User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


U.S. is poised to produce a COVID-19 vaccine, but don’t expect it soon
Manufacturers will begin producing COVID-19 vaccine doses in anticipation of approval so that if a product gets the okay for usage, distribution can begin quickly, according to Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
“We will be producing vaccine at risk, which means we’ll be [investing] considerable resources in developing doses even before we know any given candidate or candidates work,” he testified during a May 12, 2020, hearing of the Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions Committee.
During the hearing, Dr. Fauci did not elaborate on how the production at risk would be undertaken, what criteria would be in place for selecting which candidates would be in the pipeline, or how much would be spent on the advanced production of these vaccines.
And while Dr. Fauci, a member of the White House coronavirus task force, remained optimistic that one or more vaccine candidates would ultimately be viable, he cautioned that there remain many unknowns that could slow the development of a vaccine for COVID-19.
“I must warn that there’s also the possibility of negative consequences that certain vaccines can actually enhance the negative effect of the infection,” he said. “The big unknown is efficacy. Will it be present or absent and how durable will it be?”
It’s unlikely that either a vaccine or an effective treatment will be available in the next 3 months, Dr. Fauci told the committee.
Sen. Lamar Alexander (R-Tenn.), the committee chairman, asked Dr. Fauci what he would say to college, primary, and secondary school administrators about how the availability of treatments and vaccines could influence the ability to reopen campuses to students. Dr. Fauci replied that the idea of having treatments or a vaccine available to facilitate the reentry of students in the fall term would be “a bit of a bridge too far.”
The emphasis in the coming months should be on testing, contact tracing, and isolation of those infected with the virus, Dr. Fauci said.
Manufacturers will begin producing COVID-19 vaccine doses in anticipation of approval so that if a product gets the okay for usage, distribution can begin quickly, according to Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
“We will be producing vaccine at risk, which means we’ll be [investing] considerable resources in developing doses even before we know any given candidate or candidates work,” he testified during a May 12, 2020, hearing of the Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions Committee.
During the hearing, Dr. Fauci did not elaborate on how the production at risk would be undertaken, what criteria would be in place for selecting which candidates would be in the pipeline, or how much would be spent on the advanced production of these vaccines.
And while Dr. Fauci, a member of the White House coronavirus task force, remained optimistic that one or more vaccine candidates would ultimately be viable, he cautioned that there remain many unknowns that could slow the development of a vaccine for COVID-19.
“I must warn that there’s also the possibility of negative consequences that certain vaccines can actually enhance the negative effect of the infection,” he said. “The big unknown is efficacy. Will it be present or absent and how durable will it be?”
It’s unlikely that either a vaccine or an effective treatment will be available in the next 3 months, Dr. Fauci told the committee.
Sen. Lamar Alexander (R-Tenn.), the committee chairman, asked Dr. Fauci what he would say to college, primary, and secondary school administrators about how the availability of treatments and vaccines could influence the ability to reopen campuses to students. Dr. Fauci replied that the idea of having treatments or a vaccine available to facilitate the reentry of students in the fall term would be “a bit of a bridge too far.”
The emphasis in the coming months should be on testing, contact tracing, and isolation of those infected with the virus, Dr. Fauci said.
Manufacturers will begin producing COVID-19 vaccine doses in anticipation of approval so that if a product gets the okay for usage, distribution can begin quickly, according to Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
“We will be producing vaccine at risk, which means we’ll be [investing] considerable resources in developing doses even before we know any given candidate or candidates work,” he testified during a May 12, 2020, hearing of the Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions Committee.
During the hearing, Dr. Fauci did not elaborate on how the production at risk would be undertaken, what criteria would be in place for selecting which candidates would be in the pipeline, or how much would be spent on the advanced production of these vaccines.
And while Dr. Fauci, a member of the White House coronavirus task force, remained optimistic that one or more vaccine candidates would ultimately be viable, he cautioned that there remain many unknowns that could slow the development of a vaccine for COVID-19.
“I must warn that there’s also the possibility of negative consequences that certain vaccines can actually enhance the negative effect of the infection,” he said. “The big unknown is efficacy. Will it be present or absent and how durable will it be?”
It’s unlikely that either a vaccine or an effective treatment will be available in the next 3 months, Dr. Fauci told the committee.
Sen. Lamar Alexander (R-Tenn.), the committee chairman, asked Dr. Fauci what he would say to college, primary, and secondary school administrators about how the availability of treatments and vaccines could influence the ability to reopen campuses to students. Dr. Fauci replied that the idea of having treatments or a vaccine available to facilitate the reentry of students in the fall term would be “a bit of a bridge too far.”
The emphasis in the coming months should be on testing, contact tracing, and isolation of those infected with the virus, Dr. Fauci said.
States vary in vulnerability to COVID-19 impact
West Virginia’s large elderly population and high rates of chronic kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and COPD make it the most vulnerable state to the coronavirus, according to a new analysis.

Vulnerability to the virus “isn’t just health related, though, as many people are harmed by the economic effects of the pandemic,” personal finance website WalletHub said May 12.
“It’s important for the U.S. to dedicate a large portion of its resources to providing medical support during the coronavirus pandemic, but we should also support people who don’t have adequate housing or enough money to survive the pandemic,” said WalletHub analyst Jill Gonzalez.
WalletHub graded each state on 28 measures – including share of obese adults, share of homes lacking access to basic hygienic facilities, and biggest increases in unemployment because of COVID-19 – grouped into three dimensions of vulnerability: medical (60% of the total score), housing (15%), and financial (25%).
Using those measures, Louisiana is the most vulnerable state after West Virginia, followed by Mississippi, Arkansas, and Alabama. All 5 states finished in the top 6 for medical vulnerability, and 4 were in the top 10 for financial vulnerability, but only 1 (Arkansas) was in the top 10 for housing vulnerability, WalletHub said.
Among the three vulnerability dimensions, West Virginia was first in medical, Hawaii (33rd overall) was first in housing, and Louisiana was first in financial. Utah is the least vulnerable state, overall, and the least vulnerable states in each dimension are, respectively, Colorado (50th overall), the District of Columbia (29th overall), and Iowa (45th overall), the report showed.
A look at the individual metrics WalletHub used shows some serious disparities:
- New Jersey’s unemployment recipiency rate of 57.2%, the highest in the country, is 6.1 times higher than North Carolina’s 9.3%.
- The highest uninsured rate, 17.4% in Texas, is 6.2 times higher than in Massachusetts, which is the lowest at 2.8%.
- In California, the share of the homeless population that is unsheltered (71.7%) is more than 33 times higher than in North Dakota (2.2%).
“The financial damage caused by COVID-19 is leaving many Americans without the means to pay their bills and purchase necessities. … The U.S. must continue to support its financially vulnerable populations even after the virus has subsided,” Ms. Gonzalez said.
West Virginia’s large elderly population and high rates of chronic kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and COPD make it the most vulnerable state to the coronavirus, according to a new analysis.

Vulnerability to the virus “isn’t just health related, though, as many people are harmed by the economic effects of the pandemic,” personal finance website WalletHub said May 12.
“It’s important for the U.S. to dedicate a large portion of its resources to providing medical support during the coronavirus pandemic, but we should also support people who don’t have adequate housing or enough money to survive the pandemic,” said WalletHub analyst Jill Gonzalez.
WalletHub graded each state on 28 measures – including share of obese adults, share of homes lacking access to basic hygienic facilities, and biggest increases in unemployment because of COVID-19 – grouped into three dimensions of vulnerability: medical (60% of the total score), housing (15%), and financial (25%).
Using those measures, Louisiana is the most vulnerable state after West Virginia, followed by Mississippi, Arkansas, and Alabama. All 5 states finished in the top 6 for medical vulnerability, and 4 were in the top 10 for financial vulnerability, but only 1 (Arkansas) was in the top 10 for housing vulnerability, WalletHub said.
Among the three vulnerability dimensions, West Virginia was first in medical, Hawaii (33rd overall) was first in housing, and Louisiana was first in financial. Utah is the least vulnerable state, overall, and the least vulnerable states in each dimension are, respectively, Colorado (50th overall), the District of Columbia (29th overall), and Iowa (45th overall), the report showed.
A look at the individual metrics WalletHub used shows some serious disparities:
- New Jersey’s unemployment recipiency rate of 57.2%, the highest in the country, is 6.1 times higher than North Carolina’s 9.3%.
- The highest uninsured rate, 17.4% in Texas, is 6.2 times higher than in Massachusetts, which is the lowest at 2.8%.
- In California, the share of the homeless population that is unsheltered (71.7%) is more than 33 times higher than in North Dakota (2.2%).
“The financial damage caused by COVID-19 is leaving many Americans without the means to pay their bills and purchase necessities. … The U.S. must continue to support its financially vulnerable populations even after the virus has subsided,” Ms. Gonzalez said.
West Virginia’s large elderly population and high rates of chronic kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and COPD make it the most vulnerable state to the coronavirus, according to a new analysis.

Vulnerability to the virus “isn’t just health related, though, as many people are harmed by the economic effects of the pandemic,” personal finance website WalletHub said May 12.
“It’s important for the U.S. to dedicate a large portion of its resources to providing medical support during the coronavirus pandemic, but we should also support people who don’t have adequate housing or enough money to survive the pandemic,” said WalletHub analyst Jill Gonzalez.
WalletHub graded each state on 28 measures – including share of obese adults, share of homes lacking access to basic hygienic facilities, and biggest increases in unemployment because of COVID-19 – grouped into three dimensions of vulnerability: medical (60% of the total score), housing (15%), and financial (25%).
Using those measures, Louisiana is the most vulnerable state after West Virginia, followed by Mississippi, Arkansas, and Alabama. All 5 states finished in the top 6 for medical vulnerability, and 4 were in the top 10 for financial vulnerability, but only 1 (Arkansas) was in the top 10 for housing vulnerability, WalletHub said.
Among the three vulnerability dimensions, West Virginia was first in medical, Hawaii (33rd overall) was first in housing, and Louisiana was first in financial. Utah is the least vulnerable state, overall, and the least vulnerable states in each dimension are, respectively, Colorado (50th overall), the District of Columbia (29th overall), and Iowa (45th overall), the report showed.
A look at the individual metrics WalletHub used shows some serious disparities:
- New Jersey’s unemployment recipiency rate of 57.2%, the highest in the country, is 6.1 times higher than North Carolina’s 9.3%.
- The highest uninsured rate, 17.4% in Texas, is 6.2 times higher than in Massachusetts, which is the lowest at 2.8%.
- In California, the share of the homeless population that is unsheltered (71.7%) is more than 33 times higher than in North Dakota (2.2%).
“The financial damage caused by COVID-19 is leaving many Americans without the means to pay their bills and purchase necessities. … The U.S. must continue to support its financially vulnerable populations even after the virus has subsided,” Ms. Gonzalez said.
ACR gives guidance on rheumatic disease management during pandemic
When COVID-19 is suspected or confirmed in a patient with a rheumatic disease, treatment with hydroxychloroquine may be continued, but other treatments may need to be stopped or held temporarily, according to new guidance issued by the American College of Rheumatology.
That includes disease-modifying treatment with antirheumatic drugs such as sulfasalazine, methotrexate, leflunomide, and the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, as well as immunosuppressants and non-interleukin (IL)-6 biologics, and this is regardless of how severe the COVID-19 illness is. NSAIDs should also be stopped if there are respiratory symptoms.
The advice is slightly less drastic if someone with stable rheumatic disease has probably been exposed to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or are asymptomatic. In those patients, DMARDs may be continued, although there is uncertainty over whether there is a need to temporarily stop methotrexate or leflunomide. Interruption of immunosuppressive, non–IL-6, and JAK inhibitor treatment is advised pending a negative SARS-CoV-2 test result, assuming the patient’s rheumatic disease is stable.
Impetus for ACR COVID-19 guidance
“One of the earliest challenges for rheumatologists during the COVID-19 pandemic was determining how to advise our patients who were taking immunosuppressive medications and were concerned as to whether or not to discontinue their therapy,” ACR President Ellen Gravallese, MD, said in an interview about the ACR Clinical Guidance Document, which is published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“A second challenge was keeping our patients safe from exposure to the virus, while still seeing those patients in person who required office visits,” added Dr. Gravallese, who is chief of the division of rheumatology, inflammation, and immunity at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
She continued: “The ACR Clinical Guidance Document was prepared in order to assist rheumatologists with decisions as to how to handle current medications during different phases of a patient’s exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus.”
But with very little evidence available on how to manage COVID-19 patients generally, let alone specifically in those with rheumatic diseases, “it became evident that any recommendations made would need to be done in a thoughtful and organized manner, evaluating the evidence that was available and obtaining the advice of experts in infectious disease, epidemiology, and in the use of biologic and nonbiologic agents for rheumatic disease,” she said.
As such, the ACR convened a task force of 10 rheumatologists and 4 infectious disease specialists from North America to look at how best to manage patients with rheumatic disease during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our charge was to develop a guidance document for the care of adult rheumatic disease patients in the context of COVID-19 and not per se to provide guidance for the treatment of COVID-19,” explained task force member and the corresponding author for the guidance, Ted R. Mikuls, MD, MSPH, of the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Dr. Mikuls, who was speaking at a virtual town hall meeting hosted by the ACR on May 6, noted that the guidance was obviously based on the best consensus of the available data and as such represented a “living document” that “would change and be added to” as necessary.
General recommendations for adult rheumatic disease management
In terms of general recommendations for the management of adult rheumatic disease patients, Dr. Mikuls said that six statements had been made “specific to risk assessment, prevention of infection, and best practices related to glucocorticoid use and the use of ACE [angiotensin-converting enzyme] inhibitors and ARBs [angiotensin II receptor blockers] during the pandemic.”
For example, general advice is to counsel patients to keep up general preventive measures such as social distancing and regular hand washing, reducing the number of in-person health care visits, and undertaking other means to try to prevent potential SARS-CoV-2 exposure. As for general treatment advice, glucocorticoids should be used at their lowest doses possible and should not be abruptly stopped, and antihypertensive treatment should be used as indicated.
Additional guidance statements include those that address the treatment of patients with stable rheumatic disease in the absence of infection or known exposure to SARS-CoV-2, with guidance specific to the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and those with newly diagnosed or active rheumatic disease.
SLE and inflammatory arthritis recommendations
“There are several sections within the guidance document that address the treatment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus during this pandemic,” Dr. Gravallese pointed out. “In general, it is recommended that lupus patients who are currently taking hydroxychloroquine can remain on the therapy prior to and during infection and that newly diagnosed patients with lupus can be placed on this medication at full dose. It is recommended that pregnant patients with lupus remain on therapy with this drug.”
She also observed that, for the treatment of active inflammatory arthritis, “the recommendations were written to address specific medications that could be used in this setting. In general, the task force recommendations were guided by the importance of controlling inflammation prior to exposure to the virus, even during this pandemic.
Guidance raises questions
During the ACR’s town hall meeting, the task force answered several questions raised by the guidance, such as the reasoning behind recommending that the use of traditional DMARDs be discontinued in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Dr. Mikuls observed: “Maybe if you just read the guidance statements it isn’t terribly intuitive.” There was a lot of discussion about whether or not conventional DMARDs were immunosuppressive, and even though they may not have such effects, it was decided to err on the side of caution.
“I think the task force felt that, with a COVID-19–positive patient, there is a concern of potentially confusing adverse effects related to medicines or conflate those with problems from the infection,” he said. Although rare, examples of those issues could be drug-induced hypersensitivity, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, or gastrointestinal side effects of hepatitis, all of which have been described in COVID-19. “Not only could it cause confusion, but it could maybe worsen those sequalae of COVID-19,” he said.
“I think the other part of this answer was that the panel really felt that the risk in terms of the flaring of the underlying rheumatic disease was likely to be pretty low given the finite time frame you’d be taking about – usually a time frame of 2-3 weeks you’d be holding the agent – so I think that is really why the task force ended up with that recommendation.”
Similarly, for the JAK inhibitors, the decision was to err on the side of caution when COVID-19 was suspected or confirmed. “Not so much because of the risk of thromboembolic disease, but concerns over immunosuppression that these drugs carry with them and also the fact the JAK inhibitors are probably inhibitors of type 1 interferons, which play a significant role in viral immunity and could potentially have a negative impact,” said Stanley Cohen, MD, who practices rheumatology in the Dallas area.
“On the flipside, there is interest in some of the JAK inhibitors as a potential treatment for COVID-19,” Dr. Cohen said, referring to anecdotal evidence for baricitinib (Olumiant).
Michael Weinblatt, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, addressed the recent concern over the use of NSAIDs by the public.
“There’s been a lot in the lay press that NSAIDs – because of the effects on receptors in the lung – could lead to deleterious outcomes in patients with COVID and there’s very little data to support this.
“We did recommend that NSAIDs be held in the hospitalized patient and that wasn’t because of the COVID-19 issue, it really was just medical practice, and we didn’t want to confound the care of these really sick patients with potential toxicities from NSAIDs. But as far as routine rheumatological care in your outpatients, we did not recommend that nonsteroidals be stopped if they were tolerated.”
One part of the guidance that might already need revision is the recommendation on the continued use of hydroxychloroquine in patients who develop COVID-19.
“Our guidance document says it’s OK; we were all in very strong agreement to continue hydroxychloroquine in our patients with COVID-19 because at that point, just a couple of weeks ago, we thought it was part of the potential treatment,” Karen Costenbader, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, said during the town hall meeting.
“Now the pendulum has swung the other way, and we’re worried about maybe we shouldn’t be continuing it because COVID-19 patients will be getting many other medications,” Dr. Costenbader said, and these may affect the QT-interval. “They will not be getting azithromycin because the pendulum swung the other way on that one too, but definitely on many other medications when they are sick.”
Potentially, she added, “if the rheumatic disease is under good control the inpatient physicians could decide whether they should continue [hydroxychloroquine] or not. If the COVID-19 is a mild disease, I would say we probably could continue in accordance with what we put in the document, but we will have to revisit this as well.”
Guidance is a ‘living document’
“We will be providing updates to the Clinical Guidance Document as the need arises,” Dr. Gravallese emphasized. While the general recommendations are unlikely to change very much, “the task force will be interested in seeing the results of all new data, but the results of randomized, clinical trials will be particularly important as they become available,” she said. In particular, randomized, controlled trials of glucocorticoids and IL-6 receptor blockade for use in COVID-19 will be of great importance.
“In this initial document, we could not take on all of the medical scenarios our members will face. For example, we could not take on recommendations for the pediatric population as this group of patients has a very different response than adults to the SARS-CoV-2 virus,” Dr. Gravallese acknowledged. The plan is to provide guidance for that group of patients soon.
In addition, the ACR Executive Committee has appointed a Practice and Advocacy Task Force that will “address issues rheumatologists face on the practice side, including advice regarding how to effectively use telemedicine, address the frequency and safety of infusions, determine urgent versus nonurgent issues that would or would not require face-to-face visits, and help with financial challenges.”
The American College of Rheumatology supported the guidance-development process. Dr. Mikuls, Dr. Weinblatt, Dr. Cohen, and Dr. Costenbader each disclosed research support or consultancies with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Gravallese had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mikuls TR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1002/art.41301.
When COVID-19 is suspected or confirmed in a patient with a rheumatic disease, treatment with hydroxychloroquine may be continued, but other treatments may need to be stopped or held temporarily, according to new guidance issued by the American College of Rheumatology.
That includes disease-modifying treatment with antirheumatic drugs such as sulfasalazine, methotrexate, leflunomide, and the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, as well as immunosuppressants and non-interleukin (IL)-6 biologics, and this is regardless of how severe the COVID-19 illness is. NSAIDs should also be stopped if there are respiratory symptoms.
The advice is slightly less drastic if someone with stable rheumatic disease has probably been exposed to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or are asymptomatic. In those patients, DMARDs may be continued, although there is uncertainty over whether there is a need to temporarily stop methotrexate or leflunomide. Interruption of immunosuppressive, non–IL-6, and JAK inhibitor treatment is advised pending a negative SARS-CoV-2 test result, assuming the patient’s rheumatic disease is stable.
Impetus for ACR COVID-19 guidance
“One of the earliest challenges for rheumatologists during the COVID-19 pandemic was determining how to advise our patients who were taking immunosuppressive medications and were concerned as to whether or not to discontinue their therapy,” ACR President Ellen Gravallese, MD, said in an interview about the ACR Clinical Guidance Document, which is published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“A second challenge was keeping our patients safe from exposure to the virus, while still seeing those patients in person who required office visits,” added Dr. Gravallese, who is chief of the division of rheumatology, inflammation, and immunity at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
She continued: “The ACR Clinical Guidance Document was prepared in order to assist rheumatologists with decisions as to how to handle current medications during different phases of a patient’s exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus.”
But with very little evidence available on how to manage COVID-19 patients generally, let alone specifically in those with rheumatic diseases, “it became evident that any recommendations made would need to be done in a thoughtful and organized manner, evaluating the evidence that was available and obtaining the advice of experts in infectious disease, epidemiology, and in the use of biologic and nonbiologic agents for rheumatic disease,” she said.
As such, the ACR convened a task force of 10 rheumatologists and 4 infectious disease specialists from North America to look at how best to manage patients with rheumatic disease during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our charge was to develop a guidance document for the care of adult rheumatic disease patients in the context of COVID-19 and not per se to provide guidance for the treatment of COVID-19,” explained task force member and the corresponding author for the guidance, Ted R. Mikuls, MD, MSPH, of the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Dr. Mikuls, who was speaking at a virtual town hall meeting hosted by the ACR on May 6, noted that the guidance was obviously based on the best consensus of the available data and as such represented a “living document” that “would change and be added to” as necessary.
General recommendations for adult rheumatic disease management
In terms of general recommendations for the management of adult rheumatic disease patients, Dr. Mikuls said that six statements had been made “specific to risk assessment, prevention of infection, and best practices related to glucocorticoid use and the use of ACE [angiotensin-converting enzyme] inhibitors and ARBs [angiotensin II receptor blockers] during the pandemic.”
For example, general advice is to counsel patients to keep up general preventive measures such as social distancing and regular hand washing, reducing the number of in-person health care visits, and undertaking other means to try to prevent potential SARS-CoV-2 exposure. As for general treatment advice, glucocorticoids should be used at their lowest doses possible and should not be abruptly stopped, and antihypertensive treatment should be used as indicated.
Additional guidance statements include those that address the treatment of patients with stable rheumatic disease in the absence of infection or known exposure to SARS-CoV-2, with guidance specific to the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and those with newly diagnosed or active rheumatic disease.
SLE and inflammatory arthritis recommendations
“There are several sections within the guidance document that address the treatment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus during this pandemic,” Dr. Gravallese pointed out. “In general, it is recommended that lupus patients who are currently taking hydroxychloroquine can remain on the therapy prior to and during infection and that newly diagnosed patients with lupus can be placed on this medication at full dose. It is recommended that pregnant patients with lupus remain on therapy with this drug.”
She also observed that, for the treatment of active inflammatory arthritis, “the recommendations were written to address specific medications that could be used in this setting. In general, the task force recommendations were guided by the importance of controlling inflammation prior to exposure to the virus, even during this pandemic.
Guidance raises questions
During the ACR’s town hall meeting, the task force answered several questions raised by the guidance, such as the reasoning behind recommending that the use of traditional DMARDs be discontinued in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Dr. Mikuls observed: “Maybe if you just read the guidance statements it isn’t terribly intuitive.” There was a lot of discussion about whether or not conventional DMARDs were immunosuppressive, and even though they may not have such effects, it was decided to err on the side of caution.
“I think the task force felt that, with a COVID-19–positive patient, there is a concern of potentially confusing adverse effects related to medicines or conflate those with problems from the infection,” he said. Although rare, examples of those issues could be drug-induced hypersensitivity, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, or gastrointestinal side effects of hepatitis, all of which have been described in COVID-19. “Not only could it cause confusion, but it could maybe worsen those sequalae of COVID-19,” he said.
“I think the other part of this answer was that the panel really felt that the risk in terms of the flaring of the underlying rheumatic disease was likely to be pretty low given the finite time frame you’d be taking about – usually a time frame of 2-3 weeks you’d be holding the agent – so I think that is really why the task force ended up with that recommendation.”
Similarly, for the JAK inhibitors, the decision was to err on the side of caution when COVID-19 was suspected or confirmed. “Not so much because of the risk of thromboembolic disease, but concerns over immunosuppression that these drugs carry with them and also the fact the JAK inhibitors are probably inhibitors of type 1 interferons, which play a significant role in viral immunity and could potentially have a negative impact,” said Stanley Cohen, MD, who practices rheumatology in the Dallas area.
“On the flipside, there is interest in some of the JAK inhibitors as a potential treatment for COVID-19,” Dr. Cohen said, referring to anecdotal evidence for baricitinib (Olumiant).
Michael Weinblatt, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, addressed the recent concern over the use of NSAIDs by the public.
“There’s been a lot in the lay press that NSAIDs – because of the effects on receptors in the lung – could lead to deleterious outcomes in patients with COVID and there’s very little data to support this.
“We did recommend that NSAIDs be held in the hospitalized patient and that wasn’t because of the COVID-19 issue, it really was just medical practice, and we didn’t want to confound the care of these really sick patients with potential toxicities from NSAIDs. But as far as routine rheumatological care in your outpatients, we did not recommend that nonsteroidals be stopped if they were tolerated.”
One part of the guidance that might already need revision is the recommendation on the continued use of hydroxychloroquine in patients who develop COVID-19.
“Our guidance document says it’s OK; we were all in very strong agreement to continue hydroxychloroquine in our patients with COVID-19 because at that point, just a couple of weeks ago, we thought it was part of the potential treatment,” Karen Costenbader, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, said during the town hall meeting.
“Now the pendulum has swung the other way, and we’re worried about maybe we shouldn’t be continuing it because COVID-19 patients will be getting many other medications,” Dr. Costenbader said, and these may affect the QT-interval. “They will not be getting azithromycin because the pendulum swung the other way on that one too, but definitely on many other medications when they are sick.”
Potentially, she added, “if the rheumatic disease is under good control the inpatient physicians could decide whether they should continue [hydroxychloroquine] or not. If the COVID-19 is a mild disease, I would say we probably could continue in accordance with what we put in the document, but we will have to revisit this as well.”
Guidance is a ‘living document’
“We will be providing updates to the Clinical Guidance Document as the need arises,” Dr. Gravallese emphasized. While the general recommendations are unlikely to change very much, “the task force will be interested in seeing the results of all new data, but the results of randomized, clinical trials will be particularly important as they become available,” she said. In particular, randomized, controlled trials of glucocorticoids and IL-6 receptor blockade for use in COVID-19 will be of great importance.
“In this initial document, we could not take on all of the medical scenarios our members will face. For example, we could not take on recommendations for the pediatric population as this group of patients has a very different response than adults to the SARS-CoV-2 virus,” Dr. Gravallese acknowledged. The plan is to provide guidance for that group of patients soon.
In addition, the ACR Executive Committee has appointed a Practice and Advocacy Task Force that will “address issues rheumatologists face on the practice side, including advice regarding how to effectively use telemedicine, address the frequency and safety of infusions, determine urgent versus nonurgent issues that would or would not require face-to-face visits, and help with financial challenges.”
The American College of Rheumatology supported the guidance-development process. Dr. Mikuls, Dr. Weinblatt, Dr. Cohen, and Dr. Costenbader each disclosed research support or consultancies with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Gravallese had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mikuls TR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1002/art.41301.
When COVID-19 is suspected or confirmed in a patient with a rheumatic disease, treatment with hydroxychloroquine may be continued, but other treatments may need to be stopped or held temporarily, according to new guidance issued by the American College of Rheumatology.
That includes disease-modifying treatment with antirheumatic drugs such as sulfasalazine, methotrexate, leflunomide, and the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, as well as immunosuppressants and non-interleukin (IL)-6 biologics, and this is regardless of how severe the COVID-19 illness is. NSAIDs should also be stopped if there are respiratory symptoms.
The advice is slightly less drastic if someone with stable rheumatic disease has probably been exposed to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or are asymptomatic. In those patients, DMARDs may be continued, although there is uncertainty over whether there is a need to temporarily stop methotrexate or leflunomide. Interruption of immunosuppressive, non–IL-6, and JAK inhibitor treatment is advised pending a negative SARS-CoV-2 test result, assuming the patient’s rheumatic disease is stable.
Impetus for ACR COVID-19 guidance
“One of the earliest challenges for rheumatologists during the COVID-19 pandemic was determining how to advise our patients who were taking immunosuppressive medications and were concerned as to whether or not to discontinue their therapy,” ACR President Ellen Gravallese, MD, said in an interview about the ACR Clinical Guidance Document, which is published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“A second challenge was keeping our patients safe from exposure to the virus, while still seeing those patients in person who required office visits,” added Dr. Gravallese, who is chief of the division of rheumatology, inflammation, and immunity at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
She continued: “The ACR Clinical Guidance Document was prepared in order to assist rheumatologists with decisions as to how to handle current medications during different phases of a patient’s exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus.”
But with very little evidence available on how to manage COVID-19 patients generally, let alone specifically in those with rheumatic diseases, “it became evident that any recommendations made would need to be done in a thoughtful and organized manner, evaluating the evidence that was available and obtaining the advice of experts in infectious disease, epidemiology, and in the use of biologic and nonbiologic agents for rheumatic disease,” she said.
As such, the ACR convened a task force of 10 rheumatologists and 4 infectious disease specialists from North America to look at how best to manage patients with rheumatic disease during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our charge was to develop a guidance document for the care of adult rheumatic disease patients in the context of COVID-19 and not per se to provide guidance for the treatment of COVID-19,” explained task force member and the corresponding author for the guidance, Ted R. Mikuls, MD, MSPH, of the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Dr. Mikuls, who was speaking at a virtual town hall meeting hosted by the ACR on May 6, noted that the guidance was obviously based on the best consensus of the available data and as such represented a “living document” that “would change and be added to” as necessary.
General recommendations for adult rheumatic disease management
In terms of general recommendations for the management of adult rheumatic disease patients, Dr. Mikuls said that six statements had been made “specific to risk assessment, prevention of infection, and best practices related to glucocorticoid use and the use of ACE [angiotensin-converting enzyme] inhibitors and ARBs [angiotensin II receptor blockers] during the pandemic.”
For example, general advice is to counsel patients to keep up general preventive measures such as social distancing and regular hand washing, reducing the number of in-person health care visits, and undertaking other means to try to prevent potential SARS-CoV-2 exposure. As for general treatment advice, glucocorticoids should be used at their lowest doses possible and should not be abruptly stopped, and antihypertensive treatment should be used as indicated.
Additional guidance statements include those that address the treatment of patients with stable rheumatic disease in the absence of infection or known exposure to SARS-CoV-2, with guidance specific to the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and those with newly diagnosed or active rheumatic disease.
SLE and inflammatory arthritis recommendations
“There are several sections within the guidance document that address the treatment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus during this pandemic,” Dr. Gravallese pointed out. “In general, it is recommended that lupus patients who are currently taking hydroxychloroquine can remain on the therapy prior to and during infection and that newly diagnosed patients with lupus can be placed on this medication at full dose. It is recommended that pregnant patients with lupus remain on therapy with this drug.”
She also observed that, for the treatment of active inflammatory arthritis, “the recommendations were written to address specific medications that could be used in this setting. In general, the task force recommendations were guided by the importance of controlling inflammation prior to exposure to the virus, even during this pandemic.
Guidance raises questions
During the ACR’s town hall meeting, the task force answered several questions raised by the guidance, such as the reasoning behind recommending that the use of traditional DMARDs be discontinued in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Dr. Mikuls observed: “Maybe if you just read the guidance statements it isn’t terribly intuitive.” There was a lot of discussion about whether or not conventional DMARDs were immunosuppressive, and even though they may not have such effects, it was decided to err on the side of caution.
“I think the task force felt that, with a COVID-19–positive patient, there is a concern of potentially confusing adverse effects related to medicines or conflate those with problems from the infection,” he said. Although rare, examples of those issues could be drug-induced hypersensitivity, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, or gastrointestinal side effects of hepatitis, all of which have been described in COVID-19. “Not only could it cause confusion, but it could maybe worsen those sequalae of COVID-19,” he said.
“I think the other part of this answer was that the panel really felt that the risk in terms of the flaring of the underlying rheumatic disease was likely to be pretty low given the finite time frame you’d be taking about – usually a time frame of 2-3 weeks you’d be holding the agent – so I think that is really why the task force ended up with that recommendation.”
Similarly, for the JAK inhibitors, the decision was to err on the side of caution when COVID-19 was suspected or confirmed. “Not so much because of the risk of thromboembolic disease, but concerns over immunosuppression that these drugs carry with them and also the fact the JAK inhibitors are probably inhibitors of type 1 interferons, which play a significant role in viral immunity and could potentially have a negative impact,” said Stanley Cohen, MD, who practices rheumatology in the Dallas area.
“On the flipside, there is interest in some of the JAK inhibitors as a potential treatment for COVID-19,” Dr. Cohen said, referring to anecdotal evidence for baricitinib (Olumiant).
Michael Weinblatt, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, addressed the recent concern over the use of NSAIDs by the public.
“There’s been a lot in the lay press that NSAIDs – because of the effects on receptors in the lung – could lead to deleterious outcomes in patients with COVID and there’s very little data to support this.
“We did recommend that NSAIDs be held in the hospitalized patient and that wasn’t because of the COVID-19 issue, it really was just medical practice, and we didn’t want to confound the care of these really sick patients with potential toxicities from NSAIDs. But as far as routine rheumatological care in your outpatients, we did not recommend that nonsteroidals be stopped if they were tolerated.”
One part of the guidance that might already need revision is the recommendation on the continued use of hydroxychloroquine in patients who develop COVID-19.
“Our guidance document says it’s OK; we were all in very strong agreement to continue hydroxychloroquine in our patients with COVID-19 because at that point, just a couple of weeks ago, we thought it was part of the potential treatment,” Karen Costenbader, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, said during the town hall meeting.
“Now the pendulum has swung the other way, and we’re worried about maybe we shouldn’t be continuing it because COVID-19 patients will be getting many other medications,” Dr. Costenbader said, and these may affect the QT-interval. “They will not be getting azithromycin because the pendulum swung the other way on that one too, but definitely on many other medications when they are sick.”
Potentially, she added, “if the rheumatic disease is under good control the inpatient physicians could decide whether they should continue [hydroxychloroquine] or not. If the COVID-19 is a mild disease, I would say we probably could continue in accordance with what we put in the document, but we will have to revisit this as well.”
Guidance is a ‘living document’
“We will be providing updates to the Clinical Guidance Document as the need arises,” Dr. Gravallese emphasized. While the general recommendations are unlikely to change very much, “the task force will be interested in seeing the results of all new data, but the results of randomized, clinical trials will be particularly important as they become available,” she said. In particular, randomized, controlled trials of glucocorticoids and IL-6 receptor blockade for use in COVID-19 will be of great importance.
“In this initial document, we could not take on all of the medical scenarios our members will face. For example, we could not take on recommendations for the pediatric population as this group of patients has a very different response than adults to the SARS-CoV-2 virus,” Dr. Gravallese acknowledged. The plan is to provide guidance for that group of patients soon.
In addition, the ACR Executive Committee has appointed a Practice and Advocacy Task Force that will “address issues rheumatologists face on the practice side, including advice regarding how to effectively use telemedicine, address the frequency and safety of infusions, determine urgent versus nonurgent issues that would or would not require face-to-face visits, and help with financial challenges.”
The American College of Rheumatology supported the guidance-development process. Dr. Mikuls, Dr. Weinblatt, Dr. Cohen, and Dr. Costenbader each disclosed research support or consultancies with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Gravallese had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mikuls TR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1002/art.41301.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Bronchoscopy guideline for COVID-19 pandemic: Use sparingly
With little evidence available on the role of bronchoscopy during the COVID-19 pandemic, an expert panel has published a guideline recommending its spare use in COVID-19 patients and those with suspected COVID-19 infection.
The panel stated that in the context of the COVID-19 crisis, bronchoscopy and other aerosol-generating procedures put health care workers (HCWs) at particularly high risk of exposure and infection. They recommended deferring bronchoscopy in nonurgent cases, and advised practitioners to wear personal protective equipment when performing bronchoscopy, even on asymptomatic patients.
The guideline and expert panel report have been published online in the journal Chest. CHEST and the American Association for Bronchology and Interventional Pulmonology participated in selecting the 14 panelists. “The recommendation and suggestions outlined in this document were specifically created to address what were felt to be clinically common and urgent questions that frontline clinicians are likely to face,” wrote lead author and panel cochair Momen M. Wahidi, MD, MBA, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., and colleagues.
Only one of the six recommendations is based on graded evidence; the remainder are ungraded consensus-based statements. The guideline consists of the following recommendations for performing or using bronchoscopy:
- HCWs in the procedure or recovery rooms should wear either an N-95 respirator or powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR) when performing bronchoscopy on patients suspected or confirmed to have COVID-19. They should wear personal protective equipment (PPE) that includes a face shield, gown, and gloves, and they should discard N-95 respirators after performing bronchoscopy.
- A nasopharyngeal specimen in COVID-19 suspects should be obtained before performing bronchoscopy. If the patient has severe or progressive disease that requires intubation but an additional specimen is needed to confirm COVID-19 or another diagnosis that could change the treatment course, an option would be lower-respiratory specimen from the endotracheal aspirate or bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage.
- HCWs should wear an N-95 or PAPR when doing bronchoscopy on asymptomatic patients in an area with community spread of COVID-19 – again, with the PPE designated in the first recommendation.
- Test for COVID-19 before doing bronchoscopy on asymptomatic patients. Defer nonurgent bronchoscopy if the test is positive. If it’s negative, follow the recommendations regarding respirators and PPE when doing bronchoscopy.
- Perform timely bronchoscopy when indicated even in an area with known community spread of COVID-19. This is the only graded recommendation among the six (Grade 2C) and may be the most nuanced. Local teams should develop strategies for using bronchoscopy in their setting, taking into account local resources and availability of PPE, and they should send noninfected cancer patients from resource-depleted hospitals to other centers.
- Base the timing of bronchoscopy in patients recovering after COVID-19 on the indication for the procedure, disease severity, and time duration since symptoms resolved. The recommendation noted that the exact timing is still unknown, but that a wait of at least 30 days after symptoms recede is “reasonable.”
The expert panel added a noteworthy caveat to the recommendations. “We would like to stress that these protective strategies can be rendered completely ineffective if proper training on donning and doffing is not provided to HCW,” Dr. Wahidi and colleagues wrote. “Proper personnel instruction and practice for wearing PPE should receive as much attention by health facilities as the chosen strategy for protection.”
Dr. Wahidi and colleagues have no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Wahidi MM et al. CHEST. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.036.
With little evidence available on the role of bronchoscopy during the COVID-19 pandemic, an expert panel has published a guideline recommending its spare use in COVID-19 patients and those with suspected COVID-19 infection.
The panel stated that in the context of the COVID-19 crisis, bronchoscopy and other aerosol-generating procedures put health care workers (HCWs) at particularly high risk of exposure and infection. They recommended deferring bronchoscopy in nonurgent cases, and advised practitioners to wear personal protective equipment when performing bronchoscopy, even on asymptomatic patients.
The guideline and expert panel report have been published online in the journal Chest. CHEST and the American Association for Bronchology and Interventional Pulmonology participated in selecting the 14 panelists. “The recommendation and suggestions outlined in this document were specifically created to address what were felt to be clinically common and urgent questions that frontline clinicians are likely to face,” wrote lead author and panel cochair Momen M. Wahidi, MD, MBA, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., and colleagues.
Only one of the six recommendations is based on graded evidence; the remainder are ungraded consensus-based statements. The guideline consists of the following recommendations for performing or using bronchoscopy:
- HCWs in the procedure or recovery rooms should wear either an N-95 respirator or powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR) when performing bronchoscopy on patients suspected or confirmed to have COVID-19. They should wear personal protective equipment (PPE) that includes a face shield, gown, and gloves, and they should discard N-95 respirators after performing bronchoscopy.
- A nasopharyngeal specimen in COVID-19 suspects should be obtained before performing bronchoscopy. If the patient has severe or progressive disease that requires intubation but an additional specimen is needed to confirm COVID-19 or another diagnosis that could change the treatment course, an option would be lower-respiratory specimen from the endotracheal aspirate or bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage.
- HCWs should wear an N-95 or PAPR when doing bronchoscopy on asymptomatic patients in an area with community spread of COVID-19 – again, with the PPE designated in the first recommendation.
- Test for COVID-19 before doing bronchoscopy on asymptomatic patients. Defer nonurgent bronchoscopy if the test is positive. If it’s negative, follow the recommendations regarding respirators and PPE when doing bronchoscopy.
- Perform timely bronchoscopy when indicated even in an area with known community spread of COVID-19. This is the only graded recommendation among the six (Grade 2C) and may be the most nuanced. Local teams should develop strategies for using bronchoscopy in their setting, taking into account local resources and availability of PPE, and they should send noninfected cancer patients from resource-depleted hospitals to other centers.
- Base the timing of bronchoscopy in patients recovering after COVID-19 on the indication for the procedure, disease severity, and time duration since symptoms resolved. The recommendation noted that the exact timing is still unknown, but that a wait of at least 30 days after symptoms recede is “reasonable.”
The expert panel added a noteworthy caveat to the recommendations. “We would like to stress that these protective strategies can be rendered completely ineffective if proper training on donning and doffing is not provided to HCW,” Dr. Wahidi and colleagues wrote. “Proper personnel instruction and practice for wearing PPE should receive as much attention by health facilities as the chosen strategy for protection.”
Dr. Wahidi and colleagues have no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Wahidi MM et al. CHEST. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.036.
With little evidence available on the role of bronchoscopy during the COVID-19 pandemic, an expert panel has published a guideline recommending its spare use in COVID-19 patients and those with suspected COVID-19 infection.
The panel stated that in the context of the COVID-19 crisis, bronchoscopy and other aerosol-generating procedures put health care workers (HCWs) at particularly high risk of exposure and infection. They recommended deferring bronchoscopy in nonurgent cases, and advised practitioners to wear personal protective equipment when performing bronchoscopy, even on asymptomatic patients.
The guideline and expert panel report have been published online in the journal Chest. CHEST and the American Association for Bronchology and Interventional Pulmonology participated in selecting the 14 panelists. “The recommendation and suggestions outlined in this document were specifically created to address what were felt to be clinically common and urgent questions that frontline clinicians are likely to face,” wrote lead author and panel cochair Momen M. Wahidi, MD, MBA, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., and colleagues.
Only one of the six recommendations is based on graded evidence; the remainder are ungraded consensus-based statements. The guideline consists of the following recommendations for performing or using bronchoscopy:
- HCWs in the procedure or recovery rooms should wear either an N-95 respirator or powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR) when performing bronchoscopy on patients suspected or confirmed to have COVID-19. They should wear personal protective equipment (PPE) that includes a face shield, gown, and gloves, and they should discard N-95 respirators after performing bronchoscopy.
- A nasopharyngeal specimen in COVID-19 suspects should be obtained before performing bronchoscopy. If the patient has severe or progressive disease that requires intubation but an additional specimen is needed to confirm COVID-19 or another diagnosis that could change the treatment course, an option would be lower-respiratory specimen from the endotracheal aspirate or bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage.
- HCWs should wear an N-95 or PAPR when doing bronchoscopy on asymptomatic patients in an area with community spread of COVID-19 – again, with the PPE designated in the first recommendation.
- Test for COVID-19 before doing bronchoscopy on asymptomatic patients. Defer nonurgent bronchoscopy if the test is positive. If it’s negative, follow the recommendations regarding respirators and PPE when doing bronchoscopy.
- Perform timely bronchoscopy when indicated even in an area with known community spread of COVID-19. This is the only graded recommendation among the six (Grade 2C) and may be the most nuanced. Local teams should develop strategies for using bronchoscopy in their setting, taking into account local resources and availability of PPE, and they should send noninfected cancer patients from resource-depleted hospitals to other centers.
- Base the timing of bronchoscopy in patients recovering after COVID-19 on the indication for the procedure, disease severity, and time duration since symptoms resolved. The recommendation noted that the exact timing is still unknown, but that a wait of at least 30 days after symptoms recede is “reasonable.”
The expert panel added a noteworthy caveat to the recommendations. “We would like to stress that these protective strategies can be rendered completely ineffective if proper training on donning and doffing is not provided to HCW,” Dr. Wahidi and colleagues wrote. “Proper personnel instruction and practice for wearing PPE should receive as much attention by health facilities as the chosen strategy for protection.”
Dr. Wahidi and colleagues have no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Wahidi MM et al. CHEST. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.036.
FROM CHEST
Many hydroxychloroquine COVID-19 prophylaxis trials lack ECG screening
Many planned randomized trials to test the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine or related drugs for preventing COVID-19 infection have, as of the end of April 2020, failed to include ECG assessment to either exclude people at the highest risk for possibly developing a life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia or to flag people who achieve a dangerous QTc interval on treatment, according to an analysis of the posted designs of several dozen studies.
Hydroxychloroquine, the related agent chloroquine, and azithromycin have all recently received attention as potentially effective but unproven agents for both reducing the severity and duration of established COVID-19 infection as well as possibly preventing or mitigating an incident infection. As of April 30, 155 randomized, control trials listed on a major index for pending and in-progress trials, clinicaltrials.gov, had designs that intended to randomized an overall total of more than 85,000 healthy people to receive hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine, in some cases in combination with azithromycin, to test their efficacy and safety for COVID-19 prophylaxis, Michael H. Gollob, MD, said in an article posted by the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2020 May 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.008).
The problem is that all three agents are documented to potentially produce lengthening of the corrected QT interval (QTc), and if this happens in a person who starts treatment with a QTc on the high end, the incremental prolongation from drug treatment could push their heart rhythm into a range where their risk for a life-threatening arrhythmia becomes substantial, said Dr. Gollob, a cardiac arrhythmia researcher at Toronto General Hospital and the University of Toronto. As a consequence, he recommended excluding from these prophylaxis trials anyone with a resting QTc at baseline assessment of greater than 450 msec, as well as discontinuing treatment from anyone who develops a resting QTc of more than 480 ms while on treatment.
“Though this may seem like a conservative value for subject withdrawal from a study, this is a prudent QTc cut-off, particularly when the severity of the adverse event, sudden death, may be worse than the study endpoint” of reduced incidence of COVID-19 infection, he wrote in his opinion piece.
“We cannot provide an accurate number for elevated risk” faced by people whose QTc climbs above these thresholds, “but we know that events will occur, which is why most trials that involve QT-prolonging drugs typically have an ECG exclusion criterion of QTc greater than 450 msec,” Dr. Gollob said in an interview.
His analysis of the 155 planned randomized prophylaxis trials on clinicaltrials.gov that he examined in detail had enrollment goals that would translate into more than 85,000 uninfected people who would receive hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine plus, in come cases, azithromycin. Only six relatively small studies from among these 155 included a plan for ECG screening and monitoring in its design, he noted. “It is reasonable to estimate that among the 80,000 patients randomized to a QT-prolonging drug [without ECG screening or monitoring] there will certainly be arrhythmic events.” If some of these people were to then die from a drug-induced arrhythmic event that could have been prevented by ECG screening or monitoring, it would be a “tragedy,” Dr. Gollob said.
“It is not only inexplicable, but also inexcusable that clinical investigators would dare to include healthy individuals in a clinical trial involving QT-prolonging medications without bothering to screen their electrocardiogram,” commented Sami Viskin, MD, an electrophysiologist at Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center. “The fact that we needed Dr. Gollob to ring this alarm is, itself, shocking,” he said in an interview.
“ECG screening is a good option to minimize the risk. You don’t eliminate the risk, but you can minimize it,” commented Arthur Wilde, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at the Academic Medical Center in Amsterdam. Both Dr. Viskin and Dr. Wilde agreed with the QTc interval thresholds Dr. Gollob recommended using for excluding or discontinuing study participants.
In his commentary, Dr. Gollob estimated that if 85,000 otherwise healthy adults were randomized to received a drug that can increase the QTc interval, as many as about 3,400 people (4%) in the group could statistically be expected to have an especially high vulnerability to QT prolongation because of genetic variants they might carry that collectively have roughly this prevalence. In some people of African heritage, the prevalence of genetic risk for excessive QTc lengthening can be even higher, approaching about 10%, noted Dr. Wilde.
Dr. Gollob hoped the concerns he raised will prompt the organizers of many of these studies to revise their design, and he said he already knew of one study based in Toronto that recently added an ECG-monitoring strategy in response to the concerns he raised. He expressed optimism that more studies will follow.
“It’s a real issue to have these trials designed without ECG exclusions or monitoring. I’m glad that Dr. Gollob sent this warning, because he is right. ECG monitoring during treatment is important so you can stop the treatment in time,” Dr. Wilde said. Dr. Wilde also noted that many, if not most, of the studies listed on clinicaltrials.gov may not actually launch.
In April, representatives from several cardiology societies coauthored a document of considerations when using hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, or azithromycin to treat patients with a diagnosed COVID-19 infection, and highlighted a QTc interval of 500 msec or greater as flagging patients who should no longer receive these drugs (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.016). For patients who do not yet have COVID-19 disease and the goal from treatment is prevention the potential efficacy of these drugs is reasonable to explore, but “does not exclude the need to minimize risk to research participants, especially when enrolling healthy subjects,” Dr. Gollob said.
Dr. Gollob, Dr. Viskin, and Dr. Wilde had no relevant financial disclosures.
Many planned randomized trials to test the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine or related drugs for preventing COVID-19 infection have, as of the end of April 2020, failed to include ECG assessment to either exclude people at the highest risk for possibly developing a life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia or to flag people who achieve a dangerous QTc interval on treatment, according to an analysis of the posted designs of several dozen studies.
Hydroxychloroquine, the related agent chloroquine, and azithromycin have all recently received attention as potentially effective but unproven agents for both reducing the severity and duration of established COVID-19 infection as well as possibly preventing or mitigating an incident infection. As of April 30, 155 randomized, control trials listed on a major index for pending and in-progress trials, clinicaltrials.gov, had designs that intended to randomized an overall total of more than 85,000 healthy people to receive hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine, in some cases in combination with azithromycin, to test their efficacy and safety for COVID-19 prophylaxis, Michael H. Gollob, MD, said in an article posted by the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2020 May 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.008).
The problem is that all three agents are documented to potentially produce lengthening of the corrected QT interval (QTc), and if this happens in a person who starts treatment with a QTc on the high end, the incremental prolongation from drug treatment could push their heart rhythm into a range where their risk for a life-threatening arrhythmia becomes substantial, said Dr. Gollob, a cardiac arrhythmia researcher at Toronto General Hospital and the University of Toronto. As a consequence, he recommended excluding from these prophylaxis trials anyone with a resting QTc at baseline assessment of greater than 450 msec, as well as discontinuing treatment from anyone who develops a resting QTc of more than 480 ms while on treatment.
“Though this may seem like a conservative value for subject withdrawal from a study, this is a prudent QTc cut-off, particularly when the severity of the adverse event, sudden death, may be worse than the study endpoint” of reduced incidence of COVID-19 infection, he wrote in his opinion piece.
“We cannot provide an accurate number for elevated risk” faced by people whose QTc climbs above these thresholds, “but we know that events will occur, which is why most trials that involve QT-prolonging drugs typically have an ECG exclusion criterion of QTc greater than 450 msec,” Dr. Gollob said in an interview.
His analysis of the 155 planned randomized prophylaxis trials on clinicaltrials.gov that he examined in detail had enrollment goals that would translate into more than 85,000 uninfected people who would receive hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine plus, in come cases, azithromycin. Only six relatively small studies from among these 155 included a plan for ECG screening and monitoring in its design, he noted. “It is reasonable to estimate that among the 80,000 patients randomized to a QT-prolonging drug [without ECG screening or monitoring] there will certainly be arrhythmic events.” If some of these people were to then die from a drug-induced arrhythmic event that could have been prevented by ECG screening or monitoring, it would be a “tragedy,” Dr. Gollob said.
“It is not only inexplicable, but also inexcusable that clinical investigators would dare to include healthy individuals in a clinical trial involving QT-prolonging medications without bothering to screen their electrocardiogram,” commented Sami Viskin, MD, an electrophysiologist at Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center. “The fact that we needed Dr. Gollob to ring this alarm is, itself, shocking,” he said in an interview.
“ECG screening is a good option to minimize the risk. You don’t eliminate the risk, but you can minimize it,” commented Arthur Wilde, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at the Academic Medical Center in Amsterdam. Both Dr. Viskin and Dr. Wilde agreed with the QTc interval thresholds Dr. Gollob recommended using for excluding or discontinuing study participants.
In his commentary, Dr. Gollob estimated that if 85,000 otherwise healthy adults were randomized to received a drug that can increase the QTc interval, as many as about 3,400 people (4%) in the group could statistically be expected to have an especially high vulnerability to QT prolongation because of genetic variants they might carry that collectively have roughly this prevalence. In some people of African heritage, the prevalence of genetic risk for excessive QTc lengthening can be even higher, approaching about 10%, noted Dr. Wilde.
Dr. Gollob hoped the concerns he raised will prompt the organizers of many of these studies to revise their design, and he said he already knew of one study based in Toronto that recently added an ECG-monitoring strategy in response to the concerns he raised. He expressed optimism that more studies will follow.
“It’s a real issue to have these trials designed without ECG exclusions or monitoring. I’m glad that Dr. Gollob sent this warning, because he is right. ECG monitoring during treatment is important so you can stop the treatment in time,” Dr. Wilde said. Dr. Wilde also noted that many, if not most, of the studies listed on clinicaltrials.gov may not actually launch.
In April, representatives from several cardiology societies coauthored a document of considerations when using hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, or azithromycin to treat patients with a diagnosed COVID-19 infection, and highlighted a QTc interval of 500 msec or greater as flagging patients who should no longer receive these drugs (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.016). For patients who do not yet have COVID-19 disease and the goal from treatment is prevention the potential efficacy of these drugs is reasonable to explore, but “does not exclude the need to minimize risk to research participants, especially when enrolling healthy subjects,” Dr. Gollob said.
Dr. Gollob, Dr. Viskin, and Dr. Wilde had no relevant financial disclosures.
Many planned randomized trials to test the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine or related drugs for preventing COVID-19 infection have, as of the end of April 2020, failed to include ECG assessment to either exclude people at the highest risk for possibly developing a life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia or to flag people who achieve a dangerous QTc interval on treatment, according to an analysis of the posted designs of several dozen studies.
Hydroxychloroquine, the related agent chloroquine, and azithromycin have all recently received attention as potentially effective but unproven agents for both reducing the severity and duration of established COVID-19 infection as well as possibly preventing or mitigating an incident infection. As of April 30, 155 randomized, control trials listed on a major index for pending and in-progress trials, clinicaltrials.gov, had designs that intended to randomized an overall total of more than 85,000 healthy people to receive hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine, in some cases in combination with azithromycin, to test their efficacy and safety for COVID-19 prophylaxis, Michael H. Gollob, MD, said in an article posted by the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2020 May 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.008).
The problem is that all three agents are documented to potentially produce lengthening of the corrected QT interval (QTc), and if this happens in a person who starts treatment with a QTc on the high end, the incremental prolongation from drug treatment could push their heart rhythm into a range where their risk for a life-threatening arrhythmia becomes substantial, said Dr. Gollob, a cardiac arrhythmia researcher at Toronto General Hospital and the University of Toronto. As a consequence, he recommended excluding from these prophylaxis trials anyone with a resting QTc at baseline assessment of greater than 450 msec, as well as discontinuing treatment from anyone who develops a resting QTc of more than 480 ms while on treatment.
“Though this may seem like a conservative value for subject withdrawal from a study, this is a prudent QTc cut-off, particularly when the severity of the adverse event, sudden death, may be worse than the study endpoint” of reduced incidence of COVID-19 infection, he wrote in his opinion piece.
“We cannot provide an accurate number for elevated risk” faced by people whose QTc climbs above these thresholds, “but we know that events will occur, which is why most trials that involve QT-prolonging drugs typically have an ECG exclusion criterion of QTc greater than 450 msec,” Dr. Gollob said in an interview.
His analysis of the 155 planned randomized prophylaxis trials on clinicaltrials.gov that he examined in detail had enrollment goals that would translate into more than 85,000 uninfected people who would receive hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine plus, in come cases, azithromycin. Only six relatively small studies from among these 155 included a plan for ECG screening and monitoring in its design, he noted. “It is reasonable to estimate that among the 80,000 patients randomized to a QT-prolonging drug [without ECG screening or monitoring] there will certainly be arrhythmic events.” If some of these people were to then die from a drug-induced arrhythmic event that could have been prevented by ECG screening or monitoring, it would be a “tragedy,” Dr. Gollob said.
“It is not only inexplicable, but also inexcusable that clinical investigators would dare to include healthy individuals in a clinical trial involving QT-prolonging medications without bothering to screen their electrocardiogram,” commented Sami Viskin, MD, an electrophysiologist at Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center. “The fact that we needed Dr. Gollob to ring this alarm is, itself, shocking,” he said in an interview.
“ECG screening is a good option to minimize the risk. You don’t eliminate the risk, but you can minimize it,” commented Arthur Wilde, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at the Academic Medical Center in Amsterdam. Both Dr. Viskin and Dr. Wilde agreed with the QTc interval thresholds Dr. Gollob recommended using for excluding or discontinuing study participants.
In his commentary, Dr. Gollob estimated that if 85,000 otherwise healthy adults were randomized to received a drug that can increase the QTc interval, as many as about 3,400 people (4%) in the group could statistically be expected to have an especially high vulnerability to QT prolongation because of genetic variants they might carry that collectively have roughly this prevalence. In some people of African heritage, the prevalence of genetic risk for excessive QTc lengthening can be even higher, approaching about 10%, noted Dr. Wilde.
Dr. Gollob hoped the concerns he raised will prompt the organizers of many of these studies to revise their design, and he said he already knew of one study based in Toronto that recently added an ECG-monitoring strategy in response to the concerns he raised. He expressed optimism that more studies will follow.
“It’s a real issue to have these trials designed without ECG exclusions or monitoring. I’m glad that Dr. Gollob sent this warning, because he is right. ECG monitoring during treatment is important so you can stop the treatment in time,” Dr. Wilde said. Dr. Wilde also noted that many, if not most, of the studies listed on clinicaltrials.gov may not actually launch.
In April, representatives from several cardiology societies coauthored a document of considerations when using hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, or azithromycin to treat patients with a diagnosed COVID-19 infection, and highlighted a QTc interval of 500 msec or greater as flagging patients who should no longer receive these drugs (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.016). For patients who do not yet have COVID-19 disease and the goal from treatment is prevention the potential efficacy of these drugs is reasonable to explore, but “does not exclude the need to minimize risk to research participants, especially when enrolling healthy subjects,” Dr. Gollob said.
Dr. Gollob, Dr. Viskin, and Dr. Wilde had no relevant financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM JACC
COVID-19: Telehealth at the forefront of the pandemic
On Jan. 20, 2020, the first confirmed case of the 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States was admitted to Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash. Less than 3 months later, the COVID-19 pandemic has put enormous stress on the U.S. health care system, which is confronting acute resource shortage because of the surge of acute and critically ill patients, health care provider safety and burnout, and an ongoing need for managing vulnerable populations while minimizing the infection spread.
With the onset of these unprecedented challenges, telehealth has emerged as a powerful new resource for health care providers, hospitals, and health care systems across the country. This article offers a summary of government regulations that enabled telehealth expansion, and provides an overview of how two health care organizations, Providence St. Joseph Health and Sound Physicians, are employing telehealth services to combat the COVID-19 health care crisis.
The government response: Telehealth expansion
In response to the pandemic, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) have significantly increased access to telehealth services for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries. CMS swiftly put measures in place such as:
- Expanding telehealth beyond rural areas.
- Adding 80 services that can be provided in all settings, including patient homes
- Allowing providers to bill for telehealth visits at the same rate as in-person visits.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services also aided this effort by:
- Waiving requirements that physicians or other health care professionals must have licenses in the state in which they provide services, if they have an equivalent license from another state.
- Waving penalties for HIPAA violations against health care providers that serve patients in good faith through everyday communications technologies, such as FaceTime or Skype
Without prior regulatory and reimbursement restrictions, telehealth rapidly became a powerful tool in helping to solve some of the problems brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Providence Telehealth for COVID-19
Providence St. Joseph Health is a not-for-profit health care system operating 51 hospitals and 1,085 clinics across Alaska, California, Montana, New Mexico, Oregon, Texas, and Washington. Providence has developed an enterprise telemedicine network with more than 100 virtual programs. Several of these services – including Telestroke, Telepsychiatry, TeleICU, and Telehospitalist – have been scaled across several states as a clinical cloud. More than 400 telemedicine endpoints are deployed, such as robotic carts and fixed InTouch TVs. In fact, the first U.S. COVID-19 patient was treated at Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash., using the telemedical robot Vici from InTouch Health.
According to Todd Czartoski, MD, chief medical technology officer at Providence, “while telehealth has been around for many years, COVID-19 opened a lot of people’s eyes to the value of virtual care delivery.”
Providence’s telehealth response to COVID-19 has encompassed five main areas: COVID-19 home care, COVID-19 acute care, ambulatory virtual visits, behavioral health concierge (BHC) expansion, and additional support for outside partnerships.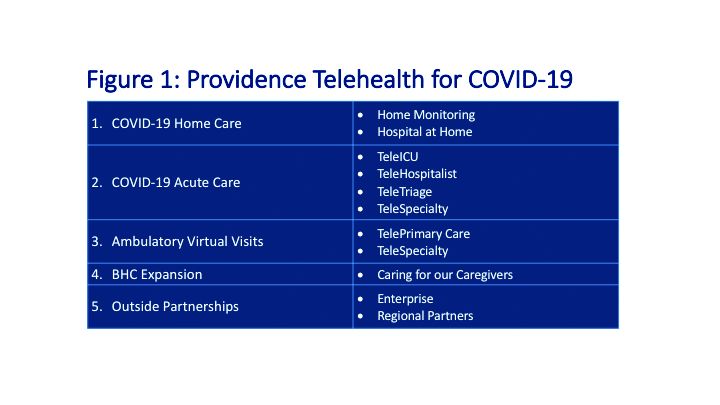
COVID-19 Home Care
Providence rapidly deployed home monitoring for nearly 2,000 positive or presumptive COVID-19 patients. Those symptomatic, clinically stable patients are given a thermometer and a pulse oximeter, and are monitored from home by a central team of nurses and physicians using the Xealth and Twistle programs.
Providence is evaluating expansion of home monitoring to other diagnoses, including higher acuity conditions.
COVID-19 Acute Care
TeleTriage expedites the triage of suspected COVID-19 patients and reduces the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by 50% per patient per day. To date, TeleTriage has resulted in the conservation of more than 90,000 PPE units.
TeleHospitalist services expanded from traditional night coverage to caring for patients in COVID-19 units around the clock. Currently, there are 25 telehospitalists who practice both in-person and virtual medicine.
TeleICU offers remote management of more than 180 ICU beds across 17 hospitals from two central command centers in Washington state and Alaska. The services include night-time intensivist and ICU nurse coverage, including medication and ventilator management, and family conferences. COVID-19 increased the demand for TeleICU, with anticipated expansion to more than 300 beds.
Core TeleSpecialty services include TeleStroke and TelePsychiatry across 135 remote sites.
Ambulatory Virtual Visits
Providence launched the COVID-19 hub microsite to help educate patients by providing accurate and timely information. A chatbot named Grace helps screen patients who are worried about COVID-19. Grace also suggests next steps, such as a video visit with a patient’s primary care provider or a visit using Express Care/Virtual team, a direct-to-consumer service available to patients within and outside of the health care system.
In less than 2 weeks, Providence enabled virtual visits for more than 7,000 outpatient providers, with more than 14,000 alternative visits now occurring daily. This has allowed primary and specialty providers to continue to manage their patient panels remotely. The number of Express Care/Virtual visits increased from 60 to more than 1,000 per day.
BHC Expansion
In the effort to improve care for its caregivers, Providence launched a behavioral health concierge (BHC) service that offers employees and their dependents virtual access to licensed mental health professionals. Over the last half of 2019, BHC provided more than 1,000 phone and virtual visits, depending on the individual preference of patients. Notably, 21% percent of users were physicians; 65% of users were seen the same day and 100% of users were seen within 48 hours.
COVID-19 increased demand for services that initially started in Seattle and rapidly expanded to Montana, Oregon, and California.
Outside Partnerships
Providence has established partnerships with outside facilities by providing services to 135 sites across eight states. COVID-19 accelerated the employment of new services, including TeleICU.
Telemedicine at Sound Physicians
Sound Physicians is a national physician-founded and -led organization that provides emergency medicine, critical care, hospital medicine, population health, and physician advisory services. Five years ago, Sound launched a telemedicine service line. I spoke with Brian Carpenter, MD, national medical director for TeleHospitalist Services at Sound, to learn about his experience implementing Telehospitalist programs across 22 hospitals and 22 skilled nursing facilities.
Prior to COVID-19, Sound offered a spectrum of telemedicine services including night-time telephonic cross coverage, as well as video-assisted admissions, transfers, and rapid responses. In 2019, Sound Telehospitalists received 88,000 connect requests, including 6,400 video-assisted new admissions and 82 rapid responses. Typically, one physician covers four to eight hospitals with back-up available for surges. The team uses a predictive model for staffing and developed an acuity-based algorithm to ensure that patients in distress are evaluated immediately, new stable admissions on average are seen within 12 minutes, and order clarifications are provided within 30 minutes.
The COVID-19 pandemic created an urgent demand for providers to support an overwhelmed health care system. Without the traditional barriers to implementation – such as lack of acceptance by medical staff, nurses and patients, strict state licensing and technology requirements, lack of reimbursement, and delays in hospital credentialing – Sound was able to develop a rapid implementation model for telemedicine services. Currently, four new hospitals are in the active implementation phase, with 40 more hospitals in the pipeline.
Implementing a telemedicine program at your hospital
In order to successfully launch a telemedicine program, Dr. Carpenter outlined the following critical implementation steps:
- In collaboration with local leadership, define the problem you are trying to solve, which helps inform the scope of the telemedicine practice and technology requirements (for example, night-time cross-coverage vs. full telemedicine service).
- Complete a discovery process (for example, existing workflow for patient admission and transfer) with the end-goal of developing a workflow and rules of engagement.
- Obtain hospital credentialing/privileges and EMR access.
- Train end-users, including physicians and nurse telepresenters.
Dr. Carpenter offered this advice to those considering a telemedicine program: “Telemedicine is not just about technology; a true telemedicine program encompasses change management, workflow development, end-user training, compliance, and mechanisms for continuous process improvement. We want to make things better for the physicians, nurses, and patients.”
Telehealth is offering support to health care providers on the front lines, patients in need of care, and health care systems managing the unprecedented surges in volume.
Dr. Farah is a hospitalist, physician adviser, and Lean Six Sigma Black Belt. She is a performance improvement consultant based in Corvallis, Ore., and a member of The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board.
On Jan. 20, 2020, the first confirmed case of the 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States was admitted to Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash. Less than 3 months later, the COVID-19 pandemic has put enormous stress on the U.S. health care system, which is confronting acute resource shortage because of the surge of acute and critically ill patients, health care provider safety and burnout, and an ongoing need for managing vulnerable populations while minimizing the infection spread.
With the onset of these unprecedented challenges, telehealth has emerged as a powerful new resource for health care providers, hospitals, and health care systems across the country. This article offers a summary of government regulations that enabled telehealth expansion, and provides an overview of how two health care organizations, Providence St. Joseph Health and Sound Physicians, are employing telehealth services to combat the COVID-19 health care crisis.
The government response: Telehealth expansion
In response to the pandemic, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) have significantly increased access to telehealth services for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries. CMS swiftly put measures in place such as:
- Expanding telehealth beyond rural areas.
- Adding 80 services that can be provided in all settings, including patient homes
- Allowing providers to bill for telehealth visits at the same rate as in-person visits.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services also aided this effort by:
- Waiving requirements that physicians or other health care professionals must have licenses in the state in which they provide services, if they have an equivalent license from another state.
- Waving penalties for HIPAA violations against health care providers that serve patients in good faith through everyday communications technologies, such as FaceTime or Skype
Without prior regulatory and reimbursement restrictions, telehealth rapidly became a powerful tool in helping to solve some of the problems brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Providence Telehealth for COVID-19
Providence St. Joseph Health is a not-for-profit health care system operating 51 hospitals and 1,085 clinics across Alaska, California, Montana, New Mexico, Oregon, Texas, and Washington. Providence has developed an enterprise telemedicine network with more than 100 virtual programs. Several of these services – including Telestroke, Telepsychiatry, TeleICU, and Telehospitalist – have been scaled across several states as a clinical cloud. More than 400 telemedicine endpoints are deployed, such as robotic carts and fixed InTouch TVs. In fact, the first U.S. COVID-19 patient was treated at Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash., using the telemedical robot Vici from InTouch Health.
According to Todd Czartoski, MD, chief medical technology officer at Providence, “while telehealth has been around for many years, COVID-19 opened a lot of people’s eyes to the value of virtual care delivery.”
Providence’s telehealth response to COVID-19 has encompassed five main areas: COVID-19 home care, COVID-19 acute care, ambulatory virtual visits, behavioral health concierge (BHC) expansion, and additional support for outside partnerships.
COVID-19 Home Care
Providence rapidly deployed home monitoring for nearly 2,000 positive or presumptive COVID-19 patients. Those symptomatic, clinically stable patients are given a thermometer and a pulse oximeter, and are monitored from home by a central team of nurses and physicians using the Xealth and Twistle programs.
Providence is evaluating expansion of home monitoring to other diagnoses, including higher acuity conditions.
COVID-19 Acute Care
TeleTriage expedites the triage of suspected COVID-19 patients and reduces the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by 50% per patient per day. To date, TeleTriage has resulted in the conservation of more than 90,000 PPE units.
TeleHospitalist services expanded from traditional night coverage to caring for patients in COVID-19 units around the clock. Currently, there are 25 telehospitalists who practice both in-person and virtual medicine.
TeleICU offers remote management of more than 180 ICU beds across 17 hospitals from two central command centers in Washington state and Alaska. The services include night-time intensivist and ICU nurse coverage, including medication and ventilator management, and family conferences. COVID-19 increased the demand for TeleICU, with anticipated expansion to more than 300 beds.
Core TeleSpecialty services include TeleStroke and TelePsychiatry across 135 remote sites.
Ambulatory Virtual Visits
Providence launched the COVID-19 hub microsite to help educate patients by providing accurate and timely information. A chatbot named Grace helps screen patients who are worried about COVID-19. Grace also suggests next steps, such as a video visit with a patient’s primary care provider or a visit using Express Care/Virtual team, a direct-to-consumer service available to patients within and outside of the health care system.
In less than 2 weeks, Providence enabled virtual visits for more than 7,000 outpatient providers, with more than 14,000 alternative visits now occurring daily. This has allowed primary and specialty providers to continue to manage their patient panels remotely. The number of Express Care/Virtual visits increased from 60 to more than 1,000 per day.
BHC Expansion
In the effort to improve care for its caregivers, Providence launched a behavioral health concierge (BHC) service that offers employees and their dependents virtual access to licensed mental health professionals. Over the last half of 2019, BHC provided more than 1,000 phone and virtual visits, depending on the individual preference of patients. Notably, 21% percent of users were physicians; 65% of users were seen the same day and 100% of users were seen within 48 hours.
COVID-19 increased demand for services that initially started in Seattle and rapidly expanded to Montana, Oregon, and California.
Outside Partnerships
Providence has established partnerships with outside facilities by providing services to 135 sites across eight states. COVID-19 accelerated the employment of new services, including TeleICU.
Telemedicine at Sound Physicians
Sound Physicians is a national physician-founded and -led organization that provides emergency medicine, critical care, hospital medicine, population health, and physician advisory services. Five years ago, Sound launched a telemedicine service line. I spoke with Brian Carpenter, MD, national medical director for TeleHospitalist Services at Sound, to learn about his experience implementing Telehospitalist programs across 22 hospitals and 22 skilled nursing facilities.
Prior to COVID-19, Sound offered a spectrum of telemedicine services including night-time telephonic cross coverage, as well as video-assisted admissions, transfers, and rapid responses. In 2019, Sound Telehospitalists received 88,000 connect requests, including 6,400 video-assisted new admissions and 82 rapid responses. Typically, one physician covers four to eight hospitals with back-up available for surges. The team uses a predictive model for staffing and developed an acuity-based algorithm to ensure that patients in distress are evaluated immediately, new stable admissions on average are seen within 12 minutes, and order clarifications are provided within 30 minutes.
The COVID-19 pandemic created an urgent demand for providers to support an overwhelmed health care system. Without the traditional barriers to implementation – such as lack of acceptance by medical staff, nurses and patients, strict state licensing and technology requirements, lack of reimbursement, and delays in hospital credentialing – Sound was able to develop a rapid implementation model for telemedicine services. Currently, four new hospitals are in the active implementation phase, with 40 more hospitals in the pipeline.
Implementing a telemedicine program at your hospital
In order to successfully launch a telemedicine program, Dr. Carpenter outlined the following critical implementation steps:
- In collaboration with local leadership, define the problem you are trying to solve, which helps inform the scope of the telemedicine practice and technology requirements (for example, night-time cross-coverage vs. full telemedicine service).
- Complete a discovery process (for example, existing workflow for patient admission and transfer) with the end-goal of developing a workflow and rules of engagement.
- Obtain hospital credentialing/privileges and EMR access.
- Train end-users, including physicians and nurse telepresenters.
Dr. Carpenter offered this advice to those considering a telemedicine program: “Telemedicine is not just about technology; a true telemedicine program encompasses change management, workflow development, end-user training, compliance, and mechanisms for continuous process improvement. We want to make things better for the physicians, nurses, and patients.”
Telehealth is offering support to health care providers on the front lines, patients in need of care, and health care systems managing the unprecedented surges in volume.
Dr. Farah is a hospitalist, physician adviser, and Lean Six Sigma Black Belt. She is a performance improvement consultant based in Corvallis, Ore., and a member of The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board.
On Jan. 20, 2020, the first confirmed case of the 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States was admitted to Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash. Less than 3 months later, the COVID-19 pandemic has put enormous stress on the U.S. health care system, which is confronting acute resource shortage because of the surge of acute and critically ill patients, health care provider safety and burnout, and an ongoing need for managing vulnerable populations while minimizing the infection spread.
With the onset of these unprecedented challenges, telehealth has emerged as a powerful new resource for health care providers, hospitals, and health care systems across the country. This article offers a summary of government regulations that enabled telehealth expansion, and provides an overview of how two health care organizations, Providence St. Joseph Health and Sound Physicians, are employing telehealth services to combat the COVID-19 health care crisis.
The government response: Telehealth expansion
In response to the pandemic, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) have significantly increased access to telehealth services for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries. CMS swiftly put measures in place such as:
- Expanding telehealth beyond rural areas.
- Adding 80 services that can be provided in all settings, including patient homes
- Allowing providers to bill for telehealth visits at the same rate as in-person visits.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services also aided this effort by:
- Waiving requirements that physicians or other health care professionals must have licenses in the state in which they provide services, if they have an equivalent license from another state.
- Waving penalties for HIPAA violations against health care providers that serve patients in good faith through everyday communications technologies, such as FaceTime or Skype
Without prior regulatory and reimbursement restrictions, telehealth rapidly became a powerful tool in helping to solve some of the problems brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Providence Telehealth for COVID-19
Providence St. Joseph Health is a not-for-profit health care system operating 51 hospitals and 1,085 clinics across Alaska, California, Montana, New Mexico, Oregon, Texas, and Washington. Providence has developed an enterprise telemedicine network with more than 100 virtual programs. Several of these services – including Telestroke, Telepsychiatry, TeleICU, and Telehospitalist – have been scaled across several states as a clinical cloud. More than 400 telemedicine endpoints are deployed, such as robotic carts and fixed InTouch TVs. In fact, the first U.S. COVID-19 patient was treated at Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash., using the telemedical robot Vici from InTouch Health.
According to Todd Czartoski, MD, chief medical technology officer at Providence, “while telehealth has been around for many years, COVID-19 opened a lot of people’s eyes to the value of virtual care delivery.”
Providence’s telehealth response to COVID-19 has encompassed five main areas: COVID-19 home care, COVID-19 acute care, ambulatory virtual visits, behavioral health concierge (BHC) expansion, and additional support for outside partnerships.
COVID-19 Home Care
Providence rapidly deployed home monitoring for nearly 2,000 positive or presumptive COVID-19 patients. Those symptomatic, clinically stable patients are given a thermometer and a pulse oximeter, and are monitored from home by a central team of nurses and physicians using the Xealth and Twistle programs.
Providence is evaluating expansion of home monitoring to other diagnoses, including higher acuity conditions.
COVID-19 Acute Care
TeleTriage expedites the triage of suspected COVID-19 patients and reduces the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by 50% per patient per day. To date, TeleTriage has resulted in the conservation of more than 90,000 PPE units.
TeleHospitalist services expanded from traditional night coverage to caring for patients in COVID-19 units around the clock. Currently, there are 25 telehospitalists who practice both in-person and virtual medicine.
TeleICU offers remote management of more than 180 ICU beds across 17 hospitals from two central command centers in Washington state and Alaska. The services include night-time intensivist and ICU nurse coverage, including medication and ventilator management, and family conferences. COVID-19 increased the demand for TeleICU, with anticipated expansion to more than 300 beds.
Core TeleSpecialty services include TeleStroke and TelePsychiatry across 135 remote sites.
Ambulatory Virtual Visits
Providence launched the COVID-19 hub microsite to help educate patients by providing accurate and timely information. A chatbot named Grace helps screen patients who are worried about COVID-19. Grace also suggests next steps, such as a video visit with a patient’s primary care provider or a visit using Express Care/Virtual team, a direct-to-consumer service available to patients within and outside of the health care system.
In less than 2 weeks, Providence enabled virtual visits for more than 7,000 outpatient providers, with more than 14,000 alternative visits now occurring daily. This has allowed primary and specialty providers to continue to manage their patient panels remotely. The number of Express Care/Virtual visits increased from 60 to more than 1,000 per day.
BHC Expansion
In the effort to improve care for its caregivers, Providence launched a behavioral health concierge (BHC) service that offers employees and their dependents virtual access to licensed mental health professionals. Over the last half of 2019, BHC provided more than 1,000 phone and virtual visits, depending on the individual preference of patients. Notably, 21% percent of users were physicians; 65% of users were seen the same day and 100% of users were seen within 48 hours.
COVID-19 increased demand for services that initially started in Seattle and rapidly expanded to Montana, Oregon, and California.
Outside Partnerships
Providence has established partnerships with outside facilities by providing services to 135 sites across eight states. COVID-19 accelerated the employment of new services, including TeleICU.
Telemedicine at Sound Physicians
Sound Physicians is a national physician-founded and -led organization that provides emergency medicine, critical care, hospital medicine, population health, and physician advisory services. Five years ago, Sound launched a telemedicine service line. I spoke with Brian Carpenter, MD, national medical director for TeleHospitalist Services at Sound, to learn about his experience implementing Telehospitalist programs across 22 hospitals and 22 skilled nursing facilities.
Prior to COVID-19, Sound offered a spectrum of telemedicine services including night-time telephonic cross coverage, as well as video-assisted admissions, transfers, and rapid responses. In 2019, Sound Telehospitalists received 88,000 connect requests, including 6,400 video-assisted new admissions and 82 rapid responses. Typically, one physician covers four to eight hospitals with back-up available for surges. The team uses a predictive model for staffing and developed an acuity-based algorithm to ensure that patients in distress are evaluated immediately, new stable admissions on average are seen within 12 minutes, and order clarifications are provided within 30 minutes.
The COVID-19 pandemic created an urgent demand for providers to support an overwhelmed health care system. Without the traditional barriers to implementation – such as lack of acceptance by medical staff, nurses and patients, strict state licensing and technology requirements, lack of reimbursement, and delays in hospital credentialing – Sound was able to develop a rapid implementation model for telemedicine services. Currently, four new hospitals are in the active implementation phase, with 40 more hospitals in the pipeline.
Implementing a telemedicine program at your hospital
In order to successfully launch a telemedicine program, Dr. Carpenter outlined the following critical implementation steps:
- In collaboration with local leadership, define the problem you are trying to solve, which helps inform the scope of the telemedicine practice and technology requirements (for example, night-time cross-coverage vs. full telemedicine service).
- Complete a discovery process (for example, existing workflow for patient admission and transfer) with the end-goal of developing a workflow and rules of engagement.
- Obtain hospital credentialing/privileges and EMR access.
- Train end-users, including physicians and nurse telepresenters.
Dr. Carpenter offered this advice to those considering a telemedicine program: “Telemedicine is not just about technology; a true telemedicine program encompasses change management, workflow development, end-user training, compliance, and mechanisms for continuous process improvement. We want to make things better for the physicians, nurses, and patients.”
Telehealth is offering support to health care providers on the front lines, patients in need of care, and health care systems managing the unprecedented surges in volume.
Dr. Farah is a hospitalist, physician adviser, and Lean Six Sigma Black Belt. She is a performance improvement consultant based in Corvallis, Ore., and a member of The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board.
Practice During the Pandemic
The first installment of my new column was obsolete on arrival. It referred to walking abroad at midday, with no mention of masks and social distancing. The whole thing was so February 2020.
My last day in the office was in mid-March. Friday the 13th.
, using stored and forwarded images.
What I had in mind was visits by patients in nursing homes or too sick at home to come in. It always bothered me to see very aged and infirm patients brought to the office at great inconvenience and expense for what often turned out to be problems like xerosis or eczema that could have been managed quite well remotely.
The HMO never got back to me, though. There were too many hurdles, mostly bureaucratic rather than medical. Would insurance pay? What about consent? Malpractice? It has been interesting to watch the current crisis sweep away the inertia of such obstacles, including licensure considerations (seeing patients across state lines for cutaneous purposes). People get around to fixing the roof when it pours. Perhaps next time there will be tests, masks, respirators. Perhaps.
Seeing patients remotely has acquainted me with all the technical headaches everyone stuck at home talks and jokes about: Balky transmission (What did you say after, “and then the blood ...”?); patients who can’t figure out how to log on, or start the video, or unmute themselves, and on and on. Picture resolution is not great, as anyone knows from watching TV newscasters interview talking heads stuck in their homes.
I was never all that image-conscious, but my beard has grown fuller and my hair unkempter. Even though I sit at my desk, I do take care to keep my trousers on. Not taking any chances.
Everyone agonizes over what the “new normal” may be. Will people come back to doctors’ offices? Will practices survive economically if many patients don’t return to the office? Stay tuned. For a long time.
Mostly, though, remote visits seem to work. Helped if needed by additional, better-resolution emailed photos, it’s possible to make useful decisions, including which lesions can wait for in-person evaluation, until ...
... Until what? In an effort to keep this column up-to-the-nanosecond, I am writing it as many countries tentatively “open up.” Careful analysis of the knowledge behind this world-wide project shows ... not much. It seems to come down to some educated guesswork about what might work and what the risks might be, which leads to advice that differs widely from state to state and country to country. It’s as if people everywhere just decided that locking everyone down is a real drag, is financially ruinous, has a duration both uncertain and longer than most people and governments think they can handle, so let’s get out there and “be careful,” whatever that is said to mean.
And the risks? Well, more people will get sick and some will die. How many “extra” deaths are ethically acceptable? Thoughtful people are working on that. They’ll get back sometime to those who are still around.
I don’t blame anyone for our staggering ignorance about this terrifying new reality. But absorbing the ignorance in real time is not reassuring.
I have nothing but sympathy for those who are not emeritus, who have practices to sustain and families to feed. I didn’t ask to be born 73 years ago, and take no credit for having done so. So much of what happens to us depends on when and where we were born – two factors for which we deserve absolutely no credit – that it’s a wonder we take such pride in praising ourselves for what we think we accomplish. Having no better choice, we do the best we can.
Meantime, I am in a “high-risk” category. If I were obese, I could try to lose weight. But my risk factor is age, which tends not to decline. Risk-wise, there is just one way to exit my group.
So I don’t expect to get back to the office anytime soon. To paraphrase a comedian who shall remain nameless: I don’t want to live on in the hearts of men. I want to live on in my house.
Dr. Rockoff, who wrote the Dermatology News column “Under My Skin,” is now semiretired, after 40 years of practice in Brookline, Mass. He served on the clinical faculty at Tufts University, Boston, and taught senior medical students and other trainees for 30 years. His second book, “Act Like a Doctor, Think Like a Patient,” is available online. Write to him at [email protected].
The first installment of my new column was obsolete on arrival. It referred to walking abroad at midday, with no mention of masks and social distancing. The whole thing was so February 2020.
My last day in the office was in mid-March. Friday the 13th.
, using stored and forwarded images.
What I had in mind was visits by patients in nursing homes or too sick at home to come in. It always bothered me to see very aged and infirm patients brought to the office at great inconvenience and expense for what often turned out to be problems like xerosis or eczema that could have been managed quite well remotely.
The HMO never got back to me, though. There were too many hurdles, mostly bureaucratic rather than medical. Would insurance pay? What about consent? Malpractice? It has been interesting to watch the current crisis sweep away the inertia of such obstacles, including licensure considerations (seeing patients across state lines for cutaneous purposes). People get around to fixing the roof when it pours. Perhaps next time there will be tests, masks, respirators. Perhaps.
Seeing patients remotely has acquainted me with all the technical headaches everyone stuck at home talks and jokes about: Balky transmission (What did you say after, “and then the blood ...”?); patients who can’t figure out how to log on, or start the video, or unmute themselves, and on and on. Picture resolution is not great, as anyone knows from watching TV newscasters interview talking heads stuck in their homes.
I was never all that image-conscious, but my beard has grown fuller and my hair unkempter. Even though I sit at my desk, I do take care to keep my trousers on. Not taking any chances.
Everyone agonizes over what the “new normal” may be. Will people come back to doctors’ offices? Will practices survive economically if many patients don’t return to the office? Stay tuned. For a long time.
Mostly, though, remote visits seem to work. Helped if needed by additional, better-resolution emailed photos, it’s possible to make useful decisions, including which lesions can wait for in-person evaluation, until ...
... Until what? In an effort to keep this column up-to-the-nanosecond, I am writing it as many countries tentatively “open up.” Careful analysis of the knowledge behind this world-wide project shows ... not much. It seems to come down to some educated guesswork about what might work and what the risks might be, which leads to advice that differs widely from state to state and country to country. It’s as if people everywhere just decided that locking everyone down is a real drag, is financially ruinous, has a duration both uncertain and longer than most people and governments think they can handle, so let’s get out there and “be careful,” whatever that is said to mean.
And the risks? Well, more people will get sick and some will die. How many “extra” deaths are ethically acceptable? Thoughtful people are working on that. They’ll get back sometime to those who are still around.
I don’t blame anyone for our staggering ignorance about this terrifying new reality. But absorbing the ignorance in real time is not reassuring.
I have nothing but sympathy for those who are not emeritus, who have practices to sustain and families to feed. I didn’t ask to be born 73 years ago, and take no credit for having done so. So much of what happens to us depends on when and where we were born – two factors for which we deserve absolutely no credit – that it’s a wonder we take such pride in praising ourselves for what we think we accomplish. Having no better choice, we do the best we can.
Meantime, I am in a “high-risk” category. If I were obese, I could try to lose weight. But my risk factor is age, which tends not to decline. Risk-wise, there is just one way to exit my group.
So I don’t expect to get back to the office anytime soon. To paraphrase a comedian who shall remain nameless: I don’t want to live on in the hearts of men. I want to live on in my house.
Dr. Rockoff, who wrote the Dermatology News column “Under My Skin,” is now semiretired, after 40 years of practice in Brookline, Mass. He served on the clinical faculty at Tufts University, Boston, and taught senior medical students and other trainees for 30 years. His second book, “Act Like a Doctor, Think Like a Patient,” is available online. Write to him at [email protected].
The first installment of my new column was obsolete on arrival. It referred to walking abroad at midday, with no mention of masks and social distancing. The whole thing was so February 2020.
My last day in the office was in mid-March. Friday the 13th.
, using stored and forwarded images.
What I had in mind was visits by patients in nursing homes or too sick at home to come in. It always bothered me to see very aged and infirm patients brought to the office at great inconvenience and expense for what often turned out to be problems like xerosis or eczema that could have been managed quite well remotely.
The HMO never got back to me, though. There were too many hurdles, mostly bureaucratic rather than medical. Would insurance pay? What about consent? Malpractice? It has been interesting to watch the current crisis sweep away the inertia of such obstacles, including licensure considerations (seeing patients across state lines for cutaneous purposes). People get around to fixing the roof when it pours. Perhaps next time there will be tests, masks, respirators. Perhaps.
Seeing patients remotely has acquainted me with all the technical headaches everyone stuck at home talks and jokes about: Balky transmission (What did you say after, “and then the blood ...”?); patients who can’t figure out how to log on, or start the video, or unmute themselves, and on and on. Picture resolution is not great, as anyone knows from watching TV newscasters interview talking heads stuck in their homes.
I was never all that image-conscious, but my beard has grown fuller and my hair unkempter. Even though I sit at my desk, I do take care to keep my trousers on. Not taking any chances.
Everyone agonizes over what the “new normal” may be. Will people come back to doctors’ offices? Will practices survive economically if many patients don’t return to the office? Stay tuned. For a long time.
Mostly, though, remote visits seem to work. Helped if needed by additional, better-resolution emailed photos, it’s possible to make useful decisions, including which lesions can wait for in-person evaluation, until ...
... Until what? In an effort to keep this column up-to-the-nanosecond, I am writing it as many countries tentatively “open up.” Careful analysis of the knowledge behind this world-wide project shows ... not much. It seems to come down to some educated guesswork about what might work and what the risks might be, which leads to advice that differs widely from state to state and country to country. It’s as if people everywhere just decided that locking everyone down is a real drag, is financially ruinous, has a duration both uncertain and longer than most people and governments think they can handle, so let’s get out there and “be careful,” whatever that is said to mean.
And the risks? Well, more people will get sick and some will die. How many “extra” deaths are ethically acceptable? Thoughtful people are working on that. They’ll get back sometime to those who are still around.
I don’t blame anyone for our staggering ignorance about this terrifying new reality. But absorbing the ignorance in real time is not reassuring.
I have nothing but sympathy for those who are not emeritus, who have practices to sustain and families to feed. I didn’t ask to be born 73 years ago, and take no credit for having done so. So much of what happens to us depends on when and where we were born – two factors for which we deserve absolutely no credit – that it’s a wonder we take such pride in praising ourselves for what we think we accomplish. Having no better choice, we do the best we can.
Meantime, I am in a “high-risk” category. If I were obese, I could try to lose weight. But my risk factor is age, which tends not to decline. Risk-wise, there is just one way to exit my group.
So I don’t expect to get back to the office anytime soon. To paraphrase a comedian who shall remain nameless: I don’t want to live on in the hearts of men. I want to live on in my house.
Dr. Rockoff, who wrote the Dermatology News column “Under My Skin,” is now semiretired, after 40 years of practice in Brookline, Mass. He served on the clinical faculty at Tufts University, Boston, and taught senior medical students and other trainees for 30 years. His second book, “Act Like a Doctor, Think Like a Patient,” is available online. Write to him at [email protected].
Obesity can shift severe COVID-19 to younger age groups
published in The Lancet.
“By itself, obesity seems to be a sufficient risk factor to start seeing younger people landing in the ICU,” said the study’s lead author, David Kass, MD, a professor of cardiology and medicine at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland.
“In that sense, there’s a simple message: If you’re very, very overweight, don’t think that if you’re 35 you’re that much safer [from severe COVID-19] than your mother or grandparents or others in their 60s or 70s,” Kass told Medscape Medical News.
The findings, which Kass describes as a “2-week snapshot” of 265 patients (58% male) in late March and early April at a handful of university hospitals in the United States reinforces other recent research indicating that obesity is one of the biggest risk factors for severe COVID-19 disease, particularly among younger patients. In addition, a large British study showed that, after adjusting for comorbidities, obesity was a significant factor associated with in-hospital death in COVID-19.
But this new analysis stands out as the only dataset to date that specifically “asks the question relative to age” of whether severe COVID-19 disease correlates to ICU treatment, he said.
The mean age of his study population of ICU patients was 55, Kass said, “and that was young, not what we were expecting.”
“Even with the first 20 patients, we were already seeing younger people and they definitely were heavier, with plenty of patients with a BMI over 35 kg/m2,” he added. “The relationship was pretty tight, pretty quick.”
“Just don’t make the assumption that any of us are too young to be vulnerable if, in fact, this is an aspect of our bodies,” he said.
Steven Heymsfield, MD, past president and a spokesperson for the Obesity Society, agrees with Kass’ conclusions.
“One thing we’ve had on our minds is that the prototype of a person with this disease is older...but now if we get [a patient] who’s symptomatic and 40 and obese, we shouldn’t assume they have some other disease,” Heymsfield told Medscape Medical News.
“We should think of them as a susceptible population.”
Kass and colleagues agree. “Public messaging to younger adults, reducing the threshold for virus testing in obese individuals, and maintaining greater vigilance for this at-risk population should reduce the prevalence of severe COVID-19 disease [among those with obesity],” they state.
“I think it’s a mental adjustment from a health care standpoint, which might hopefully help target the folks who are at higher risk before they get into trouble,” Kass told Medscape Medical News.
Trio of mechanisms explain obesity’s extra COVID-19 risks
Kass and coauthors write that, in analyzing their data, they anticipated similar results to the largest study of 1591 ICU patients from Italy in which only 203 were younger than 51 years. Common comorbidities among those patients included hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes, with similar data reported from China.
When the COVID-19 epidemic accelerated in the United States, older age was also identified as a risk factor. Obesity had not yet been added to this list, Kass noted. But following informal discussions with colleagues in other ICUs around the country, he decided to investigate further as to whether it was an underappreciated risk factor.
Kass and colleagues did a quick evaluation of the link between BMI and age of patients with COVID-19 admitted to ICUs at Johns Hopkins, University of Cincinnati, New York University, University of Washington, Florida Health, and University of Pennsylvania.
The “significant inverse correlation between age and BMI” showed younger ICU patients were more likely to be obese, with no difference by gender.
Median BMI among study participants was 29.3 kg/m2, with only a quarter having a BMI lower than 26 kg/m2 and another 25% having a BMI higher than 34.7 kg/m2.
Kass acknowledged that it wasn’t possible with this simple dataset to account for any other potential confounders, but he told Medscape Medical News that, “while diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension, for example, can occur with obesity, this is generally less so in younger populations as it takes time for the other comorbidities to develop.”
He said several mechanisms could explain why obesity predisposes patients with COVID-19 to severe disease.
For one, obesity places extra pressure on the diaphragm while lying on the back, restricting breathing.
“Morbid obesity itself is sort of proinflammatory,” he continued.
“Here we’ve got a viral infection where the early reports suggest that cytokine storms and immune mishandling of the virus are why it’s so much more severe than other forms of coronavirus we’ve seen before. So if you have someone with an already underlying proinflammatory state, this could be a reason there’s higher risk.”
Additionally, the angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) receptor to which the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 attaches is expressed in higher amounts in adipose tissue than the lungs, Kass noted.
“This could turn into kind of a viral replication depot,” he explained. “You may well be brewing more virus as a component of obesity.”
Sensitivity needed in public messaging about risks, but test sooner
With an obesity rate of about 40% in the United States, the results are particularly relevant for Americans, Kass and Heymsfield say, noting that the country’s “obesity belt” runs through the South.
Heymsfield, who wasn’t part of the new analysis, notes that public messaging around severe COVID-19 risks to younger adults with obesity is “tricky,” especially because the virus is “still pretty common in nonobese people.”
Kass agrees, noting, “it’s difficult to turn to 40% of the population and say: ‘You guys have to watch it.’ ”
But the mounting research findings necessitate linking obesity with severe COVID-19 disease and perhaps testing patients in this category for the virus sooner before symptoms become severe.
And of note, since shortness of breath is common among people with obesity regardless of illness, similar COVID-19 symptoms might catch these individuals unaware, pointed out Heymsfield, who is also a professor in the Metabolism and Body Composition Lab at Pennington Biomedical Research Center at Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge.
“They may find themselves literally unable to breathe, and the concern would be that they wait much too long to come in” for treatment, he said. Typically, people can deteriorate between day 7 and 10 of the COVID-19 infection.
Individuals with obesity “need to be educated to recognize the serious complications of COVID-19 often appear suddenly, although the virus has sometimes been working its way through the body for a long time,” he concluded.
Kass and Heymsfield have declared no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
published in The Lancet.
“By itself, obesity seems to be a sufficient risk factor to start seeing younger people landing in the ICU,” said the study’s lead author, David Kass, MD, a professor of cardiology and medicine at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland.
“In that sense, there’s a simple message: If you’re very, very overweight, don’t think that if you’re 35 you’re that much safer [from severe COVID-19] than your mother or grandparents or others in their 60s or 70s,” Kass told Medscape Medical News.
The findings, which Kass describes as a “2-week snapshot” of 265 patients (58% male) in late March and early April at a handful of university hospitals in the United States reinforces other recent research indicating that obesity is one of the biggest risk factors for severe COVID-19 disease, particularly among younger patients. In addition, a large British study showed that, after adjusting for comorbidities, obesity was a significant factor associated with in-hospital death in COVID-19.
But this new analysis stands out as the only dataset to date that specifically “asks the question relative to age” of whether severe COVID-19 disease correlates to ICU treatment, he said.
The mean age of his study population of ICU patients was 55, Kass said, “and that was young, not what we were expecting.”
“Even with the first 20 patients, we were already seeing younger people and they definitely were heavier, with plenty of patients with a BMI over 35 kg/m2,” he added. “The relationship was pretty tight, pretty quick.”
“Just don’t make the assumption that any of us are too young to be vulnerable if, in fact, this is an aspect of our bodies,” he said.
Steven Heymsfield, MD, past president and a spokesperson for the Obesity Society, agrees with Kass’ conclusions.
“One thing we’ve had on our minds is that the prototype of a person with this disease is older...but now if we get [a patient] who’s symptomatic and 40 and obese, we shouldn’t assume they have some other disease,” Heymsfield told Medscape Medical News.
“We should think of them as a susceptible population.”
Kass and colleagues agree. “Public messaging to younger adults, reducing the threshold for virus testing in obese individuals, and maintaining greater vigilance for this at-risk population should reduce the prevalence of severe COVID-19 disease [among those with obesity],” they state.
“I think it’s a mental adjustment from a health care standpoint, which might hopefully help target the folks who are at higher risk before they get into trouble,” Kass told Medscape Medical News.
Trio of mechanisms explain obesity’s extra COVID-19 risks
Kass and coauthors write that, in analyzing their data, they anticipated similar results to the largest study of 1591 ICU patients from Italy in which only 203 were younger than 51 years. Common comorbidities among those patients included hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes, with similar data reported from China.
When the COVID-19 epidemic accelerated in the United States, older age was also identified as a risk factor. Obesity had not yet been added to this list, Kass noted. But following informal discussions with colleagues in other ICUs around the country, he decided to investigate further as to whether it was an underappreciated risk factor.
Kass and colleagues did a quick evaluation of the link between BMI and age of patients with COVID-19 admitted to ICUs at Johns Hopkins, University of Cincinnati, New York University, University of Washington, Florida Health, and University of Pennsylvania.
The “significant inverse correlation between age and BMI” showed younger ICU patients were more likely to be obese, with no difference by gender.
Median BMI among study participants was 29.3 kg/m2, with only a quarter having a BMI lower than 26 kg/m2 and another 25% having a BMI higher than 34.7 kg/m2.
Kass acknowledged that it wasn’t possible with this simple dataset to account for any other potential confounders, but he told Medscape Medical News that, “while diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension, for example, can occur with obesity, this is generally less so in younger populations as it takes time for the other comorbidities to develop.”
He said several mechanisms could explain why obesity predisposes patients with COVID-19 to severe disease.
For one, obesity places extra pressure on the diaphragm while lying on the back, restricting breathing.
“Morbid obesity itself is sort of proinflammatory,” he continued.
“Here we’ve got a viral infection where the early reports suggest that cytokine storms and immune mishandling of the virus are why it’s so much more severe than other forms of coronavirus we’ve seen before. So if you have someone with an already underlying proinflammatory state, this could be a reason there’s higher risk.”
Additionally, the angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) receptor to which the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 attaches is expressed in higher amounts in adipose tissue than the lungs, Kass noted.
“This could turn into kind of a viral replication depot,” he explained. “You may well be brewing more virus as a component of obesity.”
Sensitivity needed in public messaging about risks, but test sooner
With an obesity rate of about 40% in the United States, the results are particularly relevant for Americans, Kass and Heymsfield say, noting that the country’s “obesity belt” runs through the South.
Heymsfield, who wasn’t part of the new analysis, notes that public messaging around severe COVID-19 risks to younger adults with obesity is “tricky,” especially because the virus is “still pretty common in nonobese people.”
Kass agrees, noting, “it’s difficult to turn to 40% of the population and say: ‘You guys have to watch it.’ ”
But the mounting research findings necessitate linking obesity with severe COVID-19 disease and perhaps testing patients in this category for the virus sooner before symptoms become severe.
And of note, since shortness of breath is common among people with obesity regardless of illness, similar COVID-19 symptoms might catch these individuals unaware, pointed out Heymsfield, who is also a professor in the Metabolism and Body Composition Lab at Pennington Biomedical Research Center at Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge.
“They may find themselves literally unable to breathe, and the concern would be that they wait much too long to come in” for treatment, he said. Typically, people can deteriorate between day 7 and 10 of the COVID-19 infection.
Individuals with obesity “need to be educated to recognize the serious complications of COVID-19 often appear suddenly, although the virus has sometimes been working its way through the body for a long time,” he concluded.
Kass and Heymsfield have declared no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
published in The Lancet.
“By itself, obesity seems to be a sufficient risk factor to start seeing younger people landing in the ICU,” said the study’s lead author, David Kass, MD, a professor of cardiology and medicine at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland.
“In that sense, there’s a simple message: If you’re very, very overweight, don’t think that if you’re 35 you’re that much safer [from severe COVID-19] than your mother or grandparents or others in their 60s or 70s,” Kass told Medscape Medical News.
The findings, which Kass describes as a “2-week snapshot” of 265 patients (58% male) in late March and early April at a handful of university hospitals in the United States reinforces other recent research indicating that obesity is one of the biggest risk factors for severe COVID-19 disease, particularly among younger patients. In addition, a large British study showed that, after adjusting for comorbidities, obesity was a significant factor associated with in-hospital death in COVID-19.
But this new analysis stands out as the only dataset to date that specifically “asks the question relative to age” of whether severe COVID-19 disease correlates to ICU treatment, he said.
The mean age of his study population of ICU patients was 55, Kass said, “and that was young, not what we were expecting.”
“Even with the first 20 patients, we were already seeing younger people and they definitely were heavier, with plenty of patients with a BMI over 35 kg/m2,” he added. “The relationship was pretty tight, pretty quick.”
“Just don’t make the assumption that any of us are too young to be vulnerable if, in fact, this is an aspect of our bodies,” he said.
Steven Heymsfield, MD, past president and a spokesperson for the Obesity Society, agrees with Kass’ conclusions.
“One thing we’ve had on our minds is that the prototype of a person with this disease is older...but now if we get [a patient] who’s symptomatic and 40 and obese, we shouldn’t assume they have some other disease,” Heymsfield told Medscape Medical News.
“We should think of them as a susceptible population.”
Kass and colleagues agree. “Public messaging to younger adults, reducing the threshold for virus testing in obese individuals, and maintaining greater vigilance for this at-risk population should reduce the prevalence of severe COVID-19 disease [among those with obesity],” they state.
“I think it’s a mental adjustment from a health care standpoint, which might hopefully help target the folks who are at higher risk before they get into trouble,” Kass told Medscape Medical News.
Trio of mechanisms explain obesity’s extra COVID-19 risks
Kass and coauthors write that, in analyzing their data, they anticipated similar results to the largest study of 1591 ICU patients from Italy in which only 203 were younger than 51 years. Common comorbidities among those patients included hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes, with similar data reported from China.
When the COVID-19 epidemic accelerated in the United States, older age was also identified as a risk factor. Obesity had not yet been added to this list, Kass noted. But following informal discussions with colleagues in other ICUs around the country, he decided to investigate further as to whether it was an underappreciated risk factor.
Kass and colleagues did a quick evaluation of the link between BMI and age of patients with COVID-19 admitted to ICUs at Johns Hopkins, University of Cincinnati, New York University, University of Washington, Florida Health, and University of Pennsylvania.
The “significant inverse correlation between age and BMI” showed younger ICU patients were more likely to be obese, with no difference by gender.
Median BMI among study participants was 29.3 kg/m2, with only a quarter having a BMI lower than 26 kg/m2 and another 25% having a BMI higher than 34.7 kg/m2.
Kass acknowledged that it wasn’t possible with this simple dataset to account for any other potential confounders, but he told Medscape Medical News that, “while diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension, for example, can occur with obesity, this is generally less so in younger populations as it takes time for the other comorbidities to develop.”
He said several mechanisms could explain why obesity predisposes patients with COVID-19 to severe disease.
For one, obesity places extra pressure on the diaphragm while lying on the back, restricting breathing.
“Morbid obesity itself is sort of proinflammatory,” he continued.
“Here we’ve got a viral infection where the early reports suggest that cytokine storms and immune mishandling of the virus are why it’s so much more severe than other forms of coronavirus we’ve seen before. So if you have someone with an already underlying proinflammatory state, this could be a reason there’s higher risk.”
Additionally, the angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) receptor to which the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 attaches is expressed in higher amounts in adipose tissue than the lungs, Kass noted.
“This could turn into kind of a viral replication depot,” he explained. “You may well be brewing more virus as a component of obesity.”
Sensitivity needed in public messaging about risks, but test sooner
With an obesity rate of about 40% in the United States, the results are particularly relevant for Americans, Kass and Heymsfield say, noting that the country’s “obesity belt” runs through the South.
Heymsfield, who wasn’t part of the new analysis, notes that public messaging around severe COVID-19 risks to younger adults with obesity is “tricky,” especially because the virus is “still pretty common in nonobese people.”
Kass agrees, noting, “it’s difficult to turn to 40% of the population and say: ‘You guys have to watch it.’ ”
But the mounting research findings necessitate linking obesity with severe COVID-19 disease and perhaps testing patients in this category for the virus sooner before symptoms become severe.
And of note, since shortness of breath is common among people with obesity regardless of illness, similar COVID-19 symptoms might catch these individuals unaware, pointed out Heymsfield, who is also a professor in the Metabolism and Body Composition Lab at Pennington Biomedical Research Center at Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge.
“They may find themselves literally unable to breathe, and the concern would be that they wait much too long to come in” for treatment, he said. Typically, people can deteriorate between day 7 and 10 of the COVID-19 infection.
Individuals with obesity “need to be educated to recognize the serious complications of COVID-19 often appear suddenly, although the virus has sometimes been working its way through the body for a long time,” he concluded.
Kass and Heymsfield have declared no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Triple-antiviral combo speeds COVID-19 recovery
A triple-antiviral therapy regimen of interferon-beta1, lopinavir/ritonavir, and ribavirin shortened median time to COVID-19 viral negativity by 5 days in a small trial from Hong Kong.
In an open-label, randomized phase 2 trial in patients with mild or moderate COVID-19 infections, the median time to viral negativity by nasopharyngeal swab was 7 days for 86 patients assigned to receive a 14-day course of lopinavir 400 mg and ritonavir 100 mg every 12 hours, ribavirin 400 mg every 12 hours, and three doses of 8 million international units of interferon beta-1b on alternate days, compared with a median time to negativity of 12 days for patients treated with lopinavir/ritonavir alone (P = .0010), wrote Ivan Fan-Ngai Hung, MD, from Gleaneagles Hospital in Hong Kong, and colleagues.
“Triple-antiviral therapy with interferon beta-1b, lopinavir/ritonavir, and ribavirin were safe and superior to lopinavir/ritonavir alone in shortening virus shedding, alleviating symptoms, and facilitating discharge of patients with mild to moderate COVID-19,” they wrote in a study published online in The Lancet.
Patients who received the combination also had significantly shorter time to complete alleviation of symptoms as assessed by a National Early Warning Score 2 (NEWS2, a system for detecting clinical deterioration in patients with acute illnesses) score of 0 (4 vs. 8 days, respectively; hazard ratio 3.92, P < .0001), and to a Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score of 0 (3 vs. 8 days, HR 1.89, P = .041).
The median hospital stay was 9 days for patients treated with the combination, compared with 14.5 days for controls (HR 2.72, P = .016).
In most patients treated with the combination, SARS-CoV-2 viral load was effectively suppressed in all clinical specimens, including nasopharyngeal swabs, throat and posterior oropharyngeal saliva, and stool.
In addition, serum levels of interleukin 6 (IL-6) – an inflammatory cytokine implicated in the cytokine storm frequently seen in patients with severe COVID-19 infections – were significantly lower on treatment days 2, 6, and 8 in patients treated with the combination, compared with those treated with lopinavir/ritonavir alone.
“Our trial demonstrates that early treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 with a triple combination of antiviral drugs may rapidly suppress the amount of virus in a patient’s body, relieve symptoms, and reduce the risk to health care workers by reducing the duration and quantity of viral shedding (when the virus is detectable and potentially transmissible). Furthermore, the treatment combination appeared safe and well tolerated by patients,” said lead investigator Professor Kwok-Yung Yuen from the University of Hong Kong, in a statement.
“Despite these encouraging findings,” he continued, “we must confirm in larger phase 3 trials that interferon beta-1b alone or in combination with other drugs is effective in patients with more severe illness (in whom the virus has had more time to replicate).”
Plausible rationale
Benjamin Medoff, MD, chief of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that the biologic rationale for the combination is plausible.
“I think this is a promising study that suggests that a regimen of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir/ritonavir, and ribavirin can shorten the duration of infection and improve symptoms in COVID-19 patients especially if started early in disease, in less than 7 days of symptom onset,” he said in reply to a request for expert analysis.
“The open-label nature and small size of the study limits the broad use of the regimen as noted by the authors, and it’s important to emphasize that the subjects enrolled did not have very severe disease (not in the ICU). However, the study does suggest that a larger truly randomized study is warranted,” he said.
AIDS drugs repurposed
Lopinavir/ritonavir is commonly used to treat HIV/AIDS throughout the world, and the investigators had previously reported that the antiviral agents combined with ribavirin reduced deaths and the need for intensive ventilator support among patients with SARS-CoV, the betacoronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), and antivirals have shown in vitro activity against both SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, the closely related pathogen that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome.
“ However the viral load of SARS and MERS peaks at around day 7-10 after symptom onset, whereas the viral load of COVID-19 peaks at the time of presentation, similar to influenza. Experience from the treatment of patients with influenza who are admitted to hospital suggested that a combination of multiple antiviral drugs is more effective than single-drug treatments in this setting of patients with a high viral load at presentation,” the investigators wrote.
To test this, they enrolled adults patients admitted to one of six Hong Kong Hospitals for virologically confirmed COVID-19 infections from Feb. 10 through March 20, 2020.
A total of 86 patients were randomly assigned to the combination and 41 to lopinavir/ritonavir alone as controls, at doses described above.
Patients who entered the trial within less than 7 days of symptom onset received the triple combination, with interferon dosing adjusted according to the day that treatment started. Patients recruited 1 or 2 days after symptom onset received three doses of interferon, patients started on day 3 or 4 received two doses, and those started on days 5 or 6 received one interferon dose. Patients recruited 7 days or later from symptom onset did not receive interferon beta-1b because of its proinflammatory effects.
In post-hoc analysis by day of treatment initiation, clinical and virological outcomes (except stool samples) were superior in patients admitted less than 7 days after symptom onset for the 52 patients who received a least one interferon dose plus lopinavir/ritonavir and ribavirin, compared with 24 patients randomized to the control arm (lopinavir/ritonavir only). In contrast, among patients admitted and started on treatment at day 7 or later after symptom onset, there were no differences between those who received lopinavir/ritonavir alone or combined with ribavirin.
Adverse events were reported in 41 of 86 patients in the combination group and 20 of 41 patients in the control arm. The most common adverse events were diarrhea, occurring in 52 of all 127 patients, fever in 48, nausea in 43, and elevated alanine transaminase level in 18. The side effects generally resolved within 3 days of the start of treatments.
There were no serious adverse events reported in the combination group. One patient in the control group had impaired hepatic enzymes requiring discontinuation of treatment. No patients died during the study.
The study was funded by the Shaw Foundation, Richard and Carol Yu, May Tam Mak Mei Yin, and Sanming Project of Medicine. The authors and Dr. Medoff declared no competing interests.
SOURCE: Hung IFN et al. Lancet. 2020 May 8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31101-6.
A triple-antiviral therapy regimen of interferon-beta1, lopinavir/ritonavir, and ribavirin shortened median time to COVID-19 viral negativity by 5 days in a small trial from Hong Kong.
In an open-label, randomized phase 2 trial in patients with mild or moderate COVID-19 infections, the median time to viral negativity by nasopharyngeal swab was 7 days for 86 patients assigned to receive a 14-day course of lopinavir 400 mg and ritonavir 100 mg every 12 hours, ribavirin 400 mg every 12 hours, and three doses of 8 million international units of interferon beta-1b on alternate days, compared with a median time to negativity of 12 days for patients treated with lopinavir/ritonavir alone (P = .0010), wrote Ivan Fan-Ngai Hung, MD, from Gleaneagles Hospital in Hong Kong, and colleagues.
“Triple-antiviral therapy with interferon beta-1b, lopinavir/ritonavir, and ribavirin were safe and superior to lopinavir/ritonavir alone in shortening virus shedding, alleviating symptoms, and facilitating discharge of patients with mild to moderate COVID-19,” they wrote in a study published online in The Lancet.
Patients who received the combination also had significantly shorter time to complete alleviation of symptoms as assessed by a National Early Warning Score 2 (NEWS2, a system for detecting clinical deterioration in patients with acute illnesses) score of 0 (4 vs. 8 days, respectively; hazard ratio 3.92, P < .0001), and to a Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score of 0 (3 vs. 8 days, HR 1.89, P = .041).
The median hospital stay was 9 days for patients treated with the combination, compared with 14.5 days for controls (HR 2.72, P = .016).
In most patients treated with the combination, SARS-CoV-2 viral load was effectively suppressed in all clinical specimens, including nasopharyngeal swabs, throat and posterior oropharyngeal saliva, and stool.
In addition, serum levels of interleukin 6 (IL-6) – an inflammatory cytokine implicated in the cytokine storm frequently seen in patients with severe COVID-19 infections – were significantly lower on treatment days 2, 6, and 8 in patients treated with the combination, compared with those treated with lopinavir/ritonavir alone.
“Our trial demonstrates that early treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 with a triple combination of antiviral drugs may rapidly suppress the amount of virus in a patient’s body, relieve symptoms, and reduce the risk to health care workers by reducing the duration and quantity of viral shedding (when the virus is detectable and potentially transmissible). Furthermore, the treatment combination appeared safe and well tolerated by patients,” said lead investigator Professor Kwok-Yung Yuen from the University of Hong Kong, in a statement.
“Despite these encouraging findings,” he continued, “we must confirm in larger phase 3 trials that interferon beta-1b alone or in combination with other drugs is effective in patients with more severe illness (in whom the virus has had more time to replicate).”
Plausible rationale
Benjamin Medoff, MD, chief of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that the biologic rationale for the combination is plausible.
“I think this is a promising study that suggests that a regimen of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir/ritonavir, and ribavirin can shorten the duration of infection and improve symptoms in COVID-19 patients especially if started early in disease, in less than 7 days of symptom onset,” he said in reply to a request for expert analysis.
“The open-label nature and small size of the study limits the broad use of the regimen as noted by the authors, and it’s important to emphasize that the subjects enrolled did not have very severe disease (not in the ICU). However, the study does suggest that a larger truly randomized study is warranted,” he said.
AIDS drugs repurposed
Lopinavir/ritonavir is commonly used to treat HIV/AIDS throughout the world, and the investigators had previously reported that the antiviral agents combined with ribavirin reduced deaths and the need for intensive ventilator support among patients with SARS-CoV, the betacoronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), and antivirals have shown in vitro activity against both SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, the closely related pathogen that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome.
“ However the viral load of SARS and MERS peaks at around day 7-10 after symptom onset, whereas the viral load of COVID-19 peaks at the time of presentation, similar to influenza. Experience from the treatment of patients with influenza who are admitted to hospital suggested that a combination of multiple antiviral drugs is more effective than single-drug treatments in this setting of patients with a high viral load at presentation,” the investigators wrote.
To test this, they enrolled adults patients admitted to one of six Hong Kong Hospitals for virologically confirmed COVID-19 infections from Feb. 10 through March 20, 2020.
A total of 86 patients were randomly assigned to the combination and 41 to lopinavir/ritonavir alone as controls, at doses described above.
Patients who entered the trial within less than 7 days of symptom onset received the triple combination, with interferon dosing adjusted according to the day that treatment started. Patients recruited 1 or 2 days after symptom onset received three doses of interferon, patients started on day 3 or 4 received two doses, and those started on days 5 or 6 received one interferon dose. Patients recruited 7 days or later from symptom onset did not receive interferon beta-1b because of its proinflammatory effects.
In post-hoc analysis by day of treatment initiation, clinical and virological outcomes (except stool samples) were superior in patients admitted less than 7 days after symptom onset for the 52 patients who received a least one interferon dose plus lopinavir/ritonavir and ribavirin, compared with 24 patients randomized to the control arm (lopinavir/ritonavir only). In contrast, among patients admitted and started on treatment at day 7 or later after symptom onset, there were no differences between those who received lopinavir/ritonavir alone or combined with ribavirin.
Adverse events were reported in 41 of 86 patients in the combination group and 20 of 41 patients in the control arm. The most common adverse events were diarrhea, occurring in 52 of all 127 patients, fever in 48, nausea in 43, and elevated alanine transaminase level in 18. The side effects generally resolved within 3 days of the start of treatments.
There were no serious adverse events reported in the combination group. One patient in the control group had impaired hepatic enzymes requiring discontinuation of treatment. No patients died during the study.
The study was funded by the Shaw Foundation, Richard and Carol Yu, May Tam Mak Mei Yin, and Sanming Project of Medicine. The authors and Dr. Medoff declared no competing interests.
SOURCE: Hung IFN et al. Lancet. 2020 May 8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31101-6.
A triple-antiviral therapy regimen of interferon-beta1, lopinavir/ritonavir, and ribavirin shortened median time to COVID-19 viral negativity by 5 days in a small trial from Hong Kong.
In an open-label, randomized phase 2 trial in patients with mild or moderate COVID-19 infections, the median time to viral negativity by nasopharyngeal swab was 7 days for 86 patients assigned to receive a 14-day course of lopinavir 400 mg and ritonavir 100 mg every 12 hours, ribavirin 400 mg every 12 hours, and three doses of 8 million international units of interferon beta-1b on alternate days, compared with a median time to negativity of 12 days for patients treated with lopinavir/ritonavir alone (P = .0010), wrote Ivan Fan-Ngai Hung, MD, from Gleaneagles Hospital in Hong Kong, and colleagues.
“Triple-antiviral therapy with interferon beta-1b, lopinavir/ritonavir, and ribavirin were safe and superior to lopinavir/ritonavir alone in shortening virus shedding, alleviating symptoms, and facilitating discharge of patients with mild to moderate COVID-19,” they wrote in a study published online in The Lancet.
Patients who received the combination also had significantly shorter time to complete alleviation of symptoms as assessed by a National Early Warning Score 2 (NEWS2, a system for detecting clinical deterioration in patients with acute illnesses) score of 0 (4 vs. 8 days, respectively; hazard ratio 3.92, P < .0001), and to a Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score of 0 (3 vs. 8 days, HR 1.89, P = .041).
The median hospital stay was 9 days for patients treated with the combination, compared with 14.5 days for controls (HR 2.72, P = .016).
In most patients treated with the combination, SARS-CoV-2 viral load was effectively suppressed in all clinical specimens, including nasopharyngeal swabs, throat and posterior oropharyngeal saliva, and stool.
In addition, serum levels of interleukin 6 (IL-6) – an inflammatory cytokine implicated in the cytokine storm frequently seen in patients with severe COVID-19 infections – were significantly lower on treatment days 2, 6, and 8 in patients treated with the combination, compared with those treated with lopinavir/ritonavir alone.
“Our trial demonstrates that early treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 with a triple combination of antiviral drugs may rapidly suppress the amount of virus in a patient’s body, relieve symptoms, and reduce the risk to health care workers by reducing the duration and quantity of viral shedding (when the virus is detectable and potentially transmissible). Furthermore, the treatment combination appeared safe and well tolerated by patients,” said lead investigator Professor Kwok-Yung Yuen from the University of Hong Kong, in a statement.
“Despite these encouraging findings,” he continued, “we must confirm in larger phase 3 trials that interferon beta-1b alone or in combination with other drugs is effective in patients with more severe illness (in whom the virus has had more time to replicate).”
Plausible rationale
Benjamin Medoff, MD, chief of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that the biologic rationale for the combination is plausible.
“I think this is a promising study that suggests that a regimen of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir/ritonavir, and ribavirin can shorten the duration of infection and improve symptoms in COVID-19 patients especially if started early in disease, in less than 7 days of symptom onset,” he said in reply to a request for expert analysis.
“The open-label nature and small size of the study limits the broad use of the regimen as noted by the authors, and it’s important to emphasize that the subjects enrolled did not have very severe disease (not in the ICU). However, the study does suggest that a larger truly randomized study is warranted,” he said.
AIDS drugs repurposed
Lopinavir/ritonavir is commonly used to treat HIV/AIDS throughout the world, and the investigators had previously reported that the antiviral agents combined with ribavirin reduced deaths and the need for intensive ventilator support among patients with SARS-CoV, the betacoronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), and antivirals have shown in vitro activity against both SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, the closely related pathogen that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome.
“ However the viral load of SARS and MERS peaks at around day 7-10 after symptom onset, whereas the viral load of COVID-19 peaks at the time of presentation, similar to influenza. Experience from the treatment of patients with influenza who are admitted to hospital suggested that a combination of multiple antiviral drugs is more effective than single-drug treatments in this setting of patients with a high viral load at presentation,” the investigators wrote.
To test this, they enrolled adults patients admitted to one of six Hong Kong Hospitals for virologically confirmed COVID-19 infections from Feb. 10 through March 20, 2020.
A total of 86 patients were randomly assigned to the combination and 41 to lopinavir/ritonavir alone as controls, at doses described above.
Patients who entered the trial within less than 7 days of symptom onset received the triple combination, with interferon dosing adjusted according to the day that treatment started. Patients recruited 1 or 2 days after symptom onset received three doses of interferon, patients started on day 3 or 4 received two doses, and those started on days 5 or 6 received one interferon dose. Patients recruited 7 days or later from symptom onset did not receive interferon beta-1b because of its proinflammatory effects.
In post-hoc analysis by day of treatment initiation, clinical and virological outcomes (except stool samples) were superior in patients admitted less than 7 days after symptom onset for the 52 patients who received a least one interferon dose plus lopinavir/ritonavir and ribavirin, compared with 24 patients randomized to the control arm (lopinavir/ritonavir only). In contrast, among patients admitted and started on treatment at day 7 or later after symptom onset, there were no differences between those who received lopinavir/ritonavir alone or combined with ribavirin.
Adverse events were reported in 41 of 86 patients in the combination group and 20 of 41 patients in the control arm. The most common adverse events were diarrhea, occurring in 52 of all 127 patients, fever in 48, nausea in 43, and elevated alanine transaminase level in 18. The side effects generally resolved within 3 days of the start of treatments.
There were no serious adverse events reported in the combination group. One patient in the control group had impaired hepatic enzymes requiring discontinuation of treatment. No patients died during the study.
The study was funded by the Shaw Foundation, Richard and Carol Yu, May Tam Mak Mei Yin, and Sanming Project of Medicine. The authors and Dr. Medoff declared no competing interests.
SOURCE: Hung IFN et al. Lancet. 2020 May 8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31101-6.
FROM THE LANCET
How to expand the APP role in a crisis
An opportunity to better appreciate the value of PAs, NPs
Advanced practice providers – physician assistants and nurse practitioners – at the 733-bed Emory University Hospital in Atlanta are playing an expanded role in the admission of patients into the hospital, particularly those suspected of having COVID-19.
Before the pandemic crisis, evaluation visits by the APP would have been reviewed on the same day by the supervising physician through an in-person encounter with the patient. The new protocol is not outside of scope-of-practice regulations for APPs in Georgia or of the hospital’s bylaws. But it offers a way to help limit the overall exposure of hospital staff to patients suspected of COVID-19 infection, and the total amount of time providers spend in such patients’ room. Just one provider now needs to meet the patient during the admissions process, while the attending physician can fulfill a requirement for seeing the patient within 24 hours during rounds the following day. Emergency encounters would still be done as needed.
These protocols point toward future conversations about the limits to APPs’ scope of practice, and whether more expansive approaches could be widely adopted once the current crisis is over, say advocates for the APPs’ role.
“Our APPs are primarily doing the admissions to the hospital of COVID patients and of non-COVID patients, as we’ve always done. But with COVID-infected or -suspected patients, we’re trying to minimize exposure for our providers,” explained Susan Ortiz, a certified PA, lead APP at Emory University Hospital. “In this way, we can also see more patients more efficiently.” Ms. Ortiz said she finds in talking to other APP leads in the Emory system that “each facility has its own culture and way of doing things. But for the most part, they’re all trying to do something to limit providers’ time in patients’ rooms.”
In response to the rapidly moving crisis, tactics to limit personnel in COVID patients’ rooms to the “absolutely essential” include gathering much of the needed history and other information requested from the patient by telephone, Ms. Ortiz said. This can be done either over the patient’s own cell phone or a phone placed in the room by hospital staff. Family members may be called to supplement this information, with the patient’s consent.
Once vital sign monitoring equipment is hooked up, it is possible to monitor the patient’s vital signs remotely without making frequent trips into the room. That way, in-person vital sign monitoring doesn’t need to happen routinely – at least not as often. One observation by clinicians on Ms. Ortiz’s team: listening for lung sounds with a stethoscope has not been shown to alter treatment for these patients. Once a chest X-ray shows structural changes in a patient’s lung, all lung exams are going to sound bad.
The admitting provider still needs to meet the patient in person for part of the admission visit and physical exam, but the amount of time spent in close personal contact with the patient can be much shorter, Ms. Ortiz said. For patients who are admitted, if there is a question about difficulty swallowing, they will see a speech pathologist, and if evidence of malnutrition, a nutritionist. “But we have to be extremely thoughtful about when people go into the room. So we are not ordering these ancillary services as routinely as we do during non-COVID times,” she said.
Appropriate levels of fear
Emory’s hospitalists are communicating daily about a rapidly changing situation. “We get a note by email every day, and we have a Dropbox account for downloading more information,” Ms. Ortiz said. A joint on-call system is used to provide backup coverage of APPs at the seven Emory hospitals. When replacement shifts need filling in a hurry, practitioners are able to obtain emergency credentials at any of the other hospitals. “It’s a voluntary process to sign up to be on-call,” Ms. Ortiz said. So far, that has been sufficient.
All staff have their own level of “appropriate fear” of this infection, Ms. Ortiz noted. “We have an extremely supportive group here to back up those of us who, for good reason, don’t want to be admitting the COVID patients.” Ms. Ortiz opted out of doing COVID admissions because her husband’s health places him at particular risk. “But with the cross-coverage we have, sometimes I’ll provide assistance when needed if a patient is suspected of being infected.” APPs are critical to Emory’s hospital medicine group – not ancillaries. “Everyone here feels that way. So we want to give them a lot of support. We’re all pitching in, doing it together,” she said.
“We said when we started with this, a couple of weeks before the surge started, that you could volunteer to see COVID patients,” said Emory hospitalist Jessica Nave, MD. “As we came to realize that the demand would be greater, we said you would need to opt out of seeing these patients, rather than opt in, and have a reason for doing so.” An example is pregnant staff, of which there seems to be a lot at Emory right now, Dr. Nave said, or those who are immunocompromised for other reasons. Those who don’t opt out are seeing the majority of the COVID patients, depending on actual need.
Dr. Nave is married to another hospitalist at Emory. “We can’t isolate from each other or our children. He and I have a regimented protocol for how we handle the risk, which includes taking off our shoes and clothes in the garage, showering and wiping down every place we might have touched. But those steps are not guarantees.” Other staff at Emory are isolating from their families for weeks at a time. Emory has a conference hotel offering discounted rates to staff. Nine physicians at Emory have been tested for the infection based on presenting symptoms, but at press time none had tested positive.
Streamlining code blue
Another area in which Emory has revised its policies in response to COVID-19 is for in-hospital cardiac arrest code response. Codes are inherently unpredictable, and crowd control has always been an issue for them, Dr. Nave said. “Historically, you could have 15 or more people show up when a code was called. Now, more than ever, we need to limit the number of people involved, for the same reason, avoiding unnecessary patient contact.”
The hospital’s Resuscitation Committee took the lead on developing a new policy, approved by the its Critical Care Committee and COVID Task Force, to limit the number of professionals in the room when running a code to an essential six: two doing chest compression, two managing airways, a code leader, and a critical care nurse. Outside the patient’s door, wearing the same personal protective equipment (PPE), are a pharmacist, recorder, and runner. “If you’re not one of those nine, you don’t need to be involved and should leave the area,” Dr. Nave said.
Staff have been instructed that they need to don appropriate PPE, including gown, mask, and eye wear, before entering the room for a code – even if that delays the start of intervention. “We’ve also made a code kit for each unit with quickly accessible gowns and masks. It should be used only for code blues.”
Increasing flexibility for the team
PAs and NPs in other locations are also exploring opportunities for gearing up to play larger roles in hospital care in the current crisis situation. The American Association of Physician Assistants has urged all U.S. governors to issue executive orders to waive state-specific licensing requirements for physician supervision or collaboration during the crisis, in order to increase flexibility of health care teams to deploy APPs.
AAPA believes the supervisory requirement is the biggest current barrier to mobilizing PAs and NPs. That includes those who have been furloughed from outpatient or other settings but are limited in their ability to contribute to the COVID crisis by the need to sign a supervision agreement with a physician at a new hospital.
The crisis is creating an opportunity to better appreciate the value PAs and NPs bring to health care, said Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM, vice president for advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians, a national hospitalist company based in Tacoma, Wash. The company recently sent a memo to the leadership of hospital sites at which it has contracts, requesting suspension of the hospitals’ requirements for a daily physician supervisory visit for APPs – which can be a hurdle when trying to leverage all hands on deck in the crisis.
NPs and PAs are stepping up and volunteering for COVID patients, Ms. Cardin said. Some have even taken leaves from their jobs to go to New York to help out at the epicenter of the U.S. crisis. “They want to make a difference. We’ve been deploying nonhospital medicine APPs from surgery, primary care, and elsewhere, embedding them on the hospital medicine team.”
Before the crisis, APPs at Sound Physicians weren’t always able to practice at the top of their licenses, depending on the hospital setting, added Alicia Scheffer, CNP, the company’s Great Lakes regional director for APPs. “Then COVID-19 showed up and really expedited conversations about how to maximize caseloads using APPs and about the fear of failing patients due to lack of capacity.”
In several locales, Sound Physicians is using quarantined providers to do telephone triage, or staffing ICUs with APPs backed up by telemedicine. “In APP-led ICUs, where the nurses are leading, they are intubating patients, placing central lines, things we weren’t allowed to do before,” Ms. Scheffer said.
A spirit of improvisation
There is a lot of tension at Emory University Hospital these days, reflecting the fears and uncertainties about the crisis, Dr. Nave said. “But there’s also a strangely powerful camaraderie like I’ve never seen before. When you walk onto the COVID units, you feel immediately bonded to the nurses, the techs, the phlebotomists. And you feel like you could talk about anything.”
Changes such as those made at Emory, have been talked about for a while, for example when hospitalists are having a busy night, she said. “But because this is a big cultural change, some physicians resisted it. We trust our APPs. But if the doctor’s name is on a patient chart, they want to see the patient – just for their own comfort level.”
Ms. Ortiz thinks the experience with the COVID crisis could help to advance the conversation about the appropriate role for APPs and their scope of practice in hospital medicine, once the current crisis has passed. “People were used to always doing things a certain way. This experience, hopefully, will get us to the point where attending physicians have more comfort with the APP’s ability to act autonomously,” she said.
“We’ve also talked about piloting telemedicine examinations using Zoom,” Dr. Nave added. “It’s making us think a lot of remote cross-coverage could be done that way. We’ve talked about using the hospital’s iPads with patients. This crisis really makes you think you want to innovate, in a spirit of improvisation,” she said. “Now is the time to try some of these things.”
Editors note: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitals are seeing unprecedented volumes of patients requiring hospital medicine groups to stretch their current resources and recruit providers from outside their groups to bolster their inpatient services. The Society of Hospital Medicine has put together the following stepwise guide for onboarding traditional outpatient and subspecialty-based providers to work on general medicine wards: COVID-19 nonhospitalist onboarding resources.
An opportunity to better appreciate the value of PAs, NPs
An opportunity to better appreciate the value of PAs, NPs
Advanced practice providers – physician assistants and nurse practitioners – at the 733-bed Emory University Hospital in Atlanta are playing an expanded role in the admission of patients into the hospital, particularly those suspected of having COVID-19.
Before the pandemic crisis, evaluation visits by the APP would have been reviewed on the same day by the supervising physician through an in-person encounter with the patient. The new protocol is not outside of scope-of-practice regulations for APPs in Georgia or of the hospital’s bylaws. But it offers a way to help limit the overall exposure of hospital staff to patients suspected of COVID-19 infection, and the total amount of time providers spend in such patients’ room. Just one provider now needs to meet the patient during the admissions process, while the attending physician can fulfill a requirement for seeing the patient within 24 hours during rounds the following day. Emergency encounters would still be done as needed.
These protocols point toward future conversations about the limits to APPs’ scope of practice, and whether more expansive approaches could be widely adopted once the current crisis is over, say advocates for the APPs’ role.
“Our APPs are primarily doing the admissions to the hospital of COVID patients and of non-COVID patients, as we’ve always done. But with COVID-infected or -suspected patients, we’re trying to minimize exposure for our providers,” explained Susan Ortiz, a certified PA, lead APP at Emory University Hospital. “In this way, we can also see more patients more efficiently.” Ms. Ortiz said she finds in talking to other APP leads in the Emory system that “each facility has its own culture and way of doing things. But for the most part, they’re all trying to do something to limit providers’ time in patients’ rooms.”
In response to the rapidly moving crisis, tactics to limit personnel in COVID patients’ rooms to the “absolutely essential” include gathering much of the needed history and other information requested from the patient by telephone, Ms. Ortiz said. This can be done either over the patient’s own cell phone or a phone placed in the room by hospital staff. Family members may be called to supplement this information, with the patient’s consent.
Once vital sign monitoring equipment is hooked up, it is possible to monitor the patient’s vital signs remotely without making frequent trips into the room. That way, in-person vital sign monitoring doesn’t need to happen routinely – at least not as often. One observation by clinicians on Ms. Ortiz’s team: listening for lung sounds with a stethoscope has not been shown to alter treatment for these patients. Once a chest X-ray shows structural changes in a patient’s lung, all lung exams are going to sound bad.
The admitting provider still needs to meet the patient in person for part of the admission visit and physical exam, but the amount of time spent in close personal contact with the patient can be much shorter, Ms. Ortiz said. For patients who are admitted, if there is a question about difficulty swallowing, they will see a speech pathologist, and if evidence of malnutrition, a nutritionist. “But we have to be extremely thoughtful about when people go into the room. So we are not ordering these ancillary services as routinely as we do during non-COVID times,” she said.
Appropriate levels of fear
Emory’s hospitalists are communicating daily about a rapidly changing situation. “We get a note by email every day, and we have a Dropbox account for downloading more information,” Ms. Ortiz said. A joint on-call system is used to provide backup coverage of APPs at the seven Emory hospitals. When replacement shifts need filling in a hurry, practitioners are able to obtain emergency credentials at any of the other hospitals. “It’s a voluntary process to sign up to be on-call,” Ms. Ortiz said. So far, that has been sufficient.
All staff have their own level of “appropriate fear” of this infection, Ms. Ortiz noted. “We have an extremely supportive group here to back up those of us who, for good reason, don’t want to be admitting the COVID patients.” Ms. Ortiz opted out of doing COVID admissions because her husband’s health places him at particular risk. “But with the cross-coverage we have, sometimes I’ll provide assistance when needed if a patient is suspected of being infected.” APPs are critical to Emory’s hospital medicine group – not ancillaries. “Everyone here feels that way. So we want to give them a lot of support. We’re all pitching in, doing it together,” she said.
“We said when we started with this, a couple of weeks before the surge started, that you could volunteer to see COVID patients,” said Emory hospitalist Jessica Nave, MD. “As we came to realize that the demand would be greater, we said you would need to opt out of seeing these patients, rather than opt in, and have a reason for doing so.” An example is pregnant staff, of which there seems to be a lot at Emory right now, Dr. Nave said, or those who are immunocompromised for other reasons. Those who don’t opt out are seeing the majority of the COVID patients, depending on actual need.
Dr. Nave is married to another hospitalist at Emory. “We can’t isolate from each other or our children. He and I have a regimented protocol for how we handle the risk, which includes taking off our shoes and clothes in the garage, showering and wiping down every place we might have touched. But those steps are not guarantees.” Other staff at Emory are isolating from their families for weeks at a time. Emory has a conference hotel offering discounted rates to staff. Nine physicians at Emory have been tested for the infection based on presenting symptoms, but at press time none had tested positive.
Streamlining code blue
Another area in which Emory has revised its policies in response to COVID-19 is for in-hospital cardiac arrest code response. Codes are inherently unpredictable, and crowd control has always been an issue for them, Dr. Nave said. “Historically, you could have 15 or more people show up when a code was called. Now, more than ever, we need to limit the number of people involved, for the same reason, avoiding unnecessary patient contact.”
The hospital’s Resuscitation Committee took the lead on developing a new policy, approved by the its Critical Care Committee and COVID Task Force, to limit the number of professionals in the room when running a code to an essential six: two doing chest compression, two managing airways, a code leader, and a critical care nurse. Outside the patient’s door, wearing the same personal protective equipment (PPE), are a pharmacist, recorder, and runner. “If you’re not one of those nine, you don’t need to be involved and should leave the area,” Dr. Nave said.
Staff have been instructed that they need to don appropriate PPE, including gown, mask, and eye wear, before entering the room for a code – even if that delays the start of intervention. “We’ve also made a code kit for each unit with quickly accessible gowns and masks. It should be used only for code blues.”
Increasing flexibility for the team
PAs and NPs in other locations are also exploring opportunities for gearing up to play larger roles in hospital care in the current crisis situation. The American Association of Physician Assistants has urged all U.S. governors to issue executive orders to waive state-specific licensing requirements for physician supervision or collaboration during the crisis, in order to increase flexibility of health care teams to deploy APPs.
AAPA believes the supervisory requirement is the biggest current barrier to mobilizing PAs and NPs. That includes those who have been furloughed from outpatient or other settings but are limited in their ability to contribute to the COVID crisis by the need to sign a supervision agreement with a physician at a new hospital.
The crisis is creating an opportunity to better appreciate the value PAs and NPs bring to health care, said Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM, vice president for advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians, a national hospitalist company based in Tacoma, Wash. The company recently sent a memo to the leadership of hospital sites at which it has contracts, requesting suspension of the hospitals’ requirements for a daily physician supervisory visit for APPs – which can be a hurdle when trying to leverage all hands on deck in the crisis.
NPs and PAs are stepping up and volunteering for COVID patients, Ms. Cardin said. Some have even taken leaves from their jobs to go to New York to help out at the epicenter of the U.S. crisis. “They want to make a difference. We’ve been deploying nonhospital medicine APPs from surgery, primary care, and elsewhere, embedding them on the hospital medicine team.”
Before the crisis, APPs at Sound Physicians weren’t always able to practice at the top of their licenses, depending on the hospital setting, added Alicia Scheffer, CNP, the company’s Great Lakes regional director for APPs. “Then COVID-19 showed up and really expedited conversations about how to maximize caseloads using APPs and about the fear of failing patients due to lack of capacity.”
In several locales, Sound Physicians is using quarantined providers to do telephone triage, or staffing ICUs with APPs backed up by telemedicine. “In APP-led ICUs, where the nurses are leading, they are intubating patients, placing central lines, things we weren’t allowed to do before,” Ms. Scheffer said.
A spirit of improvisation
There is a lot of tension at Emory University Hospital these days, reflecting the fears and uncertainties about the crisis, Dr. Nave said. “But there’s also a strangely powerful camaraderie like I’ve never seen before. When you walk onto the COVID units, you feel immediately bonded to the nurses, the techs, the phlebotomists. And you feel like you could talk about anything.”
Changes such as those made at Emory, have been talked about for a while, for example when hospitalists are having a busy night, she said. “But because this is a big cultural change, some physicians resisted it. We trust our APPs. But if the doctor’s name is on a patient chart, they want to see the patient – just for their own comfort level.”
Ms. Ortiz thinks the experience with the COVID crisis could help to advance the conversation about the appropriate role for APPs and their scope of practice in hospital medicine, once the current crisis has passed. “People were used to always doing things a certain way. This experience, hopefully, will get us to the point where attending physicians have more comfort with the APP’s ability to act autonomously,” she said.
“We’ve also talked about piloting telemedicine examinations using Zoom,” Dr. Nave added. “It’s making us think a lot of remote cross-coverage could be done that way. We’ve talked about using the hospital’s iPads with patients. This crisis really makes you think you want to innovate, in a spirit of improvisation,” she said. “Now is the time to try some of these things.”
Editors note: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitals are seeing unprecedented volumes of patients requiring hospital medicine groups to stretch their current resources and recruit providers from outside their groups to bolster their inpatient services. The Society of Hospital Medicine has put together the following stepwise guide for onboarding traditional outpatient and subspecialty-based providers to work on general medicine wards: COVID-19 nonhospitalist onboarding resources.
Advanced practice providers – physician assistants and nurse practitioners – at the 733-bed Emory University Hospital in Atlanta are playing an expanded role in the admission of patients into the hospital, particularly those suspected of having COVID-19.
Before the pandemic crisis, evaluation visits by the APP would have been reviewed on the same day by the supervising physician through an in-person encounter with the patient. The new protocol is not outside of scope-of-practice regulations for APPs in Georgia or of the hospital’s bylaws. But it offers a way to help limit the overall exposure of hospital staff to patients suspected of COVID-19 infection, and the total amount of time providers spend in such patients’ room. Just one provider now needs to meet the patient during the admissions process, while the attending physician can fulfill a requirement for seeing the patient within 24 hours during rounds the following day. Emergency encounters would still be done as needed.
These protocols point toward future conversations about the limits to APPs’ scope of practice, and whether more expansive approaches could be widely adopted once the current crisis is over, say advocates for the APPs’ role.
“Our APPs are primarily doing the admissions to the hospital of COVID patients and of non-COVID patients, as we’ve always done. But with COVID-infected or -suspected patients, we’re trying to minimize exposure for our providers,” explained Susan Ortiz, a certified PA, lead APP at Emory University Hospital. “In this way, we can also see more patients more efficiently.” Ms. Ortiz said she finds in talking to other APP leads in the Emory system that “each facility has its own culture and way of doing things. But for the most part, they’re all trying to do something to limit providers’ time in patients’ rooms.”
In response to the rapidly moving crisis, tactics to limit personnel in COVID patients’ rooms to the “absolutely essential” include gathering much of the needed history and other information requested from the patient by telephone, Ms. Ortiz said. This can be done either over the patient’s own cell phone or a phone placed in the room by hospital staff. Family members may be called to supplement this information, with the patient’s consent.
Once vital sign monitoring equipment is hooked up, it is possible to monitor the patient’s vital signs remotely without making frequent trips into the room. That way, in-person vital sign monitoring doesn’t need to happen routinely – at least not as often. One observation by clinicians on Ms. Ortiz’s team: listening for lung sounds with a stethoscope has not been shown to alter treatment for these patients. Once a chest X-ray shows structural changes in a patient’s lung, all lung exams are going to sound bad.
The admitting provider still needs to meet the patient in person for part of the admission visit and physical exam, but the amount of time spent in close personal contact with the patient can be much shorter, Ms. Ortiz said. For patients who are admitted, if there is a question about difficulty swallowing, they will see a speech pathologist, and if evidence of malnutrition, a nutritionist. “But we have to be extremely thoughtful about when people go into the room. So we are not ordering these ancillary services as routinely as we do during non-COVID times,” she said.
Appropriate levels of fear
Emory’s hospitalists are communicating daily about a rapidly changing situation. “We get a note by email every day, and we have a Dropbox account for downloading more information,” Ms. Ortiz said. A joint on-call system is used to provide backup coverage of APPs at the seven Emory hospitals. When replacement shifts need filling in a hurry, practitioners are able to obtain emergency credentials at any of the other hospitals. “It’s a voluntary process to sign up to be on-call,” Ms. Ortiz said. So far, that has been sufficient.
All staff have their own level of “appropriate fear” of this infection, Ms. Ortiz noted. “We have an extremely supportive group here to back up those of us who, for good reason, don’t want to be admitting the COVID patients.” Ms. Ortiz opted out of doing COVID admissions because her husband’s health places him at particular risk. “But with the cross-coverage we have, sometimes I’ll provide assistance when needed if a patient is suspected of being infected.” APPs are critical to Emory’s hospital medicine group – not ancillaries. “Everyone here feels that way. So we want to give them a lot of support. We’re all pitching in, doing it together,” she said.
“We said when we started with this, a couple of weeks before the surge started, that you could volunteer to see COVID patients,” said Emory hospitalist Jessica Nave, MD. “As we came to realize that the demand would be greater, we said you would need to opt out of seeing these patients, rather than opt in, and have a reason for doing so.” An example is pregnant staff, of which there seems to be a lot at Emory right now, Dr. Nave said, or those who are immunocompromised for other reasons. Those who don’t opt out are seeing the majority of the COVID patients, depending on actual need.
Dr. Nave is married to another hospitalist at Emory. “We can’t isolate from each other or our children. He and I have a regimented protocol for how we handle the risk, which includes taking off our shoes and clothes in the garage, showering and wiping down every place we might have touched. But those steps are not guarantees.” Other staff at Emory are isolating from their families for weeks at a time. Emory has a conference hotel offering discounted rates to staff. Nine physicians at Emory have been tested for the infection based on presenting symptoms, but at press time none had tested positive.
Streamlining code blue
Another area in which Emory has revised its policies in response to COVID-19 is for in-hospital cardiac arrest code response. Codes are inherently unpredictable, and crowd control has always been an issue for them, Dr. Nave said. “Historically, you could have 15 or more people show up when a code was called. Now, more than ever, we need to limit the number of people involved, for the same reason, avoiding unnecessary patient contact.”
The hospital’s Resuscitation Committee took the lead on developing a new policy, approved by the its Critical Care Committee and COVID Task Force, to limit the number of professionals in the room when running a code to an essential six: two doing chest compression, two managing airways, a code leader, and a critical care nurse. Outside the patient’s door, wearing the same personal protective equipment (PPE), are a pharmacist, recorder, and runner. “If you’re not one of those nine, you don’t need to be involved and should leave the area,” Dr. Nave said.
Staff have been instructed that they need to don appropriate PPE, including gown, mask, and eye wear, before entering the room for a code – even if that delays the start of intervention. “We’ve also made a code kit for each unit with quickly accessible gowns and masks. It should be used only for code blues.”
Increasing flexibility for the team
PAs and NPs in other locations are also exploring opportunities for gearing up to play larger roles in hospital care in the current crisis situation. The American Association of Physician Assistants has urged all U.S. governors to issue executive orders to waive state-specific licensing requirements for physician supervision or collaboration during the crisis, in order to increase flexibility of health care teams to deploy APPs.
AAPA believes the supervisory requirement is the biggest current barrier to mobilizing PAs and NPs. That includes those who have been furloughed from outpatient or other settings but are limited in their ability to contribute to the COVID crisis by the need to sign a supervision agreement with a physician at a new hospital.
The crisis is creating an opportunity to better appreciate the value PAs and NPs bring to health care, said Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM, vice president for advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians, a national hospitalist company based in Tacoma, Wash. The company recently sent a memo to the leadership of hospital sites at which it has contracts, requesting suspension of the hospitals’ requirements for a daily physician supervisory visit for APPs – which can be a hurdle when trying to leverage all hands on deck in the crisis.
NPs and PAs are stepping up and volunteering for COVID patients, Ms. Cardin said. Some have even taken leaves from their jobs to go to New York to help out at the epicenter of the U.S. crisis. “They want to make a difference. We’ve been deploying nonhospital medicine APPs from surgery, primary care, and elsewhere, embedding them on the hospital medicine team.”
Before the crisis, APPs at Sound Physicians weren’t always able to practice at the top of their licenses, depending on the hospital setting, added Alicia Scheffer, CNP, the company’s Great Lakes regional director for APPs. “Then COVID-19 showed up and really expedited conversations about how to maximize caseloads using APPs and about the fear of failing patients due to lack of capacity.”
In several locales, Sound Physicians is using quarantined providers to do telephone triage, or staffing ICUs with APPs backed up by telemedicine. “In APP-led ICUs, where the nurses are leading, they are intubating patients, placing central lines, things we weren’t allowed to do before,” Ms. Scheffer said.
A spirit of improvisation
There is a lot of tension at Emory University Hospital these days, reflecting the fears and uncertainties about the crisis, Dr. Nave said. “But there’s also a strangely powerful camaraderie like I’ve never seen before. When you walk onto the COVID units, you feel immediately bonded to the nurses, the techs, the phlebotomists. And you feel like you could talk about anything.”
Changes such as those made at Emory, have been talked about for a while, for example when hospitalists are having a busy night, she said. “But because this is a big cultural change, some physicians resisted it. We trust our APPs. But if the doctor’s name is on a patient chart, they want to see the patient – just for their own comfort level.”
Ms. Ortiz thinks the experience with the COVID crisis could help to advance the conversation about the appropriate role for APPs and their scope of practice in hospital medicine, once the current crisis has passed. “People were used to always doing things a certain way. This experience, hopefully, will get us to the point where attending physicians have more comfort with the APP’s ability to act autonomously,” she said.
“We’ve also talked about piloting telemedicine examinations using Zoom,” Dr. Nave added. “It’s making us think a lot of remote cross-coverage could be done that way. We’ve talked about using the hospital’s iPads with patients. This crisis really makes you think you want to innovate, in a spirit of improvisation,” she said. “Now is the time to try some of these things.”
Editors note: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitals are seeing unprecedented volumes of patients requiring hospital medicine groups to stretch their current resources and recruit providers from outside their groups to bolster their inpatient services. The Society of Hospital Medicine has put together the following stepwise guide for onboarding traditional outpatient and subspecialty-based providers to work on general medicine wards: COVID-19 nonhospitalist onboarding resources.