User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
Best diets in 2023: Mediterranean diet wins again
After all, weight loss usually lands one of the top spots on New Year’s resolution surveys.
And just in time, there’s guidance to pick the best plan, as U.S. News & World Report’s annual rankings of the best diet plans were released on Jan. 3.
Once again, the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, olive oil, and fish, got the top spot, as best diet overall. It’s the sixth consecutive year for that win. But many other diets got top marks as well.
In 2023, U.S. News, with the help of more than 30 nutritionists, doctors, and epidemiologists, ranked 24 diets in several categories to help people find a plan that meets their goals, whether it’s finding the best weight loss diet, easiest one to follow, or plans for other goals, such as managing diabetes or heart disease. Two new categories were added: Best Diets for Bone & Joint Health and Best Family-Friendly Diets.
In previous years, the publication ranked 40 diets. Even if a diet is no longer ranked, its profile with detailed information remains on the site.
“Each year we ask ourselves what we can do better or differently next time,” said Gretel Schueller, managing editor of health for U.S. News. When the publication got feedback from their experts this year, they had requests to consider sustainability of diets and whether they meet a busy family’s needs, in addition to considering many other factors.
This year’s report ranks plans in 11 categories.
The winners and the categories:
Best diets overall
After the Mediterranean diet, two others tied for second place:
- DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which fights high blood pressure and emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy.
- Flexitarian diet, which focuses on fruits, vegetables, and other healthy foods but also allows occasional meat.
Best weight-loss diets
WW, formerly known as Weight Watchers, got first place. The plan emphasizes not only weight loss but healthier eating and regular activity. The Points program, which assigns specific points to foods, with a daily Points budget, is more personalized than in the past.
- DASH got second place.
- Mayo Clinic Diet and TLC diet tied for third place. The Mayo Clinic Diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It helps people improve their eating habits. The TLC diet (Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes) focuses on vegetables, fruit, lean protein, and reducing cholesterol levels.
Best fast weight-loss diets
The keto diet got first place. It’s a high-fat, low-carb diet that aims to achieve weight loss through fat burning. Four others tied for second place:
- Atkins, a diet created by the cardiologist Robert Atkins, which begins with very few carbs and then recommends progressively eating more until the weight loss goal is achieved
- Nutrisystem, a commercial program that includes prepackaged meals and focuses on high-protein, lower-glycemic foods to stabilize blood sugar levels
- Optavia, a plan focused on low-carb, low-calorie foods and including fortified meal replacements
- SlimFast Diet, a plan of shakes, smoothies, and meal bars to replace two of three meals a day
Best diets for healthy eating
- Mediterranean
- DASH
- Flexitarian
Best heart-healthy diets
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian and Ornish tied for third. The Ornish Diet focuses on plant-based and whole foods and limiting animal products. It recommends daily exercise and stress reduction.
Best diets for diabetes
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian
Best diets for bone and joint health
DASH and Mediterranean are in a first-place tie, followed by the flexitarian diet.
Best family-friendly diets
This category has a three-way tie: the flexitarian, Mediterranean, and TLC diets.
Best plant-based diets
Mediterranean was first, then flexitarian and the MIND diet. The MIND diet combines the DASH and Mediterranean diets and focuses on “brain-healthy” foods.
Easiest diets to follow
Flexitarian and TLC tied for first, followed by a tie between DASH and Mediterranean.
Best diet programs (formerly called commercial plans)
- WW
- There was a tie for second place between Jenny Craig and Noom, the latter of which focuses on low-calorie foods, with personalized calorie ranges and coaching to help meet goals.
Methodology
A variety of factors were considered, such as whether a diet includes all food groups, how easy it is to follow, whether it can be customized to meet cultural and personal preferences, and if it has a realistic timeline for weight loss.
Response from diet plans
Representatives from two plans that received mixed reviews in the rankings responded.
Jenny Craig was ranked second for best diet program but much lower for family friendly, landing at 22nd place of 24.
“Our program is designed to address the needs of the individual through personalized experiences,” Jenny Craig CEO Mandy Dowson said. “We have many families that participate in our program together but are still evaluated separately to determine appropriate individual goals.”
Its high ranking for best diet program reflects feedback from satisfied members, she said. Among advances will be the new Jenny Fresh program, a line of entrées prepared fresh and delivered to customers’ doors.
Atkins got second place for best fast weight loss but ranked near the bottom for best overall, best weight loss, diabetes, healthy eating, and heart health. In response, Colette Heimowitz, vice president of nutrition and education for Simply Good Foods, which makes Atkins’s food products, said that low-carb eating approaches are a viable option for anyone today.
“There are more than 130 independent, peer-reviewed published studies that show the efficacy and safety of low-carb eating,” she said. “The studies have been conducted for several decades and counting.”
Expert perspective
Samantha Cassetty, a registered dietitian, nutritionist, and wellness expert in New York and author of Sugar Shock, reviewed the report for this news organization. She was not involved in the rankings.
“I think what this shows you is, the best diet overall is also the best for various conditions,” she said. For instance, the Mediterranean, the No. 1 overall, also got high ranking for diabetes, heart health, and bone and joint health.
For consumers trying to lose weight: “If you see fast weight loss, that should be a red flag. A healthy diet for weight loss is one you can sustain,” she said.
She’s not a fan of the programs with prepackaged foods. “It takes the guesswork out, but the portion sizes tend to be unsatisfying. They don’t teach you how to deal with some of the challenges [such as realizing an ‘ideal’ portion size].”
How to use the report
Ms. Schueller’s advice: “Recognize that no diet fits everyone.” When considering which plan to choose, she suggests thinking long-term.
“Whatever we choose has to work in the long run,” she said.
Consumers should consider expenses, meal prep time, and whether the diet fits their lifestyle.
Ideally, she said, the best diet “teaches you smart food preparation and how to make healthy choices, allows the flexibility to be social and eat with groups, whether family or friends.”
Before choosing a diet to follow, consult a medical professional for input on the decision, U.S. News cautioned.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After all, weight loss usually lands one of the top spots on New Year’s resolution surveys.
And just in time, there’s guidance to pick the best plan, as U.S. News & World Report’s annual rankings of the best diet plans were released on Jan. 3.
Once again, the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, olive oil, and fish, got the top spot, as best diet overall. It’s the sixth consecutive year for that win. But many other diets got top marks as well.
In 2023, U.S. News, with the help of more than 30 nutritionists, doctors, and epidemiologists, ranked 24 diets in several categories to help people find a plan that meets their goals, whether it’s finding the best weight loss diet, easiest one to follow, or plans for other goals, such as managing diabetes or heart disease. Two new categories were added: Best Diets for Bone & Joint Health and Best Family-Friendly Diets.
In previous years, the publication ranked 40 diets. Even if a diet is no longer ranked, its profile with detailed information remains on the site.
“Each year we ask ourselves what we can do better or differently next time,” said Gretel Schueller, managing editor of health for U.S. News. When the publication got feedback from their experts this year, they had requests to consider sustainability of diets and whether they meet a busy family’s needs, in addition to considering many other factors.
This year’s report ranks plans in 11 categories.
The winners and the categories:
Best diets overall
After the Mediterranean diet, two others tied for second place:
- DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which fights high blood pressure and emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy.
- Flexitarian diet, which focuses on fruits, vegetables, and other healthy foods but also allows occasional meat.
Best weight-loss diets
WW, formerly known as Weight Watchers, got first place. The plan emphasizes not only weight loss but healthier eating and regular activity. The Points program, which assigns specific points to foods, with a daily Points budget, is more personalized than in the past.
- DASH got second place.
- Mayo Clinic Diet and TLC diet tied for third place. The Mayo Clinic Diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It helps people improve their eating habits. The TLC diet (Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes) focuses on vegetables, fruit, lean protein, and reducing cholesterol levels.
Best fast weight-loss diets
The keto diet got first place. It’s a high-fat, low-carb diet that aims to achieve weight loss through fat burning. Four others tied for second place:
- Atkins, a diet created by the cardiologist Robert Atkins, which begins with very few carbs and then recommends progressively eating more until the weight loss goal is achieved
- Nutrisystem, a commercial program that includes prepackaged meals and focuses on high-protein, lower-glycemic foods to stabilize blood sugar levels
- Optavia, a plan focused on low-carb, low-calorie foods and including fortified meal replacements
- SlimFast Diet, a plan of shakes, smoothies, and meal bars to replace two of three meals a day
Best diets for healthy eating
- Mediterranean
- DASH
- Flexitarian
Best heart-healthy diets
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian and Ornish tied for third. The Ornish Diet focuses on plant-based and whole foods and limiting animal products. It recommends daily exercise and stress reduction.
Best diets for diabetes
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian
Best diets for bone and joint health
DASH and Mediterranean are in a first-place tie, followed by the flexitarian diet.
Best family-friendly diets
This category has a three-way tie: the flexitarian, Mediterranean, and TLC diets.
Best plant-based diets
Mediterranean was first, then flexitarian and the MIND diet. The MIND diet combines the DASH and Mediterranean diets and focuses on “brain-healthy” foods.
Easiest diets to follow
Flexitarian and TLC tied for first, followed by a tie between DASH and Mediterranean.
Best diet programs (formerly called commercial plans)
- WW
- There was a tie for second place between Jenny Craig and Noom, the latter of which focuses on low-calorie foods, with personalized calorie ranges and coaching to help meet goals.
Methodology
A variety of factors were considered, such as whether a diet includes all food groups, how easy it is to follow, whether it can be customized to meet cultural and personal preferences, and if it has a realistic timeline for weight loss.
Response from diet plans
Representatives from two plans that received mixed reviews in the rankings responded.
Jenny Craig was ranked second for best diet program but much lower for family friendly, landing at 22nd place of 24.
“Our program is designed to address the needs of the individual through personalized experiences,” Jenny Craig CEO Mandy Dowson said. “We have many families that participate in our program together but are still evaluated separately to determine appropriate individual goals.”
Its high ranking for best diet program reflects feedback from satisfied members, she said. Among advances will be the new Jenny Fresh program, a line of entrées prepared fresh and delivered to customers’ doors.
Atkins got second place for best fast weight loss but ranked near the bottom for best overall, best weight loss, diabetes, healthy eating, and heart health. In response, Colette Heimowitz, vice president of nutrition and education for Simply Good Foods, which makes Atkins’s food products, said that low-carb eating approaches are a viable option for anyone today.
“There are more than 130 independent, peer-reviewed published studies that show the efficacy and safety of low-carb eating,” she said. “The studies have been conducted for several decades and counting.”
Expert perspective
Samantha Cassetty, a registered dietitian, nutritionist, and wellness expert in New York and author of Sugar Shock, reviewed the report for this news organization. She was not involved in the rankings.
“I think what this shows you is, the best diet overall is also the best for various conditions,” she said. For instance, the Mediterranean, the No. 1 overall, also got high ranking for diabetes, heart health, and bone and joint health.
For consumers trying to lose weight: “If you see fast weight loss, that should be a red flag. A healthy diet for weight loss is one you can sustain,” she said.
She’s not a fan of the programs with prepackaged foods. “It takes the guesswork out, but the portion sizes tend to be unsatisfying. They don’t teach you how to deal with some of the challenges [such as realizing an ‘ideal’ portion size].”
How to use the report
Ms. Schueller’s advice: “Recognize that no diet fits everyone.” When considering which plan to choose, she suggests thinking long-term.
“Whatever we choose has to work in the long run,” she said.
Consumers should consider expenses, meal prep time, and whether the diet fits their lifestyle.
Ideally, she said, the best diet “teaches you smart food preparation and how to make healthy choices, allows the flexibility to be social and eat with groups, whether family or friends.”
Before choosing a diet to follow, consult a medical professional for input on the decision, U.S. News cautioned.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After all, weight loss usually lands one of the top spots on New Year’s resolution surveys.
And just in time, there’s guidance to pick the best plan, as U.S. News & World Report’s annual rankings of the best diet plans were released on Jan. 3.
Once again, the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, olive oil, and fish, got the top spot, as best diet overall. It’s the sixth consecutive year for that win. But many other diets got top marks as well.
In 2023, U.S. News, with the help of more than 30 nutritionists, doctors, and epidemiologists, ranked 24 diets in several categories to help people find a plan that meets their goals, whether it’s finding the best weight loss diet, easiest one to follow, or plans for other goals, such as managing diabetes or heart disease. Two new categories were added: Best Diets for Bone & Joint Health and Best Family-Friendly Diets.
In previous years, the publication ranked 40 diets. Even if a diet is no longer ranked, its profile with detailed information remains on the site.
“Each year we ask ourselves what we can do better or differently next time,” said Gretel Schueller, managing editor of health for U.S. News. When the publication got feedback from their experts this year, they had requests to consider sustainability of diets and whether they meet a busy family’s needs, in addition to considering many other factors.
This year’s report ranks plans in 11 categories.
The winners and the categories:
Best diets overall
After the Mediterranean diet, two others tied for second place:
- DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which fights high blood pressure and emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy.
- Flexitarian diet, which focuses on fruits, vegetables, and other healthy foods but also allows occasional meat.
Best weight-loss diets
WW, formerly known as Weight Watchers, got first place. The plan emphasizes not only weight loss but healthier eating and regular activity. The Points program, which assigns specific points to foods, with a daily Points budget, is more personalized than in the past.
- DASH got second place.
- Mayo Clinic Diet and TLC diet tied for third place. The Mayo Clinic Diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It helps people improve their eating habits. The TLC diet (Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes) focuses on vegetables, fruit, lean protein, and reducing cholesterol levels.
Best fast weight-loss diets
The keto diet got first place. It’s a high-fat, low-carb diet that aims to achieve weight loss through fat burning. Four others tied for second place:
- Atkins, a diet created by the cardiologist Robert Atkins, which begins with very few carbs and then recommends progressively eating more until the weight loss goal is achieved
- Nutrisystem, a commercial program that includes prepackaged meals and focuses on high-protein, lower-glycemic foods to stabilize blood sugar levels
- Optavia, a plan focused on low-carb, low-calorie foods and including fortified meal replacements
- SlimFast Diet, a plan of shakes, smoothies, and meal bars to replace two of three meals a day
Best diets for healthy eating
- Mediterranean
- DASH
- Flexitarian
Best heart-healthy diets
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian and Ornish tied for third. The Ornish Diet focuses on plant-based and whole foods and limiting animal products. It recommends daily exercise and stress reduction.
Best diets for diabetes
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian
Best diets for bone and joint health
DASH and Mediterranean are in a first-place tie, followed by the flexitarian diet.
Best family-friendly diets
This category has a three-way tie: the flexitarian, Mediterranean, and TLC diets.
Best plant-based diets
Mediterranean was first, then flexitarian and the MIND diet. The MIND diet combines the DASH and Mediterranean diets and focuses on “brain-healthy” foods.
Easiest diets to follow
Flexitarian and TLC tied for first, followed by a tie between DASH and Mediterranean.
Best diet programs (formerly called commercial plans)
- WW
- There was a tie for second place between Jenny Craig and Noom, the latter of which focuses on low-calorie foods, with personalized calorie ranges and coaching to help meet goals.
Methodology
A variety of factors were considered, such as whether a diet includes all food groups, how easy it is to follow, whether it can be customized to meet cultural and personal preferences, and if it has a realistic timeline for weight loss.
Response from diet plans
Representatives from two plans that received mixed reviews in the rankings responded.
Jenny Craig was ranked second for best diet program but much lower for family friendly, landing at 22nd place of 24.
“Our program is designed to address the needs of the individual through personalized experiences,” Jenny Craig CEO Mandy Dowson said. “We have many families that participate in our program together but are still evaluated separately to determine appropriate individual goals.”
Its high ranking for best diet program reflects feedback from satisfied members, she said. Among advances will be the new Jenny Fresh program, a line of entrées prepared fresh and delivered to customers’ doors.
Atkins got second place for best fast weight loss but ranked near the bottom for best overall, best weight loss, diabetes, healthy eating, and heart health. In response, Colette Heimowitz, vice president of nutrition and education for Simply Good Foods, which makes Atkins’s food products, said that low-carb eating approaches are a viable option for anyone today.
“There are more than 130 independent, peer-reviewed published studies that show the efficacy and safety of low-carb eating,” she said. “The studies have been conducted for several decades and counting.”
Expert perspective
Samantha Cassetty, a registered dietitian, nutritionist, and wellness expert in New York and author of Sugar Shock, reviewed the report for this news organization. She was not involved in the rankings.
“I think what this shows you is, the best diet overall is also the best for various conditions,” she said. For instance, the Mediterranean, the No. 1 overall, also got high ranking for diabetes, heart health, and bone and joint health.
For consumers trying to lose weight: “If you see fast weight loss, that should be a red flag. A healthy diet for weight loss is one you can sustain,” she said.
She’s not a fan of the programs with prepackaged foods. “It takes the guesswork out, but the portion sizes tend to be unsatisfying. They don’t teach you how to deal with some of the challenges [such as realizing an ‘ideal’ portion size].”
How to use the report
Ms. Schueller’s advice: “Recognize that no diet fits everyone.” When considering which plan to choose, she suggests thinking long-term.
“Whatever we choose has to work in the long run,” she said.
Consumers should consider expenses, meal prep time, and whether the diet fits their lifestyle.
Ideally, she said, the best diet “teaches you smart food preparation and how to make healthy choices, allows the flexibility to be social and eat with groups, whether family or friends.”
Before choosing a diet to follow, consult a medical professional for input on the decision, U.S. News cautioned.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STEMI times to treatment usually miss established goals
Therapy initiated within national treatment-time goals set a decade ago for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) remains associated with improved survival in recent years. But for many such patients, time from first symptoms to initiation of reperfusion therapy still fails to meet those goals, suggests a cross-sectional registry analysis.
For example, patients initially transported to centers with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) capability had a median treatment time of 148 minutes, in the analysis spanning the second quarter (Q2) of 2018 to the third quarter (Q3) of 2021. But the goal for centers called for treatment initiation within 90 minutes for at least 75% of such STEMI patients.
Moreover, overall STEMI treatment times and in-hospital mortality rose in tandem significantly from Q2 2018 through the first quarter (Q1) of 2021, which included the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Median time to treatment went from 86 minutes to 91 minutes during that period. Meanwhile, in-hospital mortality went from 5.6% to 8.7%, report the study authors led by James G. Jollis, MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Their report, based on 114,871 STEMI patients at 601 US hospitals contributing to the Get With The Guidelines – Coronary Artery Disease registry, was published online in JAMA.
Of those patients, 25,085 had been transferred from non-PCI hospitals, 32,483 were walk-ins, and 57,303 arrived via emergency medical services (EMS). Their median times from symptom onset to PCI were 240, 195, and 148 minutes, respectively.
In-hospital mortality was significantly reduced in an adjusted analysis for patients treated within target times, compared with those whose treatment missed the time goals, regardless of whether they were transported by EMS, walked into a hospital with on-site PCI, or were transferred from a non-PCI center (Table 1).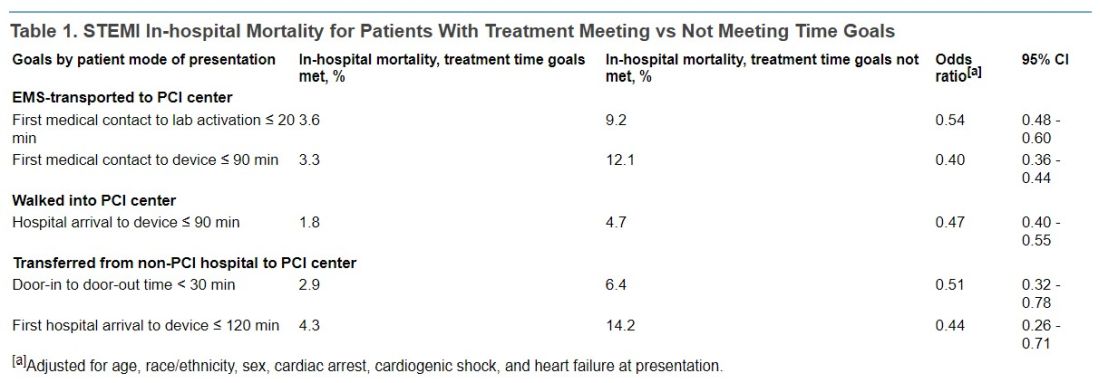
Regardless of mode of patient presentation, treatment time goals were not met most of the time, the group reports. Patients who required interhospital transfer experienced the longest system delays; only 17% were treated within 120 minutes.
Among patients who received primary PCI, 20% had a registry-defined hospital-specified reason for delay, including cardiac arrest and/or need for intubation in 6.8%, “difficulty crossing the culprit lesion” in 3.8%, and “other reasons” in 5.8%, the group reports.
“In 2020, a new reason for delay was added to the registry, ‘need for additional personal protective equipment for suspected/confirmed infectious disease.’ This reason was most commonly used in the second quarter of 2020 (6%) and then declined over time to 1% in the final 2 quarters,” they write.
“Thus, active SARS-CoV-2 infection appeared to have a smaller direct role in longer treatment times or worse outcomes.” Rather, they continue, “the pandemic potentially had a significant indirect role as hospitals were overwhelmed with patients, EMS and hospitals were challenged in maintaining paramedic and nurse staffing and intensive care bed availability, and patients experienced delayed care due to barriers to access or perceived fear of becoming entangled in an overwhelmed medical system.”
Still an important quality metric
STEMI treatment times remain an important quality metric to which hospitals should continue to pay attention because shorter times improve patient care, Deepak Bhatt, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“Having said that, as with all metrics, one needs to be thoughtful and realize that a difference of a couple of minutes is probably not a crucial thing,” said Dr. Bhatt, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, who was not involved with the current study.
Interhospital transfers indeed involve longer delays, he observed, suggesting that regional integrated health systems should develop methods for optimizing STEMI care – even, for example, if they involve bypassing non-PCI centers or stopping patients briefly for stabilization followed by rapid transport to a PCI-capable facility.
“That, of course, requires cooperation among hospitals. Sometimes that requires hospitals putting aside economic considerations and just focusing on doing the right thing for that individual patient,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Transfer delays are common for patients presenting with STEMI at hospitals without PCI capability, he noted. “Having clear protocols in place that expedite that type of transfer, I think, could go a long way in reducing the time to treatment in patients that are presenting to the hospital without cath labs. That’s an important message that these data provide.”
The onset of COVID-19 led to widespread delays in STEMI time to treatment early in the pandemic. There were concerns about exposing cath lab personnel to SARS-CoV-2 and potential adverse consequences of sick personnel being unable to provide patient care in the subsequent weeks and months, Dr. Bhatt observed.
However, “All of that seems to have quieted down, and I don’t think COVID is impacting time to treatment right now.”
‘Suboptimal compliance’ with standards
The current findings of “suboptimal compliance with national targets underscore why reassessing quality metrics, in light of changing practice patterns and other secular trends, is critical,” write Andrew S. Oseran, MD, MBA, and Robert W. Yeh, MD, both of Harvard Medical School, in an accompanying editorial.
“While the importance of coordinated and expeditious care for this high-risk patient population is undeniable, the specific actions that hospitals can – or should – take to further improve overall STEMI outcomes are less clear,” they say.
“As physicians contemplate the optimal path forward in managing the care of STEMI patients, they must recognize the clinical and operational nuance that exists in caring for this diverse population and acknowledge the trade-offs associated with uniform quality metrics,” write the editorialists.
“Global reductions in time to treatment for STEMI patients has been one of health care’s great success stories. As we move forward, it may be time to consider whether efforts to achieve additional improvement in target treatment times will result in substantive benefits, or whether we have reached the point of diminishing returns.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Therapy initiated within national treatment-time goals set a decade ago for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) remains associated with improved survival in recent years. But for many such patients, time from first symptoms to initiation of reperfusion therapy still fails to meet those goals, suggests a cross-sectional registry analysis.
For example, patients initially transported to centers with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) capability had a median treatment time of 148 minutes, in the analysis spanning the second quarter (Q2) of 2018 to the third quarter (Q3) of 2021. But the goal for centers called for treatment initiation within 90 minutes for at least 75% of such STEMI patients.
Moreover, overall STEMI treatment times and in-hospital mortality rose in tandem significantly from Q2 2018 through the first quarter (Q1) of 2021, which included the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Median time to treatment went from 86 minutes to 91 minutes during that period. Meanwhile, in-hospital mortality went from 5.6% to 8.7%, report the study authors led by James G. Jollis, MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Their report, based on 114,871 STEMI patients at 601 US hospitals contributing to the Get With The Guidelines – Coronary Artery Disease registry, was published online in JAMA.
Of those patients, 25,085 had been transferred from non-PCI hospitals, 32,483 were walk-ins, and 57,303 arrived via emergency medical services (EMS). Their median times from symptom onset to PCI were 240, 195, and 148 minutes, respectively.
In-hospital mortality was significantly reduced in an adjusted analysis for patients treated within target times, compared with those whose treatment missed the time goals, regardless of whether they were transported by EMS, walked into a hospital with on-site PCI, or were transferred from a non-PCI center (Table 1).
Regardless of mode of patient presentation, treatment time goals were not met most of the time, the group reports. Patients who required interhospital transfer experienced the longest system delays; only 17% were treated within 120 minutes.
Among patients who received primary PCI, 20% had a registry-defined hospital-specified reason for delay, including cardiac arrest and/or need for intubation in 6.8%, “difficulty crossing the culprit lesion” in 3.8%, and “other reasons” in 5.8%, the group reports.
“In 2020, a new reason for delay was added to the registry, ‘need for additional personal protective equipment for suspected/confirmed infectious disease.’ This reason was most commonly used in the second quarter of 2020 (6%) and then declined over time to 1% in the final 2 quarters,” they write.
“Thus, active SARS-CoV-2 infection appeared to have a smaller direct role in longer treatment times or worse outcomes.” Rather, they continue, “the pandemic potentially had a significant indirect role as hospitals were overwhelmed with patients, EMS and hospitals were challenged in maintaining paramedic and nurse staffing and intensive care bed availability, and patients experienced delayed care due to barriers to access or perceived fear of becoming entangled in an overwhelmed medical system.”
Still an important quality metric
STEMI treatment times remain an important quality metric to which hospitals should continue to pay attention because shorter times improve patient care, Deepak Bhatt, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“Having said that, as with all metrics, one needs to be thoughtful and realize that a difference of a couple of minutes is probably not a crucial thing,” said Dr. Bhatt, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, who was not involved with the current study.
Interhospital transfers indeed involve longer delays, he observed, suggesting that regional integrated health systems should develop methods for optimizing STEMI care – even, for example, if they involve bypassing non-PCI centers or stopping patients briefly for stabilization followed by rapid transport to a PCI-capable facility.
“That, of course, requires cooperation among hospitals. Sometimes that requires hospitals putting aside economic considerations and just focusing on doing the right thing for that individual patient,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Transfer delays are common for patients presenting with STEMI at hospitals without PCI capability, he noted. “Having clear protocols in place that expedite that type of transfer, I think, could go a long way in reducing the time to treatment in patients that are presenting to the hospital without cath labs. That’s an important message that these data provide.”
The onset of COVID-19 led to widespread delays in STEMI time to treatment early in the pandemic. There were concerns about exposing cath lab personnel to SARS-CoV-2 and potential adverse consequences of sick personnel being unable to provide patient care in the subsequent weeks and months, Dr. Bhatt observed.
However, “All of that seems to have quieted down, and I don’t think COVID is impacting time to treatment right now.”
‘Suboptimal compliance’ with standards
The current findings of “suboptimal compliance with national targets underscore why reassessing quality metrics, in light of changing practice patterns and other secular trends, is critical,” write Andrew S. Oseran, MD, MBA, and Robert W. Yeh, MD, both of Harvard Medical School, in an accompanying editorial.
“While the importance of coordinated and expeditious care for this high-risk patient population is undeniable, the specific actions that hospitals can – or should – take to further improve overall STEMI outcomes are less clear,” they say.
“As physicians contemplate the optimal path forward in managing the care of STEMI patients, they must recognize the clinical and operational nuance that exists in caring for this diverse population and acknowledge the trade-offs associated with uniform quality metrics,” write the editorialists.
“Global reductions in time to treatment for STEMI patients has been one of health care’s great success stories. As we move forward, it may be time to consider whether efforts to achieve additional improvement in target treatment times will result in substantive benefits, or whether we have reached the point of diminishing returns.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Therapy initiated within national treatment-time goals set a decade ago for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) remains associated with improved survival in recent years. But for many such patients, time from first symptoms to initiation of reperfusion therapy still fails to meet those goals, suggests a cross-sectional registry analysis.
For example, patients initially transported to centers with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) capability had a median treatment time of 148 minutes, in the analysis spanning the second quarter (Q2) of 2018 to the third quarter (Q3) of 2021. But the goal for centers called for treatment initiation within 90 minutes for at least 75% of such STEMI patients.
Moreover, overall STEMI treatment times and in-hospital mortality rose in tandem significantly from Q2 2018 through the first quarter (Q1) of 2021, which included the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Median time to treatment went from 86 minutes to 91 minutes during that period. Meanwhile, in-hospital mortality went from 5.6% to 8.7%, report the study authors led by James G. Jollis, MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Their report, based on 114,871 STEMI patients at 601 US hospitals contributing to the Get With The Guidelines – Coronary Artery Disease registry, was published online in JAMA.
Of those patients, 25,085 had been transferred from non-PCI hospitals, 32,483 were walk-ins, and 57,303 arrived via emergency medical services (EMS). Their median times from symptom onset to PCI were 240, 195, and 148 minutes, respectively.
In-hospital mortality was significantly reduced in an adjusted analysis for patients treated within target times, compared with those whose treatment missed the time goals, regardless of whether they were transported by EMS, walked into a hospital with on-site PCI, or were transferred from a non-PCI center (Table 1).
Regardless of mode of patient presentation, treatment time goals were not met most of the time, the group reports. Patients who required interhospital transfer experienced the longest system delays; only 17% were treated within 120 minutes.
Among patients who received primary PCI, 20% had a registry-defined hospital-specified reason for delay, including cardiac arrest and/or need for intubation in 6.8%, “difficulty crossing the culprit lesion” in 3.8%, and “other reasons” in 5.8%, the group reports.
“In 2020, a new reason for delay was added to the registry, ‘need for additional personal protective equipment for suspected/confirmed infectious disease.’ This reason was most commonly used in the second quarter of 2020 (6%) and then declined over time to 1% in the final 2 quarters,” they write.
“Thus, active SARS-CoV-2 infection appeared to have a smaller direct role in longer treatment times or worse outcomes.” Rather, they continue, “the pandemic potentially had a significant indirect role as hospitals were overwhelmed with patients, EMS and hospitals were challenged in maintaining paramedic and nurse staffing and intensive care bed availability, and patients experienced delayed care due to barriers to access or perceived fear of becoming entangled in an overwhelmed medical system.”
Still an important quality metric
STEMI treatment times remain an important quality metric to which hospitals should continue to pay attention because shorter times improve patient care, Deepak Bhatt, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“Having said that, as with all metrics, one needs to be thoughtful and realize that a difference of a couple of minutes is probably not a crucial thing,” said Dr. Bhatt, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, who was not involved with the current study.
Interhospital transfers indeed involve longer delays, he observed, suggesting that regional integrated health systems should develop methods for optimizing STEMI care – even, for example, if they involve bypassing non-PCI centers or stopping patients briefly for stabilization followed by rapid transport to a PCI-capable facility.
“That, of course, requires cooperation among hospitals. Sometimes that requires hospitals putting aside economic considerations and just focusing on doing the right thing for that individual patient,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Transfer delays are common for patients presenting with STEMI at hospitals without PCI capability, he noted. “Having clear protocols in place that expedite that type of transfer, I think, could go a long way in reducing the time to treatment in patients that are presenting to the hospital without cath labs. That’s an important message that these data provide.”
The onset of COVID-19 led to widespread delays in STEMI time to treatment early in the pandemic. There were concerns about exposing cath lab personnel to SARS-CoV-2 and potential adverse consequences of sick personnel being unable to provide patient care in the subsequent weeks and months, Dr. Bhatt observed.
However, “All of that seems to have quieted down, and I don’t think COVID is impacting time to treatment right now.”
‘Suboptimal compliance’ with standards
The current findings of “suboptimal compliance with national targets underscore why reassessing quality metrics, in light of changing practice patterns and other secular trends, is critical,” write Andrew S. Oseran, MD, MBA, and Robert W. Yeh, MD, both of Harvard Medical School, in an accompanying editorial.
“While the importance of coordinated and expeditious care for this high-risk patient population is undeniable, the specific actions that hospitals can – or should – take to further improve overall STEMI outcomes are less clear,” they say.
“As physicians contemplate the optimal path forward in managing the care of STEMI patients, they must recognize the clinical and operational nuance that exists in caring for this diverse population and acknowledge the trade-offs associated with uniform quality metrics,” write the editorialists.
“Global reductions in time to treatment for STEMI patients has been one of health care’s great success stories. As we move forward, it may be time to consider whether efforts to achieve additional improvement in target treatment times will result in substantive benefits, or whether we have reached the point of diminishing returns.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
Fourth Study to Show Consistent Benefit of Highly Purified Eicosapentaenoic Acid on Cardiovascular Outcomes: Results From RESPECT-EPA
In this supplement to Cardiology News, John R. Nelson, MD, FACC, FNLA, FASNC, and Matthew J. Budoff, MD, discuss results from RESPECT-EPA and the existing evidence that purified eicosapentaenoic acid significantly reduces residual CV risk in patients with CVD.
In this supplement to Cardiology News, John R. Nelson, MD, FACC, FNLA, FASNC, and Matthew J. Budoff, MD, discuss results from RESPECT-EPA and the existing evidence that purified eicosapentaenoic acid significantly reduces residual CV risk in patients with CVD.
In this supplement to Cardiology News, John R. Nelson, MD, FACC, FNLA, FASNC, and Matthew J. Budoff, MD, discuss results from RESPECT-EPA and the existing evidence that purified eicosapentaenoic acid significantly reduces residual CV risk in patients with CVD.
“The Nail in the Coffin for Fibrates”: Futility of PROMINENT Trial Definitively Settles Debate on Avoiding Use of Fibrate Class of Medications for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
In this supplement to Cardiology News, Payal Kohli, MD, FACC, and Nihar Desai, MD, MPH, discuss the PROMINENT trial and the debate on avoiding the use of fibrates for cardiovascular risk reduction.
In this supplement to Cardiology News, Payal Kohli, MD, FACC, and Nihar Desai, MD, MPH, discuss the PROMINENT trial and the debate on avoiding the use of fibrates for cardiovascular risk reduction.
In this supplement to Cardiology News, Payal Kohli, MD, FACC, and Nihar Desai, MD, MPH, discuss the PROMINENT trial and the debate on avoiding the use of fibrates for cardiovascular risk reduction.
Mediterranean diet linked with fewer pregnancy complications
Women in the United States who followed a Mediterranean-style diet – heavy on fresh foods, fish, and olive oil – around the time of conception had lower risk of developing a pregnancy complication, results of a large new study suggest.
The study included 7,798 women who had not given birth before. The group was geographically, racially, and ethnically diverse.
Researchers led by Nour Makarem, PhD, MS, with the department of epidemiology, Columbia University, New York, published their results in JAMA Network Open.
“Generally, higher intakes of vegetables, fruits, legumes, fish, and whole grains and lower intakes of red and processed meat were associated with lower risk of APOs [adverse pregnancy outcomes],” the authors wrote.
21% lower risk of complications
The investigators found that women in the study – who were part of the Nulliparous Pregnancy Outcomes Study: Monitoring Mothers-to-Be, which enrolled 10,038 women between Oct. 1, 2010, and Sept. 30, 2013, and scored high on adherence to a Mediterranean diet – had a 21% lower risk of developing any adverse pregnancy outcome (APO) than those who had low adherence. And the better the adherence, the lower the risk of adverse outcomes, especially preeclampsia or eclampsia and gestational diabetes, the researchers wrote.
The research team also studied how following the diet correlated with gestational high blood pressure, preterm birth, delivery of a small-for-gestational-age infant, and stillbirth.
Women were scored on consumption of nine components: vegetables (excluding potatoes), fruits, nuts, whole grains, legumes, fish, monounsaturated to saturated fat ratio, red and processed meats, and alcohol.
No differences by race, ethnicity, or BMI
There were no differences in adverse pregnancy outcomes by race, ethnicity, or the woman’s body mass index before pregnancy, but associations were stronger in the women who were 35 years or older, according to the paper.
The authors pointed out that the women in the study had access to prenatal care at a large academic medical center during their first 3 months of pregnancy so the study may actually underestimate the importance of the diet in the pregnancy outcomes.
Christina Han, MD, division director of maternal-fetal medicine at University of California, Los Angeles, who was not part of the study, said that the results make sense as the researchers looked at the time of conception, which is a time that reflects the way a person chooses to live their life.
“We know that your health state as you enter pregnancy can significantly affect your outcomes for that pregnancy,” she said. “We’ve known for decades now that a Mediterranean diet is good for just about everybody.”
Unequal access to foods on diet
Dr. Han said that, while it’s great the researchers were able to confirm the benefit of the Mediterranean diet, it highlights inequity as lower income people are not as likely to be able to afford fresh fruits and vegetables and fish.
“This is a call to arms for our food distribution system to even out the big divide in what patients have access to,” Dr. Han said.
She noted that most of the women in this study were married, non-Hispanic White, and had higher levels of education which may make it hard to generalize these results to the general population.
A limitation of the study is that the women were asked to report what they ate themselves, which can be less accurate than when researchers record what is eaten in a controlled setting.
The researchers suggested a next step: “Long-term intervention studies are needed to assess whether promoting a Mediterranean-style diet around the time of conception and throughout pregnancy can prevent APOs.”
Dr. Makarem reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the American Heart Association outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving grants from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development during the study. One coauthor reported receiving personal fees for serving on the board of directors for iRhythm and from fees paid through Cedars-Sinai Medical Center from Abbott Diagnostics and Sanofi outside the submitted work, and one coauthor reported serving as a clinical end point committee member for GlaxoSmithKline outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Han reported no relevant financial relationships.
Women in the United States who followed a Mediterranean-style diet – heavy on fresh foods, fish, and olive oil – around the time of conception had lower risk of developing a pregnancy complication, results of a large new study suggest.
The study included 7,798 women who had not given birth before. The group was geographically, racially, and ethnically diverse.
Researchers led by Nour Makarem, PhD, MS, with the department of epidemiology, Columbia University, New York, published their results in JAMA Network Open.
“Generally, higher intakes of vegetables, fruits, legumes, fish, and whole grains and lower intakes of red and processed meat were associated with lower risk of APOs [adverse pregnancy outcomes],” the authors wrote.
21% lower risk of complications
The investigators found that women in the study – who were part of the Nulliparous Pregnancy Outcomes Study: Monitoring Mothers-to-Be, which enrolled 10,038 women between Oct. 1, 2010, and Sept. 30, 2013, and scored high on adherence to a Mediterranean diet – had a 21% lower risk of developing any adverse pregnancy outcome (APO) than those who had low adherence. And the better the adherence, the lower the risk of adverse outcomes, especially preeclampsia or eclampsia and gestational diabetes, the researchers wrote.
The research team also studied how following the diet correlated with gestational high blood pressure, preterm birth, delivery of a small-for-gestational-age infant, and stillbirth.
Women were scored on consumption of nine components: vegetables (excluding potatoes), fruits, nuts, whole grains, legumes, fish, monounsaturated to saturated fat ratio, red and processed meats, and alcohol.
No differences by race, ethnicity, or BMI
There were no differences in adverse pregnancy outcomes by race, ethnicity, or the woman’s body mass index before pregnancy, but associations were stronger in the women who were 35 years or older, according to the paper.
The authors pointed out that the women in the study had access to prenatal care at a large academic medical center during their first 3 months of pregnancy so the study may actually underestimate the importance of the diet in the pregnancy outcomes.
Christina Han, MD, division director of maternal-fetal medicine at University of California, Los Angeles, who was not part of the study, said that the results make sense as the researchers looked at the time of conception, which is a time that reflects the way a person chooses to live their life.
“We know that your health state as you enter pregnancy can significantly affect your outcomes for that pregnancy,” she said. “We’ve known for decades now that a Mediterranean diet is good for just about everybody.”
Unequal access to foods on diet
Dr. Han said that, while it’s great the researchers were able to confirm the benefit of the Mediterranean diet, it highlights inequity as lower income people are not as likely to be able to afford fresh fruits and vegetables and fish.
“This is a call to arms for our food distribution system to even out the big divide in what patients have access to,” Dr. Han said.
She noted that most of the women in this study were married, non-Hispanic White, and had higher levels of education which may make it hard to generalize these results to the general population.
A limitation of the study is that the women were asked to report what they ate themselves, which can be less accurate than when researchers record what is eaten in a controlled setting.
The researchers suggested a next step: “Long-term intervention studies are needed to assess whether promoting a Mediterranean-style diet around the time of conception and throughout pregnancy can prevent APOs.”
Dr. Makarem reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the American Heart Association outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving grants from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development during the study. One coauthor reported receiving personal fees for serving on the board of directors for iRhythm and from fees paid through Cedars-Sinai Medical Center from Abbott Diagnostics and Sanofi outside the submitted work, and one coauthor reported serving as a clinical end point committee member for GlaxoSmithKline outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Han reported no relevant financial relationships.
Women in the United States who followed a Mediterranean-style diet – heavy on fresh foods, fish, and olive oil – around the time of conception had lower risk of developing a pregnancy complication, results of a large new study suggest.
The study included 7,798 women who had not given birth before. The group was geographically, racially, and ethnically diverse.
Researchers led by Nour Makarem, PhD, MS, with the department of epidemiology, Columbia University, New York, published their results in JAMA Network Open.
“Generally, higher intakes of vegetables, fruits, legumes, fish, and whole grains and lower intakes of red and processed meat were associated with lower risk of APOs [adverse pregnancy outcomes],” the authors wrote.
21% lower risk of complications
The investigators found that women in the study – who were part of the Nulliparous Pregnancy Outcomes Study: Monitoring Mothers-to-Be, which enrolled 10,038 women between Oct. 1, 2010, and Sept. 30, 2013, and scored high on adherence to a Mediterranean diet – had a 21% lower risk of developing any adverse pregnancy outcome (APO) than those who had low adherence. And the better the adherence, the lower the risk of adverse outcomes, especially preeclampsia or eclampsia and gestational diabetes, the researchers wrote.
The research team also studied how following the diet correlated with gestational high blood pressure, preterm birth, delivery of a small-for-gestational-age infant, and stillbirth.
Women were scored on consumption of nine components: vegetables (excluding potatoes), fruits, nuts, whole grains, legumes, fish, monounsaturated to saturated fat ratio, red and processed meats, and alcohol.
No differences by race, ethnicity, or BMI
There were no differences in adverse pregnancy outcomes by race, ethnicity, or the woman’s body mass index before pregnancy, but associations were stronger in the women who were 35 years or older, according to the paper.
The authors pointed out that the women in the study had access to prenatal care at a large academic medical center during their first 3 months of pregnancy so the study may actually underestimate the importance of the diet in the pregnancy outcomes.
Christina Han, MD, division director of maternal-fetal medicine at University of California, Los Angeles, who was not part of the study, said that the results make sense as the researchers looked at the time of conception, which is a time that reflects the way a person chooses to live their life.
“We know that your health state as you enter pregnancy can significantly affect your outcomes for that pregnancy,” she said. “We’ve known for decades now that a Mediterranean diet is good for just about everybody.”
Unequal access to foods on diet
Dr. Han said that, while it’s great the researchers were able to confirm the benefit of the Mediterranean diet, it highlights inequity as lower income people are not as likely to be able to afford fresh fruits and vegetables and fish.
“This is a call to arms for our food distribution system to even out the big divide in what patients have access to,” Dr. Han said.
She noted that most of the women in this study were married, non-Hispanic White, and had higher levels of education which may make it hard to generalize these results to the general population.
A limitation of the study is that the women were asked to report what they ate themselves, which can be less accurate than when researchers record what is eaten in a controlled setting.
The researchers suggested a next step: “Long-term intervention studies are needed to assess whether promoting a Mediterranean-style diet around the time of conception and throughout pregnancy can prevent APOs.”
Dr. Makarem reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the American Heart Association outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving grants from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development during the study. One coauthor reported receiving personal fees for serving on the board of directors for iRhythm and from fees paid through Cedars-Sinai Medical Center from Abbott Diagnostics and Sanofi outside the submitted work, and one coauthor reported serving as a clinical end point committee member for GlaxoSmithKline outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Han reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Diabetes surge expected in young people
according to a new study published in Diabetes Care.
It is expected that as many as 526,000 people younger than 20 years in the United States will have diabetes by 2060, researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report. Their projections found that the number of young people with diabetes will increase 12%, from 213,000 in 2017 to 239,000 in 2060.
The estimates include a 673% rise in the number of youth with type 2 diabetes and a 65% increase in cases of type 1 diabetes over the next 4 decades.
Most of the new cases are projected to occur among non-Hispanic Blacks, exacerbating the already significant racial disparities in type 2 diabetes in particular, the study found.
“This study’s startling projections of type 2 diabetes increases show why it is crucial to advance health equity and reduce the widespread disparities that already take a toll on people’s health,” Christopher Holliday, PhD, MPH, FACHE, director of CDC’s Division of Diabetes Translation, said in a press release about the new estimates.
Even if trends remain the same in coming decades, researchers said diagnoses of type 2 diabetes will rise almost 70% and that diagnoses of type 1 diabetes will increase by 3%.
The researchers attribute the increase in diabetes cases among youth to a variety of factors, including the growing prevalence of childhood obesity and the presence of diabetes in women of childbearing age, which is linked to obesity in their offspring.
Debra Houry, MD, MPH, acting principal director of the CDC, said the focus should be on prevention.
“This new research should serve as a wake-up call for all of us. It’s vital that we focus our efforts to ensure all Americans, especially our young people, are the healthiest they can be,” she said in a press release.
The findings come from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study, funded by the CDC and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Houry and Dr. Holliday report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study published in Diabetes Care.
It is expected that as many as 526,000 people younger than 20 years in the United States will have diabetes by 2060, researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report. Their projections found that the number of young people with diabetes will increase 12%, from 213,000 in 2017 to 239,000 in 2060.
The estimates include a 673% rise in the number of youth with type 2 diabetes and a 65% increase in cases of type 1 diabetes over the next 4 decades.
Most of the new cases are projected to occur among non-Hispanic Blacks, exacerbating the already significant racial disparities in type 2 diabetes in particular, the study found.
“This study’s startling projections of type 2 diabetes increases show why it is crucial to advance health equity and reduce the widespread disparities that already take a toll on people’s health,” Christopher Holliday, PhD, MPH, FACHE, director of CDC’s Division of Diabetes Translation, said in a press release about the new estimates.
Even if trends remain the same in coming decades, researchers said diagnoses of type 2 diabetes will rise almost 70% and that diagnoses of type 1 diabetes will increase by 3%.
The researchers attribute the increase in diabetes cases among youth to a variety of factors, including the growing prevalence of childhood obesity and the presence of diabetes in women of childbearing age, which is linked to obesity in their offspring.
Debra Houry, MD, MPH, acting principal director of the CDC, said the focus should be on prevention.
“This new research should serve as a wake-up call for all of us. It’s vital that we focus our efforts to ensure all Americans, especially our young people, are the healthiest they can be,” she said in a press release.
The findings come from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study, funded by the CDC and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Houry and Dr. Holliday report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study published in Diabetes Care.
It is expected that as many as 526,000 people younger than 20 years in the United States will have diabetes by 2060, researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report. Their projections found that the number of young people with diabetes will increase 12%, from 213,000 in 2017 to 239,000 in 2060.
The estimates include a 673% rise in the number of youth with type 2 diabetes and a 65% increase in cases of type 1 diabetes over the next 4 decades.
Most of the new cases are projected to occur among non-Hispanic Blacks, exacerbating the already significant racial disparities in type 2 diabetes in particular, the study found.
“This study’s startling projections of type 2 diabetes increases show why it is crucial to advance health equity and reduce the widespread disparities that already take a toll on people’s health,” Christopher Holliday, PhD, MPH, FACHE, director of CDC’s Division of Diabetes Translation, said in a press release about the new estimates.
Even if trends remain the same in coming decades, researchers said diagnoses of type 2 diabetes will rise almost 70% and that diagnoses of type 1 diabetes will increase by 3%.
The researchers attribute the increase in diabetes cases among youth to a variety of factors, including the growing prevalence of childhood obesity and the presence of diabetes in women of childbearing age, which is linked to obesity in their offspring.
Debra Houry, MD, MPH, acting principal director of the CDC, said the focus should be on prevention.
“This new research should serve as a wake-up call for all of us. It’s vital that we focus our efforts to ensure all Americans, especially our young people, are the healthiest they can be,” she said in a press release.
The findings come from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study, funded by the CDC and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Houry and Dr. Holliday report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETES CARE
Heart benefits begin at well under 10,000 daily steps
– and the benefits accrue at well below the widely promoted threshold of 10,000 steps per day, new research shows.
Among adults aged 60 and older, those who took roughly 6,000 to 9,000 steps per day had a 40% to 50% lower risk of CVD, compared with peers logging just 2,000 steps per day.
“We hope this study will contribute evidence to future public health and clinical guidance on how many steps we need for health,” Amanda Paluch, PhD, with University of Massachusetts Amherst, told this news organization.
Getting in more steps per day can lower an individual’s risk for heart disease – but it’s not an “all or nothing” situation, Dr. Paluch said.
“The heart health benefits begin at lower than 10,000 steps per day. So, for the many adults that may find 10,000 steps a bit out of reach, it is important to promote that even small increases in steps can be beneficial for health,” Dr. Paluch said.
The study was published online in Circulation.
Attainable step goals
As part of the Steps for Health Collaborative, Dr. Paluch and colleagues examined the dose-response relationship between steps per day and CVD in a meta-analysis of eight prospective studies involving 20,152 adults (mean age 63, 52% women).
Steps were measured in each study using one of five different commercially available step-measuring devices. Adults aged 60 years and older took a median of 4,323 steps per day (interquartile range, 2,760-6,924), while younger adults walked a bit more (median 6,911 daily steps; IQR, 4,783-9,794).
During follow-up lasting an average of 6.2 years, a total of 1,523 CVD events were reported.
In the final adjusted model, for older adults, compared with those in quartile 1 who got the fewest steps per day (median 1,811), the risk of CVD was 20% lower in those in quartile 2, who got a median of 3,823 steps per day (hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.69-0.93).
CVD risk was 38% lower in older adults in quartile 3 who got a median of 5,520 steps per day (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.52-0.74) and 49% lower in those in quartile 4 who walked the most (a median of 9,259 steps per day; HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.41-0.63).
Restricting the analysis to individuals without known CVD at baseline showed similar results.
Among six studies that excluded adults with a history of CVD at baseline, compared with the lowest quartile, the HR for incident CVD events was 0.74 (95% CI, 0.60-0.91) in the second quartile, 0.60 (95% CI, 0.47-0.77) in the third quartile, and 0.55 (95% CI, 0.40-0.76) in the fourth quartile.
Despite the inverse association of steps with CVD in older adults, there was no association in younger adults. The researchers caution, however, that CVD is a disease of aging, and the follow-up period in these studies may not have been long enough to capture CVD incidence in younger adults.
Stepping rate (pace or cadence) was not associated with CVD risk beyond that of total steps per day. However, only four of the eight studies reported data on stepping rate, so this finding should be viewed as preliminary, Dr. Paluch and colleagues say.
Start small and go from there
Dr. Paluch said the take-home message from this study and numerous others is simple.
“Move more and sit less! Being physically active, by getting in your steps, is an important part of keeping your heart healthy,” she said in an interview.
For adults who are currently inactive, Dr. Paluch suggests finding small ways to get in a few more steps per day. “It does not need to be drastic changes. Consider a brief 5- to 10-minute walking break at lunch, taking the stairs, or playing a game of hide and seek with the grandchildren,” Dr. Paluch advised.
“For adults starting at 3,000 steps a day, set a goal of 4,000, and then 5,000. Each improvement can lead to better heart health,” Dr. Paluch said. “And for those who are already active, keep it up, as there are benefits with higher volumes of steps per day as well.”
Support for this research was provided by the Intergovernmental Personnel Act Agreement through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– and the benefits accrue at well below the widely promoted threshold of 10,000 steps per day, new research shows.
Among adults aged 60 and older, those who took roughly 6,000 to 9,000 steps per day had a 40% to 50% lower risk of CVD, compared with peers logging just 2,000 steps per day.
“We hope this study will contribute evidence to future public health and clinical guidance on how many steps we need for health,” Amanda Paluch, PhD, with University of Massachusetts Amherst, told this news organization.
Getting in more steps per day can lower an individual’s risk for heart disease – but it’s not an “all or nothing” situation, Dr. Paluch said.
“The heart health benefits begin at lower than 10,000 steps per day. So, for the many adults that may find 10,000 steps a bit out of reach, it is important to promote that even small increases in steps can be beneficial for health,” Dr. Paluch said.
The study was published online in Circulation.
Attainable step goals
As part of the Steps for Health Collaborative, Dr. Paluch and colleagues examined the dose-response relationship between steps per day and CVD in a meta-analysis of eight prospective studies involving 20,152 adults (mean age 63, 52% women).
Steps were measured in each study using one of five different commercially available step-measuring devices. Adults aged 60 years and older took a median of 4,323 steps per day (interquartile range, 2,760-6,924), while younger adults walked a bit more (median 6,911 daily steps; IQR, 4,783-9,794).
During follow-up lasting an average of 6.2 years, a total of 1,523 CVD events were reported.
In the final adjusted model, for older adults, compared with those in quartile 1 who got the fewest steps per day (median 1,811), the risk of CVD was 20% lower in those in quartile 2, who got a median of 3,823 steps per day (hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.69-0.93).
CVD risk was 38% lower in older adults in quartile 3 who got a median of 5,520 steps per day (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.52-0.74) and 49% lower in those in quartile 4 who walked the most (a median of 9,259 steps per day; HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.41-0.63).
Restricting the analysis to individuals without known CVD at baseline showed similar results.
Among six studies that excluded adults with a history of CVD at baseline, compared with the lowest quartile, the HR for incident CVD events was 0.74 (95% CI, 0.60-0.91) in the second quartile, 0.60 (95% CI, 0.47-0.77) in the third quartile, and 0.55 (95% CI, 0.40-0.76) in the fourth quartile.
Despite the inverse association of steps with CVD in older adults, there was no association in younger adults. The researchers caution, however, that CVD is a disease of aging, and the follow-up period in these studies may not have been long enough to capture CVD incidence in younger adults.
Stepping rate (pace or cadence) was not associated with CVD risk beyond that of total steps per day. However, only four of the eight studies reported data on stepping rate, so this finding should be viewed as preliminary, Dr. Paluch and colleagues say.
Start small and go from there
Dr. Paluch said the take-home message from this study and numerous others is simple.
“Move more and sit less! Being physically active, by getting in your steps, is an important part of keeping your heart healthy,” she said in an interview.
For adults who are currently inactive, Dr. Paluch suggests finding small ways to get in a few more steps per day. “It does not need to be drastic changes. Consider a brief 5- to 10-minute walking break at lunch, taking the stairs, or playing a game of hide and seek with the grandchildren,” Dr. Paluch advised.
“For adults starting at 3,000 steps a day, set a goal of 4,000, and then 5,000. Each improvement can lead to better heart health,” Dr. Paluch said. “And for those who are already active, keep it up, as there are benefits with higher volumes of steps per day as well.”
Support for this research was provided by the Intergovernmental Personnel Act Agreement through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– and the benefits accrue at well below the widely promoted threshold of 10,000 steps per day, new research shows.
Among adults aged 60 and older, those who took roughly 6,000 to 9,000 steps per day had a 40% to 50% lower risk of CVD, compared with peers logging just 2,000 steps per day.
“We hope this study will contribute evidence to future public health and clinical guidance on how many steps we need for health,” Amanda Paluch, PhD, with University of Massachusetts Amherst, told this news organization.
Getting in more steps per day can lower an individual’s risk for heart disease – but it’s not an “all or nothing” situation, Dr. Paluch said.
“The heart health benefits begin at lower than 10,000 steps per day. So, for the many adults that may find 10,000 steps a bit out of reach, it is important to promote that even small increases in steps can be beneficial for health,” Dr. Paluch said.
The study was published online in Circulation.
Attainable step goals
As part of the Steps for Health Collaborative, Dr. Paluch and colleagues examined the dose-response relationship between steps per day and CVD in a meta-analysis of eight prospective studies involving 20,152 adults (mean age 63, 52% women).
Steps were measured in each study using one of five different commercially available step-measuring devices. Adults aged 60 years and older took a median of 4,323 steps per day (interquartile range, 2,760-6,924), while younger adults walked a bit more (median 6,911 daily steps; IQR, 4,783-9,794).
During follow-up lasting an average of 6.2 years, a total of 1,523 CVD events were reported.
In the final adjusted model, for older adults, compared with those in quartile 1 who got the fewest steps per day (median 1,811), the risk of CVD was 20% lower in those in quartile 2, who got a median of 3,823 steps per day (hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.69-0.93).
CVD risk was 38% lower in older adults in quartile 3 who got a median of 5,520 steps per day (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.52-0.74) and 49% lower in those in quartile 4 who walked the most (a median of 9,259 steps per day; HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.41-0.63).
Restricting the analysis to individuals without known CVD at baseline showed similar results.
Among six studies that excluded adults with a history of CVD at baseline, compared with the lowest quartile, the HR for incident CVD events was 0.74 (95% CI, 0.60-0.91) in the second quartile, 0.60 (95% CI, 0.47-0.77) in the third quartile, and 0.55 (95% CI, 0.40-0.76) in the fourth quartile.
Despite the inverse association of steps with CVD in older adults, there was no association in younger adults. The researchers caution, however, that CVD is a disease of aging, and the follow-up period in these studies may not have been long enough to capture CVD incidence in younger adults.
Stepping rate (pace or cadence) was not associated with CVD risk beyond that of total steps per day. However, only four of the eight studies reported data on stepping rate, so this finding should be viewed as preliminary, Dr. Paluch and colleagues say.
Start small and go from there
Dr. Paluch said the take-home message from this study and numerous others is simple.
“Move more and sit less! Being physically active, by getting in your steps, is an important part of keeping your heart healthy,” she said in an interview.
For adults who are currently inactive, Dr. Paluch suggests finding small ways to get in a few more steps per day. “It does not need to be drastic changes. Consider a brief 5- to 10-minute walking break at lunch, taking the stairs, or playing a game of hide and seek with the grandchildren,” Dr. Paluch advised.
“For adults starting at 3,000 steps a day, set a goal of 4,000, and then 5,000. Each improvement can lead to better heart health,” Dr. Paluch said. “And for those who are already active, keep it up, as there are benefits with higher volumes of steps per day as well.”
Support for this research was provided by the Intergovernmental Personnel Act Agreement through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
Women with cycle disorders across their life span may be at increased risk of cardiovascular disease
This finding is demonstrated in a new analysis of the Nurses’ Health Study II.
“To date, several studies have reported increased risks of cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease in connection with cycle disorders,” Yi-Xin Wang, MD, PhD, a research fellow in nutrition, and associates from the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, wrote in an article published in JAMA Network Open.
Ute Seeland, MD, speaker of the Gender Medicine in Cardiology Working Group of the German Cardiology Society, said in an interview“We know that women who have indicated in their medical history that they have irregular menstrual cycles, invariably in connection with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), more commonly develop diabetes and other metabolic disorders, as well as cardiovascular diseases.”
Cycle disorders’ role
However, the role that irregular or especially long cycles play at different points of a woman’s reproductive life span was unclear. Therefore, the research group investigated the associations in the Nurses’ Health Study II between cycle irregularity and cycle length in women of different age groups who later experienced cardiovascular events.
At the end of this study in 1989, the participants also provided information regarding the length and irregularity of their menstrual cycle from ages 14 to 17 years and again from ages 18 to 22 years. The information was updated in 1993 when the participants were aged 29-46 years. The data from 2019 to 2022 were analyzed.
“This kind of long-term cohort study is extremely rare and therefore something special,” said Dr. Seeland, who conducts research at the Institute for Social Medicine, Epidemiology, and Health Economics at the Charité – University Hospital Berlin.
The investigators used the following cycle classifications: very regular (no more than 3 or 4 days before or after the expected date), regular (within 5-7 days), usually irregular, always irregular, or no periods.
The cycle lengths were divided into the following categories: less than 21 days, 21-25 days, 26-31 days, 32-39 days, 40-50 days, more than 50 days, and too irregular to estimate the length.
The onset of cardiovascular diseases was determined using information from the participants and was confirmed by reviewing the medical files. Relevant to the study were lethal and nonlethal coronary heart diseases (such as myocardial infarction or coronary artery revascularization), as well as strokes.
Significant in adulthood
The data from 80,630 study participants were included in the analysis. At study inclusion, the average age of the participants was 37.7 years, and the average body mass index (BMI) was 25.1. “Since it was predominantly White nurses who took part in the study, the data are not transferable to other, more diverse populations,” said Dr. Seeland.
Over 24 years, 1,816 women (2.4%) had a cardiovascular event. “We observed an increased rate of cardiovascular events in women with an irregular cycle and longer cycle, both in early an in mid-adulthood,” wrote Dr. Wang and associates. “Similar trends were also observed for cycle disorders when younger, but this association was weaker than in adulthood.”
Compared with women with very regular cycles, women with irregular cycles or without periods who were aged 14-17 years, 18-22 years, or 29-49 years exhibited a 15%, 36%, and 40% higher risk of a cardiovascular event, respectively.
Similarly, women aged 18-22 years or 29-46 years with long cycles of 40 days or more had a 44% or 30% higher risk of cardiovascular disease, respectively, compared with women with cycle lengths of 26-31 days.
“The coronary heart diseases were decisive for the increase, and less so, the strokes,” wrote the researchers.
Classic risk factors?
Dr. Seeland praised the fact that the study authors tried to determine the role that classic cardiovascular risk factors played. “Compared with women with a regular cycle, women with an irregular cycle had a higher BMI, more frequently increased cholesterol levels, and an elevated blood pressure,” she said. Women with a long cycle displayed a similar pattern.
It can be assumed from this that over a woman’s life span, BMI affects the risk of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, Dr. Wang and coauthors adjusted the results on the basis of BMI, which varies over time.
Regarding other classic risk factors that may have played a role, “hypercholesterolemia, chronic high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes were only responsible in 5.4%-13.5% of the associations,” wrote the researchers.
“Our results suggest that certain characteristics of the menstrual cycle across a woman’s reproductive lifespan may constitute additional risk markers for cardiovascular disease,” according to the authors.
The highest rates of cardiovascular disease were among women with permanently irregular or long cycles in early to mid adulthood, as well as women who had regular cycles when younger but had irregular cycles in mid adulthood. “This indicates that the change from one cycle phenotype to another could be a surrogate marker for metabolic changes, which in turn contribute to the formation of cardiovascular diseases,” wrote the authors.
The study was observational and so conclusions cannot be drawn regarding causal relationships. But Dr. Wang and associates indicate that the most common cause of an irregular menstrual cycle may be PCOS. “Roughly 90% of women with cycle disorders or oligomenorrhea have signs of PCOS. And it was shown that women with PCOS have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.”
They concluded that “the associations observed between irregular and long cycles in early to mid-adulthood and cardiovascular diseases are likely attributable to underlying PCOS.”
For Dr. Seeland, however, this conclusion is “too monocausal. At no point in time did there seem to be any direct information regarding the frequency of PCOS during the data collection by the respondents.”
For now, we can only speculate about the mechanisms. “The association between a very irregular and long cycle and the increased risk of cardiovascular diseases has now only been described. More research should be done on the causes,” said Dr. Seeland.
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This finding is demonstrated in a new analysis of the Nurses’ Health Study II.
“To date, several studies have reported increased risks of cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease in connection with cycle disorders,” Yi-Xin Wang, MD, PhD, a research fellow in nutrition, and associates from the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, wrote in an article published in JAMA Network Open.
Ute Seeland, MD, speaker of the Gender Medicine in Cardiology Working Group of the German Cardiology Society, said in an interview“We know that women who have indicated in their medical history that they have irregular menstrual cycles, invariably in connection with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), more commonly develop diabetes and other metabolic disorders, as well as cardiovascular diseases.”
Cycle disorders’ role
However, the role that irregular or especially long cycles play at different points of a woman’s reproductive life span was unclear. Therefore, the research group investigated the associations in the Nurses’ Health Study II between cycle irregularity and cycle length in women of different age groups who later experienced cardiovascular events.
At the end of this study in 1989, the participants also provided information regarding the length and irregularity of their menstrual cycle from ages 14 to 17 years and again from ages 18 to 22 years. The information was updated in 1993 when the participants were aged 29-46 years. The data from 2019 to 2022 were analyzed.
“This kind of long-term cohort study is extremely rare and therefore something special,” said Dr. Seeland, who conducts research at the Institute for Social Medicine, Epidemiology, and Health Economics at the Charité – University Hospital Berlin.
The investigators used the following cycle classifications: very regular (no more than 3 or 4 days before or after the expected date), regular (within 5-7 days), usually irregular, always irregular, or no periods.
The cycle lengths were divided into the following categories: less than 21 days, 21-25 days, 26-31 days, 32-39 days, 40-50 days, more than 50 days, and too irregular to estimate the length.
The onset of cardiovascular diseases was determined using information from the participants and was confirmed by reviewing the medical files. Relevant to the study were lethal and nonlethal coronary heart diseases (such as myocardial infarction or coronary artery revascularization), as well as strokes.
Significant in adulthood
The data from 80,630 study participants were included in the analysis. At study inclusion, the average age of the participants was 37.7 years, and the average body mass index (BMI) was 25.1. “Since it was predominantly White nurses who took part in the study, the data are not transferable to other, more diverse populations,” said Dr. Seeland.
Over 24 years, 1,816 women (2.4%) had a cardiovascular event. “We observed an increased rate of cardiovascular events in women with an irregular cycle and longer cycle, both in early an in mid-adulthood,” wrote Dr. Wang and associates. “Similar trends were also observed for cycle disorders when younger, but this association was weaker than in adulthood.”
Compared with women with very regular cycles, women with irregular cycles or without periods who were aged 14-17 years, 18-22 years, or 29-49 years exhibited a 15%, 36%, and 40% higher risk of a cardiovascular event, respectively.
Similarly, women aged 18-22 years or 29-46 years with long cycles of 40 days or more had a 44% or 30% higher risk of cardiovascular disease, respectively, compared with women with cycle lengths of 26-31 days.
“The coronary heart diseases were decisive for the increase, and less so, the strokes,” wrote the researchers.
Classic risk factors?
Dr. Seeland praised the fact that the study authors tried to determine the role that classic cardiovascular risk factors played. “Compared with women with a regular cycle, women with an irregular cycle had a higher BMI, more frequently increased cholesterol levels, and an elevated blood pressure,” she said. Women with a long cycle displayed a similar pattern.
It can be assumed from this that over a woman’s life span, BMI affects the risk of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, Dr. Wang and coauthors adjusted the results on the basis of BMI, which varies over time.
Regarding other classic risk factors that may have played a role, “hypercholesterolemia, chronic high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes were only responsible in 5.4%-13.5% of the associations,” wrote the researchers.
“Our results suggest that certain characteristics of the menstrual cycle across a woman’s reproductive lifespan may constitute additional risk markers for cardiovascular disease,” according to the authors.
The highest rates of cardiovascular disease were among women with permanently irregular or long cycles in early to mid adulthood, as well as women who had regular cycles when younger but had irregular cycles in mid adulthood. “This indicates that the change from one cycle phenotype to another could be a surrogate marker for metabolic changes, which in turn contribute to the formation of cardiovascular diseases,” wrote the authors.
The study was observational and so conclusions cannot be drawn regarding causal relationships. But Dr. Wang and associates indicate that the most common cause of an irregular menstrual cycle may be PCOS. “Roughly 90% of women with cycle disorders or oligomenorrhea have signs of PCOS. And it was shown that women with PCOS have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.”
They concluded that “the associations observed between irregular and long cycles in early to mid-adulthood and cardiovascular diseases are likely attributable to underlying PCOS.”
For Dr. Seeland, however, this conclusion is “too monocausal. At no point in time did there seem to be any direct information regarding the frequency of PCOS during the data collection by the respondents.”
For now, we can only speculate about the mechanisms. “The association between a very irregular and long cycle and the increased risk of cardiovascular diseases has now only been described. More research should be done on the causes,” said Dr. Seeland.
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This finding is demonstrated in a new analysis of the Nurses’ Health Study II.
“To date, several studies have reported increased risks of cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease in connection with cycle disorders,” Yi-Xin Wang, MD, PhD, a research fellow in nutrition, and associates from the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, wrote in an article published in JAMA Network Open.
Ute Seeland, MD, speaker of the Gender Medicine in Cardiology Working Group of the German Cardiology Society, said in an interview“We know that women who have indicated in their medical history that they have irregular menstrual cycles, invariably in connection with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), more commonly develop diabetes and other metabolic disorders, as well as cardiovascular diseases.”
Cycle disorders’ role
However, the role that irregular or especially long cycles play at different points of a woman’s reproductive life span was unclear. Therefore, the research group investigated the associations in the Nurses’ Health Study II between cycle irregularity and cycle length in women of different age groups who later experienced cardiovascular events.
At the end of this study in 1989, the participants also provided information regarding the length and irregularity of their menstrual cycle from ages 14 to 17 years and again from ages 18 to 22 years. The information was updated in 1993 when the participants were aged 29-46 years. The data from 2019 to 2022 were analyzed.
“This kind of long-term cohort study is extremely rare and therefore something special,” said Dr. Seeland, who conducts research at the Institute for Social Medicine, Epidemiology, and Health Economics at the Charité – University Hospital Berlin.
The investigators used the following cycle classifications: very regular (no more than 3 or 4 days before or after the expected date), regular (within 5-7 days), usually irregular, always irregular, or no periods.
The cycle lengths were divided into the following categories: less than 21 days, 21-25 days, 26-31 days, 32-39 days, 40-50 days, more than 50 days, and too irregular to estimate the length.
The onset of cardiovascular diseases was determined using information from the participants and was confirmed by reviewing the medical files. Relevant to the study were lethal and nonlethal coronary heart diseases (such as myocardial infarction or coronary artery revascularization), as well as strokes.
Significant in adulthood
The data from 80,630 study participants were included in the analysis. At study inclusion, the average age of the participants was 37.7 years, and the average body mass index (BMI) was 25.1. “Since it was predominantly White nurses who took part in the study, the data are not transferable to other, more diverse populations,” said Dr. Seeland.
Over 24 years, 1,816 women (2.4%) had a cardiovascular event. “We observed an increased rate of cardiovascular events in women with an irregular cycle and longer cycle, both in early an in mid-adulthood,” wrote Dr. Wang and associates. “Similar trends were also observed for cycle disorders when younger, but this association was weaker than in adulthood.”
Compared with women with very regular cycles, women with irregular cycles or without periods who were aged 14-17 years, 18-22 years, or 29-49 years exhibited a 15%, 36%, and 40% higher risk of a cardiovascular event, respectively.
Similarly, women aged 18-22 years or 29-46 years with long cycles of 40 days or more had a 44% or 30% higher risk of cardiovascular disease, respectively, compared with women with cycle lengths of 26-31 days.
“The coronary heart diseases were decisive for the increase, and less so, the strokes,” wrote the researchers.
Classic risk factors?
Dr. Seeland praised the fact that the study authors tried to determine the role that classic cardiovascular risk factors played. “Compared with women with a regular cycle, women with an irregular cycle had a higher BMI, more frequently increased cholesterol levels, and an elevated blood pressure,” she said. Women with a long cycle displayed a similar pattern.
It can be assumed from this that over a woman’s life span, BMI affects the risk of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, Dr. Wang and coauthors adjusted the results on the basis of BMI, which varies over time.
Regarding other classic risk factors that may have played a role, “hypercholesterolemia, chronic high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes were only responsible in 5.4%-13.5% of the associations,” wrote the researchers.
“Our results suggest that certain characteristics of the menstrual cycle across a woman’s reproductive lifespan may constitute additional risk markers for cardiovascular disease,” according to the authors.
The highest rates of cardiovascular disease were among women with permanently irregular or long cycles in early to mid adulthood, as well as women who had regular cycles when younger but had irregular cycles in mid adulthood. “This indicates that the change from one cycle phenotype to another could be a surrogate marker for metabolic changes, which in turn contribute to the formation of cardiovascular diseases,” wrote the authors.
The study was observational and so conclusions cannot be drawn regarding causal relationships. But Dr. Wang and associates indicate that the most common cause of an irregular menstrual cycle may be PCOS. “Roughly 90% of women with cycle disorders or oligomenorrhea have signs of PCOS. And it was shown that women with PCOS have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.”
They concluded that “the associations observed between irregular and long cycles in early to mid-adulthood and cardiovascular diseases are likely attributable to underlying PCOS.”
For Dr. Seeland, however, this conclusion is “too monocausal. At no point in time did there seem to be any direct information regarding the frequency of PCOS during the data collection by the respondents.”
For now, we can only speculate about the mechanisms. “The association between a very irregular and long cycle and the increased risk of cardiovascular diseases has now only been described. More research should be done on the causes,” said Dr. Seeland.
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
FDA approves Wegovy (semaglutide) for obesity in teens 12 and up
The Food and Drug Administration has approved semaglutide 2.4 mg (Wegovy), a once-weekly subcutaneous injection, for the additional indication of treating obesity in adolescents aged 12 years and older.
This is defined as those with an initial body mass index at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex (based on CDC growth charts). Semaglutide must be administered along with lifestyle intervention of a reduced calorie meal plan and increased physical activity.
When Wegovy was approved for use in adults with obesity in June 2021, it was labeled a “game changer.”
The new approval is based on the results of the STEP TEENS phase 3 trial of once-weekly 2.4 mg of semaglutide in adolescents 12- to <18 years old with obesity, the drug’s manufacturer, Novo Nordisk, announced in a press release.
In STEP TEENS, reported at Obesity Week 2022 in November, and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine, adolescents with obesity treated with semaglutide for 68 weeks had a 16.1% reduction in BMI compared with a 0.6% increase in BMI in those receiving placebo. Both groups also received lifestyle intervention. Mean weight loss was 15.3 kg (33.7 pounds) among teens on semaglutide, while those on placebo gained 2.4 kg (5.3 pounds).
At the time, Claudia K. Fox, MD, MPH, codirector of the Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine at the University of Minnesota – who was not involved with the research – told this news organization the results were “mind-blowing ... we are getting close to bariatric surgery results” in these adolescent patients with obesity.
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 agonist, as is a related agent, also from Novo Nordisk, liraglutide (Saxenda), a daily subcutaneous injection, which was approved for use in adolescents aged 12 and older in December 2020. Wegovy is the first weekly subcutaneous injection approved for use in adolescents.
Other agents approved for obesity in those older than 12 in the United States include the combination phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules (Qsymia) in June 2022, and orlistat (Alli). Phentermine is approved for those aged 16 and older.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved semaglutide 2.4 mg (Wegovy), a once-weekly subcutaneous injection, for the additional indication of treating obesity in adolescents aged 12 years and older.
This is defined as those with an initial body mass index at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex (based on CDC growth charts). Semaglutide must be administered along with lifestyle intervention of a reduced calorie meal plan and increased physical activity.
When Wegovy was approved for use in adults with obesity in June 2021, it was labeled a “game changer.”
The new approval is based on the results of the STEP TEENS phase 3 trial of once-weekly 2.4 mg of semaglutide in adolescents 12- to <18 years old with obesity, the drug’s manufacturer, Novo Nordisk, announced in a press release.
In STEP TEENS, reported at Obesity Week 2022 in November, and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine, adolescents with obesity treated with semaglutide for 68 weeks had a 16.1% reduction in BMI compared with a 0.6% increase in BMI in those receiving placebo. Both groups also received lifestyle intervention. Mean weight loss was 15.3 kg (33.7 pounds) among teens on semaglutide, while those on placebo gained 2.4 kg (5.3 pounds).
At the time, Claudia K. Fox, MD, MPH, codirector of the Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine at the University of Minnesota – who was not involved with the research – told this news organization the results were “mind-blowing ... we are getting close to bariatric surgery results” in these adolescent patients with obesity.
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 agonist, as is a related agent, also from Novo Nordisk, liraglutide (Saxenda), a daily subcutaneous injection, which was approved for use in adolescents aged 12 and older in December 2020. Wegovy is the first weekly subcutaneous injection approved for use in adolescents.
Other agents approved for obesity in those older than 12 in the United States include the combination phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules (Qsymia) in June 2022, and orlistat (Alli). Phentermine is approved for those aged 16 and older.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved semaglutide 2.4 mg (Wegovy), a once-weekly subcutaneous injection, for the additional indication of treating obesity in adolescents aged 12 years and older.
This is defined as those with an initial body mass index at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex (based on CDC growth charts). Semaglutide must be administered along with lifestyle intervention of a reduced calorie meal plan and increased physical activity.
When Wegovy was approved for use in adults with obesity in June 2021, it was labeled a “game changer.”
The new approval is based on the results of the STEP TEENS phase 3 trial of once-weekly 2.4 mg of semaglutide in adolescents 12- to <18 years old with obesity, the drug’s manufacturer, Novo Nordisk, announced in a press release.
In STEP TEENS, reported at Obesity Week 2022 in November, and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine, adolescents with obesity treated with semaglutide for 68 weeks had a 16.1% reduction in BMI compared with a 0.6% increase in BMI in those receiving placebo. Both groups also received lifestyle intervention. Mean weight loss was 15.3 kg (33.7 pounds) among teens on semaglutide, while those on placebo gained 2.4 kg (5.3 pounds).
At the time, Claudia K. Fox, MD, MPH, codirector of the Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine at the University of Minnesota – who was not involved with the research – told this news organization the results were “mind-blowing ... we are getting close to bariatric surgery results” in these adolescent patients with obesity.
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 agonist, as is a related agent, also from Novo Nordisk, liraglutide (Saxenda), a daily subcutaneous injection, which was approved for use in adolescents aged 12 and older in December 2020. Wegovy is the first weekly subcutaneous injection approved for use in adolescents.
Other agents approved for obesity in those older than 12 in the United States include the combination phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules (Qsymia) in June 2022, and orlistat (Alli). Phentermine is approved for those aged 16 and older.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study of beliefs about what causes cancer sparks debate
The study, entitled, “Everything Causes Cancer? Beliefs and Attitudes Towards Cancer Prevention Among Anti-Vaxxers, Flat Earthers, and Reptilian Conspiracists: Online Cross Sectional Survey,” was published in the Christmas 2022 issue of The British Medical Journal (BMJ).
The authors explain that they set out to evaluate “the patterns of beliefs about cancer among people who believed in conspiracies, rejected the COVID-19 vaccine, or preferred alternative medicine.”
They sought such people on social media and online chat platforms and asked them questions about real and mythical causes of cancer.
Almost half of survey participants agreed with the statement, “It seems like everything causes cancer.”
Overall, among all participants, awareness of the actual causes of cancer was greater than awareness of the mythical causes of cancer, the authors report. However, awareness of the actual causes of cancer was lower among the unvaccinated and members of conspiracy groups than among their counterparts.
The authors are concerned that their findings suggest “a direct connection between digital misinformation and consequent potential erroneous health decisions, which may represent a further preventable fraction of cancer.”
Backlash and criticism
The study “highlights the difficulty society encounters in distinguishing the actual causes of cancer from mythical causes,” The BMJ commented on Twitter.
However, both the study and the journal received some backlash.
This is a “horrible article seeking to smear people with concerns about COVID vaccines,” commented Clare Craig, a British consultant pathologist who specializes in cancer diagnostics.
The study and its methodology were also harshly criticized on Twitter by Normal Fenton, professor of risk information management at the Queen Mary University of London.
The senior author of the study, Laura Costas, a medical epidemiologist with the Catalan Institute of Oncology, Barcelona, told this news organization that the naysayers on social media, many of whom focused their comments on the COVID-19 vaccine, prove the purpose of the study – that misinformation spreads widely on the internet.
“Most comments focused on spreading COVID-19 myths, which were not the direct subject of the study, and questioned the motivations of BMJ authors and the scientific community, assuming they had a common malevolent hidden agenda,” Ms. Costas said.
“They stated the need of having critical thinking, a trait in common with the scientific method, but dogmatically dismissed any information that comes from official sources,” she added.
Ms. Costas commented that “society encounters difficulty in differentiating actual from mythical causes of cancer owing to mass information. We therefore planned this study with a certain satire, which is in line with the essence of The BMJ Christmas issue.”
The BMJ has a long history of publishing a lighthearted Christmas edition full of original, satirical, and nontraditional studies. Previous years have seen studies that explored potential harms from holly and ivy, survival time of chocolates on hospital wards, and the question, “Were James Bond’s drinks shaken because of alcohol induced tremor?”
Study details
Ms. Costas and colleagues sought participants for their survey from online forums that included 4chan and Reddit, which are known for their controversial content posted by anonymous users. Data were also collected from ForoCoches and HispaChan, well-known Spanish online forums. These online sites were intentionally chosen because researchers thought “conspiracy beliefs would be more prevalent,” according to Ms. Costas.
Across the multiple forums, there were 1,494 participants. Of these, 209 participants were unvaccinated against COVID-19, 112 preferred alternatives rather than conventional medicine, and 62 reported that they believed the earth was flat or believed that humanoids take reptilian forms to manipulate human societies.
The team then sought to assess beliefs about actual and mythical (nonestablished) causes of cancer by presenting the participants with the closed risk factor questions on two validated scales – the Cancer Awareness Measure (CAM) and CAM–Mythical Causes Scale (CAM-MYCS).
Responses to both were recorded on a five-point scale; answers ranged from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree.”
The CAM assesses cancer risk perceptions of 11 established risk factors for cancer: smoking actively or passively, consuming alcohol, low levels of physical activity, consuming red or processed meat, getting sunburnt as a child, family history of cancer, human papillomavirus infection, being overweight, age greater than or equal to 70 years, and low vegetable and fruit consumption.
The CAM-MYCS measure includes 12 questions on risk perceptions of mythical causes of cancer – nonestablished causes that are commonly believed to cause cancer but for which there is no supporting scientific evidence, the authors explain. These items include drinking from plastic bottles; eating food containing artificial sweeteners or additives and genetically modified food; using microwave ovens, aerosol containers, mobile phones, and cleaning products; living near power lines; feeling stressed; experiencing physical trauma; and being exposed to electromagnetic frequencies/non-ionizing radiation, such as wi-fi networks, radio, and television.
The most endorsed mythical causes of cancer were eating food containing additives (63.9%) or sweeteners (50.7%), feeling stressed (59.7%), and eating genetically modified foods (38.4%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study, entitled, “Everything Causes Cancer? Beliefs and Attitudes Towards Cancer Prevention Among Anti-Vaxxers, Flat Earthers, and Reptilian Conspiracists: Online Cross Sectional Survey,” was published in the Christmas 2022 issue of The British Medical Journal (BMJ).
The authors explain that they set out to evaluate “the patterns of beliefs about cancer among people who believed in conspiracies, rejected the COVID-19 vaccine, or preferred alternative medicine.”
They sought such people on social media and online chat platforms and asked them questions about real and mythical causes of cancer.
Almost half of survey participants agreed with the statement, “It seems like everything causes cancer.”
Overall, among all participants, awareness of the actual causes of cancer was greater than awareness of the mythical causes of cancer, the authors report. However, awareness of the actual causes of cancer was lower among the unvaccinated and members of conspiracy groups than among their counterparts.
The authors are concerned that their findings suggest “a direct connection between digital misinformation and consequent potential erroneous health decisions, which may represent a further preventable fraction of cancer.”
Backlash and criticism
The study “highlights the difficulty society encounters in distinguishing the actual causes of cancer from mythical causes,” The BMJ commented on Twitter.
However, both the study and the journal received some backlash.
This is a “horrible article seeking to smear people with concerns about COVID vaccines,” commented Clare Craig, a British consultant pathologist who specializes in cancer diagnostics.
The study and its methodology were also harshly criticized on Twitter by Normal Fenton, professor of risk information management at the Queen Mary University of London.
The senior author of the study, Laura Costas, a medical epidemiologist with the Catalan Institute of Oncology, Barcelona, told this news organization that the naysayers on social media, many of whom focused their comments on the COVID-19 vaccine, prove the purpose of the study – that misinformation spreads widely on the internet.
“Most comments focused on spreading COVID-19 myths, which were not the direct subject of the study, and questioned the motivations of BMJ authors and the scientific community, assuming they had a common malevolent hidden agenda,” Ms. Costas said.
“They stated the need of having critical thinking, a trait in common with the scientific method, but dogmatically dismissed any information that comes from official sources,” she added.
Ms. Costas commented that “society encounters difficulty in differentiating actual from mythical causes of cancer owing to mass information. We therefore planned this study with a certain satire, which is in line with the essence of The BMJ Christmas issue.”
The BMJ has a long history of publishing a lighthearted Christmas edition full of original, satirical, and nontraditional studies. Previous years have seen studies that explored potential harms from holly and ivy, survival time of chocolates on hospital wards, and the question, “Were James Bond’s drinks shaken because of alcohol induced tremor?”
Study details
Ms. Costas and colleagues sought participants for their survey from online forums that included 4chan and Reddit, which are known for their controversial content posted by anonymous users. Data were also collected from ForoCoches and HispaChan, well-known Spanish online forums. These online sites were intentionally chosen because researchers thought “conspiracy beliefs would be more prevalent,” according to Ms. Costas.
Across the multiple forums, there were 1,494 participants. Of these, 209 participants were unvaccinated against COVID-19, 112 preferred alternatives rather than conventional medicine, and 62 reported that they believed the earth was flat or believed that humanoids take reptilian forms to manipulate human societies.
The team then sought to assess beliefs about actual and mythical (nonestablished) causes of cancer by presenting the participants with the closed risk factor questions on two validated scales – the Cancer Awareness Measure (CAM) and CAM–Mythical Causes Scale (CAM-MYCS).
Responses to both were recorded on a five-point scale; answers ranged from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree.”
The CAM assesses cancer risk perceptions of 11 established risk factors for cancer: smoking actively or passively, consuming alcohol, low levels of physical activity, consuming red or processed meat, getting sunburnt as a child, family history of cancer, human papillomavirus infection, being overweight, age greater than or equal to 70 years, and low vegetable and fruit consumption.
The CAM-MYCS measure includes 12 questions on risk perceptions of mythical causes of cancer – nonestablished causes that are commonly believed to cause cancer but for which there is no supporting scientific evidence, the authors explain. These items include drinking from plastic bottles; eating food containing artificial sweeteners or additives and genetically modified food; using microwave ovens, aerosol containers, mobile phones, and cleaning products; living near power lines; feeling stressed; experiencing physical trauma; and being exposed to electromagnetic frequencies/non-ionizing radiation, such as wi-fi networks, radio, and television.
The most endorsed mythical causes of cancer were eating food containing additives (63.9%) or sweeteners (50.7%), feeling stressed (59.7%), and eating genetically modified foods (38.4%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study, entitled, “Everything Causes Cancer? Beliefs and Attitudes Towards Cancer Prevention Among Anti-Vaxxers, Flat Earthers, and Reptilian Conspiracists: Online Cross Sectional Survey,” was published in the Christmas 2022 issue of The British Medical Journal (BMJ).
The authors explain that they set out to evaluate “the patterns of beliefs about cancer among people who believed in conspiracies, rejected the COVID-19 vaccine, or preferred alternative medicine.”
They sought such people on social media and online chat platforms and asked them questions about real and mythical causes of cancer.
Almost half of survey participants agreed with the statement, “It seems like everything causes cancer.”
Overall, among all participants, awareness of the actual causes of cancer was greater than awareness of the mythical causes of cancer, the authors report. However, awareness of the actual causes of cancer was lower among the unvaccinated and members of conspiracy groups than among their counterparts.
The authors are concerned that their findings suggest “a direct connection between digital misinformation and consequent potential erroneous health decisions, which may represent a further preventable fraction of cancer.”
Backlash and criticism
The study “highlights the difficulty society encounters in distinguishing the actual causes of cancer from mythical causes,” The BMJ commented on Twitter.
However, both the study and the journal received some backlash.
This is a “horrible article seeking to smear people with concerns about COVID vaccines,” commented Clare Craig, a British consultant pathologist who specializes in cancer diagnostics.
The study and its methodology were also harshly criticized on Twitter by Normal Fenton, professor of risk information management at the Queen Mary University of London.
The senior author of the study, Laura Costas, a medical epidemiologist with the Catalan Institute of Oncology, Barcelona, told this news organization that the naysayers on social media, many of whom focused their comments on the COVID-19 vaccine, prove the purpose of the study – that misinformation spreads widely on the internet.
“Most comments focused on spreading COVID-19 myths, which were not the direct subject of the study, and questioned the motivations of BMJ authors and the scientific community, assuming they had a common malevolent hidden agenda,” Ms. Costas said.
“They stated the need of having critical thinking, a trait in common with the scientific method, but dogmatically dismissed any information that comes from official sources,” she added.
Ms. Costas commented that “society encounters difficulty in differentiating actual from mythical causes of cancer owing to mass information. We therefore planned this study with a certain satire, which is in line with the essence of The BMJ Christmas issue.”
The BMJ has a long history of publishing a lighthearted Christmas edition full of original, satirical, and nontraditional studies. Previous years have seen studies that explored potential harms from holly and ivy, survival time of chocolates on hospital wards, and the question, “Were James Bond’s drinks shaken because of alcohol induced tremor?”
Study details
Ms. Costas and colleagues sought participants for their survey from online forums that included 4chan and Reddit, which are known for their controversial content posted by anonymous users. Data were also collected from ForoCoches and HispaChan, well-known Spanish online forums. These online sites were intentionally chosen because researchers thought “conspiracy beliefs would be more prevalent,” according to Ms. Costas.
Across the multiple forums, there were 1,494 participants. Of these, 209 participants were unvaccinated against COVID-19, 112 preferred alternatives rather than conventional medicine, and 62 reported that they believed the earth was flat or believed that humanoids take reptilian forms to manipulate human societies.
The team then sought to assess beliefs about actual and mythical (nonestablished) causes of cancer by presenting the participants with the closed risk factor questions on two validated scales – the Cancer Awareness Measure (CAM) and CAM–Mythical Causes Scale (CAM-MYCS).
Responses to both were recorded on a five-point scale; answers ranged from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree.”
The CAM assesses cancer risk perceptions of 11 established risk factors for cancer: smoking actively or passively, consuming alcohol, low levels of physical activity, consuming red or processed meat, getting sunburnt as a child, family history of cancer, human papillomavirus infection, being overweight, age greater than or equal to 70 years, and low vegetable and fruit consumption.
The CAM-MYCS measure includes 12 questions on risk perceptions of mythical causes of cancer – nonestablished causes that are commonly believed to cause cancer but for which there is no supporting scientific evidence, the authors explain. These items include drinking from plastic bottles; eating food containing artificial sweeteners or additives and genetically modified food; using microwave ovens, aerosol containers, mobile phones, and cleaning products; living near power lines; feeling stressed; experiencing physical trauma; and being exposed to electromagnetic frequencies/non-ionizing radiation, such as wi-fi networks, radio, and television.
The most endorsed mythical causes of cancer were eating food containing additives (63.9%) or sweeteners (50.7%), feeling stressed (59.7%), and eating genetically modified foods (38.4%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.