User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Remdesivir may keep unvaccinated out of the hospital: Study
The antiviral remdesivir, an intravenous drug given mostly to seriously ill COVID-19 patients in hospitals, could keep unvaccinated people who become infected out of the hospital if given on an outpatient basis, a new study says.
Researchers studied 562 unvaccinated people from September 2020 to April 2021, according to the study published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The study determined the risk of hospitalization or death was 87% lower in study participants who were given remdesivir than participants who received a placebo.
All participants were at high risk of developing severe COVID-19 because of their age – they were over 60 – or because they had an underlying medical condition such as diabetes or obesity.
An important caveat: The findings are based on data collected before the Delta variant surged in the summer of 2021 or the Omicron variant surged late in the year, the Washington Post reported.
The new study says the drug could be helpful in keeping vaccinated as well as unvaccinated people out of the hospital – an important factor as the Omicron surge threatens to overwhelm health systems around the world.
Remdesivir could be a boon for COVID-19 patients in parts of the world that don’t have vaccines or for patients with immunocompromised systems.
“These data provide evidence that a 3-day course of remdesivir could play a critical role in helping COVID-19 patients stay out of the hospital,” Robert L. Gottlieb, MD, PhD, the therapeutic lead for COVID-19 research at Baylor Scott & White Health in Dallas, said in a news release from Gilead Pharmaceuticals. “While our hospitals are ready to assist patients in need, prevention and early intervention are preferable to reduce the risk of disease progression and allow patients not requiring oxygen to recover from home when appropriate.”
Remdesivir was the first antiviral for COVID-19 authorized by the Food and Drug Administration. It was given to then-President Donald Trump when he was hospitalized with COVID-19 in October 2020.
Gilead released the study findings in September.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The antiviral remdesivir, an intravenous drug given mostly to seriously ill COVID-19 patients in hospitals, could keep unvaccinated people who become infected out of the hospital if given on an outpatient basis, a new study says.
Researchers studied 562 unvaccinated people from September 2020 to April 2021, according to the study published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The study determined the risk of hospitalization or death was 87% lower in study participants who were given remdesivir than participants who received a placebo.
All participants were at high risk of developing severe COVID-19 because of their age – they were over 60 – or because they had an underlying medical condition such as diabetes or obesity.
An important caveat: The findings are based on data collected before the Delta variant surged in the summer of 2021 or the Omicron variant surged late in the year, the Washington Post reported.
The new study says the drug could be helpful in keeping vaccinated as well as unvaccinated people out of the hospital – an important factor as the Omicron surge threatens to overwhelm health systems around the world.
Remdesivir could be a boon for COVID-19 patients in parts of the world that don’t have vaccines or for patients with immunocompromised systems.
“These data provide evidence that a 3-day course of remdesivir could play a critical role in helping COVID-19 patients stay out of the hospital,” Robert L. Gottlieb, MD, PhD, the therapeutic lead for COVID-19 research at Baylor Scott & White Health in Dallas, said in a news release from Gilead Pharmaceuticals. “While our hospitals are ready to assist patients in need, prevention and early intervention are preferable to reduce the risk of disease progression and allow patients not requiring oxygen to recover from home when appropriate.”
Remdesivir was the first antiviral for COVID-19 authorized by the Food and Drug Administration. It was given to then-President Donald Trump when he was hospitalized with COVID-19 in October 2020.
Gilead released the study findings in September.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The antiviral remdesivir, an intravenous drug given mostly to seriously ill COVID-19 patients in hospitals, could keep unvaccinated people who become infected out of the hospital if given on an outpatient basis, a new study says.
Researchers studied 562 unvaccinated people from September 2020 to April 2021, according to the study published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The study determined the risk of hospitalization or death was 87% lower in study participants who were given remdesivir than participants who received a placebo.
All participants were at high risk of developing severe COVID-19 because of their age – they were over 60 – or because they had an underlying medical condition such as diabetes or obesity.
An important caveat: The findings are based on data collected before the Delta variant surged in the summer of 2021 or the Omicron variant surged late in the year, the Washington Post reported.
The new study says the drug could be helpful in keeping vaccinated as well as unvaccinated people out of the hospital – an important factor as the Omicron surge threatens to overwhelm health systems around the world.
Remdesivir could be a boon for COVID-19 patients in parts of the world that don’t have vaccines or for patients with immunocompromised systems.
“These data provide evidence that a 3-day course of remdesivir could play a critical role in helping COVID-19 patients stay out of the hospital,” Robert L. Gottlieb, MD, PhD, the therapeutic lead for COVID-19 research at Baylor Scott & White Health in Dallas, said in a news release from Gilead Pharmaceuticals. “While our hospitals are ready to assist patients in need, prevention and early intervention are preferable to reduce the risk of disease progression and allow patients not requiring oxygen to recover from home when appropriate.”
Remdesivir was the first antiviral for COVID-19 authorized by the Food and Drug Administration. It was given to then-President Donald Trump when he was hospitalized with COVID-19 in October 2020.
Gilead released the study findings in September.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Tap of the brakes on gender-affirming care
In the November 2021 issue of Pediatric News are two stories that on the surface present viewpoints that couldn’t be more divergent. On page 1 under the headline “Gender dysphoria” you will read about a position statement by the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists (RANZCP) in which they strongly recommend a mental health evaluation for any child or adolescent with gender dysphoria “before any firm decisions are made on whether to prescribe hormonal treatments to transition, or perform surgeries.”
On page 6 is another story titled “Gender-affirming care ‘can save lives’ new research shows” that reports on a research study in which transgender and binary young people who received a year of gender-affirming care experienced less depression and fewer suicidal thoughts. Dr. David J. Inwards-Breland, chief of adolescent and young adult medicine at Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego and one of the authors of the study is quoted as saying “The younger we can provide gender-affirming care, the less likely [our patients are] to have depression and then negative outcomes.” One can’t avoid the impression that he is in favor of moving ahead without delay in prescribing gender-affirming care.
Where does the new recommendation by the RANZCP fit in with this sense of urgency? Does requiring a mental health evaluation constitute a delay in the institution of gender-affirming care that could increase the risk of negative mental health outcomes for gender dysphoric patients?
In one of the final paragraphs in the Pediatric News article one learns that Dr. Inwards-Breland would agree with the folks of RANZCP. He acknowledges that his study relied on screening and not diagnostic testing and says that “future studies should look at a mental health evaluation and diagnosis by a mental health provider.”
When we drill into the details there are two issues that demand clarification. First, what kind of time course are we talking about for a mental health evaluation? Are we talking weeks, or months, hopefully not years? This of course depends on the availability of mental health services for the specific patient and the depth of the evaluation required. How long a delay is acceptable?
Second, will the evaluation be performed by a provider free of bias? Can it be performed without creating the impression that the patient needs to see a mental health provider because there is something wrong with being trans and we can fix it? One would hope these evaluations would be performed in the spirit of wanting to learn more about the patient with the goal of making the process go more smoothly.
Listening to neighborhood discussions around the fire pit I find that the RANZCP plea for a broader and deeper look at each gender-dysphoric child strikes a chord with the general population. More and more people are realizing that gender-dysphoria happens and that for too long it was closeted with unfortunate consequences. However, there is a feeling, in fact one in which I share, that the rapid rise in its prevalence contains an element of social contagion. And, some irreversible decisions are being made without sufficient consideration. This may or not be a valid concern but it seems to me a thorough and sensitively done mental health evaluation might minimize the collateral damage from some gender-affirming care and at least help those patients for whom it is prescribed transition more smoothly.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
In the November 2021 issue of Pediatric News are two stories that on the surface present viewpoints that couldn’t be more divergent. On page 1 under the headline “Gender dysphoria” you will read about a position statement by the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists (RANZCP) in which they strongly recommend a mental health evaluation for any child or adolescent with gender dysphoria “before any firm decisions are made on whether to prescribe hormonal treatments to transition, or perform surgeries.”
On page 6 is another story titled “Gender-affirming care ‘can save lives’ new research shows” that reports on a research study in which transgender and binary young people who received a year of gender-affirming care experienced less depression and fewer suicidal thoughts. Dr. David J. Inwards-Breland, chief of adolescent and young adult medicine at Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego and one of the authors of the study is quoted as saying “The younger we can provide gender-affirming care, the less likely [our patients are] to have depression and then negative outcomes.” One can’t avoid the impression that he is in favor of moving ahead without delay in prescribing gender-affirming care.
Where does the new recommendation by the RANZCP fit in with this sense of urgency? Does requiring a mental health evaluation constitute a delay in the institution of gender-affirming care that could increase the risk of negative mental health outcomes for gender dysphoric patients?
In one of the final paragraphs in the Pediatric News article one learns that Dr. Inwards-Breland would agree with the folks of RANZCP. He acknowledges that his study relied on screening and not diagnostic testing and says that “future studies should look at a mental health evaluation and diagnosis by a mental health provider.”
When we drill into the details there are two issues that demand clarification. First, what kind of time course are we talking about for a mental health evaluation? Are we talking weeks, or months, hopefully not years? This of course depends on the availability of mental health services for the specific patient and the depth of the evaluation required. How long a delay is acceptable?
Second, will the evaluation be performed by a provider free of bias? Can it be performed without creating the impression that the patient needs to see a mental health provider because there is something wrong with being trans and we can fix it? One would hope these evaluations would be performed in the spirit of wanting to learn more about the patient with the goal of making the process go more smoothly.
Listening to neighborhood discussions around the fire pit I find that the RANZCP plea for a broader and deeper look at each gender-dysphoric child strikes a chord with the general population. More and more people are realizing that gender-dysphoria happens and that for too long it was closeted with unfortunate consequences. However, there is a feeling, in fact one in which I share, that the rapid rise in its prevalence contains an element of social contagion. And, some irreversible decisions are being made without sufficient consideration. This may or not be a valid concern but it seems to me a thorough and sensitively done mental health evaluation might minimize the collateral damage from some gender-affirming care and at least help those patients for whom it is prescribed transition more smoothly.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
In the November 2021 issue of Pediatric News are two stories that on the surface present viewpoints that couldn’t be more divergent. On page 1 under the headline “Gender dysphoria” you will read about a position statement by the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists (RANZCP) in which they strongly recommend a mental health evaluation for any child or adolescent with gender dysphoria “before any firm decisions are made on whether to prescribe hormonal treatments to transition, or perform surgeries.”
On page 6 is another story titled “Gender-affirming care ‘can save lives’ new research shows” that reports on a research study in which transgender and binary young people who received a year of gender-affirming care experienced less depression and fewer suicidal thoughts. Dr. David J. Inwards-Breland, chief of adolescent and young adult medicine at Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego and one of the authors of the study is quoted as saying “The younger we can provide gender-affirming care, the less likely [our patients are] to have depression and then negative outcomes.” One can’t avoid the impression that he is in favor of moving ahead without delay in prescribing gender-affirming care.
Where does the new recommendation by the RANZCP fit in with this sense of urgency? Does requiring a mental health evaluation constitute a delay in the institution of gender-affirming care that could increase the risk of negative mental health outcomes for gender dysphoric patients?
In one of the final paragraphs in the Pediatric News article one learns that Dr. Inwards-Breland would agree with the folks of RANZCP. He acknowledges that his study relied on screening and not diagnostic testing and says that “future studies should look at a mental health evaluation and diagnosis by a mental health provider.”
When we drill into the details there are two issues that demand clarification. First, what kind of time course are we talking about for a mental health evaluation? Are we talking weeks, or months, hopefully not years? This of course depends on the availability of mental health services for the specific patient and the depth of the evaluation required. How long a delay is acceptable?
Second, will the evaluation be performed by a provider free of bias? Can it be performed without creating the impression that the patient needs to see a mental health provider because there is something wrong with being trans and we can fix it? One would hope these evaluations would be performed in the spirit of wanting to learn more about the patient with the goal of making the process go more smoothly.
Listening to neighborhood discussions around the fire pit I find that the RANZCP plea for a broader and deeper look at each gender-dysphoric child strikes a chord with the general population. More and more people are realizing that gender-dysphoria happens and that for too long it was closeted with unfortunate consequences. However, there is a feeling, in fact one in which I share, that the rapid rise in its prevalence contains an element of social contagion. And, some irreversible decisions are being made without sufficient consideration. This may or not be a valid concern but it seems to me a thorough and sensitively done mental health evaluation might minimize the collateral damage from some gender-affirming care and at least help those patients for whom it is prescribed transition more smoothly.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
AD burden may be greater for those with head, neck, face, and hand involvement
of patients with AD.
“While we know that head, neck, face, and hands seem to be significantly affected by patients with AD, there is a limited evidence basis regarding the prevalence and health-related quality of life impact of AD in these areas,” presenting author Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, said during a late-breaking abstract session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium.
For the study, Dr. Eichenfield, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues evaluated 533 patients from the TARGET-DERM AD cohort, an ongoing, longitudinal, observational study launched in 2019 that captures patients with AD in 44 community or academic sites in the United States.
Adult, adolescent, and pediatric patients with moderate or severe Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD) scores at enrollment were included in the analysis. The researchers used the Patient-Oriented Scoring AD (PO-SCORAD) index to gather information on involvement of the head, neck, face, hands, or other areas, and the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM) and Dermatology Life Quality Index/Children’s DLQI (CDLQI) to measure health-related quality of life outcomes.
Of the 533 study participants, 453 (85%) had AD affecting the head, neck, face, hands, and other areas, while 80 (15%) had AD located in other body regions not including the head, neck, face, or hands. About 38% of all patients were using systemic treatments; most were using topical treatments.
Comorbid immune system disorders (including allergic and hypersensitivity disorders) were noted in 44.8% of patients, infections in 32.5%, asthma in 26.5%, hypertension in 18.6%, depression in 15.8%, and anxiety in 12.4%, with similar proportions observed in those with or without head, neck, face, and hand involvement.
However, patients with head, face, neck, and hand involvement, when compared with patients without those affected areas, were more likely to have severe vIGA scores (28.5% vs. 16.3%, P = .02) and a higher median total body surface area affected (15% vs. 10%, P ≤ .01). Also, while bivariable analyses did not detect statistical differences in POEM and DLQI/CDLQI by body region involvement, multivariable-adjusted models showed that patients with head, neck, face, and hand involvement were more than twice as likely to report higher DLQI/CDLQI (odds ratio, 2.09) and POEM (OR, 2.51) scores than those without head, face, neck, and hand involvement.
“These findings highlight the importance of detailed assessment of specific areas affected by AD to personalize treatment approaches to the needs of patients,” Dr. Eichenfield concluded.
Raj Chovatiya MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the findings confirm clinical suspicions about the unique and heightened impact of facial, head/neck, and hand dermatitis. “These data show that a detailed skin examination is necessary for a complete assessment of AD,” he said. “Future studies should focus on characterizing the optimal treatment approaches for each of these special sites.”
“This is important data,” added primary study author Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, director of clinical research in the division of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington. “We need more high-quality studies like this; we need to create long-term longitudinal data to better understand [the impact of AD on] this and other cohorts.”
TARGET-DERM is sponsored by Target RWE. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he has served as a consultant to or investigator for numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arena, Arcutis, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi-Genzyme. Dr. Silverberg disclosed that he is a consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies, receives fees for non-CME/CE services from Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, as well as contracted research fees from Galderma.
Commentary by Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH
Patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) in “visible” areas such as the head, neck, and hands experience a higher impact on their quality of life than those who do not have these areas of involvement. This is a self-evident and unsurprising result but also a particularly important one to document for several reasons. First, evidence-based demonstration of quality-of-life impact is critical as we petition carriers to support the use of newer, more expensive medications. Second, from a topical therapy standpoint, we often use different medications on the head, neck, face, and hands relative to other areas. On the head and neck area we often use either weaker topical steroids to avoid side effects or nonsteroids like topical calcineurin or phosphodiesterase inhibitors; conversely, on the hands we use stronger steroids and are less likely to use nonsteroidal agents that are perceived to be less potent. These data emphasize the need to tailor therapy but ascertain whether standard approaches are satisfactory. If patients are not responding, particularly in these sensitive areas, providers should consider the outsized impact AD may be having on quality of life.
Dr. Sidbury is chief of dermatology at Seattle Children's Hospital and professor, department of pediatrics, University of Washington, Seattle. He is a site principal investigator for dupilumab trials, for which the hospital has a contract with Regeneron.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/10/22.
of patients with AD.
“While we know that head, neck, face, and hands seem to be significantly affected by patients with AD, there is a limited evidence basis regarding the prevalence and health-related quality of life impact of AD in these areas,” presenting author Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, said during a late-breaking abstract session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium.
For the study, Dr. Eichenfield, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues evaluated 533 patients from the TARGET-DERM AD cohort, an ongoing, longitudinal, observational study launched in 2019 that captures patients with AD in 44 community or academic sites in the United States.
Adult, adolescent, and pediatric patients with moderate or severe Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD) scores at enrollment were included in the analysis. The researchers used the Patient-Oriented Scoring AD (PO-SCORAD) index to gather information on involvement of the head, neck, face, hands, or other areas, and the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM) and Dermatology Life Quality Index/Children’s DLQI (CDLQI) to measure health-related quality of life outcomes.
Of the 533 study participants, 453 (85%) had AD affecting the head, neck, face, hands, and other areas, while 80 (15%) had AD located in other body regions not including the head, neck, face, or hands. About 38% of all patients were using systemic treatments; most were using topical treatments.
Comorbid immune system disorders (including allergic and hypersensitivity disorders) were noted in 44.8% of patients, infections in 32.5%, asthma in 26.5%, hypertension in 18.6%, depression in 15.8%, and anxiety in 12.4%, with similar proportions observed in those with or without head, neck, face, and hand involvement.
However, patients with head, face, neck, and hand involvement, when compared with patients without those affected areas, were more likely to have severe vIGA scores (28.5% vs. 16.3%, P = .02) and a higher median total body surface area affected (15% vs. 10%, P ≤ .01). Also, while bivariable analyses did not detect statistical differences in POEM and DLQI/CDLQI by body region involvement, multivariable-adjusted models showed that patients with head, neck, face, and hand involvement were more than twice as likely to report higher DLQI/CDLQI (odds ratio, 2.09) and POEM (OR, 2.51) scores than those without head, face, neck, and hand involvement.
“These findings highlight the importance of detailed assessment of specific areas affected by AD to personalize treatment approaches to the needs of patients,” Dr. Eichenfield concluded.
Raj Chovatiya MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the findings confirm clinical suspicions about the unique and heightened impact of facial, head/neck, and hand dermatitis. “These data show that a detailed skin examination is necessary for a complete assessment of AD,” he said. “Future studies should focus on characterizing the optimal treatment approaches for each of these special sites.”
“This is important data,” added primary study author Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, director of clinical research in the division of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington. “We need more high-quality studies like this; we need to create long-term longitudinal data to better understand [the impact of AD on] this and other cohorts.”
TARGET-DERM is sponsored by Target RWE. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he has served as a consultant to or investigator for numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arena, Arcutis, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi-Genzyme. Dr. Silverberg disclosed that he is a consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies, receives fees for non-CME/CE services from Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, as well as contracted research fees from Galderma.
Commentary by Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH
Patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) in “visible” areas such as the head, neck, and hands experience a higher impact on their quality of life than those who do not have these areas of involvement. This is a self-evident and unsurprising result but also a particularly important one to document for several reasons. First, evidence-based demonstration of quality-of-life impact is critical as we petition carriers to support the use of newer, more expensive medications. Second, from a topical therapy standpoint, we often use different medications on the head, neck, face, and hands relative to other areas. On the head and neck area we often use either weaker topical steroids to avoid side effects or nonsteroids like topical calcineurin or phosphodiesterase inhibitors; conversely, on the hands we use stronger steroids and are less likely to use nonsteroidal agents that are perceived to be less potent. These data emphasize the need to tailor therapy but ascertain whether standard approaches are satisfactory. If patients are not responding, particularly in these sensitive areas, providers should consider the outsized impact AD may be having on quality of life.
Dr. Sidbury is chief of dermatology at Seattle Children's Hospital and professor, department of pediatrics, University of Washington, Seattle. He is a site principal investigator for dupilumab trials, for which the hospital has a contract with Regeneron.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/10/22.
of patients with AD.
“While we know that head, neck, face, and hands seem to be significantly affected by patients with AD, there is a limited evidence basis regarding the prevalence and health-related quality of life impact of AD in these areas,” presenting author Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, said during a late-breaking abstract session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium.
For the study, Dr. Eichenfield, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues evaluated 533 patients from the TARGET-DERM AD cohort, an ongoing, longitudinal, observational study launched in 2019 that captures patients with AD in 44 community or academic sites in the United States.
Adult, adolescent, and pediatric patients with moderate or severe Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD) scores at enrollment were included in the analysis. The researchers used the Patient-Oriented Scoring AD (PO-SCORAD) index to gather information on involvement of the head, neck, face, hands, or other areas, and the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM) and Dermatology Life Quality Index/Children’s DLQI (CDLQI) to measure health-related quality of life outcomes.
Of the 533 study participants, 453 (85%) had AD affecting the head, neck, face, hands, and other areas, while 80 (15%) had AD located in other body regions not including the head, neck, face, or hands. About 38% of all patients were using systemic treatments; most were using topical treatments.
Comorbid immune system disorders (including allergic and hypersensitivity disorders) were noted in 44.8% of patients, infections in 32.5%, asthma in 26.5%, hypertension in 18.6%, depression in 15.8%, and anxiety in 12.4%, with similar proportions observed in those with or without head, neck, face, and hand involvement.
However, patients with head, face, neck, and hand involvement, when compared with patients without those affected areas, were more likely to have severe vIGA scores (28.5% vs. 16.3%, P = .02) and a higher median total body surface area affected (15% vs. 10%, P ≤ .01). Also, while bivariable analyses did not detect statistical differences in POEM and DLQI/CDLQI by body region involvement, multivariable-adjusted models showed that patients with head, neck, face, and hand involvement were more than twice as likely to report higher DLQI/CDLQI (odds ratio, 2.09) and POEM (OR, 2.51) scores than those without head, face, neck, and hand involvement.
“These findings highlight the importance of detailed assessment of specific areas affected by AD to personalize treatment approaches to the needs of patients,” Dr. Eichenfield concluded.
Raj Chovatiya MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the findings confirm clinical suspicions about the unique and heightened impact of facial, head/neck, and hand dermatitis. “These data show that a detailed skin examination is necessary for a complete assessment of AD,” he said. “Future studies should focus on characterizing the optimal treatment approaches for each of these special sites.”
“This is important data,” added primary study author Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, director of clinical research in the division of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington. “We need more high-quality studies like this; we need to create long-term longitudinal data to better understand [the impact of AD on] this and other cohorts.”
TARGET-DERM is sponsored by Target RWE. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he has served as a consultant to or investigator for numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arena, Arcutis, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi-Genzyme. Dr. Silverberg disclosed that he is a consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies, receives fees for non-CME/CE services from Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, as well as contracted research fees from Galderma.
Commentary by Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH
Patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) in “visible” areas such as the head, neck, and hands experience a higher impact on their quality of life than those who do not have these areas of involvement. This is a self-evident and unsurprising result but also a particularly important one to document for several reasons. First, evidence-based demonstration of quality-of-life impact is critical as we petition carriers to support the use of newer, more expensive medications. Second, from a topical therapy standpoint, we often use different medications on the head, neck, face, and hands relative to other areas. On the head and neck area we often use either weaker topical steroids to avoid side effects or nonsteroids like topical calcineurin or phosphodiesterase inhibitors; conversely, on the hands we use stronger steroids and are less likely to use nonsteroidal agents that are perceived to be less potent. These data emphasize the need to tailor therapy but ascertain whether standard approaches are satisfactory. If patients are not responding, particularly in these sensitive areas, providers should consider the outsized impact AD may be having on quality of life.
Dr. Sidbury is chief of dermatology at Seattle Children's Hospital and professor, department of pediatrics, University of Washington, Seattle. He is a site principal investigator for dupilumab trials, for which the hospital has a contract with Regeneron.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/10/22.
FROM REVOLUTIONIZING AD 2021
iPLEDGE rollout: As frustration mounts, FDA agrees to help solve issues
, according to dermatologists, pharmacists, and patients.
When the new website and call center launched Dec. 13, hours-long hold times and repeated crashing of the website were reported as the norm, not the exception, triggering the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA) to request – and get – an emergency meeting on Dec. 16 with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, which mandates the risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) for isotretinoin due to the teratogenicity of the acne medication.
At that meeting, ‘’the FDA and HHS [U.S. Department of Health and Human Services] acknowledged the concerns of dermatologists and the need for stakeholders to work collaboratively to find a solution,” Ilona Frieden, MD, chair of the AADA’s iPLEDGE workgroup and professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an email interview. At the meeting, the AADA representatives described the severe impact on patient access to treatment that is resulting from the issues. The AADA also ‘’reiterated our call for a temporary pause to the program while stakeholders work to resolve the urgent issues with the platform,” she said.
The new approach, which is intended to make the experience more inclusive for transgender patients, reduces the previous three risk categories (females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males) to just two (those capable of getting pregnant and those not capable). The program requires physicians, patients, and pharmacists who prescribe, use, or dispense the drug to be registered, with requirements that include the use of two forms of an effective contraceptive and regular pregnancy tests by patients capable of becoming pregnant.
With reduced or no access during the technology glitches, access to the medicine was delayed for some patients. And dermatologists, pharmacists, and their staffs reported grueling hold times trying to reach the call center when the website had issues.
While the FDA agreed to help find a solution, it noted that the solution ‘’was to be found with dermatologists and pharmacists who are on the ground living the program every day,” Dr. Frieden said. No timeline for solving the issues was provided, so on Dec. 21, the AADA asked the FDA for a constructive dialogue among stakeholders within the next 24 hours, Dr. Frieden told this news organization.
While Dr. Frieden sees progress, ‘’we are disappointed that this situation continues to drag on for more than a week later, with more patients losing access to their needed medication each day.” While some prescribers have been able to log onto the portal and enter the information required, confirming some patients, large gaps remain, she said. Patients and pharmacists still report difficulties logging on. When that happens and they try to reach the call center, there are often hours-long hold times, dropped calls, or a message saying to call back.
The iPLEDGE administrator is Syneos Health, but a spokesperson for Syneos, Gary Gatyas, said the company does not maintain the system or the contact center.
So who does manage the call center and website? “The AADA has asked stakeholders, including Syneos Health, for clarification on who manages the call center and website but has not received a response,” Dr. Frieden said. “In the meeting [Dec. 16], representatives from the FDA made clear that the iPLEDGE sponsors are ultimately responsible for this REMS program,” Dr. Frieden said.
According to the FDA, isotretinoin manufacturers are part of the iPLEDGE program. On the iPLEDGE website, 12 isotretinoin products are listed, made by eight different companies.
One dermatologist maneuvering the new website who registered successfully as a provider told this news organization that he received a follow-up survey from United BioSource about the new website. This news organization contacted that company to confirm it runs the website but has not yet received a response.
Meanwhile, dermatologists continue to help frustrated patients cope with the new website and registration details. Neil S. Goldberg, MD, a dermatologist in Westchester County, New York, heard from two mothers who helped their teen daughters complete the forms by attesting they would use abstinence as contraception but then couldn’t figure out how to answer another question. As a result, their answers were interpreted as the patients saying they were using abstinence but didn’t commit to not having sexual contact with a partner capable of impregnating them. So Dr. Goldberg got an automated message back from the iPLEDGE program that the answers were a mismatch.
And in the comments section following a previous story on the problematic rollout, one reader offered a suggestion for reducing hold times to the call center: choose the Spanish option.
Dr. Frieden and Dr. Goldberg have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to dermatologists, pharmacists, and patients.
When the new website and call center launched Dec. 13, hours-long hold times and repeated crashing of the website were reported as the norm, not the exception, triggering the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA) to request – and get – an emergency meeting on Dec. 16 with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, which mandates the risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) for isotretinoin due to the teratogenicity of the acne medication.
At that meeting, ‘’the FDA and HHS [U.S. Department of Health and Human Services] acknowledged the concerns of dermatologists and the need for stakeholders to work collaboratively to find a solution,” Ilona Frieden, MD, chair of the AADA’s iPLEDGE workgroup and professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an email interview. At the meeting, the AADA representatives described the severe impact on patient access to treatment that is resulting from the issues. The AADA also ‘’reiterated our call for a temporary pause to the program while stakeholders work to resolve the urgent issues with the platform,” she said.
The new approach, which is intended to make the experience more inclusive for transgender patients, reduces the previous three risk categories (females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males) to just two (those capable of getting pregnant and those not capable). The program requires physicians, patients, and pharmacists who prescribe, use, or dispense the drug to be registered, with requirements that include the use of two forms of an effective contraceptive and regular pregnancy tests by patients capable of becoming pregnant.
With reduced or no access during the technology glitches, access to the medicine was delayed for some patients. And dermatologists, pharmacists, and their staffs reported grueling hold times trying to reach the call center when the website had issues.
While the FDA agreed to help find a solution, it noted that the solution ‘’was to be found with dermatologists and pharmacists who are on the ground living the program every day,” Dr. Frieden said. No timeline for solving the issues was provided, so on Dec. 21, the AADA asked the FDA for a constructive dialogue among stakeholders within the next 24 hours, Dr. Frieden told this news organization.
While Dr. Frieden sees progress, ‘’we are disappointed that this situation continues to drag on for more than a week later, with more patients losing access to their needed medication each day.” While some prescribers have been able to log onto the portal and enter the information required, confirming some patients, large gaps remain, she said. Patients and pharmacists still report difficulties logging on. When that happens and they try to reach the call center, there are often hours-long hold times, dropped calls, or a message saying to call back.
The iPLEDGE administrator is Syneos Health, but a spokesperson for Syneos, Gary Gatyas, said the company does not maintain the system or the contact center.
So who does manage the call center and website? “The AADA has asked stakeholders, including Syneos Health, for clarification on who manages the call center and website but has not received a response,” Dr. Frieden said. “In the meeting [Dec. 16], representatives from the FDA made clear that the iPLEDGE sponsors are ultimately responsible for this REMS program,” Dr. Frieden said.
According to the FDA, isotretinoin manufacturers are part of the iPLEDGE program. On the iPLEDGE website, 12 isotretinoin products are listed, made by eight different companies.
One dermatologist maneuvering the new website who registered successfully as a provider told this news organization that he received a follow-up survey from United BioSource about the new website. This news organization contacted that company to confirm it runs the website but has not yet received a response.
Meanwhile, dermatologists continue to help frustrated patients cope with the new website and registration details. Neil S. Goldberg, MD, a dermatologist in Westchester County, New York, heard from two mothers who helped their teen daughters complete the forms by attesting they would use abstinence as contraception but then couldn’t figure out how to answer another question. As a result, their answers were interpreted as the patients saying they were using abstinence but didn’t commit to not having sexual contact with a partner capable of impregnating them. So Dr. Goldberg got an automated message back from the iPLEDGE program that the answers were a mismatch.
And in the comments section following a previous story on the problematic rollout, one reader offered a suggestion for reducing hold times to the call center: choose the Spanish option.
Dr. Frieden and Dr. Goldberg have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to dermatologists, pharmacists, and patients.
When the new website and call center launched Dec. 13, hours-long hold times and repeated crashing of the website were reported as the norm, not the exception, triggering the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA) to request – and get – an emergency meeting on Dec. 16 with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, which mandates the risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) for isotretinoin due to the teratogenicity of the acne medication.
At that meeting, ‘’the FDA and HHS [U.S. Department of Health and Human Services] acknowledged the concerns of dermatologists and the need for stakeholders to work collaboratively to find a solution,” Ilona Frieden, MD, chair of the AADA’s iPLEDGE workgroup and professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an email interview. At the meeting, the AADA representatives described the severe impact on patient access to treatment that is resulting from the issues. The AADA also ‘’reiterated our call for a temporary pause to the program while stakeholders work to resolve the urgent issues with the platform,” she said.
The new approach, which is intended to make the experience more inclusive for transgender patients, reduces the previous three risk categories (females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males) to just two (those capable of getting pregnant and those not capable). The program requires physicians, patients, and pharmacists who prescribe, use, or dispense the drug to be registered, with requirements that include the use of two forms of an effective contraceptive and regular pregnancy tests by patients capable of becoming pregnant.
With reduced or no access during the technology glitches, access to the medicine was delayed for some patients. And dermatologists, pharmacists, and their staffs reported grueling hold times trying to reach the call center when the website had issues.
While the FDA agreed to help find a solution, it noted that the solution ‘’was to be found with dermatologists and pharmacists who are on the ground living the program every day,” Dr. Frieden said. No timeline for solving the issues was provided, so on Dec. 21, the AADA asked the FDA for a constructive dialogue among stakeholders within the next 24 hours, Dr. Frieden told this news organization.
While Dr. Frieden sees progress, ‘’we are disappointed that this situation continues to drag on for more than a week later, with more patients losing access to their needed medication each day.” While some prescribers have been able to log onto the portal and enter the information required, confirming some patients, large gaps remain, she said. Patients and pharmacists still report difficulties logging on. When that happens and they try to reach the call center, there are often hours-long hold times, dropped calls, or a message saying to call back.
The iPLEDGE administrator is Syneos Health, but a spokesperson for Syneos, Gary Gatyas, said the company does not maintain the system or the contact center.
So who does manage the call center and website? “The AADA has asked stakeholders, including Syneos Health, for clarification on who manages the call center and website but has not received a response,” Dr. Frieden said. “In the meeting [Dec. 16], representatives from the FDA made clear that the iPLEDGE sponsors are ultimately responsible for this REMS program,” Dr. Frieden said.
According to the FDA, isotretinoin manufacturers are part of the iPLEDGE program. On the iPLEDGE website, 12 isotretinoin products are listed, made by eight different companies.
One dermatologist maneuvering the new website who registered successfully as a provider told this news organization that he received a follow-up survey from United BioSource about the new website. This news organization contacted that company to confirm it runs the website but has not yet received a response.
Meanwhile, dermatologists continue to help frustrated patients cope with the new website and registration details. Neil S. Goldberg, MD, a dermatologist in Westchester County, New York, heard from two mothers who helped their teen daughters complete the forms by attesting they would use abstinence as contraception but then couldn’t figure out how to answer another question. As a result, their answers were interpreted as the patients saying they were using abstinence but didn’t commit to not having sexual contact with a partner capable of impregnating them. So Dr. Goldberg got an automated message back from the iPLEDGE program that the answers were a mismatch.
And in the comments section following a previous story on the problematic rollout, one reader offered a suggestion for reducing hold times to the call center: choose the Spanish option.
Dr. Frieden and Dr. Goldberg have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New studies suggest Omicron infections are less severe than Delta ones
People who get COVID-19 infections caused by the Omicron variant are less likely to need hospital care, compared with those infected by the Delta variant, according to two large new studies from the U.K. and South Africa.
The findings, which were released ahead of peer review, add to previous glimmers of evidence suggesting that Omicron – while extremely contagious -– may result in less severe symptoms than its predecessors.
“This is helping us quantify how much less severe Omicron is than Delta, and it appears to be between 40 to 75% reduced risk of hospitalizations, adjusted for many factors, which is very good,” said Eric Topol, MD, the editor-in-chief of Medscape and a cardiologist at Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, CA.
The first analysis, which was done by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Infectious Disease Modelling and Imperial College London, found that overall, people infected by Omicron had about a 20% reduced risk of needing any hospital care for their infections and a 40% lower risk of an overnight hospital stay, compared to those infected with Delta.
Meanwhile, people who were re-infected – meaning they caught Omicron after recovering from a previous COVID-19 infection – had a 50%-60% lower risk of needing hospital care, likely reflecting the benefits of having some prior immunity against the same family of viruses.
The study included everyone with polymerase chain reaction-confirmed COVID-19 in the U.K. during the first 2 weeks of December – roughly 56,000 Omicron cases and 269,000 Delta infections.
The second study, from researchers at the National Institute for Communicable Diseases in South Africa, included more than 29,000 COVID-19 cases that had lab results highly suggestive of Omicron infections. Compared to people infected with the Delta variant, those with presumed Omicron infections were about 70% less likely to have severe disease.
While the news is hopeful for individuals, on a population level, health care systems may still be stressed, the study authors warned.
“Given the high transmissibility of the Omicron virus, there remains the potential for health services to face increasing demand if Omicron cases continue to grow at the rate that has been seen in recent weeks,” said study author Neil Ferguson, PhD, who studies how infectious diseases spread at Imperial College London.
The study authors say their findings are specific to the U.K. and South Africa, where substantial portions of the population have some immune protection from past infection. In other words, they may not apply to countries where fewer people have been vaccinated or recovered from a bout with COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
People who get COVID-19 infections caused by the Omicron variant are less likely to need hospital care, compared with those infected by the Delta variant, according to two large new studies from the U.K. and South Africa.
The findings, which were released ahead of peer review, add to previous glimmers of evidence suggesting that Omicron – while extremely contagious -– may result in less severe symptoms than its predecessors.
“This is helping us quantify how much less severe Omicron is than Delta, and it appears to be between 40 to 75% reduced risk of hospitalizations, adjusted for many factors, which is very good,” said Eric Topol, MD, the editor-in-chief of Medscape and a cardiologist at Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, CA.
The first analysis, which was done by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Infectious Disease Modelling and Imperial College London, found that overall, people infected by Omicron had about a 20% reduced risk of needing any hospital care for their infections and a 40% lower risk of an overnight hospital stay, compared to those infected with Delta.
Meanwhile, people who were re-infected – meaning they caught Omicron after recovering from a previous COVID-19 infection – had a 50%-60% lower risk of needing hospital care, likely reflecting the benefits of having some prior immunity against the same family of viruses.
The study included everyone with polymerase chain reaction-confirmed COVID-19 in the U.K. during the first 2 weeks of December – roughly 56,000 Omicron cases and 269,000 Delta infections.
The second study, from researchers at the National Institute for Communicable Diseases in South Africa, included more than 29,000 COVID-19 cases that had lab results highly suggestive of Omicron infections. Compared to people infected with the Delta variant, those with presumed Omicron infections were about 70% less likely to have severe disease.
While the news is hopeful for individuals, on a population level, health care systems may still be stressed, the study authors warned.
“Given the high transmissibility of the Omicron virus, there remains the potential for health services to face increasing demand if Omicron cases continue to grow at the rate that has been seen in recent weeks,” said study author Neil Ferguson, PhD, who studies how infectious diseases spread at Imperial College London.
The study authors say their findings are specific to the U.K. and South Africa, where substantial portions of the population have some immune protection from past infection. In other words, they may not apply to countries where fewer people have been vaccinated or recovered from a bout with COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
People who get COVID-19 infections caused by the Omicron variant are less likely to need hospital care, compared with those infected by the Delta variant, according to two large new studies from the U.K. and South Africa.
The findings, which were released ahead of peer review, add to previous glimmers of evidence suggesting that Omicron – while extremely contagious -– may result in less severe symptoms than its predecessors.
“This is helping us quantify how much less severe Omicron is than Delta, and it appears to be between 40 to 75% reduced risk of hospitalizations, adjusted for many factors, which is very good,” said Eric Topol, MD, the editor-in-chief of Medscape and a cardiologist at Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, CA.
The first analysis, which was done by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Infectious Disease Modelling and Imperial College London, found that overall, people infected by Omicron had about a 20% reduced risk of needing any hospital care for their infections and a 40% lower risk of an overnight hospital stay, compared to those infected with Delta.
Meanwhile, people who were re-infected – meaning they caught Omicron after recovering from a previous COVID-19 infection – had a 50%-60% lower risk of needing hospital care, likely reflecting the benefits of having some prior immunity against the same family of viruses.
The study included everyone with polymerase chain reaction-confirmed COVID-19 in the U.K. during the first 2 weeks of December – roughly 56,000 Omicron cases and 269,000 Delta infections.
The second study, from researchers at the National Institute for Communicable Diseases in South Africa, included more than 29,000 COVID-19 cases that had lab results highly suggestive of Omicron infections. Compared to people infected with the Delta variant, those with presumed Omicron infections were about 70% less likely to have severe disease.
While the news is hopeful for individuals, on a population level, health care systems may still be stressed, the study authors warned.
“Given the high transmissibility of the Omicron virus, there remains the potential for health services to face increasing demand if Omicron cases continue to grow at the rate that has been seen in recent weeks,” said study author Neil Ferguson, PhD, who studies how infectious diseases spread at Imperial College London.
The study authors say their findings are specific to the U.K. and South Africa, where substantial portions of the population have some immune protection from past infection. In other words, they may not apply to countries where fewer people have been vaccinated or recovered from a bout with COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Could Fabkin hormonal complex spell the end of diabetes?
A hitherto unknown hormonal complex that regulates extracellular energy production in pancreatic islet (beta) cells could be a novel target to not only treat both type 1 and type 2 diabetes but also potentially to prevent their development in the first place, suggests basic science research led by U.S. investigators.
Fatty acid–binding protein 4 (FABP4), a recently identified hormone, was known to be elevated in type 2 diabetes, but the researchers now show that it is not only increased in type 1 diabetes but also that those increases predate its development.
They also show that antibodies against the hormone in mice models prevent type 1 diabetes and improve glycemic control in type 2 disease.
Moreover, it forms a complex with two other proteins that the researchers termed “Fabkin.”
The research, published in Nature, indicates that increased levels of the complex blunts beta cell function, while antibody treatment improves beta cell function.
“For many decades, we have been searching for the signal that communicates the status of energy reserves in adipocytes (fat cells) to generate appropriate endocrine responses, such as the insulin production from pancreatic beta cells,” said senior author Gökhan S. Hotamisligil, MD, PhD, in a press release. “We now have identified Fabkin as a novel hormone that controls this critical function through a very unusual molecular mechanism.”
Still a long way to go
Dr. Hotamisligil, who is director of the Sabri Ülker Center for Metabolic Research at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, explained in an interview that taking the findings to the clinic entails answering a number of questions.
“That will keep us busy for a long time, and there are also translational questions, which are extremely exciting,” but the team is very “optimistic” that the findings will transfer well into humans, he said.
One reason is that, in mice and humans with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, “we see exactly the same pattern of regulation” of Fabkin levels and that, “equally importantly,” sustained high levels of the hormone “correlate with poor diabetes control” in type 1 diabetes and disease severity in type 2 disease.
“This is the first strong indication that it will translate well, and the second is that, if we take human islets ... and then apply this hormone into those islets, we see the same suppression of insulin secretion and viability that we see in mice islets,” Dr. Hotamisligil said.
Moreover, blocking the hormone prevents the “negative effects” that we see on the islets, which is a “really critical” factor in suggesting that Fabkin could be a viable treatment target in humans, Dr. Hotamisligil explained.
He continued that, encouragingly, “nature has done some experiments in humans” with Fabkin, showing that “you can have a safe and healthy life with a mutation in the components of this complex ... that reduces levels of the hormone.
“These individuals have a greatly reduced risk for both diabetes and cardiovascular disease,” he said, “so this tells us that, if we can establish a safe agent that can be used in humans, this will be well tolerated for life, and it will have beneficial effects.”
Lastly, Dr. Hotamisligil said that such an agent already exists, “so it’s really just a matter of making it suitable for human use and taking it through the testing procedures.”
He cautioned, however, that “these are important pillars” for translational research “that we rarely, if ever, find in many of our projects,” and there is still a long way to go.
Study details: FABP4 levels associated with glycemic control
The team said the research was “inspired” by previous studies showing that FABP4 knockout mice had higher beta-cell mass in the pancreas and significantly increased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.
While it is “well established” that FABP4 is increased in type 2 diabetes, they initially examined whether levels are also regulated in type 1 diabetes, independently of adiposity and insulin resistance.
Looking at serum samples from normoglycemic individuals and those with new-onset type 1 diabetes in the BABYDIAB and DiMELLI cohorts, they found that FABP4 was increased approximately 1.6-fold in the latter.
In another cohort of older patients with type 1 diabetes of variation durations, serum FABP4 levels were correlated with hemoglobin A1c levels (P = .005), “which suggests that FABP4 is associated with glycemic control.”
Mouse studies indicate that FABP4 levels are increased both shortly before and during new-onset type 1 diabetes, implying that the hormone “may have a role in beta-cell failure and pathogenesis” in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Antibody targeting of FABP4 levels in mice also revealed that treatment from 10 weeks of age protected against the development of type 1 diabetes, while antibody-treated mice with diabetes had significantly reduced blood glucose and increased plasma insulin levels versus mice given control antibodies.
This, the team said, “suggests that these mice had a less severe diabetes phenotype” with the protection against type 1 diabetes similar to that seen in FABP4 knockout mice.
Mice with diet-induced obesity and nonobese mice with diabetes treated with anti-FABP4 antibodies had improved glucose tolerance tests and a significant increase in islet number and beta-cell mass versus controls.
Further work enabled the team to identify a complex formed by circulating FABP4, adenosine kinase, and nucleoside diphosphate kinase, which could be targeted by anti-FABP4 antibodies via both FABP4 and NPDK.
“We propose the name Fabkin for this new hormone complex formed by NDPK to indicate its unique constitution of a fatty acid–binding protein and kinases,” the researchers wrote.
The team then found that the Fabkin complex alters calcium homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum.
This, “results in [endoplasmic reticulum] dysfunction, increased sensitivity to environmental stress and potentiation of beta-cell death in vitro,” which are mechanisms “critical” to the pathogenesis of both type 1 and 2 diabetes.
Finally, they showed that targeting Fabkin with anti-FABP4 antibodies “preserves beta-cell mass and enhances beta-cell function to protect against diabetes in multiple models.”
Funding for this study came from National Institutes of Health and Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation grants. The Hotamisligil Lab at the Sabri Ülker Center has generated intellectual property (assigned to Harvard University) related to hormonal FABP4 and its therapeutic targeting and receives funding for this project from Lab1636, an affiliate of Deerfield Management. Dr. Hotamisligil is on the scientific advisory board of Crescenta Pharmaceuticals and holds equity. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A hitherto unknown hormonal complex that regulates extracellular energy production in pancreatic islet (beta) cells could be a novel target to not only treat both type 1 and type 2 diabetes but also potentially to prevent their development in the first place, suggests basic science research led by U.S. investigators.
Fatty acid–binding protein 4 (FABP4), a recently identified hormone, was known to be elevated in type 2 diabetes, but the researchers now show that it is not only increased in type 1 diabetes but also that those increases predate its development.
They also show that antibodies against the hormone in mice models prevent type 1 diabetes and improve glycemic control in type 2 disease.
Moreover, it forms a complex with two other proteins that the researchers termed “Fabkin.”
The research, published in Nature, indicates that increased levels of the complex blunts beta cell function, while antibody treatment improves beta cell function.
“For many decades, we have been searching for the signal that communicates the status of energy reserves in adipocytes (fat cells) to generate appropriate endocrine responses, such as the insulin production from pancreatic beta cells,” said senior author Gökhan S. Hotamisligil, MD, PhD, in a press release. “We now have identified Fabkin as a novel hormone that controls this critical function through a very unusual molecular mechanism.”
Still a long way to go
Dr. Hotamisligil, who is director of the Sabri Ülker Center for Metabolic Research at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, explained in an interview that taking the findings to the clinic entails answering a number of questions.
“That will keep us busy for a long time, and there are also translational questions, which are extremely exciting,” but the team is very “optimistic” that the findings will transfer well into humans, he said.
One reason is that, in mice and humans with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, “we see exactly the same pattern of regulation” of Fabkin levels and that, “equally importantly,” sustained high levels of the hormone “correlate with poor diabetes control” in type 1 diabetes and disease severity in type 2 disease.
“This is the first strong indication that it will translate well, and the second is that, if we take human islets ... and then apply this hormone into those islets, we see the same suppression of insulin secretion and viability that we see in mice islets,” Dr. Hotamisligil said.
Moreover, blocking the hormone prevents the “negative effects” that we see on the islets, which is a “really critical” factor in suggesting that Fabkin could be a viable treatment target in humans, Dr. Hotamisligil explained.
He continued that, encouragingly, “nature has done some experiments in humans” with Fabkin, showing that “you can have a safe and healthy life with a mutation in the components of this complex ... that reduces levels of the hormone.
“These individuals have a greatly reduced risk for both diabetes and cardiovascular disease,” he said, “so this tells us that, if we can establish a safe agent that can be used in humans, this will be well tolerated for life, and it will have beneficial effects.”
Lastly, Dr. Hotamisligil said that such an agent already exists, “so it’s really just a matter of making it suitable for human use and taking it through the testing procedures.”
He cautioned, however, that “these are important pillars” for translational research “that we rarely, if ever, find in many of our projects,” and there is still a long way to go.
Study details: FABP4 levels associated with glycemic control
The team said the research was “inspired” by previous studies showing that FABP4 knockout mice had higher beta-cell mass in the pancreas and significantly increased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.
While it is “well established” that FABP4 is increased in type 2 diabetes, they initially examined whether levels are also regulated in type 1 diabetes, independently of adiposity and insulin resistance.
Looking at serum samples from normoglycemic individuals and those with new-onset type 1 diabetes in the BABYDIAB and DiMELLI cohorts, they found that FABP4 was increased approximately 1.6-fold in the latter.
In another cohort of older patients with type 1 diabetes of variation durations, serum FABP4 levels were correlated with hemoglobin A1c levels (P = .005), “which suggests that FABP4 is associated with glycemic control.”
Mouse studies indicate that FABP4 levels are increased both shortly before and during new-onset type 1 diabetes, implying that the hormone “may have a role in beta-cell failure and pathogenesis” in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Antibody targeting of FABP4 levels in mice also revealed that treatment from 10 weeks of age protected against the development of type 1 diabetes, while antibody-treated mice with diabetes had significantly reduced blood glucose and increased plasma insulin levels versus mice given control antibodies.
This, the team said, “suggests that these mice had a less severe diabetes phenotype” with the protection against type 1 diabetes similar to that seen in FABP4 knockout mice.
Mice with diet-induced obesity and nonobese mice with diabetes treated with anti-FABP4 antibodies had improved glucose tolerance tests and a significant increase in islet number and beta-cell mass versus controls.
Further work enabled the team to identify a complex formed by circulating FABP4, adenosine kinase, and nucleoside diphosphate kinase, which could be targeted by anti-FABP4 antibodies via both FABP4 and NPDK.
“We propose the name Fabkin for this new hormone complex formed by NDPK to indicate its unique constitution of a fatty acid–binding protein and kinases,” the researchers wrote.
The team then found that the Fabkin complex alters calcium homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum.
This, “results in [endoplasmic reticulum] dysfunction, increased sensitivity to environmental stress and potentiation of beta-cell death in vitro,” which are mechanisms “critical” to the pathogenesis of both type 1 and 2 diabetes.
Finally, they showed that targeting Fabkin with anti-FABP4 antibodies “preserves beta-cell mass and enhances beta-cell function to protect against diabetes in multiple models.”
Funding for this study came from National Institutes of Health and Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation grants. The Hotamisligil Lab at the Sabri Ülker Center has generated intellectual property (assigned to Harvard University) related to hormonal FABP4 and its therapeutic targeting and receives funding for this project from Lab1636, an affiliate of Deerfield Management. Dr. Hotamisligil is on the scientific advisory board of Crescenta Pharmaceuticals and holds equity. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A hitherto unknown hormonal complex that regulates extracellular energy production in pancreatic islet (beta) cells could be a novel target to not only treat both type 1 and type 2 diabetes but also potentially to prevent their development in the first place, suggests basic science research led by U.S. investigators.
Fatty acid–binding protein 4 (FABP4), a recently identified hormone, was known to be elevated in type 2 diabetes, but the researchers now show that it is not only increased in type 1 diabetes but also that those increases predate its development.
They also show that antibodies against the hormone in mice models prevent type 1 diabetes and improve glycemic control in type 2 disease.
Moreover, it forms a complex with two other proteins that the researchers termed “Fabkin.”
The research, published in Nature, indicates that increased levels of the complex blunts beta cell function, while antibody treatment improves beta cell function.
“For many decades, we have been searching for the signal that communicates the status of energy reserves in adipocytes (fat cells) to generate appropriate endocrine responses, such as the insulin production from pancreatic beta cells,” said senior author Gökhan S. Hotamisligil, MD, PhD, in a press release. “We now have identified Fabkin as a novel hormone that controls this critical function through a very unusual molecular mechanism.”
Still a long way to go
Dr. Hotamisligil, who is director of the Sabri Ülker Center for Metabolic Research at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, explained in an interview that taking the findings to the clinic entails answering a number of questions.
“That will keep us busy for a long time, and there are also translational questions, which are extremely exciting,” but the team is very “optimistic” that the findings will transfer well into humans, he said.
One reason is that, in mice and humans with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, “we see exactly the same pattern of regulation” of Fabkin levels and that, “equally importantly,” sustained high levels of the hormone “correlate with poor diabetes control” in type 1 diabetes and disease severity in type 2 disease.
“This is the first strong indication that it will translate well, and the second is that, if we take human islets ... and then apply this hormone into those islets, we see the same suppression of insulin secretion and viability that we see in mice islets,” Dr. Hotamisligil said.
Moreover, blocking the hormone prevents the “negative effects” that we see on the islets, which is a “really critical” factor in suggesting that Fabkin could be a viable treatment target in humans, Dr. Hotamisligil explained.
He continued that, encouragingly, “nature has done some experiments in humans” with Fabkin, showing that “you can have a safe and healthy life with a mutation in the components of this complex ... that reduces levels of the hormone.
“These individuals have a greatly reduced risk for both diabetes and cardiovascular disease,” he said, “so this tells us that, if we can establish a safe agent that can be used in humans, this will be well tolerated for life, and it will have beneficial effects.”
Lastly, Dr. Hotamisligil said that such an agent already exists, “so it’s really just a matter of making it suitable for human use and taking it through the testing procedures.”
He cautioned, however, that “these are important pillars” for translational research “that we rarely, if ever, find in many of our projects,” and there is still a long way to go.
Study details: FABP4 levels associated with glycemic control
The team said the research was “inspired” by previous studies showing that FABP4 knockout mice had higher beta-cell mass in the pancreas and significantly increased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.
While it is “well established” that FABP4 is increased in type 2 diabetes, they initially examined whether levels are also regulated in type 1 diabetes, independently of adiposity and insulin resistance.
Looking at serum samples from normoglycemic individuals and those with new-onset type 1 diabetes in the BABYDIAB and DiMELLI cohorts, they found that FABP4 was increased approximately 1.6-fold in the latter.
In another cohort of older patients with type 1 diabetes of variation durations, serum FABP4 levels were correlated with hemoglobin A1c levels (P = .005), “which suggests that FABP4 is associated with glycemic control.”
Mouse studies indicate that FABP4 levels are increased both shortly before and during new-onset type 1 diabetes, implying that the hormone “may have a role in beta-cell failure and pathogenesis” in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Antibody targeting of FABP4 levels in mice also revealed that treatment from 10 weeks of age protected against the development of type 1 diabetes, while antibody-treated mice with diabetes had significantly reduced blood glucose and increased plasma insulin levels versus mice given control antibodies.
This, the team said, “suggests that these mice had a less severe diabetes phenotype” with the protection against type 1 diabetes similar to that seen in FABP4 knockout mice.
Mice with diet-induced obesity and nonobese mice with diabetes treated with anti-FABP4 antibodies had improved glucose tolerance tests and a significant increase in islet number and beta-cell mass versus controls.
Further work enabled the team to identify a complex formed by circulating FABP4, adenosine kinase, and nucleoside diphosphate kinase, which could be targeted by anti-FABP4 antibodies via both FABP4 and NPDK.
“We propose the name Fabkin for this new hormone complex formed by NDPK to indicate its unique constitution of a fatty acid–binding protein and kinases,” the researchers wrote.
The team then found that the Fabkin complex alters calcium homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum.
This, “results in [endoplasmic reticulum] dysfunction, increased sensitivity to environmental stress and potentiation of beta-cell death in vitro,” which are mechanisms “critical” to the pathogenesis of both type 1 and 2 diabetes.
Finally, they showed that targeting Fabkin with anti-FABP4 antibodies “preserves beta-cell mass and enhances beta-cell function to protect against diabetes in multiple models.”
Funding for this study came from National Institutes of Health and Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation grants. The Hotamisligil Lab at the Sabri Ülker Center has generated intellectual property (assigned to Harvard University) related to hormonal FABP4 and its therapeutic targeting and receives funding for this project from Lab1636, an affiliate of Deerfield Management. Dr. Hotamisligil is on the scientific advisory board of Crescenta Pharmaceuticals and holds equity. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE
FDA authorizes Pfizer antiviral pill for COVID-19
The Food and Drug Administration on Dec. 22, 2021, granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for a new antiviral pill to treat people with symptomatic COVID-19.
Pfizer’s ritonavir, name brand Paxlovid, can now be taken by patients ages 12 and up who weigh at least 88 pounds.
The antiviral is only for people who test positive for the coronavirus and who are at high risk for severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death. It is available by prescription only and should be taken as soon as possible after diagnosis and within 5 days of the start of symptoms.
Paxlovid is taken as three tablets together orally twice a day for 5 days, for a total of 30 tablets.
Possible side effects include a reduced sense of taste, diarrhea, high blood pressure, and muscle aches.
The authorization arrives as U.S. cases of the Omicron variant are surging, some monoclonal antibody treatments are becoming less effective, and Americans struggle to maintain some sense of tradition and normalcy around the holidays.
Paxlovid joins remdesivir as an available antiviral to treat COVID-19. Remdesivir is fully approved by the FDA but is given only intravenously in a hospital.
The COVID-19 antiviral pills come with some obvious advantages, including greater convenience for consumers – such as home use – and the potential to expand treatment for people in low- and middle-income countries.
‘An exciting step forward’
The EUA for Pfizer’s new drug has been highly anticipated, and news of its impending authorization circulated on social media on Tuesday. Eric Topol, MD, called the development an “exciting step forward.” Dr. Topol is editor in chief of Medscape, the parent company of MDedge.
He and many others also expected the FDA to grant emergency use authorization for an antiviral from Merck. But there was no immediate word Wednesday if that was still going to happen.
An accelerated authorization?
The FDA’s authorization for Pfizer’s antiviral comes about 5 weeks after the company submitted an application to the agency. In its submission, the company said a study showed the pill reduced by 89% the rate of hospitalization and death for people with mild to moderate COVID-19 illness.
In April 2021, Pfizer announced its antiviral pill for COVID-19 could be available by year’s end. In September, an official at the National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases seconded the prediction.
Merck filed its EUA application with the FDA in October. The company included results of its phase 3 study showing the treatment was linked to a 50% reduction in COVID-19 hospitalizations.
Interestingly, in September, Merck announced the findings of laboratory studies suggesting that molnupiravir would work against variants of the coronavirus because the agent does not target the virus’s spike protein. At the time, Delta was the dominant variant in the United States.
Faith-based purchasing
The U.S. government has already recognized the potential of these oral therapies, at least in terms of preorders.
Last month, it announced intentions to purchase $1 billion worth of Merck’s molnupiravir, adding to the $1.2 billion worth of the pills the U.S. ordered in June 2021. Also in November, the government announced it would purchase 10 million courses of the Pfizer pill at an estimated cost of $5.3 billion.
The government preorders of the antiviral pills for COVID-19 are separate from the orders for COVID-19 vaccines. Most recently, the Biden administration announced it will make 500 million tests for coronavirus infection available to Americans for free in early 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on Dec. 22, 2021, granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for a new antiviral pill to treat people with symptomatic COVID-19.
Pfizer’s ritonavir, name brand Paxlovid, can now be taken by patients ages 12 and up who weigh at least 88 pounds.
The antiviral is only for people who test positive for the coronavirus and who are at high risk for severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death. It is available by prescription only and should be taken as soon as possible after diagnosis and within 5 days of the start of symptoms.
Paxlovid is taken as three tablets together orally twice a day for 5 days, for a total of 30 tablets.
Possible side effects include a reduced sense of taste, diarrhea, high blood pressure, and muscle aches.
The authorization arrives as U.S. cases of the Omicron variant are surging, some monoclonal antibody treatments are becoming less effective, and Americans struggle to maintain some sense of tradition and normalcy around the holidays.
Paxlovid joins remdesivir as an available antiviral to treat COVID-19. Remdesivir is fully approved by the FDA but is given only intravenously in a hospital.
The COVID-19 antiviral pills come with some obvious advantages, including greater convenience for consumers – such as home use – and the potential to expand treatment for people in low- and middle-income countries.
‘An exciting step forward’
The EUA for Pfizer’s new drug has been highly anticipated, and news of its impending authorization circulated on social media on Tuesday. Eric Topol, MD, called the development an “exciting step forward.” Dr. Topol is editor in chief of Medscape, the parent company of MDedge.
He and many others also expected the FDA to grant emergency use authorization for an antiviral from Merck. But there was no immediate word Wednesday if that was still going to happen.
An accelerated authorization?
The FDA’s authorization for Pfizer’s antiviral comes about 5 weeks after the company submitted an application to the agency. In its submission, the company said a study showed the pill reduced by 89% the rate of hospitalization and death for people with mild to moderate COVID-19 illness.
In April 2021, Pfizer announced its antiviral pill for COVID-19 could be available by year’s end. In September, an official at the National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases seconded the prediction.
Merck filed its EUA application with the FDA in October. The company included results of its phase 3 study showing the treatment was linked to a 50% reduction in COVID-19 hospitalizations.
Interestingly, in September, Merck announced the findings of laboratory studies suggesting that molnupiravir would work against variants of the coronavirus because the agent does not target the virus’s spike protein. At the time, Delta was the dominant variant in the United States.
Faith-based purchasing
The U.S. government has already recognized the potential of these oral therapies, at least in terms of preorders.
Last month, it announced intentions to purchase $1 billion worth of Merck’s molnupiravir, adding to the $1.2 billion worth of the pills the U.S. ordered in June 2021. Also in November, the government announced it would purchase 10 million courses of the Pfizer pill at an estimated cost of $5.3 billion.
The government preorders of the antiviral pills for COVID-19 are separate from the orders for COVID-19 vaccines. Most recently, the Biden administration announced it will make 500 million tests for coronavirus infection available to Americans for free in early 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on Dec. 22, 2021, granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for a new antiviral pill to treat people with symptomatic COVID-19.
Pfizer’s ritonavir, name brand Paxlovid, can now be taken by patients ages 12 and up who weigh at least 88 pounds.
The antiviral is only for people who test positive for the coronavirus and who are at high risk for severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death. It is available by prescription only and should be taken as soon as possible after diagnosis and within 5 days of the start of symptoms.
Paxlovid is taken as three tablets together orally twice a day for 5 days, for a total of 30 tablets.
Possible side effects include a reduced sense of taste, diarrhea, high blood pressure, and muscle aches.
The authorization arrives as U.S. cases of the Omicron variant are surging, some monoclonal antibody treatments are becoming less effective, and Americans struggle to maintain some sense of tradition and normalcy around the holidays.
Paxlovid joins remdesivir as an available antiviral to treat COVID-19. Remdesivir is fully approved by the FDA but is given only intravenously in a hospital.
The COVID-19 antiviral pills come with some obvious advantages, including greater convenience for consumers – such as home use – and the potential to expand treatment for people in low- and middle-income countries.
‘An exciting step forward’
The EUA for Pfizer’s new drug has been highly anticipated, and news of its impending authorization circulated on social media on Tuesday. Eric Topol, MD, called the development an “exciting step forward.” Dr. Topol is editor in chief of Medscape, the parent company of MDedge.
He and many others also expected the FDA to grant emergency use authorization for an antiviral from Merck. But there was no immediate word Wednesday if that was still going to happen.
An accelerated authorization?
The FDA’s authorization for Pfizer’s antiviral comes about 5 weeks after the company submitted an application to the agency. In its submission, the company said a study showed the pill reduced by 89% the rate of hospitalization and death for people with mild to moderate COVID-19 illness.
In April 2021, Pfizer announced its antiviral pill for COVID-19 could be available by year’s end. In September, an official at the National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases seconded the prediction.
Merck filed its EUA application with the FDA in October. The company included results of its phase 3 study showing the treatment was linked to a 50% reduction in COVID-19 hospitalizations.
Interestingly, in September, Merck announced the findings of laboratory studies suggesting that molnupiravir would work against variants of the coronavirus because the agent does not target the virus’s spike protein. At the time, Delta was the dominant variant in the United States.
Faith-based purchasing
The U.S. government has already recognized the potential of these oral therapies, at least in terms of preorders.
Last month, it announced intentions to purchase $1 billion worth of Merck’s molnupiravir, adding to the $1.2 billion worth of the pills the U.S. ordered in June 2021. Also in November, the government announced it would purchase 10 million courses of the Pfizer pill at an estimated cost of $5.3 billion.
The government preorders of the antiviral pills for COVID-19 are separate from the orders for COVID-19 vaccines. Most recently, the Biden administration announced it will make 500 million tests for coronavirus infection available to Americans for free in early 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Pandemic poses short- and long-term risks to babies, especially boys
The pandemic has created a hostile environment for pregnant people and their babies.
Stress levels among expectant mothers have soared. Pregnant women with COVID are 5 times as likely as uninfected pregnant people to require intensive care and 22 times as likely to die. Infected moms are four times as likely to have a stillborn child.
Yet some of the pandemic’s greatest threats to infants’ health may not be apparent for years or even decades.
That’s because babies of COVID-infected moms are 60% more likely to be born very prematurely, which increases the danger of infant mortality and long-term disabilities such as cerebral palsy, asthma, and hearing loss, as well as a child’s risk of adult disease, including depression, anxiety, heart disease, and kidney disease.
Studies have linked fever and infection during pregnancy to developmental and psychiatric conditions such as autism, depression, and schizophrenia.
“Some of these conditions do not show up until middle childhood or early adult life, but they have their origins in fetal life,” said Evdokia Anagnostou, MD, a child neurologist at Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital and a pediatrics professor at the University of Toronto.
For fetuses exposed to COVID, the greatest danger is usually not the coronavirus itself, but the mother’s immune system.
Both severe COVID infections and the strain of the pandemic can expose fetuses to harmful inflammation, which can occur when a mother’s immune system is fighting a virus or when stress hormones send nonstop alarm signals.
Prenatal inflammation “changes the way the brain develops and, depending on the timing of the infection, it can change the way the heart or kidneys develop,” Dr. Anagnostou said.
Although health officials have strongly recommended COVID vaccines for pregnant people, only 35% are fully vaccinated.
At least 150,000 pregnant women have been diagnosed with COVID; more than 25,000 of them have been hospitalized, and 249 have died, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although most babies will be fine, even a small increase in the percentage of children with special medical or educational needs could have a large effect on the population, given the huge number of COVID infections, Dr. Anagnostou said.
“If someone has a baby who is doing well, that is what they should focus on,” Dr. Anagnostou said. “But from a public health point of view, we need to follow women who experienced severe COVID and their babies to understand the impact.”
Learning from history
Researchers in the United States and other countries are already studying “the COVID generation” to see whether these children have more health issues than those conceived or born before 2020.
Previous crises have shown that the challenges fetuses face in the womb – such as maternal infections, hunger, stress, and hormone-disrupting chemicals – can leave a lasting imprint on their health, as well as that of their children and grandchildren, said Frederick Kaskel, MD, director of pediatric nephrology at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, New York.
People whose mothers were pregnant during surges in the 1918 influenza pandemic, for example, had poorer health throughout their lives, compared with Americans born at other times, said John McCarthy, who is a medical student at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and cowrote a recent review in JAMA Pediatrics with Dr. Kaskel.
Researchers don’t know exactly which moms were infected with pandemic flu, Mr. McCarthy said. But women who were pregnant during major surges – when infection was widespread – had children with higher rates of heart disease or diabetes. These children were also less successful in school, less economically productive, and more likely to live with a disability.
Because organ systems develop during different periods of pregnancy, fetuses exposed during the first trimester may face different risks than those exposed toward the end of pregnancy, Mr. McCarthy said. For example, people born in the fall of 1918 were 50% more likely than others to develop kidney disease; that may reflect an exposure to the pandemic in the third trimester, while the kidneys were still developing.
Nearly 2 years into the COVID pandemic, researchers have begun to publish preliminary observations of infants exposed to COVID infections and stress before birth.
Although Dr. Anagnostou noted that it’s too early to reach definitive conclusions, “there is evidence that babies born to moms with severe COVID infections have changes to their immune system,” she said. “It’s enough to make us worry a little bit.”
Damaging a fetal security system
The good news about the coronavirus is that it seldom crosses the placenta, the organ tasked with protecting a developing fetus from infections and providing it with oxygen. So moms with COVID rarely give the virus to their children before birth.
That’s important, because some viruses that directly infect the fetus – such as Zika – can cause devastating birth defects, said Karin Nielsen-Saines, MD, a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases at University of California, Los Angeles.
But studies also suggest that inflammation from a mother’s COVID infection can injure the placenta, said Jeffery Goldstein, MD, an assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago. In a study published in American Journal of Clinical Pathology , Dr. Goldstein and his coauthors found that placentas from COVID-infected moms had more abnormal blood vessels than placentas from patients without COVID, making it harder for them to deliver sufficient oxygen to the fetus.
Placental damage can also lead to preeclampsia, a serious complication of pregnancy that can cause a mother’s blood pressure to spike.
Preeclampsia occurs when blood vessels in the placenta don’t develop or function properly, forcing the mother’s heart to work harder to get blood to the fetus, which may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. Preeclampsia also predisposes women to heart attacks and strokes later in life.
Rewiring the immune system
In some cases, COVID also appears to rewire a baby’s immune response, Dr. Nielsen-Saines said.
In an October study in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, Dr. Nielsen-Saines and her coauthors found that infants born to people with severe COVID infections had a different mix of immune cells and proteins than other babies. None of the newborns tested positive for the coronavirus.
The immune changes are concerning, Dr. Nielsen-Saines said, because this pattern of immune cells and proteins has previously been found in infants with respiratory problems and in some cases poor neurodevelopment.
Notably, all the babies in her study appear healthy, said Dr. Nielsen-Saines, who plans to follow them for 3 years to see whether these early signals translate into developmental delays, such as problems talking, walking, or interacting with others.
“How big of a difference does any of this make in the baby?” asked Dr. Anagnostou. “We won’t know for a few years. All we can do is try to be as prepared as possible.”
Increasing the risk for boys
Boys could face higher risks from COVID, even before birth.
Males are generally more vulnerable than females as fetuses and newborns; they’re more likely to be born prematurely and to die as infants. Preterm boys also have a higher risk of disability and death.
But coronavirus infection poses special dangers, said Sabra Klein, PhD, a professor of molecular microbiology and immunology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore.
That’s because boys are disproportionately affected by conditions linked to maternal infections. Boys are four times as likely as girls to be diagnosed with autism or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, for example, while men are 75% more likely than women to develop schizophrenia.
Scientists don’t fully understand why boys appear more fragile in the womb, although testosterone – which can dampen immune response – may play a role, said Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington.
Men generally mount weaker immune responses than women and more often develop severe COVID infections. Recent research suggests boys with COVID are more likely than girls to become seriously ill or develop a rare inflammatory condition called multisystem inflammatory syndrome.
New research on COVID could help illuminate this vulnerability.
In a study published in October, researchers found that the sex of a fetus influences the way its placenta responds to COVID, as well as how its mother’s immune system responds.
Pregnant people infected with COVID made fewer antibodies against the coronavirus if they were carrying male fetuses than if they were carrying females. Mothers also transferred fewer antibodies to boys than to girls, said Andrea Edlow, MD, senior author of the study and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
When examining the placentas of male fetuses after delivery, researchers found changes that could leave boys less protected against damaging inflammation.
The sex of a fetus can influence its mother’s response to other illnesses, as well.
For example, research shows that pregnant women with asthma have worse symptoms if they’re carrying a female. Women carrying males are slightly more likely to develop gestational diabetes.
Dr. Edlow said her findings raise questions about the “cross talk” between mother and baby. “The mom’s immune system is sensing there is a male fetus,” Dr. Edlow said. “And the fetus is actively communicating with the mom’s immune system.”
Boosting toxic stress
Rates of depression and stress among pregnant women have increased dramatically during the pandemic.
That’s concerning because chronic stress can lead to inflammation, affecting the babies of both infected and uninfected women, Dr. Anagnostou said.
Studies consistently show that infants born to mothers who experience significant stress during pregnancy have higher rates of short- and long-term health damage – including heart defects and obesity – than babies born to women with less stress.
“We know that inflammation directly influences the way a baby’s brain develops,” said Elinor Sullivan, PhD, an associate professor in psychiatry at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Lockdowns, travel restrictions and physical distancing left many pregnant women without the support of family and friends. The stress of losing a loved one, a job, or a home further heightens the risks to moms and babies, said Dr. Sullivan, who is following children born during the pandemic for 5 years.
In research that has not yet been published, Dr. Sullivan found that babies of women who were pregnant during the pandemic showed more sadness and negative emotions in the first year of life, compared with infants of women who were pregnant before the pandemic.
The findings show the importance of helping and protecting pregnant people before and after delivery, said Dr. Sullivan, who conducted a separate study that found women who received more social support were less depressed.
Italian researchers are also studying the effect of maternal stress on infants’ behavior, as well as the way their genes are regulated.
Although stress-related inflammation doesn’t alter the structure of a baby’s genes, it can influence whether they’re turned on and off, said Livio Provenzi, PhD, a psychologist at the C. Mondino National Institute of Neurology Foundation in Pavia, Italy.
In Dr. Provenzi’s study of 163 mother-baby pairs he found differences in how genes that regulate the stress response were activated. Genes that help people respond to stress were more likely to be turned off in babies whose moms reported the most stress during pregnancy. The same moms also reported that their babies cried more and were fussier when they were 3 months old.
Researchers usually prefer to make in-person observations of babies as they interact with their mothers, Dr. Provenzi said. But because of the pandemic, Dr. Provenzi asked mothers to fill out questionnaires about infant behavior. He plans to observe mothers and babies in person when the children are 12 months old.
While vaccinating pregnant people is the best way to protect them and their fetuses from the virus, Dr. Anagnostou said, society needs to do more to preserve expectant mothers’ mental health.
“We can’t escape the fact that we’ve lived through 2 years of a pandemic,” Dr. Anagnostou said. “But we can think about opportunities for reducing the risk.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The pandemic has created a hostile environment for pregnant people and their babies.
Stress levels among expectant mothers have soared. Pregnant women with COVID are 5 times as likely as uninfected pregnant people to require intensive care and 22 times as likely to die. Infected moms are four times as likely to have a stillborn child.
Yet some of the pandemic’s greatest threats to infants’ health may not be apparent for years or even decades.
That’s because babies of COVID-infected moms are 60% more likely to be born very prematurely, which increases the danger of infant mortality and long-term disabilities such as cerebral palsy, asthma, and hearing loss, as well as a child’s risk of adult disease, including depression, anxiety, heart disease, and kidney disease.
Studies have linked fever and infection during pregnancy to developmental and psychiatric conditions such as autism, depression, and schizophrenia.
“Some of these conditions do not show up until middle childhood or early adult life, but they have their origins in fetal life,” said Evdokia Anagnostou, MD, a child neurologist at Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital and a pediatrics professor at the University of Toronto.
For fetuses exposed to COVID, the greatest danger is usually not the coronavirus itself, but the mother’s immune system.
Both severe COVID infections and the strain of the pandemic can expose fetuses to harmful inflammation, which can occur when a mother’s immune system is fighting a virus or when stress hormones send nonstop alarm signals.
Prenatal inflammation “changes the way the brain develops and, depending on the timing of the infection, it can change the way the heart or kidneys develop,” Dr. Anagnostou said.
Although health officials have strongly recommended COVID vaccines for pregnant people, only 35% are fully vaccinated.
At least 150,000 pregnant women have been diagnosed with COVID; more than 25,000 of them have been hospitalized, and 249 have died, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although most babies will be fine, even a small increase in the percentage of children with special medical or educational needs could have a large effect on the population, given the huge number of COVID infections, Dr. Anagnostou said.
“If someone has a baby who is doing well, that is what they should focus on,” Dr. Anagnostou said. “But from a public health point of view, we need to follow women who experienced severe COVID and their babies to understand the impact.”
Learning from history
Researchers in the United States and other countries are already studying “the COVID generation” to see whether these children have more health issues than those conceived or born before 2020.
Previous crises have shown that the challenges fetuses face in the womb – such as maternal infections, hunger, stress, and hormone-disrupting chemicals – can leave a lasting imprint on their health, as well as that of their children and grandchildren, said Frederick Kaskel, MD, director of pediatric nephrology at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, New York.
People whose mothers were pregnant during surges in the 1918 influenza pandemic, for example, had poorer health throughout their lives, compared with Americans born at other times, said John McCarthy, who is a medical student at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and cowrote a recent review in JAMA Pediatrics with Dr. Kaskel.
Researchers don’t know exactly which moms were infected with pandemic flu, Mr. McCarthy said. But women who were pregnant during major surges – when infection was widespread – had children with higher rates of heart disease or diabetes. These children were also less successful in school, less economically productive, and more likely to live with a disability.
Because organ systems develop during different periods of pregnancy, fetuses exposed during the first trimester may face different risks than those exposed toward the end of pregnancy, Mr. McCarthy said. For example, people born in the fall of 1918 were 50% more likely than others to develop kidney disease; that may reflect an exposure to the pandemic in the third trimester, while the kidneys were still developing.
Nearly 2 years into the COVID pandemic, researchers have begun to publish preliminary observations of infants exposed to COVID infections and stress before birth.
Although Dr. Anagnostou noted that it’s too early to reach definitive conclusions, “there is evidence that babies born to moms with severe COVID infections have changes to their immune system,” she said. “It’s enough to make us worry a little bit.”
Damaging a fetal security system
The good news about the coronavirus is that it seldom crosses the placenta, the organ tasked with protecting a developing fetus from infections and providing it with oxygen. So moms with COVID rarely give the virus to their children before birth.
That’s important, because some viruses that directly infect the fetus – such as Zika – can cause devastating birth defects, said Karin Nielsen-Saines, MD, a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases at University of California, Los Angeles.
But studies also suggest that inflammation from a mother’s COVID infection can injure the placenta, said Jeffery Goldstein, MD, an assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago. In a study published in American Journal of Clinical Pathology , Dr. Goldstein and his coauthors found that placentas from COVID-infected moms had more abnormal blood vessels than placentas from patients without COVID, making it harder for them to deliver sufficient oxygen to the fetus.
Placental damage can also lead to preeclampsia, a serious complication of pregnancy that can cause a mother’s blood pressure to spike.
Preeclampsia occurs when blood vessels in the placenta don’t develop or function properly, forcing the mother’s heart to work harder to get blood to the fetus, which may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. Preeclampsia also predisposes women to heart attacks and strokes later in life.
Rewiring the immune system
In some cases, COVID also appears to rewire a baby’s immune response, Dr. Nielsen-Saines said.
In an October study in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, Dr. Nielsen-Saines and her coauthors found that infants born to people with severe COVID infections had a different mix of immune cells and proteins than other babies. None of the newborns tested positive for the coronavirus.
The immune changes are concerning, Dr. Nielsen-Saines said, because this pattern of immune cells and proteins has previously been found in infants with respiratory problems and in some cases poor neurodevelopment.
Notably, all the babies in her study appear healthy, said Dr. Nielsen-Saines, who plans to follow them for 3 years to see whether these early signals translate into developmental delays, such as problems talking, walking, or interacting with others.
“How big of a difference does any of this make in the baby?” asked Dr. Anagnostou. “We won’t know for a few years. All we can do is try to be as prepared as possible.”
Increasing the risk for boys
Boys could face higher risks from COVID, even before birth.
Males are generally more vulnerable than females as fetuses and newborns; they’re more likely to be born prematurely and to die as infants. Preterm boys also have a higher risk of disability and death.
But coronavirus infection poses special dangers, said Sabra Klein, PhD, a professor of molecular microbiology and immunology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore.
That’s because boys are disproportionately affected by conditions linked to maternal infections. Boys are four times as likely as girls to be diagnosed with autism or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, for example, while men are 75% more likely than women to develop schizophrenia.
Scientists don’t fully understand why boys appear more fragile in the womb, although testosterone – which can dampen immune response – may play a role, said Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington.
Men generally mount weaker immune responses than women and more often develop severe COVID infections. Recent research suggests boys with COVID are more likely than girls to become seriously ill or develop a rare inflammatory condition called multisystem inflammatory syndrome.
New research on COVID could help illuminate this vulnerability.
In a study published in October, researchers found that the sex of a fetus influences the way its placenta responds to COVID, as well as how its mother’s immune system responds.
Pregnant people infected with COVID made fewer antibodies against the coronavirus if they were carrying male fetuses than if they were carrying females. Mothers also transferred fewer antibodies to boys than to girls, said Andrea Edlow, MD, senior author of the study and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
When examining the placentas of male fetuses after delivery, researchers found changes that could leave boys less protected against damaging inflammation.
The sex of a fetus can influence its mother’s response to other illnesses, as well.
For example, research shows that pregnant women with asthma have worse symptoms if they’re carrying a female. Women carrying males are slightly more likely to develop gestational diabetes.
Dr. Edlow said her findings raise questions about the “cross talk” between mother and baby. “The mom’s immune system is sensing there is a male fetus,” Dr. Edlow said. “And the fetus is actively communicating with the mom’s immune system.”
Boosting toxic stress
Rates of depression and stress among pregnant women have increased dramatically during the pandemic.
That’s concerning because chronic stress can lead to inflammation, affecting the babies of both infected and uninfected women, Dr. Anagnostou said.
Studies consistently show that infants born to mothers who experience significant stress during pregnancy have higher rates of short- and long-term health damage – including heart defects and obesity – than babies born to women with less stress.
“We know that inflammation directly influences the way a baby’s brain develops,” said Elinor Sullivan, PhD, an associate professor in psychiatry at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Lockdowns, travel restrictions and physical distancing left many pregnant women without the support of family and friends. The stress of losing a loved one, a job, or a home further heightens the risks to moms and babies, said Dr. Sullivan, who is following children born during the pandemic for 5 years.
In research that has not yet been published, Dr. Sullivan found that babies of women who were pregnant during the pandemic showed more sadness and negative emotions in the first year of life, compared with infants of women who were pregnant before the pandemic.
The findings show the importance of helping and protecting pregnant people before and after delivery, said Dr. Sullivan, who conducted a separate study that found women who received more social support were less depressed.
Italian researchers are also studying the effect of maternal stress on infants’ behavior, as well as the way their genes are regulated.
Although stress-related inflammation doesn’t alter the structure of a baby’s genes, it can influence whether they’re turned on and off, said Livio Provenzi, PhD, a psychologist at the C. Mondino National Institute of Neurology Foundation in Pavia, Italy.
In Dr. Provenzi’s study of 163 mother-baby pairs he found differences in how genes that regulate the stress response were activated. Genes that help people respond to stress were more likely to be turned off in babies whose moms reported the most stress during pregnancy. The same moms also reported that their babies cried more and were fussier when they were 3 months old.
Researchers usually prefer to make in-person observations of babies as they interact with their mothers, Dr. Provenzi said. But because of the pandemic, Dr. Provenzi asked mothers to fill out questionnaires about infant behavior. He plans to observe mothers and babies in person when the children are 12 months old.
While vaccinating pregnant people is the best way to protect them and their fetuses from the virus, Dr. Anagnostou said, society needs to do more to preserve expectant mothers’ mental health.
“We can’t escape the fact that we’ve lived through 2 years of a pandemic,” Dr. Anagnostou said. “But we can think about opportunities for reducing the risk.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The pandemic has created a hostile environment for pregnant people and their babies.
Stress levels among expectant mothers have soared. Pregnant women with COVID are 5 times as likely as uninfected pregnant people to require intensive care and 22 times as likely to die. Infected moms are four times as likely to have a stillborn child.
Yet some of the pandemic’s greatest threats to infants’ health may not be apparent for years or even decades.
That’s because babies of COVID-infected moms are 60% more likely to be born very prematurely, which increases the danger of infant mortality and long-term disabilities such as cerebral palsy, asthma, and hearing loss, as well as a child’s risk of adult disease, including depression, anxiety, heart disease, and kidney disease.
Studies have linked fever and infection during pregnancy to developmental and psychiatric conditions such as autism, depression, and schizophrenia.
“Some of these conditions do not show up until middle childhood or early adult life, but they have their origins in fetal life,” said Evdokia Anagnostou, MD, a child neurologist at Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital and a pediatrics professor at the University of Toronto.
For fetuses exposed to COVID, the greatest danger is usually not the coronavirus itself, but the mother’s immune system.
Both severe COVID infections and the strain of the pandemic can expose fetuses to harmful inflammation, which can occur when a mother’s immune system is fighting a virus or when stress hormones send nonstop alarm signals.
Prenatal inflammation “changes the way the brain develops and, depending on the timing of the infection, it can change the way the heart or kidneys develop,” Dr. Anagnostou said.
Although health officials have strongly recommended COVID vaccines for pregnant people, only 35% are fully vaccinated.
At least 150,000 pregnant women have been diagnosed with COVID; more than 25,000 of them have been hospitalized, and 249 have died, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although most babies will be fine, even a small increase in the percentage of children with special medical or educational needs could have a large effect on the population, given the huge number of COVID infections, Dr. Anagnostou said.
“If someone has a baby who is doing well, that is what they should focus on,” Dr. Anagnostou said. “But from a public health point of view, we need to follow women who experienced severe COVID and their babies to understand the impact.”
Learning from history
Researchers in the United States and other countries are already studying “the COVID generation” to see whether these children have more health issues than those conceived or born before 2020.
Previous crises have shown that the challenges fetuses face in the womb – such as maternal infections, hunger, stress, and hormone-disrupting chemicals – can leave a lasting imprint on their health, as well as that of their children and grandchildren, said Frederick Kaskel, MD, director of pediatric nephrology at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, New York.
People whose mothers were pregnant during surges in the 1918 influenza pandemic, for example, had poorer health throughout their lives, compared with Americans born at other times, said John McCarthy, who is a medical student at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and cowrote a recent review in JAMA Pediatrics with Dr. Kaskel.
Researchers don’t know exactly which moms were infected with pandemic flu, Mr. McCarthy said. But women who were pregnant during major surges – when infection was widespread – had children with higher rates of heart disease or diabetes. These children were also less successful in school, less economically productive, and more likely to live with a disability.
Because organ systems develop during different periods of pregnancy, fetuses exposed during the first trimester may face different risks than those exposed toward the end of pregnancy, Mr. McCarthy said. For example, people born in the fall of 1918 were 50% more likely than others to develop kidney disease; that may reflect an exposure to the pandemic in the third trimester, while the kidneys were still developing.
Nearly 2 years into the COVID pandemic, researchers have begun to publish preliminary observations of infants exposed to COVID infections and stress before birth.
Although Dr. Anagnostou noted that it’s too early to reach definitive conclusions, “there is evidence that babies born to moms with severe COVID infections have changes to their immune system,” she said. “It’s enough to make us worry a little bit.”
Damaging a fetal security system
The good news about the coronavirus is that it seldom crosses the placenta, the organ tasked with protecting a developing fetus from infections and providing it with oxygen. So moms with COVID rarely give the virus to their children before birth.
That’s important, because some viruses that directly infect the fetus – such as Zika – can cause devastating birth defects, said Karin Nielsen-Saines, MD, a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases at University of California, Los Angeles.
But studies also suggest that inflammation from a mother’s COVID infection can injure the placenta, said Jeffery Goldstein, MD, an assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago. In a study published in American Journal of Clinical Pathology , Dr. Goldstein and his coauthors found that placentas from COVID-infected moms had more abnormal blood vessels than placentas from patients without COVID, making it harder for them to deliver sufficient oxygen to the fetus.
Placental damage can also lead to preeclampsia, a serious complication of pregnancy that can cause a mother’s blood pressure to spike.
Preeclampsia occurs when blood vessels in the placenta don’t develop or function properly, forcing the mother’s heart to work harder to get blood to the fetus, which may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. Preeclampsia also predisposes women to heart attacks and strokes later in life.
Rewiring the immune system
In some cases, COVID also appears to rewire a baby’s immune response, Dr. Nielsen-Saines said.
In an October study in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, Dr. Nielsen-Saines and her coauthors found that infants born to people with severe COVID infections had a different mix of immune cells and proteins than other babies. None of the newborns tested positive for the coronavirus.
The immune changes are concerning, Dr. Nielsen-Saines said, because this pattern of immune cells and proteins has previously been found in infants with respiratory problems and in some cases poor neurodevelopment.
Notably, all the babies in her study appear healthy, said Dr. Nielsen-Saines, who plans to follow them for 3 years to see whether these early signals translate into developmental delays, such as problems talking, walking, or interacting with others.
“How big of a difference does any of this make in the baby?” asked Dr. Anagnostou. “We won’t know for a few years. All we can do is try to be as prepared as possible.”
Increasing the risk for boys
Boys could face higher risks from COVID, even before birth.
Males are generally more vulnerable than females as fetuses and newborns; they’re more likely to be born prematurely and to die as infants. Preterm boys also have a higher risk of disability and death.
But coronavirus infection poses special dangers, said Sabra Klein, PhD, a professor of molecular microbiology and immunology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore.
That’s because boys are disproportionately affected by conditions linked to maternal infections. Boys are four times as likely as girls to be diagnosed with autism or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, for example, while men are 75% more likely than women to develop schizophrenia.
Scientists don’t fully understand why boys appear more fragile in the womb, although testosterone – which can dampen immune response – may play a role, said Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington.
Men generally mount weaker immune responses than women and more often develop severe COVID infections. Recent research suggests boys with COVID are more likely than girls to become seriously ill or develop a rare inflammatory condition called multisystem inflammatory syndrome.
New research on COVID could help illuminate this vulnerability.
In a study published in October, researchers found that the sex of a fetus influences the way its placenta responds to COVID, as well as how its mother’s immune system responds.
Pregnant people infected with COVID made fewer antibodies against the coronavirus if they were carrying male fetuses than if they were carrying females. Mothers also transferred fewer antibodies to boys than to girls, said Andrea Edlow, MD, senior author of the study and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
When examining the placentas of male fetuses after delivery, researchers found changes that could leave boys less protected against damaging inflammation.
The sex of a fetus can influence its mother’s response to other illnesses, as well.
For example, research shows that pregnant women with asthma have worse symptoms if they’re carrying a female. Women carrying males are slightly more likely to develop gestational diabetes.
Dr. Edlow said her findings raise questions about the “cross talk” between mother and baby. “The mom’s immune system is sensing there is a male fetus,” Dr. Edlow said. “And the fetus is actively communicating with the mom’s immune system.”
Boosting toxic stress
Rates of depression and stress among pregnant women have increased dramatically during the pandemic.
That’s concerning because chronic stress can lead to inflammation, affecting the babies of both infected and uninfected women, Dr. Anagnostou said.
Studies consistently show that infants born to mothers who experience significant stress during pregnancy have higher rates of short- and long-term health damage – including heart defects and obesity – than babies born to women with less stress.
“We know that inflammation directly influences the way a baby’s brain develops,” said Elinor Sullivan, PhD, an associate professor in psychiatry at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Lockdowns, travel restrictions and physical distancing left many pregnant women without the support of family and friends. The stress of losing a loved one, a job, or a home further heightens the risks to moms and babies, said Dr. Sullivan, who is following children born during the pandemic for 5 years.
In research that has not yet been published, Dr. Sullivan found that babies of women who were pregnant during the pandemic showed more sadness and negative emotions in the first year of life, compared with infants of women who were pregnant before the pandemic.
The findings show the importance of helping and protecting pregnant people before and after delivery, said Dr. Sullivan, who conducted a separate study that found women who received more social support were less depressed.
Italian researchers are also studying the effect of maternal stress on infants’ behavior, as well as the way their genes are regulated.
Although stress-related inflammation doesn’t alter the structure of a baby’s genes, it can influence whether they’re turned on and off, said Livio Provenzi, PhD, a psychologist at the C. Mondino National Institute of Neurology Foundation in Pavia, Italy.
In Dr. Provenzi’s study of 163 mother-baby pairs he found differences in how genes that regulate the stress response were activated. Genes that help people respond to stress were more likely to be turned off in babies whose moms reported the most stress during pregnancy. The same moms also reported that their babies cried more and were fussier when they were 3 months old.
Researchers usually prefer to make in-person observations of babies as they interact with their mothers, Dr. Provenzi said. But because of the pandemic, Dr. Provenzi asked mothers to fill out questionnaires about infant behavior. He plans to observe mothers and babies in person when the children are 12 months old.
While vaccinating pregnant people is the best way to protect them and their fetuses from the virus, Dr. Anagnostou said, society needs to do more to preserve expectant mothers’ mental health.
“We can’t escape the fact that we’ve lived through 2 years of a pandemic,” Dr. Anagnostou said. “But we can think about opportunities for reducing the risk.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
GI symptoms in kids with COVID may predict severe outcomes
Severe gastrointestinal involvement can be common in children who have had COVID-19, a new study shows.
Andrea Lo Veccio, MD, PhD, with the department of translational medical sciences, section of pediatrics, University of Naples (Italy) Federico II, and colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from a large cohort of children aged 18 years and younger who had been diagnosed with COVID-19 between Feb. 25, 2020, and Jan. 20, 2021, in 54 Italian institutions.
Overall, 685 Italian children (56.4% boys; average age, 7 years) were included in the study. Of these, 628 (91.7%) were diagnosed with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection and 57 (8.3%) with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
When children had GI symptoms, the authors found a higher risk of hospitalization (odds ratio, 2.64; 95% confidence interval, 1.89-3.69) and nearly four times the risk of ICU admission (OR, 3.90; 95% CI, 1.98-7.68).
Severe GI involvement occurred in 65 children (9.5%). The authors included the following within that category: disseminated adenomesenteritis (39.6%), appendicitis (33.5%), abdominal fluid collection (21.3%), pancreatitis (6.9%), or intussusception (4.6%). Additionally, out of these 65 children, 27 (41.5%) underwent surgery.
Older children were much more likely than preschoolers to have severe GI symptoms. Children aged 5-10 years were eight times more likely than preschoolers to show severe symptoms (OR, 8.33; 95% CI, 2.62-26.5). In those older than age 10 years, severe symptoms were six times more likely (OR, 6.37; 95% CI, 2.12-19.1).
Awareness about its frequency and presentation may help practitioners to appropriately manage children at risk of severe outcomes, the authors wrote.
The findings of this study were published online Dec. 20 in JAMA Network Open.
Study highlights the GI link
Reached for comment, William Balistreri, MD, with the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, said that it has been known that children are more likely than adults to present with GI symptoms, and also that these symptoms are especially common in children with MIS-C.
“The symptoms most commonly cited in the literature to date include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain,” he said. “What [has not been known] is the frequency, predictive markers, and clinical course of the severe GI manifestations of COVID-19.”
The findings of this study are important to clinicians to help recognize the potential for severe GI involvement, Dr. Balistreri said, adding that “the occurrence of abdominal pain, leukopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers or MIS-C should raise suspicion and lead to early evaluation.”
Margaret E. Thew, APNP, medical director in adolescent medicine and a family nurse practitioner with Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said that news reports typically emphasize the respiratory involvement, but this study provides a detailed analysis of the link between GI symptoms and COVID-19.
“Their data show that there may be less respiratory illness with children, regardless of whether they are generally healthy kids,” she said. “They may have more GI symptoms.
“We know that COVID-19 causes a lot of inflammation, and a large percentage of these kids had inflammation in their stomach or an inflamed bowel,” she added.
Dr. Thew said primary care doctors and urgent and emergency care clinicians will benefit from the findings of this study and should be on alert when kids come in with belly pain or vomiting.
Parents will benefit too, she said, if they are waiting for respiratory illness before they suspect COVID.
“You have to have a high suspicion this is going to be COVID positive,” she said. “You have to have that as part of your thought process.”
Though the study was done in Italy, Dr. Thew added that their experiences mimic those she’s seen locally.
Dr. Lo Vecchio reported receiving fees from Pfizer as an advisory board member outside the submitted work. A coauthor reported speaker’s fees from Angelini, Sobi, and X4 Pharma outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Balistreri and Dr. Thew reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe gastrointestinal involvement can be common in children who have had COVID-19, a new study shows.
Andrea Lo Veccio, MD, PhD, with the department of translational medical sciences, section of pediatrics, University of Naples (Italy) Federico II, and colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from a large cohort of children aged 18 years and younger who had been diagnosed with COVID-19 between Feb. 25, 2020, and Jan. 20, 2021, in 54 Italian institutions.
Overall, 685 Italian children (56.4% boys; average age, 7 years) were included in the study. Of these, 628 (91.7%) were diagnosed with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection and 57 (8.3%) with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
When children had GI symptoms, the authors found a higher risk of hospitalization (odds ratio, 2.64; 95% confidence interval, 1.89-3.69) and nearly four times the risk of ICU admission (OR, 3.90; 95% CI, 1.98-7.68).
Severe GI involvement occurred in 65 children (9.5%). The authors included the following within that category: disseminated adenomesenteritis (39.6%), appendicitis (33.5%), abdominal fluid collection (21.3%), pancreatitis (6.9%), or intussusception (4.6%). Additionally, out of these 65 children, 27 (41.5%) underwent surgery.
Older children were much more likely than preschoolers to have severe GI symptoms. Children aged 5-10 years were eight times more likely than preschoolers to show severe symptoms (OR, 8.33; 95% CI, 2.62-26.5). In those older than age 10 years, severe symptoms were six times more likely (OR, 6.37; 95% CI, 2.12-19.1).
Awareness about its frequency and presentation may help practitioners to appropriately manage children at risk of severe outcomes, the authors wrote.
The findings of this study were published online Dec. 20 in JAMA Network Open.
Study highlights the GI link
Reached for comment, William Balistreri, MD, with the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, said that it has been known that children are more likely than adults to present with GI symptoms, and also that these symptoms are especially common in children with MIS-C.
“The symptoms most commonly cited in the literature to date include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain,” he said. “What [has not been known] is the frequency, predictive markers, and clinical course of the severe GI manifestations of COVID-19.”
The findings of this study are important to clinicians to help recognize the potential for severe GI involvement, Dr. Balistreri said, adding that “the occurrence of abdominal pain, leukopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers or MIS-C should raise suspicion and lead to early evaluation.”
Margaret E. Thew, APNP, medical director in adolescent medicine and a family nurse practitioner with Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said that news reports typically emphasize the respiratory involvement, but this study provides a detailed analysis of the link between GI symptoms and COVID-19.
“Their data show that there may be less respiratory illness with children, regardless of whether they are generally healthy kids,” she said. “They may have more GI symptoms.
“We know that COVID-19 causes a lot of inflammation, and a large percentage of these kids had inflammation in their stomach or an inflamed bowel,” she added.
Dr. Thew said primary care doctors and urgent and emergency care clinicians will benefit from the findings of this study and should be on alert when kids come in with belly pain or vomiting.
Parents will benefit too, she said, if they are waiting for respiratory illness before they suspect COVID.
“You have to have a high suspicion this is going to be COVID positive,” she said. “You have to have that as part of your thought process.”
Though the study was done in Italy, Dr. Thew added that their experiences mimic those she’s seen locally.
Dr. Lo Vecchio reported receiving fees from Pfizer as an advisory board member outside the submitted work. A coauthor reported speaker’s fees from Angelini, Sobi, and X4 Pharma outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Balistreri and Dr. Thew reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe gastrointestinal involvement can be common in children who have had COVID-19, a new study shows.
Andrea Lo Veccio, MD, PhD, with the department of translational medical sciences, section of pediatrics, University of Naples (Italy) Federico II, and colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from a large cohort of children aged 18 years and younger who had been diagnosed with COVID-19 between Feb. 25, 2020, and Jan. 20, 2021, in 54 Italian institutions.
Overall, 685 Italian children (56.4% boys; average age, 7 years) were included in the study. Of these, 628 (91.7%) were diagnosed with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection and 57 (8.3%) with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
When children had GI symptoms, the authors found a higher risk of hospitalization (odds ratio, 2.64; 95% confidence interval, 1.89-3.69) and nearly four times the risk of ICU admission (OR, 3.90; 95% CI, 1.98-7.68).
Severe GI involvement occurred in 65 children (9.5%). The authors included the following within that category: disseminated adenomesenteritis (39.6%), appendicitis (33.5%), abdominal fluid collection (21.3%), pancreatitis (6.9%), or intussusception (4.6%). Additionally, out of these 65 children, 27 (41.5%) underwent surgery.
Older children were much more likely than preschoolers to have severe GI symptoms. Children aged 5-10 years were eight times more likely than preschoolers to show severe symptoms (OR, 8.33; 95% CI, 2.62-26.5). In those older than age 10 years, severe symptoms were six times more likely (OR, 6.37; 95% CI, 2.12-19.1).
Awareness about its frequency and presentation may help practitioners to appropriately manage children at risk of severe outcomes, the authors wrote.
The findings of this study were published online Dec. 20 in JAMA Network Open.
Study highlights the GI link
Reached for comment, William Balistreri, MD, with the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, said that it has been known that children are more likely than adults to present with GI symptoms, and also that these symptoms are especially common in children with MIS-C.
“The symptoms most commonly cited in the literature to date include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain,” he said. “What [has not been known] is the frequency, predictive markers, and clinical course of the severe GI manifestations of COVID-19.”
The findings of this study are important to clinicians to help recognize the potential for severe GI involvement, Dr. Balistreri said, adding that “the occurrence of abdominal pain, leukopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers or MIS-C should raise suspicion and lead to early evaluation.”
Margaret E. Thew, APNP, medical director in adolescent medicine and a family nurse practitioner with Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said that news reports typically emphasize the respiratory involvement, but this study provides a detailed analysis of the link between GI symptoms and COVID-19.
“Their data show that there may be less respiratory illness with children, regardless of whether they are generally healthy kids,” she said. “They may have more GI symptoms.
“We know that COVID-19 causes a lot of inflammation, and a large percentage of these kids had inflammation in their stomach or an inflamed bowel,” she added.
Dr. Thew said primary care doctors and urgent and emergency care clinicians will benefit from the findings of this study and should be on alert when kids come in with belly pain or vomiting.
Parents will benefit too, she said, if they are waiting for respiratory illness before they suspect COVID.
“You have to have a high suspicion this is going to be COVID positive,” she said. “You have to have that as part of your thought process.”
Though the study was done in Italy, Dr. Thew added that their experiences mimic those she’s seen locally.
Dr. Lo Vecchio reported receiving fees from Pfizer as an advisory board member outside the submitted work. A coauthor reported speaker’s fees from Angelini, Sobi, and X4 Pharma outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Balistreri and Dr. Thew reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Children and COVID: New cases up slightly, vaccinations continue to slow
New COVID-19 vaccinations in children were down by almost 24% in the last week as new cases rose by just 3.5%, based on new data.
That fairly low number suggests the latest case count from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association has not caught up yet to the reality of the Omicron variant, which has sent new cases climbing among all ages and now represents the majority of COVID-19 infections nationwide, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.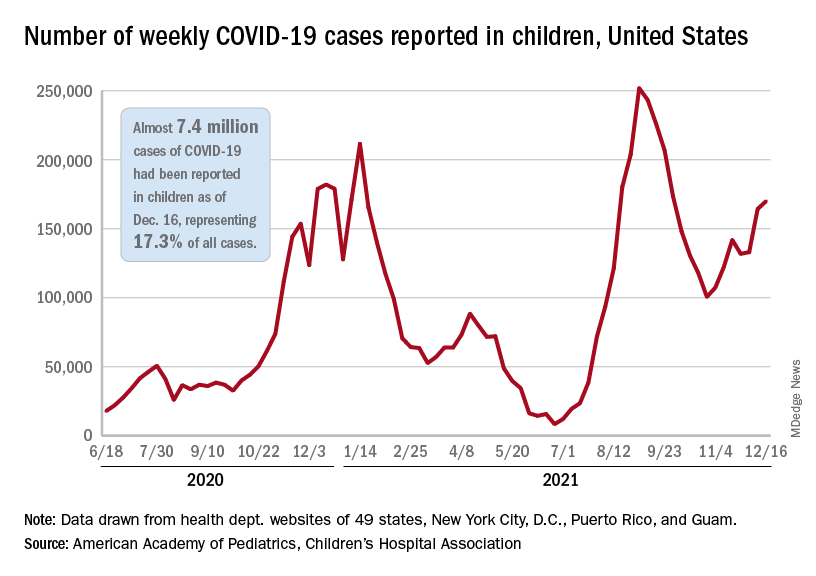
Meanwhile, in the midst of the latest surge, the United States just passed yet another sobering COVID milestone: 1,000 deaths in children aged 17 and under. The total as of Dec. 20 was 1,015, according to the CDC, with the largest share, almost 32%, occurring in children less than 5 years of age.
Regionally, the majority of that increase came in the Northeast, with a small rise in the South and decreases in the Midwest and West, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
At the state level, the largest percent increases in cases over the past 2 weeks were seen in Maine and New Hampshire, as well as Vermont, which has the nation’s highest vaccination rates for children aged 5-11 (51%) and 12-17 (84%), the AAP said in its vaccination trends report.
Nationally, new COVID vaccinations in children continue to trend downward. The number of children aged 5-17 years who had received at least one dose increased by about 498,000 for the week of Dec. 13-19, down from 654,000 (–23.9%) the previous week. Children aged 5-11 years still represented the largest share (22.7%) of all vaccine initiators in the last 2 weeks, but that proportion was 42.8% just before Thanksgiving, according to data from the CDC.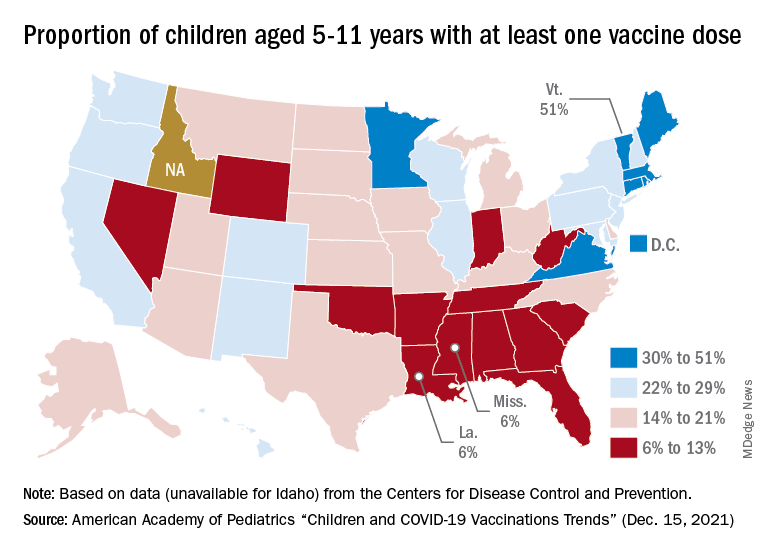
On a more positive note, children aged 5-11 made up 51% of all Americans who completed the vaccine regimen during the 2 weeks ending Dec. 20. The cumulative completion count is 3.6 million in that age group, along with almost 13.4 million children aged 12-17, and the CDC data show that 6.1 million children aged 5-11 and 15.9 million children aged 12-17 have received at least one dose.
On a less positive note, however, that means almost half (47%) of 12- to 17-year-olds still are not fully vaccinated and that over a third (37%) have received no vaccine at all, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
New COVID-19 vaccinations in children were down by almost 24% in the last week as new cases rose by just 3.5%, based on new data.
That fairly low number suggests the latest case count from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association has not caught up yet to the reality of the Omicron variant, which has sent new cases climbing among all ages and now represents the majority of COVID-19 infections nationwide, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
Meanwhile, in the midst of the latest surge, the United States just passed yet another sobering COVID milestone: 1,000 deaths in children aged 17 and under. The total as of Dec. 20 was 1,015, according to the CDC, with the largest share, almost 32%, occurring in children less than 5 years of age.
Regionally, the majority of that increase came in the Northeast, with a small rise in the South and decreases in the Midwest and West, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
At the state level, the largest percent increases in cases over the past 2 weeks were seen in Maine and New Hampshire, as well as Vermont, which has the nation’s highest vaccination rates for children aged 5-11 (51%) and 12-17 (84%), the AAP said in its vaccination trends report.
Nationally, new COVID vaccinations in children continue to trend downward. The number of children aged 5-17 years who had received at least one dose increased by about 498,000 for the week of Dec. 13-19, down from 654,000 (–23.9%) the previous week. Children aged 5-11 years still represented the largest share (22.7%) of all vaccine initiators in the last 2 weeks, but that proportion was 42.8% just before Thanksgiving, according to data from the CDC.
On a more positive note, children aged 5-11 made up 51% of all Americans who completed the vaccine regimen during the 2 weeks ending Dec. 20. The cumulative completion count is 3.6 million in that age group, along with almost 13.4 million children aged 12-17, and the CDC data show that 6.1 million children aged 5-11 and 15.9 million children aged 12-17 have received at least one dose.
On a less positive note, however, that means almost half (47%) of 12- to 17-year-olds still are not fully vaccinated and that over a third (37%) have received no vaccine at all, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
New COVID-19 vaccinations in children were down by almost 24% in the last week as new cases rose by just 3.5%, based on new data.
That fairly low number suggests the latest case count from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association has not caught up yet to the reality of the Omicron variant, which has sent new cases climbing among all ages and now represents the majority of COVID-19 infections nationwide, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
Meanwhile, in the midst of the latest surge, the United States just passed yet another sobering COVID milestone: 1,000 deaths in children aged 17 and under. The total as of Dec. 20 was 1,015, according to the CDC, with the largest share, almost 32%, occurring in children less than 5 years of age.
Regionally, the majority of that increase came in the Northeast, with a small rise in the South and decreases in the Midwest and West, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
At the state level, the largest percent increases in cases over the past 2 weeks were seen in Maine and New Hampshire, as well as Vermont, which has the nation’s highest vaccination rates for children aged 5-11 (51%) and 12-17 (84%), the AAP said in its vaccination trends report.
Nationally, new COVID vaccinations in children continue to trend downward. The number of children aged 5-17 years who had received at least one dose increased by about 498,000 for the week of Dec. 13-19, down from 654,000 (–23.9%) the previous week. Children aged 5-11 years still represented the largest share (22.7%) of all vaccine initiators in the last 2 weeks, but that proportion was 42.8% just before Thanksgiving, according to data from the CDC.
On a more positive note, children aged 5-11 made up 51% of all Americans who completed the vaccine regimen during the 2 weeks ending Dec. 20. The cumulative completion count is 3.6 million in that age group, along with almost 13.4 million children aged 12-17, and the CDC data show that 6.1 million children aged 5-11 and 15.9 million children aged 12-17 have received at least one dose.
On a less positive note, however, that means almost half (47%) of 12- to 17-year-olds still are not fully vaccinated and that over a third (37%) have received no vaccine at all, according to the COVID Data Tracker.







