User login
Phase 3 data favor axi-cel over standard care in high-risk large B-cell lymphoma
Key clinical point: Compared with the current standard-of-care chemoimmunotherapy, second-line axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) significantly prolongs the overall survival of patients with early relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL).
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 47.2 months, patients receiving axi-cel vs standard care had a significantly longer median overall survival (not reached vs 31.1 months; hazard ratio 0.73; P = .03) and an absolute improvement in overall survival (8.6 percentage points at 4 years). No new treatment-related deaths were reported since the primary event-free survival analysis.
Study details: This primary overall survival analysis of the phase 3 ZUMA-7 trial included 359 adults with LBCL (refractory to or relapsed after first-line treatment) who were randomly assigned to receive axi-cel (n = 180) or standard care (n = 179).
Disclosures: This study was funded by Kite Pharma. Some authors, including the lead author, declared serving as advisory board members, consultants, or speakers for; receiving research support, speaker fees, travel expenses, or honoraria from; or owning stock or stock options in various sources, including Kite.
Source: Westin JR et al. Survival with axicabtagene ciloleucel in large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2023 (Jun 5). doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2301665
Key clinical point: Compared with the current standard-of-care chemoimmunotherapy, second-line axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) significantly prolongs the overall survival of patients with early relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL).
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 47.2 months, patients receiving axi-cel vs standard care had a significantly longer median overall survival (not reached vs 31.1 months; hazard ratio 0.73; P = .03) and an absolute improvement in overall survival (8.6 percentage points at 4 years). No new treatment-related deaths were reported since the primary event-free survival analysis.
Study details: This primary overall survival analysis of the phase 3 ZUMA-7 trial included 359 adults with LBCL (refractory to or relapsed after first-line treatment) who were randomly assigned to receive axi-cel (n = 180) or standard care (n = 179).
Disclosures: This study was funded by Kite Pharma. Some authors, including the lead author, declared serving as advisory board members, consultants, or speakers for; receiving research support, speaker fees, travel expenses, or honoraria from; or owning stock or stock options in various sources, including Kite.
Source: Westin JR et al. Survival with axicabtagene ciloleucel in large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2023 (Jun 5). doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2301665
Key clinical point: Compared with the current standard-of-care chemoimmunotherapy, second-line axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) significantly prolongs the overall survival of patients with early relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL).
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 47.2 months, patients receiving axi-cel vs standard care had a significantly longer median overall survival (not reached vs 31.1 months; hazard ratio 0.73; P = .03) and an absolute improvement in overall survival (8.6 percentage points at 4 years). No new treatment-related deaths were reported since the primary event-free survival analysis.
Study details: This primary overall survival analysis of the phase 3 ZUMA-7 trial included 359 adults with LBCL (refractory to or relapsed after first-line treatment) who were randomly assigned to receive axi-cel (n = 180) or standard care (n = 179).
Disclosures: This study was funded by Kite Pharma. Some authors, including the lead author, declared serving as advisory board members, consultants, or speakers for; receiving research support, speaker fees, travel expenses, or honoraria from; or owning stock or stock options in various sources, including Kite.
Source: Westin JR et al. Survival with axicabtagene ciloleucel in large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2023 (Jun 5). doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2301665
Pirtobrutinib offers a promising treatment option for covalent BTK-inhibitor pretreated MCL
Key clinical point: Pirtobrutinib demonstrated durable efficacy and a favorable safety profile in patients with covalent Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (cBTKi) pretreated relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: The overall response rate was 57.8% (95% CI 46.9%-68.1%), with the complete response rate being 20.0%. At a median follow-up of 12 months, the median duration of response was 21.6 (95% CI 7.5-not reached) months. Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events were not frequent, with neutropenia (8.5%) being the most common.
Study details: This multicenter phase 1/2 BRUIN trial included 90 cBTKi pretreated patients with relapsed or refractory MCL in the primary efficacy cohort who received 25-300 mg and 200 mg pirtobrutinib once daily orally in the phases 1 and 2 of the trial, respectively.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Loxo Oncology Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly and Company. Some authors reported ties with Eli Lilly and others. Seven authors declared being employees of or stockholders in Eli Lilly.
Source: Wang ML et al. Pirtobrutinib in covalent BTK-inhibitor pre-treated mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2023 (May 16). doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.00562
Key clinical point: Pirtobrutinib demonstrated durable efficacy and a favorable safety profile in patients with covalent Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (cBTKi) pretreated relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: The overall response rate was 57.8% (95% CI 46.9%-68.1%), with the complete response rate being 20.0%. At a median follow-up of 12 months, the median duration of response was 21.6 (95% CI 7.5-not reached) months. Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events were not frequent, with neutropenia (8.5%) being the most common.
Study details: This multicenter phase 1/2 BRUIN trial included 90 cBTKi pretreated patients with relapsed or refractory MCL in the primary efficacy cohort who received 25-300 mg and 200 mg pirtobrutinib once daily orally in the phases 1 and 2 of the trial, respectively.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Loxo Oncology Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly and Company. Some authors reported ties with Eli Lilly and others. Seven authors declared being employees of or stockholders in Eli Lilly.
Source: Wang ML et al. Pirtobrutinib in covalent BTK-inhibitor pre-treated mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2023 (May 16). doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.00562
Key clinical point: Pirtobrutinib demonstrated durable efficacy and a favorable safety profile in patients with covalent Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (cBTKi) pretreated relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: The overall response rate was 57.8% (95% CI 46.9%-68.1%), with the complete response rate being 20.0%. At a median follow-up of 12 months, the median duration of response was 21.6 (95% CI 7.5-not reached) months. Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events were not frequent, with neutropenia (8.5%) being the most common.
Study details: This multicenter phase 1/2 BRUIN trial included 90 cBTKi pretreated patients with relapsed or refractory MCL in the primary efficacy cohort who received 25-300 mg and 200 mg pirtobrutinib once daily orally in the phases 1 and 2 of the trial, respectively.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Loxo Oncology Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly and Company. Some authors reported ties with Eli Lilly and others. Seven authors declared being employees of or stockholders in Eli Lilly.
Source: Wang ML et al. Pirtobrutinib in covalent BTK-inhibitor pre-treated mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2023 (May 16). doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.00562
Erythematous Dermal Facial Plaques in a Neutropenic Patient
THE DIAGNOSIS: Neutrophilic Eccrine Hidradenitis
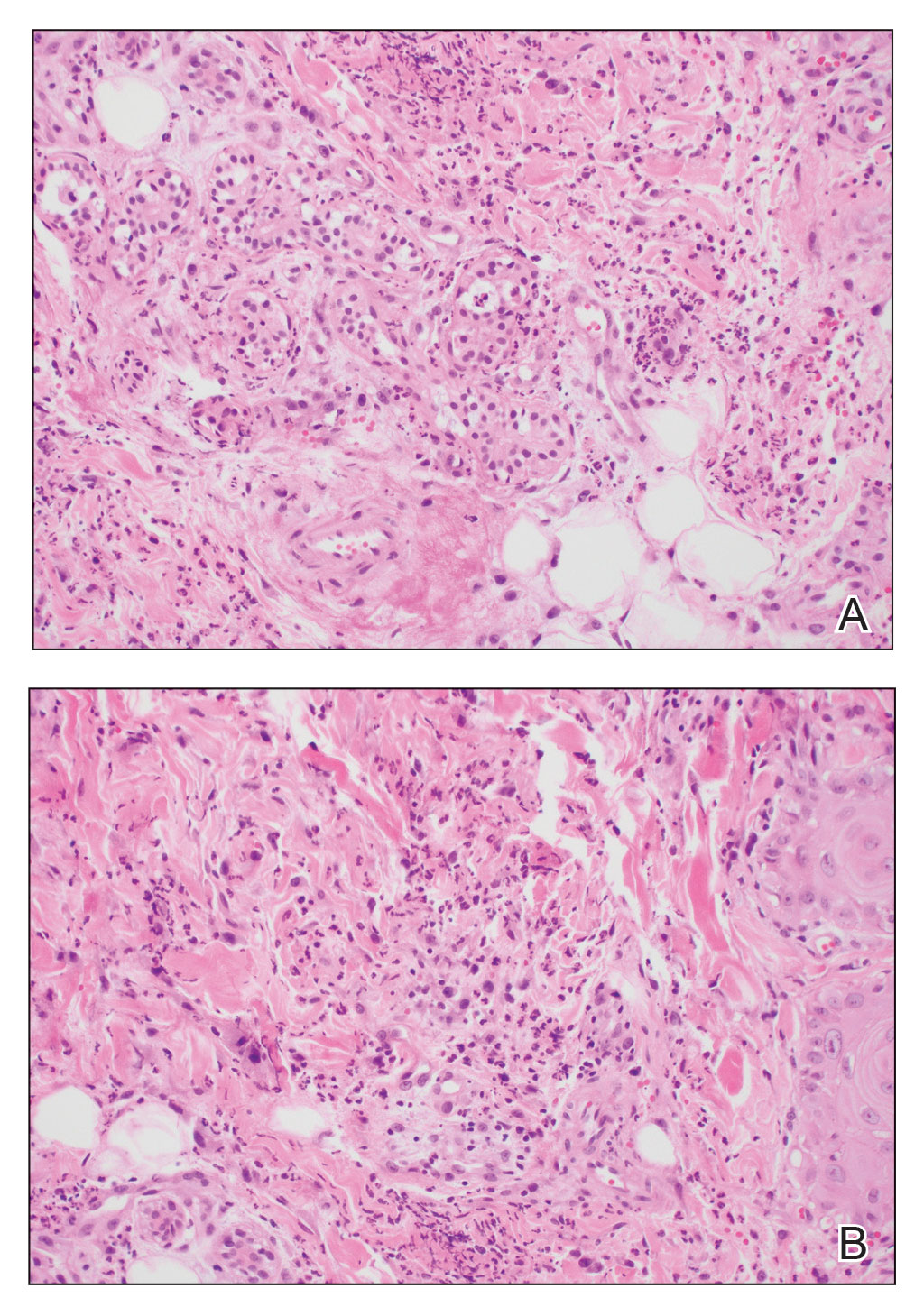
A biopsy from the left preauricular cheek demonstrated dermal neutrophilic inflammation around eccrine coils with focal necrosis (Figure). No notable diffuse dermal neutrophilic infiltrate was present, ruling out Sweet syndrome, and no notable interstitial neutrophilic infiltrate was present, making cellulitis and erysipelas less likely; panculture of tissue also was negative.1,2 Atypical cells in the deep dermis were positive for CD163 and negative for CD117, CD34, CD123, and myeloperoxidase, consistent with a diagnosis of neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis (NEH) and reactive histiocytes.3 Treatment with oral prednisone resulted in rapid improvement of symptoms.
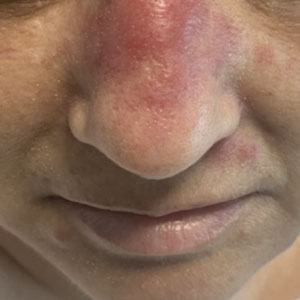
Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is a rare reactive neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by eccrine gland involvement. This benign and self-limited condition presents as asymmetric erythematous papules and plaques.2 Among 8 granulocytopenic patients with neutrophilic dermatoses, 5 were diagnosed with NEH.4 Although first identified in 1982, NEH remains poorly understood.2 Initial theories suggested that NEH developed due to cytotoxic substances secreted in sweat glands causing necrosis and neutrophil chemotaxis; however, chemotherapy exposure cannot be linked to every case of NEH. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis can be extremely difficult to differentiate clinically from conditions such as cellulitis and Sweet syndrome.
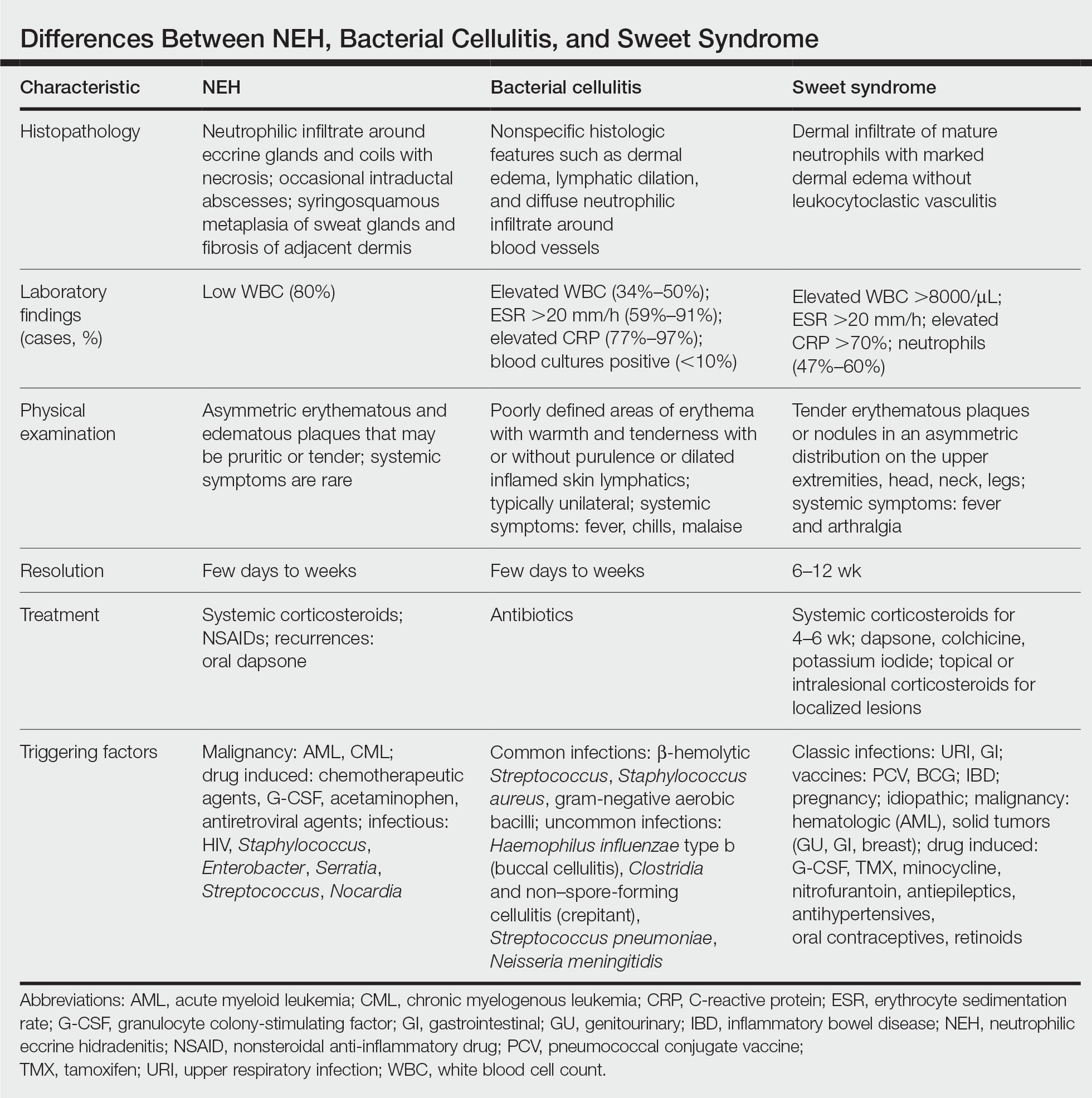
A patient history can be helpful in identifying triggering factors. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis most commonly is associated with malignant, drug-induced, or infectious triggers, while Sweet syndrome has a broad range of associations including infections, vaccines, inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy, malignancy, and drug-induced etiologies (Table).1 On average, NEH presents 10 days after chemotherapy induction, with 70% of cases presenting after the first chemotherapy cycle.5 Bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas have an infectious etiology, and patients may report symptoms such as fever, chills, or malaise. Immunosuppressed patients are at greater risk for infection; therefore, clinical signs of infection in a granulocytopenic patient should be addressed urgently.
Physical examination may have limited value in differentiating between these diagnoses, as neutrophilic dermatoses notoriously mimic infection. Cutaneous lesions can appear as pruritic or tender erythematous plaques, papules, or nodules in these conditions, though cellulitis and erysipelas tend to be unilateral and may have associated purulence or inflamed skin lymphatics. Given the potential for misdiagnosis, approaching patients with a broad differential can be helpful. In our patient, the differential diagnosis included Sweet syndrome, NEH, bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, leukemia cutis, sarcoid, and eosinophilic cellulitis.
Leukemia cutis refers to the infiltration of neoplastic leukocytes in the skin and often occurs in patients with peripheral leukemia, most often acute myeloid leukemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Patients with leukemia cutis often have a worse prognosis, as this finding signifies extramedullary spread of disease.6 Clinically, lesions can appear similar to those seen in our patient, though they typically are not symptomatic, can be nodular, tend to exhibit a violaceous hue, and occasionally may be hemorrhagic. Wells syndrome (also known as eosinophilic cellulitis) is an inflammatory dermatosis that presents as painful or pruritic, edematous and erythematous plaques.7,8 A green hue on resolution is present in some cases and may help clinicians differentiate this disease from mimickers.7 Often, eosinophilic cellulitis is misdiagnosed as bacterial cellulitis and treated with antibiotics. The presence of systemic symptoms such as fever or arthralgia is more typical of bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, eosinophilic cellulitis, or Sweet syndrome than of NEH.1 Additionally, inflammatory markers (ie, C-reactive protein) and white blood cell counts tend to be elevated in bacterial cellulitis and Sweet syndrome, while leukopenia often is seen in NEH.
Histopathology is crucial in distinguishing these disease etiologies. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is diagnosed by the characteristic neutrophilic infiltrate and necrosis surrounding eccrine glands and coils. There also may be occasional intraductal abscesses and syringosquamous metaplasia of the sweat glands along with fibrosis of the adjacent dermis. In contrast, histologic sections of Sweet syndrome show numerous mature neutrophils infiltrating the dermis with marked papillary dermal edema. The histopathology of bacterial cellulitis and erysipelas is less specific, but common features include dermal edema, lymphatic dilation, and a diffuse neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding blood vessels. Pathogenic organisms may be seen on histopathology but are not required for the diagnosis of bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas.2 Additionally, blood and tissue culture can assist in identification of both the source of infection and the causative organism, but cultures may not always be positive.
Comparatively, the histopathologic features of eosinophilic cellulitis include dermal edema, eosinophilic infiltration, and flame figures that form when eosinophils degranulate and coat collagen fibers with major basic protein. Flame figures are characteristic but not pathognomonic for eosinophilic cellulitis.7 The histopathology of leukemia cutis varies based on the leukemia classification; generally, in acute myeloid leukemia the infiltrate is composed of neoplastic cells in the early stages of development that are positive for myeloid markers such as myeloperoxidase. Atypical and immature granulocytes within the leukocytic infiltrate differentiate this condition from the other diagnoses. Treatment may entail chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and this diagnosis generally carries the worst prognosis of all the conditions in the differential.6
Differentiating between these conditions is important in guiding treatment, especially in patients with febrile neutropenia. Unnecessary steroids in immunosuppressed patients can be dangerous, especially if the patient has an infection such as bacterial cellulitis. Furthermore, unwarranted antibiotic use for noninfectious conditions may expose patients to substantial side effects and not improve the condition. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis typically is self-limited and treated symptomatically with systemic corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.3 Sweet syndrome often requires a longer course of oral steroids. Leukemia cutis worsens as the leukemia advances, and treatment of the underlying malignancy is the most effective treatment.9
Early and accurate recognition of the diagnosis can prevent harmful diagnostic delay, unnecessary antibiotic use, or extended steroid taper in neutropenic patients. Appreciating the differences between these diagnoses can assist clinicians in investigating and tailoring a broad differential to specific patient presentations, which is especially critical when considering common mimickers for life-threatening conditions.
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.0642
- Srivastava M, Scharf S, Meehan SA, et al. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis masquerading as facial cellulitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:693-696. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.07.032
- Copaescu AM, Castilloux JF, Chababi-Atallah M, et al. A classic clinical case: neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013; 5:340-346. doi:10.1159/000356229
- Aractingi S, Mallet V, Pinquier L, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses during granulocytopenia. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:1141-1145.
- Cohen PR. Neutrophilic dermatoses occurring in oncology patients. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:106-111. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.02605.x
- Wang CX, Pusic I, Anadkat MJ. Association of leukemia cutis with survival in acute myeloid leukemia. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:826. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.0052
- Chung CL, Cusack CA. Wells syndrome: an enigmatic and therapeutically challenging disease. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:908-911.
- Räßler F, Lukács J, Elsner P. Treatment of eosinophilic cellulitis (Wells syndrome): a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1465-1479. doi:10.1111/jdv.13706
- Hobbs LK, Carr PC, Gru AA, et al. Case and review: cutaneous involvement by chronic neutrophilic leukemia vs Sweet syndrome: a diagnostic dilemma. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:644-649. doi:10.1111 /cup.13925
THE DIAGNOSIS: Neutrophilic Eccrine Hidradenitis
A biopsy from the left preauricular cheek demonstrated dermal neutrophilic inflammation around eccrine coils with focal necrosis (Figure). No notable diffuse dermal neutrophilic infiltrate was present, ruling out Sweet syndrome, and no notable interstitial neutrophilic infiltrate was present, making cellulitis and erysipelas less likely; panculture of tissue also was negative.1,2 Atypical cells in the deep dermis were positive for CD163 and negative for CD117, CD34, CD123, and myeloperoxidase, consistent with a diagnosis of neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis (NEH) and reactive histiocytes.3 Treatment with oral prednisone resulted in rapid improvement of symptoms.

Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is a rare reactive neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by eccrine gland involvement. This benign and self-limited condition presents as asymmetric erythematous papules and plaques.2 Among 8 granulocytopenic patients with neutrophilic dermatoses, 5 were diagnosed with NEH.4 Although first identified in 1982, NEH remains poorly understood.2 Initial theories suggested that NEH developed due to cytotoxic substances secreted in sweat glands causing necrosis and neutrophil chemotaxis; however, chemotherapy exposure cannot be linked to every case of NEH. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis can be extremely difficult to differentiate clinically from conditions such as cellulitis and Sweet syndrome.
A patient history can be helpful in identifying triggering factors. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis most commonly is associated with malignant, drug-induced, or infectious triggers, while Sweet syndrome has a broad range of associations including infections, vaccines, inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy, malignancy, and drug-induced etiologies (Table).1 On average, NEH presents 10 days after chemotherapy induction, with 70% of cases presenting after the first chemotherapy cycle.5 Bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas have an infectious etiology, and patients may report symptoms such as fever, chills, or malaise. Immunosuppressed patients are at greater risk for infection; therefore, clinical signs of infection in a granulocytopenic patient should be addressed urgently.

Physical examination may have limited value in differentiating between these diagnoses, as neutrophilic dermatoses notoriously mimic infection. Cutaneous lesions can appear as pruritic or tender erythematous plaques, papules, or nodules in these conditions, though cellulitis and erysipelas tend to be unilateral and may have associated purulence or inflamed skin lymphatics. Given the potential for misdiagnosis, approaching patients with a broad differential can be helpful. In our patient, the differential diagnosis included Sweet syndrome, NEH, bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, leukemia cutis, sarcoid, and eosinophilic cellulitis.
Leukemia cutis refers to the infiltration of neoplastic leukocytes in the skin and often occurs in patients with peripheral leukemia, most often acute myeloid leukemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Patients with leukemia cutis often have a worse prognosis, as this finding signifies extramedullary spread of disease.6 Clinically, lesions can appear similar to those seen in our patient, though they typically are not symptomatic, can be nodular, tend to exhibit a violaceous hue, and occasionally may be hemorrhagic. Wells syndrome (also known as eosinophilic cellulitis) is an inflammatory dermatosis that presents as painful or pruritic, edematous and erythematous plaques.7,8 A green hue on resolution is present in some cases and may help clinicians differentiate this disease from mimickers.7 Often, eosinophilic cellulitis is misdiagnosed as bacterial cellulitis and treated with antibiotics. The presence of systemic symptoms such as fever or arthralgia is more typical of bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, eosinophilic cellulitis, or Sweet syndrome than of NEH.1 Additionally, inflammatory markers (ie, C-reactive protein) and white blood cell counts tend to be elevated in bacterial cellulitis and Sweet syndrome, while leukopenia often is seen in NEH.
Histopathology is crucial in distinguishing these disease etiologies. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is diagnosed by the characteristic neutrophilic infiltrate and necrosis surrounding eccrine glands and coils. There also may be occasional intraductal abscesses and syringosquamous metaplasia of the sweat glands along with fibrosis of the adjacent dermis. In contrast, histologic sections of Sweet syndrome show numerous mature neutrophils infiltrating the dermis with marked papillary dermal edema. The histopathology of bacterial cellulitis and erysipelas is less specific, but common features include dermal edema, lymphatic dilation, and a diffuse neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding blood vessels. Pathogenic organisms may be seen on histopathology but are not required for the diagnosis of bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas.2 Additionally, blood and tissue culture can assist in identification of both the source of infection and the causative organism, but cultures may not always be positive.
Comparatively, the histopathologic features of eosinophilic cellulitis include dermal edema, eosinophilic infiltration, and flame figures that form when eosinophils degranulate and coat collagen fibers with major basic protein. Flame figures are characteristic but not pathognomonic for eosinophilic cellulitis.7 The histopathology of leukemia cutis varies based on the leukemia classification; generally, in acute myeloid leukemia the infiltrate is composed of neoplastic cells in the early stages of development that are positive for myeloid markers such as myeloperoxidase. Atypical and immature granulocytes within the leukocytic infiltrate differentiate this condition from the other diagnoses. Treatment may entail chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and this diagnosis generally carries the worst prognosis of all the conditions in the differential.6
Differentiating between these conditions is important in guiding treatment, especially in patients with febrile neutropenia. Unnecessary steroids in immunosuppressed patients can be dangerous, especially if the patient has an infection such as bacterial cellulitis. Furthermore, unwarranted antibiotic use for noninfectious conditions may expose patients to substantial side effects and not improve the condition. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis typically is self-limited and treated symptomatically with systemic corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.3 Sweet syndrome often requires a longer course of oral steroids. Leukemia cutis worsens as the leukemia advances, and treatment of the underlying malignancy is the most effective treatment.9
Early and accurate recognition of the diagnosis can prevent harmful diagnostic delay, unnecessary antibiotic use, or extended steroid taper in neutropenic patients. Appreciating the differences between these diagnoses can assist clinicians in investigating and tailoring a broad differential to specific patient presentations, which is especially critical when considering common mimickers for life-threatening conditions.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Neutrophilic Eccrine Hidradenitis
A biopsy from the left preauricular cheek demonstrated dermal neutrophilic inflammation around eccrine coils with focal necrosis (Figure). No notable diffuse dermal neutrophilic infiltrate was present, ruling out Sweet syndrome, and no notable interstitial neutrophilic infiltrate was present, making cellulitis and erysipelas less likely; panculture of tissue also was negative.1,2 Atypical cells in the deep dermis were positive for CD163 and negative for CD117, CD34, CD123, and myeloperoxidase, consistent with a diagnosis of neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis (NEH) and reactive histiocytes.3 Treatment with oral prednisone resulted in rapid improvement of symptoms.

Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is a rare reactive neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by eccrine gland involvement. This benign and self-limited condition presents as asymmetric erythematous papules and plaques.2 Among 8 granulocytopenic patients with neutrophilic dermatoses, 5 were diagnosed with NEH.4 Although first identified in 1982, NEH remains poorly understood.2 Initial theories suggested that NEH developed due to cytotoxic substances secreted in sweat glands causing necrosis and neutrophil chemotaxis; however, chemotherapy exposure cannot be linked to every case of NEH. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis can be extremely difficult to differentiate clinically from conditions such as cellulitis and Sweet syndrome.
A patient history can be helpful in identifying triggering factors. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis most commonly is associated with malignant, drug-induced, or infectious triggers, while Sweet syndrome has a broad range of associations including infections, vaccines, inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy, malignancy, and drug-induced etiologies (Table).1 On average, NEH presents 10 days after chemotherapy induction, with 70% of cases presenting after the first chemotherapy cycle.5 Bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas have an infectious etiology, and patients may report symptoms such as fever, chills, or malaise. Immunosuppressed patients are at greater risk for infection; therefore, clinical signs of infection in a granulocytopenic patient should be addressed urgently.

Physical examination may have limited value in differentiating between these diagnoses, as neutrophilic dermatoses notoriously mimic infection. Cutaneous lesions can appear as pruritic or tender erythematous plaques, papules, or nodules in these conditions, though cellulitis and erysipelas tend to be unilateral and may have associated purulence or inflamed skin lymphatics. Given the potential for misdiagnosis, approaching patients with a broad differential can be helpful. In our patient, the differential diagnosis included Sweet syndrome, NEH, bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, leukemia cutis, sarcoid, and eosinophilic cellulitis.
Leukemia cutis refers to the infiltration of neoplastic leukocytes in the skin and often occurs in patients with peripheral leukemia, most often acute myeloid leukemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Patients with leukemia cutis often have a worse prognosis, as this finding signifies extramedullary spread of disease.6 Clinically, lesions can appear similar to those seen in our patient, though they typically are not symptomatic, can be nodular, tend to exhibit a violaceous hue, and occasionally may be hemorrhagic. Wells syndrome (also known as eosinophilic cellulitis) is an inflammatory dermatosis that presents as painful or pruritic, edematous and erythematous plaques.7,8 A green hue on resolution is present in some cases and may help clinicians differentiate this disease from mimickers.7 Often, eosinophilic cellulitis is misdiagnosed as bacterial cellulitis and treated with antibiotics. The presence of systemic symptoms such as fever or arthralgia is more typical of bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, eosinophilic cellulitis, or Sweet syndrome than of NEH.1 Additionally, inflammatory markers (ie, C-reactive protein) and white blood cell counts tend to be elevated in bacterial cellulitis and Sweet syndrome, while leukopenia often is seen in NEH.
Histopathology is crucial in distinguishing these disease etiologies. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is diagnosed by the characteristic neutrophilic infiltrate and necrosis surrounding eccrine glands and coils. There also may be occasional intraductal abscesses and syringosquamous metaplasia of the sweat glands along with fibrosis of the adjacent dermis. In contrast, histologic sections of Sweet syndrome show numerous mature neutrophils infiltrating the dermis with marked papillary dermal edema. The histopathology of bacterial cellulitis and erysipelas is less specific, but common features include dermal edema, lymphatic dilation, and a diffuse neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding blood vessels. Pathogenic organisms may be seen on histopathology but are not required for the diagnosis of bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas.2 Additionally, blood and tissue culture can assist in identification of both the source of infection and the causative organism, but cultures may not always be positive.
Comparatively, the histopathologic features of eosinophilic cellulitis include dermal edema, eosinophilic infiltration, and flame figures that form when eosinophils degranulate and coat collagen fibers with major basic protein. Flame figures are characteristic but not pathognomonic for eosinophilic cellulitis.7 The histopathology of leukemia cutis varies based on the leukemia classification; generally, in acute myeloid leukemia the infiltrate is composed of neoplastic cells in the early stages of development that are positive for myeloid markers such as myeloperoxidase. Atypical and immature granulocytes within the leukocytic infiltrate differentiate this condition from the other diagnoses. Treatment may entail chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and this diagnosis generally carries the worst prognosis of all the conditions in the differential.6
Differentiating between these conditions is important in guiding treatment, especially in patients with febrile neutropenia. Unnecessary steroids in immunosuppressed patients can be dangerous, especially if the patient has an infection such as bacterial cellulitis. Furthermore, unwarranted antibiotic use for noninfectious conditions may expose patients to substantial side effects and not improve the condition. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis typically is self-limited and treated symptomatically with systemic corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.3 Sweet syndrome often requires a longer course of oral steroids. Leukemia cutis worsens as the leukemia advances, and treatment of the underlying malignancy is the most effective treatment.9
Early and accurate recognition of the diagnosis can prevent harmful diagnostic delay, unnecessary antibiotic use, or extended steroid taper in neutropenic patients. Appreciating the differences between these diagnoses can assist clinicians in investigating and tailoring a broad differential to specific patient presentations, which is especially critical when considering common mimickers for life-threatening conditions.
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.0642
- Srivastava M, Scharf S, Meehan SA, et al. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis masquerading as facial cellulitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:693-696. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.07.032
- Copaescu AM, Castilloux JF, Chababi-Atallah M, et al. A classic clinical case: neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013; 5:340-346. doi:10.1159/000356229
- Aractingi S, Mallet V, Pinquier L, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses during granulocytopenia. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:1141-1145.
- Cohen PR. Neutrophilic dermatoses occurring in oncology patients. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:106-111. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.02605.x
- Wang CX, Pusic I, Anadkat MJ. Association of leukemia cutis with survival in acute myeloid leukemia. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:826. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.0052
- Chung CL, Cusack CA. Wells syndrome: an enigmatic and therapeutically challenging disease. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:908-911.
- Räßler F, Lukács J, Elsner P. Treatment of eosinophilic cellulitis (Wells syndrome): a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1465-1479. doi:10.1111/jdv.13706
- Hobbs LK, Carr PC, Gru AA, et al. Case and review: cutaneous involvement by chronic neutrophilic leukemia vs Sweet syndrome: a diagnostic dilemma. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:644-649. doi:10.1111 /cup.13925
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.0642
- Srivastava M, Scharf S, Meehan SA, et al. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis masquerading as facial cellulitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:693-696. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.07.032
- Copaescu AM, Castilloux JF, Chababi-Atallah M, et al. A classic clinical case: neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013; 5:340-346. doi:10.1159/000356229
- Aractingi S, Mallet V, Pinquier L, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses during granulocytopenia. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:1141-1145.
- Cohen PR. Neutrophilic dermatoses occurring in oncology patients. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:106-111. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.02605.x
- Wang CX, Pusic I, Anadkat MJ. Association of leukemia cutis with survival in acute myeloid leukemia. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:826. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.0052
- Chung CL, Cusack CA. Wells syndrome: an enigmatic and therapeutically challenging disease. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:908-911.
- Räßler F, Lukács J, Elsner P. Treatment of eosinophilic cellulitis (Wells syndrome): a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1465-1479. doi:10.1111/jdv.13706
- Hobbs LK, Carr PC, Gru AA, et al. Case and review: cutaneous involvement by chronic neutrophilic leukemia vs Sweet syndrome: a diagnostic dilemma. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:644-649. doi:10.1111 /cup.13925
A 50-year-old woman undergoing cytarabine induction therapy for acute myeloid leukemia developed tender, erythematous, dermal plaques on the nasal dorsum, left medial eyebrow, left preauricular cheek, and right cheek. The rash erupted 7 days after receiving the cytarabine induction regimen. She had a fever (temperature, 39.9 °C [103.8 °F]) and also was neutropenic.
CMML: GM-CSF inhibitor lenzilumab shows early promise
There is currently no international standard of care for patients with CMML, but given its overlap with other myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative syndromes, CMML is usually treated with the hypomethylating agent azacitidine (Vidaza, Onureg), which is associated with objective response rates of 40%-50% and a complete response rate of less than 20%. Alternatively, some patients are treated with the antimetabolite hydroxurea in the palliative setting.
CMML is “insidious, it’s rare, but we think the incidence is increasing because more patients are now getting sequencing done by their doctors, and therapy [related] cases, patients that have survived chemo in the last 10 years, can also develop this disease,” said Daniel Thomas, MD, PhD, from the South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute, Adelaide, in an interview.
Dr. Thomas is a co-investigator of the ongoing phase 2/3 PREACH-M trial, which is testing a novel strategy of treating CMML with mutations in the RAS pathway with a combination of azacitidine and the investigational antibody lenzilumab, which is a targeted inhibitor of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF).
Preliminary results from the trial, reported at the European Hematology Association (EHA) annual meeting, showed that among 10 patients with CMML bearing mutations in the RAS pathway, the combination was associated with durable decreases in monocyte counts, increases in platelet counts and hemoglobin levels, and reductions in both spleen size and C-reactive protein level.
Targeting GM-CSF
More than 90% of cases of CMML carry somatic mutations that are thought to be leukemogenic, with an estimated 46%-60% of cases having mutations in TET2, a tumor suppressor, and an estimated 40% having mutations in KRAS, NRAS, or CBL, all of which are involved in cellular proliferation, and which, research suggests, are sensitive to GM-CSF inhibition.
“I was very surprised that the RAS-mutant arm – so, patients that have KRAS, NRAS, or CBL mutations – are just responding beautifully to [lenzilumab], ” Dr. Thomas said.
“It’s [in the] early days, but if what we’re seeing is durable across the next 10 patients, then I think we’re looking at a game changer,” he added.
Cameron Durrant, MD, DRCOG, MRCGP, chairman and CEO of lenzilumab’s maker Humanigen, said in an interview that the development of the antibody for CMML was spurred in part by research from investigators at the Mayo Clinic, showing that patients with mutations that increased sensitivity to GM-CSF seemed to have better clinical outcomes when the growth factor was blocked.
In addition, Dr. Durrant said, preclinical research from investigators at the Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, found that myeloid and monocytic progenitors “fed” on GM-CSF and were sensitive to GM-CSF signal inhibition.
“The biological idea that’s being explored here in the clinic in this study is that by blocking, or starving, if you will, those cells of that food, then you can prevent this overgrowth of certain blood cells that lead to chronic myelomonocytic leukemia,” he said.
PREACH-M details
Lenzilumab is an engineered human immunoglobulin G1-kappa monoclonal antibody with high affinity for human GM-CSF.
In the open label, nonrandomized PREACH-M trial, 72 patients with CMML were enrolled and were assigned to receive 24 monthly cycles of therapy depending on mutational status.
Patients with RAS pathway mutations were assigned to receive azacitidine delivered subcutaneously 75 mg/m2 for 7 days, plus intravenous lenzilumab 552 mg on days 1 and 15 of cycle 1 and on day 1 only of all subsequent cycles.
Patients with TET2 mutations only were assigned to receive azacitidine on the same schedule, plus IV sodium ascorbate 30 g for 7 days, with the first dose 15 g, and subsequent doses 30 g if there is no evidence of tumor lysis syndrome. Following IV administration, patients continue on oral sodium ascorbate 1.1 g on all other days.
The primary endpoint of complete and partial responses any time during the first 12 cycles is planned for reporting at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology in December, Dr. Thomas said.
At EHA 2023, the investigators reported available data on 10 patients enrolled in the lenzilumab arm and one enrolled in the azacitidine-sodium ascorbate arm.
Among patients in the lenzilumab arm there was a 5.1-fold decrease in monocyte counts (P = .03) and 2.4-fold decrease in blast counts (P = .04) at 12 months of follow-up.
In addition there was a trend toward increased platelet counts over baseline at 12 months, a significant increase in blood hemoglobin concentration (P = .024), a significant reduction in spleen size (P = .03) and a trend toward lower levels of the inflammatory marker C-reactive protein.
There were 21 grade 3 or 4 adverse events reported, of which 5 were deemed to be possibly related to lenzilumab.
Dr. Thomas told this news organization that the investigators have been “pleasantly surprised” at how well patients tolerated the monoclonal antibody.
“We haven’t had any infusion reactions, we haven’t had any pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, [and] we haven’t had any fevers from the infusion, from the antibody,” he said.
There were some instances of neutropenia and thrombocytopenia that the investigators think may have been related to azacitidine, he noted.
The study is sponsored by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. Dr. Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Durrant is an employee and director of Humanigen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is currently no international standard of care for patients with CMML, but given its overlap with other myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative syndromes, CMML is usually treated with the hypomethylating agent azacitidine (Vidaza, Onureg), which is associated with objective response rates of 40%-50% and a complete response rate of less than 20%. Alternatively, some patients are treated with the antimetabolite hydroxurea in the palliative setting.
CMML is “insidious, it’s rare, but we think the incidence is increasing because more patients are now getting sequencing done by their doctors, and therapy [related] cases, patients that have survived chemo in the last 10 years, can also develop this disease,” said Daniel Thomas, MD, PhD, from the South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute, Adelaide, in an interview.
Dr. Thomas is a co-investigator of the ongoing phase 2/3 PREACH-M trial, which is testing a novel strategy of treating CMML with mutations in the RAS pathway with a combination of azacitidine and the investigational antibody lenzilumab, which is a targeted inhibitor of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF).
Preliminary results from the trial, reported at the European Hematology Association (EHA) annual meeting, showed that among 10 patients with CMML bearing mutations in the RAS pathway, the combination was associated with durable decreases in monocyte counts, increases in platelet counts and hemoglobin levels, and reductions in both spleen size and C-reactive protein level.
Targeting GM-CSF
More than 90% of cases of CMML carry somatic mutations that are thought to be leukemogenic, with an estimated 46%-60% of cases having mutations in TET2, a tumor suppressor, and an estimated 40% having mutations in KRAS, NRAS, or CBL, all of which are involved in cellular proliferation, and which, research suggests, are sensitive to GM-CSF inhibition.
“I was very surprised that the RAS-mutant arm – so, patients that have KRAS, NRAS, or CBL mutations – are just responding beautifully to [lenzilumab], ” Dr. Thomas said.
“It’s [in the] early days, but if what we’re seeing is durable across the next 10 patients, then I think we’re looking at a game changer,” he added.
Cameron Durrant, MD, DRCOG, MRCGP, chairman and CEO of lenzilumab’s maker Humanigen, said in an interview that the development of the antibody for CMML was spurred in part by research from investigators at the Mayo Clinic, showing that patients with mutations that increased sensitivity to GM-CSF seemed to have better clinical outcomes when the growth factor was blocked.
In addition, Dr. Durrant said, preclinical research from investigators at the Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, found that myeloid and monocytic progenitors “fed” on GM-CSF and were sensitive to GM-CSF signal inhibition.
“The biological idea that’s being explored here in the clinic in this study is that by blocking, or starving, if you will, those cells of that food, then you can prevent this overgrowth of certain blood cells that lead to chronic myelomonocytic leukemia,” he said.
PREACH-M details
Lenzilumab is an engineered human immunoglobulin G1-kappa monoclonal antibody with high affinity for human GM-CSF.
In the open label, nonrandomized PREACH-M trial, 72 patients with CMML were enrolled and were assigned to receive 24 monthly cycles of therapy depending on mutational status.
Patients with RAS pathway mutations were assigned to receive azacitidine delivered subcutaneously 75 mg/m2 for 7 days, plus intravenous lenzilumab 552 mg on days 1 and 15 of cycle 1 and on day 1 only of all subsequent cycles.
Patients with TET2 mutations only were assigned to receive azacitidine on the same schedule, plus IV sodium ascorbate 30 g for 7 days, with the first dose 15 g, and subsequent doses 30 g if there is no evidence of tumor lysis syndrome. Following IV administration, patients continue on oral sodium ascorbate 1.1 g on all other days.
The primary endpoint of complete and partial responses any time during the first 12 cycles is planned for reporting at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology in December, Dr. Thomas said.
At EHA 2023, the investigators reported available data on 10 patients enrolled in the lenzilumab arm and one enrolled in the azacitidine-sodium ascorbate arm.
Among patients in the lenzilumab arm there was a 5.1-fold decrease in monocyte counts (P = .03) and 2.4-fold decrease in blast counts (P = .04) at 12 months of follow-up.
In addition there was a trend toward increased platelet counts over baseline at 12 months, a significant increase in blood hemoglobin concentration (P = .024), a significant reduction in spleen size (P = .03) and a trend toward lower levels of the inflammatory marker C-reactive protein.
There were 21 grade 3 or 4 adverse events reported, of which 5 were deemed to be possibly related to lenzilumab.
Dr. Thomas told this news organization that the investigators have been “pleasantly surprised” at how well patients tolerated the monoclonal antibody.
“We haven’t had any infusion reactions, we haven’t had any pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, [and] we haven’t had any fevers from the infusion, from the antibody,” he said.
There were some instances of neutropenia and thrombocytopenia that the investigators think may have been related to azacitidine, he noted.
The study is sponsored by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. Dr. Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Durrant is an employee and director of Humanigen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is currently no international standard of care for patients with CMML, but given its overlap with other myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative syndromes, CMML is usually treated with the hypomethylating agent azacitidine (Vidaza, Onureg), which is associated with objective response rates of 40%-50% and a complete response rate of less than 20%. Alternatively, some patients are treated with the antimetabolite hydroxurea in the palliative setting.
CMML is “insidious, it’s rare, but we think the incidence is increasing because more patients are now getting sequencing done by their doctors, and therapy [related] cases, patients that have survived chemo in the last 10 years, can also develop this disease,” said Daniel Thomas, MD, PhD, from the South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute, Adelaide, in an interview.
Dr. Thomas is a co-investigator of the ongoing phase 2/3 PREACH-M trial, which is testing a novel strategy of treating CMML with mutations in the RAS pathway with a combination of azacitidine and the investigational antibody lenzilumab, which is a targeted inhibitor of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF).
Preliminary results from the trial, reported at the European Hematology Association (EHA) annual meeting, showed that among 10 patients with CMML bearing mutations in the RAS pathway, the combination was associated with durable decreases in monocyte counts, increases in platelet counts and hemoglobin levels, and reductions in both spleen size and C-reactive protein level.
Targeting GM-CSF
More than 90% of cases of CMML carry somatic mutations that are thought to be leukemogenic, with an estimated 46%-60% of cases having mutations in TET2, a tumor suppressor, and an estimated 40% having mutations in KRAS, NRAS, or CBL, all of which are involved in cellular proliferation, and which, research suggests, are sensitive to GM-CSF inhibition.
“I was very surprised that the RAS-mutant arm – so, patients that have KRAS, NRAS, or CBL mutations – are just responding beautifully to [lenzilumab], ” Dr. Thomas said.
“It’s [in the] early days, but if what we’re seeing is durable across the next 10 patients, then I think we’re looking at a game changer,” he added.
Cameron Durrant, MD, DRCOG, MRCGP, chairman and CEO of lenzilumab’s maker Humanigen, said in an interview that the development of the antibody for CMML was spurred in part by research from investigators at the Mayo Clinic, showing that patients with mutations that increased sensitivity to GM-CSF seemed to have better clinical outcomes when the growth factor was blocked.
In addition, Dr. Durrant said, preclinical research from investigators at the Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, found that myeloid and monocytic progenitors “fed” on GM-CSF and were sensitive to GM-CSF signal inhibition.
“The biological idea that’s being explored here in the clinic in this study is that by blocking, or starving, if you will, those cells of that food, then you can prevent this overgrowth of certain blood cells that lead to chronic myelomonocytic leukemia,” he said.
PREACH-M details
Lenzilumab is an engineered human immunoglobulin G1-kappa monoclonal antibody with high affinity for human GM-CSF.
In the open label, nonrandomized PREACH-M trial, 72 patients with CMML were enrolled and were assigned to receive 24 monthly cycles of therapy depending on mutational status.
Patients with RAS pathway mutations were assigned to receive azacitidine delivered subcutaneously 75 mg/m2 for 7 days, plus intravenous lenzilumab 552 mg on days 1 and 15 of cycle 1 and on day 1 only of all subsequent cycles.
Patients with TET2 mutations only were assigned to receive azacitidine on the same schedule, plus IV sodium ascorbate 30 g for 7 days, with the first dose 15 g, and subsequent doses 30 g if there is no evidence of tumor lysis syndrome. Following IV administration, patients continue on oral sodium ascorbate 1.1 g on all other days.
The primary endpoint of complete and partial responses any time during the first 12 cycles is planned for reporting at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology in December, Dr. Thomas said.
At EHA 2023, the investigators reported available data on 10 patients enrolled in the lenzilumab arm and one enrolled in the azacitidine-sodium ascorbate arm.
Among patients in the lenzilumab arm there was a 5.1-fold decrease in monocyte counts (P = .03) and 2.4-fold decrease in blast counts (P = .04) at 12 months of follow-up.
In addition there was a trend toward increased platelet counts over baseline at 12 months, a significant increase in blood hemoglobin concentration (P = .024), a significant reduction in spleen size (P = .03) and a trend toward lower levels of the inflammatory marker C-reactive protein.
There were 21 grade 3 or 4 adverse events reported, of which 5 were deemed to be possibly related to lenzilumab.
Dr. Thomas told this news organization that the investigators have been “pleasantly surprised” at how well patients tolerated the monoclonal antibody.
“We haven’t had any infusion reactions, we haven’t had any pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, [and] we haven’t had any fevers from the infusion, from the antibody,” he said.
There were some instances of neutropenia and thrombocytopenia that the investigators think may have been related to azacitidine, he noted.
The study is sponsored by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. Dr. Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Durrant is an employee and director of Humanigen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EHA 2023
Book review: “Sexual Citizens”
The Sexual Health Initiative to Foster Transformation (SHIFT)1 is a landmark study about sexual assault at college, which has generated 20 scientific articles and several chapters in books, but unfortunately, has not made its way into the psychiatric literature.
“Sexual Citizens: Sex, Power and Assault on Campus,” by Jennifer Hirsch and Shamus Khan, (available in audio book and paperback) was written as a follow up to the SHIFT study, so the rest of us can absorb the findings.2 This mixed-methods study included a survey of over 1,600 students aged 18-29 from Columbia University and Barnard College regarding their relationships and sexual histories, including assault. Data were collected using daily diaries, focus groups, and hundreds of hours of field work observation by young researchers. One- to 3-hour in-depth interviews exploring sexual experiences on campus were conducted with 151 students. These interviews are the focus of the book. It is a well-written, provocative story brimming with insights for those of us who lack the time to scour social science literature.
“Sexual Citizens” and the SHIFT study confirmed much of what we know. Sexual assault is common and has enduring effects. The study found that 36% of women and 15% of men had experienced unwanted, nonconsensual sexual contact by senior year. Twenty percent of women and 6% of men were rape survivors. Freshman, LGBTQ, and minority students were found at highest risk of assault. SHIFT reaffirmed that abstinence-only education is not a protective factor against college sexual assault, but neither was knowledge of affirmative consent (the practice of “ongoing and explicit” checking-in with partners) which few students ever employed. Encouragingly, students taught refusal skills were less likely to experience sexual assault.
Many of the book’s valuable lessons fall under the umbrella of failures of language and communication. For example, after drinking, they went to his room. She was expecting a social interaction, but with no other place to sit, they sat on his bed where she was coaxed or pressured into a sexual encounter. Afterward, she leaves, and it is never discussed again. One partner desires emotional intimacy, and the other, bragging rights in the fraternity or at the girls’ weekly brunch. Numerous personal stories like these, though at times heart wrenching, provide perspective on the barriers to addressing assault.
Subjects relayed experiences of assault by strangers or friends, and some provided details of their own actions as perpetrators. Stumbling around words and emotions, an avoidance of explicit language stemmed from shame, a fear of personal responsibility, the desire to maintain social cohesion, and concern for potential consequences for the perpetrator. Many subjects were resistant to calling nonconsensual sexual activity rape or even assault. Some who had perpetrated were unaware their behavior may have been experienced as assault, with recognition of this fact dawning during interviews.
This apparent limitation in self-reflective capacity may be in part due to the conceptualization of what assault is. Focus groups identified a discernible difference in how men and women understood assaults, with men believing rapes looked like a woman fighting back and screaming for help ... which is rarely what happens.
Notably absent among the interviewed are any flagrant perpetrators. The methodology section theorizes that individuals who intentionally harmed their peers were unlikely to choose to participate in this study. In addition, the characterization of assailants as “sociopathic predators” is based in a history of racialized imagery that leads us astray from the truth about campus sexual assault. Most assaults do not involve force, and SHIFT data showed 75% of victims knew their assailants. Ultimately, a major aim of the research was to study assault alongside healthy sex to “understand those pivotal moments when encounters change from being sex, to being assault.” Doing this requires understanding the where, how, and why students have sex, a more complicated undertaking than we may think.
In discussing their sexual lives, subjects frequently noted they did not have space to talk about their assaults. Though 81% of students discussed their experiences with someone, friend groups were often overburdened with stories, which minimized the victim’s experience. Furthermore, most had not sought help from the student counseling centers. Students navigating this complex field were frequently doing so in isolation. SHIFT found subjects to be eager to participate; they would often express thankfulness, and a sense of freedom in sharing with researchers. Commonly, students expressly did not want retribution for perpetrators, but simply a place to be heard without challenge. The current legal system precludes that possibility, leaving individuals without the option to confront perpetrators, and perpetrators often not knowing the extent of the damage they caused.
Where can psychiatrists have an impact right now? “Sexual Citizens” identifies four key areas for intervention to work toward a world with less sexual assault. These are:
- Improving diversity, inequality, and power distortions.
- Education about sex and sexual assault.
- Substance use.
- Mental health.
Substance use and mental health are especially relevant for psychiatrists (That substance use contributes to sexual assault is known by approximately ... everybody!). Unwanted sexual contact prior to college (20% of students) increased the odds of experiencing assault during college. Harm reduction strategies should be introduced before college, according to the SHIFT research, particularly in skills-based training on how to say “No” to unwanted sex. Psychiatrists are likely used to asking brief history questions related to sexual assault and rape. “Sexual Citizens” highlights the inadequacy of this blunt language and guides the reader toward a refined knowledge of the language needed to address sexual assault.
Dr. Whisler is a child and adolescent psychiatry fellow at the Stanford (Calif.) University. Dr. Higgins is affiliate associate professor of psychiatry and family medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
References
1. Hirsch JS et al. Social dimensions of sexual consent among cisgender heterosexual college students: Insights from ethnographic research. J Adolesc Health. 2019 Jan;64(1):26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.06.011.
2. Hirsch JS and Khan S. Sexual citizens: Sex, power, and assault on campus. New York: W.W. Norton & Company, 2020.
The Sexual Health Initiative to Foster Transformation (SHIFT)1 is a landmark study about sexual assault at college, which has generated 20 scientific articles and several chapters in books, but unfortunately, has not made its way into the psychiatric literature.
“Sexual Citizens: Sex, Power and Assault on Campus,” by Jennifer Hirsch and Shamus Khan, (available in audio book and paperback) was written as a follow up to the SHIFT study, so the rest of us can absorb the findings.2 This mixed-methods study included a survey of over 1,600 students aged 18-29 from Columbia University and Barnard College regarding their relationships and sexual histories, including assault. Data were collected using daily diaries, focus groups, and hundreds of hours of field work observation by young researchers. One- to 3-hour in-depth interviews exploring sexual experiences on campus were conducted with 151 students. These interviews are the focus of the book. It is a well-written, provocative story brimming with insights for those of us who lack the time to scour social science literature.
“Sexual Citizens” and the SHIFT study confirmed much of what we know. Sexual assault is common and has enduring effects. The study found that 36% of women and 15% of men had experienced unwanted, nonconsensual sexual contact by senior year. Twenty percent of women and 6% of men were rape survivors. Freshman, LGBTQ, and minority students were found at highest risk of assault. SHIFT reaffirmed that abstinence-only education is not a protective factor against college sexual assault, but neither was knowledge of affirmative consent (the practice of “ongoing and explicit” checking-in with partners) which few students ever employed. Encouragingly, students taught refusal skills were less likely to experience sexual assault.
Many of the book’s valuable lessons fall under the umbrella of failures of language and communication. For example, after drinking, they went to his room. She was expecting a social interaction, but with no other place to sit, they sat on his bed where she was coaxed or pressured into a sexual encounter. Afterward, she leaves, and it is never discussed again. One partner desires emotional intimacy, and the other, bragging rights in the fraternity or at the girls’ weekly brunch. Numerous personal stories like these, though at times heart wrenching, provide perspective on the barriers to addressing assault.
Subjects relayed experiences of assault by strangers or friends, and some provided details of their own actions as perpetrators. Stumbling around words and emotions, an avoidance of explicit language stemmed from shame, a fear of personal responsibility, the desire to maintain social cohesion, and concern for potential consequences for the perpetrator. Many subjects were resistant to calling nonconsensual sexual activity rape or even assault. Some who had perpetrated were unaware their behavior may have been experienced as assault, with recognition of this fact dawning during interviews.
This apparent limitation in self-reflective capacity may be in part due to the conceptualization of what assault is. Focus groups identified a discernible difference in how men and women understood assaults, with men believing rapes looked like a woman fighting back and screaming for help ... which is rarely what happens.
Notably absent among the interviewed are any flagrant perpetrators. The methodology section theorizes that individuals who intentionally harmed their peers were unlikely to choose to participate in this study. In addition, the characterization of assailants as “sociopathic predators” is based in a history of racialized imagery that leads us astray from the truth about campus sexual assault. Most assaults do not involve force, and SHIFT data showed 75% of victims knew their assailants. Ultimately, a major aim of the research was to study assault alongside healthy sex to “understand those pivotal moments when encounters change from being sex, to being assault.” Doing this requires understanding the where, how, and why students have sex, a more complicated undertaking than we may think.
In discussing their sexual lives, subjects frequently noted they did not have space to talk about their assaults. Though 81% of students discussed their experiences with someone, friend groups were often overburdened with stories, which minimized the victim’s experience. Furthermore, most had not sought help from the student counseling centers. Students navigating this complex field were frequently doing so in isolation. SHIFT found subjects to be eager to participate; they would often express thankfulness, and a sense of freedom in sharing with researchers. Commonly, students expressly did not want retribution for perpetrators, but simply a place to be heard without challenge. The current legal system precludes that possibility, leaving individuals without the option to confront perpetrators, and perpetrators often not knowing the extent of the damage they caused.
Where can psychiatrists have an impact right now? “Sexual Citizens” identifies four key areas for intervention to work toward a world with less sexual assault. These are:
- Improving diversity, inequality, and power distortions.
- Education about sex and sexual assault.
- Substance use.
- Mental health.
Substance use and mental health are especially relevant for psychiatrists (That substance use contributes to sexual assault is known by approximately ... everybody!). Unwanted sexual contact prior to college (20% of students) increased the odds of experiencing assault during college. Harm reduction strategies should be introduced before college, according to the SHIFT research, particularly in skills-based training on how to say “No” to unwanted sex. Psychiatrists are likely used to asking brief history questions related to sexual assault and rape. “Sexual Citizens” highlights the inadequacy of this blunt language and guides the reader toward a refined knowledge of the language needed to address sexual assault.
Dr. Whisler is a child and adolescent psychiatry fellow at the Stanford (Calif.) University. Dr. Higgins is affiliate associate professor of psychiatry and family medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
References
1. Hirsch JS et al. Social dimensions of sexual consent among cisgender heterosexual college students: Insights from ethnographic research. J Adolesc Health. 2019 Jan;64(1):26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.06.011.
2. Hirsch JS and Khan S. Sexual citizens: Sex, power, and assault on campus. New York: W.W. Norton & Company, 2020.
The Sexual Health Initiative to Foster Transformation (SHIFT)1 is a landmark study about sexual assault at college, which has generated 20 scientific articles and several chapters in books, but unfortunately, has not made its way into the psychiatric literature.
“Sexual Citizens: Sex, Power and Assault on Campus,” by Jennifer Hirsch and Shamus Khan, (available in audio book and paperback) was written as a follow up to the SHIFT study, so the rest of us can absorb the findings.2 This mixed-methods study included a survey of over 1,600 students aged 18-29 from Columbia University and Barnard College regarding their relationships and sexual histories, including assault. Data were collected using daily diaries, focus groups, and hundreds of hours of field work observation by young researchers. One- to 3-hour in-depth interviews exploring sexual experiences on campus were conducted with 151 students. These interviews are the focus of the book. It is a well-written, provocative story brimming with insights for those of us who lack the time to scour social science literature.
“Sexual Citizens” and the SHIFT study confirmed much of what we know. Sexual assault is common and has enduring effects. The study found that 36% of women and 15% of men had experienced unwanted, nonconsensual sexual contact by senior year. Twenty percent of women and 6% of men were rape survivors. Freshman, LGBTQ, and minority students were found at highest risk of assault. SHIFT reaffirmed that abstinence-only education is not a protective factor against college sexual assault, but neither was knowledge of affirmative consent (the practice of “ongoing and explicit” checking-in with partners) which few students ever employed. Encouragingly, students taught refusal skills were less likely to experience sexual assault.
Many of the book’s valuable lessons fall under the umbrella of failures of language and communication. For example, after drinking, they went to his room. She was expecting a social interaction, but with no other place to sit, they sat on his bed where she was coaxed or pressured into a sexual encounter. Afterward, she leaves, and it is never discussed again. One partner desires emotional intimacy, and the other, bragging rights in the fraternity or at the girls’ weekly brunch. Numerous personal stories like these, though at times heart wrenching, provide perspective on the barriers to addressing assault.
Subjects relayed experiences of assault by strangers or friends, and some provided details of their own actions as perpetrators. Stumbling around words and emotions, an avoidance of explicit language stemmed from shame, a fear of personal responsibility, the desire to maintain social cohesion, and concern for potential consequences for the perpetrator. Many subjects were resistant to calling nonconsensual sexual activity rape or even assault. Some who had perpetrated were unaware their behavior may have been experienced as assault, with recognition of this fact dawning during interviews.
This apparent limitation in self-reflective capacity may be in part due to the conceptualization of what assault is. Focus groups identified a discernible difference in how men and women understood assaults, with men believing rapes looked like a woman fighting back and screaming for help ... which is rarely what happens.
Notably absent among the interviewed are any flagrant perpetrators. The methodology section theorizes that individuals who intentionally harmed their peers were unlikely to choose to participate in this study. In addition, the characterization of assailants as “sociopathic predators” is based in a history of racialized imagery that leads us astray from the truth about campus sexual assault. Most assaults do not involve force, and SHIFT data showed 75% of victims knew their assailants. Ultimately, a major aim of the research was to study assault alongside healthy sex to “understand those pivotal moments when encounters change from being sex, to being assault.” Doing this requires understanding the where, how, and why students have sex, a more complicated undertaking than we may think.
In discussing their sexual lives, subjects frequently noted they did not have space to talk about their assaults. Though 81% of students discussed their experiences with someone, friend groups were often overburdened with stories, which minimized the victim’s experience. Furthermore, most had not sought help from the student counseling centers. Students navigating this complex field were frequently doing so in isolation. SHIFT found subjects to be eager to participate; they would often express thankfulness, and a sense of freedom in sharing with researchers. Commonly, students expressly did not want retribution for perpetrators, but simply a place to be heard without challenge. The current legal system precludes that possibility, leaving individuals without the option to confront perpetrators, and perpetrators often not knowing the extent of the damage they caused.
Where can psychiatrists have an impact right now? “Sexual Citizens” identifies four key areas for intervention to work toward a world with less sexual assault. These are:
- Improving diversity, inequality, and power distortions.
- Education about sex and sexual assault.
- Substance use.
- Mental health.
Substance use and mental health are especially relevant for psychiatrists (That substance use contributes to sexual assault is known by approximately ... everybody!). Unwanted sexual contact prior to college (20% of students) increased the odds of experiencing assault during college. Harm reduction strategies should be introduced before college, according to the SHIFT research, particularly in skills-based training on how to say “No” to unwanted sex. Psychiatrists are likely used to asking brief history questions related to sexual assault and rape. “Sexual Citizens” highlights the inadequacy of this blunt language and guides the reader toward a refined knowledge of the language needed to address sexual assault.
Dr. Whisler is a child and adolescent psychiatry fellow at the Stanford (Calif.) University. Dr. Higgins is affiliate associate professor of psychiatry and family medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
References
1. Hirsch JS et al. Social dimensions of sexual consent among cisgender heterosexual college students: Insights from ethnographic research. J Adolesc Health. 2019 Jan;64(1):26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.06.011.
2. Hirsch JS and Khan S. Sexual citizens: Sex, power, and assault on campus. New York: W.W. Norton & Company, 2020.
FDA OKs low-dose colchicine for broad CV indication
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine 0.5 mg tablets (Lodoco) as the first specific anti-inflammatory drug demonstrated to reduce the risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, and cardiovascular death in adult patients with established atherosclerotic disease or with multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
The drug, which targets residual inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, has a dosage of 0.5 mg once daily, and can be used alone or in combination with cholesterol-lowering medications.
The drug’s manufacturer, Agepha Pharma, said it anticipates that Lodoco will be available for prescription in the second half of 2023.
Colchicine has been available for many years and used at higher doses for the acute treatment of gout and pericarditis, but the current formulation is a much lower dose for long-term use in patients with atherosclerotic heart disease.
Data supporting the approval has come from two major randomized trials, LoDoCo-2 and COLCOT.
In the LoDoCo-2 trial, the anti-inflammatory drug cut the risk of cardiovascular events by one third when added to standard prevention therapies in patients with chronic coronary disease. And in the COLCOT study, use of colchicine reduced cardiovascular events by 23% compared with placebo in patients with a recent MI.
Paul Ridker, MD, director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who has been a pioneer in establishing inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, welcomed the Lodoco approval.
‘A very big day for cardiology’
“This is a very big day for cardiology,” Dr. Ridker said in an interview.
“The FDA approval of colchicine for patients with atherosclerotic disease is a huge signal that physicians need to be aware of inflammation as a key player in cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Dr. Ridker was the lead author of a recent study showing that among patients receiving contemporary statins, inflammation assessed by high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) was a stronger predictor for risk of future cardiovascular events and death than LDL cholesterol.
He pointed out that
“That is virtually identical to the indication approved for statin therapy. That shows just how important the FDA thinks this is,” he commented.
But Dr. Ridker added that, while the label does not specify that Lodoco has to be used in addition to statin therapy, he believes that it will be used as additional therapy to statins in the vast majority of patients.
“This is not an alternative to statin therapy. In the randomized trials, the benefits were seen on top of statins,” he stressed.
Dr. Ridker believes that physicians will need time to feel comfortable with this new approach.
“Initially, I think, it will be used mainly by cardiologists who know about inflammation, but I believe over time it will be widely prescribed by internists, in much the same way as statins are used today,” he commented.
Dr. Ridker said he already uses low dose colchicine in his high-risk patients who have high levels of inflammation as seen on hsCRP testing. He believes this is where the drug will mostly be used initially, as this is where it is likely to be most effective.
The prescribing information states that Lodoco is contraindicated in patients who are taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or P-glycoprotein inhibitors, such as ketoconazole, fluconazole, and clarithromycin, and in patients with preexisting blood dyscrasias, renal failure, and severe hepatic impairment.
Common side effects reported in published clinical studies and literature with the use of colchicine are gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramping) and myalgia.
More serious adverse effects are listed as blood dyscrasias such as myelosuppression, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, and aplastic anemia; and neuromuscular toxicity in the form of myotoxicity including rhabdomyolysis, which may occur, especially in combination with other drugs known to cause this effect. If these adverse effects occur, it is recommended that the drug be stopped.
The prescribing information also notes that Lodoco may rarely and transiently impair fertility in males; and that patients with renal or hepatic impairment should be monitored closely for adverse effects of colchicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine 0.5 mg tablets (Lodoco) as the first specific anti-inflammatory drug demonstrated to reduce the risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, and cardiovascular death in adult patients with established atherosclerotic disease or with multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
The drug, which targets residual inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, has a dosage of 0.5 mg once daily, and can be used alone or in combination with cholesterol-lowering medications.
The drug’s manufacturer, Agepha Pharma, said it anticipates that Lodoco will be available for prescription in the second half of 2023.
Colchicine has been available for many years and used at higher doses for the acute treatment of gout and pericarditis, but the current formulation is a much lower dose for long-term use in patients with atherosclerotic heart disease.
Data supporting the approval has come from two major randomized trials, LoDoCo-2 and COLCOT.
In the LoDoCo-2 trial, the anti-inflammatory drug cut the risk of cardiovascular events by one third when added to standard prevention therapies in patients with chronic coronary disease. And in the COLCOT study, use of colchicine reduced cardiovascular events by 23% compared with placebo in patients with a recent MI.
Paul Ridker, MD, director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who has been a pioneer in establishing inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, welcomed the Lodoco approval.
‘A very big day for cardiology’
“This is a very big day for cardiology,” Dr. Ridker said in an interview.
“The FDA approval of colchicine for patients with atherosclerotic disease is a huge signal that physicians need to be aware of inflammation as a key player in cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Dr. Ridker was the lead author of a recent study showing that among patients receiving contemporary statins, inflammation assessed by high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) was a stronger predictor for risk of future cardiovascular events and death than LDL cholesterol.
He pointed out that
“That is virtually identical to the indication approved for statin therapy. That shows just how important the FDA thinks this is,” he commented.
But Dr. Ridker added that, while the label does not specify that Lodoco has to be used in addition to statin therapy, he believes that it will be used as additional therapy to statins in the vast majority of patients.
“This is not an alternative to statin therapy. In the randomized trials, the benefits were seen on top of statins,” he stressed.
Dr. Ridker believes that physicians will need time to feel comfortable with this new approach.
“Initially, I think, it will be used mainly by cardiologists who know about inflammation, but I believe over time it will be widely prescribed by internists, in much the same way as statins are used today,” he commented.
Dr. Ridker said he already uses low dose colchicine in his high-risk patients who have high levels of inflammation as seen on hsCRP testing. He believes this is where the drug will mostly be used initially, as this is where it is likely to be most effective.
The prescribing information states that Lodoco is contraindicated in patients who are taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or P-glycoprotein inhibitors, such as ketoconazole, fluconazole, and clarithromycin, and in patients with preexisting blood dyscrasias, renal failure, and severe hepatic impairment.
Common side effects reported in published clinical studies and literature with the use of colchicine are gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramping) and myalgia.
More serious adverse effects are listed as blood dyscrasias such as myelosuppression, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, and aplastic anemia; and neuromuscular toxicity in the form of myotoxicity including rhabdomyolysis, which may occur, especially in combination with other drugs known to cause this effect. If these adverse effects occur, it is recommended that the drug be stopped.
The prescribing information also notes that Lodoco may rarely and transiently impair fertility in males; and that patients with renal or hepatic impairment should be monitored closely for adverse effects of colchicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine 0.5 mg tablets (Lodoco) as the first specific anti-inflammatory drug demonstrated to reduce the risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, and cardiovascular death in adult patients with established atherosclerotic disease or with multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
The drug, which targets residual inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, has a dosage of 0.5 mg once daily, and can be used alone or in combination with cholesterol-lowering medications.
The drug’s manufacturer, Agepha Pharma, said it anticipates that Lodoco will be available for prescription in the second half of 2023.
Colchicine has been available for many years and used at higher doses for the acute treatment of gout and pericarditis, but the current formulation is a much lower dose for long-term use in patients with atherosclerotic heart disease.
Data supporting the approval has come from two major randomized trials, LoDoCo-2 and COLCOT.
In the LoDoCo-2 trial, the anti-inflammatory drug cut the risk of cardiovascular events by one third when added to standard prevention therapies in patients with chronic coronary disease. And in the COLCOT study, use of colchicine reduced cardiovascular events by 23% compared with placebo in patients with a recent MI.
Paul Ridker, MD, director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who has been a pioneer in establishing inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, welcomed the Lodoco approval.
‘A very big day for cardiology’
“This is a very big day for cardiology,” Dr. Ridker said in an interview.
“The FDA approval of colchicine for patients with atherosclerotic disease is a huge signal that physicians need to be aware of inflammation as a key player in cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Dr. Ridker was the lead author of a recent study showing that among patients receiving contemporary statins, inflammation assessed by high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) was a stronger predictor for risk of future cardiovascular events and death than LDL cholesterol.
He pointed out that
“That is virtually identical to the indication approved for statin therapy. That shows just how important the FDA thinks this is,” he commented.
But Dr. Ridker added that, while the label does not specify that Lodoco has to be used in addition to statin therapy, he believes that it will be used as additional therapy to statins in the vast majority of patients.
“This is not an alternative to statin therapy. In the randomized trials, the benefits were seen on top of statins,” he stressed.
Dr. Ridker believes that physicians will need time to feel comfortable with this new approach.
“Initially, I think, it will be used mainly by cardiologists who know about inflammation, but I believe over time it will be widely prescribed by internists, in much the same way as statins are used today,” he commented.
Dr. Ridker said he already uses low dose colchicine in his high-risk patients who have high levels of inflammation as seen on hsCRP testing. He believes this is where the drug will mostly be used initially, as this is where it is likely to be most effective.
The prescribing information states that Lodoco is contraindicated in patients who are taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or P-glycoprotein inhibitors, such as ketoconazole, fluconazole, and clarithromycin, and in patients with preexisting blood dyscrasias, renal failure, and severe hepatic impairment.
Common side effects reported in published clinical studies and literature with the use of colchicine are gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramping) and myalgia.
More serious adverse effects are listed as blood dyscrasias such as myelosuppression, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, and aplastic anemia; and neuromuscular toxicity in the form of myotoxicity including rhabdomyolysis, which may occur, especially in combination with other drugs known to cause this effect. If these adverse effects occur, it is recommended that the drug be stopped.
The prescribing information also notes that Lodoco may rarely and transiently impair fertility in males; and that patients with renal or hepatic impairment should be monitored closely for adverse effects of colchicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NAFLD increases risk for severe infections
People with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are more likely to develop severe infections requiring hospitalization, according to findings from a large Swedish cohort study.
The increased risk was equal to one extra severe infection in every six patients with NAFLD by 20 years after diagnosis, wrote Fahim Ebrahimi, MD, of the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, and coauthors.
“Accumulating evidence suggests that NAFLD can affect multiple organ systems, which is not surprising, as the liver has multiple functions – regulating metabolism and being a central organ of the immune system,” Dr. Ebrahimi said in an interview.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
“Up to a fifth of cells in the liver are immune cells that process numerous antigens and pathogens from the gastrointestinal tract,” Dr. Ebrahimi noted. “We were intrigued by experimental studies showing that, in NAFLD, many of these key immune cells become dysfunctional at various levels, which may affect disease progression, but at the same time also increase the susceptibility to viral, bacterial, and fungal infections.”
Patients with NAFLD have metabolic risk factors known to increase infection risk, but a smaller study by a different research group had found that NAFLD could independently predispose patients to bacterial infections.
To further explore a connection between NAFLD and infection risk, the researchers looked at data for 12,133 Swedish adults with simple steatosis, nonfibrotic steatohepatitis, noncirrhotic fibrosis, or cirrhosis caused by NAFLD confirmed by liver biopsies performed between 1969 and 2017.
Each patient was matched to five or more contemporary controls from the general population by age, sex, and region of residence. The authors conducted an additional analysis that also adjusted for education, country of birth, and baseline clinical comorbidities, including diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, as well as hospitalization preceding the biopsy and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
The primary endpoint was severe infections requiring hospital admission. Secondary endpoints included seven prespecified infection subgroups: sepsis; respiratory tract; most gastrointestinal infections; bacterial peritonitis; urogenital; muscle, skin, and soft tissue; and other infections.
Elevated risk at all NAFLD stages
Dr. Ebrahimi and colleagues found that over a median follow-up of 14 years, patients with NAFLD had a higher incidence of severe infections – most often respiratory or urinary tract infections – compared with those without NAFLD (32% vs. 17%, respectively).
Biopsy-confirmed NAFLD was also associated with a 71% higher hazard and a 20-year absolute excess risk of 17.3% for severe infections requiring hospital admission versus comparators. The elevated risk showed up in patients with steatosis and increased with the severity of NAFLD. Simple steatosis saw a 64% higher risk (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.64; 95% confidence interval, 1.55-1.73), whereas patients with cirrhosis saw a more than twofold higher risk, compared with controls (aHR, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.92-2.82).
When Dr. Ebrahimi and colleagues adjusted for parameters of the metabolic syndrome, they found an independent increased risk for severe infection. For patients with NAFLD, the increased risk may come from greater susceptibility to infections in general or to a more severe course of infections.
“Our study clearly demonstrates the complexity and high disease burden associated with NAFLD,” Dr. Ebrahimi said. “We are beginning to understand the different layers involved and will eventually move away from a liver-centric view to a more holistic view of the disease.”
Clinicians caring for patients with NAFLD need to be aware of the increased risk for infection, Dr. Ebrahimi said. They also should assess their patients’ vaccination status, and seek to control modifiable risk factors, such as diabetes.
Nancy Reau, MD, of Rush University, Chicago, described the study’s message as important.
“Patients with NAFLD and advancing liver disease are at risk for severe infections,” Dr. Reau said. “When we consider the fact that patients with advanced liver disease tend to die from infectious complications, awareness leading to early recognition and efficient treatment is imperative.”
The authors acknowledged the following limitations: only severe infections requiring hospitalization could be captured; whether infection led to decompensation or vice versa among patients with cirrhosis could not be determined; and detailed data on smoking, alcohol, vaccinations, body mass, and other potentially relevant measures were not available.
The Swiss National Science Foundation, Syskonen Svensson Foundation, and Bengt Ihre Foundation provided grants to Dr. Ebrahimi or coauthors. One coauthor disclosed previous research funding from Janssen and MSD. Dr. Reau disclosed receiving research support and consulting fees from AbbVie and Gilead, as well as consulting fees from Arbutus, Intercept, and Salix.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are more likely to develop severe infections requiring hospitalization, according to findings from a large Swedish cohort study.
The increased risk was equal to one extra severe infection in every six patients with NAFLD by 20 years after diagnosis, wrote Fahim Ebrahimi, MD, of the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, and coauthors.
“Accumulating evidence suggests that NAFLD can affect multiple organ systems, which is not surprising, as the liver has multiple functions – regulating metabolism and being a central organ of the immune system,” Dr. Ebrahimi said in an interview.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
“Up to a fifth of cells in the liver are immune cells that process numerous antigens and pathogens from the gastrointestinal tract,” Dr. Ebrahimi noted. “We were intrigued by experimental studies showing that, in NAFLD, many of these key immune cells become dysfunctional at various levels, which may affect disease progression, but at the same time also increase the susceptibility to viral, bacterial, and fungal infections.”
Patients with NAFLD have metabolic risk factors known to increase infection risk, but a smaller study by a different research group had found that NAFLD could independently predispose patients to bacterial infections.
To further explore a connection between NAFLD and infection risk, the researchers looked at data for 12,133 Swedish adults with simple steatosis, nonfibrotic steatohepatitis, noncirrhotic fibrosis, or cirrhosis caused by NAFLD confirmed by liver biopsies performed between 1969 and 2017.
Each patient was matched to five or more contemporary controls from the general population by age, sex, and region of residence. The authors conducted an additional analysis that also adjusted for education, country of birth, and baseline clinical comorbidities, including diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, as well as hospitalization preceding the biopsy and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
The primary endpoint was severe infections requiring hospital admission. Secondary endpoints included seven prespecified infection subgroups: sepsis; respiratory tract; most gastrointestinal infections; bacterial peritonitis; urogenital; muscle, skin, and soft tissue; and other infections.
Elevated risk at all NAFLD stages
Dr. Ebrahimi and colleagues found that over a median follow-up of 14 years, patients with NAFLD had a higher incidence of severe infections – most often respiratory or urinary tract infections – compared with those without NAFLD (32% vs. 17%, respectively).
Biopsy-confirmed NAFLD was also associated with a 71% higher hazard and a 20-year absolute excess risk of 17.3% for severe infections requiring hospital admission versus comparators. The elevated risk showed up in patients with steatosis and increased with the severity of NAFLD. Simple steatosis saw a 64% higher risk (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.64; 95% confidence interval, 1.55-1.73), whereas patients with cirrhosis saw a more than twofold higher risk, compared with controls (aHR, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.92-2.82).
When Dr. Ebrahimi and colleagues adjusted for parameters of the metabolic syndrome, they found an independent increased risk for severe infection. For patients with NAFLD, the increased risk may come from greater susceptibility to infections in general or to a more severe course of infections.
“Our study clearly demonstrates the complexity and high disease burden associated with NAFLD,” Dr. Ebrahimi said. “We are beginning to understand the different layers involved and will eventually move away from a liver-centric view to a more holistic view of the disease.”
Clinicians caring for patients with NAFLD need to be aware of the increased risk for infection, Dr. Ebrahimi said. They also should assess their patients’ vaccination status, and seek to control modifiable risk factors, such as diabetes.
Nancy Reau, MD, of Rush University, Chicago, described the study’s message as important.
“Patients with NAFLD and advancing liver disease are at risk for severe infections,” Dr. Reau said. “When we consider the fact that patients with advanced liver disease tend to die from infectious complications, awareness leading to early recognition and efficient treatment is imperative.”
The authors acknowledged the following limitations: only severe infections requiring hospitalization could be captured; whether infection led to decompensation or vice versa among patients with cirrhosis could not be determined; and detailed data on smoking, alcohol, vaccinations, body mass, and other potentially relevant measures were not available.
The Swiss National Science Foundation, Syskonen Svensson Foundation, and Bengt Ihre Foundation provided grants to Dr. Ebrahimi or coauthors. One coauthor disclosed previous research funding from Janssen and MSD. Dr. Reau disclosed receiving research support and consulting fees from AbbVie and Gilead, as well as consulting fees from Arbutus, Intercept, and Salix.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are more likely to develop severe infections requiring hospitalization, according to findings from a large Swedish cohort study.
The increased risk was equal to one extra severe infection in every six patients with NAFLD by 20 years after diagnosis, wrote Fahim Ebrahimi, MD, of the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, and coauthors.
“Accumulating evidence suggests that NAFLD can affect multiple organ systems, which is not surprising, as the liver has multiple functions – regulating metabolism and being a central organ of the immune system,” Dr. Ebrahimi said in an interview.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
“Up to a fifth of cells in the liver are immune cells that process numerous antigens and pathogens from the gastrointestinal tract,” Dr. Ebrahimi noted. “We were intrigued by experimental studies showing that, in NAFLD, many of these key immune cells become dysfunctional at various levels, which may affect disease progression, but at the same time also increase the susceptibility to viral, bacterial, and fungal infections.”
Patients with NAFLD have metabolic risk factors known to increase infection risk, but a smaller study by a different research group had found that NAFLD could independently predispose patients to bacterial infections.
To further explore a connection between NAFLD and infection risk, the researchers looked at data for 12,133 Swedish adults with simple steatosis, nonfibrotic steatohepatitis, noncirrhotic fibrosis, or cirrhosis caused by NAFLD confirmed by liver biopsies performed between 1969 and 2017.
Each patient was matched to five or more contemporary controls from the general population by age, sex, and region of residence. The authors conducted an additional analysis that also adjusted for education, country of birth, and baseline clinical comorbidities, including diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, as well as hospitalization preceding the biopsy and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
The primary endpoint was severe infections requiring hospital admission. Secondary endpoints included seven prespecified infection subgroups: sepsis; respiratory tract; most gastrointestinal infections; bacterial peritonitis; urogenital; muscle, skin, and soft tissue; and other infections.
Elevated risk at all NAFLD stages
Dr. Ebrahimi and colleagues found that over a median follow-up of 14 years, patients with NAFLD had a higher incidence of severe infections – most often respiratory or urinary tract infections – compared with those without NAFLD (32% vs. 17%, respectively).
Biopsy-confirmed NAFLD was also associated with a 71% higher hazard and a 20-year absolute excess risk of 17.3% for severe infections requiring hospital admission versus comparators. The elevated risk showed up in patients with steatosis and increased with the severity of NAFLD. Simple steatosis saw a 64% higher risk (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.64; 95% confidence interval, 1.55-1.73), whereas patients with cirrhosis saw a more than twofold higher risk, compared with controls (aHR, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.92-2.82).
When Dr. Ebrahimi and colleagues adjusted for parameters of the metabolic syndrome, they found an independent increased risk for severe infection. For patients with NAFLD, the increased risk may come from greater susceptibility to infections in general or to a more severe course of infections.
“Our study clearly demonstrates the complexity and high disease burden associated with NAFLD,” Dr. Ebrahimi said. “We are beginning to understand the different layers involved and will eventually move away from a liver-centric view to a more holistic view of the disease.”
Clinicians caring for patients with NAFLD need to be aware of the increased risk for infection, Dr. Ebrahimi said. They also should assess their patients’ vaccination status, and seek to control modifiable risk factors, such as diabetes.
Nancy Reau, MD, of Rush University, Chicago, described the study’s message as important.
“Patients with NAFLD and advancing liver disease are at risk for severe infections,” Dr. Reau said. “When we consider the fact that patients with advanced liver disease tend to die from infectious complications, awareness leading to early recognition and efficient treatment is imperative.”
The authors acknowledged the following limitations: only severe infections requiring hospitalization could be captured; whether infection led to decompensation or vice versa among patients with cirrhosis could not be determined; and detailed data on smoking, alcohol, vaccinations, body mass, and other potentially relevant measures were not available.
The Swiss National Science Foundation, Syskonen Svensson Foundation, and Bengt Ihre Foundation provided grants to Dr. Ebrahimi or coauthors. One coauthor disclosed previous research funding from Janssen and MSD. Dr. Reau disclosed receiving research support and consulting fees from AbbVie and Gilead, as well as consulting fees from Arbutus, Intercept, and Salix.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Aspirin warning: Anemia may increase with daily use
, according to results from a new randomized controlled trial.
In the study, which was published in Annals of Internal Medicine, investigators analyzed data from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) trial and examined hemoglobin concentrations among 19,114 healthy, community-dwelling older patients.
“We knew from large clinical trials, including our ASPREE trial, that daily low-dose aspirin increased the risk of clinically significant bleeding,” said Zoe McQuilten, MBBS, PhD, a hematologist at Monash University in Australia and the study’s lead author. “From our study, we found that low-dose aspirin also increased the risk of anemia during the trial, and this was most likely due to bleeding that was not clinically apparent.”
Anemia is common among elderly patients. It can cause fatigue, fast or irregular heartbeat, headache, chest pain, and pounding or whooshing sounds in the ear, according to the Cleveland Clinic. It can also worsen conditions such as heart failure, cognitive impairment, and depression in people aged 65 and older.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force changed its recommendation on aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in 2022, recommending against initiating low-dose aspirin for adults aged 60 years or older. For adults aged 40-59 who have a 10% or greater 10-year risk for cardiovascular disease, the agency recommends that patients and clinicians make the decision to initiate low-dose aspirin use on a case-by-case basis, as the net benefit is small.
Dr. McQuilten said she spent the last 5 years designing substages of anemia and conditions such as blood cancer. In many cases of anemia, doctors are unable to determine the underlying cause, she said. One study published in the Journal of American Geriatrics Society in 2021 found that in about one-third of anemia cases, the etiology was not clear.
About 50% of people older than 60 who were involved in the latest study took aspirin for prevention from 2011 to 2018. That number likely dropped after changes were made to the guidelines in 2022, according to Dr. McQuilten, but long-term use may have continued among older patients. The researchers also examined ferritin levels, which serve as a proxy for iron levels, at baseline and after 3 years.
The incidence of anemia was 51 events per 1,000 person-years in the aspirin group compared with 43 events per 1,000 person-years in the placebo group, according to the researchers. The estimated probability of experiencing anemia within 5 years was 23.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 22.4%-24.6%) in the aspirin group and 20.3% (95% CI: 19.3% to 21.4%) in the placebo group. Aspirin therapy resulted in a 20% increase in the risk for anemia (95% CI, 1.12-1.29).
People who took aspirin were more likely to have lower serum levels of ferritin at the 3-year mark than were those who received placebo. The average decrease in ferritin among participants who took aspirin was 11.5% greater (95% CI, 9.3%-13.7%) than among those who took placebo.
Basil Eldadah, MD, PhD, supervisory medical officer at the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health, said the findings should encourage clinicians to pay closer attention to hemoglobin levels and have conversations with patients to discuss their need for taking aspirin.
“If somebody is already taking aspirin for any reason, keep an eye on hemoglobin,” said Dr. Eldadah, who was not involved in the study. “For somebody who’s taking aspirin and who’s older, and it’s not for an indication like cardiovascular disease, consider seriously whether that’s the best treatment option.”
The study did not examine the functional consequences of anemia on participants, which Dr. Eldadah said could be fodder for future research. The researchers said one limitation was that it was not clear whether anemia was sufficient to cause symptoms that affected participants’ quality of life or whether occult bleeding caused the anemia. The researchers also did not document whether patients saw their regular physicians and received treatment for anemia over the course of the trial.
The study was funded through grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. The authors reported receiving consulting fees, honoraria, and stock options, and have participated on data monitoring boards not related to the study for Vifor Pharma, ITL Biomedical, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer Healthcare, AbbVie, and Abbott Diagnostics.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to results from a new randomized controlled trial.
In the study, which was published in Annals of Internal Medicine, investigators analyzed data from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) trial and examined hemoglobin concentrations among 19,114 healthy, community-dwelling older patients.
“We knew from large clinical trials, including our ASPREE trial, that daily low-dose aspirin increased the risk of clinically significant bleeding,” said Zoe McQuilten, MBBS, PhD, a hematologist at Monash University in Australia and the study’s lead author. “From our study, we found that low-dose aspirin also increased the risk of anemia during the trial, and this was most likely due to bleeding that was not clinically apparent.”
Anemia is common among elderly patients. It can cause fatigue, fast or irregular heartbeat, headache, chest pain, and pounding or whooshing sounds in the ear, according to the Cleveland Clinic. It can also worsen conditions such as heart failure, cognitive impairment, and depression in people aged 65 and older.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force changed its recommendation on aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in 2022, recommending against initiating low-dose aspirin for adults aged 60 years or older. For adults aged 40-59 who have a 10% or greater 10-year risk for cardiovascular disease, the agency recommends that patients and clinicians make the decision to initiate low-dose aspirin use on a case-by-case basis, as the net benefit is small.
Dr. McQuilten said she spent the last 5 years designing substages of anemia and conditions such as blood cancer. In many cases of anemia, doctors are unable to determine the underlying cause, she said. One study published in the Journal of American Geriatrics Society in 2021 found that in about one-third of anemia cases, the etiology was not clear.
About 50% of people older than 60 who were involved in the latest study took aspirin for prevention from 2011 to 2018. That number likely dropped after changes were made to the guidelines in 2022, according to Dr. McQuilten, but long-term use may have continued among older patients. The researchers also examined ferritin levels, which serve as a proxy for iron levels, at baseline and after 3 years.
The incidence of anemia was 51 events per 1,000 person-years in the aspirin group compared with 43 events per 1,000 person-years in the placebo group, according to the researchers. The estimated probability of experiencing anemia within 5 years was 23.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 22.4%-24.6%) in the aspirin group and 20.3% (95% CI: 19.3% to 21.4%) in the placebo group. Aspirin therapy resulted in a 20% increase in the risk for anemia (95% CI, 1.12-1.29).
People who took aspirin were more likely to have lower serum levels of ferritin at the 3-year mark than were those who received placebo. The average decrease in ferritin among participants who took aspirin was 11.5% greater (95% CI, 9.3%-13.7%) than among those who took placebo.
Basil Eldadah, MD, PhD, supervisory medical officer at the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health, said the findings should encourage clinicians to pay closer attention to hemoglobin levels and have conversations with patients to discuss their need for taking aspirin.
“If somebody is already taking aspirin for any reason, keep an eye on hemoglobin,” said Dr. Eldadah, who was not involved in the study. “For somebody who’s taking aspirin and who’s older, and it’s not for an indication like cardiovascular disease, consider seriously whether that’s the best treatment option.”
The study did not examine the functional consequences of anemia on participants, which Dr. Eldadah said could be fodder for future research. The researchers said one limitation was that it was not clear whether anemia was sufficient to cause symptoms that affected participants’ quality of life or whether occult bleeding caused the anemia. The researchers also did not document whether patients saw their regular physicians and received treatment for anemia over the course of the trial.
The study was funded through grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. The authors reported receiving consulting fees, honoraria, and stock options, and have participated on data monitoring boards not related to the study for Vifor Pharma, ITL Biomedical, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer Healthcare, AbbVie, and Abbott Diagnostics.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to results from a new randomized controlled trial.
In the study, which was published in Annals of Internal Medicine, investigators analyzed data from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) trial and examined hemoglobin concentrations among 19,114 healthy, community-dwelling older patients.
“We knew from large clinical trials, including our ASPREE trial, that daily low-dose aspirin increased the risk of clinically significant bleeding,” said Zoe McQuilten, MBBS, PhD, a hematologist at Monash University in Australia and the study’s lead author. “From our study, we found that low-dose aspirin also increased the risk of anemia during the trial, and this was most likely due to bleeding that was not clinically apparent.”
Anemia is common among elderly patients. It can cause fatigue, fast or irregular heartbeat, headache, chest pain, and pounding or whooshing sounds in the ear, according to the Cleveland Clinic. It can also worsen conditions such as heart failure, cognitive impairment, and depression in people aged 65 and older.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force changed its recommendation on aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in 2022, recommending against initiating low-dose aspirin for adults aged 60 years or older. For adults aged 40-59 who have a 10% or greater 10-year risk for cardiovascular disease, the agency recommends that patients and clinicians make the decision to initiate low-dose aspirin use on a case-by-case basis, as the net benefit is small.
Dr. McQuilten said she spent the last 5 years designing substages of anemia and conditions such as blood cancer. In many cases of anemia, doctors are unable to determine the underlying cause, she said. One study published in the Journal of American Geriatrics Society in 2021 found that in about one-third of anemia cases, the etiology was not clear.
About 50% of people older than 60 who were involved in the latest study took aspirin for prevention from 2011 to 2018. That number likely dropped after changes were made to the guidelines in 2022, according to Dr. McQuilten, but long-term use may have continued among older patients. The researchers also examined ferritin levels, which serve as a proxy for iron levels, at baseline and after 3 years.
The incidence of anemia was 51 events per 1,000 person-years in the aspirin group compared with 43 events per 1,000 person-years in the placebo group, according to the researchers. The estimated probability of experiencing anemia within 5 years was 23.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 22.4%-24.6%) in the aspirin group and 20.3% (95% CI: 19.3% to 21.4%) in the placebo group. Aspirin therapy resulted in a 20% increase in the risk for anemia (95% CI, 1.12-1.29).
People who took aspirin were more likely to have lower serum levels of ferritin at the 3-year mark than were those who received placebo. The average decrease in ferritin among participants who took aspirin was 11.5% greater (95% CI, 9.3%-13.7%) than among those who took placebo.
Basil Eldadah, MD, PhD, supervisory medical officer at the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health, said the findings should encourage clinicians to pay closer attention to hemoglobin levels and have conversations with patients to discuss their need for taking aspirin.
“If somebody is already taking aspirin for any reason, keep an eye on hemoglobin,” said Dr. Eldadah, who was not involved in the study. “For somebody who’s taking aspirin and who’s older, and it’s not for an indication like cardiovascular disease, consider seriously whether that’s the best treatment option.”
The study did not examine the functional consequences of anemia on participants, which Dr. Eldadah said could be fodder for future research. The researchers said one limitation was that it was not clear whether anemia was sufficient to cause symptoms that affected participants’ quality of life or whether occult bleeding caused the anemia. The researchers also did not document whether patients saw their regular physicians and received treatment for anemia over the course of the trial.
The study was funded through grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. The authors reported receiving consulting fees, honoraria, and stock options, and have participated on data monitoring boards not related to the study for Vifor Pharma, ITL Biomedical, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer Healthcare, AbbVie, and Abbott Diagnostics.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Hold Ozempic before surgery to optimize patient safety?
Semaglutide and related drugs for weight loss have co-opted bariatric medicine in recent months. They have also raised serious questions for hospital-based clinicians who wonder whether the drugs may pose risks to surgery patients undergoing anesthesia.
at this point. Official guidance on best practices has not yet caught up to surging popularity of this and other glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists for weight loss.
Ozempic is indicated for treating type 2 diabetes but also is prescribed off-label for weight loss. Other GLP-1 agents from Novo Nordisk, Wegovy (semaglutide) and Saxenda (liraglutide) injections, are Food and Drug Administration–approved for weight loss. These medications work by decreasing hunger and lowering how much people eat. Semaglutide also is available as a once-daily tablet for type 2 diabetes (Rybelsus).
The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) has been working on guidance on the drugs. “It’s a really hot issue now. We are getting emails from our members looking for guidance,” ASA president Michael Champeau, MD, said in an interview.
But despite the interest in how the medications might affect surgery patients and interact with anesthesia, relatively little evidence exists in the literature beyond case studies. So the society is not issuing official recommendations at this point.
“We’re going to just be calling it ‘guidance’ for right now because of the paucity of the scientific literature,” said Dr. Champeau, adjunct clinical professor of anesthesiology, perioperative, and pain medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University. “It’s probably not going to have words like ‘must; it will probably have words like ‘should’ or ‘should consider.’ “
The ASA guidance could be out in written form soon, Dr. Champeau added.
Meanwhile, whether physicians should advise stopping these medications 24 hours, 48 hours, or up to 2 weeks before surgery remains unknown.
In search of some consensus, John Shields, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist Davie Medical Center in Bermuda Run, N.C., asked colleagues on #MedTwitter: “Anyone have guidelines for ozempic around time of surgery? – holding med? – how long NPO?”
Because a full stomach can interfere with anesthesia, clinicians often advise people to stop eating and drinking 12-24 hours before elective procedures (NPO). In the case of once-weekly GLP-1 injections, which can slow gastric emptying, the optimal timeframe remains an open question. The main concern is aspiration, where a patient actively vomits while under anesthesia or their stomach contents passively come back up.
Dr. Shields’ Twitter post garnered significant reaction and comments. Within 4 days, the post was retweeted 30 times and received 72 replies and comments. Dr. Shields noted the general consensus was to hold semaglutide for 1-2 weeks before a procedure. Other suggestions included recommending a liquid diet only for 24-48 hours before surgery, recommending an NPO protocol 24-36 hours in advance, or adjusting the weekly injection so the last dose is taken 5-6 days before surgery.
Anesthesiologist Cliff Gevirtz, MD, has encountered only a few surgical patients so far taking a GLP-1 for weight loss. “And thankfully no aspiration,” added Dr. Gevirtz, clinical director of office-based ambulatory anesthesia services at Somnia Anesthesia in Harrison, N.Y.
To minimize risk, some physicians will perform an ultrasound scan to assess the contents of the stomach. If surgery is elective in a patient with a full stomach, the procedure can get postponed. Another option is to proceed with the case but treat the patient as anesthesiologists approach an emergency procedure. To be safe, many will treat the case as if the patient has a full stomach.
Dr. Gevirtz said he would treat the patient as a ‘full stomach’ and perform a rapid sequence induction with cricoid pressure. He would then extubate the patient once laryngeal reflexes return.
A rapid-sequence induction involves giving the medicine that makes a patient go to sleep, giving another medicine that paralyzes them quickly, then inserting a breathing tube – all within about 30 seconds. Cricoid pressure involves pushing on the neck during intubation to try to seal off the top of the esophagus and again minimize the chances of food coming back up.
Giving metoclopramide 30 minutes before surgery is another option, Dr. Gevirtz said. Metoclopramide can hasten the emptying of stomach contents. Administration in advance is important because waiting for the drug to work can prolong time in the operating room.
Is holding semaglutide before surgery a relevant clinical question? “Yes, very much so,” said Ronnie Fass, MD, division director of gastroenterology and hepatology and the medical director of the Digestive Health Center at The MetroHealth System in Cleveland.
Dr. Fass recommended different strategies based on the semaglutide indication. Currently, clinicians at MetroHealth instruct patients to discontinue diabetic medications the day of surgery. For those who take semaglutide for diabetes, and because the medication is taken once a week, “there is growing discussion among surgeons that the medication should not be stopped prior to surgery. This is to ensure that patients’ diabetes is well controlled before and during surgery,” Dr. Fass said.
In patients taking semaglutide for weight loss only, “there is no clear answer at this point,” he said.
Dr. Fass said the question is complicated by the fact that the medication is taken once a week. “It brings up important questions about the use of the medication during surgery, which may increase the likelihood of side effects in general and for certain types of surgery. Personally, if a patient is taking [semaglutide] for weight loss only, I would consider stopping the medication before surgery.”
The ASA was able to act quickly because it already had an expert task force review how long people should fast before surgery last year – before the explosion in popularity of the GLP-1 agonists.
Although it is still a work in progress, Dr. Champeau offered “a peek” at the recommendations. “The guidance is going to look at how far in advance the drugs should be stopped, rather than looking at making people fast even longer” before surgery, he said. “There’s just no data on that latter question.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide and related drugs for weight loss have co-opted bariatric medicine in recent months. They have also raised serious questions for hospital-based clinicians who wonder whether the drugs may pose risks to surgery patients undergoing anesthesia.
at this point. Official guidance on best practices has not yet caught up to surging popularity of this and other glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists for weight loss.
Ozempic is indicated for treating type 2 diabetes but also is prescribed off-label for weight loss. Other GLP-1 agents from Novo Nordisk, Wegovy (semaglutide) and Saxenda (liraglutide) injections, are Food and Drug Administration–approved for weight loss. These medications work by decreasing hunger and lowering how much people eat. Semaglutide also is available as a once-daily tablet for type 2 diabetes (Rybelsus).
The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) has been working on guidance on the drugs. “It’s a really hot issue now. We are getting emails from our members looking for guidance,” ASA president Michael Champeau, MD, said in an interview.
But despite the interest in how the medications might affect surgery patients and interact with anesthesia, relatively little evidence exists in the literature beyond case studies. So the society is not issuing official recommendations at this point.
“We’re going to just be calling it ‘guidance’ for right now because of the paucity of the scientific literature,” said Dr. Champeau, adjunct clinical professor of anesthesiology, perioperative, and pain medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University. “It’s probably not going to have words like ‘must; it will probably have words like ‘should’ or ‘should consider.’ “
The ASA guidance could be out in written form soon, Dr. Champeau added.
Meanwhile, whether physicians should advise stopping these medications 24 hours, 48 hours, or up to 2 weeks before surgery remains unknown.
In search of some consensus, John Shields, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist Davie Medical Center in Bermuda Run, N.C., asked colleagues on #MedTwitter: “Anyone have guidelines for ozempic around time of surgery? – holding med? – how long NPO?”
Because a full stomach can interfere with anesthesia, clinicians often advise people to stop eating and drinking 12-24 hours before elective procedures (NPO). In the case of once-weekly GLP-1 injections, which can slow gastric emptying, the optimal timeframe remains an open question. The main concern is aspiration, where a patient actively vomits while under anesthesia or their stomach contents passively come back up.
Dr. Shields’ Twitter post garnered significant reaction and comments. Within 4 days, the post was retweeted 30 times and received 72 replies and comments. Dr. Shields noted the general consensus was to hold semaglutide for 1-2 weeks before a procedure. Other suggestions included recommending a liquid diet only for 24-48 hours before surgery, recommending an NPO protocol 24-36 hours in advance, or adjusting the weekly injection so the last dose is taken 5-6 days before surgery.
Anesthesiologist Cliff Gevirtz, MD, has encountered only a few surgical patients so far taking a GLP-1 for weight loss. “And thankfully no aspiration,” added Dr. Gevirtz, clinical director of office-based ambulatory anesthesia services at Somnia Anesthesia in Harrison, N.Y.
To minimize risk, some physicians will perform an ultrasound scan to assess the contents of the stomach. If surgery is elective in a patient with a full stomach, the procedure can get postponed. Another option is to proceed with the case but treat the patient as anesthesiologists approach an emergency procedure. To be safe, many will treat the case as if the patient has a full stomach.
Dr. Gevirtz said he would treat the patient as a ‘full stomach’ and perform a rapid sequence induction with cricoid pressure. He would then extubate the patient once laryngeal reflexes return.
A rapid-sequence induction involves giving the medicine that makes a patient go to sleep, giving another medicine that paralyzes them quickly, then inserting a breathing tube – all within about 30 seconds. Cricoid pressure involves pushing on the neck during intubation to try to seal off the top of the esophagus and again minimize the chances of food coming back up.
Giving metoclopramide 30 minutes before surgery is another option, Dr. Gevirtz said. Metoclopramide can hasten the emptying of stomach contents. Administration in advance is important because waiting for the drug to work can prolong time in the operating room.
Is holding semaglutide before surgery a relevant clinical question? “Yes, very much so,” said Ronnie Fass, MD, division director of gastroenterology and hepatology and the medical director of the Digestive Health Center at The MetroHealth System in Cleveland.
Dr. Fass recommended different strategies based on the semaglutide indication. Currently, clinicians at MetroHealth instruct patients to discontinue diabetic medications the day of surgery. For those who take semaglutide for diabetes, and because the medication is taken once a week, “there is growing discussion among surgeons that the medication should not be stopped prior to surgery. This is to ensure that patients’ diabetes is well controlled before and during surgery,” Dr. Fass said.
In patients taking semaglutide for weight loss only, “there is no clear answer at this point,” he said.
Dr. Fass said the question is complicated by the fact that the medication is taken once a week. “It brings up important questions about the use of the medication during surgery, which may increase the likelihood of side effects in general and for certain types of surgery. Personally, if a patient is taking [semaglutide] for weight loss only, I would consider stopping the medication before surgery.”
The ASA was able to act quickly because it already had an expert task force review how long people should fast before surgery last year – before the explosion in popularity of the GLP-1 agonists.
Although it is still a work in progress, Dr. Champeau offered “a peek” at the recommendations. “The guidance is going to look at how far in advance the drugs should be stopped, rather than looking at making people fast even longer” before surgery, he said. “There’s just no data on that latter question.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide and related drugs for weight loss have co-opted bariatric medicine in recent months. They have also raised serious questions for hospital-based clinicians who wonder whether the drugs may pose risks to surgery patients undergoing anesthesia.
at this point. Official guidance on best practices has not yet caught up to surging popularity of this and other glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists for weight loss.
Ozempic is indicated for treating type 2 diabetes but also is prescribed off-label for weight loss. Other GLP-1 agents from Novo Nordisk, Wegovy (semaglutide) and Saxenda (liraglutide) injections, are Food and Drug Administration–approved for weight loss. These medications work by decreasing hunger and lowering how much people eat. Semaglutide also is available as a once-daily tablet for type 2 diabetes (Rybelsus).
The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) has been working on guidance on the drugs. “It’s a really hot issue now. We are getting emails from our members looking for guidance,” ASA president Michael Champeau, MD, said in an interview.
But despite the interest in how the medications might affect surgery patients and interact with anesthesia, relatively little evidence exists in the literature beyond case studies. So the society is not issuing official recommendations at this point.
“We’re going to just be calling it ‘guidance’ for right now because of the paucity of the scientific literature,” said Dr. Champeau, adjunct clinical professor of anesthesiology, perioperative, and pain medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University. “It’s probably not going to have words like ‘must; it will probably have words like ‘should’ or ‘should consider.’ “
The ASA guidance could be out in written form soon, Dr. Champeau added.
Meanwhile, whether physicians should advise stopping these medications 24 hours, 48 hours, or up to 2 weeks before surgery remains unknown.
In search of some consensus, John Shields, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist Davie Medical Center in Bermuda Run, N.C., asked colleagues on #MedTwitter: “Anyone have guidelines for ozempic around time of surgery? – holding med? – how long NPO?”
Because a full stomach can interfere with anesthesia, clinicians often advise people to stop eating and drinking 12-24 hours before elective procedures (NPO). In the case of once-weekly GLP-1 injections, which can slow gastric emptying, the optimal timeframe remains an open question. The main concern is aspiration, where a patient actively vomits while under anesthesia or their stomach contents passively come back up.
Dr. Shields’ Twitter post garnered significant reaction and comments. Within 4 days, the post was retweeted 30 times and received 72 replies and comments. Dr. Shields noted the general consensus was to hold semaglutide for 1-2 weeks before a procedure. Other suggestions included recommending a liquid diet only for 24-48 hours before surgery, recommending an NPO protocol 24-36 hours in advance, or adjusting the weekly injection so the last dose is taken 5-6 days before surgery.
Anesthesiologist Cliff Gevirtz, MD, has encountered only a few surgical patients so far taking a GLP-1 for weight loss. “And thankfully no aspiration,” added Dr. Gevirtz, clinical director of office-based ambulatory anesthesia services at Somnia Anesthesia in Harrison, N.Y.
To minimize risk, some physicians will perform an ultrasound scan to assess the contents of the stomach. If surgery is elective in a patient with a full stomach, the procedure can get postponed. Another option is to proceed with the case but treat the patient as anesthesiologists approach an emergency procedure. To be safe, many will treat the case as if the patient has a full stomach.
Dr. Gevirtz said he would treat the patient as a ‘full stomach’ and perform a rapid sequence induction with cricoid pressure. He would then extubate the patient once laryngeal reflexes return.
A rapid-sequence induction involves giving the medicine that makes a patient go to sleep, giving another medicine that paralyzes them quickly, then inserting a breathing tube – all within about 30 seconds. Cricoid pressure involves pushing on the neck during intubation to try to seal off the top of the esophagus and again minimize the chances of food coming back up.
Giving metoclopramide 30 minutes before surgery is another option, Dr. Gevirtz said. Metoclopramide can hasten the emptying of stomach contents. Administration in advance is important because waiting for the drug to work can prolong time in the operating room.
Is holding semaglutide before surgery a relevant clinical question? “Yes, very much so,” said Ronnie Fass, MD, division director of gastroenterology and hepatology and the medical director of the Digestive Health Center at The MetroHealth System in Cleveland.
Dr. Fass recommended different strategies based on the semaglutide indication. Currently, clinicians at MetroHealth instruct patients to discontinue diabetic medications the day of surgery. For those who take semaglutide for diabetes, and because the medication is taken once a week, “there is growing discussion among surgeons that the medication should not be stopped prior to surgery. This is to ensure that patients’ diabetes is well controlled before and during surgery,” Dr. Fass said.
In patients taking semaglutide for weight loss only, “there is no clear answer at this point,” he said.
Dr. Fass said the question is complicated by the fact that the medication is taken once a week. “It brings up important questions about the use of the medication during surgery, which may increase the likelihood of side effects in general and for certain types of surgery. Personally, if a patient is taking [semaglutide] for weight loss only, I would consider stopping the medication before surgery.”
The ASA was able to act quickly because it already had an expert task force review how long people should fast before surgery last year – before the explosion in popularity of the GLP-1 agonists.
Although it is still a work in progress, Dr. Champeau offered “a peek” at the recommendations. “The guidance is going to look at how far in advance the drugs should be stopped, rather than looking at making people fast even longer” before surgery, he said. “There’s just no data on that latter question.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Docs misdiagnose aneurysm and patient dies; must pay $29M; more
and untreated, according to a story posted on Boston.com, among other news sites.
On the morning of Jan. 13, 2018, Joseph Brown awoke with shortness of breath and upper abdominal pain, which eventually spread to his chest and back. Taken to Salem Hospital’s emergency department, Mr. Brown was seen by Steven D. Browell, MD, an emergency medicine specialist.
Dr. Browell ordered tests that ruled out both a heart attack and a pulmonary embolism. He called for a blood test, which indicated that the patient’s white blood count was elevated. Suspecting an infection, Dr. Browell ordered that Mr. Brown be admitted to the hospital.
Accepting Mr. Brown’s admission was William D. Kenyon, MD, a hospitalist, who also examined the patient and concurred with Dr. Browell’s probable diagnosis. The patient was then sent to the medical floor.
There he underwent additional testing, including a chest x-ray, which proved negative except for one finding: a “mild hazy interstitial opacity that could represent a small airway inflammation or developing/early pneumonia.” Because Mr. Brown had reported that he had punctured his foot several days earlier, he also underwent a foot x-ray, which showed a possible foreign body. It was thought that might be the source of his infection.
Neither Dr. Browell nor Dr. Kenyon had completely ruled out a possible aortic aneurysm and dissection. Mr. Brown’s symptoms, after all, were in some ways suggestive of those conditions. Then again, he was very young – only 43 at the time – and his pain, while severe, didn’t correspond to the “searing” pain that, at trial, Dr. Kenyon described as typical of an aneurysm and dissection. As the hospitalist testified at trial, Mr. Brown had “a constellation of nonspecific symptoms” and an “unusual presentation of a rare condition,” typically seen in patients aged 65 and older.
Given these factors – and the results of Mr. Brown’s tests, lab studies, and physical exam – Dr. Kenyon didn’t think that the case warranted a CT scan to rule out an aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection.
By early the next morning, though, Mr. Brown’s shortness of breath and pain had intensified significantly. The on-duty doctor ordered a CT scan, which showed “a massive aneurysm at the beginning of [the patient’s] aorta and a dissection extending through most of his aorta.”
Mr. Brown was flown to Boston to undergo emergency surgery. En route to the helicopter, his aorta ruptured, stopping his heart and causing his death.
During the 8-day trial, each side introduced expert witnesses. Speaking for the plaintiffs, experts in cardiothoracic surgery and emergency medicine testified that the treating physicians were negligent in failing to order a CT scan on Jan. 13. Had they done so, the patient would have almost certainly undergone surgery earlier, which would have prevented his death.
Experts for the defense saw things differently. They testified that, given the evidence, it was reasonable and appropriate for Dr. Browell and Dr. Kenyon to have treated their patient for an infection rather than an aneurysm or dissection.
The jury found the defense’s arguments unconvincing, however. After deliberating 3 hours, it awarded the plaintiffs $20,000,000, to be paid out over time largely to Mr. Brown’s two daughters, who were aged 12 and 18 when he died. Including interest, the total award is close to $29 million.
In a statement following the verdict, lead plaintiff’s attorney Robert M. Higgins, of Lubin & Meyer, Boston, said the takeaway from the case was: “If you just treat people based on what the likelihood is, statistically, you’re going to miss a lot of life-threatening conditions. And that’s what happened in this case.”
Urologists typically prevail in BPH suits
Malpractice claims following surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) tend to be limited in scope and are typically resolved in favor of the surgeon-defendant, as a study in The Cureus Journal of Medical Science makes clear.
The study – conducted by a team of researchers that included Joao G. Porto, MD, of the Desai Sethi Urology Institute, University of Miami – investigated whether such surgeries pose a significant malpractice risk for urologists.
With information gleaned from two well-known legal databases, the team used a variety of key terms to identify BPH-related claims from January 2000 to December 2021.
Within this universe of claims, researchers identified several significant trends:
- Among BPH-related procedures, transurethral resection of the prostate was the most frequently identified (37%);
- Among the most-often cited reasons cited for a claim, allegations of inadequate postoperative care were the most common (33%);
- Of possible postsurgical complications, those that led to the greatest number of suits were urinary incontinence (23%), erectile dysfunction (13%), and urinary retention (13%); and,
- Not unexpectedly, the specialist most frequently named in a suit was a urologist (57%).
Interestingly, in all but two of the claims, the verdict favored the doctor-defendant. In the two cases in which the plaintiff prevailed, each involved unexpected and serious postsurgical complications.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
and untreated, according to a story posted on Boston.com, among other news sites.
On the morning of Jan. 13, 2018, Joseph Brown awoke with shortness of breath and upper abdominal pain, which eventually spread to his chest and back. Taken to Salem Hospital’s emergency department, Mr. Brown was seen by Steven D. Browell, MD, an emergency medicine specialist.
Dr. Browell ordered tests that ruled out both a heart attack and a pulmonary embolism. He called for a blood test, which indicated that the patient’s white blood count was elevated. Suspecting an infection, Dr. Browell ordered that Mr. Brown be admitted to the hospital.
Accepting Mr. Brown’s admission was William D. Kenyon, MD, a hospitalist, who also examined the patient and concurred with Dr. Browell’s probable diagnosis. The patient was then sent to the medical floor.
There he underwent additional testing, including a chest x-ray, which proved negative except for one finding: a “mild hazy interstitial opacity that could represent a small airway inflammation or developing/early pneumonia.” Because Mr. Brown had reported that he had punctured his foot several days earlier, he also underwent a foot x-ray, which showed a possible foreign body. It was thought that might be the source of his infection.
Neither Dr. Browell nor Dr. Kenyon had completely ruled out a possible aortic aneurysm and dissection. Mr. Brown’s symptoms, after all, were in some ways suggestive of those conditions. Then again, he was very young – only 43 at the time – and his pain, while severe, didn’t correspond to the “searing” pain that, at trial, Dr. Kenyon described as typical of an aneurysm and dissection. As the hospitalist testified at trial, Mr. Brown had “a constellation of nonspecific symptoms” and an “unusual presentation of a rare condition,” typically seen in patients aged 65 and older.
Given these factors – and the results of Mr. Brown’s tests, lab studies, and physical exam – Dr. Kenyon didn’t think that the case warranted a CT scan to rule out an aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection.
By early the next morning, though, Mr. Brown’s shortness of breath and pain had intensified significantly. The on-duty doctor ordered a CT scan, which showed “a massive aneurysm at the beginning of [the patient’s] aorta and a dissection extending through most of his aorta.”
Mr. Brown was flown to Boston to undergo emergency surgery. En route to the helicopter, his aorta ruptured, stopping his heart and causing his death.
During the 8-day trial, each side introduced expert witnesses. Speaking for the plaintiffs, experts in cardiothoracic surgery and emergency medicine testified that the treating physicians were negligent in failing to order a CT scan on Jan. 13. Had they done so, the patient would have almost certainly undergone surgery earlier, which would have prevented his death.
Experts for the defense saw things differently. They testified that, given the evidence, it was reasonable and appropriate for Dr. Browell and Dr. Kenyon to have treated their patient for an infection rather than an aneurysm or dissection.
The jury found the defense’s arguments unconvincing, however. After deliberating 3 hours, it awarded the plaintiffs $20,000,000, to be paid out over time largely to Mr. Brown’s two daughters, who were aged 12 and 18 when he died. Including interest, the total award is close to $29 million.
In a statement following the verdict, lead plaintiff’s attorney Robert M. Higgins, of Lubin & Meyer, Boston, said the takeaway from the case was: “If you just treat people based on what the likelihood is, statistically, you’re going to miss a lot of life-threatening conditions. And that’s what happened in this case.”
Urologists typically prevail in BPH suits
Malpractice claims following surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) tend to be limited in scope and are typically resolved in favor of the surgeon-defendant, as a study in The Cureus Journal of Medical Science makes clear.
The study – conducted by a team of researchers that included Joao G. Porto, MD, of the Desai Sethi Urology Institute, University of Miami – investigated whether such surgeries pose a significant malpractice risk for urologists.
With information gleaned from two well-known legal databases, the team used a variety of key terms to identify BPH-related claims from January 2000 to December 2021.
Within this universe of claims, researchers identified several significant trends:
- Among BPH-related procedures, transurethral resection of the prostate was the most frequently identified (37%);
- Among the most-often cited reasons cited for a claim, allegations of inadequate postoperative care were the most common (33%);
- Of possible postsurgical complications, those that led to the greatest number of suits were urinary incontinence (23%), erectile dysfunction (13%), and urinary retention (13%); and,
- Not unexpectedly, the specialist most frequently named in a suit was a urologist (57%).
Interestingly, in all but two of the claims, the verdict favored the doctor-defendant. In the two cases in which the plaintiff prevailed, each involved unexpected and serious postsurgical complications.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
and untreated, according to a story posted on Boston.com, among other news sites.
On the morning of Jan. 13, 2018, Joseph Brown awoke with shortness of breath and upper abdominal pain, which eventually spread to his chest and back. Taken to Salem Hospital’s emergency department, Mr. Brown was seen by Steven D. Browell, MD, an emergency medicine specialist.
Dr. Browell ordered tests that ruled out both a heart attack and a pulmonary embolism. He called for a blood test, which indicated that the patient’s white blood count was elevated. Suspecting an infection, Dr. Browell ordered that Mr. Brown be admitted to the hospital.
Accepting Mr. Brown’s admission was William D. Kenyon, MD, a hospitalist, who also examined the patient and concurred with Dr. Browell’s probable diagnosis. The patient was then sent to the medical floor.
There he underwent additional testing, including a chest x-ray, which proved negative except for one finding: a “mild hazy interstitial opacity that could represent a small airway inflammation or developing/early pneumonia.” Because Mr. Brown had reported that he had punctured his foot several days earlier, he also underwent a foot x-ray, which showed a possible foreign body. It was thought that might be the source of his infection.
Neither Dr. Browell nor Dr. Kenyon had completely ruled out a possible aortic aneurysm and dissection. Mr. Brown’s symptoms, after all, were in some ways suggestive of those conditions. Then again, he was very young – only 43 at the time – and his pain, while severe, didn’t correspond to the “searing” pain that, at trial, Dr. Kenyon described as typical of an aneurysm and dissection. As the hospitalist testified at trial, Mr. Brown had “a constellation of nonspecific symptoms” and an “unusual presentation of a rare condition,” typically seen in patients aged 65 and older.
Given these factors – and the results of Mr. Brown’s tests, lab studies, and physical exam – Dr. Kenyon didn’t think that the case warranted a CT scan to rule out an aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection.
By early the next morning, though, Mr. Brown’s shortness of breath and pain had intensified significantly. The on-duty doctor ordered a CT scan, which showed “a massive aneurysm at the beginning of [the patient’s] aorta and a dissection extending through most of his aorta.”
Mr. Brown was flown to Boston to undergo emergency surgery. En route to the helicopter, his aorta ruptured, stopping his heart and causing his death.
During the 8-day trial, each side introduced expert witnesses. Speaking for the plaintiffs, experts in cardiothoracic surgery and emergency medicine testified that the treating physicians were negligent in failing to order a CT scan on Jan. 13. Had they done so, the patient would have almost certainly undergone surgery earlier, which would have prevented his death.
Experts for the defense saw things differently. They testified that, given the evidence, it was reasonable and appropriate for Dr. Browell and Dr. Kenyon to have treated their patient for an infection rather than an aneurysm or dissection.
The jury found the defense’s arguments unconvincing, however. After deliberating 3 hours, it awarded the plaintiffs $20,000,000, to be paid out over time largely to Mr. Brown’s two daughters, who were aged 12 and 18 when he died. Including interest, the total award is close to $29 million.
In a statement following the verdict, lead plaintiff’s attorney Robert M. Higgins, of Lubin & Meyer, Boston, said the takeaway from the case was: “If you just treat people based on what the likelihood is, statistically, you’re going to miss a lot of life-threatening conditions. And that’s what happened in this case.”
Urologists typically prevail in BPH suits
Malpractice claims following surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) tend to be limited in scope and are typically resolved in favor of the surgeon-defendant, as a study in The Cureus Journal of Medical Science makes clear.
The study – conducted by a team of researchers that included Joao G. Porto, MD, of the Desai Sethi Urology Institute, University of Miami – investigated whether such surgeries pose a significant malpractice risk for urologists.
With information gleaned from two well-known legal databases, the team used a variety of key terms to identify BPH-related claims from January 2000 to December 2021.
Within this universe of claims, researchers identified several significant trends:
- Among BPH-related procedures, transurethral resection of the prostate was the most frequently identified (37%);
- Among the most-often cited reasons cited for a claim, allegations of inadequate postoperative care were the most common (33%);
- Of possible postsurgical complications, those that led to the greatest number of suits were urinary incontinence (23%), erectile dysfunction (13%), and urinary retention (13%); and,
- Not unexpectedly, the specialist most frequently named in a suit was a urologist (57%).
Interestingly, in all but two of the claims, the verdict favored the doctor-defendant. In the two cases in which the plaintiff prevailed, each involved unexpected and serious postsurgical complications.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.