User login
Circadian rhythm changes linked to future Parkinson’s disease risk
a new study suggests. “We found that men with abnormal circadian rhythms had three times the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease over an 11-year follow-up period,” lead author, Yue Leng, MD, University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
“If confirmed to be a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease, then circadian rhythmicity could be a promising intervention target and will open new opportunities for the prevention and management of Parkinson’s disease,” the researchers concluded.
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology on June 15.
Circadian disruption is very common in neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, but there isn’t much information on how it may predict the disease, Dr. Leng explained. “We wanted to see whether circadian abnormalities may predict Parkinson’s disease,” she said. “Parkinson’s disease has a long prodromal phase where brain changes have started to occur but no clinical symptoms have become evident. It would be useful to be able to identify these patients, and maybe changes in circadian rhythms may help us to do that,” she added.
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from 2,930 community-dwelling men aged 65 years or older (mean age, 76 years) who participated in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study, in which they underwent comprehensive sleep and rest-activity rhythms assessment. “Patterns of rest and activity were measured with an actigraph device, which is worn on the wrist like a watch and captures movements which are translated into a rest-activity rhythm model – one of the most commonly used and evidence-based measures of circadian rhythm,” Dr. Leng said. Men were asked to wear the actigraphs continuously for a minimum of three 24-hour periods.
Results showed that 78 men (2.7%) developed Parkinson’s disease during the 11-year follow-up. After accounting for all covariates, the risk of Parkinson’s disease increased with decreasing circadian amplitude (strength of the rhythm) with an odds ratio of 1.77 per each decrease by one standard deviation; mesor (mean level of activity) with an odds ratio of 1.64; or robustness (how closely activity follows a 24-hour pattern) with an odds ratio of 1.54.
Those in the lowest quartile of amplitude, mesor, or robustness had approximately three times the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease compared with those in the highest quartile of amplitude. The association remained after further adjustment for nighttime sleep disturbances.
“It has previously been shown that daytime napping has been linked to risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. Now we have shown that abnormalities in the overall 24-hour circadian rest activity rhythm are also present in the prodromal phase of Parkinson’s disease, and this association was independent of several confounders, including nighttime sleep disturbances,” Dr. Leng said.
“This raises awareness of the importance of circadian rhythm in older individuals and changes in their 24-hour pattern of behavior could be an early signal of Parkinson’s disease,” she said.
“This study does not tell us whether these circadian changes are causal for Parkinson’s or not,” Dr. Leng noted.
Future studies are needed to explore underlying mechanisms and to determine whether circadian disruption itself might contribute to the development of Parkinson’s disease, the researchers said.
“If there is a causal link, then using techniques to improve circadian rhythm could help to prevent or slow the onset of Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Leng suggested. There are many established therapies that act on circadian rhythm including bright light therapy, melatonin, and chronotherapy, she added.
Support for this study was provided by the National Institute on Aging (NIA); the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases; the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the Weill Pilot Award. Dr. Leng reported grants from the NIA and the University of California, San Francisco, Weill Institute for Neurosciences during the conduct of the study; and grants from Global Brain Health Institute, the Alzheimer’s Association, and the Alzheimer’s Society outside the submitted work.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
a new study suggests. “We found that men with abnormal circadian rhythms had three times the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease over an 11-year follow-up period,” lead author, Yue Leng, MD, University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
“If confirmed to be a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease, then circadian rhythmicity could be a promising intervention target and will open new opportunities for the prevention and management of Parkinson’s disease,” the researchers concluded.
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology on June 15.
Circadian disruption is very common in neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, but there isn’t much information on how it may predict the disease, Dr. Leng explained. “We wanted to see whether circadian abnormalities may predict Parkinson’s disease,” she said. “Parkinson’s disease has a long prodromal phase where brain changes have started to occur but no clinical symptoms have become evident. It would be useful to be able to identify these patients, and maybe changes in circadian rhythms may help us to do that,” she added.
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from 2,930 community-dwelling men aged 65 years or older (mean age, 76 years) who participated in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study, in which they underwent comprehensive sleep and rest-activity rhythms assessment. “Patterns of rest and activity were measured with an actigraph device, which is worn on the wrist like a watch and captures movements which are translated into a rest-activity rhythm model – one of the most commonly used and evidence-based measures of circadian rhythm,” Dr. Leng said. Men were asked to wear the actigraphs continuously for a minimum of three 24-hour periods.
Results showed that 78 men (2.7%) developed Parkinson’s disease during the 11-year follow-up. After accounting for all covariates, the risk of Parkinson’s disease increased with decreasing circadian amplitude (strength of the rhythm) with an odds ratio of 1.77 per each decrease by one standard deviation; mesor (mean level of activity) with an odds ratio of 1.64; or robustness (how closely activity follows a 24-hour pattern) with an odds ratio of 1.54.
Those in the lowest quartile of amplitude, mesor, or robustness had approximately three times the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease compared with those in the highest quartile of amplitude. The association remained after further adjustment for nighttime sleep disturbances.
“It has previously been shown that daytime napping has been linked to risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. Now we have shown that abnormalities in the overall 24-hour circadian rest activity rhythm are also present in the prodromal phase of Parkinson’s disease, and this association was independent of several confounders, including nighttime sleep disturbances,” Dr. Leng said.
“This raises awareness of the importance of circadian rhythm in older individuals and changes in their 24-hour pattern of behavior could be an early signal of Parkinson’s disease,” she said.
“This study does not tell us whether these circadian changes are causal for Parkinson’s or not,” Dr. Leng noted.
Future studies are needed to explore underlying mechanisms and to determine whether circadian disruption itself might contribute to the development of Parkinson’s disease, the researchers said.
“If there is a causal link, then using techniques to improve circadian rhythm could help to prevent or slow the onset of Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Leng suggested. There are many established therapies that act on circadian rhythm including bright light therapy, melatonin, and chronotherapy, she added.
Support for this study was provided by the National Institute on Aging (NIA); the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases; the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the Weill Pilot Award. Dr. Leng reported grants from the NIA and the University of California, San Francisco, Weill Institute for Neurosciences during the conduct of the study; and grants from Global Brain Health Institute, the Alzheimer’s Association, and the Alzheimer’s Society outside the submitted work.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
a new study suggests. “We found that men with abnormal circadian rhythms had three times the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease over an 11-year follow-up period,” lead author, Yue Leng, MD, University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
“If confirmed to be a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease, then circadian rhythmicity could be a promising intervention target and will open new opportunities for the prevention and management of Parkinson’s disease,” the researchers concluded.
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology on June 15.
Circadian disruption is very common in neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, but there isn’t much information on how it may predict the disease, Dr. Leng explained. “We wanted to see whether circadian abnormalities may predict Parkinson’s disease,” she said. “Parkinson’s disease has a long prodromal phase where brain changes have started to occur but no clinical symptoms have become evident. It would be useful to be able to identify these patients, and maybe changes in circadian rhythms may help us to do that,” she added.
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from 2,930 community-dwelling men aged 65 years or older (mean age, 76 years) who participated in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study, in which they underwent comprehensive sleep and rest-activity rhythms assessment. “Patterns of rest and activity were measured with an actigraph device, which is worn on the wrist like a watch and captures movements which are translated into a rest-activity rhythm model – one of the most commonly used and evidence-based measures of circadian rhythm,” Dr. Leng said. Men were asked to wear the actigraphs continuously for a minimum of three 24-hour periods.
Results showed that 78 men (2.7%) developed Parkinson’s disease during the 11-year follow-up. After accounting for all covariates, the risk of Parkinson’s disease increased with decreasing circadian amplitude (strength of the rhythm) with an odds ratio of 1.77 per each decrease by one standard deviation; mesor (mean level of activity) with an odds ratio of 1.64; or robustness (how closely activity follows a 24-hour pattern) with an odds ratio of 1.54.
Those in the lowest quartile of amplitude, mesor, or robustness had approximately three times the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease compared with those in the highest quartile of amplitude. The association remained after further adjustment for nighttime sleep disturbances.
“It has previously been shown that daytime napping has been linked to risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. Now we have shown that abnormalities in the overall 24-hour circadian rest activity rhythm are also present in the prodromal phase of Parkinson’s disease, and this association was independent of several confounders, including nighttime sleep disturbances,” Dr. Leng said.
“This raises awareness of the importance of circadian rhythm in older individuals and changes in their 24-hour pattern of behavior could be an early signal of Parkinson’s disease,” she said.
“This study does not tell us whether these circadian changes are causal for Parkinson’s or not,” Dr. Leng noted.
Future studies are needed to explore underlying mechanisms and to determine whether circadian disruption itself might contribute to the development of Parkinson’s disease, the researchers said.
“If there is a causal link, then using techniques to improve circadian rhythm could help to prevent or slow the onset of Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Leng suggested. There are many established therapies that act on circadian rhythm including bright light therapy, melatonin, and chronotherapy, she added.
Support for this study was provided by the National Institute on Aging (NIA); the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases; the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the Weill Pilot Award. Dr. Leng reported grants from the NIA and the University of California, San Francisco, Weill Institute for Neurosciences during the conduct of the study; and grants from Global Brain Health Institute, the Alzheimer’s Association, and the Alzheimer’s Society outside the submitted work.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
FDA gives thumbs up to tazemetostat for follicular lymphoma
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted accelerated approval of the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat (Tazverik, Epizyme, Inc) for the treatment of relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma in adult patients with tumors harboring an EZH2 mutation.
Eligible patients must have already received at least two prior systemic therapies and have tumors that are positive for an EZH2 mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test. The FDA has also approved the cobas EZH2 Mutation Test (Roche Molecular Systems, Inc) as a companion diagnostic test for tazemetostat.
The new indication is also for adult patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma who have no other satisfactory alternative treatment options.
“In our view, there remains no clear standard of care in the relapsed and/or refractory [follicular lymphoma] population, as not all patients benefit from today’s available therapies,” said Shefali Agarwal, MD, chief medical officer of Epizyme, in a company press release. “Based on this label, physicians will have the ability to use their clinical discretion to prescribe tazemetostat for their relapsed or refractory patients regardless of EZH2 mutational status and without regard to a specific line of treatment where other options are not satisfactory.”
This accelerated approval is based on overall response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for these indications may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials, the FDA notes.
Tazemetostat acts as an inhibitor of EZH2 methyltransferase. Earlier this year, the drug was approved for the treatment of metastatic or locally advanced epithelioid sarcoma in cases in which complete resection is not possible. It is the first drug with this mechanism of action and is the first to be indicated for epithelioid sarcoma.
Promising Efficacy in Phase 2 Trial
The new approval for use in follicular lymphoma was based on results from an open-label, single-arm, multicenter phase 2 clinical trial involving patients who had experienced disease progression after being treated with at least two prior systemic regimens. The cohort was divided into two treatment groups: One group consisted of 45 patients with EZH2-activating mutations, the other included 54 patients with wild-type EZH2.
All patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg administered orally twice a day. The primary efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate and duration of response, in accordance with International Working Group Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma criteria.
The median duration of follow-up was 22 months for patients with EZH2-activating mutations and 36 months for those with wild-type tumors.
Among the 45 patients with an EZH2-activating mutation, the median number of lines of prior systemic therapy was 2.0 (range, 1 – 11). In 49% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 49%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate was 69%; 12% of patients achieved a complete response, and 57% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 10.9 months and ongoing.
In the cohort of 54 patients with wild-type EZH2, the median number previous therapies was 3.0 (range, 1 – 8); in 59% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 41%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate to tazemetostat treatment was 34%; 4% of patients achieved a complete response, and 30% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 13 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients. The most common were fatigue, upper respiratory tract infection, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, and abdominal pain. Eight patients (8%) discontinued treatment during the trial because of adverse events. There were no reported deaths. No black box warnings have been published, and there are no contraindications.
“The durable responses observed with this drug are notable in the context of the safety profile and route of oral, at-home administration, and will offer an important new option for physicians as we care for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma,” said John Leonard, MD, in a company press release. He is associate dean for clinical research and Richard T. Silver Distinguished Professor of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Meyer Cancer Center, Weill Cornell Medicine and New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and an investigator in the ongoing phase 1b/3 confirmatory trial for tazemetostat.
“Follicular lymphoma remains an incurable disease, and even with the availability of new drugs in recent years, there have remained important unmet needs in the treatment of follicular lymphoma,” he commented.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted accelerated approval of the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat (Tazverik, Epizyme, Inc) for the treatment of relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma in adult patients with tumors harboring an EZH2 mutation.
Eligible patients must have already received at least two prior systemic therapies and have tumors that are positive for an EZH2 mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test. The FDA has also approved the cobas EZH2 Mutation Test (Roche Molecular Systems, Inc) as a companion diagnostic test for tazemetostat.
The new indication is also for adult patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma who have no other satisfactory alternative treatment options.
“In our view, there remains no clear standard of care in the relapsed and/or refractory [follicular lymphoma] population, as not all patients benefit from today’s available therapies,” said Shefali Agarwal, MD, chief medical officer of Epizyme, in a company press release. “Based on this label, physicians will have the ability to use their clinical discretion to prescribe tazemetostat for their relapsed or refractory patients regardless of EZH2 mutational status and without regard to a specific line of treatment where other options are not satisfactory.”
This accelerated approval is based on overall response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for these indications may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials, the FDA notes.
Tazemetostat acts as an inhibitor of EZH2 methyltransferase. Earlier this year, the drug was approved for the treatment of metastatic or locally advanced epithelioid sarcoma in cases in which complete resection is not possible. It is the first drug with this mechanism of action and is the first to be indicated for epithelioid sarcoma.
Promising Efficacy in Phase 2 Trial
The new approval for use in follicular lymphoma was based on results from an open-label, single-arm, multicenter phase 2 clinical trial involving patients who had experienced disease progression after being treated with at least two prior systemic regimens. The cohort was divided into two treatment groups: One group consisted of 45 patients with EZH2-activating mutations, the other included 54 patients with wild-type EZH2.
All patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg administered orally twice a day. The primary efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate and duration of response, in accordance with International Working Group Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma criteria.
The median duration of follow-up was 22 months for patients with EZH2-activating mutations and 36 months for those with wild-type tumors.
Among the 45 patients with an EZH2-activating mutation, the median number of lines of prior systemic therapy was 2.0 (range, 1 – 11). In 49% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 49%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate was 69%; 12% of patients achieved a complete response, and 57% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 10.9 months and ongoing.
In the cohort of 54 patients with wild-type EZH2, the median number previous therapies was 3.0 (range, 1 – 8); in 59% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 41%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate to tazemetostat treatment was 34%; 4% of patients achieved a complete response, and 30% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 13 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients. The most common were fatigue, upper respiratory tract infection, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, and abdominal pain. Eight patients (8%) discontinued treatment during the trial because of adverse events. There were no reported deaths. No black box warnings have been published, and there are no contraindications.
“The durable responses observed with this drug are notable in the context of the safety profile and route of oral, at-home administration, and will offer an important new option for physicians as we care for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma,” said John Leonard, MD, in a company press release. He is associate dean for clinical research and Richard T. Silver Distinguished Professor of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Meyer Cancer Center, Weill Cornell Medicine and New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and an investigator in the ongoing phase 1b/3 confirmatory trial for tazemetostat.
“Follicular lymphoma remains an incurable disease, and even with the availability of new drugs in recent years, there have remained important unmet needs in the treatment of follicular lymphoma,” he commented.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted accelerated approval of the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat (Tazverik, Epizyme, Inc) for the treatment of relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma in adult patients with tumors harboring an EZH2 mutation.
Eligible patients must have already received at least two prior systemic therapies and have tumors that are positive for an EZH2 mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test. The FDA has also approved the cobas EZH2 Mutation Test (Roche Molecular Systems, Inc) as a companion diagnostic test for tazemetostat.
The new indication is also for adult patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma who have no other satisfactory alternative treatment options.
“In our view, there remains no clear standard of care in the relapsed and/or refractory [follicular lymphoma] population, as not all patients benefit from today’s available therapies,” said Shefali Agarwal, MD, chief medical officer of Epizyme, in a company press release. “Based on this label, physicians will have the ability to use their clinical discretion to prescribe tazemetostat for their relapsed or refractory patients regardless of EZH2 mutational status and without regard to a specific line of treatment where other options are not satisfactory.”
This accelerated approval is based on overall response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for these indications may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials, the FDA notes.
Tazemetostat acts as an inhibitor of EZH2 methyltransferase. Earlier this year, the drug was approved for the treatment of metastatic or locally advanced epithelioid sarcoma in cases in which complete resection is not possible. It is the first drug with this mechanism of action and is the first to be indicated for epithelioid sarcoma.
Promising Efficacy in Phase 2 Trial
The new approval for use in follicular lymphoma was based on results from an open-label, single-arm, multicenter phase 2 clinical trial involving patients who had experienced disease progression after being treated with at least two prior systemic regimens. The cohort was divided into two treatment groups: One group consisted of 45 patients with EZH2-activating mutations, the other included 54 patients with wild-type EZH2.
All patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg administered orally twice a day. The primary efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate and duration of response, in accordance with International Working Group Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma criteria.
The median duration of follow-up was 22 months for patients with EZH2-activating mutations and 36 months for those with wild-type tumors.
Among the 45 patients with an EZH2-activating mutation, the median number of lines of prior systemic therapy was 2.0 (range, 1 – 11). In 49% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 49%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate was 69%; 12% of patients achieved a complete response, and 57% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 10.9 months and ongoing.
In the cohort of 54 patients with wild-type EZH2, the median number previous therapies was 3.0 (range, 1 – 8); in 59% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 41%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate to tazemetostat treatment was 34%; 4% of patients achieved a complete response, and 30% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 13 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients. The most common were fatigue, upper respiratory tract infection, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, and abdominal pain. Eight patients (8%) discontinued treatment during the trial because of adverse events. There were no reported deaths. No black box warnings have been published, and there are no contraindications.
“The durable responses observed with this drug are notable in the context of the safety profile and route of oral, at-home administration, and will offer an important new option for physicians as we care for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma,” said John Leonard, MD, in a company press release. He is associate dean for clinical research and Richard T. Silver Distinguished Professor of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Meyer Cancer Center, Weill Cornell Medicine and New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and an investigator in the ongoing phase 1b/3 confirmatory trial for tazemetostat.
“Follicular lymphoma remains an incurable disease, and even with the availability of new drugs in recent years, there have remained important unmet needs in the treatment of follicular lymphoma,” he commented.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New EPOCH for adult patients with Burkitt lymphoma
Adult patients with Burkitt lymphoma can achieve equally sound survival outcomes with dose-adjusted chemotherapy versus high-intensity regimens, but can do so while avoiding the severe toxicities, U.S. study data shows.
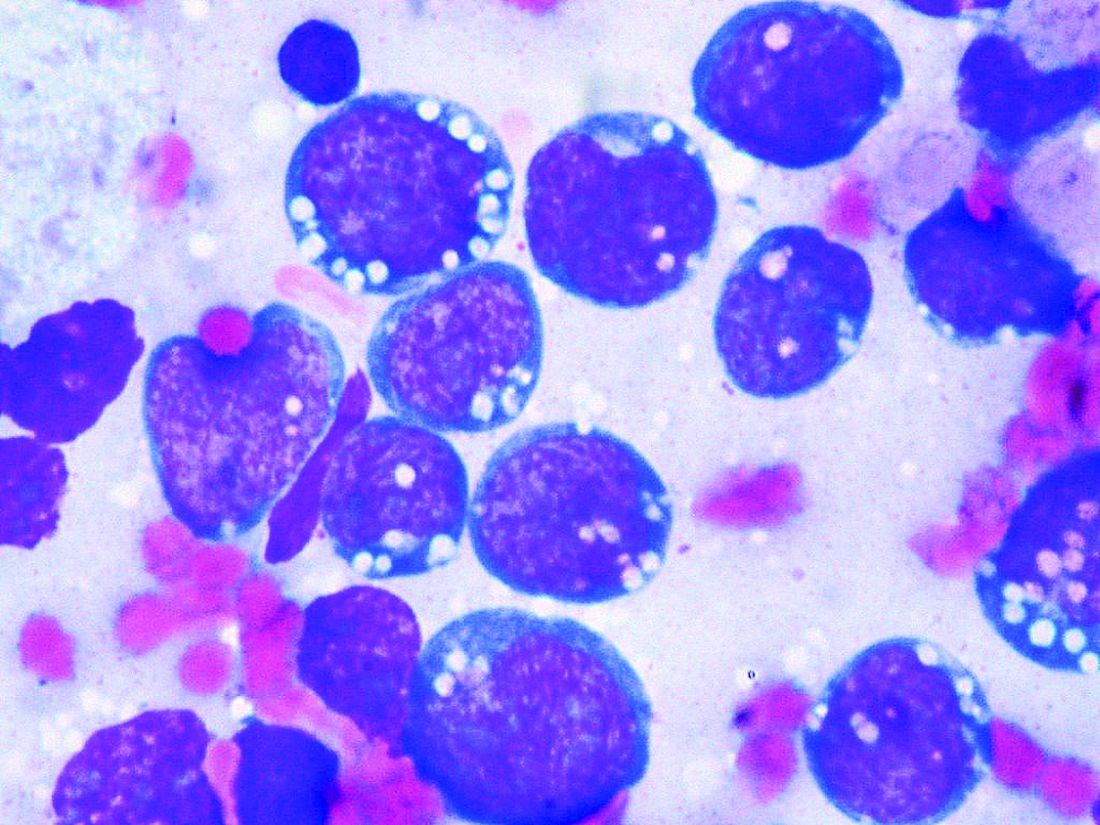
Although Burkitt lymphoma is the most common B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children, it accounts for only 1% to 2% of adult lymphoma cases.
Highly dose-intensive chemotherapy regimens, developed for children and young adults, have rendered the disease curable. But older patients in particular, and patients with comorbidities such as HIV, can suffer severe adverse effects, as well as late sequelae like second malignancies.
Mark Roschewski, MD, from the lymphoid malignancies branch at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md., and colleagues therefore examined whether a dose-adjusted regimen would maintain outcomes while reducing toxicities.
Tailoring treatment with etoposide, doxorubicin, and vincristine with prednisone, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (EPOCH-R) to whether patients had high- or low-risk disease, they achieved 4-year survival rates of higher than 85%.
The research, published by the Journal of Clinical Oncology, also showed that patients taking the regimen, which was well tolerated, had low rates of relapse in the central nervous system.
The team reports that their results with the dose-adjusted regimen “significantly improve on the complexity, cost, and toxicity profile of other regimens,” also highlighting that it is administered on an outpatient basis.
As the outcomes also “compare favorably” with those with high intensity regimens, they say the findings “support our treatment strategies to ameliorate toxicity while maintaining efficacy.”
Importantly, they suggest highly dose-intensive chemotherapy is unnecessary for cure, and carefully defined low-risk patients may be treated with limited chemotherapy.
Dr. Roschewski said in an interview that, in patients aged 40 years and older, dose-adjusted EPOCH-R is “probably the preferred choice,” despite its “weakness” in controlling the disease in patients with active CNS involvement.
However, the “real question” is what to use in younger patients, Dr. Roschewski said, as the “unknown” is whether the additional magnitude of a high-intensity regimen that “gets into the CNS” outweighs the risk of toxicities.
“What was important about our study,” he said, was that patients with CNS involvement “did the worst but it was equally split among patients that died of toxicity and patients that progressed.”
In other words, each choice increases one risk while decreasing another. “So I would have to have that discussion with the patient, and individual patient decisions are typically based on the details,” said Dr. Roschewski.
One issue, however, that could limit the adoption of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R is that, without a randomized study comparing it directly with a high-intensity regimen, clinicians may to stick to what they know.
Dr. Roschewski said that “this is particularly true of more experienced clinicians.”
“They’re less likely, I think, to adopt something else outside of a randomized study because our natural inclination with this disease has always been dose intensity is critical. ... This is a dogma, and to shift from that probably does require a higher level of evidence, at least for some practitioners,” he explained.
Further study details
Following a pilot study of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R in 30 adult patients in which the authors say the regimen showed “high efficacy,” they enrolled 113 patients with untreated Burkitt lymphoma at 22 centers between June 2010 and May 2017.
The patients were divided into low-risk and high-risk categories, with low-risk defined as stage 1 or 2 disease, normal lactate dehydrogenase levels, ECOG performance status ≤ 1, and no tumor mass ≥ 7 cm.
High-risk patients were given six cycles of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R (with rituximab on day 1 only) along with CNS prophylaxis or active therapy with intrathecal methotrexate.
In contrast, low-risk patients were given two cycles of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R, with rituximab on days 1 and 5, followed by positron emission tomography.
If that was negative, the patients had one additional treatment cycle and no CNS prophylaxis, but if it was positive, they were given four additional cycles, plus intrathecal methotrexate.
Of the 113 patients enrolled, 79% were male, median age was 49 years, and 62% were aged at least 40 years, including 26% aged at least 60 years.
The team determined that 13% of the patients were of low risk, 87% were high risk, and 11% had cerebrospinal fluid involvement. One-quarter (24.7%) were HIV positive, with a median CD4+ T-cell count of 268 cells/mm3.
The majority (87%) of low-risk patients received three treatment cycles, and 82% of high-risk patents were administered six treatment cycles.
Over a median follow-up of 58.7 months (4.9 years), the 4-year event-free survival (EFS) rate across the whole cohort was 84.5% and overall survival was 87%.
At the time of analysis, all low-risk patients were in remission; among high-risk patients, the 4-year EFS was 82.1% and overall survival was 84.9%.
The team reports that treatment was equally effective across age groups, and irrespective of HIV status and International Prognostic Index risk group.
Only 2% of high-risk patients with no pretreatment evidence of CNS involvement had relapses in the brain parenchyma. Just over half (55%) of patients with cerebrospinal fluid involvement at presentation experienced disease progression or died.
Five patients died of treatment-related toxicity. Grade 3/4 thrombocytopenia occurred during 17% of cycles, and febrile neutropenia was seen during 16%. Tumor lysis syndrome was rare, occurring in 5% of patients.
Next, the researchers are planning on focusing on CNS disease, looking at EPOCH-R as the backbone and adding intrathecal methotrexate and an additional targeted agent with known CNS penetration.
Dr. Roschewski said that is “a very attractive strategy and ... we will initiate enrollment in that study probably in the next couple of months here at the NCI,” he added, noting that it will be an early phase 1 study.
Another issue he identified that “doesn’t get spoken about quite as much but I do think is important is potentially working on supportive care guidelines for how we manage these patients.” Dr. Roschewski explained, “One of the things you see over and over in these Burkitt lymphoma studies is that some patients don’t make it through therapy because they’re so sick at the beginning, and they have certain risks.
“I think simply improving that type of care, independent of what regimen is used, can potentially improve the outcomes across patient groups.”
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, AIDS Malignancy Consortium, and the Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program and Lymphoid Malignancies Branch. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Adult patients with Burkitt lymphoma can achieve equally sound survival outcomes with dose-adjusted chemotherapy versus high-intensity regimens, but can do so while avoiding the severe toxicities, U.S. study data shows.

Although Burkitt lymphoma is the most common B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children, it accounts for only 1% to 2% of adult lymphoma cases.
Highly dose-intensive chemotherapy regimens, developed for children and young adults, have rendered the disease curable. But older patients in particular, and patients with comorbidities such as HIV, can suffer severe adverse effects, as well as late sequelae like second malignancies.
Mark Roschewski, MD, from the lymphoid malignancies branch at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md., and colleagues therefore examined whether a dose-adjusted regimen would maintain outcomes while reducing toxicities.
Tailoring treatment with etoposide, doxorubicin, and vincristine with prednisone, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (EPOCH-R) to whether patients had high- or low-risk disease, they achieved 4-year survival rates of higher than 85%.
The research, published by the Journal of Clinical Oncology, also showed that patients taking the regimen, which was well tolerated, had low rates of relapse in the central nervous system.
The team reports that their results with the dose-adjusted regimen “significantly improve on the complexity, cost, and toxicity profile of other regimens,” also highlighting that it is administered on an outpatient basis.
As the outcomes also “compare favorably” with those with high intensity regimens, they say the findings “support our treatment strategies to ameliorate toxicity while maintaining efficacy.”
Importantly, they suggest highly dose-intensive chemotherapy is unnecessary for cure, and carefully defined low-risk patients may be treated with limited chemotherapy.
Dr. Roschewski said in an interview that, in patients aged 40 years and older, dose-adjusted EPOCH-R is “probably the preferred choice,” despite its “weakness” in controlling the disease in patients with active CNS involvement.
However, the “real question” is what to use in younger patients, Dr. Roschewski said, as the “unknown” is whether the additional magnitude of a high-intensity regimen that “gets into the CNS” outweighs the risk of toxicities.
“What was important about our study,” he said, was that patients with CNS involvement “did the worst but it was equally split among patients that died of toxicity and patients that progressed.”
In other words, each choice increases one risk while decreasing another. “So I would have to have that discussion with the patient, and individual patient decisions are typically based on the details,” said Dr. Roschewski.
One issue, however, that could limit the adoption of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R is that, without a randomized study comparing it directly with a high-intensity regimen, clinicians may to stick to what they know.
Dr. Roschewski said that “this is particularly true of more experienced clinicians.”
“They’re less likely, I think, to adopt something else outside of a randomized study because our natural inclination with this disease has always been dose intensity is critical. ... This is a dogma, and to shift from that probably does require a higher level of evidence, at least for some practitioners,” he explained.
Further study details
Following a pilot study of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R in 30 adult patients in which the authors say the regimen showed “high efficacy,” they enrolled 113 patients with untreated Burkitt lymphoma at 22 centers between June 2010 and May 2017.
The patients were divided into low-risk and high-risk categories, with low-risk defined as stage 1 or 2 disease, normal lactate dehydrogenase levels, ECOG performance status ≤ 1, and no tumor mass ≥ 7 cm.
High-risk patients were given six cycles of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R (with rituximab on day 1 only) along with CNS prophylaxis or active therapy with intrathecal methotrexate.
In contrast, low-risk patients were given two cycles of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R, with rituximab on days 1 and 5, followed by positron emission tomography.
If that was negative, the patients had one additional treatment cycle and no CNS prophylaxis, but if it was positive, they were given four additional cycles, plus intrathecal methotrexate.
Of the 113 patients enrolled, 79% were male, median age was 49 years, and 62% were aged at least 40 years, including 26% aged at least 60 years.
The team determined that 13% of the patients were of low risk, 87% were high risk, and 11% had cerebrospinal fluid involvement. One-quarter (24.7%) were HIV positive, with a median CD4+ T-cell count of 268 cells/mm3.
The majority (87%) of low-risk patients received three treatment cycles, and 82% of high-risk patents were administered six treatment cycles.
Over a median follow-up of 58.7 months (4.9 years), the 4-year event-free survival (EFS) rate across the whole cohort was 84.5% and overall survival was 87%.
At the time of analysis, all low-risk patients were in remission; among high-risk patients, the 4-year EFS was 82.1% and overall survival was 84.9%.
The team reports that treatment was equally effective across age groups, and irrespective of HIV status and International Prognostic Index risk group.
Only 2% of high-risk patients with no pretreatment evidence of CNS involvement had relapses in the brain parenchyma. Just over half (55%) of patients with cerebrospinal fluid involvement at presentation experienced disease progression or died.
Five patients died of treatment-related toxicity. Grade 3/4 thrombocytopenia occurred during 17% of cycles, and febrile neutropenia was seen during 16%. Tumor lysis syndrome was rare, occurring in 5% of patients.
Next, the researchers are planning on focusing on CNS disease, looking at EPOCH-R as the backbone and adding intrathecal methotrexate and an additional targeted agent with known CNS penetration.
Dr. Roschewski said that is “a very attractive strategy and ... we will initiate enrollment in that study probably in the next couple of months here at the NCI,” he added, noting that it will be an early phase 1 study.
Another issue he identified that “doesn’t get spoken about quite as much but I do think is important is potentially working on supportive care guidelines for how we manage these patients.” Dr. Roschewski explained, “One of the things you see over and over in these Burkitt lymphoma studies is that some patients don’t make it through therapy because they’re so sick at the beginning, and they have certain risks.
“I think simply improving that type of care, independent of what regimen is used, can potentially improve the outcomes across patient groups.”
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, AIDS Malignancy Consortium, and the Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program and Lymphoid Malignancies Branch. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Adult patients with Burkitt lymphoma can achieve equally sound survival outcomes with dose-adjusted chemotherapy versus high-intensity regimens, but can do so while avoiding the severe toxicities, U.S. study data shows.

Although Burkitt lymphoma is the most common B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children, it accounts for only 1% to 2% of adult lymphoma cases.
Highly dose-intensive chemotherapy regimens, developed for children and young adults, have rendered the disease curable. But older patients in particular, and patients with comorbidities such as HIV, can suffer severe adverse effects, as well as late sequelae like second malignancies.
Mark Roschewski, MD, from the lymphoid malignancies branch at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md., and colleagues therefore examined whether a dose-adjusted regimen would maintain outcomes while reducing toxicities.
Tailoring treatment with etoposide, doxorubicin, and vincristine with prednisone, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (EPOCH-R) to whether patients had high- or low-risk disease, they achieved 4-year survival rates of higher than 85%.
The research, published by the Journal of Clinical Oncology, also showed that patients taking the regimen, which was well tolerated, had low rates of relapse in the central nervous system.
The team reports that their results with the dose-adjusted regimen “significantly improve on the complexity, cost, and toxicity profile of other regimens,” also highlighting that it is administered on an outpatient basis.
As the outcomes also “compare favorably” with those with high intensity regimens, they say the findings “support our treatment strategies to ameliorate toxicity while maintaining efficacy.”
Importantly, they suggest highly dose-intensive chemotherapy is unnecessary for cure, and carefully defined low-risk patients may be treated with limited chemotherapy.
Dr. Roschewski said in an interview that, in patients aged 40 years and older, dose-adjusted EPOCH-R is “probably the preferred choice,” despite its “weakness” in controlling the disease in patients with active CNS involvement.
However, the “real question” is what to use in younger patients, Dr. Roschewski said, as the “unknown” is whether the additional magnitude of a high-intensity regimen that “gets into the CNS” outweighs the risk of toxicities.
“What was important about our study,” he said, was that patients with CNS involvement “did the worst but it was equally split among patients that died of toxicity and patients that progressed.”
In other words, each choice increases one risk while decreasing another. “So I would have to have that discussion with the patient, and individual patient decisions are typically based on the details,” said Dr. Roschewski.
One issue, however, that could limit the adoption of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R is that, without a randomized study comparing it directly with a high-intensity regimen, clinicians may to stick to what they know.
Dr. Roschewski said that “this is particularly true of more experienced clinicians.”
“They’re less likely, I think, to adopt something else outside of a randomized study because our natural inclination with this disease has always been dose intensity is critical. ... This is a dogma, and to shift from that probably does require a higher level of evidence, at least for some practitioners,” he explained.
Further study details
Following a pilot study of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R in 30 adult patients in which the authors say the regimen showed “high efficacy,” they enrolled 113 patients with untreated Burkitt lymphoma at 22 centers between June 2010 and May 2017.
The patients were divided into low-risk and high-risk categories, with low-risk defined as stage 1 or 2 disease, normal lactate dehydrogenase levels, ECOG performance status ≤ 1, and no tumor mass ≥ 7 cm.
High-risk patients were given six cycles of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R (with rituximab on day 1 only) along with CNS prophylaxis or active therapy with intrathecal methotrexate.
In contrast, low-risk patients were given two cycles of dose-adjusted EPOCH-R, with rituximab on days 1 and 5, followed by positron emission tomography.
If that was negative, the patients had one additional treatment cycle and no CNS prophylaxis, but if it was positive, they were given four additional cycles, plus intrathecal methotrexate.
Of the 113 patients enrolled, 79% were male, median age was 49 years, and 62% were aged at least 40 years, including 26% aged at least 60 years.
The team determined that 13% of the patients were of low risk, 87% were high risk, and 11% had cerebrospinal fluid involvement. One-quarter (24.7%) were HIV positive, with a median CD4+ T-cell count of 268 cells/mm3.
The majority (87%) of low-risk patients received three treatment cycles, and 82% of high-risk patents were administered six treatment cycles.
Over a median follow-up of 58.7 months (4.9 years), the 4-year event-free survival (EFS) rate across the whole cohort was 84.5% and overall survival was 87%.
At the time of analysis, all low-risk patients were in remission; among high-risk patients, the 4-year EFS was 82.1% and overall survival was 84.9%.
The team reports that treatment was equally effective across age groups, and irrespective of HIV status and International Prognostic Index risk group.
Only 2% of high-risk patients with no pretreatment evidence of CNS involvement had relapses in the brain parenchyma. Just over half (55%) of patients with cerebrospinal fluid involvement at presentation experienced disease progression or died.
Five patients died of treatment-related toxicity. Grade 3/4 thrombocytopenia occurred during 17% of cycles, and febrile neutropenia was seen during 16%. Tumor lysis syndrome was rare, occurring in 5% of patients.
Next, the researchers are planning on focusing on CNS disease, looking at EPOCH-R as the backbone and adding intrathecal methotrexate and an additional targeted agent with known CNS penetration.
Dr. Roschewski said that is “a very attractive strategy and ... we will initiate enrollment in that study probably in the next couple of months here at the NCI,” he added, noting that it will be an early phase 1 study.
Another issue he identified that “doesn’t get spoken about quite as much but I do think is important is potentially working on supportive care guidelines for how we manage these patients.” Dr. Roschewski explained, “One of the things you see over and over in these Burkitt lymphoma studies is that some patients don’t make it through therapy because they’re so sick at the beginning, and they have certain risks.
“I think simply improving that type of care, independent of what regimen is used, can potentially improve the outcomes across patient groups.”
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, AIDS Malignancy Consortium, and the Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program and Lymphoid Malignancies Branch. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Relapsing, progressive MS classifications should be abandoned
Most disability accumulation in relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS) is not associated with overt relapses, challenging the current clinical distinction of relapsing and progressive forms of the disease, a new analysis shows. “We have to abandon the distinction between relapsing and progressive MS being different populations,” said lead author Ludwig Kappos, MD, University of Basel (Switzerland). “The disease appears to be more of a continuum of disability progression, which is sometimes also accompanied by relapses.”
The analysis was published online June 8 in JAMA Neurology.
Assessing disability progression
Noting that there are mounting data to suggest patients with relapsing MS frequently experience worsening disability over time – even when relapse activity appears well controlled – the researchers aimed to investigate the relative contributions of progression independent of relapse activity and relapse-associated worsening to overall accumulating disability in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis. To do this, they analyzed data from two identical randomized clinical trials (OPERA I and OPERA II) conducted between 2011 and 2015, which compared treatment with the new B-cell–depleting therapy ocrelizumab with interferon beta-1a in 1,656 patients with relapsing MS.
Confirmed disability accumulation was defined by an increase in 1 or more of 3 measures (Expanded Disability Status Scale, timed 25-ft walk, or 9-hole peg test), confirmed after 3 or 6 months, and was classified as being related to a clinical relapse or occurring in the absence of a relapse.
Results showed that after 96 weeks (1.8 years) of treatment, 12-week composite confirmed disability accumulation had occurred in 29.6% of patients receiving interferon beta-1a and 21.1% of those given ocrelizumab; 24-week composite confirmed disability accumulation occurred in 22.7% of interferon beta-1a patients and 16.2% of the ocrelizumab group.
In both treatment groups, the vast majority of events contributing to disability accumulation occurred independently of relapse activity. In the interferon group, 78% of events contributing to 12-week confirmed disability accumulation and 80.6% of events contributing to 24-week confirmed disability accumulation occurred in the absence of clinical relapses, with the corresponding figures in the ocrelizumab group being 88.0% (12 weeks) and 89.1% (24 weeks).
Only a minority of patients (about 17% in both groups) had confirmed disability accumulation accompanied by clinical relapses. Very few patients with confirmed disability accumulation (4% to 5%) experienced disability worsening both associated and independent of relapses. Ocrelizumab was associated with a reduced risk of both relapse-associated and relapse-independent confirmed disability accumulation, compared with interferon beta-1a.
“We found that there was progression of disability in both groups, and the really astonishing finding was that although all patients were classified as having relapsing remitting MS, actually most of the disability progression occurred without preceding relapses,” Dr. Kappos commented. He noted that there have been two previous observational studies that have shown a high rate of disability progressions without temporal association to relapses in relapsing remitting patients, but this is the first time that this progression of disability independent of relapses has been shown in the controlled setting of two prospective, randomized clinical trials over a 2-year period.
“While we expected to see some disability progression independent of relapses, we were surprised to see that the disability progression occurring in both studies was almost exclusively happening without temporal relation to relapses. That was certainly an unexpected finding,” Dr. Kappos said. “These observations make it difficult to keep the current definitions of ‘relapsing remitting’ and ‘secondary progressive’ MS, [ones] that suggest a clear-cut distinction marked by the presence or absence of relapses. This can no longer be justified,” he stressed.
“We are not saying that relapses do not contribute to disability progression. There are a lot of data to support the fact that they do. But I think what we might be seeing is that the drug therapy is quite effective in reducing disability due to relapses but only partially effective in reducing progression independent of relapses,” Dr. Kappos explained.
Although there have been many advances in reducing relapses with drug therapy, focus now needs to shift to the other more continuous process of disability progression independent of relapses, Dr. Kappos said. “There is still a lot of room for improvement here.”
“If continuous progression independent of relapses is already present in the early phases of MS, it is reasonable to study the effects of intervention on steady progression already in this early phase,” he noted. “This might help to capture patients at earlier stages who better respond to treatment aimed at halting progression.”
Dr. Kappos also called for more subtle measurements of disability than the EDSS alone, including measures such as the 9-hole peg test and the 25-ft walk as they did in this analysis. But other measures could also be added that would characterize continuous disease activity and progression, such as laboratory values (e.g., neurofilament light chain) and advanced, more tissue-specific quantitative MRI techniques and digital biomarkers to detect subtle changes in neurologic function.
An artificial distinction?
Commenting on the study, Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of the experimental therapeutics program at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research, Cleveland Clinic, said he too sees very little distinction between relapsing remitting and progressive forms of the disease.
“This study confirms what has been suspected for quite a few years –that if one looks sufficiently and carefully, there is gradual worsening of some aspects of the disease in many patients from the earliest stages,” Dr. Cohen said. “Conversely, some patients with progressive MS have superimposed relapses or MRI lesion activity.
“Thus, the distinction between relapsing-remitting and progressive MS subtypes appears artificial,” he concluded.
This study was sponsored by F. Hoffmann–La Roche. Dr. Kappos has received research support from the company.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most disability accumulation in relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS) is not associated with overt relapses, challenging the current clinical distinction of relapsing and progressive forms of the disease, a new analysis shows. “We have to abandon the distinction between relapsing and progressive MS being different populations,” said lead author Ludwig Kappos, MD, University of Basel (Switzerland). “The disease appears to be more of a continuum of disability progression, which is sometimes also accompanied by relapses.”
The analysis was published online June 8 in JAMA Neurology.
Assessing disability progression
Noting that there are mounting data to suggest patients with relapsing MS frequently experience worsening disability over time – even when relapse activity appears well controlled – the researchers aimed to investigate the relative contributions of progression independent of relapse activity and relapse-associated worsening to overall accumulating disability in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis. To do this, they analyzed data from two identical randomized clinical trials (OPERA I and OPERA II) conducted between 2011 and 2015, which compared treatment with the new B-cell–depleting therapy ocrelizumab with interferon beta-1a in 1,656 patients with relapsing MS.
Confirmed disability accumulation was defined by an increase in 1 or more of 3 measures (Expanded Disability Status Scale, timed 25-ft walk, or 9-hole peg test), confirmed after 3 or 6 months, and was classified as being related to a clinical relapse or occurring in the absence of a relapse.
Results showed that after 96 weeks (1.8 years) of treatment, 12-week composite confirmed disability accumulation had occurred in 29.6% of patients receiving interferon beta-1a and 21.1% of those given ocrelizumab; 24-week composite confirmed disability accumulation occurred in 22.7% of interferon beta-1a patients and 16.2% of the ocrelizumab group.
In both treatment groups, the vast majority of events contributing to disability accumulation occurred independently of relapse activity. In the interferon group, 78% of events contributing to 12-week confirmed disability accumulation and 80.6% of events contributing to 24-week confirmed disability accumulation occurred in the absence of clinical relapses, with the corresponding figures in the ocrelizumab group being 88.0% (12 weeks) and 89.1% (24 weeks).
Only a minority of patients (about 17% in both groups) had confirmed disability accumulation accompanied by clinical relapses. Very few patients with confirmed disability accumulation (4% to 5%) experienced disability worsening both associated and independent of relapses. Ocrelizumab was associated with a reduced risk of both relapse-associated and relapse-independent confirmed disability accumulation, compared with interferon beta-1a.
“We found that there was progression of disability in both groups, and the really astonishing finding was that although all patients were classified as having relapsing remitting MS, actually most of the disability progression occurred without preceding relapses,” Dr. Kappos commented. He noted that there have been two previous observational studies that have shown a high rate of disability progressions without temporal association to relapses in relapsing remitting patients, but this is the first time that this progression of disability independent of relapses has been shown in the controlled setting of two prospective, randomized clinical trials over a 2-year period.
“While we expected to see some disability progression independent of relapses, we were surprised to see that the disability progression occurring in both studies was almost exclusively happening without temporal relation to relapses. That was certainly an unexpected finding,” Dr. Kappos said. “These observations make it difficult to keep the current definitions of ‘relapsing remitting’ and ‘secondary progressive’ MS, [ones] that suggest a clear-cut distinction marked by the presence or absence of relapses. This can no longer be justified,” he stressed.
“We are not saying that relapses do not contribute to disability progression. There are a lot of data to support the fact that they do. But I think what we might be seeing is that the drug therapy is quite effective in reducing disability due to relapses but only partially effective in reducing progression independent of relapses,” Dr. Kappos explained.
Although there have been many advances in reducing relapses with drug therapy, focus now needs to shift to the other more continuous process of disability progression independent of relapses, Dr. Kappos said. “There is still a lot of room for improvement here.”
“If continuous progression independent of relapses is already present in the early phases of MS, it is reasonable to study the effects of intervention on steady progression already in this early phase,” he noted. “This might help to capture patients at earlier stages who better respond to treatment aimed at halting progression.”
Dr. Kappos also called for more subtle measurements of disability than the EDSS alone, including measures such as the 9-hole peg test and the 25-ft walk as they did in this analysis. But other measures could also be added that would characterize continuous disease activity and progression, such as laboratory values (e.g., neurofilament light chain) and advanced, more tissue-specific quantitative MRI techniques and digital biomarkers to detect subtle changes in neurologic function.
An artificial distinction?
Commenting on the study, Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of the experimental therapeutics program at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research, Cleveland Clinic, said he too sees very little distinction between relapsing remitting and progressive forms of the disease.
“This study confirms what has been suspected for quite a few years –that if one looks sufficiently and carefully, there is gradual worsening of some aspects of the disease in many patients from the earliest stages,” Dr. Cohen said. “Conversely, some patients with progressive MS have superimposed relapses or MRI lesion activity.
“Thus, the distinction between relapsing-remitting and progressive MS subtypes appears artificial,” he concluded.
This study was sponsored by F. Hoffmann–La Roche. Dr. Kappos has received research support from the company.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most disability accumulation in relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS) is not associated with overt relapses, challenging the current clinical distinction of relapsing and progressive forms of the disease, a new analysis shows. “We have to abandon the distinction between relapsing and progressive MS being different populations,” said lead author Ludwig Kappos, MD, University of Basel (Switzerland). “The disease appears to be more of a continuum of disability progression, which is sometimes also accompanied by relapses.”
The analysis was published online June 8 in JAMA Neurology.
Assessing disability progression
Noting that there are mounting data to suggest patients with relapsing MS frequently experience worsening disability over time – even when relapse activity appears well controlled – the researchers aimed to investigate the relative contributions of progression independent of relapse activity and relapse-associated worsening to overall accumulating disability in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis. To do this, they analyzed data from two identical randomized clinical trials (OPERA I and OPERA II) conducted between 2011 and 2015, which compared treatment with the new B-cell–depleting therapy ocrelizumab with interferon beta-1a in 1,656 patients with relapsing MS.
Confirmed disability accumulation was defined by an increase in 1 or more of 3 measures (Expanded Disability Status Scale, timed 25-ft walk, or 9-hole peg test), confirmed after 3 or 6 months, and was classified as being related to a clinical relapse or occurring in the absence of a relapse.
Results showed that after 96 weeks (1.8 years) of treatment, 12-week composite confirmed disability accumulation had occurred in 29.6% of patients receiving interferon beta-1a and 21.1% of those given ocrelizumab; 24-week composite confirmed disability accumulation occurred in 22.7% of interferon beta-1a patients and 16.2% of the ocrelizumab group.
In both treatment groups, the vast majority of events contributing to disability accumulation occurred independently of relapse activity. In the interferon group, 78% of events contributing to 12-week confirmed disability accumulation and 80.6% of events contributing to 24-week confirmed disability accumulation occurred in the absence of clinical relapses, with the corresponding figures in the ocrelizumab group being 88.0% (12 weeks) and 89.1% (24 weeks).
Only a minority of patients (about 17% in both groups) had confirmed disability accumulation accompanied by clinical relapses. Very few patients with confirmed disability accumulation (4% to 5%) experienced disability worsening both associated and independent of relapses. Ocrelizumab was associated with a reduced risk of both relapse-associated and relapse-independent confirmed disability accumulation, compared with interferon beta-1a.
“We found that there was progression of disability in both groups, and the really astonishing finding was that although all patients were classified as having relapsing remitting MS, actually most of the disability progression occurred without preceding relapses,” Dr. Kappos commented. He noted that there have been two previous observational studies that have shown a high rate of disability progressions without temporal association to relapses in relapsing remitting patients, but this is the first time that this progression of disability independent of relapses has been shown in the controlled setting of two prospective, randomized clinical trials over a 2-year period.
“While we expected to see some disability progression independent of relapses, we were surprised to see that the disability progression occurring in both studies was almost exclusively happening without temporal relation to relapses. That was certainly an unexpected finding,” Dr. Kappos said. “These observations make it difficult to keep the current definitions of ‘relapsing remitting’ and ‘secondary progressive’ MS, [ones] that suggest a clear-cut distinction marked by the presence or absence of relapses. This can no longer be justified,” he stressed.
“We are not saying that relapses do not contribute to disability progression. There are a lot of data to support the fact that they do. But I think what we might be seeing is that the drug therapy is quite effective in reducing disability due to relapses but only partially effective in reducing progression independent of relapses,” Dr. Kappos explained.
Although there have been many advances in reducing relapses with drug therapy, focus now needs to shift to the other more continuous process of disability progression independent of relapses, Dr. Kappos said. “There is still a lot of room for improvement here.”
“If continuous progression independent of relapses is already present in the early phases of MS, it is reasonable to study the effects of intervention on steady progression already in this early phase,” he noted. “This might help to capture patients at earlier stages who better respond to treatment aimed at halting progression.”
Dr. Kappos also called for more subtle measurements of disability than the EDSS alone, including measures such as the 9-hole peg test and the 25-ft walk as they did in this analysis. But other measures could also be added that would characterize continuous disease activity and progression, such as laboratory values (e.g., neurofilament light chain) and advanced, more tissue-specific quantitative MRI techniques and digital biomarkers to detect subtle changes in neurologic function.
An artificial distinction?
Commenting on the study, Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of the experimental therapeutics program at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research, Cleveland Clinic, said he too sees very little distinction between relapsing remitting and progressive forms of the disease.
“This study confirms what has been suspected for quite a few years –that if one looks sufficiently and carefully, there is gradual worsening of some aspects of the disease in many patients from the earliest stages,” Dr. Cohen said. “Conversely, some patients with progressive MS have superimposed relapses or MRI lesion activity.
“Thus, the distinction between relapsing-remitting and progressive MS subtypes appears artificial,” he concluded.
This study was sponsored by F. Hoffmann–La Roche. Dr. Kappos has received research support from the company.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves Uplizna for treatment of anti-AQP4 antibody–positive NMOSD
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Uplizna (inebilizumab-cdon) for the treatment of adult patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) who are anti-AQP4 antibody positive. Uplizna is the second approved treatment for the disorder.
Approval was based on results from the global, placebo-controlled N-MOmentum trial, which included 213 anti-AQP4 antibody–positive patients and 17 anti-AQP4 antibody–negative patients who received inebilizumab-cdon or placebo. Just under 90% of patients in the positive group remained relapse free 6 months after the initial dosing, compared with 58% of patients taking placebo. People who took inebilizumab also saw a reduction in NMOSD-related hospitalizations. There was no evidence of a benefit in patients who were anti-AQP4 antibody negative.
Inebilizumab-cdon was safe and well tolerated during the trial, with the most common adverse events being urinary tract infection (20%), nasopharyngitis (13%), infusion reaction (12%), arthralgia (11%), and headache (10%). The drug is approved as twice-yearly maintenance after initial dosing. The prescribing information for Uplizna includes a warning for infusion reactions, potential depletion of certain proteins (hypogammaglobulinemia), and potential increased risk of infection—including progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy—and potential reactivation of hepatitis B and tuberculosis.
“NMOSD is an extremely challenging disease to treat. Patients experience unpredictable attacks that can lead to permanent disability from blindness and paralysis. In addition, each subsequent attack may result in a cumulative worsening of disability,” Bruce Cree, MD, PhD, lead investigator for the N-MOmentum trial and professor of clinical neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, said in a press release. “Uplizna is an important new treatment option that provides prescribing physicians and patients living with NMOSD a therapy with proven efficacy, a favorable safety profile and a twice-a-year maintenance dosing schedule.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Uplizna (inebilizumab-cdon) for the treatment of adult patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) who are anti-AQP4 antibody positive. Uplizna is the second approved treatment for the disorder.
Approval was based on results from the global, placebo-controlled N-MOmentum trial, which included 213 anti-AQP4 antibody–positive patients and 17 anti-AQP4 antibody–negative patients who received inebilizumab-cdon or placebo. Just under 90% of patients in the positive group remained relapse free 6 months after the initial dosing, compared with 58% of patients taking placebo. People who took inebilizumab also saw a reduction in NMOSD-related hospitalizations. There was no evidence of a benefit in patients who were anti-AQP4 antibody negative.
Inebilizumab-cdon was safe and well tolerated during the trial, with the most common adverse events being urinary tract infection (20%), nasopharyngitis (13%), infusion reaction (12%), arthralgia (11%), and headache (10%). The drug is approved as twice-yearly maintenance after initial dosing. The prescribing information for Uplizna includes a warning for infusion reactions, potential depletion of certain proteins (hypogammaglobulinemia), and potential increased risk of infection—including progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy—and potential reactivation of hepatitis B and tuberculosis.
“NMOSD is an extremely challenging disease to treat. Patients experience unpredictable attacks that can lead to permanent disability from blindness and paralysis. In addition, each subsequent attack may result in a cumulative worsening of disability,” Bruce Cree, MD, PhD, lead investigator for the N-MOmentum trial and professor of clinical neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, said in a press release. “Uplizna is an important new treatment option that provides prescribing physicians and patients living with NMOSD a therapy with proven efficacy, a favorable safety profile and a twice-a-year maintenance dosing schedule.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Uplizna (inebilizumab-cdon) for the treatment of adult patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) who are anti-AQP4 antibody positive. Uplizna is the second approved treatment for the disorder.
Approval was based on results from the global, placebo-controlled N-MOmentum trial, which included 213 anti-AQP4 antibody–positive patients and 17 anti-AQP4 antibody–negative patients who received inebilizumab-cdon or placebo. Just under 90% of patients in the positive group remained relapse free 6 months after the initial dosing, compared with 58% of patients taking placebo. People who took inebilizumab also saw a reduction in NMOSD-related hospitalizations. There was no evidence of a benefit in patients who were anti-AQP4 antibody negative.
Inebilizumab-cdon was safe and well tolerated during the trial, with the most common adverse events being urinary tract infection (20%), nasopharyngitis (13%), infusion reaction (12%), arthralgia (11%), and headache (10%). The drug is approved as twice-yearly maintenance after initial dosing. The prescribing information for Uplizna includes a warning for infusion reactions, potential depletion of certain proteins (hypogammaglobulinemia), and potential increased risk of infection—including progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy—and potential reactivation of hepatitis B and tuberculosis.
“NMOSD is an extremely challenging disease to treat. Patients experience unpredictable attacks that can lead to permanent disability from blindness and paralysis. In addition, each subsequent attack may result in a cumulative worsening of disability,” Bruce Cree, MD, PhD, lead investigator for the N-MOmentum trial and professor of clinical neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, said in a press release. “Uplizna is an important new treatment option that provides prescribing physicians and patients living with NMOSD a therapy with proven efficacy, a favorable safety profile and a twice-a-year maintenance dosing schedule.”
Three-drug combo promising against high-risk CLL
For patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), first-line therapy with a triple combination of targeted agents showed encouraging response rates in the phase 2 CLL2-GIVe trial.
Among 41 patients with untreated CLL bearing deleterious TP53 mutations and/or the 17p chromosomal deletion who received the GIVe regimen consisting of obinutuzumab (Gazyva), ibrutinib (Imbruvica), and venetoclax (Venclexta), the complete response rate at final restaging was 58.5%, and 33 patients with a confirmed response were negative for minimal residual disease after a median follow-up of 18.6 months, reported Henriette Huber, MD, of University Hospital Ulm, Germany.
“The GIVe regimen is promising first-line therapy for patients with high-risk CLL,” she said in a presentation during the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
The overall safety profile of the combination was acceptable, she said, but added that “some higher-grade infections are of concern.” The rate of grade 3 or greater infections/infestations in the study was 19.5%.
Sound rationale (with caveat)
Another adverse event of concern is the rate of atrial fibrillation in the comparatively young patient population (median age 62), noted Alexey Danilov, MD, PhD, of City of Hope in Duarte Calif., who commented on the study for MDedge.
He pointed out that second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors such as acalabrutinib (Calquence) may pose a lower risk of atrial fibrillation than the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib used in the CLL2-GIVe study.
In general, however, the rationale for the combination is sound, Dr. Danilov said.
“Of all the patient populations that we deal with within CLL, this probably would be most appropriate for this type of therapy. Patients with deletion 17p or TP53 mutations still represent an unmet medical need compared to other patients who don’t have those mutations,” he said.
Patients with CLL bearing the mutations have lower clinical response rates to novel therapies and generally do not respond well to chemoimmunotherapy, he said.
“The question becomes whether using these all at the same time, versus sequential strategies – using one drug and then after that, at relapse, another – is better, and obviously this trial doesn’t address that,” he said.
Three targets
The investigators enrolled 24 men and 17 women with untreated CLL with del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations and adequate organ function (creatinine clearance rate of more than 50 mL/min). The median age was 62 (range 35-85 years); 78% of patients had Binet stage B or C disease. The median Cumulative Illness Rating Scale (CIRS) score was 3 (range 0 to 8).
All patients received treatment with the combination for 6 months. The CD20 inhibitor obinutuzumab was given in a dose of 1,000 mg on days 1, 8 and 15 of cycle 1 and day 1 of cycles 2-6. The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib was given continuously at a dose of 420 mg per day beginning on the first day of the first cycle. Venetoclax, a B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor, was started on day 22 of cycle 1, and was increased to 400 mg per day over 5 weeks until the end of cycle 12.
If patients achieved a complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi) according to International Workshop on CLL criteria at final restaging (performed with imaging at the end of cycle 12 followed by bone marrow biopsy 2 months later), ibrutinib would be stopped beginning at cycle 15. Patients who did not have a CR or CRi would continue on ibrutinib until cycle 36.
Encouraging results
All but 3 of the 41 patients reached final restaging. Analyses of efficacy and safety included all 41 patients.
The CR/CRi rate at final restaging, the primary endpoint, was accomplished in 24 patients (58.8%), and 14 patients (34.1%) had a partial response.
Of the three patients for whom responses could not be assessed, two died (one from ovarian cancer which was retrospectively determined to have been present at enrollment, and one at cycle 9 from cardiac failure), and the third patient withdrew consent at cycle 10.
In all, 33 patients (80.5%) were MRD-negative in peripheral blood, 4 remained MRD positive, and 4 were not assessed. Per protocol, 22 patients with undetectable MRD and a CR or CRi discontinued therapy at week 15. An additional 13 patients also discontinued therapy because of adverse events or other reasons, and 6 remained on therapy beyond cycle 15.
The most frequent adverse events of any grade through the end of cycle 14 were gastrointestinal disorders in 83%, none higher than grade 2; infections and infestations in 70.7%, of which 19.5% were grade 3 or greater in severity; and blood and lymphatic system disorders in 58.5%, most of which (53.7%) were grade 3 or greater.
Cardiac disorders were reported in 19.5% of all patients, including 12.2% with atrial fibrillation; grade 3 or greater atrial fibrillation occurred in 2.4% of patients.
There was one case each of cerebral aspergillosis, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (without PCR testing), urosepsis, staphylococcal sepsis and febrile infection.
Laboratory confirmed tumor lysis syndrome, all grade 3 or greater, was reported in 9.8% of patients. Infusion-related reactions were reported in 29.3% of patients, with a total of 7.3% being grade 3 or greater.
The trial was supported by Janssen-Cilag and Roche. Dr. Huber disclosed travel reimbursement from Novartis. Dr. Danilov disclosed consulting for AbbVie, Janssen, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Huber H et al. EHA Congress. Abstract S157.
For patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), first-line therapy with a triple combination of targeted agents showed encouraging response rates in the phase 2 CLL2-GIVe trial.
Among 41 patients with untreated CLL bearing deleterious TP53 mutations and/or the 17p chromosomal deletion who received the GIVe regimen consisting of obinutuzumab (Gazyva), ibrutinib (Imbruvica), and venetoclax (Venclexta), the complete response rate at final restaging was 58.5%, and 33 patients with a confirmed response were negative for minimal residual disease after a median follow-up of 18.6 months, reported Henriette Huber, MD, of University Hospital Ulm, Germany.
“The GIVe regimen is promising first-line therapy for patients with high-risk CLL,” she said in a presentation during the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
The overall safety profile of the combination was acceptable, she said, but added that “some higher-grade infections are of concern.” The rate of grade 3 or greater infections/infestations in the study was 19.5%.
Sound rationale (with caveat)
Another adverse event of concern is the rate of atrial fibrillation in the comparatively young patient population (median age 62), noted Alexey Danilov, MD, PhD, of City of Hope in Duarte Calif., who commented on the study for MDedge.
He pointed out that second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors such as acalabrutinib (Calquence) may pose a lower risk of atrial fibrillation than the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib used in the CLL2-GIVe study.
In general, however, the rationale for the combination is sound, Dr. Danilov said.
“Of all the patient populations that we deal with within CLL, this probably would be most appropriate for this type of therapy. Patients with deletion 17p or TP53 mutations still represent an unmet medical need compared to other patients who don’t have those mutations,” he said.
Patients with CLL bearing the mutations have lower clinical response rates to novel therapies and generally do not respond well to chemoimmunotherapy, he said.
“The question becomes whether using these all at the same time, versus sequential strategies – using one drug and then after that, at relapse, another – is better, and obviously this trial doesn’t address that,” he said.
Three targets
The investigators enrolled 24 men and 17 women with untreated CLL with del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations and adequate organ function (creatinine clearance rate of more than 50 mL/min). The median age was 62 (range 35-85 years); 78% of patients had Binet stage B or C disease. The median Cumulative Illness Rating Scale (CIRS) score was 3 (range 0 to 8).
All patients received treatment with the combination for 6 months. The CD20 inhibitor obinutuzumab was given in a dose of 1,000 mg on days 1, 8 and 15 of cycle 1 and day 1 of cycles 2-6. The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib was given continuously at a dose of 420 mg per day beginning on the first day of the first cycle. Venetoclax, a B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor, was started on day 22 of cycle 1, and was increased to 400 mg per day over 5 weeks until the end of cycle 12.
If patients achieved a complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi) according to International Workshop on CLL criteria at final restaging (performed with imaging at the end of cycle 12 followed by bone marrow biopsy 2 months later), ibrutinib would be stopped beginning at cycle 15. Patients who did not have a CR or CRi would continue on ibrutinib until cycle 36.
Encouraging results
All but 3 of the 41 patients reached final restaging. Analyses of efficacy and safety included all 41 patients.
The CR/CRi rate at final restaging, the primary endpoint, was accomplished in 24 patients (58.8%), and 14 patients (34.1%) had a partial response.
Of the three patients for whom responses could not be assessed, two died (one from ovarian cancer which was retrospectively determined to have been present at enrollment, and one at cycle 9 from cardiac failure), and the third patient withdrew consent at cycle 10.
In all, 33 patients (80.5%) were MRD-negative in peripheral blood, 4 remained MRD positive, and 4 were not assessed. Per protocol, 22 patients with undetectable MRD and a CR or CRi discontinued therapy at week 15. An additional 13 patients also discontinued therapy because of adverse events or other reasons, and 6 remained on therapy beyond cycle 15.
The most frequent adverse events of any grade through the end of cycle 14 were gastrointestinal disorders in 83%, none higher than grade 2; infections and infestations in 70.7%, of which 19.5% were grade 3 or greater in severity; and blood and lymphatic system disorders in 58.5%, most of which (53.7%) were grade 3 or greater.
Cardiac disorders were reported in 19.5% of all patients, including 12.2% with atrial fibrillation; grade 3 or greater atrial fibrillation occurred in 2.4% of patients.
There was one case each of cerebral aspergillosis, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (without PCR testing), urosepsis, staphylococcal sepsis and febrile infection.
Laboratory confirmed tumor lysis syndrome, all grade 3 or greater, was reported in 9.8% of patients. Infusion-related reactions were reported in 29.3% of patients, with a total of 7.3% being grade 3 or greater.
The trial was supported by Janssen-Cilag and Roche. Dr. Huber disclosed travel reimbursement from Novartis. Dr. Danilov disclosed consulting for AbbVie, Janssen, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Huber H et al. EHA Congress. Abstract S157.
For patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), first-line therapy with a triple combination of targeted agents showed encouraging response rates in the phase 2 CLL2-GIVe trial.
Among 41 patients with untreated CLL bearing deleterious TP53 mutations and/or the 17p chromosomal deletion who received the GIVe regimen consisting of obinutuzumab (Gazyva), ibrutinib (Imbruvica), and venetoclax (Venclexta), the complete response rate at final restaging was 58.5%, and 33 patients with a confirmed response were negative for minimal residual disease after a median follow-up of 18.6 months, reported Henriette Huber, MD, of University Hospital Ulm, Germany.
“The GIVe regimen is promising first-line therapy for patients with high-risk CLL,” she said in a presentation during the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
The overall safety profile of the combination was acceptable, she said, but added that “some higher-grade infections are of concern.” The rate of grade 3 or greater infections/infestations in the study was 19.5%.
Sound rationale (with caveat)
Another adverse event of concern is the rate of atrial fibrillation in the comparatively young patient population (median age 62), noted Alexey Danilov, MD, PhD, of City of Hope in Duarte Calif., who commented on the study for MDedge.
He pointed out that second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors such as acalabrutinib (Calquence) may pose a lower risk of atrial fibrillation than the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib used in the CLL2-GIVe study.
In general, however, the rationale for the combination is sound, Dr. Danilov said.
“Of all the patient populations that we deal with within CLL, this probably would be most appropriate for this type of therapy. Patients with deletion 17p or TP53 mutations still represent an unmet medical need compared to other patients who don’t have those mutations,” he said.
Patients with CLL bearing the mutations have lower clinical response rates to novel therapies and generally do not respond well to chemoimmunotherapy, he said.
“The question becomes whether using these all at the same time, versus sequential strategies – using one drug and then after that, at relapse, another – is better, and obviously this trial doesn’t address that,” he said.
Three targets
The investigators enrolled 24 men and 17 women with untreated CLL with del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations and adequate organ function (creatinine clearance rate of more than 50 mL/min). The median age was 62 (range 35-85 years); 78% of patients had Binet stage B or C disease. The median Cumulative Illness Rating Scale (CIRS) score was 3 (range 0 to 8).
All patients received treatment with the combination for 6 months. The CD20 inhibitor obinutuzumab was given in a dose of 1,000 mg on days 1, 8 and 15 of cycle 1 and day 1 of cycles 2-6. The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib was given continuously at a dose of 420 mg per day beginning on the first day of the first cycle. Venetoclax, a B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor, was started on day 22 of cycle 1, and was increased to 400 mg per day over 5 weeks until the end of cycle 12.
If patients achieved a complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi) according to International Workshop on CLL criteria at final restaging (performed with imaging at the end of cycle 12 followed by bone marrow biopsy 2 months later), ibrutinib would be stopped beginning at cycle 15. Patients who did not have a CR or CRi would continue on ibrutinib until cycle 36.
Encouraging results
All but 3 of the 41 patients reached final restaging. Analyses of efficacy and safety included all 41 patients.
The CR/CRi rate at final restaging, the primary endpoint, was accomplished in 24 patients (58.8%), and 14 patients (34.1%) had a partial response.
Of the three patients for whom responses could not be assessed, two died (one from ovarian cancer which was retrospectively determined to have been present at enrollment, and one at cycle 9 from cardiac failure), and the third patient withdrew consent at cycle 10.
In all, 33 patients (80.5%) were MRD-negative in peripheral blood, 4 remained MRD positive, and 4 were not assessed. Per protocol, 22 patients with undetectable MRD and a CR or CRi discontinued therapy at week 15. An additional 13 patients also discontinued therapy because of adverse events or other reasons, and 6 remained on therapy beyond cycle 15.
The most frequent adverse events of any grade through the end of cycle 14 were gastrointestinal disorders in 83%, none higher than grade 2; infections and infestations in 70.7%, of which 19.5% were grade 3 or greater in severity; and blood and lymphatic system disorders in 58.5%, most of which (53.7%) were grade 3 or greater.
Cardiac disorders were reported in 19.5% of all patients, including 12.2% with atrial fibrillation; grade 3 or greater atrial fibrillation occurred in 2.4% of patients.
There was one case each of cerebral aspergillosis, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (without PCR testing), urosepsis, staphylococcal sepsis and febrile infection.
Laboratory confirmed tumor lysis syndrome, all grade 3 or greater, was reported in 9.8% of patients. Infusion-related reactions were reported in 29.3% of patients, with a total of 7.3% being grade 3 or greater.
The trial was supported by Janssen-Cilag and Roche. Dr. Huber disclosed travel reimbursement from Novartis. Dr. Danilov disclosed consulting for AbbVie, Janssen, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Huber H et al. EHA Congress. Abstract S157.
FROM EHA CONGRESS
American Cancer Society update: ‘It is best not to drink alcohol’
In its updated cancer prevention guidelines, the American Cancer Society now recommends that “it is best not to drink alcohol.”
Previously, ACS suggested that, for those who consume alcoholic beverages, intake should be no more than one drink per day for women or two per day for men. That recommendation is still in place, but is now accompanied by this new, stronger directive.
The revised guidelines also place more emphasis on reducing the consumption of processed and red meat and highly processed foods, and on increasing physical activity.
But importantly, there is also a call for action from public, private, and community organizations to work to together to increase access to affordable, nutritious foods and physical activity.
“Making healthy choices can be challenging for many, and there are strategies included in the guidelines that communities can undertake to help reduce barriers to eating well and physical activity,” said Laura Makaroff, DO, American Cancer Society senior vice president. “Individual choice is an important part of a healthy lifestyle, but having the right policies and environmental factors to break down these barriers is also important, and that is something that clinicians can support.”
The guidelines were published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
The link between cancer and lifestyle factors has long been established, and for the past 4 decades, both government and leading nonprofit health organizations, including the ACS and the World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research (WCRF/AICR), have released cancer prevention guidelines and recommendations that focus on managing weight, diet, physical activity, and alcohol consumption.
In 2012, the ACS issued guidelines on diet and physical activity, and their current guideline is largely based on the WCRF/AICR systematic reviews and Continuous Update Project reports, which were last updated in 2018. The ACS guidelines also incorporated systematic reviews conducted by the International Agency on Cancer Research (IARC) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the Department of Health and Human Services (USDA/HHS) and other analyses that were published since the WCRF/AICR recommendations were released.
Emphasis on three areas
The differences between the old guidelines and the update do not differ dramatically, but Makaroff highlighted a few areas that have increased emphasis.
Time spent being physically active is critical. The recommendation has changed to encourage adults to engage in 150-300 minutes (2.5-5 hours) of moderate-intensity physical activity, or 75-150 minutes (1.25-2.5 hours) of vigorous-intensity physical activity, or an equivalent combination, per week. Achieving or exceeding the upper limit of 300 minutes is optimal.
“That is more than what we have recommended in the past, along with the continued message that children and adolescents engage in at least 1 hour of moderate- or vigorous-intensity activity each day,” she told Medscape Medical News.
The ACS has also increased emphasis on reducing the consumption of processed and red meat. “This is part of a healthy eating pattern and making sure that people are eating food that is high in nutrients that help achieve and maintain a healthy body weight,” said Makaroff.
A healthy diet should include a variety of dark green, red, and orange vegetables; fiber-rich legumes; and fruits with a variety of colors and whole grains, according to the guidelines. Sugar-sweetened beverages, highly processed foods, and refined grain products should be limited or avoided.
The revised dietary recommendations reflect a shift from a “reductionist or nutrient-centric” approach to one that is more “holistic” and that focuses on dietary patterns. In contrast to a focus on individual nutrients and bioactive compounds, the new approach is more consistent with what and how people actually eat, ACS points out.
The third area that Makaroff highlighted is alcohol, where the recommendation is to avoid or limit consumption. “The current update says not to drink alcohol, which is in line with the scientific evidence, but for those people who choose to drink alcohol, to limit it to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.”
Thus, the change here is that the previous guideline only recommended limiting alcohol consumption, while the update suggests that, optimally, it should be avoided completely.
The ACS has also called for community involvement to help implement these goals: “Public, private, and community organizations should work collaboratively at national, state, and local levels to develop, advocate for, and implement policy and environmental changes that increase access to affordable, nutritious foods; provide safe, enjoyable, and accessible opportunities for physical activity; and limit alcohol for all individuals.”
No smoking guns
Commenting on the guidelines, Steven K. Clinton, MD, PhD, associate director of the Center for Advanced Functional Foods Research and Entrepreneurship at the Ohio State University, Columbus, explained that he didn’t view the change in alcohol as that much of an evolution. “It’s been 8 years since they revised their overall guidelines, and during that time frame, there has been an enormous growth in the evidence that has been used by many organizations,” he said.
Clinton noted that the guidelines are consistent with the whole body of current scientific literature. “It’s very easy to go to the document and look for the ‘smoking gun’ – but the smoking gun is really not one thing,” he said. “It’s a pattern, and what dietitians and nutritionists are telling people is that you need to orchestrate a healthy lifestyle and diet, with a diet that has a foundation of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and modest intake of refined grains and meat. You are orchestrating an entire pattern to get the maximum benefit.”
Makaroff is an employee of the ACS. Clinton has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In its updated cancer prevention guidelines, the American Cancer Society now recommends that “it is best not to drink alcohol.”
Previously, ACS suggested that, for those who consume alcoholic beverages, intake should be no more than one drink per day for women or two per day for men. That recommendation is still in place, but is now accompanied by this new, stronger directive.
The revised guidelines also place more emphasis on reducing the consumption of processed and red meat and highly processed foods, and on increasing physical activity.
But importantly, there is also a call for action from public, private, and community organizations to work to together to increase access to affordable, nutritious foods and physical activity.
“Making healthy choices can be challenging for many, and there are strategies included in the guidelines that communities can undertake to help reduce barriers to eating well and physical activity,” said Laura Makaroff, DO, American Cancer Society senior vice president. “Individual choice is an important part of a healthy lifestyle, but having the right policies and environmental factors to break down these barriers is also important, and that is something that clinicians can support.”
The guidelines were published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
The link between cancer and lifestyle factors has long been established, and for the past 4 decades, both government and leading nonprofit health organizations, including the ACS and the World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research (WCRF/AICR), have released cancer prevention guidelines and recommendations that focus on managing weight, diet, physical activity, and alcohol consumption.
In 2012, the ACS issued guidelines on diet and physical activity, and their current guideline is largely based on the WCRF/AICR systematic reviews and Continuous Update Project reports, which were last updated in 2018. The ACS guidelines also incorporated systematic reviews conducted by the International Agency on Cancer Research (IARC) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the Department of Health and Human Services (USDA/HHS) and other analyses that were published since the WCRF/AICR recommendations were released.
Emphasis on three areas
The differences between the old guidelines and the update do not differ dramatically, but Makaroff highlighted a few areas that have increased emphasis.
Time spent being physically active is critical. The recommendation has changed to encourage adults to engage in 150-300 minutes (2.5-5 hours) of moderate-intensity physical activity, or 75-150 minutes (1.25-2.5 hours) of vigorous-intensity physical activity, or an equivalent combination, per week. Achieving or exceeding the upper limit of 300 minutes is optimal.
“That is more than what we have recommended in the past, along with the continued message that children and adolescents engage in at least 1 hour of moderate- or vigorous-intensity activity each day,” she told Medscape Medical News.
The ACS has also increased emphasis on reducing the consumption of processed and red meat. “This is part of a healthy eating pattern and making sure that people are eating food that is high in nutrients that help achieve and maintain a healthy body weight,” said Makaroff.
A healthy diet should include a variety of dark green, red, and orange vegetables; fiber-rich legumes; and fruits with a variety of colors and whole grains, according to the guidelines. Sugar-sweetened beverages, highly processed foods, and refined grain products should be limited or avoided.
The revised dietary recommendations reflect a shift from a “reductionist or nutrient-centric” approach to one that is more “holistic” and that focuses on dietary patterns. In contrast to a focus on individual nutrients and bioactive compounds, the new approach is more consistent with what and how people actually eat, ACS points out.
The third area that Makaroff highlighted is alcohol, where the recommendation is to avoid or limit consumption. “The current update says not to drink alcohol, which is in line with the scientific evidence, but for those people who choose to drink alcohol, to limit it to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.”
Thus, the change here is that the previous guideline only recommended limiting alcohol consumption, while the update suggests that, optimally, it should be avoided completely.
The ACS has also called for community involvement to help implement these goals: “Public, private, and community organizations should work collaboratively at national, state, and local levels to develop, advocate for, and implement policy and environmental changes that increase access to affordable, nutritious foods; provide safe, enjoyable, and accessible opportunities for physical activity; and limit alcohol for all individuals.”
No smoking guns
Commenting on the guidelines, Steven K. Clinton, MD, PhD, associate director of the Center for Advanced Functional Foods Research and Entrepreneurship at the Ohio State University, Columbus, explained that he didn’t view the change in alcohol as that much of an evolution. “It’s been 8 years since they revised their overall guidelines, and during that time frame, there has been an enormous growth in the evidence that has been used by many organizations,” he said.
Clinton noted that the guidelines are consistent with the whole body of current scientific literature. “It’s very easy to go to the document and look for the ‘smoking gun’ – but the smoking gun is really not one thing,” he said. “It’s a pattern, and what dietitians and nutritionists are telling people is that you need to orchestrate a healthy lifestyle and diet, with a diet that has a foundation of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and modest intake of refined grains and meat. You are orchestrating an entire pattern to get the maximum benefit.”
Makaroff is an employee of the ACS. Clinton has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In its updated cancer prevention guidelines, the American Cancer Society now recommends that “it is best not to drink alcohol.”
Previously, ACS suggested that, for those who consume alcoholic beverages, intake should be no more than one drink per day for women or two per day for men. That recommendation is still in place, but is now accompanied by this new, stronger directive.
The revised guidelines also place more emphasis on reducing the consumption of processed and red meat and highly processed foods, and on increasing physical activity.
But importantly, there is also a call for action from public, private, and community organizations to work to together to increase access to affordable, nutritious foods and physical activity.
“Making healthy choices can be challenging for many, and there are strategies included in the guidelines that communities can undertake to help reduce barriers to eating well and physical activity,” said Laura Makaroff, DO, American Cancer Society senior vice president. “Individual choice is an important part of a healthy lifestyle, but having the right policies and environmental factors to break down these barriers is also important, and that is something that clinicians can support.”
The guidelines were published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
The link between cancer and lifestyle factors has long been established, and for the past 4 decades, both government and leading nonprofit health organizations, including the ACS and the World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research (WCRF/AICR), have released cancer prevention guidelines and recommendations that focus on managing weight, diet, physical activity, and alcohol consumption.
In 2012, the ACS issued guidelines on diet and physical activity, and their current guideline is largely based on the WCRF/AICR systematic reviews and Continuous Update Project reports, which were last updated in 2018. The ACS guidelines also incorporated systematic reviews conducted by the International Agency on Cancer Research (IARC) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the Department of Health and Human Services (USDA/HHS) and other analyses that were published since the WCRF/AICR recommendations were released.
Emphasis on three areas
The differences between the old guidelines and the update do not differ dramatically, but Makaroff highlighted a few areas that have increased emphasis.
Time spent being physically active is critical. The recommendation has changed to encourage adults to engage in 150-300 minutes (2.5-5 hours) of moderate-intensity physical activity, or 75-150 minutes (1.25-2.5 hours) of vigorous-intensity physical activity, or an equivalent combination, per week. Achieving or exceeding the upper limit of 300 minutes is optimal.
“That is more than what we have recommended in the past, along with the continued message that children and adolescents engage in at least 1 hour of moderate- or vigorous-intensity activity each day,” she told Medscape Medical News.
The ACS has also increased emphasis on reducing the consumption of processed and red meat. “This is part of a healthy eating pattern and making sure that people are eating food that is high in nutrients that help achieve and maintain a healthy body weight,” said Makaroff.
A healthy diet should include a variety of dark green, red, and orange vegetables; fiber-rich legumes; and fruits with a variety of colors and whole grains, according to the guidelines. Sugar-sweetened beverages, highly processed foods, and refined grain products should be limited or avoided.
The revised dietary recommendations reflect a shift from a “reductionist or nutrient-centric” approach to one that is more “holistic” and that focuses on dietary patterns. In contrast to a focus on individual nutrients and bioactive compounds, the new approach is more consistent with what and how people actually eat, ACS points out.
The third area that Makaroff highlighted is alcohol, where the recommendation is to avoid or limit consumption. “The current update says not to drink alcohol, which is in line with the scientific evidence, but for those people who choose to drink alcohol, to limit it to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.”
Thus, the change here is that the previous guideline only recommended limiting alcohol consumption, while the update suggests that, optimally, it should be avoided completely.
The ACS has also called for community involvement to help implement these goals: “Public, private, and community organizations should work collaboratively at national, state, and local levels to develop, advocate for, and implement policy and environmental changes that increase access to affordable, nutritious foods; provide safe, enjoyable, and accessible opportunities for physical activity; and limit alcohol for all individuals.”
No smoking guns
Commenting on the guidelines, Steven K. Clinton, MD, PhD, associate director of the Center for Advanced Functional Foods Research and Entrepreneurship at the Ohio State University, Columbus, explained that he didn’t view the change in alcohol as that much of an evolution. “It’s been 8 years since they revised their overall guidelines, and during that time frame, there has been an enormous growth in the evidence that has been used by many organizations,” he said.
Clinton noted that the guidelines are consistent with the whole body of current scientific literature. “It’s very easy to go to the document and look for the ‘smoking gun’ – but the smoking gun is really not one thing,” he said. “It’s a pattern, and what dietitians and nutritionists are telling people is that you need to orchestrate a healthy lifestyle and diet, with a diet that has a foundation of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and modest intake of refined grains and meat. You are orchestrating an entire pattern to get the maximum benefit.”
Makaroff is an employee of the ACS. Clinton has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Huntington’s disease biomarkers appear 24 years before clinical symptoms
, according to a study published in the June Lancet Neurology. The data come from the Huntington’s disease Young Adult Study (HD-YAS) conducted in the United Kingdom.
The genetic cause of Huntington’s disease provides a potential target for biomarker treatment, wrote joint first authors Rachael I. Scahill, PhD, and Paul Zeun, BMBS, of University College London and colleagues.
“A detailed characterization of the premanifest period in Huntington’s disease is crucial for disease staging, informing the optimum time to initiate treatments, and identifying biomarkers for future trials in people with premanifest Huntington’s disease (preHD),” they said.
Identifying biomarkers of pre-Huntington’s disease
For their study, the researchers recruited 64 young adults with presymptomatic Huntington’s disease (preHD) and 67 controls, with an average age of 29 years. Brain imaging was conducted between Aug. 2, 2017, and April 25, 2019. Individuals with preexisting measurable cognitive and psychiatric disorders were excluded.
The researchers found no significant evidence of cognitive or psychiatric impairment in the preHD group at 23.6 years from the predicted onset of symptoms. The preHD group showed smaller putamen volumes, compared with controls, but this difference had no apparent relation to the timing of symptom onset, the researchers said.
Brain imaging revealed elevations in the CSF mutant huntingtin, neurofilament light protein (NfL), YKL-40, and plasma NfL among individuals with preHD, compared with controls. Of these, CSF NfL showed the highest effect size of measures in the study and showed a significant increasing association with estimated years to the onset of clinical symptoms of HD carriers. Overall, 53% of individuals with preHD had CSF NfL values in the normal range, and 47% had elevated values, compared with controls.
“NfL is therefore a potential candidate to provide a measure of disease progression in early preHD and might eventually be used as a marker of response to treatment in future preventive trials,” the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including potential underpowering to detect associations with age and CAG gene segment repeats, the researchers noted.
However, “By identifying a cohort of individuals with preHD and no detectable functional impairment but who begin to exhibit subtle elevations in select biological measures of neurodegeneration, we have highlighted a crucial point early in the disease process,” they concluded.
“Intervening at this stage might offer the prospect of delaying or preventing further neurodegeneration while function is intact, giving gene carriers many more years of life without impairment,” they added.
What is the best window for treatment?
The study is “particularly important since the absence of any subclinical symptoms in preHD individuals far from onset shows that the abnormal developmental aspect of Huntington’s disease has no substantial effect on adults’ clinical pattern,” wrote Anne-Catherine Bachoud-Lévi, MD, of Université Paris Est, Créteil, France, in an accompanying comment.
“The most robust findings of [the study] are the sensitiveness of NfL, compared with mutant huntingtin in CSF of individuals with preHD, and that degenerative rather than developmental disorders are clinically relevant,” she said. However, potential limitations to the study include the exclusion absence of language and calculation as part of the cognitive assessments, she noted. “Ideally, more sensitive cognitive tasks including these domains should be designed for preHD participants.”
In addition, the risks versus benefits of any long-term treatment must be considered, Dr. Bachoud-Lévi noted.
“The best window for treatment should instead target the time when a detectable subclinical slope of cognitive performance allows for predicting disease onset within a few years,” she said. “Turning to machine learning methodology, such as that in oncology, might also permit combining the best window and the best disease-modifying therapy for individuals with preHD,” she added.
The study was supported by the Wellcome Trust, CHDI Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Bachoud-Lévi disclosed grants and personal fees from Roche, and grants from the French Ministry of Health and Direction de la Recherche Clinique.
SOURCES: Scahill RI et al. Lancet Neurol. 2020 June;19:502-12; Bachoud-Lévi A-C. Lancet Neurol. 2020 June;19:473-5.
, according to a study published in the June Lancet Neurology. The data come from the Huntington’s disease Young Adult Study (HD-YAS) conducted in the United Kingdom.
The genetic cause of Huntington’s disease provides a potential target for biomarker treatment, wrote joint first authors Rachael I. Scahill, PhD, and Paul Zeun, BMBS, of University College London and colleagues.
“A detailed characterization of the premanifest period in Huntington’s disease is crucial for disease staging, informing the optimum time to initiate treatments, and identifying biomarkers for future trials in people with premanifest Huntington’s disease (preHD),” they said.
Identifying biomarkers of pre-Huntington’s disease
For their study, the researchers recruited 64 young adults with presymptomatic Huntington’s disease (preHD) and 67 controls, with an average age of 29 years. Brain imaging was conducted between Aug. 2, 2017, and April 25, 2019. Individuals with preexisting measurable cognitive and psychiatric disorders were excluded.
The researchers found no significant evidence of cognitive or psychiatric impairment in the preHD group at 23.6 years from the predicted onset of symptoms. The preHD group showed smaller putamen volumes, compared with controls, but this difference had no apparent relation to the timing of symptom onset, the researchers said.
Brain imaging revealed elevations in the CSF mutant huntingtin, neurofilament light protein (NfL), YKL-40, and plasma NfL among individuals with preHD, compared with controls. Of these, CSF NfL showed the highest effect size of measures in the study and showed a significant increasing association with estimated years to the onset of clinical symptoms of HD carriers. Overall, 53% of individuals with preHD had CSF NfL values in the normal range, and 47% had elevated values, compared with controls.
“NfL is therefore a potential candidate to provide a measure of disease progression in early preHD and might eventually be used as a marker of response to treatment in future preventive trials,” the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including potential underpowering to detect associations with age and CAG gene segment repeats, the researchers noted.
However, “By identifying a cohort of individuals with preHD and no detectable functional impairment but who begin to exhibit subtle elevations in select biological measures of neurodegeneration, we have highlighted a crucial point early in the disease process,” they concluded.
“Intervening at this stage might offer the prospect of delaying or preventing further neurodegeneration while function is intact, giving gene carriers many more years of life without impairment,” they added.
What is the best window for treatment?
The study is “particularly important since the absence of any subclinical symptoms in preHD individuals far from onset shows that the abnormal developmental aspect of Huntington’s disease has no substantial effect on adults’ clinical pattern,” wrote Anne-Catherine Bachoud-Lévi, MD, of Université Paris Est, Créteil, France, in an accompanying comment.
“The most robust findings of [the study] are the sensitiveness of NfL, compared with mutant huntingtin in CSF of individuals with preHD, and that degenerative rather than developmental disorders are clinically relevant,” she said. However, potential limitations to the study include the exclusion absence of language and calculation as part of the cognitive assessments, she noted. “Ideally, more sensitive cognitive tasks including these domains should be designed for preHD participants.”
In addition, the risks versus benefits of any long-term treatment must be considered, Dr. Bachoud-Lévi noted.
“The best window for treatment should instead target the time when a detectable subclinical slope of cognitive performance allows for predicting disease onset within a few years,” she said. “Turning to machine learning methodology, such as that in oncology, might also permit combining the best window and the best disease-modifying therapy for individuals with preHD,” she added.
The study was supported by the Wellcome Trust, CHDI Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Bachoud-Lévi disclosed grants and personal fees from Roche, and grants from the French Ministry of Health and Direction de la Recherche Clinique.
SOURCES: Scahill RI et al. Lancet Neurol. 2020 June;19:502-12; Bachoud-Lévi A-C. Lancet Neurol. 2020 June;19:473-5.
, according to a study published in the June Lancet Neurology. The data come from the Huntington’s disease Young Adult Study (HD-YAS) conducted in the United Kingdom.
The genetic cause of Huntington’s disease provides a potential target for biomarker treatment, wrote joint first authors Rachael I. Scahill, PhD, and Paul Zeun, BMBS, of University College London and colleagues.
“A detailed characterization of the premanifest period in Huntington’s disease is crucial for disease staging, informing the optimum time to initiate treatments, and identifying biomarkers for future trials in people with premanifest Huntington’s disease (preHD),” they said.
Identifying biomarkers of pre-Huntington’s disease
For their study, the researchers recruited 64 young adults with presymptomatic Huntington’s disease (preHD) and 67 controls, with an average age of 29 years. Brain imaging was conducted between Aug. 2, 2017, and April 25, 2019. Individuals with preexisting measurable cognitive and psychiatric disorders were excluded.
The researchers found no significant evidence of cognitive or psychiatric impairment in the preHD group at 23.6 years from the predicted onset of symptoms. The preHD group showed smaller putamen volumes, compared with controls, but this difference had no apparent relation to the timing of symptom onset, the researchers said.
Brain imaging revealed elevations in the CSF mutant huntingtin, neurofilament light protein (NfL), YKL-40, and plasma NfL among individuals with preHD, compared with controls. Of these, CSF NfL showed the highest effect size of measures in the study and showed a significant increasing association with estimated years to the onset of clinical symptoms of HD carriers. Overall, 53% of individuals with preHD had CSF NfL values in the normal range, and 47% had elevated values, compared with controls.
“NfL is therefore a potential candidate to provide a measure of disease progression in early preHD and might eventually be used as a marker of response to treatment in future preventive trials,” the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including potential underpowering to detect associations with age and CAG gene segment repeats, the researchers noted.
However, “By identifying a cohort of individuals with preHD and no detectable functional impairment but who begin to exhibit subtle elevations in select biological measures of neurodegeneration, we have highlighted a crucial point early in the disease process,” they concluded.
“Intervening at this stage might offer the prospect of delaying or preventing further neurodegeneration while function is intact, giving gene carriers many more years of life without impairment,” they added.
What is the best window for treatment?
The study is “particularly important since the absence of any subclinical symptoms in preHD individuals far from onset shows that the abnormal developmental aspect of Huntington’s disease has no substantial effect on adults’ clinical pattern,” wrote Anne-Catherine Bachoud-Lévi, MD, of Université Paris Est, Créteil, France, in an accompanying comment.
“The most robust findings of [the study] are the sensitiveness of NfL, compared with mutant huntingtin in CSF of individuals with preHD, and that degenerative rather than developmental disorders are clinically relevant,” she said. However, potential limitations to the study include the exclusion absence of language and calculation as part of the cognitive assessments, she noted. “Ideally, more sensitive cognitive tasks including these domains should be designed for preHD participants.”
In addition, the risks versus benefits of any long-term treatment must be considered, Dr. Bachoud-Lévi noted.
“The best window for treatment should instead target the time when a detectable subclinical slope of cognitive performance allows for predicting disease onset within a few years,” she said. “Turning to machine learning methodology, such as that in oncology, might also permit combining the best window and the best disease-modifying therapy for individuals with preHD,” she added.
The study was supported by the Wellcome Trust, CHDI Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Bachoud-Lévi disclosed grants and personal fees from Roche, and grants from the French Ministry of Health and Direction de la Recherche Clinique.
SOURCES: Scahill RI et al. Lancet Neurol. 2020 June;19:502-12; Bachoud-Lévi A-C. Lancet Neurol. 2020 June;19:473-5.
FROM LANCET NEUROLOGY
Adding avadomide shows promise for newly diagnosed DLBCL
For patients with newly diagnosed, high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding avadomide to standard therapy may reduce the likelihood of treatment failure, based on phase 1 results.
The regimen was well tolerated and had a complete response rate of 79%, reported lead author Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who presented findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Newly diagnosed DLBCL “remains a clinical challenge,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said, noting a treatment failure rate of 30%-50% for standard rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone every 21 days (R-CHOP-21), and worse outcomes among patients with high-risk disease.
In an effort to boost efficacy, the investigators turned to avadomide, a cereblon E3 ligase modulator, which previously demonstrated a complete response rate of 11% when used as monotherapy for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
The present phase 1 data included 35 adults with newly diagnosed DLBCL who had measurable lesions of at least 2.0 cm and International Prognostic Indices (IPI) between 3-5. Specifically, 51% of patients had an IPI of 3, while 49% had an IPI of 4-5.
All patients received standard R-CHOP with pegfilgrastim (to stimulate white blood cell growth), plus escalating doses of oral avadomide from 1-3 mg. Treatment was delivered, when tolerated, for up to six 21-day cycles. Depending on dose level, avadomide was given during either 2 or 3 out of 3 weeks. During treatment weeks, avadomide was given on 5 of 7 days.
The primary objectives were safety, tolerability, and complete response rate. Secondary objectives included biomarkers and additional efficacy measures, while exploratory analyses were also conducted to assess pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Out of 34 patients evaluable for efficacy, the complete response rate was 79% and the objective response rate was 88%. After a median follow-up of 10 months, the 1-year progression-free survival rate was 80%.
“The combination showed promising efficacy,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said.
The regimen was also well tolerated and demonstrated an “acceptable safety profile consistent with either therapy alone,” Dr. Mehta-Shah added.
Most patients (91%) completed all six cycles of therapy. Median relative total dose intensities were 99% and 95% for avadomide and R-CHOP-21, respectively. Approximately two out of three patients (66%) required dose interruptions of avadomide, and 9% required dose reductions because of adverse events.
Dose-limiting toxicities occurred in six patients, including sepsis, febrile neutropenia caused by skin infections, febrile neutropenia with hypotension, febrile neutropenia, pneumonia, and neutropenia with bacterial hepatic infection. Based on these findings, the recommended phase 2 dose of avadomide was determined to be 3 mg given during 2 out of 3 weeks.
About 74% of patients had grade 3-4 treatment-emergent adverse events, the most common of which were neutropenia (54%), anemia (20%), leukopenia (20%), lymphopenia (14%), hypophosphatemia (14%), and febrile neutropenia (11%).
During the second cycle of therapy, one patient died because of concurrent pneumonia. After completion of therapy, two patients developed cardiac failure, and data gathered after each cycle showed that five patients had developed elevated levels of troponin or brain natriuretic peptide.
Flow cytometry showed that avadomide had proimmunomodulatory effects, including expansion of memory T-cell populations and enhanced proliferation of T cells and NK cells. The magnitude of this latter increase was greater than that observed in previous studies involving R-CHOP and durvalumab, Dr. Mehta-Shah noted.
“We look forward to following up on this data regarding the progression-free survival over a longer period of time,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said. “The results of this trial indicate that further evaluation of cereblon-modulating compounds combined with immunochemotherapy for patients with previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is worthy of further exploration.”
Invited discussant Edward Yeh, MD, of the University of Missouri–Columbia, called cereblon modulators such as avadomide and thalidomide a “very exciting class of anticancer therapy.”
In a virtual presentation, Dr. Yeh noted that cereblon modulators have several advantages, including “good absorption, distribution, metabolism, [and] elimination,” plus relatively low susceptibility to mutation-directed drug resistance.
Despite some drawbacks, including difficulty to design and synthesize, Dr. Yeh suggested that this drug class may play a bigger role over time.
“We’re expecting more cancer therapy to come to fruition through the utilization of this posttranslational, protein-modification pathway,” he concluded.
The study was funded by Celgene. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Kyowa Hakko Kirin, AstraZeneca, Roche, and others.
SOURCE: Mehta-Shah N et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 3501.
For patients with newly diagnosed, high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding avadomide to standard therapy may reduce the likelihood of treatment failure, based on phase 1 results.
The regimen was well tolerated and had a complete response rate of 79%, reported lead author Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who presented findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Newly diagnosed DLBCL “remains a clinical challenge,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said, noting a treatment failure rate of 30%-50% for standard rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone every 21 days (R-CHOP-21), and worse outcomes among patients with high-risk disease.
In an effort to boost efficacy, the investigators turned to avadomide, a cereblon E3 ligase modulator, which previously demonstrated a complete response rate of 11% when used as monotherapy for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
The present phase 1 data included 35 adults with newly diagnosed DLBCL who had measurable lesions of at least 2.0 cm and International Prognostic Indices (IPI) between 3-5. Specifically, 51% of patients had an IPI of 3, while 49% had an IPI of 4-5.
All patients received standard R-CHOP with pegfilgrastim (to stimulate white blood cell growth), plus escalating doses of oral avadomide from 1-3 mg. Treatment was delivered, when tolerated, for up to six 21-day cycles. Depending on dose level, avadomide was given during either 2 or 3 out of 3 weeks. During treatment weeks, avadomide was given on 5 of 7 days.
The primary objectives were safety, tolerability, and complete response rate. Secondary objectives included biomarkers and additional efficacy measures, while exploratory analyses were also conducted to assess pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Out of 34 patients evaluable for efficacy, the complete response rate was 79% and the objective response rate was 88%. After a median follow-up of 10 months, the 1-year progression-free survival rate was 80%.
“The combination showed promising efficacy,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said.
The regimen was also well tolerated and demonstrated an “acceptable safety profile consistent with either therapy alone,” Dr. Mehta-Shah added.
Most patients (91%) completed all six cycles of therapy. Median relative total dose intensities were 99% and 95% for avadomide and R-CHOP-21, respectively. Approximately two out of three patients (66%) required dose interruptions of avadomide, and 9% required dose reductions because of adverse events.
Dose-limiting toxicities occurred in six patients, including sepsis, febrile neutropenia caused by skin infections, febrile neutropenia with hypotension, febrile neutropenia, pneumonia, and neutropenia with bacterial hepatic infection. Based on these findings, the recommended phase 2 dose of avadomide was determined to be 3 mg given during 2 out of 3 weeks.
About 74% of patients had grade 3-4 treatment-emergent adverse events, the most common of which were neutropenia (54%), anemia (20%), leukopenia (20%), lymphopenia (14%), hypophosphatemia (14%), and febrile neutropenia (11%).
During the second cycle of therapy, one patient died because of concurrent pneumonia. After completion of therapy, two patients developed cardiac failure, and data gathered after each cycle showed that five patients had developed elevated levels of troponin or brain natriuretic peptide.
Flow cytometry showed that avadomide had proimmunomodulatory effects, including expansion of memory T-cell populations and enhanced proliferation of T cells and NK cells. The magnitude of this latter increase was greater than that observed in previous studies involving R-CHOP and durvalumab, Dr. Mehta-Shah noted.
“We look forward to following up on this data regarding the progression-free survival over a longer period of time,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said. “The results of this trial indicate that further evaluation of cereblon-modulating compounds combined with immunochemotherapy for patients with previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is worthy of further exploration.”
Invited discussant Edward Yeh, MD, of the University of Missouri–Columbia, called cereblon modulators such as avadomide and thalidomide a “very exciting class of anticancer therapy.”
In a virtual presentation, Dr. Yeh noted that cereblon modulators have several advantages, including “good absorption, distribution, metabolism, [and] elimination,” plus relatively low susceptibility to mutation-directed drug resistance.
Despite some drawbacks, including difficulty to design and synthesize, Dr. Yeh suggested that this drug class may play a bigger role over time.
“We’re expecting more cancer therapy to come to fruition through the utilization of this posttranslational, protein-modification pathway,” he concluded.
The study was funded by Celgene. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Kyowa Hakko Kirin, AstraZeneca, Roche, and others.
SOURCE: Mehta-Shah N et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 3501.
For patients with newly diagnosed, high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding avadomide to standard therapy may reduce the likelihood of treatment failure, based on phase 1 results.
The regimen was well tolerated and had a complete response rate of 79%, reported lead author Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who presented findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Newly diagnosed DLBCL “remains a clinical challenge,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said, noting a treatment failure rate of 30%-50% for standard rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone every 21 days (R-CHOP-21), and worse outcomes among patients with high-risk disease.
In an effort to boost efficacy, the investigators turned to avadomide, a cereblon E3 ligase modulator, which previously demonstrated a complete response rate of 11% when used as monotherapy for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
The present phase 1 data included 35 adults with newly diagnosed DLBCL who had measurable lesions of at least 2.0 cm and International Prognostic Indices (IPI) between 3-5. Specifically, 51% of patients had an IPI of 3, while 49% had an IPI of 4-5.
All patients received standard R-CHOP with pegfilgrastim (to stimulate white blood cell growth), plus escalating doses of oral avadomide from 1-3 mg. Treatment was delivered, when tolerated, for up to six 21-day cycles. Depending on dose level, avadomide was given during either 2 or 3 out of 3 weeks. During treatment weeks, avadomide was given on 5 of 7 days.
The primary objectives were safety, tolerability, and complete response rate. Secondary objectives included biomarkers and additional efficacy measures, while exploratory analyses were also conducted to assess pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Out of 34 patients evaluable for efficacy, the complete response rate was 79% and the objective response rate was 88%. After a median follow-up of 10 months, the 1-year progression-free survival rate was 80%.
“The combination showed promising efficacy,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said.
The regimen was also well tolerated and demonstrated an “acceptable safety profile consistent with either therapy alone,” Dr. Mehta-Shah added.
Most patients (91%) completed all six cycles of therapy. Median relative total dose intensities were 99% and 95% for avadomide and R-CHOP-21, respectively. Approximately two out of three patients (66%) required dose interruptions of avadomide, and 9% required dose reductions because of adverse events.
Dose-limiting toxicities occurred in six patients, including sepsis, febrile neutropenia caused by skin infections, febrile neutropenia with hypotension, febrile neutropenia, pneumonia, and neutropenia with bacterial hepatic infection. Based on these findings, the recommended phase 2 dose of avadomide was determined to be 3 mg given during 2 out of 3 weeks.
About 74% of patients had grade 3-4 treatment-emergent adverse events, the most common of which were neutropenia (54%), anemia (20%), leukopenia (20%), lymphopenia (14%), hypophosphatemia (14%), and febrile neutropenia (11%).
During the second cycle of therapy, one patient died because of concurrent pneumonia. After completion of therapy, two patients developed cardiac failure, and data gathered after each cycle showed that five patients had developed elevated levels of troponin or brain natriuretic peptide.
Flow cytometry showed that avadomide had proimmunomodulatory effects, including expansion of memory T-cell populations and enhanced proliferation of T cells and NK cells. The magnitude of this latter increase was greater than that observed in previous studies involving R-CHOP and durvalumab, Dr. Mehta-Shah noted.
“We look forward to following up on this data regarding the progression-free survival over a longer period of time,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said. “The results of this trial indicate that further evaluation of cereblon-modulating compounds combined with immunochemotherapy for patients with previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is worthy of further exploration.”
Invited discussant Edward Yeh, MD, of the University of Missouri–Columbia, called cereblon modulators such as avadomide and thalidomide a “very exciting class of anticancer therapy.”
In a virtual presentation, Dr. Yeh noted that cereblon modulators have several advantages, including “good absorption, distribution, metabolism, [and] elimination,” plus relatively low susceptibility to mutation-directed drug resistance.
Despite some drawbacks, including difficulty to design and synthesize, Dr. Yeh suggested that this drug class may play a bigger role over time.
“We’re expecting more cancer therapy to come to fruition through the utilization of this posttranslational, protein-modification pathway,” he concluded.
The study was funded by Celgene. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Kyowa Hakko Kirin, AstraZeneca, Roche, and others.
SOURCE: Mehta-Shah N et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 3501.
FROM ASCO 2020
COVID-19 neurologic effects: Does the virus directly attack the brain?
A new review article summarizes what is known so far, and what clinicians need to look out for.
“We frequently see neurological conditions in people with COVID-19, but we understand very little about these effects. Is it the virus entering the brain/nerves or are they a result of a general inflammation or immune response – a bystander effect of people being severely ill. It is probably a combination of both,” said senior author Serena Spudich, MD, Gilbert H. Glaser Professor of Neurology; division chief of neurological infections & global neurology; and codirector of the Center for Neuroepidemiology and Clinical Neurological Research at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“Our message is that there are fairly frequent neurological sequelae of COVID-19 and we need to be alert to these, and to try to understand the potential long-term consequences,” she said.
The review was published online May 29 in JAMA Neurology.
Brain changes linked to loss of smell
In a separate article also published online in JAMA Neurology the same day, an Italian group describes a COVID-19 patient with anosmia (loss of sense of smell) who showed brain abnormalities on MRI in the areas associated with smell – the right gyrus rectus and the olfactory bulbs. These changes were resolved on later scan and the patient recovered her sense of smell.
“Based on the MRI findings, we can speculate that SARS-CoV-2 might invade the brain through the olfactory pathway,” conclude the researchers, led by first author Letterio S. Politi, MD, of the department of neuroradiology at IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas and Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
Can coronaviruses enter the CNS?
Dr. Spudich described this case report as “compelling evidence suggesting that loss of smell is a neurologic effect.”
“Loss of smell and/or taste is a common symptom in COVID-19, so this may suggest that an awful lot of people have some neurological involvement,” Dr. Spudich commented. “While a transient loss of smell or taste is not serious, if the virus has infected brain tissue the question is could this then spread to other parts of the brain and cause other more serious neurological effects,” she added.
In their review article, Dr. Spudich and colleagues present evidence showing that coronaviruses can enter the CNS.
“We know that SARS-1 and MERS have been shown to enter the nervous system and several coronaviruses have been shown to cause direct brain effects,” she said. “There is also some evidence that SARS-CoV-2 can do this too. As well as these latest MRI findings linked to loss of smell, there is a report of the virus being found in endothelial cells in the brain and a French autopsy study has also detected virus in the brain.”
Complications of other systemic effects?
Dr. Spudich is a neurologist specializing in neurologic consequences of infectious disease. “We don’t normally have such vast numbers of patients but in the last 3 months there has been an avalanche,” she says. From her personal experience, she believes the majority of neurologic symptoms in COVID-19 patients are most probably complications of other systemic effects, such as kidney, heart, or liver problems. But there is likely also a direct viral effect on the CNS in some patients.
“Reports from China suggested that serious neurologic effects were present in about one-third of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. I would say in our experience the figure would be less than that – maybe around 10%,” she noted.
Some COVID-19 patients are presenting with primary neurologic symptoms. For example, an elderly person may first develop confusion rather than a cough or shortness of breath; others have had severe headache as an initial COVID-19 symptom, Dr. Spudich reported. “Medical staff need to be aware of this – a severe headache in a patient who doesn’t normally get headaches could be a sign of the virus.”
Some of the neurologic symptoms could be caused by autoimmunity. Dr. Spudich explained that, in acute HIV infection a small proportion of patients can first present with autoimmune neurologic effects such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune condition of the nerves which causes a tingling sensation in the hands and feet. “This is well described in HIV, but we are also now seeing this in COVID-19 patients too,” she said. “A panoply of conditions can be caused by autoimmunity.”
On the increase in strokes that has been reported in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Spudich said, “this could be due to direct effects of the virus (e.g., causing an increase in coagulation or infecting the endothelial cells in the brain) or it could just be the final trigger for patients who were at risk of stroke anyway.”
There have been some very high-profile reports of younger patients with major strokes, she said, “but we haven’t seen that in our hospital. For the most part in my experience, strokes are happening in older COVID-19 patients with stroke risk factors such as AF [atrial fibrillation], hypertension, and diabetes. We haven’t seen a preponderance of strokes in young, otherwise healthy people.”
Even in patients who have neurologic effects as the first sign of COVID-19 infection, it is not known whether these symptoms are caused directly by the virus.
“We know that flu can cause people to have headaches, but that is because of an increase in inflammatory cytokines. On the other hand, patients with acute HIV infection often have headaches as a result of the virus getting into the brain. We don’t know where in this [cluster] COVID-19 virus falls,” Dr. Spudich said.
Much is still unknown
“The information we have is very sparse at this point. We need far more systematic information on this from CSF samples and imaging.” Dr. Spudich urged clinicians to try to collect such information in patients with neurologic symptoms.
Acknowledging that fewer such tests are being done at present because of concerns over infection risk, Dr. Spudich suggested that some changes in procedure may help. “In our hospital we have a portable MRI scanner which can be brought to the patient. This means the patient does not have to move across the hospital for a scan. This helps us to decide whether the patient has had a stroke, which can be missed when patients are on a ventilator.”
It is also unclear whether the neurologic effects seen during COVID-19 infection will last long term.
Dr. Spudich noted that there have been reports of COVID-19 patients discharged from intensive care having difficulty with higher cognitive function for some time thereafter. “This can happen after being in ICU but is it more pronounced in COVID-19 patients? An ongoing study is underway to look at this,” she said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new review article summarizes what is known so far, and what clinicians need to look out for.
“We frequently see neurological conditions in people with COVID-19, but we understand very little about these effects. Is it the virus entering the brain/nerves or are they a result of a general inflammation or immune response – a bystander effect of people being severely ill. It is probably a combination of both,” said senior author Serena Spudich, MD, Gilbert H. Glaser Professor of Neurology; division chief of neurological infections & global neurology; and codirector of the Center for Neuroepidemiology and Clinical Neurological Research at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“Our message is that there are fairly frequent neurological sequelae of COVID-19 and we need to be alert to these, and to try to understand the potential long-term consequences,” she said.
The review was published online May 29 in JAMA Neurology.
Brain changes linked to loss of smell
In a separate article also published online in JAMA Neurology the same day, an Italian group describes a COVID-19 patient with anosmia (loss of sense of smell) who showed brain abnormalities on MRI in the areas associated with smell – the right gyrus rectus and the olfactory bulbs. These changes were resolved on later scan and the patient recovered her sense of smell.
“Based on the MRI findings, we can speculate that SARS-CoV-2 might invade the brain through the olfactory pathway,” conclude the researchers, led by first author Letterio S. Politi, MD, of the department of neuroradiology at IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas and Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
Can coronaviruses enter the CNS?
Dr. Spudich described this case report as “compelling evidence suggesting that loss of smell is a neurologic effect.”
“Loss of smell and/or taste is a common symptom in COVID-19, so this may suggest that an awful lot of people have some neurological involvement,” Dr. Spudich commented. “While a transient loss of smell or taste is not serious, if the virus has infected brain tissue the question is could this then spread to other parts of the brain and cause other more serious neurological effects,” she added.
In their review article, Dr. Spudich and colleagues present evidence showing that coronaviruses can enter the CNS.
“We know that SARS-1 and MERS have been shown to enter the nervous system and several coronaviruses have been shown to cause direct brain effects,” she said. “There is also some evidence that SARS-CoV-2 can do this too. As well as these latest MRI findings linked to loss of smell, there is a report of the virus being found in endothelial cells in the brain and a French autopsy study has also detected virus in the brain.”
Complications of other systemic effects?
Dr. Spudich is a neurologist specializing in neurologic consequences of infectious disease. “We don’t normally have such vast numbers of patients but in the last 3 months there has been an avalanche,” she says. From her personal experience, she believes the majority of neurologic symptoms in COVID-19 patients are most probably complications of other systemic effects, such as kidney, heart, or liver problems. But there is likely also a direct viral effect on the CNS in some patients.
“Reports from China suggested that serious neurologic effects were present in about one-third of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. I would say in our experience the figure would be less than that – maybe around 10%,” she noted.
Some COVID-19 patients are presenting with primary neurologic symptoms. For example, an elderly person may first develop confusion rather than a cough or shortness of breath; others have had severe headache as an initial COVID-19 symptom, Dr. Spudich reported. “Medical staff need to be aware of this – a severe headache in a patient who doesn’t normally get headaches could be a sign of the virus.”
Some of the neurologic symptoms could be caused by autoimmunity. Dr. Spudich explained that, in acute HIV infection a small proportion of patients can first present with autoimmune neurologic effects such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune condition of the nerves which causes a tingling sensation in the hands and feet. “This is well described in HIV, but we are also now seeing this in COVID-19 patients too,” she said. “A panoply of conditions can be caused by autoimmunity.”
On the increase in strokes that has been reported in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Spudich said, “this could be due to direct effects of the virus (e.g., causing an increase in coagulation or infecting the endothelial cells in the brain) or it could just be the final trigger for patients who were at risk of stroke anyway.”
There have been some very high-profile reports of younger patients with major strokes, she said, “but we haven’t seen that in our hospital. For the most part in my experience, strokes are happening in older COVID-19 patients with stroke risk factors such as AF [atrial fibrillation], hypertension, and diabetes. We haven’t seen a preponderance of strokes in young, otherwise healthy people.”
Even in patients who have neurologic effects as the first sign of COVID-19 infection, it is not known whether these symptoms are caused directly by the virus.
“We know that flu can cause people to have headaches, but that is because of an increase in inflammatory cytokines. On the other hand, patients with acute HIV infection often have headaches as a result of the virus getting into the brain. We don’t know where in this [cluster] COVID-19 virus falls,” Dr. Spudich said.
Much is still unknown
“The information we have is very sparse at this point. We need far more systematic information on this from CSF samples and imaging.” Dr. Spudich urged clinicians to try to collect such information in patients with neurologic symptoms.
Acknowledging that fewer such tests are being done at present because of concerns over infection risk, Dr. Spudich suggested that some changes in procedure may help. “In our hospital we have a portable MRI scanner which can be brought to the patient. This means the patient does not have to move across the hospital for a scan. This helps us to decide whether the patient has had a stroke, which can be missed when patients are on a ventilator.”
It is also unclear whether the neurologic effects seen during COVID-19 infection will last long term.
Dr. Spudich noted that there have been reports of COVID-19 patients discharged from intensive care having difficulty with higher cognitive function for some time thereafter. “This can happen after being in ICU but is it more pronounced in COVID-19 patients? An ongoing study is underway to look at this,” she said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new review article summarizes what is known so far, and what clinicians need to look out for.
“We frequently see neurological conditions in people with COVID-19, but we understand very little about these effects. Is it the virus entering the brain/nerves or are they a result of a general inflammation or immune response – a bystander effect of people being severely ill. It is probably a combination of both,” said senior author Serena Spudich, MD, Gilbert H. Glaser Professor of Neurology; division chief of neurological infections & global neurology; and codirector of the Center for Neuroepidemiology and Clinical Neurological Research at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“Our message is that there are fairly frequent neurological sequelae of COVID-19 and we need to be alert to these, and to try to understand the potential long-term consequences,” she said.
The review was published online May 29 in JAMA Neurology.
Brain changes linked to loss of smell
In a separate article also published online in JAMA Neurology the same day, an Italian group describes a COVID-19 patient with anosmia (loss of sense of smell) who showed brain abnormalities on MRI in the areas associated with smell – the right gyrus rectus and the olfactory bulbs. These changes were resolved on later scan and the patient recovered her sense of smell.
“Based on the MRI findings, we can speculate that SARS-CoV-2 might invade the brain through the olfactory pathway,” conclude the researchers, led by first author Letterio S. Politi, MD, of the department of neuroradiology at IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas and Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
Can coronaviruses enter the CNS?
Dr. Spudich described this case report as “compelling evidence suggesting that loss of smell is a neurologic effect.”
“Loss of smell and/or taste is a common symptom in COVID-19, so this may suggest that an awful lot of people have some neurological involvement,” Dr. Spudich commented. “While a transient loss of smell or taste is not serious, if the virus has infected brain tissue the question is could this then spread to other parts of the brain and cause other more serious neurological effects,” she added.
In their review article, Dr. Spudich and colleagues present evidence showing that coronaviruses can enter the CNS.
“We know that SARS-1 and MERS have been shown to enter the nervous system and several coronaviruses have been shown to cause direct brain effects,” she said. “There is also some evidence that SARS-CoV-2 can do this too. As well as these latest MRI findings linked to loss of smell, there is a report of the virus being found in endothelial cells in the brain and a French autopsy study has also detected virus in the brain.”
Complications of other systemic effects?
Dr. Spudich is a neurologist specializing in neurologic consequences of infectious disease. “We don’t normally have such vast numbers of patients but in the last 3 months there has been an avalanche,” she says. From her personal experience, she believes the majority of neurologic symptoms in COVID-19 patients are most probably complications of other systemic effects, such as kidney, heart, or liver problems. But there is likely also a direct viral effect on the CNS in some patients.
“Reports from China suggested that serious neurologic effects were present in about one-third of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. I would say in our experience the figure would be less than that – maybe around 10%,” she noted.
Some COVID-19 patients are presenting with primary neurologic symptoms. For example, an elderly person may first develop confusion rather than a cough or shortness of breath; others have had severe headache as an initial COVID-19 symptom, Dr. Spudich reported. “Medical staff need to be aware of this – a severe headache in a patient who doesn’t normally get headaches could be a sign of the virus.”
Some of the neurologic symptoms could be caused by autoimmunity. Dr. Spudich explained that, in acute HIV infection a small proportion of patients can first present with autoimmune neurologic effects such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune condition of the nerves which causes a tingling sensation in the hands and feet. “This is well described in HIV, but we are also now seeing this in COVID-19 patients too,” she said. “A panoply of conditions can be caused by autoimmunity.”
On the increase in strokes that has been reported in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Spudich said, “this could be due to direct effects of the virus (e.g., causing an increase in coagulation or infecting the endothelial cells in the brain) or it could just be the final trigger for patients who were at risk of stroke anyway.”
There have been some very high-profile reports of younger patients with major strokes, she said, “but we haven’t seen that in our hospital. For the most part in my experience, strokes are happening in older COVID-19 patients with stroke risk factors such as AF [atrial fibrillation], hypertension, and diabetes. We haven’t seen a preponderance of strokes in young, otherwise healthy people.”
Even in patients who have neurologic effects as the first sign of COVID-19 infection, it is not known whether these symptoms are caused directly by the virus.
“We know that flu can cause people to have headaches, but that is because of an increase in inflammatory cytokines. On the other hand, patients with acute HIV infection often have headaches as a result of the virus getting into the brain. We don’t know where in this [cluster] COVID-19 virus falls,” Dr. Spudich said.
Much is still unknown
“The information we have is very sparse at this point. We need far more systematic information on this from CSF samples and imaging.” Dr. Spudich urged clinicians to try to collect such information in patients with neurologic symptoms.
Acknowledging that fewer such tests are being done at present because of concerns over infection risk, Dr. Spudich suggested that some changes in procedure may help. “In our hospital we have a portable MRI scanner which can be brought to the patient. This means the patient does not have to move across the hospital for a scan. This helps us to decide whether the patient has had a stroke, which can be missed when patients are on a ventilator.”
It is also unclear whether the neurologic effects seen during COVID-19 infection will last long term.
Dr. Spudich noted that there have been reports of COVID-19 patients discharged from intensive care having difficulty with higher cognitive function for some time thereafter. “This can happen after being in ICU but is it more pronounced in COVID-19 patients? An ongoing study is underway to look at this,” she said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.

