User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Remnant cholesterol improves CV risk prediction
, a new study suggests.
The study, which followed almost 42,000 Danish individuals without a history of ischemic cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or statin use for more than 10 years, found that elevated remnant cholesterol appropriately reclassified up to 40% of those who later experienced myocardial infarction and ischemic heart disease.
“The clinical implications of our study include that doctors and patients should be aware of remnant cholesterol levels to prevent future risk of MI and ischemic heart disease,” the authors conclude.
They suggest that the development of a cardiovascular risk algorithm, including remnant cholesterol together with LDL cholesterol, would help to better identify high-risk individuals who could be candidates for statins in a primary prevention setting.
They note that physicians are encouraged to evaluate non-HDL cholesterol and/or apolipoprotein B rather than LDL cholesterol and certainly not yet remnant cholesterol, possibly because of the limited availability of remnant cholesterol values in some parts of the world.
However, they point out that remnant cholesterol can be calculated with a standard lipid profile without additional cost, which is currently already the standard procedure in the greater Copenhagen area.
“This means that the use of remnant cholesterol is easy to introduce into daily clinical practice,” they say.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors, Takahito Doi, MD, Anne Langsted, MD, and Børge Nordestgaard, from Copenhagen University Hospital, Denmark, explain that remnant cholesterol is total cholesterol minus LDL-cholesterol minus HDL-cholesterol and includes the cholesterol content of the triglyceride-rich very-low-density lipoproteins, intermediate-density lipoproteins, and chylomicron remnants in the nonfasting state.
“When these particles enter the arterial wall, they are taken up by macrophages to produce foam cells, and therefore elevated remnant cholesterol likely enhance accumulation of cholesterol in the arterial wall, leading to progression of atherosclerosis and in consequence ischemic heart disease,” they note.
They point out that most guidelines for assessment of the 10-year risk of ischemic heart and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease include levels of total and HDL cholesterol, but remnant cholesterol levels are not included.
They conducted the current study to investigate whether elevated remnant cholesterol would lead to appropriate reclassification of individuals who later experienced MI or ischemic heart disease.
The researchers analyzed data from the Copenhagen General Population Study, which recruited individuals from the White Danish general population from 2003-2015 and followed them until 2018. Information on lifestyle, health, and medication, including statin therapy, was obtained through a questionnaire, and participants underwent physical examinations and had nonfasting blood samples drawn for biochemical measurements.
For the current study, they included 41,928 individuals aged 40-100 years enrolled before 2009 without a history of ischemic cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and statin use at baseline. The median follow-up time was 12 years. Information on diagnoses of MI and ischemic heart disease was collected from the national Danish Causes of Death Registry and all hospital admissions and diagnoses entered in the national Danish Patient Registry.
During the first 10 years of follow-up there were 1,063 MIs and 1,460 ischemic heart disease events (death of ischemic heart disease, nonfatal MI, and coronary revascularization).
Results showed that in models based on conventional risk factors estimating risk of heart disease of above or below 5% in 10 years, adding remnant cholesterol at levels above the 95th percentile, appropriately reclassified 23% of individuals who had an MI and 21% of individuals who had an ischemic heart disease event.
Using remnant cholesterol levels above the 75th percentile appropriately reclassified 10% of those who had an MI and 8% of those who had an ischemic heart disease event. No events were reclassified incorrectly.
Using measurements of remnant cholesterol also improved reclassification of individuals with heart disease risk above or below 7.5% or 10% in 10 years.
When reclassifications were combined from below to above 5%, 7.5%, and 10% risk of events, 42% of individuals with MI and 41% with ischemic heart disease events were reclassified appropriately.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the study in JACC, Peter Wilson, MD, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, and Alan Remaley, MD, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, say these findings rekindle interest in atherogenic nonfasting lipid measurements and emphasize an important role for elevated nonfasting remnant cholesterol as a value-added predictor of ischemic events.
The editorialists note that both fasting and nonfasting lipid values provide useful information for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk estimation, and elevated nonfasting remnant cholesterol appears to help identify persons at greater risk for an initial cardiovascular ischemic event.
They add that very elevated levels (above the 75th percentile) of nonfasting remnant cholesterol deserve further evaluation as a potentially valuable “modifier of ASCVD risk,” and replication of the results could move these findings forward to potentially improve prognostication and care for patients at risk for ischemic heart disease events.
An indirect measure of triglycerides
Dr. Wilson explained that remnant cholesterol is an indirect measure of triglycerides beyond LDL levels, and it is thus including a new lipid measurement in risk prediction.
“We are completely focused on LDL cholesterol,” he said. “This opens it up a bit by adding in another measure that takes into account triglycerides as well as LDL.”
He also pointed out that use of a nonfasting sample is another advantage of measuring remnant cholesterol.
“An accurate measure of LDL needs a fasting sample, which is a nuisance, whereas remnant cholesterol can be measured in a nonfasting blood sample, so it is more convenient,” Dr. Wilson said.
While this study shows this measure is helpful for risk prediction in the primary prevention population, Dr. Wilson believes remnant cholesterol could be most useful in helping to guide further medication choice in patients who are already taking statins.
“Statins mainly target LDL, but if we can also measure nonfasting triglycerides this will be helpful. It may help us select some patients who may need a different type of drug to use in addition to statins that lowers triglycerides,” he said.
This work was supported by the Global Excellence Programme, the Research Fund for the Capital Region of Denmark, the Japanese College of Cardiology Overseas Research Fellowship, and the Scandinavia Japan Sasakawa Foundation. Mr. Nordestgaard has reported consultancies or talks sponsored by AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Regeneron, Akcea, Amgen, Amarin, Kowa, Denka, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Esperion, and Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Doi has reported talks sponsored by MSD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study suggests.
The study, which followed almost 42,000 Danish individuals without a history of ischemic cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or statin use for more than 10 years, found that elevated remnant cholesterol appropriately reclassified up to 40% of those who later experienced myocardial infarction and ischemic heart disease.
“The clinical implications of our study include that doctors and patients should be aware of remnant cholesterol levels to prevent future risk of MI and ischemic heart disease,” the authors conclude.
They suggest that the development of a cardiovascular risk algorithm, including remnant cholesterol together with LDL cholesterol, would help to better identify high-risk individuals who could be candidates for statins in a primary prevention setting.
They note that physicians are encouraged to evaluate non-HDL cholesterol and/or apolipoprotein B rather than LDL cholesterol and certainly not yet remnant cholesterol, possibly because of the limited availability of remnant cholesterol values in some parts of the world.
However, they point out that remnant cholesterol can be calculated with a standard lipid profile without additional cost, which is currently already the standard procedure in the greater Copenhagen area.
“This means that the use of remnant cholesterol is easy to introduce into daily clinical practice,” they say.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors, Takahito Doi, MD, Anne Langsted, MD, and Børge Nordestgaard, from Copenhagen University Hospital, Denmark, explain that remnant cholesterol is total cholesterol minus LDL-cholesterol minus HDL-cholesterol and includes the cholesterol content of the triglyceride-rich very-low-density lipoproteins, intermediate-density lipoproteins, and chylomicron remnants in the nonfasting state.
“When these particles enter the arterial wall, they are taken up by macrophages to produce foam cells, and therefore elevated remnant cholesterol likely enhance accumulation of cholesterol in the arterial wall, leading to progression of atherosclerosis and in consequence ischemic heart disease,” they note.
They point out that most guidelines for assessment of the 10-year risk of ischemic heart and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease include levels of total and HDL cholesterol, but remnant cholesterol levels are not included.
They conducted the current study to investigate whether elevated remnant cholesterol would lead to appropriate reclassification of individuals who later experienced MI or ischemic heart disease.
The researchers analyzed data from the Copenhagen General Population Study, which recruited individuals from the White Danish general population from 2003-2015 and followed them until 2018. Information on lifestyle, health, and medication, including statin therapy, was obtained through a questionnaire, and participants underwent physical examinations and had nonfasting blood samples drawn for biochemical measurements.
For the current study, they included 41,928 individuals aged 40-100 years enrolled before 2009 without a history of ischemic cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and statin use at baseline. The median follow-up time was 12 years. Information on diagnoses of MI and ischemic heart disease was collected from the national Danish Causes of Death Registry and all hospital admissions and diagnoses entered in the national Danish Patient Registry.
During the first 10 years of follow-up there were 1,063 MIs and 1,460 ischemic heart disease events (death of ischemic heart disease, nonfatal MI, and coronary revascularization).
Results showed that in models based on conventional risk factors estimating risk of heart disease of above or below 5% in 10 years, adding remnant cholesterol at levels above the 95th percentile, appropriately reclassified 23% of individuals who had an MI and 21% of individuals who had an ischemic heart disease event.
Using remnant cholesterol levels above the 75th percentile appropriately reclassified 10% of those who had an MI and 8% of those who had an ischemic heart disease event. No events were reclassified incorrectly.
Using measurements of remnant cholesterol also improved reclassification of individuals with heart disease risk above or below 7.5% or 10% in 10 years.
When reclassifications were combined from below to above 5%, 7.5%, and 10% risk of events, 42% of individuals with MI and 41% with ischemic heart disease events were reclassified appropriately.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the study in JACC, Peter Wilson, MD, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, and Alan Remaley, MD, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, say these findings rekindle interest in atherogenic nonfasting lipid measurements and emphasize an important role for elevated nonfasting remnant cholesterol as a value-added predictor of ischemic events.
The editorialists note that both fasting and nonfasting lipid values provide useful information for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk estimation, and elevated nonfasting remnant cholesterol appears to help identify persons at greater risk for an initial cardiovascular ischemic event.
They add that very elevated levels (above the 75th percentile) of nonfasting remnant cholesterol deserve further evaluation as a potentially valuable “modifier of ASCVD risk,” and replication of the results could move these findings forward to potentially improve prognostication and care for patients at risk for ischemic heart disease events.
An indirect measure of triglycerides
Dr. Wilson explained that remnant cholesterol is an indirect measure of triglycerides beyond LDL levels, and it is thus including a new lipid measurement in risk prediction.
“We are completely focused on LDL cholesterol,” he said. “This opens it up a bit by adding in another measure that takes into account triglycerides as well as LDL.”
He also pointed out that use of a nonfasting sample is another advantage of measuring remnant cholesterol.
“An accurate measure of LDL needs a fasting sample, which is a nuisance, whereas remnant cholesterol can be measured in a nonfasting blood sample, so it is more convenient,” Dr. Wilson said.
While this study shows this measure is helpful for risk prediction in the primary prevention population, Dr. Wilson believes remnant cholesterol could be most useful in helping to guide further medication choice in patients who are already taking statins.
“Statins mainly target LDL, but if we can also measure nonfasting triglycerides this will be helpful. It may help us select some patients who may need a different type of drug to use in addition to statins that lowers triglycerides,” he said.
This work was supported by the Global Excellence Programme, the Research Fund for the Capital Region of Denmark, the Japanese College of Cardiology Overseas Research Fellowship, and the Scandinavia Japan Sasakawa Foundation. Mr. Nordestgaard has reported consultancies or talks sponsored by AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Regeneron, Akcea, Amgen, Amarin, Kowa, Denka, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Esperion, and Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Doi has reported talks sponsored by MSD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study suggests.
The study, which followed almost 42,000 Danish individuals without a history of ischemic cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or statin use for more than 10 years, found that elevated remnant cholesterol appropriately reclassified up to 40% of those who later experienced myocardial infarction and ischemic heart disease.
“The clinical implications of our study include that doctors and patients should be aware of remnant cholesterol levels to prevent future risk of MI and ischemic heart disease,” the authors conclude.
They suggest that the development of a cardiovascular risk algorithm, including remnant cholesterol together with LDL cholesterol, would help to better identify high-risk individuals who could be candidates for statins in a primary prevention setting.
They note that physicians are encouraged to evaluate non-HDL cholesterol and/or apolipoprotein B rather than LDL cholesterol and certainly not yet remnant cholesterol, possibly because of the limited availability of remnant cholesterol values in some parts of the world.
However, they point out that remnant cholesterol can be calculated with a standard lipid profile without additional cost, which is currently already the standard procedure in the greater Copenhagen area.
“This means that the use of remnant cholesterol is easy to introduce into daily clinical practice,” they say.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors, Takahito Doi, MD, Anne Langsted, MD, and Børge Nordestgaard, from Copenhagen University Hospital, Denmark, explain that remnant cholesterol is total cholesterol minus LDL-cholesterol minus HDL-cholesterol and includes the cholesterol content of the triglyceride-rich very-low-density lipoproteins, intermediate-density lipoproteins, and chylomicron remnants in the nonfasting state.
“When these particles enter the arterial wall, they are taken up by macrophages to produce foam cells, and therefore elevated remnant cholesterol likely enhance accumulation of cholesterol in the arterial wall, leading to progression of atherosclerosis and in consequence ischemic heart disease,” they note.
They point out that most guidelines for assessment of the 10-year risk of ischemic heart and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease include levels of total and HDL cholesterol, but remnant cholesterol levels are not included.
They conducted the current study to investigate whether elevated remnant cholesterol would lead to appropriate reclassification of individuals who later experienced MI or ischemic heart disease.
The researchers analyzed data from the Copenhagen General Population Study, which recruited individuals from the White Danish general population from 2003-2015 and followed them until 2018. Information on lifestyle, health, and medication, including statin therapy, was obtained through a questionnaire, and participants underwent physical examinations and had nonfasting blood samples drawn for biochemical measurements.
For the current study, they included 41,928 individuals aged 40-100 years enrolled before 2009 without a history of ischemic cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and statin use at baseline. The median follow-up time was 12 years. Information on diagnoses of MI and ischemic heart disease was collected from the national Danish Causes of Death Registry and all hospital admissions and diagnoses entered in the national Danish Patient Registry.
During the first 10 years of follow-up there were 1,063 MIs and 1,460 ischemic heart disease events (death of ischemic heart disease, nonfatal MI, and coronary revascularization).
Results showed that in models based on conventional risk factors estimating risk of heart disease of above or below 5% in 10 years, adding remnant cholesterol at levels above the 95th percentile, appropriately reclassified 23% of individuals who had an MI and 21% of individuals who had an ischemic heart disease event.
Using remnant cholesterol levels above the 75th percentile appropriately reclassified 10% of those who had an MI and 8% of those who had an ischemic heart disease event. No events were reclassified incorrectly.
Using measurements of remnant cholesterol also improved reclassification of individuals with heart disease risk above or below 7.5% or 10% in 10 years.
When reclassifications were combined from below to above 5%, 7.5%, and 10% risk of events, 42% of individuals with MI and 41% with ischemic heart disease events were reclassified appropriately.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the study in JACC, Peter Wilson, MD, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, and Alan Remaley, MD, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, say these findings rekindle interest in atherogenic nonfasting lipid measurements and emphasize an important role for elevated nonfasting remnant cholesterol as a value-added predictor of ischemic events.
The editorialists note that both fasting and nonfasting lipid values provide useful information for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk estimation, and elevated nonfasting remnant cholesterol appears to help identify persons at greater risk for an initial cardiovascular ischemic event.
They add that very elevated levels (above the 75th percentile) of nonfasting remnant cholesterol deserve further evaluation as a potentially valuable “modifier of ASCVD risk,” and replication of the results could move these findings forward to potentially improve prognostication and care for patients at risk for ischemic heart disease events.
An indirect measure of triglycerides
Dr. Wilson explained that remnant cholesterol is an indirect measure of triglycerides beyond LDL levels, and it is thus including a new lipid measurement in risk prediction.
“We are completely focused on LDL cholesterol,” he said. “This opens it up a bit by adding in another measure that takes into account triglycerides as well as LDL.”
He also pointed out that use of a nonfasting sample is another advantage of measuring remnant cholesterol.
“An accurate measure of LDL needs a fasting sample, which is a nuisance, whereas remnant cholesterol can be measured in a nonfasting blood sample, so it is more convenient,” Dr. Wilson said.
While this study shows this measure is helpful for risk prediction in the primary prevention population, Dr. Wilson believes remnant cholesterol could be most useful in helping to guide further medication choice in patients who are already taking statins.
“Statins mainly target LDL, but if we can also measure nonfasting triglycerides this will be helpful. It may help us select some patients who may need a different type of drug to use in addition to statins that lowers triglycerides,” he said.
This work was supported by the Global Excellence Programme, the Research Fund for the Capital Region of Denmark, the Japanese College of Cardiology Overseas Research Fellowship, and the Scandinavia Japan Sasakawa Foundation. Mr. Nordestgaard has reported consultancies or talks sponsored by AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Regeneron, Akcea, Amgen, Amarin, Kowa, Denka, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Esperion, and Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Doi has reported talks sponsored by MSD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves setmelanotide for obesity in Bardet-Biedl syndrome
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a supplemental indication for setmelanotide (Imcivree, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals) injection for chronic weight management in adults and pediatric patients age 6 and older with obesity due to Bardet-Biedl Syndrome (BBS).
Setmelanotide, a melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) agonist, is the first FDA-approved therapy for BBS, a rare genetic disorder that impairs a hunger signal along the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) pathway.
BBS affects an estimated 1,500-2,500 people in the United States.
Individuals with BBS typically have obesity that starts at age 1 along with insatiable hunger (hyperphagia). Available weight management options are generally unsuccessful.
Other symptoms may include retinal degeneration, reduced kidney function, or extra digits of the hands or feet.
Setmelanotide received priority review, orphan drug designation, and breakthrough designation for this new indication.
As previously reported, in November 2020, the FDA approved setmelanotide for weight management in adults and children as young as 6 years with obesity due to proopiomelanocortin (POMC), proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (PCSK1), or leptin receptor (LEPR) deficiency confirmed by genetic testing – who also have impaired hunger signaling from the brain.
These individuals have a normal weight at birth but develop persistent, severe obesity within months due to hyperphagia.
The FDA approval of Imcivree for BBS “represents a significant milestone for Rhythm [Pharmaceuticals], validating our strategy of developing Imcivree for people with hyperphagia and severe obesity caused by rare MC4R-pathway diseases and allowing us to provide our precision therapy to an established community of patients living with BBS and their families who are eagerly awaiting a new treatment option,” said David Meeker, MD, chair, president and CEO of Rhythm, in a press release.
Safety, effectiveness in 66-week trial in 44 patients
The safety and effectiveness of setmelanotidewas evaluated in a 66-week phase 3 clinical trial that enrolled 44 patients age 6 and older who had a diagnosis of BBS and obesity – defined as a body mass index greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2 or greater than or equal to 97th percentile for pediatric patients.
After an initial 14-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment period, patients entered a 52-week, open-label period.
The trial met its primary endpoint and all key secondary endpoints, with statistically significant reductions in weight and hunger at 52 weeks on therapy.
- After 52 weeks of treatment, patients taking setmelanotide lost, on average, 7.9% of their initial BMI.
- 61% of patients lost 5% or more of their initial BMI, and 39% lost 10% or more of their initial BMI.
- In the 14-week, placebo-controlled treatment, on average, BMI dropped by 4.6% in the 22 patients treated with the study drug and dropped 0.1% in the 22 patients treated with placebo.
- At 52 weeks, the 14 patients aged 12 and older who were able to self-report their hunger had a significant –2.1 mean change in hunger score.
Setmelanotide is associated with the following warnings and precautions:
- Spontaneous penile erections in males and sexual adverse reactions in females. Instruct males with erection lasting longer than 4 hours to seek emergency medical attention.
- Depression and suicidal ideation. Monitor patients for new onset or worsening depression or suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Consider discontinuing the drug if patients have suicidal thoughts or behaviors or clinically significant or persistent depression symptoms.
- Skin pigmentation and darkening of preexisting nevi (moles). Examine skin before and during treatment.
- Setmelanotide is not approved for use in neonates or infants. Serious and fatal adverse reactions including “gasping syndrome” can occur in neonates and low-birth-weight infants treated with benzyl alcohol-preserved drugs.
The most common adverse reactions (with an incidence greater than or equal to 20%) included skin hyperpigmentation, injection site reactions, nausea, headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, depression, and spontaneous penile erection.
The FDA did not approve the company’s supplemental new drug application for setmelanotide in Alström syndrome.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a supplemental indication for setmelanotide (Imcivree, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals) injection for chronic weight management in adults and pediatric patients age 6 and older with obesity due to Bardet-Biedl Syndrome (BBS).
Setmelanotide, a melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) agonist, is the first FDA-approved therapy for BBS, a rare genetic disorder that impairs a hunger signal along the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) pathway.
BBS affects an estimated 1,500-2,500 people in the United States.
Individuals with BBS typically have obesity that starts at age 1 along with insatiable hunger (hyperphagia). Available weight management options are generally unsuccessful.
Other symptoms may include retinal degeneration, reduced kidney function, or extra digits of the hands or feet.
Setmelanotide received priority review, orphan drug designation, and breakthrough designation for this new indication.
As previously reported, in November 2020, the FDA approved setmelanotide for weight management in adults and children as young as 6 years with obesity due to proopiomelanocortin (POMC), proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (PCSK1), or leptin receptor (LEPR) deficiency confirmed by genetic testing – who also have impaired hunger signaling from the brain.
These individuals have a normal weight at birth but develop persistent, severe obesity within months due to hyperphagia.
The FDA approval of Imcivree for BBS “represents a significant milestone for Rhythm [Pharmaceuticals], validating our strategy of developing Imcivree for people with hyperphagia and severe obesity caused by rare MC4R-pathway diseases and allowing us to provide our precision therapy to an established community of patients living with BBS and their families who are eagerly awaiting a new treatment option,” said David Meeker, MD, chair, president and CEO of Rhythm, in a press release.
Safety, effectiveness in 66-week trial in 44 patients
The safety and effectiveness of setmelanotidewas evaluated in a 66-week phase 3 clinical trial that enrolled 44 patients age 6 and older who had a diagnosis of BBS and obesity – defined as a body mass index greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2 or greater than or equal to 97th percentile for pediatric patients.
After an initial 14-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment period, patients entered a 52-week, open-label period.
The trial met its primary endpoint and all key secondary endpoints, with statistically significant reductions in weight and hunger at 52 weeks on therapy.
- After 52 weeks of treatment, patients taking setmelanotide lost, on average, 7.9% of their initial BMI.
- 61% of patients lost 5% or more of their initial BMI, and 39% lost 10% or more of their initial BMI.
- In the 14-week, placebo-controlled treatment, on average, BMI dropped by 4.6% in the 22 patients treated with the study drug and dropped 0.1% in the 22 patients treated with placebo.
- At 52 weeks, the 14 patients aged 12 and older who were able to self-report their hunger had a significant –2.1 mean change in hunger score.
Setmelanotide is associated with the following warnings and precautions:
- Spontaneous penile erections in males and sexual adverse reactions in females. Instruct males with erection lasting longer than 4 hours to seek emergency medical attention.
- Depression and suicidal ideation. Monitor patients for new onset or worsening depression or suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Consider discontinuing the drug if patients have suicidal thoughts or behaviors or clinically significant or persistent depression symptoms.
- Skin pigmentation and darkening of preexisting nevi (moles). Examine skin before and during treatment.
- Setmelanotide is not approved for use in neonates or infants. Serious and fatal adverse reactions including “gasping syndrome” can occur in neonates and low-birth-weight infants treated with benzyl alcohol-preserved drugs.
The most common adverse reactions (with an incidence greater than or equal to 20%) included skin hyperpigmentation, injection site reactions, nausea, headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, depression, and spontaneous penile erection.
The FDA did not approve the company’s supplemental new drug application for setmelanotide in Alström syndrome.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a supplemental indication for setmelanotide (Imcivree, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals) injection for chronic weight management in adults and pediatric patients age 6 and older with obesity due to Bardet-Biedl Syndrome (BBS).
Setmelanotide, a melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) agonist, is the first FDA-approved therapy for BBS, a rare genetic disorder that impairs a hunger signal along the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) pathway.
BBS affects an estimated 1,500-2,500 people in the United States.
Individuals with BBS typically have obesity that starts at age 1 along with insatiable hunger (hyperphagia). Available weight management options are generally unsuccessful.
Other symptoms may include retinal degeneration, reduced kidney function, or extra digits of the hands or feet.
Setmelanotide received priority review, orphan drug designation, and breakthrough designation for this new indication.
As previously reported, in November 2020, the FDA approved setmelanotide for weight management in adults and children as young as 6 years with obesity due to proopiomelanocortin (POMC), proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (PCSK1), or leptin receptor (LEPR) deficiency confirmed by genetic testing – who also have impaired hunger signaling from the brain.
These individuals have a normal weight at birth but develop persistent, severe obesity within months due to hyperphagia.
The FDA approval of Imcivree for BBS “represents a significant milestone for Rhythm [Pharmaceuticals], validating our strategy of developing Imcivree for people with hyperphagia and severe obesity caused by rare MC4R-pathway diseases and allowing us to provide our precision therapy to an established community of patients living with BBS and their families who are eagerly awaiting a new treatment option,” said David Meeker, MD, chair, president and CEO of Rhythm, in a press release.
Safety, effectiveness in 66-week trial in 44 patients
The safety and effectiveness of setmelanotidewas evaluated in a 66-week phase 3 clinical trial that enrolled 44 patients age 6 and older who had a diagnosis of BBS and obesity – defined as a body mass index greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2 or greater than or equal to 97th percentile for pediatric patients.
After an initial 14-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment period, patients entered a 52-week, open-label period.
The trial met its primary endpoint and all key secondary endpoints, with statistically significant reductions in weight and hunger at 52 weeks on therapy.
- After 52 weeks of treatment, patients taking setmelanotide lost, on average, 7.9% of their initial BMI.
- 61% of patients lost 5% or more of their initial BMI, and 39% lost 10% or more of their initial BMI.
- In the 14-week, placebo-controlled treatment, on average, BMI dropped by 4.6% in the 22 patients treated with the study drug and dropped 0.1% in the 22 patients treated with placebo.
- At 52 weeks, the 14 patients aged 12 and older who were able to self-report their hunger had a significant –2.1 mean change in hunger score.
Setmelanotide is associated with the following warnings and precautions:
- Spontaneous penile erections in males and sexual adverse reactions in females. Instruct males with erection lasting longer than 4 hours to seek emergency medical attention.
- Depression and suicidal ideation. Monitor patients for new onset or worsening depression or suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Consider discontinuing the drug if patients have suicidal thoughts or behaviors or clinically significant or persistent depression symptoms.
- Skin pigmentation and darkening of preexisting nevi (moles). Examine skin before and during treatment.
- Setmelanotide is not approved for use in neonates or infants. Serious and fatal adverse reactions including “gasping syndrome” can occur in neonates and low-birth-weight infants treated with benzyl alcohol-preserved drugs.
The most common adverse reactions (with an incidence greater than or equal to 20%) included skin hyperpigmentation, injection site reactions, nausea, headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, depression, and spontaneous penile erection.
The FDA did not approve the company’s supplemental new drug application for setmelanotide in Alström syndrome.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heart failure: Medicare cost sharing may put quadruple therapy out of reach
Out-of-pocket (OOP) costs for Medicare enrollees receiving quadruple drug therapy for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction were “substantially higher than regimens limited to generically available medications,” according to a new analysis of prescription drug plans.
“Despite the clinical benefit of quadruple therapy” consisting of beta-blockers, angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, “coverage was restricted primarily through cost sharing, and estimated annual OOP costs for beneficiaries were [over $2,000] per year under most plans,” wrote Kamil F. Faridi, MD, and associates. The findings were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.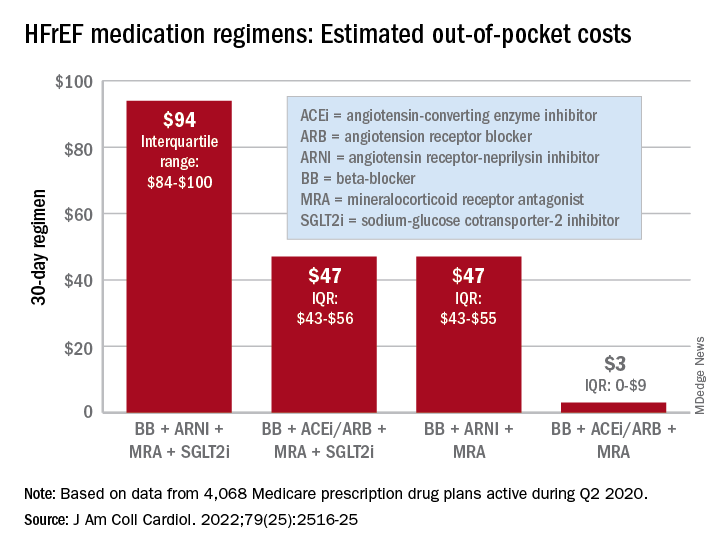
For just 1 month of quadruple drug therapy for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), the estimated median OOP cost was $94 for individuals covered by a Medicare prescription drug plan during the second quarter of 2020, with the majority coming from the ARNI (median, $47) and the SGLT2 inhibitor (median, $45). Alternative HFrEF regimens were significantly less costly, ranging from $3 to $47 OOP, the investigators reported.
Almost all of the 4,068 plans participating in Medicare at that time covered quadruple therapy for HFrEF, but more than 99% restricted coverage by instituting cost sharing for medications at tier level 3 and above on the drug formularies. Such restrictions for ARNIs and SGLT2 inhibitors “might not be readily apparent to prescribing physicians,” wrote Dr. Faridi of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and associates.
Other methods of regulating coverage were less common. Prior authorization of ARNIs was invoked by about a quarter of the plans, but none required authorization for any of the other drugs involved, and few plans used step therapy-requirements involving lower-cost alternatives, they noted.
“The use of cost sharing restricts access through high OOP costs for patients. Furthermore, these policies likely disadvantage relatively poorer patients (although the poorest Medicare patients will tend to be dual-enrolled in Medicaid and protected from cost sharing),” Jason H. Wasfy, MD, and Anna C. O’Kelly, MD, said in an accompanying editorial comment .
Since acceptable cost-effectiveness has been demonstrated for dapagliflozin, an SGLT1 inhibitor, and for the ARNIs, and because these medications have no generic equivalents, health plans should “use the discretion they have under Medicare Part D to reduce cost sharing for patients with HFrEF,” Dr. Wasfy and Dr. O’Kelly wrote, adding that the current study “demonstrates that without consensus on cost effectiveness from the societal perspective, costs can be imposed directly on patients in ways that slow uptake of cost-effective drugs.”
Data for all Medicare Advantage plans (n = 3,167) and standalone Part D plans (n = 901) came from the Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Formulary and Pricing Information Files. Annual OOP costs were estimated “using each phase of a 2020 Medicare part D standard benefit,” including deductible, standard coverage, coverage gap, and catastrophic coverage, the investigators explained.
Dr. Faridi and associates did not report any direct funding sources for their study. Dr Faridi received a grant from the National Institutes of Health outside the scope of the present work, and other investigators disclosed ties to the Food and Drug Administration, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, Cytokinetics, and the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review.
Dr. Wasfy is supported by the American Heart Association and has received consulting fees from Pfizer and honoraria from the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review. Dr. O’Kelly has no relevant disclosures.
Out-of-pocket (OOP) costs for Medicare enrollees receiving quadruple drug therapy for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction were “substantially higher than regimens limited to generically available medications,” according to a new analysis of prescription drug plans.
“Despite the clinical benefit of quadruple therapy” consisting of beta-blockers, angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, “coverage was restricted primarily through cost sharing, and estimated annual OOP costs for beneficiaries were [over $2,000] per year under most plans,” wrote Kamil F. Faridi, MD, and associates. The findings were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
For just 1 month of quadruple drug therapy for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), the estimated median OOP cost was $94 for individuals covered by a Medicare prescription drug plan during the second quarter of 2020, with the majority coming from the ARNI (median, $47) and the SGLT2 inhibitor (median, $45). Alternative HFrEF regimens were significantly less costly, ranging from $3 to $47 OOP, the investigators reported.
Almost all of the 4,068 plans participating in Medicare at that time covered quadruple therapy for HFrEF, but more than 99% restricted coverage by instituting cost sharing for medications at tier level 3 and above on the drug formularies. Such restrictions for ARNIs and SGLT2 inhibitors “might not be readily apparent to prescribing physicians,” wrote Dr. Faridi of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and associates.
Other methods of regulating coverage were less common. Prior authorization of ARNIs was invoked by about a quarter of the plans, but none required authorization for any of the other drugs involved, and few plans used step therapy-requirements involving lower-cost alternatives, they noted.
“The use of cost sharing restricts access through high OOP costs for patients. Furthermore, these policies likely disadvantage relatively poorer patients (although the poorest Medicare patients will tend to be dual-enrolled in Medicaid and protected from cost sharing),” Jason H. Wasfy, MD, and Anna C. O’Kelly, MD, said in an accompanying editorial comment .
Since acceptable cost-effectiveness has been demonstrated for dapagliflozin, an SGLT1 inhibitor, and for the ARNIs, and because these medications have no generic equivalents, health plans should “use the discretion they have under Medicare Part D to reduce cost sharing for patients with HFrEF,” Dr. Wasfy and Dr. O’Kelly wrote, adding that the current study “demonstrates that without consensus on cost effectiveness from the societal perspective, costs can be imposed directly on patients in ways that slow uptake of cost-effective drugs.”
Data for all Medicare Advantage plans (n = 3,167) and standalone Part D plans (n = 901) came from the Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Formulary and Pricing Information Files. Annual OOP costs were estimated “using each phase of a 2020 Medicare part D standard benefit,” including deductible, standard coverage, coverage gap, and catastrophic coverage, the investigators explained.
Dr. Faridi and associates did not report any direct funding sources for their study. Dr Faridi received a grant from the National Institutes of Health outside the scope of the present work, and other investigators disclosed ties to the Food and Drug Administration, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, Cytokinetics, and the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review.
Dr. Wasfy is supported by the American Heart Association and has received consulting fees from Pfizer and honoraria from the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review. Dr. O’Kelly has no relevant disclosures.
Out-of-pocket (OOP) costs for Medicare enrollees receiving quadruple drug therapy for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction were “substantially higher than regimens limited to generically available medications,” according to a new analysis of prescription drug plans.
“Despite the clinical benefit of quadruple therapy” consisting of beta-blockers, angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, “coverage was restricted primarily through cost sharing, and estimated annual OOP costs for beneficiaries were [over $2,000] per year under most plans,” wrote Kamil F. Faridi, MD, and associates. The findings were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
For just 1 month of quadruple drug therapy for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), the estimated median OOP cost was $94 for individuals covered by a Medicare prescription drug plan during the second quarter of 2020, with the majority coming from the ARNI (median, $47) and the SGLT2 inhibitor (median, $45). Alternative HFrEF regimens were significantly less costly, ranging from $3 to $47 OOP, the investigators reported.
Almost all of the 4,068 plans participating in Medicare at that time covered quadruple therapy for HFrEF, but more than 99% restricted coverage by instituting cost sharing for medications at tier level 3 and above on the drug formularies. Such restrictions for ARNIs and SGLT2 inhibitors “might not be readily apparent to prescribing physicians,” wrote Dr. Faridi of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and associates.
Other methods of regulating coverage were less common. Prior authorization of ARNIs was invoked by about a quarter of the plans, but none required authorization for any of the other drugs involved, and few plans used step therapy-requirements involving lower-cost alternatives, they noted.
“The use of cost sharing restricts access through high OOP costs for patients. Furthermore, these policies likely disadvantage relatively poorer patients (although the poorest Medicare patients will tend to be dual-enrolled in Medicaid and protected from cost sharing),” Jason H. Wasfy, MD, and Anna C. O’Kelly, MD, said in an accompanying editorial comment .
Since acceptable cost-effectiveness has been demonstrated for dapagliflozin, an SGLT1 inhibitor, and for the ARNIs, and because these medications have no generic equivalents, health plans should “use the discretion they have under Medicare Part D to reduce cost sharing for patients with HFrEF,” Dr. Wasfy and Dr. O’Kelly wrote, adding that the current study “demonstrates that without consensus on cost effectiveness from the societal perspective, costs can be imposed directly on patients in ways that slow uptake of cost-effective drugs.”
Data for all Medicare Advantage plans (n = 3,167) and standalone Part D plans (n = 901) came from the Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Formulary and Pricing Information Files. Annual OOP costs were estimated “using each phase of a 2020 Medicare part D standard benefit,” including deductible, standard coverage, coverage gap, and catastrophic coverage, the investigators explained.
Dr. Faridi and associates did not report any direct funding sources for their study. Dr Faridi received a grant from the National Institutes of Health outside the scope of the present work, and other investigators disclosed ties to the Food and Drug Administration, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, Cytokinetics, and the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review.
Dr. Wasfy is supported by the American Heart Association and has received consulting fees from Pfizer and honoraria from the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review. Dr. O’Kelly has no relevant disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL Of the AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Can the ketogenic diet treat polycystic ovary syndrome?
MADRID – During the International Scientific Symposium “New Frontiers in Scientific Research” that recently took place in Barcelona, specialists analyzed the role of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet. This analysis was in relation to three comorbidities that have a higher incidence among overweight and obese patients: polycystic ovary syndrome, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and type 2 diabetes. The experts’ aim? To analyze and update the latest evidence on the benefits of this dietary choice.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Alessandra Gambineri, MD, PhD, associate professor at the department of medicine and surgery (DIMEC) at the University of Bologna, Italy, addressed the link between obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome, which she described as a chronic disease that affects about 10% of women of childbearing age and that presents diverse phenotypes with different characteristics.
“The pathophysiology of this syndrome is characterized by the interaction of three factors: androgen excess, adipose tissue dysfunction, and insulin resistance. These factors interact with each other and are expressed differently in each phenotype,” said Dr. Gambineri.
She indicated that adipose tissue dysfunction is central to this pathology. This centrality results from its association with secretions, such as free fatty acids, proinflammatory cytokines, certain adipokines that promote insulin resistance, glucocorticosteroids, androgens, and oxidative stress.
“Similarly, the oxidative stress that characterizes this syndrome is increasingly present in obese individuals,” said Dr. Gambineri. “This oxidative stress also produces ovary hypotoxicity that aggravates ovulatory function. In this context, the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet can be useful in several ways: weight reduction; promoting the loss of mainly visceral/abdominal fat; decreasing lipotoxicity; and improving inflammation, hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance.”
This was the path followed to carry out a study that aimed to analyze the effects of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on manifestations of polycystic ovary syndrome in the obesity phenotype. Dr. Gambineri presented its results.
“The objective was to compare the effects of a very-low-calorie ketogenic diet and the standard low-calorie (hypocaloric) diet as a control group,” she said. “The effects studied include body weight, insulin resistance, menstrual cycle, ovulation, ovarian morphology, and hyperandrogenism in a population of 30 obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and insulin resistance.”
Study participants had a diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome as defined by the National Institutes of Health criteria and were aged 18-45 years. These women were randomly assigned to two groups of equal size: experimental (very-low-calorie ketogenic diet) and control (hypocaloric diet). “The women assigned to the experimental group followed the ketogenic stage for eight weeks and then moved to the second, low-calorie diet phase for an additional eight weeks, while those in the control group (hypocaloric diet) followed the low-calorie diet for all 16 weeks.”
The primary outcomes were changes in weight and body composition, specifically fat mass and lean mass, measured by bioimpedance. “The changes observed in the following aspects were considered secondary outcomes: abdominal fat distribution, metabolic parameters, ovulation, ovarian morphology, hirsutism, hyperandrogenism, psychological well-being, and psychological distress,” said Dr. Gambineri. “Any reduction in the ovarian stroma, the area where androgens are synthesized, was also analyzed.”
The study authors found that although BMI decreased in both groups, this reduction was greater in the group that followed the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet. Significant weight loss was observed in both groups, 12.4 kg versus 4.7 kg. Significant differences were also observed in waist circumference (−8.1% in the experimental group vs. −2.2% in the control group), fat mass (−15.1% vs. −8.5%), and free testosterone (−30.3% vs. +10.6%). Only the experimental group saw a reduction in insulin.
“A key point regarding hyperandrogenism, especially regarding what’s referred to as free testosterone, there was only a significant reduction in the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet group,” said Dr. Gambineri. “This reduction was especially evident in the first part of the study, coinciding with the ketogenic period. The reason for this effect lies in the significant increase in the concentration of sex hormone-binding globulins, SHB6. Said globulins bind to the testosterone present in female blood, producing a reduction in free testosterone, a very important effect considering that this syndrome is an androgenic disorder. Furthermore, current treatments for polycystic ovary syndrome do not reduce free testosterone as much as this dietary approach does.”
For the specialist, among all these positive effects in these patients, perhaps most important is the notable improvement that occurs in ovulation. “At the beginning of the study, only 38.5% of the participants in the experimental group and 14.3% of those in the control group had ovulatory cycles. After the intervention, 84.6% managed to ovulate, compared to 35.7% who achieved this goal in the other group.”
Dr. Gambineri suggested that this method is “valid for reducing fat mass and rapidly improving hyperandrogenism and ovulatory dysfunction in women with obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome.”
Reversing type 2 diabetes?
Daniela Sofrà, MD, an endocrinologist specializing in diabetology at La Source Clinic, Lausanne, Switzerland, reviewed the current evidence on the role of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet in the management of type 2 diabetes.
“It’s time to rethink diabetes treatment and focus efforts on managing obesity as an associated factor,” she said. “One of the hypotheses being examined in this regard is the twin cycle, which postulates that type 2 diabetes is the result of excess fat in the liver. This in turn is associated with insulin resistance with pancreas dysfunction.”
Dr. Sofrà added that there is a study documenting for the first time the reversibility of the morphology of the diabetic pancreas after caloric restriction with the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet. “The reason for this effect is the use of visceral and intrahepatic fat, which can lead to the remission of the clinical manifestation of type 2 diabetes, understanding as such the definition made by the American Diabetes Association: glycosylated hemoglobin < 6.5% without pharmacological therapy.”
Specifically, the results of this research showed that after following the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet and achieving a 15% weight loss (mean weight loss of the participants), liver glucose levels returned to normal levels within 7 days. Beta cell function returned to near normal within 8 weeks.
“Subsequent studies have shown the durability of remission of type 2 diabetes, thanks to the reactivation of the insulin-secreting function of beta cells that had become dedifferentiated in the face of chronic nutrient excess. Specifically, 6 out of 10 patients maintained glycosylated hemoglobin < 6% after 6 months without the need for pharmacological therapy,” Dr. Sofrà added.
Likewise, she highlighted that the probability of achieving remission is mainly determined by the duration of the disease. “The years with diabetes are one of the main predictors of the response that the patient will have with this dietary intervention. Studies have shown that remission is possible in patients with diabetes for less than 6 years, although there are other projects that indicate that it can be achieved with up to 10 years’ duration.”
Based on these data, Dr. Sofrà emphasized the pleiotropic effects of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on glycemic control, favoring the possible remission of diabetes or the reduction of drugs, as well as the reduction of the HOMA-IR index (insulin resistance) and waist circumference in people with type 2 diabetes.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
The third comorbidity of obesity that may benefit from the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet is hepatic steatosis, or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, said Hardy Walle, MD, an internal medicine specialist and director/founder of the Bodymed center, Kirkel, Germany, and one of the authors of this research.
“Recent research shows that ectopic fat and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease could be considered a cause, or at least one of the causes, of most of the diseases that affect the population as a consequence of overweight and obesity,” said Dr. Walle. “Some authors have stated that without fatty liver, there is no type 2 diabetes.”
Dr. Walle pointed out that between 30% and 40% of the adult population has nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, a percentage that increases considerably in people with obesity, reaching 70% prevalence and increasing, in the case of type 2 diabetes, to almost 90%. “Even normal weight does not rule out fatty liver; in fact, about 15% of people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are not overweight.”
In a setting where there are no approved drugs for the treatment of fatty liver (the current standard approach focuses on lifestyle interventions), a short-term hypocaloric diet (or liver fasting) is considered an effective method for management of this pathology. This principle was demonstrated by a study by the Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany, that Dr. Walle used to illustrate this statement.
“The participants (60 patients with hepatic steatosis) followed a hypocaloric diet (less than 1,000 kcal/day) for 14 days with a formula rich in protein and fiber specially developed for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. A fibroscan was then performed with controlled attenuation parameter measurement to quantify fatty liver disease. The results showed not only a significant improvement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease parameters but also a marked improvement in all relevant metabolic parameters (serum lipids, liver enzymes),” explained Dr. Walle.
“This evidence leads us to affirm that the concept of hepatic fasting (by means of a hypocaloric diet) marks a point of reference for a future treatment approach for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” he concluded.
The study that Dr. Gambineri presented was carried out with the collaboration of the Pronokal Group (Nestlé Health Science). Dr. Gambineri, Dr. Sofrà, and Dr. Walle disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID – During the International Scientific Symposium “New Frontiers in Scientific Research” that recently took place in Barcelona, specialists analyzed the role of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet. This analysis was in relation to three comorbidities that have a higher incidence among overweight and obese patients: polycystic ovary syndrome, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and type 2 diabetes. The experts’ aim? To analyze and update the latest evidence on the benefits of this dietary choice.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Alessandra Gambineri, MD, PhD, associate professor at the department of medicine and surgery (DIMEC) at the University of Bologna, Italy, addressed the link between obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome, which she described as a chronic disease that affects about 10% of women of childbearing age and that presents diverse phenotypes with different characteristics.
“The pathophysiology of this syndrome is characterized by the interaction of three factors: androgen excess, adipose tissue dysfunction, and insulin resistance. These factors interact with each other and are expressed differently in each phenotype,” said Dr. Gambineri.
She indicated that adipose tissue dysfunction is central to this pathology. This centrality results from its association with secretions, such as free fatty acids, proinflammatory cytokines, certain adipokines that promote insulin resistance, glucocorticosteroids, androgens, and oxidative stress.
“Similarly, the oxidative stress that characterizes this syndrome is increasingly present in obese individuals,” said Dr. Gambineri. “This oxidative stress also produces ovary hypotoxicity that aggravates ovulatory function. In this context, the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet can be useful in several ways: weight reduction; promoting the loss of mainly visceral/abdominal fat; decreasing lipotoxicity; and improving inflammation, hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance.”
This was the path followed to carry out a study that aimed to analyze the effects of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on manifestations of polycystic ovary syndrome in the obesity phenotype. Dr. Gambineri presented its results.
“The objective was to compare the effects of a very-low-calorie ketogenic diet and the standard low-calorie (hypocaloric) diet as a control group,” she said. “The effects studied include body weight, insulin resistance, menstrual cycle, ovulation, ovarian morphology, and hyperandrogenism in a population of 30 obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and insulin resistance.”
Study participants had a diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome as defined by the National Institutes of Health criteria and were aged 18-45 years. These women were randomly assigned to two groups of equal size: experimental (very-low-calorie ketogenic diet) and control (hypocaloric diet). “The women assigned to the experimental group followed the ketogenic stage for eight weeks and then moved to the second, low-calorie diet phase for an additional eight weeks, while those in the control group (hypocaloric diet) followed the low-calorie diet for all 16 weeks.”
The primary outcomes were changes in weight and body composition, specifically fat mass and lean mass, measured by bioimpedance. “The changes observed in the following aspects were considered secondary outcomes: abdominal fat distribution, metabolic parameters, ovulation, ovarian morphology, hirsutism, hyperandrogenism, psychological well-being, and psychological distress,” said Dr. Gambineri. “Any reduction in the ovarian stroma, the area where androgens are synthesized, was also analyzed.”
The study authors found that although BMI decreased in both groups, this reduction was greater in the group that followed the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet. Significant weight loss was observed in both groups, 12.4 kg versus 4.7 kg. Significant differences were also observed in waist circumference (−8.1% in the experimental group vs. −2.2% in the control group), fat mass (−15.1% vs. −8.5%), and free testosterone (−30.3% vs. +10.6%). Only the experimental group saw a reduction in insulin.
“A key point regarding hyperandrogenism, especially regarding what’s referred to as free testosterone, there was only a significant reduction in the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet group,” said Dr. Gambineri. “This reduction was especially evident in the first part of the study, coinciding with the ketogenic period. The reason for this effect lies in the significant increase in the concentration of sex hormone-binding globulins, SHB6. Said globulins bind to the testosterone present in female blood, producing a reduction in free testosterone, a very important effect considering that this syndrome is an androgenic disorder. Furthermore, current treatments for polycystic ovary syndrome do not reduce free testosterone as much as this dietary approach does.”
For the specialist, among all these positive effects in these patients, perhaps most important is the notable improvement that occurs in ovulation. “At the beginning of the study, only 38.5% of the participants in the experimental group and 14.3% of those in the control group had ovulatory cycles. After the intervention, 84.6% managed to ovulate, compared to 35.7% who achieved this goal in the other group.”
Dr. Gambineri suggested that this method is “valid for reducing fat mass and rapidly improving hyperandrogenism and ovulatory dysfunction in women with obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome.”
Reversing type 2 diabetes?
Daniela Sofrà, MD, an endocrinologist specializing in diabetology at La Source Clinic, Lausanne, Switzerland, reviewed the current evidence on the role of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet in the management of type 2 diabetes.
“It’s time to rethink diabetes treatment and focus efforts on managing obesity as an associated factor,” she said. “One of the hypotheses being examined in this regard is the twin cycle, which postulates that type 2 diabetes is the result of excess fat in the liver. This in turn is associated with insulin resistance with pancreas dysfunction.”
Dr. Sofrà added that there is a study documenting for the first time the reversibility of the morphology of the diabetic pancreas after caloric restriction with the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet. “The reason for this effect is the use of visceral and intrahepatic fat, which can lead to the remission of the clinical manifestation of type 2 diabetes, understanding as such the definition made by the American Diabetes Association: glycosylated hemoglobin < 6.5% without pharmacological therapy.”
Specifically, the results of this research showed that after following the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet and achieving a 15% weight loss (mean weight loss of the participants), liver glucose levels returned to normal levels within 7 days. Beta cell function returned to near normal within 8 weeks.
“Subsequent studies have shown the durability of remission of type 2 diabetes, thanks to the reactivation of the insulin-secreting function of beta cells that had become dedifferentiated in the face of chronic nutrient excess. Specifically, 6 out of 10 patients maintained glycosylated hemoglobin < 6% after 6 months without the need for pharmacological therapy,” Dr. Sofrà added.
Likewise, she highlighted that the probability of achieving remission is mainly determined by the duration of the disease. “The years with diabetes are one of the main predictors of the response that the patient will have with this dietary intervention. Studies have shown that remission is possible in patients with diabetes for less than 6 years, although there are other projects that indicate that it can be achieved with up to 10 years’ duration.”
Based on these data, Dr. Sofrà emphasized the pleiotropic effects of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on glycemic control, favoring the possible remission of diabetes or the reduction of drugs, as well as the reduction of the HOMA-IR index (insulin resistance) and waist circumference in people with type 2 diabetes.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
The third comorbidity of obesity that may benefit from the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet is hepatic steatosis, or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, said Hardy Walle, MD, an internal medicine specialist and director/founder of the Bodymed center, Kirkel, Germany, and one of the authors of this research.
“Recent research shows that ectopic fat and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease could be considered a cause, or at least one of the causes, of most of the diseases that affect the population as a consequence of overweight and obesity,” said Dr. Walle. “Some authors have stated that without fatty liver, there is no type 2 diabetes.”
Dr. Walle pointed out that between 30% and 40% of the adult population has nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, a percentage that increases considerably in people with obesity, reaching 70% prevalence and increasing, in the case of type 2 diabetes, to almost 90%. “Even normal weight does not rule out fatty liver; in fact, about 15% of people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are not overweight.”
In a setting where there are no approved drugs for the treatment of fatty liver (the current standard approach focuses on lifestyle interventions), a short-term hypocaloric diet (or liver fasting) is considered an effective method for management of this pathology. This principle was demonstrated by a study by the Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany, that Dr. Walle used to illustrate this statement.
“The participants (60 patients with hepatic steatosis) followed a hypocaloric diet (less than 1,000 kcal/day) for 14 days with a formula rich in protein and fiber specially developed for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. A fibroscan was then performed with controlled attenuation parameter measurement to quantify fatty liver disease. The results showed not only a significant improvement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease parameters but also a marked improvement in all relevant metabolic parameters (serum lipids, liver enzymes),” explained Dr. Walle.
“This evidence leads us to affirm that the concept of hepatic fasting (by means of a hypocaloric diet) marks a point of reference for a future treatment approach for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” he concluded.
The study that Dr. Gambineri presented was carried out with the collaboration of the Pronokal Group (Nestlé Health Science). Dr. Gambineri, Dr. Sofrà, and Dr. Walle disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID – During the International Scientific Symposium “New Frontiers in Scientific Research” that recently took place in Barcelona, specialists analyzed the role of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet. This analysis was in relation to three comorbidities that have a higher incidence among overweight and obese patients: polycystic ovary syndrome, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and type 2 diabetes. The experts’ aim? To analyze and update the latest evidence on the benefits of this dietary choice.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Alessandra Gambineri, MD, PhD, associate professor at the department of medicine and surgery (DIMEC) at the University of Bologna, Italy, addressed the link between obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome, which she described as a chronic disease that affects about 10% of women of childbearing age and that presents diverse phenotypes with different characteristics.
“The pathophysiology of this syndrome is characterized by the interaction of three factors: androgen excess, adipose tissue dysfunction, and insulin resistance. These factors interact with each other and are expressed differently in each phenotype,” said Dr. Gambineri.
She indicated that adipose tissue dysfunction is central to this pathology. This centrality results from its association with secretions, such as free fatty acids, proinflammatory cytokines, certain adipokines that promote insulin resistance, glucocorticosteroids, androgens, and oxidative stress.
“Similarly, the oxidative stress that characterizes this syndrome is increasingly present in obese individuals,” said Dr. Gambineri. “This oxidative stress also produces ovary hypotoxicity that aggravates ovulatory function. In this context, the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet can be useful in several ways: weight reduction; promoting the loss of mainly visceral/abdominal fat; decreasing lipotoxicity; and improving inflammation, hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance.”
This was the path followed to carry out a study that aimed to analyze the effects of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on manifestations of polycystic ovary syndrome in the obesity phenotype. Dr. Gambineri presented its results.
“The objective was to compare the effects of a very-low-calorie ketogenic diet and the standard low-calorie (hypocaloric) diet as a control group,” she said. “The effects studied include body weight, insulin resistance, menstrual cycle, ovulation, ovarian morphology, and hyperandrogenism in a population of 30 obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and insulin resistance.”
Study participants had a diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome as defined by the National Institutes of Health criteria and were aged 18-45 years. These women were randomly assigned to two groups of equal size: experimental (very-low-calorie ketogenic diet) and control (hypocaloric diet). “The women assigned to the experimental group followed the ketogenic stage for eight weeks and then moved to the second, low-calorie diet phase for an additional eight weeks, while those in the control group (hypocaloric diet) followed the low-calorie diet for all 16 weeks.”
The primary outcomes were changes in weight and body composition, specifically fat mass and lean mass, measured by bioimpedance. “The changes observed in the following aspects were considered secondary outcomes: abdominal fat distribution, metabolic parameters, ovulation, ovarian morphology, hirsutism, hyperandrogenism, psychological well-being, and psychological distress,” said Dr. Gambineri. “Any reduction in the ovarian stroma, the area where androgens are synthesized, was also analyzed.”
The study authors found that although BMI decreased in both groups, this reduction was greater in the group that followed the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet. Significant weight loss was observed in both groups, 12.4 kg versus 4.7 kg. Significant differences were also observed in waist circumference (−8.1% in the experimental group vs. −2.2% in the control group), fat mass (−15.1% vs. −8.5%), and free testosterone (−30.3% vs. +10.6%). Only the experimental group saw a reduction in insulin.
“A key point regarding hyperandrogenism, especially regarding what’s referred to as free testosterone, there was only a significant reduction in the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet group,” said Dr. Gambineri. “This reduction was especially evident in the first part of the study, coinciding with the ketogenic period. The reason for this effect lies in the significant increase in the concentration of sex hormone-binding globulins, SHB6. Said globulins bind to the testosterone present in female blood, producing a reduction in free testosterone, a very important effect considering that this syndrome is an androgenic disorder. Furthermore, current treatments for polycystic ovary syndrome do not reduce free testosterone as much as this dietary approach does.”
For the specialist, among all these positive effects in these patients, perhaps most important is the notable improvement that occurs in ovulation. “At the beginning of the study, only 38.5% of the participants in the experimental group and 14.3% of those in the control group had ovulatory cycles. After the intervention, 84.6% managed to ovulate, compared to 35.7% who achieved this goal in the other group.”
Dr. Gambineri suggested that this method is “valid for reducing fat mass and rapidly improving hyperandrogenism and ovulatory dysfunction in women with obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome.”
Reversing type 2 diabetes?
Daniela Sofrà, MD, an endocrinologist specializing in diabetology at La Source Clinic, Lausanne, Switzerland, reviewed the current evidence on the role of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet in the management of type 2 diabetes.
“It’s time to rethink diabetes treatment and focus efforts on managing obesity as an associated factor,” she said. “One of the hypotheses being examined in this regard is the twin cycle, which postulates that type 2 diabetes is the result of excess fat in the liver. This in turn is associated with insulin resistance with pancreas dysfunction.”
Dr. Sofrà added that there is a study documenting for the first time the reversibility of the morphology of the diabetic pancreas after caloric restriction with the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet. “The reason for this effect is the use of visceral and intrahepatic fat, which can lead to the remission of the clinical manifestation of type 2 diabetes, understanding as such the definition made by the American Diabetes Association: glycosylated hemoglobin < 6.5% without pharmacological therapy.”
Specifically, the results of this research showed that after following the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet and achieving a 15% weight loss (mean weight loss of the participants), liver glucose levels returned to normal levels within 7 days. Beta cell function returned to near normal within 8 weeks.
“Subsequent studies have shown the durability of remission of type 2 diabetes, thanks to the reactivation of the insulin-secreting function of beta cells that had become dedifferentiated in the face of chronic nutrient excess. Specifically, 6 out of 10 patients maintained glycosylated hemoglobin < 6% after 6 months without the need for pharmacological therapy,” Dr. Sofrà added.
Likewise, she highlighted that the probability of achieving remission is mainly determined by the duration of the disease. “The years with diabetes are one of the main predictors of the response that the patient will have with this dietary intervention. Studies have shown that remission is possible in patients with diabetes for less than 6 years, although there are other projects that indicate that it can be achieved with up to 10 years’ duration.”
Based on these data, Dr. Sofrà emphasized the pleiotropic effects of the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on glycemic control, favoring the possible remission of diabetes or the reduction of drugs, as well as the reduction of the HOMA-IR index (insulin resistance) and waist circumference in people with type 2 diabetes.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
The third comorbidity of obesity that may benefit from the very-low-calorie ketogenic diet is hepatic steatosis, or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, said Hardy Walle, MD, an internal medicine specialist and director/founder of the Bodymed center, Kirkel, Germany, and one of the authors of this research.
“Recent research shows that ectopic fat and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease could be considered a cause, or at least one of the causes, of most of the diseases that affect the population as a consequence of overweight and obesity,” said Dr. Walle. “Some authors have stated that without fatty liver, there is no type 2 diabetes.”
Dr. Walle pointed out that between 30% and 40% of the adult population has nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, a percentage that increases considerably in people with obesity, reaching 70% prevalence and increasing, in the case of type 2 diabetes, to almost 90%. “Even normal weight does not rule out fatty liver; in fact, about 15% of people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are not overweight.”
In a setting where there are no approved drugs for the treatment of fatty liver (the current standard approach focuses on lifestyle interventions), a short-term hypocaloric diet (or liver fasting) is considered an effective method for management of this pathology. This principle was demonstrated by a study by the Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany, that Dr. Walle used to illustrate this statement.
“The participants (60 patients with hepatic steatosis) followed a hypocaloric diet (less than 1,000 kcal/day) for 14 days with a formula rich in protein and fiber specially developed for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. A fibroscan was then performed with controlled attenuation parameter measurement to quantify fatty liver disease. The results showed not only a significant improvement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease parameters but also a marked improvement in all relevant metabolic parameters (serum lipids, liver enzymes),” explained Dr. Walle.
“This evidence leads us to affirm that the concept of hepatic fasting (by means of a hypocaloric diet) marks a point of reference for a future treatment approach for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” he concluded.
The study that Dr. Gambineri presented was carried out with the collaboration of the Pronokal Group (Nestlé Health Science). Dr. Gambineri, Dr. Sofrà, and Dr. Walle disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMA: Insurance should cover treatment for infertility caused by gender-affirming care
CHICAGO – Health insurance should cover treatment for infertility caused by gender-affirming medical interventions, the American Medical Association said June 13 at its House of Delegates meeting.
Speaking on behalf of the Medical Student Section, Justin Magrath, of Louisiana, said, “We as a section feel that these interventions should be considered as additional causes of iatrogenic infertility and be covered by insurance.”
Iatrogenic infertility is infertility caused by surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or other medically necessary treatment. The AMA voted June 13 to support including the phrase, “impaired fertility as a consequence of gender-affirming hormone therapy and gender-affirming surgery,” in that definition.
The AMA also supports access to fertility preservation services for people who undergo those treatments.
“I’ve had many friends who went through transitions and gender-affirming care and had no idea that these options were available and others who did know they were available but they were so expensive that they couldn’t access them,” said emergency medicine resident Sophia Spadafore, MD, delegate for the Resident and Fellow Section. “So while people might be able to access gender-affirming care, sometimes they have to make the decision between future fertility and having children and accessing this kind of lifesaving care that we support.”
The AMA already had policies that support insurance coverage of treatments for gender dysphoria and the right to seek fertility preservation services for people who undergo gender-affirming hormone therapy or surgery, but until this week, it had not addressed insurance coverage for preserving fertility in those cases.
“The transgender population already faces many barriers to care, such as provider discrimination, legal concerns, financial burden, and emotional cost,” Mr. Magrath said during a reference committee hearing on June 11. “We as a section ask our organization to continue to serve as an ally, providing equitable care for diverse populations and expanding coverage for medically necessary treatments.”
“I am a gender surgeon, so this is pretty important to me,” said Sean Figy, MD, of Nebraska, a delegate for the American Society for Reconstructive Microsurgery.
The original resolution included the words “medically necessary” when referring to gender-affirming treatments, and Dr. Figy expressed hesitancy about those words. An amendment removed them.
“I’ve seen that phrase weaponized against gender-nonconforming patients,” he said.
Ophthalmologist Charles Hickey, MD, of the Ohio delegation, spoke in favor of referral or of waiting to adopt the resolution.
“I think the different amendments being discussed here are evidence that this needs a more thorough and careful treatment than we can do at this point right now,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Health insurance should cover treatment for infertility caused by gender-affirming medical interventions, the American Medical Association said June 13 at its House of Delegates meeting.
Speaking on behalf of the Medical Student Section, Justin Magrath, of Louisiana, said, “We as a section feel that these interventions should be considered as additional causes of iatrogenic infertility and be covered by insurance.”
Iatrogenic infertility is infertility caused by surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or other medically necessary treatment. The AMA voted June 13 to support including the phrase, “impaired fertility as a consequence of gender-affirming hormone therapy and gender-affirming surgery,” in that definition.
The AMA also supports access to fertility preservation services for people who undergo those treatments.
“I’ve had many friends who went through transitions and gender-affirming care and had no idea that these options were available and others who did know they were available but they were so expensive that they couldn’t access them,” said emergency medicine resident Sophia Spadafore, MD, delegate for the Resident and Fellow Section. “So while people might be able to access gender-affirming care, sometimes they have to make the decision between future fertility and having children and accessing this kind of lifesaving care that we support.”
The AMA already had policies that support insurance coverage of treatments for gender dysphoria and the right to seek fertility preservation services for people who undergo gender-affirming hormone therapy or surgery, but until this week, it had not addressed insurance coverage for preserving fertility in those cases.
“The transgender population already faces many barriers to care, such as provider discrimination, legal concerns, financial burden, and emotional cost,” Mr. Magrath said during a reference committee hearing on June 11. “We as a section ask our organization to continue to serve as an ally, providing equitable care for diverse populations and expanding coverage for medically necessary treatments.”
“I am a gender surgeon, so this is pretty important to me,” said Sean Figy, MD, of Nebraska, a delegate for the American Society for Reconstructive Microsurgery.
The original resolution included the words “medically necessary” when referring to gender-affirming treatments, and Dr. Figy expressed hesitancy about those words. An amendment removed them.
“I’ve seen that phrase weaponized against gender-nonconforming patients,” he said.
Ophthalmologist Charles Hickey, MD, of the Ohio delegation, spoke in favor of referral or of waiting to adopt the resolution.
“I think the different amendments being discussed here are evidence that this needs a more thorough and careful treatment than we can do at this point right now,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Health insurance should cover treatment for infertility caused by gender-affirming medical interventions, the American Medical Association said June 13 at its House of Delegates meeting.
Speaking on behalf of the Medical Student Section, Justin Magrath, of Louisiana, said, “We as a section feel that these interventions should be considered as additional causes of iatrogenic infertility and be covered by insurance.”
Iatrogenic infertility is infertility caused by surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or other medically necessary treatment. The AMA voted June 13 to support including the phrase, “impaired fertility as a consequence of gender-affirming hormone therapy and gender-affirming surgery,” in that definition.
The AMA also supports access to fertility preservation services for people who undergo those treatments.
“I’ve had many friends who went through transitions and gender-affirming care and had no idea that these options were available and others who did know they were available but they were so expensive that they couldn’t access them,” said emergency medicine resident Sophia Spadafore, MD, delegate for the Resident and Fellow Section. “So while people might be able to access gender-affirming care, sometimes they have to make the decision between future fertility and having children and accessing this kind of lifesaving care that we support.”
The AMA already had policies that support insurance coverage of treatments for gender dysphoria and the right to seek fertility preservation services for people who undergo gender-affirming hormone therapy or surgery, but until this week, it had not addressed insurance coverage for preserving fertility in those cases.
“The transgender population already faces many barriers to care, such as provider discrimination, legal concerns, financial burden, and emotional cost,” Mr. Magrath said during a reference committee hearing on June 11. “We as a section ask our organization to continue to serve as an ally, providing equitable care for diverse populations and expanding coverage for medically necessary treatments.”
“I am a gender surgeon, so this is pretty important to me,” said Sean Figy, MD, of Nebraska, a delegate for the American Society for Reconstructive Microsurgery.
The original resolution included the words “medically necessary” when referring to gender-affirming treatments, and Dr. Figy expressed hesitancy about those words. An amendment removed them.
“I’ve seen that phrase weaponized against gender-nonconforming patients,” he said.
Ophthalmologist Charles Hickey, MD, of the Ohio delegation, spoke in favor of referral or of waiting to adopt the resolution.
“I think the different amendments being discussed here are evidence that this needs a more thorough and careful treatment than we can do at this point right now,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Employment and buyout agreements
. The most common question was, “Do I really need to go to the trouble and expense of negotiating them?” If you have more than one physician in your group, you absolutely do need written contracts for a variety of reasons, but mostly to avoid conflicts later on. The proverbial “handshake agreement” is worthless in a major business dispute; everyone loses in such situations except the lawyers and accountants.
Mergers and buy-ins were covered at some length in my two previous columns. If the arrangement is to be one of employer and employees rather than a merger of equal partners, you will need an employment agreement to cover duties, requirements, expectations, and benefits. They define how each practitioner/employee will be paid, along with paid time off, health insurance, expense allowances, and malpractice coverage, among other basics. The more that is spelled out in the employment agreement, the fewer disagreements you are likely to have down the road.
Many employment contracts include a “termination without cause” clause, which benefits both the practice and the practitioners. It allows a practice to terminate a new associate if it feels a mistake has been made, even if he or she has done nothing wrong. On the other hand, the newcomer has the option to terminate if a better offer arises, their spouse hates the area, or for any other reason.
Buyouts should be addressed in advance as well. Several recent correspondents told me they didn’t see the necessity of writing a buyout agreement, because they plan to eventually sell their practice, rendering any buyout conditions moot. But what happens if an associate dies, becomes permanently disabled, or abruptly decides to leave the practice? If you haven’t prepared for such eventualities, you could find yourself receiving a demand from your ex-partner (or surviving spouse) for immediate payment of that partner’s portion of the practice’s value. And your valuation of the practice is likely to be severely at odds with the other party’s. Meanwhile, remaining partners must cover all the practice’s expenses and deal with an increased patient load.
A buyout agreement avoids these problems by planning for such eventualities in advance. You must agree on how a buyout amount will be valued. As I’ve said in previous columns, I strongly advise using a formula, not a fixed amount. If a buyout is based on 15- or 20-year-old reimbursements, the buyout will have no relationship to what the partners are currently being paid. Likewise, any buyout calculated at “appraised value” is a problem, because the buyout amount remains a mystery until an appraisal is performed. If the appraised value ends up being too high, the remaining owners may refuse to pay it. Have an actuary create a formula, so that a buyout figure can be calculated at any time. This area, especially, is where you need experienced, competent legal advice.
To avoid surprises, any buyout should require ample notice (6-12 months is common) to allow time to rearrange finances and recruit a new provider. Vesting schedules, similar to those used in retirement plans, are also popular. If a partner leaves before a prescribed time period has elapsed – say, 20 years – the buyout is proportionally reduced.
Buyouts can also be useful when dealing with noncompete agreements, which are notoriously difficult (and expensive) to enforce. One solution is a buyout penalty; a departing partner can compete with his or her former practice, but at the cost of a substantially reduced buyout. This permits competition, but discourages it, and compensates the targeted practice.
Buyouts are also a potential solution to some buy-in issues. A new associate entering an established practice may not be able to contribute assets equal to existing partners’ stakes and may lack the cash necessary to make up the difference. One alternative is to agree that any inequalities will be compensated at the other end in buyout value. Those partners contributing more assets will receive larger buyouts than those contributing less.
As I’ve said many times, these are not negotiations to undertake on your own. Enlist the aid of a consultant or attorney (or both) with ample medical practice experience.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
. The most common question was, “Do I really need to go to the trouble and expense of negotiating them?” If you have more than one physician in your group, you absolutely do need written contracts for a variety of reasons, but mostly to avoid conflicts later on. The proverbial “handshake agreement” is worthless in a major business dispute; everyone loses in such situations except the lawyers and accountants.
Mergers and buy-ins were covered at some length in my two previous columns. If the arrangement is to be one of employer and employees rather than a merger of equal partners, you will need an employment agreement to cover duties, requirements, expectations, and benefits. They define how each practitioner/employee will be paid, along with paid time off, health insurance, expense allowances, and malpractice coverage, among other basics. The more that is spelled out in the employment agreement, the fewer disagreements you are likely to have down the road.
Many employment contracts include a “termination without cause” clause, which benefits both the practice and the practitioners. It allows a practice to terminate a new associate if it feels a mistake has been made, even if he or she has done nothing wrong. On the other hand, the newcomer has the option to terminate if a better offer arises, their spouse hates the area, or for any other reason.
Buyouts should be addressed in advance as well. Several recent correspondents told me they didn’t see the necessity of writing a buyout agreement, because they plan to eventually sell their practice, rendering any buyout conditions moot. But what happens if an associate dies, becomes permanently disabled, or abruptly decides to leave the practice? If you haven’t prepared for such eventualities, you could find yourself receiving a demand from your ex-partner (or surviving spouse) for immediate payment of that partner’s portion of the practice’s value. And your valuation of the practice is likely to be severely at odds with the other party’s. Meanwhile, remaining partners must cover all the practice’s expenses and deal with an increased patient load.
A buyout agreement avoids these problems by planning for such eventualities in advance. You must agree on how a buyout amount will be valued. As I’ve said in previous columns, I strongly advise using a formula, not a fixed amount. If a buyout is based on 15- or 20-year-old reimbursements, the buyout will have no relationship to what the partners are currently being paid. Likewise, any buyout calculated at “appraised value” is a problem, because the buyout amount remains a mystery until an appraisal is performed. If the appraised value ends up being too high, the remaining owners may refuse to pay it. Have an actuary create a formula, so that a buyout figure can be calculated at any time. This area, especially, is where you need experienced, competent legal advice.
To avoid surprises, any buyout should require ample notice (6-12 months is common) to allow time to rearrange finances and recruit a new provider. Vesting schedules, similar to those used in retirement plans, are also popular. If a partner leaves before a prescribed time period has elapsed – say, 20 years – the buyout is proportionally reduced.
Buyouts can also be useful when dealing with noncompete agreements, which are notoriously difficult (and expensive) to enforce. One solution is a buyout penalty; a departing partner can compete with his or her former practice, but at the cost of a substantially reduced buyout. This permits competition, but discourages it, and compensates the targeted practice.
Buyouts are also a potential solution to some buy-in issues. A new associate entering an established practice may not be able to contribute assets equal to existing partners’ stakes and may lack the cash necessary to make up the difference. One alternative is to agree that any inequalities will be compensated at the other end in buyout value. Those partners contributing more assets will receive larger buyouts than those contributing less.
As I’ve said many times, these are not negotiations to undertake on your own. Enlist the aid of a consultant or attorney (or both) with ample medical practice experience.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
. The most common question was, “Do I really need to go to the trouble and expense of negotiating them?” If you have more than one physician in your group, you absolutely do need written contracts for a variety of reasons, but mostly to avoid conflicts later on. The proverbial “handshake agreement” is worthless in a major business dispute; everyone loses in such situations except the lawyers and accountants.
Mergers and buy-ins were covered at some length in my two previous columns. If the arrangement is to be one of employer and employees rather than a merger of equal partners, you will need an employment agreement to cover duties, requirements, expectations, and benefits. They define how each practitioner/employee will be paid, along with paid time off, health insurance, expense allowances, and malpractice coverage, among other basics. The more that is spelled out in the employment agreement, the fewer disagreements you are likely to have down the road.
Many employment contracts include a “termination without cause” clause, which benefits both the practice and the practitioners. It allows a practice to terminate a new associate if it feels a mistake has been made, even if he or she has done nothing wrong. On the other hand, the newcomer has the option to terminate if a better offer arises, their spouse hates the area, or for any other reason.
Buyouts should be addressed in advance as well. Several recent correspondents told me they didn’t see the necessity of writing a buyout agreement, because they plan to eventually sell their practice, rendering any buyout conditions moot. But what happens if an associate dies, becomes permanently disabled, or abruptly decides to leave the practice? If you haven’t prepared for such eventualities, you could find yourself receiving a demand from your ex-partner (or surviving spouse) for immediate payment of that partner’s portion of the practice’s value. And your valuation of the practice is likely to be severely at odds with the other party’s. Meanwhile, remaining partners must cover all the practice’s expenses and deal with an increased patient load.
A buyout agreement avoids these problems by planning for such eventualities in advance. You must agree on how a buyout amount will be valued. As I’ve said in previous columns, I strongly advise using a formula, not a fixed amount. If a buyout is based on 15- or 20-year-old reimbursements, the buyout will have no relationship to what the partners are currently being paid. Likewise, any buyout calculated at “appraised value” is a problem, because the buyout amount remains a mystery until an appraisal is performed. If the appraised value ends up being too high, the remaining owners may refuse to pay it. Have an actuary create a formula, so that a buyout figure can be calculated at any time. This area, especially, is where you need experienced, competent legal advice.
To avoid surprises, any buyout should require ample notice (6-12 months is common) to allow time to rearrange finances and recruit a new provider. Vesting schedules, similar to those used in retirement plans, are also popular. If a partner leaves before a prescribed time period has elapsed – say, 20 years – the buyout is proportionally reduced.
Buyouts can also be useful when dealing with noncompete agreements, which are notoriously difficult (and expensive) to enforce. One solution is a buyout penalty; a departing partner can compete with his or her former practice, but at the cost of a substantially reduced buyout. This permits competition, but discourages it, and compensates the targeted practice.
Buyouts are also a potential solution to some buy-in issues. A new associate entering an established practice may not be able to contribute assets equal to existing partners’ stakes and may lack the cash necessary to make up the difference. One alternative is to agree that any inequalities will be compensated at the other end in buyout value. Those partners contributing more assets will receive larger buyouts than those contributing less.
As I’ve said many times, these are not negotiations to undertake on your own. Enlist the aid of a consultant or attorney (or both) with ample medical practice experience.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
Ultra-processed: Doctors debate whether putting this label on foods is useful
The NOVA system divides foods into “fresh or minimally processed,” such as strawberries or steel-cut oats; “processed culinary ingredients,” such as olive oil; “processed foods,” such as cheeses; and “ultra-processed foods.” UPFs are defined as “industrial formulations made by deconstructing natural food into its chemical constituents, modifying them and recombining them with additives into products liable to displace all other NOVA food groups.”
According to doctors who presented during the meeting, ultra-processed foods are drawing increased attention, because researchers have been examining them in National Institutes of Health–funded studies and journalists have been writing about them.
During the debate session at the meeting, some experts said that, with obesity and poor health skyrocketing, increased awareness and labeling of UPFs can only be a good thing. In contrast others noted at the meeting that the classification system that has come to be used for identifying UPFs – the NOVA Food Classification system – is too mushy, confusing, and, ultimately unhelpful.
Carlos Monteiro, MD, PhD, professor of nutrition and public health at the University of Sao Paolo, was part of the group favoring the NOVA system’s classifying certain foods as UPFs, during the debate. He drew attention to the extent to which the world’s population is getting its calories from UPFs.
Mexico and France get about 30% of calories from these foods. In Canada, it’s 48%. And in the United States, it’s 57%, Dr. Monteiro said.
Studies have found that UPFs, many of which are designed to be exceedingly flavorful and intended to replace consumption of unprocessed whole foods, lead to more overall energy intake, more added sugar in the diet, and less fiber and protein intake, he said.
To further support his arguments, Dr. Monteiro pointed to studies suggesting that it is not just the resulting change in the nutritional intake that is unhealthy, but the UPF manufacturing process itself. When adjusting for fat, sugar, and sodium intake, for example, health outcomes associated with UPFs remain poor, he explained.
“I’m sorry,” he said in the debate. “If you don’t reduce this, you don’t reduce your obesity, your diabetes prevalence.”
A study presented by Jacqueline Vernarelli, PhD, during a different session at the meeting suggested there may be other downsides to consuming UPFs. This research, which was based on the U.S. National Youth Fitness Survey, found that poorer locomotor skills among children aged 3-5 and poorer cardiovascular fitness among those aged 12-15 were associated with getting more calories from UPFs.
Those with lower cardiovascular fitness consumed 1,234 calories a day from UPFs, and those with higher cardiovascular fitness consumed 1,007 calories a day from UPFs (P = .002), according to the new research.
“It’s notable here that, although these differences are significant, both groups are consuming a pretty high proportion of their diet from ultra-processed foods,” said Dr. Vernarelli, associate professor of public health at Sacred Heart University, Fairfield, Conn., during her presentation.
In the debate session, Arne Astrup, MD, PhD, senior project director at the Healthy Weight Center at the Novo Nordisk Foundation, Hellerup, Denmark, presented an opposing view.
He said the definition of UPFs makes it too difficult to categorize many foods, pointing to a study from this year in which about 150 nutrition experts, doctors, and dietitians classified 120 foods. Only three marketed foods and one generic food were classified the same by all the evaluators.
Referring to the study Dr. Astrup cited, Dr. Monteiro said it was a mere “exercise,” and the experts involved in it had conflicts of interest.
Dr. Astrup touted this study’s size and its appearance in the peer-reviewed journal the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Defending his point of view, Dr. Astrup said, “The definition and classification is so ambiguous, and the risk of misclassification is so extremely high, I think we really miss the basic requirement of science, namely that we know what we are talking about,” he said.
If you take an unprocessed food, and insert a “little additive … suddenly it’s an ultra-processed food,” he added.
UPF definition doesn’t flag some unhealthy foods
Susan Roberts, PhD, professor of nutrition at Tufts University, Boston, was a discussant at the debate and touched on the merits of both sides. She noted that the UPF definition doesn’t flag some “clearly unhealthy foods,” such as table sugar, but does flag some healthy ones, such as plant-based burgers – to which Dr. Monteiro said that the system was not a system meant to divide foods into healthy and unhealthy groups, during the debate session.
The inclusion of both healthy and unhealthy foods in NOVA’s definition of a UPF is a serious problem, Dr. Roberts said.
“It’s almost like it’s an emotional classification designed to get at the food industry rather than focusing on health – and I think that’s asking for trouble because it’s just going to be such a mess to tell consumers, ‘Well, this ultra-processed food is healthy and this one isn’t,’ ” she said. What’s happening is the term ultra-processed is being used interchangeably with unhealthy.
The discussion that the UPF classification has generated is useful, Dr. Roberts continued. “This definition grew out of that recognition that we’re engaged in an unprecedented experiment of how unhealthy can you make the world without having a major catastrophe.”
She added that the UPF concept deserves a more formalized and rigorous evaluation.
“This is an important topic for the future of public health, and I think it needs big committees to address it seriously,” she said. “I think we should not be dealing with this individually in different labs.”
Doctor’s take on usefulness of discussing UPF concept with patients
Mark Corkins, MD, who did not participate in the debate at the meeting, said he talks to parents and children about nutrition at every office visit in which he sees a child with an unhealthy weight.
“Persistence wears down resistance,” said the chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics nutrition committee, in an interview.“A consistent message – you say the same thing and you say it multiple times.”
The idea of “ultra-processed foods” plays a role in those conversations, but largely in the background. It’s a topic that’s important for pediatric health, Dr. Corkins said – but he doesn’t make it the focal point.
“It’s not a direct attack on ultra-processed foods that usually I take as my direction,” said Dr. Corkins, who is also chief of pediatric gastroenterology at Le Bonheur Children’s Hospital in Memphis, Tenn.. “What I try to focus on, and what I think the American Academy of Pediatrics would focus on, is that we need to focus on making the diet better.”
He added, “Parents are aware – they don’t call it ultra-processed food, they call it junk food.”
Dr. Corkins continued that he is reluctant to directly challenge parents on feeding their children unhealthy foods – ultra-processed or not – lest he shame them and harm the relationship.
“Guilt as a motivator isn’t really highly successful,” he said, in an interview.
Dr. Astrup reported advisory committee or board member involvement with Green Leaf Medical and RNPC, France. Dr. Roberts reported advisory committee or board member involvement with Danone, and an ownership interest in Instinct Health Science. Dr. Monteiro and Dr. Corkins reported no relevant disclosures.
The NOVA system divides foods into “fresh or minimally processed,” such as strawberries or steel-cut oats; “processed culinary ingredients,” such as olive oil; “processed foods,” such as cheeses; and “ultra-processed foods.” UPFs are defined as “industrial formulations made by deconstructing natural food into its chemical constituents, modifying them and recombining them with additives into products liable to displace all other NOVA food groups.”
According to doctors who presented during the meeting, ultra-processed foods are drawing increased attention, because researchers have been examining them in National Institutes of Health–funded studies and journalists have been writing about them.
During the debate session at the meeting, some experts said that, with obesity and poor health skyrocketing, increased awareness and labeling of UPFs can only be a good thing. In contrast others noted at the meeting that the classification system that has come to be used for identifying UPFs – the NOVA Food Classification system – is too mushy, confusing, and, ultimately unhelpful.
Carlos Monteiro, MD, PhD, professor of nutrition and public health at the University of Sao Paolo, was part of the group favoring the NOVA system’s classifying certain foods as UPFs, during the debate. He drew attention to the extent to which the world’s population is getting its calories from UPFs.
Mexico and France get about 30% of calories from these foods. In Canada, it’s 48%. And in the United States, it’s 57%, Dr. Monteiro said.
Studies have found that UPFs, many of which are designed to be exceedingly flavorful and intended to replace consumption of unprocessed whole foods, lead to more overall energy intake, more added sugar in the diet, and less fiber and protein intake, he said.
To further support his arguments, Dr. Monteiro pointed to studies suggesting that it is not just the resulting change in the nutritional intake that is unhealthy, but the UPF manufacturing process itself. When adjusting for fat, sugar, and sodium intake, for example, health outcomes associated with UPFs remain poor, he explained.
“I’m sorry,” he said in the debate. “If you don’t reduce this, you don’t reduce your obesity, your diabetes prevalence.”
A study presented by Jacqueline Vernarelli, PhD, during a different session at the meeting suggested there may be other downsides to consuming UPFs. This research, which was based on the U.S. National Youth Fitness Survey, found that poorer locomotor skills among children aged 3-5 and poorer cardiovascular fitness among those aged 12-15 were associated with getting more calories from UPFs.
Those with lower cardiovascular fitness consumed 1,234 calories a day from UPFs, and those with higher cardiovascular fitness consumed 1,007 calories a day from UPFs (P = .002), according to the new research.
“It’s notable here that, although these differences are significant, both groups are consuming a pretty high proportion of their diet from ultra-processed foods,” said Dr. Vernarelli, associate professor of public health at Sacred Heart University, Fairfield, Conn., during her presentation.
In the debate session, Arne Astrup, MD, PhD, senior project director at the Healthy Weight Center at the Novo Nordisk Foundation, Hellerup, Denmark, presented an opposing view.
He said the definition of UPFs makes it too difficult to categorize many foods, pointing to a study from this year in which about 150 nutrition experts, doctors, and dietitians classified 120 foods. Only three marketed foods and one generic food were classified the same by all the evaluators.
Referring to the study Dr. Astrup cited, Dr. Monteiro said it was a mere “exercise,” and the experts involved in it had conflicts of interest.
Dr. Astrup touted this study’s size and its appearance in the peer-reviewed journal the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Defending his point of view, Dr. Astrup said, “The definition and classification is so ambiguous, and the risk of misclassification is so extremely high, I think we really miss the basic requirement of science, namely that we know what we are talking about,” he said.
If you take an unprocessed food, and insert a “little additive … suddenly it’s an ultra-processed food,” he added.
UPF definition doesn’t flag some unhealthy foods
Susan Roberts, PhD, professor of nutrition at Tufts University, Boston, was a discussant at the debate and touched on the merits of both sides. She noted that the UPF definition doesn’t flag some “clearly unhealthy foods,” such as table sugar, but does flag some healthy ones, such as plant-based burgers – to which Dr. Monteiro said that the system was not a system meant to divide foods into healthy and unhealthy groups, during the debate session.
The inclusion of both healthy and unhealthy foods in NOVA’s definition of a UPF is a serious problem, Dr. Roberts said.
“It’s almost like it’s an emotional classification designed to get at the food industry rather than focusing on health – and I think that’s asking for trouble because it’s just going to be such a mess to tell consumers, ‘Well, this ultra-processed food is healthy and this one isn’t,’ ” she said. What’s happening is the term ultra-processed is being used interchangeably with unhealthy.
The discussion that the UPF classification has generated is useful, Dr. Roberts continued. “This definition grew out of that recognition that we’re engaged in an unprecedented experiment of how unhealthy can you make the world without having a major catastrophe.”
She added that the UPF concept deserves a more formalized and rigorous evaluation.
“This is an important topic for the future of public health, and I think it needs big committees to address it seriously,” she said. “I think we should not be dealing with this individually in different labs.”
Doctor’s take on usefulness of discussing UPF concept with patients
Mark Corkins, MD, who did not participate in the debate at the meeting, said he talks to parents and children about nutrition at every office visit in which he sees a child with an unhealthy weight.
“Persistence wears down resistance,” said the chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics nutrition committee, in an interview.“A consistent message – you say the same thing and you say it multiple times.”
The idea of “ultra-processed foods” plays a role in those conversations, but largely in the background. It’s a topic that’s important for pediatric health, Dr. Corkins said – but he doesn’t make it the focal point.
“It’s not a direct attack on ultra-processed foods that usually I take as my direction,” said Dr. Corkins, who is also chief of pediatric gastroenterology at Le Bonheur Children’s Hospital in Memphis, Tenn.. “What I try to focus on, and what I think the American Academy of Pediatrics would focus on, is that we need to focus on making the diet better.”
He added, “Parents are aware – they don’t call it ultra-processed food, they call it junk food.”
Dr. Corkins continued that he is reluctant to directly challenge parents on feeding their children unhealthy foods – ultra-processed or not – lest he shame them and harm the relationship.
“Guilt as a motivator isn’t really highly successful,” he said, in an interview.
Dr. Astrup reported advisory committee or board member involvement with Green Leaf Medical and RNPC, France. Dr. Roberts reported advisory committee or board member involvement with Danone, and an ownership interest in Instinct Health Science. Dr. Monteiro and Dr. Corkins reported no relevant disclosures.
The NOVA system divides foods into “fresh or minimally processed,” such as strawberries or steel-cut oats; “processed culinary ingredients,” such as olive oil; “processed foods,” such as cheeses; and “ultra-processed foods.” UPFs are defined as “industrial formulations made by deconstructing natural food into its chemical constituents, modifying them and recombining them with additives into products liable to displace all other NOVA food groups.”
According to doctors who presented during the meeting, ultra-processed foods are drawing increased attention, because researchers have been examining them in National Institutes of Health–funded studies and journalists have been writing about them.
During the debate session at the meeting, some experts said that, with obesity and poor health skyrocketing, increased awareness and labeling of UPFs can only be a good thing. In contrast others noted at the meeting that the classification system that has come to be used for identifying UPFs – the NOVA Food Classification system – is too mushy, confusing, and, ultimately unhelpful.
Carlos Monteiro, MD, PhD, professor of nutrition and public health at the University of Sao Paolo, was part of the group favoring the NOVA system’s classifying certain foods as UPFs, during the debate. He drew attention to the extent to which the world’s population is getting its calories from UPFs.
Mexico and France get about 30% of calories from these foods. In Canada, it’s 48%. And in the United States, it’s 57%, Dr. Monteiro said.
Studies have found that UPFs, many of which are designed to be exceedingly flavorful and intended to replace consumption of unprocessed whole foods, lead to more overall energy intake, more added sugar in the diet, and less fiber and protein intake, he said.
To further support his arguments, Dr. Monteiro pointed to studies suggesting that it is not just the resulting change in the nutritional intake that is unhealthy, but the UPF manufacturing process itself. When adjusting for fat, sugar, and sodium intake, for example, health outcomes associated with UPFs remain poor, he explained.
“I’m sorry,” he said in the debate. “If you don’t reduce this, you don’t reduce your obesity, your diabetes prevalence.”
A study presented by Jacqueline Vernarelli, PhD, during a different session at the meeting suggested there may be other downsides to consuming UPFs. This research, which was based on the U.S. National Youth Fitness Survey, found that poorer locomotor skills among children aged 3-5 and poorer cardiovascular fitness among those aged 12-15 were associated with getting more calories from UPFs.
Those with lower cardiovascular fitness consumed 1,234 calories a day from UPFs, and those with higher cardiovascular fitness consumed 1,007 calories a day from UPFs (P = .002), according to the new research.
“It’s notable here that, although these differences are significant, both groups are consuming a pretty high proportion of their diet from ultra-processed foods,” said Dr. Vernarelli, associate professor of public health at Sacred Heart University, Fairfield, Conn., during her presentation.
In the debate session, Arne Astrup, MD, PhD, senior project director at the Healthy Weight Center at the Novo Nordisk Foundation, Hellerup, Denmark, presented an opposing view.
He said the definition of UPFs makes it too difficult to categorize many foods, pointing to a study from this year in which about 150 nutrition experts, doctors, and dietitians classified 120 foods. Only three marketed foods and one generic food were classified the same by all the evaluators.
Referring to the study Dr. Astrup cited, Dr. Monteiro said it was a mere “exercise,” and the experts involved in it had conflicts of interest.
Dr. Astrup touted this study’s size and its appearance in the peer-reviewed journal the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Defending his point of view, Dr. Astrup said, “The definition and classification is so ambiguous, and the risk of misclassification is so extremely high, I think we really miss the basic requirement of science, namely that we know what we are talking about,” he said.
If you take an unprocessed food, and insert a “little additive … suddenly it’s an ultra-processed food,” he added.
UPF definition doesn’t flag some unhealthy foods
Susan Roberts, PhD, professor of nutrition at Tufts University, Boston, was a discussant at the debate and touched on the merits of both sides. She noted that the UPF definition doesn’t flag some “clearly unhealthy foods,” such as table sugar, but does flag some healthy ones, such as plant-based burgers – to which Dr. Monteiro said that the system was not a system meant to divide foods into healthy and unhealthy groups, during the debate session.
The inclusion of both healthy and unhealthy foods in NOVA’s definition of a UPF is a serious problem, Dr. Roberts said.
“It’s almost like it’s an emotional classification designed to get at the food industry rather than focusing on health – and I think that’s asking for trouble because it’s just going to be such a mess to tell consumers, ‘Well, this ultra-processed food is healthy and this one isn’t,’ ” she said. What’s happening is the term ultra-processed is being used interchangeably with unhealthy.
The discussion that the UPF classification has generated is useful, Dr. Roberts continued. “This definition grew out of that recognition that we’re engaged in an unprecedented experiment of how unhealthy can you make the world without having a major catastrophe.”
She added that the UPF concept deserves a more formalized and rigorous evaluation.
“This is an important topic for the future of public health, and I think it needs big committees to address it seriously,” she said. “I think we should not be dealing with this individually in different labs.”
Doctor’s take on usefulness of discussing UPF concept with patients
Mark Corkins, MD, who did not participate in the debate at the meeting, said he talks to parents and children about nutrition at every office visit in which he sees a child with an unhealthy weight.
“Persistence wears down resistance,” said the chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics nutrition committee, in an interview.“A consistent message – you say the same thing and you say it multiple times.”
The idea of “ultra-processed foods” plays a role in those conversations, but largely in the background. It’s a topic that’s important for pediatric health, Dr. Corkins said – but he doesn’t make it the focal point.
“It’s not a direct attack on ultra-processed foods that usually I take as my direction,” said Dr. Corkins, who is also chief of pediatric gastroenterology at Le Bonheur Children’s Hospital in Memphis, Tenn.. “What I try to focus on, and what I think the American Academy of Pediatrics would focus on, is that we need to focus on making the diet better.”
He added, “Parents are aware – they don’t call it ultra-processed food, they call it junk food.”
Dr. Corkins continued that he is reluctant to directly challenge parents on feeding their children unhealthy foods – ultra-processed or not – lest he shame them and harm the relationship.
“Guilt as a motivator isn’t really highly successful,” he said, in an interview.
Dr. Astrup reported advisory committee or board member involvement with Green Leaf Medical and RNPC, France. Dr. Roberts reported advisory committee or board member involvement with Danone, and an ownership interest in Instinct Health Science. Dr. Monteiro and Dr. Corkins reported no relevant disclosures.
FROM NUTRITION 2022
Experts elevate new drugs for diabetic kidney disease
ATLANTA – U.S. clinicians caring for people with diabetes should take a more aggressive approach to using combined medical treatments proven to slow the otherwise relentless progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to a new joint statement by the American Diabetes Association and a major international nephrology organization presented during the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association (ADA).
The statement elevates treatment with an agent from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class to first-line for people with diabetes and laboratory-based evidence of advancing CKD. It also re-emphasizes the key role of concurrent first-line treatment with a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin-receptor blocker), metformin, and a statin.
The new statement also urges clinicians to rapidly add treatment with the new nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist finerenone (Kerendia) for further renal protection in the many patients suitable for treatment with this agent, and it recommends the second-line addition of a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist as the best add-on for any patient who needs additional glycemic control on top of metformin and an SGLT2 inhibitor.
The consensus joint statement with these updates came from a nine-member writing group assembled by the ADA and the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) organization.
“We’re going to try to make this feasible. We have to; I don’t think we have a choice,” commented Amy K. Mottl, MD, a nephrologist at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. Dr. Mottl was not involved with writing the consensus statement but has been active in the Diabetic Kidney Disease Collaborative of the American Society of Nephrology, another group promoting a more aggressive multidrug-class approach to treating CKD in people with diabetes.
Wider use of costly drugs
Adoption of this evidence-based approach by U.S. clinicians will both increase the number of agents that many patients receive and drive a significant uptick in the cost and complexity of patient care, a consequence acknowledged by the authors of the joint statement as well as outside experts.
But they view this as unavoidable given what’s now known about the high incidence of worsening CKD in patients with diabetes and the types of interventions proven to blunt this.
Much of the financial implication stems from the price of agents from the new drug classes now emphasized in the consensus recommendations – SGLT2 inhibitors, finerenone, and GLP-1 receptor agonists. All these drugs currently remain on-patent with relatively expensive retail prices in the range of about $600 to $1,000/month.
Commenting on the cost concerns, Dr. Mottl highlighted that she currently has several patients in her practice on agents from two or more of these newer classes, and she has generally found it possible for patients to get much of their expenses covered by insurers and through drug-company assistance programs.
“The major gap is patients on Medicare,” she noted in an interview, because the Federal health insurance program does not allow beneficiaries to receive rebates for their drug costs. “The Diabetic Kidney Disease Collaborative is currently lobbying members of Congress to lift that barrier,” she emphasized.
Improved alignment
Details of the KDIGO recommendations feature in a guideline from that organization that appeared as a draft document online in March 2022. The ADA’s version recently appeared as an update to its Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes – 2022, as reported by this news organization. A panel of five KDIGO representatives and four members appointed by the ADA produced the harmonization statement.
Recommendations from both organizations were largely in agreement at the outset, but following the panel’s review, the two groups are now “very well-aligned,” said Peter Rossing, MD, DMSc, a diabetologist and professor at the Steno Diabetes Center, Copenhagen, and a KDIGO representative to the writing committee, who presented the joint statement at the ADA meeting.
“These are very important drugs that are vastly underused,” commented Josef Coresh, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and professor at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, who specializes in CKD and was not involved with the new statement.
“Coherence and simplicity are what we need so that there are no excuses about moving forward” with the recommended combination treatment, he stressed.
Moving too slow
“No one is resisting using these new medications, but they are just moving too slowly, and data now show that it’s moving more slowly in the United States than elsewhere. That may be partly because U.S. patients are charged much more for these drugs, and partly because U.S. health care is so much more fragmented,” Dr. Coresh said in an interview.
The new joint consensus statement may help, “but the fragmentation of the United States system and COVID-19 are big enemies” for any short-term increased use of the highlighted agents, he added.
Evidence for low U.S. use of SGLT2 inhibitors, finerenone, and GLP-1 receptor agonists is becoming well known.
Dr. Rossing cited a 2019 report from the CURE-CKD registry of more than 600,000 U.S. patients with CKD showing that less than 1% received an SGLT2 inhibitor and less than 1% a GLP-1 receptor agonist. Not all these patients had diabetes, but a subgroup analysis of those with diabetes, prediabetes, or hypertension showed that usage of each of these two classes remained at less than 1% even in this group.
A separate report at the ADA meeting documented that of more than 1.3 million people with type 2 diabetes in the U.S. Veterans Affairs Healthcare System during 2019 and 2020, just 10% received an SGLT2 inhibitor and 7% a GLP-1 receptor agonist. And this is in a setting where drug cost is not a limiting factor.
In addition to focusing on the updated scheme for drug intervention in the consensus statement, Dr. Rossing highlighted several other important points that the writing committee emphasized.
Lifestyle optimization is a core first-line element of managing patients with diabetes and CKD, including a healthy diet, exercise, smoking cessation, and weight control. Other key steps for management include optimization of blood pressure, glucose, and lipids. The statement also calls out a potentially helpful role for continuous glucose monitoring in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes and CKD.
The statement notes that patients who also have atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease usually qualify for and could potentially benefit from more intensified lipid management with ezetimibe or a PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) inhibitor, as well as a potential role for treatment with antiplatelet agents.
‘If you don’t screen, you won’t find it’
Dr. Rossing also stressed the importance of regular screening for the onset of advanced CKD in patients. Patients whose estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) drops below 60 mL/min/1.73m2, as well as those who develop microalbuminuria with a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio of at least 30 mg/g (30 mg/mmol), have a stage of CKD that warrants the drug interventions he outlined.
Guidelines from both the ADA and KDIGO were already in place, recommending annual screening of patients with diabetes for both these parameters starting at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes or 5 years following initial diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.
“If you don’t screen, you won’t find it, and you won’t be able to treat,” Dr. Rossing warned. He also highlighted the panel’s recommendation to treat these patients with an SGLT2 inhibitor as long as their eGFR is at least 20 mL/min/1.73m2. Treatment can then continue even when their eGFR drops lower.
Starting treatment with finerenone requires that patients have a normal level of serum potassium, he emphasized.
One reason for developing the new ADA and KDIGO statement is that “discrepancies in clinical practice guideline recommendations from various professional organizations add to confusion that impedes understanding of best practices,” write Katherine R. Tuttle, MD, and associates in a recent commentary.
The goal of the new statement is to harmonize and promote the shared recommendations of the two organizations, added Dr. Tuttle, who is executive director for research at Providence Healthcare, Spokane, Washington, and a KDIGO representative on the statement writing panel.
Dr. Mottl has reported being a consultant to Bayer. Dr. Rossing has reported being a consultant to or speaker on behalf of Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Gilead, MSD, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi Aventis, and Vifor, as well as receiving research grants from AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Coresh has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tuttle has reported being a consultant to AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Goldfinch Bio, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, and Travere; receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio, Novo Nordisk, and Travere; and receiving research funding from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio, Novo Nordisk, and Travere.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATLANTA – U.S. clinicians caring for people with diabetes should take a more aggressive approach to using combined medical treatments proven to slow the otherwise relentless progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to a new joint statement by the American Diabetes Association and a major international nephrology organization presented during the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association (ADA).
The statement elevates treatment with an agent from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class to first-line for people with diabetes and laboratory-based evidence of advancing CKD. It also re-emphasizes the key role of concurrent first-line treatment with a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin-receptor blocker), metformin, and a statin.
The new statement also urges clinicians to rapidly add treatment with the new nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist finerenone (Kerendia) for further renal protection in the many patients suitable for treatment with this agent, and it recommends the second-line addition of a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist as the best add-on for any patient who needs additional glycemic control on top of metformin and an SGLT2 inhibitor.
The consensus joint statement with these updates came from a nine-member writing group assembled by the ADA and the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) organization.
“We’re going to try to make this feasible. We have to; I don’t think we have a choice,” commented Amy K. Mottl, MD, a nephrologist at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. Dr. Mottl was not involved with writing the consensus statement but has been active in the Diabetic Kidney Disease Collaborative of the American Society of Nephrology, another group promoting a more aggressive multidrug-class approach to treating CKD in people with diabetes.
Wider use of costly drugs
Adoption of this evidence-based approach by U.S. clinicians will both increase the number of agents that many patients receive and drive a significant uptick in the cost and complexity of patient care, a consequence acknowledged by the authors of the joint statement as well as outside experts.
But they view this as unavoidable given what’s now known about the high incidence of worsening CKD in patients with diabetes and the types of interventions proven to blunt this.
Much of the financial implication stems from the price of agents from the new drug classes now emphasized in the consensus recommendations – SGLT2 inhibitors, finerenone, and GLP-1 receptor agonists. All these drugs currently remain on-patent with relatively expensive retail prices in the range of about $600 to $1,000/month.
Commenting on the cost concerns, Dr. Mottl highlighted that she currently has several patients in her practice on agents from two or more of these newer classes, and she has generally found it possible for patients to get much of their expenses covered by insurers and through drug-company assistance programs.
“The major gap is patients on Medicare,” she noted in an interview, because the Federal health insurance program does not allow beneficiaries to receive rebates for their drug costs. “The Diabetic Kidney Disease Collaborative is currently lobbying members of Congress to lift that barrier,” she emphasized.
Improved alignment
Details of the KDIGO recommendations feature in a guideline from that organization that appeared as a draft document online in March 2022. The ADA’s version recently appeared as an update to its Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes – 2022, as reported by this news organization. A panel of five KDIGO representatives and four members appointed by the ADA produced the harmonization statement.
Recommendations from both organizations were largely in agreement at the outset, but following the panel’s review, the two groups are now “very well-aligned,” said Peter Rossing, MD, DMSc, a diabetologist and professor at the Steno Diabetes Center, Copenhagen, and a KDIGO representative to the writing committee, who presented the joint statement at the ADA meeting.
“These are very important drugs that are vastly underused,” commented Josef Coresh, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and professor at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, who specializes in CKD and was not involved with the new statement.
“Coherence and simplicity are what we need so that there are no excuses about moving forward” with the recommended combination treatment, he stressed.
Moving too slow
“No one is resisting using these new medications, but they are just moving too slowly, and data now show that it’s moving more slowly in the United States than elsewhere. That may be partly because U.S. patients are charged much more for these drugs, and partly because U.S. health care is so much more fragmented,” Dr. Coresh said in an interview.
The new joint consensus statement may help, “but the fragmentation of the United States system and COVID-19 are big enemies” for any short-term increased use of the highlighted agents, he added.
Evidence for low U.S. use of SGLT2 inhibitors, finerenone, and GLP-1 receptor agonists is becoming well known.
Dr. Rossing cited a 2019 report from the CURE-CKD registry of more than 600,000 U.S. patients with CKD showing that less than 1% received an SGLT2 inhibitor and less than 1% a GLP-1 receptor agonist. Not all these patients had diabetes, but a subgroup analysis of those with diabetes, prediabetes, or hypertension showed that usage of each of these two classes remained at less than 1% even in this group.
A separate report at the ADA meeting documented that of more than 1.3 million people with type 2 diabetes in the U.S. Veterans Affairs Healthcare System during 2019 and 2020, just 10% received an SGLT2 inhibitor and 7% a GLP-1 receptor agonist. And this is in a setting where drug cost is not a limiting factor.
In addition to focusing on the updated scheme for drug intervention in the consensus statement, Dr. Rossing highlighted several other important points that the writing committee emphasized.
Lifestyle optimization is a core first-line element of managing patients with diabetes and CKD, including a healthy diet, exercise, smoking cessation, and weight control. Other key steps for management include optimization of blood pressure, glucose, and lipids. The statement also calls out a potentially helpful role for continuous glucose monitoring in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes and CKD.
The statement notes that patients who also have atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease usually qualify for and could potentially benefit from more intensified lipid management with ezetimibe or a PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) inhibitor, as well as a potential role for treatment with antiplatelet agents.
‘If you don’t screen, you won’t find it’
Dr. Rossing also stressed the importance of regular screening for the onset of advanced CKD in patients. Patients whose estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) drops below 60 mL/min/1.73m2, as well as those who develop microalbuminuria with a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio of at least 30 mg/g (30 mg/mmol), have a stage of CKD that warrants the drug interventions he outlined.
Guidelines from both the ADA and KDIGO were already in place, recommending annual screening of patients with diabetes for both these parameters starting at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes or 5 years following initial diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.
“If you don’t screen, you won’t find it, and you won’t be able to treat,” Dr. Rossing warned. He also highlighted the panel’s recommendation to treat these patients with an SGLT2 inhibitor as long as their eGFR is at least 20 mL/min/1.73m2. Treatment can then continue even when their eGFR drops lower.
Starting treatment with finerenone requires that patients have a normal level of serum potassium, he emphasized.
One reason for developing the new ADA and KDIGO statement is that “discrepancies in clinical practice guideline recommendations from various professional organizations add to confusion that impedes understanding of best practices,” write Katherine R. Tuttle, MD, and associates in a recent commentary.
The goal of the new statement is to harmonize and promote the shared recommendations of the two organizations, added Dr. Tuttle, who is executive director for research at Providence Healthcare, Spokane, Washington, and a KDIGO representative on the statement writing panel.
Dr. Mottl has reported being a consultant to Bayer. Dr. Rossing has reported being a consultant to or speaker on behalf of Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Gilead, MSD, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi Aventis, and Vifor, as well as receiving research grants from AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Coresh has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tuttle has reported being a consultant to AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Goldfinch Bio, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, and Travere; receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio, Novo Nordisk, and Travere; and receiving research funding from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio, Novo Nordisk, and Travere.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATLANTA – U.S. clinicians caring for people with diabetes should take a more aggressive approach to using combined medical treatments proven to slow the otherwise relentless progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to a new joint statement by the American Diabetes Association and a major international nephrology organization presented during the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association (ADA).
The statement elevates treatment with an agent from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class to first-line for people with diabetes and laboratory-based evidence of advancing CKD. It also re-emphasizes the key role of concurrent first-line treatment with a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin-receptor blocker), metformin, and a statin.
The new statement also urges clinicians to rapidly add treatment with the new nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist finerenone (Kerendia) for further renal protection in the many patients suitable for treatment with this agent, and it recommends the second-line addition of a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist as the best add-on for any patient who needs additional glycemic control on top of metformin and an SGLT2 inhibitor.
The consensus joint statement with these updates came from a nine-member writing group assembled by the ADA and the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) organization.
“We’re going to try to make this feasible. We have to; I don’t think we have a choice,” commented Amy K. Mottl, MD, a nephrologist at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. Dr. Mottl was not involved with writing the consensus statement but has been active in the Diabetic Kidney Disease Collaborative of the American Society of Nephrology, another group promoting a more aggressive multidrug-class approach to treating CKD in people with diabetes.
Wider use of costly drugs
Adoption of this evidence-based approach by U.S. clinicians will both increase the number of agents that many patients receive and drive a significant uptick in the cost and complexity of patient care, a consequence acknowledged by the authors of the joint statement as well as outside experts.
But they view this as unavoidable given what’s now known about the high incidence of worsening CKD in patients with diabetes and the types of interventions proven to blunt this.
Much of the financial implication stems from the price of agents from the new drug classes now emphasized in the consensus recommendations – SGLT2 inhibitors, finerenone, and GLP-1 receptor agonists. All these drugs currently remain on-patent with relatively expensive retail prices in the range of about $600 to $1,000/month.
Commenting on the cost concerns, Dr. Mottl highlighted that she currently has several patients in her practice on agents from two or more of these newer classes, and she has generally found it possible for patients to get much of their expenses covered by insurers and through drug-company assistance programs.
“The major gap is patients on Medicare,” she noted in an interview, because the Federal health insurance program does not allow beneficiaries to receive rebates for their drug costs. “The Diabetic Kidney Disease Collaborative is currently lobbying members of Congress to lift that barrier,” she emphasized.
Improved alignment
Details of the KDIGO recommendations feature in a guideline from that organization that appeared as a draft document online in March 2022. The ADA’s version recently appeared as an update to its Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes – 2022, as reported by this news organization. A panel of five KDIGO representatives and four members appointed by the ADA produced the harmonization statement.
Recommendations from both organizations were largely in agreement at the outset, but following the panel’s review, the two groups are now “very well-aligned,” said Peter Rossing, MD, DMSc, a diabetologist and professor at the Steno Diabetes Center, Copenhagen, and a KDIGO representative to the writing committee, who presented the joint statement at the ADA meeting.
“These are very important drugs that are vastly underused,” commented Josef Coresh, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and professor at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, who specializes in CKD and was not involved with the new statement.
“Coherence and simplicity are what we need so that there are no excuses about moving forward” with the recommended combination treatment, he stressed.
Moving too slow
“No one is resisting using these new medications, but they are just moving too slowly, and data now show that it’s moving more slowly in the United States than elsewhere. That may be partly because U.S. patients are charged much more for these drugs, and partly because U.S. health care is so much more fragmented,” Dr. Coresh said in an interview.
The new joint consensus statement may help, “but the fragmentation of the United States system and COVID-19 are big enemies” for any short-term increased use of the highlighted agents, he added.
Evidence for low U.S. use of SGLT2 inhibitors, finerenone, and GLP-1 receptor agonists is becoming well known.
Dr. Rossing cited a 2019 report from the CURE-CKD registry of more than 600,000 U.S. patients with CKD showing that less than 1% received an SGLT2 inhibitor and less than 1% a GLP-1 receptor agonist. Not all these patients had diabetes, but a subgroup analysis of those with diabetes, prediabetes, or hypertension showed that usage of each of these two classes remained at less than 1% even in this group.
A separate report at the ADA meeting documented that of more than 1.3 million people with type 2 diabetes in the U.S. Veterans Affairs Healthcare System during 2019 and 2020, just 10% received an SGLT2 inhibitor and 7% a GLP-1 receptor agonist. And this is in a setting where drug cost is not a limiting factor.
In addition to focusing on the updated scheme for drug intervention in the consensus statement, Dr. Rossing highlighted several other important points that the writing committee emphasized.
Lifestyle optimization is a core first-line element of managing patients with diabetes and CKD, including a healthy diet, exercise, smoking cessation, and weight control. Other key steps for management include optimization of blood pressure, glucose, and lipids. The statement also calls out a potentially helpful role for continuous glucose monitoring in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes and CKD.
The statement notes that patients who also have atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease usually qualify for and could potentially benefit from more intensified lipid management with ezetimibe or a PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) inhibitor, as well as a potential role for treatment with antiplatelet agents.
‘If you don’t screen, you won’t find it’
Dr. Rossing also stressed the importance of regular screening for the onset of advanced CKD in patients. Patients whose estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) drops below 60 mL/min/1.73m2, as well as those who develop microalbuminuria with a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio of at least 30 mg/g (30 mg/mmol), have a stage of CKD that warrants the drug interventions he outlined.
Guidelines from both the ADA and KDIGO were already in place, recommending annual screening of patients with diabetes for both these parameters starting at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes or 5 years following initial diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.
“If you don’t screen, you won’t find it, and you won’t be able to treat,” Dr. Rossing warned. He also highlighted the panel’s recommendation to treat these patients with an SGLT2 inhibitor as long as their eGFR is at least 20 mL/min/1.73m2. Treatment can then continue even when their eGFR drops lower.
Starting treatment with finerenone requires that patients have a normal level of serum potassium, he emphasized.
One reason for developing the new ADA and KDIGO statement is that “discrepancies in clinical practice guideline recommendations from various professional organizations add to confusion that impedes understanding of best practices,” write Katherine R. Tuttle, MD, and associates in a recent commentary.
The goal of the new statement is to harmonize and promote the shared recommendations of the two organizations, added Dr. Tuttle, who is executive director for research at Providence Healthcare, Spokane, Washington, and a KDIGO representative on the statement writing panel.
Dr. Mottl has reported being a consultant to Bayer. Dr. Rossing has reported being a consultant to or speaker on behalf of Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Gilead, MSD, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi Aventis, and Vifor, as well as receiving research grants from AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Coresh has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tuttle has reported being a consultant to AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Goldfinch Bio, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, and Travere; receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio, Novo Nordisk, and Travere; and receiving research funding from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio, Novo Nordisk, and Travere.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ADA 2022
Diabetes tied to risk of long COVID, too
Individuals with diabetes who experience COVID-19 are at increased risk for long COVID compared to individuals without diabetes, according to data from a literature review of seven studies.
Diabetes remains a risk factor for severe COVID-19, but whether it is a risk factor for postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), also known as long COVID, remains unclear, Jessica L. Harding, PhD, of Emory University, said in a late-breaking poster session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Long COVID is generally defined as “sequelae that extend beyond the 4 weeks after initial infection” and may include a range of symptoms that affect multiple organs, Dr. Harding said. A study conducted in January of 2022 suggested that type 2 diabetes was one of several strong risk factors for long COVID, she noted.
Dr. Harding and colleagues reviewed data from seven studies published from Jan. 1, 2020, to Jan. 27, 2022, on the risk of PASC in people with and without diabetes. The studies included patients with a minimum of 4 weeks’ follow-up after COVID-19 diagnosis. All seven studies had a longitudinal cohort design, and included adults from high-income countries, with study populations ranging from 104 to 4,182.
Across the studies, long COVID definitions varied, but included ongoing symptoms of fatigue, cough, and dyspnea, with follow-up periods of 4 weeks to 7 months.
Overall, three of the seven studies indicated that diabetes was a risk factor for long COVID (odds ratio [OR] greater than 4 for all) and four studies indicated that diabetes was not a risk factor for long COVID (OR, 0.5-2.2).
One of the three studies showing increased risk included 2,334 individuals hospitalized with COVID-19; of these about 5% had diabetes. The odds ratio for PASC for individuals with diabetes was 4.18. In another study of 209 persons with COVID-19, of whom 22% had diabetes, diabetes was significantly correlated with respiratory viral disease (meaning at least two respiratory symptoms). The third study showing an increased risk of long COVID in diabetes patients included 104 kidney transplant patients, of whom 20% had diabetes; the odds ratio for PASC was 4.42.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the relatively small number of studies and the heterogeneity of studies regarding definitions of long COVID, specific populations at risk, follow-up times, and risk adjustment, Dr. Harding noted.
More high-quality studies across multiple populations and settings are needed to determine if diabetes is indeed a risk factor for long COVID, she said.
In the meantime, “careful monitoring of people with diabetes for development of PASC may be advised,” Dr. Harding concluded.
Findings support need for screening
“Given the devastating impact of COVID on people with diabetes, it’s important to know what data has been accumulated on long COVID for future research and discoveries in this area,” Robert A. Gabbay, MD, chief science and medical officer for the American Diabetes Association, said in an interview. “The more information we have, the better we can understand the implications.”
Dr. Gabbay said he was surprised by the current study findings. “We know very little on this subject, so yes, I am surprised to see just how significant the risk of long COVID for people with diabetes seems to be, but clearly, more research needs to be done to understand long COVID,” he emphasized.
The take-home message for clinicians is the importance of screening patients for PASC; also “ask your patients if they had COVID, to better understand any symptoms they might have that could be related to PACS,” he noted.
“It is crucial that we confirm these results and then look at risk factors in people with diabetes that might explain who is at highest risk and ultimately understand the causes and potential cure,” Dr. Gabbay added.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Harding and Dr. Gabbay had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Individuals with diabetes who experience COVID-19 are at increased risk for long COVID compared to individuals without diabetes, according to data from a literature review of seven studies.
Diabetes remains a risk factor for severe COVID-19, but whether it is a risk factor for postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), also known as long COVID, remains unclear, Jessica L. Harding, PhD, of Emory University, said in a late-breaking poster session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Long COVID is generally defined as “sequelae that extend beyond the 4 weeks after initial infection” and may include a range of symptoms that affect multiple organs, Dr. Harding said. A study conducted in January of 2022 suggested that type 2 diabetes was one of several strong risk factors for long COVID, she noted.
Dr. Harding and colleagues reviewed data from seven studies published from Jan. 1, 2020, to Jan. 27, 2022, on the risk of PASC in people with and without diabetes. The studies included patients with a minimum of 4 weeks’ follow-up after COVID-19 diagnosis. All seven studies had a longitudinal cohort design, and included adults from high-income countries, with study populations ranging from 104 to 4,182.
Across the studies, long COVID definitions varied, but included ongoing symptoms of fatigue, cough, and dyspnea, with follow-up periods of 4 weeks to 7 months.
Overall, three of the seven studies indicated that diabetes was a risk factor for long COVID (odds ratio [OR] greater than 4 for all) and four studies indicated that diabetes was not a risk factor for long COVID (OR, 0.5-2.2).
One of the three studies showing increased risk included 2,334 individuals hospitalized with COVID-19; of these about 5% had diabetes. The odds ratio for PASC for individuals with diabetes was 4.18. In another study of 209 persons with COVID-19, of whom 22% had diabetes, diabetes was significantly correlated with respiratory viral disease (meaning at least two respiratory symptoms). The third study showing an increased risk of long COVID in diabetes patients included 104 kidney transplant patients, of whom 20% had diabetes; the odds ratio for PASC was 4.42.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the relatively small number of studies and the heterogeneity of studies regarding definitions of long COVID, specific populations at risk, follow-up times, and risk adjustment, Dr. Harding noted.
More high-quality studies across multiple populations and settings are needed to determine if diabetes is indeed a risk factor for long COVID, she said.
In the meantime, “careful monitoring of people with diabetes for development of PASC may be advised,” Dr. Harding concluded.
Findings support need for screening
“Given the devastating impact of COVID on people with diabetes, it’s important to know what data has been accumulated on long COVID for future research and discoveries in this area,” Robert A. Gabbay, MD, chief science and medical officer for the American Diabetes Association, said in an interview. “The more information we have, the better we can understand the implications.”
Dr. Gabbay said he was surprised by the current study findings. “We know very little on this subject, so yes, I am surprised to see just how significant the risk of long COVID for people with diabetes seems to be, but clearly, more research needs to be done to understand long COVID,” he emphasized.
The take-home message for clinicians is the importance of screening patients for PASC; also “ask your patients if they had COVID, to better understand any symptoms they might have that could be related to PACS,” he noted.
“It is crucial that we confirm these results and then look at risk factors in people with diabetes that might explain who is at highest risk and ultimately understand the causes and potential cure,” Dr. Gabbay added.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Harding and Dr. Gabbay had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Individuals with diabetes who experience COVID-19 are at increased risk for long COVID compared to individuals without diabetes, according to data from a literature review of seven studies.
Diabetes remains a risk factor for severe COVID-19, but whether it is a risk factor for postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), also known as long COVID, remains unclear, Jessica L. Harding, PhD, of Emory University, said in a late-breaking poster session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Long COVID is generally defined as “sequelae that extend beyond the 4 weeks after initial infection” and may include a range of symptoms that affect multiple organs, Dr. Harding said. A study conducted in January of 2022 suggested that type 2 diabetes was one of several strong risk factors for long COVID, she noted.
Dr. Harding and colleagues reviewed data from seven studies published from Jan. 1, 2020, to Jan. 27, 2022, on the risk of PASC in people with and without diabetes. The studies included patients with a minimum of 4 weeks’ follow-up after COVID-19 diagnosis. All seven studies had a longitudinal cohort design, and included adults from high-income countries, with study populations ranging from 104 to 4,182.
Across the studies, long COVID definitions varied, but included ongoing symptoms of fatigue, cough, and dyspnea, with follow-up periods of 4 weeks to 7 months.
Overall, three of the seven studies indicated that diabetes was a risk factor for long COVID (odds ratio [OR] greater than 4 for all) and four studies indicated that diabetes was not a risk factor for long COVID (OR, 0.5-2.2).
One of the three studies showing increased risk included 2,334 individuals hospitalized with COVID-19; of these about 5% had diabetes. The odds ratio for PASC for individuals with diabetes was 4.18. In another study of 209 persons with COVID-19, of whom 22% had diabetes, diabetes was significantly correlated with respiratory viral disease (meaning at least two respiratory symptoms). The third study showing an increased risk of long COVID in diabetes patients included 104 kidney transplant patients, of whom 20% had diabetes; the odds ratio for PASC was 4.42.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the relatively small number of studies and the heterogeneity of studies regarding definitions of long COVID, specific populations at risk, follow-up times, and risk adjustment, Dr. Harding noted.
More high-quality studies across multiple populations and settings are needed to determine if diabetes is indeed a risk factor for long COVID, she said.
In the meantime, “careful monitoring of people with diabetes for development of PASC may be advised,” Dr. Harding concluded.
Findings support need for screening
“Given the devastating impact of COVID on people with diabetes, it’s important to know what data has been accumulated on long COVID for future research and discoveries in this area,” Robert A. Gabbay, MD, chief science and medical officer for the American Diabetes Association, said in an interview. “The more information we have, the better we can understand the implications.”
Dr. Gabbay said he was surprised by the current study findings. “We know very little on this subject, so yes, I am surprised to see just how significant the risk of long COVID for people with diabetes seems to be, but clearly, more research needs to be done to understand long COVID,” he emphasized.
The take-home message for clinicians is the importance of screening patients for PASC; also “ask your patients if they had COVID, to better understand any symptoms they might have that could be related to PACS,” he noted.
“It is crucial that we confirm these results and then look at risk factors in people with diabetes that might explain who is at highest risk and ultimately understand the causes and potential cure,” Dr. Gabbay added.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Harding and Dr. Gabbay had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ADA 2022
Why do we treat menopause as a disease?
Menopause gets a bad rap in medical literature and throughout society, say authors of a new analysis. And they argue that the negativity undermines women’s health outlook in the years that should be a natural life transition.
Menopause has been medicalized over centuries and talked about as if it were a disease, they say, and that may increase women’s anxiety and apprehension about the midlife stage.
It’s time to change the narrative, says Martha Hickey, MD, with the department of obstetrics and gynaecology at the Royal Women’s Hospital in Victoria, Australia, and her coauthors. Their analysis was published online in the BMJ.
“The message that menopause signals decay and decline, which can potentially be delayed or reversed by hormonal treatments, persists and is reinforced by the media, medical literature, and information for women, often driven by marketing interests,” they write.
Such messages may chip away at women’s confidence. Dr. Hickey and colleagues cite surveys in the United States and Ireland that found that most women (65%-77%) feel unprepared for menopause.
“Together with limited public discussion and education and shame attached to ageing in women, this may contribute to embarrassment and negative expectations about menopause,” the authors write.
The ‘untold misery of oestrogen-starved women’
These messages have deep roots. Take for instance, gynecologist Robert Wilson’s words in his 1966 book “Feminine Forever.” The authors note he recommended estrogen for all menopausal women “to treat their ‘serious, painful and often crippling disease’ and avoid the ‘untold misery of alcoholism, drug addiction, divorce, and broken
homes caused by these unstable, oestrogen-starved women.’ ”
Women experience menopause in very different ways. Experience with menopause also differs by country, the authors explain. “Women’s experience of menopause is also strongly influenced by social values around reproduction and ageing, with positive or negative ramifications,” they write.
“For example, women tend to have worse experiences of menopause in countries where their value is predicated on youth and reproductive capacity and ageing is associated with decline.”
The authors argue that the medicalization of menopause has condensed the wide range of women’s experiences at a typical age into “a narrowly defined disease requiring treatment.”
Promoting exercise, stopping smoking among positive messages
An editorial by Haitham Hamoda, MD, and Sara Moger, with the British Menopause Society, notes that more than 75% of women experiencing menopause report symptoms, and more than 25% describe severe symptoms.
The editorialists point out that the National Institute of Health and Care Excellence and others recommend an individualized approach to addressing menopause that includes a comprehensive approach – advice on exercise, weight management, stopping smoking, and reducing alcohol as well as options such as hormone therapy (HT).
The literature says the main indication for HT is for severe symptoms and not as a preventive measure. “Evidence does not support use of HT to reduce the risk of dementia,” they point out.
While some women may benefit from HT, that should not be explored to the exclusion of other avenues of help, Dr. Hickey and colleagues write. Risks must also be considered.
Menopause blamed in a difficult time of life
Jennifer Howell, MD, an obstetrician/gynecologist and certified menopause provider at Duke University in Durham, N.C., told this news organization that menopause is often blamed in a time of life when women naturally are experiencing an array of stressful and emotional changes.
It often coincides with children heading to college, navigating midlife challenges in marriage, helping aging parents, managing demanding careers, and health issues.
People want a reason for changes women experience, and too often the finger gets pointed at menopause, Dr. Howell said.
The message women hear has always been, “It’s got to be your hormones. And people want to hear that there’s a hormonal solution.”
Making menopause the target also has led to nonevidence-based “snake-oil” type remedies sold in unregulated powders, creams, and pellets, Dr. Howell noted.
Dr. Howell has treated thousands of menopausal women in her clinic and she says she spends a good deal of time with them explaining a holistic view of the process, much like what the authors describe, with lifestyle changes and treatment options.
Sometimes HT is the solution, Dr. Howell says, but “it’s become a crutch. Hormones are not a panacea.”
She is frustrated with the amount of disinformation circulating online. Groups like the North American Menopause Society put out reliable evidence-based information, but they compete “with a lot of nonsense,” she says.
The message that women should hear, she says is that “[menopause] is a natural part of aging and there may or may not be symptoms that come along with it. If there are, there are things we can do,” she says.
Menopause gets a bad rap in medical literature and throughout society, say authors of a new analysis. And they argue that the negativity undermines women’s health outlook in the years that should be a natural life transition.
Menopause has been medicalized over centuries and talked about as if it were a disease, they say, and that may increase women’s anxiety and apprehension about the midlife stage.
It’s time to change the narrative, says Martha Hickey, MD, with the department of obstetrics and gynaecology at the Royal Women’s Hospital in Victoria, Australia, and her coauthors. Their analysis was published online in the BMJ.
“The message that menopause signals decay and decline, which can potentially be delayed or reversed by hormonal treatments, persists and is reinforced by the media, medical literature, and information for women, often driven by marketing interests,” they write.
Such messages may chip away at women’s confidence. Dr. Hickey and colleagues cite surveys in the United States and Ireland that found that most women (65%-77%) feel unprepared for menopause.
“Together with limited public discussion and education and shame attached to ageing in women, this may contribute to embarrassment and negative expectations about menopause,” the authors write.
The ‘untold misery of oestrogen-starved women’
These messages have deep roots. Take for instance, gynecologist Robert Wilson’s words in his 1966 book “Feminine Forever.” The authors note he recommended estrogen for all menopausal women “to treat their ‘serious, painful and often crippling disease’ and avoid the ‘untold misery of alcoholism, drug addiction, divorce, and broken
homes caused by these unstable, oestrogen-starved women.’ ”
Women experience menopause in very different ways. Experience with menopause also differs by country, the authors explain. “Women’s experience of menopause is also strongly influenced by social values around reproduction and ageing, with positive or negative ramifications,” they write.
“For example, women tend to have worse experiences of menopause in countries where their value is predicated on youth and reproductive capacity and ageing is associated with decline.”
The authors argue that the medicalization of menopause has condensed the wide range of women’s experiences at a typical age into “a narrowly defined disease requiring treatment.”
Promoting exercise, stopping smoking among positive messages
An editorial by Haitham Hamoda, MD, and Sara Moger, with the British Menopause Society, notes that more than 75% of women experiencing menopause report symptoms, and more than 25% describe severe symptoms.
The editorialists point out that the National Institute of Health and Care Excellence and others recommend an individualized approach to addressing menopause that includes a comprehensive approach – advice on exercise, weight management, stopping smoking, and reducing alcohol as well as options such as hormone therapy (HT).
The literature says the main indication for HT is for severe symptoms and not as a preventive measure. “Evidence does not support use of HT to reduce the risk of dementia,” they point out.
While some women may benefit from HT, that should not be explored to the exclusion of other avenues of help, Dr. Hickey and colleagues write. Risks must also be considered.
Menopause blamed in a difficult time of life
Jennifer Howell, MD, an obstetrician/gynecologist and certified menopause provider at Duke University in Durham, N.C., told this news organization that menopause is often blamed in a time of life when women naturally are experiencing an array of stressful and emotional changes.
It often coincides with children heading to college, navigating midlife challenges in marriage, helping aging parents, managing demanding careers, and health issues.
People want a reason for changes women experience, and too often the finger gets pointed at menopause, Dr. Howell said.
The message women hear has always been, “It’s got to be your hormones. And people want to hear that there’s a hormonal solution.”
Making menopause the target also has led to nonevidence-based “snake-oil” type remedies sold in unregulated powders, creams, and pellets, Dr. Howell noted.
Dr. Howell has treated thousands of menopausal women in her clinic and she says she spends a good deal of time with them explaining a holistic view of the process, much like what the authors describe, with lifestyle changes and treatment options.
Sometimes HT is the solution, Dr. Howell says, but “it’s become a crutch. Hormones are not a panacea.”
She is frustrated with the amount of disinformation circulating online. Groups like the North American Menopause Society put out reliable evidence-based information, but they compete “with a lot of nonsense,” she says.
The message that women should hear, she says is that “[menopause] is a natural part of aging and there may or may not be symptoms that come along with it. If there are, there are things we can do,” she says.
Menopause gets a bad rap in medical literature and throughout society, say authors of a new analysis. And they argue that the negativity undermines women’s health outlook in the years that should be a natural life transition.
Menopause has been medicalized over centuries and talked about as if it were a disease, they say, and that may increase women’s anxiety and apprehension about the midlife stage.
It’s time to change the narrative, says Martha Hickey, MD, with the department of obstetrics and gynaecology at the Royal Women’s Hospital in Victoria, Australia, and her coauthors. Their analysis was published online in the BMJ.
“The message that menopause signals decay and decline, which can potentially be delayed or reversed by hormonal treatments, persists and is reinforced by the media, medical literature, and information for women, often driven by marketing interests,” they write.
Such messages may chip away at women’s confidence. Dr. Hickey and colleagues cite surveys in the United States and Ireland that found that most women (65%-77%) feel unprepared for menopause.
“Together with limited public discussion and education and shame attached to ageing in women, this may contribute to embarrassment and negative expectations about menopause,” the authors write.
The ‘untold misery of oestrogen-starved women’
These messages have deep roots. Take for instance, gynecologist Robert Wilson’s words in his 1966 book “Feminine Forever.” The authors note he recommended estrogen for all menopausal women “to treat their ‘serious, painful and often crippling disease’ and avoid the ‘untold misery of alcoholism, drug addiction, divorce, and broken
homes caused by these unstable, oestrogen-starved women.’ ”
Women experience menopause in very different ways. Experience with menopause also differs by country, the authors explain. “Women’s experience of menopause is also strongly influenced by social values around reproduction and ageing, with positive or negative ramifications,” they write.
“For example, women tend to have worse experiences of menopause in countries where their value is predicated on youth and reproductive capacity and ageing is associated with decline.”
The authors argue that the medicalization of menopause has condensed the wide range of women’s experiences at a typical age into “a narrowly defined disease requiring treatment.”
Promoting exercise, stopping smoking among positive messages
An editorial by Haitham Hamoda, MD, and Sara Moger, with the British Menopause Society, notes that more than 75% of women experiencing menopause report symptoms, and more than 25% describe severe symptoms.
The editorialists point out that the National Institute of Health and Care Excellence and others recommend an individualized approach to addressing menopause that includes a comprehensive approach – advice on exercise, weight management, stopping smoking, and reducing alcohol as well as options such as hormone therapy (HT).
The literature says the main indication for HT is for severe symptoms and not as a preventive measure. “Evidence does not support use of HT to reduce the risk of dementia,” they point out.
While some women may benefit from HT, that should not be explored to the exclusion of other avenues of help, Dr. Hickey and colleagues write. Risks must also be considered.
Menopause blamed in a difficult time of life
Jennifer Howell, MD, an obstetrician/gynecologist and certified menopause provider at Duke University in Durham, N.C., told this news organization that menopause is often blamed in a time of life when women naturally are experiencing an array of stressful and emotional changes.
It often coincides with children heading to college, navigating midlife challenges in marriage, helping aging parents, managing demanding careers, and health issues.
People want a reason for changes women experience, and too often the finger gets pointed at menopause, Dr. Howell said.
The message women hear has always been, “It’s got to be your hormones. And people want to hear that there’s a hormonal solution.”
Making menopause the target also has led to nonevidence-based “snake-oil” type remedies sold in unregulated powders, creams, and pellets, Dr. Howell noted.
Dr. Howell has treated thousands of menopausal women in her clinic and she says she spends a good deal of time with them explaining a holistic view of the process, much like what the authors describe, with lifestyle changes and treatment options.
Sometimes HT is the solution, Dr. Howell says, but “it’s become a crutch. Hormones are not a panacea.”
She is frustrated with the amount of disinformation circulating online. Groups like the North American Menopause Society put out reliable evidence-based information, but they compete “with a lot of nonsense,” she says.
The message that women should hear, she says is that “[menopause] is a natural part of aging and there may or may not be symptoms that come along with it. If there are, there are things we can do,” she says.
FROM BMJ









