User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
Dana-Farber Moves to Retract, Correct Dozens of Cancer Papers Amid Allegations
News of the investigation follows a blog post by British molecular biologist Sholto David, MD, who flagged almost 60 papers published between 1997 and 2017 that contained image manipulation and other errors. Some of the papers were published by Dana-Farber’s chief executive officer, Laurie Glimcher, MD, and chief operating officer, William Hahn, MD, on topics including multiple myeloma and immune cells.
Mr. David, who blogs about research integrity, highlighted numerous errors and irregularities, including copying and pasting images across multiple experiments to represent different days within the same experiment, sometimes rotating or stretching images.
In one case, Mr. David equated the manipulation with tactics used by “hapless Chinese papermills” and concluded that “a swathe of research coming out of [Dana-Farber] authored by the most senior researchers and managers appears to be hopelessly corrupt with errors that are obvious from just a cursory reading the papers.”
“Imagine what mistakes might be found in the raw data if anyone was allowed to look!” he wrote.
Barrett Rollins, MD, PhD, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute’s research integrity officer, declined to comment on whether the errors represent scientific misconduct, according to STAT. Rollins told ScienceInsider that the “presence of image discrepancies in a paper is not evidence of an author’s intent to deceive.”
Access to new artificial intelligence tools is making it easier for data sleuths, like Mr. David, to unearth data manipulation and errors.
The current investigation closely follows two other investigations into the published work of Harvard University’s former president, Claudine Gay, and Stanford University’s former president, Marc Tessier-Lavigne, which led both to resign their posts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
News of the investigation follows a blog post by British molecular biologist Sholto David, MD, who flagged almost 60 papers published between 1997 and 2017 that contained image manipulation and other errors. Some of the papers were published by Dana-Farber’s chief executive officer, Laurie Glimcher, MD, and chief operating officer, William Hahn, MD, on topics including multiple myeloma and immune cells.
Mr. David, who blogs about research integrity, highlighted numerous errors and irregularities, including copying and pasting images across multiple experiments to represent different days within the same experiment, sometimes rotating or stretching images.
In one case, Mr. David equated the manipulation with tactics used by “hapless Chinese papermills” and concluded that “a swathe of research coming out of [Dana-Farber] authored by the most senior researchers and managers appears to be hopelessly corrupt with errors that are obvious from just a cursory reading the papers.”
“Imagine what mistakes might be found in the raw data if anyone was allowed to look!” he wrote.
Barrett Rollins, MD, PhD, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute’s research integrity officer, declined to comment on whether the errors represent scientific misconduct, according to STAT. Rollins told ScienceInsider that the “presence of image discrepancies in a paper is not evidence of an author’s intent to deceive.”
Access to new artificial intelligence tools is making it easier for data sleuths, like Mr. David, to unearth data manipulation and errors.
The current investigation closely follows two other investigations into the published work of Harvard University’s former president, Claudine Gay, and Stanford University’s former president, Marc Tessier-Lavigne, which led both to resign their posts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
News of the investigation follows a blog post by British molecular biologist Sholto David, MD, who flagged almost 60 papers published between 1997 and 2017 that contained image manipulation and other errors. Some of the papers were published by Dana-Farber’s chief executive officer, Laurie Glimcher, MD, and chief operating officer, William Hahn, MD, on topics including multiple myeloma and immune cells.
Mr. David, who blogs about research integrity, highlighted numerous errors and irregularities, including copying and pasting images across multiple experiments to represent different days within the same experiment, sometimes rotating or stretching images.
In one case, Mr. David equated the manipulation with tactics used by “hapless Chinese papermills” and concluded that “a swathe of research coming out of [Dana-Farber] authored by the most senior researchers and managers appears to be hopelessly corrupt with errors that are obvious from just a cursory reading the papers.”
“Imagine what mistakes might be found in the raw data if anyone was allowed to look!” he wrote.
Barrett Rollins, MD, PhD, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute’s research integrity officer, declined to comment on whether the errors represent scientific misconduct, according to STAT. Rollins told ScienceInsider that the “presence of image discrepancies in a paper is not evidence of an author’s intent to deceive.”
Access to new artificial intelligence tools is making it easier for data sleuths, like Mr. David, to unearth data manipulation and errors.
The current investigation closely follows two other investigations into the published work of Harvard University’s former president, Claudine Gay, and Stanford University’s former president, Marc Tessier-Lavigne, which led both to resign their posts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Even Intentional Weight Loss Linked With Cancer
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
As anyone who has been through medical training will tell you, some little scenes just stick with you. I had been seeing a patient in our resident clinic in West Philly for a couple of years. She was in her mid-60s with diabetes and hypertension and a distant smoking history. She was overweight and had been trying to improve her diet and lose weight since I started seeing her. One day she came in and was delighted to report that she had finally started shedding some pounds — about 15 in the past 2 months.
I enthusiastically told my preceptor that my careful dietary counseling had finally done the job. She looked through the chart for a moment and asked, “Is she up to date on her cancer screening?” A workup revealed adenocarcinoma of the lung. The patient did well, actually, but the story stuck with me.
The textbooks call it “unintentional weight loss,” often in big, scary letters, and every doctor will go just a bit pale if a patient tells them that, despite efforts not to, they are losing weight. But true unintentional weight loss is not that common. After all, most of us are at least half-heartedly trying to lose weight all the time. Should doctors be worried when we are successful?
A new study suggests that perhaps they should. We’re talking about this study, appearing in JAMA, which combined participants from two long-running observational cohorts: 120,000 women from the Nurses’ Health Study, and 50,000 men from the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study. (These cohorts started in the 1970s and 1980s, so we’ll give them a pass on the gender-specific study designs.)
The rationale of enrolling healthcare providers in these cohort studies is that they would be reliable witnesses of their own health status. If a nurse or doctor says they have pancreatic cancer, it’s likely that they truly have pancreatic cancer. Detailed health surveys were distributed to the participants every other year, and the average follow-up was more than a decade.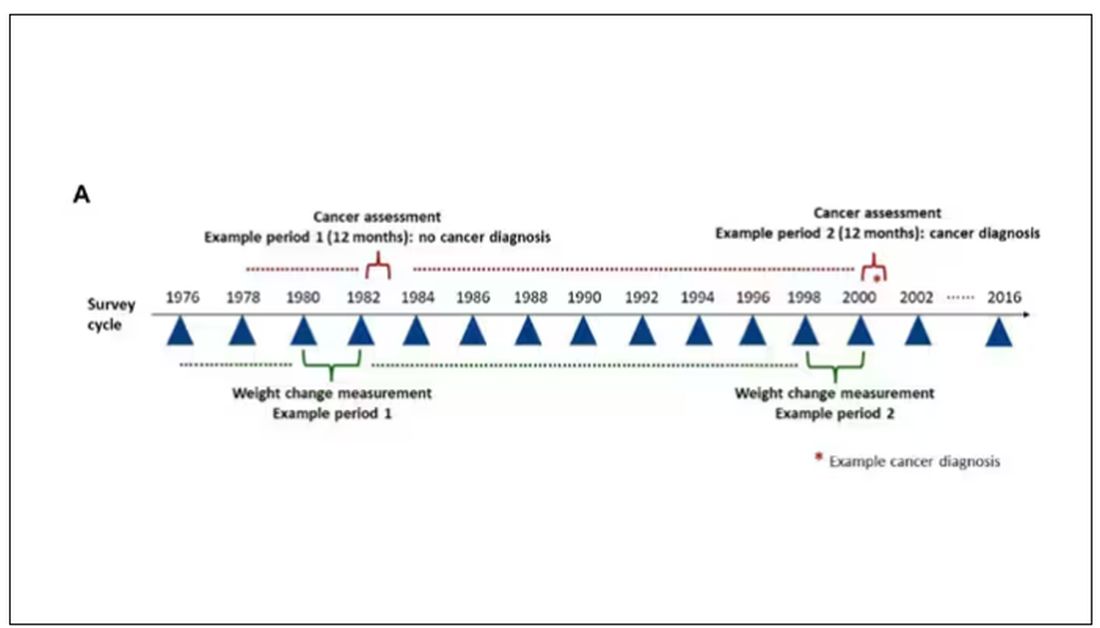
Participants recorded their weight — as an aside, a nested study found that self-reported rate was extremely well correlated with professionally measured weight — and whether they had received a cancer diagnosis since the last survey.
This allowed researchers to look at the phenomenon described above. Would weight loss precede a new diagnosis of cancer? And, more interestingly, would intentional weight loss precede a new diagnosis of cancer.
I don’t think it will surprise you to hear that individuals in the highest category of weight loss, those who lost more than 10% of their body weight over a 2-year period, had a larger risk of being diagnosed with cancer in the next year. That’s the yellow line in this graph. In fact, they had about a 40% higher risk than those who did not lose weight.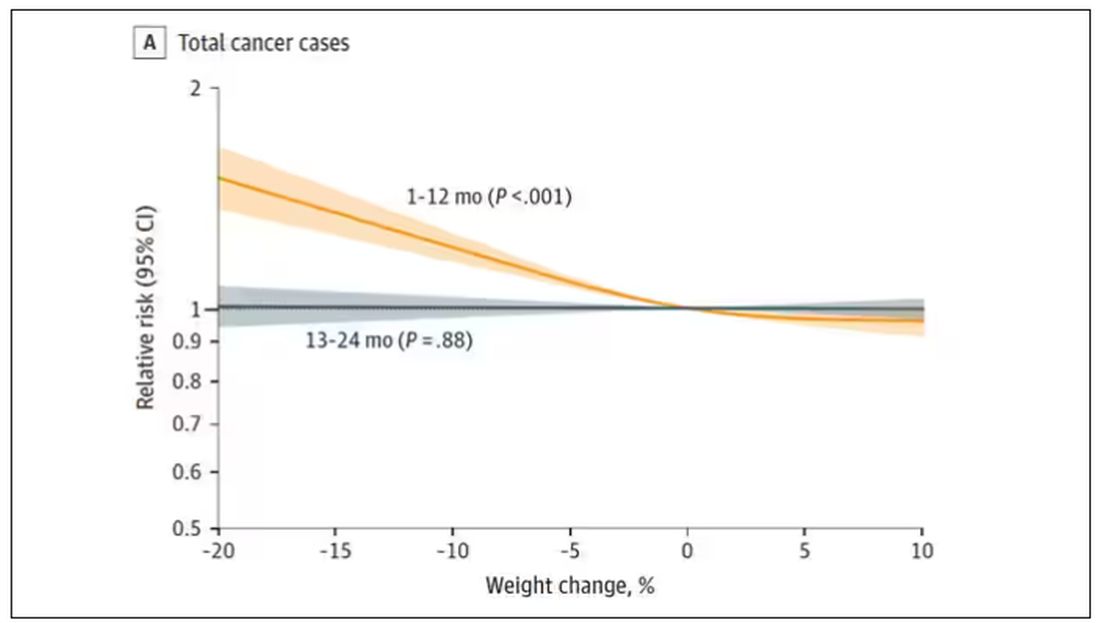
Increased risk was found across multiple cancer types, though cancers of the gastrointestinal tract, not surprisingly, were most strongly associated with antecedent weight loss.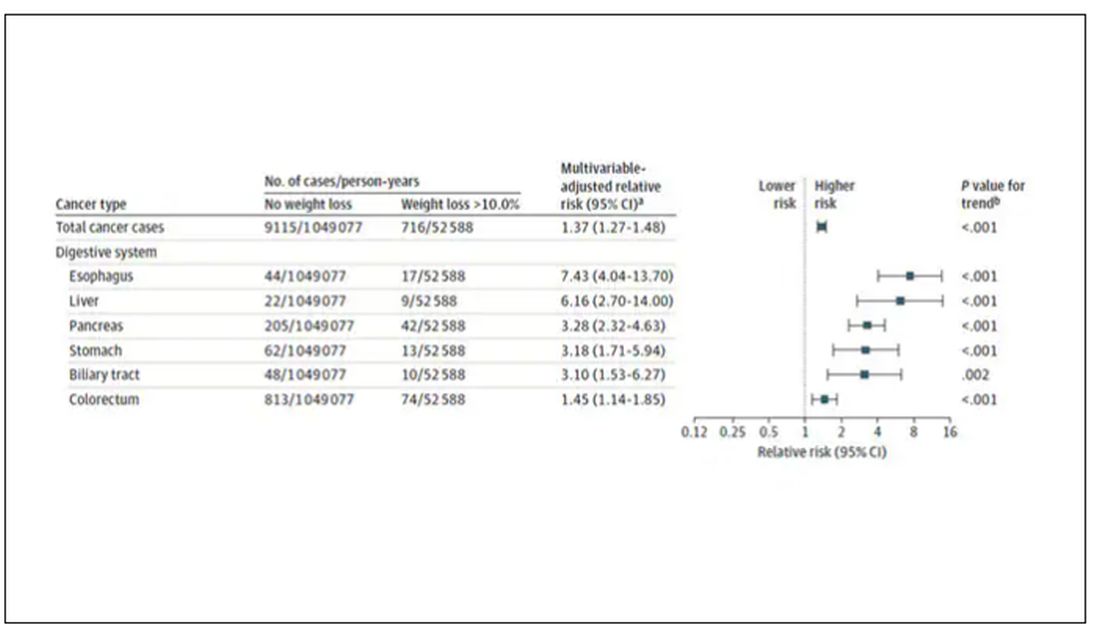
What about intentionality of weight loss? Unfortunately, the surveys did not ask participants whether they were trying to lose weight. Rather, the surveys asked about exercise and dietary habits. The researchers leveraged these responses to create three categories of participants: those who seemed to be trying to lose weight (defined as people who had increased their exercise and dietary quality); those who didn’t seem to be trying to lose weight (they changed neither exercise nor dietary behaviors); and a middle group, which changed one or the other of these behaviors but not both.
Let’s look at those who really seemed to be trying to lose weight. Over 2 years, they got more exercise and improved their diet.
If they succeeded in losing 10% or more of their body weight, they still had a higher risk for cancer than those who had not lost weight — about 30% higher, which is not that different from the 40% increased risk when you include those folks who weren’t changing their lifestyle.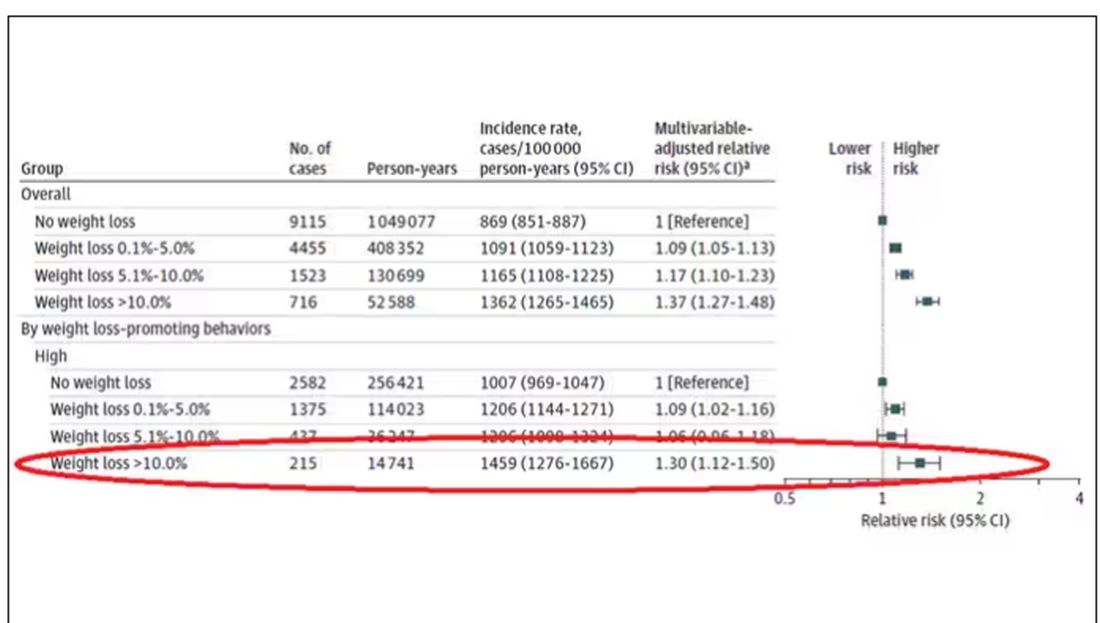
This is why this study is important. The classic teaching is that unintentional weight loss is a bad thing and needs a workup. That’s fine. But we live in a world where perhaps the majority of people are, at any given time, trying to lose weight.
We need to be careful here. I am not by any means trying to say that people who have successfully lost weight have cancer. Both of the following statements can be true:
Significant weight loss, whether intentional or not, is associated with a higher risk for cancer.
Most people with significant weight loss will not have cancer.
Both of these can be true because cancer is, fortunately, rare. Of people who lose weight, the vast majority will lose weight because they are engaging in healthier behaviors. A small number may lose weight because something else is wrong. It’s just hard to tell the two apart.
Out of the nearly 200,000 people in this study, only around 16,000 developed cancer during follow-up. Again, although the chance of having cancer is slightly higher if someone has experienced weight loss, the chance is still very low.
We also need to avoid suggesting that weight loss causes cancer. Some people lose weight because of an existing, as of yet undiagnosed cancer and its metabolic effects. This is borne out if you look at the risk of being diagnosed with cancer as you move further away from the interval of weight loss.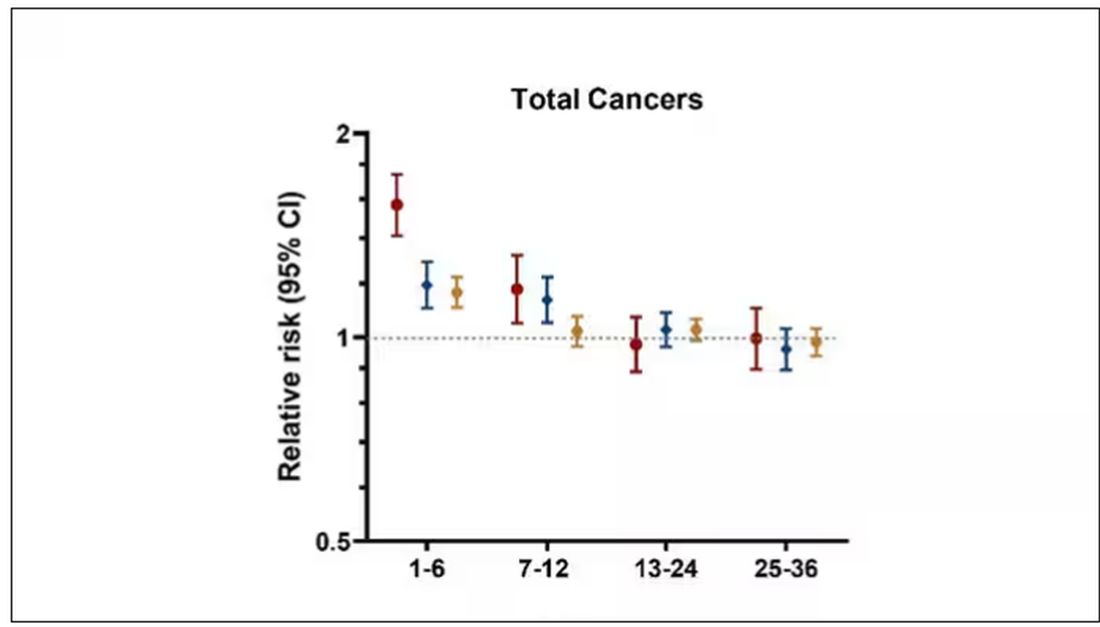
The further you get from the year of that 10% weight loss, the less likely you are to be diagnosed with cancer. Most of these cancers are diagnosed within a year of losing weight. In other words, if you’re reading this and getting worried that you lost weight 10 years ago, you’re probably out of the woods. That was, most likely, just you getting healthier.
Last thing: We have methods for weight loss now that are way more effective than diet or exercise. I’m looking at you, Ozempic. But aside from the weight loss wonder drugs, we have surgery and other interventions. This study did not capture any of that data. Ozempic wasn’t even on the market during this study, so we can’t say anything about the relationship between weight loss and cancer among people using nonlifestyle mechanisms to lose weight.
It’s a complicated system. But the clinically actionable point here is to notice if patients have lost weight. If they’ve lost it without trying, further workup is reasonable. If they’ve lost it but were trying to lose it, tell them “good job.” And consider a workup anyway.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
As anyone who has been through medical training will tell you, some little scenes just stick with you. I had been seeing a patient in our resident clinic in West Philly for a couple of years. She was in her mid-60s with diabetes and hypertension and a distant smoking history. She was overweight and had been trying to improve her diet and lose weight since I started seeing her. One day she came in and was delighted to report that she had finally started shedding some pounds — about 15 in the past 2 months.
I enthusiastically told my preceptor that my careful dietary counseling had finally done the job. She looked through the chart for a moment and asked, “Is she up to date on her cancer screening?” A workup revealed adenocarcinoma of the lung. The patient did well, actually, but the story stuck with me.
The textbooks call it “unintentional weight loss,” often in big, scary letters, and every doctor will go just a bit pale if a patient tells them that, despite efforts not to, they are losing weight. But true unintentional weight loss is not that common. After all, most of us are at least half-heartedly trying to lose weight all the time. Should doctors be worried when we are successful?
A new study suggests that perhaps they should. We’re talking about this study, appearing in JAMA, which combined participants from two long-running observational cohorts: 120,000 women from the Nurses’ Health Study, and 50,000 men from the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study. (These cohorts started in the 1970s and 1980s, so we’ll give them a pass on the gender-specific study designs.)
The rationale of enrolling healthcare providers in these cohort studies is that they would be reliable witnesses of their own health status. If a nurse or doctor says they have pancreatic cancer, it’s likely that they truly have pancreatic cancer. Detailed health surveys were distributed to the participants every other year, and the average follow-up was more than a decade.
Participants recorded their weight — as an aside, a nested study found that self-reported rate was extremely well correlated with professionally measured weight — and whether they had received a cancer diagnosis since the last survey.
This allowed researchers to look at the phenomenon described above. Would weight loss precede a new diagnosis of cancer? And, more interestingly, would intentional weight loss precede a new diagnosis of cancer.
I don’t think it will surprise you to hear that individuals in the highest category of weight loss, those who lost more than 10% of their body weight over a 2-year period, had a larger risk of being diagnosed with cancer in the next year. That’s the yellow line in this graph. In fact, they had about a 40% higher risk than those who did not lose weight.
Increased risk was found across multiple cancer types, though cancers of the gastrointestinal tract, not surprisingly, were most strongly associated with antecedent weight loss.
What about intentionality of weight loss? Unfortunately, the surveys did not ask participants whether they were trying to lose weight. Rather, the surveys asked about exercise and dietary habits. The researchers leveraged these responses to create three categories of participants: those who seemed to be trying to lose weight (defined as people who had increased their exercise and dietary quality); those who didn’t seem to be trying to lose weight (they changed neither exercise nor dietary behaviors); and a middle group, which changed one or the other of these behaviors but not both.
Let’s look at those who really seemed to be trying to lose weight. Over 2 years, they got more exercise and improved their diet.
If they succeeded in losing 10% or more of their body weight, they still had a higher risk for cancer than those who had not lost weight — about 30% higher, which is not that different from the 40% increased risk when you include those folks who weren’t changing their lifestyle.
This is why this study is important. The classic teaching is that unintentional weight loss is a bad thing and needs a workup. That’s fine. But we live in a world where perhaps the majority of people are, at any given time, trying to lose weight.
We need to be careful here. I am not by any means trying to say that people who have successfully lost weight have cancer. Both of the following statements can be true:
Significant weight loss, whether intentional or not, is associated with a higher risk for cancer.
Most people with significant weight loss will not have cancer.
Both of these can be true because cancer is, fortunately, rare. Of people who lose weight, the vast majority will lose weight because they are engaging in healthier behaviors. A small number may lose weight because something else is wrong. It’s just hard to tell the two apart.
Out of the nearly 200,000 people in this study, only around 16,000 developed cancer during follow-up. Again, although the chance of having cancer is slightly higher if someone has experienced weight loss, the chance is still very low.
We also need to avoid suggesting that weight loss causes cancer. Some people lose weight because of an existing, as of yet undiagnosed cancer and its metabolic effects. This is borne out if you look at the risk of being diagnosed with cancer as you move further away from the interval of weight loss.
The further you get from the year of that 10% weight loss, the less likely you are to be diagnosed with cancer. Most of these cancers are diagnosed within a year of losing weight. In other words, if you’re reading this and getting worried that you lost weight 10 years ago, you’re probably out of the woods. That was, most likely, just you getting healthier.
Last thing: We have methods for weight loss now that are way more effective than diet or exercise. I’m looking at you, Ozempic. But aside from the weight loss wonder drugs, we have surgery and other interventions. This study did not capture any of that data. Ozempic wasn’t even on the market during this study, so we can’t say anything about the relationship between weight loss and cancer among people using nonlifestyle mechanisms to lose weight.
It’s a complicated system. But the clinically actionable point here is to notice if patients have lost weight. If they’ve lost it without trying, further workup is reasonable. If they’ve lost it but were trying to lose it, tell them “good job.” And consider a workup anyway.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
As anyone who has been through medical training will tell you, some little scenes just stick with you. I had been seeing a patient in our resident clinic in West Philly for a couple of years. She was in her mid-60s with diabetes and hypertension and a distant smoking history. She was overweight and had been trying to improve her diet and lose weight since I started seeing her. One day she came in and was delighted to report that she had finally started shedding some pounds — about 15 in the past 2 months.
I enthusiastically told my preceptor that my careful dietary counseling had finally done the job. She looked through the chart for a moment and asked, “Is she up to date on her cancer screening?” A workup revealed adenocarcinoma of the lung. The patient did well, actually, but the story stuck with me.
The textbooks call it “unintentional weight loss,” often in big, scary letters, and every doctor will go just a bit pale if a patient tells them that, despite efforts not to, they are losing weight. But true unintentional weight loss is not that common. After all, most of us are at least half-heartedly trying to lose weight all the time. Should doctors be worried when we are successful?
A new study suggests that perhaps they should. We’re talking about this study, appearing in JAMA, which combined participants from two long-running observational cohorts: 120,000 women from the Nurses’ Health Study, and 50,000 men from the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study. (These cohorts started in the 1970s and 1980s, so we’ll give them a pass on the gender-specific study designs.)
The rationale of enrolling healthcare providers in these cohort studies is that they would be reliable witnesses of their own health status. If a nurse or doctor says they have pancreatic cancer, it’s likely that they truly have pancreatic cancer. Detailed health surveys were distributed to the participants every other year, and the average follow-up was more than a decade.
Participants recorded their weight — as an aside, a nested study found that self-reported rate was extremely well correlated with professionally measured weight — and whether they had received a cancer diagnosis since the last survey.
This allowed researchers to look at the phenomenon described above. Would weight loss precede a new diagnosis of cancer? And, more interestingly, would intentional weight loss precede a new diagnosis of cancer.
I don’t think it will surprise you to hear that individuals in the highest category of weight loss, those who lost more than 10% of their body weight over a 2-year period, had a larger risk of being diagnosed with cancer in the next year. That’s the yellow line in this graph. In fact, they had about a 40% higher risk than those who did not lose weight.
Increased risk was found across multiple cancer types, though cancers of the gastrointestinal tract, not surprisingly, were most strongly associated with antecedent weight loss.
What about intentionality of weight loss? Unfortunately, the surveys did not ask participants whether they were trying to lose weight. Rather, the surveys asked about exercise and dietary habits. The researchers leveraged these responses to create three categories of participants: those who seemed to be trying to lose weight (defined as people who had increased their exercise and dietary quality); those who didn’t seem to be trying to lose weight (they changed neither exercise nor dietary behaviors); and a middle group, which changed one or the other of these behaviors but not both.
Let’s look at those who really seemed to be trying to lose weight. Over 2 years, they got more exercise and improved their diet.
If they succeeded in losing 10% or more of their body weight, they still had a higher risk for cancer than those who had not lost weight — about 30% higher, which is not that different from the 40% increased risk when you include those folks who weren’t changing their lifestyle.
This is why this study is important. The classic teaching is that unintentional weight loss is a bad thing and needs a workup. That’s fine. But we live in a world where perhaps the majority of people are, at any given time, trying to lose weight.
We need to be careful here. I am not by any means trying to say that people who have successfully lost weight have cancer. Both of the following statements can be true:
Significant weight loss, whether intentional or not, is associated with a higher risk for cancer.
Most people with significant weight loss will not have cancer.
Both of these can be true because cancer is, fortunately, rare. Of people who lose weight, the vast majority will lose weight because they are engaging in healthier behaviors. A small number may lose weight because something else is wrong. It’s just hard to tell the two apart.
Out of the nearly 200,000 people in this study, only around 16,000 developed cancer during follow-up. Again, although the chance of having cancer is slightly higher if someone has experienced weight loss, the chance is still very low.
We also need to avoid suggesting that weight loss causes cancer. Some people lose weight because of an existing, as of yet undiagnosed cancer and its metabolic effects. This is borne out if you look at the risk of being diagnosed with cancer as you move further away from the interval of weight loss.
The further you get from the year of that 10% weight loss, the less likely you are to be diagnosed with cancer. Most of these cancers are diagnosed within a year of losing weight. In other words, if you’re reading this and getting worried that you lost weight 10 years ago, you’re probably out of the woods. That was, most likely, just you getting healthier.
Last thing: We have methods for weight loss now that are way more effective than diet or exercise. I’m looking at you, Ozempic. But aside from the weight loss wonder drugs, we have surgery and other interventions. This study did not capture any of that data. Ozempic wasn’t even on the market during this study, so we can’t say anything about the relationship between weight loss and cancer among people using nonlifestyle mechanisms to lose weight.
It’s a complicated system. But the clinically actionable point here is to notice if patients have lost weight. If they’ve lost it without trying, further workup is reasonable. If they’ve lost it but were trying to lose it, tell them “good job.” And consider a workup anyway.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hair Creams: Do You Know the Health Risks?
In late December 2023, Brazil’s National Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA) suspended the commercialization of approximately 1200 hair creams because of reports of eye irritation and temporary blindness.
A similar measure encompassing all hair creams sold in the country had already been announced by the agency in March. However, after a few weeks, ANVISA issued a resolution with rules for the products’ commercialization, allowing them back on the shelves.
With the new resolution, the sale of products that do not comply with the standards has once again been suspended. The reason is that reports of adverse events have reemerged. These events include temporary vision loss, headaches, and burning, tearing, itching, redness, and swelling of the eyes. According to reports, these adverse effects occurred mainly in people who used the specific products before swimming in the sea or in pools, or even going out in the rain.
The banned products contain 20% or more ethoxylated alcohols in their formulations. , potentially causing allergies and burns to the eyes and skin. They also have a high pulmonary and neurological toxicity. All these substances are eye irritants and can cause chemical keratitis. In extreme cases, corneal ulcers may develop, leading to vision loss.
The Brazilian Council of Ophthalmology also issued a warning on these products. It emphasized that, in addition to the sales prohibition, consumers should check the labels of hair creams to make sure that these toxic substances are not present in the product formulation.
The ANVISA website contains a list of creams that are considered safe and have not had their commercialization suspended, along with links to adverse event notifications reported by healthcare professionals or consumers.
For consumers who have recently used hair creams, the agency advises careful hair washing, including tilting the head backward to prevent the product from coming into contact with the eye area. If there is accidental eye contact, the eyes should be washed with plenty of water.
If there are any undesired effects after using these products, users should immediately seek the nearest healthcare service. Treatment should be individualized, possibly including ocular occlusion and the use of eye drops containing antibiotics or corticosteroids, among other medications.
Not every patient has easy access to an ophthalmologist in an emergency, so it is crucial for general practitioners to be prepared for initial care. In this regard, one of the most important measures is eye washing with copious amounts of clean water or saline solution for 5-10 minutes.
Eye itching is a frequent manifestation of using hair creams, and scratching the area may worsen the condition. Ocular occlusion can protect the cornea until an evaluation can be performed by a specialist.
Although we prefer our patients to stay away from these creams, it is also important to disseminate this information and advise them to read labels and use safe cosmetics.
This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In late December 2023, Brazil’s National Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA) suspended the commercialization of approximately 1200 hair creams because of reports of eye irritation and temporary blindness.
A similar measure encompassing all hair creams sold in the country had already been announced by the agency in March. However, after a few weeks, ANVISA issued a resolution with rules for the products’ commercialization, allowing them back on the shelves.
With the new resolution, the sale of products that do not comply with the standards has once again been suspended. The reason is that reports of adverse events have reemerged. These events include temporary vision loss, headaches, and burning, tearing, itching, redness, and swelling of the eyes. According to reports, these adverse effects occurred mainly in people who used the specific products before swimming in the sea or in pools, or even going out in the rain.
The banned products contain 20% or more ethoxylated alcohols in their formulations. , potentially causing allergies and burns to the eyes and skin. They also have a high pulmonary and neurological toxicity. All these substances are eye irritants and can cause chemical keratitis. In extreme cases, corneal ulcers may develop, leading to vision loss.
The Brazilian Council of Ophthalmology also issued a warning on these products. It emphasized that, in addition to the sales prohibition, consumers should check the labels of hair creams to make sure that these toxic substances are not present in the product formulation.
The ANVISA website contains a list of creams that are considered safe and have not had their commercialization suspended, along with links to adverse event notifications reported by healthcare professionals or consumers.
For consumers who have recently used hair creams, the agency advises careful hair washing, including tilting the head backward to prevent the product from coming into contact with the eye area. If there is accidental eye contact, the eyes should be washed with plenty of water.
If there are any undesired effects after using these products, users should immediately seek the nearest healthcare service. Treatment should be individualized, possibly including ocular occlusion and the use of eye drops containing antibiotics or corticosteroids, among other medications.
Not every patient has easy access to an ophthalmologist in an emergency, so it is crucial for general practitioners to be prepared for initial care. In this regard, one of the most important measures is eye washing with copious amounts of clean water or saline solution for 5-10 minutes.
Eye itching is a frequent manifestation of using hair creams, and scratching the area may worsen the condition. Ocular occlusion can protect the cornea until an evaluation can be performed by a specialist.
Although we prefer our patients to stay away from these creams, it is also important to disseminate this information and advise them to read labels and use safe cosmetics.
This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In late December 2023, Brazil’s National Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA) suspended the commercialization of approximately 1200 hair creams because of reports of eye irritation and temporary blindness.
A similar measure encompassing all hair creams sold in the country had already been announced by the agency in March. However, after a few weeks, ANVISA issued a resolution with rules for the products’ commercialization, allowing them back on the shelves.
With the new resolution, the sale of products that do not comply with the standards has once again been suspended. The reason is that reports of adverse events have reemerged. These events include temporary vision loss, headaches, and burning, tearing, itching, redness, and swelling of the eyes. According to reports, these adverse effects occurred mainly in people who used the specific products before swimming in the sea or in pools, or even going out in the rain.
The banned products contain 20% or more ethoxylated alcohols in their formulations. , potentially causing allergies and burns to the eyes and skin. They also have a high pulmonary and neurological toxicity. All these substances are eye irritants and can cause chemical keratitis. In extreme cases, corneal ulcers may develop, leading to vision loss.
The Brazilian Council of Ophthalmology also issued a warning on these products. It emphasized that, in addition to the sales prohibition, consumers should check the labels of hair creams to make sure that these toxic substances are not present in the product formulation.
The ANVISA website contains a list of creams that are considered safe and have not had their commercialization suspended, along with links to adverse event notifications reported by healthcare professionals or consumers.
For consumers who have recently used hair creams, the agency advises careful hair washing, including tilting the head backward to prevent the product from coming into contact with the eye area. If there is accidental eye contact, the eyes should be washed with plenty of water.
If there are any undesired effects after using these products, users should immediately seek the nearest healthcare service. Treatment should be individualized, possibly including ocular occlusion and the use of eye drops containing antibiotics or corticosteroids, among other medications.
Not every patient has easy access to an ophthalmologist in an emergency, so it is crucial for general practitioners to be prepared for initial care. In this regard, one of the most important measures is eye washing with copious amounts of clean water or saline solution for 5-10 minutes.
Eye itching is a frequent manifestation of using hair creams, and scratching the area may worsen the condition. Ocular occlusion can protect the cornea until an evaluation can be performed by a specialist.
Although we prefer our patients to stay away from these creams, it is also important to disseminate this information and advise them to read labels and use safe cosmetics.
This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hair Loss in Children: How to Spot and Treat Different Causes
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — There are subtleties and nuances to diagnosing, treating, and monitoring the progress of treatment of hair loss in children. Moreover, hair loss in children can be challenging because it can be caused by a range of conditions, some common and others relatively rare.
Michelle Oboite, MD, shared tips on how to distinguish types of hair loss, when to treat with medications such as topical corticosteroids or Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, and why shared decision-making is important, at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
What these conditions share is that they can negatively affect the quality of life for a child or teenager when the condition leads to anxiety, teasing, or bullying. “It is very isolating to have this condition that everyone in the world can see that you have and judge you for it,” said Dr. Oboite, an attending physician in the dermatology section of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Others are lichen planopilaris and genetic conditions, including loose anagen syndrome, uncombable hair syndrome, and “something so rare” — it has no acronym — autosomal recessive hypotrichosis with recurrent skin vesicles, Dr. Oboite said.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata can differ from child to child and can appear in different stages: A localized patch stage, a diffuse patchy stage, or alopecia universalis. In this last stage, the child has already lost most or all the hair on the scalp and eyebrows, as well as the eyelashes.
The decision to treat or not to treat, particularly in younger children, should be on the basis of shared decision-making between a healthcare provider and caregiver, said Dr. Oboite, who is also an assistant professor of clinical dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Some younger children may not experience any negative impact from the condition, so waiting until they are older is an option.
Also, consider the impact of treatment on a child. Some therapies require frequent blood draws for monitoring, and some topical therapies that are applied multiple times a day “can be very overwhelming” for young children, Dr. Oboite said.
Most children with alopecia areata are healthy and do not need extensive screening laboratory testing. However, one exception is if thyroid dysfunction, commonly associated with alopecia areata, is suspected.
For alopecia areata, Dr. Oboite recommends starting with topical therapies, either topical corticosteroids (as first line) or topical JAK inhibitors (either topical ruxolitinib or compounded topical tofacitinib, both off-label for this indication).
Topical corticosteroids can be effective, but “you want to be thoughtful of the strength you’re using, the application frequency, and then the total amount of surface area that you’re treating,” Dr. Oboite said. Too potent or too much of a topical corticosteroid increases the risk for atrophy and systemic absorption, respectively. To reduce the risk, she reserves the use of ultrahigh-potency topical corticosteroids, such as clobetasol, for children ages 10 years or older. For children younger than 10 years, she recommends using mid-high-potency topical corticosteroids instead.
She recommends once-a-day application around bedtime 5 days a week, generally Monday through Friday to make it easier to remember.
“For children who have over 50% of the scalp involved, I do consider systemic therapy,” Dr. Oboite said. This can include oral steroids such as dexamethasone, prednisone, or prednisolone. For children with recalcitrant disease, she is more likely to use the oral JAK inhibitor ritlecitinib because it was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating severe alopecia areata in children 12 years and older and in adults.
Another strategy Dr. Oboite uses is to add low-dose oral minoxidil as an adjuvant to other systemic therapy. “I find that it helps with faster hair regrowth,” she said.
Tinea Capitis
Oral treatment is indicated for tinea capitis. “Topicals just don’t really clear this,” Dr. Oboite said. Also, talk to patients and families about preventing reinfection with the dermatophyte that causes this condition. “Make sure we’re cleaning hats, combs, brushes, and pillowcases. That is really important.”
Some patients can develop a widespread rash while on treatment. But in most cases, it’s not an adverse reaction to the medication but rather an indication that the body’s response is revving up, she noted.
Griseofulvin 20 mg/kg/d is one treatment option. Another is terbinafine (using weight-based dosing). A tip with terbinafine is that because the tablet needs to be crushed for a young child, “you can put it in anything, besides applesauce or yogurt with fruit on the bottom, which can be acidic and reduce the effectiveness of the medication,” Dr. Oboite said.
For cases of severe, inflammatory tinea capitis such as a kerion, “I will say you have to hold the hands of these patients, the journey can be long,” she added.
Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania occurs when someone cannot stop pulling their own hair, and in the early phases, it can be confused with alopecia areata. A thorough history and examination of the patient can help distinguish the two conditions. Sometimes a child or teen has a history of anxiety-related behaviors like nail biting that points to trichotillomania. Another tip is to use a dermatoscope to help distinguish hair loss conditions because it avoids having to do as many biopsies in children.
Redirection therapy can work for younger children, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help older children with trichotillomania. In response to a question during the Q&A period, Dr. Oboite said psychiatrists or psychologists can perform CBT. If it takes time to get an appointment, there are some CBT apps that can help in the meantime, she said.
“One thing really important is to not blame the child,” Dr. Oboite said. “Most children don’t even know that they’re doing this. This is often not a behavior that is being done on purpose.”
Androgenetic Alopecia
Rarely, children and teenagers can also present with androgenetic alopecia, which Dr. Oboite has successfully treated with topical minoxidil, applied once a day before increasing to twice a day if tolerated. “I will tell them that when they pick it up, it will say ‘you should not use in children.’ But it actually can be used in children safely.”
Low-dose oral minoxidil is another option. Both treatments require a commitment by patients and parents because they are “taking this for a long time.”
Loose Anagen and Uncombable Hair Syndromes
A rare genetic form of hair loss is called loose anagen syndrome. Children with this disorder will have thin hair that is easily pulled out without a lot of force. Their hair appears to typically only grow to a certain length (such as to the nape of the neck) and then stops.
Another genetic hair loss condition is uncombable hair syndrome. It can cause hair to grow out of the scalp in all directions, and as the name suggests, it is almost impossible to comb or brush down. Along with loose anagen syndrome, uncombable hair syndrome tends to improve as the child gets older. “The key point here is telling parents that it can get better with time,” Dr. Oboite said.
A Condition With No Well-Known Acronym
She described a child she treated who had hair that never grew and was easily broken. The patient’s skin was prone to bruising, and her fingernails would easily fall off after trauma; her dentist noted that she had no buds for adult teeth on x-rays. These different presentations are important because hair, teeth, and nails all come from the same ectoderm germ line in embryo development, Dr. Oboite said.
Exome sequencing revealed the girl had a very rare diagnosis called autosomal recessive hypotrichosis with recurrent skin vesicles. “So, it is really important to recognize that children who are presenting with hair issues can have a genetic, underlying condition,” she said. Examining the skin, nails, and teeth, in addition to the hair, can be clues to these very rare diagnoses.
Some of these hair loss conditions in children can be challenging to diagnose and manage, Dr. Oboite said. “So don’t be afraid to ask for help on complex or rare cases.” Pediatric dermatologists “are always happy to help you. Hair loss is daunting, and hair loss in children can be even more daunting,” but the rewards of accurate diagnosis and successful treatment can be great, she said.
Dr. Oboite reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — There are subtleties and nuances to diagnosing, treating, and monitoring the progress of treatment of hair loss in children. Moreover, hair loss in children can be challenging because it can be caused by a range of conditions, some common and others relatively rare.
Michelle Oboite, MD, shared tips on how to distinguish types of hair loss, when to treat with medications such as topical corticosteroids or Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, and why shared decision-making is important, at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
What these conditions share is that they can negatively affect the quality of life for a child or teenager when the condition leads to anxiety, teasing, or bullying. “It is very isolating to have this condition that everyone in the world can see that you have and judge you for it,” said Dr. Oboite, an attending physician in the dermatology section of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Others are lichen planopilaris and genetic conditions, including loose anagen syndrome, uncombable hair syndrome, and “something so rare” — it has no acronym — autosomal recessive hypotrichosis with recurrent skin vesicles, Dr. Oboite said.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata can differ from child to child and can appear in different stages: A localized patch stage, a diffuse patchy stage, or alopecia universalis. In this last stage, the child has already lost most or all the hair on the scalp and eyebrows, as well as the eyelashes.
The decision to treat or not to treat, particularly in younger children, should be on the basis of shared decision-making between a healthcare provider and caregiver, said Dr. Oboite, who is also an assistant professor of clinical dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Some younger children may not experience any negative impact from the condition, so waiting until they are older is an option.
Also, consider the impact of treatment on a child. Some therapies require frequent blood draws for monitoring, and some topical therapies that are applied multiple times a day “can be very overwhelming” for young children, Dr. Oboite said.
Most children with alopecia areata are healthy and do not need extensive screening laboratory testing. However, one exception is if thyroid dysfunction, commonly associated with alopecia areata, is suspected.
For alopecia areata, Dr. Oboite recommends starting with topical therapies, either topical corticosteroids (as first line) or topical JAK inhibitors (either topical ruxolitinib or compounded topical tofacitinib, both off-label for this indication).
Topical corticosteroids can be effective, but “you want to be thoughtful of the strength you’re using, the application frequency, and then the total amount of surface area that you’re treating,” Dr. Oboite said. Too potent or too much of a topical corticosteroid increases the risk for atrophy and systemic absorption, respectively. To reduce the risk, she reserves the use of ultrahigh-potency topical corticosteroids, such as clobetasol, for children ages 10 years or older. For children younger than 10 years, she recommends using mid-high-potency topical corticosteroids instead.
She recommends once-a-day application around bedtime 5 days a week, generally Monday through Friday to make it easier to remember.
“For children who have over 50% of the scalp involved, I do consider systemic therapy,” Dr. Oboite said. This can include oral steroids such as dexamethasone, prednisone, or prednisolone. For children with recalcitrant disease, she is more likely to use the oral JAK inhibitor ritlecitinib because it was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating severe alopecia areata in children 12 years and older and in adults.
Another strategy Dr. Oboite uses is to add low-dose oral minoxidil as an adjuvant to other systemic therapy. “I find that it helps with faster hair regrowth,” she said.
Tinea Capitis
Oral treatment is indicated for tinea capitis. “Topicals just don’t really clear this,” Dr. Oboite said. Also, talk to patients and families about preventing reinfection with the dermatophyte that causes this condition. “Make sure we’re cleaning hats, combs, brushes, and pillowcases. That is really important.”
Some patients can develop a widespread rash while on treatment. But in most cases, it’s not an adverse reaction to the medication but rather an indication that the body’s response is revving up, she noted.
Griseofulvin 20 mg/kg/d is one treatment option. Another is terbinafine (using weight-based dosing). A tip with terbinafine is that because the tablet needs to be crushed for a young child, “you can put it in anything, besides applesauce or yogurt with fruit on the bottom, which can be acidic and reduce the effectiveness of the medication,” Dr. Oboite said.
For cases of severe, inflammatory tinea capitis such as a kerion, “I will say you have to hold the hands of these patients, the journey can be long,” she added.
Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania occurs when someone cannot stop pulling their own hair, and in the early phases, it can be confused with alopecia areata. A thorough history and examination of the patient can help distinguish the two conditions. Sometimes a child or teen has a history of anxiety-related behaviors like nail biting that points to trichotillomania. Another tip is to use a dermatoscope to help distinguish hair loss conditions because it avoids having to do as many biopsies in children.
Redirection therapy can work for younger children, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help older children with trichotillomania. In response to a question during the Q&A period, Dr. Oboite said psychiatrists or psychologists can perform CBT. If it takes time to get an appointment, there are some CBT apps that can help in the meantime, she said.
“One thing really important is to not blame the child,” Dr. Oboite said. “Most children don’t even know that they’re doing this. This is often not a behavior that is being done on purpose.”
Androgenetic Alopecia
Rarely, children and teenagers can also present with androgenetic alopecia, which Dr. Oboite has successfully treated with topical minoxidil, applied once a day before increasing to twice a day if tolerated. “I will tell them that when they pick it up, it will say ‘you should not use in children.’ But it actually can be used in children safely.”
Low-dose oral minoxidil is another option. Both treatments require a commitment by patients and parents because they are “taking this for a long time.”
Loose Anagen and Uncombable Hair Syndromes
A rare genetic form of hair loss is called loose anagen syndrome. Children with this disorder will have thin hair that is easily pulled out without a lot of force. Their hair appears to typically only grow to a certain length (such as to the nape of the neck) and then stops.
Another genetic hair loss condition is uncombable hair syndrome. It can cause hair to grow out of the scalp in all directions, and as the name suggests, it is almost impossible to comb or brush down. Along with loose anagen syndrome, uncombable hair syndrome tends to improve as the child gets older. “The key point here is telling parents that it can get better with time,” Dr. Oboite said.
A Condition With No Well-Known Acronym
She described a child she treated who had hair that never grew and was easily broken. The patient’s skin was prone to bruising, and her fingernails would easily fall off after trauma; her dentist noted that she had no buds for adult teeth on x-rays. These different presentations are important because hair, teeth, and nails all come from the same ectoderm germ line in embryo development, Dr. Oboite said.
Exome sequencing revealed the girl had a very rare diagnosis called autosomal recessive hypotrichosis with recurrent skin vesicles. “So, it is really important to recognize that children who are presenting with hair issues can have a genetic, underlying condition,” she said. Examining the skin, nails, and teeth, in addition to the hair, can be clues to these very rare diagnoses.
Some of these hair loss conditions in children can be challenging to diagnose and manage, Dr. Oboite said. “So don’t be afraid to ask for help on complex or rare cases.” Pediatric dermatologists “are always happy to help you. Hair loss is daunting, and hair loss in children can be even more daunting,” but the rewards of accurate diagnosis and successful treatment can be great, she said.
Dr. Oboite reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — There are subtleties and nuances to diagnosing, treating, and monitoring the progress of treatment of hair loss in children. Moreover, hair loss in children can be challenging because it can be caused by a range of conditions, some common and others relatively rare.
Michelle Oboite, MD, shared tips on how to distinguish types of hair loss, when to treat with medications such as topical corticosteroids or Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, and why shared decision-making is important, at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
What these conditions share is that they can negatively affect the quality of life for a child or teenager when the condition leads to anxiety, teasing, or bullying. “It is very isolating to have this condition that everyone in the world can see that you have and judge you for it,” said Dr. Oboite, an attending physician in the dermatology section of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Others are lichen planopilaris and genetic conditions, including loose anagen syndrome, uncombable hair syndrome, and “something so rare” — it has no acronym — autosomal recessive hypotrichosis with recurrent skin vesicles, Dr. Oboite said.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata can differ from child to child and can appear in different stages: A localized patch stage, a diffuse patchy stage, or alopecia universalis. In this last stage, the child has already lost most or all the hair on the scalp and eyebrows, as well as the eyelashes.
The decision to treat or not to treat, particularly in younger children, should be on the basis of shared decision-making between a healthcare provider and caregiver, said Dr. Oboite, who is also an assistant professor of clinical dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Some younger children may not experience any negative impact from the condition, so waiting until they are older is an option.
Also, consider the impact of treatment on a child. Some therapies require frequent blood draws for monitoring, and some topical therapies that are applied multiple times a day “can be very overwhelming” for young children, Dr. Oboite said.
Most children with alopecia areata are healthy and do not need extensive screening laboratory testing. However, one exception is if thyroid dysfunction, commonly associated with alopecia areata, is suspected.
For alopecia areata, Dr. Oboite recommends starting with topical therapies, either topical corticosteroids (as first line) or topical JAK inhibitors (either topical ruxolitinib or compounded topical tofacitinib, both off-label for this indication).
Topical corticosteroids can be effective, but “you want to be thoughtful of the strength you’re using, the application frequency, and then the total amount of surface area that you’re treating,” Dr. Oboite said. Too potent or too much of a topical corticosteroid increases the risk for atrophy and systemic absorption, respectively. To reduce the risk, she reserves the use of ultrahigh-potency topical corticosteroids, such as clobetasol, for children ages 10 years or older. For children younger than 10 years, she recommends using mid-high-potency topical corticosteroids instead.
She recommends once-a-day application around bedtime 5 days a week, generally Monday through Friday to make it easier to remember.
“For children who have over 50% of the scalp involved, I do consider systemic therapy,” Dr. Oboite said. This can include oral steroids such as dexamethasone, prednisone, or prednisolone. For children with recalcitrant disease, she is more likely to use the oral JAK inhibitor ritlecitinib because it was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating severe alopecia areata in children 12 years and older and in adults.
Another strategy Dr. Oboite uses is to add low-dose oral minoxidil as an adjuvant to other systemic therapy. “I find that it helps with faster hair regrowth,” she said.
Tinea Capitis
Oral treatment is indicated for tinea capitis. “Topicals just don’t really clear this,” Dr. Oboite said. Also, talk to patients and families about preventing reinfection with the dermatophyte that causes this condition. “Make sure we’re cleaning hats, combs, brushes, and pillowcases. That is really important.”
Some patients can develop a widespread rash while on treatment. But in most cases, it’s not an adverse reaction to the medication but rather an indication that the body’s response is revving up, she noted.
Griseofulvin 20 mg/kg/d is one treatment option. Another is terbinafine (using weight-based dosing). A tip with terbinafine is that because the tablet needs to be crushed for a young child, “you can put it in anything, besides applesauce or yogurt with fruit on the bottom, which can be acidic and reduce the effectiveness of the medication,” Dr. Oboite said.
For cases of severe, inflammatory tinea capitis such as a kerion, “I will say you have to hold the hands of these patients, the journey can be long,” she added.
Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania occurs when someone cannot stop pulling their own hair, and in the early phases, it can be confused with alopecia areata. A thorough history and examination of the patient can help distinguish the two conditions. Sometimes a child or teen has a history of anxiety-related behaviors like nail biting that points to trichotillomania. Another tip is to use a dermatoscope to help distinguish hair loss conditions because it avoids having to do as many biopsies in children.
Redirection therapy can work for younger children, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help older children with trichotillomania. In response to a question during the Q&A period, Dr. Oboite said psychiatrists or psychologists can perform CBT. If it takes time to get an appointment, there are some CBT apps that can help in the meantime, she said.
“One thing really important is to not blame the child,” Dr. Oboite said. “Most children don’t even know that they’re doing this. This is often not a behavior that is being done on purpose.”
Androgenetic Alopecia
Rarely, children and teenagers can also present with androgenetic alopecia, which Dr. Oboite has successfully treated with topical minoxidil, applied once a day before increasing to twice a day if tolerated. “I will tell them that when they pick it up, it will say ‘you should not use in children.’ But it actually can be used in children safely.”
Low-dose oral minoxidil is another option. Both treatments require a commitment by patients and parents because they are “taking this for a long time.”
Loose Anagen and Uncombable Hair Syndromes
A rare genetic form of hair loss is called loose anagen syndrome. Children with this disorder will have thin hair that is easily pulled out without a lot of force. Their hair appears to typically only grow to a certain length (such as to the nape of the neck) and then stops.
Another genetic hair loss condition is uncombable hair syndrome. It can cause hair to grow out of the scalp in all directions, and as the name suggests, it is almost impossible to comb or brush down. Along with loose anagen syndrome, uncombable hair syndrome tends to improve as the child gets older. “The key point here is telling parents that it can get better with time,” Dr. Oboite said.
A Condition With No Well-Known Acronym
She described a child she treated who had hair that never grew and was easily broken. The patient’s skin was prone to bruising, and her fingernails would easily fall off after trauma; her dentist noted that she had no buds for adult teeth on x-rays. These different presentations are important because hair, teeth, and nails all come from the same ectoderm germ line in embryo development, Dr. Oboite said.
Exome sequencing revealed the girl had a very rare diagnosis called autosomal recessive hypotrichosis with recurrent skin vesicles. “So, it is really important to recognize that children who are presenting with hair issues can have a genetic, underlying condition,” she said. Examining the skin, nails, and teeth, in addition to the hair, can be clues to these very rare diagnoses.
Some of these hair loss conditions in children can be challenging to diagnose and manage, Dr. Oboite said. “So don’t be afraid to ask for help on complex or rare cases.” Pediatric dermatologists “are always happy to help you. Hair loss is daunting, and hair loss in children can be even more daunting,” but the rewards of accurate diagnosis and successful treatment can be great, she said.
Dr. Oboite reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ODAC 2024
A Look at the Evidence Linking Diet to Skin Conditions
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — Amid all the hype, claims, and confusion, there is evidence linking some foods and drinks to an increased risk for acne, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, rosacea, and other common skin conditions. So, what is the connection in each case? And how can people with any of these skin conditions potentially improve their health and quality of life with dietary changes?
What is clear is that there has been an explosion of interest in learning which foods can improve or worsen skin issues in recent years. It’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with the research and also to Google ‘diet’ and ‘skin’, said Vivian Shi, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock. “As practitioners, we should be well prepared to talk about what patients want to talk about.”
Acne
One of the major areas of interest is diet and acne. “We’ve all heard sugar and dairy are bad, and the Western diet is high in sugar and dairy,” Dr. Shi said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
Dairy, red meat, and carbohydrates can break down into leucine, an essential amino acid found in protein. Leucine and sugar together, in turn, can produce insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which, through different pathways, can reach the androgen receptors throughout the body, including the skin. This results in sebogenesis, lipogenesis, and keratinization, which triggers follicular inflammation and results in more of the acne-causing bacteria Cutibacterium acnes.
Milk and other dairy products also can increase IGF-1 levels, which can alter hormonal mediators and increase acne.
Not all types of dairy milk are created equal, however, when it comes to acne. Dr. Shi wondered why 2% milk has overall color and nutritional content very similar to that of whole milk. “I looked into this.” She discovered that when milk manufacturers remove the fat, they often add whey proteins to restore some nutrients. Whey protein can increase acne, Dr. Shi added.
“So, if you’re going to choose any milk to drink, I think from an acne perspective, it’s better to use whole milk. If you can get it organic, even better.” Skim milk is the most acnegenic, she said.
Psoriasis
A systematic review of 55 studies evaluating diet and psoriasis found obesity can be an exacerbating factor. The strongest evidence for dietary weight reduction points to a hypocaloric diet in people with overweight or obesity, according to the review. Other evidence suggests alcohol can lower response to treatment and is linked with more severe psoriasis. Furthermore, a gluten-free diet or vitamin D supplements can help some subpopulations of people with psoriasis.
“An overwhelming majority of our psoriasis patients are vitamin D deficient,” Dr. Shi said.
The National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) publishes dietary modification guidelines, updated as recently as November 2023. The NPF states that “there is no diet that will cure psoriatic disease, but there are many ways in which eating healthful food may lessen the severity of symptoms and play a role in lowering the likelihood of developing comorbidities.”
Healthier choices include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat dairy products. Include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and nuts. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet has been linked to a lower severity of psoriasis.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is “one of the prototypical diseases related to diet,” Dr. Shi said. A different meta-analysis looked at randomized controlled trials of synbiotics (a combination of prebiotics and probiotics) for treatment of AD.
These researchers found that synbiotics do not prevent AD, but they can help treat it in adults and children older than 1 year. In addition, synbiotics are more beneficial than probiotics in treating the condition, although there are no head-to-head comparison studies. In addition, the meta-analysis found that prebiotics alone can lower AD severity.
However, Dr. Shi said, there are no recommendations from the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) on prebiotics or probiotics for AD, and the AAD does not recommend any supplement or essential oil for AD.
In a 2022 review, investigators ranked the efficacy of different supplements for AD based on available evidence. They found the greatest benefit associated with vitamin D supplementation, followed by vitamin E, probiotics, hemp seed oil, histidine, and oolong tea. They also noted the ‘Six Food Elimination Diet and Autoimmune Protocol’ featured the least amount of evidence to back it up.
Rosacea
Rosacea appears to be caused by “all the fun things in life” like sunlight, alcohol, chocolate, spicy foods, and caffeine, Dr. Shi said. In people with rosacea, they can cause facial flushing, edema, burning, and an inflammatory response.
Certain foods can activate skin receptors and sensory neurons, which can release neuropeptides that act on mast cells in blood that lead to flushing. The skin-gut axis may also be involved, evidence suggests. “And that is why food has a pretty profound impact on rosacea,” Dr. Shi said.
Dr. Shi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — Amid all the hype, claims, and confusion, there is evidence linking some foods and drinks to an increased risk for acne, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, rosacea, and other common skin conditions. So, what is the connection in each case? And how can people with any of these skin conditions potentially improve their health and quality of life with dietary changes?
What is clear is that there has been an explosion of interest in learning which foods can improve or worsen skin issues in recent years. It’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with the research and also to Google ‘diet’ and ‘skin’, said Vivian Shi, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock. “As practitioners, we should be well prepared to talk about what patients want to talk about.”
Acne
One of the major areas of interest is diet and acne. “We’ve all heard sugar and dairy are bad, and the Western diet is high in sugar and dairy,” Dr. Shi said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
Dairy, red meat, and carbohydrates can break down into leucine, an essential amino acid found in protein. Leucine and sugar together, in turn, can produce insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which, through different pathways, can reach the androgen receptors throughout the body, including the skin. This results in sebogenesis, lipogenesis, and keratinization, which triggers follicular inflammation and results in more of the acne-causing bacteria Cutibacterium acnes.
Milk and other dairy products also can increase IGF-1 levels, which can alter hormonal mediators and increase acne.
Not all types of dairy milk are created equal, however, when it comes to acne. Dr. Shi wondered why 2% milk has overall color and nutritional content very similar to that of whole milk. “I looked into this.” She discovered that when milk manufacturers remove the fat, they often add whey proteins to restore some nutrients. Whey protein can increase acne, Dr. Shi added.
“So, if you’re going to choose any milk to drink, I think from an acne perspective, it’s better to use whole milk. If you can get it organic, even better.” Skim milk is the most acnegenic, she said.
Psoriasis
A systematic review of 55 studies evaluating diet and psoriasis found obesity can be an exacerbating factor. The strongest evidence for dietary weight reduction points to a hypocaloric diet in people with overweight or obesity, according to the review. Other evidence suggests alcohol can lower response to treatment and is linked with more severe psoriasis. Furthermore, a gluten-free diet or vitamin D supplements can help some subpopulations of people with psoriasis.
“An overwhelming majority of our psoriasis patients are vitamin D deficient,” Dr. Shi said.
The National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) publishes dietary modification guidelines, updated as recently as November 2023. The NPF states that “there is no diet that will cure psoriatic disease, but there are many ways in which eating healthful food may lessen the severity of symptoms and play a role in lowering the likelihood of developing comorbidities.”
Healthier choices include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat dairy products. Include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and nuts. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet has been linked to a lower severity of psoriasis.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is “one of the prototypical diseases related to diet,” Dr. Shi said. A different meta-analysis looked at randomized controlled trials of synbiotics (a combination of prebiotics and probiotics) for treatment of AD.
These researchers found that synbiotics do not prevent AD, but they can help treat it in adults and children older than 1 year. In addition, synbiotics are more beneficial than probiotics in treating the condition, although there are no head-to-head comparison studies. In addition, the meta-analysis found that prebiotics alone can lower AD severity.
However, Dr. Shi said, there are no recommendations from the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) on prebiotics or probiotics for AD, and the AAD does not recommend any supplement or essential oil for AD.
In a 2022 review, investigators ranked the efficacy of different supplements for AD based on available evidence. They found the greatest benefit associated with vitamin D supplementation, followed by vitamin E, probiotics, hemp seed oil, histidine, and oolong tea. They also noted the ‘Six Food Elimination Diet and Autoimmune Protocol’ featured the least amount of evidence to back it up.
Rosacea
Rosacea appears to be caused by “all the fun things in life” like sunlight, alcohol, chocolate, spicy foods, and caffeine, Dr. Shi said. In people with rosacea, they can cause facial flushing, edema, burning, and an inflammatory response.
Certain foods can activate skin receptors and sensory neurons, which can release neuropeptides that act on mast cells in blood that lead to flushing. The skin-gut axis may also be involved, evidence suggests. “And that is why food has a pretty profound impact on rosacea,” Dr. Shi said.
Dr. Shi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — Amid all the hype, claims, and confusion, there is evidence linking some foods and drinks to an increased risk for acne, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, rosacea, and other common skin conditions. So, what is the connection in each case? And how can people with any of these skin conditions potentially improve their health and quality of life with dietary changes?
What is clear is that there has been an explosion of interest in learning which foods can improve or worsen skin issues in recent years. It’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with the research and also to Google ‘diet’ and ‘skin’, said Vivian Shi, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock. “As practitioners, we should be well prepared to talk about what patients want to talk about.”
Acne
One of the major areas of interest is diet and acne. “We’ve all heard sugar and dairy are bad, and the Western diet is high in sugar and dairy,” Dr. Shi said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
Dairy, red meat, and carbohydrates can break down into leucine, an essential amino acid found in protein. Leucine and sugar together, in turn, can produce insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which, through different pathways, can reach the androgen receptors throughout the body, including the skin. This results in sebogenesis, lipogenesis, and keratinization, which triggers follicular inflammation and results in more of the acne-causing bacteria Cutibacterium acnes.
Milk and other dairy products also can increase IGF-1 levels, which can alter hormonal mediators and increase acne.
Not all types of dairy milk are created equal, however, when it comes to acne. Dr. Shi wondered why 2% milk has overall color and nutritional content very similar to that of whole milk. “I looked into this.” She discovered that when milk manufacturers remove the fat, they often add whey proteins to restore some nutrients. Whey protein can increase acne, Dr. Shi added.
“So, if you’re going to choose any milk to drink, I think from an acne perspective, it’s better to use whole milk. If you can get it organic, even better.” Skim milk is the most acnegenic, she said.
Psoriasis
A systematic review of 55 studies evaluating diet and psoriasis found obesity can be an exacerbating factor. The strongest evidence for dietary weight reduction points to a hypocaloric diet in people with overweight or obesity, according to the review. Other evidence suggests alcohol can lower response to treatment and is linked with more severe psoriasis. Furthermore, a gluten-free diet or vitamin D supplements can help some subpopulations of people with psoriasis.
“An overwhelming majority of our psoriasis patients are vitamin D deficient,” Dr. Shi said.
The National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) publishes dietary modification guidelines, updated as recently as November 2023. The NPF states that “there is no diet that will cure psoriatic disease, but there are many ways in which eating healthful food may lessen the severity of symptoms and play a role in lowering the likelihood of developing comorbidities.”
Healthier choices include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat dairy products. Include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and nuts. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet has been linked to a lower severity of psoriasis.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is “one of the prototypical diseases related to diet,” Dr. Shi said. A different meta-analysis looked at randomized controlled trials of synbiotics (a combination of prebiotics and probiotics) for treatment of AD.
These researchers found that synbiotics do not prevent AD, but they can help treat it in adults and children older than 1 year. In addition, synbiotics are more beneficial than probiotics in treating the condition, although there are no head-to-head comparison studies. In addition, the meta-analysis found that prebiotics alone can lower AD severity.
However, Dr. Shi said, there are no recommendations from the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) on prebiotics or probiotics for AD, and the AAD does not recommend any supplement or essential oil for AD.
In a 2022 review, investigators ranked the efficacy of different supplements for AD based on available evidence. They found the greatest benefit associated with vitamin D supplementation, followed by vitamin E, probiotics, hemp seed oil, histidine, and oolong tea. They also noted the ‘Six Food Elimination Diet and Autoimmune Protocol’ featured the least amount of evidence to back it up.
Rosacea
Rosacea appears to be caused by “all the fun things in life” like sunlight, alcohol, chocolate, spicy foods, and caffeine, Dr. Shi said. In people with rosacea, they can cause facial flushing, edema, burning, and an inflammatory response.
Certain foods can activate skin receptors and sensory neurons, which can release neuropeptides that act on mast cells in blood that lead to flushing. The skin-gut axis may also be involved, evidence suggests. “And that is why food has a pretty profound impact on rosacea,” Dr. Shi said.
Dr. Shi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Novel Clinic Resulted in ‘Impressive’ Outcomes for Patients With Moderate to Severe Eczema
, results from a single-center study showed.
“A significant challenge in caring for patients with atopic dermatitis is lack of collaboration between healthcare providers, leading to disjointed care, inconsistent treatment plans, and conflicting dialogue with patients,” first author Alexis Tracy, MD, a combined allergy and dermatology research fellow at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online January 14, 2024, in Pediatric Dermatology.
Launched in 2019, the clinic, which is called the Multidisciplinary Atopic Dermatitis Program (MADP), is a collaborative effort between with Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California San Diego Health division of dermatology, division of allergy & immunology, and the hospital’s clinical pharmacy. Patients referred to the MADP undergo a concurrent, comprehensive evaluation by a dermatologist, allergist, clinical pharmacist, and others who help to assess AD severity, provide family education about the disease, and form a care plan using the model of shared decision-making (SDM). Visits take about two hours, and the frequency of follow-up visits varies.

In the dermatology realm, tools used to compare the extent and severity of AD between visits include the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM), the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI), Validated Investigator Global Assessment (vIGA), Body Surface Area (BSA), and the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS).To investigate the MADP’s success to date, Dr. Tracy and colleagues evaluated 44 patients with a history of moderate to severe, persistent AD who were referred to the clinic between April 3, 2019, and October 22, 2022, and had between one and three follow-up visits. The patients ranged from age 4 months to 18 years (mean, 7.74 years).
Compared with baseline, EASI scores of patients decreased significantly, with an average mean improvement of 9.61 by the second visit, 15.12 by the third visit, and 17.42 by the fourth visit (P <.001 for all three). These represent an average decreases of 44.20%, 63.26%, 74.35%, respectively.
At the seventh visit, the EASI score decreased by a mean of 33.48 (P = .008), which represents an average decrease of 91.52% from baseline. Of the 44 patients, 32 achieved an EASI 50 and 21 achieved an EASI 75.
In other findings, the mean vIGA improved with each visit, with the largest observed improvement at the seventh visit (a mean of 2.25 points; P = .009) and the greatest mean improvement in the POEM score was seen at the sixth visit (a mean of 11.13 points; P < .001). The mean difference in CDLQI scores also increased with each visit, with the largest improvement seen at the sixth visit (an increase of 12 points; P < .001).
Similarly, BSA progressively improved at each clinic visit, from a mean decrease of 16.02% at the second visit to a mean decrease of 56.04% at the seventh visit (P < .001 for both). Meanwhile, the largest mean improvement in pruritus was seen at the sixth visit (a mean of 4.10 points; P = .001).
In an interview, MADP’s codirector, Lawrence Eichenfield, MD, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital, said that the consistency of data showing rapid, consistent improvement with a varied set of physician assessed scores and patient-reported outcomes “was very impressive, especially given the variation in severity, extent and difficult course of many of the patients we saw, and spectrum of interventions – from topical regimens to advanced systemic therapies,” he said. “As clinicians we tend to remember the ‘tough cases,’ and it was tremendous to see the impact and utility of the clinic.”
He noted that he and Bob Geng, MD, an allergist/immunologist at Rady Children’s who co-directs the MADP, regularly discuss how much they have learned from the program. “Some take-aways are simple, like ‘do body surface area assessment in pediatric patients with moderate to serve atopic dermatitis,’ ” Dr. Eichenfield said. “These help us show the severity to the patient and family, and everyone loves to see the objective improvement measures over time.”
The MADP providers and personnel have become better at explaining AD “and understanding how families come in with broad differences in understanding of the disease, therapies and prior treatments,” he added. “And I have learned that discussing environmental allergies and food allergies, even if they might not be triggers of the AD, is appreciated by patients and families, as they are part of the family experience and they appreciate our ‘broadly caring’ beyond our narrow niches of intervention.”
Important model of care
Asked to comment on the results, pediatric dermatologist Moise L. Levy, MD, professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Texas at Austin, who was not involved with the study, characterized the MADP as an important model of care. “Multi-interdisciplinary care of such conditions is well-known to be of great help for patients and their families,” he told this news organization.
“A key part of the ‘team’ is the family/patient engagement and shared decision-making. The use of visual aides to highlight components of care was likely of great use, as well,” he said. “All such interventions impact the disease, as well as associated problems, such as itch, sleep, and mental health. Importantly, such interventions, while known to be useful as demonstrated by the authors, take time, and relate to improved outcomes as noted by the date outlined by the authors.”
The study authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the lack of a control group with single-specialty visits. “The real take-away is that taking the time to do more holistic assessments of health — with skin and allergy issues being discussed, and consistent education and messaging — helps make our medical interventions more successful, with both objective disease improvement and patient/family satisfaction,” Dr. Eichenfield said in the interview.
Pfizer and Sanofi provided financial support to MADP, and for the study. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he serves as a scientific adviser, consultant, and/or clinical trial investigator for AbbVie, Amgen, Aslan, Castle Biosciences, Dermavant, Eli Lilly and Company, Forté, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi-Genzyme, Trialspark, and UCB. Dr. Geng disclosed ties with Sanofi, Regeneron, Pfizer, and AbbVie, and is an adviser to Incyte, Galderma, Eli-Lilly, and LEO. The other authors reported having no disclosures. Dr. Levy disclosed ties with Abeona, Amgen, Arcutis, Castle Creek, Dusa Pharma, Krystal Bio, Novan, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme. He is also an investigator for Janssen.
, results from a single-center study showed.
“A significant challenge in caring for patients with atopic dermatitis is lack of collaboration between healthcare providers, leading to disjointed care, inconsistent treatment plans, and conflicting dialogue with patients,” first author Alexis Tracy, MD, a combined allergy and dermatology research fellow at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online January 14, 2024, in Pediatric Dermatology.
Launched in 2019, the clinic, which is called the Multidisciplinary Atopic Dermatitis Program (MADP), is a collaborative effort between with Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California San Diego Health division of dermatology, division of allergy & immunology, and the hospital’s clinical pharmacy. Patients referred to the MADP undergo a concurrent, comprehensive evaluation by a dermatologist, allergist, clinical pharmacist, and others who help to assess AD severity, provide family education about the disease, and form a care plan using the model of shared decision-making (SDM). Visits take about two hours, and the frequency of follow-up visits varies.

In the dermatology realm, tools used to compare the extent and severity of AD between visits include the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM), the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI), Validated Investigator Global Assessment (vIGA), Body Surface Area (BSA), and the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS).To investigate the MADP’s success to date, Dr. Tracy and colleagues evaluated 44 patients with a history of moderate to severe, persistent AD who were referred to the clinic between April 3, 2019, and October 22, 2022, and had between one and three follow-up visits. The patients ranged from age 4 months to 18 years (mean, 7.74 years).
Compared with baseline, EASI scores of patients decreased significantly, with an average mean improvement of 9.61 by the second visit, 15.12 by the third visit, and 17.42 by the fourth visit (P <.001 for all three). These represent an average decreases of 44.20%, 63.26%, 74.35%, respectively.
At the seventh visit, the EASI score decreased by a mean of 33.48 (P = .008), which represents an average decrease of 91.52% from baseline. Of the 44 patients, 32 achieved an EASI 50 and 21 achieved an EASI 75.
In other findings, the mean vIGA improved with each visit, with the largest observed improvement at the seventh visit (a mean of 2.25 points; P = .009) and the greatest mean improvement in the POEM score was seen at the sixth visit (a mean of 11.13 points; P < .001). The mean difference in CDLQI scores also increased with each visit, with the largest improvement seen at the sixth visit (an increase of 12 points; P < .001).
Similarly, BSA progressively improved at each clinic visit, from a mean decrease of 16.02% at the second visit to a mean decrease of 56.04% at the seventh visit (P < .001 for both). Meanwhile, the largest mean improvement in pruritus was seen at the sixth visit (a mean of 4.10 points; P = .001).
In an interview, MADP’s codirector, Lawrence Eichenfield, MD, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital, said that the consistency of data showing rapid, consistent improvement with a varied set of physician assessed scores and patient-reported outcomes “was very impressive, especially given the variation in severity, extent and difficult course of many of the patients we saw, and spectrum of interventions – from topical regimens to advanced systemic therapies,” he said. “As clinicians we tend to remember the ‘tough cases,’ and it was tremendous to see the impact and utility of the clinic.”
He noted that he and Bob Geng, MD, an allergist/immunologist at Rady Children’s who co-directs the MADP, regularly discuss how much they have learned from the program. “Some take-aways are simple, like ‘do body surface area assessment in pediatric patients with moderate to serve atopic dermatitis,’ ” Dr. Eichenfield said. “These help us show the severity to the patient and family, and everyone loves to see the objective improvement measures over time.”
The MADP providers and personnel have become better at explaining AD “and understanding how families come in with broad differences in understanding of the disease, therapies and prior treatments,” he added. “And I have learned that discussing environmental allergies and food allergies, even if they might not be triggers of the AD, is appreciated by patients and families, as they are part of the family experience and they appreciate our ‘broadly caring’ beyond our narrow niches of intervention.”
Important model of care
Asked to comment on the results, pediatric dermatologist Moise L. Levy, MD, professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Texas at Austin, who was not involved with the study, characterized the MADP as an important model of care. “Multi-interdisciplinary care of such conditions is well-known to be of great help for patients and their families,” he told this news organization.
“A key part of the ‘team’ is the family/patient engagement and shared decision-making. The use of visual aides to highlight components of care was likely of great use, as well,” he said. “All such interventions impact the disease, as well as associated problems, such as itch, sleep, and mental health. Importantly, such interventions, while known to be useful as demonstrated by the authors, take time, and relate to improved outcomes as noted by the date outlined by the authors.”
The study authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the lack of a control group with single-specialty visits. “The real take-away is that taking the time to do more holistic assessments of health — with skin and allergy issues being discussed, and consistent education and messaging — helps make our medical interventions more successful, with both objective disease improvement and patient/family satisfaction,” Dr. Eichenfield said in the interview.
Pfizer and Sanofi provided financial support to MADP, and for the study. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he serves as a scientific adviser, consultant, and/or clinical trial investigator for AbbVie, Amgen, Aslan, Castle Biosciences, Dermavant, Eli Lilly and Company, Forté, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi-Genzyme, Trialspark, and UCB. Dr. Geng disclosed ties with Sanofi, Regeneron, Pfizer, and AbbVie, and is an adviser to Incyte, Galderma, Eli-Lilly, and LEO. The other authors reported having no disclosures. Dr. Levy disclosed ties with Abeona, Amgen, Arcutis, Castle Creek, Dusa Pharma, Krystal Bio, Novan, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme. He is also an investigator for Janssen.
, results from a single-center study showed.
“A significant challenge in caring for patients with atopic dermatitis is lack of collaboration between healthcare providers, leading to disjointed care, inconsistent treatment plans, and conflicting dialogue with patients,” first author Alexis Tracy, MD, a combined allergy and dermatology research fellow at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online January 14, 2024, in Pediatric Dermatology.
Launched in 2019, the clinic, which is called the Multidisciplinary Atopic Dermatitis Program (MADP), is a collaborative effort between with Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California San Diego Health division of dermatology, division of allergy & immunology, and the hospital’s clinical pharmacy. Patients referred to the MADP undergo a concurrent, comprehensive evaluation by a dermatologist, allergist, clinical pharmacist, and others who help to assess AD severity, provide family education about the disease, and form a care plan using the model of shared decision-making (SDM). Visits take about two hours, and the frequency of follow-up visits varies.

In the dermatology realm, tools used to compare the extent and severity of AD between visits include the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM), the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI), Validated Investigator Global Assessment (vIGA), Body Surface Area (BSA), and the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS).To investigate the MADP’s success to date, Dr. Tracy and colleagues evaluated 44 patients with a history of moderate to severe, persistent AD who were referred to the clinic between April 3, 2019, and October 22, 2022, and had between one and three follow-up visits. The patients ranged from age 4 months to 18 years (mean, 7.74 years).
Compared with baseline, EASI scores of patients decreased significantly, with an average mean improvement of 9.61 by the second visit, 15.12 by the third visit, and 17.42 by the fourth visit (P <.001 for all three). These represent an average decreases of 44.20%, 63.26%, 74.35%, respectively.
At the seventh visit, the EASI score decreased by a mean of 33.48 (P = .008), which represents an average decrease of 91.52% from baseline. Of the 44 patients, 32 achieved an EASI 50 and 21 achieved an EASI 75.
In other findings, the mean vIGA improved with each visit, with the largest observed improvement at the seventh visit (a mean of 2.25 points; P = .009) and the greatest mean improvement in the POEM score was seen at the sixth visit (a mean of 11.13 points; P < .001). The mean difference in CDLQI scores also increased with each visit, with the largest improvement seen at the sixth visit (an increase of 12 points; P < .001).
Similarly, BSA progressively improved at each clinic visit, from a mean decrease of 16.02% at the second visit to a mean decrease of 56.04% at the seventh visit (P < .001 for both). Meanwhile, the largest mean improvement in pruritus was seen at the sixth visit (a mean of 4.10 points; P = .001).
In an interview, MADP’s codirector, Lawrence Eichenfield, MD, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital, said that the consistency of data showing rapid, consistent improvement with a varied set of physician assessed scores and patient-reported outcomes “was very impressive, especially given the variation in severity, extent and difficult course of many of the patients we saw, and spectrum of interventions – from topical regimens to advanced systemic therapies,” he said. “As clinicians we tend to remember the ‘tough cases,’ and it was tremendous to see the impact and utility of the clinic.”
He noted that he and Bob Geng, MD, an allergist/immunologist at Rady Children’s who co-directs the MADP, regularly discuss how much they have learned from the program. “Some take-aways are simple, like ‘do body surface area assessment in pediatric patients with moderate to serve atopic dermatitis,’ ” Dr. Eichenfield said. “These help us show the severity to the patient and family, and everyone loves to see the objective improvement measures over time.”
The MADP providers and personnel have become better at explaining AD “and understanding how families come in with broad differences in understanding of the disease, therapies and prior treatments,” he added. “And I have learned that discussing environmental allergies and food allergies, even if they might not be triggers of the AD, is appreciated by patients and families, as they are part of the family experience and they appreciate our ‘broadly caring’ beyond our narrow niches of intervention.”
Important model of care
Asked to comment on the results, pediatric dermatologist Moise L. Levy, MD, professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Texas at Austin, who was not involved with the study, characterized the MADP as an important model of care. “Multi-interdisciplinary care of such conditions is well-known to be of great help for patients and their families,” he told this news organization.
“A key part of the ‘team’ is the family/patient engagement and shared decision-making. The use of visual aides to highlight components of care was likely of great use, as well,” he said. “All such interventions impact the disease, as well as associated problems, such as itch, sleep, and mental health. Importantly, such interventions, while known to be useful as demonstrated by the authors, take time, and relate to improved outcomes as noted by the date outlined by the authors.”
The study authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the lack of a control group with single-specialty visits. “The real take-away is that taking the time to do more holistic assessments of health — with skin and allergy issues being discussed, and consistent education and messaging — helps make our medical interventions more successful, with both objective disease improvement and patient/family satisfaction,” Dr. Eichenfield said in the interview.
Pfizer and Sanofi provided financial support to MADP, and for the study. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he serves as a scientific adviser, consultant, and/or clinical trial investigator for AbbVie, Amgen, Aslan, Castle Biosciences, Dermavant, Eli Lilly and Company, Forté, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi-Genzyme, Trialspark, and UCB. Dr. Geng disclosed ties with Sanofi, Regeneron, Pfizer, and AbbVie, and is an adviser to Incyte, Galderma, Eli-Lilly, and LEO. The other authors reported having no disclosures. Dr. Levy disclosed ties with Abeona, Amgen, Arcutis, Castle Creek, Dusa Pharma, Krystal Bio, Novan, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme. He is also an investigator for Janssen.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Why Don’t Physicians Call In Sick?
I began practicing medicine on July 1, 1981. In the 43-plus years since then,
There are several reasons, both good and bad, why this is so: (1) like most physicians, I am a terrible patient; (2) as a solo practitioner, there was (until recently — I’ll get to that in a minute) no one else to see an office full of patients who had waited significant amounts of time for their appointments and in many cases had taken off work themselves to keep them; and (3) there is an unspoken rule against it. Taking sick days is highly frowned upon in the medical world. As a medical student, intern, and resident I was told in so many words not to call in sick, no matter how serious the illness might be.
Apparently, I was not the only doctor-in-training to receive that message. In a survey reported in JAMA Pediatrics several years ago, 95% of the physicians and advanced practice clinicians (APCs) surveyed believed that working while sick put patients at risk — yet 83% reported working sick at least one time over the prior year. They understood the risks, but did it anyway.
There is no question that this practice does put patients’ health at risk. The JAMA study linked numerous reports of outbreaks traceable to symptomatic healthcare workers. Some outbreaks of flu, staph infections, norovirus, and pertussis were shown to originate from a sick physician or supporting staff member. These associations have led to increased morbidity and mortality, as well as excess costs. Those of us who treat immunocompromised patients on a regular basis risk inducing a life-threatening illness by unnecessarily exposing them to pathogens.
The JAMA survey results also confirmed my own observation that many physicians feel boxed in by their institutions or practice situations. “The study illustrates the complex social and logistic factors that cause this behavior,” the authors wrote. “These results may inform efforts to design systems at our hospital to provide support for attending physicians and APCs and help them make the right choice to keep their patients and colleagues safe while caring for themselves.”
What might those efforts look like? For one thing, we can take the obvious and necessary steps to avoid getting sick in the first place, such as staying fit and hydrated, and eating well. We can keep up with routine health visits and measures such as colorectal screening, pap smears, and mammograms, and stay up to date with flu shots and all other essential immunizations.
Next, we can minimize the risk of spreading any illnesses we encounter in the course of our work by practicing the basic infectious disease prevention measures driven home so forcefully by the recent COVID-19 pandemic — washing our hands, using hand sanitizers, and, when appropriate, wearing gloves and masks.
Finally, we can work to overcome this institutional taboo against staying home when we do get sick. Work out a system of mutual coverage for such situations. Two years ago, I merged my solo practice with a local, larger group. I did it for a variety of reasons, but a principal one was to assure that a partner could cover for me if I became ill. Practitioners who choose to remain solo or in small groups should contact colleagues and work out a coverage agreement.
Now, during flu season, it is especially important to resist the temptation to work while sick. The CDC has guidelines for employees specific for the flu, which notes that “persons with the flu are most contagious during the first 3 days of their illness,” and should remain at home until at least 24 hours after their fever subsides (without the use of fever-reducing medications) or after symptoms have improved (at least 4-5 days after they started) — or, if they do not have a fever, after symptoms improve “for at least 4-5 days after the onset of symptoms.”
Of course, we need to remember that COVID-19 is still with us. With the constant evolution of new strains, it is especially important to avoid exposing patients and colleagues to the disease should you become infected. The most recent advice from the CDC includes the recommendation that those who are mildly ill and not moderately or severely immunocompromised should isolate after SARS-CoV-2 infection for at least 5 days after symptom onset (day 0 is the day symptoms appeared, and day 1 is the next full day thereafter) if fever has resolved for at least 24 hours (without taking fever-reducing medications) and other symptoms are improving. In addition, “a high-quality mask should be worn around others at home and in public through day 10.”
We should also extend these rules to our support staff, starting with providing them with adequate sick leave and encouraging them to use it when necessary. Research has found a direct correlation between preventative health care and the number of paid sick leave days a worker gets. In a study of over 3000 US workers, those with 10 paid sick days or more annually accessed preventative care more frequently than those without paid sick days.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
I began practicing medicine on July 1, 1981. In the 43-plus years since then,
There are several reasons, both good and bad, why this is so: (1) like most physicians, I am a terrible patient; (2) as a solo practitioner, there was (until recently — I’ll get to that in a minute) no one else to see an office full of patients who had waited significant amounts of time for their appointments and in many cases had taken off work themselves to keep them; and (3) there is an unspoken rule against it. Taking sick days is highly frowned upon in the medical world. As a medical student, intern, and resident I was told in so many words not to call in sick, no matter how serious the illness might be.
Apparently, I was not the only doctor-in-training to receive that message. In a survey reported in JAMA Pediatrics several years ago, 95% of the physicians and advanced practice clinicians (APCs) surveyed believed that working while sick put patients at risk — yet 83% reported working sick at least one time over the prior year. They understood the risks, but did it anyway.
There is no question that this practice does put patients’ health at risk. The JAMA study linked numerous reports of outbreaks traceable to symptomatic healthcare workers. Some outbreaks of flu, staph infections, norovirus, and pertussis were shown to originate from a sick physician or supporting staff member. These associations have led to increased morbidity and mortality, as well as excess costs. Those of us who treat immunocompromised patients on a regular basis risk inducing a life-threatening illness by unnecessarily exposing them to pathogens.
The JAMA survey results also confirmed my own observation that many physicians feel boxed in by their institutions or practice situations. “The study illustrates the complex social and logistic factors that cause this behavior,” the authors wrote. “These results may inform efforts to design systems at our hospital to provide support for attending physicians and APCs and help them make the right choice to keep their patients and colleagues safe while caring for themselves.”
What might those efforts look like? For one thing, we can take the obvious and necessary steps to avoid getting sick in the first place, such as staying fit and hydrated, and eating well. We can keep up with routine health visits and measures such as colorectal screening, pap smears, and mammograms, and stay up to date with flu shots and all other essential immunizations.
Next, we can minimize the risk of spreading any illnesses we encounter in the course of our work by practicing the basic infectious disease prevention measures driven home so forcefully by the recent COVID-19 pandemic — washing our hands, using hand sanitizers, and, when appropriate, wearing gloves and masks.
Finally, we can work to overcome this institutional taboo against staying home when we do get sick. Work out a system of mutual coverage for such situations. Two years ago, I merged my solo practice with a local, larger group. I did it for a variety of reasons, but a principal one was to assure that a partner could cover for me if I became ill. Practitioners who choose to remain solo or in small groups should contact colleagues and work out a coverage agreement.
Now, during flu season, it is especially important to resist the temptation to work while sick. The CDC has guidelines for employees specific for the flu, which notes that “persons with the flu are most contagious during the first 3 days of their illness,” and should remain at home until at least 24 hours after their fever subsides (without the use of fever-reducing medications) or after symptoms have improved (at least 4-5 days after they started) — or, if they do not have a fever, after symptoms improve “for at least 4-5 days after the onset of symptoms.”
Of course, we need to remember that COVID-19 is still with us. With the constant evolution of new strains, it is especially important to avoid exposing patients and colleagues to the disease should you become infected. The most recent advice from the CDC includes the recommendation that those who are mildly ill and not moderately or severely immunocompromised should isolate after SARS-CoV-2 infection for at least 5 days after symptom onset (day 0 is the day symptoms appeared, and day 1 is the next full day thereafter) if fever has resolved for at least 24 hours (without taking fever-reducing medications) and other symptoms are improving. In addition, “a high-quality mask should be worn around others at home and in public through day 10.”
We should also extend these rules to our support staff, starting with providing them with adequate sick leave and encouraging them to use it when necessary. Research has found a direct correlation between preventative health care and the number of paid sick leave days a worker gets. In a study of over 3000 US workers, those with 10 paid sick days or more annually accessed preventative care more frequently than those without paid sick days.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
I began practicing medicine on July 1, 1981. In the 43-plus years since then,
There are several reasons, both good and bad, why this is so: (1) like most physicians, I am a terrible patient; (2) as a solo practitioner, there was (until recently — I’ll get to that in a minute) no one else to see an office full of patients who had waited significant amounts of time for their appointments and in many cases had taken off work themselves to keep them; and (3) there is an unspoken rule against it. Taking sick days is highly frowned upon in the medical world. As a medical student, intern, and resident I was told in so many words not to call in sick, no matter how serious the illness might be.
Apparently, I was not the only doctor-in-training to receive that message. In a survey reported in JAMA Pediatrics several years ago, 95% of the physicians and advanced practice clinicians (APCs) surveyed believed that working while sick put patients at risk — yet 83% reported working sick at least one time over the prior year. They understood the risks, but did it anyway.
There is no question that this practice does put patients’ health at risk. The JAMA study linked numerous reports of outbreaks traceable to symptomatic healthcare workers. Some outbreaks of flu, staph infections, norovirus, and pertussis were shown to originate from a sick physician or supporting staff member. These associations have led to increased morbidity and mortality, as well as excess costs. Those of us who treat immunocompromised patients on a regular basis risk inducing a life-threatening illness by unnecessarily exposing them to pathogens.
The JAMA survey results also confirmed my own observation that many physicians feel boxed in by their institutions or practice situations. “The study illustrates the complex social and logistic factors that cause this behavior,” the authors wrote. “These results may inform efforts to design systems at our hospital to provide support for attending physicians and APCs and help them make the right choice to keep their patients and colleagues safe while caring for themselves.”
What might those efforts look like? For one thing, we can take the obvious and necessary steps to avoid getting sick in the first place, such as staying fit and hydrated, and eating well. We can keep up with routine health visits and measures such as colorectal screening, pap smears, and mammograms, and stay up to date with flu shots and all other essential immunizations.
Next, we can minimize the risk of spreading any illnesses we encounter in the course of our work by practicing the basic infectious disease prevention measures driven home so forcefully by the recent COVID-19 pandemic — washing our hands, using hand sanitizers, and, when appropriate, wearing gloves and masks.
Finally, we can work to overcome this institutional taboo against staying home when we do get sick. Work out a system of mutual coverage for such situations. Two years ago, I merged my solo practice with a local, larger group. I did it for a variety of reasons, but a principal one was to assure that a partner could cover for me if I became ill. Practitioners who choose to remain solo or in small groups should contact colleagues and work out a coverage agreement.
Now, during flu season, it is especially important to resist the temptation to work while sick. The CDC has guidelines for employees specific for the flu, which notes that “persons with the flu are most contagious during the first 3 days of their illness,” and should remain at home until at least 24 hours after their fever subsides (without the use of fever-reducing medications) or after symptoms have improved (at least 4-5 days after they started) — or, if they do not have a fever, after symptoms improve “for at least 4-5 days after the onset of symptoms.”
Of course, we need to remember that COVID-19 is still with us. With the constant evolution of new strains, it is especially important to avoid exposing patients and colleagues to the disease should you become infected. The most recent advice from the CDC includes the recommendation that those who are mildly ill and not moderately or severely immunocompromised should isolate after SARS-CoV-2 infection for at least 5 days after symptom onset (day 0 is the day symptoms appeared, and day 1 is the next full day thereafter) if fever has resolved for at least 24 hours (without taking fever-reducing medications) and other symptoms are improving. In addition, “a high-quality mask should be worn around others at home and in public through day 10.”
We should also extend these rules to our support staff, starting with providing them with adequate sick leave and encouraging them to use it when necessary. Research has found a direct correlation between preventative health care and the number of paid sick leave days a worker gets. In a study of over 3000 US workers, those with 10 paid sick days or more annually accessed preventative care more frequently than those without paid sick days.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
Smoking Associated With Increased Risk for Hair Loss Among Men
, according to a new study.
In addition, the odds of developing AGA are higher among those who smoke at least 10 cigarettes per day than among those who smoke less, the study authors found.
“Men who smoke are more likely to develop and experience progression of male pattern hair loss,” lead author Aditya Gupta, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, Toronto, and director of clinical research at Mediprobe Research Inc., London, Ontario, Canada, told this news organization.
“Our patients with male pattern baldness need to be educated about the negative effects of smoking, given that this condition can have a profound negative psychological impact on those who suffer from it,” he said.
The study was published online in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
Analyzing Smoking’s Effects
Smoking generally has been accepted as a risk factor for the development and progression of AGA or the most common form of hair loss. The research evidence on this association has been inconsistent, however, the authors wrote.
The investigators conducted a review and meta-analysis of eight observational studies to understand the links between smoking and AGA. Ever-smokers were defined as current and former smokers.
Overall, based on six studies, men who have ever smoked are 1.8 times more likely (P < .05) to develop AGA.
Based on two studies, men who smoke 10 or more cigarettes daily are about twice as likely (P < .05) to develop AGA than those who smoke up to 10 cigarettes per day.
Based on four studies, ever smoking is associated with 1.3 times higher odds of AGA progressing from mild (ie, Norwood-Hamilton stages I-III) to more severe (stages IV-VII) than among those who have never smoked.
Based on two studies, there’s no association between AGA progression and smoking intensity (as defined as smoking up to 20 cigarettes daily vs smoking 20 or more cigarettes per day).
“Though our pooled analysis found no significant association between smoking intensity and severity of male AGA, a positive correlation may exist and be detected through an analysis that is statistically better powered,” said Dr. Gupta.
The investigators noted the limitations of their analysis, such as its reliance on observational studies and its lack of data about nicotine levels, smoking intensity, and smoking cessation among study participants.
Additional studies are needed to better understand the links between smoking and hair loss, said Dr. Gupta, as well as the effects of smoking cessation.
Improving Practice and Research
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, Arash Babadjouni, MD, a dermatologist at Midwestern University, Glendale, Arizona, said, “Smoking is not only a preventable cause of significant systemic disease but also affects the follicular growth cycle and fiber pigmentation. The prevalence of hair loss and premature hair graying is higher in smokers than nonsmokers.”
Dr. Babadjouni, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched the associations between smoking and hair loss and premature hair graying.
“Evidence of this association can be used to clinically promote smoking cessation and emphasize the consequences of smoking on hair,” he said. “Smoking status should be assessed in patients who are presenting to their dermatologist and physicians alike for evaluation of alopecia and premature hair graying.”
The study was conducted without outside funding, and the authors declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Babadjouni reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new study.
In addition, the odds of developing AGA are higher among those who smoke at least 10 cigarettes per day than among those who smoke less, the study authors found.
“Men who smoke are more likely to develop and experience progression of male pattern hair loss,” lead author Aditya Gupta, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, Toronto, and director of clinical research at Mediprobe Research Inc., London, Ontario, Canada, told this news organization.
“Our patients with male pattern baldness need to be educated about the negative effects of smoking, given that this condition can have a profound negative psychological impact on those who suffer from it,” he said.
The study was published online in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
Analyzing Smoking’s Effects
Smoking generally has been accepted as a risk factor for the development and progression of AGA or the most common form of hair loss. The research evidence on this association has been inconsistent, however, the authors wrote.
The investigators conducted a review and meta-analysis of eight observational studies to understand the links between smoking and AGA. Ever-smokers were defined as current and former smokers.
Overall, based on six studies, men who have ever smoked are 1.8 times more likely (P < .05) to develop AGA.
Based on two studies, men who smoke 10 or more cigarettes daily are about twice as likely (P < .05) to develop AGA than those who smoke up to 10 cigarettes per day.
Based on four studies, ever smoking is associated with 1.3 times higher odds of AGA progressing from mild (ie, Norwood-Hamilton stages I-III) to more severe (stages IV-VII) than among those who have never smoked.
Based on two studies, there’s no association between AGA progression and smoking intensity (as defined as smoking up to 20 cigarettes daily vs smoking 20 or more cigarettes per day).
“Though our pooled analysis found no significant association between smoking intensity and severity of male AGA, a positive correlation may exist and be detected through an analysis that is statistically better powered,” said Dr. Gupta.
The investigators noted the limitations of their analysis, such as its reliance on observational studies and its lack of data about nicotine levels, smoking intensity, and smoking cessation among study participants.
Additional studies are needed to better understand the links between smoking and hair loss, said Dr. Gupta, as well as the effects of smoking cessation.
Improving Practice and Research
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, Arash Babadjouni, MD, a dermatologist at Midwestern University, Glendale, Arizona, said, “Smoking is not only a preventable cause of significant systemic disease but also affects the follicular growth cycle and fiber pigmentation. The prevalence of hair loss and premature hair graying is higher in smokers than nonsmokers.”
Dr. Babadjouni, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched the associations between smoking and hair loss and premature hair graying.
“Evidence of this association can be used to clinically promote smoking cessation and emphasize the consequences of smoking on hair,” he said. “Smoking status should be assessed in patients who are presenting to their dermatologist and physicians alike for evaluation of alopecia and premature hair graying.”
The study was conducted without outside funding, and the authors declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Babadjouni reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new study.
In addition, the odds of developing AGA are higher among those who smoke at least 10 cigarettes per day than among those who smoke less, the study authors found.
“Men who smoke are more likely to develop and experience progression of male pattern hair loss,” lead author Aditya Gupta, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, Toronto, and director of clinical research at Mediprobe Research Inc., London, Ontario, Canada, told this news organization.
“Our patients with male pattern baldness need to be educated about the negative effects of smoking, given that this condition can have a profound negative psychological impact on those who suffer from it,” he said.
The study was published online in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
Analyzing Smoking’s Effects
Smoking generally has been accepted as a risk factor for the development and progression of AGA or the most common form of hair loss. The research evidence on this association has been inconsistent, however, the authors wrote.
The investigators conducted a review and meta-analysis of eight observational studies to understand the links between smoking and AGA. Ever-smokers were defined as current and former smokers.
Overall, based on six studies, men who have ever smoked are 1.8 times more likely (P < .05) to develop AGA.
Based on two studies, men who smoke 10 or more cigarettes daily are about twice as likely (P < .05) to develop AGA than those who smoke up to 10 cigarettes per day.
Based on four studies, ever smoking is associated with 1.3 times higher odds of AGA progressing from mild (ie, Norwood-Hamilton stages I-III) to more severe (stages IV-VII) than among those who have never smoked.
Based on two studies, there’s no association between AGA progression and smoking intensity (as defined as smoking up to 20 cigarettes daily vs smoking 20 or more cigarettes per day).
“Though our pooled analysis found no significant association between smoking intensity and severity of male AGA, a positive correlation may exist and be detected through an analysis that is statistically better powered,” said Dr. Gupta.
The investigators noted the limitations of their analysis, such as its reliance on observational studies and its lack of data about nicotine levels, smoking intensity, and smoking cessation among study participants.
Additional studies are needed to better understand the links between smoking and hair loss, said Dr. Gupta, as well as the effects of smoking cessation.
Improving Practice and Research
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, Arash Babadjouni, MD, a dermatologist at Midwestern University, Glendale, Arizona, said, “Smoking is not only a preventable cause of significant systemic disease but also affects the follicular growth cycle and fiber pigmentation. The prevalence of hair loss and premature hair graying is higher in smokers than nonsmokers.”
Dr. Babadjouni, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched the associations between smoking and hair loss and premature hair graying.
“Evidence of this association can be used to clinically promote smoking cessation and emphasize the consequences of smoking on hair,” he said. “Smoking status should be assessed in patients who are presenting to their dermatologist and physicians alike for evaluation of alopecia and premature hair graying.”
The study was conducted without outside funding, and the authors declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Babadjouni reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF COSMETIC DERMATOLOGY
How much would you bet on a diagnosis?
“You have psoriasis,” I say all the time. I mean it when I say it, of course. But I don’t always to the same degree. Sometimes I’m trying to say, “You probably have psoriasis.” Other times I mean, “You most definitely have psoriasis.” I rarely use those terms though.
One 36-year-old man with a flaky scalp and scaly elbows wasn’t satisfied with my assessment. His dad has psoriasis. So does his older brother. He was in to see me to find out if he had psoriasis too. “Probably” was what I gave him. He pushed back, “What percent chance?” That’s a good question — must be an engineer. I’m unsure.
With the exception of the poker players, our species is notoriously bad at probabilities. We’re wired to notice the significance of events, but terrible at understanding their likelihood. This is salient in lottery ticket holders and some NFL offensive coordinators who persist despite very long odds of things working out. It’s also reflected in the language we use. Rarely do we say, there’s a sixty percent chance something will happen. Rather, we say, “it’s likely.” There are two problems here. One, we often misjudge the actual probability of something occurring and two, the terms we use are subjective and differences in interpretation can lead to misunderstandings.
Let’s take a look. A 55-year-old man with a chronic eczematous rash on his trunk and extremities is getting worse despite dupilumab. He recently had night sweats. Do you think he has atopic dermatitis or cutaneous T-cell lymphoma? If you had to place a $100 bet, would you change your answer? Immanuel Kant thinks you would. In his “Critique of Pure Reason,” the German philosopher proposes that betting helps clarify the mind, an antidote to brashness. The example Kant uses is of a physician who observes a patient and concludes he has phthisis (tuberculosis), but we really don’t know if the physician is confident. Kant proposes that if he had to bet on his conclusion, then we’d have insight into just how convinced he is of phthisis. So, what’s your bet?
If you’re a bad poker player, then you might bet he has cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. However, not having any additional information, the smart call is atopic dermatitis, which has a base rate 1000-fold higher than CTCL. It is therefore more probable to be eczema even in a case that worsens despite dupilumab or with recent night sweats, both of which could be a result of common variables such as weather and COVID. Failure to account for the base rate is a mistake we physicians sometimes make. Economists rarely do. Try to think like one before answering a likelihood question.
If you think about it, “probably” means something different even to me, depending on the situation. I might say I’ll probably go to Montana this summer and I’ll probably retire at 65. The actual likelihoods might be 95% and 70%. That’s a big difference. What about between probably and likely? Or possibly and maybe? Do they mean the same to you as to the person you’re speaking with? For much of the work we do, precise likelihoods aren’t critical. Yet, it can be important in decision making and in discussing probabilities, such as the risk of hepatitis on terbinafine or of melanoma recurrence after Mohs.
I told my patient “I say about a 70% chance you have psoriasis. I could do a biopsy today to confirm.” He thought for a second and asked, “What is the chance it’s psoriasis if the biopsy shows it?” “Eighty six percent,” I replied.
Seemed like a good bet to me.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at [email protected].
“You have psoriasis,” I say all the time. I mean it when I say it, of course. But I don’t always to the same degree. Sometimes I’m trying to say, “You probably have psoriasis.” Other times I mean, “You most definitely have psoriasis.” I rarely use those terms though.
One 36-year-old man with a flaky scalp and scaly elbows wasn’t satisfied with my assessment. His dad has psoriasis. So does his older brother. He was in to see me to find out if he had psoriasis too. “Probably” was what I gave him. He pushed back, “What percent chance?” That’s a good question — must be an engineer. I’m unsure.
With the exception of the poker players, our species is notoriously bad at probabilities. We’re wired to notice the significance of events, but terrible at understanding their likelihood. This is salient in lottery ticket holders and some NFL offensive coordinators who persist despite very long odds of things working out. It’s also reflected in the language we use. Rarely do we say, there’s a sixty percent chance something will happen. Rather, we say, “it’s likely.” There are two problems here. One, we often misjudge the actual probability of something occurring and two, the terms we use are subjective and differences in interpretation can lead to misunderstandings.
Let’s take a look. A 55-year-old man with a chronic eczematous rash on his trunk and extremities is getting worse despite dupilumab. He recently had night sweats. Do you think he has atopic dermatitis or cutaneous T-cell lymphoma? If you had to place a $100 bet, would you change your answer? Immanuel Kant thinks you would. In his “Critique of Pure Reason,” the German philosopher proposes that betting helps clarify the mind, an antidote to brashness. The example Kant uses is of a physician who observes a patient and concludes he has phthisis (tuberculosis), but we really don’t know if the physician is confident. Kant proposes that if he had to bet on his conclusion, then we’d have insight into just how convinced he is of phthisis. So, what’s your bet?
If you’re a bad poker player, then you might bet he has cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. However, not having any additional information, the smart call is atopic dermatitis, which has a base rate 1000-fold higher than CTCL. It is therefore more probable to be eczema even in a case that worsens despite dupilumab or with recent night sweats, both of which could be a result of common variables such as weather and COVID. Failure to account for the base rate is a mistake we physicians sometimes make. Economists rarely do. Try to think like one before answering a likelihood question.
If you think about it, “probably” means something different even to me, depending on the situation. I might say I’ll probably go to Montana this summer and I’ll probably retire at 65. The actual likelihoods might be 95% and 70%. That’s a big difference. What about between probably and likely? Or possibly and maybe? Do they mean the same to you as to the person you’re speaking with? For much of the work we do, precise likelihoods aren’t critical. Yet, it can be important in decision making and in discussing probabilities, such as the risk of hepatitis on terbinafine or of melanoma recurrence after Mohs.
I told my patient “I say about a 70% chance you have psoriasis. I could do a biopsy today to confirm.” He thought for a second and asked, “What is the chance it’s psoriasis if the biopsy shows it?” “Eighty six percent,” I replied.
Seemed like a good bet to me.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at [email protected].
“You have psoriasis,” I say all the time. I mean it when I say it, of course. But I don’t always to the same degree. Sometimes I’m trying to say, “You probably have psoriasis.” Other times I mean, “You most definitely have psoriasis.” I rarely use those terms though.
One 36-year-old man with a flaky scalp and scaly elbows wasn’t satisfied with my assessment. His dad has psoriasis. So does his older brother. He was in to see me to find out if he had psoriasis too. “Probably” was what I gave him. He pushed back, “What percent chance?” That’s a good question — must be an engineer. I’m unsure.
With the exception of the poker players, our species is notoriously bad at probabilities. We’re wired to notice the significance of events, but terrible at understanding their likelihood. This is salient in lottery ticket holders and some NFL offensive coordinators who persist despite very long odds of things working out. It’s also reflected in the language we use. Rarely do we say, there’s a sixty percent chance something will happen. Rather, we say, “it’s likely.” There are two problems here. One, we often misjudge the actual probability of something occurring and two, the terms we use are subjective and differences in interpretation can lead to misunderstandings.
Let’s take a look. A 55-year-old man with a chronic eczematous rash on his trunk and extremities is getting worse despite dupilumab. He recently had night sweats. Do you think he has atopic dermatitis or cutaneous T-cell lymphoma? If you had to place a $100 bet, would you change your answer? Immanuel Kant thinks you would. In his “Critique of Pure Reason,” the German philosopher proposes that betting helps clarify the mind, an antidote to brashness. The example Kant uses is of a physician who observes a patient and concludes he has phthisis (tuberculosis), but we really don’t know if the physician is confident. Kant proposes that if he had to bet on his conclusion, then we’d have insight into just how convinced he is of phthisis. So, what’s your bet?
If you’re a bad poker player, then you might bet he has cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. However, not having any additional information, the smart call is atopic dermatitis, which has a base rate 1000-fold higher than CTCL. It is therefore more probable to be eczema even in a case that worsens despite dupilumab or with recent night sweats, both of which could be a result of common variables such as weather and COVID. Failure to account for the base rate is a mistake we physicians sometimes make. Economists rarely do. Try to think like one before answering a likelihood question.
If you think about it, “probably” means something different even to me, depending on the situation. I might say I’ll probably go to Montana this summer and I’ll probably retire at 65. The actual likelihoods might be 95% and 70%. That’s a big difference. What about between probably and likely? Or possibly and maybe? Do they mean the same to you as to the person you’re speaking with? For much of the work we do, precise likelihoods aren’t critical. Yet, it can be important in decision making and in discussing probabilities, such as the risk of hepatitis on terbinafine or of melanoma recurrence after Mohs.
I told my patient “I say about a 70% chance you have psoriasis. I could do a biopsy today to confirm.” He thought for a second and asked, “What is the chance it’s psoriasis if the biopsy shows it?” “Eighty six percent,” I replied.
Seemed like a good bet to me.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at [email protected].
Rosemary, Part 1
A member of the Lamiaceae family, Salvia rosmarinus (rosemary),* an aromatic plant native to the Mediterranean region and now cultivated globally, has been used for centuries in cuisine and medicine, with several well-established biological activities.1-3 Thought to contribute to preventing hair loss, rosemary oil was also used for hundreds of years in hair rinses in the Mediterranean area.4 In traditional Iranian medicine, rosemary essential oil has been topically applied as an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-acne remedy.5 Rosemary is known to absorb UV light well and to impart antibacterial and antifungal activity, as well as help maintain skin homeostasis.3 It is also used and under further study for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-infective, and anticancer activity.2,6-9 The health benefits of rosemary are typically ascribed to its constituent carnosol/carnosic and ursolic acids.7 .
Chemical Constituents
The key chemical components of S. rosmarinus include bitter principle, resin, tannic acid, flavonoids, and volatile oils (made up of borneol, bornyl acetate, camphene, cineol, pinene, and camphor).10 Other important constituents of rosemary oil, in particular, include p-Cymene, linalool, gamma-terpinene, thymol, beta-pinene, alpha-pinene, eucalyptol, and carnosic acid.9 Volatile oils of rosemary have been used in various oils and lotions to treat wounds and with the intention of stimulating hair growth.10
Wound Healing
In a 2022 study in 60 adult male rats, Bulhões and colleagues found that the use of rosemary leaf essential oil-based ointments on skin lesions spurred wound healing, decreased inflammation, and enhanced angiogenesis as well as collagen fiber density.11
Three years earlier, Labib and colleagues studied the wound healing capacity of three chitosan-based topical formulations containing either tea tree essential oil, rosemary essential oil, or a mixture of both oils in an excision wound model in rats.
The combination preparation was found to be the most effective in fostering various stages of wound healing, with significant increases in wound contraction percentage observed in the combination group compared with either group treated using individual essential oils or the untreated animals.12
A 2010 in vivo study by Abu-Al-Basal using BALB/c mice with diabetes revealed that the topical application of rosemary essential oil for three days reduced inflammation, enhanced wound contraction and re-epithelialization, and promoted angiogenesis, granulation tissue regeneration, and collagen deposition.13
Anticancer Activity
Using a 7,12-dimethlybenz(a)anthracene (DMBA)-initiated and croton oil-promoted model in 2006, Sancheti and Goyal determined that rosemary extract administered orally at a dose rate of 500 mg/kg body weight/mouse significantly inhibited two-stage skin tumorigenesis in mice.14 Nearly a decade later, Cattaneo and colleagues determined that a rosemary hydroalcoholic extract displayed antiproliferative effects on the human melanoma A375 cell line.8
The polyphenols carnosic acid and rosmarinic acid are most often cited as the sources of the reputed anticancer effects of rosemary.15
Hair Health
Early in 2023, Begum and colleagues developed a 1% hair lotion including a methanolic extract of the aerial part of S. rosmarinus that they assessed for potential hair growth activity in C57BL/6 mice. Using water as a control and 2% minoxidil hair lotion as standard, the investigators determined that their rosemary hair lotion demonstrated significant hair growth promotion, exceeding that seen in the mice treated with the drug standard.1
In a randomized controlled study in C57BL/6NCrSlc mice a decade earlier, Murata and colleagues evaluated the anti-androgenic activity and hair growth potential imparted by topical rosemary oil compared with finasteride and minoxidil. Rosemary oil leaf extract, with 12-O-methylcarnosic acid as its most active component, robustly suppressed 5alpha-reductase and stimulated hair growth in vivo in both the androgenetic alopecia/testosterone-treated mouse model, as well as the hair growth activating mouse model as compared with minoxidil. Further, the inhibitory activity of rosemary was 82.4% and 94.6% at 200 mcg/mL and 500 mcg/mL, respectively, whereas finasteride demonstrated 81.9% at 250 nM.16
A human study two years later was even more encouraging. Panahi and colleagues conducted a randomized comparative trial with 100 patients to investigate the effects of rosemary oil as opposed to minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia over 6 months. By 6 months, significantly greater hair counts were observed in both groups compared with baseline and 3-month readings, but no significant variations between groups. No differences were found in the frequency of dryness, greasiness, or dandruff at any time point or between groups. Scalp itching was significantly greater at the 3- and 6-month points in both groups, particularly in the minoxidil group at both of those time points. The investigators concluded that rosemary oil compared well with minoxidil as androgenetic alopecia therapy.17
Conclusion
Rosemary has been used in traditional medicine for hundreds of years and it has been a common ingredient in cosmetic and cosmeceutical formulations for more than 20 years. Recent findings suggest a broad array of applications in modern medicine, particularly dermatology. The next column will focus on the most recent studies pertaining to the antioxidant and anti-aging activity of this aromatic shrub.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a ecommerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Begum A et al. Adv Biomed Res. 2023 Mar 21;12:60.
2. de Oliveira JR et al. J Biomed Sci. 2019 Jan 9;26(1):5.
3. González-Minero FJ et al. Cosmetics. 2020 Oct 3;7(4):77.
4. Dinkins J et al. Int J Dermatol. 2023 Aug;62(8):980-5.
5. Akbari J et al. Pharm Biol. 2015;53(10):1442-7.
6. Allegra A et al. Nutrients. 2020 Jun 10;12(6):1739.
7. de Macedo LM et al. Plants (Basel). 2020 May 21;9(5):651.
8. Cattaneo L et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0132439.
9. Borges RS et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Jan 30;229:29-45.
10. Begum A et al. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2013 Jan-Mar;12(1):61-73.
11. Bulhões AAVC et al. Acta Cir Bras. 2022 Apr 8;37(1):e370104.
12. Labib RM et al. PLoS One. 2019 Sep 16;14(9):e0219561.
13. Abu-Al-Basal MA. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Sep 15;131(2):443-50.
14. Sancheti G and Goyal PK. Phytother Res. 2006 Nov;20(11):981-6.
15. Moore J et al. Nutrients. 2016 Nov 17;8(11):731.
16. Murata K et al. Phytother Res. 2013 Feb;27(2):212-7.
17. Panahi Y et al. Skinmed. 2015 Jan-Feb;13(1):15-21.
*Correction, 2/27: This column was updated with the more recent name for rosemary, Salvia rosmarinus.
A member of the Lamiaceae family, Salvia rosmarinus (rosemary),* an aromatic plant native to the Mediterranean region and now cultivated globally, has been used for centuries in cuisine and medicine, with several well-established biological activities.1-3 Thought to contribute to preventing hair loss, rosemary oil was also used for hundreds of years in hair rinses in the Mediterranean area.4 In traditional Iranian medicine, rosemary essential oil has been topically applied as an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-acne remedy.5 Rosemary is known to absorb UV light well and to impart antibacterial and antifungal activity, as well as help maintain skin homeostasis.3 It is also used and under further study for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-infective, and anticancer activity.2,6-9 The health benefits of rosemary are typically ascribed to its constituent carnosol/carnosic and ursolic acids.7 .
Chemical Constituents
The key chemical components of S. rosmarinus include bitter principle, resin, tannic acid, flavonoids, and volatile oils (made up of borneol, bornyl acetate, camphene, cineol, pinene, and camphor).10 Other important constituents of rosemary oil, in particular, include p-Cymene, linalool, gamma-terpinene, thymol, beta-pinene, alpha-pinene, eucalyptol, and carnosic acid.9 Volatile oils of rosemary have been used in various oils and lotions to treat wounds and with the intention of stimulating hair growth.10
Wound Healing
In a 2022 study in 60 adult male rats, Bulhões and colleagues found that the use of rosemary leaf essential oil-based ointments on skin lesions spurred wound healing, decreased inflammation, and enhanced angiogenesis as well as collagen fiber density.11
Three years earlier, Labib and colleagues studied the wound healing capacity of three chitosan-based topical formulations containing either tea tree essential oil, rosemary essential oil, or a mixture of both oils in an excision wound model in rats.
The combination preparation was found to be the most effective in fostering various stages of wound healing, with significant increases in wound contraction percentage observed in the combination group compared with either group treated using individual essential oils or the untreated animals.12
A 2010 in vivo study by Abu-Al-Basal using BALB/c mice with diabetes revealed that the topical application of rosemary essential oil for three days reduced inflammation, enhanced wound contraction and re-epithelialization, and promoted angiogenesis, granulation tissue regeneration, and collagen deposition.13
Anticancer Activity
Using a 7,12-dimethlybenz(a)anthracene (DMBA)-initiated and croton oil-promoted model in 2006, Sancheti and Goyal determined that rosemary extract administered orally at a dose rate of 500 mg/kg body weight/mouse significantly inhibited two-stage skin tumorigenesis in mice.14 Nearly a decade later, Cattaneo and colleagues determined that a rosemary hydroalcoholic extract displayed antiproliferative effects on the human melanoma A375 cell line.8
The polyphenols carnosic acid and rosmarinic acid are most often cited as the sources of the reputed anticancer effects of rosemary.15
Hair Health
Early in 2023, Begum and colleagues developed a 1% hair lotion including a methanolic extract of the aerial part of S. rosmarinus that they assessed for potential hair growth activity in C57BL/6 mice. Using water as a control and 2% minoxidil hair lotion as standard, the investigators determined that their rosemary hair lotion demonstrated significant hair growth promotion, exceeding that seen in the mice treated with the drug standard.1
In a randomized controlled study in C57BL/6NCrSlc mice a decade earlier, Murata and colleagues evaluated the anti-androgenic activity and hair growth potential imparted by topical rosemary oil compared with finasteride and minoxidil. Rosemary oil leaf extract, with 12-O-methylcarnosic acid as its most active component, robustly suppressed 5alpha-reductase and stimulated hair growth in vivo in both the androgenetic alopecia/testosterone-treated mouse model, as well as the hair growth activating mouse model as compared with minoxidil. Further, the inhibitory activity of rosemary was 82.4% and 94.6% at 200 mcg/mL and 500 mcg/mL, respectively, whereas finasteride demonstrated 81.9% at 250 nM.16
A human study two years later was even more encouraging. Panahi and colleagues conducted a randomized comparative trial with 100 patients to investigate the effects of rosemary oil as opposed to minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia over 6 months. By 6 months, significantly greater hair counts were observed in both groups compared with baseline and 3-month readings, but no significant variations between groups. No differences were found in the frequency of dryness, greasiness, or dandruff at any time point or between groups. Scalp itching was significantly greater at the 3- and 6-month points in both groups, particularly in the minoxidil group at both of those time points. The investigators concluded that rosemary oil compared well with minoxidil as androgenetic alopecia therapy.17
Conclusion
Rosemary has been used in traditional medicine for hundreds of years and it has been a common ingredient in cosmetic and cosmeceutical formulations for more than 20 years. Recent findings suggest a broad array of applications in modern medicine, particularly dermatology. The next column will focus on the most recent studies pertaining to the antioxidant and anti-aging activity of this aromatic shrub.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a ecommerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Begum A et al. Adv Biomed Res. 2023 Mar 21;12:60.
2. de Oliveira JR et al. J Biomed Sci. 2019 Jan 9;26(1):5.
3. González-Minero FJ et al. Cosmetics. 2020 Oct 3;7(4):77.
4. Dinkins J et al. Int J Dermatol. 2023 Aug;62(8):980-5.
5. Akbari J et al. Pharm Biol. 2015;53(10):1442-7.
6. Allegra A et al. Nutrients. 2020 Jun 10;12(6):1739.
7. de Macedo LM et al. Plants (Basel). 2020 May 21;9(5):651.
8. Cattaneo L et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0132439.
9. Borges RS et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Jan 30;229:29-45.
10. Begum A et al. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2013 Jan-Mar;12(1):61-73.
11. Bulhões AAVC et al. Acta Cir Bras. 2022 Apr 8;37(1):e370104.
12. Labib RM et al. PLoS One. 2019 Sep 16;14(9):e0219561.
13. Abu-Al-Basal MA. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Sep 15;131(2):443-50.
14. Sancheti G and Goyal PK. Phytother Res. 2006 Nov;20(11):981-6.
15. Moore J et al. Nutrients. 2016 Nov 17;8(11):731.
16. Murata K et al. Phytother Res. 2013 Feb;27(2):212-7.
17. Panahi Y et al. Skinmed. 2015 Jan-Feb;13(1):15-21.
*Correction, 2/27: This column was updated with the more recent name for rosemary, Salvia rosmarinus.
A member of the Lamiaceae family, Salvia rosmarinus (rosemary),* an aromatic plant native to the Mediterranean region and now cultivated globally, has been used for centuries in cuisine and medicine, with several well-established biological activities.1-3 Thought to contribute to preventing hair loss, rosemary oil was also used for hundreds of years in hair rinses in the Mediterranean area.4 In traditional Iranian medicine, rosemary essential oil has been topically applied as an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-acne remedy.5 Rosemary is known to absorb UV light well and to impart antibacterial and antifungal activity, as well as help maintain skin homeostasis.3 It is also used and under further study for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-infective, and anticancer activity.2,6-9 The health benefits of rosemary are typically ascribed to its constituent carnosol/carnosic and ursolic acids.7 .
Chemical Constituents
The key chemical components of S. rosmarinus include bitter principle, resin, tannic acid, flavonoids, and volatile oils (made up of borneol, bornyl acetate, camphene, cineol, pinene, and camphor).10 Other important constituents of rosemary oil, in particular, include p-Cymene, linalool, gamma-terpinene, thymol, beta-pinene, alpha-pinene, eucalyptol, and carnosic acid.9 Volatile oils of rosemary have been used in various oils and lotions to treat wounds and with the intention of stimulating hair growth.10
Wound Healing
In a 2022 study in 60 adult male rats, Bulhões and colleagues found that the use of rosemary leaf essential oil-based ointments on skin lesions spurred wound healing, decreased inflammation, and enhanced angiogenesis as well as collagen fiber density.11
Three years earlier, Labib and colleagues studied the wound healing capacity of three chitosan-based topical formulations containing either tea tree essential oil, rosemary essential oil, or a mixture of both oils in an excision wound model in rats.
The combination preparation was found to be the most effective in fostering various stages of wound healing, with significant increases in wound contraction percentage observed in the combination group compared with either group treated using individual essential oils or the untreated animals.12
A 2010 in vivo study by Abu-Al-Basal using BALB/c mice with diabetes revealed that the topical application of rosemary essential oil for three days reduced inflammation, enhanced wound contraction and re-epithelialization, and promoted angiogenesis, granulation tissue regeneration, and collagen deposition.13
Anticancer Activity
Using a 7,12-dimethlybenz(a)anthracene (DMBA)-initiated and croton oil-promoted model in 2006, Sancheti and Goyal determined that rosemary extract administered orally at a dose rate of 500 mg/kg body weight/mouse significantly inhibited two-stage skin tumorigenesis in mice.14 Nearly a decade later, Cattaneo and colleagues determined that a rosemary hydroalcoholic extract displayed antiproliferative effects on the human melanoma A375 cell line.8
The polyphenols carnosic acid and rosmarinic acid are most often cited as the sources of the reputed anticancer effects of rosemary.15
Hair Health
Early in 2023, Begum and colleagues developed a 1% hair lotion including a methanolic extract of the aerial part of S. rosmarinus that they assessed for potential hair growth activity in C57BL/6 mice. Using water as a control and 2% minoxidil hair lotion as standard, the investigators determined that their rosemary hair lotion demonstrated significant hair growth promotion, exceeding that seen in the mice treated with the drug standard.1
In a randomized controlled study in C57BL/6NCrSlc mice a decade earlier, Murata and colleagues evaluated the anti-androgenic activity and hair growth potential imparted by topical rosemary oil compared with finasteride and minoxidil. Rosemary oil leaf extract, with 12-O-methylcarnosic acid as its most active component, robustly suppressed 5alpha-reductase and stimulated hair growth in vivo in both the androgenetic alopecia/testosterone-treated mouse model, as well as the hair growth activating mouse model as compared with minoxidil. Further, the inhibitory activity of rosemary was 82.4% and 94.6% at 200 mcg/mL and 500 mcg/mL, respectively, whereas finasteride demonstrated 81.9% at 250 nM.16
A human study two years later was even more encouraging. Panahi and colleagues conducted a randomized comparative trial with 100 patients to investigate the effects of rosemary oil as opposed to minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia over 6 months. By 6 months, significantly greater hair counts were observed in both groups compared with baseline and 3-month readings, but no significant variations between groups. No differences were found in the frequency of dryness, greasiness, or dandruff at any time point or between groups. Scalp itching was significantly greater at the 3- and 6-month points in both groups, particularly in the minoxidil group at both of those time points. The investigators concluded that rosemary oil compared well with minoxidil as androgenetic alopecia therapy.17
Conclusion
Rosemary has been used in traditional medicine for hundreds of years and it has been a common ingredient in cosmetic and cosmeceutical formulations for more than 20 years. Recent findings suggest a broad array of applications in modern medicine, particularly dermatology. The next column will focus on the most recent studies pertaining to the antioxidant and anti-aging activity of this aromatic shrub.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a ecommerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Begum A et al. Adv Biomed Res. 2023 Mar 21;12:60.
2. de Oliveira JR et al. J Biomed Sci. 2019 Jan 9;26(1):5.
3. González-Minero FJ et al. Cosmetics. 2020 Oct 3;7(4):77.
4. Dinkins J et al. Int J Dermatol. 2023 Aug;62(8):980-5.
5. Akbari J et al. Pharm Biol. 2015;53(10):1442-7.
6. Allegra A et al. Nutrients. 2020 Jun 10;12(6):1739.
7. de Macedo LM et al. Plants (Basel). 2020 May 21;9(5):651.
8. Cattaneo L et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0132439.
9. Borges RS et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Jan 30;229:29-45.
10. Begum A et al. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2013 Jan-Mar;12(1):61-73.
11. Bulhões AAVC et al. Acta Cir Bras. 2022 Apr 8;37(1):e370104.
12. Labib RM et al. PLoS One. 2019 Sep 16;14(9):e0219561.
13. Abu-Al-Basal MA. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Sep 15;131(2):443-50.
14. Sancheti G and Goyal PK. Phytother Res. 2006 Nov;20(11):981-6.
15. Moore J et al. Nutrients. 2016 Nov 17;8(11):731.
16. Murata K et al. Phytother Res. 2013 Feb;27(2):212-7.
17. Panahi Y et al. Skinmed. 2015 Jan-Feb;13(1):15-21.
*Correction, 2/27: This column was updated with the more recent name for rosemary, Salvia rosmarinus.










