User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
FDA authorizes updated COVID boosters to target newest variants
The agency cited data to support the safety and efficacy of this next generation of mRNA vaccines targeted toward variants of concern.
The Pfizer EUA corresponds to the company’s combination booster shot that includes the original COVID-19 vaccine as well as a vaccine specifically designed to protect against the most recent Omicron variants, BA.4 and BA.5.
The Moderna combination vaccine will contain both the firm’s original COVID-19 vaccine and a vaccine to protect specifically against Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 subvariants.
As of Aug. 27, BA.4 and BA.4.6 account for about 11% of circulating variants and BA.5 accounts for almost all the remaining 89%, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show.
The next step will be review of the scientific data by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which is set to meet Sept. 1 and 2. The final hurdle before distribution of the new vaccines will be sign-off on CDC recommendations for use by agency Director Rochelle Walensky, MD.
This is a developing story. A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The agency cited data to support the safety and efficacy of this next generation of mRNA vaccines targeted toward variants of concern.
The Pfizer EUA corresponds to the company’s combination booster shot that includes the original COVID-19 vaccine as well as a vaccine specifically designed to protect against the most recent Omicron variants, BA.4 and BA.5.
The Moderna combination vaccine will contain both the firm’s original COVID-19 vaccine and a vaccine to protect specifically against Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 subvariants.
As of Aug. 27, BA.4 and BA.4.6 account for about 11% of circulating variants and BA.5 accounts for almost all the remaining 89%, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show.
The next step will be review of the scientific data by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which is set to meet Sept. 1 and 2. The final hurdle before distribution of the new vaccines will be sign-off on CDC recommendations for use by agency Director Rochelle Walensky, MD.
This is a developing story. A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The agency cited data to support the safety and efficacy of this next generation of mRNA vaccines targeted toward variants of concern.
The Pfizer EUA corresponds to the company’s combination booster shot that includes the original COVID-19 vaccine as well as a vaccine specifically designed to protect against the most recent Omicron variants, BA.4 and BA.5.
The Moderna combination vaccine will contain both the firm’s original COVID-19 vaccine and a vaccine to protect specifically against Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 subvariants.
As of Aug. 27, BA.4 and BA.4.6 account for about 11% of circulating variants and BA.5 accounts for almost all the remaining 89%, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show.
The next step will be review of the scientific data by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which is set to meet Sept. 1 and 2. The final hurdle before distribution of the new vaccines will be sign-off on CDC recommendations for use by agency Director Rochelle Walensky, MD.
This is a developing story. A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: New cases increase; hospital admissions could follow
New cases of COVID-19 in children were up again after 2 weeks of declines, and preliminary data suggest that hospitalizations may be on the rise as well.
, based on data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.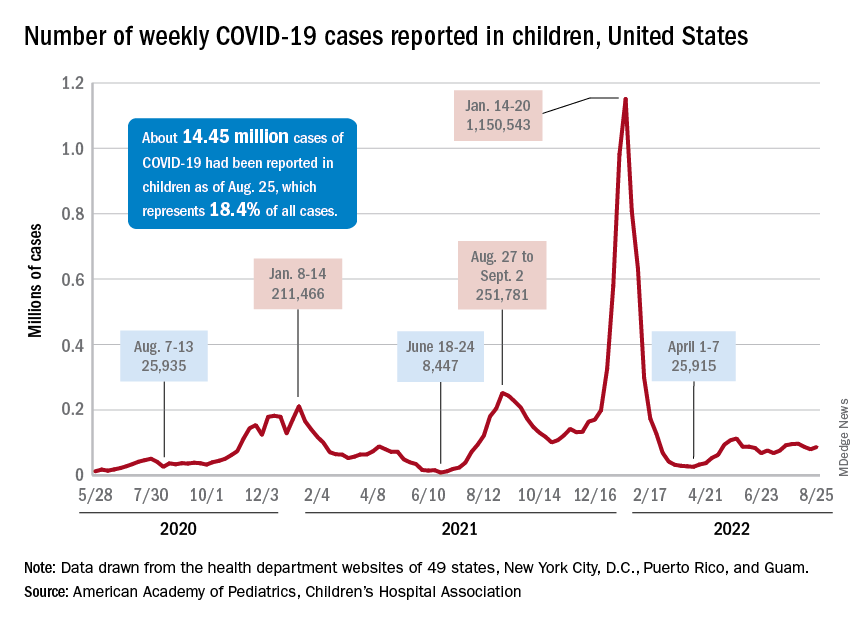
A similar increase seems to be reflected by hospital-level data. The latest 7-day (Aug. 21-27) average is 305 new admissions with diagnosed COVID per day among children aged 0-17 years, compared with 290 per day for the week of Aug. 14-20, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported, while also noting the potential for reporting delays in the most recent 7-day period.
Daily hospital admissions for COVID had been headed downward through the first half of August, falling from 0.46 per 100,000 population at the end of July to 0.40 on Aug. 19, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Since then, however, admissions have gone the other way, with the preliminary nature of the latest data suggesting that the numbers will be even higher as more hospitals report over the next few days.
Vaccine initiations continue to fall
Initiations among school-age children have fallen for 3 consecutive weeks since Aug. 3, when numbers receiving their first vaccinations reached late-summer highs for those aged 5-11 and 12-17 years. Children under age 5, included in the CDC data for the first time on Aug. 11 as separate groups – under 2 years and 2-4 years – have had vaccine initiations drop by 8.0% and 19.8% over the 2 following weeks, the CDC said.
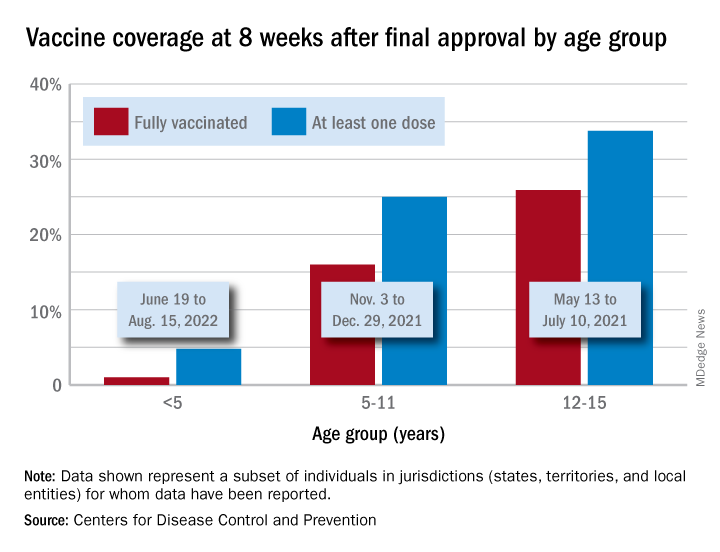
Through their first 8 weeks of vaccine eligibility (June 19 to Aug. 15), 4.8% of children under 5 years of age had received a first vaccination and 1.0% were fully vaccinated. For the two other age groups (5-11 and 12-15) who became eligible after the very first emergency authorization back in 2020, the respective proportions were 25.0% and 16.0% (5-11) and 33.8% and 26.1% (12-15) through the first 8 weeks, according to CDC data.
New cases of COVID-19 in children were up again after 2 weeks of declines, and preliminary data suggest that hospitalizations may be on the rise as well.
, based on data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.
A similar increase seems to be reflected by hospital-level data. The latest 7-day (Aug. 21-27) average is 305 new admissions with diagnosed COVID per day among children aged 0-17 years, compared with 290 per day for the week of Aug. 14-20, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported, while also noting the potential for reporting delays in the most recent 7-day period.
Daily hospital admissions for COVID had been headed downward through the first half of August, falling from 0.46 per 100,000 population at the end of July to 0.40 on Aug. 19, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Since then, however, admissions have gone the other way, with the preliminary nature of the latest data suggesting that the numbers will be even higher as more hospitals report over the next few days.
Vaccine initiations continue to fall
Initiations among school-age children have fallen for 3 consecutive weeks since Aug. 3, when numbers receiving their first vaccinations reached late-summer highs for those aged 5-11 and 12-17 years. Children under age 5, included in the CDC data for the first time on Aug. 11 as separate groups – under 2 years and 2-4 years – have had vaccine initiations drop by 8.0% and 19.8% over the 2 following weeks, the CDC said.

Through their first 8 weeks of vaccine eligibility (June 19 to Aug. 15), 4.8% of children under 5 years of age had received a first vaccination and 1.0% were fully vaccinated. For the two other age groups (5-11 and 12-15) who became eligible after the very first emergency authorization back in 2020, the respective proportions were 25.0% and 16.0% (5-11) and 33.8% and 26.1% (12-15) through the first 8 weeks, according to CDC data.
New cases of COVID-19 in children were up again after 2 weeks of declines, and preliminary data suggest that hospitalizations may be on the rise as well.
, based on data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.
A similar increase seems to be reflected by hospital-level data. The latest 7-day (Aug. 21-27) average is 305 new admissions with diagnosed COVID per day among children aged 0-17 years, compared with 290 per day for the week of Aug. 14-20, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported, while also noting the potential for reporting delays in the most recent 7-day period.
Daily hospital admissions for COVID had been headed downward through the first half of August, falling from 0.46 per 100,000 population at the end of July to 0.40 on Aug. 19, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Since then, however, admissions have gone the other way, with the preliminary nature of the latest data suggesting that the numbers will be even higher as more hospitals report over the next few days.
Vaccine initiations continue to fall
Initiations among school-age children have fallen for 3 consecutive weeks since Aug. 3, when numbers receiving their first vaccinations reached late-summer highs for those aged 5-11 and 12-17 years. Children under age 5, included in the CDC data for the first time on Aug. 11 as separate groups – under 2 years and 2-4 years – have had vaccine initiations drop by 8.0% and 19.8% over the 2 following weeks, the CDC said.

Through their first 8 weeks of vaccine eligibility (June 19 to Aug. 15), 4.8% of children under 5 years of age had received a first vaccination and 1.0% were fully vaccinated. For the two other age groups (5-11 and 12-15) who became eligible after the very first emergency authorization back in 2020, the respective proportions were 25.0% and 16.0% (5-11) and 33.8% and 26.1% (12-15) through the first 8 weeks, according to CDC data.
How do you live with COVID? One doctor’s personal experience
Early in 2020, Anne Peters, MD, caught COVID-19. The author of Medscape’s “Peters on Diabetes” column was sick in March 2020 before state-mandated lockdowns, and well before there were any vaccines.
She remembers sitting in a small exam room with two patients who had flown to her Los Angeles office from New York. The elderly couple had hearing difficulties, so Dr. Peters sat close to them, putting on a continuous glucose monitor. “At that time, we didn’t think of COVID-19 as being in L.A.,” Dr. Peters recalled, “so I think we were not terribly consistent at mask-wearing due to the need to educate.”
“Several days later, I got COVID, but I didn’t know I had COVID per se. I felt crappy, had a terrible sore throat, lost my sense of taste and smell [which was not yet described as a COVID symptom], was completely exhausted, but had no fever or cough, which were the only criteria for getting COVID tested at the time. I didn’t know I had been exposed until 2 weeks later, when the patient’s assistant returned the sensor warning us to ‘be careful’ with it because the patient and his wife were recovering from COVID.”
That early battle with COVID-19 was just the beginning of what would become a 2-year struggle, including familial loss amid her own health problems and concerns about the under-resourced patients she cares for. Here, she shares her journey through the pandemic with this news organization.
Question: Thanks for talking to us. Let’s discuss your journey over these past 2.5 years.
Answer: Everybody has their own COVID story because we all went through this together. Some of us have worse COVID stories, and some of us have better ones, but all have been impacted.
I’m not a sick person. I’m a very healthy person but COVID made me so unwell for 2 years. The brain fog and fatigue were nothing compared to the autonomic neuropathy that affected my heart. It was really limiting for me. And I still don’t know the long-term implications, looking 20-30 years from now.
Q: When you initially had COVID, what were your symptoms? What was the impact?
A: I had all the symptoms of COVID, except for a cough and fever. I lost my sense of taste and smell. I had a horrible headache, a sore throat, and I was exhausted. I couldn’t get tested because I didn’t have the right symptoms.
Despite being sick, I never stopped working but just switched to telemedicine. I also took my regular monthly trip to our cabin in Montana. I unknowingly flew on a plane with COVID. I wore a well-fitted N95 mask, so I don’t think I gave anybody COVID. I didn’t give COVID to my partner, Eric, which is hard to believe as – at 77 – he’s older than me. He has diabetes, heart disease, and every other high-risk characteristic. If he’d gotten COVID back then, it would have been terrible, as there were no treatments, but luckily he didn’t get it.
Q: When were you officially diagnosed?
A: Two or 3 months after I thought I might have had COVID, I checked my antibodies, which tested strongly positive for a prior COVID infection. That was when I knew all the symptoms I’d had were due to the disease.
Q: Not only were you dealing with your own illness, but also that of those close to you. Can you talk about that?
A: In April 2020, my mother who was in her 90s and otherwise healthy except for dementia, got COVID. She could have gotten it from me. I visited often but wore a mask. She had all the horrible pulmonary symptoms. In her advance directive, she didn’t want to be hospitalized so I kept her in her home. She died from COVID in her own bed. It was fairly brutal, but at least I kept her where she felt comforted.
My 91-year-old dad was living in a different residential facility. Throughout COVID he had become very depressed because his social patterns had changed. Prior to COVID, they all ate together, but during the pandemic they were unable to. He missed his social connections, disliked being isolated in his room, hated everyone in masks.
He was a bit demented, but not so much that he couldn’t communicate with me or remember where his grandson was going to law school. I wasn’t allowed inside the facility, which was hard on him. I hadn’t told him his wife died because the hospice social workers advised me that I shouldn’t give him news that he couldn’t process readily until I could spend time with him. Unfortunately, that time never came. In December 2020, he got COVID. One of the people in that facility had gone to the hospital, came back, and tested negative, but actually had COVID and gave it to my dad. The guy who gave it to my dad didn’t die but my dad was terribly ill. He died 2 weeks short of getting his vaccine. He was coherent enough to have a conversation. I asked him: ‘Do you want to go to the hospital?’ And he said: ‘No, because it would be too scary,’ since he couldn’t be with me. I put him on hospice and held his hand as he died from pulmonary COVID, which was awful. I couldn’t give him enough morphine or valium to ease his breathing. But his last words to me were “I love you,” and at the very end he seemed peaceful, which was a blessing.
I got an autopsy, because he wanted one. Nothing else was wrong with him other than COVID. It destroyed his lungs. The rest of him was fine – no heart disease, cancer, or anything else. He died of COVID-19, the same as my mother.
That same week, my aunt, my only surviving older relative, who was in Des Moines, Iowa, died of COVID-19. All three family members died before the vaccine came out.
It was hard to lose my parents. I’m the only surviving child because my sister died in her 20s. It’s not been an easy pandemic. But what pandemic is easy? I just happened to have lost more people than most. Ironically, my grandfather was one of the legionnaires at the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel in Philadelphia in 1976 and died of Legionnaire’s disease before we knew what was causing the outbreak.
Q: Were you still struggling with COVID?
A: COVID impacted my whole body. I lost a lot of weight. I didn’t want to eat, and my gastrointestinal system was not happy. It took a while for my sense of taste and smell to come back. Nothing tasted good. I’m not a foodie; I don’t really care about food. We could get takeout or whatever, but none of it appealed to me. I’m not so sure it was a taste thing, I just didn’t feel like eating.
I didn’t realize I had “brain fog” per se, because I felt stressed and overwhelmed by the pandemic and my patients’ concerns. But one day, about 3 months after I had developed COVID, I woke up without the fog. Which made me aware that I hadn’t been feeling right up until that point.
The worst symptoms, however, were cardiac. I noticed also immediately that my heart rate went up very quickly with minimal exertion. My pulse has always been in the 55-60 bpm range, and suddenly just walking across a room made it go up to over 140 bpm. If I did any aerobic activity, it went up over 160 and would be associated with dyspnea and chest pain. I believed these were all post-COVID symptoms and felt validated when reports of others having similar issues were published in the literature.
Q: Did you continue seeing patients?
A: Yes, of course. Patients never needed their doctors more. In East L.A., where patients don’t have easy access to telemedicine, I kept going into clinic throughout the pandemic. In the more affluent Westside of Los Angeles, we switched to telemedicine, which was quite effective for most. However, because diabetes was associated with an increased risk of hospitalization and death from COVID, my patients were understandably afraid. I’ve never been busier, but (like all health care providers), I became more of a COVID provider than a diabetologist.
Q: Do you feel your battle with COVID impacted your work?
A: It didn’t affect me at work. If I was sitting still, I was fine. Sitting at home at a desk, I didn’t notice any symptoms. But as a habitual stair-user, I would be gasping for breath in the stairwell because I couldn’t go up the stairs to my office as I once could.
I think you empathize more with people who had COVID (when you’ve had it yourself). There was such a huge patient burden. And I think that’s been the thing that’s affected health care providers the most – no matter what specialty we’re in – that nobody has answers.
Q: What happened after you had your vaccine?
A: The vaccine itself was fine. I didn’t have any reaction to the first two doses. But the first booster made my cardiac issues worse.
By this point, my cardiac problems stopped me from exercising. I even went to the ER with chest pain once because I was having palpitations and chest pressure caused by simply taking my morning shower. Fortunately, I wasn’t having an MI, but I certainly wasn’t “normal.”
My measure of my fitness is the cross-country skiing trail I use in Montana. I know exactly how far I can ski. Usually I can do the loop in 35 minutes. After COVID, I lasted 10 minutes. I would be tachycardic, short of breath with chest pain radiating down my left arm. I would rest and try to keep going. But with each rest period, I only got worse. I would be laying in the snow and strangers would ask if I needed help.
Q: What helped you?
A: I’ve read a lot about long COVID and have tried to learn from the experts. Of course, I never went to a doctor directly, although I did ask colleagues for advice. What I learned was to never push myself. I forced myself to create an exercise schedule where I only exercised three times a week with rest days in between. When exercising, the second my heart rate went above 140 bpm, I stopped until I could get it back down. I would push against this new limit, even though my limit was low.
Additionally, I worked on my breathing patterns and did meditative breathing for 10 minutes twice daily using a commercially available app.
Although progress was slow, I did improve, and by June 2022, I seemed back to normal. I was not as fit as I was prior to COVID and needed to improve, but the tachycardic response to exercise and cardiac symptoms were gone. I felt like my normal self. Normal enough to go on a spot packing trip in the Sierras in August. (Horses carried us and a mule carried the gear over the 12,000-foot pass into the mountains, and then left my friend and me high in the Sierras for a week.) We were camped above 10,000 feet and every day hiked up to another high mountain lake where we fly-fished for trout that we ate for dinner. The hikes were a challenge, but not abnormally so. Not as they would have been while I had long COVID.
Q: What is the current atmosphere in your clinic?
A: COVID is much milder now in my vaccinated patients, but I feel most health care providers are exhausted. Many of my staff left when COVID hit because they didn’t want to keep working. It made practicing medicine exhausting. There’s been a shortage of nurses, a shortage of everything. We’ve been required to do a whole lot more than we ever did before. It’s much harder to be a doctor. This pandemic is the first time I’ve ever thought of quitting. Granted, I lost my whole family, or at least the older generation, but it’s just been almost overwhelming.
On the plus side, almost every one of my patients has been vaccinated, because early on, people would ask: “Do you trust this vaccine?” I would reply: “I saw my parents die from COVID when they weren’t vaccinated, so you’re getting vaccinated. This is real and the vaccines help.” It made me very good at convincing people to get vaccines because I knew what it was like to see someone dying from COVID up close.
Q: What advice do you have for those struggling with the COVID pandemic?
A: People need to decide what their own risk is for getting sick and how many times they want to get COVID. At this point, I want people to go out, but safely. In the beginning, when my patients said, “can I go visit my granddaughter?” I said, “no,” but that was before we had the vaccine. Now I feel it is safe to go out using common sense. I still have my patients wear masks on planes. I still have patients try to eat outside as much as possible. And I tell people to take the precautions that make sense, but I tell them to go out and do things because life is short.
I had a patient in his 70s who has many risk factors like heart disease and diabetes. His granddaughter’s Bat Mitzvah in Florida was coming up. He asked: “Can I go?” I told him “Yes,” but to be safe – to wear an N95 mask on the plane and at the event, and stay in his own hotel room, rather than with the whole family. I said, “You need to do this.” Earlier in the pandemic, I saw people who literally died from loneliness and isolation.
He and his wife flew there. He sent me a picture of himself with his granddaughter. When he returned, he showed me a handwritten note from her that said, “I love you so much. Everyone else canceled, which made me cry. You’re the only one who came. You have no idea how much this meant to me.”
He’s back in L.A., and he didn’t get COVID. He said, “It was the best thing I’ve done in years.” That’s what I need to help people with, navigating this world with COVID and assessing risks and benefits. As with all of medicine, my advice is individualized. My advice changes based on the major circulating variant and the rates of the virus in the population, as well as the risk factors of the individual.
Q: What are you doing now?
A: I’m trying to avoid getting COVID again, or another booster. I could get pre-exposure monoclonal antibodies but am waiting to do anything further until I see what happens over the fall and winter. I still wear a mask inside but now do a mix of in-person and telemedicine visits. I still try to go to outdoor restaurants, which is easy in California. But I’m flying to see my son in New York and plan to go to Europe this fall for a meeting. I also go to my cabin in Montana every month to get my “dose” of the wilderness. Overall, I travel for conferences and speaking engagements much less because I have learned the joy of staying home.
Thinking back on my life as a doctor, my career began as an intern at Stanford rotating through Ward 5B, the AIDS unit at San Francisco General Hospital, and will likely end with COVID. In spite of all our medical advances, my generation of physicians, much as many generations before us, has a front-row seat to the vulnerability of humans to infectious diseases and how far we still need to go to protect our patients from communicable illness.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Anne L. Peters, MD, is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts; three books on diabetes; and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations.
Early in 2020, Anne Peters, MD, caught COVID-19. The author of Medscape’s “Peters on Diabetes” column was sick in March 2020 before state-mandated lockdowns, and well before there were any vaccines.
She remembers sitting in a small exam room with two patients who had flown to her Los Angeles office from New York. The elderly couple had hearing difficulties, so Dr. Peters sat close to them, putting on a continuous glucose monitor. “At that time, we didn’t think of COVID-19 as being in L.A.,” Dr. Peters recalled, “so I think we were not terribly consistent at mask-wearing due to the need to educate.”
“Several days later, I got COVID, but I didn’t know I had COVID per se. I felt crappy, had a terrible sore throat, lost my sense of taste and smell [which was not yet described as a COVID symptom], was completely exhausted, but had no fever or cough, which were the only criteria for getting COVID tested at the time. I didn’t know I had been exposed until 2 weeks later, when the patient’s assistant returned the sensor warning us to ‘be careful’ with it because the patient and his wife were recovering from COVID.”
That early battle with COVID-19 was just the beginning of what would become a 2-year struggle, including familial loss amid her own health problems and concerns about the under-resourced patients she cares for. Here, she shares her journey through the pandemic with this news organization.
Question: Thanks for talking to us. Let’s discuss your journey over these past 2.5 years.
Answer: Everybody has their own COVID story because we all went through this together. Some of us have worse COVID stories, and some of us have better ones, but all have been impacted.
I’m not a sick person. I’m a very healthy person but COVID made me so unwell for 2 years. The brain fog and fatigue were nothing compared to the autonomic neuropathy that affected my heart. It was really limiting for me. And I still don’t know the long-term implications, looking 20-30 years from now.
Q: When you initially had COVID, what were your symptoms? What was the impact?
A: I had all the symptoms of COVID, except for a cough and fever. I lost my sense of taste and smell. I had a horrible headache, a sore throat, and I was exhausted. I couldn’t get tested because I didn’t have the right symptoms.
Despite being sick, I never stopped working but just switched to telemedicine. I also took my regular monthly trip to our cabin in Montana. I unknowingly flew on a plane with COVID. I wore a well-fitted N95 mask, so I don’t think I gave anybody COVID. I didn’t give COVID to my partner, Eric, which is hard to believe as – at 77 – he’s older than me. He has diabetes, heart disease, and every other high-risk characteristic. If he’d gotten COVID back then, it would have been terrible, as there were no treatments, but luckily he didn’t get it.
Q: When were you officially diagnosed?
A: Two or 3 months after I thought I might have had COVID, I checked my antibodies, which tested strongly positive for a prior COVID infection. That was when I knew all the symptoms I’d had were due to the disease.
Q: Not only were you dealing with your own illness, but also that of those close to you. Can you talk about that?
A: In April 2020, my mother who was in her 90s and otherwise healthy except for dementia, got COVID. She could have gotten it from me. I visited often but wore a mask. She had all the horrible pulmonary symptoms. In her advance directive, she didn’t want to be hospitalized so I kept her in her home. She died from COVID in her own bed. It was fairly brutal, but at least I kept her where she felt comforted.
My 91-year-old dad was living in a different residential facility. Throughout COVID he had become very depressed because his social patterns had changed. Prior to COVID, they all ate together, but during the pandemic they were unable to. He missed his social connections, disliked being isolated in his room, hated everyone in masks.
He was a bit demented, but not so much that he couldn’t communicate with me or remember where his grandson was going to law school. I wasn’t allowed inside the facility, which was hard on him. I hadn’t told him his wife died because the hospice social workers advised me that I shouldn’t give him news that he couldn’t process readily until I could spend time with him. Unfortunately, that time never came. In December 2020, he got COVID. One of the people in that facility had gone to the hospital, came back, and tested negative, but actually had COVID and gave it to my dad. The guy who gave it to my dad didn’t die but my dad was terribly ill. He died 2 weeks short of getting his vaccine. He was coherent enough to have a conversation. I asked him: ‘Do you want to go to the hospital?’ And he said: ‘No, because it would be too scary,’ since he couldn’t be with me. I put him on hospice and held his hand as he died from pulmonary COVID, which was awful. I couldn’t give him enough morphine or valium to ease his breathing. But his last words to me were “I love you,” and at the very end he seemed peaceful, which was a blessing.
I got an autopsy, because he wanted one. Nothing else was wrong with him other than COVID. It destroyed his lungs. The rest of him was fine – no heart disease, cancer, or anything else. He died of COVID-19, the same as my mother.
That same week, my aunt, my only surviving older relative, who was in Des Moines, Iowa, died of COVID-19. All three family members died before the vaccine came out.
It was hard to lose my parents. I’m the only surviving child because my sister died in her 20s. It’s not been an easy pandemic. But what pandemic is easy? I just happened to have lost more people than most. Ironically, my grandfather was one of the legionnaires at the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel in Philadelphia in 1976 and died of Legionnaire’s disease before we knew what was causing the outbreak.
Q: Were you still struggling with COVID?
A: COVID impacted my whole body. I lost a lot of weight. I didn’t want to eat, and my gastrointestinal system was not happy. It took a while for my sense of taste and smell to come back. Nothing tasted good. I’m not a foodie; I don’t really care about food. We could get takeout or whatever, but none of it appealed to me. I’m not so sure it was a taste thing, I just didn’t feel like eating.
I didn’t realize I had “brain fog” per se, because I felt stressed and overwhelmed by the pandemic and my patients’ concerns. But one day, about 3 months after I had developed COVID, I woke up without the fog. Which made me aware that I hadn’t been feeling right up until that point.
The worst symptoms, however, were cardiac. I noticed also immediately that my heart rate went up very quickly with minimal exertion. My pulse has always been in the 55-60 bpm range, and suddenly just walking across a room made it go up to over 140 bpm. If I did any aerobic activity, it went up over 160 and would be associated with dyspnea and chest pain. I believed these were all post-COVID symptoms and felt validated when reports of others having similar issues were published in the literature.
Q: Did you continue seeing patients?
A: Yes, of course. Patients never needed their doctors more. In East L.A., where patients don’t have easy access to telemedicine, I kept going into clinic throughout the pandemic. In the more affluent Westside of Los Angeles, we switched to telemedicine, which was quite effective for most. However, because diabetes was associated with an increased risk of hospitalization and death from COVID, my patients were understandably afraid. I’ve never been busier, but (like all health care providers), I became more of a COVID provider than a diabetologist.
Q: Do you feel your battle with COVID impacted your work?
A: It didn’t affect me at work. If I was sitting still, I was fine. Sitting at home at a desk, I didn’t notice any symptoms. But as a habitual stair-user, I would be gasping for breath in the stairwell because I couldn’t go up the stairs to my office as I once could.
I think you empathize more with people who had COVID (when you’ve had it yourself). There was such a huge patient burden. And I think that’s been the thing that’s affected health care providers the most – no matter what specialty we’re in – that nobody has answers.
Q: What happened after you had your vaccine?
A: The vaccine itself was fine. I didn’t have any reaction to the first two doses. But the first booster made my cardiac issues worse.
By this point, my cardiac problems stopped me from exercising. I even went to the ER with chest pain once because I was having palpitations and chest pressure caused by simply taking my morning shower. Fortunately, I wasn’t having an MI, but I certainly wasn’t “normal.”
My measure of my fitness is the cross-country skiing trail I use in Montana. I know exactly how far I can ski. Usually I can do the loop in 35 minutes. After COVID, I lasted 10 minutes. I would be tachycardic, short of breath with chest pain radiating down my left arm. I would rest and try to keep going. But with each rest period, I only got worse. I would be laying in the snow and strangers would ask if I needed help.
Q: What helped you?
A: I’ve read a lot about long COVID and have tried to learn from the experts. Of course, I never went to a doctor directly, although I did ask colleagues for advice. What I learned was to never push myself. I forced myself to create an exercise schedule where I only exercised three times a week with rest days in between. When exercising, the second my heart rate went above 140 bpm, I stopped until I could get it back down. I would push against this new limit, even though my limit was low.
Additionally, I worked on my breathing patterns and did meditative breathing for 10 minutes twice daily using a commercially available app.
Although progress was slow, I did improve, and by June 2022, I seemed back to normal. I was not as fit as I was prior to COVID and needed to improve, but the tachycardic response to exercise and cardiac symptoms were gone. I felt like my normal self. Normal enough to go on a spot packing trip in the Sierras in August. (Horses carried us and a mule carried the gear over the 12,000-foot pass into the mountains, and then left my friend and me high in the Sierras for a week.) We were camped above 10,000 feet and every day hiked up to another high mountain lake where we fly-fished for trout that we ate for dinner. The hikes were a challenge, but not abnormally so. Not as they would have been while I had long COVID.
Q: What is the current atmosphere in your clinic?
A: COVID is much milder now in my vaccinated patients, but I feel most health care providers are exhausted. Many of my staff left when COVID hit because they didn’t want to keep working. It made practicing medicine exhausting. There’s been a shortage of nurses, a shortage of everything. We’ve been required to do a whole lot more than we ever did before. It’s much harder to be a doctor. This pandemic is the first time I’ve ever thought of quitting. Granted, I lost my whole family, or at least the older generation, but it’s just been almost overwhelming.
On the plus side, almost every one of my patients has been vaccinated, because early on, people would ask: “Do you trust this vaccine?” I would reply: “I saw my parents die from COVID when they weren’t vaccinated, so you’re getting vaccinated. This is real and the vaccines help.” It made me very good at convincing people to get vaccines because I knew what it was like to see someone dying from COVID up close.
Q: What advice do you have for those struggling with the COVID pandemic?
A: People need to decide what their own risk is for getting sick and how many times they want to get COVID. At this point, I want people to go out, but safely. In the beginning, when my patients said, “can I go visit my granddaughter?” I said, “no,” but that was before we had the vaccine. Now I feel it is safe to go out using common sense. I still have my patients wear masks on planes. I still have patients try to eat outside as much as possible. And I tell people to take the precautions that make sense, but I tell them to go out and do things because life is short.
I had a patient in his 70s who has many risk factors like heart disease and diabetes. His granddaughter’s Bat Mitzvah in Florida was coming up. He asked: “Can I go?” I told him “Yes,” but to be safe – to wear an N95 mask on the plane and at the event, and stay in his own hotel room, rather than with the whole family. I said, “You need to do this.” Earlier in the pandemic, I saw people who literally died from loneliness and isolation.
He and his wife flew there. He sent me a picture of himself with his granddaughter. When he returned, he showed me a handwritten note from her that said, “I love you so much. Everyone else canceled, which made me cry. You’re the only one who came. You have no idea how much this meant to me.”
He’s back in L.A., and he didn’t get COVID. He said, “It was the best thing I’ve done in years.” That’s what I need to help people with, navigating this world with COVID and assessing risks and benefits. As with all of medicine, my advice is individualized. My advice changes based on the major circulating variant and the rates of the virus in the population, as well as the risk factors of the individual.
Q: What are you doing now?
A: I’m trying to avoid getting COVID again, or another booster. I could get pre-exposure monoclonal antibodies but am waiting to do anything further until I see what happens over the fall and winter. I still wear a mask inside but now do a mix of in-person and telemedicine visits. I still try to go to outdoor restaurants, which is easy in California. But I’m flying to see my son in New York and plan to go to Europe this fall for a meeting. I also go to my cabin in Montana every month to get my “dose” of the wilderness. Overall, I travel for conferences and speaking engagements much less because I have learned the joy of staying home.
Thinking back on my life as a doctor, my career began as an intern at Stanford rotating through Ward 5B, the AIDS unit at San Francisco General Hospital, and will likely end with COVID. In spite of all our medical advances, my generation of physicians, much as many generations before us, has a front-row seat to the vulnerability of humans to infectious diseases and how far we still need to go to protect our patients from communicable illness.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Anne L. Peters, MD, is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts; three books on diabetes; and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations.
Early in 2020, Anne Peters, MD, caught COVID-19. The author of Medscape’s “Peters on Diabetes” column was sick in March 2020 before state-mandated lockdowns, and well before there were any vaccines.
She remembers sitting in a small exam room with two patients who had flown to her Los Angeles office from New York. The elderly couple had hearing difficulties, so Dr. Peters sat close to them, putting on a continuous glucose monitor. “At that time, we didn’t think of COVID-19 as being in L.A.,” Dr. Peters recalled, “so I think we were not terribly consistent at mask-wearing due to the need to educate.”
“Several days later, I got COVID, but I didn’t know I had COVID per se. I felt crappy, had a terrible sore throat, lost my sense of taste and smell [which was not yet described as a COVID symptom], was completely exhausted, but had no fever or cough, which were the only criteria for getting COVID tested at the time. I didn’t know I had been exposed until 2 weeks later, when the patient’s assistant returned the sensor warning us to ‘be careful’ with it because the patient and his wife were recovering from COVID.”
That early battle with COVID-19 was just the beginning of what would become a 2-year struggle, including familial loss amid her own health problems and concerns about the under-resourced patients she cares for. Here, she shares her journey through the pandemic with this news organization.
Question: Thanks for talking to us. Let’s discuss your journey over these past 2.5 years.
Answer: Everybody has their own COVID story because we all went through this together. Some of us have worse COVID stories, and some of us have better ones, but all have been impacted.
I’m not a sick person. I’m a very healthy person but COVID made me so unwell for 2 years. The brain fog and fatigue were nothing compared to the autonomic neuropathy that affected my heart. It was really limiting for me. And I still don’t know the long-term implications, looking 20-30 years from now.
Q: When you initially had COVID, what were your symptoms? What was the impact?
A: I had all the symptoms of COVID, except for a cough and fever. I lost my sense of taste and smell. I had a horrible headache, a sore throat, and I was exhausted. I couldn’t get tested because I didn’t have the right symptoms.
Despite being sick, I never stopped working but just switched to telemedicine. I also took my regular monthly trip to our cabin in Montana. I unknowingly flew on a plane with COVID. I wore a well-fitted N95 mask, so I don’t think I gave anybody COVID. I didn’t give COVID to my partner, Eric, which is hard to believe as – at 77 – he’s older than me. He has diabetes, heart disease, and every other high-risk characteristic. If he’d gotten COVID back then, it would have been terrible, as there were no treatments, but luckily he didn’t get it.
Q: When were you officially diagnosed?
A: Two or 3 months after I thought I might have had COVID, I checked my antibodies, which tested strongly positive for a prior COVID infection. That was when I knew all the symptoms I’d had were due to the disease.
Q: Not only were you dealing with your own illness, but also that of those close to you. Can you talk about that?
A: In April 2020, my mother who was in her 90s and otherwise healthy except for dementia, got COVID. She could have gotten it from me. I visited often but wore a mask. She had all the horrible pulmonary symptoms. In her advance directive, she didn’t want to be hospitalized so I kept her in her home. She died from COVID in her own bed. It was fairly brutal, but at least I kept her where she felt comforted.
My 91-year-old dad was living in a different residential facility. Throughout COVID he had become very depressed because his social patterns had changed. Prior to COVID, they all ate together, but during the pandemic they were unable to. He missed his social connections, disliked being isolated in his room, hated everyone in masks.
He was a bit demented, but not so much that he couldn’t communicate with me or remember where his grandson was going to law school. I wasn’t allowed inside the facility, which was hard on him. I hadn’t told him his wife died because the hospice social workers advised me that I shouldn’t give him news that he couldn’t process readily until I could spend time with him. Unfortunately, that time never came. In December 2020, he got COVID. One of the people in that facility had gone to the hospital, came back, and tested negative, but actually had COVID and gave it to my dad. The guy who gave it to my dad didn’t die but my dad was terribly ill. He died 2 weeks short of getting his vaccine. He was coherent enough to have a conversation. I asked him: ‘Do you want to go to the hospital?’ And he said: ‘No, because it would be too scary,’ since he couldn’t be with me. I put him on hospice and held his hand as he died from pulmonary COVID, which was awful. I couldn’t give him enough morphine or valium to ease his breathing. But his last words to me were “I love you,” and at the very end he seemed peaceful, which was a blessing.
I got an autopsy, because he wanted one. Nothing else was wrong with him other than COVID. It destroyed his lungs. The rest of him was fine – no heart disease, cancer, or anything else. He died of COVID-19, the same as my mother.
That same week, my aunt, my only surviving older relative, who was in Des Moines, Iowa, died of COVID-19. All three family members died before the vaccine came out.
It was hard to lose my parents. I’m the only surviving child because my sister died in her 20s. It’s not been an easy pandemic. But what pandemic is easy? I just happened to have lost more people than most. Ironically, my grandfather was one of the legionnaires at the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel in Philadelphia in 1976 and died of Legionnaire’s disease before we knew what was causing the outbreak.
Q: Were you still struggling with COVID?
A: COVID impacted my whole body. I lost a lot of weight. I didn’t want to eat, and my gastrointestinal system was not happy. It took a while for my sense of taste and smell to come back. Nothing tasted good. I’m not a foodie; I don’t really care about food. We could get takeout or whatever, but none of it appealed to me. I’m not so sure it was a taste thing, I just didn’t feel like eating.
I didn’t realize I had “brain fog” per se, because I felt stressed and overwhelmed by the pandemic and my patients’ concerns. But one day, about 3 months after I had developed COVID, I woke up without the fog. Which made me aware that I hadn’t been feeling right up until that point.
The worst symptoms, however, were cardiac. I noticed also immediately that my heart rate went up very quickly with minimal exertion. My pulse has always been in the 55-60 bpm range, and suddenly just walking across a room made it go up to over 140 bpm. If I did any aerobic activity, it went up over 160 and would be associated with dyspnea and chest pain. I believed these were all post-COVID symptoms and felt validated when reports of others having similar issues were published in the literature.
Q: Did you continue seeing patients?
A: Yes, of course. Patients never needed their doctors more. In East L.A., where patients don’t have easy access to telemedicine, I kept going into clinic throughout the pandemic. In the more affluent Westside of Los Angeles, we switched to telemedicine, which was quite effective for most. However, because diabetes was associated with an increased risk of hospitalization and death from COVID, my patients were understandably afraid. I’ve never been busier, but (like all health care providers), I became more of a COVID provider than a diabetologist.
Q: Do you feel your battle with COVID impacted your work?
A: It didn’t affect me at work. If I was sitting still, I was fine. Sitting at home at a desk, I didn’t notice any symptoms. But as a habitual stair-user, I would be gasping for breath in the stairwell because I couldn’t go up the stairs to my office as I once could.
I think you empathize more with people who had COVID (when you’ve had it yourself). There was such a huge patient burden. And I think that’s been the thing that’s affected health care providers the most – no matter what specialty we’re in – that nobody has answers.
Q: What happened after you had your vaccine?
A: The vaccine itself was fine. I didn’t have any reaction to the first two doses. But the first booster made my cardiac issues worse.
By this point, my cardiac problems stopped me from exercising. I even went to the ER with chest pain once because I was having palpitations and chest pressure caused by simply taking my morning shower. Fortunately, I wasn’t having an MI, but I certainly wasn’t “normal.”
My measure of my fitness is the cross-country skiing trail I use in Montana. I know exactly how far I can ski. Usually I can do the loop in 35 minutes. After COVID, I lasted 10 minutes. I would be tachycardic, short of breath with chest pain radiating down my left arm. I would rest and try to keep going. But with each rest period, I only got worse. I would be laying in the snow and strangers would ask if I needed help.
Q: What helped you?
A: I’ve read a lot about long COVID and have tried to learn from the experts. Of course, I never went to a doctor directly, although I did ask colleagues for advice. What I learned was to never push myself. I forced myself to create an exercise schedule where I only exercised three times a week with rest days in between. When exercising, the second my heart rate went above 140 bpm, I stopped until I could get it back down. I would push against this new limit, even though my limit was low.
Additionally, I worked on my breathing patterns and did meditative breathing for 10 minutes twice daily using a commercially available app.
Although progress was slow, I did improve, and by June 2022, I seemed back to normal. I was not as fit as I was prior to COVID and needed to improve, but the tachycardic response to exercise and cardiac symptoms were gone. I felt like my normal self. Normal enough to go on a spot packing trip in the Sierras in August. (Horses carried us and a mule carried the gear over the 12,000-foot pass into the mountains, and then left my friend and me high in the Sierras for a week.) We were camped above 10,000 feet and every day hiked up to another high mountain lake where we fly-fished for trout that we ate for dinner. The hikes were a challenge, but not abnormally so. Not as they would have been while I had long COVID.
Q: What is the current atmosphere in your clinic?
A: COVID is much milder now in my vaccinated patients, but I feel most health care providers are exhausted. Many of my staff left when COVID hit because they didn’t want to keep working. It made practicing medicine exhausting. There’s been a shortage of nurses, a shortage of everything. We’ve been required to do a whole lot more than we ever did before. It’s much harder to be a doctor. This pandemic is the first time I’ve ever thought of quitting. Granted, I lost my whole family, or at least the older generation, but it’s just been almost overwhelming.
On the plus side, almost every one of my patients has been vaccinated, because early on, people would ask: “Do you trust this vaccine?” I would reply: “I saw my parents die from COVID when they weren’t vaccinated, so you’re getting vaccinated. This is real and the vaccines help.” It made me very good at convincing people to get vaccines because I knew what it was like to see someone dying from COVID up close.
Q: What advice do you have for those struggling with the COVID pandemic?
A: People need to decide what their own risk is for getting sick and how many times they want to get COVID. At this point, I want people to go out, but safely. In the beginning, when my patients said, “can I go visit my granddaughter?” I said, “no,” but that was before we had the vaccine. Now I feel it is safe to go out using common sense. I still have my patients wear masks on planes. I still have patients try to eat outside as much as possible. And I tell people to take the precautions that make sense, but I tell them to go out and do things because life is short.
I had a patient in his 70s who has many risk factors like heart disease and diabetes. His granddaughter’s Bat Mitzvah in Florida was coming up. He asked: “Can I go?” I told him “Yes,” but to be safe – to wear an N95 mask on the plane and at the event, and stay in his own hotel room, rather than with the whole family. I said, “You need to do this.” Earlier in the pandemic, I saw people who literally died from loneliness and isolation.
He and his wife flew there. He sent me a picture of himself with his granddaughter. When he returned, he showed me a handwritten note from her that said, “I love you so much. Everyone else canceled, which made me cry. You’re the only one who came. You have no idea how much this meant to me.”
He’s back in L.A., and he didn’t get COVID. He said, “It was the best thing I’ve done in years.” That’s what I need to help people with, navigating this world with COVID and assessing risks and benefits. As with all of medicine, my advice is individualized. My advice changes based on the major circulating variant and the rates of the virus in the population, as well as the risk factors of the individual.
Q: What are you doing now?
A: I’m trying to avoid getting COVID again, or another booster. I could get pre-exposure monoclonal antibodies but am waiting to do anything further until I see what happens over the fall and winter. I still wear a mask inside but now do a mix of in-person and telemedicine visits. I still try to go to outdoor restaurants, which is easy in California. But I’m flying to see my son in New York and plan to go to Europe this fall for a meeting. I also go to my cabin in Montana every month to get my “dose” of the wilderness. Overall, I travel for conferences and speaking engagements much less because I have learned the joy of staying home.
Thinking back on my life as a doctor, my career began as an intern at Stanford rotating through Ward 5B, the AIDS unit at San Francisco General Hospital, and will likely end with COVID. In spite of all our medical advances, my generation of physicians, much as many generations before us, has a front-row seat to the vulnerability of humans to infectious diseases and how far we still need to go to protect our patients from communicable illness.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Anne L. Peters, MD, is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts; three books on diabetes; and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations.
Levels of West Nile virus higher than normal in northern Italy
Climate change has affected the spread of West Nile fever. This observation was confirmed in an Italian Ministry of Health note reporting 94 confirmed cases of infection. Of those cases, 55 were neuroinvasive, 19 were from blood donors, 19 were associated with fever, and in one case, the patient was symptomatic. Seven deaths have occurred since the start of the summer season, particularly in northern Italy.
Entomologists and veterinarians have confirmed the presence of West Nile virus (WNV) in a pool of 100 mosquitoes, 15 birds from targeted species, and 10 wild birds from passive surveillance. Four cases have been reported in horses in which clinical symptoms were attributable to a WNV infection. No cases of infection with Usutu virus (USUV) have been registered in humans. USUV is a virus in the same family as WNV. It was first identified in South Africa in the 1950s and is capable of causing encephalitis. The viral genome has been detected in a pool of 33 mosquitoes and four birds.
Currently, the regions where the circulation of WNV has been confirmed are Emilia-Romagna, Veneto, Piedmont, Lombardy, Sardinia, and Friuli Venezia Giulia. To date, USUV has been detected in Le Marche, Lombardy, Umbria, Emilia Romagna, Friuli Venezia Giulia, Lazio, and Veneto.
Current climate conditions favor the reproduction of the vector (mosquitoes of the Culex genus) and the subsequent viral circulation among wildlife, the natural reservoir of the virus, and mammals (including humans). The 2022 epidemic season is peculiar in comparison with seasons from the past 3 years. Viral circulation has started early, and a greater number of cases have been observed in the avifauna and in the mosquito pool, and there has been an increase in the number of cases in humans.
For these reasons, and considering the significance of the infection for public health, it is necessary to put all useful measures in place to limit the risk of further transmission among humans and animals.
As specified on the Italian National Institute for Health website, West Nile fever is caused by the homonymous virus of the Flaviviridae family, which was isolated for the first time in Uganda in 1937. The virus has spread to almost all continents.
The virus reservoirs are wild birds and mosquitoes (more frequently of the Culex genus). Other means of transmission, although very rare, are organ transplants, blood transfusions, and transmission from mother to fetus. West Nile fever cannot be transmitted from person to person. The virus infects other mammals, especially horses, and in some cases, dogs and rabbits.
Incubation and symptoms
The incubation period from the time of being bitten by an infected mosquito ranges from 2 to 14 days but can be up to 21 days in immunocompromised patients.
Most infected people do not show any symptoms. In around 20% of symptomatic cases, patients present with mild symptoms: fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, enlarged lymph nodes, and skin rashes. These symptoms may only last a few hours, but in rare cases, they may last a few weeks. Symptoms vary significantly, depending on the patient’s age. In children, a mild fever is most common, whereas in young people, symptoms are characterized by a fairly high fever, redness of the eyes, headache, and muscle pains. In the elderly and in debilitated patients, symptoms can be more severe.
The most serious symptoms are seen in fewer than 1% of infected patients (1 in 150 people) and include a high fever, a severe headache, muscle weakness, disorientation, tremors, visual disturbances, listlessness, and seizures, leading to paralysis and coma. Some neurologic effects may be permanent. In the most severe cases (around 1 in 1,000), the virus can cause terminal encephalitis.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is mostly made through laboratory testing for IgM antibodies on serum and, where indicated, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Antibodies can persist beyond the patient’s period of illness (up to 1 year). Therefore, a positive result may indicate a previous infection. Samples collected within 8 days of the onset of symptoms may appear negative; it is therefore advisable to repeat the laboratory test further down the line before excluding the disease. Alternatively, diagnosis may be obtained through polymerase chain reaction or viral culture testing on samples of serum or CSF.
Prevention
A vaccine for West Nile fever does not exist. Prevention consists, above all, of reducing exposure to mosquito bites.
It is advisable that people protect themselves against bites and avoid places where mosquitoes can reproduce easily. The following are recommended:
- Using repellents and wearing of trousers and long-sleeve tops when out in the open, especially at dawn and sunset.
- Using mosquito nets on windows.
- Frequently emptying vases or other containers (for example, buckets) that contain stagnant water.
- Frequently changing the water in animal drinking bowls.
- Keeping child paddling pools in a vertical position when not in use.
- Using authorized repellents and insecticides where the vector may reproduce, such as in stables. For horses, a vaccine is available for veterinary use, which can further reduce the reservoir of viral circulation.
It is important that physicians inform patients in at-risk areas of the presence of this virus, the possible symptoms, and the preventive measures to adopt.
Therapy and treatment
There is no specific therapy for West Nile fever. In most cases, symptoms appear after a few days, but they can last for a few weeks. For the most severe cases, hospital admission is necessary; occasionally, treatment in the intensive care unit is necessary.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Climate change has affected the spread of West Nile fever. This observation was confirmed in an Italian Ministry of Health note reporting 94 confirmed cases of infection. Of those cases, 55 were neuroinvasive, 19 were from blood donors, 19 were associated with fever, and in one case, the patient was symptomatic. Seven deaths have occurred since the start of the summer season, particularly in northern Italy.
Entomologists and veterinarians have confirmed the presence of West Nile virus (WNV) in a pool of 100 mosquitoes, 15 birds from targeted species, and 10 wild birds from passive surveillance. Four cases have been reported in horses in which clinical symptoms were attributable to a WNV infection. No cases of infection with Usutu virus (USUV) have been registered in humans. USUV is a virus in the same family as WNV. It was first identified in South Africa in the 1950s and is capable of causing encephalitis. The viral genome has been detected in a pool of 33 mosquitoes and four birds.
Currently, the regions where the circulation of WNV has been confirmed are Emilia-Romagna, Veneto, Piedmont, Lombardy, Sardinia, and Friuli Venezia Giulia. To date, USUV has been detected in Le Marche, Lombardy, Umbria, Emilia Romagna, Friuli Venezia Giulia, Lazio, and Veneto.
Current climate conditions favor the reproduction of the vector (mosquitoes of the Culex genus) and the subsequent viral circulation among wildlife, the natural reservoir of the virus, and mammals (including humans). The 2022 epidemic season is peculiar in comparison with seasons from the past 3 years. Viral circulation has started early, and a greater number of cases have been observed in the avifauna and in the mosquito pool, and there has been an increase in the number of cases in humans.
For these reasons, and considering the significance of the infection for public health, it is necessary to put all useful measures in place to limit the risk of further transmission among humans and animals.
As specified on the Italian National Institute for Health website, West Nile fever is caused by the homonymous virus of the Flaviviridae family, which was isolated for the first time in Uganda in 1937. The virus has spread to almost all continents.
The virus reservoirs are wild birds and mosquitoes (more frequently of the Culex genus). Other means of transmission, although very rare, are organ transplants, blood transfusions, and transmission from mother to fetus. West Nile fever cannot be transmitted from person to person. The virus infects other mammals, especially horses, and in some cases, dogs and rabbits.
Incubation and symptoms
The incubation period from the time of being bitten by an infected mosquito ranges from 2 to 14 days but can be up to 21 days in immunocompromised patients.
Most infected people do not show any symptoms. In around 20% of symptomatic cases, patients present with mild symptoms: fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, enlarged lymph nodes, and skin rashes. These symptoms may only last a few hours, but in rare cases, they may last a few weeks. Symptoms vary significantly, depending on the patient’s age. In children, a mild fever is most common, whereas in young people, symptoms are characterized by a fairly high fever, redness of the eyes, headache, and muscle pains. In the elderly and in debilitated patients, symptoms can be more severe.
The most serious symptoms are seen in fewer than 1% of infected patients (1 in 150 people) and include a high fever, a severe headache, muscle weakness, disorientation, tremors, visual disturbances, listlessness, and seizures, leading to paralysis and coma. Some neurologic effects may be permanent. In the most severe cases (around 1 in 1,000), the virus can cause terminal encephalitis.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is mostly made through laboratory testing for IgM antibodies on serum and, where indicated, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Antibodies can persist beyond the patient’s period of illness (up to 1 year). Therefore, a positive result may indicate a previous infection. Samples collected within 8 days of the onset of symptoms may appear negative; it is therefore advisable to repeat the laboratory test further down the line before excluding the disease. Alternatively, diagnosis may be obtained through polymerase chain reaction or viral culture testing on samples of serum or CSF.
Prevention
A vaccine for West Nile fever does not exist. Prevention consists, above all, of reducing exposure to mosquito bites.
It is advisable that people protect themselves against bites and avoid places where mosquitoes can reproduce easily. The following are recommended:
- Using repellents and wearing of trousers and long-sleeve tops when out in the open, especially at dawn and sunset.
- Using mosquito nets on windows.
- Frequently emptying vases or other containers (for example, buckets) that contain stagnant water.
- Frequently changing the water in animal drinking bowls.
- Keeping child paddling pools in a vertical position when not in use.
- Using authorized repellents and insecticides where the vector may reproduce, such as in stables. For horses, a vaccine is available for veterinary use, which can further reduce the reservoir of viral circulation.
It is important that physicians inform patients in at-risk areas of the presence of this virus, the possible symptoms, and the preventive measures to adopt.
Therapy and treatment
There is no specific therapy for West Nile fever. In most cases, symptoms appear after a few days, but they can last for a few weeks. For the most severe cases, hospital admission is necessary; occasionally, treatment in the intensive care unit is necessary.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Climate change has affected the spread of West Nile fever. This observation was confirmed in an Italian Ministry of Health note reporting 94 confirmed cases of infection. Of those cases, 55 were neuroinvasive, 19 were from blood donors, 19 were associated with fever, and in one case, the patient was symptomatic. Seven deaths have occurred since the start of the summer season, particularly in northern Italy.
Entomologists and veterinarians have confirmed the presence of West Nile virus (WNV) in a pool of 100 mosquitoes, 15 birds from targeted species, and 10 wild birds from passive surveillance. Four cases have been reported in horses in which clinical symptoms were attributable to a WNV infection. No cases of infection with Usutu virus (USUV) have been registered in humans. USUV is a virus in the same family as WNV. It was first identified in South Africa in the 1950s and is capable of causing encephalitis. The viral genome has been detected in a pool of 33 mosquitoes and four birds.
Currently, the regions where the circulation of WNV has been confirmed are Emilia-Romagna, Veneto, Piedmont, Lombardy, Sardinia, and Friuli Venezia Giulia. To date, USUV has been detected in Le Marche, Lombardy, Umbria, Emilia Romagna, Friuli Venezia Giulia, Lazio, and Veneto.
Current climate conditions favor the reproduction of the vector (mosquitoes of the Culex genus) and the subsequent viral circulation among wildlife, the natural reservoir of the virus, and mammals (including humans). The 2022 epidemic season is peculiar in comparison with seasons from the past 3 years. Viral circulation has started early, and a greater number of cases have been observed in the avifauna and in the mosquito pool, and there has been an increase in the number of cases in humans.
For these reasons, and considering the significance of the infection for public health, it is necessary to put all useful measures in place to limit the risk of further transmission among humans and animals.
As specified on the Italian National Institute for Health website, West Nile fever is caused by the homonymous virus of the Flaviviridae family, which was isolated for the first time in Uganda in 1937. The virus has spread to almost all continents.
The virus reservoirs are wild birds and mosquitoes (more frequently of the Culex genus). Other means of transmission, although very rare, are organ transplants, blood transfusions, and transmission from mother to fetus. West Nile fever cannot be transmitted from person to person. The virus infects other mammals, especially horses, and in some cases, dogs and rabbits.
Incubation and symptoms
The incubation period from the time of being bitten by an infected mosquito ranges from 2 to 14 days but can be up to 21 days in immunocompromised patients.
Most infected people do not show any symptoms. In around 20% of symptomatic cases, patients present with mild symptoms: fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, enlarged lymph nodes, and skin rashes. These symptoms may only last a few hours, but in rare cases, they may last a few weeks. Symptoms vary significantly, depending on the patient’s age. In children, a mild fever is most common, whereas in young people, symptoms are characterized by a fairly high fever, redness of the eyes, headache, and muscle pains. In the elderly and in debilitated patients, symptoms can be more severe.
The most serious symptoms are seen in fewer than 1% of infected patients (1 in 150 people) and include a high fever, a severe headache, muscle weakness, disorientation, tremors, visual disturbances, listlessness, and seizures, leading to paralysis and coma. Some neurologic effects may be permanent. In the most severe cases (around 1 in 1,000), the virus can cause terminal encephalitis.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is mostly made through laboratory testing for IgM antibodies on serum and, where indicated, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Antibodies can persist beyond the patient’s period of illness (up to 1 year). Therefore, a positive result may indicate a previous infection. Samples collected within 8 days of the onset of symptoms may appear negative; it is therefore advisable to repeat the laboratory test further down the line before excluding the disease. Alternatively, diagnosis may be obtained through polymerase chain reaction or viral culture testing on samples of serum or CSF.
Prevention
A vaccine for West Nile fever does not exist. Prevention consists, above all, of reducing exposure to mosquito bites.
It is advisable that people protect themselves against bites and avoid places where mosquitoes can reproduce easily. The following are recommended:
- Using repellents and wearing of trousers and long-sleeve tops when out in the open, especially at dawn and sunset.
- Using mosquito nets on windows.
- Frequently emptying vases or other containers (for example, buckets) that contain stagnant water.
- Frequently changing the water in animal drinking bowls.
- Keeping child paddling pools in a vertical position when not in use.
- Using authorized repellents and insecticides where the vector may reproduce, such as in stables. For horses, a vaccine is available for veterinary use, which can further reduce the reservoir of viral circulation.
It is important that physicians inform patients in at-risk areas of the presence of this virus, the possible symptoms, and the preventive measures to adopt.
Therapy and treatment
There is no specific therapy for West Nile fever. In most cases, symptoms appear after a few days, but they can last for a few weeks. For the most severe cases, hospital admission is necessary; occasionally, treatment in the intensive care unit is necessary.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Autoimmune disease patients’ waxing, waning response to COVID vaccination studied in-depth
A new study in The Lancet Rheumatology examines the strength and duration of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine–induced immunoglobulin-G antibody responses over time for patients with a variety of autoimmune diseases, compared with healthy controls.
The presence of humoral antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 has been shown to correlate with protection against COVID infection. But for patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs), host response to COVID infection or to vaccination is affected by the immune dysfunction imposed by the IMID and by the use of immune-modulating drugs to treat it.
This new study finds a weaker – as shown previously – and less sustained immune response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with a variety of IMIDs, including rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel diseases, and other systemic autoimmune diseases such as lupus. It also points toward the possibility of adjusting treatment and vaccination schedules and strategies for these patients based on their antibody levels, among other factors, to preserve best protection against severe COVID.
“It is important to assess immune response in these patients to see if they still have protection against severe COVID infection,” said lead author David Simon, MD, senior clinical scientist in clinical immunology and rheumatology at University Hospital Erlangen (Germany). “We know that antibody response is an immune correlate. Therefore, it is important to see how large and durable the immune response is to the coronavirus vaccine in these IMID patients, and whether specific drugs or therapies have negative effects on their immune response.”
What was studied?
For this large prospective cohort study, researchers registered 5076 coronavirus-vaccinated individuals. They analyzed serum samples obtained between December 15, 2020, and December 1, 2021, from 2,535 patients diagnosed with IMIDs and participating in a prospective coronavirus study program at the Deutsches Zentrum Immuntherapie in Erlangen. The IMID patients had a mean age of 55.0 years, and 58.9% were women.
A healthy control group of 1,198 individuals without IMID who had a mean age of 40.7 years, including 53.8% men, was also recruited for the analysis. All approved coronavirus vaccines were included, following standard vaccination schedules. Antibody response was measured over time by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay from 8 weeks after first vaccination to week 40.
Among the findings, the healthy controls had higher postvaccine antibody levels than did those with IMIDs. But the majority of vaccinated patients with IMID were able to build up a humoral immune response to SARS-CoV-2. Patients who were taking B-cell inhibitors like rituximab (Rituxan, Genentech; and biosimilars) and T-cell inhibitors like abatacept (Orencia, Bristol Myers Squibb) for IMIDs had significantly poorer antibody response.
Greater age and the use of combination therapies for IMIDs, compared with monotherapy, further reduced immune response to the vaccine. In terms of vaccination modality, messenger RNA–based vaccines induced higher antibody levels than did vector-based vaccines. The researchers noted that patients with IMID who were given a third vaccine dose could actually catch up well with the antibody responses observed in healthy controls.
“We looked at whether different IMIDs had a different humoral response, and we also assessed if there are effects from different therapeutic strategies,” Dr. Simon explained. “It doesn’t matter so much what kind of IMID patients have; much more important is the specific drug treatment and its impact on their antibody response.” Some participants were advised to briefly stop taking some immunosuppressive treatments before or after vaccination.
One of Dr. Simon’s coauthors, statistician and rheumatologist Koray Tascilar, MD, added, “This research is important because we looked not only at who responded less, which has been previously established, but who are at greater risk of losing their immune response, and how quickly.”
Need to take care
“Most treatments we as rheumatologists give to our patients don’t affect their SARS-CoV-2 humoral response,” Dr. Simon said. “However, there are specific drugs that are associated with lower antibody response. With respect to those drugs, we have to be more careful.”
It is important to be able to tell patients which drugs are safe and won’t have a negative impact on their immune response to vaccinations, Dr. Tascilar said. “But it would be too strong to say we’re ready to choose therapies based on their potential impact on protection against COVID. Yes, there is a risk from catching COVID, but we need to balance that risk with the risk of not giving patients the medications that are necessary to treat their rheumatologic condition.”
These diseases are serious, sometimes life-threatening. “We might think of strategies for how to mitigate the risk of underprotection from COVID that is brought about by these treatments,” he said. For example, offering boosters sooner or more frequently, or prophylactically treating with monoclonal antibodies.
“This study, along other recent studies, has found that antibody levels in patients with immune-mediated diseases wane more rapidly than in healthy controls, and this is especially true of those on medications that interfere with the B and T cells and anticytokine therapies,” Rebecca Haberman, MD, assistant professor, division of rheumatology, New York University Langone Health, noted in an email to this news organization.
“While there is no known antibody level that specifically correlates with clinical protection, and each patient needs to be thought of individually, these findings support the use of supplemental booster dosing in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases,” Dr. Haberman said, adding that her own research in this area has shown similar results.
“As a rheumatologist, I would be more likely to encourage my patients – especially those on immunomodulatory medications – to get boosted.”
Dr. Tascilar said his study does not directly answer the question of whether an earlier booster shot would be an effective strategy for patients with IMID. “In our department, we have an early boosting strategy, based on level of immune response.” But the decision of revaccination or not, and when, is based on a number of factors, not only on the level of antibodies. “It’s just part of the instruments we are using.”
The study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Dr. Simon and Dr. Tascilar declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study in The Lancet Rheumatology examines the strength and duration of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine–induced immunoglobulin-G antibody responses over time for patients with a variety of autoimmune diseases, compared with healthy controls.
The presence of humoral antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 has been shown to correlate with protection against COVID infection. But for patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs), host response to COVID infection or to vaccination is affected by the immune dysfunction imposed by the IMID and by the use of immune-modulating drugs to treat it.
This new study finds a weaker – as shown previously – and less sustained immune response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with a variety of IMIDs, including rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel diseases, and other systemic autoimmune diseases such as lupus. It also points toward the possibility of adjusting treatment and vaccination schedules and strategies for these patients based on their antibody levels, among other factors, to preserve best protection against severe COVID.
“It is important to assess immune response in these patients to see if they still have protection against severe COVID infection,” said lead author David Simon, MD, senior clinical scientist in clinical immunology and rheumatology at University Hospital Erlangen (Germany). “We know that antibody response is an immune correlate. Therefore, it is important to see how large and durable the immune response is to the coronavirus vaccine in these IMID patients, and whether specific drugs or therapies have negative effects on their immune response.”
What was studied?
For this large prospective cohort study, researchers registered 5076 coronavirus-vaccinated individuals. They analyzed serum samples obtained between December 15, 2020, and December 1, 2021, from 2,535 patients diagnosed with IMIDs and participating in a prospective coronavirus study program at the Deutsches Zentrum Immuntherapie in Erlangen. The IMID patients had a mean age of 55.0 years, and 58.9% were women.
A healthy control group of 1,198 individuals without IMID who had a mean age of 40.7 years, including 53.8% men, was also recruited for the analysis. All approved coronavirus vaccines were included, following standard vaccination schedules. Antibody response was measured over time by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay from 8 weeks after first vaccination to week 40.
Among the findings, the healthy controls had higher postvaccine antibody levels than did those with IMIDs. But the majority of vaccinated patients with IMID were able to build up a humoral immune response to SARS-CoV-2. Patients who were taking B-cell inhibitors like rituximab (Rituxan, Genentech; and biosimilars) and T-cell inhibitors like abatacept (Orencia, Bristol Myers Squibb) for IMIDs had significantly poorer antibody response.
Greater age and the use of combination therapies for IMIDs, compared with monotherapy, further reduced immune response to the vaccine. In terms of vaccination modality, messenger RNA–based vaccines induced higher antibody levels than did vector-based vaccines. The researchers noted that patients with IMID who were given a third vaccine dose could actually catch up well with the antibody responses observed in healthy controls.
“We looked at whether different IMIDs had a different humoral response, and we also assessed if there are effects from different therapeutic strategies,” Dr. Simon explained. “It doesn’t matter so much what kind of IMID patients have; much more important is the specific drug treatment and its impact on their antibody response.” Some participants were advised to briefly stop taking some immunosuppressive treatments before or after vaccination.
One of Dr. Simon’s coauthors, statistician and rheumatologist Koray Tascilar, MD, added, “This research is important because we looked not only at who responded less, which has been previously established, but who are at greater risk of losing their immune response, and how quickly.”
Need to take care
“Most treatments we as rheumatologists give to our patients don’t affect their SARS-CoV-2 humoral response,” Dr. Simon said. “However, there are specific drugs that are associated with lower antibody response. With respect to those drugs, we have to be more careful.”
It is important to be able to tell patients which drugs are safe and won’t have a negative impact on their immune response to vaccinations, Dr. Tascilar said. “But it would be too strong to say we’re ready to choose therapies based on their potential impact on protection against COVID. Yes, there is a risk from catching COVID, but we need to balance that risk with the risk of not giving patients the medications that are necessary to treat their rheumatologic condition.”
These diseases are serious, sometimes life-threatening. “We might think of strategies for how to mitigate the risk of underprotection from COVID that is brought about by these treatments,” he said. For example, offering boosters sooner or more frequently, or prophylactically treating with monoclonal antibodies.
“This study, along other recent studies, has found that antibody levels in patients with immune-mediated diseases wane more rapidly than in healthy controls, and this is especially true of those on medications that interfere with the B and T cells and anticytokine therapies,” Rebecca Haberman, MD, assistant professor, division of rheumatology, New York University Langone Health, noted in an email to this news organization.
“While there is no known antibody level that specifically correlates with clinical protection, and each patient needs to be thought of individually, these findings support the use of supplemental booster dosing in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases,” Dr. Haberman said, adding that her own research in this area has shown similar results.
“As a rheumatologist, I would be more likely to encourage my patients – especially those on immunomodulatory medications – to get boosted.”
Dr. Tascilar said his study does not directly answer the question of whether an earlier booster shot would be an effective strategy for patients with IMID. “In our department, we have an early boosting strategy, based on level of immune response.” But the decision of revaccination or not, and when, is based on a number of factors, not only on the level of antibodies. “It’s just part of the instruments we are using.”
The study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Dr. Simon and Dr. Tascilar declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study in The Lancet Rheumatology examines the strength and duration of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine–induced immunoglobulin-G antibody responses over time for patients with a variety of autoimmune diseases, compared with healthy controls.
The presence of humoral antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 has been shown to correlate with protection against COVID infection. But for patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs), host response to COVID infection or to vaccination is affected by the immune dysfunction imposed by the IMID and by the use of immune-modulating drugs to treat it.
This new study finds a weaker – as shown previously – and less sustained immune response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with a variety of IMIDs, including rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel diseases, and other systemic autoimmune diseases such as lupus. It also points toward the possibility of adjusting treatment and vaccination schedules and strategies for these patients based on their antibody levels, among other factors, to preserve best protection against severe COVID.
“It is important to assess immune response in these patients to see if they still have protection against severe COVID infection,” said lead author David Simon, MD, senior clinical scientist in clinical immunology and rheumatology at University Hospital Erlangen (Germany). “We know that antibody response is an immune correlate. Therefore, it is important to see how large and durable the immune response is to the coronavirus vaccine in these IMID patients, and whether specific drugs or therapies have negative effects on their immune response.”
What was studied?
For this large prospective cohort study, researchers registered 5076 coronavirus-vaccinated individuals. They analyzed serum samples obtained between December 15, 2020, and December 1, 2021, from 2,535 patients diagnosed with IMIDs and participating in a prospective coronavirus study program at the Deutsches Zentrum Immuntherapie in Erlangen. The IMID patients had a mean age of 55.0 years, and 58.9% were women.
A healthy control group of 1,198 individuals without IMID who had a mean age of 40.7 years, including 53.8% men, was also recruited for the analysis. All approved coronavirus vaccines were included, following standard vaccination schedules. Antibody response was measured over time by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay from 8 weeks after first vaccination to week 40.
Among the findings, the healthy controls had higher postvaccine antibody levels than did those with IMIDs. But the majority of vaccinated patients with IMID were able to build up a humoral immune response to SARS-CoV-2. Patients who were taking B-cell inhibitors like rituximab (Rituxan, Genentech; and biosimilars) and T-cell inhibitors like abatacept (Orencia, Bristol Myers Squibb) for IMIDs had significantly poorer antibody response.
Greater age and the use of combination therapies for IMIDs, compared with monotherapy, further reduced immune response to the vaccine. In terms of vaccination modality, messenger RNA–based vaccines induced higher antibody levels than did vector-based vaccines. The researchers noted that patients with IMID who were given a third vaccine dose could actually catch up well with the antibody responses observed in healthy controls.
“We looked at whether different IMIDs had a different humoral response, and we also assessed if there are effects from different therapeutic strategies,” Dr. Simon explained. “It doesn’t matter so much what kind of IMID patients have; much more important is the specific drug treatment and its impact on their antibody response.” Some participants were advised to briefly stop taking some immunosuppressive treatments before or after vaccination.
One of Dr. Simon’s coauthors, statistician and rheumatologist Koray Tascilar, MD, added, “This research is important because we looked not only at who responded less, which has been previously established, but who are at greater risk of losing their immune response, and how quickly.”
Need to take care
“Most treatments we as rheumatologists give to our patients don’t affect their SARS-CoV-2 humoral response,” Dr. Simon said. “However, there are specific drugs that are associated with lower antibody response. With respect to those drugs, we have to be more careful.”
It is important to be able to tell patients which drugs are safe and won’t have a negative impact on their immune response to vaccinations, Dr. Tascilar said. “But it would be too strong to say we’re ready to choose therapies based on their potential impact on protection against COVID. Yes, there is a risk from catching COVID, but we need to balance that risk with the risk of not giving patients the medications that are necessary to treat their rheumatologic condition.”
These diseases are serious, sometimes life-threatening. “We might think of strategies for how to mitigate the risk of underprotection from COVID that is brought about by these treatments,” he said. For example, offering boosters sooner or more frequently, or prophylactically treating with monoclonal antibodies.
“This study, along other recent studies, has found that antibody levels in patients with immune-mediated diseases wane more rapidly than in healthy controls, and this is especially true of those on medications that interfere with the B and T cells and anticytokine therapies,” Rebecca Haberman, MD, assistant professor, division of rheumatology, New York University Langone Health, noted in an email to this news organization.
“While there is no known antibody level that specifically correlates with clinical protection, and each patient needs to be thought of individually, these findings support the use of supplemental booster dosing in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases,” Dr. Haberman said, adding that her own research in this area has shown similar results.
“As a rheumatologist, I would be more likely to encourage my patients – especially those on immunomodulatory medications – to get boosted.”
Dr. Tascilar said his study does not directly answer the question of whether an earlier booster shot would be an effective strategy for patients with IMID. “In our department, we have an early boosting strategy, based on level of immune response.” But the decision of revaccination or not, and when, is based on a number of factors, not only on the level of antibodies. “It’s just part of the instruments we are using.”
The study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Dr. Simon and Dr. Tascilar declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET RHEUMATOLOGY
Infographic: Is physician behavior on social media really so bad?
The medical profession is held to a high standard of personal conduct, so physicians keep a sharp eye out for how fellow doctors behave. That goes for social media as well as in-person conduct.
(and it’s not as egregious as you might think). If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out the Medscape Physicians Behaving Badly Report 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The medical profession is held to a high standard of personal conduct, so physicians keep a sharp eye out for how fellow doctors behave. That goes for social media as well as in-person conduct.
(and it’s not as egregious as you might think). If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out the Medscape Physicians Behaving Badly Report 2022.

A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The medical profession is held to a high standard of personal conduct, so physicians keep a sharp eye out for how fellow doctors behave. That goes for social media as well as in-person conduct.
(and it’s not as egregious as you might think). If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out the Medscape Physicians Behaving Badly Report 2022.

A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paxlovid reduces risk of COVID death by 79% in older adults
The antiviral drug Paxlovid appears to reduce the risk of dying from COVID-19 by 79% and decrease hospitalizations by 73% in at-risk patients who are ages 65 and older, according to a new study published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The pill, which is a combination of the drugs nirmatrelvir and ritonavir, received FDA emergency use authorization in December 2021 to treat mild to moderate disease in ages 12 and older who face high risks for having severe COVID-19, hospitalization, and death.
“The results of the study show unequivocally that treatment with Paxlovid significantly reduces the risk of hospitalization and death from COVID-19,” Doron Netzer, MD, the senior study author and a researcher with Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, told The Jerusalem Post.
“We are the country’s leader in the provision of giving Paxlovid to relevant patients,” he said. “It was given to patients all over the country, with medical teams monitoring the patients who took the pills.”
, the news outlet reported. The research team analyzed information from Clalit’s electronic medical records. The health care organization covers about 52% of the Israeli population and almost two-thirds of older adults. More than 30,000 COVID-19 patients in Israel have been treated with the drug so far.
Dr. Netzer and colleagues looked at hospitalization and death data for at-risk COVID-19 patients ages 40 and older between Jan. 9 and March 31, when the original Omicron variant was the dominant strain in Israel. During that time, more than 1.1 million Clalit patients were infected with COVID-19, 109,000 patients were considered at-risk, and 3,900 patients received the drug.
The average age of the patients was 60, and 39% of the patients were 65 and older. Overall, 78% of the patients had previous COVID-19 immunity due to vaccination, prior infection, or both.
Among ages 65 and older, the rate of COVID-19 hospitalization was 14.7 cases per 100,000 person-days among treated patients, compared with 58.9 cases per 100,000 person-days among untreated patients. This represented a 73% lower chance of being hospitalized.
Among ages 40-64, the rate of hospitalization due to COVID-19 was 15.2 cases per 100,000 person-days among treated patients, compared with 15.8 cases per 100,000 person-days among untreated patients. The risk of hospitalization wasn’t significantly lower for this age group.
Among ages 65 and older, there were two deaths from COVID-19 in 2,484 treated patients, compared with 158 in the 40,337 untreated patients. This represented a 79% lower chance of dying from COVID-19.
Among ages 40-64, there was one death from COVID-19 in 1,418 treated patients, compared with 16 in the 65,015 untreated patients. The risk of death wasn’t significantly lower for this age group.
For both age groups, a lack of previous COVID-19 immunity and a previous hospitalization were most strongly linked to high rates of hospitalization during the Omicron wave.
The researchers noted that they didn’t break down the data on ages 40-64 who had cancer and other severe conditions that weaken the immune system. These patients may be more likely to benefit from Paxlovid, they said, though future studies will need to analyze the data.
The study didn’t receive any financial or in-kind support, the authors said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The antiviral drug Paxlovid appears to reduce the risk of dying from COVID-19 by 79% and decrease hospitalizations by 73% in at-risk patients who are ages 65 and older, according to a new study published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The pill, which is a combination of the drugs nirmatrelvir and ritonavir, received FDA emergency use authorization in December 2021 to treat mild to moderate disease in ages 12 and older who face high risks for having severe COVID-19, hospitalization, and death.
“The results of the study show unequivocally that treatment with Paxlovid significantly reduces the risk of hospitalization and death from COVID-19,” Doron Netzer, MD, the senior study author and a researcher with Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, told The Jerusalem Post.
“We are the country’s leader in the provision of giving Paxlovid to relevant patients,” he said. “It was given to patients all over the country, with medical teams monitoring the patients who took the pills.”
, the news outlet reported. The research team analyzed information from Clalit’s electronic medical records. The health care organization covers about 52% of the Israeli population and almost two-thirds of older adults. More than 30,000 COVID-19 patients in Israel have been treated with the drug so far.
Dr. Netzer and colleagues looked at hospitalization and death data for at-risk COVID-19 patients ages 40 and older between Jan. 9 and March 31, when the original Omicron variant was the dominant strain in Israel. During that time, more than 1.1 million Clalit patients were infected with COVID-19, 109,000 patients were considered at-risk, and 3,900 patients received the drug.
The average age of the patients was 60, and 39% of the patients were 65 and older. Overall, 78% of the patients had previous COVID-19 immunity due to vaccination, prior infection, or both.
Among ages 65 and older, the rate of COVID-19 hospitalization was 14.7 cases per 100,000 person-days among treated patients, compared with 58.9 cases per 100,000 person-days among untreated patients. This represented a 73% lower chance of being hospitalized.
Among ages 40-64, the rate of hospitalization due to COVID-19 was 15.2 cases per 100,000 person-days among treated patients, compared with 15.8 cases per 100,000 person-days among untreated patients. The risk of hospitalization wasn’t significantly lower for this age group.
Among ages 65 and older, there were two deaths from COVID-19 in 2,484 treated patients, compared with 158 in the 40,337 untreated patients. This represented a 79% lower chance of dying from COVID-19.
Among ages 40-64, there was one death from COVID-19 in 1,418 treated patients, compared with 16 in the 65,015 untreated patients. The risk of death wasn’t significantly lower for this age group.
For both age groups, a lack of previous COVID-19 immunity and a previous hospitalization were most strongly linked to high rates of hospitalization during the Omicron wave.
The researchers noted that they didn’t break down the data on ages 40-64 who had cancer and other severe conditions that weaken the immune system. These patients may be more likely to benefit from Paxlovid, they said, though future studies will need to analyze the data.
The study didn’t receive any financial or in-kind support, the authors said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The antiviral drug Paxlovid appears to reduce the risk of dying from COVID-19 by 79% and decrease hospitalizations by 73% in at-risk patients who are ages 65 and older, according to a new study published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The pill, which is a combination of the drugs nirmatrelvir and ritonavir, received FDA emergency use authorization in December 2021 to treat mild to moderate disease in ages 12 and older who face high risks for having severe COVID-19, hospitalization, and death.
“The results of the study show unequivocally that treatment with Paxlovid significantly reduces the risk of hospitalization and death from COVID-19,” Doron Netzer, MD, the senior study author and a researcher with Clalit Health Services, Tel Aviv, told The Jerusalem Post.
“We are the country’s leader in the provision of giving Paxlovid to relevant patients,” he said. “It was given to patients all over the country, with medical teams monitoring the patients who took the pills.”
, the news outlet reported. The research team analyzed information from Clalit’s electronic medical records. The health care organization covers about 52% of the Israeli population and almost two-thirds of older adults. More than 30,000 COVID-19 patients in Israel have been treated with the drug so far.
Dr. Netzer and colleagues looked at hospitalization and death data for at-risk COVID-19 patients ages 40 and older between Jan. 9 and March 31, when the original Omicron variant was the dominant strain in Israel. During that time, more than 1.1 million Clalit patients were infected with COVID-19, 109,000 patients were considered at-risk, and 3,900 patients received the drug.
The average age of the patients was 60, and 39% of the patients were 65 and older. Overall, 78% of the patients had previous COVID-19 immunity due to vaccination, prior infection, or both.
Among ages 65 and older, the rate of COVID-19 hospitalization was 14.7 cases per 100,000 person-days among treated patients, compared with 58.9 cases per 100,000 person-days among untreated patients. This represented a 73% lower chance of being hospitalized.
Among ages 40-64, the rate of hospitalization due to COVID-19 was 15.2 cases per 100,000 person-days among treated patients, compared with 15.8 cases per 100,000 person-days among untreated patients. The risk of hospitalization wasn’t significantly lower for this age group.
Among ages 65 and older, there were two deaths from COVID-19 in 2,484 treated patients, compared with 158 in the 40,337 untreated patients. This represented a 79% lower chance of dying from COVID-19.
Among ages 40-64, there was one death from COVID-19 in 1,418 treated patients, compared with 16 in the 65,015 untreated patients. The risk of death wasn’t significantly lower for this age group.
For both age groups, a lack of previous COVID-19 immunity and a previous hospitalization were most strongly linked to high rates of hospitalization during the Omicron wave.
The researchers noted that they didn’t break down the data on ages 40-64 who had cancer and other severe conditions that weaken the immune system. These patients may be more likely to benefit from Paxlovid, they said, though future studies will need to analyze the data.
The study didn’t receive any financial or in-kind support, the authors said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Vaccine hope now for leading cause of U.S. infant hospitalizations: RSV
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the leading cause of U.S. infant hospitalizations overall and across population subgroups, new data published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases confirm.
Acute bronchiolitis caused by RSV accounted for 9.6% (95% confidence interval, 9.4%-9.9%) and 9.3% (95% CI, 9.0%-9.6%) of total infant hospitalizations from January 2009 to September 2015 and October 2015 to December 2019, respectively.
Journal issue includes 14 RSV studies
The latest issue of the journal includes a special section with results from 14 studies related to the widespread, easy-to-catch virus, highlighting the urgency of finding a solution for all infants.
In one study, authors led by Mina Suh, MPH, with EpidStrategies, a division of ToxStrategies in Rockville, Md., reported that, in children under the age of 5 years in the United States, RSV caused 58,000 annual hospitalizations and from 100 to 500 annual deaths from 2009 to 2019 (the latest year data were available).
Globally, in 2015, among infants younger than 6 months, an estimated 1.4 million hospital admissions and 27,300 in-hospital deaths were attributed to RSV lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI).
The researchers used the largest publicly available, all-payer database in the United States – the National (Nationwide) Inpatient Sample – to describe the leading causes of infant hospitalizations.
The authors noted that, because clinicians don’t routinely perform lab tests for RSV, the true health care burden is likely higher and its public health impact greater than these numbers show.
Immunization candidates advance
There are no preventative options currently available to substantially cut RSV infections in all infants, though immunization candidates are advancing, showing safety and efficacy in clinical trials.
Palivizumab is currently the only available option in the United States to prevent RSV and is recommended only for a small group of infants with particular forms of heart or lung disease and those born prematurely at 29 weeks’ gestational age. Further, palivizumab has to be given monthly throughout the RSV season.
Another of the studies in the journal supplement concluded that a universal immunization strategy with one of the candidates, nirsevimab (Sanofi, AstraZeneca), an investigational long-acting monoclonal antibody, could substantially reduce the health burden and economic burden for U.S. infants in their first RSV season.
The researchers, led by Alexia Kieffer, MSc, MPH, with Sanofi, used static decision-analytic modeling for the estimates. Modeled RSV-related outcomes included primary care and ED visits, hospitalizations, including ICU admission and mechanical ventilations, and RSV-related deaths.
“The results of this model suggested that the use of nirsevimab in all infants could reduce health events by 55% and the overall costs to the payer by 49%,” the authors of the study wrote.
According to the study, universal immunization of all infants with nirsevimab is expected to reduce 290,174 RSV-related medically attended LRTI (MALRTI), 24,986 hospitalizations, and cut $612 million in costs to the health care system.
The authors wrote: “While this reduction would be driven by term infants, who account for most of the RSV-MALRTI burden; all infants, including palivizumab-eligible and preterm infants who suffer from significantly higher rates of disease, would benefit from this immunization strategy.”
Excitement for another option
Jörn-Hendrik Weitkamp, MD, professor of pediatrics and director for patient-oriented research at Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview there is much excitement in the field for nirsevimab as it has significant advantages over palivizumab.
RSV “is a huge burden to the children, the families, the hospitals, and the medical system,” he said.
Ideally there would be a vaccine to offer the best protection, he noted.
“People have spent their lives, their careers trying to develop a vaccine for RSV,” he said, but that has been elusive for more than 60 years. Therefore, passive immunization is the best of the current options, he says, and nirsevimab “seems to be very effective.”
What’s not clear, Dr. Weitkamp said, is how much nirsevimab will cost as it is not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration. However, it has the great advantage of being given only once before the season starts instead of monthly (as required for palivizumab) through the season, “which is painful, inconvenient, and traumatizing. We limit that one to the children at highest risk.”
Rolling out an infant nirsevimab program would likely vary by geographic region, Ms. Kieffer and colleagues said, to help ensure infants are protected during the peak of their region’s RSV season.
The journal’s RSV supplement was supported by Sanofi and AstraZeneca. The studies by Ms. Suh and colleagues and Ms. Kieffer and colleagues were supported by AstraZeneca and Sanofi. Ms. Suh and several coauthors are employees of EpidStrategies. One coauthor is an employee of Sanofi and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. Ms. Kieffer and several coauthors are employees of Sanofi and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. Dr. Weitkamp reported no relevant financial relationships.
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the leading cause of U.S. infant hospitalizations overall and across population subgroups, new data published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases confirm.
Acute bronchiolitis caused by RSV accounted for 9.6% (95% confidence interval, 9.4%-9.9%) and 9.3% (95% CI, 9.0%-9.6%) of total infant hospitalizations from January 2009 to September 2015 and October 2015 to December 2019, respectively.
Journal issue includes 14 RSV studies
The latest issue of the journal includes a special section with results from 14 studies related to the widespread, easy-to-catch virus, highlighting the urgency of finding a solution for all infants.
In one study, authors led by Mina Suh, MPH, with EpidStrategies, a division of ToxStrategies in Rockville, Md., reported that, in children under the age of 5 years in the United States, RSV caused 58,000 annual hospitalizations and from 100 to 500 annual deaths from 2009 to 2019 (the latest year data were available).
Globally, in 2015, among infants younger than 6 months, an estimated 1.4 million hospital admissions and 27,300 in-hospital deaths were attributed to RSV lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI).
The researchers used the largest publicly available, all-payer database in the United States – the National (Nationwide) Inpatient Sample – to describe the leading causes of infant hospitalizations.
The authors noted that, because clinicians don’t routinely perform lab tests for RSV, the true health care burden is likely higher and its public health impact greater than these numbers show.
Immunization candidates advance
There are no preventative options currently available to substantially cut RSV infections in all infants, though immunization candidates are advancing, showing safety and efficacy in clinical trials.
Palivizumab is currently the only available option in the United States to prevent RSV and is recommended only for a small group of infants with particular forms of heart or lung disease and those born prematurely at 29 weeks’ gestational age. Further, palivizumab has to be given monthly throughout the RSV season.
Another of the studies in the journal supplement concluded that a universal immunization strategy with one of the candidates, nirsevimab (Sanofi, AstraZeneca), an investigational long-acting monoclonal antibody, could substantially reduce the health burden and economic burden for U.S. infants in their first RSV season.
The researchers, led by Alexia Kieffer, MSc, MPH, with Sanofi, used static decision-analytic modeling for the estimates. Modeled RSV-related outcomes included primary care and ED visits, hospitalizations, including ICU admission and mechanical ventilations, and RSV-related deaths.
“The results of this model suggested that the use of nirsevimab in all infants could reduce health events by 55% and the overall costs to the payer by 49%,” the authors of the study wrote.
According to the study, universal immunization of all infants with nirsevimab is expected to reduce 290,174 RSV-related medically attended LRTI (MALRTI), 24,986 hospitalizations, and cut $612 million in costs to the health care system.
The authors wrote: “While this reduction would be driven by term infants, who account for most of the RSV-MALRTI burden; all infants, including palivizumab-eligible and preterm infants who suffer from significantly higher rates of disease, would benefit from this immunization strategy.”
Excitement for another option
Jörn-Hendrik Weitkamp, MD, professor of pediatrics and director for patient-oriented research at Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview there is much excitement in the field for nirsevimab as it has significant advantages over palivizumab.
RSV “is a huge burden to the children, the families, the hospitals, and the medical system,” he said.
Ideally there would be a vaccine to offer the best protection, he noted.
“People have spent their lives, their careers trying to develop a vaccine for RSV,” he said, but that has been elusive for more than 60 years. Therefore, passive immunization is the best of the current options, he says, and nirsevimab “seems to be very effective.”
What’s not clear, Dr. Weitkamp said, is how much nirsevimab will cost as it is not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration. However, it has the great advantage of being given only once before the season starts instead of monthly (as required for palivizumab) through the season, “which is painful, inconvenient, and traumatizing. We limit that one to the children at highest risk.”
Rolling out an infant nirsevimab program would likely vary by geographic region, Ms. Kieffer and colleagues said, to help ensure infants are protected during the peak of their region’s RSV season.
The journal’s RSV supplement was supported by Sanofi and AstraZeneca. The studies by Ms. Suh and colleagues and Ms. Kieffer and colleagues were supported by AstraZeneca and Sanofi. Ms. Suh and several coauthors are employees of EpidStrategies. One coauthor is an employee of Sanofi and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. Ms. Kieffer and several coauthors are employees of Sanofi and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. Dr. Weitkamp reported no relevant financial relationships.
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the leading cause of U.S. infant hospitalizations overall and across population subgroups, new data published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases confirm.
Acute bronchiolitis caused by RSV accounted for 9.6% (95% confidence interval, 9.4%-9.9%) and 9.3% (95% CI, 9.0%-9.6%) of total infant hospitalizations from January 2009 to September 2015 and October 2015 to December 2019, respectively.
Journal issue includes 14 RSV studies
The latest issue of the journal includes a special section with results from 14 studies related to the widespread, easy-to-catch virus, highlighting the urgency of finding a solution for all infants.
In one study, authors led by Mina Suh, MPH, with EpidStrategies, a division of ToxStrategies in Rockville, Md., reported that, in children under the age of 5 years in the United States, RSV caused 58,000 annual hospitalizations and from 100 to 500 annual deaths from 2009 to 2019 (the latest year data were available).
Globally, in 2015, among infants younger than 6 months, an estimated 1.4 million hospital admissions and 27,300 in-hospital deaths were attributed to RSV lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI).
The researchers used the largest publicly available, all-payer database in the United States – the National (Nationwide) Inpatient Sample – to describe the leading causes of infant hospitalizations.
The authors noted that, because clinicians don’t routinely perform lab tests for RSV, the true health care burden is likely higher and its public health impact greater than these numbers show.
Immunization candidates advance
There are no preventative options currently available to substantially cut RSV infections in all infants, though immunization candidates are advancing, showing safety and efficacy in clinical trials.
Palivizumab is currently the only available option in the United States to prevent RSV and is recommended only for a small group of infants with particular forms of heart or lung disease and those born prematurely at 29 weeks’ gestational age. Further, palivizumab has to be given monthly throughout the RSV season.
Another of the studies in the journal supplement concluded that a universal immunization strategy with one of the candidates, nirsevimab (Sanofi, AstraZeneca), an investigational long-acting monoclonal antibody, could substantially reduce the health burden and economic burden for U.S. infants in their first RSV season.
The researchers, led by Alexia Kieffer, MSc, MPH, with Sanofi, used static decision-analytic modeling for the estimates. Modeled RSV-related outcomes included primary care and ED visits, hospitalizations, including ICU admission and mechanical ventilations, and RSV-related deaths.
“The results of this model suggested that the use of nirsevimab in all infants could reduce health events by 55% and the overall costs to the payer by 49%,” the authors of the study wrote.
According to the study, universal immunization of all infants with nirsevimab is expected to reduce 290,174 RSV-related medically attended LRTI (MALRTI), 24,986 hospitalizations, and cut $612 million in costs to the health care system.
The authors wrote: “While this reduction would be driven by term infants, who account for most of the RSV-MALRTI burden; all infants, including palivizumab-eligible and preterm infants who suffer from significantly higher rates of disease, would benefit from this immunization strategy.”
Excitement for another option
Jörn-Hendrik Weitkamp, MD, professor of pediatrics and director for patient-oriented research at Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview there is much excitement in the field for nirsevimab as it has significant advantages over palivizumab.
RSV “is a huge burden to the children, the families, the hospitals, and the medical system,” he said.
Ideally there would be a vaccine to offer the best protection, he noted.
“People have spent their lives, their careers trying to develop a vaccine for RSV,” he said, but that has been elusive for more than 60 years. Therefore, passive immunization is the best of the current options, he says, and nirsevimab “seems to be very effective.”
What’s not clear, Dr. Weitkamp said, is how much nirsevimab will cost as it is not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration. However, it has the great advantage of being given only once before the season starts instead of monthly (as required for palivizumab) through the season, “which is painful, inconvenient, and traumatizing. We limit that one to the children at highest risk.”
Rolling out an infant nirsevimab program would likely vary by geographic region, Ms. Kieffer and colleagues said, to help ensure infants are protected during the peak of their region’s RSV season.
The journal’s RSV supplement was supported by Sanofi and AstraZeneca. The studies by Ms. Suh and colleagues and Ms. Kieffer and colleagues were supported by AstraZeneca and Sanofi. Ms. Suh and several coauthors are employees of EpidStrategies. One coauthor is an employee of Sanofi and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. Ms. Kieffer and several coauthors are employees of Sanofi and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. Dr. Weitkamp reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES
COVID-19 vaccine safe in patients with heart failure
Patients with heart failure (HF) who received two doses of COVID mRNA vaccines were not more likely to have worsening disease, venous thromboembolism, or myocarditis within 90 days than similar unvaccinated patients, in a case-control study in Denmark.
Moreover, in the 90 days after receiving the second shot, vaccinated patients were less likely to die of any cause, compared with unvaccinated patients during a similar 90-day period.
Caroline Sindet-Pedersen, PhD, Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Hellerup, Denmark, and colleagues presented these findings at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Major risk is not receiving vaccine
These results “confirm that the major risk for patients with HF is not receiving vaccination for COVID-19,” Marco Metra, MD, who was not involved with this research, said in an interview.
Dr. Metra was coauthor of an ESC guidance for the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular disease during the COVID-19 pandemic, published online ahead of print November 2021 in the European Heart Journal.
The guidance explains that patients with HF are at increased risk for hospitalization, need for mechanical ventilation, and death because of COVID-19, and that vaccination reduces the risk for serious illness from COVID-19, Dr. Sindet-Pedersen and colleagues explained in a press release from the ESC.
However, “concerns remain,” they added, “about the safety of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in heart failure patients, due to a perceived increased risk of cardiovascular side effects.”
The study findings suggest that “there should be no concern about cardiovascular side effects from mRNA vaccines in heart failure patients,” Dr. Sindet-Pedersen and colleagues summarized.
The results also “point to a beneficial effect of vaccination on mortality” and “indicate that patients with HF should be prioritized for COVID-19 vaccinations and boosters,” they added.
“There are ongoing concerns about the safety of COVID-19 vaccination in fragile patients and patients with heart failure,” said Dr. Metra, professor of cardiology and director of the Institute of Cardiology of the Civil Hospital and University of Brescia (Italy).
“These concerns are not based on evidence but just on reports of rare side effects (namely, myocarditis and pericarditis) in vaccinated people,” he added.
Dr. Metra also coauthored a position paper on COVID-19 vaccination in patients with HF from the Heart Failure Association of the ESC, which was published online October 2021 in the European Journal of Heart Failure.
“The current study,” he summarized, “shows a lower risk of mortality among patients vaccinated, compared with those not vaccinated.
“It has limitations,” he cautioned, “as it is not a prospective randomized study, but [rather] an observational one with comparison between vaccinated and not vaccinated patients with similar characteristics.
“However, it was done in a large population,” he noted, “and its results confirm that the major risk for patients with HF is not receiving vaccination for COVID-19.”
95% of patients with HF in Denmark double vaccinated
The group did not analyze the types of all-cause death in their study, Dr. Sindet-Pedersen clarified in an interview.
Other studies have shown that vaccines are associated with improved survival, she noted. For example, bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccines and the measles vaccines have been linked with a decreased risk for nonspecific mortality in children, and influenza vaccines are associated with decreased all-cause mortality in patients with HF.
The rates of vaccination in this study were much higher than those for patients with HF in the United States.
In a study of 7,094 patients with HF seen at the Mount Sinai Health System between January 2021 and January 2022, 31% of patients were fully vaccinated with two doses and 14.8% had also received a booster, as per Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidance. However, another 9.1% of patients were only partially vaccinated with one dose, and 45% remained unvaccinated by January 2022,
In the current study, “the uptake was very high,” Dr. Sindet-Pedersen noted, that is, “95% of the prevalent heart failure patients in 2021 received a vaccine.”
“It might be that the last 5% of the patients that did not receive a vaccine were too ill [terminal] to receive the vaccine,” she speculated, “or that was due to personal reasons.”
The researchers identified 50,893 patients with HF who were double vaccinated in 2021 and they matched them with 50,893 unvaccinated patients with HF in 2019 (prepandemic), with the same age, sex, HF duration, use of HF medications, ischemic heart disease, cancer, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, and admission with HF within 90 days.
Almost all patients in the vaccinated group received the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccine (92%) and the rest received the Moderna mRNA vaccine (8%), in 2021.
The patients had a mean age of 74, and 64% were men. They had HF for a median of 4.1 years.
During the 90-day follow-up, 1,311 patients in the unvaccinated cohort (2.56%) and 1,113 patients in the vaccinated cohort (2.23%) died; there was a significantly lower risk for all-cause death in the vaccinated cohort versus the unvaccinated cohort (–0.33 percentage points; 95% CI, –0.52 to –0.15 percentage points).
The risk for worsening heart failure was 1.1% in each group; myocarditis and venous thromboembolism were extremely rare, and risks for these conditions were not significantly different in the two groups.
The researchers and Dr. Metra declared they have no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metra is editor-in-chief of the European Journal of Heart Failure and senior consulting editor of the European Heart Journal.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with heart failure (HF) who received two doses of COVID mRNA vaccines were not more likely to have worsening disease, venous thromboembolism, or myocarditis within 90 days than similar unvaccinated patients, in a case-control study in Denmark.
Moreover, in the 90 days after receiving the second shot, vaccinated patients were less likely to die of any cause, compared with unvaccinated patients during a similar 90-day period.
Caroline Sindet-Pedersen, PhD, Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Hellerup, Denmark, and colleagues presented these findings at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Major risk is not receiving vaccine
These results “confirm that the major risk for patients with HF is not receiving vaccination for COVID-19,” Marco Metra, MD, who was not involved with this research, said in an interview.
Dr. Metra was coauthor of an ESC guidance for the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular disease during the COVID-19 pandemic, published online ahead of print November 2021 in the European Heart Journal.
The guidance explains that patients with HF are at increased risk for hospitalization, need for mechanical ventilation, and death because of COVID-19, and that vaccination reduces the risk for serious illness from COVID-19, Dr. Sindet-Pedersen and colleagues explained in a press release from the ESC.
However, “concerns remain,” they added, “about the safety of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in heart failure patients, due to a perceived increased risk of cardiovascular side effects.”
The study findings suggest that “there should be no concern about cardiovascular side effects from mRNA vaccines in heart failure patients,” Dr. Sindet-Pedersen and colleagues summarized.
The results also “point to a beneficial effect of vaccination on mortality” and “indicate that patients with HF should be prioritized for COVID-19 vaccinations and boosters,” they added.
“There are ongoing concerns about the safety of COVID-19 vaccination in fragile patients and patients with heart failure,” said Dr. Metra, professor of cardiology and director of the Institute of Cardiology of the Civil Hospital and University of Brescia (Italy).
“These concerns are not based on evidence but just on reports of rare side effects (namely, myocarditis and pericarditis) in vaccinated people,” he added.
Dr. Metra also coauthored a position paper on COVID-19 vaccination in patients with HF from the Heart Failure Association of the ESC, which was published online October 2021 in the European Journal of Heart Failure.
“The current study,” he summarized, “shows a lower risk of mortality among patients vaccinated, compared with those not vaccinated.
“It has limitations,” he cautioned, “as it is not a prospective randomized study, but [rather] an observational one with comparison between vaccinated and not vaccinated patients with similar characteristics.
“However, it was done in a large population,” he noted, “and its results confirm that the major risk for patients with HF is not receiving vaccination for COVID-19.”
95% of patients with HF in Denmark double vaccinated
The group did not analyze the types of all-cause death in their study, Dr. Sindet-Pedersen clarified in an interview.
Other studies have shown that vaccines are associated with improved survival, she noted. For example, bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccines and the measles vaccines have been linked with a decreased risk for nonspecific mortality in children, and influenza vaccines are associated with decreased all-cause mortality in patients with HF.
The rates of vaccination in this study were much higher than those for patients with HF in the United States.
In a study of 7,094 patients with HF seen at the Mount Sinai Health System between January 2021 and January 2022, 31% of patients were fully vaccinated with two doses and 14.8% had also received a booster, as per Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidance. However, another 9.1% of patients were only partially vaccinated with one dose, and 45% remained unvaccinated by January 2022,
In the current study, “the uptake was very high,” Dr. Sindet-Pedersen noted, that is, “95% of the prevalent heart failure patients in 2021 received a vaccine.”
“It might be that the last 5% of the patients that did not receive a vaccine were too ill [terminal] to receive the vaccine,” she speculated, “or that was due to personal reasons.”
The researchers identified 50,893 patients with HF who were double vaccinated in 2021 and they matched them with 50,893 unvaccinated patients with HF in 2019 (prepandemic), with the same age, sex, HF duration, use of HF medications, ischemic heart disease, cancer, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, and admission with HF within 90 days.
Almost all patients in the vaccinated group received the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccine (92%) and the rest received the Moderna mRNA vaccine (8%), in 2021.
The patients had a mean age of 74, and 64% were men. They had HF for a median of 4.1 years.
During the 90-day follow-up, 1,311 patients in the unvaccinated cohort (2.56%) and 1,113 patients in the vaccinated cohort (2.23%) died; there was a significantly lower risk for all-cause death in the vaccinated cohort versus the unvaccinated cohort (–0.33 percentage points; 95% CI, –0.52 to –0.15 percentage points).
The risk for worsening heart failure was 1.1% in each group; myocarditis and venous thromboembolism were extremely rare, and risks for these conditions were not significantly different in the two groups.
The researchers and Dr. Metra declared they have no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metra is editor-in-chief of the European Journal of Heart Failure and senior consulting editor of the European Heart Journal.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with heart failure (HF) who received two doses of COVID mRNA vaccines were not more likely to have worsening disease, venous thromboembolism, or myocarditis within 90 days than similar unvaccinated patients, in a case-control study in Denmark.
Moreover, in the 90 days after receiving the second shot, vaccinated patients were less likely to die of any cause, compared with unvaccinated patients during a similar 90-day period.
Caroline Sindet-Pedersen, PhD, Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Hellerup, Denmark, and colleagues presented these findings at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Major risk is not receiving vaccine
These results “confirm that the major risk for patients with HF is not receiving vaccination for COVID-19,” Marco Metra, MD, who was not involved with this research, said in an interview.
Dr. Metra was coauthor of an ESC guidance for the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular disease during the COVID-19 pandemic, published online ahead of print November 2021 in the European Heart Journal.
The guidance explains that patients with HF are at increased risk for hospitalization, need for mechanical ventilation, and death because of COVID-19, and that vaccination reduces the risk for serious illness from COVID-19, Dr. Sindet-Pedersen and colleagues explained in a press release from the ESC.
However, “concerns remain,” they added, “about the safety of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in heart failure patients, due to a perceived increased risk of cardiovascular side effects.”
The study findings suggest that “there should be no concern about cardiovascular side effects from mRNA vaccines in heart failure patients,” Dr. Sindet-Pedersen and colleagues summarized.
The results also “point to a beneficial effect of vaccination on mortality” and “indicate that patients with HF should be prioritized for COVID-19 vaccinations and boosters,” they added.
“There are ongoing concerns about the safety of COVID-19 vaccination in fragile patients and patients with heart failure,” said Dr. Metra, professor of cardiology and director of the Institute of Cardiology of the Civil Hospital and University of Brescia (Italy).
“These concerns are not based on evidence but just on reports of rare side effects (namely, myocarditis and pericarditis) in vaccinated people,” he added.
Dr. Metra also coauthored a position paper on COVID-19 vaccination in patients with HF from the Heart Failure Association of the ESC, which was published online October 2021 in the European Journal of Heart Failure.
“The current study,” he summarized, “shows a lower risk of mortality among patients vaccinated, compared with those not vaccinated.
“It has limitations,” he cautioned, “as it is not a prospective randomized study, but [rather] an observational one with comparison between vaccinated and not vaccinated patients with similar characteristics.
“However, it was done in a large population,” he noted, “and its results confirm that the major risk for patients with HF is not receiving vaccination for COVID-19.”
95% of patients with HF in Denmark double vaccinated
The group did not analyze the types of all-cause death in their study, Dr. Sindet-Pedersen clarified in an interview.
Other studies have shown that vaccines are associated with improved survival, she noted. For example, bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccines and the measles vaccines have been linked with a decreased risk for nonspecific mortality in children, and influenza vaccines are associated with decreased all-cause mortality in patients with HF.
The rates of vaccination in this study were much higher than those for patients with HF in the United States.
In a study of 7,094 patients with HF seen at the Mount Sinai Health System between January 2021 and January 2022, 31% of patients were fully vaccinated with two doses and 14.8% had also received a booster, as per Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidance. However, another 9.1% of patients were only partially vaccinated with one dose, and 45% remained unvaccinated by January 2022,
In the current study, “the uptake was very high,” Dr. Sindet-Pedersen noted, that is, “95% of the prevalent heart failure patients in 2021 received a vaccine.”
“It might be that the last 5% of the patients that did not receive a vaccine were too ill [terminal] to receive the vaccine,” she speculated, “or that was due to personal reasons.”
The researchers identified 50,893 patients with HF who were double vaccinated in 2021 and they matched them with 50,893 unvaccinated patients with HF in 2019 (prepandemic), with the same age, sex, HF duration, use of HF medications, ischemic heart disease, cancer, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, and admission with HF within 90 days.
Almost all patients in the vaccinated group received the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccine (92%) and the rest received the Moderna mRNA vaccine (8%), in 2021.
The patients had a mean age of 74, and 64% were men. They had HF for a median of 4.1 years.
During the 90-day follow-up, 1,311 patients in the unvaccinated cohort (2.56%) and 1,113 patients in the vaccinated cohort (2.23%) died; there was a significantly lower risk for all-cause death in the vaccinated cohort versus the unvaccinated cohort (–0.33 percentage points; 95% CI, –0.52 to –0.15 percentage points).
The risk for worsening heart failure was 1.1% in each group; myocarditis and venous thromboembolism were extremely rare, and risks for these conditions were not significantly different in the two groups.
The researchers and Dr. Metra declared they have no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metra is editor-in-chief of the European Journal of Heart Failure and senior consulting editor of the European Heart Journal.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2022
Langya, a new zoonotic virus, detected in China
Between 2018 and August 2022, These cases were reported in The New England Journal of Medicine. When asked by Nature about this emerging virus that has until now flown under the radar, scientists said that they were not overly concerned because the virus doesn’t seem to spread easily between people nor is it fatal.
Researchers think that the virus is carried by shrews. It might have infected people directly or through an intermediate animal.
First identified in Langya
The authors describe 35 cases of infection with a virus called Langya henipavirus (LayV) since 2018. It is closely related to two other henipaviruses known to infect people – Hendra virus and Nipah virus. The virus was named Langya after the town in Shandong province in China where the first patient identified with the disease was from, explained coauthor Linfa Wang, PhD, a virologist at Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore.
Langya can cause respiratory symptoms such as fever, cough, and fatigue. Hendra virus and Nipah virus also cause respiratory infections and can be fatal, the article in Nature reports.
Hendra and Nipah
According to the World Health Organization, Nipah virus, which was discovered in 1999, is a new virus responsible for a zoonosis that causes the disease in animals and humans who have had contact with infected animals. Its name comes from the location where it was first identified in Malaysia. Patients may have asymptomatic infection or symptoms such as acute respiratory infection and severe encephalitis. The case fatality rate is between 40% and 75%.
Nipah virus is closely related to another recently discovered (1994) zoonotic virus called Hendra virus, which is named after the Australian city in which it first appeared. On that day in July 2016, 53 cases were identified involving 70 horses. These incidents remained confined to the northeastern coast of Australia.
Nipah virus and Hendra virus belong to the Paramyxoviridae family. “While the members of this group of viruses are only responsible for a few limited outbreaks, the ability of these viruses to infect a wide range of hosts and cause a disease leading to high fatalities in humans has made them a public health concern,” stated the WHO.
Related to measles
The research team identified LayV while monitoring patients at three hospitals in the eastern Chinese provinces of Shandong and Henan between April 2018 and August 2021. Throughout the study period, the researchers found 35 people infected with LayV, mostly farmers, with symptoms ranging from a cough to severe pneumonia. Participants were recruited into the study if they had a fever. The team sequenced the LayV genome from a throat swab taken from the first patient identified with the disease, a 53-year-old woman.
The LayV genome showed that the virus is most closely related to Mojiang henipavirus, which was first isolated in rats in an abandoned mine in the southern Chinese province of Yunnan in 2012. Henipaviruses belong to the Paramyxoviridae family of viruses, which includes measles, mumps, and many respiratory viruses that infect humans. Several other henipaviruses have been discovered in bats, rats, and shrews from Australia to South Korea and China, but only Hendra, Nipah, and now LayV are known to infect people, according to Nature.
Animal origin likely
Because most patients stated in a questionnaire that they had been exposed to an animal during the month preceding the onset of their symptoms, the researchers tested goats, dogs, pigs, and cattle living in the villages of infected patients for antibodies against LayV. They found LayV antibodies in a handful of goats and dogs and identified LayV viral RNA in 27% of the 262 sampled shrews. These findings suggest that the shrew may be a natural reservoir of LayV, passing it between themselves “and somehow infecting people here and there by chance,” Emily Gurley, PhD, MPH, an infectious diseases epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, told Nature.
The researchers did not find strong evidence of LayV spreading between the people included in the study. There were no clusters of cases in the same family, within a short time span, or in close geographical proximity. “Of the 35 cases, not a single one is linked,” said Dr. Wang, which Dr. Gurley considered good news. It should be noted, however ,”that the study did retrospective contact tracing on only 15 family members of nine infected individuals, which makes it difficult to determine how exactly the individuals were exposed,” reported Nature.
Vigilance is needed
Should we be worried about a potential new epidemic? The replies from two experts interviewed by Nature were reassuring. “There is no particular need to worry about this virus, but ongoing surveillance is critical,” said Professor Edward Holmes, an evolutionary virologist at the University of Sydney. Regularly testing people and animals for emerging viruses is important to understand the risk for zoonotic diseases – those that can be transmitted from other animals to humans, he said.
It is still not clear how people were infected in the first place – whether directly from shrews or an intermediate animal, said Dr. Gurley. That’s why a lot of research still needs to be done to work out how the virus is spreading in shrews and how people are getting infected, she added.
Nevertheless, Dr. Gurley finds that large outbreaks of infectious diseases typically take off after a lot of false starts. “If we are actively looking for those sparks, then we are in a much better position to stop or to find something early.” Still, she noted that she didn’t see anything in the data to “cause alarm from a pandemic-threat perspective.”
Though there is not currently any cause for worry of a new pandemic, vigilance is crucial. Professor Holmes says there is an urgent need for a global surveillance system to detect virus spillovers and rapidly communicate those results to avoid more pandemics, such as the one sparked by COVID-19. “These sorts of zoonotic spillover events happen all the time,” he said. “The world needs to wake up.”
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Between 2018 and August 2022, These cases were reported in The New England Journal of Medicine. When asked by Nature about this emerging virus that has until now flown under the radar, scientists said that they were not overly concerned because the virus doesn’t seem to spread easily between people nor is it fatal.
Researchers think that the virus is carried by shrews. It might have infected people directly or through an intermediate animal.
First identified in Langya
The authors describe 35 cases of infection with a virus called Langya henipavirus (LayV) since 2018. It is closely related to two other henipaviruses known to infect people – Hendra virus and Nipah virus. The virus was named Langya after the town in Shandong province in China where the first patient identified with the disease was from, explained coauthor Linfa Wang, PhD, a virologist at Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore.
Langya can cause respiratory symptoms such as fever, cough, and fatigue. Hendra virus and Nipah virus also cause respiratory infections and can be fatal, the article in Nature reports.
Hendra and Nipah
According to the World Health Organization, Nipah virus, which was discovered in 1999, is a new virus responsible for a zoonosis that causes the disease in animals and humans who have had contact with infected animals. Its name comes from the location where it was first identified in Malaysia. Patients may have asymptomatic infection or symptoms such as acute respiratory infection and severe encephalitis. The case fatality rate is between 40% and 75%.
Nipah virus is closely related to another recently discovered (1994) zoonotic virus called Hendra virus, which is named after the Australian city in which it first appeared. On that day in July 2016, 53 cases were identified involving 70 horses. These incidents remained confined to the northeastern coast of Australia.
Nipah virus and Hendra virus belong to the Paramyxoviridae family. “While the members of this group of viruses are only responsible for a few limited outbreaks, the ability of these viruses to infect a wide range of hosts and cause a disease leading to high fatalities in humans has made them a public health concern,” stated the WHO.
Related to measles
The research team identified LayV while monitoring patients at three hospitals in the eastern Chinese provinces of Shandong and Henan between April 2018 and August 2021. Throughout the study period, the researchers found 35 people infected with LayV, mostly farmers, with symptoms ranging from a cough to severe pneumonia. Participants were recruited into the study if they had a fever. The team sequenced the LayV genome from a throat swab taken from the first patient identified with the disease, a 53-year-old woman.
The LayV genome showed that the virus is most closely related to Mojiang henipavirus, which was first isolated in rats in an abandoned mine in the southern Chinese province of Yunnan in 2012. Henipaviruses belong to the Paramyxoviridae family of viruses, which includes measles, mumps, and many respiratory viruses that infect humans. Several other henipaviruses have been discovered in bats, rats, and shrews from Australia to South Korea and China, but only Hendra, Nipah, and now LayV are known to infect people, according to Nature.
Animal origin likely
Because most patients stated in a questionnaire that they had been exposed to an animal during the month preceding the onset of their symptoms, the researchers tested goats, dogs, pigs, and cattle living in the villages of infected patients for antibodies against LayV. They found LayV antibodies in a handful of goats and dogs and identified LayV viral RNA in 27% of the 262 sampled shrews. These findings suggest that the shrew may be a natural reservoir of LayV, passing it between themselves “and somehow infecting people here and there by chance,” Emily Gurley, PhD, MPH, an infectious diseases epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, told Nature.
The researchers did not find strong evidence of LayV spreading between the people included in the study. There were no clusters of cases in the same family, within a short time span, or in close geographical proximity. “Of the 35 cases, not a single one is linked,” said Dr. Wang, which Dr. Gurley considered good news. It should be noted, however ,”that the study did retrospective contact tracing on only 15 family members of nine infected individuals, which makes it difficult to determine how exactly the individuals were exposed,” reported Nature.
Vigilance is needed
Should we be worried about a potential new epidemic? The replies from two experts interviewed by Nature were reassuring. “There is no particular need to worry about this virus, but ongoing surveillance is critical,” said Professor Edward Holmes, an evolutionary virologist at the University of Sydney. Regularly testing people and animals for emerging viruses is important to understand the risk for zoonotic diseases – those that can be transmitted from other animals to humans, he said.
It is still not clear how people were infected in the first place – whether directly from shrews or an intermediate animal, said Dr. Gurley. That’s why a lot of research still needs to be done to work out how the virus is spreading in shrews and how people are getting infected, she added.
Nevertheless, Dr. Gurley finds that large outbreaks of infectious diseases typically take off after a lot of false starts. “If we are actively looking for those sparks, then we are in a much better position to stop or to find something early.” Still, she noted that she didn’t see anything in the data to “cause alarm from a pandemic-threat perspective.”
Though there is not currently any cause for worry of a new pandemic, vigilance is crucial. Professor Holmes says there is an urgent need for a global surveillance system to detect virus spillovers and rapidly communicate those results to avoid more pandemics, such as the one sparked by COVID-19. “These sorts of zoonotic spillover events happen all the time,” he said. “The world needs to wake up.”
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Between 2018 and August 2022, These cases were reported in The New England Journal of Medicine. When asked by Nature about this emerging virus that has until now flown under the radar, scientists said that they were not overly concerned because the virus doesn’t seem to spread easily between people nor is it fatal.
Researchers think that the virus is carried by shrews. It might have infected people directly or through an intermediate animal.
First identified in Langya
The authors describe 35 cases of infection with a virus called Langya henipavirus (LayV) since 2018. It is closely related to two other henipaviruses known to infect people – Hendra virus and Nipah virus. The virus was named Langya after the town in Shandong province in China where the first patient identified with the disease was from, explained coauthor Linfa Wang, PhD, a virologist at Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore.
Langya can cause respiratory symptoms such as fever, cough, and fatigue. Hendra virus and Nipah virus also cause respiratory infections and can be fatal, the article in Nature reports.
Hendra and Nipah
According to the World Health Organization, Nipah virus, which was discovered in 1999, is a new virus responsible for a zoonosis that causes the disease in animals and humans who have had contact with infected animals. Its name comes from the location where it was first identified in Malaysia. Patients may have asymptomatic infection or symptoms such as acute respiratory infection and severe encephalitis. The case fatality rate is between 40% and 75%.
Nipah virus is closely related to another recently discovered (1994) zoonotic virus called Hendra virus, which is named after the Australian city in which it first appeared. On that day in July 2016, 53 cases were identified involving 70 horses. These incidents remained confined to the northeastern coast of Australia.
Nipah virus and Hendra virus belong to the Paramyxoviridae family. “While the members of this group of viruses are only responsible for a few limited outbreaks, the ability of these viruses to infect a wide range of hosts and cause a disease leading to high fatalities in humans has made them a public health concern,” stated the WHO.
Related to measles
The research team identified LayV while monitoring patients at three hospitals in the eastern Chinese provinces of Shandong and Henan between April 2018 and August 2021. Throughout the study period, the researchers found 35 people infected with LayV, mostly farmers, with symptoms ranging from a cough to severe pneumonia. Participants were recruited into the study if they had a fever. The team sequenced the LayV genome from a throat swab taken from the first patient identified with the disease, a 53-year-old woman.
The LayV genome showed that the virus is most closely related to Mojiang henipavirus, which was first isolated in rats in an abandoned mine in the southern Chinese province of Yunnan in 2012. Henipaviruses belong to the Paramyxoviridae family of viruses, which includes measles, mumps, and many respiratory viruses that infect humans. Several other henipaviruses have been discovered in bats, rats, and shrews from Australia to South Korea and China, but only Hendra, Nipah, and now LayV are known to infect people, according to Nature.
Animal origin likely
Because most patients stated in a questionnaire that they had been exposed to an animal during the month preceding the onset of their symptoms, the researchers tested goats, dogs, pigs, and cattle living in the villages of infected patients for antibodies against LayV. They found LayV antibodies in a handful of goats and dogs and identified LayV viral RNA in 27% of the 262 sampled shrews. These findings suggest that the shrew may be a natural reservoir of LayV, passing it between themselves “and somehow infecting people here and there by chance,” Emily Gurley, PhD, MPH, an infectious diseases epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, told Nature.
The researchers did not find strong evidence of LayV spreading between the people included in the study. There were no clusters of cases in the same family, within a short time span, or in close geographical proximity. “Of the 35 cases, not a single one is linked,” said Dr. Wang, which Dr. Gurley considered good news. It should be noted, however ,”that the study did retrospective contact tracing on only 15 family members of nine infected individuals, which makes it difficult to determine how exactly the individuals were exposed,” reported Nature.
Vigilance is needed
Should we be worried about a potential new epidemic? The replies from two experts interviewed by Nature were reassuring. “There is no particular need to worry about this virus, but ongoing surveillance is critical,” said Professor Edward Holmes, an evolutionary virologist at the University of Sydney. Regularly testing people and animals for emerging viruses is important to understand the risk for zoonotic diseases – those that can be transmitted from other animals to humans, he said.
It is still not clear how people were infected in the first place – whether directly from shrews or an intermediate animal, said Dr. Gurley. That’s why a lot of research still needs to be done to work out how the virus is spreading in shrews and how people are getting infected, she added.
Nevertheless, Dr. Gurley finds that large outbreaks of infectious diseases typically take off after a lot of false starts. “If we are actively looking for those sparks, then we are in a much better position to stop or to find something early.” Still, she noted that she didn’t see anything in the data to “cause alarm from a pandemic-threat perspective.”
Though there is not currently any cause for worry of a new pandemic, vigilance is crucial. Professor Holmes says there is an urgent need for a global surveillance system to detect virus spillovers and rapidly communicate those results to avoid more pandemics, such as the one sparked by COVID-19. “These sorts of zoonotic spillover events happen all the time,” he said. “The world needs to wake up.”
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE