User login
Clinical Psychiatry News is the online destination and multimedia properties of Clinica Psychiatry News, the independent news publication for psychiatrists. Since 1971, Clinical Psychiatry News has been the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in psychiatry as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the physician's practice.
Dear Drupal User: You're seeing this because you're logged in to Drupal, and not redirected to MDedge.com/psychiatry.
Depression
adolescent depression
adolescent major depressive disorder
adolescent schizophrenia
adolescent with major depressive disorder
animals
autism
baby
brexpiprazole
child
child bipolar
child depression
child schizophrenia
children with bipolar disorder
children with depression
children with major depressive disorder
compulsive behaviors
cure
elderly bipolar
elderly depression
elderly major depressive disorder
elderly schizophrenia
elderly with dementia
first break
first episode
gambling
gaming
geriatric depression
geriatric major depressive disorder
geriatric schizophrenia
infant
ketamine
kid
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder in adolescents
major depressive disorder in children
parenting
pediatric
pediatric bipolar
pediatric depression
pediatric major depressive disorder
pediatric schizophrenia
pregnancy
pregnant
rexulti
skin care
suicide
teen
wine
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
APA, AMA, others move to stop insurer from overturning mental health claims ruling
The American Psychiatric Association has joined with the American Medical Association and other medical societies to oppose United Behavioral Health’s (UBH) request that a court throw out a ruling that found the insurer unfairly denied tens of thousands of claims for mental health and substance use disorder services.
Wit v. United Behavioral Health, in litigation since 2014, is being closely watched by clinicians, patients, providers, and attorneys.
Reena Kapoor, MD, chair of the APA’s Committee on Judicial Action, said in an interview that the APA is hopeful that “whatever the court says about UBH should be applicable to all insurance companies that are providing employer-sponsored health benefits.”
In a friend of the court (amicus curiae) brief, the APA, AMA, the California Medical Association, Southern California Psychiatric Society, Northern California Psychiatric Society, Orange County Psychiatric Society, Central California Psychiatric Society, and San Diego Psychiatric Society argue that “despite the availability of professionally developed, evidence-based guidelines embodying generally accepted standards of care for mental health and substance use disorders, managed care organizations commonly base coverage decisions on internally developed ‘level of care guidelines’ that are inappropriately restrictive.”
The guidelines “may lead to denial of coverage for treatment that is recommended by a patient’s physician and even cut off coverage when treatment is already being delivered,” said the groups.
The U.S. Department of Labor also filed a brief in support of the plaintiffs who are suing UBH. Those individuals suffered injury when they were denied coverage, said the federal agency, which regulates employer-sponsored insurance plans.
California Attorney General Rob Bonta also made an amicus filing supporting the plaintiffs.
“When insurers limit access to this critical care, they leave Californians who need it feeling as if they have no other option than to try to cope alone,” said Mr. Bonta in a statement.
‘Discrimination must end’
Mr. Bonta said he agreed with a 2019 ruling by the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California that UBH had violated its fiduciary duties by wrongfully using its internally developed coverage determination guidelines and level of care guidelines to deny care.
The court also found that UBH’s medically necessary criteria meant that only “acute” episodes would be covered. Instead, said the court last November, chronic and comorbid conditions should always be treated, according to Maureen Gammon and Kathleen Rosenow of Willis Towers Watson, a risk advisor.
In November, the same Northern California District Court ruled on the remedies it would require of United, including that the insurer reprocess more than 67,000 claims. UBH was also barred indefinitely from using any of its guidelines to make coverage determinations. Instead, it was ordered to make determinations “consistent with generally accepted standards of care,” and consistent with state laws.
The District Court denied a request by UBH to put a hold on the claims reprocessing until it appealed the overall case. But the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals in February granted that request.
Then, in March, United appealed the District Court’s overall ruling, claiming that the plaintiffs had not proven harm.
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce has filed a brief in support of United, agreeing with its arguments.
However, the APA and other clinician groups said there is no question of harm.
“Failure to provide appropriate levels of care for treatment of mental illness and substance use disorders leads to relapse, overdose, transmission of infectious diseases, and death,” said APA CEO and Medical Director Saul Levin, MD, MPA, in a statement.
APA President Vivian Pender, MD, said guidelines that “are overly focused on stabilizing acute symptoms of mental health and substance use disorders” are not treating the underlying disease. “When the injury is physical, insurers treat the underlying disease and not just the symptoms. Discrimination against patients with mental illness must end,” she said.
No court has ever recognized the type of claims reprocessing ordered by the District Court judge, said attorneys Nathaniel Cohen and Joseph Laska of Manatt, Phelps & Phillips, in an analysis of the case.
Mr. Cohen and Mr. Laska write. “Practitioners, health plans, and health insurers would be wise to track UBH’s long-awaited appeal to the Ninth Circuit.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Psychiatric Association has joined with the American Medical Association and other medical societies to oppose United Behavioral Health’s (UBH) request that a court throw out a ruling that found the insurer unfairly denied tens of thousands of claims for mental health and substance use disorder services.
Wit v. United Behavioral Health, in litigation since 2014, is being closely watched by clinicians, patients, providers, and attorneys.
Reena Kapoor, MD, chair of the APA’s Committee on Judicial Action, said in an interview that the APA is hopeful that “whatever the court says about UBH should be applicable to all insurance companies that are providing employer-sponsored health benefits.”
In a friend of the court (amicus curiae) brief, the APA, AMA, the California Medical Association, Southern California Psychiatric Society, Northern California Psychiatric Society, Orange County Psychiatric Society, Central California Psychiatric Society, and San Diego Psychiatric Society argue that “despite the availability of professionally developed, evidence-based guidelines embodying generally accepted standards of care for mental health and substance use disorders, managed care organizations commonly base coverage decisions on internally developed ‘level of care guidelines’ that are inappropriately restrictive.”
The guidelines “may lead to denial of coverage for treatment that is recommended by a patient’s physician and even cut off coverage when treatment is already being delivered,” said the groups.
The U.S. Department of Labor also filed a brief in support of the plaintiffs who are suing UBH. Those individuals suffered injury when they were denied coverage, said the federal agency, which regulates employer-sponsored insurance plans.
California Attorney General Rob Bonta also made an amicus filing supporting the plaintiffs.
“When insurers limit access to this critical care, they leave Californians who need it feeling as if they have no other option than to try to cope alone,” said Mr. Bonta in a statement.
‘Discrimination must end’
Mr. Bonta said he agreed with a 2019 ruling by the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California that UBH had violated its fiduciary duties by wrongfully using its internally developed coverage determination guidelines and level of care guidelines to deny care.
The court also found that UBH’s medically necessary criteria meant that only “acute” episodes would be covered. Instead, said the court last November, chronic and comorbid conditions should always be treated, according to Maureen Gammon and Kathleen Rosenow of Willis Towers Watson, a risk advisor.
In November, the same Northern California District Court ruled on the remedies it would require of United, including that the insurer reprocess more than 67,000 claims. UBH was also barred indefinitely from using any of its guidelines to make coverage determinations. Instead, it was ordered to make determinations “consistent with generally accepted standards of care,” and consistent with state laws.
The District Court denied a request by UBH to put a hold on the claims reprocessing until it appealed the overall case. But the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals in February granted that request.
Then, in March, United appealed the District Court’s overall ruling, claiming that the plaintiffs had not proven harm.
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce has filed a brief in support of United, agreeing with its arguments.
However, the APA and other clinician groups said there is no question of harm.
“Failure to provide appropriate levels of care for treatment of mental illness and substance use disorders leads to relapse, overdose, transmission of infectious diseases, and death,” said APA CEO and Medical Director Saul Levin, MD, MPA, in a statement.
APA President Vivian Pender, MD, said guidelines that “are overly focused on stabilizing acute symptoms of mental health and substance use disorders” are not treating the underlying disease. “When the injury is physical, insurers treat the underlying disease and not just the symptoms. Discrimination against patients with mental illness must end,” she said.
No court has ever recognized the type of claims reprocessing ordered by the District Court judge, said attorneys Nathaniel Cohen and Joseph Laska of Manatt, Phelps & Phillips, in an analysis of the case.
Mr. Cohen and Mr. Laska write. “Practitioners, health plans, and health insurers would be wise to track UBH’s long-awaited appeal to the Ninth Circuit.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Psychiatric Association has joined with the American Medical Association and other medical societies to oppose United Behavioral Health’s (UBH) request that a court throw out a ruling that found the insurer unfairly denied tens of thousands of claims for mental health and substance use disorder services.
Wit v. United Behavioral Health, in litigation since 2014, is being closely watched by clinicians, patients, providers, and attorneys.
Reena Kapoor, MD, chair of the APA’s Committee on Judicial Action, said in an interview that the APA is hopeful that “whatever the court says about UBH should be applicable to all insurance companies that are providing employer-sponsored health benefits.”
In a friend of the court (amicus curiae) brief, the APA, AMA, the California Medical Association, Southern California Psychiatric Society, Northern California Psychiatric Society, Orange County Psychiatric Society, Central California Psychiatric Society, and San Diego Psychiatric Society argue that “despite the availability of professionally developed, evidence-based guidelines embodying generally accepted standards of care for mental health and substance use disorders, managed care organizations commonly base coverage decisions on internally developed ‘level of care guidelines’ that are inappropriately restrictive.”
The guidelines “may lead to denial of coverage for treatment that is recommended by a patient’s physician and even cut off coverage when treatment is already being delivered,” said the groups.
The U.S. Department of Labor also filed a brief in support of the plaintiffs who are suing UBH. Those individuals suffered injury when they were denied coverage, said the federal agency, which regulates employer-sponsored insurance plans.
California Attorney General Rob Bonta also made an amicus filing supporting the plaintiffs.
“When insurers limit access to this critical care, they leave Californians who need it feeling as if they have no other option than to try to cope alone,” said Mr. Bonta in a statement.
‘Discrimination must end’
Mr. Bonta said he agreed with a 2019 ruling by the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California that UBH had violated its fiduciary duties by wrongfully using its internally developed coverage determination guidelines and level of care guidelines to deny care.
The court also found that UBH’s medically necessary criteria meant that only “acute” episodes would be covered. Instead, said the court last November, chronic and comorbid conditions should always be treated, according to Maureen Gammon and Kathleen Rosenow of Willis Towers Watson, a risk advisor.
In November, the same Northern California District Court ruled on the remedies it would require of United, including that the insurer reprocess more than 67,000 claims. UBH was also barred indefinitely from using any of its guidelines to make coverage determinations. Instead, it was ordered to make determinations “consistent with generally accepted standards of care,” and consistent with state laws.
The District Court denied a request by UBH to put a hold on the claims reprocessing until it appealed the overall case. But the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals in February granted that request.
Then, in March, United appealed the District Court’s overall ruling, claiming that the plaintiffs had not proven harm.
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce has filed a brief in support of United, agreeing with its arguments.
However, the APA and other clinician groups said there is no question of harm.
“Failure to provide appropriate levels of care for treatment of mental illness and substance use disorders leads to relapse, overdose, transmission of infectious diseases, and death,” said APA CEO and Medical Director Saul Levin, MD, MPA, in a statement.
APA President Vivian Pender, MD, said guidelines that “are overly focused on stabilizing acute symptoms of mental health and substance use disorders” are not treating the underlying disease. “When the injury is physical, insurers treat the underlying disease and not just the symptoms. Discrimination against patients with mental illness must end,” she said.
No court has ever recognized the type of claims reprocessing ordered by the District Court judge, said attorneys Nathaniel Cohen and Joseph Laska of Manatt, Phelps & Phillips, in an analysis of the case.
Mr. Cohen and Mr. Laska write. “Practitioners, health plans, and health insurers would be wise to track UBH’s long-awaited appeal to the Ninth Circuit.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
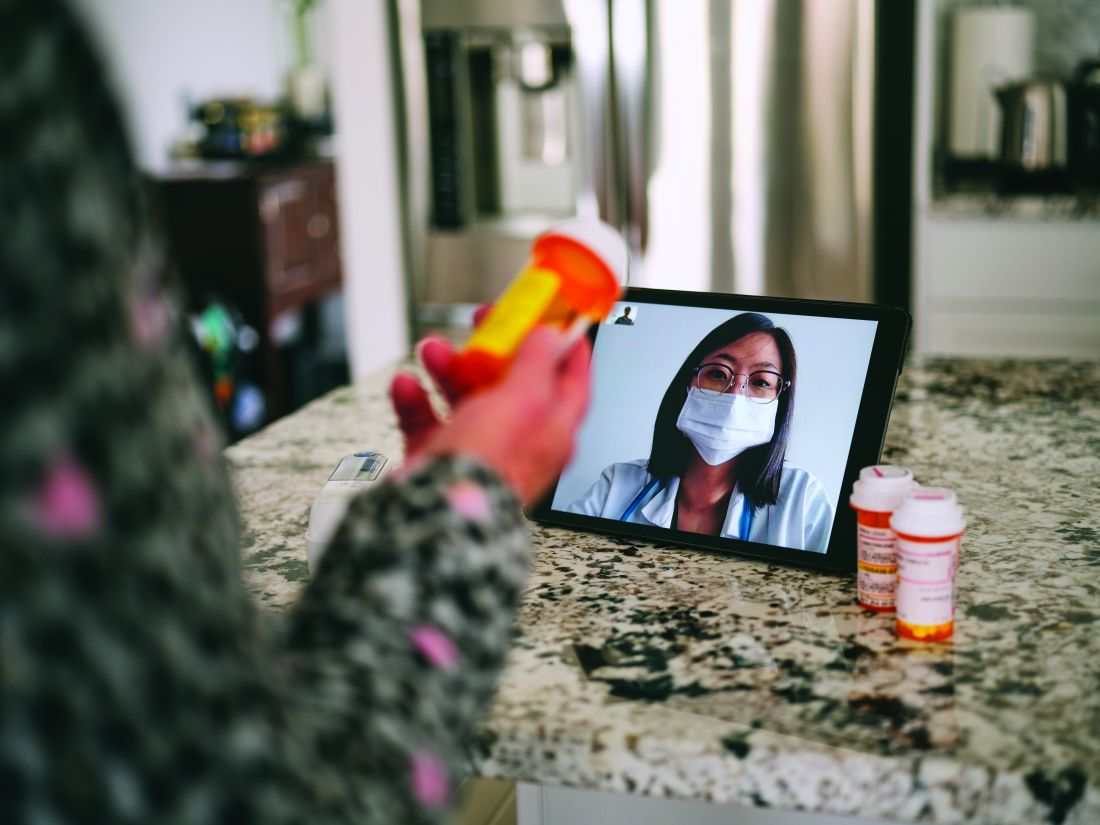
No-cancel culture: How telehealth is making it easier to keep that therapy session
When the COVID-19 pandemic forced behavioral health providers to stop seeing patients in person and instead hold therapy sessions remotely, the switch produced an unintended, positive consequence: Fewer patients skipped appointments.
That had long been a problem in mental health care. Some outpatient programs previously had no-show rates as high as 60%, according to several studies.
Only 9% of psychiatrists reported that all patients kept their appointments before the pandemic, according to an American Psychiatric Association report. Once providers switched to telepsychiatry, that number increased to 32%.
Not only that, but providers and patients say teletherapy has largely been an effective lifeline for people struggling with anxiety, depression, and other psychological issues during an extraordinarily difficult time, even though it created a new set of challenges.
Many providers say they plan to continue offering teletherapy after the pandemic. Some states are making permanent the temporary pandemic rules that allow providers to be reimbursed at the same rates as for in-person visits, which is welcome news to practitioners who take patients’ insurance.
“We are in a mental health crisis right now, so more people are struggling and may be more open to accessing services,” said psychologist Allison Dempsey, PhD, associate professor at University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “It’s much easier to connect from your living room.”
The problem for patients who didn’t show up was often as simple as a canceled ride, said Jody Long, a clinical social worker who studied the 60% rate of no-shows or late cancellations at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center psychiatric clinic in Memphis.
But sometimes it was the health problem itself. Mr. Long remembers seeing a first-time patient drive around the parking lot and then exit. The patient later called and told Mr. Long, “I just could not get out of the car; please forgive me and reschedule me.”
Mr. Long, now an assistant professor at Jacksonville (Ala.) State University, said that incident changed his perspective. “I realized when you’re having panic attacks or anxiety attacks or suffering from major depressive disorder, it’s hard,” he said. “It’s like you have built up these walls for protection and then all of a sudden you’re having to let these walls down.”
Absences strain providers whose bosses set billing and productivity expectations and those in private practice who lose billable hours, said Dr. Dempsey, who directs a program to provide mental health care for families of babies with serious medical complications. Psychotherapists often overbooked patients with the expectation that some would not show up.
Now Dr. Dempsey and colleagues no longer need to overbook. When patients don’t show up, staffers can sometimes contact a patient right away and hold the session. Other times, they can reschedule them for later that day or a different day.
And telepsychiatry performs as well as, if not better than, face-to-face delivery of mental health services, according to a World Journal of Psychiatry review of 452 studies.
Virtual visits can also save patients money, because they might not need to travel, take time off work, or pay for child care, said Jay Shore, MD, MPH, chairperson of the American Psychiatric Association’s telepsychiatry committee and a psychiatrist at the University of Colorado.
Dr. Shore started examining the potential of video conferencing to reach rural patients in the late ’90s and concluded that patients and providers can virtually build rapport, which he said is fundamental for effective therapy and medicine management.
But before the pandemic, almost 64% of psychiatrists had never used telehealth, according to the psychiatric association. Amid widespread skepticism, providers then had to do “10 years of implementations in 10 days,” said Dr. Shore, who has consulted with Dr. Dempsey and other providers.
Dr. Dempsey and colleagues faced a steep learning curve. She said she recently held a video therapy session with a mother who “seemed very out of it” before disappearing from the screen while her baby was crying.
She wondered if the patient’s exit was related to the stress of new motherhood or “something more concerning,” like addiction. She thinks she might have better understood the woman’s condition had they been in the same room. The patient called Dr. Dempsey’s team that night and told them she had relapsed into drug use and been taken to the emergency room. The mental health providers directed her to a treatment program, Dr. Dempsey said.
“We spent a lot of time reviewing what happened with that case and thinking about what we need to do differently,” Dr. Dempsey said.
Providers now routinely ask for the name of someone to call if they lose a connection and can no longer reach the patient.
In another session, Dr. Dempsey noticed that a patient seemed guarded and saw her partner hovering in the background. She said she worried about the possibility of domestic violence or “some other form of controlling behavior.”
In such cases, Dr. Dempsey called after the appointments or sent the patients secure messages to their online health portal. She asked if they felt safe and suggested they talk in person.
Such inability to maintain privacy remains a concern.
In a Walmart parking lot recently, psychologist Kristy Keefe, PsyD, of Western Illinois University, Macomb, heard a patient talking with her therapist from her car. Dr. Keefe said she wondered if the patient “had no other safe place to go to.”
To avoid that scenario, Dr. Keefe does 30-minute consultations with patients before their first telehealth appointment. She asks if they have space to talk where no one can overhear them and makes sure they have sufficient internet access and know how to use video conferencing.
To ensure that she, too, was prepared, Dr. Keefe upgraded her WiFi router, purchased two white-noise machines to drown out her conversations, and placed a stop sign on her door during appointments so her 5-year-old son knew she was seeing patients.
Dr. Keefe concluded that audio alone sometimes works better than video, which often lags. Over the phone, she and her psychology students “got really sensitive to tone fluctuations” in a patient’s voice and were better able to “pick up the emotion” than with video conferencing.
With those telehealth visits, her 20% no-show rate evaporated.
Kate Barnes, a 29-year-old middle school teacher in Fayetteville, Ark., who struggles with anxiety and depression, also has found visits easier by phone than by Zoom, because she doesn’t feel like a spotlight is on her.
“I can focus more on what I want to say,” she said.
In one of Dr. Keefe’s video sessions, though, a patient reached out, touched the camera and started to cry as she said how appreciative she was that someone was there, Dr. Keefe recalled.
“I am so very thankful that they had something in this terrible time of loss and trauma and isolation,” said Dr. Keefe.
Demand for mental health services will likely continue even after the lifting of all COVID restrictions. according to data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the National Health Interview Survey.
“That is not going to go away with snapping our fingers,” Dr. Dempsey said.
After the pandemic, Dr. Shore said, providers should review data from the past year and determine when virtual care or in-person care is more effective. He also said the health care industry needs to work to bridge the digital divide that exists because of lack of access to devices and broadband internet.
Even though Ms. Barnes said she did not see teletherapy as less effective than in-person therapy, she would like to return to seeing her therapist in person.
“When you are in person with someone, you can pick up on their body language better,” she said. “It’s a lot harder over a video call to do that.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
When the COVID-19 pandemic forced behavioral health providers to stop seeing patients in person and instead hold therapy sessions remotely, the switch produced an unintended, positive consequence: Fewer patients skipped appointments.
That had long been a problem in mental health care. Some outpatient programs previously had no-show rates as high as 60%, according to several studies.
Only 9% of psychiatrists reported that all patients kept their appointments before the pandemic, according to an American Psychiatric Association report. Once providers switched to telepsychiatry, that number increased to 32%.
Not only that, but providers and patients say teletherapy has largely been an effective lifeline for people struggling with anxiety, depression, and other psychological issues during an extraordinarily difficult time, even though it created a new set of challenges.
Many providers say they plan to continue offering teletherapy after the pandemic. Some states are making permanent the temporary pandemic rules that allow providers to be reimbursed at the same rates as for in-person visits, which is welcome news to practitioners who take patients’ insurance.
“We are in a mental health crisis right now, so more people are struggling and may be more open to accessing services,” said psychologist Allison Dempsey, PhD, associate professor at University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “It’s much easier to connect from your living room.”
The problem for patients who didn’t show up was often as simple as a canceled ride, said Jody Long, a clinical social worker who studied the 60% rate of no-shows or late cancellations at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center psychiatric clinic in Memphis.
But sometimes it was the health problem itself. Mr. Long remembers seeing a first-time patient drive around the parking lot and then exit. The patient later called and told Mr. Long, “I just could not get out of the car; please forgive me and reschedule me.”
Mr. Long, now an assistant professor at Jacksonville (Ala.) State University, said that incident changed his perspective. “I realized when you’re having panic attacks or anxiety attacks or suffering from major depressive disorder, it’s hard,” he said. “It’s like you have built up these walls for protection and then all of a sudden you’re having to let these walls down.”
Absences strain providers whose bosses set billing and productivity expectations and those in private practice who lose billable hours, said Dr. Dempsey, who directs a program to provide mental health care for families of babies with serious medical complications. Psychotherapists often overbooked patients with the expectation that some would not show up.
Now Dr. Dempsey and colleagues no longer need to overbook. When patients don’t show up, staffers can sometimes contact a patient right away and hold the session. Other times, they can reschedule them for later that day or a different day.
And telepsychiatry performs as well as, if not better than, face-to-face delivery of mental health services, according to a World Journal of Psychiatry review of 452 studies.
Virtual visits can also save patients money, because they might not need to travel, take time off work, or pay for child care, said Jay Shore, MD, MPH, chairperson of the American Psychiatric Association’s telepsychiatry committee and a psychiatrist at the University of Colorado.
Dr. Shore started examining the potential of video conferencing to reach rural patients in the late ’90s and concluded that patients and providers can virtually build rapport, which he said is fundamental for effective therapy and medicine management.
But before the pandemic, almost 64% of psychiatrists had never used telehealth, according to the psychiatric association. Amid widespread skepticism, providers then had to do “10 years of implementations in 10 days,” said Dr. Shore, who has consulted with Dr. Dempsey and other providers.
Dr. Dempsey and colleagues faced a steep learning curve. She said she recently held a video therapy session with a mother who “seemed very out of it” before disappearing from the screen while her baby was crying.
She wondered if the patient’s exit was related to the stress of new motherhood or “something more concerning,” like addiction. She thinks she might have better understood the woman’s condition had they been in the same room. The patient called Dr. Dempsey’s team that night and told them she had relapsed into drug use and been taken to the emergency room. The mental health providers directed her to a treatment program, Dr. Dempsey said.
“We spent a lot of time reviewing what happened with that case and thinking about what we need to do differently,” Dr. Dempsey said.
Providers now routinely ask for the name of someone to call if they lose a connection and can no longer reach the patient.
In another session, Dr. Dempsey noticed that a patient seemed guarded and saw her partner hovering in the background. She said she worried about the possibility of domestic violence or “some other form of controlling behavior.”
In such cases, Dr. Dempsey called after the appointments or sent the patients secure messages to their online health portal. She asked if they felt safe and suggested they talk in person.
Such inability to maintain privacy remains a concern.
In a Walmart parking lot recently, psychologist Kristy Keefe, PsyD, of Western Illinois University, Macomb, heard a patient talking with her therapist from her car. Dr. Keefe said she wondered if the patient “had no other safe place to go to.”
To avoid that scenario, Dr. Keefe does 30-minute consultations with patients before their first telehealth appointment. She asks if they have space to talk where no one can overhear them and makes sure they have sufficient internet access and know how to use video conferencing.
To ensure that she, too, was prepared, Dr. Keefe upgraded her WiFi router, purchased two white-noise machines to drown out her conversations, and placed a stop sign on her door during appointments so her 5-year-old son knew she was seeing patients.
Dr. Keefe concluded that audio alone sometimes works better than video, which often lags. Over the phone, she and her psychology students “got really sensitive to tone fluctuations” in a patient’s voice and were better able to “pick up the emotion” than with video conferencing.
With those telehealth visits, her 20% no-show rate evaporated.
Kate Barnes, a 29-year-old middle school teacher in Fayetteville, Ark., who struggles with anxiety and depression, also has found visits easier by phone than by Zoom, because she doesn’t feel like a spotlight is on her.
“I can focus more on what I want to say,” she said.
In one of Dr. Keefe’s video sessions, though, a patient reached out, touched the camera and started to cry as she said how appreciative she was that someone was there, Dr. Keefe recalled.
“I am so very thankful that they had something in this terrible time of loss and trauma and isolation,” said Dr. Keefe.
Demand for mental health services will likely continue even after the lifting of all COVID restrictions. according to data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the National Health Interview Survey.
“That is not going to go away with snapping our fingers,” Dr. Dempsey said.
After the pandemic, Dr. Shore said, providers should review data from the past year and determine when virtual care or in-person care is more effective. He also said the health care industry needs to work to bridge the digital divide that exists because of lack of access to devices and broadband internet.
Even though Ms. Barnes said she did not see teletherapy as less effective than in-person therapy, she would like to return to seeing her therapist in person.
“When you are in person with someone, you can pick up on their body language better,” she said. “It’s a lot harder over a video call to do that.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
When the COVID-19 pandemic forced behavioral health providers to stop seeing patients in person and instead hold therapy sessions remotely, the switch produced an unintended, positive consequence: Fewer patients skipped appointments.
That had long been a problem in mental health care. Some outpatient programs previously had no-show rates as high as 60%, according to several studies.
Only 9% of psychiatrists reported that all patients kept their appointments before the pandemic, according to an American Psychiatric Association report. Once providers switched to telepsychiatry, that number increased to 32%.
Not only that, but providers and patients say teletherapy has largely been an effective lifeline for people struggling with anxiety, depression, and other psychological issues during an extraordinarily difficult time, even though it created a new set of challenges.
Many providers say they plan to continue offering teletherapy after the pandemic. Some states are making permanent the temporary pandemic rules that allow providers to be reimbursed at the same rates as for in-person visits, which is welcome news to practitioners who take patients’ insurance.
“We are in a mental health crisis right now, so more people are struggling and may be more open to accessing services,” said psychologist Allison Dempsey, PhD, associate professor at University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “It’s much easier to connect from your living room.”
The problem for patients who didn’t show up was often as simple as a canceled ride, said Jody Long, a clinical social worker who studied the 60% rate of no-shows or late cancellations at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center psychiatric clinic in Memphis.
But sometimes it was the health problem itself. Mr. Long remembers seeing a first-time patient drive around the parking lot and then exit. The patient later called and told Mr. Long, “I just could not get out of the car; please forgive me and reschedule me.”
Mr. Long, now an assistant professor at Jacksonville (Ala.) State University, said that incident changed his perspective. “I realized when you’re having panic attacks or anxiety attacks or suffering from major depressive disorder, it’s hard,” he said. “It’s like you have built up these walls for protection and then all of a sudden you’re having to let these walls down.”
Absences strain providers whose bosses set billing and productivity expectations and those in private practice who lose billable hours, said Dr. Dempsey, who directs a program to provide mental health care for families of babies with serious medical complications. Psychotherapists often overbooked patients with the expectation that some would not show up.
Now Dr. Dempsey and colleagues no longer need to overbook. When patients don’t show up, staffers can sometimes contact a patient right away and hold the session. Other times, they can reschedule them for later that day or a different day.
And telepsychiatry performs as well as, if not better than, face-to-face delivery of mental health services, according to a World Journal of Psychiatry review of 452 studies.
Virtual visits can also save patients money, because they might not need to travel, take time off work, or pay for child care, said Jay Shore, MD, MPH, chairperson of the American Psychiatric Association’s telepsychiatry committee and a psychiatrist at the University of Colorado.
Dr. Shore started examining the potential of video conferencing to reach rural patients in the late ’90s and concluded that patients and providers can virtually build rapport, which he said is fundamental for effective therapy and medicine management.
But before the pandemic, almost 64% of psychiatrists had never used telehealth, according to the psychiatric association. Amid widespread skepticism, providers then had to do “10 years of implementations in 10 days,” said Dr. Shore, who has consulted with Dr. Dempsey and other providers.
Dr. Dempsey and colleagues faced a steep learning curve. She said she recently held a video therapy session with a mother who “seemed very out of it” before disappearing from the screen while her baby was crying.
She wondered if the patient’s exit was related to the stress of new motherhood or “something more concerning,” like addiction. She thinks she might have better understood the woman’s condition had they been in the same room. The patient called Dr. Dempsey’s team that night and told them she had relapsed into drug use and been taken to the emergency room. The mental health providers directed her to a treatment program, Dr. Dempsey said.
“We spent a lot of time reviewing what happened with that case and thinking about what we need to do differently,” Dr. Dempsey said.
Providers now routinely ask for the name of someone to call if they lose a connection and can no longer reach the patient.
In another session, Dr. Dempsey noticed that a patient seemed guarded and saw her partner hovering in the background. She said she worried about the possibility of domestic violence or “some other form of controlling behavior.”
In such cases, Dr. Dempsey called after the appointments or sent the patients secure messages to their online health portal. She asked if they felt safe and suggested they talk in person.
Such inability to maintain privacy remains a concern.
In a Walmart parking lot recently, psychologist Kristy Keefe, PsyD, of Western Illinois University, Macomb, heard a patient talking with her therapist from her car. Dr. Keefe said she wondered if the patient “had no other safe place to go to.”
To avoid that scenario, Dr. Keefe does 30-minute consultations with patients before their first telehealth appointment. She asks if they have space to talk where no one can overhear them and makes sure they have sufficient internet access and know how to use video conferencing.
To ensure that she, too, was prepared, Dr. Keefe upgraded her WiFi router, purchased two white-noise machines to drown out her conversations, and placed a stop sign on her door during appointments so her 5-year-old son knew she was seeing patients.
Dr. Keefe concluded that audio alone sometimes works better than video, which often lags. Over the phone, she and her psychology students “got really sensitive to tone fluctuations” in a patient’s voice and were better able to “pick up the emotion” than with video conferencing.
With those telehealth visits, her 20% no-show rate evaporated.
Kate Barnes, a 29-year-old middle school teacher in Fayetteville, Ark., who struggles with anxiety and depression, also has found visits easier by phone than by Zoom, because she doesn’t feel like a spotlight is on her.
“I can focus more on what I want to say,” she said.
In one of Dr. Keefe’s video sessions, though, a patient reached out, touched the camera and started to cry as she said how appreciative she was that someone was there, Dr. Keefe recalled.
“I am so very thankful that they had something in this terrible time of loss and trauma and isolation,” said Dr. Keefe.
Demand for mental health services will likely continue even after the lifting of all COVID restrictions. according to data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the National Health Interview Survey.
“That is not going to go away with snapping our fingers,” Dr. Dempsey said.
After the pandemic, Dr. Shore said, providers should review data from the past year and determine when virtual care or in-person care is more effective. He also said the health care industry needs to work to bridge the digital divide that exists because of lack of access to devices and broadband internet.
Even though Ms. Barnes said she did not see teletherapy as less effective than in-person therapy, she would like to return to seeing her therapist in person.
“When you are in person with someone, you can pick up on their body language better,” she said. “It’s a lot harder over a video call to do that.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
How to help vaccinated patients navigate FOGO (fear of going out)
Remember FOMO (fear of missing out)? The pandemic cured most of us of that! In its place, many are suffering from a new syndrome that has been coined “FOGO” (fear of going out). As the COVID-19 vaccines roll out, restrictions lessen, and cases decline, we face new challenges. The pandemic showed us that “we are all in it together.” Now our patients, family, friends – and even we, ourselves – may face similar anxieties as we transition back.
Our brains love routines. They save energy as we transverse the same pathway with ease. We created new patterns in the first 30 days of quarantine, and we spent more than a year engraining them. Many people are feeling even more anxiety as restrictions are lifting and expectations are rising. Those with preexisting anxiety disorders may have an even more difficult time resuming routine activities.
Since the virus is still among us, we need to maintain caution, so some degree of FOGO is wise. But when we limit our activities too much, we create a whole new host of issues. The pandemic gave us all a taste of the agoraphobic lifestyle. It is difficult to know where exactly to draw the line right now between healthy anxiety and anxiety that becomes the disease for ourselves, our families and friends – and our patients.
Recommendations for FOGO
- Talk to your families, friends, and patients about what activities you recommend, which they might resume and which they should continue to avoid. People should make plans to optimize their physical and mental health while continuing to protect themselves from COVID-19. If anxiety is becoming the main problem, psychotherapy or medication may be necessary to treat their symptoms.
- Continue to encourage those with FOGO to practice techniques to be calm. Suggest that they take deep breaths with long exhales. This breathing pattern activates the parasympathetic nervous system and will help them feel calmer. We have all been under chronic stress, and our sympathetic nervous system has been in overdrive. We need to be calm to make the best decisions so our frontal lobe can be in charge rather than our primitive, fear-based brain that has been running the show for more a year. Encourage calming activities, such as yoga, meditation, warm baths, spending time in nature, hugging a pet, and more.
- Advise sufferers to start slowly. They should resume activities where they feel the safest. Walking outside with a friend is a good way to start. We now know that transmission is remarkably low or nonexistent if both parties are vaccinated. Exercise is a great way to combat many psychological issues, including FOGO.
- FOGO sufferers should build confidence gradually. Recommend taking one day at a time and trying to find ways to enjoy new ventures out. Soon, our brains will adapt to the new routines and the days of COVID-19 will recede from our thoughts.
- Respect whatever feelings emerge. The closer we and our patients were to trauma, the more challenging it may be to recover. If you or your patients suffered from COVID-19 or had a close family member or friend who did, be prepared to reemerge more slowly. Don’t feel pressured by what others are doing. Go at your own pace. Only you can decide what is the right way to move forward in these times.
- Look for signs of substance overuse or misuse. FOGO sufferers may turn to drugs or alcohol to mask their anxiety. This is a common pothole and should be avoided. Be alert for this problem and discuss it with patients, friends, or family members who may be making unhealthy choices.
Time is a great healer, and remind others that “this too shall pass.” FOGO will give rise to another yet-to-be named syndrome. We seem to be moving in a very positive direction at a remarkable pace. As Alexander Pope so wisely wrote, “Hope springs eternal.” Better times are ahead.
Dr. Ritvo, who has almost 30 years’ experience in psychiatry, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa. Momosa Publishing, 2018). Dr. Ritvo has no disclosures.
Remember FOMO (fear of missing out)? The pandemic cured most of us of that! In its place, many are suffering from a new syndrome that has been coined “FOGO” (fear of going out). As the COVID-19 vaccines roll out, restrictions lessen, and cases decline, we face new challenges. The pandemic showed us that “we are all in it together.” Now our patients, family, friends – and even we, ourselves – may face similar anxieties as we transition back.
Our brains love routines. They save energy as we transverse the same pathway with ease. We created new patterns in the first 30 days of quarantine, and we spent more than a year engraining them. Many people are feeling even more anxiety as restrictions are lifting and expectations are rising. Those with preexisting anxiety disorders may have an even more difficult time resuming routine activities.
Since the virus is still among us, we need to maintain caution, so some degree of FOGO is wise. But when we limit our activities too much, we create a whole new host of issues. The pandemic gave us all a taste of the agoraphobic lifestyle. It is difficult to know where exactly to draw the line right now between healthy anxiety and anxiety that becomes the disease for ourselves, our families and friends – and our patients.
Recommendations for FOGO
- Talk to your families, friends, and patients about what activities you recommend, which they might resume and which they should continue to avoid. People should make plans to optimize their physical and mental health while continuing to protect themselves from COVID-19. If anxiety is becoming the main problem, psychotherapy or medication may be necessary to treat their symptoms.
- Continue to encourage those with FOGO to practice techniques to be calm. Suggest that they take deep breaths with long exhales. This breathing pattern activates the parasympathetic nervous system and will help them feel calmer. We have all been under chronic stress, and our sympathetic nervous system has been in overdrive. We need to be calm to make the best decisions so our frontal lobe can be in charge rather than our primitive, fear-based brain that has been running the show for more a year. Encourage calming activities, such as yoga, meditation, warm baths, spending time in nature, hugging a pet, and more.
- Advise sufferers to start slowly. They should resume activities where they feel the safest. Walking outside with a friend is a good way to start. We now know that transmission is remarkably low or nonexistent if both parties are vaccinated. Exercise is a great way to combat many psychological issues, including FOGO.
- FOGO sufferers should build confidence gradually. Recommend taking one day at a time and trying to find ways to enjoy new ventures out. Soon, our brains will adapt to the new routines and the days of COVID-19 will recede from our thoughts.
- Respect whatever feelings emerge. The closer we and our patients were to trauma, the more challenging it may be to recover. If you or your patients suffered from COVID-19 or had a close family member or friend who did, be prepared to reemerge more slowly. Don’t feel pressured by what others are doing. Go at your own pace. Only you can decide what is the right way to move forward in these times.
- Look for signs of substance overuse or misuse. FOGO sufferers may turn to drugs or alcohol to mask their anxiety. This is a common pothole and should be avoided. Be alert for this problem and discuss it with patients, friends, or family members who may be making unhealthy choices.
Time is a great healer, and remind others that “this too shall pass.” FOGO will give rise to another yet-to-be named syndrome. We seem to be moving in a very positive direction at a remarkable pace. As Alexander Pope so wisely wrote, “Hope springs eternal.” Better times are ahead.
Dr. Ritvo, who has almost 30 years’ experience in psychiatry, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa. Momosa Publishing, 2018). Dr. Ritvo has no disclosures.
Remember FOMO (fear of missing out)? The pandemic cured most of us of that! In its place, many are suffering from a new syndrome that has been coined “FOGO” (fear of going out). As the COVID-19 vaccines roll out, restrictions lessen, and cases decline, we face new challenges. The pandemic showed us that “we are all in it together.” Now our patients, family, friends – and even we, ourselves – may face similar anxieties as we transition back.
Our brains love routines. They save energy as we transverse the same pathway with ease. We created new patterns in the first 30 days of quarantine, and we spent more than a year engraining them. Many people are feeling even more anxiety as restrictions are lifting and expectations are rising. Those with preexisting anxiety disorders may have an even more difficult time resuming routine activities.
Since the virus is still among us, we need to maintain caution, so some degree of FOGO is wise. But when we limit our activities too much, we create a whole new host of issues. The pandemic gave us all a taste of the agoraphobic lifestyle. It is difficult to know where exactly to draw the line right now between healthy anxiety and anxiety that becomes the disease for ourselves, our families and friends – and our patients.
Recommendations for FOGO
- Talk to your families, friends, and patients about what activities you recommend, which they might resume and which they should continue to avoid. People should make plans to optimize their physical and mental health while continuing to protect themselves from COVID-19. If anxiety is becoming the main problem, psychotherapy or medication may be necessary to treat their symptoms.
- Continue to encourage those with FOGO to practice techniques to be calm. Suggest that they take deep breaths with long exhales. This breathing pattern activates the parasympathetic nervous system and will help them feel calmer. We have all been under chronic stress, and our sympathetic nervous system has been in overdrive. We need to be calm to make the best decisions so our frontal lobe can be in charge rather than our primitive, fear-based brain that has been running the show for more a year. Encourage calming activities, such as yoga, meditation, warm baths, spending time in nature, hugging a pet, and more.
- Advise sufferers to start slowly. They should resume activities where they feel the safest. Walking outside with a friend is a good way to start. We now know that transmission is remarkably low or nonexistent if both parties are vaccinated. Exercise is a great way to combat many psychological issues, including FOGO.
- FOGO sufferers should build confidence gradually. Recommend taking one day at a time and trying to find ways to enjoy new ventures out. Soon, our brains will adapt to the new routines and the days of COVID-19 will recede from our thoughts.
- Respect whatever feelings emerge. The closer we and our patients were to trauma, the more challenging it may be to recover. If you or your patients suffered from COVID-19 or had a close family member or friend who did, be prepared to reemerge more slowly. Don’t feel pressured by what others are doing. Go at your own pace. Only you can decide what is the right way to move forward in these times.
- Look for signs of substance overuse or misuse. FOGO sufferers may turn to drugs or alcohol to mask their anxiety. This is a common pothole and should be avoided. Be alert for this problem and discuss it with patients, friends, or family members who may be making unhealthy choices.
Time is a great healer, and remind others that “this too shall pass.” FOGO will give rise to another yet-to-be named syndrome. We seem to be moving in a very positive direction at a remarkable pace. As Alexander Pope so wisely wrote, “Hope springs eternal.” Better times are ahead.
Dr. Ritvo, who has almost 30 years’ experience in psychiatry, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa. Momosa Publishing, 2018). Dr. Ritvo has no disclosures.
The end of happy hour? No safe level of alcohol for the brain
There is no safe amount of alcohol consumption for the brain; even moderate drinking adversely affects brain structure and function, according a British study of more 25,000 adults.
“This is one of the largest studies of alcohol and brain health to date,” Anya Topiwala, DPhil, University of Oxford (England), told this news organization.
“There have been previous claims the relationship between alcohol and brain health are J-shaped (ie., small amounts are protective), but we formally tested this and did not find it to be the case. In fact, we found that any level of alcohol was associated with poorer brain health, compared to no alcohol,” Dr. Topiwala added.
The study, which has not yet been peer reviewed, was published online May 12 in MedRxiv.
Global impact on the brain
Participants provided detailed information on their alcohol intake. The cohort included 691 never-drinkers, 617 former drinkers, and 24,069 current drinkers.
Median alcohol intake was 13.5 units (102 g) weekly. Almost half of the sample (48.2%) were drinking above current UK low-risk guidelines (14 units, 112 g weekly), but few were heavy drinkers (>50 units, 400 g weekly).
After adjusting for all known potential confounders and multiple comparisons, a higher volume of alcohol consumed per week was associated with lower gray matter in “almost all areas of the brain,” Dr. Topiwala said in an interview.
Alcohol consumption accounted for up to 0.8% of gray matter volume variance. “The size of the effect is small, albeit greater than any other modifiable risk factor. These brain changes have been previously linked to aging, poorer performance on memory changes, and dementia,” Dr. Topiwala said.
Widespread negative associations were also found between drinking alcohol and all the measures of white matter integrity that were assessed. There was a significant positive association between alcohol consumption and resting-state functional connectivity.
Higher blood pressure and body mass index “steepened” the negative associations between alcohol and brain health, and binge drinking had additive negative effects on brain structure beyond the absolute volume consumed.
There was no evidence that the risk for alcohol-related brain harm differs according to the type of alcohol consumed (wine, beer, or spirits).
A key limitation of the study is that the study population from the UK Biobank represents a sample that is healthier, better educated, and less deprived and is characterized by less ethnic diversity than the general population. “As with any observational study, we cannot infer causality from association,” the authors note.
What remains unclear, they say, is the duration of drinking needed to cause an effect on the brain. It may be that vulnerability is increased during periods of life in which dynamic brain changes occur, such as adolescence and older age.
They also note that some studies of alcohol-dependent individuals have suggested that at least some brain damage is reversible upon abstinence. Whether that is true for moderate drinkers is unknown.
On the basis of their findings, there is “no safe dose of alcohol for the brain,” Dr. Topiwala and colleagues conclude. They suggest that current low-risk drinking guidelines be revisited to take account of brain effects.
Experts weigh in
Several experts weighed in on the study in a statement from the nonprofit UK Science Media Center.
Paul Matthews, MD, head of the department of brain sciences, Imperial College London, noted that this “carefully performed preliminary report extends our earlier UK Dementia Research Institute study of a smaller group from same UK Biobank population also showing that even moderate drinking is associated with greater atrophy of the brain, as well as injury to the heart and liver.”
Dr. Matthews said the investigators’ conclusion that there is no safe threshold below which alcohol consumption has no toxic effects “echoes our own. We join with them in suggesting that current public health guidelines concerning alcohol consumption may need to be revisited.”
Rebecca Dewey, PhD, research fellow in neuroimaging, University of Nottingham (England), cautioned that “the degree to which very small changes in brain volume are harmful” is unknown.
“While there was no threshold under which alcohol consumption did not cause changes in the brain, there may a degree of brain volume difference that is irrelevant to brain health. We don’t know what these people’s brains looked like before they drank alcohol, so the brain may have learned to cope/compensate,” Dewey said.
Sadie Boniface, PhD, head of research at the Institute of Alcohol Studies and visiting researcher at King’s College London, said, “While we can’t yet say for sure whether there is ‘no safe level’ of alcohol regarding brain health at the moment, it has been known for decades that heavy drinking is bad for brain health.
“We also shouldn’t forget alcohol affects all parts of the body and there are multiple health risks. For example, it is already known there is ‘no safe level’ of alcohol consumption for the seven types of cancer caused by alcohol, as identified by the UK chief medical officers,” Dr. Boniface said.
The study was supported in part by the Wellcome Trust, Li Ka Shing Center for Health Information and Discovery, the National Institutes of Health, and the UK Medical Research Council. Dr. Topiwala, Dr. Boniface, Dr. Dewey, and Dr. Matthews have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is no safe amount of alcohol consumption for the brain; even moderate drinking adversely affects brain structure and function, according a British study of more 25,000 adults.
“This is one of the largest studies of alcohol and brain health to date,” Anya Topiwala, DPhil, University of Oxford (England), told this news organization.
“There have been previous claims the relationship between alcohol and brain health are J-shaped (ie., small amounts are protective), but we formally tested this and did not find it to be the case. In fact, we found that any level of alcohol was associated with poorer brain health, compared to no alcohol,” Dr. Topiwala added.
The study, which has not yet been peer reviewed, was published online May 12 in MedRxiv.
Global impact on the brain
Participants provided detailed information on their alcohol intake. The cohort included 691 never-drinkers, 617 former drinkers, and 24,069 current drinkers.
Median alcohol intake was 13.5 units (102 g) weekly. Almost half of the sample (48.2%) were drinking above current UK low-risk guidelines (14 units, 112 g weekly), but few were heavy drinkers (>50 units, 400 g weekly).
After adjusting for all known potential confounders and multiple comparisons, a higher volume of alcohol consumed per week was associated with lower gray matter in “almost all areas of the brain,” Dr. Topiwala said in an interview.
Alcohol consumption accounted for up to 0.8% of gray matter volume variance. “The size of the effect is small, albeit greater than any other modifiable risk factor. These brain changes have been previously linked to aging, poorer performance on memory changes, and dementia,” Dr. Topiwala said.
Widespread negative associations were also found between drinking alcohol and all the measures of white matter integrity that were assessed. There was a significant positive association between alcohol consumption and resting-state functional connectivity.
Higher blood pressure and body mass index “steepened” the negative associations between alcohol and brain health, and binge drinking had additive negative effects on brain structure beyond the absolute volume consumed.
There was no evidence that the risk for alcohol-related brain harm differs according to the type of alcohol consumed (wine, beer, or spirits).
A key limitation of the study is that the study population from the UK Biobank represents a sample that is healthier, better educated, and less deprived and is characterized by less ethnic diversity than the general population. “As with any observational study, we cannot infer causality from association,” the authors note.
What remains unclear, they say, is the duration of drinking needed to cause an effect on the brain. It may be that vulnerability is increased during periods of life in which dynamic brain changes occur, such as adolescence and older age.
They also note that some studies of alcohol-dependent individuals have suggested that at least some brain damage is reversible upon abstinence. Whether that is true for moderate drinkers is unknown.
On the basis of their findings, there is “no safe dose of alcohol for the brain,” Dr. Topiwala and colleagues conclude. They suggest that current low-risk drinking guidelines be revisited to take account of brain effects.
Experts weigh in
Several experts weighed in on the study in a statement from the nonprofit UK Science Media Center.
Paul Matthews, MD, head of the department of brain sciences, Imperial College London, noted that this “carefully performed preliminary report extends our earlier UK Dementia Research Institute study of a smaller group from same UK Biobank population also showing that even moderate drinking is associated with greater atrophy of the brain, as well as injury to the heart and liver.”
Dr. Matthews said the investigators’ conclusion that there is no safe threshold below which alcohol consumption has no toxic effects “echoes our own. We join with them in suggesting that current public health guidelines concerning alcohol consumption may need to be revisited.”
Rebecca Dewey, PhD, research fellow in neuroimaging, University of Nottingham (England), cautioned that “the degree to which very small changes in brain volume are harmful” is unknown.
“While there was no threshold under which alcohol consumption did not cause changes in the brain, there may a degree of brain volume difference that is irrelevant to brain health. We don’t know what these people’s brains looked like before they drank alcohol, so the brain may have learned to cope/compensate,” Dewey said.
Sadie Boniface, PhD, head of research at the Institute of Alcohol Studies and visiting researcher at King’s College London, said, “While we can’t yet say for sure whether there is ‘no safe level’ of alcohol regarding brain health at the moment, it has been known for decades that heavy drinking is bad for brain health.
“We also shouldn’t forget alcohol affects all parts of the body and there are multiple health risks. For example, it is already known there is ‘no safe level’ of alcohol consumption for the seven types of cancer caused by alcohol, as identified by the UK chief medical officers,” Dr. Boniface said.
The study was supported in part by the Wellcome Trust, Li Ka Shing Center for Health Information and Discovery, the National Institutes of Health, and the UK Medical Research Council. Dr. Topiwala, Dr. Boniface, Dr. Dewey, and Dr. Matthews have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is no safe amount of alcohol consumption for the brain; even moderate drinking adversely affects brain structure and function, according a British study of more 25,000 adults.
“This is one of the largest studies of alcohol and brain health to date,” Anya Topiwala, DPhil, University of Oxford (England), told this news organization.
“There have been previous claims the relationship between alcohol and brain health are J-shaped (ie., small amounts are protective), but we formally tested this and did not find it to be the case. In fact, we found that any level of alcohol was associated with poorer brain health, compared to no alcohol,” Dr. Topiwala added.
The study, which has not yet been peer reviewed, was published online May 12 in MedRxiv.
Global impact on the brain
Participants provided detailed information on their alcohol intake. The cohort included 691 never-drinkers, 617 former drinkers, and 24,069 current drinkers.
Median alcohol intake was 13.5 units (102 g) weekly. Almost half of the sample (48.2%) were drinking above current UK low-risk guidelines (14 units, 112 g weekly), but few were heavy drinkers (>50 units, 400 g weekly).
After adjusting for all known potential confounders and multiple comparisons, a higher volume of alcohol consumed per week was associated with lower gray matter in “almost all areas of the brain,” Dr. Topiwala said in an interview.
Alcohol consumption accounted for up to 0.8% of gray matter volume variance. “The size of the effect is small, albeit greater than any other modifiable risk factor. These brain changes have been previously linked to aging, poorer performance on memory changes, and dementia,” Dr. Topiwala said.
Widespread negative associations were also found between drinking alcohol and all the measures of white matter integrity that were assessed. There was a significant positive association between alcohol consumption and resting-state functional connectivity.
Higher blood pressure and body mass index “steepened” the negative associations between alcohol and brain health, and binge drinking had additive negative effects on brain structure beyond the absolute volume consumed.
There was no evidence that the risk for alcohol-related brain harm differs according to the type of alcohol consumed (wine, beer, or spirits).
A key limitation of the study is that the study population from the UK Biobank represents a sample that is healthier, better educated, and less deprived and is characterized by less ethnic diversity than the general population. “As with any observational study, we cannot infer causality from association,” the authors note.
What remains unclear, they say, is the duration of drinking needed to cause an effect on the brain. It may be that vulnerability is increased during periods of life in which dynamic brain changes occur, such as adolescence and older age.
They also note that some studies of alcohol-dependent individuals have suggested that at least some brain damage is reversible upon abstinence. Whether that is true for moderate drinkers is unknown.
On the basis of their findings, there is “no safe dose of alcohol for the brain,” Dr. Topiwala and colleagues conclude. They suggest that current low-risk drinking guidelines be revisited to take account of brain effects.
Experts weigh in
Several experts weighed in on the study in a statement from the nonprofit UK Science Media Center.
Paul Matthews, MD, head of the department of brain sciences, Imperial College London, noted that this “carefully performed preliminary report extends our earlier UK Dementia Research Institute study of a smaller group from same UK Biobank population also showing that even moderate drinking is associated with greater atrophy of the brain, as well as injury to the heart and liver.”
Dr. Matthews said the investigators’ conclusion that there is no safe threshold below which alcohol consumption has no toxic effects “echoes our own. We join with them in suggesting that current public health guidelines concerning alcohol consumption may need to be revisited.”
Rebecca Dewey, PhD, research fellow in neuroimaging, University of Nottingham (England), cautioned that “the degree to which very small changes in brain volume are harmful” is unknown.
“While there was no threshold under which alcohol consumption did not cause changes in the brain, there may a degree of brain volume difference that is irrelevant to brain health. We don’t know what these people’s brains looked like before they drank alcohol, so the brain may have learned to cope/compensate,” Dewey said.
Sadie Boniface, PhD, head of research at the Institute of Alcohol Studies and visiting researcher at King’s College London, said, “While we can’t yet say for sure whether there is ‘no safe level’ of alcohol regarding brain health at the moment, it has been known for decades that heavy drinking is bad for brain health.
“We also shouldn’t forget alcohol affects all parts of the body and there are multiple health risks. For example, it is already known there is ‘no safe level’ of alcohol consumption for the seven types of cancer caused by alcohol, as identified by the UK chief medical officers,” Dr. Boniface said.
The study was supported in part by the Wellcome Trust, Li Ka Shing Center for Health Information and Discovery, the National Institutes of Health, and the UK Medical Research Council. Dr. Topiwala, Dr. Boniface, Dr. Dewey, and Dr. Matthews have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA reassures myocarditis rare after COVID vaccination, benefits overwhelm risks
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination “enormously outweigh” the rare possible risk for heart-related complications, including myocarditis, the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (ASA) says in new statement.
The message follows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that the agency is monitoring the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) for cases of myocarditis that have been associated with the mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 from Pfizer and Moderna.
The “relatively few” reported cases myocarditis in adolescents or young adults have involved males more often than females, more often followed the second dose rather than the first, and were usually seen in the 4 days after vaccination, the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group (VaST) found.
“Most cases appear to be mild, and follow-up of cases is ongoing,” the CDC says. “Within CDC safety monitoring systems, rates of myocarditis reports in the window following COVID-19 vaccination have not differed from expected baseline rates.”
In their statement, the AHA/ASA “strongly urge” all adults and children 12 years and older to receive a COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible.
“The evidence continues to indicate that the COVID-19 vaccines are nearly 100% effective at preventing death and hospitalization due to COVID-19 infection,” the groups say.
Although the investigation of cases of myocarditis related to COVID-19 vaccination is ongoing, the AHA/ASA notes that myocarditis is typically the result of an actual viral infection, “and it is yet to be determined if these cases have any correlation to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine.”
“We’ve lost hundreds of children, and there have been thousands who have been hospitalized, thousands who developed an inflammatory syndrome, and one of the pieces of that can be myocarditis,” Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), said today on ABC’s Good Morning America.
Still, “from my perspective, the risk of COVID is so much greater than any theoretical risk from the vaccine,” said Dr. Besser, former acting director of the CDC.
The symptoms that can occur after COVID-19 vaccination include tiredness, headache, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea, reminds the AHA/ASA statement. Such symptoms would “typically appear within 24-48 hours and usually pass within 36-48 hours after receiving the vaccine.”
All health care providers should be aware of the “very rare” adverse events that could be related to a COVID-19 vaccine, including myocarditis, blood clots, low platelets, and symptoms of severe inflammation, it says.
“Health care professionals should strongly consider inquiring about the timing of any recent COVID vaccination among patients presenting with these conditions, as needed, in order to provide appropriate treatment quickly,” the statement advises.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination “enormously outweigh” the rare possible risk for heart-related complications, including myocarditis, the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (ASA) says in new statement.
The message follows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that the agency is monitoring the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) for cases of myocarditis that have been associated with the mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 from Pfizer and Moderna.
The “relatively few” reported cases myocarditis in adolescents or young adults have involved males more often than females, more often followed the second dose rather than the first, and were usually seen in the 4 days after vaccination, the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group (VaST) found.
“Most cases appear to be mild, and follow-up of cases is ongoing,” the CDC says. “Within CDC safety monitoring systems, rates of myocarditis reports in the window following COVID-19 vaccination have not differed from expected baseline rates.”
In their statement, the AHA/ASA “strongly urge” all adults and children 12 years and older to receive a COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible.
“The evidence continues to indicate that the COVID-19 vaccines are nearly 100% effective at preventing death and hospitalization due to COVID-19 infection,” the groups say.
Although the investigation of cases of myocarditis related to COVID-19 vaccination is ongoing, the AHA/ASA notes that myocarditis is typically the result of an actual viral infection, “and it is yet to be determined if these cases have any correlation to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine.”
“We’ve lost hundreds of children, and there have been thousands who have been hospitalized, thousands who developed an inflammatory syndrome, and one of the pieces of that can be myocarditis,” Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), said today on ABC’s Good Morning America.
Still, “from my perspective, the risk of COVID is so much greater than any theoretical risk from the vaccine,” said Dr. Besser, former acting director of the CDC.
The symptoms that can occur after COVID-19 vaccination include tiredness, headache, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea, reminds the AHA/ASA statement. Such symptoms would “typically appear within 24-48 hours and usually pass within 36-48 hours after receiving the vaccine.”
All health care providers should be aware of the “very rare” adverse events that could be related to a COVID-19 vaccine, including myocarditis, blood clots, low platelets, and symptoms of severe inflammation, it says.
“Health care professionals should strongly consider inquiring about the timing of any recent COVID vaccination among patients presenting with these conditions, as needed, in order to provide appropriate treatment quickly,” the statement advises.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination “enormously outweigh” the rare possible risk for heart-related complications, including myocarditis, the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (ASA) says in new statement.
The message follows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that the agency is monitoring the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) for cases of myocarditis that have been associated with the mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 from Pfizer and Moderna.
The “relatively few” reported cases myocarditis in adolescents or young adults have involved males more often than females, more often followed the second dose rather than the first, and were usually seen in the 4 days after vaccination, the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group (VaST) found.
“Most cases appear to be mild, and follow-up of cases is ongoing,” the CDC says. “Within CDC safety monitoring systems, rates of myocarditis reports in the window following COVID-19 vaccination have not differed from expected baseline rates.”
In their statement, the AHA/ASA “strongly urge” all adults and children 12 years and older to receive a COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible.
“The evidence continues to indicate that the COVID-19 vaccines are nearly 100% effective at preventing death and hospitalization due to COVID-19 infection,” the groups say.
Although the investigation of cases of myocarditis related to COVID-19 vaccination is ongoing, the AHA/ASA notes that myocarditis is typically the result of an actual viral infection, “and it is yet to be determined if these cases have any correlation to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine.”
“We’ve lost hundreds of children, and there have been thousands who have been hospitalized, thousands who developed an inflammatory syndrome, and one of the pieces of that can be myocarditis,” Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), said today on ABC’s Good Morning America.
Still, “from my perspective, the risk of COVID is so much greater than any theoretical risk from the vaccine,” said Dr. Besser, former acting director of the CDC.
The symptoms that can occur after COVID-19 vaccination include tiredness, headache, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea, reminds the AHA/ASA statement. Such symptoms would “typically appear within 24-48 hours and usually pass within 36-48 hours after receiving the vaccine.”
All health care providers should be aware of the “very rare” adverse events that could be related to a COVID-19 vaccine, including myocarditis, blood clots, low platelets, and symptoms of severe inflammation, it says.
“Health care professionals should strongly consider inquiring about the timing of any recent COVID vaccination among patients presenting with these conditions, as needed, in order to provide appropriate treatment quickly,” the statement advises.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians’ trust in health care leadership drops in pandemic
according to a survey conducted by NORC at the University of Chicago on behalf of the American Board of Internal Medicine Foundation.
Survey results, released May 21, indicate that 30% of physicians say their trust in the U.S. health care system and health care leadership has decreased during the pandemic. Only 18% reported an increase in trust.
Physicians, however, have great trust in their fellow clinicians.
In the survey of 600 physicians, 94% said they trust doctors within their practice; 85% trusted doctors outside of their practice; and 89% trusted nurses. That trust increased during the pandemic, with 41% saying their trust in fellow physicians rose and 37% saying their trust in nurses did.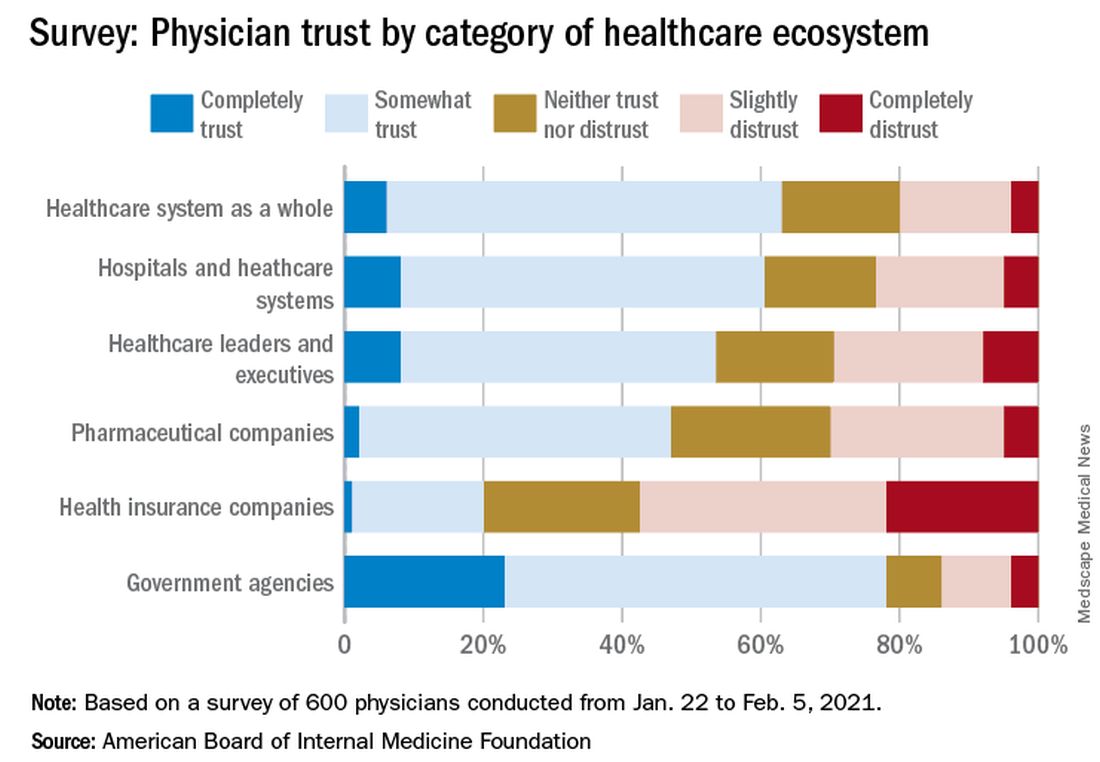
In a separate survey, NORC asked patients about their trust in various aspects of health care. Among 2,069 respondents, a wide majority reported that they trust doctors (84%) and nurses (85%), but only 64% trusted the health care system as a whole. One in three consumers (32%) said their trust in the health care system decreased during the pandemic, compared with 11% who said their trust increased.
The ABIM Foundation released the research findings on May 21 as part of Building Trust, a national campaign that aims to boost trust among patients, clinicians, system leaders, researchers, and others.
Richard J. Baron, MD, president and chief executive officer of the ABIM Foundation, said in an interview, “Clearly there’s lower trust in health care organization leaders and executives, and that’s troubling.
“Science by itself is not enough,” he said. “Becoming trustworthy has to be a core project of everybody in health care.”
Deterioration in physicians’ trust during the pandemic comes in part from failed promises of adequate personal protective equipment and some physicians’ loss of income as a result of the crisis, Dr. Baron said.
He added that the vaccine rollout was very uneven and that policies as to which elective procedures could be performed were handled differently in different parts of the country.
He also noted that, early on, transparency was lacking as to how many COVID patients hospitals were treating, which may have contributed to the decrease in trust in the system.
Fear of being known as ‘the COVID hospital’
Hospitals were afraid of being known as “the COVID hospital” and losing patients who were afraid to come there, Dr. Baron said.
He said the COVID-19 epidemic exacerbated problems regarding trust, but that trust has been declining for some time. The Building Trust campaign will focus on solutions in breaches of trust as physicians move increasingly toward being employees of huge systems, according to Dr. Baron.
However, trust works both ways, Dr. Baron notes. Physicians can be champions for their health care system or “throw the system under the bus,” he said.
For example, if a patient complains about the appointment system, clinicians who trust their institutions may say the system usually works and that they will try to make sure the patient has a better experience next time. Clinicians without trust may say they agree that the health care system doesn’t know what it is doing, and patients may further lose confidence when physicians validate their complaint, and patients may then go elsewhere.
78% of patients trust primary care doctor
When asked whether they trust their primary care physician, 78% of patients said yes. However, trust in doctors was higher among people who were older (90%), White (82%), or had high income (89%). Among people reporting lower trust, 25% said their physician spends too little time with them, and 14% said their doctor does not know or listen to them.
The survey shows that government agencies have work to do to earn trust. Responses indicate that 43% of physicians said they have “complete trust” in government health care agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is substantially higher than other parts of the health care system. However, trust in agencies declined for 43% of physician respondents and increased for 21%.
Dhruv Khullar, MD, MPP, of the department of health policy and economics at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, told this news organization the survey results match what he sees anecdotally in medicine – that physicians have been losing trust in the system but not in their colleagues.
He said the sample size of 600 is enough to be influential, though he said he would like to know the response rate, which was not calculated for this survey.
He added that, in large part, physicians’ lack of trust in their systems may come from generally being asked to see more patients and to meet more metrics during the same or shorter periods.
Physicians’ lack of trust in the system can have significant consequences, he said. It can lead to burnout, which has been linked with poorer quality of care and physician turnover, he noted.
COVID-19 led some physicians to wonder whether their system had their best interests at heart, insofar as access to adequate medicines and supplies as well as emotional support were inconsistent, Dr. Khullar said.
He said that to regain trust health care systems need to ask themselves questions in three areas. The first is whether their goals are focused on the best interest of the organization or the best interest of the patient.
“Next is competency,” Dr. Khullar said. “Maybe your motives are right, but are you able to deliver? Are you delivering a good product, whether clinical services or something else?”
The third area is transparency, he said. “Are you going to be honest and forthright in what we’re doing and where we’re going?”
Caroline Pearson, senior vice president of health care strategy for NORC, said the emailed survey was conducted between Dec. 29, 2020, and Feb. 5, 2021, with a health care survey partner that maintains a nationwide panel of physicians across specialties.
She said this report is fairly novel insofar as surveys are more typically conducted regarding patients’ trust of their doctors or of the health care system.
Ms. Pearson said because health care is delivered in teams, understanding the level of trust among the entities helps ensure that care will be delivered effectively and seamlessly with high quality.
“We want our patients to trust our doctors, but we really want doctors to trust each other and trust the hospitals and systems in which they’re working,” she said.
Dr. Baron, Ms. Pearson, and Dr. Khullar report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a survey conducted by NORC at the University of Chicago on behalf of the American Board of Internal Medicine Foundation.
Survey results, released May 21, indicate that 30% of physicians say their trust in the U.S. health care system and health care leadership has decreased during the pandemic. Only 18% reported an increase in trust.
Physicians, however, have great trust in their fellow clinicians.
In the survey of 600 physicians, 94% said they trust doctors within their practice; 85% trusted doctors outside of their practice; and 89% trusted nurses. That trust increased during the pandemic, with 41% saying their trust in fellow physicians rose and 37% saying their trust in nurses did.
In a separate survey, NORC asked patients about their trust in various aspects of health care. Among 2,069 respondents, a wide majority reported that they trust doctors (84%) and nurses (85%), but only 64% trusted the health care system as a whole. One in three consumers (32%) said their trust in the health care system decreased during the pandemic, compared with 11% who said their trust increased.
The ABIM Foundation released the research findings on May 21 as part of Building Trust, a national campaign that aims to boost trust among patients, clinicians, system leaders, researchers, and others.
Richard J. Baron, MD, president and chief executive officer of the ABIM Foundation, said in an interview, “Clearly there’s lower trust in health care organization leaders and executives, and that’s troubling.
“Science by itself is not enough,” he said. “Becoming trustworthy has to be a core project of everybody in health care.”
Deterioration in physicians’ trust during the pandemic comes in part from failed promises of adequate personal protective equipment and some physicians’ loss of income as a result of the crisis, Dr. Baron said.
He added that the vaccine rollout was very uneven and that policies as to which elective procedures could be performed were handled differently in different parts of the country.
He also noted that, early on, transparency was lacking as to how many COVID patients hospitals were treating, which may have contributed to the decrease in trust in the system.
Fear of being known as ‘the COVID hospital’
Hospitals were afraid of being known as “the COVID hospital” and losing patients who were afraid to come there, Dr. Baron said.
He said the COVID-19 epidemic exacerbated problems regarding trust, but that trust has been declining for some time. The Building Trust campaign will focus on solutions in breaches of trust as physicians move increasingly toward being employees of huge systems, according to Dr. Baron.
However, trust works both ways, Dr. Baron notes. Physicians can be champions for their health care system or “throw the system under the bus,” he said.
For example, if a patient complains about the appointment system, clinicians who trust their institutions may say the system usually works and that they will try to make sure the patient has a better experience next time. Clinicians without trust may say they agree that the health care system doesn’t know what it is doing, and patients may further lose confidence when physicians validate their complaint, and patients may then go elsewhere.
78% of patients trust primary care doctor
When asked whether they trust their primary care physician, 78% of patients said yes. However, trust in doctors was higher among people who were older (90%), White (82%), or had high income (89%). Among people reporting lower trust, 25% said their physician spends too little time with them, and 14% said their doctor does not know or listen to them.
The survey shows that government agencies have work to do to earn trust. Responses indicate that 43% of physicians said they have “complete trust” in government health care agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is substantially higher than other parts of the health care system. However, trust in agencies declined for 43% of physician respondents and increased for 21%.
Dhruv Khullar, MD, MPP, of the department of health policy and economics at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, told this news organization the survey results match what he sees anecdotally in medicine – that physicians have been losing trust in the system but not in their colleagues.
He said the sample size of 600 is enough to be influential, though he said he would like to know the response rate, which was not calculated for this survey.
He added that, in large part, physicians’ lack of trust in their systems may come from generally being asked to see more patients and to meet more metrics during the same or shorter periods.
Physicians’ lack of trust in the system can have significant consequences, he said. It can lead to burnout, which has been linked with poorer quality of care and physician turnover, he noted.
COVID-19 led some physicians to wonder whether their system had their best interests at heart, insofar as access to adequate medicines and supplies as well as emotional support were inconsistent, Dr. Khullar said.
He said that to regain trust health care systems need to ask themselves questions in three areas. The first is whether their goals are focused on the best interest of the organization or the best interest of the patient.
“Next is competency,” Dr. Khullar said. “Maybe your motives are right, but are you able to deliver? Are you delivering a good product, whether clinical services or something else?”
The third area is transparency, he said. “Are you going to be honest and forthright in what we’re doing and where we’re going?”
Caroline Pearson, senior vice president of health care strategy for NORC, said the emailed survey was conducted between Dec. 29, 2020, and Feb. 5, 2021, with a health care survey partner that maintains a nationwide panel of physicians across specialties.
She said this report is fairly novel insofar as surveys are more typically conducted regarding patients’ trust of their doctors or of the health care system.
Ms. Pearson said because health care is delivered in teams, understanding the level of trust among the entities helps ensure that care will be delivered effectively and seamlessly with high quality.
“We want our patients to trust our doctors, but we really want doctors to trust each other and trust the hospitals and systems in which they’re working,” she said.
Dr. Baron, Ms. Pearson, and Dr. Khullar report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a survey conducted by NORC at the University of Chicago on behalf of the American Board of Internal Medicine Foundation.
Survey results, released May 21, indicate that 30% of physicians say their trust in the U.S. health care system and health care leadership has decreased during the pandemic. Only 18% reported an increase in trust.
Physicians, however, have great trust in their fellow clinicians.
In the survey of 600 physicians, 94% said they trust doctors within their practice; 85% trusted doctors outside of their practice; and 89% trusted nurses. That trust increased during the pandemic, with 41% saying their trust in fellow physicians rose and 37% saying their trust in nurses did.
In a separate survey, NORC asked patients about their trust in various aspects of health care. Among 2,069 respondents, a wide majority reported that they trust doctors (84%) and nurses (85%), but only 64% trusted the health care system as a whole. One in three consumers (32%) said their trust in the health care system decreased during the pandemic, compared with 11% who said their trust increased.
The ABIM Foundation released the research findings on May 21 as part of Building Trust, a national campaign that aims to boost trust among patients, clinicians, system leaders, researchers, and others.
Richard J. Baron, MD, president and chief executive officer of the ABIM Foundation, said in an interview, “Clearly there’s lower trust in health care organization leaders and executives, and that’s troubling.
“Science by itself is not enough,” he said. “Becoming trustworthy has to be a core project of everybody in health care.”
Deterioration in physicians’ trust during the pandemic comes in part from failed promises of adequate personal protective equipment and some physicians’ loss of income as a result of the crisis, Dr. Baron said.
He added that the vaccine rollout was very uneven and that policies as to which elective procedures could be performed were handled differently in different parts of the country.
He also noted that, early on, transparency was lacking as to how many COVID patients hospitals were treating, which may have contributed to the decrease in trust in the system.
Fear of being known as ‘the COVID hospital’
Hospitals were afraid of being known as “the COVID hospital” and losing patients who were afraid to come there, Dr. Baron said.
He said the COVID-19 epidemic exacerbated problems regarding trust, but that trust has been declining for some time. The Building Trust campaign will focus on solutions in breaches of trust as physicians move increasingly toward being employees of huge systems, according to Dr. Baron.
However, trust works both ways, Dr. Baron notes. Physicians can be champions for their health care system or “throw the system under the bus,” he said.
For example, if a patient complains about the appointment system, clinicians who trust their institutions may say the system usually works and that they will try to make sure the patient has a better experience next time. Clinicians without trust may say they agree that the health care system doesn’t know what it is doing, and patients may further lose confidence when physicians validate their complaint, and patients may then go elsewhere.
78% of patients trust primary care doctor
When asked whether they trust their primary care physician, 78% of patients said yes. However, trust in doctors was higher among people who were older (90%), White (82%), or had high income (89%). Among people reporting lower trust, 25% said their physician spends too little time with them, and 14% said their doctor does not know or listen to them.
The survey shows that government agencies have work to do to earn trust. Responses indicate that 43% of physicians said they have “complete trust” in government health care agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is substantially higher than other parts of the health care system. However, trust in agencies declined for 43% of physician respondents and increased for 21%.
Dhruv Khullar, MD, MPP, of the department of health policy and economics at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, told this news organization the survey results match what he sees anecdotally in medicine – that physicians have been losing trust in the system but not in their colleagues.
He said the sample size of 600 is enough to be influential, though he said he would like to know the response rate, which was not calculated for this survey.
He added that, in large part, physicians’ lack of trust in their systems may come from generally being asked to see more patients and to meet more metrics during the same or shorter periods.
Physicians’ lack of trust in the system can have significant consequences, he said. It can lead to burnout, which has been linked with poorer quality of care and physician turnover, he noted.
COVID-19 led some physicians to wonder whether their system had their best interests at heart, insofar as access to adequate medicines and supplies as well as emotional support were inconsistent, Dr. Khullar said.
He said that to regain trust health care systems need to ask themselves questions in three areas. The first is whether their goals are focused on the best interest of the organization or the best interest of the patient.
“Next is competency,” Dr. Khullar said. “Maybe your motives are right, but are you able to deliver? Are you delivering a good product, whether clinical services or something else?”
The third area is transparency, he said. “Are you going to be honest and forthright in what we’re doing and where we’re going?”
Caroline Pearson, senior vice president of health care strategy for NORC, said the emailed survey was conducted between Dec. 29, 2020, and Feb. 5, 2021, with a health care survey partner that maintains a nationwide panel of physicians across specialties.
She said this report is fairly novel insofar as surveys are more typically conducted regarding patients’ trust of their doctors or of the health care system.
Ms. Pearson said because health care is delivered in teams, understanding the level of trust among the entities helps ensure that care will be delivered effectively and seamlessly with high quality.
“We want our patients to trust our doctors, but we really want doctors to trust each other and trust the hospitals and systems in which they’re working,” she said.
Dr. Baron, Ms. Pearson, and Dr. Khullar report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Young adults with epilepsy face higher mental illness risks
Young adults with epilepsy experience higher rates of anxiety, depression, and suicidality, compared with their counterparts in the general population, a new study shows.
The findings, based on a study of 144 young adults with epilepsy (YAWE), was published recently in Epilepsy & Behavior.
“People with epilepsy (PWE) are at a significantly higher risk of experiencing mental health difficulties, compared with healthy controls and individuals with other [long-term conditions] such as asthma and diabetes,” according to Rachel Batchelor, MSc, and Michelle D. Taylor, PhD, of the University of London (England) in Surrey.
Young adulthood, which encompasses people aged 18-25 years, has been identified as “a peak age of onset for anxiety and depression,” but mental health in young adults with epilepsy in particular has not been well studied, they wrote.
The survey measured current mental health symptoms, including anxiety, depression, and suicidality, as well as sociodemographic and epilepsy-related factors, coping strategies, and social support (Epilepsy Behav. 2021 May;118:107911. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2021.107911).
The average age of the respondents was 21.6 years, 61% were female, and 88% were of White British ethnicity. A total of 88 participants were single, 48 were in a relationship, and 8 were married or engaged. About one-third (38%) worked full-time, and 28.5% were full-time university students, 18.8% worked part-time, and 8.3% were unemployed and not students. The average age of seizure onset was 12.4 years.
Overall, 116 (80.6%) of the survey respondents met the criteria for anxiety, 110 (76.4%) for depression, and 51 (35.4%) for suicidality.
Ratings of all three of these conditions were significantly higher in females, compared with males, the researchers noted. Anxiety, depression, and suicidality also were rated higher for individuals who waited more than 1 year vs. less than 1 year for an epilepsy diagnosis from the time of seizure onset, for those suffering from anti-seizure medication side effects vs. no side effects, and for those with comorbid conditions vs. no comorbid conditions.
Avoidant-focused coping strategies were positively correlated with anxiety, depression, and suicidality, while problem-focused coping and meaning-focused coping were negatively correlated, the researchers said. In addition, those who reported greater levels of support from friends had lower rates of anxiety and depression, and those who reported greater levels of support from family had lower rates of suicidality.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the relatively homogenous population, and the absence of data on current anxiety and depression medications and additional professional support, the researchers noted.
However, the results extend the research on mental health in people with epilepsy, and the study is the first known to focus on the young adult population with epilepsy, they said.
“The high rates of anxiety, depression, and suicidality underscore the need for better integration of mental health provision into epilepsy care,” the researchers wrote. “While it would be premature to base recommendations for treating anxiety, depression, and suicidality in YAWE on the current study, investigating the efficacy of psychological interventions (for example, [acceptance and commitment therapy], [compassion-focused therapy], peer support, and family-based [therapy]) designed to address the psychosocial variables shown to independently predict mental health outcomes in YAWE would be worthy future research avenues,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding, and the researchers disclosed no financial conflicts.
Young adults with epilepsy experience higher rates of anxiety, depression, and suicidality, compared with their counterparts in the general population, a new study shows.
The findings, based on a study of 144 young adults with epilepsy (YAWE), was published recently in Epilepsy & Behavior.
“People with epilepsy (PWE) are at a significantly higher risk of experiencing mental health difficulties, compared with healthy controls and individuals with other [long-term conditions] such as asthma and diabetes,” according to Rachel Batchelor, MSc, and Michelle D. Taylor, PhD, of the University of London (England) in Surrey.
Young adulthood, which encompasses people aged 18-25 years, has been identified as “a peak age of onset for anxiety and depression,” but mental health in young adults with epilepsy in particular has not been well studied, they wrote.
The survey measured current mental health symptoms, including anxiety, depression, and suicidality, as well as sociodemographic and epilepsy-related factors, coping strategies, and social support (Epilepsy Behav. 2021 May;118:107911. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2021.107911).
The average age of the respondents was 21.6 years, 61% were female, and 88% were of White British ethnicity. A total of 88 participants were single, 48 were in a relationship, and 8 were married or engaged. About one-third (38%) worked full-time, and 28.5% were full-time university students, 18.8% worked part-time, and 8.3% were unemployed and not students. The average age of seizure onset was 12.4 years.
Overall, 116 (80.6%) of the survey respondents met the criteria for anxiety, 110 (76.4%) for depression, and 51 (35.4%) for suicidality.
Ratings of all three of these conditions were significantly higher in females, compared with males, the researchers noted. Anxiety, depression, and suicidality also were rated higher for individuals who waited more than 1 year vs. less than 1 year for an epilepsy diagnosis from the time of seizure onset, for those suffering from anti-seizure medication side effects vs. no side effects, and for those with comorbid conditions vs. no comorbid conditions.
Avoidant-focused coping strategies were positively correlated with anxiety, depression, and suicidality, while problem-focused coping and meaning-focused coping were negatively correlated, the researchers said. In addition, those who reported greater levels of support from friends had lower rates of anxiety and depression, and those who reported greater levels of support from family had lower rates of suicidality.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the relatively homogenous population, and the absence of data on current anxiety and depression medications and additional professional support, the researchers noted.
However, the results extend the research on mental health in people with epilepsy, and the study is the first known to focus on the young adult population with epilepsy, they said.
“The high rates of anxiety, depression, and suicidality underscore the need for better integration of mental health provision into epilepsy care,” the researchers wrote. “While it would be premature to base recommendations for treating anxiety, depression, and suicidality in YAWE on the current study, investigating the efficacy of psychological interventions (for example, [acceptance and commitment therapy], [compassion-focused therapy], peer support, and family-based [therapy]) designed to address the psychosocial variables shown to independently predict mental health outcomes in YAWE would be worthy future research avenues,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding, and the researchers disclosed no financial conflicts.
Young adults with epilepsy experience higher rates of anxiety, depression, and suicidality, compared with their counterparts in the general population, a new study shows.
The findings, based on a study of 144 young adults with epilepsy (YAWE), was published recently in Epilepsy & Behavior.
“People with epilepsy (PWE) are at a significantly higher risk of experiencing mental health difficulties, compared with healthy controls and individuals with other [long-term conditions] such as asthma and diabetes,” according to Rachel Batchelor, MSc, and Michelle D. Taylor, PhD, of the University of London (England) in Surrey.
Young adulthood, which encompasses people aged 18-25 years, has been identified as “a peak age of onset for anxiety and depression,” but mental health in young adults with epilepsy in particular has not been well studied, they wrote.
The survey measured current mental health symptoms, including anxiety, depression, and suicidality, as well as sociodemographic and epilepsy-related factors, coping strategies, and social support (Epilepsy Behav. 2021 May;118:107911. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2021.107911).
The average age of the respondents was 21.6 years, 61% were female, and 88% were of White British ethnicity. A total of 88 participants were single, 48 were in a relationship, and 8 were married or engaged. About one-third (38%) worked full-time, and 28.5% were full-time university students, 18.8% worked part-time, and 8.3% were unemployed and not students. The average age of seizure onset was 12.4 years.
Overall, 116 (80.6%) of the survey respondents met the criteria for anxiety, 110 (76.4%) for depression, and 51 (35.4%) for suicidality.
Ratings of all three of these conditions were significantly higher in females, compared with males, the researchers noted. Anxiety, depression, and suicidality also were rated higher for individuals who waited more than 1 year vs. less than 1 year for an epilepsy diagnosis from the time of seizure onset, for those suffering from anti-seizure medication side effects vs. no side effects, and for those with comorbid conditions vs. no comorbid conditions.
Avoidant-focused coping strategies were positively correlated with anxiety, depression, and suicidality, while problem-focused coping and meaning-focused coping were negatively correlated, the researchers said. In addition, those who reported greater levels of support from friends had lower rates of anxiety and depression, and those who reported greater levels of support from family had lower rates of suicidality.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the relatively homogenous population, and the absence of data on current anxiety and depression medications and additional professional support, the researchers noted.
However, the results extend the research on mental health in people with epilepsy, and the study is the first known to focus on the young adult population with epilepsy, they said.
“The high rates of anxiety, depression, and suicidality underscore the need for better integration of mental health provision into epilepsy care,” the researchers wrote. “While it would be premature to base recommendations for treating anxiety, depression, and suicidality in YAWE on the current study, investigating the efficacy of psychological interventions (for example, [acceptance and commitment therapy], [compassion-focused therapy], peer support, and family-based [therapy]) designed to address the psychosocial variables shown to independently predict mental health outcomes in YAWE would be worthy future research avenues,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding, and the researchers disclosed no financial conflicts.
FROM EPILEPSY & BEHAVIOR
Unhealthy drinking may worsen after weight loss surgery
Internal medicine primarily affords us the skill to cope with disorders of chronicity that rarely disappear. For every pneumococcal pneumonia we eradicate, we have multiple patients with HIV who will be treated indefinitely. Diabetes, once a lethal disease, is now a chronic condition for most patients, and even with treatment the trajectory is usually one of progression.
One gratifying exception in my professional lifetime has been the introduction of gastric surgeries that reduce morbidity and seem to extend the life span of those who successfully undergo these procedures. The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy have kept thousands of patients in better health for many years, giving them a second chance. For a subset, however, this second chance comes with a stumbling block of substance use – most notably alcohol – that exceeds their preoperative use.
Increased alcohol use after surgery
A group affiliated with the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) recently reviewed the large central database to identify changes in alcohol consumption among patients who had undergone successful bariatric surgery. The VA regularly administers the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Consumption (AUDIT-C), a survey validated as a reliable estimate of individual alcohol consumption. It is inserted into the VA electronic health record where it can be readily retrieved. By matching these survey results with individuals who underwent bariatric surgery at the VA and survived at least 8 years post op, the authors were able to follow trends in alcohol consumption, beginning 2 years before surgery through 8 years after.
Using the same database, the authors identified a larger number of nonoperative control patients with slightly less obesity but otherwise matched for several elements of comorbidity, such as hypertension, certain psychiatric disorders, and personal habits, including alcohol consumption.
Alcohol use was categorized as none, minor social use, and “unhealthy” use. Among those with no or minor social use preoperatively, 4% converted to unhealthy use at 3 years and about 5% at 8 years, significantly more than in the nonoperative control group. Those who had gastric bypass had somewhat more conversion than did those who had sleeve gastrectomy, though not significantly so.
Patients with an alcohol concern preoperatively took an interesting course. Consumption declined from 2 years pre op to the year of surgery, suggesting that curtailing its use may have been a surgical precondition. Postoperatively, they returned to unhealthy drinking levels. Those who underwent the sleeve gastrectomy consumed about the same amount of alcohol as did their matched nonoperative controls, but those who underwent bypass increased their baseline unhealthy use beyond that of the controls.
Because total abstinence is often the recommendation for treating alcoholism, the research group assessed how adherent the excessive drinkers were to abstinence. In anticipation of surgery, the rates of abstinence increased until the year of surgery, but by 3 years post op, consumption was often up to unhealthy levels, though no more than that of control participants with preexisting drinking problems.
Smoking and illicit drug use
Although increased alcohol consumption has generated the most studies, some attention has been given to smoking and illicit drug use, which may also increase over time.
One small study looked at composite tobacco, alcohol, and drug use pre- and postoperatively over 2 years, using population data. The authors found a parallel pattern of users voluntarily reducing their substance use in anticipation of surgery but relapsing as the procedure made them more functional and perhaps more independent. Of the substances people resumed, alcohol by far involved the largest increase in use from the preoperative baseline.
These studies, as important as they are, reveal what happened more effectively than they disclose why it happened. The latter requires some clinical experience. Curtailing cigarettes and alcohol use preoperatively may have been done to stay in the good graces of the surgeon. Many patients may have seen this as their path to a second chance that they intended to maintain.
The incentive to proceed to surgical weight loss, which incurs a measure of risk and forces changes in long ingrained eating habits, involves avoiding future morbidity and promoting longevity. Thus, the postoperative behaviors that threaten the long-term goal need to become a component of ongoing follow-up.
The acquisition of adverse behaviors not present preoperatively seems more difficult to sort out, and obligates those of us following these patients to ask about changes in alcohol use and provide resources for them should they need intervention.
Dr. Plotzker is a retired endocrinologist with 40 years of experience treating patients in both private practice and hospital settings.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Internal medicine primarily affords us the skill to cope with disorders of chronicity that rarely disappear. For every pneumococcal pneumonia we eradicate, we have multiple patients with HIV who will be treated indefinitely. Diabetes, once a lethal disease, is now a chronic condition for most patients, and even with treatment the trajectory is usually one of progression.
One gratifying exception in my professional lifetime has been the introduction of gastric surgeries that reduce morbidity and seem to extend the life span of those who successfully undergo these procedures. The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy have kept thousands of patients in better health for many years, giving them a second chance. For a subset, however, this second chance comes with a stumbling block of substance use – most notably alcohol – that exceeds their preoperative use.
Increased alcohol use after surgery
A group affiliated with the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) recently reviewed the large central database to identify changes in alcohol consumption among patients who had undergone successful bariatric surgery. The VA regularly administers the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Consumption (AUDIT-C), a survey validated as a reliable estimate of individual alcohol consumption. It is inserted into the VA electronic health record where it can be readily retrieved. By matching these survey results with individuals who underwent bariatric surgery at the VA and survived at least 8 years post op, the authors were able to follow trends in alcohol consumption, beginning 2 years before surgery through 8 years after.
Using the same database, the authors identified a larger number of nonoperative control patients with slightly less obesity but otherwise matched for several elements of comorbidity, such as hypertension, certain psychiatric disorders, and personal habits, including alcohol consumption.
Alcohol use was categorized as none, minor social use, and “unhealthy” use. Among those with no or minor social use preoperatively, 4% converted to unhealthy use at 3 years and about 5% at 8 years, significantly more than in the nonoperative control group. Those who had gastric bypass had somewhat more conversion than did those who had sleeve gastrectomy, though not significantly so.
Patients with an alcohol concern preoperatively took an interesting course. Consumption declined from 2 years pre op to the year of surgery, suggesting that curtailing its use may have been a surgical precondition. Postoperatively, they returned to unhealthy drinking levels. Those who underwent the sleeve gastrectomy consumed about the same amount of alcohol as did their matched nonoperative controls, but those who underwent bypass increased their baseline unhealthy use beyond that of the controls.
Because total abstinence is often the recommendation for treating alcoholism, the research group assessed how adherent the excessive drinkers were to abstinence. In anticipation of surgery, the rates of abstinence increased until the year of surgery, but by 3 years post op, consumption was often up to unhealthy levels, though no more than that of control participants with preexisting drinking problems.
Smoking and illicit drug use
Although increased alcohol consumption has generated the most studies, some attention has been given to smoking and illicit drug use, which may also increase over time.
One small study looked at composite tobacco, alcohol, and drug use pre- and postoperatively over 2 years, using population data. The authors found a parallel pattern of users voluntarily reducing their substance use in anticipation of surgery but relapsing as the procedure made them more functional and perhaps more independent. Of the substances people resumed, alcohol by far involved the largest increase in use from the preoperative baseline.
These studies, as important as they are, reveal what happened more effectively than they disclose why it happened. The latter requires some clinical experience. Curtailing cigarettes and alcohol use preoperatively may have been done to stay in the good graces of the surgeon. Many patients may have seen this as their path to a second chance that they intended to maintain.
The incentive to proceed to surgical weight loss, which incurs a measure of risk and forces changes in long ingrained eating habits, involves avoiding future morbidity and promoting longevity. Thus, the postoperative behaviors that threaten the long-term goal need to become a component of ongoing follow-up.
The acquisition of adverse behaviors not present preoperatively seems more difficult to sort out, and obligates those of us following these patients to ask about changes in alcohol use and provide resources for them should they need intervention.
Dr. Plotzker is a retired endocrinologist with 40 years of experience treating patients in both private practice and hospital settings.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Internal medicine primarily affords us the skill to cope with disorders of chronicity that rarely disappear. For every pneumococcal pneumonia we eradicate, we have multiple patients with HIV who will be treated indefinitely. Diabetes, once a lethal disease, is now a chronic condition for most patients, and even with treatment the trajectory is usually one of progression.
One gratifying exception in my professional lifetime has been the introduction of gastric surgeries that reduce morbidity and seem to extend the life span of those who successfully undergo these procedures. The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy have kept thousands of patients in better health for many years, giving them a second chance. For a subset, however, this second chance comes with a stumbling block of substance use – most notably alcohol – that exceeds their preoperative use.
Increased alcohol use after surgery
A group affiliated with the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) recently reviewed the large central database to identify changes in alcohol consumption among patients who had undergone successful bariatric surgery. The VA regularly administers the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Consumption (AUDIT-C), a survey validated as a reliable estimate of individual alcohol consumption. It is inserted into the VA electronic health record where it can be readily retrieved. By matching these survey results with individuals who underwent bariatric surgery at the VA and survived at least 8 years post op, the authors were able to follow trends in alcohol consumption, beginning 2 years before surgery through 8 years after.
Using the same database, the authors identified a larger number of nonoperative control patients with slightly less obesity but otherwise matched for several elements of comorbidity, such as hypertension, certain psychiatric disorders, and personal habits, including alcohol consumption.
Alcohol use was categorized as none, minor social use, and “unhealthy” use. Among those with no or minor social use preoperatively, 4% converted to unhealthy use at 3 years and about 5% at 8 years, significantly more than in the nonoperative control group. Those who had gastric bypass had somewhat more conversion than did those who had sleeve gastrectomy, though not significantly so.
Patients with an alcohol concern preoperatively took an interesting course. Consumption declined from 2 years pre op to the year of surgery, suggesting that curtailing its use may have been a surgical precondition. Postoperatively, they returned to unhealthy drinking levels. Those who underwent the sleeve gastrectomy consumed about the same amount of alcohol as did their matched nonoperative controls, but those who underwent bypass increased their baseline unhealthy use beyond that of the controls.
Because total abstinence is often the recommendation for treating alcoholism, the research group assessed how adherent the excessive drinkers were to abstinence. In anticipation of surgery, the rates of abstinence increased until the year of surgery, but by 3 years post op, consumption was often up to unhealthy levels, though no more than that of control participants with preexisting drinking problems.
Smoking and illicit drug use
Although increased alcohol consumption has generated the most studies, some attention has been given to smoking and illicit drug use, which may also increase over time.
One small study looked at composite tobacco, alcohol, and drug use pre- and postoperatively over 2 years, using population data. The authors found a parallel pattern of users voluntarily reducing their substance use in anticipation of surgery but relapsing as the procedure made them more functional and perhaps more independent. Of the substances people resumed, alcohol by far involved the largest increase in use from the preoperative baseline.
These studies, as important as they are, reveal what happened more effectively than they disclose why it happened. The latter requires some clinical experience. Curtailing cigarettes and alcohol use preoperatively may have been done to stay in the good graces of the surgeon. Many patients may have seen this as their path to a second chance that they intended to maintain.
The incentive to proceed to surgical weight loss, which incurs a measure of risk and forces changes in long ingrained eating habits, involves avoiding future morbidity and promoting longevity. Thus, the postoperative behaviors that threaten the long-term goal need to become a component of ongoing follow-up.
The acquisition of adverse behaviors not present preoperatively seems more difficult to sort out, and obligates those of us following these patients to ask about changes in alcohol use and provide resources for them should they need intervention.
Dr. Plotzker is a retired endocrinologist with 40 years of experience treating patients in both private practice and hospital settings.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psychosis, depression tied to neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s
Depression and psychosis are significantly associated with neuronal loss and gliosis – but not with Lewy body scores – in Parkinson’s disease, data from analyses of the brains of 175 patients suggest.
Previous research has suggested a link between neuronal loss and depression in Parkinson’s disease (PD) but the impact of Lewy bodies has not been well studied, Nicole Mercado Fischer, MPH, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
Evaluating Lewy body scores and neuronal loss/gliosis in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SN) and locus coeruleus (LC) could increase understanding of pathophysiology in PD, they said.
In a study published in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, the researchers analyzed the brains of 175 individuals with a primary diagnosis of PD.
A total of 98 participants had diagnoses of psychosis, 88 had depression, and 55 had anxiety. The average age of onset for PD was 62.4 years; 67.4% of the subjects were male, and 97.8% were White. The mean duration of illness was 16 years, and the average age at death was 78 years.
Psychosis was significantly associated with severe neuronal loss and gliosis in both the LC and SN (P = .048 and P = .042, respectively). Depression was significantly associated with severe neuronal loss in the SN (P = .042) but not in the LC. Anxiety was not associated with severe neuronal loss in either brain region. These results remained significant after a multivariate analysis, the researchers noted. However, Lewy body scores were not associated with any neuropsychiatric symptom, and severity of neuronal loss and gliosis was not correlated with Lewy body scores.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and inability to collect pathology data for all patients, the researchers noted. Also, in some cases, the collection of clinical data and observation of brain tissue pathology took place years apart, and the researchers did not assess medication records.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and “further support the notion that in vivo clinical symptoms of PD are either not caused by Lewy body pathology or that the relationship is confounded by the time of autopsy,” they said. and eventually by using new functional imaging techniques in vivo.”
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors were supported in part by the National Institutes of Health.
Depression and psychosis are significantly associated with neuronal loss and gliosis – but not with Lewy body scores – in Parkinson’s disease, data from analyses of the brains of 175 patients suggest.
Previous research has suggested a link between neuronal loss and depression in Parkinson’s disease (PD) but the impact of Lewy bodies has not been well studied, Nicole Mercado Fischer, MPH, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
Evaluating Lewy body scores and neuronal loss/gliosis in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SN) and locus coeruleus (LC) could increase understanding of pathophysiology in PD, they said.
In a study published in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, the researchers analyzed the brains of 175 individuals with a primary diagnosis of PD.
A total of 98 participants had diagnoses of psychosis, 88 had depression, and 55 had anxiety. The average age of onset for PD was 62.4 years; 67.4% of the subjects were male, and 97.8% were White. The mean duration of illness was 16 years, and the average age at death was 78 years.
Psychosis was significantly associated with severe neuronal loss and gliosis in both the LC and SN (P = .048 and P = .042, respectively). Depression was significantly associated with severe neuronal loss in the SN (P = .042) but not in the LC. Anxiety was not associated with severe neuronal loss in either brain region. These results remained significant after a multivariate analysis, the researchers noted. However, Lewy body scores were not associated with any neuropsychiatric symptom, and severity of neuronal loss and gliosis was not correlated with Lewy body scores.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and inability to collect pathology data for all patients, the researchers noted. Also, in some cases, the collection of clinical data and observation of brain tissue pathology took place years apart, and the researchers did not assess medication records.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and “further support the notion that in vivo clinical symptoms of PD are either not caused by Lewy body pathology or that the relationship is confounded by the time of autopsy,” they said. and eventually by using new functional imaging techniques in vivo.”
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors were supported in part by the National Institutes of Health.
Depression and psychosis are significantly associated with neuronal loss and gliosis – but not with Lewy body scores – in Parkinson’s disease, data from analyses of the brains of 175 patients suggest.
Previous research has suggested a link between neuronal loss and depression in Parkinson’s disease (PD) but the impact of Lewy bodies has not been well studied, Nicole Mercado Fischer, MPH, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
Evaluating Lewy body scores and neuronal loss/gliosis in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SN) and locus coeruleus (LC) could increase understanding of pathophysiology in PD, they said.
In a study published in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, the researchers analyzed the brains of 175 individuals with a primary diagnosis of PD.
A total of 98 participants had diagnoses of psychosis, 88 had depression, and 55 had anxiety. The average age of onset for PD was 62.4 years; 67.4% of the subjects were male, and 97.8% were White. The mean duration of illness was 16 years, and the average age at death was 78 years.
Psychosis was significantly associated with severe neuronal loss and gliosis in both the LC and SN (P = .048 and P = .042, respectively). Depression was significantly associated with severe neuronal loss in the SN (P = .042) but not in the LC. Anxiety was not associated with severe neuronal loss in either brain region. These results remained significant after a multivariate analysis, the researchers noted. However, Lewy body scores were not associated with any neuropsychiatric symptom, and severity of neuronal loss and gliosis was not correlated with Lewy body scores.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and inability to collect pathology data for all patients, the researchers noted. Also, in some cases, the collection of clinical data and observation of brain tissue pathology took place years apart, and the researchers did not assess medication records.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and “further support the notion that in vivo clinical symptoms of PD are either not caused by Lewy body pathology or that the relationship is confounded by the time of autopsy,” they said. and eventually by using new functional imaging techniques in vivo.”
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors were supported in part by the National Institutes of Health.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GERIATRIC PSYCHIATRY
Prevalence of psychiatric disorders higher in adult cerebral palsy patients
Adults with cerebral palsy, especially those with intellectual disabilities, are significantly more likely to be diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder, compared with the general population, a review of seven datasets shows.
The body of literature on psychiatric issues in children with cerebral palsy (CP) is increasing, but population-based studies of psychiatric issues in adults with CP have been limited in number and in scope. Most of those studies focus mainly on anxiety and depression, rather than on other issues such as psychosis or schizophrenia, Carly A. McMorris, PhD, of the University of Calgary (Alta.) and colleagues wrote.
In a retrospective, cross-sectional study published in Research in Developmental Disabilities, the researchers reviewed information from five health data sets, one registry, and census data for adults aged 18-64 years with a CP diagnosis living in Ontario, including those with and without diagnosed intellectual disabilities (ID) and a comparison group of individuals in the general population. The researchers examined the proportion of individuals with a psychiatric disorder in each of four groups: total CP, CP without ID, CP with ID, and the general population.
The study participants included 9,388 individuals with CP, 4,767 individuals with CP and ID, and a general population of 2,757,744 individuals. About half of the participants were male, and at least 85% lived in urban areas.
Overall, compared with the general population group, over a 2-year period (33.7 % vs. 24.7%). Also, the CP group was more than twice as likely to be diagnosed with a psychotic disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorder, or bipolar disorder, compared with the general population. Individuals with CP were significantly more likely to suffer from mood or affective disorders, and depression and anxiety disorders, compared with the general population, but less likely to suffer from substance use disorders.
When the data were assessed by ID status, disorders such as psychotic disorders, bipolar disorders, and schizophrenia were six times more common among individuals with CP and ID, compared with the general population (adjusted prevalence ratios, 6.26 and 6.46, respectively).
Individuals with CP and ID also had a notably higher prevalence of bipolar disorder (confidence interval, 2.06-2.89) and personality disorder, compared with the general population (aPR, 2.44 and 4.22, respectively), but this subgroup also was less likely than the general population to engage in substance use (aPR, 0.44).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the absence of universal definitions for some of the conditions studied, potential misclassification of ID, the inclusion of data on specific psychiatric diagnoses but not elevated symptoms, and by the challenges of diagnosing psychiatric disorders in individuals with ID, the researchers noted.
However, “the present study contributes important information to the existing literature, highlighting that psychiatric issues are common in adults with CP, similar to what has been reported in children and youth,” they said. “Further research is needed to determine the validity and reliability of mental health assessment measures for this population, the efficacy of evidence-based psychotherapeutic approaches ... and the underlying causes or mechanisms of psychiatric issues in individuals with CP.”
The findings also highlight the need for health care clinicians to screen for psychiatric issues in CP patients, they said.
The study was supported in part by the Province of Ontario research grants and the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences, funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. The researchers had no disclosures.
Adults with cerebral palsy, especially those with intellectual disabilities, are significantly more likely to be diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder, compared with the general population, a review of seven datasets shows.
The body of literature on psychiatric issues in children with cerebral palsy (CP) is increasing, but population-based studies of psychiatric issues in adults with CP have been limited in number and in scope. Most of those studies focus mainly on anxiety and depression, rather than on other issues such as psychosis or schizophrenia, Carly A. McMorris, PhD, of the University of Calgary (Alta.) and colleagues wrote.
In a retrospective, cross-sectional study published in Research in Developmental Disabilities, the researchers reviewed information from five health data sets, one registry, and census data for adults aged 18-64 years with a CP diagnosis living in Ontario, including those with and without diagnosed intellectual disabilities (ID) and a comparison group of individuals in the general population. The researchers examined the proportion of individuals with a psychiatric disorder in each of four groups: total CP, CP without ID, CP with ID, and the general population.
The study participants included 9,388 individuals with CP, 4,767 individuals with CP and ID, and a general population of 2,757,744 individuals. About half of the participants were male, and at least 85% lived in urban areas.
Overall, compared with the general population group, over a 2-year period (33.7 % vs. 24.7%). Also, the CP group was more than twice as likely to be diagnosed with a psychotic disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorder, or bipolar disorder, compared with the general population. Individuals with CP were significantly more likely to suffer from mood or affective disorders, and depression and anxiety disorders, compared with the general population, but less likely to suffer from substance use disorders.
When the data were assessed by ID status, disorders such as psychotic disorders, bipolar disorders, and schizophrenia were six times more common among individuals with CP and ID, compared with the general population (adjusted prevalence ratios, 6.26 and 6.46, respectively).
Individuals with CP and ID also had a notably higher prevalence of bipolar disorder (confidence interval, 2.06-2.89) and personality disorder, compared with the general population (aPR, 2.44 and 4.22, respectively), but this subgroup also was less likely than the general population to engage in substance use (aPR, 0.44).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the absence of universal definitions for some of the conditions studied, potential misclassification of ID, the inclusion of data on specific psychiatric diagnoses but not elevated symptoms, and by the challenges of diagnosing psychiatric disorders in individuals with ID, the researchers noted.
However, “the present study contributes important information to the existing literature, highlighting that psychiatric issues are common in adults with CP, similar to what has been reported in children and youth,” they said. “Further research is needed to determine the validity and reliability of mental health assessment measures for this population, the efficacy of evidence-based psychotherapeutic approaches ... and the underlying causes or mechanisms of psychiatric issues in individuals with CP.”
The findings also highlight the need for health care clinicians to screen for psychiatric issues in CP patients, they said.
The study was supported in part by the Province of Ontario research grants and the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences, funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. The researchers had no disclosures.
Adults with cerebral palsy, especially those with intellectual disabilities, are significantly more likely to be diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder, compared with the general population, a review of seven datasets shows.
The body of literature on psychiatric issues in children with cerebral palsy (CP) is increasing, but population-based studies of psychiatric issues in adults with CP have been limited in number and in scope. Most of those studies focus mainly on anxiety and depression, rather than on other issues such as psychosis or schizophrenia, Carly A. McMorris, PhD, of the University of Calgary (Alta.) and colleagues wrote.
In a retrospective, cross-sectional study published in Research in Developmental Disabilities, the researchers reviewed information from five health data sets, one registry, and census data for adults aged 18-64 years with a CP diagnosis living in Ontario, including those with and without diagnosed intellectual disabilities (ID) and a comparison group of individuals in the general population. The researchers examined the proportion of individuals with a psychiatric disorder in each of four groups: total CP, CP without ID, CP with ID, and the general population.
The study participants included 9,388 individuals with CP, 4,767 individuals with CP and ID, and a general population of 2,757,744 individuals. About half of the participants were male, and at least 85% lived in urban areas.
Overall, compared with the general population group, over a 2-year period (33.7 % vs. 24.7%). Also, the CP group was more than twice as likely to be diagnosed with a psychotic disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorder, or bipolar disorder, compared with the general population. Individuals with CP were significantly more likely to suffer from mood or affective disorders, and depression and anxiety disorders, compared with the general population, but less likely to suffer from substance use disorders.
When the data were assessed by ID status, disorders such as psychotic disorders, bipolar disorders, and schizophrenia were six times more common among individuals with CP and ID, compared with the general population (adjusted prevalence ratios, 6.26 and 6.46, respectively).
Individuals with CP and ID also had a notably higher prevalence of bipolar disorder (confidence interval, 2.06-2.89) and personality disorder, compared with the general population (aPR, 2.44 and 4.22, respectively), but this subgroup also was less likely than the general population to engage in substance use (aPR, 0.44).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the absence of universal definitions for some of the conditions studied, potential misclassification of ID, the inclusion of data on specific psychiatric diagnoses but not elevated symptoms, and by the challenges of diagnosing psychiatric disorders in individuals with ID, the researchers noted.
However, “the present study contributes important information to the existing literature, highlighting that psychiatric issues are common in adults with CP, similar to what has been reported in children and youth,” they said. “Further research is needed to determine the validity and reliability of mental health assessment measures for this population, the efficacy of evidence-based psychotherapeutic approaches ... and the underlying causes or mechanisms of psychiatric issues in individuals with CP.”
The findings also highlight the need for health care clinicians to screen for psychiatric issues in CP patients, they said.
The study was supported in part by the Province of Ontario research grants and the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences, funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. The researchers had no disclosures.
FROM RESEARCH IN DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES













