User login
AVAHO
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]


Longitudinal Dynamic in Weight Loss Impacts Clinical Outcomes for Veterans Undergoing Curative Surgery for Colorectal Cancer
In patients with gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies, malnutrition is common. In addition, it has various negative implications, including high risk for surgical complications, prolonged hospitalization, decreased quality of life (QOL), increased mortality, and poor tolerance for treatments such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy.1
A 2014 French study of 1903 patients hospitalized for cancer reported a 39% overall prevalence of malnutrition; 39% in patients with cancers of the colon/rectum, 60% for pancreatic cancer, and 67% for cancers of the esophagus/stomach.2 Malnutrition was defined as body mass index (BMI) < 18.5 for individuals aged < 75 years or BMI < 21 for individuals aged ≥ 75 years, and/or weight loss > 10% since disease onset. Malnutrition also was strongly associated with worsened performance status.
The etiology of malnutrition in GI cancers is often multifactorial. It includes systemic tumor effects, such as inflammatory mediators contributing to hypermetabolism and cachexia, local tumor-associated mechanical obstruction, GI toxicities caused by antineoplastic therapy or other medications, and psychological factors that contribute to anorexia.3 Patient-related risk factors such as older age, other chronic diseases, and history of other GI surgeries also play a role.1
Other studies have demonstrated that malnutrition in patients with GI malignancies undergoing surgical resection is associated with high rates of severe postoperative complications, increased length of stay (LOS) and time on a ventilator for patients treated in the intensive care unit, and poor QOL in the postoperative survival period.4-6 Several randomized controlled trials conducted in patients with GI cancers have shown that enteral and parenteral nutrition supplementations in the perioperative period improve various outcomes, such as reduction of postoperative complication rates, fewer readmissions, improved chemotherapy tolerance, and improved QOL.7-10 Thus, in the management of patients with GI malignancies, it is highly important to implement early nutritional screening and establish a diagnosis of malnutrition to intervene and reduce postoperative morbidity and mortality.1
However, tools and predictors of malnutrition are often imperfect. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (AND/ASPEN) weight-based criteria define malnutrition and nutritionally-at-risk as BMI < 18.5, involuntary loss of at least 10% of body weight within 6 months or 5% within 1 month, or loss of 10 lb within 6 months.11 While the ASPEN criteria are often used to define malnourishment, they may not fully capture the population at risk, and there does not exist a gold-standard tool for nutritional screening. A 2002 study that performed a critical appraisal of 44 nutritional screening tools found that no single tool was fully sufficient for application, development, evaluation, and consistent screening.12 As such, consistently screening for malnutrition to target interventions in the perioperative period for GI surgical oncology has been challenging.13 More recent tools such as the perioperative nutrition screen (PONS) have been validated as rapid, effective screening tools to predict postoperative outcomes.14 Additionally, implementation of perioperative nutritional protocols, such as enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) in colon cancer (CC) surgery, also has shown improved perioperative care and outcomes.15
Preoperative nutritional interventions have been implemented in practice and have focused mostly on the immediate perioperative period. This has been shown to improve surgical outcomes. The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) provides comprehensive care to patients in a single-payer system, allowing for capture of perioperative data and the opportunity for focused preoperative interventions to improve outcomes.
Methods
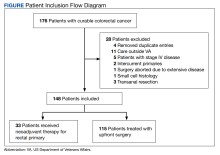
This was a retrospective record review of colorectal malignancies treated with curative intent at the Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in Michigan between January 1, 2015, and December 31, 2019. We examined nutritional status, degree of longitudinal weight loss, and subsequent clinical outcomes, including delayed postoperative recovery and delays in chemotherapy in 115 patients with CC and 33 patients with rectal cancer (RC) undergoing curative surgical resection at VAAAHS. To avoid additional confounding effects of advanced cancer, only early-stage, curable disease was included. This study was approved by the VAAAHS Institutional Review Board.
Patients with postoperative follow-up outside of VAAAHS were excluded. Patients were excluded if their surgery had noncurative intent or if they had distant metastatic disease. Data on patient weights, laboratory results, nutrition consultations, postoperative complications, delayed recovery, readmissions, and chemotherapy tolerance were abstracted by patient chart review in the VHA Computerized Patient Record System and Joint Legacy Viewer by 2 researchers.
Delayed recovery was defined as any abnormal clinical development described in inpatient progress notes, outpatient follow-up notes within 60 days, or in hospital discharge summaries. Excluded were psychiatric events without additional medical complications, postoperative bleeding not requiring an invasive intervention, urinary retention, postoperative glycemic control difficulties, cardiac events that happened before postoperative hospital discharge and not requiring readmission, and postoperative alcohol withdrawal. Complications were defined similarly to delayed recovery but excluded isolated prolonged postoperative ileus. LOS was defined in days as time from admission to discharge.
Adjuvant management course was derived from reviewing documentation from medical oncology consultations and progress notes. In patients for whom adjuvant chemotherapy was indicated and prescribed, chemotherapy was considered complete if chemotherapy was started and completed as indicated. Adjuvant chemotherapy was considered incomplete if the patient declined chemotherapy, if chemotherapy was not started when indicated, or if chemotherapy was not completed as indicated. Neoadjuvant therapy data were abstracted from medical and radiation oncology notes.
Recorded data were collected on both weight and BMI. Weights were extracted as follows: Weight 1 year before time of diagnosis, ± 4 months; weight 6 months before diagnosis ± 3 months; weight at time of diagnosis ± 2 weeks; weight at time of surgery ± 2 weeks; weight 30 days postsurgery ± 2 weeks; weight 60 days postsurgery ± 2 weeks; weight 1 year postsurgery ± 4 months. Mean percent change in weight was calculated from recorded weights between each allocated time point. A weight loss of ≥ 3% was found to be clinically relevant and was chosen as the minimal cutoff value when analyzing outcomes associated with weight trends.
Nutrition consultations were abstracted as follows: Preoperative nutrition consultations were defined as occurring between time of cancer diagnosis and surgery in either the inpatient or outpatient setting; inpatient postoperative nutrition consultations occurred during admission for surgery; readmission nutrition consultations occurred on readmission in inpatient setting, if applicable; outpatient postoperative nutrition consultations were defined as occurring up to 2 months postdischarge in the outpatient setting.
Albumin values were extracted as follows: Preoperative albumin levels were defined as up to 4 months prior to diagnosis, and postoperative albumin levels were defined as 2 to 6 months after surgery.
Analysis
The data were described using mean (SD) for continuous variables and number and percentages for categorical variables. Where appropriate, Fisher exact test, Pearson χ2 test, Spearman ρ, and Mann-Whitney U test were used for tests of significance. SAS (SAS Institute) was utilized for multivariable analysis. The significance level was P = .05 for all tests.
Results
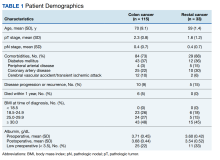
There were 115 patients in the CC cohort and 33 in the RC cohort. The mean (SD) age at diagnosis was 70 (9.1) for CC group and 59 (1.4) for RC group (Table 1).
Weight Trends
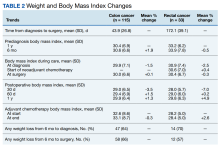
From 1 year to 6 months before diagnosis, 40 of 80 patients lost weight in the CC cohort (mean change, +1.9%) and 6 of 22 patients lost weight in the RC cohort (mean change, + 0.5%). From 6 months before diagnosis to time of diagnosis, 47 of 74 patients lost weight in the CC cohort (mean change, -1.5%) and 14 of 21 patients lost weight in the RC cohort (mean change, -2.5%). From time of diagnosis to time of surgery, 36 of 104 patients with CC and 14 of 32 patients with RC lost weight with a mean weight change of and +0.1% and -0.3%, respectively. In the 6 months before surgery, any amount of weight loss was observed in 58 patients (66%) in the CC group and in 12 patients (57%) in the RC group. In this time frame, in the CC cohort, 32 patients (36%) were observed to have at least 3% weight loss, and 23 (26%) were observed to have at least 5% weight loss (Table 3).
In patients who completed adjuvant chemotherapy in the CC group, mean (SD) BMI at the beginning and end of chemotherapy was 32.6 (8.6) and 33.1 (8.7), respectively, and a -0.3% mean change in weight was observed. In the RC group, mean (SD) BMI was 28.2 (5.0) at the initiation of adjuvant chemotherapy and 28.4 (5.0) at its completion, with a +2.6% mean change in weight.
In the immediate postoperative period, most patients were losing weight in both the CC and RC groups (mean, -3.5% and -7.0% at 1 month postoperative, respectively). At 1-year after surgery, patients had modest mean increases in weight: +1.3% for patients with CC and +4.9% for patients with RC.
A relatively large proportion of patients had missing data on weights at various data points (Table 4).
Nutrition Consultations
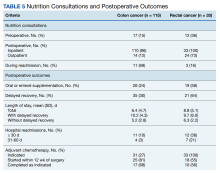
In the CC group, preoperative nutrition consultations (either inpatient or outpatient) occurred in 17 patients (15%). Inpatient postoperative nutrition evaluations occurred in 110 patients (96%) (Table 5).
In the RC group, preoperative inpatient or outpatient nutrition consultations occurred in 12 patients (36%). Eight of those occurred before initiation of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. All 33 patients received an inpatient postoperative nutrition evaluation during admission. Oral or enteral nutrition supplements were prescribed 19 times (58%). Postoperative outpatient nutrition consultations occurred for 24 patients (73%). Of the 19 patients who were readmitted to the hospital, 3 (16%) had a nutrition reconsultation on readmission.
Outcomes
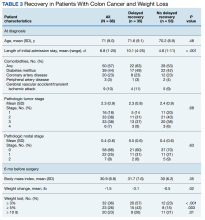
The primary outcomes observed were delayed recovery, hospital readmission and LOS, and completion of adjuvant chemotherapy as indicated. Delayed recovery was observed in 35 patients with CC (40%) and 21 patients with RC (64%). Multivariable analysis in the CC cohort demonstrated that weight change was significantly associated with delayed recovery. Among those with ≥ 3% weight loss in the 6-month preoperative period (the weight measurement 6 months prior to diagnosis to date of surgery), 20 patients (63%) had delayed recovery compared with 15 patients (27%) without ≥ 3% weight loss who experienced delayed recovery (χ2 = 10.84; P < .001).
Weight loss of ≥ 3% in the 6-month preoperative period also was significantly associated with complications. Of patients with at least 3% preoperative weight loss, 16 (50%) experienced complications, while 8 (14%) with < 3% preoperative weight loss experienced complications (χ2 = 11.20; P < .001). Notably, ≥ 3% weight loss in the 1-year preoperative period before surgery was not significantly associated with delayed recovery. Any degree of 30-day postoperative weight loss was not correlated with delayed recovery. Finally, low preoperative albumin also was not correlated with delayed recovery (Fisher exact; P = .13). Table 3 displays differences based on presence of delayed recovery in the 88 patients with CC 6 months before surgery. Of note, ≥ 10-lb weight loss in the 6 months preceding surgery also correlated with delayed recovery (P = .01).In our cohort, 3% weight loss over 6 months had a sensitivity of 57%, specificity of 77%, positive predictive value 63%, and negative predictive value 73% for delayed recovery. By comparison, a 10-lb weight loss in 6 months per ASPEN criteria had a sensitivity of 40%, specificity of 85%, positive predictive value 64%, and negative predictive value 68% for delayed recovery.
Hospital Readmissions and LOS
Hospital readmissions occurred within the first 30 days in 11 patients (10%) in the CC cohort and 12 patients (36%) in the RC cohort. Readmissions occurred between 31 and 60 days in 4 (3%) and 7 (21%) of CC and RC cohorts, respectively. The presence of ≥ 3% weight loss in the 6-month
Mean (SD) LOS was 6.4 (4.7) days (range, 1-28) for patients with CC and 8.8 (5.1) days (range, 3-23) for patients with RC. Mean (SD) LOS increased to 10.2 (4.3) days and 9.7 (6.0) days in patients with delayed recovery in the CC and RC cohorts, respectively. The mean (SD) LOS was 5.2 (2.8) days and 6.3 (2.2) days in patients without delayed recovery in the CC and RC cohorts, respectively. There was no significant difference when examining association between percent weight change and LOS for either initial admission (rs = -0.1409; 2-tailed P = .19) or for initial and readmission combined (rs = -0.13532; 2-tailed P = .21) within the CC cohort.
Chemotherapy
Within the CC cohort, 31 patients (27%) had an indication for adjuvant chemotherapy. Of these, 25 of 31 (81%) started chemotherapy within 12 weeks of surgical resection, and of these, 17 of 25 patients (68%) completed chemotherapy as indicated. Within the RC cohort all 33 patients had an indication for adjuvant chemotherapy, of these 18 of 33 patients (55%) began within 12 weeks of surgical resection, and 10 of 18 (56%) completed chemotherapy as indicated.
Among the CC cohort who began but did not complete adjuvant chemotherapy, there was no significant association between completion of chemotherapy and
Discussion
This study highlights several important findings. There were no patients in our cohort that met ASPEN malnourishment criteria with a BMI < 18.5. Twenty percent of patients lost at least 10 lb in 6 months before the operation. Notably, patients had significant associations with adverse outcomes with less pronounced weight loss than previously noted. As has been established previously, malnourishment can be difficult to screen for, and BMI also is often an imprecise tool.12 In the CC cohort, weight loss
Our findings imply that the effects of even mild malnutrition are even more profound than previously thought. Significantly, this applies to overweight and obese patients as well, as these constituted a significant fraction of our cohort. A finding of ≥ 3% weight loss at the time of CC diagnosis may provide an opportunity for a focused nutrition intervention up to the time of surgery. Second, although nutrition consultation was frequent in the inpatient setting during the hospital admission (96%-100%), rates of nutrition evaluation were as low as 15% before surgery and 12% after surgery, representing a key area for improvement and focused intervention. An optimal time for intervention and nutrition prehabilitation would be at time of diagnosis before surgery with plans for continued aggressive monitoring and subsequent follow-up. Our finding seems to provide a more sensitive tool to identify patients at risk for delayed recovery compared with the ASPEN-driven assessment. Given the simplicity and the clinical significance, our test consisting of 3% weight loss over 6 months, with its sensitivity of 57%, may be superior to the ASPEN 10-lb weight loss, with its sensitivity of 40% in our cohort.
Previous Studies
Our findings are consistent with previous studies that have demonstrated that perioperative weight loss and malnutrition are correlated with delayed recovery and complications, such as wound healing, in patients with GI cancer.2,4,5,8 In a retrospective study of more than 7000 patients with CC, those who were overweight or obese were found to have an improved overall survival compared with other BMI categories, and those who were underweight had an increased 30-day mortality and postoperative complications.16
In another retrospective study of 3799 patients with CC, those who were overweight and obese had an improved 5-year survival rate compared with patients whose weight was normal or underweight. Outcomes were found to be stage dependent.17 In this study cohort, all patients were either overweight or obese and remained in that category even with weight loss. This may have contributed to overall improved outcomes.
Implications and Next Steps
Our study has several implications. One is that BMI criteria < 18.5 may not be a good measure for malnutrition given that about 75% of the patients in our cohort were overweight or obese and none were underweight. We also show a concrete, easily identifiable finding of percent weight change that could be addressed as an automated electronic notification and potentially identify a patient at risk and serve as a trigger for both timely and early nutrition intervention. It seems to be more sensitive than the ASPEN criterion of 10-lb weight loss in 6 months before surgery. Sensitivity is especially appealing given the ease and potential of embedding this tool in an electronic health record and the clinical importance of the consequent intervention. Preoperative as opposed to perioperative nutrition optimization at time of CC diagnosis is essential, as it may help improve postsurgical outcomes as well as oncologic outcomes, including completion of adjuvant chemotherapy. Finally, although our study found that rates of inpatient postoperative nutrition consultation were high, rates of outpatient nutrition consultation in the preoperative period were low. This represents a missed opportunity for intervention before surgery. Similarly, rates of postoperative nutrition follow-up period were low, which points to an area for improvement in longitudinal and holistic care.
We suggest modifications to nutrition intervention protocols, such as ERAS, which should start at the time of GI malignancy diagnosis.18 Other suggestions include standard involvement of nutritionists in inpatient and outpatient settings with longitudinal follow-up in the preoperative and postoperative periods and patient enrollment in a nutrition program with monitoring at time of diagnosis at the VHA. Our findings as well as previous literature suggest that the preoperative period is the most important time to intervene with regard to nutrition optimization and represents an opportunity for intensive prehabilitation. Future areas of research include incorporating other important measures of malnourishment independent of BMI into future study designs, such as sarcopenia and adipose tissue density, to better assess body composition and predict prognostic risk in CC.18,19
Strengths and Limitations
This study is limited by its single-center, retrospective design and small sample sizes, and we acknowledge the limitations of our data set. However, the strength of this VHA-based study is that the single-payer system allows for complete capture of perioperative data as well as the opportunity for focused preoperative interventions to improve outcomes. To our knowledge, there is no currently existing literature on improving nutrition protocols at the VHA for patients with a GI malignancy. These retrospective data will help inform current gaps in quality improvement and supportive oncology as it relates to optimizing malnourishment in veterans undergoing surgical resection for their cancer.
Conclusions
In the CC cohort, weight loss of ≥ 3% from 6 months prior to time of surgery was significantly associated with delayed recovery, complications, and hospital readmissions. Our findings suggest that patients with CC undergoing surgery may benefit from an intensive, early nutrition prehabilitation. Preoperative nutrition optimization may help improve postsurgical outcomes as well as oncologic outcomes, including completion of adjuvant chemotherapy. Further research would be able to clarify these hypotheses.
1. Benoist S, Brouquet A. Nutritional assessment and screening for malnutrition. J Visc Surg. 2015;152:S3-S7. doi:10.1016/S1878-7886(15)30003-5
2. Hébuterne X, Lemarié E, Michallet M, de Montreuil CB, Schneider SM, Goldwasser F. Prevalence of malnutrition and current use of nutrition support in patients with cancer. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2014;38(2):196-204. doi:10.1177/0148607113502674
3. Van Cutsem E, Arends J. The causes and consequences of cancer-associated malnutrition. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2005;9:S51-S63. doi:10.1016/j.ejon.2005.09.007
4. Nishiyama VKG, Albertini SM, de Moraes CMZG, et al. Malnutrition and clinical outcomes in surgical patients with colorectal disease. Arq Gastroenterol. 2018;55(4):397-402. doi:10.1590/s0004-2803.201800000-85
5. Shpata V, Prendushi X, Kreka M, Kola I, Kurti F, Ohri I. Malnutrition at the time of surgery affects negatively the clinical outcome of critically ill patients with gastrointestinal cancer. Med Arch Sarajevo Bosnia Herzeg. 2014;68(4):263-267. doi:10.5455/medarh.2014.68.263-267
6. Lim HS, Cho GS, Park YH, Kim SK. Comparison of quality of life and nutritional status in gastric cancer patients undergoing gastrectomies. Clin Nutr Res. 2015;4(3):153-159. doi:10.7762/cnr.2015.4.3.153
7. Bozzetti F, Gavazzi C, Miceli R, et al. Perioperative total parenteral nutrition in malnourished, gastrointestinal cancer patients: a randomized, clinical trial. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2000;24(1):7-14. doi:10.1177/014860710002400107
8. Bozzetti F, Gianotti L, Braga M, Di Carlo V, Mariani L. Postoperative complications in gastrointestinal cancer patients: the joint role of the nutritional status and the nutritional support. Clin Nutr. 2007;26(6):698-709. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2007.06.009
9. Bozzetti F, Braga M, Gianotti L, Gavazzi C, Mariani L. Postoperative enteral versus parenteral nutrition in malnourished patients with gastrointestinal cancer: a randomised multicentre trial. Lancet. 2001; 358(9292):1487-1492. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06578-3
10. Meng Q, Tan S, Jiang Y, et al. Post-discharge oral nutritional supplements with dietary advice in patients at nutritional risk after surgery for gastric cancer: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr Edinb Scotl. 2021;40(1):40-46. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2020.04.043 start
11. White JV, Guenter P, Jensen G, Malone A, Schofield M. Consensus statement of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics/American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: characteristics recommended for the identification and documentation of adult malnutrition (undernutrition). J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012;112(5):730-738. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2012.03.012
12. Jones JM. The methodology of nutritional screening and assessment tools. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2002;15(1):59-71. doi:10.1046/j.1365-277X.2002.00327.x
13. Williams J, Wischmeyer P. Assessment of perioperative nutrition practices and attitudes—a national survey of colorectal and GI surgical oncology programs. Am J Surg. 2017;213(6):1010-1018. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2016.10.008
14. Williams DG, Aronson S, Murray S, et al. Validation of the perioperative nutrition screen for prediction of postoperative outcomes. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2022;46(6):1307-1315. doi:10.1002/jpen.2310
15. Besson AJ, Kei C, Djordjevic A, Carter V, Deftereos I, Yeung J. Does implementation of and adherence to enhanced recovery after surgery improve perioperative nutritional management in colorectal cancer surgery? ANZ J Surg. 2022;92(6):1382-1387. doi:10.1111/ans.17599
16. Arkenbosch JHC, van Erning FN, Rutten HJ, Zimmerman D, de Wilt JHW, Beijer S. The association between body mass index and postoperative complications, 30-day mortality and long-term survival in Dutch patients with colorectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol J Eur Soc Surg Oncol Br Assoc Surg Oncol. 2019;45(2):160-166. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2018.09.012
17. Shahjehan F, Merchea A, Cochuyt JJ, Li Z, Colibaseanu DT, Kasi PM. Body mass index and long-term outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer. Front Oncol. 2018;8:620. doi:10.3389/fonc.2018.00620
18. Nishigori T, Obama K, Sakai Y. Assessment of body composition and impact of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in patients with gastric cancer. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5:22. doi:10.21037/tgh.2019.10.13
19. Feliciano EMC, Winkels RM, Meyerhardt JA, Prado CM, Afman LA, Caan BJ. Abdominal adipose tissue radiodensity is associated with survival after colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021;114(6):1917-1924. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab285
In patients with gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies, malnutrition is common. In addition, it has various negative implications, including high risk for surgical complications, prolonged hospitalization, decreased quality of life (QOL), increased mortality, and poor tolerance for treatments such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy.1
A 2014 French study of 1903 patients hospitalized for cancer reported a 39% overall prevalence of malnutrition; 39% in patients with cancers of the colon/rectum, 60% for pancreatic cancer, and 67% for cancers of the esophagus/stomach.2 Malnutrition was defined as body mass index (BMI) < 18.5 for individuals aged < 75 years or BMI < 21 for individuals aged ≥ 75 years, and/or weight loss > 10% since disease onset. Malnutrition also was strongly associated with worsened performance status.
The etiology of malnutrition in GI cancers is often multifactorial. It includes systemic tumor effects, such as inflammatory mediators contributing to hypermetabolism and cachexia, local tumor-associated mechanical obstruction, GI toxicities caused by antineoplastic therapy or other medications, and psychological factors that contribute to anorexia.3 Patient-related risk factors such as older age, other chronic diseases, and history of other GI surgeries also play a role.1
Other studies have demonstrated that malnutrition in patients with GI malignancies undergoing surgical resection is associated with high rates of severe postoperative complications, increased length of stay (LOS) and time on a ventilator for patients treated in the intensive care unit, and poor QOL in the postoperative survival period.4-6 Several randomized controlled trials conducted in patients with GI cancers have shown that enteral and parenteral nutrition supplementations in the perioperative period improve various outcomes, such as reduction of postoperative complication rates, fewer readmissions, improved chemotherapy tolerance, and improved QOL.7-10 Thus, in the management of patients with GI malignancies, it is highly important to implement early nutritional screening and establish a diagnosis of malnutrition to intervene and reduce postoperative morbidity and mortality.1
However, tools and predictors of malnutrition are often imperfect. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (AND/ASPEN) weight-based criteria define malnutrition and nutritionally-at-risk as BMI < 18.5, involuntary loss of at least 10% of body weight within 6 months or 5% within 1 month, or loss of 10 lb within 6 months.11 While the ASPEN criteria are often used to define malnourishment, they may not fully capture the population at risk, and there does not exist a gold-standard tool for nutritional screening. A 2002 study that performed a critical appraisal of 44 nutritional screening tools found that no single tool was fully sufficient for application, development, evaluation, and consistent screening.12 As such, consistently screening for malnutrition to target interventions in the perioperative period for GI surgical oncology has been challenging.13 More recent tools such as the perioperative nutrition screen (PONS) have been validated as rapid, effective screening tools to predict postoperative outcomes.14 Additionally, implementation of perioperative nutritional protocols, such as enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) in colon cancer (CC) surgery, also has shown improved perioperative care and outcomes.15
Preoperative nutritional interventions have been implemented in practice and have focused mostly on the immediate perioperative period. This has been shown to improve surgical outcomes. The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) provides comprehensive care to patients in a single-payer system, allowing for capture of perioperative data and the opportunity for focused preoperative interventions to improve outcomes.
Methods
This was a retrospective record review of colorectal malignancies treated with curative intent at the Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in Michigan between January 1, 2015, and December 31, 2019. We examined nutritional status, degree of longitudinal weight loss, and subsequent clinical outcomes, including delayed postoperative recovery and delays in chemotherapy in 115 patients with CC and 33 patients with rectal cancer (RC) undergoing curative surgical resection at VAAAHS. To avoid additional confounding effects of advanced cancer, only early-stage, curable disease was included. This study was approved by the VAAAHS Institutional Review Board.
Patients with postoperative follow-up outside of VAAAHS were excluded. Patients were excluded if their surgery had noncurative intent or if they had distant metastatic disease. Data on patient weights, laboratory results, nutrition consultations, postoperative complications, delayed recovery, readmissions, and chemotherapy tolerance were abstracted by patient chart review in the VHA Computerized Patient Record System and Joint Legacy Viewer by 2 researchers.
Delayed recovery was defined as any abnormal clinical development described in inpatient progress notes, outpatient follow-up notes within 60 days, or in hospital discharge summaries. Excluded were psychiatric events without additional medical complications, postoperative bleeding not requiring an invasive intervention, urinary retention, postoperative glycemic control difficulties, cardiac events that happened before postoperative hospital discharge and not requiring readmission, and postoperative alcohol withdrawal. Complications were defined similarly to delayed recovery but excluded isolated prolonged postoperative ileus. LOS was defined in days as time from admission to discharge.
Adjuvant management course was derived from reviewing documentation from medical oncology consultations and progress notes. In patients for whom adjuvant chemotherapy was indicated and prescribed, chemotherapy was considered complete if chemotherapy was started and completed as indicated. Adjuvant chemotherapy was considered incomplete if the patient declined chemotherapy, if chemotherapy was not started when indicated, or if chemotherapy was not completed as indicated. Neoadjuvant therapy data were abstracted from medical and radiation oncology notes.
Recorded data were collected on both weight and BMI. Weights were extracted as follows: Weight 1 year before time of diagnosis, ± 4 months; weight 6 months before diagnosis ± 3 months; weight at time of diagnosis ± 2 weeks; weight at time of surgery ± 2 weeks; weight 30 days postsurgery ± 2 weeks; weight 60 days postsurgery ± 2 weeks; weight 1 year postsurgery ± 4 months. Mean percent change in weight was calculated from recorded weights between each allocated time point. A weight loss of ≥ 3% was found to be clinically relevant and was chosen as the minimal cutoff value when analyzing outcomes associated with weight trends.
Nutrition consultations were abstracted as follows: Preoperative nutrition consultations were defined as occurring between time of cancer diagnosis and surgery in either the inpatient or outpatient setting; inpatient postoperative nutrition consultations occurred during admission for surgery; readmission nutrition consultations occurred on readmission in inpatient setting, if applicable; outpatient postoperative nutrition consultations were defined as occurring up to 2 months postdischarge in the outpatient setting.
Albumin values were extracted as follows: Preoperative albumin levels were defined as up to 4 months prior to diagnosis, and postoperative albumin levels were defined as 2 to 6 months after surgery.
Analysis
The data were described using mean (SD) for continuous variables and number and percentages for categorical variables. Where appropriate, Fisher exact test, Pearson χ2 test, Spearman ρ, and Mann-Whitney U test were used for tests of significance. SAS (SAS Institute) was utilized for multivariable analysis. The significance level was P = .05 for all tests.
Results
There were 115 patients in the CC cohort and 33 in the RC cohort. The mean (SD) age at diagnosis was 70 (9.1) for CC group and 59 (1.4) for RC group (Table 1).
Weight Trends
From 1 year to 6 months before diagnosis, 40 of 80 patients lost weight in the CC cohort (mean change, +1.9%) and 6 of 22 patients lost weight in the RC cohort (mean change, + 0.5%). From 6 months before diagnosis to time of diagnosis, 47 of 74 patients lost weight in the CC cohort (mean change, -1.5%) and 14 of 21 patients lost weight in the RC cohort (mean change, -2.5%). From time of diagnosis to time of surgery, 36 of 104 patients with CC and 14 of 32 patients with RC lost weight with a mean weight change of and +0.1% and -0.3%, respectively. In the 6 months before surgery, any amount of weight loss was observed in 58 patients (66%) in the CC group and in 12 patients (57%) in the RC group. In this time frame, in the CC cohort, 32 patients (36%) were observed to have at least 3% weight loss, and 23 (26%) were observed to have at least 5% weight loss (Table 3).
In patients who completed adjuvant chemotherapy in the CC group, mean (SD) BMI at the beginning and end of chemotherapy was 32.6 (8.6) and 33.1 (8.7), respectively, and a -0.3% mean change in weight was observed. In the RC group, mean (SD) BMI was 28.2 (5.0) at the initiation of adjuvant chemotherapy and 28.4 (5.0) at its completion, with a +2.6% mean change in weight.
In the immediate postoperative period, most patients were losing weight in both the CC and RC groups (mean, -3.5% and -7.0% at 1 month postoperative, respectively). At 1-year after surgery, patients had modest mean increases in weight: +1.3% for patients with CC and +4.9% for patients with RC.
A relatively large proportion of patients had missing data on weights at various data points (Table 4).
Nutrition Consultations
In the CC group, preoperative nutrition consultations (either inpatient or outpatient) occurred in 17 patients (15%). Inpatient postoperative nutrition evaluations occurred in 110 patients (96%) (Table 5).
In the RC group, preoperative inpatient or outpatient nutrition consultations occurred in 12 patients (36%). Eight of those occurred before initiation of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. All 33 patients received an inpatient postoperative nutrition evaluation during admission. Oral or enteral nutrition supplements were prescribed 19 times (58%). Postoperative outpatient nutrition consultations occurred for 24 patients (73%). Of the 19 patients who were readmitted to the hospital, 3 (16%) had a nutrition reconsultation on readmission.
Outcomes
The primary outcomes observed were delayed recovery, hospital readmission and LOS, and completion of adjuvant chemotherapy as indicated. Delayed recovery was observed in 35 patients with CC (40%) and 21 patients with RC (64%). Multivariable analysis in the CC cohort demonstrated that weight change was significantly associated with delayed recovery. Among those with ≥ 3% weight loss in the 6-month preoperative period (the weight measurement 6 months prior to diagnosis to date of surgery), 20 patients (63%) had delayed recovery compared with 15 patients (27%) without ≥ 3% weight loss who experienced delayed recovery (χ2 = 10.84; P < .001).
Weight loss of ≥ 3% in the 6-month preoperative period also was significantly associated with complications. Of patients with at least 3% preoperative weight loss, 16 (50%) experienced complications, while 8 (14%) with < 3% preoperative weight loss experienced complications (χ2 = 11.20; P < .001). Notably, ≥ 3% weight loss in the 1-year preoperative period before surgery was not significantly associated with delayed recovery. Any degree of 30-day postoperative weight loss was not correlated with delayed recovery. Finally, low preoperative albumin also was not correlated with delayed recovery (Fisher exact; P = .13). Table 3 displays differences based on presence of delayed recovery in the 88 patients with CC 6 months before surgery. Of note, ≥ 10-lb weight loss in the 6 months preceding surgery also correlated with delayed recovery (P = .01).In our cohort, 3% weight loss over 6 months had a sensitivity of 57%, specificity of 77%, positive predictive value 63%, and negative predictive value 73% for delayed recovery. By comparison, a 10-lb weight loss in 6 months per ASPEN criteria had a sensitivity of 40%, specificity of 85%, positive predictive value 64%, and negative predictive value 68% for delayed recovery.
Hospital Readmissions and LOS
Hospital readmissions occurred within the first 30 days in 11 patients (10%) in the CC cohort and 12 patients (36%) in the RC cohort. Readmissions occurred between 31 and 60 days in 4 (3%) and 7 (21%) of CC and RC cohorts, respectively. The presence of ≥ 3% weight loss in the 6-month
Mean (SD) LOS was 6.4 (4.7) days (range, 1-28) for patients with CC and 8.8 (5.1) days (range, 3-23) for patients with RC. Mean (SD) LOS increased to 10.2 (4.3) days and 9.7 (6.0) days in patients with delayed recovery in the CC and RC cohorts, respectively. The mean (SD) LOS was 5.2 (2.8) days and 6.3 (2.2) days in patients without delayed recovery in the CC and RC cohorts, respectively. There was no significant difference when examining association between percent weight change and LOS for either initial admission (rs = -0.1409; 2-tailed P = .19) or for initial and readmission combined (rs = -0.13532; 2-tailed P = .21) within the CC cohort.
Chemotherapy
Within the CC cohort, 31 patients (27%) had an indication for adjuvant chemotherapy. Of these, 25 of 31 (81%) started chemotherapy within 12 weeks of surgical resection, and of these, 17 of 25 patients (68%) completed chemotherapy as indicated. Within the RC cohort all 33 patients had an indication for adjuvant chemotherapy, of these 18 of 33 patients (55%) began within 12 weeks of surgical resection, and 10 of 18 (56%) completed chemotherapy as indicated.
Among the CC cohort who began but did not complete adjuvant chemotherapy, there was no significant association between completion of chemotherapy and
Discussion
This study highlights several important findings. There were no patients in our cohort that met ASPEN malnourishment criteria with a BMI < 18.5. Twenty percent of patients lost at least 10 lb in 6 months before the operation. Notably, patients had significant associations with adverse outcomes with less pronounced weight loss than previously noted. As has been established previously, malnourishment can be difficult to screen for, and BMI also is often an imprecise tool.12 In the CC cohort, weight loss
Our findings imply that the effects of even mild malnutrition are even more profound than previously thought. Significantly, this applies to overweight and obese patients as well, as these constituted a significant fraction of our cohort. A finding of ≥ 3% weight loss at the time of CC diagnosis may provide an opportunity for a focused nutrition intervention up to the time of surgery. Second, although nutrition consultation was frequent in the inpatient setting during the hospital admission (96%-100%), rates of nutrition evaluation were as low as 15% before surgery and 12% after surgery, representing a key area for improvement and focused intervention. An optimal time for intervention and nutrition prehabilitation would be at time of diagnosis before surgery with plans for continued aggressive monitoring and subsequent follow-up. Our finding seems to provide a more sensitive tool to identify patients at risk for delayed recovery compared with the ASPEN-driven assessment. Given the simplicity and the clinical significance, our test consisting of 3% weight loss over 6 months, with its sensitivity of 57%, may be superior to the ASPEN 10-lb weight loss, with its sensitivity of 40% in our cohort.
Previous Studies
Our findings are consistent with previous studies that have demonstrated that perioperative weight loss and malnutrition are correlated with delayed recovery and complications, such as wound healing, in patients with GI cancer.2,4,5,8 In a retrospective study of more than 7000 patients with CC, those who were overweight or obese were found to have an improved overall survival compared with other BMI categories, and those who were underweight had an increased 30-day mortality and postoperative complications.16
In another retrospective study of 3799 patients with CC, those who were overweight and obese had an improved 5-year survival rate compared with patients whose weight was normal or underweight. Outcomes were found to be stage dependent.17 In this study cohort, all patients were either overweight or obese and remained in that category even with weight loss. This may have contributed to overall improved outcomes.
Implications and Next Steps
Our study has several implications. One is that BMI criteria < 18.5 may not be a good measure for malnutrition given that about 75% of the patients in our cohort were overweight or obese and none were underweight. We also show a concrete, easily identifiable finding of percent weight change that could be addressed as an automated electronic notification and potentially identify a patient at risk and serve as a trigger for both timely and early nutrition intervention. It seems to be more sensitive than the ASPEN criterion of 10-lb weight loss in 6 months before surgery. Sensitivity is especially appealing given the ease and potential of embedding this tool in an electronic health record and the clinical importance of the consequent intervention. Preoperative as opposed to perioperative nutrition optimization at time of CC diagnosis is essential, as it may help improve postsurgical outcomes as well as oncologic outcomes, including completion of adjuvant chemotherapy. Finally, although our study found that rates of inpatient postoperative nutrition consultation were high, rates of outpatient nutrition consultation in the preoperative period were low. This represents a missed opportunity for intervention before surgery. Similarly, rates of postoperative nutrition follow-up period were low, which points to an area for improvement in longitudinal and holistic care.
We suggest modifications to nutrition intervention protocols, such as ERAS, which should start at the time of GI malignancy diagnosis.18 Other suggestions include standard involvement of nutritionists in inpatient and outpatient settings with longitudinal follow-up in the preoperative and postoperative periods and patient enrollment in a nutrition program with monitoring at time of diagnosis at the VHA. Our findings as well as previous literature suggest that the preoperative period is the most important time to intervene with regard to nutrition optimization and represents an opportunity for intensive prehabilitation. Future areas of research include incorporating other important measures of malnourishment independent of BMI into future study designs, such as sarcopenia and adipose tissue density, to better assess body composition and predict prognostic risk in CC.18,19
Strengths and Limitations
This study is limited by its single-center, retrospective design and small sample sizes, and we acknowledge the limitations of our data set. However, the strength of this VHA-based study is that the single-payer system allows for complete capture of perioperative data as well as the opportunity for focused preoperative interventions to improve outcomes. To our knowledge, there is no currently existing literature on improving nutrition protocols at the VHA for patients with a GI malignancy. These retrospective data will help inform current gaps in quality improvement and supportive oncology as it relates to optimizing malnourishment in veterans undergoing surgical resection for their cancer.
Conclusions
In the CC cohort, weight loss of ≥ 3% from 6 months prior to time of surgery was significantly associated with delayed recovery, complications, and hospital readmissions. Our findings suggest that patients with CC undergoing surgery may benefit from an intensive, early nutrition prehabilitation. Preoperative nutrition optimization may help improve postsurgical outcomes as well as oncologic outcomes, including completion of adjuvant chemotherapy. Further research would be able to clarify these hypotheses.
In patients with gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies, malnutrition is common. In addition, it has various negative implications, including high risk for surgical complications, prolonged hospitalization, decreased quality of life (QOL), increased mortality, and poor tolerance for treatments such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy.1
A 2014 French study of 1903 patients hospitalized for cancer reported a 39% overall prevalence of malnutrition; 39% in patients with cancers of the colon/rectum, 60% for pancreatic cancer, and 67% for cancers of the esophagus/stomach.2 Malnutrition was defined as body mass index (BMI) < 18.5 for individuals aged < 75 years or BMI < 21 for individuals aged ≥ 75 years, and/or weight loss > 10% since disease onset. Malnutrition also was strongly associated with worsened performance status.
The etiology of malnutrition in GI cancers is often multifactorial. It includes systemic tumor effects, such as inflammatory mediators contributing to hypermetabolism and cachexia, local tumor-associated mechanical obstruction, GI toxicities caused by antineoplastic therapy or other medications, and psychological factors that contribute to anorexia.3 Patient-related risk factors such as older age, other chronic diseases, and history of other GI surgeries also play a role.1
Other studies have demonstrated that malnutrition in patients with GI malignancies undergoing surgical resection is associated with high rates of severe postoperative complications, increased length of stay (LOS) and time on a ventilator for patients treated in the intensive care unit, and poor QOL in the postoperative survival period.4-6 Several randomized controlled trials conducted in patients with GI cancers have shown that enteral and parenteral nutrition supplementations in the perioperative period improve various outcomes, such as reduction of postoperative complication rates, fewer readmissions, improved chemotherapy tolerance, and improved QOL.7-10 Thus, in the management of patients with GI malignancies, it is highly important to implement early nutritional screening and establish a diagnosis of malnutrition to intervene and reduce postoperative morbidity and mortality.1
However, tools and predictors of malnutrition are often imperfect. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (AND/ASPEN) weight-based criteria define malnutrition and nutritionally-at-risk as BMI < 18.5, involuntary loss of at least 10% of body weight within 6 months or 5% within 1 month, or loss of 10 lb within 6 months.11 While the ASPEN criteria are often used to define malnourishment, they may not fully capture the population at risk, and there does not exist a gold-standard tool for nutritional screening. A 2002 study that performed a critical appraisal of 44 nutritional screening tools found that no single tool was fully sufficient for application, development, evaluation, and consistent screening.12 As such, consistently screening for malnutrition to target interventions in the perioperative period for GI surgical oncology has been challenging.13 More recent tools such as the perioperative nutrition screen (PONS) have been validated as rapid, effective screening tools to predict postoperative outcomes.14 Additionally, implementation of perioperative nutritional protocols, such as enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) in colon cancer (CC) surgery, also has shown improved perioperative care and outcomes.15
Preoperative nutritional interventions have been implemented in practice and have focused mostly on the immediate perioperative period. This has been shown to improve surgical outcomes. The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) provides comprehensive care to patients in a single-payer system, allowing for capture of perioperative data and the opportunity for focused preoperative interventions to improve outcomes.
Methods
This was a retrospective record review of colorectal malignancies treated with curative intent at the Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in Michigan between January 1, 2015, and December 31, 2019. We examined nutritional status, degree of longitudinal weight loss, and subsequent clinical outcomes, including delayed postoperative recovery and delays in chemotherapy in 115 patients with CC and 33 patients with rectal cancer (RC) undergoing curative surgical resection at VAAAHS. To avoid additional confounding effects of advanced cancer, only early-stage, curable disease was included. This study was approved by the VAAAHS Institutional Review Board.
Patients with postoperative follow-up outside of VAAAHS were excluded. Patients were excluded if their surgery had noncurative intent or if they had distant metastatic disease. Data on patient weights, laboratory results, nutrition consultations, postoperative complications, delayed recovery, readmissions, and chemotherapy tolerance were abstracted by patient chart review in the VHA Computerized Patient Record System and Joint Legacy Viewer by 2 researchers.
Delayed recovery was defined as any abnormal clinical development described in inpatient progress notes, outpatient follow-up notes within 60 days, or in hospital discharge summaries. Excluded were psychiatric events without additional medical complications, postoperative bleeding not requiring an invasive intervention, urinary retention, postoperative glycemic control difficulties, cardiac events that happened before postoperative hospital discharge and not requiring readmission, and postoperative alcohol withdrawal. Complications were defined similarly to delayed recovery but excluded isolated prolonged postoperative ileus. LOS was defined in days as time from admission to discharge.
Adjuvant management course was derived from reviewing documentation from medical oncology consultations and progress notes. In patients for whom adjuvant chemotherapy was indicated and prescribed, chemotherapy was considered complete if chemotherapy was started and completed as indicated. Adjuvant chemotherapy was considered incomplete if the patient declined chemotherapy, if chemotherapy was not started when indicated, or if chemotherapy was not completed as indicated. Neoadjuvant therapy data were abstracted from medical and radiation oncology notes.
Recorded data were collected on both weight and BMI. Weights were extracted as follows: Weight 1 year before time of diagnosis, ± 4 months; weight 6 months before diagnosis ± 3 months; weight at time of diagnosis ± 2 weeks; weight at time of surgery ± 2 weeks; weight 30 days postsurgery ± 2 weeks; weight 60 days postsurgery ± 2 weeks; weight 1 year postsurgery ± 4 months. Mean percent change in weight was calculated from recorded weights between each allocated time point. A weight loss of ≥ 3% was found to be clinically relevant and was chosen as the minimal cutoff value when analyzing outcomes associated with weight trends.
Nutrition consultations were abstracted as follows: Preoperative nutrition consultations were defined as occurring between time of cancer diagnosis and surgery in either the inpatient or outpatient setting; inpatient postoperative nutrition consultations occurred during admission for surgery; readmission nutrition consultations occurred on readmission in inpatient setting, if applicable; outpatient postoperative nutrition consultations were defined as occurring up to 2 months postdischarge in the outpatient setting.
Albumin values were extracted as follows: Preoperative albumin levels were defined as up to 4 months prior to diagnosis, and postoperative albumin levels were defined as 2 to 6 months after surgery.
Analysis
The data were described using mean (SD) for continuous variables and number and percentages for categorical variables. Where appropriate, Fisher exact test, Pearson χ2 test, Spearman ρ, and Mann-Whitney U test were used for tests of significance. SAS (SAS Institute) was utilized for multivariable analysis. The significance level was P = .05 for all tests.
Results
There were 115 patients in the CC cohort and 33 in the RC cohort. The mean (SD) age at diagnosis was 70 (9.1) for CC group and 59 (1.4) for RC group (Table 1).
Weight Trends
From 1 year to 6 months before diagnosis, 40 of 80 patients lost weight in the CC cohort (mean change, +1.9%) and 6 of 22 patients lost weight in the RC cohort (mean change, + 0.5%). From 6 months before diagnosis to time of diagnosis, 47 of 74 patients lost weight in the CC cohort (mean change, -1.5%) and 14 of 21 patients lost weight in the RC cohort (mean change, -2.5%). From time of diagnosis to time of surgery, 36 of 104 patients with CC and 14 of 32 patients with RC lost weight with a mean weight change of and +0.1% and -0.3%, respectively. In the 6 months before surgery, any amount of weight loss was observed in 58 patients (66%) in the CC group and in 12 patients (57%) in the RC group. In this time frame, in the CC cohort, 32 patients (36%) were observed to have at least 3% weight loss, and 23 (26%) were observed to have at least 5% weight loss (Table 3).
In patients who completed adjuvant chemotherapy in the CC group, mean (SD) BMI at the beginning and end of chemotherapy was 32.6 (8.6) and 33.1 (8.7), respectively, and a -0.3% mean change in weight was observed. In the RC group, mean (SD) BMI was 28.2 (5.0) at the initiation of adjuvant chemotherapy and 28.4 (5.0) at its completion, with a +2.6% mean change in weight.
In the immediate postoperative period, most patients were losing weight in both the CC and RC groups (mean, -3.5% and -7.0% at 1 month postoperative, respectively). At 1-year after surgery, patients had modest mean increases in weight: +1.3% for patients with CC and +4.9% for patients with RC.
A relatively large proportion of patients had missing data on weights at various data points (Table 4).
Nutrition Consultations
In the CC group, preoperative nutrition consultations (either inpatient or outpatient) occurred in 17 patients (15%). Inpatient postoperative nutrition evaluations occurred in 110 patients (96%) (Table 5).
In the RC group, preoperative inpatient or outpatient nutrition consultations occurred in 12 patients (36%). Eight of those occurred before initiation of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. All 33 patients received an inpatient postoperative nutrition evaluation during admission. Oral or enteral nutrition supplements were prescribed 19 times (58%). Postoperative outpatient nutrition consultations occurred for 24 patients (73%). Of the 19 patients who were readmitted to the hospital, 3 (16%) had a nutrition reconsultation on readmission.
Outcomes
The primary outcomes observed were delayed recovery, hospital readmission and LOS, and completion of adjuvant chemotherapy as indicated. Delayed recovery was observed in 35 patients with CC (40%) and 21 patients with RC (64%). Multivariable analysis in the CC cohort demonstrated that weight change was significantly associated with delayed recovery. Among those with ≥ 3% weight loss in the 6-month preoperative period (the weight measurement 6 months prior to diagnosis to date of surgery), 20 patients (63%) had delayed recovery compared with 15 patients (27%) without ≥ 3% weight loss who experienced delayed recovery (χ2 = 10.84; P < .001).
Weight loss of ≥ 3% in the 6-month preoperative period also was significantly associated with complications. Of patients with at least 3% preoperative weight loss, 16 (50%) experienced complications, while 8 (14%) with < 3% preoperative weight loss experienced complications (χ2 = 11.20; P < .001). Notably, ≥ 3% weight loss in the 1-year preoperative period before surgery was not significantly associated with delayed recovery. Any degree of 30-day postoperative weight loss was not correlated with delayed recovery. Finally, low preoperative albumin also was not correlated with delayed recovery (Fisher exact; P = .13). Table 3 displays differences based on presence of delayed recovery in the 88 patients with CC 6 months before surgery. Of note, ≥ 10-lb weight loss in the 6 months preceding surgery also correlated with delayed recovery (P = .01).In our cohort, 3% weight loss over 6 months had a sensitivity of 57%, specificity of 77%, positive predictive value 63%, and negative predictive value 73% for delayed recovery. By comparison, a 10-lb weight loss in 6 months per ASPEN criteria had a sensitivity of 40%, specificity of 85%, positive predictive value 64%, and negative predictive value 68% for delayed recovery.
Hospital Readmissions and LOS
Hospital readmissions occurred within the first 30 days in 11 patients (10%) in the CC cohort and 12 patients (36%) in the RC cohort. Readmissions occurred between 31 and 60 days in 4 (3%) and 7 (21%) of CC and RC cohorts, respectively. The presence of ≥ 3% weight loss in the 6-month
Mean (SD) LOS was 6.4 (4.7) days (range, 1-28) for patients with CC and 8.8 (5.1) days (range, 3-23) for patients with RC. Mean (SD) LOS increased to 10.2 (4.3) days and 9.7 (6.0) days in patients with delayed recovery in the CC and RC cohorts, respectively. The mean (SD) LOS was 5.2 (2.8) days and 6.3 (2.2) days in patients without delayed recovery in the CC and RC cohorts, respectively. There was no significant difference when examining association between percent weight change and LOS for either initial admission (rs = -0.1409; 2-tailed P = .19) or for initial and readmission combined (rs = -0.13532; 2-tailed P = .21) within the CC cohort.
Chemotherapy
Within the CC cohort, 31 patients (27%) had an indication for adjuvant chemotherapy. Of these, 25 of 31 (81%) started chemotherapy within 12 weeks of surgical resection, and of these, 17 of 25 patients (68%) completed chemotherapy as indicated. Within the RC cohort all 33 patients had an indication for adjuvant chemotherapy, of these 18 of 33 patients (55%) began within 12 weeks of surgical resection, and 10 of 18 (56%) completed chemotherapy as indicated.
Among the CC cohort who began but did not complete adjuvant chemotherapy, there was no significant association between completion of chemotherapy and
Discussion
This study highlights several important findings. There were no patients in our cohort that met ASPEN malnourishment criteria with a BMI < 18.5. Twenty percent of patients lost at least 10 lb in 6 months before the operation. Notably, patients had significant associations with adverse outcomes with less pronounced weight loss than previously noted. As has been established previously, malnourishment can be difficult to screen for, and BMI also is often an imprecise tool.12 In the CC cohort, weight loss
Our findings imply that the effects of even mild malnutrition are even more profound than previously thought. Significantly, this applies to overweight and obese patients as well, as these constituted a significant fraction of our cohort. A finding of ≥ 3% weight loss at the time of CC diagnosis may provide an opportunity for a focused nutrition intervention up to the time of surgery. Second, although nutrition consultation was frequent in the inpatient setting during the hospital admission (96%-100%), rates of nutrition evaluation were as low as 15% before surgery and 12% after surgery, representing a key area for improvement and focused intervention. An optimal time for intervention and nutrition prehabilitation would be at time of diagnosis before surgery with plans for continued aggressive monitoring and subsequent follow-up. Our finding seems to provide a more sensitive tool to identify patients at risk for delayed recovery compared with the ASPEN-driven assessment. Given the simplicity and the clinical significance, our test consisting of 3% weight loss over 6 months, with its sensitivity of 57%, may be superior to the ASPEN 10-lb weight loss, with its sensitivity of 40% in our cohort.
Previous Studies
Our findings are consistent with previous studies that have demonstrated that perioperative weight loss and malnutrition are correlated with delayed recovery and complications, such as wound healing, in patients with GI cancer.2,4,5,8 In a retrospective study of more than 7000 patients with CC, those who were overweight or obese were found to have an improved overall survival compared with other BMI categories, and those who were underweight had an increased 30-day mortality and postoperative complications.16
In another retrospective study of 3799 patients with CC, those who were overweight and obese had an improved 5-year survival rate compared with patients whose weight was normal or underweight. Outcomes were found to be stage dependent.17 In this study cohort, all patients were either overweight or obese and remained in that category even with weight loss. This may have contributed to overall improved outcomes.
Implications and Next Steps
Our study has several implications. One is that BMI criteria < 18.5 may not be a good measure for malnutrition given that about 75% of the patients in our cohort were overweight or obese and none were underweight. We also show a concrete, easily identifiable finding of percent weight change that could be addressed as an automated electronic notification and potentially identify a patient at risk and serve as a trigger for both timely and early nutrition intervention. It seems to be more sensitive than the ASPEN criterion of 10-lb weight loss in 6 months before surgery. Sensitivity is especially appealing given the ease and potential of embedding this tool in an electronic health record and the clinical importance of the consequent intervention. Preoperative as opposed to perioperative nutrition optimization at time of CC diagnosis is essential, as it may help improve postsurgical outcomes as well as oncologic outcomes, including completion of adjuvant chemotherapy. Finally, although our study found that rates of inpatient postoperative nutrition consultation were high, rates of outpatient nutrition consultation in the preoperative period were low. This represents a missed opportunity for intervention before surgery. Similarly, rates of postoperative nutrition follow-up period were low, which points to an area for improvement in longitudinal and holistic care.
We suggest modifications to nutrition intervention protocols, such as ERAS, which should start at the time of GI malignancy diagnosis.18 Other suggestions include standard involvement of nutritionists in inpatient and outpatient settings with longitudinal follow-up in the preoperative and postoperative periods and patient enrollment in a nutrition program with monitoring at time of diagnosis at the VHA. Our findings as well as previous literature suggest that the preoperative period is the most important time to intervene with regard to nutrition optimization and represents an opportunity for intensive prehabilitation. Future areas of research include incorporating other important measures of malnourishment independent of BMI into future study designs, such as sarcopenia and adipose tissue density, to better assess body composition and predict prognostic risk in CC.18,19
Strengths and Limitations
This study is limited by its single-center, retrospective design and small sample sizes, and we acknowledge the limitations of our data set. However, the strength of this VHA-based study is that the single-payer system allows for complete capture of perioperative data as well as the opportunity for focused preoperative interventions to improve outcomes. To our knowledge, there is no currently existing literature on improving nutrition protocols at the VHA for patients with a GI malignancy. These retrospective data will help inform current gaps in quality improvement and supportive oncology as it relates to optimizing malnourishment in veterans undergoing surgical resection for their cancer.
Conclusions
In the CC cohort, weight loss of ≥ 3% from 6 months prior to time of surgery was significantly associated with delayed recovery, complications, and hospital readmissions. Our findings suggest that patients with CC undergoing surgery may benefit from an intensive, early nutrition prehabilitation. Preoperative nutrition optimization may help improve postsurgical outcomes as well as oncologic outcomes, including completion of adjuvant chemotherapy. Further research would be able to clarify these hypotheses.
1. Benoist S, Brouquet A. Nutritional assessment and screening for malnutrition. J Visc Surg. 2015;152:S3-S7. doi:10.1016/S1878-7886(15)30003-5
2. Hébuterne X, Lemarié E, Michallet M, de Montreuil CB, Schneider SM, Goldwasser F. Prevalence of malnutrition and current use of nutrition support in patients with cancer. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2014;38(2):196-204. doi:10.1177/0148607113502674
3. Van Cutsem E, Arends J. The causes and consequences of cancer-associated malnutrition. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2005;9:S51-S63. doi:10.1016/j.ejon.2005.09.007
4. Nishiyama VKG, Albertini SM, de Moraes CMZG, et al. Malnutrition and clinical outcomes in surgical patients with colorectal disease. Arq Gastroenterol. 2018;55(4):397-402. doi:10.1590/s0004-2803.201800000-85
5. Shpata V, Prendushi X, Kreka M, Kola I, Kurti F, Ohri I. Malnutrition at the time of surgery affects negatively the clinical outcome of critically ill patients with gastrointestinal cancer. Med Arch Sarajevo Bosnia Herzeg. 2014;68(4):263-267. doi:10.5455/medarh.2014.68.263-267
6. Lim HS, Cho GS, Park YH, Kim SK. Comparison of quality of life and nutritional status in gastric cancer patients undergoing gastrectomies. Clin Nutr Res. 2015;4(3):153-159. doi:10.7762/cnr.2015.4.3.153
7. Bozzetti F, Gavazzi C, Miceli R, et al. Perioperative total parenteral nutrition in malnourished, gastrointestinal cancer patients: a randomized, clinical trial. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2000;24(1):7-14. doi:10.1177/014860710002400107
8. Bozzetti F, Gianotti L, Braga M, Di Carlo V, Mariani L. Postoperative complications in gastrointestinal cancer patients: the joint role of the nutritional status and the nutritional support. Clin Nutr. 2007;26(6):698-709. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2007.06.009
9. Bozzetti F, Braga M, Gianotti L, Gavazzi C, Mariani L. Postoperative enteral versus parenteral nutrition in malnourished patients with gastrointestinal cancer: a randomised multicentre trial. Lancet. 2001; 358(9292):1487-1492. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06578-3
10. Meng Q, Tan S, Jiang Y, et al. Post-discharge oral nutritional supplements with dietary advice in patients at nutritional risk after surgery for gastric cancer: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr Edinb Scotl. 2021;40(1):40-46. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2020.04.043 start
11. White JV, Guenter P, Jensen G, Malone A, Schofield M. Consensus statement of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics/American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: characteristics recommended for the identification and documentation of adult malnutrition (undernutrition). J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012;112(5):730-738. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2012.03.012
12. Jones JM. The methodology of nutritional screening and assessment tools. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2002;15(1):59-71. doi:10.1046/j.1365-277X.2002.00327.x
13. Williams J, Wischmeyer P. Assessment of perioperative nutrition practices and attitudes—a national survey of colorectal and GI surgical oncology programs. Am J Surg. 2017;213(6):1010-1018. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2016.10.008
14. Williams DG, Aronson S, Murray S, et al. Validation of the perioperative nutrition screen for prediction of postoperative outcomes. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2022;46(6):1307-1315. doi:10.1002/jpen.2310
15. Besson AJ, Kei C, Djordjevic A, Carter V, Deftereos I, Yeung J. Does implementation of and adherence to enhanced recovery after surgery improve perioperative nutritional management in colorectal cancer surgery? ANZ J Surg. 2022;92(6):1382-1387. doi:10.1111/ans.17599
16. Arkenbosch JHC, van Erning FN, Rutten HJ, Zimmerman D, de Wilt JHW, Beijer S. The association between body mass index and postoperative complications, 30-day mortality and long-term survival in Dutch patients with colorectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol J Eur Soc Surg Oncol Br Assoc Surg Oncol. 2019;45(2):160-166. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2018.09.012
17. Shahjehan F, Merchea A, Cochuyt JJ, Li Z, Colibaseanu DT, Kasi PM. Body mass index and long-term outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer. Front Oncol. 2018;8:620. doi:10.3389/fonc.2018.00620
18. Nishigori T, Obama K, Sakai Y. Assessment of body composition and impact of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in patients with gastric cancer. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5:22. doi:10.21037/tgh.2019.10.13
19. Feliciano EMC, Winkels RM, Meyerhardt JA, Prado CM, Afman LA, Caan BJ. Abdominal adipose tissue radiodensity is associated with survival after colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021;114(6):1917-1924. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab285
1. Benoist S, Brouquet A. Nutritional assessment and screening for malnutrition. J Visc Surg. 2015;152:S3-S7. doi:10.1016/S1878-7886(15)30003-5
2. Hébuterne X, Lemarié E, Michallet M, de Montreuil CB, Schneider SM, Goldwasser F. Prevalence of malnutrition and current use of nutrition support in patients with cancer. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2014;38(2):196-204. doi:10.1177/0148607113502674
3. Van Cutsem E, Arends J. The causes and consequences of cancer-associated malnutrition. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2005;9:S51-S63. doi:10.1016/j.ejon.2005.09.007
4. Nishiyama VKG, Albertini SM, de Moraes CMZG, et al. Malnutrition and clinical outcomes in surgical patients with colorectal disease. Arq Gastroenterol. 2018;55(4):397-402. doi:10.1590/s0004-2803.201800000-85
5. Shpata V, Prendushi X, Kreka M, Kola I, Kurti F, Ohri I. Malnutrition at the time of surgery affects negatively the clinical outcome of critically ill patients with gastrointestinal cancer. Med Arch Sarajevo Bosnia Herzeg. 2014;68(4):263-267. doi:10.5455/medarh.2014.68.263-267
6. Lim HS, Cho GS, Park YH, Kim SK. Comparison of quality of life and nutritional status in gastric cancer patients undergoing gastrectomies. Clin Nutr Res. 2015;4(3):153-159. doi:10.7762/cnr.2015.4.3.153
7. Bozzetti F, Gavazzi C, Miceli R, et al. Perioperative total parenteral nutrition in malnourished, gastrointestinal cancer patients: a randomized, clinical trial. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2000;24(1):7-14. doi:10.1177/014860710002400107
8. Bozzetti F, Gianotti L, Braga M, Di Carlo V, Mariani L. Postoperative complications in gastrointestinal cancer patients: the joint role of the nutritional status and the nutritional support. Clin Nutr. 2007;26(6):698-709. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2007.06.009
9. Bozzetti F, Braga M, Gianotti L, Gavazzi C, Mariani L. Postoperative enteral versus parenteral nutrition in malnourished patients with gastrointestinal cancer: a randomised multicentre trial. Lancet. 2001; 358(9292):1487-1492. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06578-3
10. Meng Q, Tan S, Jiang Y, et al. Post-discharge oral nutritional supplements with dietary advice in patients at nutritional risk after surgery for gastric cancer: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr Edinb Scotl. 2021;40(1):40-46. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2020.04.043 start
11. White JV, Guenter P, Jensen G, Malone A, Schofield M. Consensus statement of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics/American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: characteristics recommended for the identification and documentation of adult malnutrition (undernutrition). J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012;112(5):730-738. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2012.03.012
12. Jones JM. The methodology of nutritional screening and assessment tools. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2002;15(1):59-71. doi:10.1046/j.1365-277X.2002.00327.x
13. Williams J, Wischmeyer P. Assessment of perioperative nutrition practices and attitudes—a national survey of colorectal and GI surgical oncology programs. Am J Surg. 2017;213(6):1010-1018. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2016.10.008
14. Williams DG, Aronson S, Murray S, et al. Validation of the perioperative nutrition screen for prediction of postoperative outcomes. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2022;46(6):1307-1315. doi:10.1002/jpen.2310
15. Besson AJ, Kei C, Djordjevic A, Carter V, Deftereos I, Yeung J. Does implementation of and adherence to enhanced recovery after surgery improve perioperative nutritional management in colorectal cancer surgery? ANZ J Surg. 2022;92(6):1382-1387. doi:10.1111/ans.17599
16. Arkenbosch JHC, van Erning FN, Rutten HJ, Zimmerman D, de Wilt JHW, Beijer S. The association between body mass index and postoperative complications, 30-day mortality and long-term survival in Dutch patients with colorectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol J Eur Soc Surg Oncol Br Assoc Surg Oncol. 2019;45(2):160-166. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2018.09.012
17. Shahjehan F, Merchea A, Cochuyt JJ, Li Z, Colibaseanu DT, Kasi PM. Body mass index and long-term outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer. Front Oncol. 2018;8:620. doi:10.3389/fonc.2018.00620
18. Nishigori T, Obama K, Sakai Y. Assessment of body composition and impact of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in patients with gastric cancer. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5:22. doi:10.21037/tgh.2019.10.13
19. Feliciano EMC, Winkels RM, Meyerhardt JA, Prado CM, Afman LA, Caan BJ. Abdominal adipose tissue radiodensity is associated with survival after colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021;114(6):1917-1924. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab285
Veterans Will Benefit if the VA Includes Telehealth in its Access Standards
The VA MISSION Act of 2018 expanded options for veterans to receive government-paid health care from private sector community health care practitioners. The act tasked the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) to develop rules that determine eligibility for outside care based on appointment wait times or distance to the nearest VA facility. As a part of those standards, VA opted not to include the availability of VA telehealth in its wait time calculations—a decision that we believe was a gross misjudgment with far-reaching consequences for veterans. Excluding telehealth from the guidelines has unnecessarily restricted veterans’ access to high-quality health care and has squandered large sums of taxpayer dollars.
The VA has reviewed its initial MISSION Act eligibility standards and proposed a correction that recognizes telehealth as a valid means of providing health care to veterans who prefer that option.1 Telehealth may not have been an essential component of health care before the COVID-19 pandemic, but now it is clear that the best action VA can take is to swiftly enact its recommended change, stipulating that both VA telehealth and in-person health care constitute access to treatment. If implemented, this correction would save taxpayers an astronomical sum—according to a VA report to Congress, about $1.1 billion in fiscal year 2021 alone.2 The cost savings from this proposed correction is reason enough to implement it. But just as importantly, increased use of VA telehealth also means higher quality, quicker, and more convenient care for veterans.
The VA is the recognized world leader in providing telehealth that is effective, timely, and veteran centric. Veterans across the country have access to telehealth services in more than 30 specialties.3 To ensure accessibility, the VA has established partnerships with major mobile broadband carriers so that veterans can receive telehealth at home without additional charges.4 The VA project Accessing Telehealth through Local Area Stations (ATLAS) brings VA telehealth to areas where existing internet infrastructure may not be adequate to support video telehealth. ATLAS is a collaboration with private organizations, including Veterans of Foreign Wars, The American Legion, and Walmart.4 The agency also provides tablets to veterans who might not have access to telehealth, fostering higher access and patient satisfaction.4
The VA can initiate telehealth care rapidly. The “Anywhere to Anywhere” VA Health Care initiative and telecare hubs eliminate geographic constraints, allowing clinicians to provide team-based services across county and state lines to veterans’ homes and communities.
VA’s telehealth effort maximizes convenience for veterans. It reduces travel time, travel expenses, depletion of sick leave, and the need for childcare. Veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder or military sexual trauma who are triggered by traffic and waiting rooms, those with mobility issues, or those facing the stigma of mental health treatment often prefer to receive care in the familiarity of their home. Nonetheless, any veteran who desires an in-person appointment would continue to have that option under the proposed VA rule change.
VA telehealth is often used for mental health care, using the same evidence-based psychotherapies that VA has championed and are superior to that available in the private sector.5,6 This advantage is largely due to VA’s rigorous training, consultation, case review, care delivery, measurement standards, and integrated care model. In a recent survey of veterans engaged in mental health care, 80% reported that VA virtual care via video and/or telephone is as helpful or more helpful than in‐person services.7 And yet, because of existing regulations, VA telemental health (TMH) does not qualify as access, resulting in hundreds of thousands of TMH visits being outsourced yearly to community practitioners that could be quickly and beneficially furnished by VA clinicians.
Telehealth has been shown to be as clinically effective as in-person care. A recent review of 38 meta-analyses covering telehealth with 10 medical disciplines found that for all disciplines, telehealth was as effective, if not more so, than conventional care.8 And because the likelihood of not showing up for telehealth appointments is lower than for in-person appointments, continuity of care is uninterrupted, and health care outcomes are improved.
Telehealth is health care. The VA must end the double standard that has handicapped it from including telehealth availability in determinations of eligibility for community care. The VA has voiced its intention to seek stakeholder input before implementing its proposed correction. The change is long overdue. It will save the VA a billion dollars annually while ensuring that veterans have quicker access to better treatment.
1 McDonough D. Statement of the honorable Denis McDonough Secretary of Veterans Affairs Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) before the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs United States Senate on veterans access to care. 117th Cong, 2nd Sess. September 21, 2022. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://www.veterans.senate.gov/2022/9/ensuring-veterans-timely-access-to-care-in-va-and-the-community/63b521ff-d308-449a-b3a3-918f4badb805
2 US Department of Veterans Affairs, Congressionally mandated report: access to care standards. September 2022.
3 US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA Secretary Press Conference, Thursday March 2, 2023. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WnkNl2whPoQ
4 US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Telehealth: bridging the digital divide. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://telehealth.va.gov/digital-divide
5 Rand Corporation. Improving the Quality of Mental Health Care for Veterans: Lessons from RAND Research. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, 2019. https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_briefs/RB10087.html.
6 Lemle, R. Choice program expansion jeopardizes high-quality VHA mental health services. Federal Pract. 2018:35(3):18-24. [link to: https://www.mdedge.com/fedprac/article/159219/mental-health/choice-program-expansion-jeopardizes-high-quality-vha-mental
7 Campbell TM. Overview of the state of mental health care services in the VHA health care system. Presentation to the National Academies’ improving access to high-quality mental health care for veterans: a workshop. April 20, 2023. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://www.nationalacademies.org/documents/embed/link/LF2255DA3DD1C41C0A42D3BEF0989ACAECE3053A6A9B/file/D2C4B73BA6FFCAA81E6C4FC7C57020A5BA54376245AD?noSaveAs=1
8 Snoswell CL, Chelberg G, De Guzman KR, et al. The clinical effectiveness of telehealth: A systematic review of meta-analyses from 2010 to 2019. J Telemed Telecare. 2021;1357633X211022907. doi:10.1177/1357633X211022907
The VA MISSION Act of 2018 expanded options for veterans to receive government-paid health care from private sector community health care practitioners. The act tasked the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) to develop rules that determine eligibility for outside care based on appointment wait times or distance to the nearest VA facility. As a part of those standards, VA opted not to include the availability of VA telehealth in its wait time calculations—a decision that we believe was a gross misjudgment with far-reaching consequences for veterans. Excluding telehealth from the guidelines has unnecessarily restricted veterans’ access to high-quality health care and has squandered large sums of taxpayer dollars.
The VA has reviewed its initial MISSION Act eligibility standards and proposed a correction that recognizes telehealth as a valid means of providing health care to veterans who prefer that option.1 Telehealth may not have been an essential component of health care before the COVID-19 pandemic, but now it is clear that the best action VA can take is to swiftly enact its recommended change, stipulating that both VA telehealth and in-person health care constitute access to treatment. If implemented, this correction would save taxpayers an astronomical sum—according to a VA report to Congress, about $1.1 billion in fiscal year 2021 alone.2 The cost savings from this proposed correction is reason enough to implement it. But just as importantly, increased use of VA telehealth also means higher quality, quicker, and more convenient care for veterans.
The VA is the recognized world leader in providing telehealth that is effective, timely, and veteran centric. Veterans across the country have access to telehealth services in more than 30 specialties.3 To ensure accessibility, the VA has established partnerships with major mobile broadband carriers so that veterans can receive telehealth at home without additional charges.4 The VA project Accessing Telehealth through Local Area Stations (ATLAS) brings VA telehealth to areas where existing internet infrastructure may not be adequate to support video telehealth. ATLAS is a collaboration with private organizations, including Veterans of Foreign Wars, The American Legion, and Walmart.4 The agency also provides tablets to veterans who might not have access to telehealth, fostering higher access and patient satisfaction.4
The VA can initiate telehealth care rapidly. The “Anywhere to Anywhere” VA Health Care initiative and telecare hubs eliminate geographic constraints, allowing clinicians to provide team-based services across county and state lines to veterans’ homes and communities.
VA’s telehealth effort maximizes convenience for veterans. It reduces travel time, travel expenses, depletion of sick leave, and the need for childcare. Veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder or military sexual trauma who are triggered by traffic and waiting rooms, those with mobility issues, or those facing the stigma of mental health treatment often prefer to receive care in the familiarity of their home. Nonetheless, any veteran who desires an in-person appointment would continue to have that option under the proposed VA rule change.
VA telehealth is often used for mental health care, using the same evidence-based psychotherapies that VA has championed and are superior to that available in the private sector.5,6 This advantage is largely due to VA’s rigorous training, consultation, case review, care delivery, measurement standards, and integrated care model. In a recent survey of veterans engaged in mental health care, 80% reported that VA virtual care via video and/or telephone is as helpful or more helpful than in‐person services.7 And yet, because of existing regulations, VA telemental health (TMH) does not qualify as access, resulting in hundreds of thousands of TMH visits being outsourced yearly to community practitioners that could be quickly and beneficially furnished by VA clinicians.
Telehealth has been shown to be as clinically effective as in-person care. A recent review of 38 meta-analyses covering telehealth with 10 medical disciplines found that for all disciplines, telehealth was as effective, if not more so, than conventional care.8 And because the likelihood of not showing up for telehealth appointments is lower than for in-person appointments, continuity of care is uninterrupted, and health care outcomes are improved.
Telehealth is health care. The VA must end the double standard that has handicapped it from including telehealth availability in determinations of eligibility for community care. The VA has voiced its intention to seek stakeholder input before implementing its proposed correction. The change is long overdue. It will save the VA a billion dollars annually while ensuring that veterans have quicker access to better treatment.
The VA MISSION Act of 2018 expanded options for veterans to receive government-paid health care from private sector community health care practitioners. The act tasked the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) to develop rules that determine eligibility for outside care based on appointment wait times or distance to the nearest VA facility. As a part of those standards, VA opted not to include the availability of VA telehealth in its wait time calculations—a decision that we believe was a gross misjudgment with far-reaching consequences for veterans. Excluding telehealth from the guidelines has unnecessarily restricted veterans’ access to high-quality health care and has squandered large sums of taxpayer dollars.
The VA has reviewed its initial MISSION Act eligibility standards and proposed a correction that recognizes telehealth as a valid means of providing health care to veterans who prefer that option.1 Telehealth may not have been an essential component of health care before the COVID-19 pandemic, but now it is clear that the best action VA can take is to swiftly enact its recommended change, stipulating that both VA telehealth and in-person health care constitute access to treatment. If implemented, this correction would save taxpayers an astronomical sum—according to a VA report to Congress, about $1.1 billion in fiscal year 2021 alone.2 The cost savings from this proposed correction is reason enough to implement it. But just as importantly, increased use of VA telehealth also means higher quality, quicker, and more convenient care for veterans.
The VA is the recognized world leader in providing telehealth that is effective, timely, and veteran centric. Veterans across the country have access to telehealth services in more than 30 specialties.3 To ensure accessibility, the VA has established partnerships with major mobile broadband carriers so that veterans can receive telehealth at home without additional charges.4 The VA project Accessing Telehealth through Local Area Stations (ATLAS) brings VA telehealth to areas where existing internet infrastructure may not be adequate to support video telehealth. ATLAS is a collaboration with private organizations, including Veterans of Foreign Wars, The American Legion, and Walmart.4 The agency also provides tablets to veterans who might not have access to telehealth, fostering higher access and patient satisfaction.4
The VA can initiate telehealth care rapidly. The “Anywhere to Anywhere” VA Health Care initiative and telecare hubs eliminate geographic constraints, allowing clinicians to provide team-based services across county and state lines to veterans’ homes and communities.
VA’s telehealth effort maximizes convenience for veterans. It reduces travel time, travel expenses, depletion of sick leave, and the need for childcare. Veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder or military sexual trauma who are triggered by traffic and waiting rooms, those with mobility issues, or those facing the stigma of mental health treatment often prefer to receive care in the familiarity of their home. Nonetheless, any veteran who desires an in-person appointment would continue to have that option under the proposed VA rule change.
VA telehealth is often used for mental health care, using the same evidence-based psychotherapies that VA has championed and are superior to that available in the private sector.5,6 This advantage is largely due to VA’s rigorous training, consultation, case review, care delivery, measurement standards, and integrated care model. In a recent survey of veterans engaged in mental health care, 80% reported that VA virtual care via video and/or telephone is as helpful or more helpful than in‐person services.7 And yet, because of existing regulations, VA telemental health (TMH) does not qualify as access, resulting in hundreds of thousands of TMH visits being outsourced yearly to community practitioners that could be quickly and beneficially furnished by VA clinicians.
Telehealth has been shown to be as clinically effective as in-person care. A recent review of 38 meta-analyses covering telehealth with 10 medical disciplines found that for all disciplines, telehealth was as effective, if not more so, than conventional care.8 And because the likelihood of not showing up for telehealth appointments is lower than for in-person appointments, continuity of care is uninterrupted, and health care outcomes are improved.
Telehealth is health care. The VA must end the double standard that has handicapped it from including telehealth availability in determinations of eligibility for community care. The VA has voiced its intention to seek stakeholder input before implementing its proposed correction. The change is long overdue. It will save the VA a billion dollars annually while ensuring that veterans have quicker access to better treatment.
1 McDonough D. Statement of the honorable Denis McDonough Secretary of Veterans Affairs Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) before the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs United States Senate on veterans access to care. 117th Cong, 2nd Sess. September 21, 2022. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://www.veterans.senate.gov/2022/9/ensuring-veterans-timely-access-to-care-in-va-and-the-community/63b521ff-d308-449a-b3a3-918f4badb805
2 US Department of Veterans Affairs, Congressionally mandated report: access to care standards. September 2022.
3 US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA Secretary Press Conference, Thursday March 2, 2023. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WnkNl2whPoQ
4 US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Telehealth: bridging the digital divide. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://telehealth.va.gov/digital-divide
5 Rand Corporation. Improving the Quality of Mental Health Care for Veterans: Lessons from RAND Research. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, 2019. https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_briefs/RB10087.html.
6 Lemle, R. Choice program expansion jeopardizes high-quality VHA mental health services. Federal Pract. 2018:35(3):18-24. [link to: https://www.mdedge.com/fedprac/article/159219/mental-health/choice-program-expansion-jeopardizes-high-quality-vha-mental
7 Campbell TM. Overview of the state of mental health care services in the VHA health care system. Presentation to the National Academies’ improving access to high-quality mental health care for veterans: a workshop. April 20, 2023. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://www.nationalacademies.org/documents/embed/link/LF2255DA3DD1C41C0A42D3BEF0989ACAECE3053A6A9B/file/D2C4B73BA6FFCAA81E6C4FC7C57020A5BA54376245AD?noSaveAs=1
8 Snoswell CL, Chelberg G, De Guzman KR, et al. The clinical effectiveness of telehealth: A systematic review of meta-analyses from 2010 to 2019. J Telemed Telecare. 2021;1357633X211022907. doi:10.1177/1357633X211022907
1 McDonough D. Statement of the honorable Denis McDonough Secretary of Veterans Affairs Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) before the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs United States Senate on veterans access to care. 117th Cong, 2nd Sess. September 21, 2022. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://www.veterans.senate.gov/2022/9/ensuring-veterans-timely-access-to-care-in-va-and-the-community/63b521ff-d308-449a-b3a3-918f4badb805
2 US Department of Veterans Affairs, Congressionally mandated report: access to care standards. September 2022.
3 US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA Secretary Press Conference, Thursday March 2, 2023. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WnkNl2whPoQ
4 US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Telehealth: bridging the digital divide. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://telehealth.va.gov/digital-divide
5 Rand Corporation. Improving the Quality of Mental Health Care for Veterans: Lessons from RAND Research. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, 2019. https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_briefs/RB10087.html.
6 Lemle, R. Choice program expansion jeopardizes high-quality VHA mental health services. Federal Pract. 2018:35(3):18-24. [link to: https://www.mdedge.com/fedprac/article/159219/mental-health/choice-program-expansion-jeopardizes-high-quality-vha-mental
7 Campbell TM. Overview of the state of mental health care services in the VHA health care system. Presentation to the National Academies’ improving access to high-quality mental health care for veterans: a workshop. April 20, 2023. Accessed May 8, 2023. https://www.nationalacademies.org/documents/embed/link/LF2255DA3DD1C41C0A42D3BEF0989ACAECE3053A6A9B/file/D2C4B73BA6FFCAA81E6C4FC7C57020A5BA54376245AD?noSaveAs=1
8 Snoswell CL, Chelberg G, De Guzman KR, et al. The clinical effectiveness of telehealth: A systematic review of meta-analyses from 2010 to 2019. J Telemed Telecare. 2021;1357633X211022907. doi:10.1177/1357633X211022907
Georgia VA Doctor Indicted on Sexual Assault Charges
A primary care physician at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Decatur, Georgia, has been indicted on several counts of sexual assault of veteran patients. Rajesh Motibhai Patel is accused of violating his patients’ constitutional right to bodily integrity while acting under color of law and of engaging in unwanted sexual contact.
According to US Attorney Ryan Buchanan, Patel allegedly “violated his oath to do no harm to patients under his care.” He allegedly sexually touched 4 female patients during routine examinations.
Patel’s alleged crimes were “horrific and unacceptable,” US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) press secretary Terrence Hayes said in a statement. “As soon as VA learned of these allegations, we removed this clinician from patient care and reassigned him to a role that had no patient interaction. Whenever a patient comes to VA, they deserve to know that they will be treated with care, compassion, and respect.”
The case is being investigated by the VA Office of Inspector General. Although Patel is only charged at present, not convicted, investigators believe he may have victimized other patients as well. Anyone with information is asked to call the VA-OIG tipline at (770) 758-6646.
A primary care physician at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Decatur, Georgia, has been indicted on several counts of sexual assault of veteran patients. Rajesh Motibhai Patel is accused of violating his patients’ constitutional right to bodily integrity while acting under color of law and of engaging in unwanted sexual contact.
According to US Attorney Ryan Buchanan, Patel allegedly “violated his oath to do no harm to patients under his care.” He allegedly sexually touched 4 female patients during routine examinations.
Patel’s alleged crimes were “horrific and unacceptable,” US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) press secretary Terrence Hayes said in a statement. “As soon as VA learned of these allegations, we removed this clinician from patient care and reassigned him to a role that had no patient interaction. Whenever a patient comes to VA, they deserve to know that they will be treated with care, compassion, and respect.”
The case is being investigated by the VA Office of Inspector General. Although Patel is only charged at present, not convicted, investigators believe he may have victimized other patients as well. Anyone with information is asked to call the VA-OIG tipline at (770) 758-6646.
A primary care physician at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Decatur, Georgia, has been indicted on several counts of sexual assault of veteran patients. Rajesh Motibhai Patel is accused of violating his patients’ constitutional right to bodily integrity while acting under color of law and of engaging in unwanted sexual contact.
According to US Attorney Ryan Buchanan, Patel allegedly “violated his oath to do no harm to patients under his care.” He allegedly sexually touched 4 female patients during routine examinations.
Patel’s alleged crimes were “horrific and unacceptable,” US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) press secretary Terrence Hayes said in a statement. “As soon as VA learned of these allegations, we removed this clinician from patient care and reassigned him to a role that had no patient interaction. Whenever a patient comes to VA, they deserve to know that they will be treated with care, compassion, and respect.”
The case is being investigated by the VA Office of Inspector General. Although Patel is only charged at present, not convicted, investigators believe he may have victimized other patients as well. Anyone with information is asked to call the VA-OIG tipline at (770) 758-6646.
The breathtaking effects of climate change
To see the harmful effects of climate change firsthand, you need look no farther than the nearest pulmonary clinic.
The causes and effects are unmistakable: pollen storms leading to allergy sufferers flooding into allergists’ offices; rising air pollution levels increasing risk for obstructive airway diseases, cardiopulmonary complications, and non–small cell lung cancer; melting snowpacks and atmospheric rivers inundating neighborhoods and leaving moldy debris and incipient fungal infections in their wake.
“The reason why we think climate change is going to change the type of disease patterns and the severity of illness that we see in patients with respiratory diseases is that it changes a lot of the environment as well as the exposures,” said Bathmapriya Balakrishnan, BMedSci, BMBS, from the section of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine in the department of medicine at West Virginia University, Morgantown.
“What we’re going to see is not just new diseases but also exacerbation of chronic diseases, things like asthma [and] COPD. And there’s also concern that patients who are otherwise healthy, because they now have more exposures that are due to climate change, can then develop these diseases,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Balakrishnan is the lead author of a comprehensive, evidence-based review focused on the effects of climate change and air pollution across the spectrum of pulmonary disorders. The review is published online ahead of print in the journal Chest.
“ To inform health care providers of evidence-based methods and improve patient counselling, further research regarding measures that limit exposure is needed. Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality and minimize exposure is a key preventative measure for decreasing morbidity and mortality while improving quality of life,” Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues write.
Similarly, in a statement on the effects of climate change on respiratory health, the American Public Health Association succinctly summarized the problem: “Warmer temperatures lead to an increase in pollutants and allergens. Poor air quality leads to reduced lung function, increased risk of asthma complications, heart attacks, heart failure, and death. Air pollution and allergens are the main exposures affecting lung and heart health in this changing climate.”
Early spring
Stanley Fineman, MD, MBA, a past president of the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology and an allergist in private practice in Atlanta, has seen firsthand how global warming and an earlier start to spring allergy season is affecting his patients.
“The season, at least in our area metro Atlanta, started earlier and has been lasting longer. The pollen counts are very high,” he told this news organization.
“In February we started seeing pollen counts over 1,000 [grams per cubic meter], which is unheard of, and in March about half the days we counted levels that were over 1,000, which is also unheard of. In April it was over 1,000 almost half the days.”
Dr. Fineman and colleagues both in Atlanta and across the country have reported sharp increases in the proportion of new adult patients and in existing patients who have experienced exacerbation of previously mild disease.
“Probably what’s happened is that they may have had some allergic sensitivity that resulted in milder manifestations, but this year they’re getting major manifestations,” Dr. Fineman said.
In a 2014 article in the journal European Respiratory Review, Gennaro D’Amato, MD, from High Speciality Hospital Antonio Cardarelli, Naples, Italy, and colleagues outlined the main effects of climate on pollen levels: “1) an increase in plant growth and faster plant growth; 2) an increase in the amount of pollen produced by each plant; 3) an increase in the amount of allergenic proteins contained in pollen; 4) an increase in the start time of plant growth and, therefore, the start of pollen production; 5) an earlier and longer pollen season; 6) change in the geospatial distribution of pollen, that is plant ranges and long-distance atmospheric transport moving polewards,” they write.
Bad air
In addition to pollen, the ambient air in many places is increasingly becoming saturated with bioallergenic proteins such as bacteria, viruses, animal dander, insects, molds, and plant species, Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues noted, adding that “atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide have also been found to increase pollen productivity. These changes result in greater over-the-counter medication use, emergency department visits, and outpatient visits for respiratory illnesses.”
The rash of violent storms that has washed over much of the United States in recent months is also likely to increase the incidence of so-called “thunderstorm asthma,” caused when large quantities of respirable particulate matter are released before or during a thunderstorm.
Air pollution from the burning of carbon-based fuels and from wildfires sparked by hotter and drier conditions increase airborne particulate matter that can seriously exacerbate asthma, COPD, and other obstructive airway conditions.
In addition, as previously reported by Medscape, exposure to particulate matter has been implicated as a possible cause of non–small cell lung cancer in persons who have never smoked.
Critical care challenges
Among the myriad other effects of climate change postulated in evidence enumerated by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues are chest infections and pleural diseases, such as aspergillosis infections that occur after catastrophic flooding; increased incidence of Mycobacterium avium complex infections and hypersensitivity pneumonitis; increased demands on critical care specialists from natural disasters; pollution-induced cardiac arrest; and heat prostration and heat stroke from increasingly prevalent heat waves.
The reviewers also examined evidence suggesting links between climate change and pulmonary hypertension, interstitial lung disease, sleep disorders, and occupational pulmonary disorders.
Power to the patients
“Pulmonologists should counsel patients on ways to minimize outdoor and indoor pollution, using tight-fitting respirators and home air-purifying systems without encroaching on patients’ beliefs and choices,” the authors advise.
“Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality daily, in inclement weather, and during disasters would help minimize exposure and thus improve overall health. The pulmonologist can play an important role in emphasizing the impact of climate change on pulmonary disorders during patient care encounters,” they write.
Ms. Balakrishan adds that another important mitigation measure that can be taken today is education.
“In medical school we don’t really learn about the impact of climate change – at least in my generation of physicians, climate change or global warming weren’t part of the medical curriculum – but now I think that there’s a lot of advocacy work being done by medical students who actually want more education on climate change and its effects on pulmonary diseases,” she said.
The study by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues was unfunded. Ms. Balakrishnan reports no relevant financial relationships. Co-author Mary-Beth Scholand, MD, has received personal fees from serving on advisory boards and speakers bureaus for Genentech, Boehringer Ingelheim, Veracyte, and United Therapeutics. Co-author Sean Callahan, MD, has received personal fees for serving on advisory boards for Gilead and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Fineman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
To see the harmful effects of climate change firsthand, you need look no farther than the nearest pulmonary clinic.
The causes and effects are unmistakable: pollen storms leading to allergy sufferers flooding into allergists’ offices; rising air pollution levels increasing risk for obstructive airway diseases, cardiopulmonary complications, and non–small cell lung cancer; melting snowpacks and atmospheric rivers inundating neighborhoods and leaving moldy debris and incipient fungal infections in their wake.
“The reason why we think climate change is going to change the type of disease patterns and the severity of illness that we see in patients with respiratory diseases is that it changes a lot of the environment as well as the exposures,” said Bathmapriya Balakrishnan, BMedSci, BMBS, from the section of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine in the department of medicine at West Virginia University, Morgantown.
“What we’re going to see is not just new diseases but also exacerbation of chronic diseases, things like asthma [and] COPD. And there’s also concern that patients who are otherwise healthy, because they now have more exposures that are due to climate change, can then develop these diseases,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Balakrishnan is the lead author of a comprehensive, evidence-based review focused on the effects of climate change and air pollution across the spectrum of pulmonary disorders. The review is published online ahead of print in the journal Chest.
“ To inform health care providers of evidence-based methods and improve patient counselling, further research regarding measures that limit exposure is needed. Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality and minimize exposure is a key preventative measure for decreasing morbidity and mortality while improving quality of life,” Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues write.
Similarly, in a statement on the effects of climate change on respiratory health, the American Public Health Association succinctly summarized the problem: “Warmer temperatures lead to an increase in pollutants and allergens. Poor air quality leads to reduced lung function, increased risk of asthma complications, heart attacks, heart failure, and death. Air pollution and allergens are the main exposures affecting lung and heart health in this changing climate.”
Early spring
Stanley Fineman, MD, MBA, a past president of the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology and an allergist in private practice in Atlanta, has seen firsthand how global warming and an earlier start to spring allergy season is affecting his patients.
“The season, at least in our area metro Atlanta, started earlier and has been lasting longer. The pollen counts are very high,” he told this news organization.
“In February we started seeing pollen counts over 1,000 [grams per cubic meter], which is unheard of, and in March about half the days we counted levels that were over 1,000, which is also unheard of. In April it was over 1,000 almost half the days.”
Dr. Fineman and colleagues both in Atlanta and across the country have reported sharp increases in the proportion of new adult patients and in existing patients who have experienced exacerbation of previously mild disease.
“Probably what’s happened is that they may have had some allergic sensitivity that resulted in milder manifestations, but this year they’re getting major manifestations,” Dr. Fineman said.
In a 2014 article in the journal European Respiratory Review, Gennaro D’Amato, MD, from High Speciality Hospital Antonio Cardarelli, Naples, Italy, and colleagues outlined the main effects of climate on pollen levels: “1) an increase in plant growth and faster plant growth; 2) an increase in the amount of pollen produced by each plant; 3) an increase in the amount of allergenic proteins contained in pollen; 4) an increase in the start time of plant growth and, therefore, the start of pollen production; 5) an earlier and longer pollen season; 6) change in the geospatial distribution of pollen, that is plant ranges and long-distance atmospheric transport moving polewards,” they write.
Bad air
In addition to pollen, the ambient air in many places is increasingly becoming saturated with bioallergenic proteins such as bacteria, viruses, animal dander, insects, molds, and plant species, Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues noted, adding that “atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide have also been found to increase pollen productivity. These changes result in greater over-the-counter medication use, emergency department visits, and outpatient visits for respiratory illnesses.”
The rash of violent storms that has washed over much of the United States in recent months is also likely to increase the incidence of so-called “thunderstorm asthma,” caused when large quantities of respirable particulate matter are released before or during a thunderstorm.
Air pollution from the burning of carbon-based fuels and from wildfires sparked by hotter and drier conditions increase airborne particulate matter that can seriously exacerbate asthma, COPD, and other obstructive airway conditions.
In addition, as previously reported by Medscape, exposure to particulate matter has been implicated as a possible cause of non–small cell lung cancer in persons who have never smoked.
Critical care challenges
Among the myriad other effects of climate change postulated in evidence enumerated by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues are chest infections and pleural diseases, such as aspergillosis infections that occur after catastrophic flooding; increased incidence of Mycobacterium avium complex infections and hypersensitivity pneumonitis; increased demands on critical care specialists from natural disasters; pollution-induced cardiac arrest; and heat prostration and heat stroke from increasingly prevalent heat waves.
The reviewers also examined evidence suggesting links between climate change and pulmonary hypertension, interstitial lung disease, sleep disorders, and occupational pulmonary disorders.
Power to the patients
“Pulmonologists should counsel patients on ways to minimize outdoor and indoor pollution, using tight-fitting respirators and home air-purifying systems without encroaching on patients’ beliefs and choices,” the authors advise.
“Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality daily, in inclement weather, and during disasters would help minimize exposure and thus improve overall health. The pulmonologist can play an important role in emphasizing the impact of climate change on pulmonary disorders during patient care encounters,” they write.
Ms. Balakrishan adds that another important mitigation measure that can be taken today is education.
“In medical school we don’t really learn about the impact of climate change – at least in my generation of physicians, climate change or global warming weren’t part of the medical curriculum – but now I think that there’s a lot of advocacy work being done by medical students who actually want more education on climate change and its effects on pulmonary diseases,” she said.
The study by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues was unfunded. Ms. Balakrishnan reports no relevant financial relationships. Co-author Mary-Beth Scholand, MD, has received personal fees from serving on advisory boards and speakers bureaus for Genentech, Boehringer Ingelheim, Veracyte, and United Therapeutics. Co-author Sean Callahan, MD, has received personal fees for serving on advisory boards for Gilead and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Fineman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
To see the harmful effects of climate change firsthand, you need look no farther than the nearest pulmonary clinic.
The causes and effects are unmistakable: pollen storms leading to allergy sufferers flooding into allergists’ offices; rising air pollution levels increasing risk for obstructive airway diseases, cardiopulmonary complications, and non–small cell lung cancer; melting snowpacks and atmospheric rivers inundating neighborhoods and leaving moldy debris and incipient fungal infections in their wake.
“The reason why we think climate change is going to change the type of disease patterns and the severity of illness that we see in patients with respiratory diseases is that it changes a lot of the environment as well as the exposures,” said Bathmapriya Balakrishnan, BMedSci, BMBS, from the section of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine in the department of medicine at West Virginia University, Morgantown.
“What we’re going to see is not just new diseases but also exacerbation of chronic diseases, things like asthma [and] COPD. And there’s also concern that patients who are otherwise healthy, because they now have more exposures that are due to climate change, can then develop these diseases,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Balakrishnan is the lead author of a comprehensive, evidence-based review focused on the effects of climate change and air pollution across the spectrum of pulmonary disorders. The review is published online ahead of print in the journal Chest.
“ To inform health care providers of evidence-based methods and improve patient counselling, further research regarding measures that limit exposure is needed. Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality and minimize exposure is a key preventative measure for decreasing morbidity and mortality while improving quality of life,” Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues write.
Similarly, in a statement on the effects of climate change on respiratory health, the American Public Health Association succinctly summarized the problem: “Warmer temperatures lead to an increase in pollutants and allergens. Poor air quality leads to reduced lung function, increased risk of asthma complications, heart attacks, heart failure, and death. Air pollution and allergens are the main exposures affecting lung and heart health in this changing climate.”
Early spring
Stanley Fineman, MD, MBA, a past president of the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology and an allergist in private practice in Atlanta, has seen firsthand how global warming and an earlier start to spring allergy season is affecting his patients.
“The season, at least in our area metro Atlanta, started earlier and has been lasting longer. The pollen counts are very high,” he told this news organization.
“In February we started seeing pollen counts over 1,000 [grams per cubic meter], which is unheard of, and in March about half the days we counted levels that were over 1,000, which is also unheard of. In April it was over 1,000 almost half the days.”
Dr. Fineman and colleagues both in Atlanta and across the country have reported sharp increases in the proportion of new adult patients and in existing patients who have experienced exacerbation of previously mild disease.
“Probably what’s happened is that they may have had some allergic sensitivity that resulted in milder manifestations, but this year they’re getting major manifestations,” Dr. Fineman said.
In a 2014 article in the journal European Respiratory Review, Gennaro D’Amato, MD, from High Speciality Hospital Antonio Cardarelli, Naples, Italy, and colleagues outlined the main effects of climate on pollen levels: “1) an increase in plant growth and faster plant growth; 2) an increase in the amount of pollen produced by each plant; 3) an increase in the amount of allergenic proteins contained in pollen; 4) an increase in the start time of plant growth and, therefore, the start of pollen production; 5) an earlier and longer pollen season; 6) change in the geospatial distribution of pollen, that is plant ranges and long-distance atmospheric transport moving polewards,” they write.
Bad air
In addition to pollen, the ambient air in many places is increasingly becoming saturated with bioallergenic proteins such as bacteria, viruses, animal dander, insects, molds, and plant species, Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues noted, adding that “atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide have also been found to increase pollen productivity. These changes result in greater over-the-counter medication use, emergency department visits, and outpatient visits for respiratory illnesses.”
The rash of violent storms that has washed over much of the United States in recent months is also likely to increase the incidence of so-called “thunderstorm asthma,” caused when large quantities of respirable particulate matter are released before or during a thunderstorm.
Air pollution from the burning of carbon-based fuels and from wildfires sparked by hotter and drier conditions increase airborne particulate matter that can seriously exacerbate asthma, COPD, and other obstructive airway conditions.
In addition, as previously reported by Medscape, exposure to particulate matter has been implicated as a possible cause of non–small cell lung cancer in persons who have never smoked.
Critical care challenges
Among the myriad other effects of climate change postulated in evidence enumerated by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues are chest infections and pleural diseases, such as aspergillosis infections that occur after catastrophic flooding; increased incidence of Mycobacterium avium complex infections and hypersensitivity pneumonitis; increased demands on critical care specialists from natural disasters; pollution-induced cardiac arrest; and heat prostration and heat stroke from increasingly prevalent heat waves.
The reviewers also examined evidence suggesting links between climate change and pulmonary hypertension, interstitial lung disease, sleep disorders, and occupational pulmonary disorders.
Power to the patients
“Pulmonologists should counsel patients on ways to minimize outdoor and indoor pollution, using tight-fitting respirators and home air-purifying systems without encroaching on patients’ beliefs and choices,” the authors advise.
“Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality daily, in inclement weather, and during disasters would help minimize exposure and thus improve overall health. The pulmonologist can play an important role in emphasizing the impact of climate change on pulmonary disorders during patient care encounters,” they write.
Ms. Balakrishan adds that another important mitigation measure that can be taken today is education.
“In medical school we don’t really learn about the impact of climate change – at least in my generation of physicians, climate change or global warming weren’t part of the medical curriculum – but now I think that there’s a lot of advocacy work being done by medical students who actually want more education on climate change and its effects on pulmonary diseases,” she said.
The study by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues was unfunded. Ms. Balakrishnan reports no relevant financial relationships. Co-author Mary-Beth Scholand, MD, has received personal fees from serving on advisory boards and speakers bureaus for Genentech, Boehringer Ingelheim, Veracyte, and United Therapeutics. Co-author Sean Callahan, MD, has received personal fees for serving on advisory boards for Gilead and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Fineman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CLL: Black patients die sooner than Whites
The findings, published in the American Journal of Hematology, hint that the racial disparity has shrunk over time, especially within the first few years of the targeted-therapy era. Still, “Black patients had a shorter median overall survival of 7 years compared to 9 years for White patients,” study coauthor Deborah Stephens, DO, of the University of Utah Huntsman Cancer Institute, said in an interview. “Clearly, more research is needed to tease out the biologic or economic barriers to achieving prolonged survival.”
As the researchers noted, CLL is far more common among White patients (5.1 cases per 100,000) than other races (Black patients: 3.2 cases per 100,000; Hispanic patients: 2.1 cases per 100,000; Asian American patients: 1.1 per 100,000). In total, non-White patients make up just 11%-13% of CLL cases in the United States.
According to Dr. Stephens, “little is known or published” about Black patients with CLL, “and it is still a mystery why fewer patients that are Black develop CLL and why this group would have shorter survival.”
Dr. Stephens and colleagues launched the new study – the largest of its kind to date – to understand disparities between White and Black patients over most of the past 20 years. The researchers especially wanted to analyze trends during the last decade, when targeted therapies revolutionized treatment of the disease.
The study authors analyzed data in the National Cancer Database for 97,804 patients diagnosed from 2004 to 2018 (90.7% White, 7.6% Black, 0.6% Asian, 1.1% other). Of patients who reported ethnicity (n = 93,555), 2.6% were Hispanic.
Black patients were more likely to have begun CLL therapy at diagnosis (35.9%) than were White patients (23.6%), a sign that Black patients had more advanced disease. Black patients also had shorter overall survival (7.0 years, 95% confidence interval [CI], 6.7–7.3 years) vs. White patients (9.1 years, 95% CI, 9.0–9.3 years, P < .001).
“This finding could be due to underlying biologic differences in the pathology of CLL, when comparing patients across racial groups,” Dr. Stephens said. “Additionally, there could be differences in access to care. Notably, there are fewer racial minorities enrolled in clinical trials, and perhaps we are not individualizing therapy for unique biologic factors seen in CLL affecting racial minorities.”
Other factors also could be at play. Black patients were more likely than were White patients to have one or more comorbidities (27.9% vs. 21.3%, P < .001), lack insurance (6.6% vs. 2.1%, P < .001) and live in lower-income neighborhoods (47.7% vs. 13.1%, P < .001).
What explains the gap in outcomes? In an interview, study lead author Victoria Vardell, MD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, noted that researchers often attribute worse medical outcomes in Black patients to economic and social disparities.
“However, when we adjusted for a number of surrogate markers of health care access, including income, comorbidities, and location, among others, this disparity remained. That indicates that this may be a more complex problem in CLL in particular. Certainly, we cannot adjust for all the socioeconomic strain placed on Black Americans, including those with CLL, but there may be molecular features related to ancestry or environmental exposures that also play a role,” Dr. Vardell said.
She added that “the high cost and difficulty obtaining many novel therapies, particularly in the clinical trial setting, places significantly higher burdens on already disadvantaged populations.”
There is some good news in the new report. “Promisingly, our data suggest that the survival disparity between White and Black patients with CLL may be improving, particularly within the last 5 years, though longer follow-up is needed to confirm significance,” the researchers reported.
Alessandra Ferrajoli, MD, of M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, who has studied racial disparities in CLL, praised the study in an interview. As she noted, it examines an impressively large population.
The explanations for the disparities are still elusive, she said, although it seems clear there are multiple factors at play. “We don’t know if the disease has the same characteristics in African-Americans as in Whites,” Dr. Ferrajoli said. However, she noted, there’s “no indication that the response to treatment is different according to race.”
Moving forward, she said, the study findings “reinforce the fact that we need to pay attention to this population and be quite attentive to their characteristics.”
No study funding was reported. The authors and Dr. Ferrajoli have no disclosures.
The findings, published in the American Journal of Hematology, hint that the racial disparity has shrunk over time, especially within the first few years of the targeted-therapy era. Still, “Black patients had a shorter median overall survival of 7 years compared to 9 years for White patients,” study coauthor Deborah Stephens, DO, of the University of Utah Huntsman Cancer Institute, said in an interview. “Clearly, more research is needed to tease out the biologic or economic barriers to achieving prolonged survival.”
As the researchers noted, CLL is far more common among White patients (5.1 cases per 100,000) than other races (Black patients: 3.2 cases per 100,000; Hispanic patients: 2.1 cases per 100,000; Asian American patients: 1.1 per 100,000). In total, non-White patients make up just 11%-13% of CLL cases in the United States.
According to Dr. Stephens, “little is known or published” about Black patients with CLL, “and it is still a mystery why fewer patients that are Black develop CLL and why this group would have shorter survival.”
Dr. Stephens and colleagues launched the new study – the largest of its kind to date – to understand disparities between White and Black patients over most of the past 20 years. The researchers especially wanted to analyze trends during the last decade, when targeted therapies revolutionized treatment of the disease.
The study authors analyzed data in the National Cancer Database for 97,804 patients diagnosed from 2004 to 2018 (90.7% White, 7.6% Black, 0.6% Asian, 1.1% other). Of patients who reported ethnicity (n = 93,555), 2.6% were Hispanic.
Black patients were more likely to have begun CLL therapy at diagnosis (35.9%) than were White patients (23.6%), a sign that Black patients had more advanced disease. Black patients also had shorter overall survival (7.0 years, 95% confidence interval [CI], 6.7–7.3 years) vs. White patients (9.1 years, 95% CI, 9.0–9.3 years, P < .001).
“This finding could be due to underlying biologic differences in the pathology of CLL, when comparing patients across racial groups,” Dr. Stephens said. “Additionally, there could be differences in access to care. Notably, there are fewer racial minorities enrolled in clinical trials, and perhaps we are not individualizing therapy for unique biologic factors seen in CLL affecting racial minorities.”
Other factors also could be at play. Black patients were more likely than were White patients to have one or more comorbidities (27.9% vs. 21.3%, P < .001), lack insurance (6.6% vs. 2.1%, P < .001) and live in lower-income neighborhoods (47.7% vs. 13.1%, P < .001).
What explains the gap in outcomes? In an interview, study lead author Victoria Vardell, MD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, noted that researchers often attribute worse medical outcomes in Black patients to economic and social disparities.
“However, when we adjusted for a number of surrogate markers of health care access, including income, comorbidities, and location, among others, this disparity remained. That indicates that this may be a more complex problem in CLL in particular. Certainly, we cannot adjust for all the socioeconomic strain placed on Black Americans, including those with CLL, but there may be molecular features related to ancestry or environmental exposures that also play a role,” Dr. Vardell said.
She added that “the high cost and difficulty obtaining many novel therapies, particularly in the clinical trial setting, places significantly higher burdens on already disadvantaged populations.”
There is some good news in the new report. “Promisingly, our data suggest that the survival disparity between White and Black patients with CLL may be improving, particularly within the last 5 years, though longer follow-up is needed to confirm significance,” the researchers reported.
Alessandra Ferrajoli, MD, of M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, who has studied racial disparities in CLL, praised the study in an interview. As she noted, it examines an impressively large population.
The explanations for the disparities are still elusive, she said, although it seems clear there are multiple factors at play. “We don’t know if the disease has the same characteristics in African-Americans as in Whites,” Dr. Ferrajoli said. However, she noted, there’s “no indication that the response to treatment is different according to race.”
Moving forward, she said, the study findings “reinforce the fact that we need to pay attention to this population and be quite attentive to their characteristics.”
No study funding was reported. The authors and Dr. Ferrajoli have no disclosures.
The findings, published in the American Journal of Hematology, hint that the racial disparity has shrunk over time, especially within the first few years of the targeted-therapy era. Still, “Black patients had a shorter median overall survival of 7 years compared to 9 years for White patients,” study coauthor Deborah Stephens, DO, of the University of Utah Huntsman Cancer Institute, said in an interview. “Clearly, more research is needed to tease out the biologic or economic barriers to achieving prolonged survival.”
As the researchers noted, CLL is far more common among White patients (5.1 cases per 100,000) than other races (Black patients: 3.2 cases per 100,000; Hispanic patients: 2.1 cases per 100,000; Asian American patients: 1.1 per 100,000). In total, non-White patients make up just 11%-13% of CLL cases in the United States.
According to Dr. Stephens, “little is known or published” about Black patients with CLL, “and it is still a mystery why fewer patients that are Black develop CLL and why this group would have shorter survival.”
Dr. Stephens and colleagues launched the new study – the largest of its kind to date – to understand disparities between White and Black patients over most of the past 20 years. The researchers especially wanted to analyze trends during the last decade, when targeted therapies revolutionized treatment of the disease.
The study authors analyzed data in the National Cancer Database for 97,804 patients diagnosed from 2004 to 2018 (90.7% White, 7.6% Black, 0.6% Asian, 1.1% other). Of patients who reported ethnicity (n = 93,555), 2.6% were Hispanic.
Black patients were more likely to have begun CLL therapy at diagnosis (35.9%) than were White patients (23.6%), a sign that Black patients had more advanced disease. Black patients also had shorter overall survival (7.0 years, 95% confidence interval [CI], 6.7–7.3 years) vs. White patients (9.1 years, 95% CI, 9.0–9.3 years, P < .001).
“This finding could be due to underlying biologic differences in the pathology of CLL, when comparing patients across racial groups,” Dr. Stephens said. “Additionally, there could be differences in access to care. Notably, there are fewer racial minorities enrolled in clinical trials, and perhaps we are not individualizing therapy for unique biologic factors seen in CLL affecting racial minorities.”
Other factors also could be at play. Black patients were more likely than were White patients to have one or more comorbidities (27.9% vs. 21.3%, P < .001), lack insurance (6.6% vs. 2.1%, P < .001) and live in lower-income neighborhoods (47.7% vs. 13.1%, P < .001).
What explains the gap in outcomes? In an interview, study lead author Victoria Vardell, MD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, noted that researchers often attribute worse medical outcomes in Black patients to economic and social disparities.
“However, when we adjusted for a number of surrogate markers of health care access, including income, comorbidities, and location, among others, this disparity remained. That indicates that this may be a more complex problem in CLL in particular. Certainly, we cannot adjust for all the socioeconomic strain placed on Black Americans, including those with CLL, but there may be molecular features related to ancestry or environmental exposures that also play a role,” Dr. Vardell said.
She added that “the high cost and difficulty obtaining many novel therapies, particularly in the clinical trial setting, places significantly higher burdens on already disadvantaged populations.”
There is some good news in the new report. “Promisingly, our data suggest that the survival disparity between White and Black patients with CLL may be improving, particularly within the last 5 years, though longer follow-up is needed to confirm significance,” the researchers reported.
Alessandra Ferrajoli, MD, of M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, who has studied racial disparities in CLL, praised the study in an interview. As she noted, it examines an impressively large population.
The explanations for the disparities are still elusive, she said, although it seems clear there are multiple factors at play. “We don’t know if the disease has the same characteristics in African-Americans as in Whites,” Dr. Ferrajoli said. However, she noted, there’s “no indication that the response to treatment is different according to race.”
Moving forward, she said, the study findings “reinforce the fact that we need to pay attention to this population and be quite attentive to their characteristics.”
No study funding was reported. The authors and Dr. Ferrajoli have no disclosures.
FROM AMERICAN JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY
CRC screening rates are higher in Medicaid expansion states
CHICAGO – presented on May 6 in Chicago at the annual Digestive Disease Week®.
Researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles, reported that states with expanded Medicaid coverage had significantly higher rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) screening than states where officials refused federal support for Medicaid expansion.
Led by Megan R. McLeod, MD, an internal medicine resident at the University of California, Los Angeles, researchers compared CRC screening rates in states that did not adopt Medicaid expansion in 2021 with screening rates in states that invested Medicaid expansion into 1,284 Federally Qualified Health Centers, which are nonprofit health centers or clinics that serve medically underserved areas and populations. In this study, 76% of these centers were in states that accepted Medicaid expansion. The median colorectal cancer screening rate was 42.1% in Medicaid expansion states, compared with 36.5% in nonexpansion states
“The impact of being uninsured on CRC screening participation was profound in nonexpansion states,” said Dr. McLeod, who will be a UCLA gastroenterology fellow this year.
The study adds to a growing body of evidence that shows Medicaid expansion, which increases access to health care services to previously uninsured or underinsured patients, can improve health outcomes and may reduce racial and economic disparities.
For example, a 2019 study based on electronic health record data presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology showed that, after Medicaid expansion, racial differences in timely cancer treatment effectively disappeared. Before Medicaid expansion, Black patients were 4.8% less likely than White patients to receive timely cancer treatment, which is defined as treatment starting within 30 days of the diagnosis of an advanced or metastatic solid tumor. After Medicaid expansion, however, the difference between the racial groups dwindled to 0.8% and was no longer statistically significant.
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medical Center in New York reported in 2020 at the virtual annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases that, 1 year after Medicaid expansion began on Jan. 1, 2014, the rate of liver-related mortality began to decline in 18 states with expanded coverage, whereas the rate of liver-related deaths continued to climb in 14 states that did not expand Medicaid.
The U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration funds Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHC) that serve nearly 29 million patients throughout the country, including a large proportion whose care is covered by Medicaid. Among patients cared for in these centers, one in three have incomes below the federal poverty line, and one in five are uninsured.
Screening rates compared
Dr. McLeod and colleagues sought to determine whether Medicaid expansion would have an effect on CRC screening rates at these centers. The final analysis included 6,940,879 patients (between 50 and 74 years), of whom 1.7% were unhoused and 17.6% were uninsured.
Medicaid expansion status appeared to have a direct impact on whether screenings were even offered to patients. Centers in rural areas and those with a high proportion of uninsured patients were found to have significantly higher odds for doing fewer CRC screenings. In Medicaid expansion states, CRC screening rates were significantly lower for patients who were male, Black, Hispanic, had low income, were unhoused, or were uninsured.
In a Q&A that followed the presentation, Steven Itzkowitz, MD, director of the GI fellowship program at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, suggested the type of CRC test patients are offered is directly related to Medicaid expansion status.
“In New York, before Cologuard (a colon and rectal cancer screening test) was covered by Medicaid, it wasn’t used very much, but once it got paid for by Medicaid, rates went up,” he said.
The study was internally supported. Dr. McLeod reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Itzkowitz has been a consultant for Exact Sciences, the maker of Cologuard.
DDW is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
CHICAGO – presented on May 6 in Chicago at the annual Digestive Disease Week®.
Researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles, reported that states with expanded Medicaid coverage had significantly higher rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) screening than states where officials refused federal support for Medicaid expansion.
Led by Megan R. McLeod, MD, an internal medicine resident at the University of California, Los Angeles, researchers compared CRC screening rates in states that did not adopt Medicaid expansion in 2021 with screening rates in states that invested Medicaid expansion into 1,284 Federally Qualified Health Centers, which are nonprofit health centers or clinics that serve medically underserved areas and populations. In this study, 76% of these centers were in states that accepted Medicaid expansion. The median colorectal cancer screening rate was 42.1% in Medicaid expansion states, compared with 36.5% in nonexpansion states
“The impact of being uninsured on CRC screening participation was profound in nonexpansion states,” said Dr. McLeod, who will be a UCLA gastroenterology fellow this year.
The study adds to a growing body of evidence that shows Medicaid expansion, which increases access to health care services to previously uninsured or underinsured patients, can improve health outcomes and may reduce racial and economic disparities.
For example, a 2019 study based on electronic health record data presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology showed that, after Medicaid expansion, racial differences in timely cancer treatment effectively disappeared. Before Medicaid expansion, Black patients were 4.8% less likely than White patients to receive timely cancer treatment, which is defined as treatment starting within 30 days of the diagnosis of an advanced or metastatic solid tumor. After Medicaid expansion, however, the difference between the racial groups dwindled to 0.8% and was no longer statistically significant.
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medical Center in New York reported in 2020 at the virtual annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases that, 1 year after Medicaid expansion began on Jan. 1, 2014, the rate of liver-related mortality began to decline in 18 states with expanded coverage, whereas the rate of liver-related deaths continued to climb in 14 states that did not expand Medicaid.
The U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration funds Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHC) that serve nearly 29 million patients throughout the country, including a large proportion whose care is covered by Medicaid. Among patients cared for in these centers, one in three have incomes below the federal poverty line, and one in five are uninsured.
Screening rates compared
Dr. McLeod and colleagues sought to determine whether Medicaid expansion would have an effect on CRC screening rates at these centers. The final analysis included 6,940,879 patients (between 50 and 74 years), of whom 1.7% were unhoused and 17.6% were uninsured.
Medicaid expansion status appeared to have a direct impact on whether screenings were even offered to patients. Centers in rural areas and those with a high proportion of uninsured patients were found to have significantly higher odds for doing fewer CRC screenings. In Medicaid expansion states, CRC screening rates were significantly lower for patients who were male, Black, Hispanic, had low income, were unhoused, or were uninsured.
In a Q&A that followed the presentation, Steven Itzkowitz, MD, director of the GI fellowship program at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, suggested the type of CRC test patients are offered is directly related to Medicaid expansion status.
“In New York, before Cologuard (a colon and rectal cancer screening test) was covered by Medicaid, it wasn’t used very much, but once it got paid for by Medicaid, rates went up,” he said.
The study was internally supported. Dr. McLeod reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Itzkowitz has been a consultant for Exact Sciences, the maker of Cologuard.
DDW is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
CHICAGO – presented on May 6 in Chicago at the annual Digestive Disease Week®.
Researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles, reported that states with expanded Medicaid coverage had significantly higher rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) screening than states where officials refused federal support for Medicaid expansion.
Led by Megan R. McLeod, MD, an internal medicine resident at the University of California, Los Angeles, researchers compared CRC screening rates in states that did not adopt Medicaid expansion in 2021 with screening rates in states that invested Medicaid expansion into 1,284 Federally Qualified Health Centers, which are nonprofit health centers or clinics that serve medically underserved areas and populations. In this study, 76% of these centers were in states that accepted Medicaid expansion. The median colorectal cancer screening rate was 42.1% in Medicaid expansion states, compared with 36.5% in nonexpansion states
“The impact of being uninsured on CRC screening participation was profound in nonexpansion states,” said Dr. McLeod, who will be a UCLA gastroenterology fellow this year.
The study adds to a growing body of evidence that shows Medicaid expansion, which increases access to health care services to previously uninsured or underinsured patients, can improve health outcomes and may reduce racial and economic disparities.
For example, a 2019 study based on electronic health record data presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology showed that, after Medicaid expansion, racial differences in timely cancer treatment effectively disappeared. Before Medicaid expansion, Black patients were 4.8% less likely than White patients to receive timely cancer treatment, which is defined as treatment starting within 30 days of the diagnosis of an advanced or metastatic solid tumor. After Medicaid expansion, however, the difference between the racial groups dwindled to 0.8% and was no longer statistically significant.
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medical Center in New York reported in 2020 at the virtual annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases that, 1 year after Medicaid expansion began on Jan. 1, 2014, the rate of liver-related mortality began to decline in 18 states with expanded coverage, whereas the rate of liver-related deaths continued to climb in 14 states that did not expand Medicaid.
The U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration funds Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHC) that serve nearly 29 million patients throughout the country, including a large proportion whose care is covered by Medicaid. Among patients cared for in these centers, one in three have incomes below the federal poverty line, and one in five are uninsured.
Screening rates compared
Dr. McLeod and colleagues sought to determine whether Medicaid expansion would have an effect on CRC screening rates at these centers. The final analysis included 6,940,879 patients (between 50 and 74 years), of whom 1.7% were unhoused and 17.6% were uninsured.
Medicaid expansion status appeared to have a direct impact on whether screenings were even offered to patients. Centers in rural areas and those with a high proportion of uninsured patients were found to have significantly higher odds for doing fewer CRC screenings. In Medicaid expansion states, CRC screening rates were significantly lower for patients who were male, Black, Hispanic, had low income, were unhoused, or were uninsured.
In a Q&A that followed the presentation, Steven Itzkowitz, MD, director of the GI fellowship program at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, suggested the type of CRC test patients are offered is directly related to Medicaid expansion status.
“In New York, before Cologuard (a colon and rectal cancer screening test) was covered by Medicaid, it wasn’t used very much, but once it got paid for by Medicaid, rates went up,” he said.
The study was internally supported. Dr. McLeod reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Itzkowitz has been a consultant for Exact Sciences, the maker of Cologuard.
DDW is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
AT DDW 2023
Familial cancer risk complex, not limited to same site
The researchers found, for instance, that children of breast cancer patients had a 27% higher risk of any discordant early-onset cancer, and patients’ siblings had a 7.6-fold higher risk of early pancreatic cancer. The analysis also indicated that children of patients’ siblings had a significantly increased risk of testicular and ovarian cancers.
“The findings suggest that the familial risk extends to discordant early-onset cancers, including ovarian, testicular, and pancreatic cancers, as well as beyond first-degree relatives,” the researchers, led by Janne M. Pitkäniemi, PhD, Finnish Cancer Registry, Institute for Statistical and Epidemiological Cancer Research, Helsinki, say. “Our findings are interesting but raise some questions about unknown [genetic] and environmental mechanisms that need to be further studied.”
Erin F. Cobain, MD, who was not involved in the research, said the findings are “not very surprising to me.”
Dr. Cobain said that at her institution, she has seen “many, many cases” of family members of early-onset breast cancer patients with discordant cancers “where we are unable to find a clear genetic cause.”
Not being able to find an identifiable cause for the clustering of early-onset cancers can be “very frustrating” for patients and their families, said Dr. Cobain, a medical oncologist at the University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor.
The study was published online in the International Journal of Cancer.
Family members of patients with early-onset breast cancer are at elevated risk for early-onset breast cancer. However, it is “unclear whether the familial risk is limited to early-onset cancer of the same site,” the authors explained.
To investigate, the researchers studied data from the Finnish Cancer Registry and the Finnish Population System, which included 54,753 relatives from 5,562 families of females diagnosed with early-onset breast cancer, defined as probands. A proband was the first member of the family diagnosed with female breast cancer at age 40 years or younger in Finland between January 1970 and December 31, 2012. Cancers were considered familial if they occurred in a family with a previously diagnosed proband and were deemed early onset if diagnosed before age 41.
The researchers found that only 5.5% of probands’ families had a family member with a discordant early-onset cancer. The most common diagnoses were testicular cancer (0.6% of families) and cancer of the thyroid gland (also 0.6%), followed by melanoma (0.5%).
Overall, the risk of any nonbreast early-onset cancer among first-degree relatives of probands was comparable with the risk in the general population (standardized incidence ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-1.16).
However, the risk was elevated for certain family members and certain cancers.
Specifically, the children of probands had an increased risk for any discordant cancer (SIR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.05-1.55).
The siblings of probands had an elevated risk for early-onset pancreatic cancer (SIR, 7.61) but not overall for any discordant cancer (SIR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.68-1.25).
And siblings’ children faced an elevated risk for testicular (SIR, 1.74) and ovarian (SIR, 2.69) cancer, though not of any discordant cancer (SIR, 1.16; 95% CI, 0.97-1.37).
The researchers also found that the fathers (SIR, 0.43), mothers (SIR, 0.48), and spouses (SIR, 0.58) of probands appeared to have a decreased risk of any discordant early-onset cancer.
A potential limitation to the study was that the authors could not identify individuals with hereditary cancer syndromes or concerning gene mutations, such as BRCA carriers, because “registry data do not include comprehensive information on the gene mutation carriage status.” But the authors note that the number of BRCA carriers is likely low because of the low number of ovarian cancers observed in first-degree relatives of probands.
Dr. Cobain noted as well that the current study is potentially limited by its “very homogeneous” cohort.
But, overall, the findings indicate that familial risk is often “a much more complicated problem, mathematically and statistically,” than were there a single genetic culprit, Dr. Cobain said. One possibility is that some shared environmental exposure may be increasing the cancer risk among members of the same family.
“Genetic diversity is so vast and understanding how the interplay of multiple genes can influence an individual’s cancer risk is so much more complicated than a single BRCA1 mutation that clearly influences your breast cancer risk,” she added. However, “we’re starting to get there.”
The study was funded by the Cancer Foundation Finland and Academy of Finland. The authors and Dr. Cobain had no relevant financial relationships to declare.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The researchers found, for instance, that children of breast cancer patients had a 27% higher risk of any discordant early-onset cancer, and patients’ siblings had a 7.6-fold higher risk of early pancreatic cancer. The analysis also indicated that children of patients’ siblings had a significantly increased risk of testicular and ovarian cancers.
“The findings suggest that the familial risk extends to discordant early-onset cancers, including ovarian, testicular, and pancreatic cancers, as well as beyond first-degree relatives,” the researchers, led by Janne M. Pitkäniemi, PhD, Finnish Cancer Registry, Institute for Statistical and Epidemiological Cancer Research, Helsinki, say. “Our findings are interesting but raise some questions about unknown [genetic] and environmental mechanisms that need to be further studied.”
Erin F. Cobain, MD, who was not involved in the research, said the findings are “not very surprising to me.”
Dr. Cobain said that at her institution, she has seen “many, many cases” of family members of early-onset breast cancer patients with discordant cancers “where we are unable to find a clear genetic cause.”
Not being able to find an identifiable cause for the clustering of early-onset cancers can be “very frustrating” for patients and their families, said Dr. Cobain, a medical oncologist at the University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor.
The study was published online in the International Journal of Cancer.
Family members of patients with early-onset breast cancer are at elevated risk for early-onset breast cancer. However, it is “unclear whether the familial risk is limited to early-onset cancer of the same site,” the authors explained.
To investigate, the researchers studied data from the Finnish Cancer Registry and the Finnish Population System, which included 54,753 relatives from 5,562 families of females diagnosed with early-onset breast cancer, defined as probands. A proband was the first member of the family diagnosed with female breast cancer at age 40 years or younger in Finland between January 1970 and December 31, 2012. Cancers were considered familial if they occurred in a family with a previously diagnosed proband and were deemed early onset if diagnosed before age 41.
The researchers found that only 5.5% of probands’ families had a family member with a discordant early-onset cancer. The most common diagnoses were testicular cancer (0.6% of families) and cancer of the thyroid gland (also 0.6%), followed by melanoma (0.5%).
Overall, the risk of any nonbreast early-onset cancer among first-degree relatives of probands was comparable with the risk in the general population (standardized incidence ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-1.16).
However, the risk was elevated for certain family members and certain cancers.
Specifically, the children of probands had an increased risk for any discordant cancer (SIR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.05-1.55).
The siblings of probands had an elevated risk for early-onset pancreatic cancer (SIR, 7.61) but not overall for any discordant cancer (SIR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.68-1.25).
And siblings’ children faced an elevated risk for testicular (SIR, 1.74) and ovarian (SIR, 2.69) cancer, though not of any discordant cancer (SIR, 1.16; 95% CI, 0.97-1.37).
The researchers also found that the fathers (SIR, 0.43), mothers (SIR, 0.48), and spouses (SIR, 0.58) of probands appeared to have a decreased risk of any discordant early-onset cancer.
A potential limitation to the study was that the authors could not identify individuals with hereditary cancer syndromes or concerning gene mutations, such as BRCA carriers, because “registry data do not include comprehensive information on the gene mutation carriage status.” But the authors note that the number of BRCA carriers is likely low because of the low number of ovarian cancers observed in first-degree relatives of probands.
Dr. Cobain noted as well that the current study is potentially limited by its “very homogeneous” cohort.
But, overall, the findings indicate that familial risk is often “a much more complicated problem, mathematically and statistically,” than were there a single genetic culprit, Dr. Cobain said. One possibility is that some shared environmental exposure may be increasing the cancer risk among members of the same family.
“Genetic diversity is so vast and understanding how the interplay of multiple genes can influence an individual’s cancer risk is so much more complicated than a single BRCA1 mutation that clearly influences your breast cancer risk,” she added. However, “we’re starting to get there.”
The study was funded by the Cancer Foundation Finland and Academy of Finland. The authors and Dr. Cobain had no relevant financial relationships to declare.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The researchers found, for instance, that children of breast cancer patients had a 27% higher risk of any discordant early-onset cancer, and patients’ siblings had a 7.6-fold higher risk of early pancreatic cancer. The analysis also indicated that children of patients’ siblings had a significantly increased risk of testicular and ovarian cancers.
“The findings suggest that the familial risk extends to discordant early-onset cancers, including ovarian, testicular, and pancreatic cancers, as well as beyond first-degree relatives,” the researchers, led by Janne M. Pitkäniemi, PhD, Finnish Cancer Registry, Institute for Statistical and Epidemiological Cancer Research, Helsinki, say. “Our findings are interesting but raise some questions about unknown [genetic] and environmental mechanisms that need to be further studied.”
Erin F. Cobain, MD, who was not involved in the research, said the findings are “not very surprising to me.”
Dr. Cobain said that at her institution, she has seen “many, many cases” of family members of early-onset breast cancer patients with discordant cancers “where we are unable to find a clear genetic cause.”
Not being able to find an identifiable cause for the clustering of early-onset cancers can be “very frustrating” for patients and their families, said Dr. Cobain, a medical oncologist at the University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor.
The study was published online in the International Journal of Cancer.
Family members of patients with early-onset breast cancer are at elevated risk for early-onset breast cancer. However, it is “unclear whether the familial risk is limited to early-onset cancer of the same site,” the authors explained.
To investigate, the researchers studied data from the Finnish Cancer Registry and the Finnish Population System, which included 54,753 relatives from 5,562 families of females diagnosed with early-onset breast cancer, defined as probands. A proband was the first member of the family diagnosed with female breast cancer at age 40 years or younger in Finland between January 1970 and December 31, 2012. Cancers were considered familial if they occurred in a family with a previously diagnosed proband and were deemed early onset if diagnosed before age 41.
The researchers found that only 5.5% of probands’ families had a family member with a discordant early-onset cancer. The most common diagnoses were testicular cancer (0.6% of families) and cancer of the thyroid gland (also 0.6%), followed by melanoma (0.5%).
Overall, the risk of any nonbreast early-onset cancer among first-degree relatives of probands was comparable with the risk in the general population (standardized incidence ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-1.16).
However, the risk was elevated for certain family members and certain cancers.
Specifically, the children of probands had an increased risk for any discordant cancer (SIR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.05-1.55).
The siblings of probands had an elevated risk for early-onset pancreatic cancer (SIR, 7.61) but not overall for any discordant cancer (SIR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.68-1.25).
And siblings’ children faced an elevated risk for testicular (SIR, 1.74) and ovarian (SIR, 2.69) cancer, though not of any discordant cancer (SIR, 1.16; 95% CI, 0.97-1.37).
The researchers also found that the fathers (SIR, 0.43), mothers (SIR, 0.48), and spouses (SIR, 0.58) of probands appeared to have a decreased risk of any discordant early-onset cancer.
A potential limitation to the study was that the authors could not identify individuals with hereditary cancer syndromes or concerning gene mutations, such as BRCA carriers, because “registry data do not include comprehensive information on the gene mutation carriage status.” But the authors note that the number of BRCA carriers is likely low because of the low number of ovarian cancers observed in first-degree relatives of probands.
Dr. Cobain noted as well that the current study is potentially limited by its “very homogeneous” cohort.
But, overall, the findings indicate that familial risk is often “a much more complicated problem, mathematically and statistically,” than were there a single genetic culprit, Dr. Cobain said. One possibility is that some shared environmental exposure may be increasing the cancer risk among members of the same family.
“Genetic diversity is so vast and understanding how the interplay of multiple genes can influence an individual’s cancer risk is so much more complicated than a single BRCA1 mutation that clearly influences your breast cancer risk,” she added. However, “we’re starting to get there.”
The study was funded by the Cancer Foundation Finland and Academy of Finland. The authors and Dr. Cobain had no relevant financial relationships to declare.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CANCER
Asthma tied to increased risk for multiple cancers
People with asthma have an elevated risk for a variety of cancers other than lung cancer, including melanoma as well as blood, kidney, and ovarian cancers, new research suggests.
But, the authors found, treatment with an inhaled steroid may lower that risk, perhaps by keeping inflammation in check.
“Using real-world data, our study is the first to provide evidence of a positive association between asthma and cancer risk in United States patients,” Yi Guo, PhD, with the University of Florida, Gainesville, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Cancer Medicine.
The relationship between chronic inflammation and cancer remains a key area of exploration in cancer etiology. Data show that the risk for developing cancer is higher in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases, and patients with asthma have complex and chronic inflammation. However, prior studies exploring a possible link between asthma and cancer have yielded mixed results.
To investigate further, Dr. Guo and colleagues analyzed electronic health records and claims data in the OneFlorida+ clinical research network for roughly 90,000 adults with asthma and a matched cohort of about 270,000 adults without asthma.
Multivariable analysis revealed that adults with asthma were more likely to develop cancer, compared with peers without asthma (hazard ratio, 1.36), the investigators found.
Adults with asthma had an elevated cancer risk for five of the 13 cancers assessed, including melanoma (HR, 1.98), ovarian cancer (HR, 1.88), lung cancer (HR, 1.56), kidney cancer (HR, 1.48), and blood cancer (HR, 1.26).
Compared with adults without asthma, those with asthma who did not treat it with an inhaled steroid had a more pronounced overall cancer risk, compared with those who were on an inhaled steroid (HR, 1.60 vs. 1.11).
For specific cancer types, the risk was elevated for nine of 13 cancers in patients with asthma not taking an inhaled steroid: prostate (HR, 1.50), lung (HR, 1.74), colorectal (HR, 1.51), blood (HR, 1.44), melanoma (HR, 2.05), corpus uteri (HR, 1.76), kidney (HR, 1.52), ovarian (HR, 2.31), and cervical (HR, 1.46).
In contrast, in patients with asthma who did use an inhaled steroid, an elevated cancer risk was observed for only two cancers, lung cancer (HR, 1.39) and melanoma (HR, 1.92), suggesting a potential protective effect of inhaled steroid use on cancer, the researchers said.
Although prior studies have shown a protective effect of inhaled steroid use on some cancers, potentially by reducing inflammation, the “speculative nature of chronic inflammation (asthma as a common example) as a driver for pan-cancer development requires more investigation,” Dr. Guo and colleagues cautioned.
And because of the observational nature of the current study, Dr. Guo’s team stressed that these findings do not prove a causal relationship between asthma and cancer.
“More in-depth studies using real-word data are needed to further explore the causal mechanisms of asthma on cancer risk,” the researchers concluded.
Funding for the study was provided in part by grants to the researchers from the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, National Institute on Aging, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This project was supported by the Cancer Informatics Shared Resource in the University of Florida Health Cancer Center. The authors have disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with asthma have an elevated risk for a variety of cancers other than lung cancer, including melanoma as well as blood, kidney, and ovarian cancers, new research suggests.
But, the authors found, treatment with an inhaled steroid may lower that risk, perhaps by keeping inflammation in check.
“Using real-world data, our study is the first to provide evidence of a positive association between asthma and cancer risk in United States patients,” Yi Guo, PhD, with the University of Florida, Gainesville, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Cancer Medicine.
The relationship between chronic inflammation and cancer remains a key area of exploration in cancer etiology. Data show that the risk for developing cancer is higher in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases, and patients with asthma have complex and chronic inflammation. However, prior studies exploring a possible link between asthma and cancer have yielded mixed results.
To investigate further, Dr. Guo and colleagues analyzed electronic health records and claims data in the OneFlorida+ clinical research network for roughly 90,000 adults with asthma and a matched cohort of about 270,000 adults without asthma.
Multivariable analysis revealed that adults with asthma were more likely to develop cancer, compared with peers without asthma (hazard ratio, 1.36), the investigators found.
Adults with asthma had an elevated cancer risk for five of the 13 cancers assessed, including melanoma (HR, 1.98), ovarian cancer (HR, 1.88), lung cancer (HR, 1.56), kidney cancer (HR, 1.48), and blood cancer (HR, 1.26).
Compared with adults without asthma, those with asthma who did not treat it with an inhaled steroid had a more pronounced overall cancer risk, compared with those who were on an inhaled steroid (HR, 1.60 vs. 1.11).
For specific cancer types, the risk was elevated for nine of 13 cancers in patients with asthma not taking an inhaled steroid: prostate (HR, 1.50), lung (HR, 1.74), colorectal (HR, 1.51), blood (HR, 1.44), melanoma (HR, 2.05), corpus uteri (HR, 1.76), kidney (HR, 1.52), ovarian (HR, 2.31), and cervical (HR, 1.46).
In contrast, in patients with asthma who did use an inhaled steroid, an elevated cancer risk was observed for only two cancers, lung cancer (HR, 1.39) and melanoma (HR, 1.92), suggesting a potential protective effect of inhaled steroid use on cancer, the researchers said.
Although prior studies have shown a protective effect of inhaled steroid use on some cancers, potentially by reducing inflammation, the “speculative nature of chronic inflammation (asthma as a common example) as a driver for pan-cancer development requires more investigation,” Dr. Guo and colleagues cautioned.
And because of the observational nature of the current study, Dr. Guo’s team stressed that these findings do not prove a causal relationship between asthma and cancer.
“More in-depth studies using real-word data are needed to further explore the causal mechanisms of asthma on cancer risk,” the researchers concluded.
Funding for the study was provided in part by grants to the researchers from the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, National Institute on Aging, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This project was supported by the Cancer Informatics Shared Resource in the University of Florida Health Cancer Center. The authors have disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with asthma have an elevated risk for a variety of cancers other than lung cancer, including melanoma as well as blood, kidney, and ovarian cancers, new research suggests.
But, the authors found, treatment with an inhaled steroid may lower that risk, perhaps by keeping inflammation in check.
“Using real-world data, our study is the first to provide evidence of a positive association between asthma and cancer risk in United States patients,” Yi Guo, PhD, with the University of Florida, Gainesville, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Cancer Medicine.
The relationship between chronic inflammation and cancer remains a key area of exploration in cancer etiology. Data show that the risk for developing cancer is higher in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases, and patients with asthma have complex and chronic inflammation. However, prior studies exploring a possible link between asthma and cancer have yielded mixed results.
To investigate further, Dr. Guo and colleagues analyzed electronic health records and claims data in the OneFlorida+ clinical research network for roughly 90,000 adults with asthma and a matched cohort of about 270,000 adults without asthma.
Multivariable analysis revealed that adults with asthma were more likely to develop cancer, compared with peers without asthma (hazard ratio, 1.36), the investigators found.
Adults with asthma had an elevated cancer risk for five of the 13 cancers assessed, including melanoma (HR, 1.98), ovarian cancer (HR, 1.88), lung cancer (HR, 1.56), kidney cancer (HR, 1.48), and blood cancer (HR, 1.26).
Compared with adults without asthma, those with asthma who did not treat it with an inhaled steroid had a more pronounced overall cancer risk, compared with those who were on an inhaled steroid (HR, 1.60 vs. 1.11).
For specific cancer types, the risk was elevated for nine of 13 cancers in patients with asthma not taking an inhaled steroid: prostate (HR, 1.50), lung (HR, 1.74), colorectal (HR, 1.51), blood (HR, 1.44), melanoma (HR, 2.05), corpus uteri (HR, 1.76), kidney (HR, 1.52), ovarian (HR, 2.31), and cervical (HR, 1.46).
In contrast, in patients with asthma who did use an inhaled steroid, an elevated cancer risk was observed for only two cancers, lung cancer (HR, 1.39) and melanoma (HR, 1.92), suggesting a potential protective effect of inhaled steroid use on cancer, the researchers said.
Although prior studies have shown a protective effect of inhaled steroid use on some cancers, potentially by reducing inflammation, the “speculative nature of chronic inflammation (asthma as a common example) as a driver for pan-cancer development requires more investigation,” Dr. Guo and colleagues cautioned.
And because of the observational nature of the current study, Dr. Guo’s team stressed that these findings do not prove a causal relationship between asthma and cancer.
“More in-depth studies using real-word data are needed to further explore the causal mechanisms of asthma on cancer risk,” the researchers concluded.
Funding for the study was provided in part by grants to the researchers from the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, National Institute on Aging, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This project was supported by the Cancer Informatics Shared Resource in the University of Florida Health Cancer Center. The authors have disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pausing endocrine therapy to attempt pregnancy is safe
The results provide the “strongest evidence to date on the short-term safety of this choice,” Sharon Giordano, MD, MPH, with University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, wrote in an editorial accompanying the study.
“Physicians should now incorporate these positive data into their shared decision-making process with patients,” Dr. Giordano said.
The POSITIVE trial findings were published online in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Before the analysis, the risks associated with taking a break from endocrine therapy among young women with hormone receptor (HR)–positive breast cancer remained unclear.
In the current trial, Ann Partridge, MD, MPH, and colleagues sought prospective data on the safety associated with taking a temporary break from therapy to attempt pregnancy.
The single-group trial enrolled more than 500 premenopausal women who had received 18-30 months of endocrine therapy for mostly stage I or II HR-positive breast cancer. After a 3-month washout, the women were given 2 years to conceive, deliver, and breastfeed, if desired, before resuming treatment. Breast cancer events – the primary outcome – were defined as local, regional, or distant recurrence of invasive breast cancer or new contralateral invasive breast cancer.
The results, initially reported at San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) 2022, showed that a temporary interruption of therapy to attempt pregnancy did not appear to lead to worse breast cancer outcomes.
Among 497 women who were followed for pregnancy status, 368 (74%) had at least one pregnancy, and 317 (64%) had at least one live birth.
After a median follow-up of 3.4 years, 44 women had had a breast cancer event – a result that was close to, but did not exceed, the safety threshold of 46 breast cancer events.
The 3-year incidence of breast cancer events was 8.9% (95% confidence interval [CI], 6.3-11.6) in the treatment-interruption group compared with 9.2% (95% CI, 7.6-10.8) among historical controls, which included women who would have met the entry criteria for the trial.
“These results suggest that although endocrine therapy for a period of 5-10 years substantially improves disease outcomes in patients with hormone receptor–positive early breast cancer, a temporary interruption of therapy to attempt pregnancy does not appear to have an appreciable negative short-term effect,” wrote Dr. Partridge, vice chair of medical oncology at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
The authors cautioned, however, that the median follow-up was only 3.4 years and that 10-year follow-up data will be “critical” to confirm the safety of interruption of adjuvant endocrine therapy.
Dr. Giordano agreed, noting that “recurrences of breast cancer are reported to occur at a steady rate for up to 20 years after diagnosis among patients with hormone receptor–positive disease; the protocol-specified 10-year follow-up data will be essential to establish longer-term safety.”
The study was supported by the International Breast Cancer Study Group and by the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology in North America in collaboration with the Breast International Group (BIG). Disclosures for authors and editorial writer are available at NEJM.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The results provide the “strongest evidence to date on the short-term safety of this choice,” Sharon Giordano, MD, MPH, with University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, wrote in an editorial accompanying the study.
“Physicians should now incorporate these positive data into their shared decision-making process with patients,” Dr. Giordano said.
The POSITIVE trial findings were published online in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Before the analysis, the risks associated with taking a break from endocrine therapy among young women with hormone receptor (HR)–positive breast cancer remained unclear.
In the current trial, Ann Partridge, MD, MPH, and colleagues sought prospective data on the safety associated with taking a temporary break from therapy to attempt pregnancy.
The single-group trial enrolled more than 500 premenopausal women who had received 18-30 months of endocrine therapy for mostly stage I or II HR-positive breast cancer. After a 3-month washout, the women were given 2 years to conceive, deliver, and breastfeed, if desired, before resuming treatment. Breast cancer events – the primary outcome – were defined as local, regional, or distant recurrence of invasive breast cancer or new contralateral invasive breast cancer.
The results, initially reported at San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) 2022, showed that a temporary interruption of therapy to attempt pregnancy did not appear to lead to worse breast cancer outcomes.
Among 497 women who were followed for pregnancy status, 368 (74%) had at least one pregnancy, and 317 (64%) had at least one live birth.
After a median follow-up of 3.4 years, 44 women had had a breast cancer event – a result that was close to, but did not exceed, the safety threshold of 46 breast cancer events.
The 3-year incidence of breast cancer events was 8.9% (95% confidence interval [CI], 6.3-11.6) in the treatment-interruption group compared with 9.2% (95% CI, 7.6-10.8) among historical controls, which included women who would have met the entry criteria for the trial.
“These results suggest that although endocrine therapy for a period of 5-10 years substantially improves disease outcomes in patients with hormone receptor–positive early breast cancer, a temporary interruption of therapy to attempt pregnancy does not appear to have an appreciable negative short-term effect,” wrote Dr. Partridge, vice chair of medical oncology at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
The authors cautioned, however, that the median follow-up was only 3.4 years and that 10-year follow-up data will be “critical” to confirm the safety of interruption of adjuvant endocrine therapy.
Dr. Giordano agreed, noting that “recurrences of breast cancer are reported to occur at a steady rate for up to 20 years after diagnosis among patients with hormone receptor–positive disease; the protocol-specified 10-year follow-up data will be essential to establish longer-term safety.”
The study was supported by the International Breast Cancer Study Group and by the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology in North America in collaboration with the Breast International Group (BIG). Disclosures for authors and editorial writer are available at NEJM.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The results provide the “strongest evidence to date on the short-term safety of this choice,” Sharon Giordano, MD, MPH, with University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, wrote in an editorial accompanying the study.
“Physicians should now incorporate these positive data into their shared decision-making process with patients,” Dr. Giordano said.
The POSITIVE trial findings were published online in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Before the analysis, the risks associated with taking a break from endocrine therapy among young women with hormone receptor (HR)–positive breast cancer remained unclear.
In the current trial, Ann Partridge, MD, MPH, and colleagues sought prospective data on the safety associated with taking a temporary break from therapy to attempt pregnancy.
The single-group trial enrolled more than 500 premenopausal women who had received 18-30 months of endocrine therapy for mostly stage I or II HR-positive breast cancer. After a 3-month washout, the women were given 2 years to conceive, deliver, and breastfeed, if desired, before resuming treatment. Breast cancer events – the primary outcome – were defined as local, regional, or distant recurrence of invasive breast cancer or new contralateral invasive breast cancer.
The results, initially reported at San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) 2022, showed that a temporary interruption of therapy to attempt pregnancy did not appear to lead to worse breast cancer outcomes.
Among 497 women who were followed for pregnancy status, 368 (74%) had at least one pregnancy, and 317 (64%) had at least one live birth.
After a median follow-up of 3.4 years, 44 women had had a breast cancer event – a result that was close to, but did not exceed, the safety threshold of 46 breast cancer events.
The 3-year incidence of breast cancer events was 8.9% (95% confidence interval [CI], 6.3-11.6) in the treatment-interruption group compared with 9.2% (95% CI, 7.6-10.8) among historical controls, which included women who would have met the entry criteria for the trial.
“These results suggest that although endocrine therapy for a period of 5-10 years substantially improves disease outcomes in patients with hormone receptor–positive early breast cancer, a temporary interruption of therapy to attempt pregnancy does not appear to have an appreciable negative short-term effect,” wrote Dr. Partridge, vice chair of medical oncology at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
The authors cautioned, however, that the median follow-up was only 3.4 years and that 10-year follow-up data will be “critical” to confirm the safety of interruption of adjuvant endocrine therapy.
Dr. Giordano agreed, noting that “recurrences of breast cancer are reported to occur at a steady rate for up to 20 years after diagnosis among patients with hormone receptor–positive disease; the protocol-specified 10-year follow-up data will be essential to establish longer-term safety.”
The study was supported by the International Breast Cancer Study Group and by the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology in North America in collaboration with the Breast International Group (BIG). Disclosures for authors and editorial writer are available at NEJM.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEJM
H. pylori eradication therapy curbs risk for stomach cancer
People with H. pylori who were treated had about a 63% lower risk of developing noncardia gastric adenocarcinoma (NCGA) after 8 years of follow-up, compared with peers with H. pylori who were not treated.
The U.S. data align with previous studies, conducted mostly in Asia, that found that treating the infection can reduce stomach cancer incidence.
The KPNC study shows the “potential for stomach cancer prevention in U.S. populations through H. pylori screening and treatment,” study investigator Dan Li, MD, gastroenterologist with the Kaiser Permanente Medical Group and Kaiser Permanente Division of Research in Oakland, Calif., said in an interview.
Judith Kim, MD, a gastroenterologist at NYU Langone Health in New York, who wasn’t involved in the research, said that the study is significant because “it is the first to show this effect in a large, diverse population in the U.S., where gastric cancer incidence is lower.”
The study was published online in Gastroenterology.
Top risk factor
About 30% of people in the United States are infected with H. pylori, which is the No. 1 known risk factor for stomach cancer, Dr. Li said.
The study cohort included 716,567 KPNC members who underwent H. pylori testing and/or treatment between 1997 and 2015.
Among H. pylori–infected individuals (based on positive nonserology test results), the subdistribution hazard ratio was 6.07 for untreated individuals and 2.68 for treated individuals, compared with H. pylori–negative individuals.
It’s not surprising that people who were treated for the infection still had a higher risk of NCGA than people who had never had the infection, Dr. Li said.
“This is likely because many people with chronic H. pylori infection had already developed some precancerous changes in their stomach before they were treated. This finding suggests that H. pylori ideally should be treated before precancerous changes develop,” he said.
When compared directly with H. pylori–positive/untreated individuals, the risk for NCGA in H. pylori–positive/treated individuals was somewhat lower at less than 8 years follow-up (sHR, 0.95) and significantly lower at 8+ years of follow-up (sHR, 0.37).
“After 7-10 years of follow-up, people with H. pylori who received treatment had nearly half the risk of developing stomach cancer as the general population,” Dr. Li said. “This is likely because most people infected with H. pylori in the general population are not screened nor treated. This highlights the impact screening and treatment can have.”
The data also show that cumulative incidence curves for H. pylori–positive/untreated and H. pylori–positive/treated largely overlapped during the first 7 years of follow-up and started to separate after 8 years.
At 10 years, cumulative NCGA incidence rates for H. pylori–positive/untreated, H. pylori–positive/treated, and H. pylori negative were 31.0, 19.7, and 3.5 per 10,000 persons, respectively (P < .0001).
This study shows that treating H. pylori reduces stomach cancer incidence in the United States, thus “filling an important research and knowledge gap,” Dr. Li said.
In the United States, Asian, Black, and Hispanic adults are much more likely to be infected with H. pylori, and they have a two- to threefold higher risk of developing stomach cancer, he noted.
“This suggests it may be reasonable to consider targeted screening and treatment in these high-risk groups. However, the optimal strategy for population-based H. pylori screening has not been established, and more research is needed to determine who should be screened for H. pylori and at what age screening should begin,” Dr. Li said.
Strong data, jury out on universal screening
For additional comment, this news organization reached out to Aaron Glatt, MD, a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases and hospital epidemiologist at Mount Sinai South Nassau in Oceanside, N.Y.
The study shows that the treatment of H. pylori “absolutely will decrease your risk of certain types of gastric carcinoma down the line. It does take a while to show that, 7 years, but this study shows that very clearly,” Dr. Glatt said.
“People who have definitely been shown to have H. pylori should be treated,” Dr. Glatt said.
“I don’t think this study yet supports that everybody should be screened, but it does make sense that people who have upper GI symptoms consistent with H. pylori should be checked for H. pylori and then appropriately treated, he noted.
Routine screening for H. pylori is recommended in countries with high incidence of gastric cancer, but not in the United States, Dr. Kim noted.
“Given the risk reduction of cancer with H. pylori treatment, consideration should be made in the U.S. for asymptomatic individuals with a family history of gastric cancer or immigrants from high-incidence countries,” she added.
The study was funded by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health Research Grants Program, the Permanente Medical Group Delivery Science & Applied Research Program, and the Permanente Medical Group. Dr. Li, Dr. Glatt, and Dr. Kim have declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
People with H. pylori who were treated had about a 63% lower risk of developing noncardia gastric adenocarcinoma (NCGA) after 8 years of follow-up, compared with peers with H. pylori who were not treated.
The U.S. data align with previous studies, conducted mostly in Asia, that found that treating the infection can reduce stomach cancer incidence.
The KPNC study shows the “potential for stomach cancer prevention in U.S. populations through H. pylori screening and treatment,” study investigator Dan Li, MD, gastroenterologist with the Kaiser Permanente Medical Group and Kaiser Permanente Division of Research in Oakland, Calif., said in an interview.
Judith Kim, MD, a gastroenterologist at NYU Langone Health in New York, who wasn’t involved in the research, said that the study is significant because “it is the first to show this effect in a large, diverse population in the U.S., where gastric cancer incidence is lower.”
The study was published online in Gastroenterology.
Top risk factor
About 30% of people in the United States are infected with H. pylori, which is the No. 1 known risk factor for stomach cancer, Dr. Li said.
The study cohort included 716,567 KPNC members who underwent H. pylori testing and/or treatment between 1997 and 2015.
Among H. pylori–infected individuals (based on positive nonserology test results), the subdistribution hazard ratio was 6.07 for untreated individuals and 2.68 for treated individuals, compared with H. pylori–negative individuals.
It’s not surprising that people who were treated for the infection still had a higher risk of NCGA than people who had never had the infection, Dr. Li said.
“This is likely because many people with chronic H. pylori infection had already developed some precancerous changes in their stomach before they were treated. This finding suggests that H. pylori ideally should be treated before precancerous changes develop,” he said.
When compared directly with H. pylori–positive/untreated individuals, the risk for NCGA in H. pylori–positive/treated individuals was somewhat lower at less than 8 years follow-up (sHR, 0.95) and significantly lower at 8+ years of follow-up (sHR, 0.37).
“After 7-10 years of follow-up, people with H. pylori who received treatment had nearly half the risk of developing stomach cancer as the general population,” Dr. Li said. “This is likely because most people infected with H. pylori in the general population are not screened nor treated. This highlights the impact screening and treatment can have.”
The data also show that cumulative incidence curves for H. pylori–positive/untreated and H. pylori–positive/treated largely overlapped during the first 7 years of follow-up and started to separate after 8 years.
At 10 years, cumulative NCGA incidence rates for H. pylori–positive/untreated, H. pylori–positive/treated, and H. pylori negative were 31.0, 19.7, and 3.5 per 10,000 persons, respectively (P < .0001).
This study shows that treating H. pylori reduces stomach cancer incidence in the United States, thus “filling an important research and knowledge gap,” Dr. Li said.
In the United States, Asian, Black, and Hispanic adults are much more likely to be infected with H. pylori, and they have a two- to threefold higher risk of developing stomach cancer, he noted.
“This suggests it may be reasonable to consider targeted screening and treatment in these high-risk groups. However, the optimal strategy for population-based H. pylori screening has not been established, and more research is needed to determine who should be screened for H. pylori and at what age screening should begin,” Dr. Li said.
Strong data, jury out on universal screening
For additional comment, this news organization reached out to Aaron Glatt, MD, a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases and hospital epidemiologist at Mount Sinai South Nassau in Oceanside, N.Y.
The study shows that the treatment of H. pylori “absolutely will decrease your risk of certain types of gastric carcinoma down the line. It does take a while to show that, 7 years, but this study shows that very clearly,” Dr. Glatt said.
“People who have definitely been shown to have H. pylori should be treated,” Dr. Glatt said.
“I don’t think this study yet supports that everybody should be screened, but it does make sense that people who have upper GI symptoms consistent with H. pylori should be checked for H. pylori and then appropriately treated, he noted.
Routine screening for H. pylori is recommended in countries with high incidence of gastric cancer, but not in the United States, Dr. Kim noted.
“Given the risk reduction of cancer with H. pylori treatment, consideration should be made in the U.S. for asymptomatic individuals with a family history of gastric cancer or immigrants from high-incidence countries,” she added.
The study was funded by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health Research Grants Program, the Permanente Medical Group Delivery Science & Applied Research Program, and the Permanente Medical Group. Dr. Li, Dr. Glatt, and Dr. Kim have declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
People with H. pylori who were treated had about a 63% lower risk of developing noncardia gastric adenocarcinoma (NCGA) after 8 years of follow-up, compared with peers with H. pylori who were not treated.
The U.S. data align with previous studies, conducted mostly in Asia, that found that treating the infection can reduce stomach cancer incidence.
The KPNC study shows the “potential for stomach cancer prevention in U.S. populations through H. pylori screening and treatment,” study investigator Dan Li, MD, gastroenterologist with the Kaiser Permanente Medical Group and Kaiser Permanente Division of Research in Oakland, Calif., said in an interview.
Judith Kim, MD, a gastroenterologist at NYU Langone Health in New York, who wasn’t involved in the research, said that the study is significant because “it is the first to show this effect in a large, diverse population in the U.S., where gastric cancer incidence is lower.”
The study was published online in Gastroenterology.
Top risk factor
About 30% of people in the United States are infected with H. pylori, which is the No. 1 known risk factor for stomach cancer, Dr. Li said.
The study cohort included 716,567 KPNC members who underwent H. pylori testing and/or treatment between 1997 and 2015.
Among H. pylori–infected individuals (based on positive nonserology test results), the subdistribution hazard ratio was 6.07 for untreated individuals and 2.68 for treated individuals, compared with H. pylori–negative individuals.
It’s not surprising that people who were treated for the infection still had a higher risk of NCGA than people who had never had the infection, Dr. Li said.
“This is likely because many people with chronic H. pylori infection had already developed some precancerous changes in their stomach before they were treated. This finding suggests that H. pylori ideally should be treated before precancerous changes develop,” he said.
When compared directly with H. pylori–positive/untreated individuals, the risk for NCGA in H. pylori–positive/treated individuals was somewhat lower at less than 8 years follow-up (sHR, 0.95) and significantly lower at 8+ years of follow-up (sHR, 0.37).
“After 7-10 years of follow-up, people with H. pylori who received treatment had nearly half the risk of developing stomach cancer as the general population,” Dr. Li said. “This is likely because most people infected with H. pylori in the general population are not screened nor treated. This highlights the impact screening and treatment can have.”
The data also show that cumulative incidence curves for H. pylori–positive/untreated and H. pylori–positive/treated largely overlapped during the first 7 years of follow-up and started to separate after 8 years.
At 10 years, cumulative NCGA incidence rates for H. pylori–positive/untreated, H. pylori–positive/treated, and H. pylori negative were 31.0, 19.7, and 3.5 per 10,000 persons, respectively (P < .0001).
This study shows that treating H. pylori reduces stomach cancer incidence in the United States, thus “filling an important research and knowledge gap,” Dr. Li said.
In the United States, Asian, Black, and Hispanic adults are much more likely to be infected with H. pylori, and they have a two- to threefold higher risk of developing stomach cancer, he noted.
“This suggests it may be reasonable to consider targeted screening and treatment in these high-risk groups. However, the optimal strategy for population-based H. pylori screening has not been established, and more research is needed to determine who should be screened for H. pylori and at what age screening should begin,” Dr. Li said.
Strong data, jury out on universal screening
For additional comment, this news organization reached out to Aaron Glatt, MD, a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases and hospital epidemiologist at Mount Sinai South Nassau in Oceanside, N.Y.
The study shows that the treatment of H. pylori “absolutely will decrease your risk of certain types of gastric carcinoma down the line. It does take a while to show that, 7 years, but this study shows that very clearly,” Dr. Glatt said.
“People who have definitely been shown to have H. pylori should be treated,” Dr. Glatt said.
“I don’t think this study yet supports that everybody should be screened, but it does make sense that people who have upper GI symptoms consistent with H. pylori should be checked for H. pylori and then appropriately treated, he noted.
Routine screening for H. pylori is recommended in countries with high incidence of gastric cancer, but not in the United States, Dr. Kim noted.
“Given the risk reduction of cancer with H. pylori treatment, consideration should be made in the U.S. for asymptomatic individuals with a family history of gastric cancer or immigrants from high-incidence countries,” she added.
The study was funded by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health Research Grants Program, the Permanente Medical Group Delivery Science & Applied Research Program, and the Permanente Medical Group. Dr. Li, Dr. Glatt, and Dr. Kim have declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY