User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Duration of breastfeeding associated with cognition in children
Breastfeeding duration is associated with improved cognitive scores at ages 5-14, even after controlling for maternal socioeconomic position and cognitive ability, said the researchers behind a new study.
Despite previous studies demonstrating an association between breastfeeding and standardized intelligence test scores – with breastfed infants scoring higher on intelligence tests than non-breastfed infants – a causal relationship is still contested.
“There is some debate about whether breastfeeding a baby for a longer period of time improves their cognitive development,” the authors of the new study said. They went on to explain how improved cognitive outcomes in breastfed infants could potentially be explained by other characteristics of the women, such as “socioeconomics and maternal intelligence.”
Important at the population level
For the study, published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, researchers from the University of Oxford (England) set out to investigate how much these confounders influenced the association between breastfeeding duration and cognitive development.
They analyzed data from the U.K. Millennium Cohort Study on 7,855 infants born in 2000 to 2002 and followed until age 14. They highlighted that although the cohort was not specifically designed to address the association between breastfeeding and cognition, it included information on duration of any breastfeeding, duration of exclusive breastfeeding, verbal cognitive scores at ages 5, 7, 11, and 14, spatial cognitive scores at ages 5, 7, and 11, as well as potential confounders, including socioeconomic characteristics and maternal cognition, based on a vocabulary test.
The researchers discovered that longer breastfeeding durations were associated with higher verbal and spatial cognitive scores at all ages up to 14 and 11, respectively.
After taking the differences in socioeconomic position and maternal cognitive ability into account, those children who were breastfed for longer scored higher in cognitive measures up to age 14, compared with children who were not breastfed. They also found that longer breastfeeding durations were associated with mean cognitive scores 0.08-0.26 standard deviations higher than the mean cognitive score of those who were never breastfed. “This difference may seem small for an individual child but could be important at the population level,” the authors commented.
Modest effect
In the United Kingdom, women who have more educational qualifications and are more economically advantaged tend to breastfeed for longer, said the authors. In addition, they added, this group tends to “score more highly on cognitive tests.”
These differences could explain why babies who breastfeed for longer do better in cognitive assessments. However, they said that in their study, “we found that even after taking these differences into account, children breastfed for longer scored higher in cognitive measures up to age 14, in comparison to children who were not breastfed.”
The authors explained that the association between breastfeeding duration and cognitive scores “persists after adjusting for socioeconomics and maternal intelligence.” However, they pointed out that “the effect was modest.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Breastfeeding duration is associated with improved cognitive scores at ages 5-14, even after controlling for maternal socioeconomic position and cognitive ability, said the researchers behind a new study.
Despite previous studies demonstrating an association between breastfeeding and standardized intelligence test scores – with breastfed infants scoring higher on intelligence tests than non-breastfed infants – a causal relationship is still contested.
“There is some debate about whether breastfeeding a baby for a longer period of time improves their cognitive development,” the authors of the new study said. They went on to explain how improved cognitive outcomes in breastfed infants could potentially be explained by other characteristics of the women, such as “socioeconomics and maternal intelligence.”
Important at the population level
For the study, published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, researchers from the University of Oxford (England) set out to investigate how much these confounders influenced the association between breastfeeding duration and cognitive development.
They analyzed data from the U.K. Millennium Cohort Study on 7,855 infants born in 2000 to 2002 and followed until age 14. They highlighted that although the cohort was not specifically designed to address the association between breastfeeding and cognition, it included information on duration of any breastfeeding, duration of exclusive breastfeeding, verbal cognitive scores at ages 5, 7, 11, and 14, spatial cognitive scores at ages 5, 7, and 11, as well as potential confounders, including socioeconomic characteristics and maternal cognition, based on a vocabulary test.
The researchers discovered that longer breastfeeding durations were associated with higher verbal and spatial cognitive scores at all ages up to 14 and 11, respectively.
After taking the differences in socioeconomic position and maternal cognitive ability into account, those children who were breastfed for longer scored higher in cognitive measures up to age 14, compared with children who were not breastfed. They also found that longer breastfeeding durations were associated with mean cognitive scores 0.08-0.26 standard deviations higher than the mean cognitive score of those who were never breastfed. “This difference may seem small for an individual child but could be important at the population level,” the authors commented.
Modest effect
In the United Kingdom, women who have more educational qualifications and are more economically advantaged tend to breastfeed for longer, said the authors. In addition, they added, this group tends to “score more highly on cognitive tests.”
These differences could explain why babies who breastfeed for longer do better in cognitive assessments. However, they said that in their study, “we found that even after taking these differences into account, children breastfed for longer scored higher in cognitive measures up to age 14, in comparison to children who were not breastfed.”
The authors explained that the association between breastfeeding duration and cognitive scores “persists after adjusting for socioeconomics and maternal intelligence.” However, they pointed out that “the effect was modest.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Breastfeeding duration is associated with improved cognitive scores at ages 5-14, even after controlling for maternal socioeconomic position and cognitive ability, said the researchers behind a new study.
Despite previous studies demonstrating an association between breastfeeding and standardized intelligence test scores – with breastfed infants scoring higher on intelligence tests than non-breastfed infants – a causal relationship is still contested.
“There is some debate about whether breastfeeding a baby for a longer period of time improves their cognitive development,” the authors of the new study said. They went on to explain how improved cognitive outcomes in breastfed infants could potentially be explained by other characteristics of the women, such as “socioeconomics and maternal intelligence.”
Important at the population level
For the study, published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, researchers from the University of Oxford (England) set out to investigate how much these confounders influenced the association between breastfeeding duration and cognitive development.
They analyzed data from the U.K. Millennium Cohort Study on 7,855 infants born in 2000 to 2002 and followed until age 14. They highlighted that although the cohort was not specifically designed to address the association between breastfeeding and cognition, it included information on duration of any breastfeeding, duration of exclusive breastfeeding, verbal cognitive scores at ages 5, 7, 11, and 14, spatial cognitive scores at ages 5, 7, and 11, as well as potential confounders, including socioeconomic characteristics and maternal cognition, based on a vocabulary test.
The researchers discovered that longer breastfeeding durations were associated with higher verbal and spatial cognitive scores at all ages up to 14 and 11, respectively.
After taking the differences in socioeconomic position and maternal cognitive ability into account, those children who were breastfed for longer scored higher in cognitive measures up to age 14, compared with children who were not breastfed. They also found that longer breastfeeding durations were associated with mean cognitive scores 0.08-0.26 standard deviations higher than the mean cognitive score of those who were never breastfed. “This difference may seem small for an individual child but could be important at the population level,” the authors commented.
Modest effect
In the United Kingdom, women who have more educational qualifications and are more economically advantaged tend to breastfeed for longer, said the authors. In addition, they added, this group tends to “score more highly on cognitive tests.”
These differences could explain why babies who breastfeed for longer do better in cognitive assessments. However, they said that in their study, “we found that even after taking these differences into account, children breastfed for longer scored higher in cognitive measures up to age 14, in comparison to children who were not breastfed.”
The authors explained that the association between breastfeeding duration and cognitive scores “persists after adjusting for socioeconomics and maternal intelligence.” However, they pointed out that “the effect was modest.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
FROM PLOS ONE
Airway injuries ‘devastating’ after battery ingestions: Review
Severe airway injuries are a “not infrequent” consequence after children swallow button batteries, which are commonly found in many household electronics, according to a systematic review published online in JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.
Most literature has focused on esophageal injury, but “the direct apposition of the esophagus to the trachea and recurrent laryngeal nerves also places these children at risk of airway injury, such as tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) (a life-threatening complication), vocal cord paresis and paralysis, tracheal stenosis, and tracheomalacia,” the researchers wrote.
Led by Justine Philteos, MD, of the department of otolaryngology–head and neck surgery at the University of Toronto, the researchers found that tracheoesophageal fistula and vocal cord paralyses were the two most common airway injuries and often required tracheostomy.
The review included 195 children pulled from the National Capital Poison Center (NCPC) database – more often young children – who had ingested the batteries. The average age at ingestion was 17.8 months and the average time between ingestion and removal was 5.8 days.
Of the 195 children, 29 (15%) underwent tracheostomy, and 11 of the 29 children (38%) ultimately had decannulation. There were 14 deaths from swallowing the batteries. All 14 patients had a TEF. The cause of death was identified for 12 of the patients: Four died of pneumonia or respiratory failure; three of massive hematemesis; three of sepsis; one of multiorgan failure, and one of anoxic encephalopathy.
Vocal cord injury occurred after a shorter button battery exposure than other airway injuries.
The authors concluded that prioritizing quick button battery removal is essential “to decrease the devastating consequences of these injuries.”
In an invited commentary, Hannah Gibbs, and Kris R. Jatana, MD, of The Ohio State University in Columbus, described what’s being done to prevent and treat these injuries and what’s next.
They noted that ingestion is often unseen so diagnosis is difficult. Therefore, they wrote, a novel coin-battery metal detector could be a radiation-free, quick screening tool. They noted a patent-pending technology has been developed at Ohio State and Nationwide Children’s Hospital.
Honey can help slow injury
Some measures can be taken at home or in the hospital if battery swallowing is discovered, the editorialists noted.
In the home or in transport to the hospital, caregivers can give 10 mL of honey every 10 minutes until arrival if the child is older than 12 months.
At the hospital, 10 mL of either honey or sucralfate may be given every 10 minutes to slow the rate of injury until the battery can be surgically removed.
“The current NCPC guidelines suggest up to six doses may be given in the prehospital setting, with three additional doses administered in the hospital,” they wrote.
“These strategies should be considered earlier than 12 hours from ingestion, when there is no clinical concern for mediastinitis or sepsis. A child with an esophageal button battery should proceed to the operating room immediately regardless of whether he or she has recently eaten,” Ms. Gibbs and Dr. Jatana wrote.
App adds convenience to boost physician reporting
Foreign body ingestions are also severely underreported, they noted. They cited a survey of more than 400 physicians who directly manage foreign body ingestions that found only 11% of button battery injuries and 4% of all foreign body ingestion or aspiration events were reported. The great majority (92%) of respondents said they would report the events if that were more convenient.
To that end, the Global Injury Research Collaborative (GIRC) has created and released a free smartphone application, the GIRC App. It is available free on the iOS system (through App Store) and soon will be available on the Android system (through Google Play), they wrote.
Ms. Gibbs and Dr. Jatana urge other measures, including safer battery compartments and battery design, to reduce the likelihood of ingestion.
They pointed out that a bill was introduced in Congress that would require the Consumer Product Safety Commission to mandate a new standard for child-resistant compartments on products containing button batteries. The act, called Reese’s Law, has been referred to the Committee on Energy and Commerce and is under review.
Dr. Jatana reported having a patent pending for a coin or battery metal detector device under development; being a shareholder in Zotarix, Landsdowne Labs, and Tivic Health Systems; serving in a leadership position on the National Button Battery Task Force; and being a board member of the Global Injury Research Collaborative, which is a U.S. Internal Revenue Service–designated, 501(c)(3) nonprofit research organization. No other relevant disclosures were reported.
Severe airway injuries are a “not infrequent” consequence after children swallow button batteries, which are commonly found in many household electronics, according to a systematic review published online in JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.
Most literature has focused on esophageal injury, but “the direct apposition of the esophagus to the trachea and recurrent laryngeal nerves also places these children at risk of airway injury, such as tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) (a life-threatening complication), vocal cord paresis and paralysis, tracheal stenosis, and tracheomalacia,” the researchers wrote.
Led by Justine Philteos, MD, of the department of otolaryngology–head and neck surgery at the University of Toronto, the researchers found that tracheoesophageal fistula and vocal cord paralyses were the two most common airway injuries and often required tracheostomy.
The review included 195 children pulled from the National Capital Poison Center (NCPC) database – more often young children – who had ingested the batteries. The average age at ingestion was 17.8 months and the average time between ingestion and removal was 5.8 days.
Of the 195 children, 29 (15%) underwent tracheostomy, and 11 of the 29 children (38%) ultimately had decannulation. There were 14 deaths from swallowing the batteries. All 14 patients had a TEF. The cause of death was identified for 12 of the patients: Four died of pneumonia or respiratory failure; three of massive hematemesis; three of sepsis; one of multiorgan failure, and one of anoxic encephalopathy.
Vocal cord injury occurred after a shorter button battery exposure than other airway injuries.
The authors concluded that prioritizing quick button battery removal is essential “to decrease the devastating consequences of these injuries.”
In an invited commentary, Hannah Gibbs, and Kris R. Jatana, MD, of The Ohio State University in Columbus, described what’s being done to prevent and treat these injuries and what’s next.
They noted that ingestion is often unseen so diagnosis is difficult. Therefore, they wrote, a novel coin-battery metal detector could be a radiation-free, quick screening tool. They noted a patent-pending technology has been developed at Ohio State and Nationwide Children’s Hospital.
Honey can help slow injury
Some measures can be taken at home or in the hospital if battery swallowing is discovered, the editorialists noted.
In the home or in transport to the hospital, caregivers can give 10 mL of honey every 10 minutes until arrival if the child is older than 12 months.
At the hospital, 10 mL of either honey or sucralfate may be given every 10 minutes to slow the rate of injury until the battery can be surgically removed.
“The current NCPC guidelines suggest up to six doses may be given in the prehospital setting, with three additional doses administered in the hospital,” they wrote.
“These strategies should be considered earlier than 12 hours from ingestion, when there is no clinical concern for mediastinitis or sepsis. A child with an esophageal button battery should proceed to the operating room immediately regardless of whether he or she has recently eaten,” Ms. Gibbs and Dr. Jatana wrote.
App adds convenience to boost physician reporting
Foreign body ingestions are also severely underreported, they noted. They cited a survey of more than 400 physicians who directly manage foreign body ingestions that found only 11% of button battery injuries and 4% of all foreign body ingestion or aspiration events were reported. The great majority (92%) of respondents said they would report the events if that were more convenient.
To that end, the Global Injury Research Collaborative (GIRC) has created and released a free smartphone application, the GIRC App. It is available free on the iOS system (through App Store) and soon will be available on the Android system (through Google Play), they wrote.
Ms. Gibbs and Dr. Jatana urge other measures, including safer battery compartments and battery design, to reduce the likelihood of ingestion.
They pointed out that a bill was introduced in Congress that would require the Consumer Product Safety Commission to mandate a new standard for child-resistant compartments on products containing button batteries. The act, called Reese’s Law, has been referred to the Committee on Energy and Commerce and is under review.
Dr. Jatana reported having a patent pending for a coin or battery metal detector device under development; being a shareholder in Zotarix, Landsdowne Labs, and Tivic Health Systems; serving in a leadership position on the National Button Battery Task Force; and being a board member of the Global Injury Research Collaborative, which is a U.S. Internal Revenue Service–designated, 501(c)(3) nonprofit research organization. No other relevant disclosures were reported.
Severe airway injuries are a “not infrequent” consequence after children swallow button batteries, which are commonly found in many household electronics, according to a systematic review published online in JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.
Most literature has focused on esophageal injury, but “the direct apposition of the esophagus to the trachea and recurrent laryngeal nerves also places these children at risk of airway injury, such as tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) (a life-threatening complication), vocal cord paresis and paralysis, tracheal stenosis, and tracheomalacia,” the researchers wrote.
Led by Justine Philteos, MD, of the department of otolaryngology–head and neck surgery at the University of Toronto, the researchers found that tracheoesophageal fistula and vocal cord paralyses were the two most common airway injuries and often required tracheostomy.
The review included 195 children pulled from the National Capital Poison Center (NCPC) database – more often young children – who had ingested the batteries. The average age at ingestion was 17.8 months and the average time between ingestion and removal was 5.8 days.
Of the 195 children, 29 (15%) underwent tracheostomy, and 11 of the 29 children (38%) ultimately had decannulation. There were 14 deaths from swallowing the batteries. All 14 patients had a TEF. The cause of death was identified for 12 of the patients: Four died of pneumonia or respiratory failure; three of massive hematemesis; three of sepsis; one of multiorgan failure, and one of anoxic encephalopathy.
Vocal cord injury occurred after a shorter button battery exposure than other airway injuries.
The authors concluded that prioritizing quick button battery removal is essential “to decrease the devastating consequences of these injuries.”
In an invited commentary, Hannah Gibbs, and Kris R. Jatana, MD, of The Ohio State University in Columbus, described what’s being done to prevent and treat these injuries and what’s next.
They noted that ingestion is often unseen so diagnosis is difficult. Therefore, they wrote, a novel coin-battery metal detector could be a radiation-free, quick screening tool. They noted a patent-pending technology has been developed at Ohio State and Nationwide Children’s Hospital.
Honey can help slow injury
Some measures can be taken at home or in the hospital if battery swallowing is discovered, the editorialists noted.
In the home or in transport to the hospital, caregivers can give 10 mL of honey every 10 minutes until arrival if the child is older than 12 months.
At the hospital, 10 mL of either honey or sucralfate may be given every 10 minutes to slow the rate of injury until the battery can be surgically removed.
“The current NCPC guidelines suggest up to six doses may be given in the prehospital setting, with three additional doses administered in the hospital,” they wrote.
“These strategies should be considered earlier than 12 hours from ingestion, when there is no clinical concern for mediastinitis or sepsis. A child with an esophageal button battery should proceed to the operating room immediately regardless of whether he or she has recently eaten,” Ms. Gibbs and Dr. Jatana wrote.
App adds convenience to boost physician reporting
Foreign body ingestions are also severely underreported, they noted. They cited a survey of more than 400 physicians who directly manage foreign body ingestions that found only 11% of button battery injuries and 4% of all foreign body ingestion or aspiration events were reported. The great majority (92%) of respondents said they would report the events if that were more convenient.
To that end, the Global Injury Research Collaborative (GIRC) has created and released a free smartphone application, the GIRC App. It is available free on the iOS system (through App Store) and soon will be available on the Android system (through Google Play), they wrote.
Ms. Gibbs and Dr. Jatana urge other measures, including safer battery compartments and battery design, to reduce the likelihood of ingestion.
They pointed out that a bill was introduced in Congress that would require the Consumer Product Safety Commission to mandate a new standard for child-resistant compartments on products containing button batteries. The act, called Reese’s Law, has been referred to the Committee on Energy and Commerce and is under review.
Dr. Jatana reported having a patent pending for a coin or battery metal detector device under development; being a shareholder in Zotarix, Landsdowne Labs, and Tivic Health Systems; serving in a leadership position on the National Button Battery Task Force; and being a board member of the Global Injury Research Collaborative, which is a U.S. Internal Revenue Service–designated, 501(c)(3) nonprofit research organization. No other relevant disclosures were reported.
FROM JAMA OTOLARYNGOLOGY–HEAD & NECK SURGERY
Most COVID long-haulers suffer long-term debilitating neurologic symptoms
Most COVID-19 long-haulers continue to have brain fog, fatigue, and compromised quality of life more than a year after the initial infection, results from the most extensive follow-up to date of a group of long COVID patients show.
Most patients continue to experience debilitating neurologic symptoms an average of 15 months from symptom onset, Igor Koralnik, MD, who oversees the Neuro COVID-19 Clinic at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, said during a press briefing.
Surprisingly, in some cases, new symptoms appear that didn’t exist before, including variation of heart rate and blood pressure, and gastrointestinal symptoms, indicating there may be a late appearance in dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system in those patients, Dr. Koralnik said.
The study was published online in Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology.
Evolving symptoms
The investigators evaluated the evolution of neurologic symptoms in 52 adults who had mild COVID-19 symptoms and were not admitted to the hospital.
Their mean age was 43 years, 73% were women and 77% had received a COVID-19 vaccine. These patients have now been followed for between 11 and 18 months since their initial infection.
Overall, between first and follow-up evaluations, there was no significant change in the frequency of most neurologic symptoms, including brain fog (81% vs. 71%), numbness/tingling (69% vs. 65%), headache (67% vs. 54%), dizziness (50% vs. 54%), blurred vision (34% vs. 44%), tinnitus (33% vs. 42%), and fatigue (87% vs. 81%).
The only neurologic symptoms that decreased over time were loss of taste (63% vs. 27%) and smell (58% vs. 21%).
Conversely, heart rate and blood pressure variation (35% vs. 56%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (27% vs. 48%; P = .04) increased at follow-up evaluations.
Patients reported subjective improvements in their recovery, cognitive function and fatigue, but quality of life measures remained lower than the average population of the United States.
There was a neutral effect of COVID vaccination on long COVID symptoms – it didn’t cure long COVID or make long COVID worse, which is a reason given by some long-haulers for not getting vaccinated, Dr. Koralnik told the briefing.
Therefore, “we continue to encourage our patients to get vaccinated and boosted according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendation,” he said.
Escape from the ‘pit of despair’
To date, the Northwestern Medicine Neuro COVID-19 Clinic has treated nearly 1,400 COVID long-haulers from across the United States.
Emily Caffee, a physical therapist from Wheaton, Ill., is one of them.
Speaking at the briefing, the 36-year-old described her saga and roller coaster of recovering from long COVID in three acts: her initial infection, followed by a descent into a pit of physical and emotional despair, followed by her eventual escape from that pit more than two years later.
Following a fairly mild case of COVID, Ms. Caffee said worsening neurologic symptoms forced her to take medical leave from her very physical and cognitively demanding job.
Ms. Caffee said she experienced crushing fatigue and brain fog, as well as rapid heart rate and blood pressure changes going from sitting to standing position.
She went from being a competitive athlete to someone who could barely get off the couch or empty the dishwasher.
With the ongoing help of her medical team, she slowly returned to daily activities and eventually to work on a limited basis.
Today, Ms. Caffee says she’s 90%-95% better but still she has some lingering symptoms and does not yet feel like her pre-COVID self.
It’s been a very slow climb out of the pit, Ms. Caffee said.
This study has no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most COVID-19 long-haulers continue to have brain fog, fatigue, and compromised quality of life more than a year after the initial infection, results from the most extensive follow-up to date of a group of long COVID patients show.
Most patients continue to experience debilitating neurologic symptoms an average of 15 months from symptom onset, Igor Koralnik, MD, who oversees the Neuro COVID-19 Clinic at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, said during a press briefing.
Surprisingly, in some cases, new symptoms appear that didn’t exist before, including variation of heart rate and blood pressure, and gastrointestinal symptoms, indicating there may be a late appearance in dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system in those patients, Dr. Koralnik said.
The study was published online in Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology.
Evolving symptoms
The investigators evaluated the evolution of neurologic symptoms in 52 adults who had mild COVID-19 symptoms and were not admitted to the hospital.
Their mean age was 43 years, 73% were women and 77% had received a COVID-19 vaccine. These patients have now been followed for between 11 and 18 months since their initial infection.
Overall, between first and follow-up evaluations, there was no significant change in the frequency of most neurologic symptoms, including brain fog (81% vs. 71%), numbness/tingling (69% vs. 65%), headache (67% vs. 54%), dizziness (50% vs. 54%), blurred vision (34% vs. 44%), tinnitus (33% vs. 42%), and fatigue (87% vs. 81%).
The only neurologic symptoms that decreased over time were loss of taste (63% vs. 27%) and smell (58% vs. 21%).
Conversely, heart rate and blood pressure variation (35% vs. 56%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (27% vs. 48%; P = .04) increased at follow-up evaluations.
Patients reported subjective improvements in their recovery, cognitive function and fatigue, but quality of life measures remained lower than the average population of the United States.
There was a neutral effect of COVID vaccination on long COVID symptoms – it didn’t cure long COVID or make long COVID worse, which is a reason given by some long-haulers for not getting vaccinated, Dr. Koralnik told the briefing.
Therefore, “we continue to encourage our patients to get vaccinated and boosted according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendation,” he said.
Escape from the ‘pit of despair’
To date, the Northwestern Medicine Neuro COVID-19 Clinic has treated nearly 1,400 COVID long-haulers from across the United States.
Emily Caffee, a physical therapist from Wheaton, Ill., is one of them.
Speaking at the briefing, the 36-year-old described her saga and roller coaster of recovering from long COVID in three acts: her initial infection, followed by a descent into a pit of physical and emotional despair, followed by her eventual escape from that pit more than two years later.
Following a fairly mild case of COVID, Ms. Caffee said worsening neurologic symptoms forced her to take medical leave from her very physical and cognitively demanding job.
Ms. Caffee said she experienced crushing fatigue and brain fog, as well as rapid heart rate and blood pressure changes going from sitting to standing position.
She went from being a competitive athlete to someone who could barely get off the couch or empty the dishwasher.
With the ongoing help of her medical team, she slowly returned to daily activities and eventually to work on a limited basis.
Today, Ms. Caffee says she’s 90%-95% better but still she has some lingering symptoms and does not yet feel like her pre-COVID self.
It’s been a very slow climb out of the pit, Ms. Caffee said.
This study has no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most COVID-19 long-haulers continue to have brain fog, fatigue, and compromised quality of life more than a year after the initial infection, results from the most extensive follow-up to date of a group of long COVID patients show.
Most patients continue to experience debilitating neurologic symptoms an average of 15 months from symptom onset, Igor Koralnik, MD, who oversees the Neuro COVID-19 Clinic at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, said during a press briefing.
Surprisingly, in some cases, new symptoms appear that didn’t exist before, including variation of heart rate and blood pressure, and gastrointestinal symptoms, indicating there may be a late appearance in dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system in those patients, Dr. Koralnik said.
The study was published online in Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology.
Evolving symptoms
The investigators evaluated the evolution of neurologic symptoms in 52 adults who had mild COVID-19 symptoms and were not admitted to the hospital.
Their mean age was 43 years, 73% were women and 77% had received a COVID-19 vaccine. These patients have now been followed for between 11 and 18 months since their initial infection.
Overall, between first and follow-up evaluations, there was no significant change in the frequency of most neurologic symptoms, including brain fog (81% vs. 71%), numbness/tingling (69% vs. 65%), headache (67% vs. 54%), dizziness (50% vs. 54%), blurred vision (34% vs. 44%), tinnitus (33% vs. 42%), and fatigue (87% vs. 81%).
The only neurologic symptoms that decreased over time were loss of taste (63% vs. 27%) and smell (58% vs. 21%).
Conversely, heart rate and blood pressure variation (35% vs. 56%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (27% vs. 48%; P = .04) increased at follow-up evaluations.
Patients reported subjective improvements in their recovery, cognitive function and fatigue, but quality of life measures remained lower than the average population of the United States.
There was a neutral effect of COVID vaccination on long COVID symptoms – it didn’t cure long COVID or make long COVID worse, which is a reason given by some long-haulers for not getting vaccinated, Dr. Koralnik told the briefing.
Therefore, “we continue to encourage our patients to get vaccinated and boosted according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendation,” he said.
Escape from the ‘pit of despair’
To date, the Northwestern Medicine Neuro COVID-19 Clinic has treated nearly 1,400 COVID long-haulers from across the United States.
Emily Caffee, a physical therapist from Wheaton, Ill., is one of them.
Speaking at the briefing, the 36-year-old described her saga and roller coaster of recovering from long COVID in three acts: her initial infection, followed by a descent into a pit of physical and emotional despair, followed by her eventual escape from that pit more than two years later.
Following a fairly mild case of COVID, Ms. Caffee said worsening neurologic symptoms forced her to take medical leave from her very physical and cognitively demanding job.
Ms. Caffee said she experienced crushing fatigue and brain fog, as well as rapid heart rate and blood pressure changes going from sitting to standing position.
She went from being a competitive athlete to someone who could barely get off the couch or empty the dishwasher.
With the ongoing help of her medical team, she slowly returned to daily activities and eventually to work on a limited basis.
Today, Ms. Caffee says she’s 90%-95% better but still she has some lingering symptoms and does not yet feel like her pre-COVID self.
It’s been a very slow climb out of the pit, Ms. Caffee said.
This study has no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND TRANSLATIONAL NEUROLOGY
Legislative efforts continue to revamp laws governing PAs
INDIANAPOLIS – That’s according to Phil Bongiorno, BA, senior vice president of advocacy and government relations at the American Academy of Physician Associates (AAPA), who spoke at the group’s annual meeting.
OTP refers to the AAPA’s goal of improving patient access to care and lessening administrative obligations by eliminating the legal requirement that there be a specific relationship between a PA, physician, or any other health care provider. This would allow a PA to practice to the full extent of their education, training, and experience, Mr. Bongiorno said.
The second tenet of OTP is to persuade states to create a separate majority PA board to regulate PAs. An alternative to this would be for states to add PAs and physicians who work with PAs to their medical or healing arts boards, he said.
Third, in an OTP environment, each state would authorize PAs to be eligible for direct payment by all public and private insurers. “We have seen that development at the federal level, as far as Medicare is concerned,” Mr. Bongiorno said. “Now, we’re focusing on making that happen in the individual states as well.”
According to Mr. Bongiorno, this year’s state advocacy priorities are to pursue new legislation in additional states, even as efforts continue to persuade state legislatures to act on carryover bills from the previous legislative session.
Mr. Bongiorno briefly summarized what he called “OTP successes” from 2021:
- Federal government: Authorized direct payment to PAs under Medicare
- Arkansas, Delaware, Illinois, Pennsylvania: Added one or more PAs to their medical boards
- Florida, Utah: Approved direct payment to PAs
- Tennessee, Wisconsin: Created a separate PA review board
- Utah, Wisconsin: Removed the relationship/agreement requirement (Wisconsin now requires 10,000 hours of practice to remove the relationship requirement)
North Central region
In Colorado, House Bill 1095 (HB1095) would have removed requirements for a legal relationship between a PA and a physician. Initially that would have happened after 3,000 hours of practice, although changing that to 5,000 hours has been a compromise measure. PAs changing specialties must collaborate for 2,000 hours, now negotiated to 3,000 hours.
HB1095 ultimately was not successful last year or this year, said Erika Miller, director of state advocacy and outreach for the AAPA. “But we do see it as a success, because in the 2022 session, we managed to get it passed in committee by a 10-to-1 vote,” she said. “It then moved to the full house and was not successful there.”
Ms. Miller said that South Dakota Senate Bill 134 would have removed the requirement for a legal PA/physician relationship after 1,040 hours, which is the requirement for nurse practitioners. “South Dakota had introduced similar legislation the year before, but also like Colorado, they went from not getting out of committee last year to making it to the senate floor this time,” she said.
In Wisconsin, the new PA-affiliated credentialing board began on April 1. It gives PAs the authority to license, discipline, and write regulations, Ms. Miller said.
South Central region
Arizona Senate Bill 1367 included direct pay, removed the relationship tether with a physician, and made each PA fully responsible for the care they provide. “The bill passed out of committee successfully but did not make it to a vote due to unexpected struggles between the Arizona medical society and PA chapter,” said Shannon Morey, senior director of state advocacy and outreach at the AAPA. “They are ready to go again next year.”
In Louisiana, Senate Bill 158 is a “strong” bill that addressed all the desired aspects of OTP, Ms. Morey said; “The legislation stands subject to call on the Senate floor, but it has been killed by the sponsor.”
Northeast region
Massachusetts Senate Bill 740 (S740) would remove the legal tether between PA and physician, said Carson Walker, senior director of state advocacy and outreach at the AAPA. “The committee decided to extend its time in committee until June,” he said. “By next month, we expect that the committee will schedule a hearing that includes S740, and we fully plan on submitting testimony.”
In New York, Senate Bill 9233 (S9233) would remove physician supervision after 3,600 hours of practice.
“Just about 10 days ago, sponsors were able to have S9233 introduced, which is the most succinct and, I think, the most effective OTP bill I have ever seen,” Mr. Walker said.
“S9233 says that after 3,600 hours a PA can practice without the supervision of a physician, and that’s all. There’s not a lot of time left in this session, but we are hopeful that it lays the groundwork for success next year.”
New Hampshire Senate Bill 228 has passed the legislature and is awaiting the governor’s signature. It will allow direct payment, make PAs responsible for the care they provide, and shift the physician-PA relationship from supervision to collaboration, Mr. Walker said.
Southeast region
Stephanie Radix, senior director of state advocacy and outreach at the AAPA, discussed North Carolina’s Senate Bill 345, which passed the Senate unanimously in 2021 and has been carried over to this year’s session. The bill defines team-based settings, eliminates the relationship tether, and establishes a supervised career entry interval of 4,000 clinical hours in the state.
The legislature is slated to adjourn June 30, Ms. Radix said: “We are very hopeful that we will get it across the finish line.”
In an interview, Mr. Bongiorno said that the AAPA’s overall advocacy progress is as expected.
“Optimal team practice is about allowing each practice to make that determination on how the team should work as a true collaboration,” he said. “The bottom line is that OTP would allow us to reach more patients, serve the community, and ensure that people are able to get healthcare, especially in underserved areas.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
INDIANAPOLIS – That’s according to Phil Bongiorno, BA, senior vice president of advocacy and government relations at the American Academy of Physician Associates (AAPA), who spoke at the group’s annual meeting.
OTP refers to the AAPA’s goal of improving patient access to care and lessening administrative obligations by eliminating the legal requirement that there be a specific relationship between a PA, physician, or any other health care provider. This would allow a PA to practice to the full extent of their education, training, and experience, Mr. Bongiorno said.
The second tenet of OTP is to persuade states to create a separate majority PA board to regulate PAs. An alternative to this would be for states to add PAs and physicians who work with PAs to their medical or healing arts boards, he said.
Third, in an OTP environment, each state would authorize PAs to be eligible for direct payment by all public and private insurers. “We have seen that development at the federal level, as far as Medicare is concerned,” Mr. Bongiorno said. “Now, we’re focusing on making that happen in the individual states as well.”
According to Mr. Bongiorno, this year’s state advocacy priorities are to pursue new legislation in additional states, even as efforts continue to persuade state legislatures to act on carryover bills from the previous legislative session.
Mr. Bongiorno briefly summarized what he called “OTP successes” from 2021:
- Federal government: Authorized direct payment to PAs under Medicare
- Arkansas, Delaware, Illinois, Pennsylvania: Added one or more PAs to their medical boards
- Florida, Utah: Approved direct payment to PAs
- Tennessee, Wisconsin: Created a separate PA review board
- Utah, Wisconsin: Removed the relationship/agreement requirement (Wisconsin now requires 10,000 hours of practice to remove the relationship requirement)
North Central region
In Colorado, House Bill 1095 (HB1095) would have removed requirements for a legal relationship between a PA and a physician. Initially that would have happened after 3,000 hours of practice, although changing that to 5,000 hours has been a compromise measure. PAs changing specialties must collaborate for 2,000 hours, now negotiated to 3,000 hours.
HB1095 ultimately was not successful last year or this year, said Erika Miller, director of state advocacy and outreach for the AAPA. “But we do see it as a success, because in the 2022 session, we managed to get it passed in committee by a 10-to-1 vote,” she said. “It then moved to the full house and was not successful there.”
Ms. Miller said that South Dakota Senate Bill 134 would have removed the requirement for a legal PA/physician relationship after 1,040 hours, which is the requirement for nurse practitioners. “South Dakota had introduced similar legislation the year before, but also like Colorado, they went from not getting out of committee last year to making it to the senate floor this time,” she said.
In Wisconsin, the new PA-affiliated credentialing board began on April 1. It gives PAs the authority to license, discipline, and write regulations, Ms. Miller said.
South Central region
Arizona Senate Bill 1367 included direct pay, removed the relationship tether with a physician, and made each PA fully responsible for the care they provide. “The bill passed out of committee successfully but did not make it to a vote due to unexpected struggles between the Arizona medical society and PA chapter,” said Shannon Morey, senior director of state advocacy and outreach at the AAPA. “They are ready to go again next year.”
In Louisiana, Senate Bill 158 is a “strong” bill that addressed all the desired aspects of OTP, Ms. Morey said; “The legislation stands subject to call on the Senate floor, but it has been killed by the sponsor.”
Northeast region
Massachusetts Senate Bill 740 (S740) would remove the legal tether between PA and physician, said Carson Walker, senior director of state advocacy and outreach at the AAPA. “The committee decided to extend its time in committee until June,” he said. “By next month, we expect that the committee will schedule a hearing that includes S740, and we fully plan on submitting testimony.”
In New York, Senate Bill 9233 (S9233) would remove physician supervision after 3,600 hours of practice.
“Just about 10 days ago, sponsors were able to have S9233 introduced, which is the most succinct and, I think, the most effective OTP bill I have ever seen,” Mr. Walker said.
“S9233 says that after 3,600 hours a PA can practice without the supervision of a physician, and that’s all. There’s not a lot of time left in this session, but we are hopeful that it lays the groundwork for success next year.”
New Hampshire Senate Bill 228 has passed the legislature and is awaiting the governor’s signature. It will allow direct payment, make PAs responsible for the care they provide, and shift the physician-PA relationship from supervision to collaboration, Mr. Walker said.
Southeast region
Stephanie Radix, senior director of state advocacy and outreach at the AAPA, discussed North Carolina’s Senate Bill 345, which passed the Senate unanimously in 2021 and has been carried over to this year’s session. The bill defines team-based settings, eliminates the relationship tether, and establishes a supervised career entry interval of 4,000 clinical hours in the state.
The legislature is slated to adjourn June 30, Ms. Radix said: “We are very hopeful that we will get it across the finish line.”
In an interview, Mr. Bongiorno said that the AAPA’s overall advocacy progress is as expected.
“Optimal team practice is about allowing each practice to make that determination on how the team should work as a true collaboration,” he said. “The bottom line is that OTP would allow us to reach more patients, serve the community, and ensure that people are able to get healthcare, especially in underserved areas.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
INDIANAPOLIS – That’s according to Phil Bongiorno, BA, senior vice president of advocacy and government relations at the American Academy of Physician Associates (AAPA), who spoke at the group’s annual meeting.
OTP refers to the AAPA’s goal of improving patient access to care and lessening administrative obligations by eliminating the legal requirement that there be a specific relationship between a PA, physician, or any other health care provider. This would allow a PA to practice to the full extent of their education, training, and experience, Mr. Bongiorno said.
The second tenet of OTP is to persuade states to create a separate majority PA board to regulate PAs. An alternative to this would be for states to add PAs and physicians who work with PAs to their medical or healing arts boards, he said.
Third, in an OTP environment, each state would authorize PAs to be eligible for direct payment by all public and private insurers. “We have seen that development at the federal level, as far as Medicare is concerned,” Mr. Bongiorno said. “Now, we’re focusing on making that happen in the individual states as well.”
According to Mr. Bongiorno, this year’s state advocacy priorities are to pursue new legislation in additional states, even as efforts continue to persuade state legislatures to act on carryover bills from the previous legislative session.
Mr. Bongiorno briefly summarized what he called “OTP successes” from 2021:
- Federal government: Authorized direct payment to PAs under Medicare
- Arkansas, Delaware, Illinois, Pennsylvania: Added one or more PAs to their medical boards
- Florida, Utah: Approved direct payment to PAs
- Tennessee, Wisconsin: Created a separate PA review board
- Utah, Wisconsin: Removed the relationship/agreement requirement (Wisconsin now requires 10,000 hours of practice to remove the relationship requirement)
North Central region
In Colorado, House Bill 1095 (HB1095) would have removed requirements for a legal relationship between a PA and a physician. Initially that would have happened after 3,000 hours of practice, although changing that to 5,000 hours has been a compromise measure. PAs changing specialties must collaborate for 2,000 hours, now negotiated to 3,000 hours.
HB1095 ultimately was not successful last year or this year, said Erika Miller, director of state advocacy and outreach for the AAPA. “But we do see it as a success, because in the 2022 session, we managed to get it passed in committee by a 10-to-1 vote,” she said. “It then moved to the full house and was not successful there.”
Ms. Miller said that South Dakota Senate Bill 134 would have removed the requirement for a legal PA/physician relationship after 1,040 hours, which is the requirement for nurse practitioners. “South Dakota had introduced similar legislation the year before, but also like Colorado, they went from not getting out of committee last year to making it to the senate floor this time,” she said.
In Wisconsin, the new PA-affiliated credentialing board began on April 1. It gives PAs the authority to license, discipline, and write regulations, Ms. Miller said.
South Central region
Arizona Senate Bill 1367 included direct pay, removed the relationship tether with a physician, and made each PA fully responsible for the care they provide. “The bill passed out of committee successfully but did not make it to a vote due to unexpected struggles between the Arizona medical society and PA chapter,” said Shannon Morey, senior director of state advocacy and outreach at the AAPA. “They are ready to go again next year.”
In Louisiana, Senate Bill 158 is a “strong” bill that addressed all the desired aspects of OTP, Ms. Morey said; “The legislation stands subject to call on the Senate floor, but it has been killed by the sponsor.”
Northeast region
Massachusetts Senate Bill 740 (S740) would remove the legal tether between PA and physician, said Carson Walker, senior director of state advocacy and outreach at the AAPA. “The committee decided to extend its time in committee until June,” he said. “By next month, we expect that the committee will schedule a hearing that includes S740, and we fully plan on submitting testimony.”
In New York, Senate Bill 9233 (S9233) would remove physician supervision after 3,600 hours of practice.
“Just about 10 days ago, sponsors were able to have S9233 introduced, which is the most succinct and, I think, the most effective OTP bill I have ever seen,” Mr. Walker said.
“S9233 says that after 3,600 hours a PA can practice without the supervision of a physician, and that’s all. There’s not a lot of time left in this session, but we are hopeful that it lays the groundwork for success next year.”
New Hampshire Senate Bill 228 has passed the legislature and is awaiting the governor’s signature. It will allow direct payment, make PAs responsible for the care they provide, and shift the physician-PA relationship from supervision to collaboration, Mr. Walker said.
Southeast region
Stephanie Radix, senior director of state advocacy and outreach at the AAPA, discussed North Carolina’s Senate Bill 345, which passed the Senate unanimously in 2021 and has been carried over to this year’s session. The bill defines team-based settings, eliminates the relationship tether, and establishes a supervised career entry interval of 4,000 clinical hours in the state.
The legislature is slated to adjourn June 30, Ms. Radix said: “We are very hopeful that we will get it across the finish line.”
In an interview, Mr. Bongiorno said that the AAPA’s overall advocacy progress is as expected.
“Optimal team practice is about allowing each practice to make that determination on how the team should work as a true collaboration,” he said. “The bottom line is that OTP would allow us to reach more patients, serve the community, and ensure that people are able to get healthcare, especially in underserved areas.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAPA 2022
Researchers find a pathway to prevent COVID infection
What’s more, they have succeeded in closing the lock to block the virus and prevent it from interacting with the cell, thereby preventing infection.
UCLouvain emphasized that this discovery, which was published in Nature Communications, is sparking hope that an aerosol antiviral therapy can be developed that would eradicate the virus in the case of an infection or a high-risk contact.
For 2 years, the team under David Alsteens, PhD, a researcher at the UCLouvain Institute of Biomolecular Science and Technology, has been working hard to understand the precise molecular mechanisms the virus uses to infect a cell. They investigated the interaction between sialic acids, a kind of sugar residue present on the surface of cells, and the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein to clarify its role in the infection process.
It was already known that the function of the sugar residues that coat the cells is to promote cell recognition, thus enabling, in particular, viruses to identify their targets more easily, but also to provide them with a point of attachment and to facilitate infection of the cells.
The researchers have now revealed a variant of these sugars that interacts more strongly with the S protein than other sugars do.
In other words, the university explained, they found the set of keys that allows the virus to open the cell door. So, the researchers decided to catch the virus in its own trap, by preventing it from attaching to its host cell. To do this, they blocked the S protein’s points of attachment, thus suppressing any interaction with the cell surface, as if a padlock had been placed on the lock on the cell’s entry door.
Th researchers added that the advantage of this discovery is that it acts on the virus, irrespective of mutations.
The team of researchers will now conduct tests on mice to apply this blocking of virus binding sites and observe whether it works on the body. The results should make it possible to develop an antiviral therapy administered by aerosol in the case of infection or at-risk contact.
This discovery is also of interest for the future to counter other viruses with similar attachment factors.
This article was translated from MediQuality; a version appeared on Medscape.com.
What’s more, they have succeeded in closing the lock to block the virus and prevent it from interacting with the cell, thereby preventing infection.
UCLouvain emphasized that this discovery, which was published in Nature Communications, is sparking hope that an aerosol antiviral therapy can be developed that would eradicate the virus in the case of an infection or a high-risk contact.
For 2 years, the team under David Alsteens, PhD, a researcher at the UCLouvain Institute of Biomolecular Science and Technology, has been working hard to understand the precise molecular mechanisms the virus uses to infect a cell. They investigated the interaction between sialic acids, a kind of sugar residue present on the surface of cells, and the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein to clarify its role in the infection process.
It was already known that the function of the sugar residues that coat the cells is to promote cell recognition, thus enabling, in particular, viruses to identify their targets more easily, but also to provide them with a point of attachment and to facilitate infection of the cells.
The researchers have now revealed a variant of these sugars that interacts more strongly with the S protein than other sugars do.
In other words, the university explained, they found the set of keys that allows the virus to open the cell door. So, the researchers decided to catch the virus in its own trap, by preventing it from attaching to its host cell. To do this, they blocked the S protein’s points of attachment, thus suppressing any interaction with the cell surface, as if a padlock had been placed on the lock on the cell’s entry door.
Th researchers added that the advantage of this discovery is that it acts on the virus, irrespective of mutations.
The team of researchers will now conduct tests on mice to apply this blocking of virus binding sites and observe whether it works on the body. The results should make it possible to develop an antiviral therapy administered by aerosol in the case of infection or at-risk contact.
This discovery is also of interest for the future to counter other viruses with similar attachment factors.
This article was translated from MediQuality; a version appeared on Medscape.com.
What’s more, they have succeeded in closing the lock to block the virus and prevent it from interacting with the cell, thereby preventing infection.
UCLouvain emphasized that this discovery, which was published in Nature Communications, is sparking hope that an aerosol antiviral therapy can be developed that would eradicate the virus in the case of an infection or a high-risk contact.
For 2 years, the team under David Alsteens, PhD, a researcher at the UCLouvain Institute of Biomolecular Science and Technology, has been working hard to understand the precise molecular mechanisms the virus uses to infect a cell. They investigated the interaction between sialic acids, a kind of sugar residue present on the surface of cells, and the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein to clarify its role in the infection process.
It was already known that the function of the sugar residues that coat the cells is to promote cell recognition, thus enabling, in particular, viruses to identify their targets more easily, but also to provide them with a point of attachment and to facilitate infection of the cells.
The researchers have now revealed a variant of these sugars that interacts more strongly with the S protein than other sugars do.
In other words, the university explained, they found the set of keys that allows the virus to open the cell door. So, the researchers decided to catch the virus in its own trap, by preventing it from attaching to its host cell. To do this, they blocked the S protein’s points of attachment, thus suppressing any interaction with the cell surface, as if a padlock had been placed on the lock on the cell’s entry door.
Th researchers added that the advantage of this discovery is that it acts on the virus, irrespective of mutations.
The team of researchers will now conduct tests on mice to apply this blocking of virus binding sites and observe whether it works on the body. The results should make it possible to develop an antiviral therapy administered by aerosol in the case of infection or at-risk contact.
This discovery is also of interest for the future to counter other viruses with similar attachment factors.
This article was translated from MediQuality; a version appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
Video game obsession: Definitions and best treatments remain elusive
NEW ORLEANS – Research into video game addiction is turning up new insights, and some treatments seem to make a difference, according to addiction psychiatry experts speaking at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. Still, understanding remains limited amid a general lack of clarity about definitions, measurements, and the most effective treatment strategies.
“Video games have the potential to be uniquely addictive, and it’s difficult to come up with treatment modalities that you can use for kids who have access to these things 24/7 on their mobile phones or laptops,” psychiatrist James C. Sherer, MD, of NYU Langone Health, said during the May 22 session, “Internet Gaming Disorder: From Harmless Fun to Dependence,” at the meeting. “It makes treating this a really complicated endeavor.”
The number of people with so-called Internet gaming disorder is unknown, but video games remain wildly popular among adults and children of all genders. According to a 2021 survey by Common Sense Media, U.S. individuals aged 8-12 and 13-18 spent an average of 1:27 hours and 1:46 hours per day, respectively, playing video games.
“Video games are an extremely important part of normal social networking among kids, and there’s a huge amount of social pressure to be good,” Dr. Sherer said. “If you’re in a particularly affluent neighborhood, it’s not unheard of for a parent to hire a coach to make their kid good at a game like Fortnite so they impress the other kids.”
The 2013 edition of the DSM-5 doesn’t list Internet gaming disorder as a mental illness but suggests that the topic warrants more research and evaluation, Dr. Sherer said.
Why are video games so addicting? According to Dr. Sherer, they’re simply designed that way. Game manufacturers “employ psychologists and behaviorists whose only job is to look at the game and determine what colors and what sounds are most likely to make you spend a little bit extra.” And with the help of the Internet, video games have evolved over the past 40 years to encourage users to make multiple purchases on single games such as Candy Crush instead of simply buying, say, a single 1980s-style Atari cartridge.
According to Dr. Sherer, research suggests that video games place users into something called the “flow state,” which a recent review article published in Frontiers in Psychology describes as “a state of full task engagement that is accompanied with low-levels of self-referential thinking” and “highly relevant for human performance and well-being.”
Diagnosing gaming addiction
How can psychiatrists diagnose video gaming addiction? Dr. Sherer, who is himself a devoted gamer, advised against focusing too much on time spent gaming in determining whether a patient has a problem. Instead, keep in mind that excessive gaming can displace exercise and normal socialization, he said, and lead to worsening mood.
Rober Aziz, MD, also of NYU Langone Health, suggested asking these questions: What types of games do you play? How long do you spend playing? What’s your reason for playing? What’s the meaning of your character choices? Does this game interfere with school or work? Have you neglected your self-care to play more?
He recommends other questions, too: Have you tried to limit your play time without success? How uncomfortable do you get if you must stop in the middle of playing? Do you get agitated if servers go down unexpectedly?
“There’s actually a lot of parallel here to other addictions that we’re very familiar with,” he said.
According to Dr. Sherer, it’s helpful to know that children who have attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder tend to struggle with gaming addiction the most. He highlighted a brain-scan study in the Journal of Attention Disorders that found that patients with gaming addiction and ADHD had less functional connectivity from the cortex to the subcortex compared to matched controls. But treatment helped increase connectivity in those with good prognoses.
The findings are “heartening,” he said. “Basically, if you’re treating ADHD, you’re treating Internet gaming disorder. And if you’re treating Internet gaming disorder, you’re treating ADHD.”
As for treatments, the speakers agreed that there is little research to point in the right direction regarding gaming addiction specifically.
According to Dr. Aziz, research has suggested that bupropion, methylphenidate, and escitalopram can be helpful. In terms of nondrug approaches, he recommends directing patients toward games that have distinct beginnings, middles, and ends instead of endlessly providing rewards. One such game is “Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild” on the Nintendo Switch platform, he said.
On the psychotherapy front, Dr. Aziz said, “reducing use rather than abstinence should be the treatment goal.” Research suggests that cognitive behavioral therapy may not help patients in the long term, he said. Other strategies, he said, include specific approaches known as “CBT for Internet addiction” and “motivational interviewing for Internet gaming disorder.”
Gaming addiction treatment centers have also popped up in the U.S., he said, and there’s now an organization called Gaming Addicts Anonymous.
The good news is that “there is a lot of active research that’s being done” into treating video game addiction, said psychiatrist Anil Thomas, MD, program director of the addiction psychiatry fellowship at NYU Langone Health and moderator of the APA session. “We just have to wait to see what the results are.”
NEW ORLEANS – Research into video game addiction is turning up new insights, and some treatments seem to make a difference, according to addiction psychiatry experts speaking at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. Still, understanding remains limited amid a general lack of clarity about definitions, measurements, and the most effective treatment strategies.
“Video games have the potential to be uniquely addictive, and it’s difficult to come up with treatment modalities that you can use for kids who have access to these things 24/7 on their mobile phones or laptops,” psychiatrist James C. Sherer, MD, of NYU Langone Health, said during the May 22 session, “Internet Gaming Disorder: From Harmless Fun to Dependence,” at the meeting. “It makes treating this a really complicated endeavor.”
The number of people with so-called Internet gaming disorder is unknown, but video games remain wildly popular among adults and children of all genders. According to a 2021 survey by Common Sense Media, U.S. individuals aged 8-12 and 13-18 spent an average of 1:27 hours and 1:46 hours per day, respectively, playing video games.
“Video games are an extremely important part of normal social networking among kids, and there’s a huge amount of social pressure to be good,” Dr. Sherer said. “If you’re in a particularly affluent neighborhood, it’s not unheard of for a parent to hire a coach to make their kid good at a game like Fortnite so they impress the other kids.”
The 2013 edition of the DSM-5 doesn’t list Internet gaming disorder as a mental illness but suggests that the topic warrants more research and evaluation, Dr. Sherer said.
Why are video games so addicting? According to Dr. Sherer, they’re simply designed that way. Game manufacturers “employ psychologists and behaviorists whose only job is to look at the game and determine what colors and what sounds are most likely to make you spend a little bit extra.” And with the help of the Internet, video games have evolved over the past 40 years to encourage users to make multiple purchases on single games such as Candy Crush instead of simply buying, say, a single 1980s-style Atari cartridge.
According to Dr. Sherer, research suggests that video games place users into something called the “flow state,” which a recent review article published in Frontiers in Psychology describes as “a state of full task engagement that is accompanied with low-levels of self-referential thinking” and “highly relevant for human performance and well-being.”
Diagnosing gaming addiction
How can psychiatrists diagnose video gaming addiction? Dr. Sherer, who is himself a devoted gamer, advised against focusing too much on time spent gaming in determining whether a patient has a problem. Instead, keep in mind that excessive gaming can displace exercise and normal socialization, he said, and lead to worsening mood.
Rober Aziz, MD, also of NYU Langone Health, suggested asking these questions: What types of games do you play? How long do you spend playing? What’s your reason for playing? What’s the meaning of your character choices? Does this game interfere with school or work? Have you neglected your self-care to play more?
He recommends other questions, too: Have you tried to limit your play time without success? How uncomfortable do you get if you must stop in the middle of playing? Do you get agitated if servers go down unexpectedly?
“There’s actually a lot of parallel here to other addictions that we’re very familiar with,” he said.
According to Dr. Sherer, it’s helpful to know that children who have attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder tend to struggle with gaming addiction the most. He highlighted a brain-scan study in the Journal of Attention Disorders that found that patients with gaming addiction and ADHD had less functional connectivity from the cortex to the subcortex compared to matched controls. But treatment helped increase connectivity in those with good prognoses.
The findings are “heartening,” he said. “Basically, if you’re treating ADHD, you’re treating Internet gaming disorder. And if you’re treating Internet gaming disorder, you’re treating ADHD.”
As for treatments, the speakers agreed that there is little research to point in the right direction regarding gaming addiction specifically.
According to Dr. Aziz, research has suggested that bupropion, methylphenidate, and escitalopram can be helpful. In terms of nondrug approaches, he recommends directing patients toward games that have distinct beginnings, middles, and ends instead of endlessly providing rewards. One such game is “Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild” on the Nintendo Switch platform, he said.
On the psychotherapy front, Dr. Aziz said, “reducing use rather than abstinence should be the treatment goal.” Research suggests that cognitive behavioral therapy may not help patients in the long term, he said. Other strategies, he said, include specific approaches known as “CBT for Internet addiction” and “motivational interviewing for Internet gaming disorder.”
Gaming addiction treatment centers have also popped up in the U.S., he said, and there’s now an organization called Gaming Addicts Anonymous.
The good news is that “there is a lot of active research that’s being done” into treating video game addiction, said psychiatrist Anil Thomas, MD, program director of the addiction psychiatry fellowship at NYU Langone Health and moderator of the APA session. “We just have to wait to see what the results are.”
NEW ORLEANS – Research into video game addiction is turning up new insights, and some treatments seem to make a difference, according to addiction psychiatry experts speaking at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. Still, understanding remains limited amid a general lack of clarity about definitions, measurements, and the most effective treatment strategies.
“Video games have the potential to be uniquely addictive, and it’s difficult to come up with treatment modalities that you can use for kids who have access to these things 24/7 on their mobile phones or laptops,” psychiatrist James C. Sherer, MD, of NYU Langone Health, said during the May 22 session, “Internet Gaming Disorder: From Harmless Fun to Dependence,” at the meeting. “It makes treating this a really complicated endeavor.”
The number of people with so-called Internet gaming disorder is unknown, but video games remain wildly popular among adults and children of all genders. According to a 2021 survey by Common Sense Media, U.S. individuals aged 8-12 and 13-18 spent an average of 1:27 hours and 1:46 hours per day, respectively, playing video games.
“Video games are an extremely important part of normal social networking among kids, and there’s a huge amount of social pressure to be good,” Dr. Sherer said. “If you’re in a particularly affluent neighborhood, it’s not unheard of for a parent to hire a coach to make their kid good at a game like Fortnite so they impress the other kids.”
The 2013 edition of the DSM-5 doesn’t list Internet gaming disorder as a mental illness but suggests that the topic warrants more research and evaluation, Dr. Sherer said.
Why are video games so addicting? According to Dr. Sherer, they’re simply designed that way. Game manufacturers “employ psychologists and behaviorists whose only job is to look at the game and determine what colors and what sounds are most likely to make you spend a little bit extra.” And with the help of the Internet, video games have evolved over the past 40 years to encourage users to make multiple purchases on single games such as Candy Crush instead of simply buying, say, a single 1980s-style Atari cartridge.
According to Dr. Sherer, research suggests that video games place users into something called the “flow state,” which a recent review article published in Frontiers in Psychology describes as “a state of full task engagement that is accompanied with low-levels of self-referential thinking” and “highly relevant for human performance and well-being.”
Diagnosing gaming addiction
How can psychiatrists diagnose video gaming addiction? Dr. Sherer, who is himself a devoted gamer, advised against focusing too much on time spent gaming in determining whether a patient has a problem. Instead, keep in mind that excessive gaming can displace exercise and normal socialization, he said, and lead to worsening mood.
Rober Aziz, MD, also of NYU Langone Health, suggested asking these questions: What types of games do you play? How long do you spend playing? What’s your reason for playing? What’s the meaning of your character choices? Does this game interfere with school or work? Have you neglected your self-care to play more?
He recommends other questions, too: Have you tried to limit your play time without success? How uncomfortable do you get if you must stop in the middle of playing? Do you get agitated if servers go down unexpectedly?
“There’s actually a lot of parallel here to other addictions that we’re very familiar with,” he said.
According to Dr. Sherer, it’s helpful to know that children who have attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder tend to struggle with gaming addiction the most. He highlighted a brain-scan study in the Journal of Attention Disorders that found that patients with gaming addiction and ADHD had less functional connectivity from the cortex to the subcortex compared to matched controls. But treatment helped increase connectivity in those with good prognoses.
The findings are “heartening,” he said. “Basically, if you’re treating ADHD, you’re treating Internet gaming disorder. And if you’re treating Internet gaming disorder, you’re treating ADHD.”
As for treatments, the speakers agreed that there is little research to point in the right direction regarding gaming addiction specifically.
According to Dr. Aziz, research has suggested that bupropion, methylphenidate, and escitalopram can be helpful. In terms of nondrug approaches, he recommends directing patients toward games that have distinct beginnings, middles, and ends instead of endlessly providing rewards. One such game is “Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild” on the Nintendo Switch platform, he said.
On the psychotherapy front, Dr. Aziz said, “reducing use rather than abstinence should be the treatment goal.” Research suggests that cognitive behavioral therapy may not help patients in the long term, he said. Other strategies, he said, include specific approaches known as “CBT for Internet addiction” and “motivational interviewing for Internet gaming disorder.”
Gaming addiction treatment centers have also popped up in the U.S., he said, and there’s now an organization called Gaming Addicts Anonymous.
The good news is that “there is a lot of active research that’s being done” into treating video game addiction, said psychiatrist Anil Thomas, MD, program director of the addiction psychiatry fellowship at NYU Langone Health and moderator of the APA session. “We just have to wait to see what the results are.”
AT APA 2022
Crohn’s disease research goes to the dogs
Why it might be better to be a dog person
Here’s that old debate again: Dogs or cats? You probably have your own opinion, but research presented at this year’s Digestive Disease Week may have tipped the scale by showing that children who lived with dogs may be less likely to have Crohn’s disease as adults.
The research was done by having approximately 4,300 people closely related to patients with Crohn’s disease fill out an environmental questionnaire. Using these data, the research team looked into environmental factors such as size of the families, where the home was, how many bathrooms the homes had, and quality of drinking water.
The researchers found that those who had or were exposed to dogs between the ages of 5 and 15 years were more likely to have healthy gut permeability and balanced microbes, which increased their protection against Crohn’s disease.
“Our study seems to add to others that have explored the ‘hygiene hypothesis’ which suggests that the lack of exposure to microbes early in life may lead to lack of immune regulation toward environmental microbes,” senior author Williams Turpin, PhD, said in the written statement.
The researchers aren’t sure why they didn’t get the same findings with cats, but Dr. Turpin theorized that dog owners tend to be outside more with their dogs or live in places with more green space, which are good protectors against Crohn’s disease.
It’s all good for dog owners, but do their pets’ parasites make you more attractive? Just more fuel for the ongoing debate.
Come for the history, stay for the fossilized parasites
Another week, another analysis of old British poop. LOTME really is your one-stop shop for all the important, hard-hitting news about historic parasites. You’re welcome, Internet.
The news this week is from Stonehenge, which is apparently kind of a big deal. Rocks in a circle, celestial calendar, cultural significance, whatever. We’re not here to talk about rocks. We’re here to talk about, uh, rocks. Smaller rocks. Specifically, coprolites, which are essentially poop turned into a rock. (Though now we’re imagining Stonehenge made out of fossilized poop rocks. Would it still be a big tourist destination? We can see both sides of the argument on that one.)
Archaeologists from the University of Cambridge have conducted an analysis of coprolites from Durrington Walls, a Neolithic settlement just a few kilometers from Stonehenge. The town dates to the same time that Stonehenge was constructed, and it’s believed that the residents were responsible for building the landmark. These coprolites, depending on what’s inside, can tell us a lot about how the builders of Stonehenge lived and, more specifically, how they ate.
In this case, the coprolites of one human and three dogs contained capillariid worm eggs. These worms come from cows, and when a human is typically infected, the eggs embed in the liver and do not pass through the body. Finding them in excrement indicates that the people were eating raw cow organs and feeding leftovers to their dogs. This is interesting, because a preponderance of pottery and cooking implements also found at the site indicates that the residents of Durrington Walls were spit-roasting or boiling their beef and pork. So the meat was cooked, but not the organs. That is an interesting dietary decision, ancient British people. Then again, modern British cuisine exists. At least now we know where they got it from.
This new research raises one other very important question: When are we going to get a full-on guided tour of all the important coprolite sites in Britain? They’ve clearly got plenty of them, and the tourist demand for ancient parasites must be sky-high. Come on, capitalism, follow through on this. We’d go.
Everyone lies: Food intake edition
Do you have any patients on special diets? Do you ask them if they are following those diets? Don’t bother, because they’re lying. Everyone lies about the food they eat. Everyone. Obese people lie, and nonobese people lie.
Investigators at the University of Essex in England asked 221 adults to keep food diaries, and then they checked on energy consumption by analyzing radioactive water levels in the participants’ urine over a 10-day period.
Underreporting of food consumption was rampant, even among those who were not obese. The obese subjects did underreport by a greater extent (1,200 calories per day) than did those who were not obese, who were off by only 800 calories, but the obese participants burned about 400 calories more each day than did the nonobese, so the difference was a wash.
Everyone ended up underreporting their calorie consumption by an average of about 900 calories, and the investigators were good enough to provide some food equivalents, tops on the list being three MacDonald’s cheeseburgers.
“Public health recommendations have historically relied heavily on self-reported energy intake values,” senior author Gavin Sandercock, PhD, said in a EurekAlert statement, and “recognising that the measures of energy intake are incorrect might result in the setting of more realistic targets.”
Maybe you can be more realistic with your patients, too. Go ahead and ask Mr. Smith about the burger sticking out of his coat pocket, because there are probably two more you can’t see. We’ve each got 900 calories hiding on us somewhere. Ours is usually pizza.
The art of the gallbladder
Ever thought you would see a portrait of a gallbladder hanging up in a gallery? Not just an artist’s rendition, but an actual photo from an actual patient? Well, you can at the Soloway Gallery in Brooklyn, N.Y., at least until June 12.
The artist? K.C. Joseph, MD, a general surgeon from St. Marie, Pa., who died in 2015. His daughter Melissa is the curator of the show and told ARTnews about the interesting connection her father had with art and surgery.
In 2010, Dr. Joseph gave his daughter a box of photos and said “Make me a famous artist,” she recalled. At first, “I was like, ‘These are weird,’ and then I put them under my bed for 10 years.”
Apparently he had been making art with his patients’ organs for about 15 years and had a system in which he put each one together. Before a surgery Dr. Joseph would make a note card with the patient’s name handwritten in calligraphy with a couple of pages taken out of the magazine from the waiting room as the backdrop. Afterward, when the patient was in recovery, the removed organ would be placed among the pages and the name card. A photo was taken with the same endoscope that was used for the procedure.
After the show’s debut, people reached out expressing their love for their photos. “I wish, before he died, I had asked him more questions about it,” Ms. Joseph told ARTnews. “I’m regretting it so much now, kicking myself.”
Who gets to take home an artsy photo of their gallbladder after getting it removed? Not us, that’s who. Each collage is a one-of-a-kind piece. They definitely should be framed and shown in an art gallery. Oh, right. Never mind.
Why it might be better to be a dog person
Here’s that old debate again: Dogs or cats? You probably have your own opinion, but research presented at this year’s Digestive Disease Week may have tipped the scale by showing that children who lived with dogs may be less likely to have Crohn’s disease as adults.
The research was done by having approximately 4,300 people closely related to patients with Crohn’s disease fill out an environmental questionnaire. Using these data, the research team looked into environmental factors such as size of the families, where the home was, how many bathrooms the homes had, and quality of drinking water.
The researchers found that those who had or were exposed to dogs between the ages of 5 and 15 years were more likely to have healthy gut permeability and balanced microbes, which increased their protection against Crohn’s disease.
“Our study seems to add to others that have explored the ‘hygiene hypothesis’ which suggests that the lack of exposure to microbes early in life may lead to lack of immune regulation toward environmental microbes,” senior author Williams Turpin, PhD, said in the written statement.
The researchers aren’t sure why they didn’t get the same findings with cats, but Dr. Turpin theorized that dog owners tend to be outside more with their dogs or live in places with more green space, which are good protectors against Crohn’s disease.
It’s all good for dog owners, but do their pets’ parasites make you more attractive? Just more fuel for the ongoing debate.
Come for the history, stay for the fossilized parasites
Another week, another analysis of old British poop. LOTME really is your one-stop shop for all the important, hard-hitting news about historic parasites. You’re welcome, Internet.
The news this week is from Stonehenge, which is apparently kind of a big deal. Rocks in a circle, celestial calendar, cultural significance, whatever. We’re not here to talk about rocks. We’re here to talk about, uh, rocks. Smaller rocks. Specifically, coprolites, which are essentially poop turned into a rock. (Though now we’re imagining Stonehenge made out of fossilized poop rocks. Would it still be a big tourist destination? We can see both sides of the argument on that one.)
Archaeologists from the University of Cambridge have conducted an analysis of coprolites from Durrington Walls, a Neolithic settlement just a few kilometers from Stonehenge. The town dates to the same time that Stonehenge was constructed, and it’s believed that the residents were responsible for building the landmark. These coprolites, depending on what’s inside, can tell us a lot about how the builders of Stonehenge lived and, more specifically, how they ate.
In this case, the coprolites of one human and three dogs contained capillariid worm eggs. These worms come from cows, and when a human is typically infected, the eggs embed in the liver and do not pass through the body. Finding them in excrement indicates that the people were eating raw cow organs and feeding leftovers to their dogs. This is interesting, because a preponderance of pottery and cooking implements also found at the site indicates that the residents of Durrington Walls were spit-roasting or boiling their beef and pork. So the meat was cooked, but not the organs. That is an interesting dietary decision, ancient British people. Then again, modern British cuisine exists. At least now we know where they got it from.
This new research raises one other very important question: When are we going to get a full-on guided tour of all the important coprolite sites in Britain? They’ve clearly got plenty of them, and the tourist demand for ancient parasites must be sky-high. Come on, capitalism, follow through on this. We’d go.
Everyone lies: Food intake edition
Do you have any patients on special diets? Do you ask them if they are following those diets? Don’t bother, because they’re lying. Everyone lies about the food they eat. Everyone. Obese people lie, and nonobese people lie.
Investigators at the University of Essex in England asked 221 adults to keep food diaries, and then they checked on energy consumption by analyzing radioactive water levels in the participants’ urine over a 10-day period.
Underreporting of food consumption was rampant, even among those who were not obese. The obese subjects did underreport by a greater extent (1,200 calories per day) than did those who were not obese, who were off by only 800 calories, but the obese participants burned about 400 calories more each day than did the nonobese, so the difference was a wash.
Everyone ended up underreporting their calorie consumption by an average of about 900 calories, and the investigators were good enough to provide some food equivalents, tops on the list being three MacDonald’s cheeseburgers.
“Public health recommendations have historically relied heavily on self-reported energy intake values,” senior author Gavin Sandercock, PhD, said in a EurekAlert statement, and “recognising that the measures of energy intake are incorrect might result in the setting of more realistic targets.”
Maybe you can be more realistic with your patients, too. Go ahead and ask Mr. Smith about the burger sticking out of his coat pocket, because there are probably two more you can’t see. We’ve each got 900 calories hiding on us somewhere. Ours is usually pizza.
The art of the gallbladder
Ever thought you would see a portrait of a gallbladder hanging up in a gallery? Not just an artist’s rendition, but an actual photo from an actual patient? Well, you can at the Soloway Gallery in Brooklyn, N.Y., at least until June 12.
The artist? K.C. Joseph, MD, a general surgeon from St. Marie, Pa., who died in 2015. His daughter Melissa is the curator of the show and told ARTnews about the interesting connection her father had with art and surgery.
In 2010, Dr. Joseph gave his daughter a box of photos and said “Make me a famous artist,” she recalled. At first, “I was like, ‘These are weird,’ and then I put them under my bed for 10 years.”
Apparently he had been making art with his patients’ organs for about 15 years and had a system in which he put each one together. Before a surgery Dr. Joseph would make a note card with the patient’s name handwritten in calligraphy with a couple of pages taken out of the magazine from the waiting room as the backdrop. Afterward, when the patient was in recovery, the removed organ would be placed among the pages and the name card. A photo was taken with the same endoscope that was used for the procedure.
After the show’s debut, people reached out expressing their love for their photos. “I wish, before he died, I had asked him more questions about it,” Ms. Joseph told ARTnews. “I’m regretting it so much now, kicking myself.”
Who gets to take home an artsy photo of their gallbladder after getting it removed? Not us, that’s who. Each collage is a one-of-a-kind piece. They definitely should be framed and shown in an art gallery. Oh, right. Never mind.
Why it might be better to be a dog person
Here’s that old debate again: Dogs or cats? You probably have your own opinion, but research presented at this year’s Digestive Disease Week may have tipped the scale by showing that children who lived with dogs may be less likely to have Crohn’s disease as adults.
The research was done by having approximately 4,300 people closely related to patients with Crohn’s disease fill out an environmental questionnaire. Using these data, the research team looked into environmental factors such as size of the families, where the home was, how many bathrooms the homes had, and quality of drinking water.
The researchers found that those who had or were exposed to dogs between the ages of 5 and 15 years were more likely to have healthy gut permeability and balanced microbes, which increased their protection against Crohn’s disease.
“Our study seems to add to others that have explored the ‘hygiene hypothesis’ which suggests that the lack of exposure to microbes early in life may lead to lack of immune regulation toward environmental microbes,” senior author Williams Turpin, PhD, said in the written statement.
The researchers aren’t sure why they didn’t get the same findings with cats, but Dr. Turpin theorized that dog owners tend to be outside more with their dogs or live in places with more green space, which are good protectors against Crohn’s disease.
It’s all good for dog owners, but do their pets’ parasites make you more attractive? Just more fuel for the ongoing debate.
Come for the history, stay for the fossilized parasites
Another week, another analysis of old British poop. LOTME really is your one-stop shop for all the important, hard-hitting news about historic parasites. You’re welcome, Internet.
The news this week is from Stonehenge, which is apparently kind of a big deal. Rocks in a circle, celestial calendar, cultural significance, whatever. We’re not here to talk about rocks. We’re here to talk about, uh, rocks. Smaller rocks. Specifically, coprolites, which are essentially poop turned into a rock. (Though now we’re imagining Stonehenge made out of fossilized poop rocks. Would it still be a big tourist destination? We can see both sides of the argument on that one.)
Archaeologists from the University of Cambridge have conducted an analysis of coprolites from Durrington Walls, a Neolithic settlement just a few kilometers from Stonehenge. The town dates to the same time that Stonehenge was constructed, and it’s believed that the residents were responsible for building the landmark. These coprolites, depending on what’s inside, can tell us a lot about how the builders of Stonehenge lived and, more specifically, how they ate.
In this case, the coprolites of one human and three dogs contained capillariid worm eggs. These worms come from cows, and when a human is typically infected, the eggs embed in the liver and do not pass through the body. Finding them in excrement indicates that the people were eating raw cow organs and feeding leftovers to their dogs. This is interesting, because a preponderance of pottery and cooking implements also found at the site indicates that the residents of Durrington Walls were spit-roasting or boiling their beef and pork. So the meat was cooked, but not the organs. That is an interesting dietary decision, ancient British people. Then again, modern British cuisine exists. At least now we know where they got it from.
This new research raises one other very important question: When are we going to get a full-on guided tour of all the important coprolite sites in Britain? They’ve clearly got plenty of them, and the tourist demand for ancient parasites must be sky-high. Come on, capitalism, follow through on this. We’d go.
Everyone lies: Food intake edition
Do you have any patients on special diets? Do you ask them if they are following those diets? Don’t bother, because they’re lying. Everyone lies about the food they eat. Everyone. Obese people lie, and nonobese people lie.
Investigators at the University of Essex in England asked 221 adults to keep food diaries, and then they checked on energy consumption by analyzing radioactive water levels in the participants’ urine over a 10-day period.
Underreporting of food consumption was rampant, even among those who were not obese. The obese subjects did underreport by a greater extent (1,200 calories per day) than did those who were not obese, who were off by only 800 calories, but the obese participants burned about 400 calories more each day than did the nonobese, so the difference was a wash.
Everyone ended up underreporting their calorie consumption by an average of about 900 calories, and the investigators were good enough to provide some food equivalents, tops on the list being three MacDonald’s cheeseburgers.
“Public health recommendations have historically relied heavily on self-reported energy intake values,” senior author Gavin Sandercock, PhD, said in a EurekAlert statement, and “recognising that the measures of energy intake are incorrect might result in the setting of more realistic targets.”
Maybe you can be more realistic with your patients, too. Go ahead and ask Mr. Smith about the burger sticking out of his coat pocket, because there are probably two more you can’t see. We’ve each got 900 calories hiding on us somewhere. Ours is usually pizza.
The art of the gallbladder
Ever thought you would see a portrait of a gallbladder hanging up in a gallery? Not just an artist’s rendition, but an actual photo from an actual patient? Well, you can at the Soloway Gallery in Brooklyn, N.Y., at least until June 12.
The artist? K.C. Joseph, MD, a general surgeon from St. Marie, Pa., who died in 2015. His daughter Melissa is the curator of the show and told ARTnews about the interesting connection her father had with art and surgery.
In 2010, Dr. Joseph gave his daughter a box of photos and said “Make me a famous artist,” she recalled. At first, “I was like, ‘These are weird,’ and then I put them under my bed for 10 years.”
Apparently he had been making art with his patients’ organs for about 15 years and had a system in which he put each one together. Before a surgery Dr. Joseph would make a note card with the patient’s name handwritten in calligraphy with a couple of pages taken out of the magazine from the waiting room as the backdrop. Afterward, when the patient was in recovery, the removed organ would be placed among the pages and the name card. A photo was taken with the same endoscope that was used for the procedure.
After the show’s debut, people reached out expressing their love for their photos. “I wish, before he died, I had asked him more questions about it,” Ms. Joseph told ARTnews. “I’m regretting it so much now, kicking myself.”
Who gets to take home an artsy photo of their gallbladder after getting it removed? Not us, that’s who. Each collage is a one-of-a-kind piece. They definitely should be framed and shown in an art gallery. Oh, right. Never mind.
$7,000 for ‘flowers’: KY doc accused in murder plot against ex
A Kentucky pediatrician accused of hiring a hitman to kill her ex-husband – and type a fake suicide text on his cell phone to disguise the plot – initially hatched the scheme 4 years ago during a custody dispute, according to court documents.
On May 19, agents with the Federal Bureau of Investigation arrested Stephanie Russell, MD, on a charge of using interstate commerce facilities in the commission of murder-for-hire, which carries a maximum 10-year sentence in federal prison.
Dr. Russell, who prosecutors said is 52, vehemently denied the plot when it was first relayed to investigators in 2020. She also dismissed suspicion from a court-appointed guardian at the time that the doctor harmed her own son, then 2, in a way “to make it appear” as if his father had hurt the child.
According to an FBI agent’s affidavit, Dr. Russell tried to recruit a killer through employees and ex-employees of Kidz Life Pediatrics, in Prospect, an upscale suburb of Louisville, Ky. She allegedly planned to time the murder during a 2-hour visitation period with her two children on the last day of the school year.
On May 24, Magistrate Judge Regina Edwards, of the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Kentucky, ordered Dr. Russell to remain in custody. A future date for the next hearing has not been set.
‘No red flags’
The case has upended the Norton Commons development in Prospect, one of Kentucky’s wealthiest communities.
“There were no red flags,” said Lance Dooley, whose two daughters had been under Dr. Russell’s care at Kidz Life. “This neighborhood was like, ‘What the hell?’ Everybody went to her and trusted and respected her judgment.”
According to prosecutors, on May 15 – after having failed to have her ex-husband murdered during the holidays – Dr. Russell contacted a person she thought she had hired to murder her ex-husband in exchange for $7,000.
On May 18, Dr. Russell placed a $3,500 down payment in a specimen drop box outside her medical office. She agreed to pay the remaining half after the murder was done, according to prosecutors. The purported hit man was an undercover FBI agent.
While making plans, Dr. Russell used several burner phones and used the word “flowers” as a code word for killing her ex-husband, Ricky Crabtree, whom she had accused of sexually abusing their children. Mr. Crabtree, a financial planner, did not return phone messages left at his office.
Family Court Judge Denise Brown had earlier appointed a guardian to represent the children and an evaluator to monitor the couple’s custodial issues.
Dr. Russell sued the judge, saying Ms. Brown acted because of allegations that Dr. Russell was “coaching” her children and inflicting “emotional harm.” Dr. Russell also objected to what she called “a vague suggestion” that previously she “‘may’ have injured the older male child in a way to make it appear that [Mr.] Crabtree had done so.”
“There wasn’t any proof of it,” said David Mour, an attorney who represented Dr. Russell in that action. The state gave custody to the father in what Mr. Mour called a “Star Chamber” action based on unsubstantiated allegations. “I don’t believe a damned thing,” he said.
In her suit against Ms. Brown, which was dismissed in 2021, Dr. Russell criticized as “preposterous” allegations that, in May 2018, she “‘attempted to hire’ a ‘hitman’ to kill [Mr.] Crabtree.”
The FBI affidavit, however, displayed numerous text messages between Dr. Russell and a former nurse, whom she thought knew a hit man, and an FBI agent posing as the purported killer. When one witness initially agreed to find an assassin who would do the job over the 2021 holiday season, Dr. Russell texted, “I am hysterically crying tears of relief.”
The witness quit Kidz Life Pediatrics and ended contact with Dr. Russell when they realized Dr. Russell was “serious” about the plot, the affidavit stated. And when Dr. Russell found a willing contractor in May, she told the hitman to write a suicide text. The killer would have to unlock Mr. Crabtree’s cell phone by having the device recognize the face of his dead body.
Mr. Dooley said Kidz Life Pediatrics was closed during business hours when he tried to retrieve his children’s medical records. He has since found another pediatrician. Dr. Russell had cared for his children for more than 4 years, he said, betraying no clue of any darkness underneath. Kidz Life Pediatrics did not return phone calls seeking comment.
“It’s very close to home,” said Mr. Dooley, who runs an advertising agency with his wife. “Dr. Russell was really good.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Kentucky pediatrician accused of hiring a hitman to kill her ex-husband – and type a fake suicide text on his cell phone to disguise the plot – initially hatched the scheme 4 years ago during a custody dispute, according to court documents.
On May 19, agents with the Federal Bureau of Investigation arrested Stephanie Russell, MD, on a charge of using interstate commerce facilities in the commission of murder-for-hire, which carries a maximum 10-year sentence in federal prison.
Dr. Russell, who prosecutors said is 52, vehemently denied the plot when it was first relayed to investigators in 2020. She also dismissed suspicion from a court-appointed guardian at the time that the doctor harmed her own son, then 2, in a way “to make it appear” as if his father had hurt the child.
According to an FBI agent’s affidavit, Dr. Russell tried to recruit a killer through employees and ex-employees of Kidz Life Pediatrics, in Prospect, an upscale suburb of Louisville, Ky. She allegedly planned to time the murder during a 2-hour visitation period with her two children on the last day of the school year.
On May 24, Magistrate Judge Regina Edwards, of the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Kentucky, ordered Dr. Russell to remain in custody. A future date for the next hearing has not been set.
‘No red flags’
The case has upended the Norton Commons development in Prospect, one of Kentucky’s wealthiest communities.
“There were no red flags,” said Lance Dooley, whose two daughters had been under Dr. Russell’s care at Kidz Life. “This neighborhood was like, ‘What the hell?’ Everybody went to her and trusted and respected her judgment.”
According to prosecutors, on May 15 – after having failed to have her ex-husband murdered during the holidays – Dr. Russell contacted a person she thought she had hired to murder her ex-husband in exchange for $7,000.
On May 18, Dr. Russell placed a $3,500 down payment in a specimen drop box outside her medical office. She agreed to pay the remaining half after the murder was done, according to prosecutors. The purported hit man was an undercover FBI agent.
While making plans, Dr. Russell used several burner phones and used the word “flowers” as a code word for killing her ex-husband, Ricky Crabtree, whom she had accused of sexually abusing their children. Mr. Crabtree, a financial planner, did not return phone messages left at his office.
Family Court Judge Denise Brown had earlier appointed a guardian to represent the children and an evaluator to monitor the couple’s custodial issues.
Dr. Russell sued the judge, saying Ms. Brown acted because of allegations that Dr. Russell was “coaching” her children and inflicting “emotional harm.” Dr. Russell also objected to what she called “a vague suggestion” that previously she “‘may’ have injured the older male child in a way to make it appear that [Mr.] Crabtree had done so.”
“There wasn’t any proof of it,” said David Mour, an attorney who represented Dr. Russell in that action. The state gave custody to the father in what Mr. Mour called a “Star Chamber” action based on unsubstantiated allegations. “I don’t believe a damned thing,” he said.
In her suit against Ms. Brown, which was dismissed in 2021, Dr. Russell criticized as “preposterous” allegations that, in May 2018, she “‘attempted to hire’ a ‘hitman’ to kill [Mr.] Crabtree.”
The FBI affidavit, however, displayed numerous text messages between Dr. Russell and a former nurse, whom she thought knew a hit man, and an FBI agent posing as the purported killer. When one witness initially agreed to find an assassin who would do the job over the 2021 holiday season, Dr. Russell texted, “I am hysterically crying tears of relief.”
The witness quit Kidz Life Pediatrics and ended contact with Dr. Russell when they realized Dr. Russell was “serious” about the plot, the affidavit stated. And when Dr. Russell found a willing contractor in May, she told the hitman to write a suicide text. The killer would have to unlock Mr. Crabtree’s cell phone by having the device recognize the face of his dead body.
Mr. Dooley said Kidz Life Pediatrics was closed during business hours when he tried to retrieve his children’s medical records. He has since found another pediatrician. Dr. Russell had cared for his children for more than 4 years, he said, betraying no clue of any darkness underneath. Kidz Life Pediatrics did not return phone calls seeking comment.
“It’s very close to home,” said Mr. Dooley, who runs an advertising agency with his wife. “Dr. Russell was really good.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Kentucky pediatrician accused of hiring a hitman to kill her ex-husband – and type a fake suicide text on his cell phone to disguise the plot – initially hatched the scheme 4 years ago during a custody dispute, according to court documents.
On May 19, agents with the Federal Bureau of Investigation arrested Stephanie Russell, MD, on a charge of using interstate commerce facilities in the commission of murder-for-hire, which carries a maximum 10-year sentence in federal prison.
Dr. Russell, who prosecutors said is 52, vehemently denied the plot when it was first relayed to investigators in 2020. She also dismissed suspicion from a court-appointed guardian at the time that the doctor harmed her own son, then 2, in a way “to make it appear” as if his father had hurt the child.
According to an FBI agent’s affidavit, Dr. Russell tried to recruit a killer through employees and ex-employees of Kidz Life Pediatrics, in Prospect, an upscale suburb of Louisville, Ky. She allegedly planned to time the murder during a 2-hour visitation period with her two children on the last day of the school year.
On May 24, Magistrate Judge Regina Edwards, of the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Kentucky, ordered Dr. Russell to remain in custody. A future date for the next hearing has not been set.
‘No red flags’
The case has upended the Norton Commons development in Prospect, one of Kentucky’s wealthiest communities.
“There were no red flags,” said Lance Dooley, whose two daughters had been under Dr. Russell’s care at Kidz Life. “This neighborhood was like, ‘What the hell?’ Everybody went to her and trusted and respected her judgment.”
According to prosecutors, on May 15 – after having failed to have her ex-husband murdered during the holidays – Dr. Russell contacted a person she thought she had hired to murder her ex-husband in exchange for $7,000.
On May 18, Dr. Russell placed a $3,500 down payment in a specimen drop box outside her medical office. She agreed to pay the remaining half after the murder was done, according to prosecutors. The purported hit man was an undercover FBI agent.
While making plans, Dr. Russell used several burner phones and used the word “flowers” as a code word for killing her ex-husband, Ricky Crabtree, whom she had accused of sexually abusing their children. Mr. Crabtree, a financial planner, did not return phone messages left at his office.
Family Court Judge Denise Brown had earlier appointed a guardian to represent the children and an evaluator to monitor the couple’s custodial issues.
Dr. Russell sued the judge, saying Ms. Brown acted because of allegations that Dr. Russell was “coaching” her children and inflicting “emotional harm.” Dr. Russell also objected to what she called “a vague suggestion” that previously she “‘may’ have injured the older male child in a way to make it appear that [Mr.] Crabtree had done so.”
“There wasn’t any proof of it,” said David Mour, an attorney who represented Dr. Russell in that action. The state gave custody to the father in what Mr. Mour called a “Star Chamber” action based on unsubstantiated allegations. “I don’t believe a damned thing,” he said.
In her suit against Ms. Brown, which was dismissed in 2021, Dr. Russell criticized as “preposterous” allegations that, in May 2018, she “‘attempted to hire’ a ‘hitman’ to kill [Mr.] Crabtree.”
The FBI affidavit, however, displayed numerous text messages between Dr. Russell and a former nurse, whom she thought knew a hit man, and an FBI agent posing as the purported killer. When one witness initially agreed to find an assassin who would do the job over the 2021 holiday season, Dr. Russell texted, “I am hysterically crying tears of relief.”
The witness quit Kidz Life Pediatrics and ended contact with Dr. Russell when they realized Dr. Russell was “serious” about the plot, the affidavit stated. And when Dr. Russell found a willing contractor in May, she told the hitman to write a suicide text. The killer would have to unlock Mr. Crabtree’s cell phone by having the device recognize the face of his dead body.
Mr. Dooley said Kidz Life Pediatrics was closed during business hours when he tried to retrieve his children’s medical records. He has since found another pediatrician. Dr. Russell had cared for his children for more than 4 years, he said, betraying no clue of any darkness underneath. Kidz Life Pediatrics did not return phone calls seeking comment.
“It’s very close to home,” said Mr. Dooley, who runs an advertising agency with his wife. “Dr. Russell was really good.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Your grandmother, the metabolic influencer
“Grandma’s workouts may have made you healthier.” The title and accompanying photo of a pair of well-worn women’s running shoes caught my eye immediately. For whatever reason, we are a family of exercisers. My wife has competed in several triathlons and won two of them. With her I have cycled across the United States. It has not surprised us that all three of our children have run at least one marathon. I have always viewed their continued devotion to an active lifestyle and their healthy bodies as a tribute to the benefits of our attempts at parenting by example. We certainly didn’t coach them, lecture them, or run family boot camps on weekends and school vacations.
I had never really given much thought as to whether their grandparents also may have played any role in their affinity for physical activity until I read that article. Apparently, my mother was a gifted athlete as a young woman. I have seen photos of her playing tennis, skiing, and diving and heard stories, but I never saw her do any of these activities except a single perfect swan dive when I must have been 8 or 9 years old.
Similarly, scrapbooks reveal that my mother-in-law had an active sports life in high school. But we never saw any evidence of her athletic activity save a devotion to a gentle backstroke in the cold Maine waters during the summer. My wife and I and our children never saw these grandmothers do anything more sporting or physically taxing than single-handedly preparing a full Thanksgiving dinner. How could their exercise habits have influenced the health of their grandchildren?
A team of researchers at the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston found that female mice who were given the opportunity to exercise produced offspring that had lower fat mass, higher bone mineral density, and insulin levels usually associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. And, in a bit of a surprise, the next generation of offspring accrued a similar benefit even though its mothers were not exercising. The role of exercise in the fathers was eliminated by experimental design.
So it appears that the first-generation offspring’s gametes and hence the third generation was being exposed in utero to something generated by the grandmothers’ exercise. It does not appear to be a behavior pattern that is passed on. It may have to do with epigenetics. Searching for this unknown factor is ongoing and broad based.
Obviously, similar studies in humans are not on the drawing board. Our reproductive cycle is significantly longer than the 2 years of the mouse. However, looking at their current data, the researchers feel comfortable encouraging a mother to exercise during pregnancy as long as it is compatible with the particulars of her obstetrical course. It would be unkind and without basis in fact to blame your mother’s or your mother-in-law’s sedentary behavior for your child’s poor metabolic health. However, it is reasonable to point out to women considering pregnancy that, in addition to avoiding alcohol and smoking, a good dose of exercise during pregnancy will benefit their children. You can point out that it may even benefit their grandchildren. And of course, once the baby is born and a mother feels comfortable returning to her exercise regime, she should go for it. Remind her also that parenting by example is still the best way to do it.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
“Grandma’s workouts may have made you healthier.” The title and accompanying photo of a pair of well-worn women’s running shoes caught my eye immediately. For whatever reason, we are a family of exercisers. My wife has competed in several triathlons and won two of them. With her I have cycled across the United States. It has not surprised us that all three of our children have run at least one marathon. I have always viewed their continued devotion to an active lifestyle and their healthy bodies as a tribute to the benefits of our attempts at parenting by example. We certainly didn’t coach them, lecture them, or run family boot camps on weekends and school vacations.
I had never really given much thought as to whether their grandparents also may have played any role in their affinity for physical activity until I read that article. Apparently, my mother was a gifted athlete as a young woman. I have seen photos of her playing tennis, skiing, and diving and heard stories, but I never saw her do any of these activities except a single perfect swan dive when I must have been 8 or 9 years old.
Similarly, scrapbooks reveal that my mother-in-law had an active sports life in high school. But we never saw any evidence of her athletic activity save a devotion to a gentle backstroke in the cold Maine waters during the summer. My wife and I and our children never saw these grandmothers do anything more sporting or physically taxing than single-handedly preparing a full Thanksgiving dinner. How could their exercise habits have influenced the health of their grandchildren?
A team of researchers at the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston found that female mice who were given the opportunity to exercise produced offspring that had lower fat mass, higher bone mineral density, and insulin levels usually associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. And, in a bit of a surprise, the next generation of offspring accrued a similar benefit even though its mothers were not exercising. The role of exercise in the fathers was eliminated by experimental design.
So it appears that the first-generation offspring’s gametes and hence the third generation was being exposed in utero to something generated by the grandmothers’ exercise. It does not appear to be a behavior pattern that is passed on. It may have to do with epigenetics. Searching for this unknown factor is ongoing and broad based.
Obviously, similar studies in humans are not on the drawing board. Our reproductive cycle is significantly longer than the 2 years of the mouse. However, looking at their current data, the researchers feel comfortable encouraging a mother to exercise during pregnancy as long as it is compatible with the particulars of her obstetrical course. It would be unkind and without basis in fact to blame your mother’s or your mother-in-law’s sedentary behavior for your child’s poor metabolic health. However, it is reasonable to point out to women considering pregnancy that, in addition to avoiding alcohol and smoking, a good dose of exercise during pregnancy will benefit their children. You can point out that it may even benefit their grandchildren. And of course, once the baby is born and a mother feels comfortable returning to her exercise regime, she should go for it. Remind her also that parenting by example is still the best way to do it.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
“Grandma’s workouts may have made you healthier.” The title and accompanying photo of a pair of well-worn women’s running shoes caught my eye immediately. For whatever reason, we are a family of exercisers. My wife has competed in several triathlons and won two of them. With her I have cycled across the United States. It has not surprised us that all three of our children have run at least one marathon. I have always viewed their continued devotion to an active lifestyle and their healthy bodies as a tribute to the benefits of our attempts at parenting by example. We certainly didn’t coach them, lecture them, or run family boot camps on weekends and school vacations.
I had never really given much thought as to whether their grandparents also may have played any role in their affinity for physical activity until I read that article. Apparently, my mother was a gifted athlete as a young woman. I have seen photos of her playing tennis, skiing, and diving and heard stories, but I never saw her do any of these activities except a single perfect swan dive when I must have been 8 or 9 years old.
Similarly, scrapbooks reveal that my mother-in-law had an active sports life in high school. But we never saw any evidence of her athletic activity save a devotion to a gentle backstroke in the cold Maine waters during the summer. My wife and I and our children never saw these grandmothers do anything more sporting or physically taxing than single-handedly preparing a full Thanksgiving dinner. How could their exercise habits have influenced the health of their grandchildren?
A team of researchers at the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston found that female mice who were given the opportunity to exercise produced offspring that had lower fat mass, higher bone mineral density, and insulin levels usually associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. And, in a bit of a surprise, the next generation of offspring accrued a similar benefit even though its mothers were not exercising. The role of exercise in the fathers was eliminated by experimental design.
So it appears that the first-generation offspring’s gametes and hence the third generation was being exposed in utero to something generated by the grandmothers’ exercise. It does not appear to be a behavior pattern that is passed on. It may have to do with epigenetics. Searching for this unknown factor is ongoing and broad based.
Obviously, similar studies in humans are not on the drawing board. Our reproductive cycle is significantly longer than the 2 years of the mouse. However, looking at their current data, the researchers feel comfortable encouraging a mother to exercise during pregnancy as long as it is compatible with the particulars of her obstetrical course. It would be unkind and without basis in fact to blame your mother’s or your mother-in-law’s sedentary behavior for your child’s poor metabolic health. However, it is reasonable to point out to women considering pregnancy that, in addition to avoiding alcohol and smoking, a good dose of exercise during pregnancy will benefit their children. You can point out that it may even benefit their grandchildren. And of course, once the baby is born and a mother feels comfortable returning to her exercise regime, she should go for it. Remind her also that parenting by example is still the best way to do it.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Children and COVID: Weekly cases keep rising past 100,000
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New cases were up by 14.6% over the previous week to just over 107,000 reported during May 13-16, marking the sixth straight increase since April 1-7, when the count was almost 26,000. Over that period, weekly cases rose 313%, based on data in the latest weekly COVID report from the AAP and CHA.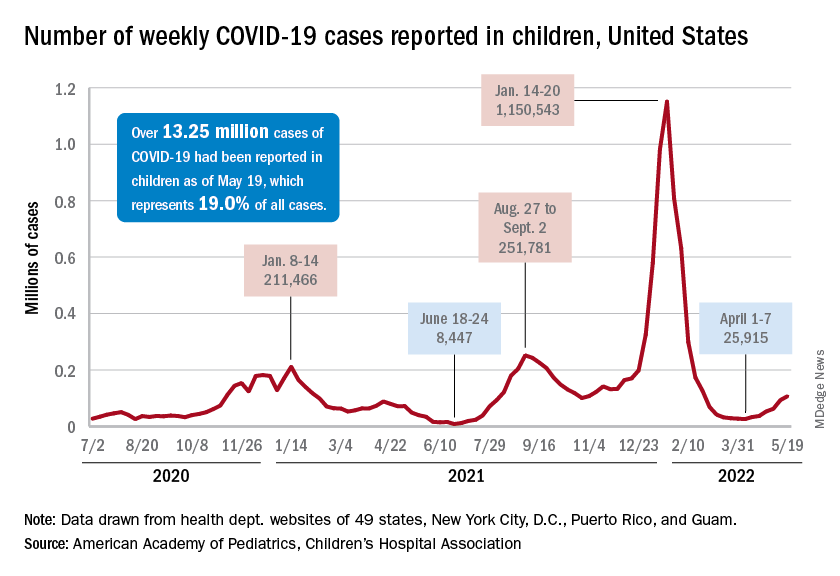
Rates reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show the same trend. Weekly cases per 100,000 population, which were down to 34.9 in children aged 0-4 years and 43.1 for those aged 5-11 on March 26, were up to 49.5 and 52.2, respectively, by April 16. The pace picked up right after that, and as of May 14, the rates of new cases were 125.4 per 100,000 in children aged 0-4 years and 143.1 in those aged 5-11, the CDC said.
Hospital admissions continue to rise as well. The rate of new admissions in children aged 0-17 was up to 0.25 per 100,000 population on May 18, nearly double the 0.13 per 100,000 recorded as late as April 13. The latest 7-day average count for new admissions, 163 per day from May 15-21, is down from the previous week’s 175 per day, but the CDC also acknowledges potential reporting delays in the most recent 7-day period.
Both of those weekly averages, however, are far below the peak rate for the pandemic, 914 per day, which occurred Jan. 10-16, 2022, during the Omicron surge. Since the CDC began keeping count at the beginning of August 2020, more than 125,000 children aged 0-17 years have been admitted with confirmed COVID-19, which is about 2.7% of all admissions over that period, the CDC’s data show.
Booster gets the green light
The week brought some positive news on the prevention side, though, as the CDC officially approved a COVID vaccine booster dose for children aged 5-11 years.
Even that good news came with a caveat, however. The vote by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices was 11:1 in favor, with the negative vote cast by Helen Keipp Talbot, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who said that “boosters are great once we’ve gotten everyone their first round. That needs to be our priority in this.”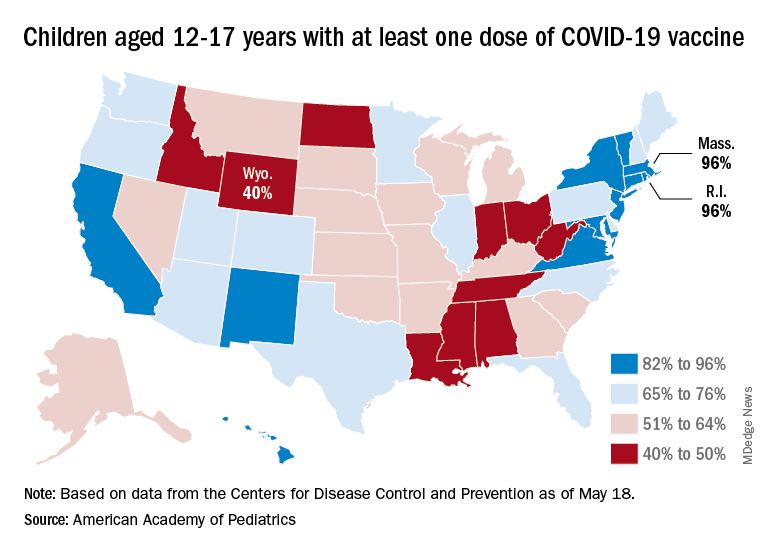
Nationally, in fact, just 35.7% of children aged 5-11 years have received at least one dose of the vaccine and only 29.0% are fully vaccinated. Those figures are nearly doubled among 12- to 17-year-olds: 69.3% have received at least one dose and 59.4% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Some states, meanwhile, are well below those national rates. In Wyoming, only 40% of children aged 12-17 have received an initial vaccine dose, and eight other states are below 50%. Among children aged 5-12, there are still five states below 20% in that measure, while the states on the other end of the spectrum – Vermont and Massachusetts – are above 60%, the AAP said in its separate vaccination report.
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New cases were up by 14.6% over the previous week to just over 107,000 reported during May 13-16, marking the sixth straight increase since April 1-7, when the count was almost 26,000. Over that period, weekly cases rose 313%, based on data in the latest weekly COVID report from the AAP and CHA.
Rates reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show the same trend. Weekly cases per 100,000 population, which were down to 34.9 in children aged 0-4 years and 43.1 for those aged 5-11 on March 26, were up to 49.5 and 52.2, respectively, by April 16. The pace picked up right after that, and as of May 14, the rates of new cases were 125.4 per 100,000 in children aged 0-4 years and 143.1 in those aged 5-11, the CDC said.
Hospital admissions continue to rise as well. The rate of new admissions in children aged 0-17 was up to 0.25 per 100,000 population on May 18, nearly double the 0.13 per 100,000 recorded as late as April 13. The latest 7-day average count for new admissions, 163 per day from May 15-21, is down from the previous week’s 175 per day, but the CDC also acknowledges potential reporting delays in the most recent 7-day period.
Both of those weekly averages, however, are far below the peak rate for the pandemic, 914 per day, which occurred Jan. 10-16, 2022, during the Omicron surge. Since the CDC began keeping count at the beginning of August 2020, more than 125,000 children aged 0-17 years have been admitted with confirmed COVID-19, which is about 2.7% of all admissions over that period, the CDC’s data show.
Booster gets the green light
The week brought some positive news on the prevention side, though, as the CDC officially approved a COVID vaccine booster dose for children aged 5-11 years.
Even that good news came with a caveat, however. The vote by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices was 11:1 in favor, with the negative vote cast by Helen Keipp Talbot, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who said that “boosters are great once we’ve gotten everyone their first round. That needs to be our priority in this.”
Nationally, in fact, just 35.7% of children aged 5-11 years have received at least one dose of the vaccine and only 29.0% are fully vaccinated. Those figures are nearly doubled among 12- to 17-year-olds: 69.3% have received at least one dose and 59.4% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Some states, meanwhile, are well below those national rates. In Wyoming, only 40% of children aged 12-17 have received an initial vaccine dose, and eight other states are below 50%. Among children aged 5-12, there are still five states below 20% in that measure, while the states on the other end of the spectrum – Vermont and Massachusetts – are above 60%, the AAP said in its separate vaccination report.
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New cases were up by 14.6% over the previous week to just over 107,000 reported during May 13-16, marking the sixth straight increase since April 1-7, when the count was almost 26,000. Over that period, weekly cases rose 313%, based on data in the latest weekly COVID report from the AAP and CHA.
Rates reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show the same trend. Weekly cases per 100,000 population, which were down to 34.9 in children aged 0-4 years and 43.1 for those aged 5-11 on March 26, were up to 49.5 and 52.2, respectively, by April 16. The pace picked up right after that, and as of May 14, the rates of new cases were 125.4 per 100,000 in children aged 0-4 years and 143.1 in those aged 5-11, the CDC said.
Hospital admissions continue to rise as well. The rate of new admissions in children aged 0-17 was up to 0.25 per 100,000 population on May 18, nearly double the 0.13 per 100,000 recorded as late as April 13. The latest 7-day average count for new admissions, 163 per day from May 15-21, is down from the previous week’s 175 per day, but the CDC also acknowledges potential reporting delays in the most recent 7-day period.
Both of those weekly averages, however, are far below the peak rate for the pandemic, 914 per day, which occurred Jan. 10-16, 2022, during the Omicron surge. Since the CDC began keeping count at the beginning of August 2020, more than 125,000 children aged 0-17 years have been admitted with confirmed COVID-19, which is about 2.7% of all admissions over that period, the CDC’s data show.
Booster gets the green light
The week brought some positive news on the prevention side, though, as the CDC officially approved a COVID vaccine booster dose for children aged 5-11 years.
Even that good news came with a caveat, however. The vote by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices was 11:1 in favor, with the negative vote cast by Helen Keipp Talbot, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who said that “boosters are great once we’ve gotten everyone their first round. That needs to be our priority in this.”
Nationally, in fact, just 35.7% of children aged 5-11 years have received at least one dose of the vaccine and only 29.0% are fully vaccinated. Those figures are nearly doubled among 12- to 17-year-olds: 69.3% have received at least one dose and 59.4% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Some states, meanwhile, are well below those national rates. In Wyoming, only 40% of children aged 12-17 have received an initial vaccine dose, and eight other states are below 50%. Among children aged 5-12, there are still five states below 20% in that measure, while the states on the other end of the spectrum – Vermont and Massachusetts – are above 60%, the AAP said in its separate vaccination report.








