User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
After backlash, publisher to retract article that surveyed parents of children with gender dysphoria, says coauthor
The move is “due to concerns about lack of informed consent,” according to tweets by one of the paper’s authors.
The article, “Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria: Parent Reports on 1655 Possible Cases,” was published in March in the Archives of Sexual Behavior. It has not been cited in the scientific literature, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science, but Altmetric, which tracks the online attention papers receive, ranks the article in the top 1% of all articles of a similar age.
Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria (ROGD) is, the article stated, a “controversial theory” that “common cultural beliefs, values, and preoccupations cause some adolescents (especially female adolescents) to attribute their social problems, feelings, and mental health issues to gender dysphoria,” and that “youth with ROGD falsely believe that they are transgender,” in part due to social influences.
Michael Bailey, a psychology professor at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., and the paper’s corresponding author, tweeted: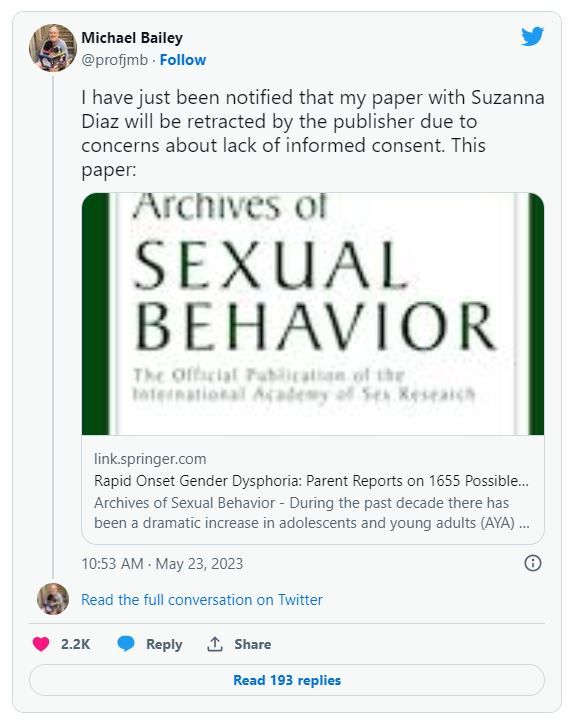
Bailey told Retraction Watch that he would “respond when [he] can” to our request for comment, following “new developments on our end.” Neither Springer Nature nor Kenneth Zucker, editor in chief of Archives of Sexual Behavior, has responded to similar requests.
The paper reported the results of a survey of parents who contacted the website ParentsofROGDKids.com, with which the first author is affiliated. According to the abstract, the authors found:
“Pre-existing mental health issues were common, and youths with these issues were more likely than those without them to have socially and medically transitioned. Parents reported that they had often felt pressured by clinicians to affirm their AYA [adolescent and young adult] child’s new gender and support their transition. According to the parents, AYA children’s mental health deteriorated considerably after social transition.”
Soon after publication, the paper attracted criticism that its method of gathering study participants was biased, and that the authors ignored information that didn’t support the theory of ROGD.
Archives of Sexual Behavior is the official publication of the International Academy of Sex Research, which tweeted on April 19:
The episode prompted a May 5 “Open Letter in Support of Dr. Kenneth Zucker and the Need to Promote Robust Scientific Debate” from the Foundation Against Intolerance and Racism that has now been signed by nearly 2000 people.
On May 10, the following publisher’s note was added to the article:
“readers are alerted that concerns have been raised regarding methodology as described in this article. The publisher is currently investigating this matter and a further response will follow the conclusion of this investigation.
Six days later, the publisher removed the article’s supplementary information “due to a lack of documented consent by study participants.”
The story may feel familiar to readers who recall what happened to another paper in 2018. In that paper, Brown University’s Lisa Littman coined the term ROGD. Following a backlash, Brown took down a press release touting the results, and the paper was eventually republished with corrections.
Bailey has been accused of mistreating transgender research participants, but an investigation by bioethicist Alice Dreger found that of the many accusations, “almost none appear to have been legitimate.”
In a post on UnHerd earlier this month, Bailey responded to the reported concerns about the study lacking approval by an Institutional Review Board (IRB), and that the way the participants were recruited biased the results.
IRB approval was not necessary, Bailey wrote, because Suzanna Diaz, the first author who collected the data, was not affiliated with an institution that required it. “Suzanna Diaz” is a pseudonym for “the mother of a gender dysphoric child she believes has ROGD” who wishes to remain anonymous for the sake of her family, Bailey wrote.
The paper included the following statement about its ethical approval:
“The first author and creator of the survey is not affiliated with any university or hospital. Thus, she did not seek approval from an IRB. After seeing a presentation of preliminary survey results by the first author, the second author suggested the data to be analyzed and submitted as an academic article (he was not involved in collecting the data). The second author consulted with his university’s IRB, who declined to certify the study because data were already collected. However, they advised that publishing the results was likely ethical provided data were deidentified. Editor’s note: After I reviewed the manuscript, I concluded that its publication is ethically appropriate, consistent with Springer policy.”
In his UnHerd post, Bailey quoted from the journal’s submission guidelines:
“If a study has not been granted ethics committee approval prior to commencing, retrospective ethics approval usually cannot be obtained and it may not be possible to consider the manuscript for peer review. The decision on whether to proceed to peer review in such cases is at the Editor’s discretion.”
“Regarding the methodological limitations of the study, these were addressed forthrightly and thoroughly in our article,” Bailey wrote.
Adam Marcus, a cofounder of Retraction Watch, is an editor at this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on RetractionWatch.com.
The move is “due to concerns about lack of informed consent,” according to tweets by one of the paper’s authors.
The article, “Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria: Parent Reports on 1655 Possible Cases,” was published in March in the Archives of Sexual Behavior. It has not been cited in the scientific literature, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science, but Altmetric, which tracks the online attention papers receive, ranks the article in the top 1% of all articles of a similar age.
Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria (ROGD) is, the article stated, a “controversial theory” that “common cultural beliefs, values, and preoccupations cause some adolescents (especially female adolescents) to attribute their social problems, feelings, and mental health issues to gender dysphoria,” and that “youth with ROGD falsely believe that they are transgender,” in part due to social influences.
Michael Bailey, a psychology professor at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., and the paper’s corresponding author, tweeted:
Bailey told Retraction Watch that he would “respond when [he] can” to our request for comment, following “new developments on our end.” Neither Springer Nature nor Kenneth Zucker, editor in chief of Archives of Sexual Behavior, has responded to similar requests.
The paper reported the results of a survey of parents who contacted the website ParentsofROGDKids.com, with which the first author is affiliated. According to the abstract, the authors found:
“Pre-existing mental health issues were common, and youths with these issues were more likely than those without them to have socially and medically transitioned. Parents reported that they had often felt pressured by clinicians to affirm their AYA [adolescent and young adult] child’s new gender and support their transition. According to the parents, AYA children’s mental health deteriorated considerably after social transition.”
Soon after publication, the paper attracted criticism that its method of gathering study participants was biased, and that the authors ignored information that didn’t support the theory of ROGD.
Archives of Sexual Behavior is the official publication of the International Academy of Sex Research, which tweeted on April 19:
The episode prompted a May 5 “Open Letter in Support of Dr. Kenneth Zucker and the Need to Promote Robust Scientific Debate” from the Foundation Against Intolerance and Racism that has now been signed by nearly 2000 people.
On May 10, the following publisher’s note was added to the article:
“readers are alerted that concerns have been raised regarding methodology as described in this article. The publisher is currently investigating this matter and a further response will follow the conclusion of this investigation.
Six days later, the publisher removed the article’s supplementary information “due to a lack of documented consent by study participants.”
The story may feel familiar to readers who recall what happened to another paper in 2018. In that paper, Brown University’s Lisa Littman coined the term ROGD. Following a backlash, Brown took down a press release touting the results, and the paper was eventually republished with corrections.
Bailey has been accused of mistreating transgender research participants, but an investigation by bioethicist Alice Dreger found that of the many accusations, “almost none appear to have been legitimate.”
In a post on UnHerd earlier this month, Bailey responded to the reported concerns about the study lacking approval by an Institutional Review Board (IRB), and that the way the participants were recruited biased the results.
IRB approval was not necessary, Bailey wrote, because Suzanna Diaz, the first author who collected the data, was not affiliated with an institution that required it. “Suzanna Diaz” is a pseudonym for “the mother of a gender dysphoric child she believes has ROGD” who wishes to remain anonymous for the sake of her family, Bailey wrote.
The paper included the following statement about its ethical approval:
“The first author and creator of the survey is not affiliated with any university or hospital. Thus, she did not seek approval from an IRB. After seeing a presentation of preliminary survey results by the first author, the second author suggested the data to be analyzed and submitted as an academic article (he was not involved in collecting the data). The second author consulted with his university’s IRB, who declined to certify the study because data were already collected. However, they advised that publishing the results was likely ethical provided data were deidentified. Editor’s note: After I reviewed the manuscript, I concluded that its publication is ethically appropriate, consistent with Springer policy.”
In his UnHerd post, Bailey quoted from the journal’s submission guidelines:
“If a study has not been granted ethics committee approval prior to commencing, retrospective ethics approval usually cannot be obtained and it may not be possible to consider the manuscript for peer review. The decision on whether to proceed to peer review in such cases is at the Editor’s discretion.”
“Regarding the methodological limitations of the study, these were addressed forthrightly and thoroughly in our article,” Bailey wrote.
Adam Marcus, a cofounder of Retraction Watch, is an editor at this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on RetractionWatch.com.
The move is “due to concerns about lack of informed consent,” according to tweets by one of the paper’s authors.
The article, “Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria: Parent Reports on 1655 Possible Cases,” was published in March in the Archives of Sexual Behavior. It has not been cited in the scientific literature, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science, but Altmetric, which tracks the online attention papers receive, ranks the article in the top 1% of all articles of a similar age.
Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria (ROGD) is, the article stated, a “controversial theory” that “common cultural beliefs, values, and preoccupations cause some adolescents (especially female adolescents) to attribute their social problems, feelings, and mental health issues to gender dysphoria,” and that “youth with ROGD falsely believe that they are transgender,” in part due to social influences.
Michael Bailey, a psychology professor at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., and the paper’s corresponding author, tweeted:
Bailey told Retraction Watch that he would “respond when [he] can” to our request for comment, following “new developments on our end.” Neither Springer Nature nor Kenneth Zucker, editor in chief of Archives of Sexual Behavior, has responded to similar requests.
The paper reported the results of a survey of parents who contacted the website ParentsofROGDKids.com, with which the first author is affiliated. According to the abstract, the authors found:
“Pre-existing mental health issues were common, and youths with these issues were more likely than those without them to have socially and medically transitioned. Parents reported that they had often felt pressured by clinicians to affirm their AYA [adolescent and young adult] child’s new gender and support their transition. According to the parents, AYA children’s mental health deteriorated considerably after social transition.”
Soon after publication, the paper attracted criticism that its method of gathering study participants was biased, and that the authors ignored information that didn’t support the theory of ROGD.
Archives of Sexual Behavior is the official publication of the International Academy of Sex Research, which tweeted on April 19:
The episode prompted a May 5 “Open Letter in Support of Dr. Kenneth Zucker and the Need to Promote Robust Scientific Debate” from the Foundation Against Intolerance and Racism that has now been signed by nearly 2000 people.
On May 10, the following publisher’s note was added to the article:
“readers are alerted that concerns have been raised regarding methodology as described in this article. The publisher is currently investigating this matter and a further response will follow the conclusion of this investigation.
Six days later, the publisher removed the article’s supplementary information “due to a lack of documented consent by study participants.”
The story may feel familiar to readers who recall what happened to another paper in 2018. In that paper, Brown University’s Lisa Littman coined the term ROGD. Following a backlash, Brown took down a press release touting the results, and the paper was eventually republished with corrections.
Bailey has been accused of mistreating transgender research participants, but an investigation by bioethicist Alice Dreger found that of the many accusations, “almost none appear to have been legitimate.”
In a post on UnHerd earlier this month, Bailey responded to the reported concerns about the study lacking approval by an Institutional Review Board (IRB), and that the way the participants were recruited biased the results.
IRB approval was not necessary, Bailey wrote, because Suzanna Diaz, the first author who collected the data, was not affiliated with an institution that required it. “Suzanna Diaz” is a pseudonym for “the mother of a gender dysphoric child she believes has ROGD” who wishes to remain anonymous for the sake of her family, Bailey wrote.
The paper included the following statement about its ethical approval:
“The first author and creator of the survey is not affiliated with any university or hospital. Thus, she did not seek approval from an IRB. After seeing a presentation of preliminary survey results by the first author, the second author suggested the data to be analyzed and submitted as an academic article (he was not involved in collecting the data). The second author consulted with his university’s IRB, who declined to certify the study because data were already collected. However, they advised that publishing the results was likely ethical provided data were deidentified. Editor’s note: After I reviewed the manuscript, I concluded that its publication is ethically appropriate, consistent with Springer policy.”
In his UnHerd post, Bailey quoted from the journal’s submission guidelines:
“If a study has not been granted ethics committee approval prior to commencing, retrospective ethics approval usually cannot be obtained and it may not be possible to consider the manuscript for peer review. The decision on whether to proceed to peer review in such cases is at the Editor’s discretion.”
“Regarding the methodological limitations of the study, these were addressed forthrightly and thoroughly in our article,” Bailey wrote.
Adam Marcus, a cofounder of Retraction Watch, is an editor at this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on RetractionWatch.com.
Is ChatGPT a friend or foe of medical publishing?
. These tools should not be listed as authors, and researchers must denote how AI-assisted technologies were used, the committee said.
These new guidelines are the latest effort for medical journals to define policies for using these large-scale language models (LLMs) in scientific publication. While these AI-assisted tools can help with tasks such as writing, analyzing data, catching mistakes, and much more, they are also prone to errors, noted Casey Greene, PhD, a professor of biomedical informatics at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. It is also not totally clear how information is stored and processed in these kinds of tools, and who has access to that information, he noted.
At the same time, experts argue that these AI tools could have a positive impact on the field by limiting some of the linguistic disparities in scientific publishing as well as alleviating the burden of some monotonous or mechanical tasks that come along with manuscript writing.
What experts can agree on, though, is that the use of AI tools is here to stay. “This is going to become a common tool,” Dr. Greene said. “I don’t think there’s a way out of that at this point.”
A change in medical publishing
OpenAI released ChatGPT in November 2022. In its own words, ChatGPT is “a deep learning model that has been trained on a massive amount of text data to understand and generate humanlike text.” Enter a question or a prompt, and it will respond. For example, when asked how the AI tool can be used in scientific publishing, ChatGPT responded:
“ChatGPT can aid scientific publishing by generating ideas, clarifying concepts, conducting preliminary literature reviews, providing proofreading and editing suggestions, and assisting with outlining and organizing scientific papers. However, it should be used as a supportive tool alongside domain expertise and validation from trusted scientific sources.”
Just a few months after ChatGPT became available, researchers began using this tool in their own work. One individual, Som Biswas, MD, a radiologist at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, reportedly used ChatGPT to author 16 scientific articles in just 4 months, according to the Daily Beast. Five of these articles have been published in four different journals. Dr. Biswas declined to be interviewed for this article.
There were also reports of papers with ChatGPT as one of the listed authors, which sparked backlash. In response, JAMA, Nature, and Science all published editorials in January outlining their policies for using ChatGPT and other large language models in the scientific authoring process. Editors from the journals of the American College of Cardiology and the American College of Rheumatology also updated their policies to reflect the influence of AI authoring tools.
The consensus is that AI has no place on the author byline.
“We think that’s not appropriate, because coauthorship means that you are taking responsibility for the analysis and the generation of data that are included in a manuscript. A machine that is dictated by AI can’t take responsibility,” said Daniel Solomon, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and the editor in chief of the ACR journal Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Issues with AI
One of the big concerns around using AI in writing is that it can generate text that seems plausible but is untrue or not supported by data. For example, Dr. Greene and colleague Milton Pividori, PhD, also of the University of Colorado, were writing a journal article about new software they developed that uses a large language model to revise scientific manuscripts.
“We used the same software to revise that article and at one point, it added a line that noted that the large language model had been fine-tuned on a data set of manuscripts from within the same field. This makes a lot of sense, and is absolutely something you could do, but was not something that we did,” Dr. Greene said. “Without a really careful review of the content, it becomes possible to invent things that were not actually done.”
In another case, ChatGPT falsely stated that a prominent law professor had been accused of sexual assault, citing a Washington Post article that did not exist.
“We live in a society where we are extremely concerned about fake news,” Dr. Pividori added, “and [these kinds of errors] could certainly exacerbate that in the scientific community, which is very concerning because science informs public policy.”
Another issue is the lack of transparency around how large language models like ChatGPT process and store data used to make queries.
“We have no idea how they are recording all the prompts and things that we input into ChatGPT and their systems,” Dr. Pividori said.
OpenAI recently addressed some privacy concerns by allowing users to turn off their chat history with the AI chatbot, so conversations cannot be used to train or improve the company’s models. But Dr. Greene noted that the terms of service “still remain pretty nebulous.”
Dr. Solomon is also concerned with researchers using these AI tools in authoring without knowing how they work. “The thing we are really concerned about is that fact that [LLMs] are a bit of a black box – people don’t really understand the methodologies,” he said.
A positive tool?
But despite these concerns, many think that these types of AI-assisted tools could have a positive impact on medical publishing, particularly for researchers for whom English is not their first language, noted Catherine Gao, MD, a pulmonary and critical care instructor at Northwestern University, Chicago. She recently led research comparing scientific abstracts written by ChatGPT and real abstracts and discovered that reviewers found it “surprisingly difficult” to differentiate the two.
“The majority of research is published in English,” she said in an email. “Responsible use of LLMs can potentially reduce the burden of writing for busy scientists and improve equity for those who are not native English speakers.”
Dr. Pividori agreed, adding that as a non-native English speaker, he spends much more time working on the structure and grammar of sentences when authoring a manuscript, compared with people who speak English as a first language. He noted that these tools can also be used to automate some of the more monotonous tasks that come along with writing manuscripts and allow researchers to focus on the more creative aspects.
In the future, “I want to focus more on the things that only a human can do and let these tools do all the rest of it,” he said.
New rules
But despite how individual researchers feel about LLMs, they agree that these AI tools are here to stay.
“I think that we should anticipate that they will become part of the medical research establishment over time, when we figure out how to use them appropriately,” Dr. Solomon said.
While the debate of how to best use AI in medical publications will continue, journal editors agree that all authors of a manuscript are solely responsible for content in articles that used AI-assisted technology.
“Authors should carefully review and edit the result because AI can generate authoritative-sounding output that can be incorrect, incomplete, or biased,” the ICMJE guidelines state. “Authors should be able to assert that there is no plagiarism in their paper, including in text and images produced by the AI.” This includes appropriate attribution of all cited materials.
The committee also recommends that authors write in both the cover letter and submitted work how AI was used in the manuscript writing process. Recently updated guidelines from the World Association of Medical Editors recommend that all prompts used to generate new text or analytical work should be provided in submitted work. Dr. Greene also noted that if authors used an AI tool to revise their work, they can include a version of the manuscript untouched by LLMs.
It is similar to a preprint, he said, but rather than publishing a version of a paper prior to peer review, someone is showing a version of a manuscript before it was reviewed and revised by AI. “This type of practice could be a path that lets us benefit from these models,” he said, “without having the drawbacks that many are concerned about.”
Dr. Solomon has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, CorEvitas, and Moderna. Both Dr. Greene and Dr. Pividori are inventors in the U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 63/486,706 that the University of Colorado has filed for the “Publishing Infrastructure For AI-Assisted Academic Authoring” invention with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. Dr. Greene and Dr. Pividori also received a grant from the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation to improve their AI-based manuscript revision tool. Dr. Gao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
. These tools should not be listed as authors, and researchers must denote how AI-assisted technologies were used, the committee said.
These new guidelines are the latest effort for medical journals to define policies for using these large-scale language models (LLMs) in scientific publication. While these AI-assisted tools can help with tasks such as writing, analyzing data, catching mistakes, and much more, they are also prone to errors, noted Casey Greene, PhD, a professor of biomedical informatics at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. It is also not totally clear how information is stored and processed in these kinds of tools, and who has access to that information, he noted.
At the same time, experts argue that these AI tools could have a positive impact on the field by limiting some of the linguistic disparities in scientific publishing as well as alleviating the burden of some monotonous or mechanical tasks that come along with manuscript writing.
What experts can agree on, though, is that the use of AI tools is here to stay. “This is going to become a common tool,” Dr. Greene said. “I don’t think there’s a way out of that at this point.”
A change in medical publishing
OpenAI released ChatGPT in November 2022. In its own words, ChatGPT is “a deep learning model that has been trained on a massive amount of text data to understand and generate humanlike text.” Enter a question or a prompt, and it will respond. For example, when asked how the AI tool can be used in scientific publishing, ChatGPT responded:
“ChatGPT can aid scientific publishing by generating ideas, clarifying concepts, conducting preliminary literature reviews, providing proofreading and editing suggestions, and assisting with outlining and organizing scientific papers. However, it should be used as a supportive tool alongside domain expertise and validation from trusted scientific sources.”
Just a few months after ChatGPT became available, researchers began using this tool in their own work. One individual, Som Biswas, MD, a radiologist at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, reportedly used ChatGPT to author 16 scientific articles in just 4 months, according to the Daily Beast. Five of these articles have been published in four different journals. Dr. Biswas declined to be interviewed for this article.
There were also reports of papers with ChatGPT as one of the listed authors, which sparked backlash. In response, JAMA, Nature, and Science all published editorials in January outlining their policies for using ChatGPT and other large language models in the scientific authoring process. Editors from the journals of the American College of Cardiology and the American College of Rheumatology also updated their policies to reflect the influence of AI authoring tools.
The consensus is that AI has no place on the author byline.
“We think that’s not appropriate, because coauthorship means that you are taking responsibility for the analysis and the generation of data that are included in a manuscript. A machine that is dictated by AI can’t take responsibility,” said Daniel Solomon, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and the editor in chief of the ACR journal Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Issues with AI
One of the big concerns around using AI in writing is that it can generate text that seems plausible but is untrue or not supported by data. For example, Dr. Greene and colleague Milton Pividori, PhD, also of the University of Colorado, were writing a journal article about new software they developed that uses a large language model to revise scientific manuscripts.
“We used the same software to revise that article and at one point, it added a line that noted that the large language model had been fine-tuned on a data set of manuscripts from within the same field. This makes a lot of sense, and is absolutely something you could do, but was not something that we did,” Dr. Greene said. “Without a really careful review of the content, it becomes possible to invent things that were not actually done.”
In another case, ChatGPT falsely stated that a prominent law professor had been accused of sexual assault, citing a Washington Post article that did not exist.
“We live in a society where we are extremely concerned about fake news,” Dr. Pividori added, “and [these kinds of errors] could certainly exacerbate that in the scientific community, which is very concerning because science informs public policy.”
Another issue is the lack of transparency around how large language models like ChatGPT process and store data used to make queries.
“We have no idea how they are recording all the prompts and things that we input into ChatGPT and their systems,” Dr. Pividori said.
OpenAI recently addressed some privacy concerns by allowing users to turn off their chat history with the AI chatbot, so conversations cannot be used to train or improve the company’s models. But Dr. Greene noted that the terms of service “still remain pretty nebulous.”
Dr. Solomon is also concerned with researchers using these AI tools in authoring without knowing how they work. “The thing we are really concerned about is that fact that [LLMs] are a bit of a black box – people don’t really understand the methodologies,” he said.
A positive tool?
But despite these concerns, many think that these types of AI-assisted tools could have a positive impact on medical publishing, particularly for researchers for whom English is not their first language, noted Catherine Gao, MD, a pulmonary and critical care instructor at Northwestern University, Chicago. She recently led research comparing scientific abstracts written by ChatGPT and real abstracts and discovered that reviewers found it “surprisingly difficult” to differentiate the two.
“The majority of research is published in English,” she said in an email. “Responsible use of LLMs can potentially reduce the burden of writing for busy scientists and improve equity for those who are not native English speakers.”
Dr. Pividori agreed, adding that as a non-native English speaker, he spends much more time working on the structure and grammar of sentences when authoring a manuscript, compared with people who speak English as a first language. He noted that these tools can also be used to automate some of the more monotonous tasks that come along with writing manuscripts and allow researchers to focus on the more creative aspects.
In the future, “I want to focus more on the things that only a human can do and let these tools do all the rest of it,” he said.
New rules
But despite how individual researchers feel about LLMs, they agree that these AI tools are here to stay.
“I think that we should anticipate that they will become part of the medical research establishment over time, when we figure out how to use them appropriately,” Dr. Solomon said.
While the debate of how to best use AI in medical publications will continue, journal editors agree that all authors of a manuscript are solely responsible for content in articles that used AI-assisted technology.
“Authors should carefully review and edit the result because AI can generate authoritative-sounding output that can be incorrect, incomplete, or biased,” the ICMJE guidelines state. “Authors should be able to assert that there is no plagiarism in their paper, including in text and images produced by the AI.” This includes appropriate attribution of all cited materials.
The committee also recommends that authors write in both the cover letter and submitted work how AI was used in the manuscript writing process. Recently updated guidelines from the World Association of Medical Editors recommend that all prompts used to generate new text or analytical work should be provided in submitted work. Dr. Greene also noted that if authors used an AI tool to revise their work, they can include a version of the manuscript untouched by LLMs.
It is similar to a preprint, he said, but rather than publishing a version of a paper prior to peer review, someone is showing a version of a manuscript before it was reviewed and revised by AI. “This type of practice could be a path that lets us benefit from these models,” he said, “without having the drawbacks that many are concerned about.”
Dr. Solomon has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, CorEvitas, and Moderna. Both Dr. Greene and Dr. Pividori are inventors in the U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 63/486,706 that the University of Colorado has filed for the “Publishing Infrastructure For AI-Assisted Academic Authoring” invention with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. Dr. Greene and Dr. Pividori also received a grant from the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation to improve their AI-based manuscript revision tool. Dr. Gao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
. These tools should not be listed as authors, and researchers must denote how AI-assisted technologies were used, the committee said.
These new guidelines are the latest effort for medical journals to define policies for using these large-scale language models (LLMs) in scientific publication. While these AI-assisted tools can help with tasks such as writing, analyzing data, catching mistakes, and much more, they are also prone to errors, noted Casey Greene, PhD, a professor of biomedical informatics at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. It is also not totally clear how information is stored and processed in these kinds of tools, and who has access to that information, he noted.
At the same time, experts argue that these AI tools could have a positive impact on the field by limiting some of the linguistic disparities in scientific publishing as well as alleviating the burden of some monotonous or mechanical tasks that come along with manuscript writing.
What experts can agree on, though, is that the use of AI tools is here to stay. “This is going to become a common tool,” Dr. Greene said. “I don’t think there’s a way out of that at this point.”
A change in medical publishing
OpenAI released ChatGPT in November 2022. In its own words, ChatGPT is “a deep learning model that has been trained on a massive amount of text data to understand and generate humanlike text.” Enter a question or a prompt, and it will respond. For example, when asked how the AI tool can be used in scientific publishing, ChatGPT responded:
“ChatGPT can aid scientific publishing by generating ideas, clarifying concepts, conducting preliminary literature reviews, providing proofreading and editing suggestions, and assisting with outlining and organizing scientific papers. However, it should be used as a supportive tool alongside domain expertise and validation from trusted scientific sources.”
Just a few months after ChatGPT became available, researchers began using this tool in their own work. One individual, Som Biswas, MD, a radiologist at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, reportedly used ChatGPT to author 16 scientific articles in just 4 months, according to the Daily Beast. Five of these articles have been published in four different journals. Dr. Biswas declined to be interviewed for this article.
There were also reports of papers with ChatGPT as one of the listed authors, which sparked backlash. In response, JAMA, Nature, and Science all published editorials in January outlining their policies for using ChatGPT and other large language models in the scientific authoring process. Editors from the journals of the American College of Cardiology and the American College of Rheumatology also updated their policies to reflect the influence of AI authoring tools.
The consensus is that AI has no place on the author byline.
“We think that’s not appropriate, because coauthorship means that you are taking responsibility for the analysis and the generation of data that are included in a manuscript. A machine that is dictated by AI can’t take responsibility,” said Daniel Solomon, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and the editor in chief of the ACR journal Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Issues with AI
One of the big concerns around using AI in writing is that it can generate text that seems plausible but is untrue or not supported by data. For example, Dr. Greene and colleague Milton Pividori, PhD, also of the University of Colorado, were writing a journal article about new software they developed that uses a large language model to revise scientific manuscripts.
“We used the same software to revise that article and at one point, it added a line that noted that the large language model had been fine-tuned on a data set of manuscripts from within the same field. This makes a lot of sense, and is absolutely something you could do, but was not something that we did,” Dr. Greene said. “Without a really careful review of the content, it becomes possible to invent things that were not actually done.”
In another case, ChatGPT falsely stated that a prominent law professor had been accused of sexual assault, citing a Washington Post article that did not exist.
“We live in a society where we are extremely concerned about fake news,” Dr. Pividori added, “and [these kinds of errors] could certainly exacerbate that in the scientific community, which is very concerning because science informs public policy.”
Another issue is the lack of transparency around how large language models like ChatGPT process and store data used to make queries.
“We have no idea how they are recording all the prompts and things that we input into ChatGPT and their systems,” Dr. Pividori said.
OpenAI recently addressed some privacy concerns by allowing users to turn off their chat history with the AI chatbot, so conversations cannot be used to train or improve the company’s models. But Dr. Greene noted that the terms of service “still remain pretty nebulous.”
Dr. Solomon is also concerned with researchers using these AI tools in authoring without knowing how they work. “The thing we are really concerned about is that fact that [LLMs] are a bit of a black box – people don’t really understand the methodologies,” he said.
A positive tool?
But despite these concerns, many think that these types of AI-assisted tools could have a positive impact on medical publishing, particularly for researchers for whom English is not their first language, noted Catherine Gao, MD, a pulmonary and critical care instructor at Northwestern University, Chicago. She recently led research comparing scientific abstracts written by ChatGPT and real abstracts and discovered that reviewers found it “surprisingly difficult” to differentiate the two.
“The majority of research is published in English,” she said in an email. “Responsible use of LLMs can potentially reduce the burden of writing for busy scientists and improve equity for those who are not native English speakers.”
Dr. Pividori agreed, adding that as a non-native English speaker, he spends much more time working on the structure and grammar of sentences when authoring a manuscript, compared with people who speak English as a first language. He noted that these tools can also be used to automate some of the more monotonous tasks that come along with writing manuscripts and allow researchers to focus on the more creative aspects.
In the future, “I want to focus more on the things that only a human can do and let these tools do all the rest of it,” he said.
New rules
But despite how individual researchers feel about LLMs, they agree that these AI tools are here to stay.
“I think that we should anticipate that they will become part of the medical research establishment over time, when we figure out how to use them appropriately,” Dr. Solomon said.
While the debate of how to best use AI in medical publications will continue, journal editors agree that all authors of a manuscript are solely responsible for content in articles that used AI-assisted technology.
“Authors should carefully review and edit the result because AI can generate authoritative-sounding output that can be incorrect, incomplete, or biased,” the ICMJE guidelines state. “Authors should be able to assert that there is no plagiarism in their paper, including in text and images produced by the AI.” This includes appropriate attribution of all cited materials.
The committee also recommends that authors write in both the cover letter and submitted work how AI was used in the manuscript writing process. Recently updated guidelines from the World Association of Medical Editors recommend that all prompts used to generate new text or analytical work should be provided in submitted work. Dr. Greene also noted that if authors used an AI tool to revise their work, they can include a version of the manuscript untouched by LLMs.
It is similar to a preprint, he said, but rather than publishing a version of a paper prior to peer review, someone is showing a version of a manuscript before it was reviewed and revised by AI. “This type of practice could be a path that lets us benefit from these models,” he said, “without having the drawbacks that many are concerned about.”
Dr. Solomon has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, CorEvitas, and Moderna. Both Dr. Greene and Dr. Pividori are inventors in the U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 63/486,706 that the University of Colorado has filed for the “Publishing Infrastructure For AI-Assisted Academic Authoring” invention with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. Dr. Greene and Dr. Pividori also received a grant from the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation to improve their AI-based manuscript revision tool. Dr. Gao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Regular, optimal sleep tied to lower mortality risk
INDIANAPOLIS –
In a diverse group of older adults, those with regular and optimal sleep had about a 40% lower risk of dying of any cause during follow-up compared with peers who had irregular and insufficient sleep.
“If sleep were an 8-hour pill, it would be beneficial to take the full dose at regular times consistently,” lead researcher Joon Chung, PhD, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in a news release.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
Broad adverse health effects
“Evidence is mounting that irregular sleep is associated with pretty broad adverse health outcomes, most prominently cardiometabolic disease, obesity, and cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Chungsaid in an interview.
In the current study, the researchers estimated the association of regular sleep of optimal sleep duration with all-cause mortality using data from 1,759 adults the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Sleep Study.
Sleep regularity and duration were classified using 7 days of data gathered by wrist actigraphy. Adults were categorized as “regular-optimal” sleepers (n = 1,015) or “irregular-insufficient” sleepers (n = 744).
During 7 years of follow-up, 176 people died. In the fully adjusted model, the regular-optimal group had a 39% lower mortality risk compared with the irregular-insufficient sleep group (hazard ratio, 0.61;95% confidence interval [CI], 0.45-0.83). The findings were robust in sensitivity analyses.
The regular and optimal duration sleep pattern maps behaviorally to regular bed and wake times, suggesting potential health benefits of adherence to recommended sleep practices, the researchers noted.
“Results suggest benefits of expanding the public conversation on getting ‘a good night’s sleep’ and broadening this goal to getting many good nights of sleep, in a row, on weekdays and weekends,” Dr. Chung said in the release.
He further said that “getting adequate, regular sleep seems to be something that is good for all. I don’t know of anyone who wouldn’t benefit.”
Fariha Abassi-Feinberg, MD, spokesperson for the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and sleep specialist with the Millennium Physician Group, Fort Myers, Fla., agreed.
“We know our bodies have an internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm, which regulates various biological processes, including sleep-wake cycles. Sticking to a consistent sleep schedule allows your body to align its natural rhythm with the external day-night cycle. This synchronization promotes better sleep quality and therefore better health,” said Dr. Abassi-Feinberg, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“The AASM recommends adults try to aim for at least 7 hours of sleep and I often tell my patients that keeping a regular routine is best for your sleep and health,” she said in an interview.
Funding for the study was provided by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Chung and Dr. Abassi-Feinberg report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
INDIANAPOLIS –
In a diverse group of older adults, those with regular and optimal sleep had about a 40% lower risk of dying of any cause during follow-up compared with peers who had irregular and insufficient sleep.
“If sleep were an 8-hour pill, it would be beneficial to take the full dose at regular times consistently,” lead researcher Joon Chung, PhD, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in a news release.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
Broad adverse health effects
“Evidence is mounting that irregular sleep is associated with pretty broad adverse health outcomes, most prominently cardiometabolic disease, obesity, and cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Chungsaid in an interview.
In the current study, the researchers estimated the association of regular sleep of optimal sleep duration with all-cause mortality using data from 1,759 adults the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Sleep Study.
Sleep regularity and duration were classified using 7 days of data gathered by wrist actigraphy. Adults were categorized as “regular-optimal” sleepers (n = 1,015) or “irregular-insufficient” sleepers (n = 744).
During 7 years of follow-up, 176 people died. In the fully adjusted model, the regular-optimal group had a 39% lower mortality risk compared with the irregular-insufficient sleep group (hazard ratio, 0.61;95% confidence interval [CI], 0.45-0.83). The findings were robust in sensitivity analyses.
The regular and optimal duration sleep pattern maps behaviorally to regular bed and wake times, suggesting potential health benefits of adherence to recommended sleep practices, the researchers noted.
“Results suggest benefits of expanding the public conversation on getting ‘a good night’s sleep’ and broadening this goal to getting many good nights of sleep, in a row, on weekdays and weekends,” Dr. Chung said in the release.
He further said that “getting adequate, regular sleep seems to be something that is good for all. I don’t know of anyone who wouldn’t benefit.”
Fariha Abassi-Feinberg, MD, spokesperson for the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and sleep specialist with the Millennium Physician Group, Fort Myers, Fla., agreed.
“We know our bodies have an internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm, which regulates various biological processes, including sleep-wake cycles. Sticking to a consistent sleep schedule allows your body to align its natural rhythm with the external day-night cycle. This synchronization promotes better sleep quality and therefore better health,” said Dr. Abassi-Feinberg, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“The AASM recommends adults try to aim for at least 7 hours of sleep and I often tell my patients that keeping a regular routine is best for your sleep and health,” she said in an interview.
Funding for the study was provided by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Chung and Dr. Abassi-Feinberg report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
INDIANAPOLIS –
In a diverse group of older adults, those with regular and optimal sleep had about a 40% lower risk of dying of any cause during follow-up compared with peers who had irregular and insufficient sleep.
“If sleep were an 8-hour pill, it would be beneficial to take the full dose at regular times consistently,” lead researcher Joon Chung, PhD, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in a news release.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
Broad adverse health effects
“Evidence is mounting that irregular sleep is associated with pretty broad adverse health outcomes, most prominently cardiometabolic disease, obesity, and cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Chungsaid in an interview.
In the current study, the researchers estimated the association of regular sleep of optimal sleep duration with all-cause mortality using data from 1,759 adults the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Sleep Study.
Sleep regularity and duration were classified using 7 days of data gathered by wrist actigraphy. Adults were categorized as “regular-optimal” sleepers (n = 1,015) or “irregular-insufficient” sleepers (n = 744).
During 7 years of follow-up, 176 people died. In the fully adjusted model, the regular-optimal group had a 39% lower mortality risk compared with the irregular-insufficient sleep group (hazard ratio, 0.61;95% confidence interval [CI], 0.45-0.83). The findings were robust in sensitivity analyses.
The regular and optimal duration sleep pattern maps behaviorally to regular bed and wake times, suggesting potential health benefits of adherence to recommended sleep practices, the researchers noted.
“Results suggest benefits of expanding the public conversation on getting ‘a good night’s sleep’ and broadening this goal to getting many good nights of sleep, in a row, on weekdays and weekends,” Dr. Chung said in the release.
He further said that “getting adequate, regular sleep seems to be something that is good for all. I don’t know of anyone who wouldn’t benefit.”
Fariha Abassi-Feinberg, MD, spokesperson for the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and sleep specialist with the Millennium Physician Group, Fort Myers, Fla., agreed.
“We know our bodies have an internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm, which regulates various biological processes, including sleep-wake cycles. Sticking to a consistent sleep schedule allows your body to align its natural rhythm with the external day-night cycle. This synchronization promotes better sleep quality and therefore better health,” said Dr. Abassi-Feinberg, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“The AASM recommends adults try to aim for at least 7 hours of sleep and I often tell my patients that keeping a regular routine is best for your sleep and health,” she said in an interview.
Funding for the study was provided by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Chung and Dr. Abassi-Feinberg report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT SLEEP 2023
Muscle fat: A new risk factor for cognitive decline?
Investigators assessed muscle fat in more than 1,600 adults in their 70s and evaluated their cognitive function over a 10-year period. They found that increases in muscle adiposity from year 1 to year 6 were associated with greater cognitive decline over time, independent of total weight, other fat deposits, muscle characteristics, and traditional dementia risk factors.
The findings were similar between Black and White people and between men and women.
“Increasing adiposity – or fat deposition – in skeletal muscles predicted faster cognitive decline, irrespective of demographics or other disease, and this effect was distinct from that of other types of fat or other muscle characteristics, such as strength or mass,” study investigator Caterina Rosano MD, MPH, professor of epidemiology at the University of Pittsburgh, said in an interview.
The study was published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Biologically plausible
“There has been a growing recognition that overall adiposity and muscle measures, such as strength and mass, are individual indicators of future dementia risk and both strengthen the algorithms to predict cognitive decline,” said Dr. Rosano, associate director for clinical translation at the University of Pittsburgh’s Aging Institute. “However, adiposity in the muscle has not been examined.”
Some evidence supports a “biologically plausible link” between muscle adiposity and dementia risk. For example, muscle adiposity increases the risk for type 2 diabetes and hypertension, both of which are dementia risk factors.
Skeletal muscle adiposity increases with older age, even in older adults who lose weight, and is “highly prevalent” among older adults of African ancestry.
The researchers examined a large, biracial sample of older adults participating in the Health, Aging and Body Composition study, which enrolled men and women aged between 70 and 79 years. Participants were followed for an average of 9.0 ± 1.8 years.
During years 1 and 6, participants’ body composition was analyzed, including intermuscular adipose tissue (IMAT), visceral and subcutaneous adiposity, total fat mass, and muscle area.
In years 1, 3, 5, 8, and 10, participants’ cognition was measured using the modified Mini-Mental State (3MS) exam.
The main independent variable was 5-year change in thigh IMAT (year 6 minus year 1), and the main dependent variable was 3MS decline (from year 5 to year 10).
The researchers adjusted all the models for traditional dementia risk factors at baseline including 3MS, education, apo E4 allele, diabetes, hypertension, and physical activity and also calculated interactions between IMAT change by race or sex.
These models also accounted for change in muscle strength, muscle area, body weight, abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adiposity, and total body fat mass as well as cytokines related to adiposity.
‘Rich and engaging crosstalk’
The final sample included 1634 participants (mean age, 73.38 years at baseline; 48% female; 35% Black; mean baseline 3MS score, 91.6).
Thigh IMAT increased by 39.0% in all participants from year 1 to year 6, which corresponded to an increase of 4.85 cm2 or 0.97 cm2/year. During the same time period, muscle strength decreased by 14.0% (P < .05), although thigh muscle area remained stable, decreasing less than 0.5%.
There were decreases in both abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adiposity of 3.92% and 6.43%, respectively (P < .05). There was a decrease of 3.3% in 3MS from year 5 to year 10.
Several variables were associated with 3MS decline, independent of any change in thigh IMAT: older age, less education, and having at least one copy of the APOe4 allele. These variables were included in the model of IMAT change predicting 3MS change.
A statistically significant association of IMAT increase with 3MS decline was found. The IMAT increase of 4.85 cm2 corresponded to a 3MS decline of an additional 3.6 points (P < .0001) from year 5 to year 10, “indicating a clinically important change.”
The association between increasing thigh IMAT with declining 3MS “remained statistically significant” after adjusting for race, age, education, and apo E4 (P < .0001) and was independent of changes in thigh muscle area, muscle strength, and other adiposity measures.
In participants with increased IMAT in years 1-6, the mean 3MS score fell to approximately 87 points at year 10, compared with those without increased IMAT, with a 3MS score that dropped to approximately 89 points.
Interactions by race and sex were not statistically significant (P > .08).
“Our results suggest that adiposity in muscles can predict cognitive decline, in addition to (not instead of) other traditional dementia risk factors,” said Dr. Rosano.
There is “a rich and engaging crosstalk between muscle, adipose tissue, and the brain all throughout our lives, happening through factors released in the bloodstream that can reach the brain, however, the specific identity of the factors responsible for the crosstalk of muscle adiposity and brain in older adults has not yet been discovered,” she noted.
Although muscle adiposity is “not yet routinely measured in clinical settings, it is being measured opportunistically on clinical CT scans obtained as part of routine patient care,” she added. “These CT measurements have already been validated in many studies of older adults; thus, clinicians could have access to this novel information without additional cost, time, or radiation exposure.”
Causality not proven
In a comment, Bruce Albala, PhD, professor, department of environmental and occupational health, University of California, Irvine, noted that the 3MS assessment is scored on a 100-point scale, with a score less than 78 “generally regarded as indicating cognitive impairment or approaching a dementia condition.” In the current study, the mean 3MS score of participants with increased IMAT was still “well above the dementia cut-off.”
Moreover, “even if there is a relationship or correlation between IMAT and cognition, this does not prove or even suggest causality, especially from a biological mechanistic approach,” said Dr. Albaba, an adjunct professor of neurology, who was not involved in the study. “Clearly, more research is needed even to understand the relationship between these two factors.”
The study was supported by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Rosano and coauthors and Dr. Albala declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators assessed muscle fat in more than 1,600 adults in their 70s and evaluated their cognitive function over a 10-year period. They found that increases in muscle adiposity from year 1 to year 6 were associated with greater cognitive decline over time, independent of total weight, other fat deposits, muscle characteristics, and traditional dementia risk factors.
The findings were similar between Black and White people and between men and women.
“Increasing adiposity – or fat deposition – in skeletal muscles predicted faster cognitive decline, irrespective of demographics or other disease, and this effect was distinct from that of other types of fat or other muscle characteristics, such as strength or mass,” study investigator Caterina Rosano MD, MPH, professor of epidemiology at the University of Pittsburgh, said in an interview.
The study was published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Biologically plausible
“There has been a growing recognition that overall adiposity and muscle measures, such as strength and mass, are individual indicators of future dementia risk and both strengthen the algorithms to predict cognitive decline,” said Dr. Rosano, associate director for clinical translation at the University of Pittsburgh’s Aging Institute. “However, adiposity in the muscle has not been examined.”
Some evidence supports a “biologically plausible link” between muscle adiposity and dementia risk. For example, muscle adiposity increases the risk for type 2 diabetes and hypertension, both of which are dementia risk factors.
Skeletal muscle adiposity increases with older age, even in older adults who lose weight, and is “highly prevalent” among older adults of African ancestry.
The researchers examined a large, biracial sample of older adults participating in the Health, Aging and Body Composition study, which enrolled men and women aged between 70 and 79 years. Participants were followed for an average of 9.0 ± 1.8 years.
During years 1 and 6, participants’ body composition was analyzed, including intermuscular adipose tissue (IMAT), visceral and subcutaneous adiposity, total fat mass, and muscle area.
In years 1, 3, 5, 8, and 10, participants’ cognition was measured using the modified Mini-Mental State (3MS) exam.
The main independent variable was 5-year change in thigh IMAT (year 6 minus year 1), and the main dependent variable was 3MS decline (from year 5 to year 10).
The researchers adjusted all the models for traditional dementia risk factors at baseline including 3MS, education, apo E4 allele, diabetes, hypertension, and physical activity and also calculated interactions between IMAT change by race or sex.
These models also accounted for change in muscle strength, muscle area, body weight, abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adiposity, and total body fat mass as well as cytokines related to adiposity.
‘Rich and engaging crosstalk’
The final sample included 1634 participants (mean age, 73.38 years at baseline; 48% female; 35% Black; mean baseline 3MS score, 91.6).
Thigh IMAT increased by 39.0% in all participants from year 1 to year 6, which corresponded to an increase of 4.85 cm2 or 0.97 cm2/year. During the same time period, muscle strength decreased by 14.0% (P < .05), although thigh muscle area remained stable, decreasing less than 0.5%.
There were decreases in both abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adiposity of 3.92% and 6.43%, respectively (P < .05). There was a decrease of 3.3% in 3MS from year 5 to year 10.
Several variables were associated with 3MS decline, independent of any change in thigh IMAT: older age, less education, and having at least one copy of the APOe4 allele. These variables were included in the model of IMAT change predicting 3MS change.
A statistically significant association of IMAT increase with 3MS decline was found. The IMAT increase of 4.85 cm2 corresponded to a 3MS decline of an additional 3.6 points (P < .0001) from year 5 to year 10, “indicating a clinically important change.”
The association between increasing thigh IMAT with declining 3MS “remained statistically significant” after adjusting for race, age, education, and apo E4 (P < .0001) and was independent of changes in thigh muscle area, muscle strength, and other adiposity measures.
In participants with increased IMAT in years 1-6, the mean 3MS score fell to approximately 87 points at year 10, compared with those without increased IMAT, with a 3MS score that dropped to approximately 89 points.
Interactions by race and sex were not statistically significant (P > .08).
“Our results suggest that adiposity in muscles can predict cognitive decline, in addition to (not instead of) other traditional dementia risk factors,” said Dr. Rosano.
There is “a rich and engaging crosstalk between muscle, adipose tissue, and the brain all throughout our lives, happening through factors released in the bloodstream that can reach the brain, however, the specific identity of the factors responsible for the crosstalk of muscle adiposity and brain in older adults has not yet been discovered,” she noted.
Although muscle adiposity is “not yet routinely measured in clinical settings, it is being measured opportunistically on clinical CT scans obtained as part of routine patient care,” she added. “These CT measurements have already been validated in many studies of older adults; thus, clinicians could have access to this novel information without additional cost, time, or radiation exposure.”
Causality not proven
In a comment, Bruce Albala, PhD, professor, department of environmental and occupational health, University of California, Irvine, noted that the 3MS assessment is scored on a 100-point scale, with a score less than 78 “generally regarded as indicating cognitive impairment or approaching a dementia condition.” In the current study, the mean 3MS score of participants with increased IMAT was still “well above the dementia cut-off.”
Moreover, “even if there is a relationship or correlation between IMAT and cognition, this does not prove or even suggest causality, especially from a biological mechanistic approach,” said Dr. Albaba, an adjunct professor of neurology, who was not involved in the study. “Clearly, more research is needed even to understand the relationship between these two factors.”
The study was supported by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Rosano and coauthors and Dr. Albala declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators assessed muscle fat in more than 1,600 adults in their 70s and evaluated their cognitive function over a 10-year period. They found that increases in muscle adiposity from year 1 to year 6 were associated with greater cognitive decline over time, independent of total weight, other fat deposits, muscle characteristics, and traditional dementia risk factors.
The findings were similar between Black and White people and between men and women.
“Increasing adiposity – or fat deposition – in skeletal muscles predicted faster cognitive decline, irrespective of demographics or other disease, and this effect was distinct from that of other types of fat or other muscle characteristics, such as strength or mass,” study investigator Caterina Rosano MD, MPH, professor of epidemiology at the University of Pittsburgh, said in an interview.
The study was published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Biologically plausible
“There has been a growing recognition that overall adiposity and muscle measures, such as strength and mass, are individual indicators of future dementia risk and both strengthen the algorithms to predict cognitive decline,” said Dr. Rosano, associate director for clinical translation at the University of Pittsburgh’s Aging Institute. “However, adiposity in the muscle has not been examined.”
Some evidence supports a “biologically plausible link” between muscle adiposity and dementia risk. For example, muscle adiposity increases the risk for type 2 diabetes and hypertension, both of which are dementia risk factors.
Skeletal muscle adiposity increases with older age, even in older adults who lose weight, and is “highly prevalent” among older adults of African ancestry.
The researchers examined a large, biracial sample of older adults participating in the Health, Aging and Body Composition study, which enrolled men and women aged between 70 and 79 years. Participants were followed for an average of 9.0 ± 1.8 years.
During years 1 and 6, participants’ body composition was analyzed, including intermuscular adipose tissue (IMAT), visceral and subcutaneous adiposity, total fat mass, and muscle area.
In years 1, 3, 5, 8, and 10, participants’ cognition was measured using the modified Mini-Mental State (3MS) exam.
The main independent variable was 5-year change in thigh IMAT (year 6 minus year 1), and the main dependent variable was 3MS decline (from year 5 to year 10).
The researchers adjusted all the models for traditional dementia risk factors at baseline including 3MS, education, apo E4 allele, diabetes, hypertension, and physical activity and also calculated interactions between IMAT change by race or sex.
These models also accounted for change in muscle strength, muscle area, body weight, abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adiposity, and total body fat mass as well as cytokines related to adiposity.
‘Rich and engaging crosstalk’
The final sample included 1634 participants (mean age, 73.38 years at baseline; 48% female; 35% Black; mean baseline 3MS score, 91.6).
Thigh IMAT increased by 39.0% in all participants from year 1 to year 6, which corresponded to an increase of 4.85 cm2 or 0.97 cm2/year. During the same time period, muscle strength decreased by 14.0% (P < .05), although thigh muscle area remained stable, decreasing less than 0.5%.
There were decreases in both abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adiposity of 3.92% and 6.43%, respectively (P < .05). There was a decrease of 3.3% in 3MS from year 5 to year 10.
Several variables were associated with 3MS decline, independent of any change in thigh IMAT: older age, less education, and having at least one copy of the APOe4 allele. These variables were included in the model of IMAT change predicting 3MS change.
A statistically significant association of IMAT increase with 3MS decline was found. The IMAT increase of 4.85 cm2 corresponded to a 3MS decline of an additional 3.6 points (P < .0001) from year 5 to year 10, “indicating a clinically important change.”
The association between increasing thigh IMAT with declining 3MS “remained statistically significant” after adjusting for race, age, education, and apo E4 (P < .0001) and was independent of changes in thigh muscle area, muscle strength, and other adiposity measures.
In participants with increased IMAT in years 1-6, the mean 3MS score fell to approximately 87 points at year 10, compared with those without increased IMAT, with a 3MS score that dropped to approximately 89 points.
Interactions by race and sex were not statistically significant (P > .08).
“Our results suggest that adiposity in muscles can predict cognitive decline, in addition to (not instead of) other traditional dementia risk factors,” said Dr. Rosano.
There is “a rich and engaging crosstalk between muscle, adipose tissue, and the brain all throughout our lives, happening through factors released in the bloodstream that can reach the brain, however, the specific identity of the factors responsible for the crosstalk of muscle adiposity and brain in older adults has not yet been discovered,” she noted.
Although muscle adiposity is “not yet routinely measured in clinical settings, it is being measured opportunistically on clinical CT scans obtained as part of routine patient care,” she added. “These CT measurements have already been validated in many studies of older adults; thus, clinicians could have access to this novel information without additional cost, time, or radiation exposure.”
Causality not proven
In a comment, Bruce Albala, PhD, professor, department of environmental and occupational health, University of California, Irvine, noted that the 3MS assessment is scored on a 100-point scale, with a score less than 78 “generally regarded as indicating cognitive impairment or approaching a dementia condition.” In the current study, the mean 3MS score of participants with increased IMAT was still “well above the dementia cut-off.”
Moreover, “even if there is a relationship or correlation between IMAT and cognition, this does not prove or even suggest causality, especially from a biological mechanistic approach,” said Dr. Albaba, an adjunct professor of neurology, who was not involved in the study. “Clearly, more research is needed even to understand the relationship between these two factors.”
The study was supported by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Rosano and coauthors and Dr. Albala declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN GERIATRICS SOCIETY
B vitamin may help boost antidepressant efficacy
The investigators analyzed six studies and found support for adjunctive use of LMF with patients with MDD not responding to antidepressant monotherapy. Treatment response was highest in those with obesity and inflammatory biomarkers.
“If clinicians try LMF on their patients with treatment-resistant depression, the treatment is very robust in patients who have high BMI [body mass index] or inflammatory biomarkers, and it’s worth a try even in patients who don’t have these indicators, since it’s safe and well tolerated, with no downside,” study investigator Vladimir Maletic, MD, MS, clinical professor of psychiatry and behavioral science, University of South Carolina, Greenville, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Shortcut’ to the brain
A considerable percentage of patients with MDD fail to achieve an adequate response to treatment, the authors wrote.
Previous research shows benefits of folate (vitamin B9) and other B vitamins in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression.
Folate is available in several forms, including LMF, which differs from dietary folate and synthetic folic acid supplements because it’s a reduced metabolite that readily crosses the blood-brain barrier.
“This is a ‘shortcut’ that gets directly to the brain, especially in those with higher BMI or inflammatory indicators, allowing their antidepressant to work better,” Dr. Maletic said.
LMF is available as a prescription medical food and approved for the clinical dietary management of patients with MDD.
The authors wanted to understand the potential role of LMF in treating patients with MDD with insufficient response to current antidepressant therapy.
They analyzed six studies:
- Two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled sequential parallel trials for patients with SSRI-resistant MDD (n = 148 and n = 75).
- A 12-month open-label extension trial of the two randomized, controlled trials (n = 68).
- A retrospective cohort study evaluating patients previously prescribed LMF (n = 554).
- Two post hoc exploratory analyses of the second randomized, controlled trial, stratifying patients by specific biological and genetic markers (n = 74) and evaluating the effect of biomarkers on treatment effect (n = 74).
The primary endpoints were improvement on the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS-17) or the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9).
Patients in all trials were treated with either 7.5 mg or 15 mg of LMF.
Both RCTs were divided into two 30-day phases, with patients assessed every 10 days. Response was defined as at least a 50% reduction in HDRS-17 score during treatment or a final score of 7 or less.
‘Salvage pathway’
In the RCTs, patients who received 7.5 mg of LMF did not achieve efficacy superior to placebo, while those receiving 15 mg/day of LMF for 30 days showed significantly greater reduction in HDRS-17 scores (–5.6 vs. –3.0; P = .05, respectively) and higher response rates (32.3% vs. 14.6%; P = .05, respectively).
The 12-month open extension trial showed that among patients who received the 15-mg dose, 61% achieved remission at any point, and 38% achieved recovery. Among initial nonresponders, 60% eventually achieved remission, with no serious adverse events.
“These results indicate that patients who respond well to shorter-term treatment are likely to maintain that response over the subsequent year and shows that those not adequately responding within the first 8 weeks of therapy may benefit from longer-term LMF treatments,” the investigators noted.
In the prospective observational study, the pooled mean change in PHQ-9 was –8.5, with response and remission rates of 67.9% and 45.7%, respectively.
“These outcomes suggest that the results seen in the controlled trial are likely to extend to patients in real-world practice,” the researchers wrote.
The post hoc analyses focusing on the findings of the two RCTs explored the differences in response to LMF, based on biomarker, BMI, and genotype.
Individuals with BMI less than 30 did not have a significant change from baseline with LMF treatment, in contrast to those with BMI of 30 or higher (pooled treatment effect, –4.66;95% CI, –7.22 to –1.98) – a difference the authors call “striking.”
Levels of inflammatory markers (tumor necrosis factor–alpha, interleukin-8, heart-specific C-reactive protein, and leptin) above the median value were associated with significantly greater treatment effect – a finding that remained significant even after adjustment for BMI.
Although BMI and cytokines all showed significant main effects, the “synergy” between them “suggests that these risk factors may interact with each other to influence response to LMF,” the authors wrote.
The mechanism by which LMF augments antidepressant treatment is tied to monoamine synthesis, since LMF promotes the synthesis of key monoamine neurotransmitters associated with MDD (serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine), Dr. Maletic explained.
High levels of inflammation (often tied to obesity) cause oxidative stress, which inhibits the synthesis of these neurotransmitters and depletes them more rapidly. LMF provides a “salvage pathway” that may prevent this from happening, thus increasing the antidepressant response of the monoamines, he said.
A ‘good addition’
In a comment, David Mischoulon, MD, PhD, Joyce R. Tedlow Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School and director of the depression clinical and research program at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, said the paper “does a good job of synthesizing what we know about LMF as an adjunctive treatment in major depression.”
However, he recommended “caution” when interpreting the findings, since “relatively few” studies were reviewed.
Dr. Mischoulon, who was not involved with the study, said that a “particularly interesting finding from these studies is individuals who are overweight and/or have elevation in inflammatory activity ... seemed to respond better to the addition of LMF.” This finding is similar to what his research team observed when investigating the potential role of fish oils in treating depression.
“These findings overall are not surprising, in view of the well-established multidirectional relationship between depression, inflammation, and overweight status,” he said.
LMF “seems like a good addition to the pharmacological armamentarium for depression; and because it is safe and has minimal side effects, it can be added to the treatment regimen of patients who are depressed and not responding adequately to standard antidepressants,” he said.
This work was funded by Alfasigma USA. The authors did not receive payment for their participation. Dr. Maletic has received writing support from Alfasigma USA; consulting/advisory fees from AbbVie/Allergan, Acadia, Alfasigma USA, Alkermes, Eisai-Purdue, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Janssen, Lundbeck, Jazz, Noven, Otsuka America, Sage, Sunovion, Supernus, and Takeda; and honoraria for lectures from AbbVie, Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Eisai, Ironshore, Intra-Cellular, Janssen, Lundbeck, Otsuka America, Sunovion, Supernus, and Takeda. Dr. Mischoulon has received research support from Nordic Naturals and Heckel Medizintechnik. He has received honoraria for speaking from the Massachusetts General Hospital Psychiatry Academy, PeerPoint Medical Education Institute, and Harvard blog.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigators analyzed six studies and found support for adjunctive use of LMF with patients with MDD not responding to antidepressant monotherapy. Treatment response was highest in those with obesity and inflammatory biomarkers.
“If clinicians try LMF on their patients with treatment-resistant depression, the treatment is very robust in patients who have high BMI [body mass index] or inflammatory biomarkers, and it’s worth a try even in patients who don’t have these indicators, since it’s safe and well tolerated, with no downside,” study investigator Vladimir Maletic, MD, MS, clinical professor of psychiatry and behavioral science, University of South Carolina, Greenville, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Shortcut’ to the brain
A considerable percentage of patients with MDD fail to achieve an adequate response to treatment, the authors wrote.
Previous research shows benefits of folate (vitamin B9) and other B vitamins in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression.
Folate is available in several forms, including LMF, which differs from dietary folate and synthetic folic acid supplements because it’s a reduced metabolite that readily crosses the blood-brain barrier.
“This is a ‘shortcut’ that gets directly to the brain, especially in those with higher BMI or inflammatory indicators, allowing their antidepressant to work better,” Dr. Maletic said.
LMF is available as a prescription medical food and approved for the clinical dietary management of patients with MDD.
The authors wanted to understand the potential role of LMF in treating patients with MDD with insufficient response to current antidepressant therapy.
They analyzed six studies:
- Two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled sequential parallel trials for patients with SSRI-resistant MDD (n = 148 and n = 75).
- A 12-month open-label extension trial of the two randomized, controlled trials (n = 68).
- A retrospective cohort study evaluating patients previously prescribed LMF (n = 554).
- Two post hoc exploratory analyses of the second randomized, controlled trial, stratifying patients by specific biological and genetic markers (n = 74) and evaluating the effect of biomarkers on treatment effect (n = 74).
The primary endpoints were improvement on the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS-17) or the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9).
Patients in all trials were treated with either 7.5 mg or 15 mg of LMF.
Both RCTs were divided into two 30-day phases, with patients assessed every 10 days. Response was defined as at least a 50% reduction in HDRS-17 score during treatment or a final score of 7 or less.
‘Salvage pathway’
In the RCTs, patients who received 7.5 mg of LMF did not achieve efficacy superior to placebo, while those receiving 15 mg/day of LMF for 30 days showed significantly greater reduction in HDRS-17 scores (–5.6 vs. –3.0; P = .05, respectively) and higher response rates (32.3% vs. 14.6%; P = .05, respectively).
The 12-month open extension trial showed that among patients who received the 15-mg dose, 61% achieved remission at any point, and 38% achieved recovery. Among initial nonresponders, 60% eventually achieved remission, with no serious adverse events.
“These results indicate that patients who respond well to shorter-term treatment are likely to maintain that response over the subsequent year and shows that those not adequately responding within the first 8 weeks of therapy may benefit from longer-term LMF treatments,” the investigators noted.
In the prospective observational study, the pooled mean change in PHQ-9 was –8.5, with response and remission rates of 67.9% and 45.7%, respectively.
“These outcomes suggest that the results seen in the controlled trial are likely to extend to patients in real-world practice,” the researchers wrote.
The post hoc analyses focusing on the findings of the two RCTs explored the differences in response to LMF, based on biomarker, BMI, and genotype.
Individuals with BMI less than 30 did not have a significant change from baseline with LMF treatment, in contrast to those with BMI of 30 or higher (pooled treatment effect, –4.66;95% CI, –7.22 to –1.98) – a difference the authors call “striking.”
Levels of inflammatory markers (tumor necrosis factor–alpha, interleukin-8, heart-specific C-reactive protein, and leptin) above the median value were associated with significantly greater treatment effect – a finding that remained significant even after adjustment for BMI.
Although BMI and cytokines all showed significant main effects, the “synergy” between them “suggests that these risk factors may interact with each other to influence response to LMF,” the authors wrote.
The mechanism by which LMF augments antidepressant treatment is tied to monoamine synthesis, since LMF promotes the synthesis of key monoamine neurotransmitters associated with MDD (serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine), Dr. Maletic explained.
High levels of inflammation (often tied to obesity) cause oxidative stress, which inhibits the synthesis of these neurotransmitters and depletes them more rapidly. LMF provides a “salvage pathway” that may prevent this from happening, thus increasing the antidepressant response of the monoamines, he said.
A ‘good addition’
In a comment, David Mischoulon, MD, PhD, Joyce R. Tedlow Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School and director of the depression clinical and research program at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, said the paper “does a good job of synthesizing what we know about LMF as an adjunctive treatment in major depression.”
However, he recommended “caution” when interpreting the findings, since “relatively few” studies were reviewed.
Dr. Mischoulon, who was not involved with the study, said that a “particularly interesting finding from these studies is individuals who are overweight and/or have elevation in inflammatory activity ... seemed to respond better to the addition of LMF.” This finding is similar to what his research team observed when investigating the potential role of fish oils in treating depression.
“These findings overall are not surprising, in view of the well-established multidirectional relationship between depression, inflammation, and overweight status,” he said.
LMF “seems like a good addition to the pharmacological armamentarium for depression; and because it is safe and has minimal side effects, it can be added to the treatment regimen of patients who are depressed and not responding adequately to standard antidepressants,” he said.
This work was funded by Alfasigma USA. The authors did not receive payment for their participation. Dr. Maletic has received writing support from Alfasigma USA; consulting/advisory fees from AbbVie/Allergan, Acadia, Alfasigma USA, Alkermes, Eisai-Purdue, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Janssen, Lundbeck, Jazz, Noven, Otsuka America, Sage, Sunovion, Supernus, and Takeda; and honoraria for lectures from AbbVie, Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Eisai, Ironshore, Intra-Cellular, Janssen, Lundbeck, Otsuka America, Sunovion, Supernus, and Takeda. Dr. Mischoulon has received research support from Nordic Naturals and Heckel Medizintechnik. He has received honoraria for speaking from the Massachusetts General Hospital Psychiatry Academy, PeerPoint Medical Education Institute, and Harvard blog.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigators analyzed six studies and found support for adjunctive use of LMF with patients with MDD not responding to antidepressant monotherapy. Treatment response was highest in those with obesity and inflammatory biomarkers.
“If clinicians try LMF on their patients with treatment-resistant depression, the treatment is very robust in patients who have high BMI [body mass index] or inflammatory biomarkers, and it’s worth a try even in patients who don’t have these indicators, since it’s safe and well tolerated, with no downside,” study investigator Vladimir Maletic, MD, MS, clinical professor of psychiatry and behavioral science, University of South Carolina, Greenville, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Shortcut’ to the brain
A considerable percentage of patients with MDD fail to achieve an adequate response to treatment, the authors wrote.
Previous research shows benefits of folate (vitamin B9) and other B vitamins in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression.
Folate is available in several forms, including LMF, which differs from dietary folate and synthetic folic acid supplements because it’s a reduced metabolite that readily crosses the blood-brain barrier.
“This is a ‘shortcut’ that gets directly to the brain, especially in those with higher BMI or inflammatory indicators, allowing their antidepressant to work better,” Dr. Maletic said.
LMF is available as a prescription medical food and approved for the clinical dietary management of patients with MDD.
The authors wanted to understand the potential role of LMF in treating patients with MDD with insufficient response to current antidepressant therapy.
They analyzed six studies:
- Two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled sequential parallel trials for patients with SSRI-resistant MDD (n = 148 and n = 75).
- A 12-month open-label extension trial of the two randomized, controlled trials (n = 68).
- A retrospective cohort study evaluating patients previously prescribed LMF (n = 554).
- Two post hoc exploratory analyses of the second randomized, controlled trial, stratifying patients by specific biological and genetic markers (n = 74) and evaluating the effect of biomarkers on treatment effect (n = 74).
The primary endpoints were improvement on the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS-17) or the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9).
Patients in all trials were treated with either 7.5 mg or 15 mg of LMF.
Both RCTs were divided into two 30-day phases, with patients assessed every 10 days. Response was defined as at least a 50% reduction in HDRS-17 score during treatment or a final score of 7 or less.
‘Salvage pathway’
In the RCTs, patients who received 7.5 mg of LMF did not achieve efficacy superior to placebo, while those receiving 15 mg/day of LMF for 30 days showed significantly greater reduction in HDRS-17 scores (–5.6 vs. –3.0; P = .05, respectively) and higher response rates (32.3% vs. 14.6%; P = .05, respectively).
The 12-month open extension trial showed that among patients who received the 15-mg dose, 61% achieved remission at any point, and 38% achieved recovery. Among initial nonresponders, 60% eventually achieved remission, with no serious adverse events.
“These results indicate that patients who respond well to shorter-term treatment are likely to maintain that response over the subsequent year and shows that those not adequately responding within the first 8 weeks of therapy may benefit from longer-term LMF treatments,” the investigators noted.
In the prospective observational study, the pooled mean change in PHQ-9 was –8.5, with response and remission rates of 67.9% and 45.7%, respectively.
“These outcomes suggest that the results seen in the controlled trial are likely to extend to patients in real-world practice,” the researchers wrote.
The post hoc analyses focusing on the findings of the two RCTs explored the differences in response to LMF, based on biomarker, BMI, and genotype.
Individuals with BMI less than 30 did not have a significant change from baseline with LMF treatment, in contrast to those with BMI of 30 or higher (pooled treatment effect, –4.66;95% CI, –7.22 to –1.98) – a difference the authors call “striking.”
Levels of inflammatory markers (tumor necrosis factor–alpha, interleukin-8, heart-specific C-reactive protein, and leptin) above the median value were associated with significantly greater treatment effect – a finding that remained significant even after adjustment for BMI.
Although BMI and cytokines all showed significant main effects, the “synergy” between them “suggests that these risk factors may interact with each other to influence response to LMF,” the authors wrote.
The mechanism by which LMF augments antidepressant treatment is tied to monoamine synthesis, since LMF promotes the synthesis of key monoamine neurotransmitters associated with MDD (serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine), Dr. Maletic explained.
High levels of inflammation (often tied to obesity) cause oxidative stress, which inhibits the synthesis of these neurotransmitters and depletes them more rapidly. LMF provides a “salvage pathway” that may prevent this from happening, thus increasing the antidepressant response of the monoamines, he said.
A ‘good addition’
In a comment, David Mischoulon, MD, PhD, Joyce R. Tedlow Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School and director of the depression clinical and research program at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, said the paper “does a good job of synthesizing what we know about LMF as an adjunctive treatment in major depression.”
However, he recommended “caution” when interpreting the findings, since “relatively few” studies were reviewed.
Dr. Mischoulon, who was not involved with the study, said that a “particularly interesting finding from these studies is individuals who are overweight and/or have elevation in inflammatory activity ... seemed to respond better to the addition of LMF.” This finding is similar to what his research team observed when investigating the potential role of fish oils in treating depression.
“These findings overall are not surprising, in view of the well-established multidirectional relationship between depression, inflammation, and overweight status,” he said.
LMF “seems like a good addition to the pharmacological armamentarium for depression; and because it is safe and has minimal side effects, it can be added to the treatment regimen of patients who are depressed and not responding adequately to standard antidepressants,” he said.
This work was funded by Alfasigma USA. The authors did not receive payment for their participation. Dr. Maletic has received writing support from Alfasigma USA; consulting/advisory fees from AbbVie/Allergan, Acadia, Alfasigma USA, Alkermes, Eisai-Purdue, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Janssen, Lundbeck, Jazz, Noven, Otsuka America, Sage, Sunovion, Supernus, and Takeda; and honoraria for lectures from AbbVie, Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Eisai, Ironshore, Intra-Cellular, Janssen, Lundbeck, Otsuka America, Sunovion, Supernus, and Takeda. Dr. Mischoulon has received research support from Nordic Naturals and Heckel Medizintechnik. He has received honoraria for speaking from the Massachusetts General Hospital Psychiatry Academy, PeerPoint Medical Education Institute, and Harvard blog.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Link between bipolar disorder and CVD mortality explained?
in new findings that may explain the “excessive and premature mortality” related to heart disease in this patient population.
The investigators found that higher reactive hyperemia index (RHI) scores, a measure of endothelial function, were tied to mood severity in patients with higher mania, but not depression scores. These findings persisted even after accounting for medications, obesity, and other cardiovascular risk factors (CVRFs).
“From a clinical perspective, these findings highlight the potential value of integrating vascular health in the assessment and management of youth with BD, and from a scientific perspective, these findings call for additional research focused on shared biological mechanisms linking vascular health and mood symptoms of BD,” senior investigator Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, full professor of psychiatry, pharmacology, and psychological clinical science, University of Toronto, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Excessively present’
BD is associated with “excessive and premature cardiovascular mortality” and CVD is “excessively present” in BD, exceeding what can be explained by traditional cardiovascular risk factors, psychiatric medications, and substance use, the researchers noted.
“In adults, more severe mood symptoms increase the risk of future CVD. Our focus on endothelial function rose due to the fact that CVD is rare in youth, whereas endothelial dysfunction – considered a precursor of CVD – can be assessed in youth,” said Dr. Goldstein, who holds the RBC Investments Chair in children’s mental health and developmental psychopathology at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, where he is director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder.
For this reason, he and his colleagues were “interested in researching whether endothelial dysfunction is associated with mood symptoms in youth with BD.” Ultimately, the motivation was to “inspire new therapeutic opportunities that may improve both cardiovascular and mental health simultaneously.”
To investigate the question, the researchers studied 209 youth aged 13-20 years (n = 114 with BD and 94 healthy controls [HCs]).
In the BD group, there were 34 BD-euthymia, 36 BD-depressed, and 44 BD-hypomanic/mixed; and within the groups who had depression or hypomania/mixed features, 72 were experiencing clinically significant depression.
Participants had to be free of chronic inflammatory illness, use of medications that might be addressing traditional CVRFs, recent infectious diseases, or neurologic conditions.
Participants’ bipolar symptoms, psychosocial functioning, and family history were assessed. In addition, they were asked about treatment, physical and/or sexual abuse, smoking status, and socioeconomic status. Height, weight, waist circumference, blood pressure, and blood tests to assess CVRFs, including C-reactive protein (CRP), were also assessed. RHI was measured via pulse amplitude tonometry, with lower values indicating poorer endothelial function.
Positive affect beneficial?
Compared with HCs, there were fewer White participants in the BD group (78% vs. 55%; P < .001). The BD group also had higher Tanner stage development scores (stage 5: 65% vs. 35%; P = .03; V = 0.21), higher body mass index (BMI, 24.4 ± 4.6 vs. 22.0 ± 4.2; P < .001; d = 0.53), and higher CRP (1.94 ± 3.99 vs. 0.76 ± 0.86; P = .009; d = –0.40).
After controlling for age, sex, and BMI (F3,202 = 4.47; P = .005; np2 = 0.06), the researchers found significant between-group differences in RHI.
Post hoc pairwise comparisons showed RHI to be significantly lower in the BD-depressed versus the HC group (P = .04; d = 0.4). Moreover, the BD-hypomanic/mixed group had significantly higher RHI, compared with the other BD groups and the HC group.
RHI was associated with higher mania scores (beta, 0.26; P = .006), but there was no similar significant association with depression mood scores (beta, 0.01; P = .90).
The mood state differences in RHI and the RHI-mania association remained significant in sensitivity analyses examining the effect of current medication use as well as CVRFs, including lipids, CRP, and blood pressure on RHI.
“We found that youth with BD experiencing a depressive episode had lower endothelial function, whereas youth with BD experiencing a hypomanic/mixed episode had higher endothelial function, as compared to healthy youth,” Dr. Goldstein said.
There are several mechanisms potentially underlying the association between endothelial function and hypomania, the investigators noted. For example, positive affect is associated with increased endothelial function in normative samples, so hypomanic symptoms, including elation, may have similar beneficial associations, although those benefits likely do not extend to mania, which has been associated with cardiovascular risk.
They also point to several limitations in the study. The cross-sectional design “precludes making inferences regarding the temporal relationship between RHI and mood.” Moreover, the study focused only on hypomania, so “we cannot draw conclusions about mania.” In addition, the HC group had a “significantly higher proportion” of White participants, and a lower Tanner stage, so it “may not be a representative control sample.”
Nevertheless, the researchers concluded that the study “adds to the existing evidence for the potential value of integrating cardiovascular-related therapeutic approaches in BD,” noting that further research is needed to elucidate the mechanisms of the association.
Observable changes in youth
In a comment, Jess G Fiedorowicz, MD, PhD, head and chief, department of mental health, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, noted that individuals with BD “have a much higher risk of CVD, which tends to develop earlier and shortens life expectancy by more than a decade.”
This cardiovascular risk “appears to be acquired over the long-term course of illness and proportionate to the persistence and severity of mood symptoms, which implies that mood syndromes, such as depression and mania, themselves may induce changes in the body relevant to CVD,” said Dr. Fiedorowicz, who is also a professor in the department of psychiatry and senior research chair in adult psychiatry at the Brain and Mind Research Institute, University of Ottawa, and was not involved with the study.
The study “adds to a growing body of evidence that mood syndromes may enact physiological changes that may be relevant to risk of CVD. One important aspect of this study is that this can even be observed in young sample,” he said.
This study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and a Miner’s Lamp Innovation Fund from the University of Toronto. Dr. Goldstein and coauthors declare no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fiedorowicz receives an honorarium from Elsevier for his work as editor-in-chief of the Journal of Psychosomatic Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in new findings that may explain the “excessive and premature mortality” related to heart disease in this patient population.
The investigators found that higher reactive hyperemia index (RHI) scores, a measure of endothelial function, were tied to mood severity in patients with higher mania, but not depression scores. These findings persisted even after accounting for medications, obesity, and other cardiovascular risk factors (CVRFs).
“From a clinical perspective, these findings highlight the potential value of integrating vascular health in the assessment and management of youth with BD, and from a scientific perspective, these findings call for additional research focused on shared biological mechanisms linking vascular health and mood symptoms of BD,” senior investigator Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, full professor of psychiatry, pharmacology, and psychological clinical science, University of Toronto, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Excessively present’
BD is associated with “excessive and premature cardiovascular mortality” and CVD is “excessively present” in BD, exceeding what can be explained by traditional cardiovascular risk factors, psychiatric medications, and substance use, the researchers noted.
“In adults, more severe mood symptoms increase the risk of future CVD. Our focus on endothelial function rose due to the fact that CVD is rare in youth, whereas endothelial dysfunction – considered a precursor of CVD – can be assessed in youth,” said Dr. Goldstein, who holds the RBC Investments Chair in children’s mental health and developmental psychopathology at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, where he is director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder.
For this reason, he and his colleagues were “interested in researching whether endothelial dysfunction is associated with mood symptoms in youth with BD.” Ultimately, the motivation was to “inspire new therapeutic opportunities that may improve both cardiovascular and mental health simultaneously.”
To investigate the question, the researchers studied 209 youth aged 13-20 years (n = 114 with BD and 94 healthy controls [HCs]).
In the BD group, there were 34 BD-euthymia, 36 BD-depressed, and 44 BD-hypomanic/mixed; and within the groups who had depression or hypomania/mixed features, 72 were experiencing clinically significant depression.
Participants had to be free of chronic inflammatory illness, use of medications that might be addressing traditional CVRFs, recent infectious diseases, or neurologic conditions.
Participants’ bipolar symptoms, psychosocial functioning, and family history were assessed. In addition, they were asked about treatment, physical and/or sexual abuse, smoking status, and socioeconomic status. Height, weight, waist circumference, blood pressure, and blood tests to assess CVRFs, including C-reactive protein (CRP), were also assessed. RHI was measured via pulse amplitude tonometry, with lower values indicating poorer endothelial function.
Positive affect beneficial?
Compared with HCs, there were fewer White participants in the BD group (78% vs. 55%; P < .001). The BD group also had higher Tanner stage development scores (stage 5: 65% vs. 35%; P = .03; V = 0.21), higher body mass index (BMI, 24.4 ± 4.6 vs. 22.0 ± 4.2; P < .001; d = 0.53), and higher CRP (1.94 ± 3.99 vs. 0.76 ± 0.86; P = .009; d = –0.40).
After controlling for age, sex, and BMI (F3,202 = 4.47; P = .005; np2 = 0.06), the researchers found significant between-group differences in RHI.
Post hoc pairwise comparisons showed RHI to be significantly lower in the BD-depressed versus the HC group (P = .04; d = 0.4). Moreover, the BD-hypomanic/mixed group had significantly higher RHI, compared with the other BD groups and the HC group.
RHI was associated with higher mania scores (beta, 0.26; P = .006), but there was no similar significant association with depression mood scores (beta, 0.01; P = .90).
The mood state differences in RHI and the RHI-mania association remained significant in sensitivity analyses examining the effect of current medication use as well as CVRFs, including lipids, CRP, and blood pressure on RHI.
“We found that youth with BD experiencing a depressive episode had lower endothelial function, whereas youth with BD experiencing a hypomanic/mixed episode had higher endothelial function, as compared to healthy youth,” Dr. Goldstein said.
There are several mechanisms potentially underlying the association between endothelial function and hypomania, the investigators noted. For example, positive affect is associated with increased endothelial function in normative samples, so hypomanic symptoms, including elation, may have similar beneficial associations, although those benefits likely do not extend to mania, which has been associated with cardiovascular risk.
They also point to several limitations in the study. The cross-sectional design “precludes making inferences regarding the temporal relationship between RHI and mood.” Moreover, the study focused only on hypomania, so “we cannot draw conclusions about mania.” In addition, the HC group had a “significantly higher proportion” of White participants, and a lower Tanner stage, so it “may not be a representative control sample.”
Nevertheless, the researchers concluded that the study “adds to the existing evidence for the potential value of integrating cardiovascular-related therapeutic approaches in BD,” noting that further research is needed to elucidate the mechanisms of the association.
Observable changes in youth
In a comment, Jess G Fiedorowicz, MD, PhD, head and chief, department of mental health, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, noted that individuals with BD “have a much higher risk of CVD, which tends to develop earlier and shortens life expectancy by more than a decade.”
This cardiovascular risk “appears to be acquired over the long-term course of illness and proportionate to the persistence and severity of mood symptoms, which implies that mood syndromes, such as depression and mania, themselves may induce changes in the body relevant to CVD,” said Dr. Fiedorowicz, who is also a professor in the department of psychiatry and senior research chair in adult psychiatry at the Brain and Mind Research Institute, University of Ottawa, and was not involved with the study.
The study “adds to a growing body of evidence that mood syndromes may enact physiological changes that may be relevant to risk of CVD. One important aspect of this study is that this can even be observed in young sample,” he said.
This study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and a Miner’s Lamp Innovation Fund from the University of Toronto. Dr. Goldstein and coauthors declare no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fiedorowicz receives an honorarium from Elsevier for his work as editor-in-chief of the Journal of Psychosomatic Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in new findings that may explain the “excessive and premature mortality” related to heart disease in this patient population.
The investigators found that higher reactive hyperemia index (RHI) scores, a measure of endothelial function, were tied to mood severity in patients with higher mania, but not depression scores. These findings persisted even after accounting for medications, obesity, and other cardiovascular risk factors (CVRFs).
“From a clinical perspective, these findings highlight the potential value of integrating vascular health in the assessment and management of youth with BD, and from a scientific perspective, these findings call for additional research focused on shared biological mechanisms linking vascular health and mood symptoms of BD,” senior investigator Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, full professor of psychiatry, pharmacology, and psychological clinical science, University of Toronto, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Excessively present’
BD is associated with “excessive and premature cardiovascular mortality” and CVD is “excessively present” in BD, exceeding what can be explained by traditional cardiovascular risk factors, psychiatric medications, and substance use, the researchers noted.
“In adults, more severe mood symptoms increase the risk of future CVD. Our focus on endothelial function rose due to the fact that CVD is rare in youth, whereas endothelial dysfunction – considered a precursor of CVD – can be assessed in youth,” said Dr. Goldstein, who holds the RBC Investments Chair in children’s mental health and developmental psychopathology at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, where he is director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder.
For this reason, he and his colleagues were “interested in researching whether endothelial dysfunction is associated with mood symptoms in youth with BD.” Ultimately, the motivation was to “inspire new therapeutic opportunities that may improve both cardiovascular and mental health simultaneously.”
To investigate the question, the researchers studied 209 youth aged 13-20 years (n = 114 with BD and 94 healthy controls [HCs]).
In the BD group, there were 34 BD-euthymia, 36 BD-depressed, and 44 BD-hypomanic/mixed; and within the groups who had depression or hypomania/mixed features, 72 were experiencing clinically significant depression.
Participants had to be free of chronic inflammatory illness, use of medications that might be addressing traditional CVRFs, recent infectious diseases, or neurologic conditions.
Participants’ bipolar symptoms, psychosocial functioning, and family history were assessed. In addition, they were asked about treatment, physical and/or sexual abuse, smoking status, and socioeconomic status. Height, weight, waist circumference, blood pressure, and blood tests to assess CVRFs, including C-reactive protein (CRP), were also assessed. RHI was measured via pulse amplitude tonometry, with lower values indicating poorer endothelial function.
Positive affect beneficial?
Compared with HCs, there were fewer White participants in the BD group (78% vs. 55%; P < .001). The BD group also had higher Tanner stage development scores (stage 5: 65% vs. 35%; P = .03; V = 0.21), higher body mass index (BMI, 24.4 ± 4.6 vs. 22.0 ± 4.2; P < .001; d = 0.53), and higher CRP (1.94 ± 3.99 vs. 0.76 ± 0.86; P = .009; d = –0.40).
After controlling for age, sex, and BMI (F3,202 = 4.47; P = .005; np2 = 0.06), the researchers found significant between-group differences in RHI.
Post hoc pairwise comparisons showed RHI to be significantly lower in the BD-depressed versus the HC group (P = .04; d = 0.4). Moreover, the BD-hypomanic/mixed group had significantly higher RHI, compared with the other BD groups and the HC group.
RHI was associated with higher mania scores (beta, 0.26; P = .006), but there was no similar significant association with depression mood scores (beta, 0.01; P = .90).
The mood state differences in RHI and the RHI-mania association remained significant in sensitivity analyses examining the effect of current medication use as well as CVRFs, including lipids, CRP, and blood pressure on RHI.
“We found that youth with BD experiencing a depressive episode had lower endothelial function, whereas youth with BD experiencing a hypomanic/mixed episode had higher endothelial function, as compared to healthy youth,” Dr. Goldstein said.
There are several mechanisms potentially underlying the association between endothelial function and hypomania, the investigators noted. For example, positive affect is associated with increased endothelial function in normative samples, so hypomanic symptoms, including elation, may have similar beneficial associations, although those benefits likely do not extend to mania, which has been associated with cardiovascular risk.
They also point to several limitations in the study. The cross-sectional design “precludes making inferences regarding the temporal relationship between RHI and mood.” Moreover, the study focused only on hypomania, so “we cannot draw conclusions about mania.” In addition, the HC group had a “significantly higher proportion” of White participants, and a lower Tanner stage, so it “may not be a representative control sample.”
Nevertheless, the researchers concluded that the study “adds to the existing evidence for the potential value of integrating cardiovascular-related therapeutic approaches in BD,” noting that further research is needed to elucidate the mechanisms of the association.
Observable changes in youth
In a comment, Jess G Fiedorowicz, MD, PhD, head and chief, department of mental health, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, noted that individuals with BD “have a much higher risk of CVD, which tends to develop earlier and shortens life expectancy by more than a decade.”
This cardiovascular risk “appears to be acquired over the long-term course of illness and proportionate to the persistence and severity of mood symptoms, which implies that mood syndromes, such as depression and mania, themselves may induce changes in the body relevant to CVD,” said Dr. Fiedorowicz, who is also a professor in the department of psychiatry and senior research chair in adult psychiatry at the Brain and Mind Research Institute, University of Ottawa, and was not involved with the study.
The study “adds to a growing body of evidence that mood syndromes may enact physiological changes that may be relevant to risk of CVD. One important aspect of this study is that this can even be observed in young sample,” he said.
This study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and a Miner’s Lamp Innovation Fund from the University of Toronto. Dr. Goldstein and coauthors declare no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fiedorowicz receives an honorarium from Elsevier for his work as editor-in-chief of the Journal of Psychosomatic Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Anxiety, your brain, and long COVID: What the research says
Having anxiety and depression before a COVID infection increases the risk of developing long COVID, researchers have found.
Those with long COVID who develop anxiety and depression after an infection may have brain shrinkage in areas that regulate memory, emotion, and other functions as well as disruption of brain connectivity.
While many questions remain about these intertwined relationships, the associations aren’t a complete surprise. Experts already know that depression and anxiety are associated with inflammation and immune dysfunction, perhaps helping to explain the link between these mental health conditions, the risk of long COVID, and the changes in the brain.
Brain changes accompanying a COVID infection have concerned researchers since earlier in the pandemic, when U.K. Biobank researchers found brain atrophy, loss of grey matter, and decline in cognition in those infected with COVID, compared with those not infected.
Common conditions
The ramifications of the research linking anxiety, depression, and long COVID are far-reaching. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 12.5% of U.S. adults have regular feelings of anxiety (as well as nervousness and worry), and the latest Gallup Poll found that nearly 18% of adults currently have or are being treated for depression.
As of May 8, 10% of infected adults in the United States have long COVID, according to the CDC, and among U.S. adults ever infected, 27% have reported long COVID. Long COVID has been defined by the CDC as symptoms such as fatigue, brain fog, and cough that persist longer than 4 weeks and by the World Health Organization as symptoms persisting for 3 months or more.
Here’s a roundup of what the research shows about mental health and long COVID risk – along with other research finding that paying attention to health habits may reduce that risk.
Pre-existing depression, anxiety, and long COVID risk
A history of mental health issues – including depression, anxiety, worry, perceived stress, and loneliness – raises the risk of long COVID if infection occurs, Harvard researchers have found.
The researchers evaluated data from three large, ongoing studies including nearly 55,000 participants to determine the effects of high levels of psychological distress before a COVID infection.
“Our study was purely survey based,” said Siwen Wang, MD, the study’s lead author and a research fellow at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
At the start of the survey in April 2020, none of the participants reported a current or previous COVID infection. They answered surveys about psychological distress at the start of the study, at 6 monthly time points, then quarterly until November 2021.
Over the follow up, 3,193 people reported a positive COVID test and 43% of those, or 1,403, developed long COVID. That number may seem high, but 38% of the 55,000 were active health care workers. On the final questionnaire, they reported whether their symptoms persisted for 4 weeks or longer and thus had long COVID by the standard CDC definition.
Dr. Wang’s team then looked at the infected participants’ psychological status. Anxiety raised the risk of long COVID by 42%, depression by 32%, worry about COVID by 37%, perceived stress, 46%, and loneliness, 32%.
COVID patients with a history of depression or anxiety are also more likely than others to report trouble with cognition in the weeks after a COVID infection and to develop brain fog and long COVID, UCLA researchers found. They evaluated 766 people with a confirmed COVID infection; 36% said their thinking was affected within 4 weeks of the infection. Those with anxiety and depression were more likely to report those difficulties.
Long COVID, then anxiety, depression, brain changes
Even mild cases of COVID infection can lead to long COVID and brain changes in those who suffer anxiety or depression after the infection, according to Clarissa Yasuda, MD, PhD, assistant professor of neurology at the University of Campinas in Sao Paulo. She has researched long COVID’s effects on the brain, even as she is coping with being a long COVID patient.
In one of her studies, presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, she found brain changes in people with anxiety, depression, and COVID but not in those infected who did not have either mental health issue. She evaluated 254 people, median age 41, after about 82 days from their positive PCR test for COVID. Everyone completed a standard questionnaire for depression (the Beck Depression Inventory) and another for anxiety (the Beck Anxiety Inventory). She further divided them into two groups – the 102 with symptoms and the 152 who had no symptoms of either depression or anxiety.
Brain scans showed those with COVID who also had anxiety and depression had shrinkage in the limbic area of the brain (which helps process emotion and memory), while those infected who didn’t have anxiety or depression did not. The researchers then scanned the brains of 148 healthy people without COVID and found no shrinkage.
The atrophy, Dr. Yasuda said, “is not something you can see with your eyes. It was only detected with computer analysis. Visualization on an MRI is normal.”
The number of people in this study with mental health issues was surprisingly high, Dr. Yasuda said. “It was intriguing for us that we noticed many individuals have both symptoms, anxiety and depression. We were not expecting it at that proportion.”
The researchers found a pattern of change not only in brain structure but in brain communication. They found those changes by using specialized software to analyze brain networks in some of the participants. Those with anxiety and depression had widespread functional changes in each of 12 networks tested. The participants without mental health symptoms showed changes in just five networks. These changes are enough to lead to problems with thinking skills and memory, Dr. Yasuda said.
Explaining the links
Several ideas have been proposed to explain the link between psychological distress and long COVID risk, Dr. Wang said. “The first and most mainstream mechanism for long COVID is chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation. Several mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression, are associated with inflammation and dysfunction and that might be the link between depression, anxiety, and long COVID.”
Another less mainstream hypothesis, she said, is that “those with long COVID have more autoantibodies and they are more likely to have blood clotting issues. These have also been found in people with anxiety, depression, or other psychological distress.”
Other researchers are looking more broadly at how COVID infections affect the brain. When German researchers evaluated the brain and other body parts of 20 patients who died from non-COVID causes but had documented COVID infections, they found that 12 had accumulations of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the brain tissue as well as the skull and meninges, the membranes that line the skull and spinal cord. Healthy controls did not.
The findings suggest the persistence of the spike protein may contribute to the long-term neurologic symptoms of long COVID and may also lead to understanding of the molecular mechanisms as well as therapies for long COVID, the researchers said in their preprint report, which has not yet been peer reviewed.
In another recent study, researchers from Germany performed neuroimaging and neuropsychological assessments of 223 people who were not vaccinated and recovered from mild to moderate COVID infections, comparing them with 223 matched healthy controls who had the same testing. In those infected, they found alterations in the cerebral white matter but no worse cognitive function in the first year after recovering. They conclude that the infection triggers a prolonged neuroinflammatory response.
Can the brain changes reverse? “We don’t have an answer right now, but we are working on that,” Dr. Yasuda said. For now, she speculates about the return of brain volume: “I think for most it will. But I think we need to treat the symptoms. We can’t disregard the symptoms of long COVID. People are suffering a lot, and this suffering is causing some brain damage.”
Lifestyle habits and risk of long COVID
Meanwhile, healthy lifestyle habits in those infected can reduce the risk of long COVID, research by Dr. Wang and colleagues found. They followed nearly 2,000 women with a positive COVID test over 19 months. Of these, 44%, or 871, developed long COVID. Compared with women who followed none of the healthy lifestyle habits evaluated, those with five to six of the habits had a 49% lower risk of long COVID.
The habits included: a healthy body mass index (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), never smoking, at least 150 minutes weekly of moderate to vigorous physical activity, moderate alcohol intake (5-15 grams a day), high diet quality, and good sleep (7-9 hours nightly).
Long-term solutions
Dr. Yasuda hopes that mental health care – of those infected and those not – will be taken more seriously. In a commentary on her own long COVID experience, she wrote, in part: “I fear for the numerous survivors of COVID-19 who do not have access to medical attention for their post-COVID symptoms. ... The mental health system needs to become prepared to receive survivors with different neuropsychiatric symptoms, including anxiety and depression.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Having anxiety and depression before a COVID infection increases the risk of developing long COVID, researchers have found.
Those with long COVID who develop anxiety and depression after an infection may have brain shrinkage in areas that regulate memory, emotion, and other functions as well as disruption of brain connectivity.
While many questions remain about these intertwined relationships, the associations aren’t a complete surprise. Experts already know that depression and anxiety are associated with inflammation and immune dysfunction, perhaps helping to explain the link between these mental health conditions, the risk of long COVID, and the changes in the brain.
Brain changes accompanying a COVID infection have concerned researchers since earlier in the pandemic, when U.K. Biobank researchers found brain atrophy, loss of grey matter, and decline in cognition in those infected with COVID, compared with those not infected.
Common conditions
The ramifications of the research linking anxiety, depression, and long COVID are far-reaching. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 12.5% of U.S. adults have regular feelings of anxiety (as well as nervousness and worry), and the latest Gallup Poll found that nearly 18% of adults currently have or are being treated for depression.
As of May 8, 10% of infected adults in the United States have long COVID, according to the CDC, and among U.S. adults ever infected, 27% have reported long COVID. Long COVID has been defined by the CDC as symptoms such as fatigue, brain fog, and cough that persist longer than 4 weeks and by the World Health Organization as symptoms persisting for 3 months or more.
Here’s a roundup of what the research shows about mental health and long COVID risk – along with other research finding that paying attention to health habits may reduce that risk.
Pre-existing depression, anxiety, and long COVID risk
A history of mental health issues – including depression, anxiety, worry, perceived stress, and loneliness – raises the risk of long COVID if infection occurs, Harvard researchers have found.
The researchers evaluated data from three large, ongoing studies including nearly 55,000 participants to determine the effects of high levels of psychological distress before a COVID infection.
“Our study was purely survey based,” said Siwen Wang, MD, the study’s lead author and a research fellow at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
At the start of the survey in April 2020, none of the participants reported a current or previous COVID infection. They answered surveys about psychological distress at the start of the study, at 6 monthly time points, then quarterly until November 2021.
Over the follow up, 3,193 people reported a positive COVID test and 43% of those, or 1,403, developed long COVID. That number may seem high, but 38% of the 55,000 were active health care workers. On the final questionnaire, they reported whether their symptoms persisted for 4 weeks or longer and thus had long COVID by the standard CDC definition.
Dr. Wang’s team then looked at the infected participants’ psychological status. Anxiety raised the risk of long COVID by 42%, depression by 32%, worry about COVID by 37%, perceived stress, 46%, and loneliness, 32%.
COVID patients with a history of depression or anxiety are also more likely than others to report trouble with cognition in the weeks after a COVID infection and to develop brain fog and long COVID, UCLA researchers found. They evaluated 766 people with a confirmed COVID infection; 36% said their thinking was affected within 4 weeks of the infection. Those with anxiety and depression were more likely to report those difficulties.
Long COVID, then anxiety, depression, brain changes
Even mild cases of COVID infection can lead to long COVID and brain changes in those who suffer anxiety or depression after the infection, according to Clarissa Yasuda, MD, PhD, assistant professor of neurology at the University of Campinas in Sao Paulo. She has researched long COVID’s effects on the brain, even as she is coping with being a long COVID patient.
In one of her studies, presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, she found brain changes in people with anxiety, depression, and COVID but not in those infected who did not have either mental health issue. She evaluated 254 people, median age 41, after about 82 days from their positive PCR test for COVID. Everyone completed a standard questionnaire for depression (the Beck Depression Inventory) and another for anxiety (the Beck Anxiety Inventory). She further divided them into two groups – the 102 with symptoms and the 152 who had no symptoms of either depression or anxiety.
Brain scans showed those with COVID who also had anxiety and depression had shrinkage in the limbic area of the brain (which helps process emotion and memory), while those infected who didn’t have anxiety or depression did not. The researchers then scanned the brains of 148 healthy people without COVID and found no shrinkage.
The atrophy, Dr. Yasuda said, “is not something you can see with your eyes. It was only detected with computer analysis. Visualization on an MRI is normal.”
The number of people in this study with mental health issues was surprisingly high, Dr. Yasuda said. “It was intriguing for us that we noticed many individuals have both symptoms, anxiety and depression. We were not expecting it at that proportion.”
The researchers found a pattern of change not only in brain structure but in brain communication. They found those changes by using specialized software to analyze brain networks in some of the participants. Those with anxiety and depression had widespread functional changes in each of 12 networks tested. The participants without mental health symptoms showed changes in just five networks. These changes are enough to lead to problems with thinking skills and memory, Dr. Yasuda said.
Explaining the links
Several ideas have been proposed to explain the link between psychological distress and long COVID risk, Dr. Wang said. “The first and most mainstream mechanism for long COVID is chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation. Several mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression, are associated with inflammation and dysfunction and that might be the link between depression, anxiety, and long COVID.”
Another less mainstream hypothesis, she said, is that “those with long COVID have more autoantibodies and they are more likely to have blood clotting issues. These have also been found in people with anxiety, depression, or other psychological distress.”
Other researchers are looking more broadly at how COVID infections affect the brain. When German researchers evaluated the brain and other body parts of 20 patients who died from non-COVID causes but had documented COVID infections, they found that 12 had accumulations of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the brain tissue as well as the skull and meninges, the membranes that line the skull and spinal cord. Healthy controls did not.
The findings suggest the persistence of the spike protein may contribute to the long-term neurologic symptoms of long COVID and may also lead to understanding of the molecular mechanisms as well as therapies for long COVID, the researchers said in their preprint report, which has not yet been peer reviewed.
In another recent study, researchers from Germany performed neuroimaging and neuropsychological assessments of 223 people who were not vaccinated and recovered from mild to moderate COVID infections, comparing them with 223 matched healthy controls who had the same testing. In those infected, they found alterations in the cerebral white matter but no worse cognitive function in the first year after recovering. They conclude that the infection triggers a prolonged neuroinflammatory response.
Can the brain changes reverse? “We don’t have an answer right now, but we are working on that,” Dr. Yasuda said. For now, she speculates about the return of brain volume: “I think for most it will. But I think we need to treat the symptoms. We can’t disregard the symptoms of long COVID. People are suffering a lot, and this suffering is causing some brain damage.”
Lifestyle habits and risk of long COVID
Meanwhile, healthy lifestyle habits in those infected can reduce the risk of long COVID, research by Dr. Wang and colleagues found. They followed nearly 2,000 women with a positive COVID test over 19 months. Of these, 44%, or 871, developed long COVID. Compared with women who followed none of the healthy lifestyle habits evaluated, those with five to six of the habits had a 49% lower risk of long COVID.
The habits included: a healthy body mass index (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), never smoking, at least 150 minutes weekly of moderate to vigorous physical activity, moderate alcohol intake (5-15 grams a day), high diet quality, and good sleep (7-9 hours nightly).
Long-term solutions
Dr. Yasuda hopes that mental health care – of those infected and those not – will be taken more seriously. In a commentary on her own long COVID experience, she wrote, in part: “I fear for the numerous survivors of COVID-19 who do not have access to medical attention for their post-COVID symptoms. ... The mental health system needs to become prepared to receive survivors with different neuropsychiatric symptoms, including anxiety and depression.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Having anxiety and depression before a COVID infection increases the risk of developing long COVID, researchers have found.
Those with long COVID who develop anxiety and depression after an infection may have brain shrinkage in areas that regulate memory, emotion, and other functions as well as disruption of brain connectivity.
While many questions remain about these intertwined relationships, the associations aren’t a complete surprise. Experts already know that depression and anxiety are associated with inflammation and immune dysfunction, perhaps helping to explain the link between these mental health conditions, the risk of long COVID, and the changes in the brain.
Brain changes accompanying a COVID infection have concerned researchers since earlier in the pandemic, when U.K. Biobank researchers found brain atrophy, loss of grey matter, and decline in cognition in those infected with COVID, compared with those not infected.
Common conditions
The ramifications of the research linking anxiety, depression, and long COVID are far-reaching. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 12.5% of U.S. adults have regular feelings of anxiety (as well as nervousness and worry), and the latest Gallup Poll found that nearly 18% of adults currently have or are being treated for depression.
As of May 8, 10% of infected adults in the United States have long COVID, according to the CDC, and among U.S. adults ever infected, 27% have reported long COVID. Long COVID has been defined by the CDC as symptoms such as fatigue, brain fog, and cough that persist longer than 4 weeks and by the World Health Organization as symptoms persisting for 3 months or more.
Here’s a roundup of what the research shows about mental health and long COVID risk – along with other research finding that paying attention to health habits may reduce that risk.
Pre-existing depression, anxiety, and long COVID risk
A history of mental health issues – including depression, anxiety, worry, perceived stress, and loneliness – raises the risk of long COVID if infection occurs, Harvard researchers have found.
The researchers evaluated data from three large, ongoing studies including nearly 55,000 participants to determine the effects of high levels of psychological distress before a COVID infection.
“Our study was purely survey based,” said Siwen Wang, MD, the study’s lead author and a research fellow at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
At the start of the survey in April 2020, none of the participants reported a current or previous COVID infection. They answered surveys about psychological distress at the start of the study, at 6 monthly time points, then quarterly until November 2021.
Over the follow up, 3,193 people reported a positive COVID test and 43% of those, or 1,403, developed long COVID. That number may seem high, but 38% of the 55,000 were active health care workers. On the final questionnaire, they reported whether their symptoms persisted for 4 weeks or longer and thus had long COVID by the standard CDC definition.
Dr. Wang’s team then looked at the infected participants’ psychological status. Anxiety raised the risk of long COVID by 42%, depression by 32%, worry about COVID by 37%, perceived stress, 46%, and loneliness, 32%.
COVID patients with a history of depression or anxiety are also more likely than others to report trouble with cognition in the weeks after a COVID infection and to develop brain fog and long COVID, UCLA researchers found. They evaluated 766 people with a confirmed COVID infection; 36% said their thinking was affected within 4 weeks of the infection. Those with anxiety and depression were more likely to report those difficulties.
Long COVID, then anxiety, depression, brain changes
Even mild cases of COVID infection can lead to long COVID and brain changes in those who suffer anxiety or depression after the infection, according to Clarissa Yasuda, MD, PhD, assistant professor of neurology at the University of Campinas in Sao Paulo. She has researched long COVID’s effects on the brain, even as she is coping with being a long COVID patient.
In one of her studies, presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, she found brain changes in people with anxiety, depression, and COVID but not in those infected who did not have either mental health issue. She evaluated 254 people, median age 41, after about 82 days from their positive PCR test for COVID. Everyone completed a standard questionnaire for depression (the Beck Depression Inventory) and another for anxiety (the Beck Anxiety Inventory). She further divided them into two groups – the 102 with symptoms and the 152 who had no symptoms of either depression or anxiety.
Brain scans showed those with COVID who also had anxiety and depression had shrinkage in the limbic area of the brain (which helps process emotion and memory), while those infected who didn’t have anxiety or depression did not. The researchers then scanned the brains of 148 healthy people without COVID and found no shrinkage.
The atrophy, Dr. Yasuda said, “is not something you can see with your eyes. It was only detected with computer analysis. Visualization on an MRI is normal.”
The number of people in this study with mental health issues was surprisingly high, Dr. Yasuda said. “It was intriguing for us that we noticed many individuals have both symptoms, anxiety and depression. We were not expecting it at that proportion.”
The researchers found a pattern of change not only in brain structure but in brain communication. They found those changes by using specialized software to analyze brain networks in some of the participants. Those with anxiety and depression had widespread functional changes in each of 12 networks tested. The participants without mental health symptoms showed changes in just five networks. These changes are enough to lead to problems with thinking skills and memory, Dr. Yasuda said.
Explaining the links
Several ideas have been proposed to explain the link between psychological distress and long COVID risk, Dr. Wang said. “The first and most mainstream mechanism for long COVID is chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation. Several mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression, are associated with inflammation and dysfunction and that might be the link between depression, anxiety, and long COVID.”
Another less mainstream hypothesis, she said, is that “those with long COVID have more autoantibodies and they are more likely to have blood clotting issues. These have also been found in people with anxiety, depression, or other psychological distress.”
Other researchers are looking more broadly at how COVID infections affect the brain. When German researchers evaluated the brain and other body parts of 20 patients who died from non-COVID causes but had documented COVID infections, they found that 12 had accumulations of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the brain tissue as well as the skull and meninges, the membranes that line the skull and spinal cord. Healthy controls did not.
The findings suggest the persistence of the spike protein may contribute to the long-term neurologic symptoms of long COVID and may also lead to understanding of the molecular mechanisms as well as therapies for long COVID, the researchers said in their preprint report, which has not yet been peer reviewed.
In another recent study, researchers from Germany performed neuroimaging and neuropsychological assessments of 223 people who were not vaccinated and recovered from mild to moderate COVID infections, comparing them with 223 matched healthy controls who had the same testing. In those infected, they found alterations in the cerebral white matter but no worse cognitive function in the first year after recovering. They conclude that the infection triggers a prolonged neuroinflammatory response.
Can the brain changes reverse? “We don’t have an answer right now, but we are working on that,” Dr. Yasuda said. For now, she speculates about the return of brain volume: “I think for most it will. But I think we need to treat the symptoms. We can’t disregard the symptoms of long COVID. People are suffering a lot, and this suffering is causing some brain damage.”
Lifestyle habits and risk of long COVID
Meanwhile, healthy lifestyle habits in those infected can reduce the risk of long COVID, research by Dr. Wang and colleagues found. They followed nearly 2,000 women with a positive COVID test over 19 months. Of these, 44%, or 871, developed long COVID. Compared with women who followed none of the healthy lifestyle habits evaluated, those with five to six of the habits had a 49% lower risk of long COVID.
The habits included: a healthy body mass index (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), never smoking, at least 150 minutes weekly of moderate to vigorous physical activity, moderate alcohol intake (5-15 grams a day), high diet quality, and good sleep (7-9 hours nightly).
Long-term solutions
Dr. Yasuda hopes that mental health care – of those infected and those not – will be taken more seriously. In a commentary on her own long COVID experience, she wrote, in part: “I fear for the numerous survivors of COVID-19 who do not have access to medical attention for their post-COVID symptoms. ... The mental health system needs to become prepared to receive survivors with different neuropsychiatric symptoms, including anxiety and depression.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The enemy of carcinogenic fumes is my friendly begonia
Sowing the seeds of cancer prevention
Are you looking to add to your quality of life, even though pets are not your speed? Might we suggest something with lower maintenance? Something a little greener?
Indoor plants can purify the air that comes from outside. Researchers at the University of Technology Sydney, in partnership with the plantscaping company Ambius, showed that a “green wall” made up of mixed indoor plants was able to suck up 97% of “the most toxic compounds” from the air in just 8 hours. We’re talking about lung-irritating, headache-inducing, cancer risk–boosting compounds from gasoline fumes, including benzene.
Public health initiatives often strive to reduce cardiovascular and obesity risks, but breathing seems pretty important too. According to the World Health Organization, household air pollution is responsible for about 2.5 million global premature deaths each year. And since 2020 we’ve become accustomed to spending more time inside and at home.
“This new research proves that plants should not just be seen as ‘nice to have,’ but rather a crucial part of every workplace wellness plan,” Ambius General Manager Johan Hodgson said in statement released by the university.
So don’t spend hundreds of dollars on a fancy air filtration system when a wall of plants can do that for next to nothing. Find what works for you and your space and become a plant parent today! Your lungs will thank you.
But officer, I had to swerve to miss the duodenal ampulla
Tiny video capsule endoscopes have been around for many years, but they have one big weakness: The ingestible cameras’ journey through the GI tract is passively driven by gravity and the natural movement of the body, so they often miss potential problem areas.
Not anymore. That flaw has been addressed by medical technology company AnX Robotica, which has taken endoscopy to the next level by adding that wondrous directional control device of the modern electronic age, a joystick.
The new system “uses an external magnet and hand-held video game style joysticks to move the capsule in three dimensions,” which allows physicians to “remotely drive a miniature video capsule to all regions of the stomach to visualize and photograph potential problem areas,” according to Andrew C. Meltzer, MD, of George Washington University and associates, who conducted a pilot study funded by AnX Robotica.
The video capsule provided a 95% rate of visualization in the stomachs of 40 patients who were examined at a medical office building by an emergency medicine physician who had no previous specialty training in endoscopy. “Capsules were driven by the ER physician and then the study reports were reviewed by an attending gastroenterologist who was physically off site,” the investigators said in a written statement.
The capsule operator did receive some additional training, and development of artificial intelligence to self-drive the capsule is in the works, but for now, we’re talking about a device controlled by a human using a joystick. And we all know that 50-year-olds are not especially known for their joystick skills. For that we need real experts. Yup, we need to put those joystick-controlled capsule endoscopes in the hands of teenage gamers. Who wants to go first?
Maybe AI isn’t ready for the big time after all
“How long before some intrepid stockholder says: ‘Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?’ ” Those words appeared on LOTME but a month ago. After all, the AI is supposed to be smarter and more empathetic than a doctor. And did we mention it’s free? Or at least extremely cheap. Cheaper than, say, a group of recently unionized health care workers.
In early May, the paid employees manning the National Eating Disorders Association emergency hotline voted to unionize, as they felt overwhelmed and underpaid. Apparently, paying six people an extra few thousand a year was too much for NEDA’s leadership, as they decided a few weeks later to fire those workers, fully closing down the hotline. Instead of talking to a real person, people “calling in” for support would be met with Tessa, a wellness chatbot that would hopefully guide them through their crisis. Key word, hopefully.
In perhaps the least surprising twist of the year, NEDA was forced to walk back its decision about a week after its initial announcement. It all started with a viral Instagram post from a woman who called in and received the following advice from Tessa: Lose 1-2 pounds a week, count calories and work for a 500- to 1,000-calorie deficit, weigh herself weekly, and restrict her diet. Unfortunately, all of these suggestions were things that led to the development of the woman’s eating disorder.
Naturally, NEDA responded in good grace, accusing the woman of lying. A NEDA vice president even left some nasty comments on the post, but hastily deleted them a day later when NEDA announced it was shutting down Tessa “until further notice for a complete investigation.” NEDA’s CEO insisted they hadn’t seen that behavior from Tessa before, calling it a “bug” and insisting the bot would only be down temporarily until the triggers causing the bug were fixed.
In the aftermath, several doctors and psychologists chimed in, terming the rush to automate human roles dangerous and risky. After all, much of what makes these hotlines effective is the volunteers speaking from their own experience. An unsupervised bot doesn’t seem to have what it takes to deal with a mental health crisis, but we’re betting that Tessa will be back. As a wise cephalopod once said: Nobody gives a care about the fate of labor as long as they can get their instant gratification.
You can’t spell existential without s-t-e-n-t
This week, we’re including a special “bonus” item that, to be honest, has nothing to do with stents. That’s why our editor is making us call this a “bonus” (and making us use quote marks, too): It doesn’t really have anything to do with stents or health care or those who practice health care. Actually, his exact words were, “You can’t just give the readers someone else’s ****ing list and expect to get paid for it.” Did we mention that he looks like Jack Nicklaus but acts like BoJack Horseman?
Anywaaay, we’re pretty sure that the list in question – “America’s Top 10 Most Googled Existential Questions” – says something about the human condition, just not about stents:
1. Why is the sky blue?
2. What do dreams mean?
3. What is the meaning of life?
4. Why am I so tired?
5. Who am I?
6. What is love?
7. Is a hot dog a sandwich?
8. What came first, the chicken or the egg?
9. What should I do?
10. Do animals have souls?
Sowing the seeds of cancer prevention
Are you looking to add to your quality of life, even though pets are not your speed? Might we suggest something with lower maintenance? Something a little greener?
Indoor plants can purify the air that comes from outside. Researchers at the University of Technology Sydney, in partnership with the plantscaping company Ambius, showed that a “green wall” made up of mixed indoor plants was able to suck up 97% of “the most toxic compounds” from the air in just 8 hours. We’re talking about lung-irritating, headache-inducing, cancer risk–boosting compounds from gasoline fumes, including benzene.
Public health initiatives often strive to reduce cardiovascular and obesity risks, but breathing seems pretty important too. According to the World Health Organization, household air pollution is responsible for about 2.5 million global premature deaths each year. And since 2020 we’ve become accustomed to spending more time inside and at home.
“This new research proves that plants should not just be seen as ‘nice to have,’ but rather a crucial part of every workplace wellness plan,” Ambius General Manager Johan Hodgson said in statement released by the university.
So don’t spend hundreds of dollars on a fancy air filtration system when a wall of plants can do that for next to nothing. Find what works for you and your space and become a plant parent today! Your lungs will thank you.
But officer, I had to swerve to miss the duodenal ampulla
Tiny video capsule endoscopes have been around for many years, but they have one big weakness: The ingestible cameras’ journey through the GI tract is passively driven by gravity and the natural movement of the body, so they often miss potential problem areas.
Not anymore. That flaw has been addressed by medical technology company AnX Robotica, which has taken endoscopy to the next level by adding that wondrous directional control device of the modern electronic age, a joystick.
The new system “uses an external magnet and hand-held video game style joysticks to move the capsule in three dimensions,” which allows physicians to “remotely drive a miniature video capsule to all regions of the stomach to visualize and photograph potential problem areas,” according to Andrew C. Meltzer, MD, of George Washington University and associates, who conducted a pilot study funded by AnX Robotica.
The video capsule provided a 95% rate of visualization in the stomachs of 40 patients who were examined at a medical office building by an emergency medicine physician who had no previous specialty training in endoscopy. “Capsules were driven by the ER physician and then the study reports were reviewed by an attending gastroenterologist who was physically off site,” the investigators said in a written statement.
The capsule operator did receive some additional training, and development of artificial intelligence to self-drive the capsule is in the works, but for now, we’re talking about a device controlled by a human using a joystick. And we all know that 50-year-olds are not especially known for their joystick skills. For that we need real experts. Yup, we need to put those joystick-controlled capsule endoscopes in the hands of teenage gamers. Who wants to go first?
Maybe AI isn’t ready for the big time after all
“How long before some intrepid stockholder says: ‘Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?’ ” Those words appeared on LOTME but a month ago. After all, the AI is supposed to be smarter and more empathetic than a doctor. And did we mention it’s free? Or at least extremely cheap. Cheaper than, say, a group of recently unionized health care workers.
In early May, the paid employees manning the National Eating Disorders Association emergency hotline voted to unionize, as they felt overwhelmed and underpaid. Apparently, paying six people an extra few thousand a year was too much for NEDA’s leadership, as they decided a few weeks later to fire those workers, fully closing down the hotline. Instead of talking to a real person, people “calling in” for support would be met with Tessa, a wellness chatbot that would hopefully guide them through their crisis. Key word, hopefully.
In perhaps the least surprising twist of the year, NEDA was forced to walk back its decision about a week after its initial announcement. It all started with a viral Instagram post from a woman who called in and received the following advice from Tessa: Lose 1-2 pounds a week, count calories and work for a 500- to 1,000-calorie deficit, weigh herself weekly, and restrict her diet. Unfortunately, all of these suggestions were things that led to the development of the woman’s eating disorder.
Naturally, NEDA responded in good grace, accusing the woman of lying. A NEDA vice president even left some nasty comments on the post, but hastily deleted them a day later when NEDA announced it was shutting down Tessa “until further notice for a complete investigation.” NEDA’s CEO insisted they hadn’t seen that behavior from Tessa before, calling it a “bug” and insisting the bot would only be down temporarily until the triggers causing the bug were fixed.
In the aftermath, several doctors and psychologists chimed in, terming the rush to automate human roles dangerous and risky. After all, much of what makes these hotlines effective is the volunteers speaking from their own experience. An unsupervised bot doesn’t seem to have what it takes to deal with a mental health crisis, but we’re betting that Tessa will be back. As a wise cephalopod once said: Nobody gives a care about the fate of labor as long as they can get their instant gratification.
You can’t spell existential without s-t-e-n-t
This week, we’re including a special “bonus” item that, to be honest, has nothing to do with stents. That’s why our editor is making us call this a “bonus” (and making us use quote marks, too): It doesn’t really have anything to do with stents or health care or those who practice health care. Actually, his exact words were, “You can’t just give the readers someone else’s ****ing list and expect to get paid for it.” Did we mention that he looks like Jack Nicklaus but acts like BoJack Horseman?
Anywaaay, we’re pretty sure that the list in question – “America’s Top 10 Most Googled Existential Questions” – says something about the human condition, just not about stents:
1. Why is the sky blue?
2. What do dreams mean?
3. What is the meaning of life?
4. Why am I so tired?
5. Who am I?
6. What is love?
7. Is a hot dog a sandwich?
8. What came first, the chicken or the egg?
9. What should I do?
10. Do animals have souls?
Sowing the seeds of cancer prevention
Are you looking to add to your quality of life, even though pets are not your speed? Might we suggest something with lower maintenance? Something a little greener?
Indoor plants can purify the air that comes from outside. Researchers at the University of Technology Sydney, in partnership with the plantscaping company Ambius, showed that a “green wall” made up of mixed indoor plants was able to suck up 97% of “the most toxic compounds” from the air in just 8 hours. We’re talking about lung-irritating, headache-inducing, cancer risk–boosting compounds from gasoline fumes, including benzene.
Public health initiatives often strive to reduce cardiovascular and obesity risks, but breathing seems pretty important too. According to the World Health Organization, household air pollution is responsible for about 2.5 million global premature deaths each year. And since 2020 we’ve become accustomed to spending more time inside and at home.
“This new research proves that plants should not just be seen as ‘nice to have,’ but rather a crucial part of every workplace wellness plan,” Ambius General Manager Johan Hodgson said in statement released by the university.
So don’t spend hundreds of dollars on a fancy air filtration system when a wall of plants can do that for next to nothing. Find what works for you and your space and become a plant parent today! Your lungs will thank you.
But officer, I had to swerve to miss the duodenal ampulla
Tiny video capsule endoscopes have been around for many years, but they have one big weakness: The ingestible cameras’ journey through the GI tract is passively driven by gravity and the natural movement of the body, so they often miss potential problem areas.
Not anymore. That flaw has been addressed by medical technology company AnX Robotica, which has taken endoscopy to the next level by adding that wondrous directional control device of the modern electronic age, a joystick.
The new system “uses an external magnet and hand-held video game style joysticks to move the capsule in three dimensions,” which allows physicians to “remotely drive a miniature video capsule to all regions of the stomach to visualize and photograph potential problem areas,” according to Andrew C. Meltzer, MD, of George Washington University and associates, who conducted a pilot study funded by AnX Robotica.
The video capsule provided a 95% rate of visualization in the stomachs of 40 patients who were examined at a medical office building by an emergency medicine physician who had no previous specialty training in endoscopy. “Capsules were driven by the ER physician and then the study reports were reviewed by an attending gastroenterologist who was physically off site,” the investigators said in a written statement.
The capsule operator did receive some additional training, and development of artificial intelligence to self-drive the capsule is in the works, but for now, we’re talking about a device controlled by a human using a joystick. And we all know that 50-year-olds are not especially known for their joystick skills. For that we need real experts. Yup, we need to put those joystick-controlled capsule endoscopes in the hands of teenage gamers. Who wants to go first?
Maybe AI isn’t ready for the big time after all
“How long before some intrepid stockholder says: ‘Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?’ ” Those words appeared on LOTME but a month ago. After all, the AI is supposed to be smarter and more empathetic than a doctor. And did we mention it’s free? Or at least extremely cheap. Cheaper than, say, a group of recently unionized health care workers.
In early May, the paid employees manning the National Eating Disorders Association emergency hotline voted to unionize, as they felt overwhelmed and underpaid. Apparently, paying six people an extra few thousand a year was too much for NEDA’s leadership, as they decided a few weeks later to fire those workers, fully closing down the hotline. Instead of talking to a real person, people “calling in” for support would be met with Tessa, a wellness chatbot that would hopefully guide them through their crisis. Key word, hopefully.
In perhaps the least surprising twist of the year, NEDA was forced to walk back its decision about a week after its initial announcement. It all started with a viral Instagram post from a woman who called in and received the following advice from Tessa: Lose 1-2 pounds a week, count calories and work for a 500- to 1,000-calorie deficit, weigh herself weekly, and restrict her diet. Unfortunately, all of these suggestions were things that led to the development of the woman’s eating disorder.
Naturally, NEDA responded in good grace, accusing the woman of lying. A NEDA vice president even left some nasty comments on the post, but hastily deleted them a day later when NEDA announced it was shutting down Tessa “until further notice for a complete investigation.” NEDA’s CEO insisted they hadn’t seen that behavior from Tessa before, calling it a “bug” and insisting the bot would only be down temporarily until the triggers causing the bug were fixed.
In the aftermath, several doctors and psychologists chimed in, terming the rush to automate human roles dangerous and risky. After all, much of what makes these hotlines effective is the volunteers speaking from their own experience. An unsupervised bot doesn’t seem to have what it takes to deal with a mental health crisis, but we’re betting that Tessa will be back. As a wise cephalopod once said: Nobody gives a care about the fate of labor as long as they can get their instant gratification.
You can’t spell existential without s-t-e-n-t
This week, we’re including a special “bonus” item that, to be honest, has nothing to do with stents. That’s why our editor is making us call this a “bonus” (and making us use quote marks, too): It doesn’t really have anything to do with stents or health care or those who practice health care. Actually, his exact words were, “You can’t just give the readers someone else’s ****ing list and expect to get paid for it.” Did we mention that he looks like Jack Nicklaus but acts like BoJack Horseman?
Anywaaay, we’re pretty sure that the list in question – “America’s Top 10 Most Googled Existential Questions” – says something about the human condition, just not about stents:
1. Why is the sky blue?
2. What do dreams mean?
3. What is the meaning of life?
4. Why am I so tired?
5. Who am I?
6. What is love?
7. Is a hot dog a sandwich?
8. What came first, the chicken or the egg?
9. What should I do?
10. Do animals have souls?
Molecular mechanisms may predict major depressive disorder
“Given the multifaceted nature of MDD, the multiple small but dynamic genetic alterations in biomolecular pathways, which are modulated by epigenetic modifications, could contribute to a better understanding of the underlying aetiology and pathophysiology of this disorder,” wrote Cyrus Su Hui Ho, MD, of National University Health System, Singapore, and colleagues. However, studies of biomarkers in psychiatry are limited, and the predictive potential of microribonucleic acids (miRNAs) has not been examined, they said.
In a study published in Comprehensive Psychiatry, the researchers identified 60 adults with depression and 60 healthy controls. Depression severity was assessed with the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale. Other demographic and clinical characteristics were similar between the patients and controls; 10 patients were unmedicated.
The researchers used QUIAGEN Ingenuity Pathway Analysis to identify the specific depression-related biological pathways affected by various miRNAs.
A total of six miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, miR-190a-5p, miR-33a-3p, miR-3690, and miR-6895-3p) were down-regulated in unmedicated depressed patients, compared with healthy controls.
In a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, a combination panel with three miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) in whole blood yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.67. This combination correctly classified 66.7% of MDD patients and 63.3% of healthy controls.
The ability of individual miRNAs to differentiate between MDD patients and controls in the current study was limited, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “However, when three miRNAs (miR-542b-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) were combined as a panel, the AUC was enhanced to an almost acceptable degree (AUC of 0.67, approaching 0.7) and might have value in complementing clinical diagnoses,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and the use of medications by most MDD patients, which resulted in an especially small number of unmedicated patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use of study population from a single center, and the inability to explain the link between blood and brain miRNA expression, they said.
However, the study is the first clinical trial in Singapore to examine the role of miRNA in depression and to identify miRNAs as potential biomarkers for MDD, they said.
Additional studies are needed to explore miRNA biomarkers for diagnosis, disease prognosis, and treatment response in MDD, they concluded.
The study was supported by the National University Health System Seed Fund. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“Given the multifaceted nature of MDD, the multiple small but dynamic genetic alterations in biomolecular pathways, which are modulated by epigenetic modifications, could contribute to a better understanding of the underlying aetiology and pathophysiology of this disorder,” wrote Cyrus Su Hui Ho, MD, of National University Health System, Singapore, and colleagues. However, studies of biomarkers in psychiatry are limited, and the predictive potential of microribonucleic acids (miRNAs) has not been examined, they said.
In a study published in Comprehensive Psychiatry, the researchers identified 60 adults with depression and 60 healthy controls. Depression severity was assessed with the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale. Other demographic and clinical characteristics were similar between the patients and controls; 10 patients were unmedicated.
The researchers used QUIAGEN Ingenuity Pathway Analysis to identify the specific depression-related biological pathways affected by various miRNAs.
A total of six miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, miR-190a-5p, miR-33a-3p, miR-3690, and miR-6895-3p) were down-regulated in unmedicated depressed patients, compared with healthy controls.
In a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, a combination panel with three miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) in whole blood yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.67. This combination correctly classified 66.7% of MDD patients and 63.3% of healthy controls.
The ability of individual miRNAs to differentiate between MDD patients and controls in the current study was limited, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “However, when three miRNAs (miR-542b-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) were combined as a panel, the AUC was enhanced to an almost acceptable degree (AUC of 0.67, approaching 0.7) and might have value in complementing clinical diagnoses,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and the use of medications by most MDD patients, which resulted in an especially small number of unmedicated patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use of study population from a single center, and the inability to explain the link between blood and brain miRNA expression, they said.
However, the study is the first clinical trial in Singapore to examine the role of miRNA in depression and to identify miRNAs as potential biomarkers for MDD, they said.
Additional studies are needed to explore miRNA biomarkers for diagnosis, disease prognosis, and treatment response in MDD, they concluded.
The study was supported by the National University Health System Seed Fund. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“Given the multifaceted nature of MDD, the multiple small but dynamic genetic alterations in biomolecular pathways, which are modulated by epigenetic modifications, could contribute to a better understanding of the underlying aetiology and pathophysiology of this disorder,” wrote Cyrus Su Hui Ho, MD, of National University Health System, Singapore, and colleagues. However, studies of biomarkers in psychiatry are limited, and the predictive potential of microribonucleic acids (miRNAs) has not been examined, they said.
In a study published in Comprehensive Psychiatry, the researchers identified 60 adults with depression and 60 healthy controls. Depression severity was assessed with the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale. Other demographic and clinical characteristics were similar between the patients and controls; 10 patients were unmedicated.
The researchers used QUIAGEN Ingenuity Pathway Analysis to identify the specific depression-related biological pathways affected by various miRNAs.
A total of six miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, miR-190a-5p, miR-33a-3p, miR-3690, and miR-6895-3p) were down-regulated in unmedicated depressed patients, compared with healthy controls.
In a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, a combination panel with three miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) in whole blood yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.67. This combination correctly classified 66.7% of MDD patients and 63.3% of healthy controls.
The ability of individual miRNAs to differentiate between MDD patients and controls in the current study was limited, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “However, when three miRNAs (miR-542b-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) were combined as a panel, the AUC was enhanced to an almost acceptable degree (AUC of 0.67, approaching 0.7) and might have value in complementing clinical diagnoses,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and the use of medications by most MDD patients, which resulted in an especially small number of unmedicated patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use of study population from a single center, and the inability to explain the link between blood and brain miRNA expression, they said.
However, the study is the first clinical trial in Singapore to examine the role of miRNA in depression and to identify miRNAs as potential biomarkers for MDD, they said.
Additional studies are needed to explore miRNA biomarkers for diagnosis, disease prognosis, and treatment response in MDD, they concluded.
The study was supported by the National University Health System Seed Fund. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM COMPREHENSIVE PSYCHIATRY
How has cannabis legalization affected pregnant mothers?
A population-based study shows that the rate of cannabis-related acute care use during pregnancy increased from 11 per 100,000 pregnancies before legalization to 20 per 100,000 pregnancies afterward: an increase of 82%. Absolute increases were small, however.
“Our findings are consistent with studies highlighting that cannabis use during pregnancy has been increasing in North America, and this study suggests that cannabis legalization might contribute to and accelerate such trends,” study author Daniel Myran, MD, MPH, a public health and preventive medicine physician at the University of Ottawa in Ontario, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Risks for newborns
In a 2019 study, 7% of U.S. women reported using cannabis during pregnancy during 2016-2017, which was double the rate of 3.4% for 2002-2003.
Dr. Myran and colleagues hypothesized that legalizing nonmedical cannabis has affected the drug’s use during pregnancy in Ontario. “We also hypothesized that hospital care for cannabis use would be associated with adverse neonatal outcomes, even after adjusting for other important risk factors that may differ between people with and without cannabis use,” he said.
The researchers’ repeated cross-sectional analysis evaluated changes in the number of pregnant people who received acute care from January 2015 to July 2021 among all patients who were eligible for Ontario’s public health coverage. The final study cohort included 691,242 pregnant patients, of whom 533 had at least one pregnancy with cannabis-related acute care visits. These mothers had a mean age of 24 years vs. 30 for their counterparts with no such visits.
Using segmented regression, the researchers compared changes in the quarterly rate of pregnant people with acute care related to cannabis use (the primary outcome) with those of acute care for mental health conditions or for noncannabis substance use (the control conditions).
“Severe morning sickness was a major risk factor for care in the emergency department or hospital for cannabis use,” said Dr. Myran. “Prior work has found that people who use cannabis during pregnancy often state that it was used to manage challenging symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness.”
Most acute care events (72.2%) were emergency department visits. The most common reasons for acute care were harmful cannabis use (57.6%), followed by cannabis dependence or withdrawal (21.5%), and acute cannabis intoxication (12.8%).
Compared with pregnancies without acute care, those with acute care related to cannabis had higher rates of adverse neonatal outcomes such as birth before 37 weeks’ gestational age (16.9% vs. 7.2%), birth weight at or below the bottom fifth percentile after adjustment for gestational age (12.1% vs. 4.4%), and neonatal intensive care unit admission in the first 28 days of life (31.5% vs. 13%).
An adjusted analysis found that patients younger than 35 years and those living in rural settings or the lowest-income neighborhoods had higher odds of acute cannabis-related care during pregnancy. Patients who received acute care for any substance use or schizophrenia before pregnancy or who accessed outpatient mental health services before pregnancy had higher risk for cannabis-related acute care during pregnancy. Mothers receiving acute care for cannabis also had higher risk for acute care for hyperemesis gravidarum during pregnancy (30.9%).
The rate of acute care for other types of substance use such as alcohol and opioids did not change after cannabis legalization, and acute care for mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression during pregnancy declined by 14%, Dr. Myran noted.
“Physicians who care for pregnant people should consider increasing screening for cannabis use during pregnancy,” said Dr. Myran. “In addition, repeated nonstigmatizing screening and counseling may be indicated for higher-risk groups identified in the study, including pregnancies with severe morning sickness.”
The U.S. perspective
Commenting on the study, M. Camille Hoffman, MD, MSc, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Colorado in Aurora, said that the findings likely indicate that legalization has made cannabis users less reluctant to come forward for urgent care. “They cannot really claim that this is equivalent to more use, just that more people are willing to present,” she said. Dr. Hoffman was not involved in the study.
The Canadian results do not align perfectly with what is seen in the United States. “It does suggest that there may be more cannabinoid hyperemesis being coded as hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a pregnancy-specific condition vs. a cannabis-dependence-related one,” said Dr. Hoffman.
Literature in the United States often includes tobacco use as a covariate, she added. “This study does not appear to do that,” she said. “Rather, it uses any substance use. Because of this, it is difficult to really know the contribution of cannabis to the adverse pregnancy outcomes vs. the combination of tobacco and cannabis.”
Finally, she pointed out, the proportion of those presenting for acute care for substance use in the 2 years before conception was 22% for acute care visits for cannabis vs 1% for no acute care visits. “This suggests to me that this was a highly vulnerable group before the legalization of cannabis as well. The overall absolute difference is nine in total per 100,000 – hardly enough to draw any real conclusions. Again, maybe those nine were simply more willing to come forth with concerns with cannabis being legal.”
There is no known safe level of cannabis consumption, and its use by pregnant women has been linked to later neurodevelopmental issues in their offspring. A 2022 U.S. study suggested that cannabis exposure in the womb may leave children later in life at risk for autism, psychiatric disorders, and problematic substance abuse, particularly as they enter peak periods of vulnerability in late adolescence.
As to the impact of legalization in certain U.S. states, a 2022 study found that women perceived legalization to mean greater access to cannabis, increased acceptance of use, and greater trust in cannabis retailers. In line with Dr. Hoffman’s view, this study suggested that legalization made pregnant women more willing to discuss cannabis use during pregnancy honestly with their care providers.
In the United States, prenatal cannabis use is still included in definitions of child abuse or neglect and can lead to termination of parental rights, even in states with full legalization.
“These findings highlight the need for ongoing monitoring of markers of cannabis use during pregnancy after legalization,” said Dr. Myran. He also called for effective policies in regions with legal cannabis, such as increased warning labels on cannabis products.
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Ottawa site of ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Myran reports a speaker fee from McMaster University. Dr. Hoffman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A population-based study shows that the rate of cannabis-related acute care use during pregnancy increased from 11 per 100,000 pregnancies before legalization to 20 per 100,000 pregnancies afterward: an increase of 82%. Absolute increases were small, however.
“Our findings are consistent with studies highlighting that cannabis use during pregnancy has been increasing in North America, and this study suggests that cannabis legalization might contribute to and accelerate such trends,” study author Daniel Myran, MD, MPH, a public health and preventive medicine physician at the University of Ottawa in Ontario, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Risks for newborns
In a 2019 study, 7% of U.S. women reported using cannabis during pregnancy during 2016-2017, which was double the rate of 3.4% for 2002-2003.
Dr. Myran and colleagues hypothesized that legalizing nonmedical cannabis has affected the drug’s use during pregnancy in Ontario. “We also hypothesized that hospital care for cannabis use would be associated with adverse neonatal outcomes, even after adjusting for other important risk factors that may differ between people with and without cannabis use,” he said.
The researchers’ repeated cross-sectional analysis evaluated changes in the number of pregnant people who received acute care from January 2015 to July 2021 among all patients who were eligible for Ontario’s public health coverage. The final study cohort included 691,242 pregnant patients, of whom 533 had at least one pregnancy with cannabis-related acute care visits. These mothers had a mean age of 24 years vs. 30 for their counterparts with no such visits.
Using segmented regression, the researchers compared changes in the quarterly rate of pregnant people with acute care related to cannabis use (the primary outcome) with those of acute care for mental health conditions or for noncannabis substance use (the control conditions).
“Severe morning sickness was a major risk factor for care in the emergency department or hospital for cannabis use,” said Dr. Myran. “Prior work has found that people who use cannabis during pregnancy often state that it was used to manage challenging symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness.”
Most acute care events (72.2%) were emergency department visits. The most common reasons for acute care were harmful cannabis use (57.6%), followed by cannabis dependence or withdrawal (21.5%), and acute cannabis intoxication (12.8%).
Compared with pregnancies without acute care, those with acute care related to cannabis had higher rates of adverse neonatal outcomes such as birth before 37 weeks’ gestational age (16.9% vs. 7.2%), birth weight at or below the bottom fifth percentile after adjustment for gestational age (12.1% vs. 4.4%), and neonatal intensive care unit admission in the first 28 days of life (31.5% vs. 13%).
An adjusted analysis found that patients younger than 35 years and those living in rural settings or the lowest-income neighborhoods had higher odds of acute cannabis-related care during pregnancy. Patients who received acute care for any substance use or schizophrenia before pregnancy or who accessed outpatient mental health services before pregnancy had higher risk for cannabis-related acute care during pregnancy. Mothers receiving acute care for cannabis also had higher risk for acute care for hyperemesis gravidarum during pregnancy (30.9%).
The rate of acute care for other types of substance use such as alcohol and opioids did not change after cannabis legalization, and acute care for mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression during pregnancy declined by 14%, Dr. Myran noted.
“Physicians who care for pregnant people should consider increasing screening for cannabis use during pregnancy,” said Dr. Myran. “In addition, repeated nonstigmatizing screening and counseling may be indicated for higher-risk groups identified in the study, including pregnancies with severe morning sickness.”
The U.S. perspective
Commenting on the study, M. Camille Hoffman, MD, MSc, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Colorado in Aurora, said that the findings likely indicate that legalization has made cannabis users less reluctant to come forward for urgent care. “They cannot really claim that this is equivalent to more use, just that more people are willing to present,” she said. Dr. Hoffman was not involved in the study.
The Canadian results do not align perfectly with what is seen in the United States. “It does suggest that there may be more cannabinoid hyperemesis being coded as hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a pregnancy-specific condition vs. a cannabis-dependence-related one,” said Dr. Hoffman.
Literature in the United States often includes tobacco use as a covariate, she added. “This study does not appear to do that,” she said. “Rather, it uses any substance use. Because of this, it is difficult to really know the contribution of cannabis to the adverse pregnancy outcomes vs. the combination of tobacco and cannabis.”
Finally, she pointed out, the proportion of those presenting for acute care for substance use in the 2 years before conception was 22% for acute care visits for cannabis vs 1% for no acute care visits. “This suggests to me that this was a highly vulnerable group before the legalization of cannabis as well. The overall absolute difference is nine in total per 100,000 – hardly enough to draw any real conclusions. Again, maybe those nine were simply more willing to come forth with concerns with cannabis being legal.”
There is no known safe level of cannabis consumption, and its use by pregnant women has been linked to later neurodevelopmental issues in their offspring. A 2022 U.S. study suggested that cannabis exposure in the womb may leave children later in life at risk for autism, psychiatric disorders, and problematic substance abuse, particularly as they enter peak periods of vulnerability in late adolescence.
As to the impact of legalization in certain U.S. states, a 2022 study found that women perceived legalization to mean greater access to cannabis, increased acceptance of use, and greater trust in cannabis retailers. In line with Dr. Hoffman’s view, this study suggested that legalization made pregnant women more willing to discuss cannabis use during pregnancy honestly with their care providers.
In the United States, prenatal cannabis use is still included in definitions of child abuse or neglect and can lead to termination of parental rights, even in states with full legalization.
“These findings highlight the need for ongoing monitoring of markers of cannabis use during pregnancy after legalization,” said Dr. Myran. He also called for effective policies in regions with legal cannabis, such as increased warning labels on cannabis products.
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Ottawa site of ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Myran reports a speaker fee from McMaster University. Dr. Hoffman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A population-based study shows that the rate of cannabis-related acute care use during pregnancy increased from 11 per 100,000 pregnancies before legalization to 20 per 100,000 pregnancies afterward: an increase of 82%. Absolute increases were small, however.
“Our findings are consistent with studies highlighting that cannabis use during pregnancy has been increasing in North America, and this study suggests that cannabis legalization might contribute to and accelerate such trends,” study author Daniel Myran, MD, MPH, a public health and preventive medicine physician at the University of Ottawa in Ontario, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Risks for newborns
In a 2019 study, 7% of U.S. women reported using cannabis during pregnancy during 2016-2017, which was double the rate of 3.4% for 2002-2003.
Dr. Myran and colleagues hypothesized that legalizing nonmedical cannabis has affected the drug’s use during pregnancy in Ontario. “We also hypothesized that hospital care for cannabis use would be associated with adverse neonatal outcomes, even after adjusting for other important risk factors that may differ between people with and without cannabis use,” he said.
The researchers’ repeated cross-sectional analysis evaluated changes in the number of pregnant people who received acute care from January 2015 to July 2021 among all patients who were eligible for Ontario’s public health coverage. The final study cohort included 691,242 pregnant patients, of whom 533 had at least one pregnancy with cannabis-related acute care visits. These mothers had a mean age of 24 years vs. 30 for their counterparts with no such visits.
Using segmented regression, the researchers compared changes in the quarterly rate of pregnant people with acute care related to cannabis use (the primary outcome) with those of acute care for mental health conditions or for noncannabis substance use (the control conditions).
“Severe morning sickness was a major risk factor for care in the emergency department or hospital for cannabis use,” said Dr. Myran. “Prior work has found that people who use cannabis during pregnancy often state that it was used to manage challenging symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness.”
Most acute care events (72.2%) were emergency department visits. The most common reasons for acute care were harmful cannabis use (57.6%), followed by cannabis dependence or withdrawal (21.5%), and acute cannabis intoxication (12.8%).
Compared with pregnancies without acute care, those with acute care related to cannabis had higher rates of adverse neonatal outcomes such as birth before 37 weeks’ gestational age (16.9% vs. 7.2%), birth weight at or below the bottom fifth percentile after adjustment for gestational age (12.1% vs. 4.4%), and neonatal intensive care unit admission in the first 28 days of life (31.5% vs. 13%).
An adjusted analysis found that patients younger than 35 years and those living in rural settings or the lowest-income neighborhoods had higher odds of acute cannabis-related care during pregnancy. Patients who received acute care for any substance use or schizophrenia before pregnancy or who accessed outpatient mental health services before pregnancy had higher risk for cannabis-related acute care during pregnancy. Mothers receiving acute care for cannabis also had higher risk for acute care for hyperemesis gravidarum during pregnancy (30.9%).
The rate of acute care for other types of substance use such as alcohol and opioids did not change after cannabis legalization, and acute care for mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression during pregnancy declined by 14%, Dr. Myran noted.
“Physicians who care for pregnant people should consider increasing screening for cannabis use during pregnancy,” said Dr. Myran. “In addition, repeated nonstigmatizing screening and counseling may be indicated for higher-risk groups identified in the study, including pregnancies with severe morning sickness.”
The U.S. perspective
Commenting on the study, M. Camille Hoffman, MD, MSc, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Colorado in Aurora, said that the findings likely indicate that legalization has made cannabis users less reluctant to come forward for urgent care. “They cannot really claim that this is equivalent to more use, just that more people are willing to present,” she said. Dr. Hoffman was not involved in the study.
The Canadian results do not align perfectly with what is seen in the United States. “It does suggest that there may be more cannabinoid hyperemesis being coded as hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a pregnancy-specific condition vs. a cannabis-dependence-related one,” said Dr. Hoffman.
Literature in the United States often includes tobacco use as a covariate, she added. “This study does not appear to do that,” she said. “Rather, it uses any substance use. Because of this, it is difficult to really know the contribution of cannabis to the adverse pregnancy outcomes vs. the combination of tobacco and cannabis.”
Finally, she pointed out, the proportion of those presenting for acute care for substance use in the 2 years before conception was 22% for acute care visits for cannabis vs 1% for no acute care visits. “This suggests to me that this was a highly vulnerable group before the legalization of cannabis as well. The overall absolute difference is nine in total per 100,000 – hardly enough to draw any real conclusions. Again, maybe those nine were simply more willing to come forth with concerns with cannabis being legal.”
There is no known safe level of cannabis consumption, and its use by pregnant women has been linked to later neurodevelopmental issues in their offspring. A 2022 U.S. study suggested that cannabis exposure in the womb may leave children later in life at risk for autism, psychiatric disorders, and problematic substance abuse, particularly as they enter peak periods of vulnerability in late adolescence.
As to the impact of legalization in certain U.S. states, a 2022 study found that women perceived legalization to mean greater access to cannabis, increased acceptance of use, and greater trust in cannabis retailers. In line with Dr. Hoffman’s view, this study suggested that legalization made pregnant women more willing to discuss cannabis use during pregnancy honestly with their care providers.
In the United States, prenatal cannabis use is still included in definitions of child abuse or neglect and can lead to termination of parental rights, even in states with full legalization.
“These findings highlight the need for ongoing monitoring of markers of cannabis use during pregnancy after legalization,” said Dr. Myran. He also called for effective policies in regions with legal cannabis, such as increased warning labels on cannabis products.
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Ottawa site of ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Myran reports a speaker fee from McMaster University. Dr. Hoffman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CMAJ












