User login
In Case You Missed It: COVID
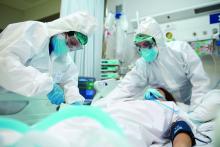
COVID exposure risk outside of work increasing for clinicians
One-third of COVID-19 exposures among health care providers (HCPs) in Minnesota are caused by family or community exposure, not patient care, according to a study conducted by the Minnesota Department of Health and published online Oct. 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. And nonwork exposures were more likely to lead to COVID-19 infections.
Between March 6 and July 11, 2020, researchers with the Minnesota Department of Health evaluated 21,406 incidences of HCP exposure to confirmed COVID-19 cases. Of those, 5,374 (25%) were classified as higher-risk exposures, meaning the provider had close contact for 15 minutes or more, or during an aerosol-generating procedure.
Two-thirds (66%) of the higher-risk exposures occurred during direct patient care and 34% were related to nonpatient care interactions (e.g., coworkers and social and household contacts). Overall, 6.9% (373) of the HCPs with a higher-risk exposure received a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result within 14 days of the exposure. Notably, HCPs with household or social exposure had the highest positivity rate across all exposure types at 13%.
“Since the time period covered in this report, we’ve seen a significant increase in the proportion of HCPs who have had higher-risk exposures outside of work due to household or social contacts,” said lead author Ashley Fell, MPH, from the Minnesota Department of Health.
“HCPs with household or social exposures are also more likely to test positive than HCPs with higher risk exposures within the healthcare setting, which is an important message for both HCPs and the community at large that more COVID-19 spreading in our communities poses a greater risk to our HCPs and health care system,” Ms. Fell said in an interview.
When evaluating personal protective equipment use among exposed HCPs, researchers found that 90% of providers in acute or ambulatory care were wearing a respirator or medical-grade face mask at time of exposure, compared with just 68% of HCPs working in congregate living or long-term care facilities.
Further, investigators found that an HCP with a positive SARS-CoV-2 test working in a congregate living or long-term care facility resulted in exposure of a median of three additional HCPs (interquartile range, 1-6), compared with a median of one additional HCP exposure in acute or ambulatory care (IQR, 1-3).
The researchers also found that, compared with HCPs in acute or ambulatory settings, HCPs working in long-term care or congregate living settings were more likely to return to work following a high-risk exposure (57% vs. 37%) and work while symptomatic (4.8% vs. 1.3%).
When asked whether these findings apply to HCPs in other states, Andrew T. Chan, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, noted: “These data are not surprising and confirm what many of us have been seeing in our own areas.
“Clearly, the risk of contracting COVID-19 is particularly high for frontline health care workers in long-term care facilities and nursing homes,” Dr. Chan said.
“Furthermore, the infection control practices in these care settings are often not as rigorous, and together these factors are probably contributing to higher risks of infection,” he said.
The authors acknowledged potential study limitations including misclassification of HCP risk for exposure or misclassification of community exposure as workplace exposure.
“We also recognize that HCPs, like the rest of the community, are experiencing COVID fatigue and that facilities have to constantly be innovative and vigilant to help HCPs maintain rigorous safety precautions with their patients and around their colleagues,” Ms. Fell concluded.
The authors and Dr. Chan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
For the latest clinical guidance, education, research and physician resources about coronavirus, visit the AGA COVID-19 Resource Center at www.gastro.org/COVID.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One-third of COVID-19 exposures among health care providers (HCPs) in Minnesota are caused by family or community exposure, not patient care, according to a study conducted by the Minnesota Department of Health and published online Oct. 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. And nonwork exposures were more likely to lead to COVID-19 infections.
Between March 6 and July 11, 2020, researchers with the Minnesota Department of Health evaluated 21,406 incidences of HCP exposure to confirmed COVID-19 cases. Of those, 5,374 (25%) were classified as higher-risk exposures, meaning the provider had close contact for 15 minutes or more, or during an aerosol-generating procedure.
Two-thirds (66%) of the higher-risk exposures occurred during direct patient care and 34% were related to nonpatient care interactions (e.g., coworkers and social and household contacts). Overall, 6.9% (373) of the HCPs with a higher-risk exposure received a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result within 14 days of the exposure. Notably, HCPs with household or social exposure had the highest positivity rate across all exposure types at 13%.
“Since the time period covered in this report, we’ve seen a significant increase in the proportion of HCPs who have had higher-risk exposures outside of work due to household or social contacts,” said lead author Ashley Fell, MPH, from the Minnesota Department of Health.
“HCPs with household or social exposures are also more likely to test positive than HCPs with higher risk exposures within the healthcare setting, which is an important message for both HCPs and the community at large that more COVID-19 spreading in our communities poses a greater risk to our HCPs and health care system,” Ms. Fell said in an interview.
When evaluating personal protective equipment use among exposed HCPs, researchers found that 90% of providers in acute or ambulatory care were wearing a respirator or medical-grade face mask at time of exposure, compared with just 68% of HCPs working in congregate living or long-term care facilities.
Further, investigators found that an HCP with a positive SARS-CoV-2 test working in a congregate living or long-term care facility resulted in exposure of a median of three additional HCPs (interquartile range, 1-6), compared with a median of one additional HCP exposure in acute or ambulatory care (IQR, 1-3).
The researchers also found that, compared with HCPs in acute or ambulatory settings, HCPs working in long-term care or congregate living settings were more likely to return to work following a high-risk exposure (57% vs. 37%) and work while symptomatic (4.8% vs. 1.3%).
When asked whether these findings apply to HCPs in other states, Andrew T. Chan, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, noted: “These data are not surprising and confirm what many of us have been seeing in our own areas.
“Clearly, the risk of contracting COVID-19 is particularly high for frontline health care workers in long-term care facilities and nursing homes,” Dr. Chan said.
“Furthermore, the infection control practices in these care settings are often not as rigorous, and together these factors are probably contributing to higher risks of infection,” he said.
The authors acknowledged potential study limitations including misclassification of HCP risk for exposure or misclassification of community exposure as workplace exposure.
“We also recognize that HCPs, like the rest of the community, are experiencing COVID fatigue and that facilities have to constantly be innovative and vigilant to help HCPs maintain rigorous safety precautions with their patients and around their colleagues,” Ms. Fell concluded.
The authors and Dr. Chan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
For the latest clinical guidance, education, research and physician resources about coronavirus, visit the AGA COVID-19 Resource Center at www.gastro.org/COVID.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One-third of COVID-19 exposures among health care providers (HCPs) in Minnesota are caused by family or community exposure, not patient care, according to a study conducted by the Minnesota Department of Health and published online Oct. 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. And nonwork exposures were more likely to lead to COVID-19 infections.
Between March 6 and July 11, 2020, researchers with the Minnesota Department of Health evaluated 21,406 incidences of HCP exposure to confirmed COVID-19 cases. Of those, 5,374 (25%) were classified as higher-risk exposures, meaning the provider had close contact for 15 minutes or more, or during an aerosol-generating procedure.
Two-thirds (66%) of the higher-risk exposures occurred during direct patient care and 34% were related to nonpatient care interactions (e.g., coworkers and social and household contacts). Overall, 6.9% (373) of the HCPs with a higher-risk exposure received a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result within 14 days of the exposure. Notably, HCPs with household or social exposure had the highest positivity rate across all exposure types at 13%.
“Since the time period covered in this report, we’ve seen a significant increase in the proportion of HCPs who have had higher-risk exposures outside of work due to household or social contacts,” said lead author Ashley Fell, MPH, from the Minnesota Department of Health.
“HCPs with household or social exposures are also more likely to test positive than HCPs with higher risk exposures within the healthcare setting, which is an important message for both HCPs and the community at large that more COVID-19 spreading in our communities poses a greater risk to our HCPs and health care system,” Ms. Fell said in an interview.
When evaluating personal protective equipment use among exposed HCPs, researchers found that 90% of providers in acute or ambulatory care were wearing a respirator or medical-grade face mask at time of exposure, compared with just 68% of HCPs working in congregate living or long-term care facilities.
Further, investigators found that an HCP with a positive SARS-CoV-2 test working in a congregate living or long-term care facility resulted in exposure of a median of three additional HCPs (interquartile range, 1-6), compared with a median of one additional HCP exposure in acute or ambulatory care (IQR, 1-3).
The researchers also found that, compared with HCPs in acute or ambulatory settings, HCPs working in long-term care or congregate living settings were more likely to return to work following a high-risk exposure (57% vs. 37%) and work while symptomatic (4.8% vs. 1.3%).
When asked whether these findings apply to HCPs in other states, Andrew T. Chan, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, noted: “These data are not surprising and confirm what many of us have been seeing in our own areas.
“Clearly, the risk of contracting COVID-19 is particularly high for frontline health care workers in long-term care facilities and nursing homes,” Dr. Chan said.
“Furthermore, the infection control practices in these care settings are often not as rigorous, and together these factors are probably contributing to higher risks of infection,” he said.
The authors acknowledged potential study limitations including misclassification of HCP risk for exposure or misclassification of community exposure as workplace exposure.
“We also recognize that HCPs, like the rest of the community, are experiencing COVID fatigue and that facilities have to constantly be innovative and vigilant to help HCPs maintain rigorous safety precautions with their patients and around their colleagues,” Ms. Fell concluded.
The authors and Dr. Chan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
For the latest clinical guidance, education, research and physician resources about coronavirus, visit the AGA COVID-19 Resource Center at www.gastro.org/COVID.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA authorizes baricitinib combo for COVID-19
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Nov. 19 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Janus kinase inhibitor baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly) in combination with remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead) for treating hospitalized adults and children at least 2 years old with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
The combination treatment is meant for patients who need supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Baricitinib/remdesivir was shown in a clinical trial to reduce time to recovery within 29 days of starting the treatment compared with a control group who received placebo/remdesivir, according to the FDA press release.
The median time to recovery from COVID-19 was 7 days for the combination group vs. 8 days for those in the placebo/remdesivir group. Recovery was defined as either discharge from the hospital or “being hospitalized but not requiring supplemental oxygen and no longer requiring ongoing medical care,” the agency explained in the press release.
The odds of a patient dying or being ventilated at day 29 was lower in the combination group compared with those taking placebo/remdesivir, the press release said without providing specific data. “For all of these endpoints, the effects were statistically significant,” the agency stated.
The safety and efficacy continues to be evaluated. Baricitinib alone is not approved as a treatment for COVID-19.
“The FDA’s emergency authorization of this combination therapy represents an incremental step forward in the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients, and FDA’s first authorization of a drug that acts on the inflammation pathway,” said Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, acting director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“Despite advances in the management of COVID-19 infection since the onset of the pandemic, we need more therapies to accelerate recovery and additional clinical research will be essential to identifying therapies that slow disease progression and lower mortality in the sicker patients,” she said.
As a JAK inhibitor, baricitinib interferes with a pathway that leads to inflammation. Baricitinib is already prescribed as an oral medication and is FDA-approved for treating moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis.
The data supporting the EUA for the combination treatment are based on a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (ACTT-2), conducted by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
The trial followed patients for 29 days and included 1,033 patients with moderate to severe COVID-19; 515 patients received baricitinib/remdesivir, and 518 patients received placebo/remdesivir.
The FDA emphasizes that an EUA is not a full FDA approval.
In reviewing the combination, the FDA “determined that it is reasonable to believe that baricitinib, in combination with remdesivir, may be effective in treating COVID-19 for the authorized population” and the known benefits outweigh the known and potential risks. Additionally, there are no adequate, approved, and available alternatives for the treatment population.
“Today’s action demonstrates the FDA’s steadfast efforts to make potential COVID-19 treatments available in a timely manner, where appropriate, while continuing to support research to further evaluate whether they are safe and effective,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD. “As part of our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA continues to use every possible avenue to facilitate new treatments for patients as quickly as possible to combat COVID-19.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Nov. 19 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Janus kinase inhibitor baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly) in combination with remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead) for treating hospitalized adults and children at least 2 years old with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
The combination treatment is meant for patients who need supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Baricitinib/remdesivir was shown in a clinical trial to reduce time to recovery within 29 days of starting the treatment compared with a control group who received placebo/remdesivir, according to the FDA press release.
The median time to recovery from COVID-19 was 7 days for the combination group vs. 8 days for those in the placebo/remdesivir group. Recovery was defined as either discharge from the hospital or “being hospitalized but not requiring supplemental oxygen and no longer requiring ongoing medical care,” the agency explained in the press release.
The odds of a patient dying or being ventilated at day 29 was lower in the combination group compared with those taking placebo/remdesivir, the press release said without providing specific data. “For all of these endpoints, the effects were statistically significant,” the agency stated.
The safety and efficacy continues to be evaluated. Baricitinib alone is not approved as a treatment for COVID-19.
“The FDA’s emergency authorization of this combination therapy represents an incremental step forward in the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients, and FDA’s first authorization of a drug that acts on the inflammation pathway,” said Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, acting director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“Despite advances in the management of COVID-19 infection since the onset of the pandemic, we need more therapies to accelerate recovery and additional clinical research will be essential to identifying therapies that slow disease progression and lower mortality in the sicker patients,” she said.
As a JAK inhibitor, baricitinib interferes with a pathway that leads to inflammation. Baricitinib is already prescribed as an oral medication and is FDA-approved for treating moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis.
The data supporting the EUA for the combination treatment are based on a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (ACTT-2), conducted by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
The trial followed patients for 29 days and included 1,033 patients with moderate to severe COVID-19; 515 patients received baricitinib/remdesivir, and 518 patients received placebo/remdesivir.
The FDA emphasizes that an EUA is not a full FDA approval.
In reviewing the combination, the FDA “determined that it is reasonable to believe that baricitinib, in combination with remdesivir, may be effective in treating COVID-19 for the authorized population” and the known benefits outweigh the known and potential risks. Additionally, there are no adequate, approved, and available alternatives for the treatment population.
“Today’s action demonstrates the FDA’s steadfast efforts to make potential COVID-19 treatments available in a timely manner, where appropriate, while continuing to support research to further evaluate whether they are safe and effective,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD. “As part of our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA continues to use every possible avenue to facilitate new treatments for patients as quickly as possible to combat COVID-19.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Nov. 19 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Janus kinase inhibitor baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly) in combination with remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead) for treating hospitalized adults and children at least 2 years old with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
The combination treatment is meant for patients who need supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Baricitinib/remdesivir was shown in a clinical trial to reduce time to recovery within 29 days of starting the treatment compared with a control group who received placebo/remdesivir, according to the FDA press release.
The median time to recovery from COVID-19 was 7 days for the combination group vs. 8 days for those in the placebo/remdesivir group. Recovery was defined as either discharge from the hospital or “being hospitalized but not requiring supplemental oxygen and no longer requiring ongoing medical care,” the agency explained in the press release.
The odds of a patient dying or being ventilated at day 29 was lower in the combination group compared with those taking placebo/remdesivir, the press release said without providing specific data. “For all of these endpoints, the effects were statistically significant,” the agency stated.
The safety and efficacy continues to be evaluated. Baricitinib alone is not approved as a treatment for COVID-19.
“The FDA’s emergency authorization of this combination therapy represents an incremental step forward in the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients, and FDA’s first authorization of a drug that acts on the inflammation pathway,” said Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, acting director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“Despite advances in the management of COVID-19 infection since the onset of the pandemic, we need more therapies to accelerate recovery and additional clinical research will be essential to identifying therapies that slow disease progression and lower mortality in the sicker patients,” she said.
As a JAK inhibitor, baricitinib interferes with a pathway that leads to inflammation. Baricitinib is already prescribed as an oral medication and is FDA-approved for treating moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis.
The data supporting the EUA for the combination treatment are based on a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (ACTT-2), conducted by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
The trial followed patients for 29 days and included 1,033 patients with moderate to severe COVID-19; 515 patients received baricitinib/remdesivir, and 518 patients received placebo/remdesivir.
The FDA emphasizes that an EUA is not a full FDA approval.
In reviewing the combination, the FDA “determined that it is reasonable to believe that baricitinib, in combination with remdesivir, may be effective in treating COVID-19 for the authorized population” and the known benefits outweigh the known and potential risks. Additionally, there are no adequate, approved, and available alternatives for the treatment population.
“Today’s action demonstrates the FDA’s steadfast efforts to make potential COVID-19 treatments available in a timely manner, where appropriate, while continuing to support research to further evaluate whether they are safe and effective,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD. “As part of our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA continues to use every possible avenue to facilitate new treatments for patients as quickly as possible to combat COVID-19.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The pandemic experience through the eyes of APPs
The evolution of hospitalist advanced practice providers
Throughout the chaos of the COVID-19 pandemic, advanced practice providers (APPs) – physician assistants (PAs) and nurse practitioners (NPs) – have become an integral component of the hospitalist response. As many physicians began shifting into telemedicine and away from direct patient care, APPs have been eagerly jumping in to fill the gaps. Their work has been changing almost as dramatically and quickly as the pandemic itself, bringing with it expected challenges but bestowing hugely satisfying, often unanticipated, rewards.
APPs on the rise
As the coronavirus pandemic evolves, the role of APPs is evolving right alongside it. With the current relaxation of hospital bylaw restrictions on APPs, their utilization has increased, said Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM, a nurse practitioner and vice president of advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians. “We have not really furloughed any advanced practice providers,” Ms. Cardin said. “In fact, I consider them to be, within hospital medicine, a key lever to finding more cost-effective care delivery models.”
Ms. Cardin said APPs have been working more independently since COVID-19 started, seeing patients on their own and using physician consultation and backup via telemedicine or telephone as needed. With the reduction in elective surgeries and patient volumes at many hospitals, APP-led care also saves money. Because one of the biggest costs is labor, Ms. Cardin said, offering this high-quality care delivery model using APPs in collaboration with physician providers helps defray some of that cost. “We’re hoping that advanced practice providers are really a solution to some of these financial pressures in a lot of different ways,” she said.
“COVID … forced us to expedite conversations about how to maximize caseloads using APPs,” said Alicia Sheffer, AGAC-AGPC NP, a nurse practitioner and Great Lakes regional director of advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians in Cincinnati. Some of those staffing model changes have included using APPs while transitioning ICUs and med-surg units to COVID cohort units, APP-led COVID cohorts, and APP-led ICUs.
“At first the hospital system had ideas about bringing in telemedicine as an alternative to seeing patients, rather than just putting APPs on the front lines and having them go in and see patients,” said Jessica Drane, APRN, PhD, DNP FNP-C, a nurse practitioner and regional director of advanced practice provider services and hospital medicine at Sound Physicians in San Antonio. In Texas at the beginning of the pandemic, hospital numbers were so low that Dr. Drane did not work at all in April. “We were all afraid we were going to lose our jobs,” she said. Then the state got slammed and APPs have been desperately needed.
Ilaria Gadalla, DMSc, PA-C, a PA at Treasure Coast Hospitalists in Port St. Lucie, Fla., and the PA program director at South University, West Palm Beach, Fla., noted that many of her APP colleagues have pivoted fluidly from other specialties to the hospitalist realm as the need for frontline workers has increased. “Hospitalists have shined through this and their value has been recognized even more than previously as a result of COVID-19,” Dr. Gadalla said.
“I don’t think it’s any surprise that hospitalists became a pillar of the COVID pandemic,” said Bridget McGrath, PA-C, a physician assistant and director of the NP/PAs service line for the section of hospital medicine at the University of Chicago. “There are just some innate traits that hospitalists have, such as the ability to be flexible, to problem solve, and to be the solution to the problem.”
Building team camaraderie
Ms. Cardin says that the need for APPs has led to an evolving integration between physicians and APPs. The growing teamwork and bonding between colleagues have been some of the most rewarding aspects of the pandemic for Dr. Gadalla. “We rely even more on each other and there isn’t really a line of, ‘I’m a physician versus an NP or PA or nurse.’ We’re all working together with the same goal,” she said.
Ms. McGrath said she has been learning what it means to lead a team during a challenging time. It has been gratifying for her to watch mentors get down to the bare bones of patient care and see everyone unify, putting aside roles and titles and coming together to care for their patients in innovative ways.
“This pandemic has really opened up a lot of doors for us because up until now, we were used almost like scribes for physicians,” Dr. Drane said. She has seen even the most resistant hospital systems beginning to rely on APPs as the pandemic has progressed. “They have become pleasantly surprised at what an APP can do.”
Work challenges
Obviously, challenges abound. Dr. Gadalla listed hers as visiting restrictions that invariably lead to slower patient visits thanks to obligatory phone calls, constantly fluctuating patient censuses, sporadic elective surgeries, watching colleagues become furloughed, and trying to balance external perceptions with what’s actually happening in the hospital.
Overall, though, “There have been a lot more rewards than barriers,” added Dr. Drane.
One of the biggest obstacles for health care workers navigating a pandemic is balancing work and home life, not to mention having time to unwind while working long hours. “Finding time for my family has been very limited. My kids feel really neglected,” said Dr. Gadalla. Some days, she gets up extra early to exercise to help clear her head, but other times she’s just too exhausted to even move.
Dr. Drane agreed that the work can get overwhelming. “We’re changing the way we practice almost every week, which can make you doubt yourself as an educator, as a practitioner. You constantly feel like you’re not sure what you’re doing, and people trust you to heal them,” she said. “Today is my first day off in 24 days. I only got it off because I said I needed a moment.”
Ms. Sheffer’s crazy days were at the beginning of the pandemic when she had to self-quarantine from her family and was working nonstop. “I would come home and sleep and work and wake up in the middle of the night and double check and triple check and go back to sleep and work, and that consumed me for several months,” she said.
The biggest challenge for Ms. Sheffer has been coping with public fear. “No matter how logical our medical approach has been, I think the constant feeling of the public threat of COVID has had this insidious effect on how patients approach their health,” she said. “We’re spending a lot more time shaping our approach to best address their fears first and not to politicize COVID so we can actually deal with the health issue at hand.”
Complications of COVID
With all the restrictions, caring for patients these days has meant learning to interact with them in different ways that aren’t as personal, Ms. McGrath said. It has been difficult to lose “that humanity of medicine, the usual ways that you interact with your patients that are going through a vulnerable time,” she noted.
Additionally, students in the medical field are being held back from graduation because they cannot participate in direct patient care. This is particularly problematic for PAs and medical students who must touch patients to graduate, Dr. Gadalla said. “All of this is slowing down future providers. We’re going to have trouble catching up. Who’s going to relieve us? That’s a huge problem and no one is finding solutions for that yet,” she said.
At the University of Chicago, Ms. McGrath explained, they created virtual rotations so that PA students could continue to do them at the university. Not only has the experience reminded Ms. McGrath how much she loves being a medical educator and fighting for the education of PA students, but she was surprised to find that her patients came to appreciate the time they spent with her students on the virtual platform as well.
“It’s isolating for patients to be in the hospital in a vulnerable state and with no support system,” she said. “I think being a part of [the PA students’] education gave some meaning to their hospitalization and highlighted that collaboration and connection is a human need.”
Despite everything, there’s a noticeable emphasis on the flowering buds of hope, unity, compassion, and pride that have been quietly blooming from the daily hardships. As Ms. Cardin puts it, “It’s so cliché to say that there’s a crisis. The other word is ‘opportunity,’ and it’s true, there are opportunities here.”
Taking care of each other
Creating resources for providers has been a priority at the University of Chicago, according to Ms. McGrath. “As hospitalists, we’re used to taking care of a variety of patients, but our section leadership and providers on the front lines quickly realized that COVID patients are more akin to trauma patients with their quick changes in health, as well as their isolation, fear, and unexpected deterioration,” she said. Her facility has implemented wellness initiatives to help prevent burnout and mental health problems in COVID providers so they can continue to give the best care to their patients.
Both Ms. Sheffer and Dr. Drane say that they have a peer network of APPs at Sound Physicians to call on for questions and support. And it’s encouraging to know you’re not alone and to keep tabs on how colleagues in other states are doing, Ms. Sheffer noted.
“The peer support system has been helpful,” Dr. Drane said. “This job, right now, takes pieces of you every day. Sometimes it’s so emotional that you can’t put it into words. You just have to cry and get it out so that you can go be with your family.”
Getting back to basics
The changes in patient care have turned into something Ms. McGrath said she appreciates. “This pandemic has really stripped away the extra fluff of medicine and brought us back to the reason why many of us have gotten into the field, because it became about the patients again,” she says. “You quickly learn your strengths and weaknesses as a provider and as a leader, and that flows into the decisions you’re making for your team and for your patients.”
Ms. Sheffer acknowledged that it is difficult to deal with patients’ family members who don’t understand that they can’t visit their sick relatives, but she said the flip side is that frontline workers become surrogate family members, an outcome she considers to be an honor.
“You step into the emotion with the family or with the patient because you’re all they have. That is a beautiful, honorable role, but it’s also tremendously emotional and sometimes devastating,” she said. “But to me, it’s one of the most beautiful things I’ve been able to offer in a time where we don’t even know what to do with COVID.”
Limited resources mixed with a healthy dose of fear can stifle creativity, Dr. Drane said. Right away, she noticed that despite the abundance of incentive spirometers at her hospital, they were not being utilized. She came in 2 hours early for 3 days to pass one out to every patient under investigation or COVID-positive patient and enlisted the help of her chief nursing officer, CEO, and regional medical director to get everyone on board.
Dr. Drane’s out-of-the-box thinking has enabled people to go home without oxygen 2 days earlier and cut the hospital’s length of stay by 5%. “It’s something so small, but it has such a great end reward,” she said. “I’m proud of this project because it didn’t take money; it was getting creative with what we already have.”
Renewed pride and passion
Dr. Drane is intensely proud of being an NP and working on the front lines. She sees that the pandemic has encouraged her and other APPs to expand their horizons.
“For me, it’s made me work to get dual certified,” she said. “APPs can be all-inclusive. I feel like I’m doing what I was meant to do and it’s not just a job anymore.”
Ms. McGrath is even more passionate about being a hospitalist now, as she has realized how valuable their unique skill sets are. “I think other people have also been able to realize that our ability to see the patient as a whole has allowed us to take care of this pandemic, because this disease impacts all organ systems and has a trickle-down effect that we as hospitalists are well versed to manage,” she said.
Ms. Cardin’s work involves communicating with APPs all around the country. Recently she had a phone exchange with an APP who needed to vent.
“She was weeping, and I thought she was going to say, ‘I can’t do this anymore, I need to go home,’ ” said Ms. Cardin. “Instead, she said, ‘I just want to make a difference in one of these people’s lives.’ And that is who the advanced practice providers are. They’re willing to go into those COVID units. They’re willing to be in the front lines. They are dedicated. They’re just intensely inspirational to me.”
The evolution of hospitalist advanced practice providers
The evolution of hospitalist advanced practice providers
Throughout the chaos of the COVID-19 pandemic, advanced practice providers (APPs) – physician assistants (PAs) and nurse practitioners (NPs) – have become an integral component of the hospitalist response. As many physicians began shifting into telemedicine and away from direct patient care, APPs have been eagerly jumping in to fill the gaps. Their work has been changing almost as dramatically and quickly as the pandemic itself, bringing with it expected challenges but bestowing hugely satisfying, often unanticipated, rewards.
APPs on the rise
As the coronavirus pandemic evolves, the role of APPs is evolving right alongside it. With the current relaxation of hospital bylaw restrictions on APPs, their utilization has increased, said Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM, a nurse practitioner and vice president of advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians. “We have not really furloughed any advanced practice providers,” Ms. Cardin said. “In fact, I consider them to be, within hospital medicine, a key lever to finding more cost-effective care delivery models.”
Ms. Cardin said APPs have been working more independently since COVID-19 started, seeing patients on their own and using physician consultation and backup via telemedicine or telephone as needed. With the reduction in elective surgeries and patient volumes at many hospitals, APP-led care also saves money. Because one of the biggest costs is labor, Ms. Cardin said, offering this high-quality care delivery model using APPs in collaboration with physician providers helps defray some of that cost. “We’re hoping that advanced practice providers are really a solution to some of these financial pressures in a lot of different ways,” she said.
“COVID … forced us to expedite conversations about how to maximize caseloads using APPs,” said Alicia Sheffer, AGAC-AGPC NP, a nurse practitioner and Great Lakes regional director of advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians in Cincinnati. Some of those staffing model changes have included using APPs while transitioning ICUs and med-surg units to COVID cohort units, APP-led COVID cohorts, and APP-led ICUs.
“At first the hospital system had ideas about bringing in telemedicine as an alternative to seeing patients, rather than just putting APPs on the front lines and having them go in and see patients,” said Jessica Drane, APRN, PhD, DNP FNP-C, a nurse practitioner and regional director of advanced practice provider services and hospital medicine at Sound Physicians in San Antonio. In Texas at the beginning of the pandemic, hospital numbers were so low that Dr. Drane did not work at all in April. “We were all afraid we were going to lose our jobs,” she said. Then the state got slammed and APPs have been desperately needed.
Ilaria Gadalla, DMSc, PA-C, a PA at Treasure Coast Hospitalists in Port St. Lucie, Fla., and the PA program director at South University, West Palm Beach, Fla., noted that many of her APP colleagues have pivoted fluidly from other specialties to the hospitalist realm as the need for frontline workers has increased. “Hospitalists have shined through this and their value has been recognized even more than previously as a result of COVID-19,” Dr. Gadalla said.
“I don’t think it’s any surprise that hospitalists became a pillar of the COVID pandemic,” said Bridget McGrath, PA-C, a physician assistant and director of the NP/PAs service line for the section of hospital medicine at the University of Chicago. “There are just some innate traits that hospitalists have, such as the ability to be flexible, to problem solve, and to be the solution to the problem.”
Building team camaraderie
Ms. Cardin says that the need for APPs has led to an evolving integration between physicians and APPs. The growing teamwork and bonding between colleagues have been some of the most rewarding aspects of the pandemic for Dr. Gadalla. “We rely even more on each other and there isn’t really a line of, ‘I’m a physician versus an NP or PA or nurse.’ We’re all working together with the same goal,” she said.
Ms. McGrath said she has been learning what it means to lead a team during a challenging time. It has been gratifying for her to watch mentors get down to the bare bones of patient care and see everyone unify, putting aside roles and titles and coming together to care for their patients in innovative ways.
“This pandemic has really opened up a lot of doors for us because up until now, we were used almost like scribes for physicians,” Dr. Drane said. She has seen even the most resistant hospital systems beginning to rely on APPs as the pandemic has progressed. “They have become pleasantly surprised at what an APP can do.”
Work challenges
Obviously, challenges abound. Dr. Gadalla listed hers as visiting restrictions that invariably lead to slower patient visits thanks to obligatory phone calls, constantly fluctuating patient censuses, sporadic elective surgeries, watching colleagues become furloughed, and trying to balance external perceptions with what’s actually happening in the hospital.
Overall, though, “There have been a lot more rewards than barriers,” added Dr. Drane.
One of the biggest obstacles for health care workers navigating a pandemic is balancing work and home life, not to mention having time to unwind while working long hours. “Finding time for my family has been very limited. My kids feel really neglected,” said Dr. Gadalla. Some days, she gets up extra early to exercise to help clear her head, but other times she’s just too exhausted to even move.
Dr. Drane agreed that the work can get overwhelming. “We’re changing the way we practice almost every week, which can make you doubt yourself as an educator, as a practitioner. You constantly feel like you’re not sure what you’re doing, and people trust you to heal them,” she said. “Today is my first day off in 24 days. I only got it off because I said I needed a moment.”
Ms. Sheffer’s crazy days were at the beginning of the pandemic when she had to self-quarantine from her family and was working nonstop. “I would come home and sleep and work and wake up in the middle of the night and double check and triple check and go back to sleep and work, and that consumed me for several months,” she said.
The biggest challenge for Ms. Sheffer has been coping with public fear. “No matter how logical our medical approach has been, I think the constant feeling of the public threat of COVID has had this insidious effect on how patients approach their health,” she said. “We’re spending a lot more time shaping our approach to best address their fears first and not to politicize COVID so we can actually deal with the health issue at hand.”
Complications of COVID
With all the restrictions, caring for patients these days has meant learning to interact with them in different ways that aren’t as personal, Ms. McGrath said. It has been difficult to lose “that humanity of medicine, the usual ways that you interact with your patients that are going through a vulnerable time,” she noted.
Additionally, students in the medical field are being held back from graduation because they cannot participate in direct patient care. This is particularly problematic for PAs and medical students who must touch patients to graduate, Dr. Gadalla said. “All of this is slowing down future providers. We’re going to have trouble catching up. Who’s going to relieve us? That’s a huge problem and no one is finding solutions for that yet,” she said.
At the University of Chicago, Ms. McGrath explained, they created virtual rotations so that PA students could continue to do them at the university. Not only has the experience reminded Ms. McGrath how much she loves being a medical educator and fighting for the education of PA students, but she was surprised to find that her patients came to appreciate the time they spent with her students on the virtual platform as well.
“It’s isolating for patients to be in the hospital in a vulnerable state and with no support system,” she said. “I think being a part of [the PA students’] education gave some meaning to their hospitalization and highlighted that collaboration and connection is a human need.”
Despite everything, there’s a noticeable emphasis on the flowering buds of hope, unity, compassion, and pride that have been quietly blooming from the daily hardships. As Ms. Cardin puts it, “It’s so cliché to say that there’s a crisis. The other word is ‘opportunity,’ and it’s true, there are opportunities here.”
Taking care of each other
Creating resources for providers has been a priority at the University of Chicago, according to Ms. McGrath. “As hospitalists, we’re used to taking care of a variety of patients, but our section leadership and providers on the front lines quickly realized that COVID patients are more akin to trauma patients with their quick changes in health, as well as their isolation, fear, and unexpected deterioration,” she said. Her facility has implemented wellness initiatives to help prevent burnout and mental health problems in COVID providers so they can continue to give the best care to their patients.
Both Ms. Sheffer and Dr. Drane say that they have a peer network of APPs at Sound Physicians to call on for questions and support. And it’s encouraging to know you’re not alone and to keep tabs on how colleagues in other states are doing, Ms. Sheffer noted.
“The peer support system has been helpful,” Dr. Drane said. “This job, right now, takes pieces of you every day. Sometimes it’s so emotional that you can’t put it into words. You just have to cry and get it out so that you can go be with your family.”
Getting back to basics
The changes in patient care have turned into something Ms. McGrath said she appreciates. “This pandemic has really stripped away the extra fluff of medicine and brought us back to the reason why many of us have gotten into the field, because it became about the patients again,” she says. “You quickly learn your strengths and weaknesses as a provider and as a leader, and that flows into the decisions you’re making for your team and for your patients.”
Ms. Sheffer acknowledged that it is difficult to deal with patients’ family members who don’t understand that they can’t visit their sick relatives, but she said the flip side is that frontline workers become surrogate family members, an outcome she considers to be an honor.
“You step into the emotion with the family or with the patient because you’re all they have. That is a beautiful, honorable role, but it’s also tremendously emotional and sometimes devastating,” she said. “But to me, it’s one of the most beautiful things I’ve been able to offer in a time where we don’t even know what to do with COVID.”
Limited resources mixed with a healthy dose of fear can stifle creativity, Dr. Drane said. Right away, she noticed that despite the abundance of incentive spirometers at her hospital, they were not being utilized. She came in 2 hours early for 3 days to pass one out to every patient under investigation or COVID-positive patient and enlisted the help of her chief nursing officer, CEO, and regional medical director to get everyone on board.
Dr. Drane’s out-of-the-box thinking has enabled people to go home without oxygen 2 days earlier and cut the hospital’s length of stay by 5%. “It’s something so small, but it has such a great end reward,” she said. “I’m proud of this project because it didn’t take money; it was getting creative with what we already have.”
Renewed pride and passion
Dr. Drane is intensely proud of being an NP and working on the front lines. She sees that the pandemic has encouraged her and other APPs to expand their horizons.
“For me, it’s made me work to get dual certified,” she said. “APPs can be all-inclusive. I feel like I’m doing what I was meant to do and it’s not just a job anymore.”
Ms. McGrath is even more passionate about being a hospitalist now, as she has realized how valuable their unique skill sets are. “I think other people have also been able to realize that our ability to see the patient as a whole has allowed us to take care of this pandemic, because this disease impacts all organ systems and has a trickle-down effect that we as hospitalists are well versed to manage,” she said.
Ms. Cardin’s work involves communicating with APPs all around the country. Recently she had a phone exchange with an APP who needed to vent.
“She was weeping, and I thought she was going to say, ‘I can’t do this anymore, I need to go home,’ ” said Ms. Cardin. “Instead, she said, ‘I just want to make a difference in one of these people’s lives.’ And that is who the advanced practice providers are. They’re willing to go into those COVID units. They’re willing to be in the front lines. They are dedicated. They’re just intensely inspirational to me.”
Throughout the chaos of the COVID-19 pandemic, advanced practice providers (APPs) – physician assistants (PAs) and nurse practitioners (NPs) – have become an integral component of the hospitalist response. As many physicians began shifting into telemedicine and away from direct patient care, APPs have been eagerly jumping in to fill the gaps. Their work has been changing almost as dramatically and quickly as the pandemic itself, bringing with it expected challenges but bestowing hugely satisfying, often unanticipated, rewards.
APPs on the rise
As the coronavirus pandemic evolves, the role of APPs is evolving right alongside it. With the current relaxation of hospital bylaw restrictions on APPs, their utilization has increased, said Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM, a nurse practitioner and vice president of advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians. “We have not really furloughed any advanced practice providers,” Ms. Cardin said. “In fact, I consider them to be, within hospital medicine, a key lever to finding more cost-effective care delivery models.”
Ms. Cardin said APPs have been working more independently since COVID-19 started, seeing patients on their own and using physician consultation and backup via telemedicine or telephone as needed. With the reduction in elective surgeries and patient volumes at many hospitals, APP-led care also saves money. Because one of the biggest costs is labor, Ms. Cardin said, offering this high-quality care delivery model using APPs in collaboration with physician providers helps defray some of that cost. “We’re hoping that advanced practice providers are really a solution to some of these financial pressures in a lot of different ways,” she said.
“COVID … forced us to expedite conversations about how to maximize caseloads using APPs,” said Alicia Sheffer, AGAC-AGPC NP, a nurse practitioner and Great Lakes regional director of advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians in Cincinnati. Some of those staffing model changes have included using APPs while transitioning ICUs and med-surg units to COVID cohort units, APP-led COVID cohorts, and APP-led ICUs.
“At first the hospital system had ideas about bringing in telemedicine as an alternative to seeing patients, rather than just putting APPs on the front lines and having them go in and see patients,” said Jessica Drane, APRN, PhD, DNP FNP-C, a nurse practitioner and regional director of advanced practice provider services and hospital medicine at Sound Physicians in San Antonio. In Texas at the beginning of the pandemic, hospital numbers were so low that Dr. Drane did not work at all in April. “We were all afraid we were going to lose our jobs,” she said. Then the state got slammed and APPs have been desperately needed.
Ilaria Gadalla, DMSc, PA-C, a PA at Treasure Coast Hospitalists in Port St. Lucie, Fla., and the PA program director at South University, West Palm Beach, Fla., noted that many of her APP colleagues have pivoted fluidly from other specialties to the hospitalist realm as the need for frontline workers has increased. “Hospitalists have shined through this and their value has been recognized even more than previously as a result of COVID-19,” Dr. Gadalla said.
“I don’t think it’s any surprise that hospitalists became a pillar of the COVID pandemic,” said Bridget McGrath, PA-C, a physician assistant and director of the NP/PAs service line for the section of hospital medicine at the University of Chicago. “There are just some innate traits that hospitalists have, such as the ability to be flexible, to problem solve, and to be the solution to the problem.”
Building team camaraderie
Ms. Cardin says that the need for APPs has led to an evolving integration between physicians and APPs. The growing teamwork and bonding between colleagues have been some of the most rewarding aspects of the pandemic for Dr. Gadalla. “We rely even more on each other and there isn’t really a line of, ‘I’m a physician versus an NP or PA or nurse.’ We’re all working together with the same goal,” she said.
Ms. McGrath said she has been learning what it means to lead a team during a challenging time. It has been gratifying for her to watch mentors get down to the bare bones of patient care and see everyone unify, putting aside roles and titles and coming together to care for their patients in innovative ways.
“This pandemic has really opened up a lot of doors for us because up until now, we were used almost like scribes for physicians,” Dr. Drane said. She has seen even the most resistant hospital systems beginning to rely on APPs as the pandemic has progressed. “They have become pleasantly surprised at what an APP can do.”
Work challenges
Obviously, challenges abound. Dr. Gadalla listed hers as visiting restrictions that invariably lead to slower patient visits thanks to obligatory phone calls, constantly fluctuating patient censuses, sporadic elective surgeries, watching colleagues become furloughed, and trying to balance external perceptions with what’s actually happening in the hospital.
Overall, though, “There have been a lot more rewards than barriers,” added Dr. Drane.
One of the biggest obstacles for health care workers navigating a pandemic is balancing work and home life, not to mention having time to unwind while working long hours. “Finding time for my family has been very limited. My kids feel really neglected,” said Dr. Gadalla. Some days, she gets up extra early to exercise to help clear her head, but other times she’s just too exhausted to even move.
Dr. Drane agreed that the work can get overwhelming. “We’re changing the way we practice almost every week, which can make you doubt yourself as an educator, as a practitioner. You constantly feel like you’re not sure what you’re doing, and people trust you to heal them,” she said. “Today is my first day off in 24 days. I only got it off because I said I needed a moment.”
Ms. Sheffer’s crazy days were at the beginning of the pandemic when she had to self-quarantine from her family and was working nonstop. “I would come home and sleep and work and wake up in the middle of the night and double check and triple check and go back to sleep and work, and that consumed me for several months,” she said.
The biggest challenge for Ms. Sheffer has been coping with public fear. “No matter how logical our medical approach has been, I think the constant feeling of the public threat of COVID has had this insidious effect on how patients approach their health,” she said. “We’re spending a lot more time shaping our approach to best address their fears first and not to politicize COVID so we can actually deal with the health issue at hand.”
Complications of COVID
With all the restrictions, caring for patients these days has meant learning to interact with them in different ways that aren’t as personal, Ms. McGrath said. It has been difficult to lose “that humanity of medicine, the usual ways that you interact with your patients that are going through a vulnerable time,” she noted.
Additionally, students in the medical field are being held back from graduation because they cannot participate in direct patient care. This is particularly problematic for PAs and medical students who must touch patients to graduate, Dr. Gadalla said. “All of this is slowing down future providers. We’re going to have trouble catching up. Who’s going to relieve us? That’s a huge problem and no one is finding solutions for that yet,” she said.
At the University of Chicago, Ms. McGrath explained, they created virtual rotations so that PA students could continue to do them at the university. Not only has the experience reminded Ms. McGrath how much she loves being a medical educator and fighting for the education of PA students, but she was surprised to find that her patients came to appreciate the time they spent with her students on the virtual platform as well.
“It’s isolating for patients to be in the hospital in a vulnerable state and with no support system,” she said. “I think being a part of [the PA students’] education gave some meaning to their hospitalization and highlighted that collaboration and connection is a human need.”
Despite everything, there’s a noticeable emphasis on the flowering buds of hope, unity, compassion, and pride that have been quietly blooming from the daily hardships. As Ms. Cardin puts it, “It’s so cliché to say that there’s a crisis. The other word is ‘opportunity,’ and it’s true, there are opportunities here.”
Taking care of each other
Creating resources for providers has been a priority at the University of Chicago, according to Ms. McGrath. “As hospitalists, we’re used to taking care of a variety of patients, but our section leadership and providers on the front lines quickly realized that COVID patients are more akin to trauma patients with their quick changes in health, as well as their isolation, fear, and unexpected deterioration,” she said. Her facility has implemented wellness initiatives to help prevent burnout and mental health problems in COVID providers so they can continue to give the best care to their patients.
Both Ms. Sheffer and Dr. Drane say that they have a peer network of APPs at Sound Physicians to call on for questions and support. And it’s encouraging to know you’re not alone and to keep tabs on how colleagues in other states are doing, Ms. Sheffer noted.
“The peer support system has been helpful,” Dr. Drane said. “This job, right now, takes pieces of you every day. Sometimes it’s so emotional that you can’t put it into words. You just have to cry and get it out so that you can go be with your family.”
Getting back to basics
The changes in patient care have turned into something Ms. McGrath said she appreciates. “This pandemic has really stripped away the extra fluff of medicine and brought us back to the reason why many of us have gotten into the field, because it became about the patients again,” she says. “You quickly learn your strengths and weaknesses as a provider and as a leader, and that flows into the decisions you’re making for your team and for your patients.”
Ms. Sheffer acknowledged that it is difficult to deal with patients’ family members who don’t understand that they can’t visit their sick relatives, but she said the flip side is that frontline workers become surrogate family members, an outcome she considers to be an honor.
“You step into the emotion with the family or with the patient because you’re all they have. That is a beautiful, honorable role, but it’s also tremendously emotional and sometimes devastating,” she said. “But to me, it’s one of the most beautiful things I’ve been able to offer in a time where we don’t even know what to do with COVID.”
Limited resources mixed with a healthy dose of fear can stifle creativity, Dr. Drane said. Right away, she noticed that despite the abundance of incentive spirometers at her hospital, they were not being utilized. She came in 2 hours early for 3 days to pass one out to every patient under investigation or COVID-positive patient and enlisted the help of her chief nursing officer, CEO, and regional medical director to get everyone on board.
Dr. Drane’s out-of-the-box thinking has enabled people to go home without oxygen 2 days earlier and cut the hospital’s length of stay by 5%. “It’s something so small, but it has such a great end reward,” she said. “I’m proud of this project because it didn’t take money; it was getting creative with what we already have.”
Renewed pride and passion
Dr. Drane is intensely proud of being an NP and working on the front lines. She sees that the pandemic has encouraged her and other APPs to expand their horizons.
“For me, it’s made me work to get dual certified,” she said. “APPs can be all-inclusive. I feel like I’m doing what I was meant to do and it’s not just a job anymore.”
Ms. McGrath is even more passionate about being a hospitalist now, as she has realized how valuable their unique skill sets are. “I think other people have also been able to realize that our ability to see the patient as a whole has allowed us to take care of this pandemic, because this disease impacts all organ systems and has a trickle-down effect that we as hospitalists are well versed to manage,” she said.
Ms. Cardin’s work involves communicating with APPs all around the country. Recently she had a phone exchange with an APP who needed to vent.
“She was weeping, and I thought she was going to say, ‘I can’t do this anymore, I need to go home,’ ” said Ms. Cardin. “Instead, she said, ‘I just want to make a difference in one of these people’s lives.’ And that is who the advanced practice providers are. They’re willing to go into those COVID units. They’re willing to be in the front lines. They are dedicated. They’re just intensely inspirational to me.”
FDA approves first at-home COVID-19 test kit
The FDA issued an emergency use authorization Tuesday for the first self-testing COVID-19 kit to use at home, which provides results in about 30 minutes.
The Lucira COVID-19 All-In-One Test-Kit is a single-use test that has a nasal swab to collect samples for people ages 14 and older. It’s available only by prescription, which can be given by a doctor who suspects a patient may have contracted the coronavirus.
“While COVID-19 diagnostic tests have been authorized for at-home collection, this is the first that can be fully self-administered and provide results at home,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in the statement.
The test kit can also be used in doctor’s offices, hospitals, urgent care centers, and emergency rooms for all ages, but samples must be collected by a health care professional if the patient is under age 14.
After using the nasal swab, the test works by swirling the sample in a vial and then placing it in the provided test unit, according to the FDA. Within 30 minutes, the results appear on the unit’s light-up display. People who receive a positive result should self-isolate and seek care from their doctor. Those who test negative but have COVID-like symptoms should follow up with their doctor, since a negative result doesn’t necessarily mean they don’t have the coronavirus.
Testing is still a key part of controlling the spread of the coronavirus, Reuters reports. The United States surpassed 11 million infections Sunday, only 8 days after passing 10 million cases.
With the at-home testing kit, public health officials still need to track and monitor results. As part of the emergency use authorization, the FDA requires doctors who prescribe the tests to report all results to public health authorities based on local, state, and federal requirements. Lucira Health, the test maker, also created box labeling and instructions to help doctors to report results.
“Now, more Americans who may have COVID-19 will be able to take immediate action, based on their results, to protect themselves and those around them,” Jeff Shuren, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in the statement.
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The FDA issued an emergency use authorization Tuesday for the first self-testing COVID-19 kit to use at home, which provides results in about 30 minutes.
The Lucira COVID-19 All-In-One Test-Kit is a single-use test that has a nasal swab to collect samples for people ages 14 and older. It’s available only by prescription, which can be given by a doctor who suspects a patient may have contracted the coronavirus.
“While COVID-19 diagnostic tests have been authorized for at-home collection, this is the first that can be fully self-administered and provide results at home,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in the statement.
The test kit can also be used in doctor’s offices, hospitals, urgent care centers, and emergency rooms for all ages, but samples must be collected by a health care professional if the patient is under age 14.
After using the nasal swab, the test works by swirling the sample in a vial and then placing it in the provided test unit, according to the FDA. Within 30 minutes, the results appear on the unit’s light-up display. People who receive a positive result should self-isolate and seek care from their doctor. Those who test negative but have COVID-like symptoms should follow up with their doctor, since a negative result doesn’t necessarily mean they don’t have the coronavirus.
Testing is still a key part of controlling the spread of the coronavirus, Reuters reports. The United States surpassed 11 million infections Sunday, only 8 days after passing 10 million cases.
With the at-home testing kit, public health officials still need to track and monitor results. As part of the emergency use authorization, the FDA requires doctors who prescribe the tests to report all results to public health authorities based on local, state, and federal requirements. Lucira Health, the test maker, also created box labeling and instructions to help doctors to report results.
“Now, more Americans who may have COVID-19 will be able to take immediate action, based on their results, to protect themselves and those around them,” Jeff Shuren, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in the statement.
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The FDA issued an emergency use authorization Tuesday for the first self-testing COVID-19 kit to use at home, which provides results in about 30 minutes.
The Lucira COVID-19 All-In-One Test-Kit is a single-use test that has a nasal swab to collect samples for people ages 14 and older. It’s available only by prescription, which can be given by a doctor who suspects a patient may have contracted the coronavirus.
“While COVID-19 diagnostic tests have been authorized for at-home collection, this is the first that can be fully self-administered and provide results at home,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in the statement.
The test kit can also be used in doctor’s offices, hospitals, urgent care centers, and emergency rooms for all ages, but samples must be collected by a health care professional if the patient is under age 14.
After using the nasal swab, the test works by swirling the sample in a vial and then placing it in the provided test unit, according to the FDA. Within 30 minutes, the results appear on the unit’s light-up display. People who receive a positive result should self-isolate and seek care from their doctor. Those who test negative but have COVID-like symptoms should follow up with their doctor, since a negative result doesn’t necessarily mean they don’t have the coronavirus.
Testing is still a key part of controlling the spread of the coronavirus, Reuters reports. The United States surpassed 11 million infections Sunday, only 8 days after passing 10 million cases.
With the at-home testing kit, public health officials still need to track and monitor results. As part of the emergency use authorization, the FDA requires doctors who prescribe the tests to report all results to public health authorities based on local, state, and federal requirements. Lucira Health, the test maker, also created box labeling and instructions to help doctors to report results.
“Now, more Americans who may have COVID-19 will be able to take immediate action, based on their results, to protect themselves and those around them,” Jeff Shuren, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in the statement.
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Can a probiotic prevent COVID-19?
On the Nov. 12 episode of the Blood & Cancer podcast, Anthony D. Sung, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., joined host David H. Henry, MD, of Penn Medicine in Philadelphia, to discuss the trial of LGG as well as other research. The following transcript of that discussion has been edited for length and clarity.
David Henry, MD: Here we are in COVID. We’re recording this the first week in November. Sadly, cases are spiking in the country. And I understand you’ve got some information that you might share about how manipulating ... the microbiome that we all exist with inside our gut might somehow play into doing better or worse with COVID.
Anthony Sung, MD: Absolutely. So, as associate director of the Duke Microbiome Center, I was approached by one of my colleagues, Paul Wischmeyer, who is a professor of anesthesiology and critical care medicine at Duke. Paul had previously done some very nice murine studies with the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, or LGG.
He showed, in a murine model of pseudomonas pneumonia, that giving LGG to mice would help modulate their microbiome and, in turn, their immune system, leading to decreased inflammation, decreased TNF-alpha, IL [interleukin]-2, and IL-6, [and] increased Treg cells [Clin Nutr. 2017;36[6]:1549-57]. This also helped prevent lung injury, and it actually significantly improved survival in mice receiving LGG [Shock. 2013;40[6]:496-503].
In addition, there has been a randomized clinical trial of LGG showing that its administration would help prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia, or VAP [Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010 Oct 15;182[8]:1058-64].
And a few years ago, there was another RCT [randomized, controlled trial], published in Nature, showing that another Lactobacillus product significantly decreased the combined endpoint of sepsis and mortality, primarily by reducing lower respiratory tract infection [Nature. 2017 Aug 24;548[7668]:407-12].
Dr. Henry: And how is that working? What is the bacillus doing to help us?
Dr. Sung: We think it’s through modulating the immune system. As mentioned in Paul’s studies, we saw significantly decreased amounts of TNF-alpha, IL-2, and IL-6, which are the same cytokines that have been implicated in COVID-19 and associated with increased lung injury in patients during this pandemic.
And we believe that by giving individuals this probiotic, LGG, we may help modulate the immune system, decrease lung injury and symptoms, and maybe even prevent COVID-19.
So with support from the Duke Microbiome Center, as well as private donations and philanthropy, we are conducting a randomized clinical trial of LGG to prevent COVID-19 in household contacts who’ve been exposed to the disease. In other words, if someone in the house gets COVID-19, we want to try to prophylax everybody else living in that house and prevent them from coming down with the same infection.
Dr. Henry: And this is an oral administration?
Dr. Sung: Correct. This is an oral pill, two pills once a day.
Dr. Henry: And it’s an ongoing study, of course, in COVID right now?
Dr. Sung: Correct. So we have an IND [investigational new drug application] from the FDA [Food and Drug Administration], and we are actively recruiting subjects both at Duke University, but also due to the unique study design, we can enroll patients anywhere across the country. Because of the importance of social distancing, everything is done remotely.
So a household contact can hear about us, either through your podcast or one of our Facebook ads or through other media. They can reach out to our study website, which is https://sites.duke.edu/protectehc, or reach out to us at our study email, [email protected].
And we can go ahead and screen them for eligibility in our trial. And if they are eligible and they consent to participate, we will mail them a package basically overnight, FedEx, containing either LGG or placebo, as well as kits so that they can self-collect their stool and nasal swabs so we can test it for SARS-CoV-2 by PCR [polymerase chain reaction] and look at the microbiome.
Dr. Sung and Dr. Henry have no relevant disclosures. Funding for the trial is provided by the Duke Microbiome Center and philanthropic giving. The LGG and placebo used in the trial are provided by DSM.
On the Nov. 12 episode of the Blood & Cancer podcast, Anthony D. Sung, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., joined host David H. Henry, MD, of Penn Medicine in Philadelphia, to discuss the trial of LGG as well as other research. The following transcript of that discussion has been edited for length and clarity.
David Henry, MD: Here we are in COVID. We’re recording this the first week in November. Sadly, cases are spiking in the country. And I understand you’ve got some information that you might share about how manipulating ... the microbiome that we all exist with inside our gut might somehow play into doing better or worse with COVID.
Anthony Sung, MD: Absolutely. So, as associate director of the Duke Microbiome Center, I was approached by one of my colleagues, Paul Wischmeyer, who is a professor of anesthesiology and critical care medicine at Duke. Paul had previously done some very nice murine studies with the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, or LGG.
He showed, in a murine model of pseudomonas pneumonia, that giving LGG to mice would help modulate their microbiome and, in turn, their immune system, leading to decreased inflammation, decreased TNF-alpha, IL [interleukin]-2, and IL-6, [and] increased Treg cells [Clin Nutr. 2017;36[6]:1549-57]. This also helped prevent lung injury, and it actually significantly improved survival in mice receiving LGG [Shock. 2013;40[6]:496-503].
In addition, there has been a randomized clinical trial of LGG showing that its administration would help prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia, or VAP [Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010 Oct 15;182[8]:1058-64].
And a few years ago, there was another RCT [randomized, controlled trial], published in Nature, showing that another Lactobacillus product significantly decreased the combined endpoint of sepsis and mortality, primarily by reducing lower respiratory tract infection [Nature. 2017 Aug 24;548[7668]:407-12].
Dr. Henry: And how is that working? What is the bacillus doing to help us?
Dr. Sung: We think it’s through modulating the immune system. As mentioned in Paul’s studies, we saw significantly decreased amounts of TNF-alpha, IL-2, and IL-6, which are the same cytokines that have been implicated in COVID-19 and associated with increased lung injury in patients during this pandemic.
And we believe that by giving individuals this probiotic, LGG, we may help modulate the immune system, decrease lung injury and symptoms, and maybe even prevent COVID-19.
So with support from the Duke Microbiome Center, as well as private donations and philanthropy, we are conducting a randomized clinical trial of LGG to prevent COVID-19 in household contacts who’ve been exposed to the disease. In other words, if someone in the house gets COVID-19, we want to try to prophylax everybody else living in that house and prevent them from coming down with the same infection.
Dr. Henry: And this is an oral administration?
Dr. Sung: Correct. This is an oral pill, two pills once a day.
Dr. Henry: And it’s an ongoing study, of course, in COVID right now?
Dr. Sung: Correct. So we have an IND [investigational new drug application] from the FDA [Food and Drug Administration], and we are actively recruiting subjects both at Duke University, but also due to the unique study design, we can enroll patients anywhere across the country. Because of the importance of social distancing, everything is done remotely.
So a household contact can hear about us, either through your podcast or one of our Facebook ads or through other media. They can reach out to our study website, which is https://sites.duke.edu/protectehc, or reach out to us at our study email, [email protected].
And we can go ahead and screen them for eligibility in our trial. And if they are eligible and they consent to participate, we will mail them a package basically overnight, FedEx, containing either LGG or placebo, as well as kits so that they can self-collect their stool and nasal swabs so we can test it for SARS-CoV-2 by PCR [polymerase chain reaction] and look at the microbiome.
Dr. Sung and Dr. Henry have no relevant disclosures. Funding for the trial is provided by the Duke Microbiome Center and philanthropic giving. The LGG and placebo used in the trial are provided by DSM.
On the Nov. 12 episode of the Blood & Cancer podcast, Anthony D. Sung, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., joined host David H. Henry, MD, of Penn Medicine in Philadelphia, to discuss the trial of LGG as well as other research. The following transcript of that discussion has been edited for length and clarity.
David Henry, MD: Here we are in COVID. We’re recording this the first week in November. Sadly, cases are spiking in the country. And I understand you’ve got some information that you might share about how manipulating ... the microbiome that we all exist with inside our gut might somehow play into doing better or worse with COVID.
Anthony Sung, MD: Absolutely. So, as associate director of the Duke Microbiome Center, I was approached by one of my colleagues, Paul Wischmeyer, who is a professor of anesthesiology and critical care medicine at Duke. Paul had previously done some very nice murine studies with the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, or LGG.
He showed, in a murine model of pseudomonas pneumonia, that giving LGG to mice would help modulate their microbiome and, in turn, their immune system, leading to decreased inflammation, decreased TNF-alpha, IL [interleukin]-2, and IL-6, [and] increased Treg cells [Clin Nutr. 2017;36[6]:1549-57]. This also helped prevent lung injury, and it actually significantly improved survival in mice receiving LGG [Shock. 2013;40[6]:496-503].
In addition, there has been a randomized clinical trial of LGG showing that its administration would help prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia, or VAP [Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010 Oct 15;182[8]:1058-64].
And a few years ago, there was another RCT [randomized, controlled trial], published in Nature, showing that another Lactobacillus product significantly decreased the combined endpoint of sepsis and mortality, primarily by reducing lower respiratory tract infection [Nature. 2017 Aug 24;548[7668]:407-12].
Dr. Henry: And how is that working? What is the bacillus doing to help us?
Dr. Sung: We think it’s through modulating the immune system. As mentioned in Paul’s studies, we saw significantly decreased amounts of TNF-alpha, IL-2, and IL-6, which are the same cytokines that have been implicated in COVID-19 and associated with increased lung injury in patients during this pandemic.
And we believe that by giving individuals this probiotic, LGG, we may help modulate the immune system, decrease lung injury and symptoms, and maybe even prevent COVID-19.
So with support from the Duke Microbiome Center, as well as private donations and philanthropy, we are conducting a randomized clinical trial of LGG to prevent COVID-19 in household contacts who’ve been exposed to the disease. In other words, if someone in the house gets COVID-19, we want to try to prophylax everybody else living in that house and prevent them from coming down with the same infection.
Dr. Henry: And this is an oral administration?
Dr. Sung: Correct. This is an oral pill, two pills once a day.
Dr. Henry: And it’s an ongoing study, of course, in COVID right now?
Dr. Sung: Correct. So we have an IND [investigational new drug application] from the FDA [Food and Drug Administration], and we are actively recruiting subjects both at Duke University, but also due to the unique study design, we can enroll patients anywhere across the country. Because of the importance of social distancing, everything is done remotely.
So a household contact can hear about us, either through your podcast or one of our Facebook ads or through other media. They can reach out to our study website, which is https://sites.duke.edu/protectehc, or reach out to us at our study email, [email protected].
And we can go ahead and screen them for eligibility in our trial. And if they are eligible and they consent to participate, we will mail them a package basically overnight, FedEx, containing either LGG or placebo, as well as kits so that they can self-collect their stool and nasal swabs so we can test it for SARS-CoV-2 by PCR [polymerase chain reaction] and look at the microbiome.
Dr. Sung and Dr. Henry have no relevant disclosures. Funding for the trial is provided by the Duke Microbiome Center and philanthropic giving. The LGG and placebo used in the trial are provided by DSM.
Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine 95% effective in final phase 3 results
After initial promising interim results on Nov. 9, Pfizer and BioNTech today announced that their mRNA vaccine, in development to prevent COVID-19, is 95% effective.
Final analysis of the randomized, phase 3 study of more than 43,000 people yielded 170 confirmed cases of COVID-19 – with 162 positive cases in the placebo group versus 8 in the BNT162b2 vaccine group.
Researchers reported 10 severe cases of COVID-19 in the trial, 9 of which occurred in the placebo group.
The study was ethnically diverse, and results were consistent across gender and age groups, with a 94% efficacy reported among participants aged older than 65 years.
Pfizer plans to file for an emergency-use authorization with the Food and Drug Administration “within days,” having now met all the FDA data endpoints, according to a news release from the two companies.
The vaccine was well tolerated with no serious safety concerns, the company stated. Two grade 3 adverse events were reported – fatigue in 3.8% of participants and headache in 2%.
The 95% efficacy places the Pfizer vaccine in the same neighborhood as the interim results of the Moderna vaccine, reported at 94.5%. Both products are two-dose mRNA vaccines.
As of Nov. 13, of 43,661 total participants in the Pfizer vaccine phase 3 trial, 41,135 received a second dose. The final results are based on two outcomes measured 7 days after the second dose: vaccine efficacy in people without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection as well as a secondary outcome in people both with and without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The 95% vaccine efficacy was statistically significant, compared with placebo (P < .0001).
‘Historic 8-month journey’
The BNT162b2 vaccine candidate is a joint effort between Pfizer and BioNTech. “The study results mark an important step in this historic 8-month journey to bring forward a vaccine capable of helping to end this devastating pandemic,” Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, Pfizer chairman and CEO, said in a statement. “With hundreds of thousands of people around the globe infected every day, we urgently need to get a safe and effective vaccine to the world.”
Ugur Sahin, MD, PhD, cofounder and CEO of BioNTech, added, “we are grateful that the first global trial to reach the final efficacy analysis mark indicates that a high rate of protection against COVID-19 can be achieved very fast after the first 30-mcg dose, underscoring the power of BNT162 in providing early protection.”
The two companies expect to produce up to 50 million vaccine doses in 2020 for global distribution. Projections for 2021 include up to 1.3 billion doses.
The companies also designed temperature-controlled thermal shipping containers with dry ice to maintain the required, approximate –70° C (–94° F) conditions. Clinicians can use the containers as temporary storage units for up to 15 days by replacing the dry ice.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After initial promising interim results on Nov. 9, Pfizer and BioNTech today announced that their mRNA vaccine, in development to prevent COVID-19, is 95% effective.
Final analysis of the randomized, phase 3 study of more than 43,000 people yielded 170 confirmed cases of COVID-19 – with 162 positive cases in the placebo group versus 8 in the BNT162b2 vaccine group.
Researchers reported 10 severe cases of COVID-19 in the trial, 9 of which occurred in the placebo group.
The study was ethnically diverse, and results were consistent across gender and age groups, with a 94% efficacy reported among participants aged older than 65 years.
Pfizer plans to file for an emergency-use authorization with the Food and Drug Administration “within days,” having now met all the FDA data endpoints, according to a news release from the two companies.
The vaccine was well tolerated with no serious safety concerns, the company stated. Two grade 3 adverse events were reported – fatigue in 3.8% of participants and headache in 2%.
The 95% efficacy places the Pfizer vaccine in the same neighborhood as the interim results of the Moderna vaccine, reported at 94.5%. Both products are two-dose mRNA vaccines.
As of Nov. 13, of 43,661 total participants in the Pfizer vaccine phase 3 trial, 41,135 received a second dose. The final results are based on two outcomes measured 7 days after the second dose: vaccine efficacy in people without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection as well as a secondary outcome in people both with and without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The 95% vaccine efficacy was statistically significant, compared with placebo (P < .0001).
‘Historic 8-month journey’
The BNT162b2 vaccine candidate is a joint effort between Pfizer and BioNTech. “The study results mark an important step in this historic 8-month journey to bring forward a vaccine capable of helping to end this devastating pandemic,” Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, Pfizer chairman and CEO, said in a statement. “With hundreds of thousands of people around the globe infected every day, we urgently need to get a safe and effective vaccine to the world.”
Ugur Sahin, MD, PhD, cofounder and CEO of BioNTech, added, “we are grateful that the first global trial to reach the final efficacy analysis mark indicates that a high rate of protection against COVID-19 can be achieved very fast after the first 30-mcg dose, underscoring the power of BNT162 in providing early protection.”
The two companies expect to produce up to 50 million vaccine doses in 2020 for global distribution. Projections for 2021 include up to 1.3 billion doses.
The companies also designed temperature-controlled thermal shipping containers with dry ice to maintain the required, approximate –70° C (–94° F) conditions. Clinicians can use the containers as temporary storage units for up to 15 days by replacing the dry ice.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After initial promising interim results on Nov. 9, Pfizer and BioNTech today announced that their mRNA vaccine, in development to prevent COVID-19, is 95% effective.
Final analysis of the randomized, phase 3 study of more than 43,000 people yielded 170 confirmed cases of COVID-19 – with 162 positive cases in the placebo group versus 8 in the BNT162b2 vaccine group.
Researchers reported 10 severe cases of COVID-19 in the trial, 9 of which occurred in the placebo group.
The study was ethnically diverse, and results were consistent across gender and age groups, with a 94% efficacy reported among participants aged older than 65 years.
Pfizer plans to file for an emergency-use authorization with the Food and Drug Administration “within days,” having now met all the FDA data endpoints, according to a news release from the two companies.
The vaccine was well tolerated with no serious safety concerns, the company stated. Two grade 3 adverse events were reported – fatigue in 3.8% of participants and headache in 2%.
The 95% efficacy places the Pfizer vaccine in the same neighborhood as the interim results of the Moderna vaccine, reported at 94.5%. Both products are two-dose mRNA vaccines.
As of Nov. 13, of 43,661 total participants in the Pfizer vaccine phase 3 trial, 41,135 received a second dose. The final results are based on two outcomes measured 7 days after the second dose: vaccine efficacy in people without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection as well as a secondary outcome in people both with and without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The 95% vaccine efficacy was statistically significant, compared with placebo (P < .0001).
‘Historic 8-month journey’
The BNT162b2 vaccine candidate is a joint effort between Pfizer and BioNTech. “The study results mark an important step in this historic 8-month journey to bring forward a vaccine capable of helping to end this devastating pandemic,” Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, Pfizer chairman and CEO, said in a statement. “With hundreds of thousands of people around the globe infected every day, we urgently need to get a safe and effective vaccine to the world.”
Ugur Sahin, MD, PhD, cofounder and CEO of BioNTech, added, “we are grateful that the first global trial to reach the final efficacy analysis mark indicates that a high rate of protection against COVID-19 can be achieved very fast after the first 30-mcg dose, underscoring the power of BNT162 in providing early protection.”
The two companies expect to produce up to 50 million vaccine doses in 2020 for global distribution. Projections for 2021 include up to 1.3 billion doses.
The companies also designed temperature-controlled thermal shipping containers with dry ice to maintain the required, approximate –70° C (–94° F) conditions. Clinicians can use the containers as temporary storage units for up to 15 days by replacing the dry ice.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Hospital at home’ increases COVID capacity in large study
A “hospital at home” (HaH) program at Atrium Health, a large integrated delivery system in the Southeast, expanded its hospital capacity during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic by providing hospital-level acute care to COVID-19 patients at home, according to a new study in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Virtual hospital programs have the potential to provide health systems with additional inpatient capacity during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond,” wrote Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, from the Atrium Health Hospitalist Group, Monroe, N.C., and colleagues.
Whereas most previous HaH programs have relied on visiting nurses and physicians, the new study uses telemedicine to connect with patients. Advocate Health Care researchers published the only other study using the telemedicine-powered model in 2015.
The new Atrium Health study evaluated 1,477 patients who received care in the HaH program between March 23 and May 7 of this year after having been diagnosed with COVID-19. The program provided home monitoring and hospital-level care in a home-based virtual observation unit (VOU) and a virtual acute care unit (VACU).
Patients were tested for the virus in Atrium emergency departments, primary care clinics, urgent care centers, and external testing sites. Those who tested positive were invited to be cared for either in the VOU, if they had mild to moderate symptoms, or in the VACU, if they were sick enough to be admitted to the hospital.
Patients hop onboard
Nearly all COVID-positive patients tested in these sites agreed to be admitted to the hospital at home, coauthor Stephanie Murphy, DO, medical director of the Atrium Health HaH program, said in an interview.
Patients with moderate symptoms were glad to be monitored at home, she said. When they got to the point where the nurse supervising their care felt they needed escalation to acute care, they were asked whether they wanted to continue to be cared for at home. Most opted to stay home rather than be admitted to the hospital, where their loved ones couldn’t visit them.
Low-acuity patients in the VOU received daily telemonitoring by a nurse to identify disease progression and escalate care as needed. For those who required more care and were admitted to the VACU, a team of paramedics and registered nurses (RNs; mobile clinicians) visited the patient’s home within 24 hours, setting up a hospital bed, other necessary medical equipment, videoconferencing gear, and a remote-monitoring kit that included a blood pressure cuff, a pulse oximeter, and a thermometer.
Dedicated hospitalists and nurses managed patients with 24/7 coverage and monitoring, bringing in other specialties as needed for virtual consults. Mobile clinician and virtual provider visits continued daily until a patient’s condition improved to the point where they could be deescalated back to the VOU. After that, patients received mobile app-driven symptom monitoring and telephone follow-up with a nurse until they got better.
Few patients go to hospital
Overall, patients had a median length of stay of 11 days in the VOU or the VACU or both. The vast majority, 1,293 patients (88%), received care in the VOU only. In that cohort, just 40 patients (3%) required hospitalization in an Atrium facility. Sixteen of those patients spent time in an ICU, seven required ventilator support, and two died in the hospital.
A total of 184 patients (12%) were admitted to the VACU. Twenty-one (11%) required intravenous fluids, 16 (9%) received antibiotics, 40 (22%) required inhaler or nebulizer treatments, 41 (22%) used supplemental oxygen, and 24 (13%) were admitted to a conventional hospital. Of the latter patients, 10 were admitted to an ICU, one required a ventilator, and none died in the hospital.
Dr. Sitammagari, a hospitalist and comedical director for quality at Atrium Health, told this news organization that, overall, the outcomes for patients in the system’s HaH were comparable to those seen in the literature among other COVID-19 cohorts.
Augmenting hospital capacity
The authors note that treating the 160 VACU patients within the HaH saved hospital beds for other patients. The HaH maintained a consistent census of between 20 and 30 patients for the first 6 weeks as COVID-19 cases spread.
Since last spring, Dr. Murphy said, the Atrium HaH’s daily census has grown to between 30 and 45 patients. “We could absorb 50 patients if our hospitals required it.”
How much capacity does that add to Atrium Health? While there are 50 hospitals in the health system, the HaH was set up mainly to care for COVID-19 patients who would otherwise have been admitted to the 10 acute-care hospitals in the Charlotte, N.C., area. In the 4 weeks ending Nov. 16, these facilities carried an average daily census of around 160 COVID-19 patients, Dr. Murphy noted. “During that time, the Atrium Health HaH has carried, on average, about 20%-25% of that census.”
If the pandemic were to overwhelm area hospitals, she added, “the structure would support flexing up our staffing and supplies to expand to crisis capacity,” which could be up to 200 patients a day.
For the nurses who make most of the phone calls to patients, patients average about 12 to 15 per RN, Dr. Murphy said, and there’s one mobile clinician for every six to nine patients. That’s pretty consistent with the staffing on med-surg floors in hospitals, she said.
The physicians in the program include hospitalists dedicated to telemedicine and some doctors who can’t work in the regular hospital because they’re immunocompromised. The physicians round virtually, covering 12-17 HaH patients per day, according to Dr. Murphy.
Prior planning paid off
Unlike some other health care systems that have launched HaH programs with the aid of outside vendors, Atrium Health developed its own HaH and brought it online just 2 weeks after deciding to launch the program. Atrium was able to do this, Dr. Sitammagari explained, because before the pandemic its hospitalist program was already developing an HaH model to improve the care of high-risk patients after hospital discharge to prevent readmission.
While Atrium’s electronic health record system wasn’t designed for hospital at home, its health information technology department and clinicians collaborated in rewriting some of the workflows and order sets in the EHR. For example, they set up a nursing questionnaire to administer after VACU admission, and they created another form for automatic admission to the HaH after a patient tested positive for COVID-19. Atrium staff also modified a patient-doctor communications app to help clinicians monitor HaH patients, Dr. Murphy noted.
Other hospital systems have gotten up to speed on HaH pretty quickly by using platforms supplied by outside vendors. Adventist Health in Los Angeles, for example, started admitting patients to its hospital at home just a month after approaching a vendor called Medically Home.
COVID vs. non-COVID patients
Atrium’s decision to focus its HaH effort on COVID-19 patients is unusual among the small but growing number of health systems that have adopted the HaH model to increase their capacity. (Atrium is now transferring some hospitalized patients with other conditions to its HaH, but is still focusing mainly on COVID-19 in its HaH program.)
Bruce Leff, MD, a professor of health policy and management at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, a leading expert on the HaH model, agrees that it can increase hospital capacity significantly.
Dr. Leff praised the Atrium Health study. “It proves that within an integrated delivery system you can quickly deploy and implement a virtual hospital in the specific-use case of COVID, and help patients and help the system at scale,” he said. “They took a bunch of people into the virtual observation unit and thereby kept people from overwhelming their [emergency department] and treated those people safely at home.”
Dr. Leff had no problem with Atrium’s focus on patients with COVID-19 rather than other conditions. “My guess is that they have the ability to take what they developed and apply it to other conditions. Once you have the ability to do acute care at home, you can do a lot at home.”
The biggest barrier to the spread of hospital at home remains the lack of insurer coverage. Dr. Murphy said that health plans are covering virtual physician consultations with patients in the HaH, as well as some other bits and pieces, but not the entire episode of acute care.
Dr. Leff believes that this will start changing soon. COVID-19 has altered the attitudes of physicians and hospitals toward telehealth, he noted, “and it has moved policy makers and payers to start thinking about the new models – home-based care in general and hospital at home in particular. For the first time in 25 years, payers are starting to get interested.”
Most of the authors are employees of Atrium Health. In addition, one coauthor reports being the cofounder of a digital health company, iEnroll, and receiving grants from The Heineman Foundation. Dr. Leff is an advisor to Medically Home, which provides support to hospital at home programs.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A “hospital at home” (HaH) program at Atrium Health, a large integrated delivery system in the Southeast, expanded its hospital capacity during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic by providing hospital-level acute care to COVID-19 patients at home, according to a new study in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Virtual hospital programs have the potential to provide health systems with additional inpatient capacity during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond,” wrote Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, from the Atrium Health Hospitalist Group, Monroe, N.C., and colleagues.
Whereas most previous HaH programs have relied on visiting nurses and physicians, the new study uses telemedicine to connect with patients. Advocate Health Care researchers published the only other study using the telemedicine-powered model in 2015.
The new Atrium Health study evaluated 1,477 patients who received care in the HaH program between March 23 and May 7 of this year after having been diagnosed with COVID-19. The program provided home monitoring and hospital-level care in a home-based virtual observation unit (VOU) and a virtual acute care unit (VACU).
Patients were tested for the virus in Atrium emergency departments, primary care clinics, urgent care centers, and external testing sites. Those who tested positive were invited to be cared for either in the VOU, if they had mild to moderate symptoms, or in the VACU, if they were sick enough to be admitted to the hospital.
Patients hop onboard
Nearly all COVID-positive patients tested in these sites agreed to be admitted to the hospital at home, coauthor Stephanie Murphy, DO, medical director of the Atrium Health HaH program, said in an interview.
Patients with moderate symptoms were glad to be monitored at home, she said. When they got to the point where the nurse supervising their care felt they needed escalation to acute care, they were asked whether they wanted to continue to be cared for at home. Most opted to stay home rather than be admitted to the hospital, where their loved ones couldn’t visit them.
Low-acuity patients in the VOU received daily telemonitoring by a nurse to identify disease progression and escalate care as needed. For those who required more care and were admitted to the VACU, a team of paramedics and registered nurses (RNs; mobile clinicians) visited the patient’s home within 24 hours, setting up a hospital bed, other necessary medical equipment, videoconferencing gear, and a remote-monitoring kit that included a blood pressure cuff, a pulse oximeter, and a thermometer.
Dedicated hospitalists and nurses managed patients with 24/7 coverage and monitoring, bringing in other specialties as needed for virtual consults. Mobile clinician and virtual provider visits continued daily until a patient’s condition improved to the point where they could be deescalated back to the VOU. After that, patients received mobile app-driven symptom monitoring and telephone follow-up with a nurse until they got better.
Few patients go to hospital
Overall, patients had a median length of stay of 11 days in the VOU or the VACU or both. The vast majority, 1,293 patients (88%), received care in the VOU only. In that cohort, just 40 patients (3%) required hospitalization in an Atrium facility. Sixteen of those patients spent time in an ICU, seven required ventilator support, and two died in the hospital.
A total of 184 patients (12%) were admitted to the VACU. Twenty-one (11%) required intravenous fluids, 16 (9%) received antibiotics, 40 (22%) required inhaler or nebulizer treatments, 41 (22%) used supplemental oxygen, and 24 (13%) were admitted to a conventional hospital. Of the latter patients, 10 were admitted to an ICU, one required a ventilator, and none died in the hospital.
Dr. Sitammagari, a hospitalist and comedical director for quality at Atrium Health, told this news organization that, overall, the outcomes for patients in the system’s HaH were comparable to those seen in the literature among other COVID-19 cohorts.
Augmenting hospital capacity
The authors note that treating the 160 VACU patients within the HaH saved hospital beds for other patients. The HaH maintained a consistent census of between 20 and 30 patients for the first 6 weeks as COVID-19 cases spread.
Since last spring, Dr. Murphy said, the Atrium HaH’s daily census has grown to between 30 and 45 patients. “We could absorb 50 patients if our hospitals required it.”
How much capacity does that add to Atrium Health? While there are 50 hospitals in the health system, the HaH was set up mainly to care for COVID-19 patients who would otherwise have been admitted to the 10 acute-care hospitals in the Charlotte, N.C., area. In the 4 weeks ending Nov. 16, these facilities carried an average daily census of around 160 COVID-19 patients, Dr. Murphy noted. “During that time, the Atrium Health HaH has carried, on average, about 20%-25% of that census.”
If the pandemic were to overwhelm area hospitals, she added, “the structure would support flexing up our staffing and supplies to expand to crisis capacity,” which could be up to 200 patients a day.
For the nurses who make most of the phone calls to patients, patients average about 12 to 15 per RN, Dr. Murphy said, and there’s one mobile clinician for every six to nine patients. That’s pretty consistent with the staffing on med-surg floors in hospitals, she said.
The physicians in the program include hospitalists dedicated to telemedicine and some doctors who can’t work in the regular hospital because they’re immunocompromised. The physicians round virtually, covering 12-17 HaH patients per day, according to Dr. Murphy.
Prior planning paid off
Unlike some other health care systems that have launched HaH programs with the aid of outside vendors, Atrium Health developed its own HaH and brought it online just 2 weeks after deciding to launch the program. Atrium was able to do this, Dr. Sitammagari explained, because before the pandemic its hospitalist program was already developing an HaH model to improve the care of high-risk patients after hospital discharge to prevent readmission.
While Atrium’s electronic health record system wasn’t designed for hospital at home, its health information technology department and clinicians collaborated in rewriting some of the workflows and order sets in the EHR. For example, they set up a nursing questionnaire to administer after VACU admission, and they created another form for automatic admission to the HaH after a patient tested positive for COVID-19. Atrium staff also modified a patient-doctor communications app to help clinicians monitor HaH patients, Dr. Murphy noted.
Other hospital systems have gotten up to speed on HaH pretty quickly by using platforms supplied by outside vendors. Adventist Health in Los Angeles, for example, started admitting patients to its hospital at home just a month after approaching a vendor called Medically Home.
COVID vs. non-COVID patients
Atrium’s decision to focus its HaH effort on COVID-19 patients is unusual among the small but growing number of health systems that have adopted the HaH model to increase their capacity. (Atrium is now transferring some hospitalized patients with other conditions to its HaH, but is still focusing mainly on COVID-19 in its HaH program.)
Bruce Leff, MD, a professor of health policy and management at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, a leading expert on the HaH model, agrees that it can increase hospital capacity significantly.
Dr. Leff praised the Atrium Health study. “It proves that within an integrated delivery system you can quickly deploy and implement a virtual hospital in the specific-use case of COVID, and help patients and help the system at scale,” he said. “They took a bunch of people into the virtual observation unit and thereby kept people from overwhelming their [emergency department] and treated those people safely at home.”
Dr. Leff had no problem with Atrium’s focus on patients with COVID-19 rather than other conditions. “My guess is that they have the ability to take what they developed and apply it to other conditions. Once you have the ability to do acute care at home, you can do a lot at home.”
The biggest barrier to the spread of hospital at home remains the lack of insurer coverage. Dr. Murphy said that health plans are covering virtual physician consultations with patients in the HaH, as well as some other bits and pieces, but not the entire episode of acute care.
Dr. Leff believes that this will start changing soon. COVID-19 has altered the attitudes of physicians and hospitals toward telehealth, he noted, “and it has moved policy makers and payers to start thinking about the new models – home-based care in general and hospital at home in particular. For the first time in 25 years, payers are starting to get interested.”
Most of the authors are employees of Atrium Health. In addition, one coauthor reports being the cofounder of a digital health company, iEnroll, and receiving grants from The Heineman Foundation. Dr. Leff is an advisor to Medically Home, which provides support to hospital at home programs.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A “hospital at home” (HaH) program at Atrium Health, a large integrated delivery system in the Southeast, expanded its hospital capacity during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic by providing hospital-level acute care to COVID-19 patients at home, according to a new study in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Virtual hospital programs have the potential to provide health systems with additional inpatient capacity during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond,” wrote Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, from the Atrium Health Hospitalist Group, Monroe, N.C., and colleagues.
Whereas most previous HaH programs have relied on visiting nurses and physicians, the new study uses telemedicine to connect with patients. Advocate Health Care researchers published the only other study using the telemedicine-powered model in 2015.
The new Atrium Health study evaluated 1,477 patients who received care in the HaH program between March 23 and May 7 of this year after having been diagnosed with COVID-19. The program provided home monitoring and hospital-level care in a home-based virtual observation unit (VOU) and a virtual acute care unit (VACU).
Patients were tested for the virus in Atrium emergency departments, primary care clinics, urgent care centers, and external testing sites. Those who tested positive were invited to be cared for either in the VOU, if they had mild to moderate symptoms, or in the VACU, if they were sick enough to be admitted to the hospital.
Patients hop onboard
Nearly all COVID-positive patients tested in these sites agreed to be admitted to the hospital at home, coauthor Stephanie Murphy, DO, medical director of the Atrium Health HaH program, said in an interview.
Patients with moderate symptoms were glad to be monitored at home, she said. When they got to the point where the nurse supervising their care felt they needed escalation to acute care, they were asked whether they wanted to continue to be cared for at home. Most opted to stay home rather than be admitted to the hospital, where their loved ones couldn’t visit them.
Low-acuity patients in the VOU received daily telemonitoring by a nurse to identify disease progression and escalate care as needed. For those who required more care and were admitted to the VACU, a team of paramedics and registered nurses (RNs; mobile clinicians) visited the patient’s home within 24 hours, setting up a hospital bed, other necessary medical equipment, videoconferencing gear, and a remote-monitoring kit that included a blood pressure cuff, a pulse oximeter, and a thermometer.
Dedicated hospitalists and nurses managed patients with 24/7 coverage and monitoring, bringing in other specialties as needed for virtual consults. Mobile clinician and virtual provider visits continued daily until a patient’s condition improved to the point where they could be deescalated back to the VOU. After that, patients received mobile app-driven symptom monitoring and telephone follow-up with a nurse until they got better.
Few patients go to hospital
Overall, patients had a median length of stay of 11 days in the VOU or the VACU or both. The vast majority, 1,293 patients (88%), received care in the VOU only. In that cohort, just 40 patients (3%) required hospitalization in an Atrium facility. Sixteen of those patients spent time in an ICU, seven required ventilator support, and two died in the hospital.
A total of 184 patients (12%) were admitted to the VACU. Twenty-one (11%) required intravenous fluids, 16 (9%) received antibiotics, 40 (22%) required inhaler or nebulizer treatments, 41 (22%) used supplemental oxygen, and 24 (13%) were admitted to a conventional hospital. Of the latter patients, 10 were admitted to an ICU, one required a ventilator, and none died in the hospital.
Dr. Sitammagari, a hospitalist and comedical director for quality at Atrium Health, told this news organization that, overall, the outcomes for patients in the system’s HaH were comparable to those seen in the literature among other COVID-19 cohorts.
Augmenting hospital capacity
The authors note that treating the 160 VACU patients within the HaH saved hospital beds for other patients. The HaH maintained a consistent census of between 20 and 30 patients for the first 6 weeks as COVID-19 cases spread.
Since last spring, Dr. Murphy said, the Atrium HaH’s daily census has grown to between 30 and 45 patients. “We could absorb 50 patients if our hospitals required it.”
How much capacity does that add to Atrium Health? While there are 50 hospitals in the health system, the HaH was set up mainly to care for COVID-19 patients who would otherwise have been admitted to the 10 acute-care hospitals in the Charlotte, N.C., area. In the 4 weeks ending Nov. 16, these facilities carried an average daily census of around 160 COVID-19 patients, Dr. Murphy noted. “During that time, the Atrium Health HaH has carried, on average, about 20%-25% of that census.”
If the pandemic were to overwhelm area hospitals, she added, “the structure would support flexing up our staffing and supplies to expand to crisis capacity,” which could be up to 200 patients a day.
For the nurses who make most of the phone calls to patients, patients average about 12 to 15 per RN, Dr. Murphy said, and there’s one mobile clinician for every six to nine patients. That’s pretty consistent with the staffing on med-surg floors in hospitals, she said.
The physicians in the program include hospitalists dedicated to telemedicine and some doctors who can’t work in the regular hospital because they’re immunocompromised. The physicians round virtually, covering 12-17 HaH patients per day, according to Dr. Murphy.
Prior planning paid off
Unlike some other health care systems that have launched HaH programs with the aid of outside vendors, Atrium Health developed its own HaH and brought it online just 2 weeks after deciding to launch the program. Atrium was able to do this, Dr. Sitammagari explained, because before the pandemic its hospitalist program was already developing an HaH model to improve the care of high-risk patients after hospital discharge to prevent readmission.
While Atrium’s electronic health record system wasn’t designed for hospital at home, its health information technology department and clinicians collaborated in rewriting some of the workflows and order sets in the EHR. For example, they set up a nursing questionnaire to administer after VACU admission, and they created another form for automatic admission to the HaH after a patient tested positive for COVID-19. Atrium staff also modified a patient-doctor communications app to help clinicians monitor HaH patients, Dr. Murphy noted.
Other hospital systems have gotten up to speed on HaH pretty quickly by using platforms supplied by outside vendors. Adventist Health in Los Angeles, for example, started admitting patients to its hospital at home just a month after approaching a vendor called Medically Home.
COVID vs. non-COVID patients
Atrium’s decision to focus its HaH effort on COVID-19 patients is unusual among the small but growing number of health systems that have adopted the HaH model to increase their capacity. (Atrium is now transferring some hospitalized patients with other conditions to its HaH, but is still focusing mainly on COVID-19 in its HaH program.)
Bruce Leff, MD, a professor of health policy and management at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, a leading expert on the HaH model, agrees that it can increase hospital capacity significantly.
Dr. Leff praised the Atrium Health study. “It proves that within an integrated delivery system you can quickly deploy and implement a virtual hospital in the specific-use case of COVID, and help patients and help the system at scale,” he said. “They took a bunch of people into the virtual observation unit and thereby kept people from overwhelming their [emergency department] and treated those people safely at home.”
Dr. Leff had no problem with Atrium’s focus on patients with COVID-19 rather than other conditions. “My guess is that they have the ability to take what they developed and apply it to other conditions. Once you have the ability to do acute care at home, you can do a lot at home.”
The biggest barrier to the spread of hospital at home remains the lack of insurer coverage. Dr. Murphy said that health plans are covering virtual physician consultations with patients in the HaH, as well as some other bits and pieces, but not the entire episode of acute care.
Dr. Leff believes that this will start changing soon. COVID-19 has altered the attitudes of physicians and hospitals toward telehealth, he noted, “and it has moved policy makers and payers to start thinking about the new models – home-based care in general and hospital at home in particular. For the first time in 25 years, payers are starting to get interested.”
Most of the authors are employees of Atrium Health. In addition, one coauthor reports being the cofounder of a digital health company, iEnroll, and receiving grants from The Heineman Foundation. Dr. Leff is an advisor to Medically Home, which provides support to hospital at home programs.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Myocarditis rare, macrophage infiltration common at COVID autopsy
An international autopsy study of 21 patients who died from COVID-19 has shown the presence of multifocal lymphocytic myocarditis in three patients (14%). In an additional six patients, focally increased interstitial T-lymphocytes within the myocardium were noted, with only focal or no myocyte injury.
However, increased interstitial macrophage infiltration, possibly related to cytokine infiltration, was seen in 86% of patients.
“One way to think about this is that, if these patients were having biopsies and not autopsies, there would be myocardial injury in the patients with myocarditis, even after they recovered. But with interstitial macrophages, there may or may not be any injury,” said cardiovascular pathologist James R. Stone, MD, PhD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Dr. Stone and colleagues from Mass General, two hospitals in Italy, the University of Amsterdam, and the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., conducted the autopsies in March and April. The results were published in the October 14 issue of the European Heart Journal.
Their technique was rigorous: a median of 20 full-thickness blocks of myocardium were examined histologically (range, 5-29 blocks).
The presence of myocarditis, defined by the presence of multiple foci of inflammation with associated myocyte injury, was determined, and the inflammatory cell composition analyzed by immunohistochemistry.
“I think one of the take-homes from this study is that you have to do a thorough sampling of the heart in order to exclude myocardial injury. You cannot exclude myocarditis with just a biopsy or two,” said Dr. Stone in an interview.
“We looked at multiple different sections of tissue preserved in paraffin for every case and found only 14% had myocarditis. The vast majority of autopsies done on patients dying from COVID-19 have short-changed the autopsy and not been done in a way to exclude myocarditis,” he added.
For all patients, COVID-19 was the underlying cause of death, but the mechanisms of death were acute respiratory distress syndrome in 15, viral pneumonia in 4, cardiogenic shock in 1, and cardiac arrest in 1. Seven patients had a history of cardiovascular disease, including atrial fibrillation in four, coronary artery disease in three, left ventricular hypertrophy in one, and previous valve replacement in one. A total of 16 had hypertension, 7 had diabetes mellitus, and 1 had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In four cases, mild pericarditis was present. Acute myocyte injury in the right ventricle, most probably from strain or overload, was also present in four cases.
A nonsignificant trend was seen toward higher serum troponin levels in the patients with myocarditis compared with those without myocarditis. There were no reports of disrupted coronary artery plaques, coronary artery aneurysms, or large pulmonary emboli.
Macrophage infiltration rather than myocarditis, myocardial injury?
The study sheds more light on previous cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging findings that have suggested that many patients who recover from COVID-19 show signs suggestive of myocarditis. These earlier studies include a recent one in competitive athletes and the earlier Puntmann and colleagues study of relatively young COVID-19 patients, which showed ongoing myocardial involvement in a majority of patients.
“It would not surprise me if some or all of the cardiac MR changes seen in some of these recent imaging studies are due to the macrophages,” said Dr. Stone.
“What we saw was not a routine pathology by any means. It was a huge amount of macrophages, higher that what we saw in SARS and more similar to a study published in 2007 that looked at patients with bacterial sepsis,” said Dr. Stone.
In an older study of SARS patients, 35% had the virus detected in myocardial tissue by polymerase chain reaction. In that subset, the degree of myocardial macrophage infiltrate was comparable to that seen in 86% of the COVID-19 cases described in this series.
Another possibility is that the macrophage infiltration reflects underlying disease rather than COVID-19. All but one of the patients had known underlying medical conditions associated with cardiac remodeling, said Nikolaos G. Frangogiannis, MD, a cardiologist who studies the mechanisms of cardiac injury, repair, and remodeling.
Frangogiannis, from Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, wrote an editorial that accompanied the autopsy study.
“The problem with this finding of increased macrophage infiltration is that it’s very hard to interpret because as we age, and especially in a less healthy population, the numbers and the density of macrophages in the heart increase, so it’s impossible to interpret as an effect of the infection itself unless you have an appropriate control population that matches the same characteristics, which is almost impossible to ask for,” he said.
“I’ve observed since the beginning of the pandemic that there seemed to be some people who wanted every single case to be myocarditis and others who had a bias toward not wanting COVID-19 to be a cause of myocarditis. I think what we’re seeing is it’s not either/or for anything with this virus, it’s a bit of everything,” said Dr. Stone.
Dr. Stone and Dr. Frangogiannis reported no conflict of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
An international autopsy study of 21 patients who died from COVID-19 has shown the presence of multifocal lymphocytic myocarditis in three patients (14%). In an additional six patients, focally increased interstitial T-lymphocytes within the myocardium were noted, with only focal or no myocyte injury.
However, increased interstitial macrophage infiltration, possibly related to cytokine infiltration, was seen in 86% of patients.
“One way to think about this is that, if these patients were having biopsies and not autopsies, there would be myocardial injury in the patients with myocarditis, even after they recovered. But with interstitial macrophages, there may or may not be any injury,” said cardiovascular pathologist James R. Stone, MD, PhD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Dr. Stone and colleagues from Mass General, two hospitals in Italy, the University of Amsterdam, and the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., conducted the autopsies in March and April. The results were published in the October 14 issue of the European Heart Journal.
Their technique was rigorous: a median of 20 full-thickness blocks of myocardium were examined histologically (range, 5-29 blocks).
The presence of myocarditis, defined by the presence of multiple foci of inflammation with associated myocyte injury, was determined, and the inflammatory cell composition analyzed by immunohistochemistry.
“I think one of the take-homes from this study is that you have to do a thorough sampling of the heart in order to exclude myocardial injury. You cannot exclude myocarditis with just a biopsy or two,” said Dr. Stone in an interview.
“We looked at multiple different sections of tissue preserved in paraffin for every case and found only 14% had myocarditis. The vast majority of autopsies done on patients dying from COVID-19 have short-changed the autopsy and not been done in a way to exclude myocarditis,” he added.
For all patients, COVID-19 was the underlying cause of death, but the mechanisms of death were acute respiratory distress syndrome in 15, viral pneumonia in 4, cardiogenic shock in 1, and cardiac arrest in 1. Seven patients had a history of cardiovascular disease, including atrial fibrillation in four, coronary artery disease in three, left ventricular hypertrophy in one, and previous valve replacement in one. A total of 16 had hypertension, 7 had diabetes mellitus, and 1 had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In four cases, mild pericarditis was present. Acute myocyte injury in the right ventricle, most probably from strain or overload, was also present in four cases.
A nonsignificant trend was seen toward higher serum troponin levels in the patients with myocarditis compared with those without myocarditis. There were no reports of disrupted coronary artery plaques, coronary artery aneurysms, or large pulmonary emboli.
Macrophage infiltration rather than myocarditis, myocardial injury?
The study sheds more light on previous cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging findings that have suggested that many patients who recover from COVID-19 show signs suggestive of myocarditis. These earlier studies include a recent one in competitive athletes and the earlier Puntmann and colleagues study of relatively young COVID-19 patients, which showed ongoing myocardial involvement in a majority of patients.
“It would not surprise me if some or all of the cardiac MR changes seen in some of these recent imaging studies are due to the macrophages,” said Dr. Stone.
“What we saw was not a routine pathology by any means. It was a huge amount of macrophages, higher that what we saw in SARS and more similar to a study published in 2007 that looked at patients with bacterial sepsis,” said Dr. Stone.
In an older study of SARS patients, 35% had the virus detected in myocardial tissue by polymerase chain reaction. In that subset, the degree of myocardial macrophage infiltrate was comparable to that seen in 86% of the COVID-19 cases described in this series.
Another possibility is that the macrophage infiltration reflects underlying disease rather than COVID-19. All but one of the patients had known underlying medical conditions associated with cardiac remodeling, said Nikolaos G. Frangogiannis, MD, a cardiologist who studies the mechanisms of cardiac injury, repair, and remodeling.
Frangogiannis, from Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, wrote an editorial that accompanied the autopsy study.
“The problem with this finding of increased macrophage infiltration is that it’s very hard to interpret because as we age, and especially in a less healthy population, the numbers and the density of macrophages in the heart increase, so it’s impossible to interpret as an effect of the infection itself unless you have an appropriate control population that matches the same characteristics, which is almost impossible to ask for,” he said.
“I’ve observed since the beginning of the pandemic that there seemed to be some people who wanted every single case to be myocarditis and others who had a bias toward not wanting COVID-19 to be a cause of myocarditis. I think what we’re seeing is it’s not either/or for anything with this virus, it’s a bit of everything,” said Dr. Stone.
Dr. Stone and Dr. Frangogiannis reported no conflict of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
An international autopsy study of 21 patients who died from COVID-19 has shown the presence of multifocal lymphocytic myocarditis in three patients (14%). In an additional six patients, focally increased interstitial T-lymphocytes within the myocardium were noted, with only focal or no myocyte injury.
However, increased interstitial macrophage infiltration, possibly related to cytokine infiltration, was seen in 86% of patients.
“One way to think about this is that, if these patients were having biopsies and not autopsies, there would be myocardial injury in the patients with myocarditis, even after they recovered. But with interstitial macrophages, there may or may not be any injury,” said cardiovascular pathologist James R. Stone, MD, PhD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Dr. Stone and colleagues from Mass General, two hospitals in Italy, the University of Amsterdam, and the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., conducted the autopsies in March and April. The results were published in the October 14 issue of the European Heart Journal.
Their technique was rigorous: a median of 20 full-thickness blocks of myocardium were examined histologically (range, 5-29 blocks).
The presence of myocarditis, defined by the presence of multiple foci of inflammation with associated myocyte injury, was determined, and the inflammatory cell composition analyzed by immunohistochemistry.
“I think one of the take-homes from this study is that you have to do a thorough sampling of the heart in order to exclude myocardial injury. You cannot exclude myocarditis with just a biopsy or two,” said Dr. Stone in an interview.
“We looked at multiple different sections of tissue preserved in paraffin for every case and found only 14% had myocarditis. The vast majority of autopsies done on patients dying from COVID-19 have short-changed the autopsy and not been done in a way to exclude myocarditis,” he added.
For all patients, COVID-19 was the underlying cause of death, but the mechanisms of death were acute respiratory distress syndrome in 15, viral pneumonia in 4, cardiogenic shock in 1, and cardiac arrest in 1. Seven patients had a history of cardiovascular disease, including atrial fibrillation in four, coronary artery disease in three, left ventricular hypertrophy in one, and previous valve replacement in one. A total of 16 had hypertension, 7 had diabetes mellitus, and 1 had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In four cases, mild pericarditis was present. Acute myocyte injury in the right ventricle, most probably from strain or overload, was also present in four cases.
A nonsignificant trend was seen toward higher serum troponin levels in the patients with myocarditis compared with those without myocarditis. There were no reports of disrupted coronary artery plaques, coronary artery aneurysms, or large pulmonary emboli.
Macrophage infiltration rather than myocarditis, myocardial injury?
The study sheds more light on previous cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging findings that have suggested that many patients who recover from COVID-19 show signs suggestive of myocarditis. These earlier studies include a recent one in competitive athletes and the earlier Puntmann and colleagues study of relatively young COVID-19 patients, which showed ongoing myocardial involvement in a majority of patients.
“It would not surprise me if some or all of the cardiac MR changes seen in some of these recent imaging studies are due to the macrophages,” said Dr. Stone.
“What we saw was not a routine pathology by any means. It was a huge amount of macrophages, higher that what we saw in SARS and more similar to a study published in 2007 that looked at patients with bacterial sepsis,” said Dr. Stone.
In an older study of SARS patients, 35% had the virus detected in myocardial tissue by polymerase chain reaction. In that subset, the degree of myocardial macrophage infiltrate was comparable to that seen in 86% of the COVID-19 cases described in this series.
Another possibility is that the macrophage infiltration reflects underlying disease rather than COVID-19. All but one of the patients had known underlying medical conditions associated with cardiac remodeling, said Nikolaos G. Frangogiannis, MD, a cardiologist who studies the mechanisms of cardiac injury, repair, and remodeling.
Frangogiannis, from Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, wrote an editorial that accompanied the autopsy study.
“The problem with this finding of increased macrophage infiltration is that it’s very hard to interpret because as we age, and especially in a less healthy population, the numbers and the density of macrophages in the heart increase, so it’s impossible to interpret as an effect of the infection itself unless you have an appropriate control population that matches the same characteristics, which is almost impossible to ask for,” he said.
“I’ve observed since the beginning of the pandemic that there seemed to be some people who wanted every single case to be myocarditis and others who had a bias toward not wanting COVID-19 to be a cause of myocarditis. I think what we’re seeing is it’s not either/or for anything with this virus, it’s a bit of everything,” said Dr. Stone.
Dr. Stone and Dr. Frangogiannis reported no conflict of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Painful ethical choices in 2020 vs. 2010: How has thinking changed?
Much has changed in the 10 years since Medscape’s first survey on what physicians would do when faced with painful choices in patient care.
A new report, Ethics 2020: Life, Death, and Painful Dilemmas, shows that physicians’ value judgments have shifted in many respects, sometimes as a result of increased regulations and fears of litigation.
End-of-life decisions
Several of the questions in the survey revolved around end-of-life decisions, and in some cases, the differences seen in just a decade were striking. One example concerned life support decisions in the context of a family’s choices.
Age also seemed to play a role in the 2020 answers to that question: Physicians younger than 45 were more likely (28%) to answer “yes” (that they would withdraw life support in that instance) than were those 45 and older (16%).
A critical care physician said, “If the family appears to have an underlying motivation that may not be in the patient’s best interest, I might be inclined to pursue a legal decision prior to withdrawing support.”
A cardiologist had a more pointed response to the question: “To me, that would be murder.”
Another example of how perspectives have changed over the past 10 years concerns whether physician-aided dying should be legal for terminally ill patients. The practice is now mandated by law in eight states and the District of Columbia, and it is mandated by court ruling in two additional states.
In 2010, 41% said “no.” That number dropped to 28% in 2020.
On legalization, a psychiatrist said, “Yes, when there is truly no hope and the quality of remaining life is too poor. We show more compassion to our sick animals than we do to our human population.”
Conversely, a neurologist answered, “No, I see younger physicians already becoming comfortable with the idea of deciding ASAP whether there is a reasonable chance of survival and then pressing for the right code status. This change would make things worse.”
Assisted death and incurable suffering
Far fewer physicians supported physician-assisted death for those who had years to live but faced incurable suffering: Thirty-seven percent said “yes,” 34% said “no,” and 29% said “it depends.”
However, support was significantly higher than it was just 2 years ago, in 2018, when only 27% supported the concept, the report authors noted.
“The shift reflects movements by many states to legalize assisted dying for the terminally ill,” Arthur Caplan, PhD, director of the division of medical ethics, New York University, said in the report. “Legalization has not been abused, so some doctors are more willing to press further beyond terminal illness as a trigger to suffering.”
Conversely, many more physicians (44% vs. 24% a decade ago) said they would provide life-sustaining therapy if the family requested it, even if the physician thought it was futile.
“Concerns over a malpractice lawsuit and potential negative patient/family online reviews are factors that play into this change,” the survey authors wrote.
Shared decision making also increased in the past decade.
Would you undertreat pain?
Primary care physicians fear the consequences of what they consider adequate pain management more than specialists do (24% vs. 17%), the survey authors noted.
Ten years ago, Medscape asked physicians whether they would undertreat a patient’s pain because of fear of repercussions or the patient’s becoming addicted: Eighty-four percent said “no,” and 6% said “yes.” The rest said “it depends.”
In 2020, the question was asked slightly differently: “Would you undertreat a patient’s pain for fear of addiction or Drug Enforcement Administration or medical board scrutiny?” This year, three times as many said “yes” (18%); 63% said “no.”
“Respondents this year talked about investigations and reprimands by medical boards, and how much they wanted to avoid that,” the survey authors wrote.
Should physicians be required to treat COVID-19 patients?
Some questions were new this year, including one on whether physicians should be required to treat COVID-19 patients. Fewer than half (47%) answered “yes,” 24% said “no,” and 29% answered “it depends.”
Doctors’ answers to this question differed slightly by gender: Fifty percent of men and 43% of women said “yes.” In their responses, many physicians said consideration should be given to risk factors, such as age, underlying conditions, risk of family members, and availability of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Another pandemic-related question asked whether physicians felt they should correct physicians who post misinformation about the pandemic on social media. Half (50%) said “yes,” 19% said “no,” and 31% said “it depends.”
Speaking out against the workplace
This year, many physicians have felt betrayed when they didn’t have adequate PPE during the pandemic.
Asked, “Is it right to speak out against your hospital or workplace when they don’t give you what you need?” 53% of physicians said “yes,” 8% said “no,” and 40% said “it depends.”
A cardiologist made the value judgment this way: “Speaking out just because you had an argument with your boss is inappropriate. Bringing to the public repeated failures to correct situations that have been brought through the proper channels is necessary to incite change.”
Random drug testing for physicians?
Another question in the survey asked whether physicians should be subjected to random drug testing for alcohol and drug abuse. About one-third (34%) said yes, 43% said no, and 23% said “it depends.” A study found that between 10% and 15% of physicians have abused a substance at some point in their careers.
The subject continues to hit a nerve in medicine.
A family physician wrote, “This should not be done unless a particular physician had a problem with drug or alcohol abuse and shows signs of impairment.”
An internist took a different view, saying, “Military service men and women, police, firefighters, airline pilots, and other professions that have responsibilities affecting people’s lives are subject to testing; why not physicians?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Much has changed in the 10 years since Medscape’s first survey on what physicians would do when faced with painful choices in patient care.
A new report, Ethics 2020: Life, Death, and Painful Dilemmas, shows that physicians’ value judgments have shifted in many respects, sometimes as a result of increased regulations and fears of litigation.
End-of-life decisions
Several of the questions in the survey revolved around end-of-life decisions, and in some cases, the differences seen in just a decade were striking. One example concerned life support decisions in the context of a family’s choices.
Age also seemed to play a role in the 2020 answers to that question: Physicians younger than 45 were more likely (28%) to answer “yes” (that they would withdraw life support in that instance) than were those 45 and older (16%).
A critical care physician said, “If the family appears to have an underlying motivation that may not be in the patient’s best interest, I might be inclined to pursue a legal decision prior to withdrawing support.”
A cardiologist had a more pointed response to the question: “To me, that would be murder.”
Another example of how perspectives have changed over the past 10 years concerns whether physician-aided dying should be legal for terminally ill patients. The practice is now mandated by law in eight states and the District of Columbia, and it is mandated by court ruling in two additional states.
In 2010, 41% said “no.” That number dropped to 28% in 2020.
On legalization, a psychiatrist said, “Yes, when there is truly no hope and the quality of remaining life is too poor. We show more compassion to our sick animals than we do to our human population.”
Conversely, a neurologist answered, “No, I see younger physicians already becoming comfortable with the idea of deciding ASAP whether there is a reasonable chance of survival and then pressing for the right code status. This change would make things worse.”
Assisted death and incurable suffering
Far fewer physicians supported physician-assisted death for those who had years to live but faced incurable suffering: Thirty-seven percent said “yes,” 34% said “no,” and 29% said “it depends.”
However, support was significantly higher than it was just 2 years ago, in 2018, when only 27% supported the concept, the report authors noted.
“The shift reflects movements by many states to legalize assisted dying for the terminally ill,” Arthur Caplan, PhD, director of the division of medical ethics, New York University, said in the report. “Legalization has not been abused, so some doctors are more willing to press further beyond terminal illness as a trigger to suffering.”
Conversely, many more physicians (44% vs. 24% a decade ago) said they would provide life-sustaining therapy if the family requested it, even if the physician thought it was futile.
“Concerns over a malpractice lawsuit and potential negative patient/family online reviews are factors that play into this change,” the survey authors wrote.
Shared decision making also increased in the past decade.
Would you undertreat pain?
Primary care physicians fear the consequences of what they consider adequate pain management more than specialists do (24% vs. 17%), the survey authors noted.
Ten years ago, Medscape asked physicians whether they would undertreat a patient’s pain because of fear of repercussions or the patient’s becoming addicted: Eighty-four percent said “no,” and 6% said “yes.” The rest said “it depends.”
In 2020, the question was asked slightly differently: “Would you undertreat a patient’s pain for fear of addiction or Drug Enforcement Administration or medical board scrutiny?” This year, three times as many said “yes” (18%); 63% said “no.”
“Respondents this year talked about investigations and reprimands by medical boards, and how much they wanted to avoid that,” the survey authors wrote.
Should physicians be required to treat COVID-19 patients?
Some questions were new this year, including one on whether physicians should be required to treat COVID-19 patients. Fewer than half (47%) answered “yes,” 24% said “no,” and 29% answered “it depends.”
Doctors’ answers to this question differed slightly by gender: Fifty percent of men and 43% of women said “yes.” In their responses, many physicians said consideration should be given to risk factors, such as age, underlying conditions, risk of family members, and availability of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Another pandemic-related question asked whether physicians felt they should correct physicians who post misinformation about the pandemic on social media. Half (50%) said “yes,” 19% said “no,” and 31% said “it depends.”
Speaking out against the workplace
This year, many physicians have felt betrayed when they didn’t have adequate PPE during the pandemic.
Asked, “Is it right to speak out against your hospital or workplace when they don’t give you what you need?” 53% of physicians said “yes,” 8% said “no,” and 40% said “it depends.”
A cardiologist made the value judgment this way: “Speaking out just because you had an argument with your boss is inappropriate. Bringing to the public repeated failures to correct situations that have been brought through the proper channels is necessary to incite change.”
Random drug testing for physicians?
Another question in the survey asked whether physicians should be subjected to random drug testing for alcohol and drug abuse. About one-third (34%) said yes, 43% said no, and 23% said “it depends.” A study found that between 10% and 15% of physicians have abused a substance at some point in their careers.
The subject continues to hit a nerve in medicine.
A family physician wrote, “This should not be done unless a particular physician had a problem with drug or alcohol abuse and shows signs of impairment.”
An internist took a different view, saying, “Military service men and women, police, firefighters, airline pilots, and other professions that have responsibilities affecting people’s lives are subject to testing; why not physicians?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Much has changed in the 10 years since Medscape’s first survey on what physicians would do when faced with painful choices in patient care.
A new report, Ethics 2020: Life, Death, and Painful Dilemmas, shows that physicians’ value judgments have shifted in many respects, sometimes as a result of increased regulations and fears of litigation.
End-of-life decisions
Several of the questions in the survey revolved around end-of-life decisions, and in some cases, the differences seen in just a decade were striking. One example concerned life support decisions in the context of a family’s choices.
Age also seemed to play a role in the 2020 answers to that question: Physicians younger than 45 were more likely (28%) to answer “yes” (that they would withdraw life support in that instance) than were those 45 and older (16%).
A critical care physician said, “If the family appears to have an underlying motivation that may not be in the patient’s best interest, I might be inclined to pursue a legal decision prior to withdrawing support.”
A cardiologist had a more pointed response to the question: “To me, that would be murder.”
Another example of how perspectives have changed over the past 10 years concerns whether physician-aided dying should be legal for terminally ill patients. The practice is now mandated by law in eight states and the District of Columbia, and it is mandated by court ruling in two additional states.
In 2010, 41% said “no.” That number dropped to 28% in 2020.
On legalization, a psychiatrist said, “Yes, when there is truly no hope and the quality of remaining life is too poor. We show more compassion to our sick animals than we do to our human population.”
Conversely, a neurologist answered, “No, I see younger physicians already becoming comfortable with the idea of deciding ASAP whether there is a reasonable chance of survival and then pressing for the right code status. This change would make things worse.”
Assisted death and incurable suffering
Far fewer physicians supported physician-assisted death for those who had years to live but faced incurable suffering: Thirty-seven percent said “yes,” 34% said “no,” and 29% said “it depends.”
However, support was significantly higher than it was just 2 years ago, in 2018, when only 27% supported the concept, the report authors noted.
“The shift reflects movements by many states to legalize assisted dying for the terminally ill,” Arthur Caplan, PhD, director of the division of medical ethics, New York University, said in the report. “Legalization has not been abused, so some doctors are more willing to press further beyond terminal illness as a trigger to suffering.”
Conversely, many more physicians (44% vs. 24% a decade ago) said they would provide life-sustaining therapy if the family requested it, even if the physician thought it was futile.
“Concerns over a malpractice lawsuit and potential negative patient/family online reviews are factors that play into this change,” the survey authors wrote.
Shared decision making also increased in the past decade.
Would you undertreat pain?
Primary care physicians fear the consequences of what they consider adequate pain management more than specialists do (24% vs. 17%), the survey authors noted.
Ten years ago, Medscape asked physicians whether they would undertreat a patient’s pain because of fear of repercussions or the patient’s becoming addicted: Eighty-four percent said “no,” and 6% said “yes.” The rest said “it depends.”
In 2020, the question was asked slightly differently: “Would you undertreat a patient’s pain for fear of addiction or Drug Enforcement Administration or medical board scrutiny?” This year, three times as many said “yes” (18%); 63% said “no.”
“Respondents this year talked about investigations and reprimands by medical boards, and how much they wanted to avoid that,” the survey authors wrote.
Should physicians be required to treat COVID-19 patients?
Some questions were new this year, including one on whether physicians should be required to treat COVID-19 patients. Fewer than half (47%) answered “yes,” 24% said “no,” and 29% answered “it depends.”
Doctors’ answers to this question differed slightly by gender: Fifty percent of men and 43% of women said “yes.” In their responses, many physicians said consideration should be given to risk factors, such as age, underlying conditions, risk of family members, and availability of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Another pandemic-related question asked whether physicians felt they should correct physicians who post misinformation about the pandemic on social media. Half (50%) said “yes,” 19% said “no,” and 31% said “it depends.”
Speaking out against the workplace
This year, many physicians have felt betrayed when they didn’t have adequate PPE during the pandemic.
Asked, “Is it right to speak out against your hospital or workplace when they don’t give you what you need?” 53% of physicians said “yes,” 8% said “no,” and 40% said “it depends.”
A cardiologist made the value judgment this way: “Speaking out just because you had an argument with your boss is inappropriate. Bringing to the public repeated failures to correct situations that have been brought through the proper channels is necessary to incite change.”
Random drug testing for physicians?
Another question in the survey asked whether physicians should be subjected to random drug testing for alcohol and drug abuse. About one-third (34%) said yes, 43% said no, and 23% said “it depends.” A study found that between 10% and 15% of physicians have abused a substance at some point in their careers.
The subject continues to hit a nerve in medicine.
A family physician wrote, “This should not be done unless a particular physician had a problem with drug or alcohol abuse and shows signs of impairment.”
An internist took a different view, saying, “Military service men and women, police, firefighters, airline pilots, and other professions that have responsibilities affecting people’s lives are subject to testing; why not physicians?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Liver injury linked to COVID-19–related coagulopathy
There is a link between liver injury and a tendency toward excessive clotting in patients with COVID-19, and the organ’s own blood vessels could be responsible, new research shows.
Cells that line the liver’s blood vessels produce high levels of factor VIII, a coagulation factor, when they are exposed to interleukin-6, an inflammatory molecule associated with COVID-19.
These findings “center the liver in global coagulopathy of COVID-19 and define a mechanism for increased coagulation factor levels that may be treatment targets,” said investigator Matthew McConnell, MD, from the Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The effect of IL-6 on the liver sinusoidal endothelial cells lining the liver blood vessels creates a prothrombotic environment that includes the release of factor VIII, said Dr. McConnell, who presented the results at the virtual annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
These associations offer insights into why COVID-19 patients with underlying liver disease can experience “devastating complications” related to improper blood vessel function in the organ, he added.
For their study, Dr. McConnell and colleagues analyzed data on ALT and hypercoagulability from 68 adults treated at the Yale–New Haven Hospital. The liver and coagulation tests were administered within 5 days of each other.
The team set the ALT cutoff for liver injury at three times the upper limit of normal. Patients with two or more parameters indicating excessive clotting were considered to have a hypercoagulable profile, which Dr. McConnell called “a signature clinical finding of COVID-19 infection.”
Patients with high levels of ALT also experienced elevations in clotting-related factors, such as fibrinogen levels and the activity of factor VIII and factor II. Furthermore, liver injury was significantly associated with hypercoagulability (P < .05).
Because COVID-19 is linked to the proinflammatory IL-6, the investigators examined how this cytokine and its receptor affect human liver sinusoidal cells. Cells exposed to IL-6 and its receptor pumped out factor VIII at levels that were significantly higher than in unexposed cells (P < .01). Exposed cells also produced significantly more von Willebrand factor (P < .05), another prothrombotic molecule, and showed increased expression of genes that induce the expression of factor VIII.
“As we learn more about COVID-19, we find that it is as much a coagulatory as a respiratory disease,” said Tien Dong, MD, PhD, from the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the study.
These findings are in line with a lot of other COVID-19-related research that suggests a link between hepatocyte injury and clotting disorders, he added.
One important factor is existing liver disease, said Dr. Dong. “If you have COVID-19 on top of that, you’re probably at risk of developing acute liver injury from the infection itself.”
That said, it’s still a good idea to check liver function in patients with COVID-19 and no known liver disease, he advised. Staying on top of these measures will keep the odds of long-term problems “a lot lower.”
There is utility in the findings beyond COVID-19, said Dr. McConnell. They provide “insights into complications of critical illness, in general, in the liver blood vessels” of patients with underlying liver disease.
Dr. McConnell and Dr. Dong have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
There is a link between liver injury and a tendency toward excessive clotting in patients with COVID-19, and the organ’s own blood vessels could be responsible, new research shows.
Cells that line the liver’s blood vessels produce high levels of factor VIII, a coagulation factor, when they are exposed to interleukin-6, an inflammatory molecule associated with COVID-19.
These findings “center the liver in global coagulopathy of COVID-19 and define a mechanism for increased coagulation factor levels that may be treatment targets,” said investigator Matthew McConnell, MD, from the Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The effect of IL-6 on the liver sinusoidal endothelial cells lining the liver blood vessels creates a prothrombotic environment that includes the release of factor VIII, said Dr. McConnell, who presented the results at the virtual annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
These associations offer insights into why COVID-19 patients with underlying liver disease can experience “devastating complications” related to improper blood vessel function in the organ, he added.
For their study, Dr. McConnell and colleagues analyzed data on ALT and hypercoagulability from 68 adults treated at the Yale–New Haven Hospital. The liver and coagulation tests were administered within 5 days of each other.
The team set the ALT cutoff for liver injury at three times the upper limit of normal. Patients with two or more parameters indicating excessive clotting were considered to have a hypercoagulable profile, which Dr. McConnell called “a signature clinical finding of COVID-19 infection.”
Patients with high levels of ALT also experienced elevations in clotting-related factors, such as fibrinogen levels and the activity of factor VIII and factor II. Furthermore, liver injury was significantly associated with hypercoagulability (P < .05).
Because COVID-19 is linked to the proinflammatory IL-6, the investigators examined how this cytokine and its receptor affect human liver sinusoidal cells. Cells exposed to IL-6 and its receptor pumped out factor VIII at levels that were significantly higher than in unexposed cells (P < .01). Exposed cells also produced significantly more von Willebrand factor (P < .05), another prothrombotic molecule, and showed increased expression of genes that induce the expression of factor VIII.
“As we learn more about COVID-19, we find that it is as much a coagulatory as a respiratory disease,” said Tien Dong, MD, PhD, from the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the study.
These findings are in line with a lot of other COVID-19-related research that suggests a link between hepatocyte injury and clotting disorders, he added.
One important factor is existing liver disease, said Dr. Dong. “If you have COVID-19 on top of that, you’re probably at risk of developing acute liver injury from the infection itself.”
That said, it’s still a good idea to check liver function in patients with COVID-19 and no known liver disease, he advised. Staying on top of these measures will keep the odds of long-term problems “a lot lower.”
There is utility in the findings beyond COVID-19, said Dr. McConnell. They provide “insights into complications of critical illness, in general, in the liver blood vessels” of patients with underlying liver disease.
Dr. McConnell and Dr. Dong have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
There is a link between liver injury and a tendency toward excessive clotting in patients with COVID-19, and the organ’s own blood vessels could be responsible, new research shows.
Cells that line the liver’s blood vessels produce high levels of factor VIII, a coagulation factor, when they are exposed to interleukin-6, an inflammatory molecule associated with COVID-19.
These findings “center the liver in global coagulopathy of COVID-19 and define a mechanism for increased coagulation factor levels that may be treatment targets,” said investigator Matthew McConnell, MD, from the Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The effect of IL-6 on the liver sinusoidal endothelial cells lining the liver blood vessels creates a prothrombotic environment that includes the release of factor VIII, said Dr. McConnell, who presented the results at the virtual annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
These associations offer insights into why COVID-19 patients with underlying liver disease can experience “devastating complications” related to improper blood vessel function in the organ, he added.
For their study, Dr. McConnell and colleagues analyzed data on ALT and hypercoagulability from 68 adults treated at the Yale–New Haven Hospital. The liver and coagulation tests were administered within 5 days of each other.
The team set the ALT cutoff for liver injury at three times the upper limit of normal. Patients with two or more parameters indicating excessive clotting were considered to have a hypercoagulable profile, which Dr. McConnell called “a signature clinical finding of COVID-19 infection.”
Patients with high levels of ALT also experienced elevations in clotting-related factors, such as fibrinogen levels and the activity of factor VIII and factor II. Furthermore, liver injury was significantly associated with hypercoagulability (P < .05).
Because COVID-19 is linked to the proinflammatory IL-6, the investigators examined how this cytokine and its receptor affect human liver sinusoidal cells. Cells exposed to IL-6 and its receptor pumped out factor VIII at levels that were significantly higher than in unexposed cells (P < .01). Exposed cells also produced significantly more von Willebrand factor (P < .05), another prothrombotic molecule, and showed increased expression of genes that induce the expression of factor VIII.
“As we learn more about COVID-19, we find that it is as much a coagulatory as a respiratory disease,” said Tien Dong, MD, PhD, from the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the study.
These findings are in line with a lot of other COVID-19-related research that suggests a link between hepatocyte injury and clotting disorders, he added.
One important factor is existing liver disease, said Dr. Dong. “If you have COVID-19 on top of that, you’re probably at risk of developing acute liver injury from the infection itself.”
That said, it’s still a good idea to check liver function in patients with COVID-19 and no known liver disease, he advised. Staying on top of these measures will keep the odds of long-term problems “a lot lower.”
There is utility in the findings beyond COVID-19, said Dr. McConnell. They provide “insights into complications of critical illness, in general, in the liver blood vessels” of patients with underlying liver disease.
Dr. McConnell and Dr. Dong have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.