User login
AVAHO
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]


Genomic analysis reveals insights into pathogenesis of neuroblastoma
Insights into the genetic drivers of the disease were identified based on data from whole-genome, whole-exome, and/or transcriptome sequencing of tumor samples.
“The comprehensive genome-wide analysis performed here allowed us to discover age-associated alterations in MYCN, TERT, PTPRD, and Ras pathway alterations, which, together with ATRX, represent the majority of common driver gene alterations in neuroblastoma,” wrote study author Samuel W. Brady, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tenn., and colleagues.
The group’s findings were published in Nature Communications.
The researchers integrated and analyzed data from 702 neuroblastomas encompassing all age and risk categories, with the goal of identifying rare driver events and age-related molecular aberrations. Among the samples, 23 were from patients who had relapsed.
The researchers found that 40% of samples had somatic alterations in known driver genes, with the most common alterations being MYCN (19%; primarily amplification), TERT (17%; structural variations [SVs]), SHANK2 (13%; SVs), PTPRD (11%; SVs and focal deletions), ALK (10%; single nucleotide variants [SNVs] and SVs), and ATRX (8%; multiple mutation types).
MYCN and TERT alterations were more common in younger children (median age of 2.3 years and 3.8 years, respectively), while ATRX alterations were more frequently seen in older patients (median age of 5.6 years).
“These findings suggest that the sympathetic nervous system, the tissue from which neuroblastoma arises, is susceptible to different oncogenic insults at different times during development, which could be explored in future investigations using animal models,” the researchers wrote.
Furthermore, they found evidence to suggest the COSMIC mutational signature 18 is the most common cause of driver SNVs in neuroblastoma, including most Ras-activating and ALK variants.
Signature 18 was enriched in neuroblastomas with increased expression of mitochondrial ribosome and electron transport–associated genes, 17q gain, and MYCN amplification.
“[T]his mutagenic process, which is caused by ROS [reactive oxygen species] in other settings (though not proven in neuroblastoma), may promote evolution and heterogeneity, as many driver SNVs, such as ALK mutations, are later events in neuroblastoma,” the researchers explained.
Based on these findings, the authors concluded that neuroblastomas with 17q gain may be amenable to precision medicines, possibly through targeting altered mitochondrial function.
“[Our] findings will identify patients who might be eligible for targeted therapy and those that may be at higher risk based on a combination of genetic alterations detected by these genome-wide sequencing methods,” commented study author Jinghui Zhang, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital.
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. One author disclosed financial affiliations with Y-mabs Therapeutics, Abpro-Labs, Eureka Therapeutics, and Biotec Pharmacon.
SOURCE: Brady SW et al. Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 14. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18987-4.
Insights into the genetic drivers of the disease were identified based on data from whole-genome, whole-exome, and/or transcriptome sequencing of tumor samples.
“The comprehensive genome-wide analysis performed here allowed us to discover age-associated alterations in MYCN, TERT, PTPRD, and Ras pathway alterations, which, together with ATRX, represent the majority of common driver gene alterations in neuroblastoma,” wrote study author Samuel W. Brady, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tenn., and colleagues.
The group’s findings were published in Nature Communications.
The researchers integrated and analyzed data from 702 neuroblastomas encompassing all age and risk categories, with the goal of identifying rare driver events and age-related molecular aberrations. Among the samples, 23 were from patients who had relapsed.
The researchers found that 40% of samples had somatic alterations in known driver genes, with the most common alterations being MYCN (19%; primarily amplification), TERT (17%; structural variations [SVs]), SHANK2 (13%; SVs), PTPRD (11%; SVs and focal deletions), ALK (10%; single nucleotide variants [SNVs] and SVs), and ATRX (8%; multiple mutation types).
MYCN and TERT alterations were more common in younger children (median age of 2.3 years and 3.8 years, respectively), while ATRX alterations were more frequently seen in older patients (median age of 5.6 years).
“These findings suggest that the sympathetic nervous system, the tissue from which neuroblastoma arises, is susceptible to different oncogenic insults at different times during development, which could be explored in future investigations using animal models,” the researchers wrote.
Furthermore, they found evidence to suggest the COSMIC mutational signature 18 is the most common cause of driver SNVs in neuroblastoma, including most Ras-activating and ALK variants.
Signature 18 was enriched in neuroblastomas with increased expression of mitochondrial ribosome and electron transport–associated genes, 17q gain, and MYCN amplification.
“[T]his mutagenic process, which is caused by ROS [reactive oxygen species] in other settings (though not proven in neuroblastoma), may promote evolution and heterogeneity, as many driver SNVs, such as ALK mutations, are later events in neuroblastoma,” the researchers explained.
Based on these findings, the authors concluded that neuroblastomas with 17q gain may be amenable to precision medicines, possibly through targeting altered mitochondrial function.
“[Our] findings will identify patients who might be eligible for targeted therapy and those that may be at higher risk based on a combination of genetic alterations detected by these genome-wide sequencing methods,” commented study author Jinghui Zhang, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital.
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. One author disclosed financial affiliations with Y-mabs Therapeutics, Abpro-Labs, Eureka Therapeutics, and Biotec Pharmacon.
SOURCE: Brady SW et al. Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 14. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18987-4.
Insights into the genetic drivers of the disease were identified based on data from whole-genome, whole-exome, and/or transcriptome sequencing of tumor samples.
“The comprehensive genome-wide analysis performed here allowed us to discover age-associated alterations in MYCN, TERT, PTPRD, and Ras pathway alterations, which, together with ATRX, represent the majority of common driver gene alterations in neuroblastoma,” wrote study author Samuel W. Brady, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tenn., and colleagues.
The group’s findings were published in Nature Communications.
The researchers integrated and analyzed data from 702 neuroblastomas encompassing all age and risk categories, with the goal of identifying rare driver events and age-related molecular aberrations. Among the samples, 23 were from patients who had relapsed.
The researchers found that 40% of samples had somatic alterations in known driver genes, with the most common alterations being MYCN (19%; primarily amplification), TERT (17%; structural variations [SVs]), SHANK2 (13%; SVs), PTPRD (11%; SVs and focal deletions), ALK (10%; single nucleotide variants [SNVs] and SVs), and ATRX (8%; multiple mutation types).
MYCN and TERT alterations were more common in younger children (median age of 2.3 years and 3.8 years, respectively), while ATRX alterations were more frequently seen in older patients (median age of 5.6 years).
“These findings suggest that the sympathetic nervous system, the tissue from which neuroblastoma arises, is susceptible to different oncogenic insults at different times during development, which could be explored in future investigations using animal models,” the researchers wrote.
Furthermore, they found evidence to suggest the COSMIC mutational signature 18 is the most common cause of driver SNVs in neuroblastoma, including most Ras-activating and ALK variants.
Signature 18 was enriched in neuroblastomas with increased expression of mitochondrial ribosome and electron transport–associated genes, 17q gain, and MYCN amplification.
“[T]his mutagenic process, which is caused by ROS [reactive oxygen species] in other settings (though not proven in neuroblastoma), may promote evolution and heterogeneity, as many driver SNVs, such as ALK mutations, are later events in neuroblastoma,” the researchers explained.
Based on these findings, the authors concluded that neuroblastomas with 17q gain may be amenable to precision medicines, possibly through targeting altered mitochondrial function.
“[Our] findings will identify patients who might be eligible for targeted therapy and those that may be at higher risk based on a combination of genetic alterations detected by these genome-wide sequencing methods,” commented study author Jinghui Zhang, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital.
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. One author disclosed financial affiliations with Y-mabs Therapeutics, Abpro-Labs, Eureka Therapeutics, and Biotec Pharmacon.
SOURCE: Brady SW et al. Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 14. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18987-4.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
One-month delay in cancer treatment linked to increase in mortality
In light of the treatment delays resulting from the pandemic, Canadian and U.K. researchers carried out a review and analysis of relevant studies published between January 2000 and April 2020.
Included studies examined data on surgical interventions, systemic therapy, or radiotherapy for seven forms of cancer – bladder, breast, colon, rectum, lung, cervix, and head and neck. Delays were measured from diagnosis to the first treatment or from the completion of one treatment to the start of the next.
The search identified 34 suitable studies for 17 indications, with data from more than 1.2 million patients. The analysis identified a significant association between delay and increased mortality for 13 of the 17 indications (P < .05).
For surgery, there was a 6%-8% increase in the risk of death for every 4-week treatment delay. Estimates for systemic treatment varied (hazard ratio range, 1.01-1.28). Four-week delays in radiotherapy were for radical radiotherapy for head and neck cancer (HR, 1.09; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-1.14), adjuvant radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery (HR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.88-1.09), and cervical cancer adjuvant radiotherapy (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.00-1.50).
Delays of up to 8 and 12 weeks further increased mortality. An 8-week delay in breast cancer surgery was linked to a 17% increased mortality, and a 12-week delay would increase mortality by 26%.
A surgical delay of 12 weeks for patients with breast cancer continuing for 1 year – which is likely to be the case as the pandemic continues – would lead to 1,400 excess deaths in the United Kingdom.
The authors said the results of this study could be used to guide policy making on the organization of cancer services, particularly as the pandemic continues and further delays are expected.
This article originally appeared on Univadis, part of the Medscape Professional Network.
In light of the treatment delays resulting from the pandemic, Canadian and U.K. researchers carried out a review and analysis of relevant studies published between January 2000 and April 2020.
Included studies examined data on surgical interventions, systemic therapy, or radiotherapy for seven forms of cancer – bladder, breast, colon, rectum, lung, cervix, and head and neck. Delays were measured from diagnosis to the first treatment or from the completion of one treatment to the start of the next.
The search identified 34 suitable studies for 17 indications, with data from more than 1.2 million patients. The analysis identified a significant association between delay and increased mortality for 13 of the 17 indications (P < .05).
For surgery, there was a 6%-8% increase in the risk of death for every 4-week treatment delay. Estimates for systemic treatment varied (hazard ratio range, 1.01-1.28). Four-week delays in radiotherapy were for radical radiotherapy for head and neck cancer (HR, 1.09; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-1.14), adjuvant radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery (HR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.88-1.09), and cervical cancer adjuvant radiotherapy (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.00-1.50).
Delays of up to 8 and 12 weeks further increased mortality. An 8-week delay in breast cancer surgery was linked to a 17% increased mortality, and a 12-week delay would increase mortality by 26%.
A surgical delay of 12 weeks for patients with breast cancer continuing for 1 year – which is likely to be the case as the pandemic continues – would lead to 1,400 excess deaths in the United Kingdom.
The authors said the results of this study could be used to guide policy making on the organization of cancer services, particularly as the pandemic continues and further delays are expected.
This article originally appeared on Univadis, part of the Medscape Professional Network.
In light of the treatment delays resulting from the pandemic, Canadian and U.K. researchers carried out a review and analysis of relevant studies published between January 2000 and April 2020.
Included studies examined data on surgical interventions, systemic therapy, or radiotherapy for seven forms of cancer – bladder, breast, colon, rectum, lung, cervix, and head and neck. Delays were measured from diagnosis to the first treatment or from the completion of one treatment to the start of the next.
The search identified 34 suitable studies for 17 indications, with data from more than 1.2 million patients. The analysis identified a significant association between delay and increased mortality for 13 of the 17 indications (P < .05).
For surgery, there was a 6%-8% increase in the risk of death for every 4-week treatment delay. Estimates for systemic treatment varied (hazard ratio range, 1.01-1.28). Four-week delays in radiotherapy were for radical radiotherapy for head and neck cancer (HR, 1.09; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-1.14), adjuvant radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery (HR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.88-1.09), and cervical cancer adjuvant radiotherapy (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.00-1.50).
Delays of up to 8 and 12 weeks further increased mortality. An 8-week delay in breast cancer surgery was linked to a 17% increased mortality, and a 12-week delay would increase mortality by 26%.
A surgical delay of 12 weeks for patients with breast cancer continuing for 1 year – which is likely to be the case as the pandemic continues – would lead to 1,400 excess deaths in the United Kingdom.
The authors said the results of this study could be used to guide policy making on the organization of cancer services, particularly as the pandemic continues and further delays are expected.
This article originally appeared on Univadis, part of the Medscape Professional Network.
The Effect of Radium-223 Therapy in Agent Orange-Related Prostate Carcinoma
Patients with metastatic castrate resistant prostate carcinoma (CRPC) have several treatment options, including radium-223 dichloride (Ra-223) radionuclide therapy, abiraterone, enzalutamide, and cabazitaxel. Ra-223 therapy has been reported to increase median survival in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma.1,2 However, ERA 223 trial data showed an increase of bone fractures with combination of Ra-223 and abiraterone.3
Agent Orange (AO) exposure has been studied as a potential risk factor for development of prostate carcinoma. AO was a commercially manufactured defoliate that was sprayed extensively during the Vietnam War. Due to a side product of chemical manufacturing, AO was contaminated with the toxin 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, a putative carcinogen. These dioxins can enter the food chain through soil contamination. There is enough evidence to link AO to hematologic malignancies and several solid tumors, including prostate carcinoma.4 Although no real estimates exist for what percentage of Vietnam veterans experienced AO exposure, Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results data showed that about 3 million veterans served in Southeast Asia where AO was used extensively in the combat theater. AO has been reported to be positively associated with a 52% increase in risk of prostate carcinoma detection at initial prostate biopsy.5
There has been no reported study of treatment efficacy in veterans with AO-related prostate carcinoma. We present a retrospective study of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC. The purpose of this study was to compare response to therapy and survival in veterans exposed to agent orange (AO+) vs veterans who were not exposed to (AO-) in a single US Department of Veteran Affairs (VA) medical center.
Methods
This was a retrospective study of veterans with metastatic CRPC to bones who received Ra-223 radionuclide therapy with standard dose of 50 kBq per kg of body weight and other sequential therapies at VA Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS) from January 2014 to January 2019. The purpose of this study was to measure difference in treatment outcome between AO+ veterans and AO- veterans.
Eligibility Criteria
All veterans had a history that included bone metastasis CRPC. They could have 2 to 3 small lymphadenopathies but not visceral metastasis. They received a minimum of 3 cycles and a maximum of 6 cycles of Ra-223 therapy, which was given in 4-week intervals. Pretreatment criteria was hemoglobin > 10 g/dL, platelet > 100
Statistics
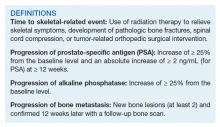
Time to study was calculated from the initiation of Ra-223 therapy. Time to skeletal-related events (SRE), progression of prostate specific antigen (PSA), bone metastasis, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were calculated in months, using unpaired t test with 2-tailed P value. Median survival was calculated in months by Kaplan Meier R log-rank test Definition).
Results
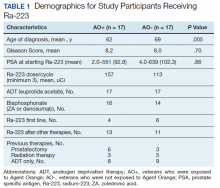
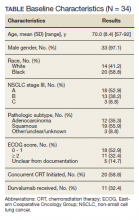
Forty-eight veterans with bone metastasis CRPC received Ra-223 therapy. Of those, 34 veterans were eligible for this retrospective study: 17 AO+ veterans and 17 AO- veterans. Mean age of diagnosis was 62 years (AO+) and 69 years (AO-) (P = .005). Mean Gleason score was 8.2 (AO+) and 8.0 (AO-) (P = .705). Veterans received initial therapy at diagnosis of prostate carcinoma, including radical prostatectomy (6 AO+ and 3 AO-), localized radiation therapy (3 AO+ and 5 AO-), and ADT (8 AO+ and 9 AO-) (Table 1).
Mean PSA at the initiation of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551) and for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639; P = .86). Mean Ra-223 dose per cycle for AO+ and AO- was 157 uCi and 113 uCi, respectively. All 34 veterans received ADT (leuprolide acetate), and 30 veterans (16 AO+ and 14 AO-) received bisphosphonates (zoledronic acid or denosumab). A total of 10 veterans (29%) received Ra-223 as a first-line therapy (4 AO+ and 6 AO-), and 24 veterans (71%) received Ra-223 after hormonal or chemotherapy (13 AO+ and 11 AO-).
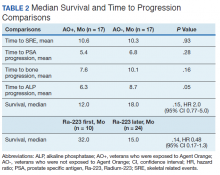
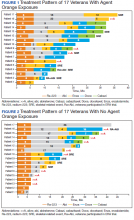
There were 12 SRE (8 AO+ and 4 AO-). Mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Three veterans received concurrent Ra-223 and abiraterone (participated in ERA 223 trial). Two AO+ veterans experienced SRE at 7 months and 11 months, respectively. Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months, respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months, respectively (P = .05). (Table 2). The treatment pattern of AO+ and AO- is depicted on a swimmer plot (Figures 1 and 2).
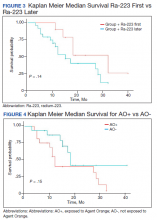
Twenty veterans (58%) had died: 13 AO+ and 7 AO- veterans. Median survival for Ra-223 first and Ra-223 later was was 32 months and 15 months, respectively (P = .14; hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). Overall median survival for AO+ veterans and AO- veterans were 12 months and 18 months, respectively (P = .15; HR, 2.0) (Figures 3 and 4).
Discussions
There has been no reported VA study of using Ra-223 and other therapies (hormonal and chemotherapy) in veterans exposed to AO. This is the first retrospective study to compare the response and survival between AO+ and AO- veterans. Even though this study featured a small sample, it is interesting to note the difference between those 2 populations. There was 1 prior study in veterans with prostate carcinoma using radiotherapy (brachytherapy) in early-stage disease. Everly and colleagues reported that AO+ veterans were less likely to remain biochemically controlled compared with AO- and nonveteran patients with prostate carcinoma.4
Ansbaugh and colleagues reported that AO was associated with a 75% increase in the risk of Gleason ≥ 7 and a 110% increase in Gleason ≥ 8. AO+ veterans are at risk for the detection of high-grade prostate carcinoma. They also tend to have an average age of diagnosis that is 4 to 5 years younger than AO- veterans.6
Our study revealed that AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age (mean 62 years) compared with that of AO- veterans (mean 69 years, P = .005). We also proved that AO veterans have a higher mean Gleason score (8.2) compared with that of AO- veterans (8.0). Veterans received therapy at the time of diagnosis of prostate carcinoma with either radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy, or ADT with leuprolide acetate. Mean PSA at the start of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551); for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639), which is not statistically significant.
Ra-223, an
In a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study by Parker and colleagues (ALSYMPCA study), 921 patients who had received, were not eligible to receive, or declined docetaxel, in a 2:1 ratio, were randomized to receive 6 injections of Ra-223 or matching placebo.2 Ra-223 significantly improved overall survival (OS) (median, 14.9 months vs 11.3 months) compared with that of placebo. Ra-223 also prolonged the time to the first symptomatic SRE (median, 15.6 months vs 9.8 months), the time to an increase in the total ALP level (median 7.4 months vs 3.8 months), and the time to an increase in the PSA level (median 3.6 months vs 3.4 months).2
In our study, the mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months respectively (P = .05). There is a trend of shorter PSA progression, bone progression, and ALP progression in AO+ veterans, though these were not statistically significant due to small sample population. In our study the median survival in for AO- was 18 months and for AO+ was 12 months, which is comparable with median survival of 14.9 months from the ALSYMPCA study.
There were 12 veterans who developed SREs. All received radiation therapy due to bone progression or impending fracture. AO+ veterans developed more SREs (n = 8) when compared with AO- veterans (n = 4). There were more AO- veterans alive (n = 10) than there were AO+ veterans (n = 4). The plausible explanation of this may be due to the aggressive pattern of prostate carcinoma in AO+ veterans (younger age and higher Gleason score).
VAPHS participated in the ERA trial between 2014 and 2016. The trial enrolled 806 patients who were randomly assigned to receive first-line Ra-223 or placebo in addition to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone.3 The study was unblinded prematurely after more fractures and deaths were noted in the Ra-223 and abiraterone group than there were in the placebo and abiraterone group. Median symptomatic SRE was 22.3 months in the Ra-223 group and 26.0 months in the placebo group. Fractures (any grade) occurred in 29% in the Ra-223 group and 11% in the placebo group. It was suggested that Ra-223 could contribute to the risk of osteoporotic fractures in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma. Median OS was 30.7 months in the Ra-223 group and 33.3 months in the placebo group.
We enrolled 3 veterans in the ERA clinical trial. Two AO+ veterans had SREs at 7 months and 11 months. In our study, the median OS for Ra-223 first line was 32 months, which is comparable with median survival of 30.7 months from ERA-223 study. Median survival for Ra-223 later was only 15 months. We recommend veterans with at least 2 to 3-bone metastasis receive Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than second- or third-line setting. In this retrospective study with Ra-223 and other therapies, we proved that AO+ veterans have a worse response and OS when compared with that of AO- veterans.
Conclusions
This is the first VA study to compare the efficacy of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC between AO+ and AO- veterans. AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age and had higher Gleason scores. There was no statistical difference between AO+ and AO- veterans in terms of time to SRE, PSA progression, and bone and ALP progression even though there was a trend of shorter duration in AO+ veterans. There was no median survival difference between veterans who received Ra-223 first vs Ra-223 later as well as between AO+ and AO- veterans, but there was a trend of worse survival in veteran who received Ra-223 later and AO+ veterans.
This study showed that AO+ veterans have a shorter duration of response to therapy and shorter median survival compared with that of AO- veterans. We recommend that veterans should get Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than after hormonal therapy and chemotherapy because their marrows are still intact. We need to investigate further whether veterans that exposed to carcinogen 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) may have different molecular biology and as such may cause inferior efficacy in the treatment of prostate carcinoma.
1. Shore ND. Radium-223 dichloride for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: the urologist’s perspective. Urology. 2015;85(4):717-724. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2014.11.031
2. Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, et al; ALSYMPCA Investigators. Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(3):213-223. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1213755
3. Smith M, Parker C, Saad F, et al. Addition of radium-223 to abiraterone acetate and prednisone or prednisolone in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer and bone metastases (ERA 223): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2019 Oct;20(10):e559]. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(3):408-419. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30860-X
4. Everly L, Merrick GS, Allen ZA, et al. Prostate cancer control and survival in Vietnam veterans exposed to Agent Orange. Brachytherapy. 2009;8(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2008.08.001
5. Altekruse S. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017 Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. 2009. 6. Ansbaugh N, Shannon J, Mori M, Farris PE, Garzotto M. Agent Orange as a risk factor for high-grade prostate cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(13):2399-2404. doi:10.1002/cncr.27941
7. Jadvar H, Quinn DI. Targeted α-particle therapy of bone metastases in prostate cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2013;38(12):966-971. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000000290
Patients with metastatic castrate resistant prostate carcinoma (CRPC) have several treatment options, including radium-223 dichloride (Ra-223) radionuclide therapy, abiraterone, enzalutamide, and cabazitaxel. Ra-223 therapy has been reported to increase median survival in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma.1,2 However, ERA 223 trial data showed an increase of bone fractures with combination of Ra-223 and abiraterone.3
Agent Orange (AO) exposure has been studied as a potential risk factor for development of prostate carcinoma. AO was a commercially manufactured defoliate that was sprayed extensively during the Vietnam War. Due to a side product of chemical manufacturing, AO was contaminated with the toxin 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, a putative carcinogen. These dioxins can enter the food chain through soil contamination. There is enough evidence to link AO to hematologic malignancies and several solid tumors, including prostate carcinoma.4 Although no real estimates exist for what percentage of Vietnam veterans experienced AO exposure, Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results data showed that about 3 million veterans served in Southeast Asia where AO was used extensively in the combat theater. AO has been reported to be positively associated with a 52% increase in risk of prostate carcinoma detection at initial prostate biopsy.5
There has been no reported study of treatment efficacy in veterans with AO-related prostate carcinoma. We present a retrospective study of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC. The purpose of this study was to compare response to therapy and survival in veterans exposed to agent orange (AO+) vs veterans who were not exposed to (AO-) in a single US Department of Veteran Affairs (VA) medical center.
Methods
This was a retrospective study of veterans with metastatic CRPC to bones who received Ra-223 radionuclide therapy with standard dose of 50 kBq per kg of body weight and other sequential therapies at VA Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS) from January 2014 to January 2019. The purpose of this study was to measure difference in treatment outcome between AO+ veterans and AO- veterans.
Eligibility Criteria
All veterans had a history that included bone metastasis CRPC. They could have 2 to 3 small lymphadenopathies but not visceral metastasis. They received a minimum of 3 cycles and a maximum of 6 cycles of Ra-223 therapy, which was given in 4-week intervals. Pretreatment criteria was hemoglobin > 10 g/dL, platelet > 100
Statistics
Time to study was calculated from the initiation of Ra-223 therapy. Time to skeletal-related events (SRE), progression of prostate specific antigen (PSA), bone metastasis, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were calculated in months, using unpaired t test with 2-tailed P value. Median survival was calculated in months by Kaplan Meier R log-rank test Definition).
Results
Forty-eight veterans with bone metastasis CRPC received Ra-223 therapy. Of those, 34 veterans were eligible for this retrospective study: 17 AO+ veterans and 17 AO- veterans. Mean age of diagnosis was 62 years (AO+) and 69 years (AO-) (P = .005). Mean Gleason score was 8.2 (AO+) and 8.0 (AO-) (P = .705). Veterans received initial therapy at diagnosis of prostate carcinoma, including radical prostatectomy (6 AO+ and 3 AO-), localized radiation therapy (3 AO+ and 5 AO-), and ADT (8 AO+ and 9 AO-) (Table 1).
Mean PSA at the initiation of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551) and for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639; P = .86). Mean Ra-223 dose per cycle for AO+ and AO- was 157 uCi and 113 uCi, respectively. All 34 veterans received ADT (leuprolide acetate), and 30 veterans (16 AO+ and 14 AO-) received bisphosphonates (zoledronic acid or denosumab). A total of 10 veterans (29%) received Ra-223 as a first-line therapy (4 AO+ and 6 AO-), and 24 veterans (71%) received Ra-223 after hormonal or chemotherapy (13 AO+ and 11 AO-).
There were 12 SRE (8 AO+ and 4 AO-). Mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Three veterans received concurrent Ra-223 and abiraterone (participated in ERA 223 trial). Two AO+ veterans experienced SRE at 7 months and 11 months, respectively. Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months, respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months, respectively (P = .05). (Table 2). The treatment pattern of AO+ and AO- is depicted on a swimmer plot (Figures 1 and 2).
Twenty veterans (58%) had died: 13 AO+ and 7 AO- veterans. Median survival for Ra-223 first and Ra-223 later was was 32 months and 15 months, respectively (P = .14; hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). Overall median survival for AO+ veterans and AO- veterans were 12 months and 18 months, respectively (P = .15; HR, 2.0) (Figures 3 and 4).
Discussions
There has been no reported VA study of using Ra-223 and other therapies (hormonal and chemotherapy) in veterans exposed to AO. This is the first retrospective study to compare the response and survival between AO+ and AO- veterans. Even though this study featured a small sample, it is interesting to note the difference between those 2 populations. There was 1 prior study in veterans with prostate carcinoma using radiotherapy (brachytherapy) in early-stage disease. Everly and colleagues reported that AO+ veterans were less likely to remain biochemically controlled compared with AO- and nonveteran patients with prostate carcinoma.4
Ansbaugh and colleagues reported that AO was associated with a 75% increase in the risk of Gleason ≥ 7 and a 110% increase in Gleason ≥ 8. AO+ veterans are at risk for the detection of high-grade prostate carcinoma. They also tend to have an average age of diagnosis that is 4 to 5 years younger than AO- veterans.6
Our study revealed that AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age (mean 62 years) compared with that of AO- veterans (mean 69 years, P = .005). We also proved that AO veterans have a higher mean Gleason score (8.2) compared with that of AO- veterans (8.0). Veterans received therapy at the time of diagnosis of prostate carcinoma with either radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy, or ADT with leuprolide acetate. Mean PSA at the start of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551); for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639), which is not statistically significant.
Ra-223, an
In a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study by Parker and colleagues (ALSYMPCA study), 921 patients who had received, were not eligible to receive, or declined docetaxel, in a 2:1 ratio, were randomized to receive 6 injections of Ra-223 or matching placebo.2 Ra-223 significantly improved overall survival (OS) (median, 14.9 months vs 11.3 months) compared with that of placebo. Ra-223 also prolonged the time to the first symptomatic SRE (median, 15.6 months vs 9.8 months), the time to an increase in the total ALP level (median 7.4 months vs 3.8 months), and the time to an increase in the PSA level (median 3.6 months vs 3.4 months).2
In our study, the mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months respectively (P = .05). There is a trend of shorter PSA progression, bone progression, and ALP progression in AO+ veterans, though these were not statistically significant due to small sample population. In our study the median survival in for AO- was 18 months and for AO+ was 12 months, which is comparable with median survival of 14.9 months from the ALSYMPCA study.
There were 12 veterans who developed SREs. All received radiation therapy due to bone progression or impending fracture. AO+ veterans developed more SREs (n = 8) when compared with AO- veterans (n = 4). There were more AO- veterans alive (n = 10) than there were AO+ veterans (n = 4). The plausible explanation of this may be due to the aggressive pattern of prostate carcinoma in AO+ veterans (younger age and higher Gleason score).
VAPHS participated in the ERA trial between 2014 and 2016. The trial enrolled 806 patients who were randomly assigned to receive first-line Ra-223 or placebo in addition to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone.3 The study was unblinded prematurely after more fractures and deaths were noted in the Ra-223 and abiraterone group than there were in the placebo and abiraterone group. Median symptomatic SRE was 22.3 months in the Ra-223 group and 26.0 months in the placebo group. Fractures (any grade) occurred in 29% in the Ra-223 group and 11% in the placebo group. It was suggested that Ra-223 could contribute to the risk of osteoporotic fractures in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma. Median OS was 30.7 months in the Ra-223 group and 33.3 months in the placebo group.
We enrolled 3 veterans in the ERA clinical trial. Two AO+ veterans had SREs at 7 months and 11 months. In our study, the median OS for Ra-223 first line was 32 months, which is comparable with median survival of 30.7 months from ERA-223 study. Median survival for Ra-223 later was only 15 months. We recommend veterans with at least 2 to 3-bone metastasis receive Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than second- or third-line setting. In this retrospective study with Ra-223 and other therapies, we proved that AO+ veterans have a worse response and OS when compared with that of AO- veterans.
Conclusions
This is the first VA study to compare the efficacy of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC between AO+ and AO- veterans. AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age and had higher Gleason scores. There was no statistical difference between AO+ and AO- veterans in terms of time to SRE, PSA progression, and bone and ALP progression even though there was a trend of shorter duration in AO+ veterans. There was no median survival difference between veterans who received Ra-223 first vs Ra-223 later as well as between AO+ and AO- veterans, but there was a trend of worse survival in veteran who received Ra-223 later and AO+ veterans.
This study showed that AO+ veterans have a shorter duration of response to therapy and shorter median survival compared with that of AO- veterans. We recommend that veterans should get Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than after hormonal therapy and chemotherapy because their marrows are still intact. We need to investigate further whether veterans that exposed to carcinogen 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) may have different molecular biology and as such may cause inferior efficacy in the treatment of prostate carcinoma.
Patients with metastatic castrate resistant prostate carcinoma (CRPC) have several treatment options, including radium-223 dichloride (Ra-223) radionuclide therapy, abiraterone, enzalutamide, and cabazitaxel. Ra-223 therapy has been reported to increase median survival in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma.1,2 However, ERA 223 trial data showed an increase of bone fractures with combination of Ra-223 and abiraterone.3
Agent Orange (AO) exposure has been studied as a potential risk factor for development of prostate carcinoma. AO was a commercially manufactured defoliate that was sprayed extensively during the Vietnam War. Due to a side product of chemical manufacturing, AO was contaminated with the toxin 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, a putative carcinogen. These dioxins can enter the food chain through soil contamination. There is enough evidence to link AO to hematologic malignancies and several solid tumors, including prostate carcinoma.4 Although no real estimates exist for what percentage of Vietnam veterans experienced AO exposure, Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results data showed that about 3 million veterans served in Southeast Asia where AO was used extensively in the combat theater. AO has been reported to be positively associated with a 52% increase in risk of prostate carcinoma detection at initial prostate biopsy.5
There has been no reported study of treatment efficacy in veterans with AO-related prostate carcinoma. We present a retrospective study of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC. The purpose of this study was to compare response to therapy and survival in veterans exposed to agent orange (AO+) vs veterans who were not exposed to (AO-) in a single US Department of Veteran Affairs (VA) medical center.
Methods
This was a retrospective study of veterans with metastatic CRPC to bones who received Ra-223 radionuclide therapy with standard dose of 50 kBq per kg of body weight and other sequential therapies at VA Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS) from January 2014 to January 2019. The purpose of this study was to measure difference in treatment outcome between AO+ veterans and AO- veterans.
Eligibility Criteria
All veterans had a history that included bone metastasis CRPC. They could have 2 to 3 small lymphadenopathies but not visceral metastasis. They received a minimum of 3 cycles and a maximum of 6 cycles of Ra-223 therapy, which was given in 4-week intervals. Pretreatment criteria was hemoglobin > 10 g/dL, platelet > 100
Statistics
Time to study was calculated from the initiation of Ra-223 therapy. Time to skeletal-related events (SRE), progression of prostate specific antigen (PSA), bone metastasis, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were calculated in months, using unpaired t test with 2-tailed P value. Median survival was calculated in months by Kaplan Meier R log-rank test Definition).
Results
Forty-eight veterans with bone metastasis CRPC received Ra-223 therapy. Of those, 34 veterans were eligible for this retrospective study: 17 AO+ veterans and 17 AO- veterans. Mean age of diagnosis was 62 years (AO+) and 69 years (AO-) (P = .005). Mean Gleason score was 8.2 (AO+) and 8.0 (AO-) (P = .705). Veterans received initial therapy at diagnosis of prostate carcinoma, including radical prostatectomy (6 AO+ and 3 AO-), localized radiation therapy (3 AO+ and 5 AO-), and ADT (8 AO+ and 9 AO-) (Table 1).
Mean PSA at the initiation of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551) and for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639; P = .86). Mean Ra-223 dose per cycle for AO+ and AO- was 157 uCi and 113 uCi, respectively. All 34 veterans received ADT (leuprolide acetate), and 30 veterans (16 AO+ and 14 AO-) received bisphosphonates (zoledronic acid or denosumab). A total of 10 veterans (29%) received Ra-223 as a first-line therapy (4 AO+ and 6 AO-), and 24 veterans (71%) received Ra-223 after hormonal or chemotherapy (13 AO+ and 11 AO-).
There were 12 SRE (8 AO+ and 4 AO-). Mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Three veterans received concurrent Ra-223 and abiraterone (participated in ERA 223 trial). Two AO+ veterans experienced SRE at 7 months and 11 months, respectively. Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months, respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months, respectively (P = .05). (Table 2). The treatment pattern of AO+ and AO- is depicted on a swimmer plot (Figures 1 and 2).
Twenty veterans (58%) had died: 13 AO+ and 7 AO- veterans. Median survival for Ra-223 first and Ra-223 later was was 32 months and 15 months, respectively (P = .14; hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). Overall median survival for AO+ veterans and AO- veterans were 12 months and 18 months, respectively (P = .15; HR, 2.0) (Figures 3 and 4).
Discussions
There has been no reported VA study of using Ra-223 and other therapies (hormonal and chemotherapy) in veterans exposed to AO. This is the first retrospective study to compare the response and survival between AO+ and AO- veterans. Even though this study featured a small sample, it is interesting to note the difference between those 2 populations. There was 1 prior study in veterans with prostate carcinoma using radiotherapy (brachytherapy) in early-stage disease. Everly and colleagues reported that AO+ veterans were less likely to remain biochemically controlled compared with AO- and nonveteran patients with prostate carcinoma.4
Ansbaugh and colleagues reported that AO was associated with a 75% increase in the risk of Gleason ≥ 7 and a 110% increase in Gleason ≥ 8. AO+ veterans are at risk for the detection of high-grade prostate carcinoma. They also tend to have an average age of diagnosis that is 4 to 5 years younger than AO- veterans.6
Our study revealed that AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age (mean 62 years) compared with that of AO- veterans (mean 69 years, P = .005). We also proved that AO veterans have a higher mean Gleason score (8.2) compared with that of AO- veterans (8.0). Veterans received therapy at the time of diagnosis of prostate carcinoma with either radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy, or ADT with leuprolide acetate. Mean PSA at the start of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551); for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639), which is not statistically significant.
Ra-223, an
In a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study by Parker and colleagues (ALSYMPCA study), 921 patients who had received, were not eligible to receive, or declined docetaxel, in a 2:1 ratio, were randomized to receive 6 injections of Ra-223 or matching placebo.2 Ra-223 significantly improved overall survival (OS) (median, 14.9 months vs 11.3 months) compared with that of placebo. Ra-223 also prolonged the time to the first symptomatic SRE (median, 15.6 months vs 9.8 months), the time to an increase in the total ALP level (median 7.4 months vs 3.8 months), and the time to an increase in the PSA level (median 3.6 months vs 3.4 months).2
In our study, the mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months respectively (P = .05). There is a trend of shorter PSA progression, bone progression, and ALP progression in AO+ veterans, though these were not statistically significant due to small sample population. In our study the median survival in for AO- was 18 months and for AO+ was 12 months, which is comparable with median survival of 14.9 months from the ALSYMPCA study.
There were 12 veterans who developed SREs. All received radiation therapy due to bone progression or impending fracture. AO+ veterans developed more SREs (n = 8) when compared with AO- veterans (n = 4). There were more AO- veterans alive (n = 10) than there were AO+ veterans (n = 4). The plausible explanation of this may be due to the aggressive pattern of prostate carcinoma in AO+ veterans (younger age and higher Gleason score).
VAPHS participated in the ERA trial between 2014 and 2016. The trial enrolled 806 patients who were randomly assigned to receive first-line Ra-223 or placebo in addition to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone.3 The study was unblinded prematurely after more fractures and deaths were noted in the Ra-223 and abiraterone group than there were in the placebo and abiraterone group. Median symptomatic SRE was 22.3 months in the Ra-223 group and 26.0 months in the placebo group. Fractures (any grade) occurred in 29% in the Ra-223 group and 11% in the placebo group. It was suggested that Ra-223 could contribute to the risk of osteoporotic fractures in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma. Median OS was 30.7 months in the Ra-223 group and 33.3 months in the placebo group.
We enrolled 3 veterans in the ERA clinical trial. Two AO+ veterans had SREs at 7 months and 11 months. In our study, the median OS for Ra-223 first line was 32 months, which is comparable with median survival of 30.7 months from ERA-223 study. Median survival for Ra-223 later was only 15 months. We recommend veterans with at least 2 to 3-bone metastasis receive Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than second- or third-line setting. In this retrospective study with Ra-223 and other therapies, we proved that AO+ veterans have a worse response and OS when compared with that of AO- veterans.
Conclusions
This is the first VA study to compare the efficacy of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC between AO+ and AO- veterans. AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age and had higher Gleason scores. There was no statistical difference between AO+ and AO- veterans in terms of time to SRE, PSA progression, and bone and ALP progression even though there was a trend of shorter duration in AO+ veterans. There was no median survival difference between veterans who received Ra-223 first vs Ra-223 later as well as between AO+ and AO- veterans, but there was a trend of worse survival in veteran who received Ra-223 later and AO+ veterans.
This study showed that AO+ veterans have a shorter duration of response to therapy and shorter median survival compared with that of AO- veterans. We recommend that veterans should get Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than after hormonal therapy and chemotherapy because their marrows are still intact. We need to investigate further whether veterans that exposed to carcinogen 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) may have different molecular biology and as such may cause inferior efficacy in the treatment of prostate carcinoma.
1. Shore ND. Radium-223 dichloride for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: the urologist’s perspective. Urology. 2015;85(4):717-724. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2014.11.031
2. Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, et al; ALSYMPCA Investigators. Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(3):213-223. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1213755
3. Smith M, Parker C, Saad F, et al. Addition of radium-223 to abiraterone acetate and prednisone or prednisolone in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer and bone metastases (ERA 223): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2019 Oct;20(10):e559]. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(3):408-419. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30860-X
4. Everly L, Merrick GS, Allen ZA, et al. Prostate cancer control and survival in Vietnam veterans exposed to Agent Orange. Brachytherapy. 2009;8(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2008.08.001
5. Altekruse S. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017 Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. 2009. 6. Ansbaugh N, Shannon J, Mori M, Farris PE, Garzotto M. Agent Orange as a risk factor for high-grade prostate cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(13):2399-2404. doi:10.1002/cncr.27941
7. Jadvar H, Quinn DI. Targeted α-particle therapy of bone metastases in prostate cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2013;38(12):966-971. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000000290
1. Shore ND. Radium-223 dichloride for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: the urologist’s perspective. Urology. 2015;85(4):717-724. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2014.11.031
2. Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, et al; ALSYMPCA Investigators. Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(3):213-223. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1213755
3. Smith M, Parker C, Saad F, et al. Addition of radium-223 to abiraterone acetate and prednisone or prednisolone in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer and bone metastases (ERA 223): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2019 Oct;20(10):e559]. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(3):408-419. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30860-X
4. Everly L, Merrick GS, Allen ZA, et al. Prostate cancer control and survival in Vietnam veterans exposed to Agent Orange. Brachytherapy. 2009;8(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2008.08.001
5. Altekruse S. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017 Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. 2009. 6. Ansbaugh N, Shannon J, Mori M, Farris PE, Garzotto M. Agent Orange as a risk factor for high-grade prostate cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(13):2399-2404. doi:10.1002/cncr.27941
7. Jadvar H, Quinn DI. Targeted α-particle therapy of bone metastases in prostate cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2013;38(12):966-971. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000000290
Guideline Concordance with Durvalumab in Unresectable Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Single Center Veterans Hospital Experience
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of durvalumab for patients with unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy (CRT).1 After 2 randomized phase 3 studies in 2017 and 2018 showed significant progression-free and overall survival respectively,2,3 durvalumab became a category 1 recommendation for the above indication per National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines.4 Adherence to guidelines have been shown to improve patient survival across several cancer types.5-7 However, guideline adherence rates have been variable across health institutions. Therefore, further study is warranted to evaluate nonadherent practices with the goal of improving the quality of cancer care delivery.8,9
Stage III NSCLC is associated with poor survival rates.10 Concurrent CRT remains the standard of care in patients with good performance status based on clinical trial populations.4 Lung cancer remains a disease of the elderly, with a median age at diagnosis of 70 years.11 Discrepancies in the treatment of lung cancer in older adults can vary widely due to a lack of evidence surrounding the treatment in those who have comorbidities and poor performance status, widening the gap between clinical trial and real-world populations.11
A recent review by Passaro and colleagues revealed that at least 11 pivotal randomized controlled trials have shown the activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in locally advanced and metastatic lung cancer. However, these studies have mostly excluded patients with a performance status of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) level ≥ 2.11
Durvalumab is one of many new therapies to enter clinical practice to demonstrate survival benefit, but its use among veterans with stage III NSCLC in adherence with National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines was not robust at the Birmingham Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Alabama. Therefore, we decided to study the level of adherence and to identify barriers to conformity to the category 1 NCCN recommendations.
Methods
The Birmingham VAMC Outpatient Oncology Clinic billing data identified all individuals diagnosed with lung cancer treated between October 2017 and August 2019. Patients who did not have NSCLC that was stage III and unresectable were excluded from our study. Patients who did not receive a majority of their treatment at US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) facilities were excluded as well. Each patient’s demographic, functional level, and tumor characteristics during the treatment planning phase and follow-up visits were obtained. Two investigators who evaluated health care provider documentation using the VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) conducted chart reviews.
The primary outcomes were the proportion of patients who received concurrent CRT and the proportion who received durvalumab consolidation. Our chart review also categorized reasons for nonreceipt of concurrent CRT and subsequent durvalumab. Documented reasons for guideline discordancy were generated empirically and broadly. We noted if documentation was unclear and included reasons for why a veteran was not a candidate for CRT, the presence of toxicities associated with CRT, and a patient’s refusal for therapy despite medical advice. Descriptive data were analyzed for all clinical or demographic characteristics and outcomes.
This was considered an internal quality improvement initiative. As such, Birmingham VAMC did not require institutional review board approval for the study. The facility is accredited by the American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer.
Results
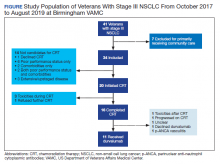
A total of 41 veterans with stage III NSCLC were identified to have established care in the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic between October 2017 and August 2019. Of these, 7 received the majority of their treatment from community-based non-VA facilities and 14 were not candidates for CRT and were excluded from this study.
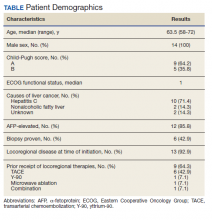
The mean (SD) age of study participants was 70.0 (8.4) years (range, 57 to 92 years). Most of the study veterans (33; 97.1%) were male and 20 (58.8%) were African American (Table). Eighteen (53%) of study participants had clinical stage IIIa NSCLC; 19 (56%) showed a squamous subtype of NSCLC. A majority (53%) of the veterans studied were evaluated to be functionally fit with an ECOG status of 0 to 1, although documentation of ECOG status was lacking in 5 (14.7%) patients in the initial treatment planning visit records. It was unclear if performance status had been reevaluated and changes noted over the course of concurrent CRT.
CRT Patients
The relative distribution of veterans who underwent CRT for stage III NSCLC plus the reasons they did not receive guideline-based treatment with durvalumab is shown in the Figure. Fourteen patients (41%) were inappropriate candidates for CRT; the most common reason for this was their poor performance status upon initial evaluation and 3 patients (8.8%) in the study had extensive disease or were upstaged upon follow-up clinic visit.
Twenty (59%) veterans in the study initiated CRT. However, only 16 (47.1%) completed CRT. Those who dropped out of CRT did so because of toxicities that included various cytopenia, gastrointestinal toxicities due to radiation and/or chemotherapy, or failure to thrive.
Durvalumab Treatment
After initiation of CRT, 9 (26.5%) patients did not go on to receive durvalumab. Three patients (8.8%) suffered toxicities during CRT. One study patient was found to have a severe respiratory infection requiring intensive care unit admission. Another study patient was found to have a new sternal lesion on follow-up positron emission tomography. One declined because of a history of severe antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies vasculitis, which made durvalumab use unsafe. Three patients (8.8%) declined treatment with CRT or durvalumab because of personal preference. Documentation was unclear as to why durvalumab was prescribed to one patient who had completed CRT.
Discussion
NCCN guidelines on the use of durvalumab in NSCLC are based on the phase 3 PACIFIC placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. This trial, which included only patients with documented performance status of ECOG 0 or 1, reported that grade 3 or 4 events occurred in 30.5% of patients randomized to consolidative durvalumab. Treatment was discontinued in 15.4% of patients due to adverse events.3
Our study examined consolidation therapy with durvalumab in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC with an ECOG performance status of 0 to 1 who had not progressed after 2 or more cycles of definitive concurrent CRT.4 Patients with previous exposure to immunotherapy, a history of immunodeficiency, active infection, unresolved toxicity from CRT, autoimmune disease, and patients who received sequential CRT were excluded.2 Surprisingly, the adherence rate to guidelines was close to 100% with appropriate documentation and justification of CRT initiation and durvalumab use. Five (14.7%) of veterans with unresectable stage III NSCLC did not have clear documentation of ECOG status on initial visit and only 1 veteran who completed CRT did not have clear documentation as to why durvalumab was not provided. Unfortunately, 23 (68.6%) veterans in the study were unable to receive durvalumab, a potentially disease-modifying drug; nearly one-third (10) of veterans were deemed poor candidates for concurrent CRT despite the fact that 52.9% (18) of veterans in the study had a documented ECOG of 0 or 1 on initial evaluation.
Clinical Trials vs Real World
The heterogeneity between anticipated study populations, those who were able to receive durvalumab in the PACIFIC trial, compared with our observed real-world veteran population, likely stems from the lack of information about how comorbidity and fitness can affect the choice of therapeutic intervention in patients with lung cancer.12 In addition, older adults who participated in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are not representative of the average older adult who presents to medical oncology clinics, making the application of guideline concordant care difficult.13
Similar real-world observations parallel to our analyses have confirmed, complemented and/or refuted findings of RCTs, and have helped impact the treatment of multiple acute and chronic conditions including influenza, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.14
A component of socioeconomic barriers and access to supportive care played roles in the decisions of certain patients who chose not to undergo concurrent CRT despite medical advice. These 2 obstacles also affected the decision making for some in the study when considering the use of durvalumab (administered by a 60-minute IV infusion every 2 weeks for 1 year) per recommended guidelines.1 These hurdles need further study in the context of their effect on quality of life and the difficulties generated by various social determinants of health.
Limitations
Study limitations included the biased and confounding factors previously described about retrospective and nonrandomized observational studies that are controlled for during RCTs.15 Electronic health record data may have been incorrectly collected resulting in missing or wrong data points that affect the validity of our conclusion. Recall bias with regard to documentation by health care providers describing reasons why CRT or durvalumab were not initiated or the patient’s ability to recall previous treatments and report ECOG status or toxicities also may have impacted our findings. Comorbidities and poor performance status, frequently occurring among veterans, negatively impact cancer treatment decisions and may result in a detection bias. For example, tobacco use, cardiovascular disease, including heart failure, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are notoriously higher in the US veteran population when compared with civilian cohorts.16-18 Also, veterans with poorly controlled depression and posttraumatic stress disorder resulting in functional impairment are a factor.19 Steps were taken to address some of these biases by performing repeat checks of tabulated data and employing 2 independent reviewers to evaluate all relevant clinical documentation, compare results, and reach a consensus.
Conlcusions
This retrospective analysis of adherence to category 1 NCCN guidelines for durvalumab use among patients at the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic reinforced our practice and identified minor deficiencies in documentation that would impact future clinical visits. More importantly, it depicted the massive disparity in treatment candidacy among Birmingham veterans compared with clinical trial populations. Efforts will be made to address factors impacting a veteran’s candidacy for CRT and explore other variables such as socioeconomic barriers to treatment. Multiple complementary tools to assess patients’ frailty, such as the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), are now being used for a variety of disorders including cancers. More robust data and standardization are needed to validate the use of these assessments in predicting response to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently being evaluated in stage III NSCLC studies and may be implemented as routine practice in the future.12 It is important to distinguish fit from frail veterans with lung cancer for treatment selection. We would like to see the expansion of the eligibility criteria for clinical trials to include patients with a performance status of ECOG 2 in order for results to be truly generalizable to the real-world population. Our hope is that such work will improve not only the quality of lung cancer care, but also the quality of care across multiple tumor types.
1. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves durvalumab after chemoradiation for unresectable stage II. Published February 20, 2018. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-durvalumab-after-chemoradiation-unresectable-stage-iii-nsclc
2. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(20):1919-1929. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1709937
3. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Overall survival with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(24):2342-2350. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1809697
4. Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL et al. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: non-small cell lung cancer. Version8.2020. Updated September 15, 2020. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf
5. Bristow RE, Chang J, Ziogas A, Campos B, Chavez LR, Anton-Culver H. Impact of National Cancer Institute Comprehensive Cancer Centers on ovarian cancer treatment and survival. J Am Coll Surg. 2015;220(5):940-950. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.01.056
6. Boland GM, Chang GJ, Haynes AB, et al. Association between adherence to National Comprehensive Cancer Network treatment guidelines and improved survival in patients with colon cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(8):1593-1601. doi:10.1002/cncr.27935
7. Schwentner L, Wöckel A, König J, et al. Adherence to treatment guidelines and survival in triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective multi-center cohort study with 9,156 patients. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:487. Published 2013 Oct 21. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-487
8. Jazieh A, Alkaiyat MO, Ali Y, Hashim MA, Abdelhafiz N, Al Olayan A. Improving adherence to lung cancer guidelines: a quality improvement project that uses chart review, audit and feedback approach. BMJ Open Qual. 2019;8(3):e000436. Published 2019 Aug 26. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2018-000436
9. Shaverdian N, Offin MD, Rimner A, et al. Utilization and factors precluding the initiation of consolidative durvalumab in unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2020;144:101-104. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2019.11.015
10. National Cancer Institute. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975-2015, Table 15.1 cancer of the lung and bronchus. Accessed October 19, 2020 https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2015/results_merged/sect_15_lung_bronchus.pdf. Updated September 10, 2018
11. Passaro A, Spitaleri G, Gyawali B, de Marinis F. Immunotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with performance status 2: clinical decision making with scant evidence. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(22):1863-1867. doi:10.1200/JCO.18.02118
12. Driessen EJM, Janssen-Heijnen MLG, Maas HA, Dingemans AC, van Loon JGM. Study protocol of the NVALT25-ELDAPT trial: selecting the optimal treatment for older patients with stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018;19(6):e849-e852. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2018.07.003
13. Schulkes KJ, Nguyen C, van den Bos F, van Elden LJ, Hamaker ME. Selection of Patients in Ongoing Clinical Trials on Lung Cancer. Lung. 2016;194(6):967-974. doi:10.1007/s00408-016-9943-7
14. Blonde L, Khunti K, Harris SB, Meizinger C, Skolnik NS. Interpretation and impact of real-world clinical data for the practicing clinician. Adv Ther. 2018;35(11):1763-1774. doi:10.1007/s12325-018-0805-y
15. Garrison LP Jr, Neumann PJ, Erickson P, Marshall D, Mullins CD. Using real-world data for coverage and payment decisions: the ISPOR Real-World Data Task Force report. Value Health. 2007;10(5):326-335. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00186.x
16. Assari S. Veterans and risk of heart disease in the United States: a cohort with 20 years of follow up. Int J Prev Med. 2014;5(6):703-709.
17. Shahoumian TA, Phillips BR, Backus LI. Cigarette smoking, reduction and quit attempts: prevalence among veterans with coronary heart disease. Prev Chronic Dis. 2016;13:E41. Published 2016 Mar 24. doi:10.5888/pcd13.150282
18. Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
19. Kozel FA, Didehbani N, DeLaRosa B, et al. Factors impacting functional status in veterans of recent conflicts with PTSD. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016;28(2):112-117. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.15070183
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of durvalumab for patients with unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy (CRT).1 After 2 randomized phase 3 studies in 2017 and 2018 showed significant progression-free and overall survival respectively,2,3 durvalumab became a category 1 recommendation for the above indication per National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines.4 Adherence to guidelines have been shown to improve patient survival across several cancer types.5-7 However, guideline adherence rates have been variable across health institutions. Therefore, further study is warranted to evaluate nonadherent practices with the goal of improving the quality of cancer care delivery.8,9
Stage III NSCLC is associated with poor survival rates.10 Concurrent CRT remains the standard of care in patients with good performance status based on clinical trial populations.4 Lung cancer remains a disease of the elderly, with a median age at diagnosis of 70 years.11 Discrepancies in the treatment of lung cancer in older adults can vary widely due to a lack of evidence surrounding the treatment in those who have comorbidities and poor performance status, widening the gap between clinical trial and real-world populations.11
A recent review by Passaro and colleagues revealed that at least 11 pivotal randomized controlled trials have shown the activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in locally advanced and metastatic lung cancer. However, these studies have mostly excluded patients with a performance status of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) level ≥ 2.11
Durvalumab is one of many new therapies to enter clinical practice to demonstrate survival benefit, but its use among veterans with stage III NSCLC in adherence with National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines was not robust at the Birmingham Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Alabama. Therefore, we decided to study the level of adherence and to identify barriers to conformity to the category 1 NCCN recommendations.
Methods
The Birmingham VAMC Outpatient Oncology Clinic billing data identified all individuals diagnosed with lung cancer treated between October 2017 and August 2019. Patients who did not have NSCLC that was stage III and unresectable were excluded from our study. Patients who did not receive a majority of their treatment at US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) facilities were excluded as well. Each patient’s demographic, functional level, and tumor characteristics during the treatment planning phase and follow-up visits were obtained. Two investigators who evaluated health care provider documentation using the VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) conducted chart reviews.
The primary outcomes were the proportion of patients who received concurrent CRT and the proportion who received durvalumab consolidation. Our chart review also categorized reasons for nonreceipt of concurrent CRT and subsequent durvalumab. Documented reasons for guideline discordancy were generated empirically and broadly. We noted if documentation was unclear and included reasons for why a veteran was not a candidate for CRT, the presence of toxicities associated with CRT, and a patient’s refusal for therapy despite medical advice. Descriptive data were analyzed for all clinical or demographic characteristics and outcomes.
This was considered an internal quality improvement initiative. As such, Birmingham VAMC did not require institutional review board approval for the study. The facility is accredited by the American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer.
Results
A total of 41 veterans with stage III NSCLC were identified to have established care in the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic between October 2017 and August 2019. Of these, 7 received the majority of their treatment from community-based non-VA facilities and 14 were not candidates for CRT and were excluded from this study.
The mean (SD) age of study participants was 70.0 (8.4) years (range, 57 to 92 years). Most of the study veterans (33; 97.1%) were male and 20 (58.8%) were African American (Table). Eighteen (53%) of study participants had clinical stage IIIa NSCLC; 19 (56%) showed a squamous subtype of NSCLC. A majority (53%) of the veterans studied were evaluated to be functionally fit with an ECOG status of 0 to 1, although documentation of ECOG status was lacking in 5 (14.7%) patients in the initial treatment planning visit records. It was unclear if performance status had been reevaluated and changes noted over the course of concurrent CRT.
CRT Patients
The relative distribution of veterans who underwent CRT for stage III NSCLC plus the reasons they did not receive guideline-based treatment with durvalumab is shown in the Figure. Fourteen patients (41%) were inappropriate candidates for CRT; the most common reason for this was their poor performance status upon initial evaluation and 3 patients (8.8%) in the study had extensive disease or were upstaged upon follow-up clinic visit.
Twenty (59%) veterans in the study initiated CRT. However, only 16 (47.1%) completed CRT. Those who dropped out of CRT did so because of toxicities that included various cytopenia, gastrointestinal toxicities due to radiation and/or chemotherapy, or failure to thrive.
Durvalumab Treatment
After initiation of CRT, 9 (26.5%) patients did not go on to receive durvalumab. Three patients (8.8%) suffered toxicities during CRT. One study patient was found to have a severe respiratory infection requiring intensive care unit admission. Another study patient was found to have a new sternal lesion on follow-up positron emission tomography. One declined because of a history of severe antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies vasculitis, which made durvalumab use unsafe. Three patients (8.8%) declined treatment with CRT or durvalumab because of personal preference. Documentation was unclear as to why durvalumab was prescribed to one patient who had completed CRT.
Discussion
NCCN guidelines on the use of durvalumab in NSCLC are based on the phase 3 PACIFIC placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. This trial, which included only patients with documented performance status of ECOG 0 or 1, reported that grade 3 or 4 events occurred in 30.5% of patients randomized to consolidative durvalumab. Treatment was discontinued in 15.4% of patients due to adverse events.3
Our study examined consolidation therapy with durvalumab in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC with an ECOG performance status of 0 to 1 who had not progressed after 2 or more cycles of definitive concurrent CRT.4 Patients with previous exposure to immunotherapy, a history of immunodeficiency, active infection, unresolved toxicity from CRT, autoimmune disease, and patients who received sequential CRT were excluded.2 Surprisingly, the adherence rate to guidelines was close to 100% with appropriate documentation and justification of CRT initiation and durvalumab use. Five (14.7%) of veterans with unresectable stage III NSCLC did not have clear documentation of ECOG status on initial visit and only 1 veteran who completed CRT did not have clear documentation as to why durvalumab was not provided. Unfortunately, 23 (68.6%) veterans in the study were unable to receive durvalumab, a potentially disease-modifying drug; nearly one-third (10) of veterans were deemed poor candidates for concurrent CRT despite the fact that 52.9% (18) of veterans in the study had a documented ECOG of 0 or 1 on initial evaluation.
Clinical Trials vs Real World
The heterogeneity between anticipated study populations, those who were able to receive durvalumab in the PACIFIC trial, compared with our observed real-world veteran population, likely stems from the lack of information about how comorbidity and fitness can affect the choice of therapeutic intervention in patients with lung cancer.12 In addition, older adults who participated in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are not representative of the average older adult who presents to medical oncology clinics, making the application of guideline concordant care difficult.13
Similar real-world observations parallel to our analyses have confirmed, complemented and/or refuted findings of RCTs, and have helped impact the treatment of multiple acute and chronic conditions including influenza, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.14
A component of socioeconomic barriers and access to supportive care played roles in the decisions of certain patients who chose not to undergo concurrent CRT despite medical advice. These 2 obstacles also affected the decision making for some in the study when considering the use of durvalumab (administered by a 60-minute IV infusion every 2 weeks for 1 year) per recommended guidelines.1 These hurdles need further study in the context of their effect on quality of life and the difficulties generated by various social determinants of health.
Limitations
Study limitations included the biased and confounding factors previously described about retrospective and nonrandomized observational studies that are controlled for during RCTs.15 Electronic health record data may have been incorrectly collected resulting in missing or wrong data points that affect the validity of our conclusion. Recall bias with regard to documentation by health care providers describing reasons why CRT or durvalumab were not initiated or the patient’s ability to recall previous treatments and report ECOG status or toxicities also may have impacted our findings. Comorbidities and poor performance status, frequently occurring among veterans, negatively impact cancer treatment decisions and may result in a detection bias. For example, tobacco use, cardiovascular disease, including heart failure, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are notoriously higher in the US veteran population when compared with civilian cohorts.16-18 Also, veterans with poorly controlled depression and posttraumatic stress disorder resulting in functional impairment are a factor.19 Steps were taken to address some of these biases by performing repeat checks of tabulated data and employing 2 independent reviewers to evaluate all relevant clinical documentation, compare results, and reach a consensus.
Conlcusions
This retrospective analysis of adherence to category 1 NCCN guidelines for durvalumab use among patients at the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic reinforced our practice and identified minor deficiencies in documentation that would impact future clinical visits. More importantly, it depicted the massive disparity in treatment candidacy among Birmingham veterans compared with clinical trial populations. Efforts will be made to address factors impacting a veteran’s candidacy for CRT and explore other variables such as socioeconomic barriers to treatment. Multiple complementary tools to assess patients’ frailty, such as the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), are now being used for a variety of disorders including cancers. More robust data and standardization are needed to validate the use of these assessments in predicting response to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently being evaluated in stage III NSCLC studies and may be implemented as routine practice in the future.12 It is important to distinguish fit from frail veterans with lung cancer for treatment selection. We would like to see the expansion of the eligibility criteria for clinical trials to include patients with a performance status of ECOG 2 in order for results to be truly generalizable to the real-world population. Our hope is that such work will improve not only the quality of lung cancer care, but also the quality of care across multiple tumor types.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of durvalumab for patients with unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy (CRT).1 After 2 randomized phase 3 studies in 2017 and 2018 showed significant progression-free and overall survival respectively,2,3 durvalumab became a category 1 recommendation for the above indication per National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines.4 Adherence to guidelines have been shown to improve patient survival across several cancer types.5-7 However, guideline adherence rates have been variable across health institutions. Therefore, further study is warranted to evaluate nonadherent practices with the goal of improving the quality of cancer care delivery.8,9
Stage III NSCLC is associated with poor survival rates.10 Concurrent CRT remains the standard of care in patients with good performance status based on clinical trial populations.4 Lung cancer remains a disease of the elderly, with a median age at diagnosis of 70 years.11 Discrepancies in the treatment of lung cancer in older adults can vary widely due to a lack of evidence surrounding the treatment in those who have comorbidities and poor performance status, widening the gap between clinical trial and real-world populations.11
A recent review by Passaro and colleagues revealed that at least 11 pivotal randomized controlled trials have shown the activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in locally advanced and metastatic lung cancer. However, these studies have mostly excluded patients with a performance status of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) level ≥ 2.11
Durvalumab is one of many new therapies to enter clinical practice to demonstrate survival benefit, but its use among veterans with stage III NSCLC in adherence with National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines was not robust at the Birmingham Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Alabama. Therefore, we decided to study the level of adherence and to identify barriers to conformity to the category 1 NCCN recommendations.
Methods
The Birmingham VAMC Outpatient Oncology Clinic billing data identified all individuals diagnosed with lung cancer treated between October 2017 and August 2019. Patients who did not have NSCLC that was stage III and unresectable were excluded from our study. Patients who did not receive a majority of their treatment at US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) facilities were excluded as well. Each patient’s demographic, functional level, and tumor characteristics during the treatment planning phase and follow-up visits were obtained. Two investigators who evaluated health care provider documentation using the VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) conducted chart reviews.
The primary outcomes were the proportion of patients who received concurrent CRT and the proportion who received durvalumab consolidation. Our chart review also categorized reasons for nonreceipt of concurrent CRT and subsequent durvalumab. Documented reasons for guideline discordancy were generated empirically and broadly. We noted if documentation was unclear and included reasons for why a veteran was not a candidate for CRT, the presence of toxicities associated with CRT, and a patient’s refusal for therapy despite medical advice. Descriptive data were analyzed for all clinical or demographic characteristics and outcomes.
This was considered an internal quality improvement initiative. As such, Birmingham VAMC did not require institutional review board approval for the study. The facility is accredited by the American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer.
Results
A total of 41 veterans with stage III NSCLC were identified to have established care in the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic between October 2017 and August 2019. Of these, 7 received the majority of their treatment from community-based non-VA facilities and 14 were not candidates for CRT and were excluded from this study.
The mean (SD) age of study participants was 70.0 (8.4) years (range, 57 to 92 years). Most of the study veterans (33; 97.1%) were male and 20 (58.8%) were African American (Table). Eighteen (53%) of study participants had clinical stage IIIa NSCLC; 19 (56%) showed a squamous subtype of NSCLC. A majority (53%) of the veterans studied were evaluated to be functionally fit with an ECOG status of 0 to 1, although documentation of ECOG status was lacking in 5 (14.7%) patients in the initial treatment planning visit records. It was unclear if performance status had been reevaluated and changes noted over the course of concurrent CRT.
CRT Patients
The relative distribution of veterans who underwent CRT for stage III NSCLC plus the reasons they did not receive guideline-based treatment with durvalumab is shown in the Figure. Fourteen patients (41%) were inappropriate candidates for CRT; the most common reason for this was their poor performance status upon initial evaluation and 3 patients (8.8%) in the study had extensive disease or were upstaged upon follow-up clinic visit.
Twenty (59%) veterans in the study initiated CRT. However, only 16 (47.1%) completed CRT. Those who dropped out of CRT did so because of toxicities that included various cytopenia, gastrointestinal toxicities due to radiation and/or chemotherapy, or failure to thrive.
Durvalumab Treatment
After initiation of CRT, 9 (26.5%) patients did not go on to receive durvalumab. Three patients (8.8%) suffered toxicities during CRT. One study patient was found to have a severe respiratory infection requiring intensive care unit admission. Another study patient was found to have a new sternal lesion on follow-up positron emission tomography. One declined because of a history of severe antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies vasculitis, which made durvalumab use unsafe. Three patients (8.8%) declined treatment with CRT or durvalumab because of personal preference. Documentation was unclear as to why durvalumab was prescribed to one patient who had completed CRT.
Discussion
NCCN guidelines on the use of durvalumab in NSCLC are based on the phase 3 PACIFIC placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. This trial, which included only patients with documented performance status of ECOG 0 or 1, reported that grade 3 or 4 events occurred in 30.5% of patients randomized to consolidative durvalumab. Treatment was discontinued in 15.4% of patients due to adverse events.3
Our study examined consolidation therapy with durvalumab in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC with an ECOG performance status of 0 to 1 who had not progressed after 2 or more cycles of definitive concurrent CRT.4 Patients with previous exposure to immunotherapy, a history of immunodeficiency, active infection, unresolved toxicity from CRT, autoimmune disease, and patients who received sequential CRT were excluded.2 Surprisingly, the adherence rate to guidelines was close to 100% with appropriate documentation and justification of CRT initiation and durvalumab use. Five (14.7%) of veterans with unresectable stage III NSCLC did not have clear documentation of ECOG status on initial visit and only 1 veteran who completed CRT did not have clear documentation as to why durvalumab was not provided. Unfortunately, 23 (68.6%) veterans in the study were unable to receive durvalumab, a potentially disease-modifying drug; nearly one-third (10) of veterans were deemed poor candidates for concurrent CRT despite the fact that 52.9% (18) of veterans in the study had a documented ECOG of 0 or 1 on initial evaluation.
Clinical Trials vs Real World
The heterogeneity between anticipated study populations, those who were able to receive durvalumab in the PACIFIC trial, compared with our observed real-world veteran population, likely stems from the lack of information about how comorbidity and fitness can affect the choice of therapeutic intervention in patients with lung cancer.12 In addition, older adults who participated in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are not representative of the average older adult who presents to medical oncology clinics, making the application of guideline concordant care difficult.13
Similar real-world observations parallel to our analyses have confirmed, complemented and/or refuted findings of RCTs, and have helped impact the treatment of multiple acute and chronic conditions including influenza, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.14
A component of socioeconomic barriers and access to supportive care played roles in the decisions of certain patients who chose not to undergo concurrent CRT despite medical advice. These 2 obstacles also affected the decision making for some in the study when considering the use of durvalumab (administered by a 60-minute IV infusion every 2 weeks for 1 year) per recommended guidelines.1 These hurdles need further study in the context of their effect on quality of life and the difficulties generated by various social determinants of health.
Limitations
Study limitations included the biased and confounding factors previously described about retrospective and nonrandomized observational studies that are controlled for during RCTs.15 Electronic health record data may have been incorrectly collected resulting in missing or wrong data points that affect the validity of our conclusion. Recall bias with regard to documentation by health care providers describing reasons why CRT or durvalumab were not initiated or the patient’s ability to recall previous treatments and report ECOG status or toxicities also may have impacted our findings. Comorbidities and poor performance status, frequently occurring among veterans, negatively impact cancer treatment decisions and may result in a detection bias. For example, tobacco use, cardiovascular disease, including heart failure, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are notoriously higher in the US veteran population when compared with civilian cohorts.16-18 Also, veterans with poorly controlled depression and posttraumatic stress disorder resulting in functional impairment are a factor.19 Steps were taken to address some of these biases by performing repeat checks of tabulated data and employing 2 independent reviewers to evaluate all relevant clinical documentation, compare results, and reach a consensus.
Conlcusions
This retrospective analysis of adherence to category 1 NCCN guidelines for durvalumab use among patients at the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic reinforced our practice and identified minor deficiencies in documentation that would impact future clinical visits. More importantly, it depicted the massive disparity in treatment candidacy among Birmingham veterans compared with clinical trial populations. Efforts will be made to address factors impacting a veteran’s candidacy for CRT and explore other variables such as socioeconomic barriers to treatment. Multiple complementary tools to assess patients’ frailty, such as the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), are now being used for a variety of disorders including cancers. More robust data and standardization are needed to validate the use of these assessments in predicting response to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently being evaluated in stage III NSCLC studies and may be implemented as routine practice in the future.12 It is important to distinguish fit from frail veterans with lung cancer for treatment selection. We would like to see the expansion of the eligibility criteria for clinical trials to include patients with a performance status of ECOG 2 in order for results to be truly generalizable to the real-world population. Our hope is that such work will improve not only the quality of lung cancer care, but also the quality of care across multiple tumor types.
1. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves durvalumab after chemoradiation for unresectable stage II. Published February 20, 2018. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-durvalumab-after-chemoradiation-unresectable-stage-iii-nsclc
2. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(20):1919-1929. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1709937
3. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Overall survival with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(24):2342-2350. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1809697
4. Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL et al. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: non-small cell lung cancer. Version8.2020. Updated September 15, 2020. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf
5. Bristow RE, Chang J, Ziogas A, Campos B, Chavez LR, Anton-Culver H. Impact of National Cancer Institute Comprehensive Cancer Centers on ovarian cancer treatment and survival. J Am Coll Surg. 2015;220(5):940-950. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.01.056
6. Boland GM, Chang GJ, Haynes AB, et al. Association between adherence to National Comprehensive Cancer Network treatment guidelines and improved survival in patients with colon cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(8):1593-1601. doi:10.1002/cncr.27935
7. Schwentner L, Wöckel A, König J, et al. Adherence to treatment guidelines and survival in triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective multi-center cohort study with 9,156 patients. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:487. Published 2013 Oct 21. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-487
8. Jazieh A, Alkaiyat MO, Ali Y, Hashim MA, Abdelhafiz N, Al Olayan A. Improving adherence to lung cancer guidelines: a quality improvement project that uses chart review, audit and feedback approach. BMJ Open Qual. 2019;8(3):e000436. Published 2019 Aug 26. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2018-000436
9. Shaverdian N, Offin MD, Rimner A, et al. Utilization and factors precluding the initiation of consolidative durvalumab in unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2020;144:101-104. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2019.11.015
10. National Cancer Institute. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975-2015, Table 15.1 cancer of the lung and bronchus. Accessed October 19, 2020 https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2015/results_merged/sect_15_lung_bronchus.pdf. Updated September 10, 2018
11. Passaro A, Spitaleri G, Gyawali B, de Marinis F. Immunotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with performance status 2: clinical decision making with scant evidence. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(22):1863-1867. doi:10.1200/JCO.18.02118
12. Driessen EJM, Janssen-Heijnen MLG, Maas HA, Dingemans AC, van Loon JGM. Study protocol of the NVALT25-ELDAPT trial: selecting the optimal treatment for older patients with stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018;19(6):e849-e852. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2018.07.003
13. Schulkes KJ, Nguyen C, van den Bos F, van Elden LJ, Hamaker ME. Selection of Patients in Ongoing Clinical Trials on Lung Cancer. Lung. 2016;194(6):967-974. doi:10.1007/s00408-016-9943-7
14. Blonde L, Khunti K, Harris SB, Meizinger C, Skolnik NS. Interpretation and impact of real-world clinical data for the practicing clinician. Adv Ther. 2018;35(11):1763-1774. doi:10.1007/s12325-018-0805-y
15. Garrison LP Jr, Neumann PJ, Erickson P, Marshall D, Mullins CD. Using real-world data for coverage and payment decisions: the ISPOR Real-World Data Task Force report. Value Health. 2007;10(5):326-335. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00186.x
16. Assari S. Veterans and risk of heart disease in the United States: a cohort with 20 years of follow up. Int J Prev Med. 2014;5(6):703-709.
17. Shahoumian TA, Phillips BR, Backus LI. Cigarette smoking, reduction and quit attempts: prevalence among veterans with coronary heart disease. Prev Chronic Dis. 2016;13:E41. Published 2016 Mar 24. doi:10.5888/pcd13.150282
18. Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
19. Kozel FA, Didehbani N, DeLaRosa B, et al. Factors impacting functional status in veterans of recent conflicts with PTSD. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016;28(2):112-117. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.15070183
1. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves durvalumab after chemoradiation for unresectable stage II. Published February 20, 2018. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-durvalumab-after-chemoradiation-unresectable-stage-iii-nsclc
2. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(20):1919-1929. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1709937
3. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Overall survival with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(24):2342-2350. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1809697
4. Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL et al. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: non-small cell lung cancer. Version8.2020. Updated September 15, 2020. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf
5. Bristow RE, Chang J, Ziogas A, Campos B, Chavez LR, Anton-Culver H. Impact of National Cancer Institute Comprehensive Cancer Centers on ovarian cancer treatment and survival. J Am Coll Surg. 2015;220(5):940-950. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.01.056
6. Boland GM, Chang GJ, Haynes AB, et al. Association between adherence to National Comprehensive Cancer Network treatment guidelines and improved survival in patients with colon cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(8):1593-1601. doi:10.1002/cncr.27935
7. Schwentner L, Wöckel A, König J, et al. Adherence to treatment guidelines and survival in triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective multi-center cohort study with 9,156 patients. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:487. Published 2013 Oct 21. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-487
8. Jazieh A, Alkaiyat MO, Ali Y, Hashim MA, Abdelhafiz N, Al Olayan A. Improving adherence to lung cancer guidelines: a quality improvement project that uses chart review, audit and feedback approach. BMJ Open Qual. 2019;8(3):e000436. Published 2019 Aug 26. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2018-000436
9. Shaverdian N, Offin MD, Rimner A, et al. Utilization and factors precluding the initiation of consolidative durvalumab in unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2020;144:101-104. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2019.11.015
10. National Cancer Institute. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975-2015, Table 15.1 cancer of the lung and bronchus. Accessed October 19, 2020 https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2015/results_merged/sect_15_lung_bronchus.pdf. Updated September 10, 2018
11. Passaro A, Spitaleri G, Gyawali B, de Marinis F. Immunotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with performance status 2: clinical decision making with scant evidence. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(22):1863-1867. doi:10.1200/JCO.18.02118
12. Driessen EJM, Janssen-Heijnen MLG, Maas HA, Dingemans AC, van Loon JGM. Study protocol of the NVALT25-ELDAPT trial: selecting the optimal treatment for older patients with stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018;19(6):e849-e852. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2018.07.003
13. Schulkes KJ, Nguyen C, van den Bos F, van Elden LJ, Hamaker ME. Selection of Patients in Ongoing Clinical Trials on Lung Cancer. Lung. 2016;194(6):967-974. doi:10.1007/s00408-016-9943-7
14. Blonde L, Khunti K, Harris SB, Meizinger C, Skolnik NS. Interpretation and impact of real-world clinical data for the practicing clinician. Adv Ther. 2018;35(11):1763-1774. doi:10.1007/s12325-018-0805-y
15. Garrison LP Jr, Neumann PJ, Erickson P, Marshall D, Mullins CD. Using real-world data for coverage and payment decisions: the ISPOR Real-World Data Task Force report. Value Health. 2007;10(5):326-335. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00186.x
16. Assari S. Veterans and risk of heart disease in the United States: a cohort with 20 years of follow up. Int J Prev Med. 2014;5(6):703-709.
17. Shahoumian TA, Phillips BR, Backus LI. Cigarette smoking, reduction and quit attempts: prevalence among veterans with coronary heart disease. Prev Chronic Dis. 2016;13:E41. Published 2016 Mar 24. doi:10.5888/pcd13.150282
18. Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
19. Kozel FA, Didehbani N, DeLaRosa B, et al. Factors impacting functional status in veterans of recent conflicts with PTSD. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016;28(2):112-117. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.15070183
Surgery may not be needed with locally advanced rectal cancer
A short course of radiation therapy followed by neoadjuvant chemotherapy resulted in a clinical complete response (CR) in almost half of 90 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer, allowing the majority of responders to skip surgical resection, a retrospective study indicates.
Specifically, at a median follow-up of 16.6 months for living patients, the initial clinical CR rate was 48% overall.
“While we do not have enough follow-up yet to know the late side-effect profile of this regimen, our preliminary results are promising,” Re-I Chin, MD, of Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
The study was presented at the virtual 2020 meeting of the American Society of Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
“Certainly, longer follow-up will be needed in this study, but none of the observed patients to date has experienced an unsalvageable failure,” said meeting discussant Amol Narang, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
He reminded conference attendees that, despite good evidence supporting equivalency in oncologic outcomes between short-course radiation and long-course chemoradiation, the former is “highly underutilized in the US” with a mere 1% usage rate between 2004 and 2014.
The current study’s short-course treatment approach was compared in this setting to long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy in the RAPIDO trial reported at the 2020 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), Narang pointed out.
Short-course patients had a higher rate of pathological complete response (pCR) and a lower rate of treatment failure compared with patients who received long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy; both patient groups underwent total mesorectal excision — which is different from the current analysis. The RAPIDO investigators concluded that the approach featuring the short course “can be considered as a new standard of care.”
Narang said the data collectively “begs the question as to whether the superiority of long-course chemoradiation should really have to be demonstrated to justify its use.”
But Chin highlighted toxicity issues. “Historically, there have been concerns regarding toxicity with short-course radiation therapy since it requires larger doses of radiation given over a shorter period of time,” Chin explained. “But [the short course] is particularly convenient for patients since it saves them more than a month of daily trips to the radiation oncology department.”
Seven local failures
The single-center study involved patients with newly diagnosed, nonmetastatic rectal adenocarcinoma treated with short-course radiation therapy followed by chemotherapy in 2018 and 2019. Nearly all (96%) had locally advanced disease, with either a T3/T4 tumor or node-positive disease. Median tumor size was 4.6 cm.
“Many of the patients in the study had low lying tumors,” Chin reported, with a median distance from the anal verge of 7 cm.
Radiation therapy was delivered in 25 Gy given in five fractions over 5 consecutive days, with the option to boost the dose to 30 Gy or 35 Gy in five fractions if extra-mesorectal lymph nodes were involved. Conventional 3D or intensity-modulated radiation was used and all patients completed treatment.
The median interval between diagnosis of rectal cancer and initiation of radiation therapy was 1.4 months, while the median interval between completion of radiation to initiation of chemotherapy was 2.7 weeks.
The most common chemotherapy regimen was FOLFOX – consisting of leucovorin, fluorouracil (5-FU), and oxaliplatin – or modified FOLFOX. For patients who received six or more cycles of chemotherapy, the median time spent on treatment was 3.9 months.
For those who completed at least six cycles of chemotherapy, the overall clinical CR was 51%, and, for patients with locally advanced disease, the clinical CR rate was 49%. Five of the 43 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR still underwent surgical resection because of patient or physician preference. Among this small group of patients, 4 of the 5 achieved a pCR, and the remaining patient achieved a pathological partial response (pPR).
A total of 42 patients (47% of the group) achieved a partial response following the radiation plus chemotherapy paradigm, and one patient had progressive disease. All underwent surgical resection. One patient did not complete chemotherapy and did not get surgery and subsequently died.
This left 38 patients to be managed nonoperatively. In this nonoperative cohort, 79% of patients continued to have a clinical CR at the end of follow-up. Of the 7 patients with local failure, 6 were salvaged by surgery, one was salvaged by chemotherapy, and all 7 treatment failures had no evidence of disease at last follow-up.
Of the small group of 5 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR following short-course radiation therapy and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, there were no further events in this group, whereas, for patients who achieved only an initial partial response or who had progressive disease, 72% remained event-free.
Approximately half of those who achieved a clinical CR to the treatment regimen had no late gastrointestinal toxicities, and no grade 3 or 4 toxicities were observed. “Surgical resection of tumors — even without a permanent stoma — can result in significantly decreased bowel function, so our goal is to treat patients without surgery and maintain good bowel function,” Chin noted.
“For rectal cancer, both short-course radiation therapy and nonoperative management are emerging treatment paradigms that may be more cost-effective and convenient compared to long-course chemoradiation followed by surgery, [especially since] the COVID-19 pandemic...has spurred changes in clinical practices in radiation oncology,” she said.
Chin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Narang reports receiving research support from Boston Scientific.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A short course of radiation therapy followed by neoadjuvant chemotherapy resulted in a clinical complete response (CR) in almost half of 90 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer, allowing the majority of responders to skip surgical resection, a retrospective study indicates.
Specifically, at a median follow-up of 16.6 months for living patients, the initial clinical CR rate was 48% overall.
“While we do not have enough follow-up yet to know the late side-effect profile of this regimen, our preliminary results are promising,” Re-I Chin, MD, of Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
The study was presented at the virtual 2020 meeting of the American Society of Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
“Certainly, longer follow-up will be needed in this study, but none of the observed patients to date has experienced an unsalvageable failure,” said meeting discussant Amol Narang, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
He reminded conference attendees that, despite good evidence supporting equivalency in oncologic outcomes between short-course radiation and long-course chemoradiation, the former is “highly underutilized in the US” with a mere 1% usage rate between 2004 and 2014.
The current study’s short-course treatment approach was compared in this setting to long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy in the RAPIDO trial reported at the 2020 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), Narang pointed out.
Short-course patients had a higher rate of pathological complete response (pCR) and a lower rate of treatment failure compared with patients who received long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy; both patient groups underwent total mesorectal excision — which is different from the current analysis. The RAPIDO investigators concluded that the approach featuring the short course “can be considered as a new standard of care.”
Narang said the data collectively “begs the question as to whether the superiority of long-course chemoradiation should really have to be demonstrated to justify its use.”
But Chin highlighted toxicity issues. “Historically, there have been concerns regarding toxicity with short-course radiation therapy since it requires larger doses of radiation given over a shorter period of time,” Chin explained. “But [the short course] is particularly convenient for patients since it saves them more than a month of daily trips to the radiation oncology department.”
Seven local failures
The single-center study involved patients with newly diagnosed, nonmetastatic rectal adenocarcinoma treated with short-course radiation therapy followed by chemotherapy in 2018 and 2019. Nearly all (96%) had locally advanced disease, with either a T3/T4 tumor or node-positive disease. Median tumor size was 4.6 cm.
“Many of the patients in the study had low lying tumors,” Chin reported, with a median distance from the anal verge of 7 cm.
Radiation therapy was delivered in 25 Gy given in five fractions over 5 consecutive days, with the option to boost the dose to 30 Gy or 35 Gy in five fractions if extra-mesorectal lymph nodes were involved. Conventional 3D or intensity-modulated radiation was used and all patients completed treatment.
The median interval between diagnosis of rectal cancer and initiation of radiation therapy was 1.4 months, while the median interval between completion of radiation to initiation of chemotherapy was 2.7 weeks.
The most common chemotherapy regimen was FOLFOX – consisting of leucovorin, fluorouracil (5-FU), and oxaliplatin – or modified FOLFOX. For patients who received six or more cycles of chemotherapy, the median time spent on treatment was 3.9 months.
For those who completed at least six cycles of chemotherapy, the overall clinical CR was 51%, and, for patients with locally advanced disease, the clinical CR rate was 49%. Five of the 43 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR still underwent surgical resection because of patient or physician preference. Among this small group of patients, 4 of the 5 achieved a pCR, and the remaining patient achieved a pathological partial response (pPR).
A total of 42 patients (47% of the group) achieved a partial response following the radiation plus chemotherapy paradigm, and one patient had progressive disease. All underwent surgical resection. One patient did not complete chemotherapy and did not get surgery and subsequently died.
This left 38 patients to be managed nonoperatively. In this nonoperative cohort, 79% of patients continued to have a clinical CR at the end of follow-up. Of the 7 patients with local failure, 6 were salvaged by surgery, one was salvaged by chemotherapy, and all 7 treatment failures had no evidence of disease at last follow-up.
Of the small group of 5 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR following short-course radiation therapy and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, there were no further events in this group, whereas, for patients who achieved only an initial partial response or who had progressive disease, 72% remained event-free.
Approximately half of those who achieved a clinical CR to the treatment regimen had no late gastrointestinal toxicities, and no grade 3 or 4 toxicities were observed. “Surgical resection of tumors — even without a permanent stoma — can result in significantly decreased bowel function, so our goal is to treat patients without surgery and maintain good bowel function,” Chin noted.
“For rectal cancer, both short-course radiation therapy and nonoperative management are emerging treatment paradigms that may be more cost-effective and convenient compared to long-course chemoradiation followed by surgery, [especially since] the COVID-19 pandemic...has spurred changes in clinical practices in radiation oncology,” she said.
Chin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Narang reports receiving research support from Boston Scientific.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A short course of radiation therapy followed by neoadjuvant chemotherapy resulted in a clinical complete response (CR) in almost half of 90 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer, allowing the majority of responders to skip surgical resection, a retrospective study indicates.
Specifically, at a median follow-up of 16.6 months for living patients, the initial clinical CR rate was 48% overall.
“While we do not have enough follow-up yet to know the late side-effect profile of this regimen, our preliminary results are promising,” Re-I Chin, MD, of Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
The study was presented at the virtual 2020 meeting of the American Society of Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
“Certainly, longer follow-up will be needed in this study, but none of the observed patients to date has experienced an unsalvageable failure,” said meeting discussant Amol Narang, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
He reminded conference attendees that, despite good evidence supporting equivalency in oncologic outcomes between short-course radiation and long-course chemoradiation, the former is “highly underutilized in the US” with a mere 1% usage rate between 2004 and 2014.
The current study’s short-course treatment approach was compared in this setting to long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy in the RAPIDO trial reported at the 2020 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), Narang pointed out.
Short-course patients had a higher rate of pathological complete response (pCR) and a lower rate of treatment failure compared with patients who received long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy; both patient groups underwent total mesorectal excision — which is different from the current analysis. The RAPIDO investigators concluded that the approach featuring the short course “can be considered as a new standard of care.”
Narang said the data collectively “begs the question as to whether the superiority of long-course chemoradiation should really have to be demonstrated to justify its use.”
But Chin highlighted toxicity issues. “Historically, there have been concerns regarding toxicity with short-course radiation therapy since it requires larger doses of radiation given over a shorter period of time,” Chin explained. “But [the short course] is particularly convenient for patients since it saves them more than a month of daily trips to the radiation oncology department.”
Seven local failures
The single-center study involved patients with newly diagnosed, nonmetastatic rectal adenocarcinoma treated with short-course radiation therapy followed by chemotherapy in 2018 and 2019. Nearly all (96%) had locally advanced disease, with either a T3/T4 tumor or node-positive disease. Median tumor size was 4.6 cm.
“Many of the patients in the study had low lying tumors,” Chin reported, with a median distance from the anal verge of 7 cm.
Radiation therapy was delivered in 25 Gy given in five fractions over 5 consecutive days, with the option to boost the dose to 30 Gy or 35 Gy in five fractions if extra-mesorectal lymph nodes were involved. Conventional 3D or intensity-modulated radiation was used and all patients completed treatment.
The median interval between diagnosis of rectal cancer and initiation of radiation therapy was 1.4 months, while the median interval between completion of radiation to initiation of chemotherapy was 2.7 weeks.
The most common chemotherapy regimen was FOLFOX – consisting of leucovorin, fluorouracil (5-FU), and oxaliplatin – or modified FOLFOX. For patients who received six or more cycles of chemotherapy, the median time spent on treatment was 3.9 months.
For those who completed at least six cycles of chemotherapy, the overall clinical CR was 51%, and, for patients with locally advanced disease, the clinical CR rate was 49%. Five of the 43 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR still underwent surgical resection because of patient or physician preference. Among this small group of patients, 4 of the 5 achieved a pCR, and the remaining patient achieved a pathological partial response (pPR).
A total of 42 patients (47% of the group) achieved a partial response following the radiation plus chemotherapy paradigm, and one patient had progressive disease. All underwent surgical resection. One patient did not complete chemotherapy and did not get surgery and subsequently died.
This left 38 patients to be managed nonoperatively. In this nonoperative cohort, 79% of patients continued to have a clinical CR at the end of follow-up. Of the 7 patients with local failure, 6 were salvaged by surgery, one was salvaged by chemotherapy, and all 7 treatment failures had no evidence of disease at last follow-up.
Of the small group of 5 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR following short-course radiation therapy and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, there were no further events in this group, whereas, for patients who achieved only an initial partial response or who had progressive disease, 72% remained event-free.
Approximately half of those who achieved a clinical CR to the treatment regimen had no late gastrointestinal toxicities, and no grade 3 or 4 toxicities were observed. “Surgical resection of tumors — even without a permanent stoma — can result in significantly decreased bowel function, so our goal is to treat patients without surgery and maintain good bowel function,” Chin noted.
“For rectal cancer, both short-course radiation therapy and nonoperative management are emerging treatment paradigms that may be more cost-effective and convenient compared to long-course chemoradiation followed by surgery, [especially since] the COVID-19 pandemic...has spurred changes in clinical practices in radiation oncology,” she said.
Chin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Narang reports receiving research support from Boston Scientific.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nivolumab Use for First-Line Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results of a Real-World Cohort of Patients
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has a poor prognosis and remains an important cause of cancer-related morbidity and mortality.1,2 Potentially curative interventions include surgical resection, radiofrequency ablation, and liver transplantation. However, the majority of patients are not eligible for these procedures because they are diagnosed at an advanced stage, when locoregional therapies are much more limited.3,4 Although the kinase inhibitors sorafenib and lenvatinib are approved as first-line systemic treatment, at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Kansas City VA Medical Center (KCVAMC) in Missouri, nivolumab was used instead because of concerns for the tolerability of the kinase inhibitors. Locoregional therapies, resection, and transplantation options were either not appropriate or had been exhausted for these patients. The objective of this retrospective study was to determine the outcomes of those veteran patients in a small cohort.
Methods
The KCVAMC Institutional Review Board approved this retrospective chart review. Patients were selected from pharmacy records at KCVAMC. We identified all patients with a diagnosis of HCC who received nivolumab from January 2016 to December 2019. We then included only the patients that had nivolumab in the front-line setting for our final analysis. At the time of initiation of treatment, all patients were informed that immunotherapy was not approved for front-line treatment, but available evidence suggested that it would be easier to tolerate than sorafenib or lenvatinib. These patients were determined to be either ineligible for sorafenib or lenvatinib therapy or expected to tolerate it poorly, and hence they consented to the use of nivolumab. Tumor response and progression were assessed by the investigator according to iRECIST (Immune Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors) criteria.5 Data were obtained from retrospective health record review.
Results
Fourteen men received nivolumab in the front-line systemic therapy setting from January 2016 to December 2019 at KCVAMC. The median age was 63.5 years (range, 58-72 years), and the median Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score was 1. The Table highlights patient characteristics.
Of the 14 patients included in the review, 2 patients had a response to nivolumab (14.3%) and 1 patient had a complete response (7.1%). The median duration of immunotherapy was 4.5 months. Immunotherapy was discontinued due to disease progression in 10 patients and toxicity in 3 patients.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) from initiation of immunotherapy was 4 months; median overall survival (OS) was 8 months. The median time from diagnosis to survival was 41 months. Only 1 patient received a second-line treatment.
Incidence of grade 3 or higher toxicity was 35%. Three deaths resulted from auto-immune hepatitis (grade 5 toxicity), as well as 1 grade 3 skin toxicity, and 1 grade 4 liver toxicity.
Discussion
Immunotherapy has shown promise in patients with HCC based on the results of the KEYNOTE-224 and Checkmate-040 studies,6,7 which led to an accelerated US Food and Drug Administration approval of nivolumab and pembrolizumab for HCC following failure of first-line sorafenib.8,9
Several clinical trials are evaluating front-line immunotherapy for HCC. The Checkmate 459 study demonstrated the median OS to be 16.4 months for nivolumab vs 14.7 months for sorafenib, a difference that was not statistically significant. However, tolerability of nivolumab was better than it was for sorafenib, thus positioning it as a potentially attractive first-line option.10 The GO30140 study evaluated
The results from our study differed from the previous studies and raise concern for the applicability of these trials to a real-world population. For example, both the GO30140 and IMbrave150 excluded patients with untreated varices.11,12 Both IMbrave150 and Checkmate 459 limited enrollment only to patients with a Child-Pugh A score for liver disease; 36% of the KCVAMC patients had a Child-Pugh B score. Three patients (21.4%) were homeless, 6 patients (42.8%) had substance abuse history and 5 patients (35.7%) had mental illness. Several psychosocial factors present in our patients, such as substance abuse, mental illness, and homelessness, would have excluded them from clinical trials. Our small cohort of patients, thus, represents a frail real-world population due to multiple medical and psychosocial comorbidities. Real-world experience with immunotherapy as second-line therapy after treatment with sorafenib has been reported, but this is the first reported real-world experience of immunotherapy in the front-line setting for HCC.13,14
Large differences in sociodemographic status and health status exist between the veteran population and typical clinical trial populations. Veterans are predominantly male and older than a clinical trial population. Veterans are more likely to belong to a minority group, more likely to have lower level education and more likely to be poor than a clinical trial population. They are more likely to have poorer health status with higher number of medical conditions and psychosocial conditions.15
Limitations
We acknowledge several limitations to our study, such as the small number of patients and the retrospective single center nature of this study. Patients were older men with multiple psychosocial comorbitities like mental illness, substance abuse, and homelessness. This cohort may not represent the non-VA population, but is an excellent representation of a frail, real-world veteran population.
Conclusions
Despite clinical trials showing the promise of immunotherapy as an attractive front-line systemic treatment option for HCC, our results show poor outcomes in a frail real-world population. In a cohort of patients who received immunotherapy as a front-line systemic treatment for HCC, results were poor with a response rate of 14.3%, a median PFS of 4 months, and a median OS of 8 months. We noted a significantly higher number of adverse effects, including 21% incidence of grade 5 hepatotoxicity. There remains an urgent need to develop more effective and safer therapies for this patient population as well as validation from larger real-world studies.
1. El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(12):1118-1127. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1001683
2. Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359-E386. doi:10.1002/ijc.29210
3. Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362(9399):1907-1917. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14964-1
4. Mittal S, El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: consider the population. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;47 Suppl(0):S2-S6. doi:10.1097/MCG.0b013e3182872f29
5. Seymour L, Bogaerts J, Perrone A, et al. iRECIST: guidelines for response criteria for use in trials testing immunotherapeutics [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2019 May;20(5):e242]. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(3):e143-e152. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30074-8
6. El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10088):2492-2502.doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31046-2
7. Zhu AX, Finn RS, Edeline J, et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): a non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2018 Sep;19(9):e440]. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(7):940-952. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30351-6
8. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to nivolumab for HCC previously treated with sorafenib. Updated September 25, 2017. Accessed October 7, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-nivolumab-hcc-previously-treated-sorafenib.
9. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to pembrolizumab for hepatocellular carcinoma. Updated December 14, 2018. Accessed October 7, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-pembrolizumab-hepatocellular-carcinoma.
10. Yau T, Park JW, Finn RS, et al. CheckMate 459: A randomized, multi-center phase 3 study of nivolumab (NIVO) vs sorafenib (SOR) as first-line (1L) treatment in patients (pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC). Presented at: ESMO 2019 Congress. Barcelona, Spain: September 27, 2019. Ann Onc. 2019;30(suppl_5):v851-v934. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdz394
11. Lee M, Ryoo BY, Hsu CH, et al. Randomised efficacy and safety results for atezolizumab (atezo) + bevacizumab (bev) in patients (pts) with previously untreated, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Presented at: ESMO 2019 Congress. Barcelona, Spain: September 27, 2019.
12. Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1894-1905.doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
13. Scheiner B, Kirstein MM, Hucke F, et al. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1)-targeted immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: efficacy and safety data from an international multicentre real-world cohort. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49(10):1323-1333. doi:10.1111/apt.15245
14. Yoon SE, Hur JY, Lee KK, et al. Real-world data on nivolumab treatment in Asian patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Presented at: ESMO 2018 Congress. Munich, Germany: October 21, 2018. Ann Onc. 2018;29(suppl_8):viii205-viii270. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdy282
15. Agha Z, Lofgren RP, VanRuiswyk JV, Layde PM. Are patients at Veterans Affairs medical centers sicker? A comparative analysis of health status and medical resource use. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(21):3252-3257. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.21.3252
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has a poor prognosis and remains an important cause of cancer-related morbidity and mortality.1,2 Potentially curative interventions include surgical resection, radiofrequency ablation, and liver transplantation. However, the majority of patients are not eligible for these procedures because they are diagnosed at an advanced stage, when locoregional therapies are much more limited.3,4 Although the kinase inhibitors sorafenib and lenvatinib are approved as first-line systemic treatment, at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Kansas City VA Medical Center (KCVAMC) in Missouri, nivolumab was used instead because of concerns for the tolerability of the kinase inhibitors. Locoregional therapies, resection, and transplantation options were either not appropriate or had been exhausted for these patients. The objective of this retrospective study was to determine the outcomes of those veteran patients in a small cohort.
Methods
The KCVAMC Institutional Review Board approved this retrospective chart review. Patients were selected from pharmacy records at KCVAMC. We identified all patients with a diagnosis of HCC who received nivolumab from January 2016 to December 2019. We then included only the patients that had nivolumab in the front-line setting for our final analysis. At the time of initiation of treatment, all patients were informed that immunotherapy was not approved for front-line treatment, but available evidence suggested that it would be easier to tolerate than sorafenib or lenvatinib. These patients were determined to be either ineligible for sorafenib or lenvatinib therapy or expected to tolerate it poorly, and hence they consented to the use of nivolumab. Tumor response and progression were assessed by the investigator according to iRECIST (Immune Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors) criteria.5 Data were obtained from retrospective health record review.
Results
Fourteen men received nivolumab in the front-line systemic therapy setting from January 2016 to December 2019 at KCVAMC. The median age was 63.5 years (range, 58-72 years), and the median Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score was 1. The Table highlights patient characteristics.
Of the 14 patients included in the review, 2 patients had a response to nivolumab (14.3%) and 1 patient had a complete response (7.1%). The median duration of immunotherapy was 4.5 months. Immunotherapy was discontinued due to disease progression in 10 patients and toxicity in 3 patients.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) from initiation of immunotherapy was 4 months; median overall survival (OS) was 8 months. The median time from diagnosis to survival was 41 months. Only 1 patient received a second-line treatment.
Incidence of grade 3 or higher toxicity was 35%. Three deaths resulted from auto-immune hepatitis (grade 5 toxicity), as well as 1 grade 3 skin toxicity, and 1 grade 4 liver toxicity.
Discussion
Immunotherapy has shown promise in patients with HCC based on the results of the KEYNOTE-224 and Checkmate-040 studies,6,7 which led to an accelerated US Food and Drug Administration approval of nivolumab and pembrolizumab for HCC following failure of first-line sorafenib.8,9
Several clinical trials are evaluating front-line immunotherapy for HCC. The Checkmate 459 study demonstrated the median OS to be 16.4 months for nivolumab vs 14.7 months for sorafenib, a difference that was not statistically significant. However, tolerability of nivolumab was better than it was for sorafenib, thus positioning it as a potentially attractive first-line option.10 The GO30140 study evaluated
The results from our study differed from the previous studies and raise concern for the applicability of these trials to a real-world population. For example, both the GO30140 and IMbrave150 excluded patients with untreated varices.11,12 Both IMbrave150 and Checkmate 459 limited enrollment only to patients with a Child-Pugh A score for liver disease; 36% of the KCVAMC patients had a Child-Pugh B score. Three patients (21.4%) were homeless, 6 patients (42.8%) had substance abuse history and 5 patients (35.7%) had mental illness. Several psychosocial factors present in our patients, such as substance abuse, mental illness, and homelessness, would have excluded them from clinical trials. Our small cohort of patients, thus, represents a frail real-world population due to multiple medical and psychosocial comorbidities. Real-world experience with immunotherapy as second-line therapy after treatment with sorafenib has been reported, but this is the first reported real-world experience of immunotherapy in the front-line setting for HCC.13,14
Large differences in sociodemographic status and health status exist between the veteran population and typical clinical trial populations. Veterans are predominantly male and older than a clinical trial population. Veterans are more likely to belong to a minority group, more likely to have lower level education and more likely to be poor than a clinical trial population. They are more likely to have poorer health status with higher number of medical conditions and psychosocial conditions.15
Limitations
We acknowledge several limitations to our study, such as the small number of patients and the retrospective single center nature of this study. Patients were older men with multiple psychosocial comorbitities like mental illness, substance abuse, and homelessness. This cohort may not represent the non-VA population, but is an excellent representation of a frail, real-world veteran population.
Conclusions
Despite clinical trials showing the promise of immunotherapy as an attractive front-line systemic treatment option for HCC, our results show poor outcomes in a frail real-world population. In a cohort of patients who received immunotherapy as a front-line systemic treatment for HCC, results were poor with a response rate of 14.3%, a median PFS of 4 months, and a median OS of 8 months. We noted a significantly higher number of adverse effects, including 21% incidence of grade 5 hepatotoxicity. There remains an urgent need to develop more effective and safer therapies for this patient population as well as validation from larger real-world studies.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has a poor prognosis and remains an important cause of cancer-related morbidity and mortality.1,2 Potentially curative interventions include surgical resection, radiofrequency ablation, and liver transplantation. However, the majority of patients are not eligible for these procedures because they are diagnosed at an advanced stage, when locoregional therapies are much more limited.3,4 Although the kinase inhibitors sorafenib and lenvatinib are approved as first-line systemic treatment, at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Kansas City VA Medical Center (KCVAMC) in Missouri, nivolumab was used instead because of concerns for the tolerability of the kinase inhibitors. Locoregional therapies, resection, and transplantation options were either not appropriate or had been exhausted for these patients. The objective of this retrospective study was to determine the outcomes of those veteran patients in a small cohort.
Methods
The KCVAMC Institutional Review Board approved this retrospective chart review. Patients were selected from pharmacy records at KCVAMC. We identified all patients with a diagnosis of HCC who received nivolumab from January 2016 to December 2019. We then included only the patients that had nivolumab in the front-line setting for our final analysis. At the time of initiation of treatment, all patients were informed that immunotherapy was not approved for front-line treatment, but available evidence suggested that it would be easier to tolerate than sorafenib or lenvatinib. These patients were determined to be either ineligible for sorafenib or lenvatinib therapy or expected to tolerate it poorly, and hence they consented to the use of nivolumab. Tumor response and progression were assessed by the investigator according to iRECIST (Immune Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors) criteria.5 Data were obtained from retrospective health record review.
Results
Fourteen men received nivolumab in the front-line systemic therapy setting from January 2016 to December 2019 at KCVAMC. The median age was 63.5 years (range, 58-72 years), and the median Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score was 1. The Table highlights patient characteristics.
Of the 14 patients included in the review, 2 patients had a response to nivolumab (14.3%) and 1 patient had a complete response (7.1%). The median duration of immunotherapy was 4.5 months. Immunotherapy was discontinued due to disease progression in 10 patients and toxicity in 3 patients.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) from initiation of immunotherapy was 4 months; median overall survival (OS) was 8 months. The median time from diagnosis to survival was 41 months. Only 1 patient received a second-line treatment.
Incidence of grade 3 or higher toxicity was 35%. Three deaths resulted from auto-immune hepatitis (grade 5 toxicity), as well as 1 grade 3 skin toxicity, and 1 grade 4 liver toxicity.
Discussion
Immunotherapy has shown promise in patients with HCC based on the results of the KEYNOTE-224 and Checkmate-040 studies,6,7 which led to an accelerated US Food and Drug Administration approval of nivolumab and pembrolizumab for HCC following failure of first-line sorafenib.8,9
Several clinical trials are evaluating front-line immunotherapy for HCC. The Checkmate 459 study demonstrated the median OS to be 16.4 months for nivolumab vs 14.7 months for sorafenib, a difference that was not statistically significant. However, tolerability of nivolumab was better than it was for sorafenib, thus positioning it as a potentially attractive first-line option.10 The GO30140 study evaluated
The results from our study differed from the previous studies and raise concern for the applicability of these trials to a real-world population. For example, both the GO30140 and IMbrave150 excluded patients with untreated varices.11,12 Both IMbrave150 and Checkmate 459 limited enrollment only to patients with a Child-Pugh A score for liver disease; 36% of the KCVAMC patients had a Child-Pugh B score. Three patients (21.4%) were homeless, 6 patients (42.8%) had substance abuse history and 5 patients (35.7%) had mental illness. Several psychosocial factors present in our patients, such as substance abuse, mental illness, and homelessness, would have excluded them from clinical trials. Our small cohort of patients, thus, represents a frail real-world population due to multiple medical and psychosocial comorbidities. Real-world experience with immunotherapy as second-line therapy after treatment with sorafenib has been reported, but this is the first reported real-world experience of immunotherapy in the front-line setting for HCC.13,14
Large differences in sociodemographic status and health status exist between the veteran population and typical clinical trial populations. Veterans are predominantly male and older than a clinical trial population. Veterans are more likely to belong to a minority group, more likely to have lower level education and more likely to be poor than a clinical trial population. They are more likely to have poorer health status with higher number of medical conditions and psychosocial conditions.15
Limitations
We acknowledge several limitations to our study, such as the small number of patients and the retrospective single center nature of this study. Patients were older men with multiple psychosocial comorbitities like mental illness, substance abuse, and homelessness. This cohort may not represent the non-VA population, but is an excellent representation of a frail, real-world veteran population.
Conclusions
Despite clinical trials showing the promise of immunotherapy as an attractive front-line systemic treatment option for HCC, our results show poor outcomes in a frail real-world population. In a cohort of patients who received immunotherapy as a front-line systemic treatment for HCC, results were poor with a response rate of 14.3%, a median PFS of 4 months, and a median OS of 8 months. We noted a significantly higher number of adverse effects, including 21% incidence of grade 5 hepatotoxicity. There remains an urgent need to develop more effective and safer therapies for this patient population as well as validation from larger real-world studies.
1. El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(12):1118-1127. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1001683
2. Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359-E386. doi:10.1002/ijc.29210
3. Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362(9399):1907-1917. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14964-1
4. Mittal S, El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: consider the population. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;47 Suppl(0):S2-S6. doi:10.1097/MCG.0b013e3182872f29
5. Seymour L, Bogaerts J, Perrone A, et al. iRECIST: guidelines for response criteria for use in trials testing immunotherapeutics [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2019 May;20(5):e242]. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(3):e143-e152. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30074-8
6. El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10088):2492-2502.doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31046-2
7. Zhu AX, Finn RS, Edeline J, et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): a non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2018 Sep;19(9):e440]. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(7):940-952. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30351-6
8. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to nivolumab for HCC previously treated with sorafenib. Updated September 25, 2017. Accessed October 7, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-nivolumab-hcc-previously-treated-sorafenib.
9. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to pembrolizumab for hepatocellular carcinoma. Updated December 14, 2018. Accessed October 7, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-pembrolizumab-hepatocellular-carcinoma.
10. Yau T, Park JW, Finn RS, et al. CheckMate 459: A randomized, multi-center phase 3 study of nivolumab (NIVO) vs sorafenib (SOR) as first-line (1L) treatment in patients (pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC). Presented at: ESMO 2019 Congress. Barcelona, Spain: September 27, 2019. Ann Onc. 2019;30(suppl_5):v851-v934. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdz394
11. Lee M, Ryoo BY, Hsu CH, et al. Randomised efficacy and safety results for atezolizumab (atezo) + bevacizumab (bev) in patients (pts) with previously untreated, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Presented at: ESMO 2019 Congress. Barcelona, Spain: September 27, 2019.
12. Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1894-1905.doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
13. Scheiner B, Kirstein MM, Hucke F, et al. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1)-targeted immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: efficacy and safety data from an international multicentre real-world cohort. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49(10):1323-1333. doi:10.1111/apt.15245
14. Yoon SE, Hur JY, Lee KK, et al. Real-world data on nivolumab treatment in Asian patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Presented at: ESMO 2018 Congress. Munich, Germany: October 21, 2018. Ann Onc. 2018;29(suppl_8):viii205-viii270. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdy282
15. Agha Z, Lofgren RP, VanRuiswyk JV, Layde PM. Are patients at Veterans Affairs medical centers sicker? A comparative analysis of health status and medical resource use. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(21):3252-3257. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.21.3252
1. El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(12):1118-1127. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1001683
2. Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359-E386. doi:10.1002/ijc.29210
3. Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362(9399):1907-1917. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14964-1
4. Mittal S, El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: consider the population. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;47 Suppl(0):S2-S6. doi:10.1097/MCG.0b013e3182872f29
5. Seymour L, Bogaerts J, Perrone A, et al. iRECIST: guidelines for response criteria for use in trials testing immunotherapeutics [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2019 May;20(5):e242]. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(3):e143-e152. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30074-8
6. El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10088):2492-2502.doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31046-2
7. Zhu AX, Finn RS, Edeline J, et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): a non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2018 Sep;19(9):e440]. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(7):940-952. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30351-6
8. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to nivolumab for HCC previously treated with sorafenib. Updated September 25, 2017. Accessed October 7, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-nivolumab-hcc-previously-treated-sorafenib.
9. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to pembrolizumab for hepatocellular carcinoma. Updated December 14, 2018. Accessed October 7, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-pembrolizumab-hepatocellular-carcinoma.
10. Yau T, Park JW, Finn RS, et al. CheckMate 459: A randomized, multi-center phase 3 study of nivolumab (NIVO) vs sorafenib (SOR) as first-line (1L) treatment in patients (pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC). Presented at: ESMO 2019 Congress. Barcelona, Spain: September 27, 2019. Ann Onc. 2019;30(suppl_5):v851-v934. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdz394
11. Lee M, Ryoo BY, Hsu CH, et al. Randomised efficacy and safety results for atezolizumab (atezo) + bevacizumab (bev) in patients (pts) with previously untreated, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Presented at: ESMO 2019 Congress. Barcelona, Spain: September 27, 2019.
12. Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1894-1905.doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
13. Scheiner B, Kirstein MM, Hucke F, et al. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1)-targeted immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: efficacy and safety data from an international multicentre real-world cohort. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49(10):1323-1333. doi:10.1111/apt.15245
14. Yoon SE, Hur JY, Lee KK, et al. Real-world data on nivolumab treatment in Asian patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Presented at: ESMO 2018 Congress. Munich, Germany: October 21, 2018. Ann Onc. 2018;29(suppl_8):viii205-viii270. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdy282
15. Agha Z, Lofgren RP, VanRuiswyk JV, Layde PM. Are patients at Veterans Affairs medical centers sicker? A comparative analysis of health status and medical resource use. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(21):3252-3257. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.21.3252
Real-world results with checkpoint inhibitors found inferior to trial results
according to research published in JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics.
However, the research also suggests that real-world patients who receive ICIs achieve longer survival than patients on standard-of-care medications.
“Patients receiving ICIs in real-world practice may differ from those enrolled in trials in a variety of ways, including age, race, performance status, and comorbidity burden,” said study author Jerry S.H. Lee, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Dr. Lee noted that only 3%-4% of cancer patients participate in clinical trials. In fact, more than half of patients with melanoma and nearly three-quarters of those with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) do not meet criteria for eligibility in clinical trials, he said.
To examine the discrepancies between real-world practice and clinical trials and to better understand which patients receive ICIs in clinical practice, Dr. Lee and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis using electronic health record data from Veterans Administration (VA) facilities nationwide.
The researchers identified 11,888 cancer patients who were treated with ICIs. The cohort included patients who are underrepresented in pivotal clinical trials, including older, non-White, and/or higher disease-burdened patients.
The majority of patients were treated for NSCLC (51.1%), followed by melanoma (14.4%), renal cell carcinoma (RCC; 8.1%), squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (6.8%), urothelial cancer (6.4%), hepatocellular carcinoma (4.5%), and other less common cancer types (8.8%).
Overall survival by indication
In general, median overall survival (OS) in the VA cohort was inferior to median OS reported in clinical trials. However, patients treated with first-line nivolumab for melanoma and second-line pembrolizumab or nivolumab for NSCLC had similar OS in the real-world and trial data.
The researchers did not report exact OS numbers from clinical trials. However, they did report the exact numbers from the VA cohort and show OS differences between the VA cohort and clinical trials graphically.
Among patients in the VA cohort, the median OS was:
- 25.5 months in melanoma patients on first-line nivolumab
- 16.3 months in RCC patients receiving nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 14 months in RCC patients on first-line ipilimumab and nivolumab
- 10.6 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab
- 9.9 months in NSCLC patients receiving pembrolizumab or nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 9.1 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab and platinum-based chemotherapy
- 6.7 months in urothelial cancer patients receiving ICIs in the second line or higher.
A number of factors may have contributed to the shorter OS observed in the VA cohort, according to the researchers. The VA cohort is predominantly male, is older, and has a higher degree of comorbidity, compared with patients in clinical trials.
In addition, no data are available to determine the cause for discontinuation of therapy, and VA patients may have received ICIs after failing multiple lines of previous therapy, while clinical trials may limit patients to only one or two previous lines of therapy.
After stratifying VA patients by frailty status, the OS among non-frail patients was more similar to the OS reported in clinical trials.
“Real-world outcomes from the VA were more similar when adjusted for frailty, which shows the importance of patient diversity in clinical trials,” Dr. Lee said. He added that the definition of frailty among VA patients included potential injury during combat and therefore differs from a generic frailty definition.
ICIs vs. standard care
The researchers also found that VA patients treated with ICIs had longer OS, compared with a cohort of VA patients receiving standard-of-care therapies.
The median OS was as follows:
- In melanoma patients on first-line treatment – 39.29 months with nivolumab and 5.75 months with chemotherapy (P < .001).
- In RCC patients on first-line treatment – 14.01 months with ipilimumab plus nivolumab and 8.63 months with targeted therapy (P = .051).
- In RCC patients on second-line or greater treatment – 12.43 months with nivolumab and 8.09 months with everolimus (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line therapy – 8.88 months with pembrolizumab and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line combination therapy – 10.59 months with pembrolizumab plus platinum chemotherapy and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on second-line or greater therapy – 10.06 months with pembrolizumab or nivolumab and 6.41 months with docetaxel (P < .001).
- In urothelial cancer patients on second-line or greater therapy – 7.66 months with an ICI and 6.31 months with chemotherapy (P = .043).
Help for treatment decisions
“The real-world survival outcomes not only indicate the breadth of indications but also represent patients who tend not to be eligible for immunotherapy trials, based on their health status,” Dr. Lee said. “We hope this dataset of national-level experience provides practicing oncologists evidence to help patients and family members in the process of decision-making about therapy.”
Real-world data can also inform oncologists who face decisions on whether to prescribe or withhold ICIs and patients who face the financial burden of paying for ICIs, he said.
This dataset will be continually updated. The researchers have already added another 10,000 VA patients who have received immunotherapies in the year since the trial began.
“In a longitudinal way, we plan to examine what causes differences in outcomes and continue to find ways to extend care to veterans with a balance of high quality of life,” Dr. Lee said.
“Patients who participate in clinical trials are, on average, younger and healthier than the general population,” said Bora Youn, PhD, a senior biostatistician at Biogen in Cambridge, Mass., who was not involved in this study.
“In the case of immunotherapies, those with poor performance status and autoimmune conditions are often excluded from trials,” Dr. Youn added. “In the real world, these patients can also receive treatments, and clinicians often need to extrapolate the results from clinical trials. It is therefore important to collect real-world data to understand the effectiveness and safety of these therapies in patients with limited evidence.”
Dr. Youn led a real-world study, published in Cancer, of 1,256 Medicare recipients who were diagnosed with NSCLC and received ICI therapy.
“We found that factors associated with poor prognosis in general, such as squamous histology and failure of aggressive prior treatment, are also predictive of decreased survival among those who initiated immunotherapies. Yet, OS of older patients was relatively comparable to those observed in clinical trials,” Dr. Youn said.
“Understanding the real-world effectiveness of these treatments will help improve the evidence base, especially for those underrepresented in clinical trials. These studies can also help identify patients who are most likely to benefit from immunotherapies,” Dr. Youn added.
This study was supported by the VA Office of Research and Development Cooperative Studies Program. Dr. Lee and Dr. Youn disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jennifer La et al. JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics. 2020:4:918-28.
according to research published in JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics.
However, the research also suggests that real-world patients who receive ICIs achieve longer survival than patients on standard-of-care medications.
“Patients receiving ICIs in real-world practice may differ from those enrolled in trials in a variety of ways, including age, race, performance status, and comorbidity burden,” said study author Jerry S.H. Lee, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Dr. Lee noted that only 3%-4% of cancer patients participate in clinical trials. In fact, more than half of patients with melanoma and nearly three-quarters of those with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) do not meet criteria for eligibility in clinical trials, he said.
To examine the discrepancies between real-world practice and clinical trials and to better understand which patients receive ICIs in clinical practice, Dr. Lee and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis using electronic health record data from Veterans Administration (VA) facilities nationwide.
The researchers identified 11,888 cancer patients who were treated with ICIs. The cohort included patients who are underrepresented in pivotal clinical trials, including older, non-White, and/or higher disease-burdened patients.
The majority of patients were treated for NSCLC (51.1%), followed by melanoma (14.4%), renal cell carcinoma (RCC; 8.1%), squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (6.8%), urothelial cancer (6.4%), hepatocellular carcinoma (4.5%), and other less common cancer types (8.8%).
Overall survival by indication
In general, median overall survival (OS) in the VA cohort was inferior to median OS reported in clinical trials. However, patients treated with first-line nivolumab for melanoma and second-line pembrolizumab or nivolumab for NSCLC had similar OS in the real-world and trial data.
The researchers did not report exact OS numbers from clinical trials. However, they did report the exact numbers from the VA cohort and show OS differences between the VA cohort and clinical trials graphically.
Among patients in the VA cohort, the median OS was:
- 25.5 months in melanoma patients on first-line nivolumab
- 16.3 months in RCC patients receiving nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 14 months in RCC patients on first-line ipilimumab and nivolumab
- 10.6 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab
- 9.9 months in NSCLC patients receiving pembrolizumab or nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 9.1 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab and platinum-based chemotherapy
- 6.7 months in urothelial cancer patients receiving ICIs in the second line or higher.
A number of factors may have contributed to the shorter OS observed in the VA cohort, according to the researchers. The VA cohort is predominantly male, is older, and has a higher degree of comorbidity, compared with patients in clinical trials.
In addition, no data are available to determine the cause for discontinuation of therapy, and VA patients may have received ICIs after failing multiple lines of previous therapy, while clinical trials may limit patients to only one or two previous lines of therapy.
After stratifying VA patients by frailty status, the OS among non-frail patients was more similar to the OS reported in clinical trials.
“Real-world outcomes from the VA were more similar when adjusted for frailty, which shows the importance of patient diversity in clinical trials,” Dr. Lee said. He added that the definition of frailty among VA patients included potential injury during combat and therefore differs from a generic frailty definition.
ICIs vs. standard care
The researchers also found that VA patients treated with ICIs had longer OS, compared with a cohort of VA patients receiving standard-of-care therapies.
The median OS was as follows:
- In melanoma patients on first-line treatment – 39.29 months with nivolumab and 5.75 months with chemotherapy (P < .001).
- In RCC patients on first-line treatment – 14.01 months with ipilimumab plus nivolumab and 8.63 months with targeted therapy (P = .051).
- In RCC patients on second-line or greater treatment – 12.43 months with nivolumab and 8.09 months with everolimus (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line therapy – 8.88 months with pembrolizumab and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line combination therapy – 10.59 months with pembrolizumab plus platinum chemotherapy and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on second-line or greater therapy – 10.06 months with pembrolizumab or nivolumab and 6.41 months with docetaxel (P < .001).
- In urothelial cancer patients on second-line or greater therapy – 7.66 months with an ICI and 6.31 months with chemotherapy (P = .043).
Help for treatment decisions
“The real-world survival outcomes not only indicate the breadth of indications but also represent patients who tend not to be eligible for immunotherapy trials, based on their health status,” Dr. Lee said. “We hope this dataset of national-level experience provides practicing oncologists evidence to help patients and family members in the process of decision-making about therapy.”
Real-world data can also inform oncologists who face decisions on whether to prescribe or withhold ICIs and patients who face the financial burden of paying for ICIs, he said.
This dataset will be continually updated. The researchers have already added another 10,000 VA patients who have received immunotherapies in the year since the trial began.
“In a longitudinal way, we plan to examine what causes differences in outcomes and continue to find ways to extend care to veterans with a balance of high quality of life,” Dr. Lee said.
“Patients who participate in clinical trials are, on average, younger and healthier than the general population,” said Bora Youn, PhD, a senior biostatistician at Biogen in Cambridge, Mass., who was not involved in this study.
“In the case of immunotherapies, those with poor performance status and autoimmune conditions are often excluded from trials,” Dr. Youn added. “In the real world, these patients can also receive treatments, and clinicians often need to extrapolate the results from clinical trials. It is therefore important to collect real-world data to understand the effectiveness and safety of these therapies in patients with limited evidence.”
Dr. Youn led a real-world study, published in Cancer, of 1,256 Medicare recipients who were diagnosed with NSCLC and received ICI therapy.
“We found that factors associated with poor prognosis in general, such as squamous histology and failure of aggressive prior treatment, are also predictive of decreased survival among those who initiated immunotherapies. Yet, OS of older patients was relatively comparable to those observed in clinical trials,” Dr. Youn said.
“Understanding the real-world effectiveness of these treatments will help improve the evidence base, especially for those underrepresented in clinical trials. These studies can also help identify patients who are most likely to benefit from immunotherapies,” Dr. Youn added.
This study was supported by the VA Office of Research and Development Cooperative Studies Program. Dr. Lee and Dr. Youn disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jennifer La et al. JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics. 2020:4:918-28.
according to research published in JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics.
However, the research also suggests that real-world patients who receive ICIs achieve longer survival than patients on standard-of-care medications.
“Patients receiving ICIs in real-world practice may differ from those enrolled in trials in a variety of ways, including age, race, performance status, and comorbidity burden,” said study author Jerry S.H. Lee, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Dr. Lee noted that only 3%-4% of cancer patients participate in clinical trials. In fact, more than half of patients with melanoma and nearly three-quarters of those with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) do not meet criteria for eligibility in clinical trials, he said.
To examine the discrepancies between real-world practice and clinical trials and to better understand which patients receive ICIs in clinical practice, Dr. Lee and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis using electronic health record data from Veterans Administration (VA) facilities nationwide.
The researchers identified 11,888 cancer patients who were treated with ICIs. The cohort included patients who are underrepresented in pivotal clinical trials, including older, non-White, and/or higher disease-burdened patients.
The majority of patients were treated for NSCLC (51.1%), followed by melanoma (14.4%), renal cell carcinoma (RCC; 8.1%), squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (6.8%), urothelial cancer (6.4%), hepatocellular carcinoma (4.5%), and other less common cancer types (8.8%).
Overall survival by indication
In general, median overall survival (OS) in the VA cohort was inferior to median OS reported in clinical trials. However, patients treated with first-line nivolumab for melanoma and second-line pembrolizumab or nivolumab for NSCLC had similar OS in the real-world and trial data.
The researchers did not report exact OS numbers from clinical trials. However, they did report the exact numbers from the VA cohort and show OS differences between the VA cohort and clinical trials graphically.
Among patients in the VA cohort, the median OS was:
- 25.5 months in melanoma patients on first-line nivolumab
- 16.3 months in RCC patients receiving nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 14 months in RCC patients on first-line ipilimumab and nivolumab
- 10.6 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab
- 9.9 months in NSCLC patients receiving pembrolizumab or nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 9.1 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab and platinum-based chemotherapy
- 6.7 months in urothelial cancer patients receiving ICIs in the second line or higher.
A number of factors may have contributed to the shorter OS observed in the VA cohort, according to the researchers. The VA cohort is predominantly male, is older, and has a higher degree of comorbidity, compared with patients in clinical trials.
In addition, no data are available to determine the cause for discontinuation of therapy, and VA patients may have received ICIs after failing multiple lines of previous therapy, while clinical trials may limit patients to only one or two previous lines of therapy.
After stratifying VA patients by frailty status, the OS among non-frail patients was more similar to the OS reported in clinical trials.
“Real-world outcomes from the VA were more similar when adjusted for frailty, which shows the importance of patient diversity in clinical trials,” Dr. Lee said. He added that the definition of frailty among VA patients included potential injury during combat and therefore differs from a generic frailty definition.
ICIs vs. standard care
The researchers also found that VA patients treated with ICIs had longer OS, compared with a cohort of VA patients receiving standard-of-care therapies.
The median OS was as follows:
- In melanoma patients on first-line treatment – 39.29 months with nivolumab and 5.75 months with chemotherapy (P < .001).
- In RCC patients on first-line treatment – 14.01 months with ipilimumab plus nivolumab and 8.63 months with targeted therapy (P = .051).
- In RCC patients on second-line or greater treatment – 12.43 months with nivolumab and 8.09 months with everolimus (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line therapy – 8.88 months with pembrolizumab and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line combination therapy – 10.59 months with pembrolizumab plus platinum chemotherapy and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on second-line or greater therapy – 10.06 months with pembrolizumab or nivolumab and 6.41 months with docetaxel (P < .001).
- In urothelial cancer patients on second-line or greater therapy – 7.66 months with an ICI and 6.31 months with chemotherapy (P = .043).
Help for treatment decisions
“The real-world survival outcomes not only indicate the breadth of indications but also represent patients who tend not to be eligible for immunotherapy trials, based on their health status,” Dr. Lee said. “We hope this dataset of national-level experience provides practicing oncologists evidence to help patients and family members in the process of decision-making about therapy.”
Real-world data can also inform oncologists who face decisions on whether to prescribe or withhold ICIs and patients who face the financial burden of paying for ICIs, he said.
This dataset will be continually updated. The researchers have already added another 10,000 VA patients who have received immunotherapies in the year since the trial began.
“In a longitudinal way, we plan to examine what causes differences in outcomes and continue to find ways to extend care to veterans with a balance of high quality of life,” Dr. Lee said.
“Patients who participate in clinical trials are, on average, younger and healthier than the general population,” said Bora Youn, PhD, a senior biostatistician at Biogen in Cambridge, Mass., who was not involved in this study.
“In the case of immunotherapies, those with poor performance status and autoimmune conditions are often excluded from trials,” Dr. Youn added. “In the real world, these patients can also receive treatments, and clinicians often need to extrapolate the results from clinical trials. It is therefore important to collect real-world data to understand the effectiveness and safety of these therapies in patients with limited evidence.”
Dr. Youn led a real-world study, published in Cancer, of 1,256 Medicare recipients who were diagnosed with NSCLC and received ICI therapy.
“We found that factors associated with poor prognosis in general, such as squamous histology and failure of aggressive prior treatment, are also predictive of decreased survival among those who initiated immunotherapies. Yet, OS of older patients was relatively comparable to those observed in clinical trials,” Dr. Youn said.
“Understanding the real-world effectiveness of these treatments will help improve the evidence base, especially for those underrepresented in clinical trials. These studies can also help identify patients who are most likely to benefit from immunotherapies,” Dr. Youn added.
This study was supported by the VA Office of Research and Development Cooperative Studies Program. Dr. Lee and Dr. Youn disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jennifer La et al. JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics. 2020:4:918-28.
FROM JCO CLINICAL CANCER INFORMATICS
New estimates for breast cancer risk with HRT
The study was published online on October 28 in The BMJ.
“The study confirms increased risk of breast cancer in patients taking HRT but shows that the magnitude of risk depends on a number of factors,” first author Yana Vinogradova, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Vinogradova is a medical statistician at the University of Nottingham (England).
The study also suggests the risk may be lower than was estimated in a large meta-analysis of 24 trials that was published in 2019 in The Lancet. In that study, researchers suggested the risk for breast cancer with HRT was higher and persisted longer than had been thought.
This conclusion from the meta-analysis was widely reported in the lay press and led to the UK Medicine and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency issuing a safety alert for HRT regarding breast cancer. Experts in the field questioned the alert and said it caused undue anxiety. The European Medicines Agency also issued a safety alert because of the study.
This new study was begun before publication of the meta-analysis. Although the results are broadly similar in suggesting increased risk for breast cancer with HRT use, findings from the new study suggest the risk is lower than had been estimated in the meta-analysis and that the risk diminishes more rapidly after stopping HRT than was suggested by the meta-analysis.
“The publicity surrounding publication of the meta-analysis highlighted unexpectedly high risks and led to a heightened level of concern in some quarters,” Dr. Vinogradova commented. “Our study, based on general population data, has not confirmed any such findings. In general, it showed lower levels of risk and clarified the variability of magnitude within them.”
Dr. Vinogradova said the discrepancy could be related to the fact that the studies were designed differently. The meta-analysis relied on results from 24 studies that were conducted around the world at different periods and included women of different ages and backgrounds. The studies in the meta-analysis used different methods, including questionnaires that relied on women’s memories and therefore could have been biased, she said.
In contrast, the new study analyzed EMR data collected prospectively by general practices in the United Kingdom. The data came from the QResearch and from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) databases, the two largest primary care databases in the United Kingdom, which were linked to hospital, mortality, and cancer registries.
Because this study used a “consistent design” and “consistent data sources,” these new results “are likely to be more accurate and reliable for assessing risks among HRT users,” Dr. Vinogradova commented.
This study used an observational design, so it cannot prove that HRT causes breast cancer. These results may better represent women in the general U.K. population, compared with the earlier meta-analysis, she added.
Commenting on the new study, Michael Jones, PhD, senior staff scientist in genetics and epidemiology at the Institute of Cancer Research, London, also emphasized that it was large and its data came from general practitioner medical records, “so the strong statistical associations are unlikely to be due to chance.
“The results of this study generally confirm what has been seen before and is well established – that the use of combined estrogen plus progestogen HRT is associated with increased risk of breast cancer, and this risk increases with duration of use. But reassuringly, after stopping HRT, the raised risk of breast cancer mostly returns to that seen in nonusers of HRT,” he said.
“It’s important to note that no one study should be considered in isolation,” he added. “Even though some risks were found to be slightly smaller than those reported in another meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence recently published in 2019, women considering use of HRT should still follow advice given to them by their [general practitioners].”
Study details
In the study, researchers evaluated all types of HRT commonly prescribed in the United Kingdom over the past 20 years, including topical estrogen, vaginal pessaries, and creams. They grouped HRT use by recent (within the past 5 years) and past (5 or more years ago) and HRT duration as short term (less than 5 years) and long term (5 years or longer). Results were adjusted for a range of factors that could affect breast cancer risk, including lifestyle, smoking, alcohol consumption, other medical conditions, family history, and use of other prescribed drugs.
The analysis included 98,611 women aged 50-79 years who were first diagnosed with breast cancer between 1998 and 2019. These women were matched by age and general practice to 457,498 women who were not diagnosed with breast cancer over these years. HRT use was reported in 34% (33,703) of women with breast cancer and in 31% (134,391) of women without breast cancer.
Overall, the risk for breast cancer was increased with use of most HRT drugs (adjusted odds ratio, 1.21; 95% confidence, 1.19-1.23), compared with not using HRT drugs. The highest risk was tied to combined estrogen/progestogen HRT (adjusted OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.24-1.29). The lowest risk was tied to estrogen-only HRT (adjusted OR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.03-1.10). Estrogen cream and vaginal estrogen were not associated with increased breast cancer risk.
In general, breast cancer risk was higher among recent HRT users and those receiving long-term therapy. HRT-associated breast cancer risk increased with age and declined after discontinuing treatment. Therapy of less than 1 year was not associated with increased breast cancer risk.
Women who had recently been receiving long-term combined estrogen/progestogen HRT had a 79% increased risk for breast cancer (adjusted OR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.73-1.85), compared with never-users. Among recent long-term users of combined HRT, breast cancer risk was highest for norethisterone (adjusted OR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.79-1.99) and lowest for dydrogesterone (adjusted OR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.03-1.48). Women who had recently been receiving long-term estrogen-only HRT had a 15% increased risk for breast cancer compared to never-users (adjusted OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.09-1.21).
Among women who discontinued HRT 5 or more years ago, risk for breast cancer was no longer increased for long-term estrogen-only therapy and short-term estrogen/progestogen therapy. However, breast cancer risk remained elevated 5 years after discontinuing long-term estrogen/progestogen (adjusted OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.11-1.21).
HRT-associated risk for breast cancer increased with age across all durations of therapy.
Compared with never-use, recent long-term estrogen-only therapy was associated with zero extra breast cancer cases per 10,000 women-years among women aged 50-59 years and eight extra cases per 10,000 women-years among women aged 70-79.
Recent long-term estrogen/progestogen use was associated with 15 extra breast cancer cases among women aged 50-59 and 36 extra cases among women aged 70-79 per 10,000 women-years.
Past long-term estrogen/progestogen use was associated with zero extra breast cancer cases among women aged 50-59 and eight extra cases among women aged 70-79 per 10,000 women-years.
Summarizing, Dr. Vinogradova said the increased risk for breast cancer with HRT appears to be “relatively small, particularly for younger women and for any women who use HRT only for a restricted period.”
Decisions about whether to use HRT and which type to use should depend on symptom severity, patient factors, and suitability of other treatment options, she commented.
“Particularly for those women who our study has shown to be most at risk, these decisions should be made through discussions between the patient and her doctor,” she concluded. “We hope that the new and more detailed information provided by our study will facilitate such prescribing decisions.”
The study was partially funded by the School for Primary Care Research of the National Institute for Health Research, by Cancer Research UK, and by the Cancer Research UK Oxford Center. Dr. Vinogradova has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Senior author Julia Hippisley-Cox is an unpaid director of QResearch and was a paid director of ClinRisk until 2019. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The study was published online on October 28 in The BMJ.
“The study confirms increased risk of breast cancer in patients taking HRT but shows that the magnitude of risk depends on a number of factors,” first author Yana Vinogradova, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Vinogradova is a medical statistician at the University of Nottingham (England).
The study also suggests the risk may be lower than was estimated in a large meta-analysis of 24 trials that was published in 2019 in The Lancet. In that study, researchers suggested the risk for breast cancer with HRT was higher and persisted longer than had been thought.
This conclusion from the meta-analysis was widely reported in the lay press and led to the UK Medicine and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency issuing a safety alert for HRT regarding breast cancer. Experts in the field questioned the alert and said it caused undue anxiety. The European Medicines Agency also issued a safety alert because of the study.
This new study was begun before publication of the meta-analysis. Although the results are broadly similar in suggesting increased risk for breast cancer with HRT use, findings from the new study suggest the risk is lower than had been estimated in the meta-analysis and that the risk diminishes more rapidly after stopping HRT than was suggested by the meta-analysis.
“The publicity surrounding publication of the meta-analysis highlighted unexpectedly high risks and led to a heightened level of concern in some quarters,” Dr. Vinogradova commented. “Our study, based on general population data, has not confirmed any such findings. In general, it showed lower levels of risk and clarified the variability of magnitude within them.”
Dr. Vinogradova said the discrepancy could be related to the fact that the studies were designed differently. The meta-analysis relied on results from 24 studies that were conducted around the world at different periods and included women of different ages and backgrounds. The studies in the meta-analysis used different methods, including questionnaires that relied on women’s memories and therefore could have been biased, she said.
In contrast, the new study analyzed EMR data collected prospectively by general practices in the United Kingdom. The data came from the QResearch and from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) databases, the two largest primary care databases in the United Kingdom, which were linked to hospital, mortality, and cancer registries.
Because this study used a “consistent design” and “consistent data sources,” these new results “are likely to be more accurate and reliable for assessing risks among HRT users,” Dr. Vinogradova commented.
This study used an observational design, so it cannot prove that HRT causes breast cancer. These results may better represent women in the general U.K. population, compared with the earlier meta-analysis, she added.
Commenting on the new study, Michael Jones, PhD, senior staff scientist in genetics and epidemiology at the Institute of Cancer Research, London, also emphasized that it was large and its data came from general practitioner medical records, “so the strong statistical associations are unlikely to be due to chance.
“The results of this study generally confirm what has been seen before and is well established – that the use of combined estrogen plus progestogen HRT is associated with increased risk of breast cancer, and this risk increases with duration of use. But reassuringly, after stopping HRT, the raised risk of breast cancer mostly returns to that seen in nonusers of HRT,” he said.
“It’s important to note that no one study should be considered in isolation,” he added. “Even though some risks were found to be slightly smaller than those reported in another meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence recently published in 2019, women considering use of HRT should still follow advice given to them by their [general practitioners].”
Study details
In the study, researchers evaluated all types of HRT commonly prescribed in the United Kingdom over the past 20 years, including topical estrogen, vaginal pessaries, and creams. They grouped HRT use by recent (within the past 5 years) and past (5 or more years ago) and HRT duration as short term (less than 5 years) and long term (5 years or longer). Results were adjusted for a range of factors that could affect breast cancer risk, including lifestyle, smoking, alcohol consumption, other medical conditions, family history, and use of other prescribed drugs.
The analysis included 98,611 women aged 50-79 years who were first diagnosed with breast cancer between 1998 and 2019. These women were matched by age and general practice to 457,498 women who were not diagnosed with breast cancer over these years. HRT use was reported in 34% (33,703) of women with breast cancer and in 31% (134,391) of women without breast cancer.
Overall, the risk for breast cancer was increased with use of most HRT drugs (adjusted odds ratio, 1.21; 95% confidence, 1.19-1.23), compared with not using HRT drugs. The highest risk was tied to combined estrogen/progestogen HRT (adjusted OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.24-1.29). The lowest risk was tied to estrogen-only HRT (adjusted OR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.03-1.10). Estrogen cream and vaginal estrogen were not associated with increased breast cancer risk.
In general, breast cancer risk was higher among recent HRT users and those receiving long-term therapy. HRT-associated breast cancer risk increased with age and declined after discontinuing treatment. Therapy of less than 1 year was not associated with increased breast cancer risk.
Women who had recently been receiving long-term combined estrogen/progestogen HRT had a 79% increased risk for breast cancer (adjusted OR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.73-1.85), compared with never-users. Among recent long-term users of combined HRT, breast cancer risk was highest for norethisterone (adjusted OR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.79-1.99) and lowest for dydrogesterone (adjusted OR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.03-1.48). Women who had recently been receiving long-term estrogen-only HRT had a 15% increased risk for breast cancer compared to never-users (adjusted OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.09-1.21).
Among women who discontinued HRT 5 or more years ago, risk for breast cancer was no longer increased for long-term estrogen-only therapy and short-term estrogen/progestogen therapy. However, breast cancer risk remained elevated 5 years after discontinuing long-term estrogen/progestogen (adjusted OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.11-1.21).
HRT-associated risk for breast cancer increased with age across all durations of therapy.
Compared with never-use, recent long-term estrogen-only therapy was associated with zero extra breast cancer cases per 10,000 women-years among women aged 50-59 years and eight extra cases per 10,000 women-years among women aged 70-79.
Recent long-term estrogen/progestogen use was associated with 15 extra breast cancer cases among women aged 50-59 and 36 extra cases among women aged 70-79 per 10,000 women-years.
Past long-term estrogen/progestogen use was associated with zero extra breast cancer cases among women aged 50-59 and eight extra cases among women aged 70-79 per 10,000 women-years.
Summarizing, Dr. Vinogradova said the increased risk for breast cancer with HRT appears to be “relatively small, particularly for younger women and for any women who use HRT only for a restricted period.”
Decisions about whether to use HRT and which type to use should depend on symptom severity, patient factors, and suitability of other treatment options, she commented.
“Particularly for those women who our study has shown to be most at risk, these decisions should be made through discussions between the patient and her doctor,” she concluded. “We hope that the new and more detailed information provided by our study will facilitate such prescribing decisions.”
The study was partially funded by the School for Primary Care Research of the National Institute for Health Research, by Cancer Research UK, and by the Cancer Research UK Oxford Center. Dr. Vinogradova has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Senior author Julia Hippisley-Cox is an unpaid director of QResearch and was a paid director of ClinRisk until 2019. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The study was published online on October 28 in The BMJ.
“The study confirms increased risk of breast cancer in patients taking HRT but shows that the magnitude of risk depends on a number of factors,” first author Yana Vinogradova, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Vinogradova is a medical statistician at the University of Nottingham (England).
The study also suggests the risk may be lower than was estimated in a large meta-analysis of 24 trials that was published in 2019 in The Lancet. In that study, researchers suggested the risk for breast cancer with HRT was higher and persisted longer than had been thought.
This conclusion from the meta-analysis was widely reported in the lay press and led to the UK Medicine and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency issuing a safety alert for HRT regarding breast cancer. Experts in the field questioned the alert and said it caused undue anxiety. The European Medicines Agency also issued a safety alert because of the study.
This new study was begun before publication of the meta-analysis. Although the results are broadly similar in suggesting increased risk for breast cancer with HRT use, findings from the new study suggest the risk is lower than had been estimated in the meta-analysis and that the risk diminishes more rapidly after stopping HRT than was suggested by the meta-analysis.
“The publicity surrounding publication of the meta-analysis highlighted unexpectedly high risks and led to a heightened level of concern in some quarters,” Dr. Vinogradova commented. “Our study, based on general population data, has not confirmed any such findings. In general, it showed lower levels of risk and clarified the variability of magnitude within them.”
Dr. Vinogradova said the discrepancy could be related to the fact that the studies were designed differently. The meta-analysis relied on results from 24 studies that were conducted around the world at different periods and included women of different ages and backgrounds. The studies in the meta-analysis used different methods, including questionnaires that relied on women’s memories and therefore could have been biased, she said.
In contrast, the new study analyzed EMR data collected prospectively by general practices in the United Kingdom. The data came from the QResearch and from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) databases, the two largest primary care databases in the United Kingdom, which were linked to hospital, mortality, and cancer registries.
Because this study used a “consistent design” and “consistent data sources,” these new results “are likely to be more accurate and reliable for assessing risks among HRT users,” Dr. Vinogradova commented.
This study used an observational design, so it cannot prove that HRT causes breast cancer. These results may better represent women in the general U.K. population, compared with the earlier meta-analysis, she added.
Commenting on the new study, Michael Jones, PhD, senior staff scientist in genetics and epidemiology at the Institute of Cancer Research, London, also emphasized that it was large and its data came from general practitioner medical records, “so the strong statistical associations are unlikely to be due to chance.
“The results of this study generally confirm what has been seen before and is well established – that the use of combined estrogen plus progestogen HRT is associated with increased risk of breast cancer, and this risk increases with duration of use. But reassuringly, after stopping HRT, the raised risk of breast cancer mostly returns to that seen in nonusers of HRT,” he said.
“It’s important to note that no one study should be considered in isolation,” he added. “Even though some risks were found to be slightly smaller than those reported in another meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence recently published in 2019, women considering use of HRT should still follow advice given to them by their [general practitioners].”
Study details
In the study, researchers evaluated all types of HRT commonly prescribed in the United Kingdom over the past 20 years, including topical estrogen, vaginal pessaries, and creams. They grouped HRT use by recent (within the past 5 years) and past (5 or more years ago) and HRT duration as short term (less than 5 years) and long term (5 years or longer). Results were adjusted for a range of factors that could affect breast cancer risk, including lifestyle, smoking, alcohol consumption, other medical conditions, family history, and use of other prescribed drugs.
The analysis included 98,611 women aged 50-79 years who were first diagnosed with breast cancer between 1998 and 2019. These women were matched by age and general practice to 457,498 women who were not diagnosed with breast cancer over these years. HRT use was reported in 34% (33,703) of women with breast cancer and in 31% (134,391) of women without breast cancer.
Overall, the risk for breast cancer was increased with use of most HRT drugs (adjusted odds ratio, 1.21; 95% confidence, 1.19-1.23), compared with not using HRT drugs. The highest risk was tied to combined estrogen/progestogen HRT (adjusted OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.24-1.29). The lowest risk was tied to estrogen-only HRT (adjusted OR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.03-1.10). Estrogen cream and vaginal estrogen were not associated with increased breast cancer risk.
In general, breast cancer risk was higher among recent HRT users and those receiving long-term therapy. HRT-associated breast cancer risk increased with age and declined after discontinuing treatment. Therapy of less than 1 year was not associated with increased breast cancer risk.
Women who had recently been receiving long-term combined estrogen/progestogen HRT had a 79% increased risk for breast cancer (adjusted OR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.73-1.85), compared with never-users. Among recent long-term users of combined HRT, breast cancer risk was highest for norethisterone (adjusted OR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.79-1.99) and lowest for dydrogesterone (adjusted OR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.03-1.48). Women who had recently been receiving long-term estrogen-only HRT had a 15% increased risk for breast cancer compared to never-users (adjusted OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.09-1.21).
Among women who discontinued HRT 5 or more years ago, risk for breast cancer was no longer increased for long-term estrogen-only therapy and short-term estrogen/progestogen therapy. However, breast cancer risk remained elevated 5 years after discontinuing long-term estrogen/progestogen (adjusted OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.11-1.21).
HRT-associated risk for breast cancer increased with age across all durations of therapy.
Compared with never-use, recent long-term estrogen-only therapy was associated with zero extra breast cancer cases per 10,000 women-years among women aged 50-59 years and eight extra cases per 10,000 women-years among women aged 70-79.
Recent long-term estrogen/progestogen use was associated with 15 extra breast cancer cases among women aged 50-59 and 36 extra cases among women aged 70-79 per 10,000 women-years.
Past long-term estrogen/progestogen use was associated with zero extra breast cancer cases among women aged 50-59 and eight extra cases among women aged 70-79 per 10,000 women-years.
Summarizing, Dr. Vinogradova said the increased risk for breast cancer with HRT appears to be “relatively small, particularly for younger women and for any women who use HRT only for a restricted period.”
Decisions about whether to use HRT and which type to use should depend on symptom severity, patient factors, and suitability of other treatment options, she commented.
“Particularly for those women who our study has shown to be most at risk, these decisions should be made through discussions between the patient and her doctor,” she concluded. “We hope that the new and more detailed information provided by our study will facilitate such prescribing decisions.”
The study was partially funded by the School for Primary Care Research of the National Institute for Health Research, by Cancer Research UK, and by the Cancer Research UK Oxford Center. Dr. Vinogradova has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Senior author Julia Hippisley-Cox is an unpaid director of QResearch and was a paid director of ClinRisk until 2019. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
PET guidance for radiation therapy improves prostate cancer outcomes
The findings were reported in a plenary session at the American Society for Radiation Oncology Annual Meeting 2020.
“Quite frankly, this is an area where we are shooting in the dark with conventional imaging, and that’s where we think molecular imaging has a potential role,” noted coprincipal investigator Ashesh B. Jani, MD, of the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“We hypothesized that radiotherapy outcomes can be improved upon by PET by excluding patients with extrapelvic disease and also by improving treatment field decisions and target definition,” Dr. Jani added.
Patients with prostate cancer were eligible for EMPIRE-1 if they had undergone prostatectomy and had a detectable prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level but negative findings on conventional imaging (a bone scan plus abdominopelvic CT and/or MRI).
A total of 165 patients were randomized to RT guided by the conventional imaging alone or combined with PET imaging using the radiotracer fluciclovine (18F). Treatment decisions in the latter group were strictly based on where uptake was seen.
Study results
The trial’s primary endpoint was treatment failure, defined as a PSA level exceeding 0.2 ng/mL from nadir followed by another rise, a continued PSA rise despite RT, progression on imaging or digital rectal exam, or initiation of systemic therapy.
“Most imaging studies tend to focus on diagnostic accuracy, pathologic correlation, and decision changes. It’s a very high bar for an imaging study to influence failure rates,” Dr. Jani pointed out.
Adding 18F-PET to conventional imaging altered the treatment decision for 35.4% of patients in that group (P < .001). It also significantly altered a range of volumetric and dosimetric parameters.
At a median follow-up of 2.48 years, the 3-year rate of failure-free survival was 63.0% with conventional imaging alone and 75.5% with the addition of 18F-PET (P = .003). The corresponding 4-year rate was 51.2% and 75.5%, respectively (P < .001).
In multivariate analysis, the conventional imaging group had double the risk of failure events relative to the PET group (hazard ratio, 2.04; P = .033).
Provider-reported data showed no significant difference between imaging groups in maximum acute or late genitourinary toxicity and gastrointestinal toxicity. An analysis of patient-reported toxicity data is pending.
“Randomized trials of imaging tests with a primary cancer control endpoint are important but uncommonly done,” Dr. Jani commented. “This is the first such trial of PET over conventional imaging in the postprostatectomy radiotherapy setting.”
“Inclusion of fluciclovine resulted in a significant improvement in failure rate at 3 years. This warrants further investigation,” he maintained.
To that end, the investigators have launched the EMPIRE-2 trial, which is comparing RT guided by 18F-PET with PET using another radiotracer that is not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration, gallium-68 prostate-specific membrane antigen.
Findings in context
“There are several remarkable aspects of the EMPIRE-1 trial worth noting,” said invited discussant Neha Vapiwala, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
She commended the trial’s randomization, given a bias that more imaging is better, and the diversity of its participants that better reflects the general population of prostate cancer patients.
“The study procedures appear to be well tolerated despite a net overall increase in the radiation volume treated in the patients who underwent PET, although we do still await patient-reported toxicity,” Dr. Vapiwala noted. “Finally, a high bar was set, with a clinically meaningful primary endpoint for an imaging study.
“This study ultimately demonstrated that, in the PET arm, better selection with PET was able to result in better patient outcomes,” she maintained.
At the same time, Dr. Vapiwala recommended caution when reducing or withholding definitive local therapy based on PET results, as occurred in 14 patients.
“We must always be able to see the forest from the trees, and when evaluating our patients with PET scans, what we see and what we don’t see is just one piece of the puzzle. Existing level 1 evidence and oncologic principles must still apply,” she said. “While PET can help paint a more complete picture, it should not define the picture itself.”
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jani disclosed advisory board service for Blue Earth Diagnostics. Dr. Vapiwala disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jani A et al. ASTRO 2020, Abstract LBA1.
The findings were reported in a plenary session at the American Society for Radiation Oncology Annual Meeting 2020.
“Quite frankly, this is an area where we are shooting in the dark with conventional imaging, and that’s where we think molecular imaging has a potential role,” noted coprincipal investigator Ashesh B. Jani, MD, of the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“We hypothesized that radiotherapy outcomes can be improved upon by PET by excluding patients with extrapelvic disease and also by improving treatment field decisions and target definition,” Dr. Jani added.
Patients with prostate cancer were eligible for EMPIRE-1 if they had undergone prostatectomy and had a detectable prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level but negative findings on conventional imaging (a bone scan plus abdominopelvic CT and/or MRI).
A total of 165 patients were randomized to RT guided by the conventional imaging alone or combined with PET imaging using the radiotracer fluciclovine (18F). Treatment decisions in the latter group were strictly based on where uptake was seen.
Study results
The trial’s primary endpoint was treatment failure, defined as a PSA level exceeding 0.2 ng/mL from nadir followed by another rise, a continued PSA rise despite RT, progression on imaging or digital rectal exam, or initiation of systemic therapy.
“Most imaging studies tend to focus on diagnostic accuracy, pathologic correlation, and decision changes. It’s a very high bar for an imaging study to influence failure rates,” Dr. Jani pointed out.
Adding 18F-PET to conventional imaging altered the treatment decision for 35.4% of patients in that group (P < .001). It also significantly altered a range of volumetric and dosimetric parameters.
At a median follow-up of 2.48 years, the 3-year rate of failure-free survival was 63.0% with conventional imaging alone and 75.5% with the addition of 18F-PET (P = .003). The corresponding 4-year rate was 51.2% and 75.5%, respectively (P < .001).
In multivariate analysis, the conventional imaging group had double the risk of failure events relative to the PET group (hazard ratio, 2.04; P = .033).
Provider-reported data showed no significant difference between imaging groups in maximum acute or late genitourinary toxicity and gastrointestinal toxicity. An analysis of patient-reported toxicity data is pending.
“Randomized trials of imaging tests with a primary cancer control endpoint are important but uncommonly done,” Dr. Jani commented. “This is the first such trial of PET over conventional imaging in the postprostatectomy radiotherapy setting.”
“Inclusion of fluciclovine resulted in a significant improvement in failure rate at 3 years. This warrants further investigation,” he maintained.
To that end, the investigators have launched the EMPIRE-2 trial, which is comparing RT guided by 18F-PET with PET using another radiotracer that is not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration, gallium-68 prostate-specific membrane antigen.
Findings in context
“There are several remarkable aspects of the EMPIRE-1 trial worth noting,” said invited discussant Neha Vapiwala, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
She commended the trial’s randomization, given a bias that more imaging is better, and the diversity of its participants that better reflects the general population of prostate cancer patients.
“The study procedures appear to be well tolerated despite a net overall increase in the radiation volume treated in the patients who underwent PET, although we do still await patient-reported toxicity,” Dr. Vapiwala noted. “Finally, a high bar was set, with a clinically meaningful primary endpoint for an imaging study.
“This study ultimately demonstrated that, in the PET arm, better selection with PET was able to result in better patient outcomes,” she maintained.
At the same time, Dr. Vapiwala recommended caution when reducing or withholding definitive local therapy based on PET results, as occurred in 14 patients.
“We must always be able to see the forest from the trees, and when evaluating our patients with PET scans, what we see and what we don’t see is just one piece of the puzzle. Existing level 1 evidence and oncologic principles must still apply,” she said. “While PET can help paint a more complete picture, it should not define the picture itself.”
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jani disclosed advisory board service for Blue Earth Diagnostics. Dr. Vapiwala disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jani A et al. ASTRO 2020, Abstract LBA1.
The findings were reported in a plenary session at the American Society for Radiation Oncology Annual Meeting 2020.
“Quite frankly, this is an area where we are shooting in the dark with conventional imaging, and that’s where we think molecular imaging has a potential role,” noted coprincipal investigator Ashesh B. Jani, MD, of the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“We hypothesized that radiotherapy outcomes can be improved upon by PET by excluding patients with extrapelvic disease and also by improving treatment field decisions and target definition,” Dr. Jani added.
Patients with prostate cancer were eligible for EMPIRE-1 if they had undergone prostatectomy and had a detectable prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level but negative findings on conventional imaging (a bone scan plus abdominopelvic CT and/or MRI).
A total of 165 patients were randomized to RT guided by the conventional imaging alone or combined with PET imaging using the radiotracer fluciclovine (18F). Treatment decisions in the latter group were strictly based on where uptake was seen.
Study results
The trial’s primary endpoint was treatment failure, defined as a PSA level exceeding 0.2 ng/mL from nadir followed by another rise, a continued PSA rise despite RT, progression on imaging or digital rectal exam, or initiation of systemic therapy.
“Most imaging studies tend to focus on diagnostic accuracy, pathologic correlation, and decision changes. It’s a very high bar for an imaging study to influence failure rates,” Dr. Jani pointed out.
Adding 18F-PET to conventional imaging altered the treatment decision for 35.4% of patients in that group (P < .001). It also significantly altered a range of volumetric and dosimetric parameters.
At a median follow-up of 2.48 years, the 3-year rate of failure-free survival was 63.0% with conventional imaging alone and 75.5% with the addition of 18F-PET (P = .003). The corresponding 4-year rate was 51.2% and 75.5%, respectively (P < .001).
In multivariate analysis, the conventional imaging group had double the risk of failure events relative to the PET group (hazard ratio, 2.04; P = .033).
Provider-reported data showed no significant difference between imaging groups in maximum acute or late genitourinary toxicity and gastrointestinal toxicity. An analysis of patient-reported toxicity data is pending.
“Randomized trials of imaging tests with a primary cancer control endpoint are important but uncommonly done,” Dr. Jani commented. “This is the first such trial of PET over conventional imaging in the postprostatectomy radiotherapy setting.”
“Inclusion of fluciclovine resulted in a significant improvement in failure rate at 3 years. This warrants further investigation,” he maintained.
To that end, the investigators have launched the EMPIRE-2 trial, which is comparing RT guided by 18F-PET with PET using another radiotracer that is not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration, gallium-68 prostate-specific membrane antigen.
Findings in context
“There are several remarkable aspects of the EMPIRE-1 trial worth noting,” said invited discussant Neha Vapiwala, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
She commended the trial’s randomization, given a bias that more imaging is better, and the diversity of its participants that better reflects the general population of prostate cancer patients.
“The study procedures appear to be well tolerated despite a net overall increase in the radiation volume treated in the patients who underwent PET, although we do still await patient-reported toxicity,” Dr. Vapiwala noted. “Finally, a high bar was set, with a clinically meaningful primary endpoint for an imaging study.
“This study ultimately demonstrated that, in the PET arm, better selection with PET was able to result in better patient outcomes,” she maintained.
At the same time, Dr. Vapiwala recommended caution when reducing or withholding definitive local therapy based on PET results, as occurred in 14 patients.
“We must always be able to see the forest from the trees, and when evaluating our patients with PET scans, what we see and what we don’t see is just one piece of the puzzle. Existing level 1 evidence and oncologic principles must still apply,” she said. “While PET can help paint a more complete picture, it should not define the picture itself.”
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jani disclosed advisory board service for Blue Earth Diagnostics. Dr. Vapiwala disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jani A et al. ASTRO 2020, Abstract LBA1.
FROM ASTRO 2020
Single and multifraction SBRT found comparable for lung metastases
This was among key findings of a randomized, phase 2 trial reported at the American Society for Radiation Oncology Annual Meeting 2020.
“Most patients [with lung metastases] are treated with lifelong anticancer drug therapy only, with little prospect for long-term cancer control,” investigator Shankar Siva, MBBS, PhD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, said in a news briefing.
“However, some patients may have limited spread to the lungs and may be suitable for either surgery, which is an invasive approach, or SBRT, which is a noninvasive approach, with the aim to prolong long-term cancer control,” he added.
Patients and treatment
Dr. Siva and colleagues enrolled in their phase 2 trial (SAFRON II/TROG 13.01) 90 patients from 13 centers in Australia and New Zealand.
All patients had one to three lung metastases (from nonhematologic malignancies) that measured up to 5 cm in diameter and were located in the periphery.
The most common primaries were colorectal cancer (47%), lung cancer (11%), and kidney cancer (10%). The trial required that all primary and extrathoracic disease had been definitively treated.
The patients were randomized evenly to lung SBRT delivered with a single-fraction regimen (28 Gy in one fraction) or a multifraction regimen (48 Gy in four fractions) that netted the same biological equivalent dose.
Safety and efficacy
The two treatment groups did not differ significantly with respect to any-grade toxicities at 1 year, with the exception of higher rates of esophagitis and radiation dermatitis in the multifraction group, Dr. Siva reported.
The rate of grade 3 or worse toxicity at 1 year – the trial’s primary endpoint – was 5% with the single fraction and 3% with multiple fractions, with overlapping 80% confidence intervals, meeting the prespecified endpoint for acceptable toxicity.
The single-fraction group had two grade 3 events that resolved with intervention and no grade 4-5 events. The multifraction group had a single grade 5 event (fatal pneumonitis in a patient with underlying interstitial lung disease) and no grade 3-4 events.
The single-fraction and multifraction groups were also similar at 1 year on rates of freedom from local failure (93% and 95%, respectively), disease-free survival (59% and 60%, respectively), and overall survival (95% and 93%, respectively), with overlapping 95% CIs for each outcome.
Analyses of quality of life and cost-effectiveness are ongoing.
Applying the results: Useful in a pandemic?
“Single-session SBRT is safe, convenient, and noninvasive, and appears to be effective, to date, for lung secondaries. This approach may be considered as a one-stop, knockout type of approach for patients who have one to three metastases to the lung,” Dr. Siva proposed.
“These findings may have implications for treatment selection in a resource-constrained environment, such as the current global pandemic, when trying to reduce footfall or thoroughfare within a radiotherapy department, and it’s quite a convenient approach for patients,” he added.
“Stereotactic radiation has an obvious advantage over conventional radiation in several ways and may have a special advantage in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic to reduce exposure to patients and our hospital personnel,” agreed news briefing moderator Sue S. Yom, MD, PhD, of the University of California, San Francisco.
However, use of stereotactic techniques remains controversial because they require technical precision and additional resources for planning and quality assurance, and they are often more expensive than conventional radiation therapy, she noted. Therefore, there must be evidence to justify their use in a palliative or metastatic setting.
The current trial is noteworthy for pushing the SBRT efficiency envelope, according to Dr. Yom.
“These findings are going to be confirmed by the study team with further follow-up at 3 years,” she pointed out. “If the findings of this study are maintained, it shows that patients with up to three metastatic tumors in the lung can have their treatment given in an extremely efficient manner over one session, which saves them time and hospital resources, and could be very significant to patients’ quality of life.”
The trial is sponsored by the Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group and the Australasian Lung Cancer Trials Group. Dr. Siva disclosed relationships with Varian Industries, Merck, AstraZeneca, Bayer Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Meyers Squibb, and Reflexion. Dr. Yom disclosed no relevant conflicts.
SOURCE: Siva S et al. ASTRO 2020, Abstract 5.
This was among key findings of a randomized, phase 2 trial reported at the American Society for Radiation Oncology Annual Meeting 2020.
“Most patients [with lung metastases] are treated with lifelong anticancer drug therapy only, with little prospect for long-term cancer control,” investigator Shankar Siva, MBBS, PhD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, said in a news briefing.
“However, some patients may have limited spread to the lungs and may be suitable for either surgery, which is an invasive approach, or SBRT, which is a noninvasive approach, with the aim to prolong long-term cancer control,” he added.
Patients and treatment
Dr. Siva and colleagues enrolled in their phase 2 trial (SAFRON II/TROG 13.01) 90 patients from 13 centers in Australia and New Zealand.
All patients had one to three lung metastases (from nonhematologic malignancies) that measured up to 5 cm in diameter and were located in the periphery.
The most common primaries were colorectal cancer (47%), lung cancer (11%), and kidney cancer (10%). The trial required that all primary and extrathoracic disease had been definitively treated.
The patients were randomized evenly to lung SBRT delivered with a single-fraction regimen (28 Gy in one fraction) or a multifraction regimen (48 Gy in four fractions) that netted the same biological equivalent dose.
Safety and efficacy
The two treatment groups did not differ significantly with respect to any-grade toxicities at 1 year, with the exception of higher rates of esophagitis and radiation dermatitis in the multifraction group, Dr. Siva reported.
The rate of grade 3 or worse toxicity at 1 year – the trial’s primary endpoint – was 5% with the single fraction and 3% with multiple fractions, with overlapping 80% confidence intervals, meeting the prespecified endpoint for acceptable toxicity.
The single-fraction group had two grade 3 events that resolved with intervention and no grade 4-5 events. The multifraction group had a single grade 5 event (fatal pneumonitis in a patient with underlying interstitial lung disease) and no grade 3-4 events.
The single-fraction and multifraction groups were also similar at 1 year on rates of freedom from local failure (93% and 95%, respectively), disease-free survival (59% and 60%, respectively), and overall survival (95% and 93%, respectively), with overlapping 95% CIs for each outcome.
Analyses of quality of life and cost-effectiveness are ongoing.
Applying the results: Useful in a pandemic?
“Single-session SBRT is safe, convenient, and noninvasive, and appears to be effective, to date, for lung secondaries. This approach may be considered as a one-stop, knockout type of approach for patients who have one to three metastases to the lung,” Dr. Siva proposed.
“These findings may have implications for treatment selection in a resource-constrained environment, such as the current global pandemic, when trying to reduce footfall or thoroughfare within a radiotherapy department, and it’s quite a convenient approach for patients,” he added.
“Stereotactic radiation has an obvious advantage over conventional radiation in several ways and may have a special advantage in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic to reduce exposure to patients and our hospital personnel,” agreed news briefing moderator Sue S. Yom, MD, PhD, of the University of California, San Francisco.
However, use of stereotactic techniques remains controversial because they require technical precision and additional resources for planning and quality assurance, and they are often more expensive than conventional radiation therapy, she noted. Therefore, there must be evidence to justify their use in a palliative or metastatic setting.
The current trial is noteworthy for pushing the SBRT efficiency envelope, according to Dr. Yom.
“These findings are going to be confirmed by the study team with further follow-up at 3 years,” she pointed out. “If the findings of this study are maintained, it shows that patients with up to three metastatic tumors in the lung can have their treatment given in an extremely efficient manner over one session, which saves them time and hospital resources, and could be very significant to patients’ quality of life.”
The trial is sponsored by the Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group and the Australasian Lung Cancer Trials Group. Dr. Siva disclosed relationships with Varian Industries, Merck, AstraZeneca, Bayer Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Meyers Squibb, and Reflexion. Dr. Yom disclosed no relevant conflicts.
SOURCE: Siva S et al. ASTRO 2020, Abstract 5.
This was among key findings of a randomized, phase 2 trial reported at the American Society for Radiation Oncology Annual Meeting 2020.
“Most patients [with lung metastases] are treated with lifelong anticancer drug therapy only, with little prospect for long-term cancer control,” investigator Shankar Siva, MBBS, PhD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, said in a news briefing.
“However, some patients may have limited spread to the lungs and may be suitable for either surgery, which is an invasive approach, or SBRT, which is a noninvasive approach, with the aim to prolong long-term cancer control,” he added.
Patients and treatment
Dr. Siva and colleagues enrolled in their phase 2 trial (SAFRON II/TROG 13.01) 90 patients from 13 centers in Australia and New Zealand.
All patients had one to three lung metastases (from nonhematologic malignancies) that measured up to 5 cm in diameter and were located in the periphery.
The most common primaries were colorectal cancer (47%), lung cancer (11%), and kidney cancer (10%). The trial required that all primary and extrathoracic disease had been definitively treated.
The patients were randomized evenly to lung SBRT delivered with a single-fraction regimen (28 Gy in one fraction) or a multifraction regimen (48 Gy in four fractions) that netted the same biological equivalent dose.
Safety and efficacy
The two treatment groups did not differ significantly with respect to any-grade toxicities at 1 year, with the exception of higher rates of esophagitis and radiation dermatitis in the multifraction group, Dr. Siva reported.
The rate of grade 3 or worse toxicity at 1 year – the trial’s primary endpoint – was 5% with the single fraction and 3% with multiple fractions, with overlapping 80% confidence intervals, meeting the prespecified endpoint for acceptable toxicity.
The single-fraction group had two grade 3 events that resolved with intervention and no grade 4-5 events. The multifraction group had a single grade 5 event (fatal pneumonitis in a patient with underlying interstitial lung disease) and no grade 3-4 events.
The single-fraction and multifraction groups were also similar at 1 year on rates of freedom from local failure (93% and 95%, respectively), disease-free survival (59% and 60%, respectively), and overall survival (95% and 93%, respectively), with overlapping 95% CIs for each outcome.
Analyses of quality of life and cost-effectiveness are ongoing.
Applying the results: Useful in a pandemic?
“Single-session SBRT is safe, convenient, and noninvasive, and appears to be effective, to date, for lung secondaries. This approach may be considered as a one-stop, knockout type of approach for patients who have one to three metastases to the lung,” Dr. Siva proposed.
“These findings may have implications for treatment selection in a resource-constrained environment, such as the current global pandemic, when trying to reduce footfall or thoroughfare within a radiotherapy department, and it’s quite a convenient approach for patients,” he added.
“Stereotactic radiation has an obvious advantage over conventional radiation in several ways and may have a special advantage in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic to reduce exposure to patients and our hospital personnel,” agreed news briefing moderator Sue S. Yom, MD, PhD, of the University of California, San Francisco.
However, use of stereotactic techniques remains controversial because they require technical precision and additional resources for planning and quality assurance, and they are often more expensive than conventional radiation therapy, she noted. Therefore, there must be evidence to justify their use in a palliative or metastatic setting.
The current trial is noteworthy for pushing the SBRT efficiency envelope, according to Dr. Yom.
“These findings are going to be confirmed by the study team with further follow-up at 3 years,” she pointed out. “If the findings of this study are maintained, it shows that patients with up to three metastatic tumors in the lung can have their treatment given in an extremely efficient manner over one session, which saves them time and hospital resources, and could be very significant to patients’ quality of life.”
The trial is sponsored by the Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group and the Australasian Lung Cancer Trials Group. Dr. Siva disclosed relationships with Varian Industries, Merck, AstraZeneca, Bayer Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Meyers Squibb, and Reflexion. Dr. Yom disclosed no relevant conflicts.
SOURCE: Siva S et al. ASTRO 2020, Abstract 5.
FROM ASTRO 2020