User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Cavernous gender gap in Medicare payments to cardiologists
Women cardiologists receive dramatically smaller payments from the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) than their male counterparts, new research suggests.
An analysis of 2016 claims data revealed male cardiologists received on average 45% more reimbursement than women in the inpatient setting, with the median payment 39% higher ($62,897 vs. $45,288).
In the outpatient setting, men received on average 62% more annual CMS payments, with the median payment 75% higher ($91,053 vs. $51,975; P < .001 for both).
The difference remained significant after the exclusion of the top and bottom 2.5% of earning physicians and cardiology subspecialties, like electrophysiology and interventional cardiology, with high procedural volumes and greater gender imbalances.
“This is one study among others which demonstrates a wage gap between men and women in medicine in cardiology,” lead author Inbar Raber, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said in an interview. “I hope by increasing awareness [and] understanding of possible etiologies, it will enable some sustainable solutions, and those include access to additional support staff and equitable models surrounding parental leave and childcare support.”
The study, published online September 8 in JAMA Cardiology, comes on the heels of a recent cross-sectional analysis that put cardiology at the bottom of 13 internal medicine subspecialties with just 21% female faculty representation and one of only three specialties in which women’s median salaries did not reach 90% of men’s.
The new findings build on a 2017 report that showed Medicare payments to women physicians in 2013 were 55% of those to male physicians across all specialties.
“It can be disheartening, especially as an early career woman cardiologist, seeing these differences, but I think the responsibility on all of us is to take these observations and really try to understand more deeply why they exist,” Nosheen Reza, MD, from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and coauthor of the cross-sectional analysis, told this news organization.
Several factors could be contributing to the disparity, but “it’s not gender discrimination from Medicare,” Dr. Raber said. “The gap in reimbursement is really driven by the types and the volume of charges submitted.”
Indeed, a direct comparison of the three most common inpatient and outpatient billing codes showed no difference in payments between the sexes.
Men, however, submitted 24% more median inpatient charges to CMS than women (1,190 vs. 959), and 94% more outpatient charges (1,685 vs. 870).
Men also submitted slightly more unique billing codes (median inpatient, 10 vs. 9; median outpatient, 11 vs. 8).
Notably, women made up just 13% of the 17,524 cardiologists who received CMS payments in the inpatient setting in 2016 and 13% of the 16,929 cardiologists who did so in the outpatient setting.
Louisiana had the dubious distinction of having the largest gender gap in mean CMS payments, with male cardiologists earning $145,323 (235%) more than women, whereas women cardiologists in Vermont out-earned men by $31,483 (38%).
Overall, male cardiologists had more years in practice than women cardiologists and cared for slightly older Medicare beneficiaries.
Differences in CMS payments persisted, however, after adjustment for years since graduation, physician subspecialty, number of charges, number of unique billing codes, and patient complexity. The resulting β coefficient was -0.06, which translates into women receiving an average of 94% of the CMS payments received by men.
“The first takeaway, if you were really crass and focused on the bottom line, might be: ‘Hey, let me get a few more male cardiologists because they’re going to bring more into the organization.’ But we shouldn’t do that because, unless you link these data with quality outcomes, they’re an interesting observation and hypothesis-generating,” said Sharonne Hayes, MD, coauthor of the 2017 report and professor of cardiovascular medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., where she has served as director of diversity and inclusion for a decade.
She noted that there are multiple examples that the style of medicine women practice, on average, may be more effective, may be more outcomes based, and may save lives, as suggested by a recent analysis of hospitalized Medicare beneficiaries.
“The gap was not much different, like within 1% or so, but when you take that over the literally millions of Medicare patients cared for each year by hospitalists, that’s a substantial number of people,” Dr. Hayes said. “So, I think we need to take a step back, and we have to include these observations on studies like this and better understand the compensation gaps.”
She pointed out that the present study lacks data on full-time-equivalent status but that female physicians are more likely to work part-time, thus reducing the volume of claims.
Women might also care for different patient populations. “I practice in a women’s heart clinic and take care of [spontaneous coronary artery dissection] SCAD patients where the average age of SCAD is 42. So, the vast majority of patients I see on a day-to-day basis aren’t going to be Medicare age,” observed Dr. Hayes.
The differences in charges might also reflect the increased obligations in nonreimbursed work that women can have, Dr. Raber said. These can be things like mentoring, teaching roles, and serving on committees, which is a hypothesis supported by a 2021 study that showed women physicians spend more time on these “citizenship tasks” than men.
Finally, there could be organizational barriers that affect women’s clinical volumes, including less access to support from health care personnel. Added support is especially important, though, amid a 100-year pandemic, the women agreed.
“Within the first year of the pandemic, we saw women leaving the workforce in droves across all sectors, including medicine, including academic medicine. And, as the pandemic goes on without any signs of abatement, those threats continue to exist and continue to be amplified,” Dr. Reza said.
The groundswell of support surrounding the importance of diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives across the board has helped bring attention to the issue, she said. Some institutions, including the National Institutes of Health, are making efforts to extend relief to women with young families, caregivers, or those in academic medicine who, for example, need extensions on grants or bridge funding.
“There’s certainly a lot left to do, but I do think within the last year, there’s been an acceleration of literature that has come out, not only pointing out the disparities, but pointing out that perhaps women physicians do have better outcomes and are better liked by their patients and that losing women in the workforce would be a huge detriment to the field overall,” Dr. Reza said.
Dr. Raber, Dr. Reza, and Dr. Hayes reports no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor conflict of interest disclosures are listed in the paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women cardiologists receive dramatically smaller payments from the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) than their male counterparts, new research suggests.
An analysis of 2016 claims data revealed male cardiologists received on average 45% more reimbursement than women in the inpatient setting, with the median payment 39% higher ($62,897 vs. $45,288).
In the outpatient setting, men received on average 62% more annual CMS payments, with the median payment 75% higher ($91,053 vs. $51,975; P < .001 for both).
The difference remained significant after the exclusion of the top and bottom 2.5% of earning physicians and cardiology subspecialties, like electrophysiology and interventional cardiology, with high procedural volumes and greater gender imbalances.
“This is one study among others which demonstrates a wage gap between men and women in medicine in cardiology,” lead author Inbar Raber, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said in an interview. “I hope by increasing awareness [and] understanding of possible etiologies, it will enable some sustainable solutions, and those include access to additional support staff and equitable models surrounding parental leave and childcare support.”
The study, published online September 8 in JAMA Cardiology, comes on the heels of a recent cross-sectional analysis that put cardiology at the bottom of 13 internal medicine subspecialties with just 21% female faculty representation and one of only three specialties in which women’s median salaries did not reach 90% of men’s.
The new findings build on a 2017 report that showed Medicare payments to women physicians in 2013 were 55% of those to male physicians across all specialties.
“It can be disheartening, especially as an early career woman cardiologist, seeing these differences, but I think the responsibility on all of us is to take these observations and really try to understand more deeply why they exist,” Nosheen Reza, MD, from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and coauthor of the cross-sectional analysis, told this news organization.
Several factors could be contributing to the disparity, but “it’s not gender discrimination from Medicare,” Dr. Raber said. “The gap in reimbursement is really driven by the types and the volume of charges submitted.”
Indeed, a direct comparison of the three most common inpatient and outpatient billing codes showed no difference in payments between the sexes.
Men, however, submitted 24% more median inpatient charges to CMS than women (1,190 vs. 959), and 94% more outpatient charges (1,685 vs. 870).
Men also submitted slightly more unique billing codes (median inpatient, 10 vs. 9; median outpatient, 11 vs. 8).
Notably, women made up just 13% of the 17,524 cardiologists who received CMS payments in the inpatient setting in 2016 and 13% of the 16,929 cardiologists who did so in the outpatient setting.
Louisiana had the dubious distinction of having the largest gender gap in mean CMS payments, with male cardiologists earning $145,323 (235%) more than women, whereas women cardiologists in Vermont out-earned men by $31,483 (38%).
Overall, male cardiologists had more years in practice than women cardiologists and cared for slightly older Medicare beneficiaries.
Differences in CMS payments persisted, however, after adjustment for years since graduation, physician subspecialty, number of charges, number of unique billing codes, and patient complexity. The resulting β coefficient was -0.06, which translates into women receiving an average of 94% of the CMS payments received by men.
“The first takeaway, if you were really crass and focused on the bottom line, might be: ‘Hey, let me get a few more male cardiologists because they’re going to bring more into the organization.’ But we shouldn’t do that because, unless you link these data with quality outcomes, they’re an interesting observation and hypothesis-generating,” said Sharonne Hayes, MD, coauthor of the 2017 report and professor of cardiovascular medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., where she has served as director of diversity and inclusion for a decade.
She noted that there are multiple examples that the style of medicine women practice, on average, may be more effective, may be more outcomes based, and may save lives, as suggested by a recent analysis of hospitalized Medicare beneficiaries.
“The gap was not much different, like within 1% or so, but when you take that over the literally millions of Medicare patients cared for each year by hospitalists, that’s a substantial number of people,” Dr. Hayes said. “So, I think we need to take a step back, and we have to include these observations on studies like this and better understand the compensation gaps.”
She pointed out that the present study lacks data on full-time-equivalent status but that female physicians are more likely to work part-time, thus reducing the volume of claims.
Women might also care for different patient populations. “I practice in a women’s heart clinic and take care of [spontaneous coronary artery dissection] SCAD patients where the average age of SCAD is 42. So, the vast majority of patients I see on a day-to-day basis aren’t going to be Medicare age,” observed Dr. Hayes.
The differences in charges might also reflect the increased obligations in nonreimbursed work that women can have, Dr. Raber said. These can be things like mentoring, teaching roles, and serving on committees, which is a hypothesis supported by a 2021 study that showed women physicians spend more time on these “citizenship tasks” than men.
Finally, there could be organizational barriers that affect women’s clinical volumes, including less access to support from health care personnel. Added support is especially important, though, amid a 100-year pandemic, the women agreed.
“Within the first year of the pandemic, we saw women leaving the workforce in droves across all sectors, including medicine, including academic medicine. And, as the pandemic goes on without any signs of abatement, those threats continue to exist and continue to be amplified,” Dr. Reza said.
The groundswell of support surrounding the importance of diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives across the board has helped bring attention to the issue, she said. Some institutions, including the National Institutes of Health, are making efforts to extend relief to women with young families, caregivers, or those in academic medicine who, for example, need extensions on grants or bridge funding.
“There’s certainly a lot left to do, but I do think within the last year, there’s been an acceleration of literature that has come out, not only pointing out the disparities, but pointing out that perhaps women physicians do have better outcomes and are better liked by their patients and that losing women in the workforce would be a huge detriment to the field overall,” Dr. Reza said.
Dr. Raber, Dr. Reza, and Dr. Hayes reports no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor conflict of interest disclosures are listed in the paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women cardiologists receive dramatically smaller payments from the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) than their male counterparts, new research suggests.
An analysis of 2016 claims data revealed male cardiologists received on average 45% more reimbursement than women in the inpatient setting, with the median payment 39% higher ($62,897 vs. $45,288).
In the outpatient setting, men received on average 62% more annual CMS payments, with the median payment 75% higher ($91,053 vs. $51,975; P < .001 for both).
The difference remained significant after the exclusion of the top and bottom 2.5% of earning physicians and cardiology subspecialties, like electrophysiology and interventional cardiology, with high procedural volumes and greater gender imbalances.
“This is one study among others which demonstrates a wage gap between men and women in medicine in cardiology,” lead author Inbar Raber, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said in an interview. “I hope by increasing awareness [and] understanding of possible etiologies, it will enable some sustainable solutions, and those include access to additional support staff and equitable models surrounding parental leave and childcare support.”
The study, published online September 8 in JAMA Cardiology, comes on the heels of a recent cross-sectional analysis that put cardiology at the bottom of 13 internal medicine subspecialties with just 21% female faculty representation and one of only three specialties in which women’s median salaries did not reach 90% of men’s.
The new findings build on a 2017 report that showed Medicare payments to women physicians in 2013 were 55% of those to male physicians across all specialties.
“It can be disheartening, especially as an early career woman cardiologist, seeing these differences, but I think the responsibility on all of us is to take these observations and really try to understand more deeply why they exist,” Nosheen Reza, MD, from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and coauthor of the cross-sectional analysis, told this news organization.
Several factors could be contributing to the disparity, but “it’s not gender discrimination from Medicare,” Dr. Raber said. “The gap in reimbursement is really driven by the types and the volume of charges submitted.”
Indeed, a direct comparison of the three most common inpatient and outpatient billing codes showed no difference in payments between the sexes.
Men, however, submitted 24% more median inpatient charges to CMS than women (1,190 vs. 959), and 94% more outpatient charges (1,685 vs. 870).
Men also submitted slightly more unique billing codes (median inpatient, 10 vs. 9; median outpatient, 11 vs. 8).
Notably, women made up just 13% of the 17,524 cardiologists who received CMS payments in the inpatient setting in 2016 and 13% of the 16,929 cardiologists who did so in the outpatient setting.
Louisiana had the dubious distinction of having the largest gender gap in mean CMS payments, with male cardiologists earning $145,323 (235%) more than women, whereas women cardiologists in Vermont out-earned men by $31,483 (38%).
Overall, male cardiologists had more years in practice than women cardiologists and cared for slightly older Medicare beneficiaries.
Differences in CMS payments persisted, however, after adjustment for years since graduation, physician subspecialty, number of charges, number of unique billing codes, and patient complexity. The resulting β coefficient was -0.06, which translates into women receiving an average of 94% of the CMS payments received by men.
“The first takeaway, if you were really crass and focused on the bottom line, might be: ‘Hey, let me get a few more male cardiologists because they’re going to bring more into the organization.’ But we shouldn’t do that because, unless you link these data with quality outcomes, they’re an interesting observation and hypothesis-generating,” said Sharonne Hayes, MD, coauthor of the 2017 report and professor of cardiovascular medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., where she has served as director of diversity and inclusion for a decade.
She noted that there are multiple examples that the style of medicine women practice, on average, may be more effective, may be more outcomes based, and may save lives, as suggested by a recent analysis of hospitalized Medicare beneficiaries.
“The gap was not much different, like within 1% or so, but when you take that over the literally millions of Medicare patients cared for each year by hospitalists, that’s a substantial number of people,” Dr. Hayes said. “So, I think we need to take a step back, and we have to include these observations on studies like this and better understand the compensation gaps.”
She pointed out that the present study lacks data on full-time-equivalent status but that female physicians are more likely to work part-time, thus reducing the volume of claims.
Women might also care for different patient populations. “I practice in a women’s heart clinic and take care of [spontaneous coronary artery dissection] SCAD patients where the average age of SCAD is 42. So, the vast majority of patients I see on a day-to-day basis aren’t going to be Medicare age,” observed Dr. Hayes.
The differences in charges might also reflect the increased obligations in nonreimbursed work that women can have, Dr. Raber said. These can be things like mentoring, teaching roles, and serving on committees, which is a hypothesis supported by a 2021 study that showed women physicians spend more time on these “citizenship tasks” than men.
Finally, there could be organizational barriers that affect women’s clinical volumes, including less access to support from health care personnel. Added support is especially important, though, amid a 100-year pandemic, the women agreed.
“Within the first year of the pandemic, we saw women leaving the workforce in droves across all sectors, including medicine, including academic medicine. And, as the pandemic goes on without any signs of abatement, those threats continue to exist and continue to be amplified,” Dr. Reza said.
The groundswell of support surrounding the importance of diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives across the board has helped bring attention to the issue, she said. Some institutions, including the National Institutes of Health, are making efforts to extend relief to women with young families, caregivers, or those in academic medicine who, for example, need extensions on grants or bridge funding.
“There’s certainly a lot left to do, but I do think within the last year, there’s been an acceleration of literature that has come out, not only pointing out the disparities, but pointing out that perhaps women physicians do have better outcomes and are better liked by their patients and that losing women in the workforce would be a huge detriment to the field overall,” Dr. Reza said.
Dr. Raber, Dr. Reza, and Dr. Hayes reports no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor conflict of interest disclosures are listed in the paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Are ESC’s new heart failure guidelines already outdated?
The new guideline on management of heart failure (HF) from the European Society of Cardiology seemed to bear an asterisk or footnote even before its full unveiling in the early hours of ESC Congress 2021.
The document would offer little new in the arena of HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), so understandably the fast-approaching presentation of a major HFpEF trial – arguably the conference’s marquee event – would feel to some like the elephant in the room.
“I’d like to highlight this unfortunate timing of the guideline, because it’s an hour or 2 before we hear the full story from EMPEROR-Preserved, which I’m sure will change the guidelines,” Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, University of Lorraine, Vandoeuvre-Les-Nancy, France, said wryly.
Anticipation of the trial’s full presentation was intense as the ESC congress got underway, in part because the top-line and incomplete message from EMPEROR-Preserved had already been released: Patients with HFpEF treated with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint of cardiovascular (CV) death or HF hospitalization.
Although empagliflozin is the first medication to achieve that status in a major HFpEF trial, conspicuously absent from the early announcement were the magnitude of “benefit” and any data. Still, the tantalizing top-line results mean that technically, at least, “we have a drug which is effective in reduced and preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. Zannad said.
But the new guideline, published online Aug. 27, 2021, in the European Heart Journal and comprehensively described that day at the congress, was never really expected to consider results from EMPEROR-Reduced. “These new indications do need to go through the regulatory authorities,” such as the European Medicines Agency and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, observed Carlos Aguiar, MD, Hospital Santa Cruz, Carnaxide, Portugal.
“It does take some time for the whole process to be concluded and, finally, as physicians, being able to implement it in clinical practice,” Dr. Aguiar said as moderator of press briefing prior to the ESC congress.
The ESC guideline’s next iteration or update could well include an SGLT2 inhibitor recommendation that applies beyond the ejection fraction limits of HFrEF. Still, the document summarized that day reflects a number of pivotal concepts with profound treatment implications. Among them are the field’s latest paradigm for medical therapy of HFrEF and the increasingly accepted division of traditional HFpEF into two entities: HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF); and HFpEF, with its left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) threshold raised to 50%.
In fact, HFmrEF in the new document is a drug-therapy indication that barely existed a few years ago but grew in prominence after secondary findings from trials like TOPCAT for spironolactone and PARAGON-HF for sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), an angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI). Still, the HFmrEF recommendations come with different class and level-of-evidence designations.
Those new guideline features and others in the realm of pharmacologic therapy were summarized by the document’s authors at the 2021 Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) meeting, and covered at the time by this news organization
The ‘fantastic four’
One of the document’s central recommendations specifies which contemporary drug classes should be initiated, and when, in patients with HFrEF. An ACE inhibitor or ARNI, a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and an SGLT2 inhibitor collectively earned a class I recommendation, “given the importance of these key HFrEF therapies, some of which have been shown to improve outcomes within a month of initiation,” observed Roy S. Gardner, MBChB, MD.
An agent from each of the four classes is to be “commenced and up-titrated as quickly and as safely as possible, whilst using the lowest effective dose of loop diuretic to relieve congestion,” said Dr. Gardner, from Golden Jubilee National Hospital, Clydebank, Scotland, when presenting the full HFrEF portion of the guidelines.
The oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo, Merck), which recently emerged from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization, gained a class IIb recommendation.
The document’s “simplified algorithm” for managing such patients overall and the advent of SGLT2 inhibitors are new twists in ESC guidelines for HF. But the way the four drug classes are started in patients is key and could take some practitioners time to get used to. There is no prespecified order of initiation.
“We’ve left the door open for clinicians to evaluate the evidence to make sure these four drugs are started, and to tailor how to do it according to the patient,” based on clinical considerations such as blood pressure or renal function, said Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, cochair of the guideline task force.
“The SGLT2 inhibitor trials were done on top of therapy with ACE inhibitors or ARNI, beta-blockers, and MRAs, so some people no doubt will choose to follow a sequenced approach,” Dr. McDonagh said. Other practitioners will consider each patient and attempt to get all four started “as quickly and safely as possible based on the phenotype.”
Importantly, clinicians “should not wait for weeks, months, or years until you have the four drugs in the patient, but you should do this within weeks,” cautioned Johann Bauersachs, MD, Hannover (Germany) Medical School, a discussant for the guideline presentation who is listed as a reviewer on the document.
Although angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors are sometimes thought of as interchangeable, the new guideline does not give them the same weight. “The angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan is a constituent of the ARNI,” Dr. McDonagh noted. “So, the place of ARBs in heart failure has been downgraded in HFrEF. They are really for those who are intolerant of an ACE inhibitor or an ARNI.”
In practice, ARBs are likely to be used as first-line therapy in some circumstances, observed Dr. Bauersachs. They are “the default option in, unfortunately, many low-income countries that may not afford sacubitril-valsartan. And I know that there are many of them.”
Tweaks to device recommendations
The new document contains several new wrinkles in the recommendations for HF device therapy, which should usually be considered only if still appropriate after at least 3 months of optimal medical therapy, Dr. Gardner said.
For example, use of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) has been demoted from its previous class I recommendation to class II, level of evidence A, in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy “in light of the data from the DANISH study,” Dr. Gardner said.
The 2016 DANISH trial was noteworthy for questioning the survival benefits of ICDs in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy, whether or not they were also receiving cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).
The new document also puts greater emphasis on a range of specific CRT patient-selection criteria. Beyond the conventional recommended standards of an LVEF of 35% or less, QRS of at least 150 ms, and left-bundle-branch block on optimal meds, consideration can be given to CRT if the QRS is only 130 ms or greater. “And where it’s appropriate to do so, an ICD could be an option,” Dr. Gardner said.
It also recommends CRT as a replacement for right ventricular pacing in patients with high-degree atrioventricular block. “And this, for the first time, includes patients with atrial fibrillation,” he said. “The previous indications for CRT were in individuals in sinus rhythm.”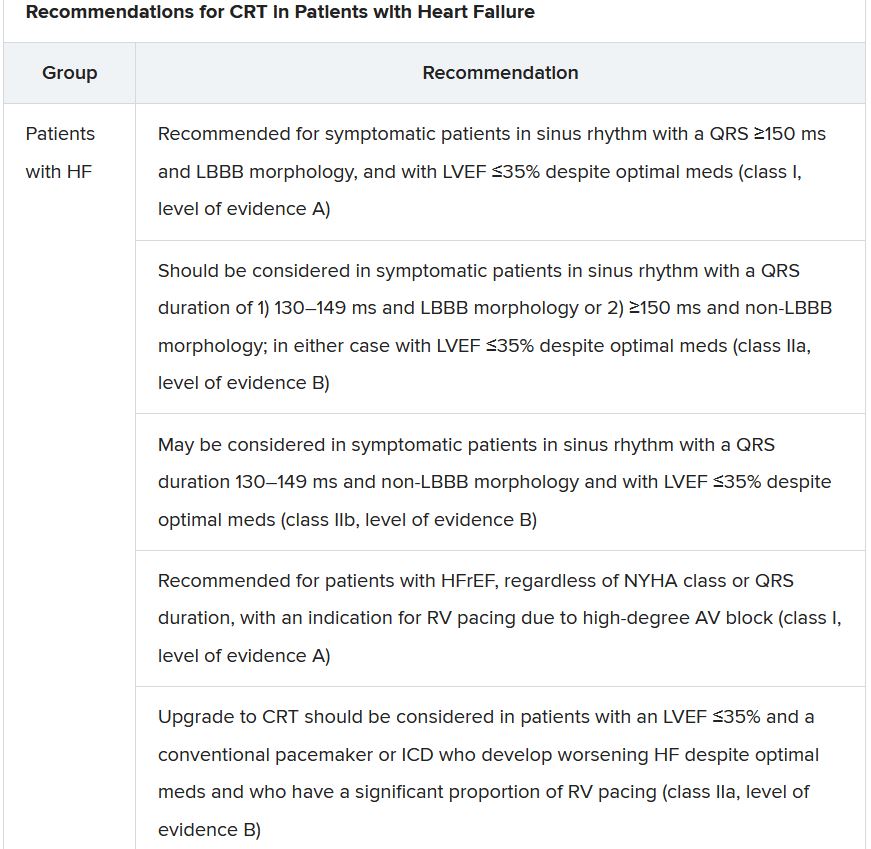
The new document recommends that HF in any patient be classified as HFrEF, defined by an LVEF of ≤40%; HFmrEF, defined by an LVEF of 41%-49%; or HFpEF, defined by an LVEF of at least 50%. “Importantly, for all forms, the presence of the clinical syndrome of heart failure is a prerequisite,” observed Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School, Singapore, at the presentation.
In a critical update from previous guidelines, the term HF with “mid-range” ejection fraction was replaced by the term specifying “mildly reduced” ejection fraction, Dr. Lam noted. The shift retains the acronym but now reflects growing appreciation that HFmrEF patients can benefit from treatments also used in HFrEF, including ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, MRAs, and sacubitril-valsartan, she said.
Support for that relationship comes largely from post hoc subgroup analyses of trials that featured some patients with LVEF 40%-49%. That includes most HFpEF trials represented in the guideline document, but also EMPEROR-Preserved, which saw gains for the primary outcome across the entire range of LVEF above 40%.
The LVEF-based definitions are consistent with a recent HF classification proposal endorsed by the ESC and subspecialty societies in Europe, North America, Japan, India, Australia, New Zealand, and China.
The document doesn’t update recommendations for HFpEF, in which “no treatment has been shown to convincingly reduce mortality or morbidity,” Dr. Lam observed. Still, she noted, the guideline task force “acknowledges that treatment options for HFpEF are being revised even as the guidelines have been published.”
That could be a reference to empagliflozin in EMPEROR-Preserved, but it also refers to the strikingly broad wording of an expanded indication for sacubitril-valsartan in the United States – “to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with chronic heart failure” – without specific restrictions on the basis of LVEF. The new indication was announced in early 2021, too late to be considered in the new guidelines.
Whither LVEF-based definitions?
During discussion after the guideline presentation, Dr. Zannad speculated on the future of HF classifications based on ventricular function, given trial evidence in recent years that some agents – notably spironolactone, sacubitril-valsartan, and now, apparently, empagliflozin – might be effective in HFpEF as well as HFrEF.
Will the field continue with “LVEF-centric” distinctions across the range of HF, or transition to “some definition in which drug therapies can be used independently across the full spectrum of ejection fraction?” Dr. Zannad posed.
“I think we need to wait and see what some of these trials with the SGLT2 inhibitors are going to show in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. McDonagh replied. “And I think that will be a step for the next guideline, completely redefining heart failure.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new guideline on management of heart failure (HF) from the European Society of Cardiology seemed to bear an asterisk or footnote even before its full unveiling in the early hours of ESC Congress 2021.
The document would offer little new in the arena of HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), so understandably the fast-approaching presentation of a major HFpEF trial – arguably the conference’s marquee event – would feel to some like the elephant in the room.
“I’d like to highlight this unfortunate timing of the guideline, because it’s an hour or 2 before we hear the full story from EMPEROR-Preserved, which I’m sure will change the guidelines,” Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, University of Lorraine, Vandoeuvre-Les-Nancy, France, said wryly.
Anticipation of the trial’s full presentation was intense as the ESC congress got underway, in part because the top-line and incomplete message from EMPEROR-Preserved had already been released: Patients with HFpEF treated with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint of cardiovascular (CV) death or HF hospitalization.
Although empagliflozin is the first medication to achieve that status in a major HFpEF trial, conspicuously absent from the early announcement were the magnitude of “benefit” and any data. Still, the tantalizing top-line results mean that technically, at least, “we have a drug which is effective in reduced and preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. Zannad said.
But the new guideline, published online Aug. 27, 2021, in the European Heart Journal and comprehensively described that day at the congress, was never really expected to consider results from EMPEROR-Reduced. “These new indications do need to go through the regulatory authorities,” such as the European Medicines Agency and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, observed Carlos Aguiar, MD, Hospital Santa Cruz, Carnaxide, Portugal.
“It does take some time for the whole process to be concluded and, finally, as physicians, being able to implement it in clinical practice,” Dr. Aguiar said as moderator of press briefing prior to the ESC congress.
The ESC guideline’s next iteration or update could well include an SGLT2 inhibitor recommendation that applies beyond the ejection fraction limits of HFrEF. Still, the document summarized that day reflects a number of pivotal concepts with profound treatment implications. Among them are the field’s latest paradigm for medical therapy of HFrEF and the increasingly accepted division of traditional HFpEF into two entities: HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF); and HFpEF, with its left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) threshold raised to 50%.
In fact, HFmrEF in the new document is a drug-therapy indication that barely existed a few years ago but grew in prominence after secondary findings from trials like TOPCAT for spironolactone and PARAGON-HF for sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), an angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI). Still, the HFmrEF recommendations come with different class and level-of-evidence designations.
Those new guideline features and others in the realm of pharmacologic therapy were summarized by the document’s authors at the 2021 Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) meeting, and covered at the time by this news organization
The ‘fantastic four’
One of the document’s central recommendations specifies which contemporary drug classes should be initiated, and when, in patients with HFrEF. An ACE inhibitor or ARNI, a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and an SGLT2 inhibitor collectively earned a class I recommendation, “given the importance of these key HFrEF therapies, some of which have been shown to improve outcomes within a month of initiation,” observed Roy S. Gardner, MBChB, MD.
An agent from each of the four classes is to be “commenced and up-titrated as quickly and as safely as possible, whilst using the lowest effective dose of loop diuretic to relieve congestion,” said Dr. Gardner, from Golden Jubilee National Hospital, Clydebank, Scotland, when presenting the full HFrEF portion of the guidelines.
The oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo, Merck), which recently emerged from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization, gained a class IIb recommendation.
The document’s “simplified algorithm” for managing such patients overall and the advent of SGLT2 inhibitors are new twists in ESC guidelines for HF. But the way the four drug classes are started in patients is key and could take some practitioners time to get used to. There is no prespecified order of initiation.
“We’ve left the door open for clinicians to evaluate the evidence to make sure these four drugs are started, and to tailor how to do it according to the patient,” based on clinical considerations such as blood pressure or renal function, said Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, cochair of the guideline task force.
“The SGLT2 inhibitor trials were done on top of therapy with ACE inhibitors or ARNI, beta-blockers, and MRAs, so some people no doubt will choose to follow a sequenced approach,” Dr. McDonagh said. Other practitioners will consider each patient and attempt to get all four started “as quickly and safely as possible based on the phenotype.”
Importantly, clinicians “should not wait for weeks, months, or years until you have the four drugs in the patient, but you should do this within weeks,” cautioned Johann Bauersachs, MD, Hannover (Germany) Medical School, a discussant for the guideline presentation who is listed as a reviewer on the document.
Although angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors are sometimes thought of as interchangeable, the new guideline does not give them the same weight. “The angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan is a constituent of the ARNI,” Dr. McDonagh noted. “So, the place of ARBs in heart failure has been downgraded in HFrEF. They are really for those who are intolerant of an ACE inhibitor or an ARNI.”
In practice, ARBs are likely to be used as first-line therapy in some circumstances, observed Dr. Bauersachs. They are “the default option in, unfortunately, many low-income countries that may not afford sacubitril-valsartan. And I know that there are many of them.”
Tweaks to device recommendations
The new document contains several new wrinkles in the recommendations for HF device therapy, which should usually be considered only if still appropriate after at least 3 months of optimal medical therapy, Dr. Gardner said.
For example, use of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) has been demoted from its previous class I recommendation to class II, level of evidence A, in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy “in light of the data from the DANISH study,” Dr. Gardner said.
The 2016 DANISH trial was noteworthy for questioning the survival benefits of ICDs in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy, whether or not they were also receiving cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).
The new document also puts greater emphasis on a range of specific CRT patient-selection criteria. Beyond the conventional recommended standards of an LVEF of 35% or less, QRS of at least 150 ms, and left-bundle-branch block on optimal meds, consideration can be given to CRT if the QRS is only 130 ms or greater. “And where it’s appropriate to do so, an ICD could be an option,” Dr. Gardner said.
It also recommends CRT as a replacement for right ventricular pacing in patients with high-degree atrioventricular block. “And this, for the first time, includes patients with atrial fibrillation,” he said. “The previous indications for CRT were in individuals in sinus rhythm.”
The new document recommends that HF in any patient be classified as HFrEF, defined by an LVEF of ≤40%; HFmrEF, defined by an LVEF of 41%-49%; or HFpEF, defined by an LVEF of at least 50%. “Importantly, for all forms, the presence of the clinical syndrome of heart failure is a prerequisite,” observed Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School, Singapore, at the presentation.
In a critical update from previous guidelines, the term HF with “mid-range” ejection fraction was replaced by the term specifying “mildly reduced” ejection fraction, Dr. Lam noted. The shift retains the acronym but now reflects growing appreciation that HFmrEF patients can benefit from treatments also used in HFrEF, including ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, MRAs, and sacubitril-valsartan, she said.
Support for that relationship comes largely from post hoc subgroup analyses of trials that featured some patients with LVEF 40%-49%. That includes most HFpEF trials represented in the guideline document, but also EMPEROR-Preserved, which saw gains for the primary outcome across the entire range of LVEF above 40%.
The LVEF-based definitions are consistent with a recent HF classification proposal endorsed by the ESC and subspecialty societies in Europe, North America, Japan, India, Australia, New Zealand, and China.
The document doesn’t update recommendations for HFpEF, in which “no treatment has been shown to convincingly reduce mortality or morbidity,” Dr. Lam observed. Still, she noted, the guideline task force “acknowledges that treatment options for HFpEF are being revised even as the guidelines have been published.”
That could be a reference to empagliflozin in EMPEROR-Preserved, but it also refers to the strikingly broad wording of an expanded indication for sacubitril-valsartan in the United States – “to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with chronic heart failure” – without specific restrictions on the basis of LVEF. The new indication was announced in early 2021, too late to be considered in the new guidelines.
Whither LVEF-based definitions?
During discussion after the guideline presentation, Dr. Zannad speculated on the future of HF classifications based on ventricular function, given trial evidence in recent years that some agents – notably spironolactone, sacubitril-valsartan, and now, apparently, empagliflozin – might be effective in HFpEF as well as HFrEF.
Will the field continue with “LVEF-centric” distinctions across the range of HF, or transition to “some definition in which drug therapies can be used independently across the full spectrum of ejection fraction?” Dr. Zannad posed.
“I think we need to wait and see what some of these trials with the SGLT2 inhibitors are going to show in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. McDonagh replied. “And I think that will be a step for the next guideline, completely redefining heart failure.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new guideline on management of heart failure (HF) from the European Society of Cardiology seemed to bear an asterisk or footnote even before its full unveiling in the early hours of ESC Congress 2021.
The document would offer little new in the arena of HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), so understandably the fast-approaching presentation of a major HFpEF trial – arguably the conference’s marquee event – would feel to some like the elephant in the room.
“I’d like to highlight this unfortunate timing of the guideline, because it’s an hour or 2 before we hear the full story from EMPEROR-Preserved, which I’m sure will change the guidelines,” Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, University of Lorraine, Vandoeuvre-Les-Nancy, France, said wryly.
Anticipation of the trial’s full presentation was intense as the ESC congress got underway, in part because the top-line and incomplete message from EMPEROR-Preserved had already been released: Patients with HFpEF treated with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint of cardiovascular (CV) death or HF hospitalization.
Although empagliflozin is the first medication to achieve that status in a major HFpEF trial, conspicuously absent from the early announcement were the magnitude of “benefit” and any data. Still, the tantalizing top-line results mean that technically, at least, “we have a drug which is effective in reduced and preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. Zannad said.
But the new guideline, published online Aug. 27, 2021, in the European Heart Journal and comprehensively described that day at the congress, was never really expected to consider results from EMPEROR-Reduced. “These new indications do need to go through the regulatory authorities,” such as the European Medicines Agency and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, observed Carlos Aguiar, MD, Hospital Santa Cruz, Carnaxide, Portugal.
“It does take some time for the whole process to be concluded and, finally, as physicians, being able to implement it in clinical practice,” Dr. Aguiar said as moderator of press briefing prior to the ESC congress.
The ESC guideline’s next iteration or update could well include an SGLT2 inhibitor recommendation that applies beyond the ejection fraction limits of HFrEF. Still, the document summarized that day reflects a number of pivotal concepts with profound treatment implications. Among them are the field’s latest paradigm for medical therapy of HFrEF and the increasingly accepted division of traditional HFpEF into two entities: HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF); and HFpEF, with its left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) threshold raised to 50%.
In fact, HFmrEF in the new document is a drug-therapy indication that barely existed a few years ago but grew in prominence after secondary findings from trials like TOPCAT for spironolactone and PARAGON-HF for sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto, Novartis), an angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI). Still, the HFmrEF recommendations come with different class and level-of-evidence designations.
Those new guideline features and others in the realm of pharmacologic therapy were summarized by the document’s authors at the 2021 Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) meeting, and covered at the time by this news organization
The ‘fantastic four’
One of the document’s central recommendations specifies which contemporary drug classes should be initiated, and when, in patients with HFrEF. An ACE inhibitor or ARNI, a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and an SGLT2 inhibitor collectively earned a class I recommendation, “given the importance of these key HFrEF therapies, some of which have been shown to improve outcomes within a month of initiation,” observed Roy S. Gardner, MBChB, MD.
An agent from each of the four classes is to be “commenced and up-titrated as quickly and as safely as possible, whilst using the lowest effective dose of loop diuretic to relieve congestion,” said Dr. Gardner, from Golden Jubilee National Hospital, Clydebank, Scotland, when presenting the full HFrEF portion of the guidelines.
The oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo, Merck), which recently emerged from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization, gained a class IIb recommendation.
The document’s “simplified algorithm” for managing such patients overall and the advent of SGLT2 inhibitors are new twists in ESC guidelines for HF. But the way the four drug classes are started in patients is key and could take some practitioners time to get used to. There is no prespecified order of initiation.
“We’ve left the door open for clinicians to evaluate the evidence to make sure these four drugs are started, and to tailor how to do it according to the patient,” based on clinical considerations such as blood pressure or renal function, said Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, cochair of the guideline task force.
“The SGLT2 inhibitor trials were done on top of therapy with ACE inhibitors or ARNI, beta-blockers, and MRAs, so some people no doubt will choose to follow a sequenced approach,” Dr. McDonagh said. Other practitioners will consider each patient and attempt to get all four started “as quickly and safely as possible based on the phenotype.”
Importantly, clinicians “should not wait for weeks, months, or years until you have the four drugs in the patient, but you should do this within weeks,” cautioned Johann Bauersachs, MD, Hannover (Germany) Medical School, a discussant for the guideline presentation who is listed as a reviewer on the document.
Although angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors are sometimes thought of as interchangeable, the new guideline does not give them the same weight. “The angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan is a constituent of the ARNI,” Dr. McDonagh noted. “So, the place of ARBs in heart failure has been downgraded in HFrEF. They are really for those who are intolerant of an ACE inhibitor or an ARNI.”
In practice, ARBs are likely to be used as first-line therapy in some circumstances, observed Dr. Bauersachs. They are “the default option in, unfortunately, many low-income countries that may not afford sacubitril-valsartan. And I know that there are many of them.”
Tweaks to device recommendations
The new document contains several new wrinkles in the recommendations for HF device therapy, which should usually be considered only if still appropriate after at least 3 months of optimal medical therapy, Dr. Gardner said.
For example, use of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) has been demoted from its previous class I recommendation to class II, level of evidence A, in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy “in light of the data from the DANISH study,” Dr. Gardner said.
The 2016 DANISH trial was noteworthy for questioning the survival benefits of ICDs in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy, whether or not they were also receiving cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).
The new document also puts greater emphasis on a range of specific CRT patient-selection criteria. Beyond the conventional recommended standards of an LVEF of 35% or less, QRS of at least 150 ms, and left-bundle-branch block on optimal meds, consideration can be given to CRT if the QRS is only 130 ms or greater. “And where it’s appropriate to do so, an ICD could be an option,” Dr. Gardner said.
It also recommends CRT as a replacement for right ventricular pacing in patients with high-degree atrioventricular block. “And this, for the first time, includes patients with atrial fibrillation,” he said. “The previous indications for CRT were in individuals in sinus rhythm.”
The new document recommends that HF in any patient be classified as HFrEF, defined by an LVEF of ≤40%; HFmrEF, defined by an LVEF of 41%-49%; or HFpEF, defined by an LVEF of at least 50%. “Importantly, for all forms, the presence of the clinical syndrome of heart failure is a prerequisite,” observed Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School, Singapore, at the presentation.
In a critical update from previous guidelines, the term HF with “mid-range” ejection fraction was replaced by the term specifying “mildly reduced” ejection fraction, Dr. Lam noted. The shift retains the acronym but now reflects growing appreciation that HFmrEF patients can benefit from treatments also used in HFrEF, including ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, MRAs, and sacubitril-valsartan, she said.
Support for that relationship comes largely from post hoc subgroup analyses of trials that featured some patients with LVEF 40%-49%. That includes most HFpEF trials represented in the guideline document, but also EMPEROR-Preserved, which saw gains for the primary outcome across the entire range of LVEF above 40%.
The LVEF-based definitions are consistent with a recent HF classification proposal endorsed by the ESC and subspecialty societies in Europe, North America, Japan, India, Australia, New Zealand, and China.
The document doesn’t update recommendations for HFpEF, in which “no treatment has been shown to convincingly reduce mortality or morbidity,” Dr. Lam observed. Still, she noted, the guideline task force “acknowledges that treatment options for HFpEF are being revised even as the guidelines have been published.”
That could be a reference to empagliflozin in EMPEROR-Preserved, but it also refers to the strikingly broad wording of an expanded indication for sacubitril-valsartan in the United States – “to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with chronic heart failure” – without specific restrictions on the basis of LVEF. The new indication was announced in early 2021, too late to be considered in the new guidelines.
Whither LVEF-based definitions?
During discussion after the guideline presentation, Dr. Zannad speculated on the future of HF classifications based on ventricular function, given trial evidence in recent years that some agents – notably spironolactone, sacubitril-valsartan, and now, apparently, empagliflozin – might be effective in HFpEF as well as HFrEF.
Will the field continue with “LVEF-centric” distinctions across the range of HF, or transition to “some definition in which drug therapies can be used independently across the full spectrum of ejection fraction?” Dr. Zannad posed.
“I think we need to wait and see what some of these trials with the SGLT2 inhibitors are going to show in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction,” Dr. McDonagh replied. “And I think that will be a step for the next guideline, completely redefining heart failure.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Novel diabetic foot ulcer cream shows promise in phase 3 trial
ON101 (Fespixon, Oneness Biotech), a first-in-class, macrophage-regulating, wound-healing cream for diabetic foot ulcers has shown benefit over absorbent dressings in a phase 3 trial, with another trial ongoing.
The product became available in Taiwan on July 4, 2021, after receiving regulatory approval from the Taiwan Food and Drug Administration based on efficacy and safety findings in a three-country phase 3 clinical trial.
Oneness Biotech has also just started a second phase 3 trial in the United States, with a planned enrollment of 208 patients with diabetic foot ulcers, which will compare ON101 cream versus placebo cream, in addition to standard care, over 20 weeks.
The company expects to complete that trial and file a new drug application with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2023, and a global launch is planned for 2025, said Oneness Biotech founder and CEO William Lu.
Current and upcoming trials
The Taiwan FDA approval of ON101 was based on a 236-patient clinical trial conducted in Taiwan, China, and the United States by Yu-Yao Huang MD, PhD, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan City, Taiwan, and colleagues, which was published online Sept. 3, 2021, in JAMA Network Open.
The study results will also be presented during an oral session at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes meeting on Sept. 30.
The published trial showed that foot ulcers treated with ON101 cream were almost three times more likely to be completely healed at 16 weeks than those treated with standard care with an absorbent dressing (Aquacel Hydrofiber, ConvaTec) (odds ratio, 2.84; P < .001).
“The findings of this study suggest that ON101, a macrophage regulator that behaves differently from moisture-retaining dressings, represents an active-healing alternative for home and primary care of patients with chronic [diabetic foot ulcers],” the researchers concluded.
“ON101 was also granted a fast track designation by the U.S. FDA in March this year,” senior author Shun-Chen Chang, MD, Taipei Medical University–Shuang Ho Hospital, New Taipei City, Taiwan, said in an interview.
“Patients in the United States can access this new drug via the expanded access program or by participating in the second phase 3 trial in the United States,” added coauthor Shawn M. Cazzell, DPM, chief medical officer, Limb Preservation Platform, Fresno, Calif., who is involved with both trials.
It is “exciting” to have a new therapy for diabetic foot ulcers, said Dr. Cazzell, because they are serious and life-threatening.
Could cream with plant extracts surpass current care?
Current standard clinical care for diabetic foot ulcer consists of debridement, off-loading, infection control, and maintaining a moist environment with dressings, Huang and colleagues explain. If the foot ulcer does not respond, growth factors, tissue-engineering products, hyperbaric oxygen, or negative pressure wound therapies may be used.
However, the number of amputations from chronic diabetic foot ulcers that do not heal is increasing, pointing to a need for better treatment options.
Hyperglycemia increases the ratio of M1 proinflammatory macrophages to M2 proregenerative macrophages, and accumulating evidence suggests this might be a potential treatment target.
Researchers at Oneness Biotech showed that ON101, which is comprised of extracts from two plants, Plectranthus amboinicus and Centella asiatica, exerts a wound-healing effect by regulating the balance between M1 and M2 macrophages.
An extract of one plant suppresses inflammation, while an extract of the other increases collagen synthesis.
In preclinical studies, these two plant extracts had a synergistic effect on balancing the ratio of M1 to M2 macrophages and accelerating wound healing in a mouse model. This was followed by promising efficacy and safety results in two trials of 24 patients and 30 patients.
Significantly better healing with ON101 than standard care
For the current phase 3, randomized clinical trial, researchers enrolled patients in 21 clinics from November 2012 to May 2020.
To be eligible for the study, patients had to be 20-80 years old, with a hemoglobin A1c less than 12%. They also had to have a Wagner grade 1 or 2 foot ulcer that was 1-25 cm2 after debridement, had been treated with standard care, and was present for at least 4 weeks.
Patients were a mean age of 57 years and 74% were men. They had a mean A1c of 8.1%, and 61% had had diabetes for more than 10 years.
Most (78%) of the diabetic foot ulcers were Wagner grade 2. The wounds had a mean area of 4.8 cm2 and had been present for a mean of 7 months.
Patients were instructed on how to self-administer ON101 cream twice a day (treatment group, n = 122) or how to apply an absorbent dressing and change it daily or two or three times a week (standard care group, n = 114). All patients were allowed to apply a sterile gauze dressing.
They visited the clinic every 2 weeks during the 16-week treatment phase and 12-week observation phase.
In the full analysis set, 74 patients (61%) in the ON101 group and 40 patients (35%) in the standard care group had complete wound healing after 16 weeks of treatment.
The subgroup of patients at higher risk of poor wound healing (A1c >9%, ulcer area >5 cm2, and diabetic foot ulcer duration >6 months) also had significantly better healing with the ON101 cream than standard care.
There were seven (5.7%) treatment-emergent adverse events in the ON101 group versus five (4.4%) in the standard care group.
There were no treatment-related serious adverse events in the ON101 group versus one (0.9%) in the comparator group.
The study was funded by Oneness Biotech, Microbio Group, and Shanghai Haihe Pharmaceutical. One author has reported receiving fees from Oneness Biotech, and Dr. Chang has reported receiving a speakers fee from Oneness Biotech. The other authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ON101 (Fespixon, Oneness Biotech), a first-in-class, macrophage-regulating, wound-healing cream for diabetic foot ulcers has shown benefit over absorbent dressings in a phase 3 trial, with another trial ongoing.
The product became available in Taiwan on July 4, 2021, after receiving regulatory approval from the Taiwan Food and Drug Administration based on efficacy and safety findings in a three-country phase 3 clinical trial.
Oneness Biotech has also just started a second phase 3 trial in the United States, with a planned enrollment of 208 patients with diabetic foot ulcers, which will compare ON101 cream versus placebo cream, in addition to standard care, over 20 weeks.
The company expects to complete that trial and file a new drug application with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2023, and a global launch is planned for 2025, said Oneness Biotech founder and CEO William Lu.
Current and upcoming trials
The Taiwan FDA approval of ON101 was based on a 236-patient clinical trial conducted in Taiwan, China, and the United States by Yu-Yao Huang MD, PhD, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan City, Taiwan, and colleagues, which was published online Sept. 3, 2021, in JAMA Network Open.
The study results will also be presented during an oral session at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes meeting on Sept. 30.
The published trial showed that foot ulcers treated with ON101 cream were almost three times more likely to be completely healed at 16 weeks than those treated with standard care with an absorbent dressing (Aquacel Hydrofiber, ConvaTec) (odds ratio, 2.84; P < .001).
“The findings of this study suggest that ON101, a macrophage regulator that behaves differently from moisture-retaining dressings, represents an active-healing alternative for home and primary care of patients with chronic [diabetic foot ulcers],” the researchers concluded.
“ON101 was also granted a fast track designation by the U.S. FDA in March this year,” senior author Shun-Chen Chang, MD, Taipei Medical University–Shuang Ho Hospital, New Taipei City, Taiwan, said in an interview.
“Patients in the United States can access this new drug via the expanded access program or by participating in the second phase 3 trial in the United States,” added coauthor Shawn M. Cazzell, DPM, chief medical officer, Limb Preservation Platform, Fresno, Calif., who is involved with both trials.
It is “exciting” to have a new therapy for diabetic foot ulcers, said Dr. Cazzell, because they are serious and life-threatening.
Could cream with plant extracts surpass current care?
Current standard clinical care for diabetic foot ulcer consists of debridement, off-loading, infection control, and maintaining a moist environment with dressings, Huang and colleagues explain. If the foot ulcer does not respond, growth factors, tissue-engineering products, hyperbaric oxygen, or negative pressure wound therapies may be used.
However, the number of amputations from chronic diabetic foot ulcers that do not heal is increasing, pointing to a need for better treatment options.
Hyperglycemia increases the ratio of M1 proinflammatory macrophages to M2 proregenerative macrophages, and accumulating evidence suggests this might be a potential treatment target.
Researchers at Oneness Biotech showed that ON101, which is comprised of extracts from two plants, Plectranthus amboinicus and Centella asiatica, exerts a wound-healing effect by regulating the balance between M1 and M2 macrophages.
An extract of one plant suppresses inflammation, while an extract of the other increases collagen synthesis.
In preclinical studies, these two plant extracts had a synergistic effect on balancing the ratio of M1 to M2 macrophages and accelerating wound healing in a mouse model. This was followed by promising efficacy and safety results in two trials of 24 patients and 30 patients.
Significantly better healing with ON101 than standard care
For the current phase 3, randomized clinical trial, researchers enrolled patients in 21 clinics from November 2012 to May 2020.
To be eligible for the study, patients had to be 20-80 years old, with a hemoglobin A1c less than 12%. They also had to have a Wagner grade 1 or 2 foot ulcer that was 1-25 cm2 after debridement, had been treated with standard care, and was present for at least 4 weeks.
Patients were a mean age of 57 years and 74% were men. They had a mean A1c of 8.1%, and 61% had had diabetes for more than 10 years.
Most (78%) of the diabetic foot ulcers were Wagner grade 2. The wounds had a mean area of 4.8 cm2 and had been present for a mean of 7 months.
Patients were instructed on how to self-administer ON101 cream twice a day (treatment group, n = 122) or how to apply an absorbent dressing and change it daily or two or three times a week (standard care group, n = 114). All patients were allowed to apply a sterile gauze dressing.
They visited the clinic every 2 weeks during the 16-week treatment phase and 12-week observation phase.
In the full analysis set, 74 patients (61%) in the ON101 group and 40 patients (35%) in the standard care group had complete wound healing after 16 weeks of treatment.
The subgroup of patients at higher risk of poor wound healing (A1c >9%, ulcer area >5 cm2, and diabetic foot ulcer duration >6 months) also had significantly better healing with the ON101 cream than standard care.
There were seven (5.7%) treatment-emergent adverse events in the ON101 group versus five (4.4%) in the standard care group.
There were no treatment-related serious adverse events in the ON101 group versus one (0.9%) in the comparator group.
The study was funded by Oneness Biotech, Microbio Group, and Shanghai Haihe Pharmaceutical. One author has reported receiving fees from Oneness Biotech, and Dr. Chang has reported receiving a speakers fee from Oneness Biotech. The other authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ON101 (Fespixon, Oneness Biotech), a first-in-class, macrophage-regulating, wound-healing cream for diabetic foot ulcers has shown benefit over absorbent dressings in a phase 3 trial, with another trial ongoing.
The product became available in Taiwan on July 4, 2021, after receiving regulatory approval from the Taiwan Food and Drug Administration based on efficacy and safety findings in a three-country phase 3 clinical trial.
Oneness Biotech has also just started a second phase 3 trial in the United States, with a planned enrollment of 208 patients with diabetic foot ulcers, which will compare ON101 cream versus placebo cream, in addition to standard care, over 20 weeks.
The company expects to complete that trial and file a new drug application with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2023, and a global launch is planned for 2025, said Oneness Biotech founder and CEO William Lu.
Current and upcoming trials
The Taiwan FDA approval of ON101 was based on a 236-patient clinical trial conducted in Taiwan, China, and the United States by Yu-Yao Huang MD, PhD, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan City, Taiwan, and colleagues, which was published online Sept. 3, 2021, in JAMA Network Open.
The study results will also be presented during an oral session at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes meeting on Sept. 30.
The published trial showed that foot ulcers treated with ON101 cream were almost three times more likely to be completely healed at 16 weeks than those treated with standard care with an absorbent dressing (Aquacel Hydrofiber, ConvaTec) (odds ratio, 2.84; P < .001).
“The findings of this study suggest that ON101, a macrophage regulator that behaves differently from moisture-retaining dressings, represents an active-healing alternative for home and primary care of patients with chronic [diabetic foot ulcers],” the researchers concluded.
“ON101 was also granted a fast track designation by the U.S. FDA in March this year,” senior author Shun-Chen Chang, MD, Taipei Medical University–Shuang Ho Hospital, New Taipei City, Taiwan, said in an interview.
“Patients in the United States can access this new drug via the expanded access program or by participating in the second phase 3 trial in the United States,” added coauthor Shawn M. Cazzell, DPM, chief medical officer, Limb Preservation Platform, Fresno, Calif., who is involved with both trials.
It is “exciting” to have a new therapy for diabetic foot ulcers, said Dr. Cazzell, because they are serious and life-threatening.
Could cream with plant extracts surpass current care?
Current standard clinical care for diabetic foot ulcer consists of debridement, off-loading, infection control, and maintaining a moist environment with dressings, Huang and colleagues explain. If the foot ulcer does not respond, growth factors, tissue-engineering products, hyperbaric oxygen, or negative pressure wound therapies may be used.
However, the number of amputations from chronic diabetic foot ulcers that do not heal is increasing, pointing to a need for better treatment options.
Hyperglycemia increases the ratio of M1 proinflammatory macrophages to M2 proregenerative macrophages, and accumulating evidence suggests this might be a potential treatment target.
Researchers at Oneness Biotech showed that ON101, which is comprised of extracts from two plants, Plectranthus amboinicus and Centella asiatica, exerts a wound-healing effect by regulating the balance between M1 and M2 macrophages.
An extract of one plant suppresses inflammation, while an extract of the other increases collagen synthesis.
In preclinical studies, these two plant extracts had a synergistic effect on balancing the ratio of M1 to M2 macrophages and accelerating wound healing in a mouse model. This was followed by promising efficacy and safety results in two trials of 24 patients and 30 patients.
Significantly better healing with ON101 than standard care
For the current phase 3, randomized clinical trial, researchers enrolled patients in 21 clinics from November 2012 to May 2020.
To be eligible for the study, patients had to be 20-80 years old, with a hemoglobin A1c less than 12%. They also had to have a Wagner grade 1 or 2 foot ulcer that was 1-25 cm2 after debridement, had been treated with standard care, and was present for at least 4 weeks.
Patients were a mean age of 57 years and 74% were men. They had a mean A1c of 8.1%, and 61% had had diabetes for more than 10 years.
Most (78%) of the diabetic foot ulcers were Wagner grade 2. The wounds had a mean area of 4.8 cm2 and had been present for a mean of 7 months.
Patients were instructed on how to self-administer ON101 cream twice a day (treatment group, n = 122) or how to apply an absorbent dressing and change it daily or two or three times a week (standard care group, n = 114). All patients were allowed to apply a sterile gauze dressing.
They visited the clinic every 2 weeks during the 16-week treatment phase and 12-week observation phase.
In the full analysis set, 74 patients (61%) in the ON101 group and 40 patients (35%) in the standard care group had complete wound healing after 16 weeks of treatment.
The subgroup of patients at higher risk of poor wound healing (A1c >9%, ulcer area >5 cm2, and diabetic foot ulcer duration >6 months) also had significantly better healing with the ON101 cream than standard care.
There were seven (5.7%) treatment-emergent adverse events in the ON101 group versus five (4.4%) in the standard care group.
There were no treatment-related serious adverse events in the ON101 group versus one (0.9%) in the comparator group.
The study was funded by Oneness Biotech, Microbio Group, and Shanghai Haihe Pharmaceutical. One author has reported receiving fees from Oneness Biotech, and Dr. Chang has reported receiving a speakers fee from Oneness Biotech. The other authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At 18 months, much still unknown about diabetes and COVID-19
At 18 months into the COVID-19 pandemic, many of the direct and indirect effects of SARS-CoV-2 on people with diabetes have become clearer, but knowledge gaps remain, say epidemiologists.
“COVID-19 has had a devastating effect on the population with diabetes, and conversely, the high prevalence of diabetes and uncontrolled diabetes has exacerbated the problem,” Edward W. Gregg, PhD, Imperial College London, lead author of a new literature review, told this news organization.
“As it becomes clear that the COVID-19 pandemic will be with us in different forms for the foreseeable future, the emphasis for people with diabetes needs to be continued primary care, glycemic management, and vaccination to reduce the long-term impact of COVID-19 in this population,” he added.
In data, mostly from case series, the review shows that more than one-third of people hospitalized with COVID-19 have diabetes. It is published in the September issue of Diabetes Care.
People with diabetes are more than three times as likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than those without diabetes, even after adjustment for age, sex, and other underlying conditions. Diabetes also accounts for 30%-40% of severe COVID-19 cases and deaths. Among those with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19, 21%-43% require intensive care, and the case fatality rate is about 25%.
In one of the few multivariate analyses that examined type 1 and type 2 diabetes separately, conducted in the U.K., the odds of in-hospital COVID-19–related deaths, compared with people without diabetes, were almost three times higher (odds ratio, 2.9) for individuals with type 1 diabetes and almost twice as high (OR, 1.8) for those with type 2, after adjustment for comorbidities.
The causes of death appear to be a combination of factors specific to the SARS-CoV-2 infection and to diabetes-related factors, Dr. Gregg said in an interview.
“Much of the increased risk is due to the fact that people with diabetes have more comorbid factors, but there are many other mechanisms that appear to further increase risk, including the inflammatory and immune responses of people with diabetes, and hyperglycemia appears to have an exacerbating effect by itself.”
Elevated glucose is clear risk factor for COVID-19 severity
Elevated A1c was identified among several other overall predictors of poor COVID-19 outcomes, including obesity as well as comorbid kidney and cardiovascular disease.
High blood glucose levels at the time of admission in people with previously diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes emerged as a clear predictor of worse outcomes. For example, among 605 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in China, those with fasting plasma glucose 6.1-6.9 mmol/L (110-125 mg/dL) and ≥7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) had odds ratios of poor outcomes within 28 days of 2.6 and 4.0 compared with FPG <6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL).
Population-based studies in the U.K. found that A1c levels measured months before COVID-19 hospitalization were associated with risk for intensive care unit admission and/or death, particularly among those with type 1 diabetes. Overall, the death rate was 36% higher for those with A1c of 9%-9.9% versus 6.5%-7%.
Despite the link between high A1c and death, there is as yet no clear evidence that normalizing blood glucose levels minimizes COVID-19 severity, Dr. Gregg said.
“There are data that suggest poor glycemic control is associated with higher risk of poor outcomes. This is indirect evidence that managing blood sugar will help, but more direct evidence is needed.”
Evidence gaps identified
Dr. Gregg and co-authors Marisa Sophiea, PhD, MSc, and Misghina Weldegiorgis, PhD, BSc, also from Imperial College London, identify three areas in which more data are needed.
First, more information is needed to determine whether exposure, infection, and hospitalization risks differ by diabetes status and how those factors affect outcomes. The same studies would also be important to identify how factors such as behavior, masking, and lockdown policies, risk factor control, and household/community environments affect risk in people with diabetes.
Second, studies are needed to better understand indirect effects of the pandemic, such as care and management factors. Some of these, such as the advent of telehealth, may turn out to be beneficial in the long run, they note.
Finally, the pandemic has “brought a wealth of natural experiments,” such as how vaccination programs and other interventions are affecting people with diabetes specifically. Finally, population studies are needed in many parts of the world beyond the U.S. and the U.K., where most of that work has been done thus far.
“Many of the most important unanswered questions lie in the potential indirect and long-term impact of the pandemic that require population-based studies,” Dr. Gregg said. “Most of our knowledge so far is from case series, which only assess patients from the time of hospitalization.”
Indeed, very little data are available for people with diabetes who get COVID-19 but are not hospitalized, so it’s not known whether they have a longer duration of illness or are at greater risk for “long COVID” than those without diabetes who experience COVID-19 at home.
“I have not seen published data on this yet, and it’s an important unanswered question,” Dr. Gregg said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At 18 months into the COVID-19 pandemic, many of the direct and indirect effects of SARS-CoV-2 on people with diabetes have become clearer, but knowledge gaps remain, say epidemiologists.
“COVID-19 has had a devastating effect on the population with diabetes, and conversely, the high prevalence of diabetes and uncontrolled diabetes has exacerbated the problem,” Edward W. Gregg, PhD, Imperial College London, lead author of a new literature review, told this news organization.
“As it becomes clear that the COVID-19 pandemic will be with us in different forms for the foreseeable future, the emphasis for people with diabetes needs to be continued primary care, glycemic management, and vaccination to reduce the long-term impact of COVID-19 in this population,” he added.
In data, mostly from case series, the review shows that more than one-third of people hospitalized with COVID-19 have diabetes. It is published in the September issue of Diabetes Care.
People with diabetes are more than three times as likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than those without diabetes, even after adjustment for age, sex, and other underlying conditions. Diabetes also accounts for 30%-40% of severe COVID-19 cases and deaths. Among those with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19, 21%-43% require intensive care, and the case fatality rate is about 25%.
In one of the few multivariate analyses that examined type 1 and type 2 diabetes separately, conducted in the U.K., the odds of in-hospital COVID-19–related deaths, compared with people without diabetes, were almost three times higher (odds ratio, 2.9) for individuals with type 1 diabetes and almost twice as high (OR, 1.8) for those with type 2, after adjustment for comorbidities.
The causes of death appear to be a combination of factors specific to the SARS-CoV-2 infection and to diabetes-related factors, Dr. Gregg said in an interview.
“Much of the increased risk is due to the fact that people with diabetes have more comorbid factors, but there are many other mechanisms that appear to further increase risk, including the inflammatory and immune responses of people with diabetes, and hyperglycemia appears to have an exacerbating effect by itself.”
Elevated glucose is clear risk factor for COVID-19 severity
Elevated A1c was identified among several other overall predictors of poor COVID-19 outcomes, including obesity as well as comorbid kidney and cardiovascular disease.
High blood glucose levels at the time of admission in people with previously diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes emerged as a clear predictor of worse outcomes. For example, among 605 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in China, those with fasting plasma glucose 6.1-6.9 mmol/L (110-125 mg/dL) and ≥7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) had odds ratios of poor outcomes within 28 days of 2.6 and 4.0 compared with FPG <6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL).
Population-based studies in the U.K. found that A1c levels measured months before COVID-19 hospitalization were associated with risk for intensive care unit admission and/or death, particularly among those with type 1 diabetes. Overall, the death rate was 36% higher for those with A1c of 9%-9.9% versus 6.5%-7%.
Despite the link between high A1c and death, there is as yet no clear evidence that normalizing blood glucose levels minimizes COVID-19 severity, Dr. Gregg said.
“There are data that suggest poor glycemic control is associated with higher risk of poor outcomes. This is indirect evidence that managing blood sugar will help, but more direct evidence is needed.”
Evidence gaps identified
Dr. Gregg and co-authors Marisa Sophiea, PhD, MSc, and Misghina Weldegiorgis, PhD, BSc, also from Imperial College London, identify three areas in which more data are needed.
First, more information is needed to determine whether exposure, infection, and hospitalization risks differ by diabetes status and how those factors affect outcomes. The same studies would also be important to identify how factors such as behavior, masking, and lockdown policies, risk factor control, and household/community environments affect risk in people with diabetes.
Second, studies are needed to better understand indirect effects of the pandemic, such as care and management factors. Some of these, such as the advent of telehealth, may turn out to be beneficial in the long run, they note.
Finally, the pandemic has “brought a wealth of natural experiments,” such as how vaccination programs and other interventions are affecting people with diabetes specifically. Finally, population studies are needed in many parts of the world beyond the U.S. and the U.K., where most of that work has been done thus far.
“Many of the most important unanswered questions lie in the potential indirect and long-term impact of the pandemic that require population-based studies,” Dr. Gregg said. “Most of our knowledge so far is from case series, which only assess patients from the time of hospitalization.”
Indeed, very little data are available for people with diabetes who get COVID-19 but are not hospitalized, so it’s not known whether they have a longer duration of illness or are at greater risk for “long COVID” than those without diabetes who experience COVID-19 at home.
“I have not seen published data on this yet, and it’s an important unanswered question,” Dr. Gregg said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At 18 months into the COVID-19 pandemic, many of the direct and indirect effects of SARS-CoV-2 on people with diabetes have become clearer, but knowledge gaps remain, say epidemiologists.
“COVID-19 has had a devastating effect on the population with diabetes, and conversely, the high prevalence of diabetes and uncontrolled diabetes has exacerbated the problem,” Edward W. Gregg, PhD, Imperial College London, lead author of a new literature review, told this news organization.
“As it becomes clear that the COVID-19 pandemic will be with us in different forms for the foreseeable future, the emphasis for people with diabetes needs to be continued primary care, glycemic management, and vaccination to reduce the long-term impact of COVID-19 in this population,” he added.
In data, mostly from case series, the review shows that more than one-third of people hospitalized with COVID-19 have diabetes. It is published in the September issue of Diabetes Care.
People with diabetes are more than three times as likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than those without diabetes, even after adjustment for age, sex, and other underlying conditions. Diabetes also accounts for 30%-40% of severe COVID-19 cases and deaths. Among those with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19, 21%-43% require intensive care, and the case fatality rate is about 25%.
In one of the few multivariate analyses that examined type 1 and type 2 diabetes separately, conducted in the U.K., the odds of in-hospital COVID-19–related deaths, compared with people without diabetes, were almost three times higher (odds ratio, 2.9) for individuals with type 1 diabetes and almost twice as high (OR, 1.8) for those with type 2, after adjustment for comorbidities.
The causes of death appear to be a combination of factors specific to the SARS-CoV-2 infection and to diabetes-related factors, Dr. Gregg said in an interview.
“Much of the increased risk is due to the fact that people with diabetes have more comorbid factors, but there are many other mechanisms that appear to further increase risk, including the inflammatory and immune responses of people with diabetes, and hyperglycemia appears to have an exacerbating effect by itself.”
Elevated glucose is clear risk factor for COVID-19 severity
Elevated A1c was identified among several other overall predictors of poor COVID-19 outcomes, including obesity as well as comorbid kidney and cardiovascular disease.
High blood glucose levels at the time of admission in people with previously diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes emerged as a clear predictor of worse outcomes. For example, among 605 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in China, those with fasting plasma glucose 6.1-6.9 mmol/L (110-125 mg/dL) and ≥7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) had odds ratios of poor outcomes within 28 days of 2.6 and 4.0 compared with FPG <6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL).
Population-based studies in the U.K. found that A1c levels measured months before COVID-19 hospitalization were associated with risk for intensive care unit admission and/or death, particularly among those with type 1 diabetes. Overall, the death rate was 36% higher for those with A1c of 9%-9.9% versus 6.5%-7%.
Despite the link between high A1c and death, there is as yet no clear evidence that normalizing blood glucose levels minimizes COVID-19 severity, Dr. Gregg said.
“There are data that suggest poor glycemic control is associated with higher risk of poor outcomes. This is indirect evidence that managing blood sugar will help, but more direct evidence is needed.”
Evidence gaps identified
Dr. Gregg and co-authors Marisa Sophiea, PhD, MSc, and Misghina Weldegiorgis, PhD, BSc, also from Imperial College London, identify three areas in which more data are needed.
First, more information is needed to determine whether exposure, infection, and hospitalization risks differ by diabetes status and how those factors affect outcomes. The same studies would also be important to identify how factors such as behavior, masking, and lockdown policies, risk factor control, and household/community environments affect risk in people with diabetes.
Second, studies are needed to better understand indirect effects of the pandemic, such as care and management factors. Some of these, such as the advent of telehealth, may turn out to be beneficial in the long run, they note.
Finally, the pandemic has “brought a wealth of natural experiments,” such as how vaccination programs and other interventions are affecting people with diabetes specifically. Finally, population studies are needed in many parts of the world beyond the U.S. and the U.K., where most of that work has been done thus far.
“Many of the most important unanswered questions lie in the potential indirect and long-term impact of the pandemic that require population-based studies,” Dr. Gregg said. “Most of our knowledge so far is from case series, which only assess patients from the time of hospitalization.”
Indeed, very little data are available for people with diabetes who get COVID-19 but are not hospitalized, so it’s not known whether they have a longer duration of illness or are at greater risk for “long COVID” than those without diabetes who experience COVID-19 at home.
“I have not seen published data on this yet, and it’s an important unanswered question,” Dr. Gregg said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA could authorize COVID-19 vaccine for ages 5-11 in October
The timeline is based on the expectation that Pfizer will have enough data from clinical trials to request Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization for the age group near the end of September. Then the FDA would likely make a decision about the vaccine’s safety and effectiveness in children within about 3 weeks, two sources told Reuters.
Anthony Fauci, MD, chief medical adviser to President Joe Biden and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, spoke about the timeline during an online town hall meeting Friday, Reuters reported. The meeting was attended by thousands of staff members at the National Institutes of Health.
If Pfizer submits paperwork to the FDA by the end of September, the vaccine could be available for kids around mid-October, Dr. Fauci said, and approval for the Moderna vaccine could come in November. Moderna will take about 3 weeks longer to collect and analyze data for ages 5-11.
Pfizer has said it would have enough data for ages 5-11 in September and would submit its documentation for FDA authorization soon after. Moderna told investors on Sept. 9 that data for ages 6-11 would be available by the end of the year.
On Sept. 10, the FDA said it would work to approve COVID-19 vaccines for children quickly once companies submit their data, according to Reuters. The agency said it would consider applications for emergency use, which would allow for faster approval.
Pfizer’s vaccine is the only one to receive full FDA approval, but only for people ages 16 and older. Adolescents ages 12-15 can receive the Pfizer vaccine under the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
For emergency use authorization, companies must submit 2 months of safety data versus 6 months for full approval. The FDA said on Sept. 10 that children in clinical trials should be monitored for at least 2 months to observe side effects.
BioNTech, Pfizer’s vaccine manufacturing partner, told a news outlet in Germany that it plans to request authorization globally for ages 5-11 in coming weeks, according to Reuters.
“Already over the next few weeks, we will file the results of our trial in 5- to 11-year-olds with regulators across the world and will request approval of the vaccine in this age group, also here in Europe,” Oezlem Tuereci, MD, the chief medical officer for BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
The company is completing the final production steps to make the vaccine at lower doses for the younger age group, she said. Pfizer and BioNTech will also seek vaccine approval for ages 6 months to 2 years later this year.
“Things are looking good, everything is going according to plan,” Ugur Sahin, MD, the CEO of BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The timeline is based on the expectation that Pfizer will have enough data from clinical trials to request Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization for the age group near the end of September. Then the FDA would likely make a decision about the vaccine’s safety and effectiveness in children within about 3 weeks, two sources told Reuters.
Anthony Fauci, MD, chief medical adviser to President Joe Biden and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, spoke about the timeline during an online town hall meeting Friday, Reuters reported. The meeting was attended by thousands of staff members at the National Institutes of Health.
If Pfizer submits paperwork to the FDA by the end of September, the vaccine could be available for kids around mid-October, Dr. Fauci said, and approval for the Moderna vaccine could come in November. Moderna will take about 3 weeks longer to collect and analyze data for ages 5-11.
Pfizer has said it would have enough data for ages 5-11 in September and would submit its documentation for FDA authorization soon after. Moderna told investors on Sept. 9 that data for ages 6-11 would be available by the end of the year.
On Sept. 10, the FDA said it would work to approve COVID-19 vaccines for children quickly once companies submit their data, according to Reuters. The agency said it would consider applications for emergency use, which would allow for faster approval.
Pfizer’s vaccine is the only one to receive full FDA approval, but only for people ages 16 and older. Adolescents ages 12-15 can receive the Pfizer vaccine under the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
For emergency use authorization, companies must submit 2 months of safety data versus 6 months for full approval. The FDA said on Sept. 10 that children in clinical trials should be monitored for at least 2 months to observe side effects.
BioNTech, Pfizer’s vaccine manufacturing partner, told a news outlet in Germany that it plans to request authorization globally for ages 5-11 in coming weeks, according to Reuters.
“Already over the next few weeks, we will file the results of our trial in 5- to 11-year-olds with regulators across the world and will request approval of the vaccine in this age group, also here in Europe,” Oezlem Tuereci, MD, the chief medical officer for BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
The company is completing the final production steps to make the vaccine at lower doses for the younger age group, she said. Pfizer and BioNTech will also seek vaccine approval for ages 6 months to 2 years later this year.
“Things are looking good, everything is going according to plan,” Ugur Sahin, MD, the CEO of BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The timeline is based on the expectation that Pfizer will have enough data from clinical trials to request Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization for the age group near the end of September. Then the FDA would likely make a decision about the vaccine’s safety and effectiveness in children within about 3 weeks, two sources told Reuters.
Anthony Fauci, MD, chief medical adviser to President Joe Biden and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, spoke about the timeline during an online town hall meeting Friday, Reuters reported. The meeting was attended by thousands of staff members at the National Institutes of Health.
If Pfizer submits paperwork to the FDA by the end of September, the vaccine could be available for kids around mid-October, Dr. Fauci said, and approval for the Moderna vaccine could come in November. Moderna will take about 3 weeks longer to collect and analyze data for ages 5-11.
Pfizer has said it would have enough data for ages 5-11 in September and would submit its documentation for FDA authorization soon after. Moderna told investors on Sept. 9 that data for ages 6-11 would be available by the end of the year.
On Sept. 10, the FDA said it would work to approve COVID-19 vaccines for children quickly once companies submit their data, according to Reuters. The agency said it would consider applications for emergency use, which would allow for faster approval.
Pfizer’s vaccine is the only one to receive full FDA approval, but only for people ages 16 and older. Adolescents ages 12-15 can receive the Pfizer vaccine under the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
For emergency use authorization, companies must submit 2 months of safety data versus 6 months for full approval. The FDA said on Sept. 10 that children in clinical trials should be monitored for at least 2 months to observe side effects.
BioNTech, Pfizer’s vaccine manufacturing partner, told a news outlet in Germany that it plans to request authorization globally for ages 5-11 in coming weeks, according to Reuters.
“Already over the next few weeks, we will file the results of our trial in 5- to 11-year-olds with regulators across the world and will request approval of the vaccine in this age group, also here in Europe,” Oezlem Tuereci, MD, the chief medical officer for BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
The company is completing the final production steps to make the vaccine at lower doses for the younger age group, she said. Pfizer and BioNTech will also seek vaccine approval for ages 6 months to 2 years later this year.
“Things are looking good, everything is going according to plan,” Ugur Sahin, MD, the CEO of BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Biden vaccine mandate rule could be ready within weeks
The emergency rule ordering large employers to require COVID-19 vaccines or weekly tests for their workers could be ready “within weeks,” officials said in a news briefing Sept. 10.
Labor Secretary Martin Walsh will oversee the Occupational Safety and Health Administration as the agency drafts what’s known as an emergency temporary standard, similar to the one that was issued a few months ago to protect health care workers during the pandemic.
The rule should be ready within weeks, said Jeff Zients, coordinator of the White House COVID-19 response team.
He said the ultimate goal of the president’s plan is to increase vaccinations as quickly as possible to keep schools open, the economy recovering, and to decrease hospitalizations and deaths from COVID.
Mr. Zients declined to set hard numbers around those goals, but other experts did.
“What we need to get to is 85% to 90% population immunity, and that’s going to be immunity both from vaccines and infections, before that really begins to have a substantial dampening effect on viral spread,” Ashish Jha, MD, dean of the Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, R.I., said on a call with reporters Sept. 9.
He said immunity needs to be that high because the Delta variant is so contagious.
Mandates are seen as the most effective way to increase immunity and do it quickly.
David Michaels, PhD, an epidemiologist and professor at George Washington University, Washington, says OSHA will have to work through a number of steps to develop the rule.
“OSHA will have to write a preamble explaining the standard, its justifications, its costs, and how it will be enforced,” says Dr. Michaels, who led OSHA for the Obama administration. After that, the rule will be reviewed by the White House. Then employers will have some time – typically 30 days – to comply.
In addition to drafting the standard, OSHA will oversee its enforcement.
Companies that refuse to follow the standard could be fined $13,600 per violation, Mr. Zients said.
Dr. Michaels said he doesn’t expect enforcement to be a big issue, and he said we’re likely to see the rule well before it is final.
“Most employers are law-abiding. When OSHA issues a standard, they try to meet whatever those requirements are, and generally that starts to happen when the rule is announced, even before it goes into effect,” he said.
The rule may face legal challenges as well. Several governors and state attorneys general, as well as the Republican National Committee, have promised lawsuits to stop the vaccine mandates.
Critics of the new mandates say they impinge on personal freedom and impose burdens on businesses.
But the president hit back at that notion Sept. 10.
“Look, I am so disappointed that, particularly some of the Republican governors, have been so cavalier with the health of these kids, so cavalier of the health of their communities,” President Biden told reporters.
“I don’t know of any scientist out there in this field who doesn’t think it makes considerable sense to do the six things I’ve suggested.”
Yet, others feel the new requirements didn’t go far enough.
“These are good steps in the right direction, but they’re not enough to get the job done,” said Leana Wen, MD, in an op-ed for The Washington Post.
Dr. Wen, an expert in public health, wondered why President Biden didn’t mandate vaccinations for plane and train travel. She was disappointed that children 12 and older weren’t required to be vaccinated, too.
“There are mandates for childhood immunizations in every state. The coronavirus vaccine should be no different,” she wrote.
Vaccines remain the cornerstone of U.S. plans to control the pandemic.
On Sept. 10, there was new research from the CDC and state health departments showing that the COVID-19 vaccines continue to be highly effective at preventing severe illness and death.
But the study also found that the vaccines became less effective in the United States after Delta became the dominant cause of infections here.
The study, which included more than 600,000 COVID-19 cases, analyzed breakthrough infections – cases where people got sick despite being fully vaccinated – in 13 jurisdictions in the United States between April 4 and July 17, 2021.
Epidemiologists compared breakthrough infections between two distinct points in time: Before and after the period when the Delta variant began causing most infections.
From April 4 to June 19, fully vaccinated people made up just 5% of cases, 7% of hospitalizations, and 8% of deaths. From June 20 to July 17, 18% of cases, 14% of hospitalizations, and 16% of deaths occurred in fully vaccinated people.
“After the week of June 20, 2021, when the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant became predominant, the percentage of fully vaccinated persons among cases increased more than expected,” the study authors wrote.
Even after Delta swept the United States, fully vaccinated people were 5 times less likely to get a COVID-19 infection and more than 10 times less likely to be hospitalized or die from one.
“As we have shown in study after study, vaccination works,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said during the White House news briefing.
“We have the scientific tools we need to turn the corner on this pandemic. Vaccination works and will protect us from the severe complications of COVID-19,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The emergency rule ordering large employers to require COVID-19 vaccines or weekly tests for their workers could be ready “within weeks,” officials said in a news briefing Sept. 10.
Labor Secretary Martin Walsh will oversee the Occupational Safety and Health Administration as the agency drafts what’s known as an emergency temporary standard, similar to the one that was issued a few months ago to protect health care workers during the pandemic.
The rule should be ready within weeks, said Jeff Zients, coordinator of the White House COVID-19 response team.
He said the ultimate goal of the president’s plan is to increase vaccinations as quickly as possible to keep schools open, the economy recovering, and to decrease hospitalizations and deaths from COVID.
Mr. Zients declined to set hard numbers around those goals, but other experts did.
“What we need to get to is 85% to 90% population immunity, and that’s going to be immunity both from vaccines and infections, before that really begins to have a substantial dampening effect on viral spread,” Ashish Jha, MD, dean of the Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, R.I., said on a call with reporters Sept. 9.
He said immunity needs to be that high because the Delta variant is so contagious.
Mandates are seen as the most effective way to increase immunity and do it quickly.
David Michaels, PhD, an epidemiologist and professor at George Washington University, Washington, says OSHA will have to work through a number of steps to develop the rule.
“OSHA will have to write a preamble explaining the standard, its justifications, its costs, and how it will be enforced,” says Dr. Michaels, who led OSHA for the Obama administration. After that, the rule will be reviewed by the White House. Then employers will have some time – typically 30 days – to comply.
In addition to drafting the standard, OSHA will oversee its enforcement.
Companies that refuse to follow the standard could be fined $13,600 per violation, Mr. Zients said.
Dr. Michaels said he doesn’t expect enforcement to be a big issue, and he said we’re likely to see the rule well before it is final.
“Most employers are law-abiding. When OSHA issues a standard, they try to meet whatever those requirements are, and generally that starts to happen when the rule is announced, even before it goes into effect,” he said.
The rule may face legal challenges as well. Several governors and state attorneys general, as well as the Republican National Committee, have promised lawsuits to stop the vaccine mandates.
Critics of the new mandates say they impinge on personal freedom and impose burdens on businesses.
But the president hit back at that notion Sept. 10.
“Look, I am so disappointed that, particularly some of the Republican governors, have been so cavalier with the health of these kids, so cavalier of the health of their communities,” President Biden told reporters.
“I don’t know of any scientist out there in this field who doesn’t think it makes considerable sense to do the six things I’ve suggested.”
Yet, others feel the new requirements didn’t go far enough.
“These are good steps in the right direction, but they’re not enough to get the job done,” said Leana Wen, MD, in an op-ed for The Washington Post.
Dr. Wen, an expert in public health, wondered why President Biden didn’t mandate vaccinations for plane and train travel. She was disappointed that children 12 and older weren’t required to be vaccinated, too.
“There are mandates for childhood immunizations in every state. The coronavirus vaccine should be no different,” she wrote.
Vaccines remain the cornerstone of U.S. plans to control the pandemic.
On Sept. 10, there was new research from the CDC and state health departments showing that the COVID-19 vaccines continue to be highly effective at preventing severe illness and death.
But the study also found that the vaccines became less effective in the United States after Delta became the dominant cause of infections here.
The study, which included more than 600,000 COVID-19 cases, analyzed breakthrough infections – cases where people got sick despite being fully vaccinated – in 13 jurisdictions in the United States between April 4 and July 17, 2021.
Epidemiologists compared breakthrough infections between two distinct points in time: Before and after the period when the Delta variant began causing most infections.
From April 4 to June 19, fully vaccinated people made up just 5% of cases, 7% of hospitalizations, and 8% of deaths. From June 20 to July 17, 18% of cases, 14% of hospitalizations, and 16% of deaths occurred in fully vaccinated people.
“After the week of June 20, 2021, when the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant became predominant, the percentage of fully vaccinated persons among cases increased more than expected,” the study authors wrote.
Even after Delta swept the United States, fully vaccinated people were 5 times less likely to get a COVID-19 infection and more than 10 times less likely to be hospitalized or die from one.
“As we have shown in study after study, vaccination works,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said during the White House news briefing.
“We have the scientific tools we need to turn the corner on this pandemic. Vaccination works and will protect us from the severe complications of COVID-19,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The emergency rule ordering large employers to require COVID-19 vaccines or weekly tests for their workers could be ready “within weeks,” officials said in a news briefing Sept. 10.
Labor Secretary Martin Walsh will oversee the Occupational Safety and Health Administration as the agency drafts what’s known as an emergency temporary standard, similar to the one that was issued a few months ago to protect health care workers during the pandemic.
The rule should be ready within weeks, said Jeff Zients, coordinator of the White House COVID-19 response team.
He said the ultimate goal of the president’s plan is to increase vaccinations as quickly as possible to keep schools open, the economy recovering, and to decrease hospitalizations and deaths from COVID.
Mr. Zients declined to set hard numbers around those goals, but other experts did.
“What we need to get to is 85% to 90% population immunity, and that’s going to be immunity both from vaccines and infections, before that really begins to have a substantial dampening effect on viral spread,” Ashish Jha, MD, dean of the Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, R.I., said on a call with reporters Sept. 9.
He said immunity needs to be that high because the Delta variant is so contagious.
Mandates are seen as the most effective way to increase immunity and do it quickly.
David Michaels, PhD, an epidemiologist and professor at George Washington University, Washington, says OSHA will have to work through a number of steps to develop the rule.
“OSHA will have to write a preamble explaining the standard, its justifications, its costs, and how it will be enforced,” says Dr. Michaels, who led OSHA for the Obama administration. After that, the rule will be reviewed by the White House. Then employers will have some time – typically 30 days – to comply.
In addition to drafting the standard, OSHA will oversee its enforcement.
Companies that refuse to follow the standard could be fined $13,600 per violation, Mr. Zients said.
Dr. Michaels said he doesn’t expect enforcement to be a big issue, and he said we’re likely to see the rule well before it is final.
“Most employers are law-abiding. When OSHA issues a standard, they try to meet whatever those requirements are, and generally that starts to happen when the rule is announced, even before it goes into effect,” he said.
The rule may face legal challenges as well. Several governors and state attorneys general, as well as the Republican National Committee, have promised lawsuits to stop the vaccine mandates.
Critics of the new mandates say they impinge on personal freedom and impose burdens on businesses.
But the president hit back at that notion Sept. 10.
“Look, I am so disappointed that, particularly some of the Republican governors, have been so cavalier with the health of these kids, so cavalier of the health of their communities,” President Biden told reporters.
“I don’t know of any scientist out there in this field who doesn’t think it makes considerable sense to do the six things I’ve suggested.”
Yet, others feel the new requirements didn’t go far enough.
“These are good steps in the right direction, but they’re not enough to get the job done,” said Leana Wen, MD, in an op-ed for The Washington Post.
Dr. Wen, an expert in public health, wondered why President Biden didn’t mandate vaccinations for plane and train travel. She was disappointed that children 12 and older weren’t required to be vaccinated, too.
“There are mandates for childhood immunizations in every state. The coronavirus vaccine should be no different,” she wrote.
Vaccines remain the cornerstone of U.S. plans to control the pandemic.
On Sept. 10, there was new research from the CDC and state health departments showing that the COVID-19 vaccines continue to be highly effective at preventing severe illness and death.
But the study also found that the vaccines became less effective in the United States after Delta became the dominant cause of infections here.
The study, which included more than 600,000 COVID-19 cases, analyzed breakthrough infections – cases where people got sick despite being fully vaccinated – in 13 jurisdictions in the United States between April 4 and July 17, 2021.
Epidemiologists compared breakthrough infections between two distinct points in time: Before and after the period when the Delta variant began causing most infections.
From April 4 to June 19, fully vaccinated people made up just 5% of cases, 7% of hospitalizations, and 8% of deaths. From June 20 to July 17, 18% of cases, 14% of hospitalizations, and 16% of deaths occurred in fully vaccinated people.
“After the week of June 20, 2021, when the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant became predominant, the percentage of fully vaccinated persons among cases increased more than expected,” the study authors wrote.
Even after Delta swept the United States, fully vaccinated people were 5 times less likely to get a COVID-19 infection and more than 10 times less likely to be hospitalized or die from one.
“As we have shown in study after study, vaccination works,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said during the White House news briefing.
“We have the scientific tools we need to turn the corner on this pandemic. Vaccination works and will protect us from the severe complications of COVID-19,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
‘Quadpill’ bests monotherapy for initial BP lowering: QUARTET
A “quadpill” containing quarter doses of four blood pressure (BP)–lowering medications was more effective than monotherapy for initial treatment of hypertension, with similar tolerability, in the 1-year, phase 3 QUARTET randomized, active-control trial.
Clara Chow, MD, PhD, academic director of the Westmead Applied Research Centre, University of Sydney, presented the findings in a late-breaking trial session at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology. The study was simultaneously published in The Lancet.
The primary outcome, mean unattended office BP at 12 weeks, dropped from 142/86 mm Hg to 120/71 mm Hg in patients who received the daily quadpill – a capsule containing irbesartan, amlodipine, indapamide, and bisoprolol – and fell from 140/83 mm Hg to 127/79 mm Hg in patients who received a daily full dose of irbesartan.
This 6.9 mm Hg greater drop in systolic BP at 12 months is clinically meaningful, Dr. Chow told this news organization. “If maintained, it would be expected to confer about a 15%-20% reduction” in heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
In the SPRINT study, she noted, the final systolic BP was 120 mm Hg in the intervention group and 134 mm Hg in the control group, and the difference was associated with a 27% reduction in the composite cardiovascular (CV) outcome.
The results of QUARTET suggest that, “even in those with stage 1 hypertension, we can safely reduce BP to a significant degree by this simple approach, compared to usual care,” Salim Yusuf, MD, DPhil, a long-time advocate of a polypill approach, said in an email.
Importantly, Dr. Chow pointed out, at 12 months, 81% of patients treated with the quadpill versus 62% of patients treated with monotherapy had BP control (<140/90 mm Hg). Patients who received monotherapy did not “catch up,” even though a higher percentage received stepped-up therapy.
The quadpill dosing strategy aligns with the latest 2018 ESC/European Society of Hypertension guidelines, which recommend starting antihypertensive treatment with more than one drug, session cochair Thomas Kahan, MD, PhD, Karolinska Institute, Danderyd Hospital, department of clinical sciences, Stockholm, commented.
“How many drugs should be in the initial step?” he asked. “Is four better than three or two, or should we have even more drugs at low doses?”
The trial was not designed to answer these questions, Dr. Chow replied. “We were really comparing [the quadpill] against what the majority of people around the planet are still doing, which is starting on one drug and slowly but surely stepping it up,” she said.
The quadpill was actually a capsule, she clarified, that contained four generic BP medications available in half doses in Australia. The half doses were cut in half and the medications were encapsulated. The control drug was prepared in an identical-looking capsule.
It is important to note that “the time to BP control was shorter in patients who received the quadpill versus monotherapy,” session cochair Felix Mahfoud, MD, internal medicine and cardiology, Saarland University Hospital, Hamburg, Germany, pointed out, because “in clinical practice we aim to get patients to BP control as quickly as possible.”
“What is new here is the use of four drugs, each given at quarter doses,” Dr. Yusuf, director of the Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., said. Although a few questions remain, “this study emphasizes the importance and potential benefits and simplicity of using combination BP-lowering drugs at low doses.”
For guidelines to be changed, he observed, the findings would have to be replicated in independent studies, and the quadpill would likely have to be shown to be superior to the dual pill.
“It took about 20 years [to change guidelines] after the first evidence that combinations of two pills were preferable to single-drug combinations,” he noted.
“I hope that in most people with elevated BP, at least a two-drug combination plus a statin plus aspirin will be prescribed,” Dr. Yusuf said. “This can reduce the risk of CVD events by 50% or more – a big impact both for the individual and for populations. The quad pill may have a role in this approach.”
Four-in-one pill
Worldwide, hypertension control is poor, Dr. Chow said, because of the need for multiple medications, treatment inertia, and concerns about adverse events.
The researchers hypothesized that initial antihypertensive treatment with a four-in-one pill with quarter doses of each medication would minimize side effects, maximize BP lowering, and overcome these treatment barriers and concerns. A pilot study of this strategy published by the group in 2017 showed promise.
QUARTET randomized 591 adults with hypertension, seen at clinics in four states in Australia from June 2017 through August 2020.
Patients were either receiving no antihypertensive medication and had an unattended standard office BP of 140/90 to 179/109 mm Hg or daytime ambulatory BP greater than 135/95 mm Hg, or they were on BP-lowering monotherapy and had a BP of 130/85 to 179/109 mm Hg or daytime ambulatory BP greater than 125/80 mm Hg. Patients who were taking antihypertensive therapy entered a washout period before the trial.
The researchers randomized 291 participants to receive 150 mg irbesartan daily (usual care or control group).
The other 300 participants received a daily quadpill containing 37.5 mg irbesartan, 1.25 mg amlodipine, 0.625 mg indapamide, and 2.5 mg bisoprolol. The first three drugs are the most commonly prescribed angiotensin II receptor blocker, calcium channel blocker, and thiazide or thiazidelike diuretic in Australia, and the last drug, a beta-blocker, has a long duration of action, the study protocol explains.
Patients in both groups had similar baseline characteristics. They were a mean age of 58 years, 40% were women, and 82% were White. They also had a mean body mass index of 31 kg/m2. About 8% were current smokers, and about 54% were not taking a BP-lowering drug.
Participants had clinic visits at baseline, 6 weeks, and 12 weeks, and if they continued the study, at 26 weeks and 52 weeks.
If a patient’s blood pressure was higher than 140/90 mm Hg, clinicians could add another medication, starting with amlodipine 5 mg.
At 12 weeks, 15% of patients in the intervention group and 40% in the control group had stepped up treatment.
Despite greater up-titration in the usual care group, BP control remained higher in the quadpill group, Dr. Chow pointed out. That is, patients in the quadpill group were more likely than patients in the usual care group to have a BP less than 140/90 mm Hg (76% vs. 58% respectively; P < .0001).
Patients in the quadpill group also had lower daytime and nighttime ambulatory systolic BP.
At 12 months, among the 417 patients who continued treatment, patients in the quadpill group had a 7.7 mm Hg greater drop in systolic BP, compared with patients in the control group, (P < .001).
There were no significant differences in adverse events, which were most commonly dizziness (31% and 25%) or muscle cramps, gastrointestinal complaints, headache, or musculoskeletal complaints.
At 12 weeks, there were seven serious adverse events in the intervention group versus three in the control group. There were 12 treatment withdrawals in the intervention group versus seven in the control group (P = .27).
Remaining questions, upcoming phase 3 U.S. study
“While the [QUARTET] results are impressive, we are left with a number of questions,” Dr. Yusuf said.
Would the results be the same with a three-drug combo or even a two-drug combo at half doses? In the HOPE 3 trial, a two-drug combo at half doses provided similar results to the current study, over a much longer mean follow-up of 5.6 years, he noted.
Also, is the quadpill associated with higher rates of diabetes or higher creatinine levels in the long term? “Given that we do not have any data on long-term clinical outcomes from a four-drug combination,” Dr. Yusuf said, “caution should be utilized.”
Would the reduced risk of CVD be greater with a combination of low doses of two BP-lowering drugs plus a statin plus aspirin? That may be superior, he said, “based on recent information published on the polypill indicating a 50% relative risk reduction in CVD events.”
The related phase 2 QUARTET US trial should shed further light on a quadpill strategy. Patients with hypertension are being randomized to a daily quadpill containing 2 mg candesartan, 1.25 mg amlodipine besylate, 0.625 mg indapamide, and 2.5 mg bisoprolol, or to usual care, 8 mg candesartan daily.
Investigators plan to enroll 87 participants in the Chicago area, with estimated study completion by March 31, 2023.
The study was supported by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council grant. The George Institute for Global Health has submitted patent applications for low–fixed-dose combination products to treat CV or cardiometabolic disease. Dr. Chow and coauthor Kris Rogers, PhD, senior biostatistician at The George Institute for Global Health, Newtown, Australia, are listed as inventors, but they do not have direct financial interests in these patent applications.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A “quadpill” containing quarter doses of four blood pressure (BP)–lowering medications was more effective than monotherapy for initial treatment of hypertension, with similar tolerability, in the 1-year, phase 3 QUARTET randomized, active-control trial.
Clara Chow, MD, PhD, academic director of the Westmead Applied Research Centre, University of Sydney, presented the findings in a late-breaking trial session at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology. The study was simultaneously published in The Lancet.
The primary outcome, mean unattended office BP at 12 weeks, dropped from 142/86 mm Hg to 120/71 mm Hg in patients who received the daily quadpill – a capsule containing irbesartan, amlodipine, indapamide, and bisoprolol – and fell from 140/83 mm Hg to 127/79 mm Hg in patients who received a daily full dose of irbesartan.
This 6.9 mm Hg greater drop in systolic BP at 12 months is clinically meaningful, Dr. Chow told this news organization. “If maintained, it would be expected to confer about a 15%-20% reduction” in heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
In the SPRINT study, she noted, the final systolic BP was 120 mm Hg in the intervention group and 134 mm Hg in the control group, and the difference was associated with a 27% reduction in the composite cardiovascular (CV) outcome.
The results of QUARTET suggest that, “even in those with stage 1 hypertension, we can safely reduce BP to a significant degree by this simple approach, compared to usual care,” Salim Yusuf, MD, DPhil, a long-time advocate of a polypill approach, said in an email.
Importantly, Dr. Chow pointed out, at 12 months, 81% of patients treated with the quadpill versus 62% of patients treated with monotherapy had BP control (<140/90 mm Hg). Patients who received monotherapy did not “catch up,” even though a higher percentage received stepped-up therapy.
The quadpill dosing strategy aligns with the latest 2018 ESC/European Society of Hypertension guidelines, which recommend starting antihypertensive treatment with more than one drug, session cochair Thomas Kahan, MD, PhD, Karolinska Institute, Danderyd Hospital, department of clinical sciences, Stockholm, commented.
“How many drugs should be in the initial step?” he asked. “Is four better than three or two, or should we have even more drugs at low doses?”
The trial was not designed to answer these questions, Dr. Chow replied. “We were really comparing [the quadpill] against what the majority of people around the planet are still doing, which is starting on one drug and slowly but surely stepping it up,” she said.
The quadpill was actually a capsule, she clarified, that contained four generic BP medications available in half doses in Australia. The half doses were cut in half and the medications were encapsulated. The control drug was prepared in an identical-looking capsule.
It is important to note that “the time to BP control was shorter in patients who received the quadpill versus monotherapy,” session cochair Felix Mahfoud, MD, internal medicine and cardiology, Saarland University Hospital, Hamburg, Germany, pointed out, because “in clinical practice we aim to get patients to BP control as quickly as possible.”
“What is new here is the use of four drugs, each given at quarter doses,” Dr. Yusuf, director of the Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., said. Although a few questions remain, “this study emphasizes the importance and potential benefits and simplicity of using combination BP-lowering drugs at low doses.”
For guidelines to be changed, he observed, the findings would have to be replicated in independent studies, and the quadpill would likely have to be shown to be superior to the dual pill.
“It took about 20 years [to change guidelines] after the first evidence that combinations of two pills were preferable to single-drug combinations,” he noted.
“I hope that in most people with elevated BP, at least a two-drug combination plus a statin plus aspirin will be prescribed,” Dr. Yusuf said. “This can reduce the risk of CVD events by 50% or more – a big impact both for the individual and for populations. The quad pill may have a role in this approach.”
Four-in-one pill
Worldwide, hypertension control is poor, Dr. Chow said, because of the need for multiple medications, treatment inertia, and concerns about adverse events.
The researchers hypothesized that initial antihypertensive treatment with a four-in-one pill with quarter doses of each medication would minimize side effects, maximize BP lowering, and overcome these treatment barriers and concerns. A pilot study of this strategy published by the group in 2017 showed promise.
QUARTET randomized 591 adults with hypertension, seen at clinics in four states in Australia from June 2017 through August 2020.
Patients were either receiving no antihypertensive medication and had an unattended standard office BP of 140/90 to 179/109 mm Hg or daytime ambulatory BP greater than 135/95 mm Hg, or they were on BP-lowering monotherapy and had a BP of 130/85 to 179/109 mm Hg or daytime ambulatory BP greater than 125/80 mm Hg. Patients who were taking antihypertensive therapy entered a washout period before the trial.
The researchers randomized 291 participants to receive 150 mg irbesartan daily (usual care or control group).
The other 300 participants received a daily quadpill containing 37.5 mg irbesartan, 1.25 mg amlodipine, 0.625 mg indapamide, and 2.5 mg bisoprolol. The first three drugs are the most commonly prescribed angiotensin II receptor blocker, calcium channel blocker, and thiazide or thiazidelike diuretic in Australia, and the last drug, a beta-blocker, has a long duration of action, the study protocol explains.
Patients in both groups had similar baseline characteristics. They were a mean age of 58 years, 40% were women, and 82% were White. They also had a mean body mass index of 31 kg/m2. About 8% were current smokers, and about 54% were not taking a BP-lowering drug.
Participants had clinic visits at baseline, 6 weeks, and 12 weeks, and if they continued the study, at 26 weeks and 52 weeks.
If a patient’s blood pressure was higher than 140/90 mm Hg, clinicians could add another medication, starting with amlodipine 5 mg.
At 12 weeks, 15% of patients in the intervention group and 40% in the control group had stepped up treatment.
Despite greater up-titration in the usual care group, BP control remained higher in the quadpill group, Dr. Chow pointed out. That is, patients in the quadpill group were more likely than patients in the usual care group to have a BP less than 140/90 mm Hg (76% vs. 58% respectively; P < .0001).
Patients in the quadpill group also had lower daytime and nighttime ambulatory systolic BP.
At 12 months, among the 417 patients who continued treatment, patients in the quadpill group had a 7.7 mm Hg greater drop in systolic BP, compared with patients in the control group, (P < .001).
There were no significant differences in adverse events, which were most commonly dizziness (31% and 25%) or muscle cramps, gastrointestinal complaints, headache, or musculoskeletal complaints.
At 12 weeks, there were seven serious adverse events in the intervention group versus three in the control group. There were 12 treatment withdrawals in the intervention group versus seven in the control group (P = .27).
Remaining questions, upcoming phase 3 U.S. study
“While the [QUARTET] results are impressive, we are left with a number of questions,” Dr. Yusuf said.
Would the results be the same with a three-drug combo or even a two-drug combo at half doses? In the HOPE 3 trial, a two-drug combo at half doses provided similar results to the current study, over a much longer mean follow-up of 5.6 years, he noted.
Also, is the quadpill associated with higher rates of diabetes or higher creatinine levels in the long term? “Given that we do not have any data on long-term clinical outcomes from a four-drug combination,” Dr. Yusuf said, “caution should be utilized.”
Would the reduced risk of CVD be greater with a combination of low doses of two BP-lowering drugs plus a statin plus aspirin? That may be superior, he said, “based on recent information published on the polypill indicating a 50% relative risk reduction in CVD events.”
The related phase 2 QUARTET US trial should shed further light on a quadpill strategy. Patients with hypertension are being randomized to a daily quadpill containing 2 mg candesartan, 1.25 mg amlodipine besylate, 0.625 mg indapamide, and 2.5 mg bisoprolol, or to usual care, 8 mg candesartan daily.
Investigators plan to enroll 87 participants in the Chicago area, with estimated study completion by March 31, 2023.
The study was supported by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council grant. The George Institute for Global Health has submitted patent applications for low–fixed-dose combination products to treat CV or cardiometabolic disease. Dr. Chow and coauthor Kris Rogers, PhD, senior biostatistician at The George Institute for Global Health, Newtown, Australia, are listed as inventors, but they do not have direct financial interests in these patent applications.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A “quadpill” containing quarter doses of four blood pressure (BP)–lowering medications was more effective than monotherapy for initial treatment of hypertension, with similar tolerability, in the 1-year, phase 3 QUARTET randomized, active-control trial.
Clara Chow, MD, PhD, academic director of the Westmead Applied Research Centre, University of Sydney, presented the findings in a late-breaking trial session at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology. The study was simultaneously published in The Lancet.
The primary outcome, mean unattended office BP at 12 weeks, dropped from 142/86 mm Hg to 120/71 mm Hg in patients who received the daily quadpill – a capsule containing irbesartan, amlodipine, indapamide, and bisoprolol – and fell from 140/83 mm Hg to 127/79 mm Hg in patients who received a daily full dose of irbesartan.
This 6.9 mm Hg greater drop in systolic BP at 12 months is clinically meaningful, Dr. Chow told this news organization. “If maintained, it would be expected to confer about a 15%-20% reduction” in heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
In the SPRINT study, she noted, the final systolic BP was 120 mm Hg in the intervention group and 134 mm Hg in the control group, and the difference was associated with a 27% reduction in the composite cardiovascular (CV) outcome.
The results of QUARTET suggest that, “even in those with stage 1 hypertension, we can safely reduce BP to a significant degree by this simple approach, compared to usual care,” Salim Yusuf, MD, DPhil, a long-time advocate of a polypill approach, said in an email.
Importantly, Dr. Chow pointed out, at 12 months, 81% of patients treated with the quadpill versus 62% of patients treated with monotherapy had BP control (<140/90 mm Hg). Patients who received monotherapy did not “catch up,” even though a higher percentage received stepped-up therapy.
The quadpill dosing strategy aligns with the latest 2018 ESC/European Society of Hypertension guidelines, which recommend starting antihypertensive treatment with more than one drug, session cochair Thomas Kahan, MD, PhD, Karolinska Institute, Danderyd Hospital, department of clinical sciences, Stockholm, commented.
“How many drugs should be in the initial step?” he asked. “Is four better than three or two, or should we have even more drugs at low doses?”
The trial was not designed to answer these questions, Dr. Chow replied. “We were really comparing [the quadpill] against what the majority of people around the planet are still doing, which is starting on one drug and slowly but surely stepping it up,” she said.
The quadpill was actually a capsule, she clarified, that contained four generic BP medications available in half doses in Australia. The half doses were cut in half and the medications were encapsulated. The control drug was prepared in an identical-looking capsule.
It is important to note that “the time to BP control was shorter in patients who received the quadpill versus monotherapy,” session cochair Felix Mahfoud, MD, internal medicine and cardiology, Saarland University Hospital, Hamburg, Germany, pointed out, because “in clinical practice we aim to get patients to BP control as quickly as possible.”
“What is new here is the use of four drugs, each given at quarter doses,” Dr. Yusuf, director of the Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., said. Although a few questions remain, “this study emphasizes the importance and potential benefits and simplicity of using combination BP-lowering drugs at low doses.”
For guidelines to be changed, he observed, the findings would have to be replicated in independent studies, and the quadpill would likely have to be shown to be superior to the dual pill.
“It took about 20 years [to change guidelines] after the first evidence that combinations of two pills were preferable to single-drug combinations,” he noted.
“I hope that in most people with elevated BP, at least a two-drug combination plus a statin plus aspirin will be prescribed,” Dr. Yusuf said. “This can reduce the risk of CVD events by 50% or more – a big impact both for the individual and for populations. The quad pill may have a role in this approach.”
Four-in-one pill
Worldwide, hypertension control is poor, Dr. Chow said, because of the need for multiple medications, treatment inertia, and concerns about adverse events.
The researchers hypothesized that initial antihypertensive treatment with a four-in-one pill with quarter doses of each medication would minimize side effects, maximize BP lowering, and overcome these treatment barriers and concerns. A pilot study of this strategy published by the group in 2017 showed promise.
QUARTET randomized 591 adults with hypertension, seen at clinics in four states in Australia from June 2017 through August 2020.
Patients were either receiving no antihypertensive medication and had an unattended standard office BP of 140/90 to 179/109 mm Hg or daytime ambulatory BP greater than 135/95 mm Hg, or they were on BP-lowering monotherapy and had a BP of 130/85 to 179/109 mm Hg or daytime ambulatory BP greater than 125/80 mm Hg. Patients who were taking antihypertensive therapy entered a washout period before the trial.
The researchers randomized 291 participants to receive 150 mg irbesartan daily (usual care or control group).
The other 300 participants received a daily quadpill containing 37.5 mg irbesartan, 1.25 mg amlodipine, 0.625 mg indapamide, and 2.5 mg bisoprolol. The first three drugs are the most commonly prescribed angiotensin II receptor blocker, calcium channel blocker, and thiazide or thiazidelike diuretic in Australia, and the last drug, a beta-blocker, has a long duration of action, the study protocol explains.
Patients in both groups had similar baseline characteristics. They were a mean age of 58 years, 40% were women, and 82% were White. They also had a mean body mass index of 31 kg/m2. About 8% were current smokers, and about 54% were not taking a BP-lowering drug.
Participants had clinic visits at baseline, 6 weeks, and 12 weeks, and if they continued the study, at 26 weeks and 52 weeks.
If a patient’s blood pressure was higher than 140/90 mm Hg, clinicians could add another medication, starting with amlodipine 5 mg.
At 12 weeks, 15% of patients in the intervention group and 40% in the control group had stepped up treatment.
Despite greater up-titration in the usual care group, BP control remained higher in the quadpill group, Dr. Chow pointed out. That is, patients in the quadpill group were more likely than patients in the usual care group to have a BP less than 140/90 mm Hg (76% vs. 58% respectively; P < .0001).
Patients in the quadpill group also had lower daytime and nighttime ambulatory systolic BP.
At 12 months, among the 417 patients who continued treatment, patients in the quadpill group had a 7.7 mm Hg greater drop in systolic BP, compared with patients in the control group, (P < .001).
There were no significant differences in adverse events, which were most commonly dizziness (31% and 25%) or muscle cramps, gastrointestinal complaints, headache, or musculoskeletal complaints.
At 12 weeks, there were seven serious adverse events in the intervention group versus three in the control group. There were 12 treatment withdrawals in the intervention group versus seven in the control group (P = .27).
Remaining questions, upcoming phase 3 U.S. study
“While the [QUARTET] results are impressive, we are left with a number of questions,” Dr. Yusuf said.
Would the results be the same with a three-drug combo or even a two-drug combo at half doses? In the HOPE 3 trial, a two-drug combo at half doses provided similar results to the current study, over a much longer mean follow-up of 5.6 years, he noted.
Also, is the quadpill associated with higher rates of diabetes or higher creatinine levels in the long term? “Given that we do not have any data on long-term clinical outcomes from a four-drug combination,” Dr. Yusuf said, “caution should be utilized.”
Would the reduced risk of CVD be greater with a combination of low doses of two BP-lowering drugs plus a statin plus aspirin? That may be superior, he said, “based on recent information published on the polypill indicating a 50% relative risk reduction in CVD events.”
The related phase 2 QUARTET US trial should shed further light on a quadpill strategy. Patients with hypertension are being randomized to a daily quadpill containing 2 mg candesartan, 1.25 mg amlodipine besylate, 0.625 mg indapamide, and 2.5 mg bisoprolol, or to usual care, 8 mg candesartan daily.
Investigators plan to enroll 87 participants in the Chicago area, with estimated study completion by March 31, 2023.
The study was supported by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council grant. The George Institute for Global Health has submitted patent applications for low–fixed-dose combination products to treat CV or cardiometabolic disease. Dr. Chow and coauthor Kris Rogers, PhD, senior biostatistician at The George Institute for Global Health, Newtown, Australia, are listed as inventors, but they do not have direct financial interests in these patent applications.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2021
Even those who just test positive at more risk for long COVID: CDC
Long-term symptoms, like those linked with COVID-19, were common in people who had even just a single positive test, new Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show.
The data show that symptoms in this group – including fatigue, cough, and headache – tended to last for more than a month.
Frequency of symptoms in people with a positive test was 1.5 times higher, compared with people whose tests had always been negative, according to the research published in the CDC’s latest Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Lead author Valentine Wanga, PhD, with the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, and colleagues conducted a non–probability-based internet panel survey of about 6,000 U.S. adults to assess long-term symptoms often associated with COVID-19 among those who had ever tested positive or always tested negative for COVID-19 between January 2020 and April 2021.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview that this research “establishes more securely than before that you don’t have to be hospitalized with COVID in order to develop long COVID symptoms.”
That’s better known among infectious disease experts, he said, but added that “this survey really gives a firm database for that.”
Study results
The study’s results showed that, compared with respondents who had a negative test result, those who received a positive result reported a significantly higher prevalence of any long-term symptom (65.9% vs. 42.9%), fatigue (22.5% vs. 12.0%), change in sense of smell or taste (17.3% vs. 1.7%), shortness of breath (15.5% vs. 5.2%), cough (14.5% vs. 4.9%), and headache (13.8% vs. 9.9%).
More people who had a positive test result (76.2%) reported persistence for more than a month of at least one initially occurring symptom, compared with those whose test results were always negative (69.6%).
The numbers are further proof, Dr. Schaffner said, that COVID not only will be an acute stressor on the health care system but patients with long COVID will need help with managing care for the long term.
“We still don’t know what the COVID virus does that results in these long COVID symptoms,” he said. Vanderbilt and many other institutions have developed “long COVID” centers as a testament to how important the problem is.
Long COVID symptoms are not well understood and most studies have looked at the effects from patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19.
In this survey, respondents self-reported whether they had ever had a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result (698), always received a negative test result (2,437), or never were tested for SARS-CoV-2 (2,750).
Compared with those who always tested negative, a larger proportion of those who tested positive (28.7% vs. 15.7%) reported believing that receiving a COVID-19 vaccine made their long-term symptoms better. No difference was found in reported beliefs that a vaccine made long-term symptoms worse.
Dr. Schaffner said he found that survey result interesting, but said that is not backed up by current data and would need further study.
“I would treat that with great caution,” he said. “I’m not dismissing it, but you can’t take that at face value. All of us who get sick and those of us who care for people who are sick – if there’s an intervention, we all hope for the best. We’re being optimistic. It’s when you do a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that you can find out whether your instincts or hopes were correct.”
The authors said that findings can inform public health preparedness, help guide care for people with post-COVID conditions, and help make the case for vaccines.
The study authors and Dr. Schaffner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long-term symptoms, like those linked with COVID-19, were common in people who had even just a single positive test, new Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show.
The data show that symptoms in this group – including fatigue, cough, and headache – tended to last for more than a month.
Frequency of symptoms in people with a positive test was 1.5 times higher, compared with people whose tests had always been negative, according to the research published in the CDC’s latest Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Lead author Valentine Wanga, PhD, with the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, and colleagues conducted a non–probability-based internet panel survey of about 6,000 U.S. adults to assess long-term symptoms often associated with COVID-19 among those who had ever tested positive or always tested negative for COVID-19 between January 2020 and April 2021.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview that this research “establishes more securely than before that you don’t have to be hospitalized with COVID in order to develop long COVID symptoms.”
That’s better known among infectious disease experts, he said, but added that “this survey really gives a firm database for that.”
Study results
The study’s results showed that, compared with respondents who had a negative test result, those who received a positive result reported a significantly higher prevalence of any long-term symptom (65.9% vs. 42.9%), fatigue (22.5% vs. 12.0%), change in sense of smell or taste (17.3% vs. 1.7%), shortness of breath (15.5% vs. 5.2%), cough (14.5% vs. 4.9%), and headache (13.8% vs. 9.9%).
More people who had a positive test result (76.2%) reported persistence for more than a month of at least one initially occurring symptom, compared with those whose test results were always negative (69.6%).
The numbers are further proof, Dr. Schaffner said, that COVID not only will be an acute stressor on the health care system but patients with long COVID will need help with managing care for the long term.
“We still don’t know what the COVID virus does that results in these long COVID symptoms,” he said. Vanderbilt and many other institutions have developed “long COVID” centers as a testament to how important the problem is.
Long COVID symptoms are not well understood and most studies have looked at the effects from patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19.
In this survey, respondents self-reported whether they had ever had a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result (698), always received a negative test result (2,437), or never were tested for SARS-CoV-2 (2,750).
Compared with those who always tested negative, a larger proportion of those who tested positive (28.7% vs. 15.7%) reported believing that receiving a COVID-19 vaccine made their long-term symptoms better. No difference was found in reported beliefs that a vaccine made long-term symptoms worse.
Dr. Schaffner said he found that survey result interesting, but said that is not backed up by current data and would need further study.
“I would treat that with great caution,” he said. “I’m not dismissing it, but you can’t take that at face value. All of us who get sick and those of us who care for people who are sick – if there’s an intervention, we all hope for the best. We’re being optimistic. It’s when you do a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that you can find out whether your instincts or hopes were correct.”
The authors said that findings can inform public health preparedness, help guide care for people with post-COVID conditions, and help make the case for vaccines.
The study authors and Dr. Schaffner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long-term symptoms, like those linked with COVID-19, were common in people who had even just a single positive test, new Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show.
The data show that symptoms in this group – including fatigue, cough, and headache – tended to last for more than a month.
Frequency of symptoms in people with a positive test was 1.5 times higher, compared with people whose tests had always been negative, according to the research published in the CDC’s latest Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Lead author Valentine Wanga, PhD, with the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, and colleagues conducted a non–probability-based internet panel survey of about 6,000 U.S. adults to assess long-term symptoms often associated with COVID-19 among those who had ever tested positive or always tested negative for COVID-19 between January 2020 and April 2021.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview that this research “establishes more securely than before that you don’t have to be hospitalized with COVID in order to develop long COVID symptoms.”
That’s better known among infectious disease experts, he said, but added that “this survey really gives a firm database for that.”
Study results
The study’s results showed that, compared with respondents who had a negative test result, those who received a positive result reported a significantly higher prevalence of any long-term symptom (65.9% vs. 42.9%), fatigue (22.5% vs. 12.0%), change in sense of smell or taste (17.3% vs. 1.7%), shortness of breath (15.5% vs. 5.2%), cough (14.5% vs. 4.9%), and headache (13.8% vs. 9.9%).
More people who had a positive test result (76.2%) reported persistence for more than a month of at least one initially occurring symptom, compared with those whose test results were always negative (69.6%).
The numbers are further proof, Dr. Schaffner said, that COVID not only will be an acute stressor on the health care system but patients with long COVID will need help with managing care for the long term.
“We still don’t know what the COVID virus does that results in these long COVID symptoms,” he said. Vanderbilt and many other institutions have developed “long COVID” centers as a testament to how important the problem is.
Long COVID symptoms are not well understood and most studies have looked at the effects from patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19.
In this survey, respondents self-reported whether they had ever had a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result (698), always received a negative test result (2,437), or never were tested for SARS-CoV-2 (2,750).
Compared with those who always tested negative, a larger proportion of those who tested positive (28.7% vs. 15.7%) reported believing that receiving a COVID-19 vaccine made their long-term symptoms better. No difference was found in reported beliefs that a vaccine made long-term symptoms worse.
Dr. Schaffner said he found that survey result interesting, but said that is not backed up by current data and would need further study.
“I would treat that with great caution,” he said. “I’m not dismissing it, but you can’t take that at face value. All of us who get sick and those of us who care for people who are sick – if there’s an intervention, we all hope for the best. We’re being optimistic. It’s when you do a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that you can find out whether your instincts or hopes were correct.”
The authors said that findings can inform public health preparedness, help guide care for people with post-COVID conditions, and help make the case for vaccines.
The study authors and Dr. Schaffner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sweeping new vaccine mandates will impact most U.S. workers
, including sweeping vaccine mandates that will affect 100 million American workers, nearly two-thirds of the country’s workforce.
“As your president, I’m announcing tonight a new plan to get more Americans vaccinated to combat those blocking public health,” he said Sept. 9.
As part of a six-part plan unveiled in a speech from the State Dining Room of the White House, President Biden said he would require vaccinations for nearly 4 million federal workers and the employees of companies that contract with the federal government.
He has also directed the Occupational Safety and Health Administration to develop a rule that will require large employers -- those with at least 100 employees -- to ensure their workers are vaccinated or tested weekly.
Nearly 17 million health care workers will face new vaccine mandates as part of the conditions of participation in the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
President Biden said the federal government will require staff at federally funded Head Start programs and schools to be vaccinated. He’s also calling on all states to mandate vaccines for teachers.
“A distinct minority of Americans, supported by a distinct minority of elected officials, are keeping us from turning the corner,” PresidentBiden said. “These pandemic politics, as I refer to them, are making people sick, causing unvaccinated people to die.”
One public health official said he was glad to see the president’s bold action.
“What I saw today was the federal government trying to use its powers to create greater safety in the American population,” said Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the school of public health at Brown University, Providence, R.I., in a call with reporters after the speech.
National Nurses United, the largest union of registered nurses in the United States, issued a statement in support of President Biden’s new vaccination requirements, but pushed back on his language.
“…as advocates for public health, registered nurses want to be extremely clear: There is no such thing as a pandemic of only the unvaccinated. The science of epidemiology tells us there is just one deadly, global pandemic that has not yet ended, and we are all in it together. To get out of it, we must act together. All of us,” the statement says.
A host of other professional groups, including the American Medical Association and the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, also issued statements of support for President Biden’s plan.
But the plan was not well received by all.
“I will pursue every legal option available to the state of Georgia to stop this blatantly unlawful overreach by the Biden Administration,” said Georgia Governor Brian Kemp, a Republican, in a Tweet.
The National Council for Occupational Safety and Health called the plan “a missed opportunity” because it failed to include workplace protections for essential workers such as grocery, postal, and transit workers.
“Social distancing, improved ventilation, shift rotation, and protective equipment to reduce exposure are important components of an overall plan to reduce risk and stop the virus. These tools are missing from the new steps President Biden announced today,” said Jessica Martinez, co-executive director of the group.
In addition to the new vaccination requirements, President Biden said extra doses would be on the way for people who have already been fully vaccinated in order to protect against waning immunity, starting on Sept. 20. But he noted that those plans would be contingent on the Food and Drug Administration’s approval for third doses and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation of the shots.
President Biden pledged to use the Defense Production Act to ramp up production of at-home tests, which have been selling out across the nation as the Delta variant spreads.
He also announced plans to expand access to COVID-19 testing, including offering testing for free at thousands of pharmacies nationwide and getting major retailers to sell at-home COVID-19 tests at cost.
The BinaxNow test kit, which currently retails for $23.99, will now cost about $15 for two tests at Kroger, Amazon, and Walmart, according to the White House. Food banks and community health centers will get free tests, too.
He called on states to set up COVID-19 testing programs at all schools.
Jha said that in his view, the big, game-changing news out of the president’s speech was the expansion of testing.
“Our country has failed to deploy tests in a way that can really bring this pandemic under control,” Jha said. “There are plenty of reasons, data, experience to indicate that if these were widely available, it would make a dramatic difference in reducing infection numbers across our country.”.
Dr. Jha said the private market had not worked effectively to make testing more widely available, so it was “absolutely a requirement of the federal government to step in and make testing more widely available,” he said.
President Biden also announced new economic stimulus programs, saying he’s expanding loan programs to small businesses and streamlining the loan forgiveness process.
President Biden said he’s boosting help for overburdened hospitals, doubling the number of federal surge response teams sent to hard-hit areas to reduce the strain on local health care workers. He said he would increase the pace of antibody treatments to states by 50%.
“We made so much progress during the past 7 months of this pandemic. Even so, we remain at a critical moment, a critical time,” he said. “We have the tools. Now, we just have to finish the job with truth, with science, with confidence and together as one nation.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, including sweeping vaccine mandates that will affect 100 million American workers, nearly two-thirds of the country’s workforce.
“As your president, I’m announcing tonight a new plan to get more Americans vaccinated to combat those blocking public health,” he said Sept. 9.
As part of a six-part plan unveiled in a speech from the State Dining Room of the White House, President Biden said he would require vaccinations for nearly 4 million federal workers and the employees of companies that contract with the federal government.
He has also directed the Occupational Safety and Health Administration to develop a rule that will require large employers -- those with at least 100 employees -- to ensure their workers are vaccinated or tested weekly.
Nearly 17 million health care workers will face new vaccine mandates as part of the conditions of participation in the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
President Biden said the federal government will require staff at federally funded Head Start programs and schools to be vaccinated. He’s also calling on all states to mandate vaccines for teachers.
“A distinct minority of Americans, supported by a distinct minority of elected officials, are keeping us from turning the corner,” PresidentBiden said. “These pandemic politics, as I refer to them, are making people sick, causing unvaccinated people to die.”
One public health official said he was glad to see the president’s bold action.
“What I saw today was the federal government trying to use its powers to create greater safety in the American population,” said Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the school of public health at Brown University, Providence, R.I., in a call with reporters after the speech.
National Nurses United, the largest union of registered nurses in the United States, issued a statement in support of President Biden’s new vaccination requirements, but pushed back on his language.
“…as advocates for public health, registered nurses want to be extremely clear: There is no such thing as a pandemic of only the unvaccinated. The science of epidemiology tells us there is just one deadly, global pandemic that has not yet ended, and we are all in it together. To get out of it, we must act together. All of us,” the statement says.
A host of other professional groups, including the American Medical Association and the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, also issued statements of support for President Biden’s plan.
But the plan was not well received by all.
“I will pursue every legal option available to the state of Georgia to stop this blatantly unlawful overreach by the Biden Administration,” said Georgia Governor Brian Kemp, a Republican, in a Tweet.
The National Council for Occupational Safety and Health called the plan “a missed opportunity” because it failed to include workplace protections for essential workers such as grocery, postal, and transit workers.
“Social distancing, improved ventilation, shift rotation, and protective equipment to reduce exposure are important components of an overall plan to reduce risk and stop the virus. These tools are missing from the new steps President Biden announced today,” said Jessica Martinez, co-executive director of the group.
In addition to the new vaccination requirements, President Biden said extra doses would be on the way for people who have already been fully vaccinated in order to protect against waning immunity, starting on Sept. 20. But he noted that those plans would be contingent on the Food and Drug Administration’s approval for third doses and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation of the shots.
President Biden pledged to use the Defense Production Act to ramp up production of at-home tests, which have been selling out across the nation as the Delta variant spreads.
He also announced plans to expand access to COVID-19 testing, including offering testing for free at thousands of pharmacies nationwide and getting major retailers to sell at-home COVID-19 tests at cost.
The BinaxNow test kit, which currently retails for $23.99, will now cost about $15 for two tests at Kroger, Amazon, and Walmart, according to the White House. Food banks and community health centers will get free tests, too.
He called on states to set up COVID-19 testing programs at all schools.
Jha said that in his view, the big, game-changing news out of the president’s speech was the expansion of testing.
“Our country has failed to deploy tests in a way that can really bring this pandemic under control,” Jha said. “There are plenty of reasons, data, experience to indicate that if these were widely available, it would make a dramatic difference in reducing infection numbers across our country.”.
Dr. Jha said the private market had not worked effectively to make testing more widely available, so it was “absolutely a requirement of the federal government to step in and make testing more widely available,” he said.
President Biden also announced new economic stimulus programs, saying he’s expanding loan programs to small businesses and streamlining the loan forgiveness process.
President Biden said he’s boosting help for overburdened hospitals, doubling the number of federal surge response teams sent to hard-hit areas to reduce the strain on local health care workers. He said he would increase the pace of antibody treatments to states by 50%.
“We made so much progress during the past 7 months of this pandemic. Even so, we remain at a critical moment, a critical time,” he said. “We have the tools. Now, we just have to finish the job with truth, with science, with confidence and together as one nation.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, including sweeping vaccine mandates that will affect 100 million American workers, nearly two-thirds of the country’s workforce.
“As your president, I’m announcing tonight a new plan to get more Americans vaccinated to combat those blocking public health,” he said Sept. 9.
As part of a six-part plan unveiled in a speech from the State Dining Room of the White House, President Biden said he would require vaccinations for nearly 4 million federal workers and the employees of companies that contract with the federal government.
He has also directed the Occupational Safety and Health Administration to develop a rule that will require large employers -- those with at least 100 employees -- to ensure their workers are vaccinated or tested weekly.
Nearly 17 million health care workers will face new vaccine mandates as part of the conditions of participation in the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
President Biden said the federal government will require staff at federally funded Head Start programs and schools to be vaccinated. He’s also calling on all states to mandate vaccines for teachers.
“A distinct minority of Americans, supported by a distinct minority of elected officials, are keeping us from turning the corner,” PresidentBiden said. “These pandemic politics, as I refer to them, are making people sick, causing unvaccinated people to die.”
One public health official said he was glad to see the president’s bold action.
“What I saw today was the federal government trying to use its powers to create greater safety in the American population,” said Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the school of public health at Brown University, Providence, R.I., in a call with reporters after the speech.
National Nurses United, the largest union of registered nurses in the United States, issued a statement in support of President Biden’s new vaccination requirements, but pushed back on his language.
“…as advocates for public health, registered nurses want to be extremely clear: There is no such thing as a pandemic of only the unvaccinated. The science of epidemiology tells us there is just one deadly, global pandemic that has not yet ended, and we are all in it together. To get out of it, we must act together. All of us,” the statement says.
A host of other professional groups, including the American Medical Association and the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, also issued statements of support for President Biden’s plan.
But the plan was not well received by all.
“I will pursue every legal option available to the state of Georgia to stop this blatantly unlawful overreach by the Biden Administration,” said Georgia Governor Brian Kemp, a Republican, in a Tweet.
The National Council for Occupational Safety and Health called the plan “a missed opportunity” because it failed to include workplace protections for essential workers such as grocery, postal, and transit workers.
“Social distancing, improved ventilation, shift rotation, and protective equipment to reduce exposure are important components of an overall plan to reduce risk and stop the virus. These tools are missing from the new steps President Biden announced today,” said Jessica Martinez, co-executive director of the group.
In addition to the new vaccination requirements, President Biden said extra doses would be on the way for people who have already been fully vaccinated in order to protect against waning immunity, starting on Sept. 20. But he noted that those plans would be contingent on the Food and Drug Administration’s approval for third doses and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation of the shots.
President Biden pledged to use the Defense Production Act to ramp up production of at-home tests, which have been selling out across the nation as the Delta variant spreads.
He also announced plans to expand access to COVID-19 testing, including offering testing for free at thousands of pharmacies nationwide and getting major retailers to sell at-home COVID-19 tests at cost.
The BinaxNow test kit, which currently retails for $23.99, will now cost about $15 for two tests at Kroger, Amazon, and Walmart, according to the White House. Food banks and community health centers will get free tests, too.
He called on states to set up COVID-19 testing programs at all schools.
Jha said that in his view, the big, game-changing news out of the president’s speech was the expansion of testing.
“Our country has failed to deploy tests in a way that can really bring this pandemic under control,” Jha said. “There are plenty of reasons, data, experience to indicate that if these were widely available, it would make a dramatic difference in reducing infection numbers across our country.”.
Dr. Jha said the private market had not worked effectively to make testing more widely available, so it was “absolutely a requirement of the federal government to step in and make testing more widely available,” he said.
President Biden also announced new economic stimulus programs, saying he’s expanding loan programs to small businesses and streamlining the loan forgiveness process.
President Biden said he’s boosting help for overburdened hospitals, doubling the number of federal surge response teams sent to hard-hit areas to reduce the strain on local health care workers. He said he would increase the pace of antibody treatments to states by 50%.
“We made so much progress during the past 7 months of this pandemic. Even so, we remain at a critical moment, a critical time,” he said. “We have the tools. Now, we just have to finish the job with truth, with science, with confidence and together as one nation.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Transgender individuals twice as likely to die as general population
Mortality is consistently twice as high in transgender people receiving hormone treatment, compared with cisgender individuals in the general population and has not decreased over time, results of a 5 decades–long study from the Netherlands indicate.
Particularly concerning is that trans women (male to female) had a mortality risk nearly double that of cis men (born and remain male) in the general Dutch population (standardized mortality ratio, 1.8), while it was nearly triple that of cis women (SMR, 2.8).
Compared with cisgender women, transgender women were more than twice as likely to die from heart disease, three times more likely to die from lung cancer, and almost nine times more likely to die from infection. HIV-related disease mortality risk was nearly 50 times higher for trans women than cis women, and the risk of suicide was almost seven times greater.
Suicide and other nonnatural causes of death were more common in trans men, compared with cis women.
The report, by Christel J.M. de Blok, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center and colleagues, was published online Sept. 2 in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
The study included trans men who received testosterone to transition from female to male and trans women who received estrogen plus an antiandrogen to transition from male to female.
Is gender-affirming hormone therapy associated with increased mortality?
Senior author Martin den Heijer, MD, also of Amsterdam University Medical Center, said: “The findings of our large, nationwide study highlight a substantially increased mortality risk among transgender people that has persisted for decades.”
But he pointed out that, overall, the data do not appear to suggest the premature deaths were related to gender-affirming hormone treatment.
However, he conceded that more work is needed on this aspect of care. “There is insufficient evidence at present to determine long-term safety of [gender-affirming hormone treatment]. More research is needed to fully establish whether it in any way affects mortality risk for transgender people,” said Dr. den Heijer.
Endocrinologist Will Malone, MD, of Twin Falls, Idaho, told this news organization, “The study confirms, like others before it, that individuals taking cross-sex hormones are more likely to die prematurely from a number of causes.”
“While the authors speculate that this higher mortality rate is not connected to cross-sex hormones, the study was not designed to be able to make such a claim,” he said, pointing to limited follow-up times.
In an accompanying commentary, Vin Tangpricha, MD, PhD, an endocrinologist from Emory University, Atlanta, noted: “Transgender men do not appear to have as significantly increased comorbidity following receipt of gender-affirming hormone therapy when compared with transgender women.”
Dr. Tangpricha added future studies should examine which factors – hormone regimen, hormone concentrations, access to health care, or other biological factors – explain the higher increased risk of morbidity and mortality observed in trans women as opposed to trans men.
However, Dr. de Blok and colleagues note that, as there were relatively few deaths among transgender men in the cohort, analysis on cause of death in this group is limited.
Transgender individuals more likely to die younger
For their study, Dutch researchers retrospectively examined data from 4,568 transgender people attending their clinic (2,927 transgender women and 1,641 transgender men) treated in 1972-2018. People were excluded if they started treatment before the age of 17 or if they had received puberty-blocking drugs.
Data on age at start of hormone treatment, type of treatment, smoking habits, medical history, and last date of follow-up were gathered from medical records. Where possible, SMRs were determined for deaths among trans men and trans women, compared with rates for the adult Dutch general population.
Median age at the start of cross-sex hormone treatment was 30 years in transgender women and 23 years in transgender men. But the median follow-up time was only 11 years in transgender women and 5 years in transgender men.
A total of 317 (10.8%) trans women died, and 44 (2.7%) trans men died. The findings were higher than expected, compared with the general population of cisgender women (SMR, 1.8) but not cisgender men (SMR 1.2).
Mortality risk did increase more in transgender people who started gender-affirming hormone treatment in the past 2 decades compared with earlier, a fact that Dr. de Blok said was surprising.
Trans men, for example, compared with cis women, had an SMR of 2.1-2.4 in 2000-2018 (compared with 1.8 overall).
“This may be due to changes in clinical practice. ... In the past, health care providers were reluctant to provide hormone treatment to people with a history of comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease. However, because of the many benefits of enabling people to access hormone therapy, nowadays this rarely results in treatment being denied,” Dr. de Blok noted.
More research needed, especially in trans-identifying youth
Dr. Malone remarked that previous studies have shown associations between taking cross-sex hormones and elevated mortality, while also “not designed to detect causality,” have “generally accepted that natal males who take estrogen have estrogen-related increases in the rates of heart disease, stroke, and deep venous thrombosis.”
He added that the risks of testosterone use in natal females were less well established, “but testosterone is also felt to increase their risk of heart disease.”
He stressed the limited follow-up times in the study by Dr. de Blok and colleagues.
This “strongly suggests that the rate of elevated mortality far exceeds the doubling measured by the study, especially for natal females.”
Dr. Malone is one of several clinicians and researchers who has formed the Society for Evidence-Based Gender Medicine, a nonprofit organization that now has at least 100 physician members. SEGM is concerned about the lack of quality evidence for the use of hormonal and surgical interventions as first-line treatment, especially for young people with gender dysphoria.
Dr. Tangpricha also highlighted that the findings do not apply to transgender people who began treatment before age 17 years or those who had taken puberty blockers before gender-affirming hormone treatment.
There are no long-term data on transgender individuals who have received gender-affirming hormone therapies close to the time of puberty.
These data, such as those from the Trans Youth Care study, should be available in the future, he added.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tangpricha has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health and served as past president of the World Professional Association for Transgender Health. He is editor-in-chief of Endocrine Practice and has provided expert testimony for Kirkland and Ellis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mortality is consistently twice as high in transgender people receiving hormone treatment, compared with cisgender individuals in the general population and has not decreased over time, results of a 5 decades–long study from the Netherlands indicate.
Particularly concerning is that trans women (male to female) had a mortality risk nearly double that of cis men (born and remain male) in the general Dutch population (standardized mortality ratio, 1.8), while it was nearly triple that of cis women (SMR, 2.8).
Compared with cisgender women, transgender women were more than twice as likely to die from heart disease, three times more likely to die from lung cancer, and almost nine times more likely to die from infection. HIV-related disease mortality risk was nearly 50 times higher for trans women than cis women, and the risk of suicide was almost seven times greater.
Suicide and other nonnatural causes of death were more common in trans men, compared with cis women.
The report, by Christel J.M. de Blok, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center and colleagues, was published online Sept. 2 in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
The study included trans men who received testosterone to transition from female to male and trans women who received estrogen plus an antiandrogen to transition from male to female.
Is gender-affirming hormone therapy associated with increased mortality?
Senior author Martin den Heijer, MD, also of Amsterdam University Medical Center, said: “The findings of our large, nationwide study highlight a substantially increased mortality risk among transgender people that has persisted for decades.”
But he pointed out that, overall, the data do not appear to suggest the premature deaths were related to gender-affirming hormone treatment.
However, he conceded that more work is needed on this aspect of care. “There is insufficient evidence at present to determine long-term safety of [gender-affirming hormone treatment]. More research is needed to fully establish whether it in any way affects mortality risk for transgender people,” said Dr. den Heijer.
Endocrinologist Will Malone, MD, of Twin Falls, Idaho, told this news organization, “The study confirms, like others before it, that individuals taking cross-sex hormones are more likely to die prematurely from a number of causes.”
“While the authors speculate that this higher mortality rate is not connected to cross-sex hormones, the study was not designed to be able to make such a claim,” he said, pointing to limited follow-up times.
In an accompanying commentary, Vin Tangpricha, MD, PhD, an endocrinologist from Emory University, Atlanta, noted: “Transgender men do not appear to have as significantly increased comorbidity following receipt of gender-affirming hormone therapy when compared with transgender women.”
Dr. Tangpricha added future studies should examine which factors – hormone regimen, hormone concentrations, access to health care, or other biological factors – explain the higher increased risk of morbidity and mortality observed in trans women as opposed to trans men.
However, Dr. de Blok and colleagues note that, as there were relatively few deaths among transgender men in the cohort, analysis on cause of death in this group is limited.
Transgender individuals more likely to die younger
For their study, Dutch researchers retrospectively examined data from 4,568 transgender people attending their clinic (2,927 transgender women and 1,641 transgender men) treated in 1972-2018. People were excluded if they started treatment before the age of 17 or if they had received puberty-blocking drugs.
Data on age at start of hormone treatment, type of treatment, smoking habits, medical history, and last date of follow-up were gathered from medical records. Where possible, SMRs were determined for deaths among trans men and trans women, compared with rates for the adult Dutch general population.
Median age at the start of cross-sex hormone treatment was 30 years in transgender women and 23 years in transgender men. But the median follow-up time was only 11 years in transgender women and 5 years in transgender men.
A total of 317 (10.8%) trans women died, and 44 (2.7%) trans men died. The findings were higher than expected, compared with the general population of cisgender women (SMR, 1.8) but not cisgender men (SMR 1.2).
Mortality risk did increase more in transgender people who started gender-affirming hormone treatment in the past 2 decades compared with earlier, a fact that Dr. de Blok said was surprising.
Trans men, for example, compared with cis women, had an SMR of 2.1-2.4 in 2000-2018 (compared with 1.8 overall).
“This may be due to changes in clinical practice. ... In the past, health care providers were reluctant to provide hormone treatment to people with a history of comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease. However, because of the many benefits of enabling people to access hormone therapy, nowadays this rarely results in treatment being denied,” Dr. de Blok noted.
More research needed, especially in trans-identifying youth
Dr. Malone remarked that previous studies have shown associations between taking cross-sex hormones and elevated mortality, while also “not designed to detect causality,” have “generally accepted that natal males who take estrogen have estrogen-related increases in the rates of heart disease, stroke, and deep venous thrombosis.”
He added that the risks of testosterone use in natal females were less well established, “but testosterone is also felt to increase their risk of heart disease.”
He stressed the limited follow-up times in the study by Dr. de Blok and colleagues.
This “strongly suggests that the rate of elevated mortality far exceeds the doubling measured by the study, especially for natal females.”
Dr. Malone is one of several clinicians and researchers who has formed the Society for Evidence-Based Gender Medicine, a nonprofit organization that now has at least 100 physician members. SEGM is concerned about the lack of quality evidence for the use of hormonal and surgical interventions as first-line treatment, especially for young people with gender dysphoria.
Dr. Tangpricha also highlighted that the findings do not apply to transgender people who began treatment before age 17 years or those who had taken puberty blockers before gender-affirming hormone treatment.
There are no long-term data on transgender individuals who have received gender-affirming hormone therapies close to the time of puberty.
These data, such as those from the Trans Youth Care study, should be available in the future, he added.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tangpricha has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health and served as past president of the World Professional Association for Transgender Health. He is editor-in-chief of Endocrine Practice and has provided expert testimony for Kirkland and Ellis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mortality is consistently twice as high in transgender people receiving hormone treatment, compared with cisgender individuals in the general population and has not decreased over time, results of a 5 decades–long study from the Netherlands indicate.
Particularly concerning is that trans women (male to female) had a mortality risk nearly double that of cis men (born and remain male) in the general Dutch population (standardized mortality ratio, 1.8), while it was nearly triple that of cis women (SMR, 2.8).
Compared with cisgender women, transgender women were more than twice as likely to die from heart disease, three times more likely to die from lung cancer, and almost nine times more likely to die from infection. HIV-related disease mortality risk was nearly 50 times higher for trans women than cis women, and the risk of suicide was almost seven times greater.
Suicide and other nonnatural causes of death were more common in trans men, compared with cis women.
The report, by Christel J.M. de Blok, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center and colleagues, was published online Sept. 2 in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
The study included trans men who received testosterone to transition from female to male and trans women who received estrogen plus an antiandrogen to transition from male to female.
Is gender-affirming hormone therapy associated with increased mortality?
Senior author Martin den Heijer, MD, also of Amsterdam University Medical Center, said: “The findings of our large, nationwide study highlight a substantially increased mortality risk among transgender people that has persisted for decades.”
But he pointed out that, overall, the data do not appear to suggest the premature deaths were related to gender-affirming hormone treatment.
However, he conceded that more work is needed on this aspect of care. “There is insufficient evidence at present to determine long-term safety of [gender-affirming hormone treatment]. More research is needed to fully establish whether it in any way affects mortality risk for transgender people,” said Dr. den Heijer.
Endocrinologist Will Malone, MD, of Twin Falls, Idaho, told this news organization, “The study confirms, like others before it, that individuals taking cross-sex hormones are more likely to die prematurely from a number of causes.”
“While the authors speculate that this higher mortality rate is not connected to cross-sex hormones, the study was not designed to be able to make such a claim,” he said, pointing to limited follow-up times.
In an accompanying commentary, Vin Tangpricha, MD, PhD, an endocrinologist from Emory University, Atlanta, noted: “Transgender men do not appear to have as significantly increased comorbidity following receipt of gender-affirming hormone therapy when compared with transgender women.”
Dr. Tangpricha added future studies should examine which factors – hormone regimen, hormone concentrations, access to health care, or other biological factors – explain the higher increased risk of morbidity and mortality observed in trans women as opposed to trans men.
However, Dr. de Blok and colleagues note that, as there were relatively few deaths among transgender men in the cohort, analysis on cause of death in this group is limited.
Transgender individuals more likely to die younger
For their study, Dutch researchers retrospectively examined data from 4,568 transgender people attending their clinic (2,927 transgender women and 1,641 transgender men) treated in 1972-2018. People were excluded if they started treatment before the age of 17 or if they had received puberty-blocking drugs.
Data on age at start of hormone treatment, type of treatment, smoking habits, medical history, and last date of follow-up were gathered from medical records. Where possible, SMRs were determined for deaths among trans men and trans women, compared with rates for the adult Dutch general population.
Median age at the start of cross-sex hormone treatment was 30 years in transgender women and 23 years in transgender men. But the median follow-up time was only 11 years in transgender women and 5 years in transgender men.
A total of 317 (10.8%) trans women died, and 44 (2.7%) trans men died. The findings were higher than expected, compared with the general population of cisgender women (SMR, 1.8) but not cisgender men (SMR 1.2).
Mortality risk did increase more in transgender people who started gender-affirming hormone treatment in the past 2 decades compared with earlier, a fact that Dr. de Blok said was surprising.
Trans men, for example, compared with cis women, had an SMR of 2.1-2.4 in 2000-2018 (compared with 1.8 overall).
“This may be due to changes in clinical practice. ... In the past, health care providers were reluctant to provide hormone treatment to people with a history of comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease. However, because of the many benefits of enabling people to access hormone therapy, nowadays this rarely results in treatment being denied,” Dr. de Blok noted.
More research needed, especially in trans-identifying youth
Dr. Malone remarked that previous studies have shown associations between taking cross-sex hormones and elevated mortality, while also “not designed to detect causality,” have “generally accepted that natal males who take estrogen have estrogen-related increases in the rates of heart disease, stroke, and deep venous thrombosis.”
He added that the risks of testosterone use in natal females were less well established, “but testosterone is also felt to increase their risk of heart disease.”
He stressed the limited follow-up times in the study by Dr. de Blok and colleagues.
This “strongly suggests that the rate of elevated mortality far exceeds the doubling measured by the study, especially for natal females.”
Dr. Malone is one of several clinicians and researchers who has formed the Society for Evidence-Based Gender Medicine, a nonprofit organization that now has at least 100 physician members. SEGM is concerned about the lack of quality evidence for the use of hormonal and surgical interventions as first-line treatment, especially for young people with gender dysphoria.
Dr. Tangpricha also highlighted that the findings do not apply to transgender people who began treatment before age 17 years or those who had taken puberty blockers before gender-affirming hormone treatment.
There are no long-term data on transgender individuals who have received gender-affirming hormone therapies close to the time of puberty.
These data, such as those from the Trans Youth Care study, should be available in the future, he added.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tangpricha has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health and served as past president of the World Professional Association for Transgender Health. He is editor-in-chief of Endocrine Practice and has provided expert testimony for Kirkland and Ellis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.