User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
Who’s Behind Cosmetic Procedures at MedSpas?
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — according to Sara Hogan, MD.
“I’m not anti-MedSpa; I’m pro-patient safety,” Dr. Hogan, clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery symposium. “The MedSpa industry is booming; it brought in $17 billion in 2023. There are as many MedSpas in the United States as there are practicing dermatologists, and that number is set to exceed the number of dermatologists.”
According to industry data from the American Med Spa Association, 63% of member MedSpas have non-MD ownership. Among MedSpas owned by physicians, 80% are of a non–core specialty, meaning a specialty other than dermatology, plastic surgery, otorhinolaryngology, or ophthalmology. Of MedSpa medical directors, 69% are from non–core physician specialties. “There’s an increasing amount of data that shows a relatively higher incidence of complications from cosmetic procedures that are delivered at MedSpas,” Dr. Hogan said. “A 2020 study suggested that this is likely due to improper training, improper technique, and/or improper device settings.”
Dr. Hogan also cited adverse effects linked to counterfeit or mishandled botulinum toxin injections that prompted the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to issue an alert to clinicians in April 2024. Clusters of 22 people in 11 states reported adverse effects after receiving injections with counterfeit botulinum toxin or injections administered by unlicensed or untrained individuals or in non-healthcare settings, such as homes or spas.
To better understand who performs cosmetic procedures, provides medical supervision, and follows safety protocols at MedSpas, Dr. Hogan and colleagues conducted a “truth in advertising” study of 127 MedSpas in the greater Chicago area. They chose this geographic location because an analysis published in 2021 identified Chicago as having the third highest number of aesthetic physicians and the fifth highest number of MedSpas in the United States. The researchers enlisted help from “secret shoppers” who contacted the MedSpas by telephone to ask about the level of training, if patients underwent a review of medical history, the level of on-site physician supervision, and the protocol for complications.
The top five cosmetic procedures offered by the 127 surveyed MedSpas were facials (85.0%), hair removal (85.0%), botulinum toxin injections (83.5%), dermal fillers (82.7%), and chemical peels (76.4%). About two thirds of cosmetic procedures were performed by aestheticians (66.9%), followed by registered nurses or licensed practical nurses (52.8%), board-certified physicians (48.8%, mostly plastic and reconstructive surgeons), nurse practitioners (27.6%), and physician assistants (9.4%).
In the realm of supervision, 16.5% of MedSpas surveyed reported that a medical director or supervising physician is always on site. “If not located on site, when asked where the physicians are, the majority of the time they were at the physician’s primary practice, clinic, or hospital,” Dr. Hogan said. “Only 65% of the MedSpas surveyed stated that they informed the patient that the supervising physician is not on site. In addition, a patient’s medical history is reviewed at only 40% of the MedSpas. To give context, in Illinois, a physician can only deliver care after a physician-patient relationship has been established, meaning that a good faith exam has been performed. And if they are to delegate any type of service, they must always be on site to provide assistance.”
Dr. Hogan noted that there are no federal statutes or agencies that regulate or oversee MedSpas. “Regulation and oversight are often delegated to state licensing agencies that are overwhelmed and often stretched thin regarding personnel and budgets,” she said. To raise awareness of this issue, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association (ASDSA) launched the Medical Spa Safety Coalition, which aims to promote model legislation for states known as the Medical Spa Safety Act. Highlights of the bill include clear definitions of medical spa and medical director, as well as the requirement of an on-site medical director who must be a physician trained in all procedures performed at the MedSpa. Coalition members include 16 state dermatology boards as well as the ASDSA, the American Academy of Dermatology Association, the American Society for Laser Medicine & Surgery, and the American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
The ASDSA provided funding to support the published study. Dr. Hogan reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — according to Sara Hogan, MD.
“I’m not anti-MedSpa; I’m pro-patient safety,” Dr. Hogan, clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery symposium. “The MedSpa industry is booming; it brought in $17 billion in 2023. There are as many MedSpas in the United States as there are practicing dermatologists, and that number is set to exceed the number of dermatologists.”
According to industry data from the American Med Spa Association, 63% of member MedSpas have non-MD ownership. Among MedSpas owned by physicians, 80% are of a non–core specialty, meaning a specialty other than dermatology, plastic surgery, otorhinolaryngology, or ophthalmology. Of MedSpa medical directors, 69% are from non–core physician specialties. “There’s an increasing amount of data that shows a relatively higher incidence of complications from cosmetic procedures that are delivered at MedSpas,” Dr. Hogan said. “A 2020 study suggested that this is likely due to improper training, improper technique, and/or improper device settings.”
Dr. Hogan also cited adverse effects linked to counterfeit or mishandled botulinum toxin injections that prompted the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to issue an alert to clinicians in April 2024. Clusters of 22 people in 11 states reported adverse effects after receiving injections with counterfeit botulinum toxin or injections administered by unlicensed or untrained individuals or in non-healthcare settings, such as homes or spas.
To better understand who performs cosmetic procedures, provides medical supervision, and follows safety protocols at MedSpas, Dr. Hogan and colleagues conducted a “truth in advertising” study of 127 MedSpas in the greater Chicago area. They chose this geographic location because an analysis published in 2021 identified Chicago as having the third highest number of aesthetic physicians and the fifth highest number of MedSpas in the United States. The researchers enlisted help from “secret shoppers” who contacted the MedSpas by telephone to ask about the level of training, if patients underwent a review of medical history, the level of on-site physician supervision, and the protocol for complications.
The top five cosmetic procedures offered by the 127 surveyed MedSpas were facials (85.0%), hair removal (85.0%), botulinum toxin injections (83.5%), dermal fillers (82.7%), and chemical peels (76.4%). About two thirds of cosmetic procedures were performed by aestheticians (66.9%), followed by registered nurses or licensed practical nurses (52.8%), board-certified physicians (48.8%, mostly plastic and reconstructive surgeons), nurse practitioners (27.6%), and physician assistants (9.4%).
In the realm of supervision, 16.5% of MedSpas surveyed reported that a medical director or supervising physician is always on site. “If not located on site, when asked where the physicians are, the majority of the time they were at the physician’s primary practice, clinic, or hospital,” Dr. Hogan said. “Only 65% of the MedSpas surveyed stated that they informed the patient that the supervising physician is not on site. In addition, a patient’s medical history is reviewed at only 40% of the MedSpas. To give context, in Illinois, a physician can only deliver care after a physician-patient relationship has been established, meaning that a good faith exam has been performed. And if they are to delegate any type of service, they must always be on site to provide assistance.”
Dr. Hogan noted that there are no federal statutes or agencies that regulate or oversee MedSpas. “Regulation and oversight are often delegated to state licensing agencies that are overwhelmed and often stretched thin regarding personnel and budgets,” she said. To raise awareness of this issue, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association (ASDSA) launched the Medical Spa Safety Coalition, which aims to promote model legislation for states known as the Medical Spa Safety Act. Highlights of the bill include clear definitions of medical spa and medical director, as well as the requirement of an on-site medical director who must be a physician trained in all procedures performed at the MedSpa. Coalition members include 16 state dermatology boards as well as the ASDSA, the American Academy of Dermatology Association, the American Society for Laser Medicine & Surgery, and the American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
The ASDSA provided funding to support the published study. Dr. Hogan reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — according to Sara Hogan, MD.
“I’m not anti-MedSpa; I’m pro-patient safety,” Dr. Hogan, clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery symposium. “The MedSpa industry is booming; it brought in $17 billion in 2023. There are as many MedSpas in the United States as there are practicing dermatologists, and that number is set to exceed the number of dermatologists.”
According to industry data from the American Med Spa Association, 63% of member MedSpas have non-MD ownership. Among MedSpas owned by physicians, 80% are of a non–core specialty, meaning a specialty other than dermatology, plastic surgery, otorhinolaryngology, or ophthalmology. Of MedSpa medical directors, 69% are from non–core physician specialties. “There’s an increasing amount of data that shows a relatively higher incidence of complications from cosmetic procedures that are delivered at MedSpas,” Dr. Hogan said. “A 2020 study suggested that this is likely due to improper training, improper technique, and/or improper device settings.”
Dr. Hogan also cited adverse effects linked to counterfeit or mishandled botulinum toxin injections that prompted the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to issue an alert to clinicians in April 2024. Clusters of 22 people in 11 states reported adverse effects after receiving injections with counterfeit botulinum toxin or injections administered by unlicensed or untrained individuals or in non-healthcare settings, such as homes or spas.
To better understand who performs cosmetic procedures, provides medical supervision, and follows safety protocols at MedSpas, Dr. Hogan and colleagues conducted a “truth in advertising” study of 127 MedSpas in the greater Chicago area. They chose this geographic location because an analysis published in 2021 identified Chicago as having the third highest number of aesthetic physicians and the fifth highest number of MedSpas in the United States. The researchers enlisted help from “secret shoppers” who contacted the MedSpas by telephone to ask about the level of training, if patients underwent a review of medical history, the level of on-site physician supervision, and the protocol for complications.
The top five cosmetic procedures offered by the 127 surveyed MedSpas were facials (85.0%), hair removal (85.0%), botulinum toxin injections (83.5%), dermal fillers (82.7%), and chemical peels (76.4%). About two thirds of cosmetic procedures were performed by aestheticians (66.9%), followed by registered nurses or licensed practical nurses (52.8%), board-certified physicians (48.8%, mostly plastic and reconstructive surgeons), nurse practitioners (27.6%), and physician assistants (9.4%).
In the realm of supervision, 16.5% of MedSpas surveyed reported that a medical director or supervising physician is always on site. “If not located on site, when asked where the physicians are, the majority of the time they were at the physician’s primary practice, clinic, or hospital,” Dr. Hogan said. “Only 65% of the MedSpas surveyed stated that they informed the patient that the supervising physician is not on site. In addition, a patient’s medical history is reviewed at only 40% of the MedSpas. To give context, in Illinois, a physician can only deliver care after a physician-patient relationship has been established, meaning that a good faith exam has been performed. And if they are to delegate any type of service, they must always be on site to provide assistance.”
Dr. Hogan noted that there are no federal statutes or agencies that regulate or oversee MedSpas. “Regulation and oversight are often delegated to state licensing agencies that are overwhelmed and often stretched thin regarding personnel and budgets,” she said. To raise awareness of this issue, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association (ASDSA) launched the Medical Spa Safety Coalition, which aims to promote model legislation for states known as the Medical Spa Safety Act. Highlights of the bill include clear definitions of medical spa and medical director, as well as the requirement of an on-site medical director who must be a physician trained in all procedures performed at the MedSpa. Coalition members include 16 state dermatology boards as well as the ASDSA, the American Academy of Dermatology Association, the American Society for Laser Medicine & Surgery, and the American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
The ASDSA provided funding to support the published study. Dr. Hogan reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors Are Seeking Professional Coaches More Often. Here’s Why
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fillers, Hyaluronidase Relieve Orofacial Changes in Patients with Scleroderma
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — In 2003, researchers asked 303 patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) what bothered them most about their disease from an aesthetic standpoint: Orofacial features, such as thin lips and mouth furrows, or non-facial features, such as fingertip ulceration and waxy changes to the skin.
Respondents expressed significant concern about specific orofacial features, including thin lips (73%), mouth furrows (80%), loss of facial lines (68%), and a smaller, tighter mouth (77%).
“Patients with systemic sclerosis may have loss of vermilion lip, microstomia, and perioral rhytids,” Kathleen Cook Suozzi, MD, who directs the Aesthetic Dermatology Program at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “How can we address these changes for our patients?”
Recent research has shown that hyaluronidase injections can help improve orofacial changes commonly experienced by patients with scleroderma. In 2019, researchers in Alabama reported the case of a 53-year-old woman treated with hyaluronidase for scleroderma-induced microstomia. After four visits over 7 months and a total hyaluronidase dose of 470 IU, the patient reported an improved Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis (MHISS) score (38 of 48); subjective improvement of symptoms, including greater ease in eating and undergoing dental treatment; and improved mouth closure.
In 2023, researchers published a cohort study of four women between the ages of 43 and 61 with autoimmune sclerosing conditions that resulted in oral microstomia. Following hyaluronidase injections, all improved in mouth opening capacity and MHISS, with change stabilizing between three and five treatments. More recently, in a study pending publication in JAAD Case Reports, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues retrospectively evaluated 12 women with scleroderma who received between 150 and 300 units of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler for microstomia between 2020 and 2023. Of the 12 women, 58% had diffuse disease, and 42% had limited disease. Overall, oral aperture width increased by 0.65 cm (P = .0027) and oral aperture height increased by 0.88 cm (P < .0001). “In general, patients needed three to four treatments to reach peak effect, and then they reached a plateau,” Dr. Suozzi said. “It wasn’t that the treatment wasn’t working anymore, but it was because their oral aperture had gotten to a size of around 5 cm, which is clinically normal. Interestingly, we found that if the patient’s disease flared and their microstomia started to return, when you rechallenged them, they continued to respond. So, patients can continue to use this treatment over time.”
In a separate case series of seven patients, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues prospectively evaluated the effect of HA soft tissue filler with Restylane Silk for lip augmentation. Study participants experienced statistically significant increases in the difference between pre- and postinjection fullness in both upper and lower lips. Also, the mean posttreatment score fell between “much improved” (2) and “improved” (3) on both the Investigator Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale and the Subject Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale.
Dr. Suozzi recommends using nerve blocks for injecting HA filler or hyaluronidase in patients with scleroderma and minimizing the injection points. “Initially, we were using 30% lidocaine preparations around the mouth for an hour before the procedure, and patients were still having pain, so now we use nerve blocks,” she said. “For hyaluronidase, we do perform a test dose of 75-100 units, usually in the commissure. It’s amazing how well it works; people will usually come back after their test dose and have improvements in their measurements. This is a really easy treatment to perform, and I think it can be done in the office of a general dermatologist. There is concern about cross-reactivity with bee venom, so you want to ask patients about that.”
Dr. Suozzi reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — In 2003, researchers asked 303 patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) what bothered them most about their disease from an aesthetic standpoint: Orofacial features, such as thin lips and mouth furrows, or non-facial features, such as fingertip ulceration and waxy changes to the skin.
Respondents expressed significant concern about specific orofacial features, including thin lips (73%), mouth furrows (80%), loss of facial lines (68%), and a smaller, tighter mouth (77%).
“Patients with systemic sclerosis may have loss of vermilion lip, microstomia, and perioral rhytids,” Kathleen Cook Suozzi, MD, who directs the Aesthetic Dermatology Program at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “How can we address these changes for our patients?”
Recent research has shown that hyaluronidase injections can help improve orofacial changes commonly experienced by patients with scleroderma. In 2019, researchers in Alabama reported the case of a 53-year-old woman treated with hyaluronidase for scleroderma-induced microstomia. After four visits over 7 months and a total hyaluronidase dose of 470 IU, the patient reported an improved Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis (MHISS) score (38 of 48); subjective improvement of symptoms, including greater ease in eating and undergoing dental treatment; and improved mouth closure.
In 2023, researchers published a cohort study of four women between the ages of 43 and 61 with autoimmune sclerosing conditions that resulted in oral microstomia. Following hyaluronidase injections, all improved in mouth opening capacity and MHISS, with change stabilizing between three and five treatments. More recently, in a study pending publication in JAAD Case Reports, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues retrospectively evaluated 12 women with scleroderma who received between 150 and 300 units of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler for microstomia between 2020 and 2023. Of the 12 women, 58% had diffuse disease, and 42% had limited disease. Overall, oral aperture width increased by 0.65 cm (P = .0027) and oral aperture height increased by 0.88 cm (P < .0001). “In general, patients needed three to four treatments to reach peak effect, and then they reached a plateau,” Dr. Suozzi said. “It wasn’t that the treatment wasn’t working anymore, but it was because their oral aperture had gotten to a size of around 5 cm, which is clinically normal. Interestingly, we found that if the patient’s disease flared and their microstomia started to return, when you rechallenged them, they continued to respond. So, patients can continue to use this treatment over time.”
In a separate case series of seven patients, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues prospectively evaluated the effect of HA soft tissue filler with Restylane Silk for lip augmentation. Study participants experienced statistically significant increases in the difference between pre- and postinjection fullness in both upper and lower lips. Also, the mean posttreatment score fell between “much improved” (2) and “improved” (3) on both the Investigator Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale and the Subject Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale.
Dr. Suozzi recommends using nerve blocks for injecting HA filler or hyaluronidase in patients with scleroderma and minimizing the injection points. “Initially, we were using 30% lidocaine preparations around the mouth for an hour before the procedure, and patients were still having pain, so now we use nerve blocks,” she said. “For hyaluronidase, we do perform a test dose of 75-100 units, usually in the commissure. It’s amazing how well it works; people will usually come back after their test dose and have improvements in their measurements. This is a really easy treatment to perform, and I think it can be done in the office of a general dermatologist. There is concern about cross-reactivity with bee venom, so you want to ask patients about that.”
Dr. Suozzi reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — In 2003, researchers asked 303 patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) what bothered them most about their disease from an aesthetic standpoint: Orofacial features, such as thin lips and mouth furrows, or non-facial features, such as fingertip ulceration and waxy changes to the skin.
Respondents expressed significant concern about specific orofacial features, including thin lips (73%), mouth furrows (80%), loss of facial lines (68%), and a smaller, tighter mouth (77%).
“Patients with systemic sclerosis may have loss of vermilion lip, microstomia, and perioral rhytids,” Kathleen Cook Suozzi, MD, who directs the Aesthetic Dermatology Program at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “How can we address these changes for our patients?”
Recent research has shown that hyaluronidase injections can help improve orofacial changes commonly experienced by patients with scleroderma. In 2019, researchers in Alabama reported the case of a 53-year-old woman treated with hyaluronidase for scleroderma-induced microstomia. After four visits over 7 months and a total hyaluronidase dose of 470 IU, the patient reported an improved Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis (MHISS) score (38 of 48); subjective improvement of symptoms, including greater ease in eating and undergoing dental treatment; and improved mouth closure.
In 2023, researchers published a cohort study of four women between the ages of 43 and 61 with autoimmune sclerosing conditions that resulted in oral microstomia. Following hyaluronidase injections, all improved in mouth opening capacity and MHISS, with change stabilizing between three and five treatments. More recently, in a study pending publication in JAAD Case Reports, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues retrospectively evaluated 12 women with scleroderma who received between 150 and 300 units of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler for microstomia between 2020 and 2023. Of the 12 women, 58% had diffuse disease, and 42% had limited disease. Overall, oral aperture width increased by 0.65 cm (P = .0027) and oral aperture height increased by 0.88 cm (P < .0001). “In general, patients needed three to four treatments to reach peak effect, and then they reached a plateau,” Dr. Suozzi said. “It wasn’t that the treatment wasn’t working anymore, but it was because their oral aperture had gotten to a size of around 5 cm, which is clinically normal. Interestingly, we found that if the patient’s disease flared and their microstomia started to return, when you rechallenged them, they continued to respond. So, patients can continue to use this treatment over time.”
In a separate case series of seven patients, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues prospectively evaluated the effect of HA soft tissue filler with Restylane Silk for lip augmentation. Study participants experienced statistically significant increases in the difference between pre- and postinjection fullness in both upper and lower lips. Also, the mean posttreatment score fell between “much improved” (2) and “improved” (3) on both the Investigator Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale and the Subject Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale.
Dr. Suozzi recommends using nerve blocks for injecting HA filler or hyaluronidase in patients with scleroderma and minimizing the injection points. “Initially, we were using 30% lidocaine preparations around the mouth for an hour before the procedure, and patients were still having pain, so now we use nerve blocks,” she said. “For hyaluronidase, we do perform a test dose of 75-100 units, usually in the commissure. It’s amazing how well it works; people will usually come back after their test dose and have improvements in their measurements. This is a really easy treatment to perform, and I think it can be done in the office of a general dermatologist. There is concern about cross-reactivity with bee venom, so you want to ask patients about that.”
Dr. Suozzi reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
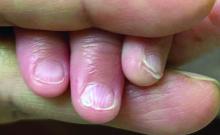
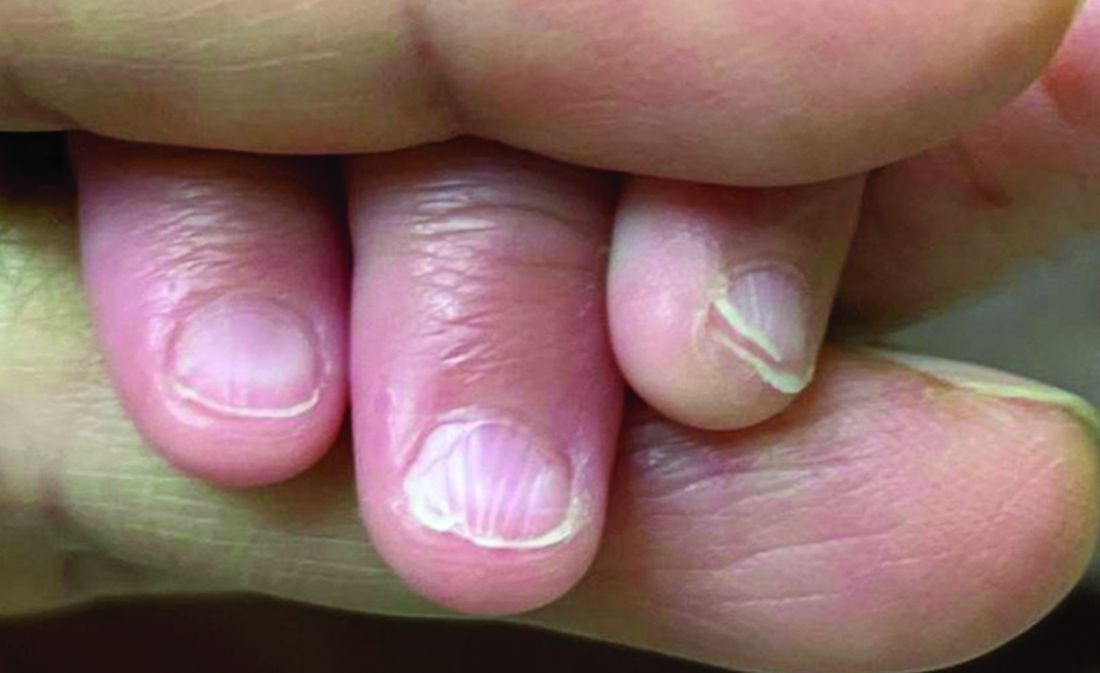
A 7-Month-Old Female Presented With Nail Changes
Given the clinical presentation and the absence of other systemic or dermatological findings, the diagnosis of chevron nails was made.
Discussion
The condition is characterized by transverse ridges on the nails that converge towards the center, forming a V or chevron shape. This condition was first described by Perry et al. and later by Shuster et al., who explained that the condition might result from axial growth of the nail with synchronous growth occurring from a chevron-shaped growing edge of the nail root. Alternatively, Shuster suggested that sequential growth, with localized variation in the nail production rate, could propagate a wave from the center of the nail to the edge.
The etiology of chevron nails is not well understood, but it is believed to result from temporary disruptions in the nail matrix, possibly related to minor illness or physiological stress during infancy.
In the case of our 7-month-old patient, the history of mild upper respiratory infections might have contributed to the development of chevron nails. However, the lack of other significant illness, skin involvement, or systemic findings supports the benign and self-limiting nature of this condition. Parents were reassured that chevron nails typically resolve on their own as the child grows and that no specific treatment is necessary.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of transverse nail changes in children includes other conditions such as trachyonychia, lichen planus, Darier disease, and pachyonychia congenita.
Trachyonychia, also known as “sandpaper nails,” trachyonychia is characterized by the roughening of the nail surface, giving it a dull and ridged appearance. The condition may affect all 20 nails and is often associated with underlying dermatological conditions such as lichen planus or alopecia areata. Unlike chevron nails, trachyonychia presents with more diffuse nail changes and does not typically feature the distinct V-shaped ridging seen in this patient.
Lichen planus is an inflammatory condition that can affect the skin, mucous membranes, and nails. Nail involvement in lichen planus can lead to longitudinal ridging, thinning, and sometimes even complete nail loss. The absence of other characteristic features of lichen planus, such as violaceous papules on the skin or white lacy patterns on mucous membranes (Wickham striae), makes this diagnosis less likely in our patient.
Darier disease, also known as keratosis follicularis, is a genetic disorder characterized by greasy, warty papules primarily on seborrheic areas of the skin, nail abnormalities, and sometimes mucosal involvement. Nail changes in Darier disease include longitudinal red and white streaks, V-shaped notching at the free edge of the nails, and subungual hyperkeratosis. These nail changes are more severe and distinct than the simple transverse ridging seen in chevron nails. The absence of other clinical signs of Darier disease, such as skin papules or characteristic nail notching, makes this diagnosis unlikely in our patient.
Pachyonychia congenita is a rare genetic disorder characterized by thickened nails (pachyonychia), painful plantar keratoderma, and sometimes oral leukokeratosis. The condition typically presents with significant nail thickening and other systemic findings, which were absent in our patient. The distinct pattern of V-shaped ridging observed in chevron nails does not align with the typical presentation of pachyonychia congenita.
Next Steps
No specific treatment is required for chevron nails. The condition is typically self-resolving, and the nails usually return to a normal appearance as the child continues to grow. Parents were advised to monitor the nails for any changes or new symptoms and were reassured about the benign nature of the findings. Follow-up was scheduled to ensure the resolution of the condition as the child develops.
Conclusion
Chevron nails are an important consideration in the differential diagnosis of transverse nail ridging in infants and young children. While the condition is benign and self-limiting, it is crucial to differentiate it from other nail dystrophies, such as trachyonychia, lichen planus, Darier disease, and pachyonychia congenita, which may require further investigation or intervention. Awareness of chevron nails can help prevent unnecessary worry and provide reassurance to parents and caregivers.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Delano S, Belazarian L. Chevron nails: A normal variant in the pediatric population. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Jan-Feb;31(1):e24-5. doi: 10.1111/pde.12193.
John JM et al. Chevron nail — An under-recognised normal variant of nail development. Arch Dis Child. 2024 Jul 18;109(8):648. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2024-326975.
Shuster S. The significance of chevron nails. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:151–152. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.1996.d01-961.x.
Starace M et al. Nail disorders in children. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018 Oct;4(4):217-229. doi: 10.1159/000486020.
Given the clinical presentation and the absence of other systemic or dermatological findings, the diagnosis of chevron nails was made.
Discussion
The condition is characterized by transverse ridges on the nails that converge towards the center, forming a V or chevron shape. This condition was first described by Perry et al. and later by Shuster et al., who explained that the condition might result from axial growth of the nail with synchronous growth occurring from a chevron-shaped growing edge of the nail root. Alternatively, Shuster suggested that sequential growth, with localized variation in the nail production rate, could propagate a wave from the center of the nail to the edge.
The etiology of chevron nails is not well understood, but it is believed to result from temporary disruptions in the nail matrix, possibly related to minor illness or physiological stress during infancy.
In the case of our 7-month-old patient, the history of mild upper respiratory infections might have contributed to the development of chevron nails. However, the lack of other significant illness, skin involvement, or systemic findings supports the benign and self-limiting nature of this condition. Parents were reassured that chevron nails typically resolve on their own as the child grows and that no specific treatment is necessary.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of transverse nail changes in children includes other conditions such as trachyonychia, lichen planus, Darier disease, and pachyonychia congenita.
Trachyonychia, also known as “sandpaper nails,” trachyonychia is characterized by the roughening of the nail surface, giving it a dull and ridged appearance. The condition may affect all 20 nails and is often associated with underlying dermatological conditions such as lichen planus or alopecia areata. Unlike chevron nails, trachyonychia presents with more diffuse nail changes and does not typically feature the distinct V-shaped ridging seen in this patient.
Lichen planus is an inflammatory condition that can affect the skin, mucous membranes, and nails. Nail involvement in lichen planus can lead to longitudinal ridging, thinning, and sometimes even complete nail loss. The absence of other characteristic features of lichen planus, such as violaceous papules on the skin or white lacy patterns on mucous membranes (Wickham striae), makes this diagnosis less likely in our patient.
Darier disease, also known as keratosis follicularis, is a genetic disorder characterized by greasy, warty papules primarily on seborrheic areas of the skin, nail abnormalities, and sometimes mucosal involvement. Nail changes in Darier disease include longitudinal red and white streaks, V-shaped notching at the free edge of the nails, and subungual hyperkeratosis. These nail changes are more severe and distinct than the simple transverse ridging seen in chevron nails. The absence of other clinical signs of Darier disease, such as skin papules or characteristic nail notching, makes this diagnosis unlikely in our patient.
Pachyonychia congenita is a rare genetic disorder characterized by thickened nails (pachyonychia), painful plantar keratoderma, and sometimes oral leukokeratosis. The condition typically presents with significant nail thickening and other systemic findings, which were absent in our patient. The distinct pattern of V-shaped ridging observed in chevron nails does not align with the typical presentation of pachyonychia congenita.
Next Steps
No specific treatment is required for chevron nails. The condition is typically self-resolving, and the nails usually return to a normal appearance as the child continues to grow. Parents were advised to monitor the nails for any changes or new symptoms and were reassured about the benign nature of the findings. Follow-up was scheduled to ensure the resolution of the condition as the child develops.
Conclusion
Chevron nails are an important consideration in the differential diagnosis of transverse nail ridging in infants and young children. While the condition is benign and self-limiting, it is crucial to differentiate it from other nail dystrophies, such as trachyonychia, lichen planus, Darier disease, and pachyonychia congenita, which may require further investigation or intervention. Awareness of chevron nails can help prevent unnecessary worry and provide reassurance to parents and caregivers.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Delano S, Belazarian L. Chevron nails: A normal variant in the pediatric population. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Jan-Feb;31(1):e24-5. doi: 10.1111/pde.12193.
John JM et al. Chevron nail — An under-recognised normal variant of nail development. Arch Dis Child. 2024 Jul 18;109(8):648. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2024-326975.
Shuster S. The significance of chevron nails. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:151–152. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.1996.d01-961.x.
Starace M et al. Nail disorders in children. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018 Oct;4(4):217-229. doi: 10.1159/000486020.
Given the clinical presentation and the absence of other systemic or dermatological findings, the diagnosis of chevron nails was made.
Discussion
The condition is characterized by transverse ridges on the nails that converge towards the center, forming a V or chevron shape. This condition was first described by Perry et al. and later by Shuster et al., who explained that the condition might result from axial growth of the nail with synchronous growth occurring from a chevron-shaped growing edge of the nail root. Alternatively, Shuster suggested that sequential growth, with localized variation in the nail production rate, could propagate a wave from the center of the nail to the edge.
The etiology of chevron nails is not well understood, but it is believed to result from temporary disruptions in the nail matrix, possibly related to minor illness or physiological stress during infancy.
In the case of our 7-month-old patient, the history of mild upper respiratory infections might have contributed to the development of chevron nails. However, the lack of other significant illness, skin involvement, or systemic findings supports the benign and self-limiting nature of this condition. Parents were reassured that chevron nails typically resolve on their own as the child grows and that no specific treatment is necessary.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of transverse nail changes in children includes other conditions such as trachyonychia, lichen planus, Darier disease, and pachyonychia congenita.
Trachyonychia, also known as “sandpaper nails,” trachyonychia is characterized by the roughening of the nail surface, giving it a dull and ridged appearance. The condition may affect all 20 nails and is often associated with underlying dermatological conditions such as lichen planus or alopecia areata. Unlike chevron nails, trachyonychia presents with more diffuse nail changes and does not typically feature the distinct V-shaped ridging seen in this patient.
Lichen planus is an inflammatory condition that can affect the skin, mucous membranes, and nails. Nail involvement in lichen planus can lead to longitudinal ridging, thinning, and sometimes even complete nail loss. The absence of other characteristic features of lichen planus, such as violaceous papules on the skin or white lacy patterns on mucous membranes (Wickham striae), makes this diagnosis less likely in our patient.
Darier disease, also known as keratosis follicularis, is a genetic disorder characterized by greasy, warty papules primarily on seborrheic areas of the skin, nail abnormalities, and sometimes mucosal involvement. Nail changes in Darier disease include longitudinal red and white streaks, V-shaped notching at the free edge of the nails, and subungual hyperkeratosis. These nail changes are more severe and distinct than the simple transverse ridging seen in chevron nails. The absence of other clinical signs of Darier disease, such as skin papules or characteristic nail notching, makes this diagnosis unlikely in our patient.
Pachyonychia congenita is a rare genetic disorder characterized by thickened nails (pachyonychia), painful plantar keratoderma, and sometimes oral leukokeratosis. The condition typically presents with significant nail thickening and other systemic findings, which were absent in our patient. The distinct pattern of V-shaped ridging observed in chevron nails does not align with the typical presentation of pachyonychia congenita.
Next Steps
No specific treatment is required for chevron nails. The condition is typically self-resolving, and the nails usually return to a normal appearance as the child continues to grow. Parents were advised to monitor the nails for any changes or new symptoms and were reassured about the benign nature of the findings. Follow-up was scheduled to ensure the resolution of the condition as the child develops.
Conclusion
Chevron nails are an important consideration in the differential diagnosis of transverse nail ridging in infants and young children. While the condition is benign and self-limiting, it is crucial to differentiate it from other nail dystrophies, such as trachyonychia, lichen planus, Darier disease, and pachyonychia congenita, which may require further investigation or intervention. Awareness of chevron nails can help prevent unnecessary worry and provide reassurance to parents and caregivers.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Delano S, Belazarian L. Chevron nails: A normal variant in the pediatric population. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Jan-Feb;31(1):e24-5. doi: 10.1111/pde.12193.
John JM et al. Chevron nail — An under-recognised normal variant of nail development. Arch Dis Child. 2024 Jul 18;109(8):648. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2024-326975.
Shuster S. The significance of chevron nails. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:151–152. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.1996.d01-961.x.
Starace M et al. Nail disorders in children. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018 Oct;4(4):217-229. doi: 10.1159/000486020.
There was no family history of similar nail findings and no relatives had a history of chronic skin conditions or congenital nail disorders.
On physical examination, several of the child’s fingernails exhibited distinct longitudinal ridges, with a characteristic pattern where the ridges converged at the center of the nail, forming a V-shape. There were no other concerning dermatologic findings, such as rashes, plaques, or erosions, and the skin and hair appeared otherwise normal. The rest of the physical exam was unremarkable.
Chronic Back Pain in Patients With Psoriasis, Uveitis, or Colitis: How Often Is It Axial Spondyloarthritis?
TOPLINE:
Patients with psoriasis, uveitis, or colitis who present with undiagnosed chronic back pain should be referred to a rheumatologist for the assessment of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), with MRI being a more accurate diagnostic method than clinical features.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the prevalence of axSpA according to the extra-articular presentation and human leukocyte antigen B27 (HLA-B27) status in two Canadian cohorts (SASPIC 1 and 2).
- Overall, 363 adult patients aged ≤ 45 years with psoriasis, uveitis, or colitis who presented with chronic undiagnosed back and/or buttock pain lasting 3 months or more were included.
- Participants were referred to rheumatologists with expertise in axSpA for structured diagnostic evaluations, including history, physical exam, levels of C-reactive protein, HLA-B27 status, and imaging studies.
- An MRI of the sacroiliac joints was conducted in all patients in the SASPIC-2 cohort and in 62.3% of those in the SASPIC-1 cohort.
- The primary outcome was the proportion of patients diagnosed with axSpA after final global evaluation, and the secondary outcome was the impact of MRI on diagnosis and classification.
TAKEAWAY:
- AxSpA diagnoses were made in 46.7% with psoriasis, 61.6% with uveitis, and 46.8% with colitis in the SASPIC-1 cohort and in 23.5%, 57.9%, and 23.3%, respectively, in the SASPIC-2 cohort.
- Being positive for HLA-B27 was linked to the presence of axSpA in 56%-88% of those in both the cohorts.
- Musculoskeletal clinical features were not helpful in differentiating between patients with and without axSpA.
- In both the cohorts, the MRI of the sacroiliac joints was indicative of axSpA in a significantly greater number of patients with psoriasis, uveitis, or colitis who were diagnosed with axSpA than in those not diagnosed with axSpA (P < .05 for all).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our data supports the benefit of recent referral recommendations that advocate referral to a rheumatologist of patients with chronic back pain and extra-articular features related to axSpA,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Walter P. Maksymowych, MB ChB, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
MRI readers had to rely on their own expertise to decide if an MRI was indeed positive and thus indicative of axSpA. This study included only patients with undiagnosed back pain, and a longer follow-up duration could have led to a higher number of patients being diagnosed with axial inflammation. In SASPIC-1, local rheumatologists conducted MRI evaluations of the spinal lesions only when necessary, while in SASPIC-2, MRI of only the sacroiliac joints was required.
DISCLOSURES:
SASPIC-1 was supported by AbbVie Canada and Janssen Canada, and SASPIC-2 was supported by AbbVie Canada. The authors disclosed receiving grants, consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria and having other ties with AbbVie and several other pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with psoriasis, uveitis, or colitis who present with undiagnosed chronic back pain should be referred to a rheumatologist for the assessment of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), with MRI being a more accurate diagnostic method than clinical features.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the prevalence of axSpA according to the extra-articular presentation and human leukocyte antigen B27 (HLA-B27) status in two Canadian cohorts (SASPIC 1 and 2).
- Overall, 363 adult patients aged ≤ 45 years with psoriasis, uveitis, or colitis who presented with chronic undiagnosed back and/or buttock pain lasting 3 months or more were included.
- Participants were referred to rheumatologists with expertise in axSpA for structured diagnostic evaluations, including history, physical exam, levels of C-reactive protein, HLA-B27 status, and imaging studies.
- An MRI of the sacroiliac joints was conducted in all patients in the SASPIC-2 cohort and in 62.3% of those in the SASPIC-1 cohort.
- The primary outcome was the proportion of patients diagnosed with axSpA after final global evaluation, and the secondary outcome was the impact of MRI on diagnosis and classification.
TAKEAWAY:
- AxSpA diagnoses were made in 46.7% with psoriasis, 61.6% with uveitis, and 46.8% with colitis in the SASPIC-1 cohort and in 23.5%, 57.9%, and 23.3%, respectively, in the SASPIC-2 cohort.
- Being positive for HLA-B27 was linked to the presence of axSpA in 56%-88% of those in both the cohorts.
- Musculoskeletal clinical features were not helpful in differentiating between patients with and without axSpA.
- In both the cohorts, the MRI of the sacroiliac joints was indicative of axSpA in a significantly greater number of patients with psoriasis, uveitis, or colitis who were diagnosed with axSpA than in those not diagnosed with axSpA (P < .05 for all).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our data supports the benefit of recent referral recommendations that advocate referral to a rheumatologist of patients with chronic back pain and extra-articular features related to axSpA,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Walter P. Maksymowych, MB ChB, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
MRI readers had to rely on their own expertise to decide if an MRI was indeed positive and thus indicative of axSpA. This study included only patients with undiagnosed back pain, and a longer follow-up duration could have led to a higher number of patients being diagnosed with axial inflammation. In SASPIC-1, local rheumatologists conducted MRI evaluations of the spinal lesions only when necessary, while in SASPIC-2, MRI of only the sacroiliac joints was required.
DISCLOSURES:
SASPIC-1 was supported by AbbVie Canada and Janssen Canada, and SASPIC-2 was supported by AbbVie Canada. The authors disclosed receiving grants, consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria and having other ties with AbbVie and several other pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with psoriasis, uveitis, or colitis who present with undiagnosed chronic back pain should be referred to a rheumatologist for the assessment of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), with MRI being a more accurate diagnostic method than clinical features.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the prevalence of axSpA according to the extra-articular presentation and human leukocyte antigen B27 (HLA-B27) status in two Canadian cohorts (SASPIC 1 and 2).
- Overall, 363 adult patients aged ≤ 45 years with psoriasis, uveitis, or colitis who presented with chronic undiagnosed back and/or buttock pain lasting 3 months or more were included.
- Participants were referred to rheumatologists with expertise in axSpA for structured diagnostic evaluations, including history, physical exam, levels of C-reactive protein, HLA-B27 status, and imaging studies.
- An MRI of the sacroiliac joints was conducted in all patients in the SASPIC-2 cohort and in 62.3% of those in the SASPIC-1 cohort.
- The primary outcome was the proportion of patients diagnosed with axSpA after final global evaluation, and the secondary outcome was the impact of MRI on diagnosis and classification.
TAKEAWAY:
- AxSpA diagnoses were made in 46.7% with psoriasis, 61.6% with uveitis, and 46.8% with colitis in the SASPIC-1 cohort and in 23.5%, 57.9%, and 23.3%, respectively, in the SASPIC-2 cohort.
- Being positive for HLA-B27 was linked to the presence of axSpA in 56%-88% of those in both the cohorts.
- Musculoskeletal clinical features were not helpful in differentiating between patients with and without axSpA.
- In both the cohorts, the MRI of the sacroiliac joints was indicative of axSpA in a significantly greater number of patients with psoriasis, uveitis, or colitis who were diagnosed with axSpA than in those not diagnosed with axSpA (P < .05 for all).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our data supports the benefit of recent referral recommendations that advocate referral to a rheumatologist of patients with chronic back pain and extra-articular features related to axSpA,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Walter P. Maksymowych, MB ChB, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
MRI readers had to rely on their own expertise to decide if an MRI was indeed positive and thus indicative of axSpA. This study included only patients with undiagnosed back pain, and a longer follow-up duration could have led to a higher number of patients being diagnosed with axial inflammation. In SASPIC-1, local rheumatologists conducted MRI evaluations of the spinal lesions only when necessary, while in SASPIC-2, MRI of only the sacroiliac joints was required.
DISCLOSURES:
SASPIC-1 was supported by AbbVie Canada and Janssen Canada, and SASPIC-2 was supported by AbbVie Canada. The authors disclosed receiving grants, consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria and having other ties with AbbVie and several other pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FTC Interim Report on Pharmacy Middlemen Is First Step of Many Needed in Addressing Drug Costs, Access
Rising consolidation among pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) allows the companies to profit at the expense of patients and independent pharmacists. That’s the conclusion of a recent Federal Trade Commission (FTC) report on interim findings from the agency’s ongoing investigation of PBMs.
Lawmakers are increasingly scrutinizing the industry amid growing concern among physicians and consumers about how PBMs exploit their market dominance. The top six PBMs managed 94% of US drug claims in 2023, with the majority handled by the industry’s three giants: CVS Caremark, Cigna’s Express Scripts, and United Healthcare’s OptumRx.
PBMs manage prescription drug benefits for health insurers, Medicare Part D drug plans, and large employers. They act as middlemen between health insurers and pharmacies, developing formularies of covered drugs and promising savings from the discounts and rebates they negotiate with drugmakers.
The FTC’s interim report found that the giant PBMs often exercise significant control over what drugs are available and at what price and which pharmacies patients can use to access their prescribed medications. Consumers suffer as a result, the report concluded.
Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations, shared her perspective on the FTC report in an email Q&A with this news organization. She is affiliated with The Rheumatology Group, based in Metairie, Louisiana.
Dr. Feldman has long tracked the PBM industry and appeared as a witness before influential government panels, including the House Energy and Commerce Committee. She has highlighted for lawmakers the challenges physicians face in helping patients get needed medicines.
For example, she shared cases of PBMs steering patients toward the more expensive of three widely used rheumatoid arthritis medicines that have a similar mechanism of action, the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, Dr. Feldman said.
One of the drugs cost roughly half of the other two — about $30,000 per year vs $65,000-$70,000. Yet only the two expensive drugs were included in the PBM formulary. As a result, the cheapest drug holds only a sliver of market share; the remainder is dominated by the two expensive products, she told the House Oversight and Accountability Committee in 2021.
This Q&A has been edited for length and clarity.
What would you want federal and state policymakers to do in response to the FTC’s report?
I think Congress needs to clearly delineate the differences between anticompetitive pharmacy issues, drug pricing issues, and their effect on formulary construction issues.
Lawmakers should demand more transparency and consider legislation that would remove perverse incentives that prompt PBMs to choose higher priced drugs for their formularies.
That may require other regulatory or legislative actions to ensure lower prices (not higher kickbacks) are incentivized. Ultimately, in order to gain true competition within the health insurance business, these oligopolies of multiple businesses need to be broken up. Anything less seems to be nibbling around the edges and allows the Big Three to continue their “whack-a mole” in circumventing piecemeal regulatory and legislative policies.
You’ve followed PBM practices closely for many years. Was there anything in this interim FTC report that surprised you?
Though not surprised, I am glad that it was released because it had been a year in investigation and there were many requests for some type of substantive report.
Two things that are missing that I feel are paramount are investigating how the three big PBMs are causing physical harm to patients as a result of the profit component in formulary construction and the profound financial impact of hidden PBM profit centers in self-insured employer health plans.
What we have seen over the years is the result of the perverse incentives for the PBMs to prefer the most profitable medications on their formularies.
They use utilization management tools such as step therapy, nonmedical switching, and exclusions to maintain their formularies’ profitability. These tools have been shown to delay and deny the proper care of patients, resulting in not just monetary but physical harm as well.
I would think the physical harm done to patients in manipulating the formularies should be addressed in this report as well and, in fact, may be the most important aspect of consumer protection of this issue.
In terms of the FTC’s mission to not “unduly burden” legitimate business, I would like to see the sector of self-insured employers addressed.
The report details how PBMs steer prescriptions to their affiliated pharmacies. The FTC says that can push smaller pharmacies out of the market, ultimately leading to higher costs and lower quality services for people. What’s your perspective?
Having more community pharmacies is better than having less. We are seeing more “pharmacy deserts” in rural areas as a result of many community pharmacies having to close.
The FTC voted 4-1 to allow staff to issue the interim report, with Commissioner Melissa Holyoak voting no. And some FTC commissioners seem divided on the usefulness of the report. Why?
Commissioner Holyoak states the “the Report leaves us without a better understanding of the competition concerns surrounding PBMs or how consumers are impacted by PBM practices.”
I do agree with her that the harm to patients’ medical status was not even addressed as far as I could tell in this report. There are multiple news articles and reports on the harms inflicted upon patients by the UM tools that drive the construction of ever changing formularies, all based on contracting with manufacturers that result in the highest profit for the PBM.
Holyoak also states, “Among other critical conclusions, the Report does not address the seemingly contradictory conclusions in the 2005 Report that PBMs, including vertically owned PBMs, generated cost savings for consumers.”
That may be true, but in 2005, the rise of PBMs was just beginning and the huge vertical and horizontal integration had yet to begin. Also, 2005 was still in the beginning of the biologic drug deluge, which did create competition to get on the formulary. Since then, PBMs have done nothing to control the rise in prices but instead, apparently have used the competition to get higher price concessions from manufacturers based on a percentage of the list price to line their pockets.
Commissioner Ferguson agreed with releasing the report but he had many issues with this report including the lack of PBM response.
I do agree with him that the FTC should have used some type of “force” to get the information they needed from the PBMs. The Big Three are known for obfuscation and delaying providing information to legislative and regulatory agencies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Rising consolidation among pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) allows the companies to profit at the expense of patients and independent pharmacists. That’s the conclusion of a recent Federal Trade Commission (FTC) report on interim findings from the agency’s ongoing investigation of PBMs.
Lawmakers are increasingly scrutinizing the industry amid growing concern among physicians and consumers about how PBMs exploit their market dominance. The top six PBMs managed 94% of US drug claims in 2023, with the majority handled by the industry’s three giants: CVS Caremark, Cigna’s Express Scripts, and United Healthcare’s OptumRx.
PBMs manage prescription drug benefits for health insurers, Medicare Part D drug plans, and large employers. They act as middlemen between health insurers and pharmacies, developing formularies of covered drugs and promising savings from the discounts and rebates they negotiate with drugmakers.
The FTC’s interim report found that the giant PBMs often exercise significant control over what drugs are available and at what price and which pharmacies patients can use to access their prescribed medications. Consumers suffer as a result, the report concluded.
Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations, shared her perspective on the FTC report in an email Q&A with this news organization. She is affiliated with The Rheumatology Group, based in Metairie, Louisiana.
Dr. Feldman has long tracked the PBM industry and appeared as a witness before influential government panels, including the House Energy and Commerce Committee. She has highlighted for lawmakers the challenges physicians face in helping patients get needed medicines.
For example, she shared cases of PBMs steering patients toward the more expensive of three widely used rheumatoid arthritis medicines that have a similar mechanism of action, the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, Dr. Feldman said.
One of the drugs cost roughly half of the other two — about $30,000 per year vs $65,000-$70,000. Yet only the two expensive drugs were included in the PBM formulary. As a result, the cheapest drug holds only a sliver of market share; the remainder is dominated by the two expensive products, she told the House Oversight and Accountability Committee in 2021.
This Q&A has been edited for length and clarity.
What would you want federal and state policymakers to do in response to the FTC’s report?
I think Congress needs to clearly delineate the differences between anticompetitive pharmacy issues, drug pricing issues, and their effect on formulary construction issues.
Lawmakers should demand more transparency and consider legislation that would remove perverse incentives that prompt PBMs to choose higher priced drugs for their formularies.
That may require other regulatory or legislative actions to ensure lower prices (not higher kickbacks) are incentivized. Ultimately, in order to gain true competition within the health insurance business, these oligopolies of multiple businesses need to be broken up. Anything less seems to be nibbling around the edges and allows the Big Three to continue their “whack-a mole” in circumventing piecemeal regulatory and legislative policies.
You’ve followed PBM practices closely for many years. Was there anything in this interim FTC report that surprised you?
Though not surprised, I am glad that it was released because it had been a year in investigation and there were many requests for some type of substantive report.
Two things that are missing that I feel are paramount are investigating how the three big PBMs are causing physical harm to patients as a result of the profit component in formulary construction and the profound financial impact of hidden PBM profit centers in self-insured employer health plans.
What we have seen over the years is the result of the perverse incentives for the PBMs to prefer the most profitable medications on their formularies.
They use utilization management tools such as step therapy, nonmedical switching, and exclusions to maintain their formularies’ profitability. These tools have been shown to delay and deny the proper care of patients, resulting in not just monetary but physical harm as well.
I would think the physical harm done to patients in manipulating the formularies should be addressed in this report as well and, in fact, may be the most important aspect of consumer protection of this issue.
In terms of the FTC’s mission to not “unduly burden” legitimate business, I would like to see the sector of self-insured employers addressed.
The report details how PBMs steer prescriptions to their affiliated pharmacies. The FTC says that can push smaller pharmacies out of the market, ultimately leading to higher costs and lower quality services for people. What’s your perspective?
Having more community pharmacies is better than having less. We are seeing more “pharmacy deserts” in rural areas as a result of many community pharmacies having to close.
The FTC voted 4-1 to allow staff to issue the interim report, with Commissioner Melissa Holyoak voting no. And some FTC commissioners seem divided on the usefulness of the report. Why?
Commissioner Holyoak states the “the Report leaves us without a better understanding of the competition concerns surrounding PBMs or how consumers are impacted by PBM practices.”
I do agree with her that the harm to patients’ medical status was not even addressed as far as I could tell in this report. There are multiple news articles and reports on the harms inflicted upon patients by the UM tools that drive the construction of ever changing formularies, all based on contracting with manufacturers that result in the highest profit for the PBM.
Holyoak also states, “Among other critical conclusions, the Report does not address the seemingly contradictory conclusions in the 2005 Report that PBMs, including vertically owned PBMs, generated cost savings for consumers.”
That may be true, but in 2005, the rise of PBMs was just beginning and the huge vertical and horizontal integration had yet to begin. Also, 2005 was still in the beginning of the biologic drug deluge, which did create competition to get on the formulary. Since then, PBMs have done nothing to control the rise in prices but instead, apparently have used the competition to get higher price concessions from manufacturers based on a percentage of the list price to line their pockets.
Commissioner Ferguson agreed with releasing the report but he had many issues with this report including the lack of PBM response.
I do agree with him that the FTC should have used some type of “force” to get the information they needed from the PBMs. The Big Three are known for obfuscation and delaying providing information to legislative and regulatory agencies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Rising consolidation among pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) allows the companies to profit at the expense of patients and independent pharmacists. That’s the conclusion of a recent Federal Trade Commission (FTC) report on interim findings from the agency’s ongoing investigation of PBMs.
Lawmakers are increasingly scrutinizing the industry amid growing concern among physicians and consumers about how PBMs exploit their market dominance. The top six PBMs managed 94% of US drug claims in 2023, with the majority handled by the industry’s three giants: CVS Caremark, Cigna’s Express Scripts, and United Healthcare’s OptumRx.
PBMs manage prescription drug benefits for health insurers, Medicare Part D drug plans, and large employers. They act as middlemen between health insurers and pharmacies, developing formularies of covered drugs and promising savings from the discounts and rebates they negotiate with drugmakers.
The FTC’s interim report found that the giant PBMs often exercise significant control over what drugs are available and at what price and which pharmacies patients can use to access their prescribed medications. Consumers suffer as a result, the report concluded.
Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations, shared her perspective on the FTC report in an email Q&A with this news organization. She is affiliated with The Rheumatology Group, based in Metairie, Louisiana.
Dr. Feldman has long tracked the PBM industry and appeared as a witness before influential government panels, including the House Energy and Commerce Committee. She has highlighted for lawmakers the challenges physicians face in helping patients get needed medicines.
For example, she shared cases of PBMs steering patients toward the more expensive of three widely used rheumatoid arthritis medicines that have a similar mechanism of action, the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, Dr. Feldman said.
One of the drugs cost roughly half of the other two — about $30,000 per year vs $65,000-$70,000. Yet only the two expensive drugs were included in the PBM formulary. As a result, the cheapest drug holds only a sliver of market share; the remainder is dominated by the two expensive products, she told the House Oversight and Accountability Committee in 2021.
This Q&A has been edited for length and clarity.
What would you want federal and state policymakers to do in response to the FTC’s report?
I think Congress needs to clearly delineate the differences between anticompetitive pharmacy issues, drug pricing issues, and their effect on formulary construction issues.
Lawmakers should demand more transparency and consider legislation that would remove perverse incentives that prompt PBMs to choose higher priced drugs for their formularies.
That may require other regulatory or legislative actions to ensure lower prices (not higher kickbacks) are incentivized. Ultimately, in order to gain true competition within the health insurance business, these oligopolies of multiple businesses need to be broken up. Anything less seems to be nibbling around the edges and allows the Big Three to continue their “whack-a mole” in circumventing piecemeal regulatory and legislative policies.
You’ve followed PBM practices closely for many years. Was there anything in this interim FTC report that surprised you?
Though not surprised, I am glad that it was released because it had been a year in investigation and there were many requests for some type of substantive report.
Two things that are missing that I feel are paramount are investigating how the three big PBMs are causing physical harm to patients as a result of the profit component in formulary construction and the profound financial impact of hidden PBM profit centers in self-insured employer health plans.
What we have seen over the years is the result of the perverse incentives for the PBMs to prefer the most profitable medications on their formularies.
They use utilization management tools such as step therapy, nonmedical switching, and exclusions to maintain their formularies’ profitability. These tools have been shown to delay and deny the proper care of patients, resulting in not just monetary but physical harm as well.
I would think the physical harm done to patients in manipulating the formularies should be addressed in this report as well and, in fact, may be the most important aspect of consumer protection of this issue.
In terms of the FTC’s mission to not “unduly burden” legitimate business, I would like to see the sector of self-insured employers addressed.
The report details how PBMs steer prescriptions to their affiliated pharmacies. The FTC says that can push smaller pharmacies out of the market, ultimately leading to higher costs and lower quality services for people. What’s your perspective?
Having more community pharmacies is better than having less. We are seeing more “pharmacy deserts” in rural areas as a result of many community pharmacies having to close.
The FTC voted 4-1 to allow staff to issue the interim report, with Commissioner Melissa Holyoak voting no. And some FTC commissioners seem divided on the usefulness of the report. Why?
Commissioner Holyoak states the “the Report leaves us without a better understanding of the competition concerns surrounding PBMs or how consumers are impacted by PBM practices.”
I do agree with her that the harm to patients’ medical status was not even addressed as far as I could tell in this report. There are multiple news articles and reports on the harms inflicted upon patients by the UM tools that drive the construction of ever changing formularies, all based on contracting with manufacturers that result in the highest profit for the PBM.
Holyoak also states, “Among other critical conclusions, the Report does not address the seemingly contradictory conclusions in the 2005 Report that PBMs, including vertically owned PBMs, generated cost savings for consumers.”
That may be true, but in 2005, the rise of PBMs was just beginning and the huge vertical and horizontal integration had yet to begin. Also, 2005 was still in the beginning of the biologic drug deluge, which did create competition to get on the formulary. Since then, PBMs have done nothing to control the rise in prices but instead, apparently have used the competition to get higher price concessions from manufacturers based on a percentage of the list price to line their pockets.
Commissioner Ferguson agreed with releasing the report but he had many issues with this report including the lack of PBM response.
I do agree with him that the FTC should have used some type of “force” to get the information they needed from the PBMs. The Big Three are known for obfuscation and delaying providing information to legislative and regulatory agencies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Could Targeting ‘Zombie Cells’ Extend a Healthy Lifespan?
What if a drug could help you live a longer, healthier life?
Scientists at the University of Connecticut are working on it. In a new study in Cell Metabolism, researchers described how to target specific cells to extend the lifespan and improve the health of mice late in life.
The study builds on a growing body of research, mostly in animals, testing interventions to slow aging and prolong health span, the length of time that one is not just alive but also healthy.
“Aging is the most important risk factor for every disease that we deal with in adult human beings,” said cardiologist Douglas Vaughan, MD, director of the Potocsnak Longevity Institute at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago. (Dr. Vaughan was not involved in the new study.) “So the big hypothesis is: If we could slow down aging just a little bit, we can push back the onset of disease.”
Senescent cells — or “zombie cells” — secrete harmful substances that disrupt tissue functioning. They’ve been linked to chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and the development of age-related diseases.
Senescence can be characterized by the accumulation of cells with high levels of specific markers like p21, or p21high cells. Almost any cell can become a p21high cell, and they accumulate with age, said Ming Xu, PhD, a professor at the UConn Center on Aging, UConn Health, Farmington, Connecticut, who led the study.
By targeting and eliminating p21high senescent cells, Dr. Xu hopes to develop novel therapies that might help people live longer and enjoy more years in good health.
Such a treatment could be ready for human trials in 2-5 years, Dr. Xu said.
What the Researchers Did
Xu and colleagues used genetic engineering to eliminate p21high cells in mice, introducing into their genome something they describe as an inducible “suicide gene.” Giving the mice a certain drug (a low dose of tamoxifen) activated the suicide gene in all p21high cells, causing them to die. Administering this treatment once a month, from age 20 months (older age) until the end of life, significantly extended the rodents’ lifespan, reduced inflammation, and decreased gene activity linked to aging.
Treated mice lived, on average, for 33 months — 3 months longer than the untreated mice. The oldest treated mouse lived to 43 months — roughly 130 in human years.
But the treated mice didn’t just live longer; they were also healthier. In humans, walking speed and grip strength can be clues of overall health and vitality. The old, treated mice were able to walk faster and grip objects with greater strength than untreated mice of the same age.
Dr. Xu’s lab is now testing drugs that target p21high cells in hopes of finding one that would work in humans. Leveraging immunotherapy technology to target these cells could be another option, Dr. Xu said.
The team also plans to test whether eliminating p21high cells could prevent or alleviate diabetes or Alzheimer’s disease.
Challenges and Criticisms
The research provides “important evidence that targeting senescence and the molecular components of that pathway might provide some benefit in the long term,” Dr. Vaughan said.
But killing senescent cells could come with downsides.
“Senescence protects us from hyperproliferative responses,” potentially blocking cells from becoming malignant, Dr. Vaughan said. “There’s this effect on aging that is desirable, but at the same time, you may enhance your risk of cancer or malignancy or excessive proliferation in some cells.”
And of course, we don’t necessarily need drugs to prolong healthy life, Dr. Vaughan pointed out.
For many people, a long healthy life is already within reach. Humans live longer on average than they used to, and simple lifestyle choices — nourishing your body well, staying active, and maintaining a healthy weight — can increase one’s chances of good health.
The most consistently demonstrated intervention for extending lifespan “in almost every animal species is caloric restriction,” Dr. Vaughan said. (Dr. Xu’s team is also investigating whether fasting and exercise can lead to a decrease in p21high cells.)
As for brain health, Dr. Vaughan and colleagues at Northwestern are studying “super agers,” people who are cognitively intact into their 90s.
“The one single thing that they found that contributes to that process, and contributes to that success, is really a social network and human bonds and interaction,” Dr. Vaughan said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What if a drug could help you live a longer, healthier life?
Scientists at the University of Connecticut are working on it. In a new study in Cell Metabolism, researchers described how to target specific cells to extend the lifespan and improve the health of mice late in life.
The study builds on a growing body of research, mostly in animals, testing interventions to slow aging and prolong health span, the length of time that one is not just alive but also healthy.
“Aging is the most important risk factor for every disease that we deal with in adult human beings,” said cardiologist Douglas Vaughan, MD, director of the Potocsnak Longevity Institute at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago. (Dr. Vaughan was not involved in the new study.) “So the big hypothesis is: If we could slow down aging just a little bit, we can push back the onset of disease.”
Senescent cells — or “zombie cells” — secrete harmful substances that disrupt tissue functioning. They’ve been linked to chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and the development of age-related diseases.
Senescence can be characterized by the accumulation of cells with high levels of specific markers like p21, or p21high cells. Almost any cell can become a p21high cell, and they accumulate with age, said Ming Xu, PhD, a professor at the UConn Center on Aging, UConn Health, Farmington, Connecticut, who led the study.
By targeting and eliminating p21high senescent cells, Dr. Xu hopes to develop novel therapies that might help people live longer and enjoy more years in good health.
Such a treatment could be ready for human trials in 2-5 years, Dr. Xu said.
What the Researchers Did
Xu and colleagues used genetic engineering to eliminate p21high cells in mice, introducing into their genome something they describe as an inducible “suicide gene.” Giving the mice a certain drug (a low dose of tamoxifen) activated the suicide gene in all p21high cells, causing them to die. Administering this treatment once a month, from age 20 months (older age) until the end of life, significantly extended the rodents’ lifespan, reduced inflammation, and decreased gene activity linked to aging.
Treated mice lived, on average, for 33 months — 3 months longer than the untreated mice. The oldest treated mouse lived to 43 months — roughly 130 in human years.
But the treated mice didn’t just live longer; they were also healthier. In humans, walking speed and grip strength can be clues of overall health and vitality. The old, treated mice were able to walk faster and grip objects with greater strength than untreated mice of the same age.
Dr. Xu’s lab is now testing drugs that target p21high cells in hopes of finding one that would work in humans. Leveraging immunotherapy technology to target these cells could be another option, Dr. Xu said.
The team also plans to test whether eliminating p21high cells could prevent or alleviate diabetes or Alzheimer’s disease.
Challenges and Criticisms
The research provides “important evidence that targeting senescence and the molecular components of that pathway might provide some benefit in the long term,” Dr. Vaughan said.
But killing senescent cells could come with downsides.
“Senescence protects us from hyperproliferative responses,” potentially blocking cells from becoming malignant, Dr. Vaughan said. “There’s this effect on aging that is desirable, but at the same time, you may enhance your risk of cancer or malignancy or excessive proliferation in some cells.”
And of course, we don’t necessarily need drugs to prolong healthy life, Dr. Vaughan pointed out.
For many people, a long healthy life is already within reach. Humans live longer on average than they used to, and simple lifestyle choices — nourishing your body well, staying active, and maintaining a healthy weight — can increase one’s chances of good health.
The most consistently demonstrated intervention for extending lifespan “in almost every animal species is caloric restriction,” Dr. Vaughan said. (Dr. Xu’s team is also investigating whether fasting and exercise can lead to a decrease in p21high cells.)
As for brain health, Dr. Vaughan and colleagues at Northwestern are studying “super agers,” people who are cognitively intact into their 90s.
“The one single thing that they found that contributes to that process, and contributes to that success, is really a social network and human bonds and interaction,” Dr. Vaughan said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What if a drug could help you live a longer, healthier life?
Scientists at the University of Connecticut are working on it. In a new study in Cell Metabolism, researchers described how to target specific cells to extend the lifespan and improve the health of mice late in life.
The study builds on a growing body of research, mostly in animals, testing interventions to slow aging and prolong health span, the length of time that one is not just alive but also healthy.
“Aging is the most important risk factor for every disease that we deal with in adult human beings,” said cardiologist Douglas Vaughan, MD, director of the Potocsnak Longevity Institute at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago. (Dr. Vaughan was not involved in the new study.) “So the big hypothesis is: If we could slow down aging just a little bit, we can push back the onset of disease.”
Senescent cells — or “zombie cells” — secrete harmful substances that disrupt tissue functioning. They’ve been linked to chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and the development of age-related diseases.
Senescence can be characterized by the accumulation of cells with high levels of specific markers like p21, or p21high cells. Almost any cell can become a p21high cell, and they accumulate with age, said Ming Xu, PhD, a professor at the UConn Center on Aging, UConn Health, Farmington, Connecticut, who led the study.
By targeting and eliminating p21high senescent cells, Dr. Xu hopes to develop novel therapies that might help people live longer and enjoy more years in good health.
Such a treatment could be ready for human trials in 2-5 years, Dr. Xu said.
What the Researchers Did
Xu and colleagues used genetic engineering to eliminate p21high cells in mice, introducing into their genome something they describe as an inducible “suicide gene.” Giving the mice a certain drug (a low dose of tamoxifen) activated the suicide gene in all p21high cells, causing them to die. Administering this treatment once a month, from age 20 months (older age) until the end of life, significantly extended the rodents’ lifespan, reduced inflammation, and decreased gene activity linked to aging.
Treated mice lived, on average, for 33 months — 3 months longer than the untreated mice. The oldest treated mouse lived to 43 months — roughly 130 in human years.
But the treated mice didn’t just live longer; they were also healthier. In humans, walking speed and grip strength can be clues of overall health and vitality. The old, treated mice were able to walk faster and grip objects with greater strength than untreated mice of the same age.
Dr. Xu’s lab is now testing drugs that target p21high cells in hopes of finding one that would work in humans. Leveraging immunotherapy technology to target these cells could be another option, Dr. Xu said.
The team also plans to test whether eliminating p21high cells could prevent or alleviate diabetes or Alzheimer’s disease.
Challenges and Criticisms
The research provides “important evidence that targeting senescence and the molecular components of that pathway might provide some benefit in the long term,” Dr. Vaughan said.
But killing senescent cells could come with downsides.
“Senescence protects us from hyperproliferative responses,” potentially blocking cells from becoming malignant, Dr. Vaughan said. “There’s this effect on aging that is desirable, but at the same time, you may enhance your risk of cancer or malignancy or excessive proliferation in some cells.”
And of course, we don’t necessarily need drugs to prolong healthy life, Dr. Vaughan pointed out.
For many people, a long healthy life is already within reach. Humans live longer on average than they used to, and simple lifestyle choices — nourishing your body well, staying active, and maintaining a healthy weight — can increase one’s chances of good health.
The most consistently demonstrated intervention for extending lifespan “in almost every animal species is caloric restriction,” Dr. Vaughan said. (Dr. Xu’s team is also investigating whether fasting and exercise can lead to a decrease in p21high cells.)
As for brain health, Dr. Vaughan and colleagues at Northwestern are studying “super agers,” people who are cognitively intact into their 90s.
“The one single thing that they found that contributes to that process, and contributes to that success, is really a social network and human bonds and interaction,” Dr. Vaughan said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What Would ‘Project 2025’ Mean for Health and Healthcare?
The Heritage Foundation sponsored and developed Project 2025 for the explicit, stated purpose of building a conservative victory through policy, personnel, and training with a 180-day game plan after a sympathetic new President of the United States takes office. To date, Project 2025 has not been formally endorsed by any presidential campaign.
Chapter 14 of the “Mandate for Leadership” is an exhaustive proposed overhaul of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), one of the major existing arms of the executive branch of the US government.
The mandate’s sweeping recommendations, if implemented, would impact the lives of all Americans and all healthcare workers, as outlined in the following excerpts.
Healthcare-Related Excerpts From Project 2025
- “From the moment of conception, every human being possesses inherent dignity and worth, and our humanity does not depend on our age, stage of development, race, or abilities. The Secretary must ensure that all HHS programs and activities are rooted in a deep respect for innocent human life from day one until natural death: Abortion and euthanasia are not health care.”
- “Unfortunately, family policies and programs under President Biden’s HHS are fraught with agenda items focusing on ‘LGBTQ+ equity,’ subsidizing single motherhood, disincentivizing work, and penalizing marriage. These policies should be repealed and replaced by policies that support the formation of stable, married, nuclear families.”
- “The next Administration should guard against the regulatory capture of our public health agencies by pharmaceutical companies, insurers, hospital conglomerates, and related economic interests that these agencies are meant to regulate. We must erect robust firewalls to mitigate these obvious financial conflicts of interest.”
- “All National Institutes of Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and Food and Drug Administration regulators should be entirely free from private biopharmaceutical funding. In this realm, ‘public–private partnerships’ is a euphemism for agency capture, a thin veneer for corporatism. Funding for agencies and individual government researchers must come directly from the government with robust congressional oversight.”
- “The CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] operates several programs related to vaccine safety including the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS); Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD); and Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment (CISA) Project. Those functions and their associated funding should be transferred to the FDA [Food and Drug Administration], which is responsible for post-market surveillance and evaluation of all other drugs and biological products.”
- “Because liberal states have now become sanctuaries for abortion tourism, HHS should use every available tool, including the cutting of funds, to ensure that every state reports exactly how many abortions take place within its borders, at what gestational age of the child, for what reason, the mother’s state of residence, and by what method. It should also ensure that statistics are separated by category: spontaneous miscarriage; treatments that incidentally result in the death of a child (such as chemotherapy); stillbirths; and induced abortion. In addition, CDC should require monitoring and reporting for complications due to abortion and every instance of children being born alive after an abortion.”
- “The CDC should immediately end its collection of data on gender identity, which legitimizes the unscientific notion that men can become women (and vice versa) and encourages the phenomenon of ever-multiplying subjective identities.”
- “A test developed by a lab in accordance with the protocols developed by another lab (non-commercial sharing) currently constitutes a ‘new’ laboratory-developed test because the lab in which it will be used is different from the initial developing lab. To encourage interlaboratory collaboration and discourage duplicative test creation (and associated regulatory and logistical burdens), the FDA should introduce mechanisms through which laboratory-developed tests can easily be shared with other laboratories without the current regulatory burdens.”
- “[FDA should] Reverse its approval of chemical abortion drugs because the politicized approval process was illegal from the start. The FDA failed to abide by its legal obligations to protect the health, safety, and welfare of girls and women.”
- “[FDA should] Stop promoting or approving mail-order abortions in violation of long-standing federal laws that prohibit the mailing and interstate carriage of abortion drugs.”
- “[HHS should] Promptly restore the ethics advisory committee to oversee abortion-derived fetal tissue research, and Congress should prohibit such research altogether.”
- “[HHS should] End intramural research projects using tissue from aborted children within the NIH, which should end its human embryonic stem cell registry.”
- “Under Francis Collins, NIH became so focused on the #MeToo movement that it refused to sponsor scientific conferences unless there were a certain number of women panelists, which violates federal civil rights law against sex discrimination. This quota practice should be ended, and the NIH Office of Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion, which pushes such unlawful actions, should be abolished.”
- “Make Medicare Advantage [MA] the default enrollment option.”
- “[Legislation reforming legacy (non-MA) Medicare should] Repeal harmful health policies enacted under the Obama and Biden Administrations such as the Medicare Shared Savings Program and Inflation Reduction Act.”
- “…the next Administration should] Add work requirements and match Medicaid benefits to beneficiary needs. Because Medicaid serves a broad and diverse group of individuals, it should be flexible enough to accommodate different designs for different groups.”
- “The No Surprises Act should scrap the dispute resolution process in favor of a truth-in-advertising approach that will protect consumers and free doctors, insurers, and arbiters from confused and conflicting standards for resolving disputes that the disputing parties can best resolve themselves.”
- “Prohibit abortion travel funding. Providing funding for abortions increases the number of abortions and violates the conscience and religious freedom rights of Americans who object to subsidizing the taking of life.”
- “Prohibit Planned Parenthood from receiving Medicaid funds. During the 2020–2021 reporting period, Planned Parenthood performed more than 383,000 abortions.”
- “Protect faith-based grant recipients from religious liberty violations and maintain a biblically based, social science–reinforced definition of marriage and family. Social science reports that assess the objective outcomes for children raised in homes aside from a heterosexual, intact marriage are clear.”
- “Allocate funding to strategy programs promoting father involvement or terminate parental rights quickly.”
- “Eliminate the Head Start program.”
- “Support palliative care. Physician-assisted suicide (PAS) is legal in 10 states and the District of Columbia. Legalizing PAS is a grave mistake that endangers the weak and vulnerable, corrupts the practice of medicine and the doctor–patient relationship, compromises the family and intergenerational commitments, and betrays human dignity and equality before the law.”
- “Eliminate men’s preventive services from the women’s preventive services mandate. In December 2021, HRSA [Health Resources and Services Administration] updated its women’s preventive services guidelines to include male condoms.”
- “Prioritize funding for home-based childcare, not universal day care.”
- “ The Office of the Secretary should eliminate the HHS Reproductive Healthcare Access Task Force and install a pro-life task force to ensure that all of the department’s divisions seek to use their authority to promote the life and health of women and their unborn children.”
- “The ASH [Assistant Secretary for Health] and SG [Surgeon General] positions should be combined into one four-star position with the rank, responsibilities, and authority of the ASH retained but with the title of Surgeon General.”
- “OCR [Office for Civil Rights] should withdraw its Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) guidance on abortion.”
Dr. Lundberg is Editor in Chief, Cancer Commons, and has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Heritage Foundation sponsored and developed Project 2025 for the explicit, stated purpose of building a conservative victory through policy, personnel, and training with a 180-day game plan after a sympathetic new President of the United States takes office. To date, Project 2025 has not been formally endorsed by any presidential campaign.
Chapter 14 of the “Mandate for Leadership” is an exhaustive proposed overhaul of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), one of the major existing arms of the executive branch of the US government.
The mandate’s sweeping recommendations, if implemented, would impact the lives of all Americans and all healthcare workers, as outlined in the following excerpts.
Healthcare-Related Excerpts From Project 2025
- “From the moment of conception, every human being possesses inherent dignity and worth, and our humanity does not depend on our age, stage of development, race, or abilities. The Secretary must ensure that all HHS programs and activities are rooted in a deep respect for innocent human life from day one until natural death: Abortion and euthanasia are not health care.”
- “Unfortunately, family policies and programs under President Biden’s HHS are fraught with agenda items focusing on ‘LGBTQ+ equity,’ subsidizing single motherhood, disincentivizing work, and penalizing marriage. These policies should be repealed and replaced by policies that support the formation of stable, married, nuclear families.”
- “The next Administration should guard against the regulatory capture of our public health agencies by pharmaceutical companies, insurers, hospital conglomerates, and related economic interests that these agencies are meant to regulate. We must erect robust firewalls to mitigate these obvious financial conflicts of interest.”
- “All National Institutes of Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and Food and Drug Administration regulators should be entirely free from private biopharmaceutical funding. In this realm, ‘public–private partnerships’ is a euphemism for agency capture, a thin veneer for corporatism. Funding for agencies and individual government researchers must come directly from the government with robust congressional oversight.”
- “The CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] operates several programs related to vaccine safety including the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS); Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD); and Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment (CISA) Project. Those functions and their associated funding should be transferred to the FDA [Food and Drug Administration], which is responsible for post-market surveillance and evaluation of all other drugs and biological products.”
- “Because liberal states have now become sanctuaries for abortion tourism, HHS should use every available tool, including the cutting of funds, to ensure that every state reports exactly how many abortions take place within its borders, at what gestational age of the child, for what reason, the mother’s state of residence, and by what method. It should also ensure that statistics are separated by category: spontaneous miscarriage; treatments that incidentally result in the death of a child (such as chemotherapy); stillbirths; and induced abortion. In addition, CDC should require monitoring and reporting for complications due to abortion and every instance of children being born alive after an abortion.”
- “The CDC should immediately end its collection of data on gender identity, which legitimizes the unscientific notion that men can become women (and vice versa) and encourages the phenomenon of ever-multiplying subjective identities.”
- “A test developed by a lab in accordance with the protocols developed by another lab (non-commercial sharing) currently constitutes a ‘new’ laboratory-developed test because the lab in which it will be used is different from the initial developing lab. To encourage interlaboratory collaboration and discourage duplicative test creation (and associated regulatory and logistical burdens), the FDA should introduce mechanisms through which laboratory-developed tests can easily be shared with other laboratories without the current regulatory burdens.”
- “[FDA should] Reverse its approval of chemical abortion drugs because the politicized approval process was illegal from the start. The FDA failed to abide by its legal obligations to protect the health, safety, and welfare of girls and women.”
- “[FDA should] Stop promoting or approving mail-order abortions in violation of long-standing federal laws that prohibit the mailing and interstate carriage of abortion drugs.”
- “[HHS should] Promptly restore the ethics advisory committee to oversee abortion-derived fetal tissue research, and Congress should prohibit such research altogether.”
- “[HHS should] End intramural research projects using tissue from aborted children within the NIH, which should end its human embryonic stem cell registry.”
- “Under Francis Collins, NIH became so focused on the #MeToo movement that it refused to sponsor scientific conferences unless there were a certain number of women panelists, which violates federal civil rights law against sex discrimination. This quota practice should be ended, and the NIH Office of Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion, which pushes such unlawful actions, should be abolished.”
- “Make Medicare Advantage [MA] the default enrollment option.”
- “[Legislation reforming legacy (non-MA) Medicare should] Repeal harmful health policies enacted under the Obama and Biden Administrations such as the Medicare Shared Savings Program and Inflation Reduction Act.”
- “…the next Administration should] Add work requirements and match Medicaid benefits to beneficiary needs. Because Medicaid serves a broad and diverse group of individuals, it should be flexible enough to accommodate different designs for different groups.”
- “The No Surprises Act should scrap the dispute resolution process in favor of a truth-in-advertising approach that will protect consumers and free doctors, insurers, and arbiters from confused and conflicting standards for resolving disputes that the disputing parties can best resolve themselves.”
- “Prohibit abortion travel funding. Providing funding for abortions increases the number of abortions and violates the conscience and religious freedom rights of Americans who object to subsidizing the taking of life.”
- “Prohibit Planned Parenthood from receiving Medicaid funds. During the 2020–2021 reporting period, Planned Parenthood performed more than 383,000 abortions.”
- “Protect faith-based grant recipients from religious liberty violations and maintain a biblically based, social science–reinforced definition of marriage and family. Social science reports that assess the objective outcomes for children raised in homes aside from a heterosexual, intact marriage are clear.”
- “Allocate funding to strategy programs promoting father involvement or terminate parental rights quickly.”
- “Eliminate the Head Start program.”
- “Support palliative care. Physician-assisted suicide (PAS) is legal in 10 states and the District of Columbia. Legalizing PAS is a grave mistake that endangers the weak and vulnerable, corrupts the practice of medicine and the doctor–patient relationship, compromises the family and intergenerational commitments, and betrays human dignity and equality before the law.”
- “Eliminate men’s preventive services from the women’s preventive services mandate. In December 2021, HRSA [Health Resources and Services Administration] updated its women’s preventive services guidelines to include male condoms.”
- “Prioritize funding for home-based childcare, not universal day care.”
- “ The Office of the Secretary should eliminate the HHS Reproductive Healthcare Access Task Force and install a pro-life task force to ensure that all of the department’s divisions seek to use their authority to promote the life and health of women and their unborn children.”
- “The ASH [Assistant Secretary for Health] and SG [Surgeon General] positions should be combined into one four-star position with the rank, responsibilities, and authority of the ASH retained but with the title of Surgeon General.”
- “OCR [Office for Civil Rights] should withdraw its Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) guidance on abortion.”
Dr. Lundberg is Editor in Chief, Cancer Commons, and has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Heritage Foundation sponsored and developed Project 2025 for the explicit, stated purpose of building a conservative victory through policy, personnel, and training with a 180-day game plan after a sympathetic new President of the United States takes office. To date, Project 2025 has not been formally endorsed by any presidential campaign.
Chapter 14 of the “Mandate for Leadership” is an exhaustive proposed overhaul of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), one of the major existing arms of the executive branch of the US government.
The mandate’s sweeping recommendations, if implemented, would impact the lives of all Americans and all healthcare workers, as outlined in the following excerpts.
Healthcare-Related Excerpts From Project 2025
- “From the moment of conception, every human being possesses inherent dignity and worth, and our humanity does not depend on our age, stage of development, race, or abilities. The Secretary must ensure that all HHS programs and activities are rooted in a deep respect for innocent human life from day one until natural death: Abortion and euthanasia are not health care.”
- “Unfortunately, family policies and programs under President Biden’s HHS are fraught with agenda items focusing on ‘LGBTQ+ equity,’ subsidizing single motherhood, disincentivizing work, and penalizing marriage. These policies should be repealed and replaced by policies that support the formation of stable, married, nuclear families.”
- “The next Administration should guard against the regulatory capture of our public health agencies by pharmaceutical companies, insurers, hospital conglomerates, and related economic interests that these agencies are meant to regulate. We must erect robust firewalls to mitigate these obvious financial conflicts of interest.”
- “All National Institutes of Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and Food and Drug Administration regulators should be entirely free from private biopharmaceutical funding. In this realm, ‘public–private partnerships’ is a euphemism for agency capture, a thin veneer for corporatism. Funding for agencies and individual government researchers must come directly from the government with robust congressional oversight.”
- “The CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] operates several programs related to vaccine safety including the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS); Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD); and Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment (CISA) Project. Those functions and their associated funding should be transferred to the FDA [Food and Drug Administration], which is responsible for post-market surveillance and evaluation of all other drugs and biological products.”
- “Because liberal states have now become sanctuaries for abortion tourism, HHS should use every available tool, including the cutting of funds, to ensure that every state reports exactly how many abortions take place within its borders, at what gestational age of the child, for what reason, the mother’s state of residence, and by what method. It should also ensure that statistics are separated by category: spontaneous miscarriage; treatments that incidentally result in the death of a child (such as chemotherapy); stillbirths; and induced abortion. In addition, CDC should require monitoring and reporting for complications due to abortion and every instance of children being born alive after an abortion.”
- “The CDC should immediately end its collection of data on gender identity, which legitimizes the unscientific notion that men can become women (and vice versa) and encourages the phenomenon of ever-multiplying subjective identities.”
- “A test developed by a lab in accordance with the protocols developed by another lab (non-commercial sharing) currently constitutes a ‘new’ laboratory-developed test because the lab in which it will be used is different from the initial developing lab. To encourage interlaboratory collaboration and discourage duplicative test creation (and associated regulatory and logistical burdens), the FDA should introduce mechanisms through which laboratory-developed tests can easily be shared with other laboratories without the current regulatory burdens.”
- “[FDA should] Reverse its approval of chemical abortion drugs because the politicized approval process was illegal from the start. The FDA failed to abide by its legal obligations to protect the health, safety, and welfare of girls and women.”
- “[FDA should] Stop promoting or approving mail-order abortions in violation of long-standing federal laws that prohibit the mailing and interstate carriage of abortion drugs.”
- “[HHS should] Promptly restore the ethics advisory committee to oversee abortion-derived fetal tissue research, and Congress should prohibit such research altogether.”
- “[HHS should] End intramural research projects using tissue from aborted children within the NIH, which should end its human embryonic stem cell registry.”
- “Under Francis Collins, NIH became so focused on the #MeToo movement that it refused to sponsor scientific conferences unless there were a certain number of women panelists, which violates federal civil rights law against sex discrimination. This quota practice should be ended, and the NIH Office of Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion, which pushes such unlawful actions, should be abolished.”
- “Make Medicare Advantage [MA] the default enrollment option.”
- “[Legislation reforming legacy (non-MA) Medicare should] Repeal harmful health policies enacted under the Obama and Biden Administrations such as the Medicare Shared Savings Program and Inflation Reduction Act.”
- “…the next Administration should] Add work requirements and match Medicaid benefits to beneficiary needs. Because Medicaid serves a broad and diverse group of individuals, it should be flexible enough to accommodate different designs for different groups.”
- “The No Surprises Act should scrap the dispute resolution process in favor of a truth-in-advertising approach that will protect consumers and free doctors, insurers, and arbiters from confused and conflicting standards for resolving disputes that the disputing parties can best resolve themselves.”
- “Prohibit abortion travel funding. Providing funding for abortions increases the number of abortions and violates the conscience and religious freedom rights of Americans who object to subsidizing the taking of life.”
- “Prohibit Planned Parenthood from receiving Medicaid funds. During the 2020–2021 reporting period, Planned Parenthood performed more than 383,000 abortions.”
- “Protect faith-based grant recipients from religious liberty violations and maintain a biblically based, social science–reinforced definition of marriage and family. Social science reports that assess the objective outcomes for children raised in homes aside from a heterosexual, intact marriage are clear.”
- “Allocate funding to strategy programs promoting father involvement or terminate parental rights quickly.”
- “Eliminate the Head Start program.”
- “Support palliative care. Physician-assisted suicide (PAS) is legal in 10 states and the District of Columbia. Legalizing PAS is a grave mistake that endangers the weak and vulnerable, corrupts the practice of medicine and the doctor–patient relationship, compromises the family and intergenerational commitments, and betrays human dignity and equality before the law.”
- “Eliminate men’s preventive services from the women’s preventive services mandate. In December 2021, HRSA [Health Resources and Services Administration] updated its women’s preventive services guidelines to include male condoms.”
- “Prioritize funding for home-based childcare, not universal day care.”
- “ The Office of the Secretary should eliminate the HHS Reproductive Healthcare Access Task Force and install a pro-life task force to ensure that all of the department’s divisions seek to use their authority to promote the life and health of women and their unborn children.”
- “The ASH [Assistant Secretary for Health] and SG [Surgeon General] positions should be combined into one four-star position with the rank, responsibilities, and authority of the ASH retained but with the title of Surgeon General.”
- “OCR [Office for Civil Rights] should withdraw its Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) guidance on abortion.”
Dr. Lundberg is Editor in Chief, Cancer Commons, and has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Does Different Types of Organ Damage From Lupus Occur? Long-Term Study Sheds Light
TOPLINE:
The first year after the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is crucial, with the highest percentage of patients experiencing organ damage. Cardiovascular issues are the second most prevalent after musculoskeletal damage in both early and later stages of SLE.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed organ damage persisting at least 6 months over different stages of lupus in 4219 patients with SLE (mean age, 35.9 years; 89.6% women) from the Spanish Society of Rheumatology Lupus Registry.
- Damage was assessed using the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index (SDI).
- Longitudinal analysis was conducted globally and by each SDI domain on 1274 patients with recorded damage event dates.
- Follow-up data were available out to 10 years in 1113 patients and to 20 years in 601.
TAKEAWAY:
- New damage was recorded in 20% of the patients with SLE within the first year after diagnosis, with the annual percentage of patients with new damage decreasing to 5% after the first 5 years of follow-up.
- In the first year, musculoskeletal damage was reported by the highest proportion of patients (21%), followed by cardiovascular damage inclusive of cerebrovascular accidents and claudication for 6 months (19%).
- The cardiovascular system remained the second most affected system even during the later stages of the diseases at years 10 and 20 of follow-up (20%-25%).
- Apart from musculoskeletal and cardiovascular damage, patients with lupus also showed renal and ocular damage in the early and later stages of the disease, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study highlights the importance of cardiovascular damage and the need for its prevention during the earliest stages of the disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Irene Altabás-González, MD, PhD, Rheumatology Department, Vigo University Hospital Group, Vigo, Spain. It was published online in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective collection of data in the study may have led to missing items; for example, the dates of damage events for the whole cohort were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The registry was supported by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology. No specific funding was received for the study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The first year after the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is crucial, with the highest percentage of patients experiencing organ damage. Cardiovascular issues are the second most prevalent after musculoskeletal damage in both early and later stages of SLE.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed organ damage persisting at least 6 months over different stages of lupus in 4219 patients with SLE (mean age, 35.9 years; 89.6% women) from the Spanish Society of Rheumatology Lupus Registry.
- Damage was assessed using the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index (SDI).
- Longitudinal analysis was conducted globally and by each SDI domain on 1274 patients with recorded damage event dates.
- Follow-up data were available out to 10 years in 1113 patients and to 20 years in 601.
TAKEAWAY:
- New damage was recorded in 20% of the patients with SLE within the first year after diagnosis, with the annual percentage of patients with new damage decreasing to 5% after the first 5 years of follow-up.
- In the first year, musculoskeletal damage was reported by the highest proportion of patients (21%), followed by cardiovascular damage inclusive of cerebrovascular accidents and claudication for 6 months (19%).
- The cardiovascular system remained the second most affected system even during the later stages of the diseases at years 10 and 20 of follow-up (20%-25%).
- Apart from musculoskeletal and cardiovascular damage, patients with lupus also showed renal and ocular damage in the early and later stages of the disease, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study highlights the importance of cardiovascular damage and the need for its prevention during the earliest stages of the disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Irene Altabás-González, MD, PhD, Rheumatology Department, Vigo University Hospital Group, Vigo, Spain. It was published online in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective collection of data in the study may have led to missing items; for example, the dates of damage events for the whole cohort were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The registry was supported by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology. No specific funding was received for the study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The first year after the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is crucial, with the highest percentage of patients experiencing organ damage. Cardiovascular issues are the second most prevalent after musculoskeletal damage in both early and later stages of SLE.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed organ damage persisting at least 6 months over different stages of lupus in 4219 patients with SLE (mean age, 35.9 years; 89.6% women) from the Spanish Society of Rheumatology Lupus Registry.
- Damage was assessed using the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index (SDI).
- Longitudinal analysis was conducted globally and by each SDI domain on 1274 patients with recorded damage event dates.
- Follow-up data were available out to 10 years in 1113 patients and to 20 years in 601.
TAKEAWAY:
- New damage was recorded in 20% of the patients with SLE within the first year after diagnosis, with the annual percentage of patients with new damage decreasing to 5% after the first 5 years of follow-up.
- In the first year, musculoskeletal damage was reported by the highest proportion of patients (21%), followed by cardiovascular damage inclusive of cerebrovascular accidents and claudication for 6 months (19%).
- The cardiovascular system remained the second most affected system even during the later stages of the diseases at years 10 and 20 of follow-up (20%-25%).
- Apart from musculoskeletal and cardiovascular damage, patients with lupus also showed renal and ocular damage in the early and later stages of the disease, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study highlights the importance of cardiovascular damage and the need for its prevention during the earliest stages of the disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Irene Altabás-González, MD, PhD, Rheumatology Department, Vigo University Hospital Group, Vigo, Spain. It was published online in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective collection of data in the study may have led to missing items; for example, the dates of damage events for the whole cohort were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The registry was supported by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology. No specific funding was received for the study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
US Experience With Infliximab Biosimilars Suggests Need for More Development Incentives
TOPLINE:
Uptake of infliximab biosimilars rose slowly across private insurance, Medicaid, and Medicare when two were available in the United States during 2016-2020 but increased significantly through 2022 after the third biosimilar became available in July 2020. However, prescriptions in Medicare still lagged behind those in private insurance and Medicaid.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed electronic health records from over 1100 US rheumatologists who participated in a national registry, the Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE), for all infliximab administrations (bio-originator or biosimilar) to patients older than 18 years from April 2016 to September 2022.
- They conducted an interrupted time series to account for autocorrelation and model the effect of each infliximab biosimilar release (infliximab-dyyb in November 2016, infliximab-abda in July 2017, and infliximab-axxq in July 2020) on uptake across Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers identified 659,988 infliximab administrations for 37,560 unique patients, with 52% on Medicare, 4.8% on Medicaid, and 43% on private insurance.
- Biosimilar uptake rose slowly with average annual increases < 5% from 2016 to June 2020 (Medicare, 3.2%; Medicaid, 5.2%; private insurance, 1.8%).
- After the third biosimilar release in July 2020, the average annual increase reached 13% for Medicaid and 16.4% for private insurance but remained low for Medicare (5.6%).
- By September 2022, biosimilar uptake was higher for Medicaid (43.8%) and private insurance (38.5%) than for Medicare (24%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results suggest policymakers may need to do more to allow biosimilars to get a foothold in the market by incentivizing the development and entry of multiple biosimilars, address anticompetitive pricing strategies, and may need to amend Medicare policy to [incentivize] uptake in order to ensure a competitive and sustainable biosimilar market that gradually reduces total drug expenditures and out-of-pocket costs over time,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Eric T. Roberts, PhD, University of California, San Francisco. It was published online on July 30, 2024, in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
First, while the biosimilar introductions are likely catalysts for many changes in the market, some changes in slopes may also be attributable to the natural growth of the market over time. Second, this study may neither be generalizable to academic medical centers, which are underrepresented in RISE, nor be generalizable to infliximab prescriptions from other specialties. Third, uptake among privately insured patients changed shortly after November-December 2020, raising the possibility that the delay reflected negotiations between insurance companies and relevant entities regarding formulary coverage.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. One author disclosed receiving consulting fees from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Bristol-Myers Squibb and grant funding from AstraZeneca, the Bristol-Myers Squibb Foundation, and Aurinia.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Uptake of infliximab biosimilars rose slowly across private insurance, Medicaid, and Medicare when two were available in the United States during 2016-2020 but increased significantly through 2022 after the third biosimilar became available in July 2020. However, prescriptions in Medicare still lagged behind those in private insurance and Medicaid.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed electronic health records from over 1100 US rheumatologists who participated in a national registry, the Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE), for all infliximab administrations (bio-originator or biosimilar) to patients older than 18 years from April 2016 to September 2022.
- They conducted an interrupted time series to account for autocorrelation and model the effect of each infliximab biosimilar release (infliximab-dyyb in November 2016, infliximab-abda in July 2017, and infliximab-axxq in July 2020) on uptake across Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers identified 659,988 infliximab administrations for 37,560 unique patients, with 52% on Medicare, 4.8% on Medicaid, and 43% on private insurance.
- Biosimilar uptake rose slowly with average annual increases < 5% from 2016 to June 2020 (Medicare, 3.2%; Medicaid, 5.2%; private insurance, 1.8%).
- After the third biosimilar release in July 2020, the average annual increase reached 13% for Medicaid and 16.4% for private insurance but remained low for Medicare (5.6%).
- By September 2022, biosimilar uptake was higher for Medicaid (43.8%) and private insurance (38.5%) than for Medicare (24%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results suggest policymakers may need to do more to allow biosimilars to get a foothold in the market by incentivizing the development and entry of multiple biosimilars, address anticompetitive pricing strategies, and may need to amend Medicare policy to [incentivize] uptake in order to ensure a competitive and sustainable biosimilar market that gradually reduces total drug expenditures and out-of-pocket costs over time,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Eric T. Roberts, PhD, University of California, San Francisco. It was published online on July 30, 2024, in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
First, while the biosimilar introductions are likely catalysts for many changes in the market, some changes in slopes may also be attributable to the natural growth of the market over time. Second, this study may neither be generalizable to academic medical centers, which are underrepresented in RISE, nor be generalizable to infliximab prescriptions from other specialties. Third, uptake among privately insured patients changed shortly after November-December 2020, raising the possibility that the delay reflected negotiations between insurance companies and relevant entities regarding formulary coverage.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. One author disclosed receiving consulting fees from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Bristol-Myers Squibb and grant funding from AstraZeneca, the Bristol-Myers Squibb Foundation, and Aurinia.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Uptake of infliximab biosimilars rose slowly across private insurance, Medicaid, and Medicare when two were available in the United States during 2016-2020 but increased significantly through 2022 after the third biosimilar became available in July 2020. However, prescriptions in Medicare still lagged behind those in private insurance and Medicaid.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed electronic health records from over 1100 US rheumatologists who participated in a national registry, the Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE), for all infliximab administrations (bio-originator or biosimilar) to patients older than 18 years from April 2016 to September 2022.
- They conducted an interrupted time series to account for autocorrelation and model the effect of each infliximab biosimilar release (infliximab-dyyb in November 2016, infliximab-abda in July 2017, and infliximab-axxq in July 2020) on uptake across Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers identified 659,988 infliximab administrations for 37,560 unique patients, with 52% on Medicare, 4.8% on Medicaid, and 43% on private insurance.
- Biosimilar uptake rose slowly with average annual increases < 5% from 2016 to June 2020 (Medicare, 3.2%; Medicaid, 5.2%; private insurance, 1.8%).
- After the third biosimilar release in July 2020, the average annual increase reached 13% for Medicaid and 16.4% for private insurance but remained low for Medicare (5.6%).
- By September 2022, biosimilar uptake was higher for Medicaid (43.8%) and private insurance (38.5%) than for Medicare (24%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results suggest policymakers may need to do more to allow biosimilars to get a foothold in the market by incentivizing the development and entry of multiple biosimilars, address anticompetitive pricing strategies, and may need to amend Medicare policy to [incentivize] uptake in order to ensure a competitive and sustainable biosimilar market that gradually reduces total drug expenditures and out-of-pocket costs over time,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Eric T. Roberts, PhD, University of California, San Francisco. It was published online on July 30, 2024, in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
First, while the biosimilar introductions are likely catalysts for many changes in the market, some changes in slopes may also be attributable to the natural growth of the market over time. Second, this study may neither be generalizable to academic medical centers, which are underrepresented in RISE, nor be generalizable to infliximab prescriptions from other specialties. Third, uptake among privately insured patients changed shortly after November-December 2020, raising the possibility that the delay reflected negotiations between insurance companies and relevant entities regarding formulary coverage.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. One author disclosed receiving consulting fees from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Bristol-Myers Squibb and grant funding from AstraZeneca, the Bristol-Myers Squibb Foundation, and Aurinia.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.