User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
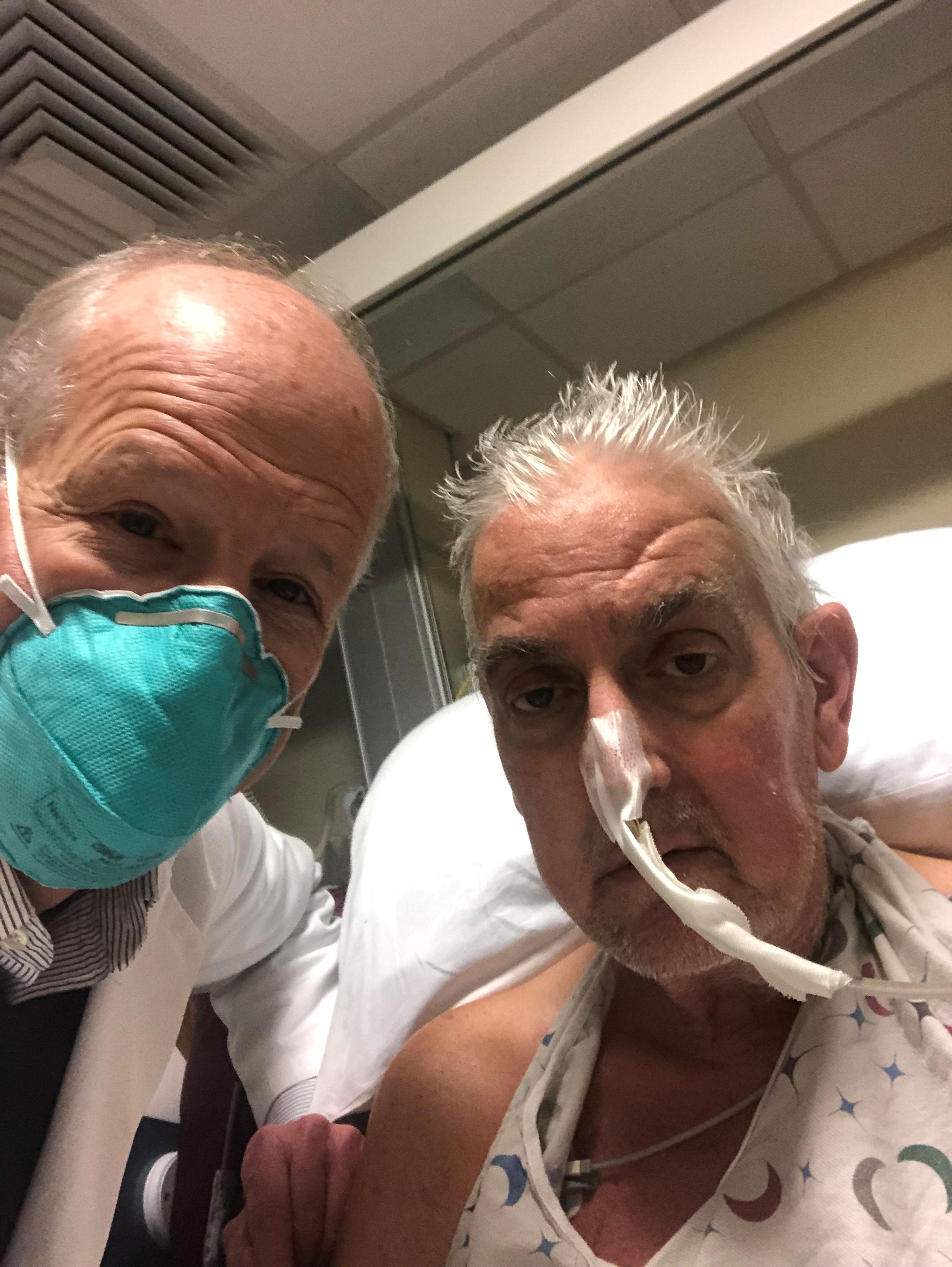
Death of pig heart transplant patient is more a beginning than an end
The genetically altered pig’s heart “worked like a rock star, beautifully functioning,” the surgeon who performed the pioneering Jan. 7 xenotransplant procedure said in a press statement on the death of the patient, David Bennett Sr.
“He wasn’t able to overcome what turned out to be devastating – the debilitation from his previous period of heart failure, which was extreme,” said Bartley P. Griffith, MD, clinical director of the cardiac xenotransplantation program at the University of Maryland, Baltimore.
Representatives of the institution aren’t offering many details on the cause of Mr. Bennett’s death on March 8, 60 days after his operation, but said they will elaborate when their findings are formally published. But their comments seem to downplay the unique nature of the implanted heart itself as a culprit and instead implicate the patient’s diminished overall clinical condition and what grew into an ongoing battle with infections.
The 57-year-old Bennett, bedridden with end-stage heart failure, judged a poor candidate for a ventricular assist device, and on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), reportedly was offered the extraordinary surgery after being turned down for a conventional transplant at several major centers.
“Until day 45 or 50, he was doing very well,” Muhammad M. Mohiuddin, MD, the xenotransplantation program’s scientific director, observed in the statement. But infections soon took advantage of his hobbled immune system.
Given his “preexisting condition and how frail his body was,” Dr. Mohiuddin said, “we were having difficulty maintaining a balance between his immunosuppression and controlling his infection.” Mr. Bennett went into multiple organ failure and “I think that resulted in his passing away.”
Beyond wildest dreams
The surgeons confidently framed Mr. Bennett’s experience as a milestone for heart xenotransplantation. “The demonstration that it was possible, beyond the wildest dreams of most people in the field, even, at this point – that we were able to take a genetically engineered organ and watch it function flawlessly for 9 weeks – is pretty positive in terms of the potential of this therapy,” Dr. Griffith said.
But enough questions linger that others were more circumspect, even as they praised the accomplishment. “There’s no question that this is a historic event,” Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, of Harvard Medical School, and director of the Center for Advanced Heart Disease at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
Still, “I don’t think we should just conclude that it was the patient’s frailty or death from infection,” Dr. Mehra said. With so few details available, “I would be very careful in prematurely concluding that the problem did not reside with the heart but with the patient. We cannot be sure.”
For example, he noted, “6 to 8 weeks is right around the time when some cardiac complications, like accelerated forms of vasculopathy, could become evident.” Immune-mediated cardiac allograft vasculopathy is a common cause of heart transplant failure.
Or, “it could as easily have been the fact that immunosuppression was modified at 6 to 7 weeks in response to potential infection, which could have led to a cardiac compromise,” Dr. Mehra said. “We just don’t know.”
“It’s really important that this be reported in a scientifically accurate way, because we will all learn from this,” Lori J. West, MD, DPhil, said in an interview.
Little seems to be known for sure about the actual cause of death, “but the fact there was not hyperacute rejection is itself a big step forward. And we know, at least from the limited information we have, that it did not occur,” observed Dr. West, who directs the Alberta Transplant Institute, Edmonton, and the Canadian Donation and Transplantation Research Program. She is a professor of pediatrics with adjunct positions in the departments of surgery and microbiology/immunology.
Dr. West also sees Mr. Bennett’s struggle with infections and adjustments to his unique immunosuppressive regimen, at least as characterized by his care team, as in line with the experience of many heart transplant recipients facing the same threat.
“We already walk this tightrope with every transplant patient,” she said. Typically, they’re put on a somewhat standardized immunosuppressant regimen, “and then we modify it a bit, either increasing or decreasing it, depending on the posttransplant course.” The regimen can become especially intense in response to new signs of rejection, “and you know that that’s going to have an impact on susceptibility to all kinds of infections.”
Full circle
The porcine heart was protected along two fronts against assault from Mr. Bennett’s immune system and other inhospitable aspects of his physiology, either of which could also have been obstacles to success: Genetic modification (Revivicor) of the pig that provided the heart, and a singularly aggressive antirejection drug regimen for the patient.
The knockout of three genes targeting specific porcine cell-surface carbohydrates that provoke a strong human antibody response reportedly averted a hyperacute rejection response that would have caused the graft to fail almost immediately.
Other genetic manipulations, some using CRISPR technology, silenced genes encoded for porcine endogenous retroviruses. Others were aimed at controlling myocardial growth and stemming graft microangiopathy.
Mr. Bennett himself was treated with powerful immunosuppressants, including an investigational anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody (KPL-404, Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals) that, according to UMSOM, inhibits a well-recognized pathway critical to B-cell proliferation, T-cell activation, and antibody production.
“I suspect the patient may not have had rejection, but unfortunately, that intense immunosuppression really set him up – even if he had been half that age – for a very difficult time,” David A. Baran, MD, a cardiologist from Sentara Advanced Heart Failure Center, Norfolk, Va., who studies transplant immunology, said in an interview.
“This is in some ways like the original heart transplant in 1967, when the ability to do the surgery evolved before understanding of the immunosuppression needed. Four or 5 years later, heart transplantation almost died out, before the development of better immunosuppressants like cyclosporine and later tacrolimus,” Dr. Baran said.
“The current age, when we use less immunosuppression than ever, is based on 30 years of progressive success,” he noted. This landmark xenotransplantation “basically turns back the clock to a time when the intensity of immunosuppression by definition had to be extremely high, because we really didn’t know what to expect.”
Emerging role of xeno-organs
Xenotransplantation has been touted as potential strategy for expanding the pool of organs available for transplantation. Mr. Bennett’s “breakthrough surgery” takes the world “one step closer to solving the organ shortage crisis,” his surgeon, Dr. Griffith, announced soon after the procedure. “There are simply not enough donor human hearts available to meet the long list of potential recipients.”
But it’s not the only proposed approach. Measures could be taken, for example, to make more efficient use of the human organs that become available, partly by opening the field to additional less-than-ideal hearts and loosening regulatory mandates for projected graft survival.
“Every year, more than two-thirds of donor organs in the United States are discarded. So it’s not actually that we don’t have enough organs, it’s that we don’t have enough organs that people are willing to take,” Dr. Baran said. Still, it’s important to pursue all promising avenues, and “the genetic manipulation pathway is remarkable.”
But “honestly, organs such as kidneys probably make the most sense” for early study of xenotransplantation from pigs, he said. “The waiting list for kidneys is also very long, but if the kidney graft were to fail, the patient wouldn’t die. It would allow us to work out the immunosuppression without putting patients’ lives at risk.”
Often overlooked in assessments of organ demand, Dr. West said, is that “a lot of patients who could benefit from a transplant will never even be listed for a transplant.” It’s not clear why; perhaps they have multiple comorbidities, live too far from a transplant center, “or they’re too big or too small. Even if there were unlimited organs, you could never meet the needs of people who could benefit from transplantation.”
So even if more available donor organs were used, she said, there would still be a gap that xenotransplantation could help fill. “I’m very much in favor of research that allows us to continue to try to find a pathway to xenotransplantation. I think it’s critically important.”
Unquestionably, “we now need to have a dialogue to entertain how a technology like this, using modern medicine with gene editing, is really going to be utilized,” Dr. Mehra said. The Bennett case “does open up the field, but it also raises caution.” There should be broad participation to move the field forward, “coordinated through either societies or nationally allocated advisory committees that oversee the movement of this technology, to the next step.”
Ideally, that next step “would be to do a safety clinical trial in the right patient,” he said. “And the right patient, by definition, would be one who does not have a life-prolonging option, either mechanical circulatory support or allograft transplantation. That would be the goal.”
Dr. Mehra has reported receiving payments to his institution from Abbott for consulting; consulting fees from Janssen, Mesoblast, Broadview Ventures, Natera, Paragonix, Moderna, and the Baim Institute for Clinical Research; and serving on a scientific advisory board NuPulseCV, Leviticus, and FineHeart. Dr. Baran disclosed consulting for Getinge and LivaNova; speaking for Pfizer; and serving on trial steering committees for CareDx and Procyrion, all unrelated to xenotransplantation. Dr. West has declared no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The genetically altered pig’s heart “worked like a rock star, beautifully functioning,” the surgeon who performed the pioneering Jan. 7 xenotransplant procedure said in a press statement on the death of the patient, David Bennett Sr.
“He wasn’t able to overcome what turned out to be devastating – the debilitation from his previous period of heart failure, which was extreme,” said Bartley P. Griffith, MD, clinical director of the cardiac xenotransplantation program at the University of Maryland, Baltimore.
Representatives of the institution aren’t offering many details on the cause of Mr. Bennett’s death on March 8, 60 days after his operation, but said they will elaborate when their findings are formally published. But their comments seem to downplay the unique nature of the implanted heart itself as a culprit and instead implicate the patient’s diminished overall clinical condition and what grew into an ongoing battle with infections.
The 57-year-old Bennett, bedridden with end-stage heart failure, judged a poor candidate for a ventricular assist device, and on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), reportedly was offered the extraordinary surgery after being turned down for a conventional transplant at several major centers.
“Until day 45 or 50, he was doing very well,” Muhammad M. Mohiuddin, MD, the xenotransplantation program’s scientific director, observed in the statement. But infections soon took advantage of his hobbled immune system.
Given his “preexisting condition and how frail his body was,” Dr. Mohiuddin said, “we were having difficulty maintaining a balance between his immunosuppression and controlling his infection.” Mr. Bennett went into multiple organ failure and “I think that resulted in his passing away.”
Beyond wildest dreams
The surgeons confidently framed Mr. Bennett’s experience as a milestone for heart xenotransplantation. “The demonstration that it was possible, beyond the wildest dreams of most people in the field, even, at this point – that we were able to take a genetically engineered organ and watch it function flawlessly for 9 weeks – is pretty positive in terms of the potential of this therapy,” Dr. Griffith said.
But enough questions linger that others were more circumspect, even as they praised the accomplishment. “There’s no question that this is a historic event,” Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, of Harvard Medical School, and director of the Center for Advanced Heart Disease at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
Still, “I don’t think we should just conclude that it was the patient’s frailty or death from infection,” Dr. Mehra said. With so few details available, “I would be very careful in prematurely concluding that the problem did not reside with the heart but with the patient. We cannot be sure.”
For example, he noted, “6 to 8 weeks is right around the time when some cardiac complications, like accelerated forms of vasculopathy, could become evident.” Immune-mediated cardiac allograft vasculopathy is a common cause of heart transplant failure.
Or, “it could as easily have been the fact that immunosuppression was modified at 6 to 7 weeks in response to potential infection, which could have led to a cardiac compromise,” Dr. Mehra said. “We just don’t know.”
“It’s really important that this be reported in a scientifically accurate way, because we will all learn from this,” Lori J. West, MD, DPhil, said in an interview.
Little seems to be known for sure about the actual cause of death, “but the fact there was not hyperacute rejection is itself a big step forward. And we know, at least from the limited information we have, that it did not occur,” observed Dr. West, who directs the Alberta Transplant Institute, Edmonton, and the Canadian Donation and Transplantation Research Program. She is a professor of pediatrics with adjunct positions in the departments of surgery and microbiology/immunology.
Dr. West also sees Mr. Bennett’s struggle with infections and adjustments to his unique immunosuppressive regimen, at least as characterized by his care team, as in line with the experience of many heart transplant recipients facing the same threat.
“We already walk this tightrope with every transplant patient,” she said. Typically, they’re put on a somewhat standardized immunosuppressant regimen, “and then we modify it a bit, either increasing or decreasing it, depending on the posttransplant course.” The regimen can become especially intense in response to new signs of rejection, “and you know that that’s going to have an impact on susceptibility to all kinds of infections.”
Full circle
The porcine heart was protected along two fronts against assault from Mr. Bennett’s immune system and other inhospitable aspects of his physiology, either of which could also have been obstacles to success: Genetic modification (Revivicor) of the pig that provided the heart, and a singularly aggressive antirejection drug regimen for the patient.
The knockout of three genes targeting specific porcine cell-surface carbohydrates that provoke a strong human antibody response reportedly averted a hyperacute rejection response that would have caused the graft to fail almost immediately.
Other genetic manipulations, some using CRISPR technology, silenced genes encoded for porcine endogenous retroviruses. Others were aimed at controlling myocardial growth and stemming graft microangiopathy.
Mr. Bennett himself was treated with powerful immunosuppressants, including an investigational anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody (KPL-404, Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals) that, according to UMSOM, inhibits a well-recognized pathway critical to B-cell proliferation, T-cell activation, and antibody production.
“I suspect the patient may not have had rejection, but unfortunately, that intense immunosuppression really set him up – even if he had been half that age – for a very difficult time,” David A. Baran, MD, a cardiologist from Sentara Advanced Heart Failure Center, Norfolk, Va., who studies transplant immunology, said in an interview.
“This is in some ways like the original heart transplant in 1967, when the ability to do the surgery evolved before understanding of the immunosuppression needed. Four or 5 years later, heart transplantation almost died out, before the development of better immunosuppressants like cyclosporine and later tacrolimus,” Dr. Baran said.
“The current age, when we use less immunosuppression than ever, is based on 30 years of progressive success,” he noted. This landmark xenotransplantation “basically turns back the clock to a time when the intensity of immunosuppression by definition had to be extremely high, because we really didn’t know what to expect.”
Emerging role of xeno-organs
Xenotransplantation has been touted as potential strategy for expanding the pool of organs available for transplantation. Mr. Bennett’s “breakthrough surgery” takes the world “one step closer to solving the organ shortage crisis,” his surgeon, Dr. Griffith, announced soon after the procedure. “There are simply not enough donor human hearts available to meet the long list of potential recipients.”
But it’s not the only proposed approach. Measures could be taken, for example, to make more efficient use of the human organs that become available, partly by opening the field to additional less-than-ideal hearts and loosening regulatory mandates for projected graft survival.
“Every year, more than two-thirds of donor organs in the United States are discarded. So it’s not actually that we don’t have enough organs, it’s that we don’t have enough organs that people are willing to take,” Dr. Baran said. Still, it’s important to pursue all promising avenues, and “the genetic manipulation pathway is remarkable.”
But “honestly, organs such as kidneys probably make the most sense” for early study of xenotransplantation from pigs, he said. “The waiting list for kidneys is also very long, but if the kidney graft were to fail, the patient wouldn’t die. It would allow us to work out the immunosuppression without putting patients’ lives at risk.”
Often overlooked in assessments of organ demand, Dr. West said, is that “a lot of patients who could benefit from a transplant will never even be listed for a transplant.” It’s not clear why; perhaps they have multiple comorbidities, live too far from a transplant center, “or they’re too big or too small. Even if there were unlimited organs, you could never meet the needs of people who could benefit from transplantation.”
So even if more available donor organs were used, she said, there would still be a gap that xenotransplantation could help fill. “I’m very much in favor of research that allows us to continue to try to find a pathway to xenotransplantation. I think it’s critically important.”
Unquestionably, “we now need to have a dialogue to entertain how a technology like this, using modern medicine with gene editing, is really going to be utilized,” Dr. Mehra said. The Bennett case “does open up the field, but it also raises caution.” There should be broad participation to move the field forward, “coordinated through either societies or nationally allocated advisory committees that oversee the movement of this technology, to the next step.”
Ideally, that next step “would be to do a safety clinical trial in the right patient,” he said. “And the right patient, by definition, would be one who does not have a life-prolonging option, either mechanical circulatory support or allograft transplantation. That would be the goal.”
Dr. Mehra has reported receiving payments to his institution from Abbott for consulting; consulting fees from Janssen, Mesoblast, Broadview Ventures, Natera, Paragonix, Moderna, and the Baim Institute for Clinical Research; and serving on a scientific advisory board NuPulseCV, Leviticus, and FineHeart. Dr. Baran disclosed consulting for Getinge and LivaNova; speaking for Pfizer; and serving on trial steering committees for CareDx and Procyrion, all unrelated to xenotransplantation. Dr. West has declared no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The genetically altered pig’s heart “worked like a rock star, beautifully functioning,” the surgeon who performed the pioneering Jan. 7 xenotransplant procedure said in a press statement on the death of the patient, David Bennett Sr.
“He wasn’t able to overcome what turned out to be devastating – the debilitation from his previous period of heart failure, which was extreme,” said Bartley P. Griffith, MD, clinical director of the cardiac xenotransplantation program at the University of Maryland, Baltimore.
Representatives of the institution aren’t offering many details on the cause of Mr. Bennett’s death on March 8, 60 days after his operation, but said they will elaborate when their findings are formally published. But their comments seem to downplay the unique nature of the implanted heart itself as a culprit and instead implicate the patient’s diminished overall clinical condition and what grew into an ongoing battle with infections.
The 57-year-old Bennett, bedridden with end-stage heart failure, judged a poor candidate for a ventricular assist device, and on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), reportedly was offered the extraordinary surgery after being turned down for a conventional transplant at several major centers.
“Until day 45 or 50, he was doing very well,” Muhammad M. Mohiuddin, MD, the xenotransplantation program’s scientific director, observed in the statement. But infections soon took advantage of his hobbled immune system.
Given his “preexisting condition and how frail his body was,” Dr. Mohiuddin said, “we were having difficulty maintaining a balance between his immunosuppression and controlling his infection.” Mr. Bennett went into multiple organ failure and “I think that resulted in his passing away.”
Beyond wildest dreams
The surgeons confidently framed Mr. Bennett’s experience as a milestone for heart xenotransplantation. “The demonstration that it was possible, beyond the wildest dreams of most people in the field, even, at this point – that we were able to take a genetically engineered organ and watch it function flawlessly for 9 weeks – is pretty positive in terms of the potential of this therapy,” Dr. Griffith said.
But enough questions linger that others were more circumspect, even as they praised the accomplishment. “There’s no question that this is a historic event,” Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, of Harvard Medical School, and director of the Center for Advanced Heart Disease at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
Still, “I don’t think we should just conclude that it was the patient’s frailty or death from infection,” Dr. Mehra said. With so few details available, “I would be very careful in prematurely concluding that the problem did not reside with the heart but with the patient. We cannot be sure.”
For example, he noted, “6 to 8 weeks is right around the time when some cardiac complications, like accelerated forms of vasculopathy, could become evident.” Immune-mediated cardiac allograft vasculopathy is a common cause of heart transplant failure.
Or, “it could as easily have been the fact that immunosuppression was modified at 6 to 7 weeks in response to potential infection, which could have led to a cardiac compromise,” Dr. Mehra said. “We just don’t know.”
“It’s really important that this be reported in a scientifically accurate way, because we will all learn from this,” Lori J. West, MD, DPhil, said in an interview.
Little seems to be known for sure about the actual cause of death, “but the fact there was not hyperacute rejection is itself a big step forward. And we know, at least from the limited information we have, that it did not occur,” observed Dr. West, who directs the Alberta Transplant Institute, Edmonton, and the Canadian Donation and Transplantation Research Program. She is a professor of pediatrics with adjunct positions in the departments of surgery and microbiology/immunology.
Dr. West also sees Mr. Bennett’s struggle with infections and adjustments to his unique immunosuppressive regimen, at least as characterized by his care team, as in line with the experience of many heart transplant recipients facing the same threat.
“We already walk this tightrope with every transplant patient,” she said. Typically, they’re put on a somewhat standardized immunosuppressant regimen, “and then we modify it a bit, either increasing or decreasing it, depending on the posttransplant course.” The regimen can become especially intense in response to new signs of rejection, “and you know that that’s going to have an impact on susceptibility to all kinds of infections.”
Full circle
The porcine heart was protected along two fronts against assault from Mr. Bennett’s immune system and other inhospitable aspects of his physiology, either of which could also have been obstacles to success: Genetic modification (Revivicor) of the pig that provided the heart, and a singularly aggressive antirejection drug regimen for the patient.
The knockout of three genes targeting specific porcine cell-surface carbohydrates that provoke a strong human antibody response reportedly averted a hyperacute rejection response that would have caused the graft to fail almost immediately.
Other genetic manipulations, some using CRISPR technology, silenced genes encoded for porcine endogenous retroviruses. Others were aimed at controlling myocardial growth and stemming graft microangiopathy.
Mr. Bennett himself was treated with powerful immunosuppressants, including an investigational anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody (KPL-404, Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals) that, according to UMSOM, inhibits a well-recognized pathway critical to B-cell proliferation, T-cell activation, and antibody production.
“I suspect the patient may not have had rejection, but unfortunately, that intense immunosuppression really set him up – even if he had been half that age – for a very difficult time,” David A. Baran, MD, a cardiologist from Sentara Advanced Heart Failure Center, Norfolk, Va., who studies transplant immunology, said in an interview.
“This is in some ways like the original heart transplant in 1967, when the ability to do the surgery evolved before understanding of the immunosuppression needed. Four or 5 years later, heart transplantation almost died out, before the development of better immunosuppressants like cyclosporine and later tacrolimus,” Dr. Baran said.
“The current age, when we use less immunosuppression than ever, is based on 30 years of progressive success,” he noted. This landmark xenotransplantation “basically turns back the clock to a time when the intensity of immunosuppression by definition had to be extremely high, because we really didn’t know what to expect.”
Emerging role of xeno-organs
Xenotransplantation has been touted as potential strategy for expanding the pool of organs available for transplantation. Mr. Bennett’s “breakthrough surgery” takes the world “one step closer to solving the organ shortage crisis,” his surgeon, Dr. Griffith, announced soon after the procedure. “There are simply not enough donor human hearts available to meet the long list of potential recipients.”
But it’s not the only proposed approach. Measures could be taken, for example, to make more efficient use of the human organs that become available, partly by opening the field to additional less-than-ideal hearts and loosening regulatory mandates for projected graft survival.
“Every year, more than two-thirds of donor organs in the United States are discarded. So it’s not actually that we don’t have enough organs, it’s that we don’t have enough organs that people are willing to take,” Dr. Baran said. Still, it’s important to pursue all promising avenues, and “the genetic manipulation pathway is remarkable.”
But “honestly, organs such as kidneys probably make the most sense” for early study of xenotransplantation from pigs, he said. “The waiting list for kidneys is also very long, but if the kidney graft were to fail, the patient wouldn’t die. It would allow us to work out the immunosuppression without putting patients’ lives at risk.”
Often overlooked in assessments of organ demand, Dr. West said, is that “a lot of patients who could benefit from a transplant will never even be listed for a transplant.” It’s not clear why; perhaps they have multiple comorbidities, live too far from a transplant center, “or they’re too big or too small. Even if there were unlimited organs, you could never meet the needs of people who could benefit from transplantation.”
So even if more available donor organs were used, she said, there would still be a gap that xenotransplantation could help fill. “I’m very much in favor of research that allows us to continue to try to find a pathway to xenotransplantation. I think it’s critically important.”
Unquestionably, “we now need to have a dialogue to entertain how a technology like this, using modern medicine with gene editing, is really going to be utilized,” Dr. Mehra said. The Bennett case “does open up the field, but it also raises caution.” There should be broad participation to move the field forward, “coordinated through either societies or nationally allocated advisory committees that oversee the movement of this technology, to the next step.”
Ideally, that next step “would be to do a safety clinical trial in the right patient,” he said. “And the right patient, by definition, would be one who does not have a life-prolonging option, either mechanical circulatory support or allograft transplantation. That would be the goal.”
Dr. Mehra has reported receiving payments to his institution from Abbott for consulting; consulting fees from Janssen, Mesoblast, Broadview Ventures, Natera, Paragonix, Moderna, and the Baim Institute for Clinical Research; and serving on a scientific advisory board NuPulseCV, Leviticus, and FineHeart. Dr. Baran disclosed consulting for Getinge and LivaNova; speaking for Pfizer; and serving on trial steering committees for CareDx and Procyrion, all unrelated to xenotransplantation. Dr. West has declared no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CPAP has only small effect on metabolic syndrome
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) may be only modestly effective for ameliorating metabolic syndrome in patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
That conclusion comes from investigators in a randomized controlled, trial, who found that, among 100 patients with OSA and a recent diagnosis of metabolic syndrome (MS), 18% of those assigned to use CPAP at night had a reversal of MS at 6 months of follow-up, compared with 4% of controls who were assigned to use nasal strips at night (P = .04).
The majority of patients assigned to CPAP still retained their MS diagnoses at 6 months, and CPAP did not significantly reduce individual components of the syndrome. Use of CPAP was, however, associated with small reductions in visceral fat and improvement in endothelial function, reported Sara Q.C. Giampa, PhD, from the University of São Paulo, and colleagues.
“Despite a significant rate of MS reversibility after CPAP therapy, most of the patients maintained the MS diagnosis. The modest effects of CPAP on MS reversibility underscore the need for combined therapy with CPAP, aiming to maximize metabolic syndrome recovery in parallel with improvements in OSA severity and related symptoms,” according to their study, reported in the journal CHEST®.
Asked whether he still recommends CPAP to patients with OSA and the metabolic syndrome, given the findings, corresponding author Luciano F. Drager, MD, PhD, replied “yes, definitely.”
“Despite the modest rate in reversing metabolic syndrome after CPAP, the rate was 5-fold higher than non-effective treatment (18% vs. 4%),” he said in an interview.
Dr. Drager noted that studies of other single interventions such as physical exercise to reverse MS in patients with OSA also had modest results.
A researcher who studies the relationship between sleep, circadian rhythms, and metabolism commented that, although the patients in the CPAP group were compliant with the assigned equipment and had both reductions in apneic events and improvement in oxygen saturation, the effect of CPAP on the metabolic syndrome was rather small.
“The CPAP was doing what we thought it was supposed to do, but it didn’t have the magnitude of effect on the metabolic syndrome as I expected or I think as the authors expected,” said Deanna Arble, PhD, assistant professor of biological science at Marquette University, Milwaukee.
She noted that the study also failed to detect a significant improvement in the blood pressure component of metabolic syndrome.
“In my experience and my review of the literature, blood pressure tends to be the one that’s improved most dramatically with CPAP,” she said.
Dr. Arble was not involved in the study.
Study details
In the trial, titled TREATOSA-MS, the investigators enrolled 100 patients with a recent diagnosis of metabolic syndrome and moderate to severe OSA, defined as 15 or more apnea-hypopnea index events per hour. The patients were stratified by body mass index and then randomized to undergo therapeutic CPAP or to use nasal strips for 6 months.
At baseline and at the end of each intervention investigators measured anthropometric variables, blood pressure, glucose, and lipid profiles. They also leptin and adiponectin, body composition, food intake, physical activity, subcutaneous and abdominal fat (visceral and hepatic), and endothelial function to control for potential confounders.
As noted previously, they found that after 6 months “most patients with OSA randomized to CPAP retained the MS diagnosis, but the rate of MS reversibility was higher than observed in the placebo group.” The difference in metabolic syndrome reversal, 18% with CPAP versus 4% with nasal strips, translated into a hazard ratio favoring CPAP of 5.27 (P = .04).
Also as noted, in analyses adjusted for baseline values, CPAP did not significantly improve either weight, liver fat, lip profiles, or the adiposity biomarkers leptin and adiponectin, but did have “very modest” influence on reducing visceral fat and improving endothelial function.
Rigorous study
Dr. Arble said that most studies of the association between OSA and metabolic syndrome have focused on only one or two of the parameters that were included in the TREATOSA-MS study, giving the findings additional weight.
“This could potentially be a very good, carefully controlled first insight into how obstructive sleep apnea is related to the metabolic syndrome,” she said.
The study was funded by grants Fundação de Amparo Q22 à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior. The authors and Dr. Arble reported having no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) may be only modestly effective for ameliorating metabolic syndrome in patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
That conclusion comes from investigators in a randomized controlled, trial, who found that, among 100 patients with OSA and a recent diagnosis of metabolic syndrome (MS), 18% of those assigned to use CPAP at night had a reversal of MS at 6 months of follow-up, compared with 4% of controls who were assigned to use nasal strips at night (P = .04).
The majority of patients assigned to CPAP still retained their MS diagnoses at 6 months, and CPAP did not significantly reduce individual components of the syndrome. Use of CPAP was, however, associated with small reductions in visceral fat and improvement in endothelial function, reported Sara Q.C. Giampa, PhD, from the University of São Paulo, and colleagues.
“Despite a significant rate of MS reversibility after CPAP therapy, most of the patients maintained the MS diagnosis. The modest effects of CPAP on MS reversibility underscore the need for combined therapy with CPAP, aiming to maximize metabolic syndrome recovery in parallel with improvements in OSA severity and related symptoms,” according to their study, reported in the journal CHEST®.
Asked whether he still recommends CPAP to patients with OSA and the metabolic syndrome, given the findings, corresponding author Luciano F. Drager, MD, PhD, replied “yes, definitely.”
“Despite the modest rate in reversing metabolic syndrome after CPAP, the rate was 5-fold higher than non-effective treatment (18% vs. 4%),” he said in an interview.
Dr. Drager noted that studies of other single interventions such as physical exercise to reverse MS in patients with OSA also had modest results.
A researcher who studies the relationship between sleep, circadian rhythms, and metabolism commented that, although the patients in the CPAP group were compliant with the assigned equipment and had both reductions in apneic events and improvement in oxygen saturation, the effect of CPAP on the metabolic syndrome was rather small.
“The CPAP was doing what we thought it was supposed to do, but it didn’t have the magnitude of effect on the metabolic syndrome as I expected or I think as the authors expected,” said Deanna Arble, PhD, assistant professor of biological science at Marquette University, Milwaukee.
She noted that the study also failed to detect a significant improvement in the blood pressure component of metabolic syndrome.
“In my experience and my review of the literature, blood pressure tends to be the one that’s improved most dramatically with CPAP,” she said.
Dr. Arble was not involved in the study.
Study details
In the trial, titled TREATOSA-MS, the investigators enrolled 100 patients with a recent diagnosis of metabolic syndrome and moderate to severe OSA, defined as 15 or more apnea-hypopnea index events per hour. The patients were stratified by body mass index and then randomized to undergo therapeutic CPAP or to use nasal strips for 6 months.
At baseline and at the end of each intervention investigators measured anthropometric variables, blood pressure, glucose, and lipid profiles. They also leptin and adiponectin, body composition, food intake, physical activity, subcutaneous and abdominal fat (visceral and hepatic), and endothelial function to control for potential confounders.
As noted previously, they found that after 6 months “most patients with OSA randomized to CPAP retained the MS diagnosis, but the rate of MS reversibility was higher than observed in the placebo group.” The difference in metabolic syndrome reversal, 18% with CPAP versus 4% with nasal strips, translated into a hazard ratio favoring CPAP of 5.27 (P = .04).
Also as noted, in analyses adjusted for baseline values, CPAP did not significantly improve either weight, liver fat, lip profiles, or the adiposity biomarkers leptin and adiponectin, but did have “very modest” influence on reducing visceral fat and improving endothelial function.
Rigorous study
Dr. Arble said that most studies of the association between OSA and metabolic syndrome have focused on only one or two of the parameters that were included in the TREATOSA-MS study, giving the findings additional weight.
“This could potentially be a very good, carefully controlled first insight into how obstructive sleep apnea is related to the metabolic syndrome,” she said.
The study was funded by grants Fundação de Amparo Q22 à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior. The authors and Dr. Arble reported having no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) may be only modestly effective for ameliorating metabolic syndrome in patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
That conclusion comes from investigators in a randomized controlled, trial, who found that, among 100 patients with OSA and a recent diagnosis of metabolic syndrome (MS), 18% of those assigned to use CPAP at night had a reversal of MS at 6 months of follow-up, compared with 4% of controls who were assigned to use nasal strips at night (P = .04).
The majority of patients assigned to CPAP still retained their MS diagnoses at 6 months, and CPAP did not significantly reduce individual components of the syndrome. Use of CPAP was, however, associated with small reductions in visceral fat and improvement in endothelial function, reported Sara Q.C. Giampa, PhD, from the University of São Paulo, and colleagues.
“Despite a significant rate of MS reversibility after CPAP therapy, most of the patients maintained the MS diagnosis. The modest effects of CPAP on MS reversibility underscore the need for combined therapy with CPAP, aiming to maximize metabolic syndrome recovery in parallel with improvements in OSA severity and related symptoms,” according to their study, reported in the journal CHEST®.
Asked whether he still recommends CPAP to patients with OSA and the metabolic syndrome, given the findings, corresponding author Luciano F. Drager, MD, PhD, replied “yes, definitely.”
“Despite the modest rate in reversing metabolic syndrome after CPAP, the rate was 5-fold higher than non-effective treatment (18% vs. 4%),” he said in an interview.
Dr. Drager noted that studies of other single interventions such as physical exercise to reverse MS in patients with OSA also had modest results.
A researcher who studies the relationship between sleep, circadian rhythms, and metabolism commented that, although the patients in the CPAP group were compliant with the assigned equipment and had both reductions in apneic events and improvement in oxygen saturation, the effect of CPAP on the metabolic syndrome was rather small.
“The CPAP was doing what we thought it was supposed to do, but it didn’t have the magnitude of effect on the metabolic syndrome as I expected or I think as the authors expected,” said Deanna Arble, PhD, assistant professor of biological science at Marquette University, Milwaukee.
She noted that the study also failed to detect a significant improvement in the blood pressure component of metabolic syndrome.
“In my experience and my review of the literature, blood pressure tends to be the one that’s improved most dramatically with CPAP,” she said.
Dr. Arble was not involved in the study.
Study details
In the trial, titled TREATOSA-MS, the investigators enrolled 100 patients with a recent diagnosis of metabolic syndrome and moderate to severe OSA, defined as 15 or more apnea-hypopnea index events per hour. The patients were stratified by body mass index and then randomized to undergo therapeutic CPAP or to use nasal strips for 6 months.
At baseline and at the end of each intervention investigators measured anthropometric variables, blood pressure, glucose, and lipid profiles. They also leptin and adiponectin, body composition, food intake, physical activity, subcutaneous and abdominal fat (visceral and hepatic), and endothelial function to control for potential confounders.
As noted previously, they found that after 6 months “most patients with OSA randomized to CPAP retained the MS diagnosis, but the rate of MS reversibility was higher than observed in the placebo group.” The difference in metabolic syndrome reversal, 18% with CPAP versus 4% with nasal strips, translated into a hazard ratio favoring CPAP of 5.27 (P = .04).
Also as noted, in analyses adjusted for baseline values, CPAP did not significantly improve either weight, liver fat, lip profiles, or the adiposity biomarkers leptin and adiponectin, but did have “very modest” influence on reducing visceral fat and improving endothelial function.
Rigorous study
Dr. Arble said that most studies of the association between OSA and metabolic syndrome have focused on only one or two of the parameters that were included in the TREATOSA-MS study, giving the findings additional weight.
“This could potentially be a very good, carefully controlled first insight into how obstructive sleep apnea is related to the metabolic syndrome,” she said.
The study was funded by grants Fundação de Amparo Q22 à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior. The authors and Dr. Arble reported having no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM CHEST
Lights on during sleep can play havoc with metabolism
“The most important finding” is that, compared with one night in a dim light environment, “one night of exposure to a moderate level of room light while sleeping with eyes closed increased heart rate and sympathetic [nervous system] activity during the entire sleep period,” said senior author Phyllis C. Zee, MD, PhD.
And on the morning following the moderate room light condition, a higher amount of insulin secretion was required to normalize glucose levels following ingestion of a bolus of glucose in an oral glucose tolerance test, consistent with higher insulin resistance, Dr. Zee, director of the center for circadian and sleep medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, told this news organization in an email.
The study by Ivy C. Mason, PhD, also of Northwestern University, and colleagues was published March 14 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Melatonin levels were similar under the two light conditions, Dr. Zee added, which “suggests that the effect of light during sleep on these cardiometabolic measures were more likely due to activation of the sympathetic [nervous] system and less likely due to changes in sleep or suppression of melatonin by light.”
“Attention to avoiding exposure to light at night during sleep may be beneficial for cardiometabolic health,” the researchers conclude.
That means “turn lights off before sleeping,” Dr. Zee elaborated. If a light is needed for safety reasons, keep it as dim as possible, she advises, and avoid exposure to blue or green light, but instead try red-amber colors.
How light during sleep may affect insulin, melatonin, heart rate
Several studies have investigated the effect of light on sleep and metabolic outcomes, the researchers explain.
In one study, light in the bedroom was associated with obesity in women, and in another study, it was associated with risk of type 2 diabetes in an elderly population.
Research has suggested that nighttime light exposure may alter glucose metabolism by increasing insulin resistance; lowering melatonin levels, which alters insulin secretion; and having an arousing effect on the sympathetic autonomic nervous system (increasing the stress hormone cortisol or heart rate, and decreasing heart rate variability).
However, the effect of a single night of moderate room light exposure across the entire nighttime sleep period has not been fully investigated.
The researchers enrolled and randomized 20 healthy young adults who were 18-40 years old and regularly went to sleep between 9 p.m. and 1 a.m. and slept 6.5-8.5 hours, to sleep 2 nights in the sleep laboratory under two conditions.
Ten participants (eight women, two men) slept in a dim light condition on night 1 and in a moderate light condition on night 2. The other 10 participants (six women, four men) slept 2 nights in the dim light condition.
The moderate light condition consisted of four 60-watt incandescent overhead ceiling light bulbs (a total of 100 lux), which “is bright enough to see, but not to read comfortably,” Dr. Zee explained. “It’s like hallway light in an apartment. But the people were sleeping, so about 90% of the light would be blocked by the eyelids.”
The dim light condition was less than 3 lux, which is dimmer than a night light.
When participants were awake, the room lighting was 240 lux.
Participants in each group were a mean age of 27 years and had a mean body mass index of 23 and 24 kg/m2.
The week before the study, participants went to bed at 11 p.m. and slept for 7 hours (based on actigraphy measures). During the laboratory stay, the participants were allowed to sleep 8 hours, during which polysomnography was performed.
They received standard meals at 2.5, 5, and 11 hours after waking and had 30 minutes to eat them. Snacking and caffeine were not permitted.
Participants were instructed to remain seated or standing in their room, but not exercise, when they were not sleeping. Blood samples to determine melatonin levels were collected hourly during wake and sleep via an intravenous line.
Participants slept for a similar time, around 7 hours, in both conditions.
Although melatonin levels were similar in both conditions, this was a relatively small sample, the researchers caution.
In the room light condition, participants spent proportionately more time in stage N2 sleep and less in slow-wave and rapid eye movement sleep. There was no increase in sleep fragmentation or arousals.
The research was partly supported by the Center for Circadian and Sleep Medicine at Northwestern University, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Institutes of Health, and the American Heart Association. The researchers have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The most important finding” is that, compared with one night in a dim light environment, “one night of exposure to a moderate level of room light while sleeping with eyes closed increased heart rate and sympathetic [nervous system] activity during the entire sleep period,” said senior author Phyllis C. Zee, MD, PhD.
And on the morning following the moderate room light condition, a higher amount of insulin secretion was required to normalize glucose levels following ingestion of a bolus of glucose in an oral glucose tolerance test, consistent with higher insulin resistance, Dr. Zee, director of the center for circadian and sleep medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, told this news organization in an email.
The study by Ivy C. Mason, PhD, also of Northwestern University, and colleagues was published March 14 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Melatonin levels were similar under the two light conditions, Dr. Zee added, which “suggests that the effect of light during sleep on these cardiometabolic measures were more likely due to activation of the sympathetic [nervous] system and less likely due to changes in sleep or suppression of melatonin by light.”
“Attention to avoiding exposure to light at night during sleep may be beneficial for cardiometabolic health,” the researchers conclude.
That means “turn lights off before sleeping,” Dr. Zee elaborated. If a light is needed for safety reasons, keep it as dim as possible, she advises, and avoid exposure to blue or green light, but instead try red-amber colors.
How light during sleep may affect insulin, melatonin, heart rate
Several studies have investigated the effect of light on sleep and metabolic outcomes, the researchers explain.
In one study, light in the bedroom was associated with obesity in women, and in another study, it was associated with risk of type 2 diabetes in an elderly population.
Research has suggested that nighttime light exposure may alter glucose metabolism by increasing insulin resistance; lowering melatonin levels, which alters insulin secretion; and having an arousing effect on the sympathetic autonomic nervous system (increasing the stress hormone cortisol or heart rate, and decreasing heart rate variability).
However, the effect of a single night of moderate room light exposure across the entire nighttime sleep period has not been fully investigated.
The researchers enrolled and randomized 20 healthy young adults who were 18-40 years old and regularly went to sleep between 9 p.m. and 1 a.m. and slept 6.5-8.5 hours, to sleep 2 nights in the sleep laboratory under two conditions.
Ten participants (eight women, two men) slept in a dim light condition on night 1 and in a moderate light condition on night 2. The other 10 participants (six women, four men) slept 2 nights in the dim light condition.
The moderate light condition consisted of four 60-watt incandescent overhead ceiling light bulbs (a total of 100 lux), which “is bright enough to see, but not to read comfortably,” Dr. Zee explained. “It’s like hallway light in an apartment. But the people were sleeping, so about 90% of the light would be blocked by the eyelids.”
The dim light condition was less than 3 lux, which is dimmer than a night light.
When participants were awake, the room lighting was 240 lux.
Participants in each group were a mean age of 27 years and had a mean body mass index of 23 and 24 kg/m2.
The week before the study, participants went to bed at 11 p.m. and slept for 7 hours (based on actigraphy measures). During the laboratory stay, the participants were allowed to sleep 8 hours, during which polysomnography was performed.
They received standard meals at 2.5, 5, and 11 hours after waking and had 30 minutes to eat them. Snacking and caffeine were not permitted.
Participants were instructed to remain seated or standing in their room, but not exercise, when they were not sleeping. Blood samples to determine melatonin levels were collected hourly during wake and sleep via an intravenous line.
Participants slept for a similar time, around 7 hours, in both conditions.
Although melatonin levels were similar in both conditions, this was a relatively small sample, the researchers caution.
In the room light condition, participants spent proportionately more time in stage N2 sleep and less in slow-wave and rapid eye movement sleep. There was no increase in sleep fragmentation or arousals.
The research was partly supported by the Center for Circadian and Sleep Medicine at Northwestern University, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Institutes of Health, and the American Heart Association. The researchers have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The most important finding” is that, compared with one night in a dim light environment, “one night of exposure to a moderate level of room light while sleeping with eyes closed increased heart rate and sympathetic [nervous system] activity during the entire sleep period,” said senior author Phyllis C. Zee, MD, PhD.
And on the morning following the moderate room light condition, a higher amount of insulin secretion was required to normalize glucose levels following ingestion of a bolus of glucose in an oral glucose tolerance test, consistent with higher insulin resistance, Dr. Zee, director of the center for circadian and sleep medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, told this news organization in an email.
The study by Ivy C. Mason, PhD, also of Northwestern University, and colleagues was published March 14 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Melatonin levels were similar under the two light conditions, Dr. Zee added, which “suggests that the effect of light during sleep on these cardiometabolic measures were more likely due to activation of the sympathetic [nervous] system and less likely due to changes in sleep or suppression of melatonin by light.”
“Attention to avoiding exposure to light at night during sleep may be beneficial for cardiometabolic health,” the researchers conclude.
That means “turn lights off before sleeping,” Dr. Zee elaborated. If a light is needed for safety reasons, keep it as dim as possible, she advises, and avoid exposure to blue or green light, but instead try red-amber colors.
How light during sleep may affect insulin, melatonin, heart rate
Several studies have investigated the effect of light on sleep and metabolic outcomes, the researchers explain.
In one study, light in the bedroom was associated with obesity in women, and in another study, it was associated with risk of type 2 diabetes in an elderly population.
Research has suggested that nighttime light exposure may alter glucose metabolism by increasing insulin resistance; lowering melatonin levels, which alters insulin secretion; and having an arousing effect on the sympathetic autonomic nervous system (increasing the stress hormone cortisol or heart rate, and decreasing heart rate variability).
However, the effect of a single night of moderate room light exposure across the entire nighttime sleep period has not been fully investigated.
The researchers enrolled and randomized 20 healthy young adults who were 18-40 years old and regularly went to sleep between 9 p.m. and 1 a.m. and slept 6.5-8.5 hours, to sleep 2 nights in the sleep laboratory under two conditions.
Ten participants (eight women, two men) slept in a dim light condition on night 1 and in a moderate light condition on night 2. The other 10 participants (six women, four men) slept 2 nights in the dim light condition.
The moderate light condition consisted of four 60-watt incandescent overhead ceiling light bulbs (a total of 100 lux), which “is bright enough to see, but not to read comfortably,” Dr. Zee explained. “It’s like hallway light in an apartment. But the people were sleeping, so about 90% of the light would be blocked by the eyelids.”
The dim light condition was less than 3 lux, which is dimmer than a night light.
When participants were awake, the room lighting was 240 lux.
Participants in each group were a mean age of 27 years and had a mean body mass index of 23 and 24 kg/m2.
The week before the study, participants went to bed at 11 p.m. and slept for 7 hours (based on actigraphy measures). During the laboratory stay, the participants were allowed to sleep 8 hours, during which polysomnography was performed.
They received standard meals at 2.5, 5, and 11 hours after waking and had 30 minutes to eat them. Snacking and caffeine were not permitted.
Participants were instructed to remain seated or standing in their room, but not exercise, when they were not sleeping. Blood samples to determine melatonin levels were collected hourly during wake and sleep via an intravenous line.
Participants slept for a similar time, around 7 hours, in both conditions.
Although melatonin levels were similar in both conditions, this was a relatively small sample, the researchers caution.
In the room light condition, participants spent proportionately more time in stage N2 sleep and less in slow-wave and rapid eye movement sleep. There was no increase in sleep fragmentation or arousals.
The research was partly supported by the Center for Circadian and Sleep Medicine at Northwestern University, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Institutes of Health, and the American Heart Association. The researchers have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Real-world data support safety of newer LAA device
More than 18 months after the Watchman FLX device was licensed by the Food and Drug Administration for closure of the left atrial appendage (LAA), a prospective analysis of registry data presented at CRT 2022, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute, supports its safely outside of the clinical trial setting.
The data, drawn from the LAA occlusion registry of the National Cardiovascular Data Registry, showed a mortality rate at 45 days of under 1.0%, which was consistent with the acceptably low rate of other adverse events, according to Samir R. Kapadia, MD, chair of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
Only 0.5% had a pericardial effusion within 45 days of LAA closure that required intervention. Of those without effusion, 95% had a leak of less than 3 mm and 82% had no leak at all, according to Dr. Kapadia.
Patients enrolled in this analysis, called SURPASS (Surveillance Post Approval Analysis Plan), had undergone left atrial closure with the device from August 2020 to September 2022. There were no exclusion criteria. Ultimately, 2 years of follow-up is planned.
With more than 16,000 patients enrolled, the data on 14,363 patients in this initial 45-day analysis represents “the largest number of Watchman FLX patients evaluated to date,” Dr. Kapadia reported.
Device implantation success 97.5%
The Watchman FLX, which is delivered to the left atrial appendage by a transcatheter approach, was deployed successfully in 97.5% of all 16,048 patients enrolled in the registry. In the 398 cases without successful deployment, the anatomy was not conducive in nearly 70%. Other reasons included failure to meet device-release criteria and change in patient condition.
The outcomes of interest at 45 days were ischemic strokes, systemic emboli, device-related thrombi, device embolization, and bleeding. The primary endpoints at 2 years will be strokes and thrombotic events.
For stroke, the incidence within 45 days was 0.39%. About 25% of the strokes were hemorrhagic and the remainder were ischemic. There was 1 systemic embolism (0.01%), 5 device embolizations (0.03%), and 30 device-related thrombotic events (0.24%). Major bleeding occurred in 508 patients (3.55%).
For context, Dr. Kapadia compared these results to those observed in the PINNACLE FLX trial, which was a nonrandomized but prospective study of the Watchman FLX published about 1 year ago. In PINNACLE FLX, the enrollment was open to patients indicated for oral anticoagulation but who had an appropriate rationale for seeking a nonpharmacological alternative.
Taken from different studies, the outcomes at 45 days should not be construed as a direct comparison, but the similarity of the results can be considered reassuring, according to Dr. Kapadia.
For the composite safety endpoint of all-cause death, ischemic stroke, systemic embolism, or implantation-related events requiring intervention, the rates in SURPASS (0.4%) and PINNACLE FLX (0.5%) were nearly identical. Device leak rates (82.0% vs. 82.8%), stroke rates (0.4% vs. 0.7%), and all-cause death rates (0.9% vs. 0.5%) were also similar.
The similarity of the SURPASS and PINNACLE FLX data provides another level of reassurance.
“The SURPASS registry confirms the safety of the Watchman Flex in the real-world experience when the device is being used by many different operators in a large patient population,” Dr. Kapadia said in an interview.
In “appropriately selected patients,” the SURPASS data confirm that the Watchman FLX device “provides a safe and effective treatment option,” he added.
Relative to the PINNACLE FLX study, which enrolled 400 patients, it is noteworthy that the median age in SURPASS was older (76 vs. 73.8 years), a potential disadvantage in demonstrating comparable safety. The proportion of non-White patients was similar (6.7% vs. 6.3%). SURPASS had a higher proportion of women (40% vs. 35.5%).
The SURPASS data are credible, according to Vivek Y. Reddy, MD, director of cardiac arrhythmia services, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
“While there are certainly limitations to registry data, I do feel pretty confident that these procedural complication and success rates [in SURPASS] do indeed reflect reality,” said Dr. Reddy, who was a coauthor of the PINNACLE FLX trial. In general, the SURPASS data “mirror most of our clinical experiences in routine clinical practice.”
With these registry data backing up multiple clinical studies, Dr. Reddy concluded, “I do believe that it is fair to say that Watchman-FLX implantation is a quite safe procedure.”
Dr. Kapadia reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Reddy reported a financial relationship with Boston Scientific.
More than 18 months after the Watchman FLX device was licensed by the Food and Drug Administration for closure of the left atrial appendage (LAA), a prospective analysis of registry data presented at CRT 2022, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute, supports its safely outside of the clinical trial setting.
The data, drawn from the LAA occlusion registry of the National Cardiovascular Data Registry, showed a mortality rate at 45 days of under 1.0%, which was consistent with the acceptably low rate of other adverse events, according to Samir R. Kapadia, MD, chair of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
Only 0.5% had a pericardial effusion within 45 days of LAA closure that required intervention. Of those without effusion, 95% had a leak of less than 3 mm and 82% had no leak at all, according to Dr. Kapadia.
Patients enrolled in this analysis, called SURPASS (Surveillance Post Approval Analysis Plan), had undergone left atrial closure with the device from August 2020 to September 2022. There were no exclusion criteria. Ultimately, 2 years of follow-up is planned.
With more than 16,000 patients enrolled, the data on 14,363 patients in this initial 45-day analysis represents “the largest number of Watchman FLX patients evaluated to date,” Dr. Kapadia reported.
Device implantation success 97.5%
The Watchman FLX, which is delivered to the left atrial appendage by a transcatheter approach, was deployed successfully in 97.5% of all 16,048 patients enrolled in the registry. In the 398 cases without successful deployment, the anatomy was not conducive in nearly 70%. Other reasons included failure to meet device-release criteria and change in patient condition.
The outcomes of interest at 45 days were ischemic strokes, systemic emboli, device-related thrombi, device embolization, and bleeding. The primary endpoints at 2 years will be strokes and thrombotic events.
For stroke, the incidence within 45 days was 0.39%. About 25% of the strokes were hemorrhagic and the remainder were ischemic. There was 1 systemic embolism (0.01%), 5 device embolizations (0.03%), and 30 device-related thrombotic events (0.24%). Major bleeding occurred in 508 patients (3.55%).
For context, Dr. Kapadia compared these results to those observed in the PINNACLE FLX trial, which was a nonrandomized but prospective study of the Watchman FLX published about 1 year ago. In PINNACLE FLX, the enrollment was open to patients indicated for oral anticoagulation but who had an appropriate rationale for seeking a nonpharmacological alternative.
Taken from different studies, the outcomes at 45 days should not be construed as a direct comparison, but the similarity of the results can be considered reassuring, according to Dr. Kapadia.
For the composite safety endpoint of all-cause death, ischemic stroke, systemic embolism, or implantation-related events requiring intervention, the rates in SURPASS (0.4%) and PINNACLE FLX (0.5%) were nearly identical. Device leak rates (82.0% vs. 82.8%), stroke rates (0.4% vs. 0.7%), and all-cause death rates (0.9% vs. 0.5%) were also similar.
The similarity of the SURPASS and PINNACLE FLX data provides another level of reassurance.
“The SURPASS registry confirms the safety of the Watchman Flex in the real-world experience when the device is being used by many different operators in a large patient population,” Dr. Kapadia said in an interview.
In “appropriately selected patients,” the SURPASS data confirm that the Watchman FLX device “provides a safe and effective treatment option,” he added.
Relative to the PINNACLE FLX study, which enrolled 400 patients, it is noteworthy that the median age in SURPASS was older (76 vs. 73.8 years), a potential disadvantage in demonstrating comparable safety. The proportion of non-White patients was similar (6.7% vs. 6.3%). SURPASS had a higher proportion of women (40% vs. 35.5%).
The SURPASS data are credible, according to Vivek Y. Reddy, MD, director of cardiac arrhythmia services, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
“While there are certainly limitations to registry data, I do feel pretty confident that these procedural complication and success rates [in SURPASS] do indeed reflect reality,” said Dr. Reddy, who was a coauthor of the PINNACLE FLX trial. In general, the SURPASS data “mirror most of our clinical experiences in routine clinical practice.”
With these registry data backing up multiple clinical studies, Dr. Reddy concluded, “I do believe that it is fair to say that Watchman-FLX implantation is a quite safe procedure.”
Dr. Kapadia reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Reddy reported a financial relationship with Boston Scientific.
More than 18 months after the Watchman FLX device was licensed by the Food and Drug Administration for closure of the left atrial appendage (LAA), a prospective analysis of registry data presented at CRT 2022, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute, supports its safely outside of the clinical trial setting.
The data, drawn from the LAA occlusion registry of the National Cardiovascular Data Registry, showed a mortality rate at 45 days of under 1.0%, which was consistent with the acceptably low rate of other adverse events, according to Samir R. Kapadia, MD, chair of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
Only 0.5% had a pericardial effusion within 45 days of LAA closure that required intervention. Of those without effusion, 95% had a leak of less than 3 mm and 82% had no leak at all, according to Dr. Kapadia.
Patients enrolled in this analysis, called SURPASS (Surveillance Post Approval Analysis Plan), had undergone left atrial closure with the device from August 2020 to September 2022. There were no exclusion criteria. Ultimately, 2 years of follow-up is planned.
With more than 16,000 patients enrolled, the data on 14,363 patients in this initial 45-day analysis represents “the largest number of Watchman FLX patients evaluated to date,” Dr. Kapadia reported.
Device implantation success 97.5%
The Watchman FLX, which is delivered to the left atrial appendage by a transcatheter approach, was deployed successfully in 97.5% of all 16,048 patients enrolled in the registry. In the 398 cases without successful deployment, the anatomy was not conducive in nearly 70%. Other reasons included failure to meet device-release criteria and change in patient condition.
The outcomes of interest at 45 days were ischemic strokes, systemic emboli, device-related thrombi, device embolization, and bleeding. The primary endpoints at 2 years will be strokes and thrombotic events.
For stroke, the incidence within 45 days was 0.39%. About 25% of the strokes were hemorrhagic and the remainder were ischemic. There was 1 systemic embolism (0.01%), 5 device embolizations (0.03%), and 30 device-related thrombotic events (0.24%). Major bleeding occurred in 508 patients (3.55%).
For context, Dr. Kapadia compared these results to those observed in the PINNACLE FLX trial, which was a nonrandomized but prospective study of the Watchman FLX published about 1 year ago. In PINNACLE FLX, the enrollment was open to patients indicated for oral anticoagulation but who had an appropriate rationale for seeking a nonpharmacological alternative.
Taken from different studies, the outcomes at 45 days should not be construed as a direct comparison, but the similarity of the results can be considered reassuring, according to Dr. Kapadia.
For the composite safety endpoint of all-cause death, ischemic stroke, systemic embolism, or implantation-related events requiring intervention, the rates in SURPASS (0.4%) and PINNACLE FLX (0.5%) were nearly identical. Device leak rates (82.0% vs. 82.8%), stroke rates (0.4% vs. 0.7%), and all-cause death rates (0.9% vs. 0.5%) were also similar.
The similarity of the SURPASS and PINNACLE FLX data provides another level of reassurance.
“The SURPASS registry confirms the safety of the Watchman Flex in the real-world experience when the device is being used by many different operators in a large patient population,” Dr. Kapadia said in an interview.
In “appropriately selected patients,” the SURPASS data confirm that the Watchman FLX device “provides a safe and effective treatment option,” he added.
Relative to the PINNACLE FLX study, which enrolled 400 patients, it is noteworthy that the median age in SURPASS was older (76 vs. 73.8 years), a potential disadvantage in demonstrating comparable safety. The proportion of non-White patients was similar (6.7% vs. 6.3%). SURPASS had a higher proportion of women (40% vs. 35.5%).
The SURPASS data are credible, according to Vivek Y. Reddy, MD, director of cardiac arrhythmia services, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
“While there are certainly limitations to registry data, I do feel pretty confident that these procedural complication and success rates [in SURPASS] do indeed reflect reality,” said Dr. Reddy, who was a coauthor of the PINNACLE FLX trial. In general, the SURPASS data “mirror most of our clinical experiences in routine clinical practice.”
With these registry data backing up multiple clinical studies, Dr. Reddy concluded, “I do believe that it is fair to say that Watchman-FLX implantation is a quite safe procedure.”
Dr. Kapadia reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Reddy reported a financial relationship with Boston Scientific.
FROM CRT 2022
Guidance seeks to improve statin treatment adherence
International experts have created recommendations on ways to improve adherence to statin therapy by offering doctors guidance on how to distinguish between true side effects of statins and those arising due to patients’ expectations of side effects.
A position paper from the International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP), a group of over 70 experts worldwide, provides a step-by-step approach to diagnosing and managing symptoms, such as muscle aches, and encourages patients to continue the statin therapy they have been prescribed.
The authors described in their paper, published in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia, and Muscle, how statins are among the most commonly prescribed drugs globally, with “strong and unambiguous evidence” that statin treatment makes a significant difference in preventing cardiovascular disease and dying from it.
They said how, although a recent meta-analysis showed the prevalence of statin intolerance is less than 10%, “as many as 1 in 2 patients stop taking statins, reduce the dose, or take them irregularly because they believe they are responsible for side effects.”
In addition to misattribution of aches and pains, a substantial proportion of statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS) result from the action of taking medicines and the expectation that medicines cause side effects. A systematic review of trials estimated that between 38% and 78% of SAMS-related statin intolerance could be attributed to expectation alone.
Nocebo/drucebo effect
President of the ILEP, Professor Maciej Banach, of the Medical University of Lodz and the University of Zielona Góra, both in Poland, who originated these recommendations, said: “There is an enormous worldwide problem with diagnosing statin intolerance correctly. In addition, we know that most diagnosed statin side effects should not, in fact, be attributed to statin therapy.”
He highlighted how as much as 70% of statin side effect symptoms may be due to a psychological phenomenon called the “nocebo” or “drucebo” effect.
“The ‘nocebo/drucebo’ effect is when patients’ expectations that they will experience side effects from the statins result in them actually experiencing these symptoms,” Professor Banach explained. Knowledge gained from the internet, leaflets, friends and family, and other sources, for example, about the most common side effects – muscle pain and liver complaints – can “result in them discontinuing their therapy and, therefore, increasing their risk of heart problems, stroke, and death,” he cautioned.
First author of the paper, Dr. Peter Penson, a reader in Cardiovascular Pharmacology at Liverpool John Moores University, England, said “the benefits of statins are not seen immediately by patients, whilst the associated adverse effects are more tangible, and so many patients stop taking statins, thereby putting themselves at risk of serious illness or death.”
A practical evidence-based guide
The authors expressed hope that their recommendations would help doctors improve patient-centered care for those patients at risk of cardiovascular disease and help these patients understand the reason for their treatment, the benefits, including that statins may prolong their lives, and the potential harms, thus enabling the patient to “make a fully informed decision about commencing and continuing therapy.”
The recommendations include:
- That health care professionals should consider the nocebo/drucebo effect when they first prescribe statins and provide information to patients about the rationale and benefits of the therapy
- The Personalized Lipid Intervention Plan (PLIP) should be used to help this process. It estimates the patient’s 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease with and without statin therapy, as well as providing clear information on adverse side effects, including that muscle symptoms are common but rarely caused by statins
- How to effectively diagnose statin intolerance and exclude nocebo/drucebo effect
- Routine follow-up to check the safety and efficacy of the therapy is recommended, and strategies for managing patients with complete statin intolerance are provided, within the recommendations. Also offered is advice about improving adherence to statin therapy and suggestions for the identification and management of the “relatively small number of patients who have true statin intolerance.”
Dr. Penson emphasized how this was the first paper to deal explicitly with the nocebo/drucebo effect and offers “practical and evidence-based suggestions” to help support individuals who are at risk of cardiovascular disease but who experience adverse effects attributable to their medicines. He added how the PLIP summarizes important lifestyle advice to help patients reduce their risk of heart attacks and strokes and also discusses the evidence for non-statin drugs that can be used to lower cholesterol.
Dr. Penson pointed out how “the vast majority of patients can take statins safely and that the benefits greatly outweigh the potential risk of side effects” and, therefore, an individual’s risk of heart problems, stroke, and death, can be reduced.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
International experts have created recommendations on ways to improve adherence to statin therapy by offering doctors guidance on how to distinguish between true side effects of statins and those arising due to patients’ expectations of side effects.
A position paper from the International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP), a group of over 70 experts worldwide, provides a step-by-step approach to diagnosing and managing symptoms, such as muscle aches, and encourages patients to continue the statin therapy they have been prescribed.
The authors described in their paper, published in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia, and Muscle, how statins are among the most commonly prescribed drugs globally, with “strong and unambiguous evidence” that statin treatment makes a significant difference in preventing cardiovascular disease and dying from it.
They said how, although a recent meta-analysis showed the prevalence of statin intolerance is less than 10%, “as many as 1 in 2 patients stop taking statins, reduce the dose, or take them irregularly because they believe they are responsible for side effects.”
In addition to misattribution of aches and pains, a substantial proportion of statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS) result from the action of taking medicines and the expectation that medicines cause side effects. A systematic review of trials estimated that between 38% and 78% of SAMS-related statin intolerance could be attributed to expectation alone.
Nocebo/drucebo effect
President of the ILEP, Professor Maciej Banach, of the Medical University of Lodz and the University of Zielona Góra, both in Poland, who originated these recommendations, said: “There is an enormous worldwide problem with diagnosing statin intolerance correctly. In addition, we know that most diagnosed statin side effects should not, in fact, be attributed to statin therapy.”
He highlighted how as much as 70% of statin side effect symptoms may be due to a psychological phenomenon called the “nocebo” or “drucebo” effect.
“The ‘nocebo/drucebo’ effect is when patients’ expectations that they will experience side effects from the statins result in them actually experiencing these symptoms,” Professor Banach explained. Knowledge gained from the internet, leaflets, friends and family, and other sources, for example, about the most common side effects – muscle pain and liver complaints – can “result in them discontinuing their therapy and, therefore, increasing their risk of heart problems, stroke, and death,” he cautioned.
First author of the paper, Dr. Peter Penson, a reader in Cardiovascular Pharmacology at Liverpool John Moores University, England, said “the benefits of statins are not seen immediately by patients, whilst the associated adverse effects are more tangible, and so many patients stop taking statins, thereby putting themselves at risk of serious illness or death.”
A practical evidence-based guide
The authors expressed hope that their recommendations would help doctors improve patient-centered care for those patients at risk of cardiovascular disease and help these patients understand the reason for their treatment, the benefits, including that statins may prolong their lives, and the potential harms, thus enabling the patient to “make a fully informed decision about commencing and continuing therapy.”
The recommendations include:
- That health care professionals should consider the nocebo/drucebo effect when they first prescribe statins and provide information to patients about the rationale and benefits of the therapy
- The Personalized Lipid Intervention Plan (PLIP) should be used to help this process. It estimates the patient’s 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease with and without statin therapy, as well as providing clear information on adverse side effects, including that muscle symptoms are common but rarely caused by statins
- How to effectively diagnose statin intolerance and exclude nocebo/drucebo effect
- Routine follow-up to check the safety and efficacy of the therapy is recommended, and strategies for managing patients with complete statin intolerance are provided, within the recommendations. Also offered is advice about improving adherence to statin therapy and suggestions for the identification and management of the “relatively small number of patients who have true statin intolerance.”
Dr. Penson emphasized how this was the first paper to deal explicitly with the nocebo/drucebo effect and offers “practical and evidence-based suggestions” to help support individuals who are at risk of cardiovascular disease but who experience adverse effects attributable to their medicines. He added how the PLIP summarizes important lifestyle advice to help patients reduce their risk of heart attacks and strokes and also discusses the evidence for non-statin drugs that can be used to lower cholesterol.
Dr. Penson pointed out how “the vast majority of patients can take statins safely and that the benefits greatly outweigh the potential risk of side effects” and, therefore, an individual’s risk of heart problems, stroke, and death, can be reduced.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
International experts have created recommendations on ways to improve adherence to statin therapy by offering doctors guidance on how to distinguish between true side effects of statins and those arising due to patients’ expectations of side effects.
A position paper from the International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP), a group of over 70 experts worldwide, provides a step-by-step approach to diagnosing and managing symptoms, such as muscle aches, and encourages patients to continue the statin therapy they have been prescribed.
The authors described in their paper, published in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia, and Muscle, how statins are among the most commonly prescribed drugs globally, with “strong and unambiguous evidence” that statin treatment makes a significant difference in preventing cardiovascular disease and dying from it.
They said how, although a recent meta-analysis showed the prevalence of statin intolerance is less than 10%, “as many as 1 in 2 patients stop taking statins, reduce the dose, or take them irregularly because they believe they are responsible for side effects.”
In addition to misattribution of aches and pains, a substantial proportion of statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS) result from the action of taking medicines and the expectation that medicines cause side effects. A systematic review of trials estimated that between 38% and 78% of SAMS-related statin intolerance could be attributed to expectation alone.
Nocebo/drucebo effect
President of the ILEP, Professor Maciej Banach, of the Medical University of Lodz and the University of Zielona Góra, both in Poland, who originated these recommendations, said: “There is an enormous worldwide problem with diagnosing statin intolerance correctly. In addition, we know that most diagnosed statin side effects should not, in fact, be attributed to statin therapy.”
He highlighted how as much as 70% of statin side effect symptoms may be due to a psychological phenomenon called the “nocebo” or “drucebo” effect.
“The ‘nocebo/drucebo’ effect is when patients’ expectations that they will experience side effects from the statins result in them actually experiencing these symptoms,” Professor Banach explained. Knowledge gained from the internet, leaflets, friends and family, and other sources, for example, about the most common side effects – muscle pain and liver complaints – can “result in them discontinuing their therapy and, therefore, increasing their risk of heart problems, stroke, and death,” he cautioned.
First author of the paper, Dr. Peter Penson, a reader in Cardiovascular Pharmacology at Liverpool John Moores University, England, said “the benefits of statins are not seen immediately by patients, whilst the associated adverse effects are more tangible, and so many patients stop taking statins, thereby putting themselves at risk of serious illness or death.”
A practical evidence-based guide
The authors expressed hope that their recommendations would help doctors improve patient-centered care for those patients at risk of cardiovascular disease and help these patients understand the reason for their treatment, the benefits, including that statins may prolong their lives, and the potential harms, thus enabling the patient to “make a fully informed decision about commencing and continuing therapy.”
The recommendations include:
- That health care professionals should consider the nocebo/drucebo effect when they first prescribe statins and provide information to patients about the rationale and benefits of the therapy
- The Personalized Lipid Intervention Plan (PLIP) should be used to help this process. It estimates the patient’s 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease with and without statin therapy, as well as providing clear information on adverse side effects, including that muscle symptoms are common but rarely caused by statins
- How to effectively diagnose statin intolerance and exclude nocebo/drucebo effect
- Routine follow-up to check the safety and efficacy of the therapy is recommended, and strategies for managing patients with complete statin intolerance are provided, within the recommendations. Also offered is advice about improving adherence to statin therapy and suggestions for the identification and management of the “relatively small number of patients who have true statin intolerance.”
Dr. Penson emphasized how this was the first paper to deal explicitly with the nocebo/drucebo effect and offers “practical and evidence-based suggestions” to help support individuals who are at risk of cardiovascular disease but who experience adverse effects attributable to their medicines. He added how the PLIP summarizes important lifestyle advice to help patients reduce their risk of heart attacks and strokes and also discusses the evidence for non-statin drugs that can be used to lower cholesterol.
Dr. Penson pointed out how “the vast majority of patients can take statins safely and that the benefits greatly outweigh the potential risk of side effects” and, therefore, an individual’s risk of heart problems, stroke, and death, can be reduced.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CACHEXIA, SARCOPENIA, AND MUSCLE
Big missed opportunities for BP control in premenopausal women
A new report shows considerable gaps in the awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in premenopausal women in the United States, with a key driver being regular access to health care.
In a nationally representative sample of women ages 35-54 with no prior cardiovascular disease, the prevalence of hypertension increased 8% from an estimated 15.2 million women between 2011 and 2014 to 16.4 million women between 2015 and 2018.
What’s more, the percentage of women with controlled hypertension dropped over the two time periods from 55% to 50%, which is well below the government’s Million Hearts target of 70%.
Missed opportunities for hypertension control in these premenopausal women were a lack of awareness of their hypertension in 23%, ineffective treatment in 34%, and a lack of health care access in 43%; increasing to 51% in non-Hispanic Black patients and 56% in Hispanic patients.
Notably, lack of health care access affected an estimated 3.1 million women (45%) in 2011-2014 and 3.5 million women (43%) in 2015-2018.
Equally stubborn over the two time periods was the lack of effective treatment, affecting 2.1 million (31%) versus 2.8 million (34%) women, and lack of awareness, affecting 1.6 million (24%) versus 1.9 million (23%) women.
“There’s been no improvement over the past decade, and there is evidence of race/ethnic disparities,” study author Susan Hennessy, PhD, said at the recent Epidemiology, Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health (EPI|Lifestyle) 2022 conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The prevalence of uncontrolled hypertension among non-Hispanic Whites was less than that of the U.S. population, at 44%, and most of the missed opportunities were due to uncontrolled blood pressure (BP), noted Dr. Hennessy, a researcher with the University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine.
However, the uncontrolled prevalence was 54% in non-Hispanic Black women and 66% in Hispanic women. “In both of these subgroups, over half of the missed opportunities occur because these women have no regular access to health care,” she said.
In women who identified as “other,” which includes non-Hispanic Asian and mixed-race populations, the uncontrolled prevalence reached 70%, and the biggest missed opportunity was in those who were untreated.
Raising awareness, empowering women, and delivery of guideline-concordant care will help premenopausal women gain control of their blood pressure, Dr. Hennessy said. “But underpinning all of this is ensuring equitable health care access, because if we fail to get women into the system, then we have no opportunity to help them lower their blood pressure.”
She reminded the audience that cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the number one killer of women in the United States and that CVD risk, mediated through hypertension, increases after menopause. Thus, managing hypertension prior to this life event is an important element of primary prevention of CVD and should be a priority.
Session moderator Sadiya S. Khan, MD, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, told this news organization that the findings should raise “alarm and concern that hypertension is not just a disease of the old but very prevalent in younger women, particularly around the time of pregnancy. And this is a clear driver of maternal morbidity and mortality as well.”
“This idea that patients should ‘Know Your Numbers’ is really important, and we talk a lot about that for hypertension, but if you don’t have a doctor, if you don’t have someone to go to, it’s very hard to know or understand what your numbers mean,” she said. “I think that’s really the main message.”
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Hennessy said there’s no simple solution to the problem, given that some women are not even in the system, whereas others are not being treated effectively, but that increasing opportunities to screen BP would be a start. That could be through community programs, similar to the Barbershop Hypertension trial, or by making BP devices available for home monitoring.
“Again, this is about empowering ourselves to take some level of control, but, as a system, we have to be able to make it equitable for everyone and make sure they have the right equipment, the right cuff size,” she said. “The disparities arise because of the social determinants of health, so if these women are struggling to put food on the table, they aren’t going to be able to afford a blood pressure cuff.”
During a discussion of the findings, audience members noted that the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data used for the analysis were somewhat dated. Dr. Hennessy also pointed out that NHANES blood pressure is measured up to three times during a single visit, which differs from clinical practice, and that responses were based on self-report and thus subject to recall bias.
The sample included 3,343 women aged 35-54 years with no prior cardiovascular disease, representing an estimated 31.6 million American women. Hypertension was defined by a systolic BP of at least 140 mm Hg or a diastolic BP of at least 90 mm Hg or current BP medication use.
The authors and Dr. Khan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new report shows considerable gaps in the awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in premenopausal women in the United States, with a key driver being regular access to health care.
In a nationally representative sample of women ages 35-54 with no prior cardiovascular disease, the prevalence of hypertension increased 8% from an estimated 15.2 million women between 2011 and 2014 to 16.4 million women between 2015 and 2018.
What’s more, the percentage of women with controlled hypertension dropped over the two time periods from 55% to 50%, which is well below the government’s Million Hearts target of 70%.
Missed opportunities for hypertension control in these premenopausal women were a lack of awareness of their hypertension in 23%, ineffective treatment in 34%, and a lack of health care access in 43%; increasing to 51% in non-Hispanic Black patients and 56% in Hispanic patients.
Notably, lack of health care access affected an estimated 3.1 million women (45%) in 2011-2014 and 3.5 million women (43%) in 2015-2018.
Equally stubborn over the two time periods was the lack of effective treatment, affecting 2.1 million (31%) versus 2.8 million (34%) women, and lack of awareness, affecting 1.6 million (24%) versus 1.9 million (23%) women.
“There’s been no improvement over the past decade, and there is evidence of race/ethnic disparities,” study author Susan Hennessy, PhD, said at the recent Epidemiology, Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health (EPI|Lifestyle) 2022 conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The prevalence of uncontrolled hypertension among non-Hispanic Whites was less than that of the U.S. population, at 44%, and most of the missed opportunities were due to uncontrolled blood pressure (BP), noted Dr. Hennessy, a researcher with the University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine.
However, the uncontrolled prevalence was 54% in non-Hispanic Black women and 66% in Hispanic women. “In both of these subgroups, over half of the missed opportunities occur because these women have no regular access to health care,” she said.
In women who identified as “other,” which includes non-Hispanic Asian and mixed-race populations, the uncontrolled prevalence reached 70%, and the biggest missed opportunity was in those who were untreated.
Raising awareness, empowering women, and delivery of guideline-concordant care will help premenopausal women gain control of their blood pressure, Dr. Hennessy said. “But underpinning all of this is ensuring equitable health care access, because if we fail to get women into the system, then we have no opportunity to help them lower their blood pressure.”
She reminded the audience that cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the number one killer of women in the United States and that CVD risk, mediated through hypertension, increases after menopause. Thus, managing hypertension prior to this life event is an important element of primary prevention of CVD and should be a priority.
Session moderator Sadiya S. Khan, MD, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, told this news organization that the findings should raise “alarm and concern that hypertension is not just a disease of the old but very prevalent in younger women, particularly around the time of pregnancy. And this is a clear driver of maternal morbidity and mortality as well.”
“This idea that patients should ‘Know Your Numbers’ is really important, and we talk a lot about that for hypertension, but if you don’t have a doctor, if you don’t have someone to go to, it’s very hard to know or understand what your numbers mean,” she said. “I think that’s really the main message.”
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Hennessy said there’s no simple solution to the problem, given that some women are not even in the system, whereas others are not being treated effectively, but that increasing opportunities to screen BP would be a start. That could be through community programs, similar to the Barbershop Hypertension trial, or by making BP devices available for home monitoring.
“Again, this is about empowering ourselves to take some level of control, but, as a system, we have to be able to make it equitable for everyone and make sure they have the right equipment, the right cuff size,” she said. “The disparities arise because of the social determinants of health, so if these women are struggling to put food on the table, they aren’t going to be able to afford a blood pressure cuff.”
During a discussion of the findings, audience members noted that the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data used for the analysis were somewhat dated. Dr. Hennessy also pointed out that NHANES blood pressure is measured up to three times during a single visit, which differs from clinical practice, and that responses were based on self-report and thus subject to recall bias.
The sample included 3,343 women aged 35-54 years with no prior cardiovascular disease, representing an estimated 31.6 million American women. Hypertension was defined by a systolic BP of at least 140 mm Hg or a diastolic BP of at least 90 mm Hg or current BP medication use.
The authors and Dr. Khan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new report shows considerable gaps in the awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in premenopausal women in the United States, with a key driver being regular access to health care.
In a nationally representative sample of women ages 35-54 with no prior cardiovascular disease, the prevalence of hypertension increased 8% from an estimated 15.2 million women between 2011 and 2014 to 16.4 million women between 2015 and 2018.
What’s more, the percentage of women with controlled hypertension dropped over the two time periods from 55% to 50%, which is well below the government’s Million Hearts target of 70%.
Missed opportunities for hypertension control in these premenopausal women were a lack of awareness of their hypertension in 23%, ineffective treatment in 34%, and a lack of health care access in 43%; increasing to 51% in non-Hispanic Black patients and 56% in Hispanic patients.
Notably, lack of health care access affected an estimated 3.1 million women (45%) in 2011-2014 and 3.5 million women (43%) in 2015-2018.
Equally stubborn over the two time periods was the lack of effective treatment, affecting 2.1 million (31%) versus 2.8 million (34%) women, and lack of awareness, affecting 1.6 million (24%) versus 1.9 million (23%) women.
“There’s been no improvement over the past decade, and there is evidence of race/ethnic disparities,” study author Susan Hennessy, PhD, said at the recent Epidemiology, Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health (EPI|Lifestyle) 2022 conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The prevalence of uncontrolled hypertension among non-Hispanic Whites was less than that of the U.S. population, at 44%, and most of the missed opportunities were due to uncontrolled blood pressure (BP), noted Dr. Hennessy, a researcher with the University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine.
However, the uncontrolled prevalence was 54% in non-Hispanic Black women and 66% in Hispanic women. “In both of these subgroups, over half of the missed opportunities occur because these women have no regular access to health care,” she said.
In women who identified as “other,” which includes non-Hispanic Asian and mixed-race populations, the uncontrolled prevalence reached 70%, and the biggest missed opportunity was in those who were untreated.
Raising awareness, empowering women, and delivery of guideline-concordant care will help premenopausal women gain control of their blood pressure, Dr. Hennessy said. “But underpinning all of this is ensuring equitable health care access, because if we fail to get women into the system, then we have no opportunity to help them lower their blood pressure.”
She reminded the audience that cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the number one killer of women in the United States and that CVD risk, mediated through hypertension, increases after menopause. Thus, managing hypertension prior to this life event is an important element of primary prevention of CVD and should be a priority.
Session moderator Sadiya S. Khan, MD, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, told this news organization that the findings should raise “alarm and concern that hypertension is not just a disease of the old but very prevalent in younger women, particularly around the time of pregnancy. And this is a clear driver of maternal morbidity and mortality as well.”
“This idea that patients should ‘Know Your Numbers’ is really important, and we talk a lot about that for hypertension, but if you don’t have a doctor, if you don’t have someone to go to, it’s very hard to know or understand what your numbers mean,” she said. “I think that’s really the main message.”
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Hennessy said there’s no simple solution to the problem, given that some women are not even in the system, whereas others are not being treated effectively, but that increasing opportunities to screen BP would be a start. That could be through community programs, similar to the Barbershop Hypertension trial, or by making BP devices available for home monitoring.
“Again, this is about empowering ourselves to take some level of control, but, as a system, we have to be able to make it equitable for everyone and make sure they have the right equipment, the right cuff size,” she said. “The disparities arise because of the social determinants of health, so if these women are struggling to put food on the table, they aren’t going to be able to afford a blood pressure cuff.”
During a discussion of the findings, audience members noted that the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data used for the analysis were somewhat dated. Dr. Hennessy also pointed out that NHANES blood pressure is measured up to three times during a single visit, which differs from clinical practice, and that responses were based on self-report and thus subject to recall bias.
The sample included 3,343 women aged 35-54 years with no prior cardiovascular disease, representing an estimated 31.6 million American women. Hypertension was defined by a systolic BP of at least 140 mm Hg or a diastolic BP of at least 90 mm Hg or current BP medication use.
The authors and Dr. Khan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiologist pleads guilty to abusive sexual contact
John Giacomini, MD, has pleaded guilty to one count of abusive sexual contact of a female physician he was supervising, the Department of Justice (DOJ) has announced.
Dr. Giacomini, 73, of Atherton, California, had practiced medicine and cardiology for more than 30 years and served as chief of the cardiology section at the VA Hospital in Palo Alto from 1985 to 2018.
According to the statement from DOJ, starting in the fall of 2017, Dr. Giacomini repeatedly subjected a subordinate doctor to unwanted and unwelcome sexual contact, which included hugging, kissing, and intimate touching while on VA premises.
The victim explicitly told Dr. Giacomini she was not interested in a romantic or sexual relationship with him and forcibly resisted his repeated attempts to kiss her, the statement notes.
The abuse continued, culminating in December 2017 with the incident of abusive sexual contact, the DOJ says.
Afterward, the victim resigned from her position at the VA, citing Dr. Giacomini’s behavior as her principal reason for leaving.
“As a federal employee for well over 30 years, [Dr.] Giacomini was trained throughout his career on the prevention of workplace sexual assault and sexual harassment,” the DOJ says.
“As a supervisor and manager, [Dr.] Giacomini had an obligation to the VA and to his subordinates to prevent workplace sexual harassment and disclose any harassing behavior of which he became aware. He failed to do this,” the DOJ says.
A federal grand jury indicted Dr. Giacomini in March 2020, charging him with one count of abusive sexual contact. Dr. Giacomini has now pleaded guilty to the charge, a felony.
Sentencing is scheduled for July 12. Dr. Giacomini faces a maximum sentence of 2 years in prison, a fine of $250,000, restitution, and supervised release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
John Giacomini, MD, has pleaded guilty to one count of abusive sexual contact of a female physician he was supervising, the Department of Justice (DOJ) has announced.
Dr. Giacomini, 73, of Atherton, California, had practiced medicine and cardiology for more than 30 years and served as chief of the cardiology section at the VA Hospital in Palo Alto from 1985 to 2018.
According to the statement from DOJ, starting in the fall of 2017, Dr. Giacomini repeatedly subjected a subordinate doctor to unwanted and unwelcome sexual contact, which included hugging, kissing, and intimate touching while on VA premises.
The victim explicitly told Dr. Giacomini she was not interested in a romantic or sexual relationship with him and forcibly resisted his repeated attempts to kiss her, the statement notes.
The abuse continued, culminating in December 2017 with the incident of abusive sexual contact, the DOJ says.
Afterward, the victim resigned from her position at the VA, citing Dr. Giacomini’s behavior as her principal reason for leaving.
“As a federal employee for well over 30 years, [Dr.] Giacomini was trained throughout his career on the prevention of workplace sexual assault and sexual harassment,” the DOJ says.
“As a supervisor and manager, [Dr.] Giacomini had an obligation to the VA and to his subordinates to prevent workplace sexual harassment and disclose any harassing behavior of which he became aware. He failed to do this,” the DOJ says.
A federal grand jury indicted Dr. Giacomini in March 2020, charging him with one count of abusive sexual contact. Dr. Giacomini has now pleaded guilty to the charge, a felony.
Sentencing is scheduled for July 12. Dr. Giacomini faces a maximum sentence of 2 years in prison, a fine of $250,000, restitution, and supervised release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
John Giacomini, MD, has pleaded guilty to one count of abusive sexual contact of a female physician he was supervising, the Department of Justice (DOJ) has announced.
Dr. Giacomini, 73, of Atherton, California, had practiced medicine and cardiology for more than 30 years and served as chief of the cardiology section at the VA Hospital in Palo Alto from 1985 to 2018.
According to the statement from DOJ, starting in the fall of 2017, Dr. Giacomini repeatedly subjected a subordinate doctor to unwanted and unwelcome sexual contact, which included hugging, kissing, and intimate touching while on VA premises.
The victim explicitly told Dr. Giacomini she was not interested in a romantic or sexual relationship with him and forcibly resisted his repeated attempts to kiss her, the statement notes.
The abuse continued, culminating in December 2017 with the incident of abusive sexual contact, the DOJ says.
Afterward, the victim resigned from her position at the VA, citing Dr. Giacomini’s behavior as her principal reason for leaving.
“As a federal employee for well over 30 years, [Dr.] Giacomini was trained throughout his career on the prevention of workplace sexual assault and sexual harassment,” the DOJ says.
“As a supervisor and manager, [Dr.] Giacomini had an obligation to the VA and to his subordinates to prevent workplace sexual harassment and disclose any harassing behavior of which he became aware. He failed to do this,” the DOJ says.
A federal grand jury indicted Dr. Giacomini in March 2020, charging him with one count of abusive sexual contact. Dr. Giacomini has now pleaded guilty to the charge, a felony.
Sentencing is scheduled for July 12. Dr. Giacomini faces a maximum sentence of 2 years in prison, a fine of $250,000, restitution, and supervised release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Resistance exercise may be best workout for a good night’s sleep
CHICAGO – A randomized trial suggests resistance exercise promotes better sleep than other workouts among inactive adults, particularly those who are poor sleepers.
“We thought resistance exercise would be somewhere in the same neighborhood as aerobic exercise or that maybe combined exercise would be a little bit better but, no, it was consistently resistance exercise, on its own, that seemed to show the most benefits across the board,” Angelique Brellenthin, PhD, told this news organization.
The results were presented at the recent Epidemiology, Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health meeting sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Even before the pandemic and bedtime “doom scrolling” took hold, research showed that a third of Americans regularly get less than 7 hours of sleep. The AHA recommends aerobic exercise to improve sleep and promote cardiovascular health, yet little is known on how it compares with other types of exercise in the general population, she said.
Dr. Brellenthin and coinvestigator Duck-chul Lee, PhD, both of Iowa State University in Ames, recruited 406 inactive adults, aged 35-70 years, who had obesity or overweight (mean body mass index, 31.2 kg/m2) and had elevated or stage 1 hypertension and randomly assigned them to no exercise or 60 minutes of supervised aerobic, resistance, or combination exercise three times per week for 12 months.
The aerobic exercise group could choose among treadmills, upright or recumbent bikes, and ellipticals, and the participants had their heart rate monitored to ensure they were continuously getting moderate- to vigorous-intensity exercise.
The resistance exercise group performed three sets of 8-16 repetitions at 50%-80% of their one-rep maximum on 12 resistance machines: a leg press, chest press, lat pulldown, leg curl, leg extension, biceps curl, triceps pushdown, shoulder press, abdominal crunch, lower back extension, torso rotation, and hip abduction.
The combination group did 30 minutes of aerobic exercise at moderate to vigorous intensity, and then two sets of 8-16 repetitions of resistance exercise on 9 machines instead of 12.
Exercise adherence over the year was 84%, 77%, and 85%, respectively.
Participants also completed the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) at baseline and 12 months. Among the 386 participants (53% women) with evaluable data, 35% had poor-quality sleep, as indicated by a global PSQI score of more than 5, and 42% regularly slept less than 7 hours per night.
In adjusted analyses, sleep duration at 12 months, on average, increased by 13 minutes in the resistance-exercise group (P = .009), decreased by 0.6 minute in the aerobic-exercise group, and increased by 2 minutes in the combined-exercise group and by 4 minutes in the control group.
Among participants who got less than 7 hours of sleep at baseline, however, sleep duration increased by 40 minutes (P < .0001), compared with increases of 23 minutes in the aerobic group, 17 minutes in the combined group, and 15 minutes in the control group.
Overall sleep efficiency, or the ratio of total sleep time to time in bed, improved in the resistance (P = .0005) and combined (P = .03) exercise groups, but not in the aerobic or control groups.
Sleep latency, or the time needed to fall asleep, decreased by 3 minutes in the resistance-exercise group, with no notable changes in the other groups.
Sleep quality and the number of sleep disturbances improved in all groups, including the control group. This could be due to simply being part of a health intervention, which included a month of lifestyle education classes, Dr. Brellenthin suggested.
It’s unclear why the aerobic-exercise group didn’t show greater gains, given the wealth of research showing it improves sleep, she said, but it had fewer poor sleepers at baseline than the resistance group (33% vs. 42%). “So it may be that people who were already getting good sleep didn’t have much room to improve.”
Among the poor-quality sleepers at baseline, resistance exercise significantly improved sleep quality (-2.4 vs. -1.0 points; P = .009) and duration (+36 vs. +3 minutes; P = .02), compared with the control group. It also improved sleep efficiency by 9.0%, compared with 0.9% in the control group (P = .002) and 8.0% for the combined-exercise group (P = .01).
“For a lot of people who know their sleep could be a bit better, this could be a place to start without resorting to medications, if they wanted to focus on a lifestyle intervention,” Dr. Brellenthin said.
It’s not fully understood how resistance exercise improves sleep, but it might contribute to better overall mental health and it might enhance the synthesis and release of certain hormones, such as testosterone and human growth hormone, which are associated with better sleep, Dr. Brellenthin said. Another hypothesis is that it causes direct microscopic damage to muscle tissue, forcing that tissue to adapt and grow over time. “So potentially that microscopic damage could provide that extra signal boost to the brain to replenish and repair, and get this person sleep.”
The study was limited by the use of self-reported sleep outcomes and a lack of detailed information on sleep medications, although 81% of participants reported taking no such medications.
The research was supported by a National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant to Dr. Lee. Dr. Brellenthin reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – A randomized trial suggests resistance exercise promotes better sleep than other workouts among inactive adults, particularly those who are poor sleepers.
“We thought resistance exercise would be somewhere in the same neighborhood as aerobic exercise or that maybe combined exercise would be a little bit better but, no, it was consistently resistance exercise, on its own, that seemed to show the most benefits across the board,” Angelique Brellenthin, PhD, told this news organization.
The results were presented at the recent Epidemiology, Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health meeting sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Even before the pandemic and bedtime “doom scrolling” took hold, research showed that a third of Americans regularly get less than 7 hours of sleep. The AHA recommends aerobic exercise to improve sleep and promote cardiovascular health, yet little is known on how it compares with other types of exercise in the general population, she said.
Dr. Brellenthin and coinvestigator Duck-chul Lee, PhD, both of Iowa State University in Ames, recruited 406 inactive adults, aged 35-70 years, who had obesity or overweight (mean body mass index, 31.2 kg/m2) and had elevated or stage 1 hypertension and randomly assigned them to no exercise or 60 minutes of supervised aerobic, resistance, or combination exercise three times per week for 12 months.
The aerobic exercise group could choose among treadmills, upright or recumbent bikes, and ellipticals, and the participants had their heart rate monitored to ensure they were continuously getting moderate- to vigorous-intensity exercise.
The resistance exercise group performed three sets of 8-16 repetitions at 50%-80% of their one-rep maximum on 12 resistance machines: a leg press, chest press, lat pulldown, leg curl, leg extension, biceps curl, triceps pushdown, shoulder press, abdominal crunch, lower back extension, torso rotation, and hip abduction.
The combination group did 30 minutes of aerobic exercise at moderate to vigorous intensity, and then two sets of 8-16 repetitions of resistance exercise on 9 machines instead of 12.
Exercise adherence over the year was 84%, 77%, and 85%, respectively.
Participants also completed the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) at baseline and 12 months. Among the 386 participants (53% women) with evaluable data, 35% had poor-quality sleep, as indicated by a global PSQI score of more than 5, and 42% regularly slept less than 7 hours per night.
In adjusted analyses, sleep duration at 12 months, on average, increased by 13 minutes in the resistance-exercise group (P = .009), decreased by 0.6 minute in the aerobic-exercise group, and increased by 2 minutes in the combined-exercise group and by 4 minutes in the control group.
Among participants who got less than 7 hours of sleep at baseline, however, sleep duration increased by 40 minutes (P < .0001), compared with increases of 23 minutes in the aerobic group, 17 minutes in the combined group, and 15 minutes in the control group.
Overall sleep efficiency, or the ratio of total sleep time to time in bed, improved in the resistance (P = .0005) and combined (P = .03) exercise groups, but not in the aerobic or control groups.
Sleep latency, or the time needed to fall asleep, decreased by 3 minutes in the resistance-exercise group, with no notable changes in the other groups.
Sleep quality and the number of sleep disturbances improved in all groups, including the control group. This could be due to simply being part of a health intervention, which included a month of lifestyle education classes, Dr. Brellenthin suggested.
It’s unclear why the aerobic-exercise group didn’t show greater gains, given the wealth of research showing it improves sleep, she said, but it had fewer poor sleepers at baseline than the resistance group (33% vs. 42%). “So it may be that people who were already getting good sleep didn’t have much room to improve.”
Among the poor-quality sleepers at baseline, resistance exercise significantly improved sleep quality (-2.4 vs. -1.0 points; P = .009) and duration (+36 vs. +3 minutes; P = .02), compared with the control group. It also improved sleep efficiency by 9.0%, compared with 0.9% in the control group (P = .002) and 8.0% for the combined-exercise group (P = .01).
“For a lot of people who know their sleep could be a bit better, this could be a place to start without resorting to medications, if they wanted to focus on a lifestyle intervention,” Dr. Brellenthin said.
It’s not fully understood how resistance exercise improves sleep, but it might contribute to better overall mental health and it might enhance the synthesis and release of certain hormones, such as testosterone and human growth hormone, which are associated with better sleep, Dr. Brellenthin said. Another hypothesis is that it causes direct microscopic damage to muscle tissue, forcing that tissue to adapt and grow over time. “So potentially that microscopic damage could provide that extra signal boost to the brain to replenish and repair, and get this person sleep.”
The study was limited by the use of self-reported sleep outcomes and a lack of detailed information on sleep medications, although 81% of participants reported taking no such medications.
The research was supported by a National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant to Dr. Lee. Dr. Brellenthin reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – A randomized trial suggests resistance exercise promotes better sleep than other workouts among inactive adults, particularly those who are poor sleepers.
“We thought resistance exercise would be somewhere in the same neighborhood as aerobic exercise or that maybe combined exercise would be a little bit better but, no, it was consistently resistance exercise, on its own, that seemed to show the most benefits across the board,” Angelique Brellenthin, PhD, told this news organization.
The results were presented at the recent Epidemiology, Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health meeting sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Even before the pandemic and bedtime “doom scrolling” took hold, research showed that a third of Americans regularly get less than 7 hours of sleep. The AHA recommends aerobic exercise to improve sleep and promote cardiovascular health, yet little is known on how it compares with other types of exercise in the general population, she said.
Dr. Brellenthin and coinvestigator Duck-chul Lee, PhD, both of Iowa State University in Ames, recruited 406 inactive adults, aged 35-70 years, who had obesity or overweight (mean body mass index, 31.2 kg/m2) and had elevated or stage 1 hypertension and randomly assigned them to no exercise or 60 minutes of supervised aerobic, resistance, or combination exercise three times per week for 12 months.
The aerobic exercise group could choose among treadmills, upright or recumbent bikes, and ellipticals, and the participants had their heart rate monitored to ensure they were continuously getting moderate- to vigorous-intensity exercise.
The resistance exercise group performed three sets of 8-16 repetitions at 50%-80% of their one-rep maximum on 12 resistance machines: a leg press, chest press, lat pulldown, leg curl, leg extension, biceps curl, triceps pushdown, shoulder press, abdominal crunch, lower back extension, torso rotation, and hip abduction.
The combination group did 30 minutes of aerobic exercise at moderate to vigorous intensity, and then two sets of 8-16 repetitions of resistance exercise on 9 machines instead of 12.
Exercise adherence over the year was 84%, 77%, and 85%, respectively.
Participants also completed the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) at baseline and 12 months. Among the 386 participants (53% women) with evaluable data, 35% had poor-quality sleep, as indicated by a global PSQI score of more than 5, and 42% regularly slept less than 7 hours per night.
In adjusted analyses, sleep duration at 12 months, on average, increased by 13 minutes in the resistance-exercise group (P = .009), decreased by 0.6 minute in the aerobic-exercise group, and increased by 2 minutes in the combined-exercise group and by 4 minutes in the control group.
Among participants who got less than 7 hours of sleep at baseline, however, sleep duration increased by 40 minutes (P < .0001), compared with increases of 23 minutes in the aerobic group, 17 minutes in the combined group, and 15 minutes in the control group.
Overall sleep efficiency, or the ratio of total sleep time to time in bed, improved in the resistance (P = .0005) and combined (P = .03) exercise groups, but not in the aerobic or control groups.
Sleep latency, or the time needed to fall asleep, decreased by 3 minutes in the resistance-exercise group, with no notable changes in the other groups.
Sleep quality and the number of sleep disturbances improved in all groups, including the control group. This could be due to simply being part of a health intervention, which included a month of lifestyle education classes, Dr. Brellenthin suggested.
It’s unclear why the aerobic-exercise group didn’t show greater gains, given the wealth of research showing it improves sleep, she said, but it had fewer poor sleepers at baseline than the resistance group (33% vs. 42%). “So it may be that people who were already getting good sleep didn’t have much room to improve.”
Among the poor-quality sleepers at baseline, resistance exercise significantly improved sleep quality (-2.4 vs. -1.0 points; P = .009) and duration (+36 vs. +3 minutes; P = .02), compared with the control group. It also improved sleep efficiency by 9.0%, compared with 0.9% in the control group (P = .002) and 8.0% for the combined-exercise group (P = .01).
“For a lot of people who know their sleep could be a bit better, this could be a place to start without resorting to medications, if they wanted to focus on a lifestyle intervention,” Dr. Brellenthin said.
It’s not fully understood how resistance exercise improves sleep, but it might contribute to better overall mental health and it might enhance the synthesis and release of certain hormones, such as testosterone and human growth hormone, which are associated with better sleep, Dr. Brellenthin said. Another hypothesis is that it causes direct microscopic damage to muscle tissue, forcing that tissue to adapt and grow over time. “So potentially that microscopic damage could provide that extra signal boost to the brain to replenish and repair, and get this person sleep.”
The study was limited by the use of self-reported sleep outcomes and a lack of detailed information on sleep medications, although 81% of participants reported taking no such medications.
The research was supported by a National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant to Dr. Lee. Dr. Brellenthin reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
REPORTING FROM EPI/LIFESTYLE 2022
Biden administration’s new test-to-treat program pits pharmacists against physicians
The Biden administration’s new test-to-treat program is simple on the surface: if you feel like you may have COVID-19, go to a pharmacy, get tested, and, if positive, get treated with an antiviral medication on the spot.
One large physicians’ group is concerned that the program leaves doctors on the margins, and may put patients at risk if there are adverse effects from the medications. Pharmacists groups, on the other hand, say the program is too restrictive, according to an article by the research group Advisory Board.
Recently, the White House announced that more than 1,000 pharmacy clinics across the United States had registered to participate in the initiative, according to CNN. Ordering of the drugs is underway in many of these clinics, a White House official told the network.
Besides retail clinics in chain pharmacies, the antivirals will also be available in community health centers, long-term-care facilities, and Veterans Health Administration clinics, according to a statement from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The two antiviral pills authorized by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration include Pfizer’s Paxlovid, for people 12 and older, and Merck’s molnupiravir, for adults. Either drug has to be taken within 5 days after symptoms appear to be effective in preventing serious illness.
The need for speed is a major reason why the government chose to work with retail clinics that are more accessible than most primary care offices. However, the American Medical Association (AMA), the National Community Pharmacists Association (NCPA), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) have publicly criticized the administration’s approach.
The pharmacists’ groups are concerned that the program is limited only to pharmacies with clinics on site, thus restricting the number of pharmacies qualified to participate. Fourteen pharmacy groups, including the NCPA and the APhA, have also sent a letter to the Biden administration urging it to remove barriers to pharmacies ordering the medications.
The groups also want permission as “clinically trained medication experts” to prescribe the drugs and ensure their safe use.
The AMA on March 4 took issue with the prescribing component, saying that “the pharmacy-based clinic component of the test-to-treat plan flouts patient safety and risks significant negative health outcomes.”
In the AMA’s view, prescribing Paxlovid without a patient’s physician being present poses a risk for adverse drug interactions, as neither the nurse practitioners in retail clinics nor the pharmacists who dispense the drug have full knowledge of a patient›s medical history.
The next day, the AMA released another statement, saying it was reassured by comments from administration officials “that patients who have access to a regular source of care should contact their physician shortly after testing positive for COVID-19 to assess their treatment options.”
“Traditional doctor-only approach”
Having patients call their doctors after testing positive for COVID in a pharmacy “strikes me as unnecessary in the vast majority of cases, and it will delay treatment,” Robert Wachter, MD, professor and chair of the department of medicine at the University of California San Francisco, said in an interview. “In this case, it seems like the AMA is taking a very traditional doctor-only approach. And the world has changed. It’s much more of a team sport than an individual sport, the way it was years ago.”
Dr. Wachter said he has the utmost respect for pharmacists’ ability to screen prescriptions for adverse drug interactions. “We’re required to do medication reconciliation when patients see us,” he says. “And in many hospitals, we delegate that to pharmacists. They’re at least as good at it if not better than physicians are.”
While it’s essential to know what other medications a patient is taking, he noted, pharmacies have computer records of all the prescriptions they’ve filled for patients. In addition, pharmacies have access to complete medication histories through Surescripts, the company that enables electronic prescribing transactions between prescribers and pharmacies.
Drug interactions “not trivial”
Preeti Malani, MD, the chief health officer and a professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, told this news organization that the potential interactions between Paxlovid and some other medications are “not trivial.”
However, she said, “The really dangerous drugs are the ones for people who have had organ transplants and the like. Those aren’t individuals who are going to shop at a pharmacy.”
Besides the antirejection drugs, Dr. Wachter said, there can be serious interactions with cholesterol-lowering medications. If a person is taking Lipitor, for instance, “Someone would have to make the decision on whether it’s ok for me to stop it for a while, or to lower the dose. But I trust the pharmacist to do that as well as anybody.”
Except for these potential drug interactions with Paxlovid, the antiviral medications are “quite safe,” he said, adding that being able to treat people who test positive for COVID-19 right away is a big advantage of the test-to-treat program, considering how difficult it is for many people to get access to a doctor. That delay could mean that the antivirals are not prescribed and taken until they are no longer effective.
Both Dr. Wachter and Dr. Malani said that the widespread distribution of pharmacies and their extended hours are other big pluses, especially for people who can’t easily leave work or travel far to visit a physician.
Dr. Malani cautioned that there are still kinks to work out in the test-to-treat program. It will be a while before the retail clinics all have the antiviral drugs, and many pharmacies don’t have clinics on site.
Still, she said people can still go to their physicians to be tested, and presumably those doctors can also write antiviral prescriptions. But it’s not clear where the antivirals will be available in the near term.
“Right now, we’re playing catch-up,” Dr. Malani said. “But pharmacies are an important piece of the puzzle.”
Looking at the big picture, she said, “We know that neither vaccination nor natural infection provides long lasting immunity, and so there will be a role for antivirals in order to make this a manageable illness. And when you’re talking about millions of cases, as we were having a few months ago, the health system can’t field all those patients. So we do need a system where I can go to a pharmacy and get a test and treatment.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Biden administration’s new test-to-treat program is simple on the surface: if you feel like you may have COVID-19, go to a pharmacy, get tested, and, if positive, get treated with an antiviral medication on the spot.
One large physicians’ group is concerned that the program leaves doctors on the margins, and may put patients at risk if there are adverse effects from the medications. Pharmacists groups, on the other hand, say the program is too restrictive, according to an article by the research group Advisory Board.
Recently, the White House announced that more than 1,000 pharmacy clinics across the United States had registered to participate in the initiative, according to CNN. Ordering of the drugs is underway in many of these clinics, a White House official told the network.
Besides retail clinics in chain pharmacies, the antivirals will also be available in community health centers, long-term-care facilities, and Veterans Health Administration clinics, according to a statement from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The two antiviral pills authorized by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration include Pfizer’s Paxlovid, for people 12 and older, and Merck’s molnupiravir, for adults. Either drug has to be taken within 5 days after symptoms appear to be effective in preventing serious illness.
The need for speed is a major reason why the government chose to work with retail clinics that are more accessible than most primary care offices. However, the American Medical Association (AMA), the National Community Pharmacists Association (NCPA), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) have publicly criticized the administration’s approach.
The pharmacists’ groups are concerned that the program is limited only to pharmacies with clinics on site, thus restricting the number of pharmacies qualified to participate. Fourteen pharmacy groups, including the NCPA and the APhA, have also sent a letter to the Biden administration urging it to remove barriers to pharmacies ordering the medications.
The groups also want permission as “clinically trained medication experts” to prescribe the drugs and ensure their safe use.
The AMA on March 4 took issue with the prescribing component, saying that “the pharmacy-based clinic component of the test-to-treat plan flouts patient safety and risks significant negative health outcomes.”
In the AMA’s view, prescribing Paxlovid without a patient’s physician being present poses a risk for adverse drug interactions, as neither the nurse practitioners in retail clinics nor the pharmacists who dispense the drug have full knowledge of a patient›s medical history.
The next day, the AMA released another statement, saying it was reassured by comments from administration officials “that patients who have access to a regular source of care should contact their physician shortly after testing positive for COVID-19 to assess their treatment options.”
“Traditional doctor-only approach”
Having patients call their doctors after testing positive for COVID in a pharmacy “strikes me as unnecessary in the vast majority of cases, and it will delay treatment,” Robert Wachter, MD, professor and chair of the department of medicine at the University of California San Francisco, said in an interview. “In this case, it seems like the AMA is taking a very traditional doctor-only approach. And the world has changed. It’s much more of a team sport than an individual sport, the way it was years ago.”
Dr. Wachter said he has the utmost respect for pharmacists’ ability to screen prescriptions for adverse drug interactions. “We’re required to do medication reconciliation when patients see us,” he says. “And in many hospitals, we delegate that to pharmacists. They’re at least as good at it if not better than physicians are.”
While it’s essential to know what other medications a patient is taking, he noted, pharmacies have computer records of all the prescriptions they’ve filled for patients. In addition, pharmacies have access to complete medication histories through Surescripts, the company that enables electronic prescribing transactions between prescribers and pharmacies.
Drug interactions “not trivial”
Preeti Malani, MD, the chief health officer and a professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, told this news organization that the potential interactions between Paxlovid and some other medications are “not trivial.”
However, she said, “The really dangerous drugs are the ones for people who have had organ transplants and the like. Those aren’t individuals who are going to shop at a pharmacy.”
Besides the antirejection drugs, Dr. Wachter said, there can be serious interactions with cholesterol-lowering medications. If a person is taking Lipitor, for instance, “Someone would have to make the decision on whether it’s ok for me to stop it for a while, or to lower the dose. But I trust the pharmacist to do that as well as anybody.”
Except for these potential drug interactions with Paxlovid, the antiviral medications are “quite safe,” he said, adding that being able to treat people who test positive for COVID-19 right away is a big advantage of the test-to-treat program, considering how difficult it is for many people to get access to a doctor. That delay could mean that the antivirals are not prescribed and taken until they are no longer effective.
Both Dr. Wachter and Dr. Malani said that the widespread distribution of pharmacies and their extended hours are other big pluses, especially for people who can’t easily leave work or travel far to visit a physician.
Dr. Malani cautioned that there are still kinks to work out in the test-to-treat program. It will be a while before the retail clinics all have the antiviral drugs, and many pharmacies don’t have clinics on site.
Still, she said people can still go to their physicians to be tested, and presumably those doctors can also write antiviral prescriptions. But it’s not clear where the antivirals will be available in the near term.
“Right now, we’re playing catch-up,” Dr. Malani said. “But pharmacies are an important piece of the puzzle.”
Looking at the big picture, she said, “We know that neither vaccination nor natural infection provides long lasting immunity, and so there will be a role for antivirals in order to make this a manageable illness. And when you’re talking about millions of cases, as we were having a few months ago, the health system can’t field all those patients. So we do need a system where I can go to a pharmacy and get a test and treatment.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Biden administration’s new test-to-treat program is simple on the surface: if you feel like you may have COVID-19, go to a pharmacy, get tested, and, if positive, get treated with an antiviral medication on the spot.
One large physicians’ group is concerned that the program leaves doctors on the margins, and may put patients at risk if there are adverse effects from the medications. Pharmacists groups, on the other hand, say the program is too restrictive, according to an article by the research group Advisory Board.
Recently, the White House announced that more than 1,000 pharmacy clinics across the United States had registered to participate in the initiative, according to CNN. Ordering of the drugs is underway in many of these clinics, a White House official told the network.
Besides retail clinics in chain pharmacies, the antivirals will also be available in community health centers, long-term-care facilities, and Veterans Health Administration clinics, according to a statement from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The two antiviral pills authorized by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration include Pfizer’s Paxlovid, for people 12 and older, and Merck’s molnupiravir, for adults. Either drug has to be taken within 5 days after symptoms appear to be effective in preventing serious illness.
The need for speed is a major reason why the government chose to work with retail clinics that are more accessible than most primary care offices. However, the American Medical Association (AMA), the National Community Pharmacists Association (NCPA), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) have publicly criticized the administration’s approach.
The pharmacists’ groups are concerned that the program is limited only to pharmacies with clinics on site, thus restricting the number of pharmacies qualified to participate. Fourteen pharmacy groups, including the NCPA and the APhA, have also sent a letter to the Biden administration urging it to remove barriers to pharmacies ordering the medications.
The groups also want permission as “clinically trained medication experts” to prescribe the drugs and ensure their safe use.
The AMA on March 4 took issue with the prescribing component, saying that “the pharmacy-based clinic component of the test-to-treat plan flouts patient safety and risks significant negative health outcomes.”
In the AMA’s view, prescribing Paxlovid without a patient’s physician being present poses a risk for adverse drug interactions, as neither the nurse practitioners in retail clinics nor the pharmacists who dispense the drug have full knowledge of a patient›s medical history.
The next day, the AMA released another statement, saying it was reassured by comments from administration officials “that patients who have access to a regular source of care should contact their physician shortly after testing positive for COVID-19 to assess their treatment options.”
“Traditional doctor-only approach”
Having patients call their doctors after testing positive for COVID in a pharmacy “strikes me as unnecessary in the vast majority of cases, and it will delay treatment,” Robert Wachter, MD, professor and chair of the department of medicine at the University of California San Francisco, said in an interview. “In this case, it seems like the AMA is taking a very traditional doctor-only approach. And the world has changed. It’s much more of a team sport than an individual sport, the way it was years ago.”
Dr. Wachter said he has the utmost respect for pharmacists’ ability to screen prescriptions for adverse drug interactions. “We’re required to do medication reconciliation when patients see us,” he says. “And in many hospitals, we delegate that to pharmacists. They’re at least as good at it if not better than physicians are.”
While it’s essential to know what other medications a patient is taking, he noted, pharmacies have computer records of all the prescriptions they’ve filled for patients. In addition, pharmacies have access to complete medication histories through Surescripts, the company that enables electronic prescribing transactions between prescribers and pharmacies.
Drug interactions “not trivial”
Preeti Malani, MD, the chief health officer and a professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, told this news organization that the potential interactions between Paxlovid and some other medications are “not trivial.”
However, she said, “The really dangerous drugs are the ones for people who have had organ transplants and the like. Those aren’t individuals who are going to shop at a pharmacy.”
Besides the antirejection drugs, Dr. Wachter said, there can be serious interactions with cholesterol-lowering medications. If a person is taking Lipitor, for instance, “Someone would have to make the decision on whether it’s ok for me to stop it for a while, or to lower the dose. But I trust the pharmacist to do that as well as anybody.”
Except for these potential drug interactions with Paxlovid, the antiviral medications are “quite safe,” he said, adding that being able to treat people who test positive for COVID-19 right away is a big advantage of the test-to-treat program, considering how difficult it is for many people to get access to a doctor. That delay could mean that the antivirals are not prescribed and taken until they are no longer effective.
Both Dr. Wachter and Dr. Malani said that the widespread distribution of pharmacies and their extended hours are other big pluses, especially for people who can’t easily leave work or travel far to visit a physician.
Dr. Malani cautioned that there are still kinks to work out in the test-to-treat program. It will be a while before the retail clinics all have the antiviral drugs, and many pharmacies don’t have clinics on site.
Still, she said people can still go to their physicians to be tested, and presumably those doctors can also write antiviral prescriptions. But it’s not clear where the antivirals will be available in the near term.
“Right now, we’re playing catch-up,” Dr. Malani said. “But pharmacies are an important piece of the puzzle.”
Looking at the big picture, she said, “We know that neither vaccination nor natural infection provides long lasting immunity, and so there will be a role for antivirals in order to make this a manageable illness. And when you’re talking about millions of cases, as we were having a few months ago, the health system can’t field all those patients. So we do need a system where I can go to a pharmacy and get a test and treatment.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pharma should stop doing business in Russia, says ethicist
Should pharmaceutical companies continue to do business in Russia, running ongoing clinical trials, starting new ones, or continuing to sell their products there?
Some argue that medicine and science must not get enmeshed in politics, staying above the fray to protect their independence and credibility. Other defenders of business-as-usual say the pharmaceutical industry deals in health and aids the vulnerable. Humanitarianism requires continued interaction with Russia.
I think both arguments fail.
We are fighting a war with Russia. It is a war of economic strangulation, social isolation, and pushing Russia as hard as we can to become a pariah state so that internal pressure on Putin will cause him to rethink his cruel, unjustified invasion or the Russian people to replace him. This pressure must be harsh and it must happen quickly. Why?
Having failed to rapidly defeat the Ukrainian army in the war’s first weeks, Russian commanders are now resorting to the horrible barbarism they used in previous wars in Chechnya and Syria: flattening cities, attacking civilians, killing children with massive and indiscriminate firepower.
To mention one recent horror among many, Russian shelling destroyed a maternity hospital in Mariupol. Ukraine’s president, Volodymyr Zelensky, in bemoaning the Russians for their continuing series of war crimes called on the world to act.
“Mariupol. Direct Strike of Russian troops at the maternity hospital,” he wrote in a Twitter post. “People, children are under the wreckage. Atrocity! How much longer will the world be an accomplice ignoring terror?”
The Russian government’s response: “It is not the first time we have seen pathetic outcries concerning the so-called atrocities,” said Minister of Foreign Affairs Sergei Lavrov, claiming the hospital was being used as a base by an “ultra-radical” Ukrainian battalion.
Health and its preservation are key parts of the aim of medicine and science. There is no way that medicine and science can ignore what war does to health, what attacks on hospitals do to the sick and those who serve them there, the psychological toll that intentional terrorism takes on civilians and their defenders, and what the destruction of infrastructure means for the long-term well-being of Ukrainians.
There can be no collusion with war criminals. There can be no denial of the inextricable link between medicine, science, and politics. Medicine and science are controlled by political forces; their use for good or evil is driven by political considerations, and each doctor, scientist, and scientific society must take a stand when politics corrodes the underlying aims of research and healing.
How far does noncooperation with Russia go? Very, very far. All research, both ongoing and new, must cease immediately. Whatever can be done to minimize harm to existing subjects in a short period of time ought to be done, but that is it.
Similarly, no sale of medicines or therapies ought to be occurring, be they life-saving or consumer products. Putin will see to it that such shipments go to the military or are sold on the black market for revenue, and there is nothing pharma companies can do to stop that.
The Russian people need to be pinched not only by the loss of cheeseburgers and boutique coffee but by products they use to maintain their well-being. War is cruel that way, but if you tolerate a government that is bombing and shelling a peaceful neighbor to oblivion, then pharma must ensure that efforts to make Putin and his kleptocratic goons feel the wrath of their fellow citizens.
Given the realities of nuclear Armageddon, the civilized world must fight obvious barbarity as best it can with sanctions, financial assaults, property seizures, and forgoing commerce, including important raw materials and health products. War, even in a fiscal form, is not without terrible costs; but achieving a rapid, just resolution against tyranny permits no exceptions for pharma or any other business if it is a war that must be fought.
Dr. Caplan is director of the division of medical ethics at New York University. He has consulted with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should pharmaceutical companies continue to do business in Russia, running ongoing clinical trials, starting new ones, or continuing to sell their products there?
Some argue that medicine and science must not get enmeshed in politics, staying above the fray to protect their independence and credibility. Other defenders of business-as-usual say the pharmaceutical industry deals in health and aids the vulnerable. Humanitarianism requires continued interaction with Russia.
I think both arguments fail.
We are fighting a war with Russia. It is a war of economic strangulation, social isolation, and pushing Russia as hard as we can to become a pariah state so that internal pressure on Putin will cause him to rethink his cruel, unjustified invasion or the Russian people to replace him. This pressure must be harsh and it must happen quickly. Why?
Having failed to rapidly defeat the Ukrainian army in the war’s first weeks, Russian commanders are now resorting to the horrible barbarism they used in previous wars in Chechnya and Syria: flattening cities, attacking civilians, killing children with massive and indiscriminate firepower.
To mention one recent horror among many, Russian shelling destroyed a maternity hospital in Mariupol. Ukraine’s president, Volodymyr Zelensky, in bemoaning the Russians for their continuing series of war crimes called on the world to act.
“Mariupol. Direct Strike of Russian troops at the maternity hospital,” he wrote in a Twitter post. “People, children are under the wreckage. Atrocity! How much longer will the world be an accomplice ignoring terror?”
The Russian government’s response: “It is not the first time we have seen pathetic outcries concerning the so-called atrocities,” said Minister of Foreign Affairs Sergei Lavrov, claiming the hospital was being used as a base by an “ultra-radical” Ukrainian battalion.
Health and its preservation are key parts of the aim of medicine and science. There is no way that medicine and science can ignore what war does to health, what attacks on hospitals do to the sick and those who serve them there, the psychological toll that intentional terrorism takes on civilians and their defenders, and what the destruction of infrastructure means for the long-term well-being of Ukrainians.
There can be no collusion with war criminals. There can be no denial of the inextricable link between medicine, science, and politics. Medicine and science are controlled by political forces; their use for good or evil is driven by political considerations, and each doctor, scientist, and scientific society must take a stand when politics corrodes the underlying aims of research and healing.
How far does noncooperation with Russia go? Very, very far. All research, both ongoing and new, must cease immediately. Whatever can be done to minimize harm to existing subjects in a short period of time ought to be done, but that is it.
Similarly, no sale of medicines or therapies ought to be occurring, be they life-saving or consumer products. Putin will see to it that such shipments go to the military or are sold on the black market for revenue, and there is nothing pharma companies can do to stop that.
The Russian people need to be pinched not only by the loss of cheeseburgers and boutique coffee but by products they use to maintain their well-being. War is cruel that way, but if you tolerate a government that is bombing and shelling a peaceful neighbor to oblivion, then pharma must ensure that efforts to make Putin and his kleptocratic goons feel the wrath of their fellow citizens.
Given the realities of nuclear Armageddon, the civilized world must fight obvious barbarity as best it can with sanctions, financial assaults, property seizures, and forgoing commerce, including important raw materials and health products. War, even in a fiscal form, is not without terrible costs; but achieving a rapid, just resolution against tyranny permits no exceptions for pharma or any other business if it is a war that must be fought.
Dr. Caplan is director of the division of medical ethics at New York University. He has consulted with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should pharmaceutical companies continue to do business in Russia, running ongoing clinical trials, starting new ones, or continuing to sell their products there?
Some argue that medicine and science must not get enmeshed in politics, staying above the fray to protect their independence and credibility. Other defenders of business-as-usual say the pharmaceutical industry deals in health and aids the vulnerable. Humanitarianism requires continued interaction with Russia.
I think both arguments fail.
We are fighting a war with Russia. It is a war of economic strangulation, social isolation, and pushing Russia as hard as we can to become a pariah state so that internal pressure on Putin will cause him to rethink his cruel, unjustified invasion or the Russian people to replace him. This pressure must be harsh and it must happen quickly. Why?
Having failed to rapidly defeat the Ukrainian army in the war’s first weeks, Russian commanders are now resorting to the horrible barbarism they used in previous wars in Chechnya and Syria: flattening cities, attacking civilians, killing children with massive and indiscriminate firepower.
To mention one recent horror among many, Russian shelling destroyed a maternity hospital in Mariupol. Ukraine’s president, Volodymyr Zelensky, in bemoaning the Russians for their continuing series of war crimes called on the world to act.
“Mariupol. Direct Strike of Russian troops at the maternity hospital,” he wrote in a Twitter post. “People, children are under the wreckage. Atrocity! How much longer will the world be an accomplice ignoring terror?”
The Russian government’s response: “It is not the first time we have seen pathetic outcries concerning the so-called atrocities,” said Minister of Foreign Affairs Sergei Lavrov, claiming the hospital was being used as a base by an “ultra-radical” Ukrainian battalion.
Health and its preservation are key parts of the aim of medicine and science. There is no way that medicine and science can ignore what war does to health, what attacks on hospitals do to the sick and those who serve them there, the psychological toll that intentional terrorism takes on civilians and their defenders, and what the destruction of infrastructure means for the long-term well-being of Ukrainians.
There can be no collusion with war criminals. There can be no denial of the inextricable link between medicine, science, and politics. Medicine and science are controlled by political forces; their use for good or evil is driven by political considerations, and each doctor, scientist, and scientific society must take a stand when politics corrodes the underlying aims of research and healing.
How far does noncooperation with Russia go? Very, very far. All research, both ongoing and new, must cease immediately. Whatever can be done to minimize harm to existing subjects in a short period of time ought to be done, but that is it.
Similarly, no sale of medicines or therapies ought to be occurring, be they life-saving or consumer products. Putin will see to it that such shipments go to the military or are sold on the black market for revenue, and there is nothing pharma companies can do to stop that.
The Russian people need to be pinched not only by the loss of cheeseburgers and boutique coffee but by products they use to maintain their well-being. War is cruel that way, but if you tolerate a government that is bombing and shelling a peaceful neighbor to oblivion, then pharma must ensure that efforts to make Putin and his kleptocratic goons feel the wrath of their fellow citizens.
Given the realities of nuclear Armageddon, the civilized world must fight obvious barbarity as best it can with sanctions, financial assaults, property seizures, and forgoing commerce, including important raw materials and health products. War, even in a fiscal form, is not without terrible costs; but achieving a rapid, just resolution against tyranny permits no exceptions for pharma or any other business if it is a war that must be fought.
Dr. Caplan is director of the division of medical ethics at New York University. He has consulted with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.