User login
Threatening to burn the house down
CASE Agitated and aggressive
Mr. X, age 61, who has Alzheimer’s disease, is brought to the emergency department (ED) by his family after he is found to be confused, becomes physically aggressive with family members, and threatens to burn the house down. His family reports that earlier that day, he was paranoid that somebody was trying to kill him and he tried to leave the house. Mr. X has been experiencing visual hallucinations and delusional thoughts that made him aggressive towards his son. After an initial laboratory workup in the ED, Mr. X’s bloodwork comes back positive for mild leukocytosis, indicating the possibility of an infectious etiology. Mr. X is admitted to the hospital for further evaluation of his altered mental status.
HISTORY Decline over 2 years
This is Mr. X’s third inpatient admission for agitation and psychosis. His current medications—twice daily divalproex sodium extended release (ER), 250 mg every morning and 500 mg at every bedtime, and prazosin, 2 mg/d at bedtime—have been only partially effective. His medical history includes osteoarthritis, back pain, and heterozygous factor V Leiden (not on anticoagulation). He quit smoking tobacco several years ago and has no history of substance use. He has no family history of dementia. Previous trials of cholinesterase inhibitors, antipsychotics, and antidepressants resulted in only minimal improvement in his agitation and psychosis.
A chart review shows that 2 years before his current hospital admission, Mr. X had presented to his primary care physician with slurred speech, forgetfulness, missing words, and transient reading difficulties. His initial laboratory workup and MRI came back normal. He was placed on short-term disability due to work-related errors. He was referred to the hospital’s Memory Clinic 2 years ago, where his Mini-Mental State Exam score was 20/30, indicating mild cognitive impairment. Stroke workup was negative. Due to significant language deficits, a differential diagnosis for Alzheimer’s disease vs primary progressive aphasia vs frontotemporal dementia was made. He screened positive for amyloid PET scan, which confirmed the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease.
Neuropsychological testing showed similarities with logopenic variant of primary progressive aphasia, which in many cases is present in Alzheimer’s disease. Mr. X was prescribed anticholinesterase inhibitors, including donepezil, 10 mg/d, and rivastigmine patch, 9.5 mg/d; and memantine, 10 mg/d, which he could not tolerate because of adverse effects. During the next year, Mr. X deteriorated and presented to the ED a few times with significant psychotic symptoms and aggression. He had a poor response to various pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions during this time.
EVALUATION Continued problematic behaviors
During his hospitalization, Mr. X continues to be agitated and paranoid and is placed in restraints. He is unable to respond to his name and cannot follow simple verbal commands. Results of his laboratory workup are within normal limits. His mild leukocytosis resolves with no active signs of infection. Psychiatry is consulted for management of his behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD).
Continue to: Mr. X is started on olanzapine...
Mr. X is started on olanzapine and lorazepam as needed for agitation, and his twice daily divalproex sodium ER is increased to 250 every morning and 750 mg at every bedtime. However, Mr. X remains agitated and requires restraints. Olanzapine is switched from an as-needed dose to scheduled doses of 10 mg every morning and 15 mg at every bedtime, to address his psychosis and agitation.
On Day 24 of hospitalization, Mr. X’s ammonia levels are checked and are found to be 69 µ/dL, which is high (normal range: 15 to 45 µ/dL). Divalproex sodium ER is eventually tapered and discontinued. Mr. X is started on carbamazepine, which is titrated to 400 mg twice daily and results in some improvement in his behavior. He continues to receive carbamazepine and is started on dextromethorphan-quinidine, 10 mg/d, and increased to 10 mg twice daily; however, Mr. X continues to be verbally aggressive with staff, throws food, wanders around, and tries to leave the hospital unit, so he is placed in restraints and continues to require a sitter.
[polldaddy:10698428]
The authors' observations
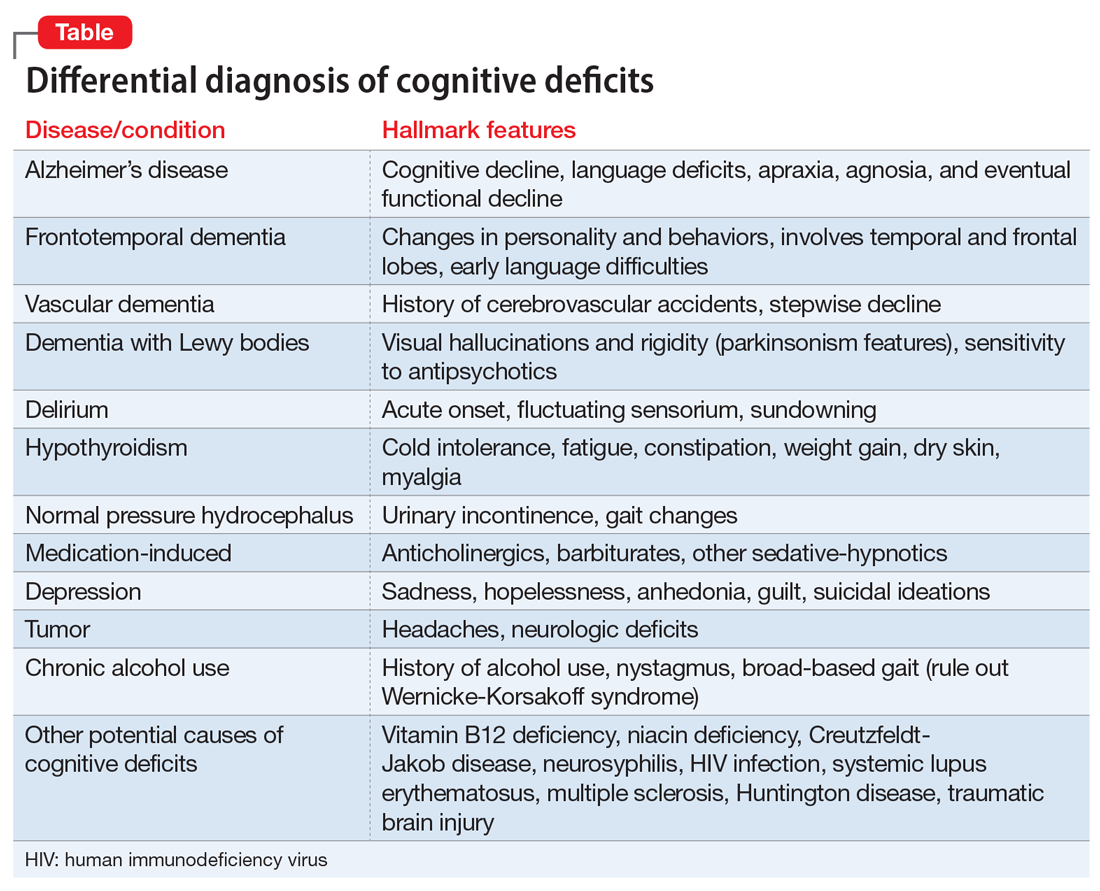
Dementia typically affects older adults, but its onset can occur before age 60. It is a syndrome rather than a specific illness; the most common types are Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies, and frontotemporal dementia. Diagnostic clarity and an evidence-based treatment plan are crucial for improving the quality of life for both the patient and their caregivers. The Table outlines the differential diagnosis of cognitive deficits. New-onset cognitive deficits warrant neuroimaging, and other testing may also be needed.
Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia
Noncognitive symptoms occur in 98% of individuals with dementia at some point in their disease and are often the most distressing to both caregivers and patients.1 Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia, including apathy, depression, sleep disorders, hallucinations, delusions, psychosis, agitation, and aggression, are exceedingly prevalent.2 Although these symptoms pose a significant burden, there are no clear published treatment guidelines; however, the American Psychiatric Association and the American Geriatric Society recommend using nonpharmacologic approaches as the first-line of treatment for patients with BPSD.3,4
Nonpharmacologic treatments
Due to the unfavorable adverse effects profiles of medications commonly used to treat dementia, nonpharmacologic treatment approaches have always played a crucial role for managing BPSD. Interventions such as music therapy, aromatherapy, art therapy, behavioral therapy, reality orientation, tailored activities, and physical exercises, have shown promising results for alleviating BPSD.5-7
Continue to: Pharmacologic therapies should be used...
Pharmacologic treatments
Pharmacologic therapies should be used when nonpharmacologic approaches are unsuccessful, or when a patient is at imminent risk to harm themselves or others.
Antipsychotics. Although there is conflicting data regarding the use of antipsychotics in older adults, these agents are the most common pharmacologic treatment for patients with BPSD. Several studies examining the efficacy of antipsychotics for treating BPSD have demonstrated an increased risk of cerebrovascular events, including stroke and death due to any cause.8 While the use of antipsychotics increases the risk of mortality in older adults, the absolute risk is still low.9
Antipsychotics used to treat BPSD include:
- Risperidone is well studied in older adults and has shown benefit for treating aggression, agitation, and psychosis.10
- Quetiapine has a favorable adverse effects profile and may help improve sleep and reduce anxiety.10
- Olanzapine. Low-dose olanzapine has been modestly effective in decreasing agitation and aggression in patients with Alzheimer’s and vascular dementias.11
- Aripiprazole has shown modest benefit in treating psychosis and agitation in patients with dementia but may be associated with insomnia or activation symptoms at lower doses.10
- Ziprasidone. Case reports have found benefit with oral and injectable forms.12
Antidepressants. In the CitAD study, which was a placebo-controlled randomized trial, citalopram titrated to a target of 30 mg/d was found to be effective in reducing BPSD.13 However, QTc prolongation limits the use of citalopram. Sertraline was studied in 1 small, randomized trial against haloperidol but showed no additional benefit.14
Mood stabilizers. In a small, randomized trial, carbamazepine was helpful for patients with BPSD who were resistant to treatment with antipsychotics, with efficacy demonstrated over 6 weeks.15 No other mood stabilizers have had significant positive results in treating BPSD.16
Anxiolytic medications. Some research suggests that the occasional use of lorazepam, as necessary, is acceptable for patients with extreme agitation or aggression when behavioral interventions or sleep aids are ineffective.17 Various case reports and case series have suggested gabapentin may be effective for BPSD.18
Prazosin. In a small randomized placebo-controlled trial, the commonly used antihypertensive agent prazosin reduced agitation and aggression in patients with Alzheimer’s dementia, at doses from 1 to 6 mg/d.19 Postural hypotension, the main adverse effect associated with prazosin, can limit its use.
Trazodone. Some research suggests trazodone can reduce irritability and aggression in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.20
Dextromethorphan/quinidine. In a 10-week phase 2 randomized clinical trial of patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease dementia, combination dextromethorphan/quinidine reduced agitation and was generally well tolerated.21
For patients such as Mr. X who do not respond to multiple pharmacologic treatments, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be an option.
Continue to: Because Mr. X does not respond...
TREATMENT A trial of ECT
Because Mr. X does not respond to the standard treatment protocols, the treatment team and Mr. X’s family discuss the use of ECT to control his agitation. Consent is obtained from his legal guardian and Mr. X is medically cleared to receive ECT. Mr. X receives 3 ECT treatments per week. During the first week, Mr. X experiences post-treatment agitation and confusion. The frequency of ECT treatments is reduced to 2 treatments per week, and then 1 session per week. Mr. X starts to show improvement in his agitation and ECT is continued at 1 session per week for 7 weeks.
The authors’ observations
Electroconvulsive therapy has been an effective treatment for patients with treatment-resistant depression and has shown benefit in treating other psychiatric conditions such as acute mania, catatonia, psychotic disorders, and Parkinson’s disease.22 Its use as an off-label treatment for chronic neuropathic pain has also been well documented.23 Although ECT is not indicated for treating agitation and aggression in patients with dementia, its effectiveness for these symptoms has been discussed extensively in the literature.22,24-26
Electroconvulsive therapy treatment can be divided into 2 phases: an acute phase during which ECT is administered 2 to 3 times a week for 4 to 5 weeks, and a maintenance phase of weekly treatments for 4 weeks and then biweekly treatments for 8 weeks.26 Although extensive research supports the safe use of ECT in older adults, concerns for worsening cognitive impairment can deter patients and families from agreeing to this treatment.
Adverse effects of ECT such as headaches and postictal confusion are generally mild and transient. Severe adverse effects such as seizures, severe confusion, and delirium are uncommon.25 The number of ECT treatments required for a good effect ranges from 2 to 18, and the most common position for electrodes placement is bilateral. Outcomes can be measured by using rating scales such as the Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory, Neuropsychiatric Inventory, Social Dysfunction and Aggression Scale, Clinical Global Impression scale, and Pittsford Agitation Scale.25 Obtaining consent from patients with dementia is generally not possible because these patients generally lack the capacity to make medical decisions. Clinicians should refer to their state laws regarding medical-decision making in such cases. The patient’s next of kin or medical power of attorney should be contacted, and the risks and benefits should be discussed before starting ECT.
OUTCOME Lasting improvement
Due to Mr. X’s improvement after ECT, on hospital Day 124, the restraints are removed and he no longer requires a sitter. He starts responding to his name and following simple verbal commands. Electroconvulsive therapy is tapered to every other week, and eventually stopped as his status improves. Mr. X continues to do well and is maintained on the same dosages of olanzapine, carbamazepine, and dextromethorphan-quinidine he had been receiving prior to discharge.
Related Resources
• Van den Berg JF, Kruithof HC, Kok RM, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for agitation and aggression in dementia: a systematic review. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018;26(4):419-434.
• Kales HC, Mulsant BH, Sajatovic M. Prescribing antipsychotics in geriatric patients: Focus on dementia. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(12):24-30.
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Carbamazepine • Tegretol
Citalopram • Celexa
Dextromethorphan- quinidine • Nuedexta
Divalproex sodium ER • Depakote
Donepezil • Aricept
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lorazepam • Ativan
Memantine • Namenda
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Prazosin • Minipress
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Rivastigmine • Exelon
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Desyrel, Oleptro
Ziprasidone • Geodon
1. Kales HC, Gitlin LN, Lyketsos CG. Management of neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia in clinical settings: recommendations from a multidisciplinary expert panel. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62(4):762-769.
2. Scarmeas N, Brandt J, Albert M, et al. Delusions and hallucinations are associated with worse outcome in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2005;62(10):1601-1608.
3. Reus VI, Fochtmann LJ, Eyler AE, et al. The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline on the use of antipsychotics to treat agitation or psychosis in patients with dementia. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173(5):543-546.
4. AGS Executive Committee. A guide to the management of psychotic disorders and neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia in older adults. The American Geriatrics Society. Published April 2011. Accessed September 24, 2020. https://qioprogram.org/sites/default/files/AGS_Guidelines_for_Telligen.pdf
5. Yang MH, Lin LC, Wu SC, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of aroma-acupressure and aromatherapy for the treatment of dementia-associated agitation. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015;15:93.
6. Cerga-Pashoja A, Lowery D, Bhattacharya R, et al. Evaluation of exercise on individuals with dementia and their carers: a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2010;11:53.
7. Chen RC, Liu CL, Lin MH, et al. Non-pharmacological treatment reducing not only behavioral symptoms, but also psychotic symptoms of older adults with dementia: a prospective cohort study in Taiwan. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2014;14(2):440-446.
8. Schneider LS, Dagerman KS, Insel P. Risk of death with atypical antipsychotic drug treatment for dementia: meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. JAMA. 2005;294(15):1934-1943.
9. Lenzer J. FDA warns about using antipsychotic drugs for dementia. BMJ. 2005;330(7497):922.
10. Burke AD, Tariot PN. Atypical antipsychotics in the elderly: a review of therapeutic trends and clinical outcomes. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009;10(15):2407-2414.
11. Moretti R, Torre R, Antonello T, et al. Olanzapine as a possible treatment of behavioral symptoms in vascular dementia: risks of cerebrovascular events. J Neurol. 2005;252(10):1186-1193.
12. Cole SA, Saleem R, Shea WP, et al. Ziprasidone for agitation or psychosis in dementia: four cases. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2005;35(1):91-98.
13. Porsteinsson AP, Drye LT, Pollock BG, et al. Effect of citalopram on agitation in Alzheimer disease: the CitAD randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014;311(7):682-691.
14. Gaber S, Ronzoli S, Bruno A, et al. Sertraline versus small doses of haloperidol in the treatment of agitated behavior in patients with dementia. Arch Gerontol Geriatr Suppl. 2001; 7:159-162.
15. Olin JT, Fox LS, Pawluczyk S, et al. A pilot randomized trial of carbamazepine for behavioral symptoms in treatment-resistant outpatients with Alzheimer disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001;9(4):400-405.
16. Konovalov S, Muralee S, Tampi RR. Anticonvulsants for the treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: a literature review. Int Psychogeriatr. 2008;20(2):293-308.
17. Davies SJC, Burhan AM, Kim D. Sequential drug treatment algorithm for agitation and aggression in Alzheimer’s and mixed dementia. J Psychopharmacol. 2018;32(5):509-523.
18. Kim Y, Wilkins KM, Tampi RR. Use of gabapentin in the treatment of behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia: a review of the evidence. Drugs Aging. 2008;25(3):187-196.
19. Wang LY, Shofer JB, Rohde K, et al. Prazosin for the treatment of behavioral symptoms in patients with Alzheimer disease with agitation and aggression. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2009; 17(9):744-751.
20. López-Pousa S, Garre-Olmo J, Vilalta-Franch J, et al. Trazodone for Alzheimer’s disease: a naturalistic follow-up study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008;47(2):207-215.
21. Cummings JL, Lyketsos CG, Peskind ER. Effect of dextromethorphan-quinidine on agitation in patients with Alzheimer disease dementia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;314(12):1242-1254.
22. Ujkaj M, Davidoff DA, Seiner SJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of electroconvulsive therapy for the treatment of agitation and aggression in patients with dementia. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012;20(1):61-72.
23. McDaniel WW. Electroconvulsive therapy in complex regional pain syndromes. J ECT. 2003;19(4):226-229.
24. Glass OM, Forester BP, Hermida AP. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) for treating agitation in dementia (major neurocognitive disorder)–a promising option. Int Psychogeriatr. 2017;29(5):717-726.
25. Van den Berg JF, Kruithof HC, Kok RM, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for agitation and aggression in dementia: a systematic review. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018;26(4):419-434.
26. Isserles M, Daskalakis ZJ, Kumar S, et al. Clinical effectiveness and tolerability of electroconvulsive therapy in patients with neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;57(1):45-51.
CASE Agitated and aggressive
Mr. X, age 61, who has Alzheimer’s disease, is brought to the emergency department (ED) by his family after he is found to be confused, becomes physically aggressive with family members, and threatens to burn the house down. His family reports that earlier that day, he was paranoid that somebody was trying to kill him and he tried to leave the house. Mr. X has been experiencing visual hallucinations and delusional thoughts that made him aggressive towards his son. After an initial laboratory workup in the ED, Mr. X’s bloodwork comes back positive for mild leukocytosis, indicating the possibility of an infectious etiology. Mr. X is admitted to the hospital for further evaluation of his altered mental status.
HISTORY Decline over 2 years
This is Mr. X’s third inpatient admission for agitation and psychosis. His current medications—twice daily divalproex sodium extended release (ER), 250 mg every morning and 500 mg at every bedtime, and prazosin, 2 mg/d at bedtime—have been only partially effective. His medical history includes osteoarthritis, back pain, and heterozygous factor V Leiden (not on anticoagulation). He quit smoking tobacco several years ago and has no history of substance use. He has no family history of dementia. Previous trials of cholinesterase inhibitors, antipsychotics, and antidepressants resulted in only minimal improvement in his agitation and psychosis.
A chart review shows that 2 years before his current hospital admission, Mr. X had presented to his primary care physician with slurred speech, forgetfulness, missing words, and transient reading difficulties. His initial laboratory workup and MRI came back normal. He was placed on short-term disability due to work-related errors. He was referred to the hospital’s Memory Clinic 2 years ago, where his Mini-Mental State Exam score was 20/30, indicating mild cognitive impairment. Stroke workup was negative. Due to significant language deficits, a differential diagnosis for Alzheimer’s disease vs primary progressive aphasia vs frontotemporal dementia was made. He screened positive for amyloid PET scan, which confirmed the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease.
Neuropsychological testing showed similarities with logopenic variant of primary progressive aphasia, which in many cases is present in Alzheimer’s disease. Mr. X was prescribed anticholinesterase inhibitors, including donepezil, 10 mg/d, and rivastigmine patch, 9.5 mg/d; and memantine, 10 mg/d, which he could not tolerate because of adverse effects. During the next year, Mr. X deteriorated and presented to the ED a few times with significant psychotic symptoms and aggression. He had a poor response to various pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions during this time.
EVALUATION Continued problematic behaviors
During his hospitalization, Mr. X continues to be agitated and paranoid and is placed in restraints. He is unable to respond to his name and cannot follow simple verbal commands. Results of his laboratory workup are within normal limits. His mild leukocytosis resolves with no active signs of infection. Psychiatry is consulted for management of his behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD).
Continue to: Mr. X is started on olanzapine...
Mr. X is started on olanzapine and lorazepam as needed for agitation, and his twice daily divalproex sodium ER is increased to 250 every morning and 750 mg at every bedtime. However, Mr. X remains agitated and requires restraints. Olanzapine is switched from an as-needed dose to scheduled doses of 10 mg every morning and 15 mg at every bedtime, to address his psychosis and agitation.
On Day 24 of hospitalization, Mr. X’s ammonia levels are checked and are found to be 69 µ/dL, which is high (normal range: 15 to 45 µ/dL). Divalproex sodium ER is eventually tapered and discontinued. Mr. X is started on carbamazepine, which is titrated to 400 mg twice daily and results in some improvement in his behavior. He continues to receive carbamazepine and is started on dextromethorphan-quinidine, 10 mg/d, and increased to 10 mg twice daily; however, Mr. X continues to be verbally aggressive with staff, throws food, wanders around, and tries to leave the hospital unit, so he is placed in restraints and continues to require a sitter.
[polldaddy:10698428]
The authors' observations
Dementia typically affects older adults, but its onset can occur before age 60. It is a syndrome rather than a specific illness; the most common types are Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies, and frontotemporal dementia. Diagnostic clarity and an evidence-based treatment plan are crucial for improving the quality of life for both the patient and their caregivers. The Table outlines the differential diagnosis of cognitive deficits. New-onset cognitive deficits warrant neuroimaging, and other testing may also be needed.

Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia
Noncognitive symptoms occur in 98% of individuals with dementia at some point in their disease and are often the most distressing to both caregivers and patients.1 Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia, including apathy, depression, sleep disorders, hallucinations, delusions, psychosis, agitation, and aggression, are exceedingly prevalent.2 Although these symptoms pose a significant burden, there are no clear published treatment guidelines; however, the American Psychiatric Association and the American Geriatric Society recommend using nonpharmacologic approaches as the first-line of treatment for patients with BPSD.3,4
Nonpharmacologic treatments
Due to the unfavorable adverse effects profiles of medications commonly used to treat dementia, nonpharmacologic treatment approaches have always played a crucial role for managing BPSD. Interventions such as music therapy, aromatherapy, art therapy, behavioral therapy, reality orientation, tailored activities, and physical exercises, have shown promising results for alleviating BPSD.5-7
Continue to: Pharmacologic therapies should be used...
Pharmacologic treatments
Pharmacologic therapies should be used when nonpharmacologic approaches are unsuccessful, or when a patient is at imminent risk to harm themselves or others.
Antipsychotics. Although there is conflicting data regarding the use of antipsychotics in older adults, these agents are the most common pharmacologic treatment for patients with BPSD. Several studies examining the efficacy of antipsychotics for treating BPSD have demonstrated an increased risk of cerebrovascular events, including stroke and death due to any cause.8 While the use of antipsychotics increases the risk of mortality in older adults, the absolute risk is still low.9
Antipsychotics used to treat BPSD include:
- Risperidone is well studied in older adults and has shown benefit for treating aggression, agitation, and psychosis.10
- Quetiapine has a favorable adverse effects profile and may help improve sleep and reduce anxiety.10
- Olanzapine. Low-dose olanzapine has been modestly effective in decreasing agitation and aggression in patients with Alzheimer’s and vascular dementias.11
- Aripiprazole has shown modest benefit in treating psychosis and agitation in patients with dementia but may be associated with insomnia or activation symptoms at lower doses.10
- Ziprasidone. Case reports have found benefit with oral and injectable forms.12
Antidepressants. In the CitAD study, which was a placebo-controlled randomized trial, citalopram titrated to a target of 30 mg/d was found to be effective in reducing BPSD.13 However, QTc prolongation limits the use of citalopram. Sertraline was studied in 1 small, randomized trial against haloperidol but showed no additional benefit.14
Mood stabilizers. In a small, randomized trial, carbamazepine was helpful for patients with BPSD who were resistant to treatment with antipsychotics, with efficacy demonstrated over 6 weeks.15 No other mood stabilizers have had significant positive results in treating BPSD.16
Anxiolytic medications. Some research suggests that the occasional use of lorazepam, as necessary, is acceptable for patients with extreme agitation or aggression when behavioral interventions or sleep aids are ineffective.17 Various case reports and case series have suggested gabapentin may be effective for BPSD.18
Prazosin. In a small randomized placebo-controlled trial, the commonly used antihypertensive agent prazosin reduced agitation and aggression in patients with Alzheimer’s dementia, at doses from 1 to 6 mg/d.19 Postural hypotension, the main adverse effect associated with prazosin, can limit its use.
Trazodone. Some research suggests trazodone can reduce irritability and aggression in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.20
Dextromethorphan/quinidine. In a 10-week phase 2 randomized clinical trial of patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease dementia, combination dextromethorphan/quinidine reduced agitation and was generally well tolerated.21
For patients such as Mr. X who do not respond to multiple pharmacologic treatments, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be an option.
Continue to: Because Mr. X does not respond...
TREATMENT A trial of ECT
Because Mr. X does not respond to the standard treatment protocols, the treatment team and Mr. X’s family discuss the use of ECT to control his agitation. Consent is obtained from his legal guardian and Mr. X is medically cleared to receive ECT. Mr. X receives 3 ECT treatments per week. During the first week, Mr. X experiences post-treatment agitation and confusion. The frequency of ECT treatments is reduced to 2 treatments per week, and then 1 session per week. Mr. X starts to show improvement in his agitation and ECT is continued at 1 session per week for 7 weeks.
The authors’ observations
Electroconvulsive therapy has been an effective treatment for patients with treatment-resistant depression and has shown benefit in treating other psychiatric conditions such as acute mania, catatonia, psychotic disorders, and Parkinson’s disease.22 Its use as an off-label treatment for chronic neuropathic pain has also been well documented.23 Although ECT is not indicated for treating agitation and aggression in patients with dementia, its effectiveness for these symptoms has been discussed extensively in the literature.22,24-26
Electroconvulsive therapy treatment can be divided into 2 phases: an acute phase during which ECT is administered 2 to 3 times a week for 4 to 5 weeks, and a maintenance phase of weekly treatments for 4 weeks and then biweekly treatments for 8 weeks.26 Although extensive research supports the safe use of ECT in older adults, concerns for worsening cognitive impairment can deter patients and families from agreeing to this treatment.
Adverse effects of ECT such as headaches and postictal confusion are generally mild and transient. Severe adverse effects such as seizures, severe confusion, and delirium are uncommon.25 The number of ECT treatments required for a good effect ranges from 2 to 18, and the most common position for electrodes placement is bilateral. Outcomes can be measured by using rating scales such as the Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory, Neuropsychiatric Inventory, Social Dysfunction and Aggression Scale, Clinical Global Impression scale, and Pittsford Agitation Scale.25 Obtaining consent from patients with dementia is generally not possible because these patients generally lack the capacity to make medical decisions. Clinicians should refer to their state laws regarding medical-decision making in such cases. The patient’s next of kin or medical power of attorney should be contacted, and the risks and benefits should be discussed before starting ECT.
OUTCOME Lasting improvement
Due to Mr. X’s improvement after ECT, on hospital Day 124, the restraints are removed and he no longer requires a sitter. He starts responding to his name and following simple verbal commands. Electroconvulsive therapy is tapered to every other week, and eventually stopped as his status improves. Mr. X continues to do well and is maintained on the same dosages of olanzapine, carbamazepine, and dextromethorphan-quinidine he had been receiving prior to discharge.
Related Resources
• Van den Berg JF, Kruithof HC, Kok RM, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for agitation and aggression in dementia: a systematic review. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018;26(4):419-434.
• Kales HC, Mulsant BH, Sajatovic M. Prescribing antipsychotics in geriatric patients: Focus on dementia. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(12):24-30.
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Carbamazepine • Tegretol
Citalopram • Celexa
Dextromethorphan- quinidine • Nuedexta
Divalproex sodium ER • Depakote
Donepezil • Aricept
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lorazepam • Ativan
Memantine • Namenda
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Prazosin • Minipress
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Rivastigmine • Exelon
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Desyrel, Oleptro
Ziprasidone • Geodon
CASE Agitated and aggressive
Mr. X, age 61, who has Alzheimer’s disease, is brought to the emergency department (ED) by his family after he is found to be confused, becomes physically aggressive with family members, and threatens to burn the house down. His family reports that earlier that day, he was paranoid that somebody was trying to kill him and he tried to leave the house. Mr. X has been experiencing visual hallucinations and delusional thoughts that made him aggressive towards his son. After an initial laboratory workup in the ED, Mr. X’s bloodwork comes back positive for mild leukocytosis, indicating the possibility of an infectious etiology. Mr. X is admitted to the hospital for further evaluation of his altered mental status.
HISTORY Decline over 2 years
This is Mr. X’s third inpatient admission for agitation and psychosis. His current medications—twice daily divalproex sodium extended release (ER), 250 mg every morning and 500 mg at every bedtime, and prazosin, 2 mg/d at bedtime—have been only partially effective. His medical history includes osteoarthritis, back pain, and heterozygous factor V Leiden (not on anticoagulation). He quit smoking tobacco several years ago and has no history of substance use. He has no family history of dementia. Previous trials of cholinesterase inhibitors, antipsychotics, and antidepressants resulted in only minimal improvement in his agitation and psychosis.
A chart review shows that 2 years before his current hospital admission, Mr. X had presented to his primary care physician with slurred speech, forgetfulness, missing words, and transient reading difficulties. His initial laboratory workup and MRI came back normal. He was placed on short-term disability due to work-related errors. He was referred to the hospital’s Memory Clinic 2 years ago, where his Mini-Mental State Exam score was 20/30, indicating mild cognitive impairment. Stroke workup was negative. Due to significant language deficits, a differential diagnosis for Alzheimer’s disease vs primary progressive aphasia vs frontotemporal dementia was made. He screened positive for amyloid PET scan, which confirmed the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease.
Neuropsychological testing showed similarities with logopenic variant of primary progressive aphasia, which in many cases is present in Alzheimer’s disease. Mr. X was prescribed anticholinesterase inhibitors, including donepezil, 10 mg/d, and rivastigmine patch, 9.5 mg/d; and memantine, 10 mg/d, which he could not tolerate because of adverse effects. During the next year, Mr. X deteriorated and presented to the ED a few times with significant psychotic symptoms and aggression. He had a poor response to various pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions during this time.
EVALUATION Continued problematic behaviors
During his hospitalization, Mr. X continues to be agitated and paranoid and is placed in restraints. He is unable to respond to his name and cannot follow simple verbal commands. Results of his laboratory workup are within normal limits. His mild leukocytosis resolves with no active signs of infection. Psychiatry is consulted for management of his behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD).
Continue to: Mr. X is started on olanzapine...
Mr. X is started on olanzapine and lorazepam as needed for agitation, and his twice daily divalproex sodium ER is increased to 250 every morning and 750 mg at every bedtime. However, Mr. X remains agitated and requires restraints. Olanzapine is switched from an as-needed dose to scheduled doses of 10 mg every morning and 15 mg at every bedtime, to address his psychosis and agitation.
On Day 24 of hospitalization, Mr. X’s ammonia levels are checked and are found to be 69 µ/dL, which is high (normal range: 15 to 45 µ/dL). Divalproex sodium ER is eventually tapered and discontinued. Mr. X is started on carbamazepine, which is titrated to 400 mg twice daily and results in some improvement in his behavior. He continues to receive carbamazepine and is started on dextromethorphan-quinidine, 10 mg/d, and increased to 10 mg twice daily; however, Mr. X continues to be verbally aggressive with staff, throws food, wanders around, and tries to leave the hospital unit, so he is placed in restraints and continues to require a sitter.
[polldaddy:10698428]
The authors' observations
Dementia typically affects older adults, but its onset can occur before age 60. It is a syndrome rather than a specific illness; the most common types are Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies, and frontotemporal dementia. Diagnostic clarity and an evidence-based treatment plan are crucial for improving the quality of life for both the patient and their caregivers. The Table outlines the differential diagnosis of cognitive deficits. New-onset cognitive deficits warrant neuroimaging, and other testing may also be needed.

Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia
Noncognitive symptoms occur in 98% of individuals with dementia at some point in their disease and are often the most distressing to both caregivers and patients.1 Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia, including apathy, depression, sleep disorders, hallucinations, delusions, psychosis, agitation, and aggression, are exceedingly prevalent.2 Although these symptoms pose a significant burden, there are no clear published treatment guidelines; however, the American Psychiatric Association and the American Geriatric Society recommend using nonpharmacologic approaches as the first-line of treatment for patients with BPSD.3,4
Nonpharmacologic treatments
Due to the unfavorable adverse effects profiles of medications commonly used to treat dementia, nonpharmacologic treatment approaches have always played a crucial role for managing BPSD. Interventions such as music therapy, aromatherapy, art therapy, behavioral therapy, reality orientation, tailored activities, and physical exercises, have shown promising results for alleviating BPSD.5-7
Continue to: Pharmacologic therapies should be used...
Pharmacologic treatments
Pharmacologic therapies should be used when nonpharmacologic approaches are unsuccessful, or when a patient is at imminent risk to harm themselves or others.
Antipsychotics. Although there is conflicting data regarding the use of antipsychotics in older adults, these agents are the most common pharmacologic treatment for patients with BPSD. Several studies examining the efficacy of antipsychotics for treating BPSD have demonstrated an increased risk of cerebrovascular events, including stroke and death due to any cause.8 While the use of antipsychotics increases the risk of mortality in older adults, the absolute risk is still low.9
Antipsychotics used to treat BPSD include:
- Risperidone is well studied in older adults and has shown benefit for treating aggression, agitation, and psychosis.10
- Quetiapine has a favorable adverse effects profile and may help improve sleep and reduce anxiety.10
- Olanzapine. Low-dose olanzapine has been modestly effective in decreasing agitation and aggression in patients with Alzheimer’s and vascular dementias.11
- Aripiprazole has shown modest benefit in treating psychosis and agitation in patients with dementia but may be associated with insomnia or activation symptoms at lower doses.10
- Ziprasidone. Case reports have found benefit with oral and injectable forms.12
Antidepressants. In the CitAD study, which was a placebo-controlled randomized trial, citalopram titrated to a target of 30 mg/d was found to be effective in reducing BPSD.13 However, QTc prolongation limits the use of citalopram. Sertraline was studied in 1 small, randomized trial against haloperidol but showed no additional benefit.14
Mood stabilizers. In a small, randomized trial, carbamazepine was helpful for patients with BPSD who were resistant to treatment with antipsychotics, with efficacy demonstrated over 6 weeks.15 No other mood stabilizers have had significant positive results in treating BPSD.16
Anxiolytic medications. Some research suggests that the occasional use of lorazepam, as necessary, is acceptable for patients with extreme agitation or aggression when behavioral interventions or sleep aids are ineffective.17 Various case reports and case series have suggested gabapentin may be effective for BPSD.18
Prazosin. In a small randomized placebo-controlled trial, the commonly used antihypertensive agent prazosin reduced agitation and aggression in patients with Alzheimer’s dementia, at doses from 1 to 6 mg/d.19 Postural hypotension, the main adverse effect associated with prazosin, can limit its use.
Trazodone. Some research suggests trazodone can reduce irritability and aggression in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.20
Dextromethorphan/quinidine. In a 10-week phase 2 randomized clinical trial of patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease dementia, combination dextromethorphan/quinidine reduced agitation and was generally well tolerated.21
For patients such as Mr. X who do not respond to multiple pharmacologic treatments, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be an option.
Continue to: Because Mr. X does not respond...
TREATMENT A trial of ECT
Because Mr. X does not respond to the standard treatment protocols, the treatment team and Mr. X’s family discuss the use of ECT to control his agitation. Consent is obtained from his legal guardian and Mr. X is medically cleared to receive ECT. Mr. X receives 3 ECT treatments per week. During the first week, Mr. X experiences post-treatment agitation and confusion. The frequency of ECT treatments is reduced to 2 treatments per week, and then 1 session per week. Mr. X starts to show improvement in his agitation and ECT is continued at 1 session per week for 7 weeks.
The authors’ observations
Electroconvulsive therapy has been an effective treatment for patients with treatment-resistant depression and has shown benefit in treating other psychiatric conditions such as acute mania, catatonia, psychotic disorders, and Parkinson’s disease.22 Its use as an off-label treatment for chronic neuropathic pain has also been well documented.23 Although ECT is not indicated for treating agitation and aggression in patients with dementia, its effectiveness for these symptoms has been discussed extensively in the literature.22,24-26
Electroconvulsive therapy treatment can be divided into 2 phases: an acute phase during which ECT is administered 2 to 3 times a week for 4 to 5 weeks, and a maintenance phase of weekly treatments for 4 weeks and then biweekly treatments for 8 weeks.26 Although extensive research supports the safe use of ECT in older adults, concerns for worsening cognitive impairment can deter patients and families from agreeing to this treatment.
Adverse effects of ECT such as headaches and postictal confusion are generally mild and transient. Severe adverse effects such as seizures, severe confusion, and delirium are uncommon.25 The number of ECT treatments required for a good effect ranges from 2 to 18, and the most common position for electrodes placement is bilateral. Outcomes can be measured by using rating scales such as the Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory, Neuropsychiatric Inventory, Social Dysfunction and Aggression Scale, Clinical Global Impression scale, and Pittsford Agitation Scale.25 Obtaining consent from patients with dementia is generally not possible because these patients generally lack the capacity to make medical decisions. Clinicians should refer to their state laws regarding medical-decision making in such cases. The patient’s next of kin or medical power of attorney should be contacted, and the risks and benefits should be discussed before starting ECT.
OUTCOME Lasting improvement
Due to Mr. X’s improvement after ECT, on hospital Day 124, the restraints are removed and he no longer requires a sitter. He starts responding to his name and following simple verbal commands. Electroconvulsive therapy is tapered to every other week, and eventually stopped as his status improves. Mr. X continues to do well and is maintained on the same dosages of olanzapine, carbamazepine, and dextromethorphan-quinidine he had been receiving prior to discharge.
Related Resources
• Van den Berg JF, Kruithof HC, Kok RM, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for agitation and aggression in dementia: a systematic review. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018;26(4):419-434.
• Kales HC, Mulsant BH, Sajatovic M. Prescribing antipsychotics in geriatric patients: Focus on dementia. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(12):24-30.
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Carbamazepine • Tegretol
Citalopram • Celexa
Dextromethorphan- quinidine • Nuedexta
Divalproex sodium ER • Depakote
Donepezil • Aricept
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lorazepam • Ativan
Memantine • Namenda
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Prazosin • Minipress
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Rivastigmine • Exelon
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Desyrel, Oleptro
Ziprasidone • Geodon
1. Kales HC, Gitlin LN, Lyketsos CG. Management of neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia in clinical settings: recommendations from a multidisciplinary expert panel. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62(4):762-769.
2. Scarmeas N, Brandt J, Albert M, et al. Delusions and hallucinations are associated with worse outcome in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2005;62(10):1601-1608.
3. Reus VI, Fochtmann LJ, Eyler AE, et al. The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline on the use of antipsychotics to treat agitation or psychosis in patients with dementia. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173(5):543-546.
4. AGS Executive Committee. A guide to the management of psychotic disorders and neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia in older adults. The American Geriatrics Society. Published April 2011. Accessed September 24, 2020. https://qioprogram.org/sites/default/files/AGS_Guidelines_for_Telligen.pdf
5. Yang MH, Lin LC, Wu SC, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of aroma-acupressure and aromatherapy for the treatment of dementia-associated agitation. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015;15:93.
6. Cerga-Pashoja A, Lowery D, Bhattacharya R, et al. Evaluation of exercise on individuals with dementia and their carers: a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2010;11:53.
7. Chen RC, Liu CL, Lin MH, et al. Non-pharmacological treatment reducing not only behavioral symptoms, but also psychotic symptoms of older adults with dementia: a prospective cohort study in Taiwan. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2014;14(2):440-446.
8. Schneider LS, Dagerman KS, Insel P. Risk of death with atypical antipsychotic drug treatment for dementia: meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. JAMA. 2005;294(15):1934-1943.
9. Lenzer J. FDA warns about using antipsychotic drugs for dementia. BMJ. 2005;330(7497):922.
10. Burke AD, Tariot PN. Atypical antipsychotics in the elderly: a review of therapeutic trends and clinical outcomes. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009;10(15):2407-2414.
11. Moretti R, Torre R, Antonello T, et al. Olanzapine as a possible treatment of behavioral symptoms in vascular dementia: risks of cerebrovascular events. J Neurol. 2005;252(10):1186-1193.
12. Cole SA, Saleem R, Shea WP, et al. Ziprasidone for agitation or psychosis in dementia: four cases. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2005;35(1):91-98.
13. Porsteinsson AP, Drye LT, Pollock BG, et al. Effect of citalopram on agitation in Alzheimer disease: the CitAD randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014;311(7):682-691.
14. Gaber S, Ronzoli S, Bruno A, et al. Sertraline versus small doses of haloperidol in the treatment of agitated behavior in patients with dementia. Arch Gerontol Geriatr Suppl. 2001; 7:159-162.
15. Olin JT, Fox LS, Pawluczyk S, et al. A pilot randomized trial of carbamazepine for behavioral symptoms in treatment-resistant outpatients with Alzheimer disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001;9(4):400-405.
16. Konovalov S, Muralee S, Tampi RR. Anticonvulsants for the treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: a literature review. Int Psychogeriatr. 2008;20(2):293-308.
17. Davies SJC, Burhan AM, Kim D. Sequential drug treatment algorithm for agitation and aggression in Alzheimer’s and mixed dementia. J Psychopharmacol. 2018;32(5):509-523.
18. Kim Y, Wilkins KM, Tampi RR. Use of gabapentin in the treatment of behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia: a review of the evidence. Drugs Aging. 2008;25(3):187-196.
19. Wang LY, Shofer JB, Rohde K, et al. Prazosin for the treatment of behavioral symptoms in patients with Alzheimer disease with agitation and aggression. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2009; 17(9):744-751.
20. López-Pousa S, Garre-Olmo J, Vilalta-Franch J, et al. Trazodone for Alzheimer’s disease: a naturalistic follow-up study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008;47(2):207-215.
21. Cummings JL, Lyketsos CG, Peskind ER. Effect of dextromethorphan-quinidine on agitation in patients with Alzheimer disease dementia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;314(12):1242-1254.
22. Ujkaj M, Davidoff DA, Seiner SJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of electroconvulsive therapy for the treatment of agitation and aggression in patients with dementia. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012;20(1):61-72.
23. McDaniel WW. Electroconvulsive therapy in complex regional pain syndromes. J ECT. 2003;19(4):226-229.
24. Glass OM, Forester BP, Hermida AP. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) for treating agitation in dementia (major neurocognitive disorder)–a promising option. Int Psychogeriatr. 2017;29(5):717-726.
25. Van den Berg JF, Kruithof HC, Kok RM, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for agitation and aggression in dementia: a systematic review. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018;26(4):419-434.
26. Isserles M, Daskalakis ZJ, Kumar S, et al. Clinical effectiveness and tolerability of electroconvulsive therapy in patients with neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;57(1):45-51.
1. Kales HC, Gitlin LN, Lyketsos CG. Management of neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia in clinical settings: recommendations from a multidisciplinary expert panel. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62(4):762-769.
2. Scarmeas N, Brandt J, Albert M, et al. Delusions and hallucinations are associated with worse outcome in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2005;62(10):1601-1608.
3. Reus VI, Fochtmann LJ, Eyler AE, et al. The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline on the use of antipsychotics to treat agitation or psychosis in patients with dementia. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173(5):543-546.
4. AGS Executive Committee. A guide to the management of psychotic disorders and neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia in older adults. The American Geriatrics Society. Published April 2011. Accessed September 24, 2020. https://qioprogram.org/sites/default/files/AGS_Guidelines_for_Telligen.pdf
5. Yang MH, Lin LC, Wu SC, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of aroma-acupressure and aromatherapy for the treatment of dementia-associated agitation. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015;15:93.
6. Cerga-Pashoja A, Lowery D, Bhattacharya R, et al. Evaluation of exercise on individuals with dementia and their carers: a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2010;11:53.
7. Chen RC, Liu CL, Lin MH, et al. Non-pharmacological treatment reducing not only behavioral symptoms, but also psychotic symptoms of older adults with dementia: a prospective cohort study in Taiwan. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2014;14(2):440-446.
8. Schneider LS, Dagerman KS, Insel P. Risk of death with atypical antipsychotic drug treatment for dementia: meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. JAMA. 2005;294(15):1934-1943.
9. Lenzer J. FDA warns about using antipsychotic drugs for dementia. BMJ. 2005;330(7497):922.
10. Burke AD, Tariot PN. Atypical antipsychotics in the elderly: a review of therapeutic trends and clinical outcomes. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009;10(15):2407-2414.
11. Moretti R, Torre R, Antonello T, et al. Olanzapine as a possible treatment of behavioral symptoms in vascular dementia: risks of cerebrovascular events. J Neurol. 2005;252(10):1186-1193.
12. Cole SA, Saleem R, Shea WP, et al. Ziprasidone for agitation or psychosis in dementia: four cases. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2005;35(1):91-98.
13. Porsteinsson AP, Drye LT, Pollock BG, et al. Effect of citalopram on agitation in Alzheimer disease: the CitAD randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014;311(7):682-691.
14. Gaber S, Ronzoli S, Bruno A, et al. Sertraline versus small doses of haloperidol in the treatment of agitated behavior in patients with dementia. Arch Gerontol Geriatr Suppl. 2001; 7:159-162.
15. Olin JT, Fox LS, Pawluczyk S, et al. A pilot randomized trial of carbamazepine for behavioral symptoms in treatment-resistant outpatients with Alzheimer disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001;9(4):400-405.
16. Konovalov S, Muralee S, Tampi RR. Anticonvulsants for the treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: a literature review. Int Psychogeriatr. 2008;20(2):293-308.
17. Davies SJC, Burhan AM, Kim D. Sequential drug treatment algorithm for agitation and aggression in Alzheimer’s and mixed dementia. J Psychopharmacol. 2018;32(5):509-523.
18. Kim Y, Wilkins KM, Tampi RR. Use of gabapentin in the treatment of behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia: a review of the evidence. Drugs Aging. 2008;25(3):187-196.
19. Wang LY, Shofer JB, Rohde K, et al. Prazosin for the treatment of behavioral symptoms in patients with Alzheimer disease with agitation and aggression. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2009; 17(9):744-751.
20. López-Pousa S, Garre-Olmo J, Vilalta-Franch J, et al. Trazodone for Alzheimer’s disease: a naturalistic follow-up study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008;47(2):207-215.
21. Cummings JL, Lyketsos CG, Peskind ER. Effect of dextromethorphan-quinidine on agitation in patients with Alzheimer disease dementia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;314(12):1242-1254.
22. Ujkaj M, Davidoff DA, Seiner SJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of electroconvulsive therapy for the treatment of agitation and aggression in patients with dementia. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012;20(1):61-72.
23. McDaniel WW. Electroconvulsive therapy in complex regional pain syndromes. J ECT. 2003;19(4):226-229.
24. Glass OM, Forester BP, Hermida AP. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) for treating agitation in dementia (major neurocognitive disorder)–a promising option. Int Psychogeriatr. 2017;29(5):717-726.
25. Van den Berg JF, Kruithof HC, Kok RM, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for agitation and aggression in dementia: a systematic review. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018;26(4):419-434.
26. Isserles M, Daskalakis ZJ, Kumar S, et al. Clinical effectiveness and tolerability of electroconvulsive therapy in patients with neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;57(1):45-51.
Dexamethasone may ‘jeopardize’ benefit of immunotherapy in glioblastoma
Dexamethasone can have a detrimental effect on survival in patients with glioblastoma who are receiving immunotherapy, according to a study published in Clinical Cancer Research.
Investigators found that baseline dexamethasone use was associated with poor overall survival (OS) in glioblastoma patients receiving anti–PD-1 or anti–PD-L1 therapy. In fact, in a multivariable analysis, baseline dexamethasone use was the strongest predictor of poor survival.
These results “support accumulating concerns that corticosteroids can be detrimental to immunotherapy for oncology patients,” wrote senior study author David Reardon, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and colleagues.
The concerns are particularly relevant for glioblastoma patients because dexamethasone is a cornerstone of glioblastoma therapy, being used to reduce tumor-associated edema. Patients often receive dexamethasone early on and in significant doses for a protracted period of time to stay ahead of evolving symptoms.
However, the current study suggests dexamethasone and other corticosteroids may be contraindicated in glioblastoma patients on immunotherapy. Therefore, Dr. Reardon and colleagues recommended “careful evaluation of dexamethasone use” in these patients.
“If a glioblastoma patient requires corticosteroids, and they often do for debilitating symptoms, only use these drugs if the patient really needs them,” Dr. Reardon advised. “Start at a low dose and use the shortest treatment interval possible.”
Preclinical and clinical results
Dr. Reardon and colleagues initially evaluated the effects of dexamethasone when administered with PD-1 blockade and/or radiotherapy in an immunocompetent syngeneic mouse model.
Most mice that received anti–PD-1 monotherapy were cured, but the benefit of anti–PD-1 therapy was significantly diminished, in a dose-dependent manner, when dexamethasone was added.
At 100 days, the OS rate was about 76% in the anti–PD-1 monotherapy group, 47% when dexamethasone was given at 1 mg/kg, 31% with dexamethasone at 2.5 mg/kg, and 27% with dexamethasone at 10 mg/kg.
A mechanistic study, including analysis of immune cells in the spleen, showed that dexamethasone decreased intratumoral T cells and systemic levels of T cells, natural killer cells, and myeloid cells, while qualitatively impairing lymphocyte function. The mechanism of T-cell depletion included induction of apoptosis, which was noted as soon as 1 hour after the dexamethasone dose, Dr. Reardon said.
The researchers also evaluated 181 consecutive glioblastoma patients treated with PD-1– or PD-L1–targeted therapy. The study included a multivariable statistical analysis that accounted for age, performance status, extent of resection, size of tumor, bulk tumor burden, and MGMT promoter methylation status.
In an initial unadjusted analysis, baseline dexamethasone decreased the median OS to 8.1 months when it was given at less than 2 mg daily and 6.3 months when given at 2 mg or more daily. The median OS was 13.1 months for patients who did not receive dexamethasone.
After multivariable adjustment, baseline dexamethasone eliminated the survival benefit of immunotherapy, the researchers said. The hazard ratio was 2.16 (P = .003) when dexamethasone was given at less than 2 mg daily and 1.97 (P = .005) with dexamethasone at 2 mg or more daily, compared with no baseline dexamethasone.
In fact, the strongest negative risk factor for OS was the use of dexamethasone at initiation of checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
Implications: Use corticosteroids ‘very judiciously’
The results of this research suggest “corticosteroids can be detrimental when used along with checkpoint inhibitors,” Dr. Reardon said. He added that this effect could extend to other immunotherapies, such as vaccines, cellular therapies, and oncolytic viruses.
“We need to understand what is driving the inflammatory response,” Dr. Reardon said. “Other targets in the downstream pathway may be regulated to avoid the detrimental effect of corticosteroids.”
Ongoing prospective clinical trials need to build in whether concurrent use of corticosteroids leads to poorer outcomes, according to Dr. Reardon.
“We are validating this prospectively in ongoing clinical trials to evaluate differences in outcome in glioblastoma patients and exploring different types of immunotherapies,” he said.
Though questions remain, Dr. Reardon advises judicious use of corticosteroids or even substituting corticosteroids with bevacizumab in glioblastoma patients.
“If a glioblastoma patient develops debilitating symptoms due to swelling in the brain and is a candidate for immunotherapy, then consider using bevacizumab to avoid using corticosteroids,” Dr. Reardon said, adding that this is being tested prospectively in a clinical trial as well.
“We know corticosteroids have a host of side effects. An additional side effect may be limiting immune function in brain cancer patients and jeopardizing the potential benefits of immunotherapy going forward. I implore practicing oncologists to use corticosteroids very judiciously and as little as possible for as little time as possible,” Dr. Reardon said.
This research was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and support from various foundations and institutions. The researchers disclosed relationships with many pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Iorgulescu JB et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Nov 25. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2291.
Dexamethasone can have a detrimental effect on survival in patients with glioblastoma who are receiving immunotherapy, according to a study published in Clinical Cancer Research.
Investigators found that baseline dexamethasone use was associated with poor overall survival (OS) in glioblastoma patients receiving anti–PD-1 or anti–PD-L1 therapy. In fact, in a multivariable analysis, baseline dexamethasone use was the strongest predictor of poor survival.
These results “support accumulating concerns that corticosteroids can be detrimental to immunotherapy for oncology patients,” wrote senior study author David Reardon, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and colleagues.
The concerns are particularly relevant for glioblastoma patients because dexamethasone is a cornerstone of glioblastoma therapy, being used to reduce tumor-associated edema. Patients often receive dexamethasone early on and in significant doses for a protracted period of time to stay ahead of evolving symptoms.
However, the current study suggests dexamethasone and other corticosteroids may be contraindicated in glioblastoma patients on immunotherapy. Therefore, Dr. Reardon and colleagues recommended “careful evaluation of dexamethasone use” in these patients.
“If a glioblastoma patient requires corticosteroids, and they often do for debilitating symptoms, only use these drugs if the patient really needs them,” Dr. Reardon advised. “Start at a low dose and use the shortest treatment interval possible.”
Preclinical and clinical results
Dr. Reardon and colleagues initially evaluated the effects of dexamethasone when administered with PD-1 blockade and/or radiotherapy in an immunocompetent syngeneic mouse model.
Most mice that received anti–PD-1 monotherapy were cured, but the benefit of anti–PD-1 therapy was significantly diminished, in a dose-dependent manner, when dexamethasone was added.
At 100 days, the OS rate was about 76% in the anti–PD-1 monotherapy group, 47% when dexamethasone was given at 1 mg/kg, 31% with dexamethasone at 2.5 mg/kg, and 27% with dexamethasone at 10 mg/kg.
A mechanistic study, including analysis of immune cells in the spleen, showed that dexamethasone decreased intratumoral T cells and systemic levels of T cells, natural killer cells, and myeloid cells, while qualitatively impairing lymphocyte function. The mechanism of T-cell depletion included induction of apoptosis, which was noted as soon as 1 hour after the dexamethasone dose, Dr. Reardon said.
The researchers also evaluated 181 consecutive glioblastoma patients treated with PD-1– or PD-L1–targeted therapy. The study included a multivariable statistical analysis that accounted for age, performance status, extent of resection, size of tumor, bulk tumor burden, and MGMT promoter methylation status.
In an initial unadjusted analysis, baseline dexamethasone decreased the median OS to 8.1 months when it was given at less than 2 mg daily and 6.3 months when given at 2 mg or more daily. The median OS was 13.1 months for patients who did not receive dexamethasone.
After multivariable adjustment, baseline dexamethasone eliminated the survival benefit of immunotherapy, the researchers said. The hazard ratio was 2.16 (P = .003) when dexamethasone was given at less than 2 mg daily and 1.97 (P = .005) with dexamethasone at 2 mg or more daily, compared with no baseline dexamethasone.
In fact, the strongest negative risk factor for OS was the use of dexamethasone at initiation of checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
Implications: Use corticosteroids ‘very judiciously’
The results of this research suggest “corticosteroids can be detrimental when used along with checkpoint inhibitors,” Dr. Reardon said. He added that this effect could extend to other immunotherapies, such as vaccines, cellular therapies, and oncolytic viruses.
“We need to understand what is driving the inflammatory response,” Dr. Reardon said. “Other targets in the downstream pathway may be regulated to avoid the detrimental effect of corticosteroids.”
Ongoing prospective clinical trials need to build in whether concurrent use of corticosteroids leads to poorer outcomes, according to Dr. Reardon.
“We are validating this prospectively in ongoing clinical trials to evaluate differences in outcome in glioblastoma patients and exploring different types of immunotherapies,” he said.
Though questions remain, Dr. Reardon advises judicious use of corticosteroids or even substituting corticosteroids with bevacizumab in glioblastoma patients.
“If a glioblastoma patient develops debilitating symptoms due to swelling in the brain and is a candidate for immunotherapy, then consider using bevacizumab to avoid using corticosteroids,” Dr. Reardon said, adding that this is being tested prospectively in a clinical trial as well.
“We know corticosteroids have a host of side effects. An additional side effect may be limiting immune function in brain cancer patients and jeopardizing the potential benefits of immunotherapy going forward. I implore practicing oncologists to use corticosteroids very judiciously and as little as possible for as little time as possible,” Dr. Reardon said.
This research was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and support from various foundations and institutions. The researchers disclosed relationships with many pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Iorgulescu JB et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Nov 25. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2291.
Dexamethasone can have a detrimental effect on survival in patients with glioblastoma who are receiving immunotherapy, according to a study published in Clinical Cancer Research.
Investigators found that baseline dexamethasone use was associated with poor overall survival (OS) in glioblastoma patients receiving anti–PD-1 or anti–PD-L1 therapy. In fact, in a multivariable analysis, baseline dexamethasone use was the strongest predictor of poor survival.
These results “support accumulating concerns that corticosteroids can be detrimental to immunotherapy for oncology patients,” wrote senior study author David Reardon, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and colleagues.
The concerns are particularly relevant for glioblastoma patients because dexamethasone is a cornerstone of glioblastoma therapy, being used to reduce tumor-associated edema. Patients often receive dexamethasone early on and in significant doses for a protracted period of time to stay ahead of evolving symptoms.
However, the current study suggests dexamethasone and other corticosteroids may be contraindicated in glioblastoma patients on immunotherapy. Therefore, Dr. Reardon and colleagues recommended “careful evaluation of dexamethasone use” in these patients.
“If a glioblastoma patient requires corticosteroids, and they often do for debilitating symptoms, only use these drugs if the patient really needs them,” Dr. Reardon advised. “Start at a low dose and use the shortest treatment interval possible.”
Preclinical and clinical results
Dr. Reardon and colleagues initially evaluated the effects of dexamethasone when administered with PD-1 blockade and/or radiotherapy in an immunocompetent syngeneic mouse model.
Most mice that received anti–PD-1 monotherapy were cured, but the benefit of anti–PD-1 therapy was significantly diminished, in a dose-dependent manner, when dexamethasone was added.
At 100 days, the OS rate was about 76% in the anti–PD-1 monotherapy group, 47% when dexamethasone was given at 1 mg/kg, 31% with dexamethasone at 2.5 mg/kg, and 27% with dexamethasone at 10 mg/kg.
A mechanistic study, including analysis of immune cells in the spleen, showed that dexamethasone decreased intratumoral T cells and systemic levels of T cells, natural killer cells, and myeloid cells, while qualitatively impairing lymphocyte function. The mechanism of T-cell depletion included induction of apoptosis, which was noted as soon as 1 hour after the dexamethasone dose, Dr. Reardon said.
The researchers also evaluated 181 consecutive glioblastoma patients treated with PD-1– or PD-L1–targeted therapy. The study included a multivariable statistical analysis that accounted for age, performance status, extent of resection, size of tumor, bulk tumor burden, and MGMT promoter methylation status.
In an initial unadjusted analysis, baseline dexamethasone decreased the median OS to 8.1 months when it was given at less than 2 mg daily and 6.3 months when given at 2 mg or more daily. The median OS was 13.1 months for patients who did not receive dexamethasone.
After multivariable adjustment, baseline dexamethasone eliminated the survival benefit of immunotherapy, the researchers said. The hazard ratio was 2.16 (P = .003) when dexamethasone was given at less than 2 mg daily and 1.97 (P = .005) with dexamethasone at 2 mg or more daily, compared with no baseline dexamethasone.
In fact, the strongest negative risk factor for OS was the use of dexamethasone at initiation of checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
Implications: Use corticosteroids ‘very judiciously’
The results of this research suggest “corticosteroids can be detrimental when used along with checkpoint inhibitors,” Dr. Reardon said. He added that this effect could extend to other immunotherapies, such as vaccines, cellular therapies, and oncolytic viruses.
“We need to understand what is driving the inflammatory response,” Dr. Reardon said. “Other targets in the downstream pathway may be regulated to avoid the detrimental effect of corticosteroids.”
Ongoing prospective clinical trials need to build in whether concurrent use of corticosteroids leads to poorer outcomes, according to Dr. Reardon.
“We are validating this prospectively in ongoing clinical trials to evaluate differences in outcome in glioblastoma patients and exploring different types of immunotherapies,” he said.
Though questions remain, Dr. Reardon advises judicious use of corticosteroids or even substituting corticosteroids with bevacizumab in glioblastoma patients.
“If a glioblastoma patient develops debilitating symptoms due to swelling in the brain and is a candidate for immunotherapy, then consider using bevacizumab to avoid using corticosteroids,” Dr. Reardon said, adding that this is being tested prospectively in a clinical trial as well.
“We know corticosteroids have a host of side effects. An additional side effect may be limiting immune function in brain cancer patients and jeopardizing the potential benefits of immunotherapy going forward. I implore practicing oncologists to use corticosteroids very judiciously and as little as possible for as little time as possible,” Dr. Reardon said.
This research was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and support from various foundations and institutions. The researchers disclosed relationships with many pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Iorgulescu JB et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Nov 25. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2291.
FROM CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH
Intense rectal cancer surveillance may be reduced
The intensity of posttreatment surveillance of patients with rectal cancer managed by a watch-and-wait approach can be safely reduced if patients achieve and maintain a clinical complete response within the first 3 years of initiation of that approach, a retrospective, multicenter registry study suggests.
“The risk of local regrowth or distant metastases after a clinical complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy after nonoperative management of rectal cancer remains an important drawback for the widespread uptake of watch and wait in clinical practice,” Laura Fernandez, MD, Champalimaud Clinical Center, Lisbon, and colleagues observe.
“Conditional survival analysis estimates suggest that patients who sustain a clinical complete response for 3 years have 5% or lower risk of developing a local regrowth and a less than 2% risk of developing systemic recurrence thereafter,” the investigators emphasize.
Achieving a complete clinical recovery and sustaining it for 1 year is the “most relevant protective factor” for patients with rectal cancer and places them in an “excellent prognostic stage,” Fernandez said in a press statement.
The study was published online Dec. 11 in The Lancet Oncology.
A watch-and-wait database
A total of 793 patients were identified from the International Watch and Wait Database, a large registry of patients who experience a clinical complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and who are managed by a watch-and-wait strategy. The registry includes data from 47 clinics in 15 countries.
The main outcome measures were the probability of patients remaining free of local regrowth and distant metastasis for an additional 2 years after sustaining a clinical complete response for 1, 3, and 5 years after the start of watch-and-wait management.
Among patients who had sustained clinical complete response for 1 year, the probability of remaining local regrowth–free for an additional 2 years – in other words, for a total of 3 years – was 88.1%.
Local regrowth–free survival rates were in the high 90 percentages after sustaining a clinical response for 3 years and for 5 years.
“Similar results were observed for distant metastasis–free survival,” Dr. Fernandez and colleagues continue. For example, 2-year conditional distant metastasis–free survival rates among patients who remained free of distant metastasis from the time the decision was made to initiate watch-and-wait management for 1 year was 93.8%; for 3 years, it was 97.8%; and for 5 years, it was 96.6%, the investigators report.
The only risk factors identified in the study for local regrowth over time was baseline clinical tumor stage and total dose of radiotherapy received.
However, after patients have achieved and sustained a complete clinical response for 1 year, known risk factors for local regrowth, such as disease stage before any treatment and the dose of radiation received by the patient, “seem to become irrelevant,” said Dr. Fernandez.
The authors say that after a patient sustains a clinical complete response for more than 3 years, it is unlikely that intensive surveillance for the detection of local regrowth would be required.
Indeed, they suggest that those who have no sign of regrowth or distant metastases at 3 years post treatment could probably be followed in established follow-up programs for rectal cancer patients who are treated with standard therapy, including radical resection.
Study limitations
Asked for comment, Joshua Smith, MD, PhD, a colorectal surgeon with the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, cautioned that there are real limitations to retrospective data as used for the current analysis, including the heterogeneity of the definitions of a clinical complete response. The investigators also tried to assess response to treatment both before and after 2010. Before 2010, intrarectal ultrasound was used to stage rectal cancer; currently, MRI is used.
There was also heterogeneity of the radiation used across the study interval. All of these factors must be taken into consideration when interpreting the investigators’ conclusions, Smith cautioned. Nevertheless, he also noted that the group is very sophisticated and that the article was well written and, in his view, not terribly overstated. “I just would be cautious with what they are saying that after 3 years, you do not need to be as strict with your surveillance,” Dr. Smith told this news organization.
“I think we still have some patients with local regrowth after that period of time, so I wouldn’t say we’re out of the woods after 3 years – I think we still have to follow these patients very closely,” he emphasized.
“The data clearly show that the longer a patient doesn’t have a local regrowth, the lower their chances are that they will develop local regrowth,” Dr. Smith said.
The study also provides clinicians with data to discuss with potential watch-and-wait candidates, he added. “The decision we make should really depend on the patient – what their goals are and what their quality-of-life perspective is,” Dr. Smith said. More definitive data on patient outcomes are expected soon from the Organ Preservation in Rectal Adenocarcinoma (OPRA) Trial.
That trial prospectively evaluates the watch-and-wait approach. Results should reflect not only what surgeons can anticipate with respect to local regrowth and distant metastases, but it should also determine the real organ preservation rate – an important endpoint of the watch-and-wait approach.
“I think it will be a paradigm-changing trial,” Dr. Smith predicted.
The study was funded by the European Registration of Cancer Care, among others organizations. Dr. Fernandez has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Smith has served as a clinical advisor to Guardant Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The intensity of posttreatment surveillance of patients with rectal cancer managed by a watch-and-wait approach can be safely reduced if patients achieve and maintain a clinical complete response within the first 3 years of initiation of that approach, a retrospective, multicenter registry study suggests.
“The risk of local regrowth or distant metastases after a clinical complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy after nonoperative management of rectal cancer remains an important drawback for the widespread uptake of watch and wait in clinical practice,” Laura Fernandez, MD, Champalimaud Clinical Center, Lisbon, and colleagues observe.
“Conditional survival analysis estimates suggest that patients who sustain a clinical complete response for 3 years have 5% or lower risk of developing a local regrowth and a less than 2% risk of developing systemic recurrence thereafter,” the investigators emphasize.
Achieving a complete clinical recovery and sustaining it for 1 year is the “most relevant protective factor” for patients with rectal cancer and places them in an “excellent prognostic stage,” Fernandez said in a press statement.
The study was published online Dec. 11 in The Lancet Oncology.
A watch-and-wait database
A total of 793 patients were identified from the International Watch and Wait Database, a large registry of patients who experience a clinical complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and who are managed by a watch-and-wait strategy. The registry includes data from 47 clinics in 15 countries.
The main outcome measures were the probability of patients remaining free of local regrowth and distant metastasis for an additional 2 years after sustaining a clinical complete response for 1, 3, and 5 years after the start of watch-and-wait management.
Among patients who had sustained clinical complete response for 1 year, the probability of remaining local regrowth–free for an additional 2 years – in other words, for a total of 3 years – was 88.1%.
Local regrowth–free survival rates were in the high 90 percentages after sustaining a clinical response for 3 years and for 5 years.
“Similar results were observed for distant metastasis–free survival,” Dr. Fernandez and colleagues continue. For example, 2-year conditional distant metastasis–free survival rates among patients who remained free of distant metastasis from the time the decision was made to initiate watch-and-wait management for 1 year was 93.8%; for 3 years, it was 97.8%; and for 5 years, it was 96.6%, the investigators report.
The only risk factors identified in the study for local regrowth over time was baseline clinical tumor stage and total dose of radiotherapy received.
However, after patients have achieved and sustained a complete clinical response for 1 year, known risk factors for local regrowth, such as disease stage before any treatment and the dose of radiation received by the patient, “seem to become irrelevant,” said Dr. Fernandez.
The authors say that after a patient sustains a clinical complete response for more than 3 years, it is unlikely that intensive surveillance for the detection of local regrowth would be required.
Indeed, they suggest that those who have no sign of regrowth or distant metastases at 3 years post treatment could probably be followed in established follow-up programs for rectal cancer patients who are treated with standard therapy, including radical resection.
Study limitations
Asked for comment, Joshua Smith, MD, PhD, a colorectal surgeon with the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, cautioned that there are real limitations to retrospective data as used for the current analysis, including the heterogeneity of the definitions of a clinical complete response. The investigators also tried to assess response to treatment both before and after 2010. Before 2010, intrarectal ultrasound was used to stage rectal cancer; currently, MRI is used.
There was also heterogeneity of the radiation used across the study interval. All of these factors must be taken into consideration when interpreting the investigators’ conclusions, Smith cautioned. Nevertheless, he also noted that the group is very sophisticated and that the article was well written and, in his view, not terribly overstated. “I just would be cautious with what they are saying that after 3 years, you do not need to be as strict with your surveillance,” Dr. Smith told this news organization.
“I think we still have some patients with local regrowth after that period of time, so I wouldn’t say we’re out of the woods after 3 years – I think we still have to follow these patients very closely,” he emphasized.
“The data clearly show that the longer a patient doesn’t have a local regrowth, the lower their chances are that they will develop local regrowth,” Dr. Smith said.
The study also provides clinicians with data to discuss with potential watch-and-wait candidates, he added. “The decision we make should really depend on the patient – what their goals are and what their quality-of-life perspective is,” Dr. Smith said. More definitive data on patient outcomes are expected soon from the Organ Preservation in Rectal Adenocarcinoma (OPRA) Trial.
That trial prospectively evaluates the watch-and-wait approach. Results should reflect not only what surgeons can anticipate with respect to local regrowth and distant metastases, but it should also determine the real organ preservation rate – an important endpoint of the watch-and-wait approach.
“I think it will be a paradigm-changing trial,” Dr. Smith predicted.
The study was funded by the European Registration of Cancer Care, among others organizations. Dr. Fernandez has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Smith has served as a clinical advisor to Guardant Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The intensity of posttreatment surveillance of patients with rectal cancer managed by a watch-and-wait approach can be safely reduced if patients achieve and maintain a clinical complete response within the first 3 years of initiation of that approach, a retrospective, multicenter registry study suggests.
“The risk of local regrowth or distant metastases after a clinical complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy after nonoperative management of rectal cancer remains an important drawback for the widespread uptake of watch and wait in clinical practice,” Laura Fernandez, MD, Champalimaud Clinical Center, Lisbon, and colleagues observe.
“Conditional survival analysis estimates suggest that patients who sustain a clinical complete response for 3 years have 5% or lower risk of developing a local regrowth and a less than 2% risk of developing systemic recurrence thereafter,” the investigators emphasize.
Achieving a complete clinical recovery and sustaining it for 1 year is the “most relevant protective factor” for patients with rectal cancer and places them in an “excellent prognostic stage,” Fernandez said in a press statement.
The study was published online Dec. 11 in The Lancet Oncology.
A watch-and-wait database
A total of 793 patients were identified from the International Watch and Wait Database, a large registry of patients who experience a clinical complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and who are managed by a watch-and-wait strategy. The registry includes data from 47 clinics in 15 countries.
The main outcome measures were the probability of patients remaining free of local regrowth and distant metastasis for an additional 2 years after sustaining a clinical complete response for 1, 3, and 5 years after the start of watch-and-wait management.
Among patients who had sustained clinical complete response for 1 year, the probability of remaining local regrowth–free for an additional 2 years – in other words, for a total of 3 years – was 88.1%.
Local regrowth–free survival rates were in the high 90 percentages after sustaining a clinical response for 3 years and for 5 years.
“Similar results were observed for distant metastasis–free survival,” Dr. Fernandez and colleagues continue. For example, 2-year conditional distant metastasis–free survival rates among patients who remained free of distant metastasis from the time the decision was made to initiate watch-and-wait management for 1 year was 93.8%; for 3 years, it was 97.8%; and for 5 years, it was 96.6%, the investigators report.
The only risk factors identified in the study for local regrowth over time was baseline clinical tumor stage and total dose of radiotherapy received.
However, after patients have achieved and sustained a complete clinical response for 1 year, known risk factors for local regrowth, such as disease stage before any treatment and the dose of radiation received by the patient, “seem to become irrelevant,” said Dr. Fernandez.
The authors say that after a patient sustains a clinical complete response for more than 3 years, it is unlikely that intensive surveillance for the detection of local regrowth would be required.
Indeed, they suggest that those who have no sign of regrowth or distant metastases at 3 years post treatment could probably be followed in established follow-up programs for rectal cancer patients who are treated with standard therapy, including radical resection.
Study limitations
Asked for comment, Joshua Smith, MD, PhD, a colorectal surgeon with the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, cautioned that there are real limitations to retrospective data as used for the current analysis, including the heterogeneity of the definitions of a clinical complete response. The investigators also tried to assess response to treatment both before and after 2010. Before 2010, intrarectal ultrasound was used to stage rectal cancer; currently, MRI is used.
There was also heterogeneity of the radiation used across the study interval. All of these factors must be taken into consideration when interpreting the investigators’ conclusions, Smith cautioned. Nevertheless, he also noted that the group is very sophisticated and that the article was well written and, in his view, not terribly overstated. “I just would be cautious with what they are saying that after 3 years, you do not need to be as strict with your surveillance,” Dr. Smith told this news organization.
“I think we still have some patients with local regrowth after that period of time, so I wouldn’t say we’re out of the woods after 3 years – I think we still have to follow these patients very closely,” he emphasized.
“The data clearly show that the longer a patient doesn’t have a local regrowth, the lower their chances are that they will develop local regrowth,” Dr. Smith said.
The study also provides clinicians with data to discuss with potential watch-and-wait candidates, he added. “The decision we make should really depend on the patient – what their goals are and what their quality-of-life perspective is,” Dr. Smith said. More definitive data on patient outcomes are expected soon from the Organ Preservation in Rectal Adenocarcinoma (OPRA) Trial.
That trial prospectively evaluates the watch-and-wait approach. Results should reflect not only what surgeons can anticipate with respect to local regrowth and distant metastases, but it should also determine the real organ preservation rate – an important endpoint of the watch-and-wait approach.
“I think it will be a paradigm-changing trial,” Dr. Smith predicted.
The study was funded by the European Registration of Cancer Care, among others organizations. Dr. Fernandez has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Smith has served as a clinical advisor to Guardant Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Letters from Maine: Role playing
It’s not unusual when I run into a former patient that I am addressed as “Doctor” Wilkoff. I guess that is to be expected because when I was in practice I seldom introduced myself as Will. However, I will admit now that I never quite felt comfortable with the “Doctor” label. Today, if you addressed me as “Doctor” I would correct you and refer to myself as the “ex-Doctor Wilkoff.”
The term doctor derived from the Latin word to teach and eventually morphed into an academic title. In common parlance it is sometimes used as verb meaning to treat, e.g., “he doctored the wound.” Regardless of what academic field we are talking about, the title “doctor” has become a term of respect for someone who has spent an unusually long time learning his or her subject or craft. The holder of a doctorate, particularly in medicine, receives a rank, earned or unearned, near the top of the social hierarchy.
When I look back at more than 50 years of doing pediatrics I’m not sure that “doctor” really captures what I was up to. I will grant you that it is nice that folks want to acknowledge all those years I spent in training. But I don’t think one could say that what I did as a primary care small town pediatrician fits in with the original definition “to teach.” I did spend a few hours teaching students every so often but my primary time was spent with patients and I don’t consider what I was doing with them as teaching. There just wasn’t enough time. I had to take as a given that families who came to see me already had a basic knowledge base either as the result of their schooling, family lore, or public service announcements from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
I certainly wasn’t doing much doctoring in the sense of treating or curing disease. If one removes administering immunizations and delivery room resuscitations, I saved very few lives.
So you may ask, if not as “doctor,” how would I prefer to be labeled? Good question, but easy for me to answer. The term “coach” quickly comes to mind. As someone who played a variety of team sports there is no term that I can think of that commands more respect than “Coach.” While the term doesn’t carry the burden of a particularly long educational journey it does imply the person is wise, observant, and experienced.
There is some teaching involved but primarily a coach is going to assess the players (or in this cases the families) he is presented with and then do the best he can to guide them toward good decisions they can make themselves given their specific situations. This requires spending most of one’s time getting to know each family and understanding their strengths and limitations. One can’t coach speed to an athlete who is slow footed. And, one isn’t going to get a family that is dominated by anxiety to become bold risk takers. The best you can do is to help them learn strategies to minimize their anxieties.
A good coach can help his players learn to set reasonable goals given their skill sets. And, a good pediatrician can coach his families how to adapt their strengths and weakness to the challenges of each of their children. For example, for a physician faced with a mother-infant dyad that is struggling with breastfeeding, once the education piece is in place, it is up to him or her to function as a coach and assist the team in setting a reasonable goal that can result in a win-win for the family.
A coach must be humble, putting his or her players’ needs first and flexible enough to adjust his or her goals to define success in terms for what is best for each individual team. “Coach” may not carry the ring of authority that can come with “Doctor” but it is a role equally as challenging and rewarding.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
It’s not unusual when I run into a former patient that I am addressed as “Doctor” Wilkoff. I guess that is to be expected because when I was in practice I seldom introduced myself as Will. However, I will admit now that I never quite felt comfortable with the “Doctor” label. Today, if you addressed me as “Doctor” I would correct you and refer to myself as the “ex-Doctor Wilkoff.”
The term doctor derived from the Latin word to teach and eventually morphed into an academic title. In common parlance it is sometimes used as verb meaning to treat, e.g., “he doctored the wound.” Regardless of what academic field we are talking about, the title “doctor” has become a term of respect for someone who has spent an unusually long time learning his or her subject or craft. The holder of a doctorate, particularly in medicine, receives a rank, earned or unearned, near the top of the social hierarchy.
When I look back at more than 50 years of doing pediatrics I’m not sure that “doctor” really captures what I was up to. I will grant you that it is nice that folks want to acknowledge all those years I spent in training. But I don’t think one could say that what I did as a primary care small town pediatrician fits in with the original definition “to teach.” I did spend a few hours teaching students every so often but my primary time was spent with patients and I don’t consider what I was doing with them as teaching. There just wasn’t enough time. I had to take as a given that families who came to see me already had a basic knowledge base either as the result of their schooling, family lore, or public service announcements from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
I certainly wasn’t doing much doctoring in the sense of treating or curing disease. If one removes administering immunizations and delivery room resuscitations, I saved very few lives.
So you may ask, if not as “doctor,” how would I prefer to be labeled? Good question, but easy for me to answer. The term “coach” quickly comes to mind. As someone who played a variety of team sports there is no term that I can think of that commands more respect than “Coach.” While the term doesn’t carry the burden of a particularly long educational journey it does imply the person is wise, observant, and experienced.
There is some teaching involved but primarily a coach is going to assess the players (or in this cases the families) he is presented with and then do the best he can to guide them toward good decisions they can make themselves given their specific situations. This requires spending most of one’s time getting to know each family and understanding their strengths and limitations. One can’t coach speed to an athlete who is slow footed. And, one isn’t going to get a family that is dominated by anxiety to become bold risk takers. The best you can do is to help them learn strategies to minimize their anxieties.
A good coach can help his players learn to set reasonable goals given their skill sets. And, a good pediatrician can coach his families how to adapt their strengths and weakness to the challenges of each of their children. For example, for a physician faced with a mother-infant dyad that is struggling with breastfeeding, once the education piece is in place, it is up to him or her to function as a coach and assist the team in setting a reasonable goal that can result in a win-win for the family.
A coach must be humble, putting his or her players’ needs first and flexible enough to adjust his or her goals to define success in terms for what is best for each individual team. “Coach” may not carry the ring of authority that can come with “Doctor” but it is a role equally as challenging and rewarding.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
It’s not unusual when I run into a former patient that I am addressed as “Doctor” Wilkoff. I guess that is to be expected because when I was in practice I seldom introduced myself as Will. However, I will admit now that I never quite felt comfortable with the “Doctor” label. Today, if you addressed me as “Doctor” I would correct you and refer to myself as the “ex-Doctor Wilkoff.”
The term doctor derived from the Latin word to teach and eventually morphed into an academic title. In common parlance it is sometimes used as verb meaning to treat, e.g., “he doctored the wound.” Regardless of what academic field we are talking about, the title “doctor” has become a term of respect for someone who has spent an unusually long time learning his or her subject or craft. The holder of a doctorate, particularly in medicine, receives a rank, earned or unearned, near the top of the social hierarchy.
When I look back at more than 50 years of doing pediatrics I’m not sure that “doctor” really captures what I was up to. I will grant you that it is nice that folks want to acknowledge all those years I spent in training. But I don’t think one could say that what I did as a primary care small town pediatrician fits in with the original definition “to teach.” I did spend a few hours teaching students every so often but my primary time was spent with patients and I don’t consider what I was doing with them as teaching. There just wasn’t enough time. I had to take as a given that families who came to see me already had a basic knowledge base either as the result of their schooling, family lore, or public service announcements from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
I certainly wasn’t doing much doctoring in the sense of treating or curing disease. If one removes administering immunizations and delivery room resuscitations, I saved very few lives.
So you may ask, if not as “doctor,” how would I prefer to be labeled? Good question, but easy for me to answer. The term “coach” quickly comes to mind. As someone who played a variety of team sports there is no term that I can think of that commands more respect than “Coach.” While the term doesn’t carry the burden of a particularly long educational journey it does imply the person is wise, observant, and experienced.
There is some teaching involved but primarily a coach is going to assess the players (or in this cases the families) he is presented with and then do the best he can to guide them toward good decisions they can make themselves given their specific situations. This requires spending most of one’s time getting to know each family and understanding their strengths and limitations. One can’t coach speed to an athlete who is slow footed. And, one isn’t going to get a family that is dominated by anxiety to become bold risk takers. The best you can do is to help them learn strategies to minimize their anxieties.
A good coach can help his players learn to set reasonable goals given their skill sets. And, a good pediatrician can coach his families how to adapt their strengths and weakness to the challenges of each of their children. For example, for a physician faced with a mother-infant dyad that is struggling with breastfeeding, once the education piece is in place, it is up to him or her to function as a coach and assist the team in setting a reasonable goal that can result in a win-win for the family.
A coach must be humble, putting his or her players’ needs first and flexible enough to adjust his or her goals to define success in terms for what is best for each individual team. “Coach” may not carry the ring of authority that can come with “Doctor” but it is a role equally as challenging and rewarding.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Child abuse visits to EDs declined in 2020, but not admissions
but the visits in 2020 were significantly more likely to result in hospitalization, based on analysis of a national ED database.
The number of ED visits involving child abuse and neglect was down by 53% during the 4-week period from March 29 to April 25, 2020, compared with the 4 weeks from March 31 to April 27, 2019. The proportion of those ED visits that ended in hospitalizations, however, increased from 2.1% in 2019 to 3.2% in 2020, Elizabeth Swedo, MD, and associates at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
“ED visits related to suspected or confirmed child abuse and neglect decreased beginning the week of March 15, 2020, coinciding with the declaration of a national emergency related to COVID-19 and implementation of community mitigation measures,” they wrote.
An earlier study involving the same database (the National Syndromic Surveillance Program) showed that, over the two same 4-week periods, the volume of all ED visits in 2020 was down 72% for children aged 10 years and younger and 71% for those aged 11-14 years.
In the current study, however, all age subgroups had significant increases in hospital admissions. The proportion of ED visits related to child abuse and neglect that resulted in hospitalization rose from 3.5% in 2019 to 5.3% in 2020 among ages 0-4 years, 0.7% to 1.3% for ages 5-11 years, and 1.6% to 2.2% for adolescents aged 12-17, Dr. Swedo and associates reported.
The absence of a corresponding drop in hospitalizations may be tied to risk factors related to the pandemic, “such as loss of income, increased stress related to parental child care and schooling responsibilities, and increased substance use and mental health conditions among adults,” the investigators added.
The National Syndromic Surveillance Program receives daily data from 3,310 EDs in 47 states, but the number of facilities meeting the investigators’ criteria averaged 2,970 a week for the 8 weeks of the study period.
SOURCE: Swedo E et al. MMWR. 2020 Dec. 11;69(49):1841-7.
but the visits in 2020 were significantly more likely to result in hospitalization, based on analysis of a national ED database.

The number of ED visits involving child abuse and neglect was down by 53% during the 4-week period from March 29 to April 25, 2020, compared with the 4 weeks from March 31 to April 27, 2019. The proportion of those ED visits that ended in hospitalizations, however, increased from 2.1% in 2019 to 3.2% in 2020, Elizabeth Swedo, MD, and associates at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
“ED visits related to suspected or confirmed child abuse and neglect decreased beginning the week of March 15, 2020, coinciding with the declaration of a national emergency related to COVID-19 and implementation of community mitigation measures,” they wrote.
An earlier study involving the same database (the National Syndromic Surveillance Program) showed that, over the two same 4-week periods, the volume of all ED visits in 2020 was down 72% for children aged 10 years and younger and 71% for those aged 11-14 years.
In the current study, however, all age subgroups had significant increases in hospital admissions. The proportion of ED visits related to child abuse and neglect that resulted in hospitalization rose from 3.5% in 2019 to 5.3% in 2020 among ages 0-4 years, 0.7% to 1.3% for ages 5-11 years, and 1.6% to 2.2% for adolescents aged 12-17, Dr. Swedo and associates reported.
The absence of a corresponding drop in hospitalizations may be tied to risk factors related to the pandemic, “such as loss of income, increased stress related to parental child care and schooling responsibilities, and increased substance use and mental health conditions among adults,” the investigators added.
The National Syndromic Surveillance Program receives daily data from 3,310 EDs in 47 states, but the number of facilities meeting the investigators’ criteria averaged 2,970 a week for the 8 weeks of the study period.
SOURCE: Swedo E et al. MMWR. 2020 Dec. 11;69(49):1841-7.
but the visits in 2020 were significantly more likely to result in hospitalization, based on analysis of a national ED database.

The number of ED visits involving child abuse and neglect was down by 53% during the 4-week period from March 29 to April 25, 2020, compared with the 4 weeks from March 31 to April 27, 2019. The proportion of those ED visits that ended in hospitalizations, however, increased from 2.1% in 2019 to 3.2% in 2020, Elizabeth Swedo, MD, and associates at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
“ED visits related to suspected or confirmed child abuse and neglect decreased beginning the week of March 15, 2020, coinciding with the declaration of a national emergency related to COVID-19 and implementation of community mitigation measures,” they wrote.
An earlier study involving the same database (the National Syndromic Surveillance Program) showed that, over the two same 4-week periods, the volume of all ED visits in 2020 was down 72% for children aged 10 years and younger and 71% for those aged 11-14 years.
In the current study, however, all age subgroups had significant increases in hospital admissions. The proportion of ED visits related to child abuse and neglect that resulted in hospitalization rose from 3.5% in 2019 to 5.3% in 2020 among ages 0-4 years, 0.7% to 1.3% for ages 5-11 years, and 1.6% to 2.2% for adolescents aged 12-17, Dr. Swedo and associates reported.
The absence of a corresponding drop in hospitalizations may be tied to risk factors related to the pandemic, “such as loss of income, increased stress related to parental child care and schooling responsibilities, and increased substance use and mental health conditions among adults,” the investigators added.
The National Syndromic Surveillance Program receives daily data from 3,310 EDs in 47 states, but the number of facilities meeting the investigators’ criteria averaged 2,970 a week for the 8 weeks of the study period.
SOURCE: Swedo E et al. MMWR. 2020 Dec. 11;69(49):1841-7.
FROM MMWR
Long-term APBI cosmetic, toxicity data reported
Long-term cosmetic and toxicity outcomes are good for both accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) delivered with 3D-conformal radiotherapy and whole-breast irradiation (WBI), with the latter having a slight edge, the IRMA trial shows.
Findings were reported at the European Society for Radiology and Oncology 2020 Online Congress by Bruno Meduri, MD, a radiation oncologist at University Hospital of Modena, Italy.
Uptake of APBI has increased since it was approved nearly 2 decades ago. However, its long-term outcomes are still being parsed, and issues such as appropriate patient selection and optimal delivery technique are still being clarified (Curr Breast Cancer Rep. 2020;18:1-10).
IRMA is a European, multicenter, phase 3 randomized controlled trial conducted among 3,279 women aged 49 years and older who underwent breast-conserving surgery for early-stage breast cancer (measuring <3 cm in diameter, and pathologic N0 or N1) with negative resection margins.
The women were randomized to APBI using 3D-conformal radiotherapy (38.5 Gy in 10 fractions, twice daily) or conventional or hypofractionated WBI (50.0 Gy in 25 fractions, once daily). All additionally received adjuvant therapy according to institutional guidelines.
Patients and physicians separately rated cosmetic outcomes on a 4-point scale using the untreated breast as a reference, and toxicity was graded with the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) scale.
Over a median follow-up of 5 years, patients rated cosmesis more favorably than physicians did at all time points, and there was a trend toward slight worsening of cosmesis in the APBI group with time, Dr. Meduri reported.
At 1 year, cosmesis did not differ significantly between treatment groups regardless of the rater. But compared with the WBI group, the APBI group more often had patient-rated fair to poor cosmesis at 3 years (12.7% vs. 9.4%; P =.02) and at 5 years (15.0% vs. 10.1%; P = .007), as well as physician-rated fair to poor cosmesis at 3 years (18.0% vs. 13.1%; P = .003) and at 5 years (18.4% vs. 14.2%; P = .04).
Women treated with APBI had less acute skin toxicity (P < .001), with 4.9% developing grade 2 toxicity, compared with 21.4% of peers treated with WBI. Late skin toxicity was also less common in the APBI group overall (P < .001), but the rate of grade 3 or 4 late skin toxicity was similar.
On the other hand, the APBI group had more late bone toxicity overall (P < .001) and late bone toxicity of grade 3 or 4 (1.0% vs. 0%; P < .05), as well as more late soft tissue (subcutaneous) toxicity overall (P < .001) and late soft tissue toxicity of grade 3 or 4 (2.6% vs. 1.1%; P < .05).
The two groups had essentially the same late lung toxicity.
Women treated with APBI had higher 5-year cumulative incidences of soft tissue toxicity of grade 2 or worse (29.7% vs. 17.9%; P < .0001) and grade 3 or worse (2.6% vs. 1.1%; P = .0016). Cumulative incidences of skin toxicity of these grades did not differ significantly.
Importantly, the prevalences of late soft tissue and skin toxicity at 5 years were much lower than the cumulative incidences, Dr. Meduri noted. “This means that the side effects in some patients tend to resolve over time.”
Although the prevalence of grade 2-4 skin toxicity increased slightly at 3 years and 5 years in both groups, the prevalence of grade 2-4 soft tissue toxicity was stable.
Finally, the volume that received at least 38.5 Gy of radiation was higher for patients who developed late grade 3 or 4 bone toxicity than for those who did not (2.1 vs. 0.82 cc; P = .027), whereas other dosimetric parameters were similar.
“The toxicity of the whole cohort was very low,” Dr. Meduri summarized. “APBI was associated with a slightly higher rate of late soft tissue and bone toxicity, with a slight decrease in cosmetic outcome at 5 years. But longer follow-up is needed to confirm these results.”
The IRMA findings confirm previous results from the RAPID trial showing that APBI delivered via 3D-conformal radiotherapy may be associated with increased rates of toxicity, Chirag Shah, MD, a radiation oncologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, said in an interview.
“While cancer control outcomes were not presented, the toxicity outcomes are important and validate why many are moving away from 3D-conformal radiotherapy APBI,” he elaborated. “We are seeing increased use of APBI in some centers in the U.S., though there has been a greater shift to IMRT [intensity-modulated radiation therapy] based on 10-year data from the Florence randomized trial, which showed reduced side effects.”
“I think the results of this study are practice-confirming,” Dr. Shah concluded. “Moving forward, shorter APBI schedules will be considered as we now have 5-fraction whole-breast regimens available, as assessed in the FAST and FAST-Forward trials.”
Dr. Meduri disclosed expert board service for MSD, and financial support for attending congresses from Ipsen, AstraZeneca, and Merck. The trial was sponsored by Regione Emilia-Romagna. Dr. Shah disclosed consulting for Impedimed and PreludeDX, and receiving grants from Varian, VisionRT, and PreludeDX.
SOURCE: Meduri B et al. ESTRO 2020. Abstract OC-0611.
Long-term cosmetic and toxicity outcomes are good for both accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) delivered with 3D-conformal radiotherapy and whole-breast irradiation (WBI), with the latter having a slight edge, the IRMA trial shows.
Findings were reported at the European Society for Radiology and Oncology 2020 Online Congress by Bruno Meduri, MD, a radiation oncologist at University Hospital of Modena, Italy.
Uptake of APBI has increased since it was approved nearly 2 decades ago. However, its long-term outcomes are still being parsed, and issues such as appropriate patient selection and optimal delivery technique are still being clarified (Curr Breast Cancer Rep. 2020;18:1-10).
IRMA is a European, multicenter, phase 3 randomized controlled trial conducted among 3,279 women aged 49 years and older who underwent breast-conserving surgery for early-stage breast cancer (measuring <3 cm in diameter, and pathologic N0 or N1) with negative resection margins.
The women were randomized to APBI using 3D-conformal radiotherapy (38.5 Gy in 10 fractions, twice daily) or conventional or hypofractionated WBI (50.0 Gy in 25 fractions, once daily). All additionally received adjuvant therapy according to institutional guidelines.
Patients and physicians separately rated cosmetic outcomes on a 4-point scale using the untreated breast as a reference, and toxicity was graded with the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) scale.
Over a median follow-up of 5 years, patients rated cosmesis more favorably than physicians did at all time points, and there was a trend toward slight worsening of cosmesis in the APBI group with time, Dr. Meduri reported.
At 1 year, cosmesis did not differ significantly between treatment groups regardless of the rater. But compared with the WBI group, the APBI group more often had patient-rated fair to poor cosmesis at 3 years (12.7% vs. 9.4%; P =.02) and at 5 years (15.0% vs. 10.1%; P = .007), as well as physician-rated fair to poor cosmesis at 3 years (18.0% vs. 13.1%; P = .003) and at 5 years (18.4% vs. 14.2%; P = .04).
Women treated with APBI had less acute skin toxicity (P < .001), with 4.9% developing grade 2 toxicity, compared with 21.4% of peers treated with WBI. Late skin toxicity was also less common in the APBI group overall (P < .001), but the rate of grade 3 or 4 late skin toxicity was similar.
On the other hand, the APBI group had more late bone toxicity overall (P < .001) and late bone toxicity of grade 3 or 4 (1.0% vs. 0%; P < .05), as well as more late soft tissue (subcutaneous) toxicity overall (P < .001) and late soft tissue toxicity of grade 3 or 4 (2.6% vs. 1.1%; P < .05).
The two groups had essentially the same late lung toxicity.
Women treated with APBI had higher 5-year cumulative incidences of soft tissue toxicity of grade 2 or worse (29.7% vs. 17.9%; P < .0001) and grade 3 or worse (2.6% vs. 1.1%; P = .0016). Cumulative incidences of skin toxicity of these grades did not differ significantly.
Importantly, the prevalences of late soft tissue and skin toxicity at 5 years were much lower than the cumulative incidences, Dr. Meduri noted. “This means that the side effects in some patients tend to resolve over time.”
Although the prevalence of grade 2-4 skin toxicity increased slightly at 3 years and 5 years in both groups, the prevalence of grade 2-4 soft tissue toxicity was stable.
Finally, the volume that received at least 38.5 Gy of radiation was higher for patients who developed late grade 3 or 4 bone toxicity than for those who did not (2.1 vs. 0.82 cc; P = .027), whereas other dosimetric parameters were similar.
“The toxicity of the whole cohort was very low,” Dr. Meduri summarized. “APBI was associated with a slightly higher rate of late soft tissue and bone toxicity, with a slight decrease in cosmetic outcome at 5 years. But longer follow-up is needed to confirm these results.”
The IRMA findings confirm previous results from the RAPID trial showing that APBI delivered via 3D-conformal radiotherapy may be associated with increased rates of toxicity, Chirag Shah, MD, a radiation oncologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, said in an interview.
“While cancer control outcomes were not presented, the toxicity outcomes are important and validate why many are moving away from 3D-conformal radiotherapy APBI,” he elaborated. “We are seeing increased use of APBI in some centers in the U.S., though there has been a greater shift to IMRT [intensity-modulated radiation therapy] based on 10-year data from the Florence randomized trial, which showed reduced side effects.”
“I think the results of this study are practice-confirming,” Dr. Shah concluded. “Moving forward, shorter APBI schedules will be considered as we now have 5-fraction whole-breast regimens available, as assessed in the FAST and FAST-Forward trials.”
Dr. Meduri disclosed expert board service for MSD, and financial support for attending congresses from Ipsen, AstraZeneca, and Merck. The trial was sponsored by Regione Emilia-Romagna. Dr. Shah disclosed consulting for Impedimed and PreludeDX, and receiving grants from Varian, VisionRT, and PreludeDX.
SOURCE: Meduri B et al. ESTRO 2020. Abstract OC-0611.
Long-term cosmetic and toxicity outcomes are good for both accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) delivered with 3D-conformal radiotherapy and whole-breast irradiation (WBI), with the latter having a slight edge, the IRMA trial shows.
Findings were reported at the European Society for Radiology and Oncology 2020 Online Congress by Bruno Meduri, MD, a radiation oncologist at University Hospital of Modena, Italy.
Uptake of APBI has increased since it was approved nearly 2 decades ago. However, its long-term outcomes are still being parsed, and issues such as appropriate patient selection and optimal delivery technique are still being clarified (Curr Breast Cancer Rep. 2020;18:1-10).
IRMA is a European, multicenter, phase 3 randomized controlled trial conducted among 3,279 women aged 49 years and older who underwent breast-conserving surgery for early-stage breast cancer (measuring <3 cm in diameter, and pathologic N0 or N1) with negative resection margins.
The women were randomized to APBI using 3D-conformal radiotherapy (38.5 Gy in 10 fractions, twice daily) or conventional or hypofractionated WBI (50.0 Gy in 25 fractions, once daily). All additionally received adjuvant therapy according to institutional guidelines.
Patients and physicians separately rated cosmetic outcomes on a 4-point scale using the untreated breast as a reference, and toxicity was graded with the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) scale.
Over a median follow-up of 5 years, patients rated cosmesis more favorably than physicians did at all time points, and there was a trend toward slight worsening of cosmesis in the APBI group with time, Dr. Meduri reported.
At 1 year, cosmesis did not differ significantly between treatment groups regardless of the rater. But compared with the WBI group, the APBI group more often had patient-rated fair to poor cosmesis at 3 years (12.7% vs. 9.4%; P =.02) and at 5 years (15.0% vs. 10.1%; P = .007), as well as physician-rated fair to poor cosmesis at 3 years (18.0% vs. 13.1%; P = .003) and at 5 years (18.4% vs. 14.2%; P = .04).
Women treated with APBI had less acute skin toxicity (P < .001), with 4.9% developing grade 2 toxicity, compared with 21.4% of peers treated with WBI. Late skin toxicity was also less common in the APBI group overall (P < .001), but the rate of grade 3 or 4 late skin toxicity was similar.
On the other hand, the APBI group had more late bone toxicity overall (P < .001) and late bone toxicity of grade 3 or 4 (1.0% vs. 0%; P < .05), as well as more late soft tissue (subcutaneous) toxicity overall (P < .001) and late soft tissue toxicity of grade 3 or 4 (2.6% vs. 1.1%; P < .05).
The two groups had essentially the same late lung toxicity.
Women treated with APBI had higher 5-year cumulative incidences of soft tissue toxicity of grade 2 or worse (29.7% vs. 17.9%; P < .0001) and grade 3 or worse (2.6% vs. 1.1%; P = .0016). Cumulative incidences of skin toxicity of these grades did not differ significantly.
Importantly, the prevalences of late soft tissue and skin toxicity at 5 years were much lower than the cumulative incidences, Dr. Meduri noted. “This means that the side effects in some patients tend to resolve over time.”
Although the prevalence of grade 2-4 skin toxicity increased slightly at 3 years and 5 years in both groups, the prevalence of grade 2-4 soft tissue toxicity was stable.
Finally, the volume that received at least 38.5 Gy of radiation was higher for patients who developed late grade 3 or 4 bone toxicity than for those who did not (2.1 vs. 0.82 cc; P = .027), whereas other dosimetric parameters were similar.
“The toxicity of the whole cohort was very low,” Dr. Meduri summarized. “APBI was associated with a slightly higher rate of late soft tissue and bone toxicity, with a slight decrease in cosmetic outcome at 5 years. But longer follow-up is needed to confirm these results.”
The IRMA findings confirm previous results from the RAPID trial showing that APBI delivered via 3D-conformal radiotherapy may be associated with increased rates of toxicity, Chirag Shah, MD, a radiation oncologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, said in an interview.
“While cancer control outcomes were not presented, the toxicity outcomes are important and validate why many are moving away from 3D-conformal radiotherapy APBI,” he elaborated. “We are seeing increased use of APBI in some centers in the U.S., though there has been a greater shift to IMRT [intensity-modulated radiation therapy] based on 10-year data from the Florence randomized trial, which showed reduced side effects.”
“I think the results of this study are practice-confirming,” Dr. Shah concluded. “Moving forward, shorter APBI schedules will be considered as we now have 5-fraction whole-breast regimens available, as assessed in the FAST and FAST-Forward trials.”
Dr. Meduri disclosed expert board service for MSD, and financial support for attending congresses from Ipsen, AstraZeneca, and Merck. The trial was sponsored by Regione Emilia-Romagna. Dr. Shah disclosed consulting for Impedimed and PreludeDX, and receiving grants from Varian, VisionRT, and PreludeDX.
SOURCE: Meduri B et al. ESTRO 2020. Abstract OC-0611.
FROM ESTRO 2020
Let’s ‘cancel’ these obsolete terms in DSM
Psychiatry has made significant scientific advances over the past century. However, it is still saddled with archaic terms, with pejorative connotations, disguised as official medical diagnoses. It is time to “cancel” those terms and replace them with ones that are neutral and have not accumulated baggage.
This process of “creative destruction” of psychiatric terminology is long overdue. It is frankly disturbing that the psychiatric jargon used around the time that the American Psychiatric Association was established 175 years ago (1844) is now considered insults and epithets. We no longer work in “lunatic asylums for the insane,” and our patients with intellectual disabilities are no longer classified as “morons,” “idiots,” or “imbeciles.” Such “diagnoses” have certainly contributed to the stigma of psychiatric brain disorders. Even the noble word “asylum” has acquired a negative valence because in the past it referred to hospitals that housed persons with serious mental illness.
Thankfully, some of the outrageous terms fabricated during the condemnable and dark era of slavery 2 centuries ago were never adopted by organized psychiatry. The absurd diagnosis of “negritude,” whose tenet was that black skin is a disease curable by whitening the skin, was “invented” by none other than Benjamin Rush, the Father of Psychiatry, whose conflicted soul was depicted by concomitantly owning a slave and positioning himself as an ardent abolitionist!
Terms that need to be replaced
Fast-forward to the modern era and consider the following:
Borderline personality disorder. It is truly tragic how this confusing and non-scientific term is used as an official diagnosis for a set of seriously ill persons. It is loaded with obloquy, indignity, and derision that completely ignore the tumult, self-harm, and disability with which patients who carry this label are burdened throughout their lives, despite being intelligent. This is a serious brain disorder that has been shown to be highly genetic and is characterized by many well-established structural brain abnormalities that have been documented in neuroimaging studies.1,2 Borderline personality should not be classified as a personality disorder but as an illness with multiple signs and symptoms, including mood lability, anger, impulsivity, self-cutting, suicidal urges, feelings of abandonment, and micro-psychotic episodes. A more clinically accurate term should be coined very soon to replace borderline personality, which should be discarded to the trash heap of obsolete psychiatric terms, and no longer inflicted on patients.
Neurosis. What is the justification for continuing to use the term “neurotic” for a person who has an anxiety disorder? Is it used because Jung and Freud propagated the term “neurosis” (after it was coined by William Cullen in 1769)? Neurosis has degenerated from a psychiatric diagnosis to a scornful snub that must never be used for any patient.
Schizophrenia. This diagnosis, coined by Eugen Bleuler to replace the narrow and pessimistic “dementia praecox” proposed by Emil Kraepelin in the 1920s, initially seemed to be a neutral description of a thought disorder (split associations, not split personality). Bleuler was perceptive enough to call his book Dementia Praecox or the Group of Schizophrenias, which is consistent with the modern scientific research that confirms schizophrenia is a very heterogeneous syndrome with hundreds of genetic and environmental biotypes with a similar phenotype but a wide range of severity, treatment response, and functional outcomes. However, in subsequent decades, schizophrenia became one of the most demeaning labels in psychiatry, casting a shadow of hopelessness and disability on the people who have this serious neurologic condition with many psychiatric symptoms. The term that should replace schizophrenia should be no more degrading than stroke, multiple sclerosis, or myocardial infarction.
Continue to: Over the past 15 years...
Over the past 15 years, an expanding group of schizophrenia experts have agreed that this term must be changed to one that reflects the core features of this syndrome, and have proposed terms such as “salience syndrome,” “psychosis-spectrum,” and “reality distortion and cognitive impairment disorder.”3 In fact, several countries have already adopted a new official diagnosis for schizophrenia.4 Japan now uses the term “integration disorder,” which has significantly reduced the stigma of this brain disorder.5 South Korea changed the name to “attunement disorder.” Hong Kong and Taiwan now use “dysfunction of thought and perception.” Some researchers recommend calling schizophrenia “Bleuler’s syndrome,” a neutral eponymous designation.
One of the most irritating things about the term schizophrenia is the widespread misconception that it means “split personality.” This prompts some sports announcers to call a football team “schizophrenic” if they play well in the first half and badly in the second. The stock market is labeled “schizophrenic” if it goes up one day and way down on the next. No other medical term is misused by the media as often as the term schizophrenia.
Narcissistic personality disorder. The origin of this diagnostic category is the concept of “malignant narcissism” coined by Erich Fromm in 1964, which he designated as “the quintessence of evil.” I strongly object to implying that evil is part of any psychiatric diagnosis. Numerous studies have found structural brain abnormalities (in both gray and white matter) in patients diagnosed with psychopathic traits.6 Later, malignant narcissism was reframed as narcissistic personality disorder in 1971 by Herbert Rosenfeld. Although malignant narcissism was never accepted by either the DSM or the International Classification of Diseases, narcissistic personality disorder has been included in the DSM for the past few decades. This diagnosis reeks of disparagement and negativity. Persons with narcissistic personality disorder have been shown to have pathological brain changes in resting-state functional connectivity,7 weakened frontostriatal white matter connectivity,8,9 and a reduced frontal thickness and cortical volume.10 A distorted sense of self and others is a socially disabling disorder that should generate empathy, not disdain. Narcissistic personality disorder should be replaced by a term that accurately describes its behavioral pathology, and should not incorporate Greek mythology.
Mania. This is another unfortunate diagnosis that immediately evokes a negative image of patients who suffer from a potentially lethal brain disorder. It was fortunate that Robert Kendall coined the term “bipolar disorder” to replace “manic-depressive illness,” but mania is still being used within bipolar disorder as a prominent clinical phase. While depression accurately describes the mood in the other phase of this disorder, the term mania evokes wild, irrational behavior. Because the actual mood symptom cluster in mania is either elation/grandiosity or irritability/anger, why not replace mania with “elation/irritability phase of bipolar disorder”? It is more descriptive of the patient’s mood and is less pejorative.
Nomenclature is vital, and words do matter, especially when used as a diagnostic medical term. Psychiatry must “cancel” its archaic names, which are infused with negative connotations. Reinventing the psychiatric lexicon is a necessary act of renewal in a specialty where a poorly worded diagnostic label can morph into the equivalent of a “scarlet letter.” Think of other contemptuous terms, such as refrigerator mother, male hysteria, moral insanity, toxic parents, inadequate personality disorder, neurasthenia, or catastrophic schizophrenia.
General medicine regularly discards many of its obsolete terms.11 These include terms such as ablepsy, ague, camp fever, bloody flux, chlorosis, catarrh, consumption, dropsy, French pox, phthisis, milk sickness, and scrumpox.
Think also of how society abandoned the antediluvian names of boys and girls. Few parents these days would name their son Ackley, Allard, Arundel, Awarnach, Beldon, Durward, Grower, Kenlm, or Legolan, or name their daughter Afton, Agrona, Arantxa, Corliss, Demelza, Eartha, Maida, Obsession, Radella, or Sacrifice.In summary, a necessary part of psychiatry’s progress is shedding obsolete terminology, even if it means slaughtering some widely used “traditional” vocabulary. It is a necessary act of renewal, and the image of psychiatry will be burnished by it.
1. Nasrallah HA. Borderline personality disorder is a heritable brain disease. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(4):19-20,32.
2. Sagarwala R, Nasrallah HA. White matter pathology in patients with borderline personality disorder: a review of controlled DTI studies. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2020;32(4):281-286.
3. Keshavan MS, Tandon R, Nasrallah HA. Renaming schizophrenia: keeping up with the facts. Schizophr Res. 2013;148(1-3):1-2.
4. Lasalvia A, Penta E, Sartorius N, et al. Should the label “schizophrenia” be abandoned? Schizophr Res. 2015;162(1-3):276-284.
5. Takahashi H, Ideno T, Okubo S, et al. Impact of changing the Japanese term for “schizophrenia” for reasons of stereotypical beliefs of schizophrenia in Japanese youth. Schizophr Res. 2009;112(1-3):149-152.
6. Johanson M, Vaurio D, Tiihunen J, et al. A systematic literature review of neuroimaging of psychopathic traits. Front Psychiatry. 2020;10:1027.
7. Yang, W, Cun L, Du X, et al. Gender differences in brain structure and resting-state functional connectivity related to narcissistic personality. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10924.
8. Chester DS, Cynam DR, Powell DK, et al. Narcissismis associated with weakened frontostriatal connectivity: a DTI study. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016;11(7):1036-1040.
9. Nenadic I, Gullmar D, Dietzek M, et al. Brain structure in narcissistic personality disorder: a VBM and DTI pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 2015;231(2):184-186.
10. Mao Y, Sang N, Wang Y, et al. Reduced frontal cortex thickness and cortical volume associated with pathological narcissism. Neuroscience. 2016;378:51-57.
11. Nasrallah HA. The transient truths of medical ‘progress.’ Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(6):23-24.
Psychiatry has made significant scientific advances over the past century. However, it is still saddled with archaic terms, with pejorative connotations, disguised as official medical diagnoses. It is time to “cancel” those terms and replace them with ones that are neutral and have not accumulated baggage.
This process of “creative destruction” of psychiatric terminology is long overdue. It is frankly disturbing that the psychiatric jargon used around the time that the American Psychiatric Association was established 175 years ago (1844) is now considered insults and epithets. We no longer work in “lunatic asylums for the insane,” and our patients with intellectual disabilities are no longer classified as “morons,” “idiots,” or “imbeciles.” Such “diagnoses” have certainly contributed to the stigma of psychiatric brain disorders. Even the noble word “asylum” has acquired a negative valence because in the past it referred to hospitals that housed persons with serious mental illness.
Thankfully, some of the outrageous terms fabricated during the condemnable and dark era of slavery 2 centuries ago were never adopted by organized psychiatry. The absurd diagnosis of “negritude,” whose tenet was that black skin is a disease curable by whitening the skin, was “invented” by none other than Benjamin Rush, the Father of Psychiatry, whose conflicted soul was depicted by concomitantly owning a slave and positioning himself as an ardent abolitionist!
Terms that need to be replaced
Fast-forward to the modern era and consider the following:
Borderline personality disorder. It is truly tragic how this confusing and non-scientific term is used as an official diagnosis for a set of seriously ill persons. It is loaded with obloquy, indignity, and derision that completely ignore the tumult, self-harm, and disability with which patients who carry this label are burdened throughout their lives, despite being intelligent. This is a serious brain disorder that has been shown to be highly genetic and is characterized by many well-established structural brain abnormalities that have been documented in neuroimaging studies.1,2 Borderline personality should not be classified as a personality disorder but as an illness with multiple signs and symptoms, including mood lability, anger, impulsivity, self-cutting, suicidal urges, feelings of abandonment, and micro-psychotic episodes. A more clinically accurate term should be coined very soon to replace borderline personality, which should be discarded to the trash heap of obsolete psychiatric terms, and no longer inflicted on patients.
Neurosis. What is the justification for continuing to use the term “neurotic” for a person who has an anxiety disorder? Is it used because Jung and Freud propagated the term “neurosis” (after it was coined by William Cullen in 1769)? Neurosis has degenerated from a psychiatric diagnosis to a scornful snub that must never be used for any patient.
Schizophrenia. This diagnosis, coined by Eugen Bleuler to replace the narrow and pessimistic “dementia praecox” proposed by Emil Kraepelin in the 1920s, initially seemed to be a neutral description of a thought disorder (split associations, not split personality). Bleuler was perceptive enough to call his book Dementia Praecox or the Group of Schizophrenias, which is consistent with the modern scientific research that confirms schizophrenia is a very heterogeneous syndrome with hundreds of genetic and environmental biotypes with a similar phenotype but a wide range of severity, treatment response, and functional outcomes. However, in subsequent decades, schizophrenia became one of the most demeaning labels in psychiatry, casting a shadow of hopelessness and disability on the people who have this serious neurologic condition with many psychiatric symptoms. The term that should replace schizophrenia should be no more degrading than stroke, multiple sclerosis, or myocardial infarction.
Continue to: Over the past 15 years...
Over the past 15 years, an expanding group of schizophrenia experts have agreed that this term must be changed to one that reflects the core features of this syndrome, and have proposed terms such as “salience syndrome,” “psychosis-spectrum,” and “reality distortion and cognitive impairment disorder.”3 In fact, several countries have already adopted a new official diagnosis for schizophrenia.4 Japan now uses the term “integration disorder,” which has significantly reduced the stigma of this brain disorder.5 South Korea changed the name to “attunement disorder.” Hong Kong and Taiwan now use “dysfunction of thought and perception.” Some researchers recommend calling schizophrenia “Bleuler’s syndrome,” a neutral eponymous designation.
One of the most irritating things about the term schizophrenia is the widespread misconception that it means “split personality.” This prompts some sports announcers to call a football team “schizophrenic” if they play well in the first half and badly in the second. The stock market is labeled “schizophrenic” if it goes up one day and way down on the next. No other medical term is misused by the media as often as the term schizophrenia.
Narcissistic personality disorder. The origin of this diagnostic category is the concept of “malignant narcissism” coined by Erich Fromm in 1964, which he designated as “the quintessence of evil.” I strongly object to implying that evil is part of any psychiatric diagnosis. Numerous studies have found structural brain abnormalities (in both gray and white matter) in patients diagnosed with psychopathic traits.6 Later, malignant narcissism was reframed as narcissistic personality disorder in 1971 by Herbert Rosenfeld. Although malignant narcissism was never accepted by either the DSM or the International Classification of Diseases, narcissistic personality disorder has been included in the DSM for the past few decades. This diagnosis reeks of disparagement and negativity. Persons with narcissistic personality disorder have been shown to have pathological brain changes in resting-state functional connectivity,7 weakened frontostriatal white matter connectivity,8,9 and a reduced frontal thickness and cortical volume.10 A distorted sense of self and others is a socially disabling disorder that should generate empathy, not disdain. Narcissistic personality disorder should be replaced by a term that accurately describes its behavioral pathology, and should not incorporate Greek mythology.
Mania. This is another unfortunate diagnosis that immediately evokes a negative image of patients who suffer from a potentially lethal brain disorder. It was fortunate that Robert Kendall coined the term “bipolar disorder” to replace “manic-depressive illness,” but mania is still being used within bipolar disorder as a prominent clinical phase. While depression accurately describes the mood in the other phase of this disorder, the term mania evokes wild, irrational behavior. Because the actual mood symptom cluster in mania is either elation/grandiosity or irritability/anger, why not replace mania with “elation/irritability phase of bipolar disorder”? It is more descriptive of the patient’s mood and is less pejorative.
Nomenclature is vital, and words do matter, especially when used as a diagnostic medical term. Psychiatry must “cancel” its archaic names, which are infused with negative connotations. Reinventing the psychiatric lexicon is a necessary act of renewal in a specialty where a poorly worded diagnostic label can morph into the equivalent of a “scarlet letter.” Think of other contemptuous terms, such as refrigerator mother, male hysteria, moral insanity, toxic parents, inadequate personality disorder, neurasthenia, or catastrophic schizophrenia.
General medicine regularly discards many of its obsolete terms.11 These include terms such as ablepsy, ague, camp fever, bloody flux, chlorosis, catarrh, consumption, dropsy, French pox, phthisis, milk sickness, and scrumpox.
Think also of how society abandoned the antediluvian names of boys and girls. Few parents these days would name their son Ackley, Allard, Arundel, Awarnach, Beldon, Durward, Grower, Kenlm, or Legolan, or name their daughter Afton, Agrona, Arantxa, Corliss, Demelza, Eartha, Maida, Obsession, Radella, or Sacrifice.In summary, a necessary part of psychiatry’s progress is shedding obsolete terminology, even if it means slaughtering some widely used “traditional” vocabulary. It is a necessary act of renewal, and the image of psychiatry will be burnished by it.
Psychiatry has made significant scientific advances over the past century. However, it is still saddled with archaic terms, with pejorative connotations, disguised as official medical diagnoses. It is time to “cancel” those terms and replace them with ones that are neutral and have not accumulated baggage.
This process of “creative destruction” of psychiatric terminology is long overdue. It is frankly disturbing that the psychiatric jargon used around the time that the American Psychiatric Association was established 175 years ago (1844) is now considered insults and epithets. We no longer work in “lunatic asylums for the insane,” and our patients with intellectual disabilities are no longer classified as “morons,” “idiots,” or “imbeciles.” Such “diagnoses” have certainly contributed to the stigma of psychiatric brain disorders. Even the noble word “asylum” has acquired a negative valence because in the past it referred to hospitals that housed persons with serious mental illness.
Thankfully, some of the outrageous terms fabricated during the condemnable and dark era of slavery 2 centuries ago were never adopted by organized psychiatry. The absurd diagnosis of “negritude,” whose tenet was that black skin is a disease curable by whitening the skin, was “invented” by none other than Benjamin Rush, the Father of Psychiatry, whose conflicted soul was depicted by concomitantly owning a slave and positioning himself as an ardent abolitionist!
Terms that need to be replaced
Fast-forward to the modern era and consider the following:
Borderline personality disorder. It is truly tragic how this confusing and non-scientific term is used as an official diagnosis for a set of seriously ill persons. It is loaded with obloquy, indignity, and derision that completely ignore the tumult, self-harm, and disability with which patients who carry this label are burdened throughout their lives, despite being intelligent. This is a serious brain disorder that has been shown to be highly genetic and is characterized by many well-established structural brain abnormalities that have been documented in neuroimaging studies.1,2 Borderline personality should not be classified as a personality disorder but as an illness with multiple signs and symptoms, including mood lability, anger, impulsivity, self-cutting, suicidal urges, feelings of abandonment, and micro-psychotic episodes. A more clinically accurate term should be coined very soon to replace borderline personality, which should be discarded to the trash heap of obsolete psychiatric terms, and no longer inflicted on patients.
Neurosis. What is the justification for continuing to use the term “neurotic” for a person who has an anxiety disorder? Is it used because Jung and Freud propagated the term “neurosis” (after it was coined by William Cullen in 1769)? Neurosis has degenerated from a psychiatric diagnosis to a scornful snub that must never be used for any patient.
Schizophrenia. This diagnosis, coined by Eugen Bleuler to replace the narrow and pessimistic “dementia praecox” proposed by Emil Kraepelin in the 1920s, initially seemed to be a neutral description of a thought disorder (split associations, not split personality). Bleuler was perceptive enough to call his book Dementia Praecox or the Group of Schizophrenias, which is consistent with the modern scientific research that confirms schizophrenia is a very heterogeneous syndrome with hundreds of genetic and environmental biotypes with a similar phenotype but a wide range of severity, treatment response, and functional outcomes. However, in subsequent decades, schizophrenia became one of the most demeaning labels in psychiatry, casting a shadow of hopelessness and disability on the people who have this serious neurologic condition with many psychiatric symptoms. The term that should replace schizophrenia should be no more degrading than stroke, multiple sclerosis, or myocardial infarction.
Continue to: Over the past 15 years...
Over the past 15 years, an expanding group of schizophrenia experts have agreed that this term must be changed to one that reflects the core features of this syndrome, and have proposed terms such as “salience syndrome,” “psychosis-spectrum,” and “reality distortion and cognitive impairment disorder.”3 In fact, several countries have already adopted a new official diagnosis for schizophrenia.4 Japan now uses the term “integration disorder,” which has significantly reduced the stigma of this brain disorder.5 South Korea changed the name to “attunement disorder.” Hong Kong and Taiwan now use “dysfunction of thought and perception.” Some researchers recommend calling schizophrenia “Bleuler’s syndrome,” a neutral eponymous designation.
One of the most irritating things about the term schizophrenia is the widespread misconception that it means “split personality.” This prompts some sports announcers to call a football team “schizophrenic” if they play well in the first half and badly in the second. The stock market is labeled “schizophrenic” if it goes up one day and way down on the next. No other medical term is misused by the media as often as the term schizophrenia.
Narcissistic personality disorder. The origin of this diagnostic category is the concept of “malignant narcissism” coined by Erich Fromm in 1964, which he designated as “the quintessence of evil.” I strongly object to implying that evil is part of any psychiatric diagnosis. Numerous studies have found structural brain abnormalities (in both gray and white matter) in patients diagnosed with psychopathic traits.6 Later, malignant narcissism was reframed as narcissistic personality disorder in 1971 by Herbert Rosenfeld. Although malignant narcissism was never accepted by either the DSM or the International Classification of Diseases, narcissistic personality disorder has been included in the DSM for the past few decades. This diagnosis reeks of disparagement and negativity. Persons with narcissistic personality disorder have been shown to have pathological brain changes in resting-state functional connectivity,7 weakened frontostriatal white matter connectivity,8,9 and a reduced frontal thickness and cortical volume.10 A distorted sense of self and others is a socially disabling disorder that should generate empathy, not disdain. Narcissistic personality disorder should be replaced by a term that accurately describes its behavioral pathology, and should not incorporate Greek mythology.
Mania. This is another unfortunate diagnosis that immediately evokes a negative image of patients who suffer from a potentially lethal brain disorder. It was fortunate that Robert Kendall coined the term “bipolar disorder” to replace “manic-depressive illness,” but mania is still being used within bipolar disorder as a prominent clinical phase. While depression accurately describes the mood in the other phase of this disorder, the term mania evokes wild, irrational behavior. Because the actual mood symptom cluster in mania is either elation/grandiosity or irritability/anger, why not replace mania with “elation/irritability phase of bipolar disorder”? It is more descriptive of the patient’s mood and is less pejorative.
Nomenclature is vital, and words do matter, especially when used as a diagnostic medical term. Psychiatry must “cancel” its archaic names, which are infused with negative connotations. Reinventing the psychiatric lexicon is a necessary act of renewal in a specialty where a poorly worded diagnostic label can morph into the equivalent of a “scarlet letter.” Think of other contemptuous terms, such as refrigerator mother, male hysteria, moral insanity, toxic parents, inadequate personality disorder, neurasthenia, or catastrophic schizophrenia.
General medicine regularly discards many of its obsolete terms.11 These include terms such as ablepsy, ague, camp fever, bloody flux, chlorosis, catarrh, consumption, dropsy, French pox, phthisis, milk sickness, and scrumpox.
Think also of how society abandoned the antediluvian names of boys and girls. Few parents these days would name their son Ackley, Allard, Arundel, Awarnach, Beldon, Durward, Grower, Kenlm, or Legolan, or name their daughter Afton, Agrona, Arantxa, Corliss, Demelza, Eartha, Maida, Obsession, Radella, or Sacrifice.In summary, a necessary part of psychiatry’s progress is shedding obsolete terminology, even if it means slaughtering some widely used “traditional” vocabulary. It is a necessary act of renewal, and the image of psychiatry will be burnished by it.
1. Nasrallah HA. Borderline personality disorder is a heritable brain disease. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(4):19-20,32.
2. Sagarwala R, Nasrallah HA. White matter pathology in patients with borderline personality disorder: a review of controlled DTI studies. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2020;32(4):281-286.
3. Keshavan MS, Tandon R, Nasrallah HA. Renaming schizophrenia: keeping up with the facts. Schizophr Res. 2013;148(1-3):1-2.
4. Lasalvia A, Penta E, Sartorius N, et al. Should the label “schizophrenia” be abandoned? Schizophr Res. 2015;162(1-3):276-284.
5. Takahashi H, Ideno T, Okubo S, et al. Impact of changing the Japanese term for “schizophrenia” for reasons of stereotypical beliefs of schizophrenia in Japanese youth. Schizophr Res. 2009;112(1-3):149-152.
6. Johanson M, Vaurio D, Tiihunen J, et al. A systematic literature review of neuroimaging of psychopathic traits. Front Psychiatry. 2020;10:1027.
7. Yang, W, Cun L, Du X, et al. Gender differences in brain structure and resting-state functional connectivity related to narcissistic personality. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10924.
8. Chester DS, Cynam DR, Powell DK, et al. Narcissismis associated with weakened frontostriatal connectivity: a DTI study. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016;11(7):1036-1040.
9. Nenadic I, Gullmar D, Dietzek M, et al. Brain structure in narcissistic personality disorder: a VBM and DTI pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 2015;231(2):184-186.
10. Mao Y, Sang N, Wang Y, et al. Reduced frontal cortex thickness and cortical volume associated with pathological narcissism. Neuroscience. 2016;378:51-57.
11. Nasrallah HA. The transient truths of medical ‘progress.’ Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(6):23-24.
1. Nasrallah HA. Borderline personality disorder is a heritable brain disease. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(4):19-20,32.
2. Sagarwala R, Nasrallah HA. White matter pathology in patients with borderline personality disorder: a review of controlled DTI studies. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2020;32(4):281-286.
3. Keshavan MS, Tandon R, Nasrallah HA. Renaming schizophrenia: keeping up with the facts. Schizophr Res. 2013;148(1-3):1-2.
4. Lasalvia A, Penta E, Sartorius N, et al. Should the label “schizophrenia” be abandoned? Schizophr Res. 2015;162(1-3):276-284.
5. Takahashi H, Ideno T, Okubo S, et al. Impact of changing the Japanese term for “schizophrenia” for reasons of stereotypical beliefs of schizophrenia in Japanese youth. Schizophr Res. 2009;112(1-3):149-152.
6. Johanson M, Vaurio D, Tiihunen J, et al. A systematic literature review of neuroimaging of psychopathic traits. Front Psychiatry. 2020;10:1027.
7. Yang, W, Cun L, Du X, et al. Gender differences in brain structure and resting-state functional connectivity related to narcissistic personality. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10924.
8. Chester DS, Cynam DR, Powell DK, et al. Narcissismis associated with weakened frontostriatal connectivity: a DTI study. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016;11(7):1036-1040.
9. Nenadic I, Gullmar D, Dietzek M, et al. Brain structure in narcissistic personality disorder: a VBM and DTI pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 2015;231(2):184-186.
10. Mao Y, Sang N, Wang Y, et al. Reduced frontal cortex thickness and cortical volume associated with pathological narcissism. Neuroscience. 2016;378:51-57.
11. Nasrallah HA. The transient truths of medical ‘progress.’ Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(6):23-24.
Caring for adults who engage in nonsuicidal self-injury
Nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI) is the direct and deliberate destruction of body tissue without intent to die.1 Cutting is the most common form of NSSI; other methods include burning, scraping/scratching skin, interfering with wound healing, hitting, biting, self-poisoning, and purposeful non-recreational risk-taking.2,3 Although most individuals who engage in NSSI have no intention to die, suicidal ideation often precedes the initial engagement in NSSI,4 and a history of repeated NSSI is a risk factor for suicide attempts.4 In a systematic review, Cipriano et al5 found that NSSI is most common among adolescents and young adults, with onset most often occurring between age 12 and 14. Prevalence rates of NSSI are 7.5% to 46.5% in adolescents, 38.9% in university students, and 4% to 23% in adults.5
Although no medications have consistently shown efficacy for treating NSSI, research suggests cognitive-behavioral therapy and dialectical behavioral therapy may be helpful. Unfortunately, these therapies are often not available during a patient’s acute crisis.3 Because a thorough review of the treatment options for NSSI is beyond the scope of this article, here I offer tips for caring for adults who engage in NSSI. Although there are slight differences in managing NSSI in adolescents (eg, the need for parental monitoring and reducing risk of contagion), these tips also can be used with adolescents.
Explore why your patient engages in NSSI. Identifying the reasons for our patients’ NSSI makes it easier for us to empathize with them, and puts us in a better position to treat them.3 The most widely reported reasons for NSSI are to cope with distress/anguish and to exert influence on others.6 In a systematic review, self-reported reasons for NSSI also included punishing oneself for having positive feelings, punishing others, managing dissociation (ie, active pursuit of numbness), sensation-seeking (ie, to generate excitement or exhilaration), averting suicide (ie, warding off suicidal thoughts), maintaining or exploring boundaries, and expressing or coping with sexuality.6 When exploring your patient’s reasons for NSSI, determine if the behavior is based on a true suicidal desire. Because NSSI is associated with mood disorders, anxiety disorders, personality disorders, and other disorders, also assess for any underlying psychiatric conditions, and treat them accordingly because mental health treatment has been empirically proven to reduce suicide rates.2,7
Conduct a suicide risk assessment. Regardless of your patient’s reasons for NSSI, an individualized and thorough suicide risk assessment is needed to identify modifiable, non-modifiable, and protective factors that you can consider when developing a treatment plan. Key components of such assessments include (but are not limited to) current and past urges to engage in NSSI, past NSSI and suicide attempts, access to lethal means, and ability to follow a safety plan.
Avoid exaggerating the danger and importance of NSSI. Treating a patient who engages in NSSI who is motivated by a true suicidal desire and/or has underlying psychiatric conditions may prompt you to consider hospitalization and/or prescribing psychotropic medications.3 However, because most NSSI is not due to a true suicidal desire, overreacting may unwittingly communicate to the patient that self-harm is a way to sustain someone’s attention, thus reinforcing that such behaviors can help them obtain support when distressed.3 Further, overreacting will not help patients comprehend and better cope with the reasons for their self-injurious behaviors.3
Restrict your patient’s access to lethal means. Restricting access to items such as firearms, sharp objects (eg, knives and razors), medications, implements for suffocation/hanging (eg, belts), and household poisons has been empirically proven to reduce suicide rates.7 Such restrictions can also potentially reduce the likelihood of NSSI. It is important to repeatedly ask your patient if they have acquired any new means, and to listen for information that indicates they possess means that they did not previously disclose. It is also important to ask if the patient has moved existing means to an area for easier access to use them.
Create a safety plan. Written safety plans can include a list of warning signs (thoughts, images, mood, situations, behaviors) that a crisis is developing, coping strategies (eg, going for a walk, exercising, engaging in a hobby, socializing with friends or family), and contact information for 24-hour crisis hotlines, emergency rooms, and mental health clinicians.8 The Suicide Prevention Resource Center offers a safety plan template at www.sprc.org/sites/default/files/resource-program/Brown_StanleySafetyPlanTemplate.pdf.8
Offer empathy. Individuals who engage in NSSI are making a desperate call for help that requires concerned and supportive responses.3 One such response is to provide empathy. In addition to expressing concern and compassion, empathy involves recognizing and sharing your patients’ emotions. Empathy also can help you avoid any resistance during the visit by considering what is appropriate to say to patients.
Manage countertransference. You may have negative feelings toward a patient who engages in NSSI, or may even view self-harm as a willful act designed to gain attention. However, such feelings could lead you to minimize or dismiss the importance of your patient’s behaviors, which may push them to engage in more dangerous self-harm.3 Acknowledging any feelings of derision for a patient who engages in NSSI and understanding why you have these emotions will help you better understand your patient, improve rapport, and ensure that you are not impeding the delivery of appropriate clinical care.
1. Nock MK. Self-injury. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2010;6:339-363.
2. Klonsky ED. Non-suicidal self-injury in United States adults: prevalence, sociodemographics, topography and functions. Psychol Med. 2011;41(9):1981-1986.
3. Gunderson JG, Choi-Kain LW. Working with patients who self-injure. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(9):976-977.
4. Glenn CR, Lanzillo EC, Esposito EC, et al. Examining the course of suicidal and nonsuicidal self-injurious thoughts and behaviors in outpatient and inpatient adolescents. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2017;45(5):971-983.
5. Cipriano A, Cella S, Cotrufo P. Nonsuicidal self-injury: a systematic review. Front Psychol. 2017;8:1946. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01946
6. Edmondson AJ, Brennan CA, House AO. Non-suicidal reasons for self-harm: a systematic review of self-reported accounts. J Affect Disord. 2016;191:109-117.
7. Mann JJ, Apter A, Bertolete J. Suicide prevention strategies: a systematic review. JAMA. 2005;294(16):2064-2074.
8. Stanley B, Brown GK. Safety planning intervention: a brief intervention to mitigate suicide risk. Cog Behav Practice. 2012;19:256-264.
Nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI) is the direct and deliberate destruction of body tissue without intent to die.1 Cutting is the most common form of NSSI; other methods include burning, scraping/scratching skin, interfering with wound healing, hitting, biting, self-poisoning, and purposeful non-recreational risk-taking.2,3 Although most individuals who engage in NSSI have no intention to die, suicidal ideation often precedes the initial engagement in NSSI,4 and a history of repeated NSSI is a risk factor for suicide attempts.4 In a systematic review, Cipriano et al5 found that NSSI is most common among adolescents and young adults, with onset most often occurring between age 12 and 14. Prevalence rates of NSSI are 7.5% to 46.5% in adolescents, 38.9% in university students, and 4% to 23% in adults.5
Although no medications have consistently shown efficacy for treating NSSI, research suggests cognitive-behavioral therapy and dialectical behavioral therapy may be helpful. Unfortunately, these therapies are often not available during a patient’s acute crisis.3 Because a thorough review of the treatment options for NSSI is beyond the scope of this article, here I offer tips for caring for adults who engage in NSSI. Although there are slight differences in managing NSSI in adolescents (eg, the need for parental monitoring and reducing risk of contagion), these tips also can be used with adolescents.
Explore why your patient engages in NSSI. Identifying the reasons for our patients’ NSSI makes it easier for us to empathize with them, and puts us in a better position to treat them.3 The most widely reported reasons for NSSI are to cope with distress/anguish and to exert influence on others.6 In a systematic review, self-reported reasons for NSSI also included punishing oneself for having positive feelings, punishing others, managing dissociation (ie, active pursuit of numbness), sensation-seeking (ie, to generate excitement or exhilaration), averting suicide (ie, warding off suicidal thoughts), maintaining or exploring boundaries, and expressing or coping with sexuality.6 When exploring your patient’s reasons for NSSI, determine if the behavior is based on a true suicidal desire. Because NSSI is associated with mood disorders, anxiety disorders, personality disorders, and other disorders, also assess for any underlying psychiatric conditions, and treat them accordingly because mental health treatment has been empirically proven to reduce suicide rates.2,7
Conduct a suicide risk assessment. Regardless of your patient’s reasons for NSSI, an individualized and thorough suicide risk assessment is needed to identify modifiable, non-modifiable, and protective factors that you can consider when developing a treatment plan. Key components of such assessments include (but are not limited to) current and past urges to engage in NSSI, past NSSI and suicide attempts, access to lethal means, and ability to follow a safety plan.
Avoid exaggerating the danger and importance of NSSI. Treating a patient who engages in NSSI who is motivated by a true suicidal desire and/or has underlying psychiatric conditions may prompt you to consider hospitalization and/or prescribing psychotropic medications.3 However, because most NSSI is not due to a true suicidal desire, overreacting may unwittingly communicate to the patient that self-harm is a way to sustain someone’s attention, thus reinforcing that such behaviors can help them obtain support when distressed.3 Further, overreacting will not help patients comprehend and better cope with the reasons for their self-injurious behaviors.3
Restrict your patient’s access to lethal means. Restricting access to items such as firearms, sharp objects (eg, knives and razors), medications, implements for suffocation/hanging (eg, belts), and household poisons has been empirically proven to reduce suicide rates.7 Such restrictions can also potentially reduce the likelihood of NSSI. It is important to repeatedly ask your patient if they have acquired any new means, and to listen for information that indicates they possess means that they did not previously disclose. It is also important to ask if the patient has moved existing means to an area for easier access to use them.
Create a safety plan. Written safety plans can include a list of warning signs (thoughts, images, mood, situations, behaviors) that a crisis is developing, coping strategies (eg, going for a walk, exercising, engaging in a hobby, socializing with friends or family), and contact information for 24-hour crisis hotlines, emergency rooms, and mental health clinicians.8 The Suicide Prevention Resource Center offers a safety plan template at www.sprc.org/sites/default/files/resource-program/Brown_StanleySafetyPlanTemplate.pdf.8
Offer empathy. Individuals who engage in NSSI are making a desperate call for help that requires concerned and supportive responses.3 One such response is to provide empathy. In addition to expressing concern and compassion, empathy involves recognizing and sharing your patients’ emotions. Empathy also can help you avoid any resistance during the visit by considering what is appropriate to say to patients.
Manage countertransference. You may have negative feelings toward a patient who engages in NSSI, or may even view self-harm as a willful act designed to gain attention. However, such feelings could lead you to minimize or dismiss the importance of your patient’s behaviors, which may push them to engage in more dangerous self-harm.3 Acknowledging any feelings of derision for a patient who engages in NSSI and understanding why you have these emotions will help you better understand your patient, improve rapport, and ensure that you are not impeding the delivery of appropriate clinical care.
Nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI) is the direct and deliberate destruction of body tissue without intent to die.1 Cutting is the most common form of NSSI; other methods include burning, scraping/scratching skin, interfering with wound healing, hitting, biting, self-poisoning, and purposeful non-recreational risk-taking.2,3 Although most individuals who engage in NSSI have no intention to die, suicidal ideation often precedes the initial engagement in NSSI,4 and a history of repeated NSSI is a risk factor for suicide attempts.4 In a systematic review, Cipriano et al5 found that NSSI is most common among adolescents and young adults, with onset most often occurring between age 12 and 14. Prevalence rates of NSSI are 7.5% to 46.5% in adolescents, 38.9% in university students, and 4% to 23% in adults.5
Although no medications have consistently shown efficacy for treating NSSI, research suggests cognitive-behavioral therapy and dialectical behavioral therapy may be helpful. Unfortunately, these therapies are often not available during a patient’s acute crisis.3 Because a thorough review of the treatment options for NSSI is beyond the scope of this article, here I offer tips for caring for adults who engage in NSSI. Although there are slight differences in managing NSSI in adolescents (eg, the need for parental monitoring and reducing risk of contagion), these tips also can be used with adolescents.
Explore why your patient engages in NSSI. Identifying the reasons for our patients’ NSSI makes it easier for us to empathize with them, and puts us in a better position to treat them.3 The most widely reported reasons for NSSI are to cope with distress/anguish and to exert influence on others.6 In a systematic review, self-reported reasons for NSSI also included punishing oneself for having positive feelings, punishing others, managing dissociation (ie, active pursuit of numbness), sensation-seeking (ie, to generate excitement or exhilaration), averting suicide (ie, warding off suicidal thoughts), maintaining or exploring boundaries, and expressing or coping with sexuality.6 When exploring your patient’s reasons for NSSI, determine if the behavior is based on a true suicidal desire. Because NSSI is associated with mood disorders, anxiety disorders, personality disorders, and other disorders, also assess for any underlying psychiatric conditions, and treat them accordingly because mental health treatment has been empirically proven to reduce suicide rates.2,7
Conduct a suicide risk assessment. Regardless of your patient’s reasons for NSSI, an individualized and thorough suicide risk assessment is needed to identify modifiable, non-modifiable, and protective factors that you can consider when developing a treatment plan. Key components of such assessments include (but are not limited to) current and past urges to engage in NSSI, past NSSI and suicide attempts, access to lethal means, and ability to follow a safety plan.
Avoid exaggerating the danger and importance of NSSI. Treating a patient who engages in NSSI who is motivated by a true suicidal desire and/or has underlying psychiatric conditions may prompt you to consider hospitalization and/or prescribing psychotropic medications.3 However, because most NSSI is not due to a true suicidal desire, overreacting may unwittingly communicate to the patient that self-harm is a way to sustain someone’s attention, thus reinforcing that such behaviors can help them obtain support when distressed.3 Further, overreacting will not help patients comprehend and better cope with the reasons for their self-injurious behaviors.3
Restrict your patient’s access to lethal means. Restricting access to items such as firearms, sharp objects (eg, knives and razors), medications, implements for suffocation/hanging (eg, belts), and household poisons has been empirically proven to reduce suicide rates.7 Such restrictions can also potentially reduce the likelihood of NSSI. It is important to repeatedly ask your patient if they have acquired any new means, and to listen for information that indicates they possess means that they did not previously disclose. It is also important to ask if the patient has moved existing means to an area for easier access to use them.
Create a safety plan. Written safety plans can include a list of warning signs (thoughts, images, mood, situations, behaviors) that a crisis is developing, coping strategies (eg, going for a walk, exercising, engaging in a hobby, socializing with friends or family), and contact information for 24-hour crisis hotlines, emergency rooms, and mental health clinicians.8 The Suicide Prevention Resource Center offers a safety plan template at www.sprc.org/sites/default/files/resource-program/Brown_StanleySafetyPlanTemplate.pdf.8
Offer empathy. Individuals who engage in NSSI are making a desperate call for help that requires concerned and supportive responses.3 One such response is to provide empathy. In addition to expressing concern and compassion, empathy involves recognizing and sharing your patients’ emotions. Empathy also can help you avoid any resistance during the visit by considering what is appropriate to say to patients.
Manage countertransference. You may have negative feelings toward a patient who engages in NSSI, or may even view self-harm as a willful act designed to gain attention. However, such feelings could lead you to minimize or dismiss the importance of your patient’s behaviors, which may push them to engage in more dangerous self-harm.3 Acknowledging any feelings of derision for a patient who engages in NSSI and understanding why you have these emotions will help you better understand your patient, improve rapport, and ensure that you are not impeding the delivery of appropriate clinical care.
1. Nock MK. Self-injury. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2010;6:339-363.
2. Klonsky ED. Non-suicidal self-injury in United States adults: prevalence, sociodemographics, topography and functions. Psychol Med. 2011;41(9):1981-1986.
3. Gunderson JG, Choi-Kain LW. Working with patients who self-injure. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(9):976-977.
4. Glenn CR, Lanzillo EC, Esposito EC, et al. Examining the course of suicidal and nonsuicidal self-injurious thoughts and behaviors in outpatient and inpatient adolescents. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2017;45(5):971-983.
5. Cipriano A, Cella S, Cotrufo P. Nonsuicidal self-injury: a systematic review. Front Psychol. 2017;8:1946. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01946
6. Edmondson AJ, Brennan CA, House AO. Non-suicidal reasons for self-harm: a systematic review of self-reported accounts. J Affect Disord. 2016;191:109-117.
7. Mann JJ, Apter A, Bertolete J. Suicide prevention strategies: a systematic review. JAMA. 2005;294(16):2064-2074.
8. Stanley B, Brown GK. Safety planning intervention: a brief intervention to mitigate suicide risk. Cog Behav Practice. 2012;19:256-264.
1. Nock MK. Self-injury. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2010;6:339-363.
2. Klonsky ED. Non-suicidal self-injury in United States adults: prevalence, sociodemographics, topography and functions. Psychol Med. 2011;41(9):1981-1986.
3. Gunderson JG, Choi-Kain LW. Working with patients who self-injure. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(9):976-977.
4. Glenn CR, Lanzillo EC, Esposito EC, et al. Examining the course of suicidal and nonsuicidal self-injurious thoughts and behaviors in outpatient and inpatient adolescents. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2017;45(5):971-983.
5. Cipriano A, Cella S, Cotrufo P. Nonsuicidal self-injury: a systematic review. Front Psychol. 2017;8:1946. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01946
6. Edmondson AJ, Brennan CA, House AO. Non-suicidal reasons for self-harm: a systematic review of self-reported accounts. J Affect Disord. 2016;191:109-117.
7. Mann JJ, Apter A, Bertolete J. Suicide prevention strategies: a systematic review. JAMA. 2005;294(16):2064-2074.
8. Stanley B, Brown GK. Safety planning intervention: a brief intervention to mitigate suicide risk. Cog Behav Practice. 2012;19:256-264.
Current PERISCOPE vaccine studies: Toward better pertussis prevention?
With increasing whooping cough numbers, developing an effective new vaccine against Bordetella pertussis is a priority. Results from the multifactorial PERISCOPE Project will help scientists and clinicians move forward.
Dominic Kelly, PhD, talked about vaccine-induced immunity and provided an overview of ongoing clinical trials in the PERISCOPE (Pertussis Correlates of Protection Europe) project in a key research session at the start of the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. Dr. Kelly, a pediatrician at the Children’s Hospital in Oxford and a member of the Oxford Vaccines Group, leads one of the studies in the project looking at infant vaccination.
Dr. Kelly began his presentation by showing a figure depicting where vaccine-induced immunity fits into the larger suite of clinical studies. These studies involve mouse models, human challenge models, and infection patients. A key theme is the use of a core group of immunoassays across all studies, with the hope that they will allow effective cross comparisons.
Dr. Kelly stated, “If we find a correlate of protection in the challenge model, we can then interpret the vaccine studies in the light of that because we are using standardized constant immunoassays.”
The assays being used depend in part on the specific study and the volume of blood available. They will generally include Bordetella-specific antibody and functional antibody assays, as well as interesting studies collecting mucosal samples from infants and adults to look at serological responses. Also under examination are a range of enzyme-linked immune absorbent spot, flow cytometry, and culture techniques looking at Memory B cells, T cells, and gene expression.
Complementing these assay studies, PERISCOPE includes a series of clinical investigations designed to throw light on three areas of interest, described below:
First, researchers hope to gain a better understanding regarding the effects of the original whole cell vaccine versus the current acellular variety. The former uses an inactivated version of the whole organism. Epidemiological studies, animal data, and experience in the field demonstrate that whole-cell vaccination results in a broad, long-lasting, and effective immune response.
By comparison, the acellular pertussis vaccine consists of between three and five protein components, which are purified from cultured Bordetella pertussis. While it is an effective vaccine, its effects are less durable; routine use in some countries is associated with cyclical outbreaks of increasing severity.
A second issue for researchers involved in the PERISCOPE project concerns the effects of maternal immunization. In the United Kingdom in 2012, for example, an increasing number of cases were noted 6-7 years after adoption of an acellular vaccine for routine vaccination in the 2nd-3rd trimester of pregnancy. Vaccination appears to effectively control neonatal disease, but whether this influences infant immune responses and long-term control of pertussis for a population is unknown.
Finally, the group is interested in the effects of an acellular booster across all age groups. While the effects may be short-lived, the booster is a potential strategy for controlling a population by repeated boosting of immunity. This is another area where using novel immunoassays may aid better understanding.
To find answers, the consortium has established four studies: the Gambia Pertussis study (GaPs) in Gambia and AWARE, the sister study to GaPs in the United Kingdom, addressing the acellular pertussis versus cellular pertussis question; the Pertussis Maternal Immunization Study in Finland (MIFI) addressing maternal immunization; and the Booster against Pertussis (BERT) study across three countries (U.K., the Netherlands, and Finland) looking at acellular booster across age groups.
Gambia pertussis study
GaPs is the largest single study in the project and is being run at the Medical Research Council–funded London School of Tropical Medicine center in Gambia. Beate Kampmann, MD, PhD, of Imperial College London, England, is the project lead. It is due to complete in 2022. GaPs seeks to enroll 600 mother/infant pairs and randomize the mothers to either an acellular pertussis booster in pregnancy or a tetanus toxoid control vaccine. Infants are subsequently randomized to an acellular or whole-cell pertussis schedule of primary immunization. The vaccine doses are being given at 2, 3, and 4 months. The primary endpoint is a serological finding being measured at 9 months of age, when the infant would usually receive yellow fever, measles, and rubella vaccination.
GaPs has a number of pathways. Within each of the four arms generated by the two randomizations, the maternal randomization and the infant randomization, there are five subgroups. They are designed to study time points in subgroups A and B after the first dose in more detail, looking at the innate immune responses using gene expression. It will enable researchers to study adaptive immune responses to T cells and B cells after the second dose of vaccine. By employing a range of subgroups, the team can explore the immune profile using the assays referred to above. Such information should provide new insights into the differences between acellular and whole-cell vaccines.
The AWARE study
AWARE is the sister study to GaPs and looks at the acellular/whole pertussis issue. Because many developed countries, such as the United Kingdom, have established maternal immunization programs, it is not possible to randomize mothers. Consequently, researchers have opted to recruit infants of mothers who have received an acellular vaccine in pregnancy and randomize them to either an acellular schedule of primary immunization or a whole-cell schedule.
The selected vaccine is ComVac5 from Bharat Biotech. This whole-cell vaccine differs from that used in Gambia. An early obstacle for AWARE has been seeking permission to import a non-conventional vaccine into Europe. It has delayed the anticipated end date to 2023. Participating infants will receive a two-dose schedule at 2 and 4 months of age per their randomization; then, both groups will go on to receive an acellular pertussis booster at 12 months. At all time points, the team will sample blood for cells and serum, as well as mucosal fluid from the nose. Because the mucosal surface is where the action is, this approach will likely generate new data around antibody responses.
The MIFI
The Pertussis Maternal Immunization Study in Finland is being run by Jussi Mertsola, of the University of Turku, Finland, and Qiushui He, of the National Public Health Institute, Turku. It is due to complete in late 2021. Where, in the United Kingdom, researchers are unable to randomize mothers because of the current guidelines, researchers in Finland do not have a maternal immunization program to consider. MIFI will randomize 80 mothers, 40 to immunization with acellular pertussis and 40 to a control group. Dr. Kelly stated that whole cell vaccines are not available for use in Finland. Participants will receive a two-dose schedule at 3 and 5 months. Blood samples will then be taken to compare the serological and cellular responses, which will help researchers understand the effects of maternal immunization. In addition, there will be sampling of mucosal fluid using a device that collects a standardized aliquot of fluid.
The BERT study
The final clinical element of PERISCOPE presented by Dr. Kelly was the Booster against Pertussis study. This study is near completion. It seeks to examine the use of an acellular booster across different age groups and three countries: the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and Finland. The study is being coordinated by Guy Berbers, PhD, at the National Institute for Public Health and the Environment in the Netherlands.
BERT comprises four cohorts (A, B, C, D) of different ages: 7-10 years (36 participants), 11-15 years (36 participants), mid-adult (25 participants), and older age (25 participants). After receiving an acellular booster, participants will undergo intense sampling. Sampling will take place immediately after immunization at day 7 and look at adaptive effects, then again at day 28 and day 365.
Because some participants will have already received whole cell or acellular vaccination, this approach will allow researchers to look at the effects of priming (i.e., how long the B cell/T cell antibody responses last).
Involving different countries across Europe ensures wide applicability of results, but also allows researchers to compare the effects of very different immunization histories.
At the end of this ESPID session, Dimitri Diavatopoulos, PhD, assistant professor at the Radboud University Medical Centre Nijmegen, the Netherlands, commented that a future problem in studying pertussis vaccines and their potential clinical application is that most vaccination schedules now involve combination products. Obtaining a stand-alone vaccination may prove difficult, and there may be resistance if it complicates current vaccination programs.
Dr. Kelly acknowledged funding for the PERISCOPE project from GlaxoSmithKline and Pasteur Sanofi.
With increasing whooping cough numbers, developing an effective new vaccine against Bordetella pertussis is a priority. Results from the multifactorial PERISCOPE Project will help scientists and clinicians move forward.
Dominic Kelly, PhD, talked about vaccine-induced immunity and provided an overview of ongoing clinical trials in the PERISCOPE (Pertussis Correlates of Protection Europe) project in a key research session at the start of the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. Dr. Kelly, a pediatrician at the Children’s Hospital in Oxford and a member of the Oxford Vaccines Group, leads one of the studies in the project looking at infant vaccination.
Dr. Kelly began his presentation by showing a figure depicting where vaccine-induced immunity fits into the larger suite of clinical studies. These studies involve mouse models, human challenge models, and infection patients. A key theme is the use of a core group of immunoassays across all studies, with the hope that they will allow effective cross comparisons.
Dr. Kelly stated, “If we find a correlate of protection in the challenge model, we can then interpret the vaccine studies in the light of that because we are using standardized constant immunoassays.”
The assays being used depend in part on the specific study and the volume of blood available. They will generally include Bordetella-specific antibody and functional antibody assays, as well as interesting studies collecting mucosal samples from infants and adults to look at serological responses. Also under examination are a range of enzyme-linked immune absorbent spot, flow cytometry, and culture techniques looking at Memory B cells, T cells, and gene expression.
Complementing these assay studies, PERISCOPE includes a series of clinical investigations designed to throw light on three areas of interest, described below:
First, researchers hope to gain a better understanding regarding the effects of the original whole cell vaccine versus the current acellular variety. The former uses an inactivated version of the whole organism. Epidemiological studies, animal data, and experience in the field demonstrate that whole-cell vaccination results in a broad, long-lasting, and effective immune response.
By comparison, the acellular pertussis vaccine consists of between three and five protein components, which are purified from cultured Bordetella pertussis. While it is an effective vaccine, its effects are less durable; routine use in some countries is associated with cyclical outbreaks of increasing severity.
A second issue for researchers involved in the PERISCOPE project concerns the effects of maternal immunization. In the United Kingdom in 2012, for example, an increasing number of cases were noted 6-7 years after adoption of an acellular vaccine for routine vaccination in the 2nd-3rd trimester of pregnancy. Vaccination appears to effectively control neonatal disease, but whether this influences infant immune responses and long-term control of pertussis for a population is unknown.
Finally, the group is interested in the effects of an acellular booster across all age groups. While the effects may be short-lived, the booster is a potential strategy for controlling a population by repeated boosting of immunity. This is another area where using novel immunoassays may aid better understanding.
To find answers, the consortium has established four studies: the Gambia Pertussis study (GaPs) in Gambia and AWARE, the sister study to GaPs in the United Kingdom, addressing the acellular pertussis versus cellular pertussis question; the Pertussis Maternal Immunization Study in Finland (MIFI) addressing maternal immunization; and the Booster against Pertussis (BERT) study across three countries (U.K., the Netherlands, and Finland) looking at acellular booster across age groups.
Gambia pertussis study
GaPs is the largest single study in the project and is being run at the Medical Research Council–funded London School of Tropical Medicine center in Gambia. Beate Kampmann, MD, PhD, of Imperial College London, England, is the project lead. It is due to complete in 2022. GaPs seeks to enroll 600 mother/infant pairs and randomize the mothers to either an acellular pertussis booster in pregnancy or a tetanus toxoid control vaccine. Infants are subsequently randomized to an acellular or whole-cell pertussis schedule of primary immunization. The vaccine doses are being given at 2, 3, and 4 months. The primary endpoint is a serological finding being measured at 9 months of age, when the infant would usually receive yellow fever, measles, and rubella vaccination.
GaPs has a number of pathways. Within each of the four arms generated by the two randomizations, the maternal randomization and the infant randomization, there are five subgroups. They are designed to study time points in subgroups A and B after the first dose in more detail, looking at the innate immune responses using gene expression. It will enable researchers to study adaptive immune responses to T cells and B cells after the second dose of vaccine. By employing a range of subgroups, the team can explore the immune profile using the assays referred to above. Such information should provide new insights into the differences between acellular and whole-cell vaccines.
The AWARE study
AWARE is the sister study to GaPs and looks at the acellular/whole pertussis issue. Because many developed countries, such as the United Kingdom, have established maternal immunization programs, it is not possible to randomize mothers. Consequently, researchers have opted to recruit infants of mothers who have received an acellular vaccine in pregnancy and randomize them to either an acellular schedule of primary immunization or a whole-cell schedule.
The selected vaccine is ComVac5 from Bharat Biotech. This whole-cell vaccine differs from that used in Gambia. An early obstacle for AWARE has been seeking permission to import a non-conventional vaccine into Europe. It has delayed the anticipated end date to 2023. Participating infants will receive a two-dose schedule at 2 and 4 months of age per their randomization; then, both groups will go on to receive an acellular pertussis booster at 12 months. At all time points, the team will sample blood for cells and serum, as well as mucosal fluid from the nose. Because the mucosal surface is where the action is, this approach will likely generate new data around antibody responses.
The MIFI
The Pertussis Maternal Immunization Study in Finland is being run by Jussi Mertsola, of the University of Turku, Finland, and Qiushui He, of the National Public Health Institute, Turku. It is due to complete in late 2021. Where, in the United Kingdom, researchers are unable to randomize mothers because of the current guidelines, researchers in Finland do not have a maternal immunization program to consider. MIFI will randomize 80 mothers, 40 to immunization with acellular pertussis and 40 to a control group. Dr. Kelly stated that whole cell vaccines are not available for use in Finland. Participants will receive a two-dose schedule at 3 and 5 months. Blood samples will then be taken to compare the serological and cellular responses, which will help researchers understand the effects of maternal immunization. In addition, there will be sampling of mucosal fluid using a device that collects a standardized aliquot of fluid.
The BERT study
The final clinical element of PERISCOPE presented by Dr. Kelly was the Booster against Pertussis study. This study is near completion. It seeks to examine the use of an acellular booster across different age groups and three countries: the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and Finland. The study is being coordinated by Guy Berbers, PhD, at the National Institute for Public Health and the Environment in the Netherlands.
BERT comprises four cohorts (A, B, C, D) of different ages: 7-10 years (36 participants), 11-15 years (36 participants), mid-adult (25 participants), and older age (25 participants). After receiving an acellular booster, participants will undergo intense sampling. Sampling will take place immediately after immunization at day 7 and look at adaptive effects, then again at day 28 and day 365.
Because some participants will have already received whole cell or acellular vaccination, this approach will allow researchers to look at the effects of priming (i.e., how long the B cell/T cell antibody responses last).
Involving different countries across Europe ensures wide applicability of results, but also allows researchers to compare the effects of very different immunization histories.
At the end of this ESPID session, Dimitri Diavatopoulos, PhD, assistant professor at the Radboud University Medical Centre Nijmegen, the Netherlands, commented that a future problem in studying pertussis vaccines and their potential clinical application is that most vaccination schedules now involve combination products. Obtaining a stand-alone vaccination may prove difficult, and there may be resistance if it complicates current vaccination programs.
Dr. Kelly acknowledged funding for the PERISCOPE project from GlaxoSmithKline and Pasteur Sanofi.
With increasing whooping cough numbers, developing an effective new vaccine against Bordetella pertussis is a priority. Results from the multifactorial PERISCOPE Project will help scientists and clinicians move forward.
Dominic Kelly, PhD, talked about vaccine-induced immunity and provided an overview of ongoing clinical trials in the PERISCOPE (Pertussis Correlates of Protection Europe) project in a key research session at the start of the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. Dr. Kelly, a pediatrician at the Children’s Hospital in Oxford and a member of the Oxford Vaccines Group, leads one of the studies in the project looking at infant vaccination.
Dr. Kelly began his presentation by showing a figure depicting where vaccine-induced immunity fits into the larger suite of clinical studies. These studies involve mouse models, human challenge models, and infection patients. A key theme is the use of a core group of immunoassays across all studies, with the hope that they will allow effective cross comparisons.
Dr. Kelly stated, “If we find a correlate of protection in the challenge model, we can then interpret the vaccine studies in the light of that because we are using standardized constant immunoassays.”
The assays being used depend in part on the specific study and the volume of blood available. They will generally include Bordetella-specific antibody and functional antibody assays, as well as interesting studies collecting mucosal samples from infants and adults to look at serological responses. Also under examination are a range of enzyme-linked immune absorbent spot, flow cytometry, and culture techniques looking at Memory B cells, T cells, and gene expression.
Complementing these assay studies, PERISCOPE includes a series of clinical investigations designed to throw light on three areas of interest, described below:
First, researchers hope to gain a better understanding regarding the effects of the original whole cell vaccine versus the current acellular variety. The former uses an inactivated version of the whole organism. Epidemiological studies, animal data, and experience in the field demonstrate that whole-cell vaccination results in a broad, long-lasting, and effective immune response.
By comparison, the acellular pertussis vaccine consists of between three and five protein components, which are purified from cultured Bordetella pertussis. While it is an effective vaccine, its effects are less durable; routine use in some countries is associated with cyclical outbreaks of increasing severity.
A second issue for researchers involved in the PERISCOPE project concerns the effects of maternal immunization. In the United Kingdom in 2012, for example, an increasing number of cases were noted 6-7 years after adoption of an acellular vaccine for routine vaccination in the 2nd-3rd trimester of pregnancy. Vaccination appears to effectively control neonatal disease, but whether this influences infant immune responses and long-term control of pertussis for a population is unknown.
Finally, the group is interested in the effects of an acellular booster across all age groups. While the effects may be short-lived, the booster is a potential strategy for controlling a population by repeated boosting of immunity. This is another area where using novel immunoassays may aid better understanding.
To find answers, the consortium has established four studies: the Gambia Pertussis study (GaPs) in Gambia and AWARE, the sister study to GaPs in the United Kingdom, addressing the acellular pertussis versus cellular pertussis question; the Pertussis Maternal Immunization Study in Finland (MIFI) addressing maternal immunization; and the Booster against Pertussis (BERT) study across three countries (U.K., the Netherlands, and Finland) looking at acellular booster across age groups.
Gambia pertussis study
GaPs is the largest single study in the project and is being run at the Medical Research Council–funded London School of Tropical Medicine center in Gambia. Beate Kampmann, MD, PhD, of Imperial College London, England, is the project lead. It is due to complete in 2022. GaPs seeks to enroll 600 mother/infant pairs and randomize the mothers to either an acellular pertussis booster in pregnancy or a tetanus toxoid control vaccine. Infants are subsequently randomized to an acellular or whole-cell pertussis schedule of primary immunization. The vaccine doses are being given at 2, 3, and 4 months. The primary endpoint is a serological finding being measured at 9 months of age, when the infant would usually receive yellow fever, measles, and rubella vaccination.
GaPs has a number of pathways. Within each of the four arms generated by the two randomizations, the maternal randomization and the infant randomization, there are five subgroups. They are designed to study time points in subgroups A and B after the first dose in more detail, looking at the innate immune responses using gene expression. It will enable researchers to study adaptive immune responses to T cells and B cells after the second dose of vaccine. By employing a range of subgroups, the team can explore the immune profile using the assays referred to above. Such information should provide new insights into the differences between acellular and whole-cell vaccines.
The AWARE study
AWARE is the sister study to GaPs and looks at the acellular/whole pertussis issue. Because many developed countries, such as the United Kingdom, have established maternal immunization programs, it is not possible to randomize mothers. Consequently, researchers have opted to recruit infants of mothers who have received an acellular vaccine in pregnancy and randomize them to either an acellular schedule of primary immunization or a whole-cell schedule.
The selected vaccine is ComVac5 from Bharat Biotech. This whole-cell vaccine differs from that used in Gambia. An early obstacle for AWARE has been seeking permission to import a non-conventional vaccine into Europe. It has delayed the anticipated end date to 2023. Participating infants will receive a two-dose schedule at 2 and 4 months of age per their randomization; then, both groups will go on to receive an acellular pertussis booster at 12 months. At all time points, the team will sample blood for cells and serum, as well as mucosal fluid from the nose. Because the mucosal surface is where the action is, this approach will likely generate new data around antibody responses.
The MIFI
The Pertussis Maternal Immunization Study in Finland is being run by Jussi Mertsola, of the University of Turku, Finland, and Qiushui He, of the National Public Health Institute, Turku. It is due to complete in late 2021. Where, in the United Kingdom, researchers are unable to randomize mothers because of the current guidelines, researchers in Finland do not have a maternal immunization program to consider. MIFI will randomize 80 mothers, 40 to immunization with acellular pertussis and 40 to a control group. Dr. Kelly stated that whole cell vaccines are not available for use in Finland. Participants will receive a two-dose schedule at 3 and 5 months. Blood samples will then be taken to compare the serological and cellular responses, which will help researchers understand the effects of maternal immunization. In addition, there will be sampling of mucosal fluid using a device that collects a standardized aliquot of fluid.
The BERT study
The final clinical element of PERISCOPE presented by Dr. Kelly was the Booster against Pertussis study. This study is near completion. It seeks to examine the use of an acellular booster across different age groups and three countries: the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and Finland. The study is being coordinated by Guy Berbers, PhD, at the National Institute for Public Health and the Environment in the Netherlands.
BERT comprises four cohorts (A, B, C, D) of different ages: 7-10 years (36 participants), 11-15 years (36 participants), mid-adult (25 participants), and older age (25 participants). After receiving an acellular booster, participants will undergo intense sampling. Sampling will take place immediately after immunization at day 7 and look at adaptive effects, then again at day 28 and day 365.
Because some participants will have already received whole cell or acellular vaccination, this approach will allow researchers to look at the effects of priming (i.e., how long the B cell/T cell antibody responses last).
Involving different countries across Europe ensures wide applicability of results, but also allows researchers to compare the effects of very different immunization histories.
At the end of this ESPID session, Dimitri Diavatopoulos, PhD, assistant professor at the Radboud University Medical Centre Nijmegen, the Netherlands, commented that a future problem in studying pertussis vaccines and their potential clinical application is that most vaccination schedules now involve combination products. Obtaining a stand-alone vaccination may prove difficult, and there may be resistance if it complicates current vaccination programs.
Dr. Kelly acknowledged funding for the PERISCOPE project from GlaxoSmithKline and Pasteur Sanofi.
FROM ESPID 2020
Career Choices: Navy Psychiatry
In this Career Choices, Siddhi Bhivandkar, MD, spoke with Captain Paulette T. Cazares, MD, MPH. Dr. Cazares is Director for Mental Health at U.S. Navy Medicine Readiness and Training Command Okinawa, Japan. She also is Assistant Professor, Department of Psychiatry, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, and serves as Secretary of the American Medical Women’s Association, Schaumburg, Illinois.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What made you choose the Navy psychiatry track, and how did your training lead you towards this path?
Dr. Cazares: I had considered a career in the Navy early on in my education, and when I was ready to apply to medical school, I saw Uniformed Services University (USU) as one of my top choices. I wasn’t 100% sure, but after a tour and my interview, I was sold on serving those who serve.
During my clinical rotations at USU, I had great experiences in inpatient and emergency psychiatry. I became fascinated with understanding all I could about brain circuitry and chemistry, and how that interacts with the environment to create or protect individuals from disease. Once I talked with some mentors, it became clear to me that I would love a career in psychiatry, and that remains true today.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What are some of the pros and cons of working in Navy psychiatry?
Dr. Cazares: As a Navy psychiatrist, I have found great reward in caring for our nation’s volunteer force. I have had wonderful colleagues with whom I have deployed, and with whom I have served in both small military hospitals and large military training and academic centers. I have been able to work in research in military mental health, and feel I have specifically advanced the field of women’s mental health in the Navy.
I had 4 children while I have been on active duty, and had paid maternity leave for all of them, as well as practices that protected my choice to breastfeed and pump, even after returning to work. I have moved to areas of the country I didn’t expect to with the Navy, and my husband’s career took unexpected turns as a result. While this can be seen as a challenge, it can also be a surprisingly rewarding experience, seeing areas of our nation and world that I otherwise would not have seen. I have deployed and been away from family. While that was a challenge, my family came through it very strong, and I found myself a more humble human and a better clinician as a result of that time.
Dr. Bhivandkar: Based on your personal experience, what should one consider when choosing a Navy psychiatry program?
Dr. Cazares: In considering a Navy training program, one should consider that in the military, our patient population is generally young and healthy, yet also exposed to unique occupational stressors. This means that we generally see routine mental health diagnoses, and some early-break severe cases. We do not typically follow long-term patients with chronic mental illness, because those patients tend to be medically retired from active duty service.
Continue to: We see many unique populations...
We see many unique populations that have specific health care needs, including service members who work on submarines, who are pilots or military police members, and those who handle and manage weapons. We get to learn the unique balance between serving our patients, and the units they work for and in. We see the impact of occupational stress on individuals, and are part of the multidisciplinary team that helps to build resilience in our young service members.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What are some of the career options and work settings for Navy psychiatrists?
Dr. Cazares: My peers and I have worked across both operational and multiple hospital settings, with both the US Marine Corps, as well as the US Navy. Psychiatrists can apply for fellowship, as the Navy regularly trains child and adolescent psychiatrists, as well as those who want to specialize in addiction psychiatry.
We can work in large Navy medical centers on faculty, in community-style Navy hospitals both in the United States and overseas, as well as on ships, with the Marines, or in headquarters jobs, advising on policy and the future of the military health system.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What are some of the challenges of working in this field?
Dr. Cazares: Health care and the military are both demanding career fields. Like many areas of medicine, work-life harmony is an important part of a career in Navy psychiatry. I work hard to balance my own needs, and model this for those I lead.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What advice do you have for those contemplating a career in Navy psychiatry?
Dr. Cazares: Consider joining a team that offers incredible purpose. I have served wonderful patients and had incredibly impressive colleagues, and I am grateful for the choice I made to take an oath and wear the uniform.
In this Career Choices, Siddhi Bhivandkar, MD, spoke with Captain Paulette T. Cazares, MD, MPH. Dr. Cazares is Director for Mental Health at U.S. Navy Medicine Readiness and Training Command Okinawa, Japan. She also is Assistant Professor, Department of Psychiatry, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, and serves as Secretary of the American Medical Women’s Association, Schaumburg, Illinois.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What made you choose the Navy psychiatry track, and how did your training lead you towards this path?
Dr. Cazares: I had considered a career in the Navy early on in my education, and when I was ready to apply to medical school, I saw Uniformed Services University (USU) as one of my top choices. I wasn’t 100% sure, but after a tour and my interview, I was sold on serving those who serve.
During my clinical rotations at USU, I had great experiences in inpatient and emergency psychiatry. I became fascinated with understanding all I could about brain circuitry and chemistry, and how that interacts with the environment to create or protect individuals from disease. Once I talked with some mentors, it became clear to me that I would love a career in psychiatry, and that remains true today.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What are some of the pros and cons of working in Navy psychiatry?
Dr. Cazares: As a Navy psychiatrist, I have found great reward in caring for our nation’s volunteer force. I have had wonderful colleagues with whom I have deployed, and with whom I have served in both small military hospitals and large military training and academic centers. I have been able to work in research in military mental health, and feel I have specifically advanced the field of women’s mental health in the Navy.
I had 4 children while I have been on active duty, and had paid maternity leave for all of them, as well as practices that protected my choice to breastfeed and pump, even after returning to work. I have moved to areas of the country I didn’t expect to with the Navy, and my husband’s career took unexpected turns as a result. While this can be seen as a challenge, it can also be a surprisingly rewarding experience, seeing areas of our nation and world that I otherwise would not have seen. I have deployed and been away from family. While that was a challenge, my family came through it very strong, and I found myself a more humble human and a better clinician as a result of that time.
Dr. Bhivandkar: Based on your personal experience, what should one consider when choosing a Navy psychiatry program?
Dr. Cazares: In considering a Navy training program, one should consider that in the military, our patient population is generally young and healthy, yet also exposed to unique occupational stressors. This means that we generally see routine mental health diagnoses, and some early-break severe cases. We do not typically follow long-term patients with chronic mental illness, because those patients tend to be medically retired from active duty service.
Continue to: We see many unique populations...
We see many unique populations that have specific health care needs, including service members who work on submarines, who are pilots or military police members, and those who handle and manage weapons. We get to learn the unique balance between serving our patients, and the units they work for and in. We see the impact of occupational stress on individuals, and are part of the multidisciplinary team that helps to build resilience in our young service members.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What are some of the career options and work settings for Navy psychiatrists?
Dr. Cazares: My peers and I have worked across both operational and multiple hospital settings, with both the US Marine Corps, as well as the US Navy. Psychiatrists can apply for fellowship, as the Navy regularly trains child and adolescent psychiatrists, as well as those who want to specialize in addiction psychiatry.
We can work in large Navy medical centers on faculty, in community-style Navy hospitals both in the United States and overseas, as well as on ships, with the Marines, or in headquarters jobs, advising on policy and the future of the military health system.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What are some of the challenges of working in this field?
Dr. Cazares: Health care and the military are both demanding career fields. Like many areas of medicine, work-life harmony is an important part of a career in Navy psychiatry. I work hard to balance my own needs, and model this for those I lead.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What advice do you have for those contemplating a career in Navy psychiatry?
Dr. Cazares: Consider joining a team that offers incredible purpose. I have served wonderful patients and had incredibly impressive colleagues, and I am grateful for the choice I made to take an oath and wear the uniform.
In this Career Choices, Siddhi Bhivandkar, MD, spoke with Captain Paulette T. Cazares, MD, MPH. Dr. Cazares is Director for Mental Health at U.S. Navy Medicine Readiness and Training Command Okinawa, Japan. She also is Assistant Professor, Department of Psychiatry, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, and serves as Secretary of the American Medical Women’s Association, Schaumburg, Illinois.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What made you choose the Navy psychiatry track, and how did your training lead you towards this path?
Dr. Cazares: I had considered a career in the Navy early on in my education, and when I was ready to apply to medical school, I saw Uniformed Services University (USU) as one of my top choices. I wasn’t 100% sure, but after a tour and my interview, I was sold on serving those who serve.
During my clinical rotations at USU, I had great experiences in inpatient and emergency psychiatry. I became fascinated with understanding all I could about brain circuitry and chemistry, and how that interacts with the environment to create or protect individuals from disease. Once I talked with some mentors, it became clear to me that I would love a career in psychiatry, and that remains true today.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What are some of the pros and cons of working in Navy psychiatry?
Dr. Cazares: As a Navy psychiatrist, I have found great reward in caring for our nation’s volunteer force. I have had wonderful colleagues with whom I have deployed, and with whom I have served in both small military hospitals and large military training and academic centers. I have been able to work in research in military mental health, and feel I have specifically advanced the field of women’s mental health in the Navy.
I had 4 children while I have been on active duty, and had paid maternity leave for all of them, as well as practices that protected my choice to breastfeed and pump, even after returning to work. I have moved to areas of the country I didn’t expect to with the Navy, and my husband’s career took unexpected turns as a result. While this can be seen as a challenge, it can also be a surprisingly rewarding experience, seeing areas of our nation and world that I otherwise would not have seen. I have deployed and been away from family. While that was a challenge, my family came through it very strong, and I found myself a more humble human and a better clinician as a result of that time.
Dr. Bhivandkar: Based on your personal experience, what should one consider when choosing a Navy psychiatry program?
Dr. Cazares: In considering a Navy training program, one should consider that in the military, our patient population is generally young and healthy, yet also exposed to unique occupational stressors. This means that we generally see routine mental health diagnoses, and some early-break severe cases. We do not typically follow long-term patients with chronic mental illness, because those patients tend to be medically retired from active duty service.
Continue to: We see many unique populations...
We see many unique populations that have specific health care needs, including service members who work on submarines, who are pilots or military police members, and those who handle and manage weapons. We get to learn the unique balance between serving our patients, and the units they work for and in. We see the impact of occupational stress on individuals, and are part of the multidisciplinary team that helps to build resilience in our young service members.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What are some of the career options and work settings for Navy psychiatrists?
Dr. Cazares: My peers and I have worked across both operational and multiple hospital settings, with both the US Marine Corps, as well as the US Navy. Psychiatrists can apply for fellowship, as the Navy regularly trains child and adolescent psychiatrists, as well as those who want to specialize in addiction psychiatry.
We can work in large Navy medical centers on faculty, in community-style Navy hospitals both in the United States and overseas, as well as on ships, with the Marines, or in headquarters jobs, advising on policy and the future of the military health system.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What are some of the challenges of working in this field?
Dr. Cazares: Health care and the military are both demanding career fields. Like many areas of medicine, work-life harmony is an important part of a career in Navy psychiatry. I work hard to balance my own needs, and model this for those I lead.
Dr. Bhivandkar: What advice do you have for those contemplating a career in Navy psychiatry?
Dr. Cazares: Consider joining a team that offers incredible purpose. I have served wonderful patients and had incredibly impressive colleagues, and I am grateful for the choice I made to take an oath and wear the uniform.