User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Loan forgiveness and med school debt: What about me?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I run the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Many of you know that President Biden created a loan forgiveness program, forgiving up to $10,000 against federal student loans, including graduate and undergraduate education. The Department of Education is supposed to provide up to $20,000 in debt cancellation to Pell Grant recipients who have loans that are held by the Department of Education. Borrowers can get this relief if their income is less than $125,000 for an individual or $250,000 for married couples.
Many people have looked at this and said, “Hey, wait a minute. I paid off my loans. I didn’t get any reimbursement. That isn’t fair.”
who often still have huge amounts of debt, and either because of the income limits or because they don’t qualify because this debt was accrued long in the past, they’re saying, “What about me? Don’t you want to give any relief to me?”
This is a topic near and dear to my heart because I happen to be at a medical school, NYU, that has decided for the two medical schools it runs – our main campus, NYU in Manhattan and NYU Langone out on Long Island – that we’re going to go tuition free. We’ve done it for a couple of years.
We did it because I think all the administrators and faculty understood the tremendous burden that debt poses on people who both carry forward their undergraduate debt and then have medical school debt. This really leads to very difficult situations – which we have great empathy for – about what specialty you’re going to go into, whether you have to moonlight, and how you’re going to manage a huge burden of debt.
Many people don’t have sympathy out in the public. They say doctors make a large amount of money and they live a nice lifestyle, so we’re not going to relieve their debt. The reality is that, whoever you are, short of Bill Gates or Elon Musk, having hundreds of thousands of dollars of debt is no easy task to live with and to work off.
Still, when we created free tuition at NYU for our medical school, there were many people who paid high tuition fees in the past. Some of them said to us, “What about me?” We decided not to try to do anything retrospectively. The plan was to build up enough money so that we could handle no-cost tuition going forward. We didn’t really have it in our pocketbook to help people who’d already paid their debts or were saddled with NYU debt. Is it fair? No, it’s probably not fair, but it’s an improvement.
That’s what I want people to think about who are saying, “What about my medical school debt? What about my undergraduate plus medical school debt?” I think we should be grateful when efforts are being made to reduce very burdensome student loans that people have. It’s good to give that benefit and move it forward.
Does that mean no one should get anything unless everyone with any kind of debt from school is covered? I don’t think so. I don’t think that’s fair either.
It is possible that we could continue to agitate politically and say, let’s go after some of the health care debt. Let’s go after some of the things that are still driving people to have to work more than they would or to choose specialties that they really don’t want to be in because they have to make up that debt.
It doesn’t mean the last word has been said about the politics of debt relief or, for that matter, the price of going to medical school in the first place and trying to see whether that can be driven down.
I don’t think it’s right to say, “If I can’t benefit, given the huge burden that I’m carrying, then I’m not going to try to give relief to others.” I think we’re relieving debt to the extent that we can do it. The nation can afford it. Going forward is a good thing. It’s wrong to create those gigantic debts in the first place.
What are we going to do about the past? We may decide that we need some sort of forgiveness or reparations for loans that were built up for others going backwards. I wouldn’t hold hostage the future and our children to what was probably a very poor, unethical practice about saddling doctors and others in the past with huge debt.
I’m Art Caplan at the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thank you for watching.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I run the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Many of you know that President Biden created a loan forgiveness program, forgiving up to $10,000 against federal student loans, including graduate and undergraduate education. The Department of Education is supposed to provide up to $20,000 in debt cancellation to Pell Grant recipients who have loans that are held by the Department of Education. Borrowers can get this relief if their income is less than $125,000 for an individual or $250,000 for married couples.
Many people have looked at this and said, “Hey, wait a minute. I paid off my loans. I didn’t get any reimbursement. That isn’t fair.”
who often still have huge amounts of debt, and either because of the income limits or because they don’t qualify because this debt was accrued long in the past, they’re saying, “What about me? Don’t you want to give any relief to me?”
This is a topic near and dear to my heart because I happen to be at a medical school, NYU, that has decided for the two medical schools it runs – our main campus, NYU in Manhattan and NYU Langone out on Long Island – that we’re going to go tuition free. We’ve done it for a couple of years.
We did it because I think all the administrators and faculty understood the tremendous burden that debt poses on people who both carry forward their undergraduate debt and then have medical school debt. This really leads to very difficult situations – which we have great empathy for – about what specialty you’re going to go into, whether you have to moonlight, and how you’re going to manage a huge burden of debt.
Many people don’t have sympathy out in the public. They say doctors make a large amount of money and they live a nice lifestyle, so we’re not going to relieve their debt. The reality is that, whoever you are, short of Bill Gates or Elon Musk, having hundreds of thousands of dollars of debt is no easy task to live with and to work off.
Still, when we created free tuition at NYU for our medical school, there were many people who paid high tuition fees in the past. Some of them said to us, “What about me?” We decided not to try to do anything retrospectively. The plan was to build up enough money so that we could handle no-cost tuition going forward. We didn’t really have it in our pocketbook to help people who’d already paid their debts or were saddled with NYU debt. Is it fair? No, it’s probably not fair, but it’s an improvement.
That’s what I want people to think about who are saying, “What about my medical school debt? What about my undergraduate plus medical school debt?” I think we should be grateful when efforts are being made to reduce very burdensome student loans that people have. It’s good to give that benefit and move it forward.
Does that mean no one should get anything unless everyone with any kind of debt from school is covered? I don’t think so. I don’t think that’s fair either.
It is possible that we could continue to agitate politically and say, let’s go after some of the health care debt. Let’s go after some of the things that are still driving people to have to work more than they would or to choose specialties that they really don’t want to be in because they have to make up that debt.
It doesn’t mean the last word has been said about the politics of debt relief or, for that matter, the price of going to medical school in the first place and trying to see whether that can be driven down.
I don’t think it’s right to say, “If I can’t benefit, given the huge burden that I’m carrying, then I’m not going to try to give relief to others.” I think we’re relieving debt to the extent that we can do it. The nation can afford it. Going forward is a good thing. It’s wrong to create those gigantic debts in the first place.
What are we going to do about the past? We may decide that we need some sort of forgiveness or reparations for loans that were built up for others going backwards. I wouldn’t hold hostage the future and our children to what was probably a very poor, unethical practice about saddling doctors and others in the past with huge debt.
I’m Art Caplan at the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thank you for watching.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I run the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Many of you know that President Biden created a loan forgiveness program, forgiving up to $10,000 against federal student loans, including graduate and undergraduate education. The Department of Education is supposed to provide up to $20,000 in debt cancellation to Pell Grant recipients who have loans that are held by the Department of Education. Borrowers can get this relief if their income is less than $125,000 for an individual or $250,000 for married couples.
Many people have looked at this and said, “Hey, wait a minute. I paid off my loans. I didn’t get any reimbursement. That isn’t fair.”
who often still have huge amounts of debt, and either because of the income limits or because they don’t qualify because this debt was accrued long in the past, they’re saying, “What about me? Don’t you want to give any relief to me?”
This is a topic near and dear to my heart because I happen to be at a medical school, NYU, that has decided for the two medical schools it runs – our main campus, NYU in Manhattan and NYU Langone out on Long Island – that we’re going to go tuition free. We’ve done it for a couple of years.
We did it because I think all the administrators and faculty understood the tremendous burden that debt poses on people who both carry forward their undergraduate debt and then have medical school debt. This really leads to very difficult situations – which we have great empathy for – about what specialty you’re going to go into, whether you have to moonlight, and how you’re going to manage a huge burden of debt.
Many people don’t have sympathy out in the public. They say doctors make a large amount of money and they live a nice lifestyle, so we’re not going to relieve their debt. The reality is that, whoever you are, short of Bill Gates or Elon Musk, having hundreds of thousands of dollars of debt is no easy task to live with and to work off.
Still, when we created free tuition at NYU for our medical school, there were many people who paid high tuition fees in the past. Some of them said to us, “What about me?” We decided not to try to do anything retrospectively. The plan was to build up enough money so that we could handle no-cost tuition going forward. We didn’t really have it in our pocketbook to help people who’d already paid their debts or were saddled with NYU debt. Is it fair? No, it’s probably not fair, but it’s an improvement.
That’s what I want people to think about who are saying, “What about my medical school debt? What about my undergraduate plus medical school debt?” I think we should be grateful when efforts are being made to reduce very burdensome student loans that people have. It’s good to give that benefit and move it forward.
Does that mean no one should get anything unless everyone with any kind of debt from school is covered? I don’t think so. I don’t think that’s fair either.
It is possible that we could continue to agitate politically and say, let’s go after some of the health care debt. Let’s go after some of the things that are still driving people to have to work more than they would or to choose specialties that they really don’t want to be in because they have to make up that debt.
It doesn’t mean the last word has been said about the politics of debt relief or, for that matter, the price of going to medical school in the first place and trying to see whether that can be driven down.
I don’t think it’s right to say, “If I can’t benefit, given the huge burden that I’m carrying, then I’m not going to try to give relief to others.” I think we’re relieving debt to the extent that we can do it. The nation can afford it. Going forward is a good thing. It’s wrong to create those gigantic debts in the first place.
What are we going to do about the past? We may decide that we need some sort of forgiveness or reparations for loans that were built up for others going backwards. I wouldn’t hold hostage the future and our children to what was probably a very poor, unethical practice about saddling doctors and others in the past with huge debt.
I’m Art Caplan at the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thank you for watching.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The marked contrast in pandemic outcomes between Japan and the United States
This article was originally published Oct. 8 on Medscape Editor-In-Chief Eric Topol’s “Ground Truths” column on Substack.
Over time it has the least cumulative deaths per capita of any major country in the world. That’s without a zero-Covid policy or any national lockdowns, which is why I have not included China as a comparator.
Before we get into that data, let’s take a look at the age pyramids for Japan and the United States. The No. 1 risk factor for death from COVID-19 is advanced age, and you can see that in Japan about 25% of the population is age 65 and older, whereas in the United States that proportion is substantially reduced at 15%. Sure there are differences in comorbidities such as obesity and diabetes, but there is also the trade-off of a much higher population density in Japan.
Besides masks, which were distributed early on by the government to the population in Japan, there was the “Avoid the 3Cs” cluster-busting strategy, widely disseminated in the spring of 2020, leveraging Pareto’s 80-20 principle, long before there were any vaccines available. For a good portion of the pandemic, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan maintained a strict policy for border control, which while hard to quantify, may certainly have contributed to its success.
Besides these factors, once vaccines became available, Japan got the population with the primary series to 83% rapidly, even after getting a late start by many months compared with the United States, which has peaked at 68%. That’s a big gap.
But that gap got much worse when it came to boosters. Ninety-five percent of Japanese eligible compared with 40.8% of Americans have had a booster shot. Of note, that 95% in Japan pertains to the whole population. In the United States the percentage of people age 65 and older who have had two boosters is currently only 42%. I’ve previously reviewed the important lifesaving impact of two boosters among people age 65 and older from five independent studies during Omicron waves throughout the world.
Now let’s turn to cumulative fatalities in the two countries. There’s a huge, nearly ninefold difference, per capita. Using today’s Covid-19 Dashboard, there are cumulatively 45,533 deaths in Japan and 1,062,560 American deaths. That translates to 1 in 2,758 people in Japan compared with 1 in 315 Americans dying of COVID.
And if we look at excess mortality instead of confirmed COVID deaths, that enormous gap doesn’t change.
Obviously it would be good to have data for other COVID outcomes, such as hospitalizations, ICUs, and Long COVID, but they are not accessible.
Comparing Japan, the country that has fared the best, with the United States, one of the worst pandemic outcome results, leaves us with a sense that Prof Ian MacKay’s “Swiss cheese model” is the best explanation. It’s not just one thing. Masks, consistent evidence-based communication (3Cs) with attention to ventilation and air quality, and the outstanding uptake of vaccines and boosters all contributed to Japan’s success.
There is another factor to add to that model – Paxlovid. Its benefit of reducing hospitalizations and deaths for people over age 65 is unquestionable.
That’s why I had previously modified the Swiss cheese model to add Paxlovid.
But in the United States, where 15% of the population is 65 and older, they account for over 75% of the daily death toll, still in the range of 400 per day. Here, with a very high proportion of people age 65 and older left vulnerable without boosters, or primary vaccines, Paxlovid is only being given to less than 25% of the eligible (age 50+), and less people age 80 and older are getting Paxlovid than those age 45. The reasons that doctors are not prescribing it – worried about interactions for a 5-day course and rebound – are not substantiated.
Bottom line: In the United States we are not protecting our population anywhere near as well as Japan, as grossly evident by the fatalities among people at the highest risk. There needs to be far better uptake of boosters and use of Paxlovid in the age 65+ group, but the need for amped up protection is not at all restricted to this age subgroup. Across all age groups age 18 and over there is an 81% reduction of hospitalizations with two boosters with the most updated CDC data available, through the Omicron BA.5 wave.
No less the previous data through May 2022 showing protection from death across all ages with two boosters
And please don’t forget that around the world, over 20 million lives were saved, just in 2021, the first year of vaccines.
We can learn so much from a model country like Japan. Yes, we need nasal and variant-proof vaccines to effectively deal with the new variants that are already getting legs in places like XBB in Singapore and ones not on the radar yet. But right now we’ve got to do far better for people getting boosters and, when a person age 65 or older gets COVID, Paxlovid. Take a look at the Chris Hayes video segment when he pleaded for Americans to get a booster shot. Every day that vaccine waning of the U.S. population exceeds the small percentage of people who get a booster, our vulnerability increases. If we don’t get that on track, it’s likely going to be a rough winter ahead.
Dr. Topol is director of the Scripps Translational Science Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health and reported conflicts of interest involving Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Quest Diagnostics, and Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published Oct. 8 on Medscape Editor-In-Chief Eric Topol’s “Ground Truths” column on Substack.
Over time it has the least cumulative deaths per capita of any major country in the world. That’s without a zero-Covid policy or any national lockdowns, which is why I have not included China as a comparator.
Before we get into that data, let’s take a look at the age pyramids for Japan and the United States. The No. 1 risk factor for death from COVID-19 is advanced age, and you can see that in Japan about 25% of the population is age 65 and older, whereas in the United States that proportion is substantially reduced at 15%. Sure there are differences in comorbidities such as obesity and diabetes, but there is also the trade-off of a much higher population density in Japan.
Besides masks, which were distributed early on by the government to the population in Japan, there was the “Avoid the 3Cs” cluster-busting strategy, widely disseminated in the spring of 2020, leveraging Pareto’s 80-20 principle, long before there were any vaccines available. For a good portion of the pandemic, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan maintained a strict policy for border control, which while hard to quantify, may certainly have contributed to its success.
Besides these factors, once vaccines became available, Japan got the population with the primary series to 83% rapidly, even after getting a late start by many months compared with the United States, which has peaked at 68%. That’s a big gap.
But that gap got much worse when it came to boosters. Ninety-five percent of Japanese eligible compared with 40.8% of Americans have had a booster shot. Of note, that 95% in Japan pertains to the whole population. In the United States the percentage of people age 65 and older who have had two boosters is currently only 42%. I’ve previously reviewed the important lifesaving impact of two boosters among people age 65 and older from five independent studies during Omicron waves throughout the world.
Now let’s turn to cumulative fatalities in the two countries. There’s a huge, nearly ninefold difference, per capita. Using today’s Covid-19 Dashboard, there are cumulatively 45,533 deaths in Japan and 1,062,560 American deaths. That translates to 1 in 2,758 people in Japan compared with 1 in 315 Americans dying of COVID.
And if we look at excess mortality instead of confirmed COVID deaths, that enormous gap doesn’t change.
Obviously it would be good to have data for other COVID outcomes, such as hospitalizations, ICUs, and Long COVID, but they are not accessible.
Comparing Japan, the country that has fared the best, with the United States, one of the worst pandemic outcome results, leaves us with a sense that Prof Ian MacKay’s “Swiss cheese model” is the best explanation. It’s not just one thing. Masks, consistent evidence-based communication (3Cs) with attention to ventilation and air quality, and the outstanding uptake of vaccines and boosters all contributed to Japan’s success.
There is another factor to add to that model – Paxlovid. Its benefit of reducing hospitalizations and deaths for people over age 65 is unquestionable.
That’s why I had previously modified the Swiss cheese model to add Paxlovid.
But in the United States, where 15% of the population is 65 and older, they account for over 75% of the daily death toll, still in the range of 400 per day. Here, with a very high proportion of people age 65 and older left vulnerable without boosters, or primary vaccines, Paxlovid is only being given to less than 25% of the eligible (age 50+), and less people age 80 and older are getting Paxlovid than those age 45. The reasons that doctors are not prescribing it – worried about interactions for a 5-day course and rebound – are not substantiated.
Bottom line: In the United States we are not protecting our population anywhere near as well as Japan, as grossly evident by the fatalities among people at the highest risk. There needs to be far better uptake of boosters and use of Paxlovid in the age 65+ group, but the need for amped up protection is not at all restricted to this age subgroup. Across all age groups age 18 and over there is an 81% reduction of hospitalizations with two boosters with the most updated CDC data available, through the Omicron BA.5 wave.
No less the previous data through May 2022 showing protection from death across all ages with two boosters
And please don’t forget that around the world, over 20 million lives were saved, just in 2021, the first year of vaccines.
We can learn so much from a model country like Japan. Yes, we need nasal and variant-proof vaccines to effectively deal with the new variants that are already getting legs in places like XBB in Singapore and ones not on the radar yet. But right now we’ve got to do far better for people getting boosters and, when a person age 65 or older gets COVID, Paxlovid. Take a look at the Chris Hayes video segment when he pleaded for Americans to get a booster shot. Every day that vaccine waning of the U.S. population exceeds the small percentage of people who get a booster, our vulnerability increases. If we don’t get that on track, it’s likely going to be a rough winter ahead.
Dr. Topol is director of the Scripps Translational Science Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health and reported conflicts of interest involving Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Quest Diagnostics, and Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published Oct. 8 on Medscape Editor-In-Chief Eric Topol’s “Ground Truths” column on Substack.
Over time it has the least cumulative deaths per capita of any major country in the world. That’s without a zero-Covid policy or any national lockdowns, which is why I have not included China as a comparator.
Before we get into that data, let’s take a look at the age pyramids for Japan and the United States. The No. 1 risk factor for death from COVID-19 is advanced age, and you can see that in Japan about 25% of the population is age 65 and older, whereas in the United States that proportion is substantially reduced at 15%. Sure there are differences in comorbidities such as obesity and diabetes, but there is also the trade-off of a much higher population density in Japan.
Besides masks, which were distributed early on by the government to the population in Japan, there was the “Avoid the 3Cs” cluster-busting strategy, widely disseminated in the spring of 2020, leveraging Pareto’s 80-20 principle, long before there were any vaccines available. For a good portion of the pandemic, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan maintained a strict policy for border control, which while hard to quantify, may certainly have contributed to its success.
Besides these factors, once vaccines became available, Japan got the population with the primary series to 83% rapidly, even after getting a late start by many months compared with the United States, which has peaked at 68%. That’s a big gap.
But that gap got much worse when it came to boosters. Ninety-five percent of Japanese eligible compared with 40.8% of Americans have had a booster shot. Of note, that 95% in Japan pertains to the whole population. In the United States the percentage of people age 65 and older who have had two boosters is currently only 42%. I’ve previously reviewed the important lifesaving impact of two boosters among people age 65 and older from five independent studies during Omicron waves throughout the world.
Now let’s turn to cumulative fatalities in the two countries. There’s a huge, nearly ninefold difference, per capita. Using today’s Covid-19 Dashboard, there are cumulatively 45,533 deaths in Japan and 1,062,560 American deaths. That translates to 1 in 2,758 people in Japan compared with 1 in 315 Americans dying of COVID.
And if we look at excess mortality instead of confirmed COVID deaths, that enormous gap doesn’t change.
Obviously it would be good to have data for other COVID outcomes, such as hospitalizations, ICUs, and Long COVID, but they are not accessible.
Comparing Japan, the country that has fared the best, with the United States, one of the worst pandemic outcome results, leaves us with a sense that Prof Ian MacKay’s “Swiss cheese model” is the best explanation. It’s not just one thing. Masks, consistent evidence-based communication (3Cs) with attention to ventilation and air quality, and the outstanding uptake of vaccines and boosters all contributed to Japan’s success.
There is another factor to add to that model – Paxlovid. Its benefit of reducing hospitalizations and deaths for people over age 65 is unquestionable.
That’s why I had previously modified the Swiss cheese model to add Paxlovid.
But in the United States, where 15% of the population is 65 and older, they account for over 75% of the daily death toll, still in the range of 400 per day. Here, with a very high proportion of people age 65 and older left vulnerable without boosters, or primary vaccines, Paxlovid is only being given to less than 25% of the eligible (age 50+), and less people age 80 and older are getting Paxlovid than those age 45. The reasons that doctors are not prescribing it – worried about interactions for a 5-day course and rebound – are not substantiated.
Bottom line: In the United States we are not protecting our population anywhere near as well as Japan, as grossly evident by the fatalities among people at the highest risk. There needs to be far better uptake of boosters and use of Paxlovid in the age 65+ group, but the need for amped up protection is not at all restricted to this age subgroup. Across all age groups age 18 and over there is an 81% reduction of hospitalizations with two boosters with the most updated CDC data available, through the Omicron BA.5 wave.
No less the previous data through May 2022 showing protection from death across all ages with two boosters
And please don’t forget that around the world, over 20 million lives were saved, just in 2021, the first year of vaccines.
We can learn so much from a model country like Japan. Yes, we need nasal and variant-proof vaccines to effectively deal with the new variants that are already getting legs in places like XBB in Singapore and ones not on the radar yet. But right now we’ve got to do far better for people getting boosters and, when a person age 65 or older gets COVID, Paxlovid. Take a look at the Chris Hayes video segment when he pleaded for Americans to get a booster shot. Every day that vaccine waning of the U.S. population exceeds the small percentage of people who get a booster, our vulnerability increases. If we don’t get that on track, it’s likely going to be a rough winter ahead.
Dr. Topol is director of the Scripps Translational Science Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health and reported conflicts of interest involving Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Quest Diagnostics, and Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
For many, long COVID’s impacts go on and on, major study says
in the same time frame, a large study out of Scotland found.
Multiple studies are evaluating people with long COVID in the hopes of figuring out why some people experience debilitating symptoms long after their primary infection ends and others either do not or recover more quickly.
This current study is notable for its large size – 96,238 people. Researchers checked in with participants at 6, 12, and 18 months, and included a group of people never infected with the coronavirus to help investigators make a stronger case.
“A lot of the symptoms of long COVID are nonspecific and therefore can occur in people never infected,” says senior study author Jill P. Pell, MD, head of the School of Health and Wellbeing at the University of Glasgow in Scotland.
Ruling out coincidence
This study shows that people experienced a wide range of symptoms after becoming infected with COVID-19 at a significantly higher rate than those who were never infected, “thereby confirming that they were genuinely associated with COVID and not merely a coincidence,” she said.
Among 21,525 people who had COVID-19 and had symptoms, tiredness, headache and muscle aches or muscle weakness were the most common ongoing symptoms.
Loss of smell was almost nine times more likely in this group compared to the never-infected group in one analysis where researchers controlled for other possible factors. The risk for loss of taste was almost six times greater, followed by risk of breathlessness at three times higher.
Long COVID risk was highest after a severe original infection and among older people, women, Black, and South Asian populations, people with socioeconomic disadvantages, and those with more than one underlying health condition.
Adding up the 6% with no recovery after 18 months and 42% with partial recovery means that between 6 and 18 months following symptomatic coronavirus infection, almost half of those infected still experience persistent symptoms.
Vaccination validated
On the plus side, people vaccinated against COVID-19 before getting infected had a lower risk for some persistent symptoms. In addition, Dr. Pell and colleagues found no evidence that people who experienced asymptomatic infection were likely to experience long COVID symptoms or challenges with activities of daily living.
The findings of the Long-COVID in Scotland Study (Long-CISS) were published in the journal Nature Communications.
‘More long COVID than ever before’
“Unfortunately, these long COVID symptoms are not getting better as the cases of COVID get milder,” said Thomas Gut, DO, medical director for the post-COVID recovery program at Staten Island (N.Y.) University Hospital. “Quite the opposite – this infection has become so common in a community because it’s so mild and spreading so rapidly that we’re seeing more long COVID symptoms than ever before.”
Although most patients he sees with long COVID resolve their symptoms within 3-6 months, “We do see some patients who require short-term disability because their symptoms continue past 6 months and out to 2 years,” said Dr. Gut, a hospitalist at Staten Island University Hospital, a member hospital of Northwell Health.
Patients with fatigue and neurocognitive symptoms “have a very tough time going back to work. Short-term disability gives them the time and finances to pursue specialty care with cardiology, pulmonary, and neurocognitive testing,” he said.
Support the whole person
The burden of living with long COVID goes beyond the persistent symptoms. “Long COVID can have wide-ranging impacts – not only on health but also quality of life and activities of daily living [including] work, mobility, self-care and more,” Dr. Pell said. “So, people with long COVID need support relevant to their individual needs and this may extend beyond the health care sector, for example including social services, school or workplace.”
Still, Lisa Penziner, RN, founder of the COVID Long Haulers Support Group in Westchester and Long Island, N.Y., said while people with the most severe cases of COVID-19 tended to have the worst long COVID symptoms, they’re not the only ones.
“We saw many post-COVID members who had mild cases and their long-haul symptoms were worse weeks later than the virus itself,” said Md. Penziner.
She estimates that 80%-90% of her support group members recover within 6 months. “However, there are others who were experiencing symptoms for much longer.”
Respiratory treatment, physical therapy, and other follow-up doctor visits are common after 6 months, for example.
“Additionally, there is a mental health component to recovery as well, meaning that the patient must learn to live while experiencing lingering, long-haul COVID symptoms in work and daily life,” said Ms. Penziner, director of special projects at North Westchester Restorative Therapy & Nursing.
In addition to ongoing medical care, people with long COVID need understanding, she said.
“While long-haul symptoms do not happen to everyone, it is proven that many do experience long-haul symptoms, and the support of the community in understanding is important.”
Limitations of the study
Dr. Pell and colleagues noted some strengths and weaknesses to their study. For example, “as a general population study, our findings provide a better indication of the overall risk and burden of long COVID than hospitalized cohorts,” they noted.
Also, the Scottish population is 96% White, so other long COVID studies with more diverse participants are warranted.
Another potential weakness is the response rate of 16% among those invited to participate in the study, which Dr. Pell and colleagues addressed: “Our cohort included a large sample (33,281) of people previously infected and the response rate of 16% overall and 20% among people who had symptomatic infection was consistent with previous studies that have used SMS text invitations as the sole method of recruitment.”
“We tell patients this should last 3-6 months, but some patients have longer recovery periods,” Dr. Gut said. “We’re here for them. We have a lot of services available to help get them through the recovery process, and we have a lot of options to help support them.”
“What we found most helpful is when there is peer-to-peer support, reaffirming to the member that they are not alone in the long-haul battle, which has been a major benefit of the support group,” Ms. Penziner said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
in the same time frame, a large study out of Scotland found.
Multiple studies are evaluating people with long COVID in the hopes of figuring out why some people experience debilitating symptoms long after their primary infection ends and others either do not or recover more quickly.
This current study is notable for its large size – 96,238 people. Researchers checked in with participants at 6, 12, and 18 months, and included a group of people never infected with the coronavirus to help investigators make a stronger case.
“A lot of the symptoms of long COVID are nonspecific and therefore can occur in people never infected,” says senior study author Jill P. Pell, MD, head of the School of Health and Wellbeing at the University of Glasgow in Scotland.
Ruling out coincidence
This study shows that people experienced a wide range of symptoms after becoming infected with COVID-19 at a significantly higher rate than those who were never infected, “thereby confirming that they were genuinely associated with COVID and not merely a coincidence,” she said.
Among 21,525 people who had COVID-19 and had symptoms, tiredness, headache and muscle aches or muscle weakness were the most common ongoing symptoms.
Loss of smell was almost nine times more likely in this group compared to the never-infected group in one analysis where researchers controlled for other possible factors. The risk for loss of taste was almost six times greater, followed by risk of breathlessness at three times higher.
Long COVID risk was highest after a severe original infection and among older people, women, Black, and South Asian populations, people with socioeconomic disadvantages, and those with more than one underlying health condition.
Adding up the 6% with no recovery after 18 months and 42% with partial recovery means that between 6 and 18 months following symptomatic coronavirus infection, almost half of those infected still experience persistent symptoms.
Vaccination validated
On the plus side, people vaccinated against COVID-19 before getting infected had a lower risk for some persistent symptoms. In addition, Dr. Pell and colleagues found no evidence that people who experienced asymptomatic infection were likely to experience long COVID symptoms or challenges with activities of daily living.
The findings of the Long-COVID in Scotland Study (Long-CISS) were published in the journal Nature Communications.
‘More long COVID than ever before’
“Unfortunately, these long COVID symptoms are not getting better as the cases of COVID get milder,” said Thomas Gut, DO, medical director for the post-COVID recovery program at Staten Island (N.Y.) University Hospital. “Quite the opposite – this infection has become so common in a community because it’s so mild and spreading so rapidly that we’re seeing more long COVID symptoms than ever before.”
Although most patients he sees with long COVID resolve their symptoms within 3-6 months, “We do see some patients who require short-term disability because their symptoms continue past 6 months and out to 2 years,” said Dr. Gut, a hospitalist at Staten Island University Hospital, a member hospital of Northwell Health.
Patients with fatigue and neurocognitive symptoms “have a very tough time going back to work. Short-term disability gives them the time and finances to pursue specialty care with cardiology, pulmonary, and neurocognitive testing,” he said.
Support the whole person
The burden of living with long COVID goes beyond the persistent symptoms. “Long COVID can have wide-ranging impacts – not only on health but also quality of life and activities of daily living [including] work, mobility, self-care and more,” Dr. Pell said. “So, people with long COVID need support relevant to their individual needs and this may extend beyond the health care sector, for example including social services, school or workplace.”
Still, Lisa Penziner, RN, founder of the COVID Long Haulers Support Group in Westchester and Long Island, N.Y., said while people with the most severe cases of COVID-19 tended to have the worst long COVID symptoms, they’re not the only ones.
“We saw many post-COVID members who had mild cases and their long-haul symptoms were worse weeks later than the virus itself,” said Md. Penziner.
She estimates that 80%-90% of her support group members recover within 6 months. “However, there are others who were experiencing symptoms for much longer.”
Respiratory treatment, physical therapy, and other follow-up doctor visits are common after 6 months, for example.
“Additionally, there is a mental health component to recovery as well, meaning that the patient must learn to live while experiencing lingering, long-haul COVID symptoms in work and daily life,” said Ms. Penziner, director of special projects at North Westchester Restorative Therapy & Nursing.
In addition to ongoing medical care, people with long COVID need understanding, she said.
“While long-haul symptoms do not happen to everyone, it is proven that many do experience long-haul symptoms, and the support of the community in understanding is important.”
Limitations of the study
Dr. Pell and colleagues noted some strengths and weaknesses to their study. For example, “as a general population study, our findings provide a better indication of the overall risk and burden of long COVID than hospitalized cohorts,” they noted.
Also, the Scottish population is 96% White, so other long COVID studies with more diverse participants are warranted.
Another potential weakness is the response rate of 16% among those invited to participate in the study, which Dr. Pell and colleagues addressed: “Our cohort included a large sample (33,281) of people previously infected and the response rate of 16% overall and 20% among people who had symptomatic infection was consistent with previous studies that have used SMS text invitations as the sole method of recruitment.”
“We tell patients this should last 3-6 months, but some patients have longer recovery periods,” Dr. Gut said. “We’re here for them. We have a lot of services available to help get them through the recovery process, and we have a lot of options to help support them.”
“What we found most helpful is when there is peer-to-peer support, reaffirming to the member that they are not alone in the long-haul battle, which has been a major benefit of the support group,” Ms. Penziner said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
in the same time frame, a large study out of Scotland found.
Multiple studies are evaluating people with long COVID in the hopes of figuring out why some people experience debilitating symptoms long after their primary infection ends and others either do not or recover more quickly.
This current study is notable for its large size – 96,238 people. Researchers checked in with participants at 6, 12, and 18 months, and included a group of people never infected with the coronavirus to help investigators make a stronger case.
“A lot of the symptoms of long COVID are nonspecific and therefore can occur in people never infected,” says senior study author Jill P. Pell, MD, head of the School of Health and Wellbeing at the University of Glasgow in Scotland.
Ruling out coincidence
This study shows that people experienced a wide range of symptoms after becoming infected with COVID-19 at a significantly higher rate than those who were never infected, “thereby confirming that they were genuinely associated with COVID and not merely a coincidence,” she said.
Among 21,525 people who had COVID-19 and had symptoms, tiredness, headache and muscle aches or muscle weakness were the most common ongoing symptoms.
Loss of smell was almost nine times more likely in this group compared to the never-infected group in one analysis where researchers controlled for other possible factors. The risk for loss of taste was almost six times greater, followed by risk of breathlessness at three times higher.
Long COVID risk was highest after a severe original infection and among older people, women, Black, and South Asian populations, people with socioeconomic disadvantages, and those with more than one underlying health condition.
Adding up the 6% with no recovery after 18 months and 42% with partial recovery means that between 6 and 18 months following symptomatic coronavirus infection, almost half of those infected still experience persistent symptoms.
Vaccination validated
On the plus side, people vaccinated against COVID-19 before getting infected had a lower risk for some persistent symptoms. In addition, Dr. Pell and colleagues found no evidence that people who experienced asymptomatic infection were likely to experience long COVID symptoms or challenges with activities of daily living.
The findings of the Long-COVID in Scotland Study (Long-CISS) were published in the journal Nature Communications.
‘More long COVID than ever before’
“Unfortunately, these long COVID symptoms are not getting better as the cases of COVID get milder,” said Thomas Gut, DO, medical director for the post-COVID recovery program at Staten Island (N.Y.) University Hospital. “Quite the opposite – this infection has become so common in a community because it’s so mild and spreading so rapidly that we’re seeing more long COVID symptoms than ever before.”
Although most patients he sees with long COVID resolve their symptoms within 3-6 months, “We do see some patients who require short-term disability because their symptoms continue past 6 months and out to 2 years,” said Dr. Gut, a hospitalist at Staten Island University Hospital, a member hospital of Northwell Health.
Patients with fatigue and neurocognitive symptoms “have a very tough time going back to work. Short-term disability gives them the time and finances to pursue specialty care with cardiology, pulmonary, and neurocognitive testing,” he said.
Support the whole person
The burden of living with long COVID goes beyond the persistent symptoms. “Long COVID can have wide-ranging impacts – not only on health but also quality of life and activities of daily living [including] work, mobility, self-care and more,” Dr. Pell said. “So, people with long COVID need support relevant to their individual needs and this may extend beyond the health care sector, for example including social services, school or workplace.”
Still, Lisa Penziner, RN, founder of the COVID Long Haulers Support Group in Westchester and Long Island, N.Y., said while people with the most severe cases of COVID-19 tended to have the worst long COVID symptoms, they’re not the only ones.
“We saw many post-COVID members who had mild cases and their long-haul symptoms were worse weeks later than the virus itself,” said Md. Penziner.
She estimates that 80%-90% of her support group members recover within 6 months. “However, there are others who were experiencing symptoms for much longer.”
Respiratory treatment, physical therapy, and other follow-up doctor visits are common after 6 months, for example.
“Additionally, there is a mental health component to recovery as well, meaning that the patient must learn to live while experiencing lingering, long-haul COVID symptoms in work and daily life,” said Ms. Penziner, director of special projects at North Westchester Restorative Therapy & Nursing.
In addition to ongoing medical care, people with long COVID need understanding, she said.
“While long-haul symptoms do not happen to everyone, it is proven that many do experience long-haul symptoms, and the support of the community in understanding is important.”
Limitations of the study
Dr. Pell and colleagues noted some strengths and weaknesses to their study. For example, “as a general population study, our findings provide a better indication of the overall risk and burden of long COVID than hospitalized cohorts,” they noted.
Also, the Scottish population is 96% White, so other long COVID studies with more diverse participants are warranted.
Another potential weakness is the response rate of 16% among those invited to participate in the study, which Dr. Pell and colleagues addressed: “Our cohort included a large sample (33,281) of people previously infected and the response rate of 16% overall and 20% among people who had symptomatic infection was consistent with previous studies that have used SMS text invitations as the sole method of recruitment.”
“We tell patients this should last 3-6 months, but some patients have longer recovery periods,” Dr. Gut said. “We’re here for them. We have a lot of services available to help get them through the recovery process, and we have a lot of options to help support them.”
“What we found most helpful is when there is peer-to-peer support, reaffirming to the member that they are not alone in the long-haul battle, which has been a major benefit of the support group,” Ms. Penziner said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
Keep menstrual cramps away the dietary prevention way
Foods for thought: Menstrual cramp prevention
For those who menstruate, it’s typical for that time of the month to bring cravings for things that may give a serotonin boost that eases the rise in stress hormones. Chocolate and other foods high in sugar fall into that category, but they could actually be adding to the problem.
About 90% of adolescent girls have menstrual pain, and it’s the leading cause of school absences for the demographic. Muscle relaxers and PMS pills are usually the recommended solution to alleviating menstrual cramps, but what if the patient doesn’t want to take any medicine?
Serah Sannoh of Rutgers University wanted to find another way to relieve her menstrual pains. The literature review she presented at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society found multiple studies that examined dietary patterns that resulted in menstrual pain.
In Ms. Sannoh’s analysis, she looked at how certain foods have an effect on cramps. Do they contribute to the pain or reduce it? Diets high in processed foods, oils, sugars, salt, and omega-6 fatty acids promote inflammation in the muscles around the uterus. Thus, cramps.
The answer, sometimes, is not to add a medicine but to change our daily practices, she suggested. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids helped reduce pain, and those who practiced a vegan diet had the lowest muscle inflammation rates. So more salmon and fewer Swedish Fish.
Stage 1 of the robot apocalypse is already upon us
The mere mention of a robot apocalypse is enough to conjure images of terrifying robot soldiers with Austrian accents harvesting and killing humanity while the survivors live blissfully in a simulation and do low-gravity kung fu with high-profile Hollywood actors. They’ll even take over the navy.
Reality is often less exciting than the movies, but rest assured, the robots will not be denied their dominion of Earth. Our future robot overlords are simply taking a more subtle, less dramatic route toward their ultimate subjugation of mankind: They’re making us all sad and burned out.
The research pulls from work conducted in multiple countries to paint a picture of a humanity filled with anxiety about jobs as robotic automation grows more common. In India, a survey of automobile manufacturing works showed that working alongside industrial robots was linked with greater reports of burnout and workplace incivility. In Singapore, a group of college students randomly assigned to read one of three articles – one about the use of robots in business, a generic article about robots, or an article unrelated to robots – were then surveyed about their job security concerns. Three guesses as to which group was most worried.
In addition, the researchers analyzed 185 U.S. metropolitan areas for robot prevalence alongside use of job-recruiting websites and found that the more robots a city used, the more common job searches were. Unemployment rates weren’t affected, suggesting people had job insecurity because of robots. Sure, there could be other, nonrobotic reasons for this, but that’s no fun. We’re here because we fear our future android rulers.
It’s not all doom and gloom, fortunately. In an online experiment, the study authors found that self-affirmation exercises, such as writing down characteristics or values important to us, can overcome the existential fears and lessen concern about robots in the workplace. One of the authors noted that, while some fear is justified, “media reports on new technologies like robots and algorithms tend to be apocalyptic in nature, so people may develop an irrational fear about them.”
Oops. Our bad.
Apocalypse, stage 2: Leaping oral superorganisms
The terms of our secret agreement with the shadowy-but-powerful dental-industrial complex stipulate that LOTME can only cover tooth-related news once a year. This is that once a year.
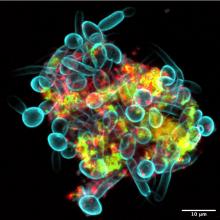
Since we’ve already dealt with a robot apocalypse, how about a sci-fi horror story? A story with a “cross-kingdom partnership” in which assemblages of bacteria and fungi perform feats greater than either could achieve on its own. A story in which new microscopy technologies allow “scientists to visualize the behavior of living microbes in real time,” according to a statement from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
While looking at saliva samples from toddlers with severe tooth decay, lead author Zhi Ren and associates “noticed the bacteria and fungi forming these assemblages and developing motions we never thought they would possess: a ‘walking-like’ and ‘leaping-like’ mobility. … It’s almost like a new organism – a superorganism – with new functions,” said senior author Hyun Koo, DDS, PhD, of Penn Dental Medicine.
Did he say “mobility”? He did, didn’t he?
To study these alleged superorganisms, they set up a laboratory system “using the bacteria, fungi, and a tooth-like material, all incubated in human saliva,” the university explained.
“Incubated in human saliva.” There’s a phrase you don’t see every day.
It only took a few hours for the investigators to observe the bacterial/fungal assemblages making leaps of more than 100 microns across the tooth-like material. “That is more than 200 times their own body length,” Dr. Ren said, “making them even better than most vertebrates, relative to body size. For example, tree frogs and grasshoppers can leap forward about 50 times and 20 times their own body length, respectively.”
So, will it be the robots or the evil superorganisms? Let us give you a word of advice: Always bet on bacteria.
Foods for thought: Menstrual cramp prevention
For those who menstruate, it’s typical for that time of the month to bring cravings for things that may give a serotonin boost that eases the rise in stress hormones. Chocolate and other foods high in sugar fall into that category, but they could actually be adding to the problem.
About 90% of adolescent girls have menstrual pain, and it’s the leading cause of school absences for the demographic. Muscle relaxers and PMS pills are usually the recommended solution to alleviating menstrual cramps, but what if the patient doesn’t want to take any medicine?
Serah Sannoh of Rutgers University wanted to find another way to relieve her menstrual pains. The literature review she presented at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society found multiple studies that examined dietary patterns that resulted in menstrual pain.
In Ms. Sannoh’s analysis, she looked at how certain foods have an effect on cramps. Do they contribute to the pain or reduce it? Diets high in processed foods, oils, sugars, salt, and omega-6 fatty acids promote inflammation in the muscles around the uterus. Thus, cramps.
The answer, sometimes, is not to add a medicine but to change our daily practices, she suggested. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids helped reduce pain, and those who practiced a vegan diet had the lowest muscle inflammation rates. So more salmon and fewer Swedish Fish.
Stage 1 of the robot apocalypse is already upon us
The mere mention of a robot apocalypse is enough to conjure images of terrifying robot soldiers with Austrian accents harvesting and killing humanity while the survivors live blissfully in a simulation and do low-gravity kung fu with high-profile Hollywood actors. They’ll even take over the navy.
Reality is often less exciting than the movies, but rest assured, the robots will not be denied their dominion of Earth. Our future robot overlords are simply taking a more subtle, less dramatic route toward their ultimate subjugation of mankind: They’re making us all sad and burned out.
The research pulls from work conducted in multiple countries to paint a picture of a humanity filled with anxiety about jobs as robotic automation grows more common. In India, a survey of automobile manufacturing works showed that working alongside industrial robots was linked with greater reports of burnout and workplace incivility. In Singapore, a group of college students randomly assigned to read one of three articles – one about the use of robots in business, a generic article about robots, or an article unrelated to robots – were then surveyed about their job security concerns. Three guesses as to which group was most worried.
In addition, the researchers analyzed 185 U.S. metropolitan areas for robot prevalence alongside use of job-recruiting websites and found that the more robots a city used, the more common job searches were. Unemployment rates weren’t affected, suggesting people had job insecurity because of robots. Sure, there could be other, nonrobotic reasons for this, but that’s no fun. We’re here because we fear our future android rulers.
It’s not all doom and gloom, fortunately. In an online experiment, the study authors found that self-affirmation exercises, such as writing down characteristics or values important to us, can overcome the existential fears and lessen concern about robots in the workplace. One of the authors noted that, while some fear is justified, “media reports on new technologies like robots and algorithms tend to be apocalyptic in nature, so people may develop an irrational fear about them.”
Oops. Our bad.
Apocalypse, stage 2: Leaping oral superorganisms
The terms of our secret agreement with the shadowy-but-powerful dental-industrial complex stipulate that LOTME can only cover tooth-related news once a year. This is that once a year.
Since we’ve already dealt with a robot apocalypse, how about a sci-fi horror story? A story with a “cross-kingdom partnership” in which assemblages of bacteria and fungi perform feats greater than either could achieve on its own. A story in which new microscopy technologies allow “scientists to visualize the behavior of living microbes in real time,” according to a statement from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
While looking at saliva samples from toddlers with severe tooth decay, lead author Zhi Ren and associates “noticed the bacteria and fungi forming these assemblages and developing motions we never thought they would possess: a ‘walking-like’ and ‘leaping-like’ mobility. … It’s almost like a new organism – a superorganism – with new functions,” said senior author Hyun Koo, DDS, PhD, of Penn Dental Medicine.
Did he say “mobility”? He did, didn’t he?
To study these alleged superorganisms, they set up a laboratory system “using the bacteria, fungi, and a tooth-like material, all incubated in human saliva,” the university explained.
“Incubated in human saliva.” There’s a phrase you don’t see every day.
It only took a few hours for the investigators to observe the bacterial/fungal assemblages making leaps of more than 100 microns across the tooth-like material. “That is more than 200 times their own body length,” Dr. Ren said, “making them even better than most vertebrates, relative to body size. For example, tree frogs and grasshoppers can leap forward about 50 times and 20 times their own body length, respectively.”
So, will it be the robots or the evil superorganisms? Let us give you a word of advice: Always bet on bacteria.
Foods for thought: Menstrual cramp prevention
For those who menstruate, it’s typical for that time of the month to bring cravings for things that may give a serotonin boost that eases the rise in stress hormones. Chocolate and other foods high in sugar fall into that category, but they could actually be adding to the problem.
About 90% of adolescent girls have menstrual pain, and it’s the leading cause of school absences for the demographic. Muscle relaxers and PMS pills are usually the recommended solution to alleviating menstrual cramps, but what if the patient doesn’t want to take any medicine?
Serah Sannoh of Rutgers University wanted to find another way to relieve her menstrual pains. The literature review she presented at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society found multiple studies that examined dietary patterns that resulted in menstrual pain.
In Ms. Sannoh’s analysis, she looked at how certain foods have an effect on cramps. Do they contribute to the pain or reduce it? Diets high in processed foods, oils, sugars, salt, and omega-6 fatty acids promote inflammation in the muscles around the uterus. Thus, cramps.
The answer, sometimes, is not to add a medicine but to change our daily practices, she suggested. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids helped reduce pain, and those who practiced a vegan diet had the lowest muscle inflammation rates. So more salmon and fewer Swedish Fish.
Stage 1 of the robot apocalypse is already upon us
The mere mention of a robot apocalypse is enough to conjure images of terrifying robot soldiers with Austrian accents harvesting and killing humanity while the survivors live blissfully in a simulation and do low-gravity kung fu with high-profile Hollywood actors. They’ll even take over the navy.
Reality is often less exciting than the movies, but rest assured, the robots will not be denied their dominion of Earth. Our future robot overlords are simply taking a more subtle, less dramatic route toward their ultimate subjugation of mankind: They’re making us all sad and burned out.
The research pulls from work conducted in multiple countries to paint a picture of a humanity filled with anxiety about jobs as robotic automation grows more common. In India, a survey of automobile manufacturing works showed that working alongside industrial robots was linked with greater reports of burnout and workplace incivility. In Singapore, a group of college students randomly assigned to read one of three articles – one about the use of robots in business, a generic article about robots, or an article unrelated to robots – were then surveyed about their job security concerns. Three guesses as to which group was most worried.
In addition, the researchers analyzed 185 U.S. metropolitan areas for robot prevalence alongside use of job-recruiting websites and found that the more robots a city used, the more common job searches were. Unemployment rates weren’t affected, suggesting people had job insecurity because of robots. Sure, there could be other, nonrobotic reasons for this, but that’s no fun. We’re here because we fear our future android rulers.
It’s not all doom and gloom, fortunately. In an online experiment, the study authors found that self-affirmation exercises, such as writing down characteristics or values important to us, can overcome the existential fears and lessen concern about robots in the workplace. One of the authors noted that, while some fear is justified, “media reports on new technologies like robots and algorithms tend to be apocalyptic in nature, so people may develop an irrational fear about them.”
Oops. Our bad.
Apocalypse, stage 2: Leaping oral superorganisms
The terms of our secret agreement with the shadowy-but-powerful dental-industrial complex stipulate that LOTME can only cover tooth-related news once a year. This is that once a year.
Since we’ve already dealt with a robot apocalypse, how about a sci-fi horror story? A story with a “cross-kingdom partnership” in which assemblages of bacteria and fungi perform feats greater than either could achieve on its own. A story in which new microscopy technologies allow “scientists to visualize the behavior of living microbes in real time,” according to a statement from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
While looking at saliva samples from toddlers with severe tooth decay, lead author Zhi Ren and associates “noticed the bacteria and fungi forming these assemblages and developing motions we never thought they would possess: a ‘walking-like’ and ‘leaping-like’ mobility. … It’s almost like a new organism – a superorganism – with new functions,” said senior author Hyun Koo, DDS, PhD, of Penn Dental Medicine.
Did he say “mobility”? He did, didn’t he?
To study these alleged superorganisms, they set up a laboratory system “using the bacteria, fungi, and a tooth-like material, all incubated in human saliva,” the university explained.
“Incubated in human saliva.” There’s a phrase you don’t see every day.
It only took a few hours for the investigators to observe the bacterial/fungal assemblages making leaps of more than 100 microns across the tooth-like material. “That is more than 200 times their own body length,” Dr. Ren said, “making them even better than most vertebrates, relative to body size. For example, tree frogs and grasshoppers can leap forward about 50 times and 20 times their own body length, respectively.”
So, will it be the robots or the evil superorganisms? Let us give you a word of advice: Always bet on bacteria.
Congenital syphilis: It’s still a significant public health problem
You’re rounding in the nursery and informed of the following about one of your new patients: He’s a 38-week-old infant delivered to a mother diagnosed with syphilis at 12 weeks’ gestation at her initial prenatal visit. Her rapid plasma reagin (RPR) was 1:64 and the fluorescent treponemal antibody–absorption (FTA-ABS) test was positive. By report she was appropriately treated. Maternal RPRs obtained at 18 and 28 weeks’ gestation were 1:16 and 1:4, respectively. Maternal RPR at delivery and the infant’s RPR obtained shortly after birth were both 1:4. The mother wants to know if her baby is infected.
One result of syphilis during pregnancy is intrauterine infection and resultant congenital disease in the infant. Before you answer this mother, let’s discuss syphilis.
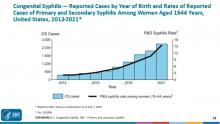
Congenital syphilis is a significant public health problem. In 2021, there were a total of 2,677 cases reported for a rate of 74.1 per 100,000 live births. Between 2020 and 2021, the number of cases of congenital syphilis increased 24.1% (2,158-2,677 cases), concurrent with a 45.8% increase (10.7-15.6 per 100,000) in the rate of primary and secondary syphilis in women aged 15-44 years. Between 2012 and 2021, the number of cases of congenital syphilis increased 701.5% (334-2,677 cases) and the increase in rates of primary and secondary syphilis in women aged 15-44 was 642.9% over the same period.
Why are the rates of congenital syphilis increasing? Most cases result from a lack of prenatal care and thus no testing for syphilis. The next most common cause is inadequate maternal treatment.
Congenital syphilis usually is acquired through transplacental transmission of spirochetes in the maternal bloodstream. Occasionally, it occurs at delivery via direct contact with maternal lesions. It is not transmitted in breast milk. Transmission of syphilis:
- Can occur any time during pregnancy.
- Is more likely to occur in women with untreated primary or secondary disease (60%-100%).
- Is approximately 40% in those with early latent syphilis and less than 8% in mothers with late latent syphilis.
- Is higher in women coinfected with HIV since they more frequently receive no prenatal care and their disease is inadequately treated.
Coinfection with syphilis may also increase the rate of mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
Untreated early syphilis during pregnancy results in spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, or perinatal death in up to 40% of cases. Infected newborns with early congenital syphilis can be asymptomatic or have evidence of hepatosplenomegaly, generalized lymphadenopathy, nasal discharge that is occasionally bloody, rash, and skeletal abnormalities (osteochondritis and periostitis). Other manifestations include edema, hemolytic anemia, jaundice, pneumonia, pseudoparalysis, and thrombocytopenia. Asymptomatic infants may have abnormal cerebrospinal fluid findings including elevated CSF white cell count, elevated protein, and a reactive venereal disease research laboratory test.
Late congenital syphilis, defined as the onset of symptoms after 2 years of age is secondary to scarring or persistent inflammation and gumma formation in a variety of tissues. It occurs in up to 40% of cases of untreated maternal disease. Most cases can be prevented by maternal treatment and treatment of the infant within the first 3 months of life. Common clinical manifestations include interstitial keratitis, sensorineural hearing loss, frontal bossing, saddle nose, Hutchinson teeth, mulberry molars, perforation of the hard palate, anterior bowing of the tibia (saber shins), and other skeletal abnormalities.
Diagnostic tests. Maternal diagnosis is dependent upon knowing the results of both a nontreponemal (RPR, VDRL) and a confirmatory treponemal test (TP-PA, TP-EIA, TP-CIA, FTA-ABS,) before or at delivery. TP-PA is the preferred test. When maternal disease is confirmed, the newborn should have the same quantitative nontreponemal test as the mother. A confirmatory treponemal test is not required
Evaluation and treatment. It’s imperative that children born to mothers with a reactive test, regardless of their treatment status, have a thorough exam performed before hospital discharge. The provider must determine what additional interventions should be performed.
The American Academy of Pediatrics and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/congenital-syphilis.htm) have developed standard algorithms for the diagnostic approach and treatment of infants born to mothers with reactive serologic tests for syphilis. It is available in the Red Book for AAP members (https://publications.aap.org/redbook). Recommendations based on various scenarios for neonates up to 1 month of age include proven or highly probable congenital syphilis, possible congenital syphilis, congenital syphilis less likely, and congenital syphilis unlikely. It is beyond the scope of this article to list the criteria and evaluation for each scenario. The reader is referred to the algorithm.
If syphilis is suspected in infants or children older than 1 month, the challenge is to determine if it is untreated congenital syphilis or acquired syphilis. Maternal syphilis status should be determined. Evaluation for congenital syphilis in this age group includes CSF analysis for VDRL, cell count and protein, CBC with differential and platelets, hepatic panel, abdominal ultrasound, long-bone radiographs, chest radiograph, neuroimaging, auditory brain stem response, and HIV testing.
Let’s go back to your patient. The mother was diagnosed with syphilis during pregnancy. You confirm that she was treated with benzathine penicillin G, and the course was completed at least 4 weeks before delivery. Treatment with any other drug during pregnancy is not appropriate. The RPR has declined, and the infant’s titer is equal to or less than four times the maternal titer. The exam is significant for generalized adenopathy and slightly bloody nasal discharge. This infant has two findings consistent with congenital syphilis regardless of RPR titer or treatment status. This places him in the proven or highly probable congenital syphilis group. Management includes CSF analysis (VDRL, cell count, and protein), CBC with differential and platelet count, and treatment with penicillin G for 10 days. Additional tests as clinically indicated include: long-bone radiograph, chest radiography, aspartate aminotranferase and alanine aminotransferase levels, neuroimaging, ophthalmologic exam, and auditory brain stem response. Despite maternal treatment, this newborn has congenital syphilis. The same nontreponemal test should be obtained every 2-3 months until it is nonreactive. It should be nonreactive by 6 months. If the infection persists to 6-12 months post treatment, reevaluation including CSF analysis and retreatment may be indicated.
Congenital syphilis can be prevented by maternal screening, diagnosis, and treatment. When that fails it is up to us to diagnosis and adequately treat our patients.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
You’re rounding in the nursery and informed of the following about one of your new patients: He’s a 38-week-old infant delivered to a mother diagnosed with syphilis at 12 weeks’ gestation at her initial prenatal visit. Her rapid plasma reagin (RPR) was 1:64 and the fluorescent treponemal antibody–absorption (FTA-ABS) test was positive. By report she was appropriately treated. Maternal RPRs obtained at 18 and 28 weeks’ gestation were 1:16 and 1:4, respectively. Maternal RPR at delivery and the infant’s RPR obtained shortly after birth were both 1:4. The mother wants to know if her baby is infected.
One result of syphilis during pregnancy is intrauterine infection and resultant congenital disease in the infant. Before you answer this mother, let’s discuss syphilis.
Congenital syphilis is a significant public health problem. In 2021, there were a total of 2,677 cases reported for a rate of 74.1 per 100,000 live births. Between 2020 and 2021, the number of cases of congenital syphilis increased 24.1% (2,158-2,677 cases), concurrent with a 45.8% increase (10.7-15.6 per 100,000) in the rate of primary and secondary syphilis in women aged 15-44 years. Between 2012 and 2021, the number of cases of congenital syphilis increased 701.5% (334-2,677 cases) and the increase in rates of primary and secondary syphilis in women aged 15-44 was 642.9% over the same period.
Why are the rates of congenital syphilis increasing? Most cases result from a lack of prenatal care and thus no testing for syphilis. The next most common cause is inadequate maternal treatment.
Congenital syphilis usually is acquired through transplacental transmission of spirochetes in the maternal bloodstream. Occasionally, it occurs at delivery via direct contact with maternal lesions. It is not transmitted in breast milk. Transmission of syphilis:
- Can occur any time during pregnancy.
- Is more likely to occur in women with untreated primary or secondary disease (60%-100%).
- Is approximately 40% in those with early latent syphilis and less than 8% in mothers with late latent syphilis.
- Is higher in women coinfected with HIV since they more frequently receive no prenatal care and their disease is inadequately treated.
Coinfection with syphilis may also increase the rate of mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
Untreated early syphilis during pregnancy results in spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, or perinatal death in up to 40% of cases. Infected newborns with early congenital syphilis can be asymptomatic or have evidence of hepatosplenomegaly, generalized lymphadenopathy, nasal discharge that is occasionally bloody, rash, and skeletal abnormalities (osteochondritis and periostitis). Other manifestations include edema, hemolytic anemia, jaundice, pneumonia, pseudoparalysis, and thrombocytopenia. Asymptomatic infants may have abnormal cerebrospinal fluid findings including elevated CSF white cell count, elevated protein, and a reactive venereal disease research laboratory test.
Late congenital syphilis, defined as the onset of symptoms after 2 years of age is secondary to scarring or persistent inflammation and gumma formation in a variety of tissues. It occurs in up to 40% of cases of untreated maternal disease. Most cases can be prevented by maternal treatment and treatment of the infant within the first 3 months of life. Common clinical manifestations include interstitial keratitis, sensorineural hearing loss, frontal bossing, saddle nose, Hutchinson teeth, mulberry molars, perforation of the hard palate, anterior bowing of the tibia (saber shins), and other skeletal abnormalities.
Diagnostic tests. Maternal diagnosis is dependent upon knowing the results of both a nontreponemal (RPR, VDRL) and a confirmatory treponemal test (TP-PA, TP-EIA, TP-CIA, FTA-ABS,) before or at delivery. TP-PA is the preferred test. When maternal disease is confirmed, the newborn should have the same quantitative nontreponemal test as the mother. A confirmatory treponemal test is not required
Evaluation and treatment. It’s imperative that children born to mothers with a reactive test, regardless of their treatment status, have a thorough exam performed before hospital discharge. The provider must determine what additional interventions should be performed.
The American Academy of Pediatrics and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/congenital-syphilis.htm) have developed standard algorithms for the diagnostic approach and treatment of infants born to mothers with reactive serologic tests for syphilis. It is available in the Red Book for AAP members (https://publications.aap.org/redbook). Recommendations based on various scenarios for neonates up to 1 month of age include proven or highly probable congenital syphilis, possible congenital syphilis, congenital syphilis less likely, and congenital syphilis unlikely. It is beyond the scope of this article to list the criteria and evaluation for each scenario. The reader is referred to the algorithm.
If syphilis is suspected in infants or children older than 1 month, the challenge is to determine if it is untreated congenital syphilis or acquired syphilis. Maternal syphilis status should be determined. Evaluation for congenital syphilis in this age group includes CSF analysis for VDRL, cell count and protein, CBC with differential and platelets, hepatic panel, abdominal ultrasound, long-bone radiographs, chest radiograph, neuroimaging, auditory brain stem response, and HIV testing.
Let’s go back to your patient. The mother was diagnosed with syphilis during pregnancy. You confirm that she was treated with benzathine penicillin G, and the course was completed at least 4 weeks before delivery. Treatment with any other drug during pregnancy is not appropriate. The RPR has declined, and the infant’s titer is equal to or less than four times the maternal titer. The exam is significant for generalized adenopathy and slightly bloody nasal discharge. This infant has two findings consistent with congenital syphilis regardless of RPR titer or treatment status. This places him in the proven or highly probable congenital syphilis group. Management includes CSF analysis (VDRL, cell count, and protein), CBC with differential and platelet count, and treatment with penicillin G for 10 days. Additional tests as clinically indicated include: long-bone radiograph, chest radiography, aspartate aminotranferase and alanine aminotransferase levels, neuroimaging, ophthalmologic exam, and auditory brain stem response. Despite maternal treatment, this newborn has congenital syphilis. The same nontreponemal test should be obtained every 2-3 months until it is nonreactive. It should be nonreactive by 6 months. If the infection persists to 6-12 months post treatment, reevaluation including CSF analysis and retreatment may be indicated.
Congenital syphilis can be prevented by maternal screening, diagnosis, and treatment. When that fails it is up to us to diagnosis and adequately treat our patients.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
You’re rounding in the nursery and informed of the following about one of your new patients: He’s a 38-week-old infant delivered to a mother diagnosed with syphilis at 12 weeks’ gestation at her initial prenatal visit. Her rapid plasma reagin (RPR) was 1:64 and the fluorescent treponemal antibody–absorption (FTA-ABS) test was positive. By report she was appropriately treated. Maternal RPRs obtained at 18 and 28 weeks’ gestation were 1:16 and 1:4, respectively. Maternal RPR at delivery and the infant’s RPR obtained shortly after birth were both 1:4. The mother wants to know if her baby is infected.
One result of syphilis during pregnancy is intrauterine infection and resultant congenital disease in the infant. Before you answer this mother, let’s discuss syphilis.
Congenital syphilis is a significant public health problem. In 2021, there were a total of 2,677 cases reported for a rate of 74.1 per 100,000 live births. Between 2020 and 2021, the number of cases of congenital syphilis increased 24.1% (2,158-2,677 cases), concurrent with a 45.8% increase (10.7-15.6 per 100,000) in the rate of primary and secondary syphilis in women aged 15-44 years. Between 2012 and 2021, the number of cases of congenital syphilis increased 701.5% (334-2,677 cases) and the increase in rates of primary and secondary syphilis in women aged 15-44 was 642.9% over the same period.
Why are the rates of congenital syphilis increasing? Most cases result from a lack of prenatal care and thus no testing for syphilis. The next most common cause is inadequate maternal treatment.
Congenital syphilis usually is acquired through transplacental transmission of spirochetes in the maternal bloodstream. Occasionally, it occurs at delivery via direct contact with maternal lesions. It is not transmitted in breast milk. Transmission of syphilis:
- Can occur any time during pregnancy.
- Is more likely to occur in women with untreated primary or secondary disease (60%-100%).
- Is approximately 40% in those with early latent syphilis and less than 8% in mothers with late latent syphilis.
- Is higher in women coinfected with HIV since they more frequently receive no prenatal care and their disease is inadequately treated.
Coinfection with syphilis may also increase the rate of mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
Untreated early syphilis during pregnancy results in spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, or perinatal death in up to 40% of cases. Infected newborns with early congenital syphilis can be asymptomatic or have evidence of hepatosplenomegaly, generalized lymphadenopathy, nasal discharge that is occasionally bloody, rash, and skeletal abnormalities (osteochondritis and periostitis). Other manifestations include edema, hemolytic anemia, jaundice, pneumonia, pseudoparalysis, and thrombocytopenia. Asymptomatic infants may have abnormal cerebrospinal fluid findings including elevated CSF white cell count, elevated protein, and a reactive venereal disease research laboratory test.
Late congenital syphilis, defined as the onset of symptoms after 2 years of age is secondary to scarring or persistent inflammation and gumma formation in a variety of tissues. It occurs in up to 40% of cases of untreated maternal disease. Most cases can be prevented by maternal treatment and treatment of the infant within the first 3 months of life. Common clinical manifestations include interstitial keratitis, sensorineural hearing loss, frontal bossing, saddle nose, Hutchinson teeth, mulberry molars, perforation of the hard palate, anterior bowing of the tibia (saber shins), and other skeletal abnormalities.
Diagnostic tests. Maternal diagnosis is dependent upon knowing the results of both a nontreponemal (RPR, VDRL) and a confirmatory treponemal test (TP-PA, TP-EIA, TP-CIA, FTA-ABS,) before or at delivery. TP-PA is the preferred test. When maternal disease is confirmed, the newborn should have the same quantitative nontreponemal test as the mother. A confirmatory treponemal test is not required
Evaluation and treatment. It’s imperative that children born to mothers with a reactive test, regardless of their treatment status, have a thorough exam performed before hospital discharge. The provider must determine what additional interventions should be performed.
The American Academy of Pediatrics and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/congenital-syphilis.htm) have developed standard algorithms for the diagnostic approach and treatment of infants born to mothers with reactive serologic tests for syphilis. It is available in the Red Book for AAP members (https://publications.aap.org/redbook). Recommendations based on various scenarios for neonates up to 1 month of age include proven or highly probable congenital syphilis, possible congenital syphilis, congenital syphilis less likely, and congenital syphilis unlikely. It is beyond the scope of this article to list the criteria and evaluation for each scenario. The reader is referred to the algorithm.
If syphilis is suspected in infants or children older than 1 month, the challenge is to determine if it is untreated congenital syphilis or acquired syphilis. Maternal syphilis status should be determined. Evaluation for congenital syphilis in this age group includes CSF analysis for VDRL, cell count and protein, CBC with differential and platelets, hepatic panel, abdominal ultrasound, long-bone radiographs, chest radiograph, neuroimaging, auditory brain stem response, and HIV testing.
Let’s go back to your patient. The mother was diagnosed with syphilis during pregnancy. You confirm that she was treated with benzathine penicillin G, and the course was completed at least 4 weeks before delivery. Treatment with any other drug during pregnancy is not appropriate. The RPR has declined, and the infant’s titer is equal to or less than four times the maternal titer. The exam is significant for generalized adenopathy and slightly bloody nasal discharge. This infant has two findings consistent with congenital syphilis regardless of RPR titer or treatment status. This places him in the proven or highly probable congenital syphilis group. Management includes CSF analysis (VDRL, cell count, and protein), CBC with differential and platelet count, and treatment with penicillin G for 10 days. Additional tests as clinically indicated include: long-bone radiograph, chest radiography, aspartate aminotranferase and alanine aminotransferase levels, neuroimaging, ophthalmologic exam, and auditory brain stem response. Despite maternal treatment, this newborn has congenital syphilis. The same nontreponemal test should be obtained every 2-3 months until it is nonreactive. It should be nonreactive by 6 months. If the infection persists to 6-12 months post treatment, reevaluation including CSF analysis and retreatment may be indicated.
Congenital syphilis can be prevented by maternal screening, diagnosis, and treatment. When that fails it is up to us to diagnosis and adequately treat our patients.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
63% of long COVID patients are women, study says
according to a new study published in JAMA.
The global study also found that about 6% of people with symptomatic infections had long COVID in 2020 and 2021. The risk for long COVID seemed to be greater among those who needed hospitalization, especially those who needed intensive care.
“Quantifying the number of individuals with long COVID may help policy makers ensure adequate access to services to guide people toward recovery, return to the workplace or school, and restore their mental health and social life,” the researchers wrote.
The study team, which included dozens of researchers across nearly every continent, analyzed data from 54 studies and two databases for more than 1 million patients in 22 countries who had symptomatic COVID infections in 2020 and 2021. They looked at three long COVID symptom types: persistent fatigue with bodily pain or mood swings, ongoing respiratory problems, and cognitive issues. The study included people aged 4-66.
Overall, 6.2% of people reported one of the long COVID symptom types, including 3.7% with ongoing respiratory problems, 3.2% with persistent fatigue and bodily pain or mood swings, and 2.2% with cognitive problems. Among those with long COVID, 38% of people reported more than one symptom cluster.
At 3 months after infection, long COVID symptoms were nearly twice as common in women who were at least 20 years old at 10.6%, compared with men who were at least 20 years old at 5.4%.
Children and teens appeared to have lower risks of long COVID. About 2.8% of patients under age 20 with symptomatic infection developed long-term issues.
The estimated average duration of long COVID symptoms was 9 months among hospitalized patients and 4 months among those who weren’t hospitalized. About 15% of people with long COVID symptoms 3 months after the initial infection continued to have symptoms at 12 months.
The study was largely based on detailed data from ongoing COVID-19 studies in the United States, Austria, the Faroe Islands, Germany, Iran, Italy, the Netherlands, Russia, Sweden, and Switzerland, according to UPI. It was supplemented by published data and research conducted as part of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries and Risk Factors Study. The dozens of researchers are referred to as “Global Burden of Disease Long COVID Collaborators.”
The study had limitations, the researchers said, including the assumption that long COVID follows a similar course in all countries. Additional studies may show how long COVID symptoms and severity may vary in different countries and continents.
Ultimately, ongoing studies of large numbers of people with long COVID could help scientists and public health officials understand risk factors and ways to treat the debilitating condition, the study authors wrote, noting that “postinfection fatigue syndrome” has been reported before, namely during the 1918 flu pandemic, after the SARS outbreak in 2003, and after the Ebola epidemic in West Africa in 2014.
“Similar symptoms have been reported after other viral infections, including the Epstein-Barr virus, mononucleosis, and dengue, as well as after nonviral infections such as Q fever, Lyme disease and giardiasis,” they wrote.
Several study investigators reported receiving grants and personal fees from a variety of sources.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study published in JAMA.
The global study also found that about 6% of people with symptomatic infections had long COVID in 2020 and 2021. The risk for long COVID seemed to be greater among those who needed hospitalization, especially those who needed intensive care.
“Quantifying the number of individuals with long COVID may help policy makers ensure adequate access to services to guide people toward recovery, return to the workplace or school, and restore their mental health and social life,” the researchers wrote.
The study team, which included dozens of researchers across nearly every continent, analyzed data from 54 studies and two databases for more than 1 million patients in 22 countries who had symptomatic COVID infections in 2020 and 2021. They looked at three long COVID symptom types: persistent fatigue with bodily pain or mood swings, ongoing respiratory problems, and cognitive issues. The study included people aged 4-66.
Overall, 6.2% of people reported one of the long COVID symptom types, including 3.7% with ongoing respiratory problems, 3.2% with persistent fatigue and bodily pain or mood swings, and 2.2% with cognitive problems. Among those with long COVID, 38% of people reported more than one symptom cluster.
At 3 months after infection, long COVID symptoms were nearly twice as common in women who were at least 20 years old at 10.6%, compared with men who were at least 20 years old at 5.4%.
Children and teens appeared to have lower risks of long COVID. About 2.8% of patients under age 20 with symptomatic infection developed long-term issues.
The estimated average duration of long COVID symptoms was 9 months among hospitalized patients and 4 months among those who weren’t hospitalized. About 15% of people with long COVID symptoms 3 months after the initial infection continued to have symptoms at 12 months.
The study was largely based on detailed data from ongoing COVID-19 studies in the United States, Austria, the Faroe Islands, Germany, Iran, Italy, the Netherlands, Russia, Sweden, and Switzerland, according to UPI. It was supplemented by published data and research conducted as part of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries and Risk Factors Study. The dozens of researchers are referred to as “Global Burden of Disease Long COVID Collaborators.”
The study had limitations, the researchers said, including the assumption that long COVID follows a similar course in all countries. Additional studies may show how long COVID symptoms and severity may vary in different countries and continents.
Ultimately, ongoing studies of large numbers of people with long COVID could help scientists and public health officials understand risk factors and ways to treat the debilitating condition, the study authors wrote, noting that “postinfection fatigue syndrome” has been reported before, namely during the 1918 flu pandemic, after the SARS outbreak in 2003, and after the Ebola epidemic in West Africa in 2014.
“Similar symptoms have been reported after other viral infections, including the Epstein-Barr virus, mononucleosis, and dengue, as well as after nonviral infections such as Q fever, Lyme disease and giardiasis,” they wrote.
Several study investigators reported receiving grants and personal fees from a variety of sources.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study published in JAMA.
The global study also found that about 6% of people with symptomatic infections had long COVID in 2020 and 2021. The risk for long COVID seemed to be greater among those who needed hospitalization, especially those who needed intensive care.
“Quantifying the number of individuals with long COVID may help policy makers ensure adequate access to services to guide people toward recovery, return to the workplace or school, and restore their mental health and social life,” the researchers wrote.
The study team, which included dozens of researchers across nearly every continent, analyzed data from 54 studies and two databases for more than 1 million patients in 22 countries who had symptomatic COVID infections in 2020 and 2021. They looked at three long COVID symptom types: persistent fatigue with bodily pain or mood swings, ongoing respiratory problems, and cognitive issues. The study included people aged 4-66.
Overall, 6.2% of people reported one of the long COVID symptom types, including 3.7% with ongoing respiratory problems, 3.2% with persistent fatigue and bodily pain or mood swings, and 2.2% with cognitive problems. Among those with long COVID, 38% of people reported more than one symptom cluster.
At 3 months after infection, long COVID symptoms were nearly twice as common in women who were at least 20 years old at 10.6%, compared with men who were at least 20 years old at 5.4%.
Children and teens appeared to have lower risks of long COVID. About 2.8% of patients under age 20 with symptomatic infection developed long-term issues.
The estimated average duration of long COVID symptoms was 9 months among hospitalized patients and 4 months among those who weren’t hospitalized. About 15% of people with long COVID symptoms 3 months after the initial infection continued to have symptoms at 12 months.
The study was largely based on detailed data from ongoing COVID-19 studies in the United States, Austria, the Faroe Islands, Germany, Iran, Italy, the Netherlands, Russia, Sweden, and Switzerland, according to UPI. It was supplemented by published data and research conducted as part of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries and Risk Factors Study. The dozens of researchers are referred to as “Global Burden of Disease Long COVID Collaborators.”
The study had limitations, the researchers said, including the assumption that long COVID follows a similar course in all countries. Additional studies may show how long COVID symptoms and severity may vary in different countries and continents.
Ultimately, ongoing studies of large numbers of people with long COVID could help scientists and public health officials understand risk factors and ways to treat the debilitating condition, the study authors wrote, noting that “postinfection fatigue syndrome” has been reported before, namely during the 1918 flu pandemic, after the SARS outbreak in 2003, and after the Ebola epidemic in West Africa in 2014.
“Similar symptoms have been reported after other viral infections, including the Epstein-Barr virus, mononucleosis, and dengue, as well as after nonviral infections such as Q fever, Lyme disease and giardiasis,” they wrote.
Several study investigators reported receiving grants and personal fees from a variety of sources.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
Why people lie about COVID
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Have you ever lied about COVID-19?
Before you get upset, before the “how dare you,” I want you to think carefully.
Did you have COVID-19 (or think you did) and not mention it to someone you were going to be with? Did you tell someone you were taking more COVID precautions than you really were? Did you tell someone you were vaccinated when you weren’t? Have you avoided getting a COVID test even though you knew you should have?
Researchers appreciated the fact that public health interventions in COVID are important but are only as good as the percentage of people who actually abide by them. So, they designed a survey to ask the questions that many people don’t want to hear the answer to.
A total of 1,733 participants – 80% of those invited – responded to the survey. By design, approximately one-third of respondents (477) had already had COVID, one-third (499) were vaccinated and not yet infected, and one-third (509) were unvaccinated and not yet infected.
Of those surveyed, 41.6% admitted that they lied about COVID or didn’t adhere to COVID guidelines - a conservative estimate, if you ask me.
Breaking down some of the results, about 20% of people who previously were infected with COVID said they didn’t mention it when meeting with someone. A similar number said they didn’t tell anyone when they were entering a public place. A bit more concerning to me, roughly 20% reported not disclosing their COVID-positive status when going to a health care provider’s office.
About 10% of those who had not been vaccinated reported lying about their vaccination status. That’s actually less than the 15% of vaccinated people who lied and told someone they weren’t vaccinated.
About 17% of people lied about the need to quarantine, and many more broke quarantine rules.
The authors tried to see if certain personal characteristics predicted people who were more likely to lie about COVID-19–related issues. Turns out there was only one thing that predicted honesty: age.
Older people were more honest about their COVID status and COVID habits. Other factors – gender, education, race, political affiliation, COVID-19 conspiracy beliefs, and where you got your COVID information – did not seem to make much of a difference. Why are older people more honest? Because older people take COVID more seriously. And they should; COVID is more severe in older people.
The problem arises, of course, because people who are at lower risk for COVID complications interact with people at higher risk – and in those situations, honesty matters more.
On the other hand, isn’t lying about COVID stuff inevitable? If you know that a positive test means you can’t go to work, and not going to work means you won’t get paid, might you not be more likely to lie about the test? Or not get the test at all?
The authors explored the reasons for dishonesty and they are fairly broad, ranging from the desire for life to feel normal (more than half of people who lied) to not believing that COVID was real (a whopping 30%). Some of the reasons for lying included:
- Wanted life to feel normal (50%).
- Freedom (45%).
- It’s no one’s business (40%).
- COVID isn’t real (30%).
In the end, though, we need to realize that public health recommendations are not going to be universally followed, and people may tell us they are following them when, in fact, they are not.
What this adds is another data point to a trend we’ve seen across the course of the pandemic, a shift from collective to individual responsibility. If you can’t be sure what others are doing in regard to COVID, you need to focus on protecting yourself. Perhaps that shift was inevitable. Doesn’t mean we have to like it.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and here on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and hosts a repository of his communication work at www.methodsman.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Have you ever lied about COVID-19?
Before you get upset, before the “how dare you,” I want you to think carefully.
Did you have COVID-19 (or think you did) and not mention it to someone you were going to be with? Did you tell someone you were taking more COVID precautions than you really were? Did you tell someone you were vaccinated when you weren’t? Have you avoided getting a COVID test even though you knew you should have?
Researchers appreciated the fact that public health interventions in COVID are important but are only as good as the percentage of people who actually abide by them. So, they designed a survey to ask the questions that many people don’t want to hear the answer to.
A total of 1,733 participants – 80% of those invited – responded to the survey. By design, approximately one-third of respondents (477) had already had COVID, one-third (499) were vaccinated and not yet infected, and one-third (509) were unvaccinated and not yet infected.
Of those surveyed, 41.6% admitted that they lied about COVID or didn’t adhere to COVID guidelines - a conservative estimate, if you ask me.
Breaking down some of the results, about 20% of people who previously were infected with COVID said they didn’t mention it when meeting with someone. A similar number said they didn’t tell anyone when they were entering a public place. A bit more concerning to me, roughly 20% reported not disclosing their COVID-positive status when going to a health care provider’s office.
About 10% of those who had not been vaccinated reported lying about their vaccination status. That’s actually less than the 15% of vaccinated people who lied and told someone they weren’t vaccinated.
About 17% of people lied about the need to quarantine, and many more broke quarantine rules.
The authors tried to see if certain personal characteristics predicted people who were more likely to lie about COVID-19–related issues. Turns out there was only one thing that predicted honesty: age.
Older people were more honest about their COVID status and COVID habits. Other factors – gender, education, race, political affiliation, COVID-19 conspiracy beliefs, and where you got your COVID information – did not seem to make much of a difference. Why are older people more honest? Because older people take COVID more seriously. And they should; COVID is more severe in older people.
The problem arises, of course, because people who are at lower risk for COVID complications interact with people at higher risk – and in those situations, honesty matters more.
On the other hand, isn’t lying about COVID stuff inevitable? If you know that a positive test means you can’t go to work, and not going to work means you won’t get paid, might you not be more likely to lie about the test? Or not get the test at all?
The authors explored the reasons for dishonesty and they are fairly broad, ranging from the desire for life to feel normal (more than half of people who lied) to not believing that COVID was real (a whopping 30%). Some of the reasons for lying included:
- Wanted life to feel normal (50%).
- Freedom (45%).
- It’s no one’s business (40%).
- COVID isn’t real (30%).
In the end, though, we need to realize that public health recommendations are not going to be universally followed, and people may tell us they are following them when, in fact, they are not.
What this adds is another data point to a trend we’ve seen across the course of the pandemic, a shift from collective to individual responsibility. If you can’t be sure what others are doing in regard to COVID, you need to focus on protecting yourself. Perhaps that shift was inevitable. Doesn’t mean we have to like it.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and here on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and hosts a repository of his communication work at www.methodsman.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Have you ever lied about COVID-19?
Before you get upset, before the “how dare you,” I want you to think carefully.
Did you have COVID-19 (or think you did) and not mention it to someone you were going to be with? Did you tell someone you were taking more COVID precautions than you really were? Did you tell someone you were vaccinated when you weren’t? Have you avoided getting a COVID test even though you knew you should have?
Researchers appreciated the fact that public health interventions in COVID are important but are only as good as the percentage of people who actually abide by them. So, they designed a survey to ask the questions that many people don’t want to hear the answer to.
A total of 1,733 participants – 80% of those invited – responded to the survey. By design, approximately one-third of respondents (477) had already had COVID, one-third (499) were vaccinated and not yet infected, and one-third (509) were unvaccinated and not yet infected.
Of those surveyed, 41.6% admitted that they lied about COVID or didn’t adhere to COVID guidelines - a conservative estimate, if you ask me.
Breaking down some of the results, about 20% of people who previously were infected with COVID said they didn’t mention it when meeting with someone. A similar number said they didn’t tell anyone when they were entering a public place. A bit more concerning to me, roughly 20% reported not disclosing their COVID-positive status when going to a health care provider’s office.
About 10% of those who had not been vaccinated reported lying about their vaccination status. That’s actually less than the 15% of vaccinated people who lied and told someone they weren’t vaccinated.
About 17% of people lied about the need to quarantine, and many more broke quarantine rules.
The authors tried to see if certain personal characteristics predicted people who were more likely to lie about COVID-19–related issues. Turns out there was only one thing that predicted honesty: age.
Older people were more honest about their COVID status and COVID habits. Other factors – gender, education, race, political affiliation, COVID-19 conspiracy beliefs, and where you got your COVID information – did not seem to make much of a difference. Why are older people more honest? Because older people take COVID more seriously. And they should; COVID is more severe in older people.
The problem arises, of course, because people who are at lower risk for COVID complications interact with people at higher risk – and in those situations, honesty matters more.
On the other hand, isn’t lying about COVID stuff inevitable? If you know that a positive test means you can’t go to work, and not going to work means you won’t get paid, might you not be more likely to lie about the test? Or not get the test at all?
The authors explored the reasons for dishonesty and they are fairly broad, ranging from the desire for life to feel normal (more than half of people who lied) to not believing that COVID was real (a whopping 30%). Some of the reasons for lying included:
- Wanted life to feel normal (50%).
- Freedom (45%).
- It’s no one’s business (40%).
- COVID isn’t real (30%).
In the end, though, we need to realize that public health recommendations are not going to be universally followed, and people may tell us they are following them when, in fact, they are not.
What this adds is another data point to a trend we’ve seen across the course of the pandemic, a shift from collective to individual responsibility. If you can’t be sure what others are doing in regard to COVID, you need to focus on protecting yourself. Perhaps that shift was inevitable. Doesn’t mean we have to like it.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and here on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and hosts a repository of his communication work at www.methodsman.com.
Epidemic of brain fog? Long COVID’s effects worry experts
Weeks after Jeannie Volpe caught COVID-19 in November 2020, she could no longer do her job running sexual assault support groups in Anniston, Ala., because she kept forgetting the details that survivors had shared with her. “People were telling me they were having to revisit their traumatic memories, which isn’t fair to anybody,” the 47-year-old says.
Ms. Volpe has been diagnosed with long-COVID autonomic dysfunction, which includes severe muscle pain, depression, anxiety, and a loss of thinking skills. Some of her symptoms are more commonly known as brain fog, and they’re among the most frequent problems reported by people who have long-term issues after a bout of COVID-19.
Many experts and medical professionals say they haven’t even begun to scratch the surface of what impact this will have in years to come.
“I’m very worried that we have an epidemic of neurologic dysfunction coming down the pike,” says Pamela Davis, MD, PhD, a research professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
In the 2 years Ms. Volpe has been living with long COVID, her executive function – the mental processes that enable people to focus attention, retain information, and multitask – has been so diminished that she had to relearn to drive. One of the various doctors assessing her has suggested speech therapy to help Ms. Volpe relearn how to form words. “I can see the words I want to say in my mind, but I can’t make them come out of my mouth,” she says in a sluggish voice that gives away her condition.
All of those symptoms make it difficult for her to care for herself. Without a job and health insurance, Ms. Volpe says she’s researched assisted suicide in the states that allow it but has ultimately decided she wants to live.
“People tell you things like you should be grateful you survived it, and you should; but you shouldn’t expect somebody to not grieve after losing their autonomy, their career, their finances.”
The findings of researchers studying the brain effects of COVID-19 reinforce what people with long COVID have been dealing with from the start. Their experiences aren’t imaginary; they’re consistent with neurological disorders – including myalgic encephalomyelitis, also known as chronic fatigue syndrome, or ME/CFS – which carry much more weight in the public imagination than the term brain fog, which can often be used dismissively.
Studies have found that COVID-19 is linked to conditions such as strokes; seizures; and mood, memory, and movement disorders.
While there are still a lot of unanswered questions about exactly how COVID-19 affects the brain and what the long-term effects are, there’s enough reason to suggest people should be trying to avoid both infection and reinfection until researchers get more answers.
Worldwide, it’s estimated that COVID-19 has contributed to more than 40 million new cases of neurological disorders, says Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist and long COVID researcher at Washington University in St. Louis. In his latest study of 14 million medical records of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the country’s largest integrated health care system, researchers found that regardless of age, gender, race, and lifestyle,
He noted that some of the conditions, such as headaches and mild decline in memory and sharpness, may improve and go away over time. But others that showed up, such as stroke, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), and Guillain-Barré syndrome (a rare disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the nerves), often lead to lasting damage. Dr. Al-Aly’s team found that neurological conditions were 7% more likely in those who had COVID-19 than in those who had never been infected.
What’s more, researchers noticed that compared with control groups, the risk of post-COVID thinking problems was more pronounced in people in their 30s, 40s, and 50s – a group that usually would be very unlikely to have these problems. For those over the age of 60, the risks stood out less because at that stage of life, such thinking problems aren’t as rare.
Another study of the veterans system last year showed that COVID-19 survivors were at a 46% higher risk of considering suicide after 1 year.
“We need to be paying attention to this,” says Dr. Al-Aly. “What we’ve seen is really the tip of the iceberg.” He worries that millions of people, including youths, will lose out on employment and education while dealing with long-term disabilities – and the economic and societal implications of such a fallout. “What we will all be left with is the aftermath of sheer devastation in some people’s lives,” he says.
Igor Koralnik, MD, chief of neuro-infectious disease and global neurology at Northwestern University, Chicago, has been running a specialized long COVID clinic. His team published a paper in March 2021 detailing what they saw in their first 100 patients. “About half the population in the study missed at least 10 days of work. This is going to have persistent impact on the workforce,” Dr. Koralnik said in a podcast posted on the Northwestern website. “We have seen that not only [do] patients have symptoms, but they have decreased quality of life.”
For older people and their caregivers, the risk of potential neurodegenerative diseases that the virus has shown to accelerate, such as dementia, is also a big concern. Alzheimer’s is already the fifth leading cause of death for people 65 and older.
In a recent study of more than 6 million people over the age of 65, Dr. Davis and her team at Case Western found the risk of Alzheimer’s in the year after COVID-19 increased by 50%-80%. The chances were especially high for women older than 85.
To date, there are no good treatments for Alzheimer’s, yet total health care costs for long-term care and hospice services for people with dementia topped $300 billion in 2020. That doesn’t even include the related costs to families.
“The downstream effect of having someone with Alzheimer’s being taken care of by a family member can be devastating on everyone,” she says. “Sometimes the caregivers don’t weather that very well.”
When Dr. Davis’s own father got Alzheimer’s at age 86, her mother took care of him until she had a stroke one morning while making breakfast. Dr. Davis attributes the stroke to the stress of caregiving. That left Dr. Davis no choice but to seek housing where both her parents could get care.
Looking at the broader picture, Dr. Davis believes widespread isolation, loneliness, and grief during the pandemic, and the disease of COVID-19 itself, will continue to have a profound impact on psychiatric diagnoses. This in turn could trigger a wave of new substance abuse as a result of unchecked mental health problems.
Still, not all brain experts are jumping to worst-case scenarios, with a lot yet to be understood before sounding the alarm. Joanna Hellmuth, MD, a neurologist and researcher at the University of California, San Francisco, cautions against reading too much into early data, including any assumptions that COVID-19 causes neurodegeneration or irreversible damage in the brain.
Even with before-and-after brain scans by University of Oxford, England, researchers that show structural changes to the brain after infection, she points out that they didn’t actually study the clinical symptoms of the people in the study, so it’s too soon to reach conclusions about associated cognitive problems.
“It’s an important piece of the puzzle, but we don’t know how that fits together with everything else,” says Dr. Hellmuth. “Some of my patients get better. … I haven’t seen a single person get worse since the pandemic started, and so I’m hopeful.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Weeks after Jeannie Volpe caught COVID-19 in November 2020, she could no longer do her job running sexual assault support groups in Anniston, Ala., because she kept forgetting the details that survivors had shared with her. “People were telling me they were having to revisit their traumatic memories, which isn’t fair to anybody,” the 47-year-old says.
Ms. Volpe has been diagnosed with long-COVID autonomic dysfunction, which includes severe muscle pain, depression, anxiety, and a loss of thinking skills. Some of her symptoms are more commonly known as brain fog, and they’re among the most frequent problems reported by people who have long-term issues after a bout of COVID-19.
Many experts and medical professionals say they haven’t even begun to scratch the surface of what impact this will have in years to come.
“I’m very worried that we have an epidemic of neurologic dysfunction coming down the pike,” says Pamela Davis, MD, PhD, a research professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
In the 2 years Ms. Volpe has been living with long COVID, her executive function – the mental processes that enable people to focus attention, retain information, and multitask – has been so diminished that she had to relearn to drive. One of the various doctors assessing her has suggested speech therapy to help Ms. Volpe relearn how to form words. “I can see the words I want to say in my mind, but I can’t make them come out of my mouth,” she says in a sluggish voice that gives away her condition.
All of those symptoms make it difficult for her to care for herself. Without a job and health insurance, Ms. Volpe says she’s researched assisted suicide in the states that allow it but has ultimately decided she wants to live.
“People tell you things like you should be grateful you survived it, and you should; but you shouldn’t expect somebody to not grieve after losing their autonomy, their career, their finances.”
The findings of researchers studying the brain effects of COVID-19 reinforce what people with long COVID have been dealing with from the start. Their experiences aren’t imaginary; they’re consistent with neurological disorders – including myalgic encephalomyelitis, also known as chronic fatigue syndrome, or ME/CFS – which carry much more weight in the public imagination than the term brain fog, which can often be used dismissively.
Studies have found that COVID-19 is linked to conditions such as strokes; seizures; and mood, memory, and movement disorders.
While there are still a lot of unanswered questions about exactly how COVID-19 affects the brain and what the long-term effects are, there’s enough reason to suggest people should be trying to avoid both infection and reinfection until researchers get more answers.
Worldwide, it’s estimated that COVID-19 has contributed to more than 40 million new cases of neurological disorders, says Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist and long COVID researcher at Washington University in St. Louis. In his latest study of 14 million medical records of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the country’s largest integrated health care system, researchers found that regardless of age, gender, race, and lifestyle,
He noted that some of the conditions, such as headaches and mild decline in memory and sharpness, may improve and go away over time. But others that showed up, such as stroke, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), and Guillain-Barré syndrome (a rare disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the nerves), often lead to lasting damage. Dr. Al-Aly’s team found that neurological conditions were 7% more likely in those who had COVID-19 than in those who had never been infected.
What’s more, researchers noticed that compared with control groups, the risk of post-COVID thinking problems was more pronounced in people in their 30s, 40s, and 50s – a group that usually would be very unlikely to have these problems. For those over the age of 60, the risks stood out less because at that stage of life, such thinking problems aren’t as rare.
Another study of the veterans system last year showed that COVID-19 survivors were at a 46% higher risk of considering suicide after 1 year.
“We need to be paying attention to this,” says Dr. Al-Aly. “What we’ve seen is really the tip of the iceberg.” He worries that millions of people, including youths, will lose out on employment and education while dealing with long-term disabilities – and the economic and societal implications of such a fallout. “What we will all be left with is the aftermath of sheer devastation in some people’s lives,” he says.
Igor Koralnik, MD, chief of neuro-infectious disease and global neurology at Northwestern University, Chicago, has been running a specialized long COVID clinic. His team published a paper in March 2021 detailing what they saw in their first 100 patients. “About half the population in the study missed at least 10 days of work. This is going to have persistent impact on the workforce,” Dr. Koralnik said in a podcast posted on the Northwestern website. “We have seen that not only [do] patients have symptoms, but they have decreased quality of life.”
For older people and their caregivers, the risk of potential neurodegenerative diseases that the virus has shown to accelerate, such as dementia, is also a big concern. Alzheimer’s is already the fifth leading cause of death for people 65 and older.
In a recent study of more than 6 million people over the age of 65, Dr. Davis and her team at Case Western found the risk of Alzheimer’s in the year after COVID-19 increased by 50%-80%. The chances were especially high for women older than 85.
To date, there are no good treatments for Alzheimer’s, yet total health care costs for long-term care and hospice services for people with dementia topped $300 billion in 2020. That doesn’t even include the related costs to families.
“The downstream effect of having someone with Alzheimer’s being taken care of by a family member can be devastating on everyone,” she says. “Sometimes the caregivers don’t weather that very well.”
When Dr. Davis’s own father got Alzheimer’s at age 86, her mother took care of him until she had a stroke one morning while making breakfast. Dr. Davis attributes the stroke to the stress of caregiving. That left Dr. Davis no choice but to seek housing where both her parents could get care.
Looking at the broader picture, Dr. Davis believes widespread isolation, loneliness, and grief during the pandemic, and the disease of COVID-19 itself, will continue to have a profound impact on psychiatric diagnoses. This in turn could trigger a wave of new substance abuse as a result of unchecked mental health problems.
Still, not all brain experts are jumping to worst-case scenarios, with a lot yet to be understood before sounding the alarm. Joanna Hellmuth, MD, a neurologist and researcher at the University of California, San Francisco, cautions against reading too much into early data, including any assumptions that COVID-19 causes neurodegeneration or irreversible damage in the brain.
Even with before-and-after brain scans by University of Oxford, England, researchers that show structural changes to the brain after infection, she points out that they didn’t actually study the clinical symptoms of the people in the study, so it’s too soon to reach conclusions about associated cognitive problems.
“It’s an important piece of the puzzle, but we don’t know how that fits together with everything else,” says Dr. Hellmuth. “Some of my patients get better. … I haven’t seen a single person get worse since the pandemic started, and so I’m hopeful.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Weeks after Jeannie Volpe caught COVID-19 in November 2020, she could no longer do her job running sexual assault support groups in Anniston, Ala., because she kept forgetting the details that survivors had shared with her. “People were telling me they were having to revisit their traumatic memories, which isn’t fair to anybody,” the 47-year-old says.
Ms. Volpe has been diagnosed with long-COVID autonomic dysfunction, which includes severe muscle pain, depression, anxiety, and a loss of thinking skills. Some of her symptoms are more commonly known as brain fog, and they’re among the most frequent problems reported by people who have long-term issues after a bout of COVID-19.
Many experts and medical professionals say they haven’t even begun to scratch the surface of what impact this will have in years to come.
“I’m very worried that we have an epidemic of neurologic dysfunction coming down the pike,” says Pamela Davis, MD, PhD, a research professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
In the 2 years Ms. Volpe has been living with long COVID, her executive function – the mental processes that enable people to focus attention, retain information, and multitask – has been so diminished that she had to relearn to drive. One of the various doctors assessing her has suggested speech therapy to help Ms. Volpe relearn how to form words. “I can see the words I want to say in my mind, but I can’t make them come out of my mouth,” she says in a sluggish voice that gives away her condition.
All of those symptoms make it difficult for her to care for herself. Without a job and health insurance, Ms. Volpe says she’s researched assisted suicide in the states that allow it but has ultimately decided she wants to live.
“People tell you things like you should be grateful you survived it, and you should; but you shouldn’t expect somebody to not grieve after losing their autonomy, their career, their finances.”
The findings of researchers studying the brain effects of COVID-19 reinforce what people with long COVID have been dealing with from the start. Their experiences aren’t imaginary; they’re consistent with neurological disorders – including myalgic encephalomyelitis, also known as chronic fatigue syndrome, or ME/CFS – which carry much more weight in the public imagination than the term brain fog, which can often be used dismissively.
Studies have found that COVID-19 is linked to conditions such as strokes; seizures; and mood, memory, and movement disorders.
While there are still a lot of unanswered questions about exactly how COVID-19 affects the brain and what the long-term effects are, there’s enough reason to suggest people should be trying to avoid both infection and reinfection until researchers get more answers.
Worldwide, it’s estimated that COVID-19 has contributed to more than 40 million new cases of neurological disorders, says Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist and long COVID researcher at Washington University in St. Louis. In his latest study of 14 million medical records of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the country’s largest integrated health care system, researchers found that regardless of age, gender, race, and lifestyle,
He noted that some of the conditions, such as headaches and mild decline in memory and sharpness, may improve and go away over time. But others that showed up, such as stroke, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), and Guillain-Barré syndrome (a rare disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the nerves), often lead to lasting damage. Dr. Al-Aly’s team found that neurological conditions were 7% more likely in those who had COVID-19 than in those who had never been infected.
What’s more, researchers noticed that compared with control groups, the risk of post-COVID thinking problems was more pronounced in people in their 30s, 40s, and 50s – a group that usually would be very unlikely to have these problems. For those over the age of 60, the risks stood out less because at that stage of life, such thinking problems aren’t as rare.
Another study of the veterans system last year showed that COVID-19 survivors were at a 46% higher risk of considering suicide after 1 year.
“We need to be paying attention to this,” says Dr. Al-Aly. “What we’ve seen is really the tip of the iceberg.” He worries that millions of people, including youths, will lose out on employment and education while dealing with long-term disabilities – and the economic and societal implications of such a fallout. “What we will all be left with is the aftermath of sheer devastation in some people’s lives,” he says.
Igor Koralnik, MD, chief of neuro-infectious disease and global neurology at Northwestern University, Chicago, has been running a specialized long COVID clinic. His team published a paper in March 2021 detailing what they saw in their first 100 patients. “About half the population in the study missed at least 10 days of work. This is going to have persistent impact on the workforce,” Dr. Koralnik said in a podcast posted on the Northwestern website. “We have seen that not only [do] patients have symptoms, but they have decreased quality of life.”
For older people and their caregivers, the risk of potential neurodegenerative diseases that the virus has shown to accelerate, such as dementia, is also a big concern. Alzheimer’s is already the fifth leading cause of death for people 65 and older.
In a recent study of more than 6 million people over the age of 65, Dr. Davis and her team at Case Western found the risk of Alzheimer’s in the year after COVID-19 increased by 50%-80%. The chances were especially high for women older than 85.
To date, there are no good treatments for Alzheimer’s, yet total health care costs for long-term care and hospice services for people with dementia topped $300 billion in 2020. That doesn’t even include the related costs to families.
“The downstream effect of having someone with Alzheimer’s being taken care of by a family member can be devastating on everyone,” she says. “Sometimes the caregivers don’t weather that very well.”
When Dr. Davis’s own father got Alzheimer’s at age 86, her mother took care of him until she had a stroke one morning while making breakfast. Dr. Davis attributes the stroke to the stress of caregiving. That left Dr. Davis no choice but to seek housing where both her parents could get care.
Looking at the broader picture, Dr. Davis believes widespread isolation, loneliness, and grief during the pandemic, and the disease of COVID-19 itself, will continue to have a profound impact on psychiatric diagnoses. This in turn could trigger a wave of new substance abuse as a result of unchecked mental health problems.
Still, not all brain experts are jumping to worst-case scenarios, with a lot yet to be understood before sounding the alarm. Joanna Hellmuth, MD, a neurologist and researcher at the University of California, San Francisco, cautions against reading too much into early data, including any assumptions that COVID-19 causes neurodegeneration or irreversible damage in the brain.
Even with before-and-after brain scans by University of Oxford, England, researchers that show structural changes to the brain after infection, she points out that they didn’t actually study the clinical symptoms of the people in the study, so it’s too soon to reach conclusions about associated cognitive problems.
“It’s an important piece of the puzzle, but we don’t know how that fits together with everything else,” says Dr. Hellmuth. “Some of my patients get better. … I haven’t seen a single person get worse since the pandemic started, and so I’m hopeful.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: Downward trend reverses with small increase in new cases
A small increase in new cases brought COVID-19’s latest losing streak to an end at 4 weeks, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The 40,656 new cases reported bring the U.S. cumulative count of child COVID-19 cases to over 14.8 million since the pandemic began, which represents 18.4% of all cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report based on state-level data.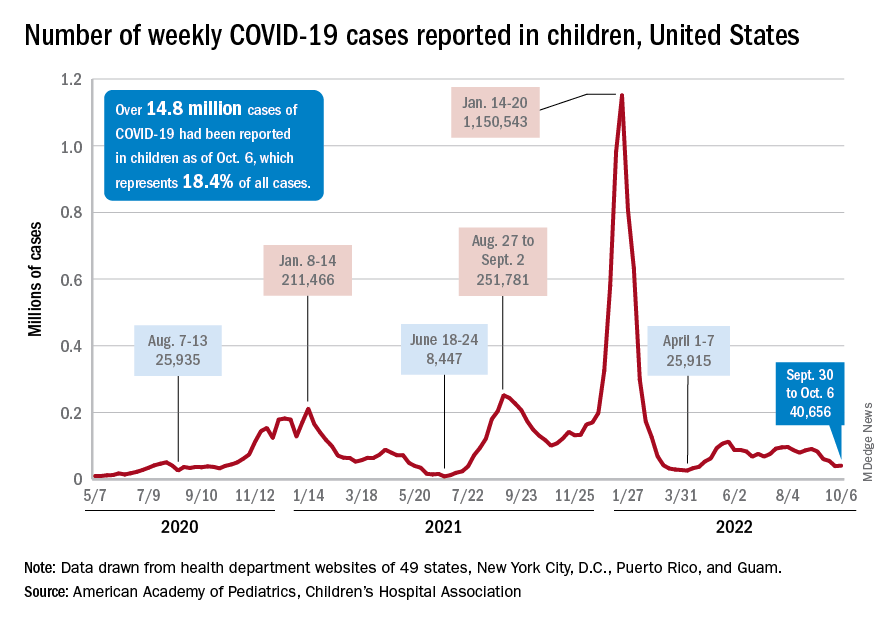
The increase in new cases was not reflected in emergency department visits or hospital admissions, which both continued sustained declines that started in August. In the week from Sept. 27 to Oct. 4, the 7-day averages for ED visits with diagnosed COVID were down by 21.5% (age 0-11), 27.3% (12-15), and 18.2% (16-17), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, while the most recent 7-day average for new admissions – 127 per day for Oct. 2-8 – among children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID was down from 161 per day the previous week, a drop of over 21%.
The state-level data that are currently available (several states are no longer reporting) show Alaska (25.5%) and Vermont (25.4%) have the highest proportions of cumulative cases in children, and Florida (12.3%) and Utah (13.5%) have the lowest. Rhode Island has the highest rate of COVID-19 per 100,000 children at 40,427, while Missouri has the lowest at 14,252. The national average is 19,687 per 100,000, the AAP and CHA reported.
Taking a look at vaccination
Vaccinations were up slightly in children aged 12-17 years, as 20,000 initial doses were given during the week of Sept. 29 to Oct. 5, compared with 17,000 and 18,000 the previous 2 weeks. Initial vaccinations in younger children, however, continued declines dating back to August, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
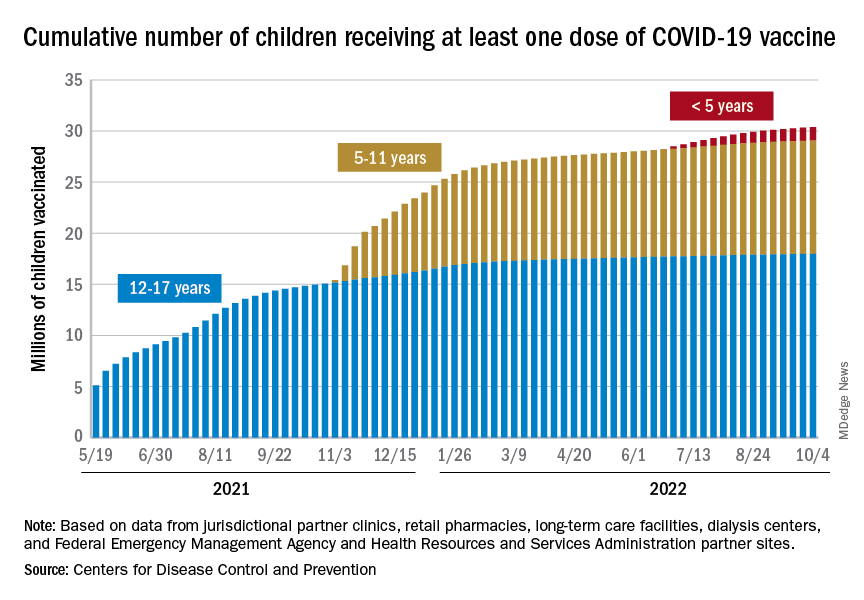
The District of Columbia and Massachusetts have the most highly vaccinated groups of 12- to 17-year-olds, as 100% and 95%, respectively, have received initial doses, while Wyoming (39%) and Idaho (42%) have the lowest. D.C. (73%) and Vermont (68%) have the highest proportions of vaccinated 5- to 11-year-olds, and Alabama (17%) and Mississippi (18%) have the lowest. For children under age 5 years, those in D.C. (33%) and Vermont (26%) are the most likely to have received an initial COVID vaccination, while Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi share national-low rates of 2%, the AAP said its report, which is based on CDC data.
When all states and territories are combined, 71% of children aged 12-17 have received at least one dose of vaccine, as have 38.6% of all children 5-11 years old and 6.7% of those under age 5. Almost 61% of the nation’s 16- to 17-year-olds have been fully vaccinated, along with 31.5% of those aged 5-11 and 2.4% of children younger than 5 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
About 42 million children – 58% of the population under the age of 18 years – have not received any vaccine yet, the AAP noted. Meanwhile, CDC data indicate that 36 children died of COVID in the last week, with pediatric deaths now totaling 1,781 over the course of the pandemic.
A small increase in new cases brought COVID-19’s latest losing streak to an end at 4 weeks, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The 40,656 new cases reported bring the U.S. cumulative count of child COVID-19 cases to over 14.8 million since the pandemic began, which represents 18.4% of all cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report based on state-level data.
The increase in new cases was not reflected in emergency department visits or hospital admissions, which both continued sustained declines that started in August. In the week from Sept. 27 to Oct. 4, the 7-day averages for ED visits with diagnosed COVID were down by 21.5% (age 0-11), 27.3% (12-15), and 18.2% (16-17), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, while the most recent 7-day average for new admissions – 127 per day for Oct. 2-8 – among children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID was down from 161 per day the previous week, a drop of over 21%.
The state-level data that are currently available (several states are no longer reporting) show Alaska (25.5%) and Vermont (25.4%) have the highest proportions of cumulative cases in children, and Florida (12.3%) and Utah (13.5%) have the lowest. Rhode Island has the highest rate of COVID-19 per 100,000 children at 40,427, while Missouri has the lowest at 14,252. The national average is 19,687 per 100,000, the AAP and CHA reported.
Taking a look at vaccination
Vaccinations were up slightly in children aged 12-17 years, as 20,000 initial doses were given during the week of Sept. 29 to Oct. 5, compared with 17,000 and 18,000 the previous 2 weeks. Initial vaccinations in younger children, however, continued declines dating back to August, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.

The District of Columbia and Massachusetts have the most highly vaccinated groups of 12- to 17-year-olds, as 100% and 95%, respectively, have received initial doses, while Wyoming (39%) and Idaho (42%) have the lowest. D.C. (73%) and Vermont (68%) have the highest proportions of vaccinated 5- to 11-year-olds, and Alabama (17%) and Mississippi (18%) have the lowest. For children under age 5 years, those in D.C. (33%) and Vermont (26%) are the most likely to have received an initial COVID vaccination, while Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi share national-low rates of 2%, the AAP said its report, which is based on CDC data.
When all states and territories are combined, 71% of children aged 12-17 have received at least one dose of vaccine, as have 38.6% of all children 5-11 years old and 6.7% of those under age 5. Almost 61% of the nation’s 16- to 17-year-olds have been fully vaccinated, along with 31.5% of those aged 5-11 and 2.4% of children younger than 5 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
About 42 million children – 58% of the population under the age of 18 years – have not received any vaccine yet, the AAP noted. Meanwhile, CDC data indicate that 36 children died of COVID in the last week, with pediatric deaths now totaling 1,781 over the course of the pandemic.
A small increase in new cases brought COVID-19’s latest losing streak to an end at 4 weeks, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The 40,656 new cases reported bring the U.S. cumulative count of child COVID-19 cases to over 14.8 million since the pandemic began, which represents 18.4% of all cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report based on state-level data.
The increase in new cases was not reflected in emergency department visits or hospital admissions, which both continued sustained declines that started in August. In the week from Sept. 27 to Oct. 4, the 7-day averages for ED visits with diagnosed COVID were down by 21.5% (age 0-11), 27.3% (12-15), and 18.2% (16-17), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, while the most recent 7-day average for new admissions – 127 per day for Oct. 2-8 – among children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID was down from 161 per day the previous week, a drop of over 21%.
The state-level data that are currently available (several states are no longer reporting) show Alaska (25.5%) and Vermont (25.4%) have the highest proportions of cumulative cases in children, and Florida (12.3%) and Utah (13.5%) have the lowest. Rhode Island has the highest rate of COVID-19 per 100,000 children at 40,427, while Missouri has the lowest at 14,252. The national average is 19,687 per 100,000, the AAP and CHA reported.
Taking a look at vaccination
Vaccinations were up slightly in children aged 12-17 years, as 20,000 initial doses were given during the week of Sept. 29 to Oct. 5, compared with 17,000 and 18,000 the previous 2 weeks. Initial vaccinations in younger children, however, continued declines dating back to August, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.

The District of Columbia and Massachusetts have the most highly vaccinated groups of 12- to 17-year-olds, as 100% and 95%, respectively, have received initial doses, while Wyoming (39%) and Idaho (42%) have the lowest. D.C. (73%) and Vermont (68%) have the highest proportions of vaccinated 5- to 11-year-olds, and Alabama (17%) and Mississippi (18%) have the lowest. For children under age 5 years, those in D.C. (33%) and Vermont (26%) are the most likely to have received an initial COVID vaccination, while Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi share national-low rates of 2%, the AAP said its report, which is based on CDC data.
When all states and territories are combined, 71% of children aged 12-17 have received at least one dose of vaccine, as have 38.6% of all children 5-11 years old and 6.7% of those under age 5. Almost 61% of the nation’s 16- to 17-year-olds have been fully vaccinated, along with 31.5% of those aged 5-11 and 2.4% of children younger than 5 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
About 42 million children – 58% of the population under the age of 18 years – have not received any vaccine yet, the AAP noted. Meanwhile, CDC data indicate that 36 children died of COVID in the last week, with pediatric deaths now totaling 1,781 over the course of the pandemic.
Previous endemic coronavirus encounters linked with long COVID
People who develop long COVID may be responding more strongly to a non–SARS-CoV-2 virus they encountered in the past than to SARS-CoV-2, a study by researchers at Harvard Medical School suggests.
Long COVID, also called postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), causes various symptoms that persist at least 4 weeks after the initial SARS-CoV-2 infection, they write in the preprint server medRxiv. Four authors explained their research into possible mechanisms of long COVID in an interview.
“Immunity to non-COVID endemic coronaviruses may play a role in who develops PASC,” co–lead author Jonathan D. Herman, MD, PhD, said. “There’s still so much more we need to understand, but it is striking that back-boosting of immune responses to coronavirus OC43 was uniquely enriched in individuals with PASC.”
“In the study, individuals with PASC preferentially generated stronger responses to previously encountered cold-causing coronaviruses,” co–senior author Galit Alter, PhD, said.
“Instead of generating strong SARS-CoV-2 immunity, they bolstered a response to a different coronavirus, potentially making their response less effective in clearing SARS-CoV-2. Surprisingly, most of the individuals had been vaccinated – and they still maintained this unusual antibody response – pointing to new therapeutic pathways to treat PASC,” Dr. Alter said.
Humoral immunity offers a clue to long-COVID origins
One-fifth of COVID-19 patients progress to long COVID, but which patients develop PASC and why are not well understood, the authors write.
“Antibodies represent powerful biomarkers that have been used for decades to diagnose disease. However, antibodies also provide a powerful source of information on previous infections. The use of antibody profiling, here, pointed to the presence of incomplete antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with PASC,” Dr. Alter said.
The researchers reviewed the medical records of patients in the Mass General Brigham health care system in Boston, including referrals from rheumatologists of participants diagnosed with COVID-19 outside the MGB system, starting on March 1, 2020.
They focused on patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs) because their tendency toward inflammation and autoantibody production may make them more susceptible to PASC and enrich for specific inflammatory-driven endotypes.
All 43 participants had COVID-19 without hospital admission and SARDs. Patients treated only for fibromyalgia, osteoarthritis, mechanical back pain, gout, or pseudogout without a SARD were excluded from the study.
Overall, 79% of participants were female, 35% had rheumatoid arthritis, 19% had psoriatic arthritis, and 95% had received a COVID-19 vaccine.
The researchers used systems serology to perform comprehensive antibody profiling against SARS-CoV-2 and a panel of endemic pathogens or routine vaccine antigens.
Long-COVID patients had a distinct immune response
Overall, 17 patients developed PASC and 26 did not, and in those with PASC, they found a distinct humoral immune response. Patients with PASC:
- harbored less inflamed and weaker Fc-gamma receptor–binding anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies;
- showed a significantly expanded and more inflamed antibody response against endemic coronavirus OC43; and
- mounted more avid IgM responses and developed expanded inflammatory OC43 S2–specific Fc-receptor–binding responses, which were linked to cross reactivity across SARS-CoV-2 and common coronaviruses.
“Strengths of the study include the detailed phenotypes of cases after COVID-19, particularly to classify PASC presence or absence, as well as the depth and breadth of antibody profiling. This allowed us to identify a humoral immune signature of PASC,” said co–senior author Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc.
“However, the study was limited in its size to investigate different types of PASC, such as fatigue or lung symptoms, that may have biologic differences. Also, all patients in the study had a preexisting rheumatic disease,” he acknowledged.
“A substantial portion of patients with COVID-19 will develop PASC, which can have substantial impact on health and quality of life,” said co–senior author Zachary S. Wallace, MD, MS. “Given the higher risk of COVID-19 in many patients with rheumatic disease, it is important to understand the etiology of PASC in this vulnerable population, to enable future diagnostic and therapeutic advances.”
Davey Smith, MD, professor of medicine and head of infectious diseases and global public health at the University of California, San Diego, in La Jolla, who was not involved in the study, called the findings interesting even though the results will not immediately affect patient care.
“There may be a link between previous non–SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus infection and PASC,” he added. “Perhaps, by understanding why some people do and do not get PASC, we can develop treatments for the condition.
“This paper is a preprint and will need to go through peer review,” Dr. Smith said. “There are many elements that need to be scrutinized. For example, there is no definition of PASC that is universally accepted, so how did that play into this study?”
Mark Cameron, PhD, associate professor in the department of population and quantitative health sciences at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, called this a strong study from a strong group, although it is a preprint prior to peer review.
“In this initial study, the scientists focused on people who had rheumatic disease before getting COVID-19, knowing they are at higher risk for lasting complications and hopefully are more immunologically similar when diagnosed with long COVID – a single ‘endotype’ or group of patients with similar clinical symptoms and background,” he noted.
“Our immune system’s memory sometimes fails to effectively fight a new virus that looks too much like a virus it saw before. This ineffective immune response can set up various problems, including the poor recoveries we see in people with long COVID,” he said.
“OC43 probably emerged in the late 1800s and probably caused a pandemic of severe respiratory illness between 1889 and 1890, previously thought to be a flu,” Dr. Cameron recalled. “OC43 is still around as an endemic coronavirus, usually causing mild or moderate upper-respiratory infections.”
COVID-19 immunity is complex, and previous SARS-CoV-2 infection doesn’t guarantee we won't get COVID-19 again, especially as new variants emerge, added Dr. Cameron, who also was not involved in the study.
“This study may help us better understand the risks and possible mechanisms associated with COVID-19 and long COVID in the face of previous coronavirus infections,” he said. “It may also help guide future COVID-19 therapies and vaccines.”
The authors plan further related research.
The study received grant support and an anonymous donation. Dr. Alter, Dr. Sparks, and Dr. Wallace report financial relationships with the pharmaceutical industry. All other authors, and Dr. Davey and Dr. Cameron, report no conflicts of interest with the study. All experts commented by email.
* This story was updated 10/12/2022.
People who develop long COVID may be responding more strongly to a non–SARS-CoV-2 virus they encountered in the past than to SARS-CoV-2, a study by researchers at Harvard Medical School suggests.
Long COVID, also called postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), causes various symptoms that persist at least 4 weeks after the initial SARS-CoV-2 infection, they write in the preprint server medRxiv. Four authors explained their research into possible mechanisms of long COVID in an interview.
“Immunity to non-COVID endemic coronaviruses may play a role in who develops PASC,” co–lead author Jonathan D. Herman, MD, PhD, said. “There’s still so much more we need to understand, but it is striking that back-boosting of immune responses to coronavirus OC43 was uniquely enriched in individuals with PASC.”
“In the study, individuals with PASC preferentially generated stronger responses to previously encountered cold-causing coronaviruses,” co–senior author Galit Alter, PhD, said.
“Instead of generating strong SARS-CoV-2 immunity, they bolstered a response to a different coronavirus, potentially making their response less effective in clearing SARS-CoV-2. Surprisingly, most of the individuals had been vaccinated – and they still maintained this unusual antibody response – pointing to new therapeutic pathways to treat PASC,” Dr. Alter said.
Humoral immunity offers a clue to long-COVID origins
One-fifth of COVID-19 patients progress to long COVID, but which patients develop PASC and why are not well understood, the authors write.
“Antibodies represent powerful biomarkers that have been used for decades to diagnose disease. However, antibodies also provide a powerful source of information on previous infections. The use of antibody profiling, here, pointed to the presence of incomplete antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with PASC,” Dr. Alter said.
The researchers reviewed the medical records of patients in the Mass General Brigham health care system in Boston, including referrals from rheumatologists of participants diagnosed with COVID-19 outside the MGB system, starting on March 1, 2020.
They focused on patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs) because their tendency toward inflammation and autoantibody production may make them more susceptible to PASC and enrich for specific inflammatory-driven endotypes.
All 43 participants had COVID-19 without hospital admission and SARDs. Patients treated only for fibromyalgia, osteoarthritis, mechanical back pain, gout, or pseudogout without a SARD were excluded from the study.
Overall, 79% of participants were female, 35% had rheumatoid arthritis, 19% had psoriatic arthritis, and 95% had received a COVID-19 vaccine.
The researchers used systems serology to perform comprehensive antibody profiling against SARS-CoV-2 and a panel of endemic pathogens or routine vaccine antigens.
Long-COVID patients had a distinct immune response
Overall, 17 patients developed PASC and 26 did not, and in those with PASC, they found a distinct humoral immune response. Patients with PASC:
- harbored less inflamed and weaker Fc-gamma receptor–binding anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies;
- showed a significantly expanded and more inflamed antibody response against endemic coronavirus OC43; and
- mounted more avid IgM responses and developed expanded inflammatory OC43 S2–specific Fc-receptor–binding responses, which were linked to cross reactivity across SARS-CoV-2 and common coronaviruses.
“Strengths of the study include the detailed phenotypes of cases after COVID-19, particularly to classify PASC presence or absence, as well as the depth and breadth of antibody profiling. This allowed us to identify a humoral immune signature of PASC,” said co–senior author Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc.
“However, the study was limited in its size to investigate different types of PASC, such as fatigue or lung symptoms, that may have biologic differences. Also, all patients in the study had a preexisting rheumatic disease,” he acknowledged.
“A substantial portion of patients with COVID-19 will develop PASC, which can have substantial impact on health and quality of life,” said co–senior author Zachary S. Wallace, MD, MS. “Given the higher risk of COVID-19 in many patients with rheumatic disease, it is important to understand the etiology of PASC in this vulnerable population, to enable future diagnostic and therapeutic advances.”
Davey Smith, MD, professor of medicine and head of infectious diseases and global public health at the University of California, San Diego, in La Jolla, who was not involved in the study, called the findings interesting even though the results will not immediately affect patient care.
“There may be a link between previous non–SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus infection and PASC,” he added. “Perhaps, by understanding why some people do and do not get PASC, we can develop treatments for the condition.
“This paper is a preprint and will need to go through peer review,” Dr. Smith said. “There are many elements that need to be scrutinized. For example, there is no definition of PASC that is universally accepted, so how did that play into this study?”
Mark Cameron, PhD, associate professor in the department of population and quantitative health sciences at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, called this a strong study from a strong group, although it is a preprint prior to peer review.
“In this initial study, the scientists focused on people who had rheumatic disease before getting COVID-19, knowing they are at higher risk for lasting complications and hopefully are more immunologically similar when diagnosed with long COVID – a single ‘endotype’ or group of patients with similar clinical symptoms and background,” he noted.
“Our immune system’s memory sometimes fails to effectively fight a new virus that looks too much like a virus it saw before. This ineffective immune response can set up various problems, including the poor recoveries we see in people with long COVID,” he said.
“OC43 probably emerged in the late 1800s and probably caused a pandemic of severe respiratory illness between 1889 and 1890, previously thought to be a flu,” Dr. Cameron recalled. “OC43 is still around as an endemic coronavirus, usually causing mild or moderate upper-respiratory infections.”
COVID-19 immunity is complex, and previous SARS-CoV-2 infection doesn’t guarantee we won't get COVID-19 again, especially as new variants emerge, added Dr. Cameron, who also was not involved in the study.
“This study may help us better understand the risks and possible mechanisms associated with COVID-19 and long COVID in the face of previous coronavirus infections,” he said. “It may also help guide future COVID-19 therapies and vaccines.”
The authors plan further related research.
The study received grant support and an anonymous donation. Dr. Alter, Dr. Sparks, and Dr. Wallace report financial relationships with the pharmaceutical industry. All other authors, and Dr. Davey and Dr. Cameron, report no conflicts of interest with the study. All experts commented by email.
* This story was updated 10/12/2022.
People who develop long COVID may be responding more strongly to a non–SARS-CoV-2 virus they encountered in the past than to SARS-CoV-2, a study by researchers at Harvard Medical School suggests.
Long COVID, also called postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), causes various symptoms that persist at least 4 weeks after the initial SARS-CoV-2 infection, they write in the preprint server medRxiv. Four authors explained their research into possible mechanisms of long COVID in an interview.
“Immunity to non-COVID endemic coronaviruses may play a role in who develops PASC,” co–lead author Jonathan D. Herman, MD, PhD, said. “There’s still so much more we need to understand, but it is striking that back-boosting of immune responses to coronavirus OC43 was uniquely enriched in individuals with PASC.”
“In the study, individuals with PASC preferentially generated stronger responses to previously encountered cold-causing coronaviruses,” co–senior author Galit Alter, PhD, said.
“Instead of generating strong SARS-CoV-2 immunity, they bolstered a response to a different coronavirus, potentially making their response less effective in clearing SARS-CoV-2. Surprisingly, most of the individuals had been vaccinated – and they still maintained this unusual antibody response – pointing to new therapeutic pathways to treat PASC,” Dr. Alter said.
Humoral immunity offers a clue to long-COVID origins
One-fifth of COVID-19 patients progress to long COVID, but which patients develop PASC and why are not well understood, the authors write.
“Antibodies represent powerful biomarkers that have been used for decades to diagnose disease. However, antibodies also provide a powerful source of information on previous infections. The use of antibody profiling, here, pointed to the presence of incomplete antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with PASC,” Dr. Alter said.
The researchers reviewed the medical records of patients in the Mass General Brigham health care system in Boston, including referrals from rheumatologists of participants diagnosed with COVID-19 outside the MGB system, starting on March 1, 2020.
They focused on patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs) because their tendency toward inflammation and autoantibody production may make them more susceptible to PASC and enrich for specific inflammatory-driven endotypes.
All 43 participants had COVID-19 without hospital admission and SARDs. Patients treated only for fibromyalgia, osteoarthritis, mechanical back pain, gout, or pseudogout without a SARD were excluded from the study.
Overall, 79% of participants were female, 35% had rheumatoid arthritis, 19% had psoriatic arthritis, and 95% had received a COVID-19 vaccine.
The researchers used systems serology to perform comprehensive antibody profiling against SARS-CoV-2 and a panel of endemic pathogens or routine vaccine antigens.
Long-COVID patients had a distinct immune response
Overall, 17 patients developed PASC and 26 did not, and in those with PASC, they found a distinct humoral immune response. Patients with PASC:
- harbored less inflamed and weaker Fc-gamma receptor–binding anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies;
- showed a significantly expanded and more inflamed antibody response against endemic coronavirus OC43; and
- mounted more avid IgM responses and developed expanded inflammatory OC43 S2–specific Fc-receptor–binding responses, which were linked to cross reactivity across SARS-CoV-2 and common coronaviruses.
“Strengths of the study include the detailed phenotypes of cases after COVID-19, particularly to classify PASC presence or absence, as well as the depth and breadth of antibody profiling. This allowed us to identify a humoral immune signature of PASC,” said co–senior author Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc.
“However, the study was limited in its size to investigate different types of PASC, such as fatigue or lung symptoms, that may have biologic differences. Also, all patients in the study had a preexisting rheumatic disease,” he acknowledged.
“A substantial portion of patients with COVID-19 will develop PASC, which can have substantial impact on health and quality of life,” said co–senior author Zachary S. Wallace, MD, MS. “Given the higher risk of COVID-19 in many patients with rheumatic disease, it is important to understand the etiology of PASC in this vulnerable population, to enable future diagnostic and therapeutic advances.”
Davey Smith, MD, professor of medicine and head of infectious diseases and global public health at the University of California, San Diego, in La Jolla, who was not involved in the study, called the findings interesting even though the results will not immediately affect patient care.
“There may be a link between previous non–SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus infection and PASC,” he added. “Perhaps, by understanding why some people do and do not get PASC, we can develop treatments for the condition.
“This paper is a preprint and will need to go through peer review,” Dr. Smith said. “There are many elements that need to be scrutinized. For example, there is no definition of PASC that is universally accepted, so how did that play into this study?”
Mark Cameron, PhD, associate professor in the department of population and quantitative health sciences at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, called this a strong study from a strong group, although it is a preprint prior to peer review.
“In this initial study, the scientists focused on people who had rheumatic disease before getting COVID-19, knowing they are at higher risk for lasting complications and hopefully are more immunologically similar when diagnosed with long COVID – a single ‘endotype’ or group of patients with similar clinical symptoms and background,” he noted.
“Our immune system’s memory sometimes fails to effectively fight a new virus that looks too much like a virus it saw before. This ineffective immune response can set up various problems, including the poor recoveries we see in people with long COVID,” he said.
“OC43 probably emerged in the late 1800s and probably caused a pandemic of severe respiratory illness between 1889 and 1890, previously thought to be a flu,” Dr. Cameron recalled. “OC43 is still around as an endemic coronavirus, usually causing mild or moderate upper-respiratory infections.”
COVID-19 immunity is complex, and previous SARS-CoV-2 infection doesn’t guarantee we won't get COVID-19 again, especially as new variants emerge, added Dr. Cameron, who also was not involved in the study.
“This study may help us better understand the risks and possible mechanisms associated with COVID-19 and long COVID in the face of previous coronavirus infections,” he said. “It may also help guide future COVID-19 therapies and vaccines.”
The authors plan further related research.
The study received grant support and an anonymous donation. Dr. Alter, Dr. Sparks, and Dr. Wallace report financial relationships with the pharmaceutical industry. All other authors, and Dr. Davey and Dr. Cameron, report no conflicts of interest with the study. All experts commented by email.
* This story was updated 10/12/2022.
FROM MEDRXIV