User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Shortage reported of antibiotic commonly used for children
The liquid form of the antibiotic amoxicillin often used to treat ear infections and strep throat in children is in short supply, just as Americans head into the season when they use the bacteria-fighting drug the most.
The FDA officially listed the shortage Oct. 28, but pharmacists, hospitals, and a supply tracking database sounded alarms earlier this month.
“The scary part is, we’re coming into the time of the year where you have the greatest need,” independent pharmacy owner Hugh Chancy, PharmD, of Georgia, told NBC News.
Thus far, reports indicate the impact of the shortages is not widespread but does affect some pharmacies, and at least one hospital has published an algorithm for offering treatment alternatives.
CVS told Bloomberg News that some stores are experiencing shortages of certain doses of amoxicillin, but a Walmart spokesperson said its diverse supply chain meant none of its pharmacies were affected.
“Hypothetically, if amoxicillin doesn’t come into stock for some time, then we’re potentially having to use less effective antibiotics with more side effects,” said Ohio pediatrician Sean Gallagher, MD, according to Bloomberg.
The shortage impacts three of the four largest amoxicillin manufacturers worldwide, according to the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) at the University of Minnesota. The FDA listed the reason for the shortage as “demand increase for drug,” except in the case of manufacturer Sandoz, for which the reason listed read “information pending.”
A company spokesperson told Bloomberg the reasons were complex.
“The combination in rapid succession of the pandemic impact and consequent demand swings, manufacturing capacity constraints, scarcity of raw materials, and the current energy crisis means we face a uniquely difficult situation in the short term,” Sandoz spokesperson Leslie Pott told Bloomberg.
According to Bloomberg, other major manufacturers are still delivering the product, but limiting new orders.
The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists issued an alert for the shortage last week via its real time drug shortage database.
“Amoxicillin comes in many forms – including capsules, powders and chewable tablets – but the most common type children take is the liquid form, which makes up at least 19 products that are part of the” shortage, Becker’s Hospital Review summarized of the database reports.
The pediatric health system Children’s Minnesota told CIDRAP that supplies are low and that alternatives are being prescribed “when appropriate.”
“As a final step, we temporarily discontinued our standard procedure of dispensing the entire bottle of amoxicillin (which comes in multiple sizes),” a spokesperson told CIDRAP. “We are instead mixing and pouring the exact amount for each course of therapy, to eliminate waste.”
The Minnesota pediatric clinic and others are particularly on alert because of the surge nationwide of a respiratory virus that particularly impacts children known as RSV.
“We have certainly observed an increase in recent use most likely correlating with the surge in RSV and other respiratory viruses with concern for superimposed bacterial infection in our critically ill and hospitalized patient population,” Laura Bio, PharmD, a clinical pharmacy specialist at Stanford Medicine Children’s Health told CIDRAP.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The liquid form of the antibiotic amoxicillin often used to treat ear infections and strep throat in children is in short supply, just as Americans head into the season when they use the bacteria-fighting drug the most.
The FDA officially listed the shortage Oct. 28, but pharmacists, hospitals, and a supply tracking database sounded alarms earlier this month.
“The scary part is, we’re coming into the time of the year where you have the greatest need,” independent pharmacy owner Hugh Chancy, PharmD, of Georgia, told NBC News.
Thus far, reports indicate the impact of the shortages is not widespread but does affect some pharmacies, and at least one hospital has published an algorithm for offering treatment alternatives.
CVS told Bloomberg News that some stores are experiencing shortages of certain doses of amoxicillin, but a Walmart spokesperson said its diverse supply chain meant none of its pharmacies were affected.
“Hypothetically, if amoxicillin doesn’t come into stock for some time, then we’re potentially having to use less effective antibiotics with more side effects,” said Ohio pediatrician Sean Gallagher, MD, according to Bloomberg.
The shortage impacts three of the four largest amoxicillin manufacturers worldwide, according to the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) at the University of Minnesota. The FDA listed the reason for the shortage as “demand increase for drug,” except in the case of manufacturer Sandoz, for which the reason listed read “information pending.”
A company spokesperson told Bloomberg the reasons were complex.
“The combination in rapid succession of the pandemic impact and consequent demand swings, manufacturing capacity constraints, scarcity of raw materials, and the current energy crisis means we face a uniquely difficult situation in the short term,” Sandoz spokesperson Leslie Pott told Bloomberg.
According to Bloomberg, other major manufacturers are still delivering the product, but limiting new orders.
The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists issued an alert for the shortage last week via its real time drug shortage database.
“Amoxicillin comes in many forms – including capsules, powders and chewable tablets – but the most common type children take is the liquid form, which makes up at least 19 products that are part of the” shortage, Becker’s Hospital Review summarized of the database reports.
The pediatric health system Children’s Minnesota told CIDRAP that supplies are low and that alternatives are being prescribed “when appropriate.”
“As a final step, we temporarily discontinued our standard procedure of dispensing the entire bottle of amoxicillin (which comes in multiple sizes),” a spokesperson told CIDRAP. “We are instead mixing and pouring the exact amount for each course of therapy, to eliminate waste.”
The Minnesota pediatric clinic and others are particularly on alert because of the surge nationwide of a respiratory virus that particularly impacts children known as RSV.
“We have certainly observed an increase in recent use most likely correlating with the surge in RSV and other respiratory viruses with concern for superimposed bacterial infection in our critically ill and hospitalized patient population,” Laura Bio, PharmD, a clinical pharmacy specialist at Stanford Medicine Children’s Health told CIDRAP.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The liquid form of the antibiotic amoxicillin often used to treat ear infections and strep throat in children is in short supply, just as Americans head into the season when they use the bacteria-fighting drug the most.
The FDA officially listed the shortage Oct. 28, but pharmacists, hospitals, and a supply tracking database sounded alarms earlier this month.
“The scary part is, we’re coming into the time of the year where you have the greatest need,” independent pharmacy owner Hugh Chancy, PharmD, of Georgia, told NBC News.
Thus far, reports indicate the impact of the shortages is not widespread but does affect some pharmacies, and at least one hospital has published an algorithm for offering treatment alternatives.
CVS told Bloomberg News that some stores are experiencing shortages of certain doses of amoxicillin, but a Walmart spokesperson said its diverse supply chain meant none of its pharmacies were affected.
“Hypothetically, if amoxicillin doesn’t come into stock for some time, then we’re potentially having to use less effective antibiotics with more side effects,” said Ohio pediatrician Sean Gallagher, MD, according to Bloomberg.
The shortage impacts three of the four largest amoxicillin manufacturers worldwide, according to the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) at the University of Minnesota. The FDA listed the reason for the shortage as “demand increase for drug,” except in the case of manufacturer Sandoz, for which the reason listed read “information pending.”
A company spokesperson told Bloomberg the reasons were complex.
“The combination in rapid succession of the pandemic impact and consequent demand swings, manufacturing capacity constraints, scarcity of raw materials, and the current energy crisis means we face a uniquely difficult situation in the short term,” Sandoz spokesperson Leslie Pott told Bloomberg.
According to Bloomberg, other major manufacturers are still delivering the product, but limiting new orders.
The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists issued an alert for the shortage last week via its real time drug shortage database.
“Amoxicillin comes in many forms – including capsules, powders and chewable tablets – but the most common type children take is the liquid form, which makes up at least 19 products that are part of the” shortage, Becker’s Hospital Review summarized of the database reports.
The pediatric health system Children’s Minnesota told CIDRAP that supplies are low and that alternatives are being prescribed “when appropriate.”
“As a final step, we temporarily discontinued our standard procedure of dispensing the entire bottle of amoxicillin (which comes in multiple sizes),” a spokesperson told CIDRAP. “We are instead mixing and pouring the exact amount for each course of therapy, to eliminate waste.”
The Minnesota pediatric clinic and others are particularly on alert because of the surge nationwide of a respiratory virus that particularly impacts children known as RSV.
“We have certainly observed an increase in recent use most likely correlating with the surge in RSV and other respiratory viruses with concern for superimposed bacterial infection in our critically ill and hospitalized patient population,” Laura Bio, PharmD, a clinical pharmacy specialist at Stanford Medicine Children’s Health told CIDRAP.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The truth of alcohol consequences
Bad drinking consequence No. 87: Joining the LOTME team
Alcohol and college students go together like peanut butter and jelly. Or peanut butter and chocolate. Or peanut butter and toothpaste. Peanut butter goes with a lot of things.
Naturally, when you combine alcohol and college students, bad decisions are sure to follow. But have you ever wondered just how many bad decisions alcohol causes? A team of researchers from Penn State University, the undisputed champion of poor drinking decisions (trust us, we know), sure has. They’ve even conducted a 4-year study of 1,700 students as they carved a drunken swath through the many fine local drinking establishments, such as East Halls or that one frat house that hosts medieval battle–style ping pong tournaments.
The students were surveyed twice a year throughout the study, and the researchers compiled a list of all the various consequences their subjects experienced. Ultimately, college students will experience an average of 102 consequences from drinking during their 4-year college careers, which is an impressive number. Try thinking up a hundred consequences for anything.
Some consequences are less common than others – we imagine “missing the Renaissance Faire because you felt drunker the morning after than while you were drinking” is pretty low on the list – but more than 96% of students reported that they’d experienced a hangover and that drinking had caused them to say or do embarrassing things. Also, more than 70% said they needed additional alcohol to feel any effect, a potential sign of alcohol use disorder.
Once they had their list, the researchers focused on 12 of the more common and severe consequences, such as blacking out, hangovers, and missing work/class, and asked the study participants how their parents would react to their drinking and those specific consequences. Students who believed their parents would disapprove of alcohol-related consequences actually experienced fewer consequences overall.
College students, it seems, really do care what their parents think, even if they don’t express it, the researchers said. That gives space for parents to offer advice about the consequences of hard drinking, making decisions while drunk, or bringing godawful Fireball whiskey to parties. Seriously, don’t do that. Stuff’s bad, and you should feel bad for bringing it. Your parents raised you better than that.
COVID ‘expert’ discusses data sharing
We interrupt our regularly scheduled programming to bring you this special news event. Elon Musk, the world’s second-most annoying human, is holding a press conference to discuss, of all things, COVID-19.
Reporter: Hey, Mr. Musketeer, what qualifies you to talk about a global pandemic?
EM: As the official king of the Twitterverse, I’m pretty much an expert on any topic.
Reporter: Okay then, Mr. Muskmelon, what can you tell us about the new study in Agricultural Economics, which looked at consumers’ knowledge of local COVID infection rates and their willingness to eat at restaurants?
EM: Well, I know that one of the investigators, Rigoberto Lopez, PhD, of the University of Connecticut, said “no news is bad news.” Restaurants located in cities where local regulations required COVID tracking recovered faster than those in areas that did not, according to data from 87 restaurants in 10 Chinese cities that were gathered between Dec. 1, 2019, and March 27, 2020. Having access to local infection rate data made customers more comfortable going out to eat, the investigators explained.
Second reporter: Interesting, Mr. Muskox, but how about this headline from CNN: “Workers flee China’s biggest iPhone factory over Covid outbreak”? Do you agree with analysts, who said that “the chaos at Zhengzhou could jeopardize Apple and Foxconn’s output in the coming weeks,” as CNN put it?
EM: I did see that a manager at Foxconn, which owns the factory and is known to its friends as Hon Hai Precision Industry, told a Chinese media outlet that “workers are panicking over the spread of the virus at the factory and lack of access to official information.” As we’ve already discussed, no news is bad news.
That’s all the time I have to chat with you today. I’m off to fire some more Twitter employees.
In case you hadn’t already guessed, Vlad Putin is officially more annoying than Elon Musk. We now return to this week’s typical LOTME shenanigans, already in progress.
The deadliest month
With climate change making the world hotter, leading to more heat stroke and organ failure, you would think the summer months would be the most deadly. In reality, though, it’s quite the opposite.
There are multiple factors that make January the most deadly month out of the year, as LiveScience discovered in a recent analysis.
Let’s go through them, shall we?
Respiratory viruses: Robert Glatter, MD, of Lenox Hill Hospital in New York, told LiveScence that winter is the time for illnesses like the flu, bacterial pneumonia, and RSV. Millions of people worldwide die from the flu, according to the CDC. And the World Health Organization reported lower respiratory infections as the fourth-leading cause of death worldwide before COVID came along.
Heart disease: Heart conditions are actually more fatal in the winter months, according to a study published in Circulation. The cold puts more stress on the heart to keep the body warm, which can be a challenge for people who already have preexisting heart conditions.
Space heaters: Dr. Glatter also told Live Science that the use of space heaters could be a factor in the cold winter months since they can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning and even fires. Silent killers.
Holiday season: A time for joy and merriment, certainly, but Christmas et al. have their downsides. By January we’re coming off a 3-month food and alcohol binge, which leads to cardiac stress. There’s also the psychological stress that comes with the season. Sometimes the most wonderful time of the year just isn’t.
So even though summer is hot, fall has hurricanes, and spring tends to have the highest suicide rate, winter still ends up being the deadliest season.
Bad drinking consequence No. 87: Joining the LOTME team
Alcohol and college students go together like peanut butter and jelly. Or peanut butter and chocolate. Or peanut butter and toothpaste. Peanut butter goes with a lot of things.
Naturally, when you combine alcohol and college students, bad decisions are sure to follow. But have you ever wondered just how many bad decisions alcohol causes? A team of researchers from Penn State University, the undisputed champion of poor drinking decisions (trust us, we know), sure has. They’ve even conducted a 4-year study of 1,700 students as they carved a drunken swath through the many fine local drinking establishments, such as East Halls or that one frat house that hosts medieval battle–style ping pong tournaments.
The students were surveyed twice a year throughout the study, and the researchers compiled a list of all the various consequences their subjects experienced. Ultimately, college students will experience an average of 102 consequences from drinking during their 4-year college careers, which is an impressive number. Try thinking up a hundred consequences for anything.
Some consequences are less common than others – we imagine “missing the Renaissance Faire because you felt drunker the morning after than while you were drinking” is pretty low on the list – but more than 96% of students reported that they’d experienced a hangover and that drinking had caused them to say or do embarrassing things. Also, more than 70% said they needed additional alcohol to feel any effect, a potential sign of alcohol use disorder.
Once they had their list, the researchers focused on 12 of the more common and severe consequences, such as blacking out, hangovers, and missing work/class, and asked the study participants how their parents would react to their drinking and those specific consequences. Students who believed their parents would disapprove of alcohol-related consequences actually experienced fewer consequences overall.
College students, it seems, really do care what their parents think, even if they don’t express it, the researchers said. That gives space for parents to offer advice about the consequences of hard drinking, making decisions while drunk, or bringing godawful Fireball whiskey to parties. Seriously, don’t do that. Stuff’s bad, and you should feel bad for bringing it. Your parents raised you better than that.
COVID ‘expert’ discusses data sharing
We interrupt our regularly scheduled programming to bring you this special news event. Elon Musk, the world’s second-most annoying human, is holding a press conference to discuss, of all things, COVID-19.
Reporter: Hey, Mr. Musketeer, what qualifies you to talk about a global pandemic?
EM: As the official king of the Twitterverse, I’m pretty much an expert on any topic.
Reporter: Okay then, Mr. Muskmelon, what can you tell us about the new study in Agricultural Economics, which looked at consumers’ knowledge of local COVID infection rates and their willingness to eat at restaurants?
EM: Well, I know that one of the investigators, Rigoberto Lopez, PhD, of the University of Connecticut, said “no news is bad news.” Restaurants located in cities where local regulations required COVID tracking recovered faster than those in areas that did not, according to data from 87 restaurants in 10 Chinese cities that were gathered between Dec. 1, 2019, and March 27, 2020. Having access to local infection rate data made customers more comfortable going out to eat, the investigators explained.
Second reporter: Interesting, Mr. Muskox, but how about this headline from CNN: “Workers flee China’s biggest iPhone factory over Covid outbreak”? Do you agree with analysts, who said that “the chaos at Zhengzhou could jeopardize Apple and Foxconn’s output in the coming weeks,” as CNN put it?
EM: I did see that a manager at Foxconn, which owns the factory and is known to its friends as Hon Hai Precision Industry, told a Chinese media outlet that “workers are panicking over the spread of the virus at the factory and lack of access to official information.” As we’ve already discussed, no news is bad news.
That’s all the time I have to chat with you today. I’m off to fire some more Twitter employees.
In case you hadn’t already guessed, Vlad Putin is officially more annoying than Elon Musk. We now return to this week’s typical LOTME shenanigans, already in progress.
The deadliest month
With climate change making the world hotter, leading to more heat stroke and organ failure, you would think the summer months would be the most deadly. In reality, though, it’s quite the opposite.
There are multiple factors that make January the most deadly month out of the year, as LiveScience discovered in a recent analysis.
Let’s go through them, shall we?
Respiratory viruses: Robert Glatter, MD, of Lenox Hill Hospital in New York, told LiveScence that winter is the time for illnesses like the flu, bacterial pneumonia, and RSV. Millions of people worldwide die from the flu, according to the CDC. And the World Health Organization reported lower respiratory infections as the fourth-leading cause of death worldwide before COVID came along.
Heart disease: Heart conditions are actually more fatal in the winter months, according to a study published in Circulation. The cold puts more stress on the heart to keep the body warm, which can be a challenge for people who already have preexisting heart conditions.
Space heaters: Dr. Glatter also told Live Science that the use of space heaters could be a factor in the cold winter months since they can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning and even fires. Silent killers.
Holiday season: A time for joy and merriment, certainly, but Christmas et al. have their downsides. By January we’re coming off a 3-month food and alcohol binge, which leads to cardiac stress. There’s also the psychological stress that comes with the season. Sometimes the most wonderful time of the year just isn’t.
So even though summer is hot, fall has hurricanes, and spring tends to have the highest suicide rate, winter still ends up being the deadliest season.
Bad drinking consequence No. 87: Joining the LOTME team
Alcohol and college students go together like peanut butter and jelly. Or peanut butter and chocolate. Or peanut butter and toothpaste. Peanut butter goes with a lot of things.
Naturally, when you combine alcohol and college students, bad decisions are sure to follow. But have you ever wondered just how many bad decisions alcohol causes? A team of researchers from Penn State University, the undisputed champion of poor drinking decisions (trust us, we know), sure has. They’ve even conducted a 4-year study of 1,700 students as they carved a drunken swath through the many fine local drinking establishments, such as East Halls or that one frat house that hosts medieval battle–style ping pong tournaments.
The students were surveyed twice a year throughout the study, and the researchers compiled a list of all the various consequences their subjects experienced. Ultimately, college students will experience an average of 102 consequences from drinking during their 4-year college careers, which is an impressive number. Try thinking up a hundred consequences for anything.
Some consequences are less common than others – we imagine “missing the Renaissance Faire because you felt drunker the morning after than while you were drinking” is pretty low on the list – but more than 96% of students reported that they’d experienced a hangover and that drinking had caused them to say or do embarrassing things. Also, more than 70% said they needed additional alcohol to feel any effect, a potential sign of alcohol use disorder.
Once they had their list, the researchers focused on 12 of the more common and severe consequences, such as blacking out, hangovers, and missing work/class, and asked the study participants how their parents would react to their drinking and those specific consequences. Students who believed their parents would disapprove of alcohol-related consequences actually experienced fewer consequences overall.
College students, it seems, really do care what their parents think, even if they don’t express it, the researchers said. That gives space for parents to offer advice about the consequences of hard drinking, making decisions while drunk, or bringing godawful Fireball whiskey to parties. Seriously, don’t do that. Stuff’s bad, and you should feel bad for bringing it. Your parents raised you better than that.
COVID ‘expert’ discusses data sharing
We interrupt our regularly scheduled programming to bring you this special news event. Elon Musk, the world’s second-most annoying human, is holding a press conference to discuss, of all things, COVID-19.
Reporter: Hey, Mr. Musketeer, what qualifies you to talk about a global pandemic?
EM: As the official king of the Twitterverse, I’m pretty much an expert on any topic.
Reporter: Okay then, Mr. Muskmelon, what can you tell us about the new study in Agricultural Economics, which looked at consumers’ knowledge of local COVID infection rates and their willingness to eat at restaurants?
EM: Well, I know that one of the investigators, Rigoberto Lopez, PhD, of the University of Connecticut, said “no news is bad news.” Restaurants located in cities where local regulations required COVID tracking recovered faster than those in areas that did not, according to data from 87 restaurants in 10 Chinese cities that were gathered between Dec. 1, 2019, and March 27, 2020. Having access to local infection rate data made customers more comfortable going out to eat, the investigators explained.
Second reporter: Interesting, Mr. Muskox, but how about this headline from CNN: “Workers flee China’s biggest iPhone factory over Covid outbreak”? Do you agree with analysts, who said that “the chaos at Zhengzhou could jeopardize Apple and Foxconn’s output in the coming weeks,” as CNN put it?
EM: I did see that a manager at Foxconn, which owns the factory and is known to its friends as Hon Hai Precision Industry, told a Chinese media outlet that “workers are panicking over the spread of the virus at the factory and lack of access to official information.” As we’ve already discussed, no news is bad news.
That’s all the time I have to chat with you today. I’m off to fire some more Twitter employees.
In case you hadn’t already guessed, Vlad Putin is officially more annoying than Elon Musk. We now return to this week’s typical LOTME shenanigans, already in progress.
The deadliest month
With climate change making the world hotter, leading to more heat stroke and organ failure, you would think the summer months would be the most deadly. In reality, though, it’s quite the opposite.
There are multiple factors that make January the most deadly month out of the year, as LiveScience discovered in a recent analysis.
Let’s go through them, shall we?
Respiratory viruses: Robert Glatter, MD, of Lenox Hill Hospital in New York, told LiveScence that winter is the time for illnesses like the flu, bacterial pneumonia, and RSV. Millions of people worldwide die from the flu, according to the CDC. And the World Health Organization reported lower respiratory infections as the fourth-leading cause of death worldwide before COVID came along.
Heart disease: Heart conditions are actually more fatal in the winter months, according to a study published in Circulation. The cold puts more stress on the heart to keep the body warm, which can be a challenge for people who already have preexisting heart conditions.
Space heaters: Dr. Glatter also told Live Science that the use of space heaters could be a factor in the cold winter months since they can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning and even fires. Silent killers.
Holiday season: A time for joy and merriment, certainly, but Christmas et al. have their downsides. By January we’re coming off a 3-month food and alcohol binge, which leads to cardiac stress. There’s also the psychological stress that comes with the season. Sometimes the most wonderful time of the year just isn’t.
So even though summer is hot, fall has hurricanes, and spring tends to have the highest suicide rate, winter still ends up being the deadliest season.
Mid-October flulike illness cases higher than past 5 years
Outpatient visits for influenzalike illness (ILI), which includes influenza, SARS-CoV-2, and RSV, were higher after 3 weeks than for any of the previous five flu seasons: 3.3% of visits reported through the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network involved ILI as of Oct. 22. The highest comparable rate in the previous 5 years was the 1.9% recorded in late October of 2021, shortly after the definition of ILI was changed to also include illnesses other than influenza.
This season’s higher flu activity is in contrast to the previous two, which were unusually mild. The change, however, is not unexpected, as William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert and professor of preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University, recently told CNN.
“Here we are in the middle of October – not the middle of November – we’re already seeing scattered influenza cases, even hospitalized influenza cases, around the country,” he said. “So we know that this virus is now spreading out in the community already. It’s gathering speed already. It looks to me to be about a month early.”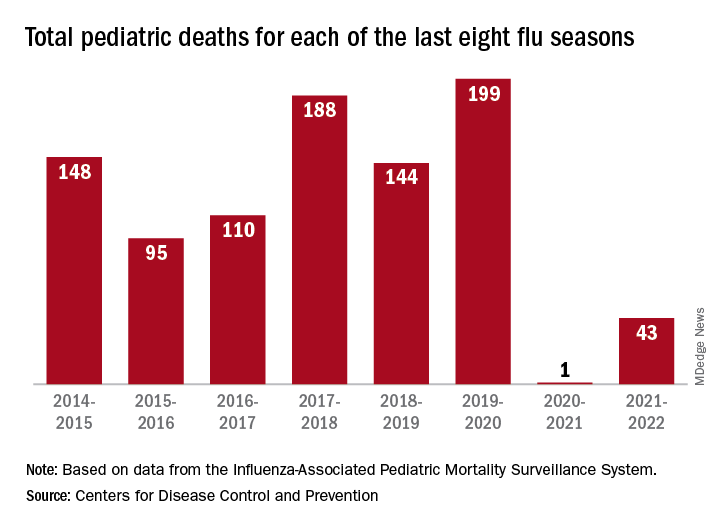
One indication of the mildness of the previous two flu seasons was the number of deaths, both pediatric and overall. Influenza-associated pediatric deaths had averaged about 110 per season over the previous eight seasons, compared with just 1 for 2020-2021 and 43 in 2021-2022. Overall flu deaths never reached 1% of all weekly deaths for either season, well below baseline levels for the flu, which range from 5.5% to 6.8%, CDC data show.
Other indicators of early severity
This season’s early rise in viral activity also can be seen in hospitalizations. The cumulative rate of flu-related admissions was 1.5 per 100,000 population as of Oct. 22, higher than the rate observed in the comparable week of previous seasons going back to 2010-2011, according to the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network.
A look at state reports of ILI outpatient visit rates shows that the District of Columbia and South Carolina are already in the very high range of the CDC’s severity scale, while 11 states are in the high range. Again going back to 2010-2011, no jurisdiction has ever been in the very high range this early in the season, based on data from the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.
Outpatient visits for influenzalike illness (ILI), which includes influenza, SARS-CoV-2, and RSV, were higher after 3 weeks than for any of the previous five flu seasons: 3.3% of visits reported through the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network involved ILI as of Oct. 22. The highest comparable rate in the previous 5 years was the 1.9% recorded in late October of 2021, shortly after the definition of ILI was changed to also include illnesses other than influenza.
This season’s higher flu activity is in contrast to the previous two, which were unusually mild. The change, however, is not unexpected, as William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert and professor of preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University, recently told CNN.
“Here we are in the middle of October – not the middle of November – we’re already seeing scattered influenza cases, even hospitalized influenza cases, around the country,” he said. “So we know that this virus is now spreading out in the community already. It’s gathering speed already. It looks to me to be about a month early.”
One indication of the mildness of the previous two flu seasons was the number of deaths, both pediatric and overall. Influenza-associated pediatric deaths had averaged about 110 per season over the previous eight seasons, compared with just 1 for 2020-2021 and 43 in 2021-2022. Overall flu deaths never reached 1% of all weekly deaths for either season, well below baseline levels for the flu, which range from 5.5% to 6.8%, CDC data show.
Other indicators of early severity
This season’s early rise in viral activity also can be seen in hospitalizations. The cumulative rate of flu-related admissions was 1.5 per 100,000 population as of Oct. 22, higher than the rate observed in the comparable week of previous seasons going back to 2010-2011, according to the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network.
A look at state reports of ILI outpatient visit rates shows that the District of Columbia and South Carolina are already in the very high range of the CDC’s severity scale, while 11 states are in the high range. Again going back to 2010-2011, no jurisdiction has ever been in the very high range this early in the season, based on data from the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.
Outpatient visits for influenzalike illness (ILI), which includes influenza, SARS-CoV-2, and RSV, were higher after 3 weeks than for any of the previous five flu seasons: 3.3% of visits reported through the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network involved ILI as of Oct. 22. The highest comparable rate in the previous 5 years was the 1.9% recorded in late October of 2021, shortly after the definition of ILI was changed to also include illnesses other than influenza.
This season’s higher flu activity is in contrast to the previous two, which were unusually mild. The change, however, is not unexpected, as William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert and professor of preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University, recently told CNN.
“Here we are in the middle of October – not the middle of November – we’re already seeing scattered influenza cases, even hospitalized influenza cases, around the country,” he said. “So we know that this virus is now spreading out in the community already. It’s gathering speed already. It looks to me to be about a month early.”
One indication of the mildness of the previous two flu seasons was the number of deaths, both pediatric and overall. Influenza-associated pediatric deaths had averaged about 110 per season over the previous eight seasons, compared with just 1 for 2020-2021 and 43 in 2021-2022. Overall flu deaths never reached 1% of all weekly deaths for either season, well below baseline levels for the flu, which range from 5.5% to 6.8%, CDC data show.
Other indicators of early severity
This season’s early rise in viral activity also can be seen in hospitalizations. The cumulative rate of flu-related admissions was 1.5 per 100,000 population as of Oct. 22, higher than the rate observed in the comparable week of previous seasons going back to 2010-2011, according to the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network.
A look at state reports of ILI outpatient visit rates shows that the District of Columbia and South Carolina are already in the very high range of the CDC’s severity scale, while 11 states are in the high range. Again going back to 2010-2011, no jurisdiction has ever been in the very high range this early in the season, based on data from the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.
FDA rejects bulevirtide for hepatitis D
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has declined to approve bulevirtide, Gilead Sciences’ drug for the treatment of hepatitis delta virus (HDV) infection and compensated liver disease.
In a complete response letter, the FDA voiced concerns over the production and delivery of bulevirtide, an investigational, first-in-class HDV entry-inhibitor that received conditional approved in Europe in 2020.
The FDA did not request new studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of bulevirtide.
As reported previously by this news organization, data from an ongoing phase 3 trial showed that after 48 weeks of treatment, almost half of those treated with bulevirtide achieved the combined primary endpoint of reduced or undetectable HDV RNA levels and normalized alanine aminotransferase levels.
Chronic HDV infection is the most severe form of viral hepatitis. It is associated with a poor prognosis and high mortality rates.
There are currently no approved treatments for HDV in the United States. Bulevirtide was granted breakthrough therapy and orphan drug designations by the FDA.
Merdad Parsey, MD, PhD, chief medical officer, Gilead Sciences, wrote in a news release that the company looks forward to “continuing our active discussions with FDA so that we may bring bulevirtide to people living with HDV in the U.S. as soon as possible.”
This is the second manufacturing-related complete response letter Gilead has received in the past 8 months. In March, the FDA rejected the long-acting HIV drug lenacapavir. The drug was sanctioned in Europe and the United Kingdom in September.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has declined to approve bulevirtide, Gilead Sciences’ drug for the treatment of hepatitis delta virus (HDV) infection and compensated liver disease.
In a complete response letter, the FDA voiced concerns over the production and delivery of bulevirtide, an investigational, first-in-class HDV entry-inhibitor that received conditional approved in Europe in 2020.
The FDA did not request new studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of bulevirtide.
As reported previously by this news organization, data from an ongoing phase 3 trial showed that after 48 weeks of treatment, almost half of those treated with bulevirtide achieved the combined primary endpoint of reduced or undetectable HDV RNA levels and normalized alanine aminotransferase levels.
Chronic HDV infection is the most severe form of viral hepatitis. It is associated with a poor prognosis and high mortality rates.
There are currently no approved treatments for HDV in the United States. Bulevirtide was granted breakthrough therapy and orphan drug designations by the FDA.
Merdad Parsey, MD, PhD, chief medical officer, Gilead Sciences, wrote in a news release that the company looks forward to “continuing our active discussions with FDA so that we may bring bulevirtide to people living with HDV in the U.S. as soon as possible.”
This is the second manufacturing-related complete response letter Gilead has received in the past 8 months. In March, the FDA rejected the long-acting HIV drug lenacapavir. The drug was sanctioned in Europe and the United Kingdom in September.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has declined to approve bulevirtide, Gilead Sciences’ drug for the treatment of hepatitis delta virus (HDV) infection and compensated liver disease.
In a complete response letter, the FDA voiced concerns over the production and delivery of bulevirtide, an investigational, first-in-class HDV entry-inhibitor that received conditional approved in Europe in 2020.
The FDA did not request new studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of bulevirtide.
As reported previously by this news organization, data from an ongoing phase 3 trial showed that after 48 weeks of treatment, almost half of those treated with bulevirtide achieved the combined primary endpoint of reduced or undetectable HDV RNA levels and normalized alanine aminotransferase levels.
Chronic HDV infection is the most severe form of viral hepatitis. It is associated with a poor prognosis and high mortality rates.
There are currently no approved treatments for HDV in the United States. Bulevirtide was granted breakthrough therapy and orphan drug designations by the FDA.
Merdad Parsey, MD, PhD, chief medical officer, Gilead Sciences, wrote in a news release that the company looks forward to “continuing our active discussions with FDA so that we may bring bulevirtide to people living with HDV in the U.S. as soon as possible.”
This is the second manufacturing-related complete response letter Gilead has received in the past 8 months. In March, the FDA rejected the long-acting HIV drug lenacapavir. The drug was sanctioned in Europe and the United Kingdom in September.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Unappreciated’ ties between COVID and gut dysbiosis
(BSIs), new research suggests.
“Collectively, these results reveal an unappreciated link between SARS-CoV-2 infection, gut microbiome dysbiosis, and a severe complication of COVID-19, BSIs,” the study team reported in Nature Communications.
“Our findings suggest that coronavirus infection directly interferes with the healthy balance of microbes in the gut, further endangering patients in the process,” microbiologist and co–senior author Ken Cadwell, PhD, New York University, added in a news release. “Now that we have uncovered the source of this bacterial imbalance, physicians can better identify those coronavirus patients most at risk of a secondary bloodstream infection.”
In a mouse model, the researchers first demonstrated that the SARS-CoV-2 infection alone induces gut microbiome dysbiosis and gut epithelial cell alterations, which correlate with markers of gut barrier permeability.
Next, they analyzed the bacterial composition of stool samples from 96 adults hospitalized with COVID-19 in 2020 in New York and New Haven, Conn.
In line with their observations in mice, they found that the SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with “severe microbiome injury,” characterized by the loss of gut microbiome diversity.
They also observed an increase in populations of several microbes known to include antibiotic-resistant species. An analysis of stool samples paired with blood cultures found that antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the gut migrated to the bloodstream in 20% of patients.
This migration could be caused by a combination of the immune-compromising effects of the viral infection and the antibiotic-driven depletion of commensal gut microbes, the researchers said.
However, COVID-19 patients are also uniquely exposed to other potential factors predisposing them to bacteremia, including immunosuppressive drugs, long hospital stays, and catheters, the investigators noted. The study is limited in its ability to investigate the individual effects of these factors.
“Our findings support a scenario in which gut-to-blood translocation of microorganisms following microbiome dysbiosis leads to dangerous BSIs during COVID-19, a complication seen in other immunocompromised patients, including patients with cancer, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and in ICU patients receiving probiotics,” the researchers wrote.
Investigating the underlying mechanism behind their observations could help inform “the judicious application of antibiotics and immunosuppressives in patients with respiratory viral infections and increase our resilience to pandemics,” they added.
Funding for the study was provided by the National Institutes of Health, the Yale School of Public Health, and numerous other sources. Dr. Cadwell has received research support from Pfizer, Takeda, Pacific Biosciences, Genentech, and AbbVie; consulted for or received an honoraria from PureTech Health, Genentech, and AbbVie; and is named as an inventor on US patent 10,722,600 and provisional patents 62/935,035 and 63/157,225.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(BSIs), new research suggests.
“Collectively, these results reveal an unappreciated link between SARS-CoV-2 infection, gut microbiome dysbiosis, and a severe complication of COVID-19, BSIs,” the study team reported in Nature Communications.
“Our findings suggest that coronavirus infection directly interferes with the healthy balance of microbes in the gut, further endangering patients in the process,” microbiologist and co–senior author Ken Cadwell, PhD, New York University, added in a news release. “Now that we have uncovered the source of this bacterial imbalance, physicians can better identify those coronavirus patients most at risk of a secondary bloodstream infection.”
In a mouse model, the researchers first demonstrated that the SARS-CoV-2 infection alone induces gut microbiome dysbiosis and gut epithelial cell alterations, which correlate with markers of gut barrier permeability.
Next, they analyzed the bacterial composition of stool samples from 96 adults hospitalized with COVID-19 in 2020 in New York and New Haven, Conn.
In line with their observations in mice, they found that the SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with “severe microbiome injury,” characterized by the loss of gut microbiome diversity.
They also observed an increase in populations of several microbes known to include antibiotic-resistant species. An analysis of stool samples paired with blood cultures found that antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the gut migrated to the bloodstream in 20% of patients.
This migration could be caused by a combination of the immune-compromising effects of the viral infection and the antibiotic-driven depletion of commensal gut microbes, the researchers said.
However, COVID-19 patients are also uniquely exposed to other potential factors predisposing them to bacteremia, including immunosuppressive drugs, long hospital stays, and catheters, the investigators noted. The study is limited in its ability to investigate the individual effects of these factors.
“Our findings support a scenario in which gut-to-blood translocation of microorganisms following microbiome dysbiosis leads to dangerous BSIs during COVID-19, a complication seen in other immunocompromised patients, including patients with cancer, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and in ICU patients receiving probiotics,” the researchers wrote.
Investigating the underlying mechanism behind their observations could help inform “the judicious application of antibiotics and immunosuppressives in patients with respiratory viral infections and increase our resilience to pandemics,” they added.
Funding for the study was provided by the National Institutes of Health, the Yale School of Public Health, and numerous other sources. Dr. Cadwell has received research support from Pfizer, Takeda, Pacific Biosciences, Genentech, and AbbVie; consulted for or received an honoraria from PureTech Health, Genentech, and AbbVie; and is named as an inventor on US patent 10,722,600 and provisional patents 62/935,035 and 63/157,225.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(BSIs), new research suggests.
“Collectively, these results reveal an unappreciated link between SARS-CoV-2 infection, gut microbiome dysbiosis, and a severe complication of COVID-19, BSIs,” the study team reported in Nature Communications.
“Our findings suggest that coronavirus infection directly interferes with the healthy balance of microbes in the gut, further endangering patients in the process,” microbiologist and co–senior author Ken Cadwell, PhD, New York University, added in a news release. “Now that we have uncovered the source of this bacterial imbalance, physicians can better identify those coronavirus patients most at risk of a secondary bloodstream infection.”
In a mouse model, the researchers first demonstrated that the SARS-CoV-2 infection alone induces gut microbiome dysbiosis and gut epithelial cell alterations, which correlate with markers of gut barrier permeability.
Next, they analyzed the bacterial composition of stool samples from 96 adults hospitalized with COVID-19 in 2020 in New York and New Haven, Conn.
In line with their observations in mice, they found that the SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with “severe microbiome injury,” characterized by the loss of gut microbiome diversity.
They also observed an increase in populations of several microbes known to include antibiotic-resistant species. An analysis of stool samples paired with blood cultures found that antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the gut migrated to the bloodstream in 20% of patients.
This migration could be caused by a combination of the immune-compromising effects of the viral infection and the antibiotic-driven depletion of commensal gut microbes, the researchers said.
However, COVID-19 patients are also uniquely exposed to other potential factors predisposing them to bacteremia, including immunosuppressive drugs, long hospital stays, and catheters, the investigators noted. The study is limited in its ability to investigate the individual effects of these factors.
“Our findings support a scenario in which gut-to-blood translocation of microorganisms following microbiome dysbiosis leads to dangerous BSIs during COVID-19, a complication seen in other immunocompromised patients, including patients with cancer, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and in ICU patients receiving probiotics,” the researchers wrote.
Investigating the underlying mechanism behind their observations could help inform “the judicious application of antibiotics and immunosuppressives in patients with respiratory viral infections and increase our resilience to pandemics,” they added.
Funding for the study was provided by the National Institutes of Health, the Yale School of Public Health, and numerous other sources. Dr. Cadwell has received research support from Pfizer, Takeda, Pacific Biosciences, Genentech, and AbbVie; consulted for or received an honoraria from PureTech Health, Genentech, and AbbVie; and is named as an inventor on US patent 10,722,600 and provisional patents 62/935,035 and 63/157,225.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
Genital HSV shedding declines rapidly in first year post infection
Shedding of genital herpes simplex virus was frequent soon after first-time infection but declined significantly during the first year, based on data from 82 individuals.
Genital herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections remain common and incurable; consequently, the population with residual infection continues to rise, Christine Johnston, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues wrote. However, data on the viral shedding trajectory of genital HSV-1 are limited, although HSV-1 accounts for an increasing number of infections.
In a study published in JAMA the researchers recruited 82 women with first-episode genital HSV-1 infections from sexual health and primary care clinics in Seattle, between 2013 and 2018. The participants supplied self-collected oral and genital swabs for daily HSV polymerase chain reaction testing for two 30-day periods at 2 months and 11 months after their initial symptoms. The study population was not pregnant and did not have HIV infection. The median age of the participants was 26 years, 54 were women, and 42 had primary HSV-1 infections. Primary HSV-1 infection was defined as the lack of HSV antibody at baseline or an evolving antibody profile, based on the University of Washington HSV Western Blot.
The primary outcome was the rates of genital and oral HSV shedding and lesions at 2 and 11 months and up to 2 years after an initial HSV-1 infection.
At 2 months, approximately two-thirds (64.6%) of the participants had HSV-1 in the genital tract and 29.3% had virus in the mouth. Genital shedding of HSV-1 was detected in 12.1% of 2,264 total testing days at 2 months, but this rate declined to 7.1% of 1,719 testing days at 11 months (relative risk, 0.52).
The researchers identified oral HSV-1 shedding on 3.9% of 2,247 testing days at 2 months, with a slight increase to 5.1% of 1,714 testing days at 11 months.
Both genital and oral lesions were rare, with reports of 2.6% and 0.4%, respectively, at 2 months and 3.8% and 0.5%, respectively, at 11 months.
The risk of genital shedding was significantly higher in individuals with primary HSV-1, compared with those with nonprimary infections (7.9% vs. 2.9%; RR, 2.75). The overall rate of genital shedding was 17.2% for those with primary HSV-1, of which 15.2% was asymptomatic. Oral shedding was similar for individuals with primary and nonprimary HSV in a multivariate analysis.
In addition, HSV-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses were identified in all participants, and these remained stable during the study period. No association appeared between rates of genital and oral shedding and the proportion of cells that expressed two, three, or four cytokines.
The current study is the first known to comprehensively assess genital and oral HSV-1 viral shedding using polymerase chain reaction, the researchers wrote. “Characterizing shedding rates is clinically important because patients with genital herpes are often concerned about transmission to sexual partners, which usually occurs in the absence of lesions.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the 22% loss of participants to follow-up by the end of the first year, and the use of data from a single location with a primarily White population, the researchers noted. Another limitation was reliance on self-reports and the potential underestimation of recurrences because of the possible use of antiviral medications between swabbing periods.
However, the results indicate the early frequency of HSV-1 shedding and suggest that suppressive therapy might benefit individuals with primary HSV-1 during their first year of infection, the researchers said.
Findings may improve HSV management
The current study helps fill a knowledge gap regarding the natural history of genital HSV-1 infections, Richard J. Whitley, MD, and Edward W. Hook III, MD, both of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, wrote in an accompanying editorial. Despite the small study population, the data represent the largest cohort to date of individuals with first-episode infection and up to 2 years’ follow-up.
Although HSV-2 shedding is greater and associated with more symptoms, seroprevalence of HSV-2 in the United States is declining, they noted. Therefore, the findings can inform patient counseling and recommendations for antiviral therapy that may extend to managing HSV-1 in pregnant women as well, although no pregnant women were included in the study.
“For clinicians, these data emphasize the importance of determining the HSV viral type in persons presenting with initial episodes of genital herpes to accurately counsel patients regarding risk of clinical recurrence, the likelihood of asymptomatic shedding of virus and hence transmission, and antiviral prophylaxis,” the editorialists emphasized. For investigators, the results should prompt additional studies of the host defense against HSV and improved serological testing.
Study supports need for attention to HSV-1
“Genital herpes is an extremely common sexually transmitted infection, and often only HSV-2 is measured,” Sarah W. Prager, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “This study shows that HSV-1 also accounts for a significant amount of genital disease, and should also be considered when determining prevalence of genital herpes.
“I was not surprised to see that viral shedding decreased significantly over the first year after diagnosis, and similarly not surprised that lesions were rare after the initial infection,” said Dr. Prager, who was not involved in the study. “I was somewhat surprised to see that genital HSV-1 shedding was more common than oral shedding.”
Dr. Prager said that she would advise clinicians against serum HSV testing unless someone has an active genital lesion. “Testing after a lesion will often reveal HSV-1, and patients should be counseled that shedding will decrease over the first year. Subsequent genital lesions are uncommon, but certainly possible, and oral lesions and shedding are both rare.” ]
More research is needed in a more diverse population, Dr. Prager emphasized. Following patients for more than a year and learning more about the use of antiviral medications also would be useful.
The study was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases through grants to several authors, including lead author Dr. Johnston. Dr. Johnston also disclosed personal fees from AbbVie, grants from Gilead, royalties from UpToDate, and personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline unrelated to the current study. Dr. Whitley disclosed personal fees from Virios Therapeutics as a board member and shareholder during the conduct of the study, royalties from Aettis unrelated to the submitted work, and serving on an advisory board for Visby Diagnostics. Dr. Hook disclosed serving on an advisory board for Visby Diagnostics unrelated to the submitted work. Dr. Prager had no conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Ob.Gyn News.
Shedding of genital herpes simplex virus was frequent soon after first-time infection but declined significantly during the first year, based on data from 82 individuals.
Genital herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections remain common and incurable; consequently, the population with residual infection continues to rise, Christine Johnston, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues wrote. However, data on the viral shedding trajectory of genital HSV-1 are limited, although HSV-1 accounts for an increasing number of infections.
In a study published in JAMA the researchers recruited 82 women with first-episode genital HSV-1 infections from sexual health and primary care clinics in Seattle, between 2013 and 2018. The participants supplied self-collected oral and genital swabs for daily HSV polymerase chain reaction testing for two 30-day periods at 2 months and 11 months after their initial symptoms. The study population was not pregnant and did not have HIV infection. The median age of the participants was 26 years, 54 were women, and 42 had primary HSV-1 infections. Primary HSV-1 infection was defined as the lack of HSV antibody at baseline or an evolving antibody profile, based on the University of Washington HSV Western Blot.
The primary outcome was the rates of genital and oral HSV shedding and lesions at 2 and 11 months and up to 2 years after an initial HSV-1 infection.
At 2 months, approximately two-thirds (64.6%) of the participants had HSV-1 in the genital tract and 29.3% had virus in the mouth. Genital shedding of HSV-1 was detected in 12.1% of 2,264 total testing days at 2 months, but this rate declined to 7.1% of 1,719 testing days at 11 months (relative risk, 0.52).
The researchers identified oral HSV-1 shedding on 3.9% of 2,247 testing days at 2 months, with a slight increase to 5.1% of 1,714 testing days at 11 months.
Both genital and oral lesions were rare, with reports of 2.6% and 0.4%, respectively, at 2 months and 3.8% and 0.5%, respectively, at 11 months.
The risk of genital shedding was significantly higher in individuals with primary HSV-1, compared with those with nonprimary infections (7.9% vs. 2.9%; RR, 2.75). The overall rate of genital shedding was 17.2% for those with primary HSV-1, of which 15.2% was asymptomatic. Oral shedding was similar for individuals with primary and nonprimary HSV in a multivariate analysis.
In addition, HSV-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses were identified in all participants, and these remained stable during the study period. No association appeared between rates of genital and oral shedding and the proportion of cells that expressed two, three, or four cytokines.
The current study is the first known to comprehensively assess genital and oral HSV-1 viral shedding using polymerase chain reaction, the researchers wrote. “Characterizing shedding rates is clinically important because patients with genital herpes are often concerned about transmission to sexual partners, which usually occurs in the absence of lesions.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the 22% loss of participants to follow-up by the end of the first year, and the use of data from a single location with a primarily White population, the researchers noted. Another limitation was reliance on self-reports and the potential underestimation of recurrences because of the possible use of antiviral medications between swabbing periods.
However, the results indicate the early frequency of HSV-1 shedding and suggest that suppressive therapy might benefit individuals with primary HSV-1 during their first year of infection, the researchers said.
Findings may improve HSV management
The current study helps fill a knowledge gap regarding the natural history of genital HSV-1 infections, Richard J. Whitley, MD, and Edward W. Hook III, MD, both of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, wrote in an accompanying editorial. Despite the small study population, the data represent the largest cohort to date of individuals with first-episode infection and up to 2 years’ follow-up.
Although HSV-2 shedding is greater and associated with more symptoms, seroprevalence of HSV-2 in the United States is declining, they noted. Therefore, the findings can inform patient counseling and recommendations for antiviral therapy that may extend to managing HSV-1 in pregnant women as well, although no pregnant women were included in the study.
“For clinicians, these data emphasize the importance of determining the HSV viral type in persons presenting with initial episodes of genital herpes to accurately counsel patients regarding risk of clinical recurrence, the likelihood of asymptomatic shedding of virus and hence transmission, and antiviral prophylaxis,” the editorialists emphasized. For investigators, the results should prompt additional studies of the host defense against HSV and improved serological testing.
Study supports need for attention to HSV-1
“Genital herpes is an extremely common sexually transmitted infection, and often only HSV-2 is measured,” Sarah W. Prager, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “This study shows that HSV-1 also accounts for a significant amount of genital disease, and should also be considered when determining prevalence of genital herpes.
“I was not surprised to see that viral shedding decreased significantly over the first year after diagnosis, and similarly not surprised that lesions were rare after the initial infection,” said Dr. Prager, who was not involved in the study. “I was somewhat surprised to see that genital HSV-1 shedding was more common than oral shedding.”
Dr. Prager said that she would advise clinicians against serum HSV testing unless someone has an active genital lesion. “Testing after a lesion will often reveal HSV-1, and patients should be counseled that shedding will decrease over the first year. Subsequent genital lesions are uncommon, but certainly possible, and oral lesions and shedding are both rare.” ]
More research is needed in a more diverse population, Dr. Prager emphasized. Following patients for more than a year and learning more about the use of antiviral medications also would be useful.
The study was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases through grants to several authors, including lead author Dr. Johnston. Dr. Johnston also disclosed personal fees from AbbVie, grants from Gilead, royalties from UpToDate, and personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline unrelated to the current study. Dr. Whitley disclosed personal fees from Virios Therapeutics as a board member and shareholder during the conduct of the study, royalties from Aettis unrelated to the submitted work, and serving on an advisory board for Visby Diagnostics. Dr. Hook disclosed serving on an advisory board for Visby Diagnostics unrelated to the submitted work. Dr. Prager had no conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Ob.Gyn News.
Shedding of genital herpes simplex virus was frequent soon after first-time infection but declined significantly during the first year, based on data from 82 individuals.
Genital herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections remain common and incurable; consequently, the population with residual infection continues to rise, Christine Johnston, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues wrote. However, data on the viral shedding trajectory of genital HSV-1 are limited, although HSV-1 accounts for an increasing number of infections.
In a study published in JAMA the researchers recruited 82 women with first-episode genital HSV-1 infections from sexual health and primary care clinics in Seattle, between 2013 and 2018. The participants supplied self-collected oral and genital swabs for daily HSV polymerase chain reaction testing for two 30-day periods at 2 months and 11 months after their initial symptoms. The study population was not pregnant and did not have HIV infection. The median age of the participants was 26 years, 54 were women, and 42 had primary HSV-1 infections. Primary HSV-1 infection was defined as the lack of HSV antibody at baseline or an evolving antibody profile, based on the University of Washington HSV Western Blot.
The primary outcome was the rates of genital and oral HSV shedding and lesions at 2 and 11 months and up to 2 years after an initial HSV-1 infection.
At 2 months, approximately two-thirds (64.6%) of the participants had HSV-1 in the genital tract and 29.3% had virus in the mouth. Genital shedding of HSV-1 was detected in 12.1% of 2,264 total testing days at 2 months, but this rate declined to 7.1% of 1,719 testing days at 11 months (relative risk, 0.52).
The researchers identified oral HSV-1 shedding on 3.9% of 2,247 testing days at 2 months, with a slight increase to 5.1% of 1,714 testing days at 11 months.
Both genital and oral lesions were rare, with reports of 2.6% and 0.4%, respectively, at 2 months and 3.8% and 0.5%, respectively, at 11 months.
The risk of genital shedding was significantly higher in individuals with primary HSV-1, compared with those with nonprimary infections (7.9% vs. 2.9%; RR, 2.75). The overall rate of genital shedding was 17.2% for those with primary HSV-1, of which 15.2% was asymptomatic. Oral shedding was similar for individuals with primary and nonprimary HSV in a multivariate analysis.
In addition, HSV-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses were identified in all participants, and these remained stable during the study period. No association appeared between rates of genital and oral shedding and the proportion of cells that expressed two, three, or four cytokines.
The current study is the first known to comprehensively assess genital and oral HSV-1 viral shedding using polymerase chain reaction, the researchers wrote. “Characterizing shedding rates is clinically important because patients with genital herpes are often concerned about transmission to sexual partners, which usually occurs in the absence of lesions.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the 22% loss of participants to follow-up by the end of the first year, and the use of data from a single location with a primarily White population, the researchers noted. Another limitation was reliance on self-reports and the potential underestimation of recurrences because of the possible use of antiviral medications between swabbing periods.
However, the results indicate the early frequency of HSV-1 shedding and suggest that suppressive therapy might benefit individuals with primary HSV-1 during their first year of infection, the researchers said.
Findings may improve HSV management
The current study helps fill a knowledge gap regarding the natural history of genital HSV-1 infections, Richard J. Whitley, MD, and Edward W. Hook III, MD, both of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, wrote in an accompanying editorial. Despite the small study population, the data represent the largest cohort to date of individuals with first-episode infection and up to 2 years’ follow-up.
Although HSV-2 shedding is greater and associated with more symptoms, seroprevalence of HSV-2 in the United States is declining, they noted. Therefore, the findings can inform patient counseling and recommendations for antiviral therapy that may extend to managing HSV-1 in pregnant women as well, although no pregnant women were included in the study.
“For clinicians, these data emphasize the importance of determining the HSV viral type in persons presenting with initial episodes of genital herpes to accurately counsel patients regarding risk of clinical recurrence, the likelihood of asymptomatic shedding of virus and hence transmission, and antiviral prophylaxis,” the editorialists emphasized. For investigators, the results should prompt additional studies of the host defense against HSV and improved serological testing.
Study supports need for attention to HSV-1
“Genital herpes is an extremely common sexually transmitted infection, and often only HSV-2 is measured,” Sarah W. Prager, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “This study shows that HSV-1 also accounts for a significant amount of genital disease, and should also be considered when determining prevalence of genital herpes.
“I was not surprised to see that viral shedding decreased significantly over the first year after diagnosis, and similarly not surprised that lesions were rare after the initial infection,” said Dr. Prager, who was not involved in the study. “I was somewhat surprised to see that genital HSV-1 shedding was more common than oral shedding.”
Dr. Prager said that she would advise clinicians against serum HSV testing unless someone has an active genital lesion. “Testing after a lesion will often reveal HSV-1, and patients should be counseled that shedding will decrease over the first year. Subsequent genital lesions are uncommon, but certainly possible, and oral lesions and shedding are both rare.” ]
More research is needed in a more diverse population, Dr. Prager emphasized. Following patients for more than a year and learning more about the use of antiviral medications also would be useful.
The study was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases through grants to several authors, including lead author Dr. Johnston. Dr. Johnston also disclosed personal fees from AbbVie, grants from Gilead, royalties from UpToDate, and personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline unrelated to the current study. Dr. Whitley disclosed personal fees from Virios Therapeutics as a board member and shareholder during the conduct of the study, royalties from Aettis unrelated to the submitted work, and serving on an advisory board for Visby Diagnostics. Dr. Hook disclosed serving on an advisory board for Visby Diagnostics unrelated to the submitted work. Dr. Prager had no conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Ob.Gyn News.
FROM JAMA
Children and COVID: Weekly cases can’t sustain downward trend
New COVID-19 cases in children inched up in late October, just 1 week after dipping to their lowest level in more than a year, and some measures of pediatric emergency visits and hospital admissions rose as well.
There was an 8% increase in the number of cases for the week of Oct. 21-27, compared with the previous week, but this week’s total was still below 25,000, and the overall trend since the beginning of September is still one of decline, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.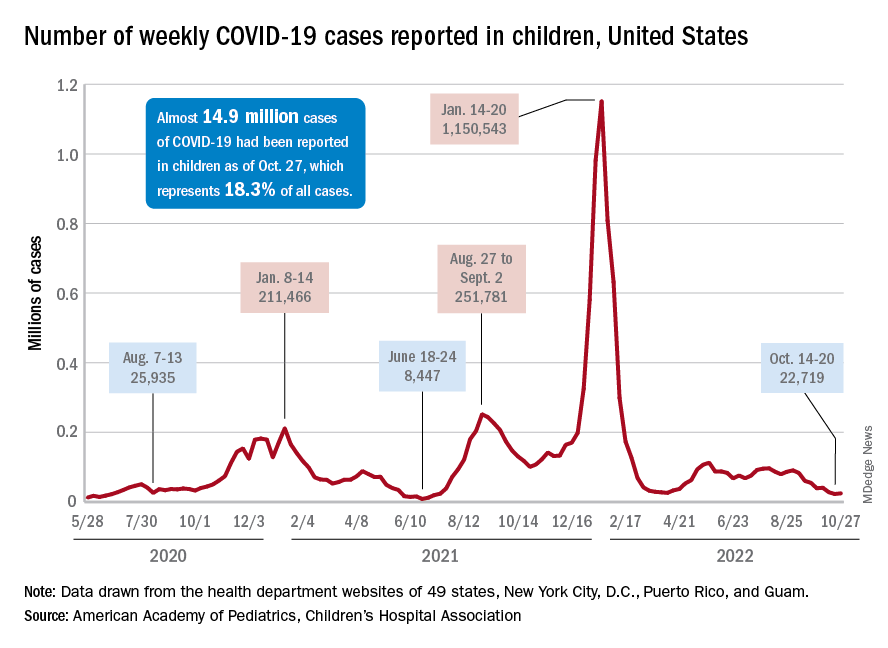
A similar increase can be seen for hospitalizations with confirmed COVID. The rate for children aged 0-17 years fell from 0.44 admissions per 100,000 population at the end of August to 0.16 per 100,000 on Oct. 23. Hospitalizations have since ticked up to 0.17 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID among children aged 16-17 years, as a percentage of all ED visits, rose from 0.6% on Oct. 21 to 0.8% on Oct. 26. ED visits for 12- to 15-year-olds rose from 0.6% to 0.7% at about the same time, with both increases coming after declines that started in late August. No such increase has occurred yet among children aged 0-11 years, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
One small milestone reached in the past week involved the proportion of all COVID cases that have occurred in children. The total number of child cases as of Oct. 27 was almost 14.9 million, which represents 18.3% of cases in all Americans, according to the AAP and CHA. That figure had been sitting at 18.4% since mid-August after reaching as high as 19.0% during the spring.
The CDC puts total COVID-related hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 at 163,588 since Aug. 1, 2020, which is 3.0% of all U.S. admissions. Total pediatric deaths number 1,843, or just about 0.2% of all COVID-related fatalities since the start of the pandemic, the CDC data show.
The latest vaccination figures show that 71.3% of children aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, as have 38.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 8.4% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 5.5% of those under age 2. Full vaccination by age group looks like this: 60.9% (12-17 years), 31.7% (5-11 years), 3.7% (2-4 years), and 2.1% (<2 years), the CDC reported. Almost 30% of children aged 12-17 have gotten a first booster dose, as have 16% of 5- to 11-year-olds.
New COVID-19 cases in children inched up in late October, just 1 week after dipping to their lowest level in more than a year, and some measures of pediatric emergency visits and hospital admissions rose as well.
There was an 8% increase in the number of cases for the week of Oct. 21-27, compared with the previous week, but this week’s total was still below 25,000, and the overall trend since the beginning of September is still one of decline, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
A similar increase can be seen for hospitalizations with confirmed COVID. The rate for children aged 0-17 years fell from 0.44 admissions per 100,000 population at the end of August to 0.16 per 100,000 on Oct. 23. Hospitalizations have since ticked up to 0.17 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID among children aged 16-17 years, as a percentage of all ED visits, rose from 0.6% on Oct. 21 to 0.8% on Oct. 26. ED visits for 12- to 15-year-olds rose from 0.6% to 0.7% at about the same time, with both increases coming after declines that started in late August. No such increase has occurred yet among children aged 0-11 years, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
One small milestone reached in the past week involved the proportion of all COVID cases that have occurred in children. The total number of child cases as of Oct. 27 was almost 14.9 million, which represents 18.3% of cases in all Americans, according to the AAP and CHA. That figure had been sitting at 18.4% since mid-August after reaching as high as 19.0% during the spring.
The CDC puts total COVID-related hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 at 163,588 since Aug. 1, 2020, which is 3.0% of all U.S. admissions. Total pediatric deaths number 1,843, or just about 0.2% of all COVID-related fatalities since the start of the pandemic, the CDC data show.
The latest vaccination figures show that 71.3% of children aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, as have 38.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 8.4% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 5.5% of those under age 2. Full vaccination by age group looks like this: 60.9% (12-17 years), 31.7% (5-11 years), 3.7% (2-4 years), and 2.1% (<2 years), the CDC reported. Almost 30% of children aged 12-17 have gotten a first booster dose, as have 16% of 5- to 11-year-olds.
New COVID-19 cases in children inched up in late October, just 1 week after dipping to their lowest level in more than a year, and some measures of pediatric emergency visits and hospital admissions rose as well.
There was an 8% increase in the number of cases for the week of Oct. 21-27, compared with the previous week, but this week’s total was still below 25,000, and the overall trend since the beginning of September is still one of decline, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
A similar increase can be seen for hospitalizations with confirmed COVID. The rate for children aged 0-17 years fell from 0.44 admissions per 100,000 population at the end of August to 0.16 per 100,000 on Oct. 23. Hospitalizations have since ticked up to 0.17 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID among children aged 16-17 years, as a percentage of all ED visits, rose from 0.6% on Oct. 21 to 0.8% on Oct. 26. ED visits for 12- to 15-year-olds rose from 0.6% to 0.7% at about the same time, with both increases coming after declines that started in late August. No such increase has occurred yet among children aged 0-11 years, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
One small milestone reached in the past week involved the proportion of all COVID cases that have occurred in children. The total number of child cases as of Oct. 27 was almost 14.9 million, which represents 18.3% of cases in all Americans, according to the AAP and CHA. That figure had been sitting at 18.4% since mid-August after reaching as high as 19.0% during the spring.
The CDC puts total COVID-related hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 at 163,588 since Aug. 1, 2020, which is 3.0% of all U.S. admissions. Total pediatric deaths number 1,843, or just about 0.2% of all COVID-related fatalities since the start of the pandemic, the CDC data show.
The latest vaccination figures show that 71.3% of children aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, as have 38.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 8.4% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 5.5% of those under age 2. Full vaccination by age group looks like this: 60.9% (12-17 years), 31.7% (5-11 years), 3.7% (2-4 years), and 2.1% (<2 years), the CDC reported. Almost 30% of children aged 12-17 have gotten a first booster dose, as have 16% of 5- to 11-year-olds.
Oral FMT on par with colonic FMT for recurrent C. difficile
A real-world analysis confirms that fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is highly effective for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection (rCDI) – and there is no difference between delivery by capsule (cap-FMT) and colonoscopy (colo-FMT).
“We present one of the largest cohorts involving people who received capsule FMT. Byron Vaughn, MD, with the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said in an interview.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The Food and Drug Administration allows FMT to be used for patients who have failed standard treatment for rCDI under a policy of enforcement discretion.
The past decade has seen an increase in the use of FMT in clinical practice, owing to an increase in cases of rCDI after failure of standard antibiotic therapy.
Unlike antibiotics, which perpetuate and worsen intestinal dysbiosis, FMT restores the diversity and function of host microbiota, effectively breaking the cycle of rCDI, the authors of the study noted. But it’s been unclear whether the efficacy and safety of FMT vary by route of administration.
Effective without procedural risks
To investigate, Dr. Vaughn and colleagues evaluated clinical outcomes and adverse events in 170 patients with rCDI who underwent cap-FMT and 96 peers who underwent colo-FMT.
FMT was performed using one of two standardized formulations of microbiota manufactured by the University of Minnesota microbiota therapeutics program: freeze-dried/encapsulated or frozen-thawed/liquid.
Overall, the cure rates of CDI were 86% at 1 month and 81% at 2 months. There was no statistically significant difference at either time between cap-FMT and colo-FMT.
The 1-month cure rate was 84% with cap-FMT and 91% with colo-FMT; at 2 months, the cure rates were 81% and 83%, respectively.
Cap-FMT has a safety and effectiveness profile similar to that of colo-FMT, without the procedural risks of colonoscopy, the researchers concluded.
They cautioned that, although FMT is highly effective overall, patient selection is a key factor to optimizing FMT success.
Older age and hemodialysis were associated with FMT failure by 2 months on multivariate logistic regression.
“These risk factors can help determine if a patient should receive FMT or an alternative therapy for rCDI. This is not to say FMT should be avoided in older patients or those on dialysis, but clinicians should be aware of these associations in light of other options for rCDI,” Dr. Vaughn said.
Confirming prior studies, antibiotic use after FMT was a major factor in its failure. Patient selection for FMT should include an assessment of the potential need for antibiotics after transplant, the researchers noted.
One serious adverse event (aspiration pneumonia) was related to colonoscopy; otherwise, no new safety signals were identified.
As reported in other studies, changes in bowel function, including diarrhea, constipation, gas, and bloating were common, although it’s tough to disentangle gastrointestinal symptoms related to FMT from those after CDI, the researchers said. Importantly, no transmission of an infectious agent related to FMT was identified.
Two good options
The researchers said their findings are “highly generalizable” because the population reflects all FMT use by participating institutions and contains a mix of academic centers and private practices.
Many patients included in the study would not have been eligible for a clinical trial, owing to their having many comorbid conditions, including immune compromise and inflammatory bowel disease, the authors noted.
“FMT is recommended by major gastroenterology and infectious disease society guidelines,” Dr. Vaughn said. “Our group, and others, have consistently found strategies that incorporate FMT as cost-effective strategies for treating rCDI.”
However, lack of access to FMT products often is a barrier to treatment, he said.
“A stool banking model, similar to the nonprofit blood banking model, may be a useful solution to ensure equitable access to FMT to all who need it,” Dr. Vaughn added.
Reached for comment, Majdi Osman, MD, MPH, told this news organization that the study is valuable, “as it nicely shows in a real-world setting that capsules and colonoscopy are good options for patients who need this.”
Dr. Osman is chief medical officer of OpenBiome, a nonprofit organization that operates a public stool bank and is the major FMT source in the United States. The organization has provided over 63,000 FMT treatments to over 1,200 hospitals in the United States.
“FMT has become standard of care for patients who failed antibiotic therapy, and certainly is being used widely as a treatment option for these patients who have often run out of existing options,” Dr. Osman said.
Support for the study was provided by a donation from Achieving Cures Together, a nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing microbiome-based research. Dr. Vaughn receives grant support from Takeda, Roche, Celgene, and Diasorin and has received consulting fees from Prometheus and AbbVie. Dr. Osman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A real-world analysis confirms that fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is highly effective for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection (rCDI) – and there is no difference between delivery by capsule (cap-FMT) and colonoscopy (colo-FMT).
“We present one of the largest cohorts involving people who received capsule FMT. Byron Vaughn, MD, with the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said in an interview.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The Food and Drug Administration allows FMT to be used for patients who have failed standard treatment for rCDI under a policy of enforcement discretion.
The past decade has seen an increase in the use of FMT in clinical practice, owing to an increase in cases of rCDI after failure of standard antibiotic therapy.
Unlike antibiotics, which perpetuate and worsen intestinal dysbiosis, FMT restores the diversity and function of host microbiota, effectively breaking the cycle of rCDI, the authors of the study noted. But it’s been unclear whether the efficacy and safety of FMT vary by route of administration.
Effective without procedural risks
To investigate, Dr. Vaughn and colleagues evaluated clinical outcomes and adverse events in 170 patients with rCDI who underwent cap-FMT and 96 peers who underwent colo-FMT.
FMT was performed using one of two standardized formulations of microbiota manufactured by the University of Minnesota microbiota therapeutics program: freeze-dried/encapsulated or frozen-thawed/liquid.
Overall, the cure rates of CDI were 86% at 1 month and 81% at 2 months. There was no statistically significant difference at either time between cap-FMT and colo-FMT.
The 1-month cure rate was 84% with cap-FMT and 91% with colo-FMT; at 2 months, the cure rates were 81% and 83%, respectively.
Cap-FMT has a safety and effectiveness profile similar to that of colo-FMT, without the procedural risks of colonoscopy, the researchers concluded.
They cautioned that, although FMT is highly effective overall, patient selection is a key factor to optimizing FMT success.
Older age and hemodialysis were associated with FMT failure by 2 months on multivariate logistic regression.
“These risk factors can help determine if a patient should receive FMT or an alternative therapy for rCDI. This is not to say FMT should be avoided in older patients or those on dialysis, but clinicians should be aware of these associations in light of other options for rCDI,” Dr. Vaughn said.
Confirming prior studies, antibiotic use after FMT was a major factor in its failure. Patient selection for FMT should include an assessment of the potential need for antibiotics after transplant, the researchers noted.
One serious adverse event (aspiration pneumonia) was related to colonoscopy; otherwise, no new safety signals were identified.
As reported in other studies, changes in bowel function, including diarrhea, constipation, gas, and bloating were common, although it’s tough to disentangle gastrointestinal symptoms related to FMT from those after CDI, the researchers said. Importantly, no transmission of an infectious agent related to FMT was identified.
Two good options
The researchers said their findings are “highly generalizable” because the population reflects all FMT use by participating institutions and contains a mix of academic centers and private practices.
Many patients included in the study would not have been eligible for a clinical trial, owing to their having many comorbid conditions, including immune compromise and inflammatory bowel disease, the authors noted.
“FMT is recommended by major gastroenterology and infectious disease society guidelines,” Dr. Vaughn said. “Our group, and others, have consistently found strategies that incorporate FMT as cost-effective strategies for treating rCDI.”
However, lack of access to FMT products often is a barrier to treatment, he said.
“A stool banking model, similar to the nonprofit blood banking model, may be a useful solution to ensure equitable access to FMT to all who need it,” Dr. Vaughn added.
Reached for comment, Majdi Osman, MD, MPH, told this news organization that the study is valuable, “as it nicely shows in a real-world setting that capsules and colonoscopy are good options for patients who need this.”
Dr. Osman is chief medical officer of OpenBiome, a nonprofit organization that operates a public stool bank and is the major FMT source in the United States. The organization has provided over 63,000 FMT treatments to over 1,200 hospitals in the United States.
“FMT has become standard of care for patients who failed antibiotic therapy, and certainly is being used widely as a treatment option for these patients who have often run out of existing options,” Dr. Osman said.
Support for the study was provided by a donation from Achieving Cures Together, a nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing microbiome-based research. Dr. Vaughn receives grant support from Takeda, Roche, Celgene, and Diasorin and has received consulting fees from Prometheus and AbbVie. Dr. Osman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A real-world analysis confirms that fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is highly effective for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection (rCDI) – and there is no difference between delivery by capsule (cap-FMT) and colonoscopy (colo-FMT).
“We present one of the largest cohorts involving people who received capsule FMT. Byron Vaughn, MD, with the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said in an interview.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The Food and Drug Administration allows FMT to be used for patients who have failed standard treatment for rCDI under a policy of enforcement discretion.
The past decade has seen an increase in the use of FMT in clinical practice, owing to an increase in cases of rCDI after failure of standard antibiotic therapy.
Unlike antibiotics, which perpetuate and worsen intestinal dysbiosis, FMT restores the diversity and function of host microbiota, effectively breaking the cycle of rCDI, the authors of the study noted. But it’s been unclear whether the efficacy and safety of FMT vary by route of administration.
Effective without procedural risks
To investigate, Dr. Vaughn and colleagues evaluated clinical outcomes and adverse events in 170 patients with rCDI who underwent cap-FMT and 96 peers who underwent colo-FMT.
FMT was performed using one of two standardized formulations of microbiota manufactured by the University of Minnesota microbiota therapeutics program: freeze-dried/encapsulated or frozen-thawed/liquid.
Overall, the cure rates of CDI were 86% at 1 month and 81% at 2 months. There was no statistically significant difference at either time between cap-FMT and colo-FMT.
The 1-month cure rate was 84% with cap-FMT and 91% with colo-FMT; at 2 months, the cure rates were 81% and 83%, respectively.
Cap-FMT has a safety and effectiveness profile similar to that of colo-FMT, without the procedural risks of colonoscopy, the researchers concluded.
They cautioned that, although FMT is highly effective overall, patient selection is a key factor to optimizing FMT success.
Older age and hemodialysis were associated with FMT failure by 2 months on multivariate logistic regression.
“These risk factors can help determine if a patient should receive FMT or an alternative therapy for rCDI. This is not to say FMT should be avoided in older patients or those on dialysis, but clinicians should be aware of these associations in light of other options for rCDI,” Dr. Vaughn said.
Confirming prior studies, antibiotic use after FMT was a major factor in its failure. Patient selection for FMT should include an assessment of the potential need for antibiotics after transplant, the researchers noted.
One serious adverse event (aspiration pneumonia) was related to colonoscopy; otherwise, no new safety signals were identified.
As reported in other studies, changes in bowel function, including diarrhea, constipation, gas, and bloating were common, although it’s tough to disentangle gastrointestinal symptoms related to FMT from those after CDI, the researchers said. Importantly, no transmission of an infectious agent related to FMT was identified.
Two good options
The researchers said their findings are “highly generalizable” because the population reflects all FMT use by participating institutions and contains a mix of academic centers and private practices.
Many patients included in the study would not have been eligible for a clinical trial, owing to their having many comorbid conditions, including immune compromise and inflammatory bowel disease, the authors noted.
“FMT is recommended by major gastroenterology and infectious disease society guidelines,” Dr. Vaughn said. “Our group, and others, have consistently found strategies that incorporate FMT as cost-effective strategies for treating rCDI.”
However, lack of access to FMT products often is a barrier to treatment, he said.
“A stool banking model, similar to the nonprofit blood banking model, may be a useful solution to ensure equitable access to FMT to all who need it,” Dr. Vaughn added.
Reached for comment, Majdi Osman, MD, MPH, told this news organization that the study is valuable, “as it nicely shows in a real-world setting that capsules and colonoscopy are good options for patients who need this.”
Dr. Osman is chief medical officer of OpenBiome, a nonprofit organization that operates a public stool bank and is the major FMT source in the United States. The organization has provided over 63,000 FMT treatments to over 1,200 hospitals in the United States.
“FMT has become standard of care for patients who failed antibiotic therapy, and certainly is being used widely as a treatment option for these patients who have often run out of existing options,” Dr. Osman said.
Support for the study was provided by a donation from Achieving Cures Together, a nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing microbiome-based research. Dr. Vaughn receives grant support from Takeda, Roche, Celgene, and Diasorin and has received consulting fees from Prometheus and AbbVie. Dr. Osman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Recurrent urinary tract infections: What’s good prophylaxis?
For those affected, recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) are sometimes stressful. However, even an informative discussion about risk factors and the imparting of behavioral recommendations can be very helpful for many women. Antibiotic prophylaxis should only be considered once all nonantibiotic therapy options have been exhausted.
One in seven women suffers at least once a year from cystitis. Around a third of those women develop a further urinary tract infection 6-12 months after the first infection. A urinary tract infection is classified as recurrent if two symptomatic episodes have occurred within the last 6 months or if three episodes have occurred within the last 12 months.
There are many different approaches to reducing the recurrence rate of urinary tract infections, Daniel Klussmann and Florian Wagenlehner, MD, of the department and outpatient clinic for urology at the University of Giessen (Germany) wrote in DMW Klinischer Fortschritt. Aside from general information and advice,
Fluids and D-mannose
An individual consultation discussion is the most important nonantibiotic strategy. Studies have shown that this strategy alone can lower the frequency of recurrent UTIs. According to the authors, special education programs on the causes and behavioral measures are especially helpful. Included in these programs is the recommendation to drink a sufficient, but not excessive, amount of fluids: approximately 1.5 liters per day. In one randomized study, this level of consumption halved UTI frequency. However, drinking an excessive amount of fluids should also be avoided, otherwise the antimicrobial peptides present in the urine become overly diluted.
The regular consumption of fruit juice, especially of that from berries, is also beneficial, according to the authors. However, study results on long-term prevention using cranberry products are inconsistent, and they are not recommended in the updated guideline. Like cranberries, D-mannose also inhibits the fimbriae of the Escherichia coli bacteria and therefore the bacteria’s ability to bind to the bladder epithelium. The authors cite a study in which, following the intake of 2 g of D-mannose dissolved in a glass of water every day, the rate of urinary tract infections dropped significantly, compared with consumption of placebo.
Additional recommendations in the S3 guideline include various phytotherapeutic products such as bearberry leaves, nasturtium herb, or horseradish root, although studies on the comparability of phytotherapeutic agents are very difficult to execute, the authors conceded.
It is already known that there is a positive correlation (by a factor of 60) between the recurrence rate of UTIs and the frequency of sexual intercourse. Even with contraceptive methods (such as vaginal suppositories, diaphragms or condoms coated with spermicide, and intrauterine devices), the risk of urinary tract infections increases by a factor of 2-14. Sexual abstinence, even if temporary, can be a remedy. Evidence for the recommendation to urinate immediately after coitus is contradictory in the literature, however. Excessive intimate hygiene clearly damages the local protective environment.
Estrogen substitution beneficial
For postmenopausal women, there is also the option of local estriol substitution (0.5 mg/day) as another nonantibiotic method of prophylaxis. This treatment serves as therapy for vaginal atrophy and reduces both vaginal colonization with uropathogens and the vaginal pH level. The authors cite Scandinavian studies that detected no increase in the risk of breast cancer from the local application of estriol.
Furthermore, the current guidelines recommend oral immunostimulation with bacterial cell wall components from uropathogenic strains of E. coli (OM-89, Uro-Vaxom). The authors reported on two meta-studies in which the average recurrence rate was reduced by 39%, compared with placebo. In addition, the treatment time for breakthrough infections decreased significantly, and prevention with OM-89 could even be started during acute therapy. Also recommended is parenteral immunostimulation with inactivated pathogens (StroVac). Acupuncture as cutaneous immunostimulation has also displayed a positive protective effect.
Only when nonantibiotic therapy fails and the patient is under a high amount of psychological strain should antibiotic prophylaxis be initiated, according to the authors. A period of 3-6 months should be the target here. When choosing an antibiotic and before starting therapy, the corresponding pathogen should be confirmed through a urine culture, and resistance testing should be performed. On the other hand, single-use, postcoital antibiotic prevention could be an alternative, particularly for women in whom a correlation between recurrent UTIs and sexual intercourse has been suspected, the authors wrote.
This article was translated from Univadis Germany. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
For those affected, recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) are sometimes stressful. However, even an informative discussion about risk factors and the imparting of behavioral recommendations can be very helpful for many women. Antibiotic prophylaxis should only be considered once all nonantibiotic therapy options have been exhausted.
One in seven women suffers at least once a year from cystitis. Around a third of those women develop a further urinary tract infection 6-12 months after the first infection. A urinary tract infection is classified as recurrent if two symptomatic episodes have occurred within the last 6 months or if three episodes have occurred within the last 12 months.
There are many different approaches to reducing the recurrence rate of urinary tract infections, Daniel Klussmann and Florian Wagenlehner, MD, of the department and outpatient clinic for urology at the University of Giessen (Germany) wrote in DMW Klinischer Fortschritt. Aside from general information and advice,
Fluids and D-mannose
An individual consultation discussion is the most important nonantibiotic strategy. Studies have shown that this strategy alone can lower the frequency of recurrent UTIs. According to the authors, special education programs on the causes and behavioral measures are especially helpful. Included in these programs is the recommendation to drink a sufficient, but not excessive, amount of fluids: approximately 1.5 liters per day. In one randomized study, this level of consumption halved UTI frequency. However, drinking an excessive amount of fluids should also be avoided, otherwise the antimicrobial peptides present in the urine become overly diluted.
The regular consumption of fruit juice, especially of that from berries, is also beneficial, according to the authors. However, study results on long-term prevention using cranberry products are inconsistent, and they are not recommended in the updated guideline. Like cranberries, D-mannose also inhibits the fimbriae of the Escherichia coli bacteria and therefore the bacteria’s ability to bind to the bladder epithelium. The authors cite a study in which, following the intake of 2 g of D-mannose dissolved in a glass of water every day, the rate of urinary tract infections dropped significantly, compared with consumption of placebo.
Additional recommendations in the S3 guideline include various phytotherapeutic products such as bearberry leaves, nasturtium herb, or horseradish root, although studies on the comparability of phytotherapeutic agents are very difficult to execute, the authors conceded.
It is already known that there is a positive correlation (by a factor of 60) between the recurrence rate of UTIs and the frequency of sexual intercourse. Even with contraceptive methods (such as vaginal suppositories, diaphragms or condoms coated with spermicide, and intrauterine devices), the risk of urinary tract infections increases by a factor of 2-14. Sexual abstinence, even if temporary, can be a remedy. Evidence for the recommendation to urinate immediately after coitus is contradictory in the literature, however. Excessive intimate hygiene clearly damages the local protective environment.
Estrogen substitution beneficial
For postmenopausal women, there is also the option of local estriol substitution (0.5 mg/day) as another nonantibiotic method of prophylaxis. This treatment serves as therapy for vaginal atrophy and reduces both vaginal colonization with uropathogens and the vaginal pH level. The authors cite Scandinavian studies that detected no increase in the risk of breast cancer from the local application of estriol.
Furthermore, the current guidelines recommend oral immunostimulation with bacterial cell wall components from uropathogenic strains of E. coli (OM-89, Uro-Vaxom). The authors reported on two meta-studies in which the average recurrence rate was reduced by 39%, compared with placebo. In addition, the treatment time for breakthrough infections decreased significantly, and prevention with OM-89 could even be started during acute therapy. Also recommended is parenteral immunostimulation with inactivated pathogens (StroVac). Acupuncture as cutaneous immunostimulation has also displayed a positive protective effect.
Only when nonantibiotic therapy fails and the patient is under a high amount of psychological strain should antibiotic prophylaxis be initiated, according to the authors. A period of 3-6 months should be the target here. When choosing an antibiotic and before starting therapy, the corresponding pathogen should be confirmed through a urine culture, and resistance testing should be performed. On the other hand, single-use, postcoital antibiotic prevention could be an alternative, particularly for women in whom a correlation between recurrent UTIs and sexual intercourse has been suspected, the authors wrote.
This article was translated from Univadis Germany. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
For those affected, recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) are sometimes stressful. However, even an informative discussion about risk factors and the imparting of behavioral recommendations can be very helpful for many women. Antibiotic prophylaxis should only be considered once all nonantibiotic therapy options have been exhausted.
One in seven women suffers at least once a year from cystitis. Around a third of those women develop a further urinary tract infection 6-12 months after the first infection. A urinary tract infection is classified as recurrent if two symptomatic episodes have occurred within the last 6 months or if three episodes have occurred within the last 12 months.
There are many different approaches to reducing the recurrence rate of urinary tract infections, Daniel Klussmann and Florian Wagenlehner, MD, of the department and outpatient clinic for urology at the University of Giessen (Germany) wrote in DMW Klinischer Fortschritt. Aside from general information and advice,
Fluids and D-mannose
An individual consultation discussion is the most important nonantibiotic strategy. Studies have shown that this strategy alone can lower the frequency of recurrent UTIs. According to the authors, special education programs on the causes and behavioral measures are especially helpful. Included in these programs is the recommendation to drink a sufficient, but not excessive, amount of fluids: approximately 1.5 liters per day. In one randomized study, this level of consumption halved UTI frequency. However, drinking an excessive amount of fluids should also be avoided, otherwise the antimicrobial peptides present in the urine become overly diluted.
The regular consumption of fruit juice, especially of that from berries, is also beneficial, according to the authors. However, study results on long-term prevention using cranberry products are inconsistent, and they are not recommended in the updated guideline. Like cranberries, D-mannose also inhibits the fimbriae of the Escherichia coli bacteria and therefore the bacteria’s ability to bind to the bladder epithelium. The authors cite a study in which, following the intake of 2 g of D-mannose dissolved in a glass of water every day, the rate of urinary tract infections dropped significantly, compared with consumption of placebo.
Additional recommendations in the S3 guideline include various phytotherapeutic products such as bearberry leaves, nasturtium herb, or horseradish root, although studies on the comparability of phytotherapeutic agents are very difficult to execute, the authors conceded.
It is already known that there is a positive correlation (by a factor of 60) between the recurrence rate of UTIs and the frequency of sexual intercourse. Even with contraceptive methods (such as vaginal suppositories, diaphragms or condoms coated with spermicide, and intrauterine devices), the risk of urinary tract infections increases by a factor of 2-14. Sexual abstinence, even if temporary, can be a remedy. Evidence for the recommendation to urinate immediately after coitus is contradictory in the literature, however. Excessive intimate hygiene clearly damages the local protective environment.
Estrogen substitution beneficial
For postmenopausal women, there is also the option of local estriol substitution (0.5 mg/day) as another nonantibiotic method of prophylaxis. This treatment serves as therapy for vaginal atrophy and reduces both vaginal colonization with uropathogens and the vaginal pH level. The authors cite Scandinavian studies that detected no increase in the risk of breast cancer from the local application of estriol.
Furthermore, the current guidelines recommend oral immunostimulation with bacterial cell wall components from uropathogenic strains of E. coli (OM-89, Uro-Vaxom). The authors reported on two meta-studies in which the average recurrence rate was reduced by 39%, compared with placebo. In addition, the treatment time for breakthrough infections decreased significantly, and prevention with OM-89 could even be started during acute therapy. Also recommended is parenteral immunostimulation with inactivated pathogens (StroVac). Acupuncture as cutaneous immunostimulation has also displayed a positive protective effect.
Only when nonantibiotic therapy fails and the patient is under a high amount of psychological strain should antibiotic prophylaxis be initiated, according to the authors. A period of 3-6 months should be the target here. When choosing an antibiotic and before starting therapy, the corresponding pathogen should be confirmed through a urine culture, and resistance testing should be performed. On the other hand, single-use, postcoital antibiotic prevention could be an alternative, particularly for women in whom a correlation between recurrent UTIs and sexual intercourse has been suspected, the authors wrote.
This article was translated from Univadis Germany. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DMW KLINISCHER FORTSCHRITT
Original COVID-19 vaccines fall short against Omicron subvariants for the immunocompromised
The effectiveness of up to three doses of COVID-19 vaccine was moderate overall and significantly lower among individuals with immunocompromising conditions, compared with the general population during the period of Omicron dominance, according to an analysis of data from more than 34,000 hospitalizations.
Previous studies have suggested lower COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness among immunocompromised individuals, compared with healthy individuals from the general population, but data from the period in which Omicron subvariants have been dominant are limited, wrote Amadea Britton, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team, and colleagues.
The CDC currently recommends an expanded primary vaccine series of three doses of an mRNA vaccine, and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has recommended a fourth dose with the new bivalent booster that contains elements of the Omicron variant, the researchers noted.
In a study published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, the researchers identified 34,220 adults with immunocompromising conditions who were hospitalized for COVID-19–like illness between Dec. 16, 2021, and Aug. 20, 2022. These conditions included solid malignancy (40.5%), hematologic malignancy (14.6%), rheumatologic or inflammatory disorder (24.4%), other intrinsic immune condition or immunodeficiency (38.5%), or organ or stem cell transplant (8.6%). They used data from the CDC’s VISION Network, a multistate database. The data include spring and summer 2022, when the BA.4 and BA.5 Omicron subvariants dominated other strains, and adults with immunocompromising conditions were eligible for a total of four vaccine doses (two primary doses and two boosters). The median age of the study population was 69 years, and 25.7%, 41.7%, and 7.0% had received two, three, and four doses, respectively, of COVID-19 vaccine.
Overall, vaccine effectiveness (VE) among immunocompromised patients was 34% after two vaccine doses, increasing to 71% during days 7-89 after a third dose, then declining to 41% 90 days or more after that dose.
During the full Omicron period, VE was 36% for 14 or more days after dose two, 69% for 7-89 days after dose three, and 44% for 90 or more days after dose three.
When VE was stratified by sublineage period, VE was higher 7 or more days after dose three during the predominance of BA.1 (67%), compared with VE during the dominant periods of BA.2/BA.2.12.1 (32%) and BA.4/BA.5 (35%).
In the later periods when Omicron BA.2/BA.2.12.1 and BA.4/BA.5 variants dominated, and individuals who had received three doses of vaccine were eligible for a fourth, VE against these variants was 32% 90 or more days after dose three and 43% 7 or more days after dose four.
VE was lowest among individuals with potentially more severe immunocompromising conditions, notably solid organ or stem cell transplants, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of ICD-9 and -10 discharge diagnosis codes for immunocompromising conditions, potential confounding in VE models, lack of data on outpatient treatments such as nirmatelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid), and lack of COVID-19 genomic sequencing data that may have affected which sublineage was identified, the researchers noted.
However, “this study confirms that even with boosters, immunocompromised adults, because of their weakened immune systems, are still at high risk of moderate to severe COVID,” said coauthor Brian Dixon, PhD, of the Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health, Indianapolis, in a press release about the study.
“Given the incomplete protection against hospitalization afforded by monovalent COVID-19 vaccines, persons with immunocompromising conditions might benefit from updated bivalent vaccine booster doses that target recently circulating Omicron sublineages, in line with ACIP [Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices] recommendations,” the researchers concluded in the study.
The study was funded by the CDC. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The VISION Network is a collaboration between the CDC, the Regenstrief Institute, and seven health care systems across the United States: Columbia University Irving Medical Center (New York), HealthPartners (Wisconsin), Intermountain Healthcare (Utah), Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Kaiser Permanente Northwest (Washington State), the University of Colorado, and Paso Del Norte Health Information Exchange (Texas).
The effectiveness of up to three doses of COVID-19 vaccine was moderate overall and significantly lower among individuals with immunocompromising conditions, compared with the general population during the period of Omicron dominance, according to an analysis of data from more than 34,000 hospitalizations.
Previous studies have suggested lower COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness among immunocompromised individuals, compared with healthy individuals from the general population, but data from the period in which Omicron subvariants have been dominant are limited, wrote Amadea Britton, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team, and colleagues.
The CDC currently recommends an expanded primary vaccine series of three doses of an mRNA vaccine, and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has recommended a fourth dose with the new bivalent booster that contains elements of the Omicron variant, the researchers noted.
In a study published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, the researchers identified 34,220 adults with immunocompromising conditions who were hospitalized for COVID-19–like illness between Dec. 16, 2021, and Aug. 20, 2022. These conditions included solid malignancy (40.5%), hematologic malignancy (14.6%), rheumatologic or inflammatory disorder (24.4%), other intrinsic immune condition or immunodeficiency (38.5%), or organ or stem cell transplant (8.6%). They used data from the CDC’s VISION Network, a multistate database. The data include spring and summer 2022, when the BA.4 and BA.5 Omicron subvariants dominated other strains, and adults with immunocompromising conditions were eligible for a total of four vaccine doses (two primary doses and two boosters). The median age of the study population was 69 years, and 25.7%, 41.7%, and 7.0% had received two, three, and four doses, respectively, of COVID-19 vaccine.
Overall, vaccine effectiveness (VE) among immunocompromised patients was 34% after two vaccine doses, increasing to 71% during days 7-89 after a third dose, then declining to 41% 90 days or more after that dose.
During the full Omicron period, VE was 36% for 14 or more days after dose two, 69% for 7-89 days after dose three, and 44% for 90 or more days after dose three.
When VE was stratified by sublineage period, VE was higher 7 or more days after dose three during the predominance of BA.1 (67%), compared with VE during the dominant periods of BA.2/BA.2.12.1 (32%) and BA.4/BA.5 (35%).
In the later periods when Omicron BA.2/BA.2.12.1 and BA.4/BA.5 variants dominated, and individuals who had received three doses of vaccine were eligible for a fourth, VE against these variants was 32% 90 or more days after dose three and 43% 7 or more days after dose four.
VE was lowest among individuals with potentially more severe immunocompromising conditions, notably solid organ or stem cell transplants, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of ICD-9 and -10 discharge diagnosis codes for immunocompromising conditions, potential confounding in VE models, lack of data on outpatient treatments such as nirmatelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid), and lack of COVID-19 genomic sequencing data that may have affected which sublineage was identified, the researchers noted.
However, “this study confirms that even with boosters, immunocompromised adults, because of their weakened immune systems, are still at high risk of moderate to severe COVID,” said coauthor Brian Dixon, PhD, of the Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health, Indianapolis, in a press release about the study.
“Given the incomplete protection against hospitalization afforded by monovalent COVID-19 vaccines, persons with immunocompromising conditions might benefit from updated bivalent vaccine booster doses that target recently circulating Omicron sublineages, in line with ACIP [Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices] recommendations,” the researchers concluded in the study.
The study was funded by the CDC. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The VISION Network is a collaboration between the CDC, the Regenstrief Institute, and seven health care systems across the United States: Columbia University Irving Medical Center (New York), HealthPartners (Wisconsin), Intermountain Healthcare (Utah), Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Kaiser Permanente Northwest (Washington State), the University of Colorado, and Paso Del Norte Health Information Exchange (Texas).
The effectiveness of up to three doses of COVID-19 vaccine was moderate overall and significantly lower among individuals with immunocompromising conditions, compared with the general population during the period of Omicron dominance, according to an analysis of data from more than 34,000 hospitalizations.
Previous studies have suggested lower COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness among immunocompromised individuals, compared with healthy individuals from the general population, but data from the period in which Omicron subvariants have been dominant are limited, wrote Amadea Britton, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team, and colleagues.
The CDC currently recommends an expanded primary vaccine series of three doses of an mRNA vaccine, and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has recommended a fourth dose with the new bivalent booster that contains elements of the Omicron variant, the researchers noted.
In a study published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, the researchers identified 34,220 adults with immunocompromising conditions who were hospitalized for COVID-19–like illness between Dec. 16, 2021, and Aug. 20, 2022. These conditions included solid malignancy (40.5%), hematologic malignancy (14.6%), rheumatologic or inflammatory disorder (24.4%), other intrinsic immune condition or immunodeficiency (38.5%), or organ or stem cell transplant (8.6%). They used data from the CDC’s VISION Network, a multistate database. The data include spring and summer 2022, when the BA.4 and BA.5 Omicron subvariants dominated other strains, and adults with immunocompromising conditions were eligible for a total of four vaccine doses (two primary doses and two boosters). The median age of the study population was 69 years, and 25.7%, 41.7%, and 7.0% had received two, three, and four doses, respectively, of COVID-19 vaccine.
Overall, vaccine effectiveness (VE) among immunocompromised patients was 34% after two vaccine doses, increasing to 71% during days 7-89 after a third dose, then declining to 41% 90 days or more after that dose.
During the full Omicron period, VE was 36% for 14 or more days after dose two, 69% for 7-89 days after dose three, and 44% for 90 or more days after dose three.
When VE was stratified by sublineage period, VE was higher 7 or more days after dose three during the predominance of BA.1 (67%), compared with VE during the dominant periods of BA.2/BA.2.12.1 (32%) and BA.4/BA.5 (35%).
In the later periods when Omicron BA.2/BA.2.12.1 and BA.4/BA.5 variants dominated, and individuals who had received three doses of vaccine were eligible for a fourth, VE against these variants was 32% 90 or more days after dose three and 43% 7 or more days after dose four.
VE was lowest among individuals with potentially more severe immunocompromising conditions, notably solid organ or stem cell transplants, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of ICD-9 and -10 discharge diagnosis codes for immunocompromising conditions, potential confounding in VE models, lack of data on outpatient treatments such as nirmatelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid), and lack of COVID-19 genomic sequencing data that may have affected which sublineage was identified, the researchers noted.
However, “this study confirms that even with boosters, immunocompromised adults, because of their weakened immune systems, are still at high risk of moderate to severe COVID,” said coauthor Brian Dixon, PhD, of the Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health, Indianapolis, in a press release about the study.
“Given the incomplete protection against hospitalization afforded by monovalent COVID-19 vaccines, persons with immunocompromising conditions might benefit from updated bivalent vaccine booster doses that target recently circulating Omicron sublineages, in line with ACIP [Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices] recommendations,” the researchers concluded in the study.
The study was funded by the CDC. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The VISION Network is a collaboration between the CDC, the Regenstrief Institute, and seven health care systems across the United States: Columbia University Irving Medical Center (New York), HealthPartners (Wisconsin), Intermountain Healthcare (Utah), Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Kaiser Permanente Northwest (Washington State), the University of Colorado, and Paso Del Norte Health Information Exchange (Texas).
FROM MMWR



