User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
‘Pandemic brain’ not limited to patients infected with COVID-19
The stress of living through a pandemic may cause brain inflammation even in those uninfected with SARS-CoV-2, a study suggests.
Healthy individuals who tested negative for the virus that causes COVID-19 had elevated levels of inflammatory markers known to be involved in depression, stress, and mental fatigue. The study indicates a possible link between pandemic-associated stressors and neuroimmune responses.
“The most important finding is the evidence of neuroinflammation in noninfected, otherwise healthy participants, which may explain the variety of sickness-behavior-like symptoms experienced by many during the pandemic,” lead author Ludovica Brusaferri, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, told this news organization.
The study was published online Feb. 16 in Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.
Impact of pandemic stress?
Reports of psychological distress have increased considerably in the United States during the pandemic, including among those not infected with SARS-CoV-2.
To better understand the effects of the pandemic on brain and mental health, the investigators retrospectively analyzed data collected from 57 people who were enrolled as control subjects for unrelated studies before the pandemic began.
They also enrolled 15 people living in Massachusetts during that state’s 2-month lockdown/stay-at-home order from March to May 2020, all of whom had tested negative for COVID-19 antibodies.
The investigators used PET and MRI imaging and blood sample analyses to investigate whether there were any differences in the brains of healthy people before and during the pandemic following the lockdown.
Compared with the control group, the pandemic cohort had elevated levels of 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) and myoinositol, inflammatory markers in the brain. Increased TSPO has been associated with depression and suicidal thoughts and elevated myoinositol has been linked to schizophrenia.
Blood levels of two inflammatory markers, interleukin-16 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, were also elevated in the pandemic cohort, although to a lesser extent.
TSPO levels were especially high in participants in the pandemic cohort who reported moodiness and mental and physical fatigue, compared with those reporting few or no symptoms.
“These findings provide support to a role for neuroinflammation in stress, an observation that, if replicated, might help guide the development of novel treatments focused on the reduction of brain inflammation,” study author Marco Loggia, PhD, codirector of the Center for Integrative Pain NeuroImaging at Mass General and Harvard Medical School, told this news organization.
Although the data showing increased neuroinflammation were collected when participants were under a stay-at-home order, the researchers said it’s not clear that this was the cause.
“We’re not saying it is the lockdown that was causing it,” Dr. Loggia said. “It could have been social isolation, changes in diet, or changes in exercise patterns. We don’t know exactly what the cause was so, maybe.”
A significant contribution
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Ning Quan, PhD, professor of biomedical science at Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, said although questions remain, the findings offer valuable information.
“This study contributes significantly to our understanding of how pandemic stress might impact our brain and behavior,” Dr. Quan said. “The main advance that this paper provides is that fatigue or brain fog could be induced in individuals with COVID infection during the pandemic.”
However, Dr. Quan added, the study has a number of limitations, including a small sample size, which makes it difficult to generalize the results.
“Another issue is the subjects of the study all lived in Massachusetts,” Dr. Quan added. “Subjects from different states or different countries could yield different results.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and by the Landreth Family Foundation. The study authors and Dr. Quan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The stress of living through a pandemic may cause brain inflammation even in those uninfected with SARS-CoV-2, a study suggests.
Healthy individuals who tested negative for the virus that causes COVID-19 had elevated levels of inflammatory markers known to be involved in depression, stress, and mental fatigue. The study indicates a possible link between pandemic-associated stressors and neuroimmune responses.
“The most important finding is the evidence of neuroinflammation in noninfected, otherwise healthy participants, which may explain the variety of sickness-behavior-like symptoms experienced by many during the pandemic,” lead author Ludovica Brusaferri, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, told this news organization.
The study was published online Feb. 16 in Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.
Impact of pandemic stress?
Reports of psychological distress have increased considerably in the United States during the pandemic, including among those not infected with SARS-CoV-2.
To better understand the effects of the pandemic on brain and mental health, the investigators retrospectively analyzed data collected from 57 people who were enrolled as control subjects for unrelated studies before the pandemic began.
They also enrolled 15 people living in Massachusetts during that state’s 2-month lockdown/stay-at-home order from March to May 2020, all of whom had tested negative for COVID-19 antibodies.
The investigators used PET and MRI imaging and blood sample analyses to investigate whether there were any differences in the brains of healthy people before and during the pandemic following the lockdown.
Compared with the control group, the pandemic cohort had elevated levels of 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) and myoinositol, inflammatory markers in the brain. Increased TSPO has been associated with depression and suicidal thoughts and elevated myoinositol has been linked to schizophrenia.
Blood levels of two inflammatory markers, interleukin-16 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, were also elevated in the pandemic cohort, although to a lesser extent.
TSPO levels were especially high in participants in the pandemic cohort who reported moodiness and mental and physical fatigue, compared with those reporting few or no symptoms.
“These findings provide support to a role for neuroinflammation in stress, an observation that, if replicated, might help guide the development of novel treatments focused on the reduction of brain inflammation,” study author Marco Loggia, PhD, codirector of the Center for Integrative Pain NeuroImaging at Mass General and Harvard Medical School, told this news organization.
Although the data showing increased neuroinflammation were collected when participants were under a stay-at-home order, the researchers said it’s not clear that this was the cause.
“We’re not saying it is the lockdown that was causing it,” Dr. Loggia said. “It could have been social isolation, changes in diet, or changes in exercise patterns. We don’t know exactly what the cause was so, maybe.”
A significant contribution
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Ning Quan, PhD, professor of biomedical science at Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, said although questions remain, the findings offer valuable information.
“This study contributes significantly to our understanding of how pandemic stress might impact our brain and behavior,” Dr. Quan said. “The main advance that this paper provides is that fatigue or brain fog could be induced in individuals with COVID infection during the pandemic.”
However, Dr. Quan added, the study has a number of limitations, including a small sample size, which makes it difficult to generalize the results.
“Another issue is the subjects of the study all lived in Massachusetts,” Dr. Quan added. “Subjects from different states or different countries could yield different results.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and by the Landreth Family Foundation. The study authors and Dr. Quan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The stress of living through a pandemic may cause brain inflammation even in those uninfected with SARS-CoV-2, a study suggests.
Healthy individuals who tested negative for the virus that causes COVID-19 had elevated levels of inflammatory markers known to be involved in depression, stress, and mental fatigue. The study indicates a possible link between pandemic-associated stressors and neuroimmune responses.
“The most important finding is the evidence of neuroinflammation in noninfected, otherwise healthy participants, which may explain the variety of sickness-behavior-like symptoms experienced by many during the pandemic,” lead author Ludovica Brusaferri, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, told this news organization.
The study was published online Feb. 16 in Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.
Impact of pandemic stress?
Reports of psychological distress have increased considerably in the United States during the pandemic, including among those not infected with SARS-CoV-2.
To better understand the effects of the pandemic on brain and mental health, the investigators retrospectively analyzed data collected from 57 people who were enrolled as control subjects for unrelated studies before the pandemic began.
They also enrolled 15 people living in Massachusetts during that state’s 2-month lockdown/stay-at-home order from March to May 2020, all of whom had tested negative for COVID-19 antibodies.
The investigators used PET and MRI imaging and blood sample analyses to investigate whether there were any differences in the brains of healthy people before and during the pandemic following the lockdown.
Compared with the control group, the pandemic cohort had elevated levels of 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) and myoinositol, inflammatory markers in the brain. Increased TSPO has been associated with depression and suicidal thoughts and elevated myoinositol has been linked to schizophrenia.
Blood levels of two inflammatory markers, interleukin-16 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, were also elevated in the pandemic cohort, although to a lesser extent.
TSPO levels were especially high in participants in the pandemic cohort who reported moodiness and mental and physical fatigue, compared with those reporting few or no symptoms.
“These findings provide support to a role for neuroinflammation in stress, an observation that, if replicated, might help guide the development of novel treatments focused on the reduction of brain inflammation,” study author Marco Loggia, PhD, codirector of the Center for Integrative Pain NeuroImaging at Mass General and Harvard Medical School, told this news organization.
Although the data showing increased neuroinflammation were collected when participants were under a stay-at-home order, the researchers said it’s not clear that this was the cause.
“We’re not saying it is the lockdown that was causing it,” Dr. Loggia said. “It could have been social isolation, changes in diet, or changes in exercise patterns. We don’t know exactly what the cause was so, maybe.”
A significant contribution
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Ning Quan, PhD, professor of biomedical science at Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, said although questions remain, the findings offer valuable information.
“This study contributes significantly to our understanding of how pandemic stress might impact our brain and behavior,” Dr. Quan said. “The main advance that this paper provides is that fatigue or brain fog could be induced in individuals with COVID infection during the pandemic.”
However, Dr. Quan added, the study has a number of limitations, including a small sample size, which makes it difficult to generalize the results.
“Another issue is the subjects of the study all lived in Massachusetts,” Dr. Quan added. “Subjects from different states or different countries could yield different results.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and by the Landreth Family Foundation. The study authors and Dr. Quan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BRAIN, BEHAVIOR, AND IMMUNITY
‘Profound implications’: COVID ups diabetes risk 40% a year later
COVID-19 infection appears to significantly raise the risk for diabetes by about 40% at 1 year, indicate new data from a very large Veterans Administration population.
“If patients have a prior history of COVID-19, that’s a risk factor for diabetes and they should certainly be screened for diabetes,” study coauthor Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a nephrologist and chief of research and development at VA St. Louis Health Care, told this news organization.
“It’s still premature to make guidelines. I think we have to process the data landscape to understand what this all really means, but it’s really, really clear that all these roads are pointing in one direction, that COVID-19 increases the risk of diabetes up to a year later. The risk is small but not negligible,” he said.
The database includes over 8 million people and 180,000 with a prior COVID-19 diagnosis. Significantly increased diabetes risks compared to those not infected ranging from 31% to more than double were found in an analysis of subgroups based on diabetes risk score, body mass index, age, race, prediabetes status, and deprivation level, even after adjustment for confounding factors.
There was a gradient of diabetes risk by COVID-19 severity – i.e., whether patients had not been hospitalized, had been hospitalized, or stayed in intensive care – but a significant excess diabetes burden was seen even among those with “mild” COVID-19. The diabetes risk was also elevated compared to both contemporary and historical controls.
The study was published March 21 in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, by Yan Xie, MPH, also of VA St Louis Health Care, along with Dr. Al-Aly.
The data align with those from another study just published from a nationwide German primary care database. That study was smaller and of shorter duration than the new VA study but consistent, said Dr. Al-Aly, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, St. Louis.
Millions more with new diabetes as late manifestation of COVID-19
“Millions of people in the U.S. have had COVID-19, so this is going to translate to literally millions more people with new-onset diabetes. Better to identify them early so they can be adequately treated,” Dr. Al-Aly said in an interview.
“The long-term implications of SARS-CoV-2 infection increasing diabetes risk are profound,” Venkat Narayan, MD, and Lisa R. Staimez, PhD, both of the Rollins School of Public Health and Emory Global Diabetes Research Center at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an accompanying editorial.
“With large and growing numbers of people worldwide infected with SARS-CoV-2 (434,154,739 cumulative cases by Feb. 28, 2022), any COVID-19-related increases in diabetes incidence could lead to unprecedented cases of diabetes worldwide – wreaking havoc on already over-stretched and under-resourced clinical and public health systems globally, with devastating tolls in terms of deaths and suffering,” they added.
Medscape Medical News contributor Eric Topol MD, of Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, Calif., agrees. He said these new data “are most profound. The researchers found a 40% increase in diabetes that wasn’t present at 1 month after COVID-19 but at 1 year, it was. Some kind of late manifestation is happening here.”
Dr. Al-Aly told this news organization that the mechanisms for the association are unknown and likely to be heterogeneous. Among the people who already had risk factors for type 2 diabetes, such as obesity or metabolic syndrome, SARS-CoV-2 could simply accelerate that process and “put them over the edge” to overt diabetes.
However, for those without diabetes risk factors, “COVID-19 with all the inflammation it provokes in the body could be leading to de novo disease.” (Diabetes status was ascertained by ICD-10 codes and only about 0.70% of the total were recorded as type 1 diabetes. But, since autoantibody testing wasn’t routinely conducted, it’s unknown how many of the cases may have been type 1 misclassified as type 2, Dr. Al-Aly acknowledged.)
Diabetes risk significantly increased after COVID-19 in all analyses
The analysis included 181,280 patients in the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs health care database with a COVID-19 diagnosis who survived for at least 30 days afterward during March 2020 through Sept. 30, 2021, with 4,118,441 contemporary controls without COVID-19 seen during 2019, and a historical control group of 4,286,911 people seen at the VA in 2017. Average follow-up was about a year.
Compared with the contemporary controls, the COVID-19 group had an excess diabetes burden of 13.46 per 1,000 person-years with a hazard ratio of 1.40. They had an increased 12.35 per 1,000 person-year risk for incident use of glucose-lowering medications, with a hazard ratio of 1.85. Similar results were seen with the historical controls.
Subgroup analyses showed an increased risk for diabetes following COVID-19 infection by age (≤ 65 years and > 65 years), race (White and Black), sex (male and female), BMI categories (> 18.5 to ≤ 25 kg/m², > 25 to ≤ 30 kg/m², and > 30 kg/m²), and area deprivation index quartiles. The increased risk was also seen across diabetes risk score quartiles.
Notably, COVID-19 significantly elevated the diabetes risk by 59% even for the subgroup with BMI between 18 and 25 kg/m², and by 38% among those with the lowest diabetes risk score quartile.
The COVID-19 population included 162,096 who were not hospitalized, 15,078 hospitalized, and 4,106 admitted to intensive care. Here, the hazard ratios for diabetes compared to the contemporary controls were 1.25, 2.73, and 3.76, respectively, all significant.
Dr. Al-Aly said that his group is now further analyzing the VA data for other outcomes including cardiovascular disease and kidney disease, as well as the now well-documented long COVID symptoms including fatigue, pain, and neurocognitive dysfunction.
They’re also investigating the impact of the COVID-19 vaccine to see whether the risks are mitigated in the case of breakthrough infections: “We’re doing a broad systematic assessment. The next paper will be more comprehensive.”
Dr. Narayan and Dr. Staimez wrote: “The potential connection between COVID-19 and diabetes highlights that infectious diseases (eg, SARS-CoV-2) and chronic diseases (eg, diabetes) cannot be viewed in siloes. When we emerge out of the pandemic, the much-neglected non-communicable diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, will continue their relentless trajectory, possibly in an accelerated manner, as the leading burdens of global health.”
Dr. Al-Aly declared support from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs for the submitted work. He has received consultation fees from Gilead Sciences and funding (unrelated to this work) from Tonix Pharmaceuticals. He is a member of the board of directors for Veterans Research and Education Foundation of Saint Louis, associate editor for the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, and a member of multiple editorial boards. Dr. Narayan and Dr. Staimez have received support from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 infection appears to significantly raise the risk for diabetes by about 40% at 1 year, indicate new data from a very large Veterans Administration population.
“If patients have a prior history of COVID-19, that’s a risk factor for diabetes and they should certainly be screened for diabetes,” study coauthor Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a nephrologist and chief of research and development at VA St. Louis Health Care, told this news organization.
“It’s still premature to make guidelines. I think we have to process the data landscape to understand what this all really means, but it’s really, really clear that all these roads are pointing in one direction, that COVID-19 increases the risk of diabetes up to a year later. The risk is small but not negligible,” he said.
The database includes over 8 million people and 180,000 with a prior COVID-19 diagnosis. Significantly increased diabetes risks compared to those not infected ranging from 31% to more than double were found in an analysis of subgroups based on diabetes risk score, body mass index, age, race, prediabetes status, and deprivation level, even after adjustment for confounding factors.
There was a gradient of diabetes risk by COVID-19 severity – i.e., whether patients had not been hospitalized, had been hospitalized, or stayed in intensive care – but a significant excess diabetes burden was seen even among those with “mild” COVID-19. The diabetes risk was also elevated compared to both contemporary and historical controls.
The study was published March 21 in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, by Yan Xie, MPH, also of VA St Louis Health Care, along with Dr. Al-Aly.
The data align with those from another study just published from a nationwide German primary care database. That study was smaller and of shorter duration than the new VA study but consistent, said Dr. Al-Aly, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, St. Louis.
Millions more with new diabetes as late manifestation of COVID-19
“Millions of people in the U.S. have had COVID-19, so this is going to translate to literally millions more people with new-onset diabetes. Better to identify them early so they can be adequately treated,” Dr. Al-Aly said in an interview.
“The long-term implications of SARS-CoV-2 infection increasing diabetes risk are profound,” Venkat Narayan, MD, and Lisa R. Staimez, PhD, both of the Rollins School of Public Health and Emory Global Diabetes Research Center at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an accompanying editorial.
“With large and growing numbers of people worldwide infected with SARS-CoV-2 (434,154,739 cumulative cases by Feb. 28, 2022), any COVID-19-related increases in diabetes incidence could lead to unprecedented cases of diabetes worldwide – wreaking havoc on already over-stretched and under-resourced clinical and public health systems globally, with devastating tolls in terms of deaths and suffering,” they added.
Medscape Medical News contributor Eric Topol MD, of Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, Calif., agrees. He said these new data “are most profound. The researchers found a 40% increase in diabetes that wasn’t present at 1 month after COVID-19 but at 1 year, it was. Some kind of late manifestation is happening here.”
Dr. Al-Aly told this news organization that the mechanisms for the association are unknown and likely to be heterogeneous. Among the people who already had risk factors for type 2 diabetes, such as obesity or metabolic syndrome, SARS-CoV-2 could simply accelerate that process and “put them over the edge” to overt diabetes.
However, for those without diabetes risk factors, “COVID-19 with all the inflammation it provokes in the body could be leading to de novo disease.” (Diabetes status was ascertained by ICD-10 codes and only about 0.70% of the total were recorded as type 1 diabetes. But, since autoantibody testing wasn’t routinely conducted, it’s unknown how many of the cases may have been type 1 misclassified as type 2, Dr. Al-Aly acknowledged.)
Diabetes risk significantly increased after COVID-19 in all analyses
The analysis included 181,280 patients in the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs health care database with a COVID-19 diagnosis who survived for at least 30 days afterward during March 2020 through Sept. 30, 2021, with 4,118,441 contemporary controls without COVID-19 seen during 2019, and a historical control group of 4,286,911 people seen at the VA in 2017. Average follow-up was about a year.
Compared with the contemporary controls, the COVID-19 group had an excess diabetes burden of 13.46 per 1,000 person-years with a hazard ratio of 1.40. They had an increased 12.35 per 1,000 person-year risk for incident use of glucose-lowering medications, with a hazard ratio of 1.85. Similar results were seen with the historical controls.
Subgroup analyses showed an increased risk for diabetes following COVID-19 infection by age (≤ 65 years and > 65 years), race (White and Black), sex (male and female), BMI categories (> 18.5 to ≤ 25 kg/m², > 25 to ≤ 30 kg/m², and > 30 kg/m²), and area deprivation index quartiles. The increased risk was also seen across diabetes risk score quartiles.
Notably, COVID-19 significantly elevated the diabetes risk by 59% even for the subgroup with BMI between 18 and 25 kg/m², and by 38% among those with the lowest diabetes risk score quartile.
The COVID-19 population included 162,096 who were not hospitalized, 15,078 hospitalized, and 4,106 admitted to intensive care. Here, the hazard ratios for diabetes compared to the contemporary controls were 1.25, 2.73, and 3.76, respectively, all significant.
Dr. Al-Aly said that his group is now further analyzing the VA data for other outcomes including cardiovascular disease and kidney disease, as well as the now well-documented long COVID symptoms including fatigue, pain, and neurocognitive dysfunction.
They’re also investigating the impact of the COVID-19 vaccine to see whether the risks are mitigated in the case of breakthrough infections: “We’re doing a broad systematic assessment. The next paper will be more comprehensive.”
Dr. Narayan and Dr. Staimez wrote: “The potential connection between COVID-19 and diabetes highlights that infectious diseases (eg, SARS-CoV-2) and chronic diseases (eg, diabetes) cannot be viewed in siloes. When we emerge out of the pandemic, the much-neglected non-communicable diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, will continue their relentless trajectory, possibly in an accelerated manner, as the leading burdens of global health.”
Dr. Al-Aly declared support from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs for the submitted work. He has received consultation fees from Gilead Sciences and funding (unrelated to this work) from Tonix Pharmaceuticals. He is a member of the board of directors for Veterans Research and Education Foundation of Saint Louis, associate editor for the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, and a member of multiple editorial boards. Dr. Narayan and Dr. Staimez have received support from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 infection appears to significantly raise the risk for diabetes by about 40% at 1 year, indicate new data from a very large Veterans Administration population.
“If patients have a prior history of COVID-19, that’s a risk factor for diabetes and they should certainly be screened for diabetes,” study coauthor Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a nephrologist and chief of research and development at VA St. Louis Health Care, told this news organization.
“It’s still premature to make guidelines. I think we have to process the data landscape to understand what this all really means, but it’s really, really clear that all these roads are pointing in one direction, that COVID-19 increases the risk of diabetes up to a year later. The risk is small but not negligible,” he said.
The database includes over 8 million people and 180,000 with a prior COVID-19 diagnosis. Significantly increased diabetes risks compared to those not infected ranging from 31% to more than double were found in an analysis of subgroups based on diabetes risk score, body mass index, age, race, prediabetes status, and deprivation level, even after adjustment for confounding factors.
There was a gradient of diabetes risk by COVID-19 severity – i.e., whether patients had not been hospitalized, had been hospitalized, or stayed in intensive care – but a significant excess diabetes burden was seen even among those with “mild” COVID-19. The diabetes risk was also elevated compared to both contemporary and historical controls.
The study was published March 21 in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, by Yan Xie, MPH, also of VA St Louis Health Care, along with Dr. Al-Aly.
The data align with those from another study just published from a nationwide German primary care database. That study was smaller and of shorter duration than the new VA study but consistent, said Dr. Al-Aly, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, St. Louis.
Millions more with new diabetes as late manifestation of COVID-19
“Millions of people in the U.S. have had COVID-19, so this is going to translate to literally millions more people with new-onset diabetes. Better to identify them early so they can be adequately treated,” Dr. Al-Aly said in an interview.
“The long-term implications of SARS-CoV-2 infection increasing diabetes risk are profound,” Venkat Narayan, MD, and Lisa R. Staimez, PhD, both of the Rollins School of Public Health and Emory Global Diabetes Research Center at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an accompanying editorial.
“With large and growing numbers of people worldwide infected with SARS-CoV-2 (434,154,739 cumulative cases by Feb. 28, 2022), any COVID-19-related increases in diabetes incidence could lead to unprecedented cases of diabetes worldwide – wreaking havoc on already over-stretched and under-resourced clinical and public health systems globally, with devastating tolls in terms of deaths and suffering,” they added.
Medscape Medical News contributor Eric Topol MD, of Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, Calif., agrees. He said these new data “are most profound. The researchers found a 40% increase in diabetes that wasn’t present at 1 month after COVID-19 but at 1 year, it was. Some kind of late manifestation is happening here.”
Dr. Al-Aly told this news organization that the mechanisms for the association are unknown and likely to be heterogeneous. Among the people who already had risk factors for type 2 diabetes, such as obesity or metabolic syndrome, SARS-CoV-2 could simply accelerate that process and “put them over the edge” to overt diabetes.
However, for those without diabetes risk factors, “COVID-19 with all the inflammation it provokes in the body could be leading to de novo disease.” (Diabetes status was ascertained by ICD-10 codes and only about 0.70% of the total were recorded as type 1 diabetes. But, since autoantibody testing wasn’t routinely conducted, it’s unknown how many of the cases may have been type 1 misclassified as type 2, Dr. Al-Aly acknowledged.)
Diabetes risk significantly increased after COVID-19 in all analyses
The analysis included 181,280 patients in the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs health care database with a COVID-19 diagnosis who survived for at least 30 days afterward during March 2020 through Sept. 30, 2021, with 4,118,441 contemporary controls without COVID-19 seen during 2019, and a historical control group of 4,286,911 people seen at the VA in 2017. Average follow-up was about a year.
Compared with the contemporary controls, the COVID-19 group had an excess diabetes burden of 13.46 per 1,000 person-years with a hazard ratio of 1.40. They had an increased 12.35 per 1,000 person-year risk for incident use of glucose-lowering medications, with a hazard ratio of 1.85. Similar results were seen with the historical controls.
Subgroup analyses showed an increased risk for diabetes following COVID-19 infection by age (≤ 65 years and > 65 years), race (White and Black), sex (male and female), BMI categories (> 18.5 to ≤ 25 kg/m², > 25 to ≤ 30 kg/m², and > 30 kg/m²), and area deprivation index quartiles. The increased risk was also seen across diabetes risk score quartiles.
Notably, COVID-19 significantly elevated the diabetes risk by 59% even for the subgroup with BMI between 18 and 25 kg/m², and by 38% among those with the lowest diabetes risk score quartile.
The COVID-19 population included 162,096 who were not hospitalized, 15,078 hospitalized, and 4,106 admitted to intensive care. Here, the hazard ratios for diabetes compared to the contemporary controls were 1.25, 2.73, and 3.76, respectively, all significant.
Dr. Al-Aly said that his group is now further analyzing the VA data for other outcomes including cardiovascular disease and kidney disease, as well as the now well-documented long COVID symptoms including fatigue, pain, and neurocognitive dysfunction.
They’re also investigating the impact of the COVID-19 vaccine to see whether the risks are mitigated in the case of breakthrough infections: “We’re doing a broad systematic assessment. The next paper will be more comprehensive.”
Dr. Narayan and Dr. Staimez wrote: “The potential connection between COVID-19 and diabetes highlights that infectious diseases (eg, SARS-CoV-2) and chronic diseases (eg, diabetes) cannot be viewed in siloes. When we emerge out of the pandemic, the much-neglected non-communicable diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, will continue their relentless trajectory, possibly in an accelerated manner, as the leading burdens of global health.”
Dr. Al-Aly declared support from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs for the submitted work. He has received consultation fees from Gilead Sciences and funding (unrelated to this work) from Tonix Pharmaceuticals. He is a member of the board of directors for Veterans Research and Education Foundation of Saint Louis, associate editor for the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, and a member of multiple editorial boards. Dr. Narayan and Dr. Staimez have received support from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET DIABETES & ENDOCRINOLOGY
Executive-function deficits a new treatment target for PTSD?
DENVER –
“To our knowledge, this study is the first to show that executive-function deficits maintain PTSD symptoms following trauma exposure,” investigators noted in research presented at the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) Anxiety & Depression conference.
The results are important in “developing precision medicine–based approaches for alleviating [posttraumatic stress] symptoms, and improving well-established PTSD treatments for those with relative deficits in executive function,” study investigator Joseph R. Bardeen, PhD, associate professor at Auburn (Ala.) University, told meeting attendees.
The findings were published in the Journal of Anxiety Disorders.
Cognitive impairment
In earlier research, deficits in EF were associated with an increased vulnerability for PTSD symptoms. However, less is known about the role of these deficits, which can impair higher-level cognitive ability, in sustaining PTSD symptoms.
To investigate, the authors conducted a longitudinal study that included 98 participants aged 18-65 years who had been identified via phone screening as experiencing clinically significant PTSD symptoms.
Participants completed self-report measures for PTSD symptoms, as well as measures for EF deficits at baseline and 6-month (n = 92) and 12-month (n = 91) follow-up sessions.
A path analysis showed a significant relationship between baseline PTSD symptoms and EF deficits at 6 months (P < .001). Baseline PTSD symptoms were associated with 12-month PTSD symptoms (P < .04).
EF deficits at 6 months were also associated with 12-month PTSD symptoms (P = .02).
Importantly, no associations were observed between baseline or 6-month PTSD symptoms and EF deficits at 12 months. However, EF deficits at 6 months drove the relationship between PTSD symptoms at baseline and at 1 year (indirect effect = .061).
“What this suggests is that executive-function deficits are a mechanism that maintains patients’ symptoms over the course of 1 year,” Dr. Bardeen said.
“And you don’t see the reverse,” he added. “You don’t see that PTSD symptoms at [6 months] mediate the relationship between [baseline] and 6 month executive-function deficits.”
Surprising finding
The findings suggest deficits in executive functioning have a stronger role in maintaining PTSD symptoms than these symptoms have in maintaining EF deficits, Dr. Bardeen told this news organization.
“I had originally hypothesized a bidirectional relationship in which PTSD symptoms influenced future executive-function deficits and executive-function deficits influenced future PTSD symptoms,” he said.
“So, it was a surprise that, when accounting for both variables in the same model, executive-function deficits predicted future PTSD symptoms, but PTSD symptoms did not significantly predict future EF deficits,” he added.
Dr. Bardeen noted this suggests that EF deficits “may be a particularly important maintenance factor.”
In addition, he recommended the use of neuropsychological assessments prior to treatment to identify individuals with EF deficits and distinguish those deficits from PTSD symptoms.
“There is certainly overlap between executive-function deficits and PTSD symptoms,” Dr. Bardeen said. “For example, several of the symptoms of PTSD, such as concentration difficulties, may be indicators of executive-function deficits.”
He noted assessments such as the Delis Kaplan Executive Function System, and Clinician Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5, when used as part of a larger assessment battery, can help differentiate between the EF deficits and PTSD.
“This would take several hours to administer, but in cases in which serious cognitive impairment is suspected, a comprehensive assessment is the way to go,” Dr. Bardeen said.
The standard approaches of prolonged exposure therapy and cognitive processing therapy can be effective in patients without EF deficits, while some modifications may benefit those with these deficits, he added.
“For example, it’s important to provide a more directive and structured environment in which the practitioner repeats key points frequently, uses concrete language, simplifies worksheets, and provides written summaries and reminder cards,” he said.
Further findings
In additional research presented at the meeting, Elsa Mattson, a PhD student from Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and colleagues reported findings further distinguishing the role of EF in PTSD.
In that study of 149 patients with chronic PTSD, those with low performing working memory, but not high working memory, had higher pre- as well as posttreatment PTSD symptom severity and depressive symptoms.
“Clinicians should consider that impairments in executive function may play a role in reduced treatment response, potentially impairing a client’s ability to learn new information in treatment,” the investigators wrote.
“Understanding how executive function processes change over the course of treatment, particularly in relation to processing the trauma memories, is an important next step,” they added.
The first study was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DENVER –
“To our knowledge, this study is the first to show that executive-function deficits maintain PTSD symptoms following trauma exposure,” investigators noted in research presented at the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) Anxiety & Depression conference.
The results are important in “developing precision medicine–based approaches for alleviating [posttraumatic stress] symptoms, and improving well-established PTSD treatments for those with relative deficits in executive function,” study investigator Joseph R. Bardeen, PhD, associate professor at Auburn (Ala.) University, told meeting attendees.
The findings were published in the Journal of Anxiety Disorders.
Cognitive impairment
In earlier research, deficits in EF were associated with an increased vulnerability for PTSD symptoms. However, less is known about the role of these deficits, which can impair higher-level cognitive ability, in sustaining PTSD symptoms.
To investigate, the authors conducted a longitudinal study that included 98 participants aged 18-65 years who had been identified via phone screening as experiencing clinically significant PTSD symptoms.
Participants completed self-report measures for PTSD symptoms, as well as measures for EF deficits at baseline and 6-month (n = 92) and 12-month (n = 91) follow-up sessions.
A path analysis showed a significant relationship between baseline PTSD symptoms and EF deficits at 6 months (P < .001). Baseline PTSD symptoms were associated with 12-month PTSD symptoms (P < .04).
EF deficits at 6 months were also associated with 12-month PTSD symptoms (P = .02).
Importantly, no associations were observed between baseline or 6-month PTSD symptoms and EF deficits at 12 months. However, EF deficits at 6 months drove the relationship between PTSD symptoms at baseline and at 1 year (indirect effect = .061).
“What this suggests is that executive-function deficits are a mechanism that maintains patients’ symptoms over the course of 1 year,” Dr. Bardeen said.
“And you don’t see the reverse,” he added. “You don’t see that PTSD symptoms at [6 months] mediate the relationship between [baseline] and 6 month executive-function deficits.”
Surprising finding
The findings suggest deficits in executive functioning have a stronger role in maintaining PTSD symptoms than these symptoms have in maintaining EF deficits, Dr. Bardeen told this news organization.
“I had originally hypothesized a bidirectional relationship in which PTSD symptoms influenced future executive-function deficits and executive-function deficits influenced future PTSD symptoms,” he said.
“So, it was a surprise that, when accounting for both variables in the same model, executive-function deficits predicted future PTSD symptoms, but PTSD symptoms did not significantly predict future EF deficits,” he added.
Dr. Bardeen noted this suggests that EF deficits “may be a particularly important maintenance factor.”
In addition, he recommended the use of neuropsychological assessments prior to treatment to identify individuals with EF deficits and distinguish those deficits from PTSD symptoms.
“There is certainly overlap between executive-function deficits and PTSD symptoms,” Dr. Bardeen said. “For example, several of the symptoms of PTSD, such as concentration difficulties, may be indicators of executive-function deficits.”
He noted assessments such as the Delis Kaplan Executive Function System, and Clinician Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5, when used as part of a larger assessment battery, can help differentiate between the EF deficits and PTSD.
“This would take several hours to administer, but in cases in which serious cognitive impairment is suspected, a comprehensive assessment is the way to go,” Dr. Bardeen said.
The standard approaches of prolonged exposure therapy and cognitive processing therapy can be effective in patients without EF deficits, while some modifications may benefit those with these deficits, he added.
“For example, it’s important to provide a more directive and structured environment in which the practitioner repeats key points frequently, uses concrete language, simplifies worksheets, and provides written summaries and reminder cards,” he said.
Further findings
In additional research presented at the meeting, Elsa Mattson, a PhD student from Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and colleagues reported findings further distinguishing the role of EF in PTSD.
In that study of 149 patients with chronic PTSD, those with low performing working memory, but not high working memory, had higher pre- as well as posttreatment PTSD symptom severity and depressive symptoms.
“Clinicians should consider that impairments in executive function may play a role in reduced treatment response, potentially impairing a client’s ability to learn new information in treatment,” the investigators wrote.
“Understanding how executive function processes change over the course of treatment, particularly in relation to processing the trauma memories, is an important next step,” they added.
The first study was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DENVER –
“To our knowledge, this study is the first to show that executive-function deficits maintain PTSD symptoms following trauma exposure,” investigators noted in research presented at the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) Anxiety & Depression conference.
The results are important in “developing precision medicine–based approaches for alleviating [posttraumatic stress] symptoms, and improving well-established PTSD treatments for those with relative deficits in executive function,” study investigator Joseph R. Bardeen, PhD, associate professor at Auburn (Ala.) University, told meeting attendees.
The findings were published in the Journal of Anxiety Disorders.
Cognitive impairment
In earlier research, deficits in EF were associated with an increased vulnerability for PTSD symptoms. However, less is known about the role of these deficits, which can impair higher-level cognitive ability, in sustaining PTSD symptoms.
To investigate, the authors conducted a longitudinal study that included 98 participants aged 18-65 years who had been identified via phone screening as experiencing clinically significant PTSD symptoms.
Participants completed self-report measures for PTSD symptoms, as well as measures for EF deficits at baseline and 6-month (n = 92) and 12-month (n = 91) follow-up sessions.
A path analysis showed a significant relationship between baseline PTSD symptoms and EF deficits at 6 months (P < .001). Baseline PTSD symptoms were associated with 12-month PTSD symptoms (P < .04).
EF deficits at 6 months were also associated with 12-month PTSD symptoms (P = .02).
Importantly, no associations were observed between baseline or 6-month PTSD symptoms and EF deficits at 12 months. However, EF deficits at 6 months drove the relationship between PTSD symptoms at baseline and at 1 year (indirect effect = .061).
“What this suggests is that executive-function deficits are a mechanism that maintains patients’ symptoms over the course of 1 year,” Dr. Bardeen said.
“And you don’t see the reverse,” he added. “You don’t see that PTSD symptoms at [6 months] mediate the relationship between [baseline] and 6 month executive-function deficits.”
Surprising finding
The findings suggest deficits in executive functioning have a stronger role in maintaining PTSD symptoms than these symptoms have in maintaining EF deficits, Dr. Bardeen told this news organization.
“I had originally hypothesized a bidirectional relationship in which PTSD symptoms influenced future executive-function deficits and executive-function deficits influenced future PTSD symptoms,” he said.
“So, it was a surprise that, when accounting for both variables in the same model, executive-function deficits predicted future PTSD symptoms, but PTSD symptoms did not significantly predict future EF deficits,” he added.
Dr. Bardeen noted this suggests that EF deficits “may be a particularly important maintenance factor.”
In addition, he recommended the use of neuropsychological assessments prior to treatment to identify individuals with EF deficits and distinguish those deficits from PTSD symptoms.
“There is certainly overlap between executive-function deficits and PTSD symptoms,” Dr. Bardeen said. “For example, several of the symptoms of PTSD, such as concentration difficulties, may be indicators of executive-function deficits.”
He noted assessments such as the Delis Kaplan Executive Function System, and Clinician Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5, when used as part of a larger assessment battery, can help differentiate between the EF deficits and PTSD.
“This would take several hours to administer, but in cases in which serious cognitive impairment is suspected, a comprehensive assessment is the way to go,” Dr. Bardeen said.
The standard approaches of prolonged exposure therapy and cognitive processing therapy can be effective in patients without EF deficits, while some modifications may benefit those with these deficits, he added.
“For example, it’s important to provide a more directive and structured environment in which the practitioner repeats key points frequently, uses concrete language, simplifies worksheets, and provides written summaries and reminder cards,” he said.
Further findings
In additional research presented at the meeting, Elsa Mattson, a PhD student from Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and colleagues reported findings further distinguishing the role of EF in PTSD.
In that study of 149 patients with chronic PTSD, those with low performing working memory, but not high working memory, had higher pre- as well as posttreatment PTSD symptom severity and depressive symptoms.
“Clinicians should consider that impairments in executive function may play a role in reduced treatment response, potentially impairing a client’s ability to learn new information in treatment,” the investigators wrote.
“Understanding how executive function processes change over the course of treatment, particularly in relation to processing the trauma memories, is an important next step,” they added.
The first study was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
REPORTING FROM ADAA 2022
Jury is out on universal screening for eating disorders
Eating disorders (binge eating disorder, bulimia nervosa, and anorexia nervosa) can cause “serious harms to physical and psychosocial health and take a tremendous toll on individuals and families,” task force member Lori Pbert, PhD, told this news organization.
“Screening for eating disorders has the potential to improve health by leading to early detection and effective treatment,” said Dr. Pbert, with the department of population and quantitative health sciences, University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
However, a “deep dive” into the available literature failed to turn up adequate evidence to recommend for or against routine screening for eating disorders for children and adolescents aged 10 years and older and for adults who have no signs or symptoms of an eating disorder or concerns about their eating and who have not previously been diagnosed with an eating disorder, Dr. Pbert said.
The task force, therefore, issued an “I” statement (insufficient evidence), meaning it cannot at this time recommend for or against screening for eating disorders.
An “I” statement is “fundamentally a call for more research,” Dr. Pbert noted.
Adolescents and adults who have signs and symptoms of an eating disorder – which include rapid weight loss; weight gain or pronounced deviation from growth trajectory; pubertal delay; bradycardia; oligomenorrhea; and amenorrhea – are not included in this recommendation.
The USPSTF recommendation statement and accompanying evidence report were published online March 15 in JAMA.
Clinical judgment key
In the absence of evidence, clinicians should use their judgment when determining whether or not to screen an individual patient for an eating disorder, Dr. Pbert advised.
One thing to consider is whether the patient is in a group at higher risk for eating disorders, such as athletes, females, young adults aged 18-29, and transgender individuals.
Another is whether the patient reports engaging in unhealthy weight control behaviors, such as fasting or skipping meals, Dr. Pbert said.
Importantly, any patient who has signs or symptoms of an eating disorder or is expressing concerns about their eating should be assessed and referred for appropriate care, Dr. Pbert said.
“The good news is that eating disorders can be treated,” she said.
Several organizations currently recommend screening in the context of monitoring changes in weight and other vital signs or signs and symptoms to determine whether a patient might have an eating disorder.
Dr. Pbert said it’s important to recognize that the USPSTF statement “doesn’t really conflict” with the recommendations of other organizations. “We all agree that patients who present with signs or symptoms of an eating disorder should be assessed further.”
Evidence gaps
The authors of an invited commentary in JAMA) say the task force has identified several “notable deficiencies” in the available data on screening for eating disorders.
“Directing attention to rigorous research to close this evidence gap will be important to find optimal approaches to identify patients with these complex disorders and improve their health outcomes,” write Evelyn Attia, MD, with Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, and Angela Guarda, MD, with Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
This “I” statement, they say, “highlights the need to prioritize research aimed at closing the evidence gap identified by USPSTF in a timely manner and underscores the need for new studies that address screening for eating disorders, treatment trials that enroll screen-detected populations from primary care settings, and screening in specific populations.
“Research on screening in primary care also should be paired with development and assessment of early brief intervention strategies for those individuals who screen positive, especially adolescents,” Dr. Attia and Dr. Guarda say.
Members of the USPSTF have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Attia has received research support from the National Institute of Mental Health and the Hilda & Preston David Foundation; royalties from UpToDate; and has served as a clinical advisor to Equip Health. Dr. Guarda has received support from the Stephen and Jean Robinson Fund and research funding from the Klarman Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Eating disorders (binge eating disorder, bulimia nervosa, and anorexia nervosa) can cause “serious harms to physical and psychosocial health and take a tremendous toll on individuals and families,” task force member Lori Pbert, PhD, told this news organization.
“Screening for eating disorders has the potential to improve health by leading to early detection and effective treatment,” said Dr. Pbert, with the department of population and quantitative health sciences, University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
However, a “deep dive” into the available literature failed to turn up adequate evidence to recommend for or against routine screening for eating disorders for children and adolescents aged 10 years and older and for adults who have no signs or symptoms of an eating disorder or concerns about their eating and who have not previously been diagnosed with an eating disorder, Dr. Pbert said.
The task force, therefore, issued an “I” statement (insufficient evidence), meaning it cannot at this time recommend for or against screening for eating disorders.
An “I” statement is “fundamentally a call for more research,” Dr. Pbert noted.
Adolescents and adults who have signs and symptoms of an eating disorder – which include rapid weight loss; weight gain or pronounced deviation from growth trajectory; pubertal delay; bradycardia; oligomenorrhea; and amenorrhea – are not included in this recommendation.
The USPSTF recommendation statement and accompanying evidence report were published online March 15 in JAMA.
Clinical judgment key
In the absence of evidence, clinicians should use their judgment when determining whether or not to screen an individual patient for an eating disorder, Dr. Pbert advised.
One thing to consider is whether the patient is in a group at higher risk for eating disorders, such as athletes, females, young adults aged 18-29, and transgender individuals.
Another is whether the patient reports engaging in unhealthy weight control behaviors, such as fasting or skipping meals, Dr. Pbert said.
Importantly, any patient who has signs or symptoms of an eating disorder or is expressing concerns about their eating should be assessed and referred for appropriate care, Dr. Pbert said.
“The good news is that eating disorders can be treated,” she said.
Several organizations currently recommend screening in the context of monitoring changes in weight and other vital signs or signs and symptoms to determine whether a patient might have an eating disorder.
Dr. Pbert said it’s important to recognize that the USPSTF statement “doesn’t really conflict” with the recommendations of other organizations. “We all agree that patients who present with signs or symptoms of an eating disorder should be assessed further.”
Evidence gaps
The authors of an invited commentary in JAMA) say the task force has identified several “notable deficiencies” in the available data on screening for eating disorders.
“Directing attention to rigorous research to close this evidence gap will be important to find optimal approaches to identify patients with these complex disorders and improve their health outcomes,” write Evelyn Attia, MD, with Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, and Angela Guarda, MD, with Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
This “I” statement, they say, “highlights the need to prioritize research aimed at closing the evidence gap identified by USPSTF in a timely manner and underscores the need for new studies that address screening for eating disorders, treatment trials that enroll screen-detected populations from primary care settings, and screening in specific populations.
“Research on screening in primary care also should be paired with development and assessment of early brief intervention strategies for those individuals who screen positive, especially adolescents,” Dr. Attia and Dr. Guarda say.
Members of the USPSTF have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Attia has received research support from the National Institute of Mental Health and the Hilda & Preston David Foundation; royalties from UpToDate; and has served as a clinical advisor to Equip Health. Dr. Guarda has received support from the Stephen and Jean Robinson Fund and research funding from the Klarman Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Eating disorders (binge eating disorder, bulimia nervosa, and anorexia nervosa) can cause “serious harms to physical and psychosocial health and take a tremendous toll on individuals and families,” task force member Lori Pbert, PhD, told this news organization.
“Screening for eating disorders has the potential to improve health by leading to early detection and effective treatment,” said Dr. Pbert, with the department of population and quantitative health sciences, University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
However, a “deep dive” into the available literature failed to turn up adequate evidence to recommend for or against routine screening for eating disorders for children and adolescents aged 10 years and older and for adults who have no signs or symptoms of an eating disorder or concerns about their eating and who have not previously been diagnosed with an eating disorder, Dr. Pbert said.
The task force, therefore, issued an “I” statement (insufficient evidence), meaning it cannot at this time recommend for or against screening for eating disorders.
An “I” statement is “fundamentally a call for more research,” Dr. Pbert noted.
Adolescents and adults who have signs and symptoms of an eating disorder – which include rapid weight loss; weight gain or pronounced deviation from growth trajectory; pubertal delay; bradycardia; oligomenorrhea; and amenorrhea – are not included in this recommendation.
The USPSTF recommendation statement and accompanying evidence report were published online March 15 in JAMA.
Clinical judgment key
In the absence of evidence, clinicians should use their judgment when determining whether or not to screen an individual patient for an eating disorder, Dr. Pbert advised.
One thing to consider is whether the patient is in a group at higher risk for eating disorders, such as athletes, females, young adults aged 18-29, and transgender individuals.
Another is whether the patient reports engaging in unhealthy weight control behaviors, such as fasting or skipping meals, Dr. Pbert said.
Importantly, any patient who has signs or symptoms of an eating disorder or is expressing concerns about their eating should be assessed and referred for appropriate care, Dr. Pbert said.
“The good news is that eating disorders can be treated,” she said.
Several organizations currently recommend screening in the context of monitoring changes in weight and other vital signs or signs and symptoms to determine whether a patient might have an eating disorder.
Dr. Pbert said it’s important to recognize that the USPSTF statement “doesn’t really conflict” with the recommendations of other organizations. “We all agree that patients who present with signs or symptoms of an eating disorder should be assessed further.”
Evidence gaps
The authors of an invited commentary in JAMA) say the task force has identified several “notable deficiencies” in the available data on screening for eating disorders.
“Directing attention to rigorous research to close this evidence gap will be important to find optimal approaches to identify patients with these complex disorders and improve their health outcomes,” write Evelyn Attia, MD, with Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, and Angela Guarda, MD, with Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
This “I” statement, they say, “highlights the need to prioritize research aimed at closing the evidence gap identified by USPSTF in a timely manner and underscores the need for new studies that address screening for eating disorders, treatment trials that enroll screen-detected populations from primary care settings, and screening in specific populations.
“Research on screening in primary care also should be paired with development and assessment of early brief intervention strategies for those individuals who screen positive, especially adolescents,” Dr. Attia and Dr. Guarda say.
Members of the USPSTF have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Attia has received research support from the National Institute of Mental Health and the Hilda & Preston David Foundation; royalties from UpToDate; and has served as a clinical advisor to Equip Health. Dr. Guarda has received support from the Stephen and Jean Robinson Fund and research funding from the Klarman Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New guidance on cannabis use for treatment-resistant epilepsy
A recent review article draws from existing clinical trials and clinical experience in New South Wales, Australia, to fill this gap with interim guidance for both pediatric and adult patients. The article was published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
The only current U.S. guidelines are from the American Academy of Neurology’s position statement on the use of medical cannabis for neurologic disorders and the American Epilepsy Society’s position statement on cannabis as a treatment for epileptic seizures. The AAN statement “highlights the current evidence, which currently only supports [Food and Drug Administration]–approved CBD [cannabidiol] (Epidiolex) for specific epilepsy syndromes,” said Daniel Freedman, DO, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of Texas at Austin and coauthor of the AAN’s position statement.
“Rescheduling marijuana will enable researchers to study CBD, THC [tetrahydrocannabinol], and other cannabinoids in high-quality studies so that we can better understand what works and for which conditions,” said Dr. Freedman, who was not involved in the Australian guidance document. He noted that little consensus exists because little evidence exists outside the handful of trials for Epidiolex.
“There are some patients with epilepsy that can benefit from high-quality, pharmaceutical-grade CBD products,” Dr. Freedman said. “These patients need to be carefully identified by a neurologist or epileptologist and prescribed a legal, safe, quality-controlled, and FDA-regulated product.”
Appropriate patient populations
Drug-resistant epilepsy, defined as failure of two appropriate antiseizure medications, affects an estimated one third of people with epilepsy, the new guideline notes. Though many over-the-counter products are available at dispensaries in the 33 U.S. states that allow use of cannabis for medical purposes, Epidiolex (cannabidiol) is the only FDA-approved drug for epilepsy that contains a substance derived from cannabis and the only one for which evidence from randomized, controlled trials exists.
Dr. Freedman notes that hemp-derived CBD oils are classified differently in the United States than marijuana-derived CBD oil, including Epidiolex, and are loosely regulated supplements or food additives commonly seen, for example at gas station.
“The point I drive home to patients is that you wouldn’t get your antibiotics from a gas station, so please don’t get your seizure medication from there,” Dr. Freedman said. “Studies have been done on ‘over-the-counter’ CBD oils and shown that they have variable quality, sometimes no detectable CBD, and sometimes other chemicals added like THC.”
Studies of Epidiolex showed that cannabidiol more effectively reduced seizure frequency than placebo for pediatric patients with Dravet syndrome (42% reduction) and for pediatric and adult patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (39% reduction) or tuberous sclerosis complex (49% reduction). Efficacy was similar across dosing from 10-50 mg/kg per day, but higher doses involved higher rates of serious adverse events.
No reliable evidence in humans exists for THC or other cannabinoids in treating epilepsy.
The Australian guidance recommends limiting cannabis treatment to patients with severe drug-resistant epilepsy; a diagnosis of Dravet syndrome, Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, or tuberous sclerosis complex; and previous treatment with four approved antiseizure medications and/or the ketogenic diet, epilepsy surgery, or neurostimulator. The authors provide specific criteria for each of these conditions and then address exceptional cases that may be considered outside that criteria, such as patients under 2 years old, severe epilepsy with extended or repeated hospitalization or ICU admission, or a dangerous seizure type. The review also includes a detailed list of exclusion criteria for CBD medicine use.
The authors advised a thorough consent process before prescribing any cannabinoids, including therapeutic goals and stopping criteria; the lack of evidence available on dosing, efficacy, and side effects; and the potential for dependence or withdrawal. Consent discussions should also note whether the products are unregistered and not covered by external payers (anything other than Epidiolex currently), any activity restrictions, and any implications for occupational drug screening.
Considerations for unapproved cannabinoids
The authors note several factors to consider if prescribing or recommending a nonapproved, nonregulated cannabis medicine, including the ”differences between registered plant-derived cannabis medicines, synthetic cannabis medicines, and unregistered hemp-derived products.” Epidiolex is plant derived while other cannabis-derived medications (Marinol, Syndos, and Cesamet) that have been approved for nonepilepsy conditions, such as nausea associated with chemotherapy, are synthetic.
The guidance document notes several reasons to use a regulated medication instead of an unregulated product:
- Manufacturing processes can differ for unregulated products, including inconsistency in batches and unknown shelf life.
- Quality control processes, including risk of impurities, are much better with regulated products, which also have a system in place for safety recalls.
- More scientific evidence is available for regulated products.
- Safety surveillance reporting is more robust and standardized for regulated products whereas adverse event reporting is less reliable for unregulated products.
- Nonregulated products are rarely covered by insurance or other reimbursement.
Legal considerations will also vary by jurisdiction. ”Right now in the U.S. we have a confused legality where state level programs are still technically illegal at the federal level and I imagine there are some quality differences amongst dispensaries and states,” Dr. Freedman said. “Whenever there is disagreement between state and federal laws, this creates tension for our patients.” He noted, for example, that a patient using a CBD product that contains THC may, even if legal in their state, be confiscated by the Transportation Security Administration at an airport since it is not FDA approved and is not legal, according to the Drug Enforcement Agency.
The authors noted that inadequate data on long-term CBD use and data on neurodevelopmental effects of THC in children, teens, and young adults means THC products should be contraindicated for these age groups. (Epidiolex has less than 2% THC.) Drug interactions should also be considered, particularly for clobazam, CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers (including St. John’s wort), digoxin, or a mechanistic target of rapamycin inhibitor.
Dr. Freedman said that most neurologists are comfortable prescribing Epidiolex since it has FDA approval while prescribing unapproved products varies more in the field. “Now that many states have compassionate use programs for medical marijuana, some neurologists do this as well,” Dr. Freedman said. Patients often ask about unregulated CBD or CBD+THC products because they’re seen as “natural and therefore better than manufactured pharmaceuticals.”
“I think this is the naturalistic fallacy at work and try to educate my patients on that since our only high-level data to show marijuana products work for epilepsy comes from a pharmaceutical company,” Dr. Freedman said. “My reasons for hesitating on compassionate use are that there is often THC, with variable amounts of concentration, and we know that THC can harm the developing pediatric brain.”
Dosing and adverse effects
Pediatric and adult dosing differences need to be considered, and “patient response (efficacy and toxicity) to these medications varies widely,” the authors noted. They advised getting serum transaminases (ALT and AST) and total bilirubin levels before beginning treatment. All patients should begin Epidiolex at a low dose, such as 2-5 mg/kg per day of CBD in two divided doses, the authors advise, and titrate slowly while monitoring for side effects (no more than 5 mg/kg per day per week). The current dosing range for CBD is 5-20 mg/kg per day in two divided doses, with higher rates involving more risk of adverse events.
“Note that some cannabinoids auto-inhibit their own metabolism and some have active metabolites with longer half-lives,” the authors wrote. “Therefore, dose or frequency may need to be reduced over time, unless tolerance occurs.” These doses, specific to Epidiolex, “cannot necessarily be applied to other oral CBD formulations or other types of epilepsy.” This guidance also does not apply to inhaled or transdermal routes of administration.
The most common adverse events were sleepiness – which occurred in up to 60% of trial participants – as well as diarrhea, decreases in appetite and weight, and drug interactions. Risk of hepatotoxicity means there’s a need to monitor liver function and adjust dosing for patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment. “Other short-term side effects reported only with THC-containing cannabinoid compounds include increased risk of cardiac and cerebrovascular events, anxiety and psychosis risk, dependency, and withdrawal,” the authors wrote.
Though no withdrawal syndrome has been linked to stopping CBD, the authors suggested decreasing the dose by 10% every 2 days if stopping is not urgent.
“The key points to this issue are that CBD and all marijuana products need to be safe and regulated,” Dr. Freedman said. “Any claims about them need to be backed by high-quality evidence looking at that specific product for that specific condition.”
Dr. Freedman noted the need for children to receive treatment from clinicians with expertise in their specific condition since many other evidence-based treatments exist even for patients with epilepsy syndromes that are difficult to treat, such as other medications, surgery, and specialized diets.
“We need to fix the inconsistent regulation between over-the-counter CBD products, state dispensaries, and federal laws,” Dr. Freedman added. “Any medicine being used to treat children should be held to the same FDA standard of safety and efficacy.”
Dr. Freedman and the authors had no conflicts of interest. No external funding was noted.
A recent review article draws from existing clinical trials and clinical experience in New South Wales, Australia, to fill this gap with interim guidance for both pediatric and adult patients. The article was published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
The only current U.S. guidelines are from the American Academy of Neurology’s position statement on the use of medical cannabis for neurologic disorders and the American Epilepsy Society’s position statement on cannabis as a treatment for epileptic seizures. The AAN statement “highlights the current evidence, which currently only supports [Food and Drug Administration]–approved CBD [cannabidiol] (Epidiolex) for specific epilepsy syndromes,” said Daniel Freedman, DO, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of Texas at Austin and coauthor of the AAN’s position statement.
“Rescheduling marijuana will enable researchers to study CBD, THC [tetrahydrocannabinol], and other cannabinoids in high-quality studies so that we can better understand what works and for which conditions,” said Dr. Freedman, who was not involved in the Australian guidance document. He noted that little consensus exists because little evidence exists outside the handful of trials for Epidiolex.
“There are some patients with epilepsy that can benefit from high-quality, pharmaceutical-grade CBD products,” Dr. Freedman said. “These patients need to be carefully identified by a neurologist or epileptologist and prescribed a legal, safe, quality-controlled, and FDA-regulated product.”
Appropriate patient populations
Drug-resistant epilepsy, defined as failure of two appropriate antiseizure medications, affects an estimated one third of people with epilepsy, the new guideline notes. Though many over-the-counter products are available at dispensaries in the 33 U.S. states that allow use of cannabis for medical purposes, Epidiolex (cannabidiol) is the only FDA-approved drug for epilepsy that contains a substance derived from cannabis and the only one for which evidence from randomized, controlled trials exists.
Dr. Freedman notes that hemp-derived CBD oils are classified differently in the United States than marijuana-derived CBD oil, including Epidiolex, and are loosely regulated supplements or food additives commonly seen, for example at gas station.
“The point I drive home to patients is that you wouldn’t get your antibiotics from a gas station, so please don’t get your seizure medication from there,” Dr. Freedman said. “Studies have been done on ‘over-the-counter’ CBD oils and shown that they have variable quality, sometimes no detectable CBD, and sometimes other chemicals added like THC.”
Studies of Epidiolex showed that cannabidiol more effectively reduced seizure frequency than placebo for pediatric patients with Dravet syndrome (42% reduction) and for pediatric and adult patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (39% reduction) or tuberous sclerosis complex (49% reduction). Efficacy was similar across dosing from 10-50 mg/kg per day, but higher doses involved higher rates of serious adverse events.
No reliable evidence in humans exists for THC or other cannabinoids in treating epilepsy.
The Australian guidance recommends limiting cannabis treatment to patients with severe drug-resistant epilepsy; a diagnosis of Dravet syndrome, Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, or tuberous sclerosis complex; and previous treatment with four approved antiseizure medications and/or the ketogenic diet, epilepsy surgery, or neurostimulator. The authors provide specific criteria for each of these conditions and then address exceptional cases that may be considered outside that criteria, such as patients under 2 years old, severe epilepsy with extended or repeated hospitalization or ICU admission, or a dangerous seizure type. The review also includes a detailed list of exclusion criteria for CBD medicine use.
The authors advised a thorough consent process before prescribing any cannabinoids, including therapeutic goals and stopping criteria; the lack of evidence available on dosing, efficacy, and side effects; and the potential for dependence or withdrawal. Consent discussions should also note whether the products are unregistered and not covered by external payers (anything other than Epidiolex currently), any activity restrictions, and any implications for occupational drug screening.
Considerations for unapproved cannabinoids
The authors note several factors to consider if prescribing or recommending a nonapproved, nonregulated cannabis medicine, including the ”differences between registered plant-derived cannabis medicines, synthetic cannabis medicines, and unregistered hemp-derived products.” Epidiolex is plant derived while other cannabis-derived medications (Marinol, Syndos, and Cesamet) that have been approved for nonepilepsy conditions, such as nausea associated with chemotherapy, are synthetic.
The guidance document notes several reasons to use a regulated medication instead of an unregulated product:
- Manufacturing processes can differ for unregulated products, including inconsistency in batches and unknown shelf life.
- Quality control processes, including risk of impurities, are much better with regulated products, which also have a system in place for safety recalls.
- More scientific evidence is available for regulated products.
- Safety surveillance reporting is more robust and standardized for regulated products whereas adverse event reporting is less reliable for unregulated products.
- Nonregulated products are rarely covered by insurance or other reimbursement.
Legal considerations will also vary by jurisdiction. ”Right now in the U.S. we have a confused legality where state level programs are still technically illegal at the federal level and I imagine there are some quality differences amongst dispensaries and states,” Dr. Freedman said. “Whenever there is disagreement between state and federal laws, this creates tension for our patients.” He noted, for example, that a patient using a CBD product that contains THC may, even if legal in their state, be confiscated by the Transportation Security Administration at an airport since it is not FDA approved and is not legal, according to the Drug Enforcement Agency.
The authors noted that inadequate data on long-term CBD use and data on neurodevelopmental effects of THC in children, teens, and young adults means THC products should be contraindicated for these age groups. (Epidiolex has less than 2% THC.) Drug interactions should also be considered, particularly for clobazam, CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers (including St. John’s wort), digoxin, or a mechanistic target of rapamycin inhibitor.
Dr. Freedman said that most neurologists are comfortable prescribing Epidiolex since it has FDA approval while prescribing unapproved products varies more in the field. “Now that many states have compassionate use programs for medical marijuana, some neurologists do this as well,” Dr. Freedman said. Patients often ask about unregulated CBD or CBD+THC products because they’re seen as “natural and therefore better than manufactured pharmaceuticals.”
“I think this is the naturalistic fallacy at work and try to educate my patients on that since our only high-level data to show marijuana products work for epilepsy comes from a pharmaceutical company,” Dr. Freedman said. “My reasons for hesitating on compassionate use are that there is often THC, with variable amounts of concentration, and we know that THC can harm the developing pediatric brain.”
Dosing and adverse effects
Pediatric and adult dosing differences need to be considered, and “patient response (efficacy and toxicity) to these medications varies widely,” the authors noted. They advised getting serum transaminases (ALT and AST) and total bilirubin levels before beginning treatment. All patients should begin Epidiolex at a low dose, such as 2-5 mg/kg per day of CBD in two divided doses, the authors advise, and titrate slowly while monitoring for side effects (no more than 5 mg/kg per day per week). The current dosing range for CBD is 5-20 mg/kg per day in two divided doses, with higher rates involving more risk of adverse events.
“Note that some cannabinoids auto-inhibit their own metabolism and some have active metabolites with longer half-lives,” the authors wrote. “Therefore, dose or frequency may need to be reduced over time, unless tolerance occurs.” These doses, specific to Epidiolex, “cannot necessarily be applied to other oral CBD formulations or other types of epilepsy.” This guidance also does not apply to inhaled or transdermal routes of administration.
The most common adverse events were sleepiness – which occurred in up to 60% of trial participants – as well as diarrhea, decreases in appetite and weight, and drug interactions. Risk of hepatotoxicity means there’s a need to monitor liver function and adjust dosing for patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment. “Other short-term side effects reported only with THC-containing cannabinoid compounds include increased risk of cardiac and cerebrovascular events, anxiety and psychosis risk, dependency, and withdrawal,” the authors wrote.
Though no withdrawal syndrome has been linked to stopping CBD, the authors suggested decreasing the dose by 10% every 2 days if stopping is not urgent.
“The key points to this issue are that CBD and all marijuana products need to be safe and regulated,” Dr. Freedman said. “Any claims about them need to be backed by high-quality evidence looking at that specific product for that specific condition.”
Dr. Freedman noted the need for children to receive treatment from clinicians with expertise in their specific condition since many other evidence-based treatments exist even for patients with epilepsy syndromes that are difficult to treat, such as other medications, surgery, and specialized diets.
“We need to fix the inconsistent regulation between over-the-counter CBD products, state dispensaries, and federal laws,” Dr. Freedman added. “Any medicine being used to treat children should be held to the same FDA standard of safety and efficacy.”
Dr. Freedman and the authors had no conflicts of interest. No external funding was noted.
A recent review article draws from existing clinical trials and clinical experience in New South Wales, Australia, to fill this gap with interim guidance for both pediatric and adult patients. The article was published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
The only current U.S. guidelines are from the American Academy of Neurology’s position statement on the use of medical cannabis for neurologic disorders and the American Epilepsy Society’s position statement on cannabis as a treatment for epileptic seizures. The AAN statement “highlights the current evidence, which currently only supports [Food and Drug Administration]–approved CBD [cannabidiol] (Epidiolex) for specific epilepsy syndromes,” said Daniel Freedman, DO, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of Texas at Austin and coauthor of the AAN’s position statement.
“Rescheduling marijuana will enable researchers to study CBD, THC [tetrahydrocannabinol], and other cannabinoids in high-quality studies so that we can better understand what works and for which conditions,” said Dr. Freedman, who was not involved in the Australian guidance document. He noted that little consensus exists because little evidence exists outside the handful of trials for Epidiolex.
“There are some patients with epilepsy that can benefit from high-quality, pharmaceutical-grade CBD products,” Dr. Freedman said. “These patients need to be carefully identified by a neurologist or epileptologist and prescribed a legal, safe, quality-controlled, and FDA-regulated product.”
Appropriate patient populations
Drug-resistant epilepsy, defined as failure of two appropriate antiseizure medications, affects an estimated one third of people with epilepsy, the new guideline notes. Though many over-the-counter products are available at dispensaries in the 33 U.S. states that allow use of cannabis for medical purposes, Epidiolex (cannabidiol) is the only FDA-approved drug for epilepsy that contains a substance derived from cannabis and the only one for which evidence from randomized, controlled trials exists.
Dr. Freedman notes that hemp-derived CBD oils are classified differently in the United States than marijuana-derived CBD oil, including Epidiolex, and are loosely regulated supplements or food additives commonly seen, for example at gas station.
“The point I drive home to patients is that you wouldn’t get your antibiotics from a gas station, so please don’t get your seizure medication from there,” Dr. Freedman said. “Studies have been done on ‘over-the-counter’ CBD oils and shown that they have variable quality, sometimes no detectable CBD, and sometimes other chemicals added like THC.”
Studies of Epidiolex showed that cannabidiol more effectively reduced seizure frequency than placebo for pediatric patients with Dravet syndrome (42% reduction) and for pediatric and adult patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (39% reduction) or tuberous sclerosis complex (49% reduction). Efficacy was similar across dosing from 10-50 mg/kg per day, but higher doses involved higher rates of serious adverse events.
No reliable evidence in humans exists for THC or other cannabinoids in treating epilepsy.
The Australian guidance recommends limiting cannabis treatment to patients with severe drug-resistant epilepsy; a diagnosis of Dravet syndrome, Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, or tuberous sclerosis complex; and previous treatment with four approved antiseizure medications and/or the ketogenic diet, epilepsy surgery, or neurostimulator. The authors provide specific criteria for each of these conditions and then address exceptional cases that may be considered outside that criteria, such as patients under 2 years old, severe epilepsy with extended or repeated hospitalization or ICU admission, or a dangerous seizure type. The review also includes a detailed list of exclusion criteria for CBD medicine use.
The authors advised a thorough consent process before prescribing any cannabinoids, including therapeutic goals and stopping criteria; the lack of evidence available on dosing, efficacy, and side effects; and the potential for dependence or withdrawal. Consent discussions should also note whether the products are unregistered and not covered by external payers (anything other than Epidiolex currently), any activity restrictions, and any implications for occupational drug screening.
Considerations for unapproved cannabinoids
The authors note several factors to consider if prescribing or recommending a nonapproved, nonregulated cannabis medicine, including the ”differences between registered plant-derived cannabis medicines, synthetic cannabis medicines, and unregistered hemp-derived products.” Epidiolex is plant derived while other cannabis-derived medications (Marinol, Syndos, and Cesamet) that have been approved for nonepilepsy conditions, such as nausea associated with chemotherapy, are synthetic.
The guidance document notes several reasons to use a regulated medication instead of an unregulated product:
- Manufacturing processes can differ for unregulated products, including inconsistency in batches and unknown shelf life.
- Quality control processes, including risk of impurities, are much better with regulated products, which also have a system in place for safety recalls.
- More scientific evidence is available for regulated products.
- Safety surveillance reporting is more robust and standardized for regulated products whereas adverse event reporting is less reliable for unregulated products.
- Nonregulated products are rarely covered by insurance or other reimbursement.
Legal considerations will also vary by jurisdiction. ”Right now in the U.S. we have a confused legality where state level programs are still technically illegal at the federal level and I imagine there are some quality differences amongst dispensaries and states,” Dr. Freedman said. “Whenever there is disagreement between state and federal laws, this creates tension for our patients.” He noted, for example, that a patient using a CBD product that contains THC may, even if legal in their state, be confiscated by the Transportation Security Administration at an airport since it is not FDA approved and is not legal, according to the Drug Enforcement Agency.
The authors noted that inadequate data on long-term CBD use and data on neurodevelopmental effects of THC in children, teens, and young adults means THC products should be contraindicated for these age groups. (Epidiolex has less than 2% THC.) Drug interactions should also be considered, particularly for clobazam, CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers (including St. John’s wort), digoxin, or a mechanistic target of rapamycin inhibitor.
Dr. Freedman said that most neurologists are comfortable prescribing Epidiolex since it has FDA approval while prescribing unapproved products varies more in the field. “Now that many states have compassionate use programs for medical marijuana, some neurologists do this as well,” Dr. Freedman said. Patients often ask about unregulated CBD or CBD+THC products because they’re seen as “natural and therefore better than manufactured pharmaceuticals.”
“I think this is the naturalistic fallacy at work and try to educate my patients on that since our only high-level data to show marijuana products work for epilepsy comes from a pharmaceutical company,” Dr. Freedman said. “My reasons for hesitating on compassionate use are that there is often THC, with variable amounts of concentration, and we know that THC can harm the developing pediatric brain.”
Dosing and adverse effects
Pediatric and adult dosing differences need to be considered, and “patient response (efficacy and toxicity) to these medications varies widely,” the authors noted. They advised getting serum transaminases (ALT and AST) and total bilirubin levels before beginning treatment. All patients should begin Epidiolex at a low dose, such as 2-5 mg/kg per day of CBD in two divided doses, the authors advise, and titrate slowly while monitoring for side effects (no more than 5 mg/kg per day per week). The current dosing range for CBD is 5-20 mg/kg per day in two divided doses, with higher rates involving more risk of adverse events.
“Note that some cannabinoids auto-inhibit their own metabolism and some have active metabolites with longer half-lives,” the authors wrote. “Therefore, dose or frequency may need to be reduced over time, unless tolerance occurs.” These doses, specific to Epidiolex, “cannot necessarily be applied to other oral CBD formulations or other types of epilepsy.” This guidance also does not apply to inhaled or transdermal routes of administration.
The most common adverse events were sleepiness – which occurred in up to 60% of trial participants – as well as diarrhea, decreases in appetite and weight, and drug interactions. Risk of hepatotoxicity means there’s a need to monitor liver function and adjust dosing for patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment. “Other short-term side effects reported only with THC-containing cannabinoid compounds include increased risk of cardiac and cerebrovascular events, anxiety and psychosis risk, dependency, and withdrawal,” the authors wrote.
Though no withdrawal syndrome has been linked to stopping CBD, the authors suggested decreasing the dose by 10% every 2 days if stopping is not urgent.
“The key points to this issue are that CBD and all marijuana products need to be safe and regulated,” Dr. Freedman said. “Any claims about them need to be backed by high-quality evidence looking at that specific product for that specific condition.”
Dr. Freedman noted the need for children to receive treatment from clinicians with expertise in their specific condition since many other evidence-based treatments exist even for patients with epilepsy syndromes that are difficult to treat, such as other medications, surgery, and specialized diets.
“We need to fix the inconsistent regulation between over-the-counter CBD products, state dispensaries, and federal laws,” Dr. Freedman added. “Any medicine being used to treat children should be held to the same FDA standard of safety and efficacy.”
Dr. Freedman and the authors had no conflicts of interest. No external funding was noted.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
U.S. health officials tracking COVID-19 increase in U.K.
according to NPR.
Daily cases counts have increased 38% in the past week, according to the latest data from the U.K. Health Security Agency. Hospitalizations are up about 25% as well.
“Over the last year or so, what happens in the U.K. usually happens here a few weeks later,” Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, told NPR.
“And right now, the U.K. is seeing somewhat of a rebound in cases,” he said.
Health officials in the United Kingdom have noted the latest increase is likely due to the contagious BA.2 Omicron subvariant, the recent loosening of coronavirus restrictions, and waning immunity from vaccinations and infections.
“All three of those factors we have here in the United States,” Dr. Fauci said. “So I would not be surprised if, in the next few weeks, we see either a plateauing … of cases or even [the curve] rebounds and slightly goes up.”
Right now, COVID-19 cases in the United Stastes have dropped to their lowest levels since July 2021, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with fewer than 30,000 daily cases. At the same time, the rate of decline in cases has slowed significantly and is beginning to plateau.
Public health experts are also pointing to wastewater surveillance data that shows an uptick in viral activity across the country. The CDC’s wastewater dashboard indicates that about 35% of sites that monitor wastewater are seeing an increase, with consistent growth in Florida, Rhode Island, and West Virginia.
“The power of wastewater surveillance is that it’s an early warning system,” Amy Kirby, the program lead for the CDC’s National Wastewater Surveillance System, told NPR.
“We are seeing evidence of increases in some communities across the country,” she said. “What looked like noise at the beginning of the week is starting to look like a true signal here at the end of the week.”
The wastewater system doesn’t distinguish between Omicron and subvariants such as BA.2. However, other CDC data has found an increase in BA.2 cases in the United States, making up about a quarter of new COVID-19 cases.
The BA.2 variant has roughly doubled each week for the last month, which means it could become the dominant coronavirus strain in the United States in coming weeks, according to USA Today. Cases appear to be spreading more quickly in the Northeast and West, making up about 39% of cases in New York and New Jersey last week.
BA.2 also accounts for nearly 39% of cases across the Northeast, including Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont, USA Today reported. In the West, which includes Arizona, California and Nevada, the subvariant makes up about 28% of new cases. In the upper West, which includes Alaska, Oregon and Washington, about 26% of cases are BA.2.
The good news is that BA.2 “doesn’t seem to evade our vaccines or immunity any more than the prior Omicron [variant]. And it doesn’t seem to lead to any more increased severity of disease,” Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told NPR’s Morning Edition on March 18.
The effects of BA.2 will likely depend on the immunity profile in the United States, including how long it’s been since someone was vaccinated, boosted, or recovered from an infection, she said.
Health officials are watching other countries with BA.2 increases, such as Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands. Many European countries have been reporting an uptick but not implementing major restrictions or shutdowns, USA Today reported.
The BA.2 variant likely won’t lead to a major surge in severe disease or strict COVID-19 measures, Dr. Fauci told NPR, but some coronavirus protocols may need to be implemented again if cases grow dramatically.
“We must be ready to pivot and, if necessary, to go back to stricter mitigation with regard to masks,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to NPR.
Daily cases counts have increased 38% in the past week, according to the latest data from the U.K. Health Security Agency. Hospitalizations are up about 25% as well.
“Over the last year or so, what happens in the U.K. usually happens here a few weeks later,” Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, told NPR.
“And right now, the U.K. is seeing somewhat of a rebound in cases,” he said.
Health officials in the United Kingdom have noted the latest increase is likely due to the contagious BA.2 Omicron subvariant, the recent loosening of coronavirus restrictions, and waning immunity from vaccinations and infections.
“All three of those factors we have here in the United States,” Dr. Fauci said. “So I would not be surprised if, in the next few weeks, we see either a plateauing … of cases or even [the curve] rebounds and slightly goes up.”
Right now, COVID-19 cases in the United Stastes have dropped to their lowest levels since July 2021, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with fewer than 30,000 daily cases. At the same time, the rate of decline in cases has slowed significantly and is beginning to plateau.
Public health experts are also pointing to wastewater surveillance data that shows an uptick in viral activity across the country. The CDC’s wastewater dashboard indicates that about 35% of sites that monitor wastewater are seeing an increase, with consistent growth in Florida, Rhode Island, and West Virginia.
“The power of wastewater surveillance is that it’s an early warning system,” Amy Kirby, the program lead for the CDC’s National Wastewater Surveillance System, told NPR.
“We are seeing evidence of increases in some communities across the country,” she said. “What looked like noise at the beginning of the week is starting to look like a true signal here at the end of the week.”
The wastewater system doesn’t distinguish between Omicron and subvariants such as BA.2. However, other CDC data has found an increase in BA.2 cases in the United States, making up about a quarter of new COVID-19 cases.
The BA.2 variant has roughly doubled each week for the last month, which means it could become the dominant coronavirus strain in the United States in coming weeks, according to USA Today. Cases appear to be spreading more quickly in the Northeast and West, making up about 39% of cases in New York and New Jersey last week.
BA.2 also accounts for nearly 39% of cases across the Northeast, including Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont, USA Today reported. In the West, which includes Arizona, California and Nevada, the subvariant makes up about 28% of new cases. In the upper West, which includes Alaska, Oregon and Washington, about 26% of cases are BA.2.
The good news is that BA.2 “doesn’t seem to evade our vaccines or immunity any more than the prior Omicron [variant]. And it doesn’t seem to lead to any more increased severity of disease,” Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told NPR’s Morning Edition on March 18.
The effects of BA.2 will likely depend on the immunity profile in the United States, including how long it’s been since someone was vaccinated, boosted, or recovered from an infection, she said.
Health officials are watching other countries with BA.2 increases, such as Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands. Many European countries have been reporting an uptick but not implementing major restrictions or shutdowns, USA Today reported.
The BA.2 variant likely won’t lead to a major surge in severe disease or strict COVID-19 measures, Dr. Fauci told NPR, but some coronavirus protocols may need to be implemented again if cases grow dramatically.
“We must be ready to pivot and, if necessary, to go back to stricter mitigation with regard to masks,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to NPR.
Daily cases counts have increased 38% in the past week, according to the latest data from the U.K. Health Security Agency. Hospitalizations are up about 25% as well.
“Over the last year or so, what happens in the U.K. usually happens here a few weeks later,” Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, told NPR.
“And right now, the U.K. is seeing somewhat of a rebound in cases,” he said.
Health officials in the United Kingdom have noted the latest increase is likely due to the contagious BA.2 Omicron subvariant, the recent loosening of coronavirus restrictions, and waning immunity from vaccinations and infections.
“All three of those factors we have here in the United States,” Dr. Fauci said. “So I would not be surprised if, in the next few weeks, we see either a plateauing … of cases or even [the curve] rebounds and slightly goes up.”
Right now, COVID-19 cases in the United Stastes have dropped to their lowest levels since July 2021, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with fewer than 30,000 daily cases. At the same time, the rate of decline in cases has slowed significantly and is beginning to plateau.
Public health experts are also pointing to wastewater surveillance data that shows an uptick in viral activity across the country. The CDC’s wastewater dashboard indicates that about 35% of sites that monitor wastewater are seeing an increase, with consistent growth in Florida, Rhode Island, and West Virginia.
“The power of wastewater surveillance is that it’s an early warning system,” Amy Kirby, the program lead for the CDC’s National Wastewater Surveillance System, told NPR.
“We are seeing evidence of increases in some communities across the country,” she said. “What looked like noise at the beginning of the week is starting to look like a true signal here at the end of the week.”
The wastewater system doesn’t distinguish between Omicron and subvariants such as BA.2. However, other CDC data has found an increase in BA.2 cases in the United States, making up about a quarter of new COVID-19 cases.
The BA.2 variant has roughly doubled each week for the last month, which means it could become the dominant coronavirus strain in the United States in coming weeks, according to USA Today. Cases appear to be spreading more quickly in the Northeast and West, making up about 39% of cases in New York and New Jersey last week.
BA.2 also accounts for nearly 39% of cases across the Northeast, including Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont, USA Today reported. In the West, which includes Arizona, California and Nevada, the subvariant makes up about 28% of new cases. In the upper West, which includes Alaska, Oregon and Washington, about 26% of cases are BA.2.
The good news is that BA.2 “doesn’t seem to evade our vaccines or immunity any more than the prior Omicron [variant]. And it doesn’t seem to lead to any more increased severity of disease,” Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told NPR’s Morning Edition on March 18.
The effects of BA.2 will likely depend on the immunity profile in the United States, including how long it’s been since someone was vaccinated, boosted, or recovered from an infection, she said.
Health officials are watching other countries with BA.2 increases, such as Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands. Many European countries have been reporting an uptick but not implementing major restrictions or shutdowns, USA Today reported.
The BA.2 variant likely won’t lead to a major surge in severe disease or strict COVID-19 measures, Dr. Fauci told NPR, but some coronavirus protocols may need to be implemented again if cases grow dramatically.
“We must be ready to pivot and, if necessary, to go back to stricter mitigation with regard to masks,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Common eye disorder in children tied to mental illness
Misaligned eyes in children are associated with an increased prevalence of mental illness, results of a large study suggest.
“Psychiatrists who have a patient with depression or anxiety and notice that patient also has strabismus might think about the link between those two conditions and refer that patient,” study investigator Stacy L. Pineles, MD, professor, department of ophthalmology, University of California, Los Angeles, told this news organization.
The study was published online March 10 in JAMA Ophthalmology.
A common condition
Strabismus, a condition in which the eyes don’t line up or are “crossed,” is one of the most common eye diseases in children, with some estimates suggesting it affects more than 1.5 million American youth.
Patients with strabismus have problems making eye contact and are affected socially and functionally, said Dr. Pineles. They’re often met with a negative bias, as shown by children’s responses to pictures of faces with and without strabismus, she said.
There is a signal from previous research suggesting that strabismus is linked to a higher risk of mental illness. However, most of these studies were small and had relatively homogenous populations, said Dr. Pineles.
The new study includes over 12 million children (mean age, 8.0 years) from a private health insurance claims database that represents diverse races and ethnicities as well as geographic regions across the United States.
The sample included 352,636 children with strabismus and 11,652,553 children with no diagnosed eye disease who served as controls. Most participants were White (51.6%), came from a family with an annual household income of $40,000 or more (51.0%), had point-of-service insurance (68.7%), and had at least one comorbid condition (64.5%).
The study evaluated five mental illness diagnoses. These included anxiety disorder, depressive disorder, substance use or addictive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
Overall, children with strabismus had a higher prevalence of all these illnesses, with the exception of substance use disorder.
After adjusting for age, sex, race and ethnicity, census region, education level of caregiver, family net worth, and presence of at least one comorbid condition, the odds ratios among those with versus without strabismus were: 2.01 (95% confidence interval, 1.99-2.04; P < .001) for anxiety disorder, 1.83 (95% CI, 1.76-1.90; P < .001) for schizophrenia, 1.64 (95% CI, 1.59-1.70; P < .001) for bipolar disorder, and 1.61 (95% CI, 1.59-1.63; P < .001) for depressive disorder.
Substance use disorder had a negative unadjusted association with strabismus, but after adjustment for confounders, the association was not significant (OR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.97-1.02; P = .48).
Dr. Pineles noted that the study participants, who were all under age 19, may be too young to have substance use disorders.
The results for substance use disorders provided something of an “internal control” and reaffirmed results for the other four conditions, said Dr. Pineles.
“When you do research on such a large database, you’re very likely to find significant associations; the dataset is so large that even very small differences become statistically significant. It was interesting that not everything gave us a positive association.”
Researchers divided the strabismus group into those with esotropia, where the eyes turn inward (52.2%), exotropia, where they turn outward (46.3%), and hypertropia, where one eye wanders upward (12.5%). Investigators found that all three conditions were associated with increased risk of anxiety disorder, depressive disorder, bipolar disorders, and schizophrenia.
Investigators note that rates in the current study were lower than in previous studies, which showed that children with congenital esotropia were 2.6 times more likely to receive a mental health diagnosis, and children with intermittent exotropia were 2.7 times more likely to receive a mental health diagnosis.
“It is probable that our study found a lower risk than these studies, because our study was cross-sectional and claims based, whereas these studies observed the children to early adulthood and were based on medical records,” the investigators note.
It’s impossible to determine from this study how strabismus is connected to mental illness. However, Dr. Pineles believes depression and anxiety might be tied to strabismus via teasing, which affects self-esteem, although genetics could also play a role. For conditions such as schizophrenia, a shared genetic link with strabismus might be more likely, she added.
“Schizophrenia is a pretty severe diagnosis, so just being teased or having poor self-esteem is probably not enough” to develop schizophrenia.
Based on her clinical experience, Dr. Pineles said that realigning the eyes of patients with milder forms of depression or anxiety “definitely anecdotally helps these patients a lot.”
Dr. Pineles and colleagues have another paper in press that examines mental illnesses and other serious eye disorders in children and shows similar findings, she said.
Implications for insurance coverage?
In an accompanying editorial, experts, led by S. Grace Prakalapakorn, MD, department of ophthalmology and pediatrics, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., noted the exclusion of children covered under government insurance or without insurance is an important study limitation, largely because socioeconomic status is a risk factor for poor mental health.
The editorialists point to studies showing that surgical correction of ocular misalignments may be associated with reduced anxiety and depression. However, health insurance coverage for such surgical correction “may not be available owing to a misconception that these conditions are ‘cosmetic’.”
Evidence of the broader association of strabismus with physical and mental health “may play an important role in shifting policy to promote insurance coverage for timely strabismus care,” they write.
As many mental health disorders begin in childhood or adolescence, “it is paramount to identify, address, and, if possible, prevent mental health disorders at a young age, because failure to intervene in a timely fashion can have lifelong health consequences,” say Dr. Prakalapakorn and colleagues.
With mental health conditions and disorders increasing worldwide, compounded by the stressors of the COVID-19 pandemic, additional studies are needed to explore the causal relationships between ocular and psychiatric phenomena, their treatment, and outcomes, they add.
The study was supported by a grant from the National Eye Institute and an unrestricted grant from Research to Prevent Blindness. Dr. Pineles has reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Commentary author Manpreet K. Singh, MD, has reported receiving research support from Stanford’s Maternal Child Health Research Institute and Stanford’s Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, the National Institute of Mental Health, the National Institute on Aging, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, Johnson & Johnson, Allergan, and the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation; serving on the advisory board for Sunovion and Skyland Trail; serving as a consultant for Johnson & Johnson; previously serving as a consultant for X, the moonshot factory, Alphabet, and Limbix Health; receiving honoraria from the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry; and receiving royalties from American Psychiatric Association Publishing and Thrive Global. Commentary author Nathan Congdon, MD, has reported receiving personal fees from Belkin Vision outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Misaligned eyes in children are associated with an increased prevalence of mental illness, results of a large study suggest.
“Psychiatrists who have a patient with depression or anxiety and notice that patient also has strabismus might think about the link between those two conditions and refer that patient,” study investigator Stacy L. Pineles, MD, professor, department of ophthalmology, University of California, Los Angeles, told this news organization.
The study was published online March 10 in JAMA Ophthalmology.
A common condition
Strabismus, a condition in which the eyes don’t line up or are “crossed,” is one of the most common eye diseases in children, with some estimates suggesting it affects more than 1.5 million American youth.
Patients with strabismus have problems making eye contact and are affected socially and functionally, said Dr. Pineles. They’re often met with a negative bias, as shown by children’s responses to pictures of faces with and without strabismus, she said.
There is a signal from previous research suggesting that strabismus is linked to a higher risk of mental illness. However, most of these studies were small and had relatively homogenous populations, said Dr. Pineles.
The new study includes over 12 million children (mean age, 8.0 years) from a private health insurance claims database that represents diverse races and ethnicities as well as geographic regions across the United States.
The sample included 352,636 children with strabismus and 11,652,553 children with no diagnosed eye disease who served as controls. Most participants were White (51.6%), came from a family with an annual household income of $40,000 or more (51.0%), had point-of-service insurance (68.7%), and had at least one comorbid condition (64.5%).
The study evaluated five mental illness diagnoses. These included anxiety disorder, depressive disorder, substance use or addictive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
Overall, children with strabismus had a higher prevalence of all these illnesses, with the exception of substance use disorder.
After adjusting for age, sex, race and ethnicity, census region, education level of caregiver, family net worth, and presence of at least one comorbid condition, the odds ratios among those with versus without strabismus were: 2.01 (95% confidence interval, 1.99-2.04; P < .001) for anxiety disorder, 1.83 (95% CI, 1.76-1.90; P < .001) for schizophrenia, 1.64 (95% CI, 1.59-1.70; P < .001) for bipolar disorder, and 1.61 (95% CI, 1.59-1.63; P < .001) for depressive disorder.
Substance use disorder had a negative unadjusted association with strabismus, but after adjustment for confounders, the association was not significant (OR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.97-1.02; P = .48).
Dr. Pineles noted that the study participants, who were all under age 19, may be too young to have substance use disorders.
The results for substance use disorders provided something of an “internal control” and reaffirmed results for the other four conditions, said Dr. Pineles.
“When you do research on such a large database, you’re very likely to find significant associations; the dataset is so large that even very small differences become statistically significant. It was interesting that not everything gave us a positive association.”
Researchers divided the strabismus group into those with esotropia, where the eyes turn inward (52.2%), exotropia, where they turn outward (46.3%), and hypertropia, where one eye wanders upward (12.5%). Investigators found that all three conditions were associated with increased risk of anxiety disorder, depressive disorder, bipolar disorders, and schizophrenia.
Investigators note that rates in the current study were lower than in previous studies, which showed that children with congenital esotropia were 2.6 times more likely to receive a mental health diagnosis, and children with intermittent exotropia were 2.7 times more likely to receive a mental health diagnosis.
“It is probable that our study found a lower risk than these studies, because our study was cross-sectional and claims based, whereas these studies observed the children to early adulthood and were based on medical records,” the investigators note.
It’s impossible to determine from this study how strabismus is connected to mental illness. However, Dr. Pineles believes depression and anxiety might be tied to strabismus via teasing, which affects self-esteem, although genetics could also play a role. For conditions such as schizophrenia, a shared genetic link with strabismus might be more likely, she added.
“Schizophrenia is a pretty severe diagnosis, so just being teased or having poor self-esteem is probably not enough” to develop schizophrenia.
Based on her clinical experience, Dr. Pineles said that realigning the eyes of patients with milder forms of depression or anxiety “definitely anecdotally helps these patients a lot.”
Dr. Pineles and colleagues have another paper in press that examines mental illnesses and other serious eye disorders in children and shows similar findings, she said.
Implications for insurance coverage?
In an accompanying editorial, experts, led by S. Grace Prakalapakorn, MD, department of ophthalmology and pediatrics, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., noted the exclusion of children covered under government insurance or without insurance is an important study limitation, largely because socioeconomic status is a risk factor for poor mental health.
The editorialists point to studies showing that surgical correction of ocular misalignments may be associated with reduced anxiety and depression. However, health insurance coverage for such surgical correction “may not be available owing to a misconception that these conditions are ‘cosmetic’.”
Evidence of the broader association of strabismus with physical and mental health “may play an important role in shifting policy to promote insurance coverage for timely strabismus care,” they write.
As many mental health disorders begin in childhood or adolescence, “it is paramount to identify, address, and, if possible, prevent mental health disorders at a young age, because failure to intervene in a timely fashion can have lifelong health consequences,” say Dr. Prakalapakorn and colleagues.
With mental health conditions and disorders increasing worldwide, compounded by the stressors of the COVID-19 pandemic, additional studies are needed to explore the causal relationships between ocular and psychiatric phenomena, their treatment, and outcomes, they add.
The study was supported by a grant from the National Eye Institute and an unrestricted grant from Research to Prevent Blindness. Dr. Pineles has reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Commentary author Manpreet K. Singh, MD, has reported receiving research support from Stanford’s Maternal Child Health Research Institute and Stanford’s Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, the National Institute of Mental Health, the National Institute on Aging, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, Johnson & Johnson, Allergan, and the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation; serving on the advisory board for Sunovion and Skyland Trail; serving as a consultant for Johnson & Johnson; previously serving as a consultant for X, the moonshot factory, Alphabet, and Limbix Health; receiving honoraria from the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry; and receiving royalties from American Psychiatric Association Publishing and Thrive Global. Commentary author Nathan Congdon, MD, has reported receiving personal fees from Belkin Vision outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Misaligned eyes in children are associated with an increased prevalence of mental illness, results of a large study suggest.
“Psychiatrists who have a patient with depression or anxiety and notice that patient also has strabismus might think about the link between those two conditions and refer that patient,” study investigator Stacy L. Pineles, MD, professor, department of ophthalmology, University of California, Los Angeles, told this news organization.
The study was published online March 10 in JAMA Ophthalmology.
A common condition
Strabismus, a condition in which the eyes don’t line up or are “crossed,” is one of the most common eye diseases in children, with some estimates suggesting it affects more than 1.5 million American youth.
Patients with strabismus have problems making eye contact and are affected socially and functionally, said Dr. Pineles. They’re often met with a negative bias, as shown by children’s responses to pictures of faces with and without strabismus, she said.
There is a signal from previous research suggesting that strabismus is linked to a higher risk of mental illness. However, most of these studies were small and had relatively homogenous populations, said Dr. Pineles.
The new study includes over 12 million children (mean age, 8.0 years) from a private health insurance claims database that represents diverse races and ethnicities as well as geographic regions across the United States.
The sample included 352,636 children with strabismus and 11,652,553 children with no diagnosed eye disease who served as controls. Most participants were White (51.6%), came from a family with an annual household income of $40,000 or more (51.0%), had point-of-service insurance (68.7%), and had at least one comorbid condition (64.5%).
The study evaluated five mental illness diagnoses. These included anxiety disorder, depressive disorder, substance use or addictive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
Overall, children with strabismus had a higher prevalence of all these illnesses, with the exception of substance use disorder.
After adjusting for age, sex, race and ethnicity, census region, education level of caregiver, family net worth, and presence of at least one comorbid condition, the odds ratios among those with versus without strabismus were: 2.01 (95% confidence interval, 1.99-2.04; P < .001) for anxiety disorder, 1.83 (95% CI, 1.76-1.90; P < .001) for schizophrenia, 1.64 (95% CI, 1.59-1.70; P < .001) for bipolar disorder, and 1.61 (95% CI, 1.59-1.63; P < .001) for depressive disorder.
Substance use disorder had a negative unadjusted association with strabismus, but after adjustment for confounders, the association was not significant (OR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.97-1.02; P = .48).
Dr. Pineles noted that the study participants, who were all under age 19, may be too young to have substance use disorders.
The results for substance use disorders provided something of an “internal control” and reaffirmed results for the other four conditions, said Dr. Pineles.
“When you do research on such a large database, you’re very likely to find significant associations; the dataset is so large that even very small differences become statistically significant. It was interesting that not everything gave us a positive association.”
Researchers divided the strabismus group into those with esotropia, where the eyes turn inward (52.2%), exotropia, where they turn outward (46.3%), and hypertropia, where one eye wanders upward (12.5%). Investigators found that all three conditions were associated with increased risk of anxiety disorder, depressive disorder, bipolar disorders, and schizophrenia.
Investigators note that rates in the current study were lower than in previous studies, which showed that children with congenital esotropia were 2.6 times more likely to receive a mental health diagnosis, and children with intermittent exotropia were 2.7 times more likely to receive a mental health diagnosis.
“It is probable that our study found a lower risk than these studies, because our study was cross-sectional and claims based, whereas these studies observed the children to early adulthood and were based on medical records,” the investigators note.
It’s impossible to determine from this study how strabismus is connected to mental illness. However, Dr. Pineles believes depression and anxiety might be tied to strabismus via teasing, which affects self-esteem, although genetics could also play a role. For conditions such as schizophrenia, a shared genetic link with strabismus might be more likely, she added.
“Schizophrenia is a pretty severe diagnosis, so just being teased or having poor self-esteem is probably not enough” to develop schizophrenia.
Based on her clinical experience, Dr. Pineles said that realigning the eyes of patients with milder forms of depression or anxiety “definitely anecdotally helps these patients a lot.”
Dr. Pineles and colleagues have another paper in press that examines mental illnesses and other serious eye disorders in children and shows similar findings, she said.
Implications for insurance coverage?
In an accompanying editorial, experts, led by S. Grace Prakalapakorn, MD, department of ophthalmology and pediatrics, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., noted the exclusion of children covered under government insurance or without insurance is an important study limitation, largely because socioeconomic status is a risk factor for poor mental health.
The editorialists point to studies showing that surgical correction of ocular misalignments may be associated with reduced anxiety and depression. However, health insurance coverage for such surgical correction “may not be available owing to a misconception that these conditions are ‘cosmetic’.”
Evidence of the broader association of strabismus with physical and mental health “may play an important role in shifting policy to promote insurance coverage for timely strabismus care,” they write.
As many mental health disorders begin in childhood or adolescence, “it is paramount to identify, address, and, if possible, prevent mental health disorders at a young age, because failure to intervene in a timely fashion can have lifelong health consequences,” say Dr. Prakalapakorn and colleagues.
With mental health conditions and disorders increasing worldwide, compounded by the stressors of the COVID-19 pandemic, additional studies are needed to explore the causal relationships between ocular and psychiatric phenomena, their treatment, and outcomes, they add.
The study was supported by a grant from the National Eye Institute and an unrestricted grant from Research to Prevent Blindness. Dr. Pineles has reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Commentary author Manpreet K. Singh, MD, has reported receiving research support from Stanford’s Maternal Child Health Research Institute and Stanford’s Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, the National Institute of Mental Health, the National Institute on Aging, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, Johnson & Johnson, Allergan, and the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation; serving on the advisory board for Sunovion and Skyland Trail; serving as a consultant for Johnson & Johnson; previously serving as a consultant for X, the moonshot factory, Alphabet, and Limbix Health; receiving honoraria from the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry; and receiving royalties from American Psychiatric Association Publishing and Thrive Global. Commentary author Nathan Congdon, MD, has reported receiving personal fees from Belkin Vision outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Alarming’ worldwide decline in mental health
The Mental Health Million project of Sapien Labs issued its second report, published online March 15, encompassing 34 countries and over 220,000 Internet-enabled adults. It found a continued decline in mental health in all age groups and genders, with English-speaking countries having the lowest mental well-being.
The decline was significantly correlated with the stringency of COVID-19 lockdown measures in each country and was directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
The youngest age group (18-24 years) reported the poorest mental well-being, with better mental health scores rising in every successively older age group.
“Some of our findings, especially regarding mental health in young adults, are alarming,” Tara Thiagarajan, PhD, Sapien Labs founder and chief scientist, told this news organization.
“Our data, which are continually updated in real time, are freely available for nonprofit, noncommercial use and research, and we hope that researchers will get involved in an interdisciplinary way that spans sociology, economics, psychiatry, and other fields,” she said.
Pioneering research
Dr. Thiagarajan and her team pioneered the Mental Health Million project, an ongoing research initiative utilizing a “free and anonymous assessment tool,” the Mental Health Quotient (MHQ), which “encompasses a comprehensive view of our emotional, social, and cognitive function and capability.”
The MHQ consists of 47 “elements of mental well-being,” with scores ranging from –100 to +200. (Negative scores indicate poorer mental well-being.) The MHQ categorizes respondents as “clinical, at-risk, enduring, managing, succeeding, and thriving” and computes scores on the basis of six broad dimensions of mental health: core cognition, complex cognition, mood and outlook, drive and motivation, social self, and mind-body connection.
As reported by this news organization, Sapien Lab’s first Mental Health State of the World report (n = 49,000 adults) was conducted in eight English-speaking countries in 2020. Participants were compared to a smaller sample of people from the same countries polled in 2019.
In this year’s report, “we expanded quite substantially,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. The project added Spanish, French, and Arabic and recruited participants from 34 countries on six continents (n = 223,087) via advertising on Google and Facebook.
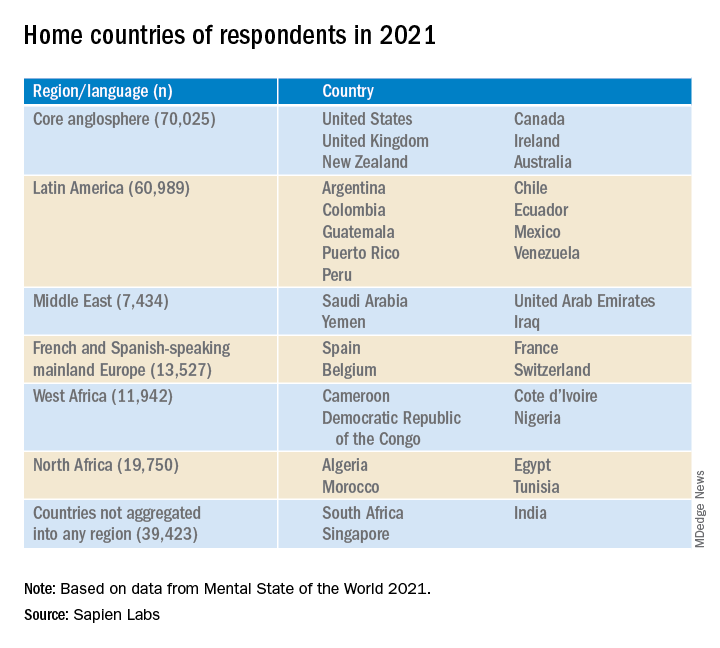
Economic prosperity not protective
Across the eight English-speaking countries, there was a decline in mental well-being of 3% from 2020 to 2021, which was smaller than the 8% decline from 2019 to 2020. The percentage of people who were “distressed or struggling” increased from 26% to 30% in 2021.
“Now that a lot of pandemic issue seems to be easing up, I hope we’ll see mental well-being coming back up, but at least it’s a smaller decline than we saw between 2019 and 2020,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
The decline across countries from 2019 to 2021 was significantly correlated with the stringency of governmental COVID-19-related measures (based on the Oxford COVID-19 Government Response Tracker, 2022; r = .54) and directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
In total, 30% of respondents in English-speaking countries had mental well-being scores in the “distressed” or “struggling” range – higher than the Middle Eastern countries, North Africa, Latin America, and Europe (23%, 23%, 24%, and 18%, respectively).
Only 36% of participants in the English-speaking countries, the Middle East, and North Africa reported “thriving or succeeding,” vs. 45% and 46% in Latin America and Europe, respectively. Venezuela topped the list with an average MHQ of 91, while the United Kingdom and South Africa had the lowest scores, at 46 each.
Mental well-being was slightly higher in males than in females but was dramatically lower in nonbinary/third-gender respondents. In fact, those identifying as nonbinary/third gender had the lowest mental well-being of any group.
Across all countries and languages, higher education was associated with better mental well-being. Employment was also associated with superior mental well-being, compared with being unemployed – particularly in core English-speaking countries.
However, “country indicators of economic prosperity were negatively correlated with mental well-being, particularly for young adults and males, belying the commonly held belief that national economic prosperity translates into greater mental well-being,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
‘Stark’ contrast
The most dramatic finding was the difference in mental well-being between younger and older adults, which was two- to threefold larger than differences in other dimensions (for example, age, gender, employment). Even the maximum difference between countries overall (15%) was still smaller than the generational gap within any region.
While only 7% (6%- 9%) of participants aged ≥65 years were “distressed and struggling” with their mental well-being to a “clinical” extent, 44% (38%-50%) of those aged 18-24 years reported mental well-being scores in the “distressed or struggling” range – representing a “growing gap between generations that, while present prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has since been exacerbated,” the authors state.
With every successive decrement in age group, mental well-being “plummeted,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. She noted that research conducted prior to 2010 in several regions of the world showed that young adults typically had the highest well-being. “Our findings stand in stark contrast to these previous patterns.”
The relationship between lockdown stringency and poorer mental health could play a role. “The impact of social isolation may be most strongly felt in younger people,” she said.
Internet a culprit?
“Within almost every region, scores for cognition and drive and motivation were highest while mood and outlook and social self were the lowest,” the authors report.
The aggregate percentage of respondents who reported being “distressed or struggling” in the various MHQ dimensions is shown in the following table.
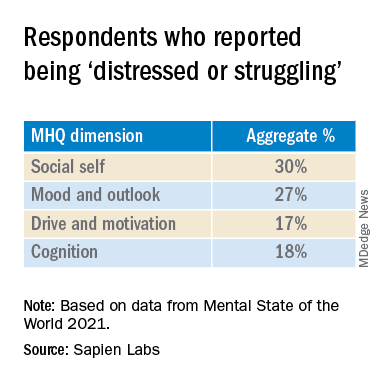
In particular, English-speaking countries scored lowest on the social self scale.
The sense of social self is “how you see yourself with respect to others, how you relate to others and the ability to form strong, stable relationships and maintain them with other people,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
Internet use might account for the “massive” difference between the youngest and the oldest generations, she suggested. “Following 2010, mobile phone penetration picked up and rose rapidly. ... Mobile phones took over the world.”
Time spent on the Internet – an estimated 7-10 hours per day – “eats into the time people in older generations used in building the social self. Kids who grow up on the Internet are losing thousands of hours in social interactions, which is challenging their ability to form relationships, how they see themselves, and how they fit into the social fabric,” Dr. Thiagarajan added
Sedentary time
Commenting for this news organization, Bernardo Ng, MD, a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on International Psychiatry and Global Health and medical director of Sun Valley Research Center, Imperial, Calif., called the report “interesting, with an impressive sample size” and an “impressive geographic distribution.”
Dr. Ng, who was not involved in the report, said, “I did not think the impact of Internet use on mental health was as dramatic before looking at this report.
“On the other hand, I have personally been interested in the impact of sedentarism in mental health – not only emotionally but also biologically. Sedentarism, which is directly related to screen use time, produces inflammation that worsens brain function.”
Also commenting, Ken Duckworth, MD, chief medical officer of the National Alliance of Mental Illness, called the survey “extremely well timed and creative, although it looked only at Internet-enabled populations, so one cannot make too many overall pronouncements, because a lot of people don’t have access to the Internet.”
The data regarding young people are particularly powerful. “The idea that young people are having a decrease in their experience of mental health across the world is something I haven’t seen before.”
Dr. Duckworth suggested the reason might “have to do with the impact of the COVID lockdown on normal development that young people go through, while older people don’t struggle with these developmental challenges in the same way.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Mental Health Million project of Sapien Labs issued its second report, published online March 15, encompassing 34 countries and over 220,000 Internet-enabled adults. It found a continued decline in mental health in all age groups and genders, with English-speaking countries having the lowest mental well-being.
The decline was significantly correlated with the stringency of COVID-19 lockdown measures in each country and was directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
The youngest age group (18-24 years) reported the poorest mental well-being, with better mental health scores rising in every successively older age group.
“Some of our findings, especially regarding mental health in young adults, are alarming,” Tara Thiagarajan, PhD, Sapien Labs founder and chief scientist, told this news organization.
“Our data, which are continually updated in real time, are freely available for nonprofit, noncommercial use and research, and we hope that researchers will get involved in an interdisciplinary way that spans sociology, economics, psychiatry, and other fields,” she said.
Pioneering research
Dr. Thiagarajan and her team pioneered the Mental Health Million project, an ongoing research initiative utilizing a “free and anonymous assessment tool,” the Mental Health Quotient (MHQ), which “encompasses a comprehensive view of our emotional, social, and cognitive function and capability.”
The MHQ consists of 47 “elements of mental well-being,” with scores ranging from –100 to +200. (Negative scores indicate poorer mental well-being.) The MHQ categorizes respondents as “clinical, at-risk, enduring, managing, succeeding, and thriving” and computes scores on the basis of six broad dimensions of mental health: core cognition, complex cognition, mood and outlook, drive and motivation, social self, and mind-body connection.
As reported by this news organization, Sapien Lab’s first Mental Health State of the World report (n = 49,000 adults) was conducted in eight English-speaking countries in 2020. Participants were compared to a smaller sample of people from the same countries polled in 2019.
In this year’s report, “we expanded quite substantially,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. The project added Spanish, French, and Arabic and recruited participants from 34 countries on six continents (n = 223,087) via advertising on Google and Facebook.

Economic prosperity not protective
Across the eight English-speaking countries, there was a decline in mental well-being of 3% from 2020 to 2021, which was smaller than the 8% decline from 2019 to 2020. The percentage of people who were “distressed or struggling” increased from 26% to 30% in 2021.
“Now that a lot of pandemic issue seems to be easing up, I hope we’ll see mental well-being coming back up, but at least it’s a smaller decline than we saw between 2019 and 2020,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
The decline across countries from 2019 to 2021 was significantly correlated with the stringency of governmental COVID-19-related measures (based on the Oxford COVID-19 Government Response Tracker, 2022; r = .54) and directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
In total, 30% of respondents in English-speaking countries had mental well-being scores in the “distressed” or “struggling” range – higher than the Middle Eastern countries, North Africa, Latin America, and Europe (23%, 23%, 24%, and 18%, respectively).
Only 36% of participants in the English-speaking countries, the Middle East, and North Africa reported “thriving or succeeding,” vs. 45% and 46% in Latin America and Europe, respectively. Venezuela topped the list with an average MHQ of 91, while the United Kingdom and South Africa had the lowest scores, at 46 each.
Mental well-being was slightly higher in males than in females but was dramatically lower in nonbinary/third-gender respondents. In fact, those identifying as nonbinary/third gender had the lowest mental well-being of any group.
Across all countries and languages, higher education was associated with better mental well-being. Employment was also associated with superior mental well-being, compared with being unemployed – particularly in core English-speaking countries.
However, “country indicators of economic prosperity were negatively correlated with mental well-being, particularly for young adults and males, belying the commonly held belief that national economic prosperity translates into greater mental well-being,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
‘Stark’ contrast
The most dramatic finding was the difference in mental well-being between younger and older adults, which was two- to threefold larger than differences in other dimensions (for example, age, gender, employment). Even the maximum difference between countries overall (15%) was still smaller than the generational gap within any region.
While only 7% (6%- 9%) of participants aged ≥65 years were “distressed and struggling” with their mental well-being to a “clinical” extent, 44% (38%-50%) of those aged 18-24 years reported mental well-being scores in the “distressed or struggling” range – representing a “growing gap between generations that, while present prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has since been exacerbated,” the authors state.
With every successive decrement in age group, mental well-being “plummeted,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. She noted that research conducted prior to 2010 in several regions of the world showed that young adults typically had the highest well-being. “Our findings stand in stark contrast to these previous patterns.”
The relationship between lockdown stringency and poorer mental health could play a role. “The impact of social isolation may be most strongly felt in younger people,” she said.
Internet a culprit?
“Within almost every region, scores for cognition and drive and motivation were highest while mood and outlook and social self were the lowest,” the authors report.
The aggregate percentage of respondents who reported being “distressed or struggling” in the various MHQ dimensions is shown in the following table.

In particular, English-speaking countries scored lowest on the social self scale.
The sense of social self is “how you see yourself with respect to others, how you relate to others and the ability to form strong, stable relationships and maintain them with other people,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
Internet use might account for the “massive” difference between the youngest and the oldest generations, she suggested. “Following 2010, mobile phone penetration picked up and rose rapidly. ... Mobile phones took over the world.”
Time spent on the Internet – an estimated 7-10 hours per day – “eats into the time people in older generations used in building the social self. Kids who grow up on the Internet are losing thousands of hours in social interactions, which is challenging their ability to form relationships, how they see themselves, and how they fit into the social fabric,” Dr. Thiagarajan added
Sedentary time
Commenting for this news organization, Bernardo Ng, MD, a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on International Psychiatry and Global Health and medical director of Sun Valley Research Center, Imperial, Calif., called the report “interesting, with an impressive sample size” and an “impressive geographic distribution.”
Dr. Ng, who was not involved in the report, said, “I did not think the impact of Internet use on mental health was as dramatic before looking at this report.
“On the other hand, I have personally been interested in the impact of sedentarism in mental health – not only emotionally but also biologically. Sedentarism, which is directly related to screen use time, produces inflammation that worsens brain function.”
Also commenting, Ken Duckworth, MD, chief medical officer of the National Alliance of Mental Illness, called the survey “extremely well timed and creative, although it looked only at Internet-enabled populations, so one cannot make too many overall pronouncements, because a lot of people don’t have access to the Internet.”
The data regarding young people are particularly powerful. “The idea that young people are having a decrease in their experience of mental health across the world is something I haven’t seen before.”
Dr. Duckworth suggested the reason might “have to do with the impact of the COVID lockdown on normal development that young people go through, while older people don’t struggle with these developmental challenges in the same way.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Mental Health Million project of Sapien Labs issued its second report, published online March 15, encompassing 34 countries and over 220,000 Internet-enabled adults. It found a continued decline in mental health in all age groups and genders, with English-speaking countries having the lowest mental well-being.
The decline was significantly correlated with the stringency of COVID-19 lockdown measures in each country and was directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
The youngest age group (18-24 years) reported the poorest mental well-being, with better mental health scores rising in every successively older age group.
“Some of our findings, especially regarding mental health in young adults, are alarming,” Tara Thiagarajan, PhD, Sapien Labs founder and chief scientist, told this news organization.
“Our data, which are continually updated in real time, are freely available for nonprofit, noncommercial use and research, and we hope that researchers will get involved in an interdisciplinary way that spans sociology, economics, psychiatry, and other fields,” she said.
Pioneering research
Dr. Thiagarajan and her team pioneered the Mental Health Million project, an ongoing research initiative utilizing a “free and anonymous assessment tool,” the Mental Health Quotient (MHQ), which “encompasses a comprehensive view of our emotional, social, and cognitive function and capability.”
The MHQ consists of 47 “elements of mental well-being,” with scores ranging from –100 to +200. (Negative scores indicate poorer mental well-being.) The MHQ categorizes respondents as “clinical, at-risk, enduring, managing, succeeding, and thriving” and computes scores on the basis of six broad dimensions of mental health: core cognition, complex cognition, mood and outlook, drive and motivation, social self, and mind-body connection.
As reported by this news organization, Sapien Lab’s first Mental Health State of the World report (n = 49,000 adults) was conducted in eight English-speaking countries in 2020. Participants were compared to a smaller sample of people from the same countries polled in 2019.
In this year’s report, “we expanded quite substantially,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. The project added Spanish, French, and Arabic and recruited participants from 34 countries on six continents (n = 223,087) via advertising on Google and Facebook.

Economic prosperity not protective
Across the eight English-speaking countries, there was a decline in mental well-being of 3% from 2020 to 2021, which was smaller than the 8% decline from 2019 to 2020. The percentage of people who were “distressed or struggling” increased from 26% to 30% in 2021.
“Now that a lot of pandemic issue seems to be easing up, I hope we’ll see mental well-being coming back up, but at least it’s a smaller decline than we saw between 2019 and 2020,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
The decline across countries from 2019 to 2021 was significantly correlated with the stringency of governmental COVID-19-related measures (based on the Oxford COVID-19 Government Response Tracker, 2022; r = .54) and directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
In total, 30% of respondents in English-speaking countries had mental well-being scores in the “distressed” or “struggling” range – higher than the Middle Eastern countries, North Africa, Latin America, and Europe (23%, 23%, 24%, and 18%, respectively).
Only 36% of participants in the English-speaking countries, the Middle East, and North Africa reported “thriving or succeeding,” vs. 45% and 46% in Latin America and Europe, respectively. Venezuela topped the list with an average MHQ of 91, while the United Kingdom and South Africa had the lowest scores, at 46 each.
Mental well-being was slightly higher in males than in females but was dramatically lower in nonbinary/third-gender respondents. In fact, those identifying as nonbinary/third gender had the lowest mental well-being of any group.
Across all countries and languages, higher education was associated with better mental well-being. Employment was also associated with superior mental well-being, compared with being unemployed – particularly in core English-speaking countries.
However, “country indicators of economic prosperity were negatively correlated with mental well-being, particularly for young adults and males, belying the commonly held belief that national economic prosperity translates into greater mental well-being,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
‘Stark’ contrast
The most dramatic finding was the difference in mental well-being between younger and older adults, which was two- to threefold larger than differences in other dimensions (for example, age, gender, employment). Even the maximum difference between countries overall (15%) was still smaller than the generational gap within any region.
While only 7% (6%- 9%) of participants aged ≥65 years were “distressed and struggling” with their mental well-being to a “clinical” extent, 44% (38%-50%) of those aged 18-24 years reported mental well-being scores in the “distressed or struggling” range – representing a “growing gap between generations that, while present prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has since been exacerbated,” the authors state.
With every successive decrement in age group, mental well-being “plummeted,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. She noted that research conducted prior to 2010 in several regions of the world showed that young adults typically had the highest well-being. “Our findings stand in stark contrast to these previous patterns.”
The relationship between lockdown stringency and poorer mental health could play a role. “The impact of social isolation may be most strongly felt in younger people,” she said.
Internet a culprit?
“Within almost every region, scores for cognition and drive and motivation were highest while mood and outlook and social self were the lowest,” the authors report.
The aggregate percentage of respondents who reported being “distressed or struggling” in the various MHQ dimensions is shown in the following table.

In particular, English-speaking countries scored lowest on the social self scale.
The sense of social self is “how you see yourself with respect to others, how you relate to others and the ability to form strong, stable relationships and maintain them with other people,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
Internet use might account for the “massive” difference between the youngest and the oldest generations, she suggested. “Following 2010, mobile phone penetration picked up and rose rapidly. ... Mobile phones took over the world.”
Time spent on the Internet – an estimated 7-10 hours per day – “eats into the time people in older generations used in building the social self. Kids who grow up on the Internet are losing thousands of hours in social interactions, which is challenging their ability to form relationships, how they see themselves, and how they fit into the social fabric,” Dr. Thiagarajan added
Sedentary time
Commenting for this news organization, Bernardo Ng, MD, a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on International Psychiatry and Global Health and medical director of Sun Valley Research Center, Imperial, Calif., called the report “interesting, with an impressive sample size” and an “impressive geographic distribution.”
Dr. Ng, who was not involved in the report, said, “I did not think the impact of Internet use on mental health was as dramatic before looking at this report.
“On the other hand, I have personally been interested in the impact of sedentarism in mental health – not only emotionally but also biologically. Sedentarism, which is directly related to screen use time, produces inflammation that worsens brain function.”
Also commenting, Ken Duckworth, MD, chief medical officer of the National Alliance of Mental Illness, called the survey “extremely well timed and creative, although it looked only at Internet-enabled populations, so one cannot make too many overall pronouncements, because a lot of people don’t have access to the Internet.”
The data regarding young people are particularly powerful. “The idea that young people are having a decrease in their experience of mental health across the world is something I haven’t seen before.”
Dr. Duckworth suggested the reason might “have to do with the impact of the COVID lockdown on normal development that young people go through, while older people don’t struggle with these developmental challenges in the same way.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sleep experts recommend permanent standard time, rather than DST
Sleep experts tend to agree with U.S. lawmakers about getting rid of the twice-per-year time shift, with one exception: They typically call for standard time rather than daylight saving time.
After the Senate voted unanimously on March 15 to make daylight saving time permanent, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine issued a statement that urged caution about adopting a fixed, year-round time with potential health risks.
“We do applaud stopping the switching during the course of the year and settling on a permanent time,” Jocelyn Cheng, MD, a member of the association’s public safety committee, told The Washington Post.
But she said.
Now it’s up to the House of Representatives to decide what to do next. The legislation, which would take effect in 2023, must be passed by the House and signed by President Joe Biden before becoming a law.
Legislators and health experts have debated the shift in recent years. In 2020, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine released a position statement in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine that recommended that the United States move to year-round standard time. Standard time is more aligned with humans’ circadian rhythms and natural light/dark cycles, the group wrote, and disrupting that rhythm has been linked to higher risks of heart disease, obesity, and depression.
At the same time, few studies have focused on the long-term effects of adopting daylight saving time. Most research has focused on the short-term risks of the seasonal shift, such as reduced sleep and increased car crashes, or circadian misalignment caused by other things. Some health experts have called for more research before deciding on a permanent time, the newspaper reported.
Still, the March 15 statement from sleep experts received support from more than 20 groups, including the National Safety Council, National Parent Teacher Association, and the World Sleep Society.
“We have all enjoyed those summer evenings with seemingly endless dusks,” David Neubauer, MD, an associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, told the Post.
But daylight saving time “does not ‘save’ evening light at all, it simply steals it from the morning, when it is necessary to maintain our healthy biological rhythms,” he said.
Permanent daylight saving time would lead to more dark mornings, which opponents have said could be dangerous for kids going to school, adults driving to work, and overall sleep cycles.
“With daylight saving time, we are perpetually out of synchronization with our internal clocks, and we often achieve less nighttime sleep, both circumstances having negative health impacts,” Dr. Neubauer said. “Extra evening light suppresses the melatonin that should be preparing us for falling asleep. The later dawn during daylight saving time deprives our biological clocks of the critical light signal.”
The pros and cons of daylight saving time and standard time were debated during a hearing held by a House Energy and Commerce subcommittee recently. Sleep experts argued in favor of standard time, while other industry experts argued for daylight saving time to reduce crime, save energy, and help businesses that benefit from more daylight in the evenings.
“Everybody advocates a permanent time, but this difference between 1 hour back or 1 hour forward is not so clear in everybody’s mind,” Dr. Cheng said. “I would like to see further debate and some due diligence done on these health consequences and public safety measures before anything else goes forward.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Sleep experts tend to agree with U.S. lawmakers about getting rid of the twice-per-year time shift, with one exception: They typically call for standard time rather than daylight saving time.
After the Senate voted unanimously on March 15 to make daylight saving time permanent, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine issued a statement that urged caution about adopting a fixed, year-round time with potential health risks.
“We do applaud stopping the switching during the course of the year and settling on a permanent time,” Jocelyn Cheng, MD, a member of the association’s public safety committee, told The Washington Post.
But she said.
Now it’s up to the House of Representatives to decide what to do next. The legislation, which would take effect in 2023, must be passed by the House and signed by President Joe Biden before becoming a law.
Legislators and health experts have debated the shift in recent years. In 2020, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine released a position statement in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine that recommended that the United States move to year-round standard time. Standard time is more aligned with humans’ circadian rhythms and natural light/dark cycles, the group wrote, and disrupting that rhythm has been linked to higher risks of heart disease, obesity, and depression.
At the same time, few studies have focused on the long-term effects of adopting daylight saving time. Most research has focused on the short-term risks of the seasonal shift, such as reduced sleep and increased car crashes, or circadian misalignment caused by other things. Some health experts have called for more research before deciding on a permanent time, the newspaper reported.
Still, the March 15 statement from sleep experts received support from more than 20 groups, including the National Safety Council, National Parent Teacher Association, and the World Sleep Society.
“We have all enjoyed those summer evenings with seemingly endless dusks,” David Neubauer, MD, an associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, told the Post.
But daylight saving time “does not ‘save’ evening light at all, it simply steals it from the morning, when it is necessary to maintain our healthy biological rhythms,” he said.
Permanent daylight saving time would lead to more dark mornings, which opponents have said could be dangerous for kids going to school, adults driving to work, and overall sleep cycles.
“With daylight saving time, we are perpetually out of synchronization with our internal clocks, and we often achieve less nighttime sleep, both circumstances having negative health impacts,” Dr. Neubauer said. “Extra evening light suppresses the melatonin that should be preparing us for falling asleep. The later dawn during daylight saving time deprives our biological clocks of the critical light signal.”
The pros and cons of daylight saving time and standard time were debated during a hearing held by a House Energy and Commerce subcommittee recently. Sleep experts argued in favor of standard time, while other industry experts argued for daylight saving time to reduce crime, save energy, and help businesses that benefit from more daylight in the evenings.
“Everybody advocates a permanent time, but this difference between 1 hour back or 1 hour forward is not so clear in everybody’s mind,” Dr. Cheng said. “I would like to see further debate and some due diligence done on these health consequences and public safety measures before anything else goes forward.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Sleep experts tend to agree with U.S. lawmakers about getting rid of the twice-per-year time shift, with one exception: They typically call for standard time rather than daylight saving time.
After the Senate voted unanimously on March 15 to make daylight saving time permanent, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine issued a statement that urged caution about adopting a fixed, year-round time with potential health risks.
“We do applaud stopping the switching during the course of the year and settling on a permanent time,” Jocelyn Cheng, MD, a member of the association’s public safety committee, told The Washington Post.
But she said.
Now it’s up to the House of Representatives to decide what to do next. The legislation, which would take effect in 2023, must be passed by the House and signed by President Joe Biden before becoming a law.
Legislators and health experts have debated the shift in recent years. In 2020, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine released a position statement in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine that recommended that the United States move to year-round standard time. Standard time is more aligned with humans’ circadian rhythms and natural light/dark cycles, the group wrote, and disrupting that rhythm has been linked to higher risks of heart disease, obesity, and depression.
At the same time, few studies have focused on the long-term effects of adopting daylight saving time. Most research has focused on the short-term risks of the seasonal shift, such as reduced sleep and increased car crashes, or circadian misalignment caused by other things. Some health experts have called for more research before deciding on a permanent time, the newspaper reported.
Still, the March 15 statement from sleep experts received support from more than 20 groups, including the National Safety Council, National Parent Teacher Association, and the World Sleep Society.
“We have all enjoyed those summer evenings with seemingly endless dusks,” David Neubauer, MD, an associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, told the Post.
But daylight saving time “does not ‘save’ evening light at all, it simply steals it from the morning, when it is necessary to maintain our healthy biological rhythms,” he said.
Permanent daylight saving time would lead to more dark mornings, which opponents have said could be dangerous for kids going to school, adults driving to work, and overall sleep cycles.
“With daylight saving time, we are perpetually out of synchronization with our internal clocks, and we often achieve less nighttime sleep, both circumstances having negative health impacts,” Dr. Neubauer said. “Extra evening light suppresses the melatonin that should be preparing us for falling asleep. The later dawn during daylight saving time deprives our biological clocks of the critical light signal.”
The pros and cons of daylight saving time and standard time were debated during a hearing held by a House Energy and Commerce subcommittee recently. Sleep experts argued in favor of standard time, while other industry experts argued for daylight saving time to reduce crime, save energy, and help businesses that benefit from more daylight in the evenings.
“Everybody advocates a permanent time, but this difference between 1 hour back or 1 hour forward is not so clear in everybody’s mind,” Dr. Cheng said. “I would like to see further debate and some due diligence done on these health consequences and public safety measures before anything else goes forward.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID surge in Western Europe puts U.S. health experts on alert
, even as states and cities continue to lift restrictions amid low case numbers.
Infectious disease experts are watching BA.2, the Omicron subvariant that appears to be more transmissible than the original strain. BA.2 is fueling outbreaks across Europe and is growing in dominance across the United States.
“It’s picking up steam. It’s across at least 12 countries … from Finland to Greece,” Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, told The Washington Post.
He has been following the surge and has posted recent charts of the outbreak on Twitter. Hospitalizations appear to be increasing in some places as well, he noted, despite the higher vaccination rates of many Western European countries.
“There’s no question there’s a significant wave there,” Dr. Topol said.
Germany recorded more than 260,000 new cases on March 15, according to the data tracker from the New York Times, but coronavirus restrictions are still being lifted this week. The U.K. is reporting more than 75,000 daily cases, and the Netherlands is reporting more than 60,000 daily cases, which are considered major numbers, compared to their population sizes. Meanwhile, France, Italy, and Switzerland are also reporting large increases in infections.
During the past 2 years, widespread outbreaks in Europe have been followed by similar surges in the U.S. weeks later. Most experts interviewed by the Post predicted that it’s likely to happen again.
In the United States, the BA.2 subvariant accounted for 23% of new COVID-19 cases for the week ending March 12, according to the latest estimate from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, while the original Omicron strain made up about 66% of cases. The BA.2 percentage is up from 13.7% of new cases for the week ending March 5, 7.1% the previous week, and 4.1% the week before that. In parts of the Northeast and New England, BA.2 makes up more than 38% of new cases.
At the same time, the 7 -day average of COVID-19 cases continues to drop in the United States, with about 31,000 daily cases currently, the New York Times data tracker shows. About 25,000 COVID-19 patients are hospitalized across the country, which has fallen 44% in the past 2 weeks, and about 1,200 deaths are being reported daily.
Several variables could affect the course of a future surge, the Post reported. Vaccination rates, coronavirus safety protocols, and access to antiviral medications could dictate how another wave unfolds across the country.
About 82% of the eligible U.S. population has received at least one vaccine dose, and 69% is fully vaccinated, according to the latest CDC data. About half of those who are eligible for booster doses have received one. In Germany, nearly 76% of people are fully vaccinated, the newspaper reported, and in the United Kingdom, about 74% are fully vaccinated.
Health experts are also considering how natural immunity from a previous infection could affect a BA.2 surge. Millions of Americans were infected with the original Omicron strain, BA.1, which could provide protection. That said, researchers aren’t quite sure whether BA.1 infection protects against BA.2.
“It’s like a weather alert. Right now, the skies are sunny and bright, and we hope they stay that way,” Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the University of Minnesota’s Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy, told CNN.
“But we could have some bad weather by evening,” he said. “We just don’t know.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, even as states and cities continue to lift restrictions amid low case numbers.
Infectious disease experts are watching BA.2, the Omicron subvariant that appears to be more transmissible than the original strain. BA.2 is fueling outbreaks across Europe and is growing in dominance across the United States.
“It’s picking up steam. It’s across at least 12 countries … from Finland to Greece,” Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, told The Washington Post.
He has been following the surge and has posted recent charts of the outbreak on Twitter. Hospitalizations appear to be increasing in some places as well, he noted, despite the higher vaccination rates of many Western European countries.
“There’s no question there’s a significant wave there,” Dr. Topol said.
Germany recorded more than 260,000 new cases on March 15, according to the data tracker from the New York Times, but coronavirus restrictions are still being lifted this week. The U.K. is reporting more than 75,000 daily cases, and the Netherlands is reporting more than 60,000 daily cases, which are considered major numbers, compared to their population sizes. Meanwhile, France, Italy, and Switzerland are also reporting large increases in infections.
During the past 2 years, widespread outbreaks in Europe have been followed by similar surges in the U.S. weeks later. Most experts interviewed by the Post predicted that it’s likely to happen again.
In the United States, the BA.2 subvariant accounted for 23% of new COVID-19 cases for the week ending March 12, according to the latest estimate from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, while the original Omicron strain made up about 66% of cases. The BA.2 percentage is up from 13.7% of new cases for the week ending March 5, 7.1% the previous week, and 4.1% the week before that. In parts of the Northeast and New England, BA.2 makes up more than 38% of new cases.
At the same time, the 7 -day average of COVID-19 cases continues to drop in the United States, with about 31,000 daily cases currently, the New York Times data tracker shows. About 25,000 COVID-19 patients are hospitalized across the country, which has fallen 44% in the past 2 weeks, and about 1,200 deaths are being reported daily.
Several variables could affect the course of a future surge, the Post reported. Vaccination rates, coronavirus safety protocols, and access to antiviral medications could dictate how another wave unfolds across the country.
About 82% of the eligible U.S. population has received at least one vaccine dose, and 69% is fully vaccinated, according to the latest CDC data. About half of those who are eligible for booster doses have received one. In Germany, nearly 76% of people are fully vaccinated, the newspaper reported, and in the United Kingdom, about 74% are fully vaccinated.
Health experts are also considering how natural immunity from a previous infection could affect a BA.2 surge. Millions of Americans were infected with the original Omicron strain, BA.1, which could provide protection. That said, researchers aren’t quite sure whether BA.1 infection protects against BA.2.
“It’s like a weather alert. Right now, the skies are sunny and bright, and we hope they stay that way,” Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the University of Minnesota’s Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy, told CNN.
“But we could have some bad weather by evening,” he said. “We just don’t know.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, even as states and cities continue to lift restrictions amid low case numbers.
Infectious disease experts are watching BA.2, the Omicron subvariant that appears to be more transmissible than the original strain. BA.2 is fueling outbreaks across Europe and is growing in dominance across the United States.
“It’s picking up steam. It’s across at least 12 countries … from Finland to Greece,” Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, told The Washington Post.
He has been following the surge and has posted recent charts of the outbreak on Twitter. Hospitalizations appear to be increasing in some places as well, he noted, despite the higher vaccination rates of many Western European countries.
“There’s no question there’s a significant wave there,” Dr. Topol said.
Germany recorded more than 260,000 new cases on March 15, according to the data tracker from the New York Times, but coronavirus restrictions are still being lifted this week. The U.K. is reporting more than 75,000 daily cases, and the Netherlands is reporting more than 60,000 daily cases, which are considered major numbers, compared to their population sizes. Meanwhile, France, Italy, and Switzerland are also reporting large increases in infections.
During the past 2 years, widespread outbreaks in Europe have been followed by similar surges in the U.S. weeks later. Most experts interviewed by the Post predicted that it’s likely to happen again.
In the United States, the BA.2 subvariant accounted for 23% of new COVID-19 cases for the week ending March 12, according to the latest estimate from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, while the original Omicron strain made up about 66% of cases. The BA.2 percentage is up from 13.7% of new cases for the week ending March 5, 7.1% the previous week, and 4.1% the week before that. In parts of the Northeast and New England, BA.2 makes up more than 38% of new cases.
At the same time, the 7 -day average of COVID-19 cases continues to drop in the United States, with about 31,000 daily cases currently, the New York Times data tracker shows. About 25,000 COVID-19 patients are hospitalized across the country, which has fallen 44% in the past 2 weeks, and about 1,200 deaths are being reported daily.
Several variables could affect the course of a future surge, the Post reported. Vaccination rates, coronavirus safety protocols, and access to antiviral medications could dictate how another wave unfolds across the country.
About 82% of the eligible U.S. population has received at least one vaccine dose, and 69% is fully vaccinated, according to the latest CDC data. About half of those who are eligible for booster doses have received one. In Germany, nearly 76% of people are fully vaccinated, the newspaper reported, and in the United Kingdom, about 74% are fully vaccinated.
Health experts are also considering how natural immunity from a previous infection could affect a BA.2 surge. Millions of Americans were infected with the original Omicron strain, BA.1, which could provide protection. That said, researchers aren’t quite sure whether BA.1 infection protects against BA.2.
“It’s like a weather alert. Right now, the skies are sunny and bright, and we hope they stay that way,” Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the University of Minnesota’s Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy, told CNN.
“But we could have some bad weather by evening,” he said. “We just don’t know.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.









