User login
Novel oral agent shows unprecedented efficacy in psoriasis
PARIS – A novel in a phase 2 clinical trial including 267 adults with moderate to severe disease, James G. Krueger, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“I would say the clinical response here is almost dead-on as a copy for ustekinumab, which is an [injectable interleukin] IL-23/IL-12 blocker. And we’re only at 12 weeks here; some of the curves look like they’re on a trajectory to go up further in terms of improvement. So I’m getting a performance with an oral drug that is just so much better than the approved alternatives that we have,” said Dr. Krueger, head of the laboratory of investigative dermatology and professor in clinical investigation at Rockefeller University in New York.
Oral apremilast (Otezla), for example, can’t touch those PASI 75 response rates in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Indeed, many psoriasis experts favor reserving apremilast for patients with moderate disease.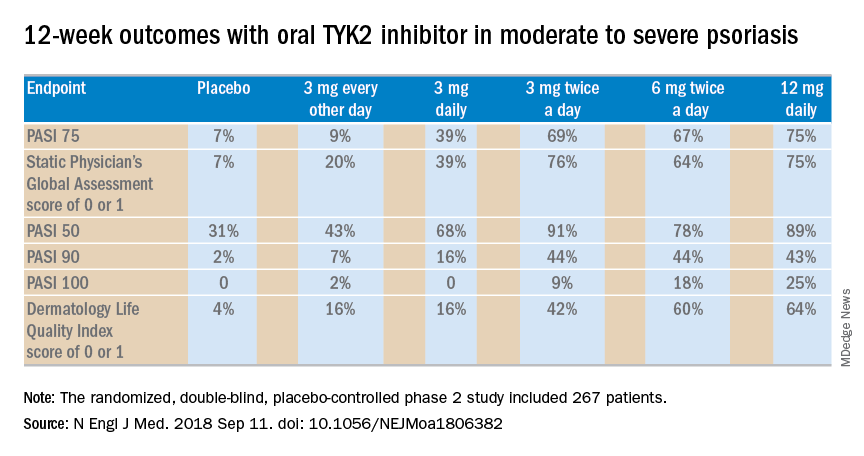
The 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted at 82 sites in the United States and seven other countries. In this dose-ranging study, participants were randomized to the oral selective tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor, known for the time being as BMS-986165, at 3 mg every other day, 3 mg daily, 3 mg twice a day, 6 mg twice a day, 12 mg daily, or to placebo.
The primary outcome was a 75% or greater reduction from baseline in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75) at week 12. The TYK2 inhibitor outperformed placebo in dose-dependent fashion starting at the 3 mg/day dose. The PASI 75 rate was 7% with placebo, 9% with 3 mg of BMS-986165 every other day, 39% with 3 mg daily, 69% with 3 mg BID, 67% with 6 mg BID, and 75% with 12 mg/day. All secondary endpoints followed suit.
A striking finding in the phase 2 study was that when the drug was stopped for a month at the end of the 12-week treatment period, for the most part, the PASI 75 response and other clinical benefits were retained.
“I would contrast this to experiments that I have personally done with cyclosporine, where I have cleared people with cyclosporine, stopped it, and a month later every single patient has rip-roaring disease back. So I think this TYK2 inhibitor has some different performance features than just blocking a downstream T-cell transduction molecule,” observed the dermatologist, who is credited as the discoverer of the importance of the T cell in psoriasis pathogenesis.
The strong multidimensional evidence of clinical efficacy in the phase 2 study was supported mechanistically by analysis of skin biopsies obtained on study days 1, 15, and 85. The laboratory studies showed that the oral drug improved molecular, cellular, and clinical biomarkers associated with treatment efficacy. For example, at doses of 3 mg twice a day or higher, the TYK2 inhibitor reduced expression of IL-19 and IL-36A, which are key drivers of keratinocyte activation and epidermal hyperplasia. The drug also markedly decreased expression of genes in the Th17 pathway and essentially normalized expression of the proinflammatory genes beta defensin and S100A9.
In contrast to the Janus kinase (JAK) 1/3 and JAK 2 inhibitors in development for treatment of psoriasis, which paint with a much broader brush, the TYK2 inhibitor is highly selective for IL-23, IL-12, and interferon alpha.
“Previous studies have shown pan-JAK inhibition can be very effective in remitting psoriasis. The problem is that if one inhibits JAK1 and JAK3, one blocks the transduction of effector cytokines that are essentially there for protective immunity. That could lead to undesirable levels of immunosuppression,” Dr. Krueger explained.
The most important cytokine in the pathogenesis of psoriasis is clearly IL-23, he continued. In cell-based assays, the TYK2 inhibitor has been shown to be 100 times more selective in inhibiting IL-23 , IL-12, and interferon-alpha than JAK 1/3 inhibitors and 3,000 times more selective than JAK 2 inhibitors. This high degree of selectivity makes for fewer off-target effects and for a favorable safety profile.
“There were no major safety signals that would lead you to be concerned,” Dr. Krueger said. Indeed, based upon the encouraging safety and efficacy demonstrated this phase 2 study, a phase 3 program known as POETYK-PSO is underway (POETYK-PSO-1 and POETYK-PSO-2).
The phase 2 clinical trial results were published online in conjunction with the EADV congress.
The TYK2 inhibitor is being developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Krueger reported receiving personal fees as well as research grants paid directly to Rockefeller University from that pharmaceutical company and numerous others.
Source: Papp K et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Sep 11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1806382.
PARIS – A novel in a phase 2 clinical trial including 267 adults with moderate to severe disease, James G. Krueger, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“I would say the clinical response here is almost dead-on as a copy for ustekinumab, which is an [injectable interleukin] IL-23/IL-12 blocker. And we’re only at 12 weeks here; some of the curves look like they’re on a trajectory to go up further in terms of improvement. So I’m getting a performance with an oral drug that is just so much better than the approved alternatives that we have,” said Dr. Krueger, head of the laboratory of investigative dermatology and professor in clinical investigation at Rockefeller University in New York.
Oral apremilast (Otezla), for example, can’t touch those PASI 75 response rates in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Indeed, many psoriasis experts favor reserving apremilast for patients with moderate disease.
The 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted at 82 sites in the United States and seven other countries. In this dose-ranging study, participants were randomized to the oral selective tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor, known for the time being as BMS-986165, at 3 mg every other day, 3 mg daily, 3 mg twice a day, 6 mg twice a day, 12 mg daily, or to placebo.
The primary outcome was a 75% or greater reduction from baseline in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75) at week 12. The TYK2 inhibitor outperformed placebo in dose-dependent fashion starting at the 3 mg/day dose. The PASI 75 rate was 7% with placebo, 9% with 3 mg of BMS-986165 every other day, 39% with 3 mg daily, 69% with 3 mg BID, 67% with 6 mg BID, and 75% with 12 mg/day. All secondary endpoints followed suit.
A striking finding in the phase 2 study was that when the drug was stopped for a month at the end of the 12-week treatment period, for the most part, the PASI 75 response and other clinical benefits were retained.
“I would contrast this to experiments that I have personally done with cyclosporine, where I have cleared people with cyclosporine, stopped it, and a month later every single patient has rip-roaring disease back. So I think this TYK2 inhibitor has some different performance features than just blocking a downstream T-cell transduction molecule,” observed the dermatologist, who is credited as the discoverer of the importance of the T cell in psoriasis pathogenesis.
The strong multidimensional evidence of clinical efficacy in the phase 2 study was supported mechanistically by analysis of skin biopsies obtained on study days 1, 15, and 85. The laboratory studies showed that the oral drug improved molecular, cellular, and clinical biomarkers associated with treatment efficacy. For example, at doses of 3 mg twice a day or higher, the TYK2 inhibitor reduced expression of IL-19 and IL-36A, which are key drivers of keratinocyte activation and epidermal hyperplasia. The drug also markedly decreased expression of genes in the Th17 pathway and essentially normalized expression of the proinflammatory genes beta defensin and S100A9.
In contrast to the Janus kinase (JAK) 1/3 and JAK 2 inhibitors in development for treatment of psoriasis, which paint with a much broader brush, the TYK2 inhibitor is highly selective for IL-23, IL-12, and interferon alpha.
“Previous studies have shown pan-JAK inhibition can be very effective in remitting psoriasis. The problem is that if one inhibits JAK1 and JAK3, one blocks the transduction of effector cytokines that are essentially there for protective immunity. That could lead to undesirable levels of immunosuppression,” Dr. Krueger explained.
The most important cytokine in the pathogenesis of psoriasis is clearly IL-23, he continued. In cell-based assays, the TYK2 inhibitor has been shown to be 100 times more selective in inhibiting IL-23 , IL-12, and interferon-alpha than JAK 1/3 inhibitors and 3,000 times more selective than JAK 2 inhibitors. This high degree of selectivity makes for fewer off-target effects and for a favorable safety profile.
“There were no major safety signals that would lead you to be concerned,” Dr. Krueger said. Indeed, based upon the encouraging safety and efficacy demonstrated this phase 2 study, a phase 3 program known as POETYK-PSO is underway (POETYK-PSO-1 and POETYK-PSO-2).
The phase 2 clinical trial results were published online in conjunction with the EADV congress.
The TYK2 inhibitor is being developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Krueger reported receiving personal fees as well as research grants paid directly to Rockefeller University from that pharmaceutical company and numerous others.
Source: Papp K et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Sep 11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1806382.
PARIS – A novel in a phase 2 clinical trial including 267 adults with moderate to severe disease, James G. Krueger, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“I would say the clinical response here is almost dead-on as a copy for ustekinumab, which is an [injectable interleukin] IL-23/IL-12 blocker. And we’re only at 12 weeks here; some of the curves look like they’re on a trajectory to go up further in terms of improvement. So I’m getting a performance with an oral drug that is just so much better than the approved alternatives that we have,” said Dr. Krueger, head of the laboratory of investigative dermatology and professor in clinical investigation at Rockefeller University in New York.
Oral apremilast (Otezla), for example, can’t touch those PASI 75 response rates in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Indeed, many psoriasis experts favor reserving apremilast for patients with moderate disease.
The 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted at 82 sites in the United States and seven other countries. In this dose-ranging study, participants were randomized to the oral selective tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor, known for the time being as BMS-986165, at 3 mg every other day, 3 mg daily, 3 mg twice a day, 6 mg twice a day, 12 mg daily, or to placebo.
The primary outcome was a 75% or greater reduction from baseline in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75) at week 12. The TYK2 inhibitor outperformed placebo in dose-dependent fashion starting at the 3 mg/day dose. The PASI 75 rate was 7% with placebo, 9% with 3 mg of BMS-986165 every other day, 39% with 3 mg daily, 69% with 3 mg BID, 67% with 6 mg BID, and 75% with 12 mg/day. All secondary endpoints followed suit.
A striking finding in the phase 2 study was that when the drug was stopped for a month at the end of the 12-week treatment period, for the most part, the PASI 75 response and other clinical benefits were retained.
“I would contrast this to experiments that I have personally done with cyclosporine, where I have cleared people with cyclosporine, stopped it, and a month later every single patient has rip-roaring disease back. So I think this TYK2 inhibitor has some different performance features than just blocking a downstream T-cell transduction molecule,” observed the dermatologist, who is credited as the discoverer of the importance of the T cell in psoriasis pathogenesis.
The strong multidimensional evidence of clinical efficacy in the phase 2 study was supported mechanistically by analysis of skin biopsies obtained on study days 1, 15, and 85. The laboratory studies showed that the oral drug improved molecular, cellular, and clinical biomarkers associated with treatment efficacy. For example, at doses of 3 mg twice a day or higher, the TYK2 inhibitor reduced expression of IL-19 and IL-36A, which are key drivers of keratinocyte activation and epidermal hyperplasia. The drug also markedly decreased expression of genes in the Th17 pathway and essentially normalized expression of the proinflammatory genes beta defensin and S100A9.
In contrast to the Janus kinase (JAK) 1/3 and JAK 2 inhibitors in development for treatment of psoriasis, which paint with a much broader brush, the TYK2 inhibitor is highly selective for IL-23, IL-12, and interferon alpha.
“Previous studies have shown pan-JAK inhibition can be very effective in remitting psoriasis. The problem is that if one inhibits JAK1 and JAK3, one blocks the transduction of effector cytokines that are essentially there for protective immunity. That could lead to undesirable levels of immunosuppression,” Dr. Krueger explained.
The most important cytokine in the pathogenesis of psoriasis is clearly IL-23, he continued. In cell-based assays, the TYK2 inhibitor has been shown to be 100 times more selective in inhibiting IL-23 , IL-12, and interferon-alpha than JAK 1/3 inhibitors and 3,000 times more selective than JAK 2 inhibitors. This high degree of selectivity makes for fewer off-target effects and for a favorable safety profile.
“There were no major safety signals that would lead you to be concerned,” Dr. Krueger said. Indeed, based upon the encouraging safety and efficacy demonstrated this phase 2 study, a phase 3 program known as POETYK-PSO is underway (POETYK-PSO-1 and POETYK-PSO-2).
The phase 2 clinical trial results were published online in conjunction with the EADV congress.
The TYK2 inhibitor is being developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Krueger reported receiving personal fees as well as research grants paid directly to Rockefeller University from that pharmaceutical company and numerous others.
Source: Papp K et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Sep 11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1806382.
REPORTING FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Key clinical point: A novel selective tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor achieves response rates previously unheard of in oral therapy for moderate to severe psoriasis.
Major finding: At the top dose of oral BMS-986165 studied to date, the PASI 75 rate at 12 weeks was 75%.
Study details: This eight-country, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 study included 267 patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. The presenter reported receiving personal fees and institutional research grants from that pharmaceutical company and numerous others.
Source: Papp K et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Sep 11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1806382.
Elevated type 2 diabetes risk seen in PsA patients
Patients with incident psoriatic arthritis are at a significantly increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes when compared against patients with psoriasis alone and with the general population, according to recent research published in Rheumatology.
Rachel Charlton, PhD, of the department of pharmacy and pharmacology at the University of Bath (England), and her colleagues performed an analysis of 6,783 incident cases of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) from the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink who were diagnosed during 1998-2014. Patients were between 18 years and 89 years old with a median age of 49 years at PsA diagnosis.
In the study, the researchers randomly matched PsA cases at a 1:4 ratio to either a cohort of general population patients with no PsA, psoriasis, or inflammatory arthritis or a cohort of patients with psoriasis but no PsA or inflammatory arthritis. Patients were followed from match to the point where they either no longer met inclusion criteria for the cohort or received a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, cerebrovascular disease (CVD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), or peripheral vascular disease (PVD) with a mean follow-up duration of approximately 5.5 years across all patient groups.
Patients in the PsA group had a significantly higher incidence of type 2 diabetes, compared with the general population (adjusted relative risk, 1.40; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.70; P = .0007) and psoriasis groups (adjusted RR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.19-1.97; P = .0009). In the PsA group, risk of CVD (adjusted RR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.99-1.56; P = .06), IHD (adjusted RR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.05-1.54; P = .02), and PVD (adjusted RR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.02-1.92; P = .04) were significantly higher than in the general population but not when compared with the psoriasis group. The overall risk of cardiovascular disease (including CVD, IHD, and PVD) for the PsA group was significantly higher (adjusted RR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.12-1.48; P = .0005), compared with the general population.
“These results support the proposal in existing clinical guidelines that, in order to reduce cardiovascular risk in patients with PsA, it is important to treat inflammatory disease as well as to screen and treat traditional risk factors early in the disease course,” Ms. Charlton and her colleagues wrote in their study.
This study was funded by a grant from the National Institute for Health Research in the United Kingdom. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Charlton RA et al. Rheumatology. 2018 Sep 6. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key286.
Patients with incident psoriatic arthritis are at a significantly increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes when compared against patients with psoriasis alone and with the general population, according to recent research published in Rheumatology.
Rachel Charlton, PhD, of the department of pharmacy and pharmacology at the University of Bath (England), and her colleagues performed an analysis of 6,783 incident cases of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) from the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink who were diagnosed during 1998-2014. Patients were between 18 years and 89 years old with a median age of 49 years at PsA diagnosis.
In the study, the researchers randomly matched PsA cases at a 1:4 ratio to either a cohort of general population patients with no PsA, psoriasis, or inflammatory arthritis or a cohort of patients with psoriasis but no PsA or inflammatory arthritis. Patients were followed from match to the point where they either no longer met inclusion criteria for the cohort or received a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, cerebrovascular disease (CVD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), or peripheral vascular disease (PVD) with a mean follow-up duration of approximately 5.5 years across all patient groups.
Patients in the PsA group had a significantly higher incidence of type 2 diabetes, compared with the general population (adjusted relative risk, 1.40; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.70; P = .0007) and psoriasis groups (adjusted RR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.19-1.97; P = .0009). In the PsA group, risk of CVD (adjusted RR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.99-1.56; P = .06), IHD (adjusted RR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.05-1.54; P = .02), and PVD (adjusted RR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.02-1.92; P = .04) were significantly higher than in the general population but not when compared with the psoriasis group. The overall risk of cardiovascular disease (including CVD, IHD, and PVD) for the PsA group was significantly higher (adjusted RR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.12-1.48; P = .0005), compared with the general population.
“These results support the proposal in existing clinical guidelines that, in order to reduce cardiovascular risk in patients with PsA, it is important to treat inflammatory disease as well as to screen and treat traditional risk factors early in the disease course,” Ms. Charlton and her colleagues wrote in their study.
This study was funded by a grant from the National Institute for Health Research in the United Kingdom. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Charlton RA et al. Rheumatology. 2018 Sep 6. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key286.
Patients with incident psoriatic arthritis are at a significantly increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes when compared against patients with psoriasis alone and with the general population, according to recent research published in Rheumatology.
Rachel Charlton, PhD, of the department of pharmacy and pharmacology at the University of Bath (England), and her colleagues performed an analysis of 6,783 incident cases of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) from the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink who were diagnosed during 1998-2014. Patients were between 18 years and 89 years old with a median age of 49 years at PsA diagnosis.
In the study, the researchers randomly matched PsA cases at a 1:4 ratio to either a cohort of general population patients with no PsA, psoriasis, or inflammatory arthritis or a cohort of patients with psoriasis but no PsA or inflammatory arthritis. Patients were followed from match to the point where they either no longer met inclusion criteria for the cohort or received a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, cerebrovascular disease (CVD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), or peripheral vascular disease (PVD) with a mean follow-up duration of approximately 5.5 years across all patient groups.
Patients in the PsA group had a significantly higher incidence of type 2 diabetes, compared with the general population (adjusted relative risk, 1.40; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.70; P = .0007) and psoriasis groups (adjusted RR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.19-1.97; P = .0009). In the PsA group, risk of CVD (adjusted RR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.99-1.56; P = .06), IHD (adjusted RR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.05-1.54; P = .02), and PVD (adjusted RR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.02-1.92; P = .04) were significantly higher than in the general population but not when compared with the psoriasis group. The overall risk of cardiovascular disease (including CVD, IHD, and PVD) for the PsA group was significantly higher (adjusted RR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.12-1.48; P = .0005), compared with the general population.
“These results support the proposal in existing clinical guidelines that, in order to reduce cardiovascular risk in patients with PsA, it is important to treat inflammatory disease as well as to screen and treat traditional risk factors early in the disease course,” Ms. Charlton and her colleagues wrote in their study.
This study was funded by a grant from the National Institute for Health Research in the United Kingdom. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Charlton RA et al. Rheumatology. 2018 Sep 6. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key286.
FROM RHEUMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: It is important to treat inflammatory disease as well as to screen and treat traditional cardiovascular risk factors early in the course of PsA.
Major finding: (adjusted RR = 1.53) and a general population control group (adjusted RR = 1.40).
Study details: An analysis of 6,783 patients with psoriatic arthritis in the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink who were diagnosed between 1998 and 2014.
Disclosures: This study was funded by a grant from the National Institute for Health Research in the United Kingdom. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
Source: Charlton RA et al. Rheumatology. 2018 Sep 6. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key286.
Infliximab biosimilar only moderately less expensive in Medicare Part D
The infliximab-dyyb biosimilar was only moderately less expensive than the originator infliximab product Remicade in the United States in 2017 under Medicare Part D, an analysis shows.
Infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra) cost 18% less than infliximab, with an annual cost exceeding $14,000 in an analysis published online Sept. 4 in JAMA by Jinoos Yazdany, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and her coauthors.
However, “without biosimilar gap discounts in 2017, beneficiaries would have paid more than $5,100 for infliximab-dyyb, or nearly $1,700 more in projected out-of-pocket costs than infliximab,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors wrote.
Biologics represent only 2% of U.S. prescriptions but made up 38% of drug spending in 2015 and accounted for 70% of growth in drug spending from 2010 to 2015, according to Dr. Yazdany and her colleagues.
Biologics for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cost more than $14,000 per year, and in 2015, 3 were among the top 15 drugs in terms of Medicare expenditures, they added.
While biosimilars are supposed to increase competition and lower prices, it’s an open question whether they actually reduce out-of-pocket expenditures for the 43 million individuals with drug benefits under Medicare Part D.
That uncertainty is due in part to the complex cost-sharing design of Part D, which includes an initial deductible, a coverage phase, a coverage gap, and catastrophic coverage.
In 2017, the plan included an initial $400 deductible, followed by the coverage phase, in which the patient paid 25% of drug costs. In the coverage gap, which started at $3,700 in total drug costs, the patient’s share of drug costs increased to 40% for biologics, and 51% for biosimilars. In the catastrophic coverage phase, triggered when out-of-pocket costs exceeded $4,950, the patient was responsible for 5% of drug costs.
“Currently, beneficiaries receive a 50% manufacturer discount during the gap for brand-name drugs and biologics, but not for biosimilars,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors said in the report.
To evaluate cost-sharing for infliximab-dyyb, which in 2016 became the first available RA biosimilar, the authors analyzed data for all Part D plans in the June 2017 Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Formulary, Pharmacy Network, and Pricing Information Files.
Out of 2,547 plans, only 10% covered the biosimilar, while 96% covered infliximab, the authors found.
The mean total cost of infliximab-dyyb was “modestly lower,” they reported. Eight-week prescription costs were $2,185 for infliximab-dyyb versus $2,667 for infliximab, while annual costs were $14,202 for the biosimilar and $17,335 for infliximab.
However, all plans required coinsurance cost-sharing for the biosimilar, they said. The mean coinsurance rate was 26.6% of the total drug cost for the biosimilar and 28.4% for infliximab.
For beneficiaries, projected annual out-of-pocket costs without the gap discount were $5,118 for infliximab-dyyb and $3,432 for infliximab, the researchers said.
Biosimilar gap discounts are set to start in 2019, according to the authors. However, they said those discounts may not substantially reduce out-of-pocket costs for Part D beneficiaries because of the high price of infliximab-dyyb and a coinsurance cost-sharing rate similar to that of infliximab.
“Further policies are needed to address affordability and access to specialty drugs,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors concluded.
The study was funded in part by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, the Robert L. Kroc Endowed Chair in Rheumatic and Connective Tissue Diseases, and other sources. Dr. Yazdany reported receiving an independent investigator award from Pfizer. Her coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
The infliximab-dyyb biosimilar was only moderately less expensive than the originator infliximab product Remicade in the United States in 2017 under Medicare Part D, an analysis shows.
Infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra) cost 18% less than infliximab, with an annual cost exceeding $14,000 in an analysis published online Sept. 4 in JAMA by Jinoos Yazdany, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and her coauthors.
However, “without biosimilar gap discounts in 2017, beneficiaries would have paid more than $5,100 for infliximab-dyyb, or nearly $1,700 more in projected out-of-pocket costs than infliximab,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors wrote.
Biologics represent only 2% of U.S. prescriptions but made up 38% of drug spending in 2015 and accounted for 70% of growth in drug spending from 2010 to 2015, according to Dr. Yazdany and her colleagues.
Biologics for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cost more than $14,000 per year, and in 2015, 3 were among the top 15 drugs in terms of Medicare expenditures, they added.
While biosimilars are supposed to increase competition and lower prices, it’s an open question whether they actually reduce out-of-pocket expenditures for the 43 million individuals with drug benefits under Medicare Part D.
That uncertainty is due in part to the complex cost-sharing design of Part D, which includes an initial deductible, a coverage phase, a coverage gap, and catastrophic coverage.
In 2017, the plan included an initial $400 deductible, followed by the coverage phase, in which the patient paid 25% of drug costs. In the coverage gap, which started at $3,700 in total drug costs, the patient’s share of drug costs increased to 40% for biologics, and 51% for biosimilars. In the catastrophic coverage phase, triggered when out-of-pocket costs exceeded $4,950, the patient was responsible for 5% of drug costs.
“Currently, beneficiaries receive a 50% manufacturer discount during the gap for brand-name drugs and biologics, but not for biosimilars,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors said in the report.
To evaluate cost-sharing for infliximab-dyyb, which in 2016 became the first available RA biosimilar, the authors analyzed data for all Part D plans in the June 2017 Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Formulary, Pharmacy Network, and Pricing Information Files.
Out of 2,547 plans, only 10% covered the biosimilar, while 96% covered infliximab, the authors found.
The mean total cost of infliximab-dyyb was “modestly lower,” they reported. Eight-week prescription costs were $2,185 for infliximab-dyyb versus $2,667 for infliximab, while annual costs were $14,202 for the biosimilar and $17,335 for infliximab.
However, all plans required coinsurance cost-sharing for the biosimilar, they said. The mean coinsurance rate was 26.6% of the total drug cost for the biosimilar and 28.4% for infliximab.
For beneficiaries, projected annual out-of-pocket costs without the gap discount were $5,118 for infliximab-dyyb and $3,432 for infliximab, the researchers said.
Biosimilar gap discounts are set to start in 2019, according to the authors. However, they said those discounts may not substantially reduce out-of-pocket costs for Part D beneficiaries because of the high price of infliximab-dyyb and a coinsurance cost-sharing rate similar to that of infliximab.
“Further policies are needed to address affordability and access to specialty drugs,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors concluded.
The study was funded in part by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, the Robert L. Kroc Endowed Chair in Rheumatic and Connective Tissue Diseases, and other sources. Dr. Yazdany reported receiving an independent investigator award from Pfizer. Her coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
The infliximab-dyyb biosimilar was only moderately less expensive than the originator infliximab product Remicade in the United States in 2017 under Medicare Part D, an analysis shows.
Infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra) cost 18% less than infliximab, with an annual cost exceeding $14,000 in an analysis published online Sept. 4 in JAMA by Jinoos Yazdany, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and her coauthors.
However, “without biosimilar gap discounts in 2017, beneficiaries would have paid more than $5,100 for infliximab-dyyb, or nearly $1,700 more in projected out-of-pocket costs than infliximab,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors wrote.
Biologics represent only 2% of U.S. prescriptions but made up 38% of drug spending in 2015 and accounted for 70% of growth in drug spending from 2010 to 2015, according to Dr. Yazdany and her colleagues.
Biologics for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cost more than $14,000 per year, and in 2015, 3 were among the top 15 drugs in terms of Medicare expenditures, they added.
While biosimilars are supposed to increase competition and lower prices, it’s an open question whether they actually reduce out-of-pocket expenditures for the 43 million individuals with drug benefits under Medicare Part D.
That uncertainty is due in part to the complex cost-sharing design of Part D, which includes an initial deductible, a coverage phase, a coverage gap, and catastrophic coverage.
In 2017, the plan included an initial $400 deductible, followed by the coverage phase, in which the patient paid 25% of drug costs. In the coverage gap, which started at $3,700 in total drug costs, the patient’s share of drug costs increased to 40% for biologics, and 51% for biosimilars. In the catastrophic coverage phase, triggered when out-of-pocket costs exceeded $4,950, the patient was responsible for 5% of drug costs.
“Currently, beneficiaries receive a 50% manufacturer discount during the gap for brand-name drugs and biologics, but not for biosimilars,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors said in the report.
To evaluate cost-sharing for infliximab-dyyb, which in 2016 became the first available RA biosimilar, the authors analyzed data for all Part D plans in the June 2017 Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Formulary, Pharmacy Network, and Pricing Information Files.
Out of 2,547 plans, only 10% covered the biosimilar, while 96% covered infliximab, the authors found.
The mean total cost of infliximab-dyyb was “modestly lower,” they reported. Eight-week prescription costs were $2,185 for infliximab-dyyb versus $2,667 for infliximab, while annual costs were $14,202 for the biosimilar and $17,335 for infliximab.
However, all plans required coinsurance cost-sharing for the biosimilar, they said. The mean coinsurance rate was 26.6% of the total drug cost for the biosimilar and 28.4% for infliximab.
For beneficiaries, projected annual out-of-pocket costs without the gap discount were $5,118 for infliximab-dyyb and $3,432 for infliximab, the researchers said.
Biosimilar gap discounts are set to start in 2019, according to the authors. However, they said those discounts may not substantially reduce out-of-pocket costs for Part D beneficiaries because of the high price of infliximab-dyyb and a coinsurance cost-sharing rate similar to that of infliximab.
“Further policies are needed to address affordability and access to specialty drugs,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors concluded.
The study was funded in part by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, the Robert L. Kroc Endowed Chair in Rheumatic and Connective Tissue Diseases, and other sources. Dr. Yazdany reported receiving an independent investigator award from Pfizer. Her coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Infliximab-dyyb was 18% less costly than infliximab, with an annual cost exceeding $14,000.
Study details: Analysis of data for 2,547 Part D plans in the June 2017 Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Formulary, Pharmacy Network, and Pricing Information Files.
Disclosures: The study was funded in part by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, the Robert L. Kroc Endowed Chair in Rheumatic and Connective Tissue Diseases, and other sources. One author reported receiving an independent investigator award from Pfizer.
Source: Yazdany J et al. JAMA. 2018;320(9):931-3.
Medication app boosts psoriasis patients’ short-term adherence
compared with those who did not use the app.
Treatment adherence remains a challenge in psoriasis, and although the field of electronic health interventions is growing, data on the effectiveness of such interventions are limited, wrote Mathias T. Svendsen, MD, of Odense University Hospital in Denmark, and his colleagues.
In a study published in the British Journal of Dermatology, 134 adults with psoriasis were randomized to use a smartphone app (68) or not (66) that provided daily medication reminders and daily information about the amount of treatment and number of product applications.
The primary outcome measure of treatment adherence was defined as once-daily application of topical medication – calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate cutaneous foam – for at least 80% of the days during the treatment period. A computer chip on the medication dispenser tracked patient use of the product and sent usage information to the patient’s smartphone via Bluetooth.
At 4 weeks, 65% of patients who used the app were adherent to treatment, versus 38% of those who didn’t use the app (P = .004).
In addition, patients who used the app showed significant improvement in disease severity, based on the secondary outcome measure of the Lattice System Physician’s Global Assessment (LS-PGA) at 4 weeks, with a mean change in score from baseline of 1.86 in the app group and 1.46 in the non-app group (P = .047). The LS-PGA and the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) were measured at all visits. No significant differences on the DLQI appeared between the groups.
During a 22-week follow-up completed by 122 patients, the effects were similar, but the differences were not statistically significant at weeks 8 and 26.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of knowledge of the correct amount of medication needed for the full benefit of the topical treatment and a lack of data on patient satisfaction with the app, the researchers noted. However, the results suggest that a medication reminder app improved disease severity as well as patient adherence rates in the short term, and that “there is potential for implementing patient-supporting apps in the dermatology clinic.”
The study was supported by LEO Pharma and by the Kirsten and Volmer Rask Nielsen’s Foundation; part of Dr. Svendsen’s salary during the study was paid by LEO Pharma, and several coauthors reported relationships with LEO Pharma.
SOURCE: Svendsen MT et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Apr 14. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16667.
compared with those who did not use the app.
Treatment adherence remains a challenge in psoriasis, and although the field of electronic health interventions is growing, data on the effectiveness of such interventions are limited, wrote Mathias T. Svendsen, MD, of Odense University Hospital in Denmark, and his colleagues.
In a study published in the British Journal of Dermatology, 134 adults with psoriasis were randomized to use a smartphone app (68) or not (66) that provided daily medication reminders and daily information about the amount of treatment and number of product applications.
The primary outcome measure of treatment adherence was defined as once-daily application of topical medication – calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate cutaneous foam – for at least 80% of the days during the treatment period. A computer chip on the medication dispenser tracked patient use of the product and sent usage information to the patient’s smartphone via Bluetooth.
At 4 weeks, 65% of patients who used the app were adherent to treatment, versus 38% of those who didn’t use the app (P = .004).
In addition, patients who used the app showed significant improvement in disease severity, based on the secondary outcome measure of the Lattice System Physician’s Global Assessment (LS-PGA) at 4 weeks, with a mean change in score from baseline of 1.86 in the app group and 1.46 in the non-app group (P = .047). The LS-PGA and the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) were measured at all visits. No significant differences on the DLQI appeared between the groups.
During a 22-week follow-up completed by 122 patients, the effects were similar, but the differences were not statistically significant at weeks 8 and 26.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of knowledge of the correct amount of medication needed for the full benefit of the topical treatment and a lack of data on patient satisfaction with the app, the researchers noted. However, the results suggest that a medication reminder app improved disease severity as well as patient adherence rates in the short term, and that “there is potential for implementing patient-supporting apps in the dermatology clinic.”
The study was supported by LEO Pharma and by the Kirsten and Volmer Rask Nielsen’s Foundation; part of Dr. Svendsen’s salary during the study was paid by LEO Pharma, and several coauthors reported relationships with LEO Pharma.
SOURCE: Svendsen MT et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Apr 14. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16667.
compared with those who did not use the app.
Treatment adherence remains a challenge in psoriasis, and although the field of electronic health interventions is growing, data on the effectiveness of such interventions are limited, wrote Mathias T. Svendsen, MD, of Odense University Hospital in Denmark, and his colleagues.
In a study published in the British Journal of Dermatology, 134 adults with psoriasis were randomized to use a smartphone app (68) or not (66) that provided daily medication reminders and daily information about the amount of treatment and number of product applications.
The primary outcome measure of treatment adherence was defined as once-daily application of topical medication – calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate cutaneous foam – for at least 80% of the days during the treatment period. A computer chip on the medication dispenser tracked patient use of the product and sent usage information to the patient’s smartphone via Bluetooth.
At 4 weeks, 65% of patients who used the app were adherent to treatment, versus 38% of those who didn’t use the app (P = .004).
In addition, patients who used the app showed significant improvement in disease severity, based on the secondary outcome measure of the Lattice System Physician’s Global Assessment (LS-PGA) at 4 weeks, with a mean change in score from baseline of 1.86 in the app group and 1.46 in the non-app group (P = .047). The LS-PGA and the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) were measured at all visits. No significant differences on the DLQI appeared between the groups.
During a 22-week follow-up completed by 122 patients, the effects were similar, but the differences were not statistically significant at weeks 8 and 26.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of knowledge of the correct amount of medication needed for the full benefit of the topical treatment and a lack of data on patient satisfaction with the app, the researchers noted. However, the results suggest that a medication reminder app improved disease severity as well as patient adherence rates in the short term, and that “there is potential for implementing patient-supporting apps in the dermatology clinic.”
The study was supported by LEO Pharma and by the Kirsten and Volmer Rask Nielsen’s Foundation; part of Dr. Svendsen’s salary during the study was paid by LEO Pharma, and several coauthors reported relationships with LEO Pharma.
SOURCE: Svendsen MT et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Apr 14. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16667.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Using a smartphone app helped patients with psoriasis significantly improve their treatment adherence.
Major finding: Significantly more patients who used the app followed their topical treatment plan, compared with the no-app controls (65% vs. 38%).
Study details: The data come from 134 adults with psoriasis who were randomized to use an app or no app for 28 days.
Disclosures: The study was supported by LEO Pharma and by the Kirsten and Volmer Rask Nielsen’s Foundation; part of Dr. Svendsen’s salary during the study was paid by LEO Pharma, and several coauthors reported relationships with LEO Pharma.
Source: Svendsen MT et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Apr 14. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16667.
Risankizumab proves more effective in psoriasis than ustekinumab
, according to results of a pair of head-to-head trials published in the Lancet.
The replicate phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active comparator–controlled trials, UltIMMa-1 (NCT02684370) and UltIMMa-2 (NCT02684375) altogether randomized 997 patients to risankizumab, ustekinumab, or placebo. The coprimary endpoints were the proportions of patients achieving 90% reduction in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 90) at 16 weeks and a static Physician Global Assessment (sPGA) score of 0 or 1, and the 15 ranked secondary endpoints included proportions of those achieving PASI 100 or sPGA 0, both of which demonstrate total clearance of psoriasis, as well as measures of quality of life improvement.
Compared with those receiving either ustekinumab or placebo, a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab achieved the coprimary endpoints, and all secondary endpoints were met. In UltIMMA-1, 75.3% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, compared with 4.9% of placebo patients and 42% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab); sPGA of 0 or 1 was achieved by 87.8% of risankizumab patients and only 7.8% of placebo patients and 63% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab). Results were similar in UltIMMA-2: 74.8% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, and 83.7% of them achieved sPGA 0 or 1 (P less than .0001 when comparing them with placebo and ustekinumab). According to results of the secondary endpoints, both studies also showed greater rates of clearance and improvements in quality of life among patients receiving risankizumab than among those receiving either placebo or ustekinumab.
The safety profiles across treatment groups were similar in both studies, with the most common adverse events including upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and diarrhea.
Risankizumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets the p19 subunit of only interleukin-23, unlike the studies’ active comparator, ustekinumab, which targets both interleukin-23 and interleukin-12. “Selectively blocking interleukin 23 with a p19 inhibitor appears to be one of the best ways to treat psoriasis,” commented Abigail Cline, MD, and Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, both of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., in an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:616-71.).
The authors of the study reported relationships with various industry entities, including AbbVie, which sponsored the studies and developed risankizumab, and Boehringer Ingelheim, which collaborated in the studies. The authors of the editorial also disclosed relationships with entities, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Gordon KB et al. Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:650-61.
, according to results of a pair of head-to-head trials published in the Lancet.
The replicate phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active comparator–controlled trials, UltIMMa-1 (NCT02684370) and UltIMMa-2 (NCT02684375) altogether randomized 997 patients to risankizumab, ustekinumab, or placebo. The coprimary endpoints were the proportions of patients achieving 90% reduction in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 90) at 16 weeks and a static Physician Global Assessment (sPGA) score of 0 or 1, and the 15 ranked secondary endpoints included proportions of those achieving PASI 100 or sPGA 0, both of which demonstrate total clearance of psoriasis, as well as measures of quality of life improvement.
Compared with those receiving either ustekinumab or placebo, a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab achieved the coprimary endpoints, and all secondary endpoints were met. In UltIMMA-1, 75.3% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, compared with 4.9% of placebo patients and 42% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab); sPGA of 0 or 1 was achieved by 87.8% of risankizumab patients and only 7.8% of placebo patients and 63% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab). Results were similar in UltIMMA-2: 74.8% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, and 83.7% of them achieved sPGA 0 or 1 (P less than .0001 when comparing them with placebo and ustekinumab). According to results of the secondary endpoints, both studies also showed greater rates of clearance and improvements in quality of life among patients receiving risankizumab than among those receiving either placebo or ustekinumab.
The safety profiles across treatment groups were similar in both studies, with the most common adverse events including upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and diarrhea.
Risankizumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets the p19 subunit of only interleukin-23, unlike the studies’ active comparator, ustekinumab, which targets both interleukin-23 and interleukin-12. “Selectively blocking interleukin 23 with a p19 inhibitor appears to be one of the best ways to treat psoriasis,” commented Abigail Cline, MD, and Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, both of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., in an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:616-71.).
The authors of the study reported relationships with various industry entities, including AbbVie, which sponsored the studies and developed risankizumab, and Boehringer Ingelheim, which collaborated in the studies. The authors of the editorial also disclosed relationships with entities, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Gordon KB et al. Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:650-61.
, according to results of a pair of head-to-head trials published in the Lancet.
The replicate phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active comparator–controlled trials, UltIMMa-1 (NCT02684370) and UltIMMa-2 (NCT02684375) altogether randomized 997 patients to risankizumab, ustekinumab, or placebo. The coprimary endpoints were the proportions of patients achieving 90% reduction in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 90) at 16 weeks and a static Physician Global Assessment (sPGA) score of 0 or 1, and the 15 ranked secondary endpoints included proportions of those achieving PASI 100 or sPGA 0, both of which demonstrate total clearance of psoriasis, as well as measures of quality of life improvement.
Compared with those receiving either ustekinumab or placebo, a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab achieved the coprimary endpoints, and all secondary endpoints were met. In UltIMMA-1, 75.3% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, compared with 4.9% of placebo patients and 42% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab); sPGA of 0 or 1 was achieved by 87.8% of risankizumab patients and only 7.8% of placebo patients and 63% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab). Results were similar in UltIMMA-2: 74.8% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, and 83.7% of them achieved sPGA 0 or 1 (P less than .0001 when comparing them with placebo and ustekinumab). According to results of the secondary endpoints, both studies also showed greater rates of clearance and improvements in quality of life among patients receiving risankizumab than among those receiving either placebo or ustekinumab.
The safety profiles across treatment groups were similar in both studies, with the most common adverse events including upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and diarrhea.
Risankizumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets the p19 subunit of only interleukin-23, unlike the studies’ active comparator, ustekinumab, which targets both interleukin-23 and interleukin-12. “Selectively blocking interleukin 23 with a p19 inhibitor appears to be one of the best ways to treat psoriasis,” commented Abigail Cline, MD, and Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, both of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., in an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:616-71.).
The authors of the study reported relationships with various industry entities, including AbbVie, which sponsored the studies and developed risankizumab, and Boehringer Ingelheim, which collaborated in the studies. The authors of the editorial also disclosed relationships with entities, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Gordon KB et al. Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:650-61.
FROM THE LANCET
Psoriasis registry study provides more data on infliximab’s infection risk
that led to hospitalization, the use of intravenous antimicrobial therapy, or death, according to a prospective cohort study of cases in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland.
The new data suggest a risk associated with infliximab treatment that previous clinical trials and observational studies were insufficiently powered to detect, according to the investigators, led by Zenas Yiu, of the University of Manchester (England). They found no associations between infection risk and treatment with etanercept, adalimumab, or ustekinumab, and they noted that there are no such data yet on more recently approved biologic therapies for psoriasis, such as secukinumab or ixekizumab.
The British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) recommends infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–blocker, only for severe cases of psoriasis (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index greater than or equal to 20 and a Dermatology Life Quality Index greater than 18), or when other biologics fail or cannot be used.
To address the insufficient power of earlier studies, the researchers used data from the BAD Biologic Interventions Register (BADBIR), a large, prospective psoriasis registry in the United Kingdom and Ireland established in 2007. The analysis included 3,421 subjects in the nonbiologic systemic therapy cohort, and 422 subjects in the all-lines infliximab cohort. The median follow-up period was 1.49 person-years (interquartile range, 2.50 person-years) for the all-lines (not just first-line) infliximab group, and 1.51 person-years (1.84 person-years) for the nonbiologics group.*
Treatment with infliximab was associated with a statistically significant increased risk of serious infection (defined as an infection associated with prolonged hospitalization or use of IV antimicrobial therapy; or an infection that resulted in death), with an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.95 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-3.75), compared with nonbiologic systemic treatments. The risk was higher in the first 6 months (adjusted HR, 3.49; 95% CI, 1.14-10.70), and from 6 months to 1 year (aHR, 2.99; 95% CI, 1.10-8.14,) but did not reach statistical significance at 1 year to 2 years (aHR, 2.03; 95% CI, 0.61-6.79).
There was also an increased risk of serious infection with infliximab compared with methotrexate (aHR, 2.96; 95% CI, 1.58-5.57).
“Given our findings of a higher risk of serious infection associated with infliximab, we provide real-world evidence to reinforce the position of infliximab in the psoriasis treatment hierarchy,” the authors wrote, adding that “patients with severe psoriasis who fulfill the criteria for the prescription of infliximab should be counseled” about the risk of serious infection.
Dr. Yiu disclosed having received nonfinancial support form Novartis, two authors had no disclosures, and the remainder had various disclosures related to pharmaceutical companies. BADBIR is funded by BAD, which receives funding from Pfizer, Janssen Cilag, AbbVie, Novartis, Samsung Bioepis and Eli Lilly for providing pharmacovigilance services.
SOURCE: Yiu ZZN et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug 2. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17036.
*This article was updated to correctly indicate that the median follow-up period was 1.49 person-years (interquartile range, 2.50 person-years) for the all-lines (not just first-line) infliximab group, and 1.51 person-years (1.84 person-years) for the nonbiologics group.
that led to hospitalization, the use of intravenous antimicrobial therapy, or death, according to a prospective cohort study of cases in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland.
The new data suggest a risk associated with infliximab treatment that previous clinical trials and observational studies were insufficiently powered to detect, according to the investigators, led by Zenas Yiu, of the University of Manchester (England). They found no associations between infection risk and treatment with etanercept, adalimumab, or ustekinumab, and they noted that there are no such data yet on more recently approved biologic therapies for psoriasis, such as secukinumab or ixekizumab.
The British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) recommends infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–blocker, only for severe cases of psoriasis (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index greater than or equal to 20 and a Dermatology Life Quality Index greater than 18), or when other biologics fail or cannot be used.
To address the insufficient power of earlier studies, the researchers used data from the BAD Biologic Interventions Register (BADBIR), a large, prospective psoriasis registry in the United Kingdom and Ireland established in 2007. The analysis included 3,421 subjects in the nonbiologic systemic therapy cohort, and 422 subjects in the all-lines infliximab cohort. The median follow-up period was 1.49 person-years (interquartile range, 2.50 person-years) for the all-lines (not just first-line) infliximab group, and 1.51 person-years (1.84 person-years) for the nonbiologics group.*
Treatment with infliximab was associated with a statistically significant increased risk of serious infection (defined as an infection associated with prolonged hospitalization or use of IV antimicrobial therapy; or an infection that resulted in death), with an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.95 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-3.75), compared with nonbiologic systemic treatments. The risk was higher in the first 6 months (adjusted HR, 3.49; 95% CI, 1.14-10.70), and from 6 months to 1 year (aHR, 2.99; 95% CI, 1.10-8.14,) but did not reach statistical significance at 1 year to 2 years (aHR, 2.03; 95% CI, 0.61-6.79).
There was also an increased risk of serious infection with infliximab compared with methotrexate (aHR, 2.96; 95% CI, 1.58-5.57).
“Given our findings of a higher risk of serious infection associated with infliximab, we provide real-world evidence to reinforce the position of infliximab in the psoriasis treatment hierarchy,” the authors wrote, adding that “patients with severe psoriasis who fulfill the criteria for the prescription of infliximab should be counseled” about the risk of serious infection.
Dr. Yiu disclosed having received nonfinancial support form Novartis, two authors had no disclosures, and the remainder had various disclosures related to pharmaceutical companies. BADBIR is funded by BAD, which receives funding from Pfizer, Janssen Cilag, AbbVie, Novartis, Samsung Bioepis and Eli Lilly for providing pharmacovigilance services.
SOURCE: Yiu ZZN et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug 2. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17036.
*This article was updated to correctly indicate that the median follow-up period was 1.49 person-years (interquartile range, 2.50 person-years) for the all-lines (not just first-line) infliximab group, and 1.51 person-years (1.84 person-years) for the nonbiologics group.
that led to hospitalization, the use of intravenous antimicrobial therapy, or death, according to a prospective cohort study of cases in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland.
The new data suggest a risk associated with infliximab treatment that previous clinical trials and observational studies were insufficiently powered to detect, according to the investigators, led by Zenas Yiu, of the University of Manchester (England). They found no associations between infection risk and treatment with etanercept, adalimumab, or ustekinumab, and they noted that there are no such data yet on more recently approved biologic therapies for psoriasis, such as secukinumab or ixekizumab.
The British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) recommends infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–blocker, only for severe cases of psoriasis (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index greater than or equal to 20 and a Dermatology Life Quality Index greater than 18), or when other biologics fail or cannot be used.
To address the insufficient power of earlier studies, the researchers used data from the BAD Biologic Interventions Register (BADBIR), a large, prospective psoriasis registry in the United Kingdom and Ireland established in 2007. The analysis included 3,421 subjects in the nonbiologic systemic therapy cohort, and 422 subjects in the all-lines infliximab cohort. The median follow-up period was 1.49 person-years (interquartile range, 2.50 person-years) for the all-lines (not just first-line) infliximab group, and 1.51 person-years (1.84 person-years) for the nonbiologics group.*
Treatment with infliximab was associated with a statistically significant increased risk of serious infection (defined as an infection associated with prolonged hospitalization or use of IV antimicrobial therapy; or an infection that resulted in death), with an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.95 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-3.75), compared with nonbiologic systemic treatments. The risk was higher in the first 6 months (adjusted HR, 3.49; 95% CI, 1.14-10.70), and from 6 months to 1 year (aHR, 2.99; 95% CI, 1.10-8.14,) but did not reach statistical significance at 1 year to 2 years (aHR, 2.03; 95% CI, 0.61-6.79).
There was also an increased risk of serious infection with infliximab compared with methotrexate (aHR, 2.96; 95% CI, 1.58-5.57).
“Given our findings of a higher risk of serious infection associated with infliximab, we provide real-world evidence to reinforce the position of infliximab in the psoriasis treatment hierarchy,” the authors wrote, adding that “patients with severe psoriasis who fulfill the criteria for the prescription of infliximab should be counseled” about the risk of serious infection.
Dr. Yiu disclosed having received nonfinancial support form Novartis, two authors had no disclosures, and the remainder had various disclosures related to pharmaceutical companies. BADBIR is funded by BAD, which receives funding from Pfizer, Janssen Cilag, AbbVie, Novartis, Samsung Bioepis and Eli Lilly for providing pharmacovigilance services.
SOURCE: Yiu ZZN et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug 2. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17036.
*This article was updated to correctly indicate that the median follow-up period was 1.49 person-years (interquartile range, 2.50 person-years) for the all-lines (not just first-line) infliximab group, and 1.51 person-years (1.84 person-years) for the nonbiologics group.
FROM BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: The study reinforces British guidelines that infliximab should be restricted to most severe cases.
Major finding: Infliximab was associated with a hazard ratio of 1.95 for severe infections, compared with non-biologic systemic therapies.
Study details: Prospective cohort analysis of a psoriasis treatment database of 3,843 individuals.
Disclosures: Dr. Yiu disclosed having received non-financial support form Novartis, two authors had no disclosures, and the remainder had various disclosures related to pharmaceutical companies. BADBIR is funded by BAD, which receives funding from Pfizer, Janssen Cilag, AbbVie, Novartis, Samsung Bioepis and Eli Lilly for providing pharmacovigilance services.
Source: Yiu ZZN et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug 2. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17036.
Latex Allergy From Biologic Injectable Devices



Latex Hypersensitivity to Injection Devices for Biologic Therapies in Psoriasis Patients
An allergic reaction is an exaggerated immune response that is known as a type I or immediate hypersensitivity reaction when provoked by reexposure to an allergen or antigen. Upon initial exposure to the antigen, dendritic cells bind it for presentation to helper T (TH2) lymphocytes. The TH2 cells then interact with B cells, stimulating them to become plasma cells and produce IgE antibodies to the antigen. When exposed to the same allergen a second time, IgE antibodies bind the allergen and cross-link on mast cells and basophils in the blood. Cross-linking stimulates degranulation of the cells, releasing histamine, leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and other cytokines. The major effects of the release of these mediators include vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and bronchoconstriction. Leukotrienes also are responsible for chemotaxis of white blood cells, further propagating the immune response.1
Effects of a type I hypersensitivity reaction can be either local or systemic, resulting in symptoms ranging from mild irritation to anaphylactic shock and death. Latex allergy is a common example of a type I hypersensitivity reaction. Latex is found in many medical products, including gloves, rubber, elastics, blood pressure cuffs, bandages, dressings, and syringes. Reactions can include runny nose, tearing eyes, itching, hives, wheals, wheezing, and in rare cases anaphylaxis.2 Diagnosis can be suspected based on history and physical examination. Screening is performed with radioallergosorbent testing, which identifies specific IgE antibodies to latex; however, the reported sensitivity and specificity for the latex-specific IgE antibody varies widely in the literature, and the test cannot reliably rule in or rule out a true latex allergy.3
Allergic responses to latex in psoriasis patients receiving frequent injections with biologic agents are not commonly reported in the literature. We report the case of a patient with a long history of psoriasis who developed an allergic response after exposure to injection devices that contained latex components while undergoing treatment with biologic agents.
Case Report
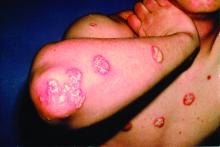
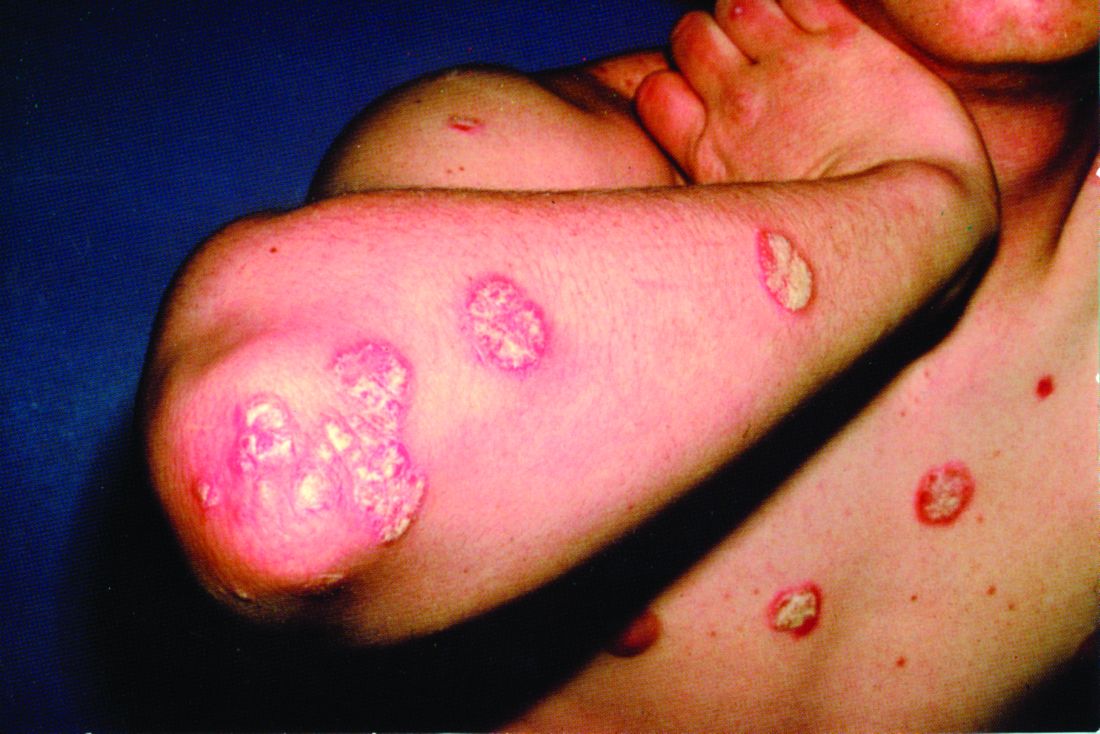
A 72-year-old man presented with an extensive history of severe psoriasis with frequent flares. Treatment with topical agents and etanercept 6 months prior at an outside facility failed. At the time of presentation, the patient had more than 10% body surface area (BSA) involvement, which included the scalp, legs, chest, and back. He subsequently was started on ustekinumab injections. He initially responded well to therapy, but after 8 months of treatment, he began to have recurrent episodes of acute eruptive rashes over the trunk with associated severe pruritus that reproducibly recurred within 24 hours after each ustekinumab injection. It was decided to discontinue ustekinumab due to concern for intolerance, and the patient was switched to secukinumab.
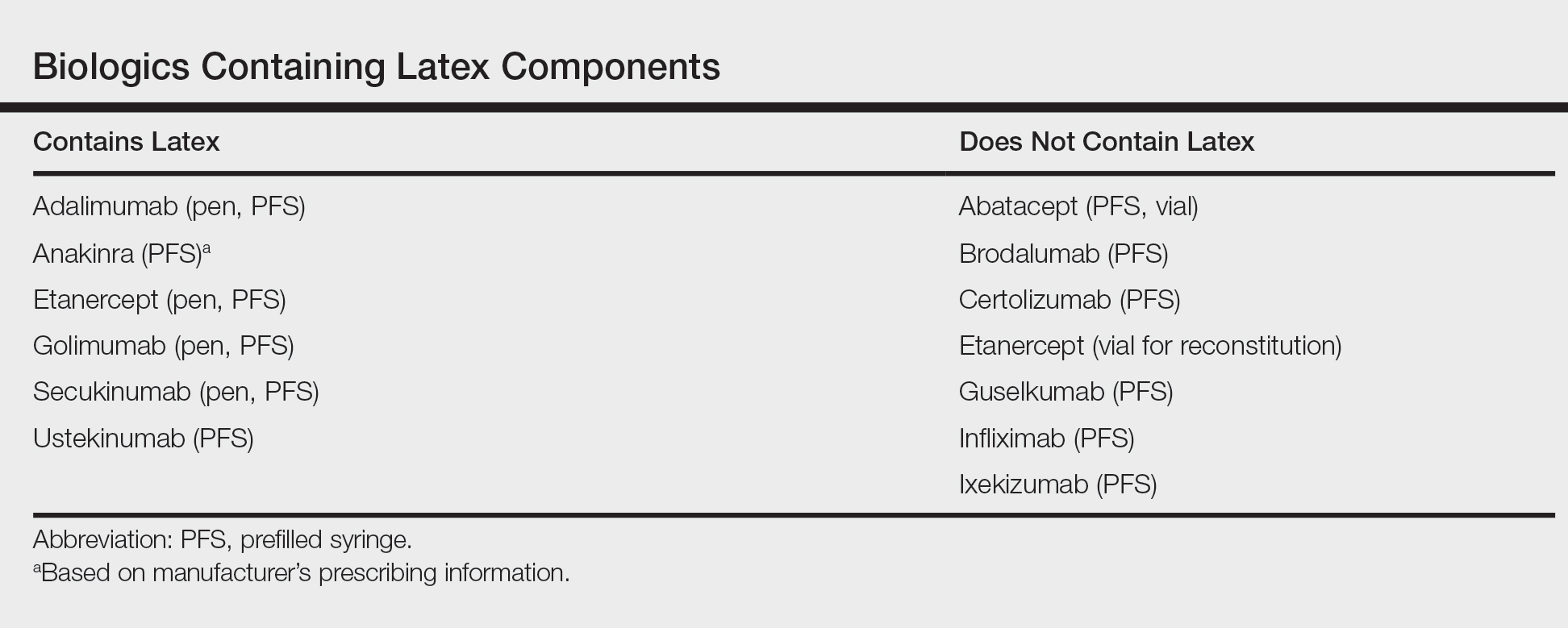
After starting secukinumab, the patient's BSA involvement was reduced to 2% after 1 month; however, he began to develop an eruptive rash with severe pruritus again that reproducibly recurred after each secukinumab injection. On physical examination the patient had ill-defined, confluent, erythematous patches over much of the trunk and extremities. Punch biopsies of the eruptive dermatitis showed spongiform psoriasis and eosinophils with dermal hypersensitivity, consistent with a drug eruption. Upon further questioning, the patient noted that he had a long history of a strong latex allergy and he would develop a blistering dermatitis when coming into contact with latex, which caused a high suspicion for a latex allergy as the cause of the patient's acute dermatitis flares from his prior ustekinumab and secukinumab injections. Although it was confirmed with the manufacturers that both the ustekinumab syringe and secukinumab pen did not contain latex, the caps of these medications (and many other biologic injections) do have latex (Table). Other differential diagnoses included an atypical paradoxical psoriasis flare and a drug eruption to secukinumab, which previously has been reported.4
Based on the suspected cause of the eruption, the patient was instructed not to touch the cap of the secukinumab pen. Despite this recommendation, the rash was still present at the next appointment 1 month later. Repeat punch biopsy showed similar findings to the one prior with likely dermal hypersensitivity. The rash improved with steroid injections and continued to improve after holding the secukinumab for 1 month.
After resolution of the hypersensitivity reaction, the patient was started on ixekizumab, which does not contain latex in any component according to the manufacturer. After 2 months of treatment, the patient had 2% BSA involvement of psoriasis and has had no further reports of itching, rash, or other symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction. On follow-up, the patient's psoriasis symptoms continue to be controlled without further reactions after injections of ixekizumab. Radioallergosorbent testing was not performed due to the lack of specificity and sensitivity of the test3 as well as the patient's known history of latex allergy and characteristic dermatitis that developed after exposure to latex and resolution with removal of the agent. These clinical manifestations are highly indicative of a type I hypersensitivity to injection devices that contain latex components during biologic therapy.
Comment
Allergic responses to latex are most commonly seen in those exposed to gloves or rubber, but little has been reported on reactions to injections with pens or syringes that contain latex components. Some case reports have demonstrated allergic responses in diabetic patients receiving insulin injections.5,6 MacCracken et al5 reported the case of a young boy who had an allergic response to an insulin injection with a syringe containing latex. The patient had a history of bladder exstrophy with a recent diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. It is well known that patients with spina bifida and other conditions who undergo frequent urological procedures more commonly develop latex allergies. This patient reported a history of swollen lips after a dentist visit, presumably due to contact with latex gloves. Because of the suspected allergy, his first insulin injection was given using a glass syringe and insulin was withdrawn with the top removed due to the top containing latex. He did not experience any complications. After being injected later with insulin drawn through the top using a syringe that contained latex, he developed a flare-up of a 0.5-cm erythematous wheal within minutes with associated pruritus.5
Towse et al6 described another patient with diabetes who developed a local allergic reaction at the site of insulin injections. Workup by the physician ruled out insulin allergy but showed elevated latex-specific IgE antibodies. Future insulin draws through a latex-containing top produced a wheal at the injection site. After switching to latex-free syringes, the allergic reaction resolved.6
Latex allergies are common in medical practice, as latex is found in a wide variety of medical supplies, including syringes used for injections and their caps. Physicians need to be aware of latex allergies in their patients and exercise extreme caution in the use of latex-containing products. In the treatment of psoriasis, care must be given when injecting biologic agents. Although many injection devices contain latex limited to the cap, it may be enough to invoke an allergic response. If such a response is elicited, therapy with injection devices that do not contain latex in either the cap or syringe should be considered.
- Druce HM. Allergic and nonallergic rhinitis. In: Middleton EM Jr, Reed CE, Ellis EF, et al, eds. Allergy: Principles and Practice. 5th ed. Vol 1. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 1998:1005-1016.
- Rochford C, Milles M. A review of the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of allergic reactions in the dental office. Quintessence Int. 2011;42:149-156.
- Hamilton RG, Peterson EL, Ownby DR. Clinical and laboratory-based methods in the diagnosis of natural rubber latex allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110(2 suppl):S47-S56.
- Shibata M, Sawada Y, Yamaguchi T, et al. Drug eruption caused by secukinumab. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27:67-68.
- MacCracken J, Stenger P, Jackson T. Latex allergy in diabetic patients: a call for latex-free insulin tops. Diabetes Care. 1996;19:184.
- Towse A, O'Brien M, Twarog FJ, et al. Local reaction secondary to insulin injection: a potential role for latex antigens in insulin vials and syringes. Diabetes Care. 1995;18:1195-1197.
An allergic reaction is an exaggerated immune response that is known as a type I or immediate hypersensitivity reaction when provoked by reexposure to an allergen or antigen. Upon initial exposure to the antigen, dendritic cells bind it for presentation to helper T (TH2) lymphocytes. The TH2 cells then interact with B cells, stimulating them to become plasma cells and produce IgE antibodies to the antigen. When exposed to the same allergen a second time, IgE antibodies bind the allergen and cross-link on mast cells and basophils in the blood. Cross-linking stimulates degranulation of the cells, releasing histamine, leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and other cytokines. The major effects of the release of these mediators include vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and bronchoconstriction. Leukotrienes also are responsible for chemotaxis of white blood cells, further propagating the immune response.1
Effects of a type I hypersensitivity reaction can be either local or systemic, resulting in symptoms ranging from mild irritation to anaphylactic shock and death. Latex allergy is a common example of a type I hypersensitivity reaction. Latex is found in many medical products, including gloves, rubber, elastics, blood pressure cuffs, bandages, dressings, and syringes. Reactions can include runny nose, tearing eyes, itching, hives, wheals, wheezing, and in rare cases anaphylaxis.2 Diagnosis can be suspected based on history and physical examination. Screening is performed with radioallergosorbent testing, which identifies specific IgE antibodies to latex; however, the reported sensitivity and specificity for the latex-specific IgE antibody varies widely in the literature, and the test cannot reliably rule in or rule out a true latex allergy.3
Allergic responses to latex in psoriasis patients receiving frequent injections with biologic agents are not commonly reported in the literature. We report the case of a patient with a long history of psoriasis who developed an allergic response after exposure to injection devices that contained latex components while undergoing treatment with biologic agents.
Case Report
A 72-year-old man presented with an extensive history of severe psoriasis with frequent flares. Treatment with topical agents and etanercept 6 months prior at an outside facility failed. At the time of presentation, the patient had more than 10% body surface area (BSA) involvement, which included the scalp, legs, chest, and back. He subsequently was started on ustekinumab injections. He initially responded well to therapy, but after 8 months of treatment, he began to have recurrent episodes of acute eruptive rashes over the trunk with associated severe pruritus that reproducibly recurred within 24 hours after each ustekinumab injection. It was decided to discontinue ustekinumab due to concern for intolerance, and the patient was switched to secukinumab.
After starting secukinumab, the patient's BSA involvement was reduced to 2% after 1 month; however, he began to develop an eruptive rash with severe pruritus again that reproducibly recurred after each secukinumab injection. On physical examination the patient had ill-defined, confluent, erythematous patches over much of the trunk and extremities. Punch biopsies of the eruptive dermatitis showed spongiform psoriasis and eosinophils with dermal hypersensitivity, consistent with a drug eruption. Upon further questioning, the patient noted that he had a long history of a strong latex allergy and he would develop a blistering dermatitis when coming into contact with latex, which caused a high suspicion for a latex allergy as the cause of the patient's acute dermatitis flares from his prior ustekinumab and secukinumab injections. Although it was confirmed with the manufacturers that both the ustekinumab syringe and secukinumab pen did not contain latex, the caps of these medications (and many other biologic injections) do have latex (Table). Other differential diagnoses included an atypical paradoxical psoriasis flare and a drug eruption to secukinumab, which previously has been reported.4
Based on the suspected cause of the eruption, the patient was instructed not to touch the cap of the secukinumab pen. Despite this recommendation, the rash was still present at the next appointment 1 month later. Repeat punch biopsy showed similar findings to the one prior with likely dermal hypersensitivity. The rash improved with steroid injections and continued to improve after holding the secukinumab for 1 month.
After resolution of the hypersensitivity reaction, the patient was started on ixekizumab, which does not contain latex in any component according to the manufacturer. After 2 months of treatment, the patient had 2% BSA involvement of psoriasis and has had no further reports of itching, rash, or other symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction. On follow-up, the patient's psoriasis symptoms continue to be controlled without further reactions after injections of ixekizumab. Radioallergosorbent testing was not performed due to the lack of specificity and sensitivity of the test3 as well as the patient's known history of latex allergy and characteristic dermatitis that developed after exposure to latex and resolution with removal of the agent. These clinical manifestations are highly indicative of a type I hypersensitivity to injection devices that contain latex components during biologic therapy.
Comment
Allergic responses to latex are most commonly seen in those exposed to gloves or rubber, but little has been reported on reactions to injections with pens or syringes that contain latex components. Some case reports have demonstrated allergic responses in diabetic patients receiving insulin injections.5,6 MacCracken et al5 reported the case of a young boy who had an allergic response to an insulin injection with a syringe containing latex. The patient had a history of bladder exstrophy with a recent diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. It is well known that patients with spina bifida and other conditions who undergo frequent urological procedures more commonly develop latex allergies. This patient reported a history of swollen lips after a dentist visit, presumably due to contact with latex gloves. Because of the suspected allergy, his first insulin injection was given using a glass syringe and insulin was withdrawn with the top removed due to the top containing latex. He did not experience any complications. After being injected later with insulin drawn through the top using a syringe that contained latex, he developed a flare-up of a 0.5-cm erythematous wheal within minutes with associated pruritus.5
Towse et al6 described another patient with diabetes who developed a local allergic reaction at the site of insulin injections. Workup by the physician ruled out insulin allergy but showed elevated latex-specific IgE antibodies. Future insulin draws through a latex-containing top produced a wheal at the injection site. After switching to latex-free syringes, the allergic reaction resolved.6
Latex allergies are common in medical practice, as latex is found in a wide variety of medical supplies, including syringes used for injections and their caps. Physicians need to be aware of latex allergies in their patients and exercise extreme caution in the use of latex-containing products. In the treatment of psoriasis, care must be given when injecting biologic agents. Although many injection devices contain latex limited to the cap, it may be enough to invoke an allergic response. If such a response is elicited, therapy with injection devices that do not contain latex in either the cap or syringe should be considered.
An allergic reaction is an exaggerated immune response that is known as a type I or immediate hypersensitivity reaction when provoked by reexposure to an allergen or antigen. Upon initial exposure to the antigen, dendritic cells bind it for presentation to helper T (TH2) lymphocytes. The TH2 cells then interact with B cells, stimulating them to become plasma cells and produce IgE antibodies to the antigen. When exposed to the same allergen a second time, IgE antibodies bind the allergen and cross-link on mast cells and basophils in the blood. Cross-linking stimulates degranulation of the cells, releasing histamine, leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and other cytokines. The major effects of the release of these mediators include vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and bronchoconstriction. Leukotrienes also are responsible for chemotaxis of white blood cells, further propagating the immune response.1
Effects of a type I hypersensitivity reaction can be either local or systemic, resulting in symptoms ranging from mild irritation to anaphylactic shock and death. Latex allergy is a common example of a type I hypersensitivity reaction. Latex is found in many medical products, including gloves, rubber, elastics, blood pressure cuffs, bandages, dressings, and syringes. Reactions can include runny nose, tearing eyes, itching, hives, wheals, wheezing, and in rare cases anaphylaxis.2 Diagnosis can be suspected based on history and physical examination. Screening is performed with radioallergosorbent testing, which identifies specific IgE antibodies to latex; however, the reported sensitivity and specificity for the latex-specific IgE antibody varies widely in the literature, and the test cannot reliably rule in or rule out a true latex allergy.3
Allergic responses to latex in psoriasis patients receiving frequent injections with biologic agents are not commonly reported in the literature. We report the case of a patient with a long history of psoriasis who developed an allergic response after exposure to injection devices that contained latex components while undergoing treatment with biologic agents.
Case Report
A 72-year-old man presented with an extensive history of severe psoriasis with frequent flares. Treatment with topical agents and etanercept 6 months prior at an outside facility failed. At the time of presentation, the patient had more than 10% body surface area (BSA) involvement, which included the scalp, legs, chest, and back. He subsequently was started on ustekinumab injections. He initially responded well to therapy, but after 8 months of treatment, he began to have recurrent episodes of acute eruptive rashes over the trunk with associated severe pruritus that reproducibly recurred within 24 hours after each ustekinumab injection. It was decided to discontinue ustekinumab due to concern for intolerance, and the patient was switched to secukinumab.
After starting secukinumab, the patient's BSA involvement was reduced to 2% after 1 month; however, he began to develop an eruptive rash with severe pruritus again that reproducibly recurred after each secukinumab injection. On physical examination the patient had ill-defined, confluent, erythematous patches over much of the trunk and extremities. Punch biopsies of the eruptive dermatitis showed spongiform psoriasis and eosinophils with dermal hypersensitivity, consistent with a drug eruption. Upon further questioning, the patient noted that he had a long history of a strong latex allergy and he would develop a blistering dermatitis when coming into contact with latex, which caused a high suspicion for a latex allergy as the cause of the patient's acute dermatitis flares from his prior ustekinumab and secukinumab injections. Although it was confirmed with the manufacturers that both the ustekinumab syringe and secukinumab pen did not contain latex, the caps of these medications (and many other biologic injections) do have latex (Table). Other differential diagnoses included an atypical paradoxical psoriasis flare and a drug eruption to secukinumab, which previously has been reported.4
Based on the suspected cause of the eruption, the patient was instructed not to touch the cap of the secukinumab pen. Despite this recommendation, the rash was still present at the next appointment 1 month later. Repeat punch biopsy showed similar findings to the one prior with likely dermal hypersensitivity. The rash improved with steroid injections and continued to improve after holding the secukinumab for 1 month.
After resolution of the hypersensitivity reaction, the patient was started on ixekizumab, which does not contain latex in any component according to the manufacturer. After 2 months of treatment, the patient had 2% BSA involvement of psoriasis and has had no further reports of itching, rash, or other symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction. On follow-up, the patient's psoriasis symptoms continue to be controlled without further reactions after injections of ixekizumab. Radioallergosorbent testing was not performed due to the lack of specificity and sensitivity of the test3 as well as the patient's known history of latex allergy and characteristic dermatitis that developed after exposure to latex and resolution with removal of the agent. These clinical manifestations are highly indicative of a type I hypersensitivity to injection devices that contain latex components during biologic therapy.
Comment
Allergic responses to latex are most commonly seen in those exposed to gloves or rubber, but little has been reported on reactions to injections with pens or syringes that contain latex components. Some case reports have demonstrated allergic responses in diabetic patients receiving insulin injections.5,6 MacCracken et al5 reported the case of a young boy who had an allergic response to an insulin injection with a syringe containing latex. The patient had a history of bladder exstrophy with a recent diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. It is well known that patients with spina bifida and other conditions who undergo frequent urological procedures more commonly develop latex allergies. This patient reported a history of swollen lips after a dentist visit, presumably due to contact with latex gloves. Because of the suspected allergy, his first insulin injection was given using a glass syringe and insulin was withdrawn with the top removed due to the top containing latex. He did not experience any complications. After being injected later with insulin drawn through the top using a syringe that contained latex, he developed a flare-up of a 0.5-cm erythematous wheal within minutes with associated pruritus.5
Towse et al6 described another patient with diabetes who developed a local allergic reaction at the site of insulin injections. Workup by the physician ruled out insulin allergy but showed elevated latex-specific IgE antibodies. Future insulin draws through a latex-containing top produced a wheal at the injection site. After switching to latex-free syringes, the allergic reaction resolved.6
Latex allergies are common in medical practice, as latex is found in a wide variety of medical supplies, including syringes used for injections and their caps. Physicians need to be aware of latex allergies in their patients and exercise extreme caution in the use of latex-containing products. In the treatment of psoriasis, care must be given when injecting biologic agents. Although many injection devices contain latex limited to the cap, it may be enough to invoke an allergic response. If such a response is elicited, therapy with injection devices that do not contain latex in either the cap or syringe should be considered.
- Druce HM. Allergic and nonallergic rhinitis. In: Middleton EM Jr, Reed CE, Ellis EF, et al, eds. Allergy: Principles and Practice. 5th ed. Vol 1. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 1998:1005-1016.
- Rochford C, Milles M. A review of the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of allergic reactions in the dental office. Quintessence Int. 2011;42:149-156.
- Hamilton RG, Peterson EL, Ownby DR. Clinical and laboratory-based methods in the diagnosis of natural rubber latex allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110(2 suppl):S47-S56.
- Shibata M, Sawada Y, Yamaguchi T, et al. Drug eruption caused by secukinumab. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27:67-68.
- MacCracken J, Stenger P, Jackson T. Latex allergy in diabetic patients: a call for latex-free insulin tops. Diabetes Care. 1996;19:184.
- Towse A, O'Brien M, Twarog FJ, et al. Local reaction secondary to insulin injection: a potential role for latex antigens in insulin vials and syringes. Diabetes Care. 1995;18:1195-1197.
- Druce HM. Allergic and nonallergic rhinitis. In: Middleton EM Jr, Reed CE, Ellis EF, et al, eds. Allergy: Principles and Practice. 5th ed. Vol 1. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 1998:1005-1016.
- Rochford C, Milles M. A review of the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of allergic reactions in the dental office. Quintessence Int. 2011;42:149-156.
- Hamilton RG, Peterson EL, Ownby DR. Clinical and laboratory-based methods in the diagnosis of natural rubber latex allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110(2 suppl):S47-S56.
- Shibata M, Sawada Y, Yamaguchi T, et al. Drug eruption caused by secukinumab. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27:67-68.
- MacCracken J, Stenger P, Jackson T. Latex allergy in diabetic patients: a call for latex-free insulin tops. Diabetes Care. 1996;19:184.
- Towse A, O'Brien M, Twarog FJ, et al. Local reaction secondary to insulin injection: a potential role for latex antigens in insulin vials and syringes. Diabetes Care. 1995;18:1195-1197.
Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus Responsive to 308-nm Excimer Laser Treatment
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a rare entity that presents with linear and pruritic psoriasiform plaques and most commonly occurs during childhood. It represents a dysregulation of keratinocytes exhibiting genetic mosaicism.1,2 Epidermal nevi may derive from keratinocytic, follicular, sebaceous, apocrine, or eccrine origin. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus is classified under the keratinocytic type of epidermal nevus and represents approximately 6% of all epidermal nevi.3 The condition presents as erythematous and verrucous plaques along the lines of Blaschko.2,4 There is a predilection for the legs, and girls are 4 times more commonly affected than boys.1 Cases of ILVEN are predominantly sporadic, though rare familial cases have been reported.4
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus is notoriously refractory to treatment. First-line therapies include topical agents such as corticosteroids, calcipotriol, retinoids, and 5-fluorouracil.3,4 Other treatments include intralesional corticosteroids, cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and surgical excision.3 Several case reports have shown promising results using the pulsed dye and ablative CO2 lasers.5-8
Case Report
An otherwise healthy 20-year-old woman presented with dry, pruritic, red lesions on the right leg that had been present and stable since she was an infant (2 weeks of age). Her medical history included acne vulgaris, but she denied any personal or family history of psoriasis as well as any arthralgia or arthritis. Physical examination revealed discrete, oval, hyperkeratotic, scaly, red plaques on the lateral right leg with a larger hyperkeratotic, linear, red plaque extending from the right popliteal fossa to the posterior thigh (Figure 1A). The nails, scalp, buttocks, and upper extremities were unaffected. Bacterial culture of the right leg demonstrated Staphylococcus aureus colonization. Biopsy of the right popliteal fossa showed psoriasiform dermatitis with psoriasiform hyperplasia, a slightly verruciform surface, broad zones of superficial pallor, and parakeratosis with conspicuous colonies of bacteria (Figure 2).
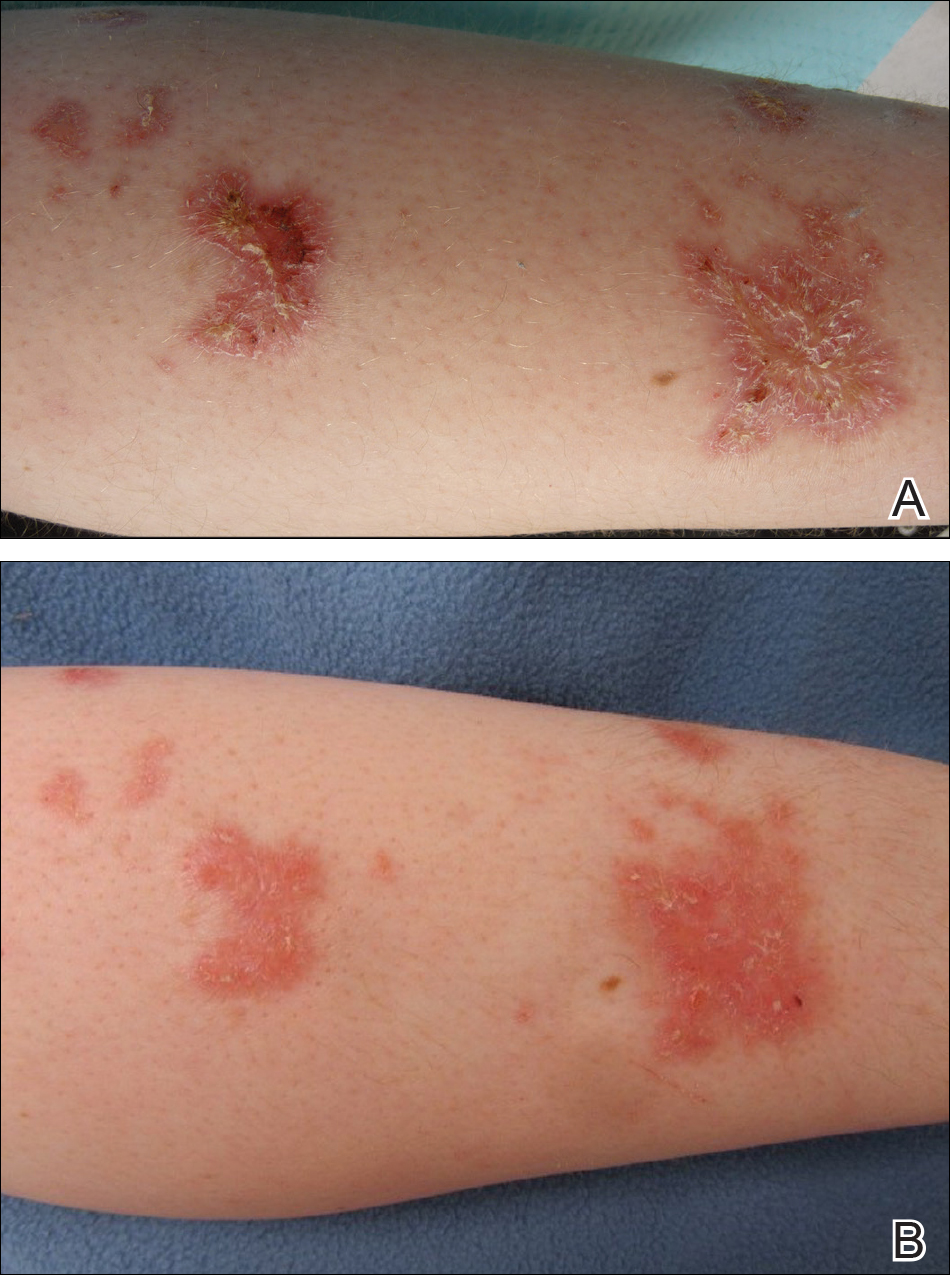
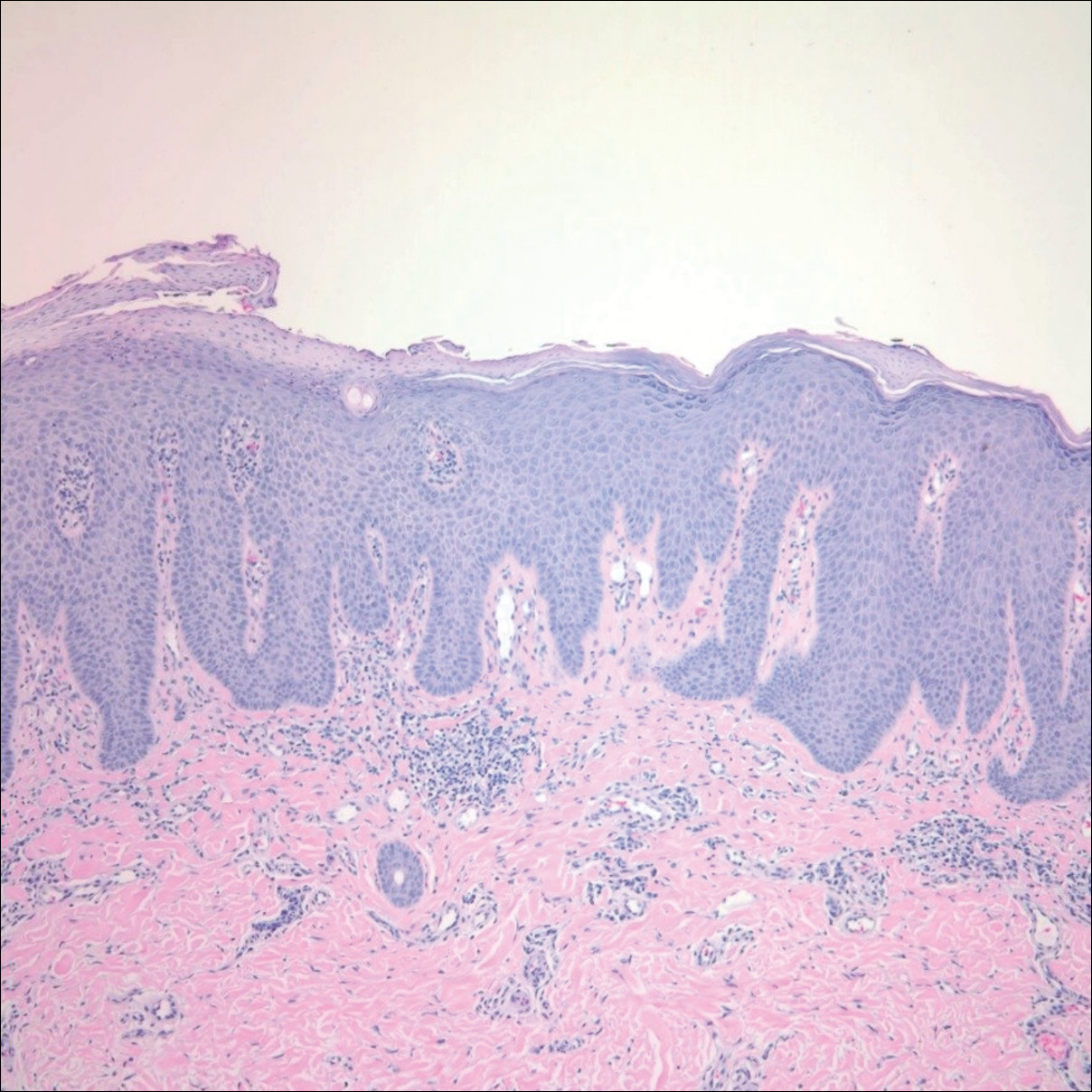
Following the positive bacterial culture, the patient was treated with a short course of oral doxycycline, which did not alter the clinical appearance of the lesions or improve symptoms of pruritus. Pruritus improved moderately with topical corticosteroid treatment, but clinically the lesions appeared unchanged. The plaque on the superior right leg was treated with a superpulsed CO2 laser and the plaque on the inferior right leg was treated with a fractional CO2 laser, both with minimal improvement.
Because of the clinical and histopathologic similarities of the patient's lesions to psoriasis, a trial of the UV 308-nm excimer laser was initiated. Following initial test spots, she completed a total of 18 treatments to all lesions with noticeable clinical improvement (Figure 1B). Initially, the patient returned for treatment biweekly for approximately 5 weeks with 2 small spots being targeted at each session, with an average surface area of approximately 16 cm2. She was started at 225 mJ/cm2 with 25% increases at each session and ultimately reached up to 1676 mJ/cm2 at the end of the 10 sessions. She tolerated the procedure well with some minor blistering. Treatment was deferred for 3 months due to the patient's schedule, then biweekly treatments resumed for 4 weeks, totaling 8 more sessions. At that time, all lesions on the right leg were targeted, with an average surface area of approximately 100 cm2. The laser settings were initiated at 225 mJ/cm2 with 20% increases at each session and ultimately reached 560 mJ/cm2. The treatment was well tolerated throughout; however, the patient initially reported residual pruritus. The plaques continued to improve, and most notably, there was thinning of the hyperkeratotic scale of the plaques in addition to decreased erythema and complete resolution of pruritus. Ultimately, treatment was discontinued because of lack of insurance coverage and financial burden. The patient was lost to follow-up.
Comment
Presentation
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus is a rare type of keratinocytic epidermal nevus4 that clinically presents as small, discrete, pruritic, scaly plaques coalescing into a linear plaque along the lines of Blaschko.9 Considerable pruritus and resistance to treatment are hallmarks of the disease.10 Histopathologically, ILVEN is characterized by alternating orthokeratosis and parakeratosis with a lack of neutrophils in an acanthotic epidermis.11-13 Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus presents at birth or in early childhood. Adult onset is rare.9,14 Approximately 75% of lesions present by 5 years of age, with a majority occurring within the first 6 months of life.15 The differential diagnosis includes linear psoriasis, epidermal nevi, linear lichen planus, linear verrucae, linear lichen simplex chronicus, and mycosis fungoides.4,11
Differentiation From Psoriasis
Despite the histopathologic overlap with psoriasis, ILVEN exhibits fewer Ki-67-positive keratinocyte nuclei (proliferative marker) and more cytokeratin 10-positive cells (epidermal differentiation marker) than psoriasis.16 Furthermore, ILVEN has demonstrated fewer CD4−, CD8−, CD45RO−, CD2−, CD25−, CD94−, and CD161+ cells within the dermis and epidermis than psoriasis.16
The clinical presentations of ILVEN and psoriasis may be similar, as some patients with linear psoriasis also present with psoriatic plaques along the lines of Blaschko.17 Additionally, ILVEN may be a precursor to psoriasis. Altman and Mehregan1 found that ILVEN patients who developed psoriasis did so in areas previously affected by ILVEN; however, they continued to distinguish the 2 pathologies as distinct entities. Another early report also hypothesized that the dermoepidermal defect caused by epidermal nevi provided a site for the development of psoriatic lesions because of the Koebner phenomenon.18
Patients with ILVEN also have been found to have extracutaneous manifestations and symptoms commonly seen in psoriasis patients. A 2012 retrospective review revealed that 37% (7/19) of patients with ILVEN also had psoriatic arthritis, cutaneous psoriatic lesions, and/or nail pitting. The authors concluded that ILVEN may lead to the onset of psoriasis later in life and may indicate an underlying psoriatic predisposition.19 Genetic theories also have been proposed, stating that ILVEN may be a mosaic of psoriasis2 or that a postzygotic mutation leads to the predisposition for developing psoriasis.20
Treatment
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus frequently is refractory to treatment; however, the associated pruritus and distressing cosmesis make treatment attempts worthwhile.11 No single therapy has been found to be successful in all patients. A widely used first-line treatment is topical or intralesional corticosteroids, with the former typically used with occlusion.13 Other treatments include adalimumab, calcipotriol,22,23 tretinoin,24 and 5-fluorouracil.24 Physical modalities such as cryotherapy, electrodesiccation, and dermabrasion have been reported with varying success.15,24 Surgical treatments include tangential25 and full-thickness excisions.26
The CO2 laser also has demonstrated success. One study showed considerable improvement of pruritus and partial resolution of lesions only 5 weeks following a single CO2 laser treatment.5 Another study showed promising results when combining CO2 pulsed laser therapy with fractional CO2 laser treatment.6 Other laser therapies including the argon27 and flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye lasers8 have been used with limited success. The use of light therapy and lasers in psoriasis have now increased the treatment options for ILVEN based on the rationale of their shared histopathologic characteristics. Photodynamic therapy also has been attempted because of its successful use in psoriasis patients. It has been found to be successful in diminishing ILVEN lesions and associated pruritus after a few weeks of therapy; however, treatment is limited by the associated pain and requirement for local anesthesia.28
The excimer laser is a form of targeted phototherapy that emits monochromatic light at 308 nm.29 It is ideal for inflammatory skin lesions because the UVB light induces apoptosis.30 Psoriasis lesions treated with the excimer laser show a decrease in keratinocyte proliferation, which in turn reverses epidermal acanthosis and causes T-cell depletion due to upregulation of p53.29,31 This mechanism of action addresses the overproliferation of keratinocytes mediated by T cells in psoriasis and contributes to the success of excimer laser treatment.31 A considerable advantage is its localized treatment, resulting in lower cumulative doses of UVB and reducing the possible carcinogenic and phototoxic risks of whole-body phototherapy.32
One study examined the antipruritic effects of the excimer laser following the treatment of epidermal hyperinnervation leading to intractable pruritus in patients with atopic dermatitis. The researchers suggested that a potential explanation for the antipruritic effect of the excimer laser may be secondary to nerve degeneration.33 Additionally, low doses of UVB light also may inhibit mast cell degranulation and prevent histamine release, further supporting the antipruritic properties of excimer laser.34
In our patient, failed treatment with other modalities led to trial of excimer laser therapy because of the overlapping clinical and histopathologic findings with psoriasis. Excimer laser improved the clinical appearance and overall texture of the ILVEN lesions and decreased pruritus. The reasons for treatment success may be two-fold. By decreasing the number of keratinocytes and mast cells, the excimer laser may have improved the epidermal hyperplasia and pruritus in the ILVEN lesions. Alternatively, because the patient had ILVEN lesions since infancy, psoriasis may have developed in the location of the ILVEN lesions due to koebnerization, resulting in the clinical response to excimer therapy; however, she had no other clinical evidence of psoriasis.
Because of the recalcitrance of ILVEN lesions to conventional therapies, it is important to investigate therapies that may be of possible benefit. Our novel case documents successful use of the excimer laser in the treatment of ILVEN.
Conclusion
Our case of ILVEN in a woman that had been present since infancy highlights the disease pathology as well as a potential new treatment modality. The patient was refractory to first-line treatments and was concerned about the cosmetic appearance of the lesions. The patient was subsequently treated with a trial of a 308-nm excimer laser with clinical improvement of the lesions. It is possible that the similarity of ILVEN and psoriasis may have contributed to the clinical improvement in our patient, but the mechanism of action remains unknown. Due to the paucity of evidence regarding optimal treatment of ILVEN, the current case offers dermatologists an option for patients who are refractory to other treatments.
- Altman J, Mehregan AH. Inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus. Arch Dermatol. 1971;104:385-389.
- Hofer T. Does inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus represent a segmental type 1/type 2 mosaic of psoriasis? Dermatology. 2006;212:103-107.
- Rogers M, McCrossin I, Commens C. Epidermal nevi and the epidermal nevus syndrome: a review of 131 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20:476-488.
- Khachemoune A, Janjua S, Guldbakke K. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: a case report and short review of the literature. Cutis. 2006;78:261-267.
- Ulkur E, Celikoz B, Yuksel F, et al. Carbon dioxide laser therapy for an inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: a case report. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2004;28:428-430.
- Conti R, Bruscino N, Campolmi P, et al. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: why a combined laser therapy. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2013;15:242-245.
- Alonso-Castro L, Boixeda P, Reig I, et al. Carbon dioxide laser treatment of epidermal nevi: response and long-term follow-up. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2012;103:910-918.
- Alster TS. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: successful treatment with the 585 nm flashlamp-pumped dye laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31:513-514.
- Kruse LL. Differential diagnosis of linear eruptions in children. Pediatr Ann. 2015;44:194-198.
- Renner R, Colsman A, Sticherling M. ILVEN: is it psoriasis? debate based on successful treatment with etanercept. Acta Derm Venereol. 2008;88:631-632.
- Lee SH, Rogers M. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevi: a review of 23 cases. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:252-256.
- Ito M, Shimizu N, Fujiwara H, et al. Histopathogenesis of inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus: histochemistry, immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure. Arch Dermatol Res. 1991;283:491-499.
- Cerio R, Jones EW, Eady RA. ILVEN responding to occlusive potent topical steroid therapy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1992;17:279-281.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Behera B, Devi B, Nayak BB, et al. Giant inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: successfully treated with full thickness excision and skin grafting. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:461-463.
- Vissers WH, Muys L, Erp PE, et al. Immunohistochemical differentiation between ILVEN and psoriasis. Eur J Dermatol. 2004;14:216-220.
- Agarwal US, Besarwal RK, Gupta R, et a. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus with psoriasiform histology. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:211.
- Bennett RG, Burns L, Wood MG. Systematized epidermal nevus: a determinant for the localization of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 1973;108:705-757.
- Tran K, Jao-Tan C, Ho N. ILVEN and psoriasis: a retrospective study among pediatric patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(suppl 1):AB163.
- Happle R. Superimposed linear psoriasis: a historical case revisited. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2011;9:1027-1028; discussion 1029.
- Özdemir M, Balevi A, Esen H. An inflammatory verrucous epidermal nevus concomitant with psoriasis: treatment with adalimumab. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:11.
- Zvulunov A, Grunwald MH, Halvy S. Topical calcipotriol for treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133:567-568.
- Gatti S, Carrozzo AM, Orlandi A, et al. Treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus with calcipotriol. Br J Dermatol. 1995;132:837-839.
- Fox BJ, Lapins NA. Comparison of treatment modalities for epidermal nevus: a case report and review. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1983;9:879-885.
- Pilanci O, Tas B, Ceran F, et al. A novel technique used in the treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: tangential excision. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014;38:1066-1067.
- Lee BJ, Mancini AJ, Renucci J, et al. Full-thickness surgical excision for the treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus. Ann Plast Surg. 2001;47:285-292.
- Hohenleutner U, Landthaler M. Laser therapy of verrucous epidermal naevi. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1993;18:124-127.
- Parera E, Gallardo F, Toll A, et al. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus successfully treated with methyl-aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:253-256.
- Situm M, Bulat V, Majcen K, et al. Benefits of controlled ultraviolet radiation in the treatment of dermatological diseases. Coll Antropol. 2014;38:1249-1253.
- Beggs S, Short J, Rengifo-Pardo M, et al. Applications of the excimer laser: a review. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41:1201-1211.
- Bianchi B, Campolmi P, Mavilia L, et al. Monochromatic excimer light (308 nm): an immunohistochemical study of cutaneous T cells and apoptosis-related molecules in psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:408-413.
- Mudigonda T, Dabade TS, Feldman SR. A review of targeted ultraviolet B phototherapy for psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:664-672.
- Kamo A, Tominaga M, Kamata Y, et al. The excimer lamp induces cutaneous nerve degeneration and reduces scratching in a dry-skin mouse model. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2977-2984.
- Bulat V, Majcen K, Dzapo A, et al. Benefits of controlled ultraviolet radiation in the treatment of dermatological diseases. Coll Antropol. 2014;38:1249-1253
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a rare entity that presents with linear and pruritic psoriasiform plaques and most commonly occurs during childhood. It represents a dysregulation of keratinocytes exhibiting genetic mosaicism.1,2 Epidermal nevi may derive from keratinocytic, follicular, sebaceous, apocrine, or eccrine origin. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus is classified under the keratinocytic type of epidermal nevus and represents approximately 6% of all epidermal nevi.3 The condition presents as erythematous and verrucous plaques along the lines of Blaschko.2,4 There is a predilection for the legs, and girls are 4 times more commonly affected than boys.1 Cases of ILVEN are predominantly sporadic, though rare familial cases have been reported.4
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus is notoriously refractory to treatment. First-line therapies include topical agents such as corticosteroids, calcipotriol, retinoids, and 5-fluorouracil.3,4 Other treatments include intralesional corticosteroids, cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and surgical excision.3 Several case reports have shown promising results using the pulsed dye and ablative CO2 lasers.5-8
Case Report
An otherwise healthy 20-year-old woman presented with dry, pruritic, red lesions on the right leg that had been present and stable since she was an infant (2 weeks of age). Her medical history included acne vulgaris, but she denied any personal or family history of psoriasis as well as any arthralgia or arthritis. Physical examination revealed discrete, oval, hyperkeratotic, scaly, red plaques on the lateral right leg with a larger hyperkeratotic, linear, red plaque extending from the right popliteal fossa to the posterior thigh (Figure 1A). The nails, scalp, buttocks, and upper extremities were unaffected. Bacterial culture of the right leg demonstrated Staphylococcus aureus colonization. Biopsy of the right popliteal fossa showed psoriasiform dermatitis with psoriasiform hyperplasia, a slightly verruciform surface, broad zones of superficial pallor, and parakeratosis with conspicuous colonies of bacteria (Figure 2).


Following the positive bacterial culture, the patient was treated with a short course of oral doxycycline, which did not alter the clinical appearance of the lesions or improve symptoms of pruritus. Pruritus improved moderately with topical corticosteroid treatment, but clinically the lesions appeared unchanged. The plaque on the superior right leg was treated with a superpulsed CO2 laser and the plaque on the inferior right leg was treated with a fractional CO2 laser, both with minimal improvement.
Because of the clinical and histopathologic similarities of the patient's lesions to psoriasis, a trial of the UV 308-nm excimer laser was initiated. Following initial test spots, she completed a total of 18 treatments to all lesions with noticeable clinical improvement (Figure 1B). Initially, the patient returned for treatment biweekly for approximately 5 weeks with 2 small spots being targeted at each session, with an average surface area of approximately 16 cm2. She was started at 225 mJ/cm2 with 25% increases at each session and ultimately reached up to 1676 mJ/cm2 at the end of the 10 sessions. She tolerated the procedure well with some minor blistering. Treatment was deferred for 3 months due to the patient's schedule, then biweekly treatments resumed for 4 weeks, totaling 8 more sessions. At that time, all lesions on the right leg were targeted, with an average surface area of approximately 100 cm2. The laser settings were initiated at 225 mJ/cm2 with 20% increases at each session and ultimately reached 560 mJ/cm2. The treatment was well tolerated throughout; however, the patient initially reported residual pruritus. The plaques continued to improve, and most notably, there was thinning of the hyperkeratotic scale of the plaques in addition to decreased erythema and complete resolution of pruritus. Ultimately, treatment was discontinued because of lack of insurance coverage and financial burden. The patient was lost to follow-up.
Comment
Presentation
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus is a rare type of keratinocytic epidermal nevus4 that clinically presents as small, discrete, pruritic, scaly plaques coalescing into a linear plaque along the lines of Blaschko.9 Considerable pruritus and resistance to treatment are hallmarks of the disease.10 Histopathologically, ILVEN is characterized by alternating orthokeratosis and parakeratosis with a lack of neutrophils in an acanthotic epidermis.11-13 Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus presents at birth or in early childhood. Adult onset is rare.9,14 Approximately 75% of lesions present by 5 years of age, with a majority occurring within the first 6 months of life.15 The differential diagnosis includes linear psoriasis, epidermal nevi, linear lichen planus, linear verrucae, linear lichen simplex chronicus, and mycosis fungoides.4,11
Differentiation From Psoriasis
Despite the histopathologic overlap with psoriasis, ILVEN exhibits fewer Ki-67-positive keratinocyte nuclei (proliferative marker) and more cytokeratin 10-positive cells (epidermal differentiation marker) than psoriasis.16 Furthermore, ILVEN has demonstrated fewer CD4−, CD8−, CD45RO−, CD2−, CD25−, CD94−, and CD161+ cells within the dermis and epidermis than psoriasis.16
The clinical presentations of ILVEN and psoriasis may be similar, as some patients with linear psoriasis also present with psoriatic plaques along the lines of Blaschko.17 Additionally, ILVEN may be a precursor to psoriasis. Altman and Mehregan1 found that ILVEN patients who developed psoriasis did so in areas previously affected by ILVEN; however, they continued to distinguish the 2 pathologies as distinct entities. Another early report also hypothesized that the dermoepidermal defect caused by epidermal nevi provided a site for the development of psoriatic lesions because of the Koebner phenomenon.18
Patients with ILVEN also have been found to have extracutaneous manifestations and symptoms commonly seen in psoriasis patients. A 2012 retrospective review revealed that 37% (7/19) of patients with ILVEN also had psoriatic arthritis, cutaneous psoriatic lesions, and/or nail pitting. The authors concluded that ILVEN may lead to the onset of psoriasis later in life and may indicate an underlying psoriatic predisposition.19 Genetic theories also have been proposed, stating that ILVEN may be a mosaic of psoriasis2 or that a postzygotic mutation leads to the predisposition for developing psoriasis.20
Treatment
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus frequently is refractory to treatment; however, the associated pruritus and distressing cosmesis make treatment attempts worthwhile.11 No single therapy has been found to be successful in all patients. A widely used first-line treatment is topical or intralesional corticosteroids, with the former typically used with occlusion.13 Other treatments include adalimumab, calcipotriol,22,23 tretinoin,24 and 5-fluorouracil.24 Physical modalities such as cryotherapy, electrodesiccation, and dermabrasion have been reported with varying success.15,24 Surgical treatments include tangential25 and full-thickness excisions.26
The CO2 laser also has demonstrated success. One study showed considerable improvement of pruritus and partial resolution of lesions only 5 weeks following a single CO2 laser treatment.5 Another study showed promising results when combining CO2 pulsed laser therapy with fractional CO2 laser treatment.6 Other laser therapies including the argon27 and flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye lasers8 have been used with limited success. The use of light therapy and lasers in psoriasis have now increased the treatment options for ILVEN based on the rationale of their shared histopathologic characteristics. Photodynamic therapy also has been attempted because of its successful use in psoriasis patients. It has been found to be successful in diminishing ILVEN lesions and associated pruritus after a few weeks of therapy; however, treatment is limited by the associated pain and requirement for local anesthesia.28
The excimer laser is a form of targeted phototherapy that emits monochromatic light at 308 nm.29 It is ideal for inflammatory skin lesions because the UVB light induces apoptosis.30 Psoriasis lesions treated with the excimer laser show a decrease in keratinocyte proliferation, which in turn reverses epidermal acanthosis and causes T-cell depletion due to upregulation of p53.29,31 This mechanism of action addresses the overproliferation of keratinocytes mediated by T cells in psoriasis and contributes to the success of excimer laser treatment.31 A considerable advantage is its localized treatment, resulting in lower cumulative doses of UVB and reducing the possible carcinogenic and phototoxic risks of whole-body phototherapy.32
One study examined the antipruritic effects of the excimer laser following the treatment of epidermal hyperinnervation leading to intractable pruritus in patients with atopic dermatitis. The researchers suggested that a potential explanation for the antipruritic effect of the excimer laser may be secondary to nerve degeneration.33 Additionally, low doses of UVB light also may inhibit mast cell degranulation and prevent histamine release, further supporting the antipruritic properties of excimer laser.34
In our patient, failed treatment with other modalities led to trial of excimer laser therapy because of the overlapping clinical and histopathologic findings with psoriasis. Excimer laser improved the clinical appearance and overall texture of the ILVEN lesions and decreased pruritus. The reasons for treatment success may be two-fold. By decreasing the number of keratinocytes and mast cells, the excimer laser may have improved the epidermal hyperplasia and pruritus in the ILVEN lesions. Alternatively, because the patient had ILVEN lesions since infancy, psoriasis may have developed in the location of the ILVEN lesions due to koebnerization, resulting in the clinical response to excimer therapy; however, she had no other clinical evidence of psoriasis.
Because of the recalcitrance of ILVEN lesions to conventional therapies, it is important to investigate therapies that may be of possible benefit. Our novel case documents successful use of the excimer laser in the treatment of ILVEN.
Conclusion
Our case of ILVEN in a woman that had been present since infancy highlights the disease pathology as well as a potential new treatment modality. The patient was refractory to first-line treatments and was concerned about the cosmetic appearance of the lesions. The patient was subsequently treated with a trial of a 308-nm excimer laser with clinical improvement of the lesions. It is possible that the similarity of ILVEN and psoriasis may have contributed to the clinical improvement in our patient, but the mechanism of action remains unknown. Due to the paucity of evidence regarding optimal treatment of ILVEN, the current case offers dermatologists an option for patients who are refractory to other treatments.
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a rare entity that presents with linear and pruritic psoriasiform plaques and most commonly occurs during childhood. It represents a dysregulation of keratinocytes exhibiting genetic mosaicism.1,2 Epidermal nevi may derive from keratinocytic, follicular, sebaceous, apocrine, or eccrine origin. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus is classified under the keratinocytic type of epidermal nevus and represents approximately 6% of all epidermal nevi.3 The condition presents as erythematous and verrucous plaques along the lines of Blaschko.2,4 There is a predilection for the legs, and girls are 4 times more commonly affected than boys.1 Cases of ILVEN are predominantly sporadic, though rare familial cases have been reported.4
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus is notoriously refractory to treatment. First-line therapies include topical agents such as corticosteroids, calcipotriol, retinoids, and 5-fluorouracil.3,4 Other treatments include intralesional corticosteroids, cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and surgical excision.3 Several case reports have shown promising results using the pulsed dye and ablative CO2 lasers.5-8
Case Report
An otherwise healthy 20-year-old woman presented with dry, pruritic, red lesions on the right leg that had been present and stable since she was an infant (2 weeks of age). Her medical history included acne vulgaris, but she denied any personal or family history of psoriasis as well as any arthralgia or arthritis. Physical examination revealed discrete, oval, hyperkeratotic, scaly, red plaques on the lateral right leg with a larger hyperkeratotic, linear, red plaque extending from the right popliteal fossa to the posterior thigh (Figure 1A). The nails, scalp, buttocks, and upper extremities were unaffected. Bacterial culture of the right leg demonstrated Staphylococcus aureus colonization. Biopsy of the right popliteal fossa showed psoriasiform dermatitis with psoriasiform hyperplasia, a slightly verruciform surface, broad zones of superficial pallor, and parakeratosis with conspicuous colonies of bacteria (Figure 2).


Following the positive bacterial culture, the patient was treated with a short course of oral doxycycline, which did not alter the clinical appearance of the lesions or improve symptoms of pruritus. Pruritus improved moderately with topical corticosteroid treatment, but clinically the lesions appeared unchanged. The plaque on the superior right leg was treated with a superpulsed CO2 laser and the plaque on the inferior right leg was treated with a fractional CO2 laser, both with minimal improvement.
Because of the clinical and histopathologic similarities of the patient's lesions to psoriasis, a trial of the UV 308-nm excimer laser was initiated. Following initial test spots, she completed a total of 18 treatments to all lesions with noticeable clinical improvement (Figure 1B). Initially, the patient returned for treatment biweekly for approximately 5 weeks with 2 small spots being targeted at each session, with an average surface area of approximately 16 cm2. She was started at 225 mJ/cm2 with 25% increases at each session and ultimately reached up to 1676 mJ/cm2 at the end of the 10 sessions. She tolerated the procedure well with some minor blistering. Treatment was deferred for 3 months due to the patient's schedule, then biweekly treatments resumed for 4 weeks, totaling 8 more sessions. At that time, all lesions on the right leg were targeted, with an average surface area of approximately 100 cm2. The laser settings were initiated at 225 mJ/cm2 with 20% increases at each session and ultimately reached 560 mJ/cm2. The treatment was well tolerated throughout; however, the patient initially reported residual pruritus. The plaques continued to improve, and most notably, there was thinning of the hyperkeratotic scale of the plaques in addition to decreased erythema and complete resolution of pruritus. Ultimately, treatment was discontinued because of lack of insurance coverage and financial burden. The patient was lost to follow-up.
Comment
Presentation
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus is a rare type of keratinocytic epidermal nevus4 that clinically presents as small, discrete, pruritic, scaly plaques coalescing into a linear plaque along the lines of Blaschko.9 Considerable pruritus and resistance to treatment are hallmarks of the disease.10 Histopathologically, ILVEN is characterized by alternating orthokeratosis and parakeratosis with a lack of neutrophils in an acanthotic epidermis.11-13 Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus presents at birth or in early childhood. Adult onset is rare.9,14 Approximately 75% of lesions present by 5 years of age, with a majority occurring within the first 6 months of life.15 The differential diagnosis includes linear psoriasis, epidermal nevi, linear lichen planus, linear verrucae, linear lichen simplex chronicus, and mycosis fungoides.4,11
Differentiation From Psoriasis
Despite the histopathologic overlap with psoriasis, ILVEN exhibits fewer Ki-67-positive keratinocyte nuclei (proliferative marker) and more cytokeratin 10-positive cells (epidermal differentiation marker) than psoriasis.16 Furthermore, ILVEN has demonstrated fewer CD4−, CD8−, CD45RO−, CD2−, CD25−, CD94−, and CD161+ cells within the dermis and epidermis than psoriasis.16
The clinical presentations of ILVEN and psoriasis may be similar, as some patients with linear psoriasis also present with psoriatic plaques along the lines of Blaschko.17 Additionally, ILVEN may be a precursor to psoriasis. Altman and Mehregan1 found that ILVEN patients who developed psoriasis did so in areas previously affected by ILVEN; however, they continued to distinguish the 2 pathologies as distinct entities. Another early report also hypothesized that the dermoepidermal defect caused by epidermal nevi provided a site for the development of psoriatic lesions because of the Koebner phenomenon.18
Patients with ILVEN also have been found to have extracutaneous manifestations and symptoms commonly seen in psoriasis patients. A 2012 retrospective review revealed that 37% (7/19) of patients with ILVEN also had psoriatic arthritis, cutaneous psoriatic lesions, and/or nail pitting. The authors concluded that ILVEN may lead to the onset of psoriasis later in life and may indicate an underlying psoriatic predisposition.19 Genetic theories also have been proposed, stating that ILVEN may be a mosaic of psoriasis2 or that a postzygotic mutation leads to the predisposition for developing psoriasis.20
Treatment
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus frequently is refractory to treatment; however, the associated pruritus and distressing cosmesis make treatment attempts worthwhile.11 No single therapy has been found to be successful in all patients. A widely used first-line treatment is topical or intralesional corticosteroids, with the former typically used with occlusion.13 Other treatments include adalimumab, calcipotriol,22,23 tretinoin,24 and 5-fluorouracil.24 Physical modalities such as cryotherapy, electrodesiccation, and dermabrasion have been reported with varying success.15,24 Surgical treatments include tangential25 and full-thickness excisions.26
The CO2 laser also has demonstrated success. One study showed considerable improvement of pruritus and partial resolution of lesions only 5 weeks following a single CO2 laser treatment.5 Another study showed promising results when combining CO2 pulsed laser therapy with fractional CO2 laser treatment.6 Other laser therapies including the argon27 and flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye lasers8 have been used with limited success. The use of light therapy and lasers in psoriasis have now increased the treatment options for ILVEN based on the rationale of their shared histopathologic characteristics. Photodynamic therapy also has been attempted because of its successful use in psoriasis patients. It has been found to be successful in diminishing ILVEN lesions and associated pruritus after a few weeks of therapy; however, treatment is limited by the associated pain and requirement for local anesthesia.28
The excimer laser is a form of targeted phototherapy that emits monochromatic light at 308 nm.29 It is ideal for inflammatory skin lesions because the UVB light induces apoptosis.30 Psoriasis lesions treated with the excimer laser show a decrease in keratinocyte proliferation, which in turn reverses epidermal acanthosis and causes T-cell depletion due to upregulation of p53.29,31 This mechanism of action addresses the overproliferation of keratinocytes mediated by T cells in psoriasis and contributes to the success of excimer laser treatment.31 A considerable advantage is its localized treatment, resulting in lower cumulative doses of UVB and reducing the possible carcinogenic and phototoxic risks of whole-body phototherapy.32
One study examined the antipruritic effects of the excimer laser following the treatment of epidermal hyperinnervation leading to intractable pruritus in patients with atopic dermatitis. The researchers suggested that a potential explanation for the antipruritic effect of the excimer laser may be secondary to nerve degeneration.33 Additionally, low doses of UVB light also may inhibit mast cell degranulation and prevent histamine release, further supporting the antipruritic properties of excimer laser.34
In our patient, failed treatment with other modalities led to trial of excimer laser therapy because of the overlapping clinical and histopathologic findings with psoriasis. Excimer laser improved the clinical appearance and overall texture of the ILVEN lesions and decreased pruritus. The reasons for treatment success may be two-fold. By decreasing the number of keratinocytes and mast cells, the excimer laser may have improved the epidermal hyperplasia and pruritus in the ILVEN lesions. Alternatively, because the patient had ILVEN lesions since infancy, psoriasis may have developed in the location of the ILVEN lesions due to koebnerization, resulting in the clinical response to excimer therapy; however, she had no other clinical evidence of psoriasis.
Because of the recalcitrance of ILVEN lesions to conventional therapies, it is important to investigate therapies that may be of possible benefit. Our novel case documents successful use of the excimer laser in the treatment of ILVEN.
Conclusion
Our case of ILVEN in a woman that had been present since infancy highlights the disease pathology as well as a potential new treatment modality. The patient was refractory to first-line treatments and was concerned about the cosmetic appearance of the lesions. The patient was subsequently treated with a trial of a 308-nm excimer laser with clinical improvement of the lesions. It is possible that the similarity of ILVEN and psoriasis may have contributed to the clinical improvement in our patient, but the mechanism of action remains unknown. Due to the paucity of evidence regarding optimal treatment of ILVEN, the current case offers dermatologists an option for patients who are refractory to other treatments.
- Altman J, Mehregan AH. Inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus. Arch Dermatol. 1971;104:385-389.
- Hofer T. Does inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus represent a segmental type 1/type 2 mosaic of psoriasis? Dermatology. 2006;212:103-107.
- Rogers M, McCrossin I, Commens C. Epidermal nevi and the epidermal nevus syndrome: a review of 131 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20:476-488.
- Khachemoune A, Janjua S, Guldbakke K. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: a case report and short review of the literature. Cutis. 2006;78:261-267.
- Ulkur E, Celikoz B, Yuksel F, et al. Carbon dioxide laser therapy for an inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: a case report. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2004;28:428-430.
- Conti R, Bruscino N, Campolmi P, et al. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: why a combined laser therapy. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2013;15:242-245.
- Alonso-Castro L, Boixeda P, Reig I, et al. Carbon dioxide laser treatment of epidermal nevi: response and long-term follow-up. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2012;103:910-918.
- Alster TS. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: successful treatment with the 585 nm flashlamp-pumped dye laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31:513-514.
- Kruse LL. Differential diagnosis of linear eruptions in children. Pediatr Ann. 2015;44:194-198.
- Renner R, Colsman A, Sticherling M. ILVEN: is it psoriasis? debate based on successful treatment with etanercept. Acta Derm Venereol. 2008;88:631-632.
- Lee SH, Rogers M. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevi: a review of 23 cases. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:252-256.
- Ito M, Shimizu N, Fujiwara H, et al. Histopathogenesis of inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus: histochemistry, immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure. Arch Dermatol Res. 1991;283:491-499.
- Cerio R, Jones EW, Eady RA. ILVEN responding to occlusive potent topical steroid therapy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1992;17:279-281.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Behera B, Devi B, Nayak BB, et al. Giant inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: successfully treated with full thickness excision and skin grafting. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:461-463.
- Vissers WH, Muys L, Erp PE, et al. Immunohistochemical differentiation between ILVEN and psoriasis. Eur J Dermatol. 2004;14:216-220.
- Agarwal US, Besarwal RK, Gupta R, et a. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus with psoriasiform histology. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:211.
- Bennett RG, Burns L, Wood MG. Systematized epidermal nevus: a determinant for the localization of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 1973;108:705-757.
- Tran K, Jao-Tan C, Ho N. ILVEN and psoriasis: a retrospective study among pediatric patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(suppl 1):AB163.
- Happle R. Superimposed linear psoriasis: a historical case revisited. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2011;9:1027-1028; discussion 1029.
- Özdemir M, Balevi A, Esen H. An inflammatory verrucous epidermal nevus concomitant with psoriasis: treatment with adalimumab. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:11.
- Zvulunov A, Grunwald MH, Halvy S. Topical calcipotriol for treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133:567-568.
- Gatti S, Carrozzo AM, Orlandi A, et al. Treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus with calcipotriol. Br J Dermatol. 1995;132:837-839.
- Fox BJ, Lapins NA. Comparison of treatment modalities for epidermal nevus: a case report and review. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1983;9:879-885.
- Pilanci O, Tas B, Ceran F, et al. A novel technique used in the treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: tangential excision. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014;38:1066-1067.
- Lee BJ, Mancini AJ, Renucci J, et al. Full-thickness surgical excision for the treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus. Ann Plast Surg. 2001;47:285-292.
- Hohenleutner U, Landthaler M. Laser therapy of verrucous epidermal naevi. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1993;18:124-127.
- Parera E, Gallardo F, Toll A, et al. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus successfully treated with methyl-aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:253-256.
- Situm M, Bulat V, Majcen K, et al. Benefits of controlled ultraviolet radiation in the treatment of dermatological diseases. Coll Antropol. 2014;38:1249-1253.
- Beggs S, Short J, Rengifo-Pardo M, et al. Applications of the excimer laser: a review. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41:1201-1211.
- Bianchi B, Campolmi P, Mavilia L, et al. Monochromatic excimer light (308 nm): an immunohistochemical study of cutaneous T cells and apoptosis-related molecules in psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:408-413.
- Mudigonda T, Dabade TS, Feldman SR. A review of targeted ultraviolet B phototherapy for psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:664-672.
- Kamo A, Tominaga M, Kamata Y, et al. The excimer lamp induces cutaneous nerve degeneration and reduces scratching in a dry-skin mouse model. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2977-2984.
- Bulat V, Majcen K, Dzapo A, et al. Benefits of controlled ultraviolet radiation in the treatment of dermatological diseases. Coll Antropol. 2014;38:1249-1253
- Altman J, Mehregan AH. Inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus. Arch Dermatol. 1971;104:385-389.
- Hofer T. Does inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus represent a segmental type 1/type 2 mosaic of psoriasis? Dermatology. 2006;212:103-107.
- Rogers M, McCrossin I, Commens C. Epidermal nevi and the epidermal nevus syndrome: a review of 131 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20:476-488.
- Khachemoune A, Janjua S, Guldbakke K. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: a case report and short review of the literature. Cutis. 2006;78:261-267.
- Ulkur E, Celikoz B, Yuksel F, et al. Carbon dioxide laser therapy for an inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: a case report. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2004;28:428-430.
- Conti R, Bruscino N, Campolmi P, et al. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: why a combined laser therapy. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2013;15:242-245.
- Alonso-Castro L, Boixeda P, Reig I, et al. Carbon dioxide laser treatment of epidermal nevi: response and long-term follow-up. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2012;103:910-918.
- Alster TS. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: successful treatment with the 585 nm flashlamp-pumped dye laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31:513-514.
- Kruse LL. Differential diagnosis of linear eruptions in children. Pediatr Ann. 2015;44:194-198.
- Renner R, Colsman A, Sticherling M. ILVEN: is it psoriasis? debate based on successful treatment with etanercept. Acta Derm Venereol. 2008;88:631-632.
- Lee SH, Rogers M. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevi: a review of 23 cases. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:252-256.
- Ito M, Shimizu N, Fujiwara H, et al. Histopathogenesis of inflammatory linear verrucose epidermal nevus: histochemistry, immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure. Arch Dermatol Res. 1991;283:491-499.
- Cerio R, Jones EW, Eady RA. ILVEN responding to occlusive potent topical steroid therapy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1992;17:279-281.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Behera B, Devi B, Nayak BB, et al. Giant inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: successfully treated with full thickness excision and skin grafting. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:461-463.
- Vissers WH, Muys L, Erp PE, et al. Immunohistochemical differentiation between ILVEN and psoriasis. Eur J Dermatol. 2004;14:216-220.
- Agarwal US, Besarwal RK, Gupta R, et a. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus with psoriasiform histology. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:211.
- Bennett RG, Burns L, Wood MG. Systematized epidermal nevus: a determinant for the localization of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 1973;108:705-757.
- Tran K, Jao-Tan C, Ho N. ILVEN and psoriasis: a retrospective study among pediatric patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(suppl 1):AB163.
- Happle R. Superimposed linear psoriasis: a historical case revisited. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2011;9:1027-1028; discussion 1029.
- Özdemir M, Balevi A, Esen H. An inflammatory verrucous epidermal nevus concomitant with psoriasis: treatment with adalimumab. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:11.
- Zvulunov A, Grunwald MH, Halvy S. Topical calcipotriol for treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133:567-568.
- Gatti S, Carrozzo AM, Orlandi A, et al. Treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal naevus with calcipotriol. Br J Dermatol. 1995;132:837-839.
- Fox BJ, Lapins NA. Comparison of treatment modalities for epidermal nevus: a case report and review. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1983;9:879-885.
- Pilanci O, Tas B, Ceran F, et al. A novel technique used in the treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: tangential excision. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014;38:1066-1067.
- Lee BJ, Mancini AJ, Renucci J, et al. Full-thickness surgical excision for the treatment of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus. Ann Plast Surg. 2001;47:285-292.
- Hohenleutner U, Landthaler M. Laser therapy of verrucous epidermal naevi. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1993;18:124-127.
- Parera E, Gallardo F, Toll A, et al. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus successfully treated with methyl-aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:253-256.
- Situm M, Bulat V, Majcen K, et al. Benefits of controlled ultraviolet radiation in the treatment of dermatological diseases. Coll Antropol. 2014;38:1249-1253.
- Beggs S, Short J, Rengifo-Pardo M, et al. Applications of the excimer laser: a review. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41:1201-1211.
- Bianchi B, Campolmi P, Mavilia L, et al. Monochromatic excimer light (308 nm): an immunohistochemical study of cutaneous T cells and apoptosis-related molecules in psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:408-413.
- Mudigonda T, Dabade TS, Feldman SR. A review of targeted ultraviolet B phototherapy for psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:664-672.
- Kamo A, Tominaga M, Kamata Y, et al. The excimer lamp induces cutaneous nerve degeneration and reduces scratching in a dry-skin mouse model. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2977-2984.
- Bulat V, Majcen K, Dzapo A, et al. Benefits of controlled ultraviolet radiation in the treatment of dermatological diseases. Coll Antropol. 2014;38:1249-1253
Psoriasis pipeline is full of biologics
CHICAGO – Most psoriasis therapies in the pipeline are biologics, including several interleukin (IL)-23 inhibitors and a promising dual inhibitor of IL-17A and IL-17F, so dermatologists are likely to gain a few more options for treating psoriasis patients who have not responded well to or tolerated existing therapies.
“The IL-23 blockers are ideal for patients who want a few injections,” Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and chair of the department of dermatology of the Mount Sinai Health System, said after the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting. He discussed clinical trial results for risankizumab, mirikizumab, certolizumab pegol (which was recently approved for psoriasis), bimekizumab, as well as tildrakizumab, which has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, but has not yet been released.
Tildrakizumab: The FDA approved tildrakizumab (Ilumya), a selective IL-23p19 inhibitor, for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in March 2018 based on data from the reSURFACE 1 and reSURFACE 2 trials. After initial doses at weeks 0 and 4, patients received a 100-mg subcutaneous injection dose every 12 weeks. Results of reSURFACE 1 showed that 14% of trial participants achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of 100 with tildrakizumab at week 12, compared with 1% of those receiving a placebo. Similarly, 35% achieved a PASI 90 and 64% achieved a PASI 75 with the drug, compared with 3% and 6%, respectively, in the placebo group. Findings for reSURFACE 2 were similar; in a pooled analysis, a quarter of the 371 patients reached PASI 100 by week 28, 36% reached PASI 90-PASI 99, 24% reached PASI 75-PASI 89, and 10% reached PASI 50-PASI 74. Efficacy remained high 2 years after treatment, although body weight affected the efficacy. “The authors concluded that PASI and PGA [Physician Global Assessment] responses were numerically greater in patients with lower versus higher body weight,” Dr. Lebwohl said at the meeting.
Tildrakizumab also has an “overall clean safety profile,” he said. Among all patients treated in the trials, the rate of severe infections, malignancies and major adverse cardiac events did not significantly differ from placebo.*
Risankizumab: Also an IL-23 inhibitor, risankizumab, under FDA review for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, outperformed both ustekinumab and adalimumab in pivotal phase 3 trials reported in October 2017. In the two ultlMMa trials, 75% of 598 total patients achieved a PASI 90 score after 16 weeks of treatment, compared with 2%-5% of placebo participants and 42%-48% of those on ustekinumab. In ultlMMa-1, just over a third of patients treated with achieved PASI 100, and just over half did in ultlMMa-2, compared with 12% and 24% of those on ustekinumab, respectively.
At 1 year, the proportion of those with PASI 90 rose to 82% in ultlMMa-1 and 81% in ultlMMa-2, with over half the participants achieving PASI 100 in both studies. The risankizumab trial findings were “among highest efficacy results reported to date, with impressive durability of response on and off drug,” Dr. Lebwohl said. “Preliminary safety is encouraging,” but “long-term data are required.”
Mirikizumab: Although not as far along in clinical trials, mirikizumab is another IL-23 inhibitor with “interesting and impressive preliminary results,” Dr. Lebwohl said. In a phase 2 trial of 205 participants whose baseline demographics indicated more severe psoriasis, 67% achieved PASI 90 at week 16 with a 300-mg dose (administered every 8 weeks). Doses of 100 mg and 30 mg resulted in 59% and 29% of participants achieving PASI 90 at week 16.
“The most common treatment emergent adverse events included upper respiratory tract infection [including viral], injection site pain, hypertension and diarrhea,” Dr. Lebwohl said. Patients are now being recruited for two phase 3 studies of mirikizumab (OASIS-1 and OASIS-2).
Certolizumab pegol: Certolizumab pegol is a tumor necrosis factor blocker approved in 2013 for treatment of psoriatic arthritis, and for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in May 2018. In a pooled data analysis of three phase 3 trials (CIMPASI-1, CIMPASI-2, and CIMPACT), 52.3% of participants taking 400 mg subcutaneously every 2 weeks and 44.5% of those taking 200 mg every 2 weeks achieved PASI 90 at week 16, compared with 1.6% of those on placebo. In addition, a trial evaluating maternal transfer of certolizumab to the fetus via placenta found minimal drug concentration levels in the umbilical cord and infant’s plasma. “Certolizumab is ideal for women of childbearing potential,” Dr. Lebwohl said after the meeting.
Bimekizumab: This is a dual inhibitor of IL-17A and IL-17F being studied for treatment of mild psoriasis but “is very promising for psoriatic arthritis, as well as psoriasis,” Dr. Lebwohl said. In the phase 2b BE ABLE 1 trial, up to 79% of patients receiving bimekizumab achieved PASI 90 at week 12, and up to 46% of psoriatic arthritis patients had at least a 50% improvement in joint symptoms, compared with 7% of those on placebo.
Dr. Lebwohl is a consultant for Allergan, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Leo and Promius Pharma, and is an employee of Mount Sinai, which receives research funds from Abbvie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen/Johnson & Johnson, Kadmon, Medimmune/AstraZeneca, Novartis, Pfizer, and ViDac Pharma.
*Correction, 8/6/18: An earlier version of this article misstated the adverse event data for tildrakizumab.
CHICAGO – Most psoriasis therapies in the pipeline are biologics, including several interleukin (IL)-23 inhibitors and a promising dual inhibitor of IL-17A and IL-17F, so dermatologists are likely to gain a few more options for treating psoriasis patients who have not responded well to or tolerated existing therapies.
“The IL-23 blockers are ideal for patients who want a few injections,” Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and chair of the department of dermatology of the Mount Sinai Health System, said after the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting. He discussed clinical trial results for risankizumab, mirikizumab, certolizumab pegol (which was recently approved for psoriasis), bimekizumab, as well as tildrakizumab, which has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, but has not yet been released.
Tildrakizumab: The FDA approved tildrakizumab (Ilumya), a selective IL-23p19 inhibitor, for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in March 2018 based on data from the reSURFACE 1 and reSURFACE 2 trials. After initial doses at weeks 0 and 4, patients received a 100-mg subcutaneous injection dose every 12 weeks. Results of reSURFACE 1 showed that 14% of trial participants achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of 100 with tildrakizumab at week 12, compared with 1% of those receiving a placebo. Similarly, 35% achieved a PASI 90 and 64% achieved a PASI 75 with the drug, compared with 3% and 6%, respectively, in the placebo group. Findings for reSURFACE 2 were similar; in a pooled analysis, a quarter of the 371 patients reached PASI 100 by week 28, 36% reached PASI 90-PASI 99, 24% reached PASI 75-PASI 89, and 10% reached PASI 50-PASI 74. Efficacy remained high 2 years after treatment, although body weight affected the efficacy. “The authors concluded that PASI and PGA [Physician Global Assessment] responses were numerically greater in patients with lower versus higher body weight,” Dr. Lebwohl said at the meeting.
Tildrakizumab also has an “overall clean safety profile,” he said. Among all patients treated in the trials, the rate of severe infections, malignancies and major adverse cardiac events did not significantly differ from placebo.*
Risankizumab: Also an IL-23 inhibitor, risankizumab, under FDA review for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, outperformed both ustekinumab and adalimumab in pivotal phase 3 trials reported in October 2017. In the two ultlMMa trials, 75% of 598 total patients achieved a PASI 90 score after 16 weeks of treatment, compared with 2%-5% of placebo participants and 42%-48% of those on ustekinumab. In ultlMMa-1, just over a third of patients treated with achieved PASI 100, and just over half did in ultlMMa-2, compared with 12% and 24% of those on ustekinumab, respectively.
At 1 year, the proportion of those with PASI 90 rose to 82% in ultlMMa-1 and 81% in ultlMMa-2, with over half the participants achieving PASI 100 in both studies. The risankizumab trial findings were “among highest efficacy results reported to date, with impressive durability of response on and off drug,” Dr. Lebwohl said. “Preliminary safety is encouraging,” but “long-term data are required.”
Mirikizumab: Although not as far along in clinical trials, mirikizumab is another IL-23 inhibitor with “interesting and impressive preliminary results,” Dr. Lebwohl said. In a phase 2 trial of 205 participants whose baseline demographics indicated more severe psoriasis, 67% achieved PASI 90 at week 16 with a 300-mg dose (administered every 8 weeks). Doses of 100 mg and 30 mg resulted in 59% and 29% of participants achieving PASI 90 at week 16.
“The most common treatment emergent adverse events included upper respiratory tract infection [including viral], injection site pain, hypertension and diarrhea,” Dr. Lebwohl said. Patients are now being recruited for two phase 3 studies of mirikizumab (OASIS-1 and OASIS-2).
Certolizumab pegol: Certolizumab pegol is a tumor necrosis factor blocker approved in 2013 for treatment of psoriatic arthritis, and for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in May 2018. In a pooled data analysis of three phase 3 trials (CIMPASI-1, CIMPASI-2, and CIMPACT), 52.3% of participants taking 400 mg subcutaneously every 2 weeks and 44.5% of those taking 200 mg every 2 weeks achieved PASI 90 at week 16, compared with 1.6% of those on placebo. In addition, a trial evaluating maternal transfer of certolizumab to the fetus via placenta found minimal drug concentration levels in the umbilical cord and infant’s plasma. “Certolizumab is ideal for women of childbearing potential,” Dr. Lebwohl said after the meeting.
Bimekizumab: This is a dual inhibitor of IL-17A and IL-17F being studied for treatment of mild psoriasis but “is very promising for psoriatic arthritis, as well as psoriasis,” Dr. Lebwohl said. In the phase 2b BE ABLE 1 trial, up to 79% of patients receiving bimekizumab achieved PASI 90 at week 12, and up to 46% of psoriatic arthritis patients had at least a 50% improvement in joint symptoms, compared with 7% of those on placebo.
Dr. Lebwohl is a consultant for Allergan, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Leo and Promius Pharma, and is an employee of Mount Sinai, which receives research funds from Abbvie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen/Johnson & Johnson, Kadmon, Medimmune/AstraZeneca, Novartis, Pfizer, and ViDac Pharma.
*Correction, 8/6/18: An earlier version of this article misstated the adverse event data for tildrakizumab.
CHICAGO – Most psoriasis therapies in the pipeline are biologics, including several interleukin (IL)-23 inhibitors and a promising dual inhibitor of IL-17A and IL-17F, so dermatologists are likely to gain a few more options for treating psoriasis patients who have not responded well to or tolerated existing therapies.
“The IL-23 blockers are ideal for patients who want a few injections,” Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and chair of the department of dermatology of the Mount Sinai Health System, said after the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting. He discussed clinical trial results for risankizumab, mirikizumab, certolizumab pegol (which was recently approved for psoriasis), bimekizumab, as well as tildrakizumab, which has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, but has not yet been released.
Tildrakizumab: The FDA approved tildrakizumab (Ilumya), a selective IL-23p19 inhibitor, for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in March 2018 based on data from the reSURFACE 1 and reSURFACE 2 trials. After initial doses at weeks 0 and 4, patients received a 100-mg subcutaneous injection dose every 12 weeks. Results of reSURFACE 1 showed that 14% of trial participants achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of 100 with tildrakizumab at week 12, compared with 1% of those receiving a placebo. Similarly, 35% achieved a PASI 90 and 64% achieved a PASI 75 with the drug, compared with 3% and 6%, respectively, in the placebo group. Findings for reSURFACE 2 were similar; in a pooled analysis, a quarter of the 371 patients reached PASI 100 by week 28, 36% reached PASI 90-PASI 99, 24% reached PASI 75-PASI 89, and 10% reached PASI 50-PASI 74. Efficacy remained high 2 years after treatment, although body weight affected the efficacy. “The authors concluded that PASI and PGA [Physician Global Assessment] responses were numerically greater in patients with lower versus higher body weight,” Dr. Lebwohl said at the meeting.
Tildrakizumab also has an “overall clean safety profile,” he said. Among all patients treated in the trials, the rate of severe infections, malignancies and major adverse cardiac events did not significantly differ from placebo.*
Risankizumab: Also an IL-23 inhibitor, risankizumab, under FDA review for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, outperformed both ustekinumab and adalimumab in pivotal phase 3 trials reported in October 2017. In the two ultlMMa trials, 75% of 598 total patients achieved a PASI 90 score after 16 weeks of treatment, compared with 2%-5% of placebo participants and 42%-48% of those on ustekinumab. In ultlMMa-1, just over a third of patients treated with achieved PASI 100, and just over half did in ultlMMa-2, compared with 12% and 24% of those on ustekinumab, respectively.
At 1 year, the proportion of those with PASI 90 rose to 82% in ultlMMa-1 and 81% in ultlMMa-2, with over half the participants achieving PASI 100 in both studies. The risankizumab trial findings were “among highest efficacy results reported to date, with impressive durability of response on and off drug,” Dr. Lebwohl said. “Preliminary safety is encouraging,” but “long-term data are required.”
Mirikizumab: Although not as far along in clinical trials, mirikizumab is another IL-23 inhibitor with “interesting and impressive preliminary results,” Dr. Lebwohl said. In a phase 2 trial of 205 participants whose baseline demographics indicated more severe psoriasis, 67% achieved PASI 90 at week 16 with a 300-mg dose (administered every 8 weeks). Doses of 100 mg and 30 mg resulted in 59% and 29% of participants achieving PASI 90 at week 16.
“The most common treatment emergent adverse events included upper respiratory tract infection [including viral], injection site pain, hypertension and diarrhea,” Dr. Lebwohl said. Patients are now being recruited for two phase 3 studies of mirikizumab (OASIS-1 and OASIS-2).
Certolizumab pegol: Certolizumab pegol is a tumor necrosis factor blocker approved in 2013 for treatment of psoriatic arthritis, and for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in May 2018. In a pooled data analysis of three phase 3 trials (CIMPASI-1, CIMPASI-2, and CIMPACT), 52.3% of participants taking 400 mg subcutaneously every 2 weeks and 44.5% of those taking 200 mg every 2 weeks achieved PASI 90 at week 16, compared with 1.6% of those on placebo. In addition, a trial evaluating maternal transfer of certolizumab to the fetus via placenta found minimal drug concentration levels in the umbilical cord and infant’s plasma. “Certolizumab is ideal for women of childbearing potential,” Dr. Lebwohl said after the meeting.
Bimekizumab: This is a dual inhibitor of IL-17A and IL-17F being studied for treatment of mild psoriasis but “is very promising for psoriatic arthritis, as well as psoriasis,” Dr. Lebwohl said. In the phase 2b BE ABLE 1 trial, up to 79% of patients receiving bimekizumab achieved PASI 90 at week 12, and up to 46% of psoriatic arthritis patients had at least a 50% improvement in joint symptoms, compared with 7% of those on placebo.
Dr. Lebwohl is a consultant for Allergan, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Leo and Promius Pharma, and is an employee of Mount Sinai, which receives research funds from Abbvie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen/Johnson & Johnson, Kadmon, Medimmune/AstraZeneca, Novartis, Pfizer, and ViDac Pharma.
*Correction, 8/6/18: An earlier version of this article misstated the adverse event data for tildrakizumab.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SUMMER AAD 2018