User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
Even light physical activity linked to lower dementia risk
Older adults who participate in even light physical activity (LPA) may have a lower risk of developing dementia, new research suggests.
In a retrospective analysis of more than 62,000 individuals aged 65 or older without preexisting dementia, 6% developed dementia.
Compared with inactive individuals, “insufficiently active,” “active,” and “highly active” individuals all had a 10%, 20%, and 28% lower risk for dementia, respectively. And this association was consistent regardless of age, sex, other comorbidities, or after the researchers censored for stroke.
Even the lowest amount of LPA was associated with reduced dementia risk, investigators noted.
“In older adults, an increased physical activity level, including a low amount of LPA, was associated with a reduced risk of dementia,” Minjae Yoon, MD, division of cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues wrote.
“Promotion of LPA might reduce the risk of dementia in older adults,” they added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Reverse causation?
Physical activity has been shown previously to be associated with reduced dementia risk. Current World Health Organization guidelines recommend that adults with normal cognition should engage in PA to reduce their risk for cognitive decline.
However, some studies have not yielded this result, “suggesting that previous findings showing a lower risk of dementia in physically active people could be attributed to reverse causation,” the investigators noted. Additionally, previous research regarding exercise intensity has been “inconsistent” concerning the role of LPA in reducing dementia risk.
Many older adults with frailty and comorbidity cannot perform intense or even moderate PA, therefore “these adults would have to gain the benefits of physical activity from LPA,” the researchers noted.
To clarify the potential association between PA and new-onset dementia, they focused specifically on the “dose-response association” between PA and dementia – especially LPA.
Between 2009 and 2012, the investigators enrolled 62,286 older individuals (60.4% women; mean age, 73.2 years) with available health checkup data from the National Health Insurance Service–Senior Database of Korea. All had no history of dementia.
Leisure-time PA was assessed with self-report questionnaires that used a 7-day recall method and included three questions regarding usual frequency (in days per week):
- Vigorous PA (VPA) for at least 20 minutes
- Moderate-intensity PA (MPA) for at least 30 minutes
- LPA for at least 30 minutes
VPA was defined as “intense exercise that caused severe shortness of breath, MPA was defined as activity causing mild shortness of breath, and LPA was defined as “walking at a slow or leisurely pace.”
PA-related energy expenditure was also calculated in metabolic equivalent (MET) minutes per week by “summing the product of frequency, intensity, and duration,” the investigators noted.
Participants were stratified on the basis of their weekly total PA levels into the following groups:
- Inactive (no LPA beyond basic movements)
- Insufficiently active (less than the recommended target range of 1-499 MET-min/wk)
- Active (meeting the recommended target range of 500-999 MET-min/wk)
- Highly active (exceeding the recommended target range of at least 1,000 MET-min/wk)
Of all participants, 35% were categorized as inactive, 25% were insufficiently active, 24.4% were active, and 15.2% were highly active.
Controversy remains
During the total median follow-up of 42 months, 6% of participants had all-cause dementia. After the researchers excluded the first 2 years, incidence of dementia was 21.6 per 1000 person-years during follow-up.
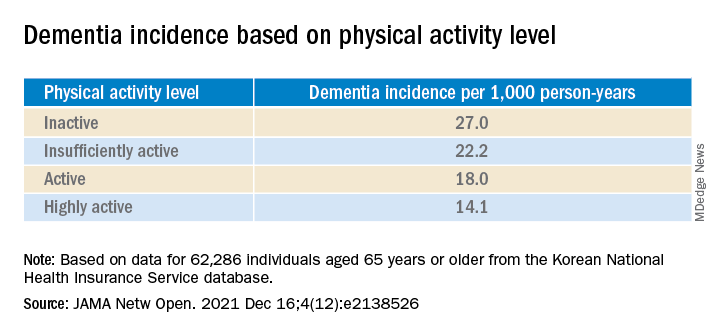
“The cumulative incidence of dementia was associated with a progressively decreasing trend with increasing physical activity” (P = .001 for trend), the investigators reported.
When using a competing-risk multivariable regression model, they found that higher levels of PA were associated with lower risk for dementia, compared with the inactive group.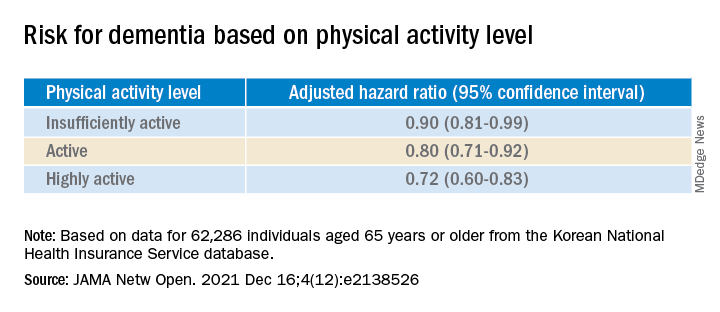
Similar findings were obtained after censoring for stroke, and were consistent for all follow-up periods. In subgroup analysis, the association between PA level and dementia risk remained consistent, regardless of age, sex, and comorbidities.
Even a low amount of LPA (1-299 MET-min/wk) was linked to reduced risk for dementia versus total sedentary behavior (adjusted HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.74-0.99).
The investigators noted that some “controversy” remains regarding the possibility of reverse causation and, because their study was observational in nature, “it cannot be used to establish causal relationship.”
Nevertheless, the study had important strengths, including the large number of older adults with available data, the assessment of dose-response association between PA and dementia, and the sensitivity analyses they performed, the researchers added.
Piece of important evidence
Commenting on the findings, Takashi Tarumi, PhD, senior research investigator, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Ibaraki, Japan, said previous studies have suggested “an inverse association between physical activity and dementia risk, such that older adults performing a higher dose of exercise may have a greater benefit for reducing the dementia risk.”
Dr. Tarumi, an associate editor at the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, added the current study “significantly extends our knowledge by showing that dementia risk can also be reduced by light physical activities when they are performed for longer hours.”
This provides “another piece of important evidence” to support clinicians recommending regular physical activity for the prevention of dementia in later life, said Dr. Tarumi, who was not involved with the research.
Also commenting, Martin Underwood, MD, Warwick Medical School, Coventry, England, described the association between reduced physical inactivity and dementia as well established – and noted the current study “appears to confirm earlier observational data showing this relationship.”
The current results have “still not been able to fully exclude the possibility of reverse causation,” said Dr. Underwood, who was also not associated with the study.
However, the finding that more physically active individuals are less likely to develop dementia “only becomes of real interest if we can show that increased physical activity prevents the onset, or slows the progression, of dementia,” he noted.
“To my knowledge this has not yet been established” in randomized clinical trials, Dr. Underwood added.
The study was supported by grants from the Patient-Centered Clinical Research Coordinating Center, funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea; and by a research grant from Yonsei University. One coauthor reported serving as a speaker for Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer, Medtronic, and Daiichi-Sankyo, and receiving research funds from Medtronic and Abbott. No other author disclosures were reported. Dr. Tarumi and Dr. Underwood have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Older adults who participate in even light physical activity (LPA) may have a lower risk of developing dementia, new research suggests.
In a retrospective analysis of more than 62,000 individuals aged 65 or older without preexisting dementia, 6% developed dementia.
Compared with inactive individuals, “insufficiently active,” “active,” and “highly active” individuals all had a 10%, 20%, and 28% lower risk for dementia, respectively. And this association was consistent regardless of age, sex, other comorbidities, or after the researchers censored for stroke.
Even the lowest amount of LPA was associated with reduced dementia risk, investigators noted.
“In older adults, an increased physical activity level, including a low amount of LPA, was associated with a reduced risk of dementia,” Minjae Yoon, MD, division of cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues wrote.
“Promotion of LPA might reduce the risk of dementia in older adults,” they added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Reverse causation?
Physical activity has been shown previously to be associated with reduced dementia risk. Current World Health Organization guidelines recommend that adults with normal cognition should engage in PA to reduce their risk for cognitive decline.
However, some studies have not yielded this result, “suggesting that previous findings showing a lower risk of dementia in physically active people could be attributed to reverse causation,” the investigators noted. Additionally, previous research regarding exercise intensity has been “inconsistent” concerning the role of LPA in reducing dementia risk.
Many older adults with frailty and comorbidity cannot perform intense or even moderate PA, therefore “these adults would have to gain the benefits of physical activity from LPA,” the researchers noted.
To clarify the potential association between PA and new-onset dementia, they focused specifically on the “dose-response association” between PA and dementia – especially LPA.
Between 2009 and 2012, the investigators enrolled 62,286 older individuals (60.4% women; mean age, 73.2 years) with available health checkup data from the National Health Insurance Service–Senior Database of Korea. All had no history of dementia.
Leisure-time PA was assessed with self-report questionnaires that used a 7-day recall method and included three questions regarding usual frequency (in days per week):
- Vigorous PA (VPA) for at least 20 minutes
- Moderate-intensity PA (MPA) for at least 30 minutes
- LPA for at least 30 minutes
VPA was defined as “intense exercise that caused severe shortness of breath, MPA was defined as activity causing mild shortness of breath, and LPA was defined as “walking at a slow or leisurely pace.”
PA-related energy expenditure was also calculated in metabolic equivalent (MET) minutes per week by “summing the product of frequency, intensity, and duration,” the investigators noted.
Participants were stratified on the basis of their weekly total PA levels into the following groups:
- Inactive (no LPA beyond basic movements)
- Insufficiently active (less than the recommended target range of 1-499 MET-min/wk)
- Active (meeting the recommended target range of 500-999 MET-min/wk)
- Highly active (exceeding the recommended target range of at least 1,000 MET-min/wk)
Of all participants, 35% were categorized as inactive, 25% were insufficiently active, 24.4% were active, and 15.2% were highly active.
Controversy remains
During the total median follow-up of 42 months, 6% of participants had all-cause dementia. After the researchers excluded the first 2 years, incidence of dementia was 21.6 per 1000 person-years during follow-up.

“The cumulative incidence of dementia was associated with a progressively decreasing trend with increasing physical activity” (P = .001 for trend), the investigators reported.
When using a competing-risk multivariable regression model, they found that higher levels of PA were associated with lower risk for dementia, compared with the inactive group.
Similar findings were obtained after censoring for stroke, and were consistent for all follow-up periods. In subgroup analysis, the association between PA level and dementia risk remained consistent, regardless of age, sex, and comorbidities.
Even a low amount of LPA (1-299 MET-min/wk) was linked to reduced risk for dementia versus total sedentary behavior (adjusted HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.74-0.99).
The investigators noted that some “controversy” remains regarding the possibility of reverse causation and, because their study was observational in nature, “it cannot be used to establish causal relationship.”
Nevertheless, the study had important strengths, including the large number of older adults with available data, the assessment of dose-response association between PA and dementia, and the sensitivity analyses they performed, the researchers added.
Piece of important evidence
Commenting on the findings, Takashi Tarumi, PhD, senior research investigator, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Ibaraki, Japan, said previous studies have suggested “an inverse association between physical activity and dementia risk, such that older adults performing a higher dose of exercise may have a greater benefit for reducing the dementia risk.”
Dr. Tarumi, an associate editor at the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, added the current study “significantly extends our knowledge by showing that dementia risk can also be reduced by light physical activities when they are performed for longer hours.”
This provides “another piece of important evidence” to support clinicians recommending regular physical activity for the prevention of dementia in later life, said Dr. Tarumi, who was not involved with the research.
Also commenting, Martin Underwood, MD, Warwick Medical School, Coventry, England, described the association between reduced physical inactivity and dementia as well established – and noted the current study “appears to confirm earlier observational data showing this relationship.”
The current results have “still not been able to fully exclude the possibility of reverse causation,” said Dr. Underwood, who was also not associated with the study.
However, the finding that more physically active individuals are less likely to develop dementia “only becomes of real interest if we can show that increased physical activity prevents the onset, or slows the progression, of dementia,” he noted.
“To my knowledge this has not yet been established” in randomized clinical trials, Dr. Underwood added.
The study was supported by grants from the Patient-Centered Clinical Research Coordinating Center, funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea; and by a research grant from Yonsei University. One coauthor reported serving as a speaker for Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer, Medtronic, and Daiichi-Sankyo, and receiving research funds from Medtronic and Abbott. No other author disclosures were reported. Dr. Tarumi and Dr. Underwood have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Older adults who participate in even light physical activity (LPA) may have a lower risk of developing dementia, new research suggests.
In a retrospective analysis of more than 62,000 individuals aged 65 or older without preexisting dementia, 6% developed dementia.
Compared with inactive individuals, “insufficiently active,” “active,” and “highly active” individuals all had a 10%, 20%, and 28% lower risk for dementia, respectively. And this association was consistent regardless of age, sex, other comorbidities, or after the researchers censored for stroke.
Even the lowest amount of LPA was associated with reduced dementia risk, investigators noted.
“In older adults, an increased physical activity level, including a low amount of LPA, was associated with a reduced risk of dementia,” Minjae Yoon, MD, division of cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues wrote.
“Promotion of LPA might reduce the risk of dementia in older adults,” they added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Reverse causation?
Physical activity has been shown previously to be associated with reduced dementia risk. Current World Health Organization guidelines recommend that adults with normal cognition should engage in PA to reduce their risk for cognitive decline.
However, some studies have not yielded this result, “suggesting that previous findings showing a lower risk of dementia in physically active people could be attributed to reverse causation,” the investigators noted. Additionally, previous research regarding exercise intensity has been “inconsistent” concerning the role of LPA in reducing dementia risk.
Many older adults with frailty and comorbidity cannot perform intense or even moderate PA, therefore “these adults would have to gain the benefits of physical activity from LPA,” the researchers noted.
To clarify the potential association between PA and new-onset dementia, they focused specifically on the “dose-response association” between PA and dementia – especially LPA.
Between 2009 and 2012, the investigators enrolled 62,286 older individuals (60.4% women; mean age, 73.2 years) with available health checkup data from the National Health Insurance Service–Senior Database of Korea. All had no history of dementia.
Leisure-time PA was assessed with self-report questionnaires that used a 7-day recall method and included three questions regarding usual frequency (in days per week):
- Vigorous PA (VPA) for at least 20 minutes
- Moderate-intensity PA (MPA) for at least 30 minutes
- LPA for at least 30 minutes
VPA was defined as “intense exercise that caused severe shortness of breath, MPA was defined as activity causing mild shortness of breath, and LPA was defined as “walking at a slow or leisurely pace.”
PA-related energy expenditure was also calculated in metabolic equivalent (MET) minutes per week by “summing the product of frequency, intensity, and duration,” the investigators noted.
Participants were stratified on the basis of their weekly total PA levels into the following groups:
- Inactive (no LPA beyond basic movements)
- Insufficiently active (less than the recommended target range of 1-499 MET-min/wk)
- Active (meeting the recommended target range of 500-999 MET-min/wk)
- Highly active (exceeding the recommended target range of at least 1,000 MET-min/wk)
Of all participants, 35% were categorized as inactive, 25% were insufficiently active, 24.4% were active, and 15.2% were highly active.
Controversy remains
During the total median follow-up of 42 months, 6% of participants had all-cause dementia. After the researchers excluded the first 2 years, incidence of dementia was 21.6 per 1000 person-years during follow-up.

“The cumulative incidence of dementia was associated with a progressively decreasing trend with increasing physical activity” (P = .001 for trend), the investigators reported.
When using a competing-risk multivariable regression model, they found that higher levels of PA were associated with lower risk for dementia, compared with the inactive group.
Similar findings were obtained after censoring for stroke, and were consistent for all follow-up periods. In subgroup analysis, the association between PA level and dementia risk remained consistent, regardless of age, sex, and comorbidities.
Even a low amount of LPA (1-299 MET-min/wk) was linked to reduced risk for dementia versus total sedentary behavior (adjusted HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.74-0.99).
The investigators noted that some “controversy” remains regarding the possibility of reverse causation and, because their study was observational in nature, “it cannot be used to establish causal relationship.”
Nevertheless, the study had important strengths, including the large number of older adults with available data, the assessment of dose-response association between PA and dementia, and the sensitivity analyses they performed, the researchers added.
Piece of important evidence
Commenting on the findings, Takashi Tarumi, PhD, senior research investigator, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Ibaraki, Japan, said previous studies have suggested “an inverse association between physical activity and dementia risk, such that older adults performing a higher dose of exercise may have a greater benefit for reducing the dementia risk.”
Dr. Tarumi, an associate editor at the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, added the current study “significantly extends our knowledge by showing that dementia risk can also be reduced by light physical activities when they are performed for longer hours.”
This provides “another piece of important evidence” to support clinicians recommending regular physical activity for the prevention of dementia in later life, said Dr. Tarumi, who was not involved with the research.
Also commenting, Martin Underwood, MD, Warwick Medical School, Coventry, England, described the association between reduced physical inactivity and dementia as well established – and noted the current study “appears to confirm earlier observational data showing this relationship.”
The current results have “still not been able to fully exclude the possibility of reverse causation,” said Dr. Underwood, who was also not associated with the study.
However, the finding that more physically active individuals are less likely to develop dementia “only becomes of real interest if we can show that increased physical activity prevents the onset, or slows the progression, of dementia,” he noted.
“To my knowledge this has not yet been established” in randomized clinical trials, Dr. Underwood added.
The study was supported by grants from the Patient-Centered Clinical Research Coordinating Center, funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea; and by a research grant from Yonsei University. One coauthor reported serving as a speaker for Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer, Medtronic, and Daiichi-Sankyo, and receiving research funds from Medtronic and Abbott. No other author disclosures were reported. Dr. Tarumi and Dr. Underwood have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fish oil: ‘No net benefit’ for depression prevention?
Fish oil supplementation does not help prevent depression or boost mood, new research suggests.
The VITAL-DEP study included more than 18,000 participants. Among adults aged 50 years or older free of clinically relevant depressive symptoms at baseline, long-term use of marine omega-3 fatty acid (omega-3) supplements did not reduce risk for depression or clinically relevant depressive symptoms — or make a difference in the quality of mood.
“While a small increase in risk of depression was inside the statistical margin of significance, there was no harmful or beneficial effect of omega-3 on the overall course of mood during the roughly 5 to 7 years of follow-up,” lead author Olivia I. Okereke, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, told Medscape Medical News.
“The takeaway from our study is that there is no net benefit of long-term use of daily omega-3 fish oil supplements for preventing depression or boosting mood,” Okereke said.
The findings were published online Dec. 21 in JAMA.
Assessing general population risk
For many years, experts have recommended omega-3 supplements for reduction in depression recurrence in some high-risk patients, Okereke noted.
“However, there are no guidelines related to the use of omega-3 supplements for preventing depression in the general population. Therefore, we undertook this study to provide clarity in the issue,” she said.
The VITAL-DEP study enrolled 18,353 older adults (mean age, 67.5 years; 49% women). Of these, 16,657 were at risk for incident depression, defined as having no previous history of depression; and 1696 were at risk for recurrent depression, defined as having a history of depression but not having undergone treatment for depression within the past 2 years.
Roughly half the participants were randomly assigned to receive marine omega-3 fatty acids (1 g/d of fish oil, including 465 mg of eicosapentaenoic acid [EPA] and 375 mg of docosahexaenoic acid [DHA]) and the other half to matching placebo for an average of 5.3 years.
“Because of the large sample size and long follow-up, we were able to test the effects of daily omega-3 fish oil supplements on universal prevention of depression in the adult population,” Okereke said.
No significant benefit
Results showed risk for depression or clinically relevant depressive symptoms (total of incident and recurrent cases) was not significantly different between the omega-3 group and the placebo group.
The omega-3 group had 651 depression or clinically relevant depressive symptom events (13.9 per 1000 person-years), and the placebo group had 583 depression or clinically relevant depressive symptom events (12.3 per 1000 person-years). The hazard ratio was 1.13 (95% CI, 1.01 - 1.26; P = .03).
There were also no significant between-group differences in longitudinal mood scores. The mean difference in change in 8-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-8) score was 0.03 points (95% CI, −0.01 to 0.07; P = .19).
“Patients, physicians, and other clinicians should understand that there are still many reasons for some people, under the guidance of their health care providers, to take omega-3 fish oil supplements,” Okereke noted.
“These supplements increasingly have been found to have benefits for cardiac disease prevention and treatment of inflammatory conditions, in addition to being used for management of existing depressive disorders in some high-risk patients,” she said.
“However, the results of our study indicate there is no reason for adults in the general population to be taking daily omega-3 fish oil supplements solely for the purpose of preventing depression or for maintaining a positive mood,” she added.
Okereke noted, however, that the VITAL-DEP study used 1 g/day of omega-3 fatty acids and there may be a greater benefit from taking higher doses, such as 4 g/day.
Cautionary notes
Commenting on the study for Medscape Medical News, Kuan-Pin Su, MD, PhD, chief of the Department of General Psychiatry, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, highlighted some of the limitations cited by the investigators.
First, depression or depressive symptoms were defined using self-rating scales, which are “convenient to screen for depressive disorders, but a high score obtained on a self-rating scale does not necessarily indicate the presence of depressive psychopathology,” said Su, who was not involved with the research.
He also noted that use of 465 mg of EPA and 375 mg of DHA in VITAL-DEP “might be too low” to have an impact.
Finally, Su said it is “very important to also address the potential for type I error, which makes the secondary and subgroup analyses less reliable.”
VITAL-DEP was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health. Pronova BioPharma donated the fish oil and matching placebo. Okereke reported receiving royalties from Springer Publishing. Su is a founding committee member of the International Society for Nutritional Psychiatry Research, the board director of the International Society for the Study of Fatty Acids, and an associate editor of the journal Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fish oil supplementation does not help prevent depression or boost mood, new research suggests.
The VITAL-DEP study included more than 18,000 participants. Among adults aged 50 years or older free of clinically relevant depressive symptoms at baseline, long-term use of marine omega-3 fatty acid (omega-3) supplements did not reduce risk for depression or clinically relevant depressive symptoms — or make a difference in the quality of mood.
“While a small increase in risk of depression was inside the statistical margin of significance, there was no harmful or beneficial effect of omega-3 on the overall course of mood during the roughly 5 to 7 years of follow-up,” lead author Olivia I. Okereke, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, told Medscape Medical News.
“The takeaway from our study is that there is no net benefit of long-term use of daily omega-3 fish oil supplements for preventing depression or boosting mood,” Okereke said.
The findings were published online Dec. 21 in JAMA.
Assessing general population risk
For many years, experts have recommended omega-3 supplements for reduction in depression recurrence in some high-risk patients, Okereke noted.
“However, there are no guidelines related to the use of omega-3 supplements for preventing depression in the general population. Therefore, we undertook this study to provide clarity in the issue,” she said.
The VITAL-DEP study enrolled 18,353 older adults (mean age, 67.5 years; 49% women). Of these, 16,657 were at risk for incident depression, defined as having no previous history of depression; and 1696 were at risk for recurrent depression, defined as having a history of depression but not having undergone treatment for depression within the past 2 years.
Roughly half the participants were randomly assigned to receive marine omega-3 fatty acids (1 g/d of fish oil, including 465 mg of eicosapentaenoic acid [EPA] and 375 mg of docosahexaenoic acid [DHA]) and the other half to matching placebo for an average of 5.3 years.
“Because of the large sample size and long follow-up, we were able to test the effects of daily omega-3 fish oil supplements on universal prevention of depression in the adult population,” Okereke said.
No significant benefit
Results showed risk for depression or clinically relevant depressive symptoms (total of incident and recurrent cases) was not significantly different between the omega-3 group and the placebo group.
The omega-3 group had 651 depression or clinically relevant depressive symptom events (13.9 per 1000 person-years), and the placebo group had 583 depression or clinically relevant depressive symptom events (12.3 per 1000 person-years). The hazard ratio was 1.13 (95% CI, 1.01 - 1.26; P = .03).
There were also no significant between-group differences in longitudinal mood scores. The mean difference in change in 8-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-8) score was 0.03 points (95% CI, −0.01 to 0.07; P = .19).
“Patients, physicians, and other clinicians should understand that there are still many reasons for some people, under the guidance of their health care providers, to take omega-3 fish oil supplements,” Okereke noted.
“These supplements increasingly have been found to have benefits for cardiac disease prevention and treatment of inflammatory conditions, in addition to being used for management of existing depressive disorders in some high-risk patients,” she said.
“However, the results of our study indicate there is no reason for adults in the general population to be taking daily omega-3 fish oil supplements solely for the purpose of preventing depression or for maintaining a positive mood,” she added.
Okereke noted, however, that the VITAL-DEP study used 1 g/day of omega-3 fatty acids and there may be a greater benefit from taking higher doses, such as 4 g/day.
Cautionary notes
Commenting on the study for Medscape Medical News, Kuan-Pin Su, MD, PhD, chief of the Department of General Psychiatry, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, highlighted some of the limitations cited by the investigators.
First, depression or depressive symptoms were defined using self-rating scales, which are “convenient to screen for depressive disorders, but a high score obtained on a self-rating scale does not necessarily indicate the presence of depressive psychopathology,” said Su, who was not involved with the research.
He also noted that use of 465 mg of EPA and 375 mg of DHA in VITAL-DEP “might be too low” to have an impact.
Finally, Su said it is “very important to also address the potential for type I error, which makes the secondary and subgroup analyses less reliable.”
VITAL-DEP was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health. Pronova BioPharma donated the fish oil and matching placebo. Okereke reported receiving royalties from Springer Publishing. Su is a founding committee member of the International Society for Nutritional Psychiatry Research, the board director of the International Society for the Study of Fatty Acids, and an associate editor of the journal Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fish oil supplementation does not help prevent depression or boost mood, new research suggests.
The VITAL-DEP study included more than 18,000 participants. Among adults aged 50 years or older free of clinically relevant depressive symptoms at baseline, long-term use of marine omega-3 fatty acid (omega-3) supplements did not reduce risk for depression or clinically relevant depressive symptoms — or make a difference in the quality of mood.
“While a small increase in risk of depression was inside the statistical margin of significance, there was no harmful or beneficial effect of omega-3 on the overall course of mood during the roughly 5 to 7 years of follow-up,” lead author Olivia I. Okereke, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, told Medscape Medical News.
“The takeaway from our study is that there is no net benefit of long-term use of daily omega-3 fish oil supplements for preventing depression or boosting mood,” Okereke said.
The findings were published online Dec. 21 in JAMA.
Assessing general population risk
For many years, experts have recommended omega-3 supplements for reduction in depression recurrence in some high-risk patients, Okereke noted.
“However, there are no guidelines related to the use of omega-3 supplements for preventing depression in the general population. Therefore, we undertook this study to provide clarity in the issue,” she said.
The VITAL-DEP study enrolled 18,353 older adults (mean age, 67.5 years; 49% women). Of these, 16,657 were at risk for incident depression, defined as having no previous history of depression; and 1696 were at risk for recurrent depression, defined as having a history of depression but not having undergone treatment for depression within the past 2 years.
Roughly half the participants were randomly assigned to receive marine omega-3 fatty acids (1 g/d of fish oil, including 465 mg of eicosapentaenoic acid [EPA] and 375 mg of docosahexaenoic acid [DHA]) and the other half to matching placebo for an average of 5.3 years.
“Because of the large sample size and long follow-up, we were able to test the effects of daily omega-3 fish oil supplements on universal prevention of depression in the adult population,” Okereke said.
No significant benefit
Results showed risk for depression or clinically relevant depressive symptoms (total of incident and recurrent cases) was not significantly different between the omega-3 group and the placebo group.
The omega-3 group had 651 depression or clinically relevant depressive symptom events (13.9 per 1000 person-years), and the placebo group had 583 depression or clinically relevant depressive symptom events (12.3 per 1000 person-years). The hazard ratio was 1.13 (95% CI, 1.01 - 1.26; P = .03).
There were also no significant between-group differences in longitudinal mood scores. The mean difference in change in 8-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-8) score was 0.03 points (95% CI, −0.01 to 0.07; P = .19).
“Patients, physicians, and other clinicians should understand that there are still many reasons for some people, under the guidance of their health care providers, to take omega-3 fish oil supplements,” Okereke noted.
“These supplements increasingly have been found to have benefits for cardiac disease prevention and treatment of inflammatory conditions, in addition to being used for management of existing depressive disorders in some high-risk patients,” she said.
“However, the results of our study indicate there is no reason for adults in the general population to be taking daily omega-3 fish oil supplements solely for the purpose of preventing depression or for maintaining a positive mood,” she added.
Okereke noted, however, that the VITAL-DEP study used 1 g/day of omega-3 fatty acids and there may be a greater benefit from taking higher doses, such as 4 g/day.
Cautionary notes
Commenting on the study for Medscape Medical News, Kuan-Pin Su, MD, PhD, chief of the Department of General Psychiatry, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, highlighted some of the limitations cited by the investigators.
First, depression or depressive symptoms were defined using self-rating scales, which are “convenient to screen for depressive disorders, but a high score obtained on a self-rating scale does not necessarily indicate the presence of depressive psychopathology,” said Su, who was not involved with the research.
He also noted that use of 465 mg of EPA and 375 mg of DHA in VITAL-DEP “might be too low” to have an impact.
Finally, Su said it is “very important to also address the potential for type I error, which makes the secondary and subgroup analyses less reliable.”
VITAL-DEP was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health. Pronova BioPharma donated the fish oil and matching placebo. Okereke reported receiving royalties from Springer Publishing. Su is a founding committee member of the International Society for Nutritional Psychiatry Research, the board director of the International Society for the Study of Fatty Acids, and an associate editor of the journal Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BMJ slams ‘incompetent’ Facebook fact-checking of vaccine article
According to an open letter written by outgoing BMJ editor-in-chief Fiona Godlee, MD, and incoming editor-in-chief Kamran Abbasi, MD, Facebook hired a third-party contractor to evaluate the article’s findings. This resulted in “inaccurate, incompetent, and irresponsible” conclusions that “should be of concern to anyone who values and relies on sources such as the BMJ for reliable medical information.”
The article in question investigated data integrity concerns at Pfizer vaccine clinical trial sites. In September 2020, the letter states, a former employee of the research group involved in Pfizer’s main vaccine trials, Ventavia, reached out to the BMJ and “began providing ... dozens of internal company documents, photos, audio recordings, and emails.” According to the company’s website, Ventavia “played a significant part in [COVID-19 clinical trial] recruitment” and “has received recognition by Pfizer for their contribution to vaccine trials.”
It was previously reported that the whistle-blower is a former regional director who was involved in Pfizer’s vaccine trials in Texas during the fall of 2020. She alleges “the company falsified data, unblinded patients, employed inadequately trained vaccinators, and was slow to follow up on adverse events reported in Pfizer’s pivotal phase 3 trial.”
The images provided to the BMJ “showed needles discarded in a plastic biohazard bag instead of a sharps container box” and another displayed “vaccine packaging materials with trial participants’ identification numbers written on them left out in the open, potentially unblinding participants.”
Despite informing Ventavia, the director’s concerns went unaddressed. She then filed a complaint with the Food and Drug Administration and was subsequently fired the same day. The FDA did not investigate the director’s allegations, said Dr. Godlee and Dr. Abbasi, even though the evidence “revealed a host of poor clinical trial research practices occurring at Ventavia that could impact data integrity and patient safety.”
Article labeled as ‘hoax,’ without pointing out errors
The BMJ hired an investigative reporter to follow up on the clinical trial claims. The findings were published in an article on Nov. 2, 2021, after the article “went through ... the usual high-level legal and editorial oversight and peer review,” according to the journal.
However, by Nov. 10, the journal began receiving complaints from readers unable to share the article on social media. Others had their posts flagged with warnings, such as “missing context ... independent fact-checkers say this information could mislead people.” Administrators of various Facebook groups were notified that posts containing the article were “partly false.”
Readers were informed that Facebook contractor Lead Stories performed the article’s “fact check.” Lead Stories is “an award-winning innovative fact checking and debunking website” and “an active part of Facebook’s partnership with third-party fact checkers” – with the latter granting them “access to listings of content that has been flagged as potentially false by Facebook’s systems or its users.” The company said they “decide independently if we want to fact check it or not.”
Lead Stories stated that they “can enter our fact checks into a tool provided by Facebook and Facebook then uses our data to help slow down the spread of false information on its platform.” Although the contractor is compensated, Lead Stories claims they have “no say or influence over what we fact check or what our conclusions are.”
Both editors question the validity of the fact check performed by Lead Stories, as it failed to provide any “assertions of fact” as to what the BMJ got wrong. Moreover, the editors take issue with Lead Stories referring to the journal as a “news blog” and using the phrase “hoax-alert” in the URL when publishing the story on its site.
The BMJ has reached out to Lead Stories and Facebook, said the letter, but Lead Stories refuses to “change anything about their article or actions that have led to Facebook flagging our article.” Requests for Facebook to remove the “fact-checking” label and allow “readers to freely share the article on [Facebook’s] platform” have been unfruitful.
Dr. Godlee and Dr. Abbasi expressed concern that other “high quality information provider[s] have been affected by the incompetence of Meta’s fact checking regime.” In November, Instagram censored Cochrane, an international provider of independent systematic medical reviews. Instagram, also owned by Meta, prohibited users from tagging Cochrane because the organization “repeatedly posted ... false content about COVID-19 or vaccines.” Cochrane refuted the allegations.
While “fact checking has been a staple of good journalism for decades,” said the editors, Meta has “apparently delegated responsibility to people incompetent in carrying out this crucial task.” They urged the company to reconsider its fact-checking strategy and review the issues that contributed to the error.
This news organization reached out to Meta for comment but did not receive a response at press time.
Lead Stories has posted a reply (Lead Stories’ Response To BMJ Open Letter Objecting To A Lead Stories Fact Check) to the BMJ’s complaint on its website.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
According to an open letter written by outgoing BMJ editor-in-chief Fiona Godlee, MD, and incoming editor-in-chief Kamran Abbasi, MD, Facebook hired a third-party contractor to evaluate the article’s findings. This resulted in “inaccurate, incompetent, and irresponsible” conclusions that “should be of concern to anyone who values and relies on sources such as the BMJ for reliable medical information.”
The article in question investigated data integrity concerns at Pfizer vaccine clinical trial sites. In September 2020, the letter states, a former employee of the research group involved in Pfizer’s main vaccine trials, Ventavia, reached out to the BMJ and “began providing ... dozens of internal company documents, photos, audio recordings, and emails.” According to the company’s website, Ventavia “played a significant part in [COVID-19 clinical trial] recruitment” and “has received recognition by Pfizer for their contribution to vaccine trials.”
It was previously reported that the whistle-blower is a former regional director who was involved in Pfizer’s vaccine trials in Texas during the fall of 2020. She alleges “the company falsified data, unblinded patients, employed inadequately trained vaccinators, and was slow to follow up on adverse events reported in Pfizer’s pivotal phase 3 trial.”
The images provided to the BMJ “showed needles discarded in a plastic biohazard bag instead of a sharps container box” and another displayed “vaccine packaging materials with trial participants’ identification numbers written on them left out in the open, potentially unblinding participants.”
Despite informing Ventavia, the director’s concerns went unaddressed. She then filed a complaint with the Food and Drug Administration and was subsequently fired the same day. The FDA did not investigate the director’s allegations, said Dr. Godlee and Dr. Abbasi, even though the evidence “revealed a host of poor clinical trial research practices occurring at Ventavia that could impact data integrity and patient safety.”
Article labeled as ‘hoax,’ without pointing out errors
The BMJ hired an investigative reporter to follow up on the clinical trial claims. The findings were published in an article on Nov. 2, 2021, after the article “went through ... the usual high-level legal and editorial oversight and peer review,” according to the journal.
However, by Nov. 10, the journal began receiving complaints from readers unable to share the article on social media. Others had their posts flagged with warnings, such as “missing context ... independent fact-checkers say this information could mislead people.” Administrators of various Facebook groups were notified that posts containing the article were “partly false.”
Readers were informed that Facebook contractor Lead Stories performed the article’s “fact check.” Lead Stories is “an award-winning innovative fact checking and debunking website” and “an active part of Facebook’s partnership with third-party fact checkers” – with the latter granting them “access to listings of content that has been flagged as potentially false by Facebook’s systems or its users.” The company said they “decide independently if we want to fact check it or not.”
Lead Stories stated that they “can enter our fact checks into a tool provided by Facebook and Facebook then uses our data to help slow down the spread of false information on its platform.” Although the contractor is compensated, Lead Stories claims they have “no say or influence over what we fact check or what our conclusions are.”
Both editors question the validity of the fact check performed by Lead Stories, as it failed to provide any “assertions of fact” as to what the BMJ got wrong. Moreover, the editors take issue with Lead Stories referring to the journal as a “news blog” and using the phrase “hoax-alert” in the URL when publishing the story on its site.
The BMJ has reached out to Lead Stories and Facebook, said the letter, but Lead Stories refuses to “change anything about their article or actions that have led to Facebook flagging our article.” Requests for Facebook to remove the “fact-checking” label and allow “readers to freely share the article on [Facebook’s] platform” have been unfruitful.
Dr. Godlee and Dr. Abbasi expressed concern that other “high quality information provider[s] have been affected by the incompetence of Meta’s fact checking regime.” In November, Instagram censored Cochrane, an international provider of independent systematic medical reviews. Instagram, also owned by Meta, prohibited users from tagging Cochrane because the organization “repeatedly posted ... false content about COVID-19 or vaccines.” Cochrane refuted the allegations.
While “fact checking has been a staple of good journalism for decades,” said the editors, Meta has “apparently delegated responsibility to people incompetent in carrying out this crucial task.” They urged the company to reconsider its fact-checking strategy and review the issues that contributed to the error.
This news organization reached out to Meta for comment but did not receive a response at press time.
Lead Stories has posted a reply (Lead Stories’ Response To BMJ Open Letter Objecting To A Lead Stories Fact Check) to the BMJ’s complaint on its website.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
According to an open letter written by outgoing BMJ editor-in-chief Fiona Godlee, MD, and incoming editor-in-chief Kamran Abbasi, MD, Facebook hired a third-party contractor to evaluate the article’s findings. This resulted in “inaccurate, incompetent, and irresponsible” conclusions that “should be of concern to anyone who values and relies on sources such as the BMJ for reliable medical information.”
The article in question investigated data integrity concerns at Pfizer vaccine clinical trial sites. In September 2020, the letter states, a former employee of the research group involved in Pfizer’s main vaccine trials, Ventavia, reached out to the BMJ and “began providing ... dozens of internal company documents, photos, audio recordings, and emails.” According to the company’s website, Ventavia “played a significant part in [COVID-19 clinical trial] recruitment” and “has received recognition by Pfizer for their contribution to vaccine trials.”
It was previously reported that the whistle-blower is a former regional director who was involved in Pfizer’s vaccine trials in Texas during the fall of 2020. She alleges “the company falsified data, unblinded patients, employed inadequately trained vaccinators, and was slow to follow up on adverse events reported in Pfizer’s pivotal phase 3 trial.”
The images provided to the BMJ “showed needles discarded in a plastic biohazard bag instead of a sharps container box” and another displayed “vaccine packaging materials with trial participants’ identification numbers written on them left out in the open, potentially unblinding participants.”
Despite informing Ventavia, the director’s concerns went unaddressed. She then filed a complaint with the Food and Drug Administration and was subsequently fired the same day. The FDA did not investigate the director’s allegations, said Dr. Godlee and Dr. Abbasi, even though the evidence “revealed a host of poor clinical trial research practices occurring at Ventavia that could impact data integrity and patient safety.”
Article labeled as ‘hoax,’ without pointing out errors
The BMJ hired an investigative reporter to follow up on the clinical trial claims. The findings were published in an article on Nov. 2, 2021, after the article “went through ... the usual high-level legal and editorial oversight and peer review,” according to the journal.
However, by Nov. 10, the journal began receiving complaints from readers unable to share the article on social media. Others had their posts flagged with warnings, such as “missing context ... independent fact-checkers say this information could mislead people.” Administrators of various Facebook groups were notified that posts containing the article were “partly false.”
Readers were informed that Facebook contractor Lead Stories performed the article’s “fact check.” Lead Stories is “an award-winning innovative fact checking and debunking website” and “an active part of Facebook’s partnership with third-party fact checkers” – with the latter granting them “access to listings of content that has been flagged as potentially false by Facebook’s systems or its users.” The company said they “decide independently if we want to fact check it or not.”
Lead Stories stated that they “can enter our fact checks into a tool provided by Facebook and Facebook then uses our data to help slow down the spread of false information on its platform.” Although the contractor is compensated, Lead Stories claims they have “no say or influence over what we fact check or what our conclusions are.”
Both editors question the validity of the fact check performed by Lead Stories, as it failed to provide any “assertions of fact” as to what the BMJ got wrong. Moreover, the editors take issue with Lead Stories referring to the journal as a “news blog” and using the phrase “hoax-alert” in the URL when publishing the story on its site.
The BMJ has reached out to Lead Stories and Facebook, said the letter, but Lead Stories refuses to “change anything about their article or actions that have led to Facebook flagging our article.” Requests for Facebook to remove the “fact-checking” label and allow “readers to freely share the article on [Facebook’s] platform” have been unfruitful.
Dr. Godlee and Dr. Abbasi expressed concern that other “high quality information provider[s] have been affected by the incompetence of Meta’s fact checking regime.” In November, Instagram censored Cochrane, an international provider of independent systematic medical reviews. Instagram, also owned by Meta, prohibited users from tagging Cochrane because the organization “repeatedly posted ... false content about COVID-19 or vaccines.” Cochrane refuted the allegations.
While “fact checking has been a staple of good journalism for decades,” said the editors, Meta has “apparently delegated responsibility to people incompetent in carrying out this crucial task.” They urged the company to reconsider its fact-checking strategy and review the issues that contributed to the error.
This news organization reached out to Meta for comment but did not receive a response at press time.
Lead Stories has posted a reply (Lead Stories’ Response To BMJ Open Letter Objecting To A Lead Stories Fact Check) to the BMJ’s complaint on its website.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many clinicians feel ill-prepared for drug overdose deaths
new research suggests.
However, results from a survey study also showed that colleagues were an important source of support in the wake of this type of event.
“A patient overdose death can change clinical decision-making for providers experiencing high levels of stress related to the overdose death,” noted the investigators, led by Amy Yule, MD, director of adolescent addiction psychiatry, Boston Medical Center, and assistant professor of psychiatry at Boston University Medical Center.
The findings were presented by Dr. Yule at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
All-time high
As reported by this news organization, there has recently been a record number of drug overdose deaths. And these deaths affect families, communities, and often providers, Dr. Yule told meeting attendees.
Previous research has looked at the impact of drug overdose deaths and the opioid epidemic on first responders and community health workers in the field of overdose prevention.
“But there’s less in the literature to my knowledge that describes the experience of providers and clinicians who are working in more formalized medical settings,” said Dr. Yule.
In December 2020, researchers sent an email to members of the Providers Clinical Support System (PCSS) inviting them to complete an anonymous survey. The PCSS program was created in response to the opioid overdose epidemic to train primary care clinicians in the prevention and treatment of opioid use disorders.
A total of 12,204 members received the email, 1,064 opened the survey link, and 523 completed the survey.
Participants were mostly White and female, with an average age of 52 years. Respondents had been practicing for an average of about 16 years.
The largest responder group was physicians (47%), followed by counselors (29%), nurse practitioners (17%), and nurses (7%).
Among physician respondents, 41% reported having received additional formal training in addiction.
Only 24% of the respondents indicated they received training in “postvention,” which refers to interventions after a suicide to support the bereaved. Such interventions “could be helpful in potentially preparing them for a drug overdose death in their practice,” said Dr. Yule.
Categories of preparedness
The survey inquired about three categories of preparedness: coping with a drug overdose death, providing support to a colleague, and talking with families who have lost a member to a drug overdose.
Overall, 59% said they felt somewhat or fairly well prepared for the first two categories and 55% for the third category.
“I think it’s notable that there is a higher percentage of people who felt not at all prepared to talk with family members (20.5%), compared to those who felt not at all prepared to cope with a drug overdose death (13.8%) or prepared to support a colleague (12%),” Dr. Yule said.
More than half of respondents (55%) indicated a drug overdose death had occurred in their own practice.
The survey also looked at frequency of consultations with colleagues, critical incident debriefing sessions, and interactions with a patient’s family.
Almost half (48%) of the sample said they consulted with a colleague after most patient overdose deaths. Only 24% said they had a critical incidence debriefing session after most of these events, and 20% said they interacted with the patient’s family.
Asked what resources they found helpful for coping with a recent patient drug overdose death, respondents flagged their colleagues and meetings with families.
The survey also examined provider trauma after a patient drug overdose death, using the Impact of Event Scale–R. “If the score is above a certain cutoff level, there is potential concern” for PTSD, Dr. Yule said.
Among the 141 respondents who had a patient drug overdose death in their practice during the previous year, 121 completed this trauma scale. Of these, 18% had “a very elevated” score, Dr. Yule reported.
Sources of support
Commenting on the survey study, Larissa Mooney, MD, associate professor and director of the addiction psychiatry division in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the University of California, Los Angeles, said it is not surprising that many providers do not feel adequately prepared to cope with an overdose death, or how to support a colleague after such an event.
“This is not routinely covered in training, and patient overdose may occur without warning signs,” said Dr. Mooney, who was not involved with the research.
However, these new findings suggest a range of potential sources of support for providers after a patient overdose death that may be helpful, “including colleagues, friends, therapy, supervision, and meeting with the patient’s family,” she said.
The study received funding from the PCSS. Dr. Yule disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
However, results from a survey study also showed that colleagues were an important source of support in the wake of this type of event.
“A patient overdose death can change clinical decision-making for providers experiencing high levels of stress related to the overdose death,” noted the investigators, led by Amy Yule, MD, director of adolescent addiction psychiatry, Boston Medical Center, and assistant professor of psychiatry at Boston University Medical Center.
The findings were presented by Dr. Yule at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
All-time high
As reported by this news organization, there has recently been a record number of drug overdose deaths. And these deaths affect families, communities, and often providers, Dr. Yule told meeting attendees.
Previous research has looked at the impact of drug overdose deaths and the opioid epidemic on first responders and community health workers in the field of overdose prevention.
“But there’s less in the literature to my knowledge that describes the experience of providers and clinicians who are working in more formalized medical settings,” said Dr. Yule.
In December 2020, researchers sent an email to members of the Providers Clinical Support System (PCSS) inviting them to complete an anonymous survey. The PCSS program was created in response to the opioid overdose epidemic to train primary care clinicians in the prevention and treatment of opioid use disorders.
A total of 12,204 members received the email, 1,064 opened the survey link, and 523 completed the survey.
Participants were mostly White and female, with an average age of 52 years. Respondents had been practicing for an average of about 16 years.
The largest responder group was physicians (47%), followed by counselors (29%), nurse practitioners (17%), and nurses (7%).
Among physician respondents, 41% reported having received additional formal training in addiction.
Only 24% of the respondents indicated they received training in “postvention,” which refers to interventions after a suicide to support the bereaved. Such interventions “could be helpful in potentially preparing them for a drug overdose death in their practice,” said Dr. Yule.
Categories of preparedness
The survey inquired about three categories of preparedness: coping with a drug overdose death, providing support to a colleague, and talking with families who have lost a member to a drug overdose.
Overall, 59% said they felt somewhat or fairly well prepared for the first two categories and 55% for the third category.
“I think it’s notable that there is a higher percentage of people who felt not at all prepared to talk with family members (20.5%), compared to those who felt not at all prepared to cope with a drug overdose death (13.8%) or prepared to support a colleague (12%),” Dr. Yule said.
More than half of respondents (55%) indicated a drug overdose death had occurred in their own practice.
The survey also looked at frequency of consultations with colleagues, critical incident debriefing sessions, and interactions with a patient’s family.
Almost half (48%) of the sample said they consulted with a colleague after most patient overdose deaths. Only 24% said they had a critical incidence debriefing session after most of these events, and 20% said they interacted with the patient’s family.
Asked what resources they found helpful for coping with a recent patient drug overdose death, respondents flagged their colleagues and meetings with families.
The survey also examined provider trauma after a patient drug overdose death, using the Impact of Event Scale–R. “If the score is above a certain cutoff level, there is potential concern” for PTSD, Dr. Yule said.
Among the 141 respondents who had a patient drug overdose death in their practice during the previous year, 121 completed this trauma scale. Of these, 18% had “a very elevated” score, Dr. Yule reported.
Sources of support
Commenting on the survey study, Larissa Mooney, MD, associate professor and director of the addiction psychiatry division in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the University of California, Los Angeles, said it is not surprising that many providers do not feel adequately prepared to cope with an overdose death, or how to support a colleague after such an event.
“This is not routinely covered in training, and patient overdose may occur without warning signs,” said Dr. Mooney, who was not involved with the research.
However, these new findings suggest a range of potential sources of support for providers after a patient overdose death that may be helpful, “including colleagues, friends, therapy, supervision, and meeting with the patient’s family,” she said.
The study received funding from the PCSS. Dr. Yule disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
However, results from a survey study also showed that colleagues were an important source of support in the wake of this type of event.
“A patient overdose death can change clinical decision-making for providers experiencing high levels of stress related to the overdose death,” noted the investigators, led by Amy Yule, MD, director of adolescent addiction psychiatry, Boston Medical Center, and assistant professor of psychiatry at Boston University Medical Center.
The findings were presented by Dr. Yule at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
All-time high
As reported by this news organization, there has recently been a record number of drug overdose deaths. And these deaths affect families, communities, and often providers, Dr. Yule told meeting attendees.
Previous research has looked at the impact of drug overdose deaths and the opioid epidemic on first responders and community health workers in the field of overdose prevention.
“But there’s less in the literature to my knowledge that describes the experience of providers and clinicians who are working in more formalized medical settings,” said Dr. Yule.
In December 2020, researchers sent an email to members of the Providers Clinical Support System (PCSS) inviting them to complete an anonymous survey. The PCSS program was created in response to the opioid overdose epidemic to train primary care clinicians in the prevention and treatment of opioid use disorders.
A total of 12,204 members received the email, 1,064 opened the survey link, and 523 completed the survey.
Participants were mostly White and female, with an average age of 52 years. Respondents had been practicing for an average of about 16 years.
The largest responder group was physicians (47%), followed by counselors (29%), nurse practitioners (17%), and nurses (7%).
Among physician respondents, 41% reported having received additional formal training in addiction.
Only 24% of the respondents indicated they received training in “postvention,” which refers to interventions after a suicide to support the bereaved. Such interventions “could be helpful in potentially preparing them for a drug overdose death in their practice,” said Dr. Yule.
Categories of preparedness
The survey inquired about three categories of preparedness: coping with a drug overdose death, providing support to a colleague, and talking with families who have lost a member to a drug overdose.
Overall, 59% said they felt somewhat or fairly well prepared for the first two categories and 55% for the third category.
“I think it’s notable that there is a higher percentage of people who felt not at all prepared to talk with family members (20.5%), compared to those who felt not at all prepared to cope with a drug overdose death (13.8%) or prepared to support a colleague (12%),” Dr. Yule said.
More than half of respondents (55%) indicated a drug overdose death had occurred in their own practice.
The survey also looked at frequency of consultations with colleagues, critical incident debriefing sessions, and interactions with a patient’s family.
Almost half (48%) of the sample said they consulted with a colleague after most patient overdose deaths. Only 24% said they had a critical incidence debriefing session after most of these events, and 20% said they interacted with the patient’s family.
Asked what resources they found helpful for coping with a recent patient drug overdose death, respondents flagged their colleagues and meetings with families.
The survey also examined provider trauma after a patient drug overdose death, using the Impact of Event Scale–R. “If the score is above a certain cutoff level, there is potential concern” for PTSD, Dr. Yule said.
Among the 141 respondents who had a patient drug overdose death in their practice during the previous year, 121 completed this trauma scale. Of these, 18% had “a very elevated” score, Dr. Yule reported.
Sources of support
Commenting on the survey study, Larissa Mooney, MD, associate professor and director of the addiction psychiatry division in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the University of California, Los Angeles, said it is not surprising that many providers do not feel adequately prepared to cope with an overdose death, or how to support a colleague after such an event.
“This is not routinely covered in training, and patient overdose may occur without warning signs,” said Dr. Mooney, who was not involved with the research.
However, these new findings suggest a range of potential sources of support for providers after a patient overdose death that may be helpful, “including colleagues, friends, therapy, supervision, and meeting with the patient’s family,” she said.
The study received funding from the PCSS. Dr. Yule disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAAP 2021
COVID-19 and coping with superimposed traumas
While 2022 is lurking around the corner, many of us still have 2020 on our minds. Social media posts are already emerging: “No new years resolutions. It is the circumstances turn to improve [sic],” one post declares. Others proclaim that it is difficult coming to terms with the idea that 2022 is actually pronounced “2020 too.” A critical difference exists between then and now – we have experienced months of living in limbo and rolling with the punches of pandemic life.
In some ways, it has become easy to think of the early pandemic days as a distant memory, yet respect that the impact of 2020 has been indelible for virtually all of us and feels palpable as if it were yesterday.
The year 2020 was marked by the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, which was accompanied by extreme uncertainty, loss of all kinds, and emotional turmoil. The early pandemic had a profound economic and social impact, with added stress tethered to political and race-related division in America that created divides among families and friends, and yielded ceaseless discourse related to divergent perspectives. This only exacerbated the stress that came with the pandemic, given that providing support and leaning on one another was more important than ever. All of this was compounded by natural disasters that have plagued the country.
So much was unprecedented. There was a collective sense of feeling “worn down,” and the burnout that was felt was quite profound. Enormous amounts of mental and physical effort were allocated to simply surviving, getting basic needs met, having enough food and supplies, and completing basic tasks. Ordinary relating felt taxing. At this stage of the pandemic, the COVID-19 experience can be conceived of as a traumatic stressor capable of eliciting a traumatic response and exacerbating other mental health symptoms. Our capacity to cope has been diminished. Anxiety rates have soared, as have rates of clinical depression. Those most affected have had lower household incomes, are unmarried, and have experienced pandemic-related stressors. The links between the impact of the pandemic on mental health have been clear.
The pandemic has forced the landscape of social support to dramatically change. Initially, we felt pulled to connect and we leaned into the use of virtual platforms to connect for all matters (simple social gatherings, big birthday events, family reunions, celebration of holidays, work duties, and academic work). However, “Zoom fatigue” began to set in, and our screen time was maxed out. There has been the added dynamic of frontline workers who did not have the option to work virtually or from home. This group largely has felt disconnected from others who didn’t understand the depth of their anxiety and loneliness of their experience. Health care workers have had to make challenging, life-and-death, patient-related decisions that called into question personal morals and ethics all while their own lives were at risk.
Fast-forward to the present, and support systems have either strengthened or worn down – which has yielded a unique dichotomy. Maintaining friendships has either felt of utmost importance given the impact of the disconnect and physical distance or has felt challenging given the mental energy expended from working and connecting virtually. Empathy burnout is also a real and important facet in the equation. We begin to ask the question: Are we checking in with others in the spirit of authentic relating, to cultivate real connection, or to check a box?
Impact of layered traumas
It is interesting to think about the pandemic’s traumatic impact being “superimposed” on top of the “ordinary traumas” experienced outside of the pandemic. We are essentially at the 2-year mark, in some ways have cultivated a sense of resilience and found ways to adapt, and in other ways at times feel right back where we were in early 2020. There were moments that felt hopeful, glimmers of normalcy, and setbacks that all ebbed and flowed – but even so, there have not been many “mental breaks,” only temporary and transient reprieves. Some got sick and died; some recovered; and others are still experiencing long-hauler syndrome and have lingering sequelae. Despite adaptation and resilience, one can’t help but wonder the impact of superimposed traumas on top of this collective trauma. Many of us have not even rebounded from the pandemic, and then are faced with loss, grief, challenges, illness, hard and big life decisions. We are challenged to answer the question: How do we endure in the face of this trauma inception?
It has been a challenging time for all, including those who are ordinarily happy-go-lucky, resilient, and see the glass half-full and are struggling with the idea of struggling. I am no “resilience expert” but gleaned much wisdom from responding to the Surfside, Fla., building collapse. This was a collective trauma that took place in the summer of 2021, and the wisdom of this event highlighted the value of collective healing and unification even in spite of the times. What happened in Surfside was a shock, and the loss was felt by those directly affected, the surrounding community, and those who were part of the disaster response efforts. All of those parties had been processing losses prior to this – loss of normalcy because of the pandemic, loss of people we loved as a result, other personal losses – and this community tragedy was yet another loss to disentangle on top of a period in U.S. history demarcated by a great lack of unity, divisiveness, anger, and hatred. The collapse highlighted the small size yet interconnectedness of the community and the power of connection and authentic relating. It was overwhelming in the moment but extremely heartening and beautiful to see the amount of willingness to drop everything and help. Despite feeling worn down from the pandemic, people drew upon their internal resources, natural goodness, and kindness “reserves” to provide support.
Responding to the collapse highlighted that resilience in the context of collective trauma requires flexibility, embracing uncertainty, cultivating unity, and paying attention to meeting basic needs/self-care. The role of kindness cannot be overemphasized. In the realm of reflecting on the notion of kindness, it is worth noting how much power there is to bearing witness to someone’s experience, especially when they are in pain. People often diminish the role or at the very least do not recognize the power of showing up for someone and just listening. Pandemic resilience, and coping with coalescing traumas, is likely composed of these same facets that were essential in the context of coping with the collapse.
It is not only the immediate impact of a trauma as much as the aftermath that needs to processed and worked through. In one sense, people feel that they should be adjusted to and accustomed to this new reality, and at the same time, one has to remember and reflect on how unnatural this experience has been. There is an impact of a cumulative onslaught of negative events, and it is hard to imagine not being phased, remaining unchanged, or not feeling affected. We may feel hardened and that there are limits to the compassion we have to offer others. We may be feel empathic. There can be desensitization and an apathy to others’ suffering when our patience is worn down and we have limited bandwidth. There are data to support the idea that a level of habituation occurs to individuals who experience multiple traumas, which yields a level of “sensitization” to the negative impact of subsequent events. It becomes easy to make comparisons of suffering. The challenge will be to rise above these and make a conscious effort to connect with who and how we were before we were worn down.
I am still in awe about how much I learned from the victims’ families, survivors, and my colleagues at Surfside – about pain, suffering, loss, resilience, coping, fortitude, and meaning making. We were all forced to think beyond ourselves, show up for others, and unify in a way that remedied this period of fragmentation. With respect to the pandemic and “where we are at now,” some elements of our lives are stabilizing; other aspects feel volatile from the fatigue of what we have been experiencing. This pandemic has not fully abated, but we can find some clarity in the value of setting boundaries and knowing our limits – but not overlooking the power of unity and kindness and the value of the reciprocating those qualities.
Dr. Feldman is a licensed clinical psychologist in private practice in Miami. She is an adjunct professor in the college of psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she teaches clinical psychology doctoral students. She also serves on the board of directors of the Southeast Florida Association for Psychoanalytic Psychology. Dr. Feldman has no disclosures.
While 2022 is lurking around the corner, many of us still have 2020 on our minds. Social media posts are already emerging: “No new years resolutions. It is the circumstances turn to improve [sic],” one post declares. Others proclaim that it is difficult coming to terms with the idea that 2022 is actually pronounced “2020 too.” A critical difference exists between then and now – we have experienced months of living in limbo and rolling with the punches of pandemic life.
In some ways, it has become easy to think of the early pandemic days as a distant memory, yet respect that the impact of 2020 has been indelible for virtually all of us and feels palpable as if it were yesterday.
The year 2020 was marked by the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, which was accompanied by extreme uncertainty, loss of all kinds, and emotional turmoil. The early pandemic had a profound economic and social impact, with added stress tethered to political and race-related division in America that created divides among families and friends, and yielded ceaseless discourse related to divergent perspectives. This only exacerbated the stress that came with the pandemic, given that providing support and leaning on one another was more important than ever. All of this was compounded by natural disasters that have plagued the country.
So much was unprecedented. There was a collective sense of feeling “worn down,” and the burnout that was felt was quite profound. Enormous amounts of mental and physical effort were allocated to simply surviving, getting basic needs met, having enough food and supplies, and completing basic tasks. Ordinary relating felt taxing. At this stage of the pandemic, the COVID-19 experience can be conceived of as a traumatic stressor capable of eliciting a traumatic response and exacerbating other mental health symptoms. Our capacity to cope has been diminished. Anxiety rates have soared, as have rates of clinical depression. Those most affected have had lower household incomes, are unmarried, and have experienced pandemic-related stressors. The links between the impact of the pandemic on mental health have been clear.
The pandemic has forced the landscape of social support to dramatically change. Initially, we felt pulled to connect and we leaned into the use of virtual platforms to connect for all matters (simple social gatherings, big birthday events, family reunions, celebration of holidays, work duties, and academic work). However, “Zoom fatigue” began to set in, and our screen time was maxed out. There has been the added dynamic of frontline workers who did not have the option to work virtually or from home. This group largely has felt disconnected from others who didn’t understand the depth of their anxiety and loneliness of their experience. Health care workers have had to make challenging, life-and-death, patient-related decisions that called into question personal morals and ethics all while their own lives were at risk.
Fast-forward to the present, and support systems have either strengthened or worn down – which has yielded a unique dichotomy. Maintaining friendships has either felt of utmost importance given the impact of the disconnect and physical distance or has felt challenging given the mental energy expended from working and connecting virtually. Empathy burnout is also a real and important facet in the equation. We begin to ask the question: Are we checking in with others in the spirit of authentic relating, to cultivate real connection, or to check a box?
Impact of layered traumas
It is interesting to think about the pandemic’s traumatic impact being “superimposed” on top of the “ordinary traumas” experienced outside of the pandemic. We are essentially at the 2-year mark, in some ways have cultivated a sense of resilience and found ways to adapt, and in other ways at times feel right back where we were in early 2020. There were moments that felt hopeful, glimmers of normalcy, and setbacks that all ebbed and flowed – but even so, there have not been many “mental breaks,” only temporary and transient reprieves. Some got sick and died; some recovered; and others are still experiencing long-hauler syndrome and have lingering sequelae. Despite adaptation and resilience, one can’t help but wonder the impact of superimposed traumas on top of this collective trauma. Many of us have not even rebounded from the pandemic, and then are faced with loss, grief, challenges, illness, hard and big life decisions. We are challenged to answer the question: How do we endure in the face of this trauma inception?
It has been a challenging time for all, including those who are ordinarily happy-go-lucky, resilient, and see the glass half-full and are struggling with the idea of struggling. I am no “resilience expert” but gleaned much wisdom from responding to the Surfside, Fla., building collapse. This was a collective trauma that took place in the summer of 2021, and the wisdom of this event highlighted the value of collective healing and unification even in spite of the times. What happened in Surfside was a shock, and the loss was felt by those directly affected, the surrounding community, and those who were part of the disaster response efforts. All of those parties had been processing losses prior to this – loss of normalcy because of the pandemic, loss of people we loved as a result, other personal losses – and this community tragedy was yet another loss to disentangle on top of a period in U.S. history demarcated by a great lack of unity, divisiveness, anger, and hatred. The collapse highlighted the small size yet interconnectedness of the community and the power of connection and authentic relating. It was overwhelming in the moment but extremely heartening and beautiful to see the amount of willingness to drop everything and help. Despite feeling worn down from the pandemic, people drew upon their internal resources, natural goodness, and kindness “reserves” to provide support.
Responding to the collapse highlighted that resilience in the context of collective trauma requires flexibility, embracing uncertainty, cultivating unity, and paying attention to meeting basic needs/self-care. The role of kindness cannot be overemphasized. In the realm of reflecting on the notion of kindness, it is worth noting how much power there is to bearing witness to someone’s experience, especially when they are in pain. People often diminish the role or at the very least do not recognize the power of showing up for someone and just listening. Pandemic resilience, and coping with coalescing traumas, is likely composed of these same facets that were essential in the context of coping with the collapse.
It is not only the immediate impact of a trauma as much as the aftermath that needs to processed and worked through. In one sense, people feel that they should be adjusted to and accustomed to this new reality, and at the same time, one has to remember and reflect on how unnatural this experience has been. There is an impact of a cumulative onslaught of negative events, and it is hard to imagine not being phased, remaining unchanged, or not feeling affected. We may feel hardened and that there are limits to the compassion we have to offer others. We may be feel empathic. There can be desensitization and an apathy to others’ suffering when our patience is worn down and we have limited bandwidth. There are data to support the idea that a level of habituation occurs to individuals who experience multiple traumas, which yields a level of “sensitization” to the negative impact of subsequent events. It becomes easy to make comparisons of suffering. The challenge will be to rise above these and make a conscious effort to connect with who and how we were before we were worn down.
I am still in awe about how much I learned from the victims’ families, survivors, and my colleagues at Surfside – about pain, suffering, loss, resilience, coping, fortitude, and meaning making. We were all forced to think beyond ourselves, show up for others, and unify in a way that remedied this period of fragmentation. With respect to the pandemic and “where we are at now,” some elements of our lives are stabilizing; other aspects feel volatile from the fatigue of what we have been experiencing. This pandemic has not fully abated, but we can find some clarity in the value of setting boundaries and knowing our limits – but not overlooking the power of unity and kindness and the value of the reciprocating those qualities.
Dr. Feldman is a licensed clinical psychologist in private practice in Miami. She is an adjunct professor in the college of psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she teaches clinical psychology doctoral students. She also serves on the board of directors of the Southeast Florida Association for Psychoanalytic Psychology. Dr. Feldman has no disclosures.
While 2022 is lurking around the corner, many of us still have 2020 on our minds. Social media posts are already emerging: “No new years resolutions. It is the circumstances turn to improve [sic],” one post declares. Others proclaim that it is difficult coming to terms with the idea that 2022 is actually pronounced “2020 too.” A critical difference exists between then and now – we have experienced months of living in limbo and rolling with the punches of pandemic life.
In some ways, it has become easy to think of the early pandemic days as a distant memory, yet respect that the impact of 2020 has been indelible for virtually all of us and feels palpable as if it were yesterday.
The year 2020 was marked by the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, which was accompanied by extreme uncertainty, loss of all kinds, and emotional turmoil. The early pandemic had a profound economic and social impact, with added stress tethered to political and race-related division in America that created divides among families and friends, and yielded ceaseless discourse related to divergent perspectives. This only exacerbated the stress that came with the pandemic, given that providing support and leaning on one another was more important than ever. All of this was compounded by natural disasters that have plagued the country.
So much was unprecedented. There was a collective sense of feeling “worn down,” and the burnout that was felt was quite profound. Enormous amounts of mental and physical effort were allocated to simply surviving, getting basic needs met, having enough food and supplies, and completing basic tasks. Ordinary relating felt taxing. At this stage of the pandemic, the COVID-19 experience can be conceived of as a traumatic stressor capable of eliciting a traumatic response and exacerbating other mental health symptoms. Our capacity to cope has been diminished. Anxiety rates have soared, as have rates of clinical depression. Those most affected have had lower household incomes, are unmarried, and have experienced pandemic-related stressors. The links between the impact of the pandemic on mental health have been clear.
The pandemic has forced the landscape of social support to dramatically change. Initially, we felt pulled to connect and we leaned into the use of virtual platforms to connect for all matters (simple social gatherings, big birthday events, family reunions, celebration of holidays, work duties, and academic work). However, “Zoom fatigue” began to set in, and our screen time was maxed out. There has been the added dynamic of frontline workers who did not have the option to work virtually or from home. This group largely has felt disconnected from others who didn’t understand the depth of their anxiety and loneliness of their experience. Health care workers have had to make challenging, life-and-death, patient-related decisions that called into question personal morals and ethics all while their own lives were at risk.
Fast-forward to the present, and support systems have either strengthened or worn down – which has yielded a unique dichotomy. Maintaining friendships has either felt of utmost importance given the impact of the disconnect and physical distance or has felt challenging given the mental energy expended from working and connecting virtually. Empathy burnout is also a real and important facet in the equation. We begin to ask the question: Are we checking in with others in the spirit of authentic relating, to cultivate real connection, or to check a box?
Impact of layered traumas
It is interesting to think about the pandemic’s traumatic impact being “superimposed” on top of the “ordinary traumas” experienced outside of the pandemic. We are essentially at the 2-year mark, in some ways have cultivated a sense of resilience and found ways to adapt, and in other ways at times feel right back where we were in early 2020. There were moments that felt hopeful, glimmers of normalcy, and setbacks that all ebbed and flowed – but even so, there have not been many “mental breaks,” only temporary and transient reprieves. Some got sick and died; some recovered; and others are still experiencing long-hauler syndrome and have lingering sequelae. Despite adaptation and resilience, one can’t help but wonder the impact of superimposed traumas on top of this collective trauma. Many of us have not even rebounded from the pandemic, and then are faced with loss, grief, challenges, illness, hard and big life decisions. We are challenged to answer the question: How do we endure in the face of this trauma inception?
It has been a challenging time for all, including those who are ordinarily happy-go-lucky, resilient, and see the glass half-full and are struggling with the idea of struggling. I am no “resilience expert” but gleaned much wisdom from responding to the Surfside, Fla., building collapse. This was a collective trauma that took place in the summer of 2021, and the wisdom of this event highlighted the value of collective healing and unification even in spite of the times. What happened in Surfside was a shock, and the loss was felt by those directly affected, the surrounding community, and those who were part of the disaster response efforts. All of those parties had been processing losses prior to this – loss of normalcy because of the pandemic, loss of people we loved as a result, other personal losses – and this community tragedy was yet another loss to disentangle on top of a period in U.S. history demarcated by a great lack of unity, divisiveness, anger, and hatred. The collapse highlighted the small size yet interconnectedness of the community and the power of connection and authentic relating. It was overwhelming in the moment but extremely heartening and beautiful to see the amount of willingness to drop everything and help. Despite feeling worn down from the pandemic, people drew upon their internal resources, natural goodness, and kindness “reserves” to provide support.
Responding to the collapse highlighted that resilience in the context of collective trauma requires flexibility, embracing uncertainty, cultivating unity, and paying attention to meeting basic needs/self-care. The role of kindness cannot be overemphasized. In the realm of reflecting on the notion of kindness, it is worth noting how much power there is to bearing witness to someone’s experience, especially when they are in pain. People often diminish the role or at the very least do not recognize the power of showing up for someone and just listening. Pandemic resilience, and coping with coalescing traumas, is likely composed of these same facets that were essential in the context of coping with the collapse.
It is not only the immediate impact of a trauma as much as the aftermath that needs to processed and worked through. In one sense, people feel that they should be adjusted to and accustomed to this new reality, and at the same time, one has to remember and reflect on how unnatural this experience has been. There is an impact of a cumulative onslaught of negative events, and it is hard to imagine not being phased, remaining unchanged, or not feeling affected. We may feel hardened and that there are limits to the compassion we have to offer others. We may be feel empathic. There can be desensitization and an apathy to others’ suffering when our patience is worn down and we have limited bandwidth. There are data to support the idea that a level of habituation occurs to individuals who experience multiple traumas, which yields a level of “sensitization” to the negative impact of subsequent events. It becomes easy to make comparisons of suffering. The challenge will be to rise above these and make a conscious effort to connect with who and how we were before we were worn down.
I am still in awe about how much I learned from the victims’ families, survivors, and my colleagues at Surfside – about pain, suffering, loss, resilience, coping, fortitude, and meaning making. We were all forced to think beyond ourselves, show up for others, and unify in a way that remedied this period of fragmentation. With respect to the pandemic and “where we are at now,” some elements of our lives are stabilizing; other aspects feel volatile from the fatigue of what we have been experiencing. This pandemic has not fully abated, but we can find some clarity in the value of setting boundaries and knowing our limits – but not overlooking the power of unity and kindness and the value of the reciprocating those qualities.
Dr. Feldman is a licensed clinical psychologist in private practice in Miami. She is an adjunct professor in the college of psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she teaches clinical psychology doctoral students. She also serves on the board of directors of the Southeast Florida Association for Psychoanalytic Psychology. Dr. Feldman has no disclosures.
Pill mill psychiatrist gets prison; must forfeit cash, luxury cars
Psychiatrist sentenced to 3 years in prison for running pill mill
, including a 2020 Porsche GT4 and a 2020 Aston Martin.
According to the U.S. Department of Justice, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration began investigating Gerald Michael Abraham, 76, after receiving a tip that he was prescribing opioids to patients who did not need the medication. The investigation, which began in October 2019, included 18 visits by undercover patients to Abraham’s cash-only clinic in Naples, Fla. Patients paid $400 per visit, according to court documents.
Even though the undercover patients pretended to have signs of drug abuse, Dr. Abraham still prescribed oxycodone, a strong opioid, on each visit without any physical examination, according to officials. He repeatedly increased the strength of the prescriptions when the patients asked. In one case, he told a patient that the patient’s medical paperwork “shows you are completely normal,” then went ahead to prescribe the oxycodone.
Dr. Abraham also gave Adderall to patients who had no legitimate medical need for the drug. As with the opioid, Dr. Abraham prescribed the frequently abused amphetamine (typically used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder) after being asked for it, without performing an examination or asking questions to justify the prescription, according to the undercover law enforcement agents.
According to the Florida Department of Health, Dr. Abraham voluntarily relinquished his license in September pending board action. His license was set to expire in January 2022.
Pennsylvania physician admits to distributing drugs resulting in patient’s death
A Pennsylvania internist pleaded guilty to unlawful prescription of controlled substances, maintaining drug-involved premises, and healthcare fraud, as well as that the death of a patient resulted from the use of the controlled drugs.
When entering his plea, Dr.Kurt Moran, 69, acknowledged that the purpose of his Scranton-based pain management practice was to distribute high doses of opioids not for medical purposes, and that he often prescribed these drugs without examining the patient to verify the illness or condition the patient claimed to have. At times, he even prescribed the drugs without seeing the patient. He admitted that he knew that such practices could result in addiction and even death, according to federal officials.
The healthcare fraud charges resulted from a scheme that took place between 2014 and 2017 in which Dr. Moran received bribes in exchange for prescribing the drug Subsys (sublingual fentanyl), which is approved for use only in cancer patients who suffer from breakthrough pain. Court documents allege that Dr. Moran was paid approximately $140,000 over a 2-year period to prescribe Subsys to patients for whom the drug was not indicated.
In order to conceal the kickbacks and bribes, the company that paid Dr. Moran is alleged to have described the payments as honoraria for educational presentations about the drug. During that period, Dr. Moran prescribed millions of micrograms of the sublingual spray to patients with no cancer diagnosis.
Subsys is manufactured by Insys, a company whose founder and CEO, John Kapoor, was sentenced in 2019 to 5½ years in prison for his role in the bribery scheme involving Dr. Moran and other physicians.
Dr. Moran faces 12 years in prison. The maximum penalty for the crimes is 10 years for each charge. As a part of his plea deal, Dr. Moran agreed to forfeit $134,000. His license to practice medicine was suspended in October 2020 according to the Pennsylvania Bureau of Professional and Occupational Affairs.
Former pharmaceutical executive charged with embezzlement
The former owner and CEO of a New Jersey pharmaceutical company is accused of embezzling millions of dollars from his company by federal officials.
According to the charging documents, John Klein, 75, of Palisades Park, N.J., hired a chief financial officer in 2016 who then created a profit-and-loss statement showing the company’s sales and receivables. According to the CFO, Mr. Klein provided information that included an account receivable of approximately $3.9 million that had not been collected.
In December 2016 and January 2017, Mr. Klein approved a reserve against the uncollected receivable in the financial statements. However, back in May 2016, $3.9 million was transferred into a company bank account that Mr. Klein controlled. In a June 2016 email, Mr. Klein acknowledged that the invoices in question had been paid in full. A review of the company bank account showed that Mr. Klein used the money to pay personal debts, such as credit card payments, property taxes, and private-school tuition for his child.
Mr. Klein is the subject of several federal lawsuits from people who worked at Cambridge Therapeutic Technologies in Teaneck, N.J., as well as individuals he collected investment money from, according to media reports.
If convicted, Mr. Klein faces up to 20 years in prison and a fine of $250,000 or twice the gross profits or twice the gross loss suffered by the victims of the fraud, whichever is greatest.
Practice administrator sentenced for defrauding medical practice
An Indiana man was sentenced to 30 months in federal prison for stealing from the ophthalmology practice where he worked for 5 years as a practice administrator.
Joshua D. Millspaugh, 42, of Westfield, Ind., pled guilty to charges of wire fraud, according to federal officials.
Mr. Millspaugh, who earned an annual salary of over $100,000, was responsible for payroll processing, purchasing, and paying the practice’s bills. After less than a year on the job, he began taking advantage of his access to company money to use the practice’s funds for himself. During his 5 years of employment, he made over 500 such transactions, making purchases, paying personal bills, and sending payroll checks to his personal bank account. He concealed these transactions with false entries in the company’s bookkeeping system. When asked about expenditures, he made up false justifications.
During Mr. Millspaugh’s sentencing, William Whitson, MD, owner and director of the practice, Whitson Vision, told the court that the loss to him and the practice was about more than money. In addition to creating long-term credit and banking problems, the situation damaged both the company’s business reputation and the morale of its other employees.
“Fraud on a small business impacts every area of that business,” said U.S. Attorney for the Southern District of Indiana Zachary A. Myers. “It also breeds mistrust, especially if the fraud is perpetrated by a trusted employee. Mr. Millspaugh exploited his position of trust for purely personal gain, and he is now being held accountable for his actions.”
In addition to the prison sentence, Mr. Millspaugh was ordered to pay $270,000 in restitution and will be federally supervised for 3 years following his release from prison.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psychiatrist sentenced to 3 years in prison for running pill mill
, including a 2020 Porsche GT4 and a 2020 Aston Martin.
According to the U.S. Department of Justice, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration began investigating Gerald Michael Abraham, 76, after receiving a tip that he was prescribing opioids to patients who did not need the medication. The investigation, which began in October 2019, included 18 visits by undercover patients to Abraham’s cash-only clinic in Naples, Fla. Patients paid $400 per visit, according to court documents.
Even though the undercover patients pretended to have signs of drug abuse, Dr. Abraham still prescribed oxycodone, a strong opioid, on each visit without any physical examination, according to officials. He repeatedly increased the strength of the prescriptions when the patients asked. In one case, he told a patient that the patient’s medical paperwork “shows you are completely normal,” then went ahead to prescribe the oxycodone.
Dr. Abraham also gave Adderall to patients who had no legitimate medical need for the drug. As with the opioid, Dr. Abraham prescribed the frequently abused amphetamine (typically used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder) after being asked for it, without performing an examination or asking questions to justify the prescription, according to the undercover law enforcement agents.
According to the Florida Department of Health, Dr. Abraham voluntarily relinquished his license in September pending board action. His license was set to expire in January 2022.
Pennsylvania physician admits to distributing drugs resulting in patient’s death
A Pennsylvania internist pleaded guilty to unlawful prescription of controlled substances, maintaining drug-involved premises, and healthcare fraud, as well as that the death of a patient resulted from the use of the controlled drugs.
When entering his plea, Dr.Kurt Moran, 69, acknowledged that the purpose of his Scranton-based pain management practice was to distribute high doses of opioids not for medical purposes, and that he often prescribed these drugs without examining the patient to verify the illness or condition the patient claimed to have. At times, he even prescribed the drugs without seeing the patient. He admitted that he knew that such practices could result in addiction and even death, according to federal officials.
The healthcare fraud charges resulted from a scheme that took place between 2014 and 2017 in which Dr. Moran received bribes in exchange for prescribing the drug Subsys (sublingual fentanyl), which is approved for use only in cancer patients who suffer from breakthrough pain. Court documents allege that Dr. Moran was paid approximately $140,000 over a 2-year period to prescribe Subsys to patients for whom the drug was not indicated.
In order to conceal the kickbacks and bribes, the company that paid Dr. Moran is alleged to have described the payments as honoraria for educational presentations about the drug. During that period, Dr. Moran prescribed millions of micrograms of the sublingual spray to patients with no cancer diagnosis.
Subsys is manufactured by Insys, a company whose founder and CEO, John Kapoor, was sentenced in 2019 to 5½ years in prison for his role in the bribery scheme involving Dr. Moran and other physicians.
Dr. Moran faces 12 years in prison. The maximum penalty for the crimes is 10 years for each charge. As a part of his plea deal, Dr. Moran agreed to forfeit $134,000. His license to practice medicine was suspended in October 2020 according to the Pennsylvania Bureau of Professional and Occupational Affairs.
Former pharmaceutical executive charged with embezzlement
The former owner and CEO of a New Jersey pharmaceutical company is accused of embezzling millions of dollars from his company by federal officials.
According to the charging documents, John Klein, 75, of Palisades Park, N.J., hired a chief financial officer in 2016 who then created a profit-and-loss statement showing the company’s sales and receivables. According to the CFO, Mr. Klein provided information that included an account receivable of approximately $3.9 million that had not been collected.
In December 2016 and January 2017, Mr. Klein approved a reserve against the uncollected receivable in the financial statements. However, back in May 2016, $3.9 million was transferred into a company bank account that Mr. Klein controlled. In a June 2016 email, Mr. Klein acknowledged that the invoices in question had been paid in full. A review of the company bank account showed that Mr. Klein used the money to pay personal debts, such as credit card payments, property taxes, and private-school tuition for his child.
Mr. Klein is the subject of several federal lawsuits from people who worked at Cambridge Therapeutic Technologies in Teaneck, N.J., as well as individuals he collected investment money from, according to media reports.
If convicted, Mr. Klein faces up to 20 years in prison and a fine of $250,000 or twice the gross profits or twice the gross loss suffered by the victims of the fraud, whichever is greatest.
Practice administrator sentenced for defrauding medical practice
An Indiana man was sentenced to 30 months in federal prison for stealing from the ophthalmology practice where he worked for 5 years as a practice administrator.
Joshua D. Millspaugh, 42, of Westfield, Ind., pled guilty to charges of wire fraud, according to federal officials.
Mr. Millspaugh, who earned an annual salary of over $100,000, was responsible for payroll processing, purchasing, and paying the practice’s bills. After less than a year on the job, he began taking advantage of his access to company money to use the practice’s funds for himself. During his 5 years of employment, he made over 500 such transactions, making purchases, paying personal bills, and sending payroll checks to his personal bank account. He concealed these transactions with false entries in the company’s bookkeeping system. When asked about expenditures, he made up false justifications.
During Mr. Millspaugh’s sentencing, William Whitson, MD, owner and director of the practice, Whitson Vision, told the court that the loss to him and the practice was about more than money. In addition to creating long-term credit and banking problems, the situation damaged both the company’s business reputation and the morale of its other employees.
“Fraud on a small business impacts every area of that business,” said U.S. Attorney for the Southern District of Indiana Zachary A. Myers. “It also breeds mistrust, especially if the fraud is perpetrated by a trusted employee. Mr. Millspaugh exploited his position of trust for purely personal gain, and he is now being held accountable for his actions.”
In addition to the prison sentence, Mr. Millspaugh was ordered to pay $270,000 in restitution and will be federally supervised for 3 years following his release from prison.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psychiatrist sentenced to 3 years in prison for running pill mill
, including a 2020 Porsche GT4 and a 2020 Aston Martin.
According to the U.S. Department of Justice, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration began investigating Gerald Michael Abraham, 76, after receiving a tip that he was prescribing opioids to patients who did not need the medication. The investigation, which began in October 2019, included 18 visits by undercover patients to Abraham’s cash-only clinic in Naples, Fla. Patients paid $400 per visit, according to court documents.
Even though the undercover patients pretended to have signs of drug abuse, Dr. Abraham still prescribed oxycodone, a strong opioid, on each visit without any physical examination, according to officials. He repeatedly increased the strength of the prescriptions when the patients asked. In one case, he told a patient that the patient’s medical paperwork “shows you are completely normal,” then went ahead to prescribe the oxycodone.
Dr. Abraham also gave Adderall to patients who had no legitimate medical need for the drug. As with the opioid, Dr. Abraham prescribed the frequently abused amphetamine (typically used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder) after being asked for it, without performing an examination or asking questions to justify the prescription, according to the undercover law enforcement agents.
According to the Florida Department of Health, Dr. Abraham voluntarily relinquished his license in September pending board action. His license was set to expire in January 2022.
Pennsylvania physician admits to distributing drugs resulting in patient’s death
A Pennsylvania internist pleaded guilty to unlawful prescription of controlled substances, maintaining drug-involved premises, and healthcare fraud, as well as that the death of a patient resulted from the use of the controlled drugs.
When entering his plea, Dr.Kurt Moran, 69, acknowledged that the purpose of his Scranton-based pain management practice was to distribute high doses of opioids not for medical purposes, and that he often prescribed these drugs without examining the patient to verify the illness or condition the patient claimed to have. At times, he even prescribed the drugs without seeing the patient. He admitted that he knew that such practices could result in addiction and even death, according to federal officials.
The healthcare fraud charges resulted from a scheme that took place between 2014 and 2017 in which Dr. Moran received bribes in exchange for prescribing the drug Subsys (sublingual fentanyl), which is approved for use only in cancer patients who suffer from breakthrough pain. Court documents allege that Dr. Moran was paid approximately $140,000 over a 2-year period to prescribe Subsys to patients for whom the drug was not indicated.
In order to conceal the kickbacks and bribes, the company that paid Dr. Moran is alleged to have described the payments as honoraria for educational presentations about the drug. During that period, Dr. Moran prescribed millions of micrograms of the sublingual spray to patients with no cancer diagnosis.
Subsys is manufactured by Insys, a company whose founder and CEO, John Kapoor, was sentenced in 2019 to 5½ years in prison for his role in the bribery scheme involving Dr. Moran and other physicians.
Dr. Moran faces 12 years in prison. The maximum penalty for the crimes is 10 years for each charge. As a part of his plea deal, Dr. Moran agreed to forfeit $134,000. His license to practice medicine was suspended in October 2020 according to the Pennsylvania Bureau of Professional and Occupational Affairs.
Former pharmaceutical executive charged with embezzlement
The former owner and CEO of a New Jersey pharmaceutical company is accused of embezzling millions of dollars from his company by federal officials.
According to the charging documents, John Klein, 75, of Palisades Park, N.J., hired a chief financial officer in 2016 who then created a profit-and-loss statement showing the company’s sales and receivables. According to the CFO, Mr. Klein provided information that included an account receivable of approximately $3.9 million that had not been collected.
In December 2016 and January 2017, Mr. Klein approved a reserve against the uncollected receivable in the financial statements. However, back in May 2016, $3.9 million was transferred into a company bank account that Mr. Klein controlled. In a June 2016 email, Mr. Klein acknowledged that the invoices in question had been paid in full. A review of the company bank account showed that Mr. Klein used the money to pay personal debts, such as credit card payments, property taxes, and private-school tuition for his child.
Mr. Klein is the subject of several federal lawsuits from people who worked at Cambridge Therapeutic Technologies in Teaneck, N.J., as well as individuals he collected investment money from, according to media reports.
If convicted, Mr. Klein faces up to 20 years in prison and a fine of $250,000 or twice the gross profits or twice the gross loss suffered by the victims of the fraud, whichever is greatest.
Practice administrator sentenced for defrauding medical practice
An Indiana man was sentenced to 30 months in federal prison for stealing from the ophthalmology practice where he worked for 5 years as a practice administrator.
Joshua D. Millspaugh, 42, of Westfield, Ind., pled guilty to charges of wire fraud, according to federal officials.
Mr. Millspaugh, who earned an annual salary of over $100,000, was responsible for payroll processing, purchasing, and paying the practice’s bills. After less than a year on the job, he began taking advantage of his access to company money to use the practice’s funds for himself. During his 5 years of employment, he made over 500 such transactions, making purchases, paying personal bills, and sending payroll checks to his personal bank account. He concealed these transactions with false entries in the company’s bookkeeping system. When asked about expenditures, he made up false justifications.
During Mr. Millspaugh’s sentencing, William Whitson, MD, owner and director of the practice, Whitson Vision, told the court that the loss to him and the practice was about more than money. In addition to creating long-term credit and banking problems, the situation damaged both the company’s business reputation and the morale of its other employees.
“Fraud on a small business impacts every area of that business,” said U.S. Attorney for the Southern District of Indiana Zachary A. Myers. “It also breeds mistrust, especially if the fraud is perpetrated by a trusted employee. Mr. Millspaugh exploited his position of trust for purely personal gain, and he is now being held accountable for his actions.”
In addition to the prison sentence, Mr. Millspaugh was ordered to pay $270,000 in restitution and will be federally supervised for 3 years following his release from prison.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA grants new indication to lumateperone (Caplyta) for bipolar depression
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded approval of lumateperone (Caplyta) to include treatment of adults with depressive episodes associated with bipolar I and II disorder, as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate.
This makes lumateperone the only FDA-approved drug for this indication.
“The efficacy, and favorable safety and tolerability profile, make Caplyta an important treatment option for the millions of patients living with bipolar I or II depression and represents a major development for these patients,” Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the mood disorders psychopharmacology unit, said in a company news release.
Lumateperone was first approved by the FDA in 2019 for the treatment of adults with schizophrenia.
‘Positioned to launch immediately’
that showed treatment with lumateperone, alone or with lithium or valproate, significantly improved depressive symptoms for patients with major depressive episodes associated with bipolar I and bipolar II disorders.
In these studies, treatment with a 42-mg once-daily dose was associated with significantly greater improvement from baseline in Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale score versus placebo.
Lumateperone also showed a statistically significant improvement in the key secondary endpoint relating to clinical global impression of bipolar disorder.
Somnolence/sedation, dizziness, nausea, and dry mouth were the most commonly reported adverse events associated with the medication. Minimal changes were observed in weight and vital signs and in results of metabolic or endocrine assessments. Incidence of extrapyramidal symptom–related events was low and was similar to those with placebo.
Sharon Mates, PhD, chairman and CEO of Intra-Cellular Therapies, noted in the same press release that the company is “positioned to launch immediately and are excited to offer Caplyta to the millions of patients living with bipolar depression.”
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded approval of lumateperone (Caplyta) to include treatment of adults with depressive episodes associated with bipolar I and II disorder, as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate.
This makes lumateperone the only FDA-approved drug for this indication.
“The efficacy, and favorable safety and tolerability profile, make Caplyta an important treatment option for the millions of patients living with bipolar I or II depression and represents a major development for these patients,” Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the mood disorders psychopharmacology unit, said in a company news release.
Lumateperone was first approved by the FDA in 2019 for the treatment of adults with schizophrenia.
‘Positioned to launch immediately’
that showed treatment with lumateperone, alone or with lithium or valproate, significantly improved depressive symptoms for patients with major depressive episodes associated with bipolar I and bipolar II disorders.
In these studies, treatment with a 42-mg once-daily dose was associated with significantly greater improvement from baseline in Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale score versus placebo.
Lumateperone also showed a statistically significant improvement in the key secondary endpoint relating to clinical global impression of bipolar disorder.
Somnolence/sedation, dizziness, nausea, and dry mouth were the most commonly reported adverse events associated with the medication. Minimal changes were observed in weight and vital signs and in results of metabolic or endocrine assessments. Incidence of extrapyramidal symptom–related events was low and was similar to those with placebo.
Sharon Mates, PhD, chairman and CEO of Intra-Cellular Therapies, noted in the same press release that the company is “positioned to launch immediately and are excited to offer Caplyta to the millions of patients living with bipolar depression.”
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded approval of lumateperone (Caplyta) to include treatment of adults with depressive episodes associated with bipolar I and II disorder, as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate.
This makes lumateperone the only FDA-approved drug for this indication.
“The efficacy, and favorable safety and tolerability profile, make Caplyta an important treatment option for the millions of patients living with bipolar I or II depression and represents a major development for these patients,” Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the mood disorders psychopharmacology unit, said in a company news release.
Lumateperone was first approved by the FDA in 2019 for the treatment of adults with schizophrenia.
‘Positioned to launch immediately’
that showed treatment with lumateperone, alone or with lithium or valproate, significantly improved depressive symptoms for patients with major depressive episodes associated with bipolar I and bipolar II disorders.
In these studies, treatment with a 42-mg once-daily dose was associated with significantly greater improvement from baseline in Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale score versus placebo.
Lumateperone also showed a statistically significant improvement in the key secondary endpoint relating to clinical global impression of bipolar disorder.
Somnolence/sedation, dizziness, nausea, and dry mouth were the most commonly reported adverse events associated with the medication. Minimal changes were observed in weight and vital signs and in results of metabolic or endocrine assessments. Incidence of extrapyramidal symptom–related events was low and was similar to those with placebo.
Sharon Mates, PhD, chairman and CEO of Intra-Cellular Therapies, noted in the same press release that the company is “positioned to launch immediately and are excited to offer Caplyta to the millions of patients living with bipolar depression.”
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID cases spike as questions remain about Omicron’s threat
The best way to stay protected is by getting vaccinated and boosted, they said.
“For the unvaccinated, you’re looking at a winter of severe illness and death – for yourselves, families, and the hospitals who may soon overwhelm,” White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Jeff Zients said at a news briefing Dec. 17. “We need the American people to do their part.”
The Omicron variant has been detected in at least 39 states and 75 countries, according to CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD.
The strain is more transmissible than the already highly infectious Delta variant, and although there was early evidence that it caused more mild disease, she said that is likely because many of those infected have been vaccinated and boosted.
“Although Delta continues to circulate widely in the United States, Omicron is increasing rapidly and we expect it to become the dominant strain in the United States, as it has in other countries, in the coming weeks,” Dr. Walensky said.
The United States is averaging close to 1,300 deaths from COVID-19 each day. New cases, deaths, and hospitalizations are higher now than in the previous winter – before vaccines were so widely available. The New York Times reported on Dec. 17 that new infections in Connecticut and Maine have grown 150% in the past 2 weeks, and Ohio and Indiana are seeing hospitalization rates nearing the worst of 2020-2021’s winter surge.
Dueling reports released recently gave cause for relief and concern about Omicron.
A study from South Africa released on Dec. 14 shows lower hospitalizations during the first 3 weeks of the Omicron wave than during earlier waves from other variants. That’s the good news.
The concerning news is out of the United Kingdom, where Imperial College London reported Dec. 17 that the risk of reinfection with COVID-19 from Omicron is more than 5 times as high and that cases of Omicron-based COVID-19 are doubling every 2 days.
What’s more, the study “finds no evidence of Omicron having lower severity than Delta, judged by either the proportion of people testing positive who report symptoms, or by the proportion of cases seeking hospital care after infection. However, hospitalization data remains very limited at this time,” the researchers said.
“We have no evidence that the virus itself is more mild,” Eric Topol, MD, executive vice president of Scripps Research and editor-in-chief of Medscape, told PBS NewsHour. “Until we have that, we have to assume that people who don’t have any protection are highly vulnerable to getting very ill.”
The White House COVID-19 team continues to urge parents and guardians to get their children vaccinated, especially in anticipation of a post-holiday spike. Dr. Walensky said the CDC’s vaccine advisory board met on Dec. 16 to continue the safety discussion about COVID-19 vaccinations in children.
So far, 20 million children under 17 and 5 million under 11 have received their shots.
“Looking specifically at vaccine safety data from over 50,000 children 5-11 years old, we found no evidence of serious safety concerns,” Dr. Walensky said.
Top infectious disease expert Anthony S. Fauci, MD, highlighted the importance of getting vaccinated and boosted to avoid serious disease from Delta and Omicron.
“We’re in a situation where we are now facing a very important Delta surge and we are looking over our shoulder at an oncoming Omicron surge,” he said. “The optimum protection is fully vaccinated plus a boost.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The best way to stay protected is by getting vaccinated and boosted, they said.
“For the unvaccinated, you’re looking at a winter of severe illness and death – for yourselves, families, and the hospitals who may soon overwhelm,” White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Jeff Zients said at a news briefing Dec. 17. “We need the American people to do their part.”
The Omicron variant has been detected in at least 39 states and 75 countries, according to CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD.
The strain is more transmissible than the already highly infectious Delta variant, and although there was early evidence that it caused more mild disease, she said that is likely because many of those infected have been vaccinated and boosted.
“Although Delta continues to circulate widely in the United States, Omicron is increasing rapidly and we expect it to become the dominant strain in the United States, as it has in other countries, in the coming weeks,” Dr. Walensky said.
The United States is averaging close to 1,300 deaths from COVID-19 each day. New cases, deaths, and hospitalizations are higher now than in the previous winter – before vaccines were so widely available. The New York Times reported on Dec. 17 that new infections in Connecticut and Maine have grown 150% in the past 2 weeks, and Ohio and Indiana are seeing hospitalization rates nearing the worst of 2020-2021’s winter surge.
Dueling reports released recently gave cause for relief and concern about Omicron.
A study from South Africa released on Dec. 14 shows lower hospitalizations during the first 3 weeks of the Omicron wave than during earlier waves from other variants. That’s the good news.
The concerning news is out of the United Kingdom, where Imperial College London reported Dec. 17 that the risk of reinfection with COVID-19 from Omicron is more than 5 times as high and that cases of Omicron-based COVID-19 are doubling every 2 days.
What’s more, the study “finds no evidence of Omicron having lower severity than Delta, judged by either the proportion of people testing positive who report symptoms, or by the proportion of cases seeking hospital care after infection. However, hospitalization data remains very limited at this time,” the researchers said.
“We have no evidence that the virus itself is more mild,” Eric Topol, MD, executive vice president of Scripps Research and editor-in-chief of Medscape, told PBS NewsHour. “Until we have that, we have to assume that people who don’t have any protection are highly vulnerable to getting very ill.”
The White House COVID-19 team continues to urge parents and guardians to get their children vaccinated, especially in anticipation of a post-holiday spike. Dr. Walensky said the CDC’s vaccine advisory board met on Dec. 16 to continue the safety discussion about COVID-19 vaccinations in children.
So far, 20 million children under 17 and 5 million under 11 have received their shots.
“Looking specifically at vaccine safety data from over 50,000 children 5-11 years old, we found no evidence of serious safety concerns,” Dr. Walensky said.
Top infectious disease expert Anthony S. Fauci, MD, highlighted the importance of getting vaccinated and boosted to avoid serious disease from Delta and Omicron.
“We’re in a situation where we are now facing a very important Delta surge and we are looking over our shoulder at an oncoming Omicron surge,” he said. “The optimum protection is fully vaccinated plus a boost.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The best way to stay protected is by getting vaccinated and boosted, they said.
“For the unvaccinated, you’re looking at a winter of severe illness and death – for yourselves, families, and the hospitals who may soon overwhelm,” White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Jeff Zients said at a news briefing Dec. 17. “We need the American people to do their part.”
The Omicron variant has been detected in at least 39 states and 75 countries, according to CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD.
The strain is more transmissible than the already highly infectious Delta variant, and although there was early evidence that it caused more mild disease, she said that is likely because many of those infected have been vaccinated and boosted.
“Although Delta continues to circulate widely in the United States, Omicron is increasing rapidly and we expect it to become the dominant strain in the United States, as it has in other countries, in the coming weeks,” Dr. Walensky said.
The United States is averaging close to 1,300 deaths from COVID-19 each day. New cases, deaths, and hospitalizations are higher now than in the previous winter – before vaccines were so widely available. The New York Times reported on Dec. 17 that new infections in Connecticut and Maine have grown 150% in the past 2 weeks, and Ohio and Indiana are seeing hospitalization rates nearing the worst of 2020-2021’s winter surge.
Dueling reports released recently gave cause for relief and concern about Omicron.
A study from South Africa released on Dec. 14 shows lower hospitalizations during the first 3 weeks of the Omicron wave than during earlier waves from other variants. That’s the good news.
The concerning news is out of the United Kingdom, where Imperial College London reported Dec. 17 that the risk of reinfection with COVID-19 from Omicron is more than 5 times as high and that cases of Omicron-based COVID-19 are doubling every 2 days.
What’s more, the study “finds no evidence of Omicron having lower severity than Delta, judged by either the proportion of people testing positive who report symptoms, or by the proportion of cases seeking hospital care after infection. However, hospitalization data remains very limited at this time,” the researchers said.
“We have no evidence that the virus itself is more mild,” Eric Topol, MD, executive vice president of Scripps Research and editor-in-chief of Medscape, told PBS NewsHour. “Until we have that, we have to assume that people who don’t have any protection are highly vulnerable to getting very ill.”
The White House COVID-19 team continues to urge parents and guardians to get their children vaccinated, especially in anticipation of a post-holiday spike. Dr. Walensky said the CDC’s vaccine advisory board met on Dec. 16 to continue the safety discussion about COVID-19 vaccinations in children.
So far, 20 million children under 17 and 5 million under 11 have received their shots.
“Looking specifically at vaccine safety data from over 50,000 children 5-11 years old, we found no evidence of serious safety concerns,” Dr. Walensky said.
Top infectious disease expert Anthony S. Fauci, MD, highlighted the importance of getting vaccinated and boosted to avoid serious disease from Delta and Omicron.
“We’re in a situation where we are now facing a very important Delta surge and we are looking over our shoulder at an oncoming Omicron surge,” he said. “The optimum protection is fully vaccinated plus a boost.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Small myocarditis risk now seen for adenovirus-based COVID-19 vaccine
The first large population study to investigate the association between different COVID-19 vaccines types and cardiac effects and adverse events shows a small increase in the risk for acute myocarditis with both the mRNA-based vaccines and – in what may a first in the literature – an adenovirus-vector vaccine.
The excess risk was seen following the first dose of the ChAdOc1 (AstraZeneca/Oxford), the adenovirus-based vaccine, and the mRNA-based BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech). It was observed after first and second doses of the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccine.
The incidence rate ratios for myocarditis 1-7 days after the first AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Moderna injections were 1.76, 1.45, and 8.38, respectively, and 23.1 after the second dose of the Moderna vaccine.
“There’s a bit more uncertainty and worry about mRNA vaccines because it’s quite a new vector for vaccination and, therefore, there’s been more focus on the potential side effects,” said Nicholas Mills, MD.
“But it doesn’t surprise me the signal is present for all types of vaccines because they’re designed to generate a systemic immune response and that is, unfortunately, where you can cause small risks for immune-mediated illnesses like myocarditis,” Dr. Mills, from the University of Edinburgh, told this news organization. Dr. Mills is a coauthor on the study, published Dec. 14 in Nature Medicine.
To put the risks in context, the group estimated between 1 and 10 additional myocarditis hospitalizations or deaths per 1 million people vaccinated, but 40 excess myocarditis events per million following a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result.
As reported, rates of excess myocarditis events associated with a first dose were 2 per million injections of the AstraZeneca vaccine, 1 per million for the Pfizer vaccine, and 6 per million with the Moderna vaccine.
Following a second dose, there were 10 additional myocarditis events per million people receiving the Moderna vaccine and none among recipients of the AstraZeneca or Pfizer vaccines.
“It was particularly seen within the first 7 days of the first dose, which is very consistent with what we see in people who have viral myocarditis,” Dr. Mills said. “So it looks like a real signal but it’s very small.”
The results are in line with previous studies of the Pfizer vaccine in Israel and studies of the Moderna vaccine in the United States, Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, told this news organization.
“What this paper does is confirm that cardiovascular complications – and they are only looking at a small component of those cardiovascular complications – are markedly higher with the COVID-19 infection than with the vaccines,” she said.
It also adds a new twist to the search for the mechanisms of myocarditis, which has focused on the immunogenicity of the RNA in the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines but also hypothesized that molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and cell antigens, antibody production against cardiac proteins, and testosterone may play a role.
“But now it doesn’t look like the risk is solely confined to the mRNA vaccine platform because it’s also happening with the adenovirus,” Dr. Bozkurt said. “The mechanisms require future experimental and clinical research and we’ll need more granular data with cohorts that are closely followed up as well as subclinical follow-up.”
James de Lemos, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and cochair of the American Heart Association’s COVID-19 CVD Registry, said he was also not surprised by a myocarditis signal with AstraZeneca’s adenovirus vaccine.
“Looking at relative risks has biological implications, but the clinical and public health implications are that the absolute risk with the adenovirus is trivial. And you see that with their estimations of absolute risk where it’s literally sort of a needle in the haystack of 1 or 2 per million,” he said in an interview.
Large-scale data
The investigators examined the rates of hospital admission or death from myocarditis, pericarditis, and cardiac arrhythmia in the 28 days following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination or infection by linking the English National Immunisation Database of COVID-19 vaccination with a national patient-level health care database of 38.6 million people, aged 16 years or older, vaccinated from Dec.1, 2020, to Aug. 24, 2021.
The number of people admitted to the hospital or who died during the study period was 1,615 for myocarditis, 1,574 for pericarditis, and 385,508 for cardiac arrhythmia.
There was no evidence of an increased risk for pericarditis or cardiac arrhythmia following vaccination, except for arrhythmia in the 28 days following a second dose of the Moderna vaccine (IRR, 1.46).
In contrast, the risk was increased for pericarditis (IRR, 2.79) and cardiac arrhythmia (IRR, 5.35) in the 28 days following a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result.
Although the scale of the analysis allows for more precise estimates than what’s been possible in smaller data sets, there is the challenge of diagnosing COVID-19 from billing codes and the potential for ascertainment bias, noted Dr. de Lemos.
“Having said that, I think it’s a really important study, because it’s the first study to put the incidence in context in the same general population the risks of myocarditis with various vaccines and with COVID-19,” he said.
“That’s really important and provides a lot of reassurance for those who are trying to balance the risks and benefits of vaccination.”
Analyses by sex and age
A subgroup analysis by age showed increased risks for myocarditis with the mRNA vaccines only in those younger than 40, whereas no association was found with the Oxford adenovirus vaccine.
“We’re not seeing any signal here that would make us change the recommendation for vaccination in children as a consequence of this risk,” Dr. Mills said during a press briefing.
Dr. Bozkurt pointed out, however, that the estimated excess in myocarditis events following a second dose of the Moderna vaccine in these younger adults reportedly exceeded that for SARS-CoV-2 infection (15 per million vs. 10 per million).
“For that age group, it’s concerning and needs further clarification. This hasn’t been seen before,” she said.
The average age was 39 years for those receiving two doses of the Moderna vaccine and 55 for recipients of the Pfizer and Oxford vaccines. The Moderna vaccine wasn’t rolled out until April 2021 in the United Kingdom, the authors noted, so the number of patients who received this vaccine is lower.
Although reports have suggested young males are at greater risk for myocarditis after vaccination, an analysis by sex found that women had an increased risk for myocarditis after a first dose of the AstraZeneca (IRR, 1.40) and Pfizer (IRR, 1.54) vaccines and following a positive COVID-19 test result (IRR, 11.00).
“Women being at increased risk is rather a new message,” Dr. Bozkurt said. “But the incidence rate ratios are being compared against the unvaccinated, so when you see the increase in women, it doesn’t mean it’s increased against men. It would be helpful for sex-specific incidence rate ratios to be reported for younger age subgroups, such as ages 16-20 and 20-30, to determine whether there’s an increased risk for males compared to females at younger ages.”
Age and sex differences are huge questions, but “I think we’ll learn a lot about myocarditis in general from what is going to be an explosion of research into the vaccine-associated causes,” Dr. de Lemos said.
“That will help us understand myocarditis more broadly and prepare us for the next generation of vaccines, which inevitably will be mRNA based.”
Dr. Mills reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Bozkurt reported consulting for Bayer and scPharmaceuticals and serving on a clinical-events committee for a trial supported by Abbott Pharmaceuticals and on a data and safety monitoring board for a trial supported by Liva Nova Pharmaceuticals. Dr. De Lemos reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first large population study to investigate the association between different COVID-19 vaccines types and cardiac effects and adverse events shows a small increase in the risk for acute myocarditis with both the mRNA-based vaccines and – in what may a first in the literature – an adenovirus-vector vaccine.
The excess risk was seen following the first dose of the ChAdOc1 (AstraZeneca/Oxford), the adenovirus-based vaccine, and the mRNA-based BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech). It was observed after first and second doses of the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccine.
The incidence rate ratios for myocarditis 1-7 days after the first AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Moderna injections were 1.76, 1.45, and 8.38, respectively, and 23.1 after the second dose of the Moderna vaccine.
“There’s a bit more uncertainty and worry about mRNA vaccines because it’s quite a new vector for vaccination and, therefore, there’s been more focus on the potential side effects,” said Nicholas Mills, MD.
“But it doesn’t surprise me the signal is present for all types of vaccines because they’re designed to generate a systemic immune response and that is, unfortunately, where you can cause small risks for immune-mediated illnesses like myocarditis,” Dr. Mills, from the University of Edinburgh, told this news organization. Dr. Mills is a coauthor on the study, published Dec. 14 in Nature Medicine.
To put the risks in context, the group estimated between 1 and 10 additional myocarditis hospitalizations or deaths per 1 million people vaccinated, but 40 excess myocarditis events per million following a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result.
As reported, rates of excess myocarditis events associated with a first dose were 2 per million injections of the AstraZeneca vaccine, 1 per million for the Pfizer vaccine, and 6 per million with the Moderna vaccine.
Following a second dose, there were 10 additional myocarditis events per million people receiving the Moderna vaccine and none among recipients of the AstraZeneca or Pfizer vaccines.
“It was particularly seen within the first 7 days of the first dose, which is very consistent with what we see in people who have viral myocarditis,” Dr. Mills said. “So it looks like a real signal but it’s very small.”
The results are in line with previous studies of the Pfizer vaccine in Israel and studies of the Moderna vaccine in the United States, Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, told this news organization.
“What this paper does is confirm that cardiovascular complications – and they are only looking at a small component of those cardiovascular complications – are markedly higher with the COVID-19 infection than with the vaccines,” she said.
It also adds a new twist to the search for the mechanisms of myocarditis, which has focused on the immunogenicity of the RNA in the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines but also hypothesized that molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and cell antigens, antibody production against cardiac proteins, and testosterone may play a role.
“But now it doesn’t look like the risk is solely confined to the mRNA vaccine platform because it’s also happening with the adenovirus,” Dr. Bozkurt said. “The mechanisms require future experimental and clinical research and we’ll need more granular data with cohorts that are closely followed up as well as subclinical follow-up.”
James de Lemos, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and cochair of the American Heart Association’s COVID-19 CVD Registry, said he was also not surprised by a myocarditis signal with AstraZeneca’s adenovirus vaccine.
“Looking at relative risks has biological implications, but the clinical and public health implications are that the absolute risk with the adenovirus is trivial. And you see that with their estimations of absolute risk where it’s literally sort of a needle in the haystack of 1 or 2 per million,” he said in an interview.
Large-scale data
The investigators examined the rates of hospital admission or death from myocarditis, pericarditis, and cardiac arrhythmia in the 28 days following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination or infection by linking the English National Immunisation Database of COVID-19 vaccination with a national patient-level health care database of 38.6 million people, aged 16 years or older, vaccinated from Dec.1, 2020, to Aug. 24, 2021.
The number of people admitted to the hospital or who died during the study period was 1,615 for myocarditis, 1,574 for pericarditis, and 385,508 for cardiac arrhythmia.
There was no evidence of an increased risk for pericarditis or cardiac arrhythmia following vaccination, except for arrhythmia in the 28 days following a second dose of the Moderna vaccine (IRR, 1.46).
In contrast, the risk was increased for pericarditis (IRR, 2.79) and cardiac arrhythmia (IRR, 5.35) in the 28 days following a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result.
Although the scale of the analysis allows for more precise estimates than what’s been possible in smaller data sets, there is the challenge of diagnosing COVID-19 from billing codes and the potential for ascertainment bias, noted Dr. de Lemos.
“Having said that, I think it’s a really important study, because it’s the first study to put the incidence in context in the same general population the risks of myocarditis with various vaccines and with COVID-19,” he said.
“That’s really important and provides a lot of reassurance for those who are trying to balance the risks and benefits of vaccination.”
Analyses by sex and age
A subgroup analysis by age showed increased risks for myocarditis with the mRNA vaccines only in those younger than 40, whereas no association was found with the Oxford adenovirus vaccine.
“We’re not seeing any signal here that would make us change the recommendation for vaccination in children as a consequence of this risk,” Dr. Mills said during a press briefing.
Dr. Bozkurt pointed out, however, that the estimated excess in myocarditis events following a second dose of the Moderna vaccine in these younger adults reportedly exceeded that for SARS-CoV-2 infection (15 per million vs. 10 per million).
“For that age group, it’s concerning and needs further clarification. This hasn’t been seen before,” she said.
The average age was 39 years for those receiving two doses of the Moderna vaccine and 55 for recipients of the Pfizer and Oxford vaccines. The Moderna vaccine wasn’t rolled out until April 2021 in the United Kingdom, the authors noted, so the number of patients who received this vaccine is lower.
Although reports have suggested young males are at greater risk for myocarditis after vaccination, an analysis by sex found that women had an increased risk for myocarditis after a first dose of the AstraZeneca (IRR, 1.40) and Pfizer (IRR, 1.54) vaccines and following a positive COVID-19 test result (IRR, 11.00).
“Women being at increased risk is rather a new message,” Dr. Bozkurt said. “But the incidence rate ratios are being compared against the unvaccinated, so when you see the increase in women, it doesn’t mean it’s increased against men. It would be helpful for sex-specific incidence rate ratios to be reported for younger age subgroups, such as ages 16-20 and 20-30, to determine whether there’s an increased risk for males compared to females at younger ages.”
Age and sex differences are huge questions, but “I think we’ll learn a lot about myocarditis in general from what is going to be an explosion of research into the vaccine-associated causes,” Dr. de Lemos said.
“That will help us understand myocarditis more broadly and prepare us for the next generation of vaccines, which inevitably will be mRNA based.”
Dr. Mills reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Bozkurt reported consulting for Bayer and scPharmaceuticals and serving on a clinical-events committee for a trial supported by Abbott Pharmaceuticals and on a data and safety monitoring board for a trial supported by Liva Nova Pharmaceuticals. Dr. De Lemos reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first large population study to investigate the association between different COVID-19 vaccines types and cardiac effects and adverse events shows a small increase in the risk for acute myocarditis with both the mRNA-based vaccines and – in what may a first in the literature – an adenovirus-vector vaccine.
The excess risk was seen following the first dose of the ChAdOc1 (AstraZeneca/Oxford), the adenovirus-based vaccine, and the mRNA-based BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech). It was observed after first and second doses of the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccine.
The incidence rate ratios for myocarditis 1-7 days after the first AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Moderna injections were 1.76, 1.45, and 8.38, respectively, and 23.1 after the second dose of the Moderna vaccine.
“There’s a bit more uncertainty and worry about mRNA vaccines because it’s quite a new vector for vaccination and, therefore, there’s been more focus on the potential side effects,” said Nicholas Mills, MD.
“But it doesn’t surprise me the signal is present for all types of vaccines because they’re designed to generate a systemic immune response and that is, unfortunately, where you can cause small risks for immune-mediated illnesses like myocarditis,” Dr. Mills, from the University of Edinburgh, told this news organization. Dr. Mills is a coauthor on the study, published Dec. 14 in Nature Medicine.
To put the risks in context, the group estimated between 1 and 10 additional myocarditis hospitalizations or deaths per 1 million people vaccinated, but 40 excess myocarditis events per million following a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result.
As reported, rates of excess myocarditis events associated with a first dose were 2 per million injections of the AstraZeneca vaccine, 1 per million for the Pfizer vaccine, and 6 per million with the Moderna vaccine.
Following a second dose, there were 10 additional myocarditis events per million people receiving the Moderna vaccine and none among recipients of the AstraZeneca or Pfizer vaccines.
“It was particularly seen within the first 7 days of the first dose, which is very consistent with what we see in people who have viral myocarditis,” Dr. Mills said. “So it looks like a real signal but it’s very small.”
The results are in line with previous studies of the Pfizer vaccine in Israel and studies of the Moderna vaccine in the United States, Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, told this news organization.
“What this paper does is confirm that cardiovascular complications – and they are only looking at a small component of those cardiovascular complications – are markedly higher with the COVID-19 infection than with the vaccines,” she said.
It also adds a new twist to the search for the mechanisms of myocarditis, which has focused on the immunogenicity of the RNA in the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines but also hypothesized that molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and cell antigens, antibody production against cardiac proteins, and testosterone may play a role.
“But now it doesn’t look like the risk is solely confined to the mRNA vaccine platform because it’s also happening with the adenovirus,” Dr. Bozkurt said. “The mechanisms require future experimental and clinical research and we’ll need more granular data with cohorts that are closely followed up as well as subclinical follow-up.”
James de Lemos, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and cochair of the American Heart Association’s COVID-19 CVD Registry, said he was also not surprised by a myocarditis signal with AstraZeneca’s adenovirus vaccine.
“Looking at relative risks has biological implications, but the clinical and public health implications are that the absolute risk with the adenovirus is trivial. And you see that with their estimations of absolute risk where it’s literally sort of a needle in the haystack of 1 or 2 per million,” he said in an interview.
Large-scale data
The investigators examined the rates of hospital admission or death from myocarditis, pericarditis, and cardiac arrhythmia in the 28 days following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination or infection by linking the English National Immunisation Database of COVID-19 vaccination with a national patient-level health care database of 38.6 million people, aged 16 years or older, vaccinated from Dec.1, 2020, to Aug. 24, 2021.
The number of people admitted to the hospital or who died during the study period was 1,615 for myocarditis, 1,574 for pericarditis, and 385,508 for cardiac arrhythmia.
There was no evidence of an increased risk for pericarditis or cardiac arrhythmia following vaccination, except for arrhythmia in the 28 days following a second dose of the Moderna vaccine (IRR, 1.46).
In contrast, the risk was increased for pericarditis (IRR, 2.79) and cardiac arrhythmia (IRR, 5.35) in the 28 days following a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result.
Although the scale of the analysis allows for more precise estimates than what’s been possible in smaller data sets, there is the challenge of diagnosing COVID-19 from billing codes and the potential for ascertainment bias, noted Dr. de Lemos.
“Having said that, I think it’s a really important study, because it’s the first study to put the incidence in context in the same general population the risks of myocarditis with various vaccines and with COVID-19,” he said.
“That’s really important and provides a lot of reassurance for those who are trying to balance the risks and benefits of vaccination.”
Analyses by sex and age
A subgroup analysis by age showed increased risks for myocarditis with the mRNA vaccines only in those younger than 40, whereas no association was found with the Oxford adenovirus vaccine.
“We’re not seeing any signal here that would make us change the recommendation for vaccination in children as a consequence of this risk,” Dr. Mills said during a press briefing.
Dr. Bozkurt pointed out, however, that the estimated excess in myocarditis events following a second dose of the Moderna vaccine in these younger adults reportedly exceeded that for SARS-CoV-2 infection (15 per million vs. 10 per million).
“For that age group, it’s concerning and needs further clarification. This hasn’t been seen before,” she said.
The average age was 39 years for those receiving two doses of the Moderna vaccine and 55 for recipients of the Pfizer and Oxford vaccines. The Moderna vaccine wasn’t rolled out until April 2021 in the United Kingdom, the authors noted, so the number of patients who received this vaccine is lower.
Although reports have suggested young males are at greater risk for myocarditis after vaccination, an analysis by sex found that women had an increased risk for myocarditis after a first dose of the AstraZeneca (IRR, 1.40) and Pfizer (IRR, 1.54) vaccines and following a positive COVID-19 test result (IRR, 11.00).
“Women being at increased risk is rather a new message,” Dr. Bozkurt said. “But the incidence rate ratios are being compared against the unvaccinated, so when you see the increase in women, it doesn’t mean it’s increased against men. It would be helpful for sex-specific incidence rate ratios to be reported for younger age subgroups, such as ages 16-20 and 20-30, to determine whether there’s an increased risk for males compared to females at younger ages.”
Age and sex differences are huge questions, but “I think we’ll learn a lot about myocarditis in general from what is going to be an explosion of research into the vaccine-associated causes,” Dr. de Lemos said.
“That will help us understand myocarditis more broadly and prepare us for the next generation of vaccines, which inevitably will be mRNA based.”
Dr. Mills reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Bozkurt reported consulting for Bayer and scPharmaceuticals and serving on a clinical-events committee for a trial supported by Abbott Pharmaceuticals and on a data and safety monitoring board for a trial supported by Liva Nova Pharmaceuticals. Dr. De Lemos reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
Most addiction specialists support legalized therapeutic psychedelics
The majority of addiction specialists, including psychiatrists, believe psychedelics are promising for the treatment of substance use disorders (SUDs) and psychiatric illnesses and, with some caveats, support legalization of the substances for these indications, results of a new survey show.
This strong positive attitude is “a surprise” given previous wariness of addiction specialists regarding legalization of marijuana, noted study investigator Amanda Kim, MD, JD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“We had hypothesized that addiction specialists would express more skepticism about psychedelics compared to nonaddiction specialists,” Dr. Kim said.
Instead, addiction experts who participated in the survey were very much in favor of psychedelics being legalized for therapeutic use, but only in a controlled setting.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
Growing interest
In recent years, there has been increased interest in the scientific community and among the general public in the therapeutic potential of psychedelics, said Dr. Kim. Previous research has shown growing positivity about psychedelics and support for their legalization among psychiatrists, she added.
Psychedelics have been decriminalized and/or legalized in several jurisdictions. The Food and Drug Administration has granted breakthrough therapy designation for 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and has granted the same designation to psilocybin in the treatment of major depressive disorder.
“Despite psychedelics increasingly entering the mainstream, we are unaware of any studies specifically assessing the current attitudes of physicians specializing in addictions regarding psychedelics,” Dr. Kim said.
For the study, investigators identified prospective survey participants from the AAAP directory. They also reached out to program directors of addiction medicine and addiction psychiatry fellowships.
In the anonymous online survey, respondents were asked to rate their level of agreement with 30 statements.
The analysis included 145 respondents (59% men; mean age, 46.2 years). Psychiatrists made up about two-thirds of the sample. The remainder specialized in internal and family medicine.
Most respondents had some clinical exposure to psychedelics.
Positive attitudes, concerns
Overall, participants expressed very positive attitudes regarding the therapeutic use of psychedelics. About 64% strongly agreed or agreed psychedelics show promise in treating SUDs, and 82% agreed they show promise in treating psychiatric disorders.
However, more than one-third of respondents (37.9%) expressed concern about the addictive potential of psychedelics. This is more than in previous research polling psychiatrists, possibly because the study’s “broad” definition of psychedelics included “nonclassic, nonserotonergic hallucinogens,” such as ketamine and MDMA, Dr. Kim noted.
Because ketamine and MDMA are both lumped into the hallucinogen category in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), “and both are known to have addictive potential, this may have obscured participant responses,” she added.
Some 28% of participants expressed concern about psychedelic use increasing the risk for subsequent psychiatric disorders and long-term cognitive impairment.
Almost three-quarters (74.5%) believe the therapeutic use of psychedelics should be legalized. However, most wanted legal therapeutic psychedelics to be highly regulated and administered only in controlled settings with specially trained providers.
Almost half of the sample believed therapeutic psychedelics should be legal in a variety of different contexts and by non-Western providers, in accordance with indigenous and/or spiritual traditions.
One surprising finding was that most respondents believed patients would be keen on using psychedelics to treat SUDs, said Dr. Kim.
“This may reflect evolving attitudes of both providers and patients about psychedelics, and it will be interesting to further study attitudes of patients toward the use of psychedelics to treat SUD in the future,” she added.
Attitudes toward psychedelics were generally similar for psychiatrists and nonpsychiatrists; but psychiatrists expressed greater comfort in discussing them with patients and were more likely to have observed complications of psychedelics use in their practice.
Dr. Kim said the study’s limitations included the small sample size and possible selection bias, as those with more favorable views of psychedelics may have been more likely to respond.
The study was supported by the Source Research Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The majority of addiction specialists, including psychiatrists, believe psychedelics are promising for the treatment of substance use disorders (SUDs) and psychiatric illnesses and, with some caveats, support legalization of the substances for these indications, results of a new survey show.
This strong positive attitude is “a surprise” given previous wariness of addiction specialists regarding legalization of marijuana, noted study investigator Amanda Kim, MD, JD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“We had hypothesized that addiction specialists would express more skepticism about psychedelics compared to nonaddiction specialists,” Dr. Kim said.
Instead, addiction experts who participated in the survey were very much in favor of psychedelics being legalized for therapeutic use, but only in a controlled setting.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
Growing interest
In recent years, there has been increased interest in the scientific community and among the general public in the therapeutic potential of psychedelics, said Dr. Kim. Previous research has shown growing positivity about psychedelics and support for their legalization among psychiatrists, she added.
Psychedelics have been decriminalized and/or legalized in several jurisdictions. The Food and Drug Administration has granted breakthrough therapy designation for 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and has granted the same designation to psilocybin in the treatment of major depressive disorder.
“Despite psychedelics increasingly entering the mainstream, we are unaware of any studies specifically assessing the current attitudes of physicians specializing in addictions regarding psychedelics,” Dr. Kim said.
For the study, investigators identified prospective survey participants from the AAAP directory. They also reached out to program directors of addiction medicine and addiction psychiatry fellowships.
In the anonymous online survey, respondents were asked to rate their level of agreement with 30 statements.
The analysis included 145 respondents (59% men; mean age, 46.2 years). Psychiatrists made up about two-thirds of the sample. The remainder specialized in internal and family medicine.
Most respondents had some clinical exposure to psychedelics.
Positive attitudes, concerns
Overall, participants expressed very positive attitudes regarding the therapeutic use of psychedelics. About 64% strongly agreed or agreed psychedelics show promise in treating SUDs, and 82% agreed they show promise in treating psychiatric disorders.
However, more than one-third of respondents (37.9%) expressed concern about the addictive potential of psychedelics. This is more than in previous research polling psychiatrists, possibly because the study’s “broad” definition of psychedelics included “nonclassic, nonserotonergic hallucinogens,” such as ketamine and MDMA, Dr. Kim noted.
Because ketamine and MDMA are both lumped into the hallucinogen category in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), “and both are known to have addictive potential, this may have obscured participant responses,” she added.
Some 28% of participants expressed concern about psychedelic use increasing the risk for subsequent psychiatric disorders and long-term cognitive impairment.
Almost three-quarters (74.5%) believe the therapeutic use of psychedelics should be legalized. However, most wanted legal therapeutic psychedelics to be highly regulated and administered only in controlled settings with specially trained providers.
Almost half of the sample believed therapeutic psychedelics should be legal in a variety of different contexts and by non-Western providers, in accordance with indigenous and/or spiritual traditions.
One surprising finding was that most respondents believed patients would be keen on using psychedelics to treat SUDs, said Dr. Kim.
“This may reflect evolving attitudes of both providers and patients about psychedelics, and it will be interesting to further study attitudes of patients toward the use of psychedelics to treat SUD in the future,” she added.
Attitudes toward psychedelics were generally similar for psychiatrists and nonpsychiatrists; but psychiatrists expressed greater comfort in discussing them with patients and were more likely to have observed complications of psychedelics use in their practice.
Dr. Kim said the study’s limitations included the small sample size and possible selection bias, as those with more favorable views of psychedelics may have been more likely to respond.
The study was supported by the Source Research Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The majority of addiction specialists, including psychiatrists, believe psychedelics are promising for the treatment of substance use disorders (SUDs) and psychiatric illnesses and, with some caveats, support legalization of the substances for these indications, results of a new survey show.
This strong positive attitude is “a surprise” given previous wariness of addiction specialists regarding legalization of marijuana, noted study investigator Amanda Kim, MD, JD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“We had hypothesized that addiction specialists would express more skepticism about psychedelics compared to nonaddiction specialists,” Dr. Kim said.
Instead, addiction experts who participated in the survey were very much in favor of psychedelics being legalized for therapeutic use, but only in a controlled setting.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
Growing interest
In recent years, there has been increased interest in the scientific community and among the general public in the therapeutic potential of psychedelics, said Dr. Kim. Previous research has shown growing positivity about psychedelics and support for their legalization among psychiatrists, she added.
Psychedelics have been decriminalized and/or legalized in several jurisdictions. The Food and Drug Administration has granted breakthrough therapy designation for 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and has granted the same designation to psilocybin in the treatment of major depressive disorder.
“Despite psychedelics increasingly entering the mainstream, we are unaware of any studies specifically assessing the current attitudes of physicians specializing in addictions regarding psychedelics,” Dr. Kim said.
For the study, investigators identified prospective survey participants from the AAAP directory. They also reached out to program directors of addiction medicine and addiction psychiatry fellowships.
In the anonymous online survey, respondents were asked to rate their level of agreement with 30 statements.
The analysis included 145 respondents (59% men; mean age, 46.2 years). Psychiatrists made up about two-thirds of the sample. The remainder specialized in internal and family medicine.
Most respondents had some clinical exposure to psychedelics.
Positive attitudes, concerns
Overall, participants expressed very positive attitudes regarding the therapeutic use of psychedelics. About 64% strongly agreed or agreed psychedelics show promise in treating SUDs, and 82% agreed they show promise in treating psychiatric disorders.
However, more than one-third of respondents (37.9%) expressed concern about the addictive potential of psychedelics. This is more than in previous research polling psychiatrists, possibly because the study’s “broad” definition of psychedelics included “nonclassic, nonserotonergic hallucinogens,” such as ketamine and MDMA, Dr. Kim noted.
Because ketamine and MDMA are both lumped into the hallucinogen category in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), “and both are known to have addictive potential, this may have obscured participant responses,” she added.
Some 28% of participants expressed concern about psychedelic use increasing the risk for subsequent psychiatric disorders and long-term cognitive impairment.
Almost three-quarters (74.5%) believe the therapeutic use of psychedelics should be legalized. However, most wanted legal therapeutic psychedelics to be highly regulated and administered only in controlled settings with specially trained providers.
Almost half of the sample believed therapeutic psychedelics should be legal in a variety of different contexts and by non-Western providers, in accordance with indigenous and/or spiritual traditions.
One surprising finding was that most respondents believed patients would be keen on using psychedelics to treat SUDs, said Dr. Kim.
“This may reflect evolving attitudes of both providers and patients about psychedelics, and it will be interesting to further study attitudes of patients toward the use of psychedelics to treat SUD in the future,” she added.
Attitudes toward psychedelics were generally similar for psychiatrists and nonpsychiatrists; but psychiatrists expressed greater comfort in discussing them with patients and were more likely to have observed complications of psychedelics use in their practice.
Dr. Kim said the study’s limitations included the small sample size and possible selection bias, as those with more favorable views of psychedelics may have been more likely to respond.
The study was supported by the Source Research Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAAP 2021