User login
News and Views that Matter to Pediatricians
The leading independent newspaper covering news and commentary in pediatrics.
Tick talk for families and pediatricians
Spring 2021 has arrived with summer quickly approaching. It is our second spring and summer during the pandemic. Travel restrictions have minimally eased for vaccinated adults. However, neither domestic nor international leisure travel is encouraged for anyone. Ironically, air travel is increasing. For many families, it is time to make decisions regarding summer activities. Outdoor activities have been encouraged throughout the pandemic, which makes it a good time to review tick-borne diseases. Depending on your location, your patients may only have to travel as far as their backyard to sustain a tick bite.
Ticks are a group of obligate, bloodsucking arthropods that feed on mammals, birds, and reptiles. There are three families of ticks. Two families, Ixodidae (hard-bodied ticks) and Argasidae (soft-bodied ticks) are responsible for transmitting the most diseases to humans in the United States. Once a tick is infected with a pathogen it usually survives and transmits it to its next host. Ticks efficiently transmit bacteria, spirochetes, protozoa, rickettsiae, nematodes, and toxins to humans during feeding when the site is exposed to infected salivary gland secretions or regurgitated midgut contents. Pathogen transmission can also occur when the feeding site is contaminated by feces or coxal fluid. Sometimes a tick can transmit multiple pathogens. Not all pathogens are infectious (e.g., tick paralysis, which occurs after exposure to a neurotoxin and red meat allergy because of alpha-gal). Ticks require a blood meal to transform to their next stage of development (larva to nymph to adult). Life cycles of hard and soft ticks differ with most hard ticks undergoing a 2-year life cycle and feeding slowly over many days. In contrast, soft ticks feed multiple times often for less than 1 hour and are capable of transmitting diseases in less than 1 minute.
Rocky Mountain spotted fever was the first recognized tick-borne disease (TBD) in humans. Since then, 18 additional pathogens transmitted by ticks have been identified with 40% being described since 1980. The increased discovery of tickborne pathogens has been attributed to physician awareness of TBD and improved diagnostics. The number of cases of TBD has risen yearly. Ticks are responsible for most vector-transmitted diseases in the United States with Lyme disease most frequently reported.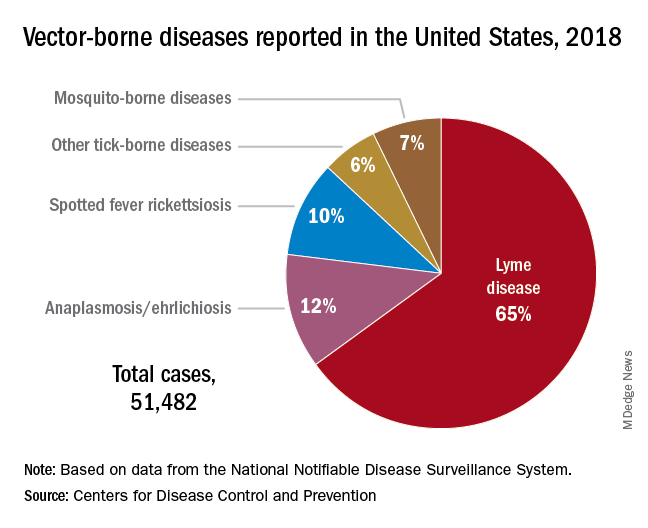
Mosquito transmission accounts for only 7% of vector-borne diseases. Three species of ticks are responsible for most human disease: Ixodes scapularis (Black-legged tick), Amblyomma americanum (Lone Star tick), and Dermacentor variabilis (American dog tick). Each is capable of transmitting agents that cause multiple diseases.
Risk for acquisition of a specific disease is dependent upon the type of tick, its geographic location, the season, and duration of the exposure.
Humans are usually incidental hosts. Tick exposure can occur year-round, but tick activity is greatest between April and September. Ticks are generally found near the ground, in brushy or wooded areas. They can climb tall grasses or shrubs and wait for a potential host to brush against them. When this occurs, they seek a site for attachment.
In the absence of a vaccine, prevention of TBD is totally dependent upon your patients/parents understanding of when and where they are at risk for exposure and for us as physicians to know which pathogens can potentially be transmitted by ticks. Data regarding potential exposure risks are based on where a TBD was diagnosed, not necessarily where it was acquired. National maps that illustrate the distribution of medically significant ticks and presence or prevalence of tick-borne pathogens in specific areas within a region previously may have been incomplete or outdated. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention initiated a national tick surveillance program in 2017; five universities were established as regional centers of excellence to help prevent and rapidly respond to emerging vector-borne diseases across the United States. One goal is to standardize tick surveillance activities at the state level. For state-specific activity go to https://www.cdc.gov/ncezid/dvbd/vital-signs/index.html.
Prevention: Here are a few environmental interventions you can recommend to your patients
- Remove leaf litter, clear tall brush, and grass around the home and at edge of lawns. Mow the lawn frequently.
- Keep playground equipment, decks, and patios away from yard edges and trees.
- Live near a wooded area? Place a 3-ft.-wide barrier of gravel or wood chips between the areas.
- Put up a fence to keep unwanted animals out.
- Keep the yard free of potential hiding place for ticks (e.g., mattresses or furniture).
- Stack wood neatly and in a dry area.
- Use pesticides, but do not rely on them solely to prevent ticks exposure.
Personal interventions for patients when outdoors
- Use Environmental Protection Agency–registered insect repellents. Note: Oil of lemon-, eucalyptus-, and para-menthane-diol–containing products should not be used in children aged3 years or less.
- Treat clothing and gear with products containing 0.5% permethrin to repel mosquitoes and ticks.
- Check cloths for ticks. Drying clothes on high heat for 10 minutes will kill ticks. If washing is needed use hot water. Lower temperatures will not kill ticks.
- Do daily body checks for ticks after coming indoors.
- Check pets for ticks.
Tick removal
- Take tweezers, grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible.
- Pull upward. Do not twist or jerk the tick. Place in a container. Ideally submit for species identification.
- After removal, clean the bite area with alcohol or soap and water.
- Never crush a tick with your fingers.
When should you include TBD in your differential for a sick child?
Headache, fever, arthralgia, and rash are symptoms for several infectious diseases. Obtaining a history of recent activities, tick bite, or travel to areas where these diseases are more prevalent is important. You must have a high index of suspicion. Clinical and laboratory clues may help.
Delay in treatment is more detrimental. If you suspect rickettsia, ehrlichiosis, or anaplasmosis, doxycycline should be started promptly regardless of age. Consultation with an infectious disease specialist is recommended.
The United States recognizes it is not adequately prepared to address the continuing rise of vector-borne diseases. In response, on Jan. 20, 2021, the CDC’s division of vector-borne diseases with input from five federal departments and the EPA developed a joint National Public Health Framework for the Prevention and Control of Vector-Borne Diseases in Humans to tackle issues including risk, detection, diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control of TBD. Stay tuned.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Spring 2021 has arrived with summer quickly approaching. It is our second spring and summer during the pandemic. Travel restrictions have minimally eased for vaccinated adults. However, neither domestic nor international leisure travel is encouraged for anyone. Ironically, air travel is increasing. For many families, it is time to make decisions regarding summer activities. Outdoor activities have been encouraged throughout the pandemic, which makes it a good time to review tick-borne diseases. Depending on your location, your patients may only have to travel as far as their backyard to sustain a tick bite.
Ticks are a group of obligate, bloodsucking arthropods that feed on mammals, birds, and reptiles. There are three families of ticks. Two families, Ixodidae (hard-bodied ticks) and Argasidae (soft-bodied ticks) are responsible for transmitting the most diseases to humans in the United States. Once a tick is infected with a pathogen it usually survives and transmits it to its next host. Ticks efficiently transmit bacteria, spirochetes, protozoa, rickettsiae, nematodes, and toxins to humans during feeding when the site is exposed to infected salivary gland secretions or regurgitated midgut contents. Pathogen transmission can also occur when the feeding site is contaminated by feces or coxal fluid. Sometimes a tick can transmit multiple pathogens. Not all pathogens are infectious (e.g., tick paralysis, which occurs after exposure to a neurotoxin and red meat allergy because of alpha-gal). Ticks require a blood meal to transform to their next stage of development (larva to nymph to adult). Life cycles of hard and soft ticks differ with most hard ticks undergoing a 2-year life cycle and feeding slowly over many days. In contrast, soft ticks feed multiple times often for less than 1 hour and are capable of transmitting diseases in less than 1 minute.
Rocky Mountain spotted fever was the first recognized tick-borne disease (TBD) in humans. Since then, 18 additional pathogens transmitted by ticks have been identified with 40% being described since 1980. The increased discovery of tickborne pathogens has been attributed to physician awareness of TBD and improved diagnostics. The number of cases of TBD has risen yearly. Ticks are responsible for most vector-transmitted diseases in the United States with Lyme disease most frequently reported.
Mosquito transmission accounts for only 7% of vector-borne diseases. Three species of ticks are responsible for most human disease: Ixodes scapularis (Black-legged tick), Amblyomma americanum (Lone Star tick), and Dermacentor variabilis (American dog tick). Each is capable of transmitting agents that cause multiple diseases.
Risk for acquisition of a specific disease is dependent upon the type of tick, its geographic location, the season, and duration of the exposure.
Humans are usually incidental hosts. Tick exposure can occur year-round, but tick activity is greatest between April and September. Ticks are generally found near the ground, in brushy or wooded areas. They can climb tall grasses or shrubs and wait for a potential host to brush against them. When this occurs, they seek a site for attachment.
In the absence of a vaccine, prevention of TBD is totally dependent upon your patients/parents understanding of when and where they are at risk for exposure and for us as physicians to know which pathogens can potentially be transmitted by ticks. Data regarding potential exposure risks are based on where a TBD was diagnosed, not necessarily where it was acquired. National maps that illustrate the distribution of medically significant ticks and presence or prevalence of tick-borne pathogens in specific areas within a region previously may have been incomplete or outdated. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention initiated a national tick surveillance program in 2017; five universities were established as regional centers of excellence to help prevent and rapidly respond to emerging vector-borne diseases across the United States. One goal is to standardize tick surveillance activities at the state level. For state-specific activity go to https://www.cdc.gov/ncezid/dvbd/vital-signs/index.html.
Prevention: Here are a few environmental interventions you can recommend to your patients
- Remove leaf litter, clear tall brush, and grass around the home and at edge of lawns. Mow the lawn frequently.
- Keep playground equipment, decks, and patios away from yard edges and trees.
- Live near a wooded area? Place a 3-ft.-wide barrier of gravel or wood chips between the areas.
- Put up a fence to keep unwanted animals out.
- Keep the yard free of potential hiding place for ticks (e.g., mattresses or furniture).
- Stack wood neatly and in a dry area.
- Use pesticides, but do not rely on them solely to prevent ticks exposure.
Personal interventions for patients when outdoors
- Use Environmental Protection Agency–registered insect repellents. Note: Oil of lemon-, eucalyptus-, and para-menthane-diol–containing products should not be used in children aged3 years or less.
- Treat clothing and gear with products containing 0.5% permethrin to repel mosquitoes and ticks.
- Check cloths for ticks. Drying clothes on high heat for 10 minutes will kill ticks. If washing is needed use hot water. Lower temperatures will not kill ticks.
- Do daily body checks for ticks after coming indoors.
- Check pets for ticks.
Tick removal
- Take tweezers, grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible.
- Pull upward. Do not twist or jerk the tick. Place in a container. Ideally submit for species identification.
- After removal, clean the bite area with alcohol or soap and water.
- Never crush a tick with your fingers.
When should you include TBD in your differential for a sick child?
Headache, fever, arthralgia, and rash are symptoms for several infectious diseases. Obtaining a history of recent activities, tick bite, or travel to areas where these diseases are more prevalent is important. You must have a high index of suspicion. Clinical and laboratory clues may help.
Delay in treatment is more detrimental. If you suspect rickettsia, ehrlichiosis, or anaplasmosis, doxycycline should be started promptly regardless of age. Consultation with an infectious disease specialist is recommended.
The United States recognizes it is not adequately prepared to address the continuing rise of vector-borne diseases. In response, on Jan. 20, 2021, the CDC’s division of vector-borne diseases with input from five federal departments and the EPA developed a joint National Public Health Framework for the Prevention and Control of Vector-Borne Diseases in Humans to tackle issues including risk, detection, diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control of TBD. Stay tuned.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Spring 2021 has arrived with summer quickly approaching. It is our second spring and summer during the pandemic. Travel restrictions have minimally eased for vaccinated adults. However, neither domestic nor international leisure travel is encouraged for anyone. Ironically, air travel is increasing. For many families, it is time to make decisions regarding summer activities. Outdoor activities have been encouraged throughout the pandemic, which makes it a good time to review tick-borne diseases. Depending on your location, your patients may only have to travel as far as their backyard to sustain a tick bite.
Ticks are a group of obligate, bloodsucking arthropods that feed on mammals, birds, and reptiles. There are three families of ticks. Two families, Ixodidae (hard-bodied ticks) and Argasidae (soft-bodied ticks) are responsible for transmitting the most diseases to humans in the United States. Once a tick is infected with a pathogen it usually survives and transmits it to its next host. Ticks efficiently transmit bacteria, spirochetes, protozoa, rickettsiae, nematodes, and toxins to humans during feeding when the site is exposed to infected salivary gland secretions or regurgitated midgut contents. Pathogen transmission can also occur when the feeding site is contaminated by feces or coxal fluid. Sometimes a tick can transmit multiple pathogens. Not all pathogens are infectious (e.g., tick paralysis, which occurs after exposure to a neurotoxin and red meat allergy because of alpha-gal). Ticks require a blood meal to transform to their next stage of development (larva to nymph to adult). Life cycles of hard and soft ticks differ with most hard ticks undergoing a 2-year life cycle and feeding slowly over many days. In contrast, soft ticks feed multiple times often for less than 1 hour and are capable of transmitting diseases in less than 1 minute.
Rocky Mountain spotted fever was the first recognized tick-borne disease (TBD) in humans. Since then, 18 additional pathogens transmitted by ticks have been identified with 40% being described since 1980. The increased discovery of tickborne pathogens has been attributed to physician awareness of TBD and improved diagnostics. The number of cases of TBD has risen yearly. Ticks are responsible for most vector-transmitted diseases in the United States with Lyme disease most frequently reported.
Mosquito transmission accounts for only 7% of vector-borne diseases. Three species of ticks are responsible for most human disease: Ixodes scapularis (Black-legged tick), Amblyomma americanum (Lone Star tick), and Dermacentor variabilis (American dog tick). Each is capable of transmitting agents that cause multiple diseases.
Risk for acquisition of a specific disease is dependent upon the type of tick, its geographic location, the season, and duration of the exposure.
Humans are usually incidental hosts. Tick exposure can occur year-round, but tick activity is greatest between April and September. Ticks are generally found near the ground, in brushy or wooded areas. They can climb tall grasses or shrubs and wait for a potential host to brush against them. When this occurs, they seek a site for attachment.
In the absence of a vaccine, prevention of TBD is totally dependent upon your patients/parents understanding of when and where they are at risk for exposure and for us as physicians to know which pathogens can potentially be transmitted by ticks. Data regarding potential exposure risks are based on where a TBD was diagnosed, not necessarily where it was acquired. National maps that illustrate the distribution of medically significant ticks and presence or prevalence of tick-borne pathogens in specific areas within a region previously may have been incomplete or outdated. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention initiated a national tick surveillance program in 2017; five universities were established as regional centers of excellence to help prevent and rapidly respond to emerging vector-borne diseases across the United States. One goal is to standardize tick surveillance activities at the state level. For state-specific activity go to https://www.cdc.gov/ncezid/dvbd/vital-signs/index.html.
Prevention: Here are a few environmental interventions you can recommend to your patients
- Remove leaf litter, clear tall brush, and grass around the home and at edge of lawns. Mow the lawn frequently.
- Keep playground equipment, decks, and patios away from yard edges and trees.
- Live near a wooded area? Place a 3-ft.-wide barrier of gravel or wood chips between the areas.
- Put up a fence to keep unwanted animals out.
- Keep the yard free of potential hiding place for ticks (e.g., mattresses or furniture).
- Stack wood neatly and in a dry area.
- Use pesticides, but do not rely on them solely to prevent ticks exposure.
Personal interventions for patients when outdoors
- Use Environmental Protection Agency–registered insect repellents. Note: Oil of lemon-, eucalyptus-, and para-menthane-diol–containing products should not be used in children aged3 years or less.
- Treat clothing and gear with products containing 0.5% permethrin to repel mosquitoes and ticks.
- Check cloths for ticks. Drying clothes on high heat for 10 minutes will kill ticks. If washing is needed use hot water. Lower temperatures will not kill ticks.
- Do daily body checks for ticks after coming indoors.
- Check pets for ticks.
Tick removal
- Take tweezers, grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible.
- Pull upward. Do not twist or jerk the tick. Place in a container. Ideally submit for species identification.
- After removal, clean the bite area with alcohol or soap and water.
- Never crush a tick with your fingers.
When should you include TBD in your differential for a sick child?
Headache, fever, arthralgia, and rash are symptoms for several infectious diseases. Obtaining a history of recent activities, tick bite, or travel to areas where these diseases are more prevalent is important. You must have a high index of suspicion. Clinical and laboratory clues may help.
Delay in treatment is more detrimental. If you suspect rickettsia, ehrlichiosis, or anaplasmosis, doxycycline should be started promptly regardless of age. Consultation with an infectious disease specialist is recommended.
The United States recognizes it is not adequately prepared to address the continuing rise of vector-borne diseases. In response, on Jan. 20, 2021, the CDC’s division of vector-borne diseases with input from five federal departments and the EPA developed a joint National Public Health Framework for the Prevention and Control of Vector-Borne Diseases in Humans to tackle issues including risk, detection, diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control of TBD. Stay tuned.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Adolescent substance use and the COVID-19 pandemic
During the past year, adolescents, families, educators, and health care providers have had to press forward through myriad challenges and stressors with flexibility and adaptability. With appropriate concern, we ask ourselves how children and youth are coping emotionally with the unprecedented changes of the past year.
Adolescent substance use represents an important area of concern. What has happened during the pandemic? Has youth substance use increased or decreased? Has access to substances increased or decreased, has monitoring and support for at-risk youth increased or decreased?
The answers to these questions are mixed. If anything, the pandemic has highlighted the heterogeneity of adolescent substance use. Now is a key time for assessment, support, and conversation with teens and families.
Monitoring the Future (MTF), a nationally representative annual survey, has provided a broad perspective on trends of adolescent substance use for decades.1 The MTF data is usually collected from February to May and was cut short in 2020 because of school closures associated with the pandemic. The sample size, though still nationally representative, was about a quarter of the typical volume. Some of the data are encouraging, including a flattening out of previous years’ stark increase in vaping of both nicotine and cannabis products (though overall numbers remain alarmingly high). Other data are more concerning including a continued increase in misuse of cough medicine, amphetamines, and inhalants among the youngest cohort surveyed (eighth graders). However, these data were largely representative of prepandemic circumstances.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly affected risk and protective factors for teen drug and alcohol use. Most notably, it has had a widely observed negative impact on adolescent mental health, across multiple disease categories.2 In addition, the cancellation of in-person academic and extracurricular activities such as arts and athletics markedly increased unstructured time, a known associated factor for higher-risk activities including substance use. This has also led to decreased contact with many supportive adults such as teachers and coaches. On the other hand, some adolescents now have more time with supportive parents and caregivers, more meals together, and more supervision, all of which are associated with decreased likelihood of substance use disorders.
The highly variable reasons for substance use affect highly variable pandemic-related changes in use. Understanding the impetus for use is a good place to start conversation and can help providers assess risk of escalation during the pandemic. Some teens primarily use for social enhancement while others use as a means of coping with stress or to mask or escape negative emotions. Still others continue use because of physiological dependence, craving, and other symptoms consistent with use disorders.
Highlighting the heterogeneity of this issue, one study assessing use early in the pandemic showed a decrease in the percentage of teens who use substances but an increase in frequency of use for those who are using.3 Though expected, an increase in frequency of use by oneself as compared with peers was also notable. Using substances alone is associated with more severe use disorders, carries greater risk of overdose, and can increase shame and secrecy, further fueling use disorders.
The pandemic has thus represented a protective pause for some experimental or socially motivated substance-using teens who have experienced a period of abstinence even if not fully by choice. For others, it has represented an acute amplification of risk factors and use has accelerated. This latter group includes those whose use represents an effort to cope with depression, anxiety, and loneliness or for whom isolation at home represents less monitoring, increased access, and greater exposure to substances.
Over the past year, in the treatment of adolescents struggling with substance use, many clinicians have observed a sifting effect during these unprecedented social changes. Many youth, who no longer have access to substances, have found they can “take it or leave it”. Other youth have been observed engaging in additional risk or going to greater lengths to access substances and continue their use. For both groups and everyone in between, this is an important time for screening, clinical assessment, and support.
While anticipating further research and data regarding broad substance use trends, including MTF data from 2021, recognizing that the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic is individual, with marked differences from adolescent to adolescent, will help us continue to act now to assess this important area of adolescent health. The first step for primary care providers is unchanged: to routinely screen for and discuss substance use in clinical settings.
Two brief, validated, easily accessible screening tools are available for primary care settings. They can both be self-administered and take less than 2 minutes to complete. Screening, Brief Intervention and Referral to Treatment and the Brief Screener for Tobacco, Alcohol and other Drugs can both be used for youth aged 12-17 years.4,5 Both screens are available online at drugabuse.gov.6
Routine screening will normalize conversations about substance use and healthy choices, provide opportunities for positive reinforcement, identify adolescents at risk, increase comfort and competence in providing brief intervention, and expedite referrals for additional support and treatment.
A false assumption that a particular adolescent isn’t using substances creates a missed opportunity to offer guidance and treatment. An oft-overlooked opportunity is that of providing positive reinforcement for an adolescent who isn’t using any substances or experimenting at all. Positive reinforcement is a strong component of reinforcing health maintenance.
Parent guidance and family assessment will also be critical tools. Parents and caregivers play a primary role in substance use treatment for teens and have a contributory impact on risk through both genes and environment. Of note, research suggests a moderate overall increase in adult substance use during the pandemic, particularly substances that are widely available such as alcohol. Adolescents may thus have greater access and exposure to substance use. A remarkably high percentage, 42%, of substance-using teens surveyed early in the pandemic indicated that they were using substances with their parents.3 Parents, who have equally been challenged by the pandemic, may need guidance in balancing compassion and support for struggling youth, while setting appropriate limits and maintaining expectations of healthy activities.
Unprecedented change and uncertainty provide an opportunity to reassess risks and openly discuss substance use with youth and families. Even with much on our minds during the COVID-19 pandemic, we can maintain focus on this significant risk to adolescent health and wellness. Our efforts now, from screening to treatment for adolescent substance use should be reinforced rather than delayed.
Dr. Jackson is assistant professor of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. Monitoringthefuture.org
2. Jones EAK et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021;18(5):2470.
3. Dumas TM et al. J Adolesc Health, 2020;67(3):354-61.
4. Levy S et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2014;168(9):822-8.
5. Kelly SM et al. Pediatrics. 2014;133(5):819-26.
6. National Institute on Drug Abuse. Adolescent Substance Use Screening Tools. 2016 Apr 27. https://www.drugabuse.gov/nidamed-medical-health-professionals/screening-tools-prevention/screening-tools-adolescent-substance-use/adolescent-substance-use-screening-tools
During the past year, adolescents, families, educators, and health care providers have had to press forward through myriad challenges and stressors with flexibility and adaptability. With appropriate concern, we ask ourselves how children and youth are coping emotionally with the unprecedented changes of the past year.
Adolescent substance use represents an important area of concern. What has happened during the pandemic? Has youth substance use increased or decreased? Has access to substances increased or decreased, has monitoring and support for at-risk youth increased or decreased?
The answers to these questions are mixed. If anything, the pandemic has highlighted the heterogeneity of adolescent substance use. Now is a key time for assessment, support, and conversation with teens and families.
Monitoring the Future (MTF), a nationally representative annual survey, has provided a broad perspective on trends of adolescent substance use for decades.1 The MTF data is usually collected from February to May and was cut short in 2020 because of school closures associated with the pandemic. The sample size, though still nationally representative, was about a quarter of the typical volume. Some of the data are encouraging, including a flattening out of previous years’ stark increase in vaping of both nicotine and cannabis products (though overall numbers remain alarmingly high). Other data are more concerning including a continued increase in misuse of cough medicine, amphetamines, and inhalants among the youngest cohort surveyed (eighth graders). However, these data were largely representative of prepandemic circumstances.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly affected risk and protective factors for teen drug and alcohol use. Most notably, it has had a widely observed negative impact on adolescent mental health, across multiple disease categories.2 In addition, the cancellation of in-person academic and extracurricular activities such as arts and athletics markedly increased unstructured time, a known associated factor for higher-risk activities including substance use. This has also led to decreased contact with many supportive adults such as teachers and coaches. On the other hand, some adolescents now have more time with supportive parents and caregivers, more meals together, and more supervision, all of which are associated with decreased likelihood of substance use disorders.
The highly variable reasons for substance use affect highly variable pandemic-related changes in use. Understanding the impetus for use is a good place to start conversation and can help providers assess risk of escalation during the pandemic. Some teens primarily use for social enhancement while others use as a means of coping with stress or to mask or escape negative emotions. Still others continue use because of physiological dependence, craving, and other symptoms consistent with use disorders.
Highlighting the heterogeneity of this issue, one study assessing use early in the pandemic showed a decrease in the percentage of teens who use substances but an increase in frequency of use for those who are using.3 Though expected, an increase in frequency of use by oneself as compared with peers was also notable. Using substances alone is associated with more severe use disorders, carries greater risk of overdose, and can increase shame and secrecy, further fueling use disorders.
The pandemic has thus represented a protective pause for some experimental or socially motivated substance-using teens who have experienced a period of abstinence even if not fully by choice. For others, it has represented an acute amplification of risk factors and use has accelerated. This latter group includes those whose use represents an effort to cope with depression, anxiety, and loneliness or for whom isolation at home represents less monitoring, increased access, and greater exposure to substances.
Over the past year, in the treatment of adolescents struggling with substance use, many clinicians have observed a sifting effect during these unprecedented social changes. Many youth, who no longer have access to substances, have found they can “take it or leave it”. Other youth have been observed engaging in additional risk or going to greater lengths to access substances and continue their use. For both groups and everyone in between, this is an important time for screening, clinical assessment, and support.
While anticipating further research and data regarding broad substance use trends, including MTF data from 2021, recognizing that the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic is individual, with marked differences from adolescent to adolescent, will help us continue to act now to assess this important area of adolescent health. The first step for primary care providers is unchanged: to routinely screen for and discuss substance use in clinical settings.
Two brief, validated, easily accessible screening tools are available for primary care settings. They can both be self-administered and take less than 2 minutes to complete. Screening, Brief Intervention and Referral to Treatment and the Brief Screener for Tobacco, Alcohol and other Drugs can both be used for youth aged 12-17 years.4,5 Both screens are available online at drugabuse.gov.6
Routine screening will normalize conversations about substance use and healthy choices, provide opportunities for positive reinforcement, identify adolescents at risk, increase comfort and competence in providing brief intervention, and expedite referrals for additional support and treatment.
A false assumption that a particular adolescent isn’t using substances creates a missed opportunity to offer guidance and treatment. An oft-overlooked opportunity is that of providing positive reinforcement for an adolescent who isn’t using any substances or experimenting at all. Positive reinforcement is a strong component of reinforcing health maintenance.
Parent guidance and family assessment will also be critical tools. Parents and caregivers play a primary role in substance use treatment for teens and have a contributory impact on risk through both genes and environment. Of note, research suggests a moderate overall increase in adult substance use during the pandemic, particularly substances that are widely available such as alcohol. Adolescents may thus have greater access and exposure to substance use. A remarkably high percentage, 42%, of substance-using teens surveyed early in the pandemic indicated that they were using substances with their parents.3 Parents, who have equally been challenged by the pandemic, may need guidance in balancing compassion and support for struggling youth, while setting appropriate limits and maintaining expectations of healthy activities.
Unprecedented change and uncertainty provide an opportunity to reassess risks and openly discuss substance use with youth and families. Even with much on our minds during the COVID-19 pandemic, we can maintain focus on this significant risk to adolescent health and wellness. Our efforts now, from screening to treatment for adolescent substance use should be reinforced rather than delayed.
Dr. Jackson is assistant professor of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. Monitoringthefuture.org
2. Jones EAK et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021;18(5):2470.
3. Dumas TM et al. J Adolesc Health, 2020;67(3):354-61.
4. Levy S et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2014;168(9):822-8.
5. Kelly SM et al. Pediatrics. 2014;133(5):819-26.
6. National Institute on Drug Abuse. Adolescent Substance Use Screening Tools. 2016 Apr 27. https://www.drugabuse.gov/nidamed-medical-health-professionals/screening-tools-prevention/screening-tools-adolescent-substance-use/adolescent-substance-use-screening-tools
During the past year, adolescents, families, educators, and health care providers have had to press forward through myriad challenges and stressors with flexibility and adaptability. With appropriate concern, we ask ourselves how children and youth are coping emotionally with the unprecedented changes of the past year.
Adolescent substance use represents an important area of concern. What has happened during the pandemic? Has youth substance use increased or decreased? Has access to substances increased or decreased, has monitoring and support for at-risk youth increased or decreased?
The answers to these questions are mixed. If anything, the pandemic has highlighted the heterogeneity of adolescent substance use. Now is a key time for assessment, support, and conversation with teens and families.
Monitoring the Future (MTF), a nationally representative annual survey, has provided a broad perspective on trends of adolescent substance use for decades.1 The MTF data is usually collected from February to May and was cut short in 2020 because of school closures associated with the pandemic. The sample size, though still nationally representative, was about a quarter of the typical volume. Some of the data are encouraging, including a flattening out of previous years’ stark increase in vaping of both nicotine and cannabis products (though overall numbers remain alarmingly high). Other data are more concerning including a continued increase in misuse of cough medicine, amphetamines, and inhalants among the youngest cohort surveyed (eighth graders). However, these data were largely representative of prepandemic circumstances.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly affected risk and protective factors for teen drug and alcohol use. Most notably, it has had a widely observed negative impact on adolescent mental health, across multiple disease categories.2 In addition, the cancellation of in-person academic and extracurricular activities such as arts and athletics markedly increased unstructured time, a known associated factor for higher-risk activities including substance use. This has also led to decreased contact with many supportive adults such as teachers and coaches. On the other hand, some adolescents now have more time with supportive parents and caregivers, more meals together, and more supervision, all of which are associated with decreased likelihood of substance use disorders.
The highly variable reasons for substance use affect highly variable pandemic-related changes in use. Understanding the impetus for use is a good place to start conversation and can help providers assess risk of escalation during the pandemic. Some teens primarily use for social enhancement while others use as a means of coping with stress or to mask or escape negative emotions. Still others continue use because of physiological dependence, craving, and other symptoms consistent with use disorders.
Highlighting the heterogeneity of this issue, one study assessing use early in the pandemic showed a decrease in the percentage of teens who use substances but an increase in frequency of use for those who are using.3 Though expected, an increase in frequency of use by oneself as compared with peers was also notable. Using substances alone is associated with more severe use disorders, carries greater risk of overdose, and can increase shame and secrecy, further fueling use disorders.
The pandemic has thus represented a protective pause for some experimental or socially motivated substance-using teens who have experienced a period of abstinence even if not fully by choice. For others, it has represented an acute amplification of risk factors and use has accelerated. This latter group includes those whose use represents an effort to cope with depression, anxiety, and loneliness or for whom isolation at home represents less monitoring, increased access, and greater exposure to substances.
Over the past year, in the treatment of adolescents struggling with substance use, many clinicians have observed a sifting effect during these unprecedented social changes. Many youth, who no longer have access to substances, have found they can “take it or leave it”. Other youth have been observed engaging in additional risk or going to greater lengths to access substances and continue their use. For both groups and everyone in between, this is an important time for screening, clinical assessment, and support.
While anticipating further research and data regarding broad substance use trends, including MTF data from 2021, recognizing that the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic is individual, with marked differences from adolescent to adolescent, will help us continue to act now to assess this important area of adolescent health. The first step for primary care providers is unchanged: to routinely screen for and discuss substance use in clinical settings.
Two brief, validated, easily accessible screening tools are available for primary care settings. They can both be self-administered and take less than 2 minutes to complete. Screening, Brief Intervention and Referral to Treatment and the Brief Screener for Tobacco, Alcohol and other Drugs can both be used for youth aged 12-17 years.4,5 Both screens are available online at drugabuse.gov.6
Routine screening will normalize conversations about substance use and healthy choices, provide opportunities for positive reinforcement, identify adolescents at risk, increase comfort and competence in providing brief intervention, and expedite referrals for additional support and treatment.
A false assumption that a particular adolescent isn’t using substances creates a missed opportunity to offer guidance and treatment. An oft-overlooked opportunity is that of providing positive reinforcement for an adolescent who isn’t using any substances or experimenting at all. Positive reinforcement is a strong component of reinforcing health maintenance.
Parent guidance and family assessment will also be critical tools. Parents and caregivers play a primary role in substance use treatment for teens and have a contributory impact on risk through both genes and environment. Of note, research suggests a moderate overall increase in adult substance use during the pandemic, particularly substances that are widely available such as alcohol. Adolescents may thus have greater access and exposure to substance use. A remarkably high percentage, 42%, of substance-using teens surveyed early in the pandemic indicated that they were using substances with their parents.3 Parents, who have equally been challenged by the pandemic, may need guidance in balancing compassion and support for struggling youth, while setting appropriate limits and maintaining expectations of healthy activities.
Unprecedented change and uncertainty provide an opportunity to reassess risks and openly discuss substance use with youth and families. Even with much on our minds during the COVID-19 pandemic, we can maintain focus on this significant risk to adolescent health and wellness. Our efforts now, from screening to treatment for adolescent substance use should be reinforced rather than delayed.
Dr. Jackson is assistant professor of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. Monitoringthefuture.org
2. Jones EAK et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021;18(5):2470.
3. Dumas TM et al. J Adolesc Health, 2020;67(3):354-61.
4. Levy S et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2014;168(9):822-8.
5. Kelly SM et al. Pediatrics. 2014;133(5):819-26.
6. National Institute on Drug Abuse. Adolescent Substance Use Screening Tools. 2016 Apr 27. https://www.drugabuse.gov/nidamed-medical-health-professionals/screening-tools-prevention/screening-tools-adolescent-substance-use/adolescent-substance-use-screening-tools
CDC panel: Pause of J&J COVID-19 vaccine to remain for now
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices decided there was not adequate information to change again recommend use of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The committee’s decision comes the day after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that J&J injections be paused after reports of rare, but serious types of blood clots in six patients among the 6.8 million people who had received the J&J vaccine in the United States.
A member of the committee, Beth Bell, MD, said: “I do not want to be sending a message that there is some huge concern here on a different order of magnitude than any other vaccine safety signals that we evaluate. And I don’t want to send a message that there is something fundamentally wrong with the vaccine because that also I don’t agree with.”
At the end of the 4-hour meeting, ACIP members decided to call a meeting in 1 or 2 weeks and evaluate more safety data, specifically reports of people who have received the J&J vaccine in the past 2 weeks.
Some, however, pointed out that delaying a decision could have substantial consequences as well in terms of unused vaccine doses and public confidence.
Committee member Camiile Kotton, MD, described the pause as “devastating.”
“Putting this vaccine on pause for those of us that are frontline health care workers has really been devastating,” she said. “I agree in general that we don’t have enough data to make a decision at this time but we were planning on using this vaccine in the state of Massachusetts for people who were homebound and otherwise not able to get a vaccine. We were planning on using it for our vulnerable inpatient population often with many comorbidities and at high risk for disease but haven’t been able to get vaccinated otherwise.”
Pausing the one-and-done vaccine that doesn’t have the significant refrigeration requirements of the others “is a significant loss,” she said.
What is known, not known
Sara Oliver, MD, who leads the COVID-19 Vaccines ACIP Work Group, summarized what is known and unknown about the blood clots.
Among the six cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System after the J&J shot, all were women aged 18-48 years and all developed the clots 6-13 days after receiving the vaccine.
No cases of these clots have been reported from either the Pfizer or Moderna shots, she noted.
In the United States, the two mRNA vaccine alternatives – the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines – are available “and based on current projections supply of both vaccines are expected to be relatively stable in the near future,” she said.
She said 14 million doses of Pfizer and Moderna are expected each week in the United States and J&J vaccines makes up less than 5% of vaccines administered in the country.
Approximately 13 million J&J doses are available to order or are already at administration sites, she said.
But much more is unknown, she said.
“There may be more cases identified in the coming days to weeks,” Dr. Oliver said, referring back to the average time from vaccination to symptom onset.
Scott Ratzan, MD, editor-in-chief of the Journal of Health Communication: International Perspectives and executive director of Business Partners to CONVINCE (BP2C), a global network of employers that promotes COVID-19 vaccination among employees, suppliers, and customers, applauded ACIP’s delay on making a decision.
Dr. Ratzan, who watched the deliberations online, said in an interview the decision “shows an admirable abundance of caution in the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines.”
“Unfortunately,” he said, “the pause also worsens the existing and pervasive vaccine hesitancy issue.
“We need a rational strategy regarding who should or should not get the J&J/Janssen vaccine since these rare adverse events appear to affect a particular group of people, females aged 18-48. It is essential that we build vaccine confidence and retain the option of using this vaccine for people who are not in this risk group.”
He pointed out there are safety red flags with the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines.
“We should feel reassured about the process of ensuring vaccine safety as the FDA and CDC have quickly addressed risk and shared the data transparently of the J&J vaccine and taken appropriate action,” he said.
ACIP’s executive secretary, Amanda Cohn, MD, said the date for the next meeting would be set by April 16.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices decided there was not adequate information to change again recommend use of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The committee’s decision comes the day after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that J&J injections be paused after reports of rare, but serious types of blood clots in six patients among the 6.8 million people who had received the J&J vaccine in the United States.
A member of the committee, Beth Bell, MD, said: “I do not want to be sending a message that there is some huge concern here on a different order of magnitude than any other vaccine safety signals that we evaluate. And I don’t want to send a message that there is something fundamentally wrong with the vaccine because that also I don’t agree with.”
At the end of the 4-hour meeting, ACIP members decided to call a meeting in 1 or 2 weeks and evaluate more safety data, specifically reports of people who have received the J&J vaccine in the past 2 weeks.
Some, however, pointed out that delaying a decision could have substantial consequences as well in terms of unused vaccine doses and public confidence.
Committee member Camiile Kotton, MD, described the pause as “devastating.”
“Putting this vaccine on pause for those of us that are frontline health care workers has really been devastating,” she said. “I agree in general that we don’t have enough data to make a decision at this time but we were planning on using this vaccine in the state of Massachusetts for people who were homebound and otherwise not able to get a vaccine. We were planning on using it for our vulnerable inpatient population often with many comorbidities and at high risk for disease but haven’t been able to get vaccinated otherwise.”
Pausing the one-and-done vaccine that doesn’t have the significant refrigeration requirements of the others “is a significant loss,” she said.
What is known, not known
Sara Oliver, MD, who leads the COVID-19 Vaccines ACIP Work Group, summarized what is known and unknown about the blood clots.
Among the six cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System after the J&J shot, all were women aged 18-48 years and all developed the clots 6-13 days after receiving the vaccine.
No cases of these clots have been reported from either the Pfizer or Moderna shots, she noted.
In the United States, the two mRNA vaccine alternatives – the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines – are available “and based on current projections supply of both vaccines are expected to be relatively stable in the near future,” she said.
She said 14 million doses of Pfizer and Moderna are expected each week in the United States and J&J vaccines makes up less than 5% of vaccines administered in the country.
Approximately 13 million J&J doses are available to order or are already at administration sites, she said.
But much more is unknown, she said.
“There may be more cases identified in the coming days to weeks,” Dr. Oliver said, referring back to the average time from vaccination to symptom onset.
Scott Ratzan, MD, editor-in-chief of the Journal of Health Communication: International Perspectives and executive director of Business Partners to CONVINCE (BP2C), a global network of employers that promotes COVID-19 vaccination among employees, suppliers, and customers, applauded ACIP’s delay on making a decision.
Dr. Ratzan, who watched the deliberations online, said in an interview the decision “shows an admirable abundance of caution in the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines.”
“Unfortunately,” he said, “the pause also worsens the existing and pervasive vaccine hesitancy issue.
“We need a rational strategy regarding who should or should not get the J&J/Janssen vaccine since these rare adverse events appear to affect a particular group of people, females aged 18-48. It is essential that we build vaccine confidence and retain the option of using this vaccine for people who are not in this risk group.”
He pointed out there are safety red flags with the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines.
“We should feel reassured about the process of ensuring vaccine safety as the FDA and CDC have quickly addressed risk and shared the data transparently of the J&J vaccine and taken appropriate action,” he said.
ACIP’s executive secretary, Amanda Cohn, MD, said the date for the next meeting would be set by April 16.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices decided there was not adequate information to change again recommend use of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The committee’s decision comes the day after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that J&J injections be paused after reports of rare, but serious types of blood clots in six patients among the 6.8 million people who had received the J&J vaccine in the United States.
A member of the committee, Beth Bell, MD, said: “I do not want to be sending a message that there is some huge concern here on a different order of magnitude than any other vaccine safety signals that we evaluate. And I don’t want to send a message that there is something fundamentally wrong with the vaccine because that also I don’t agree with.”
At the end of the 4-hour meeting, ACIP members decided to call a meeting in 1 or 2 weeks and evaluate more safety data, specifically reports of people who have received the J&J vaccine in the past 2 weeks.
Some, however, pointed out that delaying a decision could have substantial consequences as well in terms of unused vaccine doses and public confidence.
Committee member Camiile Kotton, MD, described the pause as “devastating.”
“Putting this vaccine on pause for those of us that are frontline health care workers has really been devastating,” she said. “I agree in general that we don’t have enough data to make a decision at this time but we were planning on using this vaccine in the state of Massachusetts for people who were homebound and otherwise not able to get a vaccine. We were planning on using it for our vulnerable inpatient population often with many comorbidities and at high risk for disease but haven’t been able to get vaccinated otherwise.”
Pausing the one-and-done vaccine that doesn’t have the significant refrigeration requirements of the others “is a significant loss,” she said.
What is known, not known
Sara Oliver, MD, who leads the COVID-19 Vaccines ACIP Work Group, summarized what is known and unknown about the blood clots.
Among the six cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System after the J&J shot, all were women aged 18-48 years and all developed the clots 6-13 days after receiving the vaccine.
No cases of these clots have been reported from either the Pfizer or Moderna shots, she noted.
In the United States, the two mRNA vaccine alternatives – the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines – are available “and based on current projections supply of both vaccines are expected to be relatively stable in the near future,” she said.
She said 14 million doses of Pfizer and Moderna are expected each week in the United States and J&J vaccines makes up less than 5% of vaccines administered in the country.
Approximately 13 million J&J doses are available to order or are already at administration sites, she said.
But much more is unknown, she said.
“There may be more cases identified in the coming days to weeks,” Dr. Oliver said, referring back to the average time from vaccination to symptom onset.
Scott Ratzan, MD, editor-in-chief of the Journal of Health Communication: International Perspectives and executive director of Business Partners to CONVINCE (BP2C), a global network of employers that promotes COVID-19 vaccination among employees, suppliers, and customers, applauded ACIP’s delay on making a decision.
Dr. Ratzan, who watched the deliberations online, said in an interview the decision “shows an admirable abundance of caution in the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines.”
“Unfortunately,” he said, “the pause also worsens the existing and pervasive vaccine hesitancy issue.
“We need a rational strategy regarding who should or should not get the J&J/Janssen vaccine since these rare adverse events appear to affect a particular group of people, females aged 18-48. It is essential that we build vaccine confidence and retain the option of using this vaccine for people who are not in this risk group.”
He pointed out there are safety red flags with the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines.
“We should feel reassured about the process of ensuring vaccine safety as the FDA and CDC have quickly addressed risk and shared the data transparently of the J&J vaccine and taken appropriate action,” he said.
ACIP’s executive secretary, Amanda Cohn, MD, said the date for the next meeting would be set by April 16.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
I sent my suicidal teen patient to the ED: Whew?
You read “thoughts of being better off dead” on your next patient’s PHQ-9 screen results and break into a sweat. After eliciting the teen’s realistic suicide plan and intent you send him to the ED with his parent for crisis mental health evaluation. When you call the family that evening to follow-up you hear that he was discharged with a “mental health counseling” appointment next week.
Have you done enough to prevent this child from dying at his own hand? I imagine that this haunts you as it does me. It is terrifying to know that, of youth with suicidal ideation, over one-third attempt suicide, most within 1-2 years, and 20%-40% do so without having had a plan.
We now know that certain kinds of psychotherapy have evidence for preventing subsequent suicide in teens at high risk due to suicidal ideation and past attempts. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) has the best evidence including its subtypes for youth with relevant histories: for both suicide and substance use (integrated, or I-CBT), trauma focused (TF-CBT), traumatic grief (CTG-CBT), and CBT-I, for the potent risk factor of insomnia. The other treatment shown to reduce risk is dialectical behavioral therapy–adolescent (DBT-A) focused on strengthening skills in interpersonal effectiveness, mindfulness, distress tolerance, and emotion regulation adapted to youth by adding family therapy and multifamily skills training. Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) adapted for suicidal and self-harming adolescents (IPT-SA) also has evidence.
Some school programs have shown moderate efficacy, for example (IPT-A-IN) addresses the social and interpersonal context, and Youth Aware of Mental Health, a school curriculum to increase knowledge, help-seeking, and ways of coping with depression and suicidal behavior, that cut suicide attempts by half.
You may be able to recommend, refer to, or check to see if a youth can be provided one of the above therapies with best evidence but getting any counseling at all can be hard and some, especially minority families may decline formal interventions. Any therapy – CBT, DBT, or IPT – acceptable to the youth and family can be helpful. You can often determine if the key components are being provided by asking the teen what they are working on in therapy.
It is clear that checking in regularly with teens who have been through a suicide crisis is crucial to ensure that they continue in therapy long and consistently enough, that the family is involved in treatment, and that they are taught emotion regulation, distress tolerance, and safety planning. Warm, consistent parenting, good parent-child communication, and monitoring are protective factors but also skills that can be boosted to reduce future risk of suicide. When there is family dysfunction, conflict, or weak relationships, getting help for family relationships such as through attachment-based family therapy (ABFT) or family cognitive behavioral therapy is a priority. When bereavement or parental depression is contributing to youth suicidal thoughts, addressing these specifically can reduce suicide risk.
Sometimes family members, even with counseling, are not the best supporters for a teen in pain. When youths nominated their own support team to be informed about risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment plans and to stay in contact weekly there was a 6.6-fold lower risk of death than for nonsupported youth.
But how much of this evidence-based intervention can you ensure from your position in primary care? Refer if you can but regular supportive contacts alone reduce risk so you, trusted staff, school counselors, or even the now more available teletherapists may help. You can work with your patient to fill out a written commitment-to-safety plan (e.g. U. Colorado, CHADIS) of strategies they can use when having suicidal thoughts such as self-distractions, problem-solving, listing things they are looking forward to, things to do to get their mind off suicidal thoughts, and selecting support people to understand their situation with whom to be in regular contact. Any plan needs to take into account how understanding, supportive, and available the family is, factors you are most likely to be able to judge from your ongoing relationship, but that immediate risk may change. Contact within 48 hours, check-in within 1-2 weeks, and provision of crisis hotline information are essential actions.
Recommending home safety is part of routine anticipatory guidance but reduction of lethal means is essential in these cases. Guns are the most lethal method of suicide but discussing safe gun storage has been shown to be more effective than arguing in vain for gun removal. Medication overdose, a common means, can be reduced by not prescribing tricyclics (ineffective and more lethal), and advising parents to lock up all household medications.
You can ask about and coach teens on how to avoid the hazards of participating in online discussion groups, bullying, and cyberbullying (with risk for both perpetrator and victim), all risk factors for suicide. Managing insomnia can improve depression and is within your skills. While pediatricians can’t treat the suicide risk factors of family poverty, unemployment, or loss of culture/identity, we can refer affected families to community resources.
Repeated suicide screens can help but are imperfect, so listen to the child or parent for risk signs such as the youth having self-reported worthlessness, low self-esteem, speaking negatively about self, anhedonia, or poor emotion regulation. Children with impulsive aggression, often familial, are at special risk of suicide. This trait, while more common in ADHD, is not confined to that condition. You can help by optimizing medical management of impulsivity, when appropriate.
Most youth who attempt suicide have one or more mental health diagnoses, particularly major depressive disorder (MDD), eating disorder, ADHD, conduct, or intermittent explosive disorder. When MDD is comorbid with anxiety, suicides increase 9.5-fold. Children on the autism spectrum are more likely to have been bullied and eight times more likely to commit suicide. LGBTQ youth are five times more often bullied and are at high risk for suicide. The more common issues of school failure or substance use also confer risk. While we do our best caring for children with these conditions we may not be thinking about, screening, or monitoring for their suicide risk. It may be important for us to explain that, despite black-box warnings, rates of SSRI prescribing for depression are inversely related to suicides.
Child maltreatment is the highest risk factor for suicide (population attributed risk, or PAR, 9.6%-14.5%), particularly sexual misuse. All together, adverse childhood experiences have a PAR for suicide of 80%. Continuity allows you to monitor for developmental times when distress from past experiences often reemerges, e.g., puberty, dating onset, or divorce. Getting consent and sharing these highly sensitive but potentially triggering factors as well as prior diagnoses with a newly assigned therapist can be helpful to prioritize treatments to prevent a suicide attempt, because they may be difficult to elicit and timeliness is essential.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
References
Brent DA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;58(1):25-35.
Cha CB et al. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018;59(4):460-82.
You read “thoughts of being better off dead” on your next patient’s PHQ-9 screen results and break into a sweat. After eliciting the teen’s realistic suicide plan and intent you send him to the ED with his parent for crisis mental health evaluation. When you call the family that evening to follow-up you hear that he was discharged with a “mental health counseling” appointment next week.
Have you done enough to prevent this child from dying at his own hand? I imagine that this haunts you as it does me. It is terrifying to know that, of youth with suicidal ideation, over one-third attempt suicide, most within 1-2 years, and 20%-40% do so without having had a plan.
We now know that certain kinds of psychotherapy have evidence for preventing subsequent suicide in teens at high risk due to suicidal ideation and past attempts. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) has the best evidence including its subtypes for youth with relevant histories: for both suicide and substance use (integrated, or I-CBT), trauma focused (TF-CBT), traumatic grief (CTG-CBT), and CBT-I, for the potent risk factor of insomnia. The other treatment shown to reduce risk is dialectical behavioral therapy–adolescent (DBT-A) focused on strengthening skills in interpersonal effectiveness, mindfulness, distress tolerance, and emotion regulation adapted to youth by adding family therapy and multifamily skills training. Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) adapted for suicidal and self-harming adolescents (IPT-SA) also has evidence.
Some school programs have shown moderate efficacy, for example (IPT-A-IN) addresses the social and interpersonal context, and Youth Aware of Mental Health, a school curriculum to increase knowledge, help-seeking, and ways of coping with depression and suicidal behavior, that cut suicide attempts by half.
You may be able to recommend, refer to, or check to see if a youth can be provided one of the above therapies with best evidence but getting any counseling at all can be hard and some, especially minority families may decline formal interventions. Any therapy – CBT, DBT, or IPT – acceptable to the youth and family can be helpful. You can often determine if the key components are being provided by asking the teen what they are working on in therapy.
It is clear that checking in regularly with teens who have been through a suicide crisis is crucial to ensure that they continue in therapy long and consistently enough, that the family is involved in treatment, and that they are taught emotion regulation, distress tolerance, and safety planning. Warm, consistent parenting, good parent-child communication, and monitoring are protective factors but also skills that can be boosted to reduce future risk of suicide. When there is family dysfunction, conflict, or weak relationships, getting help for family relationships such as through attachment-based family therapy (ABFT) or family cognitive behavioral therapy is a priority. When bereavement or parental depression is contributing to youth suicidal thoughts, addressing these specifically can reduce suicide risk.
Sometimes family members, even with counseling, are not the best supporters for a teen in pain. When youths nominated their own support team to be informed about risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment plans and to stay in contact weekly there was a 6.6-fold lower risk of death than for nonsupported youth.
But how much of this evidence-based intervention can you ensure from your position in primary care? Refer if you can but regular supportive contacts alone reduce risk so you, trusted staff, school counselors, or even the now more available teletherapists may help. You can work with your patient to fill out a written commitment-to-safety plan (e.g. U. Colorado, CHADIS) of strategies they can use when having suicidal thoughts such as self-distractions, problem-solving, listing things they are looking forward to, things to do to get their mind off suicidal thoughts, and selecting support people to understand their situation with whom to be in regular contact. Any plan needs to take into account how understanding, supportive, and available the family is, factors you are most likely to be able to judge from your ongoing relationship, but that immediate risk may change. Contact within 48 hours, check-in within 1-2 weeks, and provision of crisis hotline information are essential actions.
Recommending home safety is part of routine anticipatory guidance but reduction of lethal means is essential in these cases. Guns are the most lethal method of suicide but discussing safe gun storage has been shown to be more effective than arguing in vain for gun removal. Medication overdose, a common means, can be reduced by not prescribing tricyclics (ineffective and more lethal), and advising parents to lock up all household medications.
You can ask about and coach teens on how to avoid the hazards of participating in online discussion groups, bullying, and cyberbullying (with risk for both perpetrator and victim), all risk factors for suicide. Managing insomnia can improve depression and is within your skills. While pediatricians can’t treat the suicide risk factors of family poverty, unemployment, or loss of culture/identity, we can refer affected families to community resources.
Repeated suicide screens can help but are imperfect, so listen to the child or parent for risk signs such as the youth having self-reported worthlessness, low self-esteem, speaking negatively about self, anhedonia, or poor emotion regulation. Children with impulsive aggression, often familial, are at special risk of suicide. This trait, while more common in ADHD, is not confined to that condition. You can help by optimizing medical management of impulsivity, when appropriate.
Most youth who attempt suicide have one or more mental health diagnoses, particularly major depressive disorder (MDD), eating disorder, ADHD, conduct, or intermittent explosive disorder. When MDD is comorbid with anxiety, suicides increase 9.5-fold. Children on the autism spectrum are more likely to have been bullied and eight times more likely to commit suicide. LGBTQ youth are five times more often bullied and are at high risk for suicide. The more common issues of school failure or substance use also confer risk. While we do our best caring for children with these conditions we may not be thinking about, screening, or monitoring for their suicide risk. It may be important for us to explain that, despite black-box warnings, rates of SSRI prescribing for depression are inversely related to suicides.
Child maltreatment is the highest risk factor for suicide (population attributed risk, or PAR, 9.6%-14.5%), particularly sexual misuse. All together, adverse childhood experiences have a PAR for suicide of 80%. Continuity allows you to monitor for developmental times when distress from past experiences often reemerges, e.g., puberty, dating onset, or divorce. Getting consent and sharing these highly sensitive but potentially triggering factors as well as prior diagnoses with a newly assigned therapist can be helpful to prioritize treatments to prevent a suicide attempt, because they may be difficult to elicit and timeliness is essential.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
References
Brent DA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;58(1):25-35.
Cha CB et al. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018;59(4):460-82.
You read “thoughts of being better off dead” on your next patient’s PHQ-9 screen results and break into a sweat. After eliciting the teen’s realistic suicide plan and intent you send him to the ED with his parent for crisis mental health evaluation. When you call the family that evening to follow-up you hear that he was discharged with a “mental health counseling” appointment next week.
Have you done enough to prevent this child from dying at his own hand? I imagine that this haunts you as it does me. It is terrifying to know that, of youth with suicidal ideation, over one-third attempt suicide, most within 1-2 years, and 20%-40% do so without having had a plan.
We now know that certain kinds of psychotherapy have evidence for preventing subsequent suicide in teens at high risk due to suicidal ideation and past attempts. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) has the best evidence including its subtypes for youth with relevant histories: for both suicide and substance use (integrated, or I-CBT), trauma focused (TF-CBT), traumatic grief (CTG-CBT), and CBT-I, for the potent risk factor of insomnia. The other treatment shown to reduce risk is dialectical behavioral therapy–adolescent (DBT-A) focused on strengthening skills in interpersonal effectiveness, mindfulness, distress tolerance, and emotion regulation adapted to youth by adding family therapy and multifamily skills training. Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) adapted for suicidal and self-harming adolescents (IPT-SA) also has evidence.
Some school programs have shown moderate efficacy, for example (IPT-A-IN) addresses the social and interpersonal context, and Youth Aware of Mental Health, a school curriculum to increase knowledge, help-seeking, and ways of coping with depression and suicidal behavior, that cut suicide attempts by half.
You may be able to recommend, refer to, or check to see if a youth can be provided one of the above therapies with best evidence but getting any counseling at all can be hard and some, especially minority families may decline formal interventions. Any therapy – CBT, DBT, or IPT – acceptable to the youth and family can be helpful. You can often determine if the key components are being provided by asking the teen what they are working on in therapy.
It is clear that checking in regularly with teens who have been through a suicide crisis is crucial to ensure that they continue in therapy long and consistently enough, that the family is involved in treatment, and that they are taught emotion regulation, distress tolerance, and safety planning. Warm, consistent parenting, good parent-child communication, and monitoring are protective factors but also skills that can be boosted to reduce future risk of suicide. When there is family dysfunction, conflict, or weak relationships, getting help for family relationships such as through attachment-based family therapy (ABFT) or family cognitive behavioral therapy is a priority. When bereavement or parental depression is contributing to youth suicidal thoughts, addressing these specifically can reduce suicide risk.
Sometimes family members, even with counseling, are not the best supporters for a teen in pain. When youths nominated their own support team to be informed about risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment plans and to stay in contact weekly there was a 6.6-fold lower risk of death than for nonsupported youth.
But how much of this evidence-based intervention can you ensure from your position in primary care? Refer if you can but regular supportive contacts alone reduce risk so you, trusted staff, school counselors, or even the now more available teletherapists may help. You can work with your patient to fill out a written commitment-to-safety plan (e.g. U. Colorado, CHADIS) of strategies they can use when having suicidal thoughts such as self-distractions, problem-solving, listing things they are looking forward to, things to do to get their mind off suicidal thoughts, and selecting support people to understand their situation with whom to be in regular contact. Any plan needs to take into account how understanding, supportive, and available the family is, factors you are most likely to be able to judge from your ongoing relationship, but that immediate risk may change. Contact within 48 hours, check-in within 1-2 weeks, and provision of crisis hotline information are essential actions.
Recommending home safety is part of routine anticipatory guidance but reduction of lethal means is essential in these cases. Guns are the most lethal method of suicide but discussing safe gun storage has been shown to be more effective than arguing in vain for gun removal. Medication overdose, a common means, can be reduced by not prescribing tricyclics (ineffective and more lethal), and advising parents to lock up all household medications.
You can ask about and coach teens on how to avoid the hazards of participating in online discussion groups, bullying, and cyberbullying (with risk for both perpetrator and victim), all risk factors for suicide. Managing insomnia can improve depression and is within your skills. While pediatricians can’t treat the suicide risk factors of family poverty, unemployment, or loss of culture/identity, we can refer affected families to community resources.
Repeated suicide screens can help but are imperfect, so listen to the child or parent for risk signs such as the youth having self-reported worthlessness, low self-esteem, speaking negatively about self, anhedonia, or poor emotion regulation. Children with impulsive aggression, often familial, are at special risk of suicide. This trait, while more common in ADHD, is not confined to that condition. You can help by optimizing medical management of impulsivity, when appropriate.
Most youth who attempt suicide have one or more mental health diagnoses, particularly major depressive disorder (MDD), eating disorder, ADHD, conduct, or intermittent explosive disorder. When MDD is comorbid with anxiety, suicides increase 9.5-fold. Children on the autism spectrum are more likely to have been bullied and eight times more likely to commit suicide. LGBTQ youth are five times more often bullied and are at high risk for suicide. The more common issues of school failure or substance use also confer risk. While we do our best caring for children with these conditions we may not be thinking about, screening, or monitoring for their suicide risk. It may be important for us to explain that, despite black-box warnings, rates of SSRI prescribing for depression are inversely related to suicides.
Child maltreatment is the highest risk factor for suicide (population attributed risk, or PAR, 9.6%-14.5%), particularly sexual misuse. All together, adverse childhood experiences have a PAR for suicide of 80%. Continuity allows you to monitor for developmental times when distress from past experiences often reemerges, e.g., puberty, dating onset, or divorce. Getting consent and sharing these highly sensitive but potentially triggering factors as well as prior diagnoses with a newly assigned therapist can be helpful to prioritize treatments to prevent a suicide attempt, because they may be difficult to elicit and timeliness is essential.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
References
Brent DA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;58(1):25-35.
Cha CB et al. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018;59(4):460-82.
How some COVID-19 vaccines could cause rare blood clots
on April 14, 2021, after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that states hold off on using it pending a detailed review of six cases of the same kind of rare but serious event – a blood clot in the vessels that drain blood from the brain combined with a large drop in platelets, which increases the risk for bleeding.
This combination can lead to severe strokes that can lead to brain damage or death. Among the six cases reported, which came to light over the past 3 weeks, one person died, according to the CDC. All six were women and ranged in age from 18 to 48 years.
According to a report from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), which is maintained by the Department of Health & Human Services, the woman who died was 45. She developed a gradually worsening headache about a week after receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
On March 17, the day she came to the hospital, she was dry heaving. Her headache had suddenly gotten much worse, and the left side of her body was weak, which are signs of a stroke. A CT scan revealed both bleeding in her brain and a clot in her cortical vein. She died the following day.
In addition to VAERS, which accepts reports from anyone, the CDC and FDA are monitoring at least eight other safety systems maintained by hospitals, research centers, long-term care facilities, and insurance companies for signs of trouble with the vaccines. VAERS data is searchable and open to the public. Most of these systems are not publicly available to protect patient privacy. It’s unclear which systems detected the six cases cited by federal regulators.
“These are very serious and potentially fatal problems occurring in a healthy young adult. It’s serious and we need to get to the bottom of it,” said Ed Belongia, MD, director of the Center for Clinical Epidemiology and Population Health at the Marshfield (Wis.) Clinic Research Institute. Dr. Belongia leads a research team that helps the CDC monitor vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“Safety is always the highest priority, and I think what we’ve seen here in the past 24 hours is our vaccine safety monitoring system is working,” he said.
Others agree. “I think what CDC and FDA have detected is a rare, but likely real adverse event associated with this vaccine,” said Paul Offit, MD, director of vaccine education at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Although much is still unknown about these events, they follow a similar pattern of blood clots reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine in Europe. That vaccine is now sold under the brand name Vaxzevria.
This has experts questioning whether all vaccines of this type may cause these rare clots.
“I think it’s likely a class effect,” said Dr. Offit, who was a member of the FDA advisory committee that reviewed clinical trial data on the J&J vaccine before it was authorized for use.
Adenovirus vaccines scrutinized
Both the Johnson & Johnson and Vaxzevria vaccines use an adenovirus to ferry genetic instructions for making the coronaviruses spike protein into our cells.
Adenoviruses are common, relatively simple viruses that normally cause mild cold or flu symptoms. The ones used in the vaccine are disabled so they can’t make us sick. They’re more like Trojan horses.
Once inside our cells, they release the DNA instructions they carry to make the spike protein of the new coronavirus. Those cells then crank out copies of the spike protein, which then get displayed on the outer surface of the cell membrane where they are recognized by the immune system.
The immune system then makes antibodies and other defenses against the spike so that, when the real coronavirus comes along, our bodies are ready to fight the infection.
There’s no question the vaccine works. In clinical trials, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine was 66% percent effective at preventing against moderate to severe COVID-19 infection, and none of the patients who got COVID-19 after vaccination had to be admitted to the hospital or died.
The idea behind using adenoviruses in vaccines isn’t a new one. In a kind of fight-fire-with-fire approach, the idea is to use a virus, which is good at infecting us, to fight a different kind of virus.
Researchers have been working on the concept for about 10 years, but the COVID-19 vaccines that use this technology are some of the first adenovirus-vector vaccines deployed in humans.
Only one other adenovirus vaccine, for Ebola, has been approved for use in humans. It was approved in Europe last year. Before the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, no other adenovirus vector has been available for use in humans in the United States.
There are six adenovirus-vector vaccines for COVID-19. In addition to AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson, there’s the Russian-developed vaccine Sputnik V, along with CanSino from China, and the Covishield vaccine in India.
Adenovirus vaccines are more stable than the mRNA vaccines. That makes them easier to store and transport.
But they have a significant downside, too. Because adenoviruses infect humans out in the world, we already make antibodies against them. So there’s always a danger that our immune systems might recognize and react to the vaccine, rendering it ineffective. For that reason, scientists try to carefully select the adenovirus vectors, or carriers, they use.
The two vaccines under investigation for blood clots are slightly different. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine uses the vector AD26, because most of the population lacks preexisting immunity to it. Vaxzevria uses an adenovirus that infects chimpanzees, called ChAdOx1.
Vaxzevria has been widely used in Europe but has not yet been authorized in the United States.
On April 7, the European Medicines Agency, Europe’s counterpart to the FDA, ruled that unusual blood clots with low blood platelets should be listed as rare side effects on the Vaxzevria vaccine.
The decision came after reviewing 62 cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) linked to the vaccine and 25 cases of another rare type of clot, called a splanchnic vein thrombosis. Splanchnic veins drain blood from the major organs in the digestive system, including the stomach, liver, and intestines; 18 of those events were fatal.
The reports were culled from reporting in Europe and the United Kingdom, where around 25 million people have received the Vaxzevria vaccine, making these clots exceptionally rare, but serious.
So far, six cases of CVST have been reported in the United States, after more than 7 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccines have been administered.
A key question for U.S. regulators will be the background rate for these types of rare combinations of clots and deplenished platelets. The background rate is the number of events that would be expected to occur naturally in a population of unvaccinated people. On a press call on April 13, Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, was asked about the frequency of this dangerous combination. He said the combination of low platelets and clots was so rare that it was hard to pinpoint, but might be somewhere between 2 and 14 cases per million people over the course of a year.
The first Johnson & Johnson doses were given in early March. That means the six cases came to light within the first few weeks of use of the vaccine in the United States, a very short amount of time.
“These were six cases per million people for 2 weeks, which is the same thing as 25 million per year, so it’s clearly above the background rate,” Dr. Offit said.
Studies suggest possible mechanism
On April 9, the New England Journal of Medicine published a detailed evaluation of the 11 patients in Germany and Austria who developed the rare clots after their Vaxzevria vaccines.
The study detected rare antibodies to a signaling protein called platelet factor 4, which helps to coordinate clot formation.
These same type of antibodies form in some people given the blood thinning drug heparin. In those reactions, which are also exceptionally rare, the same type of syndrome develops, leading to large, devastating clots that consume circulating platelets.
It’s not yet clear whether people who develop reactions to the vaccines already have some platelet factor 4 antibodies before they are vaccinated, or whether the vaccines somehow spur the body to make these antibodies, which then launch a kind of autoimmune attack.
The researchers on the paper gave the syndrome a name, vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT).
It’s also not clear why more cases seem to be in women than in men. Andrew Eisenberger, MD, an associate professor of hematology and oncology at Columbia University, New York, said the most common causes of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis have to do with conditions that raise estrogen levels, like pregnancy and hormonal contraception.
“Estrogen naturally leads to changes in several clotting proteins in the blood that may predispose to abnormal blood clotting in a few different sites in the body,” he said. “The clotting changes we are encountering with some of COVID-19 vaccines are likely to be synergistic with the effects of estrogen on the blood.”
No matter the cause, the CDC on April 13 alerted doctors to keep a high index of suspicion for VITT in patients who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccination within the last 2 weeks. In those patients, the usual course of treatment with blood thinning drugs like heparin may be harmful.
Symptoms to watch for include severe headache or backache, new neurologic symptoms, severe abdominal pain, shortness of breath, leg swelling, tiny red spots on the skin, or easy bruising.
Grappling with evidence
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet today in an emergency session to review the cases and see if any changes are needed to use of the J&J vaccine in the United States.
Last week, for example, the United Kingdom restricted the use of the AstraZeneca vaccine in people aged younger than 30 years, saying the risks and benefits of vaccination are “more finely balanced” for this age group.
With cases of COVID-19 rising again in the United States, and the Johnson & Johnson vaccine currently the most convenient form of protection against the virus, the committee will have to weigh the risks of that infection against the risk of rare clots caused by vaccination.
They will also likely have to rule out whether any of the cases had COVID. At least one study has reported CVST clots in three patients with confirmed COVID infections. In Europe, COVID infection did not seem to play a role in the formation of the clots with low platelets.
Hilda Bastian, PhD, a clinical trials expert who cofounded the Cochrane Collaboration, said it won’t be an easy task. Much will depend on how certain the committee members feel they know about all the events linked to the vaccine.
“That’s the really, really hard issue from my point of view for them right this moment. Have we missed any? Or how many are we likely to have missed?” asked Dr. Bastian, who lives in Australia.
“In a country that size with that fragmented [of] a health care system, how sure can you be that you know them all? That’s going to be a really difficult situation for them to grapple with, the quality of information that they’ve got,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
on April 14, 2021, after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that states hold off on using it pending a detailed review of six cases of the same kind of rare but serious event – a blood clot in the vessels that drain blood from the brain combined with a large drop in platelets, which increases the risk for bleeding.
This combination can lead to severe strokes that can lead to brain damage or death. Among the six cases reported, which came to light over the past 3 weeks, one person died, according to the CDC. All six were women and ranged in age from 18 to 48 years.
According to a report from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), which is maintained by the Department of Health & Human Services, the woman who died was 45. She developed a gradually worsening headache about a week after receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
On March 17, the day she came to the hospital, she was dry heaving. Her headache had suddenly gotten much worse, and the left side of her body was weak, which are signs of a stroke. A CT scan revealed both bleeding in her brain and a clot in her cortical vein. She died the following day.
In addition to VAERS, which accepts reports from anyone, the CDC and FDA are monitoring at least eight other safety systems maintained by hospitals, research centers, long-term care facilities, and insurance companies for signs of trouble with the vaccines. VAERS data is searchable and open to the public. Most of these systems are not publicly available to protect patient privacy. It’s unclear which systems detected the six cases cited by federal regulators.
“These are very serious and potentially fatal problems occurring in a healthy young adult. It’s serious and we need to get to the bottom of it,” said Ed Belongia, MD, director of the Center for Clinical Epidemiology and Population Health at the Marshfield (Wis.) Clinic Research Institute. Dr. Belongia leads a research team that helps the CDC monitor vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“Safety is always the highest priority, and I think what we’ve seen here in the past 24 hours is our vaccine safety monitoring system is working,” he said.
Others agree. “I think what CDC and FDA have detected is a rare, but likely real adverse event associated with this vaccine,” said Paul Offit, MD, director of vaccine education at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Although much is still unknown about these events, they follow a similar pattern of blood clots reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine in Europe. That vaccine is now sold under the brand name Vaxzevria.
This has experts questioning whether all vaccines of this type may cause these rare clots.
“I think it’s likely a class effect,” said Dr. Offit, who was a member of the FDA advisory committee that reviewed clinical trial data on the J&J vaccine before it was authorized for use.
Adenovirus vaccines scrutinized
Both the Johnson & Johnson and Vaxzevria vaccines use an adenovirus to ferry genetic instructions for making the coronaviruses spike protein into our cells.
Adenoviruses are common, relatively simple viruses that normally cause mild cold or flu symptoms. The ones used in the vaccine are disabled so they can’t make us sick. They’re more like Trojan horses.
Once inside our cells, they release the DNA instructions they carry to make the spike protein of the new coronavirus. Those cells then crank out copies of the spike protein, which then get displayed on the outer surface of the cell membrane where they are recognized by the immune system.
The immune system then makes antibodies and other defenses against the spike so that, when the real coronavirus comes along, our bodies are ready to fight the infection.
There’s no question the vaccine works. In clinical trials, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine was 66% percent effective at preventing against moderate to severe COVID-19 infection, and none of the patients who got COVID-19 after vaccination had to be admitted to the hospital or died.
The idea behind using adenoviruses in vaccines isn’t a new one. In a kind of fight-fire-with-fire approach, the idea is to use a virus, which is good at infecting us, to fight a different kind of virus.
Researchers have been working on the concept for about 10 years, but the COVID-19 vaccines that use this technology are some of the first adenovirus-vector vaccines deployed in humans.
Only one other adenovirus vaccine, for Ebola, has been approved for use in humans. It was approved in Europe last year. Before the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, no other adenovirus vector has been available for use in humans in the United States.
There are six adenovirus-vector vaccines for COVID-19. In addition to AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson, there’s the Russian-developed vaccine Sputnik V, along with CanSino from China, and the Covishield vaccine in India.
Adenovirus vaccines are more stable than the mRNA vaccines. That makes them easier to store and transport.
But they have a significant downside, too. Because adenoviruses infect humans out in the world, we already make antibodies against them. So there’s always a danger that our immune systems might recognize and react to the vaccine, rendering it ineffective. For that reason, scientists try to carefully select the adenovirus vectors, or carriers, they use.
The two vaccines under investigation for blood clots are slightly different. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine uses the vector AD26, because most of the population lacks preexisting immunity to it. Vaxzevria uses an adenovirus that infects chimpanzees, called ChAdOx1.
Vaxzevria has been widely used in Europe but has not yet been authorized in the United States.
On April 7, the European Medicines Agency, Europe’s counterpart to the FDA, ruled that unusual blood clots with low blood platelets should be listed as rare side effects on the Vaxzevria vaccine.
The decision came after reviewing 62 cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) linked to the vaccine and 25 cases of another rare type of clot, called a splanchnic vein thrombosis. Splanchnic veins drain blood from the major organs in the digestive system, including the stomach, liver, and intestines; 18 of those events were fatal.
The reports were culled from reporting in Europe and the United Kingdom, where around 25 million people have received the Vaxzevria vaccine, making these clots exceptionally rare, but serious.
So far, six cases of CVST have been reported in the United States, after more than 7 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccines have been administered.
A key question for U.S. regulators will be the background rate for these types of rare combinations of clots and deplenished platelets. The background rate is the number of events that would be expected to occur naturally in a population of unvaccinated people. On a press call on April 13, Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, was asked about the frequency of this dangerous combination. He said the combination of low platelets and clots was so rare that it was hard to pinpoint, but might be somewhere between 2 and 14 cases per million people over the course of a year.
The first Johnson & Johnson doses were given in early March. That means the six cases came to light within the first few weeks of use of the vaccine in the United States, a very short amount of time.
“These were six cases per million people for 2 weeks, which is the same thing as 25 million per year, so it’s clearly above the background rate,” Dr. Offit said.
Studies suggest possible mechanism
On April 9, the New England Journal of Medicine published a detailed evaluation of the 11 patients in Germany and Austria who developed the rare clots after their Vaxzevria vaccines.
The study detected rare antibodies to a signaling protein called platelet factor 4, which helps to coordinate clot formation.
These same type of antibodies form in some people given the blood thinning drug heparin. In those reactions, which are also exceptionally rare, the same type of syndrome develops, leading to large, devastating clots that consume circulating platelets.
It’s not yet clear whether people who develop reactions to the vaccines already have some platelet factor 4 antibodies before they are vaccinated, or whether the vaccines somehow spur the body to make these antibodies, which then launch a kind of autoimmune attack.
The researchers on the paper gave the syndrome a name, vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT).
It’s also not clear why more cases seem to be in women than in men. Andrew Eisenberger, MD, an associate professor of hematology and oncology at Columbia University, New York, said the most common causes of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis have to do with conditions that raise estrogen levels, like pregnancy and hormonal contraception.
“Estrogen naturally leads to changes in several clotting proteins in the blood that may predispose to abnormal blood clotting in a few different sites in the body,” he said. “The clotting changes we are encountering with some of COVID-19 vaccines are likely to be synergistic with the effects of estrogen on the blood.”
No matter the cause, the CDC on April 13 alerted doctors to keep a high index of suspicion for VITT in patients who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccination within the last 2 weeks. In those patients, the usual course of treatment with blood thinning drugs like heparin may be harmful.
Symptoms to watch for include severe headache or backache, new neurologic symptoms, severe abdominal pain, shortness of breath, leg swelling, tiny red spots on the skin, or easy bruising.
Grappling with evidence
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet today in an emergency session to review the cases and see if any changes are needed to use of the J&J vaccine in the United States.
Last week, for example, the United Kingdom restricted the use of the AstraZeneca vaccine in people aged younger than 30 years, saying the risks and benefits of vaccination are “more finely balanced” for this age group.
With cases of COVID-19 rising again in the United States, and the Johnson & Johnson vaccine currently the most convenient form of protection against the virus, the committee will have to weigh the risks of that infection against the risk of rare clots caused by vaccination.
They will also likely have to rule out whether any of the cases had COVID. At least one study has reported CVST clots in three patients with confirmed COVID infections. In Europe, COVID infection did not seem to play a role in the formation of the clots with low platelets.
Hilda Bastian, PhD, a clinical trials expert who cofounded the Cochrane Collaboration, said it won’t be an easy task. Much will depend on how certain the committee members feel they know about all the events linked to the vaccine.
“That’s the really, really hard issue from my point of view for them right this moment. Have we missed any? Or how many are we likely to have missed?” asked Dr. Bastian, who lives in Australia.
“In a country that size with that fragmented [of] a health care system, how sure can you be that you know them all? That’s going to be a really difficult situation for them to grapple with, the quality of information that they’ve got,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
on April 14, 2021, after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that states hold off on using it pending a detailed review of six cases of the same kind of rare but serious event – a blood clot in the vessels that drain blood from the brain combined with a large drop in platelets, which increases the risk for bleeding.
This combination can lead to severe strokes that can lead to brain damage or death. Among the six cases reported, which came to light over the past 3 weeks, one person died, according to the CDC. All six were women and ranged in age from 18 to 48 years.
According to a report from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), which is maintained by the Department of Health & Human Services, the woman who died was 45. She developed a gradually worsening headache about a week after receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
On March 17, the day she came to the hospital, she was dry heaving. Her headache had suddenly gotten much worse, and the left side of her body was weak, which are signs of a stroke. A CT scan revealed both bleeding in her brain and a clot in her cortical vein. She died the following day.
In addition to VAERS, which accepts reports from anyone, the CDC and FDA are monitoring at least eight other safety systems maintained by hospitals, research centers, long-term care facilities, and insurance companies for signs of trouble with the vaccines. VAERS data is searchable and open to the public. Most of these systems are not publicly available to protect patient privacy. It’s unclear which systems detected the six cases cited by federal regulators.
“These are very serious and potentially fatal problems occurring in a healthy young adult. It’s serious and we need to get to the bottom of it,” said Ed Belongia, MD, director of the Center for Clinical Epidemiology and Population Health at the Marshfield (Wis.) Clinic Research Institute. Dr. Belongia leads a research team that helps the CDC monitor vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“Safety is always the highest priority, and I think what we’ve seen here in the past 24 hours is our vaccine safety monitoring system is working,” he said.
Others agree. “I think what CDC and FDA have detected is a rare, but likely real adverse event associated with this vaccine,” said Paul Offit, MD, director of vaccine education at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Although much is still unknown about these events, they follow a similar pattern of blood clots reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine in Europe. That vaccine is now sold under the brand name Vaxzevria.
This has experts questioning whether all vaccines of this type may cause these rare clots.
“I think it’s likely a class effect,” said Dr. Offit, who was a member of the FDA advisory committee that reviewed clinical trial data on the J&J vaccine before it was authorized for use.
Adenovirus vaccines scrutinized
Both the Johnson & Johnson and Vaxzevria vaccines use an adenovirus to ferry genetic instructions for making the coronaviruses spike protein into our cells.
Adenoviruses are common, relatively simple viruses that normally cause mild cold or flu symptoms. The ones used in the vaccine are disabled so they can’t make us sick. They’re more like Trojan horses.
Once inside our cells, they release the DNA instructions they carry to make the spike protein of the new coronavirus. Those cells then crank out copies of the spike protein, which then get displayed on the outer surface of the cell membrane where they are recognized by the immune system.
The immune system then makes antibodies and other defenses against the spike so that, when the real coronavirus comes along, our bodies are ready to fight the infection.
There’s no question the vaccine works. In clinical trials, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine was 66% percent effective at preventing against moderate to severe COVID-19 infection, and none of the patients who got COVID-19 after vaccination had to be admitted to the hospital or died.
The idea behind using adenoviruses in vaccines isn’t a new one. In a kind of fight-fire-with-fire approach, the idea is to use a virus, which is good at infecting us, to fight a different kind of virus.
Researchers have been working on the concept for about 10 years, but the COVID-19 vaccines that use this technology are some of the first adenovirus-vector vaccines deployed in humans.
Only one other adenovirus vaccine, for Ebola, has been approved for use in humans. It was approved in Europe last year. Before the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, no other adenovirus vector has been available for use in humans in the United States.
There are six adenovirus-vector vaccines for COVID-19. In addition to AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson, there’s the Russian-developed vaccine Sputnik V, along with CanSino from China, and the Covishield vaccine in India.
Adenovirus vaccines are more stable than the mRNA vaccines. That makes them easier to store and transport.
But they have a significant downside, too. Because adenoviruses infect humans out in the world, we already make antibodies against them. So there’s always a danger that our immune systems might recognize and react to the vaccine, rendering it ineffective. For that reason, scientists try to carefully select the adenovirus vectors, or carriers, they use.
The two vaccines under investigation for blood clots are slightly different. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine uses the vector AD26, because most of the population lacks preexisting immunity to it. Vaxzevria uses an adenovirus that infects chimpanzees, called ChAdOx1.
Vaxzevria has been widely used in Europe but has not yet been authorized in the United States.
On April 7, the European Medicines Agency, Europe’s counterpart to the FDA, ruled that unusual blood clots with low blood platelets should be listed as rare side effects on the Vaxzevria vaccine.
The decision came after reviewing 62 cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) linked to the vaccine and 25 cases of another rare type of clot, called a splanchnic vein thrombosis. Splanchnic veins drain blood from the major organs in the digestive system, including the stomach, liver, and intestines; 18 of those events were fatal.
The reports were culled from reporting in Europe and the United Kingdom, where around 25 million people have received the Vaxzevria vaccine, making these clots exceptionally rare, but serious.
So far, six cases of CVST have been reported in the United States, after more than 7 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccines have been administered.
A key question for U.S. regulators will be the background rate for these types of rare combinations of clots and deplenished platelets. The background rate is the number of events that would be expected to occur naturally in a population of unvaccinated people. On a press call on April 13, Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, was asked about the frequency of this dangerous combination. He said the combination of low platelets and clots was so rare that it was hard to pinpoint, but might be somewhere between 2 and 14 cases per million people over the course of a year.
The first Johnson & Johnson doses were given in early March. That means the six cases came to light within the first few weeks of use of the vaccine in the United States, a very short amount of time.
“These were six cases per million people for 2 weeks, which is the same thing as 25 million per year, so it’s clearly above the background rate,” Dr. Offit said.
Studies suggest possible mechanism
On April 9, the New England Journal of Medicine published a detailed evaluation of the 11 patients in Germany and Austria who developed the rare clots after their Vaxzevria vaccines.
The study detected rare antibodies to a signaling protein called platelet factor 4, which helps to coordinate clot formation.
These same type of antibodies form in some people given the blood thinning drug heparin. In those reactions, which are also exceptionally rare, the same type of syndrome develops, leading to large, devastating clots that consume circulating platelets.
It’s not yet clear whether people who develop reactions to the vaccines already have some platelet factor 4 antibodies before they are vaccinated, or whether the vaccines somehow spur the body to make these antibodies, which then launch a kind of autoimmune attack.
The researchers on the paper gave the syndrome a name, vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT).
It’s also not clear why more cases seem to be in women than in men. Andrew Eisenberger, MD, an associate professor of hematology and oncology at Columbia University, New York, said the most common causes of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis have to do with conditions that raise estrogen levels, like pregnancy and hormonal contraception.
“Estrogen naturally leads to changes in several clotting proteins in the blood that may predispose to abnormal blood clotting in a few different sites in the body,” he said. “The clotting changes we are encountering with some of COVID-19 vaccines are likely to be synergistic with the effects of estrogen on the blood.”
No matter the cause, the CDC on April 13 alerted doctors to keep a high index of suspicion for VITT in patients who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccination within the last 2 weeks. In those patients, the usual course of treatment with blood thinning drugs like heparin may be harmful.
Symptoms to watch for include severe headache or backache, new neurologic symptoms, severe abdominal pain, shortness of breath, leg swelling, tiny red spots on the skin, or easy bruising.
Grappling with evidence
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet today in an emergency session to review the cases and see if any changes are needed to use of the J&J vaccine in the United States.
Last week, for example, the United Kingdom restricted the use of the AstraZeneca vaccine in people aged younger than 30 years, saying the risks and benefits of vaccination are “more finely balanced” for this age group.
With cases of COVID-19 rising again in the United States, and the Johnson & Johnson vaccine currently the most convenient form of protection against the virus, the committee will have to weigh the risks of that infection against the risk of rare clots caused by vaccination.
They will also likely have to rule out whether any of the cases had COVID. At least one study has reported CVST clots in three patients with confirmed COVID infections. In Europe, COVID infection did not seem to play a role in the formation of the clots with low platelets.
Hilda Bastian, PhD, a clinical trials expert who cofounded the Cochrane Collaboration, said it won’t be an easy task. Much will depend on how certain the committee members feel they know about all the events linked to the vaccine.
“That’s the really, really hard issue from my point of view for them right this moment. Have we missed any? Or how many are we likely to have missed?” asked Dr. Bastian, who lives in Australia.
“In a country that size with that fragmented [of] a health care system, how sure can you be that you know them all? That’s going to be a really difficult situation for them to grapple with, the quality of information that they’ve got,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitalization not rare for children with COVID, study says
Nearly a third of those had severe disease that required mechanical ventilation or admission to an intensive care unit, according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open on April 9.*
That means about 1 in 9 kids with COVID-19 in this cohort needed hospitalization, and about 1 in 28 had severe COVID-19.
“Although most children with COVID-19 experience mild illness, some children develop serious illness that leads to hospitalization, use of invasive mechanical ventilation, and death,” the researchers wrote.
The research team analyzed discharge data from 869 medical facilities in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. They looked for COVID-19 patients ages 18 and under who had an in-patient or emergency department visit between March and October 2020.
More than 20,700 children with COVID-19 had an in-patient or an emergency department visit, and 2,430 were hospitalized with COVID-19. Among those, 756 children had severe COVID-19 and were admitted to an intensive care unit or needed mechanical ventilation.
About 53% of the COVID-19 patients were girls, and about 54% were between ages 12-18. In addition, about 29% had at least one chronic condition.
Similar to COVID-19 studies in adults, Hispanic, Latino and Black patients were overrepresented. About 39% of the children were Hispanic or Latino, and 24% were Black. However, the researchers didn’t find an association between severe COVID-19 and race or ethnicity.
The likelihood of severe COVID-19 increased if the patient had at least one chronic condition, was male, or was between ages 2-11.
“Understanding factors associated with severe COVID-19 disease among children could help inform prevention and control strategies,” they added. “Reducing infection risk through community mitigation strategies is critical for protecting children from COVID-19 and preventing poor outcomes.”
As of April 8, more than 3.54 million U.S. children have tested positive for COVID-19, according to the latest report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and Children’s Hospital Association. Cases among children are increasing slightly, with about 73,000 new cases reported during the first week of April.
Children represent about 13.5% of the COVID-19 cases in the country, according to the report. Among the 24 states that provide data, children represented 1% to 3% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations, and less than 2% of all child COVID-19 cases resulted in hospitalization.
“At this time, it appears that severe illness due to COVID-19 is rare among children,” the two groups wrote.
“However, there is an urgent need to collect more data on longer-term impacts of the pandemic on children, including ways the virus may harm the long-term physical health of infected children, as well as its emotional and mental health effects,” they added.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
*CORRECTION, 6/7/21 – This story has been corrected to clarify that the patient sample study reflects only those children who presented to an emergency department or received inpatient care for COVID-19 in a hospital network and were included in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. A previous version of the story incorrectly implied that 12% of all U.S. children with COVID-19 had required inpatient care.
Nearly a third of those had severe disease that required mechanical ventilation or admission to an intensive care unit, according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open on April 9.*
That means about 1 in 9 kids with COVID-19 in this cohort needed hospitalization, and about 1 in 28 had severe COVID-19.
“Although most children with COVID-19 experience mild illness, some children develop serious illness that leads to hospitalization, use of invasive mechanical ventilation, and death,” the researchers wrote.
The research team analyzed discharge data from 869 medical facilities in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. They looked for COVID-19 patients ages 18 and under who had an in-patient or emergency department visit between March and October 2020.
More than 20,700 children with COVID-19 had an in-patient or an emergency department visit, and 2,430 were hospitalized with COVID-19. Among those, 756 children had severe COVID-19 and were admitted to an intensive care unit or needed mechanical ventilation.
About 53% of the COVID-19 patients were girls, and about 54% were between ages 12-18. In addition, about 29% had at least one chronic condition.
Similar to COVID-19 studies in adults, Hispanic, Latino and Black patients were overrepresented. About 39% of the children were Hispanic or Latino, and 24% were Black. However, the researchers didn’t find an association between severe COVID-19 and race or ethnicity.
The likelihood of severe COVID-19 increased if the patient had at least one chronic condition, was male, or was between ages 2-11.
“Understanding factors associated with severe COVID-19 disease among children could help inform prevention and control strategies,” they added. “Reducing infection risk through community mitigation strategies is critical for protecting children from COVID-19 and preventing poor outcomes.”
As of April 8, more than 3.54 million U.S. children have tested positive for COVID-19, according to the latest report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and Children’s Hospital Association. Cases among children are increasing slightly, with about 73,000 new cases reported during the first week of April.
Children represent about 13.5% of the COVID-19 cases in the country, according to the report. Among the 24 states that provide data, children represented 1% to 3% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations, and less than 2% of all child COVID-19 cases resulted in hospitalization.
“At this time, it appears that severe illness due to COVID-19 is rare among children,” the two groups wrote.
“However, there is an urgent need to collect more data on longer-term impacts of the pandemic on children, including ways the virus may harm the long-term physical health of infected children, as well as its emotional and mental health effects,” they added.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
*CORRECTION, 6/7/21 – This story has been corrected to clarify that the patient sample study reflects only those children who presented to an emergency department or received inpatient care for COVID-19 in a hospital network and were included in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. A previous version of the story incorrectly implied that 12% of all U.S. children with COVID-19 had required inpatient care.
Nearly a third of those had severe disease that required mechanical ventilation or admission to an intensive care unit, according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open on April 9.*
That means about 1 in 9 kids with COVID-19 in this cohort needed hospitalization, and about 1 in 28 had severe COVID-19.
“Although most children with COVID-19 experience mild illness, some children develop serious illness that leads to hospitalization, use of invasive mechanical ventilation, and death,” the researchers wrote.
The research team analyzed discharge data from 869 medical facilities in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. They looked for COVID-19 patients ages 18 and under who had an in-patient or emergency department visit between March and October 2020.
More than 20,700 children with COVID-19 had an in-patient or an emergency department visit, and 2,430 were hospitalized with COVID-19. Among those, 756 children had severe COVID-19 and were admitted to an intensive care unit or needed mechanical ventilation.
About 53% of the COVID-19 patients were girls, and about 54% were between ages 12-18. In addition, about 29% had at least one chronic condition.
Similar to COVID-19 studies in adults, Hispanic, Latino and Black patients were overrepresented. About 39% of the children were Hispanic or Latino, and 24% were Black. However, the researchers didn’t find an association between severe COVID-19 and race or ethnicity.
The likelihood of severe COVID-19 increased if the patient had at least one chronic condition, was male, or was between ages 2-11.
“Understanding factors associated with severe COVID-19 disease among children could help inform prevention and control strategies,” they added. “Reducing infection risk through community mitigation strategies is critical for protecting children from COVID-19 and preventing poor outcomes.”
As of April 8, more than 3.54 million U.S. children have tested positive for COVID-19, according to the latest report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and Children’s Hospital Association. Cases among children are increasing slightly, with about 73,000 new cases reported during the first week of April.
Children represent about 13.5% of the COVID-19 cases in the country, according to the report. Among the 24 states that provide data, children represented 1% to 3% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations, and less than 2% of all child COVID-19 cases resulted in hospitalization.
“At this time, it appears that severe illness due to COVID-19 is rare among children,” the two groups wrote.
“However, there is an urgent need to collect more data on longer-term impacts of the pandemic on children, including ways the virus may harm the long-term physical health of infected children, as well as its emotional and mental health effects,” they added.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
*CORRECTION, 6/7/21 – This story has been corrected to clarify that the patient sample study reflects only those children who presented to an emergency department or received inpatient care for COVID-19 in a hospital network and were included in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. A previous version of the story incorrectly implied that 12% of all U.S. children with COVID-19 had required inpatient care.
How to counsel worried patients about the J&J vaccine news
On April 13, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration issued a joint statement recommending a pause in Johnson & Johnson vaccine administration, pending review of six reported U.S. cases of a rare and severe type of blood clot occurring after receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine. To date, more than 6.8 million doses of that vaccine have been given in the United States, so at this point the rate of detected cases of this problem is less than one in a million.
The six cases occurred in women aged 18-48 years, and symptoms occurred 6-13 days after vaccination. In these cases, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis was seen in addition to thrombocytopenia.
Physicians may receive calls from concerned patients who have received a COVID vaccine. However, more than 95% of the vaccine administrations in the United States to date have been the Pfizer and Moderna messenger RNA vaccines. No association between these vaccines and blood clots has been detected. Also, these six cases occurred within 2 weeks of Johnson & Johnson vaccination, so even among those receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, those who are more than 3 weeks out from their vaccination have no need for concern regarding this rare complication.
Physicians should counsel those who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine less than 3 weeks ago to watch for easy bruising, gum bleeding, nose bleeds, leg or arm pain or swelling, severe headache or abdominal pain, shortness of breath, or chest pain. If they notice one or more of those symptoms, they should seek medical attention.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will convene a meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on April 14 to review the six U.S. cases of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine and determine their significance.
Several cases of unusual thromboses and thrombocytopenia have been detected after the Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine, which uses the same adenovirus vector technology as the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, but which is not authorized for use in the United States. The Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine uses a recombinant deficient chimpanzee adenovirus to deliver the message to cells to produce antibody against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine uses a recombinant deficient human adenovirus to deliver this same message.
Two recent reports in the New England Journal of Medicine have reported on thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after the Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine in Europe. Both of these reports identified high levels of IgG antibodies to platelet factor 4–polyanion complexes, similar to the mechanism of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. The term vaccine-induced immune thrombocytopenia was proposed for this phenomenon. Treatment of this condition involves administration of intravenous immunoglobulin and nonheparin anticoagulants. Recent updates from the World Health Organization report that 169 cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and 53 of splanchnic venous thrombosis occurred after 34 million doses of the Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine was administered in the European Union and United Kingdom.
While this pause in Johnson & Johnson vaccination is disappointing news amid increased cases in parts of the country, the Johnson & Johnson vaccines make up less than 5% of the U.S. vaccine doses administered to date. According to the CDC, more than 122 million Americans have received at least one dose and more than 75 million are fully vaccinated.
Dr. Patterson has received an honorarium from Pfizer for an antifungal symposium and is a subinvestigator for the Novavax vaccine. Her spouse served as a consultant for SCYNEXIS, as a speaker for Gilead Sciences and Basilea, and has received a research grant from the National Institutes of Health for the ACTT remdesivir trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On April 13, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration issued a joint statement recommending a pause in Johnson & Johnson vaccine administration, pending review of six reported U.S. cases of a rare and severe type of blood clot occurring after receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine. To date, more than 6.8 million doses of that vaccine have been given in the United States, so at this point the rate of detected cases of this problem is less than one in a million.
The six cases occurred in women aged 18-48 years, and symptoms occurred 6-13 days after vaccination. In these cases, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis was seen in addition to thrombocytopenia.
Physicians may receive calls from concerned patients who have received a COVID vaccine. However, more than 95% of the vaccine administrations in the United States to date have been the Pfizer and Moderna messenger RNA vaccines. No association between these vaccines and blood clots has been detected. Also, these six cases occurred within 2 weeks of Johnson & Johnson vaccination, so even among those receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, those who are more than 3 weeks out from their vaccination have no need for concern regarding this rare complication.
Physicians should counsel those who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine less than 3 weeks ago to watch for easy bruising, gum bleeding, nose bleeds, leg or arm pain or swelling, severe headache or abdominal pain, shortness of breath, or chest pain. If they notice one or more of those symptoms, they should seek medical attention.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will convene a meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on April 14 to review the six U.S. cases of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine and determine their significance.
Several cases of unusual thromboses and thrombocytopenia have been detected after the Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine, which uses the same adenovirus vector technology as the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, but which is not authorized for use in the United States. The Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine uses a recombinant deficient chimpanzee adenovirus to deliver the message to cells to produce antibody against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine uses a recombinant deficient human adenovirus to deliver this same message.
Two recent reports in the New England Journal of Medicine have reported on thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after the Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine in Europe. Both of these reports identified high levels of IgG antibodies to platelet factor 4–polyanion complexes, similar to the mechanism of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. The term vaccine-induced immune thrombocytopenia was proposed for this phenomenon. Treatment of this condition involves administration of intravenous immunoglobulin and nonheparin anticoagulants. Recent updates from the World Health Organization report that 169 cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and 53 of splanchnic venous thrombosis occurred after 34 million doses of the Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine was administered in the European Union and United Kingdom.
While this pause in Johnson & Johnson vaccination is disappointing news amid increased cases in parts of the country, the Johnson & Johnson vaccines make up less than 5% of the U.S. vaccine doses administered to date. According to the CDC, more than 122 million Americans have received at least one dose and more than 75 million are fully vaccinated.
Dr. Patterson has received an honorarium from Pfizer for an antifungal symposium and is a subinvestigator for the Novavax vaccine. Her spouse served as a consultant for SCYNEXIS, as a speaker for Gilead Sciences and Basilea, and has received a research grant from the National Institutes of Health for the ACTT remdesivir trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On April 13, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration issued a joint statement recommending a pause in Johnson & Johnson vaccine administration, pending review of six reported U.S. cases of a rare and severe type of blood clot occurring after receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine. To date, more than 6.8 million doses of that vaccine have been given in the United States, so at this point the rate of detected cases of this problem is less than one in a million.
The six cases occurred in women aged 18-48 years, and symptoms occurred 6-13 days after vaccination. In these cases, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis was seen in addition to thrombocytopenia.
Physicians may receive calls from concerned patients who have received a COVID vaccine. However, more than 95% of the vaccine administrations in the United States to date have been the Pfizer and Moderna messenger RNA vaccines. No association between these vaccines and blood clots has been detected. Also, these six cases occurred within 2 weeks of Johnson & Johnson vaccination, so even among those receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, those who are more than 3 weeks out from their vaccination have no need for concern regarding this rare complication.
Physicians should counsel those who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine less than 3 weeks ago to watch for easy bruising, gum bleeding, nose bleeds, leg or arm pain or swelling, severe headache or abdominal pain, shortness of breath, or chest pain. If they notice one or more of those symptoms, they should seek medical attention.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will convene a meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on April 14 to review the six U.S. cases of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine and determine their significance.
Several cases of unusual thromboses and thrombocytopenia have been detected after the Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine, which uses the same adenovirus vector technology as the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, but which is not authorized for use in the United States. The Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine uses a recombinant deficient chimpanzee adenovirus to deliver the message to cells to produce antibody against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine uses a recombinant deficient human adenovirus to deliver this same message.
Two recent reports in the New England Journal of Medicine have reported on thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after the Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine in Europe. Both of these reports identified high levels of IgG antibodies to platelet factor 4–polyanion complexes, similar to the mechanism of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. The term vaccine-induced immune thrombocytopenia was proposed for this phenomenon. Treatment of this condition involves administration of intravenous immunoglobulin and nonheparin anticoagulants. Recent updates from the World Health Organization report that 169 cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and 53 of splanchnic venous thrombosis occurred after 34 million doses of the Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine was administered in the European Union and United Kingdom.
While this pause in Johnson & Johnson vaccination is disappointing news amid increased cases in parts of the country, the Johnson & Johnson vaccines make up less than 5% of the U.S. vaccine doses administered to date. According to the CDC, more than 122 million Americans have received at least one dose and more than 75 million are fully vaccinated.
Dr. Patterson has received an honorarium from Pfizer for an antifungal symposium and is a subinvestigator for the Novavax vaccine. Her spouse served as a consultant for SCYNEXIS, as a speaker for Gilead Sciences and Basilea, and has received a research grant from the National Institutes of Health for the ACTT remdesivir trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 vaccine failure in patients with blood cancers
COVID vaccines do not work well for patients with hematologic malignancies, new data suggest.
A small study involving 67 such patients shows that nearly half did not produce antibodies and were therefore still at risk of contracting COVID-19, even though they had all received both doses of one of the new mRNA COVID vaccines (Moderna or Pfizer).
“[This] is in stark contrast with the results of phase 1 mRNA vaccine immunogenicity trials, in which robust antibody responses were seen in essentially 100% of participants,” said the authors, led by Mounzer Agha, MD, director of the Mario Lemieux Center for Blood Cancers at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center’s Hillman Cancer Center.
“Clinicians caring for patients with hematological malignancies and other immunocompromising conditions should be aware of the possibility of COVID-19 vaccine failure,” they emphasized.
“It’s critically important for these patients to be aware of their continued risk [for SARS-CoV-2 infection] and to seek prompt medical attention if they have COVID-19 symptoms, even after vaccination,” Dr. Agha said in a statement.
The study was published online on April 9 as preprint in medRxiv and has not yet undergone peer review.
Antibody responses
The authors analyzed responses in a group of 67 patients who had a hematologic malignancy, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. Approximately 45% of the patients were receiving therapy for their cancer at the time of vaccination; the rest were under observation.
All patients received two doses of an mRNA COVID vaccine and so were considered to be fully vaccinated.
Antibody responses for these fully vaccinated patients were then analyzed. The median duration between receipt of the second dose of the vaccine and the antibody test was 23 days.
“In total ... 46.3% ... had a negative antibody result after vaccination and were therefore considered to be vaccine nonresponders,” the authors reported.
The worst responses occurred in patients with CLL, of whom only 23% produced measurable antibodies to either vaccine, although approximately 70% of these patients were not receiving any form of cancer therapy at the time of vaccination.
Older patients were more likely not to have a response to either vaccine compared with younger patients, the investigators added.
In contrast, gender, immunoglobulin G levels, the number of days between the second dose and the measurement of antibodies, and status of cancer therapy did not differ among patients who had a response to the vaccines and those who did not.
“Our findings underscore the importance of adherence to nonpharmaceutical interventions to prevent COVID-19 in hematological malignancy patients,” the authors wrote. This is particularly important, given the fact that among patients with hematologic malignancies who become infected with SARS-CoV-2, the mortality rate is in excess of 30%.
Moreover, among such patients, viral shedding may be prolonged, often lasting several months. As such, “these patients should be advised to wear masks and observe social distancing regardless of vaccination status,” the investigators advised.
As of March 2021, guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has allowed gatherings of unmasked people who have been vaccinated and of those at low risk for COVID-19 who have not yet been vaccinated. “As we see more national guidance allowing for unmasked gatherings among vaccinated people, clinicians should counsel their immunocompromised patients about the possibility that COVID-19 vaccines may not fully protect them against SARS-CoV-2,” coauthor Ghady Haidar, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, said in a statement.
“Our results show that the odds of the vaccine producing an antibody response in people with hematologic malignancies are the equivalent of a coin flip,” he said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID vaccines do not work well for patients with hematologic malignancies, new data suggest.
A small study involving 67 such patients shows that nearly half did not produce antibodies and were therefore still at risk of contracting COVID-19, even though they had all received both doses of one of the new mRNA COVID vaccines (Moderna or Pfizer).
“[This] is in stark contrast with the results of phase 1 mRNA vaccine immunogenicity trials, in which robust antibody responses were seen in essentially 100% of participants,” said the authors, led by Mounzer Agha, MD, director of the Mario Lemieux Center for Blood Cancers at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center’s Hillman Cancer Center.
“Clinicians caring for patients with hematological malignancies and other immunocompromising conditions should be aware of the possibility of COVID-19 vaccine failure,” they emphasized.
“It’s critically important for these patients to be aware of their continued risk [for SARS-CoV-2 infection] and to seek prompt medical attention if they have COVID-19 symptoms, even after vaccination,” Dr. Agha said in a statement.
The study was published online on April 9 as preprint in medRxiv and has not yet undergone peer review.
Antibody responses
The authors analyzed responses in a group of 67 patients who had a hematologic malignancy, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. Approximately 45% of the patients were receiving therapy for their cancer at the time of vaccination; the rest were under observation.
All patients received two doses of an mRNA COVID vaccine and so were considered to be fully vaccinated.
Antibody responses for these fully vaccinated patients were then analyzed. The median duration between receipt of the second dose of the vaccine and the antibody test was 23 days.
“In total ... 46.3% ... had a negative antibody result after vaccination and were therefore considered to be vaccine nonresponders,” the authors reported.
The worst responses occurred in patients with CLL, of whom only 23% produced measurable antibodies to either vaccine, although approximately 70% of these patients were not receiving any form of cancer therapy at the time of vaccination.
Older patients were more likely not to have a response to either vaccine compared with younger patients, the investigators added.
In contrast, gender, immunoglobulin G levels, the number of days between the second dose and the measurement of antibodies, and status of cancer therapy did not differ among patients who had a response to the vaccines and those who did not.
“Our findings underscore the importance of adherence to nonpharmaceutical interventions to prevent COVID-19 in hematological malignancy patients,” the authors wrote. This is particularly important, given the fact that among patients with hematologic malignancies who become infected with SARS-CoV-2, the mortality rate is in excess of 30%.
Moreover, among such patients, viral shedding may be prolonged, often lasting several months. As such, “these patients should be advised to wear masks and observe social distancing regardless of vaccination status,” the investigators advised.
As of March 2021, guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has allowed gatherings of unmasked people who have been vaccinated and of those at low risk for COVID-19 who have not yet been vaccinated. “As we see more national guidance allowing for unmasked gatherings among vaccinated people, clinicians should counsel their immunocompromised patients about the possibility that COVID-19 vaccines may not fully protect them against SARS-CoV-2,” coauthor Ghady Haidar, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, said in a statement.
“Our results show that the odds of the vaccine producing an antibody response in people with hematologic malignancies are the equivalent of a coin flip,” he said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID vaccines do not work well for patients with hematologic malignancies, new data suggest.
A small study involving 67 such patients shows that nearly half did not produce antibodies and were therefore still at risk of contracting COVID-19, even though they had all received both doses of one of the new mRNA COVID vaccines (Moderna or Pfizer).
“[This] is in stark contrast with the results of phase 1 mRNA vaccine immunogenicity trials, in which robust antibody responses were seen in essentially 100% of participants,” said the authors, led by Mounzer Agha, MD, director of the Mario Lemieux Center for Blood Cancers at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center’s Hillman Cancer Center.
“Clinicians caring for patients with hematological malignancies and other immunocompromising conditions should be aware of the possibility of COVID-19 vaccine failure,” they emphasized.
“It’s critically important for these patients to be aware of their continued risk [for SARS-CoV-2 infection] and to seek prompt medical attention if they have COVID-19 symptoms, even after vaccination,” Dr. Agha said in a statement.
The study was published online on April 9 as preprint in medRxiv and has not yet undergone peer review.
Antibody responses
The authors analyzed responses in a group of 67 patients who had a hematologic malignancy, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. Approximately 45% of the patients were receiving therapy for their cancer at the time of vaccination; the rest were under observation.
All patients received two doses of an mRNA COVID vaccine and so were considered to be fully vaccinated.
Antibody responses for these fully vaccinated patients were then analyzed. The median duration between receipt of the second dose of the vaccine and the antibody test was 23 days.
“In total ... 46.3% ... had a negative antibody result after vaccination and were therefore considered to be vaccine nonresponders,” the authors reported.
The worst responses occurred in patients with CLL, of whom only 23% produced measurable antibodies to either vaccine, although approximately 70% of these patients were not receiving any form of cancer therapy at the time of vaccination.
Older patients were more likely not to have a response to either vaccine compared with younger patients, the investigators added.
In contrast, gender, immunoglobulin G levels, the number of days between the second dose and the measurement of antibodies, and status of cancer therapy did not differ among patients who had a response to the vaccines and those who did not.
“Our findings underscore the importance of adherence to nonpharmaceutical interventions to prevent COVID-19 in hematological malignancy patients,” the authors wrote. This is particularly important, given the fact that among patients with hematologic malignancies who become infected with SARS-CoV-2, the mortality rate is in excess of 30%.
Moreover, among such patients, viral shedding may be prolonged, often lasting several months. As such, “these patients should be advised to wear masks and observe social distancing regardless of vaccination status,” the investigators advised.
As of March 2021, guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has allowed gatherings of unmasked people who have been vaccinated and of those at low risk for COVID-19 who have not yet been vaccinated. “As we see more national guidance allowing for unmasked gatherings among vaccinated people, clinicians should counsel their immunocompromised patients about the possibility that COVID-19 vaccines may not fully protect them against SARS-CoV-2,” coauthor Ghady Haidar, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, said in a statement.
“Our results show that the odds of the vaccine producing an antibody response in people with hematologic malignancies are the equivalent of a coin flip,” he said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The cost of pediatric specialization
I suspect that very few of you chose to go into pediatrics as part of a get-rich-quick scheme. But, like me, you may have assumed that by going into medicine you would always have a job buffered from the erratic winds of the economy, an assumption that it turns out did not take into account the risk of a global pandemic.
I also bet that if you chose to subspecialize it was not because you felt you might make more money. I and most of the lay public have always naively assumed that specialists generally make more money because … well, because they spent more time training. You, on the other hand, may have discovered belatedly that becoming a pediatric subspecialist isn’t as lucrative as you thought it might be.
It turns out that, when subjected to some standard money-crunching exercises, the lifetime earning potential of most pediatric subspecialists falls significantly behind that of general pediatricians. In a paper published in the April 2021 issue of Pediatrics, investigators from the departments of neurology and pediatric neurology at Johns Hopkins University have reported that, with the exception of three hospital-based, procedure-oriented specialties (cardiology, critical care, and neonatology) the earning time lost during training is usually not recouped over the course of a subspecialist’s career. This observation may be explained in many cases by the fact that the income generated by most subspecialists is similar to and not greater than that of general pediatricians. Even when the income of a subspecialist is greater, it is generally not enough to allow for catch up for the earning power lost during training. The researchers observed this effect both in academic and nonacademic settings.
It is possible that, as the results of this study become more widely distributed, more pediatricians in training will begin to think a bit more about the bottom line when they are considering fellowship training. I suspect that drift is already underway, and if it continues, we will find more subspecialties experiencing shortages. And the importance of this lack of subspecialists on both a local and national level is not something to ignore.
The authors discuss several possible solutions. One option might be to shorten the subspecialty training period. Obviously, this would raise some concerns about quality. Another might be for the government to begin a program in which student loans were selectively forgiven based on a physician’s decision to pursue a subspecialty that is experiencing a shortage.
Another option might be to subsidize the income of some subspecialists. Although this might have a similar effect as loan forgiveness, as a physician with a longstanding pride in being a generalist I would hate to see subspecialists guaranteed a higher income merely because of the narrower mix of patients they have chosen to see. I have always felt that the challenge faced by a primary care generalist who must be prepared to deal with the breadth of complaints that present themselves at the door is at least as great and in many cases greater than that of a specialist whose patients to a large extent have been presorted.
Another solution that comes to mind is that, instead of shortening fellowship programs, one could restructure basic pediatric training programs to allow physicians who have already chosen to become subspecialists to enter a fellowship program after 2 years of house officer training. Restructuring of this magnitude would not be as simple as lopping off the last year of house officer training. It would require tailoring each physician’s shortened prefellowship learning experience to maximize his or her exposure to clinical situations that will be most relevant to the anticipated subspecialty they have chosen. A plan like this also assumes that a significant number of recent medical school graduates will be ready to make choices during their internship that will channel them into careers that will span decades.
Becoming a generalist was an easy decision for me. Any of the subspecialties I was considering would have meant I would have had to live and work in or near a high-density population. I am and always have been a small town kind of guy.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I suspect that very few of you chose to go into pediatrics as part of a get-rich-quick scheme. But, like me, you may have assumed that by going into medicine you would always have a job buffered from the erratic winds of the economy, an assumption that it turns out did not take into account the risk of a global pandemic.
I also bet that if you chose to subspecialize it was not because you felt you might make more money. I and most of the lay public have always naively assumed that specialists generally make more money because … well, because they spent more time training. You, on the other hand, may have discovered belatedly that becoming a pediatric subspecialist isn’t as lucrative as you thought it might be.
It turns out that, when subjected to some standard money-crunching exercises, the lifetime earning potential of most pediatric subspecialists falls significantly behind that of general pediatricians. In a paper published in the April 2021 issue of Pediatrics, investigators from the departments of neurology and pediatric neurology at Johns Hopkins University have reported that, with the exception of three hospital-based, procedure-oriented specialties (cardiology, critical care, and neonatology) the earning time lost during training is usually not recouped over the course of a subspecialist’s career. This observation may be explained in many cases by the fact that the income generated by most subspecialists is similar to and not greater than that of general pediatricians. Even when the income of a subspecialist is greater, it is generally not enough to allow for catch up for the earning power lost during training. The researchers observed this effect both in academic and nonacademic settings.
It is possible that, as the results of this study become more widely distributed, more pediatricians in training will begin to think a bit more about the bottom line when they are considering fellowship training. I suspect that drift is already underway, and if it continues, we will find more subspecialties experiencing shortages. And the importance of this lack of subspecialists on both a local and national level is not something to ignore.
The authors discuss several possible solutions. One option might be to shorten the subspecialty training period. Obviously, this would raise some concerns about quality. Another might be for the government to begin a program in which student loans were selectively forgiven based on a physician’s decision to pursue a subspecialty that is experiencing a shortage.
Another option might be to subsidize the income of some subspecialists. Although this might have a similar effect as loan forgiveness, as a physician with a longstanding pride in being a generalist I would hate to see subspecialists guaranteed a higher income merely because of the narrower mix of patients they have chosen to see. I have always felt that the challenge faced by a primary care generalist who must be prepared to deal with the breadth of complaints that present themselves at the door is at least as great and in many cases greater than that of a specialist whose patients to a large extent have been presorted.
Another solution that comes to mind is that, instead of shortening fellowship programs, one could restructure basic pediatric training programs to allow physicians who have already chosen to become subspecialists to enter a fellowship program after 2 years of house officer training. Restructuring of this magnitude would not be as simple as lopping off the last year of house officer training. It would require tailoring each physician’s shortened prefellowship learning experience to maximize his or her exposure to clinical situations that will be most relevant to the anticipated subspecialty they have chosen. A plan like this also assumes that a significant number of recent medical school graduates will be ready to make choices during their internship that will channel them into careers that will span decades.
Becoming a generalist was an easy decision for me. Any of the subspecialties I was considering would have meant I would have had to live and work in or near a high-density population. I am and always have been a small town kind of guy.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I suspect that very few of you chose to go into pediatrics as part of a get-rich-quick scheme. But, like me, you may have assumed that by going into medicine you would always have a job buffered from the erratic winds of the economy, an assumption that it turns out did not take into account the risk of a global pandemic.
I also bet that if you chose to subspecialize it was not because you felt you might make more money. I and most of the lay public have always naively assumed that specialists generally make more money because … well, because they spent more time training. You, on the other hand, may have discovered belatedly that becoming a pediatric subspecialist isn’t as lucrative as you thought it might be.
It turns out that, when subjected to some standard money-crunching exercises, the lifetime earning potential of most pediatric subspecialists falls significantly behind that of general pediatricians. In a paper published in the April 2021 issue of Pediatrics, investigators from the departments of neurology and pediatric neurology at Johns Hopkins University have reported that, with the exception of three hospital-based, procedure-oriented specialties (cardiology, critical care, and neonatology) the earning time lost during training is usually not recouped over the course of a subspecialist’s career. This observation may be explained in many cases by the fact that the income generated by most subspecialists is similar to and not greater than that of general pediatricians. Even when the income of a subspecialist is greater, it is generally not enough to allow for catch up for the earning power lost during training. The researchers observed this effect both in academic and nonacademic settings.
It is possible that, as the results of this study become more widely distributed, more pediatricians in training will begin to think a bit more about the bottom line when they are considering fellowship training. I suspect that drift is already underway, and if it continues, we will find more subspecialties experiencing shortages. And the importance of this lack of subspecialists on both a local and national level is not something to ignore.
The authors discuss several possible solutions. One option might be to shorten the subspecialty training period. Obviously, this would raise some concerns about quality. Another might be for the government to begin a program in which student loans were selectively forgiven based on a physician’s decision to pursue a subspecialty that is experiencing a shortage.
Another option might be to subsidize the income of some subspecialists. Although this might have a similar effect as loan forgiveness, as a physician with a longstanding pride in being a generalist I would hate to see subspecialists guaranteed a higher income merely because of the narrower mix of patients they have chosen to see. I have always felt that the challenge faced by a primary care generalist who must be prepared to deal with the breadth of complaints that present themselves at the door is at least as great and in many cases greater than that of a specialist whose patients to a large extent have been presorted.
Another solution that comes to mind is that, instead of shortening fellowship programs, one could restructure basic pediatric training programs to allow physicians who have already chosen to become subspecialists to enter a fellowship program after 2 years of house officer training. Restructuring of this magnitude would not be as simple as lopping off the last year of house officer training. It would require tailoring each physician’s shortened prefellowship learning experience to maximize his or her exposure to clinical situations that will be most relevant to the anticipated subspecialty they have chosen. A plan like this also assumes that a significant number of recent medical school graduates will be ready to make choices during their internship that will channel them into careers that will span decades.
Becoming a generalist was an easy decision for me. Any of the subspecialties I was considering would have meant I would have had to live and work in or near a high-density population. I am and always have been a small town kind of guy.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Data about COVID-19-related skin manifestations in children continue to emerge
Two and stratifying children at risk for serious, systemic illness due to the virus.
In a single-center descriptive study carried out over a 9-month period, researchers in Madrid found that of 50 hospitalized children infected with COVID-19, 21 (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly exanthem, followed by conjunctival hyperemia without secretion and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue. In addition, 18 (36%) fulfilled criteria for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
“Based on findings in adult patients, the skin manifestations of COVID-19 have been classified under five categories: acral pseudo-chilblain, vesicular eruptions, urticarial lesions, maculopapular eruptions, and livedo or necrosis,” David Andina-Martinez, MD, of Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online on April 2 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Chilblain lesions in healthy children and adolescents have received much attention; these lesions resolve without complications after a few weeks,” they added. “Besides, other cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 in children have been the matter of case reports or small case series. Nevertheless, the mucocutaneous manifestations in hospitalized children infected with SARS-CoV-2 and their implications on the clinical course have not yet been extensively described.”
In an effort to describe the mucocutaneous manifestations in children hospitalized for COVID-19, the researchers evaluated 50 children up to 18 years of age who were admitted between March 1 and Nov. 30, 2020, to Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, which was designated as a pediatric reference center during the peak of the pandemic. The main reasons for admission were respiratory illness (40%) and MIS-C (40%).
Of the 50 patients, 44 (88%) had a positive RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 and 6 (12%) met clinical suspicion criteria and had a negative RT-PCR with a positive IgG serology. In 34 patients (68%), a close contact with a suspected or confirmed case of COVID-19 was referred, while the source of the infection remained unknown in the remaining 16 patients (32%).
The researchers reported that 21 patients (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly maculopapular exanthem (86%), conjunctival hyperemia (81%), and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue (43%). In addition, 18 of the 21 patients (86%) fulfilled criteria for MIS-C.
“A tricky thing about MIS-C is that it often manifests 4-5 weeks after a child had COVID-19,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study. “MIS-C is associated with characteristic bright red lips and a red tongue that might resemble a strawberry. Such oral findings should prompt rapid evaluation for other signs and symptoms. There can be redness of the eyes or other more nonspecific skin findings (large or small areas of redness on the trunk or limbs, sometimes with surface change), but more importantly, fever, a rapid heartbeat, diarrhea, or breathing issues. The risk with MIS-C is a rapid decline in a child’s health, with admission to an intensive care unit.”
Dr. Andina-Martinez and his colleagues also contrast the skin findings of MIS-C, which are not generally on the hands or feet, with the so-called “COVID toe” or finger phenomenon, which has also been associated with SARS-CoV-2, particularly in children. “Only one of the patients in this series had skin involvement of a finger, and it only appeared after recovery from MIS-C,” Dr. Ko noted. “Distinguishing COVID toes from MIS-C is important, as COVID toes has a very good outcome, while MIS-C can have severe consequences, including protracted heart disease.”
In other findings, patients who presented with mucocutaneous signs tended to be older than those without skin signs and they presented at the emergency department with poor general status and extreme tachycardia. They also had higher C-reactive protein and D-dimer levels and lower lymphocyte counts and faced a more than a 10-fold increased risk of being admitted to the PICU, compared with patients who did not have skin signs (OR, 10.24; P = .003).
In a separate study published online on April 7 in JAMA Dermatology, Zachary E. Holcomb, MD, of the combined dermatology residency program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues presented what is believed to be the first case report of reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) triggered by SARS-CoV-2. RIME is the preferred term for pediatric patients who present with mucositis and rash (often a scant or even absent skin eruption) triggered by various infectious agents.
The patient, a 17-year-old male, presented to the emergency department with 3 days of mouth pain and nonpainful penile erosions. “One week prior, he experienced transient anosmia and ageusia that had since spontaneously resolved,” the researchers wrote. “At that time, he was tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection via nasopharyngeal polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the results of which were positive.”
At presentation, the patient had no fever, his vital signs were normal, and the physical exam revealed shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities. Serum analysis revealed a normal white blood cell count with mild absolute lymphopenia, slightly elevated creatinine level, normal liver function, slightly elevated C-reactive protein level, and normal ferritin level.
Dr. Holcomb and colleagues made a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2–associated RIME based on microbiological results, which revealed positive repeated SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal PCR and negative nasopharyngeal PCR testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, adenovirus, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, human metapneumovirus, influenza A/B, parainfluenza 1 to 4, rhinovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. In addition, titers of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM levels were negative, but Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG levels were elevated.
The lesions resolved with 60 mg of oral prednisone taken daily for 4 days. A recurrence of oral mucositis 3 months later responded to 80 mg oral prednisone taken daily for 6 days.
“It’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 is yet another trigger for RIME,” said Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of the division of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was asked to comment about the case report.
“The take-home message is for clinicians to be aware of this association and distinguish these patients from those with MIS-C, because patients with MIS-C require monitoring and urgent systemic treatment. RIME and MIS-C may potentially be distinguished clinically based on the nature of the mucositis (hemorrhagic and erosive in RIME, dry, cracked lips with ‘strawberry tongue’ in MIS-C) but more importantly patients with RIME lack laboratory evidence of severe systemic inflammation,” such as ESR, CRP, or ferritin, she said.
“A final interesting point in this article was the recurrence of mucositis in this patient, which could mean that recurrent mucositis/recurrent RIME might be yet another manifestation of ‘long-COVID’ (now called post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection) in some patients,” Dr. Kirkorian added. She noted that the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatologic Societies COVID-19 Dermatology Registry and articles like these “provide invaluable ‘hot off the presses’ information for clinicians who are facing the protean manifestations of a novel viral epidemic.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Two and stratifying children at risk for serious, systemic illness due to the virus.
In a single-center descriptive study carried out over a 9-month period, researchers in Madrid found that of 50 hospitalized children infected with COVID-19, 21 (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly exanthem, followed by conjunctival hyperemia without secretion and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue. In addition, 18 (36%) fulfilled criteria for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
“Based on findings in adult patients, the skin manifestations of COVID-19 have been classified under five categories: acral pseudo-chilblain, vesicular eruptions, urticarial lesions, maculopapular eruptions, and livedo or necrosis,” David Andina-Martinez, MD, of Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online on April 2 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Chilblain lesions in healthy children and adolescents have received much attention; these lesions resolve without complications after a few weeks,” they added. “Besides, other cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 in children have been the matter of case reports or small case series. Nevertheless, the mucocutaneous manifestations in hospitalized children infected with SARS-CoV-2 and their implications on the clinical course have not yet been extensively described.”
In an effort to describe the mucocutaneous manifestations in children hospitalized for COVID-19, the researchers evaluated 50 children up to 18 years of age who were admitted between March 1 and Nov. 30, 2020, to Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, which was designated as a pediatric reference center during the peak of the pandemic. The main reasons for admission were respiratory illness (40%) and MIS-C (40%).
Of the 50 patients, 44 (88%) had a positive RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 and 6 (12%) met clinical suspicion criteria and had a negative RT-PCR with a positive IgG serology. In 34 patients (68%), a close contact with a suspected or confirmed case of COVID-19 was referred, while the source of the infection remained unknown in the remaining 16 patients (32%).
The researchers reported that 21 patients (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly maculopapular exanthem (86%), conjunctival hyperemia (81%), and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue (43%). In addition, 18 of the 21 patients (86%) fulfilled criteria for MIS-C.
“A tricky thing about MIS-C is that it often manifests 4-5 weeks after a child had COVID-19,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study. “MIS-C is associated with characteristic bright red lips and a red tongue that might resemble a strawberry. Such oral findings should prompt rapid evaluation for other signs and symptoms. There can be redness of the eyes or other more nonspecific skin findings (large or small areas of redness on the trunk or limbs, sometimes with surface change), but more importantly, fever, a rapid heartbeat, diarrhea, or breathing issues. The risk with MIS-C is a rapid decline in a child’s health, with admission to an intensive care unit.”
Dr. Andina-Martinez and his colleagues also contrast the skin findings of MIS-C, which are not generally on the hands or feet, with the so-called “COVID toe” or finger phenomenon, which has also been associated with SARS-CoV-2, particularly in children. “Only one of the patients in this series had skin involvement of a finger, and it only appeared after recovery from MIS-C,” Dr. Ko noted. “Distinguishing COVID toes from MIS-C is important, as COVID toes has a very good outcome, while MIS-C can have severe consequences, including protracted heart disease.”
In other findings, patients who presented with mucocutaneous signs tended to be older than those without skin signs and they presented at the emergency department with poor general status and extreme tachycardia. They also had higher C-reactive protein and D-dimer levels and lower lymphocyte counts and faced a more than a 10-fold increased risk of being admitted to the PICU, compared with patients who did not have skin signs (OR, 10.24; P = .003).
In a separate study published online on April 7 in JAMA Dermatology, Zachary E. Holcomb, MD, of the combined dermatology residency program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues presented what is believed to be the first case report of reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) triggered by SARS-CoV-2. RIME is the preferred term for pediatric patients who present with mucositis and rash (often a scant or even absent skin eruption) triggered by various infectious agents.
The patient, a 17-year-old male, presented to the emergency department with 3 days of mouth pain and nonpainful penile erosions. “One week prior, he experienced transient anosmia and ageusia that had since spontaneously resolved,” the researchers wrote. “At that time, he was tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection via nasopharyngeal polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the results of which were positive.”
At presentation, the patient had no fever, his vital signs were normal, and the physical exam revealed shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities. Serum analysis revealed a normal white blood cell count with mild absolute lymphopenia, slightly elevated creatinine level, normal liver function, slightly elevated C-reactive protein level, and normal ferritin level.
Dr. Holcomb and colleagues made a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2–associated RIME based on microbiological results, which revealed positive repeated SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal PCR and negative nasopharyngeal PCR testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, adenovirus, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, human metapneumovirus, influenza A/B, parainfluenza 1 to 4, rhinovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. In addition, titers of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM levels were negative, but Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG levels were elevated.
The lesions resolved with 60 mg of oral prednisone taken daily for 4 days. A recurrence of oral mucositis 3 months later responded to 80 mg oral prednisone taken daily for 6 days.
“It’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 is yet another trigger for RIME,” said Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of the division of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was asked to comment about the case report.
“The take-home message is for clinicians to be aware of this association and distinguish these patients from those with MIS-C, because patients with MIS-C require monitoring and urgent systemic treatment. RIME and MIS-C may potentially be distinguished clinically based on the nature of the mucositis (hemorrhagic and erosive in RIME, dry, cracked lips with ‘strawberry tongue’ in MIS-C) but more importantly patients with RIME lack laboratory evidence of severe systemic inflammation,” such as ESR, CRP, or ferritin, she said.
“A final interesting point in this article was the recurrence of mucositis in this patient, which could mean that recurrent mucositis/recurrent RIME might be yet another manifestation of ‘long-COVID’ (now called post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection) in some patients,” Dr. Kirkorian added. She noted that the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatologic Societies COVID-19 Dermatology Registry and articles like these “provide invaluable ‘hot off the presses’ information for clinicians who are facing the protean manifestations of a novel viral epidemic.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Two and stratifying children at risk for serious, systemic illness due to the virus.
In a single-center descriptive study carried out over a 9-month period, researchers in Madrid found that of 50 hospitalized children infected with COVID-19, 21 (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly exanthem, followed by conjunctival hyperemia without secretion and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue. In addition, 18 (36%) fulfilled criteria for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
“Based on findings in adult patients, the skin manifestations of COVID-19 have been classified under five categories: acral pseudo-chilblain, vesicular eruptions, urticarial lesions, maculopapular eruptions, and livedo or necrosis,” David Andina-Martinez, MD, of Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online on April 2 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Chilblain lesions in healthy children and adolescents have received much attention; these lesions resolve without complications after a few weeks,” they added. “Besides, other cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 in children have been the matter of case reports or small case series. Nevertheless, the mucocutaneous manifestations in hospitalized children infected with SARS-CoV-2 and their implications on the clinical course have not yet been extensively described.”
In an effort to describe the mucocutaneous manifestations in children hospitalized for COVID-19, the researchers evaluated 50 children up to 18 years of age who were admitted between March 1 and Nov. 30, 2020, to Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, which was designated as a pediatric reference center during the peak of the pandemic. The main reasons for admission were respiratory illness (40%) and MIS-C (40%).
Of the 50 patients, 44 (88%) had a positive RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 and 6 (12%) met clinical suspicion criteria and had a negative RT-PCR with a positive IgG serology. In 34 patients (68%), a close contact with a suspected or confirmed case of COVID-19 was referred, while the source of the infection remained unknown in the remaining 16 patients (32%).
The researchers reported that 21 patients (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly maculopapular exanthem (86%), conjunctival hyperemia (81%), and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue (43%). In addition, 18 of the 21 patients (86%) fulfilled criteria for MIS-C.
“A tricky thing about MIS-C is that it often manifests 4-5 weeks after a child had COVID-19,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study. “MIS-C is associated with characteristic bright red lips and a red tongue that might resemble a strawberry. Such oral findings should prompt rapid evaluation for other signs and symptoms. There can be redness of the eyes or other more nonspecific skin findings (large or small areas of redness on the trunk or limbs, sometimes with surface change), but more importantly, fever, a rapid heartbeat, diarrhea, or breathing issues. The risk with MIS-C is a rapid decline in a child’s health, with admission to an intensive care unit.”
Dr. Andina-Martinez and his colleagues also contrast the skin findings of MIS-C, which are not generally on the hands or feet, with the so-called “COVID toe” or finger phenomenon, which has also been associated with SARS-CoV-2, particularly in children. “Only one of the patients in this series had skin involvement of a finger, and it only appeared after recovery from MIS-C,” Dr. Ko noted. “Distinguishing COVID toes from MIS-C is important, as COVID toes has a very good outcome, while MIS-C can have severe consequences, including protracted heart disease.”
In other findings, patients who presented with mucocutaneous signs tended to be older than those without skin signs and they presented at the emergency department with poor general status and extreme tachycardia. They also had higher C-reactive protein and D-dimer levels and lower lymphocyte counts and faced a more than a 10-fold increased risk of being admitted to the PICU, compared with patients who did not have skin signs (OR, 10.24; P = .003).
In a separate study published online on April 7 in JAMA Dermatology, Zachary E. Holcomb, MD, of the combined dermatology residency program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues presented what is believed to be the first case report of reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) triggered by SARS-CoV-2. RIME is the preferred term for pediatric patients who present with mucositis and rash (often a scant or even absent skin eruption) triggered by various infectious agents.
The patient, a 17-year-old male, presented to the emergency department with 3 days of mouth pain and nonpainful penile erosions. “One week prior, he experienced transient anosmia and ageusia that had since spontaneously resolved,” the researchers wrote. “At that time, he was tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection via nasopharyngeal polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the results of which were positive.”
At presentation, the patient had no fever, his vital signs were normal, and the physical exam revealed shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities. Serum analysis revealed a normal white blood cell count with mild absolute lymphopenia, slightly elevated creatinine level, normal liver function, slightly elevated C-reactive protein level, and normal ferritin level.
Dr. Holcomb and colleagues made a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2–associated RIME based on microbiological results, which revealed positive repeated SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal PCR and negative nasopharyngeal PCR testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, adenovirus, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, human metapneumovirus, influenza A/B, parainfluenza 1 to 4, rhinovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. In addition, titers of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM levels were negative, but Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG levels were elevated.
The lesions resolved with 60 mg of oral prednisone taken daily for 4 days. A recurrence of oral mucositis 3 months later responded to 80 mg oral prednisone taken daily for 6 days.
“It’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 is yet another trigger for RIME,” said Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of the division of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was asked to comment about the case report.
“The take-home message is for clinicians to be aware of this association and distinguish these patients from those with MIS-C, because patients with MIS-C require monitoring and urgent systemic treatment. RIME and MIS-C may potentially be distinguished clinically based on the nature of the mucositis (hemorrhagic and erosive in RIME, dry, cracked lips with ‘strawberry tongue’ in MIS-C) but more importantly patients with RIME lack laboratory evidence of severe systemic inflammation,” such as ESR, CRP, or ferritin, she said.
“A final interesting point in this article was the recurrence of mucositis in this patient, which could mean that recurrent mucositis/recurrent RIME might be yet another manifestation of ‘long-COVID’ (now called post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection) in some patients,” Dr. Kirkorian added. She noted that the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatologic Societies COVID-19 Dermatology Registry and articles like these “provide invaluable ‘hot off the presses’ information for clinicians who are facing the protean manifestations of a novel viral epidemic.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.











