User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Monitor children’s thyroids after iodine exposure for imaging, FDA says
The Food and Drug Administration has recommended thyroid monitoring for newborns and children through 3 years of age within 3 weeks of receiving injections of iodine-containing contrast media as part of imaging procedures.
A recent FDA review showed that “underactive thyroid or a temporary decrease in thyroid hormone levels were uncommon,” according to an updated Drug Safety Communication issued on March 30, 2022.
However, early monitoring will help identify and treat any thyroid abnormalities as a result of the injections to help prevent potential complications in the future, according to the FDA, as babies and children do not generally show visible signs of thyroid problems and may not do so after an iodinated contrast media (ICM) injection.
ICM have been approved and used for decades to enhance images on x-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans, according to the communication.
The new FDA warning and recommendation for monitoring applies to the prescribing information for the entire class of ICM products. The new communication is an update to the 2015 Drug Safety Communication that advised medical professionals of the potential for underactive thyroid in response to ICM injections in newborns and young children. The update reflects new studies since that time.
The recent research showed that most reported cases of adverse effects were transient subclinical hypothyroidism and did not require treatment, according to the FDA. “The reported rate ranged from 1 percent to 15 percent and tended to be higher in neonates, particularly preterm neonates,” they said. Others at increased risk are those with underlying medical conditions, especially those with cardiac conditions who often require higher doses of contrast during invasive procedures.
In the recent studies, the time from ICM exposure to a diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction ranged from 8.5 to 138 days, but most occurred within 3 weeks, according to the update.
Patients and clinicians can report any adverse events from ICM or other medications to the FDA via FDA MedWatch program.
For more information, read the complete Drug Safety Communication.
The Food and Drug Administration has recommended thyroid monitoring for newborns and children through 3 years of age within 3 weeks of receiving injections of iodine-containing contrast media as part of imaging procedures.
A recent FDA review showed that “underactive thyroid or a temporary decrease in thyroid hormone levels were uncommon,” according to an updated Drug Safety Communication issued on March 30, 2022.
However, early monitoring will help identify and treat any thyroid abnormalities as a result of the injections to help prevent potential complications in the future, according to the FDA, as babies and children do not generally show visible signs of thyroid problems and may not do so after an iodinated contrast media (ICM) injection.
ICM have been approved and used for decades to enhance images on x-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans, according to the communication.
The new FDA warning and recommendation for monitoring applies to the prescribing information for the entire class of ICM products. The new communication is an update to the 2015 Drug Safety Communication that advised medical professionals of the potential for underactive thyroid in response to ICM injections in newborns and young children. The update reflects new studies since that time.
The recent research showed that most reported cases of adverse effects were transient subclinical hypothyroidism and did not require treatment, according to the FDA. “The reported rate ranged from 1 percent to 15 percent and tended to be higher in neonates, particularly preterm neonates,” they said. Others at increased risk are those with underlying medical conditions, especially those with cardiac conditions who often require higher doses of contrast during invasive procedures.
In the recent studies, the time from ICM exposure to a diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction ranged from 8.5 to 138 days, but most occurred within 3 weeks, according to the update.
Patients and clinicians can report any adverse events from ICM or other medications to the FDA via FDA MedWatch program.
For more information, read the complete Drug Safety Communication.
The Food and Drug Administration has recommended thyroid monitoring for newborns and children through 3 years of age within 3 weeks of receiving injections of iodine-containing contrast media as part of imaging procedures.
A recent FDA review showed that “underactive thyroid or a temporary decrease in thyroid hormone levels were uncommon,” according to an updated Drug Safety Communication issued on March 30, 2022.
However, early monitoring will help identify and treat any thyroid abnormalities as a result of the injections to help prevent potential complications in the future, according to the FDA, as babies and children do not generally show visible signs of thyroid problems and may not do so after an iodinated contrast media (ICM) injection.
ICM have been approved and used for decades to enhance images on x-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans, according to the communication.
The new FDA warning and recommendation for monitoring applies to the prescribing information for the entire class of ICM products. The new communication is an update to the 2015 Drug Safety Communication that advised medical professionals of the potential for underactive thyroid in response to ICM injections in newborns and young children. The update reflects new studies since that time.
The recent research showed that most reported cases of adverse effects were transient subclinical hypothyroidism and did not require treatment, according to the FDA. “The reported rate ranged from 1 percent to 15 percent and tended to be higher in neonates, particularly preterm neonates,” they said. Others at increased risk are those with underlying medical conditions, especially those with cardiac conditions who often require higher doses of contrast during invasive procedures.
In the recent studies, the time from ICM exposure to a diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction ranged from 8.5 to 138 days, but most occurred within 3 weeks, according to the update.
Patients and clinicians can report any adverse events from ICM or other medications to the FDA via FDA MedWatch program.
For more information, read the complete Drug Safety Communication.
You’re not on a ‘best doctor’ list – does it matter?
Thousands of doctors get a shout out every year when they make the “Top Doctor” lists in various magazines. Some may be your colleagues or competitors. Should you be concerned if you’re not on the list?
Best Doctor lists are clearly popular with readers and make money for the magazines. They can also bring in patient revenue for doctors and their employers who promote them in news releases and on their websites.
For doctors on some of the top lists, the recognition can bring not only patients, but national or international visibility.
While the dollar value is hard to come by, some doctors say that these lists have attracted new patients to their practice.
Sarah St. Louis, MD, a physician manager of Associates in Urogynecology, is one of Orlando Style magazine’s Doctors of the Year and Orlando Family Magazine’s Top Doctors.
Several new patients have told her that they read about her in the magazines’ Top Doctor lists. “Urogynecology is not a well-known specialty – it’s a helpful way to get the word out about the women’s health specialty and what I do,” said Dr. St. Louis, an early career physician who started her practice in 2017.
The additional patient revenue has been worth the cost of displaying her profile in Orlando Style, which was about $800 for a half-page spread with her photo.
Top Doctor lists also work well for specialty practices whose patients can self-refer, such as plastic surgery, dermatology, orthopedics, gastroenterology, and geriatric medicine, said Andrea Eliscu, RN, founder and president of Medical Marketing in Orlando.
Being in a competitive market also matters. If a practice is the only one in town, those doctors may not need the publicity as much as doctors in an urban practice that faces stiff competition.
How do doctors get on these lists?
In most cases, doctors have to be nominated by their peers, a process that some say is flawed because it may shut out doctors who are less popular or well-connected.
Forty-eight regional magazines, including Chicago magazine and Philadelphia Magazine , partner with Castle Connolly to use their online Top Doctor database of more than 61,000 physicians in every major metropolitan area, said Steve Leibforth, managing director of Castle Connolly’s Top Doctors.
The company says it sends annual surveys to tens of thousands of practicing doctors asking them to nominate colleagues in their specialty. The nominated doctors are vetted by Castle Connolly’s physician-led research team on several criteria including professional qualifications, education, hospital and faculty appointments, research leadership, professional reputation and disciplinary history, and outcomes data when available, said Mr. Leibforth.
Washingtonian magazine says it sends annual online surveys to 13,500 physicians in the DC metro area asking them to nominate one colleague in their specialty. The top vote-getters in each of 39 categories are designated Top Doctors.
Orlando Family Magazine says its annual Top Doctor selections are based on reader polls and doctor nominations.
Consumers’ Research Council of America uses a point system based on each year the doctor has been in practice, education and continuing education, board certification, and membership in professional medical societies.
Doctors have many ways to promote that they’re listed as a “top” doctor. Dr. St. Louis takes advantage of the magazine’s free reprints, which she puts in her waiting room.
Others buy plaques to hang up in their waiting rooms or offices and announce the distinction on their websites, blogs, or social media. “They have to maximize the magazine distinction or it’s worthless,” said Ms. Eliscu.
Employers also like to spread the word when their doctors make it on “Top Doctor” lists.
“With Emory physicians making up nearly 50 percent of the list, that’s more than any other health system in Atlanta,” said an Emory University press release after nearly half of the university’s doctors made the Top Doctors list in Atlanta magazine.
Patients may be impressed: What about your peers?
Dr. St. Louis said that making some of these lists is less impressive than having a peer-reviewed journal article or receiving professional awards.
“Just because a physician is listed in a magazine as a ‘top doctor’ does not mean they are the best. There are far more medical, clinical, and scientific points to consider than just a pretty picture in a style magazine,” she said.
Wanda Filer, MD, MBA, who practiced family medicine until last year when she became chief medical officer for VaxCare in Orlando, said she ignores the many congratulatory letters in the mail announcing that she’s made one list or another.
“I don’t put much credence in the lists. I get notifications fairly often, and to me it always looks like they’re trying to sell a plaque. I’d rather let my work speak for itself.”
Arlen Meyers, MD, MBA, president and CEO of the Society of Physician Entrepreneurs and a paid strategic adviser to RYTE, a data-driven site for “best doctors” and “best hospitals,” said he received several of these “top doctor” awards when he was a professor of otolaryngology at the University of Colorado.
He has been critical of these awards for some time. “These doctor beauty pageants may be good for business but have little value for patients.”
He would like to see a new approach that is driven by data and what patients value. “If I have a lump in my thyroid, I want to know the best doctor to treat me based on outcomes data.”
He said a good rating system would include a data-driven approach based on treatment outcomes, publicly available data, price transparency, and patient values.
Whether a physician feels honored to be named a top physician or sees little value in it, most doctors are aware of the list’s marketing value for their practices and many choose to make use of it.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Thousands of doctors get a shout out every year when they make the “Top Doctor” lists in various magazines. Some may be your colleagues or competitors. Should you be concerned if you’re not on the list?
Best Doctor lists are clearly popular with readers and make money for the magazines. They can also bring in patient revenue for doctors and their employers who promote them in news releases and on their websites.
For doctors on some of the top lists, the recognition can bring not only patients, but national or international visibility.
While the dollar value is hard to come by, some doctors say that these lists have attracted new patients to their practice.
Sarah St. Louis, MD, a physician manager of Associates in Urogynecology, is one of Orlando Style magazine’s Doctors of the Year and Orlando Family Magazine’s Top Doctors.
Several new patients have told her that they read about her in the magazines’ Top Doctor lists. “Urogynecology is not a well-known specialty – it’s a helpful way to get the word out about the women’s health specialty and what I do,” said Dr. St. Louis, an early career physician who started her practice in 2017.
The additional patient revenue has been worth the cost of displaying her profile in Orlando Style, which was about $800 for a half-page spread with her photo.
Top Doctor lists also work well for specialty practices whose patients can self-refer, such as plastic surgery, dermatology, orthopedics, gastroenterology, and geriatric medicine, said Andrea Eliscu, RN, founder and president of Medical Marketing in Orlando.
Being in a competitive market also matters. If a practice is the only one in town, those doctors may not need the publicity as much as doctors in an urban practice that faces stiff competition.
How do doctors get on these lists?
In most cases, doctors have to be nominated by their peers, a process that some say is flawed because it may shut out doctors who are less popular or well-connected.
Forty-eight regional magazines, including Chicago magazine and Philadelphia Magazine , partner with Castle Connolly to use their online Top Doctor database of more than 61,000 physicians in every major metropolitan area, said Steve Leibforth, managing director of Castle Connolly’s Top Doctors.
The company says it sends annual surveys to tens of thousands of practicing doctors asking them to nominate colleagues in their specialty. The nominated doctors are vetted by Castle Connolly’s physician-led research team on several criteria including professional qualifications, education, hospital and faculty appointments, research leadership, professional reputation and disciplinary history, and outcomes data when available, said Mr. Leibforth.
Washingtonian magazine says it sends annual online surveys to 13,500 physicians in the DC metro area asking them to nominate one colleague in their specialty. The top vote-getters in each of 39 categories are designated Top Doctors.
Orlando Family Magazine says its annual Top Doctor selections are based on reader polls and doctor nominations.
Consumers’ Research Council of America uses a point system based on each year the doctor has been in practice, education and continuing education, board certification, and membership in professional medical societies.
Doctors have many ways to promote that they’re listed as a “top” doctor. Dr. St. Louis takes advantage of the magazine’s free reprints, which she puts in her waiting room.
Others buy plaques to hang up in their waiting rooms or offices and announce the distinction on their websites, blogs, or social media. “They have to maximize the magazine distinction or it’s worthless,” said Ms. Eliscu.
Employers also like to spread the word when their doctors make it on “Top Doctor” lists.
“With Emory physicians making up nearly 50 percent of the list, that’s more than any other health system in Atlanta,” said an Emory University press release after nearly half of the university’s doctors made the Top Doctors list in Atlanta magazine.
Patients may be impressed: What about your peers?
Dr. St. Louis said that making some of these lists is less impressive than having a peer-reviewed journal article or receiving professional awards.
“Just because a physician is listed in a magazine as a ‘top doctor’ does not mean they are the best. There are far more medical, clinical, and scientific points to consider than just a pretty picture in a style magazine,” she said.
Wanda Filer, MD, MBA, who practiced family medicine until last year when she became chief medical officer for VaxCare in Orlando, said she ignores the many congratulatory letters in the mail announcing that she’s made one list or another.
“I don’t put much credence in the lists. I get notifications fairly often, and to me it always looks like they’re trying to sell a plaque. I’d rather let my work speak for itself.”
Arlen Meyers, MD, MBA, president and CEO of the Society of Physician Entrepreneurs and a paid strategic adviser to RYTE, a data-driven site for “best doctors” and “best hospitals,” said he received several of these “top doctor” awards when he was a professor of otolaryngology at the University of Colorado.
He has been critical of these awards for some time. “These doctor beauty pageants may be good for business but have little value for patients.”
He would like to see a new approach that is driven by data and what patients value. “If I have a lump in my thyroid, I want to know the best doctor to treat me based on outcomes data.”
He said a good rating system would include a data-driven approach based on treatment outcomes, publicly available data, price transparency, and patient values.
Whether a physician feels honored to be named a top physician or sees little value in it, most doctors are aware of the list’s marketing value for their practices and many choose to make use of it.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Thousands of doctors get a shout out every year when they make the “Top Doctor” lists in various magazines. Some may be your colleagues or competitors. Should you be concerned if you’re not on the list?
Best Doctor lists are clearly popular with readers and make money for the magazines. They can also bring in patient revenue for doctors and their employers who promote them in news releases and on their websites.
For doctors on some of the top lists, the recognition can bring not only patients, but national or international visibility.
While the dollar value is hard to come by, some doctors say that these lists have attracted new patients to their practice.
Sarah St. Louis, MD, a physician manager of Associates in Urogynecology, is one of Orlando Style magazine’s Doctors of the Year and Orlando Family Magazine’s Top Doctors.
Several new patients have told her that they read about her in the magazines’ Top Doctor lists. “Urogynecology is not a well-known specialty – it’s a helpful way to get the word out about the women’s health specialty and what I do,” said Dr. St. Louis, an early career physician who started her practice in 2017.
The additional patient revenue has been worth the cost of displaying her profile in Orlando Style, which was about $800 for a half-page spread with her photo.
Top Doctor lists also work well for specialty practices whose patients can self-refer, such as plastic surgery, dermatology, orthopedics, gastroenterology, and geriatric medicine, said Andrea Eliscu, RN, founder and president of Medical Marketing in Orlando.
Being in a competitive market also matters. If a practice is the only one in town, those doctors may not need the publicity as much as doctors in an urban practice that faces stiff competition.
How do doctors get on these lists?
In most cases, doctors have to be nominated by their peers, a process that some say is flawed because it may shut out doctors who are less popular or well-connected.
Forty-eight regional magazines, including Chicago magazine and Philadelphia Magazine , partner with Castle Connolly to use their online Top Doctor database of more than 61,000 physicians in every major metropolitan area, said Steve Leibforth, managing director of Castle Connolly’s Top Doctors.
The company says it sends annual surveys to tens of thousands of practicing doctors asking them to nominate colleagues in their specialty. The nominated doctors are vetted by Castle Connolly’s physician-led research team on several criteria including professional qualifications, education, hospital and faculty appointments, research leadership, professional reputation and disciplinary history, and outcomes data when available, said Mr. Leibforth.
Washingtonian magazine says it sends annual online surveys to 13,500 physicians in the DC metro area asking them to nominate one colleague in their specialty. The top vote-getters in each of 39 categories are designated Top Doctors.
Orlando Family Magazine says its annual Top Doctor selections are based on reader polls and doctor nominations.
Consumers’ Research Council of America uses a point system based on each year the doctor has been in practice, education and continuing education, board certification, and membership in professional medical societies.
Doctors have many ways to promote that they’re listed as a “top” doctor. Dr. St. Louis takes advantage of the magazine’s free reprints, which she puts in her waiting room.
Others buy plaques to hang up in their waiting rooms or offices and announce the distinction on their websites, blogs, or social media. “They have to maximize the magazine distinction or it’s worthless,” said Ms. Eliscu.
Employers also like to spread the word when their doctors make it on “Top Doctor” lists.
“With Emory physicians making up nearly 50 percent of the list, that’s more than any other health system in Atlanta,” said an Emory University press release after nearly half of the university’s doctors made the Top Doctors list in Atlanta magazine.
Patients may be impressed: What about your peers?
Dr. St. Louis said that making some of these lists is less impressive than having a peer-reviewed journal article or receiving professional awards.
“Just because a physician is listed in a magazine as a ‘top doctor’ does not mean they are the best. There are far more medical, clinical, and scientific points to consider than just a pretty picture in a style magazine,” she said.
Wanda Filer, MD, MBA, who practiced family medicine until last year when she became chief medical officer for VaxCare in Orlando, said she ignores the many congratulatory letters in the mail announcing that she’s made one list or another.
“I don’t put much credence in the lists. I get notifications fairly often, and to me it always looks like they’re trying to sell a plaque. I’d rather let my work speak for itself.”
Arlen Meyers, MD, MBA, president and CEO of the Society of Physician Entrepreneurs and a paid strategic adviser to RYTE, a data-driven site for “best doctors” and “best hospitals,” said he received several of these “top doctor” awards when he was a professor of otolaryngology at the University of Colorado.
He has been critical of these awards for some time. “These doctor beauty pageants may be good for business but have little value for patients.”
He would like to see a new approach that is driven by data and what patients value. “If I have a lump in my thyroid, I want to know the best doctor to treat me based on outcomes data.”
He said a good rating system would include a data-driven approach based on treatment outcomes, publicly available data, price transparency, and patient values.
Whether a physician feels honored to be named a top physician or sees little value in it, most doctors are aware of the list’s marketing value for their practices and many choose to make use of it.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Polio: Five African countries vaccinating 23 million children
When polio paralyzed a 3-year-old girl in Lilongwe, Malawi, in November 2021, public health experts in Malawi’s Ministry of Health responded quickly. The ministry partnered with the Global Polio Eradication Initiative, the World Health Organization, and the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund to mobilize a surge team of personnel and resources to vaccinate all 2.9 million Malawian children aged under 5 years, WHO reported in a news release.
The first of four sequential campaigns began on March 20 and expanded on March 24 to neighboring Mozambique, Tanzania, and Zambia. The multinational, multiagency effort aims to include Zimbabwean children as well and deliver over 80 million supplemental doses of bivalent oral polio vaccines to over 23 million children in these five countries by July.
Because it takes multiple polio vaccine doses to become fully immunized, the children are expected to receive four rounds of vaccine regardless of their vaccination history.
“It is important to conduct the campaigns now to boost the immunity of our children,” Annie Chauma-Mwale, MBBS, MPH, the chief medical officer of epidemiology and surveillance in Malawi’s Ministry of Health in Lilongwe, said in an interview. “Polio is not only a medical issue. Polio is also a socioeconomic issue with long-term impacts on the child, the country, and the globe.
“In Malawi, we are using our community health and health care facility structures to ensure we do not miss any eligible child,” explained Dr. Chauma-Mwale, who is also the deputy incident manager of the poliovirus outbreak response. “We aim to play our role in the global eradication of polio by protecting the vulnerable and curtailing any potential transmission as early as possible.”
Of the three variants of wild, naturally occurring poliovirus, types 2 and 3 have been eradicated, but wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1) remains endemic in Afghanistan and Pakistan.
As reported recently by this news organization, the girl in Malawi was infected with a WPV1 strain that had been circulating for years in Pakistan’s Sindh Province.
Malawi’s most recent clinically confirmed WPV1 case was reported in 1992, and this is the first WPV1 case detected in Africa since 2016. The continent was declared free of indigenous wild polio in 2020 and is still considered free of wild poliovirus because the child’s illness was imported from elsewhere.
The 3-year-old girl developed acute flaccid paralysis in November 2021. In February 2022, virus from her stool was sequenced by the National Institute of Communicable Disease in South Africa and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. On Feb. 16, Malawi was notified of the case, which was genetically linked to a sequence detected in Sindh Province around 2 years earlier.
‘Do not ignore polio’
Within 24 hours, the Government of Malawi declared a public health emergency and activated the national Emergency Operations Centre. Within 72 hours, the GPEI rapid response team arrived in the country. The Ministry of Health partnered with GPEI, WHO, and UNICEF to mobilize the campaign and begin vaccinating children on March 20.
‘’We rely on clinicians to support the surveillance of polio through case searches, both active and passive,” Mike Nenani Chisema, MBBS, MPH, the program manager of the expanded program on immunization and the polio response operations manager in Malawi’s Ministry of Health, said in an interview.
He noted that the young girl was diagnosed correctly and millions of children are now being protected against the disease, thanks to the acumen of one hospital clinician.
“Remember, we still have polio in some countries, and every country is at risk,” he cautioned. “Don’t forget to look for the obvious and do not ignore polio, regardless of economic status.’’
According to GPEI, all countries – especially those with weak immunization and other public health programs whose residents trade or travel to and from endemic countries – are at risk for imported polio.
Anita Gupta, DO, MPP, PharmD, an adjunct assistant professor of anesthesiology and critical care medicine and pain medicine at the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said that she welcomes this effort.
“Given the decades of published evidence and understanding on the vaccine’s safety and efficacy, this program in Malawi is the right step to take,” Gupta, who is not involved in the campaigns, said in an interview. “Polio is preventable, and acting now will prevent spread later.”
Dr. Chauma-Mwale and Dr. Chisema are employees of Malawi’s Ministry of Health. Dr. Gupta disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When polio paralyzed a 3-year-old girl in Lilongwe, Malawi, in November 2021, public health experts in Malawi’s Ministry of Health responded quickly. The ministry partnered with the Global Polio Eradication Initiative, the World Health Organization, and the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund to mobilize a surge team of personnel and resources to vaccinate all 2.9 million Malawian children aged under 5 years, WHO reported in a news release.
The first of four sequential campaigns began on March 20 and expanded on March 24 to neighboring Mozambique, Tanzania, and Zambia. The multinational, multiagency effort aims to include Zimbabwean children as well and deliver over 80 million supplemental doses of bivalent oral polio vaccines to over 23 million children in these five countries by July.
Because it takes multiple polio vaccine doses to become fully immunized, the children are expected to receive four rounds of vaccine regardless of their vaccination history.
“It is important to conduct the campaigns now to boost the immunity of our children,” Annie Chauma-Mwale, MBBS, MPH, the chief medical officer of epidemiology and surveillance in Malawi’s Ministry of Health in Lilongwe, said in an interview. “Polio is not only a medical issue. Polio is also a socioeconomic issue with long-term impacts on the child, the country, and the globe.
“In Malawi, we are using our community health and health care facility structures to ensure we do not miss any eligible child,” explained Dr. Chauma-Mwale, who is also the deputy incident manager of the poliovirus outbreak response. “We aim to play our role in the global eradication of polio by protecting the vulnerable and curtailing any potential transmission as early as possible.”
Of the three variants of wild, naturally occurring poliovirus, types 2 and 3 have been eradicated, but wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1) remains endemic in Afghanistan and Pakistan.
As reported recently by this news organization, the girl in Malawi was infected with a WPV1 strain that had been circulating for years in Pakistan’s Sindh Province.
Malawi’s most recent clinically confirmed WPV1 case was reported in 1992, and this is the first WPV1 case detected in Africa since 2016. The continent was declared free of indigenous wild polio in 2020 and is still considered free of wild poliovirus because the child’s illness was imported from elsewhere.
The 3-year-old girl developed acute flaccid paralysis in November 2021. In February 2022, virus from her stool was sequenced by the National Institute of Communicable Disease in South Africa and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. On Feb. 16, Malawi was notified of the case, which was genetically linked to a sequence detected in Sindh Province around 2 years earlier.
‘Do not ignore polio’
Within 24 hours, the Government of Malawi declared a public health emergency and activated the national Emergency Operations Centre. Within 72 hours, the GPEI rapid response team arrived in the country. The Ministry of Health partnered with GPEI, WHO, and UNICEF to mobilize the campaign and begin vaccinating children on March 20.
‘’We rely on clinicians to support the surveillance of polio through case searches, both active and passive,” Mike Nenani Chisema, MBBS, MPH, the program manager of the expanded program on immunization and the polio response operations manager in Malawi’s Ministry of Health, said in an interview.
He noted that the young girl was diagnosed correctly and millions of children are now being protected against the disease, thanks to the acumen of one hospital clinician.
“Remember, we still have polio in some countries, and every country is at risk,” he cautioned. “Don’t forget to look for the obvious and do not ignore polio, regardless of economic status.’’
According to GPEI, all countries – especially those with weak immunization and other public health programs whose residents trade or travel to and from endemic countries – are at risk for imported polio.
Anita Gupta, DO, MPP, PharmD, an adjunct assistant professor of anesthesiology and critical care medicine and pain medicine at the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said that she welcomes this effort.
“Given the decades of published evidence and understanding on the vaccine’s safety and efficacy, this program in Malawi is the right step to take,” Gupta, who is not involved in the campaigns, said in an interview. “Polio is preventable, and acting now will prevent spread later.”
Dr. Chauma-Mwale and Dr. Chisema are employees of Malawi’s Ministry of Health. Dr. Gupta disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When polio paralyzed a 3-year-old girl in Lilongwe, Malawi, in November 2021, public health experts in Malawi’s Ministry of Health responded quickly. The ministry partnered with the Global Polio Eradication Initiative, the World Health Organization, and the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund to mobilize a surge team of personnel and resources to vaccinate all 2.9 million Malawian children aged under 5 years, WHO reported in a news release.
The first of four sequential campaigns began on March 20 and expanded on March 24 to neighboring Mozambique, Tanzania, and Zambia. The multinational, multiagency effort aims to include Zimbabwean children as well and deliver over 80 million supplemental doses of bivalent oral polio vaccines to over 23 million children in these five countries by July.
Because it takes multiple polio vaccine doses to become fully immunized, the children are expected to receive four rounds of vaccine regardless of their vaccination history.
“It is important to conduct the campaigns now to boost the immunity of our children,” Annie Chauma-Mwale, MBBS, MPH, the chief medical officer of epidemiology and surveillance in Malawi’s Ministry of Health in Lilongwe, said in an interview. “Polio is not only a medical issue. Polio is also a socioeconomic issue with long-term impacts on the child, the country, and the globe.
“In Malawi, we are using our community health and health care facility structures to ensure we do not miss any eligible child,” explained Dr. Chauma-Mwale, who is also the deputy incident manager of the poliovirus outbreak response. “We aim to play our role in the global eradication of polio by protecting the vulnerable and curtailing any potential transmission as early as possible.”
Of the three variants of wild, naturally occurring poliovirus, types 2 and 3 have been eradicated, but wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1) remains endemic in Afghanistan and Pakistan.
As reported recently by this news organization, the girl in Malawi was infected with a WPV1 strain that had been circulating for years in Pakistan’s Sindh Province.
Malawi’s most recent clinically confirmed WPV1 case was reported in 1992, and this is the first WPV1 case detected in Africa since 2016. The continent was declared free of indigenous wild polio in 2020 and is still considered free of wild poliovirus because the child’s illness was imported from elsewhere.
The 3-year-old girl developed acute flaccid paralysis in November 2021. In February 2022, virus from her stool was sequenced by the National Institute of Communicable Disease in South Africa and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. On Feb. 16, Malawi was notified of the case, which was genetically linked to a sequence detected in Sindh Province around 2 years earlier.
‘Do not ignore polio’
Within 24 hours, the Government of Malawi declared a public health emergency and activated the national Emergency Operations Centre. Within 72 hours, the GPEI rapid response team arrived in the country. The Ministry of Health partnered with GPEI, WHO, and UNICEF to mobilize the campaign and begin vaccinating children on March 20.
‘’We rely on clinicians to support the surveillance of polio through case searches, both active and passive,” Mike Nenani Chisema, MBBS, MPH, the program manager of the expanded program on immunization and the polio response operations manager in Malawi’s Ministry of Health, said in an interview.
He noted that the young girl was diagnosed correctly and millions of children are now being protected against the disease, thanks to the acumen of one hospital clinician.
“Remember, we still have polio in some countries, and every country is at risk,” he cautioned. “Don’t forget to look for the obvious and do not ignore polio, regardless of economic status.’’
According to GPEI, all countries – especially those with weak immunization and other public health programs whose residents trade or travel to and from endemic countries – are at risk for imported polio.
Anita Gupta, DO, MPP, PharmD, an adjunct assistant professor of anesthesiology and critical care medicine and pain medicine at the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said that she welcomes this effort.
“Given the decades of published evidence and understanding on the vaccine’s safety and efficacy, this program in Malawi is the right step to take,” Gupta, who is not involved in the campaigns, said in an interview. “Polio is preventable, and acting now will prevent spread later.”
Dr. Chauma-Mwale and Dr. Chisema are employees of Malawi’s Ministry of Health. Dr. Gupta disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Senate approves bill to ban crib bumpers
The Senate on Mar. 23 approved a bill to ban the sale of padded crib bumpers, which have been deemed risky by public health experts.
The Safe Cribs Act, introduced by Sen. Rob Portman (R-Ohio) and Sen. Tammy Duckworth (D-Ill.), would prohibit making and distributing bumpers – soft pads made to protect babies from hard sides of cribs – which have been found to increase suffocation risk.
The bill will now head to the House of Representatives.
According to data from the Consumer Product Safety Commission, 107 babies died in cribs with bumpers between 1990 and 2016, and 282 nonfatal incidents with bumpers were reported, including near-misses for strangulation and suffocation.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends keeping babies’ cribs free of any objects, including bumpers.
Despite this, bumpers are still widely sold by retailers.
“The fact that these deadly products can still be found on shelves across the country is extremely confusing to new parents who don’t believe stores would be selling them if they were truly dangerous to babies,” Sen. Duckworth said in a statement.
A 2020 survey released by Johns Hopkins University found that many parents were unaware of the dangers posed by crib bumpers and assumed they would be removed from stores if found unsafe.
Maryland banned the sale of bumpers in 2013, followed by Ohio in 2017. Chicago became the first city to ban them in 2011.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Senate on Mar. 23 approved a bill to ban the sale of padded crib bumpers, which have been deemed risky by public health experts.
The Safe Cribs Act, introduced by Sen. Rob Portman (R-Ohio) and Sen. Tammy Duckworth (D-Ill.), would prohibit making and distributing bumpers – soft pads made to protect babies from hard sides of cribs – which have been found to increase suffocation risk.
The bill will now head to the House of Representatives.
According to data from the Consumer Product Safety Commission, 107 babies died in cribs with bumpers between 1990 and 2016, and 282 nonfatal incidents with bumpers were reported, including near-misses for strangulation and suffocation.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends keeping babies’ cribs free of any objects, including bumpers.
Despite this, bumpers are still widely sold by retailers.
“The fact that these deadly products can still be found on shelves across the country is extremely confusing to new parents who don’t believe stores would be selling them if they were truly dangerous to babies,” Sen. Duckworth said in a statement.
A 2020 survey released by Johns Hopkins University found that many parents were unaware of the dangers posed by crib bumpers and assumed they would be removed from stores if found unsafe.
Maryland banned the sale of bumpers in 2013, followed by Ohio in 2017. Chicago became the first city to ban them in 2011.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Senate on Mar. 23 approved a bill to ban the sale of padded crib bumpers, which have been deemed risky by public health experts.
The Safe Cribs Act, introduced by Sen. Rob Portman (R-Ohio) and Sen. Tammy Duckworth (D-Ill.), would prohibit making and distributing bumpers – soft pads made to protect babies from hard sides of cribs – which have been found to increase suffocation risk.
The bill will now head to the House of Representatives.
According to data from the Consumer Product Safety Commission, 107 babies died in cribs with bumpers between 1990 and 2016, and 282 nonfatal incidents with bumpers were reported, including near-misses for strangulation and suffocation.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends keeping babies’ cribs free of any objects, including bumpers.
Despite this, bumpers are still widely sold by retailers.
“The fact that these deadly products can still be found on shelves across the country is extremely confusing to new parents who don’t believe stores would be selling them if they were truly dangerous to babies,” Sen. Duckworth said in a statement.
A 2020 survey released by Johns Hopkins University found that many parents were unaware of the dangers posed by crib bumpers and assumed they would be removed from stores if found unsafe.
Maryland banned the sale of bumpers in 2013, followed by Ohio in 2017. Chicago became the first city to ban them in 2011.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Neonatal hypoglycemia doesn’t affect childhood academics
Children at risk of neonatal hypoglycemia who were screened and treated if needed showed no difference in educational achievement from controls at age 9-10 years, based on data from 480 children.
Previous studies have shown an increased risk of poor executive and visual-motor function in children with neonatal hypoglycemia, but the effect on later childhood academic performance remains unclear, wrote Rajesh Shah, PhD, of the University of Auckland, New Zealand, and colleagues.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA, the researchers enrolled moderate to late preterm and term infants born at increased risk for hypoglycemia; those with episodes of hypoglycemia were treated to maintain a blood glucose concentration of at least 47 mg/dL.
The study population was enrolled between 2006 and 2010 at a regional perinatal center in New Zealand, and their educational achievement was assessed 9-10 years later. The primary outcome of low educational achievement was defined as performing below the normal curriculum level in standardized tests of reading comprehension or math. The researchers also identified 47 secondary outcomes related to executive function, visual-motor function, psychosocial adaptation, and general health.
Rates of low educational achievement were not significantly different for children with and without neonatal hypoglycemia (47% vs. 48%, adjusted risk ratio 0.95).
No significant differences appeared between the two groups for any secondary outcomes, including reading comprehension, math, behavior manifestations of executive function, fine motor function, autism traits, and overall well-being, the researchers noted.
However, children with neonatal hypoglycemia were significantly less likely to be rated as below or well below reading curriculum level by teachers compared to those without neonatal hypoglycemia (24% vs. 31%).
The researchers cited a previous study of the same patient cohort at age 4.5 years, which suggested an association between adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes and infant hypoglycemia. However, the reason this association did not persist at age 9-10 years remains unclear, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Early disturbances in brain development may have diminishing effects over time due to neuroplasticity, that is, reorganization of neural networks, or delayed maturation with mid-childhood catch-up in neurocognitive function,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on several measures of cognition, notably processing speed, and a lack of adjustment for intelligence quotient at age 4.5 years, the lack of data on any treatment for developmental impairment, and the inclusion of a population with well-managed hypoglycemia, the researchers said.
However, the results were strengthened by having a sample size large enough to detect associations, the prospective design, and the accurate measure of neonatal glycemic exposure, they said. Although the results suggest that at-risk children reach similar endpoints by the end of primary school, “efforts to prevent and optimize adverse pregnancy conditions remain important, and developmental surveillance after birth should be considered for at-risk infants,” they concluded.
In a related study published in JAMA, Taygen Edwards and colleagues found that prophylactic oral dextrose gel had no significant effect on neurosensory function.
The study, a prospective follow-up of a multicenter randomized trial, included 1,197 later preterm or term infants deemed at risk for neonatal hypoglycemia. The infants (49% of whom were female) were randomized to prophylactic 40% dextrose gel or a placebo, massaged into the buccal mucosa at 1 hour after birth.
The primary outcome was neurosensory impairment at 2 years of age, which was assessed by neurologic examination, parent-reported medical questionnaires, Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, Third Edition (Bayley-III), performance-based executive function, Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function–Preschool Version, motion coherence thresholds, growth, and body composition.
At 2 years of age, the prevalence of neurosensory impairment was 21% and 19%, respectively, in infants randomized to prophylactic oral dextrose gel and placebo, a nonsignificant difference. No differences between the two groups were noted for cognitive and language delays, or low performance-based overall executive function. However, infants randomized to dextrose gel had significantly higher risk of motor delay compared to placebo (2.5% vs. 0.7%) and significantly lower Bayley-III composite scores for cognitive, language, and motor performance.
No significant differences were noted between the groups in the areas of moderate or severe neurosensory impairment, hearing impairment, cerebral palsy, developmental delay, above-average development, socioemotional and adaptive behavior, questionnaire-based executive function, low visual processing, history of seizures, allergic and infectious diseases, growth, and body composition.
The results are consistent with previous studies on the safety of dextrose gel, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, the absolute difference of 7% in the primary outcome may be clinically important, they noted. “Caution is warranted before using prophylactic dextrose gel,” they said.
The researchers noted the results of a dose-finding trial that suggested improved scores on language, executive function, and motor skills in unadjusted analysis with higher doses of dextrose gel, but the reason for these findings remains unknown, they said.
The study findings were limited by the potential underpowering to detect small, but significant differences, and possible lack of generalizability because the majority of the participants were children of mothers with diabetes.
The results were strengthened by the high follow-up rate and comprehensive assessments, and highlight the need for additional research with longer follow-up, the researchers said.
Findings fuel further exploration
Although hypoglycemia is common in newborns, its management and potential outcomes remain subjects for debate, Paul J. Rozance, MD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, wrote in an editorial accompanying both studies.
“Often, the same features that increase the risk of hypoglycemia in newborns also increase the risk for poor outcomes independent of hypoglycemia,” he said.
The study by Shah and colleagues was not a randomized trial of a specific management strategy, Dr. Rozance noted. However, the high rate of low educational attainment in children not exposed to dextrose gel emphasizes the need for more effective management of infant hypoglycemia, he said. “The findings also suggest that antenatal conditions that are associated with increased risk of hypoglycemia among newborns are associated with increased risk for impaired neurodevelopment and educational achievement, independent of neonatal hypoglycemia,” he said. The study findings contrast with those of an earlier study showing low academic achievement association with early transient hypoglycemia, which could argue for earlier intervention, he noted.
The study by Edwards and colleagues addressed the potential value of dextrose gel as an early intervention to prevent neonatal hypoglycemia, said Dr. Rozance.
“The 95% CI for the primary outcome of neurosensory impairment included up to a 7% increased risk for neurosensory impairment in the prophylactic dextrose gel group. The 7% increased risk was defined by the investigators as potentially clinically important, and the study may have been underpowered to detect small differences in the primary outcome,” he wrote.
Although the reasons for adverse outcomes in children given prophylactic dextrose gel remain unclear, “incorporation of prophylactic dextrose gel into clinical practice should await further research,” he said.
Regarding such research, Dr. Rozance proposed an “ideal study,” that would “randomize newborns with hypoglycemia to treatment or no treatment, although equipoise and ethical support for such a study are lacking. Another strategy would be to randomize newborns with hypoglycemia to receive low- or high-treatment glucose concentration goals,” he noted.
The relationship between hypoglycemia and impaired neurodevelopment is yet to be determined, but the two studies provide new evidence for the clinical importance and need for management of neonatal hypoglycemia and subsequent neurodevelopmental outcomes, he concluded.
The study by Shah and colleagues was supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand and the Maurice and Phyllis Paykel Trust. Dr. Shah disclosed a doctoral fellowship from the University of Auckland. The study by Edwards and colleagues was supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health. Ms. Edwards had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Rozance disclosed receiving a StatStrip from Nova Biomedical for use in his laboratory.
Children at risk of neonatal hypoglycemia who were screened and treated if needed showed no difference in educational achievement from controls at age 9-10 years, based on data from 480 children.
Previous studies have shown an increased risk of poor executive and visual-motor function in children with neonatal hypoglycemia, but the effect on later childhood academic performance remains unclear, wrote Rajesh Shah, PhD, of the University of Auckland, New Zealand, and colleagues.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA, the researchers enrolled moderate to late preterm and term infants born at increased risk for hypoglycemia; those with episodes of hypoglycemia were treated to maintain a blood glucose concentration of at least 47 mg/dL.
The study population was enrolled between 2006 and 2010 at a regional perinatal center in New Zealand, and their educational achievement was assessed 9-10 years later. The primary outcome of low educational achievement was defined as performing below the normal curriculum level in standardized tests of reading comprehension or math. The researchers also identified 47 secondary outcomes related to executive function, visual-motor function, psychosocial adaptation, and general health.
Rates of low educational achievement were not significantly different for children with and without neonatal hypoglycemia (47% vs. 48%, adjusted risk ratio 0.95).
No significant differences appeared between the two groups for any secondary outcomes, including reading comprehension, math, behavior manifestations of executive function, fine motor function, autism traits, and overall well-being, the researchers noted.
However, children with neonatal hypoglycemia were significantly less likely to be rated as below or well below reading curriculum level by teachers compared to those without neonatal hypoglycemia (24% vs. 31%).
The researchers cited a previous study of the same patient cohort at age 4.5 years, which suggested an association between adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes and infant hypoglycemia. However, the reason this association did not persist at age 9-10 years remains unclear, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Early disturbances in brain development may have diminishing effects over time due to neuroplasticity, that is, reorganization of neural networks, or delayed maturation with mid-childhood catch-up in neurocognitive function,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on several measures of cognition, notably processing speed, and a lack of adjustment for intelligence quotient at age 4.5 years, the lack of data on any treatment for developmental impairment, and the inclusion of a population with well-managed hypoglycemia, the researchers said.
However, the results were strengthened by having a sample size large enough to detect associations, the prospective design, and the accurate measure of neonatal glycemic exposure, they said. Although the results suggest that at-risk children reach similar endpoints by the end of primary school, “efforts to prevent and optimize adverse pregnancy conditions remain important, and developmental surveillance after birth should be considered for at-risk infants,” they concluded.
In a related study published in JAMA, Taygen Edwards and colleagues found that prophylactic oral dextrose gel had no significant effect on neurosensory function.
The study, a prospective follow-up of a multicenter randomized trial, included 1,197 later preterm or term infants deemed at risk for neonatal hypoglycemia. The infants (49% of whom were female) were randomized to prophylactic 40% dextrose gel or a placebo, massaged into the buccal mucosa at 1 hour after birth.
The primary outcome was neurosensory impairment at 2 years of age, which was assessed by neurologic examination, parent-reported medical questionnaires, Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, Third Edition (Bayley-III), performance-based executive function, Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function–Preschool Version, motion coherence thresholds, growth, and body composition.
At 2 years of age, the prevalence of neurosensory impairment was 21% and 19%, respectively, in infants randomized to prophylactic oral dextrose gel and placebo, a nonsignificant difference. No differences between the two groups were noted for cognitive and language delays, or low performance-based overall executive function. However, infants randomized to dextrose gel had significantly higher risk of motor delay compared to placebo (2.5% vs. 0.7%) and significantly lower Bayley-III composite scores for cognitive, language, and motor performance.
No significant differences were noted between the groups in the areas of moderate or severe neurosensory impairment, hearing impairment, cerebral palsy, developmental delay, above-average development, socioemotional and adaptive behavior, questionnaire-based executive function, low visual processing, history of seizures, allergic and infectious diseases, growth, and body composition.
The results are consistent with previous studies on the safety of dextrose gel, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, the absolute difference of 7% in the primary outcome may be clinically important, they noted. “Caution is warranted before using prophylactic dextrose gel,” they said.
The researchers noted the results of a dose-finding trial that suggested improved scores on language, executive function, and motor skills in unadjusted analysis with higher doses of dextrose gel, but the reason for these findings remains unknown, they said.
The study findings were limited by the potential underpowering to detect small, but significant differences, and possible lack of generalizability because the majority of the participants were children of mothers with diabetes.
The results were strengthened by the high follow-up rate and comprehensive assessments, and highlight the need for additional research with longer follow-up, the researchers said.
Findings fuel further exploration
Although hypoglycemia is common in newborns, its management and potential outcomes remain subjects for debate, Paul J. Rozance, MD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, wrote in an editorial accompanying both studies.
“Often, the same features that increase the risk of hypoglycemia in newborns also increase the risk for poor outcomes independent of hypoglycemia,” he said.
The study by Shah and colleagues was not a randomized trial of a specific management strategy, Dr. Rozance noted. However, the high rate of low educational attainment in children not exposed to dextrose gel emphasizes the need for more effective management of infant hypoglycemia, he said. “The findings also suggest that antenatal conditions that are associated with increased risk of hypoglycemia among newborns are associated with increased risk for impaired neurodevelopment and educational achievement, independent of neonatal hypoglycemia,” he said. The study findings contrast with those of an earlier study showing low academic achievement association with early transient hypoglycemia, which could argue for earlier intervention, he noted.
The study by Edwards and colleagues addressed the potential value of dextrose gel as an early intervention to prevent neonatal hypoglycemia, said Dr. Rozance.
“The 95% CI for the primary outcome of neurosensory impairment included up to a 7% increased risk for neurosensory impairment in the prophylactic dextrose gel group. The 7% increased risk was defined by the investigators as potentially clinically important, and the study may have been underpowered to detect small differences in the primary outcome,” he wrote.
Although the reasons for adverse outcomes in children given prophylactic dextrose gel remain unclear, “incorporation of prophylactic dextrose gel into clinical practice should await further research,” he said.
Regarding such research, Dr. Rozance proposed an “ideal study,” that would “randomize newborns with hypoglycemia to treatment or no treatment, although equipoise and ethical support for such a study are lacking. Another strategy would be to randomize newborns with hypoglycemia to receive low- or high-treatment glucose concentration goals,” he noted.
The relationship between hypoglycemia and impaired neurodevelopment is yet to be determined, but the two studies provide new evidence for the clinical importance and need for management of neonatal hypoglycemia and subsequent neurodevelopmental outcomes, he concluded.
The study by Shah and colleagues was supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand and the Maurice and Phyllis Paykel Trust. Dr. Shah disclosed a doctoral fellowship from the University of Auckland. The study by Edwards and colleagues was supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health. Ms. Edwards had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Rozance disclosed receiving a StatStrip from Nova Biomedical for use in his laboratory.
Children at risk of neonatal hypoglycemia who were screened and treated if needed showed no difference in educational achievement from controls at age 9-10 years, based on data from 480 children.
Previous studies have shown an increased risk of poor executive and visual-motor function in children with neonatal hypoglycemia, but the effect on later childhood academic performance remains unclear, wrote Rajesh Shah, PhD, of the University of Auckland, New Zealand, and colleagues.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA, the researchers enrolled moderate to late preterm and term infants born at increased risk for hypoglycemia; those with episodes of hypoglycemia were treated to maintain a blood glucose concentration of at least 47 mg/dL.
The study population was enrolled between 2006 and 2010 at a regional perinatal center in New Zealand, and their educational achievement was assessed 9-10 years later. The primary outcome of low educational achievement was defined as performing below the normal curriculum level in standardized tests of reading comprehension or math. The researchers also identified 47 secondary outcomes related to executive function, visual-motor function, psychosocial adaptation, and general health.
Rates of low educational achievement were not significantly different for children with and without neonatal hypoglycemia (47% vs. 48%, adjusted risk ratio 0.95).
No significant differences appeared between the two groups for any secondary outcomes, including reading comprehension, math, behavior manifestations of executive function, fine motor function, autism traits, and overall well-being, the researchers noted.
However, children with neonatal hypoglycemia were significantly less likely to be rated as below or well below reading curriculum level by teachers compared to those without neonatal hypoglycemia (24% vs. 31%).
The researchers cited a previous study of the same patient cohort at age 4.5 years, which suggested an association between adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes and infant hypoglycemia. However, the reason this association did not persist at age 9-10 years remains unclear, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Early disturbances in brain development may have diminishing effects over time due to neuroplasticity, that is, reorganization of neural networks, or delayed maturation with mid-childhood catch-up in neurocognitive function,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on several measures of cognition, notably processing speed, and a lack of adjustment for intelligence quotient at age 4.5 years, the lack of data on any treatment for developmental impairment, and the inclusion of a population with well-managed hypoglycemia, the researchers said.
However, the results were strengthened by having a sample size large enough to detect associations, the prospective design, and the accurate measure of neonatal glycemic exposure, they said. Although the results suggest that at-risk children reach similar endpoints by the end of primary school, “efforts to prevent and optimize adverse pregnancy conditions remain important, and developmental surveillance after birth should be considered for at-risk infants,” they concluded.
In a related study published in JAMA, Taygen Edwards and colleagues found that prophylactic oral dextrose gel had no significant effect on neurosensory function.
The study, a prospective follow-up of a multicenter randomized trial, included 1,197 later preterm or term infants deemed at risk for neonatal hypoglycemia. The infants (49% of whom were female) were randomized to prophylactic 40% dextrose gel or a placebo, massaged into the buccal mucosa at 1 hour after birth.
The primary outcome was neurosensory impairment at 2 years of age, which was assessed by neurologic examination, parent-reported medical questionnaires, Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, Third Edition (Bayley-III), performance-based executive function, Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function–Preschool Version, motion coherence thresholds, growth, and body composition.
At 2 years of age, the prevalence of neurosensory impairment was 21% and 19%, respectively, in infants randomized to prophylactic oral dextrose gel and placebo, a nonsignificant difference. No differences between the two groups were noted for cognitive and language delays, or low performance-based overall executive function. However, infants randomized to dextrose gel had significantly higher risk of motor delay compared to placebo (2.5% vs. 0.7%) and significantly lower Bayley-III composite scores for cognitive, language, and motor performance.
No significant differences were noted between the groups in the areas of moderate or severe neurosensory impairment, hearing impairment, cerebral palsy, developmental delay, above-average development, socioemotional and adaptive behavior, questionnaire-based executive function, low visual processing, history of seizures, allergic and infectious diseases, growth, and body composition.
The results are consistent with previous studies on the safety of dextrose gel, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, the absolute difference of 7% in the primary outcome may be clinically important, they noted. “Caution is warranted before using prophylactic dextrose gel,” they said.
The researchers noted the results of a dose-finding trial that suggested improved scores on language, executive function, and motor skills in unadjusted analysis with higher doses of dextrose gel, but the reason for these findings remains unknown, they said.
The study findings were limited by the potential underpowering to detect small, but significant differences, and possible lack of generalizability because the majority of the participants were children of mothers with diabetes.
The results were strengthened by the high follow-up rate and comprehensive assessments, and highlight the need for additional research with longer follow-up, the researchers said.
Findings fuel further exploration
Although hypoglycemia is common in newborns, its management and potential outcomes remain subjects for debate, Paul J. Rozance, MD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, wrote in an editorial accompanying both studies.
“Often, the same features that increase the risk of hypoglycemia in newborns also increase the risk for poor outcomes independent of hypoglycemia,” he said.
The study by Shah and colleagues was not a randomized trial of a specific management strategy, Dr. Rozance noted. However, the high rate of low educational attainment in children not exposed to dextrose gel emphasizes the need for more effective management of infant hypoglycemia, he said. “The findings also suggest that antenatal conditions that are associated with increased risk of hypoglycemia among newborns are associated with increased risk for impaired neurodevelopment and educational achievement, independent of neonatal hypoglycemia,” he said. The study findings contrast with those of an earlier study showing low academic achievement association with early transient hypoglycemia, which could argue for earlier intervention, he noted.
The study by Edwards and colleagues addressed the potential value of dextrose gel as an early intervention to prevent neonatal hypoglycemia, said Dr. Rozance.
“The 95% CI for the primary outcome of neurosensory impairment included up to a 7% increased risk for neurosensory impairment in the prophylactic dextrose gel group. The 7% increased risk was defined by the investigators as potentially clinically important, and the study may have been underpowered to detect small differences in the primary outcome,” he wrote.
Although the reasons for adverse outcomes in children given prophylactic dextrose gel remain unclear, “incorporation of prophylactic dextrose gel into clinical practice should await further research,” he said.
Regarding such research, Dr. Rozance proposed an “ideal study,” that would “randomize newborns with hypoglycemia to treatment or no treatment, although equipoise and ethical support for such a study are lacking. Another strategy would be to randomize newborns with hypoglycemia to receive low- or high-treatment glucose concentration goals,” he noted.
The relationship between hypoglycemia and impaired neurodevelopment is yet to be determined, but the two studies provide new evidence for the clinical importance and need for management of neonatal hypoglycemia and subsequent neurodevelopmental outcomes, he concluded.
The study by Shah and colleagues was supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand and the Maurice and Phyllis Paykel Trust. Dr. Shah disclosed a doctoral fellowship from the University of Auckland. The study by Edwards and colleagues was supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health. Ms. Edwards had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Rozance disclosed receiving a StatStrip from Nova Biomedical for use in his laboratory.
FROM JAMA
Children and COVID: The long goodbye continues
COVID-19 continues to be a diminishing issue for U.S. children, as the number of new cases declined for the ninth consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. The most recently infected children brought the total number of COVID-19 cases to just over 12.8 million since the pandemic began.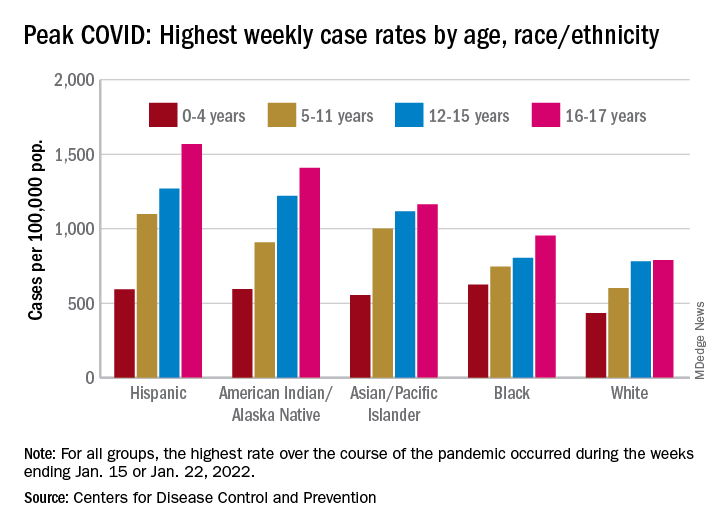
Other measures of COVID occurrence in children, such as hospital admissions and emergency department visits, also followed recent downward trends, although the sizes of the declines are beginning to decrease. Admissions dropped by 13.3% during the week ending March 26, but that followed declines of 25%, 20%, 26.5% and 24.4% for the 4 previous weeks, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.
The slowdown in ED visits started a couple of weeks earlier, but the decline is still ongoing. As of March 25, ED visits with a confirmed COVID diagnosis represented just 0.4% of all visits for children aged 0-11 years, down from 1.1% on Feb. 25 and a peak of 14.3% on Jan. 15. For children aged 12-15, the latest figure is just 0.2%, compared with 0.5% on Feb. 25 and a peak of 14.3% on Jan. 9, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
Although he was speaking of the nation as a whole and not specifically of children, Anthony Fauci, MD, the director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, recently told the Washington Post that, “unless something changes dramatically,” another major surge isn’t on the horizon.
That sentiment, however, was not entirely shared by Moderna’s chief medical officer, Paul Burton, MD, PhD. In an interview with WebMD, he said that another COVID wave is inevitable and that it’s too soon to dismantle the vaccine infrastructure: “We’ve come so far. We’ve put so much into this to now take our foot off the gas. I think it would be a mistake for public health worldwide.”
Disparities during the Omicron surge
As the country puts Omicron in its rear view mirror, a quick look back at the CDC data shows some differences in how children were affected. At the surge’s peak in early to mid-January, Hispanic children were the most likely to get COVID-19, with incidence highest in the older groups. (See graph.)
At their peak week of Jan. 2-8, Hispanic children aged 16-17 years had a COVID rate of 1,568 cases per 100,000 population, versus 790 per 100,000 for White children, whose peak occurred a week later, from Jan. 9 to 15. Hispanic children aged 5-11 (1,098 per 100,000) and 12-15 (1,269 per 100,000) also had the highest recorded rates of the largest racial/ethnic groups, while Black children had the highest one-week rate, 625 per 100,000, among the 0- to 4-year-olds, according to the CDC.
COVID-19 continues to be a diminishing issue for U.S. children, as the number of new cases declined for the ninth consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. The most recently infected children brought the total number of COVID-19 cases to just over 12.8 million since the pandemic began.
Other measures of COVID occurrence in children, such as hospital admissions and emergency department visits, also followed recent downward trends, although the sizes of the declines are beginning to decrease. Admissions dropped by 13.3% during the week ending March 26, but that followed declines of 25%, 20%, 26.5% and 24.4% for the 4 previous weeks, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.
The slowdown in ED visits started a couple of weeks earlier, but the decline is still ongoing. As of March 25, ED visits with a confirmed COVID diagnosis represented just 0.4% of all visits for children aged 0-11 years, down from 1.1% on Feb. 25 and a peak of 14.3% on Jan. 15. For children aged 12-15, the latest figure is just 0.2%, compared with 0.5% on Feb. 25 and a peak of 14.3% on Jan. 9, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
Although he was speaking of the nation as a whole and not specifically of children, Anthony Fauci, MD, the director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, recently told the Washington Post that, “unless something changes dramatically,” another major surge isn’t on the horizon.
That sentiment, however, was not entirely shared by Moderna’s chief medical officer, Paul Burton, MD, PhD. In an interview with WebMD, he said that another COVID wave is inevitable and that it’s too soon to dismantle the vaccine infrastructure: “We’ve come so far. We’ve put so much into this to now take our foot off the gas. I think it would be a mistake for public health worldwide.”
Disparities during the Omicron surge
As the country puts Omicron in its rear view mirror, a quick look back at the CDC data shows some differences in how children were affected. At the surge’s peak in early to mid-January, Hispanic children were the most likely to get COVID-19, with incidence highest in the older groups. (See graph.)
At their peak week of Jan. 2-8, Hispanic children aged 16-17 years had a COVID rate of 1,568 cases per 100,000 population, versus 790 per 100,000 for White children, whose peak occurred a week later, from Jan. 9 to 15. Hispanic children aged 5-11 (1,098 per 100,000) and 12-15 (1,269 per 100,000) also had the highest recorded rates of the largest racial/ethnic groups, while Black children had the highest one-week rate, 625 per 100,000, among the 0- to 4-year-olds, according to the CDC.
COVID-19 continues to be a diminishing issue for U.S. children, as the number of new cases declined for the ninth consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. The most recently infected children brought the total number of COVID-19 cases to just over 12.8 million since the pandemic began.
Other measures of COVID occurrence in children, such as hospital admissions and emergency department visits, also followed recent downward trends, although the sizes of the declines are beginning to decrease. Admissions dropped by 13.3% during the week ending March 26, but that followed declines of 25%, 20%, 26.5% and 24.4% for the 4 previous weeks, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.
The slowdown in ED visits started a couple of weeks earlier, but the decline is still ongoing. As of March 25, ED visits with a confirmed COVID diagnosis represented just 0.4% of all visits for children aged 0-11 years, down from 1.1% on Feb. 25 and a peak of 14.3% on Jan. 15. For children aged 12-15, the latest figure is just 0.2%, compared with 0.5% on Feb. 25 and a peak of 14.3% on Jan. 9, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
Although he was speaking of the nation as a whole and not specifically of children, Anthony Fauci, MD, the director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, recently told the Washington Post that, “unless something changes dramatically,” another major surge isn’t on the horizon.
That sentiment, however, was not entirely shared by Moderna’s chief medical officer, Paul Burton, MD, PhD. In an interview with WebMD, he said that another COVID wave is inevitable and that it’s too soon to dismantle the vaccine infrastructure: “We’ve come so far. We’ve put so much into this to now take our foot off the gas. I think it would be a mistake for public health worldwide.”
Disparities during the Omicron surge
As the country puts Omicron in its rear view mirror, a quick look back at the CDC data shows some differences in how children were affected. At the surge’s peak in early to mid-January, Hispanic children were the most likely to get COVID-19, with incidence highest in the older groups. (See graph.)
At their peak week of Jan. 2-8, Hispanic children aged 16-17 years had a COVID rate of 1,568 cases per 100,000 population, versus 790 per 100,000 for White children, whose peak occurred a week later, from Jan. 9 to 15. Hispanic children aged 5-11 (1,098 per 100,000) and 12-15 (1,269 per 100,000) also had the highest recorded rates of the largest racial/ethnic groups, while Black children had the highest one-week rate, 625 per 100,000, among the 0- to 4-year-olds, according to the CDC.
As FDA OKs another COVID booster, some experts question need
, even though many top infectious disease experts questioned the need before the agency’s decision.
The FDA granted emergency use authorization for both Pfizer and Moderna to offer the second booster – and fourth shot overall – for adults over 50 as well as those over 18 with compromised immune systems.
The Centers for Control and Prevention must still sign off before those doses start reaching American arms. That approval could come at any time.
“The general consensus, certainly the CDC’s consensus, is that the current vaccines are still really quite effective against Omicron and this new BA.2 variant in keeping people out of the hospital, and preventing the development of severe disease,” William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University in Nashville said prior to the FDA’s announcement March 29.
Of the 217.4 million Americans who are “fully vaccinated,” i.e., received two doses of either Pfizer or Moderna’s vaccines or one dose of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, only 45% have also received a booster shot, according to the CDC.
“Given that, there’s no need at the moment for the general population to get a fourth inoculation,” Dr. Schaffner says. “Our current focus ought to be on making sure that as many people as possible get that [first] booster who are eligible.”
Monica Gandhi, MD, an infectious disease specialist at the University of California, San Francisco, agreed that another booster for everyone was unnecessary. The only people who would need a fourth shot (or third, if they had the Johnson & Johnson vaccine initially) are those over age 65 or 70 years, Dr. Gandhi says.
“Older people need those antibodies up high because they’re more susceptible to severe breakthroughs,” she said, also before the latest development.
To boost or not to boost
Daniel Kuritzkes, MD, chief of infectious diseases at Brigham & Women’s Hospital in Boston, said the timing of a booster and who should be eligible depends on what the nation is trying to achieve with its vaccination strategy.
“Is the goal to prevent any symptomatic infection with COVID-19, is the goal to prevent the spread of COVID-19, or is the goal to prevent severe disease that requires hospitalization?” asked Dr. Kuritzkes.
The current vaccine — with a booster — has prevented severe disease, he said.
An Israeli study showed, for instance, that a third Pfizer dose was 93% effective against hospitalization, 92% effective against severe illness, and 81% effective against death.
A just-published study in the New England Journal of Medicine found that a booster of the Pfizer vaccine was 95% effective against COVID-19 infection and that it did not raise any new safety issues.
A small Israeli study, also published in NEJM, of a fourth Pfizer dose given to health care workers found that it prevented symptomatic infection and illness, but that it was much less effective than previous doses — maybe 65% effective against symptomatic illness, the authors write.
Giving Americans another booster now — which has been shown to lose some effectiveness after about 4 months — means it might not offer protection this fall and winter, when there could be a seasonal surge of the virus, Dr. Kuritzkes says.
And, even if people receive boosters every few months, they are still likely to get a mild respiratory virus infection, he said.
“I’m pretty convinced that we cannot boost ourselves out of this pandemic,” said Dr. Kuritzkes. “We need to first of all ensure there’s global immunization so that all the people who have not been vaccinated at all get vaccinated. That’s far more important than boosting people a fourth time.”
Booster confusion
The April 6 FDA meeting of the agency’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee comes as the two major COVID vaccine makers — Pfizer and Moderna — have applied for emergency use authorization for an additional booster.
Pfizer had asked for authorization for a fourth shot in patients over age 65 years, while Moderna wanted a booster to be available to all Americans over 18. The FDA instead granted authorization to both companies for those over 50 and anyone 18 or older who is immunocompromised.
What this means for the committee’s April 6 meeting is not clear. The original agenda says the committee will consider the evidence on safety and effectiveness of the additional vaccine doses and discuss how to set up a process — similar to that used for the influenza vaccine — to be able to determine the makeup of COVID vaccines as new variants emerge. That could lay the groundwork for an annual COVID shot, if needed.
The FDA advisers will not make recommendations nor vote on whether — and which — Americans should get a COVID booster. That is the job of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The last time a booster was considered, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, overrode the committee and recommended that all Americans — not just older individuals — get an additional COVID shot, which became the first booster.
That past action worries Dr. Gandhi, who calls it confusing, and says it may have contributed to the fact that less than half of Americans have since chosen to get a booster.
Dr. Schaffner says he expects the FDA to authorize emergency use for fourth doses of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, but he doesn’t think the CDC committee will recommend routine use. As was seen before, however, the CDC director does not have to follow the committee’s advice.
The members of ACIP “might be more conservative or narrower in scope in terms of recommending who needs to be boosted and when boosting is appropriate,” Dr. Kuritzkes says.
Dr. Gandhi says she’s concerned the FDA’s deliberations could be swayed by Moderna and Pfizer’s influence and that “pharmaceutical companies are going to have more of a say than they should in the scientific process.”
There are similar worries for Dr. Schaffner. He says he’s “a bit grumpy” that the vaccine makers have been using press releases to argue for boosters.
“Press releases are no way to make vaccine recommendations,” Dr. Schaffner said, adding that he “would advise [vaccine makers] to sit down and be quiet and let the FDA and CDC advisory committee do their thing.”
Moderna Chief Medical Officer Paul Burton, MD, however, told WebMD last week that the signs point to why a fourth shot may be needed.
“We see waning of effectiveness, antibody levels come down, and certainly effectiveness against Omicron comes down in 3 to 6 months,” Burton said. “The natural history, from what we’re seeing around the world, is that BA.2 is definitely here, it’s highly transmissible, and I think we are going to get an additional wave of BA.2 here in the United States.”
Another wave is coming, he said, and “I think there will be waning of effectiveness. We need to be prepared for that, so that’s why we need the fourth dose.”
Supply issues?
Meanwhile, the United Kingdom has begun offering boosters to anyone over 75, and Sweden’s health authority has recommended a fourth shot to people over age 80.
That puts pressure on the United States — at least on its politicians and policymakers — to, in a sense, keep up, said the infectious disease specialists.
Indeed, the White House has been keeping fourth shots in the news, warning that it is running out of money to ensure that all Americans would have access to one, if recommended.
On March 23, outgoing White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Jeff Zients said the federal government had enough vaccine for the immunocompromised to get a fourth dose “and, if authorized in the coming weeks, enough supply for fourth doses for our most vulnerable, including seniors.”
But he warned that without congressional approval of a COVID-19 funding package, “We can’t procure the necessary vaccine supply to support fourth shots for all Americans.”
Mr. Zients also noted that other countries, including Japan, Vietnam, and the Philippines had already secured future booster doses and added, “We should be securing additional supply right now.”
Dr. Schaffner says that while it would be nice to “have a booster on the shelf,” the United States needs to put more effort into creating a globally-coordinated process for ensuring that vaccines match circulating strains and that they are manufactured on a timely basis.
He says he and others “have been reminding the public that the COVID pandemic may indeed be diminishing and moving into the endemic, but that doesn’t mean COVID is over or finished or disappeared.”
Dr. Schaffner says that it may be that “perhaps we’d need a periodic reminder to our immune system to remain protected. In other words, we might have to get boosted perhaps annually like we do with influenza.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, even though many top infectious disease experts questioned the need before the agency’s decision.
The FDA granted emergency use authorization for both Pfizer and Moderna to offer the second booster – and fourth shot overall – for adults over 50 as well as those over 18 with compromised immune systems.
The Centers for Control and Prevention must still sign off before those doses start reaching American arms. That approval could come at any time.
“The general consensus, certainly the CDC’s consensus, is that the current vaccines are still really quite effective against Omicron and this new BA.2 variant in keeping people out of the hospital, and preventing the development of severe disease,” William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University in Nashville said prior to the FDA’s announcement March 29.
Of the 217.4 million Americans who are “fully vaccinated,” i.e., received two doses of either Pfizer or Moderna’s vaccines or one dose of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, only 45% have also received a booster shot, according to the CDC.
“Given that, there’s no need at the moment for the general population to get a fourth inoculation,” Dr. Schaffner says. “Our current focus ought to be on making sure that as many people as possible get that [first] booster who are eligible.”
Monica Gandhi, MD, an infectious disease specialist at the University of California, San Francisco, agreed that another booster for everyone was unnecessary. The only people who would need a fourth shot (or third, if they had the Johnson & Johnson vaccine initially) are those over age 65 or 70 years, Dr. Gandhi says.
“Older people need those antibodies up high because they’re more susceptible to severe breakthroughs,” she said, also before the latest development.
To boost or not to boost
Daniel Kuritzkes, MD, chief of infectious diseases at Brigham & Women’s Hospital in Boston, said the timing of a booster and who should be eligible depends on what the nation is trying to achieve with its vaccination strategy.
“Is the goal to prevent any symptomatic infection with COVID-19, is the goal to prevent the spread of COVID-19, or is the goal to prevent severe disease that requires hospitalization?” asked Dr. Kuritzkes.
The current vaccine — with a booster — has prevented severe disease, he said.
An Israeli study showed, for instance, that a third Pfizer dose was 93% effective against hospitalization, 92% effective against severe illness, and 81% effective against death.
A just-published study in the New England Journal of Medicine found that a booster of the Pfizer vaccine was 95% effective against COVID-19 infection and that it did not raise any new safety issues.
A small Israeli study, also published in NEJM, of a fourth Pfizer dose given to health care workers found that it prevented symptomatic infection and illness, but that it was much less effective than previous doses — maybe 65% effective against symptomatic illness, the authors write.
Giving Americans another booster now — which has been shown to lose some effectiveness after about 4 months — means it might not offer protection this fall and winter, when there could be a seasonal surge of the virus, Dr. Kuritzkes says.
And, even if people receive boosters every few months, they are still likely to get a mild respiratory virus infection, he said.
“I’m pretty convinced that we cannot boost ourselves out of this pandemic,” said Dr. Kuritzkes. “We need to first of all ensure there’s global immunization so that all the people who have not been vaccinated at all get vaccinated. That’s far more important than boosting people a fourth time.”
Booster confusion
The April 6 FDA meeting of the agency’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee comes as the two major COVID vaccine makers — Pfizer and Moderna — have applied for emergency use authorization for an additional booster.
Pfizer had asked for authorization for a fourth shot in patients over age 65 years, while Moderna wanted a booster to be available to all Americans over 18. The FDA instead granted authorization to both companies for those over 50 and anyone 18 or older who is immunocompromised.
What this means for the committee’s April 6 meeting is not clear. The original agenda says the committee will consider the evidence on safety and effectiveness of the additional vaccine doses and discuss how to set up a process — similar to that used for the influenza vaccine — to be able to determine the makeup of COVID vaccines as new variants emerge. That could lay the groundwork for an annual COVID shot, if needed.
The FDA advisers will not make recommendations nor vote on whether — and which — Americans should get a COVID booster. That is the job of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The last time a booster was considered, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, overrode the committee and recommended that all Americans — not just older individuals — get an additional COVID shot, which became the first booster.
That past action worries Dr. Gandhi, who calls it confusing, and says it may have contributed to the fact that less than half of Americans have since chosen to get a booster.
Dr. Schaffner says he expects the FDA to authorize emergency use for fourth doses of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, but he doesn’t think the CDC committee will recommend routine use. As was seen before, however, the CDC director does not have to follow the committee’s advice.
The members of ACIP “might be more conservative or narrower in scope in terms of recommending who needs to be boosted and when boosting is appropriate,” Dr. Kuritzkes says.
Dr. Gandhi says she’s concerned the FDA’s deliberations could be swayed by Moderna and Pfizer’s influence and that “pharmaceutical companies are going to have more of a say than they should in the scientific process.”
There are similar worries for Dr. Schaffner. He says he’s “a bit grumpy” that the vaccine makers have been using press releases to argue for boosters.
“Press releases are no way to make vaccine recommendations,” Dr. Schaffner said, adding that he “would advise [vaccine makers] to sit down and be quiet and let the FDA and CDC advisory committee do their thing.”
Moderna Chief Medical Officer Paul Burton, MD, however, told WebMD last week that the signs point to why a fourth shot may be needed.
“We see waning of effectiveness, antibody levels come down, and certainly effectiveness against Omicron comes down in 3 to 6 months,” Burton said. “The natural history, from what we’re seeing around the world, is that BA.2 is definitely here, it’s highly transmissible, and I think we are going to get an additional wave of BA.2 here in the United States.”
Another wave is coming, he said, and “I think there will be waning of effectiveness. We need to be prepared for that, so that’s why we need the fourth dose.”
Supply issues?
Meanwhile, the United Kingdom has begun offering boosters to anyone over 75, and Sweden’s health authority has recommended a fourth shot to people over age 80.
That puts pressure on the United States — at least on its politicians and policymakers — to, in a sense, keep up, said the infectious disease specialists.
Indeed, the White House has been keeping fourth shots in the news, warning that it is running out of money to ensure that all Americans would have access to one, if recommended.
On March 23, outgoing White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Jeff Zients said the federal government had enough vaccine for the immunocompromised to get a fourth dose “and, if authorized in the coming weeks, enough supply for fourth doses for our most vulnerable, including seniors.”
But he warned that without congressional approval of a COVID-19 funding package, “We can’t procure the necessary vaccine supply to support fourth shots for all Americans.”
Mr. Zients also noted that other countries, including Japan, Vietnam, and the Philippines had already secured future booster doses and added, “We should be securing additional supply right now.”
Dr. Schaffner says that while it would be nice to “have a booster on the shelf,” the United States needs to put more effort into creating a globally-coordinated process for ensuring that vaccines match circulating strains and that they are manufactured on a timely basis.
He says he and others “have been reminding the public that the COVID pandemic may indeed be diminishing and moving into the endemic, but that doesn’t mean COVID is over or finished or disappeared.”
Dr. Schaffner says that it may be that “perhaps we’d need a periodic reminder to our immune system to remain protected. In other words, we might have to get boosted perhaps annually like we do with influenza.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, even though many top infectious disease experts questioned the need before the agency’s decision.
The FDA granted emergency use authorization for both Pfizer and Moderna to offer the second booster – and fourth shot overall – for adults over 50 as well as those over 18 with compromised immune systems.
The Centers for Control and Prevention must still sign off before those doses start reaching American arms. That approval could come at any time.
“The general consensus, certainly the CDC’s consensus, is that the current vaccines are still really quite effective against Omicron and this new BA.2 variant in keeping people out of the hospital, and preventing the development of severe disease,” William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University in Nashville said prior to the FDA’s announcement March 29.
Of the 217.4 million Americans who are “fully vaccinated,” i.e., received two doses of either Pfizer or Moderna’s vaccines or one dose of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, only 45% have also received a booster shot, according to the CDC.
“Given that, there’s no need at the moment for the general population to get a fourth inoculation,” Dr. Schaffner says. “Our current focus ought to be on making sure that as many people as possible get that [first] booster who are eligible.”
Monica Gandhi, MD, an infectious disease specialist at the University of California, San Francisco, agreed that another booster for everyone was unnecessary. The only people who would need a fourth shot (or third, if they had the Johnson & Johnson vaccine initially) are those over age 65 or 70 years, Dr. Gandhi says.
“Older people need those antibodies up high because they’re more susceptible to severe breakthroughs,” she said, also before the latest development.
To boost or not to boost
Daniel Kuritzkes, MD, chief of infectious diseases at Brigham & Women’s Hospital in Boston, said the timing of a booster and who should be eligible depends on what the nation is trying to achieve with its vaccination strategy.
“Is the goal to prevent any symptomatic infection with COVID-19, is the goal to prevent the spread of COVID-19, or is the goal to prevent severe disease that requires hospitalization?” asked Dr. Kuritzkes.
The current vaccine — with a booster — has prevented severe disease, he said.
An Israeli study showed, for instance, that a third Pfizer dose was 93% effective against hospitalization, 92% effective against severe illness, and 81% effective against death.
A just-published study in the New England Journal of Medicine found that a booster of the Pfizer vaccine was 95% effective against COVID-19 infection and that it did not raise any new safety issues.
A small Israeli study, also published in NEJM, of a fourth Pfizer dose given to health care workers found that it prevented symptomatic infection and illness, but that it was much less effective than previous doses — maybe 65% effective against symptomatic illness, the authors write.
Giving Americans another booster now — which has been shown to lose some effectiveness after about 4 months — means it might not offer protection this fall and winter, when there could be a seasonal surge of the virus, Dr. Kuritzkes says.
And, even if people receive boosters every few months, they are still likely to get a mild respiratory virus infection, he said.
“I’m pretty convinced that we cannot boost ourselves out of this pandemic,” said Dr. Kuritzkes. “We need to first of all ensure there’s global immunization so that all the people who have not been vaccinated at all get vaccinated. That’s far more important than boosting people a fourth time.”
Booster confusion
The April 6 FDA meeting of the agency’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee comes as the two major COVID vaccine makers — Pfizer and Moderna — have applied for emergency use authorization for an additional booster.
Pfizer had asked for authorization for a fourth shot in patients over age 65 years, while Moderna wanted a booster to be available to all Americans over 18. The FDA instead granted authorization to both companies for those over 50 and anyone 18 or older who is immunocompromised.
What this means for the committee’s April 6 meeting is not clear. The original agenda says the committee will consider the evidence on safety and effectiveness of the additional vaccine doses and discuss how to set up a process — similar to that used for the influenza vaccine — to be able to determine the makeup of COVID vaccines as new variants emerge. That could lay the groundwork for an annual COVID shot, if needed.
The FDA advisers will not make recommendations nor vote on whether — and which — Americans should get a COVID booster. That is the job of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The last time a booster was considered, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, overrode the committee and recommended that all Americans — not just older individuals — get an additional COVID shot, which became the first booster.
That past action worries Dr. Gandhi, who calls it confusing, and says it may have contributed to the fact that less than half of Americans have since chosen to get a booster.
Dr. Schaffner says he expects the FDA to authorize emergency use for fourth doses of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, but he doesn’t think the CDC committee will recommend routine use. As was seen before, however, the CDC director does not have to follow the committee’s advice.
The members of ACIP “might be more conservative or narrower in scope in terms of recommending who needs to be boosted and when boosting is appropriate,” Dr. Kuritzkes says.
Dr. Gandhi says she’s concerned the FDA’s deliberations could be swayed by Moderna and Pfizer’s influence and that “pharmaceutical companies are going to have more of a say than they should in the scientific process.”
There are similar worries for Dr. Schaffner. He says he’s “a bit grumpy” that the vaccine makers have been using press releases to argue for boosters.
“Press releases are no way to make vaccine recommendations,” Dr. Schaffner said, adding that he “would advise [vaccine makers] to sit down and be quiet and let the FDA and CDC advisory committee do their thing.”
Moderna Chief Medical Officer Paul Burton, MD, however, told WebMD last week that the signs point to why a fourth shot may be needed.
“We see waning of effectiveness, antibody levels come down, and certainly effectiveness against Omicron comes down in 3 to 6 months,” Burton said. “The natural history, from what we’re seeing around the world, is that BA.2 is definitely here, it’s highly transmissible, and I think we are going to get an additional wave of BA.2 here in the United States.”
Another wave is coming, he said, and “I think there will be waning of effectiveness. We need to be prepared for that, so that’s why we need the fourth dose.”
Supply issues?
Meanwhile, the United Kingdom has begun offering boosters to anyone over 75, and Sweden’s health authority has recommended a fourth shot to people over age 80.
That puts pressure on the United States — at least on its politicians and policymakers — to, in a sense, keep up, said the infectious disease specialists.
Indeed, the White House has been keeping fourth shots in the news, warning that it is running out of money to ensure that all Americans would have access to one, if recommended.
On March 23, outgoing White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Jeff Zients said the federal government had enough vaccine for the immunocompromised to get a fourth dose “and, if authorized in the coming weeks, enough supply for fourth doses for our most vulnerable, including seniors.”
But he warned that without congressional approval of a COVID-19 funding package, “We can’t procure the necessary vaccine supply to support fourth shots for all Americans.”
Mr. Zients also noted that other countries, including Japan, Vietnam, and the Philippines had already secured future booster doses and added, “We should be securing additional supply right now.”
Dr. Schaffner says that while it would be nice to “have a booster on the shelf,” the United States needs to put more effort into creating a globally-coordinated process for ensuring that vaccines match circulating strains and that they are manufactured on a timely basis.
He says he and others “have been reminding the public that the COVID pandemic may indeed be diminishing and moving into the endemic, but that doesn’t mean COVID is over or finished or disappeared.”
Dr. Schaffner says that it may be that “perhaps we’d need a periodic reminder to our immune system to remain protected. In other words, we might have to get boosted perhaps annually like we do with influenza.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Suicide attempts in kids ages 10-12 quadrupled over 20 years
Suicide attempts spurring calls to poison control centers more than quadrupled among U.S. children aged 10-12 years from 2000 to 2020, according to research published in JAMA Pediatrics.
The reasons for the increase in suicide attempts isn’t clear from the new study, but the researchers note that popular social media networks launched during the 20-year period, and other studies have linked spending time on social media with depression in adolescence. The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in the last year the researchers looked at, also disrupted normal life and routines for children.
For all children older than age 9, the proportion of incidents in which kids ate or drank something harmful that were deemed suicide attempts increased, while those classified as misuse or abuse of potentially poisonous substances declined. Children aged 6-9 did not have an increase in suicide attempts, the study found.
“It’s a huge problem we’re seeing in [ERs]. It’s exponentially blowing up numbers across the nation,” says David Sheridan, MD, an ER pediatric doctor at the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, who led the study.
Adolescents or preteens who have attempted suicide can sit in ERs “for days or weeks” as they wait to be moved elsewhere in the hospital or to an outpatient facility for treatment, Dr. Sheridan says. The delays are not only unpleasant for the children, he says, but they also strain hospitals by leaving less space available for other patients coming to the ER.
“It’s really tough on the entire health care system, and most importantly, it’s really rough on the families who are going through a crisis,” Dr. Sheridan says. He noted that young people often attempt suicide by taking excessive quantities of common over-the-counter products found in many medicine cabinets – acetaminophen, ibuprofen, diphenhydramine – not items marked “poison.”
Twenty-year trend
The researchers examined phone calls to poison control centers about kids age 6 and up taking in potentially harmful substances from 2000-2020 recorded in the National Poison Data System, which is maintained by the American Association of Poison Control Centers.
Of more than 1.2 million total calls, 854,000 involved girls. A poison control data analyst determined if the call involved attempted suicide or the deliberate misuse or abuse of a potentially poisonous substance.
The researchers identified 1,005 deaths. About 70% of the total cases had either no effect or a minor effect on the child’s health.
Over the 20-year period, more than 90% of the calls involved children aged at least 13 years, with approximately 72,000 (5.7%) about children aged 10-12. Most calls for children 13 and older were for suicide attempts.
Suspected suicide attempts accounted for about 50% of the total calls to poison control centers among children aged 10-12 in 2000 – a figure that ballooned to 80% in 2020, the researchers found.
Both the number of calls and the proportion related to suicide attempts increased among children aged 10-12, Dr. Sheridan says. By 2020, the researchers found, poison control centers were fielding 4.5 times as many suicide-related calls among kids of this age group as they had in 2000. This jump was the largest such increase for any age group in the study, he says.
The reasons for such a large increase of suicide-related calls among preadolescents are unclear, the researchers note.
The increase became apparent around 2013, at the time many popular social media networks launched. Dr. Sheridan and his colleagues cite studies showing an association between spending more time on social media or watching television and depression in adolescence but said further research is needed to understand the root causes of this increase.
The latest study did not look specifically at the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on suicide among young people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention earlier reported a sharp rise in suicide attempts among youth during the early months of the pandemic, especially among girls aged 12-17 years. By February 2021, suicide attempts within this group had climbed by 50%, compared with 2 years earlier.
Although suicide attempts are concerning enough, deaths by suicide are even more worrisome, experts said.
The researchers’ findings are consistent with overall recent trends in youth suicide deaths, says Jeff Bridge, PhD, an epidemiologist at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus. From 2010-2020, suicide rates increased by 50% among 13- to 18-year-olds, Dr. Bridge said, and more than doubled in children aged 10-12.
The latest study captured only calls to poison control centers, so it did not count suicide attempts that did not result in a call for help. Another limitation of the study is that poison control data are not categorized by race or ethnicity, prompting Dr. Bridge to urge researchers to look specifically at the effect of race and ethnicity on these trends.
“This study supports screening for suicide risk as young as 10 years old,” Dr. Bridge says.
Dr. Sheridan agrees that prevention is essential: “The ER is where kids come when they’re in crisis. Trying to be more preventative by diagnosing or picking up on this earlier, I think, is really important.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Suicide attempts spurring calls to poison control centers more than quadrupled among U.S. children aged 10-12 years from 2000 to 2020, according to research published in JAMA Pediatrics.
The reasons for the increase in suicide attempts isn’t clear from the new study, but the researchers note that popular social media networks launched during the 20-year period, and other studies have linked spending time on social media with depression in adolescence. The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in the last year the researchers looked at, also disrupted normal life and routines for children.
For all children older than age 9, the proportion of incidents in which kids ate or drank something harmful that were deemed suicide attempts increased, while those classified as misuse or abuse of potentially poisonous substances declined. Children aged 6-9 did not have an increase in suicide attempts, the study found.
“It’s a huge problem we’re seeing in [ERs]. It’s exponentially blowing up numbers across the nation,” says David Sheridan, MD, an ER pediatric doctor at the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, who led the study.
Adolescents or preteens who have attempted suicide can sit in ERs “for days or weeks” as they wait to be moved elsewhere in the hospital or to an outpatient facility for treatment, Dr. Sheridan says. The delays are not only unpleasant for the children, he says, but they also strain hospitals by leaving less space available for other patients coming to the ER.
“It’s really tough on the entire health care system, and most importantly, it’s really rough on the families who are going through a crisis,” Dr. Sheridan says. He noted that young people often attempt suicide by taking excessive quantities of common over-the-counter products found in many medicine cabinets – acetaminophen, ibuprofen, diphenhydramine – not items marked “poison.”
Twenty-year trend
The researchers examined phone calls to poison control centers about kids age 6 and up taking in potentially harmful substances from 2000-2020 recorded in the National Poison Data System, which is maintained by the American Association of Poison Control Centers.
Of more than 1.2 million total calls, 854,000 involved girls. A poison control data analyst determined if the call involved attempted suicide or the deliberate misuse or abuse of a potentially poisonous substance.
The researchers identified 1,005 deaths. About 70% of the total cases had either no effect or a minor effect on the child’s health.
Over the 20-year period, more than 90% of the calls involved children aged at least 13 years, with approximately 72,000 (5.7%) about children aged 10-12. Most calls for children 13 and older were for suicide attempts.
Suspected suicide attempts accounted for about 50% of the total calls to poison control centers among children aged 10-12 in 2000 – a figure that ballooned to 80% in 2020, the researchers found.
Both the number of calls and the proportion related to suicide attempts increased among children aged 10-12, Dr. Sheridan says. By 2020, the researchers found, poison control centers were fielding 4.5 times as many suicide-related calls among kids of this age group as they had in 2000. This jump was the largest such increase for any age group in the study, he says.
The reasons for such a large increase of suicide-related calls among preadolescents are unclear, the researchers note.
The increase became apparent around 2013, at the time many popular social media networks launched. Dr. Sheridan and his colleagues cite studies showing an association between spending more time on social media or watching television and depression in adolescence but said further research is needed to understand the root causes of this increase.
The latest study did not look specifically at the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on suicide among young people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention earlier reported a sharp rise in suicide attempts among youth during the early months of the pandemic, especially among girls aged 12-17 years. By February 2021, suicide attempts within this group had climbed by 50%, compared with 2 years earlier.
Although suicide attempts are concerning enough, deaths by suicide are even more worrisome, experts said.
The researchers’ findings are consistent with overall recent trends in youth suicide deaths, says Jeff Bridge, PhD, an epidemiologist at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus. From 2010-2020, suicide rates increased by 50% among 13- to 18-year-olds, Dr. Bridge said, and more than doubled in children aged 10-12.
The latest study captured only calls to poison control centers, so it did not count suicide attempts that did not result in a call for help. Another limitation of the study is that poison control data are not categorized by race or ethnicity, prompting Dr. Bridge to urge researchers to look specifically at the effect of race and ethnicity on these trends.
“This study supports screening for suicide risk as young as 10 years old,” Dr. Bridge says.
Dr. Sheridan agrees that prevention is essential: “The ER is where kids come when they’re in crisis. Trying to be more preventative by diagnosing or picking up on this earlier, I think, is really important.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Suicide attempts spurring calls to poison control centers more than quadrupled among U.S. children aged 10-12 years from 2000 to 2020, according to research published in JAMA Pediatrics.
The reasons for the increase in suicide attempts isn’t clear from the new study, but the researchers note that popular social media networks launched during the 20-year period, and other studies have linked spending time on social media with depression in adolescence. The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in the last year the researchers looked at, also disrupted normal life and routines for children.
For all children older than age 9, the proportion of incidents in which kids ate or drank something harmful that were deemed suicide attempts increased, while those classified as misuse or abuse of potentially poisonous substances declined. Children aged 6-9 did not have an increase in suicide attempts, the study found.
“It’s a huge problem we’re seeing in [ERs]. It’s exponentially blowing up numbers across the nation,” says David Sheridan, MD, an ER pediatric doctor at the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, who led the study.
Adolescents or preteens who have attempted suicide can sit in ERs “for days or weeks” as they wait to be moved elsewhere in the hospital or to an outpatient facility for treatment, Dr. Sheridan says. The delays are not only unpleasant for the children, he says, but they also strain hospitals by leaving less space available for other patients coming to the ER.
“It’s really tough on the entire health care system, and most importantly, it’s really rough on the families who are going through a crisis,” Dr. Sheridan says. He noted that young people often attempt suicide by taking excessive quantities of common over-the-counter products found in many medicine cabinets – acetaminophen, ibuprofen, diphenhydramine – not items marked “poison.”
Twenty-year trend
The researchers examined phone calls to poison control centers about kids age 6 and up taking in potentially harmful substances from 2000-2020 recorded in the National Poison Data System, which is maintained by the American Association of Poison Control Centers.
Of more than 1.2 million total calls, 854,000 involved girls. A poison control data analyst determined if the call involved attempted suicide or the deliberate misuse or abuse of a potentially poisonous substance.
The researchers identified 1,005 deaths. About 70% of the total cases had either no effect or a minor effect on the child’s health.
Over the 20-year period, more than 90% of the calls involved children aged at least 13 years, with approximately 72,000 (5.7%) about children aged 10-12. Most calls for children 13 and older were for suicide attempts.
Suspected suicide attempts accounted for about 50% of the total calls to poison control centers among children aged 10-12 in 2000 – a figure that ballooned to 80% in 2020, the researchers found.
Both the number of calls and the proportion related to suicide attempts increased among children aged 10-12, Dr. Sheridan says. By 2020, the researchers found, poison control centers were fielding 4.5 times as many suicide-related calls among kids of this age group as they had in 2000. This jump was the largest such increase for any age group in the study, he says.
The reasons for such a large increase of suicide-related calls among preadolescents are unclear, the researchers note.
The increase became apparent around 2013, at the time many popular social media networks launched. Dr. Sheridan and his colleagues cite studies showing an association between spending more time on social media or watching television and depression in adolescence but said further research is needed to understand the root causes of this increase.
The latest study did not look specifically at the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on suicide among young people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention earlier reported a sharp rise in suicide attempts among youth during the early months of the pandemic, especially among girls aged 12-17 years. By February 2021, suicide attempts within this group had climbed by 50%, compared with 2 years earlier.
Although suicide attempts are concerning enough, deaths by suicide are even more worrisome, experts said.
The researchers’ findings are consistent with overall recent trends in youth suicide deaths, says Jeff Bridge, PhD, an epidemiologist at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus. From 2010-2020, suicide rates increased by 50% among 13- to 18-year-olds, Dr. Bridge said, and more than doubled in children aged 10-12.
The latest study captured only calls to poison control centers, so it did not count suicide attempts that did not result in a call for help. Another limitation of the study is that poison control data are not categorized by race or ethnicity, prompting Dr. Bridge to urge researchers to look specifically at the effect of race and ethnicity on these trends.
“This study supports screening for suicide risk as young as 10 years old,” Dr. Bridge says.
Dr. Sheridan agrees that prevention is essential: “The ER is where kids come when they’re in crisis. Trying to be more preventative by diagnosing or picking up on this earlier, I think, is really important.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Virtual and in-person pediatric visits get similar family ratings
CHICAGO – Satisfaction ratings for virtual outpatient visits for pediatric orthopedic patients were similar to those for in-person office visits across most categories in an analysis of postencounter surveys completed by patients at the Cleveland Clinic.
Satisfaction ratings for both virtual and office visits were consistently higher than 85% across all measured parameters, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Ahmed Emara, MD, a clinical research fellow in adult joint reconstruction at the Cleveland Clinic, led the study, which included data from all patients or guardians at the clinic who experienced such visits from March 2020 to March 2021.
A total of 1,686 responses were received, of which 226 (13.4%) involved virtual visits and 1,460 (86.6%) involved in-office visits. The primary endpoint was a patient-reported satisfaction score of good or excellent.
Analysis included ratings for access, care provider, telemedicine technology, and overall assessment/perception of satisfaction.
Target areas for improvement
In some areas, the virtual visits were less satisfactory than the in-office visits.
Patients had lower odds of reporting good/excellent satisfaction regarding their ability to schedule at a particularly convenient time (odds ratio, 0.1; 95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.18; P < .001). The study authors said scheduling more virtual time slots may help increase satisfaction in that area.
Satisfaction was also lower than with in-office visits with respect to providers’ explanations of patients’ conditions (OR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.17-0.91; P = .03). Providers may need to find ways to better provide educational material in addition to the virtual consultation, the authors wrote.
No significant differences in categories of satisfaction
The researchers accounted for age, sex, traumatic etiology, and anatomic location of the complaint in multivariate regression analysis and found no significant differences between the two types of visits in the odds of getting a good/excellent rating for the following areas: patient inclusion in treatment decision (P = .562), discussion of proposed treatment (P = .222), concern by the provider (P = .189), degree of care for the patient as a person (P = .208), adequacy of teamwork in care provision (P = .053), likelihood of recommending the practice to others (P = .108), ease of receiving care at a particular practice (P = .109), ease of contacting the clinic (P = .177), and likelihood of recommending a particular provider (P = .218).
Anna Dimitriovna Vergun, MD, a pediatric orthopedist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview she had been conducting virtual visits even before the pandemic, when she worked for several years at a Shriner’s children’s hospital in Los Angeles, before coming to UNC. The virtual visits were necessary because the hospital offered charity care and covered an area that included several states.
She said that during the height of the pandemic, 80% of her visits at UNC were virtual; it is down to about 5% now.
Some consultations don’t need physical visits at all, Dr. Vergun noted. For example, UNC is starting a clinic for prenatal counseling in cases in which ultrasound detects a limb deformity. Without a virtual option, she said, pregnant mothers in all parts of the state may have to drive long distances when no physical exam is necessary.
And sometimes, a visit simply involves checking in with families to see whether pain is being controlled, which is done well virtually.
“Those are particularly useful for telemedicine,” Dr. Vergun said. “There’s a lot of space for this to be useful. You sometimes don’t realize it until you start doing it and getting feedback from the families that they like it.”
Other exams may be better suited to office visits, she said. These include spine and hip exams and exams in which providers need to check reflexes.
She said she sees many cases of club feet, for which an in-person exam is needed to determine flexibility.
Expert says virtual misses nuances
Ryan Fitzgerald, MD, an orthopedic expert with Children’s Orthopaedic and Scoliosis Surgery Associates in St. Petersburg, Fla., who also was not involved in the study, said in an interview he doesn’t offer the virtual option now because he thinks those visits usually miss too much.
COSSA is a private practice that provides orthopedic services for Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital.
“I think physicians’ perspective versus the families’ perspective may be quite a bit different,” he said.
While families like the convenience, “a lot of what we do is watching the patient walk, looking at their hip range of motion, and virtually, that’s a really difficult thing to do,” he said.
You can instruct a family on how to turn a camera on the patient, but “it doesn’t always translate,” he said.
He said virtual visits also highlight disparities in access, because many families don’t own the hardware needed for such visits, and internet connections can be spotty or images pixelated.
Dr. Fitzgerald said virtual visits were helpful during the pandemic and would be beneficial for yearly checkups “if you know [the patient] well and it’s a fairly run-of-the-mill thing.”
However, he said, “everything we do is about human interaction, and I think that’s a downfall of the virtual platform right now. While it is helpful in situations like COVID and where it is a very basic follow-up, it still has a ways to go.”
Dr. Fitzgerald is a consultant for OrthoPediatrics, Medtronic, and Depuy Synthes. Dr. Vergun disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Satisfaction ratings for virtual outpatient visits for pediatric orthopedic patients were similar to those for in-person office visits across most categories in an analysis of postencounter surveys completed by patients at the Cleveland Clinic.
Satisfaction ratings for both virtual and office visits were consistently higher than 85% across all measured parameters, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Ahmed Emara, MD, a clinical research fellow in adult joint reconstruction at the Cleveland Clinic, led the study, which included data from all patients or guardians at the clinic who experienced such visits from March 2020 to March 2021.
A total of 1,686 responses were received, of which 226 (13.4%) involved virtual visits and 1,460 (86.6%) involved in-office visits. The primary endpoint was a patient-reported satisfaction score of good or excellent.
Analysis included ratings for access, care provider, telemedicine technology, and overall assessment/perception of satisfaction.
Target areas for improvement
In some areas, the virtual visits were less satisfactory than the in-office visits.
Patients had lower odds of reporting good/excellent satisfaction regarding their ability to schedule at a particularly convenient time (odds ratio, 0.1; 95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.18; P < .001). The study authors said scheduling more virtual time slots may help increase satisfaction in that area.
Satisfaction was also lower than with in-office visits with respect to providers’ explanations of patients’ conditions (OR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.17-0.91; P = .03). Providers may need to find ways to better provide educational material in addition to the virtual consultation, the authors wrote.
No significant differences in categories of satisfaction
The researchers accounted for age, sex, traumatic etiology, and anatomic location of the complaint in multivariate regression analysis and found no significant differences between the two types of visits in the odds of getting a good/excellent rating for the following areas: patient inclusion in treatment decision (P = .562), discussion of proposed treatment (P = .222), concern by the provider (P = .189), degree of care for the patient as a person (P = .208), adequacy of teamwork in care provision (P = .053), likelihood of recommending the practice to others (P = .108), ease of receiving care at a particular practice (P = .109), ease of contacting the clinic (P = .177), and likelihood of recommending a particular provider (P = .218).
Anna Dimitriovna Vergun, MD, a pediatric orthopedist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview she had been conducting virtual visits even before the pandemic, when she worked for several years at a Shriner’s children’s hospital in Los Angeles, before coming to UNC. The virtual visits were necessary because the hospital offered charity care and covered an area that included several states.
She said that during the height of the pandemic, 80% of her visits at UNC were virtual; it is down to about 5% now.
Some consultations don’t need physical visits at all, Dr. Vergun noted. For example, UNC is starting a clinic for prenatal counseling in cases in which ultrasound detects a limb deformity. Without a virtual option, she said, pregnant mothers in all parts of the state may have to drive long distances when no physical exam is necessary.
And sometimes, a visit simply involves checking in with families to see whether pain is being controlled, which is done well virtually.
“Those are particularly useful for telemedicine,” Dr. Vergun said. “There’s a lot of space for this to be useful. You sometimes don’t realize it until you start doing it and getting feedback from the families that they like it.”
Other exams may be better suited to office visits, she said. These include spine and hip exams and exams in which providers need to check reflexes.
She said she sees many cases of club feet, for which an in-person exam is needed to determine flexibility.
Expert says virtual misses nuances
Ryan Fitzgerald, MD, an orthopedic expert with Children’s Orthopaedic and Scoliosis Surgery Associates in St. Petersburg, Fla., who also was not involved in the study, said in an interview he doesn’t offer the virtual option now because he thinks those visits usually miss too much.
COSSA is a private practice that provides orthopedic services for Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital.
“I think physicians’ perspective versus the families’ perspective may be quite a bit different,” he said.
While families like the convenience, “a lot of what we do is watching the patient walk, looking at their hip range of motion, and virtually, that’s a really difficult thing to do,” he said.
You can instruct a family on how to turn a camera on the patient, but “it doesn’t always translate,” he said.
He said virtual visits also highlight disparities in access, because many families don’t own the hardware needed for such visits, and internet connections can be spotty or images pixelated.
Dr. Fitzgerald said virtual visits were helpful during the pandemic and would be beneficial for yearly checkups “if you know [the patient] well and it’s a fairly run-of-the-mill thing.”
However, he said, “everything we do is about human interaction, and I think that’s a downfall of the virtual platform right now. While it is helpful in situations like COVID and where it is a very basic follow-up, it still has a ways to go.”
Dr. Fitzgerald is a consultant for OrthoPediatrics, Medtronic, and Depuy Synthes. Dr. Vergun disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Satisfaction ratings for virtual outpatient visits for pediatric orthopedic patients were similar to those for in-person office visits across most categories in an analysis of postencounter surveys completed by patients at the Cleveland Clinic.
Satisfaction ratings for both virtual and office visits were consistently higher than 85% across all measured parameters, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Ahmed Emara, MD, a clinical research fellow in adult joint reconstruction at the Cleveland Clinic, led the study, which included data from all patients or guardians at the clinic who experienced such visits from March 2020 to March 2021.
A total of 1,686 responses were received, of which 226 (13.4%) involved virtual visits and 1,460 (86.6%) involved in-office visits. The primary endpoint was a patient-reported satisfaction score of good or excellent.
Analysis included ratings for access, care provider, telemedicine technology, and overall assessment/perception of satisfaction.
Target areas for improvement
In some areas, the virtual visits were less satisfactory than the in-office visits.
Patients had lower odds of reporting good/excellent satisfaction regarding their ability to schedule at a particularly convenient time (odds ratio, 0.1; 95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.18; P < .001). The study authors said scheduling more virtual time slots may help increase satisfaction in that area.
Satisfaction was also lower than with in-office visits with respect to providers’ explanations of patients’ conditions (OR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.17-0.91; P = .03). Providers may need to find ways to better provide educational material in addition to the virtual consultation, the authors wrote.
No significant differences in categories of satisfaction
The researchers accounted for age, sex, traumatic etiology, and anatomic location of the complaint in multivariate regression analysis and found no significant differences between the two types of visits in the odds of getting a good/excellent rating for the following areas: patient inclusion in treatment decision (P = .562), discussion of proposed treatment (P = .222), concern by the provider (P = .189), degree of care for the patient as a person (P = .208), adequacy of teamwork in care provision (P = .053), likelihood of recommending the practice to others (P = .108), ease of receiving care at a particular practice (P = .109), ease of contacting the clinic (P = .177), and likelihood of recommending a particular provider (P = .218).
Anna Dimitriovna Vergun, MD, a pediatric orthopedist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview she had been conducting virtual visits even before the pandemic, when she worked for several years at a Shriner’s children’s hospital in Los Angeles, before coming to UNC. The virtual visits were necessary because the hospital offered charity care and covered an area that included several states.
She said that during the height of the pandemic, 80% of her visits at UNC were virtual; it is down to about 5% now.
Some consultations don’t need physical visits at all, Dr. Vergun noted. For example, UNC is starting a clinic for prenatal counseling in cases in which ultrasound detects a limb deformity. Without a virtual option, she said, pregnant mothers in all parts of the state may have to drive long distances when no physical exam is necessary.
And sometimes, a visit simply involves checking in with families to see whether pain is being controlled, which is done well virtually.
“Those are particularly useful for telemedicine,” Dr. Vergun said. “There’s a lot of space for this to be useful. You sometimes don’t realize it until you start doing it and getting feedback from the families that they like it.”
Other exams may be better suited to office visits, she said. These include spine and hip exams and exams in which providers need to check reflexes.
She said she sees many cases of club feet, for which an in-person exam is needed to determine flexibility.
Expert says virtual misses nuances
Ryan Fitzgerald, MD, an orthopedic expert with Children’s Orthopaedic and Scoliosis Surgery Associates in St. Petersburg, Fla., who also was not involved in the study, said in an interview he doesn’t offer the virtual option now because he thinks those visits usually miss too much.
COSSA is a private practice that provides orthopedic services for Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital.
“I think physicians’ perspective versus the families’ perspective may be quite a bit different,” he said.
While families like the convenience, “a lot of what we do is watching the patient walk, looking at their hip range of motion, and virtually, that’s a really difficult thing to do,” he said.
You can instruct a family on how to turn a camera on the patient, but “it doesn’t always translate,” he said.
He said virtual visits also highlight disparities in access, because many families don’t own the hardware needed for such visits, and internet connections can be spotty or images pixelated.
Dr. Fitzgerald said virtual visits were helpful during the pandemic and would be beneficial for yearly checkups “if you know [the patient] well and it’s a fairly run-of-the-mill thing.”
However, he said, “everything we do is about human interaction, and I think that’s a downfall of the virtual platform right now. While it is helpful in situations like COVID and where it is a very basic follow-up, it still has a ways to go.”
Dr. Fitzgerald is a consultant for OrthoPediatrics, Medtronic, and Depuy Synthes. Dr. Vergun disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAOS 2022
Metformin use linked to birth defects in boys
researchers have found.
The association appears to involve the effects of metformin on the development of sperm during a critical window prior to conception. Female offspring were not affected. Although previous studies have linked diabetes with fertility problems in men, the latest study is the first to show that these problems can result from treatment rather than the disease itself, according to the researchers, whose findings appear in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“This is the first data to suggest that paternal metformin [use] may be associated with birth defects in children. As such, it would be early to begin to alter clinical practice,” Michael Eisenberg, MD, director of male reproductive medicine and surgery, department of urology, Stanford (Calif.) University, who is a coauthor of the study, said in an interview. “However, if it is confirmed in other populations, then it may begin to enter counseling discussions.”
Dr. Eisenberg added that eating a nutritious diet, exercising, and maintaining a healthy body weight “can improve a man’s health and likely his fertility as well.”
For the new study, Dr. Eisenberg and colleagues analyzed records in a registry of all 1.25 million births that occurred in Denmark between 1997 and 2016. The registry included information on birth defects and parental drug prescriptions.
Offspring were considered exposed to a diabetes drug if a father had filled one or more prescriptions for the medications during the 3 months prior to conception, when the fertilizing sperm would have been produced.
The final analysis included 1,116,779 offspring – all singleton births to women without a history of diabetes or essential hypertension – of whom 7,029 were exposed to diabetes drugs via the father, and 3.3% (n = 36,585) had one or more major birth defects.
Among male offspring whose fathers had taken metformin (n = 1,451), there was a 3.4-fold greater incidence of major genitourinary birth defects, according to the researchers. The study failed to find associations between birth defects and the use of insulin. Although a signal did emerge for sulfonylurea-based drugs, it did not reach statistical significance.
The risk associated with metformin did not appear for men who were prescribed the drug in the year before or after sperm development. Nor was it evident in siblings of the boys with birth defects who were not considered to have been exposed to the medication, the researchers reported.
In an editorial accompanying the journal article, Germaine Buck Louis, PhD, a reproductive and perinatal epidemiologist, wrote: “Given the prevalence of metformin use as first-line therapy for type 2 diabetes, corroboration of these findings is urgently needed.”
Dr. Louis, dean of the College of Health and Human Services at George Mason University, Washington, said a key limitation of the research is the lack of data on how well men in the study adhered to their diabetes treatment. Nevertheless, “clinical guidance is needed to help couples planning pregnancy weigh the risks and benefits of paternal metformin use relative to other medications.”
The researchers received funding from the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers have found.
The association appears to involve the effects of metformin on the development of sperm during a critical window prior to conception. Female offspring were not affected. Although previous studies have linked diabetes with fertility problems in men, the latest study is the first to show that these problems can result from treatment rather than the disease itself, according to the researchers, whose findings appear in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“This is the first data to suggest that paternal metformin [use] may be associated with birth defects in children. As such, it would be early to begin to alter clinical practice,” Michael Eisenberg, MD, director of male reproductive medicine and surgery, department of urology, Stanford (Calif.) University, who is a coauthor of the study, said in an interview. “However, if it is confirmed in other populations, then it may begin to enter counseling discussions.”
Dr. Eisenberg added that eating a nutritious diet, exercising, and maintaining a healthy body weight “can improve a man’s health and likely his fertility as well.”
For the new study, Dr. Eisenberg and colleagues analyzed records in a registry of all 1.25 million births that occurred in Denmark between 1997 and 2016. The registry included information on birth defects and parental drug prescriptions.
Offspring were considered exposed to a diabetes drug if a father had filled one or more prescriptions for the medications during the 3 months prior to conception, when the fertilizing sperm would have been produced.
The final analysis included 1,116,779 offspring – all singleton births to women without a history of diabetes or essential hypertension – of whom 7,029 were exposed to diabetes drugs via the father, and 3.3% (n = 36,585) had one or more major birth defects.
Among male offspring whose fathers had taken metformin (n = 1,451), there was a 3.4-fold greater incidence of major genitourinary birth defects, according to the researchers. The study failed to find associations between birth defects and the use of insulin. Although a signal did emerge for sulfonylurea-based drugs, it did not reach statistical significance.
The risk associated with metformin did not appear for men who were prescribed the drug in the year before or after sperm development. Nor was it evident in siblings of the boys with birth defects who were not considered to have been exposed to the medication, the researchers reported.
In an editorial accompanying the journal article, Germaine Buck Louis, PhD, a reproductive and perinatal epidemiologist, wrote: “Given the prevalence of metformin use as first-line therapy for type 2 diabetes, corroboration of these findings is urgently needed.”
Dr. Louis, dean of the College of Health and Human Services at George Mason University, Washington, said a key limitation of the research is the lack of data on how well men in the study adhered to their diabetes treatment. Nevertheless, “clinical guidance is needed to help couples planning pregnancy weigh the risks and benefits of paternal metformin use relative to other medications.”
The researchers received funding from the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers have found.
The association appears to involve the effects of metformin on the development of sperm during a critical window prior to conception. Female offspring were not affected. Although previous studies have linked diabetes with fertility problems in men, the latest study is the first to show that these problems can result from treatment rather than the disease itself, according to the researchers, whose findings appear in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“This is the first data to suggest that paternal metformin [use] may be associated with birth defects in children. As such, it would be early to begin to alter clinical practice,” Michael Eisenberg, MD, director of male reproductive medicine and surgery, department of urology, Stanford (Calif.) University, who is a coauthor of the study, said in an interview. “However, if it is confirmed in other populations, then it may begin to enter counseling discussions.”
Dr. Eisenberg added that eating a nutritious diet, exercising, and maintaining a healthy body weight “can improve a man’s health and likely his fertility as well.”
For the new study, Dr. Eisenberg and colleagues analyzed records in a registry of all 1.25 million births that occurred in Denmark between 1997 and 2016. The registry included information on birth defects and parental drug prescriptions.
Offspring were considered exposed to a diabetes drug if a father had filled one or more prescriptions for the medications during the 3 months prior to conception, when the fertilizing sperm would have been produced.
The final analysis included 1,116,779 offspring – all singleton births to women without a history of diabetes or essential hypertension – of whom 7,029 were exposed to diabetes drugs via the father, and 3.3% (n = 36,585) had one or more major birth defects.
Among male offspring whose fathers had taken metformin (n = 1,451), there was a 3.4-fold greater incidence of major genitourinary birth defects, according to the researchers. The study failed to find associations between birth defects and the use of insulin. Although a signal did emerge for sulfonylurea-based drugs, it did not reach statistical significance.
The risk associated with metformin did not appear for men who were prescribed the drug in the year before or after sperm development. Nor was it evident in siblings of the boys with birth defects who were not considered to have been exposed to the medication, the researchers reported.
In an editorial accompanying the journal article, Germaine Buck Louis, PhD, a reproductive and perinatal epidemiologist, wrote: “Given the prevalence of metformin use as first-line therapy for type 2 diabetes, corroboration of these findings is urgently needed.”
Dr. Louis, dean of the College of Health and Human Services at George Mason University, Washington, said a key limitation of the research is the lack of data on how well men in the study adhered to their diabetes treatment. Nevertheless, “clinical guidance is needed to help couples planning pregnancy weigh the risks and benefits of paternal metformin use relative to other medications.”
The researchers received funding from the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE

