User login
Machine learning can predict primary progressive MS progression
BOSTON – , according to a proof-of-concept study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The accuracy was sufficient for the lead author of the study, Michael Gurevich, PhD, head of the Neuroimmunological Laboratory in the Multiple Sclerosis Center of Sheba Medical Center in Ramat Gan, Israel, to say that it is already clinically viable even as the tool is still evolving.
“We are looking at larger sample sizes to improve the accuracy and generalizability of our model, but we can use it now to inform treatment decisions,” Dr. Gurevich said.
In patients with PPMS who have a highly variable course, the model predicts disability progression with an accuracy of approximately 70%, according to the data he presented. He said he believes this is already at a level that it is meaningful for a risk-to-benefit calculation when considering treatment.
Machine learning analyzes blood samples
The study pursues the concept that the genetic information governing highly complex pathophysiological processes is contained in RNA sequencing. While multimodal omics generate data that are too complex for human pattern recognition, there is a growing body of evidence, including that provided by this study, to suggest that machine learning can employ these same RNA profiles and predict disease activity.
In this study, blood samples were collected from patients who participated in the phase 3 clinical ORATORIO trial that led to approval of ocrelizumab for PPMS. Analyses were conducted only on blood samples from those randomized to placebo, who, like those in the active treatment arm, were evaluated at baseline and at 12-week intervals for more than 2 years.
After development of a prediction model and creation of a training dataset, machine learning was applied to the deep sequencing of the blood transcriptome data for predicting two endpoints. One was disease progression at 120 weeks defined as a 1 point or more increase in the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) among patients with confirmed disability progression for at least 12 weeks (12W-CDP).
The other was change at 120 weeks in brain morphology defined as a 1% or more reduction in brain volume (120W PBVC).
The peripheral blood samples were subjected to RNA sequencing analysis (RNA-Seq) using commercially available analysis techniques. The prediction model for the disability endpoint was based on data generated from the blood transcriptome of 135 patients of which 53 (39%) met the endpoint at 120 weeks. The prediction model for the change in brain morphology was based on the blood transcriptome from 94 patients of which 63 (67%) met the endpoint.
On the basis of 10 genes that most significantly differentiated those who met the disability endpoint from those who did not, machine recognition of patterns after training was able to predict correctly the outcome in 70.9%. The sensitivity was 55.6%, and the specificity was 79.0%. The positive and negative predictive values were 59.0% and 76.8%, respectively.
On the basis of the 12 genes the most significantly differentiated those that reached the 120W PBVC endpoint from those who did not, machine learning resulted in a correct prediction of outcomes in 75.1%. The sensitivity was 78.1%, and the specificity was 66.7%. The positive and negative predictive values were 83.3% and 58.8%, respectively
Typical of a PPMS trial population, the mean age of the patients was about 44 years. The mean disease duration was about 6 years. The majority of patients had an EDSS score below 5.5 at baseline. The baseline T2 lesion number was approximately 50.
If further validated by others and in larger studies, this type of information could play a valuable role in PPMS management, according to Dr. Gurevich. Now that there is an approved therapy for PPMS, it can help clinicians and patients determine whether to initiate treatment early to address the high risk of progression or delay treatment that might not be needed.
A useful tool
In the field of MS, most of the studies performed with machine learning have focused on the analysis of radiological images. However, others are now looking at the blood transcriptome as a potential path to better classifying a highly complex disease with substantial heterogeneity in presentation, progression, and outcome.
For example, machine learning of the blood transcriptome has also shown high accuracy in the diagnosis and classification of MS in patients with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS). One study, published in Cell Reports Medicine, was led by Cinthia Farina, PhD, Institute of Experimental Neurology, IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan.
Although she did not hear the presentation by Dr. Gurevich, Dr. Farina is enthusiastic about the potential for machine learning to help manage MS through the analysis of the blood transcriptome. “I do believe that transcriptomics in peripheral immune cells may become a useful tool for MS diagnosis and prognosis,” she said.
In her own study, in which machine learning algorithms were developed and trained on the basis of peripheral blood from patients with CIS, the tool proved accurate with a strong potential for being incorporated into routine clinical management.
“Machine learning applied to the blood transcriptomes was extremely efficient with a 95.6% accuracy in discriminating PPMS from RRMS [relapsing-remitting] MS,” she reported.
Dr. Gurevich has no potential financial conflicts of interest to report. He reported funding for the study was provided by Roche. Dr. Farina reports financial relationships with Merck-Serono, Novartis, and Teva.
BOSTON – , according to a proof-of-concept study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The accuracy was sufficient for the lead author of the study, Michael Gurevich, PhD, head of the Neuroimmunological Laboratory in the Multiple Sclerosis Center of Sheba Medical Center in Ramat Gan, Israel, to say that it is already clinically viable even as the tool is still evolving.
“We are looking at larger sample sizes to improve the accuracy and generalizability of our model, but we can use it now to inform treatment decisions,” Dr. Gurevich said.
In patients with PPMS who have a highly variable course, the model predicts disability progression with an accuracy of approximately 70%, according to the data he presented. He said he believes this is already at a level that it is meaningful for a risk-to-benefit calculation when considering treatment.
Machine learning analyzes blood samples
The study pursues the concept that the genetic information governing highly complex pathophysiological processes is contained in RNA sequencing. While multimodal omics generate data that are too complex for human pattern recognition, there is a growing body of evidence, including that provided by this study, to suggest that machine learning can employ these same RNA profiles and predict disease activity.
In this study, blood samples were collected from patients who participated in the phase 3 clinical ORATORIO trial that led to approval of ocrelizumab for PPMS. Analyses were conducted only on blood samples from those randomized to placebo, who, like those in the active treatment arm, were evaluated at baseline and at 12-week intervals for more than 2 years.
After development of a prediction model and creation of a training dataset, machine learning was applied to the deep sequencing of the blood transcriptome data for predicting two endpoints. One was disease progression at 120 weeks defined as a 1 point or more increase in the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) among patients with confirmed disability progression for at least 12 weeks (12W-CDP).
The other was change at 120 weeks in brain morphology defined as a 1% or more reduction in brain volume (120W PBVC).
The peripheral blood samples were subjected to RNA sequencing analysis (RNA-Seq) using commercially available analysis techniques. The prediction model for the disability endpoint was based on data generated from the blood transcriptome of 135 patients of which 53 (39%) met the endpoint at 120 weeks. The prediction model for the change in brain morphology was based on the blood transcriptome from 94 patients of which 63 (67%) met the endpoint.
On the basis of 10 genes that most significantly differentiated those who met the disability endpoint from those who did not, machine recognition of patterns after training was able to predict correctly the outcome in 70.9%. The sensitivity was 55.6%, and the specificity was 79.0%. The positive and negative predictive values were 59.0% and 76.8%, respectively.
On the basis of the 12 genes the most significantly differentiated those that reached the 120W PBVC endpoint from those who did not, machine learning resulted in a correct prediction of outcomes in 75.1%. The sensitivity was 78.1%, and the specificity was 66.7%. The positive and negative predictive values were 83.3% and 58.8%, respectively
Typical of a PPMS trial population, the mean age of the patients was about 44 years. The mean disease duration was about 6 years. The majority of patients had an EDSS score below 5.5 at baseline. The baseline T2 lesion number was approximately 50.
If further validated by others and in larger studies, this type of information could play a valuable role in PPMS management, according to Dr. Gurevich. Now that there is an approved therapy for PPMS, it can help clinicians and patients determine whether to initiate treatment early to address the high risk of progression or delay treatment that might not be needed.
A useful tool
In the field of MS, most of the studies performed with machine learning have focused on the analysis of radiological images. However, others are now looking at the blood transcriptome as a potential path to better classifying a highly complex disease with substantial heterogeneity in presentation, progression, and outcome.
For example, machine learning of the blood transcriptome has also shown high accuracy in the diagnosis and classification of MS in patients with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS). One study, published in Cell Reports Medicine, was led by Cinthia Farina, PhD, Institute of Experimental Neurology, IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan.
Although she did not hear the presentation by Dr. Gurevich, Dr. Farina is enthusiastic about the potential for machine learning to help manage MS through the analysis of the blood transcriptome. “I do believe that transcriptomics in peripheral immune cells may become a useful tool for MS diagnosis and prognosis,” she said.
In her own study, in which machine learning algorithms were developed and trained on the basis of peripheral blood from patients with CIS, the tool proved accurate with a strong potential for being incorporated into routine clinical management.
“Machine learning applied to the blood transcriptomes was extremely efficient with a 95.6% accuracy in discriminating PPMS from RRMS [relapsing-remitting] MS,” she reported.
Dr. Gurevich has no potential financial conflicts of interest to report. He reported funding for the study was provided by Roche. Dr. Farina reports financial relationships with Merck-Serono, Novartis, and Teva.
BOSTON – , according to a proof-of-concept study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The accuracy was sufficient for the lead author of the study, Michael Gurevich, PhD, head of the Neuroimmunological Laboratory in the Multiple Sclerosis Center of Sheba Medical Center in Ramat Gan, Israel, to say that it is already clinically viable even as the tool is still evolving.
“We are looking at larger sample sizes to improve the accuracy and generalizability of our model, but we can use it now to inform treatment decisions,” Dr. Gurevich said.
In patients with PPMS who have a highly variable course, the model predicts disability progression with an accuracy of approximately 70%, according to the data he presented. He said he believes this is already at a level that it is meaningful for a risk-to-benefit calculation when considering treatment.
Machine learning analyzes blood samples
The study pursues the concept that the genetic information governing highly complex pathophysiological processes is contained in RNA sequencing. While multimodal omics generate data that are too complex for human pattern recognition, there is a growing body of evidence, including that provided by this study, to suggest that machine learning can employ these same RNA profiles and predict disease activity.
In this study, blood samples were collected from patients who participated in the phase 3 clinical ORATORIO trial that led to approval of ocrelizumab for PPMS. Analyses were conducted only on blood samples from those randomized to placebo, who, like those in the active treatment arm, were evaluated at baseline and at 12-week intervals for more than 2 years.
After development of a prediction model and creation of a training dataset, machine learning was applied to the deep sequencing of the blood transcriptome data for predicting two endpoints. One was disease progression at 120 weeks defined as a 1 point or more increase in the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) among patients with confirmed disability progression for at least 12 weeks (12W-CDP).
The other was change at 120 weeks in brain morphology defined as a 1% or more reduction in brain volume (120W PBVC).
The peripheral blood samples were subjected to RNA sequencing analysis (RNA-Seq) using commercially available analysis techniques. The prediction model for the disability endpoint was based on data generated from the blood transcriptome of 135 patients of which 53 (39%) met the endpoint at 120 weeks. The prediction model for the change in brain morphology was based on the blood transcriptome from 94 patients of which 63 (67%) met the endpoint.
On the basis of 10 genes that most significantly differentiated those who met the disability endpoint from those who did not, machine recognition of patterns after training was able to predict correctly the outcome in 70.9%. The sensitivity was 55.6%, and the specificity was 79.0%. The positive and negative predictive values were 59.0% and 76.8%, respectively.
On the basis of the 12 genes the most significantly differentiated those that reached the 120W PBVC endpoint from those who did not, machine learning resulted in a correct prediction of outcomes in 75.1%. The sensitivity was 78.1%, and the specificity was 66.7%. The positive and negative predictive values were 83.3% and 58.8%, respectively
Typical of a PPMS trial population, the mean age of the patients was about 44 years. The mean disease duration was about 6 years. The majority of patients had an EDSS score below 5.5 at baseline. The baseline T2 lesion number was approximately 50.
If further validated by others and in larger studies, this type of information could play a valuable role in PPMS management, according to Dr. Gurevich. Now that there is an approved therapy for PPMS, it can help clinicians and patients determine whether to initiate treatment early to address the high risk of progression or delay treatment that might not be needed.
A useful tool
In the field of MS, most of the studies performed with machine learning have focused on the analysis of radiological images. However, others are now looking at the blood transcriptome as a potential path to better classifying a highly complex disease with substantial heterogeneity in presentation, progression, and outcome.
For example, machine learning of the blood transcriptome has also shown high accuracy in the diagnosis and classification of MS in patients with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS). One study, published in Cell Reports Medicine, was led by Cinthia Farina, PhD, Institute of Experimental Neurology, IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan.
Although she did not hear the presentation by Dr. Gurevich, Dr. Farina is enthusiastic about the potential for machine learning to help manage MS through the analysis of the blood transcriptome. “I do believe that transcriptomics in peripheral immune cells may become a useful tool for MS diagnosis and prognosis,” she said.
In her own study, in which machine learning algorithms were developed and trained on the basis of peripheral blood from patients with CIS, the tool proved accurate with a strong potential for being incorporated into routine clinical management.
“Machine learning applied to the blood transcriptomes was extremely efficient with a 95.6% accuracy in discriminating PPMS from RRMS [relapsing-remitting] MS,” she reported.
Dr. Gurevich has no potential financial conflicts of interest to report. He reported funding for the study was provided by Roche. Dr. Farina reports financial relationships with Merck-Serono, Novartis, and Teva.
FROM AAN 2023
Therapy to reverse muscle dystrophies shows promise
BOSTON – Becker (BMD) and Duchenne muscle dystrophy (DMD) progress largely from irreversible contraction-induced injury of skeletal muscles, making the very positive interim results of an early-phase trial with a drug that prevents these injuries worth attention.
The phase 1b data in BMD, presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, were sufficiently promising that controlled phase 2 trials in both BMD and DMD are already enrolling, reported Joanne Donovan, MD, PhD, an adjunct professor at Boston University and chief medical officer of Edgewise Therapeutics, the company developing the drug.
Phase 1 study
Early phase studies are largely focused on safety, but the
Moreover, the evidence of a clinical effect was achieved in adult patients with a North Star Ambulatory Assessment (NSAA) score of 15, signifying advanced disease. Only 12 patients were enrolled and there were no controls, but objective evidence of a favorable effect was generated by highly significant reductions in creatine kinase (CK) and fast skeletal muscle (TNNI2) troponin, which are both biomarkers commonly used to track muscular dystrophy progression.
In patients with BMD or DMD, a lack of dystrophin is a key pathogenic feature, according to Dr. Donovan. She explained that dystrophin in muscles connects contractile proteins to membranes and surrounding matrix. In the presence of dystrophin, muscle fibers support each other, but when this protein is absent, contraction causes injury.
The drug in development, currently identified as EDG-5506, is a selective fast myosin inhibitor. This agent was shown to prevent the muscle injury caused by lack of dystrophin in animal models of muscular dystrophy and is now showing the same effect in humans. Preservation of muscle is critical to preventing BMD and DMD progression according to several sets of data, according to Dr. Donovan.
For one, it has been shown that BMD or DMD patients with relatively preserved function as defined by a NSAA score above 32 have minimal muscle damage. As NSAA scores fall below 32 points, muscle mass diminishes and fat accumulates. In natural history studies of BMD, there is a 1.2-point decline in NSAA score over 5 years, and this tracks with muscle loss and not with other variables, such as patient age.
“Progression depends on the degree of muscle loss,” Dr. Donovan stated, providing the rationale for moving forward with EDG-5506.
Proof of concept
In experimental studies, modulation of fast myelin provided complete protection against muscle injury while preserving its contractile function, and this translated into protection against loss of function. Phase 1 studies in BMD patients and healthy controls have already provided evidence that EDG-5506 is well tolerated and safe, but the new phase 1b provides a proof of concept for its ability to inhibit muscle injury in BMD patients.
In this study, called ARCH, 12 adults 18 years of age or older with a dystrophin mutation and a BMD phenotype who could complete a 100-meter timed test were enrolled. The median age at entry was 32 years. Several patients had participated in a previous phase 1 safety study. The daily starting dose of 10 mg was increased from 10 mg to 15 mg at 2 months. The dose was increased again to 20 mg at 6 months, but the data presented by Dr. Donovan were restricted to the first 6 months.
At the interim 6-month analysis, creatine kinase was reduced by 40% and TINN2 was reduced by 84% (both P < 0.001). The significant reductions in these biomarkers and others, such as myoglobin, were mostly achieved within the first month, although further reductions were observed for some biomarkers subsequently.
The NSAA score at 6 months improved on average by about 1 point on treatment. Natural history studies of BMD predict a 1-point reduction in NSAA score over this period of time. The modest improvements from baseline in pain scores at 1 month were sustained at 6 months.
On the basis of a proteomic analysis, 125 proteins mostly associated with metabolic pathways consistent with muscle injury were found to be altered in BMD patients relative to healthy controls. The majority of these proteins, whether assessed collectively or individually, normalized after 1 to 2 months of treatment with EDG-5506 and have remained stable during follow-up to date, according to Dr. Donovan.
As in previous studies, the drug was well tolerated. The three most common treatment-emergent events were dizziness, somnolence, and headache. Each was reported by about 25% of patients, but no patient discontinued therapy as a result of adverse events.
Findings deemed ‘a big deal’
These data, despite the small number of patients in the study and the limited follow-up, “are a big deal,” according to Nicholas E. Johnson, MD, division chief, neuromuscular disorders, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond. He pointed out that there are no effective treatments currently for BMD, and the mechanism of action is plausible.
“I am excited about the potential of this treatment, although we clearly need longer follow-up and more patients evaluated on this treatment,” Dr. Johnson said. He said that clinicians with BMD patients should be aware of the phase 2 trial that is now recruiting adult subjects.
“Becker muscular dystrophy is highly disabling. As disease advances, most patients have very limited function,” said Dr. Johnson, emphasizing the urgent unmet need for an effective therapy.
Dr. Donovan is a full time employee of Edgewise Therapeutics, which funded this study. Dr. Johnson has financial relationships with Acceleron, Arthex, AveXis, Avidity, Biogen, Dyne Therapeutics, Entrada, Juvena, ML Bio, Sarepta Therapeutics, Triplet Therapeutics, and Vertex Pharma.
BOSTON – Becker (BMD) and Duchenne muscle dystrophy (DMD) progress largely from irreversible contraction-induced injury of skeletal muscles, making the very positive interim results of an early-phase trial with a drug that prevents these injuries worth attention.
The phase 1b data in BMD, presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, were sufficiently promising that controlled phase 2 trials in both BMD and DMD are already enrolling, reported Joanne Donovan, MD, PhD, an adjunct professor at Boston University and chief medical officer of Edgewise Therapeutics, the company developing the drug.
Phase 1 study
Early phase studies are largely focused on safety, but the
Moreover, the evidence of a clinical effect was achieved in adult patients with a North Star Ambulatory Assessment (NSAA) score of 15, signifying advanced disease. Only 12 patients were enrolled and there were no controls, but objective evidence of a favorable effect was generated by highly significant reductions in creatine kinase (CK) and fast skeletal muscle (TNNI2) troponin, which are both biomarkers commonly used to track muscular dystrophy progression.
In patients with BMD or DMD, a lack of dystrophin is a key pathogenic feature, according to Dr. Donovan. She explained that dystrophin in muscles connects contractile proteins to membranes and surrounding matrix. In the presence of dystrophin, muscle fibers support each other, but when this protein is absent, contraction causes injury.
The drug in development, currently identified as EDG-5506, is a selective fast myosin inhibitor. This agent was shown to prevent the muscle injury caused by lack of dystrophin in animal models of muscular dystrophy and is now showing the same effect in humans. Preservation of muscle is critical to preventing BMD and DMD progression according to several sets of data, according to Dr. Donovan.
For one, it has been shown that BMD or DMD patients with relatively preserved function as defined by a NSAA score above 32 have minimal muscle damage. As NSAA scores fall below 32 points, muscle mass diminishes and fat accumulates. In natural history studies of BMD, there is a 1.2-point decline in NSAA score over 5 years, and this tracks with muscle loss and not with other variables, such as patient age.
“Progression depends on the degree of muscle loss,” Dr. Donovan stated, providing the rationale for moving forward with EDG-5506.
Proof of concept
In experimental studies, modulation of fast myelin provided complete protection against muscle injury while preserving its contractile function, and this translated into protection against loss of function. Phase 1 studies in BMD patients and healthy controls have already provided evidence that EDG-5506 is well tolerated and safe, but the new phase 1b provides a proof of concept for its ability to inhibit muscle injury in BMD patients.
In this study, called ARCH, 12 adults 18 years of age or older with a dystrophin mutation and a BMD phenotype who could complete a 100-meter timed test were enrolled. The median age at entry was 32 years. Several patients had participated in a previous phase 1 safety study. The daily starting dose of 10 mg was increased from 10 mg to 15 mg at 2 months. The dose was increased again to 20 mg at 6 months, but the data presented by Dr. Donovan were restricted to the first 6 months.
At the interim 6-month analysis, creatine kinase was reduced by 40% and TINN2 was reduced by 84% (both P < 0.001). The significant reductions in these biomarkers and others, such as myoglobin, were mostly achieved within the first month, although further reductions were observed for some biomarkers subsequently.
The NSAA score at 6 months improved on average by about 1 point on treatment. Natural history studies of BMD predict a 1-point reduction in NSAA score over this period of time. The modest improvements from baseline in pain scores at 1 month were sustained at 6 months.
On the basis of a proteomic analysis, 125 proteins mostly associated with metabolic pathways consistent with muscle injury were found to be altered in BMD patients relative to healthy controls. The majority of these proteins, whether assessed collectively or individually, normalized after 1 to 2 months of treatment with EDG-5506 and have remained stable during follow-up to date, according to Dr. Donovan.
As in previous studies, the drug was well tolerated. The three most common treatment-emergent events were dizziness, somnolence, and headache. Each was reported by about 25% of patients, but no patient discontinued therapy as a result of adverse events.
Findings deemed ‘a big deal’
These data, despite the small number of patients in the study and the limited follow-up, “are a big deal,” according to Nicholas E. Johnson, MD, division chief, neuromuscular disorders, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond. He pointed out that there are no effective treatments currently for BMD, and the mechanism of action is plausible.
“I am excited about the potential of this treatment, although we clearly need longer follow-up and more patients evaluated on this treatment,” Dr. Johnson said. He said that clinicians with BMD patients should be aware of the phase 2 trial that is now recruiting adult subjects.
“Becker muscular dystrophy is highly disabling. As disease advances, most patients have very limited function,” said Dr. Johnson, emphasizing the urgent unmet need for an effective therapy.
Dr. Donovan is a full time employee of Edgewise Therapeutics, which funded this study. Dr. Johnson has financial relationships with Acceleron, Arthex, AveXis, Avidity, Biogen, Dyne Therapeutics, Entrada, Juvena, ML Bio, Sarepta Therapeutics, Triplet Therapeutics, and Vertex Pharma.
BOSTON – Becker (BMD) and Duchenne muscle dystrophy (DMD) progress largely from irreversible contraction-induced injury of skeletal muscles, making the very positive interim results of an early-phase trial with a drug that prevents these injuries worth attention.
The phase 1b data in BMD, presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, were sufficiently promising that controlled phase 2 trials in both BMD and DMD are already enrolling, reported Joanne Donovan, MD, PhD, an adjunct professor at Boston University and chief medical officer of Edgewise Therapeutics, the company developing the drug.
Phase 1 study
Early phase studies are largely focused on safety, but the
Moreover, the evidence of a clinical effect was achieved in adult patients with a North Star Ambulatory Assessment (NSAA) score of 15, signifying advanced disease. Only 12 patients were enrolled and there were no controls, but objective evidence of a favorable effect was generated by highly significant reductions in creatine kinase (CK) and fast skeletal muscle (TNNI2) troponin, which are both biomarkers commonly used to track muscular dystrophy progression.
In patients with BMD or DMD, a lack of dystrophin is a key pathogenic feature, according to Dr. Donovan. She explained that dystrophin in muscles connects contractile proteins to membranes and surrounding matrix. In the presence of dystrophin, muscle fibers support each other, but when this protein is absent, contraction causes injury.
The drug in development, currently identified as EDG-5506, is a selective fast myosin inhibitor. This agent was shown to prevent the muscle injury caused by lack of dystrophin in animal models of muscular dystrophy and is now showing the same effect in humans. Preservation of muscle is critical to preventing BMD and DMD progression according to several sets of data, according to Dr. Donovan.
For one, it has been shown that BMD or DMD patients with relatively preserved function as defined by a NSAA score above 32 have minimal muscle damage. As NSAA scores fall below 32 points, muscle mass diminishes and fat accumulates. In natural history studies of BMD, there is a 1.2-point decline in NSAA score over 5 years, and this tracks with muscle loss and not with other variables, such as patient age.
“Progression depends on the degree of muscle loss,” Dr. Donovan stated, providing the rationale for moving forward with EDG-5506.
Proof of concept
In experimental studies, modulation of fast myelin provided complete protection against muscle injury while preserving its contractile function, and this translated into protection against loss of function. Phase 1 studies in BMD patients and healthy controls have already provided evidence that EDG-5506 is well tolerated and safe, but the new phase 1b provides a proof of concept for its ability to inhibit muscle injury in BMD patients.
In this study, called ARCH, 12 adults 18 years of age or older with a dystrophin mutation and a BMD phenotype who could complete a 100-meter timed test were enrolled. The median age at entry was 32 years. Several patients had participated in a previous phase 1 safety study. The daily starting dose of 10 mg was increased from 10 mg to 15 mg at 2 months. The dose was increased again to 20 mg at 6 months, but the data presented by Dr. Donovan were restricted to the first 6 months.
At the interim 6-month analysis, creatine kinase was reduced by 40% and TINN2 was reduced by 84% (both P < 0.001). The significant reductions in these biomarkers and others, such as myoglobin, were mostly achieved within the first month, although further reductions were observed for some biomarkers subsequently.
The NSAA score at 6 months improved on average by about 1 point on treatment. Natural history studies of BMD predict a 1-point reduction in NSAA score over this period of time. The modest improvements from baseline in pain scores at 1 month were sustained at 6 months.
On the basis of a proteomic analysis, 125 proteins mostly associated with metabolic pathways consistent with muscle injury were found to be altered in BMD patients relative to healthy controls. The majority of these proteins, whether assessed collectively or individually, normalized after 1 to 2 months of treatment with EDG-5506 and have remained stable during follow-up to date, according to Dr. Donovan.
As in previous studies, the drug was well tolerated. The three most common treatment-emergent events were dizziness, somnolence, and headache. Each was reported by about 25% of patients, but no patient discontinued therapy as a result of adverse events.
Findings deemed ‘a big deal’
These data, despite the small number of patients in the study and the limited follow-up, “are a big deal,” according to Nicholas E. Johnson, MD, division chief, neuromuscular disorders, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond. He pointed out that there are no effective treatments currently for BMD, and the mechanism of action is plausible.
“I am excited about the potential of this treatment, although we clearly need longer follow-up and more patients evaluated on this treatment,” Dr. Johnson said. He said that clinicians with BMD patients should be aware of the phase 2 trial that is now recruiting adult subjects.
“Becker muscular dystrophy is highly disabling. As disease advances, most patients have very limited function,” said Dr. Johnson, emphasizing the urgent unmet need for an effective therapy.
Dr. Donovan is a full time employee of Edgewise Therapeutics, which funded this study. Dr. Johnson has financial relationships with Acceleron, Arthex, AveXis, Avidity, Biogen, Dyne Therapeutics, Entrada, Juvena, ML Bio, Sarepta Therapeutics, Triplet Therapeutics, and Vertex Pharma.
FROM AAN 2023
Phase 3 study of new levodopa/carbidopa delivery system meets all efficacy endpoints
BOSTON – presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
When compared with optimized oral immediate-release medication, the delivery system, called ND0612 (NeuroDerm, Rehovot, Israel), improved ON time without troublesome dyskinesias while improving symptoms according to ratings from both patients and clinicians, according to Alberto J. Espay, MD, professor of neurology and director of the Gardner Family Center for Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders, University of Cincinnati.
The new delivery system addresses the challenge of reducing the variability in levodopa plasma concentrations, a major factor in motor fluctuations and diminishing benefit from orally administered drug, according to Dr. Espay. He said that continuous infusion strategies have long been sought as a method to preserve levodopa efficacy.
BouNDless findings
There were two phases to this multinational trial, called BouNDless. In the first, an open-label run-in phase, 381 patients with Parkinson’s disease were dose titrated for optimization of oral immediate-release levodopa and carbidopa. They were then optimized for the same drugs delivered with ND0612. The study was conducted over 12 weeks; 122 patients left the study after this phase due to adverse events, lack of efficacy, or withdrawal of consent.
In the second phase, the 259 remaining patients were randomized to the continuous infusion arm or to immediate release oral therapy. In this double-blind, double-dummy phase, those randomized to the ND0612 infusion also received oral placebos. Those randomized to oral therapy received a placebo infusion. Efficacy and safety were assessed at the end of 12 weeks.
At the end of phase 1, the ON time increased by about 3 hours when levodopa-carbidopa dosing was optimized on either delivery method. Dr. Espay attributed the improvement to the value of optimized dosing even in patients with relatively advanced disease.
However, for the purposes of the double-blind comparison, this improvement in ON time provided a new baseline for comparison of the two delivery methods. This is important for interpreting the primary result, which was a 1.72-hour difference in ON time at the end of the study. The difference was created when ON time was maintained with ND0612 continuous drug delivery but eroded in the group randomized to oral immediate-release treatment.
Several secondary endpoints supported the greater efficacy of continuous subcutaneous delivery. These included lower OFF time (0.50 vs. 1.90 hours), less accumulation of disability on the United Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale part II-M-EDL (-0.30 vs. +2.75 points), and greater improvement on the Patient Global Impression of Change (+0.31 vs. +0.70 points), and the Clinical Global Impression of change (+0.31 vs. +0.77 points). The differences were highly statistically significant (all P < .0001).
The patients participating in the double-blind phase of the study were similar with a mean age of 63.5 years in both groups and time since Parkinson’s disease diagnosis (> 9 years). The median ON time without troublesome dyskinesias was about 12 hours at baseline in both groups and the median OFF time was about 3.5 hours.
The higher rate of treatment-related adverse events in the ND0612 group (67.2% vs. 52.7%) was largely explained by the greater rate of infusion site reactions (57.0% vs. 42.7%). The rates of severe reactions in the two groups were the same (0.8%), but both mild (43.8% vs. 36.6%) and moderate (12.5% vs. 5.3%) reactions occurred more commonly in the group receiving active therapy.
“Infusion reactions are the Achilles heel of all subcutaneous therapies,” acknowledged Dr. Espay, who expects other infusion systems in development to share this risk. He suggested that the clinical impact can be attenuated to some degree by rotating infusion sites.
BeyoND extension study
Data from an open-label extension (OLE) of the phase 2b BeyoND trial were also presented at the AAN meeting and generated generally similar results. Largely a safety study, there was no active control in the initial BeyoND or the BeyoND OLE. In BeyoND, the improvement in ON time from baseline was even greater than that seen in BouNDless, but, again, the optimization of dosing in the BouNDless run-in established a greater baseline of disease control.
In the OLE of BeyoND, presented by Aaron Ellenbogen, DO, a neurologist in Farmington, Mich., one of the notable findings was the retention of patients. After 2 years of follow-up, 82% completed at least 2 years of follow-up and 66.7% have now remained on treatment for at least 3 years. Dr. Ellenbogen maintains that this retention rate provides compelling evidence of a favorable benefit-to-risk ratio.
Fulfilling an unmet need
The favorable efficacy data from this trial represent “a big advance,” according to Ihtsham Ul Haq, MD, chief, movement disorders division, University of Miami, who was reached for comment. He noted that continuous infusion delivery has been anticipated for some time, and he expects these types of systems to fulfill an unmet need.
“This will be a useful option in a carefully selected group of patients,” said Dr. Haq, who considers the types of improvement in ON time to be highly clinically meaningful.
However, he cautioned that the nodules created by injection site reactions might limit the utility of this treatment option in at least some patients. Wearing the external device might also be a limiting factor for some patients.
In complex Parkinson’s disease, a stage that can be reached fairly rapidly in some patients but might take 15 years or more in others, all of the options involve a careful benefit-to-risk calculation, according to Dr. Haq. Deep brain stimulation is among the most effective options, but continuous infusion might appeal to some patients for delaying this procedure or as an alternative.
“We need multiple options for these types of patients, and it appears that continuous infusion will be one of them,” Dr. Haq said.
Dr. Espay has financial relationships with Acadia, Acorda, Amneal, AskBio, Bexion, Kyowa Kirin, Neuroderm, Neurocrine, and Sunovion. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva. Dr. Haq reports no potential conflicts of interest.
BOSTON – presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
When compared with optimized oral immediate-release medication, the delivery system, called ND0612 (NeuroDerm, Rehovot, Israel), improved ON time without troublesome dyskinesias while improving symptoms according to ratings from both patients and clinicians, according to Alberto J. Espay, MD, professor of neurology and director of the Gardner Family Center for Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders, University of Cincinnati.
The new delivery system addresses the challenge of reducing the variability in levodopa plasma concentrations, a major factor in motor fluctuations and diminishing benefit from orally administered drug, according to Dr. Espay. He said that continuous infusion strategies have long been sought as a method to preserve levodopa efficacy.
BouNDless findings
There were two phases to this multinational trial, called BouNDless. In the first, an open-label run-in phase, 381 patients with Parkinson’s disease were dose titrated for optimization of oral immediate-release levodopa and carbidopa. They were then optimized for the same drugs delivered with ND0612. The study was conducted over 12 weeks; 122 patients left the study after this phase due to adverse events, lack of efficacy, or withdrawal of consent.
In the second phase, the 259 remaining patients were randomized to the continuous infusion arm or to immediate release oral therapy. In this double-blind, double-dummy phase, those randomized to the ND0612 infusion also received oral placebos. Those randomized to oral therapy received a placebo infusion. Efficacy and safety were assessed at the end of 12 weeks.
At the end of phase 1, the ON time increased by about 3 hours when levodopa-carbidopa dosing was optimized on either delivery method. Dr. Espay attributed the improvement to the value of optimized dosing even in patients with relatively advanced disease.
However, for the purposes of the double-blind comparison, this improvement in ON time provided a new baseline for comparison of the two delivery methods. This is important for interpreting the primary result, which was a 1.72-hour difference in ON time at the end of the study. The difference was created when ON time was maintained with ND0612 continuous drug delivery but eroded in the group randomized to oral immediate-release treatment.
Several secondary endpoints supported the greater efficacy of continuous subcutaneous delivery. These included lower OFF time (0.50 vs. 1.90 hours), less accumulation of disability on the United Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale part II-M-EDL (-0.30 vs. +2.75 points), and greater improvement on the Patient Global Impression of Change (+0.31 vs. +0.70 points), and the Clinical Global Impression of change (+0.31 vs. +0.77 points). The differences were highly statistically significant (all P < .0001).
The patients participating in the double-blind phase of the study were similar with a mean age of 63.5 years in both groups and time since Parkinson’s disease diagnosis (> 9 years). The median ON time without troublesome dyskinesias was about 12 hours at baseline in both groups and the median OFF time was about 3.5 hours.
The higher rate of treatment-related adverse events in the ND0612 group (67.2% vs. 52.7%) was largely explained by the greater rate of infusion site reactions (57.0% vs. 42.7%). The rates of severe reactions in the two groups were the same (0.8%), but both mild (43.8% vs. 36.6%) and moderate (12.5% vs. 5.3%) reactions occurred more commonly in the group receiving active therapy.
“Infusion reactions are the Achilles heel of all subcutaneous therapies,” acknowledged Dr. Espay, who expects other infusion systems in development to share this risk. He suggested that the clinical impact can be attenuated to some degree by rotating infusion sites.
BeyoND extension study
Data from an open-label extension (OLE) of the phase 2b BeyoND trial were also presented at the AAN meeting and generated generally similar results. Largely a safety study, there was no active control in the initial BeyoND or the BeyoND OLE. In BeyoND, the improvement in ON time from baseline was even greater than that seen in BouNDless, but, again, the optimization of dosing in the BouNDless run-in established a greater baseline of disease control.
In the OLE of BeyoND, presented by Aaron Ellenbogen, DO, a neurologist in Farmington, Mich., one of the notable findings was the retention of patients. After 2 years of follow-up, 82% completed at least 2 years of follow-up and 66.7% have now remained on treatment for at least 3 years. Dr. Ellenbogen maintains that this retention rate provides compelling evidence of a favorable benefit-to-risk ratio.
Fulfilling an unmet need
The favorable efficacy data from this trial represent “a big advance,” according to Ihtsham Ul Haq, MD, chief, movement disorders division, University of Miami, who was reached for comment. He noted that continuous infusion delivery has been anticipated for some time, and he expects these types of systems to fulfill an unmet need.
“This will be a useful option in a carefully selected group of patients,” said Dr. Haq, who considers the types of improvement in ON time to be highly clinically meaningful.
However, he cautioned that the nodules created by injection site reactions might limit the utility of this treatment option in at least some patients. Wearing the external device might also be a limiting factor for some patients.
In complex Parkinson’s disease, a stage that can be reached fairly rapidly in some patients but might take 15 years or more in others, all of the options involve a careful benefit-to-risk calculation, according to Dr. Haq. Deep brain stimulation is among the most effective options, but continuous infusion might appeal to some patients for delaying this procedure or as an alternative.
“We need multiple options for these types of patients, and it appears that continuous infusion will be one of them,” Dr. Haq said.
Dr. Espay has financial relationships with Acadia, Acorda, Amneal, AskBio, Bexion, Kyowa Kirin, Neuroderm, Neurocrine, and Sunovion. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva. Dr. Haq reports no potential conflicts of interest.
BOSTON – presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
When compared with optimized oral immediate-release medication, the delivery system, called ND0612 (NeuroDerm, Rehovot, Israel), improved ON time without troublesome dyskinesias while improving symptoms according to ratings from both patients and clinicians, according to Alberto J. Espay, MD, professor of neurology and director of the Gardner Family Center for Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders, University of Cincinnati.
The new delivery system addresses the challenge of reducing the variability in levodopa plasma concentrations, a major factor in motor fluctuations and diminishing benefit from orally administered drug, according to Dr. Espay. He said that continuous infusion strategies have long been sought as a method to preserve levodopa efficacy.
BouNDless findings
There were two phases to this multinational trial, called BouNDless. In the first, an open-label run-in phase, 381 patients with Parkinson’s disease were dose titrated for optimization of oral immediate-release levodopa and carbidopa. They were then optimized for the same drugs delivered with ND0612. The study was conducted over 12 weeks; 122 patients left the study after this phase due to adverse events, lack of efficacy, or withdrawal of consent.
In the second phase, the 259 remaining patients were randomized to the continuous infusion arm or to immediate release oral therapy. In this double-blind, double-dummy phase, those randomized to the ND0612 infusion also received oral placebos. Those randomized to oral therapy received a placebo infusion. Efficacy and safety were assessed at the end of 12 weeks.
At the end of phase 1, the ON time increased by about 3 hours when levodopa-carbidopa dosing was optimized on either delivery method. Dr. Espay attributed the improvement to the value of optimized dosing even in patients with relatively advanced disease.
However, for the purposes of the double-blind comparison, this improvement in ON time provided a new baseline for comparison of the two delivery methods. This is important for interpreting the primary result, which was a 1.72-hour difference in ON time at the end of the study. The difference was created when ON time was maintained with ND0612 continuous drug delivery but eroded in the group randomized to oral immediate-release treatment.
Several secondary endpoints supported the greater efficacy of continuous subcutaneous delivery. These included lower OFF time (0.50 vs. 1.90 hours), less accumulation of disability on the United Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale part II-M-EDL (-0.30 vs. +2.75 points), and greater improvement on the Patient Global Impression of Change (+0.31 vs. +0.70 points), and the Clinical Global Impression of change (+0.31 vs. +0.77 points). The differences were highly statistically significant (all P < .0001).
The patients participating in the double-blind phase of the study were similar with a mean age of 63.5 years in both groups and time since Parkinson’s disease diagnosis (> 9 years). The median ON time without troublesome dyskinesias was about 12 hours at baseline in both groups and the median OFF time was about 3.5 hours.
The higher rate of treatment-related adverse events in the ND0612 group (67.2% vs. 52.7%) was largely explained by the greater rate of infusion site reactions (57.0% vs. 42.7%). The rates of severe reactions in the two groups were the same (0.8%), but both mild (43.8% vs. 36.6%) and moderate (12.5% vs. 5.3%) reactions occurred more commonly in the group receiving active therapy.
“Infusion reactions are the Achilles heel of all subcutaneous therapies,” acknowledged Dr. Espay, who expects other infusion systems in development to share this risk. He suggested that the clinical impact can be attenuated to some degree by rotating infusion sites.
BeyoND extension study
Data from an open-label extension (OLE) of the phase 2b BeyoND trial were also presented at the AAN meeting and generated generally similar results. Largely a safety study, there was no active control in the initial BeyoND or the BeyoND OLE. In BeyoND, the improvement in ON time from baseline was even greater than that seen in BouNDless, but, again, the optimization of dosing in the BouNDless run-in established a greater baseline of disease control.
In the OLE of BeyoND, presented by Aaron Ellenbogen, DO, a neurologist in Farmington, Mich., one of the notable findings was the retention of patients. After 2 years of follow-up, 82% completed at least 2 years of follow-up and 66.7% have now remained on treatment for at least 3 years. Dr. Ellenbogen maintains that this retention rate provides compelling evidence of a favorable benefit-to-risk ratio.
Fulfilling an unmet need
The favorable efficacy data from this trial represent “a big advance,” according to Ihtsham Ul Haq, MD, chief, movement disorders division, University of Miami, who was reached for comment. He noted that continuous infusion delivery has been anticipated for some time, and he expects these types of systems to fulfill an unmet need.
“This will be a useful option in a carefully selected group of patients,” said Dr. Haq, who considers the types of improvement in ON time to be highly clinically meaningful.
However, he cautioned that the nodules created by injection site reactions might limit the utility of this treatment option in at least some patients. Wearing the external device might also be a limiting factor for some patients.
In complex Parkinson’s disease, a stage that can be reached fairly rapidly in some patients but might take 15 years or more in others, all of the options involve a careful benefit-to-risk calculation, according to Dr. Haq. Deep brain stimulation is among the most effective options, but continuous infusion might appeal to some patients for delaying this procedure or as an alternative.
“We need multiple options for these types of patients, and it appears that continuous infusion will be one of them,” Dr. Haq said.
Dr. Espay has financial relationships with Acadia, Acorda, Amneal, AskBio, Bexion, Kyowa Kirin, Neuroderm, Neurocrine, and Sunovion. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva. Dr. Haq reports no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM AAN 2023
Explanation proposed for long-COVID symptoms in the CNS
BOSTON – , according to a collaborative study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Already documented in several other viral infections, such as influenza and human immunodeficiency virus, antigenic imprinting results in production of antibodies to previously encountered viral infections rather than to the immediate threat, according to Marianna Spatola, MD, PhD, a research fellow at the Ragon Institute, Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass.
Original antigenic sin
In the case of persistent neurologic symptoms after COVID, a condition known as neuroPASC (neurological postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV2 infection), antibodies produced for previously encountered coronaviruses rather than for SARS-CoV2 might explain most or all cases, according to the data Dr. Spatola presented.
The evidence for this explanation was drawn from a study of 112 patients evaluated months after an acute episode of COVID-19. Of these, 18 patients had persistent neurologic dysfunction. When compared with the 94 whose infection resolved without sequelae, the patients with prolonged neurologic impairments had relatively low systemic antibody response to SARS-CoV2. However, they showed relatively high antibody responses against other coronaviruses.
This is a pattern consistent with antigenic imprinting, a concept first described more than 60 years ago as original antigenic sin. When the immune system becomes imprinted with an antigen from the first encountered virus from a family of pathogens, it governs all subsequent antibody responses, according to several published studies that have described and evaluated this concept.
Additional evidence
In Dr. Spatola’s study, other differences, particularly in regard to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), further supported the role of antigenic imprinting as a cause of neuroPASC. For one, those with elevated immune responses to other common coronaviruses rather than SARS-CoV2 in the CSF relative to the periphery were more likely to have a bad outcome in regard to neurologic symptoms.
Moreover, the CSF in neuroPASC patients “was characterized by increased IgG1 and absence of IgM, suggesting compartmentalized humoral responses within the CSF through selective transfer of antibodies from the serum to the CSF across the blood-brain barrier rather than through intrathecal synthesis,” Dr. Spatola reported.
In the case of COVID-19, the propensity for antigenic imprinting is not difficult to understand.
“The common cold coronaviruses are pretty similar to SARS-CoV2, but they are not exactly the same,” Dr. Spatola said. Her work and studies by others suggest that when antigenic imprinting occurs, “it prevents full maturation of the antibody response.”
NeuroPASC is one of many manifestations of long COVID, but Dr. Spatola pointed out that the immune response in the CSF is unique and the causes of prolonged neurologic impairment after COVID-19 are likely to involve different mechanisms than other long-COVID symptoms.
“Antibodies in the brain are functionally different,” said Dr. Spatola, noting for example that antibody-directed defenses against viral threats show a greater relative reliance on phagocytosis. This might become important in the development of therapeutics for neurologic symptoms of long COVID.
A different phenomenon
The manifestations of neuroPASC are heterogeneous and can include confusion, cognitive dysfunction, headache, encephalitis, and other impairments. Neurologic symptoms occur during acute SARS-CoV2 infections, but neuroPASC appears to be a different phenomenon. These symptoms, which develop after the initial respiratory disease has resolved, were attributed by Dr. Spatola to persistent inflammation that is not necessarily directly related to ongoing infection.
“The reason why some patients develop neuroPASC is unknown, but I think the evidence has pointed to a role for the immune system rather than the virus itself,” Dr. Spatola said.
Currently, neuroPASC is a clinical diagnosis but Dr. Spatola and her coinvestigators are conducting research to identify biomarkers. A viable diagnostic test is not expected imminently. They have identified 150 different features with potential relevance to neuroPASC.
In their comparison of those who did relative to those who did not develop neuroPASC, the initial studies were undertaken 2-4 months after the acute COVID-19 symptoms had resolved. The patients with neuroPASC and those without neurologic sequelae have now been followed for 6-8 months, which Dr. Spatola said was too short to draw firm conclusions about outcomes.
An evolving concept
Despite the small sample size of this study, these are “very interesting data” for considering the pathogenesis of neuroPASC, which is “a concept that is still evolving,” according to Natalia S. Rost, MD, chief of the stroke division, department of neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Applied to SARS-CoV2, the concept of original antigenic sin “is new” but Dr. Rost said that it might help differentiate neuroPASC from acute neurologic symptoms of COVID-19, which include stroke. She indicated that the work performed by Dr. Spatola and others might eventually explain the pathology while leading to treatment strategies. She cautioned that the concepts explored in this study “need to be further developed” through larger sample sizes and the exploration of other variables that support the hypothesis.
Dr. Spatola and Dr. Rost report no potential conflicts of interest.
BOSTON – , according to a collaborative study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Already documented in several other viral infections, such as influenza and human immunodeficiency virus, antigenic imprinting results in production of antibodies to previously encountered viral infections rather than to the immediate threat, according to Marianna Spatola, MD, PhD, a research fellow at the Ragon Institute, Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass.
Original antigenic sin
In the case of persistent neurologic symptoms after COVID, a condition known as neuroPASC (neurological postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV2 infection), antibodies produced for previously encountered coronaviruses rather than for SARS-CoV2 might explain most or all cases, according to the data Dr. Spatola presented.
The evidence for this explanation was drawn from a study of 112 patients evaluated months after an acute episode of COVID-19. Of these, 18 patients had persistent neurologic dysfunction. When compared with the 94 whose infection resolved without sequelae, the patients with prolonged neurologic impairments had relatively low systemic antibody response to SARS-CoV2. However, they showed relatively high antibody responses against other coronaviruses.
This is a pattern consistent with antigenic imprinting, a concept first described more than 60 years ago as original antigenic sin. When the immune system becomes imprinted with an antigen from the first encountered virus from a family of pathogens, it governs all subsequent antibody responses, according to several published studies that have described and evaluated this concept.
Additional evidence
In Dr. Spatola’s study, other differences, particularly in regard to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), further supported the role of antigenic imprinting as a cause of neuroPASC. For one, those with elevated immune responses to other common coronaviruses rather than SARS-CoV2 in the CSF relative to the periphery were more likely to have a bad outcome in regard to neurologic symptoms.
Moreover, the CSF in neuroPASC patients “was characterized by increased IgG1 and absence of IgM, suggesting compartmentalized humoral responses within the CSF through selective transfer of antibodies from the serum to the CSF across the blood-brain barrier rather than through intrathecal synthesis,” Dr. Spatola reported.
In the case of COVID-19, the propensity for antigenic imprinting is not difficult to understand.
“The common cold coronaviruses are pretty similar to SARS-CoV2, but they are not exactly the same,” Dr. Spatola said. Her work and studies by others suggest that when antigenic imprinting occurs, “it prevents full maturation of the antibody response.”
NeuroPASC is one of many manifestations of long COVID, but Dr. Spatola pointed out that the immune response in the CSF is unique and the causes of prolonged neurologic impairment after COVID-19 are likely to involve different mechanisms than other long-COVID symptoms.
“Antibodies in the brain are functionally different,” said Dr. Spatola, noting for example that antibody-directed defenses against viral threats show a greater relative reliance on phagocytosis. This might become important in the development of therapeutics for neurologic symptoms of long COVID.
A different phenomenon
The manifestations of neuroPASC are heterogeneous and can include confusion, cognitive dysfunction, headache, encephalitis, and other impairments. Neurologic symptoms occur during acute SARS-CoV2 infections, but neuroPASC appears to be a different phenomenon. These symptoms, which develop after the initial respiratory disease has resolved, were attributed by Dr. Spatola to persistent inflammation that is not necessarily directly related to ongoing infection.
“The reason why some patients develop neuroPASC is unknown, but I think the evidence has pointed to a role for the immune system rather than the virus itself,” Dr. Spatola said.
Currently, neuroPASC is a clinical diagnosis but Dr. Spatola and her coinvestigators are conducting research to identify biomarkers. A viable diagnostic test is not expected imminently. They have identified 150 different features with potential relevance to neuroPASC.
In their comparison of those who did relative to those who did not develop neuroPASC, the initial studies were undertaken 2-4 months after the acute COVID-19 symptoms had resolved. The patients with neuroPASC and those without neurologic sequelae have now been followed for 6-8 months, which Dr. Spatola said was too short to draw firm conclusions about outcomes.
An evolving concept
Despite the small sample size of this study, these are “very interesting data” for considering the pathogenesis of neuroPASC, which is “a concept that is still evolving,” according to Natalia S. Rost, MD, chief of the stroke division, department of neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Applied to SARS-CoV2, the concept of original antigenic sin “is new” but Dr. Rost said that it might help differentiate neuroPASC from acute neurologic symptoms of COVID-19, which include stroke. She indicated that the work performed by Dr. Spatola and others might eventually explain the pathology while leading to treatment strategies. She cautioned that the concepts explored in this study “need to be further developed” through larger sample sizes and the exploration of other variables that support the hypothesis.
Dr. Spatola and Dr. Rost report no potential conflicts of interest.
BOSTON – , according to a collaborative study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Already documented in several other viral infections, such as influenza and human immunodeficiency virus, antigenic imprinting results in production of antibodies to previously encountered viral infections rather than to the immediate threat, according to Marianna Spatola, MD, PhD, a research fellow at the Ragon Institute, Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass.
Original antigenic sin
In the case of persistent neurologic symptoms after COVID, a condition known as neuroPASC (neurological postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV2 infection), antibodies produced for previously encountered coronaviruses rather than for SARS-CoV2 might explain most or all cases, according to the data Dr. Spatola presented.
The evidence for this explanation was drawn from a study of 112 patients evaluated months after an acute episode of COVID-19. Of these, 18 patients had persistent neurologic dysfunction. When compared with the 94 whose infection resolved without sequelae, the patients with prolonged neurologic impairments had relatively low systemic antibody response to SARS-CoV2. However, they showed relatively high antibody responses against other coronaviruses.
This is a pattern consistent with antigenic imprinting, a concept first described more than 60 years ago as original antigenic sin. When the immune system becomes imprinted with an antigen from the first encountered virus from a family of pathogens, it governs all subsequent antibody responses, according to several published studies that have described and evaluated this concept.
Additional evidence
In Dr. Spatola’s study, other differences, particularly in regard to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), further supported the role of antigenic imprinting as a cause of neuroPASC. For one, those with elevated immune responses to other common coronaviruses rather than SARS-CoV2 in the CSF relative to the periphery were more likely to have a bad outcome in regard to neurologic symptoms.
Moreover, the CSF in neuroPASC patients “was characterized by increased IgG1 and absence of IgM, suggesting compartmentalized humoral responses within the CSF through selective transfer of antibodies from the serum to the CSF across the blood-brain barrier rather than through intrathecal synthesis,” Dr. Spatola reported.
In the case of COVID-19, the propensity for antigenic imprinting is not difficult to understand.
“The common cold coronaviruses are pretty similar to SARS-CoV2, but they are not exactly the same,” Dr. Spatola said. Her work and studies by others suggest that when antigenic imprinting occurs, “it prevents full maturation of the antibody response.”
NeuroPASC is one of many manifestations of long COVID, but Dr. Spatola pointed out that the immune response in the CSF is unique and the causes of prolonged neurologic impairment after COVID-19 are likely to involve different mechanisms than other long-COVID symptoms.
“Antibodies in the brain are functionally different,” said Dr. Spatola, noting for example that antibody-directed defenses against viral threats show a greater relative reliance on phagocytosis. This might become important in the development of therapeutics for neurologic symptoms of long COVID.
A different phenomenon
The manifestations of neuroPASC are heterogeneous and can include confusion, cognitive dysfunction, headache, encephalitis, and other impairments. Neurologic symptoms occur during acute SARS-CoV2 infections, but neuroPASC appears to be a different phenomenon. These symptoms, which develop after the initial respiratory disease has resolved, were attributed by Dr. Spatola to persistent inflammation that is not necessarily directly related to ongoing infection.
“The reason why some patients develop neuroPASC is unknown, but I think the evidence has pointed to a role for the immune system rather than the virus itself,” Dr. Spatola said.
Currently, neuroPASC is a clinical diagnosis but Dr. Spatola and her coinvestigators are conducting research to identify biomarkers. A viable diagnostic test is not expected imminently. They have identified 150 different features with potential relevance to neuroPASC.
In their comparison of those who did relative to those who did not develop neuroPASC, the initial studies were undertaken 2-4 months after the acute COVID-19 symptoms had resolved. The patients with neuroPASC and those without neurologic sequelae have now been followed for 6-8 months, which Dr. Spatola said was too short to draw firm conclusions about outcomes.
An evolving concept
Despite the small sample size of this study, these are “very interesting data” for considering the pathogenesis of neuroPASC, which is “a concept that is still evolving,” according to Natalia S. Rost, MD, chief of the stroke division, department of neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Applied to SARS-CoV2, the concept of original antigenic sin “is new” but Dr. Rost said that it might help differentiate neuroPASC from acute neurologic symptoms of COVID-19, which include stroke. She indicated that the work performed by Dr. Spatola and others might eventually explain the pathology while leading to treatment strategies. She cautioned that the concepts explored in this study “need to be further developed” through larger sample sizes and the exploration of other variables that support the hypothesis.
Dr. Spatola and Dr. Rost report no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM AAN 2023
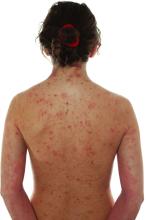
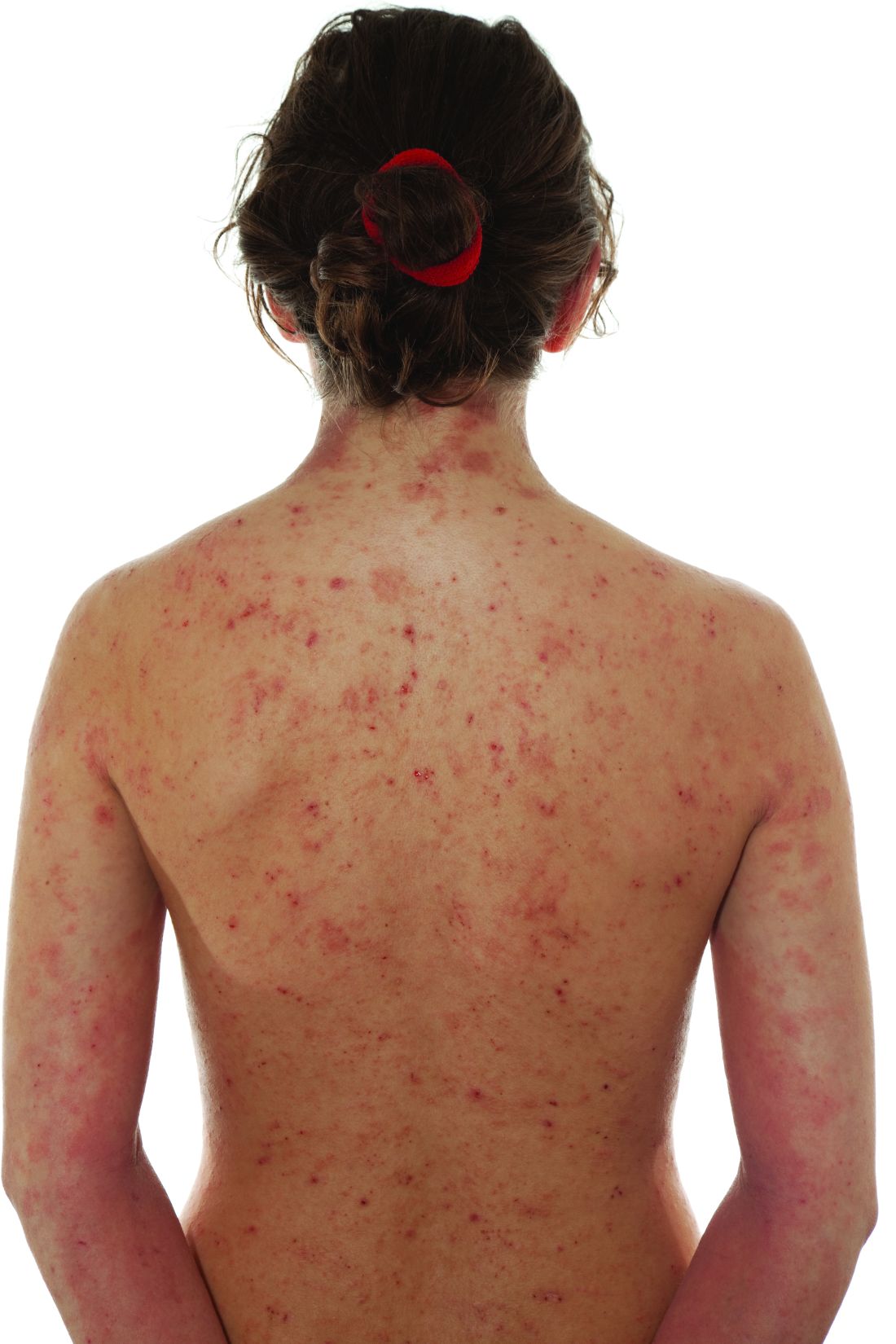
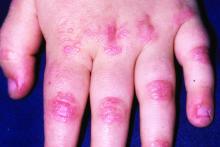
JAK inhibitor ivarmacitinib shows efficacy for atopic dermatitis in a pivotal trial
NEW ORLEANS – The presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Two doses were studied in the placebo-controlled trial and both demonstrated “a favorable benefit-to-risk profile in patients with moderate to severe AD,” reported Yan Zhao, MD, a clinician and researcher in the department of dermatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing.
In the study, called QUARTZ3, 336 patients aged 12 and older at 51 sites in China and Canada were randomized to 4 mg once-daily ivarmacitinib, 8 mg once-daily QD ivarmacitinib, or placebo. The mean age of the population was 32 years and approximately one-third were female.
The mean duration of AD for participants was 10 years. The mean baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was near 30. On the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) tool, approximately 40% had a score of 4, which is the highest score on the scale and indicates severe disease. The remaining patients had an IGA score of 3.
The co-primary endpoints were change in IGA and EASI scores at 16 weeks, and both improved rapidly, showing statistical significance relative to placebo by 4 weeks with no plateauing effect at the end of the 16-week trial. By week 16, the proportion of patients with an EASI score of 75, signifying a 75% improvement, was 66%, 54%, and 22% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups (P < .001 versus placebo for both doses of active therapy), respectively.
The pattern of the IGA response was similar. By week 16, the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) was 42%, 36%, and 9% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups, respectively. The advantage of either dose over placebo was highly significant (P < .001) at 8, 12, and 16 weeks.
For the WI-NRS (Worst Itch – Numeric Rating Scale), the advantage of the 8-mg dose relative to placebo was significant (P < .001) at the 1-week evaluation. By 2 weeks, the 4-mg dose had gained the same degree of statistical significance relative to placebo. After week 4, when the maximum proportion of patients with a WI-NRS score ≤ 4 was reached (50%, 35%, and 10% in the 8-mg, 4-mg, and placebo groups), and the relative advantage of active treatment persisted until the end of the 16-week study.
Two scales were used to evaluate change in quality of life. On the DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) and POEM (Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure), improvements were again rapid and sustained. By week 4, improvement with the 8-mg dose was about fourfold greater (P < .001) than improvement with placebo for DLQI and about sixfold greater (P < .001) for POEM. For the 4-mg dose, the relative differences were approximately threefold and fourfold greater, and both were significant (P <.001).
There was no further gain in these quality-of-life scales from week 4 to week 16, but the advantages relative to placebo were generally sustained, Dr. Zhao reported.
Ivarmacitinib was safe and well-tolerated, according to Dr. Zhao. The proportion of patients with a treatment-emergent adverse event that led to drug discontinuation was numerically higher (5.4%) in the placebo group than in the 8-mg (3.6%) or 4-mg group (2.7%). Rates of infection in the three groups were similar, and there were no major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) or thromboembolism observed in any group.
Ivarmacitinib, which has about a 10-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK2 and a more than 70-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK3, is being tested for rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and alopecia areata in addition to AD, Dr. Zhao said. She also reported that an application for new drug approval has been submitted in China. Efforts to pursue regulatory approval elsewhere are anticipated.
Currently, there are three JAK inhibitors licensed for the treatment of AD in the United States. Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) and abrocitinib (Cibinqo) are also once-daily oral JAK1-selective inhibitors. Regulatory approval for AD by the Food and Drug Administration was granted to both in early 2022 and both now have an indication for moderate to severe disease in patients ages 12 years and older.
In September 2021, the first U.S. approval of a drug in this class for AD was granted for a topical formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), which has selectivity for both JAK1 and JAK2. The indication is for mild to moderate AD in patients aged 12 years and older.
In the phase 3 clinical trial that led to approval of abrocitinib for AD, the comparator groups included placebo and active treatment with 300 mg dupilumab administered subcutaneously every other week. The higher of two doses of abrocitinib (100 mg) was numerically superior to dupilumab in terms of EASI 75 response at week 12 and was statistically superior for relief of itch at week 2.
Relative to the first-generation JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz), both of the approved oral JAK inhibitors for AD, abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have greater JAK1-selectivity. However, selectivity for all JAK inhibitors is relative rather than absolute, according to a recent review article on oral JAK inhibitors for AD. Efficacy and safety are likely determined by relative inhibition of each of the four JAK enzymes (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2). Although JAK1 appears to be an important target for AD treatment, the clinical significance of the degree of selectivity among oral JAK inhibitors is not yet clear.
In an interview, the senior author of that review article, Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, emphasized this point. She said there is no evidence and no basis on which to speculate that any one drug in this class is better than another for AD. Dr. Guttman-Yassky is a professor and system chair of dermatology and immunology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The efficacy [of ivarmacitinib] seems, in general, to be in line with other JAK inhibitors,” said Dr. Guttman-Yassky, who attended the late-breaker session during which these data were presented. Although she acknowledged that rapid control of pruritus is important clinically, she said the speed of itch relief as reported in the phase 3 ivarmacitinib trial does not distinguish it from other oral drugs in the class.
Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, agreed.
“The rapid effects on itch of ivarmacitinib are consistent with those observed by the already approved JAK1-selective inhibitors abrocitinib and upadacitinib,” he said in an interview.
This suggests that head-to-head trials will be needed to draw any conclusions about the relative efficacy and safety of existing and emerging oral JAK inhibitors for AD.
Dr. Zhao has reported a financial relationship with Reistone Biopharma, which is developing ivarmacitinib and provided funding for the trial. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Kwatra has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Aslan, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – The presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Two doses were studied in the placebo-controlled trial and both demonstrated “a favorable benefit-to-risk profile in patients with moderate to severe AD,” reported Yan Zhao, MD, a clinician and researcher in the department of dermatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing.
In the study, called QUARTZ3, 336 patients aged 12 and older at 51 sites in China and Canada were randomized to 4 mg once-daily ivarmacitinib, 8 mg once-daily QD ivarmacitinib, or placebo. The mean age of the population was 32 years and approximately one-third were female.
The mean duration of AD for participants was 10 years. The mean baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was near 30. On the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) tool, approximately 40% had a score of 4, which is the highest score on the scale and indicates severe disease. The remaining patients had an IGA score of 3.
The co-primary endpoints were change in IGA and EASI scores at 16 weeks, and both improved rapidly, showing statistical significance relative to placebo by 4 weeks with no plateauing effect at the end of the 16-week trial. By week 16, the proportion of patients with an EASI score of 75, signifying a 75% improvement, was 66%, 54%, and 22% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups (P < .001 versus placebo for both doses of active therapy), respectively.
The pattern of the IGA response was similar. By week 16, the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) was 42%, 36%, and 9% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups, respectively. The advantage of either dose over placebo was highly significant (P < .001) at 8, 12, and 16 weeks.
For the WI-NRS (Worst Itch – Numeric Rating Scale), the advantage of the 8-mg dose relative to placebo was significant (P < .001) at the 1-week evaluation. By 2 weeks, the 4-mg dose had gained the same degree of statistical significance relative to placebo. After week 4, when the maximum proportion of patients with a WI-NRS score ≤ 4 was reached (50%, 35%, and 10% in the 8-mg, 4-mg, and placebo groups), and the relative advantage of active treatment persisted until the end of the 16-week study.
Two scales were used to evaluate change in quality of life. On the DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) and POEM (Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure), improvements were again rapid and sustained. By week 4, improvement with the 8-mg dose was about fourfold greater (P < .001) than improvement with placebo for DLQI and about sixfold greater (P < .001) for POEM. For the 4-mg dose, the relative differences were approximately threefold and fourfold greater, and both were significant (P <.001).
There was no further gain in these quality-of-life scales from week 4 to week 16, but the advantages relative to placebo were generally sustained, Dr. Zhao reported.
Ivarmacitinib was safe and well-tolerated, according to Dr. Zhao. The proportion of patients with a treatment-emergent adverse event that led to drug discontinuation was numerically higher (5.4%) in the placebo group than in the 8-mg (3.6%) or 4-mg group (2.7%). Rates of infection in the three groups were similar, and there were no major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) or thromboembolism observed in any group.
Ivarmacitinib, which has about a 10-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK2 and a more than 70-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK3, is being tested for rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and alopecia areata in addition to AD, Dr. Zhao said. She also reported that an application for new drug approval has been submitted in China. Efforts to pursue regulatory approval elsewhere are anticipated.
Currently, there are three JAK inhibitors licensed for the treatment of AD in the United States. Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) and abrocitinib (Cibinqo) are also once-daily oral JAK1-selective inhibitors. Regulatory approval for AD by the Food and Drug Administration was granted to both in early 2022 and both now have an indication for moderate to severe disease in patients ages 12 years and older.
In September 2021, the first U.S. approval of a drug in this class for AD was granted for a topical formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), which has selectivity for both JAK1 and JAK2. The indication is for mild to moderate AD in patients aged 12 years and older.
In the phase 3 clinical trial that led to approval of abrocitinib for AD, the comparator groups included placebo and active treatment with 300 mg dupilumab administered subcutaneously every other week. The higher of two doses of abrocitinib (100 mg) was numerically superior to dupilumab in terms of EASI 75 response at week 12 and was statistically superior for relief of itch at week 2.
Relative to the first-generation JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz), both of the approved oral JAK inhibitors for AD, abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have greater JAK1-selectivity. However, selectivity for all JAK inhibitors is relative rather than absolute, according to a recent review article on oral JAK inhibitors for AD. Efficacy and safety are likely determined by relative inhibition of each of the four JAK enzymes (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2). Although JAK1 appears to be an important target for AD treatment, the clinical significance of the degree of selectivity among oral JAK inhibitors is not yet clear.
In an interview, the senior author of that review article, Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, emphasized this point. She said there is no evidence and no basis on which to speculate that any one drug in this class is better than another for AD. Dr. Guttman-Yassky is a professor and system chair of dermatology and immunology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The efficacy [of ivarmacitinib] seems, in general, to be in line with other JAK inhibitors,” said Dr. Guttman-Yassky, who attended the late-breaker session during which these data were presented. Although she acknowledged that rapid control of pruritus is important clinically, she said the speed of itch relief as reported in the phase 3 ivarmacitinib trial does not distinguish it from other oral drugs in the class.
Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, agreed.
“The rapid effects on itch of ivarmacitinib are consistent with those observed by the already approved JAK1-selective inhibitors abrocitinib and upadacitinib,” he said in an interview.
This suggests that head-to-head trials will be needed to draw any conclusions about the relative efficacy and safety of existing and emerging oral JAK inhibitors for AD.
Dr. Zhao has reported a financial relationship with Reistone Biopharma, which is developing ivarmacitinib and provided funding for the trial. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Kwatra has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Aslan, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – The presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Two doses were studied in the placebo-controlled trial and both demonstrated “a favorable benefit-to-risk profile in patients with moderate to severe AD,” reported Yan Zhao, MD, a clinician and researcher in the department of dermatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing.
In the study, called QUARTZ3, 336 patients aged 12 and older at 51 sites in China and Canada were randomized to 4 mg once-daily ivarmacitinib, 8 mg once-daily QD ivarmacitinib, or placebo. The mean age of the population was 32 years and approximately one-third were female.
The mean duration of AD for participants was 10 years. The mean baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was near 30. On the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) tool, approximately 40% had a score of 4, which is the highest score on the scale and indicates severe disease. The remaining patients had an IGA score of 3.
The co-primary endpoints were change in IGA and EASI scores at 16 weeks, and both improved rapidly, showing statistical significance relative to placebo by 4 weeks with no plateauing effect at the end of the 16-week trial. By week 16, the proportion of patients with an EASI score of 75, signifying a 75% improvement, was 66%, 54%, and 22% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups (P < .001 versus placebo for both doses of active therapy), respectively.
The pattern of the IGA response was similar. By week 16, the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) was 42%, 36%, and 9% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups, respectively. The advantage of either dose over placebo was highly significant (P < .001) at 8, 12, and 16 weeks.
For the WI-NRS (Worst Itch – Numeric Rating Scale), the advantage of the 8-mg dose relative to placebo was significant (P < .001) at the 1-week evaluation. By 2 weeks, the 4-mg dose had gained the same degree of statistical significance relative to placebo. After week 4, when the maximum proportion of patients with a WI-NRS score ≤ 4 was reached (50%, 35%, and 10% in the 8-mg, 4-mg, and placebo groups), and the relative advantage of active treatment persisted until the end of the 16-week study.
Two scales were used to evaluate change in quality of life. On the DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) and POEM (Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure), improvements were again rapid and sustained. By week 4, improvement with the 8-mg dose was about fourfold greater (P < .001) than improvement with placebo for DLQI and about sixfold greater (P < .001) for POEM. For the 4-mg dose, the relative differences were approximately threefold and fourfold greater, and both were significant (P <.001).
There was no further gain in these quality-of-life scales from week 4 to week 16, but the advantages relative to placebo were generally sustained, Dr. Zhao reported.
Ivarmacitinib was safe and well-tolerated, according to Dr. Zhao. The proportion of patients with a treatment-emergent adverse event that led to drug discontinuation was numerically higher (5.4%) in the placebo group than in the 8-mg (3.6%) or 4-mg group (2.7%). Rates of infection in the three groups were similar, and there were no major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) or thromboembolism observed in any group.
Ivarmacitinib, which has about a 10-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK2 and a more than 70-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK3, is being tested for rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and alopecia areata in addition to AD, Dr. Zhao said. She also reported that an application for new drug approval has been submitted in China. Efforts to pursue regulatory approval elsewhere are anticipated.
Currently, there are three JAK inhibitors licensed for the treatment of AD in the United States. Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) and abrocitinib (Cibinqo) are also once-daily oral JAK1-selective inhibitors. Regulatory approval for AD by the Food and Drug Administration was granted to both in early 2022 and both now have an indication for moderate to severe disease in patients ages 12 years and older.
In September 2021, the first U.S. approval of a drug in this class for AD was granted for a topical formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), which has selectivity for both JAK1 and JAK2. The indication is for mild to moderate AD in patients aged 12 years and older.
In the phase 3 clinical trial that led to approval of abrocitinib for AD, the comparator groups included placebo and active treatment with 300 mg dupilumab administered subcutaneously every other week. The higher of two doses of abrocitinib (100 mg) was numerically superior to dupilumab in terms of EASI 75 response at week 12 and was statistically superior for relief of itch at week 2.
Relative to the first-generation JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz), both of the approved oral JAK inhibitors for AD, abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have greater JAK1-selectivity. However, selectivity for all JAK inhibitors is relative rather than absolute, according to a recent review article on oral JAK inhibitors for AD. Efficacy and safety are likely determined by relative inhibition of each of the four JAK enzymes (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2). Although JAK1 appears to be an important target for AD treatment, the clinical significance of the degree of selectivity among oral JAK inhibitors is not yet clear.
In an interview, the senior author of that review article, Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, emphasized this point. She said there is no evidence and no basis on which to speculate that any one drug in this class is better than another for AD. Dr. Guttman-Yassky is a professor and system chair of dermatology and immunology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The efficacy [of ivarmacitinib] seems, in general, to be in line with other JAK inhibitors,” said Dr. Guttman-Yassky, who attended the late-breaker session during which these data were presented. Although she acknowledged that rapid control of pruritus is important clinically, she said the speed of itch relief as reported in the phase 3 ivarmacitinib trial does not distinguish it from other oral drugs in the class.
Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, agreed.
“The rapid effects on itch of ivarmacitinib are consistent with those observed by the already approved JAK1-selective inhibitors abrocitinib and upadacitinib,” he said in an interview.
This suggests that head-to-head trials will be needed to draw any conclusions about the relative efficacy and safety of existing and emerging oral JAK inhibitors for AD.
Dr. Zhao has reported a financial relationship with Reistone Biopharma, which is developing ivarmacitinib and provided funding for the trial. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Kwatra has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Aslan, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
New data forecast more oral PDE4 inhibitors for psoriasis
NEW ORLEANS – according to results of a phase 2 clinical trial presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The phase 2b data, which are prompting a phase 3 trial, suggest that the drug, called orismilast, “is a potential new addition to the psoriasis armamentarium,” reported Lars E. French, MD, professor and chair, department of dermatology, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany).
At the same session, findings from another study supported off-label use of oral roflumilast (Daliresp and generic), a PDE4 inhibitor approved for severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The only PDE4 inhibitors with an indication for psoriasis are roflumilast, approved as a cream (Zoryve), and apremilast (Otezla), approved as an oral therapy.
Phase 2 study of orismilast
In the orismilast trial, Dr. French attributed the efficacy observed to the potency of orismilast on the B and D subtypes of PDE4 associated with inflammation. One clue is that these specific subtypes are overly expressed in the skin of patients with either psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
“When compared to apremilast, orismilast is at least two to fivefold more potent on all PDE4 isoforms and up to 39 times more potent on some of the PDE4 B and D isoforms,” said Dr. French, referring to preclinical findings in human whole blood and blood cells and in a mouse model of chronic inflammation.
The efficacy of orismilast in an immediate-release oral formulation was previously demonstrated in a recently published phase 2a trial, but the newest study tested a modified-release formulation of orismilast to test its potential to improve tolerability.
In the study, 202 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis (Psoriasis Area Severity Index [PASI] score ≥ 12) were randomly assigned to one of three doses of orismilast or to placebo. Each of the three doses – 20 mg, 30 mg, or 40 mg – were administered twice daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI score at 16 weeks. Secondary endpoints included PASI 75 responses (signifying 75% clearance) and safety.
Relative to placebo, which was associated with a PASI improvement of 17%, all three of the tested orismilast doses were superior in a dose-dependent manner. The rates of response were 53%, 61%, and 64% for the 20-mg, 30-mg, and 40-mg twice-daily doses, respectively.
The PASI improvements were rapid, Dr. French said. At 4 weeks, PASI scores climbed from baseline by nearly 40% for those on all orismilast doses, which was more than double the improvement in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis with missing data counted as nonresponders, the proportion of patients reaching PASI-75 scores at 16 weeks were 39%, 49%, 45%, and 17%, in the 20-mg, 30-mg, 40-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. The proportion of patients experiencing complete or near-complete skin clearance defined by a PASI 90 were 24%, 22%, 28%, and 8%, respectively.
The side-effect profile was consistent with other PDE4 inhibitors. The most common adverse events included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea and nausea, as well as headache and dizziness. But the majority of these events were of low grade, and they were largely confined to the first 4 weeks of treatment, which is a pattern reported with other PDE4 inhibitors in psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory diseases, such as COPD, according to Dr. French.
“There were no discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event in the arms receiving either the 20-mg or the 30-mg doses,” Dr. French reported. There were only two serious adverse events, and neither were considered by trial investigators to be related to orismilast.
Based on the limited therapeutic gain but greater risk for adverse events on the 40-mg twice-daily dose, “the question is now whether to move forward with the 20-mg or the 30-mg dose,” said Dr. French, who said planning of a phase 3 trial is underway.
Phase 2 study of roflumilast
However, this was not the only set of data on an oral PDE4 inhibitor presented as a late-breaker at the AAD meeting. For clinicians looking for a more immediate and less expensive alternative to apremilast, another study indicated that off-label use of oral roflumilast is an option.
In an investigator-initiated, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in Denmark, the rate of response to oral roflumilast at 24 weeks, including the clear or almost clear response, was on the same general order of magnitude as that seen in the orismilast study, reported Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Copenhagen.
“At 24 weeks, 21.7% had achieved a PASI 90, and 8.7% achieved a PASI 100,” Dr. Egeberg said.
Oral roflumilast has been available for the treatment of COPD for more than 10 years and is now available in a generic formulation. This study was conducted independent of any pharmaceutical company involvement, and the high rate of response and low risk of adverse events suggests that patients can benefit from a PDE4 inhibitor in a very low-cost form.
“Generic oral roflumilast is cheaper than a Starbucks coffee,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In this trial, 46 patients were randomly assigned to placebo or to the COPD-approved roflumilast dose of 500 mcg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI scores from baseline to week 12, which Dr. Egeberg pointed out is a shorter time frame than the 16 weeks more typical of psoriasis treatment studies.
At week 12, the median improvement in PASI was 34.8% in the roflumilast group versus 0% in the placebo group. Patients were then followed for an additional 12 weeks, but those randomized to placebo were switched to the active treatment. By week 24, the switch patients had largely caught up to those initiated on roflumilast for median PASI improvement (39.1% vs. 43.5%).
Similar to orismilast, roflumilast “was generally well tolerated,” Dr. Egeberg said. The adverse events were consistent with those associated with PDE4 inhibitors in previous trials, whether in psoriasis or COPD. There was only one serious adverse event, and it was not considered treatment related. Discontinuations for adverse events “were very low.”
In a population with a relatively high rate of smoking, Dr. Egeberg further reported, lung function was improved, a remark initially interpreted as a joke by some attending the presentation. However, Dr. Egeberg confirmed that lung function was monitored, and objective improvements were recorded.
By Danish law, the investigators were required to inform the manufacturers of roflumilast. Despite the results of this study, he is not aware of any plans to seek an indication for roflumilast in psoriasis, but he noted that the drug is readily available at a low price.
For those willing to offer this therapy off label, “you can start using it tomorrow if you’d like,” he said.
Dr. French reports financial relationships with Almirall, Amgen, Biotest, Galderma, Janssen Cilag, Leo Pharma, Pincell, Regeneron, UCB, and UNION Therapeutics, which provided funding for this trial. Dr. Egeberg reports financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – according to results of a phase 2 clinical trial presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The phase 2b data, which are prompting a phase 3 trial, suggest that the drug, called orismilast, “is a potential new addition to the psoriasis armamentarium,” reported Lars E. French, MD, professor and chair, department of dermatology, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany).
At the same session, findings from another study supported off-label use of oral roflumilast (Daliresp and generic), a PDE4 inhibitor approved for severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The only PDE4 inhibitors with an indication for psoriasis are roflumilast, approved as a cream (Zoryve), and apremilast (Otezla), approved as an oral therapy.
Phase 2 study of orismilast
In the orismilast trial, Dr. French attributed the efficacy observed to the potency of orismilast on the B and D subtypes of PDE4 associated with inflammation. One clue is that these specific subtypes are overly expressed in the skin of patients with either psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
“When compared to apremilast, orismilast is at least two to fivefold more potent on all PDE4 isoforms and up to 39 times more potent on some of the PDE4 B and D isoforms,” said Dr. French, referring to preclinical findings in human whole blood and blood cells and in a mouse model of chronic inflammation.
The efficacy of orismilast in an immediate-release oral formulation was previously demonstrated in a recently published phase 2a trial, but the newest study tested a modified-release formulation of orismilast to test its potential to improve tolerability.
In the study, 202 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis (Psoriasis Area Severity Index [PASI] score ≥ 12) were randomly assigned to one of three doses of orismilast or to placebo. Each of the three doses – 20 mg, 30 mg, or 40 mg – were administered twice daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI score at 16 weeks. Secondary endpoints included PASI 75 responses (signifying 75% clearance) and safety.
Relative to placebo, which was associated with a PASI improvement of 17%, all three of the tested orismilast doses were superior in a dose-dependent manner. The rates of response were 53%, 61%, and 64% for the 20-mg, 30-mg, and 40-mg twice-daily doses, respectively.
The PASI improvements were rapid, Dr. French said. At 4 weeks, PASI scores climbed from baseline by nearly 40% for those on all orismilast doses, which was more than double the improvement in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis with missing data counted as nonresponders, the proportion of patients reaching PASI-75 scores at 16 weeks were 39%, 49%, 45%, and 17%, in the 20-mg, 30-mg, 40-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. The proportion of patients experiencing complete or near-complete skin clearance defined by a PASI 90 were 24%, 22%, 28%, and 8%, respectively.
The side-effect profile was consistent with other PDE4 inhibitors. The most common adverse events included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea and nausea, as well as headache and dizziness. But the majority of these events were of low grade, and they were largely confined to the first 4 weeks of treatment, which is a pattern reported with other PDE4 inhibitors in psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory diseases, such as COPD, according to Dr. French.
“There were no discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event in the arms receiving either the 20-mg or the 30-mg doses,” Dr. French reported. There were only two serious adverse events, and neither were considered by trial investigators to be related to orismilast.
Based on the limited therapeutic gain but greater risk for adverse events on the 40-mg twice-daily dose, “the question is now whether to move forward with the 20-mg or the 30-mg dose,” said Dr. French, who said planning of a phase 3 trial is underway.
Phase 2 study of roflumilast
However, this was not the only set of data on an oral PDE4 inhibitor presented as a late-breaker at the AAD meeting. For clinicians looking for a more immediate and less expensive alternative to apremilast, another study indicated that off-label use of oral roflumilast is an option.
In an investigator-initiated, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in Denmark, the rate of response to oral roflumilast at 24 weeks, including the clear or almost clear response, was on the same general order of magnitude as that seen in the orismilast study, reported Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Copenhagen.
“At 24 weeks, 21.7% had achieved a PASI 90, and 8.7% achieved a PASI 100,” Dr. Egeberg said.
Oral roflumilast has been available for the treatment of COPD for more than 10 years and is now available in a generic formulation. This study was conducted independent of any pharmaceutical company involvement, and the high rate of response and low risk of adverse events suggests that patients can benefit from a PDE4 inhibitor in a very low-cost form.
“Generic oral roflumilast is cheaper than a Starbucks coffee,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In this trial, 46 patients were randomly assigned to placebo or to the COPD-approved roflumilast dose of 500 mcg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI scores from baseline to week 12, which Dr. Egeberg pointed out is a shorter time frame than the 16 weeks more typical of psoriasis treatment studies.
At week 12, the median improvement in PASI was 34.8% in the roflumilast group versus 0% in the placebo group. Patients were then followed for an additional 12 weeks, but those randomized to placebo were switched to the active treatment. By week 24, the switch patients had largely caught up to those initiated on roflumilast for median PASI improvement (39.1% vs. 43.5%).
Similar to orismilast, roflumilast “was generally well tolerated,” Dr. Egeberg said. The adverse events were consistent with those associated with PDE4 inhibitors in previous trials, whether in psoriasis or COPD. There was only one serious adverse event, and it was not considered treatment related. Discontinuations for adverse events “were very low.”
In a population with a relatively high rate of smoking, Dr. Egeberg further reported, lung function was improved, a remark initially interpreted as a joke by some attending the presentation. However, Dr. Egeberg confirmed that lung function was monitored, and objective improvements were recorded.
By Danish law, the investigators were required to inform the manufacturers of roflumilast. Despite the results of this study, he is not aware of any plans to seek an indication for roflumilast in psoriasis, but he noted that the drug is readily available at a low price.
For those willing to offer this therapy off label, “you can start using it tomorrow if you’d like,” he said.
Dr. French reports financial relationships with Almirall, Amgen, Biotest, Galderma, Janssen Cilag, Leo Pharma, Pincell, Regeneron, UCB, and UNION Therapeutics, which provided funding for this trial. Dr. Egeberg reports financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – according to results of a phase 2 clinical trial presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The phase 2b data, which are prompting a phase 3 trial, suggest that the drug, called orismilast, “is a potential new addition to the psoriasis armamentarium,” reported Lars E. French, MD, professor and chair, department of dermatology, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany).
At the same session, findings from another study supported off-label use of oral roflumilast (Daliresp and generic), a PDE4 inhibitor approved for severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The only PDE4 inhibitors with an indication for psoriasis are roflumilast, approved as a cream (Zoryve), and apremilast (Otezla), approved as an oral therapy.
Phase 2 study of orismilast
In the orismilast trial, Dr. French attributed the efficacy observed to the potency of orismilast on the B and D subtypes of PDE4 associated with inflammation. One clue is that these specific subtypes are overly expressed in the skin of patients with either psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
“When compared to apremilast, orismilast is at least two to fivefold more potent on all PDE4 isoforms and up to 39 times more potent on some of the PDE4 B and D isoforms,” said Dr. French, referring to preclinical findings in human whole blood and blood cells and in a mouse model of chronic inflammation.
The efficacy of orismilast in an immediate-release oral formulation was previously demonstrated in a recently published phase 2a trial, but the newest study tested a modified-release formulation of orismilast to test its potential to improve tolerability.
In the study, 202 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis (Psoriasis Area Severity Index [PASI] score ≥ 12) were randomly assigned to one of three doses of orismilast or to placebo. Each of the three doses – 20 mg, 30 mg, or 40 mg – were administered twice daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI score at 16 weeks. Secondary endpoints included PASI 75 responses (signifying 75% clearance) and safety.
Relative to placebo, which was associated with a PASI improvement of 17%, all three of the tested orismilast doses were superior in a dose-dependent manner. The rates of response were 53%, 61%, and 64% for the 20-mg, 30-mg, and 40-mg twice-daily doses, respectively.
The PASI improvements were rapid, Dr. French said. At 4 weeks, PASI scores climbed from baseline by nearly 40% for those on all orismilast doses, which was more than double the improvement in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis with missing data counted as nonresponders, the proportion of patients reaching PASI-75 scores at 16 weeks were 39%, 49%, 45%, and 17%, in the 20-mg, 30-mg, 40-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. The proportion of patients experiencing complete or near-complete skin clearance defined by a PASI 90 were 24%, 22%, 28%, and 8%, respectively.
The side-effect profile was consistent with other PDE4 inhibitors. The most common adverse events included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea and nausea, as well as headache and dizziness. But the majority of these events were of low grade, and they were largely confined to the first 4 weeks of treatment, which is a pattern reported with other PDE4 inhibitors in psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory diseases, such as COPD, according to Dr. French.
“There were no discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event in the arms receiving either the 20-mg or the 30-mg doses,” Dr. French reported. There were only two serious adverse events, and neither were considered by trial investigators to be related to orismilast.
Based on the limited therapeutic gain but greater risk for adverse events on the 40-mg twice-daily dose, “the question is now whether to move forward with the 20-mg or the 30-mg dose,” said Dr. French, who said planning of a phase 3 trial is underway.
Phase 2 study of roflumilast
However, this was not the only set of data on an oral PDE4 inhibitor presented as a late-breaker at the AAD meeting. For clinicians looking for a more immediate and less expensive alternative to apremilast, another study indicated that off-label use of oral roflumilast is an option.
In an investigator-initiated, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in Denmark, the rate of response to oral roflumilast at 24 weeks, including the clear or almost clear response, was on the same general order of magnitude as that seen in the orismilast study, reported Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Copenhagen.
“At 24 weeks, 21.7% had achieved a PASI 90, and 8.7% achieved a PASI 100,” Dr. Egeberg said.
Oral roflumilast has been available for the treatment of COPD for more than 10 years and is now available in a generic formulation. This study was conducted independent of any pharmaceutical company involvement, and the high rate of response and low risk of adverse events suggests that patients can benefit from a PDE4 inhibitor in a very low-cost form.
“Generic oral roflumilast is cheaper than a Starbucks coffee,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In this trial, 46 patients were randomly assigned to placebo or to the COPD-approved roflumilast dose of 500 mcg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI scores from baseline to week 12, which Dr. Egeberg pointed out is a shorter time frame than the 16 weeks more typical of psoriasis treatment studies.
At week 12, the median improvement in PASI was 34.8% in the roflumilast group versus 0% in the placebo group. Patients were then followed for an additional 12 weeks, but those randomized to placebo were switched to the active treatment. By week 24, the switch patients had largely caught up to those initiated on roflumilast for median PASI improvement (39.1% vs. 43.5%).
Similar to orismilast, roflumilast “was generally well tolerated,” Dr. Egeberg said. The adverse events were consistent with those associated with PDE4 inhibitors in previous trials, whether in psoriasis or COPD. There was only one serious adverse event, and it was not considered treatment related. Discontinuations for adverse events “were very low.”
In a population with a relatively high rate of smoking, Dr. Egeberg further reported, lung function was improved, a remark initially interpreted as a joke by some attending the presentation. However, Dr. Egeberg confirmed that lung function was monitored, and objective improvements were recorded.
By Danish law, the investigators were required to inform the manufacturers of roflumilast. Despite the results of this study, he is not aware of any plans to seek an indication for roflumilast in psoriasis, but he noted that the drug is readily available at a low price.
For those willing to offer this therapy off label, “you can start using it tomorrow if you’d like,” he said.
Dr. French reports financial relationships with Almirall, Amgen, Biotest, Galderma, Janssen Cilag, Leo Pharma, Pincell, Regeneron, UCB, and UNION Therapeutics, which provided funding for this trial. Dr. Egeberg reports financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
New JAK inhibitor study data confirm benefit in alopecia areata
from clinical trials of two drugs presented at a late-breaker research session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Based on phase 3 studies that document robust hair growth in about one third of patients, deuruxolitinib (CTP-543), an inhibitor of the JAK1 and JAK2 enzymes, has the potential to become the second JAK inhibitor available for the treatment of alopecia areata. If approved, it will join baricitinib (Olumiant), which received U.S. approval almost 1 year ago.
In his talk on THRIVE-AA2, a phase 3 trial of the investigational medicine deuruxolitinib, the principal investigator, Brett A. King, MD, PhD, displayed several before-and-after photos and said, “The photos tell the whole story. This is why there is so much excitement about these drugs.”
THRIVE-AA2 was the second of two phase 3 studies of deuruxolitinib. King was a principal investigator for both pivotal trials, called THRIVE-AA1 and THRIVE AA-2. He characterized the results of the two THRIVE trials as “comparable.”
Dr. King also was a principal investigator for the trials with baricitinib, called BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE AA-2, which were published last year in the New England Journal of Medicine. The trials for both drugs had similar designs and endpoints.
Deuruxolitinib and the THRIVE studies
In the THRIVE-AA2 trial, 517 adult patients were enrolled with moderate to severe alopecia areata, defined as a SALT (Severity of Alopecia Tool) score of ≥ 50%, which signifies a hair loss of at least 50%. Like THRIVE-AA1, patients participated at treatment centers in North America and Europe. About two-thirds were female. The mean age was 39 years. The majority of patients had complete or near complete hair loss at baseline.
“Many of these patients are the ones we have historically characterized as having alopecia totalis or universalis,” Dr. King said.
Participating patients were randomly assigned to 8 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, 12 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, or placebo. The primary endpoint was a SALT score of ≤ 20% at week 24.
At 24 weeks, almost no patients in the placebo group (1%) vs. 33% and 38% in the 8 mg and 12 mg twice-daily groups, respectively, met the primary endpoint. Each active treatment group was highly significant vs. placebo.
Of the responders, the majority achieved complete or near complete hair growth as defined by a SALT score of ≤ 10%, Dr. King reported.
Based on a graph that showed a relatively steep climb over the entire 24-week study period, deuruxolitinib “had a really fast onset of action,” Dr. King said. By week 8, which was the time of the first assessment, both doses of deuruxolitinib were superior to placebo.
The majority of patients had complete or significant loss of eyebrows and eye lashes at baseline, but more than two-thirds of these patients had regrowth by week 24, Dr. King said. Again, no significant regrowth was observed in the placebo arm.
On the Satisfaction of Hair Patient Reported Outcomes (SPRO), more than half of patients on both doses reported being satisfied or very satisfied with the improvement when evaluated at 24 weeks.
“The patient satisfaction overshot what one would expect by looking at the SALT scores, but a lot of subjects were at the precipice of the primary endpoint, sitting on SALT scores of 21, 25, or 30,” Dr. King said.
High participation in extension trial
More than 90% of the patients assigned to deuruxolitinib completed the trial and have entered an open-label extension (OLE). Dr. King credited the substantial rates of hair growth and the low rate of significant adverse events for the high rate of transition to OLE. Those who experienced the response were motivated to maintain it.
“This is a devastating disease. Patients want to get better,” Dr. King said.
There were no serious treatment-emergent adverse events associated with deuruxolitinib, including no thromboembolic events or other off-target events that have been reported previously with other JAK inhibitors in other disease states, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Although some adverse events, such as nasopharyngitis, were observed more often in those taking deuruxolitinib than placebo, there were “very few” discontinuations because of an adverse event, he said.
The data of THRIVE-AA2 are wholly compatible with the previously reported 706-patient THRIVE-AA1, according to Dr. King. In THRIVE-AA1, the primary endpoint of SALT ≤ 20% was reached by 29.6%, 41.5%, and 0.8% of the 8 mg, 12 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. Patient satisfaction scores, safety, and tolerability were also similar, according to Dr. King.
The experience with deuruxolitinib in the THRIVE-AA phase 3 program is similar to the experience with baricitinib in the BRAVE-AA trials. Although they cannot be compared directly because of potential differences between study populations, the 4-mg dose of baricitinib also achieved SALT score ≤ 20 in about 35% of patients, he said. The proportion was lower in the 2-mg group but was also superior to the placebo group.
“JAK inhibitors are changing the paradigm of alopecia areata,” Dr. King said. Responding to a question about payers reluctant to reimburse therapies for a “cosmetic” condition, Dr. King added that the effective treatments are “changing the landscape of how we think about this disease.” Dr. King believes these kinds of data show that “we are literally transforming lives forever.”
Baricitinib and the BRAVE studies
When baricitinib received regulatory approval for alopecia areata last year, it was not just the first JAK inhibitor approved for this disease, but the first systemic therapy of any kind, according to Maryanne Senna, MD, an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and the director of the Lahey Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Mass. Dr. Senna was a clinical investigator of BRAVE-AA1, as well as of THRIVE-AA2.
Providing an update on the BRAVE-AA program, Dr. Senna reported 104-week data that appear to support the idea of a life-changing benefit from JAK inhibitor therapy. This is because the effects appear durable.
In the data she presented at the AAD, responders and mixed responders at 52 weeks were followed to 104 weeks. Mixed responders were defined as those without a SALT response of ≤ 20 at week 52 but who had achieved this degree of hair regrowth at some earlier point.
Of the responders, 90% maintained their response at 104 weeks. In addition, many of the mixed responders and patients with a partial response but who never achieved a SALT score ≤ 20% gained additional hair growth, including complete or near complete hair growth, when maintained on treatment over the 2 years of follow-up.
“The follow-up suggests that, if you keep patients on treatment, you can get many of them to a meaningful response,” she said.
Meanwhile, “there have been no new safety signals,” Dr. Senna said. She based this statement not only of the 104-week data but on follow-up of up to 3.6 years among patients who have remained on treatment after participating in previous studies.
According to Dr. Senna, the off-target events that have been reported previously in other diseases with other JAK inhibitors, such as major adverse cardiovascular events and thromboembolic events, have not so far been observed in the BRAVE-AA phase 3 program.
Baricitinib, much like all but one of the JAK inhibitors with dermatologic indications, carries a black box warning that lists multiple risks for drugs in this class, based on a rheumatoid arthritis study.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted deuruxolitinib Breakthrough Therapy designation for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe alopecia areata and Fast Track designation for the treatment of alopecia areata, according to its manufacturer Concert Pharmaceuticals.
Dr. King reports financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Concert Pharmaceuticals, which provided the funding for the THRIVE-AA trial program, and for Eli Lilly, which provided funding for the BRAVE-AA trial program. Dr. Senna reports financial relationships with Arena pharmaceuticals, Follica, and both Concert Pharmaceuticals and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
from clinical trials of two drugs presented at a late-breaker research session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Based on phase 3 studies that document robust hair growth in about one third of patients, deuruxolitinib (CTP-543), an inhibitor of the JAK1 and JAK2 enzymes, has the potential to become the second JAK inhibitor available for the treatment of alopecia areata. If approved, it will join baricitinib (Olumiant), which received U.S. approval almost 1 year ago.
In his talk on THRIVE-AA2, a phase 3 trial of the investigational medicine deuruxolitinib, the principal investigator, Brett A. King, MD, PhD, displayed several before-and-after photos and said, “The photos tell the whole story. This is why there is so much excitement about these drugs.”
THRIVE-AA2 was the second of two phase 3 studies of deuruxolitinib. King was a principal investigator for both pivotal trials, called THRIVE-AA1 and THRIVE AA-2. He characterized the results of the two THRIVE trials as “comparable.”
Dr. King also was a principal investigator for the trials with baricitinib, called BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE AA-2, which were published last year in the New England Journal of Medicine. The trials for both drugs had similar designs and endpoints.
Deuruxolitinib and the THRIVE studies
In the THRIVE-AA2 trial, 517 adult patients were enrolled with moderate to severe alopecia areata, defined as a SALT (Severity of Alopecia Tool) score of ≥ 50%, which signifies a hair loss of at least 50%. Like THRIVE-AA1, patients participated at treatment centers in North America and Europe. About two-thirds were female. The mean age was 39 years. The majority of patients had complete or near complete hair loss at baseline.
“Many of these patients are the ones we have historically characterized as having alopecia totalis or universalis,” Dr. King said.
Participating patients were randomly assigned to 8 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, 12 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, or placebo. The primary endpoint was a SALT score of ≤ 20% at week 24.
At 24 weeks, almost no patients in the placebo group (1%) vs. 33% and 38% in the 8 mg and 12 mg twice-daily groups, respectively, met the primary endpoint. Each active treatment group was highly significant vs. placebo.
Of the responders, the majority achieved complete or near complete hair growth as defined by a SALT score of ≤ 10%, Dr. King reported.
Based on a graph that showed a relatively steep climb over the entire 24-week study period, deuruxolitinib “had a really fast onset of action,” Dr. King said. By week 8, which was the time of the first assessment, both doses of deuruxolitinib were superior to placebo.
The majority of patients had complete or significant loss of eyebrows and eye lashes at baseline, but more than two-thirds of these patients had regrowth by week 24, Dr. King said. Again, no significant regrowth was observed in the placebo arm.
On the Satisfaction of Hair Patient Reported Outcomes (SPRO), more than half of patients on both doses reported being satisfied or very satisfied with the improvement when evaluated at 24 weeks.
“The patient satisfaction overshot what one would expect by looking at the SALT scores, but a lot of subjects were at the precipice of the primary endpoint, sitting on SALT scores of 21, 25, or 30,” Dr. King said.
High participation in extension trial
More than 90% of the patients assigned to deuruxolitinib completed the trial and have entered an open-label extension (OLE). Dr. King credited the substantial rates of hair growth and the low rate of significant adverse events for the high rate of transition to OLE. Those who experienced the response were motivated to maintain it.
“This is a devastating disease. Patients want to get better,” Dr. King said.
There were no serious treatment-emergent adverse events associated with deuruxolitinib, including no thromboembolic events or other off-target events that have been reported previously with other JAK inhibitors in other disease states, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Although some adverse events, such as nasopharyngitis, were observed more often in those taking deuruxolitinib than placebo, there were “very few” discontinuations because of an adverse event, he said.
The data of THRIVE-AA2 are wholly compatible with the previously reported 706-patient THRIVE-AA1, according to Dr. King. In THRIVE-AA1, the primary endpoint of SALT ≤ 20% was reached by 29.6%, 41.5%, and 0.8% of the 8 mg, 12 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. Patient satisfaction scores, safety, and tolerability were also similar, according to Dr. King.
The experience with deuruxolitinib in the THRIVE-AA phase 3 program is similar to the experience with baricitinib in the BRAVE-AA trials. Although they cannot be compared directly because of potential differences between study populations, the 4-mg dose of baricitinib also achieved SALT score ≤ 20 in about 35% of patients, he said. The proportion was lower in the 2-mg group but was also superior to the placebo group.
“JAK inhibitors are changing the paradigm of alopecia areata,” Dr. King said. Responding to a question about payers reluctant to reimburse therapies for a “cosmetic” condition, Dr. King added that the effective treatments are “changing the landscape of how we think about this disease.” Dr. King believes these kinds of data show that “we are literally transforming lives forever.”
Baricitinib and the BRAVE studies
When baricitinib received regulatory approval for alopecia areata last year, it was not just the first JAK inhibitor approved for this disease, but the first systemic therapy of any kind, according to Maryanne Senna, MD, an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and the director of the Lahey Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Mass. Dr. Senna was a clinical investigator of BRAVE-AA1, as well as of THRIVE-AA2.
Providing an update on the BRAVE-AA program, Dr. Senna reported 104-week data that appear to support the idea of a life-changing benefit from JAK inhibitor therapy. This is because the effects appear durable.
In the data she presented at the AAD, responders and mixed responders at 52 weeks were followed to 104 weeks. Mixed responders were defined as those without a SALT response of ≤ 20 at week 52 but who had achieved this degree of hair regrowth at some earlier point.
Of the responders, 90% maintained their response at 104 weeks. In addition, many of the mixed responders and patients with a partial response but who never achieved a SALT score ≤ 20% gained additional hair growth, including complete or near complete hair growth, when maintained on treatment over the 2 years of follow-up.
“The follow-up suggests that, if you keep patients on treatment, you can get many of them to a meaningful response,” she said.
Meanwhile, “there have been no new safety signals,” Dr. Senna said. She based this statement not only of the 104-week data but on follow-up of up to 3.6 years among patients who have remained on treatment after participating in previous studies.
According to Dr. Senna, the off-target events that have been reported previously in other diseases with other JAK inhibitors, such as major adverse cardiovascular events and thromboembolic events, have not so far been observed in the BRAVE-AA phase 3 program.
Baricitinib, much like all but one of the JAK inhibitors with dermatologic indications, carries a black box warning that lists multiple risks for drugs in this class, based on a rheumatoid arthritis study.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted deuruxolitinib Breakthrough Therapy designation for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe alopecia areata and Fast Track designation for the treatment of alopecia areata, according to its manufacturer Concert Pharmaceuticals.
Dr. King reports financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Concert Pharmaceuticals, which provided the funding for the THRIVE-AA trial program, and for Eli Lilly, which provided funding for the BRAVE-AA trial program. Dr. Senna reports financial relationships with Arena pharmaceuticals, Follica, and both Concert Pharmaceuticals and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
from clinical trials of two drugs presented at a late-breaker research session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Based on phase 3 studies that document robust hair growth in about one third of patients, deuruxolitinib (CTP-543), an inhibitor of the JAK1 and JAK2 enzymes, has the potential to become the second JAK inhibitor available for the treatment of alopecia areata. If approved, it will join baricitinib (Olumiant), which received U.S. approval almost 1 year ago.
In his talk on THRIVE-AA2, a phase 3 trial of the investigational medicine deuruxolitinib, the principal investigator, Brett A. King, MD, PhD, displayed several before-and-after photos and said, “The photos tell the whole story. This is why there is so much excitement about these drugs.”
THRIVE-AA2 was the second of two phase 3 studies of deuruxolitinib. King was a principal investigator for both pivotal trials, called THRIVE-AA1 and THRIVE AA-2. He characterized the results of the two THRIVE trials as “comparable.”
Dr. King also was a principal investigator for the trials with baricitinib, called BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE AA-2, which were published last year in the New England Journal of Medicine. The trials for both drugs had similar designs and endpoints.
Deuruxolitinib and the THRIVE studies
In the THRIVE-AA2 trial, 517 adult patients were enrolled with moderate to severe alopecia areata, defined as a SALT (Severity of Alopecia Tool) score of ≥ 50%, which signifies a hair loss of at least 50%. Like THRIVE-AA1, patients participated at treatment centers in North America and Europe. About two-thirds were female. The mean age was 39 years. The majority of patients had complete or near complete hair loss at baseline.
“Many of these patients are the ones we have historically characterized as having alopecia totalis or universalis,” Dr. King said.
Participating patients were randomly assigned to 8 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, 12 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, or placebo. The primary endpoint was a SALT score of ≤ 20% at week 24.
At 24 weeks, almost no patients in the placebo group (1%) vs. 33% and 38% in the 8 mg and 12 mg twice-daily groups, respectively, met the primary endpoint. Each active treatment group was highly significant vs. placebo.
Of the responders, the majority achieved complete or near complete hair growth as defined by a SALT score of ≤ 10%, Dr. King reported.
Based on a graph that showed a relatively steep climb over the entire 24-week study period, deuruxolitinib “had a really fast onset of action,” Dr. King said. By week 8, which was the time of the first assessment, both doses of deuruxolitinib were superior to placebo.
The majority of patients had complete or significant loss of eyebrows and eye lashes at baseline, but more than two-thirds of these patients had regrowth by week 24, Dr. King said. Again, no significant regrowth was observed in the placebo arm.
On the Satisfaction of Hair Patient Reported Outcomes (SPRO), more than half of patients on both doses reported being satisfied or very satisfied with the improvement when evaluated at 24 weeks.
“The patient satisfaction overshot what one would expect by looking at the SALT scores, but a lot of subjects were at the precipice of the primary endpoint, sitting on SALT scores of 21, 25, or 30,” Dr. King said.
High participation in extension trial
More than 90% of the patients assigned to deuruxolitinib completed the trial and have entered an open-label extension (OLE). Dr. King credited the substantial rates of hair growth and the low rate of significant adverse events for the high rate of transition to OLE. Those who experienced the response were motivated to maintain it.
“This is a devastating disease. Patients want to get better,” Dr. King said.
There were no serious treatment-emergent adverse events associated with deuruxolitinib, including no thromboembolic events or other off-target events that have been reported previously with other JAK inhibitors in other disease states, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Although some adverse events, such as nasopharyngitis, were observed more often in those taking deuruxolitinib than placebo, there were “very few” discontinuations because of an adverse event, he said.
The data of THRIVE-AA2 are wholly compatible with the previously reported 706-patient THRIVE-AA1, according to Dr. King. In THRIVE-AA1, the primary endpoint of SALT ≤ 20% was reached by 29.6%, 41.5%, and 0.8% of the 8 mg, 12 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. Patient satisfaction scores, safety, and tolerability were also similar, according to Dr. King.
The experience with deuruxolitinib in the THRIVE-AA phase 3 program is similar to the experience with baricitinib in the BRAVE-AA trials. Although they cannot be compared directly because of potential differences between study populations, the 4-mg dose of baricitinib also achieved SALT score ≤ 20 in about 35% of patients, he said. The proportion was lower in the 2-mg group but was also superior to the placebo group.
“JAK inhibitors are changing the paradigm of alopecia areata,” Dr. King said. Responding to a question about payers reluctant to reimburse therapies for a “cosmetic” condition, Dr. King added that the effective treatments are “changing the landscape of how we think about this disease.” Dr. King believes these kinds of data show that “we are literally transforming lives forever.”
Baricitinib and the BRAVE studies
When baricitinib received regulatory approval for alopecia areata last year, it was not just the first JAK inhibitor approved for this disease, but the first systemic therapy of any kind, according to Maryanne Senna, MD, an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and the director of the Lahey Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Mass. Dr. Senna was a clinical investigator of BRAVE-AA1, as well as of THRIVE-AA2.
Providing an update on the BRAVE-AA program, Dr. Senna reported 104-week data that appear to support the idea of a life-changing benefit from JAK inhibitor therapy. This is because the effects appear durable.
In the data she presented at the AAD, responders and mixed responders at 52 weeks were followed to 104 weeks. Mixed responders were defined as those without a SALT response of ≤ 20 at week 52 but who had achieved this degree of hair regrowth at some earlier point.
Of the responders, 90% maintained their response at 104 weeks. In addition, many of the mixed responders and patients with a partial response but who never achieved a SALT score ≤ 20% gained additional hair growth, including complete or near complete hair growth, when maintained on treatment over the 2 years of follow-up.
“The follow-up suggests that, if you keep patients on treatment, you can get many of them to a meaningful response,” she said.
Meanwhile, “there have been no new safety signals,” Dr. Senna said. She based this statement not only of the 104-week data but on follow-up of up to 3.6 years among patients who have remained on treatment after participating in previous studies.
According to Dr. Senna, the off-target events that have been reported previously in other diseases with other JAK inhibitors, such as major adverse cardiovascular events and thromboembolic events, have not so far been observed in the BRAVE-AA phase 3 program.
Baricitinib, much like all but one of the JAK inhibitors with dermatologic indications, carries a black box warning that lists multiple risks for drugs in this class, based on a rheumatoid arthritis study.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted deuruxolitinib Breakthrough Therapy designation for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe alopecia areata and Fast Track designation for the treatment of alopecia areata, according to its manufacturer Concert Pharmaceuticals.
Dr. King reports financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Concert Pharmaceuticals, which provided the funding for the THRIVE-AA trial program, and for Eli Lilly, which provided funding for the BRAVE-AA trial program. Dr. Senna reports financial relationships with Arena pharmaceuticals, Follica, and both Concert Pharmaceuticals and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
LAA closure device shown safe in groups omitted in trials
WASHINGTON – Left atrial appendage closure can be performed safely and effectively in older patients, those with end-stage renal disease, and likely others not included in the pivotal clinical trials, according to a series of new studies, including a late-breaker, presented on the both older and newer Watchman devices at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference.
In the case of the late-breaking clinical trial report, which included more than 60,000 patients, the goal was to look at the safety of the Watchman FLX, which is the newest of the devices in real-world practice, according to Samir R. Kapadia, MD, chairman of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
In the SURPASS registry, the number of patients discharged on the Watchman FLX climbed from zero in August 2020, when data accrual began, to 66,894 by March 2022. For the current analysis, 45-day follow-up was available for 61,963 patients and 1-year follow-up was available for 18,233.
Based on this number of patients treated by more than 2,300 clinicians at more than 740 sites, the SURPASS registry establishes that Watchman FLX “can be accomplished safely with clinical outcomes similar to pivotal trials at 45 days and 1 year,” Dr. Kapadia reported.
No surprises found in real-world outcome
At 7 days or hospital discharge (whichever came last), the rate of all-cause death was 0.18%, the rate of ischemic stroke was 0.13%, and there were no systemic emboli. By 45 days, the rate of all-cause death (0.84%) and stroke of any kind (0.32%) remained less than 1% and there were still no systemic emboli. Major bleeding events, of which about one-third occurred during hospitalization, had reached 3.34% by day 45.
By 1 year, all-cause mortality had risen to 8.3%, the stroke rate was 1.6%, and major bleeding reached 6.7%. The rate of systemic emboli remained very low (0.1%). The rates of death and stroke rose at a slow but steady rate throughout the 1-year follow-up. In contrast, major bleeding events rose steeply in the first 90 days and were followed by a much slower accrual subsequently.
At 1 year, 84.4% of patients had a complete seal. Leaks ≤ 3 mm were observed in 12.1%. The remaining leaks were larger, but just 0.7% had a leak > 5 mm.
Relative to the first-generation Watchman, the Watchman FLX has numerous design changes, including a shorter profile, more struts, and a reduced metal exposure. Most of these changes were performed to make the device easier to deploy.
When the SURPASS data are compared to the pivotal trials with Watchman FLX or to the Ewolution and National Cardiovascular Data (NCD) registries, which were created to monitor efficacy and safety with the earlier generation Watchman, the outcomes are similar or, in many cases, numerically favorable for such outcomes as bleeding and rates of stroke.
In addition to providing reassurance for the real-world safety of Watchman FLX, Dr. Kapadia said that these data establish reasonable benchmarks for centers tracking in-hospital and 1-year outcomes.
Dr. Kapadia also reported that outcomes overall in SURPASS were similar in women and men with the exception of major bleeding, a finding common to other interventional studies.
The late-breaker panelists generally agreed that SURPASS provides a robust set of data by which to be reassured, but David J. Cohen, MD, director of Clinical and Outcomes Research at the Cardiovascular Research Foundation in New York, said that he thinks the rate of bleeding is unnecessarily high.
“You really need to figure out a way to get the rate of bleeding at 45 days down,” Dr. Cohen said. He called for studies of anticoagulation in the post-procedural period that offer a better benefit-to-risk ratio.
Elderly patients benefit equally from Watchman
Yet, Watchman devices are generally regarded as a success story, and this has led investigators to evaluate safety in patients not well represented or explicitly excluded from clinical trials, such as the elderly and those with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). New data derived from experience in both of these groups were presented at the conference, which was sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
To tease out the relative safety of Watchman in octogenarians, Samian Sulaiman, MD, a cardiology fellow at West Virginia University Heart and Vascular Institute, Morgantown, performed a competing risk analysis to study the relative benefit of Watchman devices after controlling for the greater overall risk of complications in the elderly.
In raw data comparisons of those 80 years of age or older to those younger in published trials, the not-surprising result is that overall rates of death and ischemic events are far higher in the elderly, according to Dr. Sulaiman, but it’s an “unfair comparison,” he said.
“It is easy to mistakenly conclude that left atrial appendage closure is associated with worse outcomes, but older patients have far higher rates of these events independent of other factors,” Dr. Sulaiman noted.
In fact, in his comparison of 472 older patients to 1,404 younger patients, the seal rates at 45 days, 6 months, and 12 months are almost identical. Moreover, after the extensive adjustments performed for competing risk analysis, the rates of death, stroke, and bleeding were also almost identical for those 80 years or older whether or not they received a Watchman.
Although he acknowledged the risk for residual confounding, Dr. Sulaiman concluded that elderly patients derive about the same benefits as younger patients from the Watchman. He concluded age alone should not be a factor in selecting candidates for this device.
ESRD is not Watchman contraindication
A similar point was made about ESRD based on analysis of 237 patients who received either an earlier generation Watchman or the Watchman FLX. Initiated in Spain, the study was amended to collect data from centers elsewhere in Europe, the United States, and Australia.
Successful implantation was achieved in 99.2% of the patients, reported Armando Perez de Prado, MD, PhD, head of interventional cardiology at the University of Leon, Spain.
After a median follow-up of 480 days, stroke or transient ischemic attacks were observed in 3.1%, leaks > 5 mm were observed in 1.4%, and systemic emboli were observed in 0.9%. Major bleeding (BARC > 2) occurred in 13.3%.
Although the all-cause mortality over the period of follow-up was high (37.4%), most of the deaths (61.2%) were of noncardiovascular origin, according to Dr. Sulaiman. He said mortality and adverse events linked to the Watchman appeared to be roughly comparable to those seen in patients with ESRD.
“The Watchman device for patients on hemodialysis with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation is an effective and safe intervention to prevent embolic events,” he said. However, he also cautioned these the ESRD and the accompanying comorbidities place these patients at high risk of a limited life expectancy.
“Given the high mortality rate of this population, proper selection of candidates is paramount to ensure the optimal clinical benefit,” he cautioned.
Dr. Samir reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific. Dr. Cohen reported financial ties with Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Corvia Medical, Edwards Lifesciences, Impulse Dynamics, MyoKardia, Phillips, Svelte, V-Wave, and Zoll. Dr. Sulaiman reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Perez de Prado reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific.
WASHINGTON – Left atrial appendage closure can be performed safely and effectively in older patients, those with end-stage renal disease, and likely others not included in the pivotal clinical trials, according to a series of new studies, including a late-breaker, presented on the both older and newer Watchman devices at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference.
In the case of the late-breaking clinical trial report, which included more than 60,000 patients, the goal was to look at the safety of the Watchman FLX, which is the newest of the devices in real-world practice, according to Samir R. Kapadia, MD, chairman of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
In the SURPASS registry, the number of patients discharged on the Watchman FLX climbed from zero in August 2020, when data accrual began, to 66,894 by March 2022. For the current analysis, 45-day follow-up was available for 61,963 patients and 1-year follow-up was available for 18,233.
Based on this number of patients treated by more than 2,300 clinicians at more than 740 sites, the SURPASS registry establishes that Watchman FLX “can be accomplished safely with clinical outcomes similar to pivotal trials at 45 days and 1 year,” Dr. Kapadia reported.
No surprises found in real-world outcome
At 7 days or hospital discharge (whichever came last), the rate of all-cause death was 0.18%, the rate of ischemic stroke was 0.13%, and there were no systemic emboli. By 45 days, the rate of all-cause death (0.84%) and stroke of any kind (0.32%) remained less than 1% and there were still no systemic emboli. Major bleeding events, of which about one-third occurred during hospitalization, had reached 3.34% by day 45.
By 1 year, all-cause mortality had risen to 8.3%, the stroke rate was 1.6%, and major bleeding reached 6.7%. The rate of systemic emboli remained very low (0.1%). The rates of death and stroke rose at a slow but steady rate throughout the 1-year follow-up. In contrast, major bleeding events rose steeply in the first 90 days and were followed by a much slower accrual subsequently.
At 1 year, 84.4% of patients had a complete seal. Leaks ≤ 3 mm were observed in 12.1%. The remaining leaks were larger, but just 0.7% had a leak > 5 mm.
Relative to the first-generation Watchman, the Watchman FLX has numerous design changes, including a shorter profile, more struts, and a reduced metal exposure. Most of these changes were performed to make the device easier to deploy.
When the SURPASS data are compared to the pivotal trials with Watchman FLX or to the Ewolution and National Cardiovascular Data (NCD) registries, which were created to monitor efficacy and safety with the earlier generation Watchman, the outcomes are similar or, in many cases, numerically favorable for such outcomes as bleeding and rates of stroke.
In addition to providing reassurance for the real-world safety of Watchman FLX, Dr. Kapadia said that these data establish reasonable benchmarks for centers tracking in-hospital and 1-year outcomes.
Dr. Kapadia also reported that outcomes overall in SURPASS were similar in women and men with the exception of major bleeding, a finding common to other interventional studies.
The late-breaker panelists generally agreed that SURPASS provides a robust set of data by which to be reassured, but David J. Cohen, MD, director of Clinical and Outcomes Research at the Cardiovascular Research Foundation in New York, said that he thinks the rate of bleeding is unnecessarily high.
“You really need to figure out a way to get the rate of bleeding at 45 days down,” Dr. Cohen said. He called for studies of anticoagulation in the post-procedural period that offer a better benefit-to-risk ratio.
Elderly patients benefit equally from Watchman
Yet, Watchman devices are generally regarded as a success story, and this has led investigators to evaluate safety in patients not well represented or explicitly excluded from clinical trials, such as the elderly and those with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). New data derived from experience in both of these groups were presented at the conference, which was sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
To tease out the relative safety of Watchman in octogenarians, Samian Sulaiman, MD, a cardiology fellow at West Virginia University Heart and Vascular Institute, Morgantown, performed a competing risk analysis to study the relative benefit of Watchman devices after controlling for the greater overall risk of complications in the elderly.
In raw data comparisons of those 80 years of age or older to those younger in published trials, the not-surprising result is that overall rates of death and ischemic events are far higher in the elderly, according to Dr. Sulaiman, but it’s an “unfair comparison,” he said.
“It is easy to mistakenly conclude that left atrial appendage closure is associated with worse outcomes, but older patients have far higher rates of these events independent of other factors,” Dr. Sulaiman noted.
In fact, in his comparison of 472 older patients to 1,404 younger patients, the seal rates at 45 days, 6 months, and 12 months are almost identical. Moreover, after the extensive adjustments performed for competing risk analysis, the rates of death, stroke, and bleeding were also almost identical for those 80 years or older whether or not they received a Watchman.
Although he acknowledged the risk for residual confounding, Dr. Sulaiman concluded that elderly patients derive about the same benefits as younger patients from the Watchman. He concluded age alone should not be a factor in selecting candidates for this device.
ESRD is not Watchman contraindication
A similar point was made about ESRD based on analysis of 237 patients who received either an earlier generation Watchman or the Watchman FLX. Initiated in Spain, the study was amended to collect data from centers elsewhere in Europe, the United States, and Australia.
Successful implantation was achieved in 99.2% of the patients, reported Armando Perez de Prado, MD, PhD, head of interventional cardiology at the University of Leon, Spain.
After a median follow-up of 480 days, stroke or transient ischemic attacks were observed in 3.1%, leaks > 5 mm were observed in 1.4%, and systemic emboli were observed in 0.9%. Major bleeding (BARC > 2) occurred in 13.3%.
Although the all-cause mortality over the period of follow-up was high (37.4%), most of the deaths (61.2%) were of noncardiovascular origin, according to Dr. Sulaiman. He said mortality and adverse events linked to the Watchman appeared to be roughly comparable to those seen in patients with ESRD.
“The Watchman device for patients on hemodialysis with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation is an effective and safe intervention to prevent embolic events,” he said. However, he also cautioned these the ESRD and the accompanying comorbidities place these patients at high risk of a limited life expectancy.
“Given the high mortality rate of this population, proper selection of candidates is paramount to ensure the optimal clinical benefit,” he cautioned.
Dr. Samir reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific. Dr. Cohen reported financial ties with Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Corvia Medical, Edwards Lifesciences, Impulse Dynamics, MyoKardia, Phillips, Svelte, V-Wave, and Zoll. Dr. Sulaiman reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Perez de Prado reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific.
WASHINGTON – Left atrial appendage closure can be performed safely and effectively in older patients, those with end-stage renal disease, and likely others not included in the pivotal clinical trials, according to a series of new studies, including a late-breaker, presented on the both older and newer Watchman devices at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference.
In the case of the late-breaking clinical trial report, which included more than 60,000 patients, the goal was to look at the safety of the Watchman FLX, which is the newest of the devices in real-world practice, according to Samir R. Kapadia, MD, chairman of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
In the SURPASS registry, the number of patients discharged on the Watchman FLX climbed from zero in August 2020, when data accrual began, to 66,894 by March 2022. For the current analysis, 45-day follow-up was available for 61,963 patients and 1-year follow-up was available for 18,233.
Based on this number of patients treated by more than 2,300 clinicians at more than 740 sites, the SURPASS registry establishes that Watchman FLX “can be accomplished safely with clinical outcomes similar to pivotal trials at 45 days and 1 year,” Dr. Kapadia reported.
No surprises found in real-world outcome
At 7 days or hospital discharge (whichever came last), the rate of all-cause death was 0.18%, the rate of ischemic stroke was 0.13%, and there were no systemic emboli. By 45 days, the rate of all-cause death (0.84%) and stroke of any kind (0.32%) remained less than 1% and there were still no systemic emboli. Major bleeding events, of which about one-third occurred during hospitalization, had reached 3.34% by day 45.
By 1 year, all-cause mortality had risen to 8.3%, the stroke rate was 1.6%, and major bleeding reached 6.7%. The rate of systemic emboli remained very low (0.1%). The rates of death and stroke rose at a slow but steady rate throughout the 1-year follow-up. In contrast, major bleeding events rose steeply in the first 90 days and were followed by a much slower accrual subsequently.
At 1 year, 84.4% of patients had a complete seal. Leaks ≤ 3 mm were observed in 12.1%. The remaining leaks were larger, but just 0.7% had a leak > 5 mm.
Relative to the first-generation Watchman, the Watchman FLX has numerous design changes, including a shorter profile, more struts, and a reduced metal exposure. Most of these changes were performed to make the device easier to deploy.
When the SURPASS data are compared to the pivotal trials with Watchman FLX or to the Ewolution and National Cardiovascular Data (NCD) registries, which were created to monitor efficacy and safety with the earlier generation Watchman, the outcomes are similar or, in many cases, numerically favorable for such outcomes as bleeding and rates of stroke.
In addition to providing reassurance for the real-world safety of Watchman FLX, Dr. Kapadia said that these data establish reasonable benchmarks for centers tracking in-hospital and 1-year outcomes.
Dr. Kapadia also reported that outcomes overall in SURPASS were similar in women and men with the exception of major bleeding, a finding common to other interventional studies.
The late-breaker panelists generally agreed that SURPASS provides a robust set of data by which to be reassured, but David J. Cohen, MD, director of Clinical and Outcomes Research at the Cardiovascular Research Foundation in New York, said that he thinks the rate of bleeding is unnecessarily high.
“You really need to figure out a way to get the rate of bleeding at 45 days down,” Dr. Cohen said. He called for studies of anticoagulation in the post-procedural period that offer a better benefit-to-risk ratio.
Elderly patients benefit equally from Watchman
Yet, Watchman devices are generally regarded as a success story, and this has led investigators to evaluate safety in patients not well represented or explicitly excluded from clinical trials, such as the elderly and those with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). New data derived from experience in both of these groups were presented at the conference, which was sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
To tease out the relative safety of Watchman in octogenarians, Samian Sulaiman, MD, a cardiology fellow at West Virginia University Heart and Vascular Institute, Morgantown, performed a competing risk analysis to study the relative benefit of Watchman devices after controlling for the greater overall risk of complications in the elderly.
In raw data comparisons of those 80 years of age or older to those younger in published trials, the not-surprising result is that overall rates of death and ischemic events are far higher in the elderly, according to Dr. Sulaiman, but it’s an “unfair comparison,” he said.
“It is easy to mistakenly conclude that left atrial appendage closure is associated with worse outcomes, but older patients have far higher rates of these events independent of other factors,” Dr. Sulaiman noted.
In fact, in his comparison of 472 older patients to 1,404 younger patients, the seal rates at 45 days, 6 months, and 12 months are almost identical. Moreover, after the extensive adjustments performed for competing risk analysis, the rates of death, stroke, and bleeding were also almost identical for those 80 years or older whether or not they received a Watchman.
Although he acknowledged the risk for residual confounding, Dr. Sulaiman concluded that elderly patients derive about the same benefits as younger patients from the Watchman. He concluded age alone should not be a factor in selecting candidates for this device.
ESRD is not Watchman contraindication
A similar point was made about ESRD based on analysis of 237 patients who received either an earlier generation Watchman or the Watchman FLX. Initiated in Spain, the study was amended to collect data from centers elsewhere in Europe, the United States, and Australia.
Successful implantation was achieved in 99.2% of the patients, reported Armando Perez de Prado, MD, PhD, head of interventional cardiology at the University of Leon, Spain.
After a median follow-up of 480 days, stroke or transient ischemic attacks were observed in 3.1%, leaks > 5 mm were observed in 1.4%, and systemic emboli were observed in 0.9%. Major bleeding (BARC > 2) occurred in 13.3%.
Although the all-cause mortality over the period of follow-up was high (37.4%), most of the deaths (61.2%) were of noncardiovascular origin, according to Dr. Sulaiman. He said mortality and adverse events linked to the Watchman appeared to be roughly comparable to those seen in patients with ESRD.
“The Watchman device for patients on hemodialysis with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation is an effective and safe intervention to prevent embolic events,” he said. However, he also cautioned these the ESRD and the accompanying comorbidities place these patients at high risk of a limited life expectancy.
“Given the high mortality rate of this population, proper selection of candidates is paramount to ensure the optimal clinical benefit,” he cautioned.
Dr. Samir reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific. Dr. Cohen reported financial ties with Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Corvia Medical, Edwards Lifesciences, Impulse Dynamics, MyoKardia, Phillips, Svelte, V-Wave, and Zoll. Dr. Sulaiman reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Perez de Prado reported no potential conflicts of interest but stated that this study was funded by Boston Scientific.
AT CRT 2023
Novel therapy shows promise for treating skin-predominant dermatomyositis
NEW ORLEANS – in a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial, according to results presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These findings support the inhibition of IFN-beta as a promising therapeutic strategy in skin-predominant disease,” said principal investigator Aaron Mangold, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz.
Dermatomyositis, a rare autoimmune inflammatory condition that typically involves both skeletal muscles and skin, is a challenging disease with a diverse set of potential complications.
Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory agents are used with mixed success for myositis, but skin manifestations, which include papular eruptions, heliotrope rash, photoerythema, burning, and pruritus, are often the most troublesome and the most difficult to control. Treatment options other than immunomodulators that target cutaneous involvement – which include steroids, emollients, and photoprotection – are generally modestly effective, according to Dr. Mangold.
Targeting an elevated cytokine
Interest in IFN-beta, which is elevated in the blood of individuals with dermatomyositis, was triggered by evidence that this cytokine plays an important role in driving the skin inflammation, Dr. Mangold explained.
“The blood concentrations of IFN-beta are positively correlated with cutaneous disease activity and severity,” he said.
The study drug, currently known as PF-06823859 (Dazukibart), “is a potent, selective humanized IgG1-neutralizing antibody directed at IFN-beta,” Dr. Mangold said. A dose-ranging phase 1 study published 2 years ago provided evidence of acceptable pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy individuals to support treatment studies for disorders associated with elevated IFN-beta levels. In addition to dermatomyositis, this includes systemic lupus erythematosus.
In this phase 2 trial, patients whose condition was not improved by at least one standard-care therapy for skin manifestations of dermatomyositis were eligible if they had moderate to severe disease as measured with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI), according to Dr. Mangold. During the study, patients were allowed to remain on a disease modifying antirheumatic drug and/or prednisone if they had been on stable doses and did not change the dose.
After a screening run-in, the trial had two blinded stages. In stage 1, 30 patients were randomly assigned either to 600 mg of PF-06823859 or to placebo, both administered intravenously every 4 weeks. A second cohort of 25 patients was randomly assigned in stage 2 to placebo, 150 mg of PF-06823859, or 600 mg of PF-06823859. The primary endpoint assessed at 12 weeks was a greater than 5-point reduction in CDASI score or greater than 40% CDASI improvement from baseline.
Both endpoints are associated with a clinically meaningful response in regard to an improved quality of life, Dr. Mangold noted.
Both doses better than placebo
In results from the stage 1 portion, the mean reduction in CDASI at 12 weeks after three doses of the assigned therapy was 18.8 points in the active-treatment group versus 3.9 points in the placebo group. In pooled data from stage 1 and 2, the reductions were 16.6 points, 19.2 points, and 2.9 points for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Both doses achieved a highly significant advantage over placebo.
For both stages and doses, the response curves of the active-treatment groups and the placebo group diverged almost immediately. By 4 weeks, both measures of CDASI reductions on active therapy were significantly improved relative to placebo, and the response curves had a consistent downward slope through the end of the 12-week study, Dr. Mangold reported.
The majority of patients responded by either of the primary endpoint criteria. For a CDASI reduction of greater than 5 points, the response rates were 100% and 96% for the 150-mg and 600-mg doses of PF-06823859, respectively. The placebo response was 35.7%. For the CDASI reduction of greater than 40%, the rates were 80%, 82.1%, and 7.1% for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively.
“There were no major safety concerns. Most of the treatment-emergent adverse events were mild, and adverse events did not have a relationship to dose,” Dr. Mangold said. Notably, there were no cases of herpes zoster, and infections of any kind were low in all study groups.
A phase 3 study is being planned with the 600-mg dose, according to Dr. Mangold, but he acknowledged that regulatory authorities have generally required endpoints for both cutaneous and muscle manifestations in previous trials of therapies for dermatomyositis.
It is not yet certain that “there will be a carve-out for skin,” he said in answer to a question about investigations moving forward. So far, studies have been focused on skin response. However, a meaningful degree of benefit against muscle involvement, which has not yet been well studied, has not been ruled out.
Even though this is a phase 2 trial with small numbers, it was controlled and blinded, and the potential of an inhibitor of IFN-beta to control the skin manifestations of dermatomyositis “is kind of a big deal,” said Paul Nghiem, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“There is definitely an unmet need for better therapies to control the skin involvement,” Dr. Nghiem said.
Hensin Tsao, MD, PhD, clinical director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, agreed. Like Dr. Nghiem, Dr. Tsao was a panelist during the late-breaker session where the study was presented, and he was impressed by the data.
“This is something that is definitely newsworthy,” Dr. Tsao said.
Dr. Mangold reports financial relationships with Actelion, Amgen, Corbus, Eli Lilly, Incyte, miRagen, Novartis, Regeneron, Solagenix, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Teva, and Pfizer, which provided funding for this trial. Both Dr. Nghiem and Dr. Tsao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – in a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial, according to results presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These findings support the inhibition of IFN-beta as a promising therapeutic strategy in skin-predominant disease,” said principal investigator Aaron Mangold, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz.
Dermatomyositis, a rare autoimmune inflammatory condition that typically involves both skeletal muscles and skin, is a challenging disease with a diverse set of potential complications.
Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory agents are used with mixed success for myositis, but skin manifestations, which include papular eruptions, heliotrope rash, photoerythema, burning, and pruritus, are often the most troublesome and the most difficult to control. Treatment options other than immunomodulators that target cutaneous involvement – which include steroids, emollients, and photoprotection – are generally modestly effective, according to Dr. Mangold.
Targeting an elevated cytokine
Interest in IFN-beta, which is elevated in the blood of individuals with dermatomyositis, was triggered by evidence that this cytokine plays an important role in driving the skin inflammation, Dr. Mangold explained.
“The blood concentrations of IFN-beta are positively correlated with cutaneous disease activity and severity,” he said.
The study drug, currently known as PF-06823859 (Dazukibart), “is a potent, selective humanized IgG1-neutralizing antibody directed at IFN-beta,” Dr. Mangold said. A dose-ranging phase 1 study published 2 years ago provided evidence of acceptable pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy individuals to support treatment studies for disorders associated with elevated IFN-beta levels. In addition to dermatomyositis, this includes systemic lupus erythematosus.
In this phase 2 trial, patients whose condition was not improved by at least one standard-care therapy for skin manifestations of dermatomyositis were eligible if they had moderate to severe disease as measured with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI), according to Dr. Mangold. During the study, patients were allowed to remain on a disease modifying antirheumatic drug and/or prednisone if they had been on stable doses and did not change the dose.
After a screening run-in, the trial had two blinded stages. In stage 1, 30 patients were randomly assigned either to 600 mg of PF-06823859 or to placebo, both administered intravenously every 4 weeks. A second cohort of 25 patients was randomly assigned in stage 2 to placebo, 150 mg of PF-06823859, or 600 mg of PF-06823859. The primary endpoint assessed at 12 weeks was a greater than 5-point reduction in CDASI score or greater than 40% CDASI improvement from baseline.
Both endpoints are associated with a clinically meaningful response in regard to an improved quality of life, Dr. Mangold noted.
Both doses better than placebo
In results from the stage 1 portion, the mean reduction in CDASI at 12 weeks after three doses of the assigned therapy was 18.8 points in the active-treatment group versus 3.9 points in the placebo group. In pooled data from stage 1 and 2, the reductions were 16.6 points, 19.2 points, and 2.9 points for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Both doses achieved a highly significant advantage over placebo.
For both stages and doses, the response curves of the active-treatment groups and the placebo group diverged almost immediately. By 4 weeks, both measures of CDASI reductions on active therapy were significantly improved relative to placebo, and the response curves had a consistent downward slope through the end of the 12-week study, Dr. Mangold reported.
The majority of patients responded by either of the primary endpoint criteria. For a CDASI reduction of greater than 5 points, the response rates were 100% and 96% for the 150-mg and 600-mg doses of PF-06823859, respectively. The placebo response was 35.7%. For the CDASI reduction of greater than 40%, the rates were 80%, 82.1%, and 7.1% for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively.
“There were no major safety concerns. Most of the treatment-emergent adverse events were mild, and adverse events did not have a relationship to dose,” Dr. Mangold said. Notably, there were no cases of herpes zoster, and infections of any kind were low in all study groups.
A phase 3 study is being planned with the 600-mg dose, according to Dr. Mangold, but he acknowledged that regulatory authorities have generally required endpoints for both cutaneous and muscle manifestations in previous trials of therapies for dermatomyositis.
It is not yet certain that “there will be a carve-out for skin,” he said in answer to a question about investigations moving forward. So far, studies have been focused on skin response. However, a meaningful degree of benefit against muscle involvement, which has not yet been well studied, has not been ruled out.
Even though this is a phase 2 trial with small numbers, it was controlled and blinded, and the potential of an inhibitor of IFN-beta to control the skin manifestations of dermatomyositis “is kind of a big deal,” said Paul Nghiem, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“There is definitely an unmet need for better therapies to control the skin involvement,” Dr. Nghiem said.
Hensin Tsao, MD, PhD, clinical director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, agreed. Like Dr. Nghiem, Dr. Tsao was a panelist during the late-breaker session where the study was presented, and he was impressed by the data.
“This is something that is definitely newsworthy,” Dr. Tsao said.
Dr. Mangold reports financial relationships with Actelion, Amgen, Corbus, Eli Lilly, Incyte, miRagen, Novartis, Regeneron, Solagenix, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Teva, and Pfizer, which provided funding for this trial. Both Dr. Nghiem and Dr. Tsao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – in a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial, according to results presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These findings support the inhibition of IFN-beta as a promising therapeutic strategy in skin-predominant disease,” said principal investigator Aaron Mangold, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz.
Dermatomyositis, a rare autoimmune inflammatory condition that typically involves both skeletal muscles and skin, is a challenging disease with a diverse set of potential complications.
Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory agents are used with mixed success for myositis, but skin manifestations, which include papular eruptions, heliotrope rash, photoerythema, burning, and pruritus, are often the most troublesome and the most difficult to control. Treatment options other than immunomodulators that target cutaneous involvement – which include steroids, emollients, and photoprotection – are generally modestly effective, according to Dr. Mangold.
Targeting an elevated cytokine
Interest in IFN-beta, which is elevated in the blood of individuals with dermatomyositis, was triggered by evidence that this cytokine plays an important role in driving the skin inflammation, Dr. Mangold explained.
“The blood concentrations of IFN-beta are positively correlated with cutaneous disease activity and severity,” he said.
The study drug, currently known as PF-06823859 (Dazukibart), “is a potent, selective humanized IgG1-neutralizing antibody directed at IFN-beta,” Dr. Mangold said. A dose-ranging phase 1 study published 2 years ago provided evidence of acceptable pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy individuals to support treatment studies for disorders associated with elevated IFN-beta levels. In addition to dermatomyositis, this includes systemic lupus erythematosus.
In this phase 2 trial, patients whose condition was not improved by at least one standard-care therapy for skin manifestations of dermatomyositis were eligible if they had moderate to severe disease as measured with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI), according to Dr. Mangold. During the study, patients were allowed to remain on a disease modifying antirheumatic drug and/or prednisone if they had been on stable doses and did not change the dose.
After a screening run-in, the trial had two blinded stages. In stage 1, 30 patients were randomly assigned either to 600 mg of PF-06823859 or to placebo, both administered intravenously every 4 weeks. A second cohort of 25 patients was randomly assigned in stage 2 to placebo, 150 mg of PF-06823859, or 600 mg of PF-06823859. The primary endpoint assessed at 12 weeks was a greater than 5-point reduction in CDASI score or greater than 40% CDASI improvement from baseline.
Both endpoints are associated with a clinically meaningful response in regard to an improved quality of life, Dr. Mangold noted.
Both doses better than placebo
In results from the stage 1 portion, the mean reduction in CDASI at 12 weeks after three doses of the assigned therapy was 18.8 points in the active-treatment group versus 3.9 points in the placebo group. In pooled data from stage 1 and 2, the reductions were 16.6 points, 19.2 points, and 2.9 points for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Both doses achieved a highly significant advantage over placebo.
For both stages and doses, the response curves of the active-treatment groups and the placebo group diverged almost immediately. By 4 weeks, both measures of CDASI reductions on active therapy were significantly improved relative to placebo, and the response curves had a consistent downward slope through the end of the 12-week study, Dr. Mangold reported.
The majority of patients responded by either of the primary endpoint criteria. For a CDASI reduction of greater than 5 points, the response rates were 100% and 96% for the 150-mg and 600-mg doses of PF-06823859, respectively. The placebo response was 35.7%. For the CDASI reduction of greater than 40%, the rates were 80%, 82.1%, and 7.1% for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively.
“There were no major safety concerns. Most of the treatment-emergent adverse events were mild, and adverse events did not have a relationship to dose,” Dr. Mangold said. Notably, there were no cases of herpes zoster, and infections of any kind were low in all study groups.
A phase 3 study is being planned with the 600-mg dose, according to Dr. Mangold, but he acknowledged that regulatory authorities have generally required endpoints for both cutaneous and muscle manifestations in previous trials of therapies for dermatomyositis.
It is not yet certain that “there will be a carve-out for skin,” he said in answer to a question about investigations moving forward. So far, studies have been focused on skin response. However, a meaningful degree of benefit against muscle involvement, which has not yet been well studied, has not been ruled out.
Even though this is a phase 2 trial with small numbers, it was controlled and blinded, and the potential of an inhibitor of IFN-beta to control the skin manifestations of dermatomyositis “is kind of a big deal,” said Paul Nghiem, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“There is definitely an unmet need for better therapies to control the skin involvement,” Dr. Nghiem said.
Hensin Tsao, MD, PhD, clinical director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, agreed. Like Dr. Nghiem, Dr. Tsao was a panelist during the late-breaker session where the study was presented, and he was impressed by the data.
“This is something that is definitely newsworthy,” Dr. Tsao said.
Dr. Mangold reports financial relationships with Actelion, Amgen, Corbus, Eli Lilly, Incyte, miRagen, Novartis, Regeneron, Solagenix, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Teva, and Pfizer, which provided funding for this trial. Both Dr. Nghiem and Dr. Tsao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
Studies validate IL-17 as hidradenitis suppurativa drug target
NEW ORLEANS – In two phase 3 trials, bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting two types of interleukin-17 — IL-17A and IL-17F — reduced the abscess and inflammatory nodule count better than placebo in the chronic inflammatory skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), according to results presented together during a late-breaker session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“We are very excited to add this data to what we already have around IL-17 inhibition. This clearly validates this target for the control of HS,” reported lead investigator Alexa B. Kimball, MD, MPH, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
The trials, called BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II, enrolled 505 and 509 patients with HS, respectively. About 50% of patients in BE HEARD I and 60% of patients in BE HEARD II had Hurley stage 3 disease, which is the most severe of the three stratifications. The remainder were in Hurley stage 2. The mean duration of HS was 8.3 and 7.1 years, respectively.
Patients in both studies were randomized to one of four groups – either to a dosing regimen of 320 mg of bimekizumab administered by subcutaneous injection or to a placebo group. Both trials comprised double-blind 16-week initial and 32-week maintenance treatment periods.
In one experimental group, bimekizumab was given once every 2 weeks for the full course of the 48-week study (Q2W/Q2W). In another, patients started on the every-2-week schedule for 16 weeks and then were switched to every-4-week dosing (Q2W/Q4W). In the third group, patients started and remained on the every-4-week schedule (Q4W/Q4W). Patients in a fourth group started on placebo and switched at 16 weeks to the every-2-week bimekizumab schedule (placebo/Q2W).
Results at primary endpoint
The primary endpoint was HiSCR50, signifying a 50% reduction from baseline in abscess and inflammatory nodule count on the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) assessment tool. At 16 weeks, the initial Q2W dose in two of the groups outperformed the placebo in both BE HEARD I (47.8% vs. 28.7%) and BE HEARD II (52.0% vs. 32.2%). The response rates in the Q4W arm in BE HEARD I (45.3%) and BE HEARD II (53.8%) were also higher than the placebo, but the difference was only significant in BE HEARD II.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with an HiSCR50 response climbed in all groups in both trials. The patterns were generally the same with slightly higher numerical responses among the groups that received the every-2-week dosing schedule relative to the every-4-week schedule.
In BE HEARD I at 48 weeks, the HiSCR50 response rate was about 60% for those who started and remained on every-2-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q2W) or were switched at 16 weeks to every-4-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q4W). For those who started and remained on every-4-week bimekizumab and the group started on placebo and switched to every-2-week bimekizumab, the response rates were 52.7% and 45.3%, respectively.
In BE HEARD II, the HiSCR50 response rates were higher in all groups, including the placebo, and the patterns of response were similar at 48 weeks. Most patients reached the HiSCR50 response – 79.8% (Q2W/Q2W), 78.4% (Q2W/Q4W), 76.7% (Q4W/Q4W), and 65.9 % (placebo/Q2W) of patients.
It is notable that, although there was rapid increase in the proportion of placebo patients reaching HiSCR50 after the switch at 16 weeks, there appeared to be an advantage at 48 weeks for starting on full-dose bimekizumab over starting on placebo.
In this trial, patients were listed as nonresponders if they received antibiotics at any time and for any reason after randomization. This might have concealed an even greater benefit of bimekizumab, Dr. Kimball said, but the study design element was considered necessary to isolate the activity of the study drug.
“In future HS trials, it will be helpful to address the difficulty of handling the impact of antibiotics and pain medications [in assessing results],” Dr. Kimball said.
Clinically meaningful secondary endpoint
For HS patients, the secondary endpoint of HiSCR75 might be considered the most meaningful, according to Dr. Kimball. She said that this higher bar not only documents a higher level of efficacy but correlates with meaningful improvement in quality of life. In the two trials combined, more than 55% of patients on continuous bimekizumab achieved HiSCR75 at week 48 in the observed case analysis, according to a news release from biopharmaceutical company UCB, developer of bimekizumab.
In BE HEARD I, the HiSCR75 rates were 33.4% and 24.7% for the every-2-week and every-4-week bimekizumab doses, respectively. The 33.4% response was statistically superior to placebo (18.4%). In BE HEARD II, both the every-2-week dose (35.7%) and the every-4-week dose (33.7%) were superior to the 15.6% response in placebo patients.
The improvements in quality of life as measured with the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), reflected the changes in disease activity. Relative to about a 3-point reduction from baseline in the placebo groups of the two trials, the 5-point reduction for either the 2-week or 4-week bimekizumab groups in each clinical trial were highly significant, Dr. Kimball said.
Bimekizumab was relatively well tolerated, although it shares the increased risk for candidiasis observed with this agent when used in psoriasis and with other IL-17 inhibitors, such as secukinumab (Cosentyx), in general. The risk of candidiasis appeared to be dose related, but cases were generally mild and easily managed, according to Dr. Kimball. She noted that only three patients discontinued treatment for this reason. Discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event overall was less than 4% at 16 weeks.
This is only the third phase 3 trial ever completed in patients with HS. In fact, Dr. Kimball has led all of the phase 3 trials so far, including clinical studies of adalimumab (Humira), published in 2016, and of secukinumab, published earlier this year. All were positive studies.
“This is amazing news for our patients,” Dr. Kimball said. HS remains a challenging disease, even with a growing number of options showing benefit in large studies, she said, and the high rate of response, particularly at the level of HiSCR75, “is a huge milestone for what we can achieve.”
Multiple treatment options important
Her assessment was echoed by other experts, including Christopher J. Sayed, MD, an associate professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who publishes frequently about this disease.
“It is incredibly exciting to see the strong phase 3 data on bimekizumab, particularly the deep responses at the HiSCR75 in a majority of patients after the first year,” he said.
Importantly, he does not see the growing array of treatment options as necessarily competitive for a disease with heterogeneous manifestations and variable responses to any one agent.
“While this may be a major step forward, it will still be critical to see more drugs come along for those who do not respond fully enough or have comorbidities that prevent the use of IL-17 and TNF [tumor necrosis factor] antagonists,” he said.
Bimekizumab is not approved for any indication in the United States; it is approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy in the EU/EEA, where it is marketed as Bimzelx, according to UCB. Dr. Kimball reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, Kymera, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Sayed reports financial relationships with AbbVie, InflaRx, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – In two phase 3 trials, bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting two types of interleukin-17 — IL-17A and IL-17F — reduced the abscess and inflammatory nodule count better than placebo in the chronic inflammatory skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), according to results presented together during a late-breaker session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“We are very excited to add this data to what we already have around IL-17 inhibition. This clearly validates this target for the control of HS,” reported lead investigator Alexa B. Kimball, MD, MPH, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
The trials, called BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II, enrolled 505 and 509 patients with HS, respectively. About 50% of patients in BE HEARD I and 60% of patients in BE HEARD II had Hurley stage 3 disease, which is the most severe of the three stratifications. The remainder were in Hurley stage 2. The mean duration of HS was 8.3 and 7.1 years, respectively.
Patients in both studies were randomized to one of four groups – either to a dosing regimen of 320 mg of bimekizumab administered by subcutaneous injection or to a placebo group. Both trials comprised double-blind 16-week initial and 32-week maintenance treatment periods.
In one experimental group, bimekizumab was given once every 2 weeks for the full course of the 48-week study (Q2W/Q2W). In another, patients started on the every-2-week schedule for 16 weeks and then were switched to every-4-week dosing (Q2W/Q4W). In the third group, patients started and remained on the every-4-week schedule (Q4W/Q4W). Patients in a fourth group started on placebo and switched at 16 weeks to the every-2-week bimekizumab schedule (placebo/Q2W).
Results at primary endpoint
The primary endpoint was HiSCR50, signifying a 50% reduction from baseline in abscess and inflammatory nodule count on the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) assessment tool. At 16 weeks, the initial Q2W dose in two of the groups outperformed the placebo in both BE HEARD I (47.8% vs. 28.7%) and BE HEARD II (52.0% vs. 32.2%). The response rates in the Q4W arm in BE HEARD I (45.3%) and BE HEARD II (53.8%) were also higher than the placebo, but the difference was only significant in BE HEARD II.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with an HiSCR50 response climbed in all groups in both trials. The patterns were generally the same with slightly higher numerical responses among the groups that received the every-2-week dosing schedule relative to the every-4-week schedule.
In BE HEARD I at 48 weeks, the HiSCR50 response rate was about 60% for those who started and remained on every-2-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q2W) or were switched at 16 weeks to every-4-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q4W). For those who started and remained on every-4-week bimekizumab and the group started on placebo and switched to every-2-week bimekizumab, the response rates were 52.7% and 45.3%, respectively.
In BE HEARD II, the HiSCR50 response rates were higher in all groups, including the placebo, and the patterns of response were similar at 48 weeks. Most patients reached the HiSCR50 response – 79.8% (Q2W/Q2W), 78.4% (Q2W/Q4W), 76.7% (Q4W/Q4W), and 65.9 % (placebo/Q2W) of patients.
It is notable that, although there was rapid increase in the proportion of placebo patients reaching HiSCR50 after the switch at 16 weeks, there appeared to be an advantage at 48 weeks for starting on full-dose bimekizumab over starting on placebo.
In this trial, patients were listed as nonresponders if they received antibiotics at any time and for any reason after randomization. This might have concealed an even greater benefit of bimekizumab, Dr. Kimball said, but the study design element was considered necessary to isolate the activity of the study drug.
“In future HS trials, it will be helpful to address the difficulty of handling the impact of antibiotics and pain medications [in assessing results],” Dr. Kimball said.
Clinically meaningful secondary endpoint
For HS patients, the secondary endpoint of HiSCR75 might be considered the most meaningful, according to Dr. Kimball. She said that this higher bar not only documents a higher level of efficacy but correlates with meaningful improvement in quality of life. In the two trials combined, more than 55% of patients on continuous bimekizumab achieved HiSCR75 at week 48 in the observed case analysis, according to a news release from biopharmaceutical company UCB, developer of bimekizumab.
In BE HEARD I, the HiSCR75 rates were 33.4% and 24.7% for the every-2-week and every-4-week bimekizumab doses, respectively. The 33.4% response was statistically superior to placebo (18.4%). In BE HEARD II, both the every-2-week dose (35.7%) and the every-4-week dose (33.7%) were superior to the 15.6% response in placebo patients.
The improvements in quality of life as measured with the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), reflected the changes in disease activity. Relative to about a 3-point reduction from baseline in the placebo groups of the two trials, the 5-point reduction for either the 2-week or 4-week bimekizumab groups in each clinical trial were highly significant, Dr. Kimball said.
Bimekizumab was relatively well tolerated, although it shares the increased risk for candidiasis observed with this agent when used in psoriasis and with other IL-17 inhibitors, such as secukinumab (Cosentyx), in general. The risk of candidiasis appeared to be dose related, but cases were generally mild and easily managed, according to Dr. Kimball. She noted that only three patients discontinued treatment for this reason. Discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event overall was less than 4% at 16 weeks.
This is only the third phase 3 trial ever completed in patients with HS. In fact, Dr. Kimball has led all of the phase 3 trials so far, including clinical studies of adalimumab (Humira), published in 2016, and of secukinumab, published earlier this year. All were positive studies.
“This is amazing news for our patients,” Dr. Kimball said. HS remains a challenging disease, even with a growing number of options showing benefit in large studies, she said, and the high rate of response, particularly at the level of HiSCR75, “is a huge milestone for what we can achieve.”
Multiple treatment options important
Her assessment was echoed by other experts, including Christopher J. Sayed, MD, an associate professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who publishes frequently about this disease.
“It is incredibly exciting to see the strong phase 3 data on bimekizumab, particularly the deep responses at the HiSCR75 in a majority of patients after the first year,” he said.
Importantly, he does not see the growing array of treatment options as necessarily competitive for a disease with heterogeneous manifestations and variable responses to any one agent.
“While this may be a major step forward, it will still be critical to see more drugs come along for those who do not respond fully enough or have comorbidities that prevent the use of IL-17 and TNF [tumor necrosis factor] antagonists,” he said.
Bimekizumab is not approved for any indication in the United States; it is approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy in the EU/EEA, where it is marketed as Bimzelx, according to UCB. Dr. Kimball reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, Kymera, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Sayed reports financial relationships with AbbVie, InflaRx, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – In two phase 3 trials, bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting two types of interleukin-17 — IL-17A and IL-17F — reduced the abscess and inflammatory nodule count better than placebo in the chronic inflammatory skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), according to results presented together during a late-breaker session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“We are very excited to add this data to what we already have around IL-17 inhibition. This clearly validates this target for the control of HS,” reported lead investigator Alexa B. Kimball, MD, MPH, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
The trials, called BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II, enrolled 505 and 509 patients with HS, respectively. About 50% of patients in BE HEARD I and 60% of patients in BE HEARD II had Hurley stage 3 disease, which is the most severe of the three stratifications. The remainder were in Hurley stage 2. The mean duration of HS was 8.3 and 7.1 years, respectively.
Patients in both studies were randomized to one of four groups – either to a dosing regimen of 320 mg of bimekizumab administered by subcutaneous injection or to a placebo group. Both trials comprised double-blind 16-week initial and 32-week maintenance treatment periods.
In one experimental group, bimekizumab was given once every 2 weeks for the full course of the 48-week study (Q2W/Q2W). In another, patients started on the every-2-week schedule for 16 weeks and then were switched to every-4-week dosing (Q2W/Q4W). In the third group, patients started and remained on the every-4-week schedule (Q4W/Q4W). Patients in a fourth group started on placebo and switched at 16 weeks to the every-2-week bimekizumab schedule (placebo/Q2W).
Results at primary endpoint
The primary endpoint was HiSCR50, signifying a 50% reduction from baseline in abscess and inflammatory nodule count on the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) assessment tool. At 16 weeks, the initial Q2W dose in two of the groups outperformed the placebo in both BE HEARD I (47.8% vs. 28.7%) and BE HEARD II (52.0% vs. 32.2%). The response rates in the Q4W arm in BE HEARD I (45.3%) and BE HEARD II (53.8%) were also higher than the placebo, but the difference was only significant in BE HEARD II.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with an HiSCR50 response climbed in all groups in both trials. The patterns were generally the same with slightly higher numerical responses among the groups that received the every-2-week dosing schedule relative to the every-4-week schedule.
In BE HEARD I at 48 weeks, the HiSCR50 response rate was about 60% for those who started and remained on every-2-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q2W) or were switched at 16 weeks to every-4-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q4W). For those who started and remained on every-4-week bimekizumab and the group started on placebo and switched to every-2-week bimekizumab, the response rates were 52.7% and 45.3%, respectively.
In BE HEARD II, the HiSCR50 response rates were higher in all groups, including the placebo, and the patterns of response were similar at 48 weeks. Most patients reached the HiSCR50 response – 79.8% (Q2W/Q2W), 78.4% (Q2W/Q4W), 76.7% (Q4W/Q4W), and 65.9 % (placebo/Q2W) of patients.
It is notable that, although there was rapid increase in the proportion of placebo patients reaching HiSCR50 after the switch at 16 weeks, there appeared to be an advantage at 48 weeks for starting on full-dose bimekizumab over starting on placebo.
In this trial, patients were listed as nonresponders if they received antibiotics at any time and for any reason after randomization. This might have concealed an even greater benefit of bimekizumab, Dr. Kimball said, but the study design element was considered necessary to isolate the activity of the study drug.
“In future HS trials, it will be helpful to address the difficulty of handling the impact of antibiotics and pain medications [in assessing results],” Dr. Kimball said.
Clinically meaningful secondary endpoint
For HS patients, the secondary endpoint of HiSCR75 might be considered the most meaningful, according to Dr. Kimball. She said that this higher bar not only documents a higher level of efficacy but correlates with meaningful improvement in quality of life. In the two trials combined, more than 55% of patients on continuous bimekizumab achieved HiSCR75 at week 48 in the observed case analysis, according to a news release from biopharmaceutical company UCB, developer of bimekizumab.
In BE HEARD I, the HiSCR75 rates were 33.4% and 24.7% for the every-2-week and every-4-week bimekizumab doses, respectively. The 33.4% response was statistically superior to placebo (18.4%). In BE HEARD II, both the every-2-week dose (35.7%) and the every-4-week dose (33.7%) were superior to the 15.6% response in placebo patients.
The improvements in quality of life as measured with the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), reflected the changes in disease activity. Relative to about a 3-point reduction from baseline in the placebo groups of the two trials, the 5-point reduction for either the 2-week or 4-week bimekizumab groups in each clinical trial were highly significant, Dr. Kimball said.
Bimekizumab was relatively well tolerated, although it shares the increased risk for candidiasis observed with this agent when used in psoriasis and with other IL-17 inhibitors, such as secukinumab (Cosentyx), in general. The risk of candidiasis appeared to be dose related, but cases were generally mild and easily managed, according to Dr. Kimball. She noted that only three patients discontinued treatment for this reason. Discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event overall was less than 4% at 16 weeks.
This is only the third phase 3 trial ever completed in patients with HS. In fact, Dr. Kimball has led all of the phase 3 trials so far, including clinical studies of adalimumab (Humira), published in 2016, and of secukinumab, published earlier this year. All were positive studies.
“This is amazing news for our patients,” Dr. Kimball said. HS remains a challenging disease, even with a growing number of options showing benefit in large studies, she said, and the high rate of response, particularly at the level of HiSCR75, “is a huge milestone for what we can achieve.”
Multiple treatment options important
Her assessment was echoed by other experts, including Christopher J. Sayed, MD, an associate professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who publishes frequently about this disease.
“It is incredibly exciting to see the strong phase 3 data on bimekizumab, particularly the deep responses at the HiSCR75 in a majority of patients after the first year,” he said.
Importantly, he does not see the growing array of treatment options as necessarily competitive for a disease with heterogeneous manifestations and variable responses to any one agent.
“While this may be a major step forward, it will still be critical to see more drugs come along for those who do not respond fully enough or have comorbidities that prevent the use of IL-17 and TNF [tumor necrosis factor] antagonists,” he said.
Bimekizumab is not approved for any indication in the United States; it is approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy in the EU/EEA, where it is marketed as Bimzelx, according to UCB. Dr. Kimball reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, Kymera, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Sayed reports financial relationships with AbbVie, InflaRx, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023