User login
‘Remarkable’ seizure-free rates seen with adjunctive cenobamate
In addition, “high rates of seizure freedom were observed with doses of 200 mg and 400 mg,” investigators reported in the Lancet Neurology.
During a 12-week maintenance phase, 21% of patients who received cenobamate 400 mg/day and 11% who received cenobamate 200 mg/day were seizure free, compared with 1% who received placebo. “These data suggest that cenobamate might be a safe and effective treatment option in patients with uncontrolled focal (partial)-onset seizures,” the authors wrote.
On Nov. 21, 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved cenobamate tablets, marketed as Xcopri, to treat focal-onset seizures in adults. The agency noted that hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with cenobamate in two randomized, controlled studies and that one patient died when the drug was titrated rapidly during one of the studies that has not been published yet.
Researchers think that cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative, reduces neuronal excitability “by enhancing the fast and slow inactivation of sodium channels and by inhibiting the persistent component of the sodium channel current,” wrote Gregory L. Krauss, MD, a professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The rates of seizure freedom with adjunctive cenobamate in the published trial are “a remarkable finding,” wrote Stephan Arnold, MD, an epilepsy specialist at Neurozentrum Nymphenburg in Munich, in an accompanying commentary. Twenty of 95 patients in the 400-mg/day group and 11 of 98 patients in the 200-mg/day group “had no seizures during the 12-week maintenance phase, whereas only 1 patient (1%) of the placebo group remained free of seizures during this period,” Dr. Arnold wrote. “To my knowledge, a seizure freedom rate of 20% or higher has not yet been reported in a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of anticonvulsive drugs.”
Still, clinical trials in general are limited by their inclusion and exclusion criteria, relatively short maintenance phases, and the need to keep the dosage of concomitant drugs unchanged during the study, Dr. Arnold noted. “Thus, future findings under real-life conditions will reveal the clinical relevance of cenobamate.”
Hypersensitivity reactions led to protocol adjustments
During the trial, the investigators amended the protocol to lower the starting dose of cenobamate and slow the rate of up-titration to address a risk of allergic drug reactions. “Three hypersensitivity reactions, characterized as rash with involvement of at least one other body system, were reported in three patients” who were assigned to receive cenobamate 200 mg/day, the authors wrote. One case of pruritic rash accompanied by pyrexia occurred on day 10 during the initial faster titration protocol. In another case, “a rash and facial swelling occurred on day 57 in a patient who underwent the amended titration protocol.” These two patients discontinued treatment, and the rashes resolved.
“The third hypersensitivity reaction was a serious case of drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms that occurred starting on day 24 of treatment in a patient randomly assigned to receive 200 mg/day of cenobamate during the faster initial titration protocol,” the authors wrote. “Treatment was discontinued and the patient was treated with corticosteroids and recovered within 2 months.”
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events included somnolence, dizziness, and fatigue. Most events were mild or moderate. The rate of titration and an inability to adjust the dose of concomitant medications may have contributed to the rate of adverse events, the researchers noted. Treatment-emergent adverse events were most frequent in the 400-mg/day group and led to treatment discontinuation in 20% of patients in this group. An ongoing phase 3 study is assessing a lower starting dose and slower titration rate.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
The 18-week, double-blind, randomized trial published in Lancet Neurology is one of two phase 2 clinical trials of cenobamate. The other phase 2 study, which lasted 12 weeks, is pending publication. For the 18-week study, researchers at 107 centers in 16 countries enrolled more than 430 adults aged 18-70 years with uncontrolled focal epilepsy. Patients were taking one to three concomitant antiepileptic drugs at stable doses for at least 4 weeks before screening. Patients completed an 8-week baseline assessment, followed by a 6-week titration phase and a 12-week maintenance phase.
“During the 8-week baseline assessment, patients had to have eight or more focal aware (simple partial) seizures with a motor component, focal impaired awareness (complex partial) seizures, or focal to bilateral tonic-clonic (secondarily generalized) seizures, with a seizure-free interval of less than 25 days,” Dr. Krauss and colleagues wrote. In addition, participants had to have at least three of these seizures during the first 4 weeks of the baseline assessment and at least three during the last 4 weeks.
The investigators excluded patients who were taking diazepam, phenytoin, or phenobarbital within 1 month of screening because of a potential drug-drug interaction with cenobamate. Other exclusion criteria included clinically significant psychiatric illness and status epilepticus within 3 months of screening.
The researchers assigned patients 1:1:1:1 to receive cenobamate 100 mg/day, cenobamate 200 mg/day, cenobamate 400 mg/day, or placebo. Percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency averaged over 28 days during the 18-week treatment period was the primary efficacy outcome for the FDA. The responder rate (the percentage of patients with at least a 50% reduction from baseline in focal seizure frequency) during the 12-week maintenance phase was the primary efficacy outcome for the European Medicines Agency.
The investigators screened 533 patients and assigned 437 to treatment groups. The modified intention-to-treat population included 434 patients, the modified intention-to-treat maintenance-phase population included 397 patients, and the safety population included 437 patients. The most frequently used concomitant medications were levetiracetam (43%), lamotrigine (32%), and carbamazepine (28%).
The median percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency per 28 days during treatment was –24% for the placebo group and –35.5% for the cenobamate 100-mg group. The cenobamate 200 mg group and the cenobamate 400-mg/day group each had a change of –55%.
Responder rates during the maintenance phase were 25% for the placebo group, 40% for the 100-mg group, 56% for the 200-mg group, and 64% for the 400-mg group.
The implications of seizure freedom
The authors acknowledged that it is “difficult to interpret seizure freedom in clinical trials given the constraints of the study designs ... which do not reflect real-life practice. Nonetheless, seizure freedom is of great clinical significance to patient quality of life and the rates reported in this study are notable relative to all other pivotal studies of antiepileptic drug treatment in uncontrolled focal seizures over the past 25 years.”
Rates of seizure freedom represent a crucial outcome measure, Dr. Arnold wrote in his commentary.
“For individual patients, it is not a seizure reduction of 50% or even higher that counts, since this effect will not allow them to drive a car or to work under circumstances bearing increased health risks,” he wrote. “Even when seizure are infrequent, patients nevertheless face the risks of falls, fractures, drowning, and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. It is complete seizure control that gives rise for hope of an independent lifestyle.”
The study was funded by SK Life Science, the developer of cenobamate. One of the study authors is an employee of SK Life Science. Dr. Krauss is a consultant or advisor for Eisai, Otsuka, and Shire and has received research support from Biogen, SK Life Science, and UCB. Dr. Arnold had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Krauss GL et al. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30399-0.
In addition, “high rates of seizure freedom were observed with doses of 200 mg and 400 mg,” investigators reported in the Lancet Neurology.
During a 12-week maintenance phase, 21% of patients who received cenobamate 400 mg/day and 11% who received cenobamate 200 mg/day were seizure free, compared with 1% who received placebo. “These data suggest that cenobamate might be a safe and effective treatment option in patients with uncontrolled focal (partial)-onset seizures,” the authors wrote.
On Nov. 21, 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved cenobamate tablets, marketed as Xcopri, to treat focal-onset seizures in adults. The agency noted that hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with cenobamate in two randomized, controlled studies and that one patient died when the drug was titrated rapidly during one of the studies that has not been published yet.
Researchers think that cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative, reduces neuronal excitability “by enhancing the fast and slow inactivation of sodium channels and by inhibiting the persistent component of the sodium channel current,” wrote Gregory L. Krauss, MD, a professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The rates of seizure freedom with adjunctive cenobamate in the published trial are “a remarkable finding,” wrote Stephan Arnold, MD, an epilepsy specialist at Neurozentrum Nymphenburg in Munich, in an accompanying commentary. Twenty of 95 patients in the 400-mg/day group and 11 of 98 patients in the 200-mg/day group “had no seizures during the 12-week maintenance phase, whereas only 1 patient (1%) of the placebo group remained free of seizures during this period,” Dr. Arnold wrote. “To my knowledge, a seizure freedom rate of 20% or higher has not yet been reported in a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of anticonvulsive drugs.”
Still, clinical trials in general are limited by their inclusion and exclusion criteria, relatively short maintenance phases, and the need to keep the dosage of concomitant drugs unchanged during the study, Dr. Arnold noted. “Thus, future findings under real-life conditions will reveal the clinical relevance of cenobamate.”
Hypersensitivity reactions led to protocol adjustments
During the trial, the investigators amended the protocol to lower the starting dose of cenobamate and slow the rate of up-titration to address a risk of allergic drug reactions. “Three hypersensitivity reactions, characterized as rash with involvement of at least one other body system, were reported in three patients” who were assigned to receive cenobamate 200 mg/day, the authors wrote. One case of pruritic rash accompanied by pyrexia occurred on day 10 during the initial faster titration protocol. In another case, “a rash and facial swelling occurred on day 57 in a patient who underwent the amended titration protocol.” These two patients discontinued treatment, and the rashes resolved.
“The third hypersensitivity reaction was a serious case of drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms that occurred starting on day 24 of treatment in a patient randomly assigned to receive 200 mg/day of cenobamate during the faster initial titration protocol,” the authors wrote. “Treatment was discontinued and the patient was treated with corticosteroids and recovered within 2 months.”
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events included somnolence, dizziness, and fatigue. Most events were mild or moderate. The rate of titration and an inability to adjust the dose of concomitant medications may have contributed to the rate of adverse events, the researchers noted. Treatment-emergent adverse events were most frequent in the 400-mg/day group and led to treatment discontinuation in 20% of patients in this group. An ongoing phase 3 study is assessing a lower starting dose and slower titration rate.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
The 18-week, double-blind, randomized trial published in Lancet Neurology is one of two phase 2 clinical trials of cenobamate. The other phase 2 study, which lasted 12 weeks, is pending publication. For the 18-week study, researchers at 107 centers in 16 countries enrolled more than 430 adults aged 18-70 years with uncontrolled focal epilepsy. Patients were taking one to three concomitant antiepileptic drugs at stable doses for at least 4 weeks before screening. Patients completed an 8-week baseline assessment, followed by a 6-week titration phase and a 12-week maintenance phase.
“During the 8-week baseline assessment, patients had to have eight or more focal aware (simple partial) seizures with a motor component, focal impaired awareness (complex partial) seizures, or focal to bilateral tonic-clonic (secondarily generalized) seizures, with a seizure-free interval of less than 25 days,” Dr. Krauss and colleagues wrote. In addition, participants had to have at least three of these seizures during the first 4 weeks of the baseline assessment and at least three during the last 4 weeks.
The investigators excluded patients who were taking diazepam, phenytoin, or phenobarbital within 1 month of screening because of a potential drug-drug interaction with cenobamate. Other exclusion criteria included clinically significant psychiatric illness and status epilepticus within 3 months of screening.
The researchers assigned patients 1:1:1:1 to receive cenobamate 100 mg/day, cenobamate 200 mg/day, cenobamate 400 mg/day, or placebo. Percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency averaged over 28 days during the 18-week treatment period was the primary efficacy outcome for the FDA. The responder rate (the percentage of patients with at least a 50% reduction from baseline in focal seizure frequency) during the 12-week maintenance phase was the primary efficacy outcome for the European Medicines Agency.
The investigators screened 533 patients and assigned 437 to treatment groups. The modified intention-to-treat population included 434 patients, the modified intention-to-treat maintenance-phase population included 397 patients, and the safety population included 437 patients. The most frequently used concomitant medications were levetiracetam (43%), lamotrigine (32%), and carbamazepine (28%).
The median percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency per 28 days during treatment was –24% for the placebo group and –35.5% for the cenobamate 100-mg group. The cenobamate 200 mg group and the cenobamate 400-mg/day group each had a change of –55%.
Responder rates during the maintenance phase were 25% for the placebo group, 40% for the 100-mg group, 56% for the 200-mg group, and 64% for the 400-mg group.
The implications of seizure freedom
The authors acknowledged that it is “difficult to interpret seizure freedom in clinical trials given the constraints of the study designs ... which do not reflect real-life practice. Nonetheless, seizure freedom is of great clinical significance to patient quality of life and the rates reported in this study are notable relative to all other pivotal studies of antiepileptic drug treatment in uncontrolled focal seizures over the past 25 years.”
Rates of seizure freedom represent a crucial outcome measure, Dr. Arnold wrote in his commentary.
“For individual patients, it is not a seizure reduction of 50% or even higher that counts, since this effect will not allow them to drive a car or to work under circumstances bearing increased health risks,” he wrote. “Even when seizure are infrequent, patients nevertheless face the risks of falls, fractures, drowning, and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. It is complete seizure control that gives rise for hope of an independent lifestyle.”
The study was funded by SK Life Science, the developer of cenobamate. One of the study authors is an employee of SK Life Science. Dr. Krauss is a consultant or advisor for Eisai, Otsuka, and Shire and has received research support from Biogen, SK Life Science, and UCB. Dr. Arnold had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Krauss GL et al. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30399-0.
In addition, “high rates of seizure freedom were observed with doses of 200 mg and 400 mg,” investigators reported in the Lancet Neurology.
During a 12-week maintenance phase, 21% of patients who received cenobamate 400 mg/day and 11% who received cenobamate 200 mg/day were seizure free, compared with 1% who received placebo. “These data suggest that cenobamate might be a safe and effective treatment option in patients with uncontrolled focal (partial)-onset seizures,” the authors wrote.
On Nov. 21, 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved cenobamate tablets, marketed as Xcopri, to treat focal-onset seizures in adults. The agency noted that hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with cenobamate in two randomized, controlled studies and that one patient died when the drug was titrated rapidly during one of the studies that has not been published yet.
Researchers think that cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative, reduces neuronal excitability “by enhancing the fast and slow inactivation of sodium channels and by inhibiting the persistent component of the sodium channel current,” wrote Gregory L. Krauss, MD, a professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The rates of seizure freedom with adjunctive cenobamate in the published trial are “a remarkable finding,” wrote Stephan Arnold, MD, an epilepsy specialist at Neurozentrum Nymphenburg in Munich, in an accompanying commentary. Twenty of 95 patients in the 400-mg/day group and 11 of 98 patients in the 200-mg/day group “had no seizures during the 12-week maintenance phase, whereas only 1 patient (1%) of the placebo group remained free of seizures during this period,” Dr. Arnold wrote. “To my knowledge, a seizure freedom rate of 20% or higher has not yet been reported in a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of anticonvulsive drugs.”
Still, clinical trials in general are limited by their inclusion and exclusion criteria, relatively short maintenance phases, and the need to keep the dosage of concomitant drugs unchanged during the study, Dr. Arnold noted. “Thus, future findings under real-life conditions will reveal the clinical relevance of cenobamate.”
Hypersensitivity reactions led to protocol adjustments
During the trial, the investigators amended the protocol to lower the starting dose of cenobamate and slow the rate of up-titration to address a risk of allergic drug reactions. “Three hypersensitivity reactions, characterized as rash with involvement of at least one other body system, were reported in three patients” who were assigned to receive cenobamate 200 mg/day, the authors wrote. One case of pruritic rash accompanied by pyrexia occurred on day 10 during the initial faster titration protocol. In another case, “a rash and facial swelling occurred on day 57 in a patient who underwent the amended titration protocol.” These two patients discontinued treatment, and the rashes resolved.
“The third hypersensitivity reaction was a serious case of drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms that occurred starting on day 24 of treatment in a patient randomly assigned to receive 200 mg/day of cenobamate during the faster initial titration protocol,” the authors wrote. “Treatment was discontinued and the patient was treated with corticosteroids and recovered within 2 months.”
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events included somnolence, dizziness, and fatigue. Most events were mild or moderate. The rate of titration and an inability to adjust the dose of concomitant medications may have contributed to the rate of adverse events, the researchers noted. Treatment-emergent adverse events were most frequent in the 400-mg/day group and led to treatment discontinuation in 20% of patients in this group. An ongoing phase 3 study is assessing a lower starting dose and slower titration rate.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
The 18-week, double-blind, randomized trial published in Lancet Neurology is one of two phase 2 clinical trials of cenobamate. The other phase 2 study, which lasted 12 weeks, is pending publication. For the 18-week study, researchers at 107 centers in 16 countries enrolled more than 430 adults aged 18-70 years with uncontrolled focal epilepsy. Patients were taking one to three concomitant antiepileptic drugs at stable doses for at least 4 weeks before screening. Patients completed an 8-week baseline assessment, followed by a 6-week titration phase and a 12-week maintenance phase.
“During the 8-week baseline assessment, patients had to have eight or more focal aware (simple partial) seizures with a motor component, focal impaired awareness (complex partial) seizures, or focal to bilateral tonic-clonic (secondarily generalized) seizures, with a seizure-free interval of less than 25 days,” Dr. Krauss and colleagues wrote. In addition, participants had to have at least three of these seizures during the first 4 weeks of the baseline assessment and at least three during the last 4 weeks.
The investigators excluded patients who were taking diazepam, phenytoin, or phenobarbital within 1 month of screening because of a potential drug-drug interaction with cenobamate. Other exclusion criteria included clinically significant psychiatric illness and status epilepticus within 3 months of screening.
The researchers assigned patients 1:1:1:1 to receive cenobamate 100 mg/day, cenobamate 200 mg/day, cenobamate 400 mg/day, or placebo. Percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency averaged over 28 days during the 18-week treatment period was the primary efficacy outcome for the FDA. The responder rate (the percentage of patients with at least a 50% reduction from baseline in focal seizure frequency) during the 12-week maintenance phase was the primary efficacy outcome for the European Medicines Agency.
The investigators screened 533 patients and assigned 437 to treatment groups. The modified intention-to-treat population included 434 patients, the modified intention-to-treat maintenance-phase population included 397 patients, and the safety population included 437 patients. The most frequently used concomitant medications were levetiracetam (43%), lamotrigine (32%), and carbamazepine (28%).
The median percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency per 28 days during treatment was –24% for the placebo group and –35.5% for the cenobamate 100-mg group. The cenobamate 200 mg group and the cenobamate 400-mg/day group each had a change of –55%.
Responder rates during the maintenance phase were 25% for the placebo group, 40% for the 100-mg group, 56% for the 200-mg group, and 64% for the 400-mg group.
The implications of seizure freedom
The authors acknowledged that it is “difficult to interpret seizure freedom in clinical trials given the constraints of the study designs ... which do not reflect real-life practice. Nonetheless, seizure freedom is of great clinical significance to patient quality of life and the rates reported in this study are notable relative to all other pivotal studies of antiepileptic drug treatment in uncontrolled focal seizures over the past 25 years.”
Rates of seizure freedom represent a crucial outcome measure, Dr. Arnold wrote in his commentary.
“For individual patients, it is not a seizure reduction of 50% or even higher that counts, since this effect will not allow them to drive a car or to work under circumstances bearing increased health risks,” he wrote. “Even when seizure are infrequent, patients nevertheless face the risks of falls, fractures, drowning, and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. It is complete seizure control that gives rise for hope of an independent lifestyle.”
The study was funded by SK Life Science, the developer of cenobamate. One of the study authors is an employee of SK Life Science. Dr. Krauss is a consultant or advisor for Eisai, Otsuka, and Shire and has received research support from Biogen, SK Life Science, and UCB. Dr. Arnold had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Krauss GL et al. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30399-0.
FROM LANCET NEUROLOGY
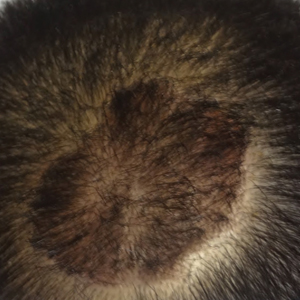
Scalp Psoriasis Considerations
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
Benefits of focused ultrasound thalamotomy for essential tremor persist for 3 years
, according to data published Nov. 20 in Neurology. Improvement from baseline remains significant at that time point, although the magnitude of effect may decrease. In addition, the treatment is not associated with progressive or delayed complications.
“For people who have disabling essential tremor that is not responding to medication, this treatment should be considered as a safe and effective option,” Casey H. Halpern, MD, assistant professor of neurosurgery at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in a press release.
Long-term follow-up of a prospective trial
Focused ultrasound thalamotomy is an emerging treatment for essential tremor. The procedure, which does not require an incision, is conducted with the guidance of magnetic resonance thermometry and patient feedback. A randomized controlled trial conducted by Elias and colleagues indicated that focused ultrasound ventral intermediate nucleus thalamotomy significantly suppressed tremor, reduced disability, and improved quality of life at 3 months, compared with sham treatment. This improvement was sustained at 12 months, and a follow-up study showed that improvements in tremor and functional disability were sustained at 24 months.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues sought to evaluate the continued safety and efficacy of focused ultrasound thalamotomy at 3 years’ follow-up in patients who participated in the original trial. Movement disorder specialists evaluated participants’ tremor severity and functional impairment using the Clinical Rating Scale for Tremor (CRST) at baseline and at 12, 24, and 36 months after treatment. Patients responded to the Quality of Life in Essential Tremor (QUEST) questionnaire, which assesses quality of life at baseline and at each follow-up visit. Neurologists evaluated and recorded all adverse events that occurred during the trial.
Postural tremor was eliminated
The original population included 75 patients who underwent focused ultrasound thalamotomy during the randomized, blinded phase or in an unblinded fashion during the crossover phase. The mean age of all treated patients was 71 years, and disease duration at treatment was 16.8 years. Fifty-two participants were observed at 36 months, and the 3-year attrition rate thus was 31%.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues found that the hand combined tremor–motor score, which was the trial’s primary endpoint, was significantly improved from baseline at 3 years. The median improvement from baseline was 56%. The median disability score decreased by 63% from baseline. Postural tremor was eliminated at 36 months, and QUEST score improved by 50%.
For patients who were missing at 3-year follow-up, data obtained at 3 months was used for comparison. These patients had less improvement in hand tremor–motor score, less reduction in disability, and less reduction in postural tremor, compared with patients who presented for 3-year follow-up. When the investigators reanalyzed their results to account for missing data, they found that the improvement from baseline remained significant.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues compared scores at 36 months and at 6 months to evaluate the durability of the treatment effect. Data were available for 49 patients at both time points, and their combined tremor–motor score had increased by a median of one point at 36 months. Disability score increased by a median of 2 points at 36 months. Posture and QUEST scores did not change significantly. About 58% of patients had at least 50% improvement in hand combined tremor–motor score at 36 months, compared with 64% at 24 months and 61% at 12 months.
The investigators described all adverse events as mild or moderate. No new procedure-related adverse events occurred between 24 and 36 months of follow-up, and none worsened during this period. Two adverse events, however, resolved between 24 and 36 months: one case of dysarthria and one of imbalance.
Reduction in improvement may have many causes
“A reduction in improvement is not unexpected, as essential tremor is a progressive disease,” wrote Dr. Halpern and colleagues. “In addition, diminishing performance of motor–functional tasks over time, particularly in this elderly population, may be multifactorial.” Decrease in tremor control has been reported after all surgical treatments for essential tremor (e.g., deep brain stimulation [DBS] and radiofrequency thalamotomy). Retreatment with invasive therapies or ionizing irradiation would be more problematic than retreatment with focused ultrasound thalamotomy, they added.
The researchers acknowledged that the main limitations of their study were the 31% dropout rate at 3 years and the fact that the cohort at 3-year follow-up differed from those at 2-year follow-up and in the original trial. The results nevertheless “demonstrate persistent, significant tremor reduction, as well as functional and quality of life improvement, with a positive safety profile,” they wrote.
Study funding was provided by the Focused Ultrasound Foundation, the Binational Industrial Research and Development Foundation of Israel, and InSightec, the maker of the focused ultrasound equipment that the researchers used. Dr. Halpern and other investigators received research funding from InSightec. One of the researchers is on the company’s medical advisory board, and another served as a consultant to the company.
Effect on axial tremor is unclear
The 50% improvement in hand tremor, disability, and quality of life that Halpern et al. report is similar to the improvement observed following DBS therapy, said Aparna Wagle Shukla, MD, director of the neurophysiology laboratory at the University of Florida in Gainesville, in an interview. Although the results are promising, neurologists should bear several points in mind, she added.
“DBS-induced side effects often are amenable to programming adjustments. However, similar to radiofrequency thalamotomy, focused ultrasound thalamotomy causes lesion effects. While the study discusses the nature of thalamotomy-induced adverse effects, the clinical practitioners also will benefit from learning about the severity of side effects and how they were individually addressed,” said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “The study acknowledges that there was a 30% dropout rate at 3 years’ follow-up. As the original plan included a 5-year follow-up, it would be beneficial to know why a large fraction of participants discontinued participation earlier than expected.”
Furthermore, the study by Halpern et al. leaves several questions unanswered. It does not indicate, for example, whether focused ultrasound thalamotomy can affect the control of axial tremor, including head and voice tremor, said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “Also, the potential of focused ultrasound thalamotomy to treat complex tremors with possible targeting of multiple brain regions such as ventralis oralis anterior and posterior and zona incerta stimulation is currently not known.
“There is no doubt that focused ultrasound thalamotomy is useful for the control of hand tremors in patients diagnosed with essential tremor, with long-term improvements in quality of life,” Dr. Wagle Shukla continued. “However, it is presently limited in its scope as a unilateral, single-target brain procedure.”
SOURCE: Halpern CH et al. Neurology. 2019 Nov 20 (Epub ahead of print).
, according to data published Nov. 20 in Neurology. Improvement from baseline remains significant at that time point, although the magnitude of effect may decrease. In addition, the treatment is not associated with progressive or delayed complications.
“For people who have disabling essential tremor that is not responding to medication, this treatment should be considered as a safe and effective option,” Casey H. Halpern, MD, assistant professor of neurosurgery at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in a press release.
Long-term follow-up of a prospective trial
Focused ultrasound thalamotomy is an emerging treatment for essential tremor. The procedure, which does not require an incision, is conducted with the guidance of magnetic resonance thermometry and patient feedback. A randomized controlled trial conducted by Elias and colleagues indicated that focused ultrasound ventral intermediate nucleus thalamotomy significantly suppressed tremor, reduced disability, and improved quality of life at 3 months, compared with sham treatment. This improvement was sustained at 12 months, and a follow-up study showed that improvements in tremor and functional disability were sustained at 24 months.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues sought to evaluate the continued safety and efficacy of focused ultrasound thalamotomy at 3 years’ follow-up in patients who participated in the original trial. Movement disorder specialists evaluated participants’ tremor severity and functional impairment using the Clinical Rating Scale for Tremor (CRST) at baseline and at 12, 24, and 36 months after treatment. Patients responded to the Quality of Life in Essential Tremor (QUEST) questionnaire, which assesses quality of life at baseline and at each follow-up visit. Neurologists evaluated and recorded all adverse events that occurred during the trial.
Postural tremor was eliminated
The original population included 75 patients who underwent focused ultrasound thalamotomy during the randomized, blinded phase or in an unblinded fashion during the crossover phase. The mean age of all treated patients was 71 years, and disease duration at treatment was 16.8 years. Fifty-two participants were observed at 36 months, and the 3-year attrition rate thus was 31%.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues found that the hand combined tremor–motor score, which was the trial’s primary endpoint, was significantly improved from baseline at 3 years. The median improvement from baseline was 56%. The median disability score decreased by 63% from baseline. Postural tremor was eliminated at 36 months, and QUEST score improved by 50%.
For patients who were missing at 3-year follow-up, data obtained at 3 months was used for comparison. These patients had less improvement in hand tremor–motor score, less reduction in disability, and less reduction in postural tremor, compared with patients who presented for 3-year follow-up. When the investigators reanalyzed their results to account for missing data, they found that the improvement from baseline remained significant.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues compared scores at 36 months and at 6 months to evaluate the durability of the treatment effect. Data were available for 49 patients at both time points, and their combined tremor–motor score had increased by a median of one point at 36 months. Disability score increased by a median of 2 points at 36 months. Posture and QUEST scores did not change significantly. About 58% of patients had at least 50% improvement in hand combined tremor–motor score at 36 months, compared with 64% at 24 months and 61% at 12 months.
The investigators described all adverse events as mild or moderate. No new procedure-related adverse events occurred between 24 and 36 months of follow-up, and none worsened during this period. Two adverse events, however, resolved between 24 and 36 months: one case of dysarthria and one of imbalance.
Reduction in improvement may have many causes
“A reduction in improvement is not unexpected, as essential tremor is a progressive disease,” wrote Dr. Halpern and colleagues. “In addition, diminishing performance of motor–functional tasks over time, particularly in this elderly population, may be multifactorial.” Decrease in tremor control has been reported after all surgical treatments for essential tremor (e.g., deep brain stimulation [DBS] and radiofrequency thalamotomy). Retreatment with invasive therapies or ionizing irradiation would be more problematic than retreatment with focused ultrasound thalamotomy, they added.
The researchers acknowledged that the main limitations of their study were the 31% dropout rate at 3 years and the fact that the cohort at 3-year follow-up differed from those at 2-year follow-up and in the original trial. The results nevertheless “demonstrate persistent, significant tremor reduction, as well as functional and quality of life improvement, with a positive safety profile,” they wrote.
Study funding was provided by the Focused Ultrasound Foundation, the Binational Industrial Research and Development Foundation of Israel, and InSightec, the maker of the focused ultrasound equipment that the researchers used. Dr. Halpern and other investigators received research funding from InSightec. One of the researchers is on the company’s medical advisory board, and another served as a consultant to the company.
Effect on axial tremor is unclear
The 50% improvement in hand tremor, disability, and quality of life that Halpern et al. report is similar to the improvement observed following DBS therapy, said Aparna Wagle Shukla, MD, director of the neurophysiology laboratory at the University of Florida in Gainesville, in an interview. Although the results are promising, neurologists should bear several points in mind, she added.
“DBS-induced side effects often are amenable to programming adjustments. However, similar to radiofrequency thalamotomy, focused ultrasound thalamotomy causes lesion effects. While the study discusses the nature of thalamotomy-induced adverse effects, the clinical practitioners also will benefit from learning about the severity of side effects and how they were individually addressed,” said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “The study acknowledges that there was a 30% dropout rate at 3 years’ follow-up. As the original plan included a 5-year follow-up, it would be beneficial to know why a large fraction of participants discontinued participation earlier than expected.”
Furthermore, the study by Halpern et al. leaves several questions unanswered. It does not indicate, for example, whether focused ultrasound thalamotomy can affect the control of axial tremor, including head and voice tremor, said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “Also, the potential of focused ultrasound thalamotomy to treat complex tremors with possible targeting of multiple brain regions such as ventralis oralis anterior and posterior and zona incerta stimulation is currently not known.
“There is no doubt that focused ultrasound thalamotomy is useful for the control of hand tremors in patients diagnosed with essential tremor, with long-term improvements in quality of life,” Dr. Wagle Shukla continued. “However, it is presently limited in its scope as a unilateral, single-target brain procedure.”
SOURCE: Halpern CH et al. Neurology. 2019 Nov 20 (Epub ahead of print).
, according to data published Nov. 20 in Neurology. Improvement from baseline remains significant at that time point, although the magnitude of effect may decrease. In addition, the treatment is not associated with progressive or delayed complications.
“For people who have disabling essential tremor that is not responding to medication, this treatment should be considered as a safe and effective option,” Casey H. Halpern, MD, assistant professor of neurosurgery at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in a press release.
Long-term follow-up of a prospective trial
Focused ultrasound thalamotomy is an emerging treatment for essential tremor. The procedure, which does not require an incision, is conducted with the guidance of magnetic resonance thermometry and patient feedback. A randomized controlled trial conducted by Elias and colleagues indicated that focused ultrasound ventral intermediate nucleus thalamotomy significantly suppressed tremor, reduced disability, and improved quality of life at 3 months, compared with sham treatment. This improvement was sustained at 12 months, and a follow-up study showed that improvements in tremor and functional disability were sustained at 24 months.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues sought to evaluate the continued safety and efficacy of focused ultrasound thalamotomy at 3 years’ follow-up in patients who participated in the original trial. Movement disorder specialists evaluated participants’ tremor severity and functional impairment using the Clinical Rating Scale for Tremor (CRST) at baseline and at 12, 24, and 36 months after treatment. Patients responded to the Quality of Life in Essential Tremor (QUEST) questionnaire, which assesses quality of life at baseline and at each follow-up visit. Neurologists evaluated and recorded all adverse events that occurred during the trial.
Postural tremor was eliminated
The original population included 75 patients who underwent focused ultrasound thalamotomy during the randomized, blinded phase or in an unblinded fashion during the crossover phase. The mean age of all treated patients was 71 years, and disease duration at treatment was 16.8 years. Fifty-two participants were observed at 36 months, and the 3-year attrition rate thus was 31%.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues found that the hand combined tremor–motor score, which was the trial’s primary endpoint, was significantly improved from baseline at 3 years. The median improvement from baseline was 56%. The median disability score decreased by 63% from baseline. Postural tremor was eliminated at 36 months, and QUEST score improved by 50%.
For patients who were missing at 3-year follow-up, data obtained at 3 months was used for comparison. These patients had less improvement in hand tremor–motor score, less reduction in disability, and less reduction in postural tremor, compared with patients who presented for 3-year follow-up. When the investigators reanalyzed their results to account for missing data, they found that the improvement from baseline remained significant.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues compared scores at 36 months and at 6 months to evaluate the durability of the treatment effect. Data were available for 49 patients at both time points, and their combined tremor–motor score had increased by a median of one point at 36 months. Disability score increased by a median of 2 points at 36 months. Posture and QUEST scores did not change significantly. About 58% of patients had at least 50% improvement in hand combined tremor–motor score at 36 months, compared with 64% at 24 months and 61% at 12 months.
The investigators described all adverse events as mild or moderate. No new procedure-related adverse events occurred between 24 and 36 months of follow-up, and none worsened during this period. Two adverse events, however, resolved between 24 and 36 months: one case of dysarthria and one of imbalance.
Reduction in improvement may have many causes
“A reduction in improvement is not unexpected, as essential tremor is a progressive disease,” wrote Dr. Halpern and colleagues. “In addition, diminishing performance of motor–functional tasks over time, particularly in this elderly population, may be multifactorial.” Decrease in tremor control has been reported after all surgical treatments for essential tremor (e.g., deep brain stimulation [DBS] and radiofrequency thalamotomy). Retreatment with invasive therapies or ionizing irradiation would be more problematic than retreatment with focused ultrasound thalamotomy, they added.
The researchers acknowledged that the main limitations of their study were the 31% dropout rate at 3 years and the fact that the cohort at 3-year follow-up differed from those at 2-year follow-up and in the original trial. The results nevertheless “demonstrate persistent, significant tremor reduction, as well as functional and quality of life improvement, with a positive safety profile,” they wrote.
Study funding was provided by the Focused Ultrasound Foundation, the Binational Industrial Research and Development Foundation of Israel, and InSightec, the maker of the focused ultrasound equipment that the researchers used. Dr. Halpern and other investigators received research funding from InSightec. One of the researchers is on the company’s medical advisory board, and another served as a consultant to the company.
Effect on axial tremor is unclear
The 50% improvement in hand tremor, disability, and quality of life that Halpern et al. report is similar to the improvement observed following DBS therapy, said Aparna Wagle Shukla, MD, director of the neurophysiology laboratory at the University of Florida in Gainesville, in an interview. Although the results are promising, neurologists should bear several points in mind, she added.
“DBS-induced side effects often are amenable to programming adjustments. However, similar to radiofrequency thalamotomy, focused ultrasound thalamotomy causes lesion effects. While the study discusses the nature of thalamotomy-induced adverse effects, the clinical practitioners also will benefit from learning about the severity of side effects and how they were individually addressed,” said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “The study acknowledges that there was a 30% dropout rate at 3 years’ follow-up. As the original plan included a 5-year follow-up, it would be beneficial to know why a large fraction of participants discontinued participation earlier than expected.”
Furthermore, the study by Halpern et al. leaves several questions unanswered. It does not indicate, for example, whether focused ultrasound thalamotomy can affect the control of axial tremor, including head and voice tremor, said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “Also, the potential of focused ultrasound thalamotomy to treat complex tremors with possible targeting of multiple brain regions such as ventralis oralis anterior and posterior and zona incerta stimulation is currently not known.
“There is no doubt that focused ultrasound thalamotomy is useful for the control of hand tremors in patients diagnosed with essential tremor, with long-term improvements in quality of life,” Dr. Wagle Shukla continued. “However, it is presently limited in its scope as a unilateral, single-target brain procedure.”
SOURCE: Halpern CH et al. Neurology. 2019 Nov 20 (Epub ahead of print).
FROM NEUROLOGY
Survey asks adults: How likely are you to develop dementia?
Donovan T. Maust, MD, and colleagues reported in a research letter published in JAMA Neurology.
More than half of study participants used crossword puzzles as a memory exercise, but only 5% said they spoke to their physician about how to reduce risk. Ironically, this lack of communication was also associated with buying unproven over-the-counter memory supplements, while still remaining ignorant of proven ways to head off dementia and other contributing chronic conditions, wrote Dr. Maust of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and coauthors.
Their analysis of the Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging found that close to half of respondents (48.5%) reported that they were at least somewhat likely to develop dementia. Another 4.2% thought dementia was “very likely” in their future.
The study comprised survey responses from 1,019 adults aged 50-64 years. Most rated their physical health either excellent (445 respondents) or good (413 respondents). Most also reported excellent or very good mental health (721 respondents); 234 reported good mental health. Many (678) were affluent, with annual incomes of $60,000 or higher. They tended to be well educated; only 337 were without at least some college education. More than half were white (753); there were 101 Hispanic respondents and 93 black respondents. Other groups made up the remainder.
A multivariate analysis found that black respondents were about half as likely to believe they would develop dementia, compared with whites – an assumption contrary to epidemiologic findings that blacks are more likely than whites to develop dementia.
People who reported fair or poor mental health were more than twice as likely to feel dementia was in their future (odds ratio, 2.3). But fair or poor physical health was not significantly associated with that concern.
“Those with fair to poor physical health did not accurately perceive that their likelihood of developing dementia was potentially higher than respondents with very good or excellent physical health,” the authors wrote. “In contrast, fair to poor mental health had the largest association with perceived likelihood of dementia, even though less evidence suggests that poor mental health is causally linked with dementia.”
Despite the concerns, just 5% of respondents said that they had spoken to their physician. Those who believed they had a high likelihood of dementia were more likely to talk with their clinician (7.1%) than those who believed they had a low risk (3.6%).
Many more, however, were using non–evidence-based compounds touted as memory supporting. These included fish oil or omega-3 fatty acids (31.6%) and vitamins or supplements (32.9%). Crossword puzzles were a very popular prevention strategy, employed by about 55% in both belief groups.
“While managing chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, could reduce dementia risk, few respondents appear to have discussed this with their physician. Given repeated failures of disease-preventing or disease-modifying treatments for dementia, interest in treatment and prevention has shifted earlier in the disease process. Adults in middle age may not accurately estimate their risk of developing dementia, which could lead to both overuse and underuse if preclinical dementia treatments become available. Policy and physicians should emphasize current evidence-based strategies of managing lifestyle and chronic medical conditions to reduce the risk of dementia,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Maust had no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Maust D et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 Nov 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.3946
I do not find it surprising that older adults fear dementia. Since they correctly perceive that there is no disease-modifying therapy (and maybe also that “getting caught with memory loss” would lead to a loss of driving privileges and other restrictions), they may be trying not to focus on it. As for asking about strategies to “prevent” dementia, that question implies unwarranted optimism about the effectiveness of any such strategy, especially in an older adult. I think we can say that a lifetime of healthy habits (regular physical exercise and careful control of any chronic conditions like diabetes being particularly important) may reduce our risk of dementia a bit, but the idea that anything a 75-year-old does is going to prevent it at that point is probably wishful thinking. Supplements and the like seem to have their own followers. It amazes me how many people suspect what they are taking probably does no good but they do it anyway out of blind hope. Sometimes we can talk them out of spending their money on such things – but not always.
Richard Caselli, MD, is associate director and clinical core director of the Alzheimer’s Disease Center at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz.
I do not find it surprising that older adults fear dementia. Since they correctly perceive that there is no disease-modifying therapy (and maybe also that “getting caught with memory loss” would lead to a loss of driving privileges and other restrictions), they may be trying not to focus on it. As for asking about strategies to “prevent” dementia, that question implies unwarranted optimism about the effectiveness of any such strategy, especially in an older adult. I think we can say that a lifetime of healthy habits (regular physical exercise and careful control of any chronic conditions like diabetes being particularly important) may reduce our risk of dementia a bit, but the idea that anything a 75-year-old does is going to prevent it at that point is probably wishful thinking. Supplements and the like seem to have their own followers. It amazes me how many people suspect what they are taking probably does no good but they do it anyway out of blind hope. Sometimes we can talk them out of spending their money on such things – but not always.
Richard Caselli, MD, is associate director and clinical core director of the Alzheimer’s Disease Center at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz.
I do not find it surprising that older adults fear dementia. Since they correctly perceive that there is no disease-modifying therapy (and maybe also that “getting caught with memory loss” would lead to a loss of driving privileges and other restrictions), they may be trying not to focus on it. As for asking about strategies to “prevent” dementia, that question implies unwarranted optimism about the effectiveness of any such strategy, especially in an older adult. I think we can say that a lifetime of healthy habits (regular physical exercise and careful control of any chronic conditions like diabetes being particularly important) may reduce our risk of dementia a bit, but the idea that anything a 75-year-old does is going to prevent it at that point is probably wishful thinking. Supplements and the like seem to have their own followers. It amazes me how many people suspect what they are taking probably does no good but they do it anyway out of blind hope. Sometimes we can talk them out of spending their money on such things – but not always.
Richard Caselli, MD, is associate director and clinical core director of the Alzheimer’s Disease Center at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Donovan T. Maust, MD, and colleagues reported in a research letter published in JAMA Neurology.
More than half of study participants used crossword puzzles as a memory exercise, but only 5% said they spoke to their physician about how to reduce risk. Ironically, this lack of communication was also associated with buying unproven over-the-counter memory supplements, while still remaining ignorant of proven ways to head off dementia and other contributing chronic conditions, wrote Dr. Maust of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and coauthors.
Their analysis of the Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging found that close to half of respondents (48.5%) reported that they were at least somewhat likely to develop dementia. Another 4.2% thought dementia was “very likely” in their future.
The study comprised survey responses from 1,019 adults aged 50-64 years. Most rated their physical health either excellent (445 respondents) or good (413 respondents). Most also reported excellent or very good mental health (721 respondents); 234 reported good mental health. Many (678) were affluent, with annual incomes of $60,000 or higher. They tended to be well educated; only 337 were without at least some college education. More than half were white (753); there were 101 Hispanic respondents and 93 black respondents. Other groups made up the remainder.
A multivariate analysis found that black respondents were about half as likely to believe they would develop dementia, compared with whites – an assumption contrary to epidemiologic findings that blacks are more likely than whites to develop dementia.
People who reported fair or poor mental health were more than twice as likely to feel dementia was in their future (odds ratio, 2.3). But fair or poor physical health was not significantly associated with that concern.
“Those with fair to poor physical health did not accurately perceive that their likelihood of developing dementia was potentially higher than respondents with very good or excellent physical health,” the authors wrote. “In contrast, fair to poor mental health had the largest association with perceived likelihood of dementia, even though less evidence suggests that poor mental health is causally linked with dementia.”
Despite the concerns, just 5% of respondents said that they had spoken to their physician. Those who believed they had a high likelihood of dementia were more likely to talk with their clinician (7.1%) than those who believed they had a low risk (3.6%).
Many more, however, were using non–evidence-based compounds touted as memory supporting. These included fish oil or omega-3 fatty acids (31.6%) and vitamins or supplements (32.9%). Crossword puzzles were a very popular prevention strategy, employed by about 55% in both belief groups.
“While managing chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, could reduce dementia risk, few respondents appear to have discussed this with their physician. Given repeated failures of disease-preventing or disease-modifying treatments for dementia, interest in treatment and prevention has shifted earlier in the disease process. Adults in middle age may not accurately estimate their risk of developing dementia, which could lead to both overuse and underuse if preclinical dementia treatments become available. Policy and physicians should emphasize current evidence-based strategies of managing lifestyle and chronic medical conditions to reduce the risk of dementia,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Maust had no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Maust D et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 Nov 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.3946
Donovan T. Maust, MD, and colleagues reported in a research letter published in JAMA Neurology.
More than half of study participants used crossword puzzles as a memory exercise, but only 5% said they spoke to their physician about how to reduce risk. Ironically, this lack of communication was also associated with buying unproven over-the-counter memory supplements, while still remaining ignorant of proven ways to head off dementia and other contributing chronic conditions, wrote Dr. Maust of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and coauthors.
Their analysis of the Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging found that close to half of respondents (48.5%) reported that they were at least somewhat likely to develop dementia. Another 4.2% thought dementia was “very likely” in their future.
The study comprised survey responses from 1,019 adults aged 50-64 years. Most rated their physical health either excellent (445 respondents) or good (413 respondents). Most also reported excellent or very good mental health (721 respondents); 234 reported good mental health. Many (678) were affluent, with annual incomes of $60,000 or higher. They tended to be well educated; only 337 were without at least some college education. More than half were white (753); there were 101 Hispanic respondents and 93 black respondents. Other groups made up the remainder.
A multivariate analysis found that black respondents were about half as likely to believe they would develop dementia, compared with whites – an assumption contrary to epidemiologic findings that blacks are more likely than whites to develop dementia.
People who reported fair or poor mental health were more than twice as likely to feel dementia was in their future (odds ratio, 2.3). But fair or poor physical health was not significantly associated with that concern.
“Those with fair to poor physical health did not accurately perceive that their likelihood of developing dementia was potentially higher than respondents with very good or excellent physical health,” the authors wrote. “In contrast, fair to poor mental health had the largest association with perceived likelihood of dementia, even though less evidence suggests that poor mental health is causally linked with dementia.”
Despite the concerns, just 5% of respondents said that they had spoken to their physician. Those who believed they had a high likelihood of dementia were more likely to talk with their clinician (7.1%) than those who believed they had a low risk (3.6%).
Many more, however, were using non–evidence-based compounds touted as memory supporting. These included fish oil or omega-3 fatty acids (31.6%) and vitamins or supplements (32.9%). Crossword puzzles were a very popular prevention strategy, employed by about 55% in both belief groups.
“While managing chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, could reduce dementia risk, few respondents appear to have discussed this with their physician. Given repeated failures of disease-preventing or disease-modifying treatments for dementia, interest in treatment and prevention has shifted earlier in the disease process. Adults in middle age may not accurately estimate their risk of developing dementia, which could lead to both overuse and underuse if preclinical dementia treatments become available. Policy and physicians should emphasize current evidence-based strategies of managing lifestyle and chronic medical conditions to reduce the risk of dementia,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Maust had no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Maust D et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 Nov 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.3946
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Study detects lower CV risk in breast cancer survivors
Breast cancer survivors may have a lower prevalence of cardiac risk factors at the time of first myocardial infarction and better outcomes compared with those having a first MI from the general population, according to findings from a retrospective study.
In addition, women without breast cancer were younger at the time of first MI compared with survivors, wrote Srikanth Yandrapalli, MD, of New York Medical College, Valhalla, and colleagues. Their report is in the American Journal of Medicine.
The researchers identified 1,644,032 women with a first MI, 56,842 of whom were breast cancer survivors. The team evaluated differences in the prevalence of cardiac risk factors and related outcomes in breast cancer survivors in comparison to the general population.
At baseline, the mean age of subjects with a history of breast cancer was 77 years (range, 11 years), while the mean age of women without breast cancer was 71 years (range, 15 years).
Clinical data were collected from the United States National Inpatient Sample for January 2005 to September 2015. Other outcomes assessed were differences in baseline characteristics and the rate of in-hospital mortality in both groups.
After analysis, the researchers found that breast cancer survivors had a lower prevalence of diabetes mellitus (30.1% vs. 33.1%), obesity (9.4% vs. 13.0%), and smoking (24.1% vs. 27.0%), but higher rates of dyslipidemia (52.7% vs. 48.4%) and hypertension (73.6% vs. 68.1%), compared with women without breast cancer (All P less than .001).
With respect to age, women without breast cancer were 6 years younger than breast cancer survivors at the time of first acute MI (mean age, 71 vs. 77 years; P less than .001).
In addition, the rate of in-hospital mortality was higher in women without breast cancer (7.9%) compared with survivors (7.1%) (P less than .001). After risk adjustment, these results remained unchanged (odds ratio, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.82-0.94).
“Breast cancer survivors in the U.S. are at least 6 years older than the general population of women without breast cancer, and they had a favorable cardiac risk factor profile at the time of first myocardial infarction,” Dr. Yandrapalli and colleagues explained. “The reason for these findings are unclear and hypothesis generating,” they added.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the retrospective design. As a result, the potential effects of residual confounding should be considered when interpreting the results.
“The favorable impact of health education and participation in cancer survivorship programs on these observed differences in breast cancer survivors should be further explored,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Yandrapalli S et al. Am J Med. 2019 Nov 9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.10.018.
Breast cancer survivors may have a lower prevalence of cardiac risk factors at the time of first myocardial infarction and better outcomes compared with those having a first MI from the general population, according to findings from a retrospective study.
In addition, women without breast cancer were younger at the time of first MI compared with survivors, wrote Srikanth Yandrapalli, MD, of New York Medical College, Valhalla, and colleagues. Their report is in the American Journal of Medicine.
The researchers identified 1,644,032 women with a first MI, 56,842 of whom were breast cancer survivors. The team evaluated differences in the prevalence of cardiac risk factors and related outcomes in breast cancer survivors in comparison to the general population.
At baseline, the mean age of subjects with a history of breast cancer was 77 years (range, 11 years), while the mean age of women without breast cancer was 71 years (range, 15 years).
Clinical data were collected from the United States National Inpatient Sample for January 2005 to September 2015. Other outcomes assessed were differences in baseline characteristics and the rate of in-hospital mortality in both groups.
After analysis, the researchers found that breast cancer survivors had a lower prevalence of diabetes mellitus (30.1% vs. 33.1%), obesity (9.4% vs. 13.0%), and smoking (24.1% vs. 27.0%), but higher rates of dyslipidemia (52.7% vs. 48.4%) and hypertension (73.6% vs. 68.1%), compared with women without breast cancer (All P less than .001).
With respect to age, women without breast cancer were 6 years younger than breast cancer survivors at the time of first acute MI (mean age, 71 vs. 77 years; P less than .001).
In addition, the rate of in-hospital mortality was higher in women without breast cancer (7.9%) compared with survivors (7.1%) (P less than .001). After risk adjustment, these results remained unchanged (odds ratio, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.82-0.94).
“Breast cancer survivors in the U.S. are at least 6 years older than the general population of women without breast cancer, and they had a favorable cardiac risk factor profile at the time of first myocardial infarction,” Dr. Yandrapalli and colleagues explained. “The reason for these findings are unclear and hypothesis generating,” they added.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the retrospective design. As a result, the potential effects of residual confounding should be considered when interpreting the results.
“The favorable impact of health education and participation in cancer survivorship programs on these observed differences in breast cancer survivors should be further explored,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Yandrapalli S et al. Am J Med. 2019 Nov 9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.10.018.
Breast cancer survivors may have a lower prevalence of cardiac risk factors at the time of first myocardial infarction and better outcomes compared with those having a first MI from the general population, according to findings from a retrospective study.
In addition, women without breast cancer were younger at the time of first MI compared with survivors, wrote Srikanth Yandrapalli, MD, of New York Medical College, Valhalla, and colleagues. Their report is in the American Journal of Medicine.
The researchers identified 1,644,032 women with a first MI, 56,842 of whom were breast cancer survivors. The team evaluated differences in the prevalence of cardiac risk factors and related outcomes in breast cancer survivors in comparison to the general population.
At baseline, the mean age of subjects with a history of breast cancer was 77 years (range, 11 years), while the mean age of women without breast cancer was 71 years (range, 15 years).
Clinical data were collected from the United States National Inpatient Sample for January 2005 to September 2015. Other outcomes assessed were differences in baseline characteristics and the rate of in-hospital mortality in both groups.
After analysis, the researchers found that breast cancer survivors had a lower prevalence of diabetes mellitus (30.1% vs. 33.1%), obesity (9.4% vs. 13.0%), and smoking (24.1% vs. 27.0%), but higher rates of dyslipidemia (52.7% vs. 48.4%) and hypertension (73.6% vs. 68.1%), compared with women without breast cancer (All P less than .001).
With respect to age, women without breast cancer were 6 years younger than breast cancer survivors at the time of first acute MI (mean age, 71 vs. 77 years; P less than .001).
In addition, the rate of in-hospital mortality was higher in women without breast cancer (7.9%) compared with survivors (7.1%) (P less than .001). After risk adjustment, these results remained unchanged (odds ratio, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.82-0.94).
“Breast cancer survivors in the U.S. are at least 6 years older than the general population of women without breast cancer, and they had a favorable cardiac risk factor profile at the time of first myocardial infarction,” Dr. Yandrapalli and colleagues explained. “The reason for these findings are unclear and hypothesis generating,” they added.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the retrospective design. As a result, the potential effects of residual confounding should be considered when interpreting the results.
“The favorable impact of health education and participation in cancer survivorship programs on these observed differences in breast cancer survivors should be further explored,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Yandrapalli S et al. Am J Med. 2019 Nov 9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.10.018.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Molecule exhibits activity in heavily pretreated, HER2-positive solid tumors
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD – PRS-343, a 4-1BB/HER2 bispecific molecule, has demonstrated safety and antitumor activity in patients with heavily pretreated, HER2-positive solid tumors, an investigator reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer.
In a phase 1 trial of 18 evaluable patients, PRS-343 produced partial responses in 2 patients and enabled 8 patients to maintain stable disease. PRS-343 was considered well tolerated at all doses and schedules tested.
“PRS-343 is a bispecific construct targeting HER2 as well as 4-1BB,” said Geoffrey Y. Ku, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York. “The HER2 component of the molecule localizes it into the tumor microenvironment of any HER2-positive cells. If the density of the HER2 protein is high enough, that facilitates cross-linkage of 4-1BB.
“4-1BB is an immune agonist that’s present in activated T cells, and cross-linkage helps to improve T-cell exhaustion and is also critical for T-cell expansion. The idea is that, by localizing 4-1BB activation to the tumor microenvironment, we can avoid some of the systemic toxicities associated with naked 4-1BB antibodies,” Dr. Ku added.
The ongoing, phase 1 trial of PRS-343 (NCT03330561) has enrolled 53 patients with a range of HER2-positive malignancies. To be eligible, patients must have progressed on standard therapy or have a tumor for which no standard therapy is available.
The most common diagnosis among enrolled patients is gastroesophageal cancer (n = 19), followed by breast cancer (n = 14), gynecologic cancers (n = 6), colorectal cancer (n = 5), and other malignancies.
The patients’ median age at baseline was 61 years (range, 29-92 years), and a majority were female (62%). Most patients (79%) had received three or more prior lines of therapy, including anti-HER2 treatments. Breast cancer patients had received a median of four anti-HER2 treatments, and gastric cancer patients had received a median of two.
The patients have been treated with PRS-343 at 11 dose levels, ranging from 0.0005 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg, given every 3 weeks. The highest dose, 8 mg/kg, was also given every 2 weeks.
Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) included infusion-related reactions (9%), fatigue (9%), chills (6%), flushing (6%), nausea (6%), diarrhea (6%), vomiting (5%), and noncardiac chest pain (4%).
“This was an extremely well-tolerated drug,” Dr. Ku said. “Out of 111 TRAEs, only a tiny proportion were grade 3, and toxicities mostly clustered around infusion-related reactions, constitutional symptoms, as well as gastrointestinal symptoms.”
Grade 3 TRAEs included infusion-related reactions (2%), fatigue (1%), flushing (3%), and noncardiac chest pain (1%). There were no grade 4-5 TRAEs.
At the data cutoff (Oct. 23, 2019), 18 patients were evaluable for a response at active dose levels (2.5 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, and 8 mg/kg).
Two patients achieved a partial response, and eight had stable disease. “This translates to a response rate of 11% and a disease control rate of 55%,” Dr. Ku noted.
Both responders received PRS-343 at 8 mg/kg every 2 weeks. One of these patients had stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma, and one had stage 4 gynecologic carcinoma.
Of the eight patients with stable disease, three received PRS-343 at 8 mg/kg every 2 weeks, two received 8 mg/kg every 3 weeks, one received the 5 mg/kg dose, and two received the 2.5 mg/kg dose.
Dr. Ku noted that the average time on treatment significantly increased in patients who received PRS-343 at 8 mg/kg every 2 weeks. Additionally, both responders and patients with stable disease had a “clear increase” in CD8+ T cells.
“[PRS-343] has demonstrated antitumor activity in heavily pretreated patients across multiple tumor types, and the treatment history, specifically the receipt of prior anti-HER2 therapy, indicates this is a 4-1BB-driven mechanism of action,” Dr. Ku said. “Based on these results, future studies are planned for continued development in defined HER2-positive indications.”
The current study is sponsored by Pieris Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Ku disclosed relationships with Arog Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Merck, Zymeworks, and Pieris Pharmaceuticals.
SOURCE: Ku GY et al. SITC 2019, Abstract O82.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD – PRS-343, a 4-1BB/HER2 bispecific molecule, has demonstrated safety and antitumor activity in patients with heavily pretreated, HER2-positive solid tumors, an investigator reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer.
In a phase 1 trial of 18 evaluable patients, PRS-343 produced partial responses in 2 patients and enabled 8 patients to maintain stable disease. PRS-343 was considered well tolerated at all doses and schedules tested.
“PRS-343 is a bispecific construct targeting HER2 as well as 4-1BB,” said Geoffrey Y. Ku, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York. “The HER2 component of the molecule localizes it into the tumor microenvironment of any HER2-positive cells. If the density of the HER2 protein is high enough, that facilitates cross-linkage of 4-1BB.
“4-1BB is an immune agonist that’s present in activated T cells, and cross-linkage helps to improve T-cell exhaustion and is also critical for T-cell expansion. The idea is that, by localizing 4-1BB activation to the tumor microenvironment, we can avoid some of the systemic toxicities associated with naked 4-1BB antibodies,” Dr. Ku added.
The ongoing, phase 1 trial of PRS-343 (NCT03330561) has enrolled 53 patients with a range of HER2-positive malignancies. To be eligible, patients must have progressed on standard therapy or have a tumor for which no standard therapy is available.
The most common diagnosis among enrolled patients is gastroesophageal cancer (n = 19), followed by breast cancer (n = 14), gynecologic cancers (n = 6), colorectal cancer (n = 5), and other malignancies.
The patients’ median age at baseline was 61 years (range, 29-92 years), and a majority were female (62%). Most patients (79%) had received three or more prior lines of therapy, including anti-HER2 treatments. Breast cancer patients had received a median of four anti-HER2 treatments, and gastric cancer patients had received a median of two.
The patients have been treated with PRS-343 at 11 dose levels, ranging from 0.0005 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg, given every 3 weeks. The highest dose, 8 mg/kg, was also given every 2 weeks.
Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) included infusion-related reactions (9%), fatigue (9%), chills (6%), flushing (6%), nausea (6%), diarrhea (6%), vomiting (5%), and noncardiac chest pain (4%).
“This was an extremely well-tolerated drug,” Dr. Ku said. “Out of 111 TRAEs, only a tiny proportion were grade 3, and toxicities mostly clustered around infusion-related reactions, constitutional symptoms, as well as gastrointestinal symptoms.”
Grade 3 TRAEs included infusion-related reactions (2%), fatigue (1%), flushing (3%), and noncardiac chest pain (1%). There were no grade 4-5 TRAEs.
At the data cutoff (Oct. 23, 2019), 18 patients were evaluable for a response at active dose levels (2.5 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, and 8 mg/kg).
Two patients achieved a partial response, and eight had stable disease. “This translates to a response rate of 11% and a disease control rate of 55%,” Dr. Ku noted.
Both responders received PRS-343 at 8 mg/kg every 2 weeks. One of these patients had stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma, and one had stage 4 gynecologic carcinoma.
Of the eight patients with stable disease, three received PRS-343 at 8 mg/kg every 2 weeks, two received 8 mg/kg every 3 weeks, one received the 5 mg/kg dose, and two received the 2.5 mg/kg dose.
Dr. Ku noted that the average time on treatment significantly increased in patients who received PRS-343 at 8 mg/kg every 2 weeks. Additionally, both responders and patients with stable disease had a “clear increase” in CD8+ T cells.
“[PRS-343] has demonstrated antitumor activity in heavily pretreated patients across multiple tumor types, and the treatment history, specifically the receipt of prior anti-HER2 therapy, indicates this is a 4-1BB-driven mechanism of action,” Dr. Ku said. “Based on these results, future studies are planned for continued development in defined HER2-positive indications.”
The current study is sponsored by Pieris Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Ku disclosed relationships with Arog Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Merck, Zymeworks, and Pieris Pharmaceuticals.
SOURCE: Ku GY et al. SITC 2019, Abstract O82.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD – PRS-343, a 4-1BB/HER2 bispecific molecule, has demonstrated safety and antitumor activity in patients with heavily pretreated, HER2-positive solid tumors, an investigator reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer.
In a phase 1 trial of 18 evaluable patients, PRS-343 produced partial responses in 2 patients and enabled 8 patients to maintain stable disease. PRS-343 was considered well tolerated at all doses and schedules tested.
“PRS-343 is a bispecific construct targeting HER2 as well as 4-1BB,” said Geoffrey Y. Ku, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York. “The HER2 component of the molecule localizes it into the tumor microenvironment of any HER2-positive cells. If the density of the HER2 protein is high enough, that facilitates cross-linkage of 4-1BB.
“4-1BB is an immune agonist that’s present in activated T cells, and cross-linkage helps to improve T-cell exhaustion and is also critical for T-cell expansion. The idea is that, by localizing 4-1BB activation to the tumor microenvironment, we can avoid some of the systemic toxicities associated with naked 4-1BB antibodies,” Dr. Ku added.
The ongoing, phase 1 trial of PRS-343 (NCT03330561) has enrolled 53 patients with a range of HER2-positive malignancies. To be eligible, patients must have progressed on standard therapy or have a tumor for which no standard therapy is available.
The most common diagnosis among enrolled patients is gastroesophageal cancer (n = 19), followed by breast cancer (n = 14), gynecologic cancers (n = 6), colorectal cancer (n = 5), and other malignancies.
The patients’ median age at baseline was 61 years (range, 29-92 years), and a majority were female (62%). Most patients (79%) had received three or more prior lines of therapy, including anti-HER2 treatments. Breast cancer patients had received a median of four anti-HER2 treatments, and gastric cancer patients had received a median of two.
The patients have been treated with PRS-343 at 11 dose levels, ranging from 0.0005 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg, given every 3 weeks. The highest dose, 8 mg/kg, was also given every 2 weeks.
Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) included infusion-related reactions (9%), fatigue (9%), chills (6%), flushing (6%), nausea (6%), diarrhea (6%), vomiting (5%), and noncardiac chest pain (4%).
“This was an extremely well-tolerated drug,” Dr. Ku said. “Out of 111 TRAEs, only a tiny proportion were grade 3, and toxicities mostly clustered around infusion-related reactions, constitutional symptoms, as well as gastrointestinal symptoms.”
Grade 3 TRAEs included infusion-related reactions (2%), fatigue (1%), flushing (3%), and noncardiac chest pain (1%). There were no grade 4-5 TRAEs.
At the data cutoff (Oct. 23, 2019), 18 patients were evaluable for a response at active dose levels (2.5 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, and 8 mg/kg).
Two patients achieved a partial response, and eight had stable disease. “This translates to a response rate of 11% and a disease control rate of 55%,” Dr. Ku noted.
Both responders received PRS-343 at 8 mg/kg every 2 weeks. One of these patients had stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma, and one had stage 4 gynecologic carcinoma.
Of the eight patients with stable disease, three received PRS-343 at 8 mg/kg every 2 weeks, two received 8 mg/kg every 3 weeks, one received the 5 mg/kg dose, and two received the 2.5 mg/kg dose.
Dr. Ku noted that the average time on treatment significantly increased in patients who received PRS-343 at 8 mg/kg every 2 weeks. Additionally, both responders and patients with stable disease had a “clear increase” in CD8+ T cells.
“[PRS-343] has demonstrated antitumor activity in heavily pretreated patients across multiple tumor types, and the treatment history, specifically the receipt of prior anti-HER2 therapy, indicates this is a 4-1BB-driven mechanism of action,” Dr. Ku said. “Based on these results, future studies are planned for continued development in defined HER2-positive indications.”
The current study is sponsored by Pieris Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Ku disclosed relationships with Arog Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Merck, Zymeworks, and Pieris Pharmaceuticals.
SOURCE: Ku GY et al. SITC 2019, Abstract O82.
REPORTING FROM SITC 2019
‘You had me at hello’: ESMO studies confirm survival benefits in NSCLC and breast cancer
In this edition of “How I will treat my next patient,” I highlight two studies that previously reported significant progression-free survival (PFS) improvements and more recently, at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress, overall survival (OS) benefit. I reflect on the significance of these new reports in the wake of previously reported data and guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN).
Osimertinib in advanced NSCLC
In the double-blind, phase 3 FLAURA trial, 556 patients with EGFR-mutated (EGFRm), advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) received osimertinib or a standard tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) as initial treatment. PFS, the primary endpoint, was clinically and statistically better for osimertinib (18.9 months vs. 10.2 months; hazard ratio 0.46; P less than .001), overall and in all major subgroups. There were fewer grade 3-4 adverse events and fewer permanent treatment discontinuations with osimertinib.
At the time of initial publication, OS data were immature, but because of the substantial survival improvements previously noted, osimertinib was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for first-line treatment of EGFRm stage IV NSCLC patients in April 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:113-25).
More recently, at ESMO 2019, Suresh Ramalingam, MD, of the department of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University, Atlanta, and colleagues reported the OS results. Crossover to osimertinib was allowed for patients on the standard TKI arm when they had progressive disease and a T790M mutation. Osimertinib produced a median OS of 38.6 months, compared with 31.8 months for standard TKI (HR, 0.799; P = .0462), a 24-month OS rate of 74% vs. 59% (with no overlap in the 95% confidence intervals), and a 36-month OS rate of 54% vs. 44%. These benefits were interpreted to be statistically significant and clinically meaningful.
The 31.8-month median OS for standard TKI was competitive with the highest reported OS for standard therapy, perhaps because crossover to osimertinib was permitted.
What this means in clinical practice
The report by Dr. Ramalingam and colleagues – and the next abstract I will review – remind me of the famous “You had me at Hello” line from “Jerry Maguire.”
For patient education – and perhaps for some national regulatory agencies – it is good that we now have definition of what the average OS is with osimertinib, compared with standard TKI followed by osimertinib. However, very few oncologists in the United States likely use the latter strategy anymore. It was clear when the impressive PFS and toxicity information appeared in 2018 in the New England Journal of Medicine that osimertinib is the best tolerated, most durably effective front-line treatment for EGFRm mNSCLC, regardless of disease extent, sex, nationality, type of EGFRm (L858R amino acid substitution in exon 21 or exon 19 deletion), or presence/absence of central nervous system metastases.
In NCCN guidelines, osimertinib was listed as the preferred TKI, prior to the OS report at ESMO 2019. The challenges going forward will be to identify high-risk patient subsets who might benefit from drug combinations or novel new agents.
MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib plus fulvestrant
In the MONARCH 2, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial, abemaciclib plus fulvestrant (abema-F) significantly improved PFS, in comparison with placebo plus fulvestrant (placebo-F; 16.9 months vs. 9.3 months; HR, 0.563) in 669 premenopausal (with concurrent ovarian function suppression) and postmenopausal women with metastatic breast cancer (mBC) who had disease progression on one to two lines of prior hormonal therapy (J Clin Oncol. 2017;35[25]:2875-84).
At ESMO 2019, George W. Sledge Jr., MD, of Stanford (Calif.) Medical Center, and colleagues reported the OS results, a secondary endpoint for the trial (JAMA Oncol. 2019 Sep 29. doi. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.4782). At the prespecified interim analysis point, median OS for abema-F was 46.7 months vs. 37.3 months for placebo-F (HR, 0.757; 95% CI 0.505-0.945; P = .0137). Patients with greatest benefit from abema-F were exactly the patients who needed the most help – those with visceral metastases (HR 0.675) and with primary resistance to prior hormonal therapy (HR, 0.686).
At 3 years, at least three times as many patients remained progression free with abema-F, compared with placebo-F, and the abema-F patients experienced prolongation in time to eventual chemotherapy (50.2 months vs. 22.1 months; HR, 0.625).
What this means in clinical practice
Many times I find myself sitting at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and thinking, “Only a medical oncologist like me would find this result exciting.” Prior to ESMO 2019, MONARCH 2 (and a similar study presented at ESMO 2019, MONALEESA-3, which employed an alternative CDK 4/6 inhibitor, ribociclib, with similar OS results) added to the body of literature that caused NCCN guidelines to list all of the approved CDK 4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy for first- or second-line use in patients with hormone-receptor positive, HER2/neu-negative mBC. NCCN guidelines have the caveat that, among patients with disease progression on CDK 4/6 inhibitors in the first-line setting, there are no data to support continuing the CDK 4/6 inhibitor or switching to an alternative CDK 4/6 inhibitor thereafter.
For that shrinking group of patients and doctors who choose to avoid CDK 4/6 inhibitors for first-line treatment, as we describe risks and benefits of using a CDK 4/6 inhibitor for second- or third-line therapy, we have high-quality OS information from ESMO 2019 to answer the “Is it worth it?” question.
Are the results of MONARCH 2 and MONALEESA-3 practice changing? No. We were already convinced. Should we be excited that we have this new information for discussions with our patients? Absolutely.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I will treat my next patient,” I highlight two studies that previously reported significant progression-free survival (PFS) improvements and more recently, at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress, overall survival (OS) benefit. I reflect on the significance of these new reports in the wake of previously reported data and guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN).
Osimertinib in advanced NSCLC
In the double-blind, phase 3 FLAURA trial, 556 patients with EGFR-mutated (EGFRm), advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) received osimertinib or a standard tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) as initial treatment. PFS, the primary endpoint, was clinically and statistically better for osimertinib (18.9 months vs. 10.2 months; hazard ratio 0.46; P less than .001), overall and in all major subgroups. There were fewer grade 3-4 adverse events and fewer permanent treatment discontinuations with osimertinib.
At the time of initial publication, OS data were immature, but because of the substantial survival improvements previously noted, osimertinib was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for first-line treatment of EGFRm stage IV NSCLC patients in April 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:113-25).
More recently, at ESMO 2019, Suresh Ramalingam, MD, of the department of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University, Atlanta, and colleagues reported the OS results. Crossover to osimertinib was allowed for patients on the standard TKI arm when they had progressive disease and a T790M mutation. Osimertinib produced a median OS of 38.6 months, compared with 31.8 months for standard TKI (HR, 0.799; P = .0462), a 24-month OS rate of 74% vs. 59% (with no overlap in the 95% confidence intervals), and a 36-month OS rate of 54% vs. 44%. These benefits were interpreted to be statistically significant and clinically meaningful.
The 31.8-month median OS for standard TKI was competitive with the highest reported OS for standard therapy, perhaps because crossover to osimertinib was permitted.
What this means in clinical practice
The report by Dr. Ramalingam and colleagues – and the next abstract I will review – remind me of the famous “You had me at Hello” line from “Jerry Maguire.”
For patient education – and perhaps for some national regulatory agencies – it is good that we now have definition of what the average OS is with osimertinib, compared with standard TKI followed by osimertinib. However, very few oncologists in the United States likely use the latter strategy anymore. It was clear when the impressive PFS and toxicity information appeared in 2018 in the New England Journal of Medicine that osimertinib is the best tolerated, most durably effective front-line treatment for EGFRm mNSCLC, regardless of disease extent, sex, nationality, type of EGFRm (L858R amino acid substitution in exon 21 or exon 19 deletion), or presence/absence of central nervous system metastases.
In NCCN guidelines, osimertinib was listed as the preferred TKI, prior to the OS report at ESMO 2019. The challenges going forward will be to identify high-risk patient subsets who might benefit from drug combinations or novel new agents.
MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib plus fulvestrant
In the MONARCH 2, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial, abemaciclib plus fulvestrant (abema-F) significantly improved PFS, in comparison with placebo plus fulvestrant (placebo-F; 16.9 months vs. 9.3 months; HR, 0.563) in 669 premenopausal (with concurrent ovarian function suppression) and postmenopausal women with metastatic breast cancer (mBC) who had disease progression on one to two lines of prior hormonal therapy (J Clin Oncol. 2017;35[25]:2875-84).
At ESMO 2019, George W. Sledge Jr., MD, of Stanford (Calif.) Medical Center, and colleagues reported the OS results, a secondary endpoint for the trial (JAMA Oncol. 2019 Sep 29. doi. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.4782). At the prespecified interim analysis point, median OS for abema-F was 46.7 months vs. 37.3 months for placebo-F (HR, 0.757; 95% CI 0.505-0.945; P = .0137). Patients with greatest benefit from abema-F were exactly the patients who needed the most help – those with visceral metastases (HR 0.675) and with primary resistance to prior hormonal therapy (HR, 0.686).
At 3 years, at least three times as many patients remained progression free with abema-F, compared with placebo-F, and the abema-F patients experienced prolongation in time to eventual chemotherapy (50.2 months vs. 22.1 months; HR, 0.625).
What this means in clinical practice
Many times I find myself sitting at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and thinking, “Only a medical oncologist like me would find this result exciting.” Prior to ESMO 2019, MONARCH 2 (and a similar study presented at ESMO 2019, MONALEESA-3, which employed an alternative CDK 4/6 inhibitor, ribociclib, with similar OS results) added to the body of literature that caused NCCN guidelines to list all of the approved CDK 4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy for first- or second-line use in patients with hormone-receptor positive, HER2/neu-negative mBC. NCCN guidelines have the caveat that, among patients with disease progression on CDK 4/6 inhibitors in the first-line setting, there are no data to support continuing the CDK 4/6 inhibitor or switching to an alternative CDK 4/6 inhibitor thereafter.
For that shrinking group of patients and doctors who choose to avoid CDK 4/6 inhibitors for first-line treatment, as we describe risks and benefits of using a CDK 4/6 inhibitor for second- or third-line therapy, we have high-quality OS information from ESMO 2019 to answer the “Is it worth it?” question.
Are the results of MONARCH 2 and MONALEESA-3 practice changing? No. We were already convinced. Should we be excited that we have this new information for discussions with our patients? Absolutely.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I will treat my next patient,” I highlight two studies that previously reported significant progression-free survival (PFS) improvements and more recently, at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress, overall survival (OS) benefit. I reflect on the significance of these new reports in the wake of previously reported data and guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN).
Osimertinib in advanced NSCLC
In the double-blind, phase 3 FLAURA trial, 556 patients with EGFR-mutated (EGFRm), advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) received osimertinib or a standard tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) as initial treatment. PFS, the primary endpoint, was clinically and statistically better for osimertinib (18.9 months vs. 10.2 months; hazard ratio 0.46; P less than .001), overall and in all major subgroups. There were fewer grade 3-4 adverse events and fewer permanent treatment discontinuations with osimertinib.
At the time of initial publication, OS data were immature, but because of the substantial survival improvements previously noted, osimertinib was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for first-line treatment of EGFRm stage IV NSCLC patients in April 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:113-25).
More recently, at ESMO 2019, Suresh Ramalingam, MD, of the department of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University, Atlanta, and colleagues reported the OS results. Crossover to osimertinib was allowed for patients on the standard TKI arm when they had progressive disease and a T790M mutation. Osimertinib produced a median OS of 38.6 months, compared with 31.8 months for standard TKI (HR, 0.799; P = .0462), a 24-month OS rate of 74% vs. 59% (with no overlap in the 95% confidence intervals), and a 36-month OS rate of 54% vs. 44%. These benefits were interpreted to be statistically significant and clinically meaningful.
The 31.8-month median OS for standard TKI was competitive with the highest reported OS for standard therapy, perhaps because crossover to osimertinib was permitted.
What this means in clinical practice
The report by Dr. Ramalingam and colleagues – and the next abstract I will review – remind me of the famous “You had me at Hello” line from “Jerry Maguire.”
For patient education – and perhaps for some national regulatory agencies – it is good that we now have definition of what the average OS is with osimertinib, compared with standard TKI followed by osimertinib. However, very few oncologists in the United States likely use the latter strategy anymore. It was clear when the impressive PFS and toxicity information appeared in 2018 in the New England Journal of Medicine that osimertinib is the best tolerated, most durably effective front-line treatment for EGFRm mNSCLC, regardless of disease extent, sex, nationality, type of EGFRm (L858R amino acid substitution in exon 21 or exon 19 deletion), or presence/absence of central nervous system metastases.
In NCCN guidelines, osimertinib was listed as the preferred TKI, prior to the OS report at ESMO 2019. The challenges going forward will be to identify high-risk patient subsets who might benefit from drug combinations or novel new agents.
MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib plus fulvestrant
In the MONARCH 2, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial, abemaciclib plus fulvestrant (abema-F) significantly improved PFS, in comparison with placebo plus fulvestrant (placebo-F; 16.9 months vs. 9.3 months; HR, 0.563) in 669 premenopausal (with concurrent ovarian function suppression) and postmenopausal women with metastatic breast cancer (mBC) who had disease progression on one to two lines of prior hormonal therapy (J Clin Oncol. 2017;35[25]:2875-84).
At ESMO 2019, George W. Sledge Jr., MD, of Stanford (Calif.) Medical Center, and colleagues reported the OS results, a secondary endpoint for the trial (JAMA Oncol. 2019 Sep 29. doi. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.4782). At the prespecified interim analysis point, median OS for abema-F was 46.7 months vs. 37.3 months for placebo-F (HR, 0.757; 95% CI 0.505-0.945; P = .0137). Patients with greatest benefit from abema-F were exactly the patients who needed the most help – those with visceral metastases (HR 0.675) and with primary resistance to prior hormonal therapy (HR, 0.686).
At 3 years, at least three times as many patients remained progression free with abema-F, compared with placebo-F, and the abema-F patients experienced prolongation in time to eventual chemotherapy (50.2 months vs. 22.1 months; HR, 0.625).
What this means in clinical practice
Many times I find myself sitting at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and thinking, “Only a medical oncologist like me would find this result exciting.” Prior to ESMO 2019, MONARCH 2 (and a similar study presented at ESMO 2019, MONALEESA-3, which employed an alternative CDK 4/6 inhibitor, ribociclib, with similar OS results) added to the body of literature that caused NCCN guidelines to list all of the approved CDK 4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy for first- or second-line use in patients with hormone-receptor positive, HER2/neu-negative mBC. NCCN guidelines have the caveat that, among patients with disease progression on CDK 4/6 inhibitors in the first-line setting, there are no data to support continuing the CDK 4/6 inhibitor or switching to an alternative CDK 4/6 inhibitor thereafter.
For that shrinking group of patients and doctors who choose to avoid CDK 4/6 inhibitors for first-line treatment, as we describe risks and benefits of using a CDK 4/6 inhibitor for second- or third-line therapy, we have high-quality OS information from ESMO 2019 to answer the “Is it worth it?” question.
Are the results of MONARCH 2 and MONALEESA-3 practice changing? No. We were already convinced. Should we be excited that we have this new information for discussions with our patients? Absolutely.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
A progressive exercise intervention improved AGFR in breast cancer survivors
BARCELONA – A progressive aerobic and resistance exercise intervention improved the android:gynoid fat ratio (AGFR) in breast cancer survivors, which could provide important health benefits.
AGFR is associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes in breast cancer survivors, therefore exercise-induced AGFR improvement may reduce the risk for such comorbid conditions, Christina Dieli-Conwright, PhD, of the University of Southern California Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, Los Angeles, and colleagues reported in a poster at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
A significant decrease in AGFR from baseline was noted in 50 survivors of stage I-III breast cancer who participated in the exercise intervention, compared with 50 such survivors randomized to a usual care group (P less than .001), and strong correlations were found between AGFR and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR; r = 0.95; P less than .01), the investigators found.
Study participants had a mean age of 53 years, 54% were overweight (body mass index greater than 25 kg/m2), 63% were Hispanic, 90% had undergone a mastectomy, and 76% received chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Adherence to the intervention, which involved three weekly sessions of supervised, progressive, moderate-to-vigorous aerobic and resistance exercise for 16 weeks, was 95%.
AGFR was calculated using whole-body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and HOMA-IR was calculated using fasting insulin and glucose levels.
“Exercise reduces fat mass in breast cancer survivors, however, few studies have focused on AGFR,” the investigators wrote.
The findings of the current study suggest that a progressive aerobic and resistance exercise intervention is an effective strategy for decreasing AGFR in breast cancer survivors, they concluded.
The National Cancer Institute funded the study. The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Dieli-Conwright C et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract 228P.
BARCELONA – A progressive aerobic and resistance exercise intervention improved the android:gynoid fat ratio (AGFR) in breast cancer survivors, which could provide important health benefits.
AGFR is associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes in breast cancer survivors, therefore exercise-induced AGFR improvement may reduce the risk for such comorbid conditions, Christina Dieli-Conwright, PhD, of the University of Southern California Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, Los Angeles, and colleagues reported in a poster at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
A significant decrease in AGFR from baseline was noted in 50 survivors of stage I-III breast cancer who participated in the exercise intervention, compared with 50 such survivors randomized to a usual care group (P less than .001), and strong correlations were found between AGFR and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR; r = 0.95; P less than .01), the investigators found.
Study participants had a mean age of 53 years, 54% were overweight (body mass index greater than 25 kg/m2), 63% were Hispanic, 90% had undergone a mastectomy, and 76% received chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Adherence to the intervention, which involved three weekly sessions of supervised, progressive, moderate-to-vigorous aerobic and resistance exercise for 16 weeks, was 95%.
AGFR was calculated using whole-body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and HOMA-IR was calculated using fasting insulin and glucose levels.
“Exercise reduces fat mass in breast cancer survivors, however, few studies have focused on AGFR,” the investigators wrote.
The findings of the current study suggest that a progressive aerobic and resistance exercise intervention is an effective strategy for decreasing AGFR in breast cancer survivors, they concluded.
The National Cancer Institute funded the study. The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Dieli-Conwright C et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract 228P.
BARCELONA – A progressive aerobic and resistance exercise intervention improved the android:gynoid fat ratio (AGFR) in breast cancer survivors, which could provide important health benefits.
AGFR is associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes in breast cancer survivors, therefore exercise-induced AGFR improvement may reduce the risk for such comorbid conditions, Christina Dieli-Conwright, PhD, of the University of Southern California Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, Los Angeles, and colleagues reported in a poster at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
A significant decrease in AGFR from baseline was noted in 50 survivors of stage I-III breast cancer who participated in the exercise intervention, compared with 50 such survivors randomized to a usual care group (P less than .001), and strong correlations were found between AGFR and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR; r = 0.95; P less than .01), the investigators found.
Study participants had a mean age of 53 years, 54% were overweight (body mass index greater than 25 kg/m2), 63% were Hispanic, 90% had undergone a mastectomy, and 76% received chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Adherence to the intervention, which involved three weekly sessions of supervised, progressive, moderate-to-vigorous aerobic and resistance exercise for 16 weeks, was 95%.
AGFR was calculated using whole-body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and HOMA-IR was calculated using fasting insulin and glucose levels.
“Exercise reduces fat mass in breast cancer survivors, however, few studies have focused on AGFR,” the investigators wrote.
The findings of the current study suggest that a progressive aerobic and resistance exercise intervention is an effective strategy for decreasing AGFR in breast cancer survivors, they concluded.
The National Cancer Institute funded the study. The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Dieli-Conwright C et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract 228P.
REPORTING FROM ESMO 2019
Bisphosphonates turn 50
ORLANDO – Cumulative evidence over the years has shown that bisphosphonates reduce distant metastases in postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer but that effect does not seem to extend to younger, premenopausal women who may experience adverse effects with bisphosphonates, nor has it been replicated in other types of cancer, such as lung or prostate, Robert Coleman MBBS, MD, said in a presentation marking the 50th anniversary of the publication of the first papers describing the then-new class of drugs.
“We have some science – at least in postmenopausal breast cancer – [showing] that we’re really making a difference, but we don’t understand why it’s not working in the other patients or in the other diseases,” said Dr. Coleman of the University of Sheffield (England) at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Mixed findings in early studies
Early studies showing the metastases-prevention effects of bisphosphonates were with clodronate. In one study, Dr. Coleman said, researchers found that oral clodronate at a dose of 1,600 mg/day as a supplementary treatment to standard treatment for primary, operable breast cancer reduced the risk of bone metastases in a cohort of 1,069 patients with stage 1-3 breast cancer (hazard ratio, 0.692; P = .043) over 5 years (Breast Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15. doi: 10.1186/bcr1384). Another trial, of 302 patients with breast cancer who received oral clodronate at 1,600 mg/day for 2 years, found that 20.4% of patients who received oral clodronate had died by 8.5 years of follow-up, compared with 40.7% of those who did not receive the intervention (Ann Oncol. 2008;19[12]:2007-11).
However, those results were in conflict with findings from an earlier study in which researchers followed patients with breast cancer who received 1,600 mg/day of oral clodronate or placebo for 3 years. They found a similar number of bone metastases in the clodronate and placebo groups (32% and 29%, respectively), as well as a lower overall disease-free survival rate at 10 years for the clodronate group, compared with the placebo group (45% vs. 58%; Acta Oncol. 2004;43[7]:650-6).“For various other reasons, clodronate did not gain traction as a therapeutic strategy in early-stage breast cancer,” said Dr. Coleman, although emerging evidence showed that other bisphosphonate agents were effective in some patients with breast cancer.
In a 2009 article, Gnant et al. reported that premenopausal patients, who underwent primary surgery for stage 1 or stage 2 breast cancer and received standard goserelin therapy for induced menopause and endocrine therapy (either tamoxifen or anastrozole) in addition to treatment with zoledronic acid, had a disease-free survival rate of 94.0% at a median 47.8 months of follow-up (N Eng J Med. 2009;360:679-91). After a median 94.4 months of follow-up, the investigators reported a lower risk of disease progression (HR, 0.77; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.99; P = .042) and death (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.43-1.02; P = .064; Ann Oncol. 2015;26[2]:313-20).
In his own group, Dr. Coleman and colleagues recruited patients with early-stage breast cancer in the AZURE trial, a phase 3 study of 3,360 patients who received standard therapy with or without zoledronic acid 4 mg every 3-4 weeks for 6 doses, followed by 8 doses every 3 months then 5 doses every 6 months (N Eng J Med. 2011;365:1396-405). “We saw no effect,” said Dr. Coleman. “[That was] very different from what was shown by [Dr.] Gnant.”
For a subgroup of postmenopausal patients, Dr. Coleman and colleagues found that the adjusted HR for disease-free survival was 0.82 for women who were more than 5 years postmenopausal (95% CI, 0.67-1.00) at the time of breast cancer and bisphosphonate treatment, but women younger than 40 years had worse survival outcomes at 10 years (HR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.09-2.22) and had a significantly higher risk of death from breast cancer (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.16-2.40; J Bone Oncol. 2018 Sep 27. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008).
Trying to reconcile disparate findings
Those findings left his group with a dilemma, said Dr. Coleman. “Do we start again and run trials, and wait another 10 years, or is there a shortcut to [understanding] what’s going on?” he asked.
In a meta-analysis of all trials from the Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group in 2015 examining adjuvant bisphosphonate treatment and placebo in patients with early-stage breast cancer, intent-to-treat analyses did not show significant benefit after therapy, but postmenopausal women (11,767 women in 36 trials) saw a clear benefit in all recurrence (rate ratio, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.78-0.94), bone recurrence (RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.60-0.86), and breast cancer–related mortality (RR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.93; Lancet. 2015 Jul 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[15]60908-4). The effect seemed to be similar, regardless of bisphosphonate type, with other results seen across trials that used clodronate, zoledronic acid, pamidronate, or ibandronate.
“Although those outcome differences might look quite small for a common disease, that’s a really big effect. Reducing one-sixth of breast cancer deaths at 10 years is the equivalent of saving 10,000 lives across the [European Union], and about half that in the United States,” said Dr. Coleman, noting that guidelines in North America from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the European Society for Medical Oncology now support adjuvant bisphosphonates in postmenopausal patients with breast cancer.
However, bisphosphonates’ effect on breast cancer does not extend to other cancers, such as non–small cell lung cancer or prostate cancer. In other absorption inhibitors such as denosumab, there also seems to be no benefit for patients with breast cancer, including in postmenopausal patient subgroups, said Dr. Coleman. “In my view, osteoclast inhibition is only part of the story,” he noted.
In the AZURE trial, secondary outcomes examined how the transcription factor MAF interacted with menopausal status and treatment with zoledronic acid. The 79% of patients with tumors that were negative for MAF fluorescence in situ hybridization had improved overall survival (0.69; 95% CI, 0.50-0.94), regardless of menopause status (J Bone Oncol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008). “There’s probably a need to merge the treatment: in this case, the bisphosphonate, the biology of the cancer, and the environment the cancer finds itself in,” noted Dr. Coleman.
“From the cancer perspective, he concluded.
Dr. Coleman reports being a paid employee of prIME Oncology (until March 2019); is a consultant for Amgen, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Scandell, and Biocon; is on the speakers bureau for Amgen and Eisai; holds intellectual property rights for a biomarker being developed by Inbiomotion; and is on the scientific advisory board for Inbiomotion.
ORLANDO – Cumulative evidence over the years has shown that bisphosphonates reduce distant metastases in postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer but that effect does not seem to extend to younger, premenopausal women who may experience adverse effects with bisphosphonates, nor has it been replicated in other types of cancer, such as lung or prostate, Robert Coleman MBBS, MD, said in a presentation marking the 50th anniversary of the publication of the first papers describing the then-new class of drugs.
“We have some science – at least in postmenopausal breast cancer – [showing] that we’re really making a difference, but we don’t understand why it’s not working in the other patients or in the other diseases,” said Dr. Coleman of the University of Sheffield (England) at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Mixed findings in early studies
Early studies showing the metastases-prevention effects of bisphosphonates were with clodronate. In one study, Dr. Coleman said, researchers found that oral clodronate at a dose of 1,600 mg/day as a supplementary treatment to standard treatment for primary, operable breast cancer reduced the risk of bone metastases in a cohort of 1,069 patients with stage 1-3 breast cancer (hazard ratio, 0.692; P = .043) over 5 years (Breast Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15. doi: 10.1186/bcr1384). Another trial, of 302 patients with breast cancer who received oral clodronate at 1,600 mg/day for 2 years, found that 20.4% of patients who received oral clodronate had died by 8.5 years of follow-up, compared with 40.7% of those who did not receive the intervention (Ann Oncol. 2008;19[12]:2007-11).
However, those results were in conflict with findings from an earlier study in which researchers followed patients with breast cancer who received 1,600 mg/day of oral clodronate or placebo for 3 years. They found a similar number of bone metastases in the clodronate and placebo groups (32% and 29%, respectively), as well as a lower overall disease-free survival rate at 10 years for the clodronate group, compared with the placebo group (45% vs. 58%; Acta Oncol. 2004;43[7]:650-6).“For various other reasons, clodronate did not gain traction as a therapeutic strategy in early-stage breast cancer,” said Dr. Coleman, although emerging evidence showed that other bisphosphonate agents were effective in some patients with breast cancer.
In a 2009 article, Gnant et al. reported that premenopausal patients, who underwent primary surgery for stage 1 or stage 2 breast cancer and received standard goserelin therapy for induced menopause and endocrine therapy (either tamoxifen or anastrozole) in addition to treatment with zoledronic acid, had a disease-free survival rate of 94.0% at a median 47.8 months of follow-up (N Eng J Med. 2009;360:679-91). After a median 94.4 months of follow-up, the investigators reported a lower risk of disease progression (HR, 0.77; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.99; P = .042) and death (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.43-1.02; P = .064; Ann Oncol. 2015;26[2]:313-20).
In his own group, Dr. Coleman and colleagues recruited patients with early-stage breast cancer in the AZURE trial, a phase 3 study of 3,360 patients who received standard therapy with or without zoledronic acid 4 mg every 3-4 weeks for 6 doses, followed by 8 doses every 3 months then 5 doses every 6 months (N Eng J Med. 2011;365:1396-405). “We saw no effect,” said Dr. Coleman. “[That was] very different from what was shown by [Dr.] Gnant.”
For a subgroup of postmenopausal patients, Dr. Coleman and colleagues found that the adjusted HR for disease-free survival was 0.82 for women who were more than 5 years postmenopausal (95% CI, 0.67-1.00) at the time of breast cancer and bisphosphonate treatment, but women younger than 40 years had worse survival outcomes at 10 years (HR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.09-2.22) and had a significantly higher risk of death from breast cancer (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.16-2.40; J Bone Oncol. 2018 Sep 27. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008).
Trying to reconcile disparate findings
Those findings left his group with a dilemma, said Dr. Coleman. “Do we start again and run trials, and wait another 10 years, or is there a shortcut to [understanding] what’s going on?” he asked.
In a meta-analysis of all trials from the Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group in 2015 examining adjuvant bisphosphonate treatment and placebo in patients with early-stage breast cancer, intent-to-treat analyses did not show significant benefit after therapy, but postmenopausal women (11,767 women in 36 trials) saw a clear benefit in all recurrence (rate ratio, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.78-0.94), bone recurrence (RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.60-0.86), and breast cancer–related mortality (RR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.93; Lancet. 2015 Jul 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[15]60908-4). The effect seemed to be similar, regardless of bisphosphonate type, with other results seen across trials that used clodronate, zoledronic acid, pamidronate, or ibandronate.
“Although those outcome differences might look quite small for a common disease, that’s a really big effect. Reducing one-sixth of breast cancer deaths at 10 years is the equivalent of saving 10,000 lives across the [European Union], and about half that in the United States,” said Dr. Coleman, noting that guidelines in North America from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the European Society for Medical Oncology now support adjuvant bisphosphonates in postmenopausal patients with breast cancer.
However, bisphosphonates’ effect on breast cancer does not extend to other cancers, such as non–small cell lung cancer or prostate cancer. In other absorption inhibitors such as denosumab, there also seems to be no benefit for patients with breast cancer, including in postmenopausal patient subgroups, said Dr. Coleman. “In my view, osteoclast inhibition is only part of the story,” he noted.
In the AZURE trial, secondary outcomes examined how the transcription factor MAF interacted with menopausal status and treatment with zoledronic acid. The 79% of patients with tumors that were negative for MAF fluorescence in situ hybridization had improved overall survival (0.69; 95% CI, 0.50-0.94), regardless of menopause status (J Bone Oncol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008). “There’s probably a need to merge the treatment: in this case, the bisphosphonate, the biology of the cancer, and the environment the cancer finds itself in,” noted Dr. Coleman.
“From the cancer perspective, he concluded.
Dr. Coleman reports being a paid employee of prIME Oncology (until March 2019); is a consultant for Amgen, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Scandell, and Biocon; is on the speakers bureau for Amgen and Eisai; holds intellectual property rights for a biomarker being developed by Inbiomotion; and is on the scientific advisory board for Inbiomotion.
ORLANDO – Cumulative evidence over the years has shown that bisphosphonates reduce distant metastases in postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer but that effect does not seem to extend to younger, premenopausal women who may experience adverse effects with bisphosphonates, nor has it been replicated in other types of cancer, such as lung or prostate, Robert Coleman MBBS, MD, said in a presentation marking the 50th anniversary of the publication of the first papers describing the then-new class of drugs.
“We have some science – at least in postmenopausal breast cancer – [showing] that we’re really making a difference, but we don’t understand why it’s not working in the other patients or in the other diseases,” said Dr. Coleman of the University of Sheffield (England) at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Mixed findings in early studies
Early studies showing the metastases-prevention effects of bisphosphonates were with clodronate. In one study, Dr. Coleman said, researchers found that oral clodronate at a dose of 1,600 mg/day as a supplementary treatment to standard treatment for primary, operable breast cancer reduced the risk of bone metastases in a cohort of 1,069 patients with stage 1-3 breast cancer (hazard ratio, 0.692; P = .043) over 5 years (Breast Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15. doi: 10.1186/bcr1384). Another trial, of 302 patients with breast cancer who received oral clodronate at 1,600 mg/day for 2 years, found that 20.4% of patients who received oral clodronate had died by 8.5 years of follow-up, compared with 40.7% of those who did not receive the intervention (Ann Oncol. 2008;19[12]:2007-11).
However, those results were in conflict with findings from an earlier study in which researchers followed patients with breast cancer who received 1,600 mg/day of oral clodronate or placebo for 3 years. They found a similar number of bone metastases in the clodronate and placebo groups (32% and 29%, respectively), as well as a lower overall disease-free survival rate at 10 years for the clodronate group, compared with the placebo group (45% vs. 58%; Acta Oncol. 2004;43[7]:650-6).“For various other reasons, clodronate did not gain traction as a therapeutic strategy in early-stage breast cancer,” said Dr. Coleman, although emerging evidence showed that other bisphosphonate agents were effective in some patients with breast cancer.
In a 2009 article, Gnant et al. reported that premenopausal patients, who underwent primary surgery for stage 1 or stage 2 breast cancer and received standard goserelin therapy for induced menopause and endocrine therapy (either tamoxifen or anastrozole) in addition to treatment with zoledronic acid, had a disease-free survival rate of 94.0% at a median 47.8 months of follow-up (N Eng J Med. 2009;360:679-91). After a median 94.4 months of follow-up, the investigators reported a lower risk of disease progression (HR, 0.77; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.99; P = .042) and death (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.43-1.02; P = .064; Ann Oncol. 2015;26[2]:313-20).
In his own group, Dr. Coleman and colleagues recruited patients with early-stage breast cancer in the AZURE trial, a phase 3 study of 3,360 patients who received standard therapy with or without zoledronic acid 4 mg every 3-4 weeks for 6 doses, followed by 8 doses every 3 months then 5 doses every 6 months (N Eng J Med. 2011;365:1396-405). “We saw no effect,” said Dr. Coleman. “[That was] very different from what was shown by [Dr.] Gnant.”
For a subgroup of postmenopausal patients, Dr. Coleman and colleagues found that the adjusted HR for disease-free survival was 0.82 for women who were more than 5 years postmenopausal (95% CI, 0.67-1.00) at the time of breast cancer and bisphosphonate treatment, but women younger than 40 years had worse survival outcomes at 10 years (HR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.09-2.22) and had a significantly higher risk of death from breast cancer (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.16-2.40; J Bone Oncol. 2018 Sep 27. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008).
Trying to reconcile disparate findings
Those findings left his group with a dilemma, said Dr. Coleman. “Do we start again and run trials, and wait another 10 years, or is there a shortcut to [understanding] what’s going on?” he asked.
In a meta-analysis of all trials from the Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group in 2015 examining adjuvant bisphosphonate treatment and placebo in patients with early-stage breast cancer, intent-to-treat analyses did not show significant benefit after therapy, but postmenopausal women (11,767 women in 36 trials) saw a clear benefit in all recurrence (rate ratio, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.78-0.94), bone recurrence (RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.60-0.86), and breast cancer–related mortality (RR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.93; Lancet. 2015 Jul 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[15]60908-4). The effect seemed to be similar, regardless of bisphosphonate type, with other results seen across trials that used clodronate, zoledronic acid, pamidronate, or ibandronate.
“Although those outcome differences might look quite small for a common disease, that’s a really big effect. Reducing one-sixth of breast cancer deaths at 10 years is the equivalent of saving 10,000 lives across the [European Union], and about half that in the United States,” said Dr. Coleman, noting that guidelines in North America from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the European Society for Medical Oncology now support adjuvant bisphosphonates in postmenopausal patients with breast cancer.
However, bisphosphonates’ effect on breast cancer does not extend to other cancers, such as non–small cell lung cancer or prostate cancer. In other absorption inhibitors such as denosumab, there also seems to be no benefit for patients with breast cancer, including in postmenopausal patient subgroups, said Dr. Coleman. “In my view, osteoclast inhibition is only part of the story,” he noted.
In the AZURE trial, secondary outcomes examined how the transcription factor MAF interacted with menopausal status and treatment with zoledronic acid. The 79% of patients with tumors that were negative for MAF fluorescence in situ hybridization had improved overall survival (0.69; 95% CI, 0.50-0.94), regardless of menopause status (J Bone Oncol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008). “There’s probably a need to merge the treatment: in this case, the bisphosphonate, the biology of the cancer, and the environment the cancer finds itself in,” noted Dr. Coleman.
“From the cancer perspective, he concluded.
Dr. Coleman reports being a paid employee of prIME Oncology (until March 2019); is a consultant for Amgen, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Scandell, and Biocon; is on the speakers bureau for Amgen and Eisai; holds intellectual property rights for a biomarker being developed by Inbiomotion; and is on the scientific advisory board for Inbiomotion.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ASBMR 2019
Exercise improved QoL, functioning in breast cancer survivors
BARCELONA – A supervised and adapted exercise program improved quality of life, physical functioning, and strength in breast cancer survivors participating in the MAMA MOVE Gaia study.
Of 19 women who initiated participation in the program, which included a 16-week control phase followed by a 16-week exercise training intervention phase, 15 completed the program, and, after the training intervention, they experienced a significant increase in handgrip strength and sit-to-stand repetitions, Ana Joaquim, MD, of Centro Hospitalar de Vila Nova de Gaia/Espinho, Portugal, and colleagues reported in a poster at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
During the control phase of the prospective nonrandomized study, participants experienced no significant changes over time in any domain of quality of life as measured by the EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaire, although a trend toward improved physical functioning was noted at an evaluation performed 8 weeks after the control phase, compared with one performed just prior to the intervention phase (77.3 to 85.3 points, P = .051), the investigators said.
After the intervention phase, however, handgrip strength improved significantly at both the limb where surgery was performed and at the nonoperated limb (from 22.2 to 25.6 kg.f and from 22.6 to 26.9 kg.f). Similar results were observed for a sit-to-stand test (improvement from 12 to 17 repetitions).
Participants in the single-arm clinical trial were assessed after 8 weeks of the control phase, immediately prior to the intervention period, 8 weeks after the control phase, and 16 weeks into the invention phase.
The intervention phase consisted of 3 60-minute sessions per week of combined moderate to vigorous aerobic and strength exercise, defined as exercise at 65%-85% of maximum heart rate or at 6-8 points on the OMNI scale. Mean compliance among the participants was 63.6%.
The participants had a median age of 59 and 15 of the 19 were diagnosed with invasive carcinoma. Following surgery, 13 underwent radiotherapy, 15 received chemotherapy, and 18 received hormone therapy.
“Treatments for early breast cancer have side effects that affect quality of life and cause deconditioning,” the investigators wrote, adding that “physical exercise might have a supportive and coadjuvant role in the rehabilitation of breast cancer survivors.”
The MAMA MOVE trial aimed to assess the potential benefits of a community-based supervised exercise training program, and the findings suggest such programs could help improve quality of life, particularly with respect to physical functioning, they concluded.
The MAMA MOVE Gaia study was funded by Liga Portuguesa Contra o Cancro. The investigators reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Joaquim A et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract 234P.
BARCELONA – A supervised and adapted exercise program improved quality of life, physical functioning, and strength in breast cancer survivors participating in the MAMA MOVE Gaia study.
Of 19 women who initiated participation in the program, which included a 16-week control phase followed by a 16-week exercise training intervention phase, 15 completed the program, and, after the training intervention, they experienced a significant increase in handgrip strength and sit-to-stand repetitions, Ana Joaquim, MD, of Centro Hospitalar de Vila Nova de Gaia/Espinho, Portugal, and colleagues reported in a poster at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
During the control phase of the prospective nonrandomized study, participants experienced no significant changes over time in any domain of quality of life as measured by the EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaire, although a trend toward improved physical functioning was noted at an evaluation performed 8 weeks after the control phase, compared with one performed just prior to the intervention phase (77.3 to 85.3 points, P = .051), the investigators said.
After the intervention phase, however, handgrip strength improved significantly at both the limb where surgery was performed and at the nonoperated limb (from 22.2 to 25.6 kg.f and from 22.6 to 26.9 kg.f). Similar results were observed for a sit-to-stand test (improvement from 12 to 17 repetitions).
Participants in the single-arm clinical trial were assessed after 8 weeks of the control phase, immediately prior to the intervention period, 8 weeks after the control phase, and 16 weeks into the invention phase.
The intervention phase consisted of 3 60-minute sessions per week of combined moderate to vigorous aerobic and strength exercise, defined as exercise at 65%-85% of maximum heart rate or at 6-8 points on the OMNI scale. Mean compliance among the participants was 63.6%.
The participants had a median age of 59 and 15 of the 19 were diagnosed with invasive carcinoma. Following surgery, 13 underwent radiotherapy, 15 received chemotherapy, and 18 received hormone therapy.
“Treatments for early breast cancer have side effects that affect quality of life and cause deconditioning,” the investigators wrote, adding that “physical exercise might have a supportive and coadjuvant role in the rehabilitation of breast cancer survivors.”
The MAMA MOVE trial aimed to assess the potential benefits of a community-based supervised exercise training program, and the findings suggest such programs could help improve quality of life, particularly with respect to physical functioning, they concluded.
The MAMA MOVE Gaia study was funded by Liga Portuguesa Contra o Cancro. The investigators reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Joaquim A et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract 234P.
BARCELONA – A supervised and adapted exercise program improved quality of life, physical functioning, and strength in breast cancer survivors participating in the MAMA MOVE Gaia study.
Of 19 women who initiated participation in the program, which included a 16-week control phase followed by a 16-week exercise training intervention phase, 15 completed the program, and, after the training intervention, they experienced a significant increase in handgrip strength and sit-to-stand repetitions, Ana Joaquim, MD, of Centro Hospitalar de Vila Nova de Gaia/Espinho, Portugal, and colleagues reported in a poster at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
During the control phase of the prospective nonrandomized study, participants experienced no significant changes over time in any domain of quality of life as measured by the EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaire, although a trend toward improved physical functioning was noted at an evaluation performed 8 weeks after the control phase, compared with one performed just prior to the intervention phase (77.3 to 85.3 points, P = .051), the investigators said.
After the intervention phase, however, handgrip strength improved significantly at both the limb where surgery was performed and at the nonoperated limb (from 22.2 to 25.6 kg.f and from 22.6 to 26.9 kg.f). Similar results were observed for a sit-to-stand test (improvement from 12 to 17 repetitions).
Participants in the single-arm clinical trial were assessed after 8 weeks of the control phase, immediately prior to the intervention period, 8 weeks after the control phase, and 16 weeks into the invention phase.
The intervention phase consisted of 3 60-minute sessions per week of combined moderate to vigorous aerobic and strength exercise, defined as exercise at 65%-85% of maximum heart rate or at 6-8 points on the OMNI scale. Mean compliance among the participants was 63.6%.
The participants had a median age of 59 and 15 of the 19 were diagnosed with invasive carcinoma. Following surgery, 13 underwent radiotherapy, 15 received chemotherapy, and 18 received hormone therapy.
“Treatments for early breast cancer have side effects that affect quality of life and cause deconditioning,” the investigators wrote, adding that “physical exercise might have a supportive and coadjuvant role in the rehabilitation of breast cancer survivors.”
The MAMA MOVE trial aimed to assess the potential benefits of a community-based supervised exercise training program, and the findings suggest such programs could help improve quality of life, particularly with respect to physical functioning, they concluded.
The MAMA MOVE Gaia study was funded by Liga Portuguesa Contra o Cancro. The investigators reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Joaquim A et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract 234P.
REPORTING FROM ESMO 2019