User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Summer flu, RSV in July, ‘super colds?’
Richard Martinello, MD, a professor of medicine and pediatric infectious diseases at Yale University, New haven, Conn., doesn’t expect to see a child hospitalized with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in the middle of summer. The illness, which can strike infants and older adults especially hard, is known as a “winter virus.”
But not this year. Over the last several weeks, he says, admissions for children with RSV have increased at the Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital. While the numbers aren’t large, they are out of the ordinary, he says, “because usually, at this time of year, we see zero. For lack of a better term, it’s weird.”
Likewise, William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, says RSV is on the rise there. Tennessee is one of 10 states taking part in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention surveillance system that tracks influenza, RSV, and COVID-19.
He says RSV cases have risen by at least a third during the past week, including all age ranges. At this time of year, he says, “We aren’t supposed to have any RSV.”
RSV isn’t the only virus thriving out of season or otherwise acting strangely. Since the pandemic began, flu seasons have been out of whack – sometimes nearly nonexistent and other times extending well beyond “normal” seasons. Some experts say one influenza “B” strain may now be extinct, while others say it will be back.
Severe colds – what some call “super colds” – also seem to be on the rise in recent warm-weather months, although that evidence is mostly based on personal experience, not science.
Trying to explain these out-of-season variations has sparked much discussion among epidemiologists and virologists, Dr. Schaffner says, with debates ongoing about whether human behavior and habits or the seasons play a bigger role in the transmission of viral illness.
On top of that, scientists are also looking at the interactions between the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 and other viruses. When people get hit with COVID-19 and other viruses at the same time, does that make COVID-19 more severe, or less?
Research is conflicting.
Summer of 2022: A repeat of 2021?
RSV. Most children contract the virus by age 2, and while it’s generally mild, about 58,000 children under age 5 years are hospitalized each year. During the pandemic, RSV cases decreased from January to April 2020, the CDC reported, and then remained at “historically low levels”: less than 1% positive RSV results a week, for the next year.
But cases began rising in April 2021.
“Last year, we did have an unusual summer,” Dr. Schaffner says. After lockdown ended, to everyone’s surprise, RSV infections rose.
That increase triggered a CDC health advisory in June 2021, telling doctors and caregivers about the increase in “interseasonal” RSV cases across parts of the Southern United States, recommending broader testing for RSV in patients who had a respiratory illness but tested negative for COVID.
Because of the reduced circulation of RSV during the winter of 2020 to 2021, the CDC warned, older infants and toddlers might have a higher risk of RSV since they weren’t exposed to typical levels of RSV for the previous 15 months.
What about 2022? “At the moment,” Dr. Schaffner says, “it looks like we are having a repeat [of 2021].”
On Twitter, other pediatricians, including those from Maine and Texas, have reported an increase in RSV cases this summer.
Influenza. From October 2020 until May 2021, flu activity was lower than during any previous flu season since at least 1997, according to the CDC.
In late 2021, researchers suggested that one line of influenza known as B/Yamagata may have become extinct.
The 2021-2022 flu season has been mild, the CDC says, but it has come in two waves, with the second wave lingering longer than previous ones. While flu activity is decreasing, last week the CDC said doctors should be alert to flu infections throughout the summer.
Colds. In reports on colds that aren’t based on science, several doctors say they are seeing more colds than usual in the summer, and they’re more severe than usual. According to the CDC, common coronaviruses and respiratory adenoviruses have been increasing since early 2021, and rhinoviruses since June 2020.
Behavior vs. seasons
In explaining the spread of viral respiratory diseases, infectious disease doctors consider two things. “One is that temperature and humidity in the winter favors longer survival of some viruses, leading to longer periods of possible transmission,” says Dean Blumberg, MD, a professor of pediatrics and chief of pediatric infectious disease at University of California Davis Health.
“The other is differences in human behavior, with people spending more time outside in the summer, which results in more distancing and [less] virus concentration due to very large air volume,” he says, and vice versa in winter.
What about the “super colds?” COVID-19 lockdowns and social distancing greatly reduced people’s exposure to common viruses like those that cause colds, says Neil A. Mabbott, PhD, a professor of immunopathology at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland).
“Immunity to these common cold viruses gained through natural infection is considered to last around 8 or 9 months or so,” he says. “Each winter, when we are exposed to the new circulating variants of these viruses, our immunity receives a natural boost.”
That explains why most people get a cold that’s relatively mild. But with all the pandemic lockdowns and the use of hand sanitizers, most people had limited exposure to other viruses, including the common cold. When people emerged from lockdown, the common cold viruses were beginning to circulate again.
“Our immune systems were less able to clear the infection than previously,” Dr. Mabbott says. “As a consequence, some may have experienced increased symptoms, giving the impression of being infected with a ‘super cold.’ ”
“The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic,” says Ian Mackay, PhD, a virologist at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia. “But there might be more of them. So I doubt they are ‘super colds’ as much as they are ‘super-perfect circumstances.’ ”
The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic. But there might be more of them.
Those super-perfect circumstances, he says, include people gathering after lockdown; a lack of immunity in new babies; viruses that have remained, even if at low levels, but continue to mutate; and our waning immunity to the range of viruses we’d normally encounter.
While lack of exposure may partly explain why some viruses become rampant out of season, it’s likely not the only reason. For example, the reduced circulation of RSV in the population as a whole also may have reduced the transfer of immunity from mothers to infants, some researchers say, making those infants more vulnerable than usual.
Interactions of viruses
Another thing that may be driving the different behavior of viruses is that the SARS-CoV-2 virus could somehow be interacting with other respiratory viruses, Dr. Schaffner says. “And if so, what sort of interactions?”
Many researchers are looking into that, and how coinfections with other respiratory diseases, including the common cold and flu, may affect the course of COVID-19. Some studies have found that the T cells – a source of deeper, cellular immunity in people – generated after a common cold “may also provide cross-protection in some people against COVID-19.”
But another study found immunity against common cold–causing coronaviruses might make COVID-19 more severe.
When researchers in the United Kingdom studied nearly 7,000 patients infected with COVID-19, including 583 also infected with RSV, flu, or adenoviruses (causing flulike or coldlike illness), those with flu or adenovirus, compared with the others, were at higher risk of death.
To be continued …
Exactly how COVID-19 will be changing what we know of other viruses is yet to be determined, too.
Even before the pandemic, Dr. Martinello says, there were already some shifts in RSV. Florida, for instance, has an RSV season longer than the rest of the country, mimicking the pattern in the tropics.
Will the atypical patterns continue? “My guess is that this will settle out,” he says, with some sort of pattern developing. At this point, there are many unknowns. “We still can’t answer whether there will be some seasonality to COVID.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Richard Martinello, MD, a professor of medicine and pediatric infectious diseases at Yale University, New haven, Conn., doesn’t expect to see a child hospitalized with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in the middle of summer. The illness, which can strike infants and older adults especially hard, is known as a “winter virus.”
But not this year. Over the last several weeks, he says, admissions for children with RSV have increased at the Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital. While the numbers aren’t large, they are out of the ordinary, he says, “because usually, at this time of year, we see zero. For lack of a better term, it’s weird.”
Likewise, William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, says RSV is on the rise there. Tennessee is one of 10 states taking part in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention surveillance system that tracks influenza, RSV, and COVID-19.
He says RSV cases have risen by at least a third during the past week, including all age ranges. At this time of year, he says, “We aren’t supposed to have any RSV.”
RSV isn’t the only virus thriving out of season or otherwise acting strangely. Since the pandemic began, flu seasons have been out of whack – sometimes nearly nonexistent and other times extending well beyond “normal” seasons. Some experts say one influenza “B” strain may now be extinct, while others say it will be back.
Severe colds – what some call “super colds” – also seem to be on the rise in recent warm-weather months, although that evidence is mostly based on personal experience, not science.
Trying to explain these out-of-season variations has sparked much discussion among epidemiologists and virologists, Dr. Schaffner says, with debates ongoing about whether human behavior and habits or the seasons play a bigger role in the transmission of viral illness.
On top of that, scientists are also looking at the interactions between the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 and other viruses. When people get hit with COVID-19 and other viruses at the same time, does that make COVID-19 more severe, or less?
Research is conflicting.
Summer of 2022: A repeat of 2021?
RSV. Most children contract the virus by age 2, and while it’s generally mild, about 58,000 children under age 5 years are hospitalized each year. During the pandemic, RSV cases decreased from January to April 2020, the CDC reported, and then remained at “historically low levels”: less than 1% positive RSV results a week, for the next year.
But cases began rising in April 2021.
“Last year, we did have an unusual summer,” Dr. Schaffner says. After lockdown ended, to everyone’s surprise, RSV infections rose.
That increase triggered a CDC health advisory in June 2021, telling doctors and caregivers about the increase in “interseasonal” RSV cases across parts of the Southern United States, recommending broader testing for RSV in patients who had a respiratory illness but tested negative for COVID.
Because of the reduced circulation of RSV during the winter of 2020 to 2021, the CDC warned, older infants and toddlers might have a higher risk of RSV since they weren’t exposed to typical levels of RSV for the previous 15 months.
What about 2022? “At the moment,” Dr. Schaffner says, “it looks like we are having a repeat [of 2021].”
On Twitter, other pediatricians, including those from Maine and Texas, have reported an increase in RSV cases this summer.
Influenza. From October 2020 until May 2021, flu activity was lower than during any previous flu season since at least 1997, according to the CDC.
In late 2021, researchers suggested that one line of influenza known as B/Yamagata may have become extinct.
The 2021-2022 flu season has been mild, the CDC says, but it has come in two waves, with the second wave lingering longer than previous ones. While flu activity is decreasing, last week the CDC said doctors should be alert to flu infections throughout the summer.
Colds. In reports on colds that aren’t based on science, several doctors say they are seeing more colds than usual in the summer, and they’re more severe than usual. According to the CDC, common coronaviruses and respiratory adenoviruses have been increasing since early 2021, and rhinoviruses since June 2020.
Behavior vs. seasons
In explaining the spread of viral respiratory diseases, infectious disease doctors consider two things. “One is that temperature and humidity in the winter favors longer survival of some viruses, leading to longer periods of possible transmission,” says Dean Blumberg, MD, a professor of pediatrics and chief of pediatric infectious disease at University of California Davis Health.
“The other is differences in human behavior, with people spending more time outside in the summer, which results in more distancing and [less] virus concentration due to very large air volume,” he says, and vice versa in winter.
What about the “super colds?” COVID-19 lockdowns and social distancing greatly reduced people’s exposure to common viruses like those that cause colds, says Neil A. Mabbott, PhD, a professor of immunopathology at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland).
“Immunity to these common cold viruses gained through natural infection is considered to last around 8 or 9 months or so,” he says. “Each winter, when we are exposed to the new circulating variants of these viruses, our immunity receives a natural boost.”
That explains why most people get a cold that’s relatively mild. But with all the pandemic lockdowns and the use of hand sanitizers, most people had limited exposure to other viruses, including the common cold. When people emerged from lockdown, the common cold viruses were beginning to circulate again.
“Our immune systems were less able to clear the infection than previously,” Dr. Mabbott says. “As a consequence, some may have experienced increased symptoms, giving the impression of being infected with a ‘super cold.’ ”
“The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic,” says Ian Mackay, PhD, a virologist at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia. “But there might be more of them. So I doubt they are ‘super colds’ as much as they are ‘super-perfect circumstances.’ ”
The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic. But there might be more of them.
Those super-perfect circumstances, he says, include people gathering after lockdown; a lack of immunity in new babies; viruses that have remained, even if at low levels, but continue to mutate; and our waning immunity to the range of viruses we’d normally encounter.
While lack of exposure may partly explain why some viruses become rampant out of season, it’s likely not the only reason. For example, the reduced circulation of RSV in the population as a whole also may have reduced the transfer of immunity from mothers to infants, some researchers say, making those infants more vulnerable than usual.
Interactions of viruses
Another thing that may be driving the different behavior of viruses is that the SARS-CoV-2 virus could somehow be interacting with other respiratory viruses, Dr. Schaffner says. “And if so, what sort of interactions?”
Many researchers are looking into that, and how coinfections with other respiratory diseases, including the common cold and flu, may affect the course of COVID-19. Some studies have found that the T cells – a source of deeper, cellular immunity in people – generated after a common cold “may also provide cross-protection in some people against COVID-19.”
But another study found immunity against common cold–causing coronaviruses might make COVID-19 more severe.
When researchers in the United Kingdom studied nearly 7,000 patients infected with COVID-19, including 583 also infected with RSV, flu, or adenoviruses (causing flulike or coldlike illness), those with flu or adenovirus, compared with the others, were at higher risk of death.
To be continued …
Exactly how COVID-19 will be changing what we know of other viruses is yet to be determined, too.
Even before the pandemic, Dr. Martinello says, there were already some shifts in RSV. Florida, for instance, has an RSV season longer than the rest of the country, mimicking the pattern in the tropics.
Will the atypical patterns continue? “My guess is that this will settle out,” he says, with some sort of pattern developing. At this point, there are many unknowns. “We still can’t answer whether there will be some seasonality to COVID.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Richard Martinello, MD, a professor of medicine and pediatric infectious diseases at Yale University, New haven, Conn., doesn’t expect to see a child hospitalized with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in the middle of summer. The illness, which can strike infants and older adults especially hard, is known as a “winter virus.”
But not this year. Over the last several weeks, he says, admissions for children with RSV have increased at the Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital. While the numbers aren’t large, they are out of the ordinary, he says, “because usually, at this time of year, we see zero. For lack of a better term, it’s weird.”
Likewise, William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, says RSV is on the rise there. Tennessee is one of 10 states taking part in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention surveillance system that tracks influenza, RSV, and COVID-19.
He says RSV cases have risen by at least a third during the past week, including all age ranges. At this time of year, he says, “We aren’t supposed to have any RSV.”
RSV isn’t the only virus thriving out of season or otherwise acting strangely. Since the pandemic began, flu seasons have been out of whack – sometimes nearly nonexistent and other times extending well beyond “normal” seasons. Some experts say one influenza “B” strain may now be extinct, while others say it will be back.
Severe colds – what some call “super colds” – also seem to be on the rise in recent warm-weather months, although that evidence is mostly based on personal experience, not science.
Trying to explain these out-of-season variations has sparked much discussion among epidemiologists and virologists, Dr. Schaffner says, with debates ongoing about whether human behavior and habits or the seasons play a bigger role in the transmission of viral illness.
On top of that, scientists are also looking at the interactions between the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 and other viruses. When people get hit with COVID-19 and other viruses at the same time, does that make COVID-19 more severe, or less?
Research is conflicting.
Summer of 2022: A repeat of 2021?
RSV. Most children contract the virus by age 2, and while it’s generally mild, about 58,000 children under age 5 years are hospitalized each year. During the pandemic, RSV cases decreased from January to April 2020, the CDC reported, and then remained at “historically low levels”: less than 1% positive RSV results a week, for the next year.
But cases began rising in April 2021.
“Last year, we did have an unusual summer,” Dr. Schaffner says. After lockdown ended, to everyone’s surprise, RSV infections rose.
That increase triggered a CDC health advisory in June 2021, telling doctors and caregivers about the increase in “interseasonal” RSV cases across parts of the Southern United States, recommending broader testing for RSV in patients who had a respiratory illness but tested negative for COVID.
Because of the reduced circulation of RSV during the winter of 2020 to 2021, the CDC warned, older infants and toddlers might have a higher risk of RSV since they weren’t exposed to typical levels of RSV for the previous 15 months.
What about 2022? “At the moment,” Dr. Schaffner says, “it looks like we are having a repeat [of 2021].”
On Twitter, other pediatricians, including those from Maine and Texas, have reported an increase in RSV cases this summer.
Influenza. From October 2020 until May 2021, flu activity was lower than during any previous flu season since at least 1997, according to the CDC.
In late 2021, researchers suggested that one line of influenza known as B/Yamagata may have become extinct.
The 2021-2022 flu season has been mild, the CDC says, but it has come in two waves, with the second wave lingering longer than previous ones. While flu activity is decreasing, last week the CDC said doctors should be alert to flu infections throughout the summer.
Colds. In reports on colds that aren’t based on science, several doctors say they are seeing more colds than usual in the summer, and they’re more severe than usual. According to the CDC, common coronaviruses and respiratory adenoviruses have been increasing since early 2021, and rhinoviruses since June 2020.
Behavior vs. seasons
In explaining the spread of viral respiratory diseases, infectious disease doctors consider two things. “One is that temperature and humidity in the winter favors longer survival of some viruses, leading to longer periods of possible transmission,” says Dean Blumberg, MD, a professor of pediatrics and chief of pediatric infectious disease at University of California Davis Health.
“The other is differences in human behavior, with people spending more time outside in the summer, which results in more distancing and [less] virus concentration due to very large air volume,” he says, and vice versa in winter.
What about the “super colds?” COVID-19 lockdowns and social distancing greatly reduced people’s exposure to common viruses like those that cause colds, says Neil A. Mabbott, PhD, a professor of immunopathology at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland).
“Immunity to these common cold viruses gained through natural infection is considered to last around 8 or 9 months or so,” he says. “Each winter, when we are exposed to the new circulating variants of these viruses, our immunity receives a natural boost.”
That explains why most people get a cold that’s relatively mild. But with all the pandemic lockdowns and the use of hand sanitizers, most people had limited exposure to other viruses, including the common cold. When people emerged from lockdown, the common cold viruses were beginning to circulate again.
“Our immune systems were less able to clear the infection than previously,” Dr. Mabbott says. “As a consequence, some may have experienced increased symptoms, giving the impression of being infected with a ‘super cold.’ ”
“The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic,” says Ian Mackay, PhD, a virologist at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia. “But there might be more of them. So I doubt they are ‘super colds’ as much as they are ‘super-perfect circumstances.’ ”
The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic. But there might be more of them.
Those super-perfect circumstances, he says, include people gathering after lockdown; a lack of immunity in new babies; viruses that have remained, even if at low levels, but continue to mutate; and our waning immunity to the range of viruses we’d normally encounter.
While lack of exposure may partly explain why some viruses become rampant out of season, it’s likely not the only reason. For example, the reduced circulation of RSV in the population as a whole also may have reduced the transfer of immunity from mothers to infants, some researchers say, making those infants more vulnerable than usual.
Interactions of viruses
Another thing that may be driving the different behavior of viruses is that the SARS-CoV-2 virus could somehow be interacting with other respiratory viruses, Dr. Schaffner says. “And if so, what sort of interactions?”
Many researchers are looking into that, and how coinfections with other respiratory diseases, including the common cold and flu, may affect the course of COVID-19. Some studies have found that the T cells – a source of deeper, cellular immunity in people – generated after a common cold “may also provide cross-protection in some people against COVID-19.”
But another study found immunity against common cold–causing coronaviruses might make COVID-19 more severe.
When researchers in the United Kingdom studied nearly 7,000 patients infected with COVID-19, including 583 also infected with RSV, flu, or adenoviruses (causing flulike or coldlike illness), those with flu or adenovirus, compared with the others, were at higher risk of death.
To be continued …
Exactly how COVID-19 will be changing what we know of other viruses is yet to be determined, too.
Even before the pandemic, Dr. Martinello says, there were already some shifts in RSV. Florida, for instance, has an RSV season longer than the rest of the country, mimicking the pattern in the tropics.
Will the atypical patterns continue? “My guess is that this will settle out,” he says, with some sort of pattern developing. At this point, there are many unknowns. “We still can’t answer whether there will be some seasonality to COVID.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Injectable HIV prevention better than pills in two trials
MONTREAL – , according to new data from two HIV Prevention Trials Network (HPTN) studies reported at the International AIDS Society Conference.
Follow-up data from the HPTN 084 trial, which compared the two regimens in 3,224 sub-Saharan persons who were assigned female sex at birth, show that three new HIV infections occurred in the CAB LA group in the 12 months since the study was unblinded, versus 20 new infections among the TDF-FTC group. That translates to an 89% lower risk of infection in the CAB LA arm across both the blinded and unblinded phases of the trial, said lead investigator Sinead Delany-Moretlwe, MD, PhD, director of research, Wits Reproductive Health and HIV Institute, the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, during a press conference.
“The trial was designed with the assumption that both drugs were highly effective in preventing HIV infection but that, given the challenges with taking a pill a day, that injectable cabotegravir may offer an adherence advantage,” she said in an interview. “Our data appear to confirm this, as most of the participants in the TDF-FTC arm who became infected with HIV had evidence of poor or inconsistent use of PrEP.”
The study also found that pregnancy incidence increased “two- to threefold” between the blinded and the unblinded period, “and this emphasizes to us the desire of women to conceive safely, without the threat of HIV, and the importance of us continuing to evaluate the safety and pharmacology of cabotegravir in pregnant and breastfeeding women during open-label extension phase of HPTN 084, so that [they] are not excluded from access to this highly effective PrEP agent,” she said. To date, no congenital anomalies have been reported in babies born during the study.
In an update report from HPTN 083, which also showed superiority of CAB LA over TDF-FTC in cisgender men and transgender women (TGW), researchers reported the safety and efficacy of CAB LA use in TGW using gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT).
Among the 4,566 participants in HPTN 083, 570 were TGW, and of those, 58% used GAHT at baseline, reported Beatriz Grinsztejn, MD, PhD, head of the STD/AIDS Clinical Research Laboratory at the Instituto Nacional de Infectologicia/Fundação Oswaldo Cruz.
CAB LA drug concentrations measured in a subset of 53 TGW who received on-time CAB injections were comparable between those taking (n = 30) and those not taking GAHT (n = 23), “suggesting the lack of a gender-affirming hormone effect on CAB pharmacokinetics,” she said. “These are very promising results, as we all know that the use of gender-affirming hormone therapy is a major priority for our transgender women community, ... so the lack of drug-drug interaction is really a very important result.”
“Cabotegravir long-acting PrEP is now approved for all at-risk populations, including men who have sex with men, transgender women, and cisgender women, after the results of HPTN 083 and 084,” commented Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, an infectious disease physician, professor of medicine, and associate chief in the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
Dr. Gandhi, who was not involved in either study, is also director of the UCSF Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital. “The incredible efficacy of long-acting PrEP for cisgender women shown by HPTN 084 is game-changing for our practice, and we have already instituted CAB LA across a range of populations at Ward 86,” she said in an interview. “The durability of the 89% additional efficacy of CAB LA over oral TDF/FTC is thrilling and will lead to a greater use of long-acting options.”
She acknowledged that information on potential interactions of GAHT was needed from the HPTN 083 trial. “That cabotegravir levels did not change with the use of estradiol or spironolactone for gender-affirming therapy is important news for our practice and to reassure our TGW that they can safely and effectively use CAB LA for HIV prevention.”
The HPTN 084 and 083 trials were funded by the National Institutes for Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Delany-Moretlwe, Dr. Grinsztejn, and Dr. Gandhi have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – , according to new data from two HIV Prevention Trials Network (HPTN) studies reported at the International AIDS Society Conference.
Follow-up data from the HPTN 084 trial, which compared the two regimens in 3,224 sub-Saharan persons who were assigned female sex at birth, show that three new HIV infections occurred in the CAB LA group in the 12 months since the study was unblinded, versus 20 new infections among the TDF-FTC group. That translates to an 89% lower risk of infection in the CAB LA arm across both the blinded and unblinded phases of the trial, said lead investigator Sinead Delany-Moretlwe, MD, PhD, director of research, Wits Reproductive Health and HIV Institute, the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, during a press conference.
“The trial was designed with the assumption that both drugs were highly effective in preventing HIV infection but that, given the challenges with taking a pill a day, that injectable cabotegravir may offer an adherence advantage,” she said in an interview. “Our data appear to confirm this, as most of the participants in the TDF-FTC arm who became infected with HIV had evidence of poor or inconsistent use of PrEP.”
The study also found that pregnancy incidence increased “two- to threefold” between the blinded and the unblinded period, “and this emphasizes to us the desire of women to conceive safely, without the threat of HIV, and the importance of us continuing to evaluate the safety and pharmacology of cabotegravir in pregnant and breastfeeding women during open-label extension phase of HPTN 084, so that [they] are not excluded from access to this highly effective PrEP agent,” she said. To date, no congenital anomalies have been reported in babies born during the study.
In an update report from HPTN 083, which also showed superiority of CAB LA over TDF-FTC in cisgender men and transgender women (TGW), researchers reported the safety and efficacy of CAB LA use in TGW using gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT).
Among the 4,566 participants in HPTN 083, 570 were TGW, and of those, 58% used GAHT at baseline, reported Beatriz Grinsztejn, MD, PhD, head of the STD/AIDS Clinical Research Laboratory at the Instituto Nacional de Infectologicia/Fundação Oswaldo Cruz.
CAB LA drug concentrations measured in a subset of 53 TGW who received on-time CAB injections were comparable between those taking (n = 30) and those not taking GAHT (n = 23), “suggesting the lack of a gender-affirming hormone effect on CAB pharmacokinetics,” she said. “These are very promising results, as we all know that the use of gender-affirming hormone therapy is a major priority for our transgender women community, ... so the lack of drug-drug interaction is really a very important result.”
“Cabotegravir long-acting PrEP is now approved for all at-risk populations, including men who have sex with men, transgender women, and cisgender women, after the results of HPTN 083 and 084,” commented Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, an infectious disease physician, professor of medicine, and associate chief in the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
Dr. Gandhi, who was not involved in either study, is also director of the UCSF Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital. “The incredible efficacy of long-acting PrEP for cisgender women shown by HPTN 084 is game-changing for our practice, and we have already instituted CAB LA across a range of populations at Ward 86,” she said in an interview. “The durability of the 89% additional efficacy of CAB LA over oral TDF/FTC is thrilling and will lead to a greater use of long-acting options.”
She acknowledged that information on potential interactions of GAHT was needed from the HPTN 083 trial. “That cabotegravir levels did not change with the use of estradiol or spironolactone for gender-affirming therapy is important news for our practice and to reassure our TGW that they can safely and effectively use CAB LA for HIV prevention.”
The HPTN 084 and 083 trials were funded by the National Institutes for Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Delany-Moretlwe, Dr. Grinsztejn, and Dr. Gandhi have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – , according to new data from two HIV Prevention Trials Network (HPTN) studies reported at the International AIDS Society Conference.
Follow-up data from the HPTN 084 trial, which compared the two regimens in 3,224 sub-Saharan persons who were assigned female sex at birth, show that three new HIV infections occurred in the CAB LA group in the 12 months since the study was unblinded, versus 20 new infections among the TDF-FTC group. That translates to an 89% lower risk of infection in the CAB LA arm across both the blinded and unblinded phases of the trial, said lead investigator Sinead Delany-Moretlwe, MD, PhD, director of research, Wits Reproductive Health and HIV Institute, the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, during a press conference.
“The trial was designed with the assumption that both drugs were highly effective in preventing HIV infection but that, given the challenges with taking a pill a day, that injectable cabotegravir may offer an adherence advantage,” she said in an interview. “Our data appear to confirm this, as most of the participants in the TDF-FTC arm who became infected with HIV had evidence of poor or inconsistent use of PrEP.”
The study also found that pregnancy incidence increased “two- to threefold” between the blinded and the unblinded period, “and this emphasizes to us the desire of women to conceive safely, without the threat of HIV, and the importance of us continuing to evaluate the safety and pharmacology of cabotegravir in pregnant and breastfeeding women during open-label extension phase of HPTN 084, so that [they] are not excluded from access to this highly effective PrEP agent,” she said. To date, no congenital anomalies have been reported in babies born during the study.
In an update report from HPTN 083, which also showed superiority of CAB LA over TDF-FTC in cisgender men and transgender women (TGW), researchers reported the safety and efficacy of CAB LA use in TGW using gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT).
Among the 4,566 participants in HPTN 083, 570 were TGW, and of those, 58% used GAHT at baseline, reported Beatriz Grinsztejn, MD, PhD, head of the STD/AIDS Clinical Research Laboratory at the Instituto Nacional de Infectologicia/Fundação Oswaldo Cruz.
CAB LA drug concentrations measured in a subset of 53 TGW who received on-time CAB injections were comparable between those taking (n = 30) and those not taking GAHT (n = 23), “suggesting the lack of a gender-affirming hormone effect on CAB pharmacokinetics,” she said. “These are very promising results, as we all know that the use of gender-affirming hormone therapy is a major priority for our transgender women community, ... so the lack of drug-drug interaction is really a very important result.”
“Cabotegravir long-acting PrEP is now approved for all at-risk populations, including men who have sex with men, transgender women, and cisgender women, after the results of HPTN 083 and 084,” commented Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, an infectious disease physician, professor of medicine, and associate chief in the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
Dr. Gandhi, who was not involved in either study, is also director of the UCSF Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital. “The incredible efficacy of long-acting PrEP for cisgender women shown by HPTN 084 is game-changing for our practice, and we have already instituted CAB LA across a range of populations at Ward 86,” she said in an interview. “The durability of the 89% additional efficacy of CAB LA over oral TDF/FTC is thrilling and will lead to a greater use of long-acting options.”
She acknowledged that information on potential interactions of GAHT was needed from the HPTN 083 trial. “That cabotegravir levels did not change with the use of estradiol or spironolactone for gender-affirming therapy is important news for our practice and to reassure our TGW that they can safely and effectively use CAB LA for HIV prevention.”
The HPTN 084 and 083 trials were funded by the National Institutes for Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Delany-Moretlwe, Dr. Grinsztejn, and Dr. Gandhi have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AIDS 2022
Children and COVID: Weekly cases top 95,000, admissions continue to rise
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.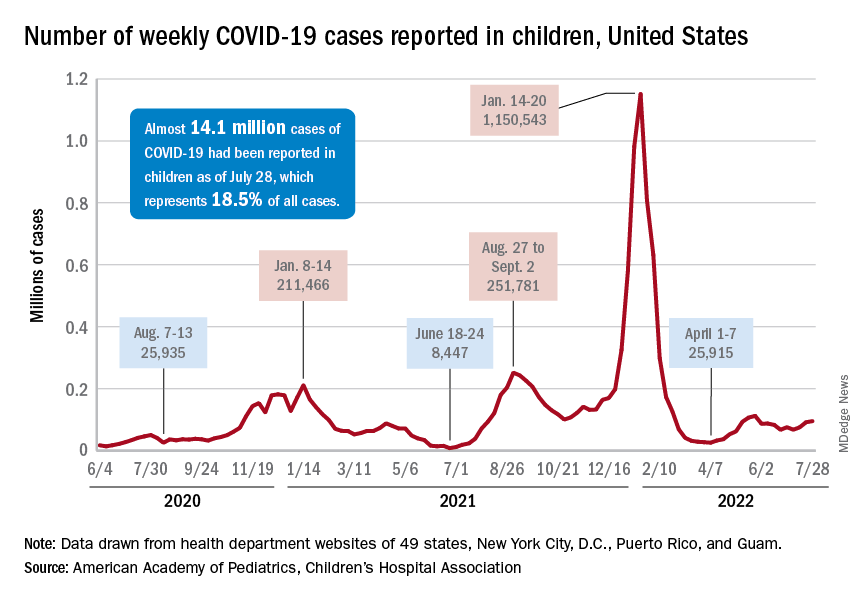
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.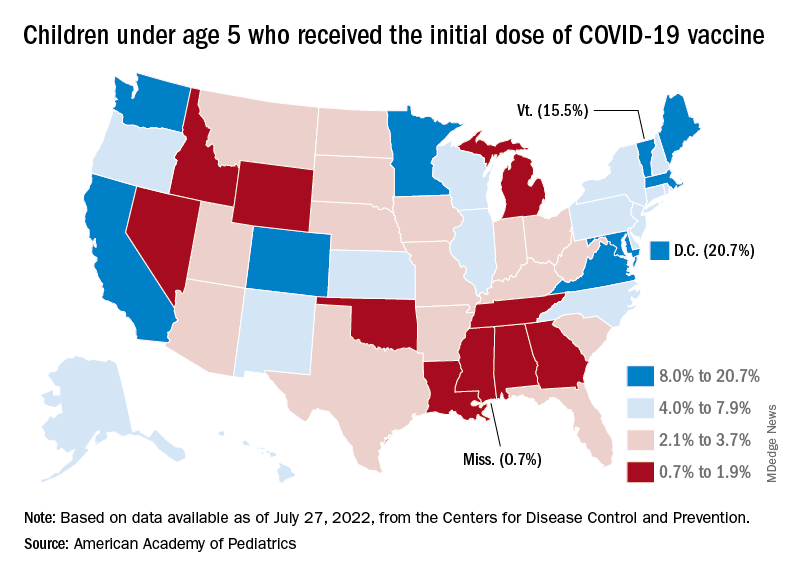
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.
Landmark ALLIANCE results offer tenofovir guidance in HIV/HBV coinfection
MONTREAL – Interim results of ALLIANCE, the first head-to-head trial comparing two different tenofovir-containing antiretroviral regimens for the treatment of HIV and hepatitis B (HBV) coinfection, demonstrate the superiority of bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF) over dolutegravir plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (DTG + F/TDF), researchers reported at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
, with more HBV DNA suppression and significantly more seroconversion, reported lead investigator Anchalee Avihingsanon, MD, PhD, at a press conference during the meeting. Dr. Avihingsanon heads the medical department of the HIV Netherlands Australia Thailand Research Collaboration (HIV-NAT) at the Thai Red Cross AIDS Research Centre, Bangkok.
The ongoing phase 3, multicountry study has 48-week results for 243 participants, who were HIV/HBV coinfected and treatment naive. All subjects received three pills of ART per day, with blinded randomization to (active B/F/TAF + placebo DTG + placebo TDF/FTC or placebo B/F/TAF + active DTG + active TDF/FTC). The primary endpoints at 48 weeks were proportion of participants with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL and plasma HBV DNA less than 29 IU/mL.
For the HIV endpoint, results showed both the B/F/TAF and DTG + F/TDF arms had high rates of suppression (95% and 91%, respectively, P = .21), but the B/F/TAF group had significantly higher rates of HBV DNA suppression (63% vs 43.4%, P = .0023) and HBeAg seroconversion (23.3% vs. 11.3%), with numerically higher, but not statistically significant differences in HBsAg loss/seroconversion (12.6% vs. 5.8% and 8.4% vs. 3.3%), HBeAg loss (25.6% vs 14.4%), and ALT normalization (73.3% vs 55.3%).
No participant developed treatment-emergent HIV-1 drug resistance while on B/F/TAF, and there were few study-drug–related AEs or discontinuations, she reported.
“There is hardly any good reason to give the two-pill DTG regimen over single-tablet BTG/TAF/FTC in HBV-coinfected people living with HIV [PLWH],” commented Babafemi Taiwo, MD, chief of infectious diseases and professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., who was not involved in the research. “This gives me confidence to prescribe bictegravir/TAF/FTC, which has the added advantage of being a single-tablet formulation, to HBV coinfected PLWH,” he said in an interview. However, he added, the results “call for some head-scratching since TAF is not known to be better than TDF for HBV treatment in persons without HIV.”
“The lower response rate of the TDF group is still poorly understood,” agreed Dr. Avihingsanon, emphasizing that “HBV and HIV/HBV are not the same, and TDF and TAF are also different. TAF has slightly more drug-drug interactions than TDF. I guess its end product in the liver might be higher. What is exciting to me is that there was such a high rate of HBsAg loss and HBs seroconversion in HIV/HBV coinfection, which is totally different from HBV monoinfection [< 1% at 48 weeks]. For me as an investigator, this important finding has additional benefit to further explore the immunologic outcome for possible HBV cure strategy.” She said the study remains blinded until week 96, at which time further data may shed light on this question.
“Perhaps a larger study would help clarify impact of TAF versus TDF on measures that did not achieve statistical significance in this study. Long-term follow up to better understand the clinical implications of these results could be helpful as well,” Dr. Taiwo added.
The study was funded by Gilead. Dr. Avihingsanon reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Taiwo disclosed that he has served as consultant to ViiV/GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck, and consulted for Gilead on COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – Interim results of ALLIANCE, the first head-to-head trial comparing two different tenofovir-containing antiretroviral regimens for the treatment of HIV and hepatitis B (HBV) coinfection, demonstrate the superiority of bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF) over dolutegravir plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (DTG + F/TDF), researchers reported at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
, with more HBV DNA suppression and significantly more seroconversion, reported lead investigator Anchalee Avihingsanon, MD, PhD, at a press conference during the meeting. Dr. Avihingsanon heads the medical department of the HIV Netherlands Australia Thailand Research Collaboration (HIV-NAT) at the Thai Red Cross AIDS Research Centre, Bangkok.
The ongoing phase 3, multicountry study has 48-week results for 243 participants, who were HIV/HBV coinfected and treatment naive. All subjects received three pills of ART per day, with blinded randomization to (active B/F/TAF + placebo DTG + placebo TDF/FTC or placebo B/F/TAF + active DTG + active TDF/FTC). The primary endpoints at 48 weeks were proportion of participants with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL and plasma HBV DNA less than 29 IU/mL.
For the HIV endpoint, results showed both the B/F/TAF and DTG + F/TDF arms had high rates of suppression (95% and 91%, respectively, P = .21), but the B/F/TAF group had significantly higher rates of HBV DNA suppression (63% vs 43.4%, P = .0023) and HBeAg seroconversion (23.3% vs. 11.3%), with numerically higher, but not statistically significant differences in HBsAg loss/seroconversion (12.6% vs. 5.8% and 8.4% vs. 3.3%), HBeAg loss (25.6% vs 14.4%), and ALT normalization (73.3% vs 55.3%).
No participant developed treatment-emergent HIV-1 drug resistance while on B/F/TAF, and there were few study-drug–related AEs or discontinuations, she reported.
“There is hardly any good reason to give the two-pill DTG regimen over single-tablet BTG/TAF/FTC in HBV-coinfected people living with HIV [PLWH],” commented Babafemi Taiwo, MD, chief of infectious diseases and professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., who was not involved in the research. “This gives me confidence to prescribe bictegravir/TAF/FTC, which has the added advantage of being a single-tablet formulation, to HBV coinfected PLWH,” he said in an interview. However, he added, the results “call for some head-scratching since TAF is not known to be better than TDF for HBV treatment in persons without HIV.”
“The lower response rate of the TDF group is still poorly understood,” agreed Dr. Avihingsanon, emphasizing that “HBV and HIV/HBV are not the same, and TDF and TAF are also different. TAF has slightly more drug-drug interactions than TDF. I guess its end product in the liver might be higher. What is exciting to me is that there was such a high rate of HBsAg loss and HBs seroconversion in HIV/HBV coinfection, which is totally different from HBV monoinfection [< 1% at 48 weeks]. For me as an investigator, this important finding has additional benefit to further explore the immunologic outcome for possible HBV cure strategy.” She said the study remains blinded until week 96, at which time further data may shed light on this question.
“Perhaps a larger study would help clarify impact of TAF versus TDF on measures that did not achieve statistical significance in this study. Long-term follow up to better understand the clinical implications of these results could be helpful as well,” Dr. Taiwo added.
The study was funded by Gilead. Dr. Avihingsanon reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Taiwo disclosed that he has served as consultant to ViiV/GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck, and consulted for Gilead on COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – Interim results of ALLIANCE, the first head-to-head trial comparing two different tenofovir-containing antiretroviral regimens for the treatment of HIV and hepatitis B (HBV) coinfection, demonstrate the superiority of bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF) over dolutegravir plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (DTG + F/TDF), researchers reported at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
, with more HBV DNA suppression and significantly more seroconversion, reported lead investigator Anchalee Avihingsanon, MD, PhD, at a press conference during the meeting. Dr. Avihingsanon heads the medical department of the HIV Netherlands Australia Thailand Research Collaboration (HIV-NAT) at the Thai Red Cross AIDS Research Centre, Bangkok.
The ongoing phase 3, multicountry study has 48-week results for 243 participants, who were HIV/HBV coinfected and treatment naive. All subjects received three pills of ART per day, with blinded randomization to (active B/F/TAF + placebo DTG + placebo TDF/FTC or placebo B/F/TAF + active DTG + active TDF/FTC). The primary endpoints at 48 weeks were proportion of participants with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL and plasma HBV DNA less than 29 IU/mL.
For the HIV endpoint, results showed both the B/F/TAF and DTG + F/TDF arms had high rates of suppression (95% and 91%, respectively, P = .21), but the B/F/TAF group had significantly higher rates of HBV DNA suppression (63% vs 43.4%, P = .0023) and HBeAg seroconversion (23.3% vs. 11.3%), with numerically higher, but not statistically significant differences in HBsAg loss/seroconversion (12.6% vs. 5.8% and 8.4% vs. 3.3%), HBeAg loss (25.6% vs 14.4%), and ALT normalization (73.3% vs 55.3%).
No participant developed treatment-emergent HIV-1 drug resistance while on B/F/TAF, and there were few study-drug–related AEs or discontinuations, she reported.
“There is hardly any good reason to give the two-pill DTG regimen over single-tablet BTG/TAF/FTC in HBV-coinfected people living with HIV [PLWH],” commented Babafemi Taiwo, MD, chief of infectious diseases and professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., who was not involved in the research. “This gives me confidence to prescribe bictegravir/TAF/FTC, which has the added advantage of being a single-tablet formulation, to HBV coinfected PLWH,” he said in an interview. However, he added, the results “call for some head-scratching since TAF is not known to be better than TDF for HBV treatment in persons without HIV.”
“The lower response rate of the TDF group is still poorly understood,” agreed Dr. Avihingsanon, emphasizing that “HBV and HIV/HBV are not the same, and TDF and TAF are also different. TAF has slightly more drug-drug interactions than TDF. I guess its end product in the liver might be higher. What is exciting to me is that there was such a high rate of HBsAg loss and HBs seroconversion in HIV/HBV coinfection, which is totally different from HBV monoinfection [< 1% at 48 weeks]. For me as an investigator, this important finding has additional benefit to further explore the immunologic outcome for possible HBV cure strategy.” She said the study remains blinded until week 96, at which time further data may shed light on this question.
“Perhaps a larger study would help clarify impact of TAF versus TDF on measures that did not achieve statistical significance in this study. Long-term follow up to better understand the clinical implications of these results could be helpful as well,” Dr. Taiwo added.
The study was funded by Gilead. Dr. Avihingsanon reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Taiwo disclosed that he has served as consultant to ViiV/GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck, and consulted for Gilead on COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AIDS 2022
Evusheld for COVID-19: Lifesaving and free, but still few takers
Evusheld (AstraZeneca), a medication used to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients at high risk, has problems: Namely, that supplies of the potentially lifesaving drug outweigh demand.
At least 7 million people who are immunocompromised could benefit from it, as could many others who are undergoing cancer treatment, have received a transplant, or who are allergic to the COVID-19 vaccines. The medication has laboratory-produced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and helps the body protect itself. It can slash the chances of becoming infected by 77%, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
And it’s free to eligible patients (although there may be an out-of-pocket administrative fee in some cases).
To meet demand, the Biden administration secured 1.7 million doses of the medicine, which was granted emergency use authorization by the FDA in December 2021. As of July 25, however, 793,348 doses have been ordered by the administration sites, and only 398,181 doses have been reported as used, a spokesperson for the Department of Health & Human Services tells this news organization.
Each week, a certain amount of doses from the 1.7 million dose stockpile is made available to state and territorial health departments. States have not been asking for their full allotment, the spokesperson said July 28.
Now, HHS and AstraZeneca have taken a number of steps to increase awareness of the medication and access to it.
- On July 27, HHS announced that individual providers and smaller sites of care that don’t currently receive Evusheld through the federal distribution process via the HHS Health Partner Order Portal can now order up to three patient courses of the medicine. These can be
- Health care providers can use the HHS’s COVID-19 Therapeutics Locator to find Evusheld in their area.
- AstraZeneca has launched a new website with educational materials and says it is working closely with patient and professional groups to inform patients and health care providers.
- A direct-to-consumer ad launched on June 22 and will run in the United States online and on TV (Yahoo, Fox, CBS Sports, MSN, ESPN) and be amplified on social and digital channels through year’s end, an AstraZeneca spokesperson said in an interview.
- AstraZeneca set up a toll-free number for providers: 1-833-EVUSHLD.
Evusheld includes two monoclonal antibodies, tixagevimab and cilgavimab. The medication is given as two consecutive intramuscular injections during a single visit to a doctor’s office, infusion center, or other health care facility. The antibodies bind to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and prevent the virus from getting into human cells and infecting them. It’s authorized for use in children and adults aged 12 years and older who weigh at least 88 pounds.
Studies have found that the medication decreases the risk of getting COVID-19 for up to 6 months after it is given. The FDA recommends repeat dosing every 6 months with the doses of 300 mg of each monoclonal antibody. In clinical trials, Evusheld reduced the incidence of COVID-19 symptomatic illness by 77%, compared with placebo.
Physicians monitor patients for an hour after administering Evusheld for allergic reactions. Other possible side effects include cardiac events, but they are not common.
Doctors and patients weigh in
Physicians – and patients – from the United States to the United Kingdom and beyond are questioning why the medication is underused while lauding the recent efforts to expand access and increase awareness.
The U.S. federal government may have underestimated the amount of communication needed to increase awareness of the medication and its applications, said infectious disease specialist William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tenn.
“HHS hasn’t made a major educational effort to promote it,” he said in an interview.
Many physicians who need to know about it, such as transplant doctors and rheumatologists, are outside the typical public health communications loop, he said.
Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Transational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape, has taken to social media to bemoan the lack of awareness.
Another infectious disease expert agrees. “In my experience, the awareness of Evusheld is low amongst many patients as well as many providers,” said Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore.
“Initially, there were scarce supplies of the drug, and certain hospital systems tiered eligibility based on degrees of immunosuppression, and only the most immunosuppressed were proactively approached for treatment.”
“Also, many community hospitals never initially ordered Evusheld – they may have been crowded out by academic centers who treat many more immunosuppressed patients and may not currently see it as a priority,” Dr. Adalja said in an interview. “As such, many immunosuppressed patients would have to seek treatment at academic medical centers, where the drug is more likely to be available.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Evusheld (AstraZeneca), a medication used to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients at high risk, has problems: Namely, that supplies of the potentially lifesaving drug outweigh demand.
At least 7 million people who are immunocompromised could benefit from it, as could many others who are undergoing cancer treatment, have received a transplant, or who are allergic to the COVID-19 vaccines. The medication has laboratory-produced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and helps the body protect itself. It can slash the chances of becoming infected by 77%, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
And it’s free to eligible patients (although there may be an out-of-pocket administrative fee in some cases).
To meet demand, the Biden administration secured 1.7 million doses of the medicine, which was granted emergency use authorization by the FDA in December 2021. As of July 25, however, 793,348 doses have been ordered by the administration sites, and only 398,181 doses have been reported as used, a spokesperson for the Department of Health & Human Services tells this news organization.
Each week, a certain amount of doses from the 1.7 million dose stockpile is made available to state and territorial health departments. States have not been asking for their full allotment, the spokesperson said July 28.
Now, HHS and AstraZeneca have taken a number of steps to increase awareness of the medication and access to it.
- On July 27, HHS announced that individual providers and smaller sites of care that don’t currently receive Evusheld through the federal distribution process via the HHS Health Partner Order Portal can now order up to three patient courses of the medicine. These can be
- Health care providers can use the HHS’s COVID-19 Therapeutics Locator to find Evusheld in their area.
- AstraZeneca has launched a new website with educational materials and says it is working closely with patient and professional groups to inform patients and health care providers.
- A direct-to-consumer ad launched on June 22 and will run in the United States online and on TV (Yahoo, Fox, CBS Sports, MSN, ESPN) and be amplified on social and digital channels through year’s end, an AstraZeneca spokesperson said in an interview.
- AstraZeneca set up a toll-free number for providers: 1-833-EVUSHLD.
Evusheld includes two monoclonal antibodies, tixagevimab and cilgavimab. The medication is given as two consecutive intramuscular injections during a single visit to a doctor’s office, infusion center, or other health care facility. The antibodies bind to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and prevent the virus from getting into human cells and infecting them. It’s authorized for use in children and adults aged 12 years and older who weigh at least 88 pounds.
Studies have found that the medication decreases the risk of getting COVID-19 for up to 6 months after it is given. The FDA recommends repeat dosing every 6 months with the doses of 300 mg of each monoclonal antibody. In clinical trials, Evusheld reduced the incidence of COVID-19 symptomatic illness by 77%, compared with placebo.
Physicians monitor patients for an hour after administering Evusheld for allergic reactions. Other possible side effects include cardiac events, but they are not common.
Doctors and patients weigh in
Physicians – and patients – from the United States to the United Kingdom and beyond are questioning why the medication is underused while lauding the recent efforts to expand access and increase awareness.
The U.S. federal government may have underestimated the amount of communication needed to increase awareness of the medication and its applications, said infectious disease specialist William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tenn.
“HHS hasn’t made a major educational effort to promote it,” he said in an interview.
Many physicians who need to know about it, such as transplant doctors and rheumatologists, are outside the typical public health communications loop, he said.
Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Transational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape, has taken to social media to bemoan the lack of awareness.
Another infectious disease expert agrees. “In my experience, the awareness of Evusheld is low amongst many patients as well as many providers,” said Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore.
“Initially, there were scarce supplies of the drug, and certain hospital systems tiered eligibility based on degrees of immunosuppression, and only the most immunosuppressed were proactively approached for treatment.”
“Also, many community hospitals never initially ordered Evusheld – they may have been crowded out by academic centers who treat many more immunosuppressed patients and may not currently see it as a priority,” Dr. Adalja said in an interview. “As such, many immunosuppressed patients would have to seek treatment at academic medical centers, where the drug is more likely to be available.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Evusheld (AstraZeneca), a medication used to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients at high risk, has problems: Namely, that supplies of the potentially lifesaving drug outweigh demand.
At least 7 million people who are immunocompromised could benefit from it, as could many others who are undergoing cancer treatment, have received a transplant, or who are allergic to the COVID-19 vaccines. The medication has laboratory-produced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and helps the body protect itself. It can slash the chances of becoming infected by 77%, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
And it’s free to eligible patients (although there may be an out-of-pocket administrative fee in some cases).
To meet demand, the Biden administration secured 1.7 million doses of the medicine, which was granted emergency use authorization by the FDA in December 2021. As of July 25, however, 793,348 doses have been ordered by the administration sites, and only 398,181 doses have been reported as used, a spokesperson for the Department of Health & Human Services tells this news organization.
Each week, a certain amount of doses from the 1.7 million dose stockpile is made available to state and territorial health departments. States have not been asking for their full allotment, the spokesperson said July 28.
Now, HHS and AstraZeneca have taken a number of steps to increase awareness of the medication and access to it.
- On July 27, HHS announced that individual providers and smaller sites of care that don’t currently receive Evusheld through the federal distribution process via the HHS Health Partner Order Portal can now order up to three patient courses of the medicine. These can be
- Health care providers can use the HHS’s COVID-19 Therapeutics Locator to find Evusheld in their area.
- AstraZeneca has launched a new website with educational materials and says it is working closely with patient and professional groups to inform patients and health care providers.
- A direct-to-consumer ad launched on June 22 and will run in the United States online and on TV (Yahoo, Fox, CBS Sports, MSN, ESPN) and be amplified on social and digital channels through year’s end, an AstraZeneca spokesperson said in an interview.
- AstraZeneca set up a toll-free number for providers: 1-833-EVUSHLD.
Evusheld includes two monoclonal antibodies, tixagevimab and cilgavimab. The medication is given as two consecutive intramuscular injections during a single visit to a doctor’s office, infusion center, or other health care facility. The antibodies bind to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and prevent the virus from getting into human cells and infecting them. It’s authorized for use in children and adults aged 12 years and older who weigh at least 88 pounds.
Studies have found that the medication decreases the risk of getting COVID-19 for up to 6 months after it is given. The FDA recommends repeat dosing every 6 months with the doses of 300 mg of each monoclonal antibody. In clinical trials, Evusheld reduced the incidence of COVID-19 symptomatic illness by 77%, compared with placebo.
Physicians monitor patients for an hour after administering Evusheld for allergic reactions. Other possible side effects include cardiac events, but they are not common.
Doctors and patients weigh in
Physicians – and patients – from the United States to the United Kingdom and beyond are questioning why the medication is underused while lauding the recent efforts to expand access and increase awareness.
The U.S. federal government may have underestimated the amount of communication needed to increase awareness of the medication and its applications, said infectious disease specialist William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tenn.
“HHS hasn’t made a major educational effort to promote it,” he said in an interview.
Many physicians who need to know about it, such as transplant doctors and rheumatologists, are outside the typical public health communications loop, he said.
Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Transational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape, has taken to social media to bemoan the lack of awareness.
Another infectious disease expert agrees. “In my experience, the awareness of Evusheld is low amongst many patients as well as many providers,” said Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore.
“Initially, there were scarce supplies of the drug, and certain hospital systems tiered eligibility based on degrees of immunosuppression, and only the most immunosuppressed were proactively approached for treatment.”
“Also, many community hospitals never initially ordered Evusheld – they may have been crowded out by academic centers who treat many more immunosuppressed patients and may not currently see it as a priority,” Dr. Adalja said in an interview. “As such, many immunosuppressed patients would have to seek treatment at academic medical centers, where the drug is more likely to be available.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Striking’ disparities in CVD deaths persist across COVID waves
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality rose significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic and persists more than 2 years on and, once again, Blacks and African Americans have been disproportionately affected, an analysis of death certificates shows.
The findings “suggest that the pandemic may reverse years or decades of work aimed at reducing gaps in cardiovascular outcomes,” Sadeer G. Al-Kindi, MD, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
Although the disparities are in line with previous research, he said, “what was surprising is the persistence of excess cardiovascular mortality approximately 2 years after the pandemic started, even during a period of low COVID-19 mortality.”
“This suggests that the pandemic resulted in a disruption of health care access and, along with disparities in COVID-19 infection and its complications, he said, “may have a long-lasting effect on health care disparities, especially among vulnerable populations.”
The study was published online in Mayo Clinic Proceedings with lead author Scott E. Janus, MD, also of Case Western Reserve University.
Impact consistently greater for Blacks
Dr. Al-Kindi and colleagues used 3,598,352 U.S. death files to investigate trends in deaths caused specifically by CVD as well as its subtypes myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure (HF) in 2018 and 2019 (prepandemic) and the pandemic years 2020 and 2021. Baseline demographics showed a higher percentage of older, female, and Black individuals among the CVD subtypes of interest.
Overall, there was an excess CVD mortality of 6.7% during the pandemic, compared with prepandemic years, including a 2.5% rise in MI deaths and an 8.5% rise in stroke deaths. HF mortality remained relatively steady, rising only 0.1%.
Subgroup analyses revealed “striking differences” in excess mortality between Blacks and Whites, the authors noted. Blacks had an overall excess mortality of 13.8% versus 5.1% for Whites, compared with the prepandemic years. The differences were consistent across subtypes: MI (9.6% vs. 1.0%); stroke (14.5% vs. 6.9%); and HF (5.1% vs. –1.2%; P value for all < .001).
When the investigators looked at deaths on a yearly basis with 2018 as the baseline, they found CVD deaths increased by 1.5% in 2019, 15.8% in 2020, and 13.5% in 2021 among Black Americans, compared with 0.5%, 5.1%, and 5.7%, respectively, among White Americans.
Excess deaths from MI rose by 9.5% in 2020 and by 6.7% in 2021 among Blacks but fell by 1.2% in 2020 and by 1.0% in 2021 among Whites.
Disparities in excess HF mortality were similar, rising 9.1% and 4.1% in 2020 and 2021 among Blacks, while dipping 0.1% and 0.8% in 2020 and 2021 among Whites.
The “most striking difference” was in excess stroke mortality, which doubled among Blacks compared with whites in 2020 (14.9% vs. 6.7%) and in 2021 (17.5% vs. 8.1%), according to the authors.
Awareness urged
Although the disparities were expected, “there is clear value in documenting and quantifying the magnitude of these disparities,” Amil M. Shah, MD, MPH, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
In addition to being observational, the main limitation of the study, he noted, is the quality and resolution of the death certificate data, which may limit the accuracy of the cause of death ascertainment and classification of race or ethnicity. “However, I think these potential inaccuracies are unlikely to materially impact the overall study findings.”
Dr. Shah, who was not involved in the study, said he would like to see additional research into the diversity and heterogeneity in risk among Black communities. “Understanding the environmental, social, and health care factors – both harmful and protective – that influence risk for CVD morbidity and mortality among Black individuals and communities offers the promise to provide actionable insights to mitigate these disparities.”
“Intervention studies testing approaches to mitigate disparities based on race/ethnicity” are also needed, he added. These may be at the policy, community, health system, or individual level, and community involvement in phases will be essential.”
Meanwhile, both Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah urged clinicians to be aware of the disparities and the need to improve access to care and address social determinants of health in vulnerable populations.
These disparities “are driven by structural factors, and are reinforced by individual behaviors. In this context, implicit bias training is important to help clinicians recognize and mitigate bias in their own practice,” Dr. Shah said. “Supporting diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts, and advocating for anti-racist policies and practices in their health systems” can also help.
Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality rose significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic and persists more than 2 years on and, once again, Blacks and African Americans have been disproportionately affected, an analysis of death certificates shows.
The findings “suggest that the pandemic may reverse years or decades of work aimed at reducing gaps in cardiovascular outcomes,” Sadeer G. Al-Kindi, MD, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
Although the disparities are in line with previous research, he said, “what was surprising is the persistence of excess cardiovascular mortality approximately 2 years after the pandemic started, even during a period of low COVID-19 mortality.”
“This suggests that the pandemic resulted in a disruption of health care access and, along with disparities in COVID-19 infection and its complications, he said, “may have a long-lasting effect on health care disparities, especially among vulnerable populations.”
The study was published online in Mayo Clinic Proceedings with lead author Scott E. Janus, MD, also of Case Western Reserve University.
Impact consistently greater for Blacks
Dr. Al-Kindi and colleagues used 3,598,352 U.S. death files to investigate trends in deaths caused specifically by CVD as well as its subtypes myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure (HF) in 2018 and 2019 (prepandemic) and the pandemic years 2020 and 2021. Baseline demographics showed a higher percentage of older, female, and Black individuals among the CVD subtypes of interest.
Overall, there was an excess CVD mortality of 6.7% during the pandemic, compared with prepandemic years, including a 2.5% rise in MI deaths and an 8.5% rise in stroke deaths. HF mortality remained relatively steady, rising only 0.1%.
Subgroup analyses revealed “striking differences” in excess mortality between Blacks and Whites, the authors noted. Blacks had an overall excess mortality of 13.8% versus 5.1% for Whites, compared with the prepandemic years. The differences were consistent across subtypes: MI (9.6% vs. 1.0%); stroke (14.5% vs. 6.9%); and HF (5.1% vs. –1.2%; P value for all < .001).
When the investigators looked at deaths on a yearly basis with 2018 as the baseline, they found CVD deaths increased by 1.5% in 2019, 15.8% in 2020, and 13.5% in 2021 among Black Americans, compared with 0.5%, 5.1%, and 5.7%, respectively, among White Americans.
Excess deaths from MI rose by 9.5% in 2020 and by 6.7% in 2021 among Blacks but fell by 1.2% in 2020 and by 1.0% in 2021 among Whites.
Disparities in excess HF mortality were similar, rising 9.1% and 4.1% in 2020 and 2021 among Blacks, while dipping 0.1% and 0.8% in 2020 and 2021 among Whites.
The “most striking difference” was in excess stroke mortality, which doubled among Blacks compared with whites in 2020 (14.9% vs. 6.7%) and in 2021 (17.5% vs. 8.1%), according to the authors.
Awareness urged
Although the disparities were expected, “there is clear value in documenting and quantifying the magnitude of these disparities,” Amil M. Shah, MD, MPH, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
In addition to being observational, the main limitation of the study, he noted, is the quality and resolution of the death certificate data, which may limit the accuracy of the cause of death ascertainment and classification of race or ethnicity. “However, I think these potential inaccuracies are unlikely to materially impact the overall study findings.”
Dr. Shah, who was not involved in the study, said he would like to see additional research into the diversity and heterogeneity in risk among Black communities. “Understanding the environmental, social, and health care factors – both harmful and protective – that influence risk for CVD morbidity and mortality among Black individuals and communities offers the promise to provide actionable insights to mitigate these disparities.”
“Intervention studies testing approaches to mitigate disparities based on race/ethnicity” are also needed, he added. These may be at the policy, community, health system, or individual level, and community involvement in phases will be essential.”
Meanwhile, both Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah urged clinicians to be aware of the disparities and the need to improve access to care and address social determinants of health in vulnerable populations.
These disparities “are driven by structural factors, and are reinforced by individual behaviors. In this context, implicit bias training is important to help clinicians recognize and mitigate bias in their own practice,” Dr. Shah said. “Supporting diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts, and advocating for anti-racist policies and practices in their health systems” can also help.
Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality rose significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic and persists more than 2 years on and, once again, Blacks and African Americans have been disproportionately affected, an analysis of death certificates shows.
The findings “suggest that the pandemic may reverse years or decades of work aimed at reducing gaps in cardiovascular outcomes,” Sadeer G. Al-Kindi, MD, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
Although the disparities are in line with previous research, he said, “what was surprising is the persistence of excess cardiovascular mortality approximately 2 years after the pandemic started, even during a period of low COVID-19 mortality.”
“This suggests that the pandemic resulted in a disruption of health care access and, along with disparities in COVID-19 infection and its complications, he said, “may have a long-lasting effect on health care disparities, especially among vulnerable populations.”
The study was published online in Mayo Clinic Proceedings with lead author Scott E. Janus, MD, also of Case Western Reserve University.
Impact consistently greater for Blacks
Dr. Al-Kindi and colleagues used 3,598,352 U.S. death files to investigate trends in deaths caused specifically by CVD as well as its subtypes myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure (HF) in 2018 and 2019 (prepandemic) and the pandemic years 2020 and 2021. Baseline demographics showed a higher percentage of older, female, and Black individuals among the CVD subtypes of interest.
Overall, there was an excess CVD mortality of 6.7% during the pandemic, compared with prepandemic years, including a 2.5% rise in MI deaths and an 8.5% rise in stroke deaths. HF mortality remained relatively steady, rising only 0.1%.
Subgroup analyses revealed “striking differences” in excess mortality between Blacks and Whites, the authors noted. Blacks had an overall excess mortality of 13.8% versus 5.1% for Whites, compared with the prepandemic years. The differences were consistent across subtypes: MI (9.6% vs. 1.0%); stroke (14.5% vs. 6.9%); and HF (5.1% vs. –1.2%; P value for all < .001).
When the investigators looked at deaths on a yearly basis with 2018 as the baseline, they found CVD deaths increased by 1.5% in 2019, 15.8% in 2020, and 13.5% in 2021 among Black Americans, compared with 0.5%, 5.1%, and 5.7%, respectively, among White Americans.
Excess deaths from MI rose by 9.5% in 2020 and by 6.7% in 2021 among Blacks but fell by 1.2% in 2020 and by 1.0% in 2021 among Whites.
Disparities in excess HF mortality were similar, rising 9.1% and 4.1% in 2020 and 2021 among Blacks, while dipping 0.1% and 0.8% in 2020 and 2021 among Whites.
The “most striking difference” was in excess stroke mortality, which doubled among Blacks compared with whites in 2020 (14.9% vs. 6.7%) and in 2021 (17.5% vs. 8.1%), according to the authors.
Awareness urged
Although the disparities were expected, “there is clear value in documenting and quantifying the magnitude of these disparities,” Amil M. Shah, MD, MPH, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
In addition to being observational, the main limitation of the study, he noted, is the quality and resolution of the death certificate data, which may limit the accuracy of the cause of death ascertainment and classification of race or ethnicity. “However, I think these potential inaccuracies are unlikely to materially impact the overall study findings.”
Dr. Shah, who was not involved in the study, said he would like to see additional research into the diversity and heterogeneity in risk among Black communities. “Understanding the environmental, social, and health care factors – both harmful and protective – that influence risk for CVD morbidity and mortality among Black individuals and communities offers the promise to provide actionable insights to mitigate these disparities.”
“Intervention studies testing approaches to mitigate disparities based on race/ethnicity” are also needed, he added. These may be at the policy, community, health system, or individual level, and community involvement in phases will be essential.”
Meanwhile, both Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah urged clinicians to be aware of the disparities and the need to improve access to care and address social determinants of health in vulnerable populations.
These disparities “are driven by structural factors, and are reinforced by individual behaviors. In this context, implicit bias training is important to help clinicians recognize and mitigate bias in their own practice,” Dr. Shah said. “Supporting diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts, and advocating for anti-racist policies and practices in their health systems” can also help.
Dr. Al-Kindi and Dr. Shah disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MAYO CLINIC PROCEEDINGS
Doxycycline cuts STI risk in men and trans women having sex with men
MONTREAL – (PrEP). The results of the open-label DoxyPEP trial were reported at a press conference at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
“It is time to take action on the data that we have and really think about incorporating it into guidelines and rolling this out in a safe and thoughtful way,” said co-principal investigator Annie Luetkemeyer, MD, of Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
The open-label trial, conducted in Seattle and San Francisco, randomized MSM/TGW living with HIV or on PrEP, and with a history of N. gonorrhoeae (GC), C. trachomatis (CT), or early syphilis in the past year, to either doxycycline or none within 72 hours of having condomless sex. It was stopped early in May when a planned interim analysis showed those randomized to take doxycycline had substantially fewer STIs than participants assigned to the control group.
The intent-to-treat analysis included 501 patients with at least one quarter of follow-up: 327 taking PrEP and 174 living with HIV. Among those taking PrEP, new STIs (GC, CT or syphilis) occurred in 31.9% of control participants vs. 10.7% of those taking doxycycline – a reduction of 66% per quarter (P < .001). Among participants living with HIV, new STIs occurred in 30.5% of controls vs. 11.8% taking doxycycline, for a 62% reduction in STIs per quarter (P < .0001).
“Participants reported taking doxycycline 87% of the time after having condomless sex, about half of participants took fewer than 10 doses per month, 30% took 10-20 doses per month, and 16% took more than 20 doses of doxycycline per month,” said Dr. Luetkemeyer, adding that there were no serious – grade 2 or greater – adverse events, and “the majority of participants reported that taking doxy was acceptable or very acceptable.”
Asked how broadly doxycycline prophylaxis could be used in other populations, Dr. Luetkemeyer was cautious. “Our study participants had a very high rate of new STIs – a 30% incidence per quarter and using doxyPEP was well tolerated and very effective to reduce new STIs. However, this is a fairly limited population,” she said. “Whether doxyPEP should be considered for other groups, such as women on PrEP or with an elevated risk for STIs, will need more data which will be forthcoming from ongoing studies.”
Dr. Luetkemeyer said her group is looking at three possible risks of antibiotic resistance with the doxyPEP regimen: the risk to bystander bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or commensal neisseria; the impact on the gut; and the risk of resistance to antibiotic treatments for STI.
For the latter, “we don’t really think this is going to be an issue in chlamydia and syphilis, and we’re looking carefully at gonorrhea,” she said, adding that it will be challenging to get definitive data from this particular study because of its short follow-up.
“Available culture data from those who had gonorrhea infections during the study demonstrated a relatively low rate of tetracycline resistance, which is a proxy for doxycycline resistance, at 20%. ... However, larger studies and population-based surveillance of those taking doxycycline as PEP are needed to understand if doxycycline use could drive the element of tetracycline resistance in gonorrhea,” she said, emphasizing that doxycycline is not used to treat active gonorrhea infections.
Calling the doxyPEP regimen a “game-changing strategy,” Sharon Lewin, AO, PhD, president-elect of the International AIDS Society, said many physicians are already prescribing it off label based on the IPERGAY study (N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2237-46) “but there’s a clear need for more evidence to guide the use of this intervention.”
“This study has huge implications for clinical care,” said Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, an infectious diseases doctor, professor of medicine, and associate chief in the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at UCSF. “Although the data on drug resistance is very important to evaluate, we should certainly consider at this point using doxycycline PEP within 72 hours of condomless sex for our patients for STI prevention,” she said in an interview.
“In our practice, we are very excited about the possibility of a simple one-pill postexposure prophylactic agent (doxycycline 200 mg) to reduce the risk of a number of STIs. We have used PEP for HIV infection for a number of years and are very familiar with the concept of preventing infections after an exposure,” said Dr. Gandhi, director of the UCSF Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital. “We are planning to institute doxycycline as PEP at my clinic after the release of these findings and will follow the remainder of the study findings closely.”
The trial was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, through grant R01AI143439. It was conducted at the HIV clinic at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and the San Francisco City Clinic, both part of the San Francisco Department of Public Health, and the Madison Clinic and the Sexual Health Clinic at Harborview Medical Center, both at the University of Washington. Medications were provided by Mayne Pharmaceuticals, and lab support by Hologic & Cepheid.
Dr. Lewin has the following disclosures: investigator-initiated, industry-funded research for Gilead, Viiv, Merck; scientific advisory board (honoraria paid to her personally) for Gilead, Merck, Viiv, Esfam, Immunocore, Vaxxinity; collaborative research (nonfunded) for AbbVie, Genentech, BMS. Dr. Luetkemeyer and Dr. Gandhi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – (PrEP). The results of the open-label DoxyPEP trial were reported at a press conference at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
“It is time to take action on the data that we have and really think about incorporating it into guidelines and rolling this out in a safe and thoughtful way,” said co-principal investigator Annie Luetkemeyer, MD, of Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
The open-label trial, conducted in Seattle and San Francisco, randomized MSM/TGW living with HIV or on PrEP, and with a history of N. gonorrhoeae (GC), C. trachomatis (CT), or early syphilis in the past year, to either doxycycline or none within 72 hours of having condomless sex. It was stopped early in May when a planned interim analysis showed those randomized to take doxycycline had substantially fewer STIs than participants assigned to the control group.
The intent-to-treat analysis included 501 patients with at least one quarter of follow-up: 327 taking PrEP and 174 living with HIV. Among those taking PrEP, new STIs (GC, CT or syphilis) occurred in 31.9% of control participants vs. 10.7% of those taking doxycycline – a reduction of 66% per quarter (P < .001). Among participants living with HIV, new STIs occurred in 30.5% of controls vs. 11.8% taking doxycycline, for a 62% reduction in STIs per quarter (P < .0001).
“Participants reported taking doxycycline 87% of the time after having condomless sex, about half of participants took fewer than 10 doses per month, 30% took 10-20 doses per month, and 16% took more than 20 doses of doxycycline per month,” said Dr. Luetkemeyer, adding that there were no serious – grade 2 or greater – adverse events, and “the majority of participants reported that taking doxy was acceptable or very acceptable.”
Asked how broadly doxycycline prophylaxis could be used in other populations, Dr. Luetkemeyer was cautious. “Our study participants had a very high rate of new STIs – a 30% incidence per quarter and using doxyPEP was well tolerated and very effective to reduce new STIs. However, this is a fairly limited population,” she said. “Whether doxyPEP should be considered for other groups, such as women on PrEP or with an elevated risk for STIs, will need more data which will be forthcoming from ongoing studies.”
Dr. Luetkemeyer said her group is looking at three possible risks of antibiotic resistance with the doxyPEP regimen: the risk to bystander bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or commensal neisseria; the impact on the gut; and the risk of resistance to antibiotic treatments for STI.
For the latter, “we don’t really think this is going to be an issue in chlamydia and syphilis, and we’re looking carefully at gonorrhea,” she said, adding that it will be challenging to get definitive data from this particular study because of its short follow-up.
“Available culture data from those who had gonorrhea infections during the study demonstrated a relatively low rate of tetracycline resistance, which is a proxy for doxycycline resistance, at 20%. ... However, larger studies and population-based surveillance of those taking doxycycline as PEP are needed to understand if doxycycline use could drive the element of tetracycline resistance in gonorrhea,” she said, emphasizing that doxycycline is not used to treat active gonorrhea infections.
Calling the doxyPEP regimen a “game-changing strategy,” Sharon Lewin, AO, PhD, president-elect of the International AIDS Society, said many physicians are already prescribing it off label based on the IPERGAY study (N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2237-46) “but there’s a clear need for more evidence to guide the use of this intervention.”
“This study has huge implications for clinical care,” said Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, an infectious diseases doctor, professor of medicine, and associate chief in the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at UCSF. “Although the data on drug resistance is very important to evaluate, we should certainly consider at this point using doxycycline PEP within 72 hours of condomless sex for our patients for STI prevention,” she said in an interview.
“In our practice, we are very excited about the possibility of a simple one-pill postexposure prophylactic agent (doxycycline 200 mg) to reduce the risk of a number of STIs. We have used PEP for HIV infection for a number of years and are very familiar with the concept of preventing infections after an exposure,” said Dr. Gandhi, director of the UCSF Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital. “We are planning to institute doxycycline as PEP at my clinic after the release of these findings and will follow the remainder of the study findings closely.”
The trial was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, through grant R01AI143439. It was conducted at the HIV clinic at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and the San Francisco City Clinic, both part of the San Francisco Department of Public Health, and the Madison Clinic and the Sexual Health Clinic at Harborview Medical Center, both at the University of Washington. Medications were provided by Mayne Pharmaceuticals, and lab support by Hologic & Cepheid.
Dr. Lewin has the following disclosures: investigator-initiated, industry-funded research for Gilead, Viiv, Merck; scientific advisory board (honoraria paid to her personally) for Gilead, Merck, Viiv, Esfam, Immunocore, Vaxxinity; collaborative research (nonfunded) for AbbVie, Genentech, BMS. Dr. Luetkemeyer and Dr. Gandhi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – (PrEP). The results of the open-label DoxyPEP trial were reported at a press conference at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
“It is time to take action on the data that we have and really think about incorporating it into guidelines and rolling this out in a safe and thoughtful way,” said co-principal investigator Annie Luetkemeyer, MD, of Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
The open-label trial, conducted in Seattle and San Francisco, randomized MSM/TGW living with HIV or on PrEP, and with a history of N. gonorrhoeae (GC), C. trachomatis (CT), or early syphilis in the past year, to either doxycycline or none within 72 hours of having condomless sex. It was stopped early in May when a planned interim analysis showed those randomized to take doxycycline had substantially fewer STIs than participants assigned to the control group.
The intent-to-treat analysis included 501 patients with at least one quarter of follow-up: 327 taking PrEP and 174 living with HIV. Among those taking PrEP, new STIs (GC, CT or syphilis) occurred in 31.9% of control participants vs. 10.7% of those taking doxycycline – a reduction of 66% per quarter (P < .001). Among participants living with HIV, new STIs occurred in 30.5% of controls vs. 11.8% taking doxycycline, for a 62% reduction in STIs per quarter (P < .0001).
“Participants reported taking doxycycline 87% of the time after having condomless sex, about half of participants took fewer than 10 doses per month, 30% took 10-20 doses per month, and 16% took more than 20 doses of doxycycline per month,” said Dr. Luetkemeyer, adding that there were no serious – grade 2 or greater – adverse events, and “the majority of participants reported that taking doxy was acceptable or very acceptable.”
Asked how broadly doxycycline prophylaxis could be used in other populations, Dr. Luetkemeyer was cautious. “Our study participants had a very high rate of new STIs – a 30% incidence per quarter and using doxyPEP was well tolerated and very effective to reduce new STIs. However, this is a fairly limited population,” she said. “Whether doxyPEP should be considered for other groups, such as women on PrEP or with an elevated risk for STIs, will need more data which will be forthcoming from ongoing studies.”
Dr. Luetkemeyer said her group is looking at three possible risks of antibiotic resistance with the doxyPEP regimen: the risk to bystander bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or commensal neisseria; the impact on the gut; and the risk of resistance to antibiotic treatments for STI.
For the latter, “we don’t really think this is going to be an issue in chlamydia and syphilis, and we’re looking carefully at gonorrhea,” she said, adding that it will be challenging to get definitive data from this particular study because of its short follow-up.
“Available culture data from those who had gonorrhea infections during the study demonstrated a relatively low rate of tetracycline resistance, which is a proxy for doxycycline resistance, at 20%. ... However, larger studies and population-based surveillance of those taking doxycycline as PEP are needed to understand if doxycycline use could drive the element of tetracycline resistance in gonorrhea,” she said, emphasizing that doxycycline is not used to treat active gonorrhea infections.
Calling the doxyPEP regimen a “game-changing strategy,” Sharon Lewin, AO, PhD, president-elect of the International AIDS Society, said many physicians are already prescribing it off label based on the IPERGAY study (N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2237-46) “but there’s a clear need for more evidence to guide the use of this intervention.”
“This study has huge implications for clinical care,” said Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, an infectious diseases doctor, professor of medicine, and associate chief in the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at UCSF. “Although the data on drug resistance is very important to evaluate, we should certainly consider at this point using doxycycline PEP within 72 hours of condomless sex for our patients for STI prevention,” she said in an interview.
“In our practice, we are very excited about the possibility of a simple one-pill postexposure prophylactic agent (doxycycline 200 mg) to reduce the risk of a number of STIs. We have used PEP for HIV infection for a number of years and are very familiar with the concept of preventing infections after an exposure,” said Dr. Gandhi, director of the UCSF Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital. “We are planning to institute doxycycline as PEP at my clinic after the release of these findings and will follow the remainder of the study findings closely.”
The trial was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, through grant R01AI143439. It was conducted at the HIV clinic at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and the San Francisco City Clinic, both part of the San Francisco Department of Public Health, and the Madison Clinic and the Sexual Health Clinic at Harborview Medical Center, both at the University of Washington. Medications were provided by Mayne Pharmaceuticals, and lab support by Hologic & Cepheid.
Dr. Lewin has the following disclosures: investigator-initiated, industry-funded research for Gilead, Viiv, Merck; scientific advisory board (honoraria paid to her personally) for Gilead, Merck, Viiv, Esfam, Immunocore, Vaxxinity; collaborative research (nonfunded) for AbbVie, Genentech, BMS. Dr. Luetkemeyer and Dr. Gandhi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AIDS 2022
U.S. clears 786,000 monkeypox vaccine doses for distribution
More than 780,000 doses of the JYNNEOS monkeypox vaccine will be available in the United States beginning July 29, the Department of Health & Human Services announced on July 28 in a press call.
HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra urged local and state public health departments to use these doses for preventive vaccination efforts to stay ahead of the virus and end the outbreak, noting that the HHS and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention do not control how vaccines are distributed at state and local levels. “We don’t have the authority to tell them what to do,” he said during the call. “We need them to work with us.”
As of July 28, there were 4,907 reported cases of monkeypox in the United States and officials expect cases will continue to rise in the coming weeks.
The vaccine is manufactured by the small Danish company Bavarian Nordic. These additional 786,000 doses were previously stored at a plant in Denmark, awaiting the completion of an inspection and authorization of the vaccine plant by the Food and Drug Administration. The agency announced on July 27 that both the vaccine doses and the manufacturing plant met standards.
With the announcement of these additional doses, the vaccine allocation plan is also being updated to take into account two important factors: the number of people at high risk in a jurisdiction and the number of new cases reported since the last vaccine allocation.
“This update gives greater weight to prioritizing vaccines to areas with the greatest number of people at risk, which includes men who have sex with men who have HIV or who are eligible for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis, while still considering where we are seeing cases increase,” said Capt. Jennifer McQuiston, DVM, deputy director of the division of high consequence pathogens and pathology at the CDC.
Capt.McQuiston also provided additional demographic information on the U.S. outbreak. The median age of people with confirmed cases is 35 years old, with a range from 17 to 76. (This does not include the two cases in children reported on July 22.) Of the cases where sex at birth was provided, 99% were individuals assigned male sex at birth. In cases with reported ethnicity and race, 37% were non-Hispanic White people, 31% were Hispanic/Latino, 27% were Black or African American, and 4% were of Asian descent. The most common symptoms were rash – present in 99% of cases – malaise, fever, and swollen lymph nodes.
HHS and CDC did not have data on how many people have received at least one dose of the monkeypox vaccine. When asked how many people need to be fully vaccinated against monkeypox to contain the outbreak, Mr. Becerra did not provide an estimate but implied that preventive vaccination could help limit the number of vaccines needed and expressed optimism about quelling the outbreak in the United States. “We believe that we have done everything we can at the federal level to work with our state and local partners and communities affected to make sure we can stay ahead of this and end this outbreak,” he said, “but everybody’s got to do their part.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 780,000 doses of the JYNNEOS monkeypox vaccine will be available in the United States beginning July 29, the Department of Health & Human Services announced on July 28 in a press call.
HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra urged local and state public health departments to use these doses for preventive vaccination efforts to stay ahead of the virus and end the outbreak, noting that the HHS and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention do not control how vaccines are distributed at state and local levels. “We don’t have the authority to tell them what to do,” he said during the call. “We need them to work with us.”
As of July 28, there were 4,907 reported cases of monkeypox in the United States and officials expect cases will continue to rise in the coming weeks.
The vaccine is manufactured by the small Danish company Bavarian Nordic. These additional 786,000 doses were previously stored at a plant in Denmark, awaiting the completion of an inspection and authorization of the vaccine plant by the Food and Drug Administration. The agency announced on July 27 that both the vaccine doses and the manufacturing plant met standards.
With the announcement of these additional doses, the vaccine allocation plan is also being updated to take into account two important factors: the number of people at high risk in a jurisdiction and the number of new cases reported since the last vaccine allocation.
“This update gives greater weight to prioritizing vaccines to areas with the greatest number of people at risk, which includes men who have sex with men who have HIV or who are eligible for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis, while still considering where we are seeing cases increase,” said Capt. Jennifer McQuiston, DVM, deputy director of the division of high consequence pathogens and pathology at the CDC.
Capt.McQuiston also provided additional demographic information on the U.S. outbreak. The median age of people with confirmed cases is 35 years old, with a range from 17 to 76. (This does not include the two cases in children reported on July 22.) Of the cases where sex at birth was provided, 99% were individuals assigned male sex at birth. In cases with reported ethnicity and race, 37% were non-Hispanic White people, 31% were Hispanic/Latino, 27% were Black or African American, and 4% were of Asian descent. The most common symptoms were rash – present in 99% of cases – malaise, fever, and swollen lymph nodes.
HHS and CDC did not have data on how many people have received at least one dose of the monkeypox vaccine. When asked how many people need to be fully vaccinated against monkeypox to contain the outbreak, Mr. Becerra did not provide an estimate but implied that preventive vaccination could help limit the number of vaccines needed and expressed optimism about quelling the outbreak in the United States. “We believe that we have done everything we can at the federal level to work with our state and local partners and communities affected to make sure we can stay ahead of this and end this outbreak,” he said, “but everybody’s got to do their part.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 780,000 doses of the JYNNEOS monkeypox vaccine will be available in the United States beginning July 29, the Department of Health & Human Services announced on July 28 in a press call.
HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra urged local and state public health departments to use these doses for preventive vaccination efforts to stay ahead of the virus and end the outbreak, noting that the HHS and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention do not control how vaccines are distributed at state and local levels. “We don’t have the authority to tell them what to do,” he said during the call. “We need them to work with us.”
As of July 28, there were 4,907 reported cases of monkeypox in the United States and officials expect cases will continue to rise in the coming weeks.
The vaccine is manufactured by the small Danish company Bavarian Nordic. These additional 786,000 doses were previously stored at a plant in Denmark, awaiting the completion of an inspection and authorization of the vaccine plant by the Food and Drug Administration. The agency announced on July 27 that both the vaccine doses and the manufacturing plant met standards.
With the announcement of these additional doses, the vaccine allocation plan is also being updated to take into account two important factors: the number of people at high risk in a jurisdiction and the number of new cases reported since the last vaccine allocation.
“This update gives greater weight to prioritizing vaccines to areas with the greatest number of people at risk, which includes men who have sex with men who have HIV or who are eligible for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis, while still considering where we are seeing cases increase,” said Capt. Jennifer McQuiston, DVM, deputy director of the division of high consequence pathogens and pathology at the CDC.
Capt.McQuiston also provided additional demographic information on the U.S. outbreak. The median age of people with confirmed cases is 35 years old, with a range from 17 to 76. (This does not include the two cases in children reported on July 22.) Of the cases where sex at birth was provided, 99% were individuals assigned male sex at birth. In cases with reported ethnicity and race, 37% were non-Hispanic White people, 31% were Hispanic/Latino, 27% were Black or African American, and 4% were of Asian descent. The most common symptoms were rash – present in 99% of cases – malaise, fever, and swollen lymph nodes.
HHS and CDC did not have data on how many people have received at least one dose of the monkeypox vaccine. When asked how many people need to be fully vaccinated against monkeypox to contain the outbreak, Mr. Becerra did not provide an estimate but implied that preventive vaccination could help limit the number of vaccines needed and expressed optimism about quelling the outbreak in the United States. “We believe that we have done everything we can at the federal level to work with our state and local partners and communities affected to make sure we can stay ahead of this and end this outbreak,” he said, “but everybody’s got to do their part.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Prolonged remission in patient with HIV may open new avenues to functional cure
MONTREAL – The case of a patient in an HIV study whose viral load dropped to undetectable levels and whose immune cells soared has captured the attention of organizers at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
Although the 59-year-old woman is one of many who are known as posttreatment controllers (PTCs) – having been in remission for more than 15 years after stopping antiretroviral therapy (ART) –
“This case opens new avenues in the HIV functional-cure field,” lead investigator Núria Climent, PhD, of the HIV unit at Hospital Clinic-IDIBAPS/University of Barcelona, told this news organization.
“As far as we know, this is the first time that the gamma-delta T cells have been identified in a PTC, and concerning the memory-like NK cells, there are very few published data and only sparse information presented in several congresses,” she said, explaining that these cells “have a high capacity to inhibit the replication of the virus in vitro. For that reason, we think that this PTC has cells able to dramatically reduce the virus amount. We think that the potential capacity to increase these cells in this PTC woman could be not only mediated by especial genetic factors ... but also mediated by early ART treatment and might be by the immunomediated treatment.”
The findings suggest the potential for “increasing the amount of those memory-like NK cells and gamma-delta T cells in order to translate this potent antiviral activity in new therapies to achieve an HIV functional cure,” she said, adding: “As far as we know, aiming to increase these specific cells has never been done before in people living with HIV.”
In a press conference during the meeting, Dr. Climent explained that the patient was enrolled in a study in which she received a combination of ART and immunomodulatory therapy. This involved a combination of cyclosporine A, low-dose interleukin 2, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and pegylated interferon alfa-2b.
“None of the other 19 patients included in the trial controlled viral replication,” senior investigator Jose Miro, MD, PhD, also from the HIV unit at Hospital Clinic-IDIBAPS/University of Barcelona, told this news organization.
Sharon Lewin, MD, president-elect of the International AIDS Society, which runs the conference, said in an interview that although the significance of the case is unclear, the IAS selected it as a highlight for the meeting. “It is important for clinicians to understand the complexities in interpreting these case reports. Their patients are probably likely to ask them about the report, and it’s important [that] they can explain it to them.”
Dr. Lewin, who is professor of medicine at the University of Melbourne and director of the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity in Melbourne, added that it is impossible to determine the mechanism of action from a single case report. “We don’t know if the intervention played a role or if this person is a ‘posttreatment controller,’ which has been previously described many times,” she said in an interview. “In this patient, the virus is at very low, but controlled, levels, and virus could be grown out. While it’s still exciting and important, this is really what we would consider a remission. The intense study of a single case such as this is certainly worthwhile and important but can only provide new ideas for research. So, I don’t think we can draw any conclusion on the role of NK cells, et cetera. We need much larger case series or controlled trials to reach any conclusion on the reasons for her remission.”
Dr. Climent disclosed no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Lewin has disclosed investigator-initiated industry-funded research (Gilead, ViiV, Merck), scientific advisory board honoraria paid to her personally (Gilead, Merck, ViiV, Esfam, Immunocore, Vaxxinity), and nonfunded collaborative research (AbbVie, Genentech, Bristol-Myers Squibb).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – The case of a patient in an HIV study whose viral load dropped to undetectable levels and whose immune cells soared has captured the attention of organizers at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
Although the 59-year-old woman is one of many who are known as posttreatment controllers (PTCs) – having been in remission for more than 15 years after stopping antiretroviral therapy (ART) –
“This case opens new avenues in the HIV functional-cure field,” lead investigator Núria Climent, PhD, of the HIV unit at Hospital Clinic-IDIBAPS/University of Barcelona, told this news organization.
“As far as we know, this is the first time that the gamma-delta T cells have been identified in a PTC, and concerning the memory-like NK cells, there are very few published data and only sparse information presented in several congresses,” she said, explaining that these cells “have a high capacity to inhibit the replication of the virus in vitro. For that reason, we think that this PTC has cells able to dramatically reduce the virus amount. We think that the potential capacity to increase these cells in this PTC woman could be not only mediated by especial genetic factors ... but also mediated by early ART treatment and might be by the immunomediated treatment.”
The findings suggest the potential for “increasing the amount of those memory-like NK cells and gamma-delta T cells in order to translate this potent antiviral activity in new therapies to achieve an HIV functional cure,” she said, adding: “As far as we know, aiming to increase these specific cells has never been done before in people living with HIV.”
In a press conference during the meeting, Dr. Climent explained that the patient was enrolled in a study in which she received a combination of ART and immunomodulatory therapy. This involved a combination of cyclosporine A, low-dose interleukin 2, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and pegylated interferon alfa-2b.
“None of the other 19 patients included in the trial controlled viral replication,” senior investigator Jose Miro, MD, PhD, also from the HIV unit at Hospital Clinic-IDIBAPS/University of Barcelona, told this news organization.
Sharon Lewin, MD, president-elect of the International AIDS Society, which runs the conference, said in an interview that although the significance of the case is unclear, the IAS selected it as a highlight for the meeting. “It is important for clinicians to understand the complexities in interpreting these case reports. Their patients are probably likely to ask them about the report, and it’s important [that] they can explain it to them.”
Dr. Lewin, who is professor of medicine at the University of Melbourne and director of the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity in Melbourne, added that it is impossible to determine the mechanism of action from a single case report. “We don’t know if the intervention played a role or if this person is a ‘posttreatment controller,’ which has been previously described many times,” she said in an interview. “In this patient, the virus is at very low, but controlled, levels, and virus could be grown out. While it’s still exciting and important, this is really what we would consider a remission. The intense study of a single case such as this is certainly worthwhile and important but can only provide new ideas for research. So, I don’t think we can draw any conclusion on the role of NK cells, et cetera. We need much larger case series or controlled trials to reach any conclusion on the reasons for her remission.”
Dr. Climent disclosed no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Lewin has disclosed investigator-initiated industry-funded research (Gilead, ViiV, Merck), scientific advisory board honoraria paid to her personally (Gilead, Merck, ViiV, Esfam, Immunocore, Vaxxinity), and nonfunded collaborative research (AbbVie, Genentech, Bristol-Myers Squibb).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – The case of a patient in an HIV study whose viral load dropped to undetectable levels and whose immune cells soared has captured the attention of organizers at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
Although the 59-year-old woman is one of many who are known as posttreatment controllers (PTCs) – having been in remission for more than 15 years after stopping antiretroviral therapy (ART) –
“This case opens new avenues in the HIV functional-cure field,” lead investigator Núria Climent, PhD, of the HIV unit at Hospital Clinic-IDIBAPS/University of Barcelona, told this news organization.
“As far as we know, this is the first time that the gamma-delta T cells have been identified in a PTC, and concerning the memory-like NK cells, there are very few published data and only sparse information presented in several congresses,” she said, explaining that these cells “have a high capacity to inhibit the replication of the virus in vitro. For that reason, we think that this PTC has cells able to dramatically reduce the virus amount. We think that the potential capacity to increase these cells in this PTC woman could be not only mediated by especial genetic factors ... but also mediated by early ART treatment and might be by the immunomediated treatment.”
The findings suggest the potential for “increasing the amount of those memory-like NK cells and gamma-delta T cells in order to translate this potent antiviral activity in new therapies to achieve an HIV functional cure,” she said, adding: “As far as we know, aiming to increase these specific cells has never been done before in people living with HIV.”
In a press conference during the meeting, Dr. Climent explained that the patient was enrolled in a study in which she received a combination of ART and immunomodulatory therapy. This involved a combination of cyclosporine A, low-dose interleukin 2, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and pegylated interferon alfa-2b.
“None of the other 19 patients included in the trial controlled viral replication,” senior investigator Jose Miro, MD, PhD, also from the HIV unit at Hospital Clinic-IDIBAPS/University of Barcelona, told this news organization.
Sharon Lewin, MD, president-elect of the International AIDS Society, which runs the conference, said in an interview that although the significance of the case is unclear, the IAS selected it as a highlight for the meeting. “It is important for clinicians to understand the complexities in interpreting these case reports. Their patients are probably likely to ask them about the report, and it’s important [that] they can explain it to them.”
Dr. Lewin, who is professor of medicine at the University of Melbourne and director of the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity in Melbourne, added that it is impossible to determine the mechanism of action from a single case report. “We don’t know if the intervention played a role or if this person is a ‘posttreatment controller,’ which has been previously described many times,” she said in an interview. “In this patient, the virus is at very low, but controlled, levels, and virus could be grown out. While it’s still exciting and important, this is really what we would consider a remission. The intense study of a single case such as this is certainly worthwhile and important but can only provide new ideas for research. So, I don’t think we can draw any conclusion on the role of NK cells, et cetera. We need much larger case series or controlled trials to reach any conclusion on the reasons for her remission.”
Dr. Climent disclosed no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Lewin has disclosed investigator-initiated industry-funded research (Gilead, ViiV, Merck), scientific advisory board honoraria paid to her personally (Gilead, Merck, ViiV, Esfam, Immunocore, Vaxxinity), and nonfunded collaborative research (AbbVie, Genentech, Bristol-Myers Squibb).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AIDS 2022
Potentially deadly bacteria detected in U.S. soil
, according to a new alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The bacteria, Burkholderia pseudomallei, was found along the Gulf Coast region in southern Mississippi. Typically, the bacteria are in tropical and subtropical climates, especially in parts of Southeast Asia, northern Australia, Central America, South America, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The bacteria can cause melioidosis, a rare and serious infectious disease that spreads to animals and humans through contact with contaminated soil and water via cuts, wounds, mucous membranes, breathing the bacteria in, or eating or drinking it. Worldwide, the disease is fatal in 10%-50% of those who become infected.
CDC and state officials are investigating the samples to find out how widespread the bacteria are within the United States. So far, modeling suggests that the environmental conditions on the Gulf Coast support the growth of B. pseudomallei.
“It is unclear how long the bacteria has been in the environment and where else it might be found in the U.S.,” according to the CDC statement. “CDC is alerting clinicians throughout the country of this discovery through a national health advisory, reminding them to be aware of the signs and symptoms of melioidosis and to consider melioidosis in patients that present with symptoms of the disease.”
Two unrelated people who live near the Gulf Coast region of Mississippi became sick with melioidosis recently – one in July 2020 and one in May 2022. Neither had traveled outside of the United States. The cases led the CDC and the Mississippi State Department of Health to collect environmental samples and test household products at the patients’ homes in June 2022. Three of the samples taken from soil and puddle water in the 2020 case tested positive for the bacteria.
Genomic sequencing revealed that both patients were infected with the same strain of the bacteria from the Western Hemisphere. They were hospitalized with sepsis due to pneumonia and had known risk factors for melioidosis. Both patients recovered after they were treated with antibiotics.
An average of 12 melioidosis cases are diagnosed in the United States each year, with most in people with recent travel to a country where the bacteria is endemic, or regularly found. Cases have also been linked to contaminated products imported from endemic countries. In late 2021, four cases in four states – Georgia, Kansas, Minnesota, and Texas – were linked to a contaminated aromatherapy spray that was imported, and Walmart issued a recall in November of that year, according to a CDC announcement. Two of the four people died.
Given the small number of cases found in the United States, the CDC believes the risk of melioidosis for the general population continues to be “very low,” and the risk of person-to-person spread is considered “extremely low.” But people who live on the Gulf Coast of Mississippi and who have health conditions that may put them at a higher risk, such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease, chronic lung disease, excessive alcohol use, and immunosuppressive conditions, should protect themselves.
The CDC recommends avoiding contact with soil or muddy water, particularly after heavy rains, and protecting open wounds with waterproof bandages. People should also wear waterproof boots when gardening, working in the yard, or doing agricultural work, which can prevent infection through the feet and lower legs, especially after flooding or storms. People should also wear gloves to protect their hands when working directly with soil.
Melioidosis has a wide range of symptoms, including fever, joint pain, headaches, coughing, chest pain, and belly pain. It can also cause conditions such as pneumonia, abscesses, and blood infections. The disease can infect any organ, including the brain. In most cases, symptoms appear within 1-21 days after exposure, with an average of 7 days after exposure.
The CDC’s health advisory for health professionals and public health officials shows that melioidosis is now considered to be locally endemic in areas of the Gulf Coast region in Mississippi.
“Once well-established in the soil, B. pseudomallei cannot feasibly be removed from the soil,” according to the advisory. “Public health efforts should focus primarily on improving identification of cases so that appropriate treatment can be administered.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The bacteria, Burkholderia pseudomallei, was found along the Gulf Coast region in southern Mississippi. Typically, the bacteria are in tropical and subtropical climates, especially in parts of Southeast Asia, northern Australia, Central America, South America, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The bacteria can cause melioidosis, a rare and serious infectious disease that spreads to animals and humans through contact with contaminated soil and water via cuts, wounds, mucous membranes, breathing the bacteria in, or eating or drinking it. Worldwide, the disease is fatal in 10%-50% of those who become infected.
CDC and state officials are investigating the samples to find out how widespread the bacteria are within the United States. So far, modeling suggests that the environmental conditions on the Gulf Coast support the growth of B. pseudomallei.
“It is unclear how long the bacteria has been in the environment and where else it might be found in the U.S.,” according to the CDC statement. “CDC is alerting clinicians throughout the country of this discovery through a national health advisory, reminding them to be aware of the signs and symptoms of melioidosis and to consider melioidosis in patients that present with symptoms of the disease.”
Two unrelated people who live near the Gulf Coast region of Mississippi became sick with melioidosis recently – one in July 2020 and one in May 2022. Neither had traveled outside of the United States. The cases led the CDC and the Mississippi State Department of Health to collect environmental samples and test household products at the patients’ homes in June 2022. Three of the samples taken from soil and puddle water in the 2020 case tested positive for the bacteria.
Genomic sequencing revealed that both patients were infected with the same strain of the bacteria from the Western Hemisphere. They were hospitalized with sepsis due to pneumonia and had known risk factors for melioidosis. Both patients recovered after they were treated with antibiotics.
An average of 12 melioidosis cases are diagnosed in the United States each year, with most in people with recent travel to a country where the bacteria is endemic, or regularly found. Cases have also been linked to contaminated products imported from endemic countries. In late 2021, four cases in four states – Georgia, Kansas, Minnesota, and Texas – were linked to a contaminated aromatherapy spray that was imported, and Walmart issued a recall in November of that year, according to a CDC announcement. Two of the four people died.
Given the small number of cases found in the United States, the CDC believes the risk of melioidosis for the general population continues to be “very low,” and the risk of person-to-person spread is considered “extremely low.” But people who live on the Gulf Coast of Mississippi and who have health conditions that may put them at a higher risk, such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease, chronic lung disease, excessive alcohol use, and immunosuppressive conditions, should protect themselves.
The CDC recommends avoiding contact with soil or muddy water, particularly after heavy rains, and protecting open wounds with waterproof bandages. People should also wear waterproof boots when gardening, working in the yard, or doing agricultural work, which can prevent infection through the feet and lower legs, especially after flooding or storms. People should also wear gloves to protect their hands when working directly with soil.
Melioidosis has a wide range of symptoms, including fever, joint pain, headaches, coughing, chest pain, and belly pain. It can also cause conditions such as pneumonia, abscesses, and blood infections. The disease can infect any organ, including the brain. In most cases, symptoms appear within 1-21 days after exposure, with an average of 7 days after exposure.
The CDC’s health advisory for health professionals and public health officials shows that melioidosis is now considered to be locally endemic in areas of the Gulf Coast region in Mississippi.
“Once well-established in the soil, B. pseudomallei cannot feasibly be removed from the soil,” according to the advisory. “Public health efforts should focus primarily on improving identification of cases so that appropriate treatment can be administered.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The bacteria, Burkholderia pseudomallei, was found along the Gulf Coast region in southern Mississippi. Typically, the bacteria are in tropical and subtropical climates, especially in parts of Southeast Asia, northern Australia, Central America, South America, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The bacteria can cause melioidosis, a rare and serious infectious disease that spreads to animals and humans through contact with contaminated soil and water via cuts, wounds, mucous membranes, breathing the bacteria in, or eating or drinking it. Worldwide, the disease is fatal in 10%-50% of those who become infected.
CDC and state officials are investigating the samples to find out how widespread the bacteria are within the United States. So far, modeling suggests that the environmental conditions on the Gulf Coast support the growth of B. pseudomallei.
“It is unclear how long the bacteria has been in the environment and where else it might be found in the U.S.,” according to the CDC statement. “CDC is alerting clinicians throughout the country of this discovery through a national health advisory, reminding them to be aware of the signs and symptoms of melioidosis and to consider melioidosis in patients that present with symptoms of the disease.”
Two unrelated people who live near the Gulf Coast region of Mississippi became sick with melioidosis recently – one in July 2020 and one in May 2022. Neither had traveled outside of the United States. The cases led the CDC and the Mississippi State Department of Health to collect environmental samples and test household products at the patients’ homes in June 2022. Three of the samples taken from soil and puddle water in the 2020 case tested positive for the bacteria.
Genomic sequencing revealed that both patients were infected with the same strain of the bacteria from the Western Hemisphere. They were hospitalized with sepsis due to pneumonia and had known risk factors for melioidosis. Both patients recovered after they were treated with antibiotics.
An average of 12 melioidosis cases are diagnosed in the United States each year, with most in people with recent travel to a country where the bacteria is endemic, or regularly found. Cases have also been linked to contaminated products imported from endemic countries. In late 2021, four cases in four states – Georgia, Kansas, Minnesota, and Texas – were linked to a contaminated aromatherapy spray that was imported, and Walmart issued a recall in November of that year, according to a CDC announcement. Two of the four people died.
Given the small number of cases found in the United States, the CDC believes the risk of melioidosis for the general population continues to be “very low,” and the risk of person-to-person spread is considered “extremely low.” But people who live on the Gulf Coast of Mississippi and who have health conditions that may put them at a higher risk, such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease, chronic lung disease, excessive alcohol use, and immunosuppressive conditions, should protect themselves.
The CDC recommends avoiding contact with soil or muddy water, particularly after heavy rains, and protecting open wounds with waterproof bandages. People should also wear waterproof boots when gardening, working in the yard, or doing agricultural work, which can prevent infection through the feet and lower legs, especially after flooding or storms. People should also wear gloves to protect their hands when working directly with soil.
Melioidosis has a wide range of symptoms, including fever, joint pain, headaches, coughing, chest pain, and belly pain. It can also cause conditions such as pneumonia, abscesses, and blood infections. The disease can infect any organ, including the brain. In most cases, symptoms appear within 1-21 days after exposure, with an average of 7 days after exposure.
The CDC’s health advisory for health professionals and public health officials shows that melioidosis is now considered to be locally endemic in areas of the Gulf Coast region in Mississippi.
“Once well-established in the soil, B. pseudomallei cannot feasibly be removed from the soil,” according to the advisory. “Public health efforts should focus primarily on improving identification of cases so that appropriate treatment can be administered.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.