User login
Antibiotic use may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease
according to a report published in Movement Disorders. Associations were found for broad-spectrum antibiotics and those that act against anaerobic bacteria and fungi. The timing of antibiotic exposure also seemed to matter.
In a nationwide case-control study, Finnish researchers compared data on antibiotic use in 13,976 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease between 1998 and 2014 with antibiotic-use data from 40,697 controls. The strongest connection with Parkinson’s disease risk was found for oral exposure to macrolides and lincosamides (adjusted odds ratio up to 1.416). After correction for multiple comparisons, exposure to antianaerobics and tetracyclines 10-15 years before the index date, and antifungal medications 1-5 years before the index date were positively associated with Parkinson’s disease risk. In post hoc analyses, further positive associations were found for broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Tuomas H. Mertsalmi, MD, from the Helsinki University Hospital and coauthors reported that this was the first study to explore a possible connection between antimicrobial use and Parkinson’s disease.
“In Parkinson’s disease, several studies have described alterations of gut microbiota composition, and changes in fecal microbiota abundance have been found to be associated with gastrointestinal and motor symptoms,” they wrote.
Commenting on the delay between the exposure and diagnosis for the most strongly associated antimicrobials, the authors noted that this 10-15 year lag was comparable with what has been found between the peripheral initiation of Parkinson’s disease and its motor manifestation.
“This would also explain the lack of association between antibiotic exposure 1-5 years before index date – if antibiotic exposure could induce or contribute to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease in the gastrointestinal tract, it would probably take several years before the clinical manifestation of Parkinson’s disease,” they wrote.
With regards to the association seen for sulfonamides and trimethoprim – which was 1-5 years before the index date – they speculated this could reflect treatment for urinary tract infections, which individuals with Parkinson’s disease might be more susceptible to in the prodromal phase of the disease.
The authors noted that infectious disease has also been associated with Parkinson’s disease, and that their analysis did not include information about why the antimicrobial agents were prescribed. However, they pointed out that the associations were only for certain antibiotic classes, which makes it unlikely that the association was related to greater burden of infectious disease among individuals with Parkinson’s disease.
The pattern of associations supports the hypothesis that effects on gut microbiota could link antibiotics to Parkinson’s disease. “The link between antibiotic exposure and Parkinson’s disease fits the current view that in a significant proportion of patients the pathology of Parkinson’s disease may originate in the gut, possibly related to microbial changes, years before the onset of typical Parkinson’s disease motor symptoms such as slowness, muscle stiffness, and shaking of the extremities. It was known that bacterial composition of the intestine in patients with Parkinson’s disease is abnormal, but the cause is unclear. Our results suggest that some commonly used antibiotics, which are known to strongly influence the gut microbiota, could be a predisposing factor,” said lead investigator Filip Scheperjans, MD, PhD, from the department of neurology at Helsinki University Hospital.
The findings may have implications for antibiotic prescribing practices in the future, said Dr. Scheperjans. “In addition to the problem of antibiotic resistance, antimicrobial prescribing should also take into account their potentially long-lasting effects on the gut microbiome and the development of certain diseases.”
The study was funded by the Finnish Parkinson Foundation, the Finnish Medical Foundation, the Maire Taponen Foundation, and the Academy of Finland. One author declared relevant patents and his position as founder and chief executive of a private company. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Mertsalmi TH et al. Mov Disord. 2019 Nov 18. doi: 10.1002/mds.27924.
according to a report published in Movement Disorders. Associations were found for broad-spectrum antibiotics and those that act against anaerobic bacteria and fungi. The timing of antibiotic exposure also seemed to matter.
In a nationwide case-control study, Finnish researchers compared data on antibiotic use in 13,976 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease between 1998 and 2014 with antibiotic-use data from 40,697 controls. The strongest connection with Parkinson’s disease risk was found for oral exposure to macrolides and lincosamides (adjusted odds ratio up to 1.416). After correction for multiple comparisons, exposure to antianaerobics and tetracyclines 10-15 years before the index date, and antifungal medications 1-5 years before the index date were positively associated with Parkinson’s disease risk. In post hoc analyses, further positive associations were found for broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Tuomas H. Mertsalmi, MD, from the Helsinki University Hospital and coauthors reported that this was the first study to explore a possible connection between antimicrobial use and Parkinson’s disease.
“In Parkinson’s disease, several studies have described alterations of gut microbiota composition, and changes in fecal microbiota abundance have been found to be associated with gastrointestinal and motor symptoms,” they wrote.
Commenting on the delay between the exposure and diagnosis for the most strongly associated antimicrobials, the authors noted that this 10-15 year lag was comparable with what has been found between the peripheral initiation of Parkinson’s disease and its motor manifestation.
“This would also explain the lack of association between antibiotic exposure 1-5 years before index date – if antibiotic exposure could induce or contribute to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease in the gastrointestinal tract, it would probably take several years before the clinical manifestation of Parkinson’s disease,” they wrote.
With regards to the association seen for sulfonamides and trimethoprim – which was 1-5 years before the index date – they speculated this could reflect treatment for urinary tract infections, which individuals with Parkinson’s disease might be more susceptible to in the prodromal phase of the disease.
The authors noted that infectious disease has also been associated with Parkinson’s disease, and that their analysis did not include information about why the antimicrobial agents were prescribed. However, they pointed out that the associations were only for certain antibiotic classes, which makes it unlikely that the association was related to greater burden of infectious disease among individuals with Parkinson’s disease.
The pattern of associations supports the hypothesis that effects on gut microbiota could link antibiotics to Parkinson’s disease. “The link between antibiotic exposure and Parkinson’s disease fits the current view that in a significant proportion of patients the pathology of Parkinson’s disease may originate in the gut, possibly related to microbial changes, years before the onset of typical Parkinson’s disease motor symptoms such as slowness, muscle stiffness, and shaking of the extremities. It was known that bacterial composition of the intestine in patients with Parkinson’s disease is abnormal, but the cause is unclear. Our results suggest that some commonly used antibiotics, which are known to strongly influence the gut microbiota, could be a predisposing factor,” said lead investigator Filip Scheperjans, MD, PhD, from the department of neurology at Helsinki University Hospital.
The findings may have implications for antibiotic prescribing practices in the future, said Dr. Scheperjans. “In addition to the problem of antibiotic resistance, antimicrobial prescribing should also take into account their potentially long-lasting effects on the gut microbiome and the development of certain diseases.”
The study was funded by the Finnish Parkinson Foundation, the Finnish Medical Foundation, the Maire Taponen Foundation, and the Academy of Finland. One author declared relevant patents and his position as founder and chief executive of a private company. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Mertsalmi TH et al. Mov Disord. 2019 Nov 18. doi: 10.1002/mds.27924.
according to a report published in Movement Disorders. Associations were found for broad-spectrum antibiotics and those that act against anaerobic bacteria and fungi. The timing of antibiotic exposure also seemed to matter.
In a nationwide case-control study, Finnish researchers compared data on antibiotic use in 13,976 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease between 1998 and 2014 with antibiotic-use data from 40,697 controls. The strongest connection with Parkinson’s disease risk was found for oral exposure to macrolides and lincosamides (adjusted odds ratio up to 1.416). After correction for multiple comparisons, exposure to antianaerobics and tetracyclines 10-15 years before the index date, and antifungal medications 1-5 years before the index date were positively associated with Parkinson’s disease risk. In post hoc analyses, further positive associations were found for broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Tuomas H. Mertsalmi, MD, from the Helsinki University Hospital and coauthors reported that this was the first study to explore a possible connection between antimicrobial use and Parkinson’s disease.
“In Parkinson’s disease, several studies have described alterations of gut microbiota composition, and changes in fecal microbiota abundance have been found to be associated with gastrointestinal and motor symptoms,” they wrote.
Commenting on the delay between the exposure and diagnosis for the most strongly associated antimicrobials, the authors noted that this 10-15 year lag was comparable with what has been found between the peripheral initiation of Parkinson’s disease and its motor manifestation.
“This would also explain the lack of association between antibiotic exposure 1-5 years before index date – if antibiotic exposure could induce or contribute to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease in the gastrointestinal tract, it would probably take several years before the clinical manifestation of Parkinson’s disease,” they wrote.
With regards to the association seen for sulfonamides and trimethoprim – which was 1-5 years before the index date – they speculated this could reflect treatment for urinary tract infections, which individuals with Parkinson’s disease might be more susceptible to in the prodromal phase of the disease.
The authors noted that infectious disease has also been associated with Parkinson’s disease, and that their analysis did not include information about why the antimicrobial agents were prescribed. However, they pointed out that the associations were only for certain antibiotic classes, which makes it unlikely that the association was related to greater burden of infectious disease among individuals with Parkinson’s disease.
The pattern of associations supports the hypothesis that effects on gut microbiota could link antibiotics to Parkinson’s disease. “The link between antibiotic exposure and Parkinson’s disease fits the current view that in a significant proportion of patients the pathology of Parkinson’s disease may originate in the gut, possibly related to microbial changes, years before the onset of typical Parkinson’s disease motor symptoms such as slowness, muscle stiffness, and shaking of the extremities. It was known that bacterial composition of the intestine in patients with Parkinson’s disease is abnormal, but the cause is unclear. Our results suggest that some commonly used antibiotics, which are known to strongly influence the gut microbiota, could be a predisposing factor,” said lead investigator Filip Scheperjans, MD, PhD, from the department of neurology at Helsinki University Hospital.
The findings may have implications for antibiotic prescribing practices in the future, said Dr. Scheperjans. “In addition to the problem of antibiotic resistance, antimicrobial prescribing should also take into account their potentially long-lasting effects on the gut microbiome and the development of certain diseases.”
The study was funded by the Finnish Parkinson Foundation, the Finnish Medical Foundation, the Maire Taponen Foundation, and the Academy of Finland. One author declared relevant patents and his position as founder and chief executive of a private company. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Mertsalmi TH et al. Mov Disord. 2019 Nov 18. doi: 10.1002/mds.27924.
FROM MOVEMENT DISORDERS
Trial finds three drugs equally effective for established status epilepticus
according to a study published Nov. 27 in the New England Journal of Medicine. The effectiveness and safety of the intravenous medications do not differ significantly, the researchers wrote.
“Having three equally effective second-line intravenous medications means that the clinician may choose a drug that takes into account individual situations,” wrote Phil E.M. Smith, MD, in an accompanying editorial (doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1913775). Clinicians may consider “factors such as the presumed underlying cause of status epilepticus; coexisting conditions, including allergy, liver and renal disease, hypotension, propensity to cardiac arrhythmia, and alcohol and drug dependence; the currently prescribed antiepileptic treatment; the cost of the medication; and governmental agency drug approval,” said Dr. Smith, who is affiliated with University Hospital of Wales in Cardiff.
A gap in guidance
Evidence supports benzodiazepines as the initial treatment for status epilepticus, but these drugs do not work in up to a third of patients, said first study author Jaideep Kapur, MBBS, PhD, and colleagues. “Clinical guidelines emphasize the need for rapid control of benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus but do not provide guidance regarding the choice of medication on the basis of either efficacy or safety,” they wrote. Dr. Kapur is a professor of neurology and the director of UVA Brain Institute at University of Virginia in Charlottesville.
Levetiracetam, fosphenytoin, and valproate are the three most commonly used medications for benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus. The Food and Drug Administration has labeled fosphenytoin for this indication in adults, and none of the drugs is approved for children. To determine the superiority or inferiority of these medications, the researchers conducted the Established Status Epilepticus Treatment Trial (ESETT). The blinded, comparative-effectiveness trial enrolled 384 patients at 57 hospital EDs in the United States. Patients were aged 2 years or older, had received a generally accepted cumulative dose of benzodiazepines for generalized convulsive seizures lasting more than 5 minutes and continued to have persistent or recurrent convulsions between 5-30 minutes after the last dose of benzodiazepine.
Patients randomly received one of the three trial drugs, which “were identical in appearance, formulation, packaging, and administration,” the authors said. The primary outcome was absence of clinically apparent seizures and improving responsiveness at 60 minutes after the start of the infusion without administration of additional anticonvulsant medication. ED physicians determined the presence of seizure and improvement in responsiveness.
Trial was stopped for futility
The trial included 400 enrollments of 384 unique patients during 2015-2017. Sixteen patients were enrolled twice, and their second enrollments were not included in the intention-to-treat analysis. A planned interim analysis after 400 enrollments to assess the likelihood of success or futility found that the trial had met the futility criterion. “There was a 1% chance of showing a most effective or least effective treatment if the trial were to continue to the maximum sample size” of 795 patients, Dr. Kapur and coauthors wrote. The researchers continued enrollment in a pediatric subcohort for a planned subgroup analysis by age.
In all, 55% of the patients were male, 43% were black, and 16% were Hispanic. The population was 39% children and adolescents, 48% adults aged 18-65 years, and 13% older than 65 years. Most patients had a final diagnosis of status epilepticus (87%). Other final diagnoses included psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (10%).
At 60 minutes after treatment administration, absence of seizures and improved responsiveness occurred in 47% of patients who received levetiracetam, 45% who received fosphenytoin, and 46% who received valproate.
In 39 patients for whom the researchers had reliable information about time to seizure cessation, median time to seizure cessation numerically favored valproate (7 minutes for valproate vs. 10.5 minutes for levetiracetam vs. 11.7 minutes for fosphenytoin), but the number of patients was limited, the authors noted.
“Hypotension and endotracheal intubation were more frequent with fosphenytoin than with the other two drugs, and deaths were more frequent with levetiracetam, but these differences were not significant,” wrote Dr. Kapur and colleagues. Seven patients who received levetiracetam died, compared with three who received fosphenytoin and two who received valproate. Life-threatening hypotension occurred in 3.2% of patients who received fosphenytoin, compared with 1.6% who received valproate and 0.7% who received levetiracetam. Endotracheal intubation occurred in 26.4% or patients who received fosphenytoin, compared with 20% of patients in the levetiracetam group and 16.8% in the valproate group.
The trial’s limitations include the enrollment of patients with psychogenic nonepileptic seizures and the use of clinical instead of electroencephalographic criteria for the primary outcome measure, the investigators wrote.
Dr. Smith noted that third- and fourth-line management of status epilepticus is not supported by high-quality evidence, and further studies are needed. Given the evidence from ESETT, “the practical challenge for the management of status epilepticus remains the same as in the past: ensuring that clinicians are familiar with, and follow, a treatment protocol,” he said.
The trial was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Kapur had no financial disclosures. A coauthor holds a patent on intravenous carbamazepine and intellectual property on intravenous topiramate. Other coauthors have ties to pharmaceutical and medical device companies.
Dr. Smith is coeditor of Practical Neurology and a member of the U.K. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidelines committee for epilepsy.
SOURCE: Kapur J et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1905795.
according to a study published Nov. 27 in the New England Journal of Medicine. The effectiveness and safety of the intravenous medications do not differ significantly, the researchers wrote.
“Having three equally effective second-line intravenous medications means that the clinician may choose a drug that takes into account individual situations,” wrote Phil E.M. Smith, MD, in an accompanying editorial (doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1913775). Clinicians may consider “factors such as the presumed underlying cause of status epilepticus; coexisting conditions, including allergy, liver and renal disease, hypotension, propensity to cardiac arrhythmia, and alcohol and drug dependence; the currently prescribed antiepileptic treatment; the cost of the medication; and governmental agency drug approval,” said Dr. Smith, who is affiliated with University Hospital of Wales in Cardiff.
A gap in guidance
Evidence supports benzodiazepines as the initial treatment for status epilepticus, but these drugs do not work in up to a third of patients, said first study author Jaideep Kapur, MBBS, PhD, and colleagues. “Clinical guidelines emphasize the need for rapid control of benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus but do not provide guidance regarding the choice of medication on the basis of either efficacy or safety,” they wrote. Dr. Kapur is a professor of neurology and the director of UVA Brain Institute at University of Virginia in Charlottesville.
Levetiracetam, fosphenytoin, and valproate are the three most commonly used medications for benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus. The Food and Drug Administration has labeled fosphenytoin for this indication in adults, and none of the drugs is approved for children. To determine the superiority or inferiority of these medications, the researchers conducted the Established Status Epilepticus Treatment Trial (ESETT). The blinded, comparative-effectiveness trial enrolled 384 patients at 57 hospital EDs in the United States. Patients were aged 2 years or older, had received a generally accepted cumulative dose of benzodiazepines for generalized convulsive seizures lasting more than 5 minutes and continued to have persistent or recurrent convulsions between 5-30 minutes after the last dose of benzodiazepine.
Patients randomly received one of the three trial drugs, which “were identical in appearance, formulation, packaging, and administration,” the authors said. The primary outcome was absence of clinically apparent seizures and improving responsiveness at 60 minutes after the start of the infusion without administration of additional anticonvulsant medication. ED physicians determined the presence of seizure and improvement in responsiveness.
Trial was stopped for futility
The trial included 400 enrollments of 384 unique patients during 2015-2017. Sixteen patients were enrolled twice, and their second enrollments were not included in the intention-to-treat analysis. A planned interim analysis after 400 enrollments to assess the likelihood of success or futility found that the trial had met the futility criterion. “There was a 1% chance of showing a most effective or least effective treatment if the trial were to continue to the maximum sample size” of 795 patients, Dr. Kapur and coauthors wrote. The researchers continued enrollment in a pediatric subcohort for a planned subgroup analysis by age.
In all, 55% of the patients were male, 43% were black, and 16% were Hispanic. The population was 39% children and adolescents, 48% adults aged 18-65 years, and 13% older than 65 years. Most patients had a final diagnosis of status epilepticus (87%). Other final diagnoses included psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (10%).
At 60 minutes after treatment administration, absence of seizures and improved responsiveness occurred in 47% of patients who received levetiracetam, 45% who received fosphenytoin, and 46% who received valproate.
In 39 patients for whom the researchers had reliable information about time to seizure cessation, median time to seizure cessation numerically favored valproate (7 minutes for valproate vs. 10.5 minutes for levetiracetam vs. 11.7 minutes for fosphenytoin), but the number of patients was limited, the authors noted.
“Hypotension and endotracheal intubation were more frequent with fosphenytoin than with the other two drugs, and deaths were more frequent with levetiracetam, but these differences were not significant,” wrote Dr. Kapur and colleagues. Seven patients who received levetiracetam died, compared with three who received fosphenytoin and two who received valproate. Life-threatening hypotension occurred in 3.2% of patients who received fosphenytoin, compared with 1.6% who received valproate and 0.7% who received levetiracetam. Endotracheal intubation occurred in 26.4% or patients who received fosphenytoin, compared with 20% of patients in the levetiracetam group and 16.8% in the valproate group.
The trial’s limitations include the enrollment of patients with psychogenic nonepileptic seizures and the use of clinical instead of electroencephalographic criteria for the primary outcome measure, the investigators wrote.
Dr. Smith noted that third- and fourth-line management of status epilepticus is not supported by high-quality evidence, and further studies are needed. Given the evidence from ESETT, “the practical challenge for the management of status epilepticus remains the same as in the past: ensuring that clinicians are familiar with, and follow, a treatment protocol,” he said.
The trial was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Kapur had no financial disclosures. A coauthor holds a patent on intravenous carbamazepine and intellectual property on intravenous topiramate. Other coauthors have ties to pharmaceutical and medical device companies.
Dr. Smith is coeditor of Practical Neurology and a member of the U.K. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidelines committee for epilepsy.
SOURCE: Kapur J et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1905795.
according to a study published Nov. 27 in the New England Journal of Medicine. The effectiveness and safety of the intravenous medications do not differ significantly, the researchers wrote.
“Having three equally effective second-line intravenous medications means that the clinician may choose a drug that takes into account individual situations,” wrote Phil E.M. Smith, MD, in an accompanying editorial (doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1913775). Clinicians may consider “factors such as the presumed underlying cause of status epilepticus; coexisting conditions, including allergy, liver and renal disease, hypotension, propensity to cardiac arrhythmia, and alcohol and drug dependence; the currently prescribed antiepileptic treatment; the cost of the medication; and governmental agency drug approval,” said Dr. Smith, who is affiliated with University Hospital of Wales in Cardiff.
A gap in guidance
Evidence supports benzodiazepines as the initial treatment for status epilepticus, but these drugs do not work in up to a third of patients, said first study author Jaideep Kapur, MBBS, PhD, and colleagues. “Clinical guidelines emphasize the need for rapid control of benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus but do not provide guidance regarding the choice of medication on the basis of either efficacy or safety,” they wrote. Dr. Kapur is a professor of neurology and the director of UVA Brain Institute at University of Virginia in Charlottesville.
Levetiracetam, fosphenytoin, and valproate are the three most commonly used medications for benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus. The Food and Drug Administration has labeled fosphenytoin for this indication in adults, and none of the drugs is approved for children. To determine the superiority or inferiority of these medications, the researchers conducted the Established Status Epilepticus Treatment Trial (ESETT). The blinded, comparative-effectiveness trial enrolled 384 patients at 57 hospital EDs in the United States. Patients were aged 2 years or older, had received a generally accepted cumulative dose of benzodiazepines for generalized convulsive seizures lasting more than 5 minutes and continued to have persistent or recurrent convulsions between 5-30 minutes after the last dose of benzodiazepine.
Patients randomly received one of the three trial drugs, which “were identical in appearance, formulation, packaging, and administration,” the authors said. The primary outcome was absence of clinically apparent seizures and improving responsiveness at 60 minutes after the start of the infusion without administration of additional anticonvulsant medication. ED physicians determined the presence of seizure and improvement in responsiveness.
Trial was stopped for futility
The trial included 400 enrollments of 384 unique patients during 2015-2017. Sixteen patients were enrolled twice, and their second enrollments were not included in the intention-to-treat analysis. A planned interim analysis after 400 enrollments to assess the likelihood of success or futility found that the trial had met the futility criterion. “There was a 1% chance of showing a most effective or least effective treatment if the trial were to continue to the maximum sample size” of 795 patients, Dr. Kapur and coauthors wrote. The researchers continued enrollment in a pediatric subcohort for a planned subgroup analysis by age.
In all, 55% of the patients were male, 43% were black, and 16% were Hispanic. The population was 39% children and adolescents, 48% adults aged 18-65 years, and 13% older than 65 years. Most patients had a final diagnosis of status epilepticus (87%). Other final diagnoses included psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (10%).
At 60 minutes after treatment administration, absence of seizures and improved responsiveness occurred in 47% of patients who received levetiracetam, 45% who received fosphenytoin, and 46% who received valproate.
In 39 patients for whom the researchers had reliable information about time to seizure cessation, median time to seizure cessation numerically favored valproate (7 minutes for valproate vs. 10.5 minutes for levetiracetam vs. 11.7 minutes for fosphenytoin), but the number of patients was limited, the authors noted.
“Hypotension and endotracheal intubation were more frequent with fosphenytoin than with the other two drugs, and deaths were more frequent with levetiracetam, but these differences were not significant,” wrote Dr. Kapur and colleagues. Seven patients who received levetiracetam died, compared with three who received fosphenytoin and two who received valproate. Life-threatening hypotension occurred in 3.2% of patients who received fosphenytoin, compared with 1.6% who received valproate and 0.7% who received levetiracetam. Endotracheal intubation occurred in 26.4% or patients who received fosphenytoin, compared with 20% of patients in the levetiracetam group and 16.8% in the valproate group.
The trial’s limitations include the enrollment of patients with psychogenic nonepileptic seizures and the use of clinical instead of electroencephalographic criteria for the primary outcome measure, the investigators wrote.
Dr. Smith noted that third- and fourth-line management of status epilepticus is not supported by high-quality evidence, and further studies are needed. Given the evidence from ESETT, “the practical challenge for the management of status epilepticus remains the same as in the past: ensuring that clinicians are familiar with, and follow, a treatment protocol,” he said.
The trial was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Kapur had no financial disclosures. A coauthor holds a patent on intravenous carbamazepine and intellectual property on intravenous topiramate. Other coauthors have ties to pharmaceutical and medical device companies.
Dr. Smith is coeditor of Practical Neurology and a member of the U.K. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidelines committee for epilepsy.
SOURCE: Kapur J et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1905795.
FROM NEJM
Key clinical point: Among children and adults with benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus, fosphenytoin, valproate, and levetiracetam each stop seizures by 60 minutes in approximately half of patients.
Major finding: Absence of seizures and improved responsiveness occurred in 47% of patients who received levetiracetam, 45% who received fosphenytoin, and 46% who received valproate.
Study details: The Established Status Epilepticus Treatment Trial (ESETT) was a blinded, comparative-effectiveness trial that enrolled 384 patients at 57 hospital EDs in the United States.
Disclosures: The trial was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Kapur had no financial disclosures. A coauthor holds a patent on intravenous carbamazepine and intellectual property on intravenous topiramate. Other coauthors have ties to pharmaceutical and medical device companies.
Source: Kapur J et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1905795.
‘Remarkable’ seizure-free rates seen with adjunctive cenobamate
In addition, “high rates of seizure freedom were observed with doses of 200 mg and 400 mg,” investigators reported in the Lancet Neurology.
During a 12-week maintenance phase, 21% of patients who received cenobamate 400 mg/day and 11% who received cenobamate 200 mg/day were seizure free, compared with 1% who received placebo. “These data suggest that cenobamate might be a safe and effective treatment option in patients with uncontrolled focal (partial)-onset seizures,” the authors wrote.
On Nov. 21, 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved cenobamate tablets, marketed as Xcopri, to treat focal-onset seizures in adults. The agency noted that hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with cenobamate in two randomized, controlled studies and that one patient died when the drug was titrated rapidly during one of the studies that has not been published yet.
Researchers think that cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative, reduces neuronal excitability “by enhancing the fast and slow inactivation of sodium channels and by inhibiting the persistent component of the sodium channel current,” wrote Gregory L. Krauss, MD, a professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The rates of seizure freedom with adjunctive cenobamate in the published trial are “a remarkable finding,” wrote Stephan Arnold, MD, an epilepsy specialist at Neurozentrum Nymphenburg in Munich, in an accompanying commentary. Twenty of 95 patients in the 400-mg/day group and 11 of 98 patients in the 200-mg/day group “had no seizures during the 12-week maintenance phase, whereas only 1 patient (1%) of the placebo group remained free of seizures during this period,” Dr. Arnold wrote. “To my knowledge, a seizure freedom rate of 20% or higher has not yet been reported in a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of anticonvulsive drugs.”
Still, clinical trials in general are limited by their inclusion and exclusion criteria, relatively short maintenance phases, and the need to keep the dosage of concomitant drugs unchanged during the study, Dr. Arnold noted. “Thus, future findings under real-life conditions will reveal the clinical relevance of cenobamate.”
Hypersensitivity reactions led to protocol adjustments
During the trial, the investigators amended the protocol to lower the starting dose of cenobamate and slow the rate of up-titration to address a risk of allergic drug reactions. “Three hypersensitivity reactions, characterized as rash with involvement of at least one other body system, were reported in three patients” who were assigned to receive cenobamate 200 mg/day, the authors wrote. One case of pruritic rash accompanied by pyrexia occurred on day 10 during the initial faster titration protocol. In another case, “a rash and facial swelling occurred on day 57 in a patient who underwent the amended titration protocol.” These two patients discontinued treatment, and the rashes resolved.
“The third hypersensitivity reaction was a serious case of drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms that occurred starting on day 24 of treatment in a patient randomly assigned to receive 200 mg/day of cenobamate during the faster initial titration protocol,” the authors wrote. “Treatment was discontinued and the patient was treated with corticosteroids and recovered within 2 months.”
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events included somnolence, dizziness, and fatigue. Most events were mild or moderate. The rate of titration and an inability to adjust the dose of concomitant medications may have contributed to the rate of adverse events, the researchers noted. Treatment-emergent adverse events were most frequent in the 400-mg/day group and led to treatment discontinuation in 20% of patients in this group. An ongoing phase 3 study is assessing a lower starting dose and slower titration rate.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
The 18-week, double-blind, randomized trial published in Lancet Neurology is one of two phase 2 clinical trials of cenobamate. The other phase 2 study, which lasted 12 weeks, is pending publication. For the 18-week study, researchers at 107 centers in 16 countries enrolled more than 430 adults aged 18-70 years with uncontrolled focal epilepsy. Patients were taking one to three concomitant antiepileptic drugs at stable doses for at least 4 weeks before screening. Patients completed an 8-week baseline assessment, followed by a 6-week titration phase and a 12-week maintenance phase.
“During the 8-week baseline assessment, patients had to have eight or more focal aware (simple partial) seizures with a motor component, focal impaired awareness (complex partial) seizures, or focal to bilateral tonic-clonic (secondarily generalized) seizures, with a seizure-free interval of less than 25 days,” Dr. Krauss and colleagues wrote. In addition, participants had to have at least three of these seizures during the first 4 weeks of the baseline assessment and at least three during the last 4 weeks.
The investigators excluded patients who were taking diazepam, phenytoin, or phenobarbital within 1 month of screening because of a potential drug-drug interaction with cenobamate. Other exclusion criteria included clinically significant psychiatric illness and status epilepticus within 3 months of screening.
The researchers assigned patients 1:1:1:1 to receive cenobamate 100 mg/day, cenobamate 200 mg/day, cenobamate 400 mg/day, or placebo. Percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency averaged over 28 days during the 18-week treatment period was the primary efficacy outcome for the FDA. The responder rate (the percentage of patients with at least a 50% reduction from baseline in focal seizure frequency) during the 12-week maintenance phase was the primary efficacy outcome for the European Medicines Agency.
The investigators screened 533 patients and assigned 437 to treatment groups. The modified intention-to-treat population included 434 patients, the modified intention-to-treat maintenance-phase population included 397 patients, and the safety population included 437 patients. The most frequently used concomitant medications were levetiracetam (43%), lamotrigine (32%), and carbamazepine (28%).
The median percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency per 28 days during treatment was –24% for the placebo group and –35.5% for the cenobamate 100-mg group. The cenobamate 200 mg group and the cenobamate 400-mg/day group each had a change of –55%.
Responder rates during the maintenance phase were 25% for the placebo group, 40% for the 100-mg group, 56% for the 200-mg group, and 64% for the 400-mg group.
The implications of seizure freedom
The authors acknowledged that it is “difficult to interpret seizure freedom in clinical trials given the constraints of the study designs ... which do not reflect real-life practice. Nonetheless, seizure freedom is of great clinical significance to patient quality of life and the rates reported in this study are notable relative to all other pivotal studies of antiepileptic drug treatment in uncontrolled focal seizures over the past 25 years.”
Rates of seizure freedom represent a crucial outcome measure, Dr. Arnold wrote in his commentary.
“For individual patients, it is not a seizure reduction of 50% or even higher that counts, since this effect will not allow them to drive a car or to work under circumstances bearing increased health risks,” he wrote. “Even when seizure are infrequent, patients nevertheless face the risks of falls, fractures, drowning, and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. It is complete seizure control that gives rise for hope of an independent lifestyle.”
The study was funded by SK Life Science, the developer of cenobamate. One of the study authors is an employee of SK Life Science. Dr. Krauss is a consultant or advisor for Eisai, Otsuka, and Shire and has received research support from Biogen, SK Life Science, and UCB. Dr. Arnold had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Krauss GL et al. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30399-0.
In addition, “high rates of seizure freedom were observed with doses of 200 mg and 400 mg,” investigators reported in the Lancet Neurology.
During a 12-week maintenance phase, 21% of patients who received cenobamate 400 mg/day and 11% who received cenobamate 200 mg/day were seizure free, compared with 1% who received placebo. “These data suggest that cenobamate might be a safe and effective treatment option in patients with uncontrolled focal (partial)-onset seizures,” the authors wrote.
On Nov. 21, 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved cenobamate tablets, marketed as Xcopri, to treat focal-onset seizures in adults. The agency noted that hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with cenobamate in two randomized, controlled studies and that one patient died when the drug was titrated rapidly during one of the studies that has not been published yet.
Researchers think that cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative, reduces neuronal excitability “by enhancing the fast and slow inactivation of sodium channels and by inhibiting the persistent component of the sodium channel current,” wrote Gregory L. Krauss, MD, a professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The rates of seizure freedom with adjunctive cenobamate in the published trial are “a remarkable finding,” wrote Stephan Arnold, MD, an epilepsy specialist at Neurozentrum Nymphenburg in Munich, in an accompanying commentary. Twenty of 95 patients in the 400-mg/day group and 11 of 98 patients in the 200-mg/day group “had no seizures during the 12-week maintenance phase, whereas only 1 patient (1%) of the placebo group remained free of seizures during this period,” Dr. Arnold wrote. “To my knowledge, a seizure freedom rate of 20% or higher has not yet been reported in a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of anticonvulsive drugs.”
Still, clinical trials in general are limited by their inclusion and exclusion criteria, relatively short maintenance phases, and the need to keep the dosage of concomitant drugs unchanged during the study, Dr. Arnold noted. “Thus, future findings under real-life conditions will reveal the clinical relevance of cenobamate.”
Hypersensitivity reactions led to protocol adjustments
During the trial, the investigators amended the protocol to lower the starting dose of cenobamate and slow the rate of up-titration to address a risk of allergic drug reactions. “Three hypersensitivity reactions, characterized as rash with involvement of at least one other body system, were reported in three patients” who were assigned to receive cenobamate 200 mg/day, the authors wrote. One case of pruritic rash accompanied by pyrexia occurred on day 10 during the initial faster titration protocol. In another case, “a rash and facial swelling occurred on day 57 in a patient who underwent the amended titration protocol.” These two patients discontinued treatment, and the rashes resolved.
“The third hypersensitivity reaction was a serious case of drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms that occurred starting on day 24 of treatment in a patient randomly assigned to receive 200 mg/day of cenobamate during the faster initial titration protocol,” the authors wrote. “Treatment was discontinued and the patient was treated with corticosteroids and recovered within 2 months.”
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events included somnolence, dizziness, and fatigue. Most events were mild or moderate. The rate of titration and an inability to adjust the dose of concomitant medications may have contributed to the rate of adverse events, the researchers noted. Treatment-emergent adverse events were most frequent in the 400-mg/day group and led to treatment discontinuation in 20% of patients in this group. An ongoing phase 3 study is assessing a lower starting dose and slower titration rate.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
The 18-week, double-blind, randomized trial published in Lancet Neurology is one of two phase 2 clinical trials of cenobamate. The other phase 2 study, which lasted 12 weeks, is pending publication. For the 18-week study, researchers at 107 centers in 16 countries enrolled more than 430 adults aged 18-70 years with uncontrolled focal epilepsy. Patients were taking one to three concomitant antiepileptic drugs at stable doses for at least 4 weeks before screening. Patients completed an 8-week baseline assessment, followed by a 6-week titration phase and a 12-week maintenance phase.
“During the 8-week baseline assessment, patients had to have eight or more focal aware (simple partial) seizures with a motor component, focal impaired awareness (complex partial) seizures, or focal to bilateral tonic-clonic (secondarily generalized) seizures, with a seizure-free interval of less than 25 days,” Dr. Krauss and colleagues wrote. In addition, participants had to have at least three of these seizures during the first 4 weeks of the baseline assessment and at least three during the last 4 weeks.
The investigators excluded patients who were taking diazepam, phenytoin, or phenobarbital within 1 month of screening because of a potential drug-drug interaction with cenobamate. Other exclusion criteria included clinically significant psychiatric illness and status epilepticus within 3 months of screening.
The researchers assigned patients 1:1:1:1 to receive cenobamate 100 mg/day, cenobamate 200 mg/day, cenobamate 400 mg/day, or placebo. Percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency averaged over 28 days during the 18-week treatment period was the primary efficacy outcome for the FDA. The responder rate (the percentage of patients with at least a 50% reduction from baseline in focal seizure frequency) during the 12-week maintenance phase was the primary efficacy outcome for the European Medicines Agency.
The investigators screened 533 patients and assigned 437 to treatment groups. The modified intention-to-treat population included 434 patients, the modified intention-to-treat maintenance-phase population included 397 patients, and the safety population included 437 patients. The most frequently used concomitant medications were levetiracetam (43%), lamotrigine (32%), and carbamazepine (28%).
The median percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency per 28 days during treatment was –24% for the placebo group and –35.5% for the cenobamate 100-mg group. The cenobamate 200 mg group and the cenobamate 400-mg/day group each had a change of –55%.
Responder rates during the maintenance phase were 25% for the placebo group, 40% for the 100-mg group, 56% for the 200-mg group, and 64% for the 400-mg group.
The implications of seizure freedom
The authors acknowledged that it is “difficult to interpret seizure freedom in clinical trials given the constraints of the study designs ... which do not reflect real-life practice. Nonetheless, seizure freedom is of great clinical significance to patient quality of life and the rates reported in this study are notable relative to all other pivotal studies of antiepileptic drug treatment in uncontrolled focal seizures over the past 25 years.”
Rates of seizure freedom represent a crucial outcome measure, Dr. Arnold wrote in his commentary.
“For individual patients, it is not a seizure reduction of 50% or even higher that counts, since this effect will not allow them to drive a car or to work under circumstances bearing increased health risks,” he wrote. “Even when seizure are infrequent, patients nevertheless face the risks of falls, fractures, drowning, and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. It is complete seizure control that gives rise for hope of an independent lifestyle.”
The study was funded by SK Life Science, the developer of cenobamate. One of the study authors is an employee of SK Life Science. Dr. Krauss is a consultant or advisor for Eisai, Otsuka, and Shire and has received research support from Biogen, SK Life Science, and UCB. Dr. Arnold had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Krauss GL et al. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30399-0.
In addition, “high rates of seizure freedom were observed with doses of 200 mg and 400 mg,” investigators reported in the Lancet Neurology.
During a 12-week maintenance phase, 21% of patients who received cenobamate 400 mg/day and 11% who received cenobamate 200 mg/day were seizure free, compared with 1% who received placebo. “These data suggest that cenobamate might be a safe and effective treatment option in patients with uncontrolled focal (partial)-onset seizures,” the authors wrote.
On Nov. 21, 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved cenobamate tablets, marketed as Xcopri, to treat focal-onset seizures in adults. The agency noted that hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with cenobamate in two randomized, controlled studies and that one patient died when the drug was titrated rapidly during one of the studies that has not been published yet.
Researchers think that cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative, reduces neuronal excitability “by enhancing the fast and slow inactivation of sodium channels and by inhibiting the persistent component of the sodium channel current,” wrote Gregory L. Krauss, MD, a professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The rates of seizure freedom with adjunctive cenobamate in the published trial are “a remarkable finding,” wrote Stephan Arnold, MD, an epilepsy specialist at Neurozentrum Nymphenburg in Munich, in an accompanying commentary. Twenty of 95 patients in the 400-mg/day group and 11 of 98 patients in the 200-mg/day group “had no seizures during the 12-week maintenance phase, whereas only 1 patient (1%) of the placebo group remained free of seizures during this period,” Dr. Arnold wrote. “To my knowledge, a seizure freedom rate of 20% or higher has not yet been reported in a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of anticonvulsive drugs.”
Still, clinical trials in general are limited by their inclusion and exclusion criteria, relatively short maintenance phases, and the need to keep the dosage of concomitant drugs unchanged during the study, Dr. Arnold noted. “Thus, future findings under real-life conditions will reveal the clinical relevance of cenobamate.”
Hypersensitivity reactions led to protocol adjustments
During the trial, the investigators amended the protocol to lower the starting dose of cenobamate and slow the rate of up-titration to address a risk of allergic drug reactions. “Three hypersensitivity reactions, characterized as rash with involvement of at least one other body system, were reported in three patients” who were assigned to receive cenobamate 200 mg/day, the authors wrote. One case of pruritic rash accompanied by pyrexia occurred on day 10 during the initial faster titration protocol. In another case, “a rash and facial swelling occurred on day 57 in a patient who underwent the amended titration protocol.” These two patients discontinued treatment, and the rashes resolved.
“The third hypersensitivity reaction was a serious case of drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms that occurred starting on day 24 of treatment in a patient randomly assigned to receive 200 mg/day of cenobamate during the faster initial titration protocol,” the authors wrote. “Treatment was discontinued and the patient was treated with corticosteroids and recovered within 2 months.”
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events included somnolence, dizziness, and fatigue. Most events were mild or moderate. The rate of titration and an inability to adjust the dose of concomitant medications may have contributed to the rate of adverse events, the researchers noted. Treatment-emergent adverse events were most frequent in the 400-mg/day group and led to treatment discontinuation in 20% of patients in this group. An ongoing phase 3 study is assessing a lower starting dose and slower titration rate.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
The 18-week, double-blind, randomized trial published in Lancet Neurology is one of two phase 2 clinical trials of cenobamate. The other phase 2 study, which lasted 12 weeks, is pending publication. For the 18-week study, researchers at 107 centers in 16 countries enrolled more than 430 adults aged 18-70 years with uncontrolled focal epilepsy. Patients were taking one to three concomitant antiepileptic drugs at stable doses for at least 4 weeks before screening. Patients completed an 8-week baseline assessment, followed by a 6-week titration phase and a 12-week maintenance phase.
“During the 8-week baseline assessment, patients had to have eight or more focal aware (simple partial) seizures with a motor component, focal impaired awareness (complex partial) seizures, or focal to bilateral tonic-clonic (secondarily generalized) seizures, with a seizure-free interval of less than 25 days,” Dr. Krauss and colleagues wrote. In addition, participants had to have at least three of these seizures during the first 4 weeks of the baseline assessment and at least three during the last 4 weeks.
The investigators excluded patients who were taking diazepam, phenytoin, or phenobarbital within 1 month of screening because of a potential drug-drug interaction with cenobamate. Other exclusion criteria included clinically significant psychiatric illness and status epilepticus within 3 months of screening.
The researchers assigned patients 1:1:1:1 to receive cenobamate 100 mg/day, cenobamate 200 mg/day, cenobamate 400 mg/day, or placebo. Percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency averaged over 28 days during the 18-week treatment period was the primary efficacy outcome for the FDA. The responder rate (the percentage of patients with at least a 50% reduction from baseline in focal seizure frequency) during the 12-week maintenance phase was the primary efficacy outcome for the European Medicines Agency.
The investigators screened 533 patients and assigned 437 to treatment groups. The modified intention-to-treat population included 434 patients, the modified intention-to-treat maintenance-phase population included 397 patients, and the safety population included 437 patients. The most frequently used concomitant medications were levetiracetam (43%), lamotrigine (32%), and carbamazepine (28%).
The median percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency per 28 days during treatment was –24% for the placebo group and –35.5% for the cenobamate 100-mg group. The cenobamate 200 mg group and the cenobamate 400-mg/day group each had a change of –55%.
Responder rates during the maintenance phase were 25% for the placebo group, 40% for the 100-mg group, 56% for the 200-mg group, and 64% for the 400-mg group.
The implications of seizure freedom
The authors acknowledged that it is “difficult to interpret seizure freedom in clinical trials given the constraints of the study designs ... which do not reflect real-life practice. Nonetheless, seizure freedom is of great clinical significance to patient quality of life and the rates reported in this study are notable relative to all other pivotal studies of antiepileptic drug treatment in uncontrolled focal seizures over the past 25 years.”
Rates of seizure freedom represent a crucial outcome measure, Dr. Arnold wrote in his commentary.
“For individual patients, it is not a seizure reduction of 50% or even higher that counts, since this effect will not allow them to drive a car or to work under circumstances bearing increased health risks,” he wrote. “Even when seizure are infrequent, patients nevertheless face the risks of falls, fractures, drowning, and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. It is complete seizure control that gives rise for hope of an independent lifestyle.”
The study was funded by SK Life Science, the developer of cenobamate. One of the study authors is an employee of SK Life Science. Dr. Krauss is a consultant or advisor for Eisai, Otsuka, and Shire and has received research support from Biogen, SK Life Science, and UCB. Dr. Arnold had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Krauss GL et al. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30399-0.
FROM LANCET NEUROLOGY
FDA approves acalabrutinib for CLL, SLL treatment
The Food and Drug Administration has approved acalabrutinib (Calquence) as initial or subsequent treatment for adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic leukemia (SLL).
The approval came as part of Project Orbis, a collaboration among the FDA, the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration, and Health Canada. The program allows for the concurrent submission of review of oncology drug applications among the various agencies.
Acalabrutinib, a bruton tyrosin kinase inhibitor, is already approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy. The FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation to acalabrutinib as a monotherapy for adults with CLL in August 2019, allowing for an expedited review.
The approval in CLL/SLL was based on results from two randomized clinical trials comparing acalabrutinib with other standard treatments. In the first trial, patients with previously untreated CLL who received acalabrutinib had a longer progression-free survival time, compared with patients who received standard treatment. A similar result was seen in the second trial among patients with previously treated CLL.
The most common adverse events associated with acalabrutinib include anemia, neutropenia, upper respiratory tract infection, thrombocytopenia, headache, diarrhea, and musculoskeletal pain. Patients receiving the drug should be monitored for symptoms of arrhythmia, serious infection, bleeding, and low blood count. Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved acalabrutinib (Calquence) as initial or subsequent treatment for adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic leukemia (SLL).
The approval came as part of Project Orbis, a collaboration among the FDA, the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration, and Health Canada. The program allows for the concurrent submission of review of oncology drug applications among the various agencies.
Acalabrutinib, a bruton tyrosin kinase inhibitor, is already approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy. The FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation to acalabrutinib as a monotherapy for adults with CLL in August 2019, allowing for an expedited review.
The approval in CLL/SLL was based on results from two randomized clinical trials comparing acalabrutinib with other standard treatments. In the first trial, patients with previously untreated CLL who received acalabrutinib had a longer progression-free survival time, compared with patients who received standard treatment. A similar result was seen in the second trial among patients with previously treated CLL.
The most common adverse events associated with acalabrutinib include anemia, neutropenia, upper respiratory tract infection, thrombocytopenia, headache, diarrhea, and musculoskeletal pain. Patients receiving the drug should be monitored for symptoms of arrhythmia, serious infection, bleeding, and low blood count. Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved acalabrutinib (Calquence) as initial or subsequent treatment for adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic leukemia (SLL).
The approval came as part of Project Orbis, a collaboration among the FDA, the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration, and Health Canada. The program allows for the concurrent submission of review of oncology drug applications among the various agencies.
Acalabrutinib, a bruton tyrosin kinase inhibitor, is already approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy. The FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation to acalabrutinib as a monotherapy for adults with CLL in August 2019, allowing for an expedited review.
The approval in CLL/SLL was based on results from two randomized clinical trials comparing acalabrutinib with other standard treatments. In the first trial, patients with previously untreated CLL who received acalabrutinib had a longer progression-free survival time, compared with patients who received standard treatment. A similar result was seen in the second trial among patients with previously treated CLL.
The most common adverse events associated with acalabrutinib include anemia, neutropenia, upper respiratory tract infection, thrombocytopenia, headache, diarrhea, and musculoskeletal pain. Patients receiving the drug should be monitored for symptoms of arrhythmia, serious infection, bleeding, and low blood count. Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website.
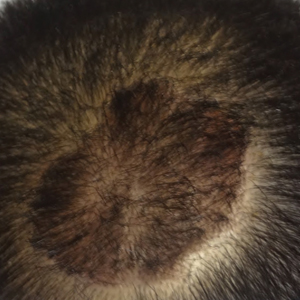
Scalp Psoriasis Considerations
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
Benefits of focused ultrasound thalamotomy for essential tremor persist for 3 years
, according to data published Nov. 20 in Neurology. Improvement from baseline remains significant at that time point, although the magnitude of effect may decrease. In addition, the treatment is not associated with progressive or delayed complications.
“For people who have disabling essential tremor that is not responding to medication, this treatment should be considered as a safe and effective option,” Casey H. Halpern, MD, assistant professor of neurosurgery at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in a press release.
Long-term follow-up of a prospective trial
Focused ultrasound thalamotomy is an emerging treatment for essential tremor. The procedure, which does not require an incision, is conducted with the guidance of magnetic resonance thermometry and patient feedback. A randomized controlled trial conducted by Elias and colleagues indicated that focused ultrasound ventral intermediate nucleus thalamotomy significantly suppressed tremor, reduced disability, and improved quality of life at 3 months, compared with sham treatment. This improvement was sustained at 12 months, and a follow-up study showed that improvements in tremor and functional disability were sustained at 24 months.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues sought to evaluate the continued safety and efficacy of focused ultrasound thalamotomy at 3 years’ follow-up in patients who participated in the original trial. Movement disorder specialists evaluated participants’ tremor severity and functional impairment using the Clinical Rating Scale for Tremor (CRST) at baseline and at 12, 24, and 36 months after treatment. Patients responded to the Quality of Life in Essential Tremor (QUEST) questionnaire, which assesses quality of life at baseline and at each follow-up visit. Neurologists evaluated and recorded all adverse events that occurred during the trial.
Postural tremor was eliminated
The original population included 75 patients who underwent focused ultrasound thalamotomy during the randomized, blinded phase or in an unblinded fashion during the crossover phase. The mean age of all treated patients was 71 years, and disease duration at treatment was 16.8 years. Fifty-two participants were observed at 36 months, and the 3-year attrition rate thus was 31%.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues found that the hand combined tremor–motor score, which was the trial’s primary endpoint, was significantly improved from baseline at 3 years. The median improvement from baseline was 56%. The median disability score decreased by 63% from baseline. Postural tremor was eliminated at 36 months, and QUEST score improved by 50%.
For patients who were missing at 3-year follow-up, data obtained at 3 months was used for comparison. These patients had less improvement in hand tremor–motor score, less reduction in disability, and less reduction in postural tremor, compared with patients who presented for 3-year follow-up. When the investigators reanalyzed their results to account for missing data, they found that the improvement from baseline remained significant.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues compared scores at 36 months and at 6 months to evaluate the durability of the treatment effect. Data were available for 49 patients at both time points, and their combined tremor–motor score had increased by a median of one point at 36 months. Disability score increased by a median of 2 points at 36 months. Posture and QUEST scores did not change significantly. About 58% of patients had at least 50% improvement in hand combined tremor–motor score at 36 months, compared with 64% at 24 months and 61% at 12 months.
The investigators described all adverse events as mild or moderate. No new procedure-related adverse events occurred between 24 and 36 months of follow-up, and none worsened during this period. Two adverse events, however, resolved between 24 and 36 months: one case of dysarthria and one of imbalance.
Reduction in improvement may have many causes
“A reduction in improvement is not unexpected, as essential tremor is a progressive disease,” wrote Dr. Halpern and colleagues. “In addition, diminishing performance of motor–functional tasks over time, particularly in this elderly population, may be multifactorial.” Decrease in tremor control has been reported after all surgical treatments for essential tremor (e.g., deep brain stimulation [DBS] and radiofrequency thalamotomy). Retreatment with invasive therapies or ionizing irradiation would be more problematic than retreatment with focused ultrasound thalamotomy, they added.
The researchers acknowledged that the main limitations of their study were the 31% dropout rate at 3 years and the fact that the cohort at 3-year follow-up differed from those at 2-year follow-up and in the original trial. The results nevertheless “demonstrate persistent, significant tremor reduction, as well as functional and quality of life improvement, with a positive safety profile,” they wrote.
Study funding was provided by the Focused Ultrasound Foundation, the Binational Industrial Research and Development Foundation of Israel, and InSightec, the maker of the focused ultrasound equipment that the researchers used. Dr. Halpern and other investigators received research funding from InSightec. One of the researchers is on the company’s medical advisory board, and another served as a consultant to the company.
Effect on axial tremor is unclear
The 50% improvement in hand tremor, disability, and quality of life that Halpern et al. report is similar to the improvement observed following DBS therapy, said Aparna Wagle Shukla, MD, director of the neurophysiology laboratory at the University of Florida in Gainesville, in an interview. Although the results are promising, neurologists should bear several points in mind, she added.
“DBS-induced side effects often are amenable to programming adjustments. However, similar to radiofrequency thalamotomy, focused ultrasound thalamotomy causes lesion effects. While the study discusses the nature of thalamotomy-induced adverse effects, the clinical practitioners also will benefit from learning about the severity of side effects and how they were individually addressed,” said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “The study acknowledges that there was a 30% dropout rate at 3 years’ follow-up. As the original plan included a 5-year follow-up, it would be beneficial to know why a large fraction of participants discontinued participation earlier than expected.”
Furthermore, the study by Halpern et al. leaves several questions unanswered. It does not indicate, for example, whether focused ultrasound thalamotomy can affect the control of axial tremor, including head and voice tremor, said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “Also, the potential of focused ultrasound thalamotomy to treat complex tremors with possible targeting of multiple brain regions such as ventralis oralis anterior and posterior and zona incerta stimulation is currently not known.
“There is no doubt that focused ultrasound thalamotomy is useful for the control of hand tremors in patients diagnosed with essential tremor, with long-term improvements in quality of life,” Dr. Wagle Shukla continued. “However, it is presently limited in its scope as a unilateral, single-target brain procedure.”
SOURCE: Halpern CH et al. Neurology. 2019 Nov 20 (Epub ahead of print).
, according to data published Nov. 20 in Neurology. Improvement from baseline remains significant at that time point, although the magnitude of effect may decrease. In addition, the treatment is not associated with progressive or delayed complications.
“For people who have disabling essential tremor that is not responding to medication, this treatment should be considered as a safe and effective option,” Casey H. Halpern, MD, assistant professor of neurosurgery at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in a press release.
Long-term follow-up of a prospective trial
Focused ultrasound thalamotomy is an emerging treatment for essential tremor. The procedure, which does not require an incision, is conducted with the guidance of magnetic resonance thermometry and patient feedback. A randomized controlled trial conducted by Elias and colleagues indicated that focused ultrasound ventral intermediate nucleus thalamotomy significantly suppressed tremor, reduced disability, and improved quality of life at 3 months, compared with sham treatment. This improvement was sustained at 12 months, and a follow-up study showed that improvements in tremor and functional disability were sustained at 24 months.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues sought to evaluate the continued safety and efficacy of focused ultrasound thalamotomy at 3 years’ follow-up in patients who participated in the original trial. Movement disorder specialists evaluated participants’ tremor severity and functional impairment using the Clinical Rating Scale for Tremor (CRST) at baseline and at 12, 24, and 36 months after treatment. Patients responded to the Quality of Life in Essential Tremor (QUEST) questionnaire, which assesses quality of life at baseline and at each follow-up visit. Neurologists evaluated and recorded all adverse events that occurred during the trial.
Postural tremor was eliminated
The original population included 75 patients who underwent focused ultrasound thalamotomy during the randomized, blinded phase or in an unblinded fashion during the crossover phase. The mean age of all treated patients was 71 years, and disease duration at treatment was 16.8 years. Fifty-two participants were observed at 36 months, and the 3-year attrition rate thus was 31%.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues found that the hand combined tremor–motor score, which was the trial’s primary endpoint, was significantly improved from baseline at 3 years. The median improvement from baseline was 56%. The median disability score decreased by 63% from baseline. Postural tremor was eliminated at 36 months, and QUEST score improved by 50%.
For patients who were missing at 3-year follow-up, data obtained at 3 months was used for comparison. These patients had less improvement in hand tremor–motor score, less reduction in disability, and less reduction in postural tremor, compared with patients who presented for 3-year follow-up. When the investigators reanalyzed their results to account for missing data, they found that the improvement from baseline remained significant.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues compared scores at 36 months and at 6 months to evaluate the durability of the treatment effect. Data were available for 49 patients at both time points, and their combined tremor–motor score had increased by a median of one point at 36 months. Disability score increased by a median of 2 points at 36 months. Posture and QUEST scores did not change significantly. About 58% of patients had at least 50% improvement in hand combined tremor–motor score at 36 months, compared with 64% at 24 months and 61% at 12 months.
The investigators described all adverse events as mild or moderate. No new procedure-related adverse events occurred between 24 and 36 months of follow-up, and none worsened during this period. Two adverse events, however, resolved between 24 and 36 months: one case of dysarthria and one of imbalance.
Reduction in improvement may have many causes
“A reduction in improvement is not unexpected, as essential tremor is a progressive disease,” wrote Dr. Halpern and colleagues. “In addition, diminishing performance of motor–functional tasks over time, particularly in this elderly population, may be multifactorial.” Decrease in tremor control has been reported after all surgical treatments for essential tremor (e.g., deep brain stimulation [DBS] and radiofrequency thalamotomy). Retreatment with invasive therapies or ionizing irradiation would be more problematic than retreatment with focused ultrasound thalamotomy, they added.
The researchers acknowledged that the main limitations of their study were the 31% dropout rate at 3 years and the fact that the cohort at 3-year follow-up differed from those at 2-year follow-up and in the original trial. The results nevertheless “demonstrate persistent, significant tremor reduction, as well as functional and quality of life improvement, with a positive safety profile,” they wrote.
Study funding was provided by the Focused Ultrasound Foundation, the Binational Industrial Research and Development Foundation of Israel, and InSightec, the maker of the focused ultrasound equipment that the researchers used. Dr. Halpern and other investigators received research funding from InSightec. One of the researchers is on the company’s medical advisory board, and another served as a consultant to the company.
Effect on axial tremor is unclear
The 50% improvement in hand tremor, disability, and quality of life that Halpern et al. report is similar to the improvement observed following DBS therapy, said Aparna Wagle Shukla, MD, director of the neurophysiology laboratory at the University of Florida in Gainesville, in an interview. Although the results are promising, neurologists should bear several points in mind, she added.
“DBS-induced side effects often are amenable to programming adjustments. However, similar to radiofrequency thalamotomy, focused ultrasound thalamotomy causes lesion effects. While the study discusses the nature of thalamotomy-induced adverse effects, the clinical practitioners also will benefit from learning about the severity of side effects and how they were individually addressed,” said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “The study acknowledges that there was a 30% dropout rate at 3 years’ follow-up. As the original plan included a 5-year follow-up, it would be beneficial to know why a large fraction of participants discontinued participation earlier than expected.”
Furthermore, the study by Halpern et al. leaves several questions unanswered. It does not indicate, for example, whether focused ultrasound thalamotomy can affect the control of axial tremor, including head and voice tremor, said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “Also, the potential of focused ultrasound thalamotomy to treat complex tremors with possible targeting of multiple brain regions such as ventralis oralis anterior and posterior and zona incerta stimulation is currently not known.
“There is no doubt that focused ultrasound thalamotomy is useful for the control of hand tremors in patients diagnosed with essential tremor, with long-term improvements in quality of life,” Dr. Wagle Shukla continued. “However, it is presently limited in its scope as a unilateral, single-target brain procedure.”
SOURCE: Halpern CH et al. Neurology. 2019 Nov 20 (Epub ahead of print).
, according to data published Nov. 20 in Neurology. Improvement from baseline remains significant at that time point, although the magnitude of effect may decrease. In addition, the treatment is not associated with progressive or delayed complications.
“For people who have disabling essential tremor that is not responding to medication, this treatment should be considered as a safe and effective option,” Casey H. Halpern, MD, assistant professor of neurosurgery at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in a press release.
Long-term follow-up of a prospective trial
Focused ultrasound thalamotomy is an emerging treatment for essential tremor. The procedure, which does not require an incision, is conducted with the guidance of magnetic resonance thermometry and patient feedback. A randomized controlled trial conducted by Elias and colleagues indicated that focused ultrasound ventral intermediate nucleus thalamotomy significantly suppressed tremor, reduced disability, and improved quality of life at 3 months, compared with sham treatment. This improvement was sustained at 12 months, and a follow-up study showed that improvements in tremor and functional disability were sustained at 24 months.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues sought to evaluate the continued safety and efficacy of focused ultrasound thalamotomy at 3 years’ follow-up in patients who participated in the original trial. Movement disorder specialists evaluated participants’ tremor severity and functional impairment using the Clinical Rating Scale for Tremor (CRST) at baseline and at 12, 24, and 36 months after treatment. Patients responded to the Quality of Life in Essential Tremor (QUEST) questionnaire, which assesses quality of life at baseline and at each follow-up visit. Neurologists evaluated and recorded all adverse events that occurred during the trial.
Postural tremor was eliminated
The original population included 75 patients who underwent focused ultrasound thalamotomy during the randomized, blinded phase or in an unblinded fashion during the crossover phase. The mean age of all treated patients was 71 years, and disease duration at treatment was 16.8 years. Fifty-two participants were observed at 36 months, and the 3-year attrition rate thus was 31%.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues found that the hand combined tremor–motor score, which was the trial’s primary endpoint, was significantly improved from baseline at 3 years. The median improvement from baseline was 56%. The median disability score decreased by 63% from baseline. Postural tremor was eliminated at 36 months, and QUEST score improved by 50%.
For patients who were missing at 3-year follow-up, data obtained at 3 months was used for comparison. These patients had less improvement in hand tremor–motor score, less reduction in disability, and less reduction in postural tremor, compared with patients who presented for 3-year follow-up. When the investigators reanalyzed their results to account for missing data, they found that the improvement from baseline remained significant.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues compared scores at 36 months and at 6 months to evaluate the durability of the treatment effect. Data were available for 49 patients at both time points, and their combined tremor–motor score had increased by a median of one point at 36 months. Disability score increased by a median of 2 points at 36 months. Posture and QUEST scores did not change significantly. About 58% of patients had at least 50% improvement in hand combined tremor–motor score at 36 months, compared with 64% at 24 months and 61% at 12 months.
The investigators described all adverse events as mild or moderate. No new procedure-related adverse events occurred between 24 and 36 months of follow-up, and none worsened during this period. Two adverse events, however, resolved between 24 and 36 months: one case of dysarthria and one of imbalance.
Reduction in improvement may have many causes
“A reduction in improvement is not unexpected, as essential tremor is a progressive disease,” wrote Dr. Halpern and colleagues. “In addition, diminishing performance of motor–functional tasks over time, particularly in this elderly population, may be multifactorial.” Decrease in tremor control has been reported after all surgical treatments for essential tremor (e.g., deep brain stimulation [DBS] and radiofrequency thalamotomy). Retreatment with invasive therapies or ionizing irradiation would be more problematic than retreatment with focused ultrasound thalamotomy, they added.
The researchers acknowledged that the main limitations of their study were the 31% dropout rate at 3 years and the fact that the cohort at 3-year follow-up differed from those at 2-year follow-up and in the original trial. The results nevertheless “demonstrate persistent, significant tremor reduction, as well as functional and quality of life improvement, with a positive safety profile,” they wrote.
Study funding was provided by the Focused Ultrasound Foundation, the Binational Industrial Research and Development Foundation of Israel, and InSightec, the maker of the focused ultrasound equipment that the researchers used. Dr. Halpern and other investigators received research funding from InSightec. One of the researchers is on the company’s medical advisory board, and another served as a consultant to the company.
Effect on axial tremor is unclear
The 50% improvement in hand tremor, disability, and quality of life that Halpern et al. report is similar to the improvement observed following DBS therapy, said Aparna Wagle Shukla, MD, director of the neurophysiology laboratory at the University of Florida in Gainesville, in an interview. Although the results are promising, neurologists should bear several points in mind, she added.
“DBS-induced side effects often are amenable to programming adjustments. However, similar to radiofrequency thalamotomy, focused ultrasound thalamotomy causes lesion effects. While the study discusses the nature of thalamotomy-induced adverse effects, the clinical practitioners also will benefit from learning about the severity of side effects and how they were individually addressed,” said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “The study acknowledges that there was a 30% dropout rate at 3 years’ follow-up. As the original plan included a 5-year follow-up, it would be beneficial to know why a large fraction of participants discontinued participation earlier than expected.”
Furthermore, the study by Halpern et al. leaves several questions unanswered. It does not indicate, for example, whether focused ultrasound thalamotomy can affect the control of axial tremor, including head and voice tremor, said Dr. Wagle Shukla. “Also, the potential of focused ultrasound thalamotomy to treat complex tremors with possible targeting of multiple brain regions such as ventralis oralis anterior and posterior and zona incerta stimulation is currently not known.
“There is no doubt that focused ultrasound thalamotomy is useful for the control of hand tremors in patients diagnosed with essential tremor, with long-term improvements in quality of life,” Dr. Wagle Shukla continued. “However, it is presently limited in its scope as a unilateral, single-target brain procedure.”
SOURCE: Halpern CH et al. Neurology. 2019 Nov 20 (Epub ahead of print).
FROM NEUROLOGY
Frontline ibrutinib saves money over chemoimmunotherapy
Ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with lower total health care costs compared with chemoimmunotherapy in the frontline treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to a retrospective study.
“This study compared time to next treatment, health care resource utilization, and total direct costs among patients with CLL initiating front-line ibrutinib single agent or chemoimmunotherapy,” wrote Bruno Emond, of Analysis Group, Montreal, and colleagues. Their report is in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed data from 1,161 patients with CLL who were started on ibrutinib monotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy from 2014 to 2017. Data were collected from the Optum Clinformatics Extended DataMart De-Identified Databases.
Between the two groups, differences in baseline characteristics were controlled for by way of inverse probability of treatment weighting. Two treatment periods were included in the study: the initial 6 months of treatment and entire duration of frontline therapy.
The team also conducted a subgroup analysis of patients treated with bendamustine and rituximab. This cohort was analyzed independently since the regimen is commonly used in clinical practice.
After analysis, the researchers found that ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with net monthly cost savings of $3,766 (P less than .0001), compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab over the frontline therapy period.
Ibrutinib patients had fewer monthly days with outpatient services (rate ratio, 0.75; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.94; P = .0200), compared with those on chemoimmunotherapy; and were less likely to initiate a next line of treatment, compared with chemoimmunotherapy patients (hazard ratio, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.33-0.90; P = .0163).
“Cost savings and reductions in health care resource utilization were even more pronounced when considering only the first 6 months of front-line treatment,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers acknowledged that two key limitations of the study were the potential influence of unobserved confounding factors and the use of claims data, which could include errors and omissions.
“These results suggest that ibrutinib single-agent is associated with lower total costs driven by lower medical costs, despite higher pharmacy costs, compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab,” they concluded.
The authors reported financial affiliations with Janssen Scientific Affairs, which funded the study, and other companies.
SOURCE: Emond B et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.08.004.
Ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with lower total health care costs compared with chemoimmunotherapy in the frontline treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to a retrospective study.
“This study compared time to next treatment, health care resource utilization, and total direct costs among patients with CLL initiating front-line ibrutinib single agent or chemoimmunotherapy,” wrote Bruno Emond, of Analysis Group, Montreal, and colleagues. Their report is in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed data from 1,161 patients with CLL who were started on ibrutinib monotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy from 2014 to 2017. Data were collected from the Optum Clinformatics Extended DataMart De-Identified Databases.
Between the two groups, differences in baseline characteristics were controlled for by way of inverse probability of treatment weighting. Two treatment periods were included in the study: the initial 6 months of treatment and entire duration of frontline therapy.
The team also conducted a subgroup analysis of patients treated with bendamustine and rituximab. This cohort was analyzed independently since the regimen is commonly used in clinical practice.
After analysis, the researchers found that ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with net monthly cost savings of $3,766 (P less than .0001), compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab over the frontline therapy period.
Ibrutinib patients had fewer monthly days with outpatient services (rate ratio, 0.75; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.94; P = .0200), compared with those on chemoimmunotherapy; and were less likely to initiate a next line of treatment, compared with chemoimmunotherapy patients (hazard ratio, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.33-0.90; P = .0163).
“Cost savings and reductions in health care resource utilization were even more pronounced when considering only the first 6 months of front-line treatment,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers acknowledged that two key limitations of the study were the potential influence of unobserved confounding factors and the use of claims data, which could include errors and omissions.
“These results suggest that ibrutinib single-agent is associated with lower total costs driven by lower medical costs, despite higher pharmacy costs, compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab,” they concluded.
The authors reported financial affiliations with Janssen Scientific Affairs, which funded the study, and other companies.
SOURCE: Emond B et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.08.004.
Ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with lower total health care costs compared with chemoimmunotherapy in the frontline treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to a retrospective study.
“This study compared time to next treatment, health care resource utilization, and total direct costs among patients with CLL initiating front-line ibrutinib single agent or chemoimmunotherapy,” wrote Bruno Emond, of Analysis Group, Montreal, and colleagues. Their report is in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed data from 1,161 patients with CLL who were started on ibrutinib monotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy from 2014 to 2017. Data were collected from the Optum Clinformatics Extended DataMart De-Identified Databases.
Between the two groups, differences in baseline characteristics were controlled for by way of inverse probability of treatment weighting. Two treatment periods were included in the study: the initial 6 months of treatment and entire duration of frontline therapy.
The team also conducted a subgroup analysis of patients treated with bendamustine and rituximab. This cohort was analyzed independently since the regimen is commonly used in clinical practice.
After analysis, the researchers found that ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with net monthly cost savings of $3,766 (P less than .0001), compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab over the frontline therapy period.
Ibrutinib patients had fewer monthly days with outpatient services (rate ratio, 0.75; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.94; P = .0200), compared with those on chemoimmunotherapy; and were less likely to initiate a next line of treatment, compared with chemoimmunotherapy patients (hazard ratio, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.33-0.90; P = .0163).
“Cost savings and reductions in health care resource utilization were even more pronounced when considering only the first 6 months of front-line treatment,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers acknowledged that two key limitations of the study were the potential influence of unobserved confounding factors and the use of claims data, which could include errors and omissions.
“These results suggest that ibrutinib single-agent is associated with lower total costs driven by lower medical costs, despite higher pharmacy costs, compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab,” they concluded.
The authors reported financial affiliations with Janssen Scientific Affairs, which funded the study, and other companies.
SOURCE: Emond B et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.08.004.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Rituximab maintenance has a durable benefit in follicular lymphoma
The benefit of rituximab maintenance therapy in follicular lymphoma is long lasting and evident out to at least 9 years, according to the final efficacy analysis of the PRIMA phase 3, randomized, controlled trial.
Previously reported results of this pivotal trial showed prolongation of progression-free survival and time to next treatment with rituximab maintenance at a follow-up of 3 years and 6 years.
“Rituximab maintenance is now widely recommended for patients with follicular lymphoma responding to first-line rituximab-based immunochemotherapy,” Emmanuel Bachy, MD, PhD, of Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale in Pierre-Bénite, France, and colleagues reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
In PRIMA, patients with previously untreated high–tumor burden follicular lymphoma received any of three immunochemotherapy induction regimens. The 1,018 patients having a response were then randomly assigned to receive 2 years of rituximab (Rituxan) maintenance or observation only.
Dr. Bachy and colleagues performed the trial’s final efficacy analyses, now at a median follow-up of 9 years.
Among the 607 patients consenting to the extended follow-up, median progression-free survival was 10.5 years in the rituximab-maintenance group, compared with 4.1 years in the observation group (hazard ratio, 0.61; P less than .001).
“Subgroup analyses showed the substantial progression-free survival improvement associated with rituximab maintenance was independent of age, sex, induction immunochemotherapy regimen, response to induction, or [Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index] risk score,” the investigators wrote.
Rituximab maintenance also prolonged the median time to next antilymphoma treatment (not reached vs. 6.1 years; hazard ratio, 0.66; P less than .001) and time to next chemotherapy treatment (not reached vs. 9.3 years; hazard ratio, 0.71; P less than .001).
But there was no significant difference in overall survival. Median overall survival was not reached in either group (hazard ratio, 1.04; P = .7948). The estimated 10-year overall survival rate was about 80% in both groups.
“This 9-year follow-up of the PRIMA study demonstrates that rituximab maintenance after induction immunochemotherapy provides a significant long-term [progression-free survival] benefit over observation,” the investigators wrote. “Despite the lack of [overall survival] advantage, it is noteworthy that more than half of the patients in the rituximab maintenance arm remain free of disease progression and have not required new antilymphoma treatment beyond 10 years.”
The trial was sponsored by the Lymphoma Study Association and supported by F. Hoffmann–La Roche and Biogen. Dr. Bachy reported financial disclosures related to Roche and other companies.
SOURCE: Bachy E et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 1;37(31):2815-24.
The benefit of rituximab maintenance therapy in follicular lymphoma is long lasting and evident out to at least 9 years, according to the final efficacy analysis of the PRIMA phase 3, randomized, controlled trial.
Previously reported results of this pivotal trial showed prolongation of progression-free survival and time to next treatment with rituximab maintenance at a follow-up of 3 years and 6 years.
“Rituximab maintenance is now widely recommended for patients with follicular lymphoma responding to first-line rituximab-based immunochemotherapy,” Emmanuel Bachy, MD, PhD, of Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale in Pierre-Bénite, France, and colleagues reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
In PRIMA, patients with previously untreated high–tumor burden follicular lymphoma received any of three immunochemotherapy induction regimens. The 1,018 patients having a response were then randomly assigned to receive 2 years of rituximab (Rituxan) maintenance or observation only.
Dr. Bachy and colleagues performed the trial’s final efficacy analyses, now at a median follow-up of 9 years.
Among the 607 patients consenting to the extended follow-up, median progression-free survival was 10.5 years in the rituximab-maintenance group, compared with 4.1 years in the observation group (hazard ratio, 0.61; P less than .001).
“Subgroup analyses showed the substantial progression-free survival improvement associated with rituximab maintenance was independent of age, sex, induction immunochemotherapy regimen, response to induction, or [Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index] risk score,” the investigators wrote.
Rituximab maintenance also prolonged the median time to next antilymphoma treatment (not reached vs. 6.1 years; hazard ratio, 0.66; P less than .001) and time to next chemotherapy treatment (not reached vs. 9.3 years; hazard ratio, 0.71; P less than .001).
But there was no significant difference in overall survival. Median overall survival was not reached in either group (hazard ratio, 1.04; P = .7948). The estimated 10-year overall survival rate was about 80% in both groups.
“This 9-year follow-up of the PRIMA study demonstrates that rituximab maintenance after induction immunochemotherapy provides a significant long-term [progression-free survival] benefit over observation,” the investigators wrote. “Despite the lack of [overall survival] advantage, it is noteworthy that more than half of the patients in the rituximab maintenance arm remain free of disease progression and have not required new antilymphoma treatment beyond 10 years.”
The trial was sponsored by the Lymphoma Study Association and supported by F. Hoffmann–La Roche and Biogen. Dr. Bachy reported financial disclosures related to Roche and other companies.
SOURCE: Bachy E et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 1;37(31):2815-24.
The benefit of rituximab maintenance therapy in follicular lymphoma is long lasting and evident out to at least 9 years, according to the final efficacy analysis of the PRIMA phase 3, randomized, controlled trial.
Previously reported results of this pivotal trial showed prolongation of progression-free survival and time to next treatment with rituximab maintenance at a follow-up of 3 years and 6 years.
“Rituximab maintenance is now widely recommended for patients with follicular lymphoma responding to first-line rituximab-based immunochemotherapy,” Emmanuel Bachy, MD, PhD, of Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale in Pierre-Bénite, France, and colleagues reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
In PRIMA, patients with previously untreated high–tumor burden follicular lymphoma received any of three immunochemotherapy induction regimens. The 1,018 patients having a response were then randomly assigned to receive 2 years of rituximab (Rituxan) maintenance or observation only.
Dr. Bachy and colleagues performed the trial’s final efficacy analyses, now at a median follow-up of 9 years.
Among the 607 patients consenting to the extended follow-up, median progression-free survival was 10.5 years in the rituximab-maintenance group, compared with 4.1 years in the observation group (hazard ratio, 0.61; P less than .001).
“Subgroup analyses showed the substantial progression-free survival improvement associated with rituximab maintenance was independent of age, sex, induction immunochemotherapy regimen, response to induction, or [Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index] risk score,” the investigators wrote.
Rituximab maintenance also prolonged the median time to next antilymphoma treatment (not reached vs. 6.1 years; hazard ratio, 0.66; P less than .001) and time to next chemotherapy treatment (not reached vs. 9.3 years; hazard ratio, 0.71; P less than .001).
But there was no significant difference in overall survival. Median overall survival was not reached in either group (hazard ratio, 1.04; P = .7948). The estimated 10-year overall survival rate was about 80% in both groups.
“This 9-year follow-up of the PRIMA study demonstrates that rituximab maintenance after induction immunochemotherapy provides a significant long-term [progression-free survival] benefit over observation,” the investigators wrote. “Despite the lack of [overall survival] advantage, it is noteworthy that more than half of the patients in the rituximab maintenance arm remain free of disease progression and have not required new antilymphoma treatment beyond 10 years.”
The trial was sponsored by the Lymphoma Study Association and supported by F. Hoffmann–La Roche and Biogen. Dr. Bachy reported financial disclosures related to Roche and other companies.
SOURCE: Bachy E et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 1;37(31):2815-24.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
CAR T-cell ‘cocktail’ may overcome antigen escape relapse
A chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell “cocktail” targeting both CD19 and CD22 could improve outcomes for patients with refractory or relapsed B-cell malignancies, according to investigators.
This dual approach, which appeared safe and effective, may be able to overcome antigen escape relapse, reported Na Wang, MD, of Huazhong University of Science and Technology in China, and colleagues.
The investigators tested this method in an open-label, single-arm pilot study involving 89 patients with refractory/relapsed B cell malignancies. Of these, 51 patients had B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), while the remaining 38 had non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). All patients had dual expression of CD19 and CD22 on malignant B cells, good performance status, and “essentially” normal organ function, the investigators reported in Blood.
Following lymphodepletion, patients were infused with CAR19 and CAR22 T cells, then evaluated for responses with imaging or bone marrow aspiration on a monthly basis for 6 months, then every 3 months thereafter.
After 30 days, most patients with ALL (96%) achieved a minimal residual disease-negative complete response or complete response with incomplete count recovery. After a median follow-up of 16.7 months, almost half of these responders relapsed (49%), median progression-free survival was 13.6 months, and overall survival was 31 months.
With a minimum follow-up of 3 months, half of the patients with NHL (50%) achieved complete responses, with the caveat that two patients who died of septic shock and severe cytokine release syndrome were excluded from this efficacy analysis. After a median follow-up of 14.4 months, in the NHL group, median progression-free survival was 9.9 months and overall survival was 18 months.
Across disease types, almost all patients (95.5%) experienced cytokine release syndrome, with more than three-quarters (77.6%) categorized as grade 1 or 2. CAR T cell-related encephalopathy syndrome (CRES) occurred in 13.5% of patients; most were low grade, apart from one case that was grade 4. In total, 12 patients died due to adverse events.
“The severe [adverse events] were mostly cytopenias and the most frequent fatal [adverse event] was lung infection, which was attributable in part to the high disease burden and heavy pretreatment of the enrolled patients,” the investigators wrote. “Nearly all the high-grade CRS and CRES were reversible and occurred in similar incidences as previously reported. Thus, the sequential infusion of CAR19/22 T-cell “cocktail” was an efficient and well-tolerated approach to circumvent antigen loss of CD19 or CD22.”
The investigators reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Wang N et al. 2019 Oct 29. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000017.
A chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell “cocktail” targeting both CD19 and CD22 could improve outcomes for patients with refractory or relapsed B-cell malignancies, according to investigators.
This dual approach, which appeared safe and effective, may be able to overcome antigen escape relapse, reported Na Wang, MD, of Huazhong University of Science and Technology in China, and colleagues.
The investigators tested this method in an open-label, single-arm pilot study involving 89 patients with refractory/relapsed B cell malignancies. Of these, 51 patients had B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), while the remaining 38 had non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). All patients had dual expression of CD19 and CD22 on malignant B cells, good performance status, and “essentially” normal organ function, the investigators reported in Blood.
Following lymphodepletion, patients were infused with CAR19 and CAR22 T cells, then evaluated for responses with imaging or bone marrow aspiration on a monthly basis for 6 months, then every 3 months thereafter.
After 30 days, most patients with ALL (96%) achieved a minimal residual disease-negative complete response or complete response with incomplete count recovery. After a median follow-up of 16.7 months, almost half of these responders relapsed (49%), median progression-free survival was 13.6 months, and overall survival was 31 months.
With a minimum follow-up of 3 months, half of the patients with NHL (50%) achieved complete responses, with the caveat that two patients who died of septic shock and severe cytokine release syndrome were excluded from this efficacy analysis. After a median follow-up of 14.4 months, in the NHL group, median progression-free survival was 9.9 months and overall survival was 18 months.
Across disease types, almost all patients (95.5%) experienced cytokine release syndrome, with more than three-quarters (77.6%) categorized as grade 1 or 2. CAR T cell-related encephalopathy syndrome (CRES) occurred in 13.5% of patients; most were low grade, apart from one case that was grade 4. In total, 12 patients died due to adverse events.
“The severe [adverse events] were mostly cytopenias and the most frequent fatal [adverse event] was lung infection, which was attributable in part to the high disease burden and heavy pretreatment of the enrolled patients,” the investigators wrote. “Nearly all the high-grade CRS and CRES were reversible and occurred in similar incidences as previously reported. Thus, the sequential infusion of CAR19/22 T-cell “cocktail” was an efficient and well-tolerated approach to circumvent antigen loss of CD19 or CD22.”
The investigators reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Wang N et al. 2019 Oct 29. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000017.
A chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell “cocktail” targeting both CD19 and CD22 could improve outcomes for patients with refractory or relapsed B-cell malignancies, according to investigators.
This dual approach, which appeared safe and effective, may be able to overcome antigen escape relapse, reported Na Wang, MD, of Huazhong University of Science and Technology in China, and colleagues.
The investigators tested this method in an open-label, single-arm pilot study involving 89 patients with refractory/relapsed B cell malignancies. Of these, 51 patients had B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), while the remaining 38 had non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). All patients had dual expression of CD19 and CD22 on malignant B cells, good performance status, and “essentially” normal organ function, the investigators reported in Blood.
Following lymphodepletion, patients were infused with CAR19 and CAR22 T cells, then evaluated for responses with imaging or bone marrow aspiration on a monthly basis for 6 months, then every 3 months thereafter.
After 30 days, most patients with ALL (96%) achieved a minimal residual disease-negative complete response or complete response with incomplete count recovery. After a median follow-up of 16.7 months, almost half of these responders relapsed (49%), median progression-free survival was 13.6 months, and overall survival was 31 months.
With a minimum follow-up of 3 months, half of the patients with NHL (50%) achieved complete responses, with the caveat that two patients who died of septic shock and severe cytokine release syndrome were excluded from this efficacy analysis. After a median follow-up of 14.4 months, in the NHL group, median progression-free survival was 9.9 months and overall survival was 18 months.
Across disease types, almost all patients (95.5%) experienced cytokine release syndrome, with more than three-quarters (77.6%) categorized as grade 1 or 2. CAR T cell-related encephalopathy syndrome (CRES) occurred in 13.5% of patients; most were low grade, apart from one case that was grade 4. In total, 12 patients died due to adverse events.
“The severe [adverse events] were mostly cytopenias and the most frequent fatal [adverse event] was lung infection, which was attributable in part to the high disease burden and heavy pretreatment of the enrolled patients,” the investigators wrote. “Nearly all the high-grade CRS and CRES were reversible and occurred in similar incidences as previously reported. Thus, the sequential infusion of CAR19/22 T-cell “cocktail” was an efficient and well-tolerated approach to circumvent antigen loss of CD19 or CD22.”
The investigators reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Wang N et al. 2019 Oct 29. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000017.
FROM BLOOD
Adding polatuzumab extends survival in relapsed/refractory DLBCL
For patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding polatuzumab vedotin to bendamustine and rituximab can improve complete response rates and extend overall survival, according to findings from a phase 1b/2 trial.
Adding polatuzumab decreased mortality risk by 58%, reported lead author Laurie H. Sehn, MD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues.
“Patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL, including those who experienced treatment failure with [autologous stem cell transplant], have dismal outcomes with limited therapeutic options,” the investigators wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. “To our knowledge, this is the first randomized trial demonstrating an [overall survival] benefit in patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL.”
In the first part of the study, 27 patients were treated with polatuzumab vedotin, bendamustine, and obinutuzumab. After a median follow-up of 27 months, this regimen returned a complete response rate of 29.6%, median progression-free survival of 6.3 months, and median overall survival of 10.8 months.
In the primary analysis, 80 patients were randomized to receive bendamustine and rituximab, with or without polatuzumab. Adding polatuzumab had a significant benefit, as 40.0% of these patients achieved a complete response, compared with 17.5% of patients who did not receive polatuzumab. After a median follow-up of 22.3 months, outcomes also were significantly improved with the addition of polatuzumab for both median progression-free survival (9.5 vs. 3.7 months) and overall survival (12.4 vs. 4.7 months).
Adding polatuzumab did come with some safety trade-offs. Rates of certain grade 3 or 4 adverse events were higher, including thrombocytopenia (41% vs. 23.1%), neutropenia (46.2% vs. 33.3%), and anemia (28.2% vs. 17.9%), while infection rates were comparable. Almost half of the patients treated with polatuzumab (43.6%) developed grade 1 or 2 peripheral neuropathy, but most cases resolved.
Combination therapy with polatuzumab, bendamustine, and rituximab “represents a novel, effective therapeutic regimen to address the unmet need of patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL,” the investigators wrote. Since just 25% of polatuzumab combination–treated patients had received prior autologous stem cell transplant, the investigators said they could not make definitive conclusions on this combination’s efficacy in the post-ASCT setting.
Additional trials involving polatuzumab in the relapsed/refractory setting are ongoing. For patients with treatment-naive DLBCL, a phase 3 trial (NCT03274492) is evaluating substitution of polatuzumab for vincristine in the R-CHOP regimen.
The study was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Genentech. The investigators reported additional relationships with AbbVie, Kite Pharma, Lundbeck, and others.
SOURCE: Sehn LH et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00172.
For patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding polatuzumab vedotin to bendamustine and rituximab can improve complete response rates and extend overall survival, according to findings from a phase 1b/2 trial.
Adding polatuzumab decreased mortality risk by 58%, reported lead author Laurie H. Sehn, MD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues.
“Patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL, including those who experienced treatment failure with [autologous stem cell transplant], have dismal outcomes with limited therapeutic options,” the investigators wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. “To our knowledge, this is the first randomized trial demonstrating an [overall survival] benefit in patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL.”
In the first part of the study, 27 patients were treated with polatuzumab vedotin, bendamustine, and obinutuzumab. After a median follow-up of 27 months, this regimen returned a complete response rate of 29.6%, median progression-free survival of 6.3 months, and median overall survival of 10.8 months.
In the primary analysis, 80 patients were randomized to receive bendamustine and rituximab, with or without polatuzumab. Adding polatuzumab had a significant benefit, as 40.0% of these patients achieved a complete response, compared with 17.5% of patients who did not receive polatuzumab. After a median follow-up of 22.3 months, outcomes also were significantly improved with the addition of polatuzumab for both median progression-free survival (9.5 vs. 3.7 months) and overall survival (12.4 vs. 4.7 months).
Adding polatuzumab did come with some safety trade-offs. Rates of certain grade 3 or 4 adverse events were higher, including thrombocytopenia (41% vs. 23.1%), neutropenia (46.2% vs. 33.3%), and anemia (28.2% vs. 17.9%), while infection rates were comparable. Almost half of the patients treated with polatuzumab (43.6%) developed grade 1 or 2 peripheral neuropathy, but most cases resolved.
Combination therapy with polatuzumab, bendamustine, and rituximab “represents a novel, effective therapeutic regimen to address the unmet need of patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL,” the investigators wrote. Since just 25% of polatuzumab combination–treated patients had received prior autologous stem cell transplant, the investigators said they could not make definitive conclusions on this combination’s efficacy in the post-ASCT setting.
Additional trials involving polatuzumab in the relapsed/refractory setting are ongoing. For patients with treatment-naive DLBCL, a phase 3 trial (NCT03274492) is evaluating substitution of polatuzumab for vincristine in the R-CHOP regimen.
The study was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Genentech. The investigators reported additional relationships with AbbVie, Kite Pharma, Lundbeck, and others.
SOURCE: Sehn LH et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00172.
For patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding polatuzumab vedotin to bendamustine and rituximab can improve complete response rates and extend overall survival, according to findings from a phase 1b/2 trial.
Adding polatuzumab decreased mortality risk by 58%, reported lead author Laurie H. Sehn, MD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues.
“Patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL, including those who experienced treatment failure with [autologous stem cell transplant], have dismal outcomes with limited therapeutic options,” the investigators wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. “To our knowledge, this is the first randomized trial demonstrating an [overall survival] benefit in patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL.”
In the first part of the study, 27 patients were treated with polatuzumab vedotin, bendamustine, and obinutuzumab. After a median follow-up of 27 months, this regimen returned a complete response rate of 29.6%, median progression-free survival of 6.3 months, and median overall survival of 10.8 months.
In the primary analysis, 80 patients were randomized to receive bendamustine and rituximab, with or without polatuzumab. Adding polatuzumab had a significant benefit, as 40.0% of these patients achieved a complete response, compared with 17.5% of patients who did not receive polatuzumab. After a median follow-up of 22.3 months, outcomes also were significantly improved with the addition of polatuzumab for both median progression-free survival (9.5 vs. 3.7 months) and overall survival (12.4 vs. 4.7 months).
Adding polatuzumab did come with some safety trade-offs. Rates of certain grade 3 or 4 adverse events were higher, including thrombocytopenia (41% vs. 23.1%), neutropenia (46.2% vs. 33.3%), and anemia (28.2% vs. 17.9%), while infection rates were comparable. Almost half of the patients treated with polatuzumab (43.6%) developed grade 1 or 2 peripheral neuropathy, but most cases resolved.
Combination therapy with polatuzumab, bendamustine, and rituximab “represents a novel, effective therapeutic regimen to address the unmet need of patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL,” the investigators wrote. Since just 25% of polatuzumab combination–treated patients had received prior autologous stem cell transplant, the investigators said they could not make definitive conclusions on this combination’s efficacy in the post-ASCT setting.
Additional trials involving polatuzumab in the relapsed/refractory setting are ongoing. For patients with treatment-naive DLBCL, a phase 3 trial (NCT03274492) is evaluating substitution of polatuzumab for vincristine in the R-CHOP regimen.
The study was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Genentech. The investigators reported additional relationships with AbbVie, Kite Pharma, Lundbeck, and others.
SOURCE: Sehn LH et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00172.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY