User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Don’t fear patients reading their clinical notes: Opinion
Doctors are learning about new rules coming this April that encourage open and transparent communication among patients, families, and clinicians. The rules, putting into effect the bipartisan 21st Century Cures Act, mandate offering patients access to notes (“open notes”) written by clinicians in electronic medical records.
A recent article from this news organization noted that for many doctors this represents both a sudden and troubling change in practice. For others, the rules codify what they have been doing as a matter of routine for a decade. Spurred by the OpenNotes movement, at least 55 million Americans are already offered access to their clinical notes, including, since 2013, more than 9 million veterans with access to the Blue Button function in Veterans Affairs practices and hospitals.
The practice is spreading beyond the United States to other countries, including Canada, Sweden, Norway, Estonia, and the United Kingdom.
In this commentary, we review what patients, clinicians, and policymakers have been learning about open notes.
The patient experience
What do patients experience? In a survey of more than 22,000 patients who read notes in three diverse health systems, more than 90% reported having a good grasp of what their doctors and other clinicians had written, and very few (3%) reported being very confused by what they read. About two-thirds described reading their notes as very important for taking care of their health, remembering details of their visits and their care plans, and understanding why a medication was prescribed.
Indeed, in a clinically exciting finding, 14% of survey respondents reported that reading their notes made them more likely to take their medications as their doctors wished. With about half of Americans with chronic illness failing to take their medicines as prescribed, which sometimes leads to compromised outcomes and associated unnecessary costs (estimated at $300 billion annually), these reports of increased adherence should be taken very seriously.
Some doctors anticipate that open notes will erode patient communication. A growing body of research reveals just the opposite. In multiple surveys, patients describe open notes as “extending the visit,” strengthening collaboration and teamwork with their doctor. Quite possibly, the invitation to read notes may in itself increase trust. Such benefits appear especially pronounced among patients who are older, less educated, are persons of color or Hispanic, or who do not speak English at home.
And in several studies, more than a third of patients also report sharing their notes with others, with older and chronically ill patients in particular sharing access with family and friends who are their care partners.
On the other hand, a small minority of patients (5%) do report being more worried by what they read. It’s unknown whether this is because they are better informed about their care or because baseline anxiety levels increase. Doctors expect also that some patients, particularly those with cancer or serious mental illness, will be upset by their notes. So far, evidence does not support that specific concern.
Conversely, withholding, delaying, or blocking notes may be a source of anxiety or even stigmatization. When clinicians find themselves worried about sharing notes, we suggest that they discuss with their patients the benefits and risks. Recall also that transparency facilitates freedom of choice; patients make their own decision, and quite a few choose to leave notes unread.
Finding mistakes early and preventing harm are important goals for health care, and open notes can make care safer. Inevitably, medical records contain errors, omissions, and inaccuracies. In a large patient survey, 21% reported finding an error in their notes, and 42% perceived the error to be serious.
Moreover, 25% of doctors with more than a year’s experience with open notes reported patients finding errors that they (the doctors) considered “serious.” In 2015, the National Academy of Medicine cited open notes as a mechanism for improving diagnostic accuracy. In regard to possible legal action from patients, most attorneys, patients, and doctors agree that more transparent communication will build trust overall and, if anything, diminish litigation. We know of no instances so far of lawsuits deriving from open notes.
The physician experience
Doctors may worry that open notes will impede workflow, that they will be compelled to “dumb down” their documentation to avoid causing offense or anxiety, and that patients will demand changes to what is written. Here, extensive survey research should allay such fears and expectations. In a survey of more than 1,600 clinicians with at least 1 year of experience with open notes, reports of disruption to workflow were uncommon.
Most doctors (84%) reported that patients contacted them with questions about their notes “less than monthly or never.” Approximately two-thirds (62%) reported spending the same amount of time writing visit notes.
After implementing open notes, many doctors do report being more mindful about their documentation. For example, 41% reported changing how they used language such as “patient denies” or “noncompliant,” and 18% reported changing their use of medical jargon or abbreviations. Might these changes undermine the utility of medical notes? A majority of doctors surveyed (78%) said no, reporting that, after implementing open notes, the value of their documentation was the same or better.
Innovations spotlight difficult and often longstanding challenges. Open notes highlight the complex role of medical records in preserving privacy, especially in the spectrum of abuse, whether domestic or involving elders, children or sexual transgressions. For families with adolescents, issues concerning confidentiality can become a two-way street, and federal and state rules at times provide conflicting and idiosyncratic guidance. It is important to emphasize that the new rules permit information blocking if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or to other third parties.
Perhaps think of open notes as a new medicine designed to help the vast majority of those who use it but with side effects and even contraindications for a few. Doctors can step in to minimize risks to vulnerable individuals, and imaginative and creative solutions to complex issues may emerge. In a growing number of practices serving adolescents, clinicians can now create two notes, with some elements of care visible on a patient portal and others held privately or visible only to the adolescent.
The shared experience
Overall, when it comes to documenting sensitive social information, open notes may act as a useful catalyst prompting deeper discussion about personal details clinically important to record, as opposed to those perhaps best left unwritten.
The implementation of open notes nationwide calls for exciting explorations. How can transparent systems maximize benefits for targeted populations in diverse settings? For patients with mental illness, can notes become part of the therapy? Given that care partners often report more benefit from reading notes than do patients themselves, how can they be mobilized to maximize their contributions to those acutely ill on hospital floors, or to family members with Alzheimer’s or in long-term care facilities?
How can we harness emerging technologies to translate notes and medical records into other languages or support lower literacy levels, while preserving the clinical detail in the notes? Should patients contribute to their own notes, cogenerating them with their clinicians? Experiments for “OurNotes” interventions are underway, and early reports from both patients and doctors hold considerable promise.
Ownership of medical records is evolving. Once firmly held by clinicians, electronic technologies have rapidly led to what may best be viewed currently as joint ownership by clinicians and patients. As apps evolve further and issues with interoperability of records diminish, it is likely that patients will eventually take control. Then it will be up to patients what to carry in their records. Clinicians will advise, but patients will decide.
The new rules herald clear changes in the fabric of care, and after a decade of study we anticipate that the benefits well outweigh the harms. But in the short run, it’s wrong to predict an avalanche. Two decades ago, when patient portals first revealed laboratory test findings to patients, doctors expected cataclysmic change in their practices. It did not occur. The vast majority of patients who registered on portals benefited and few disturbed their doctors.
Similarly, after notes were first unblinded by the OpenNotes research teams, the question we were asked most commonly by the primary care doctors who volunteered was whether the computers were actually displaying their notes. Even though many patients read them carefully, the doctors heard little from them. Clinicians have now reported the same experience in several subsequent studies.
Patients are resourceful, turning quickly to friends or the Internet for answers to their questions. They know how busy doctors are and don’t want to bother them if at all possible. When notes do trigger questions, the time taken to respond is probably offset by silence from other patients finding answers to their own questions in notes they read.
We believe that clinicians should embrace the spirit of the rules and also view them as HIPAA catching up with a computerized universe. As the new practice takes hold, ambiguities will diminish as further experience and research evolve. Warner V. Slack, MD, the first doctor to ask patients to talk to computers, opined that patients are the “largest and least utilized resource in health care.” Open and transparent communication through electronic medical records may mobilize patients (and their families) far more effectively. Patients will almost certainly benefit. Remembering Dr. Slack’s prophecy, we believe that clinicians will too.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors are learning about new rules coming this April that encourage open and transparent communication among patients, families, and clinicians. The rules, putting into effect the bipartisan 21st Century Cures Act, mandate offering patients access to notes (“open notes”) written by clinicians in electronic medical records.
A recent article from this news organization noted that for many doctors this represents both a sudden and troubling change in practice. For others, the rules codify what they have been doing as a matter of routine for a decade. Spurred by the OpenNotes movement, at least 55 million Americans are already offered access to their clinical notes, including, since 2013, more than 9 million veterans with access to the Blue Button function in Veterans Affairs practices and hospitals.
The practice is spreading beyond the United States to other countries, including Canada, Sweden, Norway, Estonia, and the United Kingdom.
In this commentary, we review what patients, clinicians, and policymakers have been learning about open notes.
The patient experience
What do patients experience? In a survey of more than 22,000 patients who read notes in three diverse health systems, more than 90% reported having a good grasp of what their doctors and other clinicians had written, and very few (3%) reported being very confused by what they read. About two-thirds described reading their notes as very important for taking care of their health, remembering details of their visits and their care plans, and understanding why a medication was prescribed.
Indeed, in a clinically exciting finding, 14% of survey respondents reported that reading their notes made them more likely to take their medications as their doctors wished. With about half of Americans with chronic illness failing to take their medicines as prescribed, which sometimes leads to compromised outcomes and associated unnecessary costs (estimated at $300 billion annually), these reports of increased adherence should be taken very seriously.
Some doctors anticipate that open notes will erode patient communication. A growing body of research reveals just the opposite. In multiple surveys, patients describe open notes as “extending the visit,” strengthening collaboration and teamwork with their doctor. Quite possibly, the invitation to read notes may in itself increase trust. Such benefits appear especially pronounced among patients who are older, less educated, are persons of color or Hispanic, or who do not speak English at home.
And in several studies, more than a third of patients also report sharing their notes with others, with older and chronically ill patients in particular sharing access with family and friends who are their care partners.
On the other hand, a small minority of patients (5%) do report being more worried by what they read. It’s unknown whether this is because they are better informed about their care or because baseline anxiety levels increase. Doctors expect also that some patients, particularly those with cancer or serious mental illness, will be upset by their notes. So far, evidence does not support that specific concern.
Conversely, withholding, delaying, or blocking notes may be a source of anxiety or even stigmatization. When clinicians find themselves worried about sharing notes, we suggest that they discuss with their patients the benefits and risks. Recall also that transparency facilitates freedom of choice; patients make their own decision, and quite a few choose to leave notes unread.
Finding mistakes early and preventing harm are important goals for health care, and open notes can make care safer. Inevitably, medical records contain errors, omissions, and inaccuracies. In a large patient survey, 21% reported finding an error in their notes, and 42% perceived the error to be serious.
Moreover, 25% of doctors with more than a year’s experience with open notes reported patients finding errors that they (the doctors) considered “serious.” In 2015, the National Academy of Medicine cited open notes as a mechanism for improving diagnostic accuracy. In regard to possible legal action from patients, most attorneys, patients, and doctors agree that more transparent communication will build trust overall and, if anything, diminish litigation. We know of no instances so far of lawsuits deriving from open notes.
The physician experience
Doctors may worry that open notes will impede workflow, that they will be compelled to “dumb down” their documentation to avoid causing offense or anxiety, and that patients will demand changes to what is written. Here, extensive survey research should allay such fears and expectations. In a survey of more than 1,600 clinicians with at least 1 year of experience with open notes, reports of disruption to workflow were uncommon.
Most doctors (84%) reported that patients contacted them with questions about their notes “less than monthly or never.” Approximately two-thirds (62%) reported spending the same amount of time writing visit notes.
After implementing open notes, many doctors do report being more mindful about their documentation. For example, 41% reported changing how they used language such as “patient denies” or “noncompliant,” and 18% reported changing their use of medical jargon or abbreviations. Might these changes undermine the utility of medical notes? A majority of doctors surveyed (78%) said no, reporting that, after implementing open notes, the value of their documentation was the same or better.
Innovations spotlight difficult and often longstanding challenges. Open notes highlight the complex role of medical records in preserving privacy, especially in the spectrum of abuse, whether domestic or involving elders, children or sexual transgressions. For families with adolescents, issues concerning confidentiality can become a two-way street, and federal and state rules at times provide conflicting and idiosyncratic guidance. It is important to emphasize that the new rules permit information blocking if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or to other third parties.
Perhaps think of open notes as a new medicine designed to help the vast majority of those who use it but with side effects and even contraindications for a few. Doctors can step in to minimize risks to vulnerable individuals, and imaginative and creative solutions to complex issues may emerge. In a growing number of practices serving adolescents, clinicians can now create two notes, with some elements of care visible on a patient portal and others held privately or visible only to the adolescent.
The shared experience
Overall, when it comes to documenting sensitive social information, open notes may act as a useful catalyst prompting deeper discussion about personal details clinically important to record, as opposed to those perhaps best left unwritten.
The implementation of open notes nationwide calls for exciting explorations. How can transparent systems maximize benefits for targeted populations in diverse settings? For patients with mental illness, can notes become part of the therapy? Given that care partners often report more benefit from reading notes than do patients themselves, how can they be mobilized to maximize their contributions to those acutely ill on hospital floors, or to family members with Alzheimer’s or in long-term care facilities?
How can we harness emerging technologies to translate notes and medical records into other languages or support lower literacy levels, while preserving the clinical detail in the notes? Should patients contribute to their own notes, cogenerating them with their clinicians? Experiments for “OurNotes” interventions are underway, and early reports from both patients and doctors hold considerable promise.
Ownership of medical records is evolving. Once firmly held by clinicians, electronic technologies have rapidly led to what may best be viewed currently as joint ownership by clinicians and patients. As apps evolve further and issues with interoperability of records diminish, it is likely that patients will eventually take control. Then it will be up to patients what to carry in their records. Clinicians will advise, but patients will decide.
The new rules herald clear changes in the fabric of care, and after a decade of study we anticipate that the benefits well outweigh the harms. But in the short run, it’s wrong to predict an avalanche. Two decades ago, when patient portals first revealed laboratory test findings to patients, doctors expected cataclysmic change in their practices. It did not occur. The vast majority of patients who registered on portals benefited and few disturbed their doctors.
Similarly, after notes were first unblinded by the OpenNotes research teams, the question we were asked most commonly by the primary care doctors who volunteered was whether the computers were actually displaying their notes. Even though many patients read them carefully, the doctors heard little from them. Clinicians have now reported the same experience in several subsequent studies.
Patients are resourceful, turning quickly to friends or the Internet for answers to their questions. They know how busy doctors are and don’t want to bother them if at all possible. When notes do trigger questions, the time taken to respond is probably offset by silence from other patients finding answers to their own questions in notes they read.
We believe that clinicians should embrace the spirit of the rules and also view them as HIPAA catching up with a computerized universe. As the new practice takes hold, ambiguities will diminish as further experience and research evolve. Warner V. Slack, MD, the first doctor to ask patients to talk to computers, opined that patients are the “largest and least utilized resource in health care.” Open and transparent communication through electronic medical records may mobilize patients (and their families) far more effectively. Patients will almost certainly benefit. Remembering Dr. Slack’s prophecy, we believe that clinicians will too.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors are learning about new rules coming this April that encourage open and transparent communication among patients, families, and clinicians. The rules, putting into effect the bipartisan 21st Century Cures Act, mandate offering patients access to notes (“open notes”) written by clinicians in electronic medical records.
A recent article from this news organization noted that for many doctors this represents both a sudden and troubling change in practice. For others, the rules codify what they have been doing as a matter of routine for a decade. Spurred by the OpenNotes movement, at least 55 million Americans are already offered access to their clinical notes, including, since 2013, more than 9 million veterans with access to the Blue Button function in Veterans Affairs practices and hospitals.
The practice is spreading beyond the United States to other countries, including Canada, Sweden, Norway, Estonia, and the United Kingdom.
In this commentary, we review what patients, clinicians, and policymakers have been learning about open notes.
The patient experience
What do patients experience? In a survey of more than 22,000 patients who read notes in three diverse health systems, more than 90% reported having a good grasp of what their doctors and other clinicians had written, and very few (3%) reported being very confused by what they read. About two-thirds described reading their notes as very important for taking care of their health, remembering details of their visits and their care plans, and understanding why a medication was prescribed.
Indeed, in a clinically exciting finding, 14% of survey respondents reported that reading their notes made them more likely to take their medications as their doctors wished. With about half of Americans with chronic illness failing to take their medicines as prescribed, which sometimes leads to compromised outcomes and associated unnecessary costs (estimated at $300 billion annually), these reports of increased adherence should be taken very seriously.
Some doctors anticipate that open notes will erode patient communication. A growing body of research reveals just the opposite. In multiple surveys, patients describe open notes as “extending the visit,” strengthening collaboration and teamwork with their doctor. Quite possibly, the invitation to read notes may in itself increase trust. Such benefits appear especially pronounced among patients who are older, less educated, are persons of color or Hispanic, or who do not speak English at home.
And in several studies, more than a third of patients also report sharing their notes with others, with older and chronically ill patients in particular sharing access with family and friends who are their care partners.
On the other hand, a small minority of patients (5%) do report being more worried by what they read. It’s unknown whether this is because they are better informed about their care or because baseline anxiety levels increase. Doctors expect also that some patients, particularly those with cancer or serious mental illness, will be upset by their notes. So far, evidence does not support that specific concern.
Conversely, withholding, delaying, or blocking notes may be a source of anxiety or even stigmatization. When clinicians find themselves worried about sharing notes, we suggest that they discuss with their patients the benefits and risks. Recall also that transparency facilitates freedom of choice; patients make their own decision, and quite a few choose to leave notes unread.
Finding mistakes early and preventing harm are important goals for health care, and open notes can make care safer. Inevitably, medical records contain errors, omissions, and inaccuracies. In a large patient survey, 21% reported finding an error in their notes, and 42% perceived the error to be serious.
Moreover, 25% of doctors with more than a year’s experience with open notes reported patients finding errors that they (the doctors) considered “serious.” In 2015, the National Academy of Medicine cited open notes as a mechanism for improving diagnostic accuracy. In regard to possible legal action from patients, most attorneys, patients, and doctors agree that more transparent communication will build trust overall and, if anything, diminish litigation. We know of no instances so far of lawsuits deriving from open notes.
The physician experience
Doctors may worry that open notes will impede workflow, that they will be compelled to “dumb down” their documentation to avoid causing offense or anxiety, and that patients will demand changes to what is written. Here, extensive survey research should allay such fears and expectations. In a survey of more than 1,600 clinicians with at least 1 year of experience with open notes, reports of disruption to workflow were uncommon.
Most doctors (84%) reported that patients contacted them with questions about their notes “less than monthly or never.” Approximately two-thirds (62%) reported spending the same amount of time writing visit notes.
After implementing open notes, many doctors do report being more mindful about their documentation. For example, 41% reported changing how they used language such as “patient denies” or “noncompliant,” and 18% reported changing their use of medical jargon or abbreviations. Might these changes undermine the utility of medical notes? A majority of doctors surveyed (78%) said no, reporting that, after implementing open notes, the value of their documentation was the same or better.
Innovations spotlight difficult and often longstanding challenges. Open notes highlight the complex role of medical records in preserving privacy, especially in the spectrum of abuse, whether domestic or involving elders, children or sexual transgressions. For families with adolescents, issues concerning confidentiality can become a two-way street, and federal and state rules at times provide conflicting and idiosyncratic guidance. It is important to emphasize that the new rules permit information blocking if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or to other third parties.
Perhaps think of open notes as a new medicine designed to help the vast majority of those who use it but with side effects and even contraindications for a few. Doctors can step in to minimize risks to vulnerable individuals, and imaginative and creative solutions to complex issues may emerge. In a growing number of practices serving adolescents, clinicians can now create two notes, with some elements of care visible on a patient portal and others held privately or visible only to the adolescent.
The shared experience
Overall, when it comes to documenting sensitive social information, open notes may act as a useful catalyst prompting deeper discussion about personal details clinically important to record, as opposed to those perhaps best left unwritten.
The implementation of open notes nationwide calls for exciting explorations. How can transparent systems maximize benefits for targeted populations in diverse settings? For patients with mental illness, can notes become part of the therapy? Given that care partners often report more benefit from reading notes than do patients themselves, how can they be mobilized to maximize their contributions to those acutely ill on hospital floors, or to family members with Alzheimer’s or in long-term care facilities?
How can we harness emerging technologies to translate notes and medical records into other languages or support lower literacy levels, while preserving the clinical detail in the notes? Should patients contribute to their own notes, cogenerating them with their clinicians? Experiments for “OurNotes” interventions are underway, and early reports from both patients and doctors hold considerable promise.
Ownership of medical records is evolving. Once firmly held by clinicians, electronic technologies have rapidly led to what may best be viewed currently as joint ownership by clinicians and patients. As apps evolve further and issues with interoperability of records diminish, it is likely that patients will eventually take control. Then it will be up to patients what to carry in their records. Clinicians will advise, but patients will decide.
The new rules herald clear changes in the fabric of care, and after a decade of study we anticipate that the benefits well outweigh the harms. But in the short run, it’s wrong to predict an avalanche. Two decades ago, when patient portals first revealed laboratory test findings to patients, doctors expected cataclysmic change in their practices. It did not occur. The vast majority of patients who registered on portals benefited and few disturbed their doctors.
Similarly, after notes were first unblinded by the OpenNotes research teams, the question we were asked most commonly by the primary care doctors who volunteered was whether the computers were actually displaying their notes. Even though many patients read them carefully, the doctors heard little from them. Clinicians have now reported the same experience in several subsequent studies.
Patients are resourceful, turning quickly to friends or the Internet for answers to their questions. They know how busy doctors are and don’t want to bother them if at all possible. When notes do trigger questions, the time taken to respond is probably offset by silence from other patients finding answers to their own questions in notes they read.
We believe that clinicians should embrace the spirit of the rules and also view them as HIPAA catching up with a computerized universe. As the new practice takes hold, ambiguities will diminish as further experience and research evolve. Warner V. Slack, MD, the first doctor to ask patients to talk to computers, opined that patients are the “largest and least utilized resource in health care.” Open and transparent communication through electronic medical records may mobilize patients (and their families) far more effectively. Patients will almost certainly benefit. Remembering Dr. Slack’s prophecy, we believe that clinicians will too.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What to do if an employee tests positive for COVID-19
An increasingly common question I’m receiving is:
As always, it depends, but here is some general advice: The specifics will vary depending on state/local laws, or your particular situation.
First, you need to determine the level of exposure, and whether it requires action. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, actionable exposure occurs 2 days prior to the onset of illness, and lasts 10 days after onset.
If action is required, you’ll need to determine who needs to quarantine and who needs to be tested. Vaccinated employees who have been exposed to suspected or confirmed COVID-19 are not required to quarantine or be tested if they are fully vaccinated and have remained asymptomatic since the exposure. Those employees should, however, follow all the usual precautions (masks, social distancing, handwashing, etc.) with increased diligence. Remind them that no vaccine is 100% effective, and suggest they self-monitor for symptoms (fever, cough, shortness of breath, etc.)
All other exposed employees should be tested. A negative test means an individual was not infected at the time the sample was collected, but that does not mean an individual will not get sick later. Some providers are retesting on days 5 and 7 post exposure.
Some experts advise that you monitor exposed employees (vaccinated or not) yourself, with daily temperature readings and inquiries regarding symptoms, and perhaps a daily pulse oximetry check, for 14 days following exposure. Document these screenings in writing. Anyone testing positive or developing a fever or other symptoms should, of course, be sent home and seek medical treatment as necessary.
Employees who develop symptoms or test positive for COVID-19 should remain out of work until all CDC “return-to-work” criteria are met. At this writing, the basic criteria include:
- At least 10 days pass after symptoms first appeared
- At least 24 hours pass after last fever without the use of fever-reducing medications
- Cough, shortness of breath, and any other symptoms improve
Anyone who is significantly immunocompromised may need more time at home, and probably consultation with an infectious disease specialist.
Your facility should be thoroughly cleaned after the exposure. Close off all areas used by the sick individual, and clean and disinfect all areas such as offices, doorknobs, bathrooms, common areas, and shared electronic equipment. Of course, the cleaners should wear gowns, gloves, masks, and goggles. Some practices are hiring cleaning crews to professionally disinfect their offices. Once the area has been disinfected, it can be reopened for use. Workers without close contact with the person who is sick can return to work immediately after disinfection.
If the potential infected area is widespread and cannot be isolated to a room or rooms where doors can be shut, it may be prudent to temporarily close your office, send staff home, and divert patients to other locations if they cannot be rescheduled. Once your facility is cleaned and disinfected and staff have been cleared, your office may reopen.
Use enhanced precautions for any staff or patients who are immunocompromised, or otherwise fall into the high-risk category, to keep them out of the path of potential exposure areas and allow them to self-quarantine if they desire.
You should continue following existing leave policies (paid time off, vacation, sick, short-term disability, leave of absence, Family and Medical Leave Act, and Americans with Disabilities Act). If the employee was exposed at work, contact your workers’ compensation carrier regarding lost wages. Unless your state laws specify otherwise, you are under no obligation to pay beyond your policies, but you may do so if you choose.
Of course, you can take proactive steps to prevent unnecessary exposure and avoid closures in the first place; for example:
- Call patients prior to their visit, or question them upon arrival, regarding fever, shortness of breath, and other COVID-19 symptoms.
- Check employees’ temperatures every morning.
- Check patients’ temperatures as they enter the office.
- Require everyone, patients and employees alike, to wear face coverings.
- Ask patients to leave friends and family members at home.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a long-time monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
An increasingly common question I’m receiving is:
As always, it depends, but here is some general advice: The specifics will vary depending on state/local laws, or your particular situation.
First, you need to determine the level of exposure, and whether it requires action. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, actionable exposure occurs 2 days prior to the onset of illness, and lasts 10 days after onset.
If action is required, you’ll need to determine who needs to quarantine and who needs to be tested. Vaccinated employees who have been exposed to suspected or confirmed COVID-19 are not required to quarantine or be tested if they are fully vaccinated and have remained asymptomatic since the exposure. Those employees should, however, follow all the usual precautions (masks, social distancing, handwashing, etc.) with increased diligence. Remind them that no vaccine is 100% effective, and suggest they self-monitor for symptoms (fever, cough, shortness of breath, etc.)
All other exposed employees should be tested. A negative test means an individual was not infected at the time the sample was collected, but that does not mean an individual will not get sick later. Some providers are retesting on days 5 and 7 post exposure.
Some experts advise that you monitor exposed employees (vaccinated or not) yourself, with daily temperature readings and inquiries regarding symptoms, and perhaps a daily pulse oximetry check, for 14 days following exposure. Document these screenings in writing. Anyone testing positive or developing a fever or other symptoms should, of course, be sent home and seek medical treatment as necessary.
Employees who develop symptoms or test positive for COVID-19 should remain out of work until all CDC “return-to-work” criteria are met. At this writing, the basic criteria include:
- At least 10 days pass after symptoms first appeared
- At least 24 hours pass after last fever without the use of fever-reducing medications
- Cough, shortness of breath, and any other symptoms improve
Anyone who is significantly immunocompromised may need more time at home, and probably consultation with an infectious disease specialist.
Your facility should be thoroughly cleaned after the exposure. Close off all areas used by the sick individual, and clean and disinfect all areas such as offices, doorknobs, bathrooms, common areas, and shared electronic equipment. Of course, the cleaners should wear gowns, gloves, masks, and goggles. Some practices are hiring cleaning crews to professionally disinfect their offices. Once the area has been disinfected, it can be reopened for use. Workers without close contact with the person who is sick can return to work immediately after disinfection.
If the potential infected area is widespread and cannot be isolated to a room or rooms where doors can be shut, it may be prudent to temporarily close your office, send staff home, and divert patients to other locations if they cannot be rescheduled. Once your facility is cleaned and disinfected and staff have been cleared, your office may reopen.
Use enhanced precautions for any staff or patients who are immunocompromised, or otherwise fall into the high-risk category, to keep them out of the path of potential exposure areas and allow them to self-quarantine if they desire.
You should continue following existing leave policies (paid time off, vacation, sick, short-term disability, leave of absence, Family and Medical Leave Act, and Americans with Disabilities Act). If the employee was exposed at work, contact your workers’ compensation carrier regarding lost wages. Unless your state laws specify otherwise, you are under no obligation to pay beyond your policies, but you may do so if you choose.
Of course, you can take proactive steps to prevent unnecessary exposure and avoid closures in the first place; for example:
- Call patients prior to their visit, or question them upon arrival, regarding fever, shortness of breath, and other COVID-19 symptoms.
- Check employees’ temperatures every morning.
- Check patients’ temperatures as they enter the office.
- Require everyone, patients and employees alike, to wear face coverings.
- Ask patients to leave friends and family members at home.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a long-time monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
An increasingly common question I’m receiving is:
As always, it depends, but here is some general advice: The specifics will vary depending on state/local laws, or your particular situation.
First, you need to determine the level of exposure, and whether it requires action. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, actionable exposure occurs 2 days prior to the onset of illness, and lasts 10 days after onset.
If action is required, you’ll need to determine who needs to quarantine and who needs to be tested. Vaccinated employees who have been exposed to suspected or confirmed COVID-19 are not required to quarantine or be tested if they are fully vaccinated and have remained asymptomatic since the exposure. Those employees should, however, follow all the usual precautions (masks, social distancing, handwashing, etc.) with increased diligence. Remind them that no vaccine is 100% effective, and suggest they self-monitor for symptoms (fever, cough, shortness of breath, etc.)
All other exposed employees should be tested. A negative test means an individual was not infected at the time the sample was collected, but that does not mean an individual will not get sick later. Some providers are retesting on days 5 and 7 post exposure.
Some experts advise that you monitor exposed employees (vaccinated or not) yourself, with daily temperature readings and inquiries regarding symptoms, and perhaps a daily pulse oximetry check, for 14 days following exposure. Document these screenings in writing. Anyone testing positive or developing a fever or other symptoms should, of course, be sent home and seek medical treatment as necessary.
Employees who develop symptoms or test positive for COVID-19 should remain out of work until all CDC “return-to-work” criteria are met. At this writing, the basic criteria include:
- At least 10 days pass after symptoms first appeared
- At least 24 hours pass after last fever without the use of fever-reducing medications
- Cough, shortness of breath, and any other symptoms improve
Anyone who is significantly immunocompromised may need more time at home, and probably consultation with an infectious disease specialist.
Your facility should be thoroughly cleaned after the exposure. Close off all areas used by the sick individual, and clean and disinfect all areas such as offices, doorknobs, bathrooms, common areas, and shared electronic equipment. Of course, the cleaners should wear gowns, gloves, masks, and goggles. Some practices are hiring cleaning crews to professionally disinfect their offices. Once the area has been disinfected, it can be reopened for use. Workers without close contact with the person who is sick can return to work immediately after disinfection.
If the potential infected area is widespread and cannot be isolated to a room or rooms where doors can be shut, it may be prudent to temporarily close your office, send staff home, and divert patients to other locations if they cannot be rescheduled. Once your facility is cleaned and disinfected and staff have been cleared, your office may reopen.
Use enhanced precautions for any staff or patients who are immunocompromised, or otherwise fall into the high-risk category, to keep them out of the path of potential exposure areas and allow them to self-quarantine if they desire.
You should continue following existing leave policies (paid time off, vacation, sick, short-term disability, leave of absence, Family and Medical Leave Act, and Americans with Disabilities Act). If the employee was exposed at work, contact your workers’ compensation carrier regarding lost wages. Unless your state laws specify otherwise, you are under no obligation to pay beyond your policies, but you may do so if you choose.
Of course, you can take proactive steps to prevent unnecessary exposure and avoid closures in the first place; for example:
- Call patients prior to their visit, or question them upon arrival, regarding fever, shortness of breath, and other COVID-19 symptoms.
- Check employees’ temperatures every morning.
- Check patients’ temperatures as they enter the office.
- Require everyone, patients and employees alike, to wear face coverings.
- Ask patients to leave friends and family members at home.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a long-time monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
One-third of health care workers leery of getting COVID-19 vaccine, survey shows
Moreover, 54% of direct care providers indicated that they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 60% of noncare providers.
The findings come from what is believed to be the largest survey of health care provider attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination, published online Jan. 25 in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
“We have shown that self-reported willingness to receive vaccination against COVID-19 differs by age, gender, race and hospital role, with physicians and research scientists showing the highest acceptance,” Jana Shaw, MD, MPH, State University of New York, Syracuse, N.Y, the study’s corresponding author, told this news organization. “Building trust in authorities and confidence in vaccines is a complex and time-consuming process that requires commitment and resources. We have to make those investments as hesitancy can severely undermine vaccination coverage. Because health care providers are members of our communities, it is possible that their views are shared by the public at large. Our findings can assist public health professionals as a starting point of discussion and engagement with communities to ensure that we vaccinate at least 80% of the public to end the pandemic.”
For the study, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues emailed an anonymous survey to 9,565 employees of State University of New York Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, an academic medical center that cares for an estimated 1.8 million people. The survey, which contained questions intended to evaluate attitudes, belief, and willingness to get vaccinated, took place between Nov. 23 and Dec. 5, about a week before the U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted the first emergency use authorization for the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine.
Survey recipients included physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, nurses, pharmacists, medical and nursing students, allied health professionals, and nonclinical ancillary staff.
Of the 9,565 surveys sent, 5,287 responses were collected and used in the final analysis, for a response rate of 55%. The mean age of respondents was 43, 73% were female, 85% were White, 6% were Asian, 5% were Black/African American, and the rest were Native American, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, or from other races. More than half of respondents (59%) reported that they provided direct patient care, and 32% said they provided care for patients with COVID-19.
Of all survey respondents, 58% expressed their intent to receive a COVID-19 vaccine, but this varied by their role in the health care system. For example, in response to the statement, “If a vaccine were offered free of charge, I would take it,” 80% of scientists and physicians agreed that they would, while colleagues in other roles were unsure whether they would take the vaccine, including 34% of registered nurses, 32% of allied health professionals, and 32% of master’s-level clinicians. These differences across roles were significant (P less than .001).
The researchers also found that direct patient care or care for COVID-19 patients was associated with lower vaccination intent. For example, 54% of direct care providers and 62% of non-care providers indicated they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 52% of those who had provided care for COVID-19 patients vs. 61% of those who had not (P less than .001).
“This was a really surprising finding,” said Dr. Shaw, who is a pediatric infectious diseases physician at SUNY Upstate. “In general, one would expect that perceived severity of disease would lead to a greater desire to get vaccinated. Because our question did not address severity of disease, it is possible that we oversampled respondents who took care of patients with mild disease (i.e., in an outpatient setting). This could have led to an underestimation of disease severity and resulted in lower vaccination intent.”
A focus on rebuilding trust
Survey respondents who agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine were older (a mean age of 44 years), compared with those who were not sure or who disagreed (a mean age of 42 vs. 38 years, respectively; P less than .001). In addition, fewer females agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine (54% vs. 73% of males), whereas those who self-identified as Black/African American were least likely to want to get vaccinated, compared with those from other ethnic groups (31%, compared with 74% of Asians, 58% of Whites, and 39% of American Indians or Alaska Natives).
“We are deeply aware of the poor decisions scientists made in the past, which led to a prevailing skepticism and ‘feeling like guinea pigs’ among people of color, especially Black adults,” Dr. Shaw said. “Black adults are less likely, compared [with] White adults, to have confidence that scientists act in the public interest. Rebuilding trust will take time and has to start with addressing health care disparities. In addition, we need to acknowledge contributions of Black researchers to science. For example, until recently very few knew that the Moderna vaccine was developed [with the help of] Dr. Kizzmekia Corbett, who is Black.”
The top five main areas of unease that all respondents expressed about a COVID-19 vaccine were concern about adverse events/side effects (47%), efficacy (15%), rushed release (11%), safety (11%), and the research and authorization process (3%).
“I think it is important that fellow clinicians recognize that, in order to boost vaccine confidence we will need careful, individually tailored communication strategies,” Dr. Shaw said. “A consideration should be given to those [strategies] that utilize interpersonal channels that deliver leadership by example and leverage influencers in the institution to encourage wider adoption of vaccination.”
Aaron M. Milstone, MD, MHS, asked to comment on the research, recommended that health care workers advocate for the vaccine and encourage their patients, friends, and loved ones to get vaccinated. “Soon, COVID-19 will have taken more than half a million lives in the U.S.,” said Dr. Milstone, a pediatric epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “Although vaccines can have side effects like fever and muscle aches, and very, very rare more serious side effects, the risks of dying from COVID are much greater than the risk of a serious vaccine reaction. The study’s authors shed light on the ongoing need for leaders of all communities to support the COVID vaccines, not just the scientific community, but religious leaders, political leaders, and community leaders.”
Addressing vaccine hesitancy
Informed by their own survey, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues have developed a plan to address vaccine hesitancy to ensure high vaccine uptake at SUNY Upstate. Those strategies include, but aren’t limited to, institution-wide forums for all employees on COVID-19 vaccine safety, risks, and benefits followed by Q&A sessions, grand rounds for providers summarizing clinical trial data on mRNA vaccines, development of an Ask COVID email line for staff to ask vaccine-related questions, and a detailed vaccine-specific FAQ document.
In addition, SUNY Upstate experts have engaged in numerous media interviews to provide education and updates on the benefits of vaccination to public and staff, stationary vaccine locations, and mobile COVID-19 vaccine carts. “To date, the COVID-19 vaccination process has been well received, and we anticipate strong vaccine uptake,” she said.
Dr. Shaw acknowledged certain limitations of the survey, including its cross-sectional design and the fact that it was conducted in a single health care system in the northeastern United States. “Thus, generalizability to other regions of the U.S. and other countries may be limited,” Dr. Shaw said. “The study was also conducted before EUA [emergency use authorization] was granted to either the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines. It is therefore likely that vaccine acceptance will change over time as more people get vaccinated.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Milstone disclosed that he has received a research grant from Merck, but it is not related to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moreover, 54% of direct care providers indicated that they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 60% of noncare providers.
The findings come from what is believed to be the largest survey of health care provider attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination, published online Jan. 25 in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
“We have shown that self-reported willingness to receive vaccination against COVID-19 differs by age, gender, race and hospital role, with physicians and research scientists showing the highest acceptance,” Jana Shaw, MD, MPH, State University of New York, Syracuse, N.Y, the study’s corresponding author, told this news organization. “Building trust in authorities and confidence in vaccines is a complex and time-consuming process that requires commitment and resources. We have to make those investments as hesitancy can severely undermine vaccination coverage. Because health care providers are members of our communities, it is possible that their views are shared by the public at large. Our findings can assist public health professionals as a starting point of discussion and engagement with communities to ensure that we vaccinate at least 80% of the public to end the pandemic.”
For the study, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues emailed an anonymous survey to 9,565 employees of State University of New York Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, an academic medical center that cares for an estimated 1.8 million people. The survey, which contained questions intended to evaluate attitudes, belief, and willingness to get vaccinated, took place between Nov. 23 and Dec. 5, about a week before the U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted the first emergency use authorization for the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine.
Survey recipients included physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, nurses, pharmacists, medical and nursing students, allied health professionals, and nonclinical ancillary staff.
Of the 9,565 surveys sent, 5,287 responses were collected and used in the final analysis, for a response rate of 55%. The mean age of respondents was 43, 73% were female, 85% were White, 6% were Asian, 5% were Black/African American, and the rest were Native American, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, or from other races. More than half of respondents (59%) reported that they provided direct patient care, and 32% said they provided care for patients with COVID-19.
Of all survey respondents, 58% expressed their intent to receive a COVID-19 vaccine, but this varied by their role in the health care system. For example, in response to the statement, “If a vaccine were offered free of charge, I would take it,” 80% of scientists and physicians agreed that they would, while colleagues in other roles were unsure whether they would take the vaccine, including 34% of registered nurses, 32% of allied health professionals, and 32% of master’s-level clinicians. These differences across roles were significant (P less than .001).
The researchers also found that direct patient care or care for COVID-19 patients was associated with lower vaccination intent. For example, 54% of direct care providers and 62% of non-care providers indicated they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 52% of those who had provided care for COVID-19 patients vs. 61% of those who had not (P less than .001).
“This was a really surprising finding,” said Dr. Shaw, who is a pediatric infectious diseases physician at SUNY Upstate. “In general, one would expect that perceived severity of disease would lead to a greater desire to get vaccinated. Because our question did not address severity of disease, it is possible that we oversampled respondents who took care of patients with mild disease (i.e., in an outpatient setting). This could have led to an underestimation of disease severity and resulted in lower vaccination intent.”
A focus on rebuilding trust
Survey respondents who agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine were older (a mean age of 44 years), compared with those who were not sure or who disagreed (a mean age of 42 vs. 38 years, respectively; P less than .001). In addition, fewer females agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine (54% vs. 73% of males), whereas those who self-identified as Black/African American were least likely to want to get vaccinated, compared with those from other ethnic groups (31%, compared with 74% of Asians, 58% of Whites, and 39% of American Indians or Alaska Natives).
“We are deeply aware of the poor decisions scientists made in the past, which led to a prevailing skepticism and ‘feeling like guinea pigs’ among people of color, especially Black adults,” Dr. Shaw said. “Black adults are less likely, compared [with] White adults, to have confidence that scientists act in the public interest. Rebuilding trust will take time and has to start with addressing health care disparities. In addition, we need to acknowledge contributions of Black researchers to science. For example, until recently very few knew that the Moderna vaccine was developed [with the help of] Dr. Kizzmekia Corbett, who is Black.”
The top five main areas of unease that all respondents expressed about a COVID-19 vaccine were concern about adverse events/side effects (47%), efficacy (15%), rushed release (11%), safety (11%), and the research and authorization process (3%).
“I think it is important that fellow clinicians recognize that, in order to boost vaccine confidence we will need careful, individually tailored communication strategies,” Dr. Shaw said. “A consideration should be given to those [strategies] that utilize interpersonal channels that deliver leadership by example and leverage influencers in the institution to encourage wider adoption of vaccination.”
Aaron M. Milstone, MD, MHS, asked to comment on the research, recommended that health care workers advocate for the vaccine and encourage their patients, friends, and loved ones to get vaccinated. “Soon, COVID-19 will have taken more than half a million lives in the U.S.,” said Dr. Milstone, a pediatric epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “Although vaccines can have side effects like fever and muscle aches, and very, very rare more serious side effects, the risks of dying from COVID are much greater than the risk of a serious vaccine reaction. The study’s authors shed light on the ongoing need for leaders of all communities to support the COVID vaccines, not just the scientific community, but religious leaders, political leaders, and community leaders.”
Addressing vaccine hesitancy
Informed by their own survey, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues have developed a plan to address vaccine hesitancy to ensure high vaccine uptake at SUNY Upstate. Those strategies include, but aren’t limited to, institution-wide forums for all employees on COVID-19 vaccine safety, risks, and benefits followed by Q&A sessions, grand rounds for providers summarizing clinical trial data on mRNA vaccines, development of an Ask COVID email line for staff to ask vaccine-related questions, and a detailed vaccine-specific FAQ document.
In addition, SUNY Upstate experts have engaged in numerous media interviews to provide education and updates on the benefits of vaccination to public and staff, stationary vaccine locations, and mobile COVID-19 vaccine carts. “To date, the COVID-19 vaccination process has been well received, and we anticipate strong vaccine uptake,” she said.
Dr. Shaw acknowledged certain limitations of the survey, including its cross-sectional design and the fact that it was conducted in a single health care system in the northeastern United States. “Thus, generalizability to other regions of the U.S. and other countries may be limited,” Dr. Shaw said. “The study was also conducted before EUA [emergency use authorization] was granted to either the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines. It is therefore likely that vaccine acceptance will change over time as more people get vaccinated.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Milstone disclosed that he has received a research grant from Merck, but it is not related to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moreover, 54% of direct care providers indicated that they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 60% of noncare providers.
The findings come from what is believed to be the largest survey of health care provider attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination, published online Jan. 25 in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
“We have shown that self-reported willingness to receive vaccination against COVID-19 differs by age, gender, race and hospital role, with physicians and research scientists showing the highest acceptance,” Jana Shaw, MD, MPH, State University of New York, Syracuse, N.Y, the study’s corresponding author, told this news organization. “Building trust in authorities and confidence in vaccines is a complex and time-consuming process that requires commitment and resources. We have to make those investments as hesitancy can severely undermine vaccination coverage. Because health care providers are members of our communities, it is possible that their views are shared by the public at large. Our findings can assist public health professionals as a starting point of discussion and engagement with communities to ensure that we vaccinate at least 80% of the public to end the pandemic.”
For the study, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues emailed an anonymous survey to 9,565 employees of State University of New York Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, an academic medical center that cares for an estimated 1.8 million people. The survey, which contained questions intended to evaluate attitudes, belief, and willingness to get vaccinated, took place between Nov. 23 and Dec. 5, about a week before the U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted the first emergency use authorization for the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine.
Survey recipients included physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, nurses, pharmacists, medical and nursing students, allied health professionals, and nonclinical ancillary staff.
Of the 9,565 surveys sent, 5,287 responses were collected and used in the final analysis, for a response rate of 55%. The mean age of respondents was 43, 73% were female, 85% were White, 6% were Asian, 5% were Black/African American, and the rest were Native American, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, or from other races. More than half of respondents (59%) reported that they provided direct patient care, and 32% said they provided care for patients with COVID-19.
Of all survey respondents, 58% expressed their intent to receive a COVID-19 vaccine, but this varied by their role in the health care system. For example, in response to the statement, “If a vaccine were offered free of charge, I would take it,” 80% of scientists and physicians agreed that they would, while colleagues in other roles were unsure whether they would take the vaccine, including 34% of registered nurses, 32% of allied health professionals, and 32% of master’s-level clinicians. These differences across roles were significant (P less than .001).
The researchers also found that direct patient care or care for COVID-19 patients was associated with lower vaccination intent. For example, 54% of direct care providers and 62% of non-care providers indicated they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 52% of those who had provided care for COVID-19 patients vs. 61% of those who had not (P less than .001).
“This was a really surprising finding,” said Dr. Shaw, who is a pediatric infectious diseases physician at SUNY Upstate. “In general, one would expect that perceived severity of disease would lead to a greater desire to get vaccinated. Because our question did not address severity of disease, it is possible that we oversampled respondents who took care of patients with mild disease (i.e., in an outpatient setting). This could have led to an underestimation of disease severity and resulted in lower vaccination intent.”
A focus on rebuilding trust
Survey respondents who agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine were older (a mean age of 44 years), compared with those who were not sure or who disagreed (a mean age of 42 vs. 38 years, respectively; P less than .001). In addition, fewer females agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine (54% vs. 73% of males), whereas those who self-identified as Black/African American were least likely to want to get vaccinated, compared with those from other ethnic groups (31%, compared with 74% of Asians, 58% of Whites, and 39% of American Indians or Alaska Natives).
“We are deeply aware of the poor decisions scientists made in the past, which led to a prevailing skepticism and ‘feeling like guinea pigs’ among people of color, especially Black adults,” Dr. Shaw said. “Black adults are less likely, compared [with] White adults, to have confidence that scientists act in the public interest. Rebuilding trust will take time and has to start with addressing health care disparities. In addition, we need to acknowledge contributions of Black researchers to science. For example, until recently very few knew that the Moderna vaccine was developed [with the help of] Dr. Kizzmekia Corbett, who is Black.”
The top five main areas of unease that all respondents expressed about a COVID-19 vaccine were concern about adverse events/side effects (47%), efficacy (15%), rushed release (11%), safety (11%), and the research and authorization process (3%).
“I think it is important that fellow clinicians recognize that, in order to boost vaccine confidence we will need careful, individually tailored communication strategies,” Dr. Shaw said. “A consideration should be given to those [strategies] that utilize interpersonal channels that deliver leadership by example and leverage influencers in the institution to encourage wider adoption of vaccination.”
Aaron M. Milstone, MD, MHS, asked to comment on the research, recommended that health care workers advocate for the vaccine and encourage their patients, friends, and loved ones to get vaccinated. “Soon, COVID-19 will have taken more than half a million lives in the U.S.,” said Dr. Milstone, a pediatric epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “Although vaccines can have side effects like fever and muscle aches, and very, very rare more serious side effects, the risks of dying from COVID are much greater than the risk of a serious vaccine reaction. The study’s authors shed light on the ongoing need for leaders of all communities to support the COVID vaccines, not just the scientific community, but religious leaders, political leaders, and community leaders.”
Addressing vaccine hesitancy
Informed by their own survey, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues have developed a plan to address vaccine hesitancy to ensure high vaccine uptake at SUNY Upstate. Those strategies include, but aren’t limited to, institution-wide forums for all employees on COVID-19 vaccine safety, risks, and benefits followed by Q&A sessions, grand rounds for providers summarizing clinical trial data on mRNA vaccines, development of an Ask COVID email line for staff to ask vaccine-related questions, and a detailed vaccine-specific FAQ document.
In addition, SUNY Upstate experts have engaged in numerous media interviews to provide education and updates on the benefits of vaccination to public and staff, stationary vaccine locations, and mobile COVID-19 vaccine carts. “To date, the COVID-19 vaccination process has been well received, and we anticipate strong vaccine uptake,” she said.
Dr. Shaw acknowledged certain limitations of the survey, including its cross-sectional design and the fact that it was conducted in a single health care system in the northeastern United States. “Thus, generalizability to other regions of the U.S. and other countries may be limited,” Dr. Shaw said. “The study was also conducted before EUA [emergency use authorization] was granted to either the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines. It is therefore likely that vaccine acceptance will change over time as more people get vaccinated.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Milstone disclosed that he has received a research grant from Merck, but it is not related to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Prospective data support delaying antibiotics for pediatric respiratory infections
For pediatric patients with respiratory tract infections (RTIs), immediately prescribing antibiotics may do more harm than good, based on prospective data from 436 children treated by primary care pediatricians in Spain.
In the largest trial of its kind to date, children who were immediately prescribed antibiotics showed no significant difference in symptom severity or duration from those who received a delayed prescription for antibiotics, or no prescription at all; yet those in the immediate-prescription group had a higher rate of gastrointestinal adverse events, reported lead author Gemma Mas-Dalmau, MD, of the Sant Pau Institute for Biomedical Research, Barcelona, and colleagues.
“Most RTIs are self-limiting, and antibiotics hardly alter the course of the condition, yet antibiotics are frequently prescribed for these conditions,” the investigators wrote in Pediatrics. “Antibiotic prescription for RTIs in children is especially considered to be inappropriately high.”
This clinical behavior is driven by several factors, according to Dr. Mas-Dalmau and colleagues, including limited diagnostics in primary care, pressure to meet parental expectations, and concern for possible complications if antibiotics are withheld or delayed.
In an accompanying editorial, Jeffrey S. Gerber, MD, PhD and Bonnie F. Offit, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, noted that “children in the United States receive more than one antibiotic prescription per year, driven largely by acute RTIs.”
Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit noted that some RTIs are indeed caused by bacteria, and therefore benefit from antibiotics, but it’s “not always easy” to identify these cases.
“Primary care, urgent care, and emergency medicine clinicians have a hard job,” they wrote.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, delayed prescription of antibiotics, in which a prescription is filled upon persistence or worsening of symptoms, can balance clinical caution and antibiotic stewardship.
“An example of this approach is acute otitis media, in which delayed prescribing has been shown to safely reduce antibiotic exposure,” wrote Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit.
In a 2017 Cochrane systematic review of both adults and children with RTIs, antibiotic prescriptions, whether immediate, delayed, or not given at all, had no significant effect on most symptoms or complications. Although several randomized trials have evaluated delayed antibiotic prescriptions in children, Dr. Mas-Dalmau and colleagues described the current body of evidence as “scant.”
The present study built upon this knowledge base by prospectively following 436 children treated at 39 primary care centers in Spain from 2012 to 2016. Patients were between 2 and 14 years of age and presented for rhinosinusitis, pharyngitis, acute otitis media, or acute bronchitis. Inclusion in the study required the pediatrician to have “reasonable doubts about the need to prescribe an antibiotic.” Clinics with access to rapid streptococcal testing did not enroll patients with pharyngitis.
Patients were randomized in approximately equal groups to receive either immediate prescription of antibiotics, delayed prescription, or no prescription. In the delayed group, caregivers were advised to fill prescriptions if any of following three events occurred:
- No symptom improvement after a certain amount of days, depending on presenting complaint (acute otitis media, 4 days; pharyngitis, 7 days; acute rhinosinusitis, 15 days; acute bronchitis, 20 days).
- Temperature of at least 39° C after 24 hours, or at least 38° C but less than 39° C after 48 hours.
- Patient feeling “much worse.”
Primary outcomes were severity and duration of symptoms over 30 days, while secondary outcomes included antibiotic use over 30 days, additional unscheduled visits to primary care over 30 days, and parental satisfaction and beliefs regarding antibiotic efficacy.
In the final dataset, 148 patients received immediate antibiotic prescriptions, while 146 received delayed prescriptions, and 142 received no prescription. Rate of antibiotic use was highest in the immediate prescription group, at 96%, versus 25.3% in the delayed group and 12% among those who received no prescription upon first presentation (P < .001).
Although the mean duration of severe symptoms was longest in the delayed-prescription group, at 12.4 days, versus 10.9 days in the no-prescription group and 10.1 days in the immediate-prescription group, these differences were not statistically significant (P = .539). Median score for greatest severity of any symptom was also similar across groups. Secondary outcomes echoed this pattern, in which reconsultation rates and caregiver satisfaction were statistically similar regardless of treatment type.
In contrast, patients who received immediate antibiotic prescriptions had a significantly higher rate of gastrointestinal adverse events (8.8%) than those who received a delayed prescription (3.4%) or no prescription (2.8%; P = .037).
“Delayed antibiotic prescription is an efficacious and safe strategy for reducing inappropriate antibiotic treatment of uncomplicated RTIs in children when the doctor has reasonable doubts regarding the indication,” the investigators concluded. “[It] is therefore a useful tool for addressing the public health issue of bacterial resistance. However, no antibiotic prescription remains the recommended strategy when it is clear that antibiotics are not indicated, like in most cases of acute bronchitis.”
“These data are reassuring,” wrote Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit; however, they went on to suggest that the data “might not substantially move the needle.”
“With rare exceptions, children with acute pharyngitis should first receive a group A streptococcal test,” they wrote. “If results are positive, all patients should get antibiotics; if results are negative, no one gets them. Acute bronchitis (whatever that is in children) is viral. Acute sinusitis with persistent symptoms (the most commonly diagnosed variety) already has a delayed option, and the current study ... was not powered for this outcome. We are left with acute otitis media, which dominated enrollment but already has an evidence-based guideline.”
Still, Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit suggested that the findings should further encourage pediatricians to prescribe antibiotics judiciously, and when elected, to choose the shortest duration and narrowest spectrum possible.
In a joint comment, Rana El Feghaly, MD, MSCI, director of outpatient antibiotic stewardship at Children’s Mercy, Kansas City, and her colleague, Mary Anne Jackson, MD, noted that the findings are “in accordance” with the 2017 Cochrane review.
Dr. Feghaly and Dr. Jackson said that these new data provide greater support for conservative use of antibiotics, which is badly needed, considering approximately 50% of outpatient prescriptions are unnecessary or inappropriate .
Delayed antibiotic prescription is part of a multifaceted approach to the issue, they said, joining “communication skills training, antibiotic justification documentation, audit and feedback reporting with peer comparison, diagnostic stewardship, [and] the use of clinician education on practice-based guidelines.”
“Leveraging delayed antibiotic prescription may be an excellent way to combat antibiotic overuse in the outpatient setting, while avoiding provider and parental fear of the ‘no antibiotic’ approach,” Dr. Feghaly and Dr. Jackson said.
Karlyn Kinsella, MD, of Pediatric Associates of Cheshire, Conn., suggested that clinicians discuss these findings with parents who request antibiotics for “otitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, or sinusitis.”
“We can cite this study that antibiotics have no effect on symptom duration or severity for these illnesses,” Dr. Kinsella said. “Of course, our clinical opinion in each case takes precedent.”
According to Dr. Kinsella, conversations with parents also need to cover reasonable expectations, as the study did, with clear time frames for each condition in which children should start to get better.
“I think this is really key in our anticipatory guidance so that patients know what to expect,” she said.
The study was funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III, the European Union, and the Spanish Ministry of Health, Social Services, and Equality. The investigators and interviewees reported no conflicts of interest.
For pediatric patients with respiratory tract infections (RTIs), immediately prescribing antibiotics may do more harm than good, based on prospective data from 436 children treated by primary care pediatricians in Spain.
In the largest trial of its kind to date, children who were immediately prescribed antibiotics showed no significant difference in symptom severity or duration from those who received a delayed prescription for antibiotics, or no prescription at all; yet those in the immediate-prescription group had a higher rate of gastrointestinal adverse events, reported lead author Gemma Mas-Dalmau, MD, of the Sant Pau Institute for Biomedical Research, Barcelona, and colleagues.
“Most RTIs are self-limiting, and antibiotics hardly alter the course of the condition, yet antibiotics are frequently prescribed for these conditions,” the investigators wrote in Pediatrics. “Antibiotic prescription for RTIs in children is especially considered to be inappropriately high.”
This clinical behavior is driven by several factors, according to Dr. Mas-Dalmau and colleagues, including limited diagnostics in primary care, pressure to meet parental expectations, and concern for possible complications if antibiotics are withheld or delayed.
In an accompanying editorial, Jeffrey S. Gerber, MD, PhD and Bonnie F. Offit, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, noted that “children in the United States receive more than one antibiotic prescription per year, driven largely by acute RTIs.”
Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit noted that some RTIs are indeed caused by bacteria, and therefore benefit from antibiotics, but it’s “not always easy” to identify these cases.
“Primary care, urgent care, and emergency medicine clinicians have a hard job,” they wrote.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, delayed prescription of antibiotics, in which a prescription is filled upon persistence or worsening of symptoms, can balance clinical caution and antibiotic stewardship.
“An example of this approach is acute otitis media, in which delayed prescribing has been shown to safely reduce antibiotic exposure,” wrote Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit.
In a 2017 Cochrane systematic review of both adults and children with RTIs, antibiotic prescriptions, whether immediate, delayed, or not given at all, had no significant effect on most symptoms or complications. Although several randomized trials have evaluated delayed antibiotic prescriptions in children, Dr. Mas-Dalmau and colleagues described the current body of evidence as “scant.”
The present study built upon this knowledge base by prospectively following 436 children treated at 39 primary care centers in Spain from 2012 to 2016. Patients were between 2 and 14 years of age and presented for rhinosinusitis, pharyngitis, acute otitis media, or acute bronchitis. Inclusion in the study required the pediatrician to have “reasonable doubts about the need to prescribe an antibiotic.” Clinics with access to rapid streptococcal testing did not enroll patients with pharyngitis.
Patients were randomized in approximately equal groups to receive either immediate prescription of antibiotics, delayed prescription, or no prescription. In the delayed group, caregivers were advised to fill prescriptions if any of following three events occurred:
- No symptom improvement after a certain amount of days, depending on presenting complaint (acute otitis media, 4 days; pharyngitis, 7 days; acute rhinosinusitis, 15 days; acute bronchitis, 20 days).
- Temperature of at least 39° C after 24 hours, or at least 38° C but less than 39° C after 48 hours.
- Patient feeling “much worse.”
Primary outcomes were severity and duration of symptoms over 30 days, while secondary outcomes included antibiotic use over 30 days, additional unscheduled visits to primary care over 30 days, and parental satisfaction and beliefs regarding antibiotic efficacy.
In the final dataset, 148 patients received immediate antibiotic prescriptions, while 146 received delayed prescriptions, and 142 received no prescription. Rate of antibiotic use was highest in the immediate prescription group, at 96%, versus 25.3% in the delayed group and 12% among those who received no prescription upon first presentation (P < .001).
Although the mean duration of severe symptoms was longest in the delayed-prescription group, at 12.4 days, versus 10.9 days in the no-prescription group and 10.1 days in the immediate-prescription group, these differences were not statistically significant (P = .539). Median score for greatest severity of any symptom was also similar across groups. Secondary outcomes echoed this pattern, in which reconsultation rates and caregiver satisfaction were statistically similar regardless of treatment type.
In contrast, patients who received immediate antibiotic prescriptions had a significantly higher rate of gastrointestinal adverse events (8.8%) than those who received a delayed prescription (3.4%) or no prescription (2.8%; P = .037).
“Delayed antibiotic prescription is an efficacious and safe strategy for reducing inappropriate antibiotic treatment of uncomplicated RTIs in children when the doctor has reasonable doubts regarding the indication,” the investigators concluded. “[It] is therefore a useful tool for addressing the public health issue of bacterial resistance. However, no antibiotic prescription remains the recommended strategy when it is clear that antibiotics are not indicated, like in most cases of acute bronchitis.”
“These data are reassuring,” wrote Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit; however, they went on to suggest that the data “might not substantially move the needle.”
“With rare exceptions, children with acute pharyngitis should first receive a group A streptococcal test,” they wrote. “If results are positive, all patients should get antibiotics; if results are negative, no one gets them. Acute bronchitis (whatever that is in children) is viral. Acute sinusitis with persistent symptoms (the most commonly diagnosed variety) already has a delayed option, and the current study ... was not powered for this outcome. We are left with acute otitis media, which dominated enrollment but already has an evidence-based guideline.”
Still, Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit suggested that the findings should further encourage pediatricians to prescribe antibiotics judiciously, and when elected, to choose the shortest duration and narrowest spectrum possible.
In a joint comment, Rana El Feghaly, MD, MSCI, director of outpatient antibiotic stewardship at Children’s Mercy, Kansas City, and her colleague, Mary Anne Jackson, MD, noted that the findings are “in accordance” with the 2017 Cochrane review.
Dr. Feghaly and Dr. Jackson said that these new data provide greater support for conservative use of antibiotics, which is badly needed, considering approximately 50% of outpatient prescriptions are unnecessary or inappropriate .
Delayed antibiotic prescription is part of a multifaceted approach to the issue, they said, joining “communication skills training, antibiotic justification documentation, audit and feedback reporting with peer comparison, diagnostic stewardship, [and] the use of clinician education on practice-based guidelines.”
“Leveraging delayed antibiotic prescription may be an excellent way to combat antibiotic overuse in the outpatient setting, while avoiding provider and parental fear of the ‘no antibiotic’ approach,” Dr. Feghaly and Dr. Jackson said.
Karlyn Kinsella, MD, of Pediatric Associates of Cheshire, Conn., suggested that clinicians discuss these findings with parents who request antibiotics for “otitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, or sinusitis.”
“We can cite this study that antibiotics have no effect on symptom duration or severity for these illnesses,” Dr. Kinsella said. “Of course, our clinical opinion in each case takes precedent.”
According to Dr. Kinsella, conversations with parents also need to cover reasonable expectations, as the study did, with clear time frames for each condition in which children should start to get better.
“I think this is really key in our anticipatory guidance so that patients know what to expect,” she said.
The study was funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III, the European Union, and the Spanish Ministry of Health, Social Services, and Equality. The investigators and interviewees reported no conflicts of interest.
For pediatric patients with respiratory tract infections (RTIs), immediately prescribing antibiotics may do more harm than good, based on prospective data from 436 children treated by primary care pediatricians in Spain.
In the largest trial of its kind to date, children who were immediately prescribed antibiotics showed no significant difference in symptom severity or duration from those who received a delayed prescription for antibiotics, or no prescription at all; yet those in the immediate-prescription group had a higher rate of gastrointestinal adverse events, reported lead author Gemma Mas-Dalmau, MD, of the Sant Pau Institute for Biomedical Research, Barcelona, and colleagues.
“Most RTIs are self-limiting, and antibiotics hardly alter the course of the condition, yet antibiotics are frequently prescribed for these conditions,” the investigators wrote in Pediatrics. “Antibiotic prescription for RTIs in children is especially considered to be inappropriately high.”
This clinical behavior is driven by several factors, according to Dr. Mas-Dalmau and colleagues, including limited diagnostics in primary care, pressure to meet parental expectations, and concern for possible complications if antibiotics are withheld or delayed.
In an accompanying editorial, Jeffrey S. Gerber, MD, PhD and Bonnie F. Offit, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, noted that “children in the United States receive more than one antibiotic prescription per year, driven largely by acute RTIs.”
Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit noted that some RTIs are indeed caused by bacteria, and therefore benefit from antibiotics, but it’s “not always easy” to identify these cases.
“Primary care, urgent care, and emergency medicine clinicians have a hard job,” they wrote.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, delayed prescription of antibiotics, in which a prescription is filled upon persistence or worsening of symptoms, can balance clinical caution and antibiotic stewardship.
“An example of this approach is acute otitis media, in which delayed prescribing has been shown to safely reduce antibiotic exposure,” wrote Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit.
In a 2017 Cochrane systematic review of both adults and children with RTIs, antibiotic prescriptions, whether immediate, delayed, or not given at all, had no significant effect on most symptoms or complications. Although several randomized trials have evaluated delayed antibiotic prescriptions in children, Dr. Mas-Dalmau and colleagues described the current body of evidence as “scant.”
The present study built upon this knowledge base by prospectively following 436 children treated at 39 primary care centers in Spain from 2012 to 2016. Patients were between 2 and 14 years of age and presented for rhinosinusitis, pharyngitis, acute otitis media, or acute bronchitis. Inclusion in the study required the pediatrician to have “reasonable doubts about the need to prescribe an antibiotic.” Clinics with access to rapid streptococcal testing did not enroll patients with pharyngitis.
Patients were randomized in approximately equal groups to receive either immediate prescription of antibiotics, delayed prescription, or no prescription. In the delayed group, caregivers were advised to fill prescriptions if any of following three events occurred:
- No symptom improvement after a certain amount of days, depending on presenting complaint (acute otitis media, 4 days; pharyngitis, 7 days; acute rhinosinusitis, 15 days; acute bronchitis, 20 days).
- Temperature of at least 39° C after 24 hours, or at least 38° C but less than 39° C after 48 hours.
- Patient feeling “much worse.”
Primary outcomes were severity and duration of symptoms over 30 days, while secondary outcomes included antibiotic use over 30 days, additional unscheduled visits to primary care over 30 days, and parental satisfaction and beliefs regarding antibiotic efficacy.
In the final dataset, 148 patients received immediate antibiotic prescriptions, while 146 received delayed prescriptions, and 142 received no prescription. Rate of antibiotic use was highest in the immediate prescription group, at 96%, versus 25.3% in the delayed group and 12% among those who received no prescription upon first presentation (P < .001).
Although the mean duration of severe symptoms was longest in the delayed-prescription group, at 12.4 days, versus 10.9 days in the no-prescription group and 10.1 days in the immediate-prescription group, these differences were not statistically significant (P = .539). Median score for greatest severity of any symptom was also similar across groups. Secondary outcomes echoed this pattern, in which reconsultation rates and caregiver satisfaction were statistically similar regardless of treatment type.
In contrast, patients who received immediate antibiotic prescriptions had a significantly higher rate of gastrointestinal adverse events (8.8%) than those who received a delayed prescription (3.4%) or no prescription (2.8%; P = .037).
“Delayed antibiotic prescription is an efficacious and safe strategy for reducing inappropriate antibiotic treatment of uncomplicated RTIs in children when the doctor has reasonable doubts regarding the indication,” the investigators concluded. “[It] is therefore a useful tool for addressing the public health issue of bacterial resistance. However, no antibiotic prescription remains the recommended strategy when it is clear that antibiotics are not indicated, like in most cases of acute bronchitis.”
“These data are reassuring,” wrote Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit; however, they went on to suggest that the data “might not substantially move the needle.”
“With rare exceptions, children with acute pharyngitis should first receive a group A streptococcal test,” they wrote. “If results are positive, all patients should get antibiotics; if results are negative, no one gets them. Acute bronchitis (whatever that is in children) is viral. Acute sinusitis with persistent symptoms (the most commonly diagnosed variety) already has a delayed option, and the current study ... was not powered for this outcome. We are left with acute otitis media, which dominated enrollment but already has an evidence-based guideline.”
Still, Dr. Gerber and Dr. Offit suggested that the findings should further encourage pediatricians to prescribe antibiotics judiciously, and when elected, to choose the shortest duration and narrowest spectrum possible.
In a joint comment, Rana El Feghaly, MD, MSCI, director of outpatient antibiotic stewardship at Children’s Mercy, Kansas City, and her colleague, Mary Anne Jackson, MD, noted that the findings are “in accordance” with the 2017 Cochrane review.
Dr. Feghaly and Dr. Jackson said that these new data provide greater support for conservative use of antibiotics, which is badly needed, considering approximately 50% of outpatient prescriptions are unnecessary or inappropriate .
Delayed antibiotic prescription is part of a multifaceted approach to the issue, they said, joining “communication skills training, antibiotic justification documentation, audit and feedback reporting with peer comparison, diagnostic stewardship, [and] the use of clinician education on practice-based guidelines.”
“Leveraging delayed antibiotic prescription may be an excellent way to combat antibiotic overuse in the outpatient setting, while avoiding provider and parental fear of the ‘no antibiotic’ approach,” Dr. Feghaly and Dr. Jackson said.
Karlyn Kinsella, MD, of Pediatric Associates of Cheshire, Conn., suggested that clinicians discuss these findings with parents who request antibiotics for “otitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, or sinusitis.”
“We can cite this study that antibiotics have no effect on symptom duration or severity for these illnesses,” Dr. Kinsella said. “Of course, our clinical opinion in each case takes precedent.”
According to Dr. Kinsella, conversations with parents also need to cover reasonable expectations, as the study did, with clear time frames for each condition in which children should start to get better.
“I think this is really key in our anticipatory guidance so that patients know what to expect,” she said.
The study was funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III, the European Union, and the Spanish Ministry of Health, Social Services, and Equality. The investigators and interviewees reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Zika vaccine candidate shows promise in phase 1 trial
in a phase 1 study.
Although Zika cases have declined in recent years, “geographic expansion of the Aedes aegypti mosquito to areas where population-level immunity is low poses a substantial risk for future epidemics,” wrote Nadine C. Salisch, PhD, of Janssen Vaccines and Prevention, Leiden, the Netherlands, and colleagues in a paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
No vaccine against Zika is yet available, although more than 10 candidates have been studied in preclinical trials to date, they said.
The researchers randomized 100 healthy adult volunteers to an experimental Zika vaccine candidate known as Ad26.ZIKV.001 in either one-dose or two-dose regimens of 5x1010 viral particles (low dose) or 1x1011 viral particles (high dose) or placebo. Approximately half (55%) of the participants were women, and 72% were White.
Approximately 80% of patients in both two-dose groups showed antibody responses for a year after vaccination. Geometric mean titers (GMTs) reached peak of 823.4 in the low-dose/low-dose group and 961.5 in the high-dose/high-dose group. At day 365, the GMTs for these groups were 68.7 and 87.0, respectively.
A single high-dose vaccine achieved a similar level of neutralizing antibody titers, but lower peak neutralizing responses than the two-dose strategies, the researchers noted.
Most of the reported adverse events were mild to moderate, and short lived; the most common were injection site pain or tenderness, headache, and fatigue, the researchers said. After the first vaccination, 75% of participants in the low-dose groups, 88% of participants in high-dose groups, and 45% of participants receiving placebo reported local adverse events. In addition, 73%, 83%, and 40% of the participants in the low-dose, high-dose, and placebo groups, respectively, reported systemic adverse events. Reports were similar after the second vaccination. Two serious adverse events not related to vaccination were reported; one case of right lower lobe pneumonia and one case of incomplete spontaneous abortion.
The researchers also explored protective efficacy through a nonlethal mouse challenge model. “Transfer of 6 mg of IgG from Ad26.ZIKV.001 vaccines conferred complete protection from viremia in most recipient animals, with statistically significantly decreased breakthrough rates and cumulative viral loads per group compared with placebo,” they said.
The study findings were limited by the inability to assess safety and immunogenicity in an endemic area, the researchers noted. However, “Ad26.ZIKV.001 induces potent ZIKV-specific neutralizing responses with durability of at least 1 year, which supports further clinical development if an unmet medical need reemerges,” they said. “In addition, these data underscore the performance of the Ad26 vaccine platform, which Janssen is using for different infectious diseases, including COVID-19,” they noted.
Ad26 vector platform shows consistency
“Development of the investigational Janssen Zika vaccine candidate was initiated in 2015, and while the incidence of Zika virus has declined since the 2015-2016 outbreak, spread of the ‘carrier’ Aedes aegypti mosquito to areas where population-level immunity is low poses a substantial risk for future epidemics,” lead author Dr. Salisch said in an interview. For this reason, researchers say the vaccine warrants further development should the need reemerge, she said.
“Our research has found that while a single higher-dose regimen had lower peak neutralizing responses than a two-dose regimen, it achieved a similar level of neutralizing antibody responses at 1 year, an encouraging finding that shows our vaccine may be a useful tool to curb Zika epidemics,” Dr. Salisch noted. “Previous experience with the Ad26 vector platform across our investigational vaccine programs have yielded similarly promising results, most recently with our investigational Janssen COVID-19 vaccine program, for which phase 3 data show a single-dose vaccine met all primary and key secondary endpoints,” she said.
“The biggest barrier [to further development of the candidate vaccine] is one that we actually consider ourselves fortunate to have: The very low incidence of reported Zika cases currently reported worldwide,” Dr. Salisch said. “However, the current Zika case rate can change at any time, and in the event the situation demands it, we are open to alternative regulatory pathways to help us glean the necessary insights on vaccine safety and efficacy to further advance the development of this candidate,” she emphasized.
As for additional research, “there are still questions surrounding Zika transmission and the pathomechanism of congenital Zika syndrome,” said Dr. Salisch. “Our hope is that a correlate of protection against Zika disease, and in particular against congenital Zika syndrome, can be identified,” she said.
Consider pregnant women in next phase of research
“A major hurdle in ZIKV vaccine development is the inability to conduct large efficacy studies in the absence of a current outbreak,” Ann Chahroudi, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and Sallie Permar, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The current study provided some efficacy data using a mouse model, but “these data are obviously not conclusive for human protection,” they said.
“A further challenge for ZIKV vaccine efficacy trials will be to demonstrate fetal protection from [congenital Zika syndrome] after adult immunization. There should be a clear plan to readily deploy phase 3 trials for the most promising vaccines to emerge from phase 1 and 2 in the event of an outbreak, as was implemented for Ebola, including infant follow-up,” they emphasized.
The editorialists noted that the study did not include pregnant women, who represent a major target for immunization, but they said that vaccination of pregnant women against other neonatal pathogens such as influenza and tetanus has been effective. “Candidate ZIKV vaccines proven safe in phase 1 trials should immediately be assessed for safety and efficacy in pregnant women,” they said. Although Zika infections are not at epidemic levels currently, resurgence remains a possibility and the coronavirus pandemic “has taught us that preparedness for emerging infections is crucial,” they said.
Zika vaccine research is a challenge worth pursuing
“It is important to continue Zika vaccine research because of the unpredictable nature of that infection,” Kevin Ault, MD, of the University of Kansas, Kansas City, said in an interview. “Several times Zika has gained a foothold in unexposed and vulnerable populations,” Dr. Ault said. “Additionally, there are some data about using this vector during pregnancy, and eventually this vaccine may prevent the birth defects associated with Zika infections during pregnancy, he noted.
Dr. Ault said he was not surprised by the study findings. “This is a promising early phase vaccine candidate, and this adenovirus vector has been used in other similar trials,” he said. Potential barriers to vaccine development include the challenge of conducting late phase clinical trials in pregnant women, he noted. “The relevant endpoint is going to be clinical disease, and one of the most critical populations is pregnant women,” he said. In addition, “later phase 3 trials would be conducted in a population where there is an ongoing Zika outbreak,” Dr. Ault emphasized.
The study was supported by Janssen Vaccines and Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Chahroudi had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Permar disclosed grants from Merck and Moderna unrelated to the current study. Dr. Ault had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose; he has served as an adviser to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the World Medical Association, the National Vaccine Program Office, and the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases. He is a fellow of the Infectious Disease Society of American and a fellow of ACOG.
in a phase 1 study.
Although Zika cases have declined in recent years, “geographic expansion of the Aedes aegypti mosquito to areas where population-level immunity is low poses a substantial risk for future epidemics,” wrote Nadine C. Salisch, PhD, of Janssen Vaccines and Prevention, Leiden, the Netherlands, and colleagues in a paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
No vaccine against Zika is yet available, although more than 10 candidates have been studied in preclinical trials to date, they said.
The researchers randomized 100 healthy adult volunteers to an experimental Zika vaccine candidate known as Ad26.ZIKV.001 in either one-dose or two-dose regimens of 5x1010 viral particles (low dose) or 1x1011 viral particles (high dose) or placebo. Approximately half (55%) of the participants were women, and 72% were White.
Approximately 80% of patients in both two-dose groups showed antibody responses for a year after vaccination. Geometric mean titers (GMTs) reached peak of 823.4 in the low-dose/low-dose group and 961.5 in the high-dose/high-dose group. At day 365, the GMTs for these groups were 68.7 and 87.0, respectively.
A single high-dose vaccine achieved a similar level of neutralizing antibody titers, but lower peak neutralizing responses than the two-dose strategies, the researchers noted.
Most of the reported adverse events were mild to moderate, and short lived; the most common were injection site pain or tenderness, headache, and fatigue, the researchers said. After the first vaccination, 75% of participants in the low-dose groups, 88% of participants in high-dose groups, and 45% of participants receiving placebo reported local adverse events. In addition, 73%, 83%, and 40% of the participants in the low-dose, high-dose, and placebo groups, respectively, reported systemic adverse events. Reports were similar after the second vaccination. Two serious adverse events not related to vaccination were reported; one case of right lower lobe pneumonia and one case of incomplete spontaneous abortion.
The researchers also explored protective efficacy through a nonlethal mouse challenge model. “Transfer of 6 mg of IgG from Ad26.ZIKV.001 vaccines conferred complete protection from viremia in most recipient animals, with statistically significantly decreased breakthrough rates and cumulative viral loads per group compared with placebo,” they said.
The study findings were limited by the inability to assess safety and immunogenicity in an endemic area, the researchers noted. However, “Ad26.ZIKV.001 induces potent ZIKV-specific neutralizing responses with durability of at least 1 year, which supports further clinical development if an unmet medical need reemerges,” they said. “In addition, these data underscore the performance of the Ad26 vaccine platform, which Janssen is using for different infectious diseases, including COVID-19,” they noted.
Ad26 vector platform shows consistency
“Development of the investigational Janssen Zika vaccine candidate was initiated in 2015, and while the incidence of Zika virus has declined since the 2015-2016 outbreak, spread of the ‘carrier’ Aedes aegypti mosquito to areas where population-level immunity is low poses a substantial risk for future epidemics,” lead author Dr. Salisch said in an interview. For this reason, researchers say the vaccine warrants further development should the need reemerge, she said.
“Our research has found that while a single higher-dose regimen had lower peak neutralizing responses than a two-dose regimen, it achieved a similar level of neutralizing antibody responses at 1 year, an encouraging finding that shows our vaccine may be a useful tool to curb Zika epidemics,” Dr. Salisch noted. “Previous experience with the Ad26 vector platform across our investigational vaccine programs have yielded similarly promising results, most recently with our investigational Janssen COVID-19 vaccine program, for which phase 3 data show a single-dose vaccine met all primary and key secondary endpoints,” she said.
“The biggest barrier [to further development of the candidate vaccine] is one that we actually consider ourselves fortunate to have: The very low incidence of reported Zika cases currently reported worldwide,” Dr. Salisch said. “However, the current Zika case rate can change at any time, and in the event the situation demands it, we are open to alternative regulatory pathways to help us glean the necessary insights on vaccine safety and efficacy to further advance the development of this candidate,” she emphasized.
As for additional research, “there are still questions surrounding Zika transmission and the pathomechanism of congenital Zika syndrome,” said Dr. Salisch. “Our hope is that a correlate of protection against Zika disease, and in particular against congenital Zika syndrome, can be identified,” she said.
Consider pregnant women in next phase of research
“A major hurdle in ZIKV vaccine development is the inability to conduct large efficacy studies in the absence of a current outbreak,” Ann Chahroudi, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and Sallie Permar, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The current study provided some efficacy data using a mouse model, but “these data are obviously not conclusive for human protection,” they said.
“A further challenge for ZIKV vaccine efficacy trials will be to demonstrate fetal protection from [congenital Zika syndrome] after adult immunization. There should be a clear plan to readily deploy phase 3 trials for the most promising vaccines to emerge from phase 1 and 2 in the event of an outbreak, as was implemented for Ebola, including infant follow-up,” they emphasized.
The editorialists noted that the study did not include pregnant women, who represent a major target for immunization, but they said that vaccination of pregnant women against other neonatal pathogens such as influenza and tetanus has been effective. “Candidate ZIKV vaccines proven safe in phase 1 trials should immediately be assessed for safety and efficacy in pregnant women,” they said. Although Zika infections are not at epidemic levels currently, resurgence remains a possibility and the coronavirus pandemic “has taught us that preparedness for emerging infections is crucial,” they said.
Zika vaccine research is a challenge worth pursuing
“It is important to continue Zika vaccine research because of the unpredictable nature of that infection,” Kevin Ault, MD, of the University of Kansas, Kansas City, said in an interview. “Several times Zika has gained a foothold in unexposed and vulnerable populations,” Dr. Ault said. “Additionally, there are some data about using this vector during pregnancy, and eventually this vaccine may prevent the birth defects associated with Zika infections during pregnancy, he noted.
Dr. Ault said he was not surprised by the study findings. “This is a promising early phase vaccine candidate, and this adenovirus vector has been used in other similar trials,” he said. Potential barriers to vaccine development include the challenge of conducting late phase clinical trials in pregnant women, he noted. “The relevant endpoint is going to be clinical disease, and one of the most critical populations is pregnant women,” he said. In addition, “later phase 3 trials would be conducted in a population where there is an ongoing Zika outbreak,” Dr. Ault emphasized.
The study was supported by Janssen Vaccines and Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Chahroudi had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Permar disclosed grants from Merck and Moderna unrelated to the current study. Dr. Ault had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose; he has served as an adviser to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the World Medical Association, the National Vaccine Program Office, and the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases. He is a fellow of the Infectious Disease Society of American and a fellow of ACOG.
in a phase 1 study.
Although Zika cases have declined in recent years, “geographic expansion of the Aedes aegypti mosquito to areas where population-level immunity is low poses a substantial risk for future epidemics,” wrote Nadine C. Salisch, PhD, of Janssen Vaccines and Prevention, Leiden, the Netherlands, and colleagues in a paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
No vaccine against Zika is yet available, although more than 10 candidates have been studied in preclinical trials to date, they said.
The researchers randomized 100 healthy adult volunteers to an experimental Zika vaccine candidate known as Ad26.ZIKV.001 in either one-dose or two-dose regimens of 5x1010 viral particles (low dose) or 1x1011 viral particles (high dose) or placebo. Approximately half (55%) of the participants were women, and 72% were White.
Approximately 80% of patients in both two-dose groups showed antibody responses for a year after vaccination. Geometric mean titers (GMTs) reached peak of 823.4 in the low-dose/low-dose group and 961.5 in the high-dose/high-dose group. At day 365, the GMTs for these groups were 68.7 and 87.0, respectively.
A single high-dose vaccine achieved a similar level of neutralizing antibody titers, but lower peak neutralizing responses than the two-dose strategies, the researchers noted.
Most of the reported adverse events were mild to moderate, and short lived; the most common were injection site pain or tenderness, headache, and fatigue, the researchers said. After the first vaccination, 75% of participants in the low-dose groups, 88% of participants in high-dose groups, and 45% of participants receiving placebo reported local adverse events. In addition, 73%, 83%, and 40% of the participants in the low-dose, high-dose, and placebo groups, respectively, reported systemic adverse events. Reports were similar after the second vaccination. Two serious adverse events not related to vaccination were reported; one case of right lower lobe pneumonia and one case of incomplete spontaneous abortion.
The researchers also explored protective efficacy through a nonlethal mouse challenge model. “Transfer of 6 mg of IgG from Ad26.ZIKV.001 vaccines conferred complete protection from viremia in most recipient animals, with statistically significantly decreased breakthrough rates and cumulative viral loads per group compared with placebo,” they said.
The study findings were limited by the inability to assess safety and immunogenicity in an endemic area, the researchers noted. However, “Ad26.ZIKV.001 induces potent ZIKV-specific neutralizing responses with durability of at least 1 year, which supports further clinical development if an unmet medical need reemerges,” they said. “In addition, these data underscore the performance of the Ad26 vaccine platform, which Janssen is using for different infectious diseases, including COVID-19,” they noted.
Ad26 vector platform shows consistency
“Development of the investigational Janssen Zika vaccine candidate was initiated in 2015, and while the incidence of Zika virus has declined since the 2015-2016 outbreak, spread of the ‘carrier’ Aedes aegypti mosquito to areas where population-level immunity is low poses a substantial risk for future epidemics,” lead author Dr. Salisch said in an interview. For this reason, researchers say the vaccine warrants further development should the need reemerge, she said.
“Our research has found that while a single higher-dose regimen had lower peak neutralizing responses than a two-dose regimen, it achieved a similar level of neutralizing antibody responses at 1 year, an encouraging finding that shows our vaccine may be a useful tool to curb Zika epidemics,” Dr. Salisch noted. “Previous experience with the Ad26 vector platform across our investigational vaccine programs have yielded similarly promising results, most recently with our investigational Janssen COVID-19 vaccine program, for which phase 3 data show a single-dose vaccine met all primary and key secondary endpoints,” she said.
“The biggest barrier [to further development of the candidate vaccine] is one that we actually consider ourselves fortunate to have: The very low incidence of reported Zika cases currently reported worldwide,” Dr. Salisch said. “However, the current Zika case rate can change at any time, and in the event the situation demands it, we are open to alternative regulatory pathways to help us glean the necessary insights on vaccine safety and efficacy to further advance the development of this candidate,” she emphasized.
As for additional research, “there are still questions surrounding Zika transmission and the pathomechanism of congenital Zika syndrome,” said Dr. Salisch. “Our hope is that a correlate of protection against Zika disease, and in particular against congenital Zika syndrome, can be identified,” she said.
Consider pregnant women in next phase of research
“A major hurdle in ZIKV vaccine development is the inability to conduct large efficacy studies in the absence of a current outbreak,” Ann Chahroudi, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and Sallie Permar, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The current study provided some efficacy data using a mouse model, but “these data are obviously not conclusive for human protection,” they said.
“A further challenge for ZIKV vaccine efficacy trials will be to demonstrate fetal protection from [congenital Zika syndrome] after adult immunization. There should be a clear plan to readily deploy phase 3 trials for the most promising vaccines to emerge from phase 1 and 2 in the event of an outbreak, as was implemented for Ebola, including infant follow-up,” they emphasized.
The editorialists noted that the study did not include pregnant women, who represent a major target for immunization, but they said that vaccination of pregnant women against other neonatal pathogens such as influenza and tetanus has been effective. “Candidate ZIKV vaccines proven safe in phase 1 trials should immediately be assessed for safety and efficacy in pregnant women,” they said. Although Zika infections are not at epidemic levels currently, resurgence remains a possibility and the coronavirus pandemic “has taught us that preparedness for emerging infections is crucial,” they said.
Zika vaccine research is a challenge worth pursuing
“It is important to continue Zika vaccine research because of the unpredictable nature of that infection,” Kevin Ault, MD, of the University of Kansas, Kansas City, said in an interview. “Several times Zika has gained a foothold in unexposed and vulnerable populations,” Dr. Ault said. “Additionally, there are some data about using this vector during pregnancy, and eventually this vaccine may prevent the birth defects associated with Zika infections during pregnancy, he noted.
Dr. Ault said he was not surprised by the study findings. “This is a promising early phase vaccine candidate, and this adenovirus vector has been used in other similar trials,” he said. Potential barriers to vaccine development include the challenge of conducting late phase clinical trials in pregnant women, he noted. “The relevant endpoint is going to be clinical disease, and one of the most critical populations is pregnant women,” he said. In addition, “later phase 3 trials would be conducted in a population where there is an ongoing Zika outbreak,” Dr. Ault emphasized.
The study was supported by Janssen Vaccines and Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Chahroudi had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Permar disclosed grants from Merck and Moderna unrelated to the current study. Dr. Ault had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose; he has served as an adviser to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the World Medical Association, the National Vaccine Program Office, and the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases. He is a fellow of the Infectious Disease Society of American and a fellow of ACOG.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
The importance of family acceptance for LGBTQ youth
It is well established that LGBTQ individuals experience more health disparities compared with their cisgender, heterosexual counterparts. In general, LGBTQ adolescents and young adults have higher levels of depression, suicide attempts, and substance use than those of their heterosexual peers. However, a key protective factor is family acceptance and support. By encouraging families to modify and change behaviors that are experienced by their LGBTQ children as rejecting and to engage in supportive and affirming behaviors, providers can help families to decrease risk and promote healthy outcomes for LGBTQ youth and young adults. 
We all know that a supportive family can make a difference for any child, but this is especially true for LGBTQ youth and is critical during a pandemic when young people are confined with families and separated from peers and supportive adults outside the home. Several research studies show that family support can improve outcomes related to suicide, depression, homelessness, drug use, and HIV in LGBTQ young people. Family acceptance improves health outcomes, while rejection undermines family relationships and worsens both health and other serious outcomes such as homelessness and placement in custodial care. Pediatricians can help their patients by educating parents and caregivers with LGBTQ children about the critical role of family support – both those who see themselves as accepting and those who believe that being gay or transgender is wrong and are struggling with parenting a child who identifies as LGBTQ or who is gender diverse.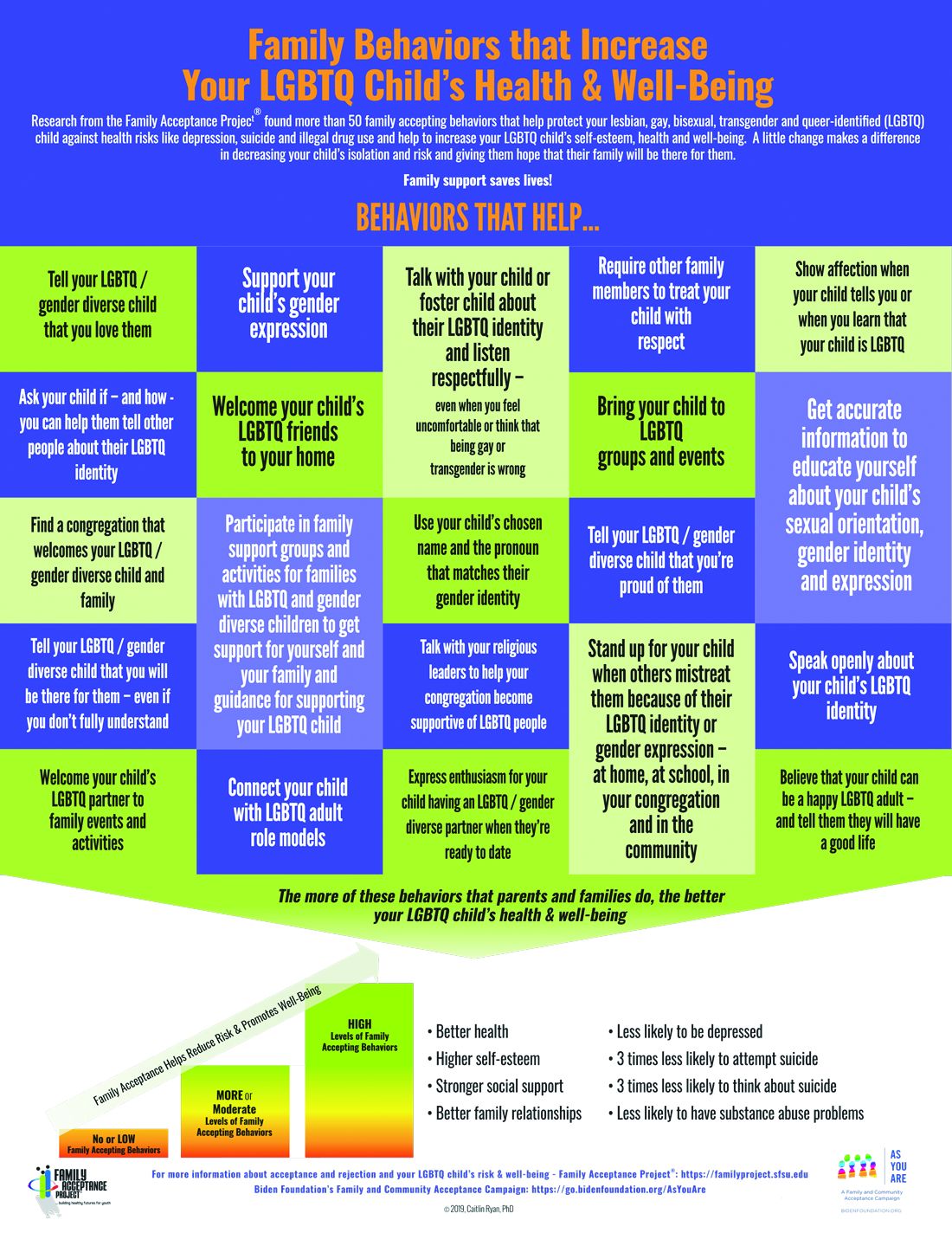
The Family Acceptance Project (FAP) at San Francisco State University conducted the first research on LGBTQ youth and families, developed the first evidence-informed family support model, and has published a range of studies and evidence-based resources that demonstrate the harm caused by family rejection, validate the importance of family acceptance, and provide guidance to increase family support. FAP’s research found that parents and caregivers that engage in rejecting behaviors are typically motivated by care and concern and by trying to protect their children from harm. They believe such behaviors will help their LGBTQ children fit in, have a good life, meet cultural and religious expectations, and be respected by others.1 FAP’s research identified and measured more than 50 rejecting behaviors that parents and caregivers use to respond to their LGBTQ children. Some of these commonly expressed rejecting behaviors include ridiculing and making disparaging comments about their child and other LGBTQ people; excluding them from family activities; blaming their child when others mistreat them because they are LGBTQ; blocking access to LGBTQ resources including friends, support groups, and activities; and trying to change their child’s sexual orientation and gender identity.2 LGBTQ youth experience these and other such behaviors as hurtful, harmful, and traumatic and may feel that they need to hide or repress their identity which can affect their self-esteem, increase isolation, depression, and risky behaviors.3 Providers working with families of LGBTQ youth should focus on shared goals, such as reducing risk and having a happy, healthy child. Most parents love their children and fear for their well-being. However, many are uninformed about their child’s gender identity and sexual orientation and don’t know how to nurture and support them.
In FAP’s initial study, LGB young people who reported higher levels of family rejection had substantially higher rates of attempted suicide, depression, illegal drug use, and unprotected sex.4 These rates were even more significant among Latino gay and bisexual men.4 Those who are rejected by family are less likely to want to have a family or to be parents themselves5 and have lower educational and income levels.6
To reduce risk, pediatricians should ask LGBTQ patients about family rejecting behaviors and help parents and caregivers to identify and understand the effect of such behaviors to reduce health risks and conflict that can lead to running away, expulsion, and removal from the home. Even decreasing rejecting behaviors to moderate levels can significantly improve negative outcomes.5
Caitlin Ryan, PhD, and her team also identified and measured more than 50 family accepting behaviors that help protect against risk and promote well-being. They found that young adults who experience high levels of family acceptance during adolescence report significantly higher levels of self-esteem, social support, and general health with much lower levels of depression, suicidality, and substance abuse.7 Family accepting and supportive behaviors include talking with the child about their LGBTQ identity; advocating for their LGBTQ child when others mistreat them; requiring other family members to treat their LGBTQ child with respect; and supporting their child’s gender identity.5 FAP has developed an evidence-informed family support model and multilingual educational resources for families, providers, youth and religious leaders to decrease rejection and increase family support. These are available in print copies and for download at familyproject.sfsu.edu.
In addition, Dr. Ryan and colleagues1,4,8 recommend the following guidance for providers:
- Ask LGBTQ adolescents about family reactions to their sexual orientation, gender identity, and expression, and refer to LGBTQ community support programs and for supportive counseling, as needed.
- Identify LGBTQ community support programs and online resources to educate parents about how to help their children. Parents need culturally relevant peer support to help decrease rejection and increase family support.
- Advise parents that negative reactions to their adolescent’s LGBTQ identity may negatively impact their child’s health and mental health while supportive and affirming reactions promote well-being.
- Advise parents and caregivers to modify and change family rejecting behaviors that increase their child’s risk for suicide, depression, substance abuse ,and risky sexual behaviors.
- Expand anticipatory guidance to include information on the need for support and the link between family rejection and negative health problems.
- Provide guidance on sexual orientation and gender identity as part of normative child development during well-baby and early childhood care.
- Use FAP’s multilingual family education booklets and Healthy Futures poster series in family and patient education and provide these materials in clinical and community settings. FAP’s Healthy Futures posters include a poster guidance, a version on family acceptance, a version on family rejection and a family acceptance version for conservative families and settings. They are available in camera-ready art in four sizes in English and Spanish and are forthcoming in five Asian languages: familyproject.sfsu.edu/poster.
Dr. Lawlis is assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and an adolescent medicine specialist at OU Children’s. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
Resources
• Family Acceptance Project – consultation and training; evidence-based educational materials for families, providers, religious leaders and youth.
• PFLAG – peer support for parents and friends with LGBTQ children in all states and several other countries.
References
1. Ryan C. Generating a revolution in prevention, wellness & care for LGBT children & youth. Temple Political & Civil Rights Law Review. 2014;23(2):331-44.
2. Ryan C. Healthy Futures Poster Series – Family Accepting & Rejecting Behaviors That Impact LGBTQ Children’s Health & Well-Being. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2019.
3. Ryan C. Family Acceptance Project: Culturally grounded framework for supporting LGBTQ children and youth. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatr. 2019;58(10):S58-9.
4. Ryan C et al. Family rejection as a predictor of negative health outcomes in White and Latino lesbian, gay, and bisexual young adults. Pediatrics. 2009;123(1):346-52.
5. Ryan C. Supportive families, healthy children: Helping families with lesbian, gay, bisexual & transgender children. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2009.
6. Ryan C et al. Parent-initiated sexual orientation change efforts with LGBT adolescents: Implications for young adult mental health and adjustment. J Homosexuality. 2020;67(2):159-73.
7. Ryan C et al. Family acceptance in adolescence and the health of LGBT young adults. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nursing. 2010;23(4):205-13. 8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. A Practitioner’s Guide: Helping Families to Support Their LGBT Children. In: Administration SAaMhS, ed. Vol PEP14-LGBTKIDS. Rockville, MD: HHS Publication; 2014.
It is well established that LGBTQ individuals experience more health disparities compared with their cisgender, heterosexual counterparts. In general, LGBTQ adolescents and young adults have higher levels of depression, suicide attempts, and substance use than those of their heterosexual peers. However, a key protective factor is family acceptance and support. By encouraging families to modify and change behaviors that are experienced by their LGBTQ children as rejecting and to engage in supportive and affirming behaviors, providers can help families to decrease risk and promote healthy outcomes for LGBTQ youth and young adults. 
We all know that a supportive family can make a difference for any child, but this is especially true for LGBTQ youth and is critical during a pandemic when young people are confined with families and separated from peers and supportive adults outside the home. Several research studies show that family support can improve outcomes related to suicide, depression, homelessness, drug use, and HIV in LGBTQ young people. Family acceptance improves health outcomes, while rejection undermines family relationships and worsens both health and other serious outcomes such as homelessness and placement in custodial care. Pediatricians can help their patients by educating parents and caregivers with LGBTQ children about the critical role of family support – both those who see themselves as accepting and those who believe that being gay or transgender is wrong and are struggling with parenting a child who identifies as LGBTQ or who is gender diverse.
The Family Acceptance Project (FAP) at San Francisco State University conducted the first research on LGBTQ youth and families, developed the first evidence-informed family support model, and has published a range of studies and evidence-based resources that demonstrate the harm caused by family rejection, validate the importance of family acceptance, and provide guidance to increase family support. FAP’s research found that parents and caregivers that engage in rejecting behaviors are typically motivated by care and concern and by trying to protect their children from harm. They believe such behaviors will help their LGBTQ children fit in, have a good life, meet cultural and religious expectations, and be respected by others.1 FAP’s research identified and measured more than 50 rejecting behaviors that parents and caregivers use to respond to their LGBTQ children. Some of these commonly expressed rejecting behaviors include ridiculing and making disparaging comments about their child and other LGBTQ people; excluding them from family activities; blaming their child when others mistreat them because they are LGBTQ; blocking access to LGBTQ resources including friends, support groups, and activities; and trying to change their child’s sexual orientation and gender identity.2 LGBTQ youth experience these and other such behaviors as hurtful, harmful, and traumatic and may feel that they need to hide or repress their identity which can affect their self-esteem, increase isolation, depression, and risky behaviors.3 Providers working with families of LGBTQ youth should focus on shared goals, such as reducing risk and having a happy, healthy child. Most parents love their children and fear for their well-being. However, many are uninformed about their child’s gender identity and sexual orientation and don’t know how to nurture and support them.
In FAP’s initial study, LGB young people who reported higher levels of family rejection had substantially higher rates of attempted suicide, depression, illegal drug use, and unprotected sex.4 These rates were even more significant among Latino gay and bisexual men.4 Those who are rejected by family are less likely to want to have a family or to be parents themselves5 and have lower educational and income levels.6
To reduce risk, pediatricians should ask LGBTQ patients about family rejecting behaviors and help parents and caregivers to identify and understand the effect of such behaviors to reduce health risks and conflict that can lead to running away, expulsion, and removal from the home. Even decreasing rejecting behaviors to moderate levels can significantly improve negative outcomes.5
Caitlin Ryan, PhD, and her team also identified and measured more than 50 family accepting behaviors that help protect against risk and promote well-being. They found that young adults who experience high levels of family acceptance during adolescence report significantly higher levels of self-esteem, social support, and general health with much lower levels of depression, suicidality, and substance abuse.7 Family accepting and supportive behaviors include talking with the child about their LGBTQ identity; advocating for their LGBTQ child when others mistreat them; requiring other family members to treat their LGBTQ child with respect; and supporting their child’s gender identity.5 FAP has developed an evidence-informed family support model and multilingual educational resources for families, providers, youth and religious leaders to decrease rejection and increase family support. These are available in print copies and for download at familyproject.sfsu.edu.
In addition, Dr. Ryan and colleagues1,4,8 recommend the following guidance for providers:
- Ask LGBTQ adolescents about family reactions to their sexual orientation, gender identity, and expression, and refer to LGBTQ community support programs and for supportive counseling, as needed.
- Identify LGBTQ community support programs and online resources to educate parents about how to help their children. Parents need culturally relevant peer support to help decrease rejection and increase family support.
- Advise parents that negative reactions to their adolescent’s LGBTQ identity may negatively impact their child’s health and mental health while supportive and affirming reactions promote well-being.
- Advise parents and caregivers to modify and change family rejecting behaviors that increase their child’s risk for suicide, depression, substance abuse ,and risky sexual behaviors.
- Expand anticipatory guidance to include information on the need for support and the link between family rejection and negative health problems.
- Provide guidance on sexual orientation and gender identity as part of normative child development during well-baby and early childhood care.
- Use FAP’s multilingual family education booklets and Healthy Futures poster series in family and patient education and provide these materials in clinical and community settings. FAP’s Healthy Futures posters include a poster guidance, a version on family acceptance, a version on family rejection and a family acceptance version for conservative families and settings. They are available in camera-ready art in four sizes in English and Spanish and are forthcoming in five Asian languages: familyproject.sfsu.edu/poster.
Dr. Lawlis is assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and an adolescent medicine specialist at OU Children’s. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
Resources
• Family Acceptance Project – consultation and training; evidence-based educational materials for families, providers, religious leaders and youth.
• PFLAG – peer support for parents and friends with LGBTQ children in all states and several other countries.
References
1. Ryan C. Generating a revolution in prevention, wellness & care for LGBT children & youth. Temple Political & Civil Rights Law Review. 2014;23(2):331-44.
2. Ryan C. Healthy Futures Poster Series – Family Accepting & Rejecting Behaviors That Impact LGBTQ Children’s Health & Well-Being. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2019.
3. Ryan C. Family Acceptance Project: Culturally grounded framework for supporting LGBTQ children and youth. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatr. 2019;58(10):S58-9.
4. Ryan C et al. Family rejection as a predictor of negative health outcomes in White and Latino lesbian, gay, and bisexual young adults. Pediatrics. 2009;123(1):346-52.
5. Ryan C. Supportive families, healthy children: Helping families with lesbian, gay, bisexual & transgender children. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2009.
6. Ryan C et al. Parent-initiated sexual orientation change efforts with LGBT adolescents: Implications for young adult mental health and adjustment. J Homosexuality. 2020;67(2):159-73.
7. Ryan C et al. Family acceptance in adolescence and the health of LGBT young adults. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nursing. 2010;23(4):205-13. 8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. A Practitioner’s Guide: Helping Families to Support Their LGBT Children. In: Administration SAaMhS, ed. Vol PEP14-LGBTKIDS. Rockville, MD: HHS Publication; 2014.
It is well established that LGBTQ individuals experience more health disparities compared with their cisgender, heterosexual counterparts. In general, LGBTQ adolescents and young adults have higher levels of depression, suicide attempts, and substance use than those of their heterosexual peers. However, a key protective factor is family acceptance and support. By encouraging families to modify and change behaviors that are experienced by their LGBTQ children as rejecting and to engage in supportive and affirming behaviors, providers can help families to decrease risk and promote healthy outcomes for LGBTQ youth and young adults. 
We all know that a supportive family can make a difference for any child, but this is especially true for LGBTQ youth and is critical during a pandemic when young people are confined with families and separated from peers and supportive adults outside the home. Several research studies show that family support can improve outcomes related to suicide, depression, homelessness, drug use, and HIV in LGBTQ young people. Family acceptance improves health outcomes, while rejection undermines family relationships and worsens both health and other serious outcomes such as homelessness and placement in custodial care. Pediatricians can help their patients by educating parents and caregivers with LGBTQ children about the critical role of family support – both those who see themselves as accepting and those who believe that being gay or transgender is wrong and are struggling with parenting a child who identifies as LGBTQ or who is gender diverse.
The Family Acceptance Project (FAP) at San Francisco State University conducted the first research on LGBTQ youth and families, developed the first evidence-informed family support model, and has published a range of studies and evidence-based resources that demonstrate the harm caused by family rejection, validate the importance of family acceptance, and provide guidance to increase family support. FAP’s research found that parents and caregivers that engage in rejecting behaviors are typically motivated by care and concern and by trying to protect their children from harm. They believe such behaviors will help their LGBTQ children fit in, have a good life, meet cultural and religious expectations, and be respected by others.1 FAP’s research identified and measured more than 50 rejecting behaviors that parents and caregivers use to respond to their LGBTQ children. Some of these commonly expressed rejecting behaviors include ridiculing and making disparaging comments about their child and other LGBTQ people; excluding them from family activities; blaming their child when others mistreat them because they are LGBTQ; blocking access to LGBTQ resources including friends, support groups, and activities; and trying to change their child’s sexual orientation and gender identity.2 LGBTQ youth experience these and other such behaviors as hurtful, harmful, and traumatic and may feel that they need to hide or repress their identity which can affect their self-esteem, increase isolation, depression, and risky behaviors.3 Providers working with families of LGBTQ youth should focus on shared goals, such as reducing risk and having a happy, healthy child. Most parents love their children and fear for their well-being. However, many are uninformed about their child’s gender identity and sexual orientation and don’t know how to nurture and support them.
In FAP’s initial study, LGB young people who reported higher levels of family rejection had substantially higher rates of attempted suicide, depression, illegal drug use, and unprotected sex.4 These rates were even more significant among Latino gay and bisexual men.4 Those who are rejected by family are less likely to want to have a family or to be parents themselves5 and have lower educational and income levels.6
To reduce risk, pediatricians should ask LGBTQ patients about family rejecting behaviors and help parents and caregivers to identify and understand the effect of such behaviors to reduce health risks and conflict that can lead to running away, expulsion, and removal from the home. Even decreasing rejecting behaviors to moderate levels can significantly improve negative outcomes.5
Caitlin Ryan, PhD, and her team also identified and measured more than 50 family accepting behaviors that help protect against risk and promote well-being. They found that young adults who experience high levels of family acceptance during adolescence report significantly higher levels of self-esteem, social support, and general health with much lower levels of depression, suicidality, and substance abuse.7 Family accepting and supportive behaviors include talking with the child about their LGBTQ identity; advocating for their LGBTQ child when others mistreat them; requiring other family members to treat their LGBTQ child with respect; and supporting their child’s gender identity.5 FAP has developed an evidence-informed family support model and multilingual educational resources for families, providers, youth and religious leaders to decrease rejection and increase family support. These are available in print copies and for download at familyproject.sfsu.edu.
In addition, Dr. Ryan and colleagues1,4,8 recommend the following guidance for providers:
- Ask LGBTQ adolescents about family reactions to their sexual orientation, gender identity, and expression, and refer to LGBTQ community support programs and for supportive counseling, as needed.
- Identify LGBTQ community support programs and online resources to educate parents about how to help their children. Parents need culturally relevant peer support to help decrease rejection and increase family support.
- Advise parents that negative reactions to their adolescent’s LGBTQ identity may negatively impact their child’s health and mental health while supportive and affirming reactions promote well-being.
- Advise parents and caregivers to modify and change family rejecting behaviors that increase their child’s risk for suicide, depression, substance abuse ,and risky sexual behaviors.
- Expand anticipatory guidance to include information on the need for support and the link between family rejection and negative health problems.
- Provide guidance on sexual orientation and gender identity as part of normative child development during well-baby and early childhood care.
- Use FAP’s multilingual family education booklets and Healthy Futures poster series in family and patient education and provide these materials in clinical and community settings. FAP’s Healthy Futures posters include a poster guidance, a version on family acceptance, a version on family rejection and a family acceptance version for conservative families and settings. They are available in camera-ready art in four sizes in English and Spanish and are forthcoming in five Asian languages: familyproject.sfsu.edu/poster.
Dr. Lawlis is assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and an adolescent medicine specialist at OU Children’s. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
Resources
• Family Acceptance Project – consultation and training; evidence-based educational materials for families, providers, religious leaders and youth.
• PFLAG – peer support for parents and friends with LGBTQ children in all states and several other countries.
References
1. Ryan C. Generating a revolution in prevention, wellness & care for LGBT children & youth. Temple Political & Civil Rights Law Review. 2014;23(2):331-44.
2. Ryan C. Healthy Futures Poster Series – Family Accepting & Rejecting Behaviors That Impact LGBTQ Children’s Health & Well-Being. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2019.
3. Ryan C. Family Acceptance Project: Culturally grounded framework for supporting LGBTQ children and youth. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatr. 2019;58(10):S58-9.
4. Ryan C et al. Family rejection as a predictor of negative health outcomes in White and Latino lesbian, gay, and bisexual young adults. Pediatrics. 2009;123(1):346-52.
5. Ryan C. Supportive families, healthy children: Helping families with lesbian, gay, bisexual & transgender children. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2009.
6. Ryan C et al. Parent-initiated sexual orientation change efforts with LGBT adolescents: Implications for young adult mental health and adjustment. J Homosexuality. 2020;67(2):159-73.
7. Ryan C et al. Family acceptance in adolescence and the health of LGBT young adults. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nursing. 2010;23(4):205-13. 8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. A Practitioner’s Guide: Helping Families to Support Their LGBT Children. In: Administration SAaMhS, ed. Vol PEP14-LGBTKIDS. Rockville, MD: HHS Publication; 2014.
Child ‘Mis’behavior – What’s ‘mis’ing?
“What kind of parent are you? Why don’t you straighten him out!” rants the woman being jostled in the grocery store by your patient. “Easy for you to say,” thinks your patient’s frazzled and now insulted parent.
Blaming the parent for an out-of-control child has historically been a common refrain of neighbors, relatives, and even strangers. But considering child behavior as resulting from both parent and child factors is central to the current transactional model of child development. In this model, mismatch of the parent’s and child’s response patterns is seen as setting them up for chronically rough interactions around parent requests/demands. A parent escalating quickly from a briefly stated request to a tirade may create more tension paired with an anxious child who takes time to act, for example. Once a parent (and ultimately the child) recognize patterns in what leads to conflict, they can become more proactive in predicting and negotiating these situations. Ross Greene, PhD, explains this in his book “The Explosive Child,” calling the method Collaborative Problem Solving (now Collaborative & Proactive Solutions or CPS).
While there are general principles parents can use to modify what they consider “mis”behaviors, these methods often do not account for the “missing” skills of the individual child (and parent) predisposing to those “mis”takes. Thinking of misbehaviors as being because of a kind of “learning disability” in the child rather than willful defiance can help cool off interactions by instead focusing on solving the underlying problem.
What kinds of “gaps in skills” set a child up for defiant or explosive reactions? If you think about what features of children, and parent-child relationships are associated with harmonious interactions this becomes evident. Children over 3 who are patient, easygoing, flexible or adaptable, and good at transitions and problem-solving can delay gratification and tolerate frustration, regulate their emotions, explain their desires, and multitask. They are better at reading the parent’s needs and intent and tend to interpret requests as positive or at least neutral and are more likely to comply with parent requests without a fuss.
What? No kid you know is great at all of these? These skills, at best variable, develop with maturation. Some are part of temperament, considered normal variation in personality. For example, so-called difficult temperament includes low adaptability, high-intensity reactions, low regularity, tendency to withdraw, and negative mood. But in the extreme, weaknesses in these skills are core to or comorbid with diagnosable mental health disorders. Defiance and irritable responses are criteria for oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), and less severe categories called aggressive/oppositional problem or variation. ODD is often found in children diagnosed with ADHD (65%), Tourette’s (15%-65%), depression (70% if severe), bipolar disorder (85%), OCD, anxiety (45%), autism, and language-processing disorders (55%), or trauma. These conditions variably include lower emotion regulation, poorer executive functioning including poor task shifting and impulsivity, obsessiveness, lower expressive and receptive communication skills, and less social awareness that facilitates harmonious problem solving.
The basic components of the CPS approach to addressing parent-child conflict sound intuitive but defining them clearly is important when families are stuck. There are three levels of plans. If the problem is an emergency or nonnegotiable, e.g., child hurting the cat, it may call for Plan A – parent-imposed solutions, sometimes with consequences or rewards. As children mature, Plan A should be used less frequently. If solving the problem is not a top life priority, Plan C – postponing action, may be appropriate. Plan C highlights that behavior change is a long-term project and “picking your fights” is important.
The biggest value of CPS for resolving behavior problems comes from intermediate Plan B. In Plan B the first step of problem solving for parents facing child defiance or upset is to empathically and nonjudgmentally figure out the child’s concern. Questions such as “I’ve noticed that when I remind you that it is trash night you start shouting. What’s up with that?” then patiently asking about the who, what, where, and when of their concern and checking to ensure understanding. Specificity is important as well as noting times when the reaction occurs or not.
Once the child’s concern is clear, e.g., feeling that the demand to take out the trash now interrupts his games during the only time his friends are online, the parents should echo the child’s concern then express their own concern about how the behavior is affecting them and others, potentially including the child; e.g., mother is so upset by the shouting that she can’t sleep, and worry that the child is not learning responsibility, and then checking for child understanding.
Finally, the parent invites brainstorming for a solution that addresses both of their concerns, first asking the child for suggestions, aiming for a strategy that is realistic and specific. Children reluctant to make suggestions may need more time and the parent may be wondering “if there is a way for both of our concerns to be addressed.” Solutions chosen are then tried for several weeks, success tracked, and needed changes negotiated.
For parents, using a collaborative approach to dealing with their child’s behavior takes skills they may not have at the moment, or ever. Especially under the stresses of COVID-19 lockdown, taking a step back from an encounter to consider lack of a skill to turn off the video game promptly when a Zoom meeting starts is challenging. Parents may also genetically share the child’s predisposing ADHD, anxiety, depression, OCD, or weakness in communication or social sensitivity.
Sometimes part of the solution for a conflict is for the parent to reduce expectations. This requires understanding and accepting the child’s cognitive or emotional limitations. Reducing expectations is ideally done before a request rather than by giving in after it, which reinforces protests. For authoritarian adults rigid in their belief that parents are boss, changing expectations can be tough and can feel like losing control or failing as a leader. One benefit of working with a CPS coach (see livesinthebalance.org or ThinkKids.org) is to help parents identify their own limitations.
Predicting the types of demands that tend to create conflict, such as to act immediately or be flexible about options, allows parents to prioritize those requests for calmer moments or when there is more time for discussion. Reviewing a checklist of common gaps in skills and creating a list of expectations and triggers that are difficult for the child helps the family be more proactive in developing solutions. Authors of CPS have validated a checklist of skill deficits, “Thinking Skills Inventory,” to facilitate detection of gaps that is educational plus useful for planning specific solutions.
CPS has been shown in randomized trials with both parent groups and in home counseling to be as effective as Parent Training in reducing oppositional behavior and reducing maternal stress, with effects lasting even longer.
CPS Plan B notably has no reward or punishment components as it assumes the child wants to behave acceptably but can’t; has the “will but not the skill.” When skill deficits are worked around the child is satisfied with complying and pleasing the parents. The idea of a “function” of the misbehavior for the child of gaining attention or reward or avoiding consequences is reinterpreted as serving to communicate the problem the child is having trouble in meeting the parent’s demand. When the parent understands and helps the child solve the problem his/her misbehavior is no longer needed. A benefit of the communication and mutual problem solving used in CPS is on not only improving behavior but empowering parents and children, building parental empathy, and improving child skills.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She has no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication is as a paid expert to MDedge News. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
Greene RW et al. A transactional model of oppositional behavior: Underpinnings of the Collaborative Problem Solving approach. J Psychosom Res. 2003;55(1):67-75.
“What kind of parent are you? Why don’t you straighten him out!” rants the woman being jostled in the grocery store by your patient. “Easy for you to say,” thinks your patient’s frazzled and now insulted parent.
Blaming the parent for an out-of-control child has historically been a common refrain of neighbors, relatives, and even strangers. But considering child behavior as resulting from both parent and child factors is central to the current transactional model of child development. In this model, mismatch of the parent’s and child’s response patterns is seen as setting them up for chronically rough interactions around parent requests/demands. A parent escalating quickly from a briefly stated request to a tirade may create more tension paired with an anxious child who takes time to act, for example. Once a parent (and ultimately the child) recognize patterns in what leads to conflict, they can become more proactive in predicting and negotiating these situations. Ross Greene, PhD, explains this in his book “The Explosive Child,” calling the method Collaborative Problem Solving (now Collaborative & Proactive Solutions or CPS).
While there are general principles parents can use to modify what they consider “mis”behaviors, these methods often do not account for the “missing” skills of the individual child (and parent) predisposing to those “mis”takes. Thinking of misbehaviors as being because of a kind of “learning disability” in the child rather than willful defiance can help cool off interactions by instead focusing on solving the underlying problem.
What kinds of “gaps in skills” set a child up for defiant or explosive reactions? If you think about what features of children, and parent-child relationships are associated with harmonious interactions this becomes evident. Children over 3 who are patient, easygoing, flexible or adaptable, and good at transitions and problem-solving can delay gratification and tolerate frustration, regulate their emotions, explain their desires, and multitask. They are better at reading the parent’s needs and intent and tend to interpret requests as positive or at least neutral and are more likely to comply with parent requests without a fuss.
What? No kid you know is great at all of these? These skills, at best variable, develop with maturation. Some are part of temperament, considered normal variation in personality. For example, so-called difficult temperament includes low adaptability, high-intensity reactions, low regularity, tendency to withdraw, and negative mood. But in the extreme, weaknesses in these skills are core to or comorbid with diagnosable mental health disorders. Defiance and irritable responses are criteria for oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), and less severe categories called aggressive/oppositional problem or variation. ODD is often found in children diagnosed with ADHD (65%), Tourette’s (15%-65%), depression (70% if severe), bipolar disorder (85%), OCD, anxiety (45%), autism, and language-processing disorders (55%), or trauma. These conditions variably include lower emotion regulation, poorer executive functioning including poor task shifting and impulsivity, obsessiveness, lower expressive and receptive communication skills, and less social awareness that facilitates harmonious problem solving.
The basic components of the CPS approach to addressing parent-child conflict sound intuitive but defining them clearly is important when families are stuck. There are three levels of plans. If the problem is an emergency or nonnegotiable, e.g., child hurting the cat, it may call for Plan A – parent-imposed solutions, sometimes with consequences or rewards. As children mature, Plan A should be used less frequently. If solving the problem is not a top life priority, Plan C – postponing action, may be appropriate. Plan C highlights that behavior change is a long-term project and “picking your fights” is important.
The biggest value of CPS for resolving behavior problems comes from intermediate Plan B. In Plan B the first step of problem solving for parents facing child defiance or upset is to empathically and nonjudgmentally figure out the child’s concern. Questions such as “I’ve noticed that when I remind you that it is trash night you start shouting. What’s up with that?” then patiently asking about the who, what, where, and when of their concern and checking to ensure understanding. Specificity is important as well as noting times when the reaction occurs or not.
Once the child’s concern is clear, e.g., feeling that the demand to take out the trash now interrupts his games during the only time his friends are online, the parents should echo the child’s concern then express their own concern about how the behavior is affecting them and others, potentially including the child; e.g., mother is so upset by the shouting that she can’t sleep, and worry that the child is not learning responsibility, and then checking for child understanding.
Finally, the parent invites brainstorming for a solution that addresses both of their concerns, first asking the child for suggestions, aiming for a strategy that is realistic and specific. Children reluctant to make suggestions may need more time and the parent may be wondering “if there is a way for both of our concerns to be addressed.” Solutions chosen are then tried for several weeks, success tracked, and needed changes negotiated.
For parents, using a collaborative approach to dealing with their child’s behavior takes skills they may not have at the moment, or ever. Especially under the stresses of COVID-19 lockdown, taking a step back from an encounter to consider lack of a skill to turn off the video game promptly when a Zoom meeting starts is challenging. Parents may also genetically share the child’s predisposing ADHD, anxiety, depression, OCD, or weakness in communication or social sensitivity.
Sometimes part of the solution for a conflict is for the parent to reduce expectations. This requires understanding and accepting the child’s cognitive or emotional limitations. Reducing expectations is ideally done before a request rather than by giving in after it, which reinforces protests. For authoritarian adults rigid in their belief that parents are boss, changing expectations can be tough and can feel like losing control or failing as a leader. One benefit of working with a CPS coach (see livesinthebalance.org or ThinkKids.org) is to help parents identify their own limitations.
Predicting the types of demands that tend to create conflict, such as to act immediately or be flexible about options, allows parents to prioritize those requests for calmer moments or when there is more time for discussion. Reviewing a checklist of common gaps in skills and creating a list of expectations and triggers that are difficult for the child helps the family be more proactive in developing solutions. Authors of CPS have validated a checklist of skill deficits, “Thinking Skills Inventory,” to facilitate detection of gaps that is educational plus useful for planning specific solutions.
CPS has been shown in randomized trials with both parent groups and in home counseling to be as effective as Parent Training in reducing oppositional behavior and reducing maternal stress, with effects lasting even longer.
CPS Plan B notably has no reward or punishment components as it assumes the child wants to behave acceptably but can’t; has the “will but not the skill.” When skill deficits are worked around the child is satisfied with complying and pleasing the parents. The idea of a “function” of the misbehavior for the child of gaining attention or reward or avoiding consequences is reinterpreted as serving to communicate the problem the child is having trouble in meeting the parent’s demand. When the parent understands and helps the child solve the problem his/her misbehavior is no longer needed. A benefit of the communication and mutual problem solving used in CPS is on not only improving behavior but empowering parents and children, building parental empathy, and improving child skills.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She has no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication is as a paid expert to MDedge News. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
Greene RW et al. A transactional model of oppositional behavior: Underpinnings of the Collaborative Problem Solving approach. J Psychosom Res. 2003;55(1):67-75.
“What kind of parent are you? Why don’t you straighten him out!” rants the woman being jostled in the grocery store by your patient. “Easy for you to say,” thinks your patient’s frazzled and now insulted parent.
Blaming the parent for an out-of-control child has historically been a common refrain of neighbors, relatives, and even strangers. But considering child behavior as resulting from both parent and child factors is central to the current transactional model of child development. In this model, mismatch of the parent’s and child’s response patterns is seen as setting them up for chronically rough interactions around parent requests/demands. A parent escalating quickly from a briefly stated request to a tirade may create more tension paired with an anxious child who takes time to act, for example. Once a parent (and ultimately the child) recognize patterns in what leads to conflict, they can become more proactive in predicting and negotiating these situations. Ross Greene, PhD, explains this in his book “The Explosive Child,” calling the method Collaborative Problem Solving (now Collaborative & Proactive Solutions or CPS).
While there are general principles parents can use to modify what they consider “mis”behaviors, these methods often do not account for the “missing” skills of the individual child (and parent) predisposing to those “mis”takes. Thinking of misbehaviors as being because of a kind of “learning disability” in the child rather than willful defiance can help cool off interactions by instead focusing on solving the underlying problem.
What kinds of “gaps in skills” set a child up for defiant or explosive reactions? If you think about what features of children, and parent-child relationships are associated with harmonious interactions this becomes evident. Children over 3 who are patient, easygoing, flexible or adaptable, and good at transitions and problem-solving can delay gratification and tolerate frustration, regulate their emotions, explain their desires, and multitask. They are better at reading the parent’s needs and intent and tend to interpret requests as positive or at least neutral and are more likely to comply with parent requests without a fuss.
What? No kid you know is great at all of these? These skills, at best variable, develop with maturation. Some are part of temperament, considered normal variation in personality. For example, so-called difficult temperament includes low adaptability, high-intensity reactions, low regularity, tendency to withdraw, and negative mood. But in the extreme, weaknesses in these skills are core to or comorbid with diagnosable mental health disorders. Defiance and irritable responses are criteria for oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), and less severe categories called aggressive/oppositional problem or variation. ODD is often found in children diagnosed with ADHD (65%), Tourette’s (15%-65%), depression (70% if severe), bipolar disorder (85%), OCD, anxiety (45%), autism, and language-processing disorders (55%), or trauma. These conditions variably include lower emotion regulation, poorer executive functioning including poor task shifting and impulsivity, obsessiveness, lower expressive and receptive communication skills, and less social awareness that facilitates harmonious problem solving.
The basic components of the CPS approach to addressing parent-child conflict sound intuitive but defining them clearly is important when families are stuck. There are three levels of plans. If the problem is an emergency or nonnegotiable, e.g., child hurting the cat, it may call for Plan A – parent-imposed solutions, sometimes with consequences or rewards. As children mature, Plan A should be used less frequently. If solving the problem is not a top life priority, Plan C – postponing action, may be appropriate. Plan C highlights that behavior change is a long-term project and “picking your fights” is important.
The biggest value of CPS for resolving behavior problems comes from intermediate Plan B. In Plan B the first step of problem solving for parents facing child defiance or upset is to empathically and nonjudgmentally figure out the child’s concern. Questions such as “I’ve noticed that when I remind you that it is trash night you start shouting. What’s up with that?” then patiently asking about the who, what, where, and when of their concern and checking to ensure understanding. Specificity is important as well as noting times when the reaction occurs or not.
Once the child’s concern is clear, e.g., feeling that the demand to take out the trash now interrupts his games during the only time his friends are online, the parents should echo the child’s concern then express their own concern about how the behavior is affecting them and others, potentially including the child; e.g., mother is so upset by the shouting that she can’t sleep, and worry that the child is not learning responsibility, and then checking for child understanding.
Finally, the parent invites brainstorming for a solution that addresses both of their concerns, first asking the child for suggestions, aiming for a strategy that is realistic and specific. Children reluctant to make suggestions may need more time and the parent may be wondering “if there is a way for both of our concerns to be addressed.” Solutions chosen are then tried for several weeks, success tracked, and needed changes negotiated.
For parents, using a collaborative approach to dealing with their child’s behavior takes skills they may not have at the moment, or ever. Especially under the stresses of COVID-19 lockdown, taking a step back from an encounter to consider lack of a skill to turn off the video game promptly when a Zoom meeting starts is challenging. Parents may also genetically share the child’s predisposing ADHD, anxiety, depression, OCD, or weakness in communication or social sensitivity.
Sometimes part of the solution for a conflict is for the parent to reduce expectations. This requires understanding and accepting the child’s cognitive or emotional limitations. Reducing expectations is ideally done before a request rather than by giving in after it, which reinforces protests. For authoritarian adults rigid in their belief that parents are boss, changing expectations can be tough and can feel like losing control or failing as a leader. One benefit of working with a CPS coach (see livesinthebalance.org or ThinkKids.org) is to help parents identify their own limitations.
Predicting the types of demands that tend to create conflict, such as to act immediately or be flexible about options, allows parents to prioritize those requests for calmer moments or when there is more time for discussion. Reviewing a checklist of common gaps in skills and creating a list of expectations and triggers that are difficult for the child helps the family be more proactive in developing solutions. Authors of CPS have validated a checklist of skill deficits, “Thinking Skills Inventory,” to facilitate detection of gaps that is educational plus useful for planning specific solutions.
CPS has been shown in randomized trials with both parent groups and in home counseling to be as effective as Parent Training in reducing oppositional behavior and reducing maternal stress, with effects lasting even longer.
CPS Plan B notably has no reward or punishment components as it assumes the child wants to behave acceptably but can’t; has the “will but not the skill.” When skill deficits are worked around the child is satisfied with complying and pleasing the parents. The idea of a “function” of the misbehavior for the child of gaining attention or reward or avoiding consequences is reinterpreted as serving to communicate the problem the child is having trouble in meeting the parent’s demand. When the parent understands and helps the child solve the problem his/her misbehavior is no longer needed. A benefit of the communication and mutual problem solving used in CPS is on not only improving behavior but empowering parents and children, building parental empathy, and improving child skills.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She has no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication is as a paid expert to MDedge News. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
Greene RW et al. A transactional model of oppositional behavior: Underpinnings of the Collaborative Problem Solving approach. J Psychosom Res. 2003;55(1):67-75.
The lost year – even for common respiratory viruses
In this column in September 2020, you read how common respiratory viruses’ seasons are usually so predictable, each virus arising, peaking, and then dying out in a predictable virus parade (Figure 1).1 Well, the predictable virus seasonal pattern was lost in 2020. Since March of 2020, it is striking how little activity was detected for the usual seasonal viruses in Kansas City after mid-March 2020 (Figure 2).2 So, my concern in September 2020 for possible rampant coinfections of common viruses with or in tandem with SARS-CoV-2 did not pan out. That said, the seasons for non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses did change; I just didn’t expect they would nearly disappear.
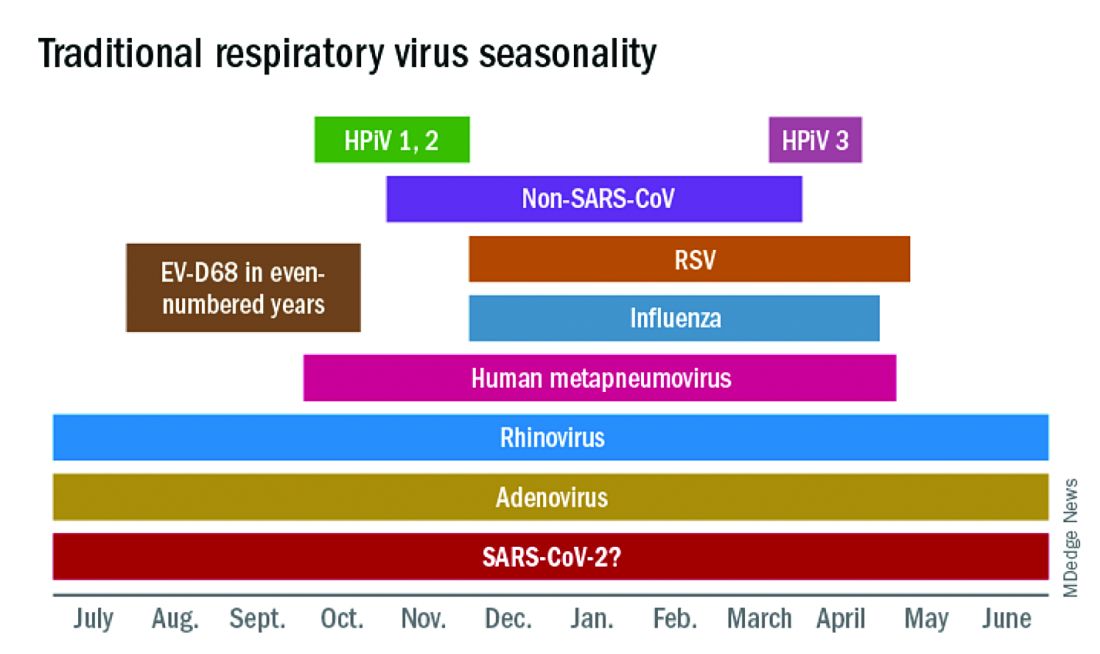
The 2020 winter-spring. In the first quarter (the last part of the overall 2019-2020 respiratory viral season), viral detections were chugging along as usual up to mid-March (Figure 2); influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and rhinovirus were the big players.
Influenza. In most years, influenza type B leads off and is quickly replaced by type A only to see B reemerge to end influenza season in March-April. In early 2020, both influenza type A and influenza type B cocirculated nearly equally, but both dropped like a rock in mid-March (Figure 2).2 Neither type has been seen since with the exception of sporadic detections – perhaps being false positives.
RSV. In the usual year in temperate mid-latitudes of the northern hemisphere, RSV season usually starts in early December, peaks in January-March, and declines gradually until the end of RSV season in April (Figure 1). In southern latitudes, RSV is less seasonal, being present most of the year, but peaking in “winter” months.3 But in 2020, RSV also disappeared in mid-March and has yet to reappear.
Other viruses. Small bumps in detection of parainfluenza of varying types usually frame influenza season, one B bump in early autumn and another in April-May. In most years, human metapneumovirus is detected on and off, with worse years at 2- to 3-year intervals. Adenovirus occurs year-round with bumps as children get back to school in autumn. Yet in 2020, almost no parainfluenza, adenovirus, common coronaviruses, or human metapneumovirus were detected in either spring or autumn. This was supposed to be a banner summer-autumn for EV-D68 – but almost none was detected. Interestingly, the cockroach of viruses, rhinovirus, has its usual year (Figure 2).
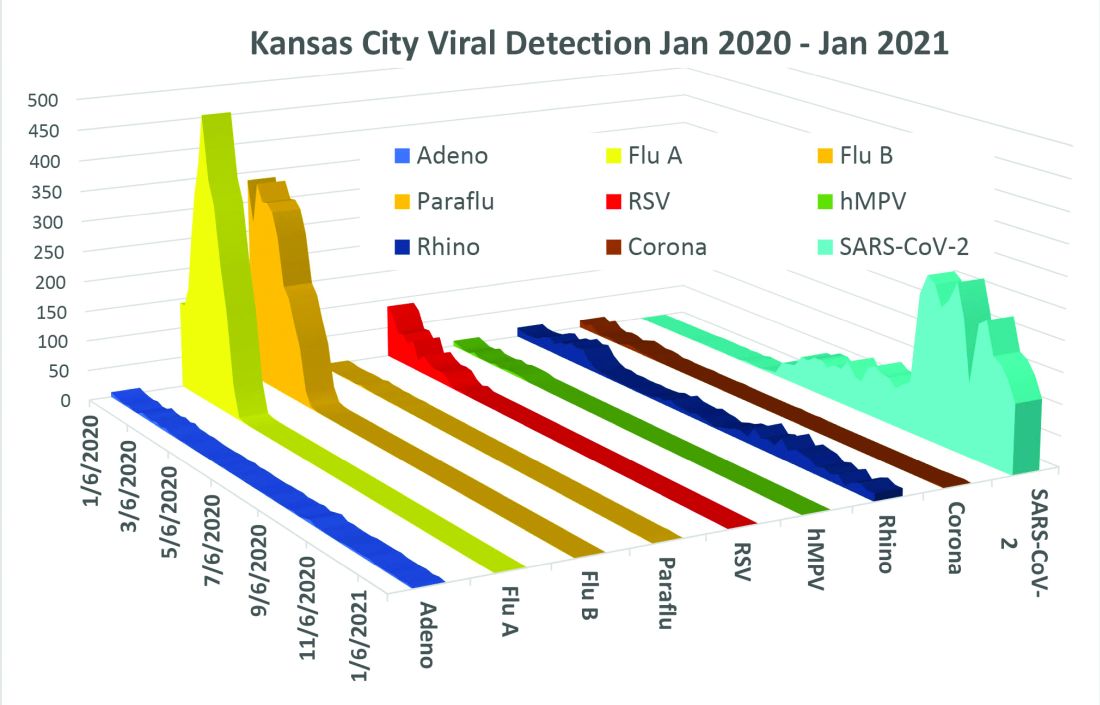
What happened? Intense social mitigation interventions, including social distancing and closing daycares and schools, were likely major factors.4 For influenza, vaccine may have helped but uptake was not remarkably better than most prior years. There may have been “viral competition,”where a new or highly transmissible virus outcompetes less-transmissible viruses with lower affinity for respiratory receptors.5,6 Note that SARS-CoV-2 has very high affinity for the ACE2 receptor and has been highly prevalent. So, SARS-CoV-2 could fit the theoretical mold for a virus that outcompetes others.
Does it matter for the future? Blunted 2019-2020 and nearly absent 2020-2021 respiratory virus season may have set the stage for intense 2021-2022 rebounds for the non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses. We now have two whole and one partial birth cohort with no experience with seasonal respiratory viruses, including EV-D68 (and nonrespiratory viruses too – like norovirus, parechovirus, and other enteroviruses). Most viruses have particularly bad seasons every 2-3 years, thought to be caused by increasing accumulation of susceptible individuals in consecutive birth cohorts until a critical mass of susceptible individuals is achieved. The excess in susceptible individuals means that each contagious case is likely to expose one or more susceptible individuals, enhancing transmission and infection numbers in an ever-extending ripple effect. We have never had this many children aged under 3 years with no immunity to influenza, RSV, etc. So unless mother nature is kind (when has that happened lately?), expect rebound years for seasonal viruses as children return to daycare/schools and as social mitigation becomes less necessary in the waning pandemic.
Options? If you ramped up telehealth visits for the pandemic, that may be a saving grace, i.e., more efficiency so more “visits” can be completed per day, and less potential contact in reception rooms between well and ill children. And if there was ever a time to really intensify efforts to immunize all our pediatric patients, the next two seasons are just that. Adding a bit of a warning to families with young children also seems warranted. If they understand that, while 2021-2022 will be better for SARS-CoV-2, it is likely going to be worse for the other viruses.
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Harrison CJ. 2020-2021 respiratory viral season: Onset, presentations, and testing likely to differ in pandemic, Pediatric News: September 17, 2020.
2. Olsen SJ et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1305-9.
3. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Surveillance. http://www.floridahealth.gov/diseases-and-conditions/respiratory-syncytial-virus/_documents/2021-w4-rsv-summary.pdf
4. Baker RE et al. PNAS. Dec 2020 117;(48):30547-53.
5. Sema Nickbakhsh et al. PNAS. Dec 2019 116;(52):27142-50.
6. Kirsten M et al. PNAS. Mar 2020 117;(13):6987.
In this column in September 2020, you read how common respiratory viruses’ seasons are usually so predictable, each virus arising, peaking, and then dying out in a predictable virus parade (Figure 1).1 Well, the predictable virus seasonal pattern was lost in 2020. Since March of 2020, it is striking how little activity was detected for the usual seasonal viruses in Kansas City after mid-March 2020 (Figure 2).2 So, my concern in September 2020 for possible rampant coinfections of common viruses with or in tandem with SARS-CoV-2 did not pan out. That said, the seasons for non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses did change; I just didn’t expect they would nearly disappear.

The 2020 winter-spring. In the first quarter (the last part of the overall 2019-2020 respiratory viral season), viral detections were chugging along as usual up to mid-March (Figure 2); influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and rhinovirus were the big players.
Influenza. In most years, influenza type B leads off and is quickly replaced by type A only to see B reemerge to end influenza season in March-April. In early 2020, both influenza type A and influenza type B cocirculated nearly equally, but both dropped like a rock in mid-March (Figure 2).2 Neither type has been seen since with the exception of sporadic detections – perhaps being false positives.
RSV. In the usual year in temperate mid-latitudes of the northern hemisphere, RSV season usually starts in early December, peaks in January-March, and declines gradually until the end of RSV season in April (Figure 1). In southern latitudes, RSV is less seasonal, being present most of the year, but peaking in “winter” months.3 But in 2020, RSV also disappeared in mid-March and has yet to reappear.
Other viruses. Small bumps in detection of parainfluenza of varying types usually frame influenza season, one B bump in early autumn and another in April-May. In most years, human metapneumovirus is detected on and off, with worse years at 2- to 3-year intervals. Adenovirus occurs year-round with bumps as children get back to school in autumn. Yet in 2020, almost no parainfluenza, adenovirus, common coronaviruses, or human metapneumovirus were detected in either spring or autumn. This was supposed to be a banner summer-autumn for EV-D68 – but almost none was detected. Interestingly, the cockroach of viruses, rhinovirus, has its usual year (Figure 2).

What happened? Intense social mitigation interventions, including social distancing and closing daycares and schools, were likely major factors.4 For influenza, vaccine may have helped but uptake was not remarkably better than most prior years. There may have been “viral competition,”where a new or highly transmissible virus outcompetes less-transmissible viruses with lower affinity for respiratory receptors.5,6 Note that SARS-CoV-2 has very high affinity for the ACE2 receptor and has been highly prevalent. So, SARS-CoV-2 could fit the theoretical mold for a virus that outcompetes others.
Does it matter for the future? Blunted 2019-2020 and nearly absent 2020-2021 respiratory virus season may have set the stage for intense 2021-2022 rebounds for the non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses. We now have two whole and one partial birth cohort with no experience with seasonal respiratory viruses, including EV-D68 (and nonrespiratory viruses too – like norovirus, parechovirus, and other enteroviruses). Most viruses have particularly bad seasons every 2-3 years, thought to be caused by increasing accumulation of susceptible individuals in consecutive birth cohorts until a critical mass of susceptible individuals is achieved. The excess in susceptible individuals means that each contagious case is likely to expose one or more susceptible individuals, enhancing transmission and infection numbers in an ever-extending ripple effect. We have never had this many children aged under 3 years with no immunity to influenza, RSV, etc. So unless mother nature is kind (when has that happened lately?), expect rebound years for seasonal viruses as children return to daycare/schools and as social mitigation becomes less necessary in the waning pandemic.
Options? If you ramped up telehealth visits for the pandemic, that may be a saving grace, i.e., more efficiency so more “visits” can be completed per day, and less potential contact in reception rooms between well and ill children. And if there was ever a time to really intensify efforts to immunize all our pediatric patients, the next two seasons are just that. Adding a bit of a warning to families with young children also seems warranted. If they understand that, while 2021-2022 will be better for SARS-CoV-2, it is likely going to be worse for the other viruses.
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Harrison CJ. 2020-2021 respiratory viral season: Onset, presentations, and testing likely to differ in pandemic, Pediatric News: September 17, 2020.
2. Olsen SJ et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1305-9.
3. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Surveillance. http://www.floridahealth.gov/diseases-and-conditions/respiratory-syncytial-virus/_documents/2021-w4-rsv-summary.pdf
4. Baker RE et al. PNAS. Dec 2020 117;(48):30547-53.
5. Sema Nickbakhsh et al. PNAS. Dec 2019 116;(52):27142-50.
6. Kirsten M et al. PNAS. Mar 2020 117;(13):6987.
In this column in September 2020, you read how common respiratory viruses’ seasons are usually so predictable, each virus arising, peaking, and then dying out in a predictable virus parade (Figure 1).1 Well, the predictable virus seasonal pattern was lost in 2020. Since March of 2020, it is striking how little activity was detected for the usual seasonal viruses in Kansas City after mid-March 2020 (Figure 2).2 So, my concern in September 2020 for possible rampant coinfections of common viruses with or in tandem with SARS-CoV-2 did not pan out. That said, the seasons for non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses did change; I just didn’t expect they would nearly disappear.

The 2020 winter-spring. In the first quarter (the last part of the overall 2019-2020 respiratory viral season), viral detections were chugging along as usual up to mid-March (Figure 2); influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and rhinovirus were the big players.
Influenza. In most years, influenza type B leads off and is quickly replaced by type A only to see B reemerge to end influenza season in March-April. In early 2020, both influenza type A and influenza type B cocirculated nearly equally, but both dropped like a rock in mid-March (Figure 2).2 Neither type has been seen since with the exception of sporadic detections – perhaps being false positives.
RSV. In the usual year in temperate mid-latitudes of the northern hemisphere, RSV season usually starts in early December, peaks in January-March, and declines gradually until the end of RSV season in April (Figure 1). In southern latitudes, RSV is less seasonal, being present most of the year, but peaking in “winter” months.3 But in 2020, RSV also disappeared in mid-March and has yet to reappear.
Other viruses. Small bumps in detection of parainfluenza of varying types usually frame influenza season, one B bump in early autumn and another in April-May. In most years, human metapneumovirus is detected on and off, with worse years at 2- to 3-year intervals. Adenovirus occurs year-round with bumps as children get back to school in autumn. Yet in 2020, almost no parainfluenza, adenovirus, common coronaviruses, or human metapneumovirus were detected in either spring or autumn. This was supposed to be a banner summer-autumn for EV-D68 – but almost none was detected. Interestingly, the cockroach of viruses, rhinovirus, has its usual year (Figure 2).

What happened? Intense social mitigation interventions, including social distancing and closing daycares and schools, were likely major factors.4 For influenza, vaccine may have helped but uptake was not remarkably better than most prior years. There may have been “viral competition,”where a new or highly transmissible virus outcompetes less-transmissible viruses with lower affinity for respiratory receptors.5,6 Note that SARS-CoV-2 has very high affinity for the ACE2 receptor and has been highly prevalent. So, SARS-CoV-2 could fit the theoretical mold for a virus that outcompetes others.
Does it matter for the future? Blunted 2019-2020 and nearly absent 2020-2021 respiratory virus season may have set the stage for intense 2021-2022 rebounds for the non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses. We now have two whole and one partial birth cohort with no experience with seasonal respiratory viruses, including EV-D68 (and nonrespiratory viruses too – like norovirus, parechovirus, and other enteroviruses). Most viruses have particularly bad seasons every 2-3 years, thought to be caused by increasing accumulation of susceptible individuals in consecutive birth cohorts until a critical mass of susceptible individuals is achieved. The excess in susceptible individuals means that each contagious case is likely to expose one or more susceptible individuals, enhancing transmission and infection numbers in an ever-extending ripple effect. We have never had this many children aged under 3 years with no immunity to influenza, RSV, etc. So unless mother nature is kind (when has that happened lately?), expect rebound years for seasonal viruses as children return to daycare/schools and as social mitigation becomes less necessary in the waning pandemic.
Options? If you ramped up telehealth visits for the pandemic, that may be a saving grace, i.e., more efficiency so more “visits” can be completed per day, and less potential contact in reception rooms between well and ill children. And if there was ever a time to really intensify efforts to immunize all our pediatric patients, the next two seasons are just that. Adding a bit of a warning to families with young children also seems warranted. If they understand that, while 2021-2022 will be better for SARS-CoV-2, it is likely going to be worse for the other viruses.
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Harrison CJ. 2020-2021 respiratory viral season: Onset, presentations, and testing likely to differ in pandemic, Pediatric News: September 17, 2020.
2. Olsen SJ et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1305-9.
3. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Surveillance. http://www.floridahealth.gov/diseases-and-conditions/respiratory-syncytial-virus/_documents/2021-w4-rsv-summary.pdf
4. Baker RE et al. PNAS. Dec 2020 117;(48):30547-53.
5. Sema Nickbakhsh et al. PNAS. Dec 2019 116;(52):27142-50.
6. Kirsten M et al. PNAS. Mar 2020 117;(13):6987.
Antibiotic exposure in pregnancy linked to childhood asthma risk in study
in a Danish birth cohort study.
The reason behind the correlation is unclear. Maternal infections, rather than antibiotics, “could explain the observed association,” said study author Cecilie Skaarup Uldbjerg, a researcher in the department of public health at Aarhus University in Denmark.
Still, the “results are in keeping with the hypothesis that effects of antibiotics impact the maternally derived microbiome in vaginally born children and that this may increase the odds of childhood asthma,” Ms. Uldbjerg and coauthors wrote in their study, which was published online Feb. 9 in Archives of Disease in Childhood . “However, this observational study did not address underlying mechanisms, and this interpretation, while plausible, remains speculative.”
Antibiotic use in pregnancy likely to continue
Patrick Duff, MD, who was not involved in the research, does not expect the findings will alter clinical practice.
The association was relatively weak, and the study does not account for factors such as antibiotic exposure during early childhood or tobacco smoke in the house, said Dr. Duff, professor of maternal-fetal medicine at University of Florida, Gainesville.
“Although I agree that we should not use antibiotics indiscriminately during pregnancy, we definitely need to treat certain infections,” Dr. Duff said. “Thus we cannot avoid some degree of antibiotic exposure.”
Although prior research has indicated that antibiotic use in pregnancy may increase the risk of asthma in children, results have been inconsistent.
To study whether antibiotic exposure during pregnancy is associated with childhood asthma and whether the timing of antibiotic exposure or mode of delivery influence the relationship, the investigators analyzed data from more than 32,000 children in the Danish National Birth Cohort, which was established in 1996.
Children of mothers who took and did not take antibiotics compared
In all, 17% of the children were born to mothers who used antibiotics during pregnancy. Compared with mothers who did not take antibiotics, those who did reported more maternal asthma, smoking during pregnancy, and having overweight or obesity. In addition, they were less likely to have been in their first pregnancy.
During follow-up at age 11 years, 4,238 children (13%) had asthma, including 12.7% of those whose mothers had not been exposed to antibiotics, and 14.6% of those whose mothers had used antibiotics during pregnancy.
In adjusted analyses, children born to mothers who received antibiotics were more likely to have asthma (OR, 1.14).
Antibiotic exposure in the second to third trimester, but not in the first trimester, was associated with asthma. The association was observed in vaginally born children, but not in children born by cesarean section.
The study is limited by its reliance on maternal reporting for data about antibiotics and asthma diagnoses, the authors noted. Mothers completed telephone interviews twice during pregnancy and once at 6 months postpartum. They completed online questionnaires to provide follow-up information at 11 years.
Mode of delivery may matter
The researchers said their analysis indicates that mode of delivery may modify the association between antibiotic exposure during pregnancy and childhood asthma.
Fourteen percent of the children in the study were delivered by cesarean section. Further research may clarify the relationship between antibiotics in pregnancy, mode of delivery, and asthma risk, another doctor who was not involved the study added.
“I do not think that the evidence indicates that mode of delivery clearly has an impact,” said Santina J. G. Wheat, MD, MPH, associate professor of family and community medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago, “as the number of cesarean deliveries was not large enough to fully support such a statement.
“It will be interesting to see if an association holds in future studies with increased cesarean deliveries,” Dr. Wheat said.
How and why antibiotics were used may be other important factors to investigate, Dr. Duff suggested.
“The authors did not provide any specific information about which antibiotics were used by the mothers, duration of use, and indication for use. Those are very important confounders,” Dr. Duff said. “Perhaps the key exposure is to a particular maternal infection rather than to the antibiotic per se.”
The Danish National Birth Cohort was established with a grant from the Danish National Research Foundation and support from regional committees and other organizations. Its biobank has been supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation and the Lundbeck Foundation, and follow-up of mothers and children has been supported by the Danish Medical Research Council, the Lundbeck Foundation, Innovation Fund Denmark, the Nordea Foundation, Aarhus Ideas, a University of Copenhagen strategic grant, and the Danish Council for Independent Research. The study was partially funded by the Health Research Fund of Central Denmark Region, which supported one of the authors. Other authors were supported by the DHB Foundation and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. One author is affiliated with Murdoch Children’s Research Institute in Australia, where the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program supports research.
The authors had no competing interests. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. Dr. Duff had no relevant financial disclosures.
in a Danish birth cohort study.
The reason behind the correlation is unclear. Maternal infections, rather than antibiotics, “could explain the observed association,” said study author Cecilie Skaarup Uldbjerg, a researcher in the department of public health at Aarhus University in Denmark.
Still, the “results are in keeping with the hypothesis that effects of antibiotics impact the maternally derived microbiome in vaginally born children and that this may increase the odds of childhood asthma,” Ms. Uldbjerg and coauthors wrote in their study, which was published online Feb. 9 in Archives of Disease in Childhood . “However, this observational study did not address underlying mechanisms, and this interpretation, while plausible, remains speculative.”
Antibiotic use in pregnancy likely to continue
Patrick Duff, MD, who was not involved in the research, does not expect the findings will alter clinical practice.
The association was relatively weak, and the study does not account for factors such as antibiotic exposure during early childhood or tobacco smoke in the house, said Dr. Duff, professor of maternal-fetal medicine at University of Florida, Gainesville.
“Although I agree that we should not use antibiotics indiscriminately during pregnancy, we definitely need to treat certain infections,” Dr. Duff said. “Thus we cannot avoid some degree of antibiotic exposure.”
Although prior research has indicated that antibiotic use in pregnancy may increase the risk of asthma in children, results have been inconsistent.
To study whether antibiotic exposure during pregnancy is associated with childhood asthma and whether the timing of antibiotic exposure or mode of delivery influence the relationship, the investigators analyzed data from more than 32,000 children in the Danish National Birth Cohort, which was established in 1996.
Children of mothers who took and did not take antibiotics compared
In all, 17% of the children were born to mothers who used antibiotics during pregnancy. Compared with mothers who did not take antibiotics, those who did reported more maternal asthma, smoking during pregnancy, and having overweight or obesity. In addition, they were less likely to have been in their first pregnancy.
During follow-up at age 11 years, 4,238 children (13%) had asthma, including 12.7% of those whose mothers had not been exposed to antibiotics, and 14.6% of those whose mothers had used antibiotics during pregnancy.
In adjusted analyses, children born to mothers who received antibiotics were more likely to have asthma (OR, 1.14).
Antibiotic exposure in the second to third trimester, but not in the first trimester, was associated with asthma. The association was observed in vaginally born children, but not in children born by cesarean section.
The study is limited by its reliance on maternal reporting for data about antibiotics and asthma diagnoses, the authors noted. Mothers completed telephone interviews twice during pregnancy and once at 6 months postpartum. They completed online questionnaires to provide follow-up information at 11 years.
Mode of delivery may matter
The researchers said their analysis indicates that mode of delivery may modify the association between antibiotic exposure during pregnancy and childhood asthma.
Fourteen percent of the children in the study were delivered by cesarean section. Further research may clarify the relationship between antibiotics in pregnancy, mode of delivery, and asthma risk, another doctor who was not involved the study added.
“I do not think that the evidence indicates that mode of delivery clearly has an impact,” said Santina J. G. Wheat, MD, MPH, associate professor of family and community medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago, “as the number of cesarean deliveries was not large enough to fully support such a statement.
“It will be interesting to see if an association holds in future studies with increased cesarean deliveries,” Dr. Wheat said.
How and why antibiotics were used may be other important factors to investigate, Dr. Duff suggested.
“The authors did not provide any specific information about which antibiotics were used by the mothers, duration of use, and indication for use. Those are very important confounders,” Dr. Duff said. “Perhaps the key exposure is to a particular maternal infection rather than to the antibiotic per se.”
The Danish National Birth Cohort was established with a grant from the Danish National Research Foundation and support from regional committees and other organizations. Its biobank has been supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation and the Lundbeck Foundation, and follow-up of mothers and children has been supported by the Danish Medical Research Council, the Lundbeck Foundation, Innovation Fund Denmark, the Nordea Foundation, Aarhus Ideas, a University of Copenhagen strategic grant, and the Danish Council for Independent Research. The study was partially funded by the Health Research Fund of Central Denmark Region, which supported one of the authors. Other authors were supported by the DHB Foundation and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. One author is affiliated with Murdoch Children’s Research Institute in Australia, where the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program supports research.
The authors had no competing interests. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. Dr. Duff had no relevant financial disclosures.
in a Danish birth cohort study.
The reason behind the correlation is unclear. Maternal infections, rather than antibiotics, “could explain the observed association,” said study author Cecilie Skaarup Uldbjerg, a researcher in the department of public health at Aarhus University in Denmark.
Still, the “results are in keeping with the hypothesis that effects of antibiotics impact the maternally derived microbiome in vaginally born children and that this may increase the odds of childhood asthma,” Ms. Uldbjerg and coauthors wrote in their study, which was published online Feb. 9 in Archives of Disease in Childhood . “However, this observational study did not address underlying mechanisms, and this interpretation, while plausible, remains speculative.”
Antibiotic use in pregnancy likely to continue
Patrick Duff, MD, who was not involved in the research, does not expect the findings will alter clinical practice.
The association was relatively weak, and the study does not account for factors such as antibiotic exposure during early childhood or tobacco smoke in the house, said Dr. Duff, professor of maternal-fetal medicine at University of Florida, Gainesville.
“Although I agree that we should not use antibiotics indiscriminately during pregnancy, we definitely need to treat certain infections,” Dr. Duff said. “Thus we cannot avoid some degree of antibiotic exposure.”
Although prior research has indicated that antibiotic use in pregnancy may increase the risk of asthma in children, results have been inconsistent.
To study whether antibiotic exposure during pregnancy is associated with childhood asthma and whether the timing of antibiotic exposure or mode of delivery influence the relationship, the investigators analyzed data from more than 32,000 children in the Danish National Birth Cohort, which was established in 1996.
Children of mothers who took and did not take antibiotics compared
In all, 17% of the children were born to mothers who used antibiotics during pregnancy. Compared with mothers who did not take antibiotics, those who did reported more maternal asthma, smoking during pregnancy, and having overweight or obesity. In addition, they were less likely to have been in their first pregnancy.
During follow-up at age 11 years, 4,238 children (13%) had asthma, including 12.7% of those whose mothers had not been exposed to antibiotics, and 14.6% of those whose mothers had used antibiotics during pregnancy.
In adjusted analyses, children born to mothers who received antibiotics were more likely to have asthma (OR, 1.14).
Antibiotic exposure in the second to third trimester, but not in the first trimester, was associated with asthma. The association was observed in vaginally born children, but not in children born by cesarean section.
The study is limited by its reliance on maternal reporting for data about antibiotics and asthma diagnoses, the authors noted. Mothers completed telephone interviews twice during pregnancy and once at 6 months postpartum. They completed online questionnaires to provide follow-up information at 11 years.
Mode of delivery may matter
The researchers said their analysis indicates that mode of delivery may modify the association between antibiotic exposure during pregnancy and childhood asthma.
Fourteen percent of the children in the study were delivered by cesarean section. Further research may clarify the relationship between antibiotics in pregnancy, mode of delivery, and asthma risk, another doctor who was not involved the study added.
“I do not think that the evidence indicates that mode of delivery clearly has an impact,” said Santina J. G. Wheat, MD, MPH, associate professor of family and community medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago, “as the number of cesarean deliveries was not large enough to fully support such a statement.
“It will be interesting to see if an association holds in future studies with increased cesarean deliveries,” Dr. Wheat said.
How and why antibiotics were used may be other important factors to investigate, Dr. Duff suggested.
“The authors did not provide any specific information about which antibiotics were used by the mothers, duration of use, and indication for use. Those are very important confounders,” Dr. Duff said. “Perhaps the key exposure is to a particular maternal infection rather than to the antibiotic per se.”
The Danish National Birth Cohort was established with a grant from the Danish National Research Foundation and support from regional committees and other organizations. Its biobank has been supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation and the Lundbeck Foundation, and follow-up of mothers and children has been supported by the Danish Medical Research Council, the Lundbeck Foundation, Innovation Fund Denmark, the Nordea Foundation, Aarhus Ideas, a University of Copenhagen strategic grant, and the Danish Council for Independent Research. The study was partially funded by the Health Research Fund of Central Denmark Region, which supported one of the authors. Other authors were supported by the DHB Foundation and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. One author is affiliated with Murdoch Children’s Research Institute in Australia, where the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program supports research.
The authors had no competing interests. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. Dr. Duff had no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM ARCHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD
Study finds benefits of increasing length of NICU stay unclear
Gestational age and weight at discharge for infants aged 24-29 weeks increased steadily between 2005 and 2018, reported Erika M. Edwards, PhD, MPH, of the Vermont Oxford Network, Burlington, and associates.
Although they discussed several possible influencing factors, the authors were unable to explain the associated benefits, costs, and harms associated with increased age and weight at discharge, which remain undetermined. Infants are separated a week longer than they were at the beginning of the study period, the prolonged effects of which cannot be underestimated, Dr. Edwards and colleagues observed in a large cohort study in Pediatrics.
A total of 314,811 infants 24-29 weeks’ gestational age who were admitted to 824 neonatal ICUs (NICUs) throughout the United States survived to initial discharge. The median postmenstrual age at hospital discharge was 38.3 weeks. Over the 14-year period from 2005 to 2018, unadjusted postmenstrual age at discharge increased a median 9 days, compared with a median adjusted age of 8 days.
Of the 273,109 infants initially discharged from the hospital to home, median weight at discharge was 2,600 g. Over the 14 years from 2005 to 2018, median unadjusted discharge weight increased 360 g, compared with median adjusted weight, which was estimated to have increased 316 g.
Median unadjusted z scores for weight increased 0.22 standard units over the 14-year period, compared with median adjusted z scores for weight at discharge, which increased an estimated 0.19 standard units.
The proportion of infants who were consuming human milk at discharge increased over the study period from 40% in 2005 to 48% in 2018. The use of cardiorespiratory monitors and oxygen decreased from 49% to 26%, and 27% to 22% respectively. The number of infants who were never transferred to specialized care before discharge to home also improved, from 71% to 76%.
Despite the unknowns, good news for managing pediatricians?
In a separate interview, study author Dr. Edwards noted that “infants born very preterm, who are discharged home from the NICU today, are larger and more physiologically mature than they were in 2005. Pediatricians will likely find this news to be positive as it may be easier to manage care for a more physiologically mature [infant],” and it may reduce risk of readmission.
“Infants stayed, on average, 8 days longer in 2018 than they did in 2005. That is 8 days when they were not at home with their families. Despite efforts by NICU teams to increase family-centered care, the NICU is not the same as being at home. ... That extra time in the NICU cost [some families] an estimated $28,000. ... As health care costs continue to rise, we need to understand the true cost [behind] this increase,” added Dr. Edwards, noting that more research is needed to understand what may be driving the increase in NICU length of stay and the possible implications. More research to investigate whether babies did better after discharge also is needed.
Going forward, Dr. Edwards indicated that she and her colleagues are exploring ways to measure apnea of prematurity (AOP) and use of continuous pulse oximetry (CPO) as the subject of future studies. In our study, we showed that the number of infants discharged home on a cardiorespiratory monitor decreased, but we do not know if that is explained by differences in management of AOP and CPO. “Understanding the influence of AOP and CPO management on discharge age would be an important contribution [to future research].”
AOP may drive increase in postmenstrual age
In an accompanying editorial, Cody Arnold, MD, and Alexis S. Davis, MD, said: “We have focused on apnea of prematurity and discharge countdowns in this commentary because we believe that changes in related practices are likely the most important drivers of the increases in postmenstrual age” reported by the authors in this study. “Other factors, such as increasing availability of NICU beds or decreasing availability of home support services, may have contributed to longer length of stay. But these questions should be answered by research, not by speculation,” said Dr. Arnold, neonatologist, University of Texas Health Sciences Center, Houston, and Dr. Davis, clinical associate professor, Stanford (Calif.) University.
“Prospective research comparing alternative countdown strategies on the basis of readmission rates and other outpatient outcomes is overdue.” Additional research is needed operationally to clearly outline parameters for countdown events, countdown duration, indications for CPO, outpatient caffeine use, and parental shared decision-making.”
The study was funded by the Vermont Oxford Network. Dr. Edwards received a grant from the Vermont Oxford Network; several others also had ties to the Network. Dr. Arnold and Dr. Davis had no conflicts of interest and reported no disclosures.
Gestational age and weight at discharge for infants aged 24-29 weeks increased steadily between 2005 and 2018, reported Erika M. Edwards, PhD, MPH, of the Vermont Oxford Network, Burlington, and associates.
Although they discussed several possible influencing factors, the authors were unable to explain the associated benefits, costs, and harms associated with increased age and weight at discharge, which remain undetermined. Infants are separated a week longer than they were at the beginning of the study period, the prolonged effects of which cannot be underestimated, Dr. Edwards and colleagues observed in a large cohort study in Pediatrics.
A total of 314,811 infants 24-29 weeks’ gestational age who were admitted to 824 neonatal ICUs (NICUs) throughout the United States survived to initial discharge. The median postmenstrual age at hospital discharge was 38.3 weeks. Over the 14-year period from 2005 to 2018, unadjusted postmenstrual age at discharge increased a median 9 days, compared with a median adjusted age of 8 days.
Of the 273,109 infants initially discharged from the hospital to home, median weight at discharge was 2,600 g. Over the 14 years from 2005 to 2018, median unadjusted discharge weight increased 360 g, compared with median adjusted weight, which was estimated to have increased 316 g.
Median unadjusted z scores for weight increased 0.22 standard units over the 14-year period, compared with median adjusted z scores for weight at discharge, which increased an estimated 0.19 standard units.
The proportion of infants who were consuming human milk at discharge increased over the study period from 40% in 2005 to 48% in 2018. The use of cardiorespiratory monitors and oxygen decreased from 49% to 26%, and 27% to 22% respectively. The number of infants who were never transferred to specialized care before discharge to home also improved, from 71% to 76%.
Despite the unknowns, good news for managing pediatricians?
In a separate interview, study author Dr. Edwards noted that “infants born very preterm, who are discharged home from the NICU today, are larger and more physiologically mature than they were in 2005. Pediatricians will likely find this news to be positive as it may be easier to manage care for a more physiologically mature [infant],” and it may reduce risk of readmission.
“Infants stayed, on average, 8 days longer in 2018 than they did in 2005. That is 8 days when they were not at home with their families. Despite efforts by NICU teams to increase family-centered care, the NICU is not the same as being at home. ... That extra time in the NICU cost [some families] an estimated $28,000. ... As health care costs continue to rise, we need to understand the true cost [behind] this increase,” added Dr. Edwards, noting that more research is needed to understand what may be driving the increase in NICU length of stay and the possible implications. More research to investigate whether babies did better after discharge also is needed.
Going forward, Dr. Edwards indicated that she and her colleagues are exploring ways to measure apnea of prematurity (AOP) and use of continuous pulse oximetry (CPO) as the subject of future studies. In our study, we showed that the number of infants discharged home on a cardiorespiratory monitor decreased, but we do not know if that is explained by differences in management of AOP and CPO. “Understanding the influence of AOP and CPO management on discharge age would be an important contribution [to future research].”
AOP may drive increase in postmenstrual age
In an accompanying editorial, Cody Arnold, MD, and Alexis S. Davis, MD, said: “We have focused on apnea of prematurity and discharge countdowns in this commentary because we believe that changes in related practices are likely the most important drivers of the increases in postmenstrual age” reported by the authors in this study. “Other factors, such as increasing availability of NICU beds or decreasing availability of home support services, may have contributed to longer length of stay. But these questions should be answered by research, not by speculation,” said Dr. Arnold, neonatologist, University of Texas Health Sciences Center, Houston, and Dr. Davis, clinical associate professor, Stanford (Calif.) University.
“Prospective research comparing alternative countdown strategies on the basis of readmission rates and other outpatient outcomes is overdue.” Additional research is needed operationally to clearly outline parameters for countdown events, countdown duration, indications for CPO, outpatient caffeine use, and parental shared decision-making.”
The study was funded by the Vermont Oxford Network. Dr. Edwards received a grant from the Vermont Oxford Network; several others also had ties to the Network. Dr. Arnold and Dr. Davis had no conflicts of interest and reported no disclosures.
Gestational age and weight at discharge for infants aged 24-29 weeks increased steadily between 2005 and 2018, reported Erika M. Edwards, PhD, MPH, of the Vermont Oxford Network, Burlington, and associates.
Although they discussed several possible influencing factors, the authors were unable to explain the associated benefits, costs, and harms associated with increased age and weight at discharge, which remain undetermined. Infants are separated a week longer than they were at the beginning of the study period, the prolonged effects of which cannot be underestimated, Dr. Edwards and colleagues observed in a large cohort study in Pediatrics.
A total of 314,811 infants 24-29 weeks’ gestational age who were admitted to 824 neonatal ICUs (NICUs) throughout the United States survived to initial discharge. The median postmenstrual age at hospital discharge was 38.3 weeks. Over the 14-year period from 2005 to 2018, unadjusted postmenstrual age at discharge increased a median 9 days, compared with a median adjusted age of 8 days.
Of the 273,109 infants initially discharged from the hospital to home, median weight at discharge was 2,600 g. Over the 14 years from 2005 to 2018, median unadjusted discharge weight increased 360 g, compared with median adjusted weight, which was estimated to have increased 316 g.
Median unadjusted z scores for weight increased 0.22 standard units over the 14-year period, compared with median adjusted z scores for weight at discharge, which increased an estimated 0.19 standard units.
The proportion of infants who were consuming human milk at discharge increased over the study period from 40% in 2005 to 48% in 2018. The use of cardiorespiratory monitors and oxygen decreased from 49% to 26%, and 27% to 22% respectively. The number of infants who were never transferred to specialized care before discharge to home also improved, from 71% to 76%.
Despite the unknowns, good news for managing pediatricians?
In a separate interview, study author Dr. Edwards noted that “infants born very preterm, who are discharged home from the NICU today, are larger and more physiologically mature than they were in 2005. Pediatricians will likely find this news to be positive as it may be easier to manage care for a more physiologically mature [infant],” and it may reduce risk of readmission.
“Infants stayed, on average, 8 days longer in 2018 than they did in 2005. That is 8 days when they were not at home with their families. Despite efforts by NICU teams to increase family-centered care, the NICU is not the same as being at home. ... That extra time in the NICU cost [some families] an estimated $28,000. ... As health care costs continue to rise, we need to understand the true cost [behind] this increase,” added Dr. Edwards, noting that more research is needed to understand what may be driving the increase in NICU length of stay and the possible implications. More research to investigate whether babies did better after discharge also is needed.
Going forward, Dr. Edwards indicated that she and her colleagues are exploring ways to measure apnea of prematurity (AOP) and use of continuous pulse oximetry (CPO) as the subject of future studies. In our study, we showed that the number of infants discharged home on a cardiorespiratory monitor decreased, but we do not know if that is explained by differences in management of AOP and CPO. “Understanding the influence of AOP and CPO management on discharge age would be an important contribution [to future research].”
AOP may drive increase in postmenstrual age
In an accompanying editorial, Cody Arnold, MD, and Alexis S. Davis, MD, said: “We have focused on apnea of prematurity and discharge countdowns in this commentary because we believe that changes in related practices are likely the most important drivers of the increases in postmenstrual age” reported by the authors in this study. “Other factors, such as increasing availability of NICU beds or decreasing availability of home support services, may have contributed to longer length of stay. But these questions should be answered by research, not by speculation,” said Dr. Arnold, neonatologist, University of Texas Health Sciences Center, Houston, and Dr. Davis, clinical associate professor, Stanford (Calif.) University.
“Prospective research comparing alternative countdown strategies on the basis of readmission rates and other outpatient outcomes is overdue.” Additional research is needed operationally to clearly outline parameters for countdown events, countdown duration, indications for CPO, outpatient caffeine use, and parental shared decision-making.”
The study was funded by the Vermont Oxford Network. Dr. Edwards received a grant from the Vermont Oxford Network; several others also had ties to the Network. Dr. Arnold and Dr. Davis had no conflicts of interest and reported no disclosures.
FROM PEDIATRICS