User login
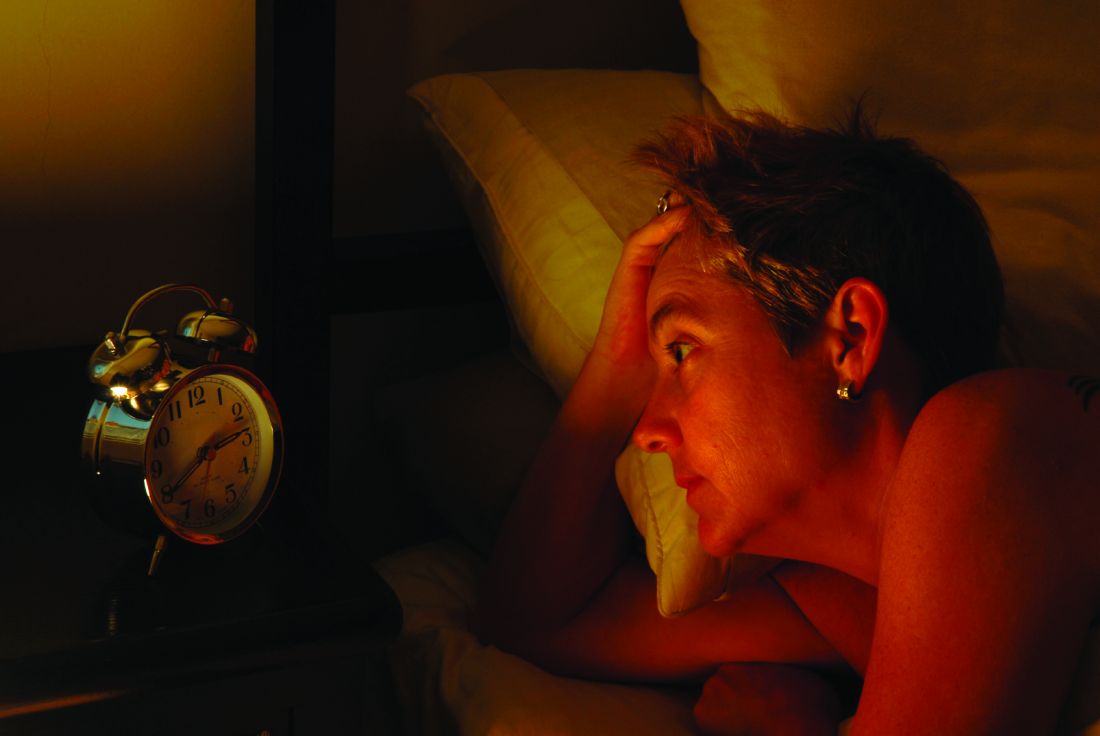
Survey asks adults: How likely are you to develop dementia?
Donovan T. Maust, MD, and colleagues reported in a research letter published in JAMA Neurology.
More than half of study participants used crossword puzzles as a memory exercise, but only 5% said they spoke to their physician about how to reduce risk. Ironically, this lack of communication was also associated with buying unproven over-the-counter memory supplements, while still remaining ignorant of proven ways to head off dementia and other contributing chronic conditions, wrote Dr. Maust of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and coauthors.
Their analysis of the Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging found that close to half of respondents (48.5%) reported that they were at least somewhat likely to develop dementia. Another 4.2% thought dementia was “very likely” in their future.
The study comprised survey responses from 1,019 adults aged 50-64 years. Most rated their physical health either excellent (445 respondents) or good (413 respondents). Most also reported excellent or very good mental health (721 respondents); 234 reported good mental health. Many (678) were affluent, with annual incomes of $60,000 or higher. They tended to be well educated; only 337 were without at least some college education. More than half were white (753); there were 101 Hispanic respondents and 93 black respondents. Other groups made up the remainder.
A multivariate analysis found that black respondents were about half as likely to believe they would develop dementia, compared with whites – an assumption contrary to epidemiologic findings that blacks are more likely than whites to develop dementia.
People who reported fair or poor mental health were more than twice as likely to feel dementia was in their future (odds ratio, 2.3). But fair or poor physical health was not significantly associated with that concern.
“Those with fair to poor physical health did not accurately perceive that their likelihood of developing dementia was potentially higher than respondents with very good or excellent physical health,” the authors wrote. “In contrast, fair to poor mental health had the largest association with perceived likelihood of dementia, even though less evidence suggests that poor mental health is causally linked with dementia.”
Despite the concerns, just 5% of respondents said that they had spoken to their physician. Those who believed they had a high likelihood of dementia were more likely to talk with their clinician (7.1%) than those who believed they had a low risk (3.6%).
Many more, however, were using non–evidence-based compounds touted as memory supporting. These included fish oil or omega-3 fatty acids (31.6%) and vitamins or supplements (32.9%). Crossword puzzles were a very popular prevention strategy, employed by about 55% in both belief groups.
“While managing chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, could reduce dementia risk, few respondents appear to have discussed this with their physician. Given repeated failures of disease-preventing or disease-modifying treatments for dementia, interest in treatment and prevention has shifted earlier in the disease process. Adults in middle age may not accurately estimate their risk of developing dementia, which could lead to both overuse and underuse if preclinical dementia treatments become available. Policy and physicians should emphasize current evidence-based strategies of managing lifestyle and chronic medical conditions to reduce the risk of dementia,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Maust had no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Maust D et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 Nov 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.3946
I do not find it surprising that older adults fear dementia. Since they correctly perceive that there is no disease-modifying therapy (and maybe also that “getting caught with memory loss” would lead to a loss of driving privileges and other restrictions), they may be trying not to focus on it. As for asking about strategies to “prevent” dementia, that question implies unwarranted optimism about the effectiveness of any such strategy, especially in an older adult. I think we can say that a lifetime of healthy habits (regular physical exercise and careful control of any chronic conditions like diabetes being particularly important) may reduce our risk of dementia a bit, but the idea that anything a 75-year-old does is going to prevent it at that point is probably wishful thinking. Supplements and the like seem to have their own followers. It amazes me how many people suspect what they are taking probably does no good but they do it anyway out of blind hope. Sometimes we can talk them out of spending their money on such things – but not always.
Richard Caselli, MD, is associate director and clinical core director of the Alzheimer’s Disease Center at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz.
I do not find it surprising that older adults fear dementia. Since they correctly perceive that there is no disease-modifying therapy (and maybe also that “getting caught with memory loss” would lead to a loss of driving privileges and other restrictions), they may be trying not to focus on it. As for asking about strategies to “prevent” dementia, that question implies unwarranted optimism about the effectiveness of any such strategy, especially in an older adult. I think we can say that a lifetime of healthy habits (regular physical exercise and careful control of any chronic conditions like diabetes being particularly important) may reduce our risk of dementia a bit, but the idea that anything a 75-year-old does is going to prevent it at that point is probably wishful thinking. Supplements and the like seem to have their own followers. It amazes me how many people suspect what they are taking probably does no good but they do it anyway out of blind hope. Sometimes we can talk them out of spending their money on such things – but not always.
Richard Caselli, MD, is associate director and clinical core director of the Alzheimer’s Disease Center at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz.
I do not find it surprising that older adults fear dementia. Since they correctly perceive that there is no disease-modifying therapy (and maybe also that “getting caught with memory loss” would lead to a loss of driving privileges and other restrictions), they may be trying not to focus on it. As for asking about strategies to “prevent” dementia, that question implies unwarranted optimism about the effectiveness of any such strategy, especially in an older adult. I think we can say that a lifetime of healthy habits (regular physical exercise and careful control of any chronic conditions like diabetes being particularly important) may reduce our risk of dementia a bit, but the idea that anything a 75-year-old does is going to prevent it at that point is probably wishful thinking. Supplements and the like seem to have their own followers. It amazes me how many people suspect what they are taking probably does no good but they do it anyway out of blind hope. Sometimes we can talk them out of spending their money on such things – but not always.
Richard Caselli, MD, is associate director and clinical core director of the Alzheimer’s Disease Center at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Donovan T. Maust, MD, and colleagues reported in a research letter published in JAMA Neurology.
More than half of study participants used crossword puzzles as a memory exercise, but only 5% said they spoke to their physician about how to reduce risk. Ironically, this lack of communication was also associated with buying unproven over-the-counter memory supplements, while still remaining ignorant of proven ways to head off dementia and other contributing chronic conditions, wrote Dr. Maust of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and coauthors.
Their analysis of the Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging found that close to half of respondents (48.5%) reported that they were at least somewhat likely to develop dementia. Another 4.2% thought dementia was “very likely” in their future.
The study comprised survey responses from 1,019 adults aged 50-64 years. Most rated their physical health either excellent (445 respondents) or good (413 respondents). Most also reported excellent or very good mental health (721 respondents); 234 reported good mental health. Many (678) were affluent, with annual incomes of $60,000 or higher. They tended to be well educated; only 337 were without at least some college education. More than half were white (753); there were 101 Hispanic respondents and 93 black respondents. Other groups made up the remainder.
A multivariate analysis found that black respondents were about half as likely to believe they would develop dementia, compared with whites – an assumption contrary to epidemiologic findings that blacks are more likely than whites to develop dementia.
People who reported fair or poor mental health were more than twice as likely to feel dementia was in their future (odds ratio, 2.3). But fair or poor physical health was not significantly associated with that concern.
“Those with fair to poor physical health did not accurately perceive that their likelihood of developing dementia was potentially higher than respondents with very good or excellent physical health,” the authors wrote. “In contrast, fair to poor mental health had the largest association with perceived likelihood of dementia, even though less evidence suggests that poor mental health is causally linked with dementia.”
Despite the concerns, just 5% of respondents said that they had spoken to their physician. Those who believed they had a high likelihood of dementia were more likely to talk with their clinician (7.1%) than those who believed they had a low risk (3.6%).
Many more, however, were using non–evidence-based compounds touted as memory supporting. These included fish oil or omega-3 fatty acids (31.6%) and vitamins or supplements (32.9%). Crossword puzzles were a very popular prevention strategy, employed by about 55% in both belief groups.
“While managing chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, could reduce dementia risk, few respondents appear to have discussed this with their physician. Given repeated failures of disease-preventing or disease-modifying treatments for dementia, interest in treatment and prevention has shifted earlier in the disease process. Adults in middle age may not accurately estimate their risk of developing dementia, which could lead to both overuse and underuse if preclinical dementia treatments become available. Policy and physicians should emphasize current evidence-based strategies of managing lifestyle and chronic medical conditions to reduce the risk of dementia,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Maust had no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Maust D et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 Nov 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.3946
Donovan T. Maust, MD, and colleagues reported in a research letter published in JAMA Neurology.
More than half of study participants used crossword puzzles as a memory exercise, but only 5% said they spoke to their physician about how to reduce risk. Ironically, this lack of communication was also associated with buying unproven over-the-counter memory supplements, while still remaining ignorant of proven ways to head off dementia and other contributing chronic conditions, wrote Dr. Maust of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and coauthors.
Their analysis of the Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging found that close to half of respondents (48.5%) reported that they were at least somewhat likely to develop dementia. Another 4.2% thought dementia was “very likely” in their future.
The study comprised survey responses from 1,019 adults aged 50-64 years. Most rated their physical health either excellent (445 respondents) or good (413 respondents). Most also reported excellent or very good mental health (721 respondents); 234 reported good mental health. Many (678) were affluent, with annual incomes of $60,000 or higher. They tended to be well educated; only 337 were without at least some college education. More than half were white (753); there were 101 Hispanic respondents and 93 black respondents. Other groups made up the remainder.
A multivariate analysis found that black respondents were about half as likely to believe they would develop dementia, compared with whites – an assumption contrary to epidemiologic findings that blacks are more likely than whites to develop dementia.
People who reported fair or poor mental health were more than twice as likely to feel dementia was in their future (odds ratio, 2.3). But fair or poor physical health was not significantly associated with that concern.
“Those with fair to poor physical health did not accurately perceive that their likelihood of developing dementia was potentially higher than respondents with very good or excellent physical health,” the authors wrote. “In contrast, fair to poor mental health had the largest association with perceived likelihood of dementia, even though less evidence suggests that poor mental health is causally linked with dementia.”
Despite the concerns, just 5% of respondents said that they had spoken to their physician. Those who believed they had a high likelihood of dementia were more likely to talk with their clinician (7.1%) than those who believed they had a low risk (3.6%).
Many more, however, were using non–evidence-based compounds touted as memory supporting. These included fish oil or omega-3 fatty acids (31.6%) and vitamins or supplements (32.9%). Crossword puzzles were a very popular prevention strategy, employed by about 55% in both belief groups.
“While managing chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, could reduce dementia risk, few respondents appear to have discussed this with their physician. Given repeated failures of disease-preventing or disease-modifying treatments for dementia, interest in treatment and prevention has shifted earlier in the disease process. Adults in middle age may not accurately estimate their risk of developing dementia, which could lead to both overuse and underuse if preclinical dementia treatments become available. Policy and physicians should emphasize current evidence-based strategies of managing lifestyle and chronic medical conditions to reduce the risk of dementia,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Maust had no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Maust D et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 Nov 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.3946
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
FDA approves Brukinsa for relapsed, refractory MCL
The Food and Drug Administration has approved zanubrutinib (Brukinsa) for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is based on results from two separate studies; in a global phase 1/2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory MCL who received zanubrutinib had an overall response rate of 84%, with 22% experiencing a complete response and 62% experiencing partial response. Median duration of response was 18.5 months. The ORR in the second study – a multicenter phase 2 trial – was also 84%, but with 59% experiencing a complete response and 24% experiencing partial response; duration of response was 19.5 months.
The most common adverse events reported during the trials were decreased neutrophil count, decreased platelet count, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased white blood cell count, decreased hemoglobin, rash, bruising, diarrhea, cough, musculoskeletal pain, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, hematuria, fatigue, constipation, and hemorrhage. The most common serious adverse events were pneumonia and hemorrhage.
Of the 118 patients with MCL treated with zanubrutinib over the two trials, 8 had to be discontinued because of adverse events.
The recommended dose of zanubrutinib is 320 mg, taken orally 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily, with or without food.
“BTK [Bruton kinase] inhibition is an established mode of treatment for patients with MCL, but many patients treated with previously approved BTK inhibitors do not fully respond to BTK therapy or are forced to discontinue treatment early due to side effects. Today we have a new option for our adult patients who have received one prior systemic or targeted therapy and are living with MCL,” Luhua (Michael) Wang, MD, clinical trial investigator and professor in the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a statement.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved zanubrutinib (Brukinsa) for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is based on results from two separate studies; in a global phase 1/2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory MCL who received zanubrutinib had an overall response rate of 84%, with 22% experiencing a complete response and 62% experiencing partial response. Median duration of response was 18.5 months. The ORR in the second study – a multicenter phase 2 trial – was also 84%, but with 59% experiencing a complete response and 24% experiencing partial response; duration of response was 19.5 months.
The most common adverse events reported during the trials were decreased neutrophil count, decreased platelet count, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased white blood cell count, decreased hemoglobin, rash, bruising, diarrhea, cough, musculoskeletal pain, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, hematuria, fatigue, constipation, and hemorrhage. The most common serious adverse events were pneumonia and hemorrhage.
Of the 118 patients with MCL treated with zanubrutinib over the two trials, 8 had to be discontinued because of adverse events.
The recommended dose of zanubrutinib is 320 mg, taken orally 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily, with or without food.
“BTK [Bruton kinase] inhibition is an established mode of treatment for patients with MCL, but many patients treated with previously approved BTK inhibitors do not fully respond to BTK therapy or are forced to discontinue treatment early due to side effects. Today we have a new option for our adult patients who have received one prior systemic or targeted therapy and are living with MCL,” Luhua (Michael) Wang, MD, clinical trial investigator and professor in the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a statement.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved zanubrutinib (Brukinsa) for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is based on results from two separate studies; in a global phase 1/2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory MCL who received zanubrutinib had an overall response rate of 84%, with 22% experiencing a complete response and 62% experiencing partial response. Median duration of response was 18.5 months. The ORR in the second study – a multicenter phase 2 trial – was also 84%, but with 59% experiencing a complete response and 24% experiencing partial response; duration of response was 19.5 months.
The most common adverse events reported during the trials were decreased neutrophil count, decreased platelet count, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased white blood cell count, decreased hemoglobin, rash, bruising, diarrhea, cough, musculoskeletal pain, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, hematuria, fatigue, constipation, and hemorrhage. The most common serious adverse events were pneumonia and hemorrhage.
Of the 118 patients with MCL treated with zanubrutinib over the two trials, 8 had to be discontinued because of adverse events.
The recommended dose of zanubrutinib is 320 mg, taken orally 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily, with or without food.
“BTK [Bruton kinase] inhibition is an established mode of treatment for patients with MCL, but many patients treated with previously approved BTK inhibitors do not fully respond to BTK therapy or are forced to discontinue treatment early due to side effects. Today we have a new option for our adult patients who have received one prior systemic or targeted therapy and are living with MCL,” Luhua (Michael) Wang, MD, clinical trial investigator and professor in the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a statement.
Gene signature may help guide initial CLL treatment choice
A novel 17-gene expression signature may help guide the choice of initial treatment in patients with IGHV-unmutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to findings of a retrospective dual cohort study.
“[Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab] was the first regimen to improve progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, and has become a gold-standard chemoimmunotherapy regimen in physically fit patients,” wrote the investigators, who were led by Carmen D. Herling, MD, of the Center for Integrated Oncology, Cologne, Germany; and Kevin R. Coombes, PhD, of Ohio State University, Columbus.
While several studies demonstrate that young, fit patients with mutated IGHV gene and no high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities achieve durable remission with the FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) regimen, there have been no studies to identify if this is true for patients with unmutated IGHV gene, they reported in the Lancet Oncology.
The investigators performed transcriptional profiling using peripheral blood samples collected from two cohorts of patients with CLL who were treated with frontline FCR.
The discovery and training cohort consisted of 101 patients (65% with IGHV-unmutated disease) treated at the MD Anderson Cancer Center who had a median follow-up of about 12 years. The validation cohort consisted of 109 patients with IGHV-unmutated disease treated on the German CLL8 single-arm trial who had a median follow-up of about 6 years.
A total of 1,136 genes showed a significant univariate association with time to progression. Ultimately, 17 of these genes – most of them involved in purine metabolism and oxidative phosphorylation – were included in the expression signature.
Among patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL, the 17-gene signature discriminated between two groups having differing time to progression after their frontline FCR chemoimmunotherapy: an unfavorable prognosis group and an intermediate prognosis group.
The unfavorable prognosis group had a significantly higher relative risk of progression in both the discovery/training cohort (hazard ratio, 3.83; P less than .0001) and the validation cohort (HR, 1.90; P = .008). In the validation cohort, the median time to progression was 39 months among patients with a signature-defined unfavorable prognosis, compared with 59 months among patients with a signature-defined intermediate prognosis.
“We would recommend testing the value of the 17-gene signature in a prospective study that compares FCR treatment with alternative therapies, such as ibrutinib, as part of a randomised clinical trial,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Herling reported financial disclosures related to Hoffmann-La Roche, and Dr. Coombes reported grants from the National Institutes of Health. The study was funded by the Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Global Research Foundation and the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Herling CD et al. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(11):1576-86.
A novel 17-gene expression signature may help guide the choice of initial treatment in patients with IGHV-unmutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to findings of a retrospective dual cohort study.
“[Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab] was the first regimen to improve progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, and has become a gold-standard chemoimmunotherapy regimen in physically fit patients,” wrote the investigators, who were led by Carmen D. Herling, MD, of the Center for Integrated Oncology, Cologne, Germany; and Kevin R. Coombes, PhD, of Ohio State University, Columbus.
While several studies demonstrate that young, fit patients with mutated IGHV gene and no high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities achieve durable remission with the FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) regimen, there have been no studies to identify if this is true for patients with unmutated IGHV gene, they reported in the Lancet Oncology.
The investigators performed transcriptional profiling using peripheral blood samples collected from two cohorts of patients with CLL who were treated with frontline FCR.
The discovery and training cohort consisted of 101 patients (65% with IGHV-unmutated disease) treated at the MD Anderson Cancer Center who had a median follow-up of about 12 years. The validation cohort consisted of 109 patients with IGHV-unmutated disease treated on the German CLL8 single-arm trial who had a median follow-up of about 6 years.
A total of 1,136 genes showed a significant univariate association with time to progression. Ultimately, 17 of these genes – most of them involved in purine metabolism and oxidative phosphorylation – were included in the expression signature.
Among patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL, the 17-gene signature discriminated between two groups having differing time to progression after their frontline FCR chemoimmunotherapy: an unfavorable prognosis group and an intermediate prognosis group.
The unfavorable prognosis group had a significantly higher relative risk of progression in both the discovery/training cohort (hazard ratio, 3.83; P less than .0001) and the validation cohort (HR, 1.90; P = .008). In the validation cohort, the median time to progression was 39 months among patients with a signature-defined unfavorable prognosis, compared with 59 months among patients with a signature-defined intermediate prognosis.
“We would recommend testing the value of the 17-gene signature in a prospective study that compares FCR treatment with alternative therapies, such as ibrutinib, as part of a randomised clinical trial,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Herling reported financial disclosures related to Hoffmann-La Roche, and Dr. Coombes reported grants from the National Institutes of Health. The study was funded by the Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Global Research Foundation and the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Herling CD et al. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(11):1576-86.
A novel 17-gene expression signature may help guide the choice of initial treatment in patients with IGHV-unmutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to findings of a retrospective dual cohort study.
“[Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab] was the first regimen to improve progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, and has become a gold-standard chemoimmunotherapy regimen in physically fit patients,” wrote the investigators, who were led by Carmen D. Herling, MD, of the Center for Integrated Oncology, Cologne, Germany; and Kevin R. Coombes, PhD, of Ohio State University, Columbus.
While several studies demonstrate that young, fit patients with mutated IGHV gene and no high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities achieve durable remission with the FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) regimen, there have been no studies to identify if this is true for patients with unmutated IGHV gene, they reported in the Lancet Oncology.
The investigators performed transcriptional profiling using peripheral blood samples collected from two cohorts of patients with CLL who were treated with frontline FCR.
The discovery and training cohort consisted of 101 patients (65% with IGHV-unmutated disease) treated at the MD Anderson Cancer Center who had a median follow-up of about 12 years. The validation cohort consisted of 109 patients with IGHV-unmutated disease treated on the German CLL8 single-arm trial who had a median follow-up of about 6 years.
A total of 1,136 genes showed a significant univariate association with time to progression. Ultimately, 17 of these genes – most of them involved in purine metabolism and oxidative phosphorylation – were included in the expression signature.
Among patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL, the 17-gene signature discriminated between two groups having differing time to progression after their frontline FCR chemoimmunotherapy: an unfavorable prognosis group and an intermediate prognosis group.
The unfavorable prognosis group had a significantly higher relative risk of progression in both the discovery/training cohort (hazard ratio, 3.83; P less than .0001) and the validation cohort (HR, 1.90; P = .008). In the validation cohort, the median time to progression was 39 months among patients with a signature-defined unfavorable prognosis, compared with 59 months among patients with a signature-defined intermediate prognosis.
“We would recommend testing the value of the 17-gene signature in a prospective study that compares FCR treatment with alternative therapies, such as ibrutinib, as part of a randomised clinical trial,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Herling reported financial disclosures related to Hoffmann-La Roche, and Dr. Coombes reported grants from the National Institutes of Health. The study was funded by the Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Global Research Foundation and the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Herling CD et al. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(11):1576-86.
FROM LANCET ONCOLOGY
Armored CAR T cells elicit responses in NHL patients
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD – An armored chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has demonstrated efficacy in vitro and in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer.
ICTCAR014, a dominant negative PD-1 armored CAR T-cell therapy, proved more cytotoxic than traditional CAR T-cell therapy in vitro and produced responses in 12 of 13 NHL patients who received it.
Xiaobin Victor Lu, PhD, of Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, Shanghai, China, presented results with ICTCAR014 at the meeting.
Dr. Lu explained that ICTCAR014 consists of CD19-targeted CAR T cells genetically engineered to overexpress a PD-1 dominant negative protein with an altered intracellular signaling domain. The dominant negative protein can act as a “decoy receptor” to bind and block the PD-L1/2 inhibitory signal, thereby enhancing the efficacy of CAR T cells.
Innovative Cellular Therapeutics is developing ICTCAR014 because there is “some room to improve” with commercially available CAR T-cell products, Dr. Lu said. Specifically, tisagenlecleucel produced a 52% response rate in the JULIET trial (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:45-56), and axicabtagene ciloleucel produced an 82% response rate in the ZUMA-1 trial (N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2531-44).
There is also evidence to suggest that PD-1 blockade can modulate and “refuel” CAR T cells in relapsed/refractory NHL patients who fail or relapse after traditional anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy (Blood. 2017 Feb 23;129[8]:1039-41). This finding has prompted researchers to conduct trials of PD-1 inhibitors in combination with CAR T-cell therapies. But this combination approach may be expensive and cause more side effects than the armored CAR T-cell approach, Dr. Lu said.
In preclinical studies, Dr. Lu and colleagues found that ICTCAR014 was more effective than traditional anti-CD19 CAR T cells in killing Nalm6-PDL1 cells. In addition, the PD-1 dominant negative protein protected CAR T cells from exhaustion.
Dr. Lu also presented results in 13 NHL patients who have received ICTCAR014 in a phase 1 trial in China. Eleven patients had diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and two had follicular lymphoma.
The objective response rate was 92.3% (12/13), which included five partial responses (38.5%) and seven complete responses (53.8%). Both follicular lymphoma patients and five DLBCL patients achieved a complete response. Five DLBCL patients achieved a partial response, and the remaining DLBCL patient did not respond.
Dr. Lu did not present safety data. However, he reported that there was no increased incidence of cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity in these patients, compared with patients receiving traditional CAR T-cell therapy.
Dr. Lu is employed by Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, which funded the research and is developing ICTCAR014.
SOURCE: Lu V et al. SITC 2019, Abstract O25.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD – An armored chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has demonstrated efficacy in vitro and in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer.
ICTCAR014, a dominant negative PD-1 armored CAR T-cell therapy, proved more cytotoxic than traditional CAR T-cell therapy in vitro and produced responses in 12 of 13 NHL patients who received it.
Xiaobin Victor Lu, PhD, of Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, Shanghai, China, presented results with ICTCAR014 at the meeting.
Dr. Lu explained that ICTCAR014 consists of CD19-targeted CAR T cells genetically engineered to overexpress a PD-1 dominant negative protein with an altered intracellular signaling domain. The dominant negative protein can act as a “decoy receptor” to bind and block the PD-L1/2 inhibitory signal, thereby enhancing the efficacy of CAR T cells.
Innovative Cellular Therapeutics is developing ICTCAR014 because there is “some room to improve” with commercially available CAR T-cell products, Dr. Lu said. Specifically, tisagenlecleucel produced a 52% response rate in the JULIET trial (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:45-56), and axicabtagene ciloleucel produced an 82% response rate in the ZUMA-1 trial (N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2531-44).
There is also evidence to suggest that PD-1 blockade can modulate and “refuel” CAR T cells in relapsed/refractory NHL patients who fail or relapse after traditional anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy (Blood. 2017 Feb 23;129[8]:1039-41). This finding has prompted researchers to conduct trials of PD-1 inhibitors in combination with CAR T-cell therapies. But this combination approach may be expensive and cause more side effects than the armored CAR T-cell approach, Dr. Lu said.
In preclinical studies, Dr. Lu and colleagues found that ICTCAR014 was more effective than traditional anti-CD19 CAR T cells in killing Nalm6-PDL1 cells. In addition, the PD-1 dominant negative protein protected CAR T cells from exhaustion.
Dr. Lu also presented results in 13 NHL patients who have received ICTCAR014 in a phase 1 trial in China. Eleven patients had diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and two had follicular lymphoma.
The objective response rate was 92.3% (12/13), which included five partial responses (38.5%) and seven complete responses (53.8%). Both follicular lymphoma patients and five DLBCL patients achieved a complete response. Five DLBCL patients achieved a partial response, and the remaining DLBCL patient did not respond.
Dr. Lu did not present safety data. However, he reported that there was no increased incidence of cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity in these patients, compared with patients receiving traditional CAR T-cell therapy.
Dr. Lu is employed by Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, which funded the research and is developing ICTCAR014.
SOURCE: Lu V et al. SITC 2019, Abstract O25.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD – An armored chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has demonstrated efficacy in vitro and in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer.
ICTCAR014, a dominant negative PD-1 armored CAR T-cell therapy, proved more cytotoxic than traditional CAR T-cell therapy in vitro and produced responses in 12 of 13 NHL patients who received it.
Xiaobin Victor Lu, PhD, of Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, Shanghai, China, presented results with ICTCAR014 at the meeting.
Dr. Lu explained that ICTCAR014 consists of CD19-targeted CAR T cells genetically engineered to overexpress a PD-1 dominant negative protein with an altered intracellular signaling domain. The dominant negative protein can act as a “decoy receptor” to bind and block the PD-L1/2 inhibitory signal, thereby enhancing the efficacy of CAR T cells.
Innovative Cellular Therapeutics is developing ICTCAR014 because there is “some room to improve” with commercially available CAR T-cell products, Dr. Lu said. Specifically, tisagenlecleucel produced a 52% response rate in the JULIET trial (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:45-56), and axicabtagene ciloleucel produced an 82% response rate in the ZUMA-1 trial (N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2531-44).
There is also evidence to suggest that PD-1 blockade can modulate and “refuel” CAR T cells in relapsed/refractory NHL patients who fail or relapse after traditional anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy (Blood. 2017 Feb 23;129[8]:1039-41). This finding has prompted researchers to conduct trials of PD-1 inhibitors in combination with CAR T-cell therapies. But this combination approach may be expensive and cause more side effects than the armored CAR T-cell approach, Dr. Lu said.
In preclinical studies, Dr. Lu and colleagues found that ICTCAR014 was more effective than traditional anti-CD19 CAR T cells in killing Nalm6-PDL1 cells. In addition, the PD-1 dominant negative protein protected CAR T cells from exhaustion.
Dr. Lu also presented results in 13 NHL patients who have received ICTCAR014 in a phase 1 trial in China. Eleven patients had diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and two had follicular lymphoma.
The objective response rate was 92.3% (12/13), which included five partial responses (38.5%) and seven complete responses (53.8%). Both follicular lymphoma patients and five DLBCL patients achieved a complete response. Five DLBCL patients achieved a partial response, and the remaining DLBCL patient did not respond.
Dr. Lu did not present safety data. However, he reported that there was no increased incidence of cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity in these patients, compared with patients receiving traditional CAR T-cell therapy.
Dr. Lu is employed by Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, which funded the research and is developing ICTCAR014.
SOURCE: Lu V et al. SITC 2019, Abstract O25.
REPORTING FROM SITC 2019
Insomnia symptoms increase likelihood of stroke and heart disease
, according to a large cohort study of adults in China. A greater number of insomnia symptoms is associated with increased risk, and this relationship is more evident in younger adults and in adults without hypertension at baseline, researchers reported Nov. 6 in Neurology.
“These results suggest that, if we can target people who are having trouble sleeping with behavioral therapies, it’s possible that we could reduce the number of cases of stroke, heart attack, and other diseases later down the line,” study author Liming Li, MD, professor of epidemiology at Peking University, Beijing, said in a news release.
To clarify the relationships between individual insomnia symptoms, cardiocerebral vascular diseases, and potential effect modifiers, Dr. Li and colleagues analyzed data from the China Kadoorie Biobank Study. For this study, more than 500,000 adults in China aged 30-79 years completed a baseline survey during 2004-2008. The present analysis included data from 487,200 participants who did not have a history of stroke, coronary heart disease, or cancer at baseline.
For the baseline survey, participants answered questions about whether specific insomnia symptoms occurred at least 3 days per week during the past month. The symptoms included difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep (that is, sleep onset latency of 30 minutes or more after going to bed or waking up in the middle of the night); waking too early and being unable to fall back asleep; and trouble functioning during the day because of bad sleep.
The researchers assessed the incidence of cardiocerebral vascular diseases through 2016 by examining disease registries, national health insurance claims databases, and local records. Investigators identified participants with any cardiocerebral vascular disease and assessed the incidence of ischemic heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, hemorrhagic stroke, and ischemic stroke. The researchers followed each participant until the diagnosis of a cardiocerebral vascular disease outcome, death from any cause, loss to follow-up, or Dec. 31, 2016. The researchers used Cox proportional hazard models to estimate hazard ratios for the association between each insomnia symptom and cardiocerebral vascular disease outcomes. They adjusted the models for established and potential confounding factors, including age, income, smoking status, diet, and physical activity.
More than 16% had any insomnia symptom
Of the 487,200 participants, 11.3% had difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, 10.4% had early morning awakening, and 2.2% had daytime dysfunction attributed to poor sleep. Compared with participants without insomnia symptoms, participants with insomnia symptoms tended to be older and were more likely to be female, not married, and from a rural area. In addition, those with insomnia symptoms were more likely have depression or anxiety symptoms, lower education level, lower household income, and lower body mass index. They also were more likely to have a history of diabetes mellitus. During a median follow-up of 9.6 years, 130,032 cases of cardiocerebral vascular disease occurred, including 40,348 cases of ischemic heart disease and 45,316 cases of stroke.
After adjustment for potential confounders, each insomnia symptom was associated with greater risk of cardiocerebral vascular disease. For difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, the hazard ratio was 1.09. For early-morning awakening, the HR was 1.07. For daytime dysfunction, the HR was 1.13. Each insomnia symptom was associated with increased risk of ischemic heart disease and ischemic stroke, whereas only difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep was associated with increased risk of acute MI.
In all, 16.4% of participants reported any insomnia symptom; 10% had one symptom, 5.2% had two symptoms, and 1.2% had three symptoms. “Compared with those without any insomnia symptoms, participants with one, two, or three symptoms had a 7%, 10%, or 18% higher risk of total [cardiocerebral vascular disease] incidence, respectively,” the authors wrote. “Our study is the first large-scale cohort study that identified positive dose-response relationships between the number of insomnia symptoms and risks of [cardiocerebral vascular diseases, ischemic heart disease] and stroke incidence.”
Opportunity for intervention
Compared with clinical diagnostic criteria for insomnia, “individual insomnia symptoms are better defined and more feasible to assess with questionnaires in large-scale population studies and clinical practice,” Dr. Li and colleagues wrote. “Moreover, it is reasonable that insomnia symptoms are more modifiable and precisely targetable through behavioral therapies before developing into clinically significant insomnia disorder. Therefore, future clinical trials or community-based intervention studies should be conducted to test whether lifestyle or sleep hygiene interventions for insomnia symptoms can reduce subsequent [cardiocerebral vascular disease] risks.”
The results suggest that efforts aimed at early detection and intervention should include a focus on younger adults and people who do not have high blood pressure, Dr. Li said.
The self-reported insomnia symptoms used in this study have not been fully validated, the investigators noted. The researchers also lacked information about potential confounders, such as shift work and obstructive sleep apnea, that are risk factors for coronary heart disease or stroke and may interfere with insomnia symptoms. In addition, the study did not capture changes in insomnia symptoms over time.
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The China Kadoorie Biobank surveys were supported by grants from the Kadoorie Charitable Foundation and the U.K. Wellcome Trust. The authors had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Zheng B et al. Neurology. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008581.
, according to a large cohort study of adults in China. A greater number of insomnia symptoms is associated with increased risk, and this relationship is more evident in younger adults and in adults without hypertension at baseline, researchers reported Nov. 6 in Neurology.
“These results suggest that, if we can target people who are having trouble sleeping with behavioral therapies, it’s possible that we could reduce the number of cases of stroke, heart attack, and other diseases later down the line,” study author Liming Li, MD, professor of epidemiology at Peking University, Beijing, said in a news release.
To clarify the relationships between individual insomnia symptoms, cardiocerebral vascular diseases, and potential effect modifiers, Dr. Li and colleagues analyzed data from the China Kadoorie Biobank Study. For this study, more than 500,000 adults in China aged 30-79 years completed a baseline survey during 2004-2008. The present analysis included data from 487,200 participants who did not have a history of stroke, coronary heart disease, or cancer at baseline.
For the baseline survey, participants answered questions about whether specific insomnia symptoms occurred at least 3 days per week during the past month. The symptoms included difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep (that is, sleep onset latency of 30 minutes or more after going to bed or waking up in the middle of the night); waking too early and being unable to fall back asleep; and trouble functioning during the day because of bad sleep.
The researchers assessed the incidence of cardiocerebral vascular diseases through 2016 by examining disease registries, national health insurance claims databases, and local records. Investigators identified participants with any cardiocerebral vascular disease and assessed the incidence of ischemic heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, hemorrhagic stroke, and ischemic stroke. The researchers followed each participant until the diagnosis of a cardiocerebral vascular disease outcome, death from any cause, loss to follow-up, or Dec. 31, 2016. The researchers used Cox proportional hazard models to estimate hazard ratios for the association between each insomnia symptom and cardiocerebral vascular disease outcomes. They adjusted the models for established and potential confounding factors, including age, income, smoking status, diet, and physical activity.
More than 16% had any insomnia symptom
Of the 487,200 participants, 11.3% had difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, 10.4% had early morning awakening, and 2.2% had daytime dysfunction attributed to poor sleep. Compared with participants without insomnia symptoms, participants with insomnia symptoms tended to be older and were more likely to be female, not married, and from a rural area. In addition, those with insomnia symptoms were more likely have depression or anxiety symptoms, lower education level, lower household income, and lower body mass index. They also were more likely to have a history of diabetes mellitus. During a median follow-up of 9.6 years, 130,032 cases of cardiocerebral vascular disease occurred, including 40,348 cases of ischemic heart disease and 45,316 cases of stroke.
After adjustment for potential confounders, each insomnia symptom was associated with greater risk of cardiocerebral vascular disease. For difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, the hazard ratio was 1.09. For early-morning awakening, the HR was 1.07. For daytime dysfunction, the HR was 1.13. Each insomnia symptom was associated with increased risk of ischemic heart disease and ischemic stroke, whereas only difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep was associated with increased risk of acute MI.
In all, 16.4% of participants reported any insomnia symptom; 10% had one symptom, 5.2% had two symptoms, and 1.2% had three symptoms. “Compared with those without any insomnia symptoms, participants with one, two, or three symptoms had a 7%, 10%, or 18% higher risk of total [cardiocerebral vascular disease] incidence, respectively,” the authors wrote. “Our study is the first large-scale cohort study that identified positive dose-response relationships between the number of insomnia symptoms and risks of [cardiocerebral vascular diseases, ischemic heart disease] and stroke incidence.”
Opportunity for intervention
Compared with clinical diagnostic criteria for insomnia, “individual insomnia symptoms are better defined and more feasible to assess with questionnaires in large-scale population studies and clinical practice,” Dr. Li and colleagues wrote. “Moreover, it is reasonable that insomnia symptoms are more modifiable and precisely targetable through behavioral therapies before developing into clinically significant insomnia disorder. Therefore, future clinical trials or community-based intervention studies should be conducted to test whether lifestyle or sleep hygiene interventions for insomnia symptoms can reduce subsequent [cardiocerebral vascular disease] risks.”
The results suggest that efforts aimed at early detection and intervention should include a focus on younger adults and people who do not have high blood pressure, Dr. Li said.
The self-reported insomnia symptoms used in this study have not been fully validated, the investigators noted. The researchers also lacked information about potential confounders, such as shift work and obstructive sleep apnea, that are risk factors for coronary heart disease or stroke and may interfere with insomnia symptoms. In addition, the study did not capture changes in insomnia symptoms over time.
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The China Kadoorie Biobank surveys were supported by grants from the Kadoorie Charitable Foundation and the U.K. Wellcome Trust. The authors had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Zheng B et al. Neurology. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008581.
, according to a large cohort study of adults in China. A greater number of insomnia symptoms is associated with increased risk, and this relationship is more evident in younger adults and in adults without hypertension at baseline, researchers reported Nov. 6 in Neurology.
“These results suggest that, if we can target people who are having trouble sleeping with behavioral therapies, it’s possible that we could reduce the number of cases of stroke, heart attack, and other diseases later down the line,” study author Liming Li, MD, professor of epidemiology at Peking University, Beijing, said in a news release.
To clarify the relationships between individual insomnia symptoms, cardiocerebral vascular diseases, and potential effect modifiers, Dr. Li and colleagues analyzed data from the China Kadoorie Biobank Study. For this study, more than 500,000 adults in China aged 30-79 years completed a baseline survey during 2004-2008. The present analysis included data from 487,200 participants who did not have a history of stroke, coronary heart disease, or cancer at baseline.
For the baseline survey, participants answered questions about whether specific insomnia symptoms occurred at least 3 days per week during the past month. The symptoms included difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep (that is, sleep onset latency of 30 minutes or more after going to bed or waking up in the middle of the night); waking too early and being unable to fall back asleep; and trouble functioning during the day because of bad sleep.
The researchers assessed the incidence of cardiocerebral vascular diseases through 2016 by examining disease registries, national health insurance claims databases, and local records. Investigators identified participants with any cardiocerebral vascular disease and assessed the incidence of ischemic heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, hemorrhagic stroke, and ischemic stroke. The researchers followed each participant until the diagnosis of a cardiocerebral vascular disease outcome, death from any cause, loss to follow-up, or Dec. 31, 2016. The researchers used Cox proportional hazard models to estimate hazard ratios for the association between each insomnia symptom and cardiocerebral vascular disease outcomes. They adjusted the models for established and potential confounding factors, including age, income, smoking status, diet, and physical activity.
More than 16% had any insomnia symptom
Of the 487,200 participants, 11.3% had difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, 10.4% had early morning awakening, and 2.2% had daytime dysfunction attributed to poor sleep. Compared with participants without insomnia symptoms, participants with insomnia symptoms tended to be older and were more likely to be female, not married, and from a rural area. In addition, those with insomnia symptoms were more likely have depression or anxiety symptoms, lower education level, lower household income, and lower body mass index. They also were more likely to have a history of diabetes mellitus. During a median follow-up of 9.6 years, 130,032 cases of cardiocerebral vascular disease occurred, including 40,348 cases of ischemic heart disease and 45,316 cases of stroke.
After adjustment for potential confounders, each insomnia symptom was associated with greater risk of cardiocerebral vascular disease. For difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, the hazard ratio was 1.09. For early-morning awakening, the HR was 1.07. For daytime dysfunction, the HR was 1.13. Each insomnia symptom was associated with increased risk of ischemic heart disease and ischemic stroke, whereas only difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep was associated with increased risk of acute MI.
In all, 16.4% of participants reported any insomnia symptom; 10% had one symptom, 5.2% had two symptoms, and 1.2% had three symptoms. “Compared with those without any insomnia symptoms, participants with one, two, or three symptoms had a 7%, 10%, or 18% higher risk of total [cardiocerebral vascular disease] incidence, respectively,” the authors wrote. “Our study is the first large-scale cohort study that identified positive dose-response relationships between the number of insomnia symptoms and risks of [cardiocerebral vascular diseases, ischemic heart disease] and stroke incidence.”
Opportunity for intervention
Compared with clinical diagnostic criteria for insomnia, “individual insomnia symptoms are better defined and more feasible to assess with questionnaires in large-scale population studies and clinical practice,” Dr. Li and colleagues wrote. “Moreover, it is reasonable that insomnia symptoms are more modifiable and precisely targetable through behavioral therapies before developing into clinically significant insomnia disorder. Therefore, future clinical trials or community-based intervention studies should be conducted to test whether lifestyle or sleep hygiene interventions for insomnia symptoms can reduce subsequent [cardiocerebral vascular disease] risks.”
The results suggest that efforts aimed at early detection and intervention should include a focus on younger adults and people who do not have high blood pressure, Dr. Li said.
The self-reported insomnia symptoms used in this study have not been fully validated, the investigators noted. The researchers also lacked information about potential confounders, such as shift work and obstructive sleep apnea, that are risk factors for coronary heart disease or stroke and may interfere with insomnia symptoms. In addition, the study did not capture changes in insomnia symptoms over time.
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The China Kadoorie Biobank surveys were supported by grants from the Kadoorie Charitable Foundation and the U.K. Wellcome Trust. The authors had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Zheng B et al. Neurology. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008581.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Key clinical point: The presence of insomnia symptoms increases the likelihood of cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease during approximately 10 years of follow-up.
Major finding: After adjustment for potential confounders, each insomnia symptom was associated with greater risk of cardiocerebral vascular disease. For difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, the hazard ratio was 1.09. For early-morning awakening, the HR was 1.07. For daytime dysfunction, the HR was 1.13.
Study details: An analysis of data from 487,200 adults in China aged 30-79 years who completed a baseline survey during 2004-2008 and were followed through 2016.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The China Kadoorie Biobank surveys were supported by grants from the Kadoorie Charitable Foundation and the U.K. Wellcome Trust. The authors had no relevant disclosures.
Source: Zheng B et al. Neurology. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008581.
Survival ‘excellent’ after rituximab-bendamustine induction in transplant-eligible MCL
The combination of rituximab and bendamustine (RB) provided “excellent” survival with less toxicity, compared with a cytarabine-based induction regimen, in transplant-eligible patients with mantle cell lymphoma, according to a long-term follow-up report from randomized phase 2 trial.
The 5-year survival rates for RB were “provocatively similar” to what was achieved with the standard, intensive R-hyperCVAD regimen, investigators said in this update on the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) S1106 study.
By contrast, the R-hyperCVAD regimen was associated with more toxicity and higher failure rates for stem cell mobilization, according to the report’s lead author, Manali Kamdar, MD, of the University of Colorado, Denver, and coauthors.
“Overall, S1106 demonstrated that an outpatient-based, less intensive induction therapy of bendamustine plus rituximab is highly effective, safe, and durable in untreated transplant-eligible MCL patients,” Dr. Kamdar and her colleagues reported in Blood Advances.
The results have guided the design of an upcoming study, EA4181, in which patients with mantle cell lymphoma will be treated with an RB backbone plus cytarabine, the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib, or both, according to the authors.
In the present study, S1106, patients with mantle cell lymphoma were randomized to receive RB or the R-hyperCVAD regimen, which consisted of rituximab with hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone, alternating with high-dose cytarabine and methotrexate. Both regimens were followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
The stem cell mobilization failure rate was 29% in the R-hyperCVAD arm in an interim analysis conducted after 53 of a planned 160 patients had been enrolled, including 35 in the RB arm and 17 in the R-hyperCVAD arm, according to a report published in the British Journal of Haematology (2016 Dec 19. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14480). That analysis triggered a shutdown of the study, based on a rule stating that either arm would be deemed “unacceptably toxic” if the mobilization rate exceeded 10%.
Accordingly, R-hyperCVAD is “not an ideal platform” for future trials, the investigators said. At that time, the estimated 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 81% versus 82% for RB and R-hyperCVAD, respectively, while overall survival (OS) was 87% versus 88%.
With additional follow-up, the 5-year PFS is 66% and 62% in the RB and R-hyperCVAD arms, respectively, while 5-year OS is 80% and 74%, according to the investigators.
The RB regimen also results in “excellent” minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, they added.
MRD status was evaluated in 12 paired pre- and postinduction therapy specimens, of which 2 pairs were from patients in the R-hyperCVAD arm, and 10 pairs were from patients in the RB arm.
In the R-hyperCVAD arm, both patients were MRD positive at baseline, and MRD negative after induction, according to the investigators. Similarly, 9 of 10 patients in the RB arm were MRD positive at baseline, and of those, 7 converted to MRD negative following induction.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, and in part by Sequenta (Adaptive Biotechnologies). Dr. Kamdar reported being on the speakers bureau of Seattle Genetics and receiving consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Celgene, and Genentech. Co-authors of the study provided disclosures related to Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Affimed, Seattle Genetics, Pharmacyclics, and Merck, among others.
SOURCE: Kamdar M et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 22;3(20):3132-5.
The combination of rituximab and bendamustine (RB) provided “excellent” survival with less toxicity, compared with a cytarabine-based induction regimen, in transplant-eligible patients with mantle cell lymphoma, according to a long-term follow-up report from randomized phase 2 trial.
The 5-year survival rates for RB were “provocatively similar” to what was achieved with the standard, intensive R-hyperCVAD regimen, investigators said in this update on the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) S1106 study.
By contrast, the R-hyperCVAD regimen was associated with more toxicity and higher failure rates for stem cell mobilization, according to the report’s lead author, Manali Kamdar, MD, of the University of Colorado, Denver, and coauthors.
“Overall, S1106 demonstrated that an outpatient-based, less intensive induction therapy of bendamustine plus rituximab is highly effective, safe, and durable in untreated transplant-eligible MCL patients,” Dr. Kamdar and her colleagues reported in Blood Advances.
The results have guided the design of an upcoming study, EA4181, in which patients with mantle cell lymphoma will be treated with an RB backbone plus cytarabine, the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib, or both, according to the authors.
In the present study, S1106, patients with mantle cell lymphoma were randomized to receive RB or the R-hyperCVAD regimen, which consisted of rituximab with hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone, alternating with high-dose cytarabine and methotrexate. Both regimens were followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
The stem cell mobilization failure rate was 29% in the R-hyperCVAD arm in an interim analysis conducted after 53 of a planned 160 patients had been enrolled, including 35 in the RB arm and 17 in the R-hyperCVAD arm, according to a report published in the British Journal of Haematology (2016 Dec 19. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14480). That analysis triggered a shutdown of the study, based on a rule stating that either arm would be deemed “unacceptably toxic” if the mobilization rate exceeded 10%.
Accordingly, R-hyperCVAD is “not an ideal platform” for future trials, the investigators said. At that time, the estimated 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 81% versus 82% for RB and R-hyperCVAD, respectively, while overall survival (OS) was 87% versus 88%.
With additional follow-up, the 5-year PFS is 66% and 62% in the RB and R-hyperCVAD arms, respectively, while 5-year OS is 80% and 74%, according to the investigators.
The RB regimen also results in “excellent” minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, they added.
MRD status was evaluated in 12 paired pre- and postinduction therapy specimens, of which 2 pairs were from patients in the R-hyperCVAD arm, and 10 pairs were from patients in the RB arm.
In the R-hyperCVAD arm, both patients were MRD positive at baseline, and MRD negative after induction, according to the investigators. Similarly, 9 of 10 patients in the RB arm were MRD positive at baseline, and of those, 7 converted to MRD negative following induction.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, and in part by Sequenta (Adaptive Biotechnologies). Dr. Kamdar reported being on the speakers bureau of Seattle Genetics and receiving consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Celgene, and Genentech. Co-authors of the study provided disclosures related to Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Affimed, Seattle Genetics, Pharmacyclics, and Merck, among others.
SOURCE: Kamdar M et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 22;3(20):3132-5.
The combination of rituximab and bendamustine (RB) provided “excellent” survival with less toxicity, compared with a cytarabine-based induction regimen, in transplant-eligible patients with mantle cell lymphoma, according to a long-term follow-up report from randomized phase 2 trial.
The 5-year survival rates for RB were “provocatively similar” to what was achieved with the standard, intensive R-hyperCVAD regimen, investigators said in this update on the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) S1106 study.
By contrast, the R-hyperCVAD regimen was associated with more toxicity and higher failure rates for stem cell mobilization, according to the report’s lead author, Manali Kamdar, MD, of the University of Colorado, Denver, and coauthors.
“Overall, S1106 demonstrated that an outpatient-based, less intensive induction therapy of bendamustine plus rituximab is highly effective, safe, and durable in untreated transplant-eligible MCL patients,” Dr. Kamdar and her colleagues reported in Blood Advances.
The results have guided the design of an upcoming study, EA4181, in which patients with mantle cell lymphoma will be treated with an RB backbone plus cytarabine, the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib, or both, according to the authors.
In the present study, S1106, patients with mantle cell lymphoma were randomized to receive RB or the R-hyperCVAD regimen, which consisted of rituximab with hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone, alternating with high-dose cytarabine and methotrexate. Both regimens were followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
The stem cell mobilization failure rate was 29% in the R-hyperCVAD arm in an interim analysis conducted after 53 of a planned 160 patients had been enrolled, including 35 in the RB arm and 17 in the R-hyperCVAD arm, according to a report published in the British Journal of Haematology (2016 Dec 19. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14480). That analysis triggered a shutdown of the study, based on a rule stating that either arm would be deemed “unacceptably toxic” if the mobilization rate exceeded 10%.
Accordingly, R-hyperCVAD is “not an ideal platform” for future trials, the investigators said. At that time, the estimated 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 81% versus 82% for RB and R-hyperCVAD, respectively, while overall survival (OS) was 87% versus 88%.
With additional follow-up, the 5-year PFS is 66% and 62% in the RB and R-hyperCVAD arms, respectively, while 5-year OS is 80% and 74%, according to the investigators.
The RB regimen also results in “excellent” minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, they added.
MRD status was evaluated in 12 paired pre- and postinduction therapy specimens, of which 2 pairs were from patients in the R-hyperCVAD arm, and 10 pairs were from patients in the RB arm.
In the R-hyperCVAD arm, both patients were MRD positive at baseline, and MRD negative after induction, according to the investigators. Similarly, 9 of 10 patients in the RB arm were MRD positive at baseline, and of those, 7 converted to MRD negative following induction.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, and in part by Sequenta (Adaptive Biotechnologies). Dr. Kamdar reported being on the speakers bureau of Seattle Genetics and receiving consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Celgene, and Genentech. Co-authors of the study provided disclosures related to Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Affimed, Seattle Genetics, Pharmacyclics, and Merck, among others.
SOURCE: Kamdar M et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 22;3(20):3132-5.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
Interview with Clyde E. Markowitz, MD on switching therapies during MS treatment
Clyde E. Markowitz, MD, is the director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center at Penn Neuroscience Center and an Associate Professor of Neurology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. We sat down with Dr. Markowitz to talk about different multiple sclerosis (MS) therapies and how to determine when it might be time to switch a patient’s current regimen.
Why would an MS specialist switch a patient from one drug therapy to another?
The main reason we switch a patient from one treatment to another is usually related to an inadequate response to their current treatment. This can be seen when a patient is having new clinical symptoms suggestive of a relapse. Additional situations which would cause us to consider a switch in treatment include if the patient has had a new abnormalities seen on MRI scans, such as new T2 lesions or gadolinium- enhancing lesions. We might also switch a patient due to intolerance towards the medication they are on. For example, if they are experiencing flu-like symptoms or having Gastrointestinal issues.
In addition, the expectation that the treatment should slow the rate of progression may not be adequately demonstrating the desired effect. In that setting, we may consider a switch to a drug with a different mechanism of action to hopefully better control disease progression.
Laboratory abnormalities while on treatment might also be a consideration for a switch in therapy. Elevated LFTs, or low WBCs can occur on DMTs and may require a change in treatment. Patients on Natalizumab, require JC virus antibody testing. If the patient’s JCV Ab status changes from negative to positive or a rising index may require a change in therapy to avoid the development of PML.
What are some special considerations for patients during a switch in therapy?
We need to take into consideration the patient’s comorbidities. Does the patient have a history of diabetes, hypertension, cardiac concerns or a risk for infectious complications? What is the patient’s age? As individuals age the immune system becomes less robust at fighting infections or surveillance for malignancies. Some of the medications are immunosuppressive and might increase the risk of developing opportunistic infections or cancers.
Family planning should be taken into consideration during the discussion of which medications might be appropriate. Is the patient planning to have a pregnancy in the near future? Some medications might not be appropriate in that case.
Route of administration could be a factor to consider, since there are several medications that are administered as an infusion in a medical office or hospital setting. This could create issues for some patients who are employed and may have to miss work during these infusions. This could be as frequent as monthly or 2-3 times per year. Some patients just starting a new job, may feel uncomfortable taking time off or disclosing that they have MS leading to concerns for job security.
We also consider the side effects of the new treatment. What side effects and safety monitoring are required for a particular medication? Are there frequent blood tests, cardiac monitoring, dermatologic and ophthalmologic monitoring? How will this impact the patient’s quality of life?
In the end, it comes down to the level of monitoring required for a particular treatment, where the patient is in his or her life, and where he or she is in the disease course.
What are some potential complications when switching therapies?
When switching therapies, one of the bigger concerns is how quickly can we get the patient on the new therapy. Some medications when stopped can lead to return of disease activity or possibly lead to a rebound phenomenon with significant inflammatory activity. We focus on transitioning a patient quickly to a new drug that has a rapid mechanism of action thus limiting the amount of time that a patient is without a treatment. However, based on the mechanism of action of the drug you must consider if a wash out is necessary. The question is how quickly can the patient start the new drug thus preventing a rebound phenomenon. Ideally, no wash out would protect the patient best but might have safety concerns depending on the switch drug profile. If the switch was related to concerns for high JC virus antibody titer going off of natalizumab, there may be a need to make sure the patient does not have PML before making the switch. This may require MRIs and CSF analysis prior to switching.
Ultimately, we consider whether the drug we are switching the patient to is going to be more efficacious than the drug that the patient was previously on. We consider the safety and side effect profile of the new medication. We balance the risk of the disease with the risk of the medication. We must factor in the patient’s tolerance for risk as well and make the best decision with all the available factors considered.
Clyde E. Markowitz, MD, is the director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center at Penn Neuroscience Center and an Associate Professor of Neurology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. We sat down with Dr. Markowitz to talk about different multiple sclerosis (MS) therapies and how to determine when it might be time to switch a patient’s current regimen.
Why would an MS specialist switch a patient from one drug therapy to another?
The main reason we switch a patient from one treatment to another is usually related to an inadequate response to their current treatment. This can be seen when a patient is having new clinical symptoms suggestive of a relapse. Additional situations which would cause us to consider a switch in treatment include if the patient has had a new abnormalities seen on MRI scans, such as new T2 lesions or gadolinium- enhancing lesions. We might also switch a patient due to intolerance towards the medication they are on. For example, if they are experiencing flu-like symptoms or having Gastrointestinal issues.
In addition, the expectation that the treatment should slow the rate of progression may not be adequately demonstrating the desired effect. In that setting, we may consider a switch to a drug with a different mechanism of action to hopefully better control disease progression.
Laboratory abnormalities while on treatment might also be a consideration for a switch in therapy. Elevated LFTs, or low WBCs can occur on DMTs and may require a change in treatment. Patients on Natalizumab, require JC virus antibody testing. If the patient’s JCV Ab status changes from negative to positive or a rising index may require a change in therapy to avoid the development of PML.
What are some special considerations for patients during a switch in therapy?
We need to take into consideration the patient’s comorbidities. Does the patient have a history of diabetes, hypertension, cardiac concerns or a risk for infectious complications? What is the patient’s age? As individuals age the immune system becomes less robust at fighting infections or surveillance for malignancies. Some of the medications are immunosuppressive and might increase the risk of developing opportunistic infections or cancers.
Family planning should be taken into consideration during the discussion of which medications might be appropriate. Is the patient planning to have a pregnancy in the near future? Some medications might not be appropriate in that case.
Route of administration could be a factor to consider, since there are several medications that are administered as an infusion in a medical office or hospital setting. This could create issues for some patients who are employed and may have to miss work during these infusions. This could be as frequent as monthly or 2-3 times per year. Some patients just starting a new job, may feel uncomfortable taking time off or disclosing that they have MS leading to concerns for job security.
We also consider the side effects of the new treatment. What side effects and safety monitoring are required for a particular medication? Are there frequent blood tests, cardiac monitoring, dermatologic and ophthalmologic monitoring? How will this impact the patient’s quality of life?
In the end, it comes down to the level of monitoring required for a particular treatment, where the patient is in his or her life, and where he or she is in the disease course.
What are some potential complications when switching therapies?
When switching therapies, one of the bigger concerns is how quickly can we get the patient on the new therapy. Some medications when stopped can lead to return of disease activity or possibly lead to a rebound phenomenon with significant inflammatory activity. We focus on transitioning a patient quickly to a new drug that has a rapid mechanism of action thus limiting the amount of time that a patient is without a treatment. However, based on the mechanism of action of the drug you must consider if a wash out is necessary. The question is how quickly can the patient start the new drug thus preventing a rebound phenomenon. Ideally, no wash out would protect the patient best but might have safety concerns depending on the switch drug profile. If the switch was related to concerns for high JC virus antibody titer going off of natalizumab, there may be a need to make sure the patient does not have PML before making the switch. This may require MRIs and CSF analysis prior to switching.
Ultimately, we consider whether the drug we are switching the patient to is going to be more efficacious than the drug that the patient was previously on. We consider the safety and side effect profile of the new medication. We balance the risk of the disease with the risk of the medication. We must factor in the patient’s tolerance for risk as well and make the best decision with all the available factors considered.
Clyde E. Markowitz, MD, is the director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center at Penn Neuroscience Center and an Associate Professor of Neurology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. We sat down with Dr. Markowitz to talk about different multiple sclerosis (MS) therapies and how to determine when it might be time to switch a patient’s current regimen.
Why would an MS specialist switch a patient from one drug therapy to another?
The main reason we switch a patient from one treatment to another is usually related to an inadequate response to their current treatment. This can be seen when a patient is having new clinical symptoms suggestive of a relapse. Additional situations which would cause us to consider a switch in treatment include if the patient has had a new abnormalities seen on MRI scans, such as new T2 lesions or gadolinium- enhancing lesions. We might also switch a patient due to intolerance towards the medication they are on. For example, if they are experiencing flu-like symptoms or having Gastrointestinal issues.
In addition, the expectation that the treatment should slow the rate of progression may not be adequately demonstrating the desired effect. In that setting, we may consider a switch to a drug with a different mechanism of action to hopefully better control disease progression.
Laboratory abnormalities while on treatment might also be a consideration for a switch in therapy. Elevated LFTs, or low WBCs can occur on DMTs and may require a change in treatment. Patients on Natalizumab, require JC virus antibody testing. If the patient’s JCV Ab status changes from negative to positive or a rising index may require a change in therapy to avoid the development of PML.
What are some special considerations for patients during a switch in therapy?
We need to take into consideration the patient’s comorbidities. Does the patient have a history of diabetes, hypertension, cardiac concerns or a risk for infectious complications? What is the patient’s age? As individuals age the immune system becomes less robust at fighting infections or surveillance for malignancies. Some of the medications are immunosuppressive and might increase the risk of developing opportunistic infections or cancers.
Family planning should be taken into consideration during the discussion of which medications might be appropriate. Is the patient planning to have a pregnancy in the near future? Some medications might not be appropriate in that case.
Route of administration could be a factor to consider, since there are several medications that are administered as an infusion in a medical office or hospital setting. This could create issues for some patients who are employed and may have to miss work during these infusions. This could be as frequent as monthly or 2-3 times per year. Some patients just starting a new job, may feel uncomfortable taking time off or disclosing that they have MS leading to concerns for job security.
We also consider the side effects of the new treatment. What side effects and safety monitoring are required for a particular medication? Are there frequent blood tests, cardiac monitoring, dermatologic and ophthalmologic monitoring? How will this impact the patient’s quality of life?
In the end, it comes down to the level of monitoring required for a particular treatment, where the patient is in his or her life, and where he or she is in the disease course.
What are some potential complications when switching therapies?
When switching therapies, one of the bigger concerns is how quickly can we get the patient on the new therapy. Some medications when stopped can lead to return of disease activity or possibly lead to a rebound phenomenon with significant inflammatory activity. We focus on transitioning a patient quickly to a new drug that has a rapid mechanism of action thus limiting the amount of time that a patient is without a treatment. However, based on the mechanism of action of the drug you must consider if a wash out is necessary. The question is how quickly can the patient start the new drug thus preventing a rebound phenomenon. Ideally, no wash out would protect the patient best but might have safety concerns depending on the switch drug profile. If the switch was related to concerns for high JC virus antibody titer going off of natalizumab, there may be a need to make sure the patient does not have PML before making the switch. This may require MRIs and CSF analysis prior to switching.
Ultimately, we consider whether the drug we are switching the patient to is going to be more efficacious than the drug that the patient was previously on. We consider the safety and side effect profile of the new medication. We balance the risk of the disease with the risk of the medication. We must factor in the patient’s tolerance for risk as well and make the best decision with all the available factors considered.
FDA approves diroximel fumarate for relapsing MS
The Food and Drug Administration has approved diroximel fumarate (Vumerity) for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) in adults, including clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, according to an Oct. 30 announcement from its developers, Biogen and Alkermes.
The approval is based on pharmacokinetic studies that established the bioequivalence of diroximel fumarate and dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera), and it relied in part on the safety and efficacy data for dimethyl fumarate, which was approved in 2013. Diroximel fumarate rapidly converts to monomethyl fumarate, the same active metabolite as dimethyl fumarate.
Diroximel fumarate may be better tolerated than dimethyl fumarate. A trial found that the newer drug has significantly better gastrointestinal tolerability, the developers of the drug announced in July. In addition, the drug application for diroximel fumarate included interim data from EVOLVE-MS-1, an ongoing, open-label, 2-year safety study evaluating diroximel fumarate in patients with relapsing-remitting MS. Researchers found a 6.3% rate of treatment discontinuation attributable to adverse events. Less than 1% of patients discontinued treatment because of gastrointestinal adverse events.
Serious side effects of diroximel fumarate may include allergic reaction, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, decreases in white blood cell count, and liver problems. Flushing and stomach problems are the most common side effects, which may decrease over time.
Biogen plans to make diroximel fumarate available in the United States in the near future, the company said. Prescribing information is available online.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved diroximel fumarate (Vumerity) for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) in adults, including clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, according to an Oct. 30 announcement from its developers, Biogen and Alkermes.
The approval is based on pharmacokinetic studies that established the bioequivalence of diroximel fumarate and dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera), and it relied in part on the safety and efficacy data for dimethyl fumarate, which was approved in 2013. Diroximel fumarate rapidly converts to monomethyl fumarate, the same active metabolite as dimethyl fumarate.
Diroximel fumarate may be better tolerated than dimethyl fumarate. A trial found that the newer drug has significantly better gastrointestinal tolerability, the developers of the drug announced in July. In addition, the drug application for diroximel fumarate included interim data from EVOLVE-MS-1, an ongoing, open-label, 2-year safety study evaluating diroximel fumarate in patients with relapsing-remitting MS. Researchers found a 6.3% rate of treatment discontinuation attributable to adverse events. Less than 1% of patients discontinued treatment because of gastrointestinal adverse events.
Serious side effects of diroximel fumarate may include allergic reaction, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, decreases in white blood cell count, and liver problems. Flushing and stomach problems are the most common side effects, which may decrease over time.
Biogen plans to make diroximel fumarate available in the United States in the near future, the company said. Prescribing information is available online.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved diroximel fumarate (Vumerity) for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) in adults, including clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, according to an Oct. 30 announcement from its developers, Biogen and Alkermes.
The approval is based on pharmacokinetic studies that established the bioequivalence of diroximel fumarate and dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera), and it relied in part on the safety and efficacy data for dimethyl fumarate, which was approved in 2013. Diroximel fumarate rapidly converts to monomethyl fumarate, the same active metabolite as dimethyl fumarate.
Diroximel fumarate may be better tolerated than dimethyl fumarate. A trial found that the newer drug has significantly better gastrointestinal tolerability, the developers of the drug announced in July. In addition, the drug application for diroximel fumarate included interim data from EVOLVE-MS-1, an ongoing, open-label, 2-year safety study evaluating diroximel fumarate in patients with relapsing-remitting MS. Researchers found a 6.3% rate of treatment discontinuation attributable to adverse events. Less than 1% of patients discontinued treatment because of gastrointestinal adverse events.
Serious side effects of diroximel fumarate may include allergic reaction, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, decreases in white blood cell count, and liver problems. Flushing and stomach problems are the most common side effects, which may decrease over time.
Biogen plans to make diroximel fumarate available in the United States in the near future, the company said. Prescribing information is available online.
Consider renal function in TLS risk assessment of venetoclax-treated CLL
EDINBURGH – Impaired renal function may indicate excess risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) in venetoclax-treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients and should be considered when assessing TLS risk, according to findings from a retrospective cohort study.
Complex karyotype may also affect TLS risk, Anthony Mato, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Of 339 CLL patients who were treated with venetoclax, 38%, 34%, and 28% were considered to have low, medium, or high risk for TLS, respectively, according to the standard definition based on absolute lymphocyte count as a measure of tumor burden and/or lymph node size.
TLS occurred in 35 patients (10%), including 26 cases of laboratory-confirmed TLS and 9 clinical TLS cases; 1 patient required dialysis and 1 death occurred, which was attributable to the TLS, Dr. Mato of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues reported in a poster at the workshop.
Univariate analysis was performed to “understand baseline factors associated with TLS development during dose escalation,” and it examined sex, creatinine clearance (CrCl), complex karyotype, immunoglobulin heavy chain variable mutation status, prior ibrutinib exposure, venetoclax monotherapy vs. combination therapy, and TLS risk group. The investigators observed no significant difference between the low- and medium-risk patients, therefore those two groups were combined and compared with the high-risk patients.
The univariate analysis showed significant associations between TLS and CrCl (odds ratio, 2.9 for 80 mL/min or less vs. greater than 80 mL/min), complex karyotype (OR, 2.2), and low/medium vs. high TLS risk based on the standard definition (OR, 2.56).
A multivariable analysis of the predictors identified as significant in the univariate analyses showed that standard TLS risk group and CrCl remained independent predictors of TLS.
“Although the odds ratio for complex karyotype suggested potential clinical significance, this did not meet the threshold for statistical significance and was not included in the final model,” they wrote.
The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for a model including TLS risk group and CrCl was 74.6%, compared with 65% for the area under the ROC curve using the standard tumor burden/lymph node size approach for defining TLS risk, which is described in the venetoclax package insert.
Patients included in the study had a median age of 67 years at venetoclax initiation, 69% were men, 85% were white, and 13% were treated on a clinical trial. Complex karyotype was present in 39%, del(17p) in 43%, and 84% had immunoglobulin heavy chain variable–unmutated disease.
Most patients received venetoclax monotherapy (79%), had relapsed/refractory disease (94%), and had previously received ibrutinib (78%). The median number of prior therapies was 3, but the number ranged from 0-15, the investigators noted.
The findings of this study suggest that, in addition to defining risk based on absolute lymphocyte count and lymph node size, patients with CrCl less than 80 mL/min – indicating impaired renal function – have excess risk of TLS.
Although complex karyotype did not reach statistical significance as an independent predictor of TLS, the findings in this study suggest it “may impact TLS risk and is worthy of further study in larger samples,” they said, concluding that consideration of baseline renal function, and possibly karyotype, could “further guide practitioners in their approach to prophylaxis and patient counseling, allowing for improved safety in the use of this effective agent in CLL.”
Additional planned analyses will focus on TLS risk score development and further refinement of TLS risk stratification, they noted.
Dr. Mato has received grant support, consulting fees, and/or fees for serving on a data and safety monitoring board or advisory board from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Janssen, TG Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics, Loxo, Sunesis, prIME Oncology, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Regeneron.
EDINBURGH – Impaired renal function may indicate excess risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) in venetoclax-treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients and should be considered when assessing TLS risk, according to findings from a retrospective cohort study.
Complex karyotype may also affect TLS risk, Anthony Mato, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Of 339 CLL patients who were treated with venetoclax, 38%, 34%, and 28% were considered to have low, medium, or high risk for TLS, respectively, according to the standard definition based on absolute lymphocyte count as a measure of tumor burden and/or lymph node size.
TLS occurred in 35 patients (10%), including 26 cases of laboratory-confirmed TLS and 9 clinical TLS cases; 1 patient required dialysis and 1 death occurred, which was attributable to the TLS, Dr. Mato of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues reported in a poster at the workshop.
Univariate analysis was performed to “understand baseline factors associated with TLS development during dose escalation,” and it examined sex, creatinine clearance (CrCl), complex karyotype, immunoglobulin heavy chain variable mutation status, prior ibrutinib exposure, venetoclax monotherapy vs. combination therapy, and TLS risk group. The investigators observed no significant difference between the low- and medium-risk patients, therefore those two groups were combined and compared with the high-risk patients.
The univariate analysis showed significant associations between TLS and CrCl (odds ratio, 2.9 for 80 mL/min or less vs. greater than 80 mL/min), complex karyotype (OR, 2.2), and low/medium vs. high TLS risk based on the standard definition (OR, 2.56).
A multivariable analysis of the predictors identified as significant in the univariate analyses showed that standard TLS risk group and CrCl remained independent predictors of TLS.
“Although the odds ratio for complex karyotype suggested potential clinical significance, this did not meet the threshold for statistical significance and was not included in the final model,” they wrote.
The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for a model including TLS risk group and CrCl was 74.6%, compared with 65% for the area under the ROC curve using the standard tumor burden/lymph node size approach for defining TLS risk, which is described in the venetoclax package insert.
Patients included in the study had a median age of 67 years at venetoclax initiation, 69% were men, 85% were white, and 13% were treated on a clinical trial. Complex karyotype was present in 39%, del(17p) in 43%, and 84% had immunoglobulin heavy chain variable–unmutated disease.
Most patients received venetoclax monotherapy (79%), had relapsed/refractory disease (94%), and had previously received ibrutinib (78%). The median number of prior therapies was 3, but the number ranged from 0-15, the investigators noted.
The findings of this study suggest that, in addition to defining risk based on absolute lymphocyte count and lymph node size, patients with CrCl less than 80 mL/min – indicating impaired renal function – have excess risk of TLS.
Although complex karyotype did not reach statistical significance as an independent predictor of TLS, the findings in this study suggest it “may impact TLS risk and is worthy of further study in larger samples,” they said, concluding that consideration of baseline renal function, and possibly karyotype, could “further guide practitioners in their approach to prophylaxis and patient counseling, allowing for improved safety in the use of this effective agent in CLL.”
Additional planned analyses will focus on TLS risk score development and further refinement of TLS risk stratification, they noted.
Dr. Mato has received grant support, consulting fees, and/or fees for serving on a data and safety monitoring board or advisory board from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Janssen, TG Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics, Loxo, Sunesis, prIME Oncology, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Regeneron.
EDINBURGH – Impaired renal function may indicate excess risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) in venetoclax-treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients and should be considered when assessing TLS risk, according to findings from a retrospective cohort study.
Complex karyotype may also affect TLS risk, Anthony Mato, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Of 339 CLL patients who were treated with venetoclax, 38%, 34%, and 28% were considered to have low, medium, or high risk for TLS, respectively, according to the standard definition based on absolute lymphocyte count as a measure of tumor burden and/or lymph node size.
TLS occurred in 35 patients (10%), including 26 cases of laboratory-confirmed TLS and 9 clinical TLS cases; 1 patient required dialysis and 1 death occurred, which was attributable to the TLS, Dr. Mato of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues reported in a poster at the workshop.
Univariate analysis was performed to “understand baseline factors associated with TLS development during dose escalation,” and it examined sex, creatinine clearance (CrCl), complex karyotype, immunoglobulin heavy chain variable mutation status, prior ibrutinib exposure, venetoclax monotherapy vs. combination therapy, and TLS risk group. The investigators observed no significant difference between the low- and medium-risk patients, therefore those two groups were combined and compared with the high-risk patients.
The univariate analysis showed significant associations between TLS and CrCl (odds ratio, 2.9 for 80 mL/min or less vs. greater than 80 mL/min), complex karyotype (OR, 2.2), and low/medium vs. high TLS risk based on the standard definition (OR, 2.56).
A multivariable analysis of the predictors identified as significant in the univariate analyses showed that standard TLS risk group and CrCl remained independent predictors of TLS.
“Although the odds ratio for complex karyotype suggested potential clinical significance, this did not meet the threshold for statistical significance and was not included in the final model,” they wrote.
The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for a model including TLS risk group and CrCl was 74.6%, compared with 65% for the area under the ROC curve using the standard tumor burden/lymph node size approach for defining TLS risk, which is described in the venetoclax package insert.
Patients included in the study had a median age of 67 years at venetoclax initiation, 69% were men, 85% were white, and 13% were treated on a clinical trial. Complex karyotype was present in 39%, del(17p) in 43%, and 84% had immunoglobulin heavy chain variable–unmutated disease.
Most patients received venetoclax monotherapy (79%), had relapsed/refractory disease (94%), and had previously received ibrutinib (78%). The median number of prior therapies was 3, but the number ranged from 0-15, the investigators noted.
The findings of this study suggest that, in addition to defining risk based on absolute lymphocyte count and lymph node size, patients with CrCl less than 80 mL/min – indicating impaired renal function – have excess risk of TLS.
Although complex karyotype did not reach statistical significance as an independent predictor of TLS, the findings in this study suggest it “may impact TLS risk and is worthy of further study in larger samples,” they said, concluding that consideration of baseline renal function, and possibly karyotype, could “further guide practitioners in their approach to prophylaxis and patient counseling, allowing for improved safety in the use of this effective agent in CLL.”
Additional planned analyses will focus on TLS risk score development and further refinement of TLS risk stratification, they noted.
Dr. Mato has received grant support, consulting fees, and/or fees for serving on a data and safety monitoring board or advisory board from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Janssen, TG Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics, Loxo, Sunesis, prIME Oncology, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Regeneron.
REPORTING FROM iwCLL 2019
Pembrolizumab shows promise for relapsed/refractory PMBCL
The programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor pembrolizumab showed manageable safety and promising clinical activity in patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to results from two early-phase studies.
The phase 1b KEYNOTE-013 study included an expansion cohort that evaluated pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL. Based on preliminary findings from KEYNOTE-013, the phase 2 KEYNOTE-170 study was initiated to validate these results.
Philippe Armand, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and colleagues reported results from 53 patients in KEYNOTE-170 and extended follow-up of 21 patients in KEYNOTE-013. Data from these two trials formed the basis of an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration of pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL in June 2018.
“Frequent amplification and translocation events occur at 9p24.1 in PMBCL, resulting in tumor expression of the programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. This suggests susceptibility of PMBCL to PD-1 blockade,” the researchers wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
KEYNOTE-170 included patients with relapsed or refractory disease who were transplant-ineligible and had failed a minimum of two prior lines of treatment. KEYNOTE-013 enrolled patients who relapsed following autologous stem cell transplantation or were ineligible for transplant.
Among patients in KEYNOTE-013 and KEYNOTE-170, the objective response rates were 48% and 45%, respectively. In total, 33% of patients in KEYNOTE-013 and 13% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 achieved a complete response. Among these patients, no disease progression was observed.
The median progression-free survival in KEYNOTE-170 was 5.5 months and 10.4 months in KEYNOTE-013. In KEYNOTE-170, median overall survival was not reached, while in KEYNOTE-013, the median overall survival was 31.4 months.
After a median follow-up time of 29.1 months in KEYNOTE-013 and 12.5 months in KEYNOTE-170, the median duration of response was not reached in either trial, the researchers reported.
With respect to safety, pembrolizumab-related grade 3 or 4 adverse events were observed in 23% and 24% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 and KEYNOTE-013, respectively. The most common adverse event in both trials was neutropenia. No deaths related to pembrolizumab were observed.
Response rates were lower in KEYNOTE-170, compared with KEYNOTE-013, but the researchers noted that longer follow-up could change these results.
“Although the small numbers allow only a tentative hypothesis, they raise the question of whether PD-1 blockade in this setting might resensitize tumors to chemotherapy, as recently suggested. If this can be further validated, it could have profound implication for the management of patients with [relapsed/refractory] PMBCL,” the researchers wrote.
The study was supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, the Harold and Virginia Lash Foundation, the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, and the Center for Immuno-Oncology of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. The authors reported financial affiliations with Merck Sharp & Dohme and several other companies.
SOURCE: Armand P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01389.
The programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor pembrolizumab showed manageable safety and promising clinical activity in patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to results from two early-phase studies.
The phase 1b KEYNOTE-013 study included an expansion cohort that evaluated pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL. Based on preliminary findings from KEYNOTE-013, the phase 2 KEYNOTE-170 study was initiated to validate these results.
Philippe Armand, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and colleagues reported results from 53 patients in KEYNOTE-170 and extended follow-up of 21 patients in KEYNOTE-013. Data from these two trials formed the basis of an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration of pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL in June 2018.
“Frequent amplification and translocation events occur at 9p24.1 in PMBCL, resulting in tumor expression of the programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. This suggests susceptibility of PMBCL to PD-1 blockade,” the researchers wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
KEYNOTE-170 included patients with relapsed or refractory disease who were transplant-ineligible and had failed a minimum of two prior lines of treatment. KEYNOTE-013 enrolled patients who relapsed following autologous stem cell transplantation or were ineligible for transplant.
Among patients in KEYNOTE-013 and KEYNOTE-170, the objective response rates were 48% and 45%, respectively. In total, 33% of patients in KEYNOTE-013 and 13% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 achieved a complete response. Among these patients, no disease progression was observed.
The median progression-free survival in KEYNOTE-170 was 5.5 months and 10.4 months in KEYNOTE-013. In KEYNOTE-170, median overall survival was not reached, while in KEYNOTE-013, the median overall survival was 31.4 months.
After a median follow-up time of 29.1 months in KEYNOTE-013 and 12.5 months in KEYNOTE-170, the median duration of response was not reached in either trial, the researchers reported.
With respect to safety, pembrolizumab-related grade 3 or 4 adverse events were observed in 23% and 24% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 and KEYNOTE-013, respectively. The most common adverse event in both trials was neutropenia. No deaths related to pembrolizumab were observed.
Response rates were lower in KEYNOTE-170, compared with KEYNOTE-013, but the researchers noted that longer follow-up could change these results.
“Although the small numbers allow only a tentative hypothesis, they raise the question of whether PD-1 blockade in this setting might resensitize tumors to chemotherapy, as recently suggested. If this can be further validated, it could have profound implication for the management of patients with [relapsed/refractory] PMBCL,” the researchers wrote.
The study was supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, the Harold and Virginia Lash Foundation, the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, and the Center for Immuno-Oncology of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. The authors reported financial affiliations with Merck Sharp & Dohme and several other companies.
SOURCE: Armand P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01389.
The programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor pembrolizumab showed manageable safety and promising clinical activity in patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to results from two early-phase studies.
The phase 1b KEYNOTE-013 study included an expansion cohort that evaluated pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL. Based on preliminary findings from KEYNOTE-013, the phase 2 KEYNOTE-170 study was initiated to validate these results.
Philippe Armand, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and colleagues reported results from 53 patients in KEYNOTE-170 and extended follow-up of 21 patients in KEYNOTE-013. Data from these two trials formed the basis of an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration of pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL in June 2018.
“Frequent amplification and translocation events occur at 9p24.1 in PMBCL, resulting in tumor expression of the programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. This suggests susceptibility of PMBCL to PD-1 blockade,” the researchers wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
KEYNOTE-170 included patients with relapsed or refractory disease who were transplant-ineligible and had failed a minimum of two prior lines of treatment. KEYNOTE-013 enrolled patients who relapsed following autologous stem cell transplantation or were ineligible for transplant.
Among patients in KEYNOTE-013 and KEYNOTE-170, the objective response rates were 48% and 45%, respectively. In total, 33% of patients in KEYNOTE-013 and 13% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 achieved a complete response. Among these patients, no disease progression was observed.
The median progression-free survival in KEYNOTE-170 was 5.5 months and 10.4 months in KEYNOTE-013. In KEYNOTE-170, median overall survival was not reached, while in KEYNOTE-013, the median overall survival was 31.4 months.
After a median follow-up time of 29.1 months in KEYNOTE-013 and 12.5 months in KEYNOTE-170, the median duration of response was not reached in either trial, the researchers reported.
With respect to safety, pembrolizumab-related grade 3 or 4 adverse events were observed in 23% and 24% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 and KEYNOTE-013, respectively. The most common adverse event in both trials was neutropenia. No deaths related to pembrolizumab were observed.
Response rates were lower in KEYNOTE-170, compared with KEYNOTE-013, but the researchers noted that longer follow-up could change these results.
“Although the small numbers allow only a tentative hypothesis, they raise the question of whether PD-1 blockade in this setting might resensitize tumors to chemotherapy, as recently suggested. If this can be further validated, it could have profound implication for the management of patients with [relapsed/refractory] PMBCL,” the researchers wrote.
The study was supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, the Harold and Virginia Lash Foundation, the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, and the Center for Immuno-Oncology of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. The authors reported financial affiliations with Merck Sharp & Dohme and several other companies.
SOURCE: Armand P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01389.
FROM JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY