User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
A doctor saves a drowning family in a dangerous river
Is There a Doctor in the House? is a new series telling these stories.
I live on the Maumee River in Ohio, about 50 yards from the water. I had an early quit time and came home to meet my wife for lunch. Afterward, I went up to my barn across the main road to tinker around. It was a nice day out, so my wife had opened some windows. Suddenly, she heard screaming from the river. It did not sound like fun.
She ran down to the river’s edge and saw a dad and three boys struggling in the water. She phoned me screaming: “They’re drowning! They’re drowning!” I jumped in my truck and drove up our driveway through the yard right down to the river.
My wife was on the phone with 911 at that point, and I could see them about 75-100 yards out. The dad had two of the boys clinging around his neck. They were going under the water and coming up and going under again. The other boy was just floating nearby, face down, motionless.
I threw my shoes and scrubs off and started to walk towards the water. My wife screamed at me, “You’re not going in there!” I said, “I’m not going to stand here and watch this. It’s not going to happen.”
I’m not a kid anymore, but I was a high school swimmer, and to this day I work out all the time. I felt like I had to try something. So, I went in the water despite my wife yelling and I swam towards them.
What happens when you get in that deep water is that you panic. You can’t hear anyone because of the rapids, and your instinct is to swim back towards where you went in, which is against the current. Unless you’re a very strong swimmer, you’re just wasting your time, swimming in place.
But these guys weren’t trying to go anywhere. Dad was just trying to stay up and keep the boys alive. He was in about 10 feet of water. What they didn’t see or just didn’t know: About 20 yards upstream from that deep water is a little island.
When I got to them, I yelled at the dad to move towards the island, “Go backwards! Go back!” I flipped the boy over who wasn’t moving. He was the oldest of the three, around 10 or 11 years old. When I turned him over, he was blue and wasn’t breathing. I put my fingers on his neck and didn’t feel a pulse.
So, I’m treading water, holding him. I put an arm behind his back and started doing chest compressions on him. I probably did a dozen to 15 compressions – nothing. I thought, I’ve got to get some air in this kid. So, I gave him two deep breaths and then started doing compressions again. I know ACLS and CPR training would say we don’t do that anymore. But I couldn’t just sit there and give up. Shortly after that, he coughed out a large amount of water and started breathing.
The dad and the other two boys had made it to the island. So, I started moving towards it with the boy. It was a few minutes before he regained consciousness. Of course, he was unaware of what had happened. He started to scream, because here’s this strange man holding him. But he was breathing. That’s all I cared about.
When we got to the island, I saw that my neighbor downstream had launched his canoe. He’s a retired gentleman who lives next to me, a very physically fit man. He started rolling as hard as he could towards us, against the stream. I kind of gave him a thumbs up, like, “we’re safe now. We’re standing.” We loaded the kids and the dad in the canoe and made it back against the stream to the parking lot where they went in.
All this took probably 10 or 15 minutes, and by then the paramedics were there. Life Flight had been dispatched up by my barn where there’s room to land. So, they drove up there in the ambulance. The boy I revived was flown to the hospital. The others went in the ambulance.
I know all the ED docs, so I talked to somebody later who, with permission from the family, said they were all doing fine. They were getting x-rays on the boy’s lungs. And then I heard the dad and two boys were released that night. The other boy I worked on was observed overnight and discharged the following morning.
Four or 5 days later, I heard from their pediatrician, who also had permission to share. He sent me a very nice note through Epic that he had seen the boys. Besides some mental trauma, they were all healthy and doing fine.
The family lives in the area and the kids go to school 5 miles from my house. So, the following weekend they came over. It was Father’s Day, which was kind of cool. They brought me some flowers and candy and a card the boys had drawn to thank me.
I learned that the dad had brought the boys to the fishing site. They were horsing around in knee deep water. One of the boys walked off a little way and didn’t realize there was a drop off. He went in, and of course the dad went after him, and the other two followed.
I said to the parents: “Look, things like this happen for a reason. People like your son are saved and go on in this world because they’ve got special things to do. I can’t wait to see what kind of man he becomes.”
Two or 3 months later, it was football season, and I got at a message from the dad saying their son was playing football on Saturday at the school. He wondered if I could drop by. So, I kind of snuck over and watched, but I didn’t go say hi. There’s trauma there, and I didn’t want them to have to relive that.
I’m very fortunate that I exercise every day and I know how to do CPR and swim. And thank God the boy was floating when I got to him, or I never would’ve found him. The Maumee River is known as the “muddy Maumee.” You can’t see anything under the water.
Depending on the time of year, the river can be almost dry or overflowing into the parking lot with the current rushing hard. If it had been like that, I wouldn’t have considered going in. And they wouldn’t they have been there in the first place. They’d have been a mile downstream.
I took a risk. I could have gone out there and had the dad and two other kids jump on top of me. Then we all would have been in trouble. But like I told my wife, I couldn’t stand there and watch it. I’m just not that person.
I think it was also about being a dad myself and having grandkids now. Doctor or no doctor, I felt like I was in reasonably good shape and I had to go in there to help. This dad was trying his butt off, but three little kids is too many. You can’t do that by yourself. They were not going to make it.
I go to the hospital and I save lives as part of my job, and I don’t even come home and talk about it. But this is a whole different thing. Being able to save someone’s life when put in this situation is very gratifying. It’s a tremendous feeling. There’s a reason that young man is here today, and I’ll be watching for great things from him.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Daniel Cassavar, MD, is a cardiologist with ProMedica in Perrysburg, Ohio.
Is There a Doctor in the House? is a new series telling these stories.
I live on the Maumee River in Ohio, about 50 yards from the water. I had an early quit time and came home to meet my wife for lunch. Afterward, I went up to my barn across the main road to tinker around. It was a nice day out, so my wife had opened some windows. Suddenly, she heard screaming from the river. It did not sound like fun.
She ran down to the river’s edge and saw a dad and three boys struggling in the water. She phoned me screaming: “They’re drowning! They’re drowning!” I jumped in my truck and drove up our driveway through the yard right down to the river.
My wife was on the phone with 911 at that point, and I could see them about 75-100 yards out. The dad had two of the boys clinging around his neck. They were going under the water and coming up and going under again. The other boy was just floating nearby, face down, motionless.
I threw my shoes and scrubs off and started to walk towards the water. My wife screamed at me, “You’re not going in there!” I said, “I’m not going to stand here and watch this. It’s not going to happen.”
I’m not a kid anymore, but I was a high school swimmer, and to this day I work out all the time. I felt like I had to try something. So, I went in the water despite my wife yelling and I swam towards them.
What happens when you get in that deep water is that you panic. You can’t hear anyone because of the rapids, and your instinct is to swim back towards where you went in, which is against the current. Unless you’re a very strong swimmer, you’re just wasting your time, swimming in place.
But these guys weren’t trying to go anywhere. Dad was just trying to stay up and keep the boys alive. He was in about 10 feet of water. What they didn’t see or just didn’t know: About 20 yards upstream from that deep water is a little island.
When I got to them, I yelled at the dad to move towards the island, “Go backwards! Go back!” I flipped the boy over who wasn’t moving. He was the oldest of the three, around 10 or 11 years old. When I turned him over, he was blue and wasn’t breathing. I put my fingers on his neck and didn’t feel a pulse.
So, I’m treading water, holding him. I put an arm behind his back and started doing chest compressions on him. I probably did a dozen to 15 compressions – nothing. I thought, I’ve got to get some air in this kid. So, I gave him two deep breaths and then started doing compressions again. I know ACLS and CPR training would say we don’t do that anymore. But I couldn’t just sit there and give up. Shortly after that, he coughed out a large amount of water and started breathing.
The dad and the other two boys had made it to the island. So, I started moving towards it with the boy. It was a few minutes before he regained consciousness. Of course, he was unaware of what had happened. He started to scream, because here’s this strange man holding him. But he was breathing. That’s all I cared about.
When we got to the island, I saw that my neighbor downstream had launched his canoe. He’s a retired gentleman who lives next to me, a very physically fit man. He started rolling as hard as he could towards us, against the stream. I kind of gave him a thumbs up, like, “we’re safe now. We’re standing.” We loaded the kids and the dad in the canoe and made it back against the stream to the parking lot where they went in.
All this took probably 10 or 15 minutes, and by then the paramedics were there. Life Flight had been dispatched up by my barn where there’s room to land. So, they drove up there in the ambulance. The boy I revived was flown to the hospital. The others went in the ambulance.
I know all the ED docs, so I talked to somebody later who, with permission from the family, said they were all doing fine. They were getting x-rays on the boy’s lungs. And then I heard the dad and two boys were released that night. The other boy I worked on was observed overnight and discharged the following morning.
Four or 5 days later, I heard from their pediatrician, who also had permission to share. He sent me a very nice note through Epic that he had seen the boys. Besides some mental trauma, they were all healthy and doing fine.
The family lives in the area and the kids go to school 5 miles from my house. So, the following weekend they came over. It was Father’s Day, which was kind of cool. They brought me some flowers and candy and a card the boys had drawn to thank me.
I learned that the dad had brought the boys to the fishing site. They were horsing around in knee deep water. One of the boys walked off a little way and didn’t realize there was a drop off. He went in, and of course the dad went after him, and the other two followed.
I said to the parents: “Look, things like this happen for a reason. People like your son are saved and go on in this world because they’ve got special things to do. I can’t wait to see what kind of man he becomes.”
Two or 3 months later, it was football season, and I got at a message from the dad saying their son was playing football on Saturday at the school. He wondered if I could drop by. So, I kind of snuck over and watched, but I didn’t go say hi. There’s trauma there, and I didn’t want them to have to relive that.
I’m very fortunate that I exercise every day and I know how to do CPR and swim. And thank God the boy was floating when I got to him, or I never would’ve found him. The Maumee River is known as the “muddy Maumee.” You can’t see anything under the water.
Depending on the time of year, the river can be almost dry or overflowing into the parking lot with the current rushing hard. If it had been like that, I wouldn’t have considered going in. And they wouldn’t they have been there in the first place. They’d have been a mile downstream.
I took a risk. I could have gone out there and had the dad and two other kids jump on top of me. Then we all would have been in trouble. But like I told my wife, I couldn’t stand there and watch it. I’m just not that person.
I think it was also about being a dad myself and having grandkids now. Doctor or no doctor, I felt like I was in reasonably good shape and I had to go in there to help. This dad was trying his butt off, but three little kids is too many. You can’t do that by yourself. They were not going to make it.
I go to the hospital and I save lives as part of my job, and I don’t even come home and talk about it. But this is a whole different thing. Being able to save someone’s life when put in this situation is very gratifying. It’s a tremendous feeling. There’s a reason that young man is here today, and I’ll be watching for great things from him.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Daniel Cassavar, MD, is a cardiologist with ProMedica in Perrysburg, Ohio.
Is There a Doctor in the House? is a new series telling these stories.
I live on the Maumee River in Ohio, about 50 yards from the water. I had an early quit time and came home to meet my wife for lunch. Afterward, I went up to my barn across the main road to tinker around. It was a nice day out, so my wife had opened some windows. Suddenly, she heard screaming from the river. It did not sound like fun.
She ran down to the river’s edge and saw a dad and three boys struggling in the water. She phoned me screaming: “They’re drowning! They’re drowning!” I jumped in my truck and drove up our driveway through the yard right down to the river.
My wife was on the phone with 911 at that point, and I could see them about 75-100 yards out. The dad had two of the boys clinging around his neck. They were going under the water and coming up and going under again. The other boy was just floating nearby, face down, motionless.
I threw my shoes and scrubs off and started to walk towards the water. My wife screamed at me, “You’re not going in there!” I said, “I’m not going to stand here and watch this. It’s not going to happen.”
I’m not a kid anymore, but I was a high school swimmer, and to this day I work out all the time. I felt like I had to try something. So, I went in the water despite my wife yelling and I swam towards them.
What happens when you get in that deep water is that you panic. You can’t hear anyone because of the rapids, and your instinct is to swim back towards where you went in, which is against the current. Unless you’re a very strong swimmer, you’re just wasting your time, swimming in place.
But these guys weren’t trying to go anywhere. Dad was just trying to stay up and keep the boys alive. He was in about 10 feet of water. What they didn’t see or just didn’t know: About 20 yards upstream from that deep water is a little island.
When I got to them, I yelled at the dad to move towards the island, “Go backwards! Go back!” I flipped the boy over who wasn’t moving. He was the oldest of the three, around 10 or 11 years old. When I turned him over, he was blue and wasn’t breathing. I put my fingers on his neck and didn’t feel a pulse.
So, I’m treading water, holding him. I put an arm behind his back and started doing chest compressions on him. I probably did a dozen to 15 compressions – nothing. I thought, I’ve got to get some air in this kid. So, I gave him two deep breaths and then started doing compressions again. I know ACLS and CPR training would say we don’t do that anymore. But I couldn’t just sit there and give up. Shortly after that, he coughed out a large amount of water and started breathing.
The dad and the other two boys had made it to the island. So, I started moving towards it with the boy. It was a few minutes before he regained consciousness. Of course, he was unaware of what had happened. He started to scream, because here’s this strange man holding him. But he was breathing. That’s all I cared about.
When we got to the island, I saw that my neighbor downstream had launched his canoe. He’s a retired gentleman who lives next to me, a very physically fit man. He started rolling as hard as he could towards us, against the stream. I kind of gave him a thumbs up, like, “we’re safe now. We’re standing.” We loaded the kids and the dad in the canoe and made it back against the stream to the parking lot where they went in.
All this took probably 10 or 15 minutes, and by then the paramedics were there. Life Flight had been dispatched up by my barn where there’s room to land. So, they drove up there in the ambulance. The boy I revived was flown to the hospital. The others went in the ambulance.
I know all the ED docs, so I talked to somebody later who, with permission from the family, said they were all doing fine. They were getting x-rays on the boy’s lungs. And then I heard the dad and two boys were released that night. The other boy I worked on was observed overnight and discharged the following morning.
Four or 5 days later, I heard from their pediatrician, who also had permission to share. He sent me a very nice note through Epic that he had seen the boys. Besides some mental trauma, they were all healthy and doing fine.
The family lives in the area and the kids go to school 5 miles from my house. So, the following weekend they came over. It was Father’s Day, which was kind of cool. They brought me some flowers and candy and a card the boys had drawn to thank me.
I learned that the dad had brought the boys to the fishing site. They were horsing around in knee deep water. One of the boys walked off a little way and didn’t realize there was a drop off. He went in, and of course the dad went after him, and the other two followed.
I said to the parents: “Look, things like this happen for a reason. People like your son are saved and go on in this world because they’ve got special things to do. I can’t wait to see what kind of man he becomes.”
Two or 3 months later, it was football season, and I got at a message from the dad saying their son was playing football on Saturday at the school. He wondered if I could drop by. So, I kind of snuck over and watched, but I didn’t go say hi. There’s trauma there, and I didn’t want them to have to relive that.
I’m very fortunate that I exercise every day and I know how to do CPR and swim. And thank God the boy was floating when I got to him, or I never would’ve found him. The Maumee River is known as the “muddy Maumee.” You can’t see anything under the water.
Depending on the time of year, the river can be almost dry or overflowing into the parking lot with the current rushing hard. If it had been like that, I wouldn’t have considered going in. And they wouldn’t they have been there in the first place. They’d have been a mile downstream.
I took a risk. I could have gone out there and had the dad and two other kids jump on top of me. Then we all would have been in trouble. But like I told my wife, I couldn’t stand there and watch it. I’m just not that person.
I think it was also about being a dad myself and having grandkids now. Doctor or no doctor, I felt like I was in reasonably good shape and I had to go in there to help. This dad was trying his butt off, but three little kids is too many. You can’t do that by yourself. They were not going to make it.
I go to the hospital and I save lives as part of my job, and I don’t even come home and talk about it. But this is a whole different thing. Being able to save someone’s life when put in this situation is very gratifying. It’s a tremendous feeling. There’s a reason that young man is here today, and I’ll be watching for great things from him.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Daniel Cassavar, MD, is a cardiologist with ProMedica in Perrysburg, Ohio.
Endocarditis tied to drug use on the rise, spiked during COVID
A new study provides more evidence that endocarditis associated with drug use is a significant and growing health concern, and further demonstrates that this risk has been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The rate of infective endocarditis among individuals in the United States with opioid or cocaine use disorder increased in the 11-year period 2011 to 2022, with the steepest increase logged during the COVID-19 pandemic (2021-2022), according to the study.
A diagnosis of COVID-19 more than doubled the risk for a new diagnosis of endocarditis in patients with either cocaine (hazard ratio, 2.24) or opioid use disorder (HR, 2.23).
“Our data suggests that, in addition to the major social disruption from the pandemic, including disrupted access to health care, COVID-19 infection itself is a significant risk factor for new diagnosis of endocarditis in drug using populations,” authors Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and colleagues wrote.
“Drug-using populations, particularly those who use cocaine or opioids, have some of the highest risk for endocarditis, and here we show that having a COVID-19 diagnoses further increases this risk,” they added.
The study was published online in Molecular Psychiatry.
The researchers analyzed electronic health record data collected from January 2011 to August 2022 for more than 109 million people across the United States, including more than 736,000 with an opioid use disorder and more than 379,000 with a cocaine use disorder.
In 2011, there were 4 cases of endocarditis per day for every 1 million people with opioid use disorder. By 2022, the rate had increased to 30 cases per day per 1 million people with opioid use disorder.
For people with cocaine use disorder, cases of endocarditis increased from 5 per 1 million in 2011 to 23 per 1 million in 2022.
Among individuals with cocaine or opioid use disorder, the risk of being hospitalized within 180 days following a diagnosis of endocarditis was higher in those with than without COVID-19 (67.5% vs. 58.7%; HR, 1.21).
The risk of dying within 180 days following new diagnosis of endocarditis was also higher in those with than without COVID-19 (9.2% vs. 8%; HR, 1.16).
The study also showed that Black and Hispanic individuals had a lower risk for COVID-19-associated endocarditis than non-Hispanic White individuals, which is consistent with a higher prevalence of injection drug use in non-Hispanic White populations, compared with Black or Hispanic populations, the researchers pointed out.
Dr. Volkow and colleagues said their findings highlight the need to screen drug users for endocarditis and link them to infectious disease and addiction treatment if they contract COVID-19.
“People with substance use disorder already face major impediments to proper health care due to lack of access and stigma,” Dr. Volkow said in a news release.
“Proven techniques like syringe service programs, which help people avoid infection from reused or shared injection equipment, can help prevent this often fatal and costly condition,” Dr. Volkow added.
The authors said it will also be important to determine exactly how SARS-CoV-2 viral infection exacerbates the risk for endocarditis in drug users.
Support for the study was provided by the National Institute on Aging, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative of Cleveland, and the National Cancer Institute Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study provides more evidence that endocarditis associated with drug use is a significant and growing health concern, and further demonstrates that this risk has been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The rate of infective endocarditis among individuals in the United States with opioid or cocaine use disorder increased in the 11-year period 2011 to 2022, with the steepest increase logged during the COVID-19 pandemic (2021-2022), according to the study.
A diagnosis of COVID-19 more than doubled the risk for a new diagnosis of endocarditis in patients with either cocaine (hazard ratio, 2.24) or opioid use disorder (HR, 2.23).
“Our data suggests that, in addition to the major social disruption from the pandemic, including disrupted access to health care, COVID-19 infection itself is a significant risk factor for new diagnosis of endocarditis in drug using populations,” authors Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and colleagues wrote.
“Drug-using populations, particularly those who use cocaine or opioids, have some of the highest risk for endocarditis, and here we show that having a COVID-19 diagnoses further increases this risk,” they added.
The study was published online in Molecular Psychiatry.
The researchers analyzed electronic health record data collected from January 2011 to August 2022 for more than 109 million people across the United States, including more than 736,000 with an opioid use disorder and more than 379,000 with a cocaine use disorder.
In 2011, there were 4 cases of endocarditis per day for every 1 million people with opioid use disorder. By 2022, the rate had increased to 30 cases per day per 1 million people with opioid use disorder.
For people with cocaine use disorder, cases of endocarditis increased from 5 per 1 million in 2011 to 23 per 1 million in 2022.
Among individuals with cocaine or opioid use disorder, the risk of being hospitalized within 180 days following a diagnosis of endocarditis was higher in those with than without COVID-19 (67.5% vs. 58.7%; HR, 1.21).
The risk of dying within 180 days following new diagnosis of endocarditis was also higher in those with than without COVID-19 (9.2% vs. 8%; HR, 1.16).
The study also showed that Black and Hispanic individuals had a lower risk for COVID-19-associated endocarditis than non-Hispanic White individuals, which is consistent with a higher prevalence of injection drug use in non-Hispanic White populations, compared with Black or Hispanic populations, the researchers pointed out.
Dr. Volkow and colleagues said their findings highlight the need to screen drug users for endocarditis and link them to infectious disease and addiction treatment if they contract COVID-19.
“People with substance use disorder already face major impediments to proper health care due to lack of access and stigma,” Dr. Volkow said in a news release.
“Proven techniques like syringe service programs, which help people avoid infection from reused or shared injection equipment, can help prevent this often fatal and costly condition,” Dr. Volkow added.
The authors said it will also be important to determine exactly how SARS-CoV-2 viral infection exacerbates the risk for endocarditis in drug users.
Support for the study was provided by the National Institute on Aging, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative of Cleveland, and the National Cancer Institute Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study provides more evidence that endocarditis associated with drug use is a significant and growing health concern, and further demonstrates that this risk has been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The rate of infective endocarditis among individuals in the United States with opioid or cocaine use disorder increased in the 11-year period 2011 to 2022, with the steepest increase logged during the COVID-19 pandemic (2021-2022), according to the study.
A diagnosis of COVID-19 more than doubled the risk for a new diagnosis of endocarditis in patients with either cocaine (hazard ratio, 2.24) or opioid use disorder (HR, 2.23).
“Our data suggests that, in addition to the major social disruption from the pandemic, including disrupted access to health care, COVID-19 infection itself is a significant risk factor for new diagnosis of endocarditis in drug using populations,” authors Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and colleagues wrote.
“Drug-using populations, particularly those who use cocaine or opioids, have some of the highest risk for endocarditis, and here we show that having a COVID-19 diagnoses further increases this risk,” they added.
The study was published online in Molecular Psychiatry.
The researchers analyzed electronic health record data collected from January 2011 to August 2022 for more than 109 million people across the United States, including more than 736,000 with an opioid use disorder and more than 379,000 with a cocaine use disorder.
In 2011, there were 4 cases of endocarditis per day for every 1 million people with opioid use disorder. By 2022, the rate had increased to 30 cases per day per 1 million people with opioid use disorder.
For people with cocaine use disorder, cases of endocarditis increased from 5 per 1 million in 2011 to 23 per 1 million in 2022.
Among individuals with cocaine or opioid use disorder, the risk of being hospitalized within 180 days following a diagnosis of endocarditis was higher in those with than without COVID-19 (67.5% vs. 58.7%; HR, 1.21).
The risk of dying within 180 days following new diagnosis of endocarditis was also higher in those with than without COVID-19 (9.2% vs. 8%; HR, 1.16).
The study also showed that Black and Hispanic individuals had a lower risk for COVID-19-associated endocarditis than non-Hispanic White individuals, which is consistent with a higher prevalence of injection drug use in non-Hispanic White populations, compared with Black or Hispanic populations, the researchers pointed out.
Dr. Volkow and colleagues said their findings highlight the need to screen drug users for endocarditis and link them to infectious disease and addiction treatment if they contract COVID-19.
“People with substance use disorder already face major impediments to proper health care due to lack of access and stigma,” Dr. Volkow said in a news release.
“Proven techniques like syringe service programs, which help people avoid infection from reused or shared injection equipment, can help prevent this often fatal and costly condition,” Dr. Volkow added.
The authors said it will also be important to determine exactly how SARS-CoV-2 viral infection exacerbates the risk for endocarditis in drug users.
Support for the study was provided by the National Institute on Aging, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative of Cleveland, and the National Cancer Institute Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MOLECULAR PSYCHIATRY
All the National Health Service wants for Christmas is tea and biscuits
Three cups of tea, two biscuit packs, and a Christmas study from the BMJ
Warning: The following content may contain excessive Britishness. Continue at your own risk.
It’s no secret that the world economy is in an … interesting spot right now. Belt tightening is occurring around the world despite the holiday season, and hospitals across the pond in Great Britain are no exception.
It was a simple sign that prompted the study, published in the Christmas edition of the BMJ: “Please do not take excessive quantities of these refreshments.” And if we all know one thing, you do not get between Brits and their tea and biscuits. So the researchers behind the study drafted a survey and sent it around to nearly 2,000 British health care workers and asked what they considered to be excessive consumption of work-provided hot drinks and biscuits.
In the hot drinks department (tea and coffee, though we appreciate the two people who voiced a preference for free hot whiskey, if it was available) the survey participants decreed that 3.32 drinks was the maximum before consumption became excessive. That’s pretty close to the actual number of hot drinks respondents drank daily (3.04), so it’s pretty fair to say that British health care workers do a good job of self-limiting.
It’s much the same story with biscuits: Health care workers reported that consuming 2.25 packets of free biscuits would be excessive. Notably, doctors would take more than nondoctors (2.35 vs. 2.14 – typical doctor behavior), and those who had been in their role for less than 2 years would consume nearly 3 packets a day before calling it quits.
The study did not include an official cost analysis, but calculations conducted on a biscuit wrapper (that’s not a joke, by the way) estimated that the combined cost for providing every National Health Service employee with three free drinks and two free biscuit packages a day would be about 160 million pounds a year. Now, that’s a lot of money for tea and biscuits, but, they added, it’s a meager 0.1% of the NHS annual budget. They also noted that most employees consider free hot drinks a more valuable workplace perk than free support for mental health.
In conclusion, the authors wrote, “As a target for cost-saving initiatives, limiting free refreshment consumption is really scraping the biscuit barrel (although some limits on hot whiskey availability may be necessary), and implementing, or continuing, perks that improve staff morale seems justifiable. … Healthcare employers should allow biscuits and hot drinks to be freely available to staff, and they should leave these grateful recipients to judge for themselves what constitutes reasonable consumption.”
Now there’s a Christmas sentiment we can all get behind.
We come not to bury sugar, but to improve it
When we think about sugar, healthy isn’t the first thing that comes to mind. Research also shows that artificial sweeteners, as well as processed foods in general, are bad for your body and brain. People, however, love the stuff. That’s why one of the leading brands in processed foods, Kraft Heinz, partnered with the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard to find a way to reduce consumers’ sugar consumption.
The question that Kraft Heinz presented to Wyss was this: How could it reduce the fructose in its products without losing the functionality of regular sugar.
The Wyss team’s approach seems pretty simple: Use a naturally occurring enzyme to convert sugar to fiber. The trick was to add the enzymes into the food so they could convert the sugar to fiber after being consumed. The enzymes also needed to be able to be added to existing food products without changing their existing recipes, Kraft Heinz insisted.
How does it work? The crafted enzyme is encapsulated to remain dormant in the food until exposed to an increased pH level, as is found in the GI tract between the stomach and the intestine. It reduces the amount of sugar absorbed in the bloodstream and creates a healthy prebiotic fiber, the institute explained.
This opens a whole new window for consumers. People with diabetes can enjoy their favorite cookies from time to time, while parents can feel less guilty about their children bathing their chicken nuggets in unholy amounts of ketchup.
New genes, or not new genes? That is the question
… and the police report that no capybaras were harmed in the incident. What a relief. Now Action News 8 brings you Carol Espinosa’s exclusive interview with legendary scientist and zombie, Charles Darwin.
Carol: Thanks, Daryl. Tell us, Prof. Darwin, what have you been up to lately?
Prof. Darwin: Please, Carol, call me Chuck. As always, I’ve got my hands full with the whole evolution thing. The big news right now is a study published in Cell Reports that offers evidence of the continuing evolution of humans. Can I eat your brain now?
Carol: No, Chuck, you may not. So people are still evolving? It sure seems like we’ve reverted to survival of the dumbest.
Chuck Darwin: Good one, Carol, but evolution hasn’t stopped. The investigators used a previously published dataset of functionally relevant new genes to create an ancestral tree comparing humans with other vertebrate species. By tracking the genes across evolution, they found 155 from regions of unique DNA that arose from scratch and not from duplication events in the existing genome. That’s a big deal.
Carol: Anything made from scratch is always better. Everyone knows that. What else can you tell us, Chuck?
Chuck Darwin: So these 155 genes didn’t exist when humans separated from chimpanzees nearly 7 million years ago. Turns out that 44 of them are associated with growth defects in cell cultures and three “have disease-associated DNA markers that point to connections with ailments such as muscular dystrophy, retinitis pigmentosa, and Alazami syndrome.” At least that’s what the investigators said in a written statement. I must say, Carol, that your brain is looking particularly delicious tonight.
Carol: Ironic. For years I’ve been hoping a man would appreciate me for my brain, and now I get this. Back to you, Daryl.
Three cups of tea, two biscuit packs, and a Christmas study from the BMJ
Warning: The following content may contain excessive Britishness. Continue at your own risk.
It’s no secret that the world economy is in an … interesting spot right now. Belt tightening is occurring around the world despite the holiday season, and hospitals across the pond in Great Britain are no exception.
It was a simple sign that prompted the study, published in the Christmas edition of the BMJ: “Please do not take excessive quantities of these refreshments.” And if we all know one thing, you do not get between Brits and their tea and biscuits. So the researchers behind the study drafted a survey and sent it around to nearly 2,000 British health care workers and asked what they considered to be excessive consumption of work-provided hot drinks and biscuits.
In the hot drinks department (tea and coffee, though we appreciate the two people who voiced a preference for free hot whiskey, if it was available) the survey participants decreed that 3.32 drinks was the maximum before consumption became excessive. That’s pretty close to the actual number of hot drinks respondents drank daily (3.04), so it’s pretty fair to say that British health care workers do a good job of self-limiting.
It’s much the same story with biscuits: Health care workers reported that consuming 2.25 packets of free biscuits would be excessive. Notably, doctors would take more than nondoctors (2.35 vs. 2.14 – typical doctor behavior), and those who had been in their role for less than 2 years would consume nearly 3 packets a day before calling it quits.
The study did not include an official cost analysis, but calculations conducted on a biscuit wrapper (that’s not a joke, by the way) estimated that the combined cost for providing every National Health Service employee with three free drinks and two free biscuit packages a day would be about 160 million pounds a year. Now, that’s a lot of money for tea and biscuits, but, they added, it’s a meager 0.1% of the NHS annual budget. They also noted that most employees consider free hot drinks a more valuable workplace perk than free support for mental health.
In conclusion, the authors wrote, “As a target for cost-saving initiatives, limiting free refreshment consumption is really scraping the biscuit barrel (although some limits on hot whiskey availability may be necessary), and implementing, or continuing, perks that improve staff morale seems justifiable. … Healthcare employers should allow biscuits and hot drinks to be freely available to staff, and they should leave these grateful recipients to judge for themselves what constitutes reasonable consumption.”
Now there’s a Christmas sentiment we can all get behind.
We come not to bury sugar, but to improve it
When we think about sugar, healthy isn’t the first thing that comes to mind. Research also shows that artificial sweeteners, as well as processed foods in general, are bad for your body and brain. People, however, love the stuff. That’s why one of the leading brands in processed foods, Kraft Heinz, partnered with the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard to find a way to reduce consumers’ sugar consumption.
The question that Kraft Heinz presented to Wyss was this: How could it reduce the fructose in its products without losing the functionality of regular sugar.
The Wyss team’s approach seems pretty simple: Use a naturally occurring enzyme to convert sugar to fiber. The trick was to add the enzymes into the food so they could convert the sugar to fiber after being consumed. The enzymes also needed to be able to be added to existing food products without changing their existing recipes, Kraft Heinz insisted.
How does it work? The crafted enzyme is encapsulated to remain dormant in the food until exposed to an increased pH level, as is found in the GI tract between the stomach and the intestine. It reduces the amount of sugar absorbed in the bloodstream and creates a healthy prebiotic fiber, the institute explained.
This opens a whole new window for consumers. People with diabetes can enjoy their favorite cookies from time to time, while parents can feel less guilty about their children bathing their chicken nuggets in unholy amounts of ketchup.
New genes, or not new genes? That is the question
… and the police report that no capybaras were harmed in the incident. What a relief. Now Action News 8 brings you Carol Espinosa’s exclusive interview with legendary scientist and zombie, Charles Darwin.
Carol: Thanks, Daryl. Tell us, Prof. Darwin, what have you been up to lately?
Prof. Darwin: Please, Carol, call me Chuck. As always, I’ve got my hands full with the whole evolution thing. The big news right now is a study published in Cell Reports that offers evidence of the continuing evolution of humans. Can I eat your brain now?
Carol: No, Chuck, you may not. So people are still evolving? It sure seems like we’ve reverted to survival of the dumbest.
Chuck Darwin: Good one, Carol, but evolution hasn’t stopped. The investigators used a previously published dataset of functionally relevant new genes to create an ancestral tree comparing humans with other vertebrate species. By tracking the genes across evolution, they found 155 from regions of unique DNA that arose from scratch and not from duplication events in the existing genome. That’s a big deal.
Carol: Anything made from scratch is always better. Everyone knows that. What else can you tell us, Chuck?
Chuck Darwin: So these 155 genes didn’t exist when humans separated from chimpanzees nearly 7 million years ago. Turns out that 44 of them are associated with growth defects in cell cultures and three “have disease-associated DNA markers that point to connections with ailments such as muscular dystrophy, retinitis pigmentosa, and Alazami syndrome.” At least that’s what the investigators said in a written statement. I must say, Carol, that your brain is looking particularly delicious tonight.
Carol: Ironic. For years I’ve been hoping a man would appreciate me for my brain, and now I get this. Back to you, Daryl.
Three cups of tea, two biscuit packs, and a Christmas study from the BMJ
Warning: The following content may contain excessive Britishness. Continue at your own risk.
It’s no secret that the world economy is in an … interesting spot right now. Belt tightening is occurring around the world despite the holiday season, and hospitals across the pond in Great Britain are no exception.
It was a simple sign that prompted the study, published in the Christmas edition of the BMJ: “Please do not take excessive quantities of these refreshments.” And if we all know one thing, you do not get between Brits and their tea and biscuits. So the researchers behind the study drafted a survey and sent it around to nearly 2,000 British health care workers and asked what they considered to be excessive consumption of work-provided hot drinks and biscuits.
In the hot drinks department (tea and coffee, though we appreciate the two people who voiced a preference for free hot whiskey, if it was available) the survey participants decreed that 3.32 drinks was the maximum before consumption became excessive. That’s pretty close to the actual number of hot drinks respondents drank daily (3.04), so it’s pretty fair to say that British health care workers do a good job of self-limiting.
It’s much the same story with biscuits: Health care workers reported that consuming 2.25 packets of free biscuits would be excessive. Notably, doctors would take more than nondoctors (2.35 vs. 2.14 – typical doctor behavior), and those who had been in their role for less than 2 years would consume nearly 3 packets a day before calling it quits.
The study did not include an official cost analysis, but calculations conducted on a biscuit wrapper (that’s not a joke, by the way) estimated that the combined cost for providing every National Health Service employee with three free drinks and two free biscuit packages a day would be about 160 million pounds a year. Now, that’s a lot of money for tea and biscuits, but, they added, it’s a meager 0.1% of the NHS annual budget. They also noted that most employees consider free hot drinks a more valuable workplace perk than free support for mental health.
In conclusion, the authors wrote, “As a target for cost-saving initiatives, limiting free refreshment consumption is really scraping the biscuit barrel (although some limits on hot whiskey availability may be necessary), and implementing, or continuing, perks that improve staff morale seems justifiable. … Healthcare employers should allow biscuits and hot drinks to be freely available to staff, and they should leave these grateful recipients to judge for themselves what constitutes reasonable consumption.”
Now there’s a Christmas sentiment we can all get behind.
We come not to bury sugar, but to improve it
When we think about sugar, healthy isn’t the first thing that comes to mind. Research also shows that artificial sweeteners, as well as processed foods in general, are bad for your body and brain. People, however, love the stuff. That’s why one of the leading brands in processed foods, Kraft Heinz, partnered with the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard to find a way to reduce consumers’ sugar consumption.
The question that Kraft Heinz presented to Wyss was this: How could it reduce the fructose in its products without losing the functionality of regular sugar.
The Wyss team’s approach seems pretty simple: Use a naturally occurring enzyme to convert sugar to fiber. The trick was to add the enzymes into the food so they could convert the sugar to fiber after being consumed. The enzymes also needed to be able to be added to existing food products without changing their existing recipes, Kraft Heinz insisted.
How does it work? The crafted enzyme is encapsulated to remain dormant in the food until exposed to an increased pH level, as is found in the GI tract between the stomach and the intestine. It reduces the amount of sugar absorbed in the bloodstream and creates a healthy prebiotic fiber, the institute explained.
This opens a whole new window for consumers. People with diabetes can enjoy their favorite cookies from time to time, while parents can feel less guilty about their children bathing their chicken nuggets in unholy amounts of ketchup.
New genes, or not new genes? That is the question
… and the police report that no capybaras were harmed in the incident. What a relief. Now Action News 8 brings you Carol Espinosa’s exclusive interview with legendary scientist and zombie, Charles Darwin.
Carol: Thanks, Daryl. Tell us, Prof. Darwin, what have you been up to lately?
Prof. Darwin: Please, Carol, call me Chuck. As always, I’ve got my hands full with the whole evolution thing. The big news right now is a study published in Cell Reports that offers evidence of the continuing evolution of humans. Can I eat your brain now?
Carol: No, Chuck, you may not. So people are still evolving? It sure seems like we’ve reverted to survival of the dumbest.
Chuck Darwin: Good one, Carol, but evolution hasn’t stopped. The investigators used a previously published dataset of functionally relevant new genes to create an ancestral tree comparing humans with other vertebrate species. By tracking the genes across evolution, they found 155 from regions of unique DNA that arose from scratch and not from duplication events in the existing genome. That’s a big deal.
Carol: Anything made from scratch is always better. Everyone knows that. What else can you tell us, Chuck?
Chuck Darwin: So these 155 genes didn’t exist when humans separated from chimpanzees nearly 7 million years ago. Turns out that 44 of them are associated with growth defects in cell cultures and three “have disease-associated DNA markers that point to connections with ailments such as muscular dystrophy, retinitis pigmentosa, and Alazami syndrome.” At least that’s what the investigators said in a written statement. I must say, Carol, that your brain is looking particularly delicious tonight.
Carol: Ironic. For years I’ve been hoping a man would appreciate me for my brain, and now I get this. Back to you, Daryl.
GLP-1 agonists for weight loss: What you need to know
Obesity and overweight, with or without metabolic dysregulation, pose vexing problems for many patients with mood, anxiety, or psychotic disorders. More than one-half of individuals with severe mental illnesses are obese or overweight,1 resulting from multiple factors that may include psychiatric symptoms (eg, anergia and hyperphagia), poor dietary choices, sedentary lifestyle, underlying inflammatory processes, medical comorbidities, and iatrogenic consequences of certain medications. Unfortunately, numerous psychotropic medications can increase weight and appetite due to a variety of mechanisms, including antihistaminergic effects, direct appetite-stimulating effects, and proclivities to cause insulin resistance. While individual agents can vary, a recent review identified an overall 2-fold increased risk for rapid, significant weight gain during treatment with antipsychotics as a class.2 In addition to lifestyle modifications (diet and exercise), many pharmacologic strategies have been proposed to counter iatrogenic weight gain, including appetite suppressants (eg, pro-dopaminergic agents such as phentermine, stimulants, and amantadine), pro-anorectant anticonvulsants (eg, topiramate or zonisamide), opioid receptor antagonists (eg, olanzapine/samidorphan or naltrexone) and oral hypoglycemics such as metformin. However, the magnitude of impact for most of these agents to reverse iatrogenic weight gain tends to be modest, particularly once significant weight gain (ie, ≥7% of initial body weight) has already occurred.
Pharmacologic strategies to modulate or enhance the effects of insulin hold particular importance for combatting psychotropic-associated weight gain. Insulin transports glucose from the intravascular space to end organs for fuel consumption; to varying degrees, second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) and some other psychotropic medications can cause insulin resistance. This in turn leads to excessive storage of underutilized glucose in the liver (glycogenesis), the potential for developing fatty liver (ie, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis), and conversion of excess carbohydrates to fatty acids and triglycerides, with subsequent storage in adipose tissue. Medications that can enhance the activity of insulin (so-called incretin mimetics) can help to overcome insulin resistance caused by SGAs (and potentially by other psychotropic medications) and essentially lead to weight loss through enhanced “fuel efficiency.”
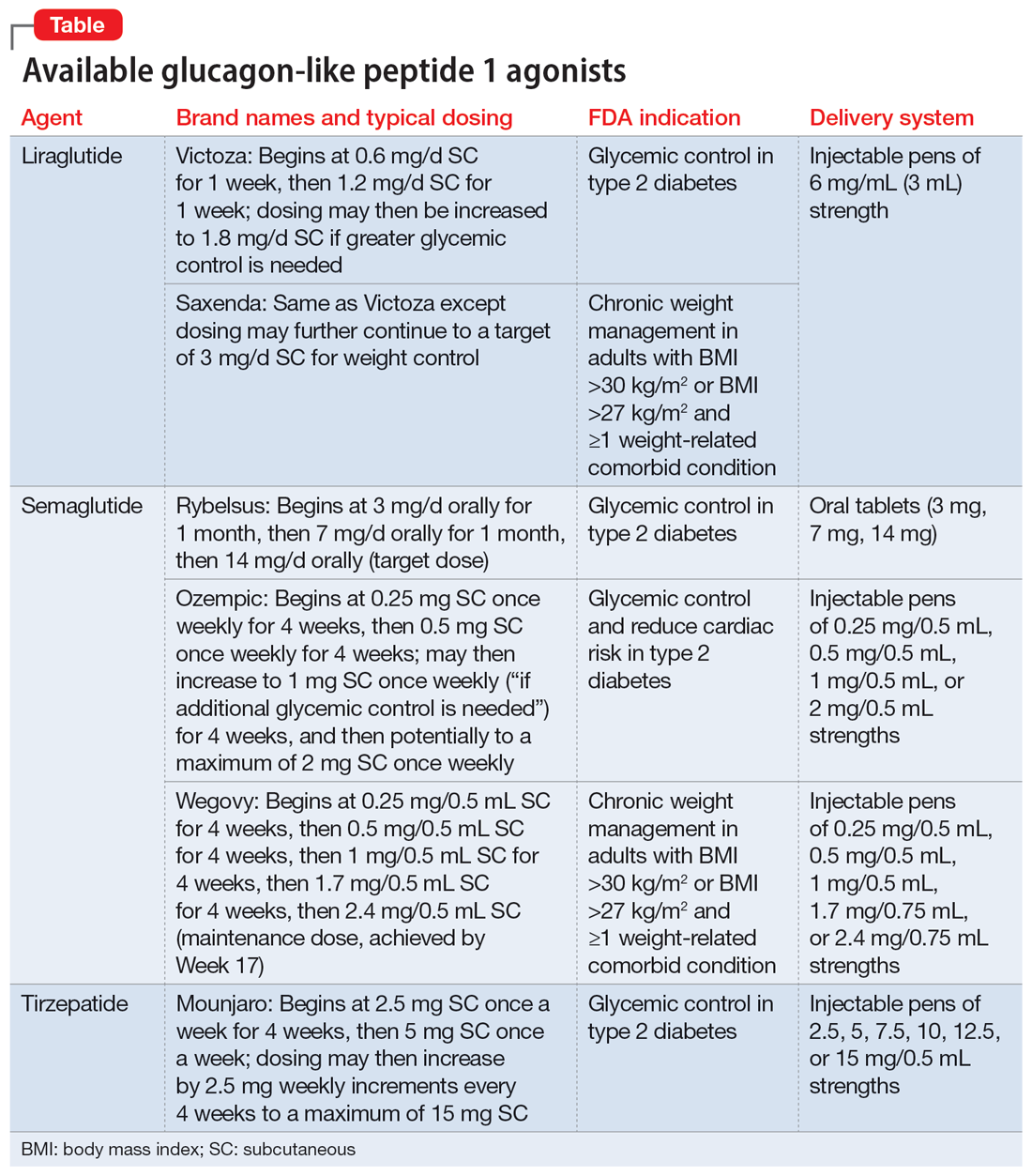
Metformin, typically dosed up to 1,000 mg twice daily with meals, has increasingly become recognized as a first-line strategy to attenuate weight gain and glycemic dysregulation from SGAs via its ability to reduce insulin resistance. Yet meta-analyses have shown that although results are significantly better than placebo, overall long-term weight loss from metformin alone tends to be rather modest (<4 kg) and associated with a reduction in body mass index (BMI) of only approximately 1 point.3 Psychiatrists (and other clinicians who prescribe psychotropic medications that can cause weight gain or metabolic dysregulation) therefore need to become familiar with alternative or adjunctive weight loss options. The use of a relatively new class of incretin mimetics called glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists (Table) has been associated with profound and often dramatic weight loss and improvement of glycemic parameters in patients with obesity and glycemic dysregulation.
What are GLP-1 agonists?
GLP-1 is a hormone secreted by L cells in the intestinal mucosa in response to food. GLP-1 agonists reduce blood sugar by increasing insulin secretion, decreasing glucagon release (thus downregulating further increases in blood sugar), and reducing insulin resistance. GLP-1 agonists also reduce appetite by directly stimulating the satiety center and slowing gastric emptying and GI motility. In addition to GLP-1 agonism, some medications in this family (notably tirzepatide) also agonize a second hormone, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, which can further induce insulin secretion as well as decrease stomach acid secretion, potentially delivering an even more substantial reduction in appetite and weight.
Routes of administration and FDA indications
Due to limited bioavailability, most GLP-1 agonists require subcutaneous (SC) injections (the sole exception is the Rybelsus brand of semaglutide, which comes in a daily pill form). Most are FDA-approved not specifically for weight loss but for patients with type 2 diabetes (defined as a hemoglobin A1C ≥6.5% or a fasting blood glucose level ≥126 mg/dL). Weight loss represents a secondary outcome for GLP-1 agonists FDA-approved for glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. The 2 current exceptions to this classification are the Wegovy brand of semaglutide (ie, dosing of 2.4 mg) and the Saxenda brand of liraglutide, both of which carry FDA indications for chronic weight management alone (when paired with dietary and lifestyle modification) in individuals who are obese (BMI >30 kg/m2) regardless of the presence or absence of diabetes, or for persons who are overweight (BMI >27 kg/m2) and have ≥1 weight-related comorbid condition (eg, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, or dyslipidemia). Although patients at risk for diabetes (ie, prediabetes, defined as a hemoglobin A1C 5.7% to 6.4% or a fasting blood glucose level 100 to 125 mg/dL) were included in FDA registration trials of Saxenda or Wegovy, prediabetes is not an FDA indication for any GLP-1 agonist.
Data in weight loss
Most of the existing empirical data on weight loss with GLP-1 agonists come from studies of individuals who are overweight or obese, with or without type 2 diabetes, rather than from studies using these agents to counteract iatrogenic weight gain. In a retrospective cohort study of patients with type 2 diabetes, coadministration with serotonergic antidepressants (eg, citalopram/escitalopram) was associated with attenuation of the weight loss effects of GLP-1 agonists.4
Liraglutide currently is the sole GLP-1 agonist studied for treating SGA-associated weight gain. A 16-week randomized trial compared once-daily SC injected liraglutide vs placebo in patients with schizophrenia who incurred weight gain and prediabetes after taking olanzapine or clozapine.5 Significantly more patients taking liraglutide than placebo developed normal glucose tolerance (64% vs 16%), and body weight decreased by a mean of 5.3 kg.
Continue to: In studies of semaglutide...
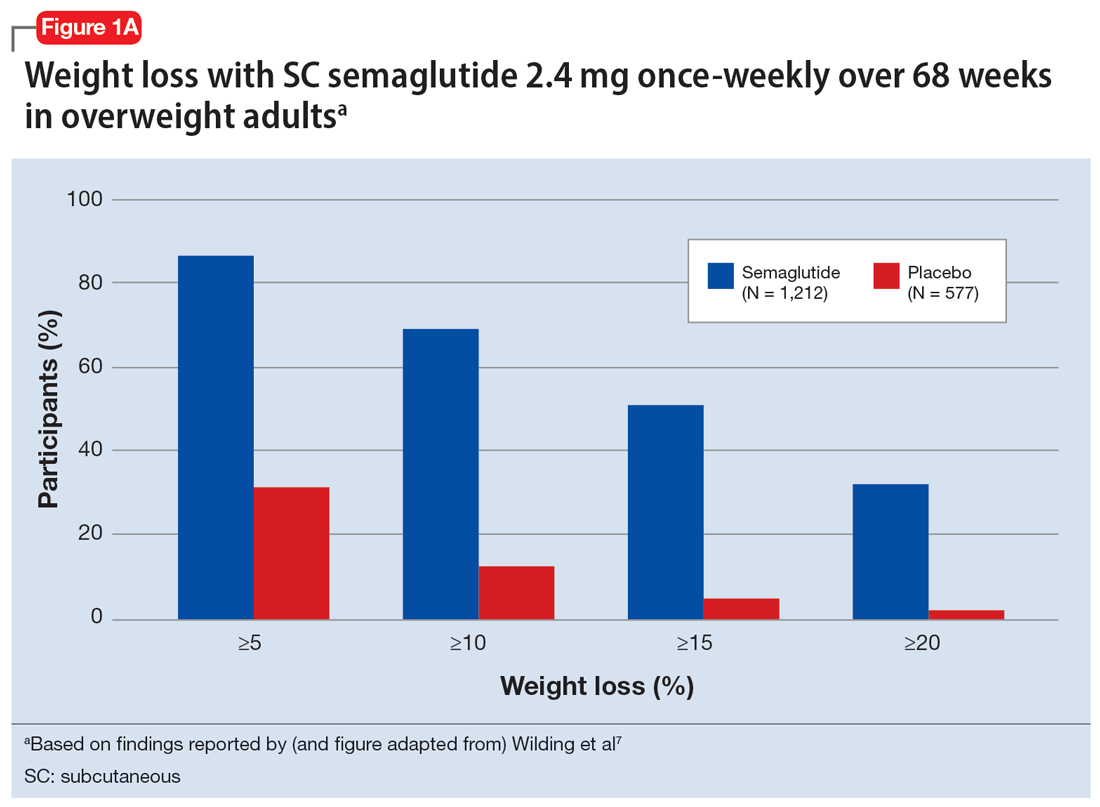
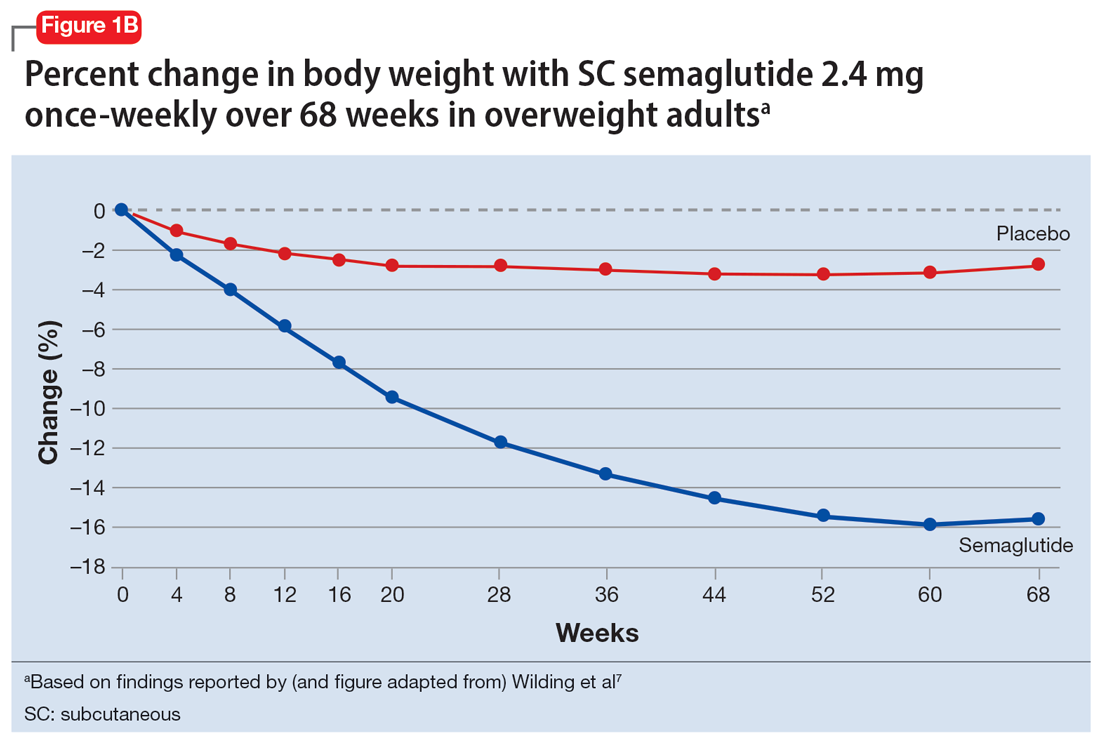
In studies of semaglutide for overweight/obese patients with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes, clinical trials of oral semaglutide (Rybelsus) found a mean weight loss over 26 weeks of -1.0 kg with dosing at 7 mg/d and -2.6 kg with dosing at 14 mg/d.6 A 68-week placebo-controlled trial of semaglutide (dosed at 2.4 mg SC weekly) for overweight/obese adults who did not have diabetes yielded a -15.3 kg weight loss (vs -2.6 kg with placebo); one-half of those who received semaglutide lost 15% of their initial body weight (Figure 1A and Figure 1B).7 Similar findings with semaglutide 2.4 mg SC weekly (Wegovy) were observed in overweight/obese adolescents, with 73% of participants losing ≥5% of their baseline weight.8 A comparative randomized trial in patients with type 2 diabetes also found modestly but significantly greater weight loss with oral semaglutide than with SC liraglutide.9
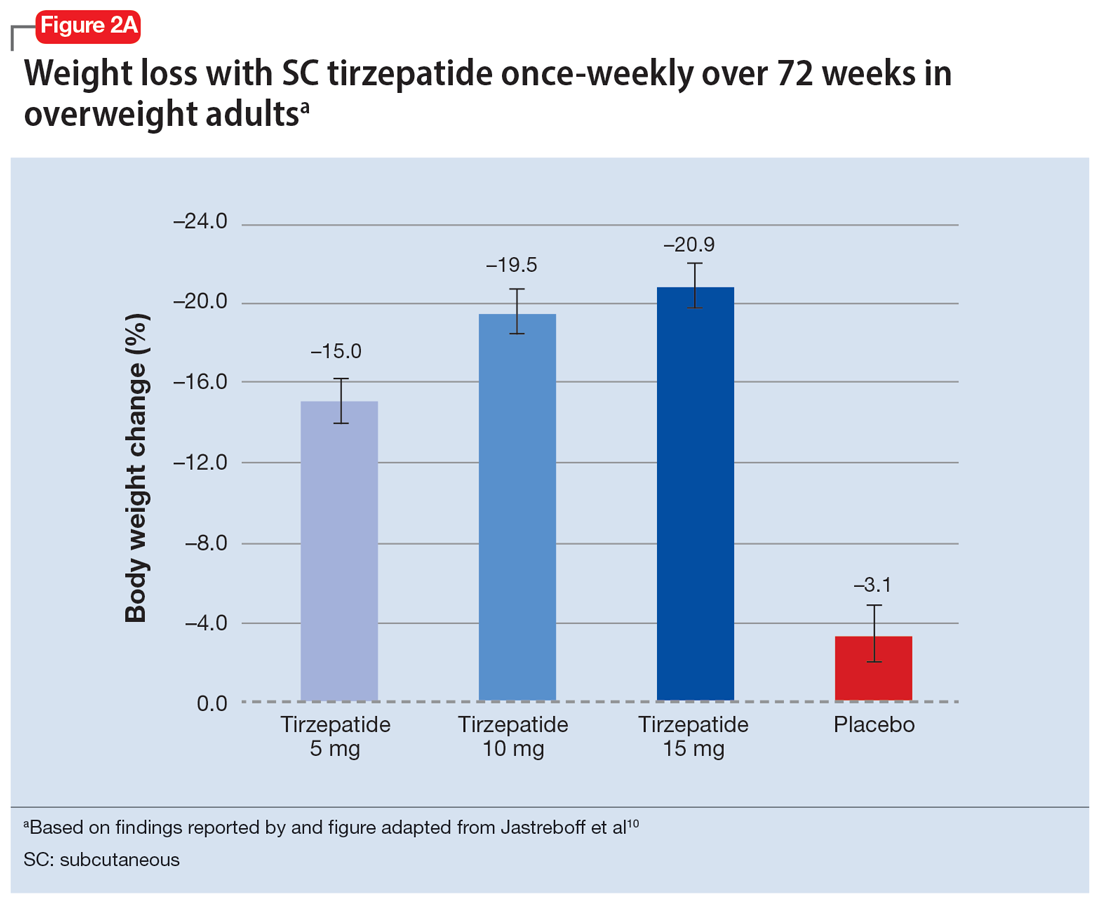
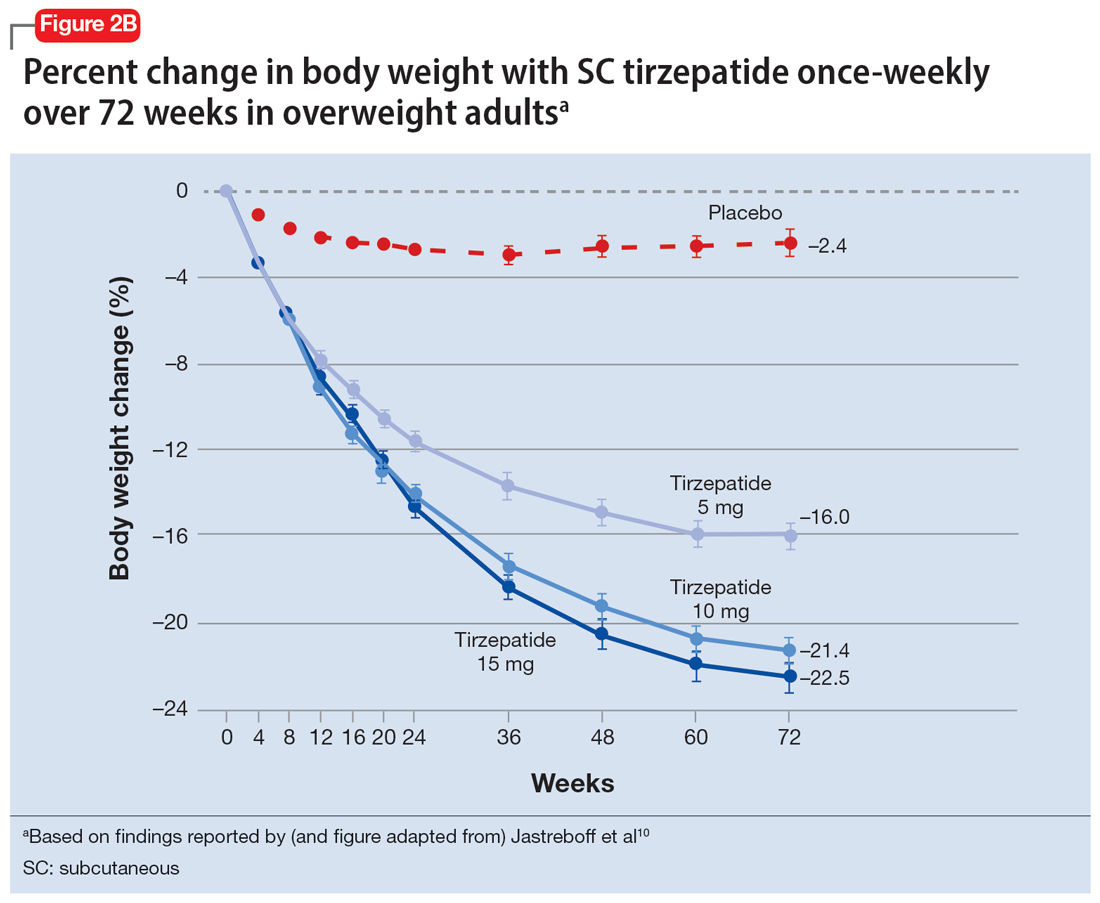
In a 72-week study of tirzepatide specifically for weight loss in nondiabetic patients who were overweight or obese, findings were especially dramatic (Figure 2A and Figure 2B).10 An overall 15% decrease in body weight was observed with 5 mg/week dosing alongside a 19.5% decrease in body weight with 10 mg/week dosing and a 20.9% weight reduction with 15 mg/week dosing.10 As noted in Figure 2B, the observed pattern of weight loss occurred along an exponential decay curve. Notably, a comparative study of tirzepatide vs once-weekly semaglutide (1 mg) in patients with type 2 diabetes11 found significantly greater dose-dependent weight loss with tirzepatide than semaglutide (-1.9 kg at 5 mg, -3.6 kg at 10 mg, and -5.5 kg at 15 mg)—although the somewhat low dosing of semaglutide may have limited its optimal possible weight loss benefit.
Tolerability
Adverse effects with GLP-1 agonists are mainly gastrointestinal (eg, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or constipation)5-11 and generally transient. SC administration is performed in fatty tissue of the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm; site rotation is recommended to minimize injection site pain. All GLP-1 agonists carry manufacturers’ warning and precaution statements identifying the rare potential for acute pancreatitis, acute gall bladder disease, acute kidney injury, and hypoglycemia. Animal studies also have suggested an increased, dose-dependent risk for thyroid C-cell tumors with GLP-1 agonists; this has not been observed in human trials, although postmarketing pharmacovigilance reports have identified cases of medullary thyroid carcinoma in patients who took liraglutide. A manufacturer’s boxed warning indicates that a personal or family history of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid poses a contraindication for taking semaglutide, liraglutide, or tirzepatide.
Initial evidence prompts additional questions
GLP-1 agonists represent an emerging class of novel agents that can modulate glycemic dysregulation and overweight/obesity, often with dramatic results whose magnitude rivals the efficacy of bariatric surgery. Once-weekly formulations of semaglutide (Wegovy) and daily liraglutide (Saxenda) are FDA-approved for weight loss in patients who are overweight or obese while other existing formulations are approved solely for patients with type 2 diabetes, although it is likely that broader indications for weight loss (regardless of glycemic status) are forthcoming. Targeted use of GLP-1 agonists to counteract SGA-associated weight gain is supported by a handful of preliminary reports, with additional studies likely to come. Unanswered questions include:
- When should GLP-1 agonists be considered within a treatment algorithm for iatrogenic weight gain relative to other antidote strategies such as metformin or appetite-suppressing anticonvulsants?
- How effective might GLP-1 agonists be for iatrogenic weight gain from non-SGA psychotropic medications, such as serotonergic antidepressants?
- When and how can GLP-1 agonists be safely coprescribed with other nonincretin mimetic weight loss medications?
- When should psychiatrists prescribe GLP-1 agonists, or do so collaboratively with primary care physicians or endocrinologists, particularly in patients with metabolic syndrome?
Followers of the rapidly emerging literature in this area will likely find themselves best positioned to address these and other questions about optimal management of psychotropic-induced weight gain for the patients they treat.
Bottom Line
The use of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists, a relatively new class of incretin mimetics, has been associated with profound and often dramatic weight loss and improvement of glycemic parameters in patients with obesity and glycemic dysregulation. Preliminary reports support the potential targeted use of GLP-1 agonists to counteract weight gain associated with second-generation antipsychotics.
Related Resources
- Singh F, Allen A, Ianni A. Managing metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(12):20-24,26. doi:10.12788/cp.0064
- Ard J, Fitch A, Fruh S, et al. Weight loss and maintenance related to the mechanism of action of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists. Adv Ther. 2021;38(6):2821- 2839. doi:10.1007/s12325-021-01710-0
Drug Brand Names
Amantadine • Gocovri
Citalopram • Celexa
Clozapine • Clozaril
Escitalopram • Lexapro
Liraglutide • Victoza, Saxenda
Metformin • Glucophage
Naltrexone • ReVia
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Olanzapine/samidorphan • Lybalvi
Phentermine • Ionamin
Semaglutide • Rybelsus, Ozempic, Wegovy
Tirzepatide • Mounjaro
Topiramate • Topamax
Zonisamide • Zonegran
1. Afzal M, Siddiqi N, Ahmad B, et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in people with severe mental illness: systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;25;12:769309.
2. Barton BB, Segger F, Fischer K, et al. Update on weight-gain caused by antipsychotics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Opin Drug Safety. 2020;19(3):295-314.
3. de Silva AV, Suraweera C, Ratnatunga SS, et al. Metformin in prevention and treatment of antipsychotic induced weight gain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry. 2016;16(1):341.
4. Durell N, Franks R, Coon S, et al. Effects of antidepressants on glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist-related weight loss. J Pharm Technol. 2022;38(5):283-288.
5. Larsen JR, Vedtofte L, Jakobsen MSL, et al. Effect of liraglutide treatment on prediabetes and overweight or obesity in clozapine- or olanzapine-treated patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(7):719-728.
6. Aroda VR, Rosenstock J, Terauchi Y, et al. PIONEER 1: randomized clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy in comparison with placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(9):1724-1732.
7. Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(11):989-1002.
8. Weghuber D, Barrett T, Barrientos-Pérez M, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adolescents with obesity. N Engl J Med. Published online November 2, 2022. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2208601.
9. Pratley R, Amod A, Hoff ST, et al. Oral semaglutide versus subcutaneous liraglutide and placebo in type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 4): a randomized, double-blind, phase 3a trial. Lancet. 2019;394(10192):39-50.
10. Jastreboff AM, Aronne LJ, Ahmad NN, et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(3):205-216.
11. Frías JP, Davies MJ, Rosenstock J, et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(6):503-515.
Obesity and overweight, with or without metabolic dysregulation, pose vexing problems for many patients with mood, anxiety, or psychotic disorders. More than one-half of individuals with severe mental illnesses are obese or overweight,1 resulting from multiple factors that may include psychiatric symptoms (eg, anergia and hyperphagia), poor dietary choices, sedentary lifestyle, underlying inflammatory processes, medical comorbidities, and iatrogenic consequences of certain medications. Unfortunately, numerous psychotropic medications can increase weight and appetite due to a variety of mechanisms, including antihistaminergic effects, direct appetite-stimulating effects, and proclivities to cause insulin resistance. While individual agents can vary, a recent review identified an overall 2-fold increased risk for rapid, significant weight gain during treatment with antipsychotics as a class.2 In addition to lifestyle modifications (diet and exercise), many pharmacologic strategies have been proposed to counter iatrogenic weight gain, including appetite suppressants (eg, pro-dopaminergic agents such as phentermine, stimulants, and amantadine), pro-anorectant anticonvulsants (eg, topiramate or zonisamide), opioid receptor antagonists (eg, olanzapine/samidorphan or naltrexone) and oral hypoglycemics such as metformin. However, the magnitude of impact for most of these agents to reverse iatrogenic weight gain tends to be modest, particularly once significant weight gain (ie, ≥7% of initial body weight) has already occurred.
Pharmacologic strategies to modulate or enhance the effects of insulin hold particular importance for combatting psychotropic-associated weight gain. Insulin transports glucose from the intravascular space to end organs for fuel consumption; to varying degrees, second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) and some other psychotropic medications can cause insulin resistance. This in turn leads to excessive storage of underutilized glucose in the liver (glycogenesis), the potential for developing fatty liver (ie, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis), and conversion of excess carbohydrates to fatty acids and triglycerides, with subsequent storage in adipose tissue. Medications that can enhance the activity of insulin (so-called incretin mimetics) can help to overcome insulin resistance caused by SGAs (and potentially by other psychotropic medications) and essentially lead to weight loss through enhanced “fuel efficiency.”
Metformin, typically dosed up to 1,000 mg twice daily with meals, has increasingly become recognized as a first-line strategy to attenuate weight gain and glycemic dysregulation from SGAs via its ability to reduce insulin resistance. Yet meta-analyses have shown that although results are significantly better than placebo, overall long-term weight loss from metformin alone tends to be rather modest (<4 kg) and associated with a reduction in body mass index (BMI) of only approximately 1 point.3 Psychiatrists (and other clinicians who prescribe psychotropic medications that can cause weight gain or metabolic dysregulation) therefore need to become familiar with alternative or adjunctive weight loss options. The use of a relatively new class of incretin mimetics called glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists (Table) has been associated with profound and often dramatic weight loss and improvement of glycemic parameters in patients with obesity and glycemic dysregulation.

What are GLP-1 agonists?
GLP-1 is a hormone secreted by L cells in the intestinal mucosa in response to food. GLP-1 agonists reduce blood sugar by increasing insulin secretion, decreasing glucagon release (thus downregulating further increases in blood sugar), and reducing insulin resistance. GLP-1 agonists also reduce appetite by directly stimulating the satiety center and slowing gastric emptying and GI motility. In addition to GLP-1 agonism, some medications in this family (notably tirzepatide) also agonize a second hormone, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, which can further induce insulin secretion as well as decrease stomach acid secretion, potentially delivering an even more substantial reduction in appetite and weight.
Routes of administration and FDA indications
Due to limited bioavailability, most GLP-1 agonists require subcutaneous (SC) injections (the sole exception is the Rybelsus brand of semaglutide, which comes in a daily pill form). Most are FDA-approved not specifically for weight loss but for patients with type 2 diabetes (defined as a hemoglobin A1C ≥6.5% or a fasting blood glucose level ≥126 mg/dL). Weight loss represents a secondary outcome for GLP-1 agonists FDA-approved for glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. The 2 current exceptions to this classification are the Wegovy brand of semaglutide (ie, dosing of 2.4 mg) and the Saxenda brand of liraglutide, both of which carry FDA indications for chronic weight management alone (when paired with dietary and lifestyle modification) in individuals who are obese (BMI >30 kg/m2) regardless of the presence or absence of diabetes, or for persons who are overweight (BMI >27 kg/m2) and have ≥1 weight-related comorbid condition (eg, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, or dyslipidemia). Although patients at risk for diabetes (ie, prediabetes, defined as a hemoglobin A1C 5.7% to 6.4% or a fasting blood glucose level 100 to 125 mg/dL) were included in FDA registration trials of Saxenda or Wegovy, prediabetes is not an FDA indication for any GLP-1 agonist.
Data in weight loss
Most of the existing empirical data on weight loss with GLP-1 agonists come from studies of individuals who are overweight or obese, with or without type 2 diabetes, rather than from studies using these agents to counteract iatrogenic weight gain. In a retrospective cohort study of patients with type 2 diabetes, coadministration with serotonergic antidepressants (eg, citalopram/escitalopram) was associated with attenuation of the weight loss effects of GLP-1 agonists.4
Liraglutide currently is the sole GLP-1 agonist studied for treating SGA-associated weight gain. A 16-week randomized trial compared once-daily SC injected liraglutide vs placebo in patients with schizophrenia who incurred weight gain and prediabetes after taking olanzapine or clozapine.5 Significantly more patients taking liraglutide than placebo developed normal glucose tolerance (64% vs 16%), and body weight decreased by a mean of 5.3 kg.
Continue to: In studies of semaglutide...
In studies of semaglutide for overweight/obese patients with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes, clinical trials of oral semaglutide (Rybelsus) found a mean weight loss over 26 weeks of -1.0 kg with dosing at 7 mg/d and -2.6 kg with dosing at 14 mg/d.6 A 68-week placebo-controlled trial of semaglutide (dosed at 2.4 mg SC weekly) for overweight/obese adults who did not have diabetes yielded a -15.3 kg weight loss (vs -2.6 kg with placebo); one-half of those who received semaglutide lost 15% of their initial body weight (Figure 1A and Figure 1B).7 Similar findings with semaglutide 2.4 mg SC weekly (Wegovy) were observed in overweight/obese adolescents, with 73% of participants losing ≥5% of their baseline weight.8 A comparative randomized trial in patients with type 2 diabetes also found modestly but significantly greater weight loss with oral semaglutide than with SC liraglutide.9


In a 72-week study of tirzepatide specifically for weight loss in nondiabetic patients who were overweight or obese, findings were especially dramatic (Figure 2A and Figure 2B).10 An overall 15% decrease in body weight was observed with 5 mg/week dosing alongside a 19.5% decrease in body weight with 10 mg/week dosing and a 20.9% weight reduction with 15 mg/week dosing.10 As noted in Figure 2B, the observed pattern of weight loss occurred along an exponential decay curve. Notably, a comparative study of tirzepatide vs once-weekly semaglutide (1 mg) in patients with type 2 diabetes11 found significantly greater dose-dependent weight loss with tirzepatide than semaglutide (-1.9 kg at 5 mg, -3.6 kg at 10 mg, and -5.5 kg at 15 mg)—although the somewhat low dosing of semaglutide may have limited its optimal possible weight loss benefit.


Tolerability
Adverse effects with GLP-1 agonists are mainly gastrointestinal (eg, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or constipation)5-11 and generally transient. SC administration is performed in fatty tissue of the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm; site rotation is recommended to minimize injection site pain. All GLP-1 agonists carry manufacturers’ warning and precaution statements identifying the rare potential for acute pancreatitis, acute gall bladder disease, acute kidney injury, and hypoglycemia. Animal studies also have suggested an increased, dose-dependent risk for thyroid C-cell tumors with GLP-1 agonists; this has not been observed in human trials, although postmarketing pharmacovigilance reports have identified cases of medullary thyroid carcinoma in patients who took liraglutide. A manufacturer’s boxed warning indicates that a personal or family history of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid poses a contraindication for taking semaglutide, liraglutide, or tirzepatide.
Initial evidence prompts additional questions
GLP-1 agonists represent an emerging class of novel agents that can modulate glycemic dysregulation and overweight/obesity, often with dramatic results whose magnitude rivals the efficacy of bariatric surgery. Once-weekly formulations of semaglutide (Wegovy) and daily liraglutide (Saxenda) are FDA-approved for weight loss in patients who are overweight or obese while other existing formulations are approved solely for patients with type 2 diabetes, although it is likely that broader indications for weight loss (regardless of glycemic status) are forthcoming. Targeted use of GLP-1 agonists to counteract SGA-associated weight gain is supported by a handful of preliminary reports, with additional studies likely to come. Unanswered questions include:
- When should GLP-1 agonists be considered within a treatment algorithm for iatrogenic weight gain relative to other antidote strategies such as metformin or appetite-suppressing anticonvulsants?
- How effective might GLP-1 agonists be for iatrogenic weight gain from non-SGA psychotropic medications, such as serotonergic antidepressants?
- When and how can GLP-1 agonists be safely coprescribed with other nonincretin mimetic weight loss medications?
- When should psychiatrists prescribe GLP-1 agonists, or do so collaboratively with primary care physicians or endocrinologists, particularly in patients with metabolic syndrome?
Followers of the rapidly emerging literature in this area will likely find themselves best positioned to address these and other questions about optimal management of psychotropic-induced weight gain for the patients they treat.
Bottom Line
The use of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists, a relatively new class of incretin mimetics, has been associated with profound and often dramatic weight loss and improvement of glycemic parameters in patients with obesity and glycemic dysregulation. Preliminary reports support the potential targeted use of GLP-1 agonists to counteract weight gain associated with second-generation antipsychotics.
Related Resources
- Singh F, Allen A, Ianni A. Managing metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(12):20-24,26. doi:10.12788/cp.0064
- Ard J, Fitch A, Fruh S, et al. Weight loss and maintenance related to the mechanism of action of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists. Adv Ther. 2021;38(6):2821- 2839. doi:10.1007/s12325-021-01710-0
Drug Brand Names
Amantadine • Gocovri
Citalopram • Celexa
Clozapine • Clozaril
Escitalopram • Lexapro
Liraglutide • Victoza, Saxenda
Metformin • Glucophage
Naltrexone • ReVia
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Olanzapine/samidorphan • Lybalvi
Phentermine • Ionamin
Semaglutide • Rybelsus, Ozempic, Wegovy
Tirzepatide • Mounjaro
Topiramate • Topamax
Zonisamide • Zonegran
Obesity and overweight, with or without metabolic dysregulation, pose vexing problems for many patients with mood, anxiety, or psychotic disorders. More than one-half of individuals with severe mental illnesses are obese or overweight,1 resulting from multiple factors that may include psychiatric symptoms (eg, anergia and hyperphagia), poor dietary choices, sedentary lifestyle, underlying inflammatory processes, medical comorbidities, and iatrogenic consequences of certain medications. Unfortunately, numerous psychotropic medications can increase weight and appetite due to a variety of mechanisms, including antihistaminergic effects, direct appetite-stimulating effects, and proclivities to cause insulin resistance. While individual agents can vary, a recent review identified an overall 2-fold increased risk for rapid, significant weight gain during treatment with antipsychotics as a class.2 In addition to lifestyle modifications (diet and exercise), many pharmacologic strategies have been proposed to counter iatrogenic weight gain, including appetite suppressants (eg, pro-dopaminergic agents such as phentermine, stimulants, and amantadine), pro-anorectant anticonvulsants (eg, topiramate or zonisamide), opioid receptor antagonists (eg, olanzapine/samidorphan or naltrexone) and oral hypoglycemics such as metformin. However, the magnitude of impact for most of these agents to reverse iatrogenic weight gain tends to be modest, particularly once significant weight gain (ie, ≥7% of initial body weight) has already occurred.
Pharmacologic strategies to modulate or enhance the effects of insulin hold particular importance for combatting psychotropic-associated weight gain. Insulin transports glucose from the intravascular space to end organs for fuel consumption; to varying degrees, second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) and some other psychotropic medications can cause insulin resistance. This in turn leads to excessive storage of underutilized glucose in the liver (glycogenesis), the potential for developing fatty liver (ie, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis), and conversion of excess carbohydrates to fatty acids and triglycerides, with subsequent storage in adipose tissue. Medications that can enhance the activity of insulin (so-called incretin mimetics) can help to overcome insulin resistance caused by SGAs (and potentially by other psychotropic medications) and essentially lead to weight loss through enhanced “fuel efficiency.”
Metformin, typically dosed up to 1,000 mg twice daily with meals, has increasingly become recognized as a first-line strategy to attenuate weight gain and glycemic dysregulation from SGAs via its ability to reduce insulin resistance. Yet meta-analyses have shown that although results are significantly better than placebo, overall long-term weight loss from metformin alone tends to be rather modest (<4 kg) and associated with a reduction in body mass index (BMI) of only approximately 1 point.3 Psychiatrists (and other clinicians who prescribe psychotropic medications that can cause weight gain or metabolic dysregulation) therefore need to become familiar with alternative or adjunctive weight loss options. The use of a relatively new class of incretin mimetics called glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists (Table) has been associated with profound and often dramatic weight loss and improvement of glycemic parameters in patients with obesity and glycemic dysregulation.

What are GLP-1 agonists?
GLP-1 is a hormone secreted by L cells in the intestinal mucosa in response to food. GLP-1 agonists reduce blood sugar by increasing insulin secretion, decreasing glucagon release (thus downregulating further increases in blood sugar), and reducing insulin resistance. GLP-1 agonists also reduce appetite by directly stimulating the satiety center and slowing gastric emptying and GI motility. In addition to GLP-1 agonism, some medications in this family (notably tirzepatide) also agonize a second hormone, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, which can further induce insulin secretion as well as decrease stomach acid secretion, potentially delivering an even more substantial reduction in appetite and weight.
Routes of administration and FDA indications
Due to limited bioavailability, most GLP-1 agonists require subcutaneous (SC) injections (the sole exception is the Rybelsus brand of semaglutide, which comes in a daily pill form). Most are FDA-approved not specifically for weight loss but for patients with type 2 diabetes (defined as a hemoglobin A1C ≥6.5% or a fasting blood glucose level ≥126 mg/dL). Weight loss represents a secondary outcome for GLP-1 agonists FDA-approved for glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. The 2 current exceptions to this classification are the Wegovy brand of semaglutide (ie, dosing of 2.4 mg) and the Saxenda brand of liraglutide, both of which carry FDA indications for chronic weight management alone (when paired with dietary and lifestyle modification) in individuals who are obese (BMI >30 kg/m2) regardless of the presence or absence of diabetes, or for persons who are overweight (BMI >27 kg/m2) and have ≥1 weight-related comorbid condition (eg, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, or dyslipidemia). Although patients at risk for diabetes (ie, prediabetes, defined as a hemoglobin A1C 5.7% to 6.4% or a fasting blood glucose level 100 to 125 mg/dL) were included in FDA registration trials of Saxenda or Wegovy, prediabetes is not an FDA indication for any GLP-1 agonist.
Data in weight loss
Most of the existing empirical data on weight loss with GLP-1 agonists come from studies of individuals who are overweight or obese, with or without type 2 diabetes, rather than from studies using these agents to counteract iatrogenic weight gain. In a retrospective cohort study of patients with type 2 diabetes, coadministration with serotonergic antidepressants (eg, citalopram/escitalopram) was associated with attenuation of the weight loss effects of GLP-1 agonists.4
Liraglutide currently is the sole GLP-1 agonist studied for treating SGA-associated weight gain. A 16-week randomized trial compared once-daily SC injected liraglutide vs placebo in patients with schizophrenia who incurred weight gain and prediabetes after taking olanzapine or clozapine.5 Significantly more patients taking liraglutide than placebo developed normal glucose tolerance (64% vs 16%), and body weight decreased by a mean of 5.3 kg.
Continue to: In studies of semaglutide...
In studies of semaglutide for overweight/obese patients with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes, clinical trials of oral semaglutide (Rybelsus) found a mean weight loss over 26 weeks of -1.0 kg with dosing at 7 mg/d and -2.6 kg with dosing at 14 mg/d.6 A 68-week placebo-controlled trial of semaglutide (dosed at 2.4 mg SC weekly) for overweight/obese adults who did not have diabetes yielded a -15.3 kg weight loss (vs -2.6 kg with placebo); one-half of those who received semaglutide lost 15% of their initial body weight (Figure 1A and Figure 1B).7 Similar findings with semaglutide 2.4 mg SC weekly (Wegovy) were observed in overweight/obese adolescents, with 73% of participants losing ≥5% of their baseline weight.8 A comparative randomized trial in patients with type 2 diabetes also found modestly but significantly greater weight loss with oral semaglutide than with SC liraglutide.9


In a 72-week study of tirzepatide specifically for weight loss in nondiabetic patients who were overweight or obese, findings were especially dramatic (Figure 2A and Figure 2B).10 An overall 15% decrease in body weight was observed with 5 mg/week dosing alongside a 19.5% decrease in body weight with 10 mg/week dosing and a 20.9% weight reduction with 15 mg/week dosing.10 As noted in Figure 2B, the observed pattern of weight loss occurred along an exponential decay curve. Notably, a comparative study of tirzepatide vs once-weekly semaglutide (1 mg) in patients with type 2 diabetes11 found significantly greater dose-dependent weight loss with tirzepatide than semaglutide (-1.9 kg at 5 mg, -3.6 kg at 10 mg, and -5.5 kg at 15 mg)—although the somewhat low dosing of semaglutide may have limited its optimal possible weight loss benefit.


Tolerability
Adverse effects with GLP-1 agonists are mainly gastrointestinal (eg, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or constipation)5-11 and generally transient. SC administration is performed in fatty tissue of the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm; site rotation is recommended to minimize injection site pain. All GLP-1 agonists carry manufacturers’ warning and precaution statements identifying the rare potential for acute pancreatitis, acute gall bladder disease, acute kidney injury, and hypoglycemia. Animal studies also have suggested an increased, dose-dependent risk for thyroid C-cell tumors with GLP-1 agonists; this has not been observed in human trials, although postmarketing pharmacovigilance reports have identified cases of medullary thyroid carcinoma in patients who took liraglutide. A manufacturer’s boxed warning indicates that a personal or family history of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid poses a contraindication for taking semaglutide, liraglutide, or tirzepatide.
Initial evidence prompts additional questions
GLP-1 agonists represent an emerging class of novel agents that can modulate glycemic dysregulation and overweight/obesity, often with dramatic results whose magnitude rivals the efficacy of bariatric surgery. Once-weekly formulations of semaglutide (Wegovy) and daily liraglutide (Saxenda) are FDA-approved for weight loss in patients who are overweight or obese while other existing formulations are approved solely for patients with type 2 diabetes, although it is likely that broader indications for weight loss (regardless of glycemic status) are forthcoming. Targeted use of GLP-1 agonists to counteract SGA-associated weight gain is supported by a handful of preliminary reports, with additional studies likely to come. Unanswered questions include:
- When should GLP-1 agonists be considered within a treatment algorithm for iatrogenic weight gain relative to other antidote strategies such as metformin or appetite-suppressing anticonvulsants?
- How effective might GLP-1 agonists be for iatrogenic weight gain from non-SGA psychotropic medications, such as serotonergic antidepressants?
- When and how can GLP-1 agonists be safely coprescribed with other nonincretin mimetic weight loss medications?
- When should psychiatrists prescribe GLP-1 agonists, or do so collaboratively with primary care physicians or endocrinologists, particularly in patients with metabolic syndrome?
Followers of the rapidly emerging literature in this area will likely find themselves best positioned to address these and other questions about optimal management of psychotropic-induced weight gain for the patients they treat.
Bottom Line
The use of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists, a relatively new class of incretin mimetics, has been associated with profound and often dramatic weight loss and improvement of glycemic parameters in patients with obesity and glycemic dysregulation. Preliminary reports support the potential targeted use of GLP-1 agonists to counteract weight gain associated with second-generation antipsychotics.
Related Resources
- Singh F, Allen A, Ianni A. Managing metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(12):20-24,26. doi:10.12788/cp.0064
- Ard J, Fitch A, Fruh S, et al. Weight loss and maintenance related to the mechanism of action of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists. Adv Ther. 2021;38(6):2821- 2839. doi:10.1007/s12325-021-01710-0
Drug Brand Names
Amantadine • Gocovri
Citalopram • Celexa
Clozapine • Clozaril
Escitalopram • Lexapro
Liraglutide • Victoza, Saxenda
Metformin • Glucophage
Naltrexone • ReVia
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Olanzapine/samidorphan • Lybalvi
Phentermine • Ionamin
Semaglutide • Rybelsus, Ozempic, Wegovy
Tirzepatide • Mounjaro
Topiramate • Topamax
Zonisamide • Zonegran
1. Afzal M, Siddiqi N, Ahmad B, et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in people with severe mental illness: systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;25;12:769309.
2. Barton BB, Segger F, Fischer K, et al. Update on weight-gain caused by antipsychotics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Opin Drug Safety. 2020;19(3):295-314.
3. de Silva AV, Suraweera C, Ratnatunga SS, et al. Metformin in prevention and treatment of antipsychotic induced weight gain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry. 2016;16(1):341.
4. Durell N, Franks R, Coon S, et al. Effects of antidepressants on glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist-related weight loss. J Pharm Technol. 2022;38(5):283-288.
5. Larsen JR, Vedtofte L, Jakobsen MSL, et al. Effect of liraglutide treatment on prediabetes and overweight or obesity in clozapine- or olanzapine-treated patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(7):719-728.
6. Aroda VR, Rosenstock J, Terauchi Y, et al. PIONEER 1: randomized clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy in comparison with placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(9):1724-1732.
7. Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(11):989-1002.
8. Weghuber D, Barrett T, Barrientos-Pérez M, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adolescents with obesity. N Engl J Med. Published online November 2, 2022. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2208601.
9. Pratley R, Amod A, Hoff ST, et al. Oral semaglutide versus subcutaneous liraglutide and placebo in type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 4): a randomized, double-blind, phase 3a trial. Lancet. 2019;394(10192):39-50.
10. Jastreboff AM, Aronne LJ, Ahmad NN, et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(3):205-216.
11. Frías JP, Davies MJ, Rosenstock J, et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(6):503-515.
1. Afzal M, Siddiqi N, Ahmad B, et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in people with severe mental illness: systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;25;12:769309.
2. Barton BB, Segger F, Fischer K, et al. Update on weight-gain caused by antipsychotics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Opin Drug Safety. 2020;19(3):295-314.
3. de Silva AV, Suraweera C, Ratnatunga SS, et al. Metformin in prevention and treatment of antipsychotic induced weight gain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry. 2016;16(1):341.
4. Durell N, Franks R, Coon S, et al. Effects of antidepressants on glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist-related weight loss. J Pharm Technol. 2022;38(5):283-288.
5. Larsen JR, Vedtofte L, Jakobsen MSL, et al. Effect of liraglutide treatment on prediabetes and overweight or obesity in clozapine- or olanzapine-treated patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(7):719-728.
6. Aroda VR, Rosenstock J, Terauchi Y, et al. PIONEER 1: randomized clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy in comparison with placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(9):1724-1732.
7. Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(11):989-1002.
8. Weghuber D, Barrett T, Barrientos-Pérez M, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adolescents with obesity. N Engl J Med. Published online November 2, 2022. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2208601.
9. Pratley R, Amod A, Hoff ST, et al. Oral semaglutide versus subcutaneous liraglutide and placebo in type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 4): a randomized, double-blind, phase 3a trial. Lancet. 2019;394(10192):39-50.
10. Jastreboff AM, Aronne LJ, Ahmad NN, et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(3):205-216.
11. Frías JP, Davies MJ, Rosenstock J, et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(6):503-515.
Managing excited catatonia: A suggested approach
Catatonia is often difficult to identify and treat. The excited catatonia subtype can be particularly challenging to diagnose because it can present with symptoms similar to those seen in mania or psychosis. In this article, we present 3 cases of excited catatonia that illustrate how to identify it, how to treat the catatonia as well as the underlying pathology, and factors to consider during this process to mitigate the risk of adverse outcomes. We also outline a treatment algorithm we used for the 3 cases. Although we describe using this approach for patients with excited catatonia, it is generalizable to other types of catatonia.
Many causes, varying presentations
Catatonia is a psychomotor syndrome characterized by mutism, negativism, stereotypy, waxy flexibility, and other symptoms.1 It is defined by the presence of ≥3 of the 12 symptoms listed in the Table.2 Causes of catatonia include metabolic abnormalities, endocrine disorders, drug intoxication, neurodevelopmental disorders, medication adverse effects, psychosis, and mood disorders.1,3
A subtype of this syndrome, excited catatonia, can present with restlessness, agitation, emotional lability, poor sleep, and altered mental status in addition to the more typical symptoms.1,4 Because excited catatonia can resemble mania or psychosis, it is particularly challenging to identify the underlying disorder causing it and appropriate treatment. Fink et al4 discussed how clinicians have interpreted the different presentations of excited catatonia to gain insight into the underlying diagnosis. If the patient’s thought process appears disorganized, psychosis may be suspected.4 If the patient is delusional and grandiose, they may be manic, and when altered mental status dominates the presentation, delirium may be the culprit.4
Regardless of the underlying cause, the first step is to treat the catatonia. Benzodiazepines and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) are the most well validated treatments for catatonia and have been used to treat excited catatonia.1 Excited catatonia is often misdiagnosed and subsequently mistreated. In the following 3 cases, excited catatonia was successfully identified and treated using the same approach (Figure).
Case 1
Mr. A, age 27, has a history of bipolar I disorder. He was brought to the hospital by ambulance after being found to be yelling and acting belligerently, and he was admitted to the inpatient psychiatry unit for manic decompensation due to medication nonadherence. He was started on divalproex sodium 500 mg twice a day for mood stabilization, risperidone 1 mg twice a day for adjunct mood stabilization and psychosis, and lorazepam 1 mg 3 times a day for agitation. Mr. A exhibited odd behavior; he would take off his clothes in the hallway, run around the unit, and randomly yell at staff or to himself. At other times, he would stay silent, repeat the same statements, or oddly posture in the hallway for minutes at a time. These behaviors were seen primarily in the hour or 2 preceding lorazepam administration and improved after he received lorazepam.
Mr. A’s treating team completed the Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale (BFCRS), which yielded a positive catatonia screen of 7/14. As a result, divalproex sodium and risperidone were held, and lorazepam was increased to 2 mg twice a day.
After several days, Mr. A was no longer acting oddly and was able to speak more spontaneously; however, he began to exhibit overt signs of mania. He would speak rapidly and make grandiose claims about managing millions of dollars as the CEO of a famous company. Divalproex sodium was restarted at 500 mg twice a day and increased to 500 mg 3 times a day for mood stabilization. Mr. A continued to receive lorazepam 2 mg 3 times a day for catatonia, and risperidone was restarted at 1 mg twice a day to more effectively target his manic symptoms. Risperidone was increased to 2 mg twice a day. After this change, Mr. A’s grandiosity dissipated, his speech normalized, and his thought process became organized. He was discharged on lorazepam 2 mg 3 times a day, divalproex sodium 500 mg 3 times a day, and risperidone 2 mg twice a day. Mr. A’s length of stay (LOS) for this admission was 11 days.
Continue to: Case 2
Case 2
Mr. B, age 49, presented with irritability and odd posturing. He has a history of schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type for which he was receiving a maintenance regimen of lithium 600 mg/d at bedtime and risperidone 2 mg/d at bedtime. He had multiple previous psychiatric admissions for catatonia. On this admission, Mr. B was irritable and difficult to redirect. He yelled at staff members and had a stiff gait. The BFCRS yielded a positive screening score of 3/14 and a severity score of 8/23. As a result, the treatment team conducted a lorazepam challenge.
After Mr. B received lorazepam 1 mg IM, his thought organization and irritability improved, which allowed him to have a coherent conversation with the interviewer. His gait stiffness also improved. His risperidone and lithium were held, and oral lorazepam 1 mg 3 times a day was started for catatonia. Lorazepam was gradually increased to 4 mg 3 times a day. Mr. B became euthymic and redirectable, and had an improved gait. However, he was also tangential and hyperverbal; these symptoms were indicative of the underlying mania that precipitated his catatonia.
Divalproex sodium extended release (ER) was started and increased to 1,500 mg/d at bedtime for mood stabilization. Lithium was restarted and increased to 300 mg twice a day for adjunct mood stabilization. Risperidone was not restarted. Toward the end of his admission, Mr. B was noted to be overly sedated, so the lorazepam dosage was decreased. He was discharged on lorazepam 2 mg 3 times a day, divalproex sodium ER 1,500 mg/d at bedtime, and lithium 300 mg twice a day. At discharge, Mr. B was calm and euthymic, with a linear thought process. His LOS was 25 days.
Case 3
Mr. C, age 62, presented to the emergency department (ED) because he had exhibited erratic behavior and had not slept for the past week. He has a history of bipolar I disorder, hypothyroidism, diabetes, and hypertension. For many years, he had been stable on divalproex sodium ER 2,500 mg/d at bedtime for mood stabilization and clozapine 100 mg/d at bedtime for adjunct mood stabilization and psychosis. In the ED, Mr. C was irritable, distractible, and tangential. On admission, he was speaking slowly with increased speech latency in response to questions, exhibiting stereotypy, repeating statements over and over, and walking very slowly.
The BFCRS yielded a positive screening score of 5/14 and a severity score of 10/23. Lorazepam 1 mg IM was administered. After 15 minutes, Mr. C’s speech, gait, and distractibility improved. As a result, clozapine and divalproex sodium were held, and he was started on oral lorazepam 1 mg 3 times a day. After several days, Mr. C was speaking fluently and no longer exhibiting stereotypy or having outbursts where he would make repetitive statements. However, he was tangential and irritable at times, which were signs of his underlying mania. Divalproex sodium ER was restarted at 250 mg/d at bedtime for mood stabilization and gradually increased to 2,500 mg/d at bedtime. Clozapine was also restarted at 25 mg/d at bedtime and gradually increased to 200 mg/d at bedtime. The lorazepam was gradually tapered and discontinued over the course of 3 weeks due to oversedation.
Continue to: At discharge...
At discharge, Mr. C was euthymic, calm, linear, and goal-directed. He was discharged on divalproex sodium ER 2,500 mg/d at bedtime and clozapine 200 mg/d at bedtime. His LOS for this admission was 22 days.
A stepwise approach can improve outcomes
The Figure outlines the method we used to manage excited catatonia in these 3 cases. Each of these patients exhibited signs of excited catatonia, but because those symptoms were nearly identical to those of mania, it was initially difficult to identify catatonia. Excited catatonia was suspected after more typical catatonic symptoms—such as a stiff gait, slowed speech, and stereotypy—were observed. The BFCRS was completed to get an objective measure of the likelihood that the patient was catatonic. In all 3 cases, the BFCRS resulted in a positive screen for catatonia. Following this, the patients described in Case 2 and Case 3 received a lorazepam challenge, which confirmed their catatonia. No lorazepam challenge was performed in Case 1 because the patient was already receiving lorazepam when the BFCRS was completed. Although most catatonic patients will respond to a lorazepam challenge, not all will. Therefore, clinicians should maintain some degree of suspicion for catatonia if a patient has a positive screen on the BFCRS but a negative lorazepam challenge.
In all 3 cases, after catatonia was confirmed, the patient’s psychotropic medications were discontinued. In all 3 cases, the antipsychotic was held to prevent progression to neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) or malignant catatonia. Rasmussen et al3 found that 3.6% of the catatonic patients in their sample who were treated with antipsychotics developed NMS. A review of prospective studies looking at patients treated with antipsychotics found the incidence of NMS was .07% to 1.8%.5 Because NMS is often clinically indistinguishable from malignant catatonia,4,6 this incidence of NMS may have represented an increased incidence in malignant catatonia.
In all 3 cases, the mood stabilizer was held to prevent it from complicating the clinical picture. Discontinuing the mood stabilizer and focusing on treating the catatonia before targeting the underlying mania increased the likelihood of differentiating the patient’s catatonic symptoms from manic symptoms. This resulted in more precise medication selection and titration by allowing us to identify the specific symptoms that were being targeted by each medication.
Oral lorazepam was prescribed to target catatonia in all 3 cases, and the dosage was gradually increased until symptoms began to resolve. As the catatonia resolved, the manic symptoms became more easily identifiable, and at this point a mood stabilizer was started and titrated to a therapeutic dose to target the mania. In Case 1 and Case 3, the antipsychotic was restarted to treat the mania more effectively. It was not restarted in Case 2 because the patient’s mania was effectively being managed by 2 mood stabilizers. The risks and benefits of starting an antipsychotic in a catatonic or recently catatonic patient should be carefully considered. In the 2 cases where the antipsychotic was restarted, the patients were closely monitored, and there were no signs of NMS or malignant catatonia.
Continue to: As discharge approached...
As discharge approached, the dosages of oral lorazepam were reevaluated. Catatonic patients can typically tolerate high doses of benzodiazepines without becoming overly sedated, but each patient has a different threshold at which the dosage causes oversedation. In all 3 patients, lorazepam was initially titrated to a dose that treated their catatonic symptoms without causing intolerable sedation. In Case 2 and Case 3, as the catatonia began to resolve, the patients became increasingly sedated on their existing lorazepam dosage, so it was decreased. Because the patient in Case 1 did not become overly sedated, his lorazepam dosage did not need to be reduced.
For 2 of these patients, our approach resulted in a shorter LOS compared to their previous hospitalizations. The LOS in Case 2 was 25 days; 5 years earlier, he had a 49-day LOS for mania and catatonia. During the past admission, the identification and treatment of the catatonia was delayed, which resulted in the patient requiring multiple transfers to the medical unit for unstable vital signs. The LOS in Case 3 was 22 days; 6 months prior to this admission, the patient had 2 psychiatric admissions that totaled 37 days. Although the patient’s presentation in the 2 previous admissions was similar to his presentation as described in Case 3, catatonia had not been identified or treated in either admission. Since his catatonia and mania were treated in Case 3, he has not required a readmission. The patient in Case 1 was previously hospitalized, but information about the LOS of these admissions was not available. These results suggest that early identification and treatment of catatonia via the approach we used can improve patient outcomes.
Bottom Line
Excited catatonia can be challenging to diagnose and treat because it can present with symptoms similar to those seen in mania or psychosis. We describe 3 cases in which we used a stepwise approach to optimize treatment and improve outcomes for patients with excited catatonia. This approach may work equally well for other catatonia subtypes.
Related Resources
- Dubovsky SL, Dubovsky AN. Catatonia: how to identify and treat it. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):16-26.
- Crouse EL, Joel B. Moran JB. Catatonia: recognition, management, and prevention of complications. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(12):45-49.
Drug Brand Names
Clozapine • Clozaril
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
Risperidone • Risperdal
Divalproex sodium • Depakote
1. Fink M, Taylor MA. The many varieties of catatonia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;251(Suppl 1):8-13.
2. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013:119-121.
3. Rasmussen SA, Mazurek MF, Rosebush PI. Catatonia: our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. World J Psychiatry. 2016;6(4):391-398.
4. Fink M, Taylor MA. Catatonia: A Clinician’s Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment. Cambridge University Press; 2003.
5. Adityanjee, Aderibigbe YA, Matthews T. Epidemiology of neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1999;22(3):151-158.
6. Strawn JR, Keck PE Jr, Caroff SN. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(6):870-876.
Catatonia is often difficult to identify and treat. The excited catatonia subtype can be particularly challenging to diagnose because it can present with symptoms similar to those seen in mania or psychosis. In this article, we present 3 cases of excited catatonia that illustrate how to identify it, how to treat the catatonia as well as the underlying pathology, and factors to consider during this process to mitigate the risk of adverse outcomes. We also outline a treatment algorithm we used for the 3 cases. Although we describe using this approach for patients with excited catatonia, it is generalizable to other types of catatonia.
Many causes, varying presentations
Catatonia is a psychomotor syndrome characterized by mutism, negativism, stereotypy, waxy flexibility, and other symptoms.1 It is defined by the presence of ≥3 of the 12 symptoms listed in the Table.2 Causes of catatonia include metabolic abnormalities, endocrine disorders, drug intoxication, neurodevelopmental disorders, medication adverse effects, psychosis, and mood disorders.1,3

A subtype of this syndrome, excited catatonia, can present with restlessness, agitation, emotional lability, poor sleep, and altered mental status in addition to the more typical symptoms.1,4 Because excited catatonia can resemble mania or psychosis, it is particularly challenging to identify the underlying disorder causing it and appropriate treatment. Fink et al4 discussed how clinicians have interpreted the different presentations of excited catatonia to gain insight into the underlying diagnosis. If the patient’s thought process appears disorganized, psychosis may be suspected.4 If the patient is delusional and grandiose, they may be manic, and when altered mental status dominates the presentation, delirium may be the culprit.4
Regardless of the underlying cause, the first step is to treat the catatonia. Benzodiazepines and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) are the most well validated treatments for catatonia and have been used to treat excited catatonia.1 Excited catatonia is often misdiagnosed and subsequently mistreated. In the following 3 cases, excited catatonia was successfully identified and treated using the same approach (Figure).

Case 1
Mr. A, age 27, has a history of bipolar I disorder. He was brought to the hospital by ambulance after being found to be yelling and acting belligerently, and he was admitted to the inpatient psychiatry unit for manic decompensation due to medication nonadherence. He was started on divalproex sodium 500 mg twice a day for mood stabilization, risperidone 1 mg twice a day for adjunct mood stabilization and psychosis, and lorazepam 1 mg 3 times a day for agitation. Mr. A exhibited odd behavior; he would take off his clothes in the hallway, run around the unit, and randomly yell at staff or to himself. At other times, he would stay silent, repeat the same statements, or oddly posture in the hallway for minutes at a time. These behaviors were seen primarily in the hour or 2 preceding lorazepam administration and improved after he received lorazepam.
Mr. A’s treating team completed the Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale (BFCRS), which yielded a positive catatonia screen of 7/14. As a result, divalproex sodium and risperidone were held, and lorazepam was increased to 2 mg twice a day.
After several days, Mr. A was no longer acting oddly and was able to speak more spontaneously; however, he began to exhibit overt signs of mania. He would speak rapidly and make grandiose claims about managing millions of dollars as the CEO of a famous company. Divalproex sodium was restarted at 500 mg twice a day and increased to 500 mg 3 times a day for mood stabilization. Mr. A continued to receive lorazepam 2 mg 3 times a day for catatonia, and risperidone was restarted at 1 mg twice a day to more effectively target his manic symptoms. Risperidone was increased to 2 mg twice a day. After this change, Mr. A’s grandiosity dissipated, his speech normalized, and his thought process became organized. He was discharged on lorazepam 2 mg 3 times a day, divalproex sodium 500 mg 3 times a day, and risperidone 2 mg twice a day. Mr. A’s length of stay (LOS) for this admission was 11 days.
Continue to: Case 2
Case 2
Mr. B, age 49, presented with irritability and odd posturing. He has a history of schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type for which he was receiving a maintenance regimen of lithium 600 mg/d at bedtime and risperidone 2 mg/d at bedtime. He had multiple previous psychiatric admissions for catatonia. On this admission, Mr. B was irritable and difficult to redirect. He yelled at staff members and had a stiff gait. The BFCRS yielded a positive screening score of 3/14 and a severity score of 8/23. As a result, the treatment team conducted a lorazepam challenge.
After Mr. B received lorazepam 1 mg IM, his thought organization and irritability improved, which allowed him to have a coherent conversation with the interviewer. His gait stiffness also improved. His risperidone and lithium were held, and oral lorazepam 1 mg 3 times a day was started for catatonia. Lorazepam was gradually increased to 4 mg 3 times a day. Mr. B became euthymic and redirectable, and had an improved gait. However, he was also tangential and hyperverbal; these symptoms were indicative of the underlying mania that precipitated his catatonia.
Divalproex sodium extended release (ER) was started and increased to 1,500 mg/d at bedtime for mood stabilization. Lithium was restarted and increased to 300 mg twice a day for adjunct mood stabilization. Risperidone was not restarted. Toward the end of his admission, Mr. B was noted to be overly sedated, so the lorazepam dosage was decreased. He was discharged on lorazepam 2 mg 3 times a day, divalproex sodium ER 1,500 mg/d at bedtime, and lithium 300 mg twice a day. At discharge, Mr. B was calm and euthymic, with a linear thought process. His LOS was 25 days.
Case 3
Mr. C, age 62, presented to the emergency department (ED) because he had exhibited erratic behavior and had not slept for the past week. He has a history of bipolar I disorder, hypothyroidism, diabetes, and hypertension. For many years, he had been stable on divalproex sodium ER 2,500 mg/d at bedtime for mood stabilization and clozapine 100 mg/d at bedtime for adjunct mood stabilization and psychosis. In the ED, Mr. C was irritable, distractible, and tangential. On admission, he was speaking slowly with increased speech latency in response to questions, exhibiting stereotypy, repeating statements over and over, and walking very slowly.
The BFCRS yielded a positive screening score of 5/14 and a severity score of 10/23. Lorazepam 1 mg IM was administered. After 15 minutes, Mr. C’s speech, gait, and distractibility improved. As a result, clozapine and divalproex sodium were held, and he was started on oral lorazepam 1 mg 3 times a day. After several days, Mr. C was speaking fluently and no longer exhibiting stereotypy or having outbursts where he would make repetitive statements. However, he was tangential and irritable at times, which were signs of his underlying mania. Divalproex sodium ER was restarted at 250 mg/d at bedtime for mood stabilization and gradually increased to 2,500 mg/d at bedtime. Clozapine was also restarted at 25 mg/d at bedtime and gradually increased to 200 mg/d at bedtime. The lorazepam was gradually tapered and discontinued over the course of 3 weeks due to oversedation.
Continue to: At discharge...
At discharge, Mr. C was euthymic, calm, linear, and goal-directed. He was discharged on divalproex sodium ER 2,500 mg/d at bedtime and clozapine 200 mg/d at bedtime. His LOS for this admission was 22 days.
A stepwise approach can improve outcomes
The Figure outlines the method we used to manage excited catatonia in these 3 cases. Each of these patients exhibited signs of excited catatonia, but because those symptoms were nearly identical to those of mania, it was initially difficult to identify catatonia. Excited catatonia was suspected after more typical catatonic symptoms—such as a stiff gait, slowed speech, and stereotypy—were observed. The BFCRS was completed to get an objective measure of the likelihood that the patient was catatonic. In all 3 cases, the BFCRS resulted in a positive screen for catatonia. Following this, the patients described in Case 2 and Case 3 received a lorazepam challenge, which confirmed their catatonia. No lorazepam challenge was performed in Case 1 because the patient was already receiving lorazepam when the BFCRS was completed. Although most catatonic patients will respond to a lorazepam challenge, not all will. Therefore, clinicians should maintain some degree of suspicion for catatonia if a patient has a positive screen on the BFCRS but a negative lorazepam challenge.
In all 3 cases, after catatonia was confirmed, the patient’s psychotropic medications were discontinued. In all 3 cases, the antipsychotic was held to prevent progression to neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) or malignant catatonia. Rasmussen et al3 found that 3.6% of the catatonic patients in their sample who were treated with antipsychotics developed NMS. A review of prospective studies looking at patients treated with antipsychotics found the incidence of NMS was .07% to 1.8%.5 Because NMS is often clinically indistinguishable from malignant catatonia,4,6 this incidence of NMS may have represented an increased incidence in malignant catatonia.
In all 3 cases, the mood stabilizer was held to prevent it from complicating the clinical picture. Discontinuing the mood stabilizer and focusing on treating the catatonia before targeting the underlying mania increased the likelihood of differentiating the patient’s catatonic symptoms from manic symptoms. This resulted in more precise medication selection and titration by allowing us to identify the specific symptoms that were being targeted by each medication.
Oral lorazepam was prescribed to target catatonia in all 3 cases, and the dosage was gradually increased until symptoms began to resolve. As the catatonia resolved, the manic symptoms became more easily identifiable, and at this point a mood stabilizer was started and titrated to a therapeutic dose to target the mania. In Case 1 and Case 3, the antipsychotic was restarted to treat the mania more effectively. It was not restarted in Case 2 because the patient’s mania was effectively being managed by 2 mood stabilizers. The risks and benefits of starting an antipsychotic in a catatonic or recently catatonic patient should be carefully considered. In the 2 cases where the antipsychotic was restarted, the patients were closely monitored, and there were no signs of NMS or malignant catatonia.
Continue to: As discharge approached...
As discharge approached, the dosages of oral lorazepam were reevaluated. Catatonic patients can typically tolerate high doses of benzodiazepines without becoming overly sedated, but each patient has a different threshold at which the dosage causes oversedation. In all 3 patients, lorazepam was initially titrated to a dose that treated their catatonic symptoms without causing intolerable sedation. In Case 2 and Case 3, as the catatonia began to resolve, the patients became increasingly sedated on their existing lorazepam dosage, so it was decreased. Because the patient in Case 1 did not become overly sedated, his lorazepam dosage did not need to be reduced.
For 2 of these patients, our approach resulted in a shorter LOS compared to their previous hospitalizations. The LOS in Case 2 was 25 days; 5 years earlier, he had a 49-day LOS for mania and catatonia. During the past admission, the identification and treatment of the catatonia was delayed, which resulted in the patient requiring multiple transfers to the medical unit for unstable vital signs. The LOS in Case 3 was 22 days; 6 months prior to this admission, the patient had 2 psychiatric admissions that totaled 37 days. Although the patient’s presentation in the 2 previous admissions was similar to his presentation as described in Case 3, catatonia had not been identified or treated in either admission. Since his catatonia and mania were treated in Case 3, he has not required a readmission. The patient in Case 1 was previously hospitalized, but information about the LOS of these admissions was not available. These results suggest that early identification and treatment of catatonia via the approach we used can improve patient outcomes.
Bottom Line
Excited catatonia can be challenging to diagnose and treat because it can present with symptoms similar to those seen in mania or psychosis. We describe 3 cases in which we used a stepwise approach to optimize treatment and improve outcomes for patients with excited catatonia. This approach may work equally well for other catatonia subtypes.
Related Resources
- Dubovsky SL, Dubovsky AN. Catatonia: how to identify and treat it. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):16-26.
- Crouse EL, Joel B. Moran JB. Catatonia: recognition, management, and prevention of complications. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(12):45-49.
Drug Brand Names
Clozapine • Clozaril
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
Risperidone • Risperdal
Divalproex sodium • Depakote
Catatonia is often difficult to identify and treat. The excited catatonia subtype can be particularly challenging to diagnose because it can present with symptoms similar to those seen in mania or psychosis. In this article, we present 3 cases of excited catatonia that illustrate how to identify it, how to treat the catatonia as well as the underlying pathology, and factors to consider during this process to mitigate the risk of adverse outcomes. We also outline a treatment algorithm we used for the 3 cases. Although we describe using this approach for patients with excited catatonia, it is generalizable to other types of catatonia.
Many causes, varying presentations
Catatonia is a psychomotor syndrome characterized by mutism, negativism, stereotypy, waxy flexibility, and other symptoms.1 It is defined by the presence of ≥3 of the 12 symptoms listed in the Table.2 Causes of catatonia include metabolic abnormalities, endocrine disorders, drug intoxication, neurodevelopmental disorders, medication adverse effects, psychosis, and mood disorders.1,3

A subtype of this syndrome, excited catatonia, can present with restlessness, agitation, emotional lability, poor sleep, and altered mental status in addition to the more typical symptoms.1,4 Because excited catatonia can resemble mania or psychosis, it is particularly challenging to identify the underlying disorder causing it and appropriate treatment. Fink et al4 discussed how clinicians have interpreted the different presentations of excited catatonia to gain insight into the underlying diagnosis. If the patient’s thought process appears disorganized, psychosis may be suspected.4 If the patient is delusional and grandiose, they may be manic, and when altered mental status dominates the presentation, delirium may be the culprit.4
Regardless of the underlying cause, the first step is to treat the catatonia. Benzodiazepines and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) are the most well validated treatments for catatonia and have been used to treat excited catatonia.1 Excited catatonia is often misdiagnosed and subsequently mistreated. In the following 3 cases, excited catatonia was successfully identified and treated using the same approach (Figure).

Case 1
Mr. A, age 27, has a history of bipolar I disorder. He was brought to the hospital by ambulance after being found to be yelling and acting belligerently, and he was admitted to the inpatient psychiatry unit for manic decompensation due to medication nonadherence. He was started on divalproex sodium 500 mg twice a day for mood stabilization, risperidone 1 mg twice a day for adjunct mood stabilization and psychosis, and lorazepam 1 mg 3 times a day for agitation. Mr. A exhibited odd behavior; he would take off his clothes in the hallway, run around the unit, and randomly yell at staff or to himself. At other times, he would stay silent, repeat the same statements, or oddly posture in the hallway for minutes at a time. These behaviors were seen primarily in the hour or 2 preceding lorazepam administration and improved after he received lorazepam.
Mr. A’s treating team completed the Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale (BFCRS), which yielded a positive catatonia screen of 7/14. As a result, divalproex sodium and risperidone were held, and lorazepam was increased to 2 mg twice a day.
After several days, Mr. A was no longer acting oddly and was able to speak more spontaneously; however, he began to exhibit overt signs of mania. He would speak rapidly and make grandiose claims about managing millions of dollars as the CEO of a famous company. Divalproex sodium was restarted at 500 mg twice a day and increased to 500 mg 3 times a day for mood stabilization. Mr. A continued to receive lorazepam 2 mg 3 times a day for catatonia, and risperidone was restarted at 1 mg twice a day to more effectively target his manic symptoms. Risperidone was increased to 2 mg twice a day. After this change, Mr. A’s grandiosity dissipated, his speech normalized, and his thought process became organized. He was discharged on lorazepam 2 mg 3 times a day, divalproex sodium 500 mg 3 times a day, and risperidone 2 mg twice a day. Mr. A’s length of stay (LOS) for this admission was 11 days.
Continue to: Case 2
Case 2
Mr. B, age 49, presented with irritability and odd posturing. He has a history of schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type for which he was receiving a maintenance regimen of lithium 600 mg/d at bedtime and risperidone 2 mg/d at bedtime. He had multiple previous psychiatric admissions for catatonia. On this admission, Mr. B was irritable and difficult to redirect. He yelled at staff members and had a stiff gait. The BFCRS yielded a positive screening score of 3/14 and a severity score of 8/23. As a result, the treatment team conducted a lorazepam challenge.
After Mr. B received lorazepam 1 mg IM, his thought organization and irritability improved, which allowed him to have a coherent conversation with the interviewer. His gait stiffness also improved. His risperidone and lithium were held, and oral lorazepam 1 mg 3 times a day was started for catatonia. Lorazepam was gradually increased to 4 mg 3 times a day. Mr. B became euthymic and redirectable, and had an improved gait. However, he was also tangential and hyperverbal; these symptoms were indicative of the underlying mania that precipitated his catatonia.
Divalproex sodium extended release (ER) was started and increased to 1,500 mg/d at bedtime for mood stabilization. Lithium was restarted and increased to 300 mg twice a day for adjunct mood stabilization. Risperidone was not restarted. Toward the end of his admission, Mr. B was noted to be overly sedated, so the lorazepam dosage was decreased. He was discharged on lorazepam 2 mg 3 times a day, divalproex sodium ER 1,500 mg/d at bedtime, and lithium 300 mg twice a day. At discharge, Mr. B was calm and euthymic, with a linear thought process. His LOS was 25 days.
Case 3
Mr. C, age 62, presented to the emergency department (ED) because he had exhibited erratic behavior and had not slept for the past week. He has a history of bipolar I disorder, hypothyroidism, diabetes, and hypertension. For many years, he had been stable on divalproex sodium ER 2,500 mg/d at bedtime for mood stabilization and clozapine 100 mg/d at bedtime for adjunct mood stabilization and psychosis. In the ED, Mr. C was irritable, distractible, and tangential. On admission, he was speaking slowly with increased speech latency in response to questions, exhibiting stereotypy, repeating statements over and over, and walking very slowly.
The BFCRS yielded a positive screening score of 5/14 and a severity score of 10/23. Lorazepam 1 mg IM was administered. After 15 minutes, Mr. C’s speech, gait, and distractibility improved. As a result, clozapine and divalproex sodium were held, and he was started on oral lorazepam 1 mg 3 times a day. After several days, Mr. C was speaking fluently and no longer exhibiting stereotypy or having outbursts where he would make repetitive statements. However, he was tangential and irritable at times, which were signs of his underlying mania. Divalproex sodium ER was restarted at 250 mg/d at bedtime for mood stabilization and gradually increased to 2,500 mg/d at bedtime. Clozapine was also restarted at 25 mg/d at bedtime and gradually increased to 200 mg/d at bedtime. The lorazepam was gradually tapered and discontinued over the course of 3 weeks due to oversedation.
Continue to: At discharge...
At discharge, Mr. C was euthymic, calm, linear, and goal-directed. He was discharged on divalproex sodium ER 2,500 mg/d at bedtime and clozapine 200 mg/d at bedtime. His LOS for this admission was 22 days.
A stepwise approach can improve outcomes
The Figure outlines the method we used to manage excited catatonia in these 3 cases. Each of these patients exhibited signs of excited catatonia, but because those symptoms were nearly identical to those of mania, it was initially difficult to identify catatonia. Excited catatonia was suspected after more typical catatonic symptoms—such as a stiff gait, slowed speech, and stereotypy—were observed. The BFCRS was completed to get an objective measure of the likelihood that the patient was catatonic. In all 3 cases, the BFCRS resulted in a positive screen for catatonia. Following this, the patients described in Case 2 and Case 3 received a lorazepam challenge, which confirmed their catatonia. No lorazepam challenge was performed in Case 1 because the patient was already receiving lorazepam when the BFCRS was completed. Although most catatonic patients will respond to a lorazepam challenge, not all will. Therefore, clinicians should maintain some degree of suspicion for catatonia if a patient has a positive screen on the BFCRS but a negative lorazepam challenge.
In all 3 cases, after catatonia was confirmed, the patient’s psychotropic medications were discontinued. In all 3 cases, the antipsychotic was held to prevent progression to neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) or malignant catatonia. Rasmussen et al3 found that 3.6% of the catatonic patients in their sample who were treated with antipsychotics developed NMS. A review of prospective studies looking at patients treated with antipsychotics found the incidence of NMS was .07% to 1.8%.5 Because NMS is often clinically indistinguishable from malignant catatonia,4,6 this incidence of NMS may have represented an increased incidence in malignant catatonia.
In all 3 cases, the mood stabilizer was held to prevent it from complicating the clinical picture. Discontinuing the mood stabilizer and focusing on treating the catatonia before targeting the underlying mania increased the likelihood of differentiating the patient’s catatonic symptoms from manic symptoms. This resulted in more precise medication selection and titration by allowing us to identify the specific symptoms that were being targeted by each medication.
Oral lorazepam was prescribed to target catatonia in all 3 cases, and the dosage was gradually increased until symptoms began to resolve. As the catatonia resolved, the manic symptoms became more easily identifiable, and at this point a mood stabilizer was started and titrated to a therapeutic dose to target the mania. In Case 1 and Case 3, the antipsychotic was restarted to treat the mania more effectively. It was not restarted in Case 2 because the patient’s mania was effectively being managed by 2 mood stabilizers. The risks and benefits of starting an antipsychotic in a catatonic or recently catatonic patient should be carefully considered. In the 2 cases where the antipsychotic was restarted, the patients were closely monitored, and there were no signs of NMS or malignant catatonia.
Continue to: As discharge approached...
As discharge approached, the dosages of oral lorazepam were reevaluated. Catatonic patients can typically tolerate high doses of benzodiazepines without becoming overly sedated, but each patient has a different threshold at which the dosage causes oversedation. In all 3 patients, lorazepam was initially titrated to a dose that treated their catatonic symptoms without causing intolerable sedation. In Case 2 and Case 3, as the catatonia began to resolve, the patients became increasingly sedated on their existing lorazepam dosage, so it was decreased. Because the patient in Case 1 did not become overly sedated, his lorazepam dosage did not need to be reduced.
For 2 of these patients, our approach resulted in a shorter LOS compared to their previous hospitalizations. The LOS in Case 2 was 25 days; 5 years earlier, he had a 49-day LOS for mania and catatonia. During the past admission, the identification and treatment of the catatonia was delayed, which resulted in the patient requiring multiple transfers to the medical unit for unstable vital signs. The LOS in Case 3 was 22 days; 6 months prior to this admission, the patient had 2 psychiatric admissions that totaled 37 days. Although the patient’s presentation in the 2 previous admissions was similar to his presentation as described in Case 3, catatonia had not been identified or treated in either admission. Since his catatonia and mania were treated in Case 3, he has not required a readmission. The patient in Case 1 was previously hospitalized, but information about the LOS of these admissions was not available. These results suggest that early identification and treatment of catatonia via the approach we used can improve patient outcomes.
Bottom Line
Excited catatonia can be challenging to diagnose and treat because it can present with symptoms similar to those seen in mania or psychosis. We describe 3 cases in which we used a stepwise approach to optimize treatment and improve outcomes for patients with excited catatonia. This approach may work equally well for other catatonia subtypes.
Related Resources
- Dubovsky SL, Dubovsky AN. Catatonia: how to identify and treat it. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):16-26.
- Crouse EL, Joel B. Moran JB. Catatonia: recognition, management, and prevention of complications. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(12):45-49.
Drug Brand Names
Clozapine • Clozaril
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
Risperidone • Risperdal
Divalproex sodium • Depakote
1. Fink M, Taylor MA. The many varieties of catatonia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;251(Suppl 1):8-13.
2. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013:119-121.
3. Rasmussen SA, Mazurek MF, Rosebush PI. Catatonia: our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. World J Psychiatry. 2016;6(4):391-398.
4. Fink M, Taylor MA. Catatonia: A Clinician’s Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment. Cambridge University Press; 2003.
5. Adityanjee, Aderibigbe YA, Matthews T. Epidemiology of neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1999;22(3):151-158.
6. Strawn JR, Keck PE Jr, Caroff SN. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(6):870-876.
1. Fink M, Taylor MA. The many varieties of catatonia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;251(Suppl 1):8-13.
2. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013:119-121.
3. Rasmussen SA, Mazurek MF, Rosebush PI. Catatonia: our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. World J Psychiatry. 2016;6(4):391-398.
4. Fink M, Taylor MA. Catatonia: A Clinician’s Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment. Cambridge University Press; 2003.
5. Adityanjee, Aderibigbe YA, Matthews T. Epidemiology of neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1999;22(3):151-158.
6. Strawn JR, Keck PE Jr, Caroff SN. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(6):870-876.
Cluster headache tied to high risk of mental and neurologic disorders
, leading to significant disability and absenteeism, new research shows.
Results from a Swedish register-based study also showed that patients with cluster headache had a sixfold increased risk for central nervous system disorders and a twofold increased risk for musculoskeletal disorders.
Although cluster headaches are often more prevalent in men, researchers found that multimorbidity rates were significantly higher in women. In addition, rates of external injuries were significantly higher among individuals with cluster headache than among persons without cluster headache.
“The findings very clearly indicate that cluster headache patients suffer from other health issues as well and that they are at risk of having longer periods of times when they cannot work,” said lead investigator Caroline Ran, PhD, a research specialist in the department of neuroscience at the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm.
“It’s really important for clinicians to look at cluster headache from a broader perspective and make sure that patients are followed up so that they don’t risk ending up in a situation where they have several comorbidities,” Dr. Ran added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
‘Striking’ finding
Cluster headache is one of the most severe and debilitating types of headache. It causes intense pain behind the eyes, which has been described as being worse than pain associated with childbirth or kidney stones.
Attacks can occur multiple times in a single day and can last up to 3 hours. Cluster headache is rare, occurring in about 1 in 1,000 individuals, and is more common in men. Underdiagnosis is common – especially in women.
The study drew on two Swedish population-based registries and included 3,240 patients with cluster headache aged 16-64 years and 16,200 matched control persons. The analysis covered medical visits from 2001 to 2010.
Results showed that 91.9% of participants with cluster headache had some type of multimorbidity. By comparison, 77.6% of the control group had some type of multimorbidity (odds ratio, 3.26; P < .0001).
Prior studies have shown a higher incidence of mental health and behavioral disorders among patients with cluster headache. However, when the researchers removed those conditions along with external injuries from the dataset, patients with headache were still significantly more likely to have multiple co-occurring illnesses (86.7% vs. 68.8%; OR, 2.95; P < .0001).
The most common comorbid conditions in the overall cluster headache group were diseases of the nervous system (OR, 5.9; 95% CI, 5.46 -6.42); 51.8% of the cluster headache group reported these disorders, compared with just 15.4% of the control group.
Diseases of the eye, the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal systems, and connective tissue were also significantly more common among patients with cluster headache.
“For each diagnosis that we investigated, we found a higher incidence in the cluster headache group, and we thought this was a very striking finding and worth discussing in the clinical setting that these patients are at risk of general ill health,” Dr. Ran said.
Risky behavior?
Another novel finding was the higher rate of external injuries among the cluster headache group, compared with the control group. The finding seems to back up the theory that patients with cluster headache are more likely to engage in risky behaviors, the researchers noted.
In the cluster headache group, external injuries were reported by 47.1% of men and 41% of women, versus 34.9% and 26.0%, respectively, in the control group.
“Now we can also show that cluster headache patients have more injuries and that is totally unrelated to the biological health of the individuals, so that could also indicate higher risk taking,” Dr. Ran said.
Overall multimorbidity rates and diagnoses in each medical category except external injury were higher among women with cluster headache than men with headaches. In addition, the mean number of days on sick leave and disability pension was higher among women with cluster headache than among men with cluster headache (83.71 days vs. 52.56 days).
Overall, the mean number of sickness absence and disability pension net days in 2010 was nearly twice as high in the cluster headache group as in the control group (63.15 days vs. 34.08 days).
Removing mental and behavioral health disorders from the mix did not lower those numbers.
“Our numbers indicate that the mental health issues that are related to cluster headache might not impact their work situation as much as the other comorbidities,” Dr. Ran said.
Struggle is real
Commenting on the findings, Heidi Schwarz, MD, professor of clinical neurology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, called the study a “valuable contribution” to the field and to the treatment of cluster headache.
“It’s a good study that addresses factors that really need to be considered as you take care of these patients,” said Dr. Schwarz, who was not involved with the research.
“The most salient features of this is that cluster headache is quite disabling, and if you add a comorbidity to it, it’s even more disabling,” she said.
Dr. Schwarz noted that cluster headache is often misdiagnosed as migraine or is overlooked altogether, especially in women. These data underscore that, although cluster headache is more common in men, it affects women too and could lead to even greater disability.
“This has a direct impact on patient quality of life, and in the end, that really should be what we’re looking to enhance,” Dr. Schwarz said. “When a patient with cluster comes in and they tell you they’re really struggling, believe them because it’s quite real.”
The findings also fill a gap in the literature and offer the kind of data that could not be collected in the United States, she noted. Sweden provides paid sick time for all workers aged 16 and older and offers a disability pension to all workers whose ability to work is temporarily or permanently inhibited because of illness or injury.
“You will never get this kind of data in the United States because this kind of data comes from two datasets that are extremely inclusive and detailed in a society, Sweden, where they have a social support system,” Dr. Schwarz said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Brain Foundation, and Mellby Gård, Region Stockholm, Märta Lundkvist stiftelse and Karolinska Institutet research funds. Dr. Ran and Dr. Schwarz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, leading to significant disability and absenteeism, new research shows.
Results from a Swedish register-based study also showed that patients with cluster headache had a sixfold increased risk for central nervous system disorders and a twofold increased risk for musculoskeletal disorders.
Although cluster headaches are often more prevalent in men, researchers found that multimorbidity rates were significantly higher in women. In addition, rates of external injuries were significantly higher among individuals with cluster headache than among persons without cluster headache.
“The findings very clearly indicate that cluster headache patients suffer from other health issues as well and that they are at risk of having longer periods of times when they cannot work,” said lead investigator Caroline Ran, PhD, a research specialist in the department of neuroscience at the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm.
“It’s really important for clinicians to look at cluster headache from a broader perspective and make sure that patients are followed up so that they don’t risk ending up in a situation where they have several comorbidities,” Dr. Ran added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
‘Striking’ finding
Cluster headache is one of the most severe and debilitating types of headache. It causes intense pain behind the eyes, which has been described as being worse than pain associated with childbirth or kidney stones.
Attacks can occur multiple times in a single day and can last up to 3 hours. Cluster headache is rare, occurring in about 1 in 1,000 individuals, and is more common in men. Underdiagnosis is common – especially in women.
The study drew on two Swedish population-based registries and included 3,240 patients with cluster headache aged 16-64 years and 16,200 matched control persons. The analysis covered medical visits from 2001 to 2010.
Results showed that 91.9% of participants with cluster headache had some type of multimorbidity. By comparison, 77.6% of the control group had some type of multimorbidity (odds ratio, 3.26; P < .0001).
Prior studies have shown a higher incidence of mental health and behavioral disorders among patients with cluster headache. However, when the researchers removed those conditions along with external injuries from the dataset, patients with headache were still significantly more likely to have multiple co-occurring illnesses (86.7% vs. 68.8%; OR, 2.95; P < .0001).
The most common comorbid conditions in the overall cluster headache group were diseases of the nervous system (OR, 5.9; 95% CI, 5.46 -6.42); 51.8% of the cluster headache group reported these disorders, compared with just 15.4% of the control group.
Diseases of the eye, the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal systems, and connective tissue were also significantly more common among patients with cluster headache.
“For each diagnosis that we investigated, we found a higher incidence in the cluster headache group, and we thought this was a very striking finding and worth discussing in the clinical setting that these patients are at risk of general ill health,” Dr. Ran said.
Risky behavior?
Another novel finding was the higher rate of external injuries among the cluster headache group, compared with the control group. The finding seems to back up the theory that patients with cluster headache are more likely to engage in risky behaviors, the researchers noted.
In the cluster headache group, external injuries were reported by 47.1% of men and 41% of women, versus 34.9% and 26.0%, respectively, in the control group.
“Now we can also show that cluster headache patients have more injuries and that is totally unrelated to the biological health of the individuals, so that could also indicate higher risk taking,” Dr. Ran said.
Overall multimorbidity rates and diagnoses in each medical category except external injury were higher among women with cluster headache than men with headaches. In addition, the mean number of days on sick leave and disability pension was higher among women with cluster headache than among men with cluster headache (83.71 days vs. 52.56 days).
Overall, the mean number of sickness absence and disability pension net days in 2010 was nearly twice as high in the cluster headache group as in the control group (63.15 days vs. 34.08 days).
Removing mental and behavioral health disorders from the mix did not lower those numbers.
“Our numbers indicate that the mental health issues that are related to cluster headache might not impact their work situation as much as the other comorbidities,” Dr. Ran said.
Struggle is real
Commenting on the findings, Heidi Schwarz, MD, professor of clinical neurology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, called the study a “valuable contribution” to the field and to the treatment of cluster headache.
“It’s a good study that addresses factors that really need to be considered as you take care of these patients,” said Dr. Schwarz, who was not involved with the research.
“The most salient features of this is that cluster headache is quite disabling, and if you add a comorbidity to it, it’s even more disabling,” she said.
Dr. Schwarz noted that cluster headache is often misdiagnosed as migraine or is overlooked altogether, especially in women. These data underscore that, although cluster headache is more common in men, it affects women too and could lead to even greater disability.
“This has a direct impact on patient quality of life, and in the end, that really should be what we’re looking to enhance,” Dr. Schwarz said. “When a patient with cluster comes in and they tell you they’re really struggling, believe them because it’s quite real.”
The findings also fill a gap in the literature and offer the kind of data that could not be collected in the United States, she noted. Sweden provides paid sick time for all workers aged 16 and older and offers a disability pension to all workers whose ability to work is temporarily or permanently inhibited because of illness or injury.
“You will never get this kind of data in the United States because this kind of data comes from two datasets that are extremely inclusive and detailed in a society, Sweden, where they have a social support system,” Dr. Schwarz said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Brain Foundation, and Mellby Gård, Region Stockholm, Märta Lundkvist stiftelse and Karolinska Institutet research funds. Dr. Ran and Dr. Schwarz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, leading to significant disability and absenteeism, new research shows.
Results from a Swedish register-based study also showed that patients with cluster headache had a sixfold increased risk for central nervous system disorders and a twofold increased risk for musculoskeletal disorders.
Although cluster headaches are often more prevalent in men, researchers found that multimorbidity rates were significantly higher in women. In addition, rates of external injuries were significantly higher among individuals with cluster headache than among persons without cluster headache.
“The findings very clearly indicate that cluster headache patients suffer from other health issues as well and that they are at risk of having longer periods of times when they cannot work,” said lead investigator Caroline Ran, PhD, a research specialist in the department of neuroscience at the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm.
“It’s really important for clinicians to look at cluster headache from a broader perspective and make sure that patients are followed up so that they don’t risk ending up in a situation where they have several comorbidities,” Dr. Ran added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
‘Striking’ finding
Cluster headache is one of the most severe and debilitating types of headache. It causes intense pain behind the eyes, which has been described as being worse than pain associated with childbirth or kidney stones.
Attacks can occur multiple times in a single day and can last up to 3 hours. Cluster headache is rare, occurring in about 1 in 1,000 individuals, and is more common in men. Underdiagnosis is common – especially in women.
The study drew on two Swedish population-based registries and included 3,240 patients with cluster headache aged 16-64 years and 16,200 matched control persons. The analysis covered medical visits from 2001 to 2010.
Results showed that 91.9% of participants with cluster headache had some type of multimorbidity. By comparison, 77.6% of the control group had some type of multimorbidity (odds ratio, 3.26; P < .0001).
Prior studies have shown a higher incidence of mental health and behavioral disorders among patients with cluster headache. However, when the researchers removed those conditions along with external injuries from the dataset, patients with headache were still significantly more likely to have multiple co-occurring illnesses (86.7% vs. 68.8%; OR, 2.95; P < .0001).
The most common comorbid conditions in the overall cluster headache group were diseases of the nervous system (OR, 5.9; 95% CI, 5.46 -6.42); 51.8% of the cluster headache group reported these disorders, compared with just 15.4% of the control group.
Diseases of the eye, the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal systems, and connective tissue were also significantly more common among patients with cluster headache.
“For each diagnosis that we investigated, we found a higher incidence in the cluster headache group, and we thought this was a very striking finding and worth discussing in the clinical setting that these patients are at risk of general ill health,” Dr. Ran said.
Risky behavior?
Another novel finding was the higher rate of external injuries among the cluster headache group, compared with the control group. The finding seems to back up the theory that patients with cluster headache are more likely to engage in risky behaviors, the researchers noted.
In the cluster headache group, external injuries were reported by 47.1% of men and 41% of women, versus 34.9% and 26.0%, respectively, in the control group.
“Now we can also show that cluster headache patients have more injuries and that is totally unrelated to the biological health of the individuals, so that could also indicate higher risk taking,” Dr. Ran said.
Overall multimorbidity rates and diagnoses in each medical category except external injury were higher among women with cluster headache than men with headaches. In addition, the mean number of days on sick leave and disability pension was higher among women with cluster headache than among men with cluster headache (83.71 days vs. 52.56 days).
Overall, the mean number of sickness absence and disability pension net days in 2010 was nearly twice as high in the cluster headache group as in the control group (63.15 days vs. 34.08 days).
Removing mental and behavioral health disorders from the mix did not lower those numbers.
“Our numbers indicate that the mental health issues that are related to cluster headache might not impact their work situation as much as the other comorbidities,” Dr. Ran said.
Struggle is real
Commenting on the findings, Heidi Schwarz, MD, professor of clinical neurology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, called the study a “valuable contribution” to the field and to the treatment of cluster headache.
“It’s a good study that addresses factors that really need to be considered as you take care of these patients,” said Dr. Schwarz, who was not involved with the research.
“The most salient features of this is that cluster headache is quite disabling, and if you add a comorbidity to it, it’s even more disabling,” she said.
Dr. Schwarz noted that cluster headache is often misdiagnosed as migraine or is overlooked altogether, especially in women. These data underscore that, although cluster headache is more common in men, it affects women too and could lead to even greater disability.
“This has a direct impact on patient quality of life, and in the end, that really should be what we’re looking to enhance,” Dr. Schwarz said. “When a patient with cluster comes in and they tell you they’re really struggling, believe them because it’s quite real.”
The findings also fill a gap in the literature and offer the kind of data that could not be collected in the United States, she noted. Sweden provides paid sick time for all workers aged 16 and older and offers a disability pension to all workers whose ability to work is temporarily or permanently inhibited because of illness or injury.
“You will never get this kind of data in the United States because this kind of data comes from two datasets that are extremely inclusive and detailed in a society, Sweden, where they have a social support system,” Dr. Schwarz said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Brain Foundation, and Mellby Gård, Region Stockholm, Märta Lundkvist stiftelse and Karolinska Institutet research funds. Dr. Ran and Dr. Schwarz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Greater handgrip strength tied to lower risk for depression
, new research suggests.
In a study of more than 115,000 adults, there was a significant association between stronger handgrip, up to 40 kg in men and 27 kg in women, and lower depression risk.
Investigators add that there was a “dose-response” association between physical strength and risk for depression.
“Being physically strong may serve as a preventive factor for depression in older adults, but this is limited to a maximum specific threshold for men and women,” Ruben Lopez-Bueno, PhD, of the department of physical medicine and nursing, University of Zaragoza, Spain, and colleagues write.
The findings were published online in the British Journal of Psychiatry.
Easy, fast, reliable
Depression is a major public health problem, and studies “aimed at examining preventive factors to tackle the increase in depression are required,” the investigators write.
They add that a “growing body of research” is examining the link between depression and muscle strength, with handgrip as an estimator, in healthy middle-aged and older adults.
Handgrip strength is an “easy-to-use, fast and reliable indicator of both sarcopenia (age-related loss of muscle mass) and dynapenia (age-related loss of muscle strength), both of which have been associated with depression,” the researchers note.
It is plausible that there is a “regulatory role of skeletal muscle on brain function affecting this condition,” they add.
They note that exercise seems to play a “key role” because it can improve muscle strength as well as muscle mass, downregulate systemic inflammation, and improve neuroplasticity, neuroendocrine, and oxidative stress responses.
Previous studies have relied either on cross-sectional or prospective cohort models and have focused mostly on a specific country, “not accounting for time-varying changes of both handgrip strength and relevant covariables.”
Moreover, previous evidence has been mixed regarding the “extent to which handgrip strength levels may associate with lower risk of depression, with study results ranging from weak to strong associations,” the investigators write.
So “higher-quality research with representative samples from different countries is required to better clarify the strength of such an association and to confirm directionality,” they add.
SHARE data
To fill this gap, the researchers turned to data from waves 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, and 7 of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE). This encompassed 115,601 individuals aged 50 years and older (mean age, 64.3 years; 54.3% women) residing in European countries and Israel (24 countries total).
Data from wave 3 were not used because handgrip measures were not used in that wave. In the other waves, a handheld dynamometer was used to measure handgrip strength.
The participants were divided into tertiles of handgrip strength, with the “first third” being the lowest tertile of strength and the “final third” representing the highest strength.
All participants were followed for a median of 7.3 years (792,459 person-years), during which 26.1% experienced a risk for depression, as reflected by scores on the EURO-D 12-item scale.
The investigators set the time scale as the months from study entry until either a first depression onset or the end of follow-up.
Covariates that the researchers accounted for included gender, age, education, country, body mass index, physical inactivity, smoking, alcohol consumption, whether living with a partner, wave of inclusion, chronic diseases, consumption of prescribed drugs, and fruit and vegetable consumption.
The researchers used two models: the first adjusted for gender and age at time of the interview, and the second adjusted for all confounders.
In the model that was adjusted only for gender and age, greater handgrip strength was associated with a significantly reduced risk for depression among participants in the second, third, and the final third in comparison with the first third (hazard ratio, 0.65; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.68; and HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.48-0.53, respectively).
The associations remained consistent in the fully adjusted model, although risk for depression was slightly attenuated in the second and final thirds compared with the first third (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.71-0.81; and HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.59-0.69, respectively).
When the researchers conducted analyses using restricted cubic spline modeling, they found a significant association for each kilogram increase of handgrip strength and depression, up to 40 kg in men and 27 kg in women (HR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.08-1.71; and HR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.05-1.55, respectively).
There was no greater reduction in depression risk in those with handgrip strength above those values.
Potential depression screen
The investigators suggest several explanations for their findings. For example, handgrip strength has “been used as an overall indicator of health status, including sarcopenia,” they write.
Adults with sarcopenia have been found to be at greater risk for depression because of reduced muscle strength, since neurotrophins are produced by skeletal muscle, among other tissues, and are associated with improvement in mood.
From a psychological point of view, “being physically strong may lead to a sensation of psychological wellbeing,” the researchers write.
Moreover, being physically active “across the lifespan also promotes structural and functional changes in the brain, benefiting cognitive functioning and reducing the risk of neurodegeneration,” they write.
This can be important because aging adults with cognitive impairments can also experience neuromuscular impairments that “presumably will contribute to becoming weaker,” they note.
Overall, the findings “warrant strength training programmes aimed at older adults to reduce depression risk,” the investigators write. Clinicians “may consider using the observed handgrip strength thresholds to screen for potential depression risk in older adults,” they add.
Protective factor?
Commenting for this news organization, Julian Mutz, PhD, postdoctoral research associate at the Social, Genetic and Developmental Psychiatry Centre, King’s College, London, said the study “provides further evidence that physical strength may be a protective factor against depression in older adults.”
This confirms a “plethora of cross-sectional and longitudinal studies,” including one recently conducted by Dr. Mutz’s group.
The design of the current study “allowed the authors to address a number of key limitations of previous studies, for example, by including repeated measurements of grip strength and adjustment for potential confounding factors over time,” said Dr. Mutz, who was not involved with the research.
Additionally, “an important contribution of this study is that the authors show that higher grip strength is only associated with a lower risk of depression up to a specific threshold,” he noted.
“The clinical implication of this finding is that only individuals with grip strength below this threshold are at a higher risk of depression. These individuals especially may benefit from interventions aimed at increasing physical strength,” Dr. Mutz said.
The SHARE data collection has been funded by the European Commission and by DG Employment, Social Affairs and Inclusion. Additional funding was obtained from the German Ministry of Education and Research, the Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science, and the U.S. National Institute on Aging. Dr. Lopez-Bueno is supported by the European Union – Next Generation EU. The other investigators and Dr. Mutz have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a study of more than 115,000 adults, there was a significant association between stronger handgrip, up to 40 kg in men and 27 kg in women, and lower depression risk.
Investigators add that there was a “dose-response” association between physical strength and risk for depression.
“Being physically strong may serve as a preventive factor for depression in older adults, but this is limited to a maximum specific threshold for men and women,” Ruben Lopez-Bueno, PhD, of the department of physical medicine and nursing, University of Zaragoza, Spain, and colleagues write.
The findings were published online in the British Journal of Psychiatry.
Easy, fast, reliable
Depression is a major public health problem, and studies “aimed at examining preventive factors to tackle the increase in depression are required,” the investigators write.
They add that a “growing body of research” is examining the link between depression and muscle strength, with handgrip as an estimator, in healthy middle-aged and older adults.
Handgrip strength is an “easy-to-use, fast and reliable indicator of both sarcopenia (age-related loss of muscle mass) and dynapenia (age-related loss of muscle strength), both of which have been associated with depression,” the researchers note.
It is plausible that there is a “regulatory role of skeletal muscle on brain function affecting this condition,” they add.
They note that exercise seems to play a “key role” because it can improve muscle strength as well as muscle mass, downregulate systemic inflammation, and improve neuroplasticity, neuroendocrine, and oxidative stress responses.
Previous studies have relied either on cross-sectional or prospective cohort models and have focused mostly on a specific country, “not accounting for time-varying changes of both handgrip strength and relevant covariables.”
Moreover, previous evidence has been mixed regarding the “extent to which handgrip strength levels may associate with lower risk of depression, with study results ranging from weak to strong associations,” the investigators write.
So “higher-quality research with representative samples from different countries is required to better clarify the strength of such an association and to confirm directionality,” they add.
SHARE data
To fill this gap, the researchers turned to data from waves 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, and 7 of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE). This encompassed 115,601 individuals aged 50 years and older (mean age, 64.3 years; 54.3% women) residing in European countries and Israel (24 countries total).
Data from wave 3 were not used because handgrip measures were not used in that wave. In the other waves, a handheld dynamometer was used to measure handgrip strength.
The participants were divided into tertiles of handgrip strength, with the “first third” being the lowest tertile of strength and the “final third” representing the highest strength.
All participants were followed for a median of 7.3 years (792,459 person-years), during which 26.1% experienced a risk for depression, as reflected by scores on the EURO-D 12-item scale.
The investigators set the time scale as the months from study entry until either a first depression onset or the end of follow-up.
Covariates that the researchers accounted for included gender, age, education, country, body mass index, physical inactivity, smoking, alcohol consumption, whether living with a partner, wave of inclusion, chronic diseases, consumption of prescribed drugs, and fruit and vegetable consumption.
The researchers used two models: the first adjusted for gender and age at time of the interview, and the second adjusted for all confounders.
In the model that was adjusted only for gender and age, greater handgrip strength was associated with a significantly reduced risk for depression among participants in the second, third, and the final third in comparison with the first third (hazard ratio, 0.65; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.68; and HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.48-0.53, respectively).
The associations remained consistent in the fully adjusted model, although risk for depression was slightly attenuated in the second and final thirds compared with the first third (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.71-0.81; and HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.59-0.69, respectively).
When the researchers conducted analyses using restricted cubic spline modeling, they found a significant association for each kilogram increase of handgrip strength and depression, up to 40 kg in men and 27 kg in women (HR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.08-1.71; and HR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.05-1.55, respectively).
There was no greater reduction in depression risk in those with handgrip strength above those values.
Potential depression screen
The investigators suggest several explanations for their findings. For example, handgrip strength has “been used as an overall indicator of health status, including sarcopenia,” they write.
Adults with sarcopenia have been found to be at greater risk for depression because of reduced muscle strength, since neurotrophins are produced by skeletal muscle, among other tissues, and are associated with improvement in mood.
From a psychological point of view, “being physically strong may lead to a sensation of psychological wellbeing,” the researchers write.
Moreover, being physically active “across the lifespan also promotes structural and functional changes in the brain, benefiting cognitive functioning and reducing the risk of neurodegeneration,” they write.
This can be important because aging adults with cognitive impairments can also experience neuromuscular impairments that “presumably will contribute to becoming weaker,” they note.
Overall, the findings “warrant strength training programmes aimed at older adults to reduce depression risk,” the investigators write. Clinicians “may consider using the observed handgrip strength thresholds to screen for potential depression risk in older adults,” they add.
Protective factor?
Commenting for this news organization, Julian Mutz, PhD, postdoctoral research associate at the Social, Genetic and Developmental Psychiatry Centre, King’s College, London, said the study “provides further evidence that physical strength may be a protective factor against depression in older adults.”
This confirms a “plethora of cross-sectional and longitudinal studies,” including one recently conducted by Dr. Mutz’s group.
The design of the current study “allowed the authors to address a number of key limitations of previous studies, for example, by including repeated measurements of grip strength and adjustment for potential confounding factors over time,” said Dr. Mutz, who was not involved with the research.
Additionally, “an important contribution of this study is that the authors show that higher grip strength is only associated with a lower risk of depression up to a specific threshold,” he noted.
“The clinical implication of this finding is that only individuals with grip strength below this threshold are at a higher risk of depression. These individuals especially may benefit from interventions aimed at increasing physical strength,” Dr. Mutz said.
The SHARE data collection has been funded by the European Commission and by DG Employment, Social Affairs and Inclusion. Additional funding was obtained from the German Ministry of Education and Research, the Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science, and the U.S. National Institute on Aging. Dr. Lopez-Bueno is supported by the European Union – Next Generation EU. The other investigators and Dr. Mutz have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a study of more than 115,000 adults, there was a significant association between stronger handgrip, up to 40 kg in men and 27 kg in women, and lower depression risk.
Investigators add that there was a “dose-response” association between physical strength and risk for depression.
“Being physically strong may serve as a preventive factor for depression in older adults, but this is limited to a maximum specific threshold for men and women,” Ruben Lopez-Bueno, PhD, of the department of physical medicine and nursing, University of Zaragoza, Spain, and colleagues write.
The findings were published online in the British Journal of Psychiatry.
Easy, fast, reliable
Depression is a major public health problem, and studies “aimed at examining preventive factors to tackle the increase in depression are required,” the investigators write.
They add that a “growing body of research” is examining the link between depression and muscle strength, with handgrip as an estimator, in healthy middle-aged and older adults.
Handgrip strength is an “easy-to-use, fast and reliable indicator of both sarcopenia (age-related loss of muscle mass) and dynapenia (age-related loss of muscle strength), both of which have been associated with depression,” the researchers note.
It is plausible that there is a “regulatory role of skeletal muscle on brain function affecting this condition,” they add.
They note that exercise seems to play a “key role” because it can improve muscle strength as well as muscle mass, downregulate systemic inflammation, and improve neuroplasticity, neuroendocrine, and oxidative stress responses.
Previous studies have relied either on cross-sectional or prospective cohort models and have focused mostly on a specific country, “not accounting for time-varying changes of both handgrip strength and relevant covariables.”
Moreover, previous evidence has been mixed regarding the “extent to which handgrip strength levels may associate with lower risk of depression, with study results ranging from weak to strong associations,” the investigators write.
So “higher-quality research with representative samples from different countries is required to better clarify the strength of such an association and to confirm directionality,” they add.
SHARE data
To fill this gap, the researchers turned to data from waves 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, and 7 of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE). This encompassed 115,601 individuals aged 50 years and older (mean age, 64.3 years; 54.3% women) residing in European countries and Israel (24 countries total).
Data from wave 3 were not used because handgrip measures were not used in that wave. In the other waves, a handheld dynamometer was used to measure handgrip strength.
The participants were divided into tertiles of handgrip strength, with the “first third” being the lowest tertile of strength and the “final third” representing the highest strength.
All participants were followed for a median of 7.3 years (792,459 person-years), during which 26.1% experienced a risk for depression, as reflected by scores on the EURO-D 12-item scale.
The investigators set the time scale as the months from study entry until either a first depression onset or the end of follow-up.
Covariates that the researchers accounted for included gender, age, education, country, body mass index, physical inactivity, smoking, alcohol consumption, whether living with a partner, wave of inclusion, chronic diseases, consumption of prescribed drugs, and fruit and vegetable consumption.
The researchers used two models: the first adjusted for gender and age at time of the interview, and the second adjusted for all confounders.
In the model that was adjusted only for gender and age, greater handgrip strength was associated with a significantly reduced risk for depression among participants in the second, third, and the final third in comparison with the first third (hazard ratio, 0.65; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.68; and HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.48-0.53, respectively).
The associations remained consistent in the fully adjusted model, although risk for depression was slightly attenuated in the second and final thirds compared with the first third (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.71-0.81; and HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.59-0.69, respectively).
When the researchers conducted analyses using restricted cubic spline modeling, they found a significant association for each kilogram increase of handgrip strength and depression, up to 40 kg in men and 27 kg in women (HR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.08-1.71; and HR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.05-1.55, respectively).
There was no greater reduction in depression risk in those with handgrip strength above those values.
Potential depression screen
The investigators suggest several explanations for their findings. For example, handgrip strength has “been used as an overall indicator of health status, including sarcopenia,” they write.
Adults with sarcopenia have been found to be at greater risk for depression because of reduced muscle strength, since neurotrophins are produced by skeletal muscle, among other tissues, and are associated with improvement in mood.
From a psychological point of view, “being physically strong may lead to a sensation of psychological wellbeing,” the researchers write.
Moreover, being physically active “across the lifespan also promotes structural and functional changes in the brain, benefiting cognitive functioning and reducing the risk of neurodegeneration,” they write.
This can be important because aging adults with cognitive impairments can also experience neuromuscular impairments that “presumably will contribute to becoming weaker,” they note.
Overall, the findings “warrant strength training programmes aimed at older adults to reduce depression risk,” the investigators write. Clinicians “may consider using the observed handgrip strength thresholds to screen for potential depression risk in older adults,” they add.
Protective factor?
Commenting for this news organization, Julian Mutz, PhD, postdoctoral research associate at the Social, Genetic and Developmental Psychiatry Centre, King’s College, London, said the study “provides further evidence that physical strength may be a protective factor against depression in older adults.”
This confirms a “plethora of cross-sectional and longitudinal studies,” including one recently conducted by Dr. Mutz’s group.
The design of the current study “allowed the authors to address a number of key limitations of previous studies, for example, by including repeated measurements of grip strength and adjustment for potential confounding factors over time,” said Dr. Mutz, who was not involved with the research.
Additionally, “an important contribution of this study is that the authors show that higher grip strength is only associated with a lower risk of depression up to a specific threshold,” he noted.
“The clinical implication of this finding is that only individuals with grip strength below this threshold are at a higher risk of depression. These individuals especially may benefit from interventions aimed at increasing physical strength,” Dr. Mutz said.
The SHARE data collection has been funded by the European Commission and by DG Employment, Social Affairs and Inclusion. Additional funding was obtained from the German Ministry of Education and Research, the Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science, and the U.S. National Institute on Aging. Dr. Lopez-Bueno is supported by the European Union – Next Generation EU. The other investigators and Dr. Mutz have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY
Can a common artificial sweetener fuel anxiety?
In a new preclinical study, investigators observed that mice that drank water containing aspartame exhibited pronounced anxiety-like behaviors in a variety of maze tests.
This behavior occurred at aspartame doses equivalent to less than 15% of the maximum daily human intake recommended by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
“It was such a robust anxiety-like trait that I don’t think any of us were anticipating we would see. It was completely unexpected. Usually you see subtle changes,” lead author Sara Jones, doctoral candidate at Florida State University, Tallahassee, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Transgenerational transmission
When consumed, aspartame becomes aspartic acid, phenylalanine, and methanol – all of which can have potent effects on the central nervous system, the researchers point out.
Exposing the mice to aspartame also produced changes in the expression of genes regulating excitation-inhibition balance in the amygdala, a brain region that regulates anxiety and fear.
Giving the mice diazepam, which is used to treat generalized anxiety disorder, alleviated the anxiety behavior in the animals.
“The anxiety, its response to diazepam, and the changes in amygdala gene expression are not limited to the aspartame-exposed individuals but also appear in up to two generations descending from the aspartame-exposed males,” the researchers report.
“Extrapolation of the findings to humans suggests that aspartame consumption at doses below the FDA recommended maximum daily intake may produce neurobehavioral changes in aspartame-consuming individuals and their descendants,” they write.
“Thus, human population at risk of aspartame’s potential mental health effects may be larger than current expectations, which only include aspartame-consuming individuals,” they add.
Far from harmless?
The investigators plan to publish additional data from the study that focus on how aspartame affected memory in the mice.
In future research, they hope to identify molecular mechanisms that influence the transmission of aspartame’s effect across generations.
The Florida State University study joins several others that discount the long-held notion that aspartame and other nonnutritive sweeteners have no effect on the body.
As reported by this news organization, in a recent study researchers found that these sugar substitutes are not metabolically inert and can alter the gut microbiome in a way that can influence blood glucose levels.
Artificial sweeteners have also been linked to an increased risk for heart disease and stroke and for cancer.
The study was funded by the Jim and Betty Ann Rodgers Chair Fund at Florida State University and by the Bryan Robinson Foundation. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a new preclinical study, investigators observed that mice that drank water containing aspartame exhibited pronounced anxiety-like behaviors in a variety of maze tests.
This behavior occurred at aspartame doses equivalent to less than 15% of the maximum daily human intake recommended by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
“It was such a robust anxiety-like trait that I don’t think any of us were anticipating we would see. It was completely unexpected. Usually you see subtle changes,” lead author Sara Jones, doctoral candidate at Florida State University, Tallahassee, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Transgenerational transmission
When consumed, aspartame becomes aspartic acid, phenylalanine, and methanol – all of which can have potent effects on the central nervous system, the researchers point out.
Exposing the mice to aspartame also produced changes in the expression of genes regulating excitation-inhibition balance in the amygdala, a brain region that regulates anxiety and fear.
Giving the mice diazepam, which is used to treat generalized anxiety disorder, alleviated the anxiety behavior in the animals.
“The anxiety, its response to diazepam, and the changes in amygdala gene expression are not limited to the aspartame-exposed individuals but also appear in up to two generations descending from the aspartame-exposed males,” the researchers report.
“Extrapolation of the findings to humans suggests that aspartame consumption at doses below the FDA recommended maximum daily intake may produce neurobehavioral changes in aspartame-consuming individuals and their descendants,” they write.
“Thus, human population at risk of aspartame’s potential mental health effects may be larger than current expectations, which only include aspartame-consuming individuals,” they add.
Far from harmless?
The investigators plan to publish additional data from the study that focus on how aspartame affected memory in the mice.
In future research, they hope to identify molecular mechanisms that influence the transmission of aspartame’s effect across generations.
The Florida State University study joins several others that discount the long-held notion that aspartame and other nonnutritive sweeteners have no effect on the body.
As reported by this news organization, in a recent study researchers found that these sugar substitutes are not metabolically inert and can alter the gut microbiome in a way that can influence blood glucose levels.
Artificial sweeteners have also been linked to an increased risk for heart disease and stroke and for cancer.
The study was funded by the Jim and Betty Ann Rodgers Chair Fund at Florida State University and by the Bryan Robinson Foundation. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a new preclinical study, investigators observed that mice that drank water containing aspartame exhibited pronounced anxiety-like behaviors in a variety of maze tests.
This behavior occurred at aspartame doses equivalent to less than 15% of the maximum daily human intake recommended by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
“It was such a robust anxiety-like trait that I don’t think any of us were anticipating we would see. It was completely unexpected. Usually you see subtle changes,” lead author Sara Jones, doctoral candidate at Florida State University, Tallahassee, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Transgenerational transmission
When consumed, aspartame becomes aspartic acid, phenylalanine, and methanol – all of which can have potent effects on the central nervous system, the researchers point out.
Exposing the mice to aspartame also produced changes in the expression of genes regulating excitation-inhibition balance in the amygdala, a brain region that regulates anxiety and fear.
Giving the mice diazepam, which is used to treat generalized anxiety disorder, alleviated the anxiety behavior in the animals.
“The anxiety, its response to diazepam, and the changes in amygdala gene expression are not limited to the aspartame-exposed individuals but also appear in up to two generations descending from the aspartame-exposed males,” the researchers report.
“Extrapolation of the findings to humans suggests that aspartame consumption at doses below the FDA recommended maximum daily intake may produce neurobehavioral changes in aspartame-consuming individuals and their descendants,” they write.
“Thus, human population at risk of aspartame’s potential mental health effects may be larger than current expectations, which only include aspartame-consuming individuals,” they add.
Far from harmless?
The investigators plan to publish additional data from the study that focus on how aspartame affected memory in the mice.
In future research, they hope to identify molecular mechanisms that influence the transmission of aspartame’s effect across generations.
The Florida State University study joins several others that discount the long-held notion that aspartame and other nonnutritive sweeteners have no effect on the body.
As reported by this news organization, in a recent study researchers found that these sugar substitutes are not metabolically inert and can alter the gut microbiome in a way that can influence blood glucose levels.
Artificial sweeteners have also been linked to an increased risk for heart disease and stroke and for cancer.
The study was funded by the Jim and Betty Ann Rodgers Chair Fund at Florida State University and by the Bryan Robinson Foundation. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Rise of ‘alarming’ subvariants of COVID ‘worrisome’ for winter
It’s a story perhaps more appropriate for Halloween than for the festive holiday season, given its scary implications.
Not too dire so far, until the researchers’ other findings are considered.
The BQ.1, BQ1.1, XBB, and XBB.1 subvariants are the most resistant to neutralizing antibodies, researcher Qian Wang, PhD, and colleagues wrote in a study published online in the journal Cell. This means people have no or “markedly reduced” protection against infection from these four strains, even if they’ve already had COVID-19 or are vaccinated and boosted multiple times, including with a bivalent vaccine.
On top of that, all available monoclonal antibody treatments are mostly or completely ineffective against these subvariants.
What does that mean for the immediate future? The findings are definitely “worrisome,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Translational Research Institute in La Jolla, Calif.
But evidence from other countries, specifically Singapore and France, show that at least two of these variants turned out not to be as damaging as expected, likely because of high numbers of people vaccinated or who survived previous infections, he said.
Still, there is little to celebrate in the new findings, except that COVID-19 vaccinations and prior infections can still reduce the risk for serious outcomes such as hospitalization and death, the researchers wrote.
In fact, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data released on Dec. 16 shows that people who have received four shots of the original COVID-19 vaccines as well as the bivalent booster were 57% less likely to visit an urgent care clinic or emergency room, regardless of age.
It comes at a time when BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 account for about 70% of the circulating variants, data show. In addition, hospitalizations are up 18% over the past 2 weeks and COVID-19 deaths are up 50% nationwide, The New York Times reported.
Globally, in many places, an “immunity wall” that has been built, Dr. Topol said. That may not be the case in the United States.
“The problem in the United States, making it harder to predict, is that we have a very low rate of recent boosters, in the past 6 months, especially in seniors,” he said. For example, only 36% of Americans aged 65 years and older, the group with highest risk, have received an updated bivalent booster.
An evolving virus
The subvariants are successfully replacing BA.5, which reigned as one of the most common Omicron variants over the past year. The latest CDC data show that BA.5 now accounts for only about 10% of the circulating virus. The researchers wrote: “This rapid replacement of virus strains is raising the specter of yet another wave of infections in the coming months.”
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 evolved directly from BA.5 – adding more and some novel mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. XBB and XBB.1 are the “offspring” of a combination of two other strains, known as BJ.1 and BA.2.75.
The story sounds familiar to the researchers. “The rapid rise of these subvariants and their extensive array of spike mutations are reminiscent of the appearance of the first Omicron variant last year, thus raising concerns that they may further compromise the efficacy of current COVID-19 vaccines and monoclonal antibody therapeutics,” they wrote. “We now report findings that indicate that such concerns are, sadly, justified, especially so for the XBB and XBB.1 subvariants.”
To figure out how effective existing antibodies could be against these newer subvariants, Dr. Wang and colleagues used blood samples from five groups of people. They tested serum from people who had three doses of the original COVID-19 vaccine, four doses of the original vaccine, those who received a bivalent booster, people who experienced a breakthrough infection with the BA.2 Omicron variant, and those who had a breakthrough with a BA.4 or BA.5 variant.
Adding the new subvariants to these serum samples revealed that the existing antibodies in the blood were ineffective at wiping out or neutralizing BQ.1, BQ.1.1, XBB, and XBB.1.
The BQ.1 subvariant was six times more resistant to antibodies than BA.5, its parent strain, and XBB.1 was 63 times more resistant compared with its predecessor, BA.2.
This shift in the ability of vaccines to stop the subvariants “is particularly concerning,” the researchers wrote.
Wiping out treatments too
Dr. Wang and colleagues also tested how well a panel of 23 different monoclonal antibody drugs might work against the four subvariants. The therapies all worked well against the original Omicron variant and included some approved for use through the Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization (EUA) program at the time of the study.
They found that 19 of these 23 monoclonal antibodies lost effectiveness “greatly or completely” against XBB and XBB.1, for example.
This is not the first time that monoclonal antibody therapies have gone from effective to ineffective. Previous variants have come out that no longer responded to treatment with bamlanivimab, etesevimab, imdevimab, casirivimab, tixagevimab, cilgavimab, and sotrovimab. Bebtelovimab now joins this list and is no longer available from Eli Lilly under EUA because of this lack of effectiveness.
The lack of an effective monoclonal antibody treatment “poses a serious problem for millions of immunocompromised individuals who do not respond robustly to COVID-19 vaccines,” the researchers wrote, adding that “the urgent need to develop active monoclonal antibodies for clinical use is obvious.”
A limitation of the study is that the work is done in blood samples. The effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination against the BQ and XBB subvariants should be evaluated in people in clinical studies, the authors noted.
Also, the current study looked at how well antibodies could neutralize the viral strains, but future research, they added, should look at how well “cellular immunity” or other aspects of the immune system might protect people.
Going forward, the challenge remains to develop vaccines and treatments that offer broad protection as the coronavirus continues to evolve.
In an alarming ending, the researchers wrote: “We have collectively chased after SARS-CoV-2 variants for over 2 years, and yet, the virus continues to evolve and evade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s a story perhaps more appropriate for Halloween than for the festive holiday season, given its scary implications.
Not too dire so far, until the researchers’ other findings are considered.
The BQ.1, BQ1.1, XBB, and XBB.1 subvariants are the most resistant to neutralizing antibodies, researcher Qian Wang, PhD, and colleagues wrote in a study published online in the journal Cell. This means people have no or “markedly reduced” protection against infection from these four strains, even if they’ve already had COVID-19 or are vaccinated and boosted multiple times, including with a bivalent vaccine.
On top of that, all available monoclonal antibody treatments are mostly or completely ineffective against these subvariants.
What does that mean for the immediate future? The findings are definitely “worrisome,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Translational Research Institute in La Jolla, Calif.
But evidence from other countries, specifically Singapore and France, show that at least two of these variants turned out not to be as damaging as expected, likely because of high numbers of people vaccinated or who survived previous infections, he said.
Still, there is little to celebrate in the new findings, except that COVID-19 vaccinations and prior infections can still reduce the risk for serious outcomes such as hospitalization and death, the researchers wrote.
In fact, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data released on Dec. 16 shows that people who have received four shots of the original COVID-19 vaccines as well as the bivalent booster were 57% less likely to visit an urgent care clinic or emergency room, regardless of age.
It comes at a time when BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 account for about 70% of the circulating variants, data show. In addition, hospitalizations are up 18% over the past 2 weeks and COVID-19 deaths are up 50% nationwide, The New York Times reported.
Globally, in many places, an “immunity wall” that has been built, Dr. Topol said. That may not be the case in the United States.
“The problem in the United States, making it harder to predict, is that we have a very low rate of recent boosters, in the past 6 months, especially in seniors,” he said. For example, only 36% of Americans aged 65 years and older, the group with highest risk, have received an updated bivalent booster.
An evolving virus
The subvariants are successfully replacing BA.5, which reigned as one of the most common Omicron variants over the past year. The latest CDC data show that BA.5 now accounts for only about 10% of the circulating virus. The researchers wrote: “This rapid replacement of virus strains is raising the specter of yet another wave of infections in the coming months.”
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 evolved directly from BA.5 – adding more and some novel mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. XBB and XBB.1 are the “offspring” of a combination of two other strains, known as BJ.1 and BA.2.75.
The story sounds familiar to the researchers. “The rapid rise of these subvariants and their extensive array of spike mutations are reminiscent of the appearance of the first Omicron variant last year, thus raising concerns that they may further compromise the efficacy of current COVID-19 vaccines and monoclonal antibody therapeutics,” they wrote. “We now report findings that indicate that such concerns are, sadly, justified, especially so for the XBB and XBB.1 subvariants.”
To figure out how effective existing antibodies could be against these newer subvariants, Dr. Wang and colleagues used blood samples from five groups of people. They tested serum from people who had three doses of the original COVID-19 vaccine, four doses of the original vaccine, those who received a bivalent booster, people who experienced a breakthrough infection with the BA.2 Omicron variant, and those who had a breakthrough with a BA.4 or BA.5 variant.
Adding the new subvariants to these serum samples revealed that the existing antibodies in the blood were ineffective at wiping out or neutralizing BQ.1, BQ.1.1, XBB, and XBB.1.
The BQ.1 subvariant was six times more resistant to antibodies than BA.5, its parent strain, and XBB.1 was 63 times more resistant compared with its predecessor, BA.2.
This shift in the ability of vaccines to stop the subvariants “is particularly concerning,” the researchers wrote.
Wiping out treatments too
Dr. Wang and colleagues also tested how well a panel of 23 different monoclonal antibody drugs might work against the four subvariants. The therapies all worked well against the original Omicron variant and included some approved for use through the Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization (EUA) program at the time of the study.
They found that 19 of these 23 monoclonal antibodies lost effectiveness “greatly or completely” against XBB and XBB.1, for example.
This is not the first time that monoclonal antibody therapies have gone from effective to ineffective. Previous variants have come out that no longer responded to treatment with bamlanivimab, etesevimab, imdevimab, casirivimab, tixagevimab, cilgavimab, and sotrovimab. Bebtelovimab now joins this list and is no longer available from Eli Lilly under EUA because of this lack of effectiveness.
The lack of an effective monoclonal antibody treatment “poses a serious problem for millions of immunocompromised individuals who do not respond robustly to COVID-19 vaccines,” the researchers wrote, adding that “the urgent need to develop active monoclonal antibodies for clinical use is obvious.”
A limitation of the study is that the work is done in blood samples. The effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination against the BQ and XBB subvariants should be evaluated in people in clinical studies, the authors noted.
Also, the current study looked at how well antibodies could neutralize the viral strains, but future research, they added, should look at how well “cellular immunity” or other aspects of the immune system might protect people.
Going forward, the challenge remains to develop vaccines and treatments that offer broad protection as the coronavirus continues to evolve.
In an alarming ending, the researchers wrote: “We have collectively chased after SARS-CoV-2 variants for over 2 years, and yet, the virus continues to evolve and evade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s a story perhaps more appropriate for Halloween than for the festive holiday season, given its scary implications.
Not too dire so far, until the researchers’ other findings are considered.
The BQ.1, BQ1.1, XBB, and XBB.1 subvariants are the most resistant to neutralizing antibodies, researcher Qian Wang, PhD, and colleagues wrote in a study published online in the journal Cell. This means people have no or “markedly reduced” protection against infection from these four strains, even if they’ve already had COVID-19 or are vaccinated and boosted multiple times, including with a bivalent vaccine.
On top of that, all available monoclonal antibody treatments are mostly or completely ineffective against these subvariants.
What does that mean for the immediate future? The findings are definitely “worrisome,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Translational Research Institute in La Jolla, Calif.
But evidence from other countries, specifically Singapore and France, show that at least two of these variants turned out not to be as damaging as expected, likely because of high numbers of people vaccinated or who survived previous infections, he said.
Still, there is little to celebrate in the new findings, except that COVID-19 vaccinations and prior infections can still reduce the risk for serious outcomes such as hospitalization and death, the researchers wrote.
In fact, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data released on Dec. 16 shows that people who have received four shots of the original COVID-19 vaccines as well as the bivalent booster were 57% less likely to visit an urgent care clinic or emergency room, regardless of age.
It comes at a time when BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 account for about 70% of the circulating variants, data show. In addition, hospitalizations are up 18% over the past 2 weeks and COVID-19 deaths are up 50% nationwide, The New York Times reported.
Globally, in many places, an “immunity wall” that has been built, Dr. Topol said. That may not be the case in the United States.
“The problem in the United States, making it harder to predict, is that we have a very low rate of recent boosters, in the past 6 months, especially in seniors,” he said. For example, only 36% of Americans aged 65 years and older, the group with highest risk, have received an updated bivalent booster.
An evolving virus
The subvariants are successfully replacing BA.5, which reigned as one of the most common Omicron variants over the past year. The latest CDC data show that BA.5 now accounts for only about 10% of the circulating virus. The researchers wrote: “This rapid replacement of virus strains is raising the specter of yet another wave of infections in the coming months.”
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 evolved directly from BA.5 – adding more and some novel mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. XBB and XBB.1 are the “offspring” of a combination of two other strains, known as BJ.1 and BA.2.75.
The story sounds familiar to the researchers. “The rapid rise of these subvariants and their extensive array of spike mutations are reminiscent of the appearance of the first Omicron variant last year, thus raising concerns that they may further compromise the efficacy of current COVID-19 vaccines and monoclonal antibody therapeutics,” they wrote. “We now report findings that indicate that such concerns are, sadly, justified, especially so for the XBB and XBB.1 subvariants.”
To figure out how effective existing antibodies could be against these newer subvariants, Dr. Wang and colleagues used blood samples from five groups of people. They tested serum from people who had three doses of the original COVID-19 vaccine, four doses of the original vaccine, those who received a bivalent booster, people who experienced a breakthrough infection with the BA.2 Omicron variant, and those who had a breakthrough with a BA.4 or BA.5 variant.
Adding the new subvariants to these serum samples revealed that the existing antibodies in the blood were ineffective at wiping out or neutralizing BQ.1, BQ.1.1, XBB, and XBB.1.
The BQ.1 subvariant was six times more resistant to antibodies than BA.5, its parent strain, and XBB.1 was 63 times more resistant compared with its predecessor, BA.2.
This shift in the ability of vaccines to stop the subvariants “is particularly concerning,” the researchers wrote.
Wiping out treatments too
Dr. Wang and colleagues also tested how well a panel of 23 different monoclonal antibody drugs might work against the four subvariants. The therapies all worked well against the original Omicron variant and included some approved for use through the Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization (EUA) program at the time of the study.
They found that 19 of these 23 monoclonal antibodies lost effectiveness “greatly or completely” against XBB and XBB.1, for example.
This is not the first time that monoclonal antibody therapies have gone from effective to ineffective. Previous variants have come out that no longer responded to treatment with bamlanivimab, etesevimab, imdevimab, casirivimab, tixagevimab, cilgavimab, and sotrovimab. Bebtelovimab now joins this list and is no longer available from Eli Lilly under EUA because of this lack of effectiveness.
The lack of an effective monoclonal antibody treatment “poses a serious problem for millions of immunocompromised individuals who do not respond robustly to COVID-19 vaccines,” the researchers wrote, adding that “the urgent need to develop active monoclonal antibodies for clinical use is obvious.”
A limitation of the study is that the work is done in blood samples. The effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination against the BQ and XBB subvariants should be evaluated in people in clinical studies, the authors noted.
Also, the current study looked at how well antibodies could neutralize the viral strains, but future research, they added, should look at how well “cellular immunity” or other aspects of the immune system might protect people.
Going forward, the challenge remains to develop vaccines and treatments that offer broad protection as the coronavirus continues to evolve.
In an alarming ending, the researchers wrote: “We have collectively chased after SARS-CoV-2 variants for over 2 years, and yet, the virus continues to evolve and evade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CELL
Behavioral treatment tied to lower medical, pharmacy costs
Results of a large retrospective study showed that patients newly diagnosed with a BHC who receive OPBHT following diagnosis incur lower medical and pharmacy costs over roughly the next 1 to 2 years, compared with peers who don’t receive OPBHT.
“Our findings suggest that promoting OPBHT as part of a population health strategy is associated with improved overall medical spending, particularly among adults,” the investigators write.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Common, undertreated
Nearly a quarter of adults in the United States have a BHC, and they incur greater medical costs than those without a BHC. However, diagnosis of a BHC is often delayed, and most affected individuals receive little to no treatment.
In their cost analysis, Johanna Bellon, PhD, and colleagues with Evernorth Health, St. Louis, analyzed commercial insurance claims data for 203,401 U.S. individuals newly diagnosed with one or more BHCs between 2017 and 2018.
About half of participants had depression and/or anxiety, 11% had substance use or alcohol use disorder, and 6% had a higher-acuity diagnosis, such as bipolar disorder, severe depression, eating disorder, psychotic disorder, or autism spectrum disorder.
About 1 in 5 (22%) had at least one chronic medical condition along with their BHC.
The researchers found that having at least one OPBHT visit was associated with lower medical and pharmacy costs during 15- and 27-month follow-up periods.
Over 15 months, the adjusted mean per member per month (PMPM) medical/pharmacy cost was $686 with no OPBHT visit, compared with $571 with one or more OPBHT visits.
Over 27 months, the adjusted mean PMPM was $464 with no OPBHT, versus $391 with one or more OPBHT visits.
Dose-response effect
In addition, there was a “dose-response” relationship between OPBHT and medical/pharmacy costs, such that estimated cost savings were significantly lower in the treated versus the untreated groups at almost every level of treatment.
“Our findings were also largely age independent, especially over 15 months, suggesting that OPBHT has favorable effects among children, young adults, and adults,” the researchers report.
“This is promising given that disease etiology and progression, treatment paradigms, presence of comorbid medical conditions, and overall medical and pharmacy costs differ among the three groups,” they say.
Notably, the dataset largely encompassed in-person OPBHT, because the study period preceded the transition into virtual care that occurred in 2020.
However, overall use of OPBHT was low – older adults, adults with lower income, individuals with comorbid medical conditions, and persons of racial and ethnic minorities were less likely to receive OPBHT, they found.
“These findings support the cost-effectiveness of practitioner- and insurance-based interventions to increase OPBHT utilization, which is a critical resource as new BHC diagnoses continue to increase,” the researchers say.
“Future research should validate these findings in other populations, including government-insured individuals, and explore data by chronic disease category, over longer time horizons, by type and quality of OPBHT, by type of medical spending, within subpopulations with BHCs, and including virtual and digital behavioral health services,” they suggest.
The study had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results of a large retrospective study showed that patients newly diagnosed with a BHC who receive OPBHT following diagnosis incur lower medical and pharmacy costs over roughly the next 1 to 2 years, compared with peers who don’t receive OPBHT.
“Our findings suggest that promoting OPBHT as part of a population health strategy is associated with improved overall medical spending, particularly among adults,” the investigators write.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Common, undertreated
Nearly a quarter of adults in the United States have a BHC, and they incur greater medical costs than those without a BHC. However, diagnosis of a BHC is often delayed, and most affected individuals receive little to no treatment.
In their cost analysis, Johanna Bellon, PhD, and colleagues with Evernorth Health, St. Louis, analyzed commercial insurance claims data for 203,401 U.S. individuals newly diagnosed with one or more BHCs between 2017 and 2018.
About half of participants had depression and/or anxiety, 11% had substance use or alcohol use disorder, and 6% had a higher-acuity diagnosis, such as bipolar disorder, severe depression, eating disorder, psychotic disorder, or autism spectrum disorder.
About 1 in 5 (22%) had at least one chronic medical condition along with their BHC.
The researchers found that having at least one OPBHT visit was associated with lower medical and pharmacy costs during 15- and 27-month follow-up periods.
Over 15 months, the adjusted mean per member per month (PMPM) medical/pharmacy cost was $686 with no OPBHT visit, compared with $571 with one or more OPBHT visits.
Over 27 months, the adjusted mean PMPM was $464 with no OPBHT, versus $391 with one or more OPBHT visits.
Dose-response effect
In addition, there was a “dose-response” relationship between OPBHT and medical/pharmacy costs, such that estimated cost savings were significantly lower in the treated versus the untreated groups at almost every level of treatment.
“Our findings were also largely age independent, especially over 15 months, suggesting that OPBHT has favorable effects among children, young adults, and adults,” the researchers report.
“This is promising given that disease etiology and progression, treatment paradigms, presence of comorbid medical conditions, and overall medical and pharmacy costs differ among the three groups,” they say.
Notably, the dataset largely encompassed in-person OPBHT, because the study period preceded the transition into virtual care that occurred in 2020.
However, overall use of OPBHT was low – older adults, adults with lower income, individuals with comorbid medical conditions, and persons of racial and ethnic minorities were less likely to receive OPBHT, they found.
“These findings support the cost-effectiveness of practitioner- and insurance-based interventions to increase OPBHT utilization, which is a critical resource as new BHC diagnoses continue to increase,” the researchers say.
“Future research should validate these findings in other populations, including government-insured individuals, and explore data by chronic disease category, over longer time horizons, by type and quality of OPBHT, by type of medical spending, within subpopulations with BHCs, and including virtual and digital behavioral health services,” they suggest.
The study had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results of a large retrospective study showed that patients newly diagnosed with a BHC who receive OPBHT following diagnosis incur lower medical and pharmacy costs over roughly the next 1 to 2 years, compared with peers who don’t receive OPBHT.
“Our findings suggest that promoting OPBHT as part of a population health strategy is associated with improved overall medical spending, particularly among adults,” the investigators write.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Common, undertreated
Nearly a quarter of adults in the United States have a BHC, and they incur greater medical costs than those without a BHC. However, diagnosis of a BHC is often delayed, and most affected individuals receive little to no treatment.
In their cost analysis, Johanna Bellon, PhD, and colleagues with Evernorth Health, St. Louis, analyzed commercial insurance claims data for 203,401 U.S. individuals newly diagnosed with one or more BHCs between 2017 and 2018.
About half of participants had depression and/or anxiety, 11% had substance use or alcohol use disorder, and 6% had a higher-acuity diagnosis, such as bipolar disorder, severe depression, eating disorder, psychotic disorder, or autism spectrum disorder.
About 1 in 5 (22%) had at least one chronic medical condition along with their BHC.
The researchers found that having at least one OPBHT visit was associated with lower medical and pharmacy costs during 15- and 27-month follow-up periods.
Over 15 months, the adjusted mean per member per month (PMPM) medical/pharmacy cost was $686 with no OPBHT visit, compared with $571 with one or more OPBHT visits.
Over 27 months, the adjusted mean PMPM was $464 with no OPBHT, versus $391 with one or more OPBHT visits.
Dose-response effect
In addition, there was a “dose-response” relationship between OPBHT and medical/pharmacy costs, such that estimated cost savings were significantly lower in the treated versus the untreated groups at almost every level of treatment.
“Our findings were also largely age independent, especially over 15 months, suggesting that OPBHT has favorable effects among children, young adults, and adults,” the researchers report.
“This is promising given that disease etiology and progression, treatment paradigms, presence of comorbid medical conditions, and overall medical and pharmacy costs differ among the three groups,” they say.
Notably, the dataset largely encompassed in-person OPBHT, because the study period preceded the transition into virtual care that occurred in 2020.
However, overall use of OPBHT was low – older adults, adults with lower income, individuals with comorbid medical conditions, and persons of racial and ethnic minorities were less likely to receive OPBHT, they found.
“These findings support the cost-effectiveness of practitioner- and insurance-based interventions to increase OPBHT utilization, which is a critical resource as new BHC diagnoses continue to increase,” the researchers say.
“Future research should validate these findings in other populations, including government-insured individuals, and explore data by chronic disease category, over longer time horizons, by type and quality of OPBHT, by type of medical spending, within subpopulations with BHCs, and including virtual and digital behavioral health services,” they suggest.
The study had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN





