User login
Official news magazine of the Society of Hospital Medicine
Copyright by Society of Hospital Medicine or related companies. All rights reserved. ISSN 1553-085X
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-hospitalist')]


United States adds nearly 74,000 more children with COVID-19
The new weekly high for COVID-19 cases in children announced last week has been surpassed already, as the United States experienced almost 74,000 new pediatric cases for the week ending Nov. 5, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
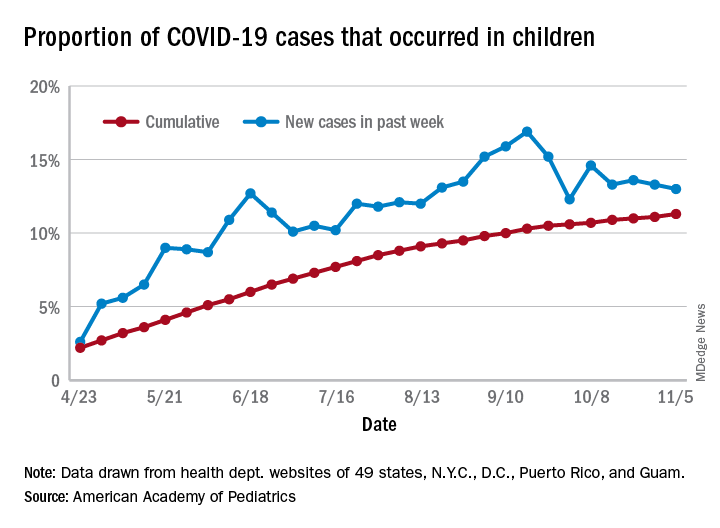
The total number of COVID-19 cases in children is now 927,518 in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report.
Cumulatively, children represent 11.3% of all COVID-19 cases in those jurisdictions, up from 11.1% a week ago. For just the past week, those 73,883 children represent 13.0% of the 567,672 new cases reported among all ages. That proportion peaked at 16.9% in mid-September, the AAP/CHA data show.
Dropping down to the state level, cumulative proportions as of Nov. 5 range from 5.2% in New Jersey to 23.3% in Wyoming, with 11 other states over 15%. California has had more cases, 100,856, than any other state, and Vermont the fewest at 329, the AAP and CHA said.
The national rate per 100,000 children is now 1,232, up from 1,134 the previous week and more than doubled since mid-August (582.2 per 100,000 on Aug. 20). North Dakota’s rate of 3,990 per 100,000 children is the highest of any state (South Dakota is next at 2,779), while Vermont is again the lowest at 245 per 100,000, based on data collected from state health department websites.
Two COVID-19–related deaths in children were reported during the week ending Nov. 5, bringing the total to 123 but leaving the overall proportion of deaths in children unchanged at 0.06% of all deaths. Texas has reported the most COVID-19 deaths in children with 29, while 15 states have recorded no deaths so far (mortality data in children reported by 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA said.
The new weekly high for COVID-19 cases in children announced last week has been surpassed already, as the United States experienced almost 74,000 new pediatric cases for the week ending Nov. 5, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of COVID-19 cases in children is now 927,518 in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report.
Cumulatively, children represent 11.3% of all COVID-19 cases in those jurisdictions, up from 11.1% a week ago. For just the past week, those 73,883 children represent 13.0% of the 567,672 new cases reported among all ages. That proportion peaked at 16.9% in mid-September, the AAP/CHA data show.
Dropping down to the state level, cumulative proportions as of Nov. 5 range from 5.2% in New Jersey to 23.3% in Wyoming, with 11 other states over 15%. California has had more cases, 100,856, than any other state, and Vermont the fewest at 329, the AAP and CHA said.
The national rate per 100,000 children is now 1,232, up from 1,134 the previous week and more than doubled since mid-August (582.2 per 100,000 on Aug. 20). North Dakota’s rate of 3,990 per 100,000 children is the highest of any state (South Dakota is next at 2,779), while Vermont is again the lowest at 245 per 100,000, based on data collected from state health department websites.
Two COVID-19–related deaths in children were reported during the week ending Nov. 5, bringing the total to 123 but leaving the overall proportion of deaths in children unchanged at 0.06% of all deaths. Texas has reported the most COVID-19 deaths in children with 29, while 15 states have recorded no deaths so far (mortality data in children reported by 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA said.
The new weekly high for COVID-19 cases in children announced last week has been surpassed already, as the United States experienced almost 74,000 new pediatric cases for the week ending Nov. 5, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of COVID-19 cases in children is now 927,518 in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report.
Cumulatively, children represent 11.3% of all COVID-19 cases in those jurisdictions, up from 11.1% a week ago. For just the past week, those 73,883 children represent 13.0% of the 567,672 new cases reported among all ages. That proportion peaked at 16.9% in mid-September, the AAP/CHA data show.
Dropping down to the state level, cumulative proportions as of Nov. 5 range from 5.2% in New Jersey to 23.3% in Wyoming, with 11 other states over 15%. California has had more cases, 100,856, than any other state, and Vermont the fewest at 329, the AAP and CHA said.
The national rate per 100,000 children is now 1,232, up from 1,134 the previous week and more than doubled since mid-August (582.2 per 100,000 on Aug. 20). North Dakota’s rate of 3,990 per 100,000 children is the highest of any state (South Dakota is next at 2,779), while Vermont is again the lowest at 245 per 100,000, based on data collected from state health department websites.
Two COVID-19–related deaths in children were reported during the week ending Nov. 5, bringing the total to 123 but leaving the overall proportion of deaths in children unchanged at 0.06% of all deaths. Texas has reported the most COVID-19 deaths in children with 29, while 15 states have recorded no deaths so far (mortality data in children reported by 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA said.
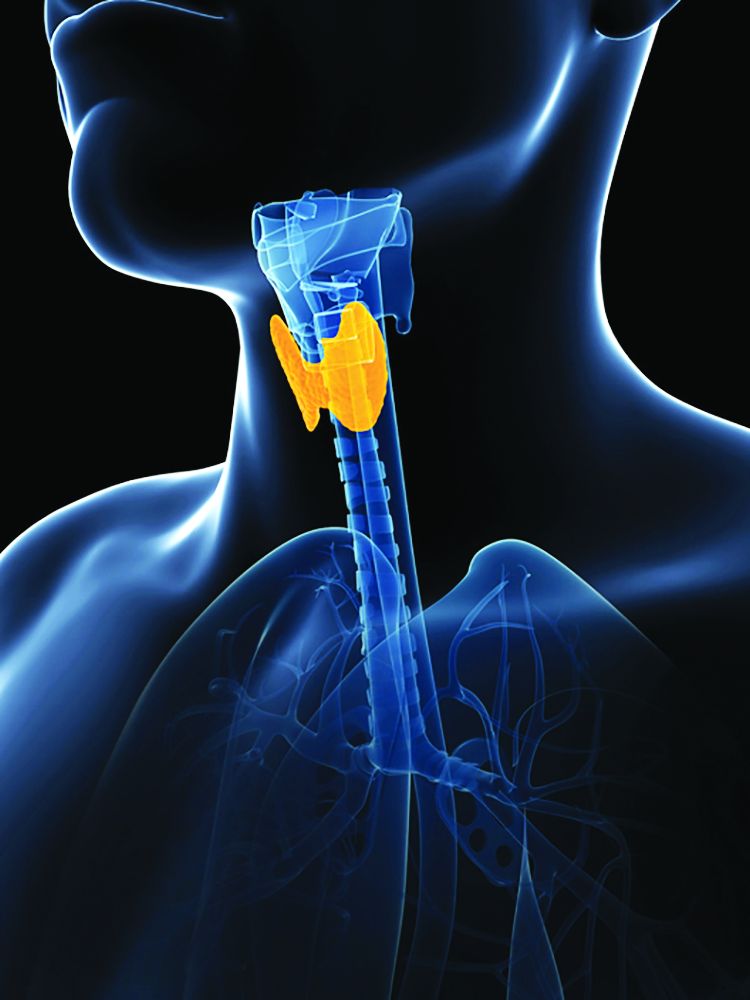
No link shown between thyroid dysfunction and heart failure
Thyroid dysfunction had virtually no independent impact on survival in a retrospective study of nearly 5,000 English patients with chronic heart failure, adding to evidence that subclinical thyroid disorders in these patients requires no special management beyond ongoing monitoring.
“Although thyroid dysfunction is related to outcome in patients with chronic heart failure, the association disappears when adjustment is made for established prognostic variables, such as age, NT-proBNP [N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide], and [New York Heart Association] class,” wrote Nathan A. Samuel, MBChB, and coauthors in the American Journal of Cardiology.
Results from several earlier studies had shown evidence for reduced survival in heart failure patients with thyroid dysfunction, but in analyses that did not adjust for heart failure severity, such as a 2013 report that used data from the Sudden Cardiac Death in Heart Failure Trial SCD-HeFT. Other studies that adjusted for heart failure severity based on serum level of natriuretic peptides did not show significant associations between thyroid function and mortality, and when those results couple with the new report they together minimize the immediate risk from subclinical thyroid dysfunction faced by heart failure patients, wrote the authors of the new report.
Don’t treat subclinical thyroid dysfunction
“Our results suggest that subclinical thyroid disease has little impact on outcomes, and that we should not treat subclinical hypothyroidism in the expectation of improving outlook,” said Andrew L. Clark, MD, senior author on the new report and professor and head of the department of academic cardiology at Hull (England) York Medical School.
“Both hyper-and hypothyroidism can cause heart failure, so thyroid function should always be checked in patients when they present with heart failure. A small proportion of patients have heart failure that is potentially reversible” with thyroid-directed treatment, Dr. Clark said in an interview.
But “subclinical disease should probably not be treated, although we have not conducted a clinical trial that proves this assertion. We speculate, based on our findings, that such a trial is unlikely to be positive.”
Patients with subclinical thyroid disorders, particularly subclinical hypothyroidism, “need to be followed and treated should they develop clinical disease,” he maintained. “Except in extreme circumstances, such as the handful of patients who might have gross myxedema and may be near coma, thyroid replacement therapy for those [with heart failure] who have clinical hypothyroidism should follow standard lines.”
It is important to monitor thyroid function,” agreed Dr. Samuel, a researcher in the department of academic cardiology at Hull York Medical School. “We found that thyroxine use was most common among patients with hyperthyroidism, suggesting that they were previously hypothyroid and had received inappropriate treatment.”
Confounder adjustment mitigates the thyroid link
The new analysis used data collected from 6,782 consecutive heart failure patients enrolled during 2000-2018 at a community heart failure clinic that serves patients in the region of Hull, England. The researchers identified 4,992 of these patients with confirmed heart failure and adequate data for their analyses, including 2,997 (60%) with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and 1,995 (40%) with heart failure with normal ejection fraction (HFnEF, the term used by the authors but often called heart failure with preserved ejection fraction).
Thyroid hormone levels showed that 90% of these patients were euthyroid, 6% were hyperthyroid, and 4% were hypothyroid, rates consistent with prior reports for both the general population and heart failure patients. Only 12 patients (0.2%) had overt hypothyroidism, and fewer that 1% (about 45 patients) had overt hyperthyroidism. Patients averaged about 73 years of age, and during a median 4.6 years of follow-up 58% died.
Both the hypo- and hyperthyroid patients showed significantly higher mortality rates than euthyroid patients in a univariate analysis. But the patients with thyroid dysfunction also had more comorbidities, more severe heart failure symptoms measured by NYHA functional class, and more severe heart failure measured as higher serum levels of NT-proBNP.
In a multivariate analysis that adjusted for these factors, the significant differences disappeared among the entire group of heart failure patients for the outcomes of all-cause mortality, and mortality or hospitalization with heart failure. The multivariate analysis also showed no significant association between higher levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and all-cause death or death plus heart failure hospitalization among the patients with HFrEF.
Among patients with HFnEF, the multivariate adjusted analysis showed a small increase in both mortality and mortality plus hospitalization for heart failure, a 2% rise for each of these two endpoints for each 1 mIU/L increase in TSH, the authors reported. Although the P value for each of these two significant differences among patients with HFnEF was .02, the 95% confidence interval included 1.00 and ranged from 1.00 to 1.04.
The multivariate analysis identified three variables with the strongest associations with all-cause mortality: older age, higher levels of NT-proBNP, and higher NYHA class indicating greater functional impairment.
The results support the hypothesis that “worsening heart failure can lead to down-regulation of thyroid hormone signaling,” the authors suggested. Their study is also “the first to examine the prognostic significance of thyroid dysfunction in a large population of patients with HFnEF.” This analysis showed a “weak but significant association between increasing TSH and both mortality and the composite endpoint in patients with HFnEF.”
“HFnEF is a heterogeneous group of conditions that are difficult to diagnose in many cases. Therefore, future studies are needed to provide further clarity on the effect of thyroid dysfunction in these patients,” Dr. Samuel said.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Samuel and Dr. Clark had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Samuel NA et al. Am J Cardiol. 2020 Oct 24. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.10.034.
Thyroid dysfunction had virtually no independent impact on survival in a retrospective study of nearly 5,000 English patients with chronic heart failure, adding to evidence that subclinical thyroid disorders in these patients requires no special management beyond ongoing monitoring.
“Although thyroid dysfunction is related to outcome in patients with chronic heart failure, the association disappears when adjustment is made for established prognostic variables, such as age, NT-proBNP [N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide], and [New York Heart Association] class,” wrote Nathan A. Samuel, MBChB, and coauthors in the American Journal of Cardiology.
Results from several earlier studies had shown evidence for reduced survival in heart failure patients with thyroid dysfunction, but in analyses that did not adjust for heart failure severity, such as a 2013 report that used data from the Sudden Cardiac Death in Heart Failure Trial SCD-HeFT. Other studies that adjusted for heart failure severity based on serum level of natriuretic peptides did not show significant associations between thyroid function and mortality, and when those results couple with the new report they together minimize the immediate risk from subclinical thyroid dysfunction faced by heart failure patients, wrote the authors of the new report.
Don’t treat subclinical thyroid dysfunction
“Our results suggest that subclinical thyroid disease has little impact on outcomes, and that we should not treat subclinical hypothyroidism in the expectation of improving outlook,” said Andrew L. Clark, MD, senior author on the new report and professor and head of the department of academic cardiology at Hull (England) York Medical School.
“Both hyper-and hypothyroidism can cause heart failure, so thyroid function should always be checked in patients when they present with heart failure. A small proportion of patients have heart failure that is potentially reversible” with thyroid-directed treatment, Dr. Clark said in an interview.
But “subclinical disease should probably not be treated, although we have not conducted a clinical trial that proves this assertion. We speculate, based on our findings, that such a trial is unlikely to be positive.”
Patients with subclinical thyroid disorders, particularly subclinical hypothyroidism, “need to be followed and treated should they develop clinical disease,” he maintained. “Except in extreme circumstances, such as the handful of patients who might have gross myxedema and may be near coma, thyroid replacement therapy for those [with heart failure] who have clinical hypothyroidism should follow standard lines.”
It is important to monitor thyroid function,” agreed Dr. Samuel, a researcher in the department of academic cardiology at Hull York Medical School. “We found that thyroxine use was most common among patients with hyperthyroidism, suggesting that they were previously hypothyroid and had received inappropriate treatment.”
Confounder adjustment mitigates the thyroid link
The new analysis used data collected from 6,782 consecutive heart failure patients enrolled during 2000-2018 at a community heart failure clinic that serves patients in the region of Hull, England. The researchers identified 4,992 of these patients with confirmed heart failure and adequate data for their analyses, including 2,997 (60%) with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and 1,995 (40%) with heart failure with normal ejection fraction (HFnEF, the term used by the authors but often called heart failure with preserved ejection fraction).
Thyroid hormone levels showed that 90% of these patients were euthyroid, 6% were hyperthyroid, and 4% were hypothyroid, rates consistent with prior reports for both the general population and heart failure patients. Only 12 patients (0.2%) had overt hypothyroidism, and fewer that 1% (about 45 patients) had overt hyperthyroidism. Patients averaged about 73 years of age, and during a median 4.6 years of follow-up 58% died.
Both the hypo- and hyperthyroid patients showed significantly higher mortality rates than euthyroid patients in a univariate analysis. But the patients with thyroid dysfunction also had more comorbidities, more severe heart failure symptoms measured by NYHA functional class, and more severe heart failure measured as higher serum levels of NT-proBNP.
In a multivariate analysis that adjusted for these factors, the significant differences disappeared among the entire group of heart failure patients for the outcomes of all-cause mortality, and mortality or hospitalization with heart failure. The multivariate analysis also showed no significant association between higher levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and all-cause death or death plus heart failure hospitalization among the patients with HFrEF.
Among patients with HFnEF, the multivariate adjusted analysis showed a small increase in both mortality and mortality plus hospitalization for heart failure, a 2% rise for each of these two endpoints for each 1 mIU/L increase in TSH, the authors reported. Although the P value for each of these two significant differences among patients with HFnEF was .02, the 95% confidence interval included 1.00 and ranged from 1.00 to 1.04.
The multivariate analysis identified three variables with the strongest associations with all-cause mortality: older age, higher levels of NT-proBNP, and higher NYHA class indicating greater functional impairment.
The results support the hypothesis that “worsening heart failure can lead to down-regulation of thyroid hormone signaling,” the authors suggested. Their study is also “the first to examine the prognostic significance of thyroid dysfunction in a large population of patients with HFnEF.” This analysis showed a “weak but significant association between increasing TSH and both mortality and the composite endpoint in patients with HFnEF.”
“HFnEF is a heterogeneous group of conditions that are difficult to diagnose in many cases. Therefore, future studies are needed to provide further clarity on the effect of thyroid dysfunction in these patients,” Dr. Samuel said.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Samuel and Dr. Clark had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Samuel NA et al. Am J Cardiol. 2020 Oct 24. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.10.034.
Thyroid dysfunction had virtually no independent impact on survival in a retrospective study of nearly 5,000 English patients with chronic heart failure, adding to evidence that subclinical thyroid disorders in these patients requires no special management beyond ongoing monitoring.
“Although thyroid dysfunction is related to outcome in patients with chronic heart failure, the association disappears when adjustment is made for established prognostic variables, such as age, NT-proBNP [N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide], and [New York Heart Association] class,” wrote Nathan A. Samuel, MBChB, and coauthors in the American Journal of Cardiology.
Results from several earlier studies had shown evidence for reduced survival in heart failure patients with thyroid dysfunction, but in analyses that did not adjust for heart failure severity, such as a 2013 report that used data from the Sudden Cardiac Death in Heart Failure Trial SCD-HeFT. Other studies that adjusted for heart failure severity based on serum level of natriuretic peptides did not show significant associations between thyroid function and mortality, and when those results couple with the new report they together minimize the immediate risk from subclinical thyroid dysfunction faced by heart failure patients, wrote the authors of the new report.
Don’t treat subclinical thyroid dysfunction
“Our results suggest that subclinical thyroid disease has little impact on outcomes, and that we should not treat subclinical hypothyroidism in the expectation of improving outlook,” said Andrew L. Clark, MD, senior author on the new report and professor and head of the department of academic cardiology at Hull (England) York Medical School.
“Both hyper-and hypothyroidism can cause heart failure, so thyroid function should always be checked in patients when they present with heart failure. A small proportion of patients have heart failure that is potentially reversible” with thyroid-directed treatment, Dr. Clark said in an interview.
But “subclinical disease should probably not be treated, although we have not conducted a clinical trial that proves this assertion. We speculate, based on our findings, that such a trial is unlikely to be positive.”
Patients with subclinical thyroid disorders, particularly subclinical hypothyroidism, “need to be followed and treated should they develop clinical disease,” he maintained. “Except in extreme circumstances, such as the handful of patients who might have gross myxedema and may be near coma, thyroid replacement therapy for those [with heart failure] who have clinical hypothyroidism should follow standard lines.”
It is important to monitor thyroid function,” agreed Dr. Samuel, a researcher in the department of academic cardiology at Hull York Medical School. “We found that thyroxine use was most common among patients with hyperthyroidism, suggesting that they were previously hypothyroid and had received inappropriate treatment.”
Confounder adjustment mitigates the thyroid link
The new analysis used data collected from 6,782 consecutive heart failure patients enrolled during 2000-2018 at a community heart failure clinic that serves patients in the region of Hull, England. The researchers identified 4,992 of these patients with confirmed heart failure and adequate data for their analyses, including 2,997 (60%) with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and 1,995 (40%) with heart failure with normal ejection fraction (HFnEF, the term used by the authors but often called heart failure with preserved ejection fraction).
Thyroid hormone levels showed that 90% of these patients were euthyroid, 6% were hyperthyroid, and 4% were hypothyroid, rates consistent with prior reports for both the general population and heart failure patients. Only 12 patients (0.2%) had overt hypothyroidism, and fewer that 1% (about 45 patients) had overt hyperthyroidism. Patients averaged about 73 years of age, and during a median 4.6 years of follow-up 58% died.
Both the hypo- and hyperthyroid patients showed significantly higher mortality rates than euthyroid patients in a univariate analysis. But the patients with thyroid dysfunction also had more comorbidities, more severe heart failure symptoms measured by NYHA functional class, and more severe heart failure measured as higher serum levels of NT-proBNP.
In a multivariate analysis that adjusted for these factors, the significant differences disappeared among the entire group of heart failure patients for the outcomes of all-cause mortality, and mortality or hospitalization with heart failure. The multivariate analysis also showed no significant association between higher levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and all-cause death or death plus heart failure hospitalization among the patients with HFrEF.
Among patients with HFnEF, the multivariate adjusted analysis showed a small increase in both mortality and mortality plus hospitalization for heart failure, a 2% rise for each of these two endpoints for each 1 mIU/L increase in TSH, the authors reported. Although the P value for each of these two significant differences among patients with HFnEF was .02, the 95% confidence interval included 1.00 and ranged from 1.00 to 1.04.
The multivariate analysis identified three variables with the strongest associations with all-cause mortality: older age, higher levels of NT-proBNP, and higher NYHA class indicating greater functional impairment.
The results support the hypothesis that “worsening heart failure can lead to down-regulation of thyroid hormone signaling,” the authors suggested. Their study is also “the first to examine the prognostic significance of thyroid dysfunction in a large population of patients with HFnEF.” This analysis showed a “weak but significant association between increasing TSH and both mortality and the composite endpoint in patients with HFnEF.”
“HFnEF is a heterogeneous group of conditions that are difficult to diagnose in many cases. Therefore, future studies are needed to provide further clarity on the effect of thyroid dysfunction in these patients,” Dr. Samuel said.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Samuel and Dr. Clark had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Samuel NA et al. Am J Cardiol. 2020 Oct 24. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.10.034.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CARDIOLOGY
Whales, seals, and dolphins: Will SARS-CoV-2–contaminated wastewater prove a killer?
Zoonoses are no respecter of biological boundaries and are notorious for crossing genus and even higher taxonomic boundaries. SARS-CoV-2 is no exception, the current outbreak most probably having originated in bats, a common source of human-affecting zoonoses throughout history. But it is not a one-way street, and the virus has been shown to spread from infected humans to a variety of other land mammals, including our domesticated animals and kept zoo species.
A recent troubling report, however, has indicated that sea mammals may be part of a next wave of likely candidates for infection, put at risk by the current human pandemic and environmental degradation on a global scale, according to a the results of a genomic analysis of four major groups of sea mammals.
Researchers Sabateeshan Mathavarajah and colleagues from Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., examined the sequences of the ACE2 receptors in the various marine mammal species. The ACE2 receptor has recently been identified as the SARS-CoV-2 receptor, which allows for infection.
The researchers examined genomic databases of the marine species to determine if their ACE2 receptor sequences indicated the potential for high, medium, or low susceptibility to infection, as reported in Science of the Total Environment. Database analysis was performed for four groups: Cetacea (whales and dolphins), Pinnepidia (seals), Sirenia (sea cows), and Fissipedia (sea otters and polar bears).
The researchers defined susceptibility values based on comparable binding with the receptor and came up with the following subgroups: higher than human, high (resembles human ACE2), medium (resembles cat ACE2), and low (resembles dog ACE2). It has yet to be established if these marine mammals actually are infected with SARS-CoV-2 and what the impact of such an infection might have on animal health or humans who come in contact with infected animals.
They also cross-referenced for the level of species endangerment and with maps of potential wastewater contamination for certain areas that species came in contact with, using Alaska as the model.
Populations in danger
The researchers found 15 species that are already at risk globally that fall under the categories of near threatened, vulnerable, endangered, and critically endangered that were predicted to be medium to higher susceptibility to the SARS-CoV-2 virus than humans. Cross infection is of particular concern because other coronaviruses have been shown to have severe and lethal effects among many of these species.
Among the potentially impacted species were the near threatened–status Antarctic Mink whale and the stellar sea lion; the vulnerable sperm whale, northern fur seal, and Atlantic walrus; the endangered northern and southern sea otters, the North Pacific right whale, and the Amazon River dolphin; and the critically threatened Baiji and Vaquita dolphin species.
Pollution risks
In Alaska, as of Aug. 7th, 2020, there were 4,221 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and this number continues to rise, according to the researchers. Since there is a diversity of marine mammals in Alaska and their populations are well documented, they compared this information with available data on the wastewater treatment plants in the state. They were thus able to determine the potential geographic locations and species at high risk for transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via wastewater effluent.
Among their findings, the city of Cold Bay discharges wastewater into Cold Bay, where there are Northern sea otter populations that are predicted to be highly susceptible to the virus. Beluga whales are also predicted to have high susceptibility and they can be found in Bristol Bay near Naknek, a city which relies only on lagoon treatment prior to the discharge of wastewater effluent; the city of Dillingham discharges wastewater into the Nushagak River where beluga whales are found. In Palmer, wastewater effluent flows into the Talkeetna River, which is a tributary to the Susitna River and home to two species predicted to have high susceptibility, beluga whales and harbor seals, the authors added.
Based on these results, the researchers predicted that there was likely a significant risk to sea mammals across the globe, especially where less-adequate treatment facilities and high population densities may lead to greater wastewater contamination.
“Given the proximity of marine animals to high-risk environments where viral spill over is likely, we must act with foresight to protect marine mammal species predicted to be at risk and mitigate the environmental impact of the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mathavarajah S et al. Sci Total Environ. 2020 Oct 29. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143346.
Zoonoses are no respecter of biological boundaries and are notorious for crossing genus and even higher taxonomic boundaries. SARS-CoV-2 is no exception, the current outbreak most probably having originated in bats, a common source of human-affecting zoonoses throughout history. But it is not a one-way street, and the virus has been shown to spread from infected humans to a variety of other land mammals, including our domesticated animals and kept zoo species.
A recent troubling report, however, has indicated that sea mammals may be part of a next wave of likely candidates for infection, put at risk by the current human pandemic and environmental degradation on a global scale, according to a the results of a genomic analysis of four major groups of sea mammals.
Researchers Sabateeshan Mathavarajah and colleagues from Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., examined the sequences of the ACE2 receptors in the various marine mammal species. The ACE2 receptor has recently been identified as the SARS-CoV-2 receptor, which allows for infection.
The researchers examined genomic databases of the marine species to determine if their ACE2 receptor sequences indicated the potential for high, medium, or low susceptibility to infection, as reported in Science of the Total Environment. Database analysis was performed for four groups: Cetacea (whales and dolphins), Pinnepidia (seals), Sirenia (sea cows), and Fissipedia (sea otters and polar bears).
The researchers defined susceptibility values based on comparable binding with the receptor and came up with the following subgroups: higher than human, high (resembles human ACE2), medium (resembles cat ACE2), and low (resembles dog ACE2). It has yet to be established if these marine mammals actually are infected with SARS-CoV-2 and what the impact of such an infection might have on animal health or humans who come in contact with infected animals.
They also cross-referenced for the level of species endangerment and with maps of potential wastewater contamination for certain areas that species came in contact with, using Alaska as the model.
Populations in danger
The researchers found 15 species that are already at risk globally that fall under the categories of near threatened, vulnerable, endangered, and critically endangered that were predicted to be medium to higher susceptibility to the SARS-CoV-2 virus than humans. Cross infection is of particular concern because other coronaviruses have been shown to have severe and lethal effects among many of these species.
Among the potentially impacted species were the near threatened–status Antarctic Mink whale and the stellar sea lion; the vulnerable sperm whale, northern fur seal, and Atlantic walrus; the endangered northern and southern sea otters, the North Pacific right whale, and the Amazon River dolphin; and the critically threatened Baiji and Vaquita dolphin species.
Pollution risks
In Alaska, as of Aug. 7th, 2020, there were 4,221 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and this number continues to rise, according to the researchers. Since there is a diversity of marine mammals in Alaska and their populations are well documented, they compared this information with available data on the wastewater treatment plants in the state. They were thus able to determine the potential geographic locations and species at high risk for transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via wastewater effluent.
Among their findings, the city of Cold Bay discharges wastewater into Cold Bay, where there are Northern sea otter populations that are predicted to be highly susceptible to the virus. Beluga whales are also predicted to have high susceptibility and they can be found in Bristol Bay near Naknek, a city which relies only on lagoon treatment prior to the discharge of wastewater effluent; the city of Dillingham discharges wastewater into the Nushagak River where beluga whales are found. In Palmer, wastewater effluent flows into the Talkeetna River, which is a tributary to the Susitna River and home to two species predicted to have high susceptibility, beluga whales and harbor seals, the authors added.
Based on these results, the researchers predicted that there was likely a significant risk to sea mammals across the globe, especially where less-adequate treatment facilities and high population densities may lead to greater wastewater contamination.
“Given the proximity of marine animals to high-risk environments where viral spill over is likely, we must act with foresight to protect marine mammal species predicted to be at risk and mitigate the environmental impact of the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mathavarajah S et al. Sci Total Environ. 2020 Oct 29. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143346.
Zoonoses are no respecter of biological boundaries and are notorious for crossing genus and even higher taxonomic boundaries. SARS-CoV-2 is no exception, the current outbreak most probably having originated in bats, a common source of human-affecting zoonoses throughout history. But it is not a one-way street, and the virus has been shown to spread from infected humans to a variety of other land mammals, including our domesticated animals and kept zoo species.
A recent troubling report, however, has indicated that sea mammals may be part of a next wave of likely candidates for infection, put at risk by the current human pandemic and environmental degradation on a global scale, according to a the results of a genomic analysis of four major groups of sea mammals.
Researchers Sabateeshan Mathavarajah and colleagues from Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., examined the sequences of the ACE2 receptors in the various marine mammal species. The ACE2 receptor has recently been identified as the SARS-CoV-2 receptor, which allows for infection.
The researchers examined genomic databases of the marine species to determine if their ACE2 receptor sequences indicated the potential for high, medium, or low susceptibility to infection, as reported in Science of the Total Environment. Database analysis was performed for four groups: Cetacea (whales and dolphins), Pinnepidia (seals), Sirenia (sea cows), and Fissipedia (sea otters and polar bears).
The researchers defined susceptibility values based on comparable binding with the receptor and came up with the following subgroups: higher than human, high (resembles human ACE2), medium (resembles cat ACE2), and low (resembles dog ACE2). It has yet to be established if these marine mammals actually are infected with SARS-CoV-2 and what the impact of such an infection might have on animal health or humans who come in contact with infected animals.
They also cross-referenced for the level of species endangerment and with maps of potential wastewater contamination for certain areas that species came in contact with, using Alaska as the model.
Populations in danger
The researchers found 15 species that are already at risk globally that fall under the categories of near threatened, vulnerable, endangered, and critically endangered that were predicted to be medium to higher susceptibility to the SARS-CoV-2 virus than humans. Cross infection is of particular concern because other coronaviruses have been shown to have severe and lethal effects among many of these species.
Among the potentially impacted species were the near threatened–status Antarctic Mink whale and the stellar sea lion; the vulnerable sperm whale, northern fur seal, and Atlantic walrus; the endangered northern and southern sea otters, the North Pacific right whale, and the Amazon River dolphin; and the critically threatened Baiji and Vaquita dolphin species.
Pollution risks
In Alaska, as of Aug. 7th, 2020, there were 4,221 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and this number continues to rise, according to the researchers. Since there is a diversity of marine mammals in Alaska and their populations are well documented, they compared this information with available data on the wastewater treatment plants in the state. They were thus able to determine the potential geographic locations and species at high risk for transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via wastewater effluent.
Among their findings, the city of Cold Bay discharges wastewater into Cold Bay, where there are Northern sea otter populations that are predicted to be highly susceptible to the virus. Beluga whales are also predicted to have high susceptibility and they can be found in Bristol Bay near Naknek, a city which relies only on lagoon treatment prior to the discharge of wastewater effluent; the city of Dillingham discharges wastewater into the Nushagak River where beluga whales are found. In Palmer, wastewater effluent flows into the Talkeetna River, which is a tributary to the Susitna River and home to two species predicted to have high susceptibility, beluga whales and harbor seals, the authors added.
Based on these results, the researchers predicted that there was likely a significant risk to sea mammals across the globe, especially where less-adequate treatment facilities and high population densities may lead to greater wastewater contamination.
“Given the proximity of marine animals to high-risk environments where viral spill over is likely, we must act with foresight to protect marine mammal species predicted to be at risk and mitigate the environmental impact of the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mathavarajah S et al. Sci Total Environ. 2020 Oct 29. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143346.
FROM SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT
Pfizer vaccine data show 90% efficacy in early results
A vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2 has been found to be 90% effective in preventing COVID-19 in trial volunteers who were without evidence of prior infection of the virus, results from an interim analysis of a phase 3 study demonstrated.
BTN162b2, a messenger RNA–based vaccine candidate that requires two doses, is being developed by Pfizer and BioNTech SE independently of the Trump administration’s Operation Warp Speed. A global phase 3 clinical trial of BTN162b2 began on July 27 and has enrolled 43,538 participants to date; 42% of enrollees have racially and ethnically diverse backgrounds.
According to a press release issued by the two companies, 38,955 trial volunteers had received a second dose of either vaccine or placebo as of Nov. 8. An interim analysis of 94 individuals conducted by an independent data monitoring committee (DMC) found that the vaccine efficacy rate was above 90% 7 days after the second dose. This means that protection was achieved 28 days after the first vaccine dose.
“It’s promising in that it validates the genetic strategy – whether it’s mRNA vaccines or DNA vaccines,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told Medscape Medical News. Offit is a member of the US Food and Drug Administraiton’s COVID-19 Vaccine Advisory Committee. “All of them have the same approach, which is that they introduce the gene that codes for the coronavirus spike protein into the cell. Your cell makes the spike protein, and your immune system makes antibodies to the spike protein. At least in these preliminary data, which involved 94 people getting sick, it looks like it’s effective. That’s good. We knew that it seemed to work in experimental animals, but you never know until you put it into people.”
According to Pfizer and BioNTech SE, a final data analysis is planned once 164 confirmed COVID-19 cases have accrued. So far, the DMC has not reported any serious safety concerns. It recommends that the study continue to collect safety and efficacy data as planned. The companies plan to apply to the FDA for emergency use authorization soon after the required safety milestone is achieved.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, added in a separate press release, “It’s important to note that we cannot apply for FDA Emergency Use Authorization based on these efficacy results alone. More data on safety is also needed, and we are continuing to accumulate that safety data as part of our ongoing clinical study.
“We estimate that a median of two months of safety data following the second and final dose of the vaccine candidate – required by FDA’s guidance for potential Emergency Use Authorization – will be available by the third week of November.”
Offit, professor of pediatrics in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said that, if BTN162b2 is approved, administering it will be tricky. “This particular vaccine has to be shipped and stored at –70° C or –80° C, which we’ve never done before in this country,” he said. “That means maintaining the product on dry ice. That’s going to be a challenge for distribution, I think.”
Good news, but…
In the press release, BioNTech SE’s cofounder and CEO, Ugur Sahin, MD, characterized the findings as “a victory for innovation, science and a global collaborative effort. When we embarked on this journey 10 months ago this is what we aspired to achieve. Especially today, while we are all in the midst of a second wave and many of us in lockdown, we appreciate even more how important this milestone is on our path towards ending this pandemic and for all of us to regain a sense of normality.”
President-elect Joe Biden also weighed in, calling the results “excellent news” in a news release.
“At the same time, it is also important to understand that the end of the battle against COVID-19 is still months away,” he said. “This news follows a previously announced timeline by industry officials that forecast vaccine approval by late November. Even if that is achieved, and some Americans are vaccinated later this year, it will be many more months before there is widespread vaccination in this country.
“Today’s news does not change this urgent reality. Americans will have to rely on masking, distancing, contact tracing, hand washing, and other measures to keep themselves safe well into next year,” Biden added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2 has been found to be 90% effective in preventing COVID-19 in trial volunteers who were without evidence of prior infection of the virus, results from an interim analysis of a phase 3 study demonstrated.
BTN162b2, a messenger RNA–based vaccine candidate that requires two doses, is being developed by Pfizer and BioNTech SE independently of the Trump administration’s Operation Warp Speed. A global phase 3 clinical trial of BTN162b2 began on July 27 and has enrolled 43,538 participants to date; 42% of enrollees have racially and ethnically diverse backgrounds.
According to a press release issued by the two companies, 38,955 trial volunteers had received a second dose of either vaccine or placebo as of Nov. 8. An interim analysis of 94 individuals conducted by an independent data monitoring committee (DMC) found that the vaccine efficacy rate was above 90% 7 days after the second dose. This means that protection was achieved 28 days after the first vaccine dose.
“It’s promising in that it validates the genetic strategy – whether it’s mRNA vaccines or DNA vaccines,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told Medscape Medical News. Offit is a member of the US Food and Drug Administraiton’s COVID-19 Vaccine Advisory Committee. “All of them have the same approach, which is that they introduce the gene that codes for the coronavirus spike protein into the cell. Your cell makes the spike protein, and your immune system makes antibodies to the spike protein. At least in these preliminary data, which involved 94 people getting sick, it looks like it’s effective. That’s good. We knew that it seemed to work in experimental animals, but you never know until you put it into people.”
According to Pfizer and BioNTech SE, a final data analysis is planned once 164 confirmed COVID-19 cases have accrued. So far, the DMC has not reported any serious safety concerns. It recommends that the study continue to collect safety and efficacy data as planned. The companies plan to apply to the FDA for emergency use authorization soon after the required safety milestone is achieved.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, added in a separate press release, “It’s important to note that we cannot apply for FDA Emergency Use Authorization based on these efficacy results alone. More data on safety is also needed, and we are continuing to accumulate that safety data as part of our ongoing clinical study.
“We estimate that a median of two months of safety data following the second and final dose of the vaccine candidate – required by FDA’s guidance for potential Emergency Use Authorization – will be available by the third week of November.”
Offit, professor of pediatrics in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said that, if BTN162b2 is approved, administering it will be tricky. “This particular vaccine has to be shipped and stored at –70° C or –80° C, which we’ve never done before in this country,” he said. “That means maintaining the product on dry ice. That’s going to be a challenge for distribution, I think.”
Good news, but…
In the press release, BioNTech SE’s cofounder and CEO, Ugur Sahin, MD, characterized the findings as “a victory for innovation, science and a global collaborative effort. When we embarked on this journey 10 months ago this is what we aspired to achieve. Especially today, while we are all in the midst of a second wave and many of us in lockdown, we appreciate even more how important this milestone is on our path towards ending this pandemic and for all of us to regain a sense of normality.”
President-elect Joe Biden also weighed in, calling the results “excellent news” in a news release.
“At the same time, it is also important to understand that the end of the battle against COVID-19 is still months away,” he said. “This news follows a previously announced timeline by industry officials that forecast vaccine approval by late November. Even if that is achieved, and some Americans are vaccinated later this year, it will be many more months before there is widespread vaccination in this country.
“Today’s news does not change this urgent reality. Americans will have to rely on masking, distancing, contact tracing, hand washing, and other measures to keep themselves safe well into next year,” Biden added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2 has been found to be 90% effective in preventing COVID-19 in trial volunteers who were without evidence of prior infection of the virus, results from an interim analysis of a phase 3 study demonstrated.
BTN162b2, a messenger RNA–based vaccine candidate that requires two doses, is being developed by Pfizer and BioNTech SE independently of the Trump administration’s Operation Warp Speed. A global phase 3 clinical trial of BTN162b2 began on July 27 and has enrolled 43,538 participants to date; 42% of enrollees have racially and ethnically diverse backgrounds.
According to a press release issued by the two companies, 38,955 trial volunteers had received a second dose of either vaccine or placebo as of Nov. 8. An interim analysis of 94 individuals conducted by an independent data monitoring committee (DMC) found that the vaccine efficacy rate was above 90% 7 days after the second dose. This means that protection was achieved 28 days after the first vaccine dose.
“It’s promising in that it validates the genetic strategy – whether it’s mRNA vaccines or DNA vaccines,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told Medscape Medical News. Offit is a member of the US Food and Drug Administraiton’s COVID-19 Vaccine Advisory Committee. “All of them have the same approach, which is that they introduce the gene that codes for the coronavirus spike protein into the cell. Your cell makes the spike protein, and your immune system makes antibodies to the spike protein. At least in these preliminary data, which involved 94 people getting sick, it looks like it’s effective. That’s good. We knew that it seemed to work in experimental animals, but you never know until you put it into people.”
According to Pfizer and BioNTech SE, a final data analysis is planned once 164 confirmed COVID-19 cases have accrued. So far, the DMC has not reported any serious safety concerns. It recommends that the study continue to collect safety and efficacy data as planned. The companies plan to apply to the FDA for emergency use authorization soon after the required safety milestone is achieved.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, added in a separate press release, “It’s important to note that we cannot apply for FDA Emergency Use Authorization based on these efficacy results alone. More data on safety is also needed, and we are continuing to accumulate that safety data as part of our ongoing clinical study.
“We estimate that a median of two months of safety data following the second and final dose of the vaccine candidate – required by FDA’s guidance for potential Emergency Use Authorization – will be available by the third week of November.”
Offit, professor of pediatrics in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said that, if BTN162b2 is approved, administering it will be tricky. “This particular vaccine has to be shipped and stored at –70° C or –80° C, which we’ve never done before in this country,” he said. “That means maintaining the product on dry ice. That’s going to be a challenge for distribution, I think.”
Good news, but…
In the press release, BioNTech SE’s cofounder and CEO, Ugur Sahin, MD, characterized the findings as “a victory for innovation, science and a global collaborative effort. When we embarked on this journey 10 months ago this is what we aspired to achieve. Especially today, while we are all in the midst of a second wave and many of us in lockdown, we appreciate even more how important this milestone is on our path towards ending this pandemic and for all of us to regain a sense of normality.”
President-elect Joe Biden also weighed in, calling the results “excellent news” in a news release.
“At the same time, it is also important to understand that the end of the battle against COVID-19 is still months away,” he said. “This news follows a previously announced timeline by industry officials that forecast vaccine approval by late November. Even if that is achieved, and some Americans are vaccinated later this year, it will be many more months before there is widespread vaccination in this country.
“Today’s news does not change this urgent reality. Americans will have to rely on masking, distancing, contact tracing, hand washing, and other measures to keep themselves safe well into next year,” Biden added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VA joins Pentagon in recruiting volunteers for COVID vaccine trials
according to officials with the VA and Operation Warp Speed, the Trump administration’s initiative to fast-track a coronavirus vaccine.
The largely unpublicized effort follows a Department of Defense announcement in September that it has partnered with AstraZeneca to recruit volunteers at five of its medical facilities, which are separate from the VA system. DOD is also is in talks with developers of other vaccine candidates, although officials won’t say which ones.
Both federal departments have long experience in medical research and diverse populations – a crucial component of effective clinical trials, said J. Stephen Morrison, senior vice president and director of global health policy at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, a bipartisan think tank in Washington.
Since active troops are essential to national security, and veterans are extremely vulnerable to COVID-19, both departments have a vested interest in supporting the development of safe, effective vaccines, Mr. Morrison said.
“On the DOD active servicemen and -women side, it’s a question of making sure they’re ready, they are protected,” Mr. Morrison said. “With VA, their population, all elderly and infirm with underlying conditions, they could really be suffering if we don’t get a vaccine.”
According to a VA website, of its 20 medical centers involved, 17 would be part of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine trial, while the three others are recruiting – or have completed recruitment – for advanced-stage trials for Moderna, AstraZeneca, and Pfizer vaccines.
Matthew Hepburn, MD, head of vaccine development at Operation Warp Speed, said the VA effort lets veterans contribute to the overall well-being of the country.
“This is another way they can continue to serve in this way, fighting the pandemic as a volunteer,” Dr. Hepburn said during a discussion of vaccine and therapeutics development hosted by the Heritage Foundation on Oct. 27.
It’s not unusual for the military to participate in multicenter trials for treatments of ailments as diverse as cancer and trauma. Historically, many vaccines have been tested first by the military.
In the general population, clinicians often have difficulty recruiting African Americans and other minorities for medical research, and “the military provides a rich opportunity to find volunteers for those groups,” said retired Rear Adm. Thomas Cullison, MD, a doctor and former deputy surgeon general for the Navy.
Military health facilities are held to the same standards as private research facilities, he said.
No service members will be required to participate in the COVID vaccine trials. All volunteers will be paid by the developer.
Support for routine vaccinations runs high in the military, but some have expressed concerns about new vaccines and mandatory inoculations, especially for anthrax. In a 2002 federal study, 85% of those who received that vaccine reported an adverse reaction, with just under half noticing minor redness at the injection site. But nearly a quarter of the side effects reported were more systemic, including fevers, chills, fatigue and joint pain.
That survey of a small group of National Guard and Reserve members found that, while 73% said they believe immunizations are effective, two-thirds said they did not support the mandatory anthrax program, and 6 in 10 said they were not satisfied with the information they were given on the vaccines.
To quell concerns over the military’s role in supporting COVID vaccine development, the Pentagon has reiterated that troops or their dependents interested in participating in the research must provide voluntary written consent, and they will be allowed to take part only if they will be in the same location for the length of the research, expected to last at least 2 years.
In addition, active-duty members such as new recruits and boot camp participants will not be allowed to volunteer because they are “considered vulnerable from an ethical and regulatory standpoint,” an official said.
At the VA, officials are seeking to recruit healthy veterans aged 18-65 years old who are not pregnant and may be at risk for exposure. As with trials conducted in civilian facilities, participants will be paid by the developer, VA spokesperson Christina Noel said.
Also, VA nurses and caseworkers also are being asked to identify their sickest, highest-risk patients to determine who should be at the top of the list once a vaccine is approved, according to a VA nurse and other health officials who asked not to be identified because they were not authorized to speak with the press.
The U.S. military has a long history of contributing to research on vaccines, including a key role in developing inoculations against yellow fever and adenovirus, and the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research is developing its own vaccine against the coronavirus.
Some segments of the population remain skeptical of federal medical experiments. A survey by AP-NORC in May found that Black people are particularly reluctant to get the coronavirus vaccine. Many have concerns about federal research in part because of associations with the infamous Tuskegee Institute syphilis experiments, in which U.S. Public Health Service officials intentionally withheld a cure from Black men infected with the disease.
But Mr. Morrison, of the Center for Strategic and International Studies, said the Defense Department and VA are a “natural fit” for the COVID vaccine trials.
“DOD has lots of expertise. They know how to vaccinate; they know how to reach communities. They have a whole science infrastructure and research-and-development infrastructure. And when you are thinking what the mission of VA is, [VA] sees this is part of their mission,” Mr. Morrison said.
The Defense Department announced its agreement with AstraZeneca in September, shortly before the drugmaker’s vaccine trial was put on hold to study a serious medical condition that one participant reported. That research was approved by the Food and Drug Administration to begin again Oct. 23. The military plans to restart its efforts to recruit 3,000 volunteers.
The Pentagon has also signed an agreement with another vaccine developer, the head of the Defense Health Agency, Army Lt. Gen. Ronald Place, told reporters Oct. 8. He wouldn’t provide the company’s name.
Senator Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.) and Senator Mazie Hirono (D-Hawaii) have called, unsuccessfully, for the Senate Armed Services Committee to investigate what they say is a lack of Pentagon transparency on its role in vaccine development and distribution. The Defense Department has awarded more than $6 billion in Operation Warp Speed contracts through an intermediary, Advanced Technology International, and the two senators want more information about those contracts.
“There may well be a valuable role for DoD officials in [Operation Warp Speed] – particularly given the department’s logistical capacity,” they wrote to the committee chair and ranking member. “But it is important that Congress conduct appropriate oversight of, and understand, DoD’s activities in this area.”
Neither department has disclosed the financial arrangements they have made with developers to support the vaccine research.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
according to officials with the VA and Operation Warp Speed, the Trump administration’s initiative to fast-track a coronavirus vaccine.
The largely unpublicized effort follows a Department of Defense announcement in September that it has partnered with AstraZeneca to recruit volunteers at five of its medical facilities, which are separate from the VA system. DOD is also is in talks with developers of other vaccine candidates, although officials won’t say which ones.
Both federal departments have long experience in medical research and diverse populations – a crucial component of effective clinical trials, said J. Stephen Morrison, senior vice president and director of global health policy at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, a bipartisan think tank in Washington.
Since active troops are essential to national security, and veterans are extremely vulnerable to COVID-19, both departments have a vested interest in supporting the development of safe, effective vaccines, Mr. Morrison said.
“On the DOD active servicemen and -women side, it’s a question of making sure they’re ready, they are protected,” Mr. Morrison said. “With VA, their population, all elderly and infirm with underlying conditions, they could really be suffering if we don’t get a vaccine.”
According to a VA website, of its 20 medical centers involved, 17 would be part of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine trial, while the three others are recruiting – or have completed recruitment – for advanced-stage trials for Moderna, AstraZeneca, and Pfizer vaccines.
Matthew Hepburn, MD, head of vaccine development at Operation Warp Speed, said the VA effort lets veterans contribute to the overall well-being of the country.
“This is another way they can continue to serve in this way, fighting the pandemic as a volunteer,” Dr. Hepburn said during a discussion of vaccine and therapeutics development hosted by the Heritage Foundation on Oct. 27.
It’s not unusual for the military to participate in multicenter trials for treatments of ailments as diverse as cancer and trauma. Historically, many vaccines have been tested first by the military.
In the general population, clinicians often have difficulty recruiting African Americans and other minorities for medical research, and “the military provides a rich opportunity to find volunteers for those groups,” said retired Rear Adm. Thomas Cullison, MD, a doctor and former deputy surgeon general for the Navy.
Military health facilities are held to the same standards as private research facilities, he said.
No service members will be required to participate in the COVID vaccine trials. All volunteers will be paid by the developer.
Support for routine vaccinations runs high in the military, but some have expressed concerns about new vaccines and mandatory inoculations, especially for anthrax. In a 2002 federal study, 85% of those who received that vaccine reported an adverse reaction, with just under half noticing minor redness at the injection site. But nearly a quarter of the side effects reported were more systemic, including fevers, chills, fatigue and joint pain.
That survey of a small group of National Guard and Reserve members found that, while 73% said they believe immunizations are effective, two-thirds said they did not support the mandatory anthrax program, and 6 in 10 said they were not satisfied with the information they were given on the vaccines.
To quell concerns over the military’s role in supporting COVID vaccine development, the Pentagon has reiterated that troops or their dependents interested in participating in the research must provide voluntary written consent, and they will be allowed to take part only if they will be in the same location for the length of the research, expected to last at least 2 years.
In addition, active-duty members such as new recruits and boot camp participants will not be allowed to volunteer because they are “considered vulnerable from an ethical and regulatory standpoint,” an official said.
At the VA, officials are seeking to recruit healthy veterans aged 18-65 years old who are not pregnant and may be at risk for exposure. As with trials conducted in civilian facilities, participants will be paid by the developer, VA spokesperson Christina Noel said.
Also, VA nurses and caseworkers also are being asked to identify their sickest, highest-risk patients to determine who should be at the top of the list once a vaccine is approved, according to a VA nurse and other health officials who asked not to be identified because they were not authorized to speak with the press.
The U.S. military has a long history of contributing to research on vaccines, including a key role in developing inoculations against yellow fever and adenovirus, and the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research is developing its own vaccine against the coronavirus.
Some segments of the population remain skeptical of federal medical experiments. A survey by AP-NORC in May found that Black people are particularly reluctant to get the coronavirus vaccine. Many have concerns about federal research in part because of associations with the infamous Tuskegee Institute syphilis experiments, in which U.S. Public Health Service officials intentionally withheld a cure from Black men infected with the disease.
But Mr. Morrison, of the Center for Strategic and International Studies, said the Defense Department and VA are a “natural fit” for the COVID vaccine trials.
“DOD has lots of expertise. They know how to vaccinate; they know how to reach communities. They have a whole science infrastructure and research-and-development infrastructure. And when you are thinking what the mission of VA is, [VA] sees this is part of their mission,” Mr. Morrison said.
The Defense Department announced its agreement with AstraZeneca in September, shortly before the drugmaker’s vaccine trial was put on hold to study a serious medical condition that one participant reported. That research was approved by the Food and Drug Administration to begin again Oct. 23. The military plans to restart its efforts to recruit 3,000 volunteers.
The Pentagon has also signed an agreement with another vaccine developer, the head of the Defense Health Agency, Army Lt. Gen. Ronald Place, told reporters Oct. 8. He wouldn’t provide the company’s name.
Senator Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.) and Senator Mazie Hirono (D-Hawaii) have called, unsuccessfully, for the Senate Armed Services Committee to investigate what they say is a lack of Pentagon transparency on its role in vaccine development and distribution. The Defense Department has awarded more than $6 billion in Operation Warp Speed contracts through an intermediary, Advanced Technology International, and the two senators want more information about those contracts.
“There may well be a valuable role for DoD officials in [Operation Warp Speed] – particularly given the department’s logistical capacity,” they wrote to the committee chair and ranking member. “But it is important that Congress conduct appropriate oversight of, and understand, DoD’s activities in this area.”
Neither department has disclosed the financial arrangements they have made with developers to support the vaccine research.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
according to officials with the VA and Operation Warp Speed, the Trump administration’s initiative to fast-track a coronavirus vaccine.
The largely unpublicized effort follows a Department of Defense announcement in September that it has partnered with AstraZeneca to recruit volunteers at five of its medical facilities, which are separate from the VA system. DOD is also is in talks with developers of other vaccine candidates, although officials won’t say which ones.
Both federal departments have long experience in medical research and diverse populations – a crucial component of effective clinical trials, said J. Stephen Morrison, senior vice president and director of global health policy at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, a bipartisan think tank in Washington.
Since active troops are essential to national security, and veterans are extremely vulnerable to COVID-19, both departments have a vested interest in supporting the development of safe, effective vaccines, Mr. Morrison said.
“On the DOD active servicemen and -women side, it’s a question of making sure they’re ready, they are protected,” Mr. Morrison said. “With VA, their population, all elderly and infirm with underlying conditions, they could really be suffering if we don’t get a vaccine.”
According to a VA website, of its 20 medical centers involved, 17 would be part of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine trial, while the three others are recruiting – or have completed recruitment – for advanced-stage trials for Moderna, AstraZeneca, and Pfizer vaccines.
Matthew Hepburn, MD, head of vaccine development at Operation Warp Speed, said the VA effort lets veterans contribute to the overall well-being of the country.
“This is another way they can continue to serve in this way, fighting the pandemic as a volunteer,” Dr. Hepburn said during a discussion of vaccine and therapeutics development hosted by the Heritage Foundation on Oct. 27.
It’s not unusual for the military to participate in multicenter trials for treatments of ailments as diverse as cancer and trauma. Historically, many vaccines have been tested first by the military.
In the general population, clinicians often have difficulty recruiting African Americans and other minorities for medical research, and “the military provides a rich opportunity to find volunteers for those groups,” said retired Rear Adm. Thomas Cullison, MD, a doctor and former deputy surgeon general for the Navy.
Military health facilities are held to the same standards as private research facilities, he said.
No service members will be required to participate in the COVID vaccine trials. All volunteers will be paid by the developer.
Support for routine vaccinations runs high in the military, but some have expressed concerns about new vaccines and mandatory inoculations, especially for anthrax. In a 2002 federal study, 85% of those who received that vaccine reported an adverse reaction, with just under half noticing minor redness at the injection site. But nearly a quarter of the side effects reported were more systemic, including fevers, chills, fatigue and joint pain.
That survey of a small group of National Guard and Reserve members found that, while 73% said they believe immunizations are effective, two-thirds said they did not support the mandatory anthrax program, and 6 in 10 said they were not satisfied with the information they were given on the vaccines.
To quell concerns over the military’s role in supporting COVID vaccine development, the Pentagon has reiterated that troops or their dependents interested in participating in the research must provide voluntary written consent, and they will be allowed to take part only if they will be in the same location for the length of the research, expected to last at least 2 years.
In addition, active-duty members such as new recruits and boot camp participants will not be allowed to volunteer because they are “considered vulnerable from an ethical and regulatory standpoint,” an official said.
At the VA, officials are seeking to recruit healthy veterans aged 18-65 years old who are not pregnant and may be at risk for exposure. As with trials conducted in civilian facilities, participants will be paid by the developer, VA spokesperson Christina Noel said.
Also, VA nurses and caseworkers also are being asked to identify their sickest, highest-risk patients to determine who should be at the top of the list once a vaccine is approved, according to a VA nurse and other health officials who asked not to be identified because they were not authorized to speak with the press.
The U.S. military has a long history of contributing to research on vaccines, including a key role in developing inoculations against yellow fever and adenovirus, and the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research is developing its own vaccine against the coronavirus.
Some segments of the population remain skeptical of federal medical experiments. A survey by AP-NORC in May found that Black people are particularly reluctant to get the coronavirus vaccine. Many have concerns about federal research in part because of associations with the infamous Tuskegee Institute syphilis experiments, in which U.S. Public Health Service officials intentionally withheld a cure from Black men infected with the disease.
But Mr. Morrison, of the Center for Strategic and International Studies, said the Defense Department and VA are a “natural fit” for the COVID vaccine trials.
“DOD has lots of expertise. They know how to vaccinate; they know how to reach communities. They have a whole science infrastructure and research-and-development infrastructure. And when you are thinking what the mission of VA is, [VA] sees this is part of their mission,” Mr. Morrison said.
The Defense Department announced its agreement with AstraZeneca in September, shortly before the drugmaker’s vaccine trial was put on hold to study a serious medical condition that one participant reported. That research was approved by the Food and Drug Administration to begin again Oct. 23. The military plans to restart its efforts to recruit 3,000 volunteers.
The Pentagon has also signed an agreement with another vaccine developer, the head of the Defense Health Agency, Army Lt. Gen. Ronald Place, told reporters Oct. 8. He wouldn’t provide the company’s name.
Senator Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.) and Senator Mazie Hirono (D-Hawaii) have called, unsuccessfully, for the Senate Armed Services Committee to investigate what they say is a lack of Pentagon transparency on its role in vaccine development and distribution. The Defense Department has awarded more than $6 billion in Operation Warp Speed contracts through an intermediary, Advanced Technology International, and the two senators want more information about those contracts.
“There may well be a valuable role for DoD officials in [Operation Warp Speed] – particularly given the department’s logistical capacity,” they wrote to the committee chair and ranking member. “But it is important that Congress conduct appropriate oversight of, and understand, DoD’s activities in this area.”
Neither department has disclosed the financial arrangements they have made with developers to support the vaccine research.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
What to know as ACA heads to Supreme Court – again
The case, California v. Texas, is the result of a change to the health law made by Congress in 2017. As part of a major tax bill, Congress reduced to zero the penalty for not having health insurance. But it was that penalty – a tax – that the high court ruled made the law constitutional in a 2012 decision, argues a group of Republican state attorneys general. Without the tax, they say in their suit, the rest of the law must fall, too.
After originally contending that the entire law should not be struck down when the suit was filed in 2018, the Trump administration changed course in 2019 and joined the GOP officials who brought the case.
Here are some key questions and answers about the case.
What are the possibilities for how the court could rule?
There is a long list of ways this could play out.
The justices could declare the entire law unconstitutional – which is what a federal district judge in Texas ruled in December 2018. But legal experts say that’s not the most likely outcome of this case.
First, the court may avoid deciding the case on its merits entirely by ruling that the plaintiffs do not have “standing” to sue. The central issue in the case is whether the requirement in the law to have insurance – which remains even though Congress eliminated the penalty or tax – is constitutional. But states are not subject to the so-called individual mandate, so some analysts suggest the Republican officials have no standing. In addition, questions have been raised about the individual plaintiffs in the case, two consultants from Texas who argue that they felt compelled to buy insurance even without a possible penalty.
The court could also rule that, by eliminating the penalty but not the rest of the mandate (which Congress could not do in that 2017 tax bill for procedural reasons), lawmakers “didn’t mean to coerce anyone to do anything, and so there’s no constitutional problem,” University of Michigan law professor Nicholas Bagley said in a recent webinar for the NIHCM Foundation, the Commonwealth Fund, and the University of Southern California’s Center for Health Journalism.
Or, said Bagley, the court could rule that, without the tax, the requirement to have health insurance is unconstitutional, but the rest of the law is not. In that case, the justices might strike the mandate only, which would have basically no impact.
It gets more complicated if the court decides that, as the plaintiffs argue, the individual mandate language without the penalty is unconstitutional and so closely tied to other parts of the law that some of them must fall as well.
Even there the court has choices. One option would be, as the Trump administration originally argued, to strike down the mandate and just the pieces of the law most closely related to it – which happen to include the insurance protections for people with preexisting conditions, an extremely popular provision of the law. The two parts are connected because the original purpose of the mandate was to make sure enough healthy people sign up for insurance to offset the added costs to insurers of sicker people.
Another option, of course, would be for the court to follow the lead of the Texas judge and strike down the entire law.
While that’s not the most likely outcome, said Bagley, if it happens it could be “a hot mess” for the nation’s entire health care system. As just one example, he said, “every hospital is getting paid pursuant to changes made by the ACA. How do you even go about making payments if the thing that you are looking to guide what those payments ought to be is itself invalid?”
What impact will new Justice Amy Coney Barrett have?
Perhaps a lot. Before the death of Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg, most court observers thought the case was highly unlikely to result in the entire law being struck down. That’s because Chief Justice John Roberts voted to uphold the law in 2012, and again when it was challenged in a less sweeping way in 2015.
But with Barrett replacing Ginsburg, even if Roberts joined the court’s remaining three liberals they could still be outvoted by the other five conservatives. Barrett was coy about her views on the Affordable Care Act during her confirmation hearings in October, but she has written that she thinks Roberts was wrong to uphold the law in 2012.
Could a new president and Congress make the case go away?
Many have suggested that, if Joe Biden assumes the presidency, his Justice Department could simply drop the case. But the administration did not bring the case; the GOP state officials did. And while normally the Justice Department’s job is to defend existing laws in court, in this case the ACA is being defended by a group of Democratic state attorneys general. A new administration could change that position, but that’s not the same as dropping the case.
Congress, on the other hand, could easily make the case moot. It could add back even a nominal financial penalty for not having insurance. It could eliminate the mandate altogether, although that would require 60 votes in the Senate under current rules. Congress could also pass a “severability” provision saying that, if any portion of the law is struck down, the rest should remain.
“The problem is not technical,” said Bagley. “It’s political.”
What is the timeline for a decision? Could the court delay implementation of its ruling?
The court usually hears oral arguments in a case months before it issues a decision. Unless the decision is unanimous or turns out to be very simple, Bagley said, he would expect to see an opinion “sometime in the spring.”
As to whether the court could find some or all of the law unconstitutional but delay when its decision takes effect, Bagley said that happened from time to time as recently as the 1970s. “That practice has been more or less abandoned,” he said, but in the case of a law so large, “you could imagine the Supreme Court using its discretion to say the decision wouldn’t take effect immediately.”
If the court does invalidate the entire ACA, Congress could act to fix things, but it’s unclear if it will be able to, especially if Republicans still control the Senate. If the justices strike the law, Bagley said, “I honestly think the likeliest outcome is that Congress runs around like a chicken with its head cut off, doesn’t come to a deal, and we’re back to where we were before 2010” when the ACA passed.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
The case, California v. Texas, is the result of a change to the health law made by Congress in 2017. As part of a major tax bill, Congress reduced to zero the penalty for not having health insurance. But it was that penalty – a tax – that the high court ruled made the law constitutional in a 2012 decision, argues a group of Republican state attorneys general. Without the tax, they say in their suit, the rest of the law must fall, too.
After originally contending that the entire law should not be struck down when the suit was filed in 2018, the Trump administration changed course in 2019 and joined the GOP officials who brought the case.
Here are some key questions and answers about the case.
What are the possibilities for how the court could rule?
There is a long list of ways this could play out.
The justices could declare the entire law unconstitutional – which is what a federal district judge in Texas ruled in December 2018. But legal experts say that’s not the most likely outcome of this case.
First, the court may avoid deciding the case on its merits entirely by ruling that the plaintiffs do not have “standing” to sue. The central issue in the case is whether the requirement in the law to have insurance – which remains even though Congress eliminated the penalty or tax – is constitutional. But states are not subject to the so-called individual mandate, so some analysts suggest the Republican officials have no standing. In addition, questions have been raised about the individual plaintiffs in the case, two consultants from Texas who argue that they felt compelled to buy insurance even without a possible penalty.
The court could also rule that, by eliminating the penalty but not the rest of the mandate (which Congress could not do in that 2017 tax bill for procedural reasons), lawmakers “didn’t mean to coerce anyone to do anything, and so there’s no constitutional problem,” University of Michigan law professor Nicholas Bagley said in a recent webinar for the NIHCM Foundation, the Commonwealth Fund, and the University of Southern California’s Center for Health Journalism.
Or, said Bagley, the court could rule that, without the tax, the requirement to have health insurance is unconstitutional, but the rest of the law is not. In that case, the justices might strike the mandate only, which would have basically no impact.
It gets more complicated if the court decides that, as the plaintiffs argue, the individual mandate language without the penalty is unconstitutional and so closely tied to other parts of the law that some of them must fall as well.
Even there the court has choices. One option would be, as the Trump administration originally argued, to strike down the mandate and just the pieces of the law most closely related to it – which happen to include the insurance protections for people with preexisting conditions, an extremely popular provision of the law. The two parts are connected because the original purpose of the mandate was to make sure enough healthy people sign up for insurance to offset the added costs to insurers of sicker people.
Another option, of course, would be for the court to follow the lead of the Texas judge and strike down the entire law.
While that’s not the most likely outcome, said Bagley, if it happens it could be “a hot mess” for the nation’s entire health care system. As just one example, he said, “every hospital is getting paid pursuant to changes made by the ACA. How do you even go about making payments if the thing that you are looking to guide what those payments ought to be is itself invalid?”
What impact will new Justice Amy Coney Barrett have?
Perhaps a lot. Before the death of Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg, most court observers thought the case was highly unlikely to result in the entire law being struck down. That’s because Chief Justice John Roberts voted to uphold the law in 2012, and again when it was challenged in a less sweeping way in 2015.
But with Barrett replacing Ginsburg, even if Roberts joined the court’s remaining three liberals they could still be outvoted by the other five conservatives. Barrett was coy about her views on the Affordable Care Act during her confirmation hearings in October, but she has written that she thinks Roberts was wrong to uphold the law in 2012.
Could a new president and Congress make the case go away?
Many have suggested that, if Joe Biden assumes the presidency, his Justice Department could simply drop the case. But the administration did not bring the case; the GOP state officials did. And while normally the Justice Department’s job is to defend existing laws in court, in this case the ACA is being defended by a group of Democratic state attorneys general. A new administration could change that position, but that’s not the same as dropping the case.
Congress, on the other hand, could easily make the case moot. It could add back even a nominal financial penalty for not having insurance. It could eliminate the mandate altogether, although that would require 60 votes in the Senate under current rules. Congress could also pass a “severability” provision saying that, if any portion of the law is struck down, the rest should remain.
“The problem is not technical,” said Bagley. “It’s political.”
What is the timeline for a decision? Could the court delay implementation of its ruling?
The court usually hears oral arguments in a case months before it issues a decision. Unless the decision is unanimous or turns out to be very simple, Bagley said, he would expect to see an opinion “sometime in the spring.”
As to whether the court could find some or all of the law unconstitutional but delay when its decision takes effect, Bagley said that happened from time to time as recently as the 1970s. “That practice has been more or less abandoned,” he said, but in the case of a law so large, “you could imagine the Supreme Court using its discretion to say the decision wouldn’t take effect immediately.”
If the court does invalidate the entire ACA, Congress could act to fix things, but it’s unclear if it will be able to, especially if Republicans still control the Senate. If the justices strike the law, Bagley said, “I honestly think the likeliest outcome is that Congress runs around like a chicken with its head cut off, doesn’t come to a deal, and we’re back to where we were before 2010” when the ACA passed.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
The case, California v. Texas, is the result of a change to the health law made by Congress in 2017. As part of a major tax bill, Congress reduced to zero the penalty for not having health insurance. But it was that penalty – a tax – that the high court ruled made the law constitutional in a 2012 decision, argues a group of Republican state attorneys general. Without the tax, they say in their suit, the rest of the law must fall, too.
After originally contending that the entire law should not be struck down when the suit was filed in 2018, the Trump administration changed course in 2019 and joined the GOP officials who brought the case.
Here are some key questions and answers about the case.
What are the possibilities for how the court could rule?
There is a long list of ways this could play out.
The justices could declare the entire law unconstitutional – which is what a federal district judge in Texas ruled in December 2018. But legal experts say that’s not the most likely outcome of this case.
First, the court may avoid deciding the case on its merits entirely by ruling that the plaintiffs do not have “standing” to sue. The central issue in the case is whether the requirement in the law to have insurance – which remains even though Congress eliminated the penalty or tax – is constitutional. But states are not subject to the so-called individual mandate, so some analysts suggest the Republican officials have no standing. In addition, questions have been raised about the individual plaintiffs in the case, two consultants from Texas who argue that they felt compelled to buy insurance even without a possible penalty.
The court could also rule that, by eliminating the penalty but not the rest of the mandate (which Congress could not do in that 2017 tax bill for procedural reasons), lawmakers “didn’t mean to coerce anyone to do anything, and so there’s no constitutional problem,” University of Michigan law professor Nicholas Bagley said in a recent webinar for the NIHCM Foundation, the Commonwealth Fund, and the University of Southern California’s Center for Health Journalism.
Or, said Bagley, the court could rule that, without the tax, the requirement to have health insurance is unconstitutional, but the rest of the law is not. In that case, the justices might strike the mandate only, which would have basically no impact.
It gets more complicated if the court decides that, as the plaintiffs argue, the individual mandate language without the penalty is unconstitutional and so closely tied to other parts of the law that some of them must fall as well.
Even there the court has choices. One option would be, as the Trump administration originally argued, to strike down the mandate and just the pieces of the law most closely related to it – which happen to include the insurance protections for people with preexisting conditions, an extremely popular provision of the law. The two parts are connected because the original purpose of the mandate was to make sure enough healthy people sign up for insurance to offset the added costs to insurers of sicker people.
Another option, of course, would be for the court to follow the lead of the Texas judge and strike down the entire law.
While that’s not the most likely outcome, said Bagley, if it happens it could be “a hot mess” for the nation’s entire health care system. As just one example, he said, “every hospital is getting paid pursuant to changes made by the ACA. How do you even go about making payments if the thing that you are looking to guide what those payments ought to be is itself invalid?”
What impact will new Justice Amy Coney Barrett have?
Perhaps a lot. Before the death of Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg, most court observers thought the case was highly unlikely to result in the entire law being struck down. That’s because Chief Justice John Roberts voted to uphold the law in 2012, and again when it was challenged in a less sweeping way in 2015.
But with Barrett replacing Ginsburg, even if Roberts joined the court’s remaining three liberals they could still be outvoted by the other five conservatives. Barrett was coy about her views on the Affordable Care Act during her confirmation hearings in October, but she has written that she thinks Roberts was wrong to uphold the law in 2012.
Could a new president and Congress make the case go away?
Many have suggested that, if Joe Biden assumes the presidency, his Justice Department could simply drop the case. But the administration did not bring the case; the GOP state officials did. And while normally the Justice Department’s job is to defend existing laws in court, in this case the ACA is being defended by a group of Democratic state attorneys general. A new administration could change that position, but that’s not the same as dropping the case.
Congress, on the other hand, could easily make the case moot. It could add back even a nominal financial penalty for not having insurance. It could eliminate the mandate altogether, although that would require 60 votes in the Senate under current rules. Congress could also pass a “severability” provision saying that, if any portion of the law is struck down, the rest should remain.
“The problem is not technical,” said Bagley. “It’s political.”
What is the timeline for a decision? Could the court delay implementation of its ruling?
The court usually hears oral arguments in a case months before it issues a decision. Unless the decision is unanimous or turns out to be very simple, Bagley said, he would expect to see an opinion “sometime in the spring.”
As to whether the court could find some or all of the law unconstitutional but delay when its decision takes effect, Bagley said that happened from time to time as recently as the 1970s. “That practice has been more or less abandoned,” he said, but in the case of a law so large, “you could imagine the Supreme Court using its discretion to say the decision wouldn’t take effect immediately.”
If the court does invalidate the entire ACA, Congress could act to fix things, but it’s unclear if it will be able to, especially if Republicans still control the Senate. If the justices strike the law, Bagley said, “I honestly think the likeliest outcome is that Congress runs around like a chicken with its head cut off, doesn’t come to a deal, and we’re back to where we were before 2010” when the ACA passed.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Higher cardiovascular risks in Kawasaki disease persist 10-plus years
Risks are highest in first year.
Survivors of Kawasaki disease remain at a higher long-term risk for cardiovascular events into young adulthood, including myocardial infarction, compared to people without the disease, new evidence reveals. The elevated risks emerged in survivors both with and without cardiovascular involvement at the time of initial diagnosis.
Overall risk of cardiovascular events was highest in the first year following Kawasaki disease diagnosis, and about 10 times greater than in healthy children, Cal Robinson, MD, said during a press conference at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“The risk gradually decreased over time. However, even 10 years after diagnosis of their illness, they still had a 39% higher risk,” said study author Dr. Robinson, a PGY4 pediatric nephrology fellow at The Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
Dr. Robinson also put the numbers in perspective. “We fully acknowledged these are very rare events in children, especially healthy children, which is why we needed such a large cohort to study this. Interpret the numbers cautiously.”
In terms of patient and family counseling, “I would say children with Kawasaki disease have a higher risk of myocardial infarction, but the absolute risk is still low,” he added. For example, 16 Kawasaki disease survivors experienced a heart attack during follow-up, or 0.4% of the affected study population, compared to a rate of 0.1% among matched controls.
“These families are often very frightened after the initial Kawasaki disease diagnosis,” Dr. Robinson said. “We have to balance some discussion with what we know about Kawasaki disease without overly scaring or terrifying these families, who are already anxious.”
To quantify the incidence and timing of cardiovascular events and cardiac disease following diagnosis, Dr. Robinson and colleagues assessed large databases representing approximately 3 million children. They focused on children hospitalized with a Kawasaki disease diagnosis between 1995 and 2018. These children had a median length of stay of 3 days and 2.5% were admitted to critical care. The investigators matched his population 1:100 to unaffected children in Ontario.
Follow-up was up to 24 years (median, 11 years) in this retrospective, population-based cohort study.
Risks raised over a decade and beyond
Compared to matched controls, Kawasaki disease survivors had a higher risk for a cardiac event in the first year following diagnosis (adjusted hazard ratio, 11.65; 95% confidence interval, 10.34-13.13). The 1- to 5-year risk was lower (aHR, 3.35), a trend that continued between 5 and 10 years (aHR, 1.87) and as well as after more than 10 years (aHR, 1.39).
The risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE, a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular death) was likewise highest in the first year after diagnosis (aHR, 3.27), followed by a 51% greater risk at 1-5 years, a 113% increased risk at 5-10 years, and a 17% elevated risk after 10 years.
The investigators compared the 144 Kawasaki disease survivors who experienced a coronary artery aneurysm (CAA) within 90 days of hospital admission to the 4,453 others who did not have a CAA. The risk for a composite cardiovascular event was elevated at each time point among those with a history of CAA, especially in the first year. The adjusted HR was 33.12 in the CAA group versus 10.44 in the non-CAA group.
“The most interesting finding of this study was that children with Kawasaki syndrome are at higher risk for composite cardiovascular events and major adverse cardiac events even if they were not diagnosed with coronary artery aneurysm,” session comoderator Shervin Assassi, MD, professor of medicine and director of division of rheumatology at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, said when asked to comment.
Dr. Robinson and colleagues also looked at outcomes based on presence or absence of coronary involvement at the time of Kawasaki disease diagnosis. For example, among those with initial coronary involvement, 15% later experienced a cardiovascular event and 10% experienced a major cardiovascular event.
“However, we were specifically interested in looking at children without initial coronary involvement. In this group, we also found these children were at increased risk for cardiovascular events compared to children without Kawasaki disease,” Dr. Robinson said. He said the distinction is important because approximately 95% of children diagnosed with Kawasaki disease do not feature initial coronary involvement.
In terms of clinical care, “our data provides an early signal that Kawasaki disease survivors – including those without initial coronary involvement – may be at higher risk of cardiovascular events into early adulthood.”
A call for closer monitoring
“Based on our results, we find that Kawasaki disease survivors may benefit from additional follow-up and surveillance for cardiovascular disease risk factors, such as obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol,” Dr. Robinson said. Early identification of heightened risk could allow physicians to more closely monitor this subgroup and emphasize potentially beneficial lifestyle modifications, including increasing physical activity, implementing a heart healthy diet, and avoiding smoking.
Mortality was not significantly different between groups. “Despite the risk of cardiac events we found, death was uncommon,” Dr. Robinson said. Among children with Kawasaki disease, 1 in 500 died during follow-up, so “the risk of death was actually lower than for children without Kawasaki disease.”
Similar findings of lower mortality have been reported in research out of Japan, he added during a plenary presentation at ACR 2020. Future research is warranted to evaluate this finding further, Dr. Robinson said.
Future plans
Going forward, the investigators plan to evaluate noncardiovascular outcomes in this patient population. They would also like to examine health care utilization following a diagnosis of Kawasaki disease “to better understand what kind of follow-up is happening now in Ontario,” Dr. Robinson said.
Another unanswered question is whether the cardiovascular events observed in the study stem from atherosclerotic disease or a different mechanism among survivors of Kawasaki disease.
The research was supported by a McMaster University Resident Research Grant, a Hamilton Health Sciences New Investigator Award, and Ontario’s Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Robinson had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Robinson C et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10): Abstract 0937.
Risks are highest in first year.
Risks are highest in first year.
Survivors of Kawasaki disease remain at a higher long-term risk for cardiovascular events into young adulthood, including myocardial infarction, compared to people without the disease, new evidence reveals. The elevated risks emerged in survivors both with and without cardiovascular involvement at the time of initial diagnosis.
Overall risk of cardiovascular events was highest in the first year following Kawasaki disease diagnosis, and about 10 times greater than in healthy children, Cal Robinson, MD, said during a press conference at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“The risk gradually decreased over time. However, even 10 years after diagnosis of their illness, they still had a 39% higher risk,” said study author Dr. Robinson, a PGY4 pediatric nephrology fellow at The Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
Dr. Robinson also put the numbers in perspective. “We fully acknowledged these are very rare events in children, especially healthy children, which is why we needed such a large cohort to study this. Interpret the numbers cautiously.”
In terms of patient and family counseling, “I would say children with Kawasaki disease have a higher risk of myocardial infarction, but the absolute risk is still low,” he added. For example, 16 Kawasaki disease survivors experienced a heart attack during follow-up, or 0.4% of the affected study population, compared to a rate of 0.1% among matched controls.
“These families are often very frightened after the initial Kawasaki disease diagnosis,” Dr. Robinson said. “We have to balance some discussion with what we know about Kawasaki disease without overly scaring or terrifying these families, who are already anxious.”
To quantify the incidence and timing of cardiovascular events and cardiac disease following diagnosis, Dr. Robinson and colleagues assessed large databases representing approximately 3 million children. They focused on children hospitalized with a Kawasaki disease diagnosis between 1995 and 2018. These children had a median length of stay of 3 days and 2.5% were admitted to critical care. The investigators matched his population 1:100 to unaffected children in Ontario.
Follow-up was up to 24 years (median, 11 years) in this retrospective, population-based cohort study.
Risks raised over a decade and beyond
Compared to matched controls, Kawasaki disease survivors had a higher risk for a cardiac event in the first year following diagnosis (adjusted hazard ratio, 11.65; 95% confidence interval, 10.34-13.13). The 1- to 5-year risk was lower (aHR, 3.35), a trend that continued between 5 and 10 years (aHR, 1.87) and as well as after more than 10 years (aHR, 1.39).
The risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE, a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular death) was likewise highest in the first year after diagnosis (aHR, 3.27), followed by a 51% greater risk at 1-5 years, a 113% increased risk at 5-10 years, and a 17% elevated risk after 10 years.
The investigators compared the 144 Kawasaki disease survivors who experienced a coronary artery aneurysm (CAA) within 90 days of hospital admission to the 4,453 others who did not have a CAA. The risk for a composite cardiovascular event was elevated at each time point among those with a history of CAA, especially in the first year. The adjusted HR was 33.12 in the CAA group versus 10.44 in the non-CAA group.
“The most interesting finding of this study was that children with Kawasaki syndrome are at higher risk for composite cardiovascular events and major adverse cardiac events even if they were not diagnosed with coronary artery aneurysm,” session comoderator Shervin Assassi, MD, professor of medicine and director of division of rheumatology at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, said when asked to comment.
Dr. Robinson and colleagues also looked at outcomes based on presence or absence of coronary involvement at the time of Kawasaki disease diagnosis. For example, among those with initial coronary involvement, 15% later experienced a cardiovascular event and 10% experienced a major cardiovascular event.
“However, we were specifically interested in looking at children without initial coronary involvement. In this group, we also found these children were at increased risk for cardiovascular events compared to children without Kawasaki disease,” Dr. Robinson said. He said the distinction is important because approximately 95% of children diagnosed with Kawasaki disease do not feature initial coronary involvement.
In terms of clinical care, “our data provides an early signal that Kawasaki disease survivors – including those without initial coronary involvement – may be at higher risk of cardiovascular events into early adulthood.”
A call for closer monitoring
“Based on our results, we find that Kawasaki disease survivors may benefit from additional follow-up and surveillance for cardiovascular disease risk factors, such as obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol,” Dr. Robinson said. Early identification of heightened risk could allow physicians to more closely monitor this subgroup and emphasize potentially beneficial lifestyle modifications, including increasing physical activity, implementing a heart healthy diet, and avoiding smoking.
Mortality was not significantly different between groups. “Despite the risk of cardiac events we found, death was uncommon,” Dr. Robinson said. Among children with Kawasaki disease, 1 in 500 died during follow-up, so “the risk of death was actually lower than for children without Kawasaki disease.”
Similar findings of lower mortality have been reported in research out of Japan, he added during a plenary presentation at ACR 2020. Future research is warranted to evaluate this finding further, Dr. Robinson said.
Future plans
Going forward, the investigators plan to evaluate noncardiovascular outcomes in this patient population. They would also like to examine health care utilization following a diagnosis of Kawasaki disease “to better understand what kind of follow-up is happening now in Ontario,” Dr. Robinson said.
Another unanswered question is whether the cardiovascular events observed in the study stem from atherosclerotic disease or a different mechanism among survivors of Kawasaki disease.
The research was supported by a McMaster University Resident Research Grant, a Hamilton Health Sciences New Investigator Award, and Ontario’s Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Robinson had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Robinson C et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10): Abstract 0937.
Survivors of Kawasaki disease remain at a higher long-term risk for cardiovascular events into young adulthood, including myocardial infarction, compared to people without the disease, new evidence reveals. The elevated risks emerged in survivors both with and without cardiovascular involvement at the time of initial diagnosis.
Overall risk of cardiovascular events was highest in the first year following Kawasaki disease diagnosis, and about 10 times greater than in healthy children, Cal Robinson, MD, said during a press conference at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“The risk gradually decreased over time. However, even 10 years after diagnosis of their illness, they still had a 39% higher risk,” said study author Dr. Robinson, a PGY4 pediatric nephrology fellow at The Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
Dr. Robinson also put the numbers in perspective. “We fully acknowledged these are very rare events in children, especially healthy children, which is why we needed such a large cohort to study this. Interpret the numbers cautiously.”
In terms of patient and family counseling, “I would say children with Kawasaki disease have a higher risk of myocardial infarction, but the absolute risk is still low,” he added. For example, 16 Kawasaki disease survivors experienced a heart attack during follow-up, or 0.4% of the affected study population, compared to a rate of 0.1% among matched controls.
“These families are often very frightened after the initial Kawasaki disease diagnosis,” Dr. Robinson said. “We have to balance some discussion with what we know about Kawasaki disease without overly scaring or terrifying these families, who are already anxious.”
To quantify the incidence and timing of cardiovascular events and cardiac disease following diagnosis, Dr. Robinson and colleagues assessed large databases representing approximately 3 million children. They focused on children hospitalized with a Kawasaki disease diagnosis between 1995 and 2018. These children had a median length of stay of 3 days and 2.5% were admitted to critical care. The investigators matched his population 1:100 to unaffected children in Ontario.
Follow-up was up to 24 years (median, 11 years) in this retrospective, population-based cohort study.
Risks raised over a decade and beyond
Compared to matched controls, Kawasaki disease survivors had a higher risk for a cardiac event in the first year following diagnosis (adjusted hazard ratio, 11.65; 95% confidence interval, 10.34-13.13). The 1- to 5-year risk was lower (aHR, 3.35), a trend that continued between 5 and 10 years (aHR, 1.87) and as well as after more than 10 years (aHR, 1.39).
The risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE, a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular death) was likewise highest in the first year after diagnosis (aHR, 3.27), followed by a 51% greater risk at 1-5 years, a 113% increased risk at 5-10 years, and a 17% elevated risk after 10 years.
The investigators compared the 144 Kawasaki disease survivors who experienced a coronary artery aneurysm (CAA) within 90 days of hospital admission to the 4,453 others who did not have a CAA. The risk for a composite cardiovascular event was elevated at each time point among those with a history of CAA, especially in the first year. The adjusted HR was 33.12 in the CAA group versus 10.44 in the non-CAA group.
“The most interesting finding of this study was that children with Kawasaki syndrome are at higher risk for composite cardiovascular events and major adverse cardiac events even if they were not diagnosed with coronary artery aneurysm,” session comoderator Shervin Assassi, MD, professor of medicine and director of division of rheumatology at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, said when asked to comment.
Dr. Robinson and colleagues also looked at outcomes based on presence or absence of coronary involvement at the time of Kawasaki disease diagnosis. For example, among those with initial coronary involvement, 15% later experienced a cardiovascular event and 10% experienced a major cardiovascular event.
“However, we were specifically interested in looking at children without initial coronary involvement. In this group, we also found these children were at increased risk for cardiovascular events compared to children without Kawasaki disease,” Dr. Robinson said. He said the distinction is important because approximately 95% of children diagnosed with Kawasaki disease do not feature initial coronary involvement.
In terms of clinical care, “our data provides an early signal that Kawasaki disease survivors – including those without initial coronary involvement – may be at higher risk of cardiovascular events into early adulthood.”
A call for closer monitoring
“Based on our results, we find that Kawasaki disease survivors may benefit from additional follow-up and surveillance for cardiovascular disease risk factors, such as obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol,” Dr. Robinson said. Early identification of heightened risk could allow physicians to more closely monitor this subgroup and emphasize potentially beneficial lifestyle modifications, including increasing physical activity, implementing a heart healthy diet, and avoiding smoking.
Mortality was not significantly different between groups. “Despite the risk of cardiac events we found, death was uncommon,” Dr. Robinson said. Among children with Kawasaki disease, 1 in 500 died during follow-up, so “the risk of death was actually lower than for children without Kawasaki disease.”
Similar findings of lower mortality have been reported in research out of Japan, he added during a plenary presentation at ACR 2020. Future research is warranted to evaluate this finding further, Dr. Robinson said.
Future plans
Going forward, the investigators plan to evaluate noncardiovascular outcomes in this patient population. They would also like to examine health care utilization following a diagnosis of Kawasaki disease “to better understand what kind of follow-up is happening now in Ontario,” Dr. Robinson said.
Another unanswered question is whether the cardiovascular events observed in the study stem from atherosclerotic disease or a different mechanism among survivors of Kawasaki disease.
The research was supported by a McMaster University Resident Research Grant, a Hamilton Health Sciences New Investigator Award, and Ontario’s Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Robinson had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Robinson C et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10): Abstract 0937.
FROM ACR 2020
Key clinical point: Kawasaki disease survivors remain at elevated long-term risk for cardiovascular events.
Major finding: Overall cardiovascular event risk was 39% higher, even after 10 years.
Study details: A retrospective, population-based cohort study of more than 4,597 Kawasaki disease survivors and 459,700 matched children without Kawasaki disease.
Disclosures: The research was supported by a McMaster University Resident Research Grant, a Hamilton Health Sciences New Investigator Award, and Ontario’s Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Robinson had no relevant financial disclosures.
Source: Robinson C et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10): Abstract 0937.
COVID-19 risks in rheumatic disease remain unclear
ACR 2020 studies offer conflicting findings.
Among people with COVID-19, those with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases had an elevated 30-day risk of hospitalization, ICU admission, need for mechanical ventilation, and acute kidney injury, compared to a group without rheumatic diseases at 4 months in a match-controlled study.
When investigators expanded the study to 6 months, the difference in need for mechanical ventilation disappeared. However, relative risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE) emerged as 74% higher among people with COVID-19 and with rheumatic disease, said Kristin D’Silva, MD, who presented the findings during a plenary session at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. She noted that rheumatic disease itself could contribute to VTE risk.
Comorbidities including hypertension, diabetes, and asthma were more common among people with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs). After adjustment for comorbidities, “the risks of hospitalization and ICU admission were attenuated, suggesting comorbidities are likely key mediators of the increased risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes observed in SARDs patients versus comparators,” Dr. D’Silva, a rheumatology fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview.
“The risk of venous thromboembolism persisted even after adjusting for comorbidities,” Dr. D’Silva said. Patients with SARDs should be closely monitored for VTE during COVID-19 infection, she added. “Patients with significant cardiovascular, pulmonary, and metabolic comorbidities should be closely monitored for severe COVID-19.”
At the same time, a systematic review of 15 published studies revealed a low incidence of COVID-19 infection among people with rheumatic disease. Furthermore, most experienced a mild clinical course and low mortality, Akhil Sood, MD, said when presenting results of his poster at the meeting.
Underlying immunosuppression, chronic inflammation, comorbidities, and disparities based on racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic status could predispose people with rheumatic disease to poorer COVID-19 outcomes. However, the risks and outcomes of COVID-19 infection among this population “are not well understood,” said Dr. Sood, a second-year resident in internal medicine at the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston.
Elevated risks in match-controlled study
Dr. D’Silva and colleagues examined a COVID-19 population and compared 716 people with SARDs and another 716 people from the general public at 4 months, as well as 2,379 people each in similar groups at 6 months. They used real-time electronic medical record data from the TriNetX research network to identify ICD-10 codes for inflammatory arthritis, connective tissue diseases, and systemic vasculitis. They also used ICD-10 codes and positive PCR tests to identify people with COVID-19.
Mean age was 57 years and women accounted for 79% of both groups evaluated at 4 months. Those with SARDs were 23% more likely to be hospitalized (relative risk, 1.23; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.50). This group was 75% more likely to be admitted to the ICU (RR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.11-2.75), 77% more likely to require mechanical ventilation (RR, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.06-2.96), and 83% more likely to experience acute kidney injury (RR, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.11-3.00).
Risk of death was not significantly higher in the SARDs group (RR, 1.16; 95% CI, 0.73-1.86).
When Dr. D’Silva expanded the study to more people at 6 months, they added additional 30-day outcomes of interest: renal replacement therapy, VTE, and ischemic stroke. Risk of need for renal replacement therapy, for example, was 81% higher in the SARDs group (RR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.07-3.07). Risk of stroke was not significantly different between groups.The improvement in mechanical ventilation risk between 4 and 6 months was not completely unexpected, Dr. D’Silva said. The relative risk dropped from 1.77 to 1.05. “This is not particularly surprising given national trends in the general population reporting decreased severe outcomes of COVID-19 including mortality as the pandemic progresses. This is likely multifactorial including changes in COVID-19 management (such as increasing use of nonintubated prone positioning rather than early intubation and treatments such as dexamethasone and remdesivir), decreased strain on hospitals and staffing compared to the early crisis phase of the pandemic, and higher testing capacity leading to detection of milder cases.”
When the 6-month analysis was further adjusted for comorbidities and a history of prior hospitalization within 1 year, only risk for acute kidney injury and VTE remained significant with relative risks of 1.33 and 1.60, respectively, likely because comorbidities are causal intermediates of COVID-19 30-day outcomes rather than confounders.
When asked to comment on the results, session comoderator Victoria K. Shanmugam, MD, said in an interview that the study “is of great interest both to rheumatologists and to patients with rheumatic disease.”
The higher risk of hospitalization, ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, acute kidney injury, and heart failure “is an important finding with implications for how our patients navigate risk during this pandemic,” said Dr. Shanmugam, director of the division of rheumatology at George Washington University in Washington.
Lower risks emerge in systematic review
The 15 observational studies in the systematic review included 11,815 participants. A total of 179, or 1.5%, tested positive for COVID-19.
“The incidence of COVID-19 infection among patients with rheumatic disease was low,” Dr. Sood said.
Within the COVID-19-positive group, almost 50% required hospitalization, 10% required ICU admission, and 8% died. The pooled event rate for hospitalization was 0.440 (95% CI, 0.296-0.596), while for ICU admission it was 0.132 (95% CI, 0.087-0.194) and for death it was 0.125 (95% CI, 0.082-0.182).
Different calculations of risk
The two studies seem to offer contradictory findings, but the disparities could be explained by study design differences. For example, Dr. D’Silva’s study evaluated a population with COVID-19 and compared those with SARDs versus a matched group from the general public. Dr. Sood and colleagues assessed study populations with rheumatic disease and assessed incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection and difference in outcomes.
“We are asking very different questions,” Dr. D’Silva said.
“The study by D’Silva et al. was able to account for different factors to reduce confounding,” Dr. Sood said, adding that Dr. D’Silva and colleagues included a high proportion of minorities, compared with a less diverse population in the systematic review, which featured a large number of studies from Italy.
The authors of the two studies had no relevant financial disclosures to report.
SOURCES: D’Silva K et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10): Abstract 0430, and Sood A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10): Abstract 0008.
ACR 2020 studies offer conflicting findings.
ACR 2020 studies offer conflicting findings.
Among people with COVID-19, those with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases had an elevated 30-day risk of hospitalization, ICU admission, need for mechanical ventilation, and acute kidney injury, compared to a group without rheumatic diseases at 4 months in a match-controlled study.
When investigators expanded the study to 6 months, the difference in need for mechanical ventilation disappeared. However, relative risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE) emerged as 74% higher among people with COVID-19 and with rheumatic disease, said Kristin D’Silva, MD, who presented the findings during a plenary session at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. She noted that rheumatic disease itself could contribute to VTE risk.
Comorbidities including hypertension, diabetes, and asthma were more common among people with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs). After adjustment for comorbidities, “the risks of hospitalization and ICU admission were attenuated, suggesting comorbidities are likely key mediators of the increased risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes observed in SARDs patients versus comparators,” Dr. D’Silva, a rheumatology fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview.
“The risk of venous thromboembolism persisted even after adjusting for comorbidities,” Dr. D’Silva said. Patients with SARDs should be closely monitored for VTE during COVID-19 infection, she added. “Patients with significant cardiovascular, pulmonary, and metabolic comorbidities should be closely monitored for severe COVID-19.”
At the same time, a systematic review of 15 published studies revealed a low incidence of COVID-19 infection among people with rheumatic disease. Furthermore, most experienced a mild clinical course and low mortality, Akhil Sood, MD, said when presenting results of his poster at the meeting.
Underlying immunosuppression, chronic inflammation, comorbidities, and disparities based on racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic status could predispose people with rheumatic disease to poorer COVID-19 outcomes. However, the risks and outcomes of COVID-19 infection among this population “are not well understood,” said Dr. Sood, a second-year resident in internal medicine at the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston.
Elevated risks in match-controlled study
Dr. D’Silva and colleagues examined a COVID-19 population and compared 716 people with SARDs and another 716 people from the general public at 4 months, as well as 2,379 people each in similar groups at 6 months. They used real-time electronic medical record data from the TriNetX research network to identify ICD-10 codes for inflammatory arthritis, connective tissue diseases, and systemic vasculitis. They also used ICD-10 codes and positive PCR tests to identify people with COVID-19.
Mean age was 57 years and women accounted for 79% of both groups evaluated at 4 months. Those with SARDs were 23% more likely to be hospitalized (relative risk, 1.23; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.50). This group was 75% more likely to be admitted to the ICU (RR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.11-2.75), 77% more likely to require mechanical ventilation (RR, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.06-2.96), and 83% more likely to experience acute kidney injury (RR, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.11-3.00).
Risk of death was not significantly higher in the SARDs group (RR, 1.16; 95% CI, 0.73-1.86).
When Dr. D’Silva expanded the study to more people at 6 months, they added additional 30-day outcomes of interest: renal replacement therapy, VTE, and ischemic stroke. Risk of need for renal replacement therapy, for example, was 81% higher in the SARDs group (RR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.07-3.07). Risk of stroke was not significantly different between groups.The improvement in mechanical ventilation risk between 4 and 6 months was not completely unexpected, Dr. D’Silva said. The relative risk dropped from 1.77 to 1.05. “This is not particularly surprising given national trends in the general population reporting decreased severe outcomes of COVID-19 including mortality as the pandemic progresses. This is likely multifactorial including changes in COVID-19 management (such as increasing use of nonintubated prone positioning rather than early intubation and treatments such as dexamethasone and remdesivir), decreased strain on hospitals and staffing compared to the early crisis phase of the pandemic, and higher testing capacity leading to detection of milder cases.”
When the 6-month analysis was further adjusted for comorbidities and a history of prior hospitalization within 1 year, only risk for acute kidney injury and VTE remained significant with relative risks of 1.33 and 1.60, respectively, likely because comorbidities are causal intermediates of COVID-19 30-day outcomes rather than confounders.
When asked to comment on the results, session comoderator Victoria K. Shanmugam, MD, said in an interview that the study “is of great interest both to rheumatologists and to patients with rheumatic disease.”
The higher risk of hospitalization, ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, acute kidney injury, and heart failure “is an important finding with implications for how our patients navigate risk during this pandemic,” said Dr. Shanmugam, director of the division of rheumatology at George Washington University in Washington.
Lower risks emerge in systematic review
The 15 observational studies in the systematic review included 11,815 participants. A total of 179, or 1.5%, tested positive for COVID-19.
“The incidence of COVID-19 infection among patients with rheumatic disease was low,” Dr. Sood said.
Within the COVID-19-positive group, almost 50% required hospitalization, 10% required ICU admission, and 8% died. The pooled event rate for hospitalization was 0.440 (95% CI, 0.296-0.596), while for ICU admission it was 0.132 (95% CI, 0.087-0.194) and for death it was 0.125 (95% CI, 0.082-0.182).
Different calculations of risk
The two studies seem to offer contradictory findings, but the disparities could be explained by study design differences. For example, Dr. D’Silva’s study evaluated a population with COVID-19 and compared those with SARDs versus a matched group from the general public. Dr. Sood and colleagues assessed study populations with rheumatic disease and assessed incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection and difference in outcomes.
“We are asking very different questions,” Dr. D’Silva said.
“The study by D’Silva et al. was able to account for different factors to reduce confounding,” Dr. Sood said, adding that Dr. D’Silva and colleagues included a high proportion of minorities, compared with a less diverse population in the systematic review, which featured a large number of studies from Italy.
The authors of the two studies had no relevant financial disclosures to report.
SOURCES: D’Silva K et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10): Abstract 0430, and Sood A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10): Abstract 0008.
Among people with COVID-19, those with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases had an elevated 30-day risk of hospitalization, ICU admission, need for mechanical ventilation, and acute kidney injury, compared to a group without rheumatic diseases at 4 months in a match-controlled study.
When investigators expanded the study to 6 months, the difference in need for mechanical ventilation disappeared. However, relative risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE) emerged as 74% higher among people with COVID-19 and with rheumatic disease, said Kristin D’Silva, MD, who presented the findings during a plenary session at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. She noted that rheumatic disease itself could contribute to VTE risk.
Comorbidities including hypertension, diabetes, and asthma were more common among people with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs). After adjustment for comorbidities, “the risks of hospitalization and ICU admission were attenuated, suggesting comorbidities are likely key mediators of the increased risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes observed in SARDs patients versus comparators,” Dr. D’Silva, a rheumatology fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview.
“The risk of venous thromboembolism persisted even after adjusting for comorbidities,” Dr. D’Silva said. Patients with SARDs should be closely monitored for VTE during COVID-19 infection, she added. “Patients with significant cardiovascular, pulmonary, and metabolic comorbidities should be closely monitored for severe COVID-19.”
At the same time, a systematic review of 15 published studies revealed a low incidence of COVID-19 infection among people with rheumatic disease. Furthermore, most experienced a mild clinical course and low mortality, Akhil Sood, MD, said when presenting results of his poster at the meeting.
Underlying immunosuppression, chronic inflammation, comorbidities, and disparities based on racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic status could predispose people with rheumatic disease to poorer COVID-19 outcomes. However, the risks and outcomes of COVID-19 infection among this population “are not well understood,” said Dr. Sood, a second-year resident in internal medicine at the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston.
Elevated risks in match-controlled study
Dr. D’Silva and colleagues examined a COVID-19 population and compared 716 people with SARDs and another 716 people from the general public at 4 months, as well as 2,379 people each in similar groups at 6 months. They used real-time electronic medical record data from the TriNetX research network to identify ICD-10 codes for inflammatory arthritis, connective tissue diseases, and systemic vasculitis. They also used ICD-10 codes and positive PCR tests to identify people with COVID-19.
Mean age was 57 years and women accounted for 79% of both groups evaluated at 4 months. Those with SARDs were 23% more likely to be hospitalized (relative risk, 1.23; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.50). This group was 75% more likely to be admitted to the ICU (RR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.11-2.75), 77% more likely to require mechanical ventilation (RR, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.06-2.96), and 83% more likely to experience acute kidney injury (RR, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.11-3.00).
Risk of death was not significantly higher in the SARDs group (RR, 1.16; 95% CI, 0.73-1.86).
When Dr. D’Silva expanded the study to more people at 6 months, they added additional 30-day outcomes of interest: renal replacement therapy, VTE, and ischemic stroke. Risk of need for renal replacement therapy, for example, was 81% higher in the SARDs group (RR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.07-3.07). Risk of stroke was not significantly different between groups.The improvement in mechanical ventilation risk between 4 and 6 months was not completely unexpected, Dr. D’Silva said. The relative risk dropped from 1.77 to 1.05. “This is not particularly surprising given national trends in the general population reporting decreased severe outcomes of COVID-19 including mortality as the pandemic progresses. This is likely multifactorial including changes in COVID-19 management (such as increasing use of nonintubated prone positioning rather than early intubation and treatments such as dexamethasone and remdesivir), decreased strain on hospitals and staffing compared to the early crisis phase of the pandemic, and higher testing capacity leading to detection of milder cases.”
When the 6-month analysis was further adjusted for comorbidities and a history of prior hospitalization within 1 year, only risk for acute kidney injury and VTE remained significant with relative risks of 1.33 and 1.60, respectively, likely because comorbidities are causal intermediates of COVID-19 30-day outcomes rather than confounders.
When asked to comment on the results, session comoderator Victoria K. Shanmugam, MD, said in an interview that the study “is of great interest both to rheumatologists and to patients with rheumatic disease.”
The higher risk of hospitalization, ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, acute kidney injury, and heart failure “is an important finding with implications for how our patients navigate risk during this pandemic,” said Dr. Shanmugam, director of the division of rheumatology at George Washington University in Washington.
Lower risks emerge in systematic review
The 15 observational studies in the systematic review included 11,815 participants. A total of 179, or 1.5%, tested positive for COVID-19.
“The incidence of COVID-19 infection among patients with rheumatic disease was low,” Dr. Sood said.
Within the COVID-19-positive group, almost 50% required hospitalization, 10% required ICU admission, and 8% died. The pooled event rate for hospitalization was 0.440 (95% CI, 0.296-0.596), while for ICU admission it was 0.132 (95% CI, 0.087-0.194) and for death it was 0.125 (95% CI, 0.082-0.182).
Different calculations of risk
The two studies seem to offer contradictory findings, but the disparities could be explained by study design differences. For example, Dr. D’Silva’s study evaluated a population with COVID-19 and compared those with SARDs versus a matched group from the general public. Dr. Sood and colleagues assessed study populations with rheumatic disease and assessed incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection and difference in outcomes.
“We are asking very different questions,” Dr. D’Silva said.
“The study by D’Silva et al. was able to account for different factors to reduce confounding,” Dr. Sood said, adding that Dr. D’Silva and colleagues included a high proportion of minorities, compared with a less diverse population in the systematic review, which featured a large number of studies from Italy.
The authors of the two studies had no relevant financial disclosures to report.
SOURCES: D’Silva K et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10): Abstract 0430, and Sood A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10): Abstract 0008.
FROM ACR 2020
Biden victory: What it means for COVID, health care
The former vice president has sketched out a big health agenda: ramping up the federal response to COVID-19, boosting the Affordable Care Act, creating a new “public option” to cover uninsured Americans, and expanding Medicare and Medicaid.
But the president-elect’s long to-do list on health is likely to face significant roadblocks in Congress and the courts, experts say.
For instance, Biden’s ambitious proposals on COVID-19 -- including his recent call for a national mask mandate -- could be waylaid by legal challenges and run into political hurdles on Capitol Hill, where he may face a divided Congress.
Joseph Antos, PhD, a health policy expert with the conservative American Enterprise Institute, predicts Biden will encounter the same type of congressional “gridlock situation” that President Barack Obama ran into during his second term.
“We have a situation that has been like this for a very, very long time -- lack of cooperation, lack of recognition that either party is capable of rising above their own electoral views to deal with problems that the country actually has.”
Antos also suggests that Biden may also face enormous political pressure to address the economic fallout from the coronavirus, including record unemployment and business closures, before anything else.
“I think it’s really going to be efforts that are intended to promote economic development and promote the economy,” he says.
In addition, Biden’s plans to expand Obamacare might face a new challenge from the Supreme Court in the year ahead. This month, the high court will take up a new case seeking to overturn the law.
Even so, experts say Biden’s plans on COVID-19 and expanding health care are likely to define his tenure in the White House as a central focus of his presidency.
“Health care will be at the very top of the list of the president’s priorities,” says Sabrina Corlette, JD, co-director of the Center on Health Insurance Reforms at Georgetown University’s McCourt School of Public Policy. “I do think, however, that the administration is going to be very preoccupied with the response to COVID-19 and the economic fallout … particularly in the first year.”
Here’s a closer look at what we can expect from a Biden presidency.
COVID-19: Federalizing response efforts
Biden will move to federalize the response to COVID-19. He has said he will take back major responsibilities from the states -- such as setting national policies on mask wearing, social distancing, and the reopening of schools and businesses, based on CDC guidance. In the days leading up to the election, Biden called for a national mask mandate, after waffling on the issue throughout the summer.
He has said he will let public health science drive political policy. Biden is also planning to create his own task force to advise officials during the transition on managing the new surge in COVID-19 cases, vaccine safety and protecting at-risk populations, Politico reported this week. He received a virtual briefing on the pandemic from a panel of experts as he awaited the election’s outcome.
“I think we will no longer have this confused and contradictory public messaging,” Corlette says, “but I also think there will be humility and the recognition that the evidence is evolving -- that we don’t have all the answers, but we’re learning as we go.”
But national mandates on masks and social distancing will be challenging to enforce, experts say. They are also likely to face pushback from business interests, opposition from public officials in GOP-led states, and even legal challenges.
Biden’s ability to work with Congress -- or not -- may determine whether he is able to implement some of the key components of his coronavirus action plan, which includes:
- Providing free COVID-19 testing for all Americans
- Hiring 100,000 contact tracers
- Eliminating out-of-pocket expenses for coronavirus treatment
- Delivering “sufficient” PPE for essential workers
- Supporting science-backed vaccines and medical treatments being developed
- Requiring the reopening of businesses, workplaces, and schools only after “sufficient” reductions in community transmission -- under evidence-based protocols put forward by the CDC
- Giving emergency paid leave for workers dislocated by the pandemic and more financial aid for workers, families, and small businesses
- Shoring up safeguards to protect at-risk Americans, including older people
- Boosting pay for health care workers on the front lines
Biden has not detailed how he would pay for many of these, beyond promising to force wealthy Americans to “pay their fair share” of taxes to help. He has proposed a tax increase on Americans making more than $400,000 a year, which would require congressional approval.
Antos says he expects Biden’s proposed COVID-19 action plan to be virtually the same as Trump’s in two areas: efforts to develop a vaccine and antiviral treatments.
The administration has spent some $225 million on COVID-19 testing efforts, with a particular focus on rural areas.
Trump launched Operation Warp Speed to fast-track a vaccine. As part of that, the federal government has contracted with six drug companies, spending nearly $11 billion. The operation aims to provide at least 300 million doses of a coronavirus vaccine by January 2021.
Antos would like to see “a more sophisticated approach to social distancing” from the president-elect that takes into account the different challenges facing Americans depending on their income, work situation, and other factors during the pandemic.
“There are a lot of people in this country where working from home is fine and their jobs are secure,” he notes. “It’s the person who used to work at a restaurant that closed, it’s the line worker at a factory that has severely cut back its hours. It’s basically lower-middle-class people, low-income people, middle-class people, and it’s not the elite.
“And the policies have not given enough consideration to the fact that their circumstances and their tradeoffs would differ from the tradeoffs of somebody who doesn’t have anything to worry about economically.
“So, what we need is a more supple policy [that] will give people the information they need and give them the financial support that they also need … so they can make good decisions for themselves and their families. And we basically haven’t done that.”
Obamacare on the blocks?
The Supreme Court’s decision to take up another case seeking to overturn the Affordable Care Act could hand Biden’s health agenda a major setback -- and put the medical care for millions of Americans in jeopardy.
On Nov. 10, the high court will hear oral arguments on a lawsuit that would strike down all of Obamacare. A decision is not expected until next year.
The court has previously upheld the 2010 law, which Biden helped usher through Congress as vice president. But the addition of right-leaning Supreme Court Justice Amy Coney Barrett to the bench last month gives the court a clear conservative majority that could mean the end of Obamacare, legal experts say.
Republicans have opposed the law since its passage, but they have been unable to muster the votes to repeal it, or to pass an alternative
Antos, from the American Enterprise Institute, notes conservatives believe the law has increased costs for health care and insurance over the past decade, in part because of its protections for Americans with preexisting conditions and requiring insurers to provide comprehensive “gold-plated” policies.
“It’s driven up costs, offers plans that are not very strong, put high-risk folks into the same [insurance pool], which has increased costs for everyone, the employer mandate … these are all the reasons,” he says.
The Supreme Court isn’t expected to deliver a decision on the Affordable Care Act before the middle of next year. But the uncertainty will likely push back Biden’s proposals to expand on the law.
Overturning Obamacare would have huge impacts on millions of Americans:
- As many as 133 million Americans -- roughly half the U.S. population -- with preexisting conditions could find it harder, if not impossible, to find affordable health insurance. That figure does not include Americans infected with COVID-19.
- About 165 million who require expensive treatments -- for cancer and other conditions -- would no longer be protected from huge costs for care by federal caps on out-of-pocket expenditures the Affordable Care Act requires.
- An estimated 21 million who now buy insurance through the Obamacare Marketplaces could lose their coverage.
- Another 12 million on Medicaid could find themselves without insurance.
- At least 2 million young adults ages 26 and under, now on their parents’ health policies, could be kicked off.
- Millions of people who use Medicare could face higher costs.
- Federal subsidies for lower-income Americans to buy policies would disappear.
Throughout the campaign, Biden repeatedly stressed the need to preserve the law’s provision barring insurance companies from refusing coverage for Americans with preexisting conditions, such as diabetes, cancer, and heart disease. It also outlaws charging higher premiums on the basis of health status, age, or gender.
Biden has also pledged to bolster the law as president.
He has proposed a variety of add-ons to the Affordable Care Act he says will “insure more than an estimated 97% of Americans,” according to the Biden campaign site.
Biden’s proposals include offering larger federal subsidies to help low- and middle-income Americans pay for policies purchased through Obamacare insurance Marketplaces.
The boldest of Biden’s proposals is the creation of a “public option” for insurance -- a Medicare-like program that small businesses and individuals could choose if they do not have coverage, cannot afford it, or don’t like their employer-based coverage.
It would also automatically enroll millions of uninsured Americans living in the 14 states that have not expanded Medicaid, which covers low-income people.
But such a plan would require congressional approval -- including a “super majority” of 60 Senate votes to block a likely GOP filibuster. That will be a significant challenge Biden will have to overcome, with Congress so evenly divided.
The White House would also have to defeat heavy lobbying from some of the most influential industry interest groups in Washington, Corlette says.
“I’m not even confident they would get all the Democrat votes,” she says.
“So, it’s a going to be an uphill battle to get a public option passed.”
Taken together, Biden’s plans for expanding Obamacare are projected to cost $750 billion over 10 years. He has said much of that financing would come from increasing taxes on the wealthy.
That means it would likely require congressional approval, which Antos suggests is unlikely given the polarization on Capitol Hill.
Medicare, Medicaid, and drug costs
Biden has called for a host of reforms targeting Medicare, Medicaid, and rising drug costs.
On Medicare, which primarily covers seniors 65 and older, Biden has proposed lowering the eligibility age from 65 to 60. That could extend Medicare to up to 20 million more Americans.
On Medicaid, the health care safety net for low-income and disabled Americans, the president-elect supports increased federal funding to states during the current economic crisis, and potentially beyond.
Medicare is likely to become a key focus of the new administration, in light of the pressures the pandemic is placing on Medicare funding.
In April, Medicare’s trustees said that the Part A trust fund for the program, which pays for hospital and inpatient care, could start to run dry in 2026.
But those projections did not include the impact of COVID-19. Some economists have since projected that Medicare Part A could become insolvent as early as 2022.
Medicare Part B, which pays for doctor and outpatient costs, is funded by general tax funding and beneficiary insurance premiums, so it is not in danger of drying up.
Adding to those pressures is an executive order Trump signed in August temporarily deferring payroll taxes, a primary funding vehicle for Medicare and Social Security.
Under these taxes, employees pay 6.2% of their earnings (on annual income up to $137,700) toward Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare taxes each pay period. Employers pay the same rate per paycheck, adding up to a combined 12.4% Social Security tax and 2.9% Medicare tax.
Biden has said he would reverse the tax cut when he takes office.
But to get a handle on Medicare and Medicaid funding issues, he is likely to need congressional support. Corlette and other experts say that could be a challenge while the nation remains in the grip of the coronavirus pandemic.
In addition to his Medicare and Medicaid reforms, Biden has proposed several plans to lower drug prices, a subset of rising health care and insurance costs.
U.S. spending on prescription drugs has increased nearly 42% over the past decade -- from $253.1 billion in 2010 to $358.7 billion in 2020 (projected) -- according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
In 2020, retail prices for 460 commonly prescribed drugs have spiked an average of 5.2%, according to new analysis by 3 Axis Advisors, a health research firm.
That’s more than double the projected rate of inflation.
To control drug costs, Biden supports legislation approved by the Democratic-led House of Representatives last year that would empower Medicare to negotiate drug prices with drug companies, as private insurers do.
Federal law now bars Medicare from negotiating prices on behalf of the 67.7 million Americans who use it. Drug companies and many GOP leaders argue that the current law is necessary to allow them to spend more on research and development of new medications.
In addition, Biden supports the idea of lifting bans on importing drugs from foreign countries with lower costs.
He also backs creating an independent review board to set price caps for new medications with no competitors; making high-quality generics more available; ending tax breaks for drug company advertising; and limiting their leeway in raising prices.
All of these proposals would likely require congressional approval and could face legal challenges in the courts.
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The former vice president has sketched out a big health agenda: ramping up the federal response to COVID-19, boosting the Affordable Care Act, creating a new “public option” to cover uninsured Americans, and expanding Medicare and Medicaid.
But the president-elect’s long to-do list on health is likely to face significant roadblocks in Congress and the courts, experts say.
For instance, Biden’s ambitious proposals on COVID-19 -- including his recent call for a national mask mandate -- could be waylaid by legal challenges and run into political hurdles on Capitol Hill, where he may face a divided Congress.
Joseph Antos, PhD, a health policy expert with the conservative American Enterprise Institute, predicts Biden will encounter the same type of congressional “gridlock situation” that President Barack Obama ran into during his second term.
“We have a situation that has been like this for a very, very long time -- lack of cooperation, lack of recognition that either party is capable of rising above their own electoral views to deal with problems that the country actually has.”
Antos also suggests that Biden may also face enormous political pressure to address the economic fallout from the coronavirus, including record unemployment and business closures, before anything else.
“I think it’s really going to be efforts that are intended to promote economic development and promote the economy,” he says.
In addition, Biden’s plans to expand Obamacare might face a new challenge from the Supreme Court in the year ahead. This month, the high court will take up a new case seeking to overturn the law.
Even so, experts say Biden’s plans on COVID-19 and expanding health care are likely to define his tenure in the White House as a central focus of his presidency.
“Health care will be at the very top of the list of the president’s priorities,” says Sabrina Corlette, JD, co-director of the Center on Health Insurance Reforms at Georgetown University’s McCourt School of Public Policy. “I do think, however, that the administration is going to be very preoccupied with the response to COVID-19 and the economic fallout … particularly in the first year.”
Here’s a closer look at what we can expect from a Biden presidency.
COVID-19: Federalizing response efforts
Biden will move to federalize the response to COVID-19. He has said he will take back major responsibilities from the states -- such as setting national policies on mask wearing, social distancing, and the reopening of schools and businesses, based on CDC guidance. In the days leading up to the election, Biden called for a national mask mandate, after waffling on the issue throughout the summer.
He has said he will let public health science drive political policy. Biden is also planning to create his own task force to advise officials during the transition on managing the new surge in COVID-19 cases, vaccine safety and protecting at-risk populations, Politico reported this week. He received a virtual briefing on the pandemic from a panel of experts as he awaited the election’s outcome.
“I think we will no longer have this confused and contradictory public messaging,” Corlette says, “but I also think there will be humility and the recognition that the evidence is evolving -- that we don’t have all the answers, but we’re learning as we go.”
But national mandates on masks and social distancing will be challenging to enforce, experts say. They are also likely to face pushback from business interests, opposition from public officials in GOP-led states, and even legal challenges.
Biden’s ability to work with Congress -- or not -- may determine whether he is able to implement some of the key components of his coronavirus action plan, which includes:
- Providing free COVID-19 testing for all Americans
- Hiring 100,000 contact tracers
- Eliminating out-of-pocket expenses for coronavirus treatment
- Delivering “sufficient” PPE for essential workers
- Supporting science-backed vaccines and medical treatments being developed
- Requiring the reopening of businesses, workplaces, and schools only after “sufficient” reductions in community transmission -- under evidence-based protocols put forward by the CDC
- Giving emergency paid leave for workers dislocated by the pandemic and more financial aid for workers, families, and small businesses
- Shoring up safeguards to protect at-risk Americans, including older people
- Boosting pay for health care workers on the front lines
Biden has not detailed how he would pay for many of these, beyond promising to force wealthy Americans to “pay their fair share” of taxes to help. He has proposed a tax increase on Americans making more than $400,000 a year, which would require congressional approval.
Antos says he expects Biden’s proposed COVID-19 action plan to be virtually the same as Trump’s in two areas: efforts to develop a vaccine and antiviral treatments.
The administration has spent some $225 million on COVID-19 testing efforts, with a particular focus on rural areas.
Trump launched Operation Warp Speed to fast-track a vaccine. As part of that, the federal government has contracted with six drug companies, spending nearly $11 billion. The operation aims to provide at least 300 million doses of a coronavirus vaccine by January 2021.
Antos would like to see “a more sophisticated approach to social distancing” from the president-elect that takes into account the different challenges facing Americans depending on their income, work situation, and other factors during the pandemic.
“There are a lot of people in this country where working from home is fine and their jobs are secure,” he notes. “It’s the person who used to work at a restaurant that closed, it’s the line worker at a factory that has severely cut back its hours. It’s basically lower-middle-class people, low-income people, middle-class people, and it’s not the elite.
“And the policies have not given enough consideration to the fact that their circumstances and their tradeoffs would differ from the tradeoffs of somebody who doesn’t have anything to worry about economically.
“So, what we need is a more supple policy [that] will give people the information they need and give them the financial support that they also need … so they can make good decisions for themselves and their families. And we basically haven’t done that.”
Obamacare on the blocks?
The Supreme Court’s decision to take up another case seeking to overturn the Affordable Care Act could hand Biden’s health agenda a major setback -- and put the medical care for millions of Americans in jeopardy.
On Nov. 10, the high court will hear oral arguments on a lawsuit that would strike down all of Obamacare. A decision is not expected until next year.
The court has previously upheld the 2010 law, which Biden helped usher through Congress as vice president. But the addition of right-leaning Supreme Court Justice Amy Coney Barrett to the bench last month gives the court a clear conservative majority that could mean the end of Obamacare, legal experts say.
Republicans have opposed the law since its passage, but they have been unable to muster the votes to repeal it, or to pass an alternative
Antos, from the American Enterprise Institute, notes conservatives believe the law has increased costs for health care and insurance over the past decade, in part because of its protections for Americans with preexisting conditions and requiring insurers to provide comprehensive “gold-plated” policies.
“It’s driven up costs, offers plans that are not very strong, put high-risk folks into the same [insurance pool], which has increased costs for everyone, the employer mandate … these are all the reasons,” he says.
The Supreme Court isn’t expected to deliver a decision on the Affordable Care Act before the middle of next year. But the uncertainty will likely push back Biden’s proposals to expand on the law.
Overturning Obamacare would have huge impacts on millions of Americans:
- As many as 133 million Americans -- roughly half the U.S. population -- with preexisting conditions could find it harder, if not impossible, to find affordable health insurance. That figure does not include Americans infected with COVID-19.
- About 165 million who require expensive treatments -- for cancer and other conditions -- would no longer be protected from huge costs for care by federal caps on out-of-pocket expenditures the Affordable Care Act requires.
- An estimated 21 million who now buy insurance through the Obamacare Marketplaces could lose their coverage.
- Another 12 million on Medicaid could find themselves without insurance.
- At least 2 million young adults ages 26 and under, now on their parents’ health policies, could be kicked off.
- Millions of people who use Medicare could face higher costs.
- Federal subsidies for lower-income Americans to buy policies would disappear.
Throughout the campaign, Biden repeatedly stressed the need to preserve the law’s provision barring insurance companies from refusing coverage for Americans with preexisting conditions, such as diabetes, cancer, and heart disease. It also outlaws charging higher premiums on the basis of health status, age, or gender.
Biden has also pledged to bolster the law as president.
He has proposed a variety of add-ons to the Affordable Care Act he says will “insure more than an estimated 97% of Americans,” according to the Biden campaign site.
Biden’s proposals include offering larger federal subsidies to help low- and middle-income Americans pay for policies purchased through Obamacare insurance Marketplaces.
The boldest of Biden’s proposals is the creation of a “public option” for insurance -- a Medicare-like program that small businesses and individuals could choose if they do not have coverage, cannot afford it, or don’t like their employer-based coverage.
It would also automatically enroll millions of uninsured Americans living in the 14 states that have not expanded Medicaid, which covers low-income people.
But such a plan would require congressional approval -- including a “super majority” of 60 Senate votes to block a likely GOP filibuster. That will be a significant challenge Biden will have to overcome, with Congress so evenly divided.
The White House would also have to defeat heavy lobbying from some of the most influential industry interest groups in Washington, Corlette says.
“I’m not even confident they would get all the Democrat votes,” she says.
“So, it’s a going to be an uphill battle to get a public option passed.”
Taken together, Biden’s plans for expanding Obamacare are projected to cost $750 billion over 10 years. He has said much of that financing would come from increasing taxes on the wealthy.
That means it would likely require congressional approval, which Antos suggests is unlikely given the polarization on Capitol Hill.
Medicare, Medicaid, and drug costs
Biden has called for a host of reforms targeting Medicare, Medicaid, and rising drug costs.
On Medicare, which primarily covers seniors 65 and older, Biden has proposed lowering the eligibility age from 65 to 60. That could extend Medicare to up to 20 million more Americans.
On Medicaid, the health care safety net for low-income and disabled Americans, the president-elect supports increased federal funding to states during the current economic crisis, and potentially beyond.
Medicare is likely to become a key focus of the new administration, in light of the pressures the pandemic is placing on Medicare funding.
In April, Medicare’s trustees said that the Part A trust fund for the program, which pays for hospital and inpatient care, could start to run dry in 2026.
But those projections did not include the impact of COVID-19. Some economists have since projected that Medicare Part A could become insolvent as early as 2022.
Medicare Part B, which pays for doctor and outpatient costs, is funded by general tax funding and beneficiary insurance premiums, so it is not in danger of drying up.
Adding to those pressures is an executive order Trump signed in August temporarily deferring payroll taxes, a primary funding vehicle for Medicare and Social Security.
Under these taxes, employees pay 6.2% of their earnings (on annual income up to $137,700) toward Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare taxes each pay period. Employers pay the same rate per paycheck, adding up to a combined 12.4% Social Security tax and 2.9% Medicare tax.
Biden has said he would reverse the tax cut when he takes office.
But to get a handle on Medicare and Medicaid funding issues, he is likely to need congressional support. Corlette and other experts say that could be a challenge while the nation remains in the grip of the coronavirus pandemic.
In addition to his Medicare and Medicaid reforms, Biden has proposed several plans to lower drug prices, a subset of rising health care and insurance costs.
U.S. spending on prescription drugs has increased nearly 42% over the past decade -- from $253.1 billion in 2010 to $358.7 billion in 2020 (projected) -- according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
In 2020, retail prices for 460 commonly prescribed drugs have spiked an average of 5.2%, according to new analysis by 3 Axis Advisors, a health research firm.
That’s more than double the projected rate of inflation.
To control drug costs, Biden supports legislation approved by the Democratic-led House of Representatives last year that would empower Medicare to negotiate drug prices with drug companies, as private insurers do.
Federal law now bars Medicare from negotiating prices on behalf of the 67.7 million Americans who use it. Drug companies and many GOP leaders argue that the current law is necessary to allow them to spend more on research and development of new medications.
In addition, Biden supports the idea of lifting bans on importing drugs from foreign countries with lower costs.
He also backs creating an independent review board to set price caps for new medications with no competitors; making high-quality generics more available; ending tax breaks for drug company advertising; and limiting their leeway in raising prices.
All of these proposals would likely require congressional approval and could face legal challenges in the courts.
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The former vice president has sketched out a big health agenda: ramping up the federal response to COVID-19, boosting the Affordable Care Act, creating a new “public option” to cover uninsured Americans, and expanding Medicare and Medicaid.
But the president-elect’s long to-do list on health is likely to face significant roadblocks in Congress and the courts, experts say.
For instance, Biden’s ambitious proposals on COVID-19 -- including his recent call for a national mask mandate -- could be waylaid by legal challenges and run into political hurdles on Capitol Hill, where he may face a divided Congress.
Joseph Antos, PhD, a health policy expert with the conservative American Enterprise Institute, predicts Biden will encounter the same type of congressional “gridlock situation” that President Barack Obama ran into during his second term.
“We have a situation that has been like this for a very, very long time -- lack of cooperation, lack of recognition that either party is capable of rising above their own electoral views to deal with problems that the country actually has.”
Antos also suggests that Biden may also face enormous political pressure to address the economic fallout from the coronavirus, including record unemployment and business closures, before anything else.
“I think it’s really going to be efforts that are intended to promote economic development and promote the economy,” he says.
In addition, Biden’s plans to expand Obamacare might face a new challenge from the Supreme Court in the year ahead. This month, the high court will take up a new case seeking to overturn the law.
Even so, experts say Biden’s plans on COVID-19 and expanding health care are likely to define his tenure in the White House as a central focus of his presidency.
“Health care will be at the very top of the list of the president’s priorities,” says Sabrina Corlette, JD, co-director of the Center on Health Insurance Reforms at Georgetown University’s McCourt School of Public Policy. “I do think, however, that the administration is going to be very preoccupied with the response to COVID-19 and the economic fallout … particularly in the first year.”
Here’s a closer look at what we can expect from a Biden presidency.
COVID-19: Federalizing response efforts
Biden will move to federalize the response to COVID-19. He has said he will take back major responsibilities from the states -- such as setting national policies on mask wearing, social distancing, and the reopening of schools and businesses, based on CDC guidance. In the days leading up to the election, Biden called for a national mask mandate, after waffling on the issue throughout the summer.
He has said he will let public health science drive political policy. Biden is also planning to create his own task force to advise officials during the transition on managing the new surge in COVID-19 cases, vaccine safety and protecting at-risk populations, Politico reported this week. He received a virtual briefing on the pandemic from a panel of experts as he awaited the election’s outcome.
“I think we will no longer have this confused and contradictory public messaging,” Corlette says, “but I also think there will be humility and the recognition that the evidence is evolving -- that we don’t have all the answers, but we’re learning as we go.”
But national mandates on masks and social distancing will be challenging to enforce, experts say. They are also likely to face pushback from business interests, opposition from public officials in GOP-led states, and even legal challenges.
Biden’s ability to work with Congress -- or not -- may determine whether he is able to implement some of the key components of his coronavirus action plan, which includes:
- Providing free COVID-19 testing for all Americans
- Hiring 100,000 contact tracers
- Eliminating out-of-pocket expenses for coronavirus treatment
- Delivering “sufficient” PPE for essential workers
- Supporting science-backed vaccines and medical treatments being developed
- Requiring the reopening of businesses, workplaces, and schools only after “sufficient” reductions in community transmission -- under evidence-based protocols put forward by the CDC
- Giving emergency paid leave for workers dislocated by the pandemic and more financial aid for workers, families, and small businesses
- Shoring up safeguards to protect at-risk Americans, including older people
- Boosting pay for health care workers on the front lines
Biden has not detailed how he would pay for many of these, beyond promising to force wealthy Americans to “pay their fair share” of taxes to help. He has proposed a tax increase on Americans making more than $400,000 a year, which would require congressional approval.
Antos says he expects Biden’s proposed COVID-19 action plan to be virtually the same as Trump’s in two areas: efforts to develop a vaccine and antiviral treatments.
The administration has spent some $225 million on COVID-19 testing efforts, with a particular focus on rural areas.
Trump launched Operation Warp Speed to fast-track a vaccine. As part of that, the federal government has contracted with six drug companies, spending nearly $11 billion. The operation aims to provide at least 300 million doses of a coronavirus vaccine by January 2021.
Antos would like to see “a more sophisticated approach to social distancing” from the president-elect that takes into account the different challenges facing Americans depending on their income, work situation, and other factors during the pandemic.
“There are a lot of people in this country where working from home is fine and their jobs are secure,” he notes. “It’s the person who used to work at a restaurant that closed, it’s the line worker at a factory that has severely cut back its hours. It’s basically lower-middle-class people, low-income people, middle-class people, and it’s not the elite.
“And the policies have not given enough consideration to the fact that their circumstances and their tradeoffs would differ from the tradeoffs of somebody who doesn’t have anything to worry about economically.
“So, what we need is a more supple policy [that] will give people the information they need and give them the financial support that they also need … so they can make good decisions for themselves and their families. And we basically haven’t done that.”
Obamacare on the blocks?
The Supreme Court’s decision to take up another case seeking to overturn the Affordable Care Act could hand Biden’s health agenda a major setback -- and put the medical care for millions of Americans in jeopardy.
On Nov. 10, the high court will hear oral arguments on a lawsuit that would strike down all of Obamacare. A decision is not expected until next year.
The court has previously upheld the 2010 law, which Biden helped usher through Congress as vice president. But the addition of right-leaning Supreme Court Justice Amy Coney Barrett to the bench last month gives the court a clear conservative majority that could mean the end of Obamacare, legal experts say.
Republicans have opposed the law since its passage, but they have been unable to muster the votes to repeal it, or to pass an alternative
Antos, from the American Enterprise Institute, notes conservatives believe the law has increased costs for health care and insurance over the past decade, in part because of its protections for Americans with preexisting conditions and requiring insurers to provide comprehensive “gold-plated” policies.
“It’s driven up costs, offers plans that are not very strong, put high-risk folks into the same [insurance pool], which has increased costs for everyone, the employer mandate … these are all the reasons,” he says.
The Supreme Court isn’t expected to deliver a decision on the Affordable Care Act before the middle of next year. But the uncertainty will likely push back Biden’s proposals to expand on the law.
Overturning Obamacare would have huge impacts on millions of Americans:
- As many as 133 million Americans -- roughly half the U.S. population -- with preexisting conditions could find it harder, if not impossible, to find affordable health insurance. That figure does not include Americans infected with COVID-19.
- About 165 million who require expensive treatments -- for cancer and other conditions -- would no longer be protected from huge costs for care by federal caps on out-of-pocket expenditures the Affordable Care Act requires.
- An estimated 21 million who now buy insurance through the Obamacare Marketplaces could lose their coverage.
- Another 12 million on Medicaid could find themselves without insurance.
- At least 2 million young adults ages 26 and under, now on their parents’ health policies, could be kicked off.
- Millions of people who use Medicare could face higher costs.
- Federal subsidies for lower-income Americans to buy policies would disappear.
Throughout the campaign, Biden repeatedly stressed the need to preserve the law’s provision barring insurance companies from refusing coverage for Americans with preexisting conditions, such as diabetes, cancer, and heart disease. It also outlaws charging higher premiums on the basis of health status, age, or gender.
Biden has also pledged to bolster the law as president.
He has proposed a variety of add-ons to the Affordable Care Act he says will “insure more than an estimated 97% of Americans,” according to the Biden campaign site.
Biden’s proposals include offering larger federal subsidies to help low- and middle-income Americans pay for policies purchased through Obamacare insurance Marketplaces.
The boldest of Biden’s proposals is the creation of a “public option” for insurance -- a Medicare-like program that small businesses and individuals could choose if they do not have coverage, cannot afford it, or don’t like their employer-based coverage.
It would also automatically enroll millions of uninsured Americans living in the 14 states that have not expanded Medicaid, which covers low-income people.
But such a plan would require congressional approval -- including a “super majority” of 60 Senate votes to block a likely GOP filibuster. That will be a significant challenge Biden will have to overcome, with Congress so evenly divided.
The White House would also have to defeat heavy lobbying from some of the most influential industry interest groups in Washington, Corlette says.
“I’m not even confident they would get all the Democrat votes,” she says.
“So, it’s a going to be an uphill battle to get a public option passed.”
Taken together, Biden’s plans for expanding Obamacare are projected to cost $750 billion over 10 years. He has said much of that financing would come from increasing taxes on the wealthy.
That means it would likely require congressional approval, which Antos suggests is unlikely given the polarization on Capitol Hill.
Medicare, Medicaid, and drug costs
Biden has called for a host of reforms targeting Medicare, Medicaid, and rising drug costs.
On Medicare, which primarily covers seniors 65 and older, Biden has proposed lowering the eligibility age from 65 to 60. That could extend Medicare to up to 20 million more Americans.
On Medicaid, the health care safety net for low-income and disabled Americans, the president-elect supports increased federal funding to states during the current economic crisis, and potentially beyond.
Medicare is likely to become a key focus of the new administration, in light of the pressures the pandemic is placing on Medicare funding.
In April, Medicare’s trustees said that the Part A trust fund for the program, which pays for hospital and inpatient care, could start to run dry in 2026.
But those projections did not include the impact of COVID-19. Some economists have since projected that Medicare Part A could become insolvent as early as 2022.
Medicare Part B, which pays for doctor and outpatient costs, is funded by general tax funding and beneficiary insurance premiums, so it is not in danger of drying up.
Adding to those pressures is an executive order Trump signed in August temporarily deferring payroll taxes, a primary funding vehicle for Medicare and Social Security.
Under these taxes, employees pay 6.2% of their earnings (on annual income up to $137,700) toward Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare taxes each pay period. Employers pay the same rate per paycheck, adding up to a combined 12.4% Social Security tax and 2.9% Medicare tax.
Biden has said he would reverse the tax cut when he takes office.
But to get a handle on Medicare and Medicaid funding issues, he is likely to need congressional support. Corlette and other experts say that could be a challenge while the nation remains in the grip of the coronavirus pandemic.
In addition to his Medicare and Medicaid reforms, Biden has proposed several plans to lower drug prices, a subset of rising health care and insurance costs.
U.S. spending on prescription drugs has increased nearly 42% over the past decade -- from $253.1 billion in 2010 to $358.7 billion in 2020 (projected) -- according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
In 2020, retail prices for 460 commonly prescribed drugs have spiked an average of 5.2%, according to new analysis by 3 Axis Advisors, a health research firm.
That’s more than double the projected rate of inflation.
To control drug costs, Biden supports legislation approved by the Democratic-led House of Representatives last year that would empower Medicare to negotiate drug prices with drug companies, as private insurers do.
Federal law now bars Medicare from negotiating prices on behalf of the 67.7 million Americans who use it. Drug companies and many GOP leaders argue that the current law is necessary to allow them to spend more on research and development of new medications.
In addition, Biden supports the idea of lifting bans on importing drugs from foreign countries with lower costs.
He also backs creating an independent review board to set price caps for new medications with no competitors; making high-quality generics more available; ending tax breaks for drug company advertising; and limiting their leeway in raising prices.
All of these proposals would likely require congressional approval and could face legal challenges in the courts.
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FBI warns of ‘imminent’ cyberattacks on U.S. hospitals
Amid recent reports of hackers targeting and blackmailing health care systems and even patients, the Federal Bureau of Investigation and other agencies have issued warning of “imminent” cyberattacks on more U.S. hospitals.
A new report released by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, part of the Department of Homeland Security, noted that the FBI and the Department of Health & Human Services have “credible information of an increased and imminent cybercrime threat to U.S. hospitals and health care providers.”
The agencies are urging “timely and reasonable precautions” to protect health care networks from these threats.
As reported, hackers accessed patient records at Vastaamo, Finland’s largest private psychotherapy system, and emailed some patients last month demanding €200 in bitcoin or else personal health data would be released online.
In June, the University of California, San Francisco, experienced an information technology (IT) “security incident” that led to the payout of $1.14 million to individuals responsible for a malware attack in exchange for the return of data.
In addition, last week, Sky Lakes Medical Center in Klamath Falls, Ore., released a statement in which it said there had been a ransomware attack on its computer systems. Although “there is no evidence that patient information has been compromised,” some of its systems are still down.
“We’re open for business, it’s just not business as usual,” Tom Hottman, public information officer at Sky Lakes, said in an interview.
Paul S. Appelbaum, MD, Dollard Professor of Psychiatry, Medicine, and Law at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview, “People have known for a long time that there are nefarious actors out there.” He said all health care systems should be prepared to deal with these problems.
“In the face of a warning from the FBI, I’d say that’s even more important now,” Dr. Appelbaum added.
‘Malicious cyber actors’
In the new CISA report, the agency noted that it, the FBI, and the HHS have been assessing “malicious cyber actors” targeting health care systems with malware loaders such as TrickBot and BazarLoader, which often lead to data theft, ransomware attacks, and service disruptions.
“The cybercriminal enterprise behind TrickBot, which is likely also the creator of BazarLoader malware, has continued to develop new functionality and tools, increasing the ease, speed, and profitability of victimization,” the report authors wrote.
Phishing campaigns often contain attachments with malware or links to malicious websites. “Loaders start the infection chain by distributing the payload,” the report noted. A backdoor mechanism is then installed on the victim’s device.
In addition to TrickBot and BazarLoader (or BazarBackdoor), the report discussed other malicious tools, including Ryuk and Conti, which are types of ransomware that can infect systems for hackers’ financial gain.
“These issues will be particularly challenging for organizations within the COVID-19 pandemic; therefore, administrators will need to balance this risk when determining their cybersecurity investments,” the agencies wrote.
Dr. Appelbaum said his organization is taking the warning seriously.
“When the report first came out, I received emails from every system that I’m affiliated with warning about it and encouraging me as a member of the medical staff to take the usual prudent precautions,” such as not opening attachments or links from unknown sources, he said.
“The FBI warning has what seems like very reasonable advice, which is that every system should automatically back up their data off site in a separate system that’s differently accessible,” he added.
After a ransomware attack, the most recently entered information may not be backed up and could get lost, but “that’s a lot easier to deal with then losing access to all of your medical records,” said Dr. Appelbaum.
Ipsit Vahia, MD, medical director at the Institute for Technology and Psychiatry at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., noted that, in answer to the FBI warning, he has heard that many centers, including his own, are warning their clinicians not to open any email attachments at this time.
Recent attacks
UCSF issued a statement noting that malware detected in early June led to the encryption of “a limited number of servers” in its medical school, making them temporarily inaccessible.
“We do not currently believe patient medical records were exposed,” the university said in the statement.
It added that because the encrypted data were necessary for “some of the academic work” conducted at UCSF, they agreed to pay a portion of the ransom demand – about $1.14 million. The hackers then provided a tool that unlocked the encrypted data.
“We continue to cooperate with law enforcement and we appreciate everyone’s understanding that we are limited in what we can share while we continue our investigation,” the statement reads. UCSF declined a request for further comment.
At Sky Lakes Medical Center, computer systems are still down after its ransomware attack, including use of electronic medical records, but the Oregon-based health care system is still seeing patients.
They are “being interviewed old school,” with the admitting process being conducted on paper, “but patient care goes on,” said Mr. Hottman.
In addition to a teaching hospital, Sky Lakes comprises specialty and primary care clinics, including a cancer treatment center. All remain open to patients at this time.
Diagnostic imaging is also continuing, but “getting the image to a place it can be read” has become more complicated, said Mr. Hottman.
“We have some work-arounds in process, and a plan is being assembled that we think will be in place as early as this weekend so that we can get those images read starting next week,” he said.
In addition, “scheduling is a little clunky,” he reported. However, “we have an awesome staff with a good attitude, so there’s still a whole lot we can do.”
He also noted that his institution has reconfirmed that, as of Nov. 4, no patient data had been compromised.
‘Especially chilling’
Targeting hospitals through cyberattacks isn’t new. In 2017, the WannaCry virus affected more than 200,000 computers in 150 countries, including the operating system of the U.K. National Health Service. The cyberattack locked clinicians out of NHS patient records and other digital tools for 3 days.
Dr. Appelbaum noted that, as hospital systems become more dependent on the Internet and on electronic communications, they become more vulnerable to data breaches.
“I think it’s clear that there have been concerted efforts lately to undertake attacks on health care IT systems to either hold them hostage, as in a ransomware attack, or to download files and use that information for profit,” he said.
Still, Dr. Vahia noted that contacting patients directly, which occurred in the Finland data breach and blackmail scheme, is something new. It is “especially chilling” that individual psychiatric patients were targeted.
It’s difficult to overstate how big a deal this is, and we should be treating it with the appropriate level of urgency,” he said in an interview.
“It shows how badly things can go wrong when security is compromised; and it should make us take a step back and survey the world of digital health to gain recognition of how much risk there might be that we haven’t really understood before,” Dr. Vahia said.
Clinical tips
Asked whether he had any tips to share with clinicians, Mr. Hottman noted that the best time to have a plan is before something dire happens.
“I would make [the possibility of cyberattacks] part of the emergency preparedness program. What if you don’t have access to computers? What do you do?” It’s important to answer those questions prior to systems going down, he said.
Mr. Hottman reported that after a mechanical failure last year put their computer systems offline for a day, “we started putting all critical information on paper and in a binder,” including phone numbers for the state police.
Dr. Vahia noted that another important step for clinicians “is to just pause and take stock of how digitally dependent” health care is becoming. He also warned that precautions should be taken regarding wearables and apps, as well as for electronic medical records. He noted the importance of strong passwords and two-step verification processes.
Even with the risks, digital technology has had a major impact on health care efficiency. “It’s not perfect, the work is ongoing, and there are big questions that need to be addressed, but in the end, the ability of technology when used right and securely” leads to better patient care, he said.
John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, agreed that digital health care is and will remain very important; but at the same time, security issues need proper attention.
“When you look back at medical hacks that have happened, there’s often a human error behind it. It’s rare for someone to break encryption. I think we have pretty darn good security, but we need to realize that sometimes errors will happen,” he said in an interview.
As an example, Dr. Torous, who is also chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Health and Technology Committee, cited phishing emails, which depend on a user clicking a link that can cause a virus to be downloaded into their network.
“You can be cautious, but it takes just one person to download an attachment with a virus in it” to cause disruptions, Dr. Torous said.
Telehealth implications
After its data breach, Vastaamo posted on its website a notice that video is never recorded during the centers’ telehealth sessions, and so patients need not worry that any videos could be leaked online.
Asked whether video is commonly recorded during telehealth sessions in the United States, Dr. Vahia said that he was not aware of sessions being recorded, especially because the amount of the data would be too great to store indefinitely.
Dr. Appelbaum agreed and said that, to his knowledge, no clinicians at Columbia University are recording telehealth sessions. He said that it would represent a privacy threat, and he noted that most health care providers “don’t have the time to go back and watch videos of their interactions with patients.”
In the case of recordings for research purposes, he emphasized that it would be important to get consent and then store the health information offline.
As for other telehealth security risks, Dr. Vahia noted that it is possible that if a computer or device is compromised, an individual could hack into a camera and observe the session. In addition to microphones, “these pose some especially high vulnerabilities,” he said. “Clinicians need to pay attention as to whether the cameras they’re using for telecare are on or if they’re covered when not in use. And they should pay attention to security settings on smartphones and ensure microphones are not turned on as the default.”
Dr. Appelbaum said the HIPAA requires that telehealth sessions be conducted on secure systems, so clinicians need to ascertain whether the system they’re using complies with that rule.
“Particularly people who are not part of larger systems and would not usually take on that responsibility, maybe they’re in private practice or a small group, they really need to check on the security level and on HIPAA compliance and not just assume that it is adequately secure,” he said.
Dr. Appelbaum, who is also a past president of the APA and director of the Center for Law, Ethics, and Psychiatry at Columbia University, noted that the major risk for hospitals after a cyberattack is probably not liability to individual patients.
“It’s much more likely that they would face fines from HIPAA if it’s found that they failed to live up to HIPAA requirements,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Amid recent reports of hackers targeting and blackmailing health care systems and even patients, the Federal Bureau of Investigation and other agencies have issued warning of “imminent” cyberattacks on more U.S. hospitals.
A new report released by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, part of the Department of Homeland Security, noted that the FBI and the Department of Health & Human Services have “credible information of an increased and imminent cybercrime threat to U.S. hospitals and health care providers.”
The agencies are urging “timely and reasonable precautions” to protect health care networks from these threats.
As reported, hackers accessed patient records at Vastaamo, Finland’s largest private psychotherapy system, and emailed some patients last month demanding €200 in bitcoin or else personal health data would be released online.
In June, the University of California, San Francisco, experienced an information technology (IT) “security incident” that led to the payout of $1.14 million to individuals responsible for a malware attack in exchange for the return of data.
In addition, last week, Sky Lakes Medical Center in Klamath Falls, Ore., released a statement in which it said there had been a ransomware attack on its computer systems. Although “there is no evidence that patient information has been compromised,” some of its systems are still down.
“We’re open for business, it’s just not business as usual,” Tom Hottman, public information officer at Sky Lakes, said in an interview.
Paul S. Appelbaum, MD, Dollard Professor of Psychiatry, Medicine, and Law at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview, “People have known for a long time that there are nefarious actors out there.” He said all health care systems should be prepared to deal with these problems.
“In the face of a warning from the FBI, I’d say that’s even more important now,” Dr. Appelbaum added.
‘Malicious cyber actors’
In the new CISA report, the agency noted that it, the FBI, and the HHS have been assessing “malicious cyber actors” targeting health care systems with malware loaders such as TrickBot and BazarLoader, which often lead to data theft, ransomware attacks, and service disruptions.
“The cybercriminal enterprise behind TrickBot, which is likely also the creator of BazarLoader malware, has continued to develop new functionality and tools, increasing the ease, speed, and profitability of victimization,” the report authors wrote.
Phishing campaigns often contain attachments with malware or links to malicious websites. “Loaders start the infection chain by distributing the payload,” the report noted. A backdoor mechanism is then installed on the victim’s device.
In addition to TrickBot and BazarLoader (or BazarBackdoor), the report discussed other malicious tools, including Ryuk and Conti, which are types of ransomware that can infect systems for hackers’ financial gain.
“These issues will be particularly challenging for organizations within the COVID-19 pandemic; therefore, administrators will need to balance this risk when determining their cybersecurity investments,” the agencies wrote.
Dr. Appelbaum said his organization is taking the warning seriously.
“When the report first came out, I received emails from every system that I’m affiliated with warning about it and encouraging me as a member of the medical staff to take the usual prudent precautions,” such as not opening attachments or links from unknown sources, he said.
“The FBI warning has what seems like very reasonable advice, which is that every system should automatically back up their data off site in a separate system that’s differently accessible,” he added.
After a ransomware attack, the most recently entered information may not be backed up and could get lost, but “that’s a lot easier to deal with then losing access to all of your medical records,” said Dr. Appelbaum.
Ipsit Vahia, MD, medical director at the Institute for Technology and Psychiatry at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., noted that, in answer to the FBI warning, he has heard that many centers, including his own, are warning their clinicians not to open any email attachments at this time.
Recent attacks
UCSF issued a statement noting that malware detected in early June led to the encryption of “a limited number of servers” in its medical school, making them temporarily inaccessible.
“We do not currently believe patient medical records were exposed,” the university said in the statement.
It added that because the encrypted data were necessary for “some of the academic work” conducted at UCSF, they agreed to pay a portion of the ransom demand – about $1.14 million. The hackers then provided a tool that unlocked the encrypted data.
“We continue to cooperate with law enforcement and we appreciate everyone’s understanding that we are limited in what we can share while we continue our investigation,” the statement reads. UCSF declined a request for further comment.
At Sky Lakes Medical Center, computer systems are still down after its ransomware attack, including use of electronic medical records, but the Oregon-based health care system is still seeing patients.
They are “being interviewed old school,” with the admitting process being conducted on paper, “but patient care goes on,” said Mr. Hottman.
In addition to a teaching hospital, Sky Lakes comprises specialty and primary care clinics, including a cancer treatment center. All remain open to patients at this time.
Diagnostic imaging is also continuing, but “getting the image to a place it can be read” has become more complicated, said Mr. Hottman.
“We have some work-arounds in process, and a plan is being assembled that we think will be in place as early as this weekend so that we can get those images read starting next week,” he said.
In addition, “scheduling is a little clunky,” he reported. However, “we have an awesome staff with a good attitude, so there’s still a whole lot we can do.”
He also noted that his institution has reconfirmed that, as of Nov. 4, no patient data had been compromised.
‘Especially chilling’
Targeting hospitals through cyberattacks isn’t new. In 2017, the WannaCry virus affected more than 200,000 computers in 150 countries, including the operating system of the U.K. National Health Service. The cyberattack locked clinicians out of NHS patient records and other digital tools for 3 days.
Dr. Appelbaum noted that, as hospital systems become more dependent on the Internet and on electronic communications, they become more vulnerable to data breaches.
“I think it’s clear that there have been concerted efforts lately to undertake attacks on health care IT systems to either hold them hostage, as in a ransomware attack, or to download files and use that information for profit,” he said.
Still, Dr. Vahia noted that contacting patients directly, which occurred in the Finland data breach and blackmail scheme, is something new. It is “especially chilling” that individual psychiatric patients were targeted.
It’s difficult to overstate how big a deal this is, and we should be treating it with the appropriate level of urgency,” he said in an interview.
“It shows how badly things can go wrong when security is compromised; and it should make us take a step back and survey the world of digital health to gain recognition of how much risk there might be that we haven’t really understood before,” Dr. Vahia said.
Clinical tips
Asked whether he had any tips to share with clinicians, Mr. Hottman noted that the best time to have a plan is before something dire happens.
“I would make [the possibility of cyberattacks] part of the emergency preparedness program. What if you don’t have access to computers? What do you do?” It’s important to answer those questions prior to systems going down, he said.
Mr. Hottman reported that after a mechanical failure last year put their computer systems offline for a day, “we started putting all critical information on paper and in a binder,” including phone numbers for the state police.
Dr. Vahia noted that another important step for clinicians “is to just pause and take stock of how digitally dependent” health care is becoming. He also warned that precautions should be taken regarding wearables and apps, as well as for electronic medical records. He noted the importance of strong passwords and two-step verification processes.
Even with the risks, digital technology has had a major impact on health care efficiency. “It’s not perfect, the work is ongoing, and there are big questions that need to be addressed, but in the end, the ability of technology when used right and securely” leads to better patient care, he said.
John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, agreed that digital health care is and will remain very important; but at the same time, security issues need proper attention.
“When you look back at medical hacks that have happened, there’s often a human error behind it. It’s rare for someone to break encryption. I think we have pretty darn good security, but we need to realize that sometimes errors will happen,” he said in an interview.
As an example, Dr. Torous, who is also chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Health and Technology Committee, cited phishing emails, which depend on a user clicking a link that can cause a virus to be downloaded into their network.
“You can be cautious, but it takes just one person to download an attachment with a virus in it” to cause disruptions, Dr. Torous said.
Telehealth implications
After its data breach, Vastaamo posted on its website a notice that video is never recorded during the centers’ telehealth sessions, and so patients need not worry that any videos could be leaked online.
Asked whether video is commonly recorded during telehealth sessions in the United States, Dr. Vahia said that he was not aware of sessions being recorded, especially because the amount of the data would be too great to store indefinitely.
Dr. Appelbaum agreed and said that, to his knowledge, no clinicians at Columbia University are recording telehealth sessions. He said that it would represent a privacy threat, and he noted that most health care providers “don’t have the time to go back and watch videos of their interactions with patients.”
In the case of recordings for research purposes, he emphasized that it would be important to get consent and then store the health information offline.
As for other telehealth security risks, Dr. Vahia noted that it is possible that if a computer or device is compromised, an individual could hack into a camera and observe the session. In addition to microphones, “these pose some especially high vulnerabilities,” he said. “Clinicians need to pay attention as to whether the cameras they’re using for telecare are on or if they’re covered when not in use. And they should pay attention to security settings on smartphones and ensure microphones are not turned on as the default.”
Dr. Appelbaum said the HIPAA requires that telehealth sessions be conducted on secure systems, so clinicians need to ascertain whether the system they’re using complies with that rule.
“Particularly people who are not part of larger systems and would not usually take on that responsibility, maybe they’re in private practice or a small group, they really need to check on the security level and on HIPAA compliance and not just assume that it is adequately secure,” he said.
Dr. Appelbaum, who is also a past president of the APA and director of the Center for Law, Ethics, and Psychiatry at Columbia University, noted that the major risk for hospitals after a cyberattack is probably not liability to individual patients.
“It’s much more likely that they would face fines from HIPAA if it’s found that they failed to live up to HIPAA requirements,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Amid recent reports of hackers targeting and blackmailing health care systems and even patients, the Federal Bureau of Investigation and other agencies have issued warning of “imminent” cyberattacks on more U.S. hospitals.
A new report released by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, part of the Department of Homeland Security, noted that the FBI and the Department of Health & Human Services have “credible information of an increased and imminent cybercrime threat to U.S. hospitals and health care providers.”
The agencies are urging “timely and reasonable precautions” to protect health care networks from these threats.
As reported, hackers accessed patient records at Vastaamo, Finland’s largest private psychotherapy system, and emailed some patients last month demanding €200 in bitcoin or else personal health data would be released online.
In June, the University of California, San Francisco, experienced an information technology (IT) “security incident” that led to the payout of $1.14 million to individuals responsible for a malware attack in exchange for the return of data.
In addition, last week, Sky Lakes Medical Center in Klamath Falls, Ore., released a statement in which it said there had been a ransomware attack on its computer systems. Although “there is no evidence that patient information has been compromised,” some of its systems are still down.
“We’re open for business, it’s just not business as usual,” Tom Hottman, public information officer at Sky Lakes, said in an interview.
Paul S. Appelbaum, MD, Dollard Professor of Psychiatry, Medicine, and Law at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview, “People have known for a long time that there are nefarious actors out there.” He said all health care systems should be prepared to deal with these problems.
“In the face of a warning from the FBI, I’d say that’s even more important now,” Dr. Appelbaum added.
‘Malicious cyber actors’
In the new CISA report, the agency noted that it, the FBI, and the HHS have been assessing “malicious cyber actors” targeting health care systems with malware loaders such as TrickBot and BazarLoader, which often lead to data theft, ransomware attacks, and service disruptions.
“The cybercriminal enterprise behind TrickBot, which is likely also the creator of BazarLoader malware, has continued to develop new functionality and tools, increasing the ease, speed, and profitability of victimization,” the report authors wrote.
Phishing campaigns often contain attachments with malware or links to malicious websites. “Loaders start the infection chain by distributing the payload,” the report noted. A backdoor mechanism is then installed on the victim’s device.
In addition to TrickBot and BazarLoader (or BazarBackdoor), the report discussed other malicious tools, including Ryuk and Conti, which are types of ransomware that can infect systems for hackers’ financial gain.
“These issues will be particularly challenging for organizations within the COVID-19 pandemic; therefore, administrators will need to balance this risk when determining their cybersecurity investments,” the agencies wrote.
Dr. Appelbaum said his organization is taking the warning seriously.
“When the report first came out, I received emails from every system that I’m affiliated with warning about it and encouraging me as a member of the medical staff to take the usual prudent precautions,” such as not opening attachments or links from unknown sources, he said.
“The FBI warning has what seems like very reasonable advice, which is that every system should automatically back up their data off site in a separate system that’s differently accessible,” he added.
After a ransomware attack, the most recently entered information may not be backed up and could get lost, but “that’s a lot easier to deal with then losing access to all of your medical records,” said Dr. Appelbaum.
Ipsit Vahia, MD, medical director at the Institute for Technology and Psychiatry at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., noted that, in answer to the FBI warning, he has heard that many centers, including his own, are warning their clinicians not to open any email attachments at this time.
Recent attacks
UCSF issued a statement noting that malware detected in early June led to the encryption of “a limited number of servers” in its medical school, making them temporarily inaccessible.
“We do not currently believe patient medical records were exposed,” the university said in the statement.
It added that because the encrypted data were necessary for “some of the academic work” conducted at UCSF, they agreed to pay a portion of the ransom demand – about $1.14 million. The hackers then provided a tool that unlocked the encrypted data.
“We continue to cooperate with law enforcement and we appreciate everyone’s understanding that we are limited in what we can share while we continue our investigation,” the statement reads. UCSF declined a request for further comment.
At Sky Lakes Medical Center, computer systems are still down after its ransomware attack, including use of electronic medical records, but the Oregon-based health care system is still seeing patients.
They are “being interviewed old school,” with the admitting process being conducted on paper, “but patient care goes on,” said Mr. Hottman.
In addition to a teaching hospital, Sky Lakes comprises specialty and primary care clinics, including a cancer treatment center. All remain open to patients at this time.
Diagnostic imaging is also continuing, but “getting the image to a place it can be read” has become more complicated, said Mr. Hottman.
“We have some work-arounds in process, and a plan is being assembled that we think will be in place as early as this weekend so that we can get those images read starting next week,” he said.
In addition, “scheduling is a little clunky,” he reported. However, “we have an awesome staff with a good attitude, so there’s still a whole lot we can do.”
He also noted that his institution has reconfirmed that, as of Nov. 4, no patient data had been compromised.
‘Especially chilling’
Targeting hospitals through cyberattacks isn’t new. In 2017, the WannaCry virus affected more than 200,000 computers in 150 countries, including the operating system of the U.K. National Health Service. The cyberattack locked clinicians out of NHS patient records and other digital tools for 3 days.
Dr. Appelbaum noted that, as hospital systems become more dependent on the Internet and on electronic communications, they become more vulnerable to data breaches.
“I think it’s clear that there have been concerted efforts lately to undertake attacks on health care IT systems to either hold them hostage, as in a ransomware attack, or to download files and use that information for profit,” he said.
Still, Dr. Vahia noted that contacting patients directly, which occurred in the Finland data breach and blackmail scheme, is something new. It is “especially chilling” that individual psychiatric patients were targeted.
It’s difficult to overstate how big a deal this is, and we should be treating it with the appropriate level of urgency,” he said in an interview.
“It shows how badly things can go wrong when security is compromised; and it should make us take a step back and survey the world of digital health to gain recognition of how much risk there might be that we haven’t really understood before,” Dr. Vahia said.
Clinical tips
Asked whether he had any tips to share with clinicians, Mr. Hottman noted that the best time to have a plan is before something dire happens.
“I would make [the possibility of cyberattacks] part of the emergency preparedness program. What if you don’t have access to computers? What do you do?” It’s important to answer those questions prior to systems going down, he said.
Mr. Hottman reported that after a mechanical failure last year put their computer systems offline for a day, “we started putting all critical information on paper and in a binder,” including phone numbers for the state police.
Dr. Vahia noted that another important step for clinicians “is to just pause and take stock of how digitally dependent” health care is becoming. He also warned that precautions should be taken regarding wearables and apps, as well as for electronic medical records. He noted the importance of strong passwords and two-step verification processes.
Even with the risks, digital technology has had a major impact on health care efficiency. “It’s not perfect, the work is ongoing, and there are big questions that need to be addressed, but in the end, the ability of technology when used right and securely” leads to better patient care, he said.
John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, agreed that digital health care is and will remain very important; but at the same time, security issues need proper attention.
“When you look back at medical hacks that have happened, there’s often a human error behind it. It’s rare for someone to break encryption. I think we have pretty darn good security, but we need to realize that sometimes errors will happen,” he said in an interview.
As an example, Dr. Torous, who is also chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Health and Technology Committee, cited phishing emails, which depend on a user clicking a link that can cause a virus to be downloaded into their network.
“You can be cautious, but it takes just one person to download an attachment with a virus in it” to cause disruptions, Dr. Torous said.
Telehealth implications
After its data breach, Vastaamo posted on its website a notice that video is never recorded during the centers’ telehealth sessions, and so patients need not worry that any videos could be leaked online.
Asked whether video is commonly recorded during telehealth sessions in the United States, Dr. Vahia said that he was not aware of sessions being recorded, especially because the amount of the data would be too great to store indefinitely.
Dr. Appelbaum agreed and said that, to his knowledge, no clinicians at Columbia University are recording telehealth sessions. He said that it would represent a privacy threat, and he noted that most health care providers “don’t have the time to go back and watch videos of their interactions with patients.”
In the case of recordings for research purposes, he emphasized that it would be important to get consent and then store the health information offline.
As for other telehealth security risks, Dr. Vahia noted that it is possible that if a computer or device is compromised, an individual could hack into a camera and observe the session. In addition to microphones, “these pose some especially high vulnerabilities,” he said. “Clinicians need to pay attention as to whether the cameras they’re using for telecare are on or if they’re covered when not in use. And they should pay attention to security settings on smartphones and ensure microphones are not turned on as the default.”
Dr. Appelbaum said the HIPAA requires that telehealth sessions be conducted on secure systems, so clinicians need to ascertain whether the system they’re using complies with that rule.
“Particularly people who are not part of larger systems and would not usually take on that responsibility, maybe they’re in private practice or a small group, they really need to check on the security level and on HIPAA compliance and not just assume that it is adequately secure,” he said.
Dr. Appelbaum, who is also a past president of the APA and director of the Center for Law, Ethics, and Psychiatry at Columbia University, noted that the major risk for hospitals after a cyberattack is probably not liability to individual patients.
“It’s much more likely that they would face fines from HIPAA if it’s found that they failed to live up to HIPAA requirements,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.