User login
News and Views that Matter to Pediatricians
The leading independent newspaper covering news and commentary in pediatrics.
Underinsurance rises among U.S. children
The proportion of U.S. children who are underinsured for health care increased by 3.4% from 2016 to 2019, reflecting approximately 2.4 million underinsured children, based on data from the National Survey of Children’s Health.
Children with inconsistent or inadequate medical coverage are more likely to forgo medical care, including preventive well-child visits, and to have unmet medical needs such as prescription medications, Justin Yu, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, and colleagues wrote. Although the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Healthy People 2030 guidelines have endorsed increasing the proportion of children with adequate coverage, recent studies suggest that advances in insuring children in the wake of the Affordable Care Act have stalled, and trends in child insurance have not been well described, the researchers said.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from the combined 2016-2019 datasets of the National Survey of Children’s Health, a survey funded by the Maternal and Child Health Bureau of the Health Resources and Services Administration.
Adequate insurance was defined as a composite with three questions; whether the benefits “usually” or “always” meet the child’s needs; the benefits “usually” or “always” allow the child to see needed providers; and whether out-of-pocket expenses are either absent or “usually” or “always” reasonable.
Overall, the proportion of children with underinsurance increased from 30.6% in 2016 to 34.0% in 2019.
Underinsurance was significantly associated with increased health complexity and private insurance, with adjusted odds ratios of 1.9 and 3.5, respectively. In addition, underinsurance was significantly associated with child age of 6 years or older, non-Black racial identity, U.S. nonnative status, and a family income of at least 100% above the Federal Poverty Level. Notably, underinsurance grew significantly among White children living in “middle-income” families, the researchers said.
The increase in underinsurance was driven primarily by increased insurance inadequacy, which rose from 24.8% to 27.9% over the study period. The increase in insurance inadequacy was described primarily as unreasonable out-of-pocket medical expenses, according to the survey respondents.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to show causality or to describe changes in outcomes for individual children, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the reliance on parent reports and the lack of a definitive definition of underinsurance.
However, the results highlight the ongoing problem of underinsurance in children, and the need to address the factors that contribute to inadequate insurance for children, the researchers said.
“Our data, demonstrating a shift from public to private insurance that is more likely to be inadequate, in conjunction with existing literature linking Medicaid/CHIP [Children’s Health Insurance Program] coverage with improved access to medical care as well as improved long-term outcomes in adulthood, should give policy makers and payers pause as they contemplate strategies to improve child health,” they concluded.
Nationwide action needed to fight underinsurance
The authors should be commended for highlighting the disturbing trend in underinsurance among children in the United States, Tim Joos, MD, a Seattle-based clinician with a combination internal medicine/pediatrics practice, said in an interview.
“With the passage of the Affordable Care Act, the population of uninsured and underinsured had shrunk quite a bit, but in the past few years, the numbers are growing again. This population has often been called the working poor; the vast majority are legal residents who make too much to qualify for Medicaid/CHIP programs, and whose employers don’t offer affordable robust health care coverage,” Dr. Joos said.
“These families have to make the risky decisions of how much of the family budget to spend on insurance plans, often to the detriment of their own and their children’s health,” he explained. “If you believe the old adage about ‘an ounce of prevention,’ then the money we spend on preserving the health of our children will more than pay for itself in benefits of increased productivity and health care savings in the 1-2 decades later when they reach adulthood. It is time for us as a nation to come up with a more comprehensive baseline coverage for all pediatric patients and take away any barriers for families to access basic health care for children.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
The proportion of U.S. children who are underinsured for health care increased by 3.4% from 2016 to 2019, reflecting approximately 2.4 million underinsured children, based on data from the National Survey of Children’s Health.
Children with inconsistent or inadequate medical coverage are more likely to forgo medical care, including preventive well-child visits, and to have unmet medical needs such as prescription medications, Justin Yu, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, and colleagues wrote. Although the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Healthy People 2030 guidelines have endorsed increasing the proportion of children with adequate coverage, recent studies suggest that advances in insuring children in the wake of the Affordable Care Act have stalled, and trends in child insurance have not been well described, the researchers said.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from the combined 2016-2019 datasets of the National Survey of Children’s Health, a survey funded by the Maternal and Child Health Bureau of the Health Resources and Services Administration.
Adequate insurance was defined as a composite with three questions; whether the benefits “usually” or “always” meet the child’s needs; the benefits “usually” or “always” allow the child to see needed providers; and whether out-of-pocket expenses are either absent or “usually” or “always” reasonable.
Overall, the proportion of children with underinsurance increased from 30.6% in 2016 to 34.0% in 2019.
Underinsurance was significantly associated with increased health complexity and private insurance, with adjusted odds ratios of 1.9 and 3.5, respectively. In addition, underinsurance was significantly associated with child age of 6 years or older, non-Black racial identity, U.S. nonnative status, and a family income of at least 100% above the Federal Poverty Level. Notably, underinsurance grew significantly among White children living in “middle-income” families, the researchers said.
The increase in underinsurance was driven primarily by increased insurance inadequacy, which rose from 24.8% to 27.9% over the study period. The increase in insurance inadequacy was described primarily as unreasonable out-of-pocket medical expenses, according to the survey respondents.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to show causality or to describe changes in outcomes for individual children, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the reliance on parent reports and the lack of a definitive definition of underinsurance.
However, the results highlight the ongoing problem of underinsurance in children, and the need to address the factors that contribute to inadequate insurance for children, the researchers said.
“Our data, demonstrating a shift from public to private insurance that is more likely to be inadequate, in conjunction with existing literature linking Medicaid/CHIP [Children’s Health Insurance Program] coverage with improved access to medical care as well as improved long-term outcomes in adulthood, should give policy makers and payers pause as they contemplate strategies to improve child health,” they concluded.
Nationwide action needed to fight underinsurance
The authors should be commended for highlighting the disturbing trend in underinsurance among children in the United States, Tim Joos, MD, a Seattle-based clinician with a combination internal medicine/pediatrics practice, said in an interview.
“With the passage of the Affordable Care Act, the population of uninsured and underinsured had shrunk quite a bit, but in the past few years, the numbers are growing again. This population has often been called the working poor; the vast majority are legal residents who make too much to qualify for Medicaid/CHIP programs, and whose employers don’t offer affordable robust health care coverage,” Dr. Joos said.
“These families have to make the risky decisions of how much of the family budget to spend on insurance plans, often to the detriment of their own and their children’s health,” he explained. “If you believe the old adage about ‘an ounce of prevention,’ then the money we spend on preserving the health of our children will more than pay for itself in benefits of increased productivity and health care savings in the 1-2 decades later when they reach adulthood. It is time for us as a nation to come up with a more comprehensive baseline coverage for all pediatric patients and take away any barriers for families to access basic health care for children.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
The proportion of U.S. children who are underinsured for health care increased by 3.4% from 2016 to 2019, reflecting approximately 2.4 million underinsured children, based on data from the National Survey of Children’s Health.
Children with inconsistent or inadequate medical coverage are more likely to forgo medical care, including preventive well-child visits, and to have unmet medical needs such as prescription medications, Justin Yu, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, and colleagues wrote. Although the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Healthy People 2030 guidelines have endorsed increasing the proportion of children with adequate coverage, recent studies suggest that advances in insuring children in the wake of the Affordable Care Act have stalled, and trends in child insurance have not been well described, the researchers said.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from the combined 2016-2019 datasets of the National Survey of Children’s Health, a survey funded by the Maternal and Child Health Bureau of the Health Resources and Services Administration.
Adequate insurance was defined as a composite with three questions; whether the benefits “usually” or “always” meet the child’s needs; the benefits “usually” or “always” allow the child to see needed providers; and whether out-of-pocket expenses are either absent or “usually” or “always” reasonable.
Overall, the proportion of children with underinsurance increased from 30.6% in 2016 to 34.0% in 2019.
Underinsurance was significantly associated with increased health complexity and private insurance, with adjusted odds ratios of 1.9 and 3.5, respectively. In addition, underinsurance was significantly associated with child age of 6 years or older, non-Black racial identity, U.S. nonnative status, and a family income of at least 100% above the Federal Poverty Level. Notably, underinsurance grew significantly among White children living in “middle-income” families, the researchers said.
The increase in underinsurance was driven primarily by increased insurance inadequacy, which rose from 24.8% to 27.9% over the study period. The increase in insurance inadequacy was described primarily as unreasonable out-of-pocket medical expenses, according to the survey respondents.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to show causality or to describe changes in outcomes for individual children, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the reliance on parent reports and the lack of a definitive definition of underinsurance.
However, the results highlight the ongoing problem of underinsurance in children, and the need to address the factors that contribute to inadequate insurance for children, the researchers said.
“Our data, demonstrating a shift from public to private insurance that is more likely to be inadequate, in conjunction with existing literature linking Medicaid/CHIP [Children’s Health Insurance Program] coverage with improved access to medical care as well as improved long-term outcomes in adulthood, should give policy makers and payers pause as they contemplate strategies to improve child health,” they concluded.
Nationwide action needed to fight underinsurance
The authors should be commended for highlighting the disturbing trend in underinsurance among children in the United States, Tim Joos, MD, a Seattle-based clinician with a combination internal medicine/pediatrics practice, said in an interview.
“With the passage of the Affordable Care Act, the population of uninsured and underinsured had shrunk quite a bit, but in the past few years, the numbers are growing again. This population has often been called the working poor; the vast majority are legal residents who make too much to qualify for Medicaid/CHIP programs, and whose employers don’t offer affordable robust health care coverage,” Dr. Joos said.
“These families have to make the risky decisions of how much of the family budget to spend on insurance plans, often to the detriment of their own and their children’s health,” he explained. “If you believe the old adage about ‘an ounce of prevention,’ then the money we spend on preserving the health of our children will more than pay for itself in benefits of increased productivity and health care savings in the 1-2 decades later when they reach adulthood. It is time for us as a nation to come up with a more comprehensive baseline coverage for all pediatric patients and take away any barriers for families to access basic health care for children.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Mumps: Sometimes forgotten but not gone
The 7-year-old boy sat at the edge of a stretcher in the emergency department, looking miserable, as his mother recounted his symptoms to a senior resident physician on duty. Low-grade fever, fatigue, and myalgias prompted rapid SARS-CoV-2 testing at his school. That test, as well as a repeat test at the pediatrician’s office, were negative. A triage protocol in the emergency department prompted a third test, which was also negative.
“Everyone has told me that it’s likely just a different virus,” the mother said. “But then his cheek started to swell. Have you ever seen anything like this?”
The boy turned his head, revealing a diffuse swelling that extended down his right cheek to the angle of his jaw.
“Only in textbooks,” the resident physician responded.
It is a credit to our national immunization program that most practicing clinicians have never actually seen a case of mumps. Before vaccination was introduced in 1967, infection in childhood was nearly universal. Unilateral or bilateral tender swelling of the parotid gland is the typical clinical finding. Low-grade fever, myalgias, decreased appetite, malaise, and headache may precede parotid swelling in some patients. Other patients infected with mumps may have only respiratory symptoms, and some may have no symptoms at all.
Two doses of measles-mumps-rubella vaccine have been recommended for children in the United States since 1989, with the first dose administered at 12-15 months of age. According to data collected through the National Immunization Survey, more than 92% of children in the United States receive at least one dose of measles-mumps-rubella vaccine by 24 months of age. The vaccine is immunogenic, with 94% of recipients developing measurable mumps antibody (range, 89%-97%). The vaccine has been a public health success: Overall, mumps cases declined more than 99% between 1967 and 2005.
But in the mid-2000s, mumps cases started to rise again, with more than 28,000 reported between 2007 and 2019. Annual cases ranged from 229 to 6,369 and while large, localized outbreaks have contributed to peak years, mumps has been reported from all 50 states and the District of Columbia. According to a recently published paper in Pediatrics, nearly a third of these cases occurred in children <18 years of age and most had been appropriately immunized for age.
Of the 9,172 cases reported in children, 5,461 or 60% occurred between 2015 and 2019. Of these, 55% were in boys. While cases occurred in children of all ages, 54% were in children 11-17 years of age, and 33% were in children 5-10 years of age. Non-Hispanic Asian and/or Pacific Islander children accounted for 38% of cases. Only 2% of cases were associated with international travel and were presumed to have been acquired outside the United States
The reason for the increase in mumps cases in recent years is not well understood. Outbreaks in fully immunized college students have prompted concern about poor B-cell memory after vaccination resulting in waning immunity over time. In the past, antibodies against mumps were boosted by exposure to wild-type mumps virus but such exposures have become fortunately rare for most of us. Cases in recently immunized children suggest there is more to the story. Notably, there is a mismatch between the genotype A mumps virus contained in the current MMR and MMRV vaccines and the genotype G virus currently circulating in the United States.
With the onset of the pandemic and implementation of mitigation measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19, circulation of some common respiratory viruses, including respiratory syncytial virus and influenza, was sharply curtailed. Mumps continued to circulate, albeit at reduced levels, with 616 cases reported in 2020. In 2021, 30 states and jurisdictions reported 139 cases through Dec. 1.
Clinicians should suspect mumps in all cases of parotitis, regardless of an individual’s age, vaccination status, or travel history. Laboratory testing is required to distinguish mumps from other infectious and noninfectious causes of parotitis. Infectious causes include gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial infection, as well as other viral infections, including Epstein-Barr virus, coxsackie viruses, parainfluenza, and rarely, influenza. Case reports also describe parotitis coincident with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
When parotitis has been present for 3 days or less, a buccal swab for RT-PCR should be obtained, massaging the parotid gland for 30 seconds before specimen collection. When parotitis has been present for >3 days, a mumps Immunoglobulin M serum antibody should be collected in addition to the buccal swab PCR. A negative IgM does not exclude the possibility of infection, especially in immunized individuals. Mumps is a nationally notifiable disease, and all confirmed and suspect cases should be reported to the state or local health department.
Back in the emergency department, the mother was counseled about the potential diagnosis of mumps and the need for her son to isolate at home for 5 days after the onset of the parotid swelling. She was also educated about potential complications of mumps, including orchitis, aseptic meningitis and encephalitis, and hearing loss. Fortunately, complications are less common in individuals who have been immunized, and orchitis rarely occurs in prepubertal boys.
The resident physician also confirmed that other members of the household had been appropriately immunized for age. While the MMR vaccine does not prevent illness in those already infected with mumps and is not indicated as postexposure prophylaxis, providing vaccine to those not already immunized can protect against future exposures. A third dose of MMR vaccine is only indicated in the setting of an outbreak and when specifically recommended by public health authorities for those deemed to be in a high-risk group. Additional information about mumps is available at www.cdc.gov/mumps/hcp.html#report.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
The 7-year-old boy sat at the edge of a stretcher in the emergency department, looking miserable, as his mother recounted his symptoms to a senior resident physician on duty. Low-grade fever, fatigue, and myalgias prompted rapid SARS-CoV-2 testing at his school. That test, as well as a repeat test at the pediatrician’s office, were negative. A triage protocol in the emergency department prompted a third test, which was also negative.
“Everyone has told me that it’s likely just a different virus,” the mother said. “But then his cheek started to swell. Have you ever seen anything like this?”
The boy turned his head, revealing a diffuse swelling that extended down his right cheek to the angle of his jaw.
“Only in textbooks,” the resident physician responded.
It is a credit to our national immunization program that most practicing clinicians have never actually seen a case of mumps. Before vaccination was introduced in 1967, infection in childhood was nearly universal. Unilateral or bilateral tender swelling of the parotid gland is the typical clinical finding. Low-grade fever, myalgias, decreased appetite, malaise, and headache may precede parotid swelling in some patients. Other patients infected with mumps may have only respiratory symptoms, and some may have no symptoms at all.
Two doses of measles-mumps-rubella vaccine have been recommended for children in the United States since 1989, with the first dose administered at 12-15 months of age. According to data collected through the National Immunization Survey, more than 92% of children in the United States receive at least one dose of measles-mumps-rubella vaccine by 24 months of age. The vaccine is immunogenic, with 94% of recipients developing measurable mumps antibody (range, 89%-97%). The vaccine has been a public health success: Overall, mumps cases declined more than 99% between 1967 and 2005.
But in the mid-2000s, mumps cases started to rise again, with more than 28,000 reported between 2007 and 2019. Annual cases ranged from 229 to 6,369 and while large, localized outbreaks have contributed to peak years, mumps has been reported from all 50 states and the District of Columbia. According to a recently published paper in Pediatrics, nearly a third of these cases occurred in children <18 years of age and most had been appropriately immunized for age.
Of the 9,172 cases reported in children, 5,461 or 60% occurred between 2015 and 2019. Of these, 55% were in boys. While cases occurred in children of all ages, 54% were in children 11-17 years of age, and 33% were in children 5-10 years of age. Non-Hispanic Asian and/or Pacific Islander children accounted for 38% of cases. Only 2% of cases were associated with international travel and were presumed to have been acquired outside the United States
The reason for the increase in mumps cases in recent years is not well understood. Outbreaks in fully immunized college students have prompted concern about poor B-cell memory after vaccination resulting in waning immunity over time. In the past, antibodies against mumps were boosted by exposure to wild-type mumps virus but such exposures have become fortunately rare for most of us. Cases in recently immunized children suggest there is more to the story. Notably, there is a mismatch between the genotype A mumps virus contained in the current MMR and MMRV vaccines and the genotype G virus currently circulating in the United States.
With the onset of the pandemic and implementation of mitigation measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19, circulation of some common respiratory viruses, including respiratory syncytial virus and influenza, was sharply curtailed. Mumps continued to circulate, albeit at reduced levels, with 616 cases reported in 2020. In 2021, 30 states and jurisdictions reported 139 cases through Dec. 1.
Clinicians should suspect mumps in all cases of parotitis, regardless of an individual’s age, vaccination status, or travel history. Laboratory testing is required to distinguish mumps from other infectious and noninfectious causes of parotitis. Infectious causes include gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial infection, as well as other viral infections, including Epstein-Barr virus, coxsackie viruses, parainfluenza, and rarely, influenza. Case reports also describe parotitis coincident with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
When parotitis has been present for 3 days or less, a buccal swab for RT-PCR should be obtained, massaging the parotid gland for 30 seconds before specimen collection. When parotitis has been present for >3 days, a mumps Immunoglobulin M serum antibody should be collected in addition to the buccal swab PCR. A negative IgM does not exclude the possibility of infection, especially in immunized individuals. Mumps is a nationally notifiable disease, and all confirmed and suspect cases should be reported to the state or local health department.
Back in the emergency department, the mother was counseled about the potential diagnosis of mumps and the need for her son to isolate at home for 5 days after the onset of the parotid swelling. She was also educated about potential complications of mumps, including orchitis, aseptic meningitis and encephalitis, and hearing loss. Fortunately, complications are less common in individuals who have been immunized, and orchitis rarely occurs in prepubertal boys.
The resident physician also confirmed that other members of the household had been appropriately immunized for age. While the MMR vaccine does not prevent illness in those already infected with mumps and is not indicated as postexposure prophylaxis, providing vaccine to those not already immunized can protect against future exposures. A third dose of MMR vaccine is only indicated in the setting of an outbreak and when specifically recommended by public health authorities for those deemed to be in a high-risk group. Additional information about mumps is available at www.cdc.gov/mumps/hcp.html#report.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
The 7-year-old boy sat at the edge of a stretcher in the emergency department, looking miserable, as his mother recounted his symptoms to a senior resident physician on duty. Low-grade fever, fatigue, and myalgias prompted rapid SARS-CoV-2 testing at his school. That test, as well as a repeat test at the pediatrician’s office, were negative. A triage protocol in the emergency department prompted a third test, which was also negative.
“Everyone has told me that it’s likely just a different virus,” the mother said. “But then his cheek started to swell. Have you ever seen anything like this?”
The boy turned his head, revealing a diffuse swelling that extended down his right cheek to the angle of his jaw.
“Only in textbooks,” the resident physician responded.
It is a credit to our national immunization program that most practicing clinicians have never actually seen a case of mumps. Before vaccination was introduced in 1967, infection in childhood was nearly universal. Unilateral or bilateral tender swelling of the parotid gland is the typical clinical finding. Low-grade fever, myalgias, decreased appetite, malaise, and headache may precede parotid swelling in some patients. Other patients infected with mumps may have only respiratory symptoms, and some may have no symptoms at all.
Two doses of measles-mumps-rubella vaccine have been recommended for children in the United States since 1989, with the first dose administered at 12-15 months of age. According to data collected through the National Immunization Survey, more than 92% of children in the United States receive at least one dose of measles-mumps-rubella vaccine by 24 months of age. The vaccine is immunogenic, with 94% of recipients developing measurable mumps antibody (range, 89%-97%). The vaccine has been a public health success: Overall, mumps cases declined more than 99% between 1967 and 2005.
But in the mid-2000s, mumps cases started to rise again, with more than 28,000 reported between 2007 and 2019. Annual cases ranged from 229 to 6,369 and while large, localized outbreaks have contributed to peak years, mumps has been reported from all 50 states and the District of Columbia. According to a recently published paper in Pediatrics, nearly a third of these cases occurred in children <18 years of age and most had been appropriately immunized for age.
Of the 9,172 cases reported in children, 5,461 or 60% occurred between 2015 and 2019. Of these, 55% were in boys. While cases occurred in children of all ages, 54% were in children 11-17 years of age, and 33% were in children 5-10 years of age. Non-Hispanic Asian and/or Pacific Islander children accounted for 38% of cases. Only 2% of cases were associated with international travel and were presumed to have been acquired outside the United States
The reason for the increase in mumps cases in recent years is not well understood. Outbreaks in fully immunized college students have prompted concern about poor B-cell memory after vaccination resulting in waning immunity over time. In the past, antibodies against mumps were boosted by exposure to wild-type mumps virus but such exposures have become fortunately rare for most of us. Cases in recently immunized children suggest there is more to the story. Notably, there is a mismatch between the genotype A mumps virus contained in the current MMR and MMRV vaccines and the genotype G virus currently circulating in the United States.
With the onset of the pandemic and implementation of mitigation measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19, circulation of some common respiratory viruses, including respiratory syncytial virus and influenza, was sharply curtailed. Mumps continued to circulate, albeit at reduced levels, with 616 cases reported in 2020. In 2021, 30 states and jurisdictions reported 139 cases through Dec. 1.
Clinicians should suspect mumps in all cases of parotitis, regardless of an individual’s age, vaccination status, or travel history. Laboratory testing is required to distinguish mumps from other infectious and noninfectious causes of parotitis. Infectious causes include gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial infection, as well as other viral infections, including Epstein-Barr virus, coxsackie viruses, parainfluenza, and rarely, influenza. Case reports also describe parotitis coincident with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
When parotitis has been present for 3 days or less, a buccal swab for RT-PCR should be obtained, massaging the parotid gland for 30 seconds before specimen collection. When parotitis has been present for >3 days, a mumps Immunoglobulin M serum antibody should be collected in addition to the buccal swab PCR. A negative IgM does not exclude the possibility of infection, especially in immunized individuals. Mumps is a nationally notifiable disease, and all confirmed and suspect cases should be reported to the state or local health department.
Back in the emergency department, the mother was counseled about the potential diagnosis of mumps and the need for her son to isolate at home for 5 days after the onset of the parotid swelling. She was also educated about potential complications of mumps, including orchitis, aseptic meningitis and encephalitis, and hearing loss. Fortunately, complications are less common in individuals who have been immunized, and orchitis rarely occurs in prepubertal boys.
The resident physician also confirmed that other members of the household had been appropriately immunized for age. While the MMR vaccine does not prevent illness in those already infected with mumps and is not indicated as postexposure prophylaxis, providing vaccine to those not already immunized can protect against future exposures. A third dose of MMR vaccine is only indicated in the setting of an outbreak and when specifically recommended by public health authorities for those deemed to be in a high-risk group. Additional information about mumps is available at www.cdc.gov/mumps/hcp.html#report.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
New HIV PrEP guidelines call for clinicians to talk to patients about HIV prevention meds
Starting Dec. 8, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends all clinicians talk to their sexually active adolescent and adult patients about HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) at least once and prescribe the prevention pills to anyone who asks for them, whether or not you understand their need for it.
“PrEP is a part of good primary care,” Demetre Daskalakis, MD, CDC’s director of the division of HIV/AIDS prevention, said in an interview. “Listening to people and what they need, as opposed to assessing what you think they need, is a seismic shift in how PrEP should be offered.”
The expanded recommendation comes as part of the 2021 update to the U.S. Public Health Service’s PrEP prescribing guidelines. It’s the third iteration since the Food and Drug Administration approved the first HIV prevention pill in 2012, and the first to include guidance on how to prescribe and monitor an injectable version of PrEP, which the FDA may approve as early as December 2021.
There are currently two pills, Truvada (emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, Gilead Sciences and generic) and Descovy (emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide, Gilead Sciences). The pills have been found to be up to 99% effective in preventing HIV acquisition. The new injectable cabotegravir appears to be even more effective.
The broadened guidance is part of an effort from the country’s top health officials to expand PrEP prescribing from infectious disease specialists and sexual health clinics to health care professionals, including gynecologists, internal medicine physicians, and family practice clinicians. It appears to be necessary. In 2020, just 25% of the 1.2 million Americans who could benefit from PrEP were taking it, according to CDC data.
But those rates belie stark disparities in PrEP use by race and gender. The vast majority of those using PrEP are White Americans and men. About 66% of White Americans who could benefit from PrEP used it in 2020, and more than a quarter of the men who could benefit used it. By contrast, just 16% of Latinx people who could benefit had a prescription. And fewer than 1 in 10 Black Americans, who make up nearly half of those with indications for PrEP, had a prescription. The same was true for the women who could benefit.
Researchers and data from early PrEP demonstration projects have documented that clinicians are less likely to refer or prescribe the HIV prevention pills to Black people, especially the Black cisgender and transgender women and same-gender-loving men who bear the disproportionate burden of new cases in the United States, as well as fail to prescribe the medication to people who inject drugs.
Normalizing PrEP in primary care
When Courtney Sherman, DNP, APRN, first heard about PrEP in the early 2010s, she joked that her reaction was: “You’re ridiculous. You’re making that up. That’s not real.”
Ms. Sherman is now launching a tele-PrEP program from CAN Community Health, a nonprofit network of community health centers in southern Florida. The tele-PrEP program is meant to serve people in Florida and beyond, to increase access to the pill in areas with few health care professionals, or clinicians unwilling to prescribe it.
“When I go other places, I can’t do what I do for a living without getting some sort of bizarre comment or look,” she said. But the looks don’t just come from family, friends, or her children’s teachers. They come from colleagues, too. “What I’ve learned is that anybody – anybody – can be impacted [by HIV] and the illusion that ‘those people who live over there do things that me and my kind don’t do’ is just garbage.”
That’s the PrEP stigma that the universal PrEP counseling in the guidelines is meant to override, said Dr. Daskalakis. Going forward, he said that informing people about PrEP should be treated as normally as counseling people about smoking.
“You can change the blank: You talk to all adolescents and adults about not smoking,” he said. “This is: ‘Tell adolescents and adults about ways you can prevent HIV, and PrEP is one of them.’ ”
The guidelines also simplify for monitoring lab levels for the current daily pills, checking creatinine clearance levels twice a year in people older than age 50 and once a year in those younger than 50 taking the oral pills. Dr. Daskalakis said that should ease the burden of monitoring PrEP patients for health care professionals with busy caseloads.
It’s a move that drew praise from Shawnika Hull, PhD, assistant professor of health communications at Rutgers University, New Brunswick, N.J.. Dr. Hull’s recent data showed that clinicians who espoused more biased racial views were also less likely to prescribe PrEP to Black women who asked for it.
“Public health practitioners and scientists have been advocating for this as a strategy, as one way to address several ongoing barriers to PrEP specifically but also equity in PrEP,” said Dr. Hull. “This sort of universal provision of information is really an important strategy to try to undo some of the deeply intertwined barriers to uptake.”
‘Don’t grill them’
The updated guidelines keep the number and proportion of Americans who could benefit from PrEP the same: 1.2 million Americans, with nearly half of those Black. And the reasons people would qualify for PrEP remain the same: inconsistent condom use, sharing injection drug equipment, and a STI diagnosis in the last 6 months. There are also 57 jurisdictions, including seven rural states, where dating and having sex carries an increased risk of acquiring HIV because of high rates of untreated HIV in the community.
That’s why the other big change in the update is guidance to prescribe PrEP to whoever asks for it, whether the patient divulges their risk or not. Or as Dr. Daskalakis puts it: “If someone asks for PrEP, don’t grill them.”
There are lots of reasons that someone might ask for PrEP without divulging their risk behaviors, said Dr. Daskalakis, who was an infectious disease doctor in New York back in 2012 (and a member of the FDA committee) when the first pill for PrEP was approved. He said he’s seen this particularly with women who ask about it. Asking for PrEP ends up being an “ice breaker” to discussing the woman’s sexual and injection drug use history, which can then improve the kinds of tests and vaccinations clinicians suggest for her.
“So many women will open the door and say, ‘I want to do this,’ and not necessarily want to go into the details,” he said. “Now, will they go into the details later? Absolutely. That’s how you create trust and connection.”
A mandate and a guideline
Leisha McKinley-Beach, MPH, a member of the U.S. Women and PrEP Working Group, has been urging greater funding and mandates to expand PrEP to women since the first pill was approved. And still, Ms. McKinley-Beach said she recently met a woman who worked for a community group scheduling PrEP appointments for gay men. But the woman didn’t know that she, too, could take it.
The American Academy of Family Physicians recommends health care professionals offer PrEP to those who can benefit. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists have a 2014 committee opinion stating that PrEP “may be a useful tool for women at highest risk of HIV acquisition.”
But the ACOG opinion is not a recommendation, stating that it “should not be construed as dictating an exclusive course of treatment or procedure to be followed.” Ms. McKinley-Beach said she hopes that the new CDC guidelines will prompt ACOG and other professional organizations to issue statements to include PrEP education in all health assessments. A spokesperson for ACOG said that the organization had not seen the new CDC guidelines and had no statement on them, but pointed out that the 2014 committee opinion is one of the “highest level of documents we produce.
“We have failed for nearly a decade to raise awareness that PrEP is also a prevention strategy for women,” Ms. McKinley-Beach said in an interview. “In many ways, we’re still back in 2012 as it relates to women.”
Dr. Hull reported having done previous research funded by Gilead Sciences and having received consulting fees from Gilead Sciences in 2018. Ms. McKinley-Beach reported receiving honoraria from ViiV Healthcare. Ms. Sherman and Dr. Daskalakis disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Starting Dec. 8, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends all clinicians talk to their sexually active adolescent and adult patients about HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) at least once and prescribe the prevention pills to anyone who asks for them, whether or not you understand their need for it.
“PrEP is a part of good primary care,” Demetre Daskalakis, MD, CDC’s director of the division of HIV/AIDS prevention, said in an interview. “Listening to people and what they need, as opposed to assessing what you think they need, is a seismic shift in how PrEP should be offered.”
The expanded recommendation comes as part of the 2021 update to the U.S. Public Health Service’s PrEP prescribing guidelines. It’s the third iteration since the Food and Drug Administration approved the first HIV prevention pill in 2012, and the first to include guidance on how to prescribe and monitor an injectable version of PrEP, which the FDA may approve as early as December 2021.
There are currently two pills, Truvada (emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, Gilead Sciences and generic) and Descovy (emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide, Gilead Sciences). The pills have been found to be up to 99% effective in preventing HIV acquisition. The new injectable cabotegravir appears to be even more effective.
The broadened guidance is part of an effort from the country’s top health officials to expand PrEP prescribing from infectious disease specialists and sexual health clinics to health care professionals, including gynecologists, internal medicine physicians, and family practice clinicians. It appears to be necessary. In 2020, just 25% of the 1.2 million Americans who could benefit from PrEP were taking it, according to CDC data.
But those rates belie stark disparities in PrEP use by race and gender. The vast majority of those using PrEP are White Americans and men. About 66% of White Americans who could benefit from PrEP used it in 2020, and more than a quarter of the men who could benefit used it. By contrast, just 16% of Latinx people who could benefit had a prescription. And fewer than 1 in 10 Black Americans, who make up nearly half of those with indications for PrEP, had a prescription. The same was true for the women who could benefit.
Researchers and data from early PrEP demonstration projects have documented that clinicians are less likely to refer or prescribe the HIV prevention pills to Black people, especially the Black cisgender and transgender women and same-gender-loving men who bear the disproportionate burden of new cases in the United States, as well as fail to prescribe the medication to people who inject drugs.
Normalizing PrEP in primary care
When Courtney Sherman, DNP, APRN, first heard about PrEP in the early 2010s, she joked that her reaction was: “You’re ridiculous. You’re making that up. That’s not real.”
Ms. Sherman is now launching a tele-PrEP program from CAN Community Health, a nonprofit network of community health centers in southern Florida. The tele-PrEP program is meant to serve people in Florida and beyond, to increase access to the pill in areas with few health care professionals, or clinicians unwilling to prescribe it.
“When I go other places, I can’t do what I do for a living without getting some sort of bizarre comment or look,” she said. But the looks don’t just come from family, friends, or her children’s teachers. They come from colleagues, too. “What I’ve learned is that anybody – anybody – can be impacted [by HIV] and the illusion that ‘those people who live over there do things that me and my kind don’t do’ is just garbage.”
That’s the PrEP stigma that the universal PrEP counseling in the guidelines is meant to override, said Dr. Daskalakis. Going forward, he said that informing people about PrEP should be treated as normally as counseling people about smoking.
“You can change the blank: You talk to all adolescents and adults about not smoking,” he said. “This is: ‘Tell adolescents and adults about ways you can prevent HIV, and PrEP is one of them.’ ”
The guidelines also simplify for monitoring lab levels for the current daily pills, checking creatinine clearance levels twice a year in people older than age 50 and once a year in those younger than 50 taking the oral pills. Dr. Daskalakis said that should ease the burden of monitoring PrEP patients for health care professionals with busy caseloads.
It’s a move that drew praise from Shawnika Hull, PhD, assistant professor of health communications at Rutgers University, New Brunswick, N.J.. Dr. Hull’s recent data showed that clinicians who espoused more biased racial views were also less likely to prescribe PrEP to Black women who asked for it.
“Public health practitioners and scientists have been advocating for this as a strategy, as one way to address several ongoing barriers to PrEP specifically but also equity in PrEP,” said Dr. Hull. “This sort of universal provision of information is really an important strategy to try to undo some of the deeply intertwined barriers to uptake.”
‘Don’t grill them’
The updated guidelines keep the number and proportion of Americans who could benefit from PrEP the same: 1.2 million Americans, with nearly half of those Black. And the reasons people would qualify for PrEP remain the same: inconsistent condom use, sharing injection drug equipment, and a STI diagnosis in the last 6 months. There are also 57 jurisdictions, including seven rural states, where dating and having sex carries an increased risk of acquiring HIV because of high rates of untreated HIV in the community.
That’s why the other big change in the update is guidance to prescribe PrEP to whoever asks for it, whether the patient divulges their risk or not. Or as Dr. Daskalakis puts it: “If someone asks for PrEP, don’t grill them.”
There are lots of reasons that someone might ask for PrEP without divulging their risk behaviors, said Dr. Daskalakis, who was an infectious disease doctor in New York back in 2012 (and a member of the FDA committee) when the first pill for PrEP was approved. He said he’s seen this particularly with women who ask about it. Asking for PrEP ends up being an “ice breaker” to discussing the woman’s sexual and injection drug use history, which can then improve the kinds of tests and vaccinations clinicians suggest for her.
“So many women will open the door and say, ‘I want to do this,’ and not necessarily want to go into the details,” he said. “Now, will they go into the details later? Absolutely. That’s how you create trust and connection.”
A mandate and a guideline
Leisha McKinley-Beach, MPH, a member of the U.S. Women and PrEP Working Group, has been urging greater funding and mandates to expand PrEP to women since the first pill was approved. And still, Ms. McKinley-Beach said she recently met a woman who worked for a community group scheduling PrEP appointments for gay men. But the woman didn’t know that she, too, could take it.
The American Academy of Family Physicians recommends health care professionals offer PrEP to those who can benefit. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists have a 2014 committee opinion stating that PrEP “may be a useful tool for women at highest risk of HIV acquisition.”
But the ACOG opinion is not a recommendation, stating that it “should not be construed as dictating an exclusive course of treatment or procedure to be followed.” Ms. McKinley-Beach said she hopes that the new CDC guidelines will prompt ACOG and other professional organizations to issue statements to include PrEP education in all health assessments. A spokesperson for ACOG said that the organization had not seen the new CDC guidelines and had no statement on them, but pointed out that the 2014 committee opinion is one of the “highest level of documents we produce.
“We have failed for nearly a decade to raise awareness that PrEP is also a prevention strategy for women,” Ms. McKinley-Beach said in an interview. “In many ways, we’re still back in 2012 as it relates to women.”
Dr. Hull reported having done previous research funded by Gilead Sciences and having received consulting fees from Gilead Sciences in 2018. Ms. McKinley-Beach reported receiving honoraria from ViiV Healthcare. Ms. Sherman and Dr. Daskalakis disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Starting Dec. 8, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends all clinicians talk to their sexually active adolescent and adult patients about HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) at least once and prescribe the prevention pills to anyone who asks for them, whether or not you understand their need for it.
“PrEP is a part of good primary care,” Demetre Daskalakis, MD, CDC’s director of the division of HIV/AIDS prevention, said in an interview. “Listening to people and what they need, as opposed to assessing what you think they need, is a seismic shift in how PrEP should be offered.”
The expanded recommendation comes as part of the 2021 update to the U.S. Public Health Service’s PrEP prescribing guidelines. It’s the third iteration since the Food and Drug Administration approved the first HIV prevention pill in 2012, and the first to include guidance on how to prescribe and monitor an injectable version of PrEP, which the FDA may approve as early as December 2021.
There are currently two pills, Truvada (emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, Gilead Sciences and generic) and Descovy (emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide, Gilead Sciences). The pills have been found to be up to 99% effective in preventing HIV acquisition. The new injectable cabotegravir appears to be even more effective.
The broadened guidance is part of an effort from the country’s top health officials to expand PrEP prescribing from infectious disease specialists and sexual health clinics to health care professionals, including gynecologists, internal medicine physicians, and family practice clinicians. It appears to be necessary. In 2020, just 25% of the 1.2 million Americans who could benefit from PrEP were taking it, according to CDC data.
But those rates belie stark disparities in PrEP use by race and gender. The vast majority of those using PrEP are White Americans and men. About 66% of White Americans who could benefit from PrEP used it in 2020, and more than a quarter of the men who could benefit used it. By contrast, just 16% of Latinx people who could benefit had a prescription. And fewer than 1 in 10 Black Americans, who make up nearly half of those with indications for PrEP, had a prescription. The same was true for the women who could benefit.
Researchers and data from early PrEP demonstration projects have documented that clinicians are less likely to refer or prescribe the HIV prevention pills to Black people, especially the Black cisgender and transgender women and same-gender-loving men who bear the disproportionate burden of new cases in the United States, as well as fail to prescribe the medication to people who inject drugs.
Normalizing PrEP in primary care
When Courtney Sherman, DNP, APRN, first heard about PrEP in the early 2010s, she joked that her reaction was: “You’re ridiculous. You’re making that up. That’s not real.”
Ms. Sherman is now launching a tele-PrEP program from CAN Community Health, a nonprofit network of community health centers in southern Florida. The tele-PrEP program is meant to serve people in Florida and beyond, to increase access to the pill in areas with few health care professionals, or clinicians unwilling to prescribe it.
“When I go other places, I can’t do what I do for a living without getting some sort of bizarre comment or look,” she said. But the looks don’t just come from family, friends, or her children’s teachers. They come from colleagues, too. “What I’ve learned is that anybody – anybody – can be impacted [by HIV] and the illusion that ‘those people who live over there do things that me and my kind don’t do’ is just garbage.”
That’s the PrEP stigma that the universal PrEP counseling in the guidelines is meant to override, said Dr. Daskalakis. Going forward, he said that informing people about PrEP should be treated as normally as counseling people about smoking.
“You can change the blank: You talk to all adolescents and adults about not smoking,” he said. “This is: ‘Tell adolescents and adults about ways you can prevent HIV, and PrEP is one of them.’ ”
The guidelines also simplify for monitoring lab levels for the current daily pills, checking creatinine clearance levels twice a year in people older than age 50 and once a year in those younger than 50 taking the oral pills. Dr. Daskalakis said that should ease the burden of monitoring PrEP patients for health care professionals with busy caseloads.
It’s a move that drew praise from Shawnika Hull, PhD, assistant professor of health communications at Rutgers University, New Brunswick, N.J.. Dr. Hull’s recent data showed that clinicians who espoused more biased racial views were also less likely to prescribe PrEP to Black women who asked for it.
“Public health practitioners and scientists have been advocating for this as a strategy, as one way to address several ongoing barriers to PrEP specifically but also equity in PrEP,” said Dr. Hull. “This sort of universal provision of information is really an important strategy to try to undo some of the deeply intertwined barriers to uptake.”
‘Don’t grill them’
The updated guidelines keep the number and proportion of Americans who could benefit from PrEP the same: 1.2 million Americans, with nearly half of those Black. And the reasons people would qualify for PrEP remain the same: inconsistent condom use, sharing injection drug equipment, and a STI diagnosis in the last 6 months. There are also 57 jurisdictions, including seven rural states, where dating and having sex carries an increased risk of acquiring HIV because of high rates of untreated HIV in the community.
That’s why the other big change in the update is guidance to prescribe PrEP to whoever asks for it, whether the patient divulges their risk or not. Or as Dr. Daskalakis puts it: “If someone asks for PrEP, don’t grill them.”
There are lots of reasons that someone might ask for PrEP without divulging their risk behaviors, said Dr. Daskalakis, who was an infectious disease doctor in New York back in 2012 (and a member of the FDA committee) when the first pill for PrEP was approved. He said he’s seen this particularly with women who ask about it. Asking for PrEP ends up being an “ice breaker” to discussing the woman’s sexual and injection drug use history, which can then improve the kinds of tests and vaccinations clinicians suggest for her.
“So many women will open the door and say, ‘I want to do this,’ and not necessarily want to go into the details,” he said. “Now, will they go into the details later? Absolutely. That’s how you create trust and connection.”
A mandate and a guideline
Leisha McKinley-Beach, MPH, a member of the U.S. Women and PrEP Working Group, has been urging greater funding and mandates to expand PrEP to women since the first pill was approved. And still, Ms. McKinley-Beach said she recently met a woman who worked for a community group scheduling PrEP appointments for gay men. But the woman didn’t know that she, too, could take it.
The American Academy of Family Physicians recommends health care professionals offer PrEP to those who can benefit. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists have a 2014 committee opinion stating that PrEP “may be a useful tool for women at highest risk of HIV acquisition.”
But the ACOG opinion is not a recommendation, stating that it “should not be construed as dictating an exclusive course of treatment or procedure to be followed.” Ms. McKinley-Beach said she hopes that the new CDC guidelines will prompt ACOG and other professional organizations to issue statements to include PrEP education in all health assessments. A spokesperson for ACOG said that the organization had not seen the new CDC guidelines and had no statement on them, but pointed out that the 2014 committee opinion is one of the “highest level of documents we produce.
“We have failed for nearly a decade to raise awareness that PrEP is also a prevention strategy for women,” Ms. McKinley-Beach said in an interview. “In many ways, we’re still back in 2012 as it relates to women.”
Dr. Hull reported having done previous research funded by Gilead Sciences and having received consulting fees from Gilead Sciences in 2018. Ms. McKinley-Beach reported receiving honoraria from ViiV Healthcare. Ms. Sherman and Dr. Daskalakis disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Spam filter failure: Selling physician emails equals big $$
Despite the best efforts of my institution’s spam filter, I’ve realized that I spend at least 4 minutes every day of the week removing junk email from my in basket: EMR vendors, predatory journals trying to lure me into paying their outrageous publication fees, people who want to help me with my billing software (evidently that .edu extension hasn’t clicked for them yet), headhunters trying to fill specialty positions in other states, market researchers offering a gift card for 40 minutes filling out a survey.
If you do the math, 4 minutes daily is 1,460 minutes per year. That’s an entire day of my life lost each year to this useless nonsense, which I never agreed to receive in the first place. Now multiply that by the 22 million health care workers in the United States, or even just by the 985,000 licensed physicians in this country. Then factor in the $638 per hour in gross revenue generated by the average primary care physician, as a conservative, well-documented value.
By my reckoning, these bozos owe the United States alone over $15 billion in lost GDP each year.
So why don’t we shut it down!? The CAN-SPAM Act of 2003 attempted to at least mitigate the problem. It applies only to commercial entities (I know, I’d love to report some political groups, too). To avoid violating the law and risking fines of up to $16,000 per individual email, senders must:
- Not use misleading header info (including domain name and email address)
- Not use deceptive subject lines
- Clearly label the email as an ad
- Give an actual physical address of the sender
- Tell recipients how to opt out of future emails
- Honor opt-out requests within 10 business days
- Monitor the activities of any subcontractor sending email on their behalf
I can say with certainty that much of the trash in my inbox violates at least one of these. But that doesn’t matter if there is not an efficient way to report the violators and ensure that they’ll be tracked down. Hard enough if they live here, impossible if the email is routed from overseas, as much of it clearly is.
If you receive email in violation of the act, experts recommend that you write down the email address and the business name of the sender, fill out a complaint form on the Federal Trade Commission website, or send an email to [email protected], then send an email to your Internet service provider’s abuse desk. If you’re not working within a big institution like mine that has hot and cold running IT personnel that operate their own abuse prevention office, the address you’ll need is likely abuse@domain_name or postmaster@domain_name. Just hitting the spam button at the top of your browser/email software may do the trick. There’s more good advice at the FTC’s consumer spam page.
The answer came, ironically, to my email inbox in the form of one of those emails that did indeed violate the law.
I rolled my eyes and started into my reporting subroutine but then stopped cold. Just 1 second. If this person is selling lists of email addresses of conference attendees, somebody within the conference structure must be providing them. How is that legal? I have never agreed, in registering for a medical conference, to allow them to share my email address with anyone. To think that they are making money from that is extremely galling.
Vermont, at least, has enacted a law requiring companies that traffic in such email lists to register with the state. Although it has been in effect for 2 years, the jury is out regarding its efficacy. Our European counterparts are protected by the General Data Protection Regulation, which specifies that commercial email can be sent only to individuals who have explicitly opted into such mailings, and that purchased email lists are not compliant with the requirement.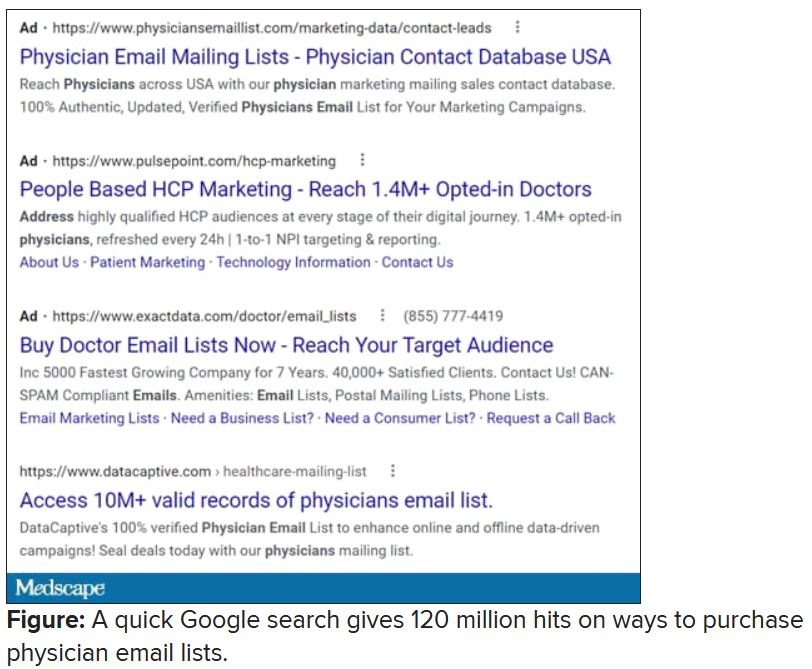
Anybody have the inside scoop on this? Can we demand that our professional societies safeguard their attendee databases so this won’t happen? If they won’t, why am I paying big money to attend their conferences, only for them to make even more money at my expense?
Dr. Hitchcock is assistant professor, department of radiation oncology, at the University of Florida, Gainesville. She reported receiving research grant money from Merck. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite the best efforts of my institution’s spam filter, I’ve realized that I spend at least 4 minutes every day of the week removing junk email from my in basket: EMR vendors, predatory journals trying to lure me into paying their outrageous publication fees, people who want to help me with my billing software (evidently that .edu extension hasn’t clicked for them yet), headhunters trying to fill specialty positions in other states, market researchers offering a gift card for 40 minutes filling out a survey.
If you do the math, 4 minutes daily is 1,460 minutes per year. That’s an entire day of my life lost each year to this useless nonsense, which I never agreed to receive in the first place. Now multiply that by the 22 million health care workers in the United States, or even just by the 985,000 licensed physicians in this country. Then factor in the $638 per hour in gross revenue generated by the average primary care physician, as a conservative, well-documented value.
By my reckoning, these bozos owe the United States alone over $15 billion in lost GDP each year.
So why don’t we shut it down!? The CAN-SPAM Act of 2003 attempted to at least mitigate the problem. It applies only to commercial entities (I know, I’d love to report some political groups, too). To avoid violating the law and risking fines of up to $16,000 per individual email, senders must:
- Not use misleading header info (including domain name and email address)
- Not use deceptive subject lines
- Clearly label the email as an ad
- Give an actual physical address of the sender
- Tell recipients how to opt out of future emails
- Honor opt-out requests within 10 business days
- Monitor the activities of any subcontractor sending email on their behalf
I can say with certainty that much of the trash in my inbox violates at least one of these. But that doesn’t matter if there is not an efficient way to report the violators and ensure that they’ll be tracked down. Hard enough if they live here, impossible if the email is routed from overseas, as much of it clearly is.
If you receive email in violation of the act, experts recommend that you write down the email address and the business name of the sender, fill out a complaint form on the Federal Trade Commission website, or send an email to [email protected], then send an email to your Internet service provider’s abuse desk. If you’re not working within a big institution like mine that has hot and cold running IT personnel that operate their own abuse prevention office, the address you’ll need is likely abuse@domain_name or postmaster@domain_name. Just hitting the spam button at the top of your browser/email software may do the trick. There’s more good advice at the FTC’s consumer spam page.
The answer came, ironically, to my email inbox in the form of one of those emails that did indeed violate the law.
I rolled my eyes and started into my reporting subroutine but then stopped cold. Just 1 second. If this person is selling lists of email addresses of conference attendees, somebody within the conference structure must be providing them. How is that legal? I have never agreed, in registering for a medical conference, to allow them to share my email address with anyone. To think that they are making money from that is extremely galling.
Vermont, at least, has enacted a law requiring companies that traffic in such email lists to register with the state. Although it has been in effect for 2 years, the jury is out regarding its efficacy. Our European counterparts are protected by the General Data Protection Regulation, which specifies that commercial email can be sent only to individuals who have explicitly opted into such mailings, and that purchased email lists are not compliant with the requirement.
Anybody have the inside scoop on this? Can we demand that our professional societies safeguard their attendee databases so this won’t happen? If they won’t, why am I paying big money to attend their conferences, only for them to make even more money at my expense?
Dr. Hitchcock is assistant professor, department of radiation oncology, at the University of Florida, Gainesville. She reported receiving research grant money from Merck. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite the best efforts of my institution’s spam filter, I’ve realized that I spend at least 4 minutes every day of the week removing junk email from my in basket: EMR vendors, predatory journals trying to lure me into paying their outrageous publication fees, people who want to help me with my billing software (evidently that .edu extension hasn’t clicked for them yet), headhunters trying to fill specialty positions in other states, market researchers offering a gift card for 40 minutes filling out a survey.
If you do the math, 4 minutes daily is 1,460 minutes per year. That’s an entire day of my life lost each year to this useless nonsense, which I never agreed to receive in the first place. Now multiply that by the 22 million health care workers in the United States, or even just by the 985,000 licensed physicians in this country. Then factor in the $638 per hour in gross revenue generated by the average primary care physician, as a conservative, well-documented value.
By my reckoning, these bozos owe the United States alone over $15 billion in lost GDP each year.
So why don’t we shut it down!? The CAN-SPAM Act of 2003 attempted to at least mitigate the problem. It applies only to commercial entities (I know, I’d love to report some political groups, too). To avoid violating the law and risking fines of up to $16,000 per individual email, senders must:
- Not use misleading header info (including domain name and email address)
- Not use deceptive subject lines
- Clearly label the email as an ad
- Give an actual physical address of the sender
- Tell recipients how to opt out of future emails
- Honor opt-out requests within 10 business days
- Monitor the activities of any subcontractor sending email on their behalf
I can say with certainty that much of the trash in my inbox violates at least one of these. But that doesn’t matter if there is not an efficient way to report the violators and ensure that they’ll be tracked down. Hard enough if they live here, impossible if the email is routed from overseas, as much of it clearly is.
If you receive email in violation of the act, experts recommend that you write down the email address and the business name of the sender, fill out a complaint form on the Federal Trade Commission website, or send an email to [email protected], then send an email to your Internet service provider’s abuse desk. If you’re not working within a big institution like mine that has hot and cold running IT personnel that operate their own abuse prevention office, the address you’ll need is likely abuse@domain_name or postmaster@domain_name. Just hitting the spam button at the top of your browser/email software may do the trick. There’s more good advice at the FTC’s consumer spam page.
The answer came, ironically, to my email inbox in the form of one of those emails that did indeed violate the law.
I rolled my eyes and started into my reporting subroutine but then stopped cold. Just 1 second. If this person is selling lists of email addresses of conference attendees, somebody within the conference structure must be providing them. How is that legal? I have never agreed, in registering for a medical conference, to allow them to share my email address with anyone. To think that they are making money from that is extremely galling.
Vermont, at least, has enacted a law requiring companies that traffic in such email lists to register with the state. Although it has been in effect for 2 years, the jury is out regarding its efficacy. Our European counterparts are protected by the General Data Protection Regulation, which specifies that commercial email can be sent only to individuals who have explicitly opted into such mailings, and that purchased email lists are not compliant with the requirement.
Anybody have the inside scoop on this? Can we demand that our professional societies safeguard their attendee databases so this won’t happen? If they won’t, why am I paying big money to attend their conferences, only for them to make even more money at my expense?
Dr. Hitchcock is assistant professor, department of radiation oncology, at the University of Florida, Gainesville. She reported receiving research grant money from Merck. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New insights into psychogenic seizures in teens
, results of a small study suggest.
The school experience of teens with PNES is overwhelmingly negative, study investigator Andrea Tanner, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at Indiana University School of Nursing, Indianapolis.
She hopes this research will spur a collaborative effort between students, schools, families, and health care providers “to develop an effective plan to help these adolescents cope, to manage this condition, and hopefully reach seizure freedom.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Anxiety, perfectionism
Although psychogenic seizures resemble epileptic seizures, they have a psychological basis and, unlike epilepsy, are not caused by abnormal electrical brain activity.
While the school experience has previously been identified as a source of predisposing, precipitating, and perpetuating factors for PNES, little is known about the school experience of adolescents with the disorder and the role it may play in PNES management, the investigators noted.
During her 20 years as a school nurse, Dr. Tanner saw firsthand how school staff struggled with responding appropriately to teens with PNES. “They wanted to call 911 every time; they wanted to respond as if it [were] an epileptic seizure.”
For the study, she interviewed 10 teens with PNES, aged 12 to 19 years, whom she found mostly through Facebook support groups but also through flyers. All participants had undergone video EEG and been diagnosed with PNES.
From the interviews, Dr. Tanner and colleagues conducted a qualitative content analysis and uncovered “overarching” themes.
A main theme was stress, some of which focused on bullying by peers or harassment by school personnel, much of which was related to accusations of the children “faking” seizures to get attention, said Dr. Tanner.
Some teens reported being banned from school events, such as field trips, out of concern they would be a “distraction,” which led to feelings of isolation and exclusion, said Dr. Tanner.
Research points to a growing incidence of PNES among adolescents. This may be because it is now better recognized, or it may stem from the unique stressors today’s teens face, said Dr. Tanner.
Adolescents discussed the pressures they feel to be the best at everything. “They wanted to be good in athletics; they wanted to be good in academics; they wanted to get into a good college,” said Dr. Tanner.
Some study participants had undergone psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, and others had investigated mindfulness-based therapy. However, not all were receiving treatment. For some, such care was inaccessible, while others had tried a mental health care intervention but had abandoned it.
Although all the study participants were female, Dr. Tanner has interviewed males outside this study and found their experiences are similar.
Her next research step is to try to quantify the findings. “I would like to begin to look at what would be the appropriate outcomes if I were to do an intervention to improve the school experience.”
Her message for doctors is to see school nurses as a “partner” or “liaison” who “can bridge the world of health care and education.”
Important, novel research
Commenting on the research, Barbara Dworetzky, MD, Chief, Epilepsy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, said it’s “important and novel.”
The study focuses on the main factors – or themes – that lead to increased stress, such as bullying, isolation, and “not being believed,” that are likely triggers for PNES, said Dr. Dworetzky.
The study is also important because it focuses on factors that help make the girls “feel supported and protected” – for example, having staff “take the episodes seriously,” she said.
The study’s qualitative measures “are a valid way of understanding these girls and giving them a voice,” said Dr. Dworetzky. She added the study provides “practical information” that could help target treatments to improve outcomes in this group.
A limitation of the study was that the very small cohort of teenage girls was selected only through families in Facebook support groups or flyers to school nurses, said Dr. Dworetzky.
“There are likely many other groups who don’t even have families trying to help them. Larger cohorts without this type of bias may be next steps.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, results of a small study suggest.
The school experience of teens with PNES is overwhelmingly negative, study investigator Andrea Tanner, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at Indiana University School of Nursing, Indianapolis.
She hopes this research will spur a collaborative effort between students, schools, families, and health care providers “to develop an effective plan to help these adolescents cope, to manage this condition, and hopefully reach seizure freedom.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Anxiety, perfectionism
Although psychogenic seizures resemble epileptic seizures, they have a psychological basis and, unlike epilepsy, are not caused by abnormal electrical brain activity.
While the school experience has previously been identified as a source of predisposing, precipitating, and perpetuating factors for PNES, little is known about the school experience of adolescents with the disorder and the role it may play in PNES management, the investigators noted.
During her 20 years as a school nurse, Dr. Tanner saw firsthand how school staff struggled with responding appropriately to teens with PNES. “They wanted to call 911 every time; they wanted to respond as if it [were] an epileptic seizure.”
For the study, she interviewed 10 teens with PNES, aged 12 to 19 years, whom she found mostly through Facebook support groups but also through flyers. All participants had undergone video EEG and been diagnosed with PNES.
From the interviews, Dr. Tanner and colleagues conducted a qualitative content analysis and uncovered “overarching” themes.
A main theme was stress, some of which focused on bullying by peers or harassment by school personnel, much of which was related to accusations of the children “faking” seizures to get attention, said Dr. Tanner.
Some teens reported being banned from school events, such as field trips, out of concern they would be a “distraction,” which led to feelings of isolation and exclusion, said Dr. Tanner.
Research points to a growing incidence of PNES among adolescents. This may be because it is now better recognized, or it may stem from the unique stressors today’s teens face, said Dr. Tanner.
Adolescents discussed the pressures they feel to be the best at everything. “They wanted to be good in athletics; they wanted to be good in academics; they wanted to get into a good college,” said Dr. Tanner.
Some study participants had undergone psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, and others had investigated mindfulness-based therapy. However, not all were receiving treatment. For some, such care was inaccessible, while others had tried a mental health care intervention but had abandoned it.
Although all the study participants were female, Dr. Tanner has interviewed males outside this study and found their experiences are similar.
Her next research step is to try to quantify the findings. “I would like to begin to look at what would be the appropriate outcomes if I were to do an intervention to improve the school experience.”
Her message for doctors is to see school nurses as a “partner” or “liaison” who “can bridge the world of health care and education.”
Important, novel research
Commenting on the research, Barbara Dworetzky, MD, Chief, Epilepsy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, said it’s “important and novel.”
The study focuses on the main factors – or themes – that lead to increased stress, such as bullying, isolation, and “not being believed,” that are likely triggers for PNES, said Dr. Dworetzky.
The study is also important because it focuses on factors that help make the girls “feel supported and protected” – for example, having staff “take the episodes seriously,” she said.
The study’s qualitative measures “are a valid way of understanding these girls and giving them a voice,” said Dr. Dworetzky. She added the study provides “practical information” that could help target treatments to improve outcomes in this group.
A limitation of the study was that the very small cohort of teenage girls was selected only through families in Facebook support groups or flyers to school nurses, said Dr. Dworetzky.
“There are likely many other groups who don’t even have families trying to help them. Larger cohorts without this type of bias may be next steps.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, results of a small study suggest.
The school experience of teens with PNES is overwhelmingly negative, study investigator Andrea Tanner, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at Indiana University School of Nursing, Indianapolis.
She hopes this research will spur a collaborative effort between students, schools, families, and health care providers “to develop an effective plan to help these adolescents cope, to manage this condition, and hopefully reach seizure freedom.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Anxiety, perfectionism
Although psychogenic seizures resemble epileptic seizures, they have a psychological basis and, unlike epilepsy, are not caused by abnormal electrical brain activity.
While the school experience has previously been identified as a source of predisposing, precipitating, and perpetuating factors for PNES, little is known about the school experience of adolescents with the disorder and the role it may play in PNES management, the investigators noted.
During her 20 years as a school nurse, Dr. Tanner saw firsthand how school staff struggled with responding appropriately to teens with PNES. “They wanted to call 911 every time; they wanted to respond as if it [were] an epileptic seizure.”
For the study, she interviewed 10 teens with PNES, aged 12 to 19 years, whom she found mostly through Facebook support groups but also through flyers. All participants had undergone video EEG and been diagnosed with PNES.
From the interviews, Dr. Tanner and colleagues conducted a qualitative content analysis and uncovered “overarching” themes.
A main theme was stress, some of which focused on bullying by peers or harassment by school personnel, much of which was related to accusations of the children “faking” seizures to get attention, said Dr. Tanner.
Some teens reported being banned from school events, such as field trips, out of concern they would be a “distraction,” which led to feelings of isolation and exclusion, said Dr. Tanner.
Research points to a growing incidence of PNES among adolescents. This may be because it is now better recognized, or it may stem from the unique stressors today’s teens face, said Dr. Tanner.
Adolescents discussed the pressures they feel to be the best at everything. “They wanted to be good in athletics; they wanted to be good in academics; they wanted to get into a good college,” said Dr. Tanner.
Some study participants had undergone psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, and others had investigated mindfulness-based therapy. However, not all were receiving treatment. For some, such care was inaccessible, while others had tried a mental health care intervention but had abandoned it.
Although all the study participants were female, Dr. Tanner has interviewed males outside this study and found their experiences are similar.
Her next research step is to try to quantify the findings. “I would like to begin to look at what would be the appropriate outcomes if I were to do an intervention to improve the school experience.”
Her message for doctors is to see school nurses as a “partner” or “liaison” who “can bridge the world of health care and education.”
Important, novel research
Commenting on the research, Barbara Dworetzky, MD, Chief, Epilepsy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, said it’s “important and novel.”
The study focuses on the main factors – or themes – that lead to increased stress, such as bullying, isolation, and “not being believed,” that are likely triggers for PNES, said Dr. Dworetzky.
The study is also important because it focuses on factors that help make the girls “feel supported and protected” – for example, having staff “take the episodes seriously,” she said.
The study’s qualitative measures “are a valid way of understanding these girls and giving them a voice,” said Dr. Dworetzky. She added the study provides “practical information” that could help target treatments to improve outcomes in this group.
A limitation of the study was that the very small cohort of teenage girls was selected only through families in Facebook support groups or flyers to school nurses, said Dr. Dworetzky.
“There are likely many other groups who don’t even have families trying to help them. Larger cohorts without this type of bias may be next steps.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
From AES 2021
Advocating for children’s health, one page at a time
Everyone can remember a book from their childhood that helped transform them, reinvent them, or turned the world on its head. Characters such as Harry Potter, Franklin the Turtle, Matilda, the Very Hungry Caterpillar, Corduroy, and Nancy Drew, among others, continue to exist in the cultural zeitgeist because they remind us of our childhood and the experience of discovering something innovative and exciting for the first time.
For many young children, introductions to these timeless characters first come from an adult reading to them. Those interactions, starting with watching mouths form words, to exploring pictures, to eventually reading along, leave a lasting impression. “Adults remember being read to,” says pediatrician Perri Klass, MD. “It’s a very powerful thing.”
Dr. Klass serves as national medical director of Reach Out and Read, a nonprofit organization that champions the positive effects of reading and other language-rich activities with young children.
And what better partners to involve in this mission than pediatricians? Before a child reaches the age of 4, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommends that a child visit the pediatrician at least seven times. The Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics suggests as many as 13 pediatrician visits before the child reaches that same milestone. Regardless of the exact number, almost all children are encountering a pediatrician multiple times during the most crucial years of their brain development.
In 1989, physicians Barry Zuckerman, MD, and Robert Needleman, MD, at Boston City Hospital (now Boston Medical Center) realized that they could reach a large population of children and parents, especially those coming from disadvantaged backgrounds, in the pediatrics ward of offices and hospitals all over the country.
The design of Reach Out and Read, the organization they founded, is to work with pediatricians in how they can best support parents in making reading to their children a part of their daily routine, advocating for the importance of books for children, and making sure that a child leaves the office with a book to take home.
Rather than just dumping books onto nervous or busy parents, the organization trains doctors on how to teach parents to read to their children: how to hold the books, how to make it as active as possible, how to point to the pictures and make them come to life, and how to make sure the child is grasping the language.
“You don’t just prop a baby up and read to them,” Dr. Klass told this news organization. “You have to make it interactive.”
Physician-driven success
Now an international organization, Dr. Klass has watched the nonprofit grow tremendously since it began during her fellowship in Boston over three decades ago. The initiative has over 6,100 sites in all 50 states and is able to get books into the hands of 4.2 million children every single year through government aid, individual contributions, and in-kind donations. On average, the organization is able to give parents 6.4 million books annually. Half of the children served every year by the program come from low-income backgrounds.
Dr. Klass ascribed some of the organization’s longevity and success to “practical realism,” its “mission-driven” approach, and its creation by people in primary care who understood the constraints, the upkeep, and the scaling.
“Our organization isn’t looking to pile 10 more things on to the hands of pediatricians who are already very busy,” she said. “We understand that conversation is important with our care providers. We always hear that watching children happily interacting with literature is one of the most rewarding parts of their job. So, we’re saying to them, ‘I want to help you do what you enjoy most.’”
Both Dr. Klass, who is also a presidential appointee to the Advisory Board of the National Institute For Literacy, and Brian Gallagher, MPA, the CEO of Reach Out and Read, said one of the most rewarding parts of their attachment to the organization is working with dedicated physicians all over the country.
“We hear all the time that physicians say working with these tools [from Reach Out and Read] is the most joyful part of their day,” said Mr. Gallagher. “Children are hope for the future and books help them grow.”
Amy Shriver, MD, an Iowa pediatrician and medical director of the Reach Out and Read Iowa Board, admitted that at first she just thought of the organization as a book drive. As Dr. Shriver got closer to the organization, though, she realized how she could utilize the book as a surveillance tool.
“At 6 months through 2 years, I hand the book to the patient, and I can always tell which children are familiar with books by their responses,” she said. After learning about and implementing Reach Out and Read’s ‘model, observe, coach’ methodology, Dr. Shriver said she was wowed by how much it helped families who weren’t reading to their child understand not only how to read with their children but why it’s so important.”
Dr. Shriver said that her clinic has purchased more diverse books to meet the needs of its patient population and has partnered with local libraries and a science center to promote early brain development. The biggest change is that Dr. Shriver finds herself spending more time observing and talking about parent/child relationships since starting with Reach Out and Read.
Mr. Gallagher attributed the organization’s success to the massive amounts of research that back up the practices of the organization. “Our model isn’t just a nice thing to do,” Mr. Gallagher said. “Our practice has been proven to be effective, and that’s why pediatricians continue to work with us. We’ve heard experts say that when they’re advocating for children’s health, they say ‘vaccines, sleep, and Reach Out and Read.’”
Nineteen independent studies have been done profiling the work of Reach Out and Read since its inception. The research has shown that exposure to the organization results in parents reading more often to their children, higher language scores, as well as an improvement in clinic culture and clinician well-being.
In 2014, the American Academy of Pediatrics quoted the research of Reach Out and Read in its policy statement “Literacy Promotion: An Essential Component of Primary Care Pediatric Practice,” which argued that pediatrics should advocate for literacy from birth. The abstract of the study suggests that practicing pediatricians “advise all parents that reading aloud with young children can enhance parent-child relationships and prepare young minds to learn language and early literacy skills ... provide developmentally appropriate books given at health supervision visits for all high-risk, low-income young children ... partnering with other child advocates to influence national messaging and policies that support and promote these key, early shared-reading experiences.”
Adapting to benefit children and parents
Reach Out and Read is not afraid to change with the times. When it began in 1989, there was no guidance for pediatricians on the importance of reading. Mr. Gallagher said that a common question Reach Out and Read received was, “Why not focus on physical health?” The organization was more interested in the shift in pediatric practice overtime.
“We used to advocate starting off kids with books at 6 months old, but we always listen to the research,” Mr. Gallagher said. Now, the organization as well as the American Academy of Pediatrics advocate for beginning at birth. Other publications such as Green Child Magazine and Psychology Today speak of the importance of reading to babies still in the womb. The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences published an article in 2013 that suggests that third-trimester babies can not only pick up on language patterns but also can identify words first heard in the womb.
“We aren’t afraid to adjust our practice if it will be more effective and beneficial for children,” Mr. Gallagher said, “We follow the research and share the work that we are doing. It’s important to stay as up to date as possible.”
Although the focus is largely on the health of children, the impact on parents is crucial as well. Mr. Gallagher described the books at the center of the mission as “a vehicle for bonding” between parents and their children. “The relationship-building we see between families is truly quite magical,” he said.
“Parents will say it’s a respite in their day,” Dr. Klass said of the daily practice of reading aloud. She recalled a memory of talking to a mother with two rowdy young boys, who would sit down and read to them, immediately calming them down.
“When parents sit down to read to their children they don’t have to make anything up. It’s a script, it’s a prompt. You have this story, a picture to show. And kids get preferences,” she said. “When they pick a book that they want you to read, they get to exercise some control. It’s a satisfying routine for parents. It helps open up the world to your child. And when kids come over and hand a book to you for you to read together, it’s them saying, ‘I like the way you look, sound, and interact with me when we do this together.’”
A study from Ambulatory Pediatrics demonstrated that families working with Reach Out and Read were more likely to report reading aloud at bedtime, to read aloud three or more days per week, to mention reading aloud as a favorite parenting activity, and to own 10 or more children’s books. The American Journal of Diseases for Children, in a 1991 article co-authored by Needleman and Zuckerman, noted that the effects of Reach Out and Read were greater for those families who were receiving Aid to Families with Dependent Children. In 2015, the Pew Research Center unveiled a report, “Parenting in America” on raising a child in the modern age, the first generation in American history expected, on average, to make less than their parents.
The report stated that “a broad, demographically-based look at the landscape of American families reveals stark parenting divides linked less to philosophies or values and more to economic circumstances and changing family structure.”
As questions of access and privilege loom over the growing world of education, Reach Out and Read is trying to shorten the gap one book at a time. They are hoping, in time, that their model will be able to reach 90% of children in the United States and foster a relationship with reading and protecting children from toxic stress.
“Every time I look at a newborn, I think about the power of relationships,” said Dr. Shriver, the Iowa-based pediatrician. “I think about how much love passes between infants and their parents, and how shared reading is such a powerful way to show our children we love them. I know from my own experiences how good it feels to snuggle every night and read together. Those moments when the world falls away, and it’s just you, your child, and a book are magical.”
“I want every parent and child to have that experience and create those loving memories. I want all children to feel safe, secure, and loved. I want every child to have the opportunity to use books as a mirror to see themselves and as a window to see the world.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Everyone can remember a book from their childhood that helped transform them, reinvent them, or turned the world on its head. Characters such as Harry Potter, Franklin the Turtle, Matilda, the Very Hungry Caterpillar, Corduroy, and Nancy Drew, among others, continue to exist in the cultural zeitgeist because they remind us of our childhood and the experience of discovering something innovative and exciting for the first time.
For many young children, introductions to these timeless characters first come from an adult reading to them. Those interactions, starting with watching mouths form words, to exploring pictures, to eventually reading along, leave a lasting impression. “Adults remember being read to,” says pediatrician Perri Klass, MD. “It’s a very powerful thing.”
Dr. Klass serves as national medical director of Reach Out and Read, a nonprofit organization that champions the positive effects of reading and other language-rich activities with young children.
And what better partners to involve in this mission than pediatricians? Before a child reaches the age of 4, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommends that a child visit the pediatrician at least seven times. The Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics suggests as many as 13 pediatrician visits before the child reaches that same milestone. Regardless of the exact number, almost all children are encountering a pediatrician multiple times during the most crucial years of their brain development.
In 1989, physicians Barry Zuckerman, MD, and Robert Needleman, MD, at Boston City Hospital (now Boston Medical Center) realized that they could reach a large population of children and parents, especially those coming from disadvantaged backgrounds, in the pediatrics ward of offices and hospitals all over the country.
The design of Reach Out and Read, the organization they founded, is to work with pediatricians in how they can best support parents in making reading to their children a part of their daily routine, advocating for the importance of books for children, and making sure that a child leaves the office with a book to take home.
Rather than just dumping books onto nervous or busy parents, the organization trains doctors on how to teach parents to read to their children: how to hold the books, how to make it as active as possible, how to point to the pictures and make them come to life, and how to make sure the child is grasping the language.
“You don’t just prop a baby up and read to them,” Dr. Klass told this news organization. “You have to make it interactive.”
Physician-driven success
Now an international organization, Dr. Klass has watched the nonprofit grow tremendously since it began during her fellowship in Boston over three decades ago. The initiative has over 6,100 sites in all 50 states and is able to get books into the hands of 4.2 million children every single year through government aid, individual contributions, and in-kind donations. On average, the organization is able to give parents 6.4 million books annually. Half of the children served every year by the program come from low-income backgrounds.
Dr. Klass ascribed some of the organization’s longevity and success to “practical realism,” its “mission-driven” approach, and its creation by people in primary care who understood the constraints, the upkeep, and the scaling.
“Our organization isn’t looking to pile 10 more things on to the hands of pediatricians who are already very busy,” she said. “We understand that conversation is important with our care providers. We always hear that watching children happily interacting with literature is one of the most rewarding parts of their job. So, we’re saying to them, ‘I want to help you do what you enjoy most.’”
Both Dr. Klass, who is also a presidential appointee to the Advisory Board of the National Institute For Literacy, and Brian Gallagher, MPA, the CEO of Reach Out and Read, said one of the most rewarding parts of their attachment to the organization is working with dedicated physicians all over the country.
“We hear all the time that physicians say working with these tools [from Reach Out and Read] is the most joyful part of their day,” said Mr. Gallagher. “Children are hope for the future and books help them grow.”
Amy Shriver, MD, an Iowa pediatrician and medical director of the Reach Out and Read Iowa Board, admitted that at first she just thought of the organization as a book drive. As Dr. Shriver got closer to the organization, though, she realized how she could utilize the book as a surveillance tool.
“At 6 months through 2 years, I hand the book to the patient, and I can always tell which children are familiar with books by their responses,” she said. After learning about and implementing Reach Out and Read’s ‘model, observe, coach’ methodology, Dr. Shriver said she was wowed by how much it helped families who weren’t reading to their child understand not only how to read with their children but why it’s so important.”
Dr. Shriver said that her clinic has purchased more diverse books to meet the needs of its patient population and has partnered with local libraries and a science center to promote early brain development. The biggest change is that Dr. Shriver finds herself spending more time observing and talking about parent/child relationships since starting with Reach Out and Read.
Mr. Gallagher attributed the organization’s success to the massive amounts of research that back up the practices of the organization. “Our model isn’t just a nice thing to do,” Mr. Gallagher said. “Our practice has been proven to be effective, and that’s why pediatricians continue to work with us. We’ve heard experts say that when they’re advocating for children’s health, they say ‘vaccines, sleep, and Reach Out and Read.’”
Nineteen independent studies have been done profiling the work of Reach Out and Read since its inception. The research has shown that exposure to the organization results in parents reading more often to their children, higher language scores, as well as an improvement in clinic culture and clinician well-being.
In 2014, the American Academy of Pediatrics quoted the research of Reach Out and Read in its policy statement “Literacy Promotion: An Essential Component of Primary Care Pediatric Practice,” which argued that pediatrics should advocate for literacy from birth. The abstract of the study suggests that practicing pediatricians “advise all parents that reading aloud with young children can enhance parent-child relationships and prepare young minds to learn language and early literacy skills ... provide developmentally appropriate books given at health supervision visits for all high-risk, low-income young children ... partnering with other child advocates to influence national messaging and policies that support and promote these key, early shared-reading experiences.”
Adapting to benefit children and parents
Reach Out and Read is not afraid to change with the times. When it began in 1989, there was no guidance for pediatricians on the importance of reading. Mr. Gallagher said that a common question Reach Out and Read received was, “Why not focus on physical health?” The organization was more interested in the shift in pediatric practice overtime.
“We used to advocate starting off kids with books at 6 months old, but we always listen to the research,” Mr. Gallagher said. Now, the organization as well as the American Academy of Pediatrics advocate for beginning at birth. Other publications such as Green Child Magazine and Psychology Today speak of the importance of reading to babies still in the womb. The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences published an article in 2013 that suggests that third-trimester babies can not only pick up on language patterns but also can identify words first heard in the womb.
“We aren’t afraid to adjust our practice if it will be more effective and beneficial for children,” Mr. Gallagher said, “We follow the research and share the work that we are doing. It’s important to stay as up to date as possible.”
Although the focus is largely on the health of children, the impact on parents is crucial as well. Mr. Gallagher described the books at the center of the mission as “a vehicle for bonding” between parents and their children. “The relationship-building we see between families is truly quite magical,” he said.
“Parents will say it’s a respite in their day,” Dr. Klass said of the daily practice of reading aloud. She recalled a memory of talking to a mother with two rowdy young boys, who would sit down and read to them, immediately calming them down.
“When parents sit down to read to their children they don’t have to make anything up. It’s a script, it’s a prompt. You have this story, a picture to show. And kids get preferences,” she said. “When they pick a book that they want you to read, they get to exercise some control. It’s a satisfying routine for parents. It helps open up the world to your child. And when kids come over and hand a book to you for you to read together, it’s them saying, ‘I like the way you look, sound, and interact with me when we do this together.’”
A study from Ambulatory Pediatrics demonstrated that families working with Reach Out and Read were more likely to report reading aloud at bedtime, to read aloud three or more days per week, to mention reading aloud as a favorite parenting activity, and to own 10 or more children’s books. The American Journal of Diseases for Children, in a 1991 article co-authored by Needleman and Zuckerman, noted that the effects of Reach Out and Read were greater for those families who were receiving Aid to Families with Dependent Children. In 2015, the Pew Research Center unveiled a report, “Parenting in America” on raising a child in the modern age, the first generation in American history expected, on average, to make less than their parents.
The report stated that “a broad, demographically-based look at the landscape of American families reveals stark parenting divides linked less to philosophies or values and more to economic circumstances and changing family structure.”
As questions of access and privilege loom over the growing world of education, Reach Out and Read is trying to shorten the gap one book at a time. They are hoping, in time, that their model will be able to reach 90% of children in the United States and foster a relationship with reading and protecting children from toxic stress.
“Every time I look at a newborn, I think about the power of relationships,” said Dr. Shriver, the Iowa-based pediatrician. “I think about how much love passes between infants and their parents, and how shared reading is such a powerful way to show our children we love them. I know from my own experiences how good it feels to snuggle every night and read together. Those moments when the world falls away, and it’s just you, your child, and a book are magical.”
“I want every parent and child to have that experience and create those loving memories. I want all children to feel safe, secure, and loved. I want every child to have the opportunity to use books as a mirror to see themselves and as a window to see the world.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Everyone can remember a book from their childhood that helped transform them, reinvent them, or turned the world on its head. Characters such as Harry Potter, Franklin the Turtle, Matilda, the Very Hungry Caterpillar, Corduroy, and Nancy Drew, among others, continue to exist in the cultural zeitgeist because they remind us of our childhood and the experience of discovering something innovative and exciting for the first time.
For many young children, introductions to these timeless characters first come from an adult reading to them. Those interactions, starting with watching mouths form words, to exploring pictures, to eventually reading along, leave a lasting impression. “Adults remember being read to,” says pediatrician Perri Klass, MD. “It’s a very powerful thing.”
Dr. Klass serves as national medical director of Reach Out and Read, a nonprofit organization that champions the positive effects of reading and other language-rich activities with young children.
And what better partners to involve in this mission than pediatricians? Before a child reaches the age of 4, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommends that a child visit the pediatrician at least seven times. The Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics suggests as many as 13 pediatrician visits before the child reaches that same milestone. Regardless of the exact number, almost all children are encountering a pediatrician multiple times during the most crucial years of their brain development.
In 1989, physicians Barry Zuckerman, MD, and Robert Needleman, MD, at Boston City Hospital (now Boston Medical Center) realized that they could reach a large population of children and parents, especially those coming from disadvantaged backgrounds, in the pediatrics ward of offices and hospitals all over the country.
The design of Reach Out and Read, the organization they founded, is to work with pediatricians in how they can best support parents in making reading to their children a part of their daily routine, advocating for the importance of books for children, and making sure that a child leaves the office with a book to take home.
Rather than just dumping books onto nervous or busy parents, the organization trains doctors on how to teach parents to read to their children: how to hold the books, how to make it as active as possible, how to point to the pictures and make them come to life, and how to make sure the child is grasping the language.
“You don’t just prop a baby up and read to them,” Dr. Klass told this news organization. “You have to make it interactive.”
Physician-driven success
Now an international organization, Dr. Klass has watched the nonprofit grow tremendously since it began during her fellowship in Boston over three decades ago. The initiative has over 6,100 sites in all 50 states and is able to get books into the hands of 4.2 million children every single year through government aid, individual contributions, and in-kind donations. On average, the organization is able to give parents 6.4 million books annually. Half of the children served every year by the program come from low-income backgrounds.
Dr. Klass ascribed some of the organization’s longevity and success to “practical realism,” its “mission-driven” approach, and its creation by people in primary care who understood the constraints, the upkeep, and the scaling.
“Our organization isn’t looking to pile 10 more things on to the hands of pediatricians who are already very busy,” she said. “We understand that conversation is important with our care providers. We always hear that watching children happily interacting with literature is one of the most rewarding parts of their job. So, we’re saying to them, ‘I want to help you do what you enjoy most.’”
Both Dr. Klass, who is also a presidential appointee to the Advisory Board of the National Institute For Literacy, and Brian Gallagher, MPA, the CEO of Reach Out and Read, said one of the most rewarding parts of their attachment to the organization is working with dedicated physicians all over the country.
“We hear all the time that physicians say working with these tools [from Reach Out and Read] is the most joyful part of their day,” said Mr. Gallagher. “Children are hope for the future and books help them grow.”
Amy Shriver, MD, an Iowa pediatrician and medical director of the Reach Out and Read Iowa Board, admitted that at first she just thought of the organization as a book drive. As Dr. Shriver got closer to the organization, though, she realized how she could utilize the book as a surveillance tool.
“At 6 months through 2 years, I hand the book to the patient, and I can always tell which children are familiar with books by their responses,” she said. After learning about and implementing Reach Out and Read’s ‘model, observe, coach’ methodology, Dr. Shriver said she was wowed by how much it helped families who weren’t reading to their child understand not only how to read with their children but why it’s so important.”
Dr. Shriver said that her clinic has purchased more diverse books to meet the needs of its patient population and has partnered with local libraries and a science center to promote early brain development. The biggest change is that Dr. Shriver finds herself spending more time observing and talking about parent/child relationships since starting with Reach Out and Read.
Mr. Gallagher attributed the organization’s success to the massive amounts of research that back up the practices of the organization. “Our model isn’t just a nice thing to do,” Mr. Gallagher said. “Our practice has been proven to be effective, and that’s why pediatricians continue to work with us. We’ve heard experts say that when they’re advocating for children’s health, they say ‘vaccines, sleep, and Reach Out and Read.’”
Nineteen independent studies have been done profiling the work of Reach Out and Read since its inception. The research has shown that exposure to the organization results in parents reading more often to their children, higher language scores, as well as an improvement in clinic culture and clinician well-being.
In 2014, the American Academy of Pediatrics quoted the research of Reach Out and Read in its policy statement “Literacy Promotion: An Essential Component of Primary Care Pediatric Practice,” which argued that pediatrics should advocate for literacy from birth. The abstract of the study suggests that practicing pediatricians “advise all parents that reading aloud with young children can enhance parent-child relationships and prepare young minds to learn language and early literacy skills ... provide developmentally appropriate books given at health supervision visits for all high-risk, low-income young children ... partnering with other child advocates to influence national messaging and policies that support and promote these key, early shared-reading experiences.”
Adapting to benefit children and parents
Reach Out and Read is not afraid to change with the times. When it began in 1989, there was no guidance for pediatricians on the importance of reading. Mr. Gallagher said that a common question Reach Out and Read received was, “Why not focus on physical health?” The organization was more interested in the shift in pediatric practice overtime.
“We used to advocate starting off kids with books at 6 months old, but we always listen to the research,” Mr. Gallagher said. Now, the organization as well as the American Academy of Pediatrics advocate for beginning at birth. Other publications such as Green Child Magazine and Psychology Today speak of the importance of reading to babies still in the womb. The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences published an article in 2013 that suggests that third-trimester babies can not only pick up on language patterns but also can identify words first heard in the womb.
“We aren’t afraid to adjust our practice if it will be more effective and beneficial for children,” Mr. Gallagher said, “We follow the research and share the work that we are doing. It’s important to stay as up to date as possible.”
Although the focus is largely on the health of children, the impact on parents is crucial as well. Mr. Gallagher described the books at the center of the mission as “a vehicle for bonding” between parents and their children. “The relationship-building we see between families is truly quite magical,” he said.
“Parents will say it’s a respite in their day,” Dr. Klass said of the daily practice of reading aloud. She recalled a memory of talking to a mother with two rowdy young boys, who would sit down and read to them, immediately calming them down.
“When parents sit down to read to their children they don’t have to make anything up. It’s a script, it’s a prompt. You have this story, a picture to show. And kids get preferences,” she said. “When they pick a book that they want you to read, they get to exercise some control. It’s a satisfying routine for parents. It helps open up the world to your child. And when kids come over and hand a book to you for you to read together, it’s them saying, ‘I like the way you look, sound, and interact with me when we do this together.’”
A study from Ambulatory Pediatrics demonstrated that families working with Reach Out and Read were more likely to report reading aloud at bedtime, to read aloud three or more days per week, to mention reading aloud as a favorite parenting activity, and to own 10 or more children’s books. The American Journal of Diseases for Children, in a 1991 article co-authored by Needleman and Zuckerman, noted that the effects of Reach Out and Read were greater for those families who were receiving Aid to Families with Dependent Children. In 2015, the Pew Research Center unveiled a report, “Parenting in America” on raising a child in the modern age, the first generation in American history expected, on average, to make less than their parents.
The report stated that “a broad, demographically-based look at the landscape of American families reveals stark parenting divides linked less to philosophies or values and more to economic circumstances and changing family structure.”
As questions of access and privilege loom over the growing world of education, Reach Out and Read is trying to shorten the gap one book at a time. They are hoping, in time, that their model will be able to reach 90% of children in the United States and foster a relationship with reading and protecting children from toxic stress.
“Every time I look at a newborn, I think about the power of relationships,” said Dr. Shriver, the Iowa-based pediatrician. “I think about how much love passes between infants and their parents, and how shared reading is such a powerful way to show our children we love them. I know from my own experiences how good it feels to snuggle every night and read together. Those moments when the world falls away, and it’s just you, your child, and a book are magical.”
“I want every parent and child to have that experience and create those loving memories. I want all children to feel safe, secure, and loved. I want every child to have the opportunity to use books as a mirror to see themselves and as a window to see the world.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A very strange place to find a tooth
A nose for the tooth
Have you ever had a stuffy nose that just wouldn’t go away? Those irritating head colds have nothing on the stuffy nose a man in New York recently had to go through. A stuffy nose to top all stuffy noses. One stuffy nose to rule them all, as it were.
This man went to a Mount Sinai clinic with difficulty breathing through his right nostril, a problem that had been going on for years. Let us repeat that: A stuffy nose that lasted for years. The exam revealed a white mass jutting through the back of the septum and a CT scan confirmed the diagnosis. Perhaps you’ve already guessed, since the headline does give things away. Yes, this man had a tooth growing into his nose.
The problem was a half-inch-long ectopic tooth. Ectopic teeth are rare, occurring in less than 1% of people, but an ectopic tooth growing backward into the nasal cavity? Well, that’s so uncommon that this man got a case report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
This story does have a happy ending. Not all ectopic teeth need to be treated, but this one really did have to go. The offending tooth was surgically removed and, at a 3-month follow-up, the stuffy nose issue was completely resolved. So our friend gets the best of both worlds: His issue gets cured and he gets a case report in a major medical publication. If that’s not living the dream, we don’t know what is, and that’s the tooth.
Lettuce recommend you a sleep aid
Lettuce is great for many things. The star in a salad? Of course. The fresh element in a BLT? Yep. A sleep aid? According to a TikTok hack with almost 5 million views, the pinch hitter in a sandwich is switching leagues to be used like a tea for faster sleep. But, does it really work? Researchers say yes and no, according to a recent report at Tyla.com.
Studies conducted in 2013 and 2017 pointed toward a compound called lactucin, which is found in the plant’s n-butanol fraction. In the 2013 study, mice that received n-butanol fraction fell asleep faster and stayed asleep longer. In 2017, researchers found that lettuce made mice sleep longer and helped protect against cell inflammation and damage.
OK, so it works on mice. But what about humans? In the TikTok video, user Shapla Hoque pours hot water on a few lettuce leaves in a mug with a peppermint tea bag (for flavor). After 10 minutes, when the leaves are soaked and soggy, she removes them and drinks the lettuce tea. By the end of the video she’s visibly drowsy and ready to crash. Does this hold water?
Here’s the no. Dr. Charlotte Norton of the Slimming Clinic told Tyla.com that yeah, there are some properties in lettuce that will help you fall asleep, such as lactucarium, which is prominent in romaine. But you would need a massive amount of lettuce to get any effect. The TikTok video, she said, is an example of the placebo effect.
Brains get a rise out of Viagra
A lot of medications are used off label. Antidepressants for COVID have taken the cake recently, but here’s a new one: Viagra for Alzheimer’s disease.
Although there’s no definite link yet between the two, neuron models derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with Alzheimer’s suggest that sildenafil increases neurite growth and decreases phospho-tau expression, Jiansong Fang, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and associates said in Nature Aging.
Their research is an attempt to find untapped sources of new treatments among existing drugs. They began the search with 1,600 approved drugs and focused on those that target the buildup of beta amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, according to the Daily Beast.
Since sildenafil is obviously for men, more research will need to be done on how this drug affects women. Don’t start stocking up just yet.
Omicron is not a social-distancing robot
COVID, safe to say, has not been your typical, run-of-the-mill pandemic. People have protested social distancing. People have protested lockdowns. People have protested mask mandates. People have protested vaccine mandates. People have protested people protesting vaccine mandates.
Someone used a fake arm to get a COVID vaccine card. People have tried to reverse their COVID vaccinations. People had COVID contamination parties.
The common denominator? People. Humans. Maybe what we need is a nonhuman intervention. To fight COVID, we need a hero. A robotic hero.
And where can we find such a hero? The University of Maryland, of course, where computer scientists and engineers are working on an autonomous mobile robot to enforce indoor social-distancing rules.
Their robot can detect lapses in social distancing using cameras, both thermal and visual, along with a LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor. It then sorts the offenders into various groups depending on whether they are standing still or moving and predicts their future movement using a state-of-the-art hybrid collision avoidance method known as Frozone, Adarsh Jagan Sathyamoorthy and associates explained in PLOS One.
“Once it reaches the breach, the robot encourages people to move apart via text that appears on a mounted display,” ScienceDaily said.
Maybe you were expecting a Terminator-type robot coming to enforce social distancing requirements rather than a simple text message. Let’s just hope that all COVID guidelines are followed, including social distancing, so the pandemic will finally end and won’t “be back.”
A nose for the tooth
Have you ever had a stuffy nose that just wouldn’t go away? Those irritating head colds have nothing on the stuffy nose a man in New York recently had to go through. A stuffy nose to top all stuffy noses. One stuffy nose to rule them all, as it were.
This man went to a Mount Sinai clinic with difficulty breathing through his right nostril, a problem that had been going on for years. Let us repeat that: A stuffy nose that lasted for years. The exam revealed a white mass jutting through the back of the septum and a CT scan confirmed the diagnosis. Perhaps you’ve already guessed, since the headline does give things away. Yes, this man had a tooth growing into his nose.
The problem was a half-inch-long ectopic tooth. Ectopic teeth are rare, occurring in less than 1% of people, but an ectopic tooth growing backward into the nasal cavity? Well, that’s so uncommon that this man got a case report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
This story does have a happy ending. Not all ectopic teeth need to be treated, but this one really did have to go. The offending tooth was surgically removed and, at a 3-month follow-up, the stuffy nose issue was completely resolved. So our friend gets the best of both worlds: His issue gets cured and he gets a case report in a major medical publication. If that’s not living the dream, we don’t know what is, and that’s the tooth.
Lettuce recommend you a sleep aid
Lettuce is great for many things. The star in a salad? Of course. The fresh element in a BLT? Yep. A sleep aid? According to a TikTok hack with almost 5 million views, the pinch hitter in a sandwich is switching leagues to be used like a tea for faster sleep. But, does it really work? Researchers say yes and no, according to a recent report at Tyla.com.
Studies conducted in 2013 and 2017 pointed toward a compound called lactucin, which is found in the plant’s n-butanol fraction. In the 2013 study, mice that received n-butanol fraction fell asleep faster and stayed asleep longer. In 2017, researchers found that lettuce made mice sleep longer and helped protect against cell inflammation and damage.
OK, so it works on mice. But what about humans? In the TikTok video, user Shapla Hoque pours hot water on a few lettuce leaves in a mug with a peppermint tea bag (for flavor). After 10 minutes, when the leaves are soaked and soggy, she removes them and drinks the lettuce tea. By the end of the video she’s visibly drowsy and ready to crash. Does this hold water?
Here’s the no. Dr. Charlotte Norton of the Slimming Clinic told Tyla.com that yeah, there are some properties in lettuce that will help you fall asleep, such as lactucarium, which is prominent in romaine. But you would need a massive amount of lettuce to get any effect. The TikTok video, she said, is an example of the placebo effect.
Brains get a rise out of Viagra
A lot of medications are used off label. Antidepressants for COVID have taken the cake recently, but here’s a new one: Viagra for Alzheimer’s disease.
Although there’s no definite link yet between the two, neuron models derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with Alzheimer’s suggest that sildenafil increases neurite growth and decreases phospho-tau expression, Jiansong Fang, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and associates said in Nature Aging.
Their research is an attempt to find untapped sources of new treatments among existing drugs. They began the search with 1,600 approved drugs and focused on those that target the buildup of beta amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, according to the Daily Beast.
Since sildenafil is obviously for men, more research will need to be done on how this drug affects women. Don’t start stocking up just yet.
Omicron is not a social-distancing robot
COVID, safe to say, has not been your typical, run-of-the-mill pandemic. People have protested social distancing. People have protested lockdowns. People have protested mask mandates. People have protested vaccine mandates. People have protested people protesting vaccine mandates.
Someone used a fake arm to get a COVID vaccine card. People have tried to reverse their COVID vaccinations. People had COVID contamination parties.
The common denominator? People. Humans. Maybe what we need is a nonhuman intervention. To fight COVID, we need a hero. A robotic hero.
And where can we find such a hero? The University of Maryland, of course, where computer scientists and engineers are working on an autonomous mobile robot to enforce indoor social-distancing rules.
Their robot can detect lapses in social distancing using cameras, both thermal and visual, along with a LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor. It then sorts the offenders into various groups depending on whether they are standing still or moving and predicts their future movement using a state-of-the-art hybrid collision avoidance method known as Frozone, Adarsh Jagan Sathyamoorthy and associates explained in PLOS One.
“Once it reaches the breach, the robot encourages people to move apart via text that appears on a mounted display,” ScienceDaily said.
Maybe you were expecting a Terminator-type robot coming to enforce social distancing requirements rather than a simple text message. Let’s just hope that all COVID guidelines are followed, including social distancing, so the pandemic will finally end and won’t “be back.”
A nose for the tooth
Have you ever had a stuffy nose that just wouldn’t go away? Those irritating head colds have nothing on the stuffy nose a man in New York recently had to go through. A stuffy nose to top all stuffy noses. One stuffy nose to rule them all, as it were.
This man went to a Mount Sinai clinic with difficulty breathing through his right nostril, a problem that had been going on for years. Let us repeat that: A stuffy nose that lasted for years. The exam revealed a white mass jutting through the back of the septum and a CT scan confirmed the diagnosis. Perhaps you’ve already guessed, since the headline does give things away. Yes, this man had a tooth growing into his nose.
The problem was a half-inch-long ectopic tooth. Ectopic teeth are rare, occurring in less than 1% of people, but an ectopic tooth growing backward into the nasal cavity? Well, that’s so uncommon that this man got a case report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
This story does have a happy ending. Not all ectopic teeth need to be treated, but this one really did have to go. The offending tooth was surgically removed and, at a 3-month follow-up, the stuffy nose issue was completely resolved. So our friend gets the best of both worlds: His issue gets cured and he gets a case report in a major medical publication. If that’s not living the dream, we don’t know what is, and that’s the tooth.
Lettuce recommend you a sleep aid
Lettuce is great for many things. The star in a salad? Of course. The fresh element in a BLT? Yep. A sleep aid? According to a TikTok hack with almost 5 million views, the pinch hitter in a sandwich is switching leagues to be used like a tea for faster sleep. But, does it really work? Researchers say yes and no, according to a recent report at Tyla.com.
Studies conducted in 2013 and 2017 pointed toward a compound called lactucin, which is found in the plant’s n-butanol fraction. In the 2013 study, mice that received n-butanol fraction fell asleep faster and stayed asleep longer. In 2017, researchers found that lettuce made mice sleep longer and helped protect against cell inflammation and damage.
OK, so it works on mice. But what about humans? In the TikTok video, user Shapla Hoque pours hot water on a few lettuce leaves in a mug with a peppermint tea bag (for flavor). After 10 minutes, when the leaves are soaked and soggy, she removes them and drinks the lettuce tea. By the end of the video she’s visibly drowsy and ready to crash. Does this hold water?
Here’s the no. Dr. Charlotte Norton of the Slimming Clinic told Tyla.com that yeah, there are some properties in lettuce that will help you fall asleep, such as lactucarium, which is prominent in romaine. But you would need a massive amount of lettuce to get any effect. The TikTok video, she said, is an example of the placebo effect.
Brains get a rise out of Viagra
A lot of medications are used off label. Antidepressants for COVID have taken the cake recently, but here’s a new one: Viagra for Alzheimer’s disease.
Although there’s no definite link yet between the two, neuron models derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with Alzheimer’s suggest that sildenafil increases neurite growth and decreases phospho-tau expression, Jiansong Fang, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and associates said in Nature Aging.
Their research is an attempt to find untapped sources of new treatments among existing drugs. They began the search with 1,600 approved drugs and focused on those that target the buildup of beta amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, according to the Daily Beast.
Since sildenafil is obviously for men, more research will need to be done on how this drug affects women. Don’t start stocking up just yet.
Omicron is not a social-distancing robot
COVID, safe to say, has not been your typical, run-of-the-mill pandemic. People have protested social distancing. People have protested lockdowns. People have protested mask mandates. People have protested vaccine mandates. People have protested people protesting vaccine mandates.
Someone used a fake arm to get a COVID vaccine card. People have tried to reverse their COVID vaccinations. People had COVID contamination parties.
The common denominator? People. Humans. Maybe what we need is a nonhuman intervention. To fight COVID, we need a hero. A robotic hero.
And where can we find such a hero? The University of Maryland, of course, where computer scientists and engineers are working on an autonomous mobile robot to enforce indoor social-distancing rules.
Their robot can detect lapses in social distancing using cameras, both thermal and visual, along with a LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor. It then sorts the offenders into various groups depending on whether they are standing still or moving and predicts their future movement using a state-of-the-art hybrid collision avoidance method known as Frozone, Adarsh Jagan Sathyamoorthy and associates explained in PLOS One.
“Once it reaches the breach, the robot encourages people to move apart via text that appears on a mounted display,” ScienceDaily said.
Maybe you were expecting a Terminator-type robot coming to enforce social distancing requirements rather than a simple text message. Let’s just hope that all COVID guidelines are followed, including social distancing, so the pandemic will finally end and won’t “be back.”
Vaccine protection drops against Omicron, making boosters crucial
A raft of new
The new studies, from teams of researchers in Germany, South Africa, Sweden, and the drug company Pfizer, showed 25 to 40-fold drops in the ability of antibodies created by two doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine to neutralize the virus.
But there seemed to be a bright spot in the studies too. The virus didn’t completely escape the immunity from the vaccines, and giving a third, booster dose appeared to restore antibodies to a level that’s been associated with protection against variants in the past.
“One of the silver linings of this pandemic so far is that mRNA vaccines manufactured based on the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 continue to work in the laboratory and, importantly, in real life against variant strains,” said Hana El Sahly, MD, professor of molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. “The strains so far vary by their degree of being neutralized by the antibodies from these vaccines, but they are being neutralized nonetheless.”
Dr. El Sahly points out that the Beta variant was associated with a 10-fold drop in antibodies, but two doses of the vaccines still protected against it.
President Biden hailed the study results as good news.
“That Pfizer lab report came back saying that the expectation is that the existing vaccines protect against Omicron. But if you get the booster, you’re really in good shape. And so that’s very encouraging,” he said in a press briefing Dec. 8.
More research needed
Other scientists, however, stressed that these studies are from lab tests, and don’t necessarily reflect what will happen with Omicron in the real world. They cautioned about a worldwide push for boosters with so many countries still struggling to give first doses of vaccines.
Soumya Swaminathan, MD, chief scientist for the World Health Organization, stressed in a press briefing Dec. 8 that the results from the four studies varied widely, showing dips in neutralizing activity with Omicron that ranged from 5-fold to 40-fold.
The types of lab tests that were run were different, too, and involved small numbers of blood samples from patients.
She stressed that immunity depends not just on neutralizing antibodies, which act as a first line of defense when a virus invades, but also on B cells and T cells, and so far, tests show that these crucial components — which are important for preventing severe disease and death — had been less impacted than antibodies.
“So, I think it’s premature to conclude that this reduction in neutralizing activity would result in a significant reduction in vaccine effectiveness,” she said.
Whether or not these first-generation vaccines will be enough to stop Omicron, though, remains to be seen. A study of the Pfizer, Moderna, and AstraZeneca vaccines, led by German physician Sandra Ciesek, MD, who directs the Institute of Medical Virology at the University of Frankfurt, shows a booster didn’t appear to hold up well over time.
Dr. Ciesek and her team exposed Omicron viruses to the antibodies of volunteers who had been boosted with the Pfizer vaccine 3 months prior.
She also compared the results to what happened to those same 3-month antibody levels against Delta variant viruses. She found only a 25% neutralization of Omicron compared with a 95% neutralization of Delta. That represented about a 37-fold reduction in the ability of the antibodies to neutralize Omicron vs Delta.
“The data confirm that developing a vaccine adapted for Omicron makes sense,” she tweeted as part of a long thread she posted on her results.
Retool the vaccines?
Both Pfizer and Moderna are retooling their vaccines to better match them to the changes in the Omicron variant. In a press release, Pfizer said it could start deliveries of that updated vaccine by March, pending U.S. Food and Drug Administration authorization.
“What the booster really does in neutralizing Omicron right now, they don’t know, they have no idea,” said Peter Palese, PhD, chair of the department of microbiology at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City.
Dr. Palese said he was definitely concerned about a possible Omicron wave.
“There are four major sites on the spike protein targeted by antibodies from the vaccines, and all four sites have mutations,” he said. “All these important antigenic sites are changed.
“If Omicron becomes the new Delta, and the old vaccines really aren’t good enough, then we have to make new Omicron vaccines. Then we have to revaccinate everybody twice,” he said, and the costs could be staggering. “I am worried.”
Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD, director general of the WHO, urged countries to move quickly.
“Don’t wait. Act now,” he said, even before all the science is in hand. “All of us, every government, every individual should use all the tools we have right now,” to drive down transmission, increase testing and surveillance, and share scientific findings.
“We can prevent Omicron [from] becoming a global crisis right now,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A raft of new
The new studies, from teams of researchers in Germany, South Africa, Sweden, and the drug company Pfizer, showed 25 to 40-fold drops in the ability of antibodies created by two doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine to neutralize the virus.
But there seemed to be a bright spot in the studies too. The virus didn’t completely escape the immunity from the vaccines, and giving a third, booster dose appeared to restore antibodies to a level that’s been associated with protection against variants in the past.
“One of the silver linings of this pandemic so far is that mRNA vaccines manufactured based on the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 continue to work in the laboratory and, importantly, in real life against variant strains,” said Hana El Sahly, MD, professor of molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. “The strains so far vary by their degree of being neutralized by the antibodies from these vaccines, but they are being neutralized nonetheless.”
Dr. El Sahly points out that the Beta variant was associated with a 10-fold drop in antibodies, but two doses of the vaccines still protected against it.
President Biden hailed the study results as good news.
“That Pfizer lab report came back saying that the expectation is that the existing vaccines protect against Omicron. But if you get the booster, you’re really in good shape. And so that’s very encouraging,” he said in a press briefing Dec. 8.
More research needed
Other scientists, however, stressed that these studies are from lab tests, and don’t necessarily reflect what will happen with Omicron in the real world. They cautioned about a worldwide push for boosters with so many countries still struggling to give first doses of vaccines.
Soumya Swaminathan, MD, chief scientist for the World Health Organization, stressed in a press briefing Dec. 8 that the results from the four studies varied widely, showing dips in neutralizing activity with Omicron that ranged from 5-fold to 40-fold.
The types of lab tests that were run were different, too, and involved small numbers of blood samples from patients.
She stressed that immunity depends not just on neutralizing antibodies, which act as a first line of defense when a virus invades, but also on B cells and T cells, and so far, tests show that these crucial components — which are important for preventing severe disease and death — had been less impacted than antibodies.
“So, I think it’s premature to conclude that this reduction in neutralizing activity would result in a significant reduction in vaccine effectiveness,” she said.
Whether or not these first-generation vaccines will be enough to stop Omicron, though, remains to be seen. A study of the Pfizer, Moderna, and AstraZeneca vaccines, led by German physician Sandra Ciesek, MD, who directs the Institute of Medical Virology at the University of Frankfurt, shows a booster didn’t appear to hold up well over time.
Dr. Ciesek and her team exposed Omicron viruses to the antibodies of volunteers who had been boosted with the Pfizer vaccine 3 months prior.
She also compared the results to what happened to those same 3-month antibody levels against Delta variant viruses. She found only a 25% neutralization of Omicron compared with a 95% neutralization of Delta. That represented about a 37-fold reduction in the ability of the antibodies to neutralize Omicron vs Delta.
“The data confirm that developing a vaccine adapted for Omicron makes sense,” she tweeted as part of a long thread she posted on her results.
Retool the vaccines?
Both Pfizer and Moderna are retooling their vaccines to better match them to the changes in the Omicron variant. In a press release, Pfizer said it could start deliveries of that updated vaccine by March, pending U.S. Food and Drug Administration authorization.
“What the booster really does in neutralizing Omicron right now, they don’t know, they have no idea,” said Peter Palese, PhD, chair of the department of microbiology at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City.
Dr. Palese said he was definitely concerned about a possible Omicron wave.
“There are four major sites on the spike protein targeted by antibodies from the vaccines, and all four sites have mutations,” he said. “All these important antigenic sites are changed.
“If Omicron becomes the new Delta, and the old vaccines really aren’t good enough, then we have to make new Omicron vaccines. Then we have to revaccinate everybody twice,” he said, and the costs could be staggering. “I am worried.”
Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD, director general of the WHO, urged countries to move quickly.
“Don’t wait. Act now,” he said, even before all the science is in hand. “All of us, every government, every individual should use all the tools we have right now,” to drive down transmission, increase testing and surveillance, and share scientific findings.
“We can prevent Omicron [from] becoming a global crisis right now,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A raft of new
The new studies, from teams of researchers in Germany, South Africa, Sweden, and the drug company Pfizer, showed 25 to 40-fold drops in the ability of antibodies created by two doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine to neutralize the virus.
But there seemed to be a bright spot in the studies too. The virus didn’t completely escape the immunity from the vaccines, and giving a third, booster dose appeared to restore antibodies to a level that’s been associated with protection against variants in the past.
“One of the silver linings of this pandemic so far is that mRNA vaccines manufactured based on the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 continue to work in the laboratory and, importantly, in real life against variant strains,” said Hana El Sahly, MD, professor of molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. “The strains so far vary by their degree of being neutralized by the antibodies from these vaccines, but they are being neutralized nonetheless.”
Dr. El Sahly points out that the Beta variant was associated with a 10-fold drop in antibodies, but two doses of the vaccines still protected against it.
President Biden hailed the study results as good news.
“That Pfizer lab report came back saying that the expectation is that the existing vaccines protect against Omicron. But if you get the booster, you’re really in good shape. And so that’s very encouraging,” he said in a press briefing Dec. 8.
More research needed
Other scientists, however, stressed that these studies are from lab tests, and don’t necessarily reflect what will happen with Omicron in the real world. They cautioned about a worldwide push for boosters with so many countries still struggling to give first doses of vaccines.
Soumya Swaminathan, MD, chief scientist for the World Health Organization, stressed in a press briefing Dec. 8 that the results from the four studies varied widely, showing dips in neutralizing activity with Omicron that ranged from 5-fold to 40-fold.
The types of lab tests that were run were different, too, and involved small numbers of blood samples from patients.
She stressed that immunity depends not just on neutralizing antibodies, which act as a first line of defense when a virus invades, but also on B cells and T cells, and so far, tests show that these crucial components — which are important for preventing severe disease and death — had been less impacted than antibodies.
“So, I think it’s premature to conclude that this reduction in neutralizing activity would result in a significant reduction in vaccine effectiveness,” she said.
Whether or not these first-generation vaccines will be enough to stop Omicron, though, remains to be seen. A study of the Pfizer, Moderna, and AstraZeneca vaccines, led by German physician Sandra Ciesek, MD, who directs the Institute of Medical Virology at the University of Frankfurt, shows a booster didn’t appear to hold up well over time.
Dr. Ciesek and her team exposed Omicron viruses to the antibodies of volunteers who had been boosted with the Pfizer vaccine 3 months prior.
She also compared the results to what happened to those same 3-month antibody levels against Delta variant viruses. She found only a 25% neutralization of Omicron compared with a 95% neutralization of Delta. That represented about a 37-fold reduction in the ability of the antibodies to neutralize Omicron vs Delta.
“The data confirm that developing a vaccine adapted for Omicron makes sense,” she tweeted as part of a long thread she posted on her results.
Retool the vaccines?
Both Pfizer and Moderna are retooling their vaccines to better match them to the changes in the Omicron variant. In a press release, Pfizer said it could start deliveries of that updated vaccine by March, pending U.S. Food and Drug Administration authorization.
“What the booster really does in neutralizing Omicron right now, they don’t know, they have no idea,” said Peter Palese, PhD, chair of the department of microbiology at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City.
Dr. Palese said he was definitely concerned about a possible Omicron wave.
“There are four major sites on the spike protein targeted by antibodies from the vaccines, and all four sites have mutations,” he said. “All these important antigenic sites are changed.
“If Omicron becomes the new Delta, and the old vaccines really aren’t good enough, then we have to make new Omicron vaccines. Then we have to revaccinate everybody twice,” he said, and the costs could be staggering. “I am worried.”
Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD, director general of the WHO, urged countries to move quickly.
“Don’t wait. Act now,” he said, even before all the science is in hand. “All of us, every government, every individual should use all the tools we have right now,” to drive down transmission, increase testing and surveillance, and share scientific findings.
“We can prevent Omicron [from] becoming a global crisis right now,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data on rare myocarditis after COVID-19 vaccination
Adolescents and adults younger than age 21 who develop myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination frequently have abnormal findings on cardiac MRI (cMRI) but most have a mild clinical course with rapid resolution of symptoms, a new study concludes.
“This study supports what we’ve been seeing. People identified and treated early and appropriately for the rare complication of COVID-19 vaccine-related myocarditis typically experienced only mild cases and short recovery times,” American Heart Association President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a podcast.
“Overwhelmingly, the data continue to indicate [that] the benefits of COVID-19 vaccine far outweigh any very rare risks of adverse events from the vaccine, including myocarditis,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
The study was published online Dec. 6 in Circulation.
Using data from 26 pediatric medical centers across the United States and Canada, the researchers reviewed the medical records of 139 patients younger than 21 with suspected myocarditis within 1 month of receiving a COVID-19 vaccination.
They made the following key observations:
- Most patients were male (90.6%), White (66.2%) and with a median age of 15.8 years.
- Suspected myocarditis occurred in 136 patients (97.8%) following mRNA vaccine, with 131 (94.2%) following the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine; 128 cases (91.4%) occurred after the second dose.
- Symptoms started a median of 2 days (range 0 to 22 days) following vaccination administration.
- Chest pain was the most common symptom (99.3%), with fever present in 30.9% of patients and shortness of breath in 27.3%.
- Patients were treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (81.3%), intravenous immunoglobulin (21.6%), glucocorticoids (21.6%), colchicine (7.9%) or no anti-inflammatory therapies (8.6%).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) were admitted to the intensive care unit; 2 received inotropic/vasoactive support; none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or died.
- Median time spent in the hospital was 2 days.
- A total of 111 patients had elevated troponin I (8.12 ng/mL) and 28 had elevated troponin T (0.61 ng/mL).
- More than two-thirds (69.8%) had abnormal electrocardiograms and/or arrhythmias (7 with nonsustained ventricular tachycardia).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) had left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 55% on echocardiogram; LVEF had returned to normal in the 25 who returned for follow-up.
- 75 of 97 patients (77.3%) who underwent cMRI at a median of 5 days from symptom onset had abnormal findings; 74 (76.3%) had late gadolinium enhancement, 54 (55.7%) had myocardial edema, and 49 (50.5%) met Lake Louise criteria for myocarditis.
“These data suggest that most cases of suspected COVID-19 vaccine–related myocarditis in people younger than 21 are mild and resolve quickly,” corresponding author Dongngan Truong, MD, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“We were very happy to see that type of recovery. However, we are awaiting further studies to better understand the long-term outcomes of patients who have had COVID-19 vaccination-related myocarditis. We also need to study the risk factors and mechanisms for this rare complication,” Dr. Truong added.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones said these findings support the AHA’s position that COVID-19 vaccines are “safe, highly effective, and fundamental to saving lives, protecting our families and communities against COVID-19, and ending the pandemic.”
The study received no funding. Dr. Truong consults for Pfizer on vaccine-associated myocarditis. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adolescents and adults younger than age 21 who develop myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination frequently have abnormal findings on cardiac MRI (cMRI) but most have a mild clinical course with rapid resolution of symptoms, a new study concludes.
“This study supports what we’ve been seeing. People identified and treated early and appropriately for the rare complication of COVID-19 vaccine-related myocarditis typically experienced only mild cases and short recovery times,” American Heart Association President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a podcast.
“Overwhelmingly, the data continue to indicate [that] the benefits of COVID-19 vaccine far outweigh any very rare risks of adverse events from the vaccine, including myocarditis,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
The study was published online Dec. 6 in Circulation.
Using data from 26 pediatric medical centers across the United States and Canada, the researchers reviewed the medical records of 139 patients younger than 21 with suspected myocarditis within 1 month of receiving a COVID-19 vaccination.
They made the following key observations:
- Most patients were male (90.6%), White (66.2%) and with a median age of 15.8 years.
- Suspected myocarditis occurred in 136 patients (97.8%) following mRNA vaccine, with 131 (94.2%) following the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine; 128 cases (91.4%) occurred after the second dose.
- Symptoms started a median of 2 days (range 0 to 22 days) following vaccination administration.
- Chest pain was the most common symptom (99.3%), with fever present in 30.9% of patients and shortness of breath in 27.3%.
- Patients were treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (81.3%), intravenous immunoglobulin (21.6%), glucocorticoids (21.6%), colchicine (7.9%) or no anti-inflammatory therapies (8.6%).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) were admitted to the intensive care unit; 2 received inotropic/vasoactive support; none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or died.
- Median time spent in the hospital was 2 days.
- A total of 111 patients had elevated troponin I (8.12 ng/mL) and 28 had elevated troponin T (0.61 ng/mL).
- More than two-thirds (69.8%) had abnormal electrocardiograms and/or arrhythmias (7 with nonsustained ventricular tachycardia).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) had left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 55% on echocardiogram; LVEF had returned to normal in the 25 who returned for follow-up.
- 75 of 97 patients (77.3%) who underwent cMRI at a median of 5 days from symptom onset had abnormal findings; 74 (76.3%) had late gadolinium enhancement, 54 (55.7%) had myocardial edema, and 49 (50.5%) met Lake Louise criteria for myocarditis.
“These data suggest that most cases of suspected COVID-19 vaccine–related myocarditis in people younger than 21 are mild and resolve quickly,” corresponding author Dongngan Truong, MD, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“We were very happy to see that type of recovery. However, we are awaiting further studies to better understand the long-term outcomes of patients who have had COVID-19 vaccination-related myocarditis. We also need to study the risk factors and mechanisms for this rare complication,” Dr. Truong added.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones said these findings support the AHA’s position that COVID-19 vaccines are “safe, highly effective, and fundamental to saving lives, protecting our families and communities against COVID-19, and ending the pandemic.”
The study received no funding. Dr. Truong consults for Pfizer on vaccine-associated myocarditis. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adolescents and adults younger than age 21 who develop myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination frequently have abnormal findings on cardiac MRI (cMRI) but most have a mild clinical course with rapid resolution of symptoms, a new study concludes.
“This study supports what we’ve been seeing. People identified and treated early and appropriately for the rare complication of COVID-19 vaccine-related myocarditis typically experienced only mild cases and short recovery times,” American Heart Association President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a podcast.
“Overwhelmingly, the data continue to indicate [that] the benefits of COVID-19 vaccine far outweigh any very rare risks of adverse events from the vaccine, including myocarditis,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
The study was published online Dec. 6 in Circulation.
Using data from 26 pediatric medical centers across the United States and Canada, the researchers reviewed the medical records of 139 patients younger than 21 with suspected myocarditis within 1 month of receiving a COVID-19 vaccination.
They made the following key observations:
- Most patients were male (90.6%), White (66.2%) and with a median age of 15.8 years.
- Suspected myocarditis occurred in 136 patients (97.8%) following mRNA vaccine, with 131 (94.2%) following the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine; 128 cases (91.4%) occurred after the second dose.
- Symptoms started a median of 2 days (range 0 to 22 days) following vaccination administration.
- Chest pain was the most common symptom (99.3%), with fever present in 30.9% of patients and shortness of breath in 27.3%.
- Patients were treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (81.3%), intravenous immunoglobulin (21.6%), glucocorticoids (21.6%), colchicine (7.9%) or no anti-inflammatory therapies (8.6%).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) were admitted to the intensive care unit; 2 received inotropic/vasoactive support; none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or died.
- Median time spent in the hospital was 2 days.
- A total of 111 patients had elevated troponin I (8.12 ng/mL) and 28 had elevated troponin T (0.61 ng/mL).
- More than two-thirds (69.8%) had abnormal electrocardiograms and/or arrhythmias (7 with nonsustained ventricular tachycardia).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) had left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 55% on echocardiogram; LVEF had returned to normal in the 25 who returned for follow-up.
- 75 of 97 patients (77.3%) who underwent cMRI at a median of 5 days from symptom onset had abnormal findings; 74 (76.3%) had late gadolinium enhancement, 54 (55.7%) had myocardial edema, and 49 (50.5%) met Lake Louise criteria for myocarditis.
“These data suggest that most cases of suspected COVID-19 vaccine–related myocarditis in people younger than 21 are mild and resolve quickly,” corresponding author Dongngan Truong, MD, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“We were very happy to see that type of recovery. However, we are awaiting further studies to better understand the long-term outcomes of patients who have had COVID-19 vaccination-related myocarditis. We also need to study the risk factors and mechanisms for this rare complication,” Dr. Truong added.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones said these findings support the AHA’s position that COVID-19 vaccines are “safe, highly effective, and fundamental to saving lives, protecting our families and communities against COVID-19, and ending the pandemic.”
The study received no funding. Dr. Truong consults for Pfizer on vaccine-associated myocarditis. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA challenges diet doctor’s study alleging COVID vax risks
An abstract and poster presentation questioning the safety of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, embraced by some and lambasted by others, has drawn an “expression of concern” from the American Heart Association, along with a bid for correction.
The abstract in question concludes that COVID vaccines “dramatically increase” levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, and therefore, the 5-year risk of acute coronary syndromes (ACS), based on pre- and post-vaccination results of an obscure blood panel called the PULS Cardiac Test (GD Biosciences). The findings were presented at the AHA’s 2021 Scientific Sessionsas, an uncontrolled observational study of 566 patients in a preventive cardiology practice.
Some on social media have seized on the abstract as evidence of serious potential harm from the two available mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and mRNA-1273 (Moderna). But others contend that the study’s described design and findings are specious and its conclusions overstated.
They also point to the notoriety of its one listed author, Steven R. Gundry, MD, who promotes his diet books and supplements as well as fringe, highly criticized theories about diet and disease on several websites, including drgundry.com. Dr. Gundry has not responded to requests for an interview.
Dr. Gundry’s abstract from the AHA Scientific Sessions 2021, available on the meeting’s program planner, was marked with an “expression of concern” by the AHA that is to stand “until a suitable correction is published, to indicate that the abstract in its current version may not be reliable.”
The expression of concern statement, also published online Nov. 24 in Circulation, says “potential errors in the abstract” were brought to the attention of the meeting planners. “Specifically, there are several typographical errors, there is no data in the abstract regarding myocardial T-cell infiltration, there are no statistical analyses for significance provided, and the author is not clear that only anecdotal data was used.”
The biomarker elevations on which the abstract’s conclusions are based included hepatocyte growth factor, “which serves as a marker for chemotaxis of T-cells into epithelium and cardiac tissue,” it states.
“The expression of concern about the abstract will remain in place until a correction is accepted and published” in Circulation, AHA spokesperson Suzanne Grant told this news organization by email.
“The specific data needed will be up to the abstract author to determine and supply,” she said, noting that Dr. Gundry “has been in communication with the journal throughout this process.”
Submitting researchers “must always attest to the validity of the abstract,” Ms. Grant said. “Abstracts are then curated by independent review panels, blinded to the identities of the abstract authors, and are considered based on the potential to add to the diversity of scientific issues and views discussed at the meeting.”
Regarding the AHA’s system for vetting abstracts vying for acceptance to the scientific sessions, she said it is not primarily intended to “evaluate scientific validity” and that the organization is “currently reviewing its existing abstract submission processes.”
A recent Reuters report reviews the controversy and provides links to criticisms of the study on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An abstract and poster presentation questioning the safety of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, embraced by some and lambasted by others, has drawn an “expression of concern” from the American Heart Association, along with a bid for correction.
The abstract in question concludes that COVID vaccines “dramatically increase” levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, and therefore, the 5-year risk of acute coronary syndromes (ACS), based on pre- and post-vaccination results of an obscure blood panel called the PULS Cardiac Test (GD Biosciences). The findings were presented at the AHA’s 2021 Scientific Sessionsas, an uncontrolled observational study of 566 patients in a preventive cardiology practice.
Some on social media have seized on the abstract as evidence of serious potential harm from the two available mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and mRNA-1273 (Moderna). But others contend that the study’s described design and findings are specious and its conclusions overstated.
They also point to the notoriety of its one listed author, Steven R. Gundry, MD, who promotes his diet books and supplements as well as fringe, highly criticized theories about diet and disease on several websites, including drgundry.com. Dr. Gundry has not responded to requests for an interview.
Dr. Gundry’s abstract from the AHA Scientific Sessions 2021, available on the meeting’s program planner, was marked with an “expression of concern” by the AHA that is to stand “until a suitable correction is published, to indicate that the abstract in its current version may not be reliable.”
The expression of concern statement, also published online Nov. 24 in Circulation, says “potential errors in the abstract” were brought to the attention of the meeting planners. “Specifically, there are several typographical errors, there is no data in the abstract regarding myocardial T-cell infiltration, there are no statistical analyses for significance provided, and the author is not clear that only anecdotal data was used.”
The biomarker elevations on which the abstract’s conclusions are based included hepatocyte growth factor, “which serves as a marker for chemotaxis of T-cells into epithelium and cardiac tissue,” it states.
“The expression of concern about the abstract will remain in place until a correction is accepted and published” in Circulation, AHA spokesperson Suzanne Grant told this news organization by email.
“The specific data needed will be up to the abstract author to determine and supply,” she said, noting that Dr. Gundry “has been in communication with the journal throughout this process.”
Submitting researchers “must always attest to the validity of the abstract,” Ms. Grant said. “Abstracts are then curated by independent review panels, blinded to the identities of the abstract authors, and are considered based on the potential to add to the diversity of scientific issues and views discussed at the meeting.”
Regarding the AHA’s system for vetting abstracts vying for acceptance to the scientific sessions, she said it is not primarily intended to “evaluate scientific validity” and that the organization is “currently reviewing its existing abstract submission processes.”
A recent Reuters report reviews the controversy and provides links to criticisms of the study on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An abstract and poster presentation questioning the safety of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, embraced by some and lambasted by others, has drawn an “expression of concern” from the American Heart Association, along with a bid for correction.
The abstract in question concludes that COVID vaccines “dramatically increase” levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, and therefore, the 5-year risk of acute coronary syndromes (ACS), based on pre- and post-vaccination results of an obscure blood panel called the PULS Cardiac Test (GD Biosciences). The findings were presented at the AHA’s 2021 Scientific Sessionsas, an uncontrolled observational study of 566 patients in a preventive cardiology practice.
Some on social media have seized on the abstract as evidence of serious potential harm from the two available mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and mRNA-1273 (Moderna). But others contend that the study’s described design and findings are specious and its conclusions overstated.
They also point to the notoriety of its one listed author, Steven R. Gundry, MD, who promotes his diet books and supplements as well as fringe, highly criticized theories about diet and disease on several websites, including drgundry.com. Dr. Gundry has not responded to requests for an interview.
Dr. Gundry’s abstract from the AHA Scientific Sessions 2021, available on the meeting’s program planner, was marked with an “expression of concern” by the AHA that is to stand “until a suitable correction is published, to indicate that the abstract in its current version may not be reliable.”
The expression of concern statement, also published online Nov. 24 in Circulation, says “potential errors in the abstract” were brought to the attention of the meeting planners. “Specifically, there are several typographical errors, there is no data in the abstract regarding myocardial T-cell infiltration, there are no statistical analyses for significance provided, and the author is not clear that only anecdotal data was used.”
The biomarker elevations on which the abstract’s conclusions are based included hepatocyte growth factor, “which serves as a marker for chemotaxis of T-cells into epithelium and cardiac tissue,” it states.
“The expression of concern about the abstract will remain in place until a correction is accepted and published” in Circulation, AHA spokesperson Suzanne Grant told this news organization by email.
“The specific data needed will be up to the abstract author to determine and supply,” she said, noting that Dr. Gundry “has been in communication with the journal throughout this process.”
Submitting researchers “must always attest to the validity of the abstract,” Ms. Grant said. “Abstracts are then curated by independent review panels, blinded to the identities of the abstract authors, and are considered based on the potential to add to the diversity of scientific issues and views discussed at the meeting.”
Regarding the AHA’s system for vetting abstracts vying for acceptance to the scientific sessions, she said it is not primarily intended to “evaluate scientific validity” and that the organization is “currently reviewing its existing abstract submission processes.”
A recent Reuters report reviews the controversy and provides links to criticisms of the study on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.