User login
News and Views that Matter to Pediatricians
The leading independent newspaper covering news and commentary in pediatrics.
Probiotic LGG doesn’t lessen eczema, asthma, or rhinitis risk by age 7
Giving the probiotic supplement Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) to high-risk infants in the first 6 months of life is not effective in lessening incidence of eczema, asthma, or rhinitis in later childhood, researchers have found.
The researchers, led by Michael D. Cabana, MD, MPH, with the Children’s Hospital of Montefiore, New York, said they cannot support its use in this population of children at high risk for allergic disease. Findings were published in Pediatrics.
Jonathan Spergel, MD, PhD, chief of the allergy program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, who was not part of the study, said the “small, but very interesting study adds to the literature indicating that allergy prevention needs to be a multifactorial approach and simply adding LGG in a select population makes no difference.”
He noted that the study of probiotics for allergic conditions is complex as it depends on many factors, such as the child’s environment, including exposure to pets and pollution, and whether the child was delivered vaginally or by cesarean section.
Study builds on previous work
The new study builds on the same researchers’ randomized, double-masked, parallel-arm, controlled Trial of Infant Probiotic Supplementation (TIPS). That study investigated whether daily administration of LGG in the first 6 months to children at high risk for allergic disease because of asthma in a parent, could decrease their cumulative incidence of eczema. Investigators found LGG had no effect.
These additional results included participants at least 7 years old and also included physician-diagnosed asthma and physician-diagnosed rhinitis as secondary outcomes.
Retention rate over the 7-year follow-up was 56%; 49 (53%) of 92 in the intervention group and 54 (59%) of 92 in the control group.
The researchers performed modified intention-to-treat analyses with all children who received treatment in the study arm to which they had been randomized.
Eczema was diagnosed in 78 participants, asthma in 32, and rhinitis in 15. Incidence of eczema was high in infancy, but low thereafter. Incidence rates for asthma and rhinitis were constant throughout childhood.
The researchers used modeling to compare the incidence of each outcome between the intervention and control groups, adjusting for mode of delivery and how long a child was breastfed.
Cesarean delivery was linked to a greater incidence of rhinitis, with a hazard ratio of 3.33 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-9.21).
Finding the right strain
Heather Cassell, MD, a pediatric allergist and immunologist at University of Arizona, Tucson, who was not part of the study, said in an interview that many researchers, including those at her institution, are trying to find which strain of probiotic might be beneficial in lowering risk for allergic disease.
Though it appears LGG doesn’t have an effect, she said, another strain might be successful and this helps zero in on the right one.
The TIPS trial showed that there were no significant side effects from giving LGG early, which is good information to have as the search resumes for the right strain, she said.
“We know that there’s probably some immune dysregulation in kids with asthma, eczema, other allergies, but we don’t fully know the extent of it,” she said, adding that it may be that skin flora or respiratory flora and microbiomes in other parts of the body play a role.
“We don’t have bacteria just in our guts,” she noted. “It may be a combination of strains or a combination of bacteria.”
The authors, Dr. Spergel, and Dr. Cassell reported no relevant financial relationships.
Giving the probiotic supplement Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) to high-risk infants in the first 6 months of life is not effective in lessening incidence of eczema, asthma, or rhinitis in later childhood, researchers have found.
The researchers, led by Michael D. Cabana, MD, MPH, with the Children’s Hospital of Montefiore, New York, said they cannot support its use in this population of children at high risk for allergic disease. Findings were published in Pediatrics.
Jonathan Spergel, MD, PhD, chief of the allergy program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, who was not part of the study, said the “small, but very interesting study adds to the literature indicating that allergy prevention needs to be a multifactorial approach and simply adding LGG in a select population makes no difference.”
He noted that the study of probiotics for allergic conditions is complex as it depends on many factors, such as the child’s environment, including exposure to pets and pollution, and whether the child was delivered vaginally or by cesarean section.
Study builds on previous work
The new study builds on the same researchers’ randomized, double-masked, parallel-arm, controlled Trial of Infant Probiotic Supplementation (TIPS). That study investigated whether daily administration of LGG in the first 6 months to children at high risk for allergic disease because of asthma in a parent, could decrease their cumulative incidence of eczema. Investigators found LGG had no effect.
These additional results included participants at least 7 years old and also included physician-diagnosed asthma and physician-diagnosed rhinitis as secondary outcomes.
Retention rate over the 7-year follow-up was 56%; 49 (53%) of 92 in the intervention group and 54 (59%) of 92 in the control group.
The researchers performed modified intention-to-treat analyses with all children who received treatment in the study arm to which they had been randomized.
Eczema was diagnosed in 78 participants, asthma in 32, and rhinitis in 15. Incidence of eczema was high in infancy, but low thereafter. Incidence rates for asthma and rhinitis were constant throughout childhood.
The researchers used modeling to compare the incidence of each outcome between the intervention and control groups, adjusting for mode of delivery and how long a child was breastfed.
Cesarean delivery was linked to a greater incidence of rhinitis, with a hazard ratio of 3.33 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-9.21).
Finding the right strain
Heather Cassell, MD, a pediatric allergist and immunologist at University of Arizona, Tucson, who was not part of the study, said in an interview that many researchers, including those at her institution, are trying to find which strain of probiotic might be beneficial in lowering risk for allergic disease.
Though it appears LGG doesn’t have an effect, she said, another strain might be successful and this helps zero in on the right one.
The TIPS trial showed that there were no significant side effects from giving LGG early, which is good information to have as the search resumes for the right strain, she said.
“We know that there’s probably some immune dysregulation in kids with asthma, eczema, other allergies, but we don’t fully know the extent of it,” she said, adding that it may be that skin flora or respiratory flora and microbiomes in other parts of the body play a role.
“We don’t have bacteria just in our guts,” she noted. “It may be a combination of strains or a combination of bacteria.”
The authors, Dr. Spergel, and Dr. Cassell reported no relevant financial relationships.
Giving the probiotic supplement Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) to high-risk infants in the first 6 months of life is not effective in lessening incidence of eczema, asthma, or rhinitis in later childhood, researchers have found.
The researchers, led by Michael D. Cabana, MD, MPH, with the Children’s Hospital of Montefiore, New York, said they cannot support its use in this population of children at high risk for allergic disease. Findings were published in Pediatrics.
Jonathan Spergel, MD, PhD, chief of the allergy program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, who was not part of the study, said the “small, but very interesting study adds to the literature indicating that allergy prevention needs to be a multifactorial approach and simply adding LGG in a select population makes no difference.”
He noted that the study of probiotics for allergic conditions is complex as it depends on many factors, such as the child’s environment, including exposure to pets and pollution, and whether the child was delivered vaginally or by cesarean section.
Study builds on previous work
The new study builds on the same researchers’ randomized, double-masked, parallel-arm, controlled Trial of Infant Probiotic Supplementation (TIPS). That study investigated whether daily administration of LGG in the first 6 months to children at high risk for allergic disease because of asthma in a parent, could decrease their cumulative incidence of eczema. Investigators found LGG had no effect.
These additional results included participants at least 7 years old and also included physician-diagnosed asthma and physician-diagnosed rhinitis as secondary outcomes.
Retention rate over the 7-year follow-up was 56%; 49 (53%) of 92 in the intervention group and 54 (59%) of 92 in the control group.
The researchers performed modified intention-to-treat analyses with all children who received treatment in the study arm to which they had been randomized.
Eczema was diagnosed in 78 participants, asthma in 32, and rhinitis in 15. Incidence of eczema was high in infancy, but low thereafter. Incidence rates for asthma and rhinitis were constant throughout childhood.
The researchers used modeling to compare the incidence of each outcome between the intervention and control groups, adjusting for mode of delivery and how long a child was breastfed.
Cesarean delivery was linked to a greater incidence of rhinitis, with a hazard ratio of 3.33 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-9.21).
Finding the right strain
Heather Cassell, MD, a pediatric allergist and immunologist at University of Arizona, Tucson, who was not part of the study, said in an interview that many researchers, including those at her institution, are trying to find which strain of probiotic might be beneficial in lowering risk for allergic disease.
Though it appears LGG doesn’t have an effect, she said, another strain might be successful and this helps zero in on the right one.
The TIPS trial showed that there were no significant side effects from giving LGG early, which is good information to have as the search resumes for the right strain, she said.
“We know that there’s probably some immune dysregulation in kids with asthma, eczema, other allergies, but we don’t fully know the extent of it,” she said, adding that it may be that skin flora or respiratory flora and microbiomes in other parts of the body play a role.
“We don’t have bacteria just in our guts,” she noted. “It may be a combination of strains or a combination of bacteria.”
The authors, Dr. Spergel, and Dr. Cassell reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM PEDIATRICS
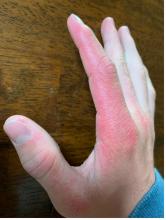
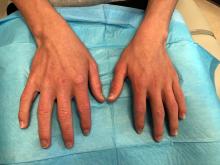
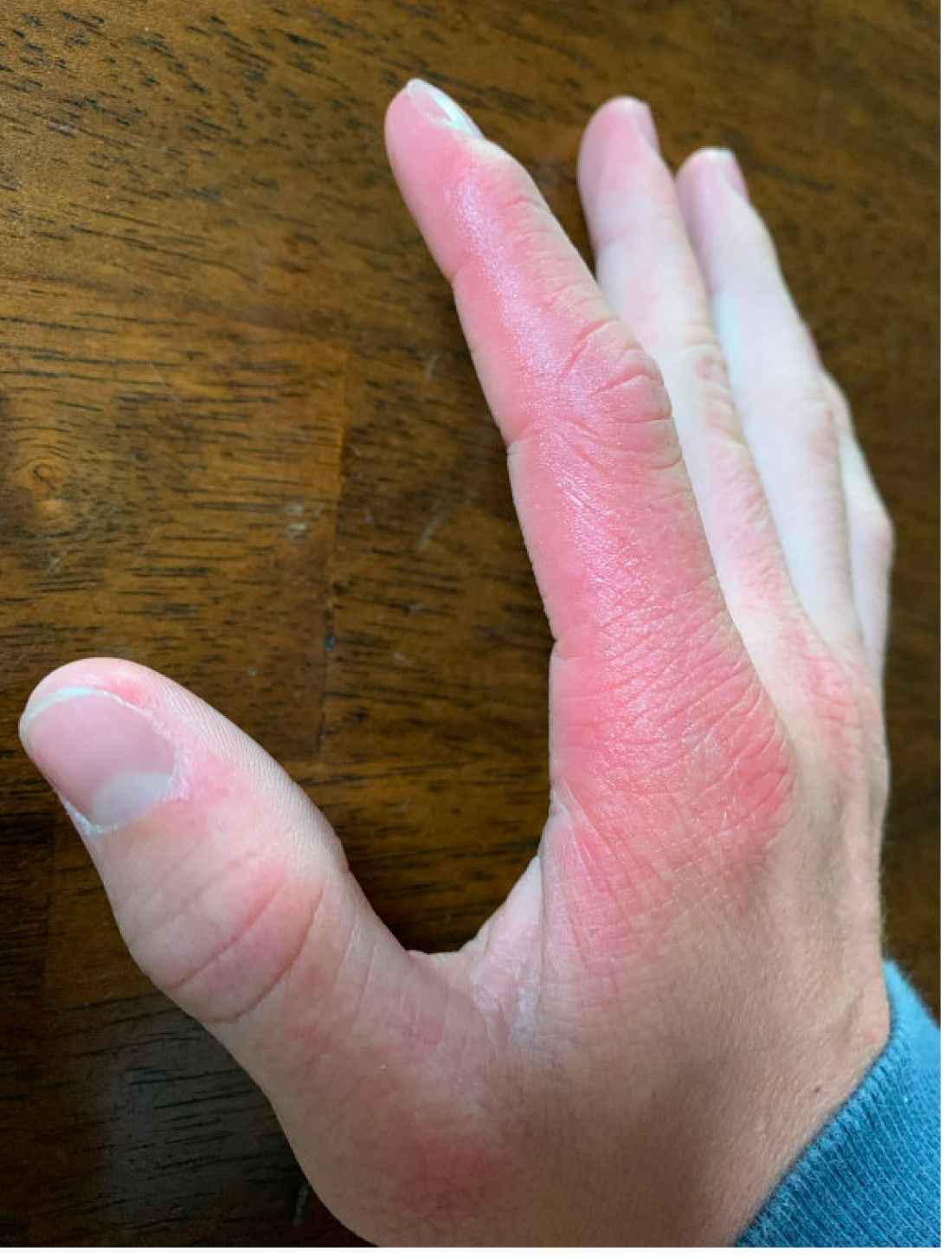
A 14-year-old male presents to clinic with a new-onset rash of the hands
Photosensitivity due to doxycycline
As the patient’s rash presented in sun-exposed areas with both skin and nail changes, our patient was diagnosed with a phototoxic reaction to doxycycline, the oral antibiotic used to treat his acne.
Photosensitive cutaneous drug eruptions are reactions that occur after exposure to a medication and subsequent exposure to UV radiation or visible light. Reactions can be classified into two ways based on their mechanism of action: phototoxic or photoallergic.1 Phototoxic reactions are more common and are a result of direct keratinocyte damage and cellular necrosis. Many classes of medications may cause this adverse effect, but the tetracycline class of antibiotics is a common culprit.2 Photoallergic reactions are less common and are a result of a type IV immune reaction to the offending agent.1
Phototoxic reactions generally present shortly after sun or UV exposure with a photo-distributed eruption pattern.3 Commonly involved areas include the face, the neck, and the extensor surfaces of extremities, with sparing of relatively protected skin such as the upper eyelids and the skin folds.2 Erythema may initially develop in the exposed skin areas, followed by appearance of edema, vesicles, or bullae.1-3 The eruption may be painful and itchy, with some patients reporting severe pain.3
Doxycycline phototoxicity may also cause onycholysis of the nails.2 The reaction is dose dependent, with higher doses of medication leading to a higher likelihood of symptoms.1,2 It is also more prevalent in patients with Fitzpatrick skin type I and II. The usual UVA wavelength required to induce this reaction appears to be in the 320-400 nm range of the UV spectrum.4 By contrast, photoallergic reactions are dose independent, and require a sensitization period prior to the eruption.1 An eczematous eruption is most commonly seen with photoallergic reactions.3
Treatment of drug-induced photosensitivity reactions requires proper identification of the diagnosis and the offending agent, followed by cessation of the medication. If cessation is not possible, then lowering the dose can help to minimize worsening of the condition. However, for photoallergic reactions, the reaction is dose independent so switching to another tolerated agent is likely required. For persistent symptoms following medication withdrawal, topical or systemic steroids and oral antihistamine can help with symptom management.1 For patients with photo-onycholysis, treatment involves stopping the medication and waiting for the intact nail plate to grow.
Prevention is key in the management of photosensitivity reactions. Patients should be counseled about the increased risk of photosensitivity while on tetracycline medications and encouraged to engage in enhanced sun protection measures such as wearing sun protective hats and clothing, increasing use of sunscreen that provides mainly UVA but also UVB protection, and avoiding the sun during the midday when the UV index is highest.1-3
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune condition that presents with skin lesions as well as systemic findings such as myositis. The cutaneous findings are variable, but pathognomonic findings include Gottron papules of the hands, Gottron’s sign on the elbows, knees, and ankles, and the heliotrope rash of the face. Eighty percent of patients have myopathy presenting as muscle weakness, and commonly have elevated creatine kinase, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase values.5 Diagnosis may be confirmed through skin or muscle biopsy, though antibody studies can also play a helpful role in diagnosis. Treatment is generally with oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants as well as sun protection.6 The rash seen in our patient could have been seen in patients with dermatomyositis, though it was not in the typical location on the knuckles (Gottron papules) as it also affected the lateral sides of the fingers.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune condition characterized by systemic and cutaneous manifestations. Systemic symptoms may include weight loss, fever, fatigue, arthralgia, or arthritis; patients are at risk of renal, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and neurologic complications of SLE.7 The most common cutaneous finding is malar rash, though there are myriad dermatologic manifestations that can occur associated with photosensitivity. Diagnosis is made based on history, physical, and laboratory testing. Treatment options include NSAIDs, oral glucocorticoids, antimalarial drugs, and immunosuppressants.7 Though our patient exhibited photosensitivity, he had none of the systemic findings associated with SLE, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, and may present as acute, subacute, or chronic dermatitis. The clinical findings vary based on chronicity. Acute ACD presents as pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles or bullae, similar to how it occurred in our patient, though our patient’s lesions were more tender than pruritic. Chronic ACD presents with erythematous lesions with pruritis, lichenification, scaling, and/or fissuring. Observing shapes or sharp demarcation of lesions may help with diagnosis. Patch testing is also useful in the diagnosis of ACD.
Treatment generally involves avoiding the offending agent with topical corticosteroids for symptom management.8
Polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) is a delayed, type IV hypersensitivity reaction to UV-induced antigens, though these antigens are unknown. PLE presents hours to days following solar or UV exposure and presents only in sun-exposed areas. Itching and burning are always present, but lesion morphology varies from erythema and papules to vesico-papules and blisters. Notably, PLE must be distinguished from drug photosensitivity through history. Treatment generally involves symptom management with topical steroids and sun protective measures for prevention.9 While PLE may present similarly to drug photosensitivity reactions, our patient’s use of a known phototoxic agent makes PLE a less likely diagnosis.
Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate and medical student at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Appiah has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Montgomery S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40(1):57-63.
2. Blakely KM et al. Drug Saf. 2019;42(7):827-47.
3. Goetze S et al. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;30(2):76-80.
4. Odorici G et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34(4):e14978.
5. DeWane ME et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):267-81.
6. Waldman R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):283-96.
7. Kiriakidou M et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81-ITC96.
8. Nassau S et al. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(1):61-76.
9. Guarrera M. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:61-70.
Photosensitivity due to doxycycline
As the patient’s rash presented in sun-exposed areas with both skin and nail changes, our patient was diagnosed with a phototoxic reaction to doxycycline, the oral antibiotic used to treat his acne.
Photosensitive cutaneous drug eruptions are reactions that occur after exposure to a medication and subsequent exposure to UV radiation or visible light. Reactions can be classified into two ways based on their mechanism of action: phototoxic or photoallergic.1 Phototoxic reactions are more common and are a result of direct keratinocyte damage and cellular necrosis. Many classes of medications may cause this adverse effect, but the tetracycline class of antibiotics is a common culprit.2 Photoallergic reactions are less common and are a result of a type IV immune reaction to the offending agent.1
Phototoxic reactions generally present shortly after sun or UV exposure with a photo-distributed eruption pattern.3 Commonly involved areas include the face, the neck, and the extensor surfaces of extremities, with sparing of relatively protected skin such as the upper eyelids and the skin folds.2 Erythema may initially develop in the exposed skin areas, followed by appearance of edema, vesicles, or bullae.1-3 The eruption may be painful and itchy, with some patients reporting severe pain.3
Doxycycline phototoxicity may also cause onycholysis of the nails.2 The reaction is dose dependent, with higher doses of medication leading to a higher likelihood of symptoms.1,2 It is also more prevalent in patients with Fitzpatrick skin type I and II. The usual UVA wavelength required to induce this reaction appears to be in the 320-400 nm range of the UV spectrum.4 By contrast, photoallergic reactions are dose independent, and require a sensitization period prior to the eruption.1 An eczematous eruption is most commonly seen with photoallergic reactions.3
Treatment of drug-induced photosensitivity reactions requires proper identification of the diagnosis and the offending agent, followed by cessation of the medication. If cessation is not possible, then lowering the dose can help to minimize worsening of the condition. However, for photoallergic reactions, the reaction is dose independent so switching to another tolerated agent is likely required. For persistent symptoms following medication withdrawal, topical or systemic steroids and oral antihistamine can help with symptom management.1 For patients with photo-onycholysis, treatment involves stopping the medication and waiting for the intact nail plate to grow.
Prevention is key in the management of photosensitivity reactions. Patients should be counseled about the increased risk of photosensitivity while on tetracycline medications and encouraged to engage in enhanced sun protection measures such as wearing sun protective hats and clothing, increasing use of sunscreen that provides mainly UVA but also UVB protection, and avoiding the sun during the midday when the UV index is highest.1-3
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune condition that presents with skin lesions as well as systemic findings such as myositis. The cutaneous findings are variable, but pathognomonic findings include Gottron papules of the hands, Gottron’s sign on the elbows, knees, and ankles, and the heliotrope rash of the face. Eighty percent of patients have myopathy presenting as muscle weakness, and commonly have elevated creatine kinase, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase values.5 Diagnosis may be confirmed through skin or muscle biopsy, though antibody studies can also play a helpful role in diagnosis. Treatment is generally with oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants as well as sun protection.6 The rash seen in our patient could have been seen in patients with dermatomyositis, though it was not in the typical location on the knuckles (Gottron papules) as it also affected the lateral sides of the fingers.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune condition characterized by systemic and cutaneous manifestations. Systemic symptoms may include weight loss, fever, fatigue, arthralgia, or arthritis; patients are at risk of renal, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and neurologic complications of SLE.7 The most common cutaneous finding is malar rash, though there are myriad dermatologic manifestations that can occur associated with photosensitivity. Diagnosis is made based on history, physical, and laboratory testing. Treatment options include NSAIDs, oral glucocorticoids, antimalarial drugs, and immunosuppressants.7 Though our patient exhibited photosensitivity, he had none of the systemic findings associated with SLE, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, and may present as acute, subacute, or chronic dermatitis. The clinical findings vary based on chronicity. Acute ACD presents as pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles or bullae, similar to how it occurred in our patient, though our patient’s lesions were more tender than pruritic. Chronic ACD presents with erythematous lesions with pruritis, lichenification, scaling, and/or fissuring. Observing shapes or sharp demarcation of lesions may help with diagnosis. Patch testing is also useful in the diagnosis of ACD.
Treatment generally involves avoiding the offending agent with topical corticosteroids for symptom management.8
Polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) is a delayed, type IV hypersensitivity reaction to UV-induced antigens, though these antigens are unknown. PLE presents hours to days following solar or UV exposure and presents only in sun-exposed areas. Itching and burning are always present, but lesion morphology varies from erythema and papules to vesico-papules and blisters. Notably, PLE must be distinguished from drug photosensitivity through history. Treatment generally involves symptom management with topical steroids and sun protective measures for prevention.9 While PLE may present similarly to drug photosensitivity reactions, our patient’s use of a known phototoxic agent makes PLE a less likely diagnosis.
Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate and medical student at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Appiah has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Montgomery S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40(1):57-63.
2. Blakely KM et al. Drug Saf. 2019;42(7):827-47.
3. Goetze S et al. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;30(2):76-80.
4. Odorici G et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34(4):e14978.
5. DeWane ME et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):267-81.
6. Waldman R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):283-96.
7. Kiriakidou M et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81-ITC96.
8. Nassau S et al. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(1):61-76.
9. Guarrera M. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:61-70.
Photosensitivity due to doxycycline
As the patient’s rash presented in sun-exposed areas with both skin and nail changes, our patient was diagnosed with a phototoxic reaction to doxycycline, the oral antibiotic used to treat his acne.
Photosensitive cutaneous drug eruptions are reactions that occur after exposure to a medication and subsequent exposure to UV radiation or visible light. Reactions can be classified into two ways based on their mechanism of action: phototoxic or photoallergic.1 Phototoxic reactions are more common and are a result of direct keratinocyte damage and cellular necrosis. Many classes of medications may cause this adverse effect, but the tetracycline class of antibiotics is a common culprit.2 Photoallergic reactions are less common and are a result of a type IV immune reaction to the offending agent.1
Phototoxic reactions generally present shortly after sun or UV exposure with a photo-distributed eruption pattern.3 Commonly involved areas include the face, the neck, and the extensor surfaces of extremities, with sparing of relatively protected skin such as the upper eyelids and the skin folds.2 Erythema may initially develop in the exposed skin areas, followed by appearance of edema, vesicles, or bullae.1-3 The eruption may be painful and itchy, with some patients reporting severe pain.3
Doxycycline phototoxicity may also cause onycholysis of the nails.2 The reaction is dose dependent, with higher doses of medication leading to a higher likelihood of symptoms.1,2 It is also more prevalent in patients with Fitzpatrick skin type I and II. The usual UVA wavelength required to induce this reaction appears to be in the 320-400 nm range of the UV spectrum.4 By contrast, photoallergic reactions are dose independent, and require a sensitization period prior to the eruption.1 An eczematous eruption is most commonly seen with photoallergic reactions.3
Treatment of drug-induced photosensitivity reactions requires proper identification of the diagnosis and the offending agent, followed by cessation of the medication. If cessation is not possible, then lowering the dose can help to minimize worsening of the condition. However, for photoallergic reactions, the reaction is dose independent so switching to another tolerated agent is likely required. For persistent symptoms following medication withdrawal, topical or systemic steroids and oral antihistamine can help with symptom management.1 For patients with photo-onycholysis, treatment involves stopping the medication and waiting for the intact nail plate to grow.
Prevention is key in the management of photosensitivity reactions. Patients should be counseled about the increased risk of photosensitivity while on tetracycline medications and encouraged to engage in enhanced sun protection measures such as wearing sun protective hats and clothing, increasing use of sunscreen that provides mainly UVA but also UVB protection, and avoiding the sun during the midday when the UV index is highest.1-3
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune condition that presents with skin lesions as well as systemic findings such as myositis. The cutaneous findings are variable, but pathognomonic findings include Gottron papules of the hands, Gottron’s sign on the elbows, knees, and ankles, and the heliotrope rash of the face. Eighty percent of patients have myopathy presenting as muscle weakness, and commonly have elevated creatine kinase, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase values.5 Diagnosis may be confirmed through skin or muscle biopsy, though antibody studies can also play a helpful role in diagnosis. Treatment is generally with oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants as well as sun protection.6 The rash seen in our patient could have been seen in patients with dermatomyositis, though it was not in the typical location on the knuckles (Gottron papules) as it also affected the lateral sides of the fingers.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune condition characterized by systemic and cutaneous manifestations. Systemic symptoms may include weight loss, fever, fatigue, arthralgia, or arthritis; patients are at risk of renal, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and neurologic complications of SLE.7 The most common cutaneous finding is malar rash, though there are myriad dermatologic manifestations that can occur associated with photosensitivity. Diagnosis is made based on history, physical, and laboratory testing. Treatment options include NSAIDs, oral glucocorticoids, antimalarial drugs, and immunosuppressants.7 Though our patient exhibited photosensitivity, he had none of the systemic findings associated with SLE, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, and may present as acute, subacute, or chronic dermatitis. The clinical findings vary based on chronicity. Acute ACD presents as pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles or bullae, similar to how it occurred in our patient, though our patient’s lesions were more tender than pruritic. Chronic ACD presents with erythematous lesions with pruritis, lichenification, scaling, and/or fissuring. Observing shapes or sharp demarcation of lesions may help with diagnosis. Patch testing is also useful in the diagnosis of ACD.
Treatment generally involves avoiding the offending agent with topical corticosteroids for symptom management.8
Polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) is a delayed, type IV hypersensitivity reaction to UV-induced antigens, though these antigens are unknown. PLE presents hours to days following solar or UV exposure and presents only in sun-exposed areas. Itching and burning are always present, but lesion morphology varies from erythema and papules to vesico-papules and blisters. Notably, PLE must be distinguished from drug photosensitivity through history. Treatment generally involves symptom management with topical steroids and sun protective measures for prevention.9 While PLE may present similarly to drug photosensitivity reactions, our patient’s use of a known phototoxic agent makes PLE a less likely diagnosis.
Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate and medical student at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Appiah has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Montgomery S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40(1):57-63.
2. Blakely KM et al. Drug Saf. 2019;42(7):827-47.
3. Goetze S et al. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;30(2):76-80.
4. Odorici G et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34(4):e14978.
5. DeWane ME et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):267-81.
6. Waldman R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):283-96.
7. Kiriakidou M et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81-ITC96.
8. Nassau S et al. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(1):61-76.
9. Guarrera M. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:61-70.
He reported no hiking or gardening, no new topical products such as new sunscreens or lotions, and no new medications. The patient had a history of acne, for which he used over-the-counter benzoyl peroxide wash, adapalene gel, and an oral antibiotic for 3 months. His review of systems was negative for fevers, chills, muscle weakness, mouth sores, or joint pain and no prior rashes following sun exposure.
On physical exam he presented with pink plaques with thin vesicles on the dorsum of the hands that were more noticeable on the lateral aspect of both the first and second fingers (Figures 1 and 2). His nails also had a yellow discoloration.
University of Washington, Harvard ranked top medical schools for second year
It may seem like déjà vu, as not much has changed regarding the rankings of top U.S. medical schools over the past 2 years.
The University of Washington, Seattle retained its ranking from the U.S. News & World Report as the top medical school for primary care for 2023. Also repeating its 2022 standing as the top medical school for research is Harvard University.
In the primary care ranking, the top 10 schools after the University of Washington were the University of California, San Francisco; the University of Minnesota; Oregon Health and Science University; the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; the University of Colorado; the University of Nebraska Medical Center; the University of California, Davis; and Harvard. Three schools tied for the no. 10 slot: the University of Kansas Medical Center, the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical Center, and the University of Pittsburgh.
The top five schools with the most graduates practicing in primary care specialties are Des Moines University, Iowa (50.6%); the University of Pikeville (Ky.) (46.8%); Western University of Health Sciences, Pomona, California (46%); William Carey University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Hattiesburg, Mississippi (44.7%); and A.T. Still University of Health Sciences, Kirksville, Missouri (44.3%).
Best for research
When it comes to schools ranking the highest for research, the Grossman School of Medicine at New York University takes the no. 2 spot after Harvard. Three schools were tied for the no. 3 spot: Columbia University, Johns Hopkins University, and the University of California, San Francisco; and two schools for no. 6: Duke University and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. No. 8 goes to Stanford University, followed by the University of Washington. Rounding out the top 10 is Yale University.
Specialty ranks
The top-ranked schools in eight specialties are as follows:
- Anesthesiology: Harvard
- Family medicine: the University of Washington
- Internal medicine: Johns Hopkins
- Obstetrics/gynecology: Harvard
- Pediatrics: the University of Pennsylvania (Perelman)
- Psychiatry: Harvard
- Radiology: Johns Hopkins
- Surgery: Harvard
Most diverse student body
If you’re looking for a school with significant minority representation, Howard University, Washington, D.C., ranked highest (76.8%), followed by the Wertheim College of Medicine at Florida International University, Miami (43.2%). The University of California, Davis (40%), Sacramento, California, and the University of Vermont (Larner), Burlington (14.1%), tied for third.
Three southern schools take top honors for the most graduates practicing in underserved areas, starting with the University of South Carolina (70.9%), followed by the University of Mississippi (66.2%), and East Tennessee State University (Quillen), Johnson City, Tennessee (65.8%).
The colleges with the most graduates practicing in rural areas are William Carey University College of Osteopathic Medicine (28%), the University of Pikesville (25.6%), and the University of Mississippi (22.1%).
College debt
The medical school where graduates have the most debt is Nova Southeastern University Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida. Graduates incurred an average debt of $309,206. Western University of Health Sciences graduates racked up $276,840 in debt, followed by graduates of West Virginia School of Osteopathic Medicine, owing $268,416.
Ranking criteria
Each year, U.S. News ranks hundreds of U.S. colleges and universities. Medical schools fall under the rankings for best graduate schools.
U.S. News surveyed 192 medical and osteopathic schools accredited in 2021 by the Liaison Committee on Medical Education or the American Osteopathic Association. Among the schools surveyed in fall 2021 and early 2022, 130 schools responded. Of those, 124 were included in both the research and primary care rankings.
The criteria for ranking include faculty resources, academic achievements of entering students, and qualitative assessments by schools and residency directors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It may seem like déjà vu, as not much has changed regarding the rankings of top U.S. medical schools over the past 2 years.
The University of Washington, Seattle retained its ranking from the U.S. News & World Report as the top medical school for primary care for 2023. Also repeating its 2022 standing as the top medical school for research is Harvard University.
In the primary care ranking, the top 10 schools after the University of Washington were the University of California, San Francisco; the University of Minnesota; Oregon Health and Science University; the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; the University of Colorado; the University of Nebraska Medical Center; the University of California, Davis; and Harvard. Three schools tied for the no. 10 slot: the University of Kansas Medical Center, the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical Center, and the University of Pittsburgh.
The top five schools with the most graduates practicing in primary care specialties are Des Moines University, Iowa (50.6%); the University of Pikeville (Ky.) (46.8%); Western University of Health Sciences, Pomona, California (46%); William Carey University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Hattiesburg, Mississippi (44.7%); and A.T. Still University of Health Sciences, Kirksville, Missouri (44.3%).
Best for research
When it comes to schools ranking the highest for research, the Grossman School of Medicine at New York University takes the no. 2 spot after Harvard. Three schools were tied for the no. 3 spot: Columbia University, Johns Hopkins University, and the University of California, San Francisco; and two schools for no. 6: Duke University and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. No. 8 goes to Stanford University, followed by the University of Washington. Rounding out the top 10 is Yale University.
Specialty ranks
The top-ranked schools in eight specialties are as follows:
- Anesthesiology: Harvard
- Family medicine: the University of Washington
- Internal medicine: Johns Hopkins
- Obstetrics/gynecology: Harvard
- Pediatrics: the University of Pennsylvania (Perelman)
- Psychiatry: Harvard
- Radiology: Johns Hopkins
- Surgery: Harvard
Most diverse student body
If you’re looking for a school with significant minority representation, Howard University, Washington, D.C., ranked highest (76.8%), followed by the Wertheim College of Medicine at Florida International University, Miami (43.2%). The University of California, Davis (40%), Sacramento, California, and the University of Vermont (Larner), Burlington (14.1%), tied for third.
Three southern schools take top honors for the most graduates practicing in underserved areas, starting with the University of South Carolina (70.9%), followed by the University of Mississippi (66.2%), and East Tennessee State University (Quillen), Johnson City, Tennessee (65.8%).
The colleges with the most graduates practicing in rural areas are William Carey University College of Osteopathic Medicine (28%), the University of Pikesville (25.6%), and the University of Mississippi (22.1%).
College debt
The medical school where graduates have the most debt is Nova Southeastern University Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida. Graduates incurred an average debt of $309,206. Western University of Health Sciences graduates racked up $276,840 in debt, followed by graduates of West Virginia School of Osteopathic Medicine, owing $268,416.
Ranking criteria
Each year, U.S. News ranks hundreds of U.S. colleges and universities. Medical schools fall under the rankings for best graduate schools.
U.S. News surveyed 192 medical and osteopathic schools accredited in 2021 by the Liaison Committee on Medical Education or the American Osteopathic Association. Among the schools surveyed in fall 2021 and early 2022, 130 schools responded. Of those, 124 were included in both the research and primary care rankings.
The criteria for ranking include faculty resources, academic achievements of entering students, and qualitative assessments by schools and residency directors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It may seem like déjà vu, as not much has changed regarding the rankings of top U.S. medical schools over the past 2 years.
The University of Washington, Seattle retained its ranking from the U.S. News & World Report as the top medical school for primary care for 2023. Also repeating its 2022 standing as the top medical school for research is Harvard University.
In the primary care ranking, the top 10 schools after the University of Washington were the University of California, San Francisco; the University of Minnesota; Oregon Health and Science University; the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; the University of Colorado; the University of Nebraska Medical Center; the University of California, Davis; and Harvard. Three schools tied for the no. 10 slot: the University of Kansas Medical Center, the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical Center, and the University of Pittsburgh.
The top five schools with the most graduates practicing in primary care specialties are Des Moines University, Iowa (50.6%); the University of Pikeville (Ky.) (46.8%); Western University of Health Sciences, Pomona, California (46%); William Carey University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Hattiesburg, Mississippi (44.7%); and A.T. Still University of Health Sciences, Kirksville, Missouri (44.3%).
Best for research
When it comes to schools ranking the highest for research, the Grossman School of Medicine at New York University takes the no. 2 spot after Harvard. Three schools were tied for the no. 3 spot: Columbia University, Johns Hopkins University, and the University of California, San Francisco; and two schools for no. 6: Duke University and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. No. 8 goes to Stanford University, followed by the University of Washington. Rounding out the top 10 is Yale University.
Specialty ranks
The top-ranked schools in eight specialties are as follows:
- Anesthesiology: Harvard
- Family medicine: the University of Washington
- Internal medicine: Johns Hopkins
- Obstetrics/gynecology: Harvard
- Pediatrics: the University of Pennsylvania (Perelman)
- Psychiatry: Harvard
- Radiology: Johns Hopkins
- Surgery: Harvard
Most diverse student body
If you’re looking for a school with significant minority representation, Howard University, Washington, D.C., ranked highest (76.8%), followed by the Wertheim College of Medicine at Florida International University, Miami (43.2%). The University of California, Davis (40%), Sacramento, California, and the University of Vermont (Larner), Burlington (14.1%), tied for third.
Three southern schools take top honors for the most graduates practicing in underserved areas, starting with the University of South Carolina (70.9%), followed by the University of Mississippi (66.2%), and East Tennessee State University (Quillen), Johnson City, Tennessee (65.8%).
The colleges with the most graduates practicing in rural areas are William Carey University College of Osteopathic Medicine (28%), the University of Pikesville (25.6%), and the University of Mississippi (22.1%).
College debt
The medical school where graduates have the most debt is Nova Southeastern University Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida. Graduates incurred an average debt of $309,206. Western University of Health Sciences graduates racked up $276,840 in debt, followed by graduates of West Virginia School of Osteopathic Medicine, owing $268,416.
Ranking criteria
Each year, U.S. News ranks hundreds of U.S. colleges and universities. Medical schools fall under the rankings for best graduate schools.
U.S. News surveyed 192 medical and osteopathic schools accredited in 2021 by the Liaison Committee on Medical Education or the American Osteopathic Association. Among the schools surveyed in fall 2021 and early 2022, 130 schools responded. Of those, 124 were included in both the research and primary care rankings.
The criteria for ranking include faculty resources, academic achievements of entering students, and qualitative assessments by schools and residency directors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Methylphenidate is overprescribed to children in France
The prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder is difficult to evaluate, and the diagnosis is based primarily on clinical criteria. In 2008, a French study estimated the prevalence to be between 3.5% and 5.6%, but the study’s design was questionable.
Treatment of this disorder consists first and foremost of educational, social, and psychotherapeutic management. Only if such treatment fails is methylphenidate (MPH), the only drug that has been approved in France for this indication, to be considered, according to the recommendations.
The drug’s short-term efficacy has been proven, but it has not shown any effect on the long-term risks for academic failure, delinquency, and drug addiction associated with ADHD. In contrast, its adverse effects are numerous. Cases of nervousness, sleep disorders, headaches, weight loss, risk for aggravation of psychiatric conditions, and progression to violent or suicidal behavior have all been documented extensively, as well as cases of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease. Moreover, MPH is classified as a narcotic.
Inappropriate prescribing conditions
A study that appeared in the French journal of neuropsychiatry in minors, Neuropsychiatrie de l’Enfance et de l’Adolescence, investigated the prescribing procedures for this drug in France. Researchers examined Social Security data for 144,509 patients between the ages of 0 and 17 years who had received at least one prescription between 2010 and 2019. The researchers made the following observations about prescribing patterns and usage during this period:
- New MPH prescriptions increased by 56% per year, and the total number of annual prescriptions increased by 116%. In 3- to 17-year-olds, the prevalence was estimated at 0.61% to 0.75% of the pediatric population in 2019. Boys accounted for most of this consumption (82.5% to 80.8% over this period).
- In 2011, the median duration of consumption by children 6 years of age and older was 5.5 years. For 25% of those children, it was more than 8 years.
- Contrary to the labeling, some prescriptions were written for children younger than 6 years.
- Twenty-five percent of initial prescriptions and 50% of annual renewals were not written by a hospital specialist, in violation of the regulatory requirements in effect until Sept. 13, 2021. On that date, the French National Authority for Health (HAS) decided that initial hospital prescription of MPH should end.
- Eighty-four percent of children did not have any medical consultations at the prescribing hospital department in the 13 months after starting MPH. While the prevalence of ADHD has more than doubled, the number of consultations at specialist French medical, psychological, and educational centers for minors (CMPPs) is now less than a fourth of what it was – a drop from 4.1% to 0.8%.
- The prescribing of MPH is not always associated with an ADHD diagnosis, even though ADHD is its only indication.
- Of children and adolescents who use MPH, 22.8% received one or more other psychotropic drugs in the year following the initial prescription, including the following: neuroleptics (64.5%), anxiolytics (35.5%), antidepressants (16.2%), antiepileptics (11%), hypnotics (4.8%), and antiparkinsonian drugs (3%). “These co-prescriptions are often way off-label and are not within HAS recommendations,” according to the authors.
- For the youngest children in school classes (those born in December rather than in January), between 2010 and 2019, there was on average a 54% increased risk of being medicated.
- In 2019, 21.7% of children who received MPH lived in families with Universal Health Coverage or a similar plan. Yet, according to the French National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies, only 7.8% of the French population had this type of assistance.
A minority of practitioners
The authors of this article state that “the distribution of consumption suggests a predominant role of a minority of practitioners and hospital departments in the prescription of methylphenidate.” They note that “in European countries and in North America, the prescription rate of psychotropic drugs for ADHD has stabilized or shown a clear trend toward stabilization since 2008. The same cannot be said for France, where this rate is continuously increasing; so much so that in 2019, it reached a higher level than in other European countries like Great Britain.” The reasons for this are disputed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder is difficult to evaluate, and the diagnosis is based primarily on clinical criteria. In 2008, a French study estimated the prevalence to be between 3.5% and 5.6%, but the study’s design was questionable.
Treatment of this disorder consists first and foremost of educational, social, and psychotherapeutic management. Only if such treatment fails is methylphenidate (MPH), the only drug that has been approved in France for this indication, to be considered, according to the recommendations.
The drug’s short-term efficacy has been proven, but it has not shown any effect on the long-term risks for academic failure, delinquency, and drug addiction associated with ADHD. In contrast, its adverse effects are numerous. Cases of nervousness, sleep disorders, headaches, weight loss, risk for aggravation of psychiatric conditions, and progression to violent or suicidal behavior have all been documented extensively, as well as cases of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease. Moreover, MPH is classified as a narcotic.
Inappropriate prescribing conditions
A study that appeared in the French journal of neuropsychiatry in minors, Neuropsychiatrie de l’Enfance et de l’Adolescence, investigated the prescribing procedures for this drug in France. Researchers examined Social Security data for 144,509 patients between the ages of 0 and 17 years who had received at least one prescription between 2010 and 2019. The researchers made the following observations about prescribing patterns and usage during this period:
- New MPH prescriptions increased by 56% per year, and the total number of annual prescriptions increased by 116%. In 3- to 17-year-olds, the prevalence was estimated at 0.61% to 0.75% of the pediatric population in 2019. Boys accounted for most of this consumption (82.5% to 80.8% over this period).
- In 2011, the median duration of consumption by children 6 years of age and older was 5.5 years. For 25% of those children, it was more than 8 years.
- Contrary to the labeling, some prescriptions were written for children younger than 6 years.
- Twenty-five percent of initial prescriptions and 50% of annual renewals were not written by a hospital specialist, in violation of the regulatory requirements in effect until Sept. 13, 2021. On that date, the French National Authority for Health (HAS) decided that initial hospital prescription of MPH should end.
- Eighty-four percent of children did not have any medical consultations at the prescribing hospital department in the 13 months after starting MPH. While the prevalence of ADHD has more than doubled, the number of consultations at specialist French medical, psychological, and educational centers for minors (CMPPs) is now less than a fourth of what it was – a drop from 4.1% to 0.8%.
- The prescribing of MPH is not always associated with an ADHD diagnosis, even though ADHD is its only indication.
- Of children and adolescents who use MPH, 22.8% received one or more other psychotropic drugs in the year following the initial prescription, including the following: neuroleptics (64.5%), anxiolytics (35.5%), antidepressants (16.2%), antiepileptics (11%), hypnotics (4.8%), and antiparkinsonian drugs (3%). “These co-prescriptions are often way off-label and are not within HAS recommendations,” according to the authors.
- For the youngest children in school classes (those born in December rather than in January), between 2010 and 2019, there was on average a 54% increased risk of being medicated.
- In 2019, 21.7% of children who received MPH lived in families with Universal Health Coverage or a similar plan. Yet, according to the French National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies, only 7.8% of the French population had this type of assistance.
A minority of practitioners
The authors of this article state that “the distribution of consumption suggests a predominant role of a minority of practitioners and hospital departments in the prescription of methylphenidate.” They note that “in European countries and in North America, the prescription rate of psychotropic drugs for ADHD has stabilized or shown a clear trend toward stabilization since 2008. The same cannot be said for France, where this rate is continuously increasing; so much so that in 2019, it reached a higher level than in other European countries like Great Britain.” The reasons for this are disputed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder is difficult to evaluate, and the diagnosis is based primarily on clinical criteria. In 2008, a French study estimated the prevalence to be between 3.5% and 5.6%, but the study’s design was questionable.
Treatment of this disorder consists first and foremost of educational, social, and psychotherapeutic management. Only if such treatment fails is methylphenidate (MPH), the only drug that has been approved in France for this indication, to be considered, according to the recommendations.
The drug’s short-term efficacy has been proven, but it has not shown any effect on the long-term risks for academic failure, delinquency, and drug addiction associated with ADHD. In contrast, its adverse effects are numerous. Cases of nervousness, sleep disorders, headaches, weight loss, risk for aggravation of psychiatric conditions, and progression to violent or suicidal behavior have all been documented extensively, as well as cases of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease. Moreover, MPH is classified as a narcotic.
Inappropriate prescribing conditions
A study that appeared in the French journal of neuropsychiatry in minors, Neuropsychiatrie de l’Enfance et de l’Adolescence, investigated the prescribing procedures for this drug in France. Researchers examined Social Security data for 144,509 patients between the ages of 0 and 17 years who had received at least one prescription between 2010 and 2019. The researchers made the following observations about prescribing patterns and usage during this period:
- New MPH prescriptions increased by 56% per year, and the total number of annual prescriptions increased by 116%. In 3- to 17-year-olds, the prevalence was estimated at 0.61% to 0.75% of the pediatric population in 2019. Boys accounted for most of this consumption (82.5% to 80.8% over this period).
- In 2011, the median duration of consumption by children 6 years of age and older was 5.5 years. For 25% of those children, it was more than 8 years.
- Contrary to the labeling, some prescriptions were written for children younger than 6 years.
- Twenty-five percent of initial prescriptions and 50% of annual renewals were not written by a hospital specialist, in violation of the regulatory requirements in effect until Sept. 13, 2021. On that date, the French National Authority for Health (HAS) decided that initial hospital prescription of MPH should end.
- Eighty-four percent of children did not have any medical consultations at the prescribing hospital department in the 13 months after starting MPH. While the prevalence of ADHD has more than doubled, the number of consultations at specialist French medical, psychological, and educational centers for minors (CMPPs) is now less than a fourth of what it was – a drop from 4.1% to 0.8%.
- The prescribing of MPH is not always associated with an ADHD diagnosis, even though ADHD is its only indication.
- Of children and adolescents who use MPH, 22.8% received one or more other psychotropic drugs in the year following the initial prescription, including the following: neuroleptics (64.5%), anxiolytics (35.5%), antidepressants (16.2%), antiepileptics (11%), hypnotics (4.8%), and antiparkinsonian drugs (3%). “These co-prescriptions are often way off-label and are not within HAS recommendations,” according to the authors.
- For the youngest children in school classes (those born in December rather than in January), between 2010 and 2019, there was on average a 54% increased risk of being medicated.
- In 2019, 21.7% of children who received MPH lived in families with Universal Health Coverage or a similar plan. Yet, according to the French National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies, only 7.8% of the French population had this type of assistance.
A minority of practitioners
The authors of this article state that “the distribution of consumption suggests a predominant role of a minority of practitioners and hospital departments in the prescription of methylphenidate.” They note that “in European countries and in North America, the prescription rate of psychotropic drugs for ADHD has stabilized or shown a clear trend toward stabilization since 2008. The same cannot be said for France, where this rate is continuously increasing; so much so that in 2019, it reached a higher level than in other European countries like Great Britain.” The reasons for this are disputed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Babies die as congenital syphilis continues a decade-long surge across the U.S.
For a decade, the number of babies born with syphilis in the United States has surged, undeterred. Data released Apr. 12 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows just how dire the outbreak has become.
In 2012, 332 babies were born infected with the disease. In 2021, that number had climbed nearly sevenfold, to at least 2,268, according to preliminary estimates. And 166 of those babies died.
About 7% of babies diagnosed with syphilis in recent years have died; thousands of others born with the disease have faced problems that include brain and bone malformations, blindness, and organ damage.
For public health officials, the situation is all the more heartbreaking, considering that congenital syphilis rates reached near-historic modern lows from 2000 to 2012 amid ambitious prevention and education efforts. By 2020, following a sharp erosion in funding and attention, the nationwide case rate was more than seven times that of 2012.
“The really depressing thing about it is we had this thing virtually eradicated back in the year 2000,” said William Andrews, a public information officer for Oklahoma’s sexual health and harm reduction service. “Now it’s back with a vengeance. We are really trying to get the message out that sexual health is health. It’s nothing to be ashamed of.”
Even as caseloads soar, the CDC budget for STD prevention – the primary funding source for most public health departments – has been largely stagnant for two decades, its purchasing power dragged even lower by inflation.
The CDC report on STD trends provides official data on congenital syphilis cases for 2020, as well as preliminary case counts for 2021 that are expected to increase. CDC data shows that congenital syphilis rates in 2020 continued to climb in already overwhelmed states like Texas, California, and Nevada and that the disease is now present in almost every state in the nation. All but three states – Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont – reported congenital syphilis cases in 2020.
From 2011 to 2020, congenital syphilis resulted in 633 documented stillbirths and infant deaths, according to the new CDC data.
Preventing congenital syphilis – the term used when syphilis is transferred to a fetus in utero – is from a medical standpoint exceedingly simple: If a pregnant woman is diagnosed at least a month before giving birth, just a few shots of penicillin have a near-perfect cure rate for mother and baby. But funding cuts and competing priorities in the nation’s fragmented public health care system have vastly narrowed access to such services.
The reasons pregnant people with syphilis go undiagnosed or untreated vary geographically, according to data collected by states and analyzed by the CDC.
In Western states, the largest share of cases involve women who have received little to no prenatal care and aren’t tested for syphilis until they give birth. Many have substance use disorders, primarily related to methamphetamines. “They’ve felt a lot of judgment and stigma by the medical community,” said Stephanie Pierce, MD, a maternal fetal medicine specialist at the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City, who runs a clinic for women with high-risk pregnancies.
In Southern states, a CDC study of 2018 data found that the largest share of congenital syphilis cases were among women who had been tested and diagnosed but hadn’t received treatment. That year, among Black moms who gave birth to a baby with syphilis, 37% had not been treated adequately even though they’d received a timely diagnosis. Among white moms, that number was 24%. Longstanding racism in medical care, poverty, transportation issues, poorly funded public health departments, and crowded clinics whose employees are too overworked to follow up with patients all contribute to the problem, according to infectious disease experts.
Doctors are also noticing a growing number of women who are treated for syphilis but reinfected during pregnancy. Amid rising cases and stagnant resources, some states have focused disease investigations on pregnant women of childbearing age; they can no longer prioritize treating sexual partners who are also infected.
Eric McGrath, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Wayne State University, Detroit, said that he’d seen several newborns in recent years whose mothers had been treated for syphilis but then were re-exposed during pregnancy by partners who hadn’t been treated.
Treating a newborn baby for syphilis isn’t trivial. Penicillin carries little risk, but delivering it to a baby often involves a lumbar puncture and other painful procedures. And treatment typically means keeping the baby in the hospital for 10 days, interrupting an important time for family bonding.
Dr. McGrath has seen a couple of babies in his career who weren’t diagnosed or treated at birth and later came to him with full-blown syphilis complications, including full-body rashes and inflamed livers. It was an awful experience he doesn’t want to repeat. The preferred course, he said, is to spare the baby the ordeal and treat parents early in the pregnancy.
But in some places, providers aren’t routinely testing for syphilis. Although most states mandate testing at some point during pregnancy, as of last year just 14 required it for everyone in the third trimester. The CDC recommends third-trimester testing in areas with high rates of syphilis, a growing share of the United States.
After Arizona declared a statewide outbreak in 2018, state health officials wanted to know whether widespread testing in the third trimester could have prevented infections. Looking at 18 months of data, analysts found that nearly three-quarters of the more than 200 pregnant women diagnosed with syphilis in 2017 and the first half of 2018 got treatment. That left 57 babies born with syphilis, nine of whom died. The analysts estimated that a third of the infections could have been prevented with testing in the third trimester.
Based on the numbers they saw in those 18 months, officials estimated that screening all women on Medicaid in the third trimester would cost the state $113,300 annually, and that treating all cases of syphilis that screening would catch could be done for just $113. Factoring in the hospitalization costs for infected infants, the officials concluded the additional testing would save the state money.
And yet prevention money has been hard to come by. Taking inflation into account, CDC prevention funding for STDs has fallen 41% since 2003, according to an analysis by the National Coalition of STD Directors. That’s even as cases have risen, leaving public health departments saddled with more work and far less money.
Janine Waters, STD program manager for the state of New Mexico, has watched the unraveling. When Ms. Waters started her career more than 20 years ago, she and her colleagues followed up on every case of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis reported, not only making sure that people got treatment but also getting in touch with their sexual partners, with the aim of stopping the spread of infection. In a 2019 interview with Kaiser Health News, she said her team was struggling to keep up with syphilis alone, even as they registered with dread congenital syphilis cases surging in neighboring Texas and Arizona.
By 2020, New Mexico had the highest rate of congenital syphilis in the country.
The COVID-19 pandemic drained the remaining resources. Half of health departments across the country discontinued STD fieldwork altogether, diverting their resources to COVID. In California, which for years has struggled with high rates of congenital syphilis, three-quarters of local health departments dispatched more than half of their STD staffers to work on COVID.
As the pandemic ebbs – at least in the short term – many public health departments are turning their attention back to syphilis and other diseases. And they are doing it with reinforcements. Although the Biden administration’s proposed STD prevention budget for 2023 remains flat, the American Rescue Plan Act included $200 million to help health departments boost contact tracing and surveillance for covid and other infectious diseases. Many departments are funneling that money toward STDs.
The money is an infusion that state health officials say will make a difference. But when taking inflation into account, it essentially brings STD prevention funding back to what it was in 2003, said Stephanie Arnold Pang of the National Coalition of STD Directors. And the American Rescue Plan money doesn’t cover some aspects of STD prevention, including clinical services.
The coalition wants to revive dedicated STD clinics, where people can drop in for testing and treatment at little to no cost. Advocates say that would fill a void that has plagued treatment efforts since public clinics closed en masse in the wake of the 2008 recession.
Texas, battling its own pervasive outbreak, will use its share of American Rescue Plan money to fill 94 new positions focused on various aspects of STD prevention. Those hires will bolster a range of measures the state put in place before the pandemic, including an updated data system to track infections, review boards in major cities that examine what went wrong for every case of congenital syphilis, and a requirement that providers test for syphilis during the third trimester of pregnancy. The suite of interventions seems to be working, but it could be a while before cases go down, said Amy Carter, the state’s congenital syphilis coordinator.
“The growth didn’t happen overnight,” Ms. Carter said. “So our prevention efforts aren’t going to have a direct impact overnight either.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation
For a decade, the number of babies born with syphilis in the United States has surged, undeterred. Data released Apr. 12 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows just how dire the outbreak has become.
In 2012, 332 babies were born infected with the disease. In 2021, that number had climbed nearly sevenfold, to at least 2,268, according to preliminary estimates. And 166 of those babies died.
About 7% of babies diagnosed with syphilis in recent years have died; thousands of others born with the disease have faced problems that include brain and bone malformations, blindness, and organ damage.
For public health officials, the situation is all the more heartbreaking, considering that congenital syphilis rates reached near-historic modern lows from 2000 to 2012 amid ambitious prevention and education efforts. By 2020, following a sharp erosion in funding and attention, the nationwide case rate was more than seven times that of 2012.
“The really depressing thing about it is we had this thing virtually eradicated back in the year 2000,” said William Andrews, a public information officer for Oklahoma’s sexual health and harm reduction service. “Now it’s back with a vengeance. We are really trying to get the message out that sexual health is health. It’s nothing to be ashamed of.”
Even as caseloads soar, the CDC budget for STD prevention – the primary funding source for most public health departments – has been largely stagnant for two decades, its purchasing power dragged even lower by inflation.
The CDC report on STD trends provides official data on congenital syphilis cases for 2020, as well as preliminary case counts for 2021 that are expected to increase. CDC data shows that congenital syphilis rates in 2020 continued to climb in already overwhelmed states like Texas, California, and Nevada and that the disease is now present in almost every state in the nation. All but three states – Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont – reported congenital syphilis cases in 2020.
From 2011 to 2020, congenital syphilis resulted in 633 documented stillbirths and infant deaths, according to the new CDC data.
Preventing congenital syphilis – the term used when syphilis is transferred to a fetus in utero – is from a medical standpoint exceedingly simple: If a pregnant woman is diagnosed at least a month before giving birth, just a few shots of penicillin have a near-perfect cure rate for mother and baby. But funding cuts and competing priorities in the nation’s fragmented public health care system have vastly narrowed access to such services.
The reasons pregnant people with syphilis go undiagnosed or untreated vary geographically, according to data collected by states and analyzed by the CDC.
In Western states, the largest share of cases involve women who have received little to no prenatal care and aren’t tested for syphilis until they give birth. Many have substance use disorders, primarily related to methamphetamines. “They’ve felt a lot of judgment and stigma by the medical community,” said Stephanie Pierce, MD, a maternal fetal medicine specialist at the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City, who runs a clinic for women with high-risk pregnancies.
In Southern states, a CDC study of 2018 data found that the largest share of congenital syphilis cases were among women who had been tested and diagnosed but hadn’t received treatment. That year, among Black moms who gave birth to a baby with syphilis, 37% had not been treated adequately even though they’d received a timely diagnosis. Among white moms, that number was 24%. Longstanding racism in medical care, poverty, transportation issues, poorly funded public health departments, and crowded clinics whose employees are too overworked to follow up with patients all contribute to the problem, according to infectious disease experts.
Doctors are also noticing a growing number of women who are treated for syphilis but reinfected during pregnancy. Amid rising cases and stagnant resources, some states have focused disease investigations on pregnant women of childbearing age; they can no longer prioritize treating sexual partners who are also infected.
Eric McGrath, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Wayne State University, Detroit, said that he’d seen several newborns in recent years whose mothers had been treated for syphilis but then were re-exposed during pregnancy by partners who hadn’t been treated.
Treating a newborn baby for syphilis isn’t trivial. Penicillin carries little risk, but delivering it to a baby often involves a lumbar puncture and other painful procedures. And treatment typically means keeping the baby in the hospital for 10 days, interrupting an important time for family bonding.
Dr. McGrath has seen a couple of babies in his career who weren’t diagnosed or treated at birth and later came to him with full-blown syphilis complications, including full-body rashes and inflamed livers. It was an awful experience he doesn’t want to repeat. The preferred course, he said, is to spare the baby the ordeal and treat parents early in the pregnancy.
But in some places, providers aren’t routinely testing for syphilis. Although most states mandate testing at some point during pregnancy, as of last year just 14 required it for everyone in the third trimester. The CDC recommends third-trimester testing in areas with high rates of syphilis, a growing share of the United States.
After Arizona declared a statewide outbreak in 2018, state health officials wanted to know whether widespread testing in the third trimester could have prevented infections. Looking at 18 months of data, analysts found that nearly three-quarters of the more than 200 pregnant women diagnosed with syphilis in 2017 and the first half of 2018 got treatment. That left 57 babies born with syphilis, nine of whom died. The analysts estimated that a third of the infections could have been prevented with testing in the third trimester.
Based on the numbers they saw in those 18 months, officials estimated that screening all women on Medicaid in the third trimester would cost the state $113,300 annually, and that treating all cases of syphilis that screening would catch could be done for just $113. Factoring in the hospitalization costs for infected infants, the officials concluded the additional testing would save the state money.
And yet prevention money has been hard to come by. Taking inflation into account, CDC prevention funding for STDs has fallen 41% since 2003, according to an analysis by the National Coalition of STD Directors. That’s even as cases have risen, leaving public health departments saddled with more work and far less money.
Janine Waters, STD program manager for the state of New Mexico, has watched the unraveling. When Ms. Waters started her career more than 20 years ago, she and her colleagues followed up on every case of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis reported, not only making sure that people got treatment but also getting in touch with their sexual partners, with the aim of stopping the spread of infection. In a 2019 interview with Kaiser Health News, she said her team was struggling to keep up with syphilis alone, even as they registered with dread congenital syphilis cases surging in neighboring Texas and Arizona.
By 2020, New Mexico had the highest rate of congenital syphilis in the country.
The COVID-19 pandemic drained the remaining resources. Half of health departments across the country discontinued STD fieldwork altogether, diverting their resources to COVID. In California, which for years has struggled with high rates of congenital syphilis, three-quarters of local health departments dispatched more than half of their STD staffers to work on COVID.
As the pandemic ebbs – at least in the short term – many public health departments are turning their attention back to syphilis and other diseases. And they are doing it with reinforcements. Although the Biden administration’s proposed STD prevention budget for 2023 remains flat, the American Rescue Plan Act included $200 million to help health departments boost contact tracing and surveillance for covid and other infectious diseases. Many departments are funneling that money toward STDs.
The money is an infusion that state health officials say will make a difference. But when taking inflation into account, it essentially brings STD prevention funding back to what it was in 2003, said Stephanie Arnold Pang of the National Coalition of STD Directors. And the American Rescue Plan money doesn’t cover some aspects of STD prevention, including clinical services.
The coalition wants to revive dedicated STD clinics, where people can drop in for testing and treatment at little to no cost. Advocates say that would fill a void that has plagued treatment efforts since public clinics closed en masse in the wake of the 2008 recession.
Texas, battling its own pervasive outbreak, will use its share of American Rescue Plan money to fill 94 new positions focused on various aspects of STD prevention. Those hires will bolster a range of measures the state put in place before the pandemic, including an updated data system to track infections, review boards in major cities that examine what went wrong for every case of congenital syphilis, and a requirement that providers test for syphilis during the third trimester of pregnancy. The suite of interventions seems to be working, but it could be a while before cases go down, said Amy Carter, the state’s congenital syphilis coordinator.
“The growth didn’t happen overnight,” Ms. Carter said. “So our prevention efforts aren’t going to have a direct impact overnight either.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation
For a decade, the number of babies born with syphilis in the United States has surged, undeterred. Data released Apr. 12 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows just how dire the outbreak has become.
In 2012, 332 babies were born infected with the disease. In 2021, that number had climbed nearly sevenfold, to at least 2,268, according to preliminary estimates. And 166 of those babies died.
About 7% of babies diagnosed with syphilis in recent years have died; thousands of others born with the disease have faced problems that include brain and bone malformations, blindness, and organ damage.
For public health officials, the situation is all the more heartbreaking, considering that congenital syphilis rates reached near-historic modern lows from 2000 to 2012 amid ambitious prevention and education efforts. By 2020, following a sharp erosion in funding and attention, the nationwide case rate was more than seven times that of 2012.
“The really depressing thing about it is we had this thing virtually eradicated back in the year 2000,” said William Andrews, a public information officer for Oklahoma’s sexual health and harm reduction service. “Now it’s back with a vengeance. We are really trying to get the message out that sexual health is health. It’s nothing to be ashamed of.”
Even as caseloads soar, the CDC budget for STD prevention – the primary funding source for most public health departments – has been largely stagnant for two decades, its purchasing power dragged even lower by inflation.
The CDC report on STD trends provides official data on congenital syphilis cases for 2020, as well as preliminary case counts for 2021 that are expected to increase. CDC data shows that congenital syphilis rates in 2020 continued to climb in already overwhelmed states like Texas, California, and Nevada and that the disease is now present in almost every state in the nation. All but three states – Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont – reported congenital syphilis cases in 2020.
From 2011 to 2020, congenital syphilis resulted in 633 documented stillbirths and infant deaths, according to the new CDC data.
Preventing congenital syphilis – the term used when syphilis is transferred to a fetus in utero – is from a medical standpoint exceedingly simple: If a pregnant woman is diagnosed at least a month before giving birth, just a few shots of penicillin have a near-perfect cure rate for mother and baby. But funding cuts and competing priorities in the nation’s fragmented public health care system have vastly narrowed access to such services.
The reasons pregnant people with syphilis go undiagnosed or untreated vary geographically, according to data collected by states and analyzed by the CDC.
In Western states, the largest share of cases involve women who have received little to no prenatal care and aren’t tested for syphilis until they give birth. Many have substance use disorders, primarily related to methamphetamines. “They’ve felt a lot of judgment and stigma by the medical community,” said Stephanie Pierce, MD, a maternal fetal medicine specialist at the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City, who runs a clinic for women with high-risk pregnancies.
In Southern states, a CDC study of 2018 data found that the largest share of congenital syphilis cases were among women who had been tested and diagnosed but hadn’t received treatment. That year, among Black moms who gave birth to a baby with syphilis, 37% had not been treated adequately even though they’d received a timely diagnosis. Among white moms, that number was 24%. Longstanding racism in medical care, poverty, transportation issues, poorly funded public health departments, and crowded clinics whose employees are too overworked to follow up with patients all contribute to the problem, according to infectious disease experts.
Doctors are also noticing a growing number of women who are treated for syphilis but reinfected during pregnancy. Amid rising cases and stagnant resources, some states have focused disease investigations on pregnant women of childbearing age; they can no longer prioritize treating sexual partners who are also infected.
Eric McGrath, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Wayne State University, Detroit, said that he’d seen several newborns in recent years whose mothers had been treated for syphilis but then were re-exposed during pregnancy by partners who hadn’t been treated.
Treating a newborn baby for syphilis isn’t trivial. Penicillin carries little risk, but delivering it to a baby often involves a lumbar puncture and other painful procedures. And treatment typically means keeping the baby in the hospital for 10 days, interrupting an important time for family bonding.
Dr. McGrath has seen a couple of babies in his career who weren’t diagnosed or treated at birth and later came to him with full-blown syphilis complications, including full-body rashes and inflamed livers. It was an awful experience he doesn’t want to repeat. The preferred course, he said, is to spare the baby the ordeal and treat parents early in the pregnancy.
But in some places, providers aren’t routinely testing for syphilis. Although most states mandate testing at some point during pregnancy, as of last year just 14 required it for everyone in the third trimester. The CDC recommends third-trimester testing in areas with high rates of syphilis, a growing share of the United States.
After Arizona declared a statewide outbreak in 2018, state health officials wanted to know whether widespread testing in the third trimester could have prevented infections. Looking at 18 months of data, analysts found that nearly three-quarters of the more than 200 pregnant women diagnosed with syphilis in 2017 and the first half of 2018 got treatment. That left 57 babies born with syphilis, nine of whom died. The analysts estimated that a third of the infections could have been prevented with testing in the third trimester.
Based on the numbers they saw in those 18 months, officials estimated that screening all women on Medicaid in the third trimester would cost the state $113,300 annually, and that treating all cases of syphilis that screening would catch could be done for just $113. Factoring in the hospitalization costs for infected infants, the officials concluded the additional testing would save the state money.
And yet prevention money has been hard to come by. Taking inflation into account, CDC prevention funding for STDs has fallen 41% since 2003, according to an analysis by the National Coalition of STD Directors. That’s even as cases have risen, leaving public health departments saddled with more work and far less money.
Janine Waters, STD program manager for the state of New Mexico, has watched the unraveling. When Ms. Waters started her career more than 20 years ago, she and her colleagues followed up on every case of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis reported, not only making sure that people got treatment but also getting in touch with their sexual partners, with the aim of stopping the spread of infection. In a 2019 interview with Kaiser Health News, she said her team was struggling to keep up with syphilis alone, even as they registered with dread congenital syphilis cases surging in neighboring Texas and Arizona.
By 2020, New Mexico had the highest rate of congenital syphilis in the country.
The COVID-19 pandemic drained the remaining resources. Half of health departments across the country discontinued STD fieldwork altogether, diverting their resources to COVID. In California, which for years has struggled with high rates of congenital syphilis, three-quarters of local health departments dispatched more than half of their STD staffers to work on COVID.
As the pandemic ebbs – at least in the short term – many public health departments are turning their attention back to syphilis and other diseases. And they are doing it with reinforcements. Although the Biden administration’s proposed STD prevention budget for 2023 remains flat, the American Rescue Plan Act included $200 million to help health departments boost contact tracing and surveillance for covid and other infectious diseases. Many departments are funneling that money toward STDs.
The money is an infusion that state health officials say will make a difference. But when taking inflation into account, it essentially brings STD prevention funding back to what it was in 2003, said Stephanie Arnold Pang of the National Coalition of STD Directors. And the American Rescue Plan money doesn’t cover some aspects of STD prevention, including clinical services.
The coalition wants to revive dedicated STD clinics, where people can drop in for testing and treatment at little to no cost. Advocates say that would fill a void that has plagued treatment efforts since public clinics closed en masse in the wake of the 2008 recession.
Texas, battling its own pervasive outbreak, will use its share of American Rescue Plan money to fill 94 new positions focused on various aspects of STD prevention. Those hires will bolster a range of measures the state put in place before the pandemic, including an updated data system to track infections, review boards in major cities that examine what went wrong for every case of congenital syphilis, and a requirement that providers test for syphilis during the third trimester of pregnancy. The suite of interventions seems to be working, but it could be a while before cases go down, said Amy Carter, the state’s congenital syphilis coordinator.
“The growth didn’t happen overnight,” Ms. Carter said. “So our prevention efforts aren’t going to have a direct impact overnight either.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation
Weigh but don’t tell
Reports of long waiting times at mental health clinics and anecdotal observations by health care providers suggest the pandemic has generated a dramatic increase in the incidence of eating disorders among the pediatric population. Of course this should come as no surprise to pediatricians.
Eating disorders come in many different forms and a triggering event is sometimes difficult to define. Often the adolescent or preadolescent is searching for some sense of stability in a life tossed on a stormy sea roiled by hormonal and physical change. Wresting control of their bodies during a period of uncertainty may result in a downward spiral into dangerously unhealthy weight loss. If nothing else, the pandemic has been a period of dramatic uncertainty unlike what most children and few adults in this country have ever experienced.
With the unprecedented increase in eating disorder cases, providers in several disciplines are searching for novel strategies to ease the burden on their patients and their practices. I recently learned of a pediatric practice in California that is considering blinding all patients aged 12 and older to the body mass measurements obtained at their health maintenance visits.
Blind weight checks for children with eating disorders, particularly those who seem to be nearing recovery, has been a common and often helpful practice. However, I am unaware of any practice that has made it a universal office policy. I’m unsure of the rationale behind this practice’s policy, but on several fronts, suppressing body mass measurements in the age group most vulnerable to eating disorders makes some sense.
Universal blind weight checks could minimize the risk of in-office shaming. However, careful training of support staff and thoughtful placement of the scales could serve the same purpose. This new policy acknowledges not only the ubiquity of the problem but also that many, maybe even most, children with eating disorders appear normal. And of course, there is the unfortunate fact that body mass is a poor screening test for eating disorders.
As I thought more about this novel approach I came to see its educational value for patients, parents, and even physicians. I can envision how a 13-year-old’s first health maintenance visit would go after the roll-out of the new policy. “Dr. Smith, aren’t you going to tell us how much I (or my daughter Jenny) weigh(s)?” This could, or more likely, should launch a discussion about weight and body image. It might continue with questions like, “How much do you think you weigh?” Or, “Do you think you are too heavy or too thin?”
Or, the conversation could include the provider’s observations that weight is just one measure of health and in fact not a very good one. Other ingredients in a healthy life style, such as sleep and physical activity, are not as easy to measure as weight but in many cases are more important.
As my mind struggled to restructure a health maintenance schedule that included blind weight checks, I wondered why we should wait until age 12. Of course, it is unreasonable to expect parents to stick with a pediatric practice that seems to ignore their infant’s weight. I’m sure that, like me, you have always discouraged new parents from having a baby scale at home because in the first few months too-frequent weighings can usually cause more angst than good.
It might make sense to remove a within-earshot discussion of a child’s weight from the health maintenance visit as soon as the child can absorb and digest the discussion; say, around age 3 years. In a perfect world, the provider should have already elicited a history that suggested a young child’s vulnerability to obesity before the scale and the growth chart told the unfortunate story. But, neither you nor I are perfect providers and so we will always need the scale to document our concerns. However, when and how we report that one vital sign to the patient and his or her parents is a topic ripe for discussion and improvement.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Reports of long waiting times at mental health clinics and anecdotal observations by health care providers suggest the pandemic has generated a dramatic increase in the incidence of eating disorders among the pediatric population. Of course this should come as no surprise to pediatricians.
Eating disorders come in many different forms and a triggering event is sometimes difficult to define. Often the adolescent or preadolescent is searching for some sense of stability in a life tossed on a stormy sea roiled by hormonal and physical change. Wresting control of their bodies during a period of uncertainty may result in a downward spiral into dangerously unhealthy weight loss. If nothing else, the pandemic has been a period of dramatic uncertainty unlike what most children and few adults in this country have ever experienced.
With the unprecedented increase in eating disorder cases, providers in several disciplines are searching for novel strategies to ease the burden on their patients and their practices. I recently learned of a pediatric practice in California that is considering blinding all patients aged 12 and older to the body mass measurements obtained at their health maintenance visits.
Blind weight checks for children with eating disorders, particularly those who seem to be nearing recovery, has been a common and often helpful practice. However, I am unaware of any practice that has made it a universal office policy. I’m unsure of the rationale behind this practice’s policy, but on several fronts, suppressing body mass measurements in the age group most vulnerable to eating disorders makes some sense.
Universal blind weight checks could minimize the risk of in-office shaming. However, careful training of support staff and thoughtful placement of the scales could serve the same purpose. This new policy acknowledges not only the ubiquity of the problem but also that many, maybe even most, children with eating disorders appear normal. And of course, there is the unfortunate fact that body mass is a poor screening test for eating disorders.
As I thought more about this novel approach I came to see its educational value for patients, parents, and even physicians. I can envision how a 13-year-old’s first health maintenance visit would go after the roll-out of the new policy. “Dr. Smith, aren’t you going to tell us how much I (or my daughter Jenny) weigh(s)?” This could, or more likely, should launch a discussion about weight and body image. It might continue with questions like, “How much do you think you weigh?” Or, “Do you think you are too heavy or too thin?”
Or, the conversation could include the provider’s observations that weight is just one measure of health and in fact not a very good one. Other ingredients in a healthy life style, such as sleep and physical activity, are not as easy to measure as weight but in many cases are more important.
As my mind struggled to restructure a health maintenance schedule that included blind weight checks, I wondered why we should wait until age 12. Of course, it is unreasonable to expect parents to stick with a pediatric practice that seems to ignore their infant’s weight. I’m sure that, like me, you have always discouraged new parents from having a baby scale at home because in the first few months too-frequent weighings can usually cause more angst than good.
It might make sense to remove a within-earshot discussion of a child’s weight from the health maintenance visit as soon as the child can absorb and digest the discussion; say, around age 3 years. In a perfect world, the provider should have already elicited a history that suggested a young child’s vulnerability to obesity before the scale and the growth chart told the unfortunate story. But, neither you nor I are perfect providers and so we will always need the scale to document our concerns. However, when and how we report that one vital sign to the patient and his or her parents is a topic ripe for discussion and improvement.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Reports of long waiting times at mental health clinics and anecdotal observations by health care providers suggest the pandemic has generated a dramatic increase in the incidence of eating disorders among the pediatric population. Of course this should come as no surprise to pediatricians.
Eating disorders come in many different forms and a triggering event is sometimes difficult to define. Often the adolescent or preadolescent is searching for some sense of stability in a life tossed on a stormy sea roiled by hormonal and physical change. Wresting control of their bodies during a period of uncertainty may result in a downward spiral into dangerously unhealthy weight loss. If nothing else, the pandemic has been a period of dramatic uncertainty unlike what most children and few adults in this country have ever experienced.
With the unprecedented increase in eating disorder cases, providers in several disciplines are searching for novel strategies to ease the burden on their patients and their practices. I recently learned of a pediatric practice in California that is considering blinding all patients aged 12 and older to the body mass measurements obtained at their health maintenance visits.
Blind weight checks for children with eating disorders, particularly those who seem to be nearing recovery, has been a common and often helpful practice. However, I am unaware of any practice that has made it a universal office policy. I’m unsure of the rationale behind this practice’s policy, but on several fronts, suppressing body mass measurements in the age group most vulnerable to eating disorders makes some sense.
Universal blind weight checks could minimize the risk of in-office shaming. However, careful training of support staff and thoughtful placement of the scales could serve the same purpose. This new policy acknowledges not only the ubiquity of the problem but also that many, maybe even most, children with eating disorders appear normal. And of course, there is the unfortunate fact that body mass is a poor screening test for eating disorders.
As I thought more about this novel approach I came to see its educational value for patients, parents, and even physicians. I can envision how a 13-year-old’s first health maintenance visit would go after the roll-out of the new policy. “Dr. Smith, aren’t you going to tell us how much I (or my daughter Jenny) weigh(s)?” This could, or more likely, should launch a discussion about weight and body image. It might continue with questions like, “How much do you think you weigh?” Or, “Do you think you are too heavy or too thin?”
Or, the conversation could include the provider’s observations that weight is just one measure of health and in fact not a very good one. Other ingredients in a healthy life style, such as sleep and physical activity, are not as easy to measure as weight but in many cases are more important.
As my mind struggled to restructure a health maintenance schedule that included blind weight checks, I wondered why we should wait until age 12. Of course, it is unreasonable to expect parents to stick with a pediatric practice that seems to ignore their infant’s weight. I’m sure that, like me, you have always discouraged new parents from having a baby scale at home because in the first few months too-frequent weighings can usually cause more angst than good.
It might make sense to remove a within-earshot discussion of a child’s weight from the health maintenance visit as soon as the child can absorb and digest the discussion; say, around age 3 years. In a perfect world, the provider should have already elicited a history that suggested a young child’s vulnerability to obesity before the scale and the growth chart told the unfortunate story. But, neither you nor I are perfect providers and so we will always need the scale to document our concerns. However, when and how we report that one vital sign to the patient and his or her parents is a topic ripe for discussion and improvement.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Cardiac issues after COVID infection and vaccination: New data
The new information comes from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet) and from a separate large international clinical study published online in Circulation.
CDC data
The CDC study analyzed electronic health record data from 40 U.S. health care systems from Jan. 1, 2021, to Jan. 31, 2022, on more than 15 million people aged 5 years or older.
It reports a rate of myocarditis or pericarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination of 0-35.9 per 100,000 for males and 0-10.9 per 100,000 for females across different age groups and vaccine cohorts.
Rates of myocarditis or pericarditis after SARS-CoV-2 infection ranged from 12.6 to 114 per 100,000 for males and from 5.4 to 61.7 per 100,000 for females across different age groups.
Even among males aged 12-17 years, the group with the highest incidence of cardiac complications after receipt of a second mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose, the risk was 1.8-5.6 times higher after SARS-CoV-2 infection than after vaccination, the CDC report notes.
“These findings provide important context for balancing risks and benefits of mRNA COVID-19 vaccination among eligible persons greater than or equal to 5 years,” the report states. They also “support the continued use of recommended mRNA vaccines among all eligible persons aged greater than or equal to 5 years,” it concludes.
International study
The international study focused on prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of clinically manifest acute myocarditis in patients with COVID-19 infection.
The study showed a rate of acute myocarditis of 2.4 per 1,000 patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
“A small study previously indicated acute myocarditis is a rare occurrence in people infected with COVID-19. Our analysis of international data offers better insight to the occurrence of acute myocarditis during COVID-19 hospitalization, particularly before the COVID-19 vaccines were widely available,” coauthor Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, commented.
“This analysis indicates that, although rare, hospitalized patients with acute myocarditis associated with COVID-19 infection have a much greater need for intensive care unit admission, in up to 70.5% of the cases, despite the average age of the individuals in the study being much younger than expected, at 38 years old,” added coauthor Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia, Italy.
The researchers report that the use of corticosteroids in patients with acute myocarditis appeared safe, and, in most cases, a rapid increase in the left ventricular ejection fraction was observed. In addition, they say that discharged patients with acute myocarditis had “an excellent short-term prognosis without occurrence of cardiovascular events.”
The authors also point out that these data show much higher frequency and severity of acute myocarditis linked to COVID-19 infection, compared with myocarditis cases linked to the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
The international study examined health data on 56,963 patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19 at 23 hospitals across the United States and Europe from February 2020 through April 2021.
Among these patients, 97 with possible acute myocarditis were identified (4.1 per 1,000), of whom 54 (2.4 per 1,000) were classified as having “definite or probable” acute myocarditis supported by endomyocardial biopsy (31.5% of cases) or magnetic resonance imaging (92.6% of cases).
The median age of definite/probable acute myocarditis cases was 38 years, and 39% were female. On admission, chest pain and dyspnea were the most frequent symptoms (55.5% and 53.7%, respectively), and 31 cases (57.4%) occurred in the absence of COVID-19–associated pneumonia. A fulminant presentation requiring inotropic support or temporary mechanical circulatory support occurred in 21 cases (39%).
Overall, 38 patients (70.4%) were admitted to the intensive care unit for a median time of 6 days. Ten patients (18.5%) received temporary mechanical circulatory support for a median time of 5 days. Three patients died (5.5%) during the index hospitalization, all of whom also had pneumonia. At 120 days, estimated mortality was 6.6%. Patients with pneumonia were more likely to develop hemodynamic instability, require mechanical circulatory support, and die, compared with those without pneumonia.
The authors note that their reported prevalence of acute myocarditis associated with COVID-19 is lower, compared with studies that performed universal cardiac MRI screening during the convalescent COVID-19 period.
They say that underestimation of the prevalence of mild or subclinical acute myocarditis is likely in this study because of the retrospective nature of the registry, the lack of systematic cardiac MRI, and the possibility of missing some diagnoses, particularly during the first pandemic wave when cardiac MRI and endomyocardial biopsy were less frequently performed.
The authors also point out that data on myocarditis after COVID-19 vaccination suggest that vaccination-linked myocarditis is milder than that associated with the virus itself.
With regard to the prevalence of acute myocarditis after vaccination, they report that among 2.8 million doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in the armed forces, 23 individuals had evidence of acute myocarditis, suggesting a prevalence of less than 1 case of acute myocarditis per 100,000 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine doses.
They note that the CDC has also reported 399 reports of myocarditis among 129 million fully vaccinated individuals with the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
“These figures appear reassuring, compared with the prevalence of clinically manifest acute myocarditis observed in this study among hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” they conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new information comes from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet) and from a separate large international clinical study published online in Circulation.
CDC data
The CDC study analyzed electronic health record data from 40 U.S. health care systems from Jan. 1, 2021, to Jan. 31, 2022, on more than 15 million people aged 5 years or older.
It reports a rate of myocarditis or pericarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination of 0-35.9 per 100,000 for males and 0-10.9 per 100,000 for females across different age groups and vaccine cohorts.
Rates of myocarditis or pericarditis after SARS-CoV-2 infection ranged from 12.6 to 114 per 100,000 for males and from 5.4 to 61.7 per 100,000 for females across different age groups.
Even among males aged 12-17 years, the group with the highest incidence of cardiac complications after receipt of a second mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose, the risk was 1.8-5.6 times higher after SARS-CoV-2 infection than after vaccination, the CDC report notes.
“These findings provide important context for balancing risks and benefits of mRNA COVID-19 vaccination among eligible persons greater than or equal to 5 years,” the report states. They also “support the continued use of recommended mRNA vaccines among all eligible persons aged greater than or equal to 5 years,” it concludes.
International study
The international study focused on prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of clinically manifest acute myocarditis in patients with COVID-19 infection.
The study showed a rate of acute myocarditis of 2.4 per 1,000 patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
“A small study previously indicated acute myocarditis is a rare occurrence in people infected with COVID-19. Our analysis of international data offers better insight to the occurrence of acute myocarditis during COVID-19 hospitalization, particularly before the COVID-19 vaccines were widely available,” coauthor Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, commented.
“This analysis indicates that, although rare, hospitalized patients with acute myocarditis associated with COVID-19 infection have a much greater need for intensive care unit admission, in up to 70.5% of the cases, despite the average age of the individuals in the study being much younger than expected, at 38 years old,” added coauthor Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia, Italy.
The researchers report that the use of corticosteroids in patients with acute myocarditis appeared safe, and, in most cases, a rapid increase in the left ventricular ejection fraction was observed. In addition, they say that discharged patients with acute myocarditis had “an excellent short-term prognosis without occurrence of cardiovascular events.”
The authors also point out that these data show much higher frequency and severity of acute myocarditis linked to COVID-19 infection, compared with myocarditis cases linked to the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
The international study examined health data on 56,963 patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19 at 23 hospitals across the United States and Europe from February 2020 through April 2021.
Among these patients, 97 with possible acute myocarditis were identified (4.1 per 1,000), of whom 54 (2.4 per 1,000) were classified as having “definite or probable” acute myocarditis supported by endomyocardial biopsy (31.5% of cases) or magnetic resonance imaging (92.6% of cases).
The median age of definite/probable acute myocarditis cases was 38 years, and 39% were female. On admission, chest pain and dyspnea were the most frequent symptoms (55.5% and 53.7%, respectively), and 31 cases (57.4%) occurred in the absence of COVID-19–associated pneumonia. A fulminant presentation requiring inotropic support or temporary mechanical circulatory support occurred in 21 cases (39%).
Overall, 38 patients (70.4%) were admitted to the intensive care unit for a median time of 6 days. Ten patients (18.5%) received temporary mechanical circulatory support for a median time of 5 days. Three patients died (5.5%) during the index hospitalization, all of whom also had pneumonia. At 120 days, estimated mortality was 6.6%. Patients with pneumonia were more likely to develop hemodynamic instability, require mechanical circulatory support, and die, compared with those without pneumonia.
The authors note that their reported prevalence of acute myocarditis associated with COVID-19 is lower, compared with studies that performed universal cardiac MRI screening during the convalescent COVID-19 period.
They say that underestimation of the prevalence of mild or subclinical acute myocarditis is likely in this study because of the retrospective nature of the registry, the lack of systematic cardiac MRI, and the possibility of missing some diagnoses, particularly during the first pandemic wave when cardiac MRI and endomyocardial biopsy were less frequently performed.
The authors also point out that data on myocarditis after COVID-19 vaccination suggest that vaccination-linked myocarditis is milder than that associated with the virus itself.
With regard to the prevalence of acute myocarditis after vaccination, they report that among 2.8 million doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in the armed forces, 23 individuals had evidence of acute myocarditis, suggesting a prevalence of less than 1 case of acute myocarditis per 100,000 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine doses.
They note that the CDC has also reported 399 reports of myocarditis among 129 million fully vaccinated individuals with the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
“These figures appear reassuring, compared with the prevalence of clinically manifest acute myocarditis observed in this study among hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” they conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new information comes from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet) and from a separate large international clinical study published online in Circulation.
CDC data
The CDC study analyzed electronic health record data from 40 U.S. health care systems from Jan. 1, 2021, to Jan. 31, 2022, on more than 15 million people aged 5 years or older.
It reports a rate of myocarditis or pericarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination of 0-35.9 per 100,000 for males and 0-10.9 per 100,000 for females across different age groups and vaccine cohorts.
Rates of myocarditis or pericarditis after SARS-CoV-2 infection ranged from 12.6 to 114 per 100,000 for males and from 5.4 to 61.7 per 100,000 for females across different age groups.
Even among males aged 12-17 years, the group with the highest incidence of cardiac complications after receipt of a second mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose, the risk was 1.8-5.6 times higher after SARS-CoV-2 infection than after vaccination, the CDC report notes.
“These findings provide important context for balancing risks and benefits of mRNA COVID-19 vaccination among eligible persons greater than or equal to 5 years,” the report states. They also “support the continued use of recommended mRNA vaccines among all eligible persons aged greater than or equal to 5 years,” it concludes.
International study
The international study focused on prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of clinically manifest acute myocarditis in patients with COVID-19 infection.
The study showed a rate of acute myocarditis of 2.4 per 1,000 patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
“A small study previously indicated acute myocarditis is a rare occurrence in people infected with COVID-19. Our analysis of international data offers better insight to the occurrence of acute myocarditis during COVID-19 hospitalization, particularly before the COVID-19 vaccines were widely available,” coauthor Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, commented.
“This analysis indicates that, although rare, hospitalized patients with acute myocarditis associated with COVID-19 infection have a much greater need for intensive care unit admission, in up to 70.5% of the cases, despite the average age of the individuals in the study being much younger than expected, at 38 years old,” added coauthor Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia, Italy.
The researchers report that the use of corticosteroids in patients with acute myocarditis appeared safe, and, in most cases, a rapid increase in the left ventricular ejection fraction was observed. In addition, they say that discharged patients with acute myocarditis had “an excellent short-term prognosis without occurrence of cardiovascular events.”
The authors also point out that these data show much higher frequency and severity of acute myocarditis linked to COVID-19 infection, compared with myocarditis cases linked to the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
The international study examined health data on 56,963 patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19 at 23 hospitals across the United States and Europe from February 2020 through April 2021.
Among these patients, 97 with possible acute myocarditis were identified (4.1 per 1,000), of whom 54 (2.4 per 1,000) were classified as having “definite or probable” acute myocarditis supported by endomyocardial biopsy (31.5% of cases) or magnetic resonance imaging (92.6% of cases).
The median age of definite/probable acute myocarditis cases was 38 years, and 39% were female. On admission, chest pain and dyspnea were the most frequent symptoms (55.5% and 53.7%, respectively), and 31 cases (57.4%) occurred in the absence of COVID-19–associated pneumonia. A fulminant presentation requiring inotropic support or temporary mechanical circulatory support occurred in 21 cases (39%).
Overall, 38 patients (70.4%) were admitted to the intensive care unit for a median time of 6 days. Ten patients (18.5%) received temporary mechanical circulatory support for a median time of 5 days. Three patients died (5.5%) during the index hospitalization, all of whom also had pneumonia. At 120 days, estimated mortality was 6.6%. Patients with pneumonia were more likely to develop hemodynamic instability, require mechanical circulatory support, and die, compared with those without pneumonia.
The authors note that their reported prevalence of acute myocarditis associated with COVID-19 is lower, compared with studies that performed universal cardiac MRI screening during the convalescent COVID-19 period.
They say that underestimation of the prevalence of mild or subclinical acute myocarditis is likely in this study because of the retrospective nature of the registry, the lack of systematic cardiac MRI, and the possibility of missing some diagnoses, particularly during the first pandemic wave when cardiac MRI and endomyocardial biopsy were less frequently performed.
The authors also point out that data on myocarditis after COVID-19 vaccination suggest that vaccination-linked myocarditis is milder than that associated with the virus itself.
With regard to the prevalence of acute myocarditis after vaccination, they report that among 2.8 million doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in the armed forces, 23 individuals had evidence of acute myocarditis, suggesting a prevalence of less than 1 case of acute myocarditis per 100,000 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine doses.
They note that the CDC has also reported 399 reports of myocarditis among 129 million fully vaccinated individuals with the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
“These figures appear reassuring, compared with the prevalence of clinically manifest acute myocarditis observed in this study among hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” they conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Woman who faked medical degree practiced for 3 years
Who needs medical degrees anyway?
It’s no secret that doctors make a fair chunk of change. It’s a lucrative profession, but that big fat paycheck is siloed behind long, tough years of medical school and residency. It’s not an easy path doctors walk. Or at least, it’s not supposed to be. Anything’s easy if you’re willing to lie.
That brings us to Sonia, a 31-year-old woman from northern France with a bachelor’s degree in real estate management who wasn’t bringing in enough money for her three children, at least not to her satisfaction. Naturally, the only decision was to forge some diplomas from the University of Strasbourg, as well as a certificate from the French Order of Physicians. Sonia got hired as a general practitioner by using the identities of two doctors who shared her name. She had no experience, had no idea what she was doing, and was wearing a GPS tagging bracelet for an unrelated crime, so she was quickly caught and exposed in October 2021, after, um, 3 years of fake doctoring, according to France Live.
Not to be deterred by this temporary setback, Sonia proceeded to immediately find work as an ophthalmologist, a career that requires more than 10 years of training, continuing her fraudulent medical career until recently, when she was caught again and sentenced to 3 years in prison. She did make 70,000 euros a year as a fake doctor, which isn’t exactly huge money, but certainly not bad either.
We certainly hope she’s learned her lesson about impersonating a doctor, at this point, but maybe she should just go to medical school. If not, northern France might just end up with a new endocrinologist or oncologist floating around in 3 years.
No need to ‘guess what size horse you are’
Is COVID-19 warming up for yet another surge? Maybe. That means it’s also time for the return of its remora-like follower, ivermectin. Our thanks go out to the Tennessee state legislature for bringing the proven-to-be-ineffective treatment for COVID back into our hearts and minds and emergency rooms.
Both the state House and Senate have approved a bill that allows pharmacists to dispense the antiparasitic drug without a prescription while shielding them “from any liability that could arise from dispensing ivermectin,” Nashville Public Radio reported.
The drug’s manufacturer, Merck, said over a year ago that there is “no scientific basis for a potential therapeutic effect against COVID-19 from preclinical studies … and a concerning lack of safety data.” More recently, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that ivermectin treatment had no important benefits in patients with COVID.
Last week, the bill’s Senate sponsor, Frank Niceley of Strawberry Plains, said that it was all about safety, as he explained to NPR station WPLN: “It’s a lot safer to go to your pharmacist and let him tell you how much ivermectin to take than it is to go to the co-op and guess what size horse you are.”
And on that note, here are a few more items of business that just might end up on the legislature’s calendar:
- Horses will be allowed to “share” their unused ivermectin with humans and other mammals.
- An apple a day not only keeps the doctor away, but the IRS and the FDA as well.
- Colon cleansing is more fun than humans should be allowed to have.
- TikTok videos qualify as CME.
Who needs medical degrees anyway?
It’s no secret that doctors make a fair chunk of change. It’s a lucrative profession, but that big fat paycheck is siloed behind long, tough years of medical school and residency. It’s not an easy path doctors walk. Or at least, it’s not supposed to be. Anything’s easy if you’re willing to lie.
That brings us to Sonia, a 31-year-old woman from northern France with a bachelor’s degree in real estate management who wasn’t bringing in enough money for her three children, at least not to her satisfaction. Naturally, the only decision was to forge some diplomas from the University of Strasbourg, as well as a certificate from the French Order of Physicians. Sonia got hired as a general practitioner by using the identities of two doctors who shared her name. She had no experience, had no idea what she was doing, and was wearing a GPS tagging bracelet for an unrelated crime, so she was quickly caught and exposed in October 2021, after, um, 3 years of fake doctoring, according to France Live.
Not to be deterred by this temporary setback, Sonia proceeded to immediately find work as an ophthalmologist, a career that requires more than 10 years of training, continuing her fraudulent medical career until recently, when she was caught again and sentenced to 3 years in prison. She did make 70,000 euros a year as a fake doctor, which isn’t exactly huge money, but certainly not bad either.
We certainly hope she’s learned her lesson about impersonating a doctor, at this point, but maybe she should just go to medical school. If not, northern France might just end up with a new endocrinologist or oncologist floating around in 3 years.
Speak louder, I can’t see you
With the introduction of FaceTime and the pandemic pushing work and social events to Zoom, video calls have become ubiquitous. Along the way, however, we’ve had to learn to adjust to technical difficulties. Often by yelling at the screen when the video quality is disrupted. Waving our hands and arms, speaking louder. Sound like you?
Well, a new study published in Royal Society Open Science shows that it sounds like a lot of us.
James Trujillo of the Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, who was lead author of the paper, said on Eurekalert that “previous research has shown that speech and gestures are linked, but ours is the first to look into how visuals impact our behavior in those fields.”
He and his associates set up 40 participants in separate rooms to have conversations in pairs over a video chat. Over the course of 40 minutes, the video quality started to deteriorate from clear to extremely blurry. When the video quality was affected, participants started with gestures but as the quality continued to lessen the gestures increased and so did the decibels of their voices.
Even when the participants could barely see each other, they still gestured and their voices were even louder, positively supporting the idea that gestures and speech are a dynamically linked when it comes to communication. Even on regular phone calls, when we can’t see each other at all, people make small movements and gestures, Mr. Trujillo said.
So, the next time the Wifi is terrible and your video calls keep cutting out, don’t worry about looking foolish screaming at the computer. We’ve all been there.
Seek a doctor if standing at attention for more than 4 hours
Imbrochável. In Brazil, it means “unfloppable” or “flaccid proof.” It’s also a word that Brazilian president Jair Bolsonaro likes to use when referring to himself. Gives you a good idea of what he’s all about. Imagine his embarrassment when news recently broke about more than 30,000 pills of Viagra that had been secretly distributed to the Brazilian military.
The military offered a simple and plausible explanation: The Viagra had been prescribed to treat pulmonary hypertension. Fair, but when a Brazilian newspaper dug a little deeper, they found that this was not the case. The Viagra was, in general, being used for its, shall we say, traditional purpose.
Many Brazilians reacted poorly to the news that their tax dollars were being used to provide Brazilian soldiers with downstairs assistance, with the standard associated furor on social media. A rival politician, Ciro Gomes, who is planning on challenging the president in an upcoming election, had perhaps the best remark on the situation: “Unless they’re able to prove they’re developing some kind of secret weapon – capable of revolutionizing the international arms industry – it’ll be tough to justify the purchase of 35,000 units of a erectile dysfunction drug.”
Hmm, secret weapon. Well, a certain Russian fellow has made a bit of a thrust into world affairs recently. Does anyone know if Putin is sitting on a big Viagra stash?
Who needs medical degrees anyway?
It’s no secret that doctors make a fair chunk of change. It’s a lucrative profession, but that big fat paycheck is siloed behind long, tough years of medical school and residency. It’s not an easy path doctors walk. Or at least, it’s not supposed to be. Anything’s easy if you’re willing to lie.
That brings us to Sonia, a 31-year-old woman from northern France with a bachelor’s degree in real estate management who wasn’t bringing in enough money for her three children, at least not to her satisfaction. Naturally, the only decision was to forge some diplomas from the University of Strasbourg, as well as a certificate from the French Order of Physicians. Sonia got hired as a general practitioner by using the identities of two doctors who shared her name. She had no experience, had no idea what she was doing, and was wearing a GPS tagging bracelet for an unrelated crime, so she was quickly caught and exposed in October 2021, after, um, 3 years of fake doctoring, according to France Live.
Not to be deterred by this temporary setback, Sonia proceeded to immediately find work as an ophthalmologist, a career that requires more than 10 years of training, continuing her fraudulent medical career until recently, when she was caught again and sentenced to 3 years in prison. She did make 70,000 euros a year as a fake doctor, which isn’t exactly huge money, but certainly not bad either.
We certainly hope she’s learned her lesson about impersonating a doctor, at this point, but maybe she should just go to medical school. If not, northern France might just end up with a new endocrinologist or oncologist floating around in 3 years.
No need to ‘guess what size horse you are’
Is COVID-19 warming up for yet another surge? Maybe. That means it’s also time for the return of its remora-like follower, ivermectin. Our thanks go out to the Tennessee state legislature for bringing the proven-to-be-ineffective treatment for COVID back into our hearts and minds and emergency rooms.
Both the state House and Senate have approved a bill that allows pharmacists to dispense the antiparasitic drug without a prescription while shielding them “from any liability that could arise from dispensing ivermectin,” Nashville Public Radio reported.
The drug’s manufacturer, Merck, said over a year ago that there is “no scientific basis for a potential therapeutic effect against COVID-19 from preclinical studies … and a concerning lack of safety data.” More recently, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that ivermectin treatment had no important benefits in patients with COVID.
Last week, the bill’s Senate sponsor, Frank Niceley of Strawberry Plains, said that it was all about safety, as he explained to NPR station WPLN: “It’s a lot safer to go to your pharmacist and let him tell you how much ivermectin to take than it is to go to the co-op and guess what size horse you are.”
And on that note, here are a few more items of business that just might end up on the legislature’s calendar:
- Horses will be allowed to “share” their unused ivermectin with humans and other mammals.
- An apple a day not only keeps the doctor away, but the IRS and the FDA as well.
- Colon cleansing is more fun than humans should be allowed to have.
- TikTok videos qualify as CME.
Who needs medical degrees anyway?
It’s no secret that doctors make a fair chunk of change. It’s a lucrative profession, but that big fat paycheck is siloed behind long, tough years of medical school and residency. It’s not an easy path doctors walk. Or at least, it’s not supposed to be. Anything’s easy if you’re willing to lie.
That brings us to Sonia, a 31-year-old woman from northern France with a bachelor’s degree in real estate management who wasn’t bringing in enough money for her three children, at least not to her satisfaction. Naturally, the only decision was to forge some diplomas from the University of Strasbourg, as well as a certificate from the French Order of Physicians. Sonia got hired as a general practitioner by using the identities of two doctors who shared her name. She had no experience, had no idea what she was doing, and was wearing a GPS tagging bracelet for an unrelated crime, so she was quickly caught and exposed in October 2021, after, um, 3 years of fake doctoring, according to France Live.
Not to be deterred by this temporary setback, Sonia proceeded to immediately find work as an ophthalmologist, a career that requires more than 10 years of training, continuing her fraudulent medical career until recently, when she was caught again and sentenced to 3 years in prison. She did make 70,000 euros a year as a fake doctor, which isn’t exactly huge money, but certainly not bad either.
We certainly hope she’s learned her lesson about impersonating a doctor, at this point, but maybe she should just go to medical school. If not, northern France might just end up with a new endocrinologist or oncologist floating around in 3 years.
Speak louder, I can’t see you
With the introduction of FaceTime and the pandemic pushing work and social events to Zoom, video calls have become ubiquitous. Along the way, however, we’ve had to learn to adjust to technical difficulties. Often by yelling at the screen when the video quality is disrupted. Waving our hands and arms, speaking louder. Sound like you?
Well, a new study published in Royal Society Open Science shows that it sounds like a lot of us.
James Trujillo of the Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, who was lead author of the paper, said on Eurekalert that “previous research has shown that speech and gestures are linked, but ours is the first to look into how visuals impact our behavior in those fields.”
He and his associates set up 40 participants in separate rooms to have conversations in pairs over a video chat. Over the course of 40 minutes, the video quality started to deteriorate from clear to extremely blurry. When the video quality was affected, participants started with gestures but as the quality continued to lessen the gestures increased and so did the decibels of their voices.
Even when the participants could barely see each other, they still gestured and their voices were even louder, positively supporting the idea that gestures and speech are a dynamically linked when it comes to communication. Even on regular phone calls, when we can’t see each other at all, people make small movements and gestures, Mr. Trujillo said.
So, the next time the Wifi is terrible and your video calls keep cutting out, don’t worry about looking foolish screaming at the computer. We’ve all been there.
Seek a doctor if standing at attention for more than 4 hours
Imbrochável. In Brazil, it means “unfloppable” or “flaccid proof.” It’s also a word that Brazilian president Jair Bolsonaro likes to use when referring to himself. Gives you a good idea of what he’s all about. Imagine his embarrassment when news recently broke about more than 30,000 pills of Viagra that had been secretly distributed to the Brazilian military.
The military offered a simple and plausible explanation: The Viagra had been prescribed to treat pulmonary hypertension. Fair, but when a Brazilian newspaper dug a little deeper, they found that this was not the case. The Viagra was, in general, being used for its, shall we say, traditional purpose.
Many Brazilians reacted poorly to the news that their tax dollars were being used to provide Brazilian soldiers with downstairs assistance, with the standard associated furor on social media. A rival politician, Ciro Gomes, who is planning on challenging the president in an upcoming election, had perhaps the best remark on the situation: “Unless they’re able to prove they’re developing some kind of secret weapon – capable of revolutionizing the international arms industry – it’ll be tough to justify the purchase of 35,000 units of a erectile dysfunction drug.”
Hmm, secret weapon. Well, a certain Russian fellow has made a bit of a thrust into world affairs recently. Does anyone know if Putin is sitting on a big Viagra stash?
Who needs medical degrees anyway?
It’s no secret that doctors make a fair chunk of change. It’s a lucrative profession, but that big fat paycheck is siloed behind long, tough years of medical school and residency. It’s not an easy path doctors walk. Or at least, it’s not supposed to be. Anything’s easy if you’re willing to lie.
That brings us to Sonia, a 31-year-old woman from northern France with a bachelor’s degree in real estate management who wasn’t bringing in enough money for her three children, at least not to her satisfaction. Naturally, the only decision was to forge some diplomas from the University of Strasbourg, as well as a certificate from the French Order of Physicians. Sonia got hired as a general practitioner by using the identities of two doctors who shared her name. She had no experience, had no idea what she was doing, and was wearing a GPS tagging bracelet for an unrelated crime, so she was quickly caught and exposed in October 2021, after, um, 3 years of fake doctoring, according to France Live.
Not to be deterred by this temporary setback, Sonia proceeded to immediately find work as an ophthalmologist, a career that requires more than 10 years of training, continuing her fraudulent medical career until recently, when she was caught again and sentenced to 3 years in prison. She did make 70,000 euros a year as a fake doctor, which isn’t exactly huge money, but certainly not bad either.
We certainly hope she’s learned her lesson about impersonating a doctor, at this point, but maybe she should just go to medical school. If not, northern France might just end up with a new endocrinologist or oncologist floating around in 3 years.
No need to ‘guess what size horse you are’
Is COVID-19 warming up for yet another surge? Maybe. That means it’s also time for the return of its remora-like follower, ivermectin. Our thanks go out to the Tennessee state legislature for bringing the proven-to-be-ineffective treatment for COVID back into our hearts and minds and emergency rooms.
Both the state House and Senate have approved a bill that allows pharmacists to dispense the antiparasitic drug without a prescription while shielding them “from any liability that could arise from dispensing ivermectin,” Nashville Public Radio reported.
The drug’s manufacturer, Merck, said over a year ago that there is “no scientific basis for a potential therapeutic effect against COVID-19 from preclinical studies … and a concerning lack of safety data.” More recently, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that ivermectin treatment had no important benefits in patients with COVID.
Last week, the bill’s Senate sponsor, Frank Niceley of Strawberry Plains, said that it was all about safety, as he explained to NPR station WPLN: “It’s a lot safer to go to your pharmacist and let him tell you how much ivermectin to take than it is to go to the co-op and guess what size horse you are.”
And on that note, here are a few more items of business that just might end up on the legislature’s calendar:
- Horses will be allowed to “share” their unused ivermectin with humans and other mammals.
- An apple a day not only keeps the doctor away, but the IRS and the FDA as well.
- Colon cleansing is more fun than humans should be allowed to have.
- TikTok videos qualify as CME.
Who needs medical degrees anyway?
It’s no secret that doctors make a fair chunk of change. It’s a lucrative profession, but that big fat paycheck is siloed behind long, tough years of medical school and residency. It’s not an easy path doctors walk. Or at least, it’s not supposed to be. Anything’s easy if you’re willing to lie.
That brings us to Sonia, a 31-year-old woman from northern France with a bachelor’s degree in real estate management who wasn’t bringing in enough money for her three children, at least not to her satisfaction. Naturally, the only decision was to forge some diplomas from the University of Strasbourg, as well as a certificate from the French Order of Physicians. Sonia got hired as a general practitioner by using the identities of two doctors who shared her name. She had no experience, had no idea what she was doing, and was wearing a GPS tagging bracelet for an unrelated crime, so she was quickly caught and exposed in October 2021, after, um, 3 years of fake doctoring, according to France Live.
Not to be deterred by this temporary setback, Sonia proceeded to immediately find work as an ophthalmologist, a career that requires more than 10 years of training, continuing her fraudulent medical career until recently, when she was caught again and sentenced to 3 years in prison. She did make 70,000 euros a year as a fake doctor, which isn’t exactly huge money, but certainly not bad either.
We certainly hope she’s learned her lesson about impersonating a doctor, at this point, but maybe she should just go to medical school. If not, northern France might just end up with a new endocrinologist or oncologist floating around in 3 years.
Speak louder, I can’t see you
With the introduction of FaceTime and the pandemic pushing work and social events to Zoom, video calls have become ubiquitous. Along the way, however, we’ve had to learn to adjust to technical difficulties. Often by yelling at the screen when the video quality is disrupted. Waving our hands and arms, speaking louder. Sound like you?
Well, a new study published in Royal Society Open Science shows that it sounds like a lot of us.
James Trujillo of the Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, who was lead author of the paper, said on Eurekalert that “previous research has shown that speech and gestures are linked, but ours is the first to look into how visuals impact our behavior in those fields.”
He and his associates set up 40 participants in separate rooms to have conversations in pairs over a video chat. Over the course of 40 minutes, the video quality started to deteriorate from clear to extremely blurry. When the video quality was affected, participants started with gestures but as the quality continued to lessen the gestures increased and so did the decibels of their voices.
Even when the participants could barely see each other, they still gestured and their voices were even louder, positively supporting the idea that gestures and speech are a dynamically linked when it comes to communication. Even on regular phone calls, when we can’t see each other at all, people make small movements and gestures, Mr. Trujillo said.
So, the next time the Wifi is terrible and your video calls keep cutting out, don’t worry about looking foolish screaming at the computer. We’ve all been there.
Seek a doctor if standing at attention for more than 4 hours
Imbrochável. In Brazil, it means “unfloppable” or “flaccid proof.” It’s also a word that Brazilian president Jair Bolsonaro likes to use when referring to himself. Gives you a good idea of what he’s all about. Imagine his embarrassment when news recently broke about more than 30,000 pills of Viagra that had been secretly distributed to the Brazilian military.
The military offered a simple and plausible explanation: The Viagra had been prescribed to treat pulmonary hypertension. Fair, but when a Brazilian newspaper dug a little deeper, they found that this was not the case. The Viagra was, in general, being used for its, shall we say, traditional purpose.
Many Brazilians reacted poorly to the news that their tax dollars were being used to provide Brazilian soldiers with downstairs assistance, with the standard associated furor on social media. A rival politician, Ciro Gomes, who is planning on challenging the president in an upcoming election, had perhaps the best remark on the situation: “Unless they’re able to prove they’re developing some kind of secret weapon – capable of revolutionizing the international arms industry – it’ll be tough to justify the purchase of 35,000 units of a erectile dysfunction drug.”
Hmm, secret weapon. Well, a certain Russian fellow has made a bit of a thrust into world affairs recently. Does anyone know if Putin is sitting on a big Viagra stash?
Treat or refer? New primary care flow diagrams for allergy patients
Most patients with allergy problems first see PCPs, not allergists, the authors write in Allergy. The new flow diagrams help PCPs treat anaphylaxis, asthma, drug allergy, food allergy, and urticaria.
“The European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology established the Logogram Task Force to create a set of simple flow diagrams to assist allergy nonspecialist, generalist, and primary care teams in the diagnosis of five common allergic diseases encountered in primary care,” lead author Dermot Ryan, MB BCh, BAO, FRGCP, of the University of Edinburgh told this news organization.
“The source documents were mainstream guidelines coupled with ancillary literature,” he added in an email. “A multi-disciplinary taskforce ... distilled these guidelines into accessible, comprehensible, usable, and context-specific flow diagrams.”
The flow diagrams developed in Europe can be used by providers in the United States and elsewhere
“These diagrams are consistent with practices in the U.S.,” Christina E. Ciaccio, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics and the section chief of pediatric allergy and immunology at the University of Chicago Medicine, said in an email. “They will prove helpful to PCPs in the U.S. and elsewhere, particularly to young physicians new to practice.
“Treating allergies is part of the ‘bread-and-butter’ practice of primary care physicians in the U.S.,” Dr. Ciaccio, who was not involved in developing the flow diagrams, explained. “Up to 30% of Americans are atopic, and the vast majority seek treatment advice from their PCP first.”
The flow diagrams can help providers in developing countries, where allergic diseases are common, provide the best patient care possible, she said.
At some point, a PCP may need to think beyond flow diagrams and refer the patient to an allergist
“If the treatment plan for a patient falls outside first- or second-line medications, or if a diagnosis is unclear with preliminary testing, a PCP may reach out to an allergy/immunology specialist to assist in providing care,” Dr. Ciaccio advised. “Allergists may provide treatment options, such as immunotherapy, that the PCP does not offer. PCPs also often reach out to allergy team members for help with patients whose allergies are not ‘run-of-the-mill.’
“The flow diagrams are complex and may not be practical in the middle of a busy clinic,” she cautioned. “However, when a patient comes into a primary care clinic with an atypical presentation of an allergic disease, the diagrams are likely to help a physician feel confident that an allergist is the right physician for consultation.”
Patricia Lynne Lugar, MD, an associate professor of medicine in pulmonary, allergy, and critical care medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C., noted that providers in the U.S. can use the flow diagrams because the definitions, differential diagnosis, and treatments for the conditions they cover are similar.
“The flow diagrams are comprehensive, and they attempt to condense a great deal of information into summary points. They are very useful in the U.S., and not just for generalists,” Dr. Lugar, who also was not involved in the project, said. “Even emergency rooms would benefit from these flow diagrams, especially regarding the recognition of symptoms and differential diagnosis.”
Asthma and seasonal and environmental allergies are often managed by PCPs, and the flow diagrams would help them decide when to refer their patients to an allergist, she added in an email.
Dr. Lugar advises PCPs to “recognize the symptoms of an allergic condition, offer treatment based on confidence the diagnosis is correct, and offer a referral for testing to confirm the allergy.
“Because 50% or more of asthmatics are allergic, all asthmatics should be offered an allergy evaluation to determine their allergies and avoid exacerbating the asthma,” she added. “I do not see the flow diagrams as comprehensive enough to manage chronic urticaria, asthma, venom allergy, and drug allergy.”
With food allergy, environmental allergy, venom allergy, or anaphylaxis, “allergists are experts at considering the differential diagnosis and providing the next steps in the diagnostic workup,” Dr. Lugar said. “Allergists can also provide special treatments, such as allergen-specific immunotherapy or desensitization.”
The flow diagrams guide nonspecialists in diagnosis and treatment of their patients with allergy, with supplementary information as needed. The diagrams recommend referral to a specialist when appropriate, as in cases of anaphylaxis, or chronic urticaria.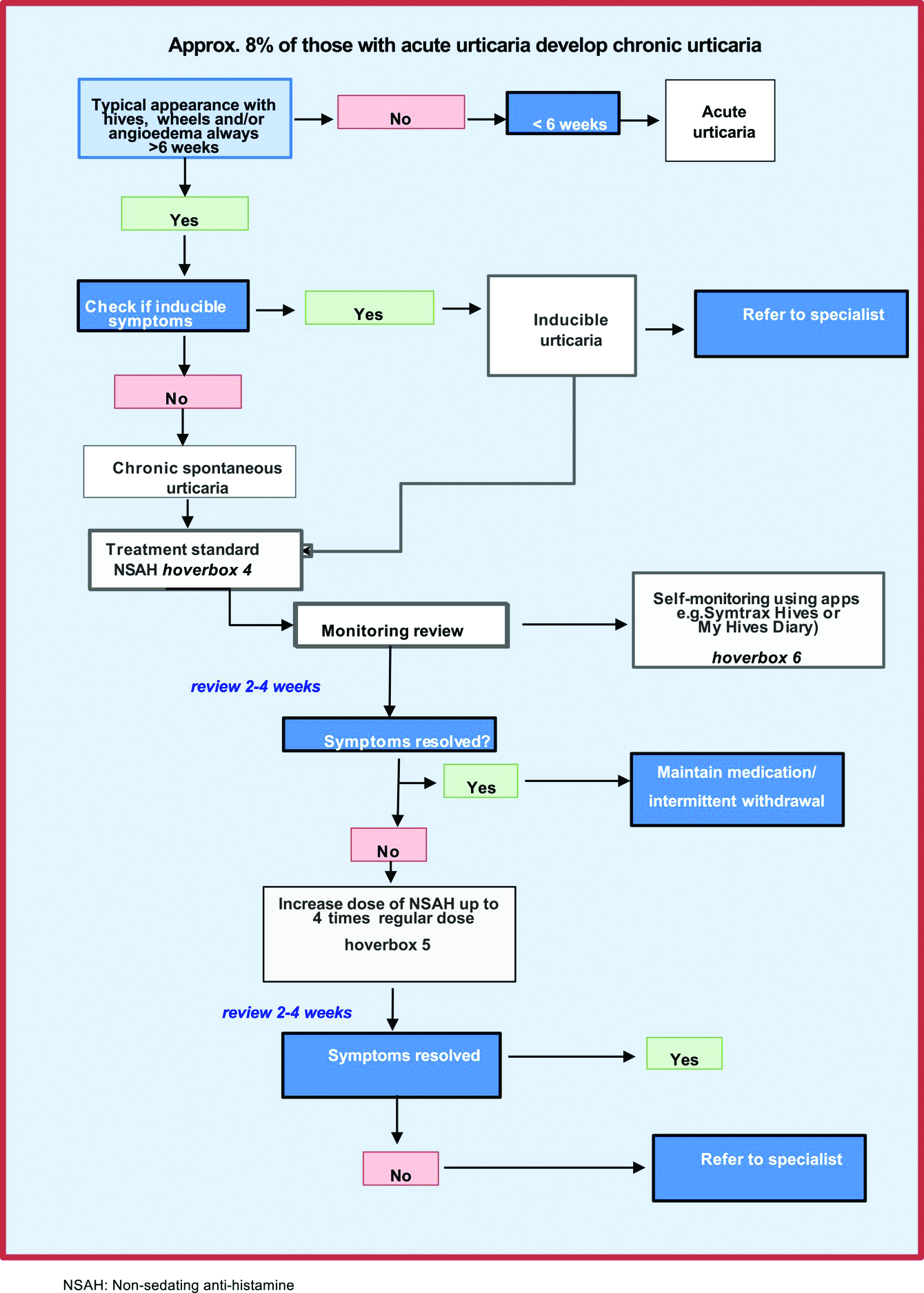
The task force was funded by EAACI. Dr. Ryan and several other authors report financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Ciaccio and Dr. Lugar report no such relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most patients with allergy problems first see PCPs, not allergists, the authors write in Allergy. The new flow diagrams help PCPs treat anaphylaxis, asthma, drug allergy, food allergy, and urticaria.
“The European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology established the Logogram Task Force to create a set of simple flow diagrams to assist allergy nonspecialist, generalist, and primary care teams in the diagnosis of five common allergic diseases encountered in primary care,” lead author Dermot Ryan, MB BCh, BAO, FRGCP, of the University of Edinburgh told this news organization.
“The source documents were mainstream guidelines coupled with ancillary literature,” he added in an email. “A multi-disciplinary taskforce ... distilled these guidelines into accessible, comprehensible, usable, and context-specific flow diagrams.”
The flow diagrams developed in Europe can be used by providers in the United States and elsewhere
“These diagrams are consistent with practices in the U.S.,” Christina E. Ciaccio, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics and the section chief of pediatric allergy and immunology at the University of Chicago Medicine, said in an email. “They will prove helpful to PCPs in the U.S. and elsewhere, particularly to young physicians new to practice.
“Treating allergies is part of the ‘bread-and-butter’ practice of primary care physicians in the U.S.,” Dr. Ciaccio, who was not involved in developing the flow diagrams, explained. “Up to 30% of Americans are atopic, and the vast majority seek treatment advice from their PCP first.”
The flow diagrams can help providers in developing countries, where allergic diseases are common, provide the best patient care possible, she said.
At some point, a PCP may need to think beyond flow diagrams and refer the patient to an allergist
“If the treatment plan for a patient falls outside first- or second-line medications, or if a diagnosis is unclear with preliminary testing, a PCP may reach out to an allergy/immunology specialist to assist in providing care,” Dr. Ciaccio advised. “Allergists may provide treatment options, such as immunotherapy, that the PCP does not offer. PCPs also often reach out to allergy team members for help with patients whose allergies are not ‘run-of-the-mill.’
“The flow diagrams are complex and may not be practical in the middle of a busy clinic,” she cautioned. “However, when a patient comes into a primary care clinic with an atypical presentation of an allergic disease, the diagrams are likely to help a physician feel confident that an allergist is the right physician for consultation.”
Patricia Lynne Lugar, MD, an associate professor of medicine in pulmonary, allergy, and critical care medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C., noted that providers in the U.S. can use the flow diagrams because the definitions, differential diagnosis, and treatments for the conditions they cover are similar.
“The flow diagrams are comprehensive, and they attempt to condense a great deal of information into summary points. They are very useful in the U.S., and not just for generalists,” Dr. Lugar, who also was not involved in the project, said. “Even emergency rooms would benefit from these flow diagrams, especially regarding the recognition of symptoms and differential diagnosis.”
Asthma and seasonal and environmental allergies are often managed by PCPs, and the flow diagrams would help them decide when to refer their patients to an allergist, she added in an email.
Dr. Lugar advises PCPs to “recognize the symptoms of an allergic condition, offer treatment based on confidence the diagnosis is correct, and offer a referral for testing to confirm the allergy.
“Because 50% or more of asthmatics are allergic, all asthmatics should be offered an allergy evaluation to determine their allergies and avoid exacerbating the asthma,” she added. “I do not see the flow diagrams as comprehensive enough to manage chronic urticaria, asthma, venom allergy, and drug allergy.”
With food allergy, environmental allergy, venom allergy, or anaphylaxis, “allergists are experts at considering the differential diagnosis and providing the next steps in the diagnostic workup,” Dr. Lugar said. “Allergists can also provide special treatments, such as allergen-specific immunotherapy or desensitization.”
The flow diagrams guide nonspecialists in diagnosis and treatment of their patients with allergy, with supplementary information as needed. The diagrams recommend referral to a specialist when appropriate, as in cases of anaphylaxis, or chronic urticaria.
The task force was funded by EAACI. Dr. Ryan and several other authors report financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Ciaccio and Dr. Lugar report no such relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most patients with allergy problems first see PCPs, not allergists, the authors write in Allergy. The new flow diagrams help PCPs treat anaphylaxis, asthma, drug allergy, food allergy, and urticaria.
“The European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology established the Logogram Task Force to create a set of simple flow diagrams to assist allergy nonspecialist, generalist, and primary care teams in the diagnosis of five common allergic diseases encountered in primary care,” lead author Dermot Ryan, MB BCh, BAO, FRGCP, of the University of Edinburgh told this news organization.
“The source documents were mainstream guidelines coupled with ancillary literature,” he added in an email. “A multi-disciplinary taskforce ... distilled these guidelines into accessible, comprehensible, usable, and context-specific flow diagrams.”
The flow diagrams developed in Europe can be used by providers in the United States and elsewhere
“These diagrams are consistent with practices in the U.S.,” Christina E. Ciaccio, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics and the section chief of pediatric allergy and immunology at the University of Chicago Medicine, said in an email. “They will prove helpful to PCPs in the U.S. and elsewhere, particularly to young physicians new to practice.
“Treating allergies is part of the ‘bread-and-butter’ practice of primary care physicians in the U.S.,” Dr. Ciaccio, who was not involved in developing the flow diagrams, explained. “Up to 30% of Americans are atopic, and the vast majority seek treatment advice from their PCP first.”
The flow diagrams can help providers in developing countries, where allergic diseases are common, provide the best patient care possible, she said.
At some point, a PCP may need to think beyond flow diagrams and refer the patient to an allergist
“If the treatment plan for a patient falls outside first- or second-line medications, or if a diagnosis is unclear with preliminary testing, a PCP may reach out to an allergy/immunology specialist to assist in providing care,” Dr. Ciaccio advised. “Allergists may provide treatment options, such as immunotherapy, that the PCP does not offer. PCPs also often reach out to allergy team members for help with patients whose allergies are not ‘run-of-the-mill.’
“The flow diagrams are complex and may not be practical in the middle of a busy clinic,” she cautioned. “However, when a patient comes into a primary care clinic with an atypical presentation of an allergic disease, the diagrams are likely to help a physician feel confident that an allergist is the right physician for consultation.”
Patricia Lynne Lugar, MD, an associate professor of medicine in pulmonary, allergy, and critical care medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C., noted that providers in the U.S. can use the flow diagrams because the definitions, differential diagnosis, and treatments for the conditions they cover are similar.
“The flow diagrams are comprehensive, and they attempt to condense a great deal of information into summary points. They are very useful in the U.S., and not just for generalists,” Dr. Lugar, who also was not involved in the project, said. “Even emergency rooms would benefit from these flow diagrams, especially regarding the recognition of symptoms and differential diagnosis.”
Asthma and seasonal and environmental allergies are often managed by PCPs, and the flow diagrams would help them decide when to refer their patients to an allergist, she added in an email.
Dr. Lugar advises PCPs to “recognize the symptoms of an allergic condition, offer treatment based on confidence the diagnosis is correct, and offer a referral for testing to confirm the allergy.
“Because 50% or more of asthmatics are allergic, all asthmatics should be offered an allergy evaluation to determine their allergies and avoid exacerbating the asthma,” she added. “I do not see the flow diagrams as comprehensive enough to manage chronic urticaria, asthma, venom allergy, and drug allergy.”
With food allergy, environmental allergy, venom allergy, or anaphylaxis, “allergists are experts at considering the differential diagnosis and providing the next steps in the diagnostic workup,” Dr. Lugar said. “Allergists can also provide special treatments, such as allergen-specific immunotherapy or desensitization.”
The flow diagrams guide nonspecialists in diagnosis and treatment of their patients with allergy, with supplementary information as needed. The diagrams recommend referral to a specialist when appropriate, as in cases of anaphylaxis, or chronic urticaria.
The task force was funded by EAACI. Dr. Ryan and several other authors report financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Ciaccio and Dr. Lugar report no such relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ALLERGY
Commentary: Babies die as congenital syphilis continues a decade-long surge across the U.S.
The data are shocking: Almost 35,000 U.S. syphilis cases by mid-July 2022 with the highest rates per/100,000 population in Nevada (n = 21), California (n = 19), and Mississippi (n = 16). Excluding Nevada, California, and Oklahoma, rates over 12/100,000 were concentrated in the southernmost U.S. states. Overall, the 2,268 congenital syphilis cases in U.S. children born in 2021 was a 6% increase over 2020, and a 680% increase over 2012. (Note: All 2021 data are not yet available because of public health STI resources being diverted to COVID-19 control.) A telling number is the 166 congenital syphilis deaths in babies born in 2021 – a 1,000% increase over 2012. Another concern is that 50% of U.S. counties reported at least one congenital syphilis case in 2019 – the last time frame from which county-specific data are available.
Syphilis afflicts the underserved and underprivileged more than other demographic groups, particularly when public health budgets are not adequate (funding for public health STI prevention/treatment efforts has lagged for more than a decade), and/or when public health emergencies such as the pandemic divert public health resources away from STI prevention/treatment efforts.
As pediatric care providers, we can help by heightening our vigilance and appropriately testing for and treating syphilis, particularly in newborns/infants, regardless of where we work. And we can advocate for increased public health STI funding allocation whenever possible. It is a smart economic move because it costs nearly 1,000 times more to manage congenital syphilis and its sequelae than to prevent or treat it.
Christopher J. Harrison, MD, is professor, University of Missouri Kansas City School of Medicine, department of medicine, infectious diseases section, Kansas City. He has no financial conflicts of interest.
The data are shocking: Almost 35,000 U.S. syphilis cases by mid-July 2022 with the highest rates per/100,000 population in Nevada (n = 21), California (n = 19), and Mississippi (n = 16). Excluding Nevada, California, and Oklahoma, rates over 12/100,000 were concentrated in the southernmost U.S. states. Overall, the 2,268 congenital syphilis cases in U.S. children born in 2021 was a 6% increase over 2020, and a 680% increase over 2012. (Note: All 2021 data are not yet available because of public health STI resources being diverted to COVID-19 control.) A telling number is the 166 congenital syphilis deaths in babies born in 2021 – a 1,000% increase over 2012. Another concern is that 50% of U.S. counties reported at least one congenital syphilis case in 2019 – the last time frame from which county-specific data are available.
Syphilis afflicts the underserved and underprivileged more than other demographic groups, particularly when public health budgets are not adequate (funding for public health STI prevention/treatment efforts has lagged for more than a decade), and/or when public health emergencies such as the pandemic divert public health resources away from STI prevention/treatment efforts.
As pediatric care providers, we can help by heightening our vigilance and appropriately testing for and treating syphilis, particularly in newborns/infants, regardless of where we work. And we can advocate for increased public health STI funding allocation whenever possible. It is a smart economic move because it costs nearly 1,000 times more to manage congenital syphilis and its sequelae than to prevent or treat it.
Christopher J. Harrison, MD, is professor, University of Missouri Kansas City School of Medicine, department of medicine, infectious diseases section, Kansas City. He has no financial conflicts of interest.
The data are shocking: Almost 35,000 U.S. syphilis cases by mid-July 2022 with the highest rates per/100,000 population in Nevada (n = 21), California (n = 19), and Mississippi (n = 16). Excluding Nevada, California, and Oklahoma, rates over 12/100,000 were concentrated in the southernmost U.S. states. Overall, the 2,268 congenital syphilis cases in U.S. children born in 2021 was a 6% increase over 2020, and a 680% increase over 2012. (Note: All 2021 data are not yet available because of public health STI resources being diverted to COVID-19 control.) A telling number is the 166 congenital syphilis deaths in babies born in 2021 – a 1,000% increase over 2012. Another concern is that 50% of U.S. counties reported at least one congenital syphilis case in 2019 – the last time frame from which county-specific data are available.
Syphilis afflicts the underserved and underprivileged more than other demographic groups, particularly when public health budgets are not adequate (funding for public health STI prevention/treatment efforts has lagged for more than a decade), and/or when public health emergencies such as the pandemic divert public health resources away from STI prevention/treatment efforts.
As pediatric care providers, we can help by heightening our vigilance and appropriately testing for and treating syphilis, particularly in newborns/infants, regardless of where we work. And we can advocate for increased public health STI funding allocation whenever possible. It is a smart economic move because it costs nearly 1,000 times more to manage congenital syphilis and its sequelae than to prevent or treat it.
Christopher J. Harrison, MD, is professor, University of Missouri Kansas City School of Medicine, department of medicine, infectious diseases section, Kansas City. He has no financial conflicts of interest.