User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Scientific doubt tempers COVID-19 vaccine optimism
US government and industry projections that a COVID-19 vaccine will be ready by this fall or even January would take compressing what usually takes at least a decade into months, with little room for error or safety surprises.
“If all the cards fall into the right place and all the stars are aligned, you definitely could get a vaccine by December or January,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said last week.
But Fauci said a more realistic timeline is still 12 to 18 months, and experts interviewed by Medscape Medical News agree. They say that although recent developments are encouraging, history and scientific reason say the day when a COVID-19 vaccine is widely available will not come this year and may not come by the end of 2021.
The encouraging signals come primarily from two recent announcements: the $1.2 billion United States backing last week of one vaccine platform and the announcement on May 18 that the first human trials of another have produced some positive phase 1 results.
Recent developments
On May 21, the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) under “Operation Warp Speed” announced that the US will give AstraZeneca $1.2 billion “to make available at least 300 million doses of a coronavirus vaccine called AZD1222, with the first doses delivered as early as October 2020.”
On May 18, the Massachusetts-based biotechnology company Moderna announced that phase 1 clinical results showed that its vaccine candidate, which uses a new messenger RNA (mRNA) technology, appeared safe. Eight participants in the human trials were able to produce neutralizing antibodies that researchers believe are important in developing protection from the virus.
Moderna Chief Medical Officer Tal Zaks, MD, PhD told CNN that if the vaccine candidate does well in phase 2, “it could be ready by January 2021.”
The two candidates are among 10 in clinical trials for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The AstraZeneca/ AZD1222 candidate (also called ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, in collaboration with the University of Oxford) has entered phase 2/3.
Moderna’s candidate and another being developed in Beijing, China, are in phase 2, WHO reports. As of yesterday, 115 other candidates are in preclinical evaluation.
Maria Elena Bottazzi, PhD, associate dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, told Medscape Medical News it’s important to realize that, in the case of the $1.2 billion US investment, “what they’re talking about is manufacturing.”
The idea, she said, is to pay AstraZeneca up front so that manufacturing can start before it is known whether the vaccine candidate is safe or effective, the reverse of how the clinical trial process usually works.
That way, if the candidate is deemed safe and effective, time is not lost by then deciding how to make it and distribute it.
By the end of this year, she said, “Maybe we will have many vaccines made and stored in a refrigerator somewhere. But between now and December, there’s absolutely no way you can show efficacy of the vaccine at the same time you confirm that it’s safe.”
“Take these things with a grain of salt”
Animal testing for the AstraZeneca candidate, made in partnership with the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom, has yielded lackluster results, according to results on the preprint server BioRxiv, which have not been peer-reviewed.
“The results were not bad, but they were not gangbusters,” Bottazzi said. The results show the vaccine offered only partial protection.
“Partial protection is better than no protection,” she noted. “You have to take these things with a grain of salt. We don’t know what’s going to happen in humans.”
As for the Moderna candidate, Bottazzi said, “the good news is they found an appropriate safety profile. But from an eight-person group to make the extrapolation that they have efficacy — it’s unrealistic.”
Nicole Lurie, MD, MSPH, is senior adviser to the CEO for the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovation (CEPI), a nongovernmental organization funded by the Wellcome Trust, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the European Commission, and eight countries (Australia, Belgium, Canada, Ethiopia, Germany, Japan, Norway, and the United Kingdom) charged with supporting development of vaccines for pathogens on WHO’s priority list.
She and her colleagues write in a paper published online in the New England Journal of Medicine on March 30 that “it typically takes multiple candidates and many years to produce a licensed vaccine.”
The fastest time for developing a vaccine to date is 4 years, for the mumps vaccine, licensed in 1967.
As to whether she would expect a rollout of any vaccine by the end of the year, Lurie told Medscape Medical News, “If everything goes according to plan in every way, shape or form, well then maybe you can get there. But I wouldn’t hold my breath.”
Lurie and her colleagues write that “it’s far from certain that these new platforms will be scalable or that existing capacity can provide sufficient quantities of vaccine fast enough.”
On a call with reporters today, leaders of some of the words largest pharmaceutical companies said that one of the key bottlenecks is the sheer number of vials needed in order to distribute billions of doses of a successful vaccine.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, said, “Typically we are producing vaccines in single-dose vials. We are exploring with governments right now if it would be more convenient if there were 5-dose vials or 10-dose vials. I think we can resolve a significant part of the bottleneck.”
Despite the challenges, experts interviewed for this article agree that it will be possible to make a vaccine for COVID-19. They don’t expect attempts to meet the same complications that HIV researchers have seen over decades as the virus continues to confound with mutations.
Fred Ledley, MD, director of the Center for Integration of Science and Industry at Bentley University in Waltham, Massachusetts, told Medscape Medical News, “There doesn’t appear to be anything terribly diabolical about this virus. The mutation rate doesn’t appear to be anything like HIV. It appears to have some big, ugly proteins on the surface, which is good for vaccines — proteins with a lot of physical features look distinguishable from healthy cells. Signs all point to that it should be possible to make a vaccine.”
History raises safety concerns
However, Ledley said, “The idea of doing it in 6 months is largely unrealistic.”
He says 18 months is more realistic, primarily because of the sheer number of people that would have to be enrolled in a phase 3 study to truly test whether the endpoints are being met.
Vaccines are given to healthy volunteers. If safety signals arise, they may not be apparent until massive numbers of people are tested in phase 3.
“You’re never going to see the rates cut to 0%, but to see the difference between 10 people getting sick and seven people getting sick, takes very, very large numbers,” Ledley said. “There’s no way that can be done in 6 months. You’re talking about tens of thousands of people enrolled.”
He notes at this point it’s unclear what the endpoints will be and what the safety thresholds will be after consideration of risks and benefit.
Another big question for Ledley: “We don’t know what type of immunity we need to protect us against the virus. Do you just need the antibodies in your blood or do you need cells that are primed to attack the virus? Is it more of a chemical clearance or do the cells need to physically go in and digest the virus?”
History also points to the need for rigorous safety precautions that scientists fear could be compromised as trial phases overlap and processes are run in parallel instead of one step at a time.
An early batch of the Salk vaccine for polio in 1955, for example, turned out to be contaminated and caused paralysis in some children and 10 deaths, he points out.
CEPI’s Lurie adds that early candidates for another coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), “caused a reaction in the lungs that was very dangerous” before development was halted.
She also pointed to previous findings that a vaccine for dengue fever could worsen the disease in some people through a phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement.
Lurie and colleagues write in their paper that “it’s critical that vaccines also be developed using the tried-and-true methods, even if they may take longer to enter clinical trials or to result in large numbers of doses.”
Live attenuated vaccine
Raul Andino, PhD, a virologist at the University of California San Francisco, is among the scientists working with a tried-and-true method — a live attenuated vaccine — and he told Medscape Medical News he’s predicting it will take 2 years to develop.
He said it is cheaper to produce because scientists just have to learn how to grow the virus. Because the technology is already proven, a live attenuated vaccine could be rapidly produced on a worldwide scale.
The hope is also that a live attenuated vaccine would be given once in a lifetime and therefore be more affordable, especially in poorer countries.
“While a Moderna vaccine might be good for Europe and the United States,” he said, “It’s not going to be good for Africa, India, Brazil.”
Andino said, “I would bet money” that the front-runner vaccines so far will not be one-time vaccines.
He points out that most of the vaccine candidates are trying to protect people from disease. While there’s nothing wrong with that, he said, “In my opinion that is the lower-hanging fruit.”
“In my mind we need something that interrupts the chain of transmission and induces protection,” Andino said, important for developing herd immunity.
The reason this type of approach takes longer is because you are introducing a weakened form of the virus to the body and you have to make sure it doesn’t cause disease, not just in a small test population, but in populations who may be more susceptible to the disease, Andino said.
A call for unified strategies
Universities, countries, international consortiums, and public-private partnerships are all racing to find several safe and effective vaccines as no one entity will likely be able to provide the global solution.
Some of the efforts involve overlap of entities but with different focuses.
Along with “Operation Warp Speed” and CEPI, other collaborations include Gavi the Vaccine Alliance, whose core partners include WHO, UNICEF, the World Bank, and the Gates Foundation; and “Accelerating Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV) partnership,” led by the National Institutes of Health.
Industry partners in ACTIV (18 biopharmaceutical companies), according to a May 18 article published online in the Journal of the American Medical Association, have said they will contribute their respective clinical trial capacities, regardless of which agent is studied.
Some, however, have called for more streamlining of efforts.
“Ideally we’d be working together,” Lurie told Medscape Medical News.
“I’m hopeful we will find ways to collaborate scientifically,” she said. “The US government’s responsibility is to make doses for the US. CEPI’s responsibility is to make doses for the world. A big focus of CEPI is to make sure we have manufacturing capacity outside of the US so those doses can be available to the world and they don’t get seized by wealthy countries.”
Bottazzi, Ledley, Lurie, and Andino report no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
US government and industry projections that a COVID-19 vaccine will be ready by this fall or even January would take compressing what usually takes at least a decade into months, with little room for error or safety surprises.
“If all the cards fall into the right place and all the stars are aligned, you definitely could get a vaccine by December or January,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said last week.
But Fauci said a more realistic timeline is still 12 to 18 months, and experts interviewed by Medscape Medical News agree. They say that although recent developments are encouraging, history and scientific reason say the day when a COVID-19 vaccine is widely available will not come this year and may not come by the end of 2021.
The encouraging signals come primarily from two recent announcements: the $1.2 billion United States backing last week of one vaccine platform and the announcement on May 18 that the first human trials of another have produced some positive phase 1 results.
Recent developments
On May 21, the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) under “Operation Warp Speed” announced that the US will give AstraZeneca $1.2 billion “to make available at least 300 million doses of a coronavirus vaccine called AZD1222, with the first doses delivered as early as October 2020.”
On May 18, the Massachusetts-based biotechnology company Moderna announced that phase 1 clinical results showed that its vaccine candidate, which uses a new messenger RNA (mRNA) technology, appeared safe. Eight participants in the human trials were able to produce neutralizing antibodies that researchers believe are important in developing protection from the virus.
Moderna Chief Medical Officer Tal Zaks, MD, PhD told CNN that if the vaccine candidate does well in phase 2, “it could be ready by January 2021.”
The two candidates are among 10 in clinical trials for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The AstraZeneca/ AZD1222 candidate (also called ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, in collaboration with the University of Oxford) has entered phase 2/3.
Moderna’s candidate and another being developed in Beijing, China, are in phase 2, WHO reports. As of yesterday, 115 other candidates are in preclinical evaluation.
Maria Elena Bottazzi, PhD, associate dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, told Medscape Medical News it’s important to realize that, in the case of the $1.2 billion US investment, “what they’re talking about is manufacturing.”
The idea, she said, is to pay AstraZeneca up front so that manufacturing can start before it is known whether the vaccine candidate is safe or effective, the reverse of how the clinical trial process usually works.
That way, if the candidate is deemed safe and effective, time is not lost by then deciding how to make it and distribute it.
By the end of this year, she said, “Maybe we will have many vaccines made and stored in a refrigerator somewhere. But between now and December, there’s absolutely no way you can show efficacy of the vaccine at the same time you confirm that it’s safe.”
“Take these things with a grain of salt”
Animal testing for the AstraZeneca candidate, made in partnership with the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom, has yielded lackluster results, according to results on the preprint server BioRxiv, which have not been peer-reviewed.
“The results were not bad, but they were not gangbusters,” Bottazzi said. The results show the vaccine offered only partial protection.
“Partial protection is better than no protection,” she noted. “You have to take these things with a grain of salt. We don’t know what’s going to happen in humans.”
As for the Moderna candidate, Bottazzi said, “the good news is they found an appropriate safety profile. But from an eight-person group to make the extrapolation that they have efficacy — it’s unrealistic.”
Nicole Lurie, MD, MSPH, is senior adviser to the CEO for the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovation (CEPI), a nongovernmental organization funded by the Wellcome Trust, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the European Commission, and eight countries (Australia, Belgium, Canada, Ethiopia, Germany, Japan, Norway, and the United Kingdom) charged with supporting development of vaccines for pathogens on WHO’s priority list.
She and her colleagues write in a paper published online in the New England Journal of Medicine on March 30 that “it typically takes multiple candidates and many years to produce a licensed vaccine.”
The fastest time for developing a vaccine to date is 4 years, for the mumps vaccine, licensed in 1967.
As to whether she would expect a rollout of any vaccine by the end of the year, Lurie told Medscape Medical News, “If everything goes according to plan in every way, shape or form, well then maybe you can get there. But I wouldn’t hold my breath.”
Lurie and her colleagues write that “it’s far from certain that these new platforms will be scalable or that existing capacity can provide sufficient quantities of vaccine fast enough.”
On a call with reporters today, leaders of some of the words largest pharmaceutical companies said that one of the key bottlenecks is the sheer number of vials needed in order to distribute billions of doses of a successful vaccine.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, said, “Typically we are producing vaccines in single-dose vials. We are exploring with governments right now if it would be more convenient if there were 5-dose vials or 10-dose vials. I think we can resolve a significant part of the bottleneck.”
Despite the challenges, experts interviewed for this article agree that it will be possible to make a vaccine for COVID-19. They don’t expect attempts to meet the same complications that HIV researchers have seen over decades as the virus continues to confound with mutations.
Fred Ledley, MD, director of the Center for Integration of Science and Industry at Bentley University in Waltham, Massachusetts, told Medscape Medical News, “There doesn’t appear to be anything terribly diabolical about this virus. The mutation rate doesn’t appear to be anything like HIV. It appears to have some big, ugly proteins on the surface, which is good for vaccines — proteins with a lot of physical features look distinguishable from healthy cells. Signs all point to that it should be possible to make a vaccine.”
History raises safety concerns
However, Ledley said, “The idea of doing it in 6 months is largely unrealistic.”
He says 18 months is more realistic, primarily because of the sheer number of people that would have to be enrolled in a phase 3 study to truly test whether the endpoints are being met.
Vaccines are given to healthy volunteers. If safety signals arise, they may not be apparent until massive numbers of people are tested in phase 3.
“You’re never going to see the rates cut to 0%, but to see the difference between 10 people getting sick and seven people getting sick, takes very, very large numbers,” Ledley said. “There’s no way that can be done in 6 months. You’re talking about tens of thousands of people enrolled.”
He notes at this point it’s unclear what the endpoints will be and what the safety thresholds will be after consideration of risks and benefit.
Another big question for Ledley: “We don’t know what type of immunity we need to protect us against the virus. Do you just need the antibodies in your blood or do you need cells that are primed to attack the virus? Is it more of a chemical clearance or do the cells need to physically go in and digest the virus?”
History also points to the need for rigorous safety precautions that scientists fear could be compromised as trial phases overlap and processes are run in parallel instead of one step at a time.
An early batch of the Salk vaccine for polio in 1955, for example, turned out to be contaminated and caused paralysis in some children and 10 deaths, he points out.
CEPI’s Lurie adds that early candidates for another coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), “caused a reaction in the lungs that was very dangerous” before development was halted.
She also pointed to previous findings that a vaccine for dengue fever could worsen the disease in some people through a phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement.
Lurie and colleagues write in their paper that “it’s critical that vaccines also be developed using the tried-and-true methods, even if they may take longer to enter clinical trials or to result in large numbers of doses.”
Live attenuated vaccine
Raul Andino, PhD, a virologist at the University of California San Francisco, is among the scientists working with a tried-and-true method — a live attenuated vaccine — and he told Medscape Medical News he’s predicting it will take 2 years to develop.
He said it is cheaper to produce because scientists just have to learn how to grow the virus. Because the technology is already proven, a live attenuated vaccine could be rapidly produced on a worldwide scale.
The hope is also that a live attenuated vaccine would be given once in a lifetime and therefore be more affordable, especially in poorer countries.
“While a Moderna vaccine might be good for Europe and the United States,” he said, “It’s not going to be good for Africa, India, Brazil.”
Andino said, “I would bet money” that the front-runner vaccines so far will not be one-time vaccines.
He points out that most of the vaccine candidates are trying to protect people from disease. While there’s nothing wrong with that, he said, “In my opinion that is the lower-hanging fruit.”
“In my mind we need something that interrupts the chain of transmission and induces protection,” Andino said, important for developing herd immunity.
The reason this type of approach takes longer is because you are introducing a weakened form of the virus to the body and you have to make sure it doesn’t cause disease, not just in a small test population, but in populations who may be more susceptible to the disease, Andino said.
A call for unified strategies
Universities, countries, international consortiums, and public-private partnerships are all racing to find several safe and effective vaccines as no one entity will likely be able to provide the global solution.
Some of the efforts involve overlap of entities but with different focuses.
Along with “Operation Warp Speed” and CEPI, other collaborations include Gavi the Vaccine Alliance, whose core partners include WHO, UNICEF, the World Bank, and the Gates Foundation; and “Accelerating Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV) partnership,” led by the National Institutes of Health.
Industry partners in ACTIV (18 biopharmaceutical companies), according to a May 18 article published online in the Journal of the American Medical Association, have said they will contribute their respective clinical trial capacities, regardless of which agent is studied.
Some, however, have called for more streamlining of efforts.
“Ideally we’d be working together,” Lurie told Medscape Medical News.
“I’m hopeful we will find ways to collaborate scientifically,” she said. “The US government’s responsibility is to make doses for the US. CEPI’s responsibility is to make doses for the world. A big focus of CEPI is to make sure we have manufacturing capacity outside of the US so those doses can be available to the world and they don’t get seized by wealthy countries.”
Bottazzi, Ledley, Lurie, and Andino report no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
US government and industry projections that a COVID-19 vaccine will be ready by this fall or even January would take compressing what usually takes at least a decade into months, with little room for error or safety surprises.
“If all the cards fall into the right place and all the stars are aligned, you definitely could get a vaccine by December or January,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said last week.
But Fauci said a more realistic timeline is still 12 to 18 months, and experts interviewed by Medscape Medical News agree. They say that although recent developments are encouraging, history and scientific reason say the day when a COVID-19 vaccine is widely available will not come this year and may not come by the end of 2021.
The encouraging signals come primarily from two recent announcements: the $1.2 billion United States backing last week of one vaccine platform and the announcement on May 18 that the first human trials of another have produced some positive phase 1 results.
Recent developments
On May 21, the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) under “Operation Warp Speed” announced that the US will give AstraZeneca $1.2 billion “to make available at least 300 million doses of a coronavirus vaccine called AZD1222, with the first doses delivered as early as October 2020.”
On May 18, the Massachusetts-based biotechnology company Moderna announced that phase 1 clinical results showed that its vaccine candidate, which uses a new messenger RNA (mRNA) technology, appeared safe. Eight participants in the human trials were able to produce neutralizing antibodies that researchers believe are important in developing protection from the virus.
Moderna Chief Medical Officer Tal Zaks, MD, PhD told CNN that if the vaccine candidate does well in phase 2, “it could be ready by January 2021.”
The two candidates are among 10 in clinical trials for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The AstraZeneca/ AZD1222 candidate (also called ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, in collaboration with the University of Oxford) has entered phase 2/3.
Moderna’s candidate and another being developed in Beijing, China, are in phase 2, WHO reports. As of yesterday, 115 other candidates are in preclinical evaluation.
Maria Elena Bottazzi, PhD, associate dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, told Medscape Medical News it’s important to realize that, in the case of the $1.2 billion US investment, “what they’re talking about is manufacturing.”
The idea, she said, is to pay AstraZeneca up front so that manufacturing can start before it is known whether the vaccine candidate is safe or effective, the reverse of how the clinical trial process usually works.
That way, if the candidate is deemed safe and effective, time is not lost by then deciding how to make it and distribute it.
By the end of this year, she said, “Maybe we will have many vaccines made and stored in a refrigerator somewhere. But between now and December, there’s absolutely no way you can show efficacy of the vaccine at the same time you confirm that it’s safe.”
“Take these things with a grain of salt”
Animal testing for the AstraZeneca candidate, made in partnership with the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom, has yielded lackluster results, according to results on the preprint server BioRxiv, which have not been peer-reviewed.
“The results were not bad, but they were not gangbusters,” Bottazzi said. The results show the vaccine offered only partial protection.
“Partial protection is better than no protection,” she noted. “You have to take these things with a grain of salt. We don’t know what’s going to happen in humans.”
As for the Moderna candidate, Bottazzi said, “the good news is they found an appropriate safety profile. But from an eight-person group to make the extrapolation that they have efficacy — it’s unrealistic.”
Nicole Lurie, MD, MSPH, is senior adviser to the CEO for the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovation (CEPI), a nongovernmental organization funded by the Wellcome Trust, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the European Commission, and eight countries (Australia, Belgium, Canada, Ethiopia, Germany, Japan, Norway, and the United Kingdom) charged with supporting development of vaccines for pathogens on WHO’s priority list.
She and her colleagues write in a paper published online in the New England Journal of Medicine on March 30 that “it typically takes multiple candidates and many years to produce a licensed vaccine.”
The fastest time for developing a vaccine to date is 4 years, for the mumps vaccine, licensed in 1967.
As to whether she would expect a rollout of any vaccine by the end of the year, Lurie told Medscape Medical News, “If everything goes according to plan in every way, shape or form, well then maybe you can get there. But I wouldn’t hold my breath.”
Lurie and her colleagues write that “it’s far from certain that these new platforms will be scalable or that existing capacity can provide sufficient quantities of vaccine fast enough.”
On a call with reporters today, leaders of some of the words largest pharmaceutical companies said that one of the key bottlenecks is the sheer number of vials needed in order to distribute billions of doses of a successful vaccine.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, said, “Typically we are producing vaccines in single-dose vials. We are exploring with governments right now if it would be more convenient if there were 5-dose vials or 10-dose vials. I think we can resolve a significant part of the bottleneck.”
Despite the challenges, experts interviewed for this article agree that it will be possible to make a vaccine for COVID-19. They don’t expect attempts to meet the same complications that HIV researchers have seen over decades as the virus continues to confound with mutations.
Fred Ledley, MD, director of the Center for Integration of Science and Industry at Bentley University in Waltham, Massachusetts, told Medscape Medical News, “There doesn’t appear to be anything terribly diabolical about this virus. The mutation rate doesn’t appear to be anything like HIV. It appears to have some big, ugly proteins on the surface, which is good for vaccines — proteins with a lot of physical features look distinguishable from healthy cells. Signs all point to that it should be possible to make a vaccine.”
History raises safety concerns
However, Ledley said, “The idea of doing it in 6 months is largely unrealistic.”
He says 18 months is more realistic, primarily because of the sheer number of people that would have to be enrolled in a phase 3 study to truly test whether the endpoints are being met.
Vaccines are given to healthy volunteers. If safety signals arise, they may not be apparent until massive numbers of people are tested in phase 3.
“You’re never going to see the rates cut to 0%, but to see the difference between 10 people getting sick and seven people getting sick, takes very, very large numbers,” Ledley said. “There’s no way that can be done in 6 months. You’re talking about tens of thousands of people enrolled.”
He notes at this point it’s unclear what the endpoints will be and what the safety thresholds will be after consideration of risks and benefit.
Another big question for Ledley: “We don’t know what type of immunity we need to protect us against the virus. Do you just need the antibodies in your blood or do you need cells that are primed to attack the virus? Is it more of a chemical clearance or do the cells need to physically go in and digest the virus?”
History also points to the need for rigorous safety precautions that scientists fear could be compromised as trial phases overlap and processes are run in parallel instead of one step at a time.
An early batch of the Salk vaccine for polio in 1955, for example, turned out to be contaminated and caused paralysis in some children and 10 deaths, he points out.
CEPI’s Lurie adds that early candidates for another coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), “caused a reaction in the lungs that was very dangerous” before development was halted.
She also pointed to previous findings that a vaccine for dengue fever could worsen the disease in some people through a phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement.
Lurie and colleagues write in their paper that “it’s critical that vaccines also be developed using the tried-and-true methods, even if they may take longer to enter clinical trials or to result in large numbers of doses.”
Live attenuated vaccine
Raul Andino, PhD, a virologist at the University of California San Francisco, is among the scientists working with a tried-and-true method — a live attenuated vaccine — and he told Medscape Medical News he’s predicting it will take 2 years to develop.
He said it is cheaper to produce because scientists just have to learn how to grow the virus. Because the technology is already proven, a live attenuated vaccine could be rapidly produced on a worldwide scale.
The hope is also that a live attenuated vaccine would be given once in a lifetime and therefore be more affordable, especially in poorer countries.
“While a Moderna vaccine might be good for Europe and the United States,” he said, “It’s not going to be good for Africa, India, Brazil.”
Andino said, “I would bet money” that the front-runner vaccines so far will not be one-time vaccines.
He points out that most of the vaccine candidates are trying to protect people from disease. While there’s nothing wrong with that, he said, “In my opinion that is the lower-hanging fruit.”
“In my mind we need something that interrupts the chain of transmission and induces protection,” Andino said, important for developing herd immunity.
The reason this type of approach takes longer is because you are introducing a weakened form of the virus to the body and you have to make sure it doesn’t cause disease, not just in a small test population, but in populations who may be more susceptible to the disease, Andino said.
A call for unified strategies
Universities, countries, international consortiums, and public-private partnerships are all racing to find several safe and effective vaccines as no one entity will likely be able to provide the global solution.
Some of the efforts involve overlap of entities but with different focuses.
Along with “Operation Warp Speed” and CEPI, other collaborations include Gavi the Vaccine Alliance, whose core partners include WHO, UNICEF, the World Bank, and the Gates Foundation; and “Accelerating Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV) partnership,” led by the National Institutes of Health.
Industry partners in ACTIV (18 biopharmaceutical companies), according to a May 18 article published online in the Journal of the American Medical Association, have said they will contribute their respective clinical trial capacities, regardless of which agent is studied.
Some, however, have called for more streamlining of efforts.
“Ideally we’d be working together,” Lurie told Medscape Medical News.
“I’m hopeful we will find ways to collaborate scientifically,” she said. “The US government’s responsibility is to make doses for the US. CEPI’s responsibility is to make doses for the world. A big focus of CEPI is to make sure we have manufacturing capacity outside of the US so those doses can be available to the world and they don’t get seized by wealthy countries.”
Bottazzi, Ledley, Lurie, and Andino report no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians still unaware of need for genetic testing in NSCLC
Moreover, the majority of these clinicians believe that fewer than 50% of patients in their country undergo molecular testing, the same survey showed.
The survey was conducted by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC); 2537 questionnaires from 102 countries were returned and analyzed.
It was published online May 20 in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology.
The results are concerning because “the risk of death for patients with NSCLC is substantially reduced when a gene alteration is identified and the available targeted therapy is administered,” the authors emphasize.
“Specific protocols to initiate reflex testing for guideline-recommended molecular markers would help providers consider molecular testing earlier and optimize tissue,” they suggest.
Surprised that clinicians were unaware of guidelines
“I was not surprised that we found suboptimal testing rates based on other research that has demonstrated the need to improve the quality of lung cancer in some areas,” corresponding author Matthew Smeltzer, PhD, University of Memphis, Tennessee, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
“However, I was surprised that so many respondents were unaware of guidelines,” he said.
The College of American Pathologists, IASLC, and Association for Molecular Pathology established evidence-based standards for the selection of NSCLC patients for molecular testing in 2013, and these guidelines were subsequently endorsed by the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“We suspect that the level of access a provider has to targeted therapies does affect molecular testing rates,” Smeltzer acknowledged.
Molecular testing survey
“The survey included a seven-question introduction for all respondents and then divided respondents into one of three tracks,” the authors explain.
These tracks included respondents who requested tests and who treated patients (medical oncologists), those who analyzed and interpreted assays (pathologists), and those who acquired tissue samples (surgeons, pulmonologists, radiologists).
Countries were also grouped into five geographic regions — Asia, Europe, Latin America, United States, and Canada — and the rest of the world (ROW).
“Overall, respondents reported that molecular testing rates were lower than we would like but they were not satisfied with the current state of testing, and they reported higher testing rates in their own clinics,” Smeltzer noted.
However, when tests were ordered, “we found 99% of respondents in the requesting/treating track ordered tests for EGFR, 95% for ALK, 79% for ROS1, and < 50% ordered other tests,” the authors observe.
Indeed, EGFR, ALK, and ROS1 were the top three tests ordered across all regions, though less frequently so in the ROW, they add.
More than half of requesting/treating track respondents also order multiplex assays, although Latin America and the ROW did this less frequently than other regions.
Over 90% of respondents who perform or interpret assays indicated that they perform EGFR testing, while 83% of the same group do ALK testing; 69% tested for KRAS; 68% for BRAF, 64% for ROS1, and 56% for HER2. Fewer than half of them performed other tests.
Survey results also showed that EGFR, ALK, and KRAS are the top three tests performed across all regions, with no regional differences.
“Respondents also reported on the acquisition and testing of liquid biopsies,” survey authors point out.
Here, 87% of requesting/treating track respondents indicated that they “sometimes” request molecular testing on liquid biopsies, but the proportions of those who sometimes use liquid biopsy varied by region and were lowest in Latin America and the ROW.
A lower proportion of those who perform and interpret assays, at 69%, also offer tests on liquid biopsies, but this percentage, too, varied significantly by region, being the least frequently done in the United States and Canada, as well as in the ROW.
All the above tests are for genetic mutations or alterations that guide clinicians on use of targeted therapy directed at particular mutations, for example, drugs like erlotinib for EGFR and crizotinib for ALK.
However, immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has also made a big impact on the treatment of NSCLC, and the use of these agents is sometimes guided by testing for programmed cell-death ligand (PD-L1).
PD-L1 is not a molecular marker per se, the authors note.
Nevertheless, “we found that 84% of respondents in the requesting/treating track ordered PD-L1 and 68% of respondents who perform or interpret assays report PD-L1 is offered in their own lab,” the authors observe.
Smeltzer commented that both approaches — targeted therapies and immunotherapy — have made inroads into the treatment of NSCLC, in some cases replacing chemotherapy.
He emphasized that “it is important to know if a specific oncogene driver is present before initiating immunotherapy treatment,” and noted that when tissue is sent out for both types of testing, the results for PD-L1 are usually available before the results for the full molecular testing panel are back.
Barriers to testing
“The most frequent barrier to molecular testing in every region was cost,” the survey authors note.
Insufficient amount of tumor cells was the main reason for molecular testing failures along with inadequate tissue quality.
The majority of respondents who order tests and treat patients were sure that the laboratories they use perform appropriate validation of molecular tests, while almost all of those who perform or interpret assays said they perform validation tests in their labs.
Only 30% of respondents who request tests and treat patients have access to molecular testing labs within their own institutions; the remaining respondents have to outsource testing completely or partially.
Most respondents who test and treat patients also have multidisciplinary tumor boards to discuss patients with NSCLC, but almost one quarter of the same group indicated their board met less than once a month.
“Turnaround time is a barrier to molecular testing across the world,” the authors continue, with 29% of those who request tests and treat patients reporting that it typically takes 10 days or more to receive molecular testing results.
Interestingly, the highest percentage of respondents who reported this long turnaround time were in North America.
Perhaps encouragingly, 41% of respondents who perform or interpret assays indicated they were dissatisfied with the condition of molecular testing in their country, although in this regard, the United States and Canada had the lowest rates of dissatisfaction.
In fact, 39% of those who request tests and treat patients ranked the conditions of molecular testing in their country as “average or below,” while 42% of respondents in the tissue acquisition track ranked the conditions of molecular testing as average or below, the worst rankings coming from Latin America and the ROW.
Low quality of tissue samples was another reason respondents expressed dissatisfaction with the current state of molecular testing in their country.
Smeltzer is a research consultant for the Association of Community Cancer Centers.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moreover, the majority of these clinicians believe that fewer than 50% of patients in their country undergo molecular testing, the same survey showed.
The survey was conducted by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC); 2537 questionnaires from 102 countries were returned and analyzed.
It was published online May 20 in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology.
The results are concerning because “the risk of death for patients with NSCLC is substantially reduced when a gene alteration is identified and the available targeted therapy is administered,” the authors emphasize.
“Specific protocols to initiate reflex testing for guideline-recommended molecular markers would help providers consider molecular testing earlier and optimize tissue,” they suggest.
Surprised that clinicians were unaware of guidelines
“I was not surprised that we found suboptimal testing rates based on other research that has demonstrated the need to improve the quality of lung cancer in some areas,” corresponding author Matthew Smeltzer, PhD, University of Memphis, Tennessee, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
“However, I was surprised that so many respondents were unaware of guidelines,” he said.
The College of American Pathologists, IASLC, and Association for Molecular Pathology established evidence-based standards for the selection of NSCLC patients for molecular testing in 2013, and these guidelines were subsequently endorsed by the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“We suspect that the level of access a provider has to targeted therapies does affect molecular testing rates,” Smeltzer acknowledged.
Molecular testing survey
“The survey included a seven-question introduction for all respondents and then divided respondents into one of three tracks,” the authors explain.
These tracks included respondents who requested tests and who treated patients (medical oncologists), those who analyzed and interpreted assays (pathologists), and those who acquired tissue samples (surgeons, pulmonologists, radiologists).
Countries were also grouped into five geographic regions — Asia, Europe, Latin America, United States, and Canada — and the rest of the world (ROW).
“Overall, respondents reported that molecular testing rates were lower than we would like but they were not satisfied with the current state of testing, and they reported higher testing rates in their own clinics,” Smeltzer noted.
However, when tests were ordered, “we found 99% of respondents in the requesting/treating track ordered tests for EGFR, 95% for ALK, 79% for ROS1, and < 50% ordered other tests,” the authors observe.
Indeed, EGFR, ALK, and ROS1 were the top three tests ordered across all regions, though less frequently so in the ROW, they add.
More than half of requesting/treating track respondents also order multiplex assays, although Latin America and the ROW did this less frequently than other regions.
Over 90% of respondents who perform or interpret assays indicated that they perform EGFR testing, while 83% of the same group do ALK testing; 69% tested for KRAS; 68% for BRAF, 64% for ROS1, and 56% for HER2. Fewer than half of them performed other tests.
Survey results also showed that EGFR, ALK, and KRAS are the top three tests performed across all regions, with no regional differences.
“Respondents also reported on the acquisition and testing of liquid biopsies,” survey authors point out.
Here, 87% of requesting/treating track respondents indicated that they “sometimes” request molecular testing on liquid biopsies, but the proportions of those who sometimes use liquid biopsy varied by region and were lowest in Latin America and the ROW.
A lower proportion of those who perform and interpret assays, at 69%, also offer tests on liquid biopsies, but this percentage, too, varied significantly by region, being the least frequently done in the United States and Canada, as well as in the ROW.
All the above tests are for genetic mutations or alterations that guide clinicians on use of targeted therapy directed at particular mutations, for example, drugs like erlotinib for EGFR and crizotinib for ALK.
However, immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has also made a big impact on the treatment of NSCLC, and the use of these agents is sometimes guided by testing for programmed cell-death ligand (PD-L1).
PD-L1 is not a molecular marker per se, the authors note.
Nevertheless, “we found that 84% of respondents in the requesting/treating track ordered PD-L1 and 68% of respondents who perform or interpret assays report PD-L1 is offered in their own lab,” the authors observe.
Smeltzer commented that both approaches — targeted therapies and immunotherapy — have made inroads into the treatment of NSCLC, in some cases replacing chemotherapy.
He emphasized that “it is important to know if a specific oncogene driver is present before initiating immunotherapy treatment,” and noted that when tissue is sent out for both types of testing, the results for PD-L1 are usually available before the results for the full molecular testing panel are back.
Barriers to testing
“The most frequent barrier to molecular testing in every region was cost,” the survey authors note.
Insufficient amount of tumor cells was the main reason for molecular testing failures along with inadequate tissue quality.
The majority of respondents who order tests and treat patients were sure that the laboratories they use perform appropriate validation of molecular tests, while almost all of those who perform or interpret assays said they perform validation tests in their labs.
Only 30% of respondents who request tests and treat patients have access to molecular testing labs within their own institutions; the remaining respondents have to outsource testing completely or partially.
Most respondents who test and treat patients also have multidisciplinary tumor boards to discuss patients with NSCLC, but almost one quarter of the same group indicated their board met less than once a month.
“Turnaround time is a barrier to molecular testing across the world,” the authors continue, with 29% of those who request tests and treat patients reporting that it typically takes 10 days or more to receive molecular testing results.
Interestingly, the highest percentage of respondents who reported this long turnaround time were in North America.
Perhaps encouragingly, 41% of respondents who perform or interpret assays indicated they were dissatisfied with the condition of molecular testing in their country, although in this regard, the United States and Canada had the lowest rates of dissatisfaction.
In fact, 39% of those who request tests and treat patients ranked the conditions of molecular testing in their country as “average or below,” while 42% of respondents in the tissue acquisition track ranked the conditions of molecular testing as average or below, the worst rankings coming from Latin America and the ROW.
Low quality of tissue samples was another reason respondents expressed dissatisfaction with the current state of molecular testing in their country.
Smeltzer is a research consultant for the Association of Community Cancer Centers.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moreover, the majority of these clinicians believe that fewer than 50% of patients in their country undergo molecular testing, the same survey showed.
The survey was conducted by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC); 2537 questionnaires from 102 countries were returned and analyzed.
It was published online May 20 in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology.
The results are concerning because “the risk of death for patients with NSCLC is substantially reduced when a gene alteration is identified and the available targeted therapy is administered,” the authors emphasize.
“Specific protocols to initiate reflex testing for guideline-recommended molecular markers would help providers consider molecular testing earlier and optimize tissue,” they suggest.
Surprised that clinicians were unaware of guidelines
“I was not surprised that we found suboptimal testing rates based on other research that has demonstrated the need to improve the quality of lung cancer in some areas,” corresponding author Matthew Smeltzer, PhD, University of Memphis, Tennessee, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
“However, I was surprised that so many respondents were unaware of guidelines,” he said.
The College of American Pathologists, IASLC, and Association for Molecular Pathology established evidence-based standards for the selection of NSCLC patients for molecular testing in 2013, and these guidelines were subsequently endorsed by the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“We suspect that the level of access a provider has to targeted therapies does affect molecular testing rates,” Smeltzer acknowledged.
Molecular testing survey
“The survey included a seven-question introduction for all respondents and then divided respondents into one of three tracks,” the authors explain.
These tracks included respondents who requested tests and who treated patients (medical oncologists), those who analyzed and interpreted assays (pathologists), and those who acquired tissue samples (surgeons, pulmonologists, radiologists).
Countries were also grouped into five geographic regions — Asia, Europe, Latin America, United States, and Canada — and the rest of the world (ROW).
“Overall, respondents reported that molecular testing rates were lower than we would like but they were not satisfied with the current state of testing, and they reported higher testing rates in their own clinics,” Smeltzer noted.
However, when tests were ordered, “we found 99% of respondents in the requesting/treating track ordered tests for EGFR, 95% for ALK, 79% for ROS1, and < 50% ordered other tests,” the authors observe.
Indeed, EGFR, ALK, and ROS1 were the top three tests ordered across all regions, though less frequently so in the ROW, they add.
More than half of requesting/treating track respondents also order multiplex assays, although Latin America and the ROW did this less frequently than other regions.
Over 90% of respondents who perform or interpret assays indicated that they perform EGFR testing, while 83% of the same group do ALK testing; 69% tested for KRAS; 68% for BRAF, 64% for ROS1, and 56% for HER2. Fewer than half of them performed other tests.
Survey results also showed that EGFR, ALK, and KRAS are the top three tests performed across all regions, with no regional differences.
“Respondents also reported on the acquisition and testing of liquid biopsies,” survey authors point out.
Here, 87% of requesting/treating track respondents indicated that they “sometimes” request molecular testing on liquid biopsies, but the proportions of those who sometimes use liquid biopsy varied by region and were lowest in Latin America and the ROW.
A lower proportion of those who perform and interpret assays, at 69%, also offer tests on liquid biopsies, but this percentage, too, varied significantly by region, being the least frequently done in the United States and Canada, as well as in the ROW.
All the above tests are for genetic mutations or alterations that guide clinicians on use of targeted therapy directed at particular mutations, for example, drugs like erlotinib for EGFR and crizotinib for ALK.
However, immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has also made a big impact on the treatment of NSCLC, and the use of these agents is sometimes guided by testing for programmed cell-death ligand (PD-L1).
PD-L1 is not a molecular marker per se, the authors note.
Nevertheless, “we found that 84% of respondents in the requesting/treating track ordered PD-L1 and 68% of respondents who perform or interpret assays report PD-L1 is offered in their own lab,” the authors observe.
Smeltzer commented that both approaches — targeted therapies and immunotherapy — have made inroads into the treatment of NSCLC, in some cases replacing chemotherapy.
He emphasized that “it is important to know if a specific oncogene driver is present before initiating immunotherapy treatment,” and noted that when tissue is sent out for both types of testing, the results for PD-L1 are usually available before the results for the full molecular testing panel are back.
Barriers to testing
“The most frequent barrier to molecular testing in every region was cost,” the survey authors note.
Insufficient amount of tumor cells was the main reason for molecular testing failures along with inadequate tissue quality.
The majority of respondents who order tests and treat patients were sure that the laboratories they use perform appropriate validation of molecular tests, while almost all of those who perform or interpret assays said they perform validation tests in their labs.
Only 30% of respondents who request tests and treat patients have access to molecular testing labs within their own institutions; the remaining respondents have to outsource testing completely or partially.
Most respondents who test and treat patients also have multidisciplinary tumor boards to discuss patients with NSCLC, but almost one quarter of the same group indicated their board met less than once a month.
“Turnaround time is a barrier to molecular testing across the world,” the authors continue, with 29% of those who request tests and treat patients reporting that it typically takes 10 days or more to receive molecular testing results.
Interestingly, the highest percentage of respondents who reported this long turnaround time were in North America.
Perhaps encouragingly, 41% of respondents who perform or interpret assays indicated they were dissatisfied with the condition of molecular testing in their country, although in this regard, the United States and Canada had the lowest rates of dissatisfaction.
In fact, 39% of those who request tests and treat patients ranked the conditions of molecular testing in their country as “average or below,” while 42% of respondents in the tissue acquisition track ranked the conditions of molecular testing as average or below, the worst rankings coming from Latin America and the ROW.
Low quality of tissue samples was another reason respondents expressed dissatisfaction with the current state of molecular testing in their country.
Smeltzer is a research consultant for the Association of Community Cancer Centers.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19: Putting distance between projection and reality
When it comes to COVID-19, studies show that social distancing flattened the curve.
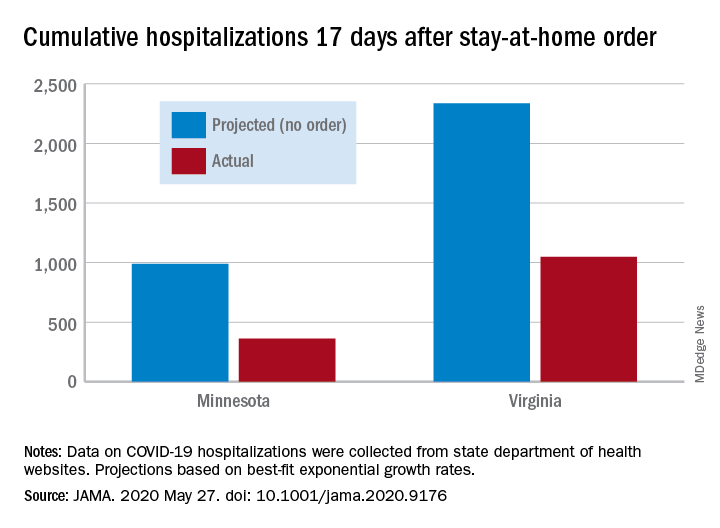
Cumulative hospitalizations in four states with stay-at-home orders were well short of the projected exponential growth curves, Soumya Sen, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and associates reported May 27 in a research letter in JAMA. All states were observed through April 28.
The deviations between observed cases and worst-case projections in the four states – Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia – all began within 8-10 days of the stay-at-home orders. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In Virginia, the corresponding numbers were 1,048 observed and 2,335 projected, they reported.
“Observed hospitalizations consistently fell outside of the 95% prediction bands of the projected exponential growth curve,” Dr. Sen and associates noted.
In a separate Canadian study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention, Ashleigh R. Tuite, PhD, MPH, of the University of Toronto and associates wrote May 27 in a letter in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Their model, based on a 70% reduction in physical contacts for March 19–May 3, projected 2.0 cases per 100,000 population with physical distancing and 37.4 per 100,000 without. Deaths among those ICU patients were projected at 2.5 per 100,000 with distancing and 12.7 per 100,000 without intervention, they reported.
“Our modeling also shows the challenges associated with relaxation of physical distancing measures without a concomitant increase in other public health measures. Specifically, when the number of contacts between persons returns to more than 50% of normal, we expect disease activity to resurge rapidly and ICUs to quickly reach capacity,” they wrote.
The study published in JAMA used publicly available data from the University of Minnesota COVID-19 Hospitalization Project, which is partially funded by the University of Minnesota Office of Academic Clinical Affairs and United Health Foundation.
SOURCES: Sen S et al. JAMA. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9176; Tuite AR et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.7326/M20-2945.
When it comes to COVID-19, studies show that social distancing flattened the curve.

Cumulative hospitalizations in four states with stay-at-home orders were well short of the projected exponential growth curves, Soumya Sen, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and associates reported May 27 in a research letter in JAMA. All states were observed through April 28.
The deviations between observed cases and worst-case projections in the four states – Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia – all began within 8-10 days of the stay-at-home orders. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In Virginia, the corresponding numbers were 1,048 observed and 2,335 projected, they reported.
“Observed hospitalizations consistently fell outside of the 95% prediction bands of the projected exponential growth curve,” Dr. Sen and associates noted.
In a separate Canadian study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention, Ashleigh R. Tuite, PhD, MPH, of the University of Toronto and associates wrote May 27 in a letter in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Their model, based on a 70% reduction in physical contacts for March 19–May 3, projected 2.0 cases per 100,000 population with physical distancing and 37.4 per 100,000 without. Deaths among those ICU patients were projected at 2.5 per 100,000 with distancing and 12.7 per 100,000 without intervention, they reported.
“Our modeling also shows the challenges associated with relaxation of physical distancing measures without a concomitant increase in other public health measures. Specifically, when the number of contacts between persons returns to more than 50% of normal, we expect disease activity to resurge rapidly and ICUs to quickly reach capacity,” they wrote.
The study published in JAMA used publicly available data from the University of Minnesota COVID-19 Hospitalization Project, which is partially funded by the University of Minnesota Office of Academic Clinical Affairs and United Health Foundation.
SOURCES: Sen S et al. JAMA. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9176; Tuite AR et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.7326/M20-2945.
When it comes to COVID-19, studies show that social distancing flattened the curve.

Cumulative hospitalizations in four states with stay-at-home orders were well short of the projected exponential growth curves, Soumya Sen, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and associates reported May 27 in a research letter in JAMA. All states were observed through April 28.
The deviations between observed cases and worst-case projections in the four states – Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia – all began within 8-10 days of the stay-at-home orders. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In Virginia, the corresponding numbers were 1,048 observed and 2,335 projected, they reported.
“Observed hospitalizations consistently fell outside of the 95% prediction bands of the projected exponential growth curve,” Dr. Sen and associates noted.
In a separate Canadian study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention, Ashleigh R. Tuite, PhD, MPH, of the University of Toronto and associates wrote May 27 in a letter in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Their model, based on a 70% reduction in physical contacts for March 19–May 3, projected 2.0 cases per 100,000 population with physical distancing and 37.4 per 100,000 without. Deaths among those ICU patients were projected at 2.5 per 100,000 with distancing and 12.7 per 100,000 without intervention, they reported.
“Our modeling also shows the challenges associated with relaxation of physical distancing measures without a concomitant increase in other public health measures. Specifically, when the number of contacts between persons returns to more than 50% of normal, we expect disease activity to resurge rapidly and ICUs to quickly reach capacity,” they wrote.
The study published in JAMA used publicly available data from the University of Minnesota COVID-19 Hospitalization Project, which is partially funded by the University of Minnesota Office of Academic Clinical Affairs and United Health Foundation.
SOURCES: Sen S et al. JAMA. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9176; Tuite AR et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.7326/M20-2945.
Patients find CAC more persuasive than ASCVD risk score for statin decisions
Patients who received a protocol-driven recommendation to initiate statin therapy for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease based upon their CT angiography coronary artery calcium score were twice as likely to actually start on the drug than those whose recommendation was guided by the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Pooled Cohort Equations Risk Calculator, according to the results of the randomized CorCal Vanguard study.
These results suggest that patients – and their primary care physicians – find the conventional method of screening for cardiovascular risk using the Pooled Cohort Equations to estimate the 10-year risk of MI or stroke, as recommended in ACC/AHA guidelines, to be less persuasive than screening for the presence or absence of actual disease as captured by CT angiography images and the associated coronary artery calcium (CAC) score, Joseph B. Muhlestein, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the ACC and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The CorCal Vanguard study included 601 patients with an average baseline LDL cholesterol of 120 mg/dL, an average age of 60 years, and no history of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or prior statin therapy. They were randomized to decision-making regarding statin therapy based on either the ACC/AHA guideline–endorsed Pooled Cohort Equations, which use an estimated 10-year risk of 7.5% or more as the threshold for statin initiation, or their CAC score.
If a patient’s CAC score was 0, the recommendation was against starting a statin. Everyone with a CAC greater than 100 received a recommendation for high-intensity statin therapy. And for those with a CAC of 1-100, the decision defaulted to the results of the Pooled Cohort Equations. The screening results were provided to a patient’s primary physician so they could engage in joint decision-making regarding initiation of statin therapy. Adherence to a screening-based recommendation to start on a statin was assessed at 3 and 12 months of follow-up, explained Dr. Muhlestein, a cardiologist at the Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute in Salt Lake City.
He noted that CorCal Vanguard was merely a feasibility study. Based on the study results he presented at ACC 2020, the full 9,000-patient CorCal primary prevention trial is now enrolling participants. CorCal is the first randomized trial to pit the Pooled Cohort Equations against the CAC score in a large study looking for differences in downstream clinical outcomes.
The rationale for this line of clinical research lies in the known limitations of the ACC/AHA risk calculator. “It may overestimate risk in some populations, patients aren’t always adherent to Pooled Cohort Equations Risk Calculator recommendations, and it doesn’t include novel risk markers such as C-reactive protein that some consider important for risk assessment. And the big question: Should we continue risk screening to determine potential benefit from drug therapy, or should we switch to disease screening?” the cardiologist commented.
The CorCal Vanguard results
A recommendation to start statin therapy was made in 48% of patients in the Pooled Cohort Equations group, versus 36% of the group randomized to CAC. However, only 17% of patients in the Pooled Cohort Equations group actually initiated a statin, a significantly lower rate than the 26% figure in the CAC arm. Fully 70% of patients who received a recommendation to start taking a statin on the basis of their CAC score actually did so, compared to just 36% of those whose recommendation was based upon their Pooled Cohort Equations Risk Calculator.
At 3 months of follow-up, 61% of patients who received an initial recommendation to start statin therapy based upon their CAC screening were actually taking a statin, compared with 41% of those whose recommendation was based upon the Pooled Cohort Equations. At 12 months, the figures were 64% and 49%.
In both groups, at 12 months of follow-up, the No. 1 reason patients weren’t taking a statin as recommended was that their personal physician had advised against it or never prescribed it. That accounted for roughly half of the nonadherence. Another quarter was because of a preference to try lifestyle change first. Fear of drug side effects was a less common reason.
Putting the CorCal Vanguard study results in perspective, Dr. Muhlestein observed that, prior to the screening study, none of the participants had ever been on a statin, yet 37% of them were found by one screening method or the other to be at high cardiovascular risk. Of those high-risk patients, 51% actually initiated statin therapy and the majority of them were still taking their medication 12 months later.
“That has to be a good thing. It emphasizes what can be done when proactive primary prevention is practiced,” the cardiologist said.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding the CorCal study, which was funded by a grant from the Dell Loy Hansen Cardiovascular Research Fund.
SOURCE: Muhlestein JB et al. ACC 2020, Abstract 909-12.
Patients who received a protocol-driven recommendation to initiate statin therapy for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease based upon their CT angiography coronary artery calcium score were twice as likely to actually start on the drug than those whose recommendation was guided by the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Pooled Cohort Equations Risk Calculator, according to the results of the randomized CorCal Vanguard study.
These results suggest that patients – and their primary care physicians – find the conventional method of screening for cardiovascular risk using the Pooled Cohort Equations to estimate the 10-year risk of MI or stroke, as recommended in ACC/AHA guidelines, to be less persuasive than screening for the presence or absence of actual disease as captured by CT angiography images and the associated coronary artery calcium (CAC) score, Joseph B. Muhlestein, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the ACC and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The CorCal Vanguard study included 601 patients with an average baseline LDL cholesterol of 120 mg/dL, an average age of 60 years, and no history of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or prior statin therapy. They were randomized to decision-making regarding statin therapy based on either the ACC/AHA guideline–endorsed Pooled Cohort Equations, which use an estimated 10-year risk of 7.5% or more as the threshold for statin initiation, or their CAC score.
If a patient’s CAC score was 0, the recommendation was against starting a statin. Everyone with a CAC greater than 100 received a recommendation for high-intensity statin therapy. And for those with a CAC of 1-100, the decision defaulted to the results of the Pooled Cohort Equations. The screening results were provided to a patient’s primary physician so they could engage in joint decision-making regarding initiation of statin therapy. Adherence to a screening-based recommendation to start on a statin was assessed at 3 and 12 months of follow-up, explained Dr. Muhlestein, a cardiologist at the Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute in Salt Lake City.
He noted that CorCal Vanguard was merely a feasibility study. Based on the study results he presented at ACC 2020, the full 9,000-patient CorCal primary prevention trial is now enrolling participants. CorCal is the first randomized trial to pit the Pooled Cohort Equations against the CAC score in a large study looking for differences in downstream clinical outcomes.
The rationale for this line of clinical research lies in the known limitations of the ACC/AHA risk calculator. “It may overestimate risk in some populations, patients aren’t always adherent to Pooled Cohort Equations Risk Calculator recommendations, and it doesn’t include novel risk markers such as C-reactive protein that some consider important for risk assessment. And the big question: Should we continue risk screening to determine potential benefit from drug therapy, or should we switch to disease screening?” the cardiologist commented.
The CorCal Vanguard results
A recommendation to start statin therapy was made in 48% of patients in the Pooled Cohort Equations group, versus 36% of the group randomized to CAC. However, only 17% of patients in the Pooled Cohort Equations group actually initiated a statin, a significantly lower rate than the 26% figure in the CAC arm. Fully 70% of patients who received a recommendation to start taking a statin on the basis of their CAC score actually did so, compared to just 36% of those whose recommendation was based upon their Pooled Cohort Equations Risk Calculator.
At 3 months of follow-up, 61% of patients who received an initial recommendation to start statin therapy based upon their CAC screening were actually taking a statin, compared with 41% of those whose recommendation was based upon the Pooled Cohort Equations. At 12 months, the figures were 64% and 49%.
In both groups, at 12 months of follow-up, the No. 1 reason patients weren’t taking a statin as recommended was that their personal physician had advised against it or never prescribed it. That accounted for roughly half of the nonadherence. Another quarter was because of a preference to try lifestyle change first. Fear of drug side effects was a less common reason.
Putting the CorCal Vanguard study results in perspective, Dr. Muhlestein observed that, prior to the screening study, none of the participants had ever been on a statin, yet 37% of them were found by one screening method or the other to be at high cardiovascular risk. Of those high-risk patients, 51% actually initiated statin therapy and the majority of them were still taking their medication 12 months later.
“That has to be a good thing. It emphasizes what can be done when proactive primary prevention is practiced,” the cardiologist said.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding the CorCal study, which was funded by a grant from the Dell Loy Hansen Cardiovascular Research Fund.
SOURCE: Muhlestein JB et al. ACC 2020, Abstract 909-12.
Patients who received a protocol-driven recommendation to initiate statin therapy for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease based upon their CT angiography coronary artery calcium score were twice as likely to actually start on the drug than those whose recommendation was guided by the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Pooled Cohort Equations Risk Calculator, according to the results of the randomized CorCal Vanguard study.
These results suggest that patients – and their primary care physicians – find the conventional method of screening for cardiovascular risk using the Pooled Cohort Equations to estimate the 10-year risk of MI or stroke, as recommended in ACC/AHA guidelines, to be less persuasive than screening for the presence or absence of actual disease as captured by CT angiography images and the associated coronary artery calcium (CAC) score, Joseph B. Muhlestein, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the ACC and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The CorCal Vanguard study included 601 patients with an average baseline LDL cholesterol of 120 mg/dL, an average age of 60 years, and no history of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or prior statin therapy. They were randomized to decision-making regarding statin therapy based on either the ACC/AHA guideline–endorsed Pooled Cohort Equations, which use an estimated 10-year risk of 7.5% or more as the threshold for statin initiation, or their CAC score.
If a patient’s CAC score was 0, the recommendation was against starting a statin. Everyone with a CAC greater than 100 received a recommendation for high-intensity statin therapy. And for those with a CAC of 1-100, the decision defaulted to the results of the Pooled Cohort Equations. The screening results were provided to a patient’s primary physician so they could engage in joint decision-making regarding initiation of statin therapy. Adherence to a screening-based recommendation to start on a statin was assessed at 3 and 12 months of follow-up, explained Dr. Muhlestein, a cardiologist at the Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute in Salt Lake City.
He noted that CorCal Vanguard was merely a feasibility study. Based on the study results he presented at ACC 2020, the full 9,000-patient CorCal primary prevention trial is now enrolling participants. CorCal is the first randomized trial to pit the Pooled Cohort Equations against the CAC score in a large study looking for differences in downstream clinical outcomes.
The rationale for this line of clinical research lies in the known limitations of the ACC/AHA risk calculator. “It may overestimate risk in some populations, patients aren’t always adherent to Pooled Cohort Equations Risk Calculator recommendations, and it doesn’t include novel risk markers such as C-reactive protein that some consider important for risk assessment. And the big question: Should we continue risk screening to determine potential benefit from drug therapy, or should we switch to disease screening?” the cardiologist commented.
The CorCal Vanguard results
A recommendation to start statin therapy was made in 48% of patients in the Pooled Cohort Equations group, versus 36% of the group randomized to CAC. However, only 17% of patients in the Pooled Cohort Equations group actually initiated a statin, a significantly lower rate than the 26% figure in the CAC arm. Fully 70% of patients who received a recommendation to start taking a statin on the basis of their CAC score actually did so, compared to just 36% of those whose recommendation was based upon their Pooled Cohort Equations Risk Calculator.
At 3 months of follow-up, 61% of patients who received an initial recommendation to start statin therapy based upon their CAC screening were actually taking a statin, compared with 41% of those whose recommendation was based upon the Pooled Cohort Equations. At 12 months, the figures were 64% and 49%.
In both groups, at 12 months of follow-up, the No. 1 reason patients weren’t taking a statin as recommended was that their personal physician had advised against it or never prescribed it. That accounted for roughly half of the nonadherence. Another quarter was because of a preference to try lifestyle change first. Fear of drug side effects was a less common reason.
Putting the CorCal Vanguard study results in perspective, Dr. Muhlestein observed that, prior to the screening study, none of the participants had ever been on a statin, yet 37% of them were found by one screening method or the other to be at high cardiovascular risk. Of those high-risk patients, 51% actually initiated statin therapy and the majority of them were still taking their medication 12 months later.
“That has to be a good thing. It emphasizes what can be done when proactive primary prevention is practiced,” the cardiologist said.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding the CorCal study, which was funded by a grant from the Dell Loy Hansen Cardiovascular Research Fund.
SOURCE: Muhlestein JB et al. ACC 2020, Abstract 909-12.
FROM ACC 2020
Active cancer increases death risk in patients with COVID-19
Patients with COVID-19 and progressing cancer had a fivefold increase in the risk of 30-day mortality, compared with COVID-19–positive cancer patients who were in remission or had no evidence of cancer, according to data from the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium (CCC19) registry.
Other independent risk factors for death in patients with COVID-19 and cancer were older age, male sex, former smoking, number of comorbidities, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 2 or greater, and treatment with hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin.
In fact, patients who received hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin had a nearly threefold higher risk of death than did patients who had not received the combination. However, this finding was of “uncertain validity due to a high risk of residual confounding; for example, patients receiving this combination were more likely to have severe disease or more likely to be hospitalized,” said Jeremy L. Warner, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee.
Dr. Warner presented these findings in an online press briefing. Additional findings from the CCC19 registry are set to be presented as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) virtual scientific program. The findings were also published in The Lancet.
‘Severe impact’ in cancer patients
“For people with cancer, the impact of COVID-19 is especially severe, whether they have been exposed to the virus or not. Patients with cancer are typically older adults, often with other underlying conditions, and their immune systems may be suppressed by the cancer, or due to chemotherapy, radiation, or other treatment,” commented ASCO President Howard A. Burris III, MD, who moderated the press briefing but was not involved in the study of CCC19 registry data.
“ASCO members tell us that they have had to delay or modify treatment plans to reduce patients’ risk of infection, and we’re unclear what the impact of these changes will be. Delays in cancer screening and diagnosis are also a major concern,” Dr. Burris continued.
“This does confirm reports that have come out from other centers, including other parts of the world, where they have found that people who have cancer and COVID-19 have a worse outcome,” said Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, who was not involved in the research.
Dr. Chan’s group has developed a COVID-19 symptom study app with the aim of defining whether people living with cancer are at increased risk for infections, in addition to whether cancer is an independent risk factor for COVID-19 severity or mortality.
“Using data from our app, we were able to show that people who reported living with cancer did have a higher risk of developing COVID and were more likely to be hospitalized related to COVID,” Dr. Chan said in an interview.
Study details
The CCC19 registry collects information from 104 participating institutions in the United States and Canada, as well as anonymous data from individuals in the United States, Argentina, Canada, the European Union, and the United Kingdom.
The sample of 928 patients Dr. Warner presented was evenly balanced by sex. The median age was 66 years, and 30% of patients were aged 75 years or older.
In all, 39% of patients were on active anticancer therapy, and 43% had measurable disease. Breast cancer was the most common diagnosis, followed by prostate cancer, gastrointestinal cancers, lymphomas, and thoracic cancers.
Two-thirds of the patients (68%) had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1, 8% had a performance status of 2, and 5% a status of 3 or 4. The remaining patients had unknown performance status.
Slightly more than half of patients (52%) were never smokers, 37% were former smokers, and 5% were current smokers. The remaining 6% of patients had unknown smoking status.
At a median follow-up of 21 days, 121 patients (13%) had died. All deaths occurred within 30 days of COVID-19 diagnosis. Among patients who died, 78 were male, 64 were former smokers, 70 were aged 75 years or older, 41 had active stable or responding cancer, 25 had progressing cancer, and 42 had an ECOG performance status of 2 or higher.
In all, 466 patients were hospitalized, and 106 in this group (23%) died. Among the 132 patients admitted to an ICU, 50 (38%) died, including 27 patients aged 75 years or older, and 15 with an ECOG performance status of 2 or greater. Of the 116 patients who required intubation, 50 (43%) died, including 26 who were 75 years or older, and 11 who had a performance status of 2 or greater.
It’s early days yet, and a larger sample size with longer follow-up will be needed to get a more complete picture of how COVID-19 affects specific patient subsets over time, Dr. Warner said.
ASCO has established its own COVID-19 registry to collect both near-term and longitudinal data during the pandemic.
“We’ll be able to learn about both how the pandemic has impacted delivery of cancer care, as well as the longer-term effects of COVID-19 on cancer patients and understand what care approaches are working best,” said Richard L. Schilsky, MD, chief medical officer and executive vice president of ASCO, during the briefing.
The study of CCC19 registry data was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health and the American Cancer Society. Dr. Warner disclosed stock/ownership in HemOnc.org, consulting for IBM and Westat, and travel expenses from IBM. Dr. Burris, Dr. Schilsky, and Dr. Chan reported no disclosures relevant to the study.
SOURCE: Warner J L et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract LBA110.
Patients with COVID-19 and progressing cancer had a fivefold increase in the risk of 30-day mortality, compared with COVID-19–positive cancer patients who were in remission or had no evidence of cancer, according to data from the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium (CCC19) registry.
Other independent risk factors for death in patients with COVID-19 and cancer were older age, male sex, former smoking, number of comorbidities, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 2 or greater, and treatment with hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin.
In fact, patients who received hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin had a nearly threefold higher risk of death than did patients who had not received the combination. However, this finding was of “uncertain validity due to a high risk of residual confounding; for example, patients receiving this combination were more likely to have severe disease or more likely to be hospitalized,” said Jeremy L. Warner, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee.
Dr. Warner presented these findings in an online press briefing. Additional findings from the CCC19 registry are set to be presented as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) virtual scientific program. The findings were also published in The Lancet.
‘Severe impact’ in cancer patients
“For people with cancer, the impact of COVID-19 is especially severe, whether they have been exposed to the virus or not. Patients with cancer are typically older adults, often with other underlying conditions, and their immune systems may be suppressed by the cancer, or due to chemotherapy, radiation, or other treatment,” commented ASCO President Howard A. Burris III, MD, who moderated the press briefing but was not involved in the study of CCC19 registry data.
“ASCO members tell us that they have had to delay or modify treatment plans to reduce patients’ risk of infection, and we’re unclear what the impact of these changes will be. Delays in cancer screening and diagnosis are also a major concern,” Dr. Burris continued.
“This does confirm reports that have come out from other centers, including other parts of the world, where they have found that people who have cancer and COVID-19 have a worse outcome,” said Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, who was not involved in the research.
Dr. Chan’s group has developed a COVID-19 symptom study app with the aim of defining whether people living with cancer are at increased risk for infections, in addition to whether cancer is an independent risk factor for COVID-19 severity or mortality.
“Using data from our app, we were able to show that people who reported living with cancer did have a higher risk of developing COVID and were more likely to be hospitalized related to COVID,” Dr. Chan said in an interview.
Study details
The CCC19 registry collects information from 104 participating institutions in the United States and Canada, as well as anonymous data from individuals in the United States, Argentina, Canada, the European Union, and the United Kingdom.
The sample of 928 patients Dr. Warner presented was evenly balanced by sex. The median age was 66 years, and 30% of patients were aged 75 years or older.
In all, 39% of patients were on active anticancer therapy, and 43% had measurable disease. Breast cancer was the most common diagnosis, followed by prostate cancer, gastrointestinal cancers, lymphomas, and thoracic cancers.
Two-thirds of the patients (68%) had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1, 8% had a performance status of 2, and 5% a status of 3 or 4. The remaining patients had unknown performance status.
Slightly more than half of patients (52%) were never smokers, 37% were former smokers, and 5% were current smokers. The remaining 6% of patients had unknown smoking status.
At a median follow-up of 21 days, 121 patients (13%) had died. All deaths occurred within 30 days of COVID-19 diagnosis. Among patients who died, 78 were male, 64 were former smokers, 70 were aged 75 years or older, 41 had active stable or responding cancer, 25 had progressing cancer, and 42 had an ECOG performance status of 2 or higher.
In all, 466 patients were hospitalized, and 106 in this group (23%) died. Among the 132 patients admitted to an ICU, 50 (38%) died, including 27 patients aged 75 years or older, and 15 with an ECOG performance status of 2 or greater. Of the 116 patients who required intubation, 50 (43%) died, including 26 who were 75 years or older, and 11 who had a performance status of 2 or greater.
It’s early days yet, and a larger sample size with longer follow-up will be needed to get a more complete picture of how COVID-19 affects specific patient subsets over time, Dr. Warner said.
ASCO has established its own COVID-19 registry to collect both near-term and longitudinal data during the pandemic.
“We’ll be able to learn about both how the pandemic has impacted delivery of cancer care, as well as the longer-term effects of COVID-19 on cancer patients and understand what care approaches are working best,” said Richard L. Schilsky, MD, chief medical officer and executive vice president of ASCO, during the briefing.
The study of CCC19 registry data was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health and the American Cancer Society. Dr. Warner disclosed stock/ownership in HemOnc.org, consulting for IBM and Westat, and travel expenses from IBM. Dr. Burris, Dr. Schilsky, and Dr. Chan reported no disclosures relevant to the study.
SOURCE: Warner J L et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract LBA110.
Patients with COVID-19 and progressing cancer had a fivefold increase in the risk of 30-day mortality, compared with COVID-19–positive cancer patients who were in remission or had no evidence of cancer, according to data from the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium (CCC19) registry.
Other independent risk factors for death in patients with COVID-19 and cancer were older age, male sex, former smoking, number of comorbidities, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 2 or greater, and treatment with hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin.
In fact, patients who received hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin had a nearly threefold higher risk of death than did patients who had not received the combination. However, this finding was of “uncertain validity due to a high risk of residual confounding; for example, patients receiving this combination were more likely to have severe disease or more likely to be hospitalized,” said Jeremy L. Warner, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee.
Dr. Warner presented these findings in an online press briefing. Additional findings from the CCC19 registry are set to be presented as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) virtual scientific program. The findings were also published in The Lancet.
‘Severe impact’ in cancer patients
“For people with cancer, the impact of COVID-19 is especially severe, whether they have been exposed to the virus or not. Patients with cancer are typically older adults, often with other underlying conditions, and their immune systems may be suppressed by the cancer, or due to chemotherapy, radiation, or other treatment,” commented ASCO President Howard A. Burris III, MD, who moderated the press briefing but was not involved in the study of CCC19 registry data.
“ASCO members tell us that they have had to delay or modify treatment plans to reduce patients’ risk of infection, and we’re unclear what the impact of these changes will be. Delays in cancer screening and diagnosis are also a major concern,” Dr. Burris continued.
“This does confirm reports that have come out from other centers, including other parts of the world, where they have found that people who have cancer and COVID-19 have a worse outcome,” said Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, who was not involved in the research.
Dr. Chan’s group has developed a COVID-19 symptom study app with the aim of defining whether people living with cancer are at increased risk for infections, in addition to whether cancer is an independent risk factor for COVID-19 severity or mortality.
“Using data from our app, we were able to show that people who reported living with cancer did have a higher risk of developing COVID and were more likely to be hospitalized related to COVID,” Dr. Chan said in an interview.
Study details
The CCC19 registry collects information from 104 participating institutions in the United States and Canada, as well as anonymous data from individuals in the United States, Argentina, Canada, the European Union, and the United Kingdom.
The sample of 928 patients Dr. Warner presented was evenly balanced by sex. The median age was 66 years, and 30% of patients were aged 75 years or older.
In all, 39% of patients were on active anticancer therapy, and 43% had measurable disease. Breast cancer was the most common diagnosis, followed by prostate cancer, gastrointestinal cancers, lymphomas, and thoracic cancers.
Two-thirds of the patients (68%) had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1, 8% had a performance status of 2, and 5% a status of 3 or 4. The remaining patients had unknown performance status.
Slightly more than half of patients (52%) were never smokers, 37% were former smokers, and 5% were current smokers. The remaining 6% of patients had unknown smoking status.
At a median follow-up of 21 days, 121 patients (13%) had died. All deaths occurred within 30 days of COVID-19 diagnosis. Among patients who died, 78 were male, 64 were former smokers, 70 were aged 75 years or older, 41 had active stable or responding cancer, 25 had progressing cancer, and 42 had an ECOG performance status of 2 or higher.
In all, 466 patients were hospitalized, and 106 in this group (23%) died. Among the 132 patients admitted to an ICU, 50 (38%) died, including 27 patients aged 75 years or older, and 15 with an ECOG performance status of 2 or greater. Of the 116 patients who required intubation, 50 (43%) died, including 26 who were 75 years or older, and 11 who had a performance status of 2 or greater.
It’s early days yet, and a larger sample size with longer follow-up will be needed to get a more complete picture of how COVID-19 affects specific patient subsets over time, Dr. Warner said.
ASCO has established its own COVID-19 registry to collect both near-term and longitudinal data during the pandemic.
“We’ll be able to learn about both how the pandemic has impacted delivery of cancer care, as well as the longer-term effects of COVID-19 on cancer patients and understand what care approaches are working best,” said Richard L. Schilsky, MD, chief medical officer and executive vice president of ASCO, during the briefing.
The study of CCC19 registry data was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health and the American Cancer Society. Dr. Warner disclosed stock/ownership in HemOnc.org, consulting for IBM and Westat, and travel expenses from IBM. Dr. Burris, Dr. Schilsky, and Dr. Chan reported no disclosures relevant to the study.
SOURCE: Warner J L et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract LBA110.
FROM ASCO 2020
Key clinical point: Patients with progressing cancer and COVID-19 are at an especially high risk of 30-day mortality.
Major finding: Patients with COVID-19 whose cancers were progressing had a fivefold increase in the risk of 30-day mortality, compared with COVID-19–positive cancer patients in remission or with no evidence of cancer.
Study details: Analysis of data on 928 patients enrolled in the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium (CCC19) registry.
Disclosures: The research was supported, in part, by the National Institutes of Health and the American Cancer Society. Dr. Warner disclosed relationships with HemOnc.org, IBM, and Westat.
Source: Warner J L et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract LBA110.
Adjuvant osimertinib extends DFS in localized NSCLC
, results of the ADAURA trial showed.
The randomized, phase 3 trial was a comparison of osimertinib treatment with placebo following complete resection of localized or locally advanced NSCLC with negative margins. The trial was unblinded early and halted on the recommendation of the independent data-monitoring committee, due to the efficacy of osimertinib.
“If I were on the committee, I would have done the same thing. These are extraordinary results,” said study investigator Roy S. Herbst, MD, PhD, chief of medical oncology at the Yale Cancer Center and Smilow Cancer Center at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Herbst is scheduled to present results from ADAURA as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
In an online briefing prior to the meeting, Dr. Herbst said the impressive results reminded him of a lesson imparted by his mentor, the late Isaiah Fidler, DVM, PhD.
“He taught me, he taught all of us, that metastasis is a spread of tumor that kills patients,” Dr. Herbst said. “Drugs such as this, based on biology, given to patients at the earliest possible time, prevent those metastases and allow patients to live longer and with a better quality of life.”
Results from the ADAURA trial provide compelling evidence of the benefit of adjuvant osimertinib for a select group of patients, according to Tina Cascone, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the department of thoracic head and neck medical oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. She was not involved in the study.
“These are unprecedented results for a potentially curable, resected population of patients,” Dr. Cascone said in an interview. “This definitely has the potential to shift the paradigm in the treatments that we have available for patients with resected disease. It’s very important to emphasize how much we’ve learned from the metastatic setting and how we’re bringing what we’ve learned into early stage disease.”
High recurrence rates
An estimated 30% of patients with NSCLC present with resectable disease at diagnosis, but 5-year recurrence rates following surgery and cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy remain high, ranging from 45% among patients with stage IB disease to 62% for patients with stage II NSCLC and 76% for patients with stage III disease, Dr. Herbst noted.
Osimertinib is a third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) targeted to EGFR. It has been shown to offer improvements in both progression-free survival and overall survival compared with the EGFR-TKIs erlotinib and gefitinib for patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC, as well as in patients with central nervous system metastases.
Osimertinib’s efficacy and safety profile against advanced disease suggests it may also be effective against early stage disease, a hypothesis the ADAURA trial was designed to test.
Study details
The phase 3, randomized, double-blind trial was conducted at centers in the United States, Europe, Asia, and Australia. A total of 682 patients with completely resected stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC, with or without planned adjuvant chemotherapy, were enrolled.
After stratification by stage, EGFR mutation, and race (Asian vs. non-Asian), patients were randomized on a 1:1 basis to receive either osimertinib at 80 mg once daily or placebo. The planned treatment duration was a maximum of 3 years.
Members of the independent data-monitoring committee held a meeting in April 2020. Although they had not planned an efficacy analysis at that time, they decided the results were clearly in favor of osimertinib. So they recommended unblinding and halting of the trial.
At the time of unblinding, the study had completed enrollment, and all patients had been followed for at least 1 year.
Efficacy and safety
For the primary endpoint of disease-free survival (DFS) in patients with stage II to IIIA disease, the median DFS was not reached for patients assigned to osimertinib, but it was 20.4 months for patients assigned to placebo (hazard ratio, 0.17; P < .0001).
The numbers were similar for the secondary endpoint of DFS in the overall population, including patients with stage IB disease. The median DFS was not reached for patients on osimertinib but was 28.1 months for patients on placebo (HR, 0.21; P < .0001).
DFS was significantly superior with osimertinib across all subgroups in the overall population, including sex, age, smoking status, race, stage, EGFR mutation, and adjuvant chemotherapy (yes or no).
Dr. Herbst said patients tolerated osimertinib well, and the drug’s safety profile was consistent with that already known. There were no adverse events leading to death in the osimertinib arm, and the incidence of grade 3 or 4 adverse events of any kind was low.
In all, 10 patients (3%) in the osimertinib arm were reported to have interstitial lung disease. Prolongation of the QT interval was reported in 22 patients (7%) on osimertinib and 4 patients (1%) in the placebo arm.
The results show that “adjuvant osimertinib provides a highly effective, practice-changing treatment for patients with stage IB, II, IIIA, EGFR mutation-positive non–small cell lung cancer after complete tumor resection,” Dr. Herbst said.
Dr. Herbst disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, which funded the study, as well as Jun Shi Pharmaceuticals and other companies. Dr. Cascone is the international principal investigator of the NeoCOAST trial evaluating durvalumab, an AstraZeneca product.
SOURCE: Herbst RS et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract LBA5.
, results of the ADAURA trial showed.
The randomized, phase 3 trial was a comparison of osimertinib treatment with placebo following complete resection of localized or locally advanced NSCLC with negative margins. The trial was unblinded early and halted on the recommendation of the independent data-monitoring committee, due to the efficacy of osimertinib.
“If I were on the committee, I would have done the same thing. These are extraordinary results,” said study investigator Roy S. Herbst, MD, PhD, chief of medical oncology at the Yale Cancer Center and Smilow Cancer Center at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Herbst is scheduled to present results from ADAURA as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
In an online briefing prior to the meeting, Dr. Herbst said the impressive results reminded him of a lesson imparted by his mentor, the late Isaiah Fidler, DVM, PhD.
“He taught me, he taught all of us, that metastasis is a spread of tumor that kills patients,” Dr. Herbst said. “Drugs such as this, based on biology, given to patients at the earliest possible time, prevent those metastases and allow patients to live longer and with a better quality of life.”
Results from the ADAURA trial provide compelling evidence of the benefit of adjuvant osimertinib for a select group of patients, according to Tina Cascone, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the department of thoracic head and neck medical oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. She was not involved in the study.
“These are unprecedented results for a potentially curable, resected population of patients,” Dr. Cascone said in an interview. “This definitely has the potential to shift the paradigm in the treatments that we have available for patients with resected disease. It’s very important to emphasize how much we’ve learned from the metastatic setting and how we’re bringing what we’ve learned into early stage disease.”
High recurrence rates
An estimated 30% of patients with NSCLC present with resectable disease at diagnosis, but 5-year recurrence rates following surgery and cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy remain high, ranging from 45% among patients with stage IB disease to 62% for patients with stage II NSCLC and 76% for patients with stage III disease, Dr. Herbst noted.
Osimertinib is a third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) targeted to EGFR. It has been shown to offer improvements in both progression-free survival and overall survival compared with the EGFR-TKIs erlotinib and gefitinib for patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC, as well as in patients with central nervous system metastases.
Osimertinib’s efficacy and safety profile against advanced disease suggests it may also be effective against early stage disease, a hypothesis the ADAURA trial was designed to test.
Study details
The phase 3, randomized, double-blind trial was conducted at centers in the United States, Europe, Asia, and Australia. A total of 682 patients with completely resected stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC, with or without planned adjuvant chemotherapy, were enrolled.
After stratification by stage, EGFR mutation, and race (Asian vs. non-Asian), patients were randomized on a 1:1 basis to receive either osimertinib at 80 mg once daily or placebo. The planned treatment duration was a maximum of 3 years.
Members of the independent data-monitoring committee held a meeting in April 2020. Although they had not planned an efficacy analysis at that time, they decided the results were clearly in favor of osimertinib. So they recommended unblinding and halting of the trial.
At the time of unblinding, the study had completed enrollment, and all patients had been followed for at least 1 year.
Efficacy and safety
For the primary endpoint of disease-free survival (DFS) in patients with stage II to IIIA disease, the median DFS was not reached for patients assigned to osimertinib, but it was 20.4 months for patients assigned to placebo (hazard ratio, 0.17; P < .0001).
The numbers were similar for the secondary endpoint of DFS in the overall population, including patients with stage IB disease. The median DFS was not reached for patients on osimertinib but was 28.1 months for patients on placebo (HR, 0.21; P < .0001).
DFS was significantly superior with osimertinib across all subgroups in the overall population, including sex, age, smoking status, race, stage, EGFR mutation, and adjuvant chemotherapy (yes or no).
Dr. Herbst said patients tolerated osimertinib well, and the drug’s safety profile was consistent with that already known. There were no adverse events leading to death in the osimertinib arm, and the incidence of grade 3 or 4 adverse events of any kind was low.
In all, 10 patients (3%) in the osimertinib arm were reported to have interstitial lung disease. Prolongation of the QT interval was reported in 22 patients (7%) on osimertinib and 4 patients (1%) in the placebo arm.
The results show that “adjuvant osimertinib provides a highly effective, practice-changing treatment for patients with stage IB, II, IIIA, EGFR mutation-positive non–small cell lung cancer after complete tumor resection,” Dr. Herbst said.
Dr. Herbst disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, which funded the study, as well as Jun Shi Pharmaceuticals and other companies. Dr. Cascone is the international principal investigator of the NeoCOAST trial evaluating durvalumab, an AstraZeneca product.
SOURCE: Herbst RS et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract LBA5.
, results of the ADAURA trial showed.
The randomized, phase 3 trial was a comparison of osimertinib treatment with placebo following complete resection of localized or locally advanced NSCLC with negative margins. The trial was unblinded early and halted on the recommendation of the independent data-monitoring committee, due to the efficacy of osimertinib.
“If I were on the committee, I would have done the same thing. These are extraordinary results,” said study investigator Roy S. Herbst, MD, PhD, chief of medical oncology at the Yale Cancer Center and Smilow Cancer Center at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Herbst is scheduled to present results from ADAURA as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
In an online briefing prior to the meeting, Dr. Herbst said the impressive results reminded him of a lesson imparted by his mentor, the late Isaiah Fidler, DVM, PhD.
“He taught me, he taught all of us, that metastasis is a spread of tumor that kills patients,” Dr. Herbst said. “Drugs such as this, based on biology, given to patients at the earliest possible time, prevent those metastases and allow patients to live longer and with a better quality of life.”
Results from the ADAURA trial provide compelling evidence of the benefit of adjuvant osimertinib for a select group of patients, according to Tina Cascone, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the department of thoracic head and neck medical oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. She was not involved in the study.
“These are unprecedented results for a potentially curable, resected population of patients,” Dr. Cascone said in an interview. “This definitely has the potential to shift the paradigm in the treatments that we have available for patients with resected disease. It’s very important to emphasize how much we’ve learned from the metastatic setting and how we’re bringing what we’ve learned into early stage disease.”
High recurrence rates
An estimated 30% of patients with NSCLC present with resectable disease at diagnosis, but 5-year recurrence rates following surgery and cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy remain high, ranging from 45% among patients with stage IB disease to 62% for patients with stage II NSCLC and 76% for patients with stage III disease, Dr. Herbst noted.
Osimertinib is a third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) targeted to EGFR. It has been shown to offer improvements in both progression-free survival and overall survival compared with the EGFR-TKIs erlotinib and gefitinib for patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC, as well as in patients with central nervous system metastases.
Osimertinib’s efficacy and safety profile against advanced disease suggests it may also be effective against early stage disease, a hypothesis the ADAURA trial was designed to test.
Study details
The phase 3, randomized, double-blind trial was conducted at centers in the United States, Europe, Asia, and Australia. A total of 682 patients with completely resected stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC, with or without planned adjuvant chemotherapy, were enrolled.
After stratification by stage, EGFR mutation, and race (Asian vs. non-Asian), patients were randomized on a 1:1 basis to receive either osimertinib at 80 mg once daily or placebo. The planned treatment duration was a maximum of 3 years.
Members of the independent data-monitoring committee held a meeting in April 2020. Although they had not planned an efficacy analysis at that time, they decided the results were clearly in favor of osimertinib. So they recommended unblinding and halting of the trial.
At the time of unblinding, the study had completed enrollment, and all patients had been followed for at least 1 year.
Efficacy and safety
For the primary endpoint of disease-free survival (DFS) in patients with stage II to IIIA disease, the median DFS was not reached for patients assigned to osimertinib, but it was 20.4 months for patients assigned to placebo (hazard ratio, 0.17; P < .0001).
The numbers were similar for the secondary endpoint of DFS in the overall population, including patients with stage IB disease. The median DFS was not reached for patients on osimertinib but was 28.1 months for patients on placebo (HR, 0.21; P < .0001).
DFS was significantly superior with osimertinib across all subgroups in the overall population, including sex, age, smoking status, race, stage, EGFR mutation, and adjuvant chemotherapy (yes or no).
Dr. Herbst said patients tolerated osimertinib well, and the drug’s safety profile was consistent with that already known. There were no adverse events leading to death in the osimertinib arm, and the incidence of grade 3 or 4 adverse events of any kind was low.
In all, 10 patients (3%) in the osimertinib arm were reported to have interstitial lung disease. Prolongation of the QT interval was reported in 22 patients (7%) on osimertinib and 4 patients (1%) in the placebo arm.
The results show that “adjuvant osimertinib provides a highly effective, practice-changing treatment for patients with stage IB, II, IIIA, EGFR mutation-positive non–small cell lung cancer after complete tumor resection,” Dr. Herbst said.
Dr. Herbst disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, which funded the study, as well as Jun Shi Pharmaceuticals and other companies. Dr. Cascone is the international principal investigator of the NeoCOAST trial evaluating durvalumab, an AstraZeneca product.
SOURCE: Herbst RS et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract LBA5.
FROM ASCO 2020
Key clinical point: Adjuvant osimertinib extended disease-free survival, compared with placebo, in patients with EGFR-mutated non–small cell lung cancer.
Major finding: In the overall population, the median disease-free survival was not reached for patients on osimertinib and was 28.1 months for patients on placebo (hazard ratio, 0.21, P < .0001).
Study details: Randomized, double-blind, phase 3 trial of 682 patients with stage IB-IIIA non–small cell lung cancer bearing EGFR mutations.
Disclosures: Dr. Herbst disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, which funded the study, as well as Jun Shi Pharmaceuticals and other companies.
Source: Herbst RS et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract LBA5.
Today’s top news highlights: Coping with addiction during COVID, lung rehab part of recovery
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Long road to recovery includes lung rehab
For seriously ill COVID-19 patients, there may a long recovery period even after leaving the intensive care unit. Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, is one of those patients. For 28 days, he was on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab. “The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University. READ MORE.
Detox unit keeps running during COVID-19
Substance use disorder doesn’t take a break for a pandemic. In fact, the stressors from the current COVID-19 situation have increased substance use. In a commentary published on MDedge, Keji Fagbemi, MD, a hospitalist at the BronxCare Health System, shared how his hospital kept its inpatient detoxification unit running, despite the challenges presented by COVID-19. “At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service,” he wrote. “In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.” READ MORE.
Air pollution linked to MS risk
Air pollution may be another environmental risk factor for developing multiple sclerosis, suggests new research released as part of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020. The findings, which are based on a large cohort study of nearly 550,000 individuals in Italy, appear to confirm the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in prior studies. “Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy. READ MORE.
Trials produce conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease
High-dose aducanumab, a human monoclonal antibody in development for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, significantly reduced clinical decline in people with early disease in one randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. But there was no statistically significant change in outcomes in an identical study. “We believe that the difference between the results was largely due to patients’ greater exposure to the high dose of aducanumab,” said Samantha Budd Haeberlein, PhD, one of the study investigators and senior vice president and head of the neurodegeneration development unit at Biogen, which is developing the drug. READ MORE.
Pregnant patients have asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
The rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16% among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, according to recent study results. “If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” researchers wrote in Obstetrics & Gynecology. READ MORE.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Long road to recovery includes lung rehab
For seriously ill COVID-19 patients, there may a long recovery period even after leaving the intensive care unit. Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, is one of those patients. For 28 days, he was on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab. “The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University. READ MORE.
Detox unit keeps running during COVID-19
Substance use disorder doesn’t take a break for a pandemic. In fact, the stressors from the current COVID-19 situation have increased substance use. In a commentary published on MDedge, Keji Fagbemi, MD, a hospitalist at the BronxCare Health System, shared how his hospital kept its inpatient detoxification unit running, despite the challenges presented by COVID-19. “At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service,” he wrote. “In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.” READ MORE.
Air pollution linked to MS risk
Air pollution may be another environmental risk factor for developing multiple sclerosis, suggests new research released as part of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020. The findings, which are based on a large cohort study of nearly 550,000 individuals in Italy, appear to confirm the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in prior studies. “Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy. READ MORE.
Trials produce conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease
High-dose aducanumab, a human monoclonal antibody in development for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, significantly reduced clinical decline in people with early disease in one randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. But there was no statistically significant change in outcomes in an identical study. “We believe that the difference between the results was largely due to patients’ greater exposure to the high dose of aducanumab,” said Samantha Budd Haeberlein, PhD, one of the study investigators and senior vice president and head of the neurodegeneration development unit at Biogen, which is developing the drug. READ MORE.
Pregnant patients have asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
The rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16% among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, according to recent study results. “If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” researchers wrote in Obstetrics & Gynecology. READ MORE.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Long road to recovery includes lung rehab
For seriously ill COVID-19 patients, there may a long recovery period even after leaving the intensive care unit. Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, is one of those patients. For 28 days, he was on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab. “The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University. READ MORE.
Detox unit keeps running during COVID-19
Substance use disorder doesn’t take a break for a pandemic. In fact, the stressors from the current COVID-19 situation have increased substance use. In a commentary published on MDedge, Keji Fagbemi, MD, a hospitalist at the BronxCare Health System, shared how his hospital kept its inpatient detoxification unit running, despite the challenges presented by COVID-19. “At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service,” he wrote. “In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.” READ MORE.
Air pollution linked to MS risk
Air pollution may be another environmental risk factor for developing multiple sclerosis, suggests new research released as part of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020. The findings, which are based on a large cohort study of nearly 550,000 individuals in Italy, appear to confirm the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in prior studies. “Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy. READ MORE.
Trials produce conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease
High-dose aducanumab, a human monoclonal antibody in development for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, significantly reduced clinical decline in people with early disease in one randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. But there was no statistically significant change in outcomes in an identical study. “We believe that the difference between the results was largely due to patients’ greater exposure to the high dose of aducanumab,” said Samantha Budd Haeberlein, PhD, one of the study investigators and senior vice president and head of the neurodegeneration development unit at Biogen, which is developing the drug. READ MORE.
Pregnant patients have asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
The rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16% among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, according to recent study results. “If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” researchers wrote in Obstetrics & Gynecology. READ MORE.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
New York City inpatient detox unit keeps running: Here’s how
Substance use disorder and its daily consequences take no breaks even during a pandemic. The stressors created by COVID-19, including deaths of loved ones and the disruptions to normal life from policies aimed at flattening the curve, seem to have increased substance use.
I practice as a hospitalist with an internal medicine background and specialty in addiction medicine at BronxCare Health System’s inpatient detoxification unit, a 24/7, 20-bed medically-supervised unit in South Bronx in New York City. It is one of the comprehensive services provided by the BronxCare’s life recovery center and addiction services, which also includes an outpatient clinic, opioid treatment program, inpatient rehab, and a half-way house. Inpatient detoxification units like ours are designed to treat serious addictions and chemical dependency and prevent and treat life-threatening withdrawal symptoms and signs or complications. Our patients come from all over the city and its adjoining suburbs, including from emergency room referrals, referral clinics, courts and the justice system, walk-ins, and self-referrals.
At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service. In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.
Individuals with substance use disorder have historically been a vulnerable and underserved population and possess high risk for multiple health problems as well as preexisting conditions. Many have limited life options financially, educationally, and with housing, and encounter barriers to accessing primary health care services, including preventive services. The introduction of the COVID-19 pandemic into these patients’ precarious health situations only made things worse as many of the limited resources for patients with substance use disorder were diverted to battling the pandemic. Numerous inpatient and outpatient addiction services, for example, were temporarily shut down. This has led to an increase in domestic violence, and psychiatric decompensation, including psychosis, suicidal attempts, and worsening of medical comorbidities in these patients.
Our wake-up call came when the first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in New York in early March. Within a short period of time the state became the epicenter for COVID-19. With the projection of millions of cases being positive and the number of new cases doubling every third day at the onset in New York City, we knew we had a battle brewing and needed to radically transform our mode of operation fast.
Our first task was to ensure the safety of our patients and the dedicated health workers attending to them. We streamlined the patient point of entry through one screening site, while also brushing up on our history-taking to intently screen for COVID-19. This included not just focusing on travels from China, but from Europe and other parts of the world.
Yes, we did ask patients about cough, fever, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling fatigued, severe body ache, and possible contact with someone who is sick or has traveled overseas. But we were also attuned to the increased rate of community spread and the presentation of other symptoms, such as loss of taste and smell, early in the process. Hence we were able to triage patients with suspected cases to the appropriate sections of the hospital for further screening, testing, and evaluation, instead of having those patients admitted to the detox unit.
Early in the process a huddle team was instituted with daily briefing of staff lasting 30 minutes or less. This team consists of physicians, nurses, a physician assistant, a social worker, and a counselor. In addition to discussing treatment plans for the patient, they deliberate on the public health information from the hospital’s COVID-19 command center, New York State Department of Health, the Office of Mental Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the latest evidence-based information. These discussions have helped us modify our policies and practices.
We instituted a no visiting rule during a short hospital stay of 5-7 days, and this was initiated weeks in advance of many institutions, including nursing homes with vulnerable populations. Our admitting criteria was reviewed to allow for admission of only those patients who absolutely needed inpatient substance use disorder treatment, including patients with severe withdrawal symptoms and signs, comorbidities, or neuropsychiatric manifestations that made them unsafe for outpatient or home detoxification. Others were triaged to the outpatient services which was amply supported with telemedicine. Rooms and designated areas of the building were earmarked as places for isolation/quarantine if suspected COVID-19 cases were identified pending testing. To assess patients’ risk of COVID-19, we do point-of-care nasopharyngeal swab testing with polymerase chain reaction.
Regarding face masks, patients and staff were fitted with ones early in the process. Additionally, staff were trained on the importance of face mask use and how to ensure you have a tight seal around the mouth and nose and were provided with other appropriate personal protective equipment. Concerning social distancing, we reduced the patient population capacity for the unit down to 50% and offered only single room admissions. Social distancing was encouraged in the unit, including in the television and recreation room and dining room, and during small treatment groups of less than six individuals. Daily temperature checks with noncontact handheld thermometers were enforced for staff and anyone coming into the life recovery center.
Patients are continuously being educated on the presentations of COVID-19 and encouraged to report any symptoms. Any staff feeling sick or having symptoms are encouraged to stay home. Rigorous and continuous cleaning of surfaces, especially of areas subjected to common use, is done frequently by the hospital housekeeping and environmental crew and is the order of the day.
Dr. Fagbemi is a hospitalist at BronxCare Health System, a not-for-profit health and teaching hospital system serving South and Central Bronx in New York. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Substance use disorder and its daily consequences take no breaks even during a pandemic. The stressors created by COVID-19, including deaths of loved ones and the disruptions to normal life from policies aimed at flattening the curve, seem to have increased substance use.
I practice as a hospitalist with an internal medicine background and specialty in addiction medicine at BronxCare Health System’s inpatient detoxification unit, a 24/7, 20-bed medically-supervised unit in South Bronx in New York City. It is one of the comprehensive services provided by the BronxCare’s life recovery center and addiction services, which also includes an outpatient clinic, opioid treatment program, inpatient rehab, and a half-way house. Inpatient detoxification units like ours are designed to treat serious addictions and chemical dependency and prevent and treat life-threatening withdrawal symptoms and signs or complications. Our patients come from all over the city and its adjoining suburbs, including from emergency room referrals, referral clinics, courts and the justice system, walk-ins, and self-referrals.
At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service. In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.
Individuals with substance use disorder have historically been a vulnerable and underserved population and possess high risk for multiple health problems as well as preexisting conditions. Many have limited life options financially, educationally, and with housing, and encounter barriers to accessing primary health care services, including preventive services. The introduction of the COVID-19 pandemic into these patients’ precarious health situations only made things worse as many of the limited resources for patients with substance use disorder were diverted to battling the pandemic. Numerous inpatient and outpatient addiction services, for example, were temporarily shut down. This has led to an increase in domestic violence, and psychiatric decompensation, including psychosis, suicidal attempts, and worsening of medical comorbidities in these patients.
Our wake-up call came when the first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in New York in early March. Within a short period of time the state became the epicenter for COVID-19. With the projection of millions of cases being positive and the number of new cases doubling every third day at the onset in New York City, we knew we had a battle brewing and needed to radically transform our mode of operation fast.
Our first task was to ensure the safety of our patients and the dedicated health workers attending to them. We streamlined the patient point of entry through one screening site, while also brushing up on our history-taking to intently screen for COVID-19. This included not just focusing on travels from China, but from Europe and other parts of the world.
Yes, we did ask patients about cough, fever, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling fatigued, severe body ache, and possible contact with someone who is sick or has traveled overseas. But we were also attuned to the increased rate of community spread and the presentation of other symptoms, such as loss of taste and smell, early in the process. Hence we were able to triage patients with suspected cases to the appropriate sections of the hospital for further screening, testing, and evaluation, instead of having those patients admitted to the detox unit.
Early in the process a huddle team was instituted with daily briefing of staff lasting 30 minutes or less. This team consists of physicians, nurses, a physician assistant, a social worker, and a counselor. In addition to discussing treatment plans for the patient, they deliberate on the public health information from the hospital’s COVID-19 command center, New York State Department of Health, the Office of Mental Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the latest evidence-based information. These discussions have helped us modify our policies and practices.
We instituted a no visiting rule during a short hospital stay of 5-7 days, and this was initiated weeks in advance of many institutions, including nursing homes with vulnerable populations. Our admitting criteria was reviewed to allow for admission of only those patients who absolutely needed inpatient substance use disorder treatment, including patients with severe withdrawal symptoms and signs, comorbidities, or neuropsychiatric manifestations that made them unsafe for outpatient or home detoxification. Others were triaged to the outpatient services which was amply supported with telemedicine. Rooms and designated areas of the building were earmarked as places for isolation/quarantine if suspected COVID-19 cases were identified pending testing. To assess patients’ risk of COVID-19, we do point-of-care nasopharyngeal swab testing with polymerase chain reaction.
Regarding face masks, patients and staff were fitted with ones early in the process. Additionally, staff were trained on the importance of face mask use and how to ensure you have a tight seal around the mouth and nose and were provided with other appropriate personal protective equipment. Concerning social distancing, we reduced the patient population capacity for the unit down to 50% and offered only single room admissions. Social distancing was encouraged in the unit, including in the television and recreation room and dining room, and during small treatment groups of less than six individuals. Daily temperature checks with noncontact handheld thermometers were enforced for staff and anyone coming into the life recovery center.
Patients are continuously being educated on the presentations of COVID-19 and encouraged to report any symptoms. Any staff feeling sick or having symptoms are encouraged to stay home. Rigorous and continuous cleaning of surfaces, especially of areas subjected to common use, is done frequently by the hospital housekeeping and environmental crew and is the order of the day.
Dr. Fagbemi is a hospitalist at BronxCare Health System, a not-for-profit health and teaching hospital system serving South and Central Bronx in New York. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Substance use disorder and its daily consequences take no breaks even during a pandemic. The stressors created by COVID-19, including deaths of loved ones and the disruptions to normal life from policies aimed at flattening the curve, seem to have increased substance use.
I practice as a hospitalist with an internal medicine background and specialty in addiction medicine at BronxCare Health System’s inpatient detoxification unit, a 24/7, 20-bed medically-supervised unit in South Bronx in New York City. It is one of the comprehensive services provided by the BronxCare’s life recovery center and addiction services, which also includes an outpatient clinic, opioid treatment program, inpatient rehab, and a half-way house. Inpatient detoxification units like ours are designed to treat serious addictions and chemical dependency and prevent and treat life-threatening withdrawal symptoms and signs or complications. Our patients come from all over the city and its adjoining suburbs, including from emergency room referrals, referral clinics, courts and the justice system, walk-ins, and self-referrals.
At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service. In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.
Individuals with substance use disorder have historically been a vulnerable and underserved population and possess high risk for multiple health problems as well as preexisting conditions. Many have limited life options financially, educationally, and with housing, and encounter barriers to accessing primary health care services, including preventive services. The introduction of the COVID-19 pandemic into these patients’ precarious health situations only made things worse as many of the limited resources for patients with substance use disorder were diverted to battling the pandemic. Numerous inpatient and outpatient addiction services, for example, were temporarily shut down. This has led to an increase in domestic violence, and psychiatric decompensation, including psychosis, suicidal attempts, and worsening of medical comorbidities in these patients.
Our wake-up call came when the first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in New York in early March. Within a short period of time the state became the epicenter for COVID-19. With the projection of millions of cases being positive and the number of new cases doubling every third day at the onset in New York City, we knew we had a battle brewing and needed to radically transform our mode of operation fast.
Our first task was to ensure the safety of our patients and the dedicated health workers attending to them. We streamlined the patient point of entry through one screening site, while also brushing up on our history-taking to intently screen for COVID-19. This included not just focusing on travels from China, but from Europe and other parts of the world.
Yes, we did ask patients about cough, fever, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling fatigued, severe body ache, and possible contact with someone who is sick or has traveled overseas. But we were also attuned to the increased rate of community spread and the presentation of other symptoms, such as loss of taste and smell, early in the process. Hence we were able to triage patients with suspected cases to the appropriate sections of the hospital for further screening, testing, and evaluation, instead of having those patients admitted to the detox unit.
Early in the process a huddle team was instituted with daily briefing of staff lasting 30 minutes or less. This team consists of physicians, nurses, a physician assistant, a social worker, and a counselor. In addition to discussing treatment plans for the patient, they deliberate on the public health information from the hospital’s COVID-19 command center, New York State Department of Health, the Office of Mental Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the latest evidence-based information. These discussions have helped us modify our policies and practices.
We instituted a no visiting rule during a short hospital stay of 5-7 days, and this was initiated weeks in advance of many institutions, including nursing homes with vulnerable populations. Our admitting criteria was reviewed to allow for admission of only those patients who absolutely needed inpatient substance use disorder treatment, including patients with severe withdrawal symptoms and signs, comorbidities, or neuropsychiatric manifestations that made them unsafe for outpatient or home detoxification. Others were triaged to the outpatient services which was amply supported with telemedicine. Rooms and designated areas of the building were earmarked as places for isolation/quarantine if suspected COVID-19 cases were identified pending testing. To assess patients’ risk of COVID-19, we do point-of-care nasopharyngeal swab testing with polymerase chain reaction.
Regarding face masks, patients and staff were fitted with ones early in the process. Additionally, staff were trained on the importance of face mask use and how to ensure you have a tight seal around the mouth and nose and were provided with other appropriate personal protective equipment. Concerning social distancing, we reduced the patient population capacity for the unit down to 50% and offered only single room admissions. Social distancing was encouraged in the unit, including in the television and recreation room and dining room, and during small treatment groups of less than six individuals. Daily temperature checks with noncontact handheld thermometers were enforced for staff and anyone coming into the life recovery center.
Patients are continuously being educated on the presentations of COVID-19 and encouraged to report any symptoms. Any staff feeling sick or having symptoms are encouraged to stay home. Rigorous and continuous cleaning of surfaces, especially of areas subjected to common use, is done frequently by the hospital housekeeping and environmental crew and is the order of the day.
Dr. Fagbemi is a hospitalist at BronxCare Health System, a not-for-profit health and teaching hospital system serving South and Central Bronx in New York. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Placental injury reported in women with COVID-19
Neonates appear healthy so far
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
Neonates appear healthy so far
Neonates appear healthy so far
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY
SARS-CoV-2 infection rate 16% in asymptomatic pregnant women at delivery
Among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, the rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Among the patients’ designated support persons, the asymptomatic carrier rate was 10%.
“If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” wrote the researchers affiliated with the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Angela Bianco, MD, and colleagues conducted an observational study of women who were scheduled for a planned delivery within the Mount Sinai Health System between April 4 and April 15, 2020. Patients and their designated support person completed a telephone screen and underwent COVID-19 testing the day before a scheduled delivery. If support persons screened positive during the telephone interview about COVID-19 symptoms, they could not attend the birth, and patients could contact a different support person to be screened and tested. “All patients and their support persons were informed of their SARS-CoV-2 test results before admission,” the investigators wrote. “Those who tested positive were counseled regarding symptomatology that should prompt medical attention.”
In all, researchers screened 158 patients with a planned delivery, and 155 agreed to undergo COVID-19 testing. Of the 155 women tested, 24 (16%) tested positive for SARS CoV-2 infection. Among 146 support persons who had a negative interview screen and underwent SARS-CoV-2 testing, 14 (10%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Test results were substantially concordant among patient and support person pairs. “Among patients who tested positive for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, 11 of 19 (58%) support persons also tested positive for COVID-19 infection,” the authors reported. “Among patients who tested negative for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, only 3 of 127 (2.4%) support persons tested positive for COVID-19 infection.”
Telephone screening did not identify any of the COVID-19–positive cases. Of the 24 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, none of their newborns tested positive at birth.
“Universal testing ... provides a mechanism for more accurate counseling of patients regarding issues such as newborn skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding,” noted Dr. Bianco and colleagues. At their institution, parents with COVID-19 are instructed to wear a mask and practice proper hand hygiene when caring for their newborns.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, said in an interview that the study by Bianco et al. underscores the high rate of asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic COVID-19 infections detected with universal screening in a hospital at the U.S. epicenter of the pandemic. “Each state and hospital will need to evaluate their own data to determine the value of universal screening for their patient population. In rural parts of America that have yet to see cases, universal screening may not make sense, but these areas are likely to be few and far between. The rest of America will need to quickly get on board with universal screening to protect their labor and delivery staff.”
Testing the partner was a strength of the study. “It is reassuring that when a pregnant woman tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the rate was very, very low (2.4%) that her partner would test positive. However, it was disconcerting that telephone screening for common symptoms associated with COVID-19 was not very helpful in identifying cases,” said Dr. Waldorf, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. She was not involved in the study by Bianco et al.
One study author receives payment from the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology for serving as a board examiner, receives payment from UpToDate, and serves as an expert witness in malpractice and products liability cases. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bianco A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003985.
Among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, the rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Among the patients’ designated support persons, the asymptomatic carrier rate was 10%.
“If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” wrote the researchers affiliated with the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Angela Bianco, MD, and colleagues conducted an observational study of women who were scheduled for a planned delivery within the Mount Sinai Health System between April 4 and April 15, 2020. Patients and their designated support person completed a telephone screen and underwent COVID-19 testing the day before a scheduled delivery. If support persons screened positive during the telephone interview about COVID-19 symptoms, they could not attend the birth, and patients could contact a different support person to be screened and tested. “All patients and their support persons were informed of their SARS-CoV-2 test results before admission,” the investigators wrote. “Those who tested positive were counseled regarding symptomatology that should prompt medical attention.”
In all, researchers screened 158 patients with a planned delivery, and 155 agreed to undergo COVID-19 testing. Of the 155 women tested, 24 (16%) tested positive for SARS CoV-2 infection. Among 146 support persons who had a negative interview screen and underwent SARS-CoV-2 testing, 14 (10%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Test results were substantially concordant among patient and support person pairs. “Among patients who tested positive for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, 11 of 19 (58%) support persons also tested positive for COVID-19 infection,” the authors reported. “Among patients who tested negative for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, only 3 of 127 (2.4%) support persons tested positive for COVID-19 infection.”
Telephone screening did not identify any of the COVID-19–positive cases. Of the 24 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, none of their newborns tested positive at birth.
“Universal testing ... provides a mechanism for more accurate counseling of patients regarding issues such as newborn skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding,” noted Dr. Bianco and colleagues. At their institution, parents with COVID-19 are instructed to wear a mask and practice proper hand hygiene when caring for their newborns.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, said in an interview that the study by Bianco et al. underscores the high rate of asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic COVID-19 infections detected with universal screening in a hospital at the U.S. epicenter of the pandemic. “Each state and hospital will need to evaluate their own data to determine the value of universal screening for their patient population. In rural parts of America that have yet to see cases, universal screening may not make sense, but these areas are likely to be few and far between. The rest of America will need to quickly get on board with universal screening to protect their labor and delivery staff.”
Testing the partner was a strength of the study. “It is reassuring that when a pregnant woman tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the rate was very, very low (2.4%) that her partner would test positive. However, it was disconcerting that telephone screening for common symptoms associated with COVID-19 was not very helpful in identifying cases,” said Dr. Waldorf, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. She was not involved in the study by Bianco et al.
One study author receives payment from the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology for serving as a board examiner, receives payment from UpToDate, and serves as an expert witness in malpractice and products liability cases. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bianco A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003985.
Among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, the rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Among the patients’ designated support persons, the asymptomatic carrier rate was 10%.
“If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” wrote the researchers affiliated with the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Angela Bianco, MD, and colleagues conducted an observational study of women who were scheduled for a planned delivery within the Mount Sinai Health System between April 4 and April 15, 2020. Patients and their designated support person completed a telephone screen and underwent COVID-19 testing the day before a scheduled delivery. If support persons screened positive during the telephone interview about COVID-19 symptoms, they could not attend the birth, and patients could contact a different support person to be screened and tested. “All patients and their support persons were informed of their SARS-CoV-2 test results before admission,” the investigators wrote. “Those who tested positive were counseled regarding symptomatology that should prompt medical attention.”
In all, researchers screened 158 patients with a planned delivery, and 155 agreed to undergo COVID-19 testing. Of the 155 women tested, 24 (16%) tested positive for SARS CoV-2 infection. Among 146 support persons who had a negative interview screen and underwent SARS-CoV-2 testing, 14 (10%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Test results were substantially concordant among patient and support person pairs. “Among patients who tested positive for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, 11 of 19 (58%) support persons also tested positive for COVID-19 infection,” the authors reported. “Among patients who tested negative for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, only 3 of 127 (2.4%) support persons tested positive for COVID-19 infection.”
Telephone screening did not identify any of the COVID-19–positive cases. Of the 24 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, none of their newborns tested positive at birth.
“Universal testing ... provides a mechanism for more accurate counseling of patients regarding issues such as newborn skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding,” noted Dr. Bianco and colleagues. At their institution, parents with COVID-19 are instructed to wear a mask and practice proper hand hygiene when caring for their newborns.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, said in an interview that the study by Bianco et al. underscores the high rate of asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic COVID-19 infections detected with universal screening in a hospital at the U.S. epicenter of the pandemic. “Each state and hospital will need to evaluate their own data to determine the value of universal screening for their patient population. In rural parts of America that have yet to see cases, universal screening may not make sense, but these areas are likely to be few and far between. The rest of America will need to quickly get on board with universal screening to protect their labor and delivery staff.”
Testing the partner was a strength of the study. “It is reassuring that when a pregnant woman tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the rate was very, very low (2.4%) that her partner would test positive. However, it was disconcerting that telephone screening for common symptoms associated with COVID-19 was not very helpful in identifying cases,” said Dr. Waldorf, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. She was not involved in the study by Bianco et al.
One study author receives payment from the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology for serving as a board examiner, receives payment from UpToDate, and serves as an expert witness in malpractice and products liability cases. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bianco A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003985.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY