User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
FDA approves self-administered, SubQ furosemide preparation
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a furosemide preparation (Furoscix, scPharmaceuticals) intended for subcutaneous self-administration by outpatients with chronic heart failure and volume overload, the company has announced.
The product is indicated for use with a SmartDose On-Body Infuser (West Pharmaceutical Services) single-use subcutaneous administration device, which affixes to the abdomen.
The infuser is loaded by the patient or caregiver with a prefilled cartridge and is programmed to deliver Furoscix 30 mg over 1 hour followed by a 4-hour infusion at 12.5 mg/h, for a total fixed dose of 80 mg, scPharmaceuticals said in a press release on the drug approval.
Furosemide, a loop diuretic and one of the world’s most frequently used drugs, is conventionally given intravenously in the hospital or orally on an outpatient basis.
The company describes its furosemide preparation, used with the infuser, as “the first and only FDA-approved subcutaneous loop diuretic that delivers [intravenous]-equivalent diuresis at home.” It has been shown to “produce similar diuresis and natriuresis compared to intravenous furosemide.”
“This marks a tremendous opportunity to improve the at-home management of worsening congestion in patients with heart failure who display reduced responsiveness to oral diuretics and require administration of [intravenous] diuretics, which typically requires admission to the hospital,” William T. Abraham, MD, said in the press release.
The FDA approval “is significant and will allow patients to be treated outside of the hospital setting,” said Dr. Abraham, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and an scPharmaceuticals board member.
The Furoscix indication doesn’t cover emergent use or use in acute pulmonary edema, nor is it meant to be used chronically “and should be replaced with oral diuretics as soon as practical,” the company states.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a furosemide preparation (Furoscix, scPharmaceuticals) intended for subcutaneous self-administration by outpatients with chronic heart failure and volume overload, the company has announced.
The product is indicated for use with a SmartDose On-Body Infuser (West Pharmaceutical Services) single-use subcutaneous administration device, which affixes to the abdomen.
The infuser is loaded by the patient or caregiver with a prefilled cartridge and is programmed to deliver Furoscix 30 mg over 1 hour followed by a 4-hour infusion at 12.5 mg/h, for a total fixed dose of 80 mg, scPharmaceuticals said in a press release on the drug approval.
Furosemide, a loop diuretic and one of the world’s most frequently used drugs, is conventionally given intravenously in the hospital or orally on an outpatient basis.
The company describes its furosemide preparation, used with the infuser, as “the first and only FDA-approved subcutaneous loop diuretic that delivers [intravenous]-equivalent diuresis at home.” It has been shown to “produce similar diuresis and natriuresis compared to intravenous furosemide.”
“This marks a tremendous opportunity to improve the at-home management of worsening congestion in patients with heart failure who display reduced responsiveness to oral diuretics and require administration of [intravenous] diuretics, which typically requires admission to the hospital,” William T. Abraham, MD, said in the press release.
The FDA approval “is significant and will allow patients to be treated outside of the hospital setting,” said Dr. Abraham, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and an scPharmaceuticals board member.
The Furoscix indication doesn’t cover emergent use or use in acute pulmonary edema, nor is it meant to be used chronically “and should be replaced with oral diuretics as soon as practical,” the company states.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a furosemide preparation (Furoscix, scPharmaceuticals) intended for subcutaneous self-administration by outpatients with chronic heart failure and volume overload, the company has announced.
The product is indicated for use with a SmartDose On-Body Infuser (West Pharmaceutical Services) single-use subcutaneous administration device, which affixes to the abdomen.
The infuser is loaded by the patient or caregiver with a prefilled cartridge and is programmed to deliver Furoscix 30 mg over 1 hour followed by a 4-hour infusion at 12.5 mg/h, for a total fixed dose of 80 mg, scPharmaceuticals said in a press release on the drug approval.
Furosemide, a loop diuretic and one of the world’s most frequently used drugs, is conventionally given intravenously in the hospital or orally on an outpatient basis.
The company describes its furosemide preparation, used with the infuser, as “the first and only FDA-approved subcutaneous loop diuretic that delivers [intravenous]-equivalent diuresis at home.” It has been shown to “produce similar diuresis and natriuresis compared to intravenous furosemide.”
“This marks a tremendous opportunity to improve the at-home management of worsening congestion in patients with heart failure who display reduced responsiveness to oral diuretics and require administration of [intravenous] diuretics, which typically requires admission to the hospital,” William T. Abraham, MD, said in the press release.
The FDA approval “is significant and will allow patients to be treated outside of the hospital setting,” said Dr. Abraham, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and an scPharmaceuticals board member.
The Furoscix indication doesn’t cover emergent use or use in acute pulmonary edema, nor is it meant to be used chronically “and should be replaced with oral diuretics as soon as practical,” the company states.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Loan forgiveness and med school debt: What about me?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I run the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Many of you know that President Biden created a loan forgiveness program, forgiving up to $10,000 against federal student loans, including graduate and undergraduate education. The Department of Education is supposed to provide up to $20,000 in debt cancellation to Pell Grant recipients who have loans that are held by the Department of Education. Borrowers can get this relief if their income is less than $125,000 for an individual or $250,000 for married couples.
Many people have looked at this and said, “Hey, wait a minute. I paid off my loans. I didn’t get any reimbursement. That isn’t fair.”
who often still have huge amounts of debt, and either because of the income limits or because they don’t qualify because this debt was accrued long in the past, they’re saying, “What about me? Don’t you want to give any relief to me?”
This is a topic near and dear to my heart because I happen to be at a medical school, NYU, that has decided for the two medical schools it runs – our main campus, NYU in Manhattan and NYU Langone out on Long Island – that we’re going to go tuition free. We’ve done it for a couple of years.
We did it because I think all the administrators and faculty understood the tremendous burden that debt poses on people who both carry forward their undergraduate debt and then have medical school debt. This really leads to very difficult situations – which we have great empathy for – about what specialty you’re going to go into, whether you have to moonlight, and how you’re going to manage a huge burden of debt.
Many people don’t have sympathy out in the public. They say doctors make a large amount of money and they live a nice lifestyle, so we’re not going to relieve their debt. The reality is that, whoever you are, short of Bill Gates or Elon Musk, having hundreds of thousands of dollars of debt is no easy task to live with and to work off.
Still, when we created free tuition at NYU for our medical school, there were many people who paid high tuition fees in the past. Some of them said to us, “What about me?” We decided not to try to do anything retrospectively. The plan was to build up enough money so that we could handle no-cost tuition going forward. We didn’t really have it in our pocketbook to help people who’d already paid their debts or were saddled with NYU debt. Is it fair? No, it’s probably not fair, but it’s an improvement.
That’s what I want people to think about who are saying, “What about my medical school debt? What about my undergraduate plus medical school debt?” I think we should be grateful when efforts are being made to reduce very burdensome student loans that people have. It’s good to give that benefit and move it forward.
Does that mean no one should get anything unless everyone with any kind of debt from school is covered? I don’t think so. I don’t think that’s fair either.
It is possible that we could continue to agitate politically and say, let’s go after some of the health care debt. Let’s go after some of the things that are still driving people to have to work more than they would or to choose specialties that they really don’t want to be in because they have to make up that debt.
It doesn’t mean the last word has been said about the politics of debt relief or, for that matter, the price of going to medical school in the first place and trying to see whether that can be driven down.
I don’t think it’s right to say, “If I can’t benefit, given the huge burden that I’m carrying, then I’m not going to try to give relief to others.” I think we’re relieving debt to the extent that we can do it. The nation can afford it. Going forward is a good thing. It’s wrong to create those gigantic debts in the first place.
What are we going to do about the past? We may decide that we need some sort of forgiveness or reparations for loans that were built up for others going backwards. I wouldn’t hold hostage the future and our children to what was probably a very poor, unethical practice about saddling doctors and others in the past with huge debt.
I’m Art Caplan at the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thank you for watching.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I run the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Many of you know that President Biden created a loan forgiveness program, forgiving up to $10,000 against federal student loans, including graduate and undergraduate education. The Department of Education is supposed to provide up to $20,000 in debt cancellation to Pell Grant recipients who have loans that are held by the Department of Education. Borrowers can get this relief if their income is less than $125,000 for an individual or $250,000 for married couples.
Many people have looked at this and said, “Hey, wait a minute. I paid off my loans. I didn’t get any reimbursement. That isn’t fair.”
who often still have huge amounts of debt, and either because of the income limits or because they don’t qualify because this debt was accrued long in the past, they’re saying, “What about me? Don’t you want to give any relief to me?”
This is a topic near and dear to my heart because I happen to be at a medical school, NYU, that has decided for the two medical schools it runs – our main campus, NYU in Manhattan and NYU Langone out on Long Island – that we’re going to go tuition free. We’ve done it for a couple of years.
We did it because I think all the administrators and faculty understood the tremendous burden that debt poses on people who both carry forward their undergraduate debt and then have medical school debt. This really leads to very difficult situations – which we have great empathy for – about what specialty you’re going to go into, whether you have to moonlight, and how you’re going to manage a huge burden of debt.
Many people don’t have sympathy out in the public. They say doctors make a large amount of money and they live a nice lifestyle, so we’re not going to relieve their debt. The reality is that, whoever you are, short of Bill Gates or Elon Musk, having hundreds of thousands of dollars of debt is no easy task to live with and to work off.
Still, when we created free tuition at NYU for our medical school, there were many people who paid high tuition fees in the past. Some of them said to us, “What about me?” We decided not to try to do anything retrospectively. The plan was to build up enough money so that we could handle no-cost tuition going forward. We didn’t really have it in our pocketbook to help people who’d already paid their debts or were saddled with NYU debt. Is it fair? No, it’s probably not fair, but it’s an improvement.
That’s what I want people to think about who are saying, “What about my medical school debt? What about my undergraduate plus medical school debt?” I think we should be grateful when efforts are being made to reduce very burdensome student loans that people have. It’s good to give that benefit and move it forward.
Does that mean no one should get anything unless everyone with any kind of debt from school is covered? I don’t think so. I don’t think that’s fair either.
It is possible that we could continue to agitate politically and say, let’s go after some of the health care debt. Let’s go after some of the things that are still driving people to have to work more than they would or to choose specialties that they really don’t want to be in because they have to make up that debt.
It doesn’t mean the last word has been said about the politics of debt relief or, for that matter, the price of going to medical school in the first place and trying to see whether that can be driven down.
I don’t think it’s right to say, “If I can’t benefit, given the huge burden that I’m carrying, then I’m not going to try to give relief to others.” I think we’re relieving debt to the extent that we can do it. The nation can afford it. Going forward is a good thing. It’s wrong to create those gigantic debts in the first place.
What are we going to do about the past? We may decide that we need some sort of forgiveness or reparations for loans that were built up for others going backwards. I wouldn’t hold hostage the future and our children to what was probably a very poor, unethical practice about saddling doctors and others in the past with huge debt.
I’m Art Caplan at the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thank you for watching.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I run the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Many of you know that President Biden created a loan forgiveness program, forgiving up to $10,000 against federal student loans, including graduate and undergraduate education. The Department of Education is supposed to provide up to $20,000 in debt cancellation to Pell Grant recipients who have loans that are held by the Department of Education. Borrowers can get this relief if their income is less than $125,000 for an individual or $250,000 for married couples.
Many people have looked at this and said, “Hey, wait a minute. I paid off my loans. I didn’t get any reimbursement. That isn’t fair.”
who often still have huge amounts of debt, and either because of the income limits or because they don’t qualify because this debt was accrued long in the past, they’re saying, “What about me? Don’t you want to give any relief to me?”
This is a topic near and dear to my heart because I happen to be at a medical school, NYU, that has decided for the two medical schools it runs – our main campus, NYU in Manhattan and NYU Langone out on Long Island – that we’re going to go tuition free. We’ve done it for a couple of years.
We did it because I think all the administrators and faculty understood the tremendous burden that debt poses on people who both carry forward their undergraduate debt and then have medical school debt. This really leads to very difficult situations – which we have great empathy for – about what specialty you’re going to go into, whether you have to moonlight, and how you’re going to manage a huge burden of debt.
Many people don’t have sympathy out in the public. They say doctors make a large amount of money and they live a nice lifestyle, so we’re not going to relieve their debt. The reality is that, whoever you are, short of Bill Gates or Elon Musk, having hundreds of thousands of dollars of debt is no easy task to live with and to work off.
Still, when we created free tuition at NYU for our medical school, there were many people who paid high tuition fees in the past. Some of them said to us, “What about me?” We decided not to try to do anything retrospectively. The plan was to build up enough money so that we could handle no-cost tuition going forward. We didn’t really have it in our pocketbook to help people who’d already paid their debts or were saddled with NYU debt. Is it fair? No, it’s probably not fair, but it’s an improvement.
That’s what I want people to think about who are saying, “What about my medical school debt? What about my undergraduate plus medical school debt?” I think we should be grateful when efforts are being made to reduce very burdensome student loans that people have. It’s good to give that benefit and move it forward.
Does that mean no one should get anything unless everyone with any kind of debt from school is covered? I don’t think so. I don’t think that’s fair either.
It is possible that we could continue to agitate politically and say, let’s go after some of the health care debt. Let’s go after some of the things that are still driving people to have to work more than they would or to choose specialties that they really don’t want to be in because they have to make up that debt.
It doesn’t mean the last word has been said about the politics of debt relief or, for that matter, the price of going to medical school in the first place and trying to see whether that can be driven down.
I don’t think it’s right to say, “If I can’t benefit, given the huge burden that I’m carrying, then I’m not going to try to give relief to others.” I think we’re relieving debt to the extent that we can do it. The nation can afford it. Going forward is a good thing. It’s wrong to create those gigantic debts in the first place.
What are we going to do about the past? We may decide that we need some sort of forgiveness or reparations for loans that were built up for others going backwards. I wouldn’t hold hostage the future and our children to what was probably a very poor, unethical practice about saddling doctors and others in the past with huge debt.
I’m Art Caplan at the division of medical ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thank you for watching.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The marked contrast in pandemic outcomes between Japan and the United States
This article was originally published Oct. 8 on Medscape Editor-In-Chief Eric Topol’s “Ground Truths” column on Substack.
Over time it has the least cumulative deaths per capita of any major country in the world. That’s without a zero-Covid policy or any national lockdowns, which is why I have not included China as a comparator.
Before we get into that data, let’s take a look at the age pyramids for Japan and the United States. The No. 1 risk factor for death from COVID-19 is advanced age, and you can see that in Japan about 25% of the population is age 65 and older, whereas in the United States that proportion is substantially reduced at 15%. Sure there are differences in comorbidities such as obesity and diabetes, but there is also the trade-off of a much higher population density in Japan.
Besides masks, which were distributed early on by the government to the population in Japan, there was the “Avoid the 3Cs” cluster-busting strategy, widely disseminated in the spring of 2020, leveraging Pareto’s 80-20 principle, long before there were any vaccines available. For a good portion of the pandemic, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan maintained a strict policy for border control, which while hard to quantify, may certainly have contributed to its success.
Besides these factors, once vaccines became available, Japan got the population with the primary series to 83% rapidly, even after getting a late start by many months compared with the United States, which has peaked at 68%. That’s a big gap.
But that gap got much worse when it came to boosters. Ninety-five percent of Japanese eligible compared with 40.8% of Americans have had a booster shot. Of note, that 95% in Japan pertains to the whole population. In the United States the percentage of people age 65 and older who have had two boosters is currently only 42%. I’ve previously reviewed the important lifesaving impact of two boosters among people age 65 and older from five independent studies during Omicron waves throughout the world.
Now let’s turn to cumulative fatalities in the two countries. There’s a huge, nearly ninefold difference, per capita. Using today’s Covid-19 Dashboard, there are cumulatively 45,533 deaths in Japan and 1,062,560 American deaths. That translates to 1 in 2,758 people in Japan compared with 1 in 315 Americans dying of COVID.
And if we look at excess mortality instead of confirmed COVID deaths, that enormous gap doesn’t change.
Obviously it would be good to have data for other COVID outcomes, such as hospitalizations, ICUs, and Long COVID, but they are not accessible.
Comparing Japan, the country that has fared the best, with the United States, one of the worst pandemic outcome results, leaves us with a sense that Prof Ian MacKay’s “Swiss cheese model” is the best explanation. It’s not just one thing. Masks, consistent evidence-based communication (3Cs) with attention to ventilation and air quality, and the outstanding uptake of vaccines and boosters all contributed to Japan’s success.
There is another factor to add to that model – Paxlovid. Its benefit of reducing hospitalizations and deaths for people over age 65 is unquestionable.
That’s why I had previously modified the Swiss cheese model to add Paxlovid.
But in the United States, where 15% of the population is 65 and older, they account for over 75% of the daily death toll, still in the range of 400 per day. Here, with a very high proportion of people age 65 and older left vulnerable without boosters, or primary vaccines, Paxlovid is only being given to less than 25% of the eligible (age 50+), and less people age 80 and older are getting Paxlovid than those age 45. The reasons that doctors are not prescribing it – worried about interactions for a 5-day course and rebound – are not substantiated.
Bottom line: In the United States we are not protecting our population anywhere near as well as Japan, as grossly evident by the fatalities among people at the highest risk. There needs to be far better uptake of boosters and use of Paxlovid in the age 65+ group, but the need for amped up protection is not at all restricted to this age subgroup. Across all age groups age 18 and over there is an 81% reduction of hospitalizations with two boosters with the most updated CDC data available, through the Omicron BA.5 wave.
No less the previous data through May 2022 showing protection from death across all ages with two boosters
And please don’t forget that around the world, over 20 million lives were saved, just in 2021, the first year of vaccines.
We can learn so much from a model country like Japan. Yes, we need nasal and variant-proof vaccines to effectively deal with the new variants that are already getting legs in places like XBB in Singapore and ones not on the radar yet. But right now we’ve got to do far better for people getting boosters and, when a person age 65 or older gets COVID, Paxlovid. Take a look at the Chris Hayes video segment when he pleaded for Americans to get a booster shot. Every day that vaccine waning of the U.S. population exceeds the small percentage of people who get a booster, our vulnerability increases. If we don’t get that on track, it’s likely going to be a rough winter ahead.
Dr. Topol is director of the Scripps Translational Science Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health and reported conflicts of interest involving Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Quest Diagnostics, and Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published Oct. 8 on Medscape Editor-In-Chief Eric Topol’s “Ground Truths” column on Substack.
Over time it has the least cumulative deaths per capita of any major country in the world. That’s without a zero-Covid policy or any national lockdowns, which is why I have not included China as a comparator.
Before we get into that data, let’s take a look at the age pyramids for Japan and the United States. The No. 1 risk factor for death from COVID-19 is advanced age, and you can see that in Japan about 25% of the population is age 65 and older, whereas in the United States that proportion is substantially reduced at 15%. Sure there are differences in comorbidities such as obesity and diabetes, but there is also the trade-off of a much higher population density in Japan.
Besides masks, which were distributed early on by the government to the population in Japan, there was the “Avoid the 3Cs” cluster-busting strategy, widely disseminated in the spring of 2020, leveraging Pareto’s 80-20 principle, long before there were any vaccines available. For a good portion of the pandemic, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan maintained a strict policy for border control, which while hard to quantify, may certainly have contributed to its success.
Besides these factors, once vaccines became available, Japan got the population with the primary series to 83% rapidly, even after getting a late start by many months compared with the United States, which has peaked at 68%. That’s a big gap.
But that gap got much worse when it came to boosters. Ninety-five percent of Japanese eligible compared with 40.8% of Americans have had a booster shot. Of note, that 95% in Japan pertains to the whole population. In the United States the percentage of people age 65 and older who have had two boosters is currently only 42%. I’ve previously reviewed the important lifesaving impact of two boosters among people age 65 and older from five independent studies during Omicron waves throughout the world.
Now let’s turn to cumulative fatalities in the two countries. There’s a huge, nearly ninefold difference, per capita. Using today’s Covid-19 Dashboard, there are cumulatively 45,533 deaths in Japan and 1,062,560 American deaths. That translates to 1 in 2,758 people in Japan compared with 1 in 315 Americans dying of COVID.
And if we look at excess mortality instead of confirmed COVID deaths, that enormous gap doesn’t change.
Obviously it would be good to have data for other COVID outcomes, such as hospitalizations, ICUs, and Long COVID, but they are not accessible.
Comparing Japan, the country that has fared the best, with the United States, one of the worst pandemic outcome results, leaves us with a sense that Prof Ian MacKay’s “Swiss cheese model” is the best explanation. It’s not just one thing. Masks, consistent evidence-based communication (3Cs) with attention to ventilation and air quality, and the outstanding uptake of vaccines and boosters all contributed to Japan’s success.
There is another factor to add to that model – Paxlovid. Its benefit of reducing hospitalizations and deaths for people over age 65 is unquestionable.
That’s why I had previously modified the Swiss cheese model to add Paxlovid.
But in the United States, where 15% of the population is 65 and older, they account for over 75% of the daily death toll, still in the range of 400 per day. Here, with a very high proportion of people age 65 and older left vulnerable without boosters, or primary vaccines, Paxlovid is only being given to less than 25% of the eligible (age 50+), and less people age 80 and older are getting Paxlovid than those age 45. The reasons that doctors are not prescribing it – worried about interactions for a 5-day course and rebound – are not substantiated.
Bottom line: In the United States we are not protecting our population anywhere near as well as Japan, as grossly evident by the fatalities among people at the highest risk. There needs to be far better uptake of boosters and use of Paxlovid in the age 65+ group, but the need for amped up protection is not at all restricted to this age subgroup. Across all age groups age 18 and over there is an 81% reduction of hospitalizations with two boosters with the most updated CDC data available, through the Omicron BA.5 wave.
No less the previous data through May 2022 showing protection from death across all ages with two boosters
And please don’t forget that around the world, over 20 million lives were saved, just in 2021, the first year of vaccines.
We can learn so much from a model country like Japan. Yes, we need nasal and variant-proof vaccines to effectively deal with the new variants that are already getting legs in places like XBB in Singapore and ones not on the radar yet. But right now we’ve got to do far better for people getting boosters and, when a person age 65 or older gets COVID, Paxlovid. Take a look at the Chris Hayes video segment when he pleaded for Americans to get a booster shot. Every day that vaccine waning of the U.S. population exceeds the small percentage of people who get a booster, our vulnerability increases. If we don’t get that on track, it’s likely going to be a rough winter ahead.
Dr. Topol is director of the Scripps Translational Science Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health and reported conflicts of interest involving Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Quest Diagnostics, and Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published Oct. 8 on Medscape Editor-In-Chief Eric Topol’s “Ground Truths” column on Substack.
Over time it has the least cumulative deaths per capita of any major country in the world. That’s without a zero-Covid policy or any national lockdowns, which is why I have not included China as a comparator.
Before we get into that data, let’s take a look at the age pyramids for Japan and the United States. The No. 1 risk factor for death from COVID-19 is advanced age, and you can see that in Japan about 25% of the population is age 65 and older, whereas in the United States that proportion is substantially reduced at 15%. Sure there are differences in comorbidities such as obesity and diabetes, but there is also the trade-off of a much higher population density in Japan.
Besides masks, which were distributed early on by the government to the population in Japan, there was the “Avoid the 3Cs” cluster-busting strategy, widely disseminated in the spring of 2020, leveraging Pareto’s 80-20 principle, long before there were any vaccines available. For a good portion of the pandemic, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan maintained a strict policy for border control, which while hard to quantify, may certainly have contributed to its success.
Besides these factors, once vaccines became available, Japan got the population with the primary series to 83% rapidly, even after getting a late start by many months compared with the United States, which has peaked at 68%. That’s a big gap.
But that gap got much worse when it came to boosters. Ninety-five percent of Japanese eligible compared with 40.8% of Americans have had a booster shot. Of note, that 95% in Japan pertains to the whole population. In the United States the percentage of people age 65 and older who have had two boosters is currently only 42%. I’ve previously reviewed the important lifesaving impact of two boosters among people age 65 and older from five independent studies during Omicron waves throughout the world.
Now let’s turn to cumulative fatalities in the two countries. There’s a huge, nearly ninefold difference, per capita. Using today’s Covid-19 Dashboard, there are cumulatively 45,533 deaths in Japan and 1,062,560 American deaths. That translates to 1 in 2,758 people in Japan compared with 1 in 315 Americans dying of COVID.
And if we look at excess mortality instead of confirmed COVID deaths, that enormous gap doesn’t change.
Obviously it would be good to have data for other COVID outcomes, such as hospitalizations, ICUs, and Long COVID, but they are not accessible.
Comparing Japan, the country that has fared the best, with the United States, one of the worst pandemic outcome results, leaves us with a sense that Prof Ian MacKay’s “Swiss cheese model” is the best explanation. It’s not just one thing. Masks, consistent evidence-based communication (3Cs) with attention to ventilation and air quality, and the outstanding uptake of vaccines and boosters all contributed to Japan’s success.
There is another factor to add to that model – Paxlovid. Its benefit of reducing hospitalizations and deaths for people over age 65 is unquestionable.
That’s why I had previously modified the Swiss cheese model to add Paxlovid.
But in the United States, where 15% of the population is 65 and older, they account for over 75% of the daily death toll, still in the range of 400 per day. Here, with a very high proportion of people age 65 and older left vulnerable without boosters, or primary vaccines, Paxlovid is only being given to less than 25% of the eligible (age 50+), and less people age 80 and older are getting Paxlovid than those age 45. The reasons that doctors are not prescribing it – worried about interactions for a 5-day course and rebound – are not substantiated.
Bottom line: In the United States we are not protecting our population anywhere near as well as Japan, as grossly evident by the fatalities among people at the highest risk. There needs to be far better uptake of boosters and use of Paxlovid in the age 65+ group, but the need for amped up protection is not at all restricted to this age subgroup. Across all age groups age 18 and over there is an 81% reduction of hospitalizations with two boosters with the most updated CDC data available, through the Omicron BA.5 wave.
No less the previous data through May 2022 showing protection from death across all ages with two boosters
And please don’t forget that around the world, over 20 million lives were saved, just in 2021, the first year of vaccines.
We can learn so much from a model country like Japan. Yes, we need nasal and variant-proof vaccines to effectively deal with the new variants that are already getting legs in places like XBB in Singapore and ones not on the radar yet. But right now we’ve got to do far better for people getting boosters and, when a person age 65 or older gets COVID, Paxlovid. Take a look at the Chris Hayes video segment when he pleaded for Americans to get a booster shot. Every day that vaccine waning of the U.S. population exceeds the small percentage of people who get a booster, our vulnerability increases. If we don’t get that on track, it’s likely going to be a rough winter ahead.
Dr. Topol is director of the Scripps Translational Science Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health and reported conflicts of interest involving Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Quest Diagnostics, and Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tirzepatide’s benefits expand: Lean mass up, serum lipids down
STOCKHOLM – New insights into the benefits of treatment with the “twincretin” tirzepatide for people with overweight or obesity – with or without diabetes – come from new findings reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
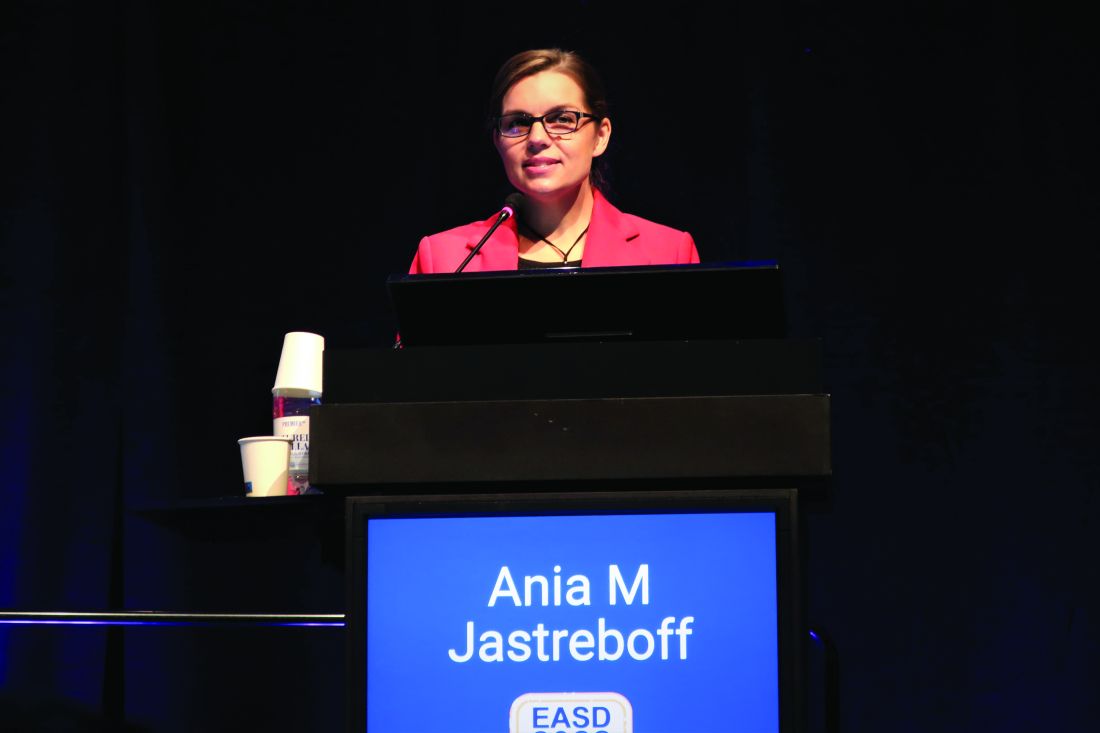
Additional results from the SURMOUNT-1 trial, which matched tirzepatide against placebo in people with overweight or obesity, provide further details on the favorable changes produced by 72 weeks of tirzepatide treatment on outcomes that included fat and lean mass, insulin sensitivity, and patient-reported outcomes related to functional health and well being, reported Ania M. Jastreboff, MD, PhD.
And results from a meta-analysis of six trials that compared tirzepatide (Mounjaro) against several different comparators in patients with type 2 diabetes further confirm the drug’s ability to reliably produce positive changes in blood lipids, especially by significantly lowering levels of triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and very LDL (VLDL) cholesterol, said Thomas Karagiannis, MD, PhD, in a separate report at the meeting.
Tirzepatide works as an agonist on receptors for both the glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1), and for the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, and received Food and Drug Administration approval for treating people with type 2 diabetes in May 2022. On the basis of results from SURMOUNT-1, the FDA on Oct. 6 granted tirzepatide fast-track designation for a proposed labeling of the agent for treating people with overweight or obesity. This FDA decision will likely remain pending at least until results from a second trial in people with overweight or obesity but without diabetes, SURMOUNT-2, become available in 2023.
SURMOUNT-1 randomized 2,539 people with obesity or overweight and at least one weight-related complication to a weekly injection of tirzepatide or placebo for 72 weeks. The study’s primary efficacy endpoints were the average reduction in weight from baseline, and the percentage of people in each treatment arm achieving weight loss of at least 5% from baseline.
For both endpoints, the outcomes with tirzepatide significantly surpassed placebo effects. Average weight loss ranged from 15%-21% from baseline, depending on dose, compared with 3% on placebo. The rate of participants with at least a 5% weight loss ranged from 85% to 91%, compared with 35% with placebo, as reported in July 2022 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Cutting fat mass, boosting lean mass
New results from the trial reported by Dr. Jastreboff included a cut in fat mass from 46.2% of total body mass at baseline to 38.5% after 72 weeks, compared with a change from 46.8% at baseline to 44.7% after 72 weeks in the placebo group. Concurrently, lean mass increased with tirzepatide treatment from 51.0% at baseline to 58.1% after 72 weeks.
Participants who received tirzepatide, compared with those who received placebo, had “proportionately greater decrease in fat mass and proportionately greater increase in lean mass” compared with those who received placebo, said Dr. Jastreboff, an endocrinologist and obesity medicine specialist with Yale Medicine in New Haven, Conn. “I was impressed by the amount of visceral fat lost.”
These effects translated into a significant reduction in fat mass-to-lean mass ratio among the people treated with tirzepatide, with the greatest reduction in those who lost at least 15% of their starting weight. In that subgroup the fat-to-lean mass ratio dropped from 0.94 at baseline to 0.64 after 72 weeks of treatment, she said.
Focus on diet quality
People treated with tirzepatide “eat so little food that we need to improve the quality of what they eat to protect their muscle,” commented Carel le Roux, MBChB, PhD, a professor in the Diabetes Complications Research Centre of University College Dublin. “You no longer need a dietitian to help people lose weight, because the drug does that. You need dietitians to look after the nutritional health of patients while they lose weight,” Dr. le Roux said in a separate session at the meeting.
Additional tests showed that blood glucose and insulin levels were all significantly lower among trial participants on all three doses of tirzepatide compared with those on placebo, and the tirzepatide-treated subjects also had significant, roughly twofold elevations in their insulin sensitivity measured by the Matsuda Index.
The impact of tirzepatide on glucose and insulin levels and on insulin sensitivity was similar regardless of whether study participants had normoglycemia or prediabetes at entry. By design, no study participants had diabetes.
The trial assessed patient-reported quality-of-life outcomes using the 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36). Participants had significant increases in all eight domains within the SF-36 at all three tirzepatide doses, compared with placebo, at 72 weeks, Dr. Jastreboff reported. Improvements in the physical function domain increased most notably among study participants on tirzepatide who had functional limitations at baseline. Heart rate rose among participants who received either of the two highest tirzepatide doses by 2.3-2.5 beats/min, comparable with the effect of other injected incretin-based treatments.
Lipids improve in those with type 2 diabetes
Tirzepatide treatment also results in a “secondary effect” of improving levels of several lipids in people with type 2 diabetes, according to a meta-analysis of findings from six randomized trials. The meta-analysis collectively involved 4,502 participants treated for numerous weeks with one of three doses of tirzepatide and 2,144 people in comparator groups, reported Dr. Karagiannis, a diabetes researcher at Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (Greece).
Among the significant lipid changes linked with tirzepatide treatment, compared with placebo, were an average 13 mg/dL decrease in LDL cholesterol, an average 6 mg/dL decrease in VLDL cholesterol, and an average 50 mg/dL decrease in triglycerides. In comparison to a GLP-1 receptor agonist, an average 25 mg/dL decrease in triglycerides and an average 4 mg/dL reduction in VLDL cholesterol were seen. And trials comparing tirzepatide with basal insulin saw average reductions of 7% in LDL cholesterol, 15% in VLDL cholesterol, 15% in triglycerides, and an 8% increase in HDL cholesterol.
Dr. Karagiannis highlighted that the clinical impact of these effects is unclear, although he noted that the average reduction in LDL cholesterol relative to placebo is of a magnitude that could have a modest effect on long-term outcomes.
These lipid effects of tirzepatide “should be considered alongside” tirzepatide’s “key metabolic effects” on weight and hemoglobin A1c as well as the drug’s safety, concluded Dr. Karagiannis.
The tirzepatide trials were all funded by Eli Lilly, which markets tirzepatide (Mounjaro). Dr. Jastreboff has been an adviser and consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Scholars, Roche, and Weight Watchers, and she has received research funding from Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Karagiannis had no disclosures. Dr. le Roux has had financial relationships with Eli Lilly, as well as with Boehringer Ingelheim, Consilient Health, Covidion, Fractyl, GL Dynamics, Herbalife, Johnson & Johnson, Keyron, and Novo Nordisk.
STOCKHOLM – New insights into the benefits of treatment with the “twincretin” tirzepatide for people with overweight or obesity – with or without diabetes – come from new findings reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Additional results from the SURMOUNT-1 trial, which matched tirzepatide against placebo in people with overweight or obesity, provide further details on the favorable changes produced by 72 weeks of tirzepatide treatment on outcomes that included fat and lean mass, insulin sensitivity, and patient-reported outcomes related to functional health and well being, reported Ania M. Jastreboff, MD, PhD.
And results from a meta-analysis of six trials that compared tirzepatide (Mounjaro) against several different comparators in patients with type 2 diabetes further confirm the drug’s ability to reliably produce positive changes in blood lipids, especially by significantly lowering levels of triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and very LDL (VLDL) cholesterol, said Thomas Karagiannis, MD, PhD, in a separate report at the meeting.
Tirzepatide works as an agonist on receptors for both the glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1), and for the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, and received Food and Drug Administration approval for treating people with type 2 diabetes in May 2022. On the basis of results from SURMOUNT-1, the FDA on Oct. 6 granted tirzepatide fast-track designation for a proposed labeling of the agent for treating people with overweight or obesity. This FDA decision will likely remain pending at least until results from a second trial in people with overweight or obesity but without diabetes, SURMOUNT-2, become available in 2023.
SURMOUNT-1 randomized 2,539 people with obesity or overweight and at least one weight-related complication to a weekly injection of tirzepatide or placebo for 72 weeks. The study’s primary efficacy endpoints were the average reduction in weight from baseline, and the percentage of people in each treatment arm achieving weight loss of at least 5% from baseline.
For both endpoints, the outcomes with tirzepatide significantly surpassed placebo effects. Average weight loss ranged from 15%-21% from baseline, depending on dose, compared with 3% on placebo. The rate of participants with at least a 5% weight loss ranged from 85% to 91%, compared with 35% with placebo, as reported in July 2022 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Cutting fat mass, boosting lean mass
New results from the trial reported by Dr. Jastreboff included a cut in fat mass from 46.2% of total body mass at baseline to 38.5% after 72 weeks, compared with a change from 46.8% at baseline to 44.7% after 72 weeks in the placebo group. Concurrently, lean mass increased with tirzepatide treatment from 51.0% at baseline to 58.1% after 72 weeks.
Participants who received tirzepatide, compared with those who received placebo, had “proportionately greater decrease in fat mass and proportionately greater increase in lean mass” compared with those who received placebo, said Dr. Jastreboff, an endocrinologist and obesity medicine specialist with Yale Medicine in New Haven, Conn. “I was impressed by the amount of visceral fat lost.”
These effects translated into a significant reduction in fat mass-to-lean mass ratio among the people treated with tirzepatide, with the greatest reduction in those who lost at least 15% of their starting weight. In that subgroup the fat-to-lean mass ratio dropped from 0.94 at baseline to 0.64 after 72 weeks of treatment, she said.
Focus on diet quality
People treated with tirzepatide “eat so little food that we need to improve the quality of what they eat to protect their muscle,” commented Carel le Roux, MBChB, PhD, a professor in the Diabetes Complications Research Centre of University College Dublin. “You no longer need a dietitian to help people lose weight, because the drug does that. You need dietitians to look after the nutritional health of patients while they lose weight,” Dr. le Roux said in a separate session at the meeting.
Additional tests showed that blood glucose and insulin levels were all significantly lower among trial participants on all three doses of tirzepatide compared with those on placebo, and the tirzepatide-treated subjects also had significant, roughly twofold elevations in their insulin sensitivity measured by the Matsuda Index.
The impact of tirzepatide on glucose and insulin levels and on insulin sensitivity was similar regardless of whether study participants had normoglycemia or prediabetes at entry. By design, no study participants had diabetes.
The trial assessed patient-reported quality-of-life outcomes using the 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36). Participants had significant increases in all eight domains within the SF-36 at all three tirzepatide doses, compared with placebo, at 72 weeks, Dr. Jastreboff reported. Improvements in the physical function domain increased most notably among study participants on tirzepatide who had functional limitations at baseline. Heart rate rose among participants who received either of the two highest tirzepatide doses by 2.3-2.5 beats/min, comparable with the effect of other injected incretin-based treatments.
Lipids improve in those with type 2 diabetes
Tirzepatide treatment also results in a “secondary effect” of improving levels of several lipids in people with type 2 diabetes, according to a meta-analysis of findings from six randomized trials. The meta-analysis collectively involved 4,502 participants treated for numerous weeks with one of three doses of tirzepatide and 2,144 people in comparator groups, reported Dr. Karagiannis, a diabetes researcher at Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (Greece).
Among the significant lipid changes linked with tirzepatide treatment, compared with placebo, were an average 13 mg/dL decrease in LDL cholesterol, an average 6 mg/dL decrease in VLDL cholesterol, and an average 50 mg/dL decrease in triglycerides. In comparison to a GLP-1 receptor agonist, an average 25 mg/dL decrease in triglycerides and an average 4 mg/dL reduction in VLDL cholesterol were seen. And trials comparing tirzepatide with basal insulin saw average reductions of 7% in LDL cholesterol, 15% in VLDL cholesterol, 15% in triglycerides, and an 8% increase in HDL cholesterol.
Dr. Karagiannis highlighted that the clinical impact of these effects is unclear, although he noted that the average reduction in LDL cholesterol relative to placebo is of a magnitude that could have a modest effect on long-term outcomes.
These lipid effects of tirzepatide “should be considered alongside” tirzepatide’s “key metabolic effects” on weight and hemoglobin A1c as well as the drug’s safety, concluded Dr. Karagiannis.
The tirzepatide trials were all funded by Eli Lilly, which markets tirzepatide (Mounjaro). Dr. Jastreboff has been an adviser and consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Scholars, Roche, and Weight Watchers, and she has received research funding from Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Karagiannis had no disclosures. Dr. le Roux has had financial relationships with Eli Lilly, as well as with Boehringer Ingelheim, Consilient Health, Covidion, Fractyl, GL Dynamics, Herbalife, Johnson & Johnson, Keyron, and Novo Nordisk.
STOCKHOLM – New insights into the benefits of treatment with the “twincretin” tirzepatide for people with overweight or obesity – with or without diabetes – come from new findings reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Additional results from the SURMOUNT-1 trial, which matched tirzepatide against placebo in people with overweight or obesity, provide further details on the favorable changes produced by 72 weeks of tirzepatide treatment on outcomes that included fat and lean mass, insulin sensitivity, and patient-reported outcomes related to functional health and well being, reported Ania M. Jastreboff, MD, PhD.
And results from a meta-analysis of six trials that compared tirzepatide (Mounjaro) against several different comparators in patients with type 2 diabetes further confirm the drug’s ability to reliably produce positive changes in blood lipids, especially by significantly lowering levels of triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and very LDL (VLDL) cholesterol, said Thomas Karagiannis, MD, PhD, in a separate report at the meeting.
Tirzepatide works as an agonist on receptors for both the glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1), and for the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, and received Food and Drug Administration approval for treating people with type 2 diabetes in May 2022. On the basis of results from SURMOUNT-1, the FDA on Oct. 6 granted tirzepatide fast-track designation for a proposed labeling of the agent for treating people with overweight or obesity. This FDA decision will likely remain pending at least until results from a second trial in people with overweight or obesity but without diabetes, SURMOUNT-2, become available in 2023.
SURMOUNT-1 randomized 2,539 people with obesity or overweight and at least one weight-related complication to a weekly injection of tirzepatide or placebo for 72 weeks. The study’s primary efficacy endpoints were the average reduction in weight from baseline, and the percentage of people in each treatment arm achieving weight loss of at least 5% from baseline.
For both endpoints, the outcomes with tirzepatide significantly surpassed placebo effects. Average weight loss ranged from 15%-21% from baseline, depending on dose, compared with 3% on placebo. The rate of participants with at least a 5% weight loss ranged from 85% to 91%, compared with 35% with placebo, as reported in July 2022 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Cutting fat mass, boosting lean mass
New results from the trial reported by Dr. Jastreboff included a cut in fat mass from 46.2% of total body mass at baseline to 38.5% after 72 weeks, compared with a change from 46.8% at baseline to 44.7% after 72 weeks in the placebo group. Concurrently, lean mass increased with tirzepatide treatment from 51.0% at baseline to 58.1% after 72 weeks.
Participants who received tirzepatide, compared with those who received placebo, had “proportionately greater decrease in fat mass and proportionately greater increase in lean mass” compared with those who received placebo, said Dr. Jastreboff, an endocrinologist and obesity medicine specialist with Yale Medicine in New Haven, Conn. “I was impressed by the amount of visceral fat lost.”
These effects translated into a significant reduction in fat mass-to-lean mass ratio among the people treated with tirzepatide, with the greatest reduction in those who lost at least 15% of their starting weight. In that subgroup the fat-to-lean mass ratio dropped from 0.94 at baseline to 0.64 after 72 weeks of treatment, she said.
Focus on diet quality
People treated with tirzepatide “eat so little food that we need to improve the quality of what they eat to protect their muscle,” commented Carel le Roux, MBChB, PhD, a professor in the Diabetes Complications Research Centre of University College Dublin. “You no longer need a dietitian to help people lose weight, because the drug does that. You need dietitians to look after the nutritional health of patients while they lose weight,” Dr. le Roux said in a separate session at the meeting.
Additional tests showed that blood glucose and insulin levels were all significantly lower among trial participants on all three doses of tirzepatide compared with those on placebo, and the tirzepatide-treated subjects also had significant, roughly twofold elevations in their insulin sensitivity measured by the Matsuda Index.
The impact of tirzepatide on glucose and insulin levels and on insulin sensitivity was similar regardless of whether study participants had normoglycemia or prediabetes at entry. By design, no study participants had diabetes.
The trial assessed patient-reported quality-of-life outcomes using the 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36). Participants had significant increases in all eight domains within the SF-36 at all three tirzepatide doses, compared with placebo, at 72 weeks, Dr. Jastreboff reported. Improvements in the physical function domain increased most notably among study participants on tirzepatide who had functional limitations at baseline. Heart rate rose among participants who received either of the two highest tirzepatide doses by 2.3-2.5 beats/min, comparable with the effect of other injected incretin-based treatments.
Lipids improve in those with type 2 diabetes
Tirzepatide treatment also results in a “secondary effect” of improving levels of several lipids in people with type 2 diabetes, according to a meta-analysis of findings from six randomized trials. The meta-analysis collectively involved 4,502 participants treated for numerous weeks with one of three doses of tirzepatide and 2,144 people in comparator groups, reported Dr. Karagiannis, a diabetes researcher at Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (Greece).
Among the significant lipid changes linked with tirzepatide treatment, compared with placebo, were an average 13 mg/dL decrease in LDL cholesterol, an average 6 mg/dL decrease in VLDL cholesterol, and an average 50 mg/dL decrease in triglycerides. In comparison to a GLP-1 receptor agonist, an average 25 mg/dL decrease in triglycerides and an average 4 mg/dL reduction in VLDL cholesterol were seen. And trials comparing tirzepatide with basal insulin saw average reductions of 7% in LDL cholesterol, 15% in VLDL cholesterol, 15% in triglycerides, and an 8% increase in HDL cholesterol.
Dr. Karagiannis highlighted that the clinical impact of these effects is unclear, although he noted that the average reduction in LDL cholesterol relative to placebo is of a magnitude that could have a modest effect on long-term outcomes.
These lipid effects of tirzepatide “should be considered alongside” tirzepatide’s “key metabolic effects” on weight and hemoglobin A1c as well as the drug’s safety, concluded Dr. Karagiannis.
The tirzepatide trials were all funded by Eli Lilly, which markets tirzepatide (Mounjaro). Dr. Jastreboff has been an adviser and consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Scholars, Roche, and Weight Watchers, and she has received research funding from Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Karagiannis had no disclosures. Dr. le Roux has had financial relationships with Eli Lilly, as well as with Boehringer Ingelheim, Consilient Health, Covidion, Fractyl, GL Dynamics, Herbalife, Johnson & Johnson, Keyron, and Novo Nordisk.
AT EASD 2022
For many, long COVID’s impacts go on and on, major study says
in the same time frame, a large study out of Scotland found.
Multiple studies are evaluating people with long COVID in the hopes of figuring out why some people experience debilitating symptoms long after their primary infection ends and others either do not or recover more quickly.
This current study is notable for its large size – 96,238 people. Researchers checked in with participants at 6, 12, and 18 months, and included a group of people never infected with the coronavirus to help investigators make a stronger case.
“A lot of the symptoms of long COVID are nonspecific and therefore can occur in people never infected,” says senior study author Jill P. Pell, MD, head of the School of Health and Wellbeing at the University of Glasgow in Scotland.
Ruling out coincidence
This study shows that people experienced a wide range of symptoms after becoming infected with COVID-19 at a significantly higher rate than those who were never infected, “thereby confirming that they were genuinely associated with COVID and not merely a coincidence,” she said.
Among 21,525 people who had COVID-19 and had symptoms, tiredness, headache and muscle aches or muscle weakness were the most common ongoing symptoms.
Loss of smell was almost nine times more likely in this group compared to the never-infected group in one analysis where researchers controlled for other possible factors. The risk for loss of taste was almost six times greater, followed by risk of breathlessness at three times higher.
Long COVID risk was highest after a severe original infection and among older people, women, Black, and South Asian populations, people with socioeconomic disadvantages, and those with more than one underlying health condition.
Adding up the 6% with no recovery after 18 months and 42% with partial recovery means that between 6 and 18 months following symptomatic coronavirus infection, almost half of those infected still experience persistent symptoms.
Vaccination validated
On the plus side, people vaccinated against COVID-19 before getting infected had a lower risk for some persistent symptoms. In addition, Dr. Pell and colleagues found no evidence that people who experienced asymptomatic infection were likely to experience long COVID symptoms or challenges with activities of daily living.
The findings of the Long-COVID in Scotland Study (Long-CISS) were published in the journal Nature Communications.
‘More long COVID than ever before’
“Unfortunately, these long COVID symptoms are not getting better as the cases of COVID get milder,” said Thomas Gut, DO, medical director for the post-COVID recovery program at Staten Island (N.Y.) University Hospital. “Quite the opposite – this infection has become so common in a community because it’s so mild and spreading so rapidly that we’re seeing more long COVID symptoms than ever before.”
Although most patients he sees with long COVID resolve their symptoms within 3-6 months, “We do see some patients who require short-term disability because their symptoms continue past 6 months and out to 2 years,” said Dr. Gut, a hospitalist at Staten Island University Hospital, a member hospital of Northwell Health.
Patients with fatigue and neurocognitive symptoms “have a very tough time going back to work. Short-term disability gives them the time and finances to pursue specialty care with cardiology, pulmonary, and neurocognitive testing,” he said.
Support the whole person
The burden of living with long COVID goes beyond the persistent symptoms. “Long COVID can have wide-ranging impacts – not only on health but also quality of life and activities of daily living [including] work, mobility, self-care and more,” Dr. Pell said. “So, people with long COVID need support relevant to their individual needs and this may extend beyond the health care sector, for example including social services, school or workplace.”
Still, Lisa Penziner, RN, founder of the COVID Long Haulers Support Group in Westchester and Long Island, N.Y., said while people with the most severe cases of COVID-19 tended to have the worst long COVID symptoms, they’re not the only ones.
“We saw many post-COVID members who had mild cases and their long-haul symptoms were worse weeks later than the virus itself,” said Md. Penziner.
She estimates that 80%-90% of her support group members recover within 6 months. “However, there are others who were experiencing symptoms for much longer.”
Respiratory treatment, physical therapy, and other follow-up doctor visits are common after 6 months, for example.
“Additionally, there is a mental health component to recovery as well, meaning that the patient must learn to live while experiencing lingering, long-haul COVID symptoms in work and daily life,” said Ms. Penziner, director of special projects at North Westchester Restorative Therapy & Nursing.
In addition to ongoing medical care, people with long COVID need understanding, she said.
“While long-haul symptoms do not happen to everyone, it is proven that many do experience long-haul symptoms, and the support of the community in understanding is important.”
Limitations of the study
Dr. Pell and colleagues noted some strengths and weaknesses to their study. For example, “as a general population study, our findings provide a better indication of the overall risk and burden of long COVID than hospitalized cohorts,” they noted.
Also, the Scottish population is 96% White, so other long COVID studies with more diverse participants are warranted.
Another potential weakness is the response rate of 16% among those invited to participate in the study, which Dr. Pell and colleagues addressed: “Our cohort included a large sample (33,281) of people previously infected and the response rate of 16% overall and 20% among people who had symptomatic infection was consistent with previous studies that have used SMS text invitations as the sole method of recruitment.”
“We tell patients this should last 3-6 months, but some patients have longer recovery periods,” Dr. Gut said. “We’re here for them. We have a lot of services available to help get them through the recovery process, and we have a lot of options to help support them.”
“What we found most helpful is when there is peer-to-peer support, reaffirming to the member that they are not alone in the long-haul battle, which has been a major benefit of the support group,” Ms. Penziner said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
in the same time frame, a large study out of Scotland found.
Multiple studies are evaluating people with long COVID in the hopes of figuring out why some people experience debilitating symptoms long after their primary infection ends and others either do not or recover more quickly.
This current study is notable for its large size – 96,238 people. Researchers checked in with participants at 6, 12, and 18 months, and included a group of people never infected with the coronavirus to help investigators make a stronger case.
“A lot of the symptoms of long COVID are nonspecific and therefore can occur in people never infected,” says senior study author Jill P. Pell, MD, head of the School of Health and Wellbeing at the University of Glasgow in Scotland.
Ruling out coincidence
This study shows that people experienced a wide range of symptoms after becoming infected with COVID-19 at a significantly higher rate than those who were never infected, “thereby confirming that they were genuinely associated with COVID and not merely a coincidence,” she said.
Among 21,525 people who had COVID-19 and had symptoms, tiredness, headache and muscle aches or muscle weakness were the most common ongoing symptoms.
Loss of smell was almost nine times more likely in this group compared to the never-infected group in one analysis where researchers controlled for other possible factors. The risk for loss of taste was almost six times greater, followed by risk of breathlessness at three times higher.
Long COVID risk was highest after a severe original infection and among older people, women, Black, and South Asian populations, people with socioeconomic disadvantages, and those with more than one underlying health condition.
Adding up the 6% with no recovery after 18 months and 42% with partial recovery means that between 6 and 18 months following symptomatic coronavirus infection, almost half of those infected still experience persistent symptoms.
Vaccination validated
On the plus side, people vaccinated against COVID-19 before getting infected had a lower risk for some persistent symptoms. In addition, Dr. Pell and colleagues found no evidence that people who experienced asymptomatic infection were likely to experience long COVID symptoms or challenges with activities of daily living.
The findings of the Long-COVID in Scotland Study (Long-CISS) were published in the journal Nature Communications.
‘More long COVID than ever before’
“Unfortunately, these long COVID symptoms are not getting better as the cases of COVID get milder,” said Thomas Gut, DO, medical director for the post-COVID recovery program at Staten Island (N.Y.) University Hospital. “Quite the opposite – this infection has become so common in a community because it’s so mild and spreading so rapidly that we’re seeing more long COVID symptoms than ever before.”
Although most patients he sees with long COVID resolve their symptoms within 3-6 months, “We do see some patients who require short-term disability because their symptoms continue past 6 months and out to 2 years,” said Dr. Gut, a hospitalist at Staten Island University Hospital, a member hospital of Northwell Health.
Patients with fatigue and neurocognitive symptoms “have a very tough time going back to work. Short-term disability gives them the time and finances to pursue specialty care with cardiology, pulmonary, and neurocognitive testing,” he said.
Support the whole person
The burden of living with long COVID goes beyond the persistent symptoms. “Long COVID can have wide-ranging impacts – not only on health but also quality of life and activities of daily living [including] work, mobility, self-care and more,” Dr. Pell said. “So, people with long COVID need support relevant to their individual needs and this may extend beyond the health care sector, for example including social services, school or workplace.”
Still, Lisa Penziner, RN, founder of the COVID Long Haulers Support Group in Westchester and Long Island, N.Y., said while people with the most severe cases of COVID-19 tended to have the worst long COVID symptoms, they’re not the only ones.
“We saw many post-COVID members who had mild cases and their long-haul symptoms were worse weeks later than the virus itself,” said Md. Penziner.
She estimates that 80%-90% of her support group members recover within 6 months. “However, there are others who were experiencing symptoms for much longer.”
Respiratory treatment, physical therapy, and other follow-up doctor visits are common after 6 months, for example.
“Additionally, there is a mental health component to recovery as well, meaning that the patient must learn to live while experiencing lingering, long-haul COVID symptoms in work and daily life,” said Ms. Penziner, director of special projects at North Westchester Restorative Therapy & Nursing.
In addition to ongoing medical care, people with long COVID need understanding, she said.
“While long-haul symptoms do not happen to everyone, it is proven that many do experience long-haul symptoms, and the support of the community in understanding is important.”
Limitations of the study
Dr. Pell and colleagues noted some strengths and weaknesses to their study. For example, “as a general population study, our findings provide a better indication of the overall risk and burden of long COVID than hospitalized cohorts,” they noted.
Also, the Scottish population is 96% White, so other long COVID studies with more diverse participants are warranted.
Another potential weakness is the response rate of 16% among those invited to participate in the study, which Dr. Pell and colleagues addressed: “Our cohort included a large sample (33,281) of people previously infected and the response rate of 16% overall and 20% among people who had symptomatic infection was consistent with previous studies that have used SMS text invitations as the sole method of recruitment.”
“We tell patients this should last 3-6 months, but some patients have longer recovery periods,” Dr. Gut said. “We’re here for them. We have a lot of services available to help get them through the recovery process, and we have a lot of options to help support them.”
“What we found most helpful is when there is peer-to-peer support, reaffirming to the member that they are not alone in the long-haul battle, which has been a major benefit of the support group,” Ms. Penziner said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
in the same time frame, a large study out of Scotland found.
Multiple studies are evaluating people with long COVID in the hopes of figuring out why some people experience debilitating symptoms long after their primary infection ends and others either do not or recover more quickly.
This current study is notable for its large size – 96,238 people. Researchers checked in with participants at 6, 12, and 18 months, and included a group of people never infected with the coronavirus to help investigators make a stronger case.
“A lot of the symptoms of long COVID are nonspecific and therefore can occur in people never infected,” says senior study author Jill P. Pell, MD, head of the School of Health and Wellbeing at the University of Glasgow in Scotland.
Ruling out coincidence
This study shows that people experienced a wide range of symptoms after becoming infected with COVID-19 at a significantly higher rate than those who were never infected, “thereby confirming that they were genuinely associated with COVID and not merely a coincidence,” she said.
Among 21,525 people who had COVID-19 and had symptoms, tiredness, headache and muscle aches or muscle weakness were the most common ongoing symptoms.
Loss of smell was almost nine times more likely in this group compared to the never-infected group in one analysis where researchers controlled for other possible factors. The risk for loss of taste was almost six times greater, followed by risk of breathlessness at three times higher.
Long COVID risk was highest after a severe original infection and among older people, women, Black, and South Asian populations, people with socioeconomic disadvantages, and those with more than one underlying health condition.
Adding up the 6% with no recovery after 18 months and 42% with partial recovery means that between 6 and 18 months following symptomatic coronavirus infection, almost half of those infected still experience persistent symptoms.
Vaccination validated
On the plus side, people vaccinated against COVID-19 before getting infected had a lower risk for some persistent symptoms. In addition, Dr. Pell and colleagues found no evidence that people who experienced asymptomatic infection were likely to experience long COVID symptoms or challenges with activities of daily living.
The findings of the Long-COVID in Scotland Study (Long-CISS) were published in the journal Nature Communications.
‘More long COVID than ever before’
“Unfortunately, these long COVID symptoms are not getting better as the cases of COVID get milder,” said Thomas Gut, DO, medical director for the post-COVID recovery program at Staten Island (N.Y.) University Hospital. “Quite the opposite – this infection has become so common in a community because it’s so mild and spreading so rapidly that we’re seeing more long COVID symptoms than ever before.”
Although most patients he sees with long COVID resolve their symptoms within 3-6 months, “We do see some patients who require short-term disability because their symptoms continue past 6 months and out to 2 years,” said Dr. Gut, a hospitalist at Staten Island University Hospital, a member hospital of Northwell Health.
Patients with fatigue and neurocognitive symptoms “have a very tough time going back to work. Short-term disability gives them the time and finances to pursue specialty care with cardiology, pulmonary, and neurocognitive testing,” he said.
Support the whole person
The burden of living with long COVID goes beyond the persistent symptoms. “Long COVID can have wide-ranging impacts – not only on health but also quality of life and activities of daily living [including] work, mobility, self-care and more,” Dr. Pell said. “So, people with long COVID need support relevant to their individual needs and this may extend beyond the health care sector, for example including social services, school or workplace.”
Still, Lisa Penziner, RN, founder of the COVID Long Haulers Support Group in Westchester and Long Island, N.Y., said while people with the most severe cases of COVID-19 tended to have the worst long COVID symptoms, they’re not the only ones.
“We saw many post-COVID members who had mild cases and their long-haul symptoms were worse weeks later than the virus itself,” said Md. Penziner.
She estimates that 80%-90% of her support group members recover within 6 months. “However, there are others who were experiencing symptoms for much longer.”
Respiratory treatment, physical therapy, and other follow-up doctor visits are common after 6 months, for example.
“Additionally, there is a mental health component to recovery as well, meaning that the patient must learn to live while experiencing lingering, long-haul COVID symptoms in work and daily life,” said Ms. Penziner, director of special projects at North Westchester Restorative Therapy & Nursing.
In addition to ongoing medical care, people with long COVID need understanding, she said.
“While long-haul symptoms do not happen to everyone, it is proven that many do experience long-haul symptoms, and the support of the community in understanding is important.”
Limitations of the study
Dr. Pell and colleagues noted some strengths and weaknesses to their study. For example, “as a general population study, our findings provide a better indication of the overall risk and burden of long COVID than hospitalized cohorts,” they noted.
Also, the Scottish population is 96% White, so other long COVID studies with more diverse participants are warranted.
Another potential weakness is the response rate of 16% among those invited to participate in the study, which Dr. Pell and colleagues addressed: “Our cohort included a large sample (33,281) of people previously infected and the response rate of 16% overall and 20% among people who had symptomatic infection was consistent with previous studies that have used SMS text invitations as the sole method of recruitment.”
“We tell patients this should last 3-6 months, but some patients have longer recovery periods,” Dr. Gut said. “We’re here for them. We have a lot of services available to help get them through the recovery process, and we have a lot of options to help support them.”
“What we found most helpful is when there is peer-to-peer support, reaffirming to the member that they are not alone in the long-haul battle, which has been a major benefit of the support group,” Ms. Penziner said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
Keep menstrual cramps away the dietary prevention way
Foods for thought: Menstrual cramp prevention
For those who menstruate, it’s typical for that time of the month to bring cravings for things that may give a serotonin boost that eases the rise in stress hormones. Chocolate and other foods high in sugar fall into that category, but they could actually be adding to the problem.
About 90% of adolescent girls have menstrual pain, and it’s the leading cause of school absences for the demographic. Muscle relaxers and PMS pills are usually the recommended solution to alleviating menstrual cramps, but what if the patient doesn’t want to take any medicine?
Serah Sannoh of Rutgers University wanted to find another way to relieve her menstrual pains. The literature review she presented at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society found multiple studies that examined dietary patterns that resulted in menstrual pain.
In Ms. Sannoh’s analysis, she looked at how certain foods have an effect on cramps. Do they contribute to the pain or reduce it? Diets high in processed foods, oils, sugars, salt, and omega-6 fatty acids promote inflammation in the muscles around the uterus. Thus, cramps.
The answer, sometimes, is not to add a medicine but to change our daily practices, she suggested. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids helped reduce pain, and those who practiced a vegan diet had the lowest muscle inflammation rates. So more salmon and fewer Swedish Fish.
Stage 1 of the robot apocalypse is already upon us
The mere mention of a robot apocalypse is enough to conjure images of terrifying robot soldiers with Austrian accents harvesting and killing humanity while the survivors live blissfully in a simulation and do low-gravity kung fu with high-profile Hollywood actors. They’ll even take over the navy.
Reality is often less exciting than the movies, but rest assured, the robots will not be denied their dominion of Earth. Our future robot overlords are simply taking a more subtle, less dramatic route toward their ultimate subjugation of mankind: They’re making us all sad and burned out.
The research pulls from work conducted in multiple countries to paint a picture of a humanity filled with anxiety about jobs as robotic automation grows more common. In India, a survey of automobile manufacturing works showed that working alongside industrial robots was linked with greater reports of burnout and workplace incivility. In Singapore, a group of college students randomly assigned to read one of three articles – one about the use of robots in business, a generic article about robots, or an article unrelated to robots – were then surveyed about their job security concerns. Three guesses as to which group was most worried.
In addition, the researchers analyzed 185 U.S. metropolitan areas for robot prevalence alongside use of job-recruiting websites and found that the more robots a city used, the more common job searches were. Unemployment rates weren’t affected, suggesting people had job insecurity because of robots. Sure, there could be other, nonrobotic reasons for this, but that’s no fun. We’re here because we fear our future android rulers.
It’s not all doom and gloom, fortunately. In an online experiment, the study authors found that self-affirmation exercises, such as writing down characteristics or values important to us, can overcome the existential fears and lessen concern about robots in the workplace. One of the authors noted that, while some fear is justified, “media reports on new technologies like robots and algorithms tend to be apocalyptic in nature, so people may develop an irrational fear about them.”
Oops. Our bad.
Apocalypse, stage 2: Leaping oral superorganisms
The terms of our secret agreement with the shadowy-but-powerful dental-industrial complex stipulate that LOTME can only cover tooth-related news once a year. This is that once a year.
Since we’ve already dealt with a robot apocalypse, how about a sci-fi horror story? A story with a “cross-kingdom partnership” in which assemblages of bacteria and fungi perform feats greater than either could achieve on its own. A story in which new microscopy technologies allow “scientists to visualize the behavior of living microbes in real time,” according to a statement from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
While looking at saliva samples from toddlers with severe tooth decay, lead author Zhi Ren and associates “noticed the bacteria and fungi forming these assemblages and developing motions we never thought they would possess: a ‘walking-like’ and ‘leaping-like’ mobility. … It’s almost like a new organism – a superorganism – with new functions,” said senior author Hyun Koo, DDS, PhD, of Penn Dental Medicine.
Did he say “mobility”? He did, didn’t he?
To study these alleged superorganisms, they set up a laboratory system “using the bacteria, fungi, and a tooth-like material, all incubated in human saliva,” the university explained.
“Incubated in human saliva.” There’s a phrase you don’t see every day.
It only took a few hours for the investigators to observe the bacterial/fungal assemblages making leaps of more than 100 microns across the tooth-like material. “That is more than 200 times their own body length,” Dr. Ren said, “making them even better than most vertebrates, relative to body size. For example, tree frogs and grasshoppers can leap forward about 50 times and 20 times their own body length, respectively.”
So, will it be the robots or the evil superorganisms? Let us give you a word of advice: Always bet on bacteria.
Foods for thought: Menstrual cramp prevention
For those who menstruate, it’s typical for that time of the month to bring cravings for things that may give a serotonin boost that eases the rise in stress hormones. Chocolate and other foods high in sugar fall into that category, but they could actually be adding to the problem.
About 90% of adolescent girls have menstrual pain, and it’s the leading cause of school absences for the demographic. Muscle relaxers and PMS pills are usually the recommended solution to alleviating menstrual cramps, but what if the patient doesn’t want to take any medicine?
Serah Sannoh of Rutgers University wanted to find another way to relieve her menstrual pains. The literature review she presented at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society found multiple studies that examined dietary patterns that resulted in menstrual pain.
In Ms. Sannoh’s analysis, she looked at how certain foods have an effect on cramps. Do they contribute to the pain or reduce it? Diets high in processed foods, oils, sugars, salt, and omega-6 fatty acids promote inflammation in the muscles around the uterus. Thus, cramps.
The answer, sometimes, is not to add a medicine but to change our daily practices, she suggested. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids helped reduce pain, and those who practiced a vegan diet had the lowest muscle inflammation rates. So more salmon and fewer Swedish Fish.
Stage 1 of the robot apocalypse is already upon us
The mere mention of a robot apocalypse is enough to conjure images of terrifying robot soldiers with Austrian accents harvesting and killing humanity while the survivors live blissfully in a simulation and do low-gravity kung fu with high-profile Hollywood actors. They’ll even take over the navy.
Reality is often less exciting than the movies, but rest assured, the robots will not be denied their dominion of Earth. Our future robot overlords are simply taking a more subtle, less dramatic route toward their ultimate subjugation of mankind: They’re making us all sad and burned out.
The research pulls from work conducted in multiple countries to paint a picture of a humanity filled with anxiety about jobs as robotic automation grows more common. In India, a survey of automobile manufacturing works showed that working alongside industrial robots was linked with greater reports of burnout and workplace incivility. In Singapore, a group of college students randomly assigned to read one of three articles – one about the use of robots in business, a generic article about robots, or an article unrelated to robots – were then surveyed about their job security concerns. Three guesses as to which group was most worried.
In addition, the researchers analyzed 185 U.S. metropolitan areas for robot prevalence alongside use of job-recruiting websites and found that the more robots a city used, the more common job searches were. Unemployment rates weren’t affected, suggesting people had job insecurity because of robots. Sure, there could be other, nonrobotic reasons for this, but that’s no fun. We’re here because we fear our future android rulers.
It’s not all doom and gloom, fortunately. In an online experiment, the study authors found that self-affirmation exercises, such as writing down characteristics or values important to us, can overcome the existential fears and lessen concern about robots in the workplace. One of the authors noted that, while some fear is justified, “media reports on new technologies like robots and algorithms tend to be apocalyptic in nature, so people may develop an irrational fear about them.”
Oops. Our bad.
Apocalypse, stage 2: Leaping oral superorganisms
The terms of our secret agreement with the shadowy-but-powerful dental-industrial complex stipulate that LOTME can only cover tooth-related news once a year. This is that once a year.
Since we’ve already dealt with a robot apocalypse, how about a sci-fi horror story? A story with a “cross-kingdom partnership” in which assemblages of bacteria and fungi perform feats greater than either could achieve on its own. A story in which new microscopy technologies allow “scientists to visualize the behavior of living microbes in real time,” according to a statement from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
While looking at saliva samples from toddlers with severe tooth decay, lead author Zhi Ren and associates “noticed the bacteria and fungi forming these assemblages and developing motions we never thought they would possess: a ‘walking-like’ and ‘leaping-like’ mobility. … It’s almost like a new organism – a superorganism – with new functions,” said senior author Hyun Koo, DDS, PhD, of Penn Dental Medicine.
Did he say “mobility”? He did, didn’t he?
To study these alleged superorganisms, they set up a laboratory system “using the bacteria, fungi, and a tooth-like material, all incubated in human saliva,” the university explained.
“Incubated in human saliva.” There’s a phrase you don’t see every day.
It only took a few hours for the investigators to observe the bacterial/fungal assemblages making leaps of more than 100 microns across the tooth-like material. “That is more than 200 times their own body length,” Dr. Ren said, “making them even better than most vertebrates, relative to body size. For example, tree frogs and grasshoppers can leap forward about 50 times and 20 times their own body length, respectively.”
So, will it be the robots or the evil superorganisms? Let us give you a word of advice: Always bet on bacteria.
Foods for thought: Menstrual cramp prevention
For those who menstruate, it’s typical for that time of the month to bring cravings for things that may give a serotonin boost that eases the rise in stress hormones. Chocolate and other foods high in sugar fall into that category, but they could actually be adding to the problem.
About 90% of adolescent girls have menstrual pain, and it’s the leading cause of school absences for the demographic. Muscle relaxers and PMS pills are usually the recommended solution to alleviating menstrual cramps, but what if the patient doesn’t want to take any medicine?
Serah Sannoh of Rutgers University wanted to find another way to relieve her menstrual pains. The literature review she presented at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society found multiple studies that examined dietary patterns that resulted in menstrual pain.
In Ms. Sannoh’s analysis, she looked at how certain foods have an effect on cramps. Do they contribute to the pain or reduce it? Diets high in processed foods, oils, sugars, salt, and omega-6 fatty acids promote inflammation in the muscles around the uterus. Thus, cramps.
The answer, sometimes, is not to add a medicine but to change our daily practices, she suggested. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids helped reduce pain, and those who practiced a vegan diet had the lowest muscle inflammation rates. So more salmon and fewer Swedish Fish.
Stage 1 of the robot apocalypse is already upon us
The mere mention of a robot apocalypse is enough to conjure images of terrifying robot soldiers with Austrian accents harvesting and killing humanity while the survivors live blissfully in a simulation and do low-gravity kung fu with high-profile Hollywood actors. They’ll even take over the navy.
Reality is often less exciting than the movies, but rest assured, the robots will not be denied their dominion of Earth. Our future robot overlords are simply taking a more subtle, less dramatic route toward their ultimate subjugation of mankind: They’re making us all sad and burned out.
The research pulls from work conducted in multiple countries to paint a picture of a humanity filled with anxiety about jobs as robotic automation grows more common. In India, a survey of automobile manufacturing works showed that working alongside industrial robots was linked with greater reports of burnout and workplace incivility. In Singapore, a group of college students randomly assigned to read one of three articles – one about the use of robots in business, a generic article about robots, or an article unrelated to robots – were then surveyed about their job security concerns. Three guesses as to which group was most worried.
In addition, the researchers analyzed 185 U.S. metropolitan areas for robot prevalence alongside use of job-recruiting websites and found that the more robots a city used, the more common job searches were. Unemployment rates weren’t affected, suggesting people had job insecurity because of robots. Sure, there could be other, nonrobotic reasons for this, but that’s no fun. We’re here because we fear our future android rulers.
It’s not all doom and gloom, fortunately. In an online experiment, the study authors found that self-affirmation exercises, such as writing down characteristics or values important to us, can overcome the existential fears and lessen concern about robots in the workplace. One of the authors noted that, while some fear is justified, “media reports on new technologies like robots and algorithms tend to be apocalyptic in nature, so people may develop an irrational fear about them.”
Oops. Our bad.
Apocalypse, stage 2: Leaping oral superorganisms
The terms of our secret agreement with the shadowy-but-powerful dental-industrial complex stipulate that LOTME can only cover tooth-related news once a year. This is that once a year.
Since we’ve already dealt with a robot apocalypse, how about a sci-fi horror story? A story with a “cross-kingdom partnership” in which assemblages of bacteria and fungi perform feats greater than either could achieve on its own. A story in which new microscopy technologies allow “scientists to visualize the behavior of living microbes in real time,” according to a statement from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
While looking at saliva samples from toddlers with severe tooth decay, lead author Zhi Ren and associates “noticed the bacteria and fungi forming these assemblages and developing motions we never thought they would possess: a ‘walking-like’ and ‘leaping-like’ mobility. … It’s almost like a new organism – a superorganism – with new functions,” said senior author Hyun Koo, DDS, PhD, of Penn Dental Medicine.
Did he say “mobility”? He did, didn’t he?
To study these alleged superorganisms, they set up a laboratory system “using the bacteria, fungi, and a tooth-like material, all incubated in human saliva,” the university explained.
“Incubated in human saliva.” There’s a phrase you don’t see every day.
It only took a few hours for the investigators to observe the bacterial/fungal assemblages making leaps of more than 100 microns across the tooth-like material. “That is more than 200 times their own body length,” Dr. Ren said, “making them even better than most vertebrates, relative to body size. For example, tree frogs and grasshoppers can leap forward about 50 times and 20 times their own body length, respectively.”
So, will it be the robots or the evil superorganisms? Let us give you a word of advice: Always bet on bacteria.
63% of long COVID patients are women, study says
according to a new study published in JAMA.
The global study also found that about 6% of people with symptomatic infections had long COVID in 2020 and 2021. The risk for long COVID seemed to be greater among those who needed hospitalization, especially those who needed intensive care.
“Quantifying the number of individuals with long COVID may help policy makers ensure adequate access to services to guide people toward recovery, return to the workplace or school, and restore their mental health and social life,” the researchers wrote.
The study team, which included dozens of researchers across nearly every continent, analyzed data from 54 studies and two databases for more than 1 million patients in 22 countries who had symptomatic COVID infections in 2020 and 2021. They looked at three long COVID symptom types: persistent fatigue with bodily pain or mood swings, ongoing respiratory problems, and cognitive issues. The study included people aged 4-66.
Overall, 6.2% of people reported one of the long COVID symptom types, including 3.7% with ongoing respiratory problems, 3.2% with persistent fatigue and bodily pain or mood swings, and 2.2% with cognitive problems. Among those with long COVID, 38% of people reported more than one symptom cluster.
At 3 months after infection, long COVID symptoms were nearly twice as common in women who were at least 20 years old at 10.6%, compared with men who were at least 20 years old at 5.4%.
Children and teens appeared to have lower risks of long COVID. About 2.8% of patients under age 20 with symptomatic infection developed long-term issues.
The estimated average duration of long COVID symptoms was 9 months among hospitalized patients and 4 months among those who weren’t hospitalized. About 15% of people with long COVID symptoms 3 months after the initial infection continued to have symptoms at 12 months.
The study was largely based on detailed data from ongoing COVID-19 studies in the United States, Austria, the Faroe Islands, Germany, Iran, Italy, the Netherlands, Russia, Sweden, and Switzerland, according to UPI. It was supplemented by published data and research conducted as part of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries and Risk Factors Study. The dozens of researchers are referred to as “Global Burden of Disease Long COVID Collaborators.”
The study had limitations, the researchers said, including the assumption that long COVID follows a similar course in all countries. Additional studies may show how long COVID symptoms and severity may vary in different countries and continents.
Ultimately, ongoing studies of large numbers of people with long COVID could help scientists and public health officials understand risk factors and ways to treat the debilitating condition, the study authors wrote, noting that “postinfection fatigue syndrome” has been reported before, namely during the 1918 flu pandemic, after the SARS outbreak in 2003, and after the Ebola epidemic in West Africa in 2014.
“Similar symptoms have been reported after other viral infections, including the Epstein-Barr virus, mononucleosis, and dengue, as well as after nonviral infections such as Q fever, Lyme disease and giardiasis,” they wrote.
Several study investigators reported receiving grants and personal fees from a variety of sources.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study published in JAMA.
The global study also found that about 6% of people with symptomatic infections had long COVID in 2020 and 2021. The risk for long COVID seemed to be greater among those who needed hospitalization, especially those who needed intensive care.
“Quantifying the number of individuals with long COVID may help policy makers ensure adequate access to services to guide people toward recovery, return to the workplace or school, and restore their mental health and social life,” the researchers wrote.
The study team, which included dozens of researchers across nearly every continent, analyzed data from 54 studies and two databases for more than 1 million patients in 22 countries who had symptomatic COVID infections in 2020 and 2021. They looked at three long COVID symptom types: persistent fatigue with bodily pain or mood swings, ongoing respiratory problems, and cognitive issues. The study included people aged 4-66.
Overall, 6.2% of people reported one of the long COVID symptom types, including 3.7% with ongoing respiratory problems, 3.2% with persistent fatigue and bodily pain or mood swings, and 2.2% with cognitive problems. Among those with long COVID, 38% of people reported more than one symptom cluster.
At 3 months after infection, long COVID symptoms were nearly twice as common in women who were at least 20 years old at 10.6%, compared with men who were at least 20 years old at 5.4%.
Children and teens appeared to have lower risks of long COVID. About 2.8% of patients under age 20 with symptomatic infection developed long-term issues.
The estimated average duration of long COVID symptoms was 9 months among hospitalized patients and 4 months among those who weren’t hospitalized. About 15% of people with long COVID symptoms 3 months after the initial infection continued to have symptoms at 12 months.
The study was largely based on detailed data from ongoing COVID-19 studies in the United States, Austria, the Faroe Islands, Germany, Iran, Italy, the Netherlands, Russia, Sweden, and Switzerland, according to UPI. It was supplemented by published data and research conducted as part of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries and Risk Factors Study. The dozens of researchers are referred to as “Global Burden of Disease Long COVID Collaborators.”
The study had limitations, the researchers said, including the assumption that long COVID follows a similar course in all countries. Additional studies may show how long COVID symptoms and severity may vary in different countries and continents.
Ultimately, ongoing studies of large numbers of people with long COVID could help scientists and public health officials understand risk factors and ways to treat the debilitating condition, the study authors wrote, noting that “postinfection fatigue syndrome” has been reported before, namely during the 1918 flu pandemic, after the SARS outbreak in 2003, and after the Ebola epidemic in West Africa in 2014.
“Similar symptoms have been reported after other viral infections, including the Epstein-Barr virus, mononucleosis, and dengue, as well as after nonviral infections such as Q fever, Lyme disease and giardiasis,” they wrote.
Several study investigators reported receiving grants and personal fees from a variety of sources.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study published in JAMA.
The global study also found that about 6% of people with symptomatic infections had long COVID in 2020 and 2021. The risk for long COVID seemed to be greater among those who needed hospitalization, especially those who needed intensive care.
“Quantifying the number of individuals with long COVID may help policy makers ensure adequate access to services to guide people toward recovery, return to the workplace or school, and restore their mental health and social life,” the researchers wrote.
The study team, which included dozens of researchers across nearly every continent, analyzed data from 54 studies and two databases for more than 1 million patients in 22 countries who had symptomatic COVID infections in 2020 and 2021. They looked at three long COVID symptom types: persistent fatigue with bodily pain or mood swings, ongoing respiratory problems, and cognitive issues. The study included people aged 4-66.
Overall, 6.2% of people reported one of the long COVID symptom types, including 3.7% with ongoing respiratory problems, 3.2% with persistent fatigue and bodily pain or mood swings, and 2.2% with cognitive problems. Among those with long COVID, 38% of people reported more than one symptom cluster.
At 3 months after infection, long COVID symptoms were nearly twice as common in women who were at least 20 years old at 10.6%, compared with men who were at least 20 years old at 5.4%.
Children and teens appeared to have lower risks of long COVID. About 2.8% of patients under age 20 with symptomatic infection developed long-term issues.
The estimated average duration of long COVID symptoms was 9 months among hospitalized patients and 4 months among those who weren’t hospitalized. About 15% of people with long COVID symptoms 3 months after the initial infection continued to have symptoms at 12 months.
The study was largely based on detailed data from ongoing COVID-19 studies in the United States, Austria, the Faroe Islands, Germany, Iran, Italy, the Netherlands, Russia, Sweden, and Switzerland, according to UPI. It was supplemented by published data and research conducted as part of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries and Risk Factors Study. The dozens of researchers are referred to as “Global Burden of Disease Long COVID Collaborators.”
The study had limitations, the researchers said, including the assumption that long COVID follows a similar course in all countries. Additional studies may show how long COVID symptoms and severity may vary in different countries and continents.
Ultimately, ongoing studies of large numbers of people with long COVID could help scientists and public health officials understand risk factors and ways to treat the debilitating condition, the study authors wrote, noting that “postinfection fatigue syndrome” has been reported before, namely during the 1918 flu pandemic, after the SARS outbreak in 2003, and after the Ebola epidemic in West Africa in 2014.
“Similar symptoms have been reported after other viral infections, including the Epstein-Barr virus, mononucleosis, and dengue, as well as after nonviral infections such as Q fever, Lyme disease and giardiasis,” they wrote.
Several study investigators reported receiving grants and personal fees from a variety of sources.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
ACC issues guidance on ED evaluation of acute chest pain
Chest pain accounts for more than 7 million ED visits annually. A major challenge is to quickly identify the small number of patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) among the large number of patients who have noncardiac conditions.
The new document is intended to provide guidance on how to “practically apply” recommendations from the 2021 American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Guideline for the Evaluation and Diagnosis of Chest Pain, focusing specifically on patients who present to the ED, the writing group explains.
“A systematic approach – both at the level of the institution and the individual patient – is essential to achieve optimal outcomes for patients presenting with chest pain to the ED,” say writing group chair Michael Kontos, MD, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and colleagues.
At the institution level, this decision pathway recommends high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) assays coupled with a clinical decision pathway (CDP) to reduce ED “dwell” times and increase the number of patients with chest pain who can safely be discharged without additional testing. This will decrease ED crowding and limit unnecessary testing, they point out.
At the individual patient level, this document aims to provide structure for the ED evaluation of chest pain, accelerating the evaluation process and matching the intensity of testing and treatment to patient risk.
The 36-page document was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Key summary points in the document include the following:
- Electrocardiogram remains the best initial test for evaluation of chest pain in the ED and should be performed and interpreted within 10 minutes of ED arrival.
- In patients who arrive via ambulance, the prehospital ECG should be reviewed, because ischemic changes may have resolved before ED arrival.
- When the ECG shows evidence of acute infarction or ischemia, subsequent care should follow current guidelines for management of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non–ST-segment elevation ACS (NSTE-ACS).
- Patients with a nonischemic ECG can enter an accelerated CDP designed to provide rapid risk assessment and exclusion of ACS.
- Patients who are hemodynamically unstable, have significant arrhythmias, or evidence of significant heart failure should be evaluated and treated appropriately and are not candidates for an accelerated CDP.
- High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT) and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) are the preferred biomarkers for evaluation of possible ACS.
- Patients classified as low risk (rule out) using the current hs-cTn-based CDPs can generally be discharged directly from the ED without additional testing, although outpatient testing may be considered in selected cases.
- Patients with substantially elevated initial hs-cTn values or those with significant dynamic changes over 1-3 hours are assigned to the abnormal/high-risk category and should be further classified according to the universal definition of myocardial infarction type 1 or 2 or acute or chronic nonischemic cardiac injury.
- High-risk patients should usually be admitted to an inpatient setting for further evaluation and treatment.
- Patients determined to be intermediate risk with the CDP should undergo additional observation with repeat hs-cTn measurements at 3-6 hours and risk assessment using either the modified HEART (history, ECG, age, risk factors, and troponin) score or the ED assessment of chest pain score (EDACS).
- Noninvasive testing should be considered for the intermediate-risk group unless low-risk features are identified using risk scores or noninvasive testing has been performed recently with normal or low-risk findings.
The writing group notes that “safe and efficient” management of chest pain in the ED requires appropriate follow-up after discharge. Timing of follow-up and referral for outpatient noninvasive testing should be influenced by patient risk and results of cardiac testing.
Disclosures for members of the writing group are available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chest pain accounts for more than 7 million ED visits annually. A major challenge is to quickly identify the small number of patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) among the large number of patients who have noncardiac conditions.
The new document is intended to provide guidance on how to “practically apply” recommendations from the 2021 American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Guideline for the Evaluation and Diagnosis of Chest Pain, focusing specifically on patients who present to the ED, the writing group explains.
“A systematic approach – both at the level of the institution and the individual patient – is essential to achieve optimal outcomes for patients presenting with chest pain to the ED,” say writing group chair Michael Kontos, MD, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and colleagues.
At the institution level, this decision pathway recommends high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) assays coupled with a clinical decision pathway (CDP) to reduce ED “dwell” times and increase the number of patients with chest pain who can safely be discharged without additional testing. This will decrease ED crowding and limit unnecessary testing, they point out.
At the individual patient level, this document aims to provide structure for the ED evaluation of chest pain, accelerating the evaluation process and matching the intensity of testing and treatment to patient risk.
The 36-page document was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Key summary points in the document include the following:
- Electrocardiogram remains the best initial test for evaluation of chest pain in the ED and should be performed and interpreted within 10 minutes of ED arrival.
- In patients who arrive via ambulance, the prehospital ECG should be reviewed, because ischemic changes may have resolved before ED arrival.
- When the ECG shows evidence of acute infarction or ischemia, subsequent care should follow current guidelines for management of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non–ST-segment elevation ACS (NSTE-ACS).
- Patients with a nonischemic ECG can enter an accelerated CDP designed to provide rapid risk assessment and exclusion of ACS.
- Patients who are hemodynamically unstable, have significant arrhythmias, or evidence of significant heart failure should be evaluated and treated appropriately and are not candidates for an accelerated CDP.
- High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT) and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) are the preferred biomarkers for evaluation of possible ACS.
- Patients classified as low risk (rule out) using the current hs-cTn-based CDPs can generally be discharged directly from the ED without additional testing, although outpatient testing may be considered in selected cases.
- Patients with substantially elevated initial hs-cTn values or those with significant dynamic changes over 1-3 hours are assigned to the abnormal/high-risk category and should be further classified according to the universal definition of myocardial infarction type 1 or 2 or acute or chronic nonischemic cardiac injury.
- High-risk patients should usually be admitted to an inpatient setting for further evaluation and treatment.
- Patients determined to be intermediate risk with the CDP should undergo additional observation with repeat hs-cTn measurements at 3-6 hours and risk assessment using either the modified HEART (history, ECG, age, risk factors, and troponin) score or the ED assessment of chest pain score (EDACS).
- Noninvasive testing should be considered for the intermediate-risk group unless low-risk features are identified using risk scores or noninvasive testing has been performed recently with normal or low-risk findings.
The writing group notes that “safe and efficient” management of chest pain in the ED requires appropriate follow-up after discharge. Timing of follow-up and referral for outpatient noninvasive testing should be influenced by patient risk and results of cardiac testing.
Disclosures for members of the writing group are available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chest pain accounts for more than 7 million ED visits annually. A major challenge is to quickly identify the small number of patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) among the large number of patients who have noncardiac conditions.
The new document is intended to provide guidance on how to “practically apply” recommendations from the 2021 American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Guideline for the Evaluation and Diagnosis of Chest Pain, focusing specifically on patients who present to the ED, the writing group explains.
“A systematic approach – both at the level of the institution and the individual patient – is essential to achieve optimal outcomes for patients presenting with chest pain to the ED,” say writing group chair Michael Kontos, MD, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and colleagues.
At the institution level, this decision pathway recommends high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) assays coupled with a clinical decision pathway (CDP) to reduce ED “dwell” times and increase the number of patients with chest pain who can safely be discharged without additional testing. This will decrease ED crowding and limit unnecessary testing, they point out.
At the individual patient level, this document aims to provide structure for the ED evaluation of chest pain, accelerating the evaluation process and matching the intensity of testing and treatment to patient risk.
The 36-page document was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Key summary points in the document include the following:
- Electrocardiogram remains the best initial test for evaluation of chest pain in the ED and should be performed and interpreted within 10 minutes of ED arrival.
- In patients who arrive via ambulance, the prehospital ECG should be reviewed, because ischemic changes may have resolved before ED arrival.
- When the ECG shows evidence of acute infarction or ischemia, subsequent care should follow current guidelines for management of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non–ST-segment elevation ACS (NSTE-ACS).
- Patients with a nonischemic ECG can enter an accelerated CDP designed to provide rapid risk assessment and exclusion of ACS.
- Patients who are hemodynamically unstable, have significant arrhythmias, or evidence of significant heart failure should be evaluated and treated appropriately and are not candidates for an accelerated CDP.
- High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT) and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) are the preferred biomarkers for evaluation of possible ACS.
- Patients classified as low risk (rule out) using the current hs-cTn-based CDPs can generally be discharged directly from the ED without additional testing, although outpatient testing may be considered in selected cases.
- Patients with substantially elevated initial hs-cTn values or those with significant dynamic changes over 1-3 hours are assigned to the abnormal/high-risk category and should be further classified according to the universal definition of myocardial infarction type 1 or 2 or acute or chronic nonischemic cardiac injury.
- High-risk patients should usually be admitted to an inpatient setting for further evaluation and treatment.
- Patients determined to be intermediate risk with the CDP should undergo additional observation with repeat hs-cTn measurements at 3-6 hours and risk assessment using either the modified HEART (history, ECG, age, risk factors, and troponin) score or the ED assessment of chest pain score (EDACS).
- Noninvasive testing should be considered for the intermediate-risk group unless low-risk features are identified using risk scores or noninvasive testing has been performed recently with normal or low-risk findings.
The writing group notes that “safe and efficient” management of chest pain in the ED requires appropriate follow-up after discharge. Timing of follow-up and referral for outpatient noninvasive testing should be influenced by patient risk and results of cardiac testing.
Disclosures for members of the writing group are available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
New advice on artificial pancreas insulin delivery systems
A new consensus statement summarizes the benefits, limitations, and challenges of using automated insulin delivery (AID) systems and provides recommendations for use by people with diabetes.
“Automated insulin delivery systems” is becoming the standard terminology – including by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration – to refer to systems that integrate data from a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system via a control algorithm into an insulin pump in order to automate subcutaneous insulin delivery. “Hybrid AID” or “hybrid closed-loop” refers to the current status of these systems, which still require some degree of user input to control glucose levels.
The term “artificial pancreas” was used interchangeably with AID in the past, but it doesn’t take into account exocrine pancreatic function. The term “bionic pancreas” refers to a specific system in development that would ultimately include glucagon along with insulin.
The new consensus report, titled “Automated insulin delivery: Benefits, challenges, and recommendations,” was published online in Diabetes Care and Diabetologia.
The document is geared toward not only diabetologists and other specialists, but also diabetes nurses and specialist dietitians. Colleagues working at regulatory agencies, health care organizations, and related media might also benefit from reading it.
It is endorsed by two professional societies – the European Association for the Study of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association – and contrasts with other statements about AID systems that are sponsored by their manufacturers, noted document co-author Mark Evans, PhD, professor of diabetic medicine, University of Cambridge, England, in a statement.
“Many clinically relevant aspects, including safety, are addressed in this report. The aim ... is to encourage ongoing improvement of this technology, its safe and effective use, and its accessibility to all who can benefit from it,” Dr. Evans said.
Lead author Jennifer Sherr, MD, PhD, pediatric endocrinology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., commented that the report “addresses the clinical usage of AID systems from a practical point of view rather than as ... a meta-analysis or a review of all relevant clinical studies. ... As such, the benefits and limitations of systems are discussed while also considering safety, regulatory pathways, and access to this technology.”
AID systems do not mean diabetes is “cured”
Separate recommendations provided at the end of the document are aimed at specific stakeholders, including health care providers, patients and their caregivers, manufacturers, regulatory agencies, and the research community.
The authors make clear in the introduction that, while representing “a significant movement toward optimizing glucose management for individuals with diabetes,” the use of AID systems doesn’t mean that diabetes is “cured.” Rather, “expectations need to be set adequately so that individuals with diabetes and providers understand what such systems can and cannot do.”
In particular, current commercially available AID systems require user input for mealtime insulin dosing and sometimes for correction doses of high blood glucose levels, although the systems at least partially automate that.
“When integrated into care, AID systems hold promise to relieve some of the daily burdens of diabetes care,” the authors write.
The statement also details problems that may arise with the physical devices, including skin irritation from adhesives, occlusion of insulin infusion sets, early CGM sensor failure, and inadequate dosing algorithms.
“Individuals with diabetes who are considering this type of advanced diabetes therapy should not only have appropriate technical understanding of the system but also be able to revert to standard diabetes treatment (that is, nonautomated subcutaneous insulin delivery by pump or injections) in case the AID system fails. They should be able to independently troubleshoot and have access to their health care provider if needed.”
To monitor the impact of the technology, the authors emphasize the importance of the time-in-range metric derived from CGM, with the goal of achieving 70% or greater time in target blood glucose range.
Separate sections of the document address the benefits and limitations of AID systems, education and expectations for both patients and providers, and patient and provider perspectives, including how to handle urgent questions.
Other sections cover special populations such as pregnant women and people with type 2 diabetes, considerations for patient selection for current AID systems, safety, improving access to the technology, liability, and do-it-yourself systems.
Recommendations for health care professionals
A table near the end of the document provides specific recommendations for health care professionals, including the following:
- Be knowledgeable about AID systems and nuances of different systems, including their distinguishing features as well as strengths and weaknesses.
- Inform patients with diabetes about AID systems, including review of currently available systems, and create realistic expectations for device use.
- Involve patients with diabetes in shared decision-making when considering use of AID systems.
- Share information with patients with diabetes, as well as their peers, about general standards set by national and international guidelines on AID systems.
- Provide an on-call number or method by which a person with diabetes can always access support from a health care provider at the practice, including weekends and nights.
- Implement, potentially, protocols on times when AID systems should not be used.
- Use an individual’s health data to improve quality of care and health outcomes.
Most members of the ADA/EASD Diabetes Technology Working Group work with industry, but industry had no input on the project. Dr. Sherr has reported conducting clinical trials for Eli Lilly, Insulet, and Medtronic, and has received in-kind support for research studies from Dexcom and Medtronic. She has also reported consulting for Eli Lilly, Lexicon, Medtronic, and Sanofi, and being an advisory board member for Bigfoot Biomedical, Cecelia Health, Eli Lilly, Insulet, T1D Fund, and Vertex Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Evans has reported conducting clinical trials or research collaborations for, serving on advisory boards for, or receiving speakers fees or travel support from Medtronic, Roche, Abbott Diabetes Care, Dexcom, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Zucara Therapeutics, Pila Pharma, and AstraZeneca. The University of Cambridge has received salary support for Dr. Evans from the National Health Service.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new consensus statement summarizes the benefits, limitations, and challenges of using automated insulin delivery (AID) systems and provides recommendations for use by people with diabetes.
“Automated insulin delivery systems” is becoming the standard terminology – including by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration – to refer to systems that integrate data from a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system via a control algorithm into an insulin pump in order to automate subcutaneous insulin delivery. “Hybrid AID” or “hybrid closed-loop” refers to the current status of these systems, which still require some degree of user input to control glucose levels.
The term “artificial pancreas” was used interchangeably with AID in the past, but it doesn’t take into account exocrine pancreatic function. The term “bionic pancreas” refers to a specific system in development that would ultimately include glucagon along with insulin.
The new consensus report, titled “Automated insulin delivery: Benefits, challenges, and recommendations,” was published online in Diabetes Care and Diabetologia.
The document is geared toward not only diabetologists and other specialists, but also diabetes nurses and specialist dietitians. Colleagues working at regulatory agencies, health care organizations, and related media might also benefit from reading it.
It is endorsed by two professional societies – the European Association for the Study of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association – and contrasts with other statements about AID systems that are sponsored by their manufacturers, noted document co-author Mark Evans, PhD, professor of diabetic medicine, University of Cambridge, England, in a statement.
“Many clinically relevant aspects, including safety, are addressed in this report. The aim ... is to encourage ongoing improvement of this technology, its safe and effective use, and its accessibility to all who can benefit from it,” Dr. Evans said.
Lead author Jennifer Sherr, MD, PhD, pediatric endocrinology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., commented that the report “addresses the clinical usage of AID systems from a practical point of view rather than as ... a meta-analysis or a review of all relevant clinical studies. ... As such, the benefits and limitations of systems are discussed while also considering safety, regulatory pathways, and access to this technology.”
AID systems do not mean diabetes is “cured”
Separate recommendations provided at the end of the document are aimed at specific stakeholders, including health care providers, patients and their caregivers, manufacturers, regulatory agencies, and the research community.
The authors make clear in the introduction that, while representing “a significant movement toward optimizing glucose management for individuals with diabetes,” the use of AID systems doesn’t mean that diabetes is “cured.” Rather, “expectations need to be set adequately so that individuals with diabetes and providers understand what such systems can and cannot do.”
In particular, current commercially available AID systems require user input for mealtime insulin dosing and sometimes for correction doses of high blood glucose levels, although the systems at least partially automate that.
“When integrated into care, AID systems hold promise to relieve some of the daily burdens of diabetes care,” the authors write.
The statement also details problems that may arise with the physical devices, including skin irritation from adhesives, occlusion of insulin infusion sets, early CGM sensor failure, and inadequate dosing algorithms.
“Individuals with diabetes who are considering this type of advanced diabetes therapy should not only have appropriate technical understanding of the system but also be able to revert to standard diabetes treatment (that is, nonautomated subcutaneous insulin delivery by pump or injections) in case the AID system fails. They should be able to independently troubleshoot and have access to their health care provider if needed.”
To monitor the impact of the technology, the authors emphasize the importance of the time-in-range metric derived from CGM, with the goal of achieving 70% or greater time in target blood glucose range.
Separate sections of the document address the benefits and limitations of AID systems, education and expectations for both patients and providers, and patient and provider perspectives, including how to handle urgent questions.
Other sections cover special populations such as pregnant women and people with type 2 diabetes, considerations for patient selection for current AID systems, safety, improving access to the technology, liability, and do-it-yourself systems.
Recommendations for health care professionals
A table near the end of the document provides specific recommendations for health care professionals, including the following:
- Be knowledgeable about AID systems and nuances of different systems, including their distinguishing features as well as strengths and weaknesses.
- Inform patients with diabetes about AID systems, including review of currently available systems, and create realistic expectations for device use.
- Involve patients with diabetes in shared decision-making when considering use of AID systems.
- Share information with patients with diabetes, as well as their peers, about general standards set by national and international guidelines on AID systems.
- Provide an on-call number or method by which a person with diabetes can always access support from a health care provider at the practice, including weekends and nights.
- Implement, potentially, protocols on times when AID systems should not be used.
- Use an individual’s health data to improve quality of care and health outcomes.
Most members of the ADA/EASD Diabetes Technology Working Group work with industry, but industry had no input on the project. Dr. Sherr has reported conducting clinical trials for Eli Lilly, Insulet, and Medtronic, and has received in-kind support for research studies from Dexcom and Medtronic. She has also reported consulting for Eli Lilly, Lexicon, Medtronic, and Sanofi, and being an advisory board member for Bigfoot Biomedical, Cecelia Health, Eli Lilly, Insulet, T1D Fund, and Vertex Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Evans has reported conducting clinical trials or research collaborations for, serving on advisory boards for, or receiving speakers fees or travel support from Medtronic, Roche, Abbott Diabetes Care, Dexcom, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Zucara Therapeutics, Pila Pharma, and AstraZeneca. The University of Cambridge has received salary support for Dr. Evans from the National Health Service.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new consensus statement summarizes the benefits, limitations, and challenges of using automated insulin delivery (AID) systems and provides recommendations for use by people with diabetes.
“Automated insulin delivery systems” is becoming the standard terminology – including by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration – to refer to systems that integrate data from a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system via a control algorithm into an insulin pump in order to automate subcutaneous insulin delivery. “Hybrid AID” or “hybrid closed-loop” refers to the current status of these systems, which still require some degree of user input to control glucose levels.
The term “artificial pancreas” was used interchangeably with AID in the past, but it doesn’t take into account exocrine pancreatic function. The term “bionic pancreas” refers to a specific system in development that would ultimately include glucagon along with insulin.
The new consensus report, titled “Automated insulin delivery: Benefits, challenges, and recommendations,” was published online in Diabetes Care and Diabetologia.
The document is geared toward not only diabetologists and other specialists, but also diabetes nurses and specialist dietitians. Colleagues working at regulatory agencies, health care organizations, and related media might also benefit from reading it.
It is endorsed by two professional societies – the European Association for the Study of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association – and contrasts with other statements about AID systems that are sponsored by their manufacturers, noted document co-author Mark Evans, PhD, professor of diabetic medicine, University of Cambridge, England, in a statement.
“Many clinically relevant aspects, including safety, are addressed in this report. The aim ... is to encourage ongoing improvement of this technology, its safe and effective use, and its accessibility to all who can benefit from it,” Dr. Evans said.
Lead author Jennifer Sherr, MD, PhD, pediatric endocrinology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., commented that the report “addresses the clinical usage of AID systems from a practical point of view rather than as ... a meta-analysis or a review of all relevant clinical studies. ... As such, the benefits and limitations of systems are discussed while also considering safety, regulatory pathways, and access to this technology.”
AID systems do not mean diabetes is “cured”
Separate recommendations provided at the end of the document are aimed at specific stakeholders, including health care providers, patients and their caregivers, manufacturers, regulatory agencies, and the research community.
The authors make clear in the introduction that, while representing “a significant movement toward optimizing glucose management for individuals with diabetes,” the use of AID systems doesn’t mean that diabetes is “cured.” Rather, “expectations need to be set adequately so that individuals with diabetes and providers understand what such systems can and cannot do.”
In particular, current commercially available AID systems require user input for mealtime insulin dosing and sometimes for correction doses of high blood glucose levels, although the systems at least partially automate that.
“When integrated into care, AID systems hold promise to relieve some of the daily burdens of diabetes care,” the authors write.
The statement also details problems that may arise with the physical devices, including skin irritation from adhesives, occlusion of insulin infusion sets, early CGM sensor failure, and inadequate dosing algorithms.
“Individuals with diabetes who are considering this type of advanced diabetes therapy should not only have appropriate technical understanding of the system but also be able to revert to standard diabetes treatment (that is, nonautomated subcutaneous insulin delivery by pump or injections) in case the AID system fails. They should be able to independently troubleshoot and have access to their health care provider if needed.”
To monitor the impact of the technology, the authors emphasize the importance of the time-in-range metric derived from CGM, with the goal of achieving 70% or greater time in target blood glucose range.
Separate sections of the document address the benefits and limitations of AID systems, education and expectations for both patients and providers, and patient and provider perspectives, including how to handle urgent questions.
Other sections cover special populations such as pregnant women and people with type 2 diabetes, considerations for patient selection for current AID systems, safety, improving access to the technology, liability, and do-it-yourself systems.
Recommendations for health care professionals
A table near the end of the document provides specific recommendations for health care professionals, including the following:
- Be knowledgeable about AID systems and nuances of different systems, including their distinguishing features as well as strengths and weaknesses.
- Inform patients with diabetes about AID systems, including review of currently available systems, and create realistic expectations for device use.
- Involve patients with diabetes in shared decision-making when considering use of AID systems.
- Share information with patients with diabetes, as well as their peers, about general standards set by national and international guidelines on AID systems.
- Provide an on-call number or method by which a person with diabetes can always access support from a health care provider at the practice, including weekends and nights.
- Implement, potentially, protocols on times when AID systems should not be used.
- Use an individual’s health data to improve quality of care and health outcomes.
Most members of the ADA/EASD Diabetes Technology Working Group work with industry, but industry had no input on the project. Dr. Sherr has reported conducting clinical trials for Eli Lilly, Insulet, and Medtronic, and has received in-kind support for research studies from Dexcom and Medtronic. She has also reported consulting for Eli Lilly, Lexicon, Medtronic, and Sanofi, and being an advisory board member for Bigfoot Biomedical, Cecelia Health, Eli Lilly, Insulet, T1D Fund, and Vertex Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Evans has reported conducting clinical trials or research collaborations for, serving on advisory boards for, or receiving speakers fees or travel support from Medtronic, Roche, Abbott Diabetes Care, Dexcom, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Zucara Therapeutics, Pila Pharma, and AstraZeneca. The University of Cambridge has received salary support for Dr. Evans from the National Health Service.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETES CARE AND DIABETOLOGIA
At the front lines of long COVID, local clinics prove vital
Big-name hospital chains across the United States are opening dedicated centers to help patients dealing with long COVID. But so are the lower-profile clinics and hospitals run by cities, counties and states – including Harborview Medical Center in Seattle.
They serve areas ranging from Campbell County, Wyo., with 47,000 residents, to New York City, with its 8.4 million people. Many providers working there are searching for innovative ways to approach this lingering illness with its variety of symptoms, from brain fog to shortness of breath to depression and more.
Their efforts often fall below the radar, with still-scant serious media attention to long COVID or the public health employees working to treat ailing patients.
Why are state and local health agencies taking on these duties?
They’re leading the way in part because the federal government has made only limited efforts, said Lisa McCorkell, a cofounder of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative. The international group was founded in spring 2020 by researchers who are also long COVID patients.
“It’s a big reason why long COVID isn’t talked about as much,” Ms. McCorkell said. “It’s definitely a national issue. But it trickles down to state and local health departments, and there’s not enough resources.”
The government clinics may be accessible to people without insurance and often are cheaper than clinics at private hospitals.
Harborview has treated more than 1,000 patients with long COVID, and another 200 patients are awaiting treatment, said Jessica Bender, MD, a codirector of the University of Washington Post-COVID Rehabilitation and Recovery Clinic in Seattle’s First Hill neighborhood.
The group Survivor Corps offers lists by states of clinics. While the publicly run clinics may be less expensive or even free for some patients, methods of payment vary from clinic to clinic. Federally qualified health clinics offer treatment on a sliding scale. For instance, the Riverside University Health System in California has federally qualified centers. And other providers who are not federally qualified also offer care paid for on a sliding scale. They include Campbell County Health, where some residents are eligible for discounts of 25%-100%, said spokesperson Norberto Orellana.
At Harborview, Dr. Bender said the public hospital’s post-COVID clinic initially began with a staff of rehabilitation doctors but expanded in 2021 to include family and internal medicine doctors. And it offers mental health programs with rehabilitation psychologists who instruct on how to deal with doctors or loved ones who don’t believe that long COVID exists.
“I have patients who really have been devastated by the lack of support from coworkers [and] family,” Dr. Bender said.
In Campbell County, Wyo., the pandemic surge did not arrive in earnest until late 2021. Physical therapists at Campbell County’s Health Rehabilitation Services organized a rehabilitation program for residents with long COVID after recognizing the need, said Shannon Sorensen, rehabilitation director at Campbell County Health.
“We had patients coming in showing chest pain, or heart palpitations. There were people trying to get back to work. They were frustrated,” Ms. Sorensen said.
Myalgic encephalomyelitis and chronic fatigue syndrome activists have embraced the fight to recognize and help long COVID patients, noting the similarities between the conditions, and hope to help kickstart more organized research, treatment and benefits for long COVID sufferers and myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients alike.
In Ft. Collins, Colo., disability activist Alison Sbrana has long had myalgic encephalomyelitis. She and other members of the local chapter of ME Action have met with state officials for several years and are finally seeing the results of those efforts.
Colorado Gov. Jared Polis has created the full-time position of policy adviser for long COVID and post–viral infection planning.
“This is one way forward of how state governments are (finally) paying attention to infection-triggered chronic illnesses and starting to think ahead on them,” Ms. Sbrana said.
New York City’s Health + Hospitals launched what may be the most expansive long COVID treatment program in the nation in April 2021. Called AfterCare, it provides physical and mental health services as well as community support systems and financial assistance.
A persistent issue for patients is that there isn’t yet a test for long COVID, like there is for COVID-19, said Amanda Johnson, MD, assistant vice president for ambulatory care and population health at New York Health + Hospitals. “It’s in many ways a diagnosis of exclusion. You have to make sure their shortness of breath isn’t caused by something else. The same with anemia,” she said.
California’s Department of Public Health has a detailed website devoted to the topic, including videos of “long haulers” describing their experiences.
Vermont is one of several states studying long COVID, said Mark Levine, MD, the state health commissioner. The state, in collaboration with the University of Vermont, has established a surveillance project to determine how many people have long COVID, as well as how severe it is, how long it lasts, and potential predispositions.
The University of Utah, Salt Lake City, established a comprehensive COVID-19 clinic more than a year ago that also handles long COVID patients, said Jeannette Brown, MD, PhD, an associate professor at the school and director of the COVID-19 clinic.
Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, MPH, already had a deep understanding of long COVID when she landed in Riverside County, Calif., in the summer of 2021. She came from Atlanta, where as part of her job as an epidemic intelligence service officer at the CDC, she heard stories of COVID-19 patients who were not getting better.
Now she is a deputy public health officer for Riverside County, in a region known for its deserts, sizzling summer temperatures and diverse populations. She said her department has helped launch programs such as post–COVID-19 follow-up phone calls and long COVID training programs that reach out to the many Latino residents in this county of 2.4 million people. It also includes Black and Native American residents.
“We’re making sure information is circulated with community and faith-based organizations, and community health workers,” she said.
Ms. McCorkell said there is still much work to do to raise public awareness of the risks of long COVID and how to obtain care for patients. She would like to see a national public health campaign about long COVID, possibly spearheaded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in partnership with local health workers and community-based organizations.
“That,” she said, “could make a big difference.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Big-name hospital chains across the United States are opening dedicated centers to help patients dealing with long COVID. But so are the lower-profile clinics and hospitals run by cities, counties and states – including Harborview Medical Center in Seattle.
They serve areas ranging from Campbell County, Wyo., with 47,000 residents, to New York City, with its 8.4 million people. Many providers working there are searching for innovative ways to approach this lingering illness with its variety of symptoms, from brain fog to shortness of breath to depression and more.
Their efforts often fall below the radar, with still-scant serious media attention to long COVID or the public health employees working to treat ailing patients.
Why are state and local health agencies taking on these duties?
They’re leading the way in part because the federal government has made only limited efforts, said Lisa McCorkell, a cofounder of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative. The international group was founded in spring 2020 by researchers who are also long COVID patients.
“It’s a big reason why long COVID isn’t talked about as much,” Ms. McCorkell said. “It’s definitely a national issue. But it trickles down to state and local health departments, and there’s not enough resources.”
The government clinics may be accessible to people without insurance and often are cheaper than clinics at private hospitals.
Harborview has treated more than 1,000 patients with long COVID, and another 200 patients are awaiting treatment, said Jessica Bender, MD, a codirector of the University of Washington Post-COVID Rehabilitation and Recovery Clinic in Seattle’s First Hill neighborhood.
The group Survivor Corps offers lists by states of clinics. While the publicly run clinics may be less expensive or even free for some patients, methods of payment vary from clinic to clinic. Federally qualified health clinics offer treatment on a sliding scale. For instance, the Riverside University Health System in California has federally qualified centers. And other providers who are not federally qualified also offer care paid for on a sliding scale. They include Campbell County Health, where some residents are eligible for discounts of 25%-100%, said spokesperson Norberto Orellana.
At Harborview, Dr. Bender said the public hospital’s post-COVID clinic initially began with a staff of rehabilitation doctors but expanded in 2021 to include family and internal medicine doctors. And it offers mental health programs with rehabilitation psychologists who instruct on how to deal with doctors or loved ones who don’t believe that long COVID exists.
“I have patients who really have been devastated by the lack of support from coworkers [and] family,” Dr. Bender said.
In Campbell County, Wyo., the pandemic surge did not arrive in earnest until late 2021. Physical therapists at Campbell County’s Health Rehabilitation Services organized a rehabilitation program for residents with long COVID after recognizing the need, said Shannon Sorensen, rehabilitation director at Campbell County Health.
“We had patients coming in showing chest pain, or heart palpitations. There were people trying to get back to work. They were frustrated,” Ms. Sorensen said.
Myalgic encephalomyelitis and chronic fatigue syndrome activists have embraced the fight to recognize and help long COVID patients, noting the similarities between the conditions, and hope to help kickstart more organized research, treatment and benefits for long COVID sufferers and myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients alike.
In Ft. Collins, Colo., disability activist Alison Sbrana has long had myalgic encephalomyelitis. She and other members of the local chapter of ME Action have met with state officials for several years and are finally seeing the results of those efforts.
Colorado Gov. Jared Polis has created the full-time position of policy adviser for long COVID and post–viral infection planning.
“This is one way forward of how state governments are (finally) paying attention to infection-triggered chronic illnesses and starting to think ahead on them,” Ms. Sbrana said.
New York City’s Health + Hospitals launched what may be the most expansive long COVID treatment program in the nation in April 2021. Called AfterCare, it provides physical and mental health services as well as community support systems and financial assistance.
A persistent issue for patients is that there isn’t yet a test for long COVID, like there is for COVID-19, said Amanda Johnson, MD, assistant vice president for ambulatory care and population health at New York Health + Hospitals. “It’s in many ways a diagnosis of exclusion. You have to make sure their shortness of breath isn’t caused by something else. The same with anemia,” she said.
California’s Department of Public Health has a detailed website devoted to the topic, including videos of “long haulers” describing their experiences.
Vermont is one of several states studying long COVID, said Mark Levine, MD, the state health commissioner. The state, in collaboration with the University of Vermont, has established a surveillance project to determine how many people have long COVID, as well as how severe it is, how long it lasts, and potential predispositions.
The University of Utah, Salt Lake City, established a comprehensive COVID-19 clinic more than a year ago that also handles long COVID patients, said Jeannette Brown, MD, PhD, an associate professor at the school and director of the COVID-19 clinic.
Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, MPH, already had a deep understanding of long COVID when she landed in Riverside County, Calif., in the summer of 2021. She came from Atlanta, where as part of her job as an epidemic intelligence service officer at the CDC, she heard stories of COVID-19 patients who were not getting better.
Now she is a deputy public health officer for Riverside County, in a region known for its deserts, sizzling summer temperatures and diverse populations. She said her department has helped launch programs such as post–COVID-19 follow-up phone calls and long COVID training programs that reach out to the many Latino residents in this county of 2.4 million people. It also includes Black and Native American residents.
“We’re making sure information is circulated with community and faith-based organizations, and community health workers,” she said.
Ms. McCorkell said there is still much work to do to raise public awareness of the risks of long COVID and how to obtain care for patients. She would like to see a national public health campaign about long COVID, possibly spearheaded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in partnership with local health workers and community-based organizations.
“That,” she said, “could make a big difference.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Big-name hospital chains across the United States are opening dedicated centers to help patients dealing with long COVID. But so are the lower-profile clinics and hospitals run by cities, counties and states – including Harborview Medical Center in Seattle.
They serve areas ranging from Campbell County, Wyo., with 47,000 residents, to New York City, with its 8.4 million people. Many providers working there are searching for innovative ways to approach this lingering illness with its variety of symptoms, from brain fog to shortness of breath to depression and more.
Their efforts often fall below the radar, with still-scant serious media attention to long COVID or the public health employees working to treat ailing patients.
Why are state and local health agencies taking on these duties?
They’re leading the way in part because the federal government has made only limited efforts, said Lisa McCorkell, a cofounder of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative. The international group was founded in spring 2020 by researchers who are also long COVID patients.
“It’s a big reason why long COVID isn’t talked about as much,” Ms. McCorkell said. “It’s definitely a national issue. But it trickles down to state and local health departments, and there’s not enough resources.”
The government clinics may be accessible to people without insurance and often are cheaper than clinics at private hospitals.
Harborview has treated more than 1,000 patients with long COVID, and another 200 patients are awaiting treatment, said Jessica Bender, MD, a codirector of the University of Washington Post-COVID Rehabilitation and Recovery Clinic in Seattle’s First Hill neighborhood.
The group Survivor Corps offers lists by states of clinics. While the publicly run clinics may be less expensive or even free for some patients, methods of payment vary from clinic to clinic. Federally qualified health clinics offer treatment on a sliding scale. For instance, the Riverside University Health System in California has federally qualified centers. And other providers who are not federally qualified also offer care paid for on a sliding scale. They include Campbell County Health, where some residents are eligible for discounts of 25%-100%, said spokesperson Norberto Orellana.
At Harborview, Dr. Bender said the public hospital’s post-COVID clinic initially began with a staff of rehabilitation doctors but expanded in 2021 to include family and internal medicine doctors. And it offers mental health programs with rehabilitation psychologists who instruct on how to deal with doctors or loved ones who don’t believe that long COVID exists.
“I have patients who really have been devastated by the lack of support from coworkers [and] family,” Dr. Bender said.
In Campbell County, Wyo., the pandemic surge did not arrive in earnest until late 2021. Physical therapists at Campbell County’s Health Rehabilitation Services organized a rehabilitation program for residents with long COVID after recognizing the need, said Shannon Sorensen, rehabilitation director at Campbell County Health.
“We had patients coming in showing chest pain, or heart palpitations. There were people trying to get back to work. They were frustrated,” Ms. Sorensen said.
Myalgic encephalomyelitis and chronic fatigue syndrome activists have embraced the fight to recognize and help long COVID patients, noting the similarities between the conditions, and hope to help kickstart more organized research, treatment and benefits for long COVID sufferers and myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients alike.
In Ft. Collins, Colo., disability activist Alison Sbrana has long had myalgic encephalomyelitis. She and other members of the local chapter of ME Action have met with state officials for several years and are finally seeing the results of those efforts.
Colorado Gov. Jared Polis has created the full-time position of policy adviser for long COVID and post–viral infection planning.
“This is one way forward of how state governments are (finally) paying attention to infection-triggered chronic illnesses and starting to think ahead on them,” Ms. Sbrana said.
New York City’s Health + Hospitals launched what may be the most expansive long COVID treatment program in the nation in April 2021. Called AfterCare, it provides physical and mental health services as well as community support systems and financial assistance.
A persistent issue for patients is that there isn’t yet a test for long COVID, like there is for COVID-19, said Amanda Johnson, MD, assistant vice president for ambulatory care and population health at New York Health + Hospitals. “It’s in many ways a diagnosis of exclusion. You have to make sure their shortness of breath isn’t caused by something else. The same with anemia,” she said.
California’s Department of Public Health has a detailed website devoted to the topic, including videos of “long haulers” describing their experiences.
Vermont is one of several states studying long COVID, said Mark Levine, MD, the state health commissioner. The state, in collaboration with the University of Vermont, has established a surveillance project to determine how many people have long COVID, as well as how severe it is, how long it lasts, and potential predispositions.
The University of Utah, Salt Lake City, established a comprehensive COVID-19 clinic more than a year ago that also handles long COVID patients, said Jeannette Brown, MD, PhD, an associate professor at the school and director of the COVID-19 clinic.
Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, MPH, already had a deep understanding of long COVID when she landed in Riverside County, Calif., in the summer of 2021. She came from Atlanta, where as part of her job as an epidemic intelligence service officer at the CDC, she heard stories of COVID-19 patients who were not getting better.
Now she is a deputy public health officer for Riverside County, in a region known for its deserts, sizzling summer temperatures and diverse populations. She said her department has helped launch programs such as post–COVID-19 follow-up phone calls and long COVID training programs that reach out to the many Latino residents in this county of 2.4 million people. It also includes Black and Native American residents.
“We’re making sure information is circulated with community and faith-based organizations, and community health workers,” she said.
Ms. McCorkell said there is still much work to do to raise public awareness of the risks of long COVID and how to obtain care for patients. She would like to see a national public health campaign about long COVID, possibly spearheaded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in partnership with local health workers and community-based organizations.
“That,” she said, “could make a big difference.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.