User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
Melatonin as a sleep aid: Are you prescribing it correctly?
Difficulty achieving regular restorative sleep is a common symptom of many psychiatric illnesses and can pose a pharmaceutical challenge, particularly for patients who have contraindications to benzodiazepines or sedative-hypnotics. Melatonin is commonly used to treat insomnia and circadian rhythm disorders in hospitalized patients because it is largely considered safe, nonhabit forming, unlikely to interact with other medications, and possibly protective against delirium.1 We support its short-term use in patients with sleep disruption, even if they do not meet the diagnostic criteria for insomnia or a circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorder. However, this use should be guided by consideration of the known physiological actions of melatonin, and not by an assumption that it acts as a simple sedative-hypnotic.
How melatonin works
Melatonin is an endogenous neurohormone involved in circadian rhythm regulation (sleep/wake regulation), a fundamental process in the functioning of the CNS and in the development of psychiatric disorders.2 Melatonin is commonly described as a sleep-promoting neurotransmitter, but it is more accurately described as a “darkness hormone.”3 With an onset at dusk and offset at sunrise, melatonin is the signal for biological night, not the signal for sleep. Melanopsin-containing retina neurons sensitive to blue light sense the diminishing light of the evening and communicate this cue to the brain’s master clock in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus (via the retinohypothalamic pathway). The SCN then releases its inhibition on the pineal gland, allowing it to release melatonin into the bloodstream and CSF. The timing of this release is known as the dim-light melatonin onset (DLMO).
Selecting the optimal timing and dose
Studies in laboratory and home settings have consistently shown that the DLMO precedes the onset of sleep by approximately 2 to 4 hours.4 Thus, we recommend scheduling melatonin administration for 2 to 4 hours before the intended bedtime.
Lower doses better replicate physiological levels of melatonin. A lower dose is also less likely to lead to a compromise of the entrainment process and the induction of a delayed sleep phase due to the lingering presence of melatonin, or the phase-delaying effects of a strong melatonin signal much later than the ideal DLMO. Giving higher doses at bedtime will induce sleep but may cause a circadian phase delay, effectively “jet lagging” the patient. We recommend prescribing low-dose melatonin (LDM; 0.5 to 1 mg) 2 to 4 hours before the intended bedtime rather than higher doses (≥5 mg) given at bedtime as is common practice and recommended by many melatonin manufacturers. LDM better simulates the natural release and function of melatonin and avoids potential adverse circadian phase delays. T
1. Joseph SG. Melatonin supplementation for the prevention of hospital-associated delirium. Ment Health Clin. 2018;7(4):143-146. doi:10.9740/mhc.2017.07.143
2. Arendt J, Skene DJ. Melatonin as a chronobiotic. Sleep Med Rev. 2005;9(1):25-39. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2004.05.002
3. Tallavajhula S, Rodgers JJ, Slater JD. Sleep and sleep-wake disorders. In: Arciniengas DB, Yudofsky SC, Hales RE, eds. Textbook of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2018:373-393.
4. Sletten TL, Vincenzi S, Redman JR, et al. Timing of sleep and its relationship with the endogenous melatonin rhythm. Front Neurol. 2010;1:137. doi:10.3389/fneur.2010.00137
Difficulty achieving regular restorative sleep is a common symptom of many psychiatric illnesses and can pose a pharmaceutical challenge, particularly for patients who have contraindications to benzodiazepines or sedative-hypnotics. Melatonin is commonly used to treat insomnia and circadian rhythm disorders in hospitalized patients because it is largely considered safe, nonhabit forming, unlikely to interact with other medications, and possibly protective against delirium.1 We support its short-term use in patients with sleep disruption, even if they do not meet the diagnostic criteria for insomnia or a circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorder. However, this use should be guided by consideration of the known physiological actions of melatonin, and not by an assumption that it acts as a simple sedative-hypnotic.
How melatonin works
Melatonin is an endogenous neurohormone involved in circadian rhythm regulation (sleep/wake regulation), a fundamental process in the functioning of the CNS and in the development of psychiatric disorders.2 Melatonin is commonly described as a sleep-promoting neurotransmitter, but it is more accurately described as a “darkness hormone.”3 With an onset at dusk and offset at sunrise, melatonin is the signal for biological night, not the signal for sleep. Melanopsin-containing retina neurons sensitive to blue light sense the diminishing light of the evening and communicate this cue to the brain’s master clock in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus (via the retinohypothalamic pathway). The SCN then releases its inhibition on the pineal gland, allowing it to release melatonin into the bloodstream and CSF. The timing of this release is known as the dim-light melatonin onset (DLMO).
Selecting the optimal timing and dose
Studies in laboratory and home settings have consistently shown that the DLMO precedes the onset of sleep by approximately 2 to 4 hours.4 Thus, we recommend scheduling melatonin administration for 2 to 4 hours before the intended bedtime.
Lower doses better replicate physiological levels of melatonin. A lower dose is also less likely to lead to a compromise of the entrainment process and the induction of a delayed sleep phase due to the lingering presence of melatonin, or the phase-delaying effects of a strong melatonin signal much later than the ideal DLMO. Giving higher doses at bedtime will induce sleep but may cause a circadian phase delay, effectively “jet lagging” the patient. We recommend prescribing low-dose melatonin (LDM; 0.5 to 1 mg) 2 to 4 hours before the intended bedtime rather than higher doses (≥5 mg) given at bedtime as is common practice and recommended by many melatonin manufacturers. LDM better simulates the natural release and function of melatonin and avoids potential adverse circadian phase delays. T
Difficulty achieving regular restorative sleep is a common symptom of many psychiatric illnesses and can pose a pharmaceutical challenge, particularly for patients who have contraindications to benzodiazepines or sedative-hypnotics. Melatonin is commonly used to treat insomnia and circadian rhythm disorders in hospitalized patients because it is largely considered safe, nonhabit forming, unlikely to interact with other medications, and possibly protective against delirium.1 We support its short-term use in patients with sleep disruption, even if they do not meet the diagnostic criteria for insomnia or a circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorder. However, this use should be guided by consideration of the known physiological actions of melatonin, and not by an assumption that it acts as a simple sedative-hypnotic.
How melatonin works
Melatonin is an endogenous neurohormone involved in circadian rhythm regulation (sleep/wake regulation), a fundamental process in the functioning of the CNS and in the development of psychiatric disorders.2 Melatonin is commonly described as a sleep-promoting neurotransmitter, but it is more accurately described as a “darkness hormone.”3 With an onset at dusk and offset at sunrise, melatonin is the signal for biological night, not the signal for sleep. Melanopsin-containing retina neurons sensitive to blue light sense the diminishing light of the evening and communicate this cue to the brain’s master clock in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus (via the retinohypothalamic pathway). The SCN then releases its inhibition on the pineal gland, allowing it to release melatonin into the bloodstream and CSF. The timing of this release is known as the dim-light melatonin onset (DLMO).
Selecting the optimal timing and dose
Studies in laboratory and home settings have consistently shown that the DLMO precedes the onset of sleep by approximately 2 to 4 hours.4 Thus, we recommend scheduling melatonin administration for 2 to 4 hours before the intended bedtime.
Lower doses better replicate physiological levels of melatonin. A lower dose is also less likely to lead to a compromise of the entrainment process and the induction of a delayed sleep phase due to the lingering presence of melatonin, or the phase-delaying effects of a strong melatonin signal much later than the ideal DLMO. Giving higher doses at bedtime will induce sleep but may cause a circadian phase delay, effectively “jet lagging” the patient. We recommend prescribing low-dose melatonin (LDM; 0.5 to 1 mg) 2 to 4 hours before the intended bedtime rather than higher doses (≥5 mg) given at bedtime as is common practice and recommended by many melatonin manufacturers. LDM better simulates the natural release and function of melatonin and avoids potential adverse circadian phase delays. T
1. Joseph SG. Melatonin supplementation for the prevention of hospital-associated delirium. Ment Health Clin. 2018;7(4):143-146. doi:10.9740/mhc.2017.07.143
2. Arendt J, Skene DJ. Melatonin as a chronobiotic. Sleep Med Rev. 2005;9(1):25-39. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2004.05.002
3. Tallavajhula S, Rodgers JJ, Slater JD. Sleep and sleep-wake disorders. In: Arciniengas DB, Yudofsky SC, Hales RE, eds. Textbook of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2018:373-393.
4. Sletten TL, Vincenzi S, Redman JR, et al. Timing of sleep and its relationship with the endogenous melatonin rhythm. Front Neurol. 2010;1:137. doi:10.3389/fneur.2010.00137
1. Joseph SG. Melatonin supplementation for the prevention of hospital-associated delirium. Ment Health Clin. 2018;7(4):143-146. doi:10.9740/mhc.2017.07.143
2. Arendt J, Skene DJ. Melatonin as a chronobiotic. Sleep Med Rev. 2005;9(1):25-39. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2004.05.002
3. Tallavajhula S, Rodgers JJ, Slater JD. Sleep and sleep-wake disorders. In: Arciniengas DB, Yudofsky SC, Hales RE, eds. Textbook of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2018:373-393.
4. Sletten TL, Vincenzi S, Redman JR, et al. Timing of sleep and its relationship with the endogenous melatonin rhythm. Front Neurol. 2010;1:137. doi:10.3389/fneur.2010.00137
Proposal for a new diagnosis: Acute anxiety disorder
Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
Mr. F, age 42, says he has always been a very anxious person and has chronically found his worrying to negatively affect his life. He says that over the last month his anxiety has been “off the charts” and he is worrying “24/7” due to taking on new responsibilities at his job and his son being diagnosed with lupus. He says his constant worrying is significantly impairing his ability to focus at his job, and he is considering taking a mental health leave from work. His wife reports that she is extremely frustrated because Mr. F has been isolating himself from family and friends; he admits this is true and attributes it to being preoccupied by his worries.
Mr. F endorses chronic insomnia, muscle tension, and irritability associated with anxiety; these have all substantially worsened over the last month. He admits that recently he has occasionally thought it would be easier if he weren’t alive. Mr. F denies having problems with his energy or motivation levels and insists that he generally feels very anxious, but not depressed. He says he drinks 1 alcoholic drink per week and denies any other substance use. Mr. F is overweight and has slightly elevated cholesterol but denies any other health conditions. He takes melatonin to help him sleep but does not take any prescribed medications.
Although this vignette provides limited details, on the surface it appears that Mr. F is experiencing an exacerbation of chronic generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). However, in this article, I propose establishing a new diagnosis: “acute anxiety disorder,” which would encapsulate severe exacerbations of a pre-existing anxiety disorder. Among the patients I have encountered for whom this diagnosis would fit, most have pre-existing GAD or panic disorder.
A look at the differential diagnosis
It is important to determine whether Mr. F is using any substances or has a medical condition that could be contributing to his anxiety. Other psychiatric diagnoses that could be considered include:
Adjustment disorder. This diagnosis would make sense if Mr. F didn’t have an apparent chronic history of symptoms that meet criteria for GAD.
Major depressive disorder with anxious distress. Many patients experiencing a major depressive episode meet the criteria for the specifier “with anxious distress,” even those who do not have a comorbid anxiety disorder.1 However, it is not evident from this vignette that Mr. F is experiencing a major depressive episode.
Continue to: Panic disorder and GAD...
Panic disorder and GAD. It is possible for a patient with GAD to develop panic disorder, which, at times, occurs after experiencing significant life stressors. Panic disorder requires the presence of recurrent panic attacks. Mr. F describes experiencing chronic, intense symptoms of anxiety rather than the discreet episodes of acute symptoms that characterize panic attacks.
Acute stress disorder. This diagnosis involves psychological symptoms that occur in response to exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violation. Mr. F was not exposed to any of these stressors.
Why this new diagnosis would be helpful
A new diagnosis, acute anxiety disorder, would indicate that a patient is currently experiencing an acute exacerbation of a chronic anxiety disorder that is leading to a significant decrease in their baseline functioning. My proposed criteria for acute anxiety disorder appear in the Table. Here are some reasons this diagnosis would be helpful:

Signifier of severity. Anxiety disorders such as GAD are generally not considered severe conditions and not considered to fall under the rubric of SPMI (severe and persistent mental illness).2 Posttraumatic stress disorder is the anxiety disorder–like condition most often found in the SPMI category. A diagnosis of acute anxiety disorder would indicate a patient is experiencing an episode of anxiety that is distinct from their chronic anxiety condition due to its severe impact on functional capabilities. Acute anxiety disorder would certainly not qualify as a “SPMI diagnosis” that would facilitate someone being considered eligible for supplemental security income, but it might be a legitimate justification for someone to receive short-term disability.
Treatment approach. The pharmacologic treatment of anxiety disorders usually involves a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). However, these medications can sometimes briefly increase anxiety when they are started. Individuals with acute anxiety are the most vulnerable to the possibility of experiencing increased anxiety when starting an SSRI or SNRI and may benefit from a slower titration of these medications. In light of this and the length of time required for SSRIs or SNRIs to exert a positive effect (typically a few weeks), patients with acute anxiety are best served by treatment with a medication with an immediate onset of action, such as a benzodiazepine or a sleep medication (eg, zolpidem). Benzodiazepines and hypnotics such as zolpidem are best prescribed for as-needed use because they carry a risk of dependence. One might consider prescribing mirtazapine or pregabalin (both of which are used off-label to treat anxiety) because these medications also have a relatively rapid onset of action and can treat both anxiety and insomnia (particularly mirtazapine).
Research considerations. It would be helpful to study which treatments are most effective for the subset of patients who experience acute anxiety disorder as I define it. Perhaps psychotherapy treatment protocols could be adapted or created. Treatment with esketamine or IV ketamine might be further studied as a treatment for acute anxiety because some evidence suggests ketamine is efficacious for this indication.3
1. Otsubo T, Hokama C, Sano N, et al. How significant is the assessment of the DSM-5 ‘anxious distress’ specifier in patients with major depressive disorder without comorbid anxiety disorders in the continuation/maintenance phase? Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2021;25(4):385-392. doi:10.1080/13651501.2021.1907415
2. Butler H, O’Brien AJ. Access to specialist palliative care services by people with severe and persistent mental illness: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2018;27(2):737-746. doi:10.1111/inm.12360
3. Glue P, Neehoff SM, Medlicott NJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of maintenance ketamine treatment in patients with treatment-refractory generalised anxiety and social anxiety disorders. J Psychopharmacol. 2018;32(6):663-667. doi:10.1177/0269881118762073
Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
Mr. F, age 42, says he has always been a very anxious person and has chronically found his worrying to negatively affect his life. He says that over the last month his anxiety has been “off the charts” and he is worrying “24/7” due to taking on new responsibilities at his job and his son being diagnosed with lupus. He says his constant worrying is significantly impairing his ability to focus at his job, and he is considering taking a mental health leave from work. His wife reports that she is extremely frustrated because Mr. F has been isolating himself from family and friends; he admits this is true and attributes it to being preoccupied by his worries.
Mr. F endorses chronic insomnia, muscle tension, and irritability associated with anxiety; these have all substantially worsened over the last month. He admits that recently he has occasionally thought it would be easier if he weren’t alive. Mr. F denies having problems with his energy or motivation levels and insists that he generally feels very anxious, but not depressed. He says he drinks 1 alcoholic drink per week and denies any other substance use. Mr. F is overweight and has slightly elevated cholesterol but denies any other health conditions. He takes melatonin to help him sleep but does not take any prescribed medications.
Although this vignette provides limited details, on the surface it appears that Mr. F is experiencing an exacerbation of chronic generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). However, in this article, I propose establishing a new diagnosis: “acute anxiety disorder,” which would encapsulate severe exacerbations of a pre-existing anxiety disorder. Among the patients I have encountered for whom this diagnosis would fit, most have pre-existing GAD or panic disorder.
A look at the differential diagnosis
It is important to determine whether Mr. F is using any substances or has a medical condition that could be contributing to his anxiety. Other psychiatric diagnoses that could be considered include:
Adjustment disorder. This diagnosis would make sense if Mr. F didn’t have an apparent chronic history of symptoms that meet criteria for GAD.
Major depressive disorder with anxious distress. Many patients experiencing a major depressive episode meet the criteria for the specifier “with anxious distress,” even those who do not have a comorbid anxiety disorder.1 However, it is not evident from this vignette that Mr. F is experiencing a major depressive episode.
Continue to: Panic disorder and GAD...
Panic disorder and GAD. It is possible for a patient with GAD to develop panic disorder, which, at times, occurs after experiencing significant life stressors. Panic disorder requires the presence of recurrent panic attacks. Mr. F describes experiencing chronic, intense symptoms of anxiety rather than the discreet episodes of acute symptoms that characterize panic attacks.
Acute stress disorder. This diagnosis involves psychological symptoms that occur in response to exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violation. Mr. F was not exposed to any of these stressors.
Why this new diagnosis would be helpful
A new diagnosis, acute anxiety disorder, would indicate that a patient is currently experiencing an acute exacerbation of a chronic anxiety disorder that is leading to a significant decrease in their baseline functioning. My proposed criteria for acute anxiety disorder appear in the Table. Here are some reasons this diagnosis would be helpful:

Signifier of severity. Anxiety disorders such as GAD are generally not considered severe conditions and not considered to fall under the rubric of SPMI (severe and persistent mental illness).2 Posttraumatic stress disorder is the anxiety disorder–like condition most often found in the SPMI category. A diagnosis of acute anxiety disorder would indicate a patient is experiencing an episode of anxiety that is distinct from their chronic anxiety condition due to its severe impact on functional capabilities. Acute anxiety disorder would certainly not qualify as a “SPMI diagnosis” that would facilitate someone being considered eligible for supplemental security income, but it might be a legitimate justification for someone to receive short-term disability.
Treatment approach. The pharmacologic treatment of anxiety disorders usually involves a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). However, these medications can sometimes briefly increase anxiety when they are started. Individuals with acute anxiety are the most vulnerable to the possibility of experiencing increased anxiety when starting an SSRI or SNRI and may benefit from a slower titration of these medications. In light of this and the length of time required for SSRIs or SNRIs to exert a positive effect (typically a few weeks), patients with acute anxiety are best served by treatment with a medication with an immediate onset of action, such as a benzodiazepine or a sleep medication (eg, zolpidem). Benzodiazepines and hypnotics such as zolpidem are best prescribed for as-needed use because they carry a risk of dependence. One might consider prescribing mirtazapine or pregabalin (both of which are used off-label to treat anxiety) because these medications also have a relatively rapid onset of action and can treat both anxiety and insomnia (particularly mirtazapine).
Research considerations. It would be helpful to study which treatments are most effective for the subset of patients who experience acute anxiety disorder as I define it. Perhaps psychotherapy treatment protocols could be adapted or created. Treatment with esketamine or IV ketamine might be further studied as a treatment for acute anxiety because some evidence suggests ketamine is efficacious for this indication.3
Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
Mr. F, age 42, says he has always been a very anxious person and has chronically found his worrying to negatively affect his life. He says that over the last month his anxiety has been “off the charts” and he is worrying “24/7” due to taking on new responsibilities at his job and his son being diagnosed with lupus. He says his constant worrying is significantly impairing his ability to focus at his job, and he is considering taking a mental health leave from work. His wife reports that she is extremely frustrated because Mr. F has been isolating himself from family and friends; he admits this is true and attributes it to being preoccupied by his worries.
Mr. F endorses chronic insomnia, muscle tension, and irritability associated with anxiety; these have all substantially worsened over the last month. He admits that recently he has occasionally thought it would be easier if he weren’t alive. Mr. F denies having problems with his energy or motivation levels and insists that he generally feels very anxious, but not depressed. He says he drinks 1 alcoholic drink per week and denies any other substance use. Mr. F is overweight and has slightly elevated cholesterol but denies any other health conditions. He takes melatonin to help him sleep but does not take any prescribed medications.
Although this vignette provides limited details, on the surface it appears that Mr. F is experiencing an exacerbation of chronic generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). However, in this article, I propose establishing a new diagnosis: “acute anxiety disorder,” which would encapsulate severe exacerbations of a pre-existing anxiety disorder. Among the patients I have encountered for whom this diagnosis would fit, most have pre-existing GAD or panic disorder.
A look at the differential diagnosis
It is important to determine whether Mr. F is using any substances or has a medical condition that could be contributing to his anxiety. Other psychiatric diagnoses that could be considered include:
Adjustment disorder. This diagnosis would make sense if Mr. F didn’t have an apparent chronic history of symptoms that meet criteria for GAD.
Major depressive disorder with anxious distress. Many patients experiencing a major depressive episode meet the criteria for the specifier “with anxious distress,” even those who do not have a comorbid anxiety disorder.1 However, it is not evident from this vignette that Mr. F is experiencing a major depressive episode.
Continue to: Panic disorder and GAD...
Panic disorder and GAD. It is possible for a patient with GAD to develop panic disorder, which, at times, occurs after experiencing significant life stressors. Panic disorder requires the presence of recurrent panic attacks. Mr. F describes experiencing chronic, intense symptoms of anxiety rather than the discreet episodes of acute symptoms that characterize panic attacks.
Acute stress disorder. This diagnosis involves psychological symptoms that occur in response to exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violation. Mr. F was not exposed to any of these stressors.
Why this new diagnosis would be helpful
A new diagnosis, acute anxiety disorder, would indicate that a patient is currently experiencing an acute exacerbation of a chronic anxiety disorder that is leading to a significant decrease in their baseline functioning. My proposed criteria for acute anxiety disorder appear in the Table. Here are some reasons this diagnosis would be helpful:

Signifier of severity. Anxiety disorders such as GAD are generally not considered severe conditions and not considered to fall under the rubric of SPMI (severe and persistent mental illness).2 Posttraumatic stress disorder is the anxiety disorder–like condition most often found in the SPMI category. A diagnosis of acute anxiety disorder would indicate a patient is experiencing an episode of anxiety that is distinct from their chronic anxiety condition due to its severe impact on functional capabilities. Acute anxiety disorder would certainly not qualify as a “SPMI diagnosis” that would facilitate someone being considered eligible for supplemental security income, but it might be a legitimate justification for someone to receive short-term disability.
Treatment approach. The pharmacologic treatment of anxiety disorders usually involves a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). However, these medications can sometimes briefly increase anxiety when they are started. Individuals with acute anxiety are the most vulnerable to the possibility of experiencing increased anxiety when starting an SSRI or SNRI and may benefit from a slower titration of these medications. In light of this and the length of time required for SSRIs or SNRIs to exert a positive effect (typically a few weeks), patients with acute anxiety are best served by treatment with a medication with an immediate onset of action, such as a benzodiazepine or a sleep medication (eg, zolpidem). Benzodiazepines and hypnotics such as zolpidem are best prescribed for as-needed use because they carry a risk of dependence. One might consider prescribing mirtazapine or pregabalin (both of which are used off-label to treat anxiety) because these medications also have a relatively rapid onset of action and can treat both anxiety and insomnia (particularly mirtazapine).
Research considerations. It would be helpful to study which treatments are most effective for the subset of patients who experience acute anxiety disorder as I define it. Perhaps psychotherapy treatment protocols could be adapted or created. Treatment with esketamine or IV ketamine might be further studied as a treatment for acute anxiety because some evidence suggests ketamine is efficacious for this indication.3
1. Otsubo T, Hokama C, Sano N, et al. How significant is the assessment of the DSM-5 ‘anxious distress’ specifier in patients with major depressive disorder without comorbid anxiety disorders in the continuation/maintenance phase? Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2021;25(4):385-392. doi:10.1080/13651501.2021.1907415
2. Butler H, O’Brien AJ. Access to specialist palliative care services by people with severe and persistent mental illness: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2018;27(2):737-746. doi:10.1111/inm.12360
3. Glue P, Neehoff SM, Medlicott NJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of maintenance ketamine treatment in patients with treatment-refractory generalised anxiety and social anxiety disorders. J Psychopharmacol. 2018;32(6):663-667. doi:10.1177/0269881118762073
1. Otsubo T, Hokama C, Sano N, et al. How significant is the assessment of the DSM-5 ‘anxious distress’ specifier in patients with major depressive disorder without comorbid anxiety disorders in the continuation/maintenance phase? Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2021;25(4):385-392. doi:10.1080/13651501.2021.1907415
2. Butler H, O’Brien AJ. Access to specialist palliative care services by people with severe and persistent mental illness: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2018;27(2):737-746. doi:10.1111/inm.12360
3. Glue P, Neehoff SM, Medlicott NJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of maintenance ketamine treatment in patients with treatment-refractory generalised anxiety and social anxiety disorders. J Psychopharmacol. 2018;32(6):663-667. doi:10.1177/0269881118762073
Neurosurgical treatment of OCD: Patient selection, safety, and access
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is typically a severe, chronic illness in which patients have recurrent, unwanted thoughts, urges, and compulsions.1 It causes significant morbidity and lost potential over time, and is the world’s 10th-most disabling disorder in terms of lost income and decreased quality of life, and the fifth-most disabling mental health condition.2 Patients with OCD (and their clinicians) are often desperate for an efficacious treatment, but we must ensure that those who are not helped by traditional psychotherapeutic and/or pharmacologic treatments are appropriate for safe neurosurgical intervention.
Pros and cons of neurosurgical therapies
Most patients with OCD are effectively treated with cognitive-behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy in the form of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, clomipramine, or second-generation antipsychotics. However, up to 5% of individuals with OCD will have symptoms refractory to these traditional therapies.3 These cases require more aggressive forms of therapy, including radiofrequency ablation surgeries and deep brain stimulation (DBS). The efficacy of both therapies is similar at 40% to 60%.4,5 While these treatments can be life-changing for patients fortunate to receive them, they are not without issue.
Only a limited number of institutions offer these neurosurgical techniques, and for many patients, those locations may be inaccessible. Patients may not experience relief simply due to where they live, difficult logistics, and the high cost requisite to receive care. If fortunate enough to live near a participating institution or have the means to travel to one, the patient and clinician must then choose the best option based on the nuances of the patient’s situation.
Ablation techniques, such as gamma knife or magnetic resonance–guided ultrasound, are simpler and more cost-effective. A drawback of this approach, however, is that it is irreversible. Lesioned structures are irreparable, as are the adverse effects of the surgery, which, while rare, may include a persistent minimally conscious state or necrotic cysts.4 A benefit of this approach is that there is no need for lengthy follow-up as seen with DBS.
DBS is more complicated. In addition to having to undergo an open neurosurgical procedure, these patients require long-term follow-up and monitoring. A positive aspect is the device can be turned off or removed. However, the amount of follow-up and adjustments is significant. These patients need access to clinicians skilled in DBS device management.
Finally, we must consider the chronically ill patient’s perspective after successful treatment. While the patient’s symptoms may improve, their lives and identities likely developed around their symptoms. Bosanac et al6 describe this reality well in a case study in which a patient with OCD was “burdened with normality” after successful DBS treatment. He was finally able to work, build meaningful relationships, and approach previously unattainable social milestones. This was an overwhelming experience for him, and he and his family needed guidance into the world in which most of us find comfort.
As ablation techniques, DBS, and other cutting-edge therapies for OCD come to the forefront of modern care, clinicians must remember to keep patient safety first. Verify follow-up care before committing patients to invasive and irreversible treatments. While general access is currently poor, participating institutions should consider advertising and communicating that there is an accessible network available for these chronically ill individuals.
1. Ruscio AM, Stein DJ, Chiu WT, et al. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15(1):53-63.
2. World Health Organization. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. World Health Organization; 2008.
3. Jenike MA, Rauch SL. Managing the patient with treatment-resistant obsessive compulsive disorder: current strategies. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994;55 Suppl:11-17.
4. Rasmussen SA, Noren G, Greenberg BD, et al. Gamma ventral capsulotomy in intractable obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;84(5):355-364.
5. Kumar KK, Appelboom, G, Lamsam L, et al. Comparative effectiveness of neuroablation and deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a meta-analytic study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019;90(4):469-473.
6. Bosanac P, Hamilton BE, Lucak J, et al. Identity challenges and ‘burden of normality’ after DBS for severe OCD: a narrative case study. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18(1):186.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is typically a severe, chronic illness in which patients have recurrent, unwanted thoughts, urges, and compulsions.1 It causes significant morbidity and lost potential over time, and is the world’s 10th-most disabling disorder in terms of lost income and decreased quality of life, and the fifth-most disabling mental health condition.2 Patients with OCD (and their clinicians) are often desperate for an efficacious treatment, but we must ensure that those who are not helped by traditional psychotherapeutic and/or pharmacologic treatments are appropriate for safe neurosurgical intervention.
Pros and cons of neurosurgical therapies
Most patients with OCD are effectively treated with cognitive-behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy in the form of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, clomipramine, or second-generation antipsychotics. However, up to 5% of individuals with OCD will have symptoms refractory to these traditional therapies.3 These cases require more aggressive forms of therapy, including radiofrequency ablation surgeries and deep brain stimulation (DBS). The efficacy of both therapies is similar at 40% to 60%.4,5 While these treatments can be life-changing for patients fortunate to receive them, they are not without issue.
Only a limited number of institutions offer these neurosurgical techniques, and for many patients, those locations may be inaccessible. Patients may not experience relief simply due to where they live, difficult logistics, and the high cost requisite to receive care. If fortunate enough to live near a participating institution or have the means to travel to one, the patient and clinician must then choose the best option based on the nuances of the patient’s situation.
Ablation techniques, such as gamma knife or magnetic resonance–guided ultrasound, are simpler and more cost-effective. A drawback of this approach, however, is that it is irreversible. Lesioned structures are irreparable, as are the adverse effects of the surgery, which, while rare, may include a persistent minimally conscious state or necrotic cysts.4 A benefit of this approach is that there is no need for lengthy follow-up as seen with DBS.
DBS is more complicated. In addition to having to undergo an open neurosurgical procedure, these patients require long-term follow-up and monitoring. A positive aspect is the device can be turned off or removed. However, the amount of follow-up and adjustments is significant. These patients need access to clinicians skilled in DBS device management.
Finally, we must consider the chronically ill patient’s perspective after successful treatment. While the patient’s symptoms may improve, their lives and identities likely developed around their symptoms. Bosanac et al6 describe this reality well in a case study in which a patient with OCD was “burdened with normality” after successful DBS treatment. He was finally able to work, build meaningful relationships, and approach previously unattainable social milestones. This was an overwhelming experience for him, and he and his family needed guidance into the world in which most of us find comfort.
As ablation techniques, DBS, and other cutting-edge therapies for OCD come to the forefront of modern care, clinicians must remember to keep patient safety first. Verify follow-up care before committing patients to invasive and irreversible treatments. While general access is currently poor, participating institutions should consider advertising and communicating that there is an accessible network available for these chronically ill individuals.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is typically a severe, chronic illness in which patients have recurrent, unwanted thoughts, urges, and compulsions.1 It causes significant morbidity and lost potential over time, and is the world’s 10th-most disabling disorder in terms of lost income and decreased quality of life, and the fifth-most disabling mental health condition.2 Patients with OCD (and their clinicians) are often desperate for an efficacious treatment, but we must ensure that those who are not helped by traditional psychotherapeutic and/or pharmacologic treatments are appropriate for safe neurosurgical intervention.
Pros and cons of neurosurgical therapies
Most patients with OCD are effectively treated with cognitive-behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy in the form of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, clomipramine, or second-generation antipsychotics. However, up to 5% of individuals with OCD will have symptoms refractory to these traditional therapies.3 These cases require more aggressive forms of therapy, including radiofrequency ablation surgeries and deep brain stimulation (DBS). The efficacy of both therapies is similar at 40% to 60%.4,5 While these treatments can be life-changing for patients fortunate to receive them, they are not without issue.
Only a limited number of institutions offer these neurosurgical techniques, and for many patients, those locations may be inaccessible. Patients may not experience relief simply due to where they live, difficult logistics, and the high cost requisite to receive care. If fortunate enough to live near a participating institution or have the means to travel to one, the patient and clinician must then choose the best option based on the nuances of the patient’s situation.
Ablation techniques, such as gamma knife or magnetic resonance–guided ultrasound, are simpler and more cost-effective. A drawback of this approach, however, is that it is irreversible. Lesioned structures are irreparable, as are the adverse effects of the surgery, which, while rare, may include a persistent minimally conscious state or necrotic cysts.4 A benefit of this approach is that there is no need for lengthy follow-up as seen with DBS.
DBS is more complicated. In addition to having to undergo an open neurosurgical procedure, these patients require long-term follow-up and monitoring. A positive aspect is the device can be turned off or removed. However, the amount of follow-up and adjustments is significant. These patients need access to clinicians skilled in DBS device management.
Finally, we must consider the chronically ill patient’s perspective after successful treatment. While the patient’s symptoms may improve, their lives and identities likely developed around their symptoms. Bosanac et al6 describe this reality well in a case study in which a patient with OCD was “burdened with normality” after successful DBS treatment. He was finally able to work, build meaningful relationships, and approach previously unattainable social milestones. This was an overwhelming experience for him, and he and his family needed guidance into the world in which most of us find comfort.
As ablation techniques, DBS, and other cutting-edge therapies for OCD come to the forefront of modern care, clinicians must remember to keep patient safety first. Verify follow-up care before committing patients to invasive and irreversible treatments. While general access is currently poor, participating institutions should consider advertising and communicating that there is an accessible network available for these chronically ill individuals.
1. Ruscio AM, Stein DJ, Chiu WT, et al. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15(1):53-63.
2. World Health Organization. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. World Health Organization; 2008.
3. Jenike MA, Rauch SL. Managing the patient with treatment-resistant obsessive compulsive disorder: current strategies. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994;55 Suppl:11-17.
4. Rasmussen SA, Noren G, Greenberg BD, et al. Gamma ventral capsulotomy in intractable obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;84(5):355-364.
5. Kumar KK, Appelboom, G, Lamsam L, et al. Comparative effectiveness of neuroablation and deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a meta-analytic study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019;90(4):469-473.
6. Bosanac P, Hamilton BE, Lucak J, et al. Identity challenges and ‘burden of normality’ after DBS for severe OCD: a narrative case study. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18(1):186.
1. Ruscio AM, Stein DJ, Chiu WT, et al. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15(1):53-63.
2. World Health Organization. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. World Health Organization; 2008.
3. Jenike MA, Rauch SL. Managing the patient with treatment-resistant obsessive compulsive disorder: current strategies. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994;55 Suppl:11-17.
4. Rasmussen SA, Noren G, Greenberg BD, et al. Gamma ventral capsulotomy in intractable obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;84(5):355-364.
5. Kumar KK, Appelboom, G, Lamsam L, et al. Comparative effectiveness of neuroablation and deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a meta-analytic study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019;90(4):469-473.
6. Bosanac P, Hamilton BE, Lucak J, et al. Identity challenges and ‘burden of normality’ after DBS for severe OCD: a narrative case study. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18(1):186.
Inhaled, systemic steroids linked to changes in brain structure
New research links the use of glucocorticoids with changes in white matter microstructure – which may explain the development of anxiety, depression, and other neuropsychiatric side effects related to these drugs, investigators say.
Results from a cross-sectional study showed that use of both systemic and inhaled glucocorticoids was associated with widespread reductions in fractional anisotropy (FA) and increases in mean diffusivity.
Glucocorticoids have “a whole catalogue” of adverse events, and effects on brain structure “adds to the list,” co-investigator Onno C. Meijer, PhD, professor of molecular neuroendocrinology of corticosteroids, department of medicine, Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands, told this news organization.
The findings should encourage clinicians to consider whether doses they are prescribing are too high, said Dr. Meijer. He added that the negative effect of glucocorticoids on the brain was also found in those using inhalers, such as patients with asthma.
The findings were published online in the BMJ Open.
Serious side effects
Glucocorticoids, a class of synthetic steroids with immunosuppressive properties, are prescribed for a wide range of conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and asthma.
However, they are also associated with potentially serious metabolic, cardiovascular, and musculoskeletal side effects as well as neuropsychiatric side effects such as depression, mania, and cognitive impairment.
About 1 in 3 patients exposed to “quite a lot of these drugs” will experience neuropsychiatric symptoms, Dr. Meijer said.
Most previous studies that investigated effects from high levels of glucocorticoids on brain structure have been small and involved selected populations, such as those with Cushing disease.
The new study included participants from the UK Biobank, a large population-based cohort. Participants had undergone imaging and did not have a history of psychiatric disease – although they could have conditions associated with glucocorticoid use, including anxiety, depression, mania, or delirium.
The analysis included 222 patients using oral or parenteral glucocorticoids at the time of imaging (systemic group), 557 using inhaled glucocorticoids, and 24,106 not using glucocorticoids (the control group).
Inhaled steroids target the lungs, whereas a steroid in pill form “travels in the blood and reaches each and every organ and cell in the body and typically requires higher doses,” Dr. Meijer noted.
The groups were similar with respect to sex, education, and smoking status. However, the systemic glucocorticoid group was slightly older (mean age, 66.1 years vs. 63.3 years for inhaled glucocorticoid users and 63.5 years for the control group).
In addition to age, researchers adjusted for sex, education level, head position in the scanner, head size, assessment center, and year of imaging.
Imaging analyses
Imaging analyses showed systemic glucocorticoid use was associated with reduced global FA (adjusted mean difference, -3.7e-3; 95% confidence interval, -6.4e-3 to 1.0e-3), and reductions in regional FA in the body and genu of the corpus callosum versus the control group.
Inhaled glucocorticoid use was associated with reduced global FA (AMD, -2.3e-3; 95% CI, -4.0e-3 to -5.7e-4), and lower FA in the splenium of the corpus callosum and the cingulum of the hippocampus.
Global mean diffusivity was higher in systemic glucocorticoid users (AMD, 7.2e-6; 95% CI, 3.2e-6 to 1.1e-5) and inhaled glucocorticoid users (AMD, 2.7e-6; 95% CI, 1.7e-7 to 5.2e-6), compared with the control group.
The effects of glucocorticoids on white matter were “pervasive,” and the “most important finding” of the study, Dr. Meijer said. “We were impressed by the fact white matter is so sensitive to these drugs.”
He noted that it is likely that functional connectivity between brain regions is affected by use of glucocorticoids. “You could say communication between brain regions is probably somewhat impaired or challenged,” he said.
Subgroup analyses among participants using glucocorticoids chronically, defined as reported at two consecutive visits, suggested a potential dose-dependent or duration-dependent effect of glucocorticoids on white matter microstructure.
Systemic glucocorticoid use was also associated with an increase in total and grey matter volume of the caudate nucleus.
In addition, there was a significant association between inhaled glucocorticoid use and decreased grey matter volume of the amygdala, which Dr. Meijer said was surprising because studies have shown that glucocorticoids “can drive amygdala big time.”
Move away from ‘one dose for all’?
Another surprise was that the results showed no hippocampal volume differences with steroid use, Dr. Meijer noted.
The modest association between glucocorticoid use and brain volumes could indicate that white matter integrity is more sensitive to glucocorticoids than is grey matter volume, “at least at the structural level,” he said.
He added that longer use or higher doses may be necessary to also induce volumetric changes.
Participants also completed a questionnaire to assess mood over the previous 2 weeks. Systemic glucocorticoid users had more depressive symptoms, disinterest, tenseness/restlessness, and tiredness/lethargy, compared with the control group. Inhaled glucocorticoid users only reported more tiredness/lethargy.
The investigators note that mood-related effects could be linked to the condition for which glucocorticoids were prescribed: for example, rheumatoid arthritis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
In terms of cognition, systemic glucocorticoid users performed significantly worse on the symbol digit substitution task, compared with participants in the control group.
In light of these findings, pharmaceutical companies that make inhaled corticosteroids “should perhaps find out if glucocorticoids can be dosed by kilogram body weight rather than simply one dose fits all,” which is currently the case, Dr. Meijer said.
Impressive, but several limitations
Commenting on the findings, E. Sherwood Brown, MD, PhD, Distinguished Chair in Psychiatric Research and professor and vice chair for clinical research, department of psychiatry, The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, called the study sample size “impressive.”
In addition, the study is the first to look at systemic as well as inhaled corticosteroids, said Dr. Brown, who was not involved with the research. He noted that previously, there had been only case reports of psychiatric symptoms with inhaled corticosteroids.
That results are in the same direction but greater with systemic, compared with inhaled corticosteroids, is “particularly interesting” because this might suggest dose-dependent effects, Dr. Brown said.
He noted that cognitive differences were also only observed with systemic corticosteroids.
Some study observations, such as smaller amygdala volume with inhaled but not systemic corticosteroids, “are harder to understand,” said Dr. Brown.
However, he pointed out some study limitations. For example, data were apparently unavailable for verbal and declarative memory test data, despite corticosteroids probably affecting the hippocampus and causing memory changes.
Other drawbacks were that the dose and duration of corticosteroid use, as well as the medical histories of study participants, were not available, Dr. Brown said.
No study funding was reported. Dr. Meijer has received research grants and honorariums from Corcept Therapeutics and a speakers’ fee from Ipsen. Dr. Brown is on an advisory board for Sage Pharmaceuticals, which is developing neurosteroids (not corticosteroids) for mood disorders. He is also on a Medscape advisory board related to bipolar disorder.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research links the use of glucocorticoids with changes in white matter microstructure – which may explain the development of anxiety, depression, and other neuropsychiatric side effects related to these drugs, investigators say.
Results from a cross-sectional study showed that use of both systemic and inhaled glucocorticoids was associated with widespread reductions in fractional anisotropy (FA) and increases in mean diffusivity.
Glucocorticoids have “a whole catalogue” of adverse events, and effects on brain structure “adds to the list,” co-investigator Onno C. Meijer, PhD, professor of molecular neuroendocrinology of corticosteroids, department of medicine, Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands, told this news organization.
The findings should encourage clinicians to consider whether doses they are prescribing are too high, said Dr. Meijer. He added that the negative effect of glucocorticoids on the brain was also found in those using inhalers, such as patients with asthma.
The findings were published online in the BMJ Open.
Serious side effects
Glucocorticoids, a class of synthetic steroids with immunosuppressive properties, are prescribed for a wide range of conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and asthma.
However, they are also associated with potentially serious metabolic, cardiovascular, and musculoskeletal side effects as well as neuropsychiatric side effects such as depression, mania, and cognitive impairment.
About 1 in 3 patients exposed to “quite a lot of these drugs” will experience neuropsychiatric symptoms, Dr. Meijer said.
Most previous studies that investigated effects from high levels of glucocorticoids on brain structure have been small and involved selected populations, such as those with Cushing disease.
The new study included participants from the UK Biobank, a large population-based cohort. Participants had undergone imaging and did not have a history of psychiatric disease – although they could have conditions associated with glucocorticoid use, including anxiety, depression, mania, or delirium.
The analysis included 222 patients using oral or parenteral glucocorticoids at the time of imaging (systemic group), 557 using inhaled glucocorticoids, and 24,106 not using glucocorticoids (the control group).
Inhaled steroids target the lungs, whereas a steroid in pill form “travels in the blood and reaches each and every organ and cell in the body and typically requires higher doses,” Dr. Meijer noted.
The groups were similar with respect to sex, education, and smoking status. However, the systemic glucocorticoid group was slightly older (mean age, 66.1 years vs. 63.3 years for inhaled glucocorticoid users and 63.5 years for the control group).
In addition to age, researchers adjusted for sex, education level, head position in the scanner, head size, assessment center, and year of imaging.
Imaging analyses
Imaging analyses showed systemic glucocorticoid use was associated with reduced global FA (adjusted mean difference, -3.7e-3; 95% confidence interval, -6.4e-3 to 1.0e-3), and reductions in regional FA in the body and genu of the corpus callosum versus the control group.
Inhaled glucocorticoid use was associated with reduced global FA (AMD, -2.3e-3; 95% CI, -4.0e-3 to -5.7e-4), and lower FA in the splenium of the corpus callosum and the cingulum of the hippocampus.
Global mean diffusivity was higher in systemic glucocorticoid users (AMD, 7.2e-6; 95% CI, 3.2e-6 to 1.1e-5) and inhaled glucocorticoid users (AMD, 2.7e-6; 95% CI, 1.7e-7 to 5.2e-6), compared with the control group.
The effects of glucocorticoids on white matter were “pervasive,” and the “most important finding” of the study, Dr. Meijer said. “We were impressed by the fact white matter is so sensitive to these drugs.”
He noted that it is likely that functional connectivity between brain regions is affected by use of glucocorticoids. “You could say communication between brain regions is probably somewhat impaired or challenged,” he said.
Subgroup analyses among participants using glucocorticoids chronically, defined as reported at two consecutive visits, suggested a potential dose-dependent or duration-dependent effect of glucocorticoids on white matter microstructure.
Systemic glucocorticoid use was also associated with an increase in total and grey matter volume of the caudate nucleus.
In addition, there was a significant association between inhaled glucocorticoid use and decreased grey matter volume of the amygdala, which Dr. Meijer said was surprising because studies have shown that glucocorticoids “can drive amygdala big time.”
Move away from ‘one dose for all’?
Another surprise was that the results showed no hippocampal volume differences with steroid use, Dr. Meijer noted.
The modest association between glucocorticoid use and brain volumes could indicate that white matter integrity is more sensitive to glucocorticoids than is grey matter volume, “at least at the structural level,” he said.
He added that longer use or higher doses may be necessary to also induce volumetric changes.
Participants also completed a questionnaire to assess mood over the previous 2 weeks. Systemic glucocorticoid users had more depressive symptoms, disinterest, tenseness/restlessness, and tiredness/lethargy, compared with the control group. Inhaled glucocorticoid users only reported more tiredness/lethargy.
The investigators note that mood-related effects could be linked to the condition for which glucocorticoids were prescribed: for example, rheumatoid arthritis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
In terms of cognition, systemic glucocorticoid users performed significantly worse on the symbol digit substitution task, compared with participants in the control group.
In light of these findings, pharmaceutical companies that make inhaled corticosteroids “should perhaps find out if glucocorticoids can be dosed by kilogram body weight rather than simply one dose fits all,” which is currently the case, Dr. Meijer said.
Impressive, but several limitations
Commenting on the findings, E. Sherwood Brown, MD, PhD, Distinguished Chair in Psychiatric Research and professor and vice chair for clinical research, department of psychiatry, The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, called the study sample size “impressive.”
In addition, the study is the first to look at systemic as well as inhaled corticosteroids, said Dr. Brown, who was not involved with the research. He noted that previously, there had been only case reports of psychiatric symptoms with inhaled corticosteroids.
That results are in the same direction but greater with systemic, compared with inhaled corticosteroids, is “particularly interesting” because this might suggest dose-dependent effects, Dr. Brown said.
He noted that cognitive differences were also only observed with systemic corticosteroids.
Some study observations, such as smaller amygdala volume with inhaled but not systemic corticosteroids, “are harder to understand,” said Dr. Brown.
However, he pointed out some study limitations. For example, data were apparently unavailable for verbal and declarative memory test data, despite corticosteroids probably affecting the hippocampus and causing memory changes.
Other drawbacks were that the dose and duration of corticosteroid use, as well as the medical histories of study participants, were not available, Dr. Brown said.
No study funding was reported. Dr. Meijer has received research grants and honorariums from Corcept Therapeutics and a speakers’ fee from Ipsen. Dr. Brown is on an advisory board for Sage Pharmaceuticals, which is developing neurosteroids (not corticosteroids) for mood disorders. He is also on a Medscape advisory board related to bipolar disorder.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research links the use of glucocorticoids with changes in white matter microstructure – which may explain the development of anxiety, depression, and other neuropsychiatric side effects related to these drugs, investigators say.
Results from a cross-sectional study showed that use of both systemic and inhaled glucocorticoids was associated with widespread reductions in fractional anisotropy (FA) and increases in mean diffusivity.
Glucocorticoids have “a whole catalogue” of adverse events, and effects on brain structure “adds to the list,” co-investigator Onno C. Meijer, PhD, professor of molecular neuroendocrinology of corticosteroids, department of medicine, Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands, told this news organization.
The findings should encourage clinicians to consider whether doses they are prescribing are too high, said Dr. Meijer. He added that the negative effect of glucocorticoids on the brain was also found in those using inhalers, such as patients with asthma.
The findings were published online in the BMJ Open.
Serious side effects
Glucocorticoids, a class of synthetic steroids with immunosuppressive properties, are prescribed for a wide range of conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and asthma.
However, they are also associated with potentially serious metabolic, cardiovascular, and musculoskeletal side effects as well as neuropsychiatric side effects such as depression, mania, and cognitive impairment.
About 1 in 3 patients exposed to “quite a lot of these drugs” will experience neuropsychiatric symptoms, Dr. Meijer said.
Most previous studies that investigated effects from high levels of glucocorticoids on brain structure have been small and involved selected populations, such as those with Cushing disease.
The new study included participants from the UK Biobank, a large population-based cohort. Participants had undergone imaging and did not have a history of psychiatric disease – although they could have conditions associated with glucocorticoid use, including anxiety, depression, mania, or delirium.
The analysis included 222 patients using oral or parenteral glucocorticoids at the time of imaging (systemic group), 557 using inhaled glucocorticoids, and 24,106 not using glucocorticoids (the control group).
Inhaled steroids target the lungs, whereas a steroid in pill form “travels in the blood and reaches each and every organ and cell in the body and typically requires higher doses,” Dr. Meijer noted.
The groups were similar with respect to sex, education, and smoking status. However, the systemic glucocorticoid group was slightly older (mean age, 66.1 years vs. 63.3 years for inhaled glucocorticoid users and 63.5 years for the control group).
In addition to age, researchers adjusted for sex, education level, head position in the scanner, head size, assessment center, and year of imaging.
Imaging analyses
Imaging analyses showed systemic glucocorticoid use was associated with reduced global FA (adjusted mean difference, -3.7e-3; 95% confidence interval, -6.4e-3 to 1.0e-3), and reductions in regional FA in the body and genu of the corpus callosum versus the control group.
Inhaled glucocorticoid use was associated with reduced global FA (AMD, -2.3e-3; 95% CI, -4.0e-3 to -5.7e-4), and lower FA in the splenium of the corpus callosum and the cingulum of the hippocampus.
Global mean diffusivity was higher in systemic glucocorticoid users (AMD, 7.2e-6; 95% CI, 3.2e-6 to 1.1e-5) and inhaled glucocorticoid users (AMD, 2.7e-6; 95% CI, 1.7e-7 to 5.2e-6), compared with the control group.
The effects of glucocorticoids on white matter were “pervasive,” and the “most important finding” of the study, Dr. Meijer said. “We were impressed by the fact white matter is so sensitive to these drugs.”
He noted that it is likely that functional connectivity between brain regions is affected by use of glucocorticoids. “You could say communication between brain regions is probably somewhat impaired or challenged,” he said.
Subgroup analyses among participants using glucocorticoids chronically, defined as reported at two consecutive visits, suggested a potential dose-dependent or duration-dependent effect of glucocorticoids on white matter microstructure.
Systemic glucocorticoid use was also associated with an increase in total and grey matter volume of the caudate nucleus.
In addition, there was a significant association between inhaled glucocorticoid use and decreased grey matter volume of the amygdala, which Dr. Meijer said was surprising because studies have shown that glucocorticoids “can drive amygdala big time.”
Move away from ‘one dose for all’?
Another surprise was that the results showed no hippocampal volume differences with steroid use, Dr. Meijer noted.
The modest association between glucocorticoid use and brain volumes could indicate that white matter integrity is more sensitive to glucocorticoids than is grey matter volume, “at least at the structural level,” he said.
He added that longer use or higher doses may be necessary to also induce volumetric changes.
Participants also completed a questionnaire to assess mood over the previous 2 weeks. Systemic glucocorticoid users had more depressive symptoms, disinterest, tenseness/restlessness, and tiredness/lethargy, compared with the control group. Inhaled glucocorticoid users only reported more tiredness/lethargy.
The investigators note that mood-related effects could be linked to the condition for which glucocorticoids were prescribed: for example, rheumatoid arthritis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
In terms of cognition, systemic glucocorticoid users performed significantly worse on the symbol digit substitution task, compared with participants in the control group.
In light of these findings, pharmaceutical companies that make inhaled corticosteroids “should perhaps find out if glucocorticoids can be dosed by kilogram body weight rather than simply one dose fits all,” which is currently the case, Dr. Meijer said.
Impressive, but several limitations
Commenting on the findings, E. Sherwood Brown, MD, PhD, Distinguished Chair in Psychiatric Research and professor and vice chair for clinical research, department of psychiatry, The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, called the study sample size “impressive.”
In addition, the study is the first to look at systemic as well as inhaled corticosteroids, said Dr. Brown, who was not involved with the research. He noted that previously, there had been only case reports of psychiatric symptoms with inhaled corticosteroids.
That results are in the same direction but greater with systemic, compared with inhaled corticosteroids, is “particularly interesting” because this might suggest dose-dependent effects, Dr. Brown said.
He noted that cognitive differences were also only observed with systemic corticosteroids.
Some study observations, such as smaller amygdala volume with inhaled but not systemic corticosteroids, “are harder to understand,” said Dr. Brown.
However, he pointed out some study limitations. For example, data were apparently unavailable for verbal and declarative memory test data, despite corticosteroids probably affecting the hippocampus and causing memory changes.
Other drawbacks were that the dose and duration of corticosteroid use, as well as the medical histories of study participants, were not available, Dr. Brown said.
No study funding was reported. Dr. Meijer has received research grants and honorariums from Corcept Therapeutics and a speakers’ fee from Ipsen. Dr. Brown is on an advisory board for Sage Pharmaceuticals, which is developing neurosteroids (not corticosteroids) for mood disorders. He is also on a Medscape advisory board related to bipolar disorder.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BMJ OPEN
Omega-3 fatty acids and depression: Are they protective?
New research is suggesting that there are “meaningful” associations between higher dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids and lower risk for depressive episodes.
In addition, consumption of total fatty acids and alpha-linolenic acid was associated with a reduced risk for incident depressive episodes (9% and 29%, respectively).
“Our results showed an important protective effect from the consumption of omega-3,” Maria de Jesus Mendes da Fonseca, University of the State of Rio de Janeiro, and colleagues write.
The findings were published online in Nutrients.
Mixed bag of studies
Epidemiologic evidence suggests that deficient dietary omega-3 intake is a modifiable risk factor for depression and that individuals with low consumption of omega-3 food sources have more depressive symptoms.
However, the results are inconsistent, and few longitudinal studies have addressed this association, the investigators note.
The new analysis included 13,879 adults (aged 39-65 years or older) participating in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil) from 2008 to 2014.
Data on depressive episodes were obtained with the Clinical Interview Schedule Revised (CIS-R), and food consumption was measured with the Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ).
The target dietary components were total polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) and the omega-3 fatty acids: alpha-linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and docosapentaenoic acid (DPA).
The majority of participants had adequate dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids, and none was taking omega-3 supplements.
In the fully adjusted model, consumption of fatty acids from the omega-3 family had a protective effect against maintenance of depressive episodes, showing “important associations, although the significance levels are borderline, possibly due to the sample size,” the researchers report.
In regard to onset of depressive episodes, estimates from the fully adjusted model suggest that a higher consumption of omega-3 acids (total and subtypes) is associated with lower risk for depressive episodes – with significant associations for omega-3 and alpha-linolenic acid.
The investigators note that strengths of the study include “its originality, as it is the first to assess associations between maintenance and incidence of depressive episodes and consumption of omega-3, besides the use of data from the ELSA-Brasil Study, with rigorous data collection protocols and reliable and validated instruments, thus guaranteeing the quality of the sample and the data.”
A study limitation, however, was that the ELSA-Brasil sample consists only of public employees, with the potential for a selection bias such as healthy worker phenomenon, the researchers note. Another was the use of the FFQ, which may underestimate daily intake of foods and depends on individual participant recall – all of which could possibly lead to a differential classification bias.
Interpret cautiously
Commenting on the study, David Mischoulon, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, and director of the depression clinical and research program at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, said that data on omega-3s in depression are “very mixed.”
“A lot of the studies don’t necessarily agree with each other. Certainly, in studies that try to seek an association between omega-3 use and depression, it’s always complicated because it can be difficult to control for all variables that could be contributing to the result that you get,” said Dr. Mischoulon, who is also a member of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America and was not involved in the research.
A caveat to the current study was that diet was assessed only at baseline, “so we don’t really know whether there were any substantial dietary changes over time, he noted.
He also cautioned that it is hard to draw any firm conclusions from this type of study.
“In general, in studies with a large sample, which this study has, it’s easier to find statistically significant differences. But you need to ask yourself: Does it really matter? Is it enough to have a clinical impact and make a difference?” Dr. Mischoulon said.
The ELSA-Brasil study was funded by the Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation and by the Ministry of Health. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mischoulon has received research support from Nordic Naturals and heckel medizintechnik GmbH and honoraria for speaking from the Massachusetts General Hospital Psychiatry Academy. He also works with the MGH Clinical Trials Network and Institute, which has received research funding from multiple pharmaceutical companies and the National Institute of Mental Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research is suggesting that there are “meaningful” associations between higher dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids and lower risk for depressive episodes.
In addition, consumption of total fatty acids and alpha-linolenic acid was associated with a reduced risk for incident depressive episodes (9% and 29%, respectively).
“Our results showed an important protective effect from the consumption of omega-3,” Maria de Jesus Mendes da Fonseca, University of the State of Rio de Janeiro, and colleagues write.
The findings were published online in Nutrients.
Mixed bag of studies
Epidemiologic evidence suggests that deficient dietary omega-3 intake is a modifiable risk factor for depression and that individuals with low consumption of omega-3 food sources have more depressive symptoms.
However, the results are inconsistent, and few longitudinal studies have addressed this association, the investigators note.
The new analysis included 13,879 adults (aged 39-65 years or older) participating in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil) from 2008 to 2014.
Data on depressive episodes were obtained with the Clinical Interview Schedule Revised (CIS-R), and food consumption was measured with the Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ).
The target dietary components were total polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) and the omega-3 fatty acids: alpha-linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and docosapentaenoic acid (DPA).
The majority of participants had adequate dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids, and none was taking omega-3 supplements.
In the fully adjusted model, consumption of fatty acids from the omega-3 family had a protective effect against maintenance of depressive episodes, showing “important associations, although the significance levels are borderline, possibly due to the sample size,” the researchers report.
In regard to onset of depressive episodes, estimates from the fully adjusted model suggest that a higher consumption of omega-3 acids (total and subtypes) is associated with lower risk for depressive episodes – with significant associations for omega-3 and alpha-linolenic acid.
The investigators note that strengths of the study include “its originality, as it is the first to assess associations between maintenance and incidence of depressive episodes and consumption of omega-3, besides the use of data from the ELSA-Brasil Study, with rigorous data collection protocols and reliable and validated instruments, thus guaranteeing the quality of the sample and the data.”
A study limitation, however, was that the ELSA-Brasil sample consists only of public employees, with the potential for a selection bias such as healthy worker phenomenon, the researchers note. Another was the use of the FFQ, which may underestimate daily intake of foods and depends on individual participant recall – all of which could possibly lead to a differential classification bias.
Interpret cautiously
Commenting on the study, David Mischoulon, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, and director of the depression clinical and research program at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, said that data on omega-3s in depression are “very mixed.”
“A lot of the studies don’t necessarily agree with each other. Certainly, in studies that try to seek an association between omega-3 use and depression, it’s always complicated because it can be difficult to control for all variables that could be contributing to the result that you get,” said Dr. Mischoulon, who is also a member of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America and was not involved in the research.
A caveat to the current study was that diet was assessed only at baseline, “so we don’t really know whether there were any substantial dietary changes over time, he noted.
He also cautioned that it is hard to draw any firm conclusions from this type of study.
“In general, in studies with a large sample, which this study has, it’s easier to find statistically significant differences. But you need to ask yourself: Does it really matter? Is it enough to have a clinical impact and make a difference?” Dr. Mischoulon said.
The ELSA-Brasil study was funded by the Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation and by the Ministry of Health. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mischoulon has received research support from Nordic Naturals and heckel medizintechnik GmbH and honoraria for speaking from the Massachusetts General Hospital Psychiatry Academy. He also works with the MGH Clinical Trials Network and Institute, which has received research funding from multiple pharmaceutical companies and the National Institute of Mental Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research is suggesting that there are “meaningful” associations between higher dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids and lower risk for depressive episodes.
In addition, consumption of total fatty acids and alpha-linolenic acid was associated with a reduced risk for incident depressive episodes (9% and 29%, respectively).
“Our results showed an important protective effect from the consumption of omega-3,” Maria de Jesus Mendes da Fonseca, University of the State of Rio de Janeiro, and colleagues write.
The findings were published online in Nutrients.
Mixed bag of studies
Epidemiologic evidence suggests that deficient dietary omega-3 intake is a modifiable risk factor for depression and that individuals with low consumption of omega-3 food sources have more depressive symptoms.
However, the results are inconsistent, and few longitudinal studies have addressed this association, the investigators note.
The new analysis included 13,879 adults (aged 39-65 years or older) participating in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil) from 2008 to 2014.
Data on depressive episodes were obtained with the Clinical Interview Schedule Revised (CIS-R), and food consumption was measured with the Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ).
The target dietary components were total polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) and the omega-3 fatty acids: alpha-linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and docosapentaenoic acid (DPA).
The majority of participants had adequate dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids, and none was taking omega-3 supplements.
In the fully adjusted model, consumption of fatty acids from the omega-3 family had a protective effect against maintenance of depressive episodes, showing “important associations, although the significance levels are borderline, possibly due to the sample size,” the researchers report.
In regard to onset of depressive episodes, estimates from the fully adjusted model suggest that a higher consumption of omega-3 acids (total and subtypes) is associated with lower risk for depressive episodes – with significant associations for omega-3 and alpha-linolenic acid.
The investigators note that strengths of the study include “its originality, as it is the first to assess associations between maintenance and incidence of depressive episodes and consumption of omega-3, besides the use of data from the ELSA-Brasil Study, with rigorous data collection protocols and reliable and validated instruments, thus guaranteeing the quality of the sample and the data.”
A study limitation, however, was that the ELSA-Brasil sample consists only of public employees, with the potential for a selection bias such as healthy worker phenomenon, the researchers note. Another was the use of the FFQ, which may underestimate daily intake of foods and depends on individual participant recall – all of which could possibly lead to a differential classification bias.
Interpret cautiously
Commenting on the study, David Mischoulon, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, and director of the depression clinical and research program at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, said that data on omega-3s in depression are “very mixed.”
“A lot of the studies don’t necessarily agree with each other. Certainly, in studies that try to seek an association between omega-3 use and depression, it’s always complicated because it can be difficult to control for all variables that could be contributing to the result that you get,” said Dr. Mischoulon, who is also a member of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America and was not involved in the research.
A caveat to the current study was that diet was assessed only at baseline, “so we don’t really know whether there were any substantial dietary changes over time, he noted.
He also cautioned that it is hard to draw any firm conclusions from this type of study.
“In general, in studies with a large sample, which this study has, it’s easier to find statistically significant differences. But you need to ask yourself: Does it really matter? Is it enough to have a clinical impact and make a difference?” Dr. Mischoulon said.
The ELSA-Brasil study was funded by the Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation and by the Ministry of Health. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mischoulon has received research support from Nordic Naturals and heckel medizintechnik GmbH and honoraria for speaking from the Massachusetts General Hospital Psychiatry Academy. He also works with the MGH Clinical Trials Network and Institute, which has received research funding from multiple pharmaceutical companies and the National Institute of Mental Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NUTRIENTS
‘Doomscrolling’ may be a significant driver of poor mental health
The past 2 years have been filled with worrisome global events, from the pandemic to the war in Ukraine, large-scale protests, mass shootings, and devastating wildfires. The 24-hour media coverage of these events can take a toll on “news addicts” who have an excessive urge to constantly check the news, researchers note.
Results from an online survey of more than 1,000 adults showed that nearly 17% showed signs of “severely problematic” news consumption.
These “doomscrollers” or “doomsurfers” scored high on all five problematic news consumption dimensions: being absorbed in news content, being consumed by thoughts about the news, attempting to alleviate feelings of threat by consuming more news, losing control over news consumption, and having news consumption interfere in daily life.
“We anticipated that a sizable portion of our sample would show signs of problematic news consumption. However, we were surprised to find that 17% of study participants suffer from the most severe level of problematic news consumption,” lead author Bryan McLaughlin, PhD, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, told this news organization. “This is certainly concerning and suggests the problem may be more widespread than we expected,” he said.
In addition, 74% of those with severe levels of problematic news consumption reported experiencing mental problems, and 61% reported physical problems.
“It’s important for health care providers to be aware that problematic news consumption may be a significant driver of mental and physical ill-being, especially because a lot of people might be unaware of the negative impact the news is having on their health,” Dr. McLaughlin said.
The findings were published online in Health Communication.
Emotionally invested
The researchers assessed data from an online survey of 1,100 adults (mean age, 40.5 years; 51% women) in the United States who were recruited in August 2021.
Among those surveyed, 27.3% reported “moderately problematic” news consumption, 27.5% reported minimally problematic news consumption, and 28.7% reported no problematic news consumption.
Perhaps not surprisingly, respondents with higher levels of problematic news consumption were significantly more likely to experience mental and physical ill-being than those with lower levels, even after accounting for demographics, personality traits, and overall news use, the researchers note.
Nearly three-quarters (74%) of those with severe levels of problematic news consumption reported experiencing mental ill-being “quite a bit” or “very much” – whereas frequent symptoms were only reported by 8% of all other study participants.
In addition, 61% of adults with severe problematic news consumption reported experiencing physical ill-being “quite a bit” or “very much,” compared with only 6.1% for all other study participants.
Dr. McLaughlin noted that one way to combat this problem is to help individuals develop a healthier relationship with the news – and mindfulness training may be one way to accomplish that.
“We have some preliminary evidence that individuals with high levels of mindfulness are much less susceptible to developing higher levels of problematic news consumption,” he said.
“Given this, mindfulness-based training could potentially help problematic news consumers follow the news without becoming so emotionally invested in it. We hope to examine the effectiveness of a mindfulness intervention in our future research,” he added.
Increased distress
Commenting on the study, Steven R. Thorp, PhD, ABPP, a professor at California School of Professional Psychology, Alliant International University, San Diego, said that he and his colleagues have noticed an increase in clients reporting distress about news consumption.
The survey by Dr. McLaughlin and colleagues “appears to be representative and has sufficient statistical power to address the issues,” said Dr. Thorp, who was not involved with the research.
“However, as the researchers note, it is a cross-sectional and correlational survey. So it’s possible that, as implied, people who ‘doomscroll’ are more likely to have physical and mental health problems that interfere with their functioning,” he added.
It is also possible that individuals with physical and mental health problems are more likely to be isolated and have restricted activities, thus leading to greater news consumption, Dr. Thorp noted. Alternatively, there could be an independent link between health and news consumption.
Most news is “sensational and not representative,” Dr. Thorp pointed out.
For example, “we are far more likely to hear about deaths from terrorist attacks or plane crashes than from heart attacks, though deaths from heart attacks are far more common,” he said.
“News also tends to be negative, rather than uplifting, and most news is not directly relevant to a person’s day-to-day functioning. Thus, for most people, the consumption of news may have more downsides than upsides,” Dr. Thorp added.
Still, many people want to stay informed about national and international events. So rather than following a “cold turkey” or abstinence model of stopping all news consumption, individuals could consider a “harm reduction” model of reducing time spent consuming news, Dr. Thorp noted.
Another thing to consider is the news source. “Some outlets and social media sites are designed to instill outrage, fear, or anger and to increase polarization, while others have been shown to provide balanced and less sensational coverage,” Dr. Thorp said.
“I also think it’s a good idea for providers to regularly ask about news consumption, along with learning about other daily activities that may enhance or diminish mental and physical health,” he added.
The research had no specific funding. Dr. McLaughlin and Dr. Thorp have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The past 2 years have been filled with worrisome global events, from the pandemic to the war in Ukraine, large-scale protests, mass shootings, and devastating wildfires. The 24-hour media coverage of these events can take a toll on “news addicts” who have an excessive urge to constantly check the news, researchers note.
Results from an online survey of more than 1,000 adults showed that nearly 17% showed signs of “severely problematic” news consumption.
These “doomscrollers” or “doomsurfers” scored high on all five problematic news consumption dimensions: being absorbed in news content, being consumed by thoughts about the news, attempting to alleviate feelings of threat by consuming more news, losing control over news consumption, and having news consumption interfere in daily life.
“We anticipated that a sizable portion of our sample would show signs of problematic news consumption. However, we were surprised to find that 17% of study participants suffer from the most severe level of problematic news consumption,” lead author Bryan McLaughlin, PhD, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, told this news organization. “This is certainly concerning and suggests the problem may be more widespread than we expected,” he said.
In addition, 74% of those with severe levels of problematic news consumption reported experiencing mental problems, and 61% reported physical problems.
“It’s important for health care providers to be aware that problematic news consumption may be a significant driver of mental and physical ill-being, especially because a lot of people might be unaware of the negative impact the news is having on their health,” Dr. McLaughlin said.
The findings were published online in Health Communication.
Emotionally invested
The researchers assessed data from an online survey of 1,100 adults (mean age, 40.5 years; 51% women) in the United States who were recruited in August 2021.
Among those surveyed, 27.3% reported “moderately problematic” news consumption, 27.5% reported minimally problematic news consumption, and 28.7% reported no problematic news consumption.
Perhaps not surprisingly, respondents with higher levels of problematic news consumption were significantly more likely to experience mental and physical ill-being than those with lower levels, even after accounting for demographics, personality traits, and overall news use, the researchers note.
Nearly three-quarters (74%) of those with severe levels of problematic news consumption reported experiencing mental ill-being “quite a bit” or “very much” – whereas frequent symptoms were only reported by 8% of all other study participants.
In addition, 61% of adults with severe problematic news consumption reported experiencing physical ill-being “quite a bit” or “very much,” compared with only 6.1% for all other study participants.
Dr. McLaughlin noted that one way to combat this problem is to help individuals develop a healthier relationship with the news – and mindfulness training may be one way to accomplish that.
“We have some preliminary evidence that individuals with high levels of mindfulness are much less susceptible to developing higher levels of problematic news consumption,” he said.
“Given this, mindfulness-based training could potentially help problematic news consumers follow the news without becoming so emotionally invested in it. We hope to examine the effectiveness of a mindfulness intervention in our future research,” he added.
Increased distress
Commenting on the study, Steven R. Thorp, PhD, ABPP, a professor at California School of Professional Psychology, Alliant International University, San Diego, said that he and his colleagues have noticed an increase in clients reporting distress about news consumption.
The survey by Dr. McLaughlin and colleagues “appears to be representative and has sufficient statistical power to address the issues,” said Dr. Thorp, who was not involved with the research.
“However, as the researchers note, it is a cross-sectional and correlational survey. So it’s possible that, as implied, people who ‘doomscroll’ are more likely to have physical and mental health problems that interfere with their functioning,” he added.
It is also possible that individuals with physical and mental health problems are more likely to be isolated and have restricted activities, thus leading to greater news consumption, Dr. Thorp noted. Alternatively, there could be an independent link between health and news consumption.
Most news is “sensational and not representative,” Dr. Thorp pointed out.
For example, “we are far more likely to hear about deaths from terrorist attacks or plane crashes than from heart attacks, though deaths from heart attacks are far more common,” he said.
“News also tends to be negative, rather than uplifting, and most news is not directly relevant to a person’s day-to-day functioning. Thus, for most people, the consumption of news may have more downsides than upsides,” Dr. Thorp added.
Still, many people want to stay informed about national and international events. So rather than following a “cold turkey” or abstinence model of stopping all news consumption, individuals could consider a “harm reduction” model of reducing time spent consuming news, Dr. Thorp noted.
Another thing to consider is the news source. “Some outlets and social media sites are designed to instill outrage, fear, or anger and to increase polarization, while others have been shown to provide balanced and less sensational coverage,” Dr. Thorp said.
“I also think it’s a good idea for providers to regularly ask about news consumption, along with learning about other daily activities that may enhance or diminish mental and physical health,” he added.
The research had no specific funding. Dr. McLaughlin and Dr. Thorp have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The past 2 years have been filled with worrisome global events, from the pandemic to the war in Ukraine, large-scale protests, mass shootings, and devastating wildfires. The 24-hour media coverage of these events can take a toll on “news addicts” who have an excessive urge to constantly check the news, researchers note.
Results from an online survey of more than 1,000 adults showed that nearly 17% showed signs of “severely problematic” news consumption.
These “doomscrollers” or “doomsurfers” scored high on all five problematic news consumption dimensions: being absorbed in news content, being consumed by thoughts about the news, attempting to alleviate feelings of threat by consuming more news, losing control over news consumption, and having news consumption interfere in daily life.
“We anticipated that a sizable portion of our sample would show signs of problematic news consumption. However, we were surprised to find that 17% of study participants suffer from the most severe level of problematic news consumption,” lead author Bryan McLaughlin, PhD, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, told this news organization. “This is certainly concerning and suggests the problem may be more widespread than we expected,” he said.
In addition, 74% of those with severe levels of problematic news consumption reported experiencing mental problems, and 61% reported physical problems.
“It’s important for health care providers to be aware that problematic news consumption may be a significant driver of mental and physical ill-being, especially because a lot of people might be unaware of the negative impact the news is having on their health,” Dr. McLaughlin said.
The findings were published online in Health Communication.
Emotionally invested
The researchers assessed data from an online survey of 1,100 adults (mean age, 40.5 years; 51% women) in the United States who were recruited in August 2021.
Among those surveyed, 27.3% reported “moderately problematic” news consumption, 27.5% reported minimally problematic news consumption, and 28.7% reported no problematic news consumption.
Perhaps not surprisingly, respondents with higher levels of problematic news consumption were significantly more likely to experience mental and physical ill-being than those with lower levels, even after accounting for demographics, personality traits, and overall news use, the researchers note.
Nearly three-quarters (74%) of those with severe levels of problematic news consumption reported experiencing mental ill-being “quite a bit” or “very much” – whereas frequent symptoms were only reported by 8% of all other study participants.
In addition, 61% of adults with severe problematic news consumption reported experiencing physical ill-being “quite a bit” or “very much,” compared with only 6.1% for all other study participants.
Dr. McLaughlin noted that one way to combat this problem is to help individuals develop a healthier relationship with the news – and mindfulness training may be one way to accomplish that.
“We have some preliminary evidence that individuals with high levels of mindfulness are much less susceptible to developing higher levels of problematic news consumption,” he said.
“Given this, mindfulness-based training could potentially help problematic news consumers follow the news without becoming so emotionally invested in it. We hope to examine the effectiveness of a mindfulness intervention in our future research,” he added.
Increased distress
Commenting on the study, Steven R. Thorp, PhD, ABPP, a professor at California School of Professional Psychology, Alliant International University, San Diego, said that he and his colleagues have noticed an increase in clients reporting distress about news consumption.
The survey by Dr. McLaughlin and colleagues “appears to be representative and has sufficient statistical power to address the issues,” said Dr. Thorp, who was not involved with the research.
“However, as the researchers note, it is a cross-sectional and correlational survey. So it’s possible that, as implied, people who ‘doomscroll’ are more likely to have physical and mental health problems that interfere with their functioning,” he added.
It is also possible that individuals with physical and mental health problems are more likely to be isolated and have restricted activities, thus leading to greater news consumption, Dr. Thorp noted. Alternatively, there could be an independent link between health and news consumption.
Most news is “sensational and not representative,” Dr. Thorp pointed out.
For example, “we are far more likely to hear about deaths from terrorist attacks or plane crashes than from heart attacks, though deaths from heart attacks are far more common,” he said.
“News also tends to be negative, rather than uplifting, and most news is not directly relevant to a person’s day-to-day functioning. Thus, for most people, the consumption of news may have more downsides than upsides,” Dr. Thorp added.
Still, many people want to stay informed about national and international events. So rather than following a “cold turkey” or abstinence model of stopping all news consumption, individuals could consider a “harm reduction” model of reducing time spent consuming news, Dr. Thorp noted.
Another thing to consider is the news source. “Some outlets and social media sites are designed to instill outrage, fear, or anger and to increase polarization, while others have been shown to provide balanced and less sensational coverage,” Dr. Thorp said.
“I also think it’s a good idea for providers to regularly ask about news consumption, along with learning about other daily activities that may enhance or diminish mental and physical health,” he added.
The research had no specific funding. Dr. McLaughlin and Dr. Thorp have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HEALTH COMMUNICATION
Distorted time perception during the pandemic tied to stress, poor mental health
ranging from difficulty keeping track of the days of the week to feeling that the hours either crawled by or sped up, new research suggests.
Results showed the sense of present focus, blurring weekdays and weekends together, and uncertainly about the future were reported by over 65% of the 5,661 survey respondents. And more than half reported the experience of feeling “time speeding up or slowing down,” report the investigators, led by E. Alison Holman, PhD, professor at the University of California, Irvine.
Significant predictors of these time distortions included being exposed to daily pandemic-related media and having a mental health diagnosis prior to the pandemic; secondary stress such as school closures and lockdown; financial stress; lifetime stress; and lifetime trauma exposure.
“Continuity between past experiences, present life, and future hopes is critical to one’s well-being, and disruption of that synergy presents mental health challenges,” Dr. Holman said in a news release.
“We were able to measure this in a nationally representative sample of Americans as they were experiencing a protracted collective trauma, which has never been done before, and this study is the first to document the prevalence and early predictors of these time distortions,” added Dr. Holman.
The findings were published online in Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy.
Unique opportunity
During the pandemic, many people’s time perspective (TP), defined as “our view of time as it spans from our past into the future,” shifted as they “focused on the immediate, present danger of the COVID-19 pandemic and future plans became uncertain,” the investigators wrote.
Studies of convenience samples “suggested that many people experienced time slowing down, stopping, and/or speeding up as they coped with the challenges of the pandemic” – a phenomenon known as temporal disintegration (TD) in psychiatric literature.
Dr. Holman said in an interview that she researched TD after the Sept.11, 2001 World Trade Center attacks.
“We found that people who experienced that early sense of TD, the sense of ‘time falling apart,’ were more prone to getting stuck in the past and staying focused on the past event,” which led to feeling “more distress over time,” she said.
Research examining the prevalence of and psychosocial factors predicting TD are “quite rare” and studies examining TD “during an unfolding, protracted collective trauma are even rarer,” the researchers note. The COVID pandemic “presented a unique opportunity to conduct such a study,” the researchers wrote.
For their study, the investigators surveyed participants in the NORC AmeriSpeak online panel, a “probability-based panel” of 35,000 U.S. households selected at random from across the country.
The study was conducted in two waves: the first survey was administered March–April 2020, the second in September–October 2020.
Speeding up, slowing down
At wave 2, participants completed a 7-item index of TD symptoms experienced over the previous 6 months. To adjust for psychological processes that may have predisposed individuals to experience TD during the pandemic, the researchers included a Wave 1 measure of future uncertainty as a covariate.
Prepandemic health data had been collected prior to the current study.
Wave 1 participants completed a checklist reporting personal, work, and community-wide exposure to the COVID outbreak, including contracting the virus, sheltering in place, and experiencing secondary stressors. The extent and type of pandemic-related media exposure were also assessed.
At wave 2, they reported the extent of exposure to the coronavirus, financial exposures, and secondary stressors. They also completed a non–COVID-related stress/trauma exposure checklist and were asked to indicate whether the trauma, disaster, or bereavement took place prior to or during the pandemic.
The final sample consisted of 5,661 adults (52% female) who completed the wave 2 survey. Participants were divided into four age groups: 18-34, 35-49, 50-64, and 65 and older.
The most common experiences (reported by more than 65% of respondents) included being focused on the present moment, feeling that weekdays and weekends were the same, and feeling uncertain about the future.
Over half of respondents (50.4%) reported feeling as though time was speeding up, and 55.2% reported feeling as though time was slowing down. Some also reported feeling uncertain about the time of day (46.4%) and forgetting events they had just experienced (35.2%).
When the researchers controlled for feeling uncertain about the future, they found that women reported more TD than men (b = 0.11; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.14; P < .001).
At wave 1, associations were found between TD and COVID-related media exposure, prepandemic mental health diagnoses, and prepandemic non–COVID-related stress and trauma. At wave 2, associations were found between TD and COVID-related secondary and financial stressors (P < .001 for all).
In contrast, COVID-related work exposure at wave 1, being 45-59 years old, and living in the Midwest region were negatively associated with TD.
“The sense of the flow of the past into the present, and the present into the future is important for our mental health,” Dr. Holman said. “We need to remember who we have been, how that shaped who we are today, and where we want to go with our lives.”
Staying in the present moment is “good, when you’re doing it mindfully. But you still need to feel you can shape and work toward the future and have some sense of control,” she added.
Dr. Homan also recommended time-perspective therapy, which helps patients with PTSD to “build continuity across time – to understand and learn from the past, live in the present, and move toward the future.”
Widespread distortion
In an interview, Ruth Ogden, PhD, a lecturer at Liverpool (England) John Moores University, said the findings “confirm those reported in Europe, South America, and the Middle East, that widespread distortion to time was common during the pandemic and that distortions to time were greatest amongst those most negatively affected by the pandemic.”
The results also support her own recent research in the United Kingdom “suggesting that distortions to time during the pandemic extend to our memory for the length of the pandemic, with most people believing that lockdowns lasted far longer than they actually did,” said Dr. Ogden, who was not involved with Dr. Holman and colleagues’ current study.
“This type of subjective lengthening of the pandemic may reinforce trauma by making the traumatic period seem longer, further damaging health and well-being,” she noted. “As the negative fallouts of the pandemic continue, it is important to establish the long-term effects of time distortions during the pandemic on mental health and well-being.”
The study was funded by U.S. National Science Foundation and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Ogden receives funding from the Wellcome Trust.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ranging from difficulty keeping track of the days of the week to feeling that the hours either crawled by or sped up, new research suggests.
Results showed the sense of present focus, blurring weekdays and weekends together, and uncertainly about the future were reported by over 65% of the 5,661 survey respondents. And more than half reported the experience of feeling “time speeding up or slowing down,” report the investigators, led by E. Alison Holman, PhD, professor at the University of California, Irvine.
Significant predictors of these time distortions included being exposed to daily pandemic-related media and having a mental health diagnosis prior to the pandemic; secondary stress such as school closures and lockdown; financial stress; lifetime stress; and lifetime trauma exposure.
“Continuity between past experiences, present life, and future hopes is critical to one’s well-being, and disruption of that synergy presents mental health challenges,” Dr. Holman said in a news release.
“We were able to measure this in a nationally representative sample of Americans as they were experiencing a protracted collective trauma, which has never been done before, and this study is the first to document the prevalence and early predictors of these time distortions,” added Dr. Holman.
The findings were published online in Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy.
Unique opportunity
During the pandemic, many people’s time perspective (TP), defined as “our view of time as it spans from our past into the future,” shifted as they “focused on the immediate, present danger of the COVID-19 pandemic and future plans became uncertain,” the investigators wrote.
Studies of convenience samples “suggested that many people experienced time slowing down, stopping, and/or speeding up as they coped with the challenges of the pandemic” – a phenomenon known as temporal disintegration (TD) in psychiatric literature.
Dr. Holman said in an interview that she researched TD after the Sept.11, 2001 World Trade Center attacks.
“We found that people who experienced that early sense of TD, the sense of ‘time falling apart,’ were more prone to getting stuck in the past and staying focused on the past event,” which led to feeling “more distress over time,” she said.
Research examining the prevalence of and psychosocial factors predicting TD are “quite rare” and studies examining TD “during an unfolding, protracted collective trauma are even rarer,” the researchers note. The COVID pandemic “presented a unique opportunity to conduct such a study,” the researchers wrote.
For their study, the investigators surveyed participants in the NORC AmeriSpeak online panel, a “probability-based panel” of 35,000 U.S. households selected at random from across the country.
The study was conducted in two waves: the first survey was administered March–April 2020, the second in September–October 2020.
Speeding up, slowing down
At wave 2, participants completed a 7-item index of TD symptoms experienced over the previous 6 months. To adjust for psychological processes that may have predisposed individuals to experience TD during the pandemic, the researchers included a Wave 1 measure of future uncertainty as a covariate.
Prepandemic health data had been collected prior to the current study.
Wave 1 participants completed a checklist reporting personal, work, and community-wide exposure to the COVID outbreak, including contracting the virus, sheltering in place, and experiencing secondary stressors. The extent and type of pandemic-related media exposure were also assessed.
At wave 2, they reported the extent of exposure to the coronavirus, financial exposures, and secondary stressors. They also completed a non–COVID-related stress/trauma exposure checklist and were asked to indicate whether the trauma, disaster, or bereavement took place prior to or during the pandemic.
The final sample consisted of 5,661 adults (52% female) who completed the wave 2 survey. Participants were divided into four age groups: 18-34, 35-49, 50-64, and 65 and older.
The most common experiences (reported by more than 65% of respondents) included being focused on the present moment, feeling that weekdays and weekends were the same, and feeling uncertain about the future.
Over half of respondents (50.4%) reported feeling as though time was speeding up, and 55.2% reported feeling as though time was slowing down. Some also reported feeling uncertain about the time of day (46.4%) and forgetting events they had just experienced (35.2%).
When the researchers controlled for feeling uncertain about the future, they found that women reported more TD than men (b = 0.11; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.14; P < .001).
At wave 1, associations were found between TD and COVID-related media exposure, prepandemic mental health diagnoses, and prepandemic non–COVID-related stress and trauma. At wave 2, associations were found between TD and COVID-related secondary and financial stressors (P < .001 for all).
In contrast, COVID-related work exposure at wave 1, being 45-59 years old, and living in the Midwest region were negatively associated with TD.
“The sense of the flow of the past into the present, and the present into the future is important for our mental health,” Dr. Holman said. “We need to remember who we have been, how that shaped who we are today, and where we want to go with our lives.”
Staying in the present moment is “good, when you’re doing it mindfully. But you still need to feel you can shape and work toward the future and have some sense of control,” she added.
Dr. Homan also recommended time-perspective therapy, which helps patients with PTSD to “build continuity across time – to understand and learn from the past, live in the present, and move toward the future.”
Widespread distortion
In an interview, Ruth Ogden, PhD, a lecturer at Liverpool (England) John Moores University, said the findings “confirm those reported in Europe, South America, and the Middle East, that widespread distortion to time was common during the pandemic and that distortions to time were greatest amongst those most negatively affected by the pandemic.”
The results also support her own recent research in the United Kingdom “suggesting that distortions to time during the pandemic extend to our memory for the length of the pandemic, with most people believing that lockdowns lasted far longer than they actually did,” said Dr. Ogden, who was not involved with Dr. Holman and colleagues’ current study.
“This type of subjective lengthening of the pandemic may reinforce trauma by making the traumatic period seem longer, further damaging health and well-being,” she noted. “As the negative fallouts of the pandemic continue, it is important to establish the long-term effects of time distortions during the pandemic on mental health and well-being.”
The study was funded by U.S. National Science Foundation and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Ogden receives funding from the Wellcome Trust.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ranging from difficulty keeping track of the days of the week to feeling that the hours either crawled by or sped up, new research suggests.
Results showed the sense of present focus, blurring weekdays and weekends together, and uncertainly about the future were reported by over 65% of the 5,661 survey respondents. And more than half reported the experience of feeling “time speeding up or slowing down,” report the investigators, led by E. Alison Holman, PhD, professor at the University of California, Irvine.
Significant predictors of these time distortions included being exposed to daily pandemic-related media and having a mental health diagnosis prior to the pandemic; secondary stress such as school closures and lockdown; financial stress; lifetime stress; and lifetime trauma exposure.
“Continuity between past experiences, present life, and future hopes is critical to one’s well-being, and disruption of that synergy presents mental health challenges,” Dr. Holman said in a news release.
“We were able to measure this in a nationally representative sample of Americans as they were experiencing a protracted collective trauma, which has never been done before, and this study is the first to document the prevalence and early predictors of these time distortions,” added Dr. Holman.
The findings were published online in Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy.
Unique opportunity
During the pandemic, many people’s time perspective (TP), defined as “our view of time as it spans from our past into the future,” shifted as they “focused on the immediate, present danger of the COVID-19 pandemic and future plans became uncertain,” the investigators wrote.
Studies of convenience samples “suggested that many people experienced time slowing down, stopping, and/or speeding up as they coped with the challenges of the pandemic” – a phenomenon known as temporal disintegration (TD) in psychiatric literature.
Dr. Holman said in an interview that she researched TD after the Sept.11, 2001 World Trade Center attacks.
“We found that people who experienced that early sense of TD, the sense of ‘time falling apart,’ were more prone to getting stuck in the past and staying focused on the past event,” which led to feeling “more distress over time,” she said.
Research examining the prevalence of and psychosocial factors predicting TD are “quite rare” and studies examining TD “during an unfolding, protracted collective trauma are even rarer,” the researchers note. The COVID pandemic “presented a unique opportunity to conduct such a study,” the researchers wrote.
For their study, the investigators surveyed participants in the NORC AmeriSpeak online panel, a “probability-based panel” of 35,000 U.S. households selected at random from across the country.
The study was conducted in two waves: the first survey was administered March–April 2020, the second in September–October 2020.
Speeding up, slowing down
At wave 2, participants completed a 7-item index of TD symptoms experienced over the previous 6 months. To adjust for psychological processes that may have predisposed individuals to experience TD during the pandemic, the researchers included a Wave 1 measure of future uncertainty as a covariate.
Prepandemic health data had been collected prior to the current study.
Wave 1 participants completed a checklist reporting personal, work, and community-wide exposure to the COVID outbreak, including contracting the virus, sheltering in place, and experiencing secondary stressors. The extent and type of pandemic-related media exposure were also assessed.
At wave 2, they reported the extent of exposure to the coronavirus, financial exposures, and secondary stressors. They also completed a non–COVID-related stress/trauma exposure checklist and were asked to indicate whether the trauma, disaster, or bereavement took place prior to or during the pandemic.
The final sample consisted of 5,661 adults (52% female) who completed the wave 2 survey. Participants were divided into four age groups: 18-34, 35-49, 50-64, and 65 and older.
The most common experiences (reported by more than 65% of respondents) included being focused on the present moment, feeling that weekdays and weekends were the same, and feeling uncertain about the future.
Over half of respondents (50.4%) reported feeling as though time was speeding up, and 55.2% reported feeling as though time was slowing down. Some also reported feeling uncertain about the time of day (46.4%) and forgetting events they had just experienced (35.2%).
When the researchers controlled for feeling uncertain about the future, they found that women reported more TD than men (b = 0.11; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.14; P < .001).
At wave 1, associations were found between TD and COVID-related media exposure, prepandemic mental health diagnoses, and prepandemic non–COVID-related stress and trauma. At wave 2, associations were found between TD and COVID-related secondary and financial stressors (P < .001 for all).
In contrast, COVID-related work exposure at wave 1, being 45-59 years old, and living in the Midwest region were negatively associated with TD.
“The sense of the flow of the past into the present, and the present into the future is important for our mental health,” Dr. Holman said. “We need to remember who we have been, how that shaped who we are today, and where we want to go with our lives.”
Staying in the present moment is “good, when you’re doing it mindfully. But you still need to feel you can shape and work toward the future and have some sense of control,” she added.
Dr. Homan also recommended time-perspective therapy, which helps patients with PTSD to “build continuity across time – to understand and learn from the past, live in the present, and move toward the future.”
Widespread distortion
In an interview, Ruth Ogden, PhD, a lecturer at Liverpool (England) John Moores University, said the findings “confirm those reported in Europe, South America, and the Middle East, that widespread distortion to time was common during the pandemic and that distortions to time were greatest amongst those most negatively affected by the pandemic.”
The results also support her own recent research in the United Kingdom “suggesting that distortions to time during the pandemic extend to our memory for the length of the pandemic, with most people believing that lockdowns lasted far longer than they actually did,” said Dr. Ogden, who was not involved with Dr. Holman and colleagues’ current study.
“This type of subjective lengthening of the pandemic may reinforce trauma by making the traumatic period seem longer, further damaging health and well-being,” she noted. “As the negative fallouts of the pandemic continue, it is important to establish the long-term effects of time distortions during the pandemic on mental health and well-being.”
The study was funded by U.S. National Science Foundation and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Ogden receives funding from the Wellcome Trust.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PSYCHOLOGICAL TRAUMA: THEORY, RESEARCH, PRACTICE, AND POLICY
How do you live with COVID? One doctor’s personal experience
Early in 2020, Anne Peters, MD, caught COVID-19. The author of Medscape’s “Peters on Diabetes” column was sick in March 2020 before state-mandated lockdowns, and well before there were any vaccines.
She remembers sitting in a small exam room with two patients who had flown to her Los Angeles office from New York. The elderly couple had hearing difficulties, so Dr. Peters sat close to them, putting on a continuous glucose monitor. “At that time, we didn’t think of COVID-19 as being in L.A.,” Dr. Peters recalled, “so I think we were not terribly consistent at mask-wearing due to the need to educate.”
“Several days later, I got COVID, but I didn’t know I had COVID per se. I felt crappy, had a terrible sore throat, lost my sense of taste and smell [which was not yet described as a COVID symptom], was completely exhausted, but had no fever or cough, which were the only criteria for getting COVID tested at the time. I didn’t know I had been exposed until 2 weeks later, when the patient’s assistant returned the sensor warning us to ‘be careful’ with it because the patient and his wife were recovering from COVID.”
That early battle with COVID-19 was just the beginning of what would become a 2-year struggle, including familial loss amid her own health problems and concerns about the under-resourced patients she cares for. Here, she shares her journey through the pandemic with this news organization.
Question: Thanks for talking to us. Let’s discuss your journey over these past 2.5 years.
Answer: Everybody has their own COVID story because we all went through this together. Some of us have worse COVID stories, and some of us have better ones, but all have been impacted.
I’m not a sick person. I’m a very healthy person but COVID made me so unwell for 2 years. The brain fog and fatigue were nothing compared to the autonomic neuropathy that affected my heart. It was really limiting for me. And I still don’t know the long-term implications, looking 20-30 years from now.
Q: When you initially had COVID, what were your symptoms? What was the impact?
A: I had all the symptoms of COVID, except for a cough and fever. I lost my sense of taste and smell. I had a horrible headache, a sore throat, and I was exhausted. I couldn’t get tested because I didn’t have the right symptoms.
Despite being sick, I never stopped working but just switched to telemedicine. I also took my regular monthly trip to our cabin in Montana. I unknowingly flew on a plane with COVID. I wore a well-fitted N95 mask, so I don’t think I gave anybody COVID. I didn’t give COVID to my partner, Eric, which is hard to believe as – at 77 – he’s older than me. He has diabetes, heart disease, and every other high-risk characteristic. If he’d gotten COVID back then, it would have been terrible, as there were no treatments, but luckily he didn’t get it.
Q: When were you officially diagnosed?
A: Two or 3 months after I thought I might have had COVID, I checked my antibodies, which tested strongly positive for a prior COVID infection. That was when I knew all the symptoms I’d had were due to the disease.
Q: Not only were you dealing with your own illness, but also that of those close to you. Can you talk about that?
A: In April 2020, my mother who was in her 90s and otherwise healthy except for dementia, got COVID. She could have gotten it from me. I visited often but wore a mask. She had all the horrible pulmonary symptoms. In her advance directive, she didn’t want to be hospitalized so I kept her in her home. She died from COVID in her own bed. It was fairly brutal, but at least I kept her where she felt comforted.
My 91-year-old dad was living in a different residential facility. Throughout COVID he had become very depressed because his social patterns had changed. Prior to COVID, they all ate together, but during the pandemic they were unable to. He missed his social connections, disliked being isolated in his room, hated everyone in masks.
He was a bit demented, but not so much that he couldn’t communicate with me or remember where his grandson was going to law school. I wasn’t allowed inside the facility, which was hard on him. I hadn’t told him his wife died because the hospice social workers advised me that I shouldn’t give him news that he couldn’t process readily until I could spend time with him. Unfortunately, that time never came. In December 2020, he got COVID. One of the people in that facility had gone to the hospital, came back, and tested negative, but actually had COVID and gave it to my dad. The guy who gave it to my dad didn’t die but my dad was terribly ill. He died 2 weeks short of getting his vaccine. He was coherent enough to have a conversation. I asked him: ‘Do you want to go to the hospital?’ And he said: ‘No, because it would be too scary,’ since he couldn’t be with me. I put him on hospice and held his hand as he died from pulmonary COVID, which was awful. I couldn’t give him enough morphine or valium to ease his breathing. But his last words to me were “I love you,” and at the very end he seemed peaceful, which was a blessing.
I got an autopsy, because he wanted one. Nothing else was wrong with him other than COVID. It destroyed his lungs. The rest of him was fine – no heart disease, cancer, or anything else. He died of COVID-19, the same as my mother.
That same week, my aunt, my only surviving older relative, who was in Des Moines, Iowa, died of COVID-19. All three family members died before the vaccine came out.
It was hard to lose my parents. I’m the only surviving child because my sister died in her 20s. It’s not been an easy pandemic. But what pandemic is easy? I just happened to have lost more people than most. Ironically, my grandfather was one of the legionnaires at the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel in Philadelphia in 1976 and died of Legionnaire’s disease before we knew what was causing the outbreak.
Q: Were you still struggling with COVID?
A: COVID impacted my whole body. I lost a lot of weight. I didn’t want to eat, and my gastrointestinal system was not happy. It took a while for my sense of taste and smell to come back. Nothing tasted good. I’m not a foodie; I don’t really care about food. We could get takeout or whatever, but none of it appealed to me. I’m not so sure it was a taste thing, I just didn’t feel like eating.
I didn’t realize I had “brain fog” per se, because I felt stressed and overwhelmed by the pandemic and my patients’ concerns. But one day, about 3 months after I had developed COVID, I woke up without the fog. Which made me aware that I hadn’t been feeling right up until that point.
The worst symptoms, however, were cardiac. I noticed also immediately that my heart rate went up very quickly with minimal exertion. My pulse has always been in the 55-60 bpm range, and suddenly just walking across a room made it go up to over 140 bpm. If I did any aerobic activity, it went up over 160 and would be associated with dyspnea and chest pain. I believed these were all post-COVID symptoms and felt validated when reports of others having similar issues were published in the literature.
Q: Did you continue seeing patients?
A: Yes, of course. Patients never needed their doctors more. In East L.A., where patients don’t have easy access to telemedicine, I kept going into clinic throughout the pandemic. In the more affluent Westside of Los Angeles, we switched to telemedicine, which was quite effective for most. However, because diabetes was associated with an increased risk of hospitalization and death from COVID, my patients were understandably afraid. I’ve never been busier, but (like all health care providers), I became more of a COVID provider than a diabetologist.
Q: Do you feel your battle with COVID impacted your work?
A: It didn’t affect me at work. If I was sitting still, I was fine. Sitting at home at a desk, I didn’t notice any symptoms. But as a habitual stair-user, I would be gasping for breath in the stairwell because I couldn’t go up the stairs to my office as I once could.
I think you empathize more with people who had COVID (when you’ve had it yourself). There was such a huge patient burden. And I think that’s been the thing that’s affected health care providers the most – no matter what specialty we’re in – that nobody has answers.
Q: What happened after you had your vaccine?
A: The vaccine itself was fine. I didn’t have any reaction to the first two doses. But the first booster made my cardiac issues worse.
By this point, my cardiac problems stopped me from exercising. I even went to the ER with chest pain once because I was having palpitations and chest pressure caused by simply taking my morning shower. Fortunately, I wasn’t having an MI, but I certainly wasn’t “normal.”
My measure of my fitness is the cross-country skiing trail I use in Montana. I know exactly how far I can ski. Usually I can do the loop in 35 minutes. After COVID, I lasted 10 minutes. I would be tachycardic, short of breath with chest pain radiating down my left arm. I would rest and try to keep going. But with each rest period, I only got worse. I would be laying in the snow and strangers would ask if I needed help.
Q: What helped you?
A: I’ve read a lot about long COVID and have tried to learn from the experts. Of course, I never went to a doctor directly, although I did ask colleagues for advice. What I learned was to never push myself. I forced myself to create an exercise schedule where I only exercised three times a week with rest days in between. When exercising, the second my heart rate went above 140 bpm, I stopped until I could get it back down. I would push against this new limit, even though my limit was low.
Additionally, I worked on my breathing patterns and did meditative breathing for 10 minutes twice daily using a commercially available app.
Although progress was slow, I did improve, and by June 2022, I seemed back to normal. I was not as fit as I was prior to COVID and needed to improve, but the tachycardic response to exercise and cardiac symptoms were gone. I felt like my normal self. Normal enough to go on a spot packing trip in the Sierras in August. (Horses carried us and a mule carried the gear over the 12,000-foot pass into the mountains, and then left my friend and me high in the Sierras for a week.) We were camped above 10,000 feet and every day hiked up to another high mountain lake where we fly-fished for trout that we ate for dinner. The hikes were a challenge, but not abnormally so. Not as they would have been while I had long COVID.
Q: What is the current atmosphere in your clinic?
A: COVID is much milder now in my vaccinated patients, but I feel most health care providers are exhausted. Many of my staff left when COVID hit because they didn’t want to keep working. It made practicing medicine exhausting. There’s been a shortage of nurses, a shortage of everything. We’ve been required to do a whole lot more than we ever did before. It’s much harder to be a doctor. This pandemic is the first time I’ve ever thought of quitting. Granted, I lost my whole family, or at least the older generation, but it’s just been almost overwhelming.
On the plus side, almost every one of my patients has been vaccinated, because early on, people would ask: “Do you trust this vaccine?” I would reply: “I saw my parents die from COVID when they weren’t vaccinated, so you’re getting vaccinated. This is real and the vaccines help.” It made me very good at convincing people to get vaccines because I knew what it was like to see someone dying from COVID up close.
Q: What advice do you have for those struggling with the COVID pandemic?
A: People need to decide what their own risk is for getting sick and how many times they want to get COVID. At this point, I want people to go out, but safely. In the beginning, when my patients said, “can I go visit my granddaughter?” I said, “no,” but that was before we had the vaccine. Now I feel it is safe to go out using common sense. I still have my patients wear masks on planes. I still have patients try to eat outside as much as possible. And I tell people to take the precautions that make sense, but I tell them to go out and do things because life is short.
I had a patient in his 70s who has many risk factors like heart disease and diabetes. His granddaughter’s Bat Mitzvah in Florida was coming up. He asked: “Can I go?” I told him “Yes,” but to be safe – to wear an N95 mask on the plane and at the event, and stay in his own hotel room, rather than with the whole family. I said, “You need to do this.” Earlier in the pandemic, I saw people who literally died from loneliness and isolation.
He and his wife flew there. He sent me a picture of himself with his granddaughter. When he returned, he showed me a handwritten note from her that said, “I love you so much. Everyone else canceled, which made me cry. You’re the only one who came. You have no idea how much this meant to me.”
He’s back in L.A., and he didn’t get COVID. He said, “It was the best thing I’ve done in years.” That’s what I need to help people with, navigating this world with COVID and assessing risks and benefits. As with all of medicine, my advice is individualized. My advice changes based on the major circulating variant and the rates of the virus in the population, as well as the risk factors of the individual.
Q: What are you doing now?
A: I’m trying to avoid getting COVID again, or another booster. I could get pre-exposure monoclonal antibodies but am waiting to do anything further until I see what happens over the fall and winter. I still wear a mask inside but now do a mix of in-person and telemedicine visits. I still try to go to outdoor restaurants, which is easy in California. But I’m flying to see my son in New York and plan to go to Europe this fall for a meeting. I also go to my cabin in Montana every month to get my “dose” of the wilderness. Overall, I travel for conferences and speaking engagements much less because I have learned the joy of staying home.
Thinking back on my life as a doctor, my career began as an intern at Stanford rotating through Ward 5B, the AIDS unit at San Francisco General Hospital, and will likely end with COVID. In spite of all our medical advances, my generation of physicians, much as many generations before us, has a front-row seat to the vulnerability of humans to infectious diseases and how far we still need to go to protect our patients from communicable illness.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Anne L. Peters, MD, is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts; three books on diabetes; and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations.
Early in 2020, Anne Peters, MD, caught COVID-19. The author of Medscape’s “Peters on Diabetes” column was sick in March 2020 before state-mandated lockdowns, and well before there were any vaccines.
She remembers sitting in a small exam room with two patients who had flown to her Los Angeles office from New York. The elderly couple had hearing difficulties, so Dr. Peters sat close to them, putting on a continuous glucose monitor. “At that time, we didn’t think of COVID-19 as being in L.A.,” Dr. Peters recalled, “so I think we were not terribly consistent at mask-wearing due to the need to educate.”
“Several days later, I got COVID, but I didn’t know I had COVID per se. I felt crappy, had a terrible sore throat, lost my sense of taste and smell [which was not yet described as a COVID symptom], was completely exhausted, but had no fever or cough, which were the only criteria for getting COVID tested at the time. I didn’t know I had been exposed until 2 weeks later, when the patient’s assistant returned the sensor warning us to ‘be careful’ with it because the patient and his wife were recovering from COVID.”
That early battle with COVID-19 was just the beginning of what would become a 2-year struggle, including familial loss amid her own health problems and concerns about the under-resourced patients she cares for. Here, she shares her journey through the pandemic with this news organization.
Question: Thanks for talking to us. Let’s discuss your journey over these past 2.5 years.
Answer: Everybody has their own COVID story because we all went through this together. Some of us have worse COVID stories, and some of us have better ones, but all have been impacted.
I’m not a sick person. I’m a very healthy person but COVID made me so unwell for 2 years. The brain fog and fatigue were nothing compared to the autonomic neuropathy that affected my heart. It was really limiting for me. And I still don’t know the long-term implications, looking 20-30 years from now.
Q: When you initially had COVID, what were your symptoms? What was the impact?
A: I had all the symptoms of COVID, except for a cough and fever. I lost my sense of taste and smell. I had a horrible headache, a sore throat, and I was exhausted. I couldn’t get tested because I didn’t have the right symptoms.
Despite being sick, I never stopped working but just switched to telemedicine. I also took my regular monthly trip to our cabin in Montana. I unknowingly flew on a plane with COVID. I wore a well-fitted N95 mask, so I don’t think I gave anybody COVID. I didn’t give COVID to my partner, Eric, which is hard to believe as – at 77 – he’s older than me. He has diabetes, heart disease, and every other high-risk characteristic. If he’d gotten COVID back then, it would have been terrible, as there were no treatments, but luckily he didn’t get it.
Q: When were you officially diagnosed?
A: Two or 3 months after I thought I might have had COVID, I checked my antibodies, which tested strongly positive for a prior COVID infection. That was when I knew all the symptoms I’d had were due to the disease.
Q: Not only were you dealing with your own illness, but also that of those close to you. Can you talk about that?
A: In April 2020, my mother who was in her 90s and otherwise healthy except for dementia, got COVID. She could have gotten it from me. I visited often but wore a mask. She had all the horrible pulmonary symptoms. In her advance directive, she didn’t want to be hospitalized so I kept her in her home. She died from COVID in her own bed. It was fairly brutal, but at least I kept her where she felt comforted.
My 91-year-old dad was living in a different residential facility. Throughout COVID he had become very depressed because his social patterns had changed. Prior to COVID, they all ate together, but during the pandemic they were unable to. He missed his social connections, disliked being isolated in his room, hated everyone in masks.
He was a bit demented, but not so much that he couldn’t communicate with me or remember where his grandson was going to law school. I wasn’t allowed inside the facility, which was hard on him. I hadn’t told him his wife died because the hospice social workers advised me that I shouldn’t give him news that he couldn’t process readily until I could spend time with him. Unfortunately, that time never came. In December 2020, he got COVID. One of the people in that facility had gone to the hospital, came back, and tested negative, but actually had COVID and gave it to my dad. The guy who gave it to my dad didn’t die but my dad was terribly ill. He died 2 weeks short of getting his vaccine. He was coherent enough to have a conversation. I asked him: ‘Do you want to go to the hospital?’ And he said: ‘No, because it would be too scary,’ since he couldn’t be with me. I put him on hospice and held his hand as he died from pulmonary COVID, which was awful. I couldn’t give him enough morphine or valium to ease his breathing. But his last words to me were “I love you,” and at the very end he seemed peaceful, which was a blessing.
I got an autopsy, because he wanted one. Nothing else was wrong with him other than COVID. It destroyed his lungs. The rest of him was fine – no heart disease, cancer, or anything else. He died of COVID-19, the same as my mother.
That same week, my aunt, my only surviving older relative, who was in Des Moines, Iowa, died of COVID-19. All three family members died before the vaccine came out.
It was hard to lose my parents. I’m the only surviving child because my sister died in her 20s. It’s not been an easy pandemic. But what pandemic is easy? I just happened to have lost more people than most. Ironically, my grandfather was one of the legionnaires at the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel in Philadelphia in 1976 and died of Legionnaire’s disease before we knew what was causing the outbreak.
Q: Were you still struggling with COVID?
A: COVID impacted my whole body. I lost a lot of weight. I didn’t want to eat, and my gastrointestinal system was not happy. It took a while for my sense of taste and smell to come back. Nothing tasted good. I’m not a foodie; I don’t really care about food. We could get takeout or whatever, but none of it appealed to me. I’m not so sure it was a taste thing, I just didn’t feel like eating.
I didn’t realize I had “brain fog” per se, because I felt stressed and overwhelmed by the pandemic and my patients’ concerns. But one day, about 3 months after I had developed COVID, I woke up without the fog. Which made me aware that I hadn’t been feeling right up until that point.
The worst symptoms, however, were cardiac. I noticed also immediately that my heart rate went up very quickly with minimal exertion. My pulse has always been in the 55-60 bpm range, and suddenly just walking across a room made it go up to over 140 bpm. If I did any aerobic activity, it went up over 160 and would be associated with dyspnea and chest pain. I believed these were all post-COVID symptoms and felt validated when reports of others having similar issues were published in the literature.
Q: Did you continue seeing patients?
A: Yes, of course. Patients never needed their doctors more. In East L.A., where patients don’t have easy access to telemedicine, I kept going into clinic throughout the pandemic. In the more affluent Westside of Los Angeles, we switched to telemedicine, which was quite effective for most. However, because diabetes was associated with an increased risk of hospitalization and death from COVID, my patients were understandably afraid. I’ve never been busier, but (like all health care providers), I became more of a COVID provider than a diabetologist.
Q: Do you feel your battle with COVID impacted your work?
A: It didn’t affect me at work. If I was sitting still, I was fine. Sitting at home at a desk, I didn’t notice any symptoms. But as a habitual stair-user, I would be gasping for breath in the stairwell because I couldn’t go up the stairs to my office as I once could.
I think you empathize more with people who had COVID (when you’ve had it yourself). There was such a huge patient burden. And I think that’s been the thing that’s affected health care providers the most – no matter what specialty we’re in – that nobody has answers.
Q: What happened after you had your vaccine?
A: The vaccine itself was fine. I didn’t have any reaction to the first two doses. But the first booster made my cardiac issues worse.
By this point, my cardiac problems stopped me from exercising. I even went to the ER with chest pain once because I was having palpitations and chest pressure caused by simply taking my morning shower. Fortunately, I wasn’t having an MI, but I certainly wasn’t “normal.”
My measure of my fitness is the cross-country skiing trail I use in Montana. I know exactly how far I can ski. Usually I can do the loop in 35 minutes. After COVID, I lasted 10 minutes. I would be tachycardic, short of breath with chest pain radiating down my left arm. I would rest and try to keep going. But with each rest period, I only got worse. I would be laying in the snow and strangers would ask if I needed help.
Q: What helped you?
A: I’ve read a lot about long COVID and have tried to learn from the experts. Of course, I never went to a doctor directly, although I did ask colleagues for advice. What I learned was to never push myself. I forced myself to create an exercise schedule where I only exercised three times a week with rest days in between. When exercising, the second my heart rate went above 140 bpm, I stopped until I could get it back down. I would push against this new limit, even though my limit was low.
Additionally, I worked on my breathing patterns and did meditative breathing for 10 minutes twice daily using a commercially available app.
Although progress was slow, I did improve, and by June 2022, I seemed back to normal. I was not as fit as I was prior to COVID and needed to improve, but the tachycardic response to exercise and cardiac symptoms were gone. I felt like my normal self. Normal enough to go on a spot packing trip in the Sierras in August. (Horses carried us and a mule carried the gear over the 12,000-foot pass into the mountains, and then left my friend and me high in the Sierras for a week.) We were camped above 10,000 feet and every day hiked up to another high mountain lake where we fly-fished for trout that we ate for dinner. The hikes were a challenge, but not abnormally so. Not as they would have been while I had long COVID.
Q: What is the current atmosphere in your clinic?
A: COVID is much milder now in my vaccinated patients, but I feel most health care providers are exhausted. Many of my staff left when COVID hit because they didn’t want to keep working. It made practicing medicine exhausting. There’s been a shortage of nurses, a shortage of everything. We’ve been required to do a whole lot more than we ever did before. It’s much harder to be a doctor. This pandemic is the first time I’ve ever thought of quitting. Granted, I lost my whole family, or at least the older generation, but it’s just been almost overwhelming.
On the plus side, almost every one of my patients has been vaccinated, because early on, people would ask: “Do you trust this vaccine?” I would reply: “I saw my parents die from COVID when they weren’t vaccinated, so you’re getting vaccinated. This is real and the vaccines help.” It made me very good at convincing people to get vaccines because I knew what it was like to see someone dying from COVID up close.
Q: What advice do you have for those struggling with the COVID pandemic?
A: People need to decide what their own risk is for getting sick and how many times they want to get COVID. At this point, I want people to go out, but safely. In the beginning, when my patients said, “can I go visit my granddaughter?” I said, “no,” but that was before we had the vaccine. Now I feel it is safe to go out using common sense. I still have my patients wear masks on planes. I still have patients try to eat outside as much as possible. And I tell people to take the precautions that make sense, but I tell them to go out and do things because life is short.
I had a patient in his 70s who has many risk factors like heart disease and diabetes. His granddaughter’s Bat Mitzvah in Florida was coming up. He asked: “Can I go?” I told him “Yes,” but to be safe – to wear an N95 mask on the plane and at the event, and stay in his own hotel room, rather than with the whole family. I said, “You need to do this.” Earlier in the pandemic, I saw people who literally died from loneliness and isolation.
He and his wife flew there. He sent me a picture of himself with his granddaughter. When he returned, he showed me a handwritten note from her that said, “I love you so much. Everyone else canceled, which made me cry. You’re the only one who came. You have no idea how much this meant to me.”
He’s back in L.A., and he didn’t get COVID. He said, “It was the best thing I’ve done in years.” That’s what I need to help people with, navigating this world with COVID and assessing risks and benefits. As with all of medicine, my advice is individualized. My advice changes based on the major circulating variant and the rates of the virus in the population, as well as the risk factors of the individual.
Q: What are you doing now?
A: I’m trying to avoid getting COVID again, or another booster. I could get pre-exposure monoclonal antibodies but am waiting to do anything further until I see what happens over the fall and winter. I still wear a mask inside but now do a mix of in-person and telemedicine visits. I still try to go to outdoor restaurants, which is easy in California. But I’m flying to see my son in New York and plan to go to Europe this fall for a meeting. I also go to my cabin in Montana every month to get my “dose” of the wilderness. Overall, I travel for conferences and speaking engagements much less because I have learned the joy of staying home.
Thinking back on my life as a doctor, my career began as an intern at Stanford rotating through Ward 5B, the AIDS unit at San Francisco General Hospital, and will likely end with COVID. In spite of all our medical advances, my generation of physicians, much as many generations before us, has a front-row seat to the vulnerability of humans to infectious diseases and how far we still need to go to protect our patients from communicable illness.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Anne L. Peters, MD, is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts; three books on diabetes; and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations.
Early in 2020, Anne Peters, MD, caught COVID-19. The author of Medscape’s “Peters on Diabetes” column was sick in March 2020 before state-mandated lockdowns, and well before there were any vaccines.
She remembers sitting in a small exam room with two patients who had flown to her Los Angeles office from New York. The elderly couple had hearing difficulties, so Dr. Peters sat close to them, putting on a continuous glucose monitor. “At that time, we didn’t think of COVID-19 as being in L.A.,” Dr. Peters recalled, “so I think we were not terribly consistent at mask-wearing due to the need to educate.”
“Several days later, I got COVID, but I didn’t know I had COVID per se. I felt crappy, had a terrible sore throat, lost my sense of taste and smell [which was not yet described as a COVID symptom], was completely exhausted, but had no fever or cough, which were the only criteria for getting COVID tested at the time. I didn’t know I had been exposed until 2 weeks later, when the patient’s assistant returned the sensor warning us to ‘be careful’ with it because the patient and his wife were recovering from COVID.”
That early battle with COVID-19 was just the beginning of what would become a 2-year struggle, including familial loss amid her own health problems and concerns about the under-resourced patients she cares for. Here, she shares her journey through the pandemic with this news organization.
Question: Thanks for talking to us. Let’s discuss your journey over these past 2.5 years.
Answer: Everybody has their own COVID story because we all went through this together. Some of us have worse COVID stories, and some of us have better ones, but all have been impacted.
I’m not a sick person. I’m a very healthy person but COVID made me so unwell for 2 years. The brain fog and fatigue were nothing compared to the autonomic neuropathy that affected my heart. It was really limiting for me. And I still don’t know the long-term implications, looking 20-30 years from now.
Q: When you initially had COVID, what were your symptoms? What was the impact?
A: I had all the symptoms of COVID, except for a cough and fever. I lost my sense of taste and smell. I had a horrible headache, a sore throat, and I was exhausted. I couldn’t get tested because I didn’t have the right symptoms.
Despite being sick, I never stopped working but just switched to telemedicine. I also took my regular monthly trip to our cabin in Montana. I unknowingly flew on a plane with COVID. I wore a well-fitted N95 mask, so I don’t think I gave anybody COVID. I didn’t give COVID to my partner, Eric, which is hard to believe as – at 77 – he’s older than me. He has diabetes, heart disease, and every other high-risk characteristic. If he’d gotten COVID back then, it would have been terrible, as there were no treatments, but luckily he didn’t get it.
Q: When were you officially diagnosed?
A: Two or 3 months after I thought I might have had COVID, I checked my antibodies, which tested strongly positive for a prior COVID infection. That was when I knew all the symptoms I’d had were due to the disease.
Q: Not only were you dealing with your own illness, but also that of those close to you. Can you talk about that?
A: In April 2020, my mother who was in her 90s and otherwise healthy except for dementia, got COVID. She could have gotten it from me. I visited often but wore a mask. She had all the horrible pulmonary symptoms. In her advance directive, she didn’t want to be hospitalized so I kept her in her home. She died from COVID in her own bed. It was fairly brutal, but at least I kept her where she felt comforted.
My 91-year-old dad was living in a different residential facility. Throughout COVID he had become very depressed because his social patterns had changed. Prior to COVID, they all ate together, but during the pandemic they were unable to. He missed his social connections, disliked being isolated in his room, hated everyone in masks.
He was a bit demented, but not so much that he couldn’t communicate with me or remember where his grandson was going to law school. I wasn’t allowed inside the facility, which was hard on him. I hadn’t told him his wife died because the hospice social workers advised me that I shouldn’t give him news that he couldn’t process readily until I could spend time with him. Unfortunately, that time never came. In December 2020, he got COVID. One of the people in that facility had gone to the hospital, came back, and tested negative, but actually had COVID and gave it to my dad. The guy who gave it to my dad didn’t die but my dad was terribly ill. He died 2 weeks short of getting his vaccine. He was coherent enough to have a conversation. I asked him: ‘Do you want to go to the hospital?’ And he said: ‘No, because it would be too scary,’ since he couldn’t be with me. I put him on hospice and held his hand as he died from pulmonary COVID, which was awful. I couldn’t give him enough morphine or valium to ease his breathing. But his last words to me were “I love you,” and at the very end he seemed peaceful, which was a blessing.
I got an autopsy, because he wanted one. Nothing else was wrong with him other than COVID. It destroyed his lungs. The rest of him was fine – no heart disease, cancer, or anything else. He died of COVID-19, the same as my mother.
That same week, my aunt, my only surviving older relative, who was in Des Moines, Iowa, died of COVID-19. All three family members died before the vaccine came out.
It was hard to lose my parents. I’m the only surviving child because my sister died in her 20s. It’s not been an easy pandemic. But what pandemic is easy? I just happened to have lost more people than most. Ironically, my grandfather was one of the legionnaires at the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel in Philadelphia in 1976 and died of Legionnaire’s disease before we knew what was causing the outbreak.
Q: Were you still struggling with COVID?
A: COVID impacted my whole body. I lost a lot of weight. I didn’t want to eat, and my gastrointestinal system was not happy. It took a while for my sense of taste and smell to come back. Nothing tasted good. I’m not a foodie; I don’t really care about food. We could get takeout or whatever, but none of it appealed to me. I’m not so sure it was a taste thing, I just didn’t feel like eating.
I didn’t realize I had “brain fog” per se, because I felt stressed and overwhelmed by the pandemic and my patients’ concerns. But one day, about 3 months after I had developed COVID, I woke up without the fog. Which made me aware that I hadn’t been feeling right up until that point.
The worst symptoms, however, were cardiac. I noticed also immediately that my heart rate went up very quickly with minimal exertion. My pulse has always been in the 55-60 bpm range, and suddenly just walking across a room made it go up to over 140 bpm. If I did any aerobic activity, it went up over 160 and would be associated with dyspnea and chest pain. I believed these were all post-COVID symptoms and felt validated when reports of others having similar issues were published in the literature.
Q: Did you continue seeing patients?
A: Yes, of course. Patients never needed their doctors more. In East L.A., where patients don’t have easy access to telemedicine, I kept going into clinic throughout the pandemic. In the more affluent Westside of Los Angeles, we switched to telemedicine, which was quite effective for most. However, because diabetes was associated with an increased risk of hospitalization and death from COVID, my patients were understandably afraid. I’ve never been busier, but (like all health care providers), I became more of a COVID provider than a diabetologist.
Q: Do you feel your battle with COVID impacted your work?
A: It didn’t affect me at work. If I was sitting still, I was fine. Sitting at home at a desk, I didn’t notice any symptoms. But as a habitual stair-user, I would be gasping for breath in the stairwell because I couldn’t go up the stairs to my office as I once could.
I think you empathize more with people who had COVID (when you’ve had it yourself). There was such a huge patient burden. And I think that’s been the thing that’s affected health care providers the most – no matter what specialty we’re in – that nobody has answers.
Q: What happened after you had your vaccine?
A: The vaccine itself was fine. I didn’t have any reaction to the first two doses. But the first booster made my cardiac issues worse.
By this point, my cardiac problems stopped me from exercising. I even went to the ER with chest pain once because I was having palpitations and chest pressure caused by simply taking my morning shower. Fortunately, I wasn’t having an MI, but I certainly wasn’t “normal.”
My measure of my fitness is the cross-country skiing trail I use in Montana. I know exactly how far I can ski. Usually I can do the loop in 35 minutes. After COVID, I lasted 10 minutes. I would be tachycardic, short of breath with chest pain radiating down my left arm. I would rest and try to keep going. But with each rest period, I only got worse. I would be laying in the snow and strangers would ask if I needed help.
Q: What helped you?
A: I’ve read a lot about long COVID and have tried to learn from the experts. Of course, I never went to a doctor directly, although I did ask colleagues for advice. What I learned was to never push myself. I forced myself to create an exercise schedule where I only exercised three times a week with rest days in between. When exercising, the second my heart rate went above 140 bpm, I stopped until I could get it back down. I would push against this new limit, even though my limit was low.
Additionally, I worked on my breathing patterns and did meditative breathing for 10 minutes twice daily using a commercially available app.
Although progress was slow, I did improve, and by June 2022, I seemed back to normal. I was not as fit as I was prior to COVID and needed to improve, but the tachycardic response to exercise and cardiac symptoms were gone. I felt like my normal self. Normal enough to go on a spot packing trip in the Sierras in August. (Horses carried us and a mule carried the gear over the 12,000-foot pass into the mountains, and then left my friend and me high in the Sierras for a week.) We were camped above 10,000 feet and every day hiked up to another high mountain lake where we fly-fished for trout that we ate for dinner. The hikes were a challenge, but not abnormally so. Not as they would have been while I had long COVID.
Q: What is the current atmosphere in your clinic?
A: COVID is much milder now in my vaccinated patients, but I feel most health care providers are exhausted. Many of my staff left when COVID hit because they didn’t want to keep working. It made practicing medicine exhausting. There’s been a shortage of nurses, a shortage of everything. We’ve been required to do a whole lot more than we ever did before. It’s much harder to be a doctor. This pandemic is the first time I’ve ever thought of quitting. Granted, I lost my whole family, or at least the older generation, but it’s just been almost overwhelming.
On the plus side, almost every one of my patients has been vaccinated, because early on, people would ask: “Do you trust this vaccine?” I would reply: “I saw my parents die from COVID when they weren’t vaccinated, so you’re getting vaccinated. This is real and the vaccines help.” It made me very good at convincing people to get vaccines because I knew what it was like to see someone dying from COVID up close.
Q: What advice do you have for those struggling with the COVID pandemic?
A: People need to decide what their own risk is for getting sick and how many times they want to get COVID. At this point, I want people to go out, but safely. In the beginning, when my patients said, “can I go visit my granddaughter?” I said, “no,” but that was before we had the vaccine. Now I feel it is safe to go out using common sense. I still have my patients wear masks on planes. I still have patients try to eat outside as much as possible. And I tell people to take the precautions that make sense, but I tell them to go out and do things because life is short.
I had a patient in his 70s who has many risk factors like heart disease and diabetes. His granddaughter’s Bat Mitzvah in Florida was coming up. He asked: “Can I go?” I told him “Yes,” but to be safe – to wear an N95 mask on the plane and at the event, and stay in his own hotel room, rather than with the whole family. I said, “You need to do this.” Earlier in the pandemic, I saw people who literally died from loneliness and isolation.
He and his wife flew there. He sent me a picture of himself with his granddaughter. When he returned, he showed me a handwritten note from her that said, “I love you so much. Everyone else canceled, which made me cry. You’re the only one who came. You have no idea how much this meant to me.”
He’s back in L.A., and he didn’t get COVID. He said, “It was the best thing I’ve done in years.” That’s what I need to help people with, navigating this world with COVID and assessing risks and benefits. As with all of medicine, my advice is individualized. My advice changes based on the major circulating variant and the rates of the virus in the population, as well as the risk factors of the individual.
Q: What are you doing now?
A: I’m trying to avoid getting COVID again, or another booster. I could get pre-exposure monoclonal antibodies but am waiting to do anything further until I see what happens over the fall and winter. I still wear a mask inside but now do a mix of in-person and telemedicine visits. I still try to go to outdoor restaurants, which is easy in California. But I’m flying to see my son in New York and plan to go to Europe this fall for a meeting. I also go to my cabin in Montana every month to get my “dose” of the wilderness. Overall, I travel for conferences and speaking engagements much less because I have learned the joy of staying home.
Thinking back on my life as a doctor, my career began as an intern at Stanford rotating through Ward 5B, the AIDS unit at San Francisco General Hospital, and will likely end with COVID. In spite of all our medical advances, my generation of physicians, much as many generations before us, has a front-row seat to the vulnerability of humans to infectious diseases and how far we still need to go to protect our patients from communicable illness.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Anne L. Peters, MD, is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts; three books on diabetes; and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations.
Stable, long-term opioid therapy safer than tapering?
Investigators analyzed data for almost 200,000 patients who did not have signs of opioid use disorder (OUD) and were receiving opioid treatment. The investigators compared three dosing strategies: abrupt withdrawal, gradual tapering, and continuation of the current stable dosage.
Results showed a higher adjusted cumulative incidence of opioid overdose or suicide events 11 months after baseline among participants for whom a tapered dosing strategy was utilized, compared with those who continued taking a stable dosage. The risk difference was 0.15% between taper and stable dosage and 0.33% between abrupt discontinuation and stable dosage.
“This study identified a small absolute increase in risk of harms associated with opioid tapering compared with a stable opioid dosage,” Marc LaRochelle, MD, MPH, assistant professor, Boston University, and colleagues write.
“These results do not suggest that policies of mandatory dosage tapering for individuals receiving a stable long-term opioid dosage without evidence of opioid misuse will reduce short-term harm via suicide and overdose,” they add.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Benefits vs. harms
The investigators note that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in its 2016 Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain, “recommended tapering opioid dosages if benefits no longer outweigh harms.”
In response, “some health systems and U.S. states enacted stringent dose limits that were applied with few exceptions, regardless of individual patients’ risk of harms,” they write. By contrast, there have been “increasing reports of patients experiencing adverse effects from forced opioid tapers.”
Previous studies that identified harms associated with opioid tapering and discontinuation had several limitations, including a focus on discontinuation, which is “likely more destabilizing than gradual tapering,” the researchers write. There is also “a high potential for confounding” in these studies, they add.
The investigators sought to fill the research gap by drawing on 8-year data (Jan. 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2018) from a large database that includes adjudicated pharmacy, outpatient, and inpatient medical claims for individuals with commercial or Medicare Advantage insurance encompassing all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico.
Notably, individuals who had received a diagnosis of substance use, abuse, or dependence or for whom there were indicators consistent with OUD were excluded.
The researchers compared the three treatment strategies during a 4-month treatment strategy assignment period (“grace period”) after baseline. Tapering was defined as “2 consecutive months with a mean MME [morphine milligram equivalent] reduction of 15% or more compared with the baseline month.”
All estimates were adjusted for potential confounders, including demographic and treatment characteristics, baseline year, region, insurance plan type, comorbid psychiatric and medical conditions, and the prescribing of other psychiatric medications, such as benzodiazepines, gabapentin, or pregabalin.
Patient-centered approaches
The final cohort that met inclusion criteria consisted of 199,836 individuals (45.1% men; mean age, 56.9 years). Of the total group, 57.6% were aged 45-64 years. There were 415,123 qualifying long-term opioid therapy episodes.
The largest percentage of the cohort (41.2%) were receiving a baseline mean MME of 50-89 mg/day, while 34% were receiving 90-199 mg/day and 23.5% were receiving at least 200 mg/day.
During the 6-month eligibility assessment period, 34.8% of the cohort were receiving benzodiazepine prescriptions, 18% had been diagnosed with comorbid anxiety, and 19.7% had been diagnosed with comorbid depression.
After the treatment assignment period, most treatment episodes (87.1%) were considered stable, 11.1% were considered a taper, and 1.8% were considered abrupt discontinuation.
Eleven months after baseline, the adjusted cumulative incidence of opioid overdose or suicide events was lowest for those who continued to receive a stable dose.

The risk differences between taper vs. stable dosage were 0.15% (95% confidence interval, 0.03%-0.26%), and the risk differences between abrupt discontinuation and stable dose were 0.33% (95% CI, −0.03%-0.74%). The risk ratios associated with taper vs. stable dosage and abrupt discontinuation vs. stable dosage were 1.15 (95% CI, 1.04-1.27) and 1.34 (95% CI, 0.97-1.79), respectively.
The adjusted cumulative incidence curves for overdose or suicide diverged at month 4 when comparing stable dosage and taper, with a higher incidence associated with the taper vs. stable dosage treatment strategies thereafter. However, when the researchers compared stable dosage with abrupt discontinuation, the event rates were similar.
A per protocol analysis, in which the researchers censored episodes involving lack of adherence to assigned treatment, yielded results similar to those of the main analysis.
“Policies establishing dosage thresholds or mandating tapers for all patients receiving long-term opioid therapy are not supported by existing data in terms of anticipated benefits even if, as we found, the rate of adverse outcomes is small,” the investigators write.
Instead, they encourage health care systems and clinicians to “continue to develop and implement patient-centered approaches to pain management for patients with established long-term opioid therapy.”
Protracted withdrawal?
Commenting on the study, A. Benjamin Srivastava, MD, assistant professor of clinical psychiatry, division on substance use disorders, Columbia University Medical Center, New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York, called the study “an important contribution to the literature” that “sheds further light on the risks associated with tapering.”
Dr. Srivastava, who was not involved with the research, noted that previous studies showing an increased prevalence of adverse events with tapering included participants with OUD or signs of opioid misuse, “potentially confounding findings.”
By contrast, the current study investigators specifically excluded patients with OUD/opioid misuse but still found a “slight increase in risk for opioid overdose and suicide, even when excluding for potential confounders,” he said.
Although causal implications require further investigation, “a source of these adverse outcomes may be unmanaged withdrawal that may be protracted,” Dr. Srivastava noted.
While abrupt discontinuation “may result in significant acute withdrawal symptoms, these should subside by 1-2 weeks at most,” he said.
Lowering the dose without discontinuation may lead to patients’ entering into “a dyshomeostatic state characterized by anxiety and dysphoria ... that may not be recognized by the prescribing clinician,” he added.
The brain “is still being primed by opioids [and] ‘wanting’ a higher dose. Thus, particular attention to withdrawal symptoms, both physical and psychiatric, is prudent when choosing to taper opioids vs. maintaining or discontinuing,” Dr. Srivastava said.
The study was funded by a grant from the CDC and a grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse to one of the investigators. Dr. LaRochelle received grants from the CDC and NIDA during the conduct of the study and has received consulting fees for research paid to his institution from OptumLabs outside the submitted work. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Srivastava reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators analyzed data for almost 200,000 patients who did not have signs of opioid use disorder (OUD) and were receiving opioid treatment. The investigators compared three dosing strategies: abrupt withdrawal, gradual tapering, and continuation of the current stable dosage.
Results showed a higher adjusted cumulative incidence of opioid overdose or suicide events 11 months after baseline among participants for whom a tapered dosing strategy was utilized, compared with those who continued taking a stable dosage. The risk difference was 0.15% between taper and stable dosage and 0.33% between abrupt discontinuation and stable dosage.
“This study identified a small absolute increase in risk of harms associated with opioid tapering compared with a stable opioid dosage,” Marc LaRochelle, MD, MPH, assistant professor, Boston University, and colleagues write.
“These results do not suggest that policies of mandatory dosage tapering for individuals receiving a stable long-term opioid dosage without evidence of opioid misuse will reduce short-term harm via suicide and overdose,” they add.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Benefits vs. harms
The investigators note that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in its 2016 Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain, “recommended tapering opioid dosages if benefits no longer outweigh harms.”
In response, “some health systems and U.S. states enacted stringent dose limits that were applied with few exceptions, regardless of individual patients’ risk of harms,” they write. By contrast, there have been “increasing reports of patients experiencing adverse effects from forced opioid tapers.”
Previous studies that identified harms associated with opioid tapering and discontinuation had several limitations, including a focus on discontinuation, which is “likely more destabilizing than gradual tapering,” the researchers write. There is also “a high potential for confounding” in these studies, they add.
The investigators sought to fill the research gap by drawing on 8-year data (Jan. 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2018) from a large database that includes adjudicated pharmacy, outpatient, and inpatient medical claims for individuals with commercial or Medicare Advantage insurance encompassing all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico.
Notably, individuals who had received a diagnosis of substance use, abuse, or dependence or for whom there were indicators consistent with OUD were excluded.
The researchers compared the three treatment strategies during a 4-month treatment strategy assignment period (“grace period”) after baseline. Tapering was defined as “2 consecutive months with a mean MME [morphine milligram equivalent] reduction of 15% or more compared with the baseline month.”
All estimates were adjusted for potential confounders, including demographic and treatment characteristics, baseline year, region, insurance plan type, comorbid psychiatric and medical conditions, and the prescribing of other psychiatric medications, such as benzodiazepines, gabapentin, or pregabalin.
Patient-centered approaches
The final cohort that met inclusion criteria consisted of 199,836 individuals (45.1% men; mean age, 56.9 years). Of the total group, 57.6% were aged 45-64 years. There were 415,123 qualifying long-term opioid therapy episodes.
The largest percentage of the cohort (41.2%) were receiving a baseline mean MME of 50-89 mg/day, while 34% were receiving 90-199 mg/day and 23.5% were receiving at least 200 mg/day.
During the 6-month eligibility assessment period, 34.8% of the cohort were receiving benzodiazepine prescriptions, 18% had been diagnosed with comorbid anxiety, and 19.7% had been diagnosed with comorbid depression.
After the treatment assignment period, most treatment episodes (87.1%) were considered stable, 11.1% were considered a taper, and 1.8% were considered abrupt discontinuation.
Eleven months after baseline, the adjusted cumulative incidence of opioid overdose or suicide events was lowest for those who continued to receive a stable dose.

The risk differences between taper vs. stable dosage were 0.15% (95% confidence interval, 0.03%-0.26%), and the risk differences between abrupt discontinuation and stable dose were 0.33% (95% CI, −0.03%-0.74%). The risk ratios associated with taper vs. stable dosage and abrupt discontinuation vs. stable dosage were 1.15 (95% CI, 1.04-1.27) and 1.34 (95% CI, 0.97-1.79), respectively.
The adjusted cumulative incidence curves for overdose or suicide diverged at month 4 when comparing stable dosage and taper, with a higher incidence associated with the taper vs. stable dosage treatment strategies thereafter. However, when the researchers compared stable dosage with abrupt discontinuation, the event rates were similar.
A per protocol analysis, in which the researchers censored episodes involving lack of adherence to assigned treatment, yielded results similar to those of the main analysis.
“Policies establishing dosage thresholds or mandating tapers for all patients receiving long-term opioid therapy are not supported by existing data in terms of anticipated benefits even if, as we found, the rate of adverse outcomes is small,” the investigators write.
Instead, they encourage health care systems and clinicians to “continue to develop and implement patient-centered approaches to pain management for patients with established long-term opioid therapy.”
Protracted withdrawal?
Commenting on the study, A. Benjamin Srivastava, MD, assistant professor of clinical psychiatry, division on substance use disorders, Columbia University Medical Center, New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York, called the study “an important contribution to the literature” that “sheds further light on the risks associated with tapering.”
Dr. Srivastava, who was not involved with the research, noted that previous studies showing an increased prevalence of adverse events with tapering included participants with OUD or signs of opioid misuse, “potentially confounding findings.”
By contrast, the current study investigators specifically excluded patients with OUD/opioid misuse but still found a “slight increase in risk for opioid overdose and suicide, even when excluding for potential confounders,” he said.
Although causal implications require further investigation, “a source of these adverse outcomes may be unmanaged withdrawal that may be protracted,” Dr. Srivastava noted.
While abrupt discontinuation “may result in significant acute withdrawal symptoms, these should subside by 1-2 weeks at most,” he said.
Lowering the dose without discontinuation may lead to patients’ entering into “a dyshomeostatic state characterized by anxiety and dysphoria ... that may not be recognized by the prescribing clinician,” he added.
The brain “is still being primed by opioids [and] ‘wanting’ a higher dose. Thus, particular attention to withdrawal symptoms, both physical and psychiatric, is prudent when choosing to taper opioids vs. maintaining or discontinuing,” Dr. Srivastava said.
The study was funded by a grant from the CDC and a grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse to one of the investigators. Dr. LaRochelle received grants from the CDC and NIDA during the conduct of the study and has received consulting fees for research paid to his institution from OptumLabs outside the submitted work. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Srivastava reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators analyzed data for almost 200,000 patients who did not have signs of opioid use disorder (OUD) and were receiving opioid treatment. The investigators compared three dosing strategies: abrupt withdrawal, gradual tapering, and continuation of the current stable dosage.
Results showed a higher adjusted cumulative incidence of opioid overdose or suicide events 11 months after baseline among participants for whom a tapered dosing strategy was utilized, compared with those who continued taking a stable dosage. The risk difference was 0.15% between taper and stable dosage and 0.33% between abrupt discontinuation and stable dosage.
“This study identified a small absolute increase in risk of harms associated with opioid tapering compared with a stable opioid dosage,” Marc LaRochelle, MD, MPH, assistant professor, Boston University, and colleagues write.
“These results do not suggest that policies of mandatory dosage tapering for individuals receiving a stable long-term opioid dosage without evidence of opioid misuse will reduce short-term harm via suicide and overdose,” they add.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Benefits vs. harms
The investigators note that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in its 2016 Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain, “recommended tapering opioid dosages if benefits no longer outweigh harms.”
In response, “some health systems and U.S. states enacted stringent dose limits that were applied with few exceptions, regardless of individual patients’ risk of harms,” they write. By contrast, there have been “increasing reports of patients experiencing adverse effects from forced opioid tapers.”
Previous studies that identified harms associated with opioid tapering and discontinuation had several limitations, including a focus on discontinuation, which is “likely more destabilizing than gradual tapering,” the researchers write. There is also “a high potential for confounding” in these studies, they add.
The investigators sought to fill the research gap by drawing on 8-year data (Jan. 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2018) from a large database that includes adjudicated pharmacy, outpatient, and inpatient medical claims for individuals with commercial or Medicare Advantage insurance encompassing all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico.
Notably, individuals who had received a diagnosis of substance use, abuse, or dependence or for whom there were indicators consistent with OUD were excluded.
The researchers compared the three treatment strategies during a 4-month treatment strategy assignment period (“grace period”) after baseline. Tapering was defined as “2 consecutive months with a mean MME [morphine milligram equivalent] reduction of 15% or more compared with the baseline month.”
All estimates were adjusted for potential confounders, including demographic and treatment characteristics, baseline year, region, insurance plan type, comorbid psychiatric and medical conditions, and the prescribing of other psychiatric medications, such as benzodiazepines, gabapentin, or pregabalin.
Patient-centered approaches
The final cohort that met inclusion criteria consisted of 199,836 individuals (45.1% men; mean age, 56.9 years). Of the total group, 57.6% were aged 45-64 years. There were 415,123 qualifying long-term opioid therapy episodes.
The largest percentage of the cohort (41.2%) were receiving a baseline mean MME of 50-89 mg/day, while 34% were receiving 90-199 mg/day and 23.5% were receiving at least 200 mg/day.
During the 6-month eligibility assessment period, 34.8% of the cohort were receiving benzodiazepine prescriptions, 18% had been diagnosed with comorbid anxiety, and 19.7% had been diagnosed with comorbid depression.
After the treatment assignment period, most treatment episodes (87.1%) were considered stable, 11.1% were considered a taper, and 1.8% were considered abrupt discontinuation.
Eleven months after baseline, the adjusted cumulative incidence of opioid overdose or suicide events was lowest for those who continued to receive a stable dose.

The risk differences between taper vs. stable dosage were 0.15% (95% confidence interval, 0.03%-0.26%), and the risk differences between abrupt discontinuation and stable dose were 0.33% (95% CI, −0.03%-0.74%). The risk ratios associated with taper vs. stable dosage and abrupt discontinuation vs. stable dosage were 1.15 (95% CI, 1.04-1.27) and 1.34 (95% CI, 0.97-1.79), respectively.
The adjusted cumulative incidence curves for overdose or suicide diverged at month 4 when comparing stable dosage and taper, with a higher incidence associated with the taper vs. stable dosage treatment strategies thereafter. However, when the researchers compared stable dosage with abrupt discontinuation, the event rates were similar.
A per protocol analysis, in which the researchers censored episodes involving lack of adherence to assigned treatment, yielded results similar to those of the main analysis.
“Policies establishing dosage thresholds or mandating tapers for all patients receiving long-term opioid therapy are not supported by existing data in terms of anticipated benefits even if, as we found, the rate of adverse outcomes is small,” the investigators write.
Instead, they encourage health care systems and clinicians to “continue to develop and implement patient-centered approaches to pain management for patients with established long-term opioid therapy.”
Protracted withdrawal?
Commenting on the study, A. Benjamin Srivastava, MD, assistant professor of clinical psychiatry, division on substance use disorders, Columbia University Medical Center, New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York, called the study “an important contribution to the literature” that “sheds further light on the risks associated with tapering.”
Dr. Srivastava, who was not involved with the research, noted that previous studies showing an increased prevalence of adverse events with tapering included participants with OUD or signs of opioid misuse, “potentially confounding findings.”
By contrast, the current study investigators specifically excluded patients with OUD/opioid misuse but still found a “slight increase in risk for opioid overdose and suicide, even when excluding for potential confounders,” he said.
Although causal implications require further investigation, “a source of these adverse outcomes may be unmanaged withdrawal that may be protracted,” Dr. Srivastava noted.
While abrupt discontinuation “may result in significant acute withdrawal symptoms, these should subside by 1-2 weeks at most,” he said.
Lowering the dose without discontinuation may lead to patients’ entering into “a dyshomeostatic state characterized by anxiety and dysphoria ... that may not be recognized by the prescribing clinician,” he added.
The brain “is still being primed by opioids [and] ‘wanting’ a higher dose. Thus, particular attention to withdrawal symptoms, both physical and psychiatric, is prudent when choosing to taper opioids vs. maintaining or discontinuing,” Dr. Srivastava said.
The study was funded by a grant from the CDC and a grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse to one of the investigators. Dr. LaRochelle received grants from the CDC and NIDA during the conduct of the study and has received consulting fees for research paid to his institution from OptumLabs outside the submitted work. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Srivastava reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Infographic: Is physician behavior on social media really so bad?
The medical profession is held to a high standard of personal conduct, so physicians keep a sharp eye out for how fellow doctors behave. That goes for social media as well as in-person conduct.
(and it’s not as egregious as you might think). If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out the Medscape Physicians Behaving Badly Report 2022.
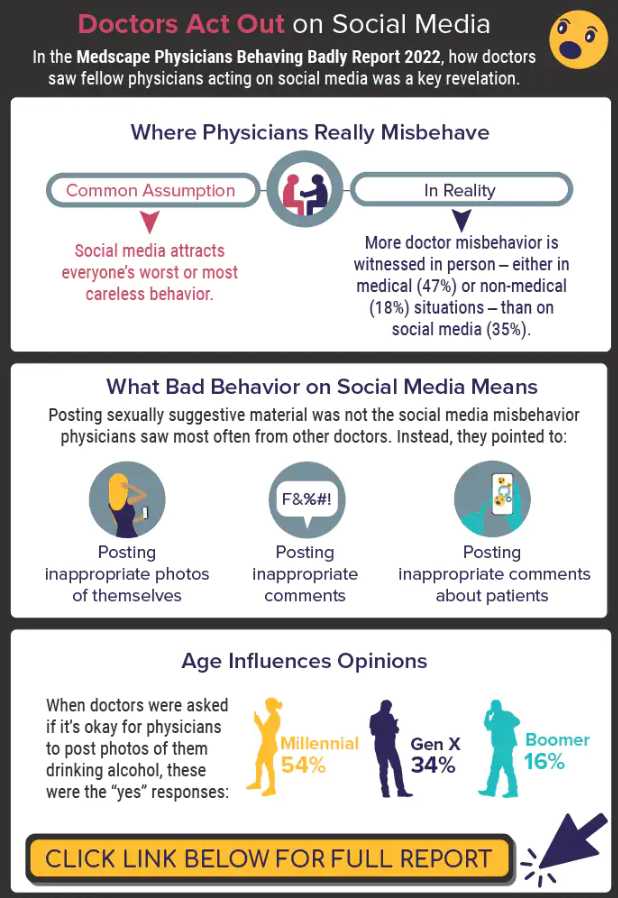
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The medical profession is held to a high standard of personal conduct, so physicians keep a sharp eye out for how fellow doctors behave. That goes for social media as well as in-person conduct.
(and it’s not as egregious as you might think). If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out the Medscape Physicians Behaving Badly Report 2022.

A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The medical profession is held to a high standard of personal conduct, so physicians keep a sharp eye out for how fellow doctors behave. That goes for social media as well as in-person conduct.
(and it’s not as egregious as you might think). If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out the Medscape Physicians Behaving Badly Report 2022.

A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.










