User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Dining restrictions, mask mandates tied to less illness, death, CDC reaffirms
The numbers are in to back up two policies designed to restrict the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) found that when states lifted restrictions on dining on premises at restaurants, rates of daily COVID-19 cases jumped 41-100 days later. COVID-19-related deaths also increased significantly after 60 days.
On the other hand, the same report demonstrates that state mask mandates slowed the spread of SARS-CoV-2 within a few weeks.
The study was published online March 5 in the CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The investigators did not distinguish between outdoor and indoor restaurant dining. But they did compare COVID-19 case and death rates before and after most states banned restaurants from serving patrons on-premises in March and April 2020.
They found, for example, that COVID-19 daily cases increased by 0.9% at 41-60 days after on-premise dining was permitted. Similarly, rates jumped by 1.2% at 61-80 days, and 1.1% at 81-100 days after the restaurant restrictions were lifted.
The differences were statistically significant, with P values of .02, <.01, and .04, respectively.
COVID-19–related death rates did not increase significantly at first – but did jump 2.2% between 61 and 80 days after the return of on-premises dining, for example. Deaths also increased by 3% at 81-100 days.
Both these differences were statistically significant (P < .01).
This is not the first report where the CDC announced reservations about in-person dining. In September 2020, CDC investigators implicated the inability to wear a mask while eating and drinking as likely contributing to the heightened risk.
Masks make a difference
The CDC report also provided more evidence to back mask-wearing policies for public spaces. Between March 1 and Dec. 31, 2020, 74% of U.S. counties issued mask mandates.
Investigators found that these policies had a more immediate effect, reducing daily COVID-19 cases by 0.5% in the first 20 days. Mask mandates likewise were linked to daily cases dropping 1.1% between 21 and 40 days, 1.5% between 41 and 60 days, 1.7% between 61 and 80 days, and 1.8% between 81 and 100 days.
These decreases in daily COVID-19 cases were statistically significant (P < .01) compared with a reference period before March 1, 2020.
The CDC also linked mask mandates to lower mortality. For example, these state policies were associated with 0.7% fewer deaths at 1-20 days post implementation. The effect increased thereafter – 1.0% drop at 21-40 days, 1.4% decrease at 41-60 days, 1.6% drop between 61 and 80 days, and 1.9% fewer deaths between 81 and 100 days.
The decrease in deaths was statistically significant at 1-20 days after the mask mandate (P = .03), as well as during the other periods (each P < .01) compared with the reference period.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, reacted to the new findings at a White House press briefing. She cited how increases in COVID-19 cases and death rates “slowed significantly within 20 days of putting mask mandates into place. This is why I’m asking you to double down on prevention measures.
“We have seen this movie before,” Dr. Walensky added. “When prevention measures like mask-wearing mandates are lifted, cases go up.”
Recently, multiple states have announced plans to roll back restrictions related to the pandemic, including mask mandates, which prompted warnings from some public health officials.
These are not the first CDC data to show that mask mandates make a difference.
In February 2021, for example, the agency pointed out that state-wide mask mandates reduced COVID-19 hospitalizations by 5.5% among adults 18-64 years old within 3 weeks of implementation.
Restrictions regarding on-premises restaurant dining and implementation of state-wide mask mandates are two tactics within a more comprehensive CDC strategy to reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2. The researchers note that “such efforts are increasingly important given the emergence of highly transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States.”
The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The numbers are in to back up two policies designed to restrict the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) found that when states lifted restrictions on dining on premises at restaurants, rates of daily COVID-19 cases jumped 41-100 days later. COVID-19-related deaths also increased significantly after 60 days.
On the other hand, the same report demonstrates that state mask mandates slowed the spread of SARS-CoV-2 within a few weeks.
The study was published online March 5 in the CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The investigators did not distinguish between outdoor and indoor restaurant dining. But they did compare COVID-19 case and death rates before and after most states banned restaurants from serving patrons on-premises in March and April 2020.
They found, for example, that COVID-19 daily cases increased by 0.9% at 41-60 days after on-premise dining was permitted. Similarly, rates jumped by 1.2% at 61-80 days, and 1.1% at 81-100 days after the restaurant restrictions were lifted.
The differences were statistically significant, with P values of .02, <.01, and .04, respectively.
COVID-19–related death rates did not increase significantly at first – but did jump 2.2% between 61 and 80 days after the return of on-premises dining, for example. Deaths also increased by 3% at 81-100 days.
Both these differences were statistically significant (P < .01).
This is not the first report where the CDC announced reservations about in-person dining. In September 2020, CDC investigators implicated the inability to wear a mask while eating and drinking as likely contributing to the heightened risk.
Masks make a difference
The CDC report also provided more evidence to back mask-wearing policies for public spaces. Between March 1 and Dec. 31, 2020, 74% of U.S. counties issued mask mandates.
Investigators found that these policies had a more immediate effect, reducing daily COVID-19 cases by 0.5% in the first 20 days. Mask mandates likewise were linked to daily cases dropping 1.1% between 21 and 40 days, 1.5% between 41 and 60 days, 1.7% between 61 and 80 days, and 1.8% between 81 and 100 days.
These decreases in daily COVID-19 cases were statistically significant (P < .01) compared with a reference period before March 1, 2020.
The CDC also linked mask mandates to lower mortality. For example, these state policies were associated with 0.7% fewer deaths at 1-20 days post implementation. The effect increased thereafter – 1.0% drop at 21-40 days, 1.4% decrease at 41-60 days, 1.6% drop between 61 and 80 days, and 1.9% fewer deaths between 81 and 100 days.
The decrease in deaths was statistically significant at 1-20 days after the mask mandate (P = .03), as well as during the other periods (each P < .01) compared with the reference period.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, reacted to the new findings at a White House press briefing. She cited how increases in COVID-19 cases and death rates “slowed significantly within 20 days of putting mask mandates into place. This is why I’m asking you to double down on prevention measures.
“We have seen this movie before,” Dr. Walensky added. “When prevention measures like mask-wearing mandates are lifted, cases go up.”
Recently, multiple states have announced plans to roll back restrictions related to the pandemic, including mask mandates, which prompted warnings from some public health officials.
These are not the first CDC data to show that mask mandates make a difference.
In February 2021, for example, the agency pointed out that state-wide mask mandates reduced COVID-19 hospitalizations by 5.5% among adults 18-64 years old within 3 weeks of implementation.
Restrictions regarding on-premises restaurant dining and implementation of state-wide mask mandates are two tactics within a more comprehensive CDC strategy to reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2. The researchers note that “such efforts are increasingly important given the emergence of highly transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States.”
The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The numbers are in to back up two policies designed to restrict the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) found that when states lifted restrictions on dining on premises at restaurants, rates of daily COVID-19 cases jumped 41-100 days later. COVID-19-related deaths also increased significantly after 60 days.
On the other hand, the same report demonstrates that state mask mandates slowed the spread of SARS-CoV-2 within a few weeks.
The study was published online March 5 in the CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The investigators did not distinguish between outdoor and indoor restaurant dining. But they did compare COVID-19 case and death rates before and after most states banned restaurants from serving patrons on-premises in March and April 2020.
They found, for example, that COVID-19 daily cases increased by 0.9% at 41-60 days after on-premise dining was permitted. Similarly, rates jumped by 1.2% at 61-80 days, and 1.1% at 81-100 days after the restaurant restrictions were lifted.
The differences were statistically significant, with P values of .02, <.01, and .04, respectively.
COVID-19–related death rates did not increase significantly at first – but did jump 2.2% between 61 and 80 days after the return of on-premises dining, for example. Deaths also increased by 3% at 81-100 days.
Both these differences were statistically significant (P < .01).
This is not the first report where the CDC announced reservations about in-person dining. In September 2020, CDC investigators implicated the inability to wear a mask while eating and drinking as likely contributing to the heightened risk.
Masks make a difference
The CDC report also provided more evidence to back mask-wearing policies for public spaces. Between March 1 and Dec. 31, 2020, 74% of U.S. counties issued mask mandates.
Investigators found that these policies had a more immediate effect, reducing daily COVID-19 cases by 0.5% in the first 20 days. Mask mandates likewise were linked to daily cases dropping 1.1% between 21 and 40 days, 1.5% between 41 and 60 days, 1.7% between 61 and 80 days, and 1.8% between 81 and 100 days.
These decreases in daily COVID-19 cases were statistically significant (P < .01) compared with a reference period before March 1, 2020.
The CDC also linked mask mandates to lower mortality. For example, these state policies were associated with 0.7% fewer deaths at 1-20 days post implementation. The effect increased thereafter – 1.0% drop at 21-40 days, 1.4% decrease at 41-60 days, 1.6% drop between 61 and 80 days, and 1.9% fewer deaths between 81 and 100 days.
The decrease in deaths was statistically significant at 1-20 days after the mask mandate (P = .03), as well as during the other periods (each P < .01) compared with the reference period.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, reacted to the new findings at a White House press briefing. She cited how increases in COVID-19 cases and death rates “slowed significantly within 20 days of putting mask mandates into place. This is why I’m asking you to double down on prevention measures.
“We have seen this movie before,” Dr. Walensky added. “When prevention measures like mask-wearing mandates are lifted, cases go up.”
Recently, multiple states have announced plans to roll back restrictions related to the pandemic, including mask mandates, which prompted warnings from some public health officials.
These are not the first CDC data to show that mask mandates make a difference.
In February 2021, for example, the agency pointed out that state-wide mask mandates reduced COVID-19 hospitalizations by 5.5% among adults 18-64 years old within 3 weeks of implementation.
Restrictions regarding on-premises restaurant dining and implementation of state-wide mask mandates are two tactics within a more comprehensive CDC strategy to reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2. The researchers note that “such efforts are increasingly important given the emergence of highly transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States.”
The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tocilizumab (Actemra) scores FDA approval for systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease
The Food and Drug Administration has approved subcutaneously-injected tocilizumab (Actemra) to reduce the rate of pulmonary function decline in systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) patients, according to a press release from manufacturer Genentech.
Tocilizumab is the first biologic to be approved by the agency for adults with SSc-ILD, a rare and potentially life-threatening condition that may affect up to 80% of SSc patients and lead to lung inflammation and scarring.
The approval was based primarily on data from a phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (the focuSSced trial) that included 212 adults with SSc. Although that study failed to meet its primary endpoint of change from baseline to 48 weeks in the modified Rodnan Skin Score, the researchers observed a significantly reduced lung function decline as measured by forced vital capacity (FVC) and percent predicted forced vital capacity (ppFVC) among tocilizumab-treated patients, compared with those who received placebo. A total of 68 patients (65%) in the tocilizumab group and 68 patients (64%) in the placebo group had SSc-ILD at baseline.
In a subgroup analysis, patients taking tocilizumab had a smaller decline in mean ppFVC, compared with placebo patients (0.07% vs. –6.4%; mean difference, 6.47%), and a smaller decline in FVC (mean change –14 mL vs. –255 mL with placebo; mean difference, 241 mL).
The mean change from baseline to week 48 in modified Rodnan Skin Score was –5.88 for patients on tocilizumab and –3.77 with placebo.
Safety data were similar between tocilizumab and placebo groups through 48 weeks, and similar for patients with and without SSc-ILD. In general, tocilizumab side effects include increased susceptibility to infections, and serious side effects may include stomach tears, hepatotoxicity, and increased risk of cancer and hepatitis B, according to the prescribing information. However, the most common side effects are upper respiratory tract infections, headache, hypertension, and injection-site reactions.
Tocilizumab, an interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, is already approved for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis, as well as for adult patients with giant cell arteritis; patients aged 2 years and older with active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis or active systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis; and adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with chimeric antigen receptor T-cell–induced severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome.
Prescribing information is available here.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved subcutaneously-injected tocilizumab (Actemra) to reduce the rate of pulmonary function decline in systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) patients, according to a press release from manufacturer Genentech.
Tocilizumab is the first biologic to be approved by the agency for adults with SSc-ILD, a rare and potentially life-threatening condition that may affect up to 80% of SSc patients and lead to lung inflammation and scarring.
The approval was based primarily on data from a phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (the focuSSced trial) that included 212 adults with SSc. Although that study failed to meet its primary endpoint of change from baseline to 48 weeks in the modified Rodnan Skin Score, the researchers observed a significantly reduced lung function decline as measured by forced vital capacity (FVC) and percent predicted forced vital capacity (ppFVC) among tocilizumab-treated patients, compared with those who received placebo. A total of 68 patients (65%) in the tocilizumab group and 68 patients (64%) in the placebo group had SSc-ILD at baseline.
In a subgroup analysis, patients taking tocilizumab had a smaller decline in mean ppFVC, compared with placebo patients (0.07% vs. –6.4%; mean difference, 6.47%), and a smaller decline in FVC (mean change –14 mL vs. –255 mL with placebo; mean difference, 241 mL).
The mean change from baseline to week 48 in modified Rodnan Skin Score was –5.88 for patients on tocilizumab and –3.77 with placebo.
Safety data were similar between tocilizumab and placebo groups through 48 weeks, and similar for patients with and without SSc-ILD. In general, tocilizumab side effects include increased susceptibility to infections, and serious side effects may include stomach tears, hepatotoxicity, and increased risk of cancer and hepatitis B, according to the prescribing information. However, the most common side effects are upper respiratory tract infections, headache, hypertension, and injection-site reactions.
Tocilizumab, an interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, is already approved for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis, as well as for adult patients with giant cell arteritis; patients aged 2 years and older with active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis or active systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis; and adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with chimeric antigen receptor T-cell–induced severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome.
Prescribing information is available here.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved subcutaneously-injected tocilizumab (Actemra) to reduce the rate of pulmonary function decline in systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) patients, according to a press release from manufacturer Genentech.
Tocilizumab is the first biologic to be approved by the agency for adults with SSc-ILD, a rare and potentially life-threatening condition that may affect up to 80% of SSc patients and lead to lung inflammation and scarring.
The approval was based primarily on data from a phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (the focuSSced trial) that included 212 adults with SSc. Although that study failed to meet its primary endpoint of change from baseline to 48 weeks in the modified Rodnan Skin Score, the researchers observed a significantly reduced lung function decline as measured by forced vital capacity (FVC) and percent predicted forced vital capacity (ppFVC) among tocilizumab-treated patients, compared with those who received placebo. A total of 68 patients (65%) in the tocilizumab group and 68 patients (64%) in the placebo group had SSc-ILD at baseline.
In a subgroup analysis, patients taking tocilizumab had a smaller decline in mean ppFVC, compared with placebo patients (0.07% vs. –6.4%; mean difference, 6.47%), and a smaller decline in FVC (mean change –14 mL vs. –255 mL with placebo; mean difference, 241 mL).
The mean change from baseline to week 48 in modified Rodnan Skin Score was –5.88 for patients on tocilizumab and –3.77 with placebo.
Safety data were similar between tocilizumab and placebo groups through 48 weeks, and similar for patients with and without SSc-ILD. In general, tocilizumab side effects include increased susceptibility to infections, and serious side effects may include stomach tears, hepatotoxicity, and increased risk of cancer and hepatitis B, according to the prescribing information. However, the most common side effects are upper respiratory tract infections, headache, hypertension, and injection-site reactions.
Tocilizumab, an interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, is already approved for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis, as well as for adult patients with giant cell arteritis; patients aged 2 years and older with active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis or active systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis; and adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with chimeric antigen receptor T-cell–induced severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome.
Prescribing information is available here.
Routine vaccinations missed by older adults during pandemic
Physicians are going to have to play catch-up when it comes to getting older patients their routine, but important, vaccinations missed during the pandemic.
and have recovered only partially and gradually, according to a report by Kai Hong, PhD, and colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “As the pandemic continues,” the investigators stated, “vaccination providers should continue efforts to resolve disruptions in routine adult vaccination.”
The CDC issued guidance recommending postponement of routine adult vaccination in response to the March 13, 2020, COVID-19 national emergency declaration by the U.S. government and also to state and local shelter-in-place orders. Health care facility operations were restricted because of safety concerns around exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The result was a significant drop in routine medical care including adult vaccinations.
The investigators examined Medicare enrollment and claims data to assess the change in weekly receipt of four routine adult vaccines by Medicare beneficiaries aged ≥65 during the pandemic: (13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine [PCV13], 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine [PPSV23], tetanus-diphtheria or tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis vaccine [Td/Tdap], and recombinant zoster vaccine [RZV]). The comparison periods were Jan. 6–July 20, 2019, and Jan. 5–July 18, 2020.
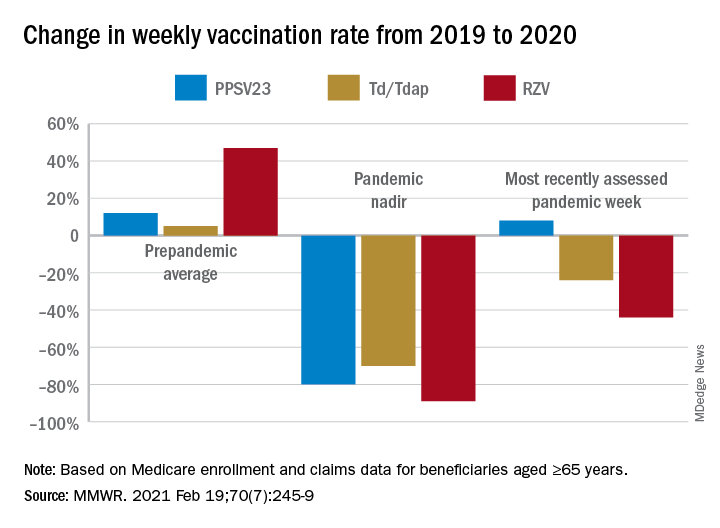
Of the Medicare enrollees in the study sample, 85% were White, 7% Black, 2% Asian, 2% Hispanic, and 4% other racial and ethnic groups. For each of the four vaccines overall, weekly rates of vaccination declined sharply after the emergency declaration, compared with corresponding weeks in 2019. In the period prior to the emergency declaration (Jan. 5–March 14, 2020), weekly percentages of Medicare beneficiaries vaccinated with PPSV23, Td/Tdap, and RZV were consistently higher than rates during the same period in 2019.
After the March 13 declaration, while weekly vaccination rates plummeted 25% for PPSV23 and 62% for RZV in the first week, the greatest weekly declines were during April 5-11, 2020, for PCV13, PPSV23, and Td/Tdap, and during April 12-18, 2020, for RZV. The pandemic weekly vaccination rate nadirs revealed declines of 88% for PCV13, 80% for PPSV23, 70% for Td/Tdap, and 89% for RZV.
Routine vaccinations increased midyear
Vaccination rates recovered gradually. For the most recently assessed pandemic week (July 12-18, 2020), the rate for PPSV23 was 8% higher than in the corresponding period in 2019. Weekly corresponding rates for other examined vaccines, however, remained much lower than in 2019: 44% lower for RZV, 24% lower for Td/Tdap and 43% lower for PCV13. The CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted in June 2019 to stop recommending PCV13 for adults aged ≥65 years and so vaccination with PCV13 among this population declined in 2020, compared with that in 2019.
Another significant drop in the rates of adult vaccinations may have occurred because of the surge in COVID-19 infections in the fall of 2020 and subsequent closures and renewal of lockdown in many localities.
Disparities in routine vaccination trends
Dr. Hong and colleagues noted that their findings are consistent with prior reports of declines in pediatric vaccine ordering, administration, and coverage during the pandemic. While the reductions were similar across all racial and ethnic groups, the magnitudes of recovery varied, with vaccination rates lower among racial and ethnic minority adults than among White adults.
In view of the disproportionate COVID-19 pandemic effects among some racial and ethnic minorities, the investigators recommended monitoring and subsequent early intervention to mitigate similar indirect pandemic effects, such as reduced utilization of other preventive services. “Many members of racial and ethnic minority groups face barriers to routine medical care, which means they have fewer opportunities to receive preventive interventions such as vaccination,” Dr. Hong said in an interview. “When clinicians are following up with patients who have missed vaccinations, it is important for them to remember that patients may face new barriers to vaccination such as loss of income or health insurance, and to work with them to remove those barriers,” he added.
“If vaccination is deferred, older adults and adults with underlying medical conditions who subsequently become infected with a vaccine-preventable disease are at increased risk for complications,” Dr. Hong said. “The most important thing clinicians can do is identify patients who are due for or who have missed vaccinations, and contact them to schedule visits. Immunization Information Systems and electronic health records may be able to support this work. In addition, the vaccination status of all patients should be assessed at every health care visit to reduce missed opportunities for vaccination.”
Physicians are going to have to play catch-up when it comes to getting older patients their routine, but important, vaccinations missed during the pandemic.
and have recovered only partially and gradually, according to a report by Kai Hong, PhD, and colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “As the pandemic continues,” the investigators stated, “vaccination providers should continue efforts to resolve disruptions in routine adult vaccination.”
The CDC issued guidance recommending postponement of routine adult vaccination in response to the March 13, 2020, COVID-19 national emergency declaration by the U.S. government and also to state and local shelter-in-place orders. Health care facility operations were restricted because of safety concerns around exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The result was a significant drop in routine medical care including adult vaccinations.
The investigators examined Medicare enrollment and claims data to assess the change in weekly receipt of four routine adult vaccines by Medicare beneficiaries aged ≥65 during the pandemic: (13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine [PCV13], 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine [PPSV23], tetanus-diphtheria or tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis vaccine [Td/Tdap], and recombinant zoster vaccine [RZV]). The comparison periods were Jan. 6–July 20, 2019, and Jan. 5–July 18, 2020.
Of the Medicare enrollees in the study sample, 85% were White, 7% Black, 2% Asian, 2% Hispanic, and 4% other racial and ethnic groups. For each of the four vaccines overall, weekly rates of vaccination declined sharply after the emergency declaration, compared with corresponding weeks in 2019. In the period prior to the emergency declaration (Jan. 5–March 14, 2020), weekly percentages of Medicare beneficiaries vaccinated with PPSV23, Td/Tdap, and RZV were consistently higher than rates during the same period in 2019.
After the March 13 declaration, while weekly vaccination rates plummeted 25% for PPSV23 and 62% for RZV in the first week, the greatest weekly declines were during April 5-11, 2020, for PCV13, PPSV23, and Td/Tdap, and during April 12-18, 2020, for RZV. The pandemic weekly vaccination rate nadirs revealed declines of 88% for PCV13, 80% for PPSV23, 70% for Td/Tdap, and 89% for RZV.
Routine vaccinations increased midyear
Vaccination rates recovered gradually. For the most recently assessed pandemic week (July 12-18, 2020), the rate for PPSV23 was 8% higher than in the corresponding period in 2019. Weekly corresponding rates for other examined vaccines, however, remained much lower than in 2019: 44% lower for RZV, 24% lower for Td/Tdap and 43% lower for PCV13. The CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted in June 2019 to stop recommending PCV13 for adults aged ≥65 years and so vaccination with PCV13 among this population declined in 2020, compared with that in 2019.
Another significant drop in the rates of adult vaccinations may have occurred because of the surge in COVID-19 infections in the fall of 2020 and subsequent closures and renewal of lockdown in many localities.
Disparities in routine vaccination trends
Dr. Hong and colleagues noted that their findings are consistent with prior reports of declines in pediatric vaccine ordering, administration, and coverage during the pandemic. While the reductions were similar across all racial and ethnic groups, the magnitudes of recovery varied, with vaccination rates lower among racial and ethnic minority adults than among White adults.

In view of the disproportionate COVID-19 pandemic effects among some racial and ethnic minorities, the investigators recommended monitoring and subsequent early intervention to mitigate similar indirect pandemic effects, such as reduced utilization of other preventive services. “Many members of racial and ethnic minority groups face barriers to routine medical care, which means they have fewer opportunities to receive preventive interventions such as vaccination,” Dr. Hong said in an interview. “When clinicians are following up with patients who have missed vaccinations, it is important for them to remember that patients may face new barriers to vaccination such as loss of income or health insurance, and to work with them to remove those barriers,” he added.
“If vaccination is deferred, older adults and adults with underlying medical conditions who subsequently become infected with a vaccine-preventable disease are at increased risk for complications,” Dr. Hong said. “The most important thing clinicians can do is identify patients who are due for or who have missed vaccinations, and contact them to schedule visits. Immunization Information Systems and electronic health records may be able to support this work. In addition, the vaccination status of all patients should be assessed at every health care visit to reduce missed opportunities for vaccination.”
Physicians are going to have to play catch-up when it comes to getting older patients their routine, but important, vaccinations missed during the pandemic.
and have recovered only partially and gradually, according to a report by Kai Hong, PhD, and colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “As the pandemic continues,” the investigators stated, “vaccination providers should continue efforts to resolve disruptions in routine adult vaccination.”
The CDC issued guidance recommending postponement of routine adult vaccination in response to the March 13, 2020, COVID-19 national emergency declaration by the U.S. government and also to state and local shelter-in-place orders. Health care facility operations were restricted because of safety concerns around exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The result was a significant drop in routine medical care including adult vaccinations.
The investigators examined Medicare enrollment and claims data to assess the change in weekly receipt of four routine adult vaccines by Medicare beneficiaries aged ≥65 during the pandemic: (13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine [PCV13], 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine [PPSV23], tetanus-diphtheria or tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis vaccine [Td/Tdap], and recombinant zoster vaccine [RZV]). The comparison periods were Jan. 6–July 20, 2019, and Jan. 5–July 18, 2020.
Of the Medicare enrollees in the study sample, 85% were White, 7% Black, 2% Asian, 2% Hispanic, and 4% other racial and ethnic groups. For each of the four vaccines overall, weekly rates of vaccination declined sharply after the emergency declaration, compared with corresponding weeks in 2019. In the period prior to the emergency declaration (Jan. 5–March 14, 2020), weekly percentages of Medicare beneficiaries vaccinated with PPSV23, Td/Tdap, and RZV were consistently higher than rates during the same period in 2019.
After the March 13 declaration, while weekly vaccination rates plummeted 25% for PPSV23 and 62% for RZV in the first week, the greatest weekly declines were during April 5-11, 2020, for PCV13, PPSV23, and Td/Tdap, and during April 12-18, 2020, for RZV. The pandemic weekly vaccination rate nadirs revealed declines of 88% for PCV13, 80% for PPSV23, 70% for Td/Tdap, and 89% for RZV.
Routine vaccinations increased midyear
Vaccination rates recovered gradually. For the most recently assessed pandemic week (July 12-18, 2020), the rate for PPSV23 was 8% higher than in the corresponding period in 2019. Weekly corresponding rates for other examined vaccines, however, remained much lower than in 2019: 44% lower for RZV, 24% lower for Td/Tdap and 43% lower for PCV13. The CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted in June 2019 to stop recommending PCV13 for adults aged ≥65 years and so vaccination with PCV13 among this population declined in 2020, compared with that in 2019.
Another significant drop in the rates of adult vaccinations may have occurred because of the surge in COVID-19 infections in the fall of 2020 and subsequent closures and renewal of lockdown in many localities.
Disparities in routine vaccination trends
Dr. Hong and colleagues noted that their findings are consistent with prior reports of declines in pediatric vaccine ordering, administration, and coverage during the pandemic. While the reductions were similar across all racial and ethnic groups, the magnitudes of recovery varied, with vaccination rates lower among racial and ethnic minority adults than among White adults.

In view of the disproportionate COVID-19 pandemic effects among some racial and ethnic minorities, the investigators recommended monitoring and subsequent early intervention to mitigate similar indirect pandemic effects, such as reduced utilization of other preventive services. “Many members of racial and ethnic minority groups face barriers to routine medical care, which means they have fewer opportunities to receive preventive interventions such as vaccination,” Dr. Hong said in an interview. “When clinicians are following up with patients who have missed vaccinations, it is important for them to remember that patients may face new barriers to vaccination such as loss of income or health insurance, and to work with them to remove those barriers,” he added.
“If vaccination is deferred, older adults and adults with underlying medical conditions who subsequently become infected with a vaccine-preventable disease are at increased risk for complications,” Dr. Hong said. “The most important thing clinicians can do is identify patients who are due for or who have missed vaccinations, and contact them to schedule visits. Immunization Information Systems and electronic health records may be able to support this work. In addition, the vaccination status of all patients should be assessed at every health care visit to reduce missed opportunities for vaccination.”
FROM MMWR
BMI, age, and sex affect COVID-19 vaccine antibody response
The capacity to mount humoral immune responses to COVID-19 vaccinations may be reduced among people who are heavier, older, and male, new findings suggest.
The data pertain specifically to the mRNA vaccine, BNT162b2, developed by BioNTech and Pfizer. The study was conducted by Italian researchers and was published Feb. 26 as a preprint.
The study involved 248 health care workers who each received two doses of the vaccine. Of the participants, 99.5% developed a humoral immune response after the second dose. Those responses varied by body mass index (BMI), age, and sex.
“The findings imply that female, lean, and young people have an increased capacity to mount humoral immune responses, compared to male, overweight, and older populations,” Raul Pellini, MD, professor at the IRCCS Regina Elena National Cancer Institute, Rome, and colleagues said.
“To our knowledge, this study is the first to analyze Covid-19 vaccine response in correlation to BMI,” they noted.
“Although further studies are needed, this data may have important implications to the development of vaccination strategies for COVID-19, particularly in obese people,” they wrote. If the data are confirmed by larger studies, “giving obese people an extra dose of the vaccine or a higher dose could be options to be evaluated in this population.”
Results contrast with Pfizer trials of vaccine
The BMI finding seemingly contrasts with final data from the phase 3 clinical trial of the vaccine, which were reported in a supplement to an article published Dec. 31, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine. In that study, vaccine efficacy did not differ by obesity status.
Akiko Iwasaki, PhD, professor of immunology at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and an investigator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., noted that, although the current Italian study showed somewhat lower levels of antibodies in people with obesity, compared with people who did not have obesity, the phase 3 trial found no difference in symptomatic infection rates.
“These results indicate that even with a slightly lower level of antibody induced in obese people, that level was sufficient to protect against symptomatic infection,” Dr. Iwasaki said in an interview.
Indeed, Dr. Pellini and colleagues pointed out that responses to vaccines against influenza, hepatitis B, and rabies are also reduced in those with obesity, compared with lean individuals.
However, they said, it was especially important to study the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in people with obesity, because obesity is a major risk factor for morbidity and mortality in COVID-19.
“The constant state of low-grade inflammation, present in overweight people, can weaken some immune responses, including those launched by T cells, which can directly kill infected cells,” the authors noted.
Findings reported in British newspapers
The findings of the Italian study were widely covered in the lay press in the United Kingdom, with headlines such as “Pfizer Vaccine May Be Less Effective in People With Obesity, Says Study” and “Pfizer Vaccine: Overweight People Might Need Bigger Dose, Italian Study Says.” In tabloid newspapers, some headlines were slightly more stigmatizing.
The reports do stress that the Italian research was published as a preprint and has not been peer reviewed, or “is yet to be scrutinized by fellow scientists.”
Most make the point that there were only 26 people with obesity among the 248 persons in the study.
“We always knew that BMI was an enormous predictor of poor immune response to vaccines, so this paper is definitely interesting, although it is based on a rather small preliminary dataset,” Danny Altmann, PhD, a professor of immunology at Imperial College London, told the Guardian.
“It confirms that having a vaccinated population isn’t synonymous with having an immune population, especially in a country with high obesity, and emphasizes the vital need for long-term immune monitoring programs,” he added.
Antibody responses differ by BMI, age, and sex
In the Italian study, the participants – 158 women and 90 men – were assigned to receive a priming BNT162b2 vaccine dose with a booster at day 21. Blood and nasopharyngeal swabs were collected at baseline and 7 days after the second vaccine dose.
After the second dose, 99.5% of participants developed a humoral immune response; one person did not respond. None tested positive for SARS-CoV-2.
Titers of SARS-CoV-2–binding antibodies were greater in younger than in older participants. There were statistically significant differences between those aged 37 years and younger (453.5 AU/mL) and those aged 47-56 years (239.8 AU/mL; P = .005), those aged 37 years and younger versus those older than 56 years (453.5 vs 182.4 AU/mL; P < .0001), and those aged 37-47 years versus those older than 56 years (330.9 vs. 182.4 AU/mL; P = .01).
Antibody response was significantly greater for women than for men (338.5 vs. 212.6 AU/mL; P = .001).
Humoral responses were greater in persons of normal-weight BMI (18.5-24.9 kg/m2; 325.8 AU/mL) and those of underweight BMI (<18.5 kg/m2; 455.4 AU/mL), compared with persons with preobesity, defined as BMI of 25-29.9 (222.4 AU/mL), and those with obesity (BMI ≥30; 167.0 AU/mL; P < .0001). This association remained after adjustment for age (P = .003).
“Our data stresses the importance of close vaccination monitoring of obese people, considering the growing list of countries with obesity problems,” the researchers noted.
Hypertension was also associated with lower antibody titers (P = .006), but that lost statistical significance after matching for age (P = .22).
“We strongly believe that our results are extremely encouraging and useful for the scientific community,” Dr. Pellini and colleagues concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Iwasaki is a cofounder of RIGImmune and is a member of its scientific advisory board.
This article was updated on 3/8/21.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The capacity to mount humoral immune responses to COVID-19 vaccinations may be reduced among people who are heavier, older, and male, new findings suggest.
The data pertain specifically to the mRNA vaccine, BNT162b2, developed by BioNTech and Pfizer. The study was conducted by Italian researchers and was published Feb. 26 as a preprint.
The study involved 248 health care workers who each received two doses of the vaccine. Of the participants, 99.5% developed a humoral immune response after the second dose. Those responses varied by body mass index (BMI), age, and sex.
“The findings imply that female, lean, and young people have an increased capacity to mount humoral immune responses, compared to male, overweight, and older populations,” Raul Pellini, MD, professor at the IRCCS Regina Elena National Cancer Institute, Rome, and colleagues said.
“To our knowledge, this study is the first to analyze Covid-19 vaccine response in correlation to BMI,” they noted.
“Although further studies are needed, this data may have important implications to the development of vaccination strategies for COVID-19, particularly in obese people,” they wrote. If the data are confirmed by larger studies, “giving obese people an extra dose of the vaccine or a higher dose could be options to be evaluated in this population.”
Results contrast with Pfizer trials of vaccine
The BMI finding seemingly contrasts with final data from the phase 3 clinical trial of the vaccine, which were reported in a supplement to an article published Dec. 31, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine. In that study, vaccine efficacy did not differ by obesity status.
Akiko Iwasaki, PhD, professor of immunology at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and an investigator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., noted that, although the current Italian study showed somewhat lower levels of antibodies in people with obesity, compared with people who did not have obesity, the phase 3 trial found no difference in symptomatic infection rates.
“These results indicate that even with a slightly lower level of antibody induced in obese people, that level was sufficient to protect against symptomatic infection,” Dr. Iwasaki said in an interview.
Indeed, Dr. Pellini and colleagues pointed out that responses to vaccines against influenza, hepatitis B, and rabies are also reduced in those with obesity, compared with lean individuals.
However, they said, it was especially important to study the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in people with obesity, because obesity is a major risk factor for morbidity and mortality in COVID-19.
“The constant state of low-grade inflammation, present in overweight people, can weaken some immune responses, including those launched by T cells, which can directly kill infected cells,” the authors noted.
Findings reported in British newspapers
The findings of the Italian study were widely covered in the lay press in the United Kingdom, with headlines such as “Pfizer Vaccine May Be Less Effective in People With Obesity, Says Study” and “Pfizer Vaccine: Overweight People Might Need Bigger Dose, Italian Study Says.” In tabloid newspapers, some headlines were slightly more stigmatizing.
The reports do stress that the Italian research was published as a preprint and has not been peer reviewed, or “is yet to be scrutinized by fellow scientists.”
Most make the point that there were only 26 people with obesity among the 248 persons in the study.
“We always knew that BMI was an enormous predictor of poor immune response to vaccines, so this paper is definitely interesting, although it is based on a rather small preliminary dataset,” Danny Altmann, PhD, a professor of immunology at Imperial College London, told the Guardian.
“It confirms that having a vaccinated population isn’t synonymous with having an immune population, especially in a country with high obesity, and emphasizes the vital need for long-term immune monitoring programs,” he added.
Antibody responses differ by BMI, age, and sex
In the Italian study, the participants – 158 women and 90 men – were assigned to receive a priming BNT162b2 vaccine dose with a booster at day 21. Blood and nasopharyngeal swabs were collected at baseline and 7 days after the second vaccine dose.
After the second dose, 99.5% of participants developed a humoral immune response; one person did not respond. None tested positive for SARS-CoV-2.
Titers of SARS-CoV-2–binding antibodies were greater in younger than in older participants. There were statistically significant differences between those aged 37 years and younger (453.5 AU/mL) and those aged 47-56 years (239.8 AU/mL; P = .005), those aged 37 years and younger versus those older than 56 years (453.5 vs 182.4 AU/mL; P < .0001), and those aged 37-47 years versus those older than 56 years (330.9 vs. 182.4 AU/mL; P = .01).
Antibody response was significantly greater for women than for men (338.5 vs. 212.6 AU/mL; P = .001).
Humoral responses were greater in persons of normal-weight BMI (18.5-24.9 kg/m2; 325.8 AU/mL) and those of underweight BMI (<18.5 kg/m2; 455.4 AU/mL), compared with persons with preobesity, defined as BMI of 25-29.9 (222.4 AU/mL), and those with obesity (BMI ≥30; 167.0 AU/mL; P < .0001). This association remained after adjustment for age (P = .003).
“Our data stresses the importance of close vaccination monitoring of obese people, considering the growing list of countries with obesity problems,” the researchers noted.
Hypertension was also associated with lower antibody titers (P = .006), but that lost statistical significance after matching for age (P = .22).
“We strongly believe that our results are extremely encouraging and useful for the scientific community,” Dr. Pellini and colleagues concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Iwasaki is a cofounder of RIGImmune and is a member of its scientific advisory board.
This article was updated on 3/8/21.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The capacity to mount humoral immune responses to COVID-19 vaccinations may be reduced among people who are heavier, older, and male, new findings suggest.
The data pertain specifically to the mRNA vaccine, BNT162b2, developed by BioNTech and Pfizer. The study was conducted by Italian researchers and was published Feb. 26 as a preprint.
The study involved 248 health care workers who each received two doses of the vaccine. Of the participants, 99.5% developed a humoral immune response after the second dose. Those responses varied by body mass index (BMI), age, and sex.
“The findings imply that female, lean, and young people have an increased capacity to mount humoral immune responses, compared to male, overweight, and older populations,” Raul Pellini, MD, professor at the IRCCS Regina Elena National Cancer Institute, Rome, and colleagues said.
“To our knowledge, this study is the first to analyze Covid-19 vaccine response in correlation to BMI,” they noted.
“Although further studies are needed, this data may have important implications to the development of vaccination strategies for COVID-19, particularly in obese people,” they wrote. If the data are confirmed by larger studies, “giving obese people an extra dose of the vaccine or a higher dose could be options to be evaluated in this population.”
Results contrast with Pfizer trials of vaccine
The BMI finding seemingly contrasts with final data from the phase 3 clinical trial of the vaccine, which were reported in a supplement to an article published Dec. 31, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine. In that study, vaccine efficacy did not differ by obesity status.
Akiko Iwasaki, PhD, professor of immunology at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and an investigator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., noted that, although the current Italian study showed somewhat lower levels of antibodies in people with obesity, compared with people who did not have obesity, the phase 3 trial found no difference in symptomatic infection rates.
“These results indicate that even with a slightly lower level of antibody induced in obese people, that level was sufficient to protect against symptomatic infection,” Dr. Iwasaki said in an interview.
Indeed, Dr. Pellini and colleagues pointed out that responses to vaccines against influenza, hepatitis B, and rabies are also reduced in those with obesity, compared with lean individuals.
However, they said, it was especially important to study the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in people with obesity, because obesity is a major risk factor for morbidity and mortality in COVID-19.
“The constant state of low-grade inflammation, present in overweight people, can weaken some immune responses, including those launched by T cells, which can directly kill infected cells,” the authors noted.
Findings reported in British newspapers
The findings of the Italian study were widely covered in the lay press in the United Kingdom, with headlines such as “Pfizer Vaccine May Be Less Effective in People With Obesity, Says Study” and “Pfizer Vaccine: Overweight People Might Need Bigger Dose, Italian Study Says.” In tabloid newspapers, some headlines were slightly more stigmatizing.
The reports do stress that the Italian research was published as a preprint and has not been peer reviewed, or “is yet to be scrutinized by fellow scientists.”
Most make the point that there were only 26 people with obesity among the 248 persons in the study.
“We always knew that BMI was an enormous predictor of poor immune response to vaccines, so this paper is definitely interesting, although it is based on a rather small preliminary dataset,” Danny Altmann, PhD, a professor of immunology at Imperial College London, told the Guardian.
“It confirms that having a vaccinated population isn’t synonymous with having an immune population, especially in a country with high obesity, and emphasizes the vital need for long-term immune monitoring programs,” he added.
Antibody responses differ by BMI, age, and sex
In the Italian study, the participants – 158 women and 90 men – were assigned to receive a priming BNT162b2 vaccine dose with a booster at day 21. Blood and nasopharyngeal swabs were collected at baseline and 7 days after the second vaccine dose.
After the second dose, 99.5% of participants developed a humoral immune response; one person did not respond. None tested positive for SARS-CoV-2.
Titers of SARS-CoV-2–binding antibodies were greater in younger than in older participants. There were statistically significant differences between those aged 37 years and younger (453.5 AU/mL) and those aged 47-56 years (239.8 AU/mL; P = .005), those aged 37 years and younger versus those older than 56 years (453.5 vs 182.4 AU/mL; P < .0001), and those aged 37-47 years versus those older than 56 years (330.9 vs. 182.4 AU/mL; P = .01).
Antibody response was significantly greater for women than for men (338.5 vs. 212.6 AU/mL; P = .001).
Humoral responses were greater in persons of normal-weight BMI (18.5-24.9 kg/m2; 325.8 AU/mL) and those of underweight BMI (<18.5 kg/m2; 455.4 AU/mL), compared with persons with preobesity, defined as BMI of 25-29.9 (222.4 AU/mL), and those with obesity (BMI ≥30; 167.0 AU/mL; P < .0001). This association remained after adjustment for age (P = .003).
“Our data stresses the importance of close vaccination monitoring of obese people, considering the growing list of countries with obesity problems,” the researchers noted.
Hypertension was also associated with lower antibody titers (P = .006), but that lost statistical significance after matching for age (P = .22).
“We strongly believe that our results are extremely encouraging and useful for the scientific community,” Dr. Pellini and colleagues concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Iwasaki is a cofounder of RIGImmune and is a member of its scientific advisory board.
This article was updated on 3/8/21.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sleep apnea and cognitive impairment are common bedfellows
“The study shows obstructive sleep apnea is common in patients with cognitive impairment. The results suggest that people with cognitive impairment should be assessed for sleep apnea if they have difficulty with sleep or if they demonstrate sleep-related symptoms,” said study investigator David Colelli, MSc, research coordinator at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto.
The findings were released ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology..
Linked to cognitive impairment
OSA is a common sleep disorder and is associated with an increased risk of developing cognitive impairment. It is also prevalent in the general population, but even more common among patients with dementia.
However, the investigators noted, the frequency and predictors of OSA have not been well established in Alzheimer’s disease and other related conditions such as vascular dementia.
The investigators had conducted a previous feasibility study investigating a home sleep monitor as an OSA screening tool. The current research examined potential correlations between OSA detected by this monitor and cognitive impairment.
The study included 67 patients with cognitive impairment due to neurodegenerative or vascular disease. The range of disorders included Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment caused by Alzheimer’s disease, dementia caused by Parkinson’s or Lewy body disease, and vascular conditions.
Participants had a mean age of 72.8 years and 44.8% were male. The mean body mass index (BMI) was 25.6 kg/m2.
These participants completed a home sleep apnea test, which is an alternative to polysomnography for the detection of OSA.
Researchers identified OSA in 52.2% of the study population. This, Mr. Colelli said, “is in the range” of other research investigating sleep and cognitive impairment.
“In the general population, however, this number is a lot lower – in the 10%-20% range depending on the population or country you’re looking at,” Mr. Colelli said.
He emphasized that, without an objective sleep test, some patients may be unaware of their sleep issues. Those with cognitive impairment may “misjudge how they’re sleeping,” especially if they sleep without a partner, so it’s possible that sleep disorder symptoms often go undetected.
Bidirectional relationship?
Participants answered questionnaires on sleep, cognition, and mood. They also completed the 30-point Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) to assess language, visuospatial abilities, memory and recall, and abstract thinking.
Scores on this test range from 0 to 30, with a score of 26 or higher signifying normal, 18-25 indicating mild cognitive impairment, and 17 or lower indicating moderate to severe cognitive impairment. The average score for study participants with OSA was 20.5, compared with 23.6 for those without the sleep disorder.
Results showed OSA was significantly associated with a lower score on the MoCA scale (odds ratio, 0.40; P = .048). “This demonstrated an association of OSA with lower cognitive scores,” Mr. Colelli said.
The analysis also showed that OSA severity was correlated with actigraphy-derived sleep variables, including lower total sleep time, greater sleep onset latency, lower sleep efficiency, and more awakenings.
The study was too small to determine whether a specific diagnosis of cognitive impairment affected the link to OSA, Mr. Colelli said. “But definitely future research should be directed towards looking at this.”
Obesity is a risk factor for OSA, but the mean BMI in the study was not in the obese range of 30 and over. This, Mr. Colelli said, suggests that sleep apnea may present differently in those with cognitive impairment.
“Sleep apnea in this population might not present with the typical risk factors of obesity or snoring or feeling tired.”
While the new study “adds to the understanding that there’s a link between sleep and cognitive impairment, the direction of that link isn’t entirely clear,” Mr. Colelli said.
“It’s slowly becoming appreciated that the relationship might be bidirectionality, where sleep apnea might be contributing to the cognitive impairment and cognitive impairment could be contributing to the sleep issues.”
The study highlights how essential sleep is to mental health, Mr. Colelli said. “I feel, and I’m sure you do too, that if you don’t get good sleep, you feel tired during the day and you may not have the best concentration or memory.”
Identifying sleep issues in patients with cognitive impairment is important, as treatment and management of these issues could affect outcomes including cognition and quality of life, he added.
“Future research should be directed to see if treatment of sleep disorders with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), which is the gold standard, and various other treatments, can improve outcomes.” Future research should also examine OSA prevalence in larger cohorts.
Common, undertreated
Commenting on the resaerch, Lei Gao, MD, assistant professor of anesthesia at Harvard Medical School, Boston, whose areas of expertise include disorders of cognition, sleep, and circadian rhythm, believes the findings are important. “It highlights how common and potentially undertreated OSA is in this age group, and in particular, its link to cognitive impairment.”
OSA is often associated with significant comorbidities, as well as sleep disruption, Dr. Gao noted. One of the study’s strengths was including objective assessment of sleep using actigraphy. “It will be interesting to see to what extent the OSA link to cognitive impairment is via poor sleep or disrupted circadian rest/activity cycles.”
It would also be interesting “to tease out whether OSA is more linked to dementia of vascular etiologies due to common risk factors, or whether it is pervasive to all forms of dementia,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The study shows obstructive sleep apnea is common in patients with cognitive impairment. The results suggest that people with cognitive impairment should be assessed for sleep apnea if they have difficulty with sleep or if they demonstrate sleep-related symptoms,” said study investigator David Colelli, MSc, research coordinator at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto.
The findings were released ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology..
Linked to cognitive impairment
OSA is a common sleep disorder and is associated with an increased risk of developing cognitive impairment. It is also prevalent in the general population, but even more common among patients with dementia.
However, the investigators noted, the frequency and predictors of OSA have not been well established in Alzheimer’s disease and other related conditions such as vascular dementia.
The investigators had conducted a previous feasibility study investigating a home sleep monitor as an OSA screening tool. The current research examined potential correlations between OSA detected by this monitor and cognitive impairment.
The study included 67 patients with cognitive impairment due to neurodegenerative or vascular disease. The range of disorders included Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment caused by Alzheimer’s disease, dementia caused by Parkinson’s or Lewy body disease, and vascular conditions.
Participants had a mean age of 72.8 years and 44.8% were male. The mean body mass index (BMI) was 25.6 kg/m2.
These participants completed a home sleep apnea test, which is an alternative to polysomnography for the detection of OSA.
Researchers identified OSA in 52.2% of the study population. This, Mr. Colelli said, “is in the range” of other research investigating sleep and cognitive impairment.
“In the general population, however, this number is a lot lower – in the 10%-20% range depending on the population or country you’re looking at,” Mr. Colelli said.
He emphasized that, without an objective sleep test, some patients may be unaware of their sleep issues. Those with cognitive impairment may “misjudge how they’re sleeping,” especially if they sleep without a partner, so it’s possible that sleep disorder symptoms often go undetected.
Bidirectional relationship?
Participants answered questionnaires on sleep, cognition, and mood. They also completed the 30-point Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) to assess language, visuospatial abilities, memory and recall, and abstract thinking.
Scores on this test range from 0 to 30, with a score of 26 or higher signifying normal, 18-25 indicating mild cognitive impairment, and 17 or lower indicating moderate to severe cognitive impairment. The average score for study participants with OSA was 20.5, compared with 23.6 for those without the sleep disorder.
Results showed OSA was significantly associated with a lower score on the MoCA scale (odds ratio, 0.40; P = .048). “This demonstrated an association of OSA with lower cognitive scores,” Mr. Colelli said.
The analysis also showed that OSA severity was correlated with actigraphy-derived sleep variables, including lower total sleep time, greater sleep onset latency, lower sleep efficiency, and more awakenings.
The study was too small to determine whether a specific diagnosis of cognitive impairment affected the link to OSA, Mr. Colelli said. “But definitely future research should be directed towards looking at this.”
Obesity is a risk factor for OSA, but the mean BMI in the study was not in the obese range of 30 and over. This, Mr. Colelli said, suggests that sleep apnea may present differently in those with cognitive impairment.
“Sleep apnea in this population might not present with the typical risk factors of obesity or snoring or feeling tired.”
While the new study “adds to the understanding that there’s a link between sleep and cognitive impairment, the direction of that link isn’t entirely clear,” Mr. Colelli said.
“It’s slowly becoming appreciated that the relationship might be bidirectionality, where sleep apnea might be contributing to the cognitive impairment and cognitive impairment could be contributing to the sleep issues.”
The study highlights how essential sleep is to mental health, Mr. Colelli said. “I feel, and I’m sure you do too, that if you don’t get good sleep, you feel tired during the day and you may not have the best concentration or memory.”
Identifying sleep issues in patients with cognitive impairment is important, as treatment and management of these issues could affect outcomes including cognition and quality of life, he added.
“Future research should be directed to see if treatment of sleep disorders with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), which is the gold standard, and various other treatments, can improve outcomes.” Future research should also examine OSA prevalence in larger cohorts.
Common, undertreated
Commenting on the resaerch, Lei Gao, MD, assistant professor of anesthesia at Harvard Medical School, Boston, whose areas of expertise include disorders of cognition, sleep, and circadian rhythm, believes the findings are important. “It highlights how common and potentially undertreated OSA is in this age group, and in particular, its link to cognitive impairment.”
OSA is often associated with significant comorbidities, as well as sleep disruption, Dr. Gao noted. One of the study’s strengths was including objective assessment of sleep using actigraphy. “It will be interesting to see to what extent the OSA link to cognitive impairment is via poor sleep or disrupted circadian rest/activity cycles.”
It would also be interesting “to tease out whether OSA is more linked to dementia of vascular etiologies due to common risk factors, or whether it is pervasive to all forms of dementia,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The study shows obstructive sleep apnea is common in patients with cognitive impairment. The results suggest that people with cognitive impairment should be assessed for sleep apnea if they have difficulty with sleep or if they demonstrate sleep-related symptoms,” said study investigator David Colelli, MSc, research coordinator at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto.
The findings were released ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology..
Linked to cognitive impairment
OSA is a common sleep disorder and is associated with an increased risk of developing cognitive impairment. It is also prevalent in the general population, but even more common among patients with dementia.
However, the investigators noted, the frequency and predictors of OSA have not been well established in Alzheimer’s disease and other related conditions such as vascular dementia.
The investigators had conducted a previous feasibility study investigating a home sleep monitor as an OSA screening tool. The current research examined potential correlations between OSA detected by this monitor and cognitive impairment.
The study included 67 patients with cognitive impairment due to neurodegenerative or vascular disease. The range of disorders included Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment caused by Alzheimer’s disease, dementia caused by Parkinson’s or Lewy body disease, and vascular conditions.
Participants had a mean age of 72.8 years and 44.8% were male. The mean body mass index (BMI) was 25.6 kg/m2.
These participants completed a home sleep apnea test, which is an alternative to polysomnography for the detection of OSA.
Researchers identified OSA in 52.2% of the study population. This, Mr. Colelli said, “is in the range” of other research investigating sleep and cognitive impairment.
“In the general population, however, this number is a lot lower – in the 10%-20% range depending on the population or country you’re looking at,” Mr. Colelli said.
He emphasized that, without an objective sleep test, some patients may be unaware of their sleep issues. Those with cognitive impairment may “misjudge how they’re sleeping,” especially if they sleep without a partner, so it’s possible that sleep disorder symptoms often go undetected.
Bidirectional relationship?
Participants answered questionnaires on sleep, cognition, and mood. They also completed the 30-point Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) to assess language, visuospatial abilities, memory and recall, and abstract thinking.
Scores on this test range from 0 to 30, with a score of 26 or higher signifying normal, 18-25 indicating mild cognitive impairment, and 17 or lower indicating moderate to severe cognitive impairment. The average score for study participants with OSA was 20.5, compared with 23.6 for those without the sleep disorder.
Results showed OSA was significantly associated with a lower score on the MoCA scale (odds ratio, 0.40; P = .048). “This demonstrated an association of OSA with lower cognitive scores,” Mr. Colelli said.
The analysis also showed that OSA severity was correlated with actigraphy-derived sleep variables, including lower total sleep time, greater sleep onset latency, lower sleep efficiency, and more awakenings.
The study was too small to determine whether a specific diagnosis of cognitive impairment affected the link to OSA, Mr. Colelli said. “But definitely future research should be directed towards looking at this.”
Obesity is a risk factor for OSA, but the mean BMI in the study was not in the obese range of 30 and over. This, Mr. Colelli said, suggests that sleep apnea may present differently in those with cognitive impairment.
“Sleep apnea in this population might not present with the typical risk factors of obesity or snoring or feeling tired.”
While the new study “adds to the understanding that there’s a link between sleep and cognitive impairment, the direction of that link isn’t entirely clear,” Mr. Colelli said.
“It’s slowly becoming appreciated that the relationship might be bidirectionality, where sleep apnea might be contributing to the cognitive impairment and cognitive impairment could be contributing to the sleep issues.”
The study highlights how essential sleep is to mental health, Mr. Colelli said. “I feel, and I’m sure you do too, that if you don’t get good sleep, you feel tired during the day and you may not have the best concentration or memory.”
Identifying sleep issues in patients with cognitive impairment is important, as treatment and management of these issues could affect outcomes including cognition and quality of life, he added.
“Future research should be directed to see if treatment of sleep disorders with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), which is the gold standard, and various other treatments, can improve outcomes.” Future research should also examine OSA prevalence in larger cohorts.
Common, undertreated
Commenting on the resaerch, Lei Gao, MD, assistant professor of anesthesia at Harvard Medical School, Boston, whose areas of expertise include disorders of cognition, sleep, and circadian rhythm, believes the findings are important. “It highlights how common and potentially undertreated OSA is in this age group, and in particular, its link to cognitive impairment.”
OSA is often associated with significant comorbidities, as well as sleep disruption, Dr. Gao noted. One of the study’s strengths was including objective assessment of sleep using actigraphy. “It will be interesting to see to what extent the OSA link to cognitive impairment is via poor sleep or disrupted circadian rest/activity cycles.”
It would also be interesting “to tease out whether OSA is more linked to dementia of vascular etiologies due to common risk factors, or whether it is pervasive to all forms of dementia,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAN 2021
JAMA podcast on racism in medicine faces backlash
Published on Feb. 23, the episode is hosted on JAMA’s learning platform for doctors and is available for continuing medical education credits.
“No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast,” JAMA wrote in a Twitter post to promote the episode. That tweet has since been deleted.
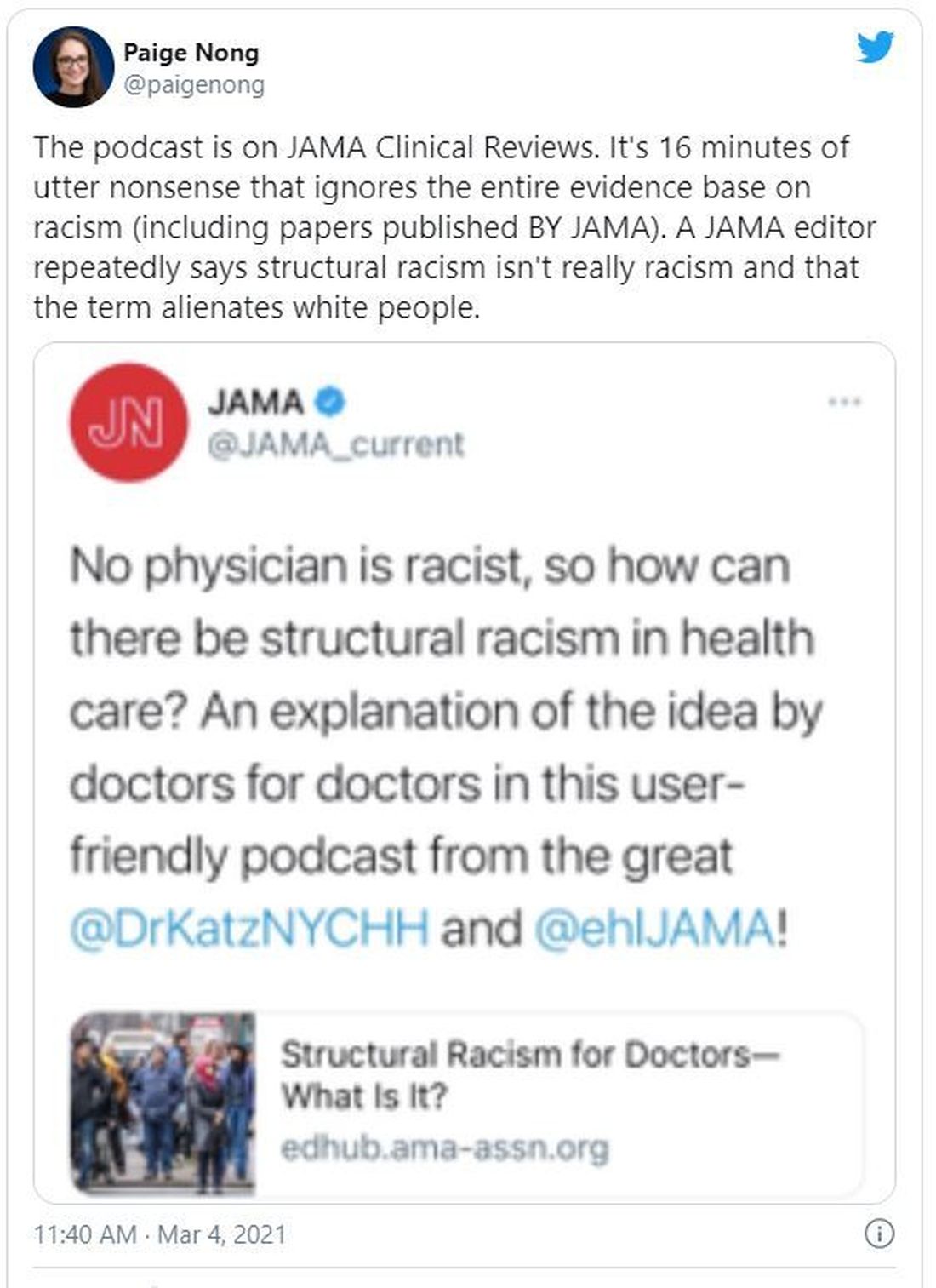
The episode features host Ed Livingston, MD, deputy editor for clinical reviews and education at JAMA, and guest Mitchell Katz, MD, president and CEO for NYC Health + Hospitals and deputy editor for JAMA Internal Medicine. Dr. Livingston approaches the episode as “structural racism for skeptics,” and Dr. Katz tries to explain how structural racism deepens health disparities and what health systems can do about it.
“Many physicians are skeptical of structural racism, the idea that economic, educational, and other societal systems preferentially disadvantage Black Americans and other communities of color,” the episode description says.
In the podcast, Dr. Livingston and Dr. Katz speak about health care disparities and racial inequality. Dr. Livingston, who says he “didn’t understand the concept” going into the episode, suggests that racism was made illegal in the 1960s and that the discussion of “structural racism” should shift away from the term “racism” and focus on socioeconomic status instead.
“What you’re talking about isn’t so much racism ... it isn’t their race, it isn’t their color, it’s their socioeconomic status,” Dr. Livingston says. “Is that a fair statement?”
But Dr. Katz says that “acknowledging structural racism can be helpful to us. Structural racism refers to a system in which policies or practices or how we look at people perpetuates racial inequality.”
Dr. Katz points to the creation of a hospital in San Francisco in the 1880s to treat patients of Chinese ethnicity separately. Outside of health care, he talks about environmental racism between neighborhoods with inequalities in hospitals, schools, and social services.
“All of those things have an impact on that minority person,” Dr. Katz says. “The big thing we can all do is move away from trying to interrogate each other’s opinions and move to a place where we are looking at the policies of our institutions and making sure that they promote equality.”
Dr. Livingston concludes the episode by reemphasizing that “racism” should be taken out of the conversation and it should instead focus on the “structural” aspect of socioeconomics.
“Minorities ... aren’t [in those neighborhoods] because they’re not allowed to buy houses or they can’t get a job because they’re Black or Hispanic. That would be illegal,” Dr. Livingston says. “But disproportionality does exist.”
Efforts to reach Dr. Livingston were unsuccessful. Dr. Katz distanced himself from Dr. Livingston in a statement released on March 4.
“Systemic and interpersonal racism both still exist in our country — they must be rooted out. I do not share the JAMA host’s belief of doing away with the word ‘racism’ will help us be more successful in ending inequities that exists across racial and ethnic lines,” Dr. Katz said. “Further, I believe that we will only produce an equitable society when social and political structures do not continue to produce and perpetuate disparate results based on social race and ethnicity.”
Dr. Katz reiterated that both interpersonal and structural racism continue to exist in the United States, “and it is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it.”
He also recommended JAMA use this controversy “as a learning opportunity for continued dialogue and create another podcast series as an open conversation that invites diverse experts in the field to have an open discussion about structural racism in healthcare.”
The podcast and JAMA’s tweet promoting it were widely criticized on Twitter. In interviews with WebMD, many doctors expressed disbelief that such a respected journal would lend its name to this podcast episode.
B. Bobby Chiong, MD, a radiologist in New York, said although JAMA’s effort to engage with its audience about racism is laudable, it missed the mark.
“I think the backlash comes from how they tried to make a podcast about the subject and somehow made themselves an example of unconscious bias and unfamiliarity with just how embedded in our system is structural racism,” he said.
Perhaps the podcast’s worst offense was its failure to address the painful history of racial bias in this country that still permeates the medical community, says Tamara Saint-Surin, MD, assistant professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“For physicians in leadership to have the belief that structural racism does not exist in medicine, they don’t really appreciate what affects their patients and what their patients were dealing with,” Dr. Saint-Surin said in an interview. “It was a very harmful podcast and goes to show we still have so much work to do.”
Along with a flawed premise, she says, the podcast was not nearly long enough to address such a nuanced issue. And Dr. Livingston focused on interpersonal racism rather than structural racism, she said, failing to address widespread problems such as higher rates of asthma among Black populations living in areas with poor air quality.
The number of Black doctors remains low and the lack of representation adds to an environment already rife with racism, according to many medical professionals.
Shirlene Obuobi, MD, an internal medicine doctor in Chicago, said JAMA failed to live up to its own standards by publishing material that lacked research and expertise.
“I can’t submit a clinical trial to JAMA without them combing through methods with a fine-tooth comb,” Dr. Obuobi said. “They didn’t uphold the standards they normally apply to anyone else.”
Both the editor of JAMA and the head of the American Medical Association issued statements criticizing the episode and the tweet that promoted it.
JAMA Editor-in-Chief Howard Bauchner, MD, said, “The language of the tweet, and some portions of the podcast, do not reflect my commitment as editorial leader of JAMA and JAMA Network to call out and discuss the adverse effects of injustice, inequity, and racism in society and medicine as JAMA has done for many years.” He said JAMA will schedule a future podcast to address the concerns raised about the recent episode.
AMA CEO James L. Madara, MD, said, “The AMA’s House of Delegates passed policy stating that racism is structural, systemic, cultural, and interpersonal, and we are deeply disturbed – and angered – by a recent JAMA podcast that questioned the existence of structural racism and the affiliated tweet that promoted the podcast and stated ‘no physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care?’ ”
He continued: “JAMA has editorial independence from AMA, but this tweet and podcast are inconsistent with the policies and views of AMA, and I’m concerned about and acknowledge the harms they have caused. Structural racism in health care and our society exists, and it is incumbent on all of us to fix it.”
This article was updated 3/5/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Published on Feb. 23, the episode is hosted on JAMA’s learning platform for doctors and is available for continuing medical education credits.
“No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast,” JAMA wrote in a Twitter post to promote the episode. That tweet has since been deleted.

The episode features host Ed Livingston, MD, deputy editor for clinical reviews and education at JAMA, and guest Mitchell Katz, MD, president and CEO for NYC Health + Hospitals and deputy editor for JAMA Internal Medicine. Dr. Livingston approaches the episode as “structural racism for skeptics,” and Dr. Katz tries to explain how structural racism deepens health disparities and what health systems can do about it.
“Many physicians are skeptical of structural racism, the idea that economic, educational, and other societal systems preferentially disadvantage Black Americans and other communities of color,” the episode description says.
In the podcast, Dr. Livingston and Dr. Katz speak about health care disparities and racial inequality. Dr. Livingston, who says he “didn’t understand the concept” going into the episode, suggests that racism was made illegal in the 1960s and that the discussion of “structural racism” should shift away from the term “racism” and focus on socioeconomic status instead.
“What you’re talking about isn’t so much racism ... it isn’t their race, it isn’t their color, it’s their socioeconomic status,” Dr. Livingston says. “Is that a fair statement?”
But Dr. Katz says that “acknowledging structural racism can be helpful to us. Structural racism refers to a system in which policies or practices or how we look at people perpetuates racial inequality.”
Dr. Katz points to the creation of a hospital in San Francisco in the 1880s to treat patients of Chinese ethnicity separately. Outside of health care, he talks about environmental racism between neighborhoods with inequalities in hospitals, schools, and social services.
“All of those things have an impact on that minority person,” Dr. Katz says. “The big thing we can all do is move away from trying to interrogate each other’s opinions and move to a place where we are looking at the policies of our institutions and making sure that they promote equality.”
Dr. Livingston concludes the episode by reemphasizing that “racism” should be taken out of the conversation and it should instead focus on the “structural” aspect of socioeconomics.
“Minorities ... aren’t [in those neighborhoods] because they’re not allowed to buy houses or they can’t get a job because they’re Black or Hispanic. That would be illegal,” Dr. Livingston says. “But disproportionality does exist.”
Efforts to reach Dr. Livingston were unsuccessful. Dr. Katz distanced himself from Dr. Livingston in a statement released on March 4.
“Systemic and interpersonal racism both still exist in our country — they must be rooted out. I do not share the JAMA host’s belief of doing away with the word ‘racism’ will help us be more successful in ending inequities that exists across racial and ethnic lines,” Dr. Katz said. “Further, I believe that we will only produce an equitable society when social and political structures do not continue to produce and perpetuate disparate results based on social race and ethnicity.”
Dr. Katz reiterated that both interpersonal and structural racism continue to exist in the United States, “and it is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it.”
He also recommended JAMA use this controversy “as a learning opportunity for continued dialogue and create another podcast series as an open conversation that invites diverse experts in the field to have an open discussion about structural racism in healthcare.”
The podcast and JAMA’s tweet promoting it were widely criticized on Twitter. In interviews with WebMD, many doctors expressed disbelief that such a respected journal would lend its name to this podcast episode.
B. Bobby Chiong, MD, a radiologist in New York, said although JAMA’s effort to engage with its audience about racism is laudable, it missed the mark.
“I think the backlash comes from how they tried to make a podcast about the subject and somehow made themselves an example of unconscious bias and unfamiliarity with just how embedded in our system is structural racism,” he said.
Perhaps the podcast’s worst offense was its failure to address the painful history of racial bias in this country that still permeates the medical community, says Tamara Saint-Surin, MD, assistant professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“For physicians in leadership to have the belief that structural racism does not exist in medicine, they don’t really appreciate what affects their patients and what their patients were dealing with,” Dr. Saint-Surin said in an interview. “It was a very harmful podcast and goes to show we still have so much work to do.”
Along with a flawed premise, she says, the podcast was not nearly long enough to address such a nuanced issue. And Dr. Livingston focused on interpersonal racism rather than structural racism, she said, failing to address widespread problems such as higher rates of asthma among Black populations living in areas with poor air quality.
The number of Black doctors remains low and the lack of representation adds to an environment already rife with racism, according to many medical professionals.
Shirlene Obuobi, MD, an internal medicine doctor in Chicago, said JAMA failed to live up to its own standards by publishing material that lacked research and expertise.
“I can’t submit a clinical trial to JAMA without them combing through methods with a fine-tooth comb,” Dr. Obuobi said. “They didn’t uphold the standards they normally apply to anyone else.”
Both the editor of JAMA and the head of the American Medical Association issued statements criticizing the episode and the tweet that promoted it.
JAMA Editor-in-Chief Howard Bauchner, MD, said, “The language of the tweet, and some portions of the podcast, do not reflect my commitment as editorial leader of JAMA and JAMA Network to call out and discuss the adverse effects of injustice, inequity, and racism in society and medicine as JAMA has done for many years.” He said JAMA will schedule a future podcast to address the concerns raised about the recent episode.
AMA CEO James L. Madara, MD, said, “The AMA’s House of Delegates passed policy stating that racism is structural, systemic, cultural, and interpersonal, and we are deeply disturbed – and angered – by a recent JAMA podcast that questioned the existence of structural racism and the affiliated tweet that promoted the podcast and stated ‘no physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care?’ ”
He continued: “JAMA has editorial independence from AMA, but this tweet and podcast are inconsistent with the policies and views of AMA, and I’m concerned about and acknowledge the harms they have caused. Structural racism in health care and our society exists, and it is incumbent on all of us to fix it.”
This article was updated 3/5/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Published on Feb. 23, the episode is hosted on JAMA’s learning platform for doctors and is available for continuing medical education credits.
“No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast,” JAMA wrote in a Twitter post to promote the episode. That tweet has since been deleted.

The episode features host Ed Livingston, MD, deputy editor for clinical reviews and education at JAMA, and guest Mitchell Katz, MD, president and CEO for NYC Health + Hospitals and deputy editor for JAMA Internal Medicine. Dr. Livingston approaches the episode as “structural racism for skeptics,” and Dr. Katz tries to explain how structural racism deepens health disparities and what health systems can do about it.
“Many physicians are skeptical of structural racism, the idea that economic, educational, and other societal systems preferentially disadvantage Black Americans and other communities of color,” the episode description says.
In the podcast, Dr. Livingston and Dr. Katz speak about health care disparities and racial inequality. Dr. Livingston, who says he “didn’t understand the concept” going into the episode, suggests that racism was made illegal in the 1960s and that the discussion of “structural racism” should shift away from the term “racism” and focus on socioeconomic status instead.
“What you’re talking about isn’t so much racism ... it isn’t their race, it isn’t their color, it’s their socioeconomic status,” Dr. Livingston says. “Is that a fair statement?”
But Dr. Katz says that “acknowledging structural racism can be helpful to us. Structural racism refers to a system in which policies or practices or how we look at people perpetuates racial inequality.”
Dr. Katz points to the creation of a hospital in San Francisco in the 1880s to treat patients of Chinese ethnicity separately. Outside of health care, he talks about environmental racism between neighborhoods with inequalities in hospitals, schools, and social services.
“All of those things have an impact on that minority person,” Dr. Katz says. “The big thing we can all do is move away from trying to interrogate each other’s opinions and move to a place where we are looking at the policies of our institutions and making sure that they promote equality.”
Dr. Livingston concludes the episode by reemphasizing that “racism” should be taken out of the conversation and it should instead focus on the “structural” aspect of socioeconomics.
“Minorities ... aren’t [in those neighborhoods] because they’re not allowed to buy houses or they can’t get a job because they’re Black or Hispanic. That would be illegal,” Dr. Livingston says. “But disproportionality does exist.”
Efforts to reach Dr. Livingston were unsuccessful. Dr. Katz distanced himself from Dr. Livingston in a statement released on March 4.
“Systemic and interpersonal racism both still exist in our country — they must be rooted out. I do not share the JAMA host’s belief of doing away with the word ‘racism’ will help us be more successful in ending inequities that exists across racial and ethnic lines,” Dr. Katz said. “Further, I believe that we will only produce an equitable society when social and political structures do not continue to produce and perpetuate disparate results based on social race and ethnicity.”
Dr. Katz reiterated that both interpersonal and structural racism continue to exist in the United States, “and it is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it.”
He also recommended JAMA use this controversy “as a learning opportunity for continued dialogue and create another podcast series as an open conversation that invites diverse experts in the field to have an open discussion about structural racism in healthcare.”
The podcast and JAMA’s tweet promoting it were widely criticized on Twitter. In interviews with WebMD, many doctors expressed disbelief that such a respected journal would lend its name to this podcast episode.
B. Bobby Chiong, MD, a radiologist in New York, said although JAMA’s effort to engage with its audience about racism is laudable, it missed the mark.
“I think the backlash comes from how they tried to make a podcast about the subject and somehow made themselves an example of unconscious bias and unfamiliarity with just how embedded in our system is structural racism,” he said.
Perhaps the podcast’s worst offense was its failure to address the painful history of racial bias in this country that still permeates the medical community, says Tamara Saint-Surin, MD, assistant professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“For physicians in leadership to have the belief that structural racism does not exist in medicine, they don’t really appreciate what affects their patients and what their patients were dealing with,” Dr. Saint-Surin said in an interview. “It was a very harmful podcast and goes to show we still have so much work to do.”
Along with a flawed premise, she says, the podcast was not nearly long enough to address such a nuanced issue. And Dr. Livingston focused on interpersonal racism rather than structural racism, she said, failing to address widespread problems such as higher rates of asthma among Black populations living in areas with poor air quality.
The number of Black doctors remains low and the lack of representation adds to an environment already rife with racism, according to many medical professionals.
Shirlene Obuobi, MD, an internal medicine doctor in Chicago, said JAMA failed to live up to its own standards by publishing material that lacked research and expertise.
“I can’t submit a clinical trial to JAMA without them combing through methods with a fine-tooth comb,” Dr. Obuobi said. “They didn’t uphold the standards they normally apply to anyone else.”
Both the editor of JAMA and the head of the American Medical Association issued statements criticizing the episode and the tweet that promoted it.
JAMA Editor-in-Chief Howard Bauchner, MD, said, “The language of the tweet, and some portions of the podcast, do not reflect my commitment as editorial leader of JAMA and JAMA Network to call out and discuss the adverse effects of injustice, inequity, and racism in society and medicine as JAMA has done for many years.” He said JAMA will schedule a future podcast to address the concerns raised about the recent episode.
AMA CEO James L. Madara, MD, said, “The AMA’s House of Delegates passed policy stating that racism is structural, systemic, cultural, and interpersonal, and we are deeply disturbed – and angered – by a recent JAMA podcast that questioned the existence of structural racism and the affiliated tweet that promoted the podcast and stated ‘no physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care?’ ”
He continued: “JAMA has editorial independence from AMA, but this tweet and podcast are inconsistent with the policies and views of AMA, and I’m concerned about and acknowledge the harms they have caused. Structural racism in health care and our society exists, and it is incumbent on all of us to fix it.”
This article was updated 3/5/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Docs become dog groomers and warehouse workers after COVID-19 work loss
One of the biggest conundrums of the COVID-19 pandemic has been the simultaneous panic-hiring of medical professionals in hot spots and significant downsizing of staff across the country. From huge hospital systems to private practices, the stoppage of breast reductions and knee replacements, not to mention the drops in motor vehicle accidents and bar fights, have quieted operating rooms and emergency departments and put doctors’ jobs on the chopping block. A widely cited survey suggests that 21% of doctors have had a work reduction due to COVID-19.
For many American doctors, this is their first extended period of unemployment. Unlike engineers or those with MBAs who might see their fortunes rise and fall with the whims of recessions and boom times, physicians are not exactly accustomed to being laid off. However, doctors were already smarting for years due to falling salaries and decreased autonomy, punctuated by endless clicks on electronic medical records software.
Stephanie Eschenbach Morgan, MD, a breast radiologist in North Carolina, trained for 10 years after college before earning a true physician’s salary.
“Being furloughed was awful. Initially, it was only going to be 2 weeks, and then it turned into 2 months with no pay,” she reflected.
Dr. Eschenbach Morgan and her surgeon husband, who lost a full quarter’s salary, had to ask for grace periods on their credit card and mortgage payments because they had paid a large tax bill right before the pandemic began. “We couldn’t get any stimulus help, so that added insult to injury,” she said.
With her time spent waiting in a holding pattern, Dr. Eschenbach Morgan homeschooled her two young children and started putting a home gym together. She went on a home organizing spree, started a garden, and, perhaps most impressively, caught up with 5 years of photo albums.
A bonus she noted: “I didn’t set an alarm for 2 months.”
Shella Farooki, MD, a radiologist in California, was also focused on homeschooling, itself a demanding job, and veered toward retirement. When one of her work contracts furloughed her (“at one point, I made $30K a month for [their business]”), she started saving money at home, teaching the kids, and applied for a Paycheck Protection Program loan. Her husband, a hospitalist, had had his shifts cut. Dr. Farooki tried a radiology artificial intelligence firm but backed out when she was asked to read 9,200 studies for them for $2,000 per month.
Now, she thinks about leaving medicine “every day.”
Some doctors are questioning whether they should be in medicine in the first place. Family medicine physician Jonathan Polak, MD, faced with his own pink slip, turned to pink T-shirts instead. His girlfriend manages an outlet of the teen fashion retailer Justice. Dr. Polak, who finished his residency just 2 years ago, didn’t hesitate to take a $10-an-hour gig as a stock doc, once even finding himself delivering a shelving unit from the shuttering store to a physician fleeing the city for rural New Hampshire to “escape.”
There’s no escape for him – yet. Saddled with “astronomical” student loans, he had considered grocery store work as well. Dr. Polak knows he can’t work part time or go into teaching long term, as he might like.
Even so, he’s doing everything he can to not be in patient care for the long haul – it’s just not what he thought it would be.
“The culture of medicine, bureaucracy, endless paperwork and charting, and threat of litigation sucks a lot of the joy out of it to the point that I don’t see myself doing it forever when imagining myself 5-10 years into it.”
Still, he recently took an 18-month hospital contract that will force him to move to Florida, but he’s also been turning himself into a veritable Renaissance man; composing music, training for an ultramarathon, studying the latest medical findings, roadtripping, and launching a podcast about dog grooming with a master groomer. “We found parallels between medicine and dog grooming,” he says, somewhat convincingly.
Also working the ruff life is Jen Tserng, MD, a former forensic pathologist who landed on news websites in recent years for becoming a professional dogwalker and housesitter without a permanent home. Dr. Tserng knows doctors were restless and unhappy before COVID-19, their thoughts wandering where the grass might be greener.
As her profile grew, she found her inbox gathering messages from disaffected medical minions: students with a fear of failing or staring down residency application season and employed doctors sick of the constant grind. As she recounted those de facto life coach conversations (“What do you really enjoy?” “Do you really like dogs?”) by phone from New York, she said matter-of-factly, “They don’t call because of COVID. They call because they hate their lives.”
Michelle Mudge-Riley, MD, a physician in Texas, has been seeing this shift for some time as well. She recently held a virtual version of her Physicians Helping Physicians conference, where doctors hear from their peers working successfully in fields like pharmaceuticals and real estate investing.
When COVID-19 hit, Dr. Mudge-Riley quickly pivoted to a virtual platform, where the MDs and DOs huddled in breakout rooms having honest chats about their fears and tentative hopes about their new careers.
“There has been increased interest in nonclinical exploration into full- and part-time careers, as well as side hustles, since COVID began,” she said. “Many physicians have had their hours or pay cut, and some have been laid off. Others are furloughed. Some just want out of an environment where they don’t feel safe.”
An ear, nose, and throat surgeon, Maansi Doshi, MD, from central California, didn’t feel safe – so she left. She had returned from India sick with a mystery virus right as the pandemic began (she said her COVID-19 tests were all negative) and was waiting to get well enough to go back to her private practice job. However, she said she clashed with Trump-supporting colleagues she feared might not be taking the pandemic seriously enough.
Finally getting over a relapse of her mystery virus, Dr. Doshi emailed her resignation in May. Her husband, family practice doctor Mark Mangiapane, MD, gave his job notice weeks later in solidarity because he worked in the same building. Together, they have embraced gardening, a Peloton splurge, and learning business skills to open private practices – solo primary care for him; ENT with a focus on her favorite surgery, rhinoplasty, for her.
Dr. Mangiapane had considered editing medical brochures and also tried to apply for a job as a county public health officer in rural California, but he received his own shock when he learned the county intended to open schools in the midst of the pandemic despite advisement to the contrary by the former health officer.
He retreated from job listings altogether after hearing his would-be peers were getting death threats – targeting their children.
Both doctors felt COVID-19 pushed them beyond their comfort zones. “If COVID hadn’t happened, I would be working. ... Be ‘owned.’ In a weird way, COVID made me more independent and take a risk with my career.”
Obstetrician Kwandaa Roberts, MD, certainly did; she took a budding interest in decorating dollhouses straight to Instagram and national news fame, and she is now a TV-show expert on “Sell This House.”
Like Dr. Doshi and Dr. Mangiapane, Dr. Polak wants to be more in control of his future – even if selling T-shirts at a mall means a certain loss of status along the way.
“Aside from my passion to learn and to have that connection with people, I went into medicine ... because of the job security I thought existed,” he said. “I would say that my getting furloughed has changed my view of the United States in a dramatic way. I do not feel as confident in the U.S. economy and general way of life as I did a year ago. And I am taking a number of steps to put myself in a more fluid, adaptable position in case another crisis like this occurs or if the current state of things worsens.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One of the biggest conundrums of the COVID-19 pandemic has been the simultaneous panic-hiring of medical professionals in hot spots and significant downsizing of staff across the country. From huge hospital systems to private practices, the stoppage of breast reductions and knee replacements, not to mention the drops in motor vehicle accidents and bar fights, have quieted operating rooms and emergency departments and put doctors’ jobs on the chopping block. A widely cited survey suggests that 21% of doctors have had a work reduction due to COVID-19.
For many American doctors, this is their first extended period of unemployment. Unlike engineers or those with MBAs who might see their fortunes rise and fall with the whims of recessions and boom times, physicians are not exactly accustomed to being laid off. However, doctors were already smarting for years due to falling salaries and decreased autonomy, punctuated by endless clicks on electronic medical records software.
Stephanie Eschenbach Morgan, MD, a breast radiologist in North Carolina, trained for 10 years after college before earning a true physician’s salary.
“Being furloughed was awful. Initially, it was only going to be 2 weeks, and then it turned into 2 months with no pay,” she reflected.
Dr. Eschenbach Morgan and her surgeon husband, who lost a full quarter’s salary, had to ask for grace periods on their credit card and mortgage payments because they had paid a large tax bill right before the pandemic began. “We couldn’t get any stimulus help, so that added insult to injury,” she said.
With her time spent waiting in a holding pattern, Dr. Eschenbach Morgan homeschooled her two young children and started putting a home gym together. She went on a home organizing spree, started a garden, and, perhaps most impressively, caught up with 5 years of photo albums.
A bonus she noted: “I didn’t set an alarm for 2 months.”
Shella Farooki, MD, a radiologist in California, was also focused on homeschooling, itself a demanding job, and veered toward retirement. When one of her work contracts furloughed her (“at one point, I made $30K a month for [their business]”), she started saving money at home, teaching the kids, and applied for a Paycheck Protection Program loan. Her husband, a hospitalist, had had his shifts cut. Dr. Farooki tried a radiology artificial intelligence firm but backed out when she was asked to read 9,200 studies for them for $2,000 per month.
Now, she thinks about leaving medicine “every day.”
Some doctors are questioning whether they should be in medicine in the first place. Family medicine physician Jonathan Polak, MD, faced with his own pink slip, turned to pink T-shirts instead. His girlfriend manages an outlet of the teen fashion retailer Justice. Dr. Polak, who finished his residency just 2 years ago, didn’t hesitate to take a $10-an-hour gig as a stock doc, once even finding himself delivering a shelving unit from the shuttering store to a physician fleeing the city for rural New Hampshire to “escape.”
There’s no escape for him – yet. Saddled with “astronomical” student loans, he had considered grocery store work as well. Dr. Polak knows he can’t work part time or go into teaching long term, as he might like.
Even so, he’s doing everything he can to not be in patient care for the long haul – it’s just not what he thought it would be.
“The culture of medicine, bureaucracy, endless paperwork and charting, and threat of litigation sucks a lot of the joy out of it to the point that I don’t see myself doing it forever when imagining myself 5-10 years into it.”
Still, he recently took an 18-month hospital contract that will force him to move to Florida, but he’s also been turning himself into a veritable Renaissance man; composing music, training for an ultramarathon, studying the latest medical findings, roadtripping, and launching a podcast about dog grooming with a master groomer. “We found parallels between medicine and dog grooming,” he says, somewhat convincingly.
Also working the ruff life is Jen Tserng, MD, a former forensic pathologist who landed on news websites in recent years for becoming a professional dogwalker and housesitter without a permanent home. Dr. Tserng knows doctors were restless and unhappy before COVID-19, their thoughts wandering where the grass might be greener.
As her profile grew, she found her inbox gathering messages from disaffected medical minions: students with a fear of failing or staring down residency application season and employed doctors sick of the constant grind. As she recounted those de facto life coach conversations (“What do you really enjoy?” “Do you really like dogs?”) by phone from New York, she said matter-of-factly, “They don’t call because of COVID. They call because they hate their lives.”
Michelle Mudge-Riley, MD, a physician in Texas, has been seeing this shift for some time as well. She recently held a virtual version of her Physicians Helping Physicians conference, where doctors hear from their peers working successfully in fields like pharmaceuticals and real estate investing.
When COVID-19 hit, Dr. Mudge-Riley quickly pivoted to a virtual platform, where the MDs and DOs huddled in breakout rooms having honest chats about their fears and tentative hopes about their new careers.
“There has been increased interest in nonclinical exploration into full- and part-time careers, as well as side hustles, since COVID began,” she said. “Many physicians have had their hours or pay cut, and some have been laid off. Others are furloughed. Some just want out of an environment where they don’t feel safe.”
An ear, nose, and throat surgeon, Maansi Doshi, MD, from central California, didn’t feel safe – so she left. She had returned from India sick with a mystery virus right as the pandemic began (she said her COVID-19 tests were all negative) and was waiting to get well enough to go back to her private practice job. However, she said she clashed with Trump-supporting colleagues she feared might not be taking the pandemic seriously enough.
Finally getting over a relapse of her mystery virus, Dr. Doshi emailed her resignation in May. Her husband, family practice doctor Mark Mangiapane, MD, gave his job notice weeks later in solidarity because he worked in the same building. Together, they have embraced gardening, a Peloton splurge, and learning business skills to open private practices – solo primary care for him; ENT with a focus on her favorite surgery, rhinoplasty, for her.
Dr. Mangiapane had considered editing medical brochures and also tried to apply for a job as a county public health officer in rural California, but he received his own shock when he learned the county intended to open schools in the midst of the pandemic despite advisement to the contrary by the former health officer.
He retreated from job listings altogether after hearing his would-be peers were getting death threats – targeting their children.
Both doctors felt COVID-19 pushed them beyond their comfort zones. “If COVID hadn’t happened, I would be working. ... Be ‘owned.’ In a weird way, COVID made me more independent and take a risk with my career.”
Obstetrician Kwandaa Roberts, MD, certainly did; she took a budding interest in decorating dollhouses straight to Instagram and national news fame, and she is now a TV-show expert on “Sell This House.”
Like Dr. Doshi and Dr. Mangiapane, Dr. Polak wants to be more in control of his future – even if selling T-shirts at a mall means a certain loss of status along the way.
“Aside from my passion to learn and to have that connection with people, I went into medicine ... because of the job security I thought existed,” he said. “I would say that my getting furloughed has changed my view of the United States in a dramatic way. I do not feel as confident in the U.S. economy and general way of life as I did a year ago. And I am taking a number of steps to put myself in a more fluid, adaptable position in case another crisis like this occurs or if the current state of things worsens.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One of the biggest conundrums of the COVID-19 pandemic has been the simultaneous panic-hiring of medical professionals in hot spots and significant downsizing of staff across the country. From huge hospital systems to private practices, the stoppage of breast reductions and knee replacements, not to mention the drops in motor vehicle accidents and bar fights, have quieted operating rooms and emergency departments and put doctors’ jobs on the chopping block. A widely cited survey suggests that 21% of doctors have had a work reduction due to COVID-19.
For many American doctors, this is their first extended period of unemployment. Unlike engineers or those with MBAs who might see their fortunes rise and fall with the whims of recessions and boom times, physicians are not exactly accustomed to being laid off. However, doctors were already smarting for years due to falling salaries and decreased autonomy, punctuated by endless clicks on electronic medical records software.
Stephanie Eschenbach Morgan, MD, a breast radiologist in North Carolina, trained for 10 years after college before earning a true physician’s salary.
“Being furloughed was awful. Initially, it was only going to be 2 weeks, and then it turned into 2 months with no pay,” she reflected.
Dr. Eschenbach Morgan and her surgeon husband, who lost a full quarter’s salary, had to ask for grace periods on their credit card and mortgage payments because they had paid a large tax bill right before the pandemic began. “We couldn’t get any stimulus help, so that added insult to injury,” she said.
With her time spent waiting in a holding pattern, Dr. Eschenbach Morgan homeschooled her two young children and started putting a home gym together. She went on a home organizing spree, started a garden, and, perhaps most impressively, caught up with 5 years of photo albums.
A bonus she noted: “I didn’t set an alarm for 2 months.”
Shella Farooki, MD, a radiologist in California, was also focused on homeschooling, itself a demanding job, and veered toward retirement. When one of her work contracts furloughed her (“at one point, I made $30K a month for [their business]”), she started saving money at home, teaching the kids, and applied for a Paycheck Protection Program loan. Her husband, a hospitalist, had had his shifts cut. Dr. Farooki tried a radiology artificial intelligence firm but backed out when she was asked to read 9,200 studies for them for $2,000 per month.
Now, she thinks about leaving medicine “every day.”
Some doctors are questioning whether they should be in medicine in the first place. Family medicine physician Jonathan Polak, MD, faced with his own pink slip, turned to pink T-shirts instead. His girlfriend manages an outlet of the teen fashion retailer Justice. Dr. Polak, who finished his residency just 2 years ago, didn’t hesitate to take a $10-an-hour gig as a stock doc, once even finding himself delivering a shelving unit from the shuttering store to a physician fleeing the city for rural New Hampshire to “escape.”
There’s no escape for him – yet. Saddled with “astronomical” student loans, he had considered grocery store work as well. Dr. Polak knows he can’t work part time or go into teaching long term, as he might like.
Even so, he’s doing everything he can to not be in patient care for the long haul – it’s just not what he thought it would be.
“The culture of medicine, bureaucracy, endless paperwork and charting, and threat of litigation sucks a lot of the joy out of it to the point that I don’t see myself doing it forever when imagining myself 5-10 years into it.”
Still, he recently took an 18-month hospital contract that will force him to move to Florida, but he’s also been turning himself into a veritable Renaissance man; composing music, training for an ultramarathon, studying the latest medical findings, roadtripping, and launching a podcast about dog grooming with a master groomer. “We found parallels between medicine and dog grooming,” he says, somewhat convincingly.
Also working the ruff life is Jen Tserng, MD, a former forensic pathologist who landed on news websites in recent years for becoming a professional dogwalker and housesitter without a permanent home. Dr. Tserng knows doctors were restless and unhappy before COVID-19, their thoughts wandering where the grass might be greener.
As her profile grew, she found her inbox gathering messages from disaffected medical minions: students with a fear of failing or staring down residency application season and employed doctors sick of the constant grind. As she recounted those de facto life coach conversations (“What do you really enjoy?” “Do you really like dogs?”) by phone from New York, she said matter-of-factly, “They don’t call because of COVID. They call because they hate their lives.”
Michelle Mudge-Riley, MD, a physician in Texas, has been seeing this shift for some time as well. She recently held a virtual version of her Physicians Helping Physicians conference, where doctors hear from their peers working successfully in fields like pharmaceuticals and real estate investing.
When COVID-19 hit, Dr. Mudge-Riley quickly pivoted to a virtual platform, where the MDs and DOs huddled in breakout rooms having honest chats about their fears and tentative hopes about their new careers.
“There has been increased interest in nonclinical exploration into full- and part-time careers, as well as side hustles, since COVID began,” she said. “Many physicians have had their hours or pay cut, and some have been laid off. Others are furloughed. Some just want out of an environment where they don’t feel safe.”
An ear, nose, and throat surgeon, Maansi Doshi, MD, from central California, didn’t feel safe – so she left. She had returned from India sick with a mystery virus right as the pandemic began (she said her COVID-19 tests were all negative) and was waiting to get well enough to go back to her private practice job. However, she said she clashed with Trump-supporting colleagues she feared might not be taking the pandemic seriously enough.
Finally getting over a relapse of her mystery virus, Dr. Doshi emailed her resignation in May. Her husband, family practice doctor Mark Mangiapane, MD, gave his job notice weeks later in solidarity because he worked in the same building. Together, they have embraced gardening, a Peloton splurge, and learning business skills to open private practices – solo primary care for him; ENT with a focus on her favorite surgery, rhinoplasty, for her.
Dr. Mangiapane had considered editing medical brochures and also tried to apply for a job as a county public health officer in rural California, but he received his own shock when he learned the county intended to open schools in the midst of the pandemic despite advisement to the contrary by the former health officer.
He retreated from job listings altogether after hearing his would-be peers were getting death threats – targeting their children.
Both doctors felt COVID-19 pushed them beyond their comfort zones. “If COVID hadn’t happened, I would be working. ... Be ‘owned.’ In a weird way, COVID made me more independent and take a risk with my career.”
Obstetrician Kwandaa Roberts, MD, certainly did; she took a budding interest in decorating dollhouses straight to Instagram and national news fame, and she is now a TV-show expert on “Sell This House.”
Like Dr. Doshi and Dr. Mangiapane, Dr. Polak wants to be more in control of his future – even if selling T-shirts at a mall means a certain loss of status along the way.
“Aside from my passion to learn and to have that connection with people, I went into medicine ... because of the job security I thought existed,” he said. “I would say that my getting furloughed has changed my view of the United States in a dramatic way. I do not feel as confident in the U.S. economy and general way of life as I did a year ago. And I am taking a number of steps to put myself in a more fluid, adaptable position in case another crisis like this occurs or if the current state of things worsens.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Novel oral agent effective in teens with atopic dermatitis
Abrocitinib, an investigational drug proven to be a safe and effective treatment for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults 18 years and older, is also safe and effective in patients aged 12-17 years, according to a randomized trial of the oral, once-daily Janus kinase (JAK) 1 selective inhibitor, used in combination with medicated topical therapy.
The results, from the phase 3 JADE TEEN study, were presented during an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, held virtually this year.
“We’re very excited about the introduction of oral JAKs into our armamentarium for atopic dermatitis,” lead author Lawrence Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, University of California, San Diego, and chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego, said in an interview.
AD ranges in severity, and there is a great deal of moderate to severe AD that has a tremendous negative impact on the individual, Dr. Eichenfield said. “Traditionally we have treated it with intermittent topical corticosteroids, but this has left a significant percentage of patients without long-term disease control.”
JAK inhibitors are effective mediators of the inflammation response that occurs in moderate to severe AD. They inhibit the stimulation of the JAK pathway and allow anti-inflammatory effects and therefore have potential, especially in more severe disease, Dr. Eichenfield said.
In the current study, which is a spin-off of the original study that looked at abrocitinib in adults, he and his team randomly assigned 285 teens (mean age, 14.9 years; 50.9% male; 56.1% White) with moderate to severe AD to receive one of the following treatments for 12 weeks: abrocitinib 200 mg plus topical therapy (95); abrocitinib 100 mg plus topical therapy (95); or placebo, which consisted of topical therapy alone (95).
The primary endpoints were an Investigator’s Global Assessment response of clear or almost clear (scores of 0 and 1, respectively), with an improvement of at least 2 points, and an improvement in Eczema Area and Severity Index score of at least 75% at week 12.
Secondary endpoints included an improvement in Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (PP-NRS) response of at least 4 points at week 12.
The teens who received abrocitinib along with medicated topical therapy showed significant improvement in the severity of their AD at the end of the 12-week period, compared with those in the placebo group.
“The percentage of patients achieving essentially no itch, as captured in the fact that more than half of those on the higher dose of abrocitinib made it to no itch, is a new data point and is important to note,” Dr. Eichenfield said. “A lot of the other medicines don’t really get a significant percentage of the population to an itch score of 0 to 1. This drug brought about a rapid and profound itch relief.”
He added: “The results from JADE TEEN extend the drug’s utility in this younger population and show that abrocitinib performs the same with regard to efficacy and safety in the teenagers. Having atopic dermatitis that does not respond to treatment is especially hard for adolescents, but now we know that abrocitinib will be safe and effective and so we now have something to offer these kids.”
“Abrocitinib achieved a good response in this study that was statistically significant, compared to standard treatment,” Jonathan A. Bernstein, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Cincinnati, commented in an interview.
“JAK inhibitors are very promising, and this study adds to that promise. They play an important role in atopic dermatitis, so obviously, teenagers with AD represent an important population,” said Dr. Bernstein, who was not part of the study. “These results are very encouraging, and I think that we will probably see some of these JAK inhibitors approved by the FDA, if not this year, probably next.”
The study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Eichenfield serves as an investigator, speaker, and consultant for Pfizer; and as an investigator, speaker, consultant, and/or is on a data safety monitoring board for AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Arcutis, Asana, Dermavant, Dermira, Forte, Galderma, Ichnos/Glenmark, Incyte, LEO, Lilly, L’Oreal, Novartis, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica. Dr. Bernstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Abrocitinib, an investigational drug proven to be a safe and effective treatment for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults 18 years and older, is also safe and effective in patients aged 12-17 years, according to a randomized trial of the oral, once-daily Janus kinase (JAK) 1 selective inhibitor, used in combination with medicated topical therapy.
The results, from the phase 3 JADE TEEN study, were presented during an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, held virtually this year.
“We’re very excited about the introduction of oral JAKs into our armamentarium for atopic dermatitis,” lead author Lawrence Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, University of California, San Diego, and chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego, said in an interview.
AD ranges in severity, and there is a great deal of moderate to severe AD that has a tremendous negative impact on the individual, Dr. Eichenfield said. “Traditionally we have treated it with intermittent topical corticosteroids, but this has left a significant percentage of patients without long-term disease control.”
JAK inhibitors are effective mediators of the inflammation response that occurs in moderate to severe AD. They inhibit the stimulation of the JAK pathway and allow anti-inflammatory effects and therefore have potential, especially in more severe disease, Dr. Eichenfield said.
In the current study, which is a spin-off of the original study that looked at abrocitinib in adults, he and his team randomly assigned 285 teens (mean age, 14.9 years; 50.9% male; 56.1% White) with moderate to severe AD to receive one of the following treatments for 12 weeks: abrocitinib 200 mg plus topical therapy (95); abrocitinib 100 mg plus topical therapy (95); or placebo, which consisted of topical therapy alone (95).
The primary endpoints were an Investigator’s Global Assessment response of clear or almost clear (scores of 0 and 1, respectively), with an improvement of at least 2 points, and an improvement in Eczema Area and Severity Index score of at least 75% at week 12.
Secondary endpoints included an improvement in Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (PP-NRS) response of at least 4 points at week 12.
The teens who received abrocitinib along with medicated topical therapy showed significant improvement in the severity of their AD at the end of the 12-week period, compared with those in the placebo group.
“The percentage of patients achieving essentially no itch, as captured in the fact that more than half of those on the higher dose of abrocitinib made it to no itch, is a new data point and is important to note,” Dr. Eichenfield said. “A lot of the other medicines don’t really get a significant percentage of the population to an itch score of 0 to 1. This drug brought about a rapid and profound itch relief.”
He added: “The results from JADE TEEN extend the drug’s utility in this younger population and show that abrocitinib performs the same with regard to efficacy and safety in the teenagers. Having atopic dermatitis that does not respond to treatment is especially hard for adolescents, but now we know that abrocitinib will be safe and effective and so we now have something to offer these kids.”
“Abrocitinib achieved a good response in this study that was statistically significant, compared to standard treatment,” Jonathan A. Bernstein, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Cincinnati, commented in an interview.
“JAK inhibitors are very promising, and this study adds to that promise. They play an important role in atopic dermatitis, so obviously, teenagers with AD represent an important population,” said Dr. Bernstein, who was not part of the study. “These results are very encouraging, and I think that we will probably see some of these JAK inhibitors approved by the FDA, if not this year, probably next.”
The study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Eichenfield serves as an investigator, speaker, and consultant for Pfizer; and as an investigator, speaker, consultant, and/or is on a data safety monitoring board for AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Arcutis, Asana, Dermavant, Dermira, Forte, Galderma, Ichnos/Glenmark, Incyte, LEO, Lilly, L’Oreal, Novartis, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica. Dr. Bernstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Abrocitinib, an investigational drug proven to be a safe and effective treatment for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults 18 years and older, is also safe and effective in patients aged 12-17 years, according to a randomized trial of the oral, once-daily Janus kinase (JAK) 1 selective inhibitor, used in combination with medicated topical therapy.
The results, from the phase 3 JADE TEEN study, were presented during an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, held virtually this year.
“We’re very excited about the introduction of oral JAKs into our armamentarium for atopic dermatitis,” lead author Lawrence Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, University of California, San Diego, and chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego, said in an interview.
AD ranges in severity, and there is a great deal of moderate to severe AD that has a tremendous negative impact on the individual, Dr. Eichenfield said. “Traditionally we have treated it with intermittent topical corticosteroids, but this has left a significant percentage of patients without long-term disease control.”
JAK inhibitors are effective mediators of the inflammation response that occurs in moderate to severe AD. They inhibit the stimulation of the JAK pathway and allow anti-inflammatory effects and therefore have potential, especially in more severe disease, Dr. Eichenfield said.
In the current study, which is a spin-off of the original study that looked at abrocitinib in adults, he and his team randomly assigned 285 teens (mean age, 14.9 years; 50.9% male; 56.1% White) with moderate to severe AD to receive one of the following treatments for 12 weeks: abrocitinib 200 mg plus topical therapy (95); abrocitinib 100 mg plus topical therapy (95); or placebo, which consisted of topical therapy alone (95).
The primary endpoints were an Investigator’s Global Assessment response of clear or almost clear (scores of 0 and 1, respectively), with an improvement of at least 2 points, and an improvement in Eczema Area and Severity Index score of at least 75% at week 12.
Secondary endpoints included an improvement in Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (PP-NRS) response of at least 4 points at week 12.
The teens who received abrocitinib along with medicated topical therapy showed significant improvement in the severity of their AD at the end of the 12-week period, compared with those in the placebo group.
“The percentage of patients achieving essentially no itch, as captured in the fact that more than half of those on the higher dose of abrocitinib made it to no itch, is a new data point and is important to note,” Dr. Eichenfield said. “A lot of the other medicines don’t really get a significant percentage of the population to an itch score of 0 to 1. This drug brought about a rapid and profound itch relief.”
He added: “The results from JADE TEEN extend the drug’s utility in this younger population and show that abrocitinib performs the same with regard to efficacy and safety in the teenagers. Having atopic dermatitis that does not respond to treatment is especially hard for adolescents, but now we know that abrocitinib will be safe and effective and so we now have something to offer these kids.”
“Abrocitinib achieved a good response in this study that was statistically significant, compared to standard treatment,” Jonathan A. Bernstein, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Cincinnati, commented in an interview.
“JAK inhibitors are very promising, and this study adds to that promise. They play an important role in atopic dermatitis, so obviously, teenagers with AD represent an important population,” said Dr. Bernstein, who was not part of the study. “These results are very encouraging, and I think that we will probably see some of these JAK inhibitors approved by the FDA, if not this year, probably next.”
The study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Eichenfield serves as an investigator, speaker, and consultant for Pfizer; and as an investigator, speaker, consultant, and/or is on a data safety monitoring board for AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Arcutis, Asana, Dermavant, Dermira, Forte, Galderma, Ichnos/Glenmark, Incyte, LEO, Lilly, L’Oreal, Novartis, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica. Dr. Bernstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pembrolizumab SCLC indication withdrawn in U.S.
The move does not affect any of the drug’s other indications. The immunotherapy is used in the treatment of many different types of cancer.
The SCLC indication had been granted an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration in 2019 based on tumor response rate and durability of response data from patient cohorts in two trials. However, the anti-PD-1 therapy failed to demonstrate statistically significant improved overall survival in a confirmatory trial, which is mandated after an accelerated approval.
The FDA is conducting “an industry-wide evaluation of indications based on accelerated approvals that have not yet met their postmarketing requirements,” said Merck.
In February of 2021, an indication for durvalumab (Imfinzi) was withdrawn by AstraZeneca in concert with the FDA after the drug failed to improve overall survival in unresectable metastatic bladder cancer in a confirmatory trial, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
“We will continue to rigorously evaluate the benefits of [pembrolizumab] in small cell lung cancer and other types of cancer, in pursuit of Merck’s mission to save and improve lives,” Roy Baynes, MD, chief medical officer, Merck Research Laboratories, said in the company statement
Dr. Baynes also championed the value of accelerated approvals.
“The accelerated pathways created by the FDA have been integral to the remarkable progress in oncology care over the past 5 years and have helped many cancer patients with advanced disease, including small cell lung cancer, access new treatments,” he said.
However, in the past, the FDA has been criticized for approving new cancer drugs based on surrogate markers such as response rates because, in many cases, subsequent studies often show that the drug fails to improve overall survival.
For example, a 2015 study found that 36 (67%) of 54 cancer drug approvals from 2008 to 2012 were made on the basis of surrogate markers – either tumor response rate or progression-free survival. Over a median follow-up period of 4.4 years, only 5 of those 36 drugs were shown in randomized studies to improve overall survival, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The FDA says that it instituted the accelerated approval program to “allow for earlier approval of drugs that treat serious conditions, and that fill an unmet medical need based on a surrogate endpoint.” The program was started in 1992, in the midst of the HIV/AIDS epidemic.
In 2020, the nonprofit Friends of Cancer Research issued a white paper calling for reform in the accelerated approval process, which included a proposal to add risk assessment to surrogate endpoints that would factor in variables such as toxicity.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The move does not affect any of the drug’s other indications. The immunotherapy is used in the treatment of many different types of cancer.
The SCLC indication had been granted an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration in 2019 based on tumor response rate and durability of response data from patient cohorts in two trials. However, the anti-PD-1 therapy failed to demonstrate statistically significant improved overall survival in a confirmatory trial, which is mandated after an accelerated approval.
The FDA is conducting “an industry-wide evaluation of indications based on accelerated approvals that have not yet met their postmarketing requirements,” said Merck.
In February of 2021, an indication for durvalumab (Imfinzi) was withdrawn by AstraZeneca in concert with the FDA after the drug failed to improve overall survival in unresectable metastatic bladder cancer in a confirmatory trial, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
“We will continue to rigorously evaluate the benefits of [pembrolizumab] in small cell lung cancer and other types of cancer, in pursuit of Merck’s mission to save and improve lives,” Roy Baynes, MD, chief medical officer, Merck Research Laboratories, said in the company statement
Dr. Baynes also championed the value of accelerated approvals.
“The accelerated pathways created by the FDA have been integral to the remarkable progress in oncology care over the past 5 years and have helped many cancer patients with advanced disease, including small cell lung cancer, access new treatments,” he said.
However, in the past, the FDA has been criticized for approving new cancer drugs based on surrogate markers such as response rates because, in many cases, subsequent studies often show that the drug fails to improve overall survival.
For example, a 2015 study found that 36 (67%) of 54 cancer drug approvals from 2008 to 2012 were made on the basis of surrogate markers – either tumor response rate or progression-free survival. Over a median follow-up period of 4.4 years, only 5 of those 36 drugs were shown in randomized studies to improve overall survival, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The FDA says that it instituted the accelerated approval program to “allow for earlier approval of drugs that treat serious conditions, and that fill an unmet medical need based on a surrogate endpoint.” The program was started in 1992, in the midst of the HIV/AIDS epidemic.
In 2020, the nonprofit Friends of Cancer Research issued a white paper calling for reform in the accelerated approval process, which included a proposal to add risk assessment to surrogate endpoints that would factor in variables such as toxicity.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The move does not affect any of the drug’s other indications. The immunotherapy is used in the treatment of many different types of cancer.
The SCLC indication had been granted an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration in 2019 based on tumor response rate and durability of response data from patient cohorts in two trials. However, the anti-PD-1 therapy failed to demonstrate statistically significant improved overall survival in a confirmatory trial, which is mandated after an accelerated approval.
The FDA is conducting “an industry-wide evaluation of indications based on accelerated approvals that have not yet met their postmarketing requirements,” said Merck.
In February of 2021, an indication for durvalumab (Imfinzi) was withdrawn by AstraZeneca in concert with the FDA after the drug failed to improve overall survival in unresectable metastatic bladder cancer in a confirmatory trial, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
“We will continue to rigorously evaluate the benefits of [pembrolizumab] in small cell lung cancer and other types of cancer, in pursuit of Merck’s mission to save and improve lives,” Roy Baynes, MD, chief medical officer, Merck Research Laboratories, said in the company statement
Dr. Baynes also championed the value of accelerated approvals.
“The accelerated pathways created by the FDA have been integral to the remarkable progress in oncology care over the past 5 years and have helped many cancer patients with advanced disease, including small cell lung cancer, access new treatments,” he said.
However, in the past, the FDA has been criticized for approving new cancer drugs based on surrogate markers such as response rates because, in many cases, subsequent studies often show that the drug fails to improve overall survival.
For example, a 2015 study found that 36 (67%) of 54 cancer drug approvals from 2008 to 2012 were made on the basis of surrogate markers – either tumor response rate or progression-free survival. Over a median follow-up period of 4.4 years, only 5 of those 36 drugs were shown in randomized studies to improve overall survival, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The FDA says that it instituted the accelerated approval program to “allow for earlier approval of drugs that treat serious conditions, and that fill an unmet medical need based on a surrogate endpoint.” The program was started in 1992, in the midst of the HIV/AIDS epidemic.
In 2020, the nonprofit Friends of Cancer Research issued a white paper calling for reform in the accelerated approval process, which included a proposal to add risk assessment to surrogate endpoints that would factor in variables such as toxicity.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Earlier antibiotic initiation for sepsis did not lead to overuse
There has been a marked increase in the time to antibiotic administration for ICU patients with sepsis across Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals, but there is no evidence that they are being given inappropriately, according to new findings.
Accelerating time-to-antibiotics in sepsis means that patients will be treated earlier, but it could also result in more patients receiving antibiotics, including those without infection. This in turn may contribute to antimicrobial resistance.
“The time to antibiotics for sepsis accelerated across VA hospitals, and declined from 5.8 to 4.8 hours between 2013 and 2018,” said lead study author Sarah Seelye, PhD, data scientist at the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Ann Arbor, Mich. “Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis.”
The results were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine, which was held virtually this year.
“Many hospitals have initiated programs like this to accelerate the use of antibiotics in patients with severe sepsis, but at the same time, there is growing concern that earlier antibiotic initiation may result in increased antibiotic treatment overall, including those without infection,” said Dr. Seelye. “However, to date, there is little evidence to support this claim.”
The goal of their study was to investigate whether hospital-level acceleration in antibiotic timing for sepsis was associated with increasing antibiotic use among patients hospitalized with potential infection.
They identified 1,101,239 hospitalizations for potential infection in 132 VA hospitals during the period from 2013 to 2018. Of these patients, 608,128 (55.2%) received antibiotics within 48 hours of presentation to the emergency department. A total of 117,435 (10.7%) met the criteria for sepsis.
Hospitals were classified into tertiles of antibiotic acceleration for sepsis: rapid, slow, and flat.
In the VA system, patients with severe sepsis began receiving faster antibiotic treatment in 2017, compared with earlier years. In 2017-2018 more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
In 2017-2018, more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
Hospitals categorized as rapid accelerators decreased their time to antibiotic initiation from 6.4 hours to 4.5 hours, while slow accelerators went from 5.6 to 4.6 hours from 2013 to 2018, and flat accelerators remained stable during the time period (5.3 hours down to 5.2 hours).
However, statistical analysis showed no real difference between the three groups in antibiotic prescribing.
“Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital-level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis,” said Dr. Seelye.
Weighing in on the study results, Craig M. Coopersmith, MD, professor of surgery at Emory University, Atlanta, noted that these results are very convincing, considering the size of the study and that it encompassed 132 different facilities.
“It’s difficult to say how generalizable these results are but they are definitely generalizable to all hospitals in the VA system,” he said. “In general, there are similarities between large health care systems, and it would be surprising if we found the opposite to be true in non-VA health systems.”
However, he emphasized that there is some possibility that the results would not be identical because different health care systems have different methods of providing care.
“This paper does show that you can get antibiotics into patients faster, which can be life saving, without inappropriately using them on everybody,” Dr. Coopersmith said.
He explained that there is more attention being paid now to antibiotic stewardship, compared with 10 or 15 years ago. “Given the choice of giving someone a single dose of antibiotics who may not need it, as opposed to withholding them from someone who is septic which is life threatening, the risk benefit ratio weighs heavily towards starting them early,” he said. “And then escalate rapidly.”
There has been a marked increase in the time to antibiotic administration for ICU patients with sepsis across Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals, but there is no evidence that they are being given inappropriately, according to new findings.
Accelerating time-to-antibiotics in sepsis means that patients will be treated earlier, but it could also result in more patients receiving antibiotics, including those without infection. This in turn may contribute to antimicrobial resistance.
“The time to antibiotics for sepsis accelerated across VA hospitals, and declined from 5.8 to 4.8 hours between 2013 and 2018,” said lead study author Sarah Seelye, PhD, data scientist at the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Ann Arbor, Mich. “Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis.”
The results were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine, which was held virtually this year.
“Many hospitals have initiated programs like this to accelerate the use of antibiotics in patients with severe sepsis, but at the same time, there is growing concern that earlier antibiotic initiation may result in increased antibiotic treatment overall, including those without infection,” said Dr. Seelye. “However, to date, there is little evidence to support this claim.”
The goal of their study was to investigate whether hospital-level acceleration in antibiotic timing for sepsis was associated with increasing antibiotic use among patients hospitalized with potential infection.
They identified 1,101,239 hospitalizations for potential infection in 132 VA hospitals during the period from 2013 to 2018. Of these patients, 608,128 (55.2%) received antibiotics within 48 hours of presentation to the emergency department. A total of 117,435 (10.7%) met the criteria for sepsis.
Hospitals were classified into tertiles of antibiotic acceleration for sepsis: rapid, slow, and flat.
In the VA system, patients with severe sepsis began receiving faster antibiotic treatment in 2017, compared with earlier years. In 2017-2018 more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
In 2017-2018, more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
Hospitals categorized as rapid accelerators decreased their time to antibiotic initiation from 6.4 hours to 4.5 hours, while slow accelerators went from 5.6 to 4.6 hours from 2013 to 2018, and flat accelerators remained stable during the time period (5.3 hours down to 5.2 hours).
However, statistical analysis showed no real difference between the three groups in antibiotic prescribing.
“Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital-level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis,” said Dr. Seelye.
Weighing in on the study results, Craig M. Coopersmith, MD, professor of surgery at Emory University, Atlanta, noted that these results are very convincing, considering the size of the study and that it encompassed 132 different facilities.
“It’s difficult to say how generalizable these results are but they are definitely generalizable to all hospitals in the VA system,” he said. “In general, there are similarities between large health care systems, and it would be surprising if we found the opposite to be true in non-VA health systems.”
However, he emphasized that there is some possibility that the results would not be identical because different health care systems have different methods of providing care.
“This paper does show that you can get antibiotics into patients faster, which can be life saving, without inappropriately using them on everybody,” Dr. Coopersmith said.
He explained that there is more attention being paid now to antibiotic stewardship, compared with 10 or 15 years ago. “Given the choice of giving someone a single dose of antibiotics who may not need it, as opposed to withholding them from someone who is septic which is life threatening, the risk benefit ratio weighs heavily towards starting them early,” he said. “And then escalate rapidly.”
There has been a marked increase in the time to antibiotic administration for ICU patients with sepsis across Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals, but there is no evidence that they are being given inappropriately, according to new findings.
Accelerating time-to-antibiotics in sepsis means that patients will be treated earlier, but it could also result in more patients receiving antibiotics, including those without infection. This in turn may contribute to antimicrobial resistance.
“The time to antibiotics for sepsis accelerated across VA hospitals, and declined from 5.8 to 4.8 hours between 2013 and 2018,” said lead study author Sarah Seelye, PhD, data scientist at the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Ann Arbor, Mich. “Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis.”
The results were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine, which was held virtually this year.
“Many hospitals have initiated programs like this to accelerate the use of antibiotics in patients with severe sepsis, but at the same time, there is growing concern that earlier antibiotic initiation may result in increased antibiotic treatment overall, including those without infection,” said Dr. Seelye. “However, to date, there is little evidence to support this claim.”
The goal of their study was to investigate whether hospital-level acceleration in antibiotic timing for sepsis was associated with increasing antibiotic use among patients hospitalized with potential infection.
They identified 1,101,239 hospitalizations for potential infection in 132 VA hospitals during the period from 2013 to 2018. Of these patients, 608,128 (55.2%) received antibiotics within 48 hours of presentation to the emergency department. A total of 117,435 (10.7%) met the criteria for sepsis.
Hospitals were classified into tertiles of antibiotic acceleration for sepsis: rapid, slow, and flat.
In the VA system, patients with severe sepsis began receiving faster antibiotic treatment in 2017, compared with earlier years. In 2017-2018 more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
In 2017-2018, more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
Hospitals categorized as rapid accelerators decreased their time to antibiotic initiation from 6.4 hours to 4.5 hours, while slow accelerators went from 5.6 to 4.6 hours from 2013 to 2018, and flat accelerators remained stable during the time period (5.3 hours down to 5.2 hours).
However, statistical analysis showed no real difference between the three groups in antibiotic prescribing.
“Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital-level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis,” said Dr. Seelye.
Weighing in on the study results, Craig M. Coopersmith, MD, professor of surgery at Emory University, Atlanta, noted that these results are very convincing, considering the size of the study and that it encompassed 132 different facilities.
“It’s difficult to say how generalizable these results are but they are definitely generalizable to all hospitals in the VA system,” he said. “In general, there are similarities between large health care systems, and it would be surprising if we found the opposite to be true in non-VA health systems.”
However, he emphasized that there is some possibility that the results would not be identical because different health care systems have different methods of providing care.
“This paper does show that you can get antibiotics into patients faster, which can be life saving, without inappropriately using them on everybody,” Dr. Coopersmith said.
He explained that there is more attention being paid now to antibiotic stewardship, compared with 10 or 15 years ago. “Given the choice of giving someone a single dose of antibiotics who may not need it, as opposed to withholding them from someone who is septic which is life threatening, the risk benefit ratio weighs heavily towards starting them early,” he said. “And then escalate rapidly.”
FROM CCC50