User login
Racial disparities in maternal morbidity persist even with equal access to care
An analysis of data from the U.S. military suggests that the maternal morbidity disparities between Black and White women cannot be attributed solely to differences in access to care and socioeconomics.
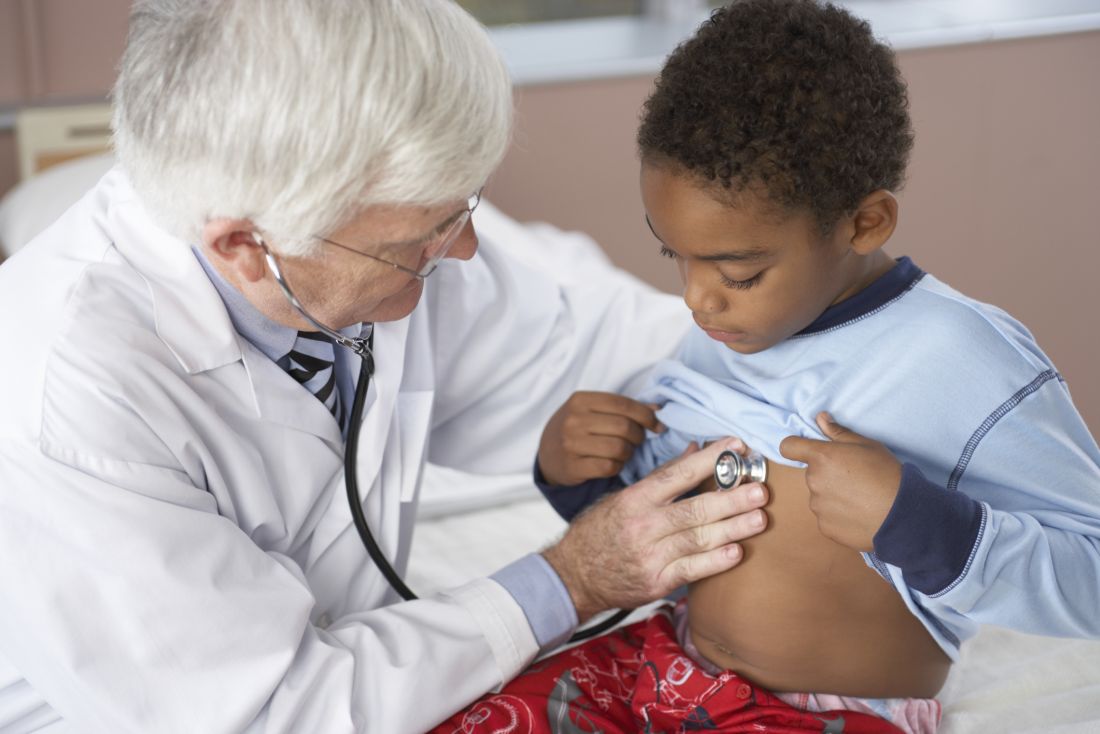
Even in the U.S. military health care system, where all service members have universal access to the same facilities and providers, researchers found substantial racial disparities in cesarean deliveries, maternal ICU admission, and overall severe maternal morbidity and mortality between Black patients and White patients, according to findings from a new study presented Jan. 28, 2021, at a meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
“This was surprising given some of the driving theories behind maternal race disparities encountered in this country, such as access to care and socioeconomic status, are controlled for in this health care system,” Capt. Jameaka Hamilton, MD, who presented the research, said in an interview. “Our findings indicate that there are likely additional factors at play which impact the obstetrical outcomes of women based upon their race, including systems-based barriers to accessing the military health care system which contribute to health care disparities, or in systemic or implicit biases which occur within our health care delivery.”
Plenty of recent research has documented the rise in maternal morbidity and mortality in the United States and the considerable racial disparities within those statistics. Black women are twice as likely to suffer morbidity and three to four times more likely to die in childbirth, compared with White women, Dr. Hamilton, an ob.gyn. from the San Antonio Uniformed Services Health Education Consortium at Ft. Sam Houston in San Antonio, Texas, reminded attendees. So far, much of this disparity has been attributed to social determinants of health.
Military retirees, active-duty personnel, and dependents, however, have equal access to federal health insurance and care at military health care facilities, or at covered civilian facilities where needed. Hence the researchers’ hypothesis that the military medical system would not show the same disparities by race that are seen in civilian populations.
The researchers analyzed maternal morbidity data from the Neonatal Perinatal Information Center from April 2018 to March 2019. The retrospective study included data from 13 military treatment facilities that had more than 1,000 deliveries per year. In addition to statistics on cesarean delivery and adult ICU admission, the researchers compared numbers on overall severe maternal morbidity based on the indicators defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The 15,305 deliveries included 23% Black patients and 77% White patients from the Air Force, Army, and Navy branches.
The cesarean delivery rate ranged from 19.4% to 35.5%. ICU admissions totaled 38 women, 190 women had postpartum hemorrhage, and 282 women experienced severe maternal morbidity. All three measures revealed racial disparities:
- Overall severe maternal morbidity occurred in 2.66% of Black women and 1.66% of White women (P =.0001).
- ICU admission occurred in 0.49% of Black women and 0.18% of White women (P =.0026).
- 31.68% of Black women had a cesarean delivery, compared with 23.58% of White women (P <.0001).
After excluding cases with blood transfusions, Black women were twice as likely to have severe maternal morbidity (0.64% vs. 0.32%). There were no significant differences in postpartum hemorrhage rates between Black and White women, but this analysis was limited by the small overall numbers of postpartum hemorrhage.
Among the study’s limitations were the inability to stratify patients by retiree, active duty, or dependent status, and the lack of data on preeclampsia rates, maternal age, obesity, or other preexisting conditions. In addition, the initial dataset included 61% of patients who reported their race as “other” than Black or White, limiting the number of patients whose data could be analyzed. Since low-volume hospitals were excluded, the outcomes could be skewed if lower-volume facilities are more likely to care for more complex cases, Dr. Hamilton added.
Allison Bryant Mantha, MD, MPH, vice chair for quality, equity, and safety in the ob.gyn. department at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, praised Dr. Hamilton’s work for revealing that differential access – though still problematic – cannot fully explain inequities between Black women and other women.
“The findings are not shocking given that what underlies some of these inequities – namely structural and institutional racism, and differential treatment within the system – are not exclusive to civilian health care settings,” Dr. Bryant Mantha, who moderated the session, said in an interview. “That said, doing the work to demonstrate this is extremely valuable.”
Although the causes of these disparities are systemic, Dr. Hamilton said individual providers can play a role in addressing them.
“There can certainly be more done to address this dangerous trend at the provider, hospital/institution, and national level,” she said. I think we as providers should continue to self-reflect and address our own biases. Hospitals and institutions should continue to develop policies that draw attention health care disparities.”
Completely removing these inequalities, however, will require confronting the racism embedded in U.S. health care at all levels, Dr. Bryant Mantha suggested.
“Ultimately, moving to an antiracist health care system – and criminal justice system, educational system, political system, etc. – and dismantling the existing structural racism in policies and practices will be needed to drive this change,” Dr. Bryant Mantha said. “Individual clinicians can use their voices to advocate for these changes in their health systems, communities, and states. Awareness of these inequities is critical, as is a sense of collective efficacy that we can, indeed, change the status quo.”
Dr. Hamilton and Dr. Bryant Mantha reported no disclosures.
An analysis of data from the U.S. military suggests that the maternal morbidity disparities between Black and White women cannot be attributed solely to differences in access to care and socioeconomics.
Even in the U.S. military health care system, where all service members have universal access to the same facilities and providers, researchers found substantial racial disparities in cesarean deliveries, maternal ICU admission, and overall severe maternal morbidity and mortality between Black patients and White patients, according to findings from a new study presented Jan. 28, 2021, at a meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
“This was surprising given some of the driving theories behind maternal race disparities encountered in this country, such as access to care and socioeconomic status, are controlled for in this health care system,” Capt. Jameaka Hamilton, MD, who presented the research, said in an interview. “Our findings indicate that there are likely additional factors at play which impact the obstetrical outcomes of women based upon their race, including systems-based barriers to accessing the military health care system which contribute to health care disparities, or in systemic or implicit biases which occur within our health care delivery.”
Plenty of recent research has documented the rise in maternal morbidity and mortality in the United States and the considerable racial disparities within those statistics. Black women are twice as likely to suffer morbidity and three to four times more likely to die in childbirth, compared with White women, Dr. Hamilton, an ob.gyn. from the San Antonio Uniformed Services Health Education Consortium at Ft. Sam Houston in San Antonio, Texas, reminded attendees. So far, much of this disparity has been attributed to social determinants of health.
Military retirees, active-duty personnel, and dependents, however, have equal access to federal health insurance and care at military health care facilities, or at covered civilian facilities where needed. Hence the researchers’ hypothesis that the military medical system would not show the same disparities by race that are seen in civilian populations.
The researchers analyzed maternal morbidity data from the Neonatal Perinatal Information Center from April 2018 to March 2019. The retrospective study included data from 13 military treatment facilities that had more than 1,000 deliveries per year. In addition to statistics on cesarean delivery and adult ICU admission, the researchers compared numbers on overall severe maternal morbidity based on the indicators defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The 15,305 deliveries included 23% Black patients and 77% White patients from the Air Force, Army, and Navy branches.
The cesarean delivery rate ranged from 19.4% to 35.5%. ICU admissions totaled 38 women, 190 women had postpartum hemorrhage, and 282 women experienced severe maternal morbidity. All three measures revealed racial disparities:
- Overall severe maternal morbidity occurred in 2.66% of Black women and 1.66% of White women (P =.0001).
- ICU admission occurred in 0.49% of Black women and 0.18% of White women (P =.0026).
- 31.68% of Black women had a cesarean delivery, compared with 23.58% of White women (P <.0001).
After excluding cases with blood transfusions, Black women were twice as likely to have severe maternal morbidity (0.64% vs. 0.32%). There were no significant differences in postpartum hemorrhage rates between Black and White women, but this analysis was limited by the small overall numbers of postpartum hemorrhage.
Among the study’s limitations were the inability to stratify patients by retiree, active duty, or dependent status, and the lack of data on preeclampsia rates, maternal age, obesity, or other preexisting conditions. In addition, the initial dataset included 61% of patients who reported their race as “other” than Black or White, limiting the number of patients whose data could be analyzed. Since low-volume hospitals were excluded, the outcomes could be skewed if lower-volume facilities are more likely to care for more complex cases, Dr. Hamilton added.
Allison Bryant Mantha, MD, MPH, vice chair for quality, equity, and safety in the ob.gyn. department at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, praised Dr. Hamilton’s work for revealing that differential access – though still problematic – cannot fully explain inequities between Black women and other women.
“The findings are not shocking given that what underlies some of these inequities – namely structural and institutional racism, and differential treatment within the system – are not exclusive to civilian health care settings,” Dr. Bryant Mantha, who moderated the session, said in an interview. “That said, doing the work to demonstrate this is extremely valuable.”
Although the causes of these disparities are systemic, Dr. Hamilton said individual providers can play a role in addressing them.
“There can certainly be more done to address this dangerous trend at the provider, hospital/institution, and national level,” she said. I think we as providers should continue to self-reflect and address our own biases. Hospitals and institutions should continue to develop policies that draw attention health care disparities.”
Completely removing these inequalities, however, will require confronting the racism embedded in U.S. health care at all levels, Dr. Bryant Mantha suggested.
“Ultimately, moving to an antiracist health care system – and criminal justice system, educational system, political system, etc. – and dismantling the existing structural racism in policies and practices will be needed to drive this change,” Dr. Bryant Mantha said. “Individual clinicians can use their voices to advocate for these changes in their health systems, communities, and states. Awareness of these inequities is critical, as is a sense of collective efficacy that we can, indeed, change the status quo.”
Dr. Hamilton and Dr. Bryant Mantha reported no disclosures.
An analysis of data from the U.S. military suggests that the maternal morbidity disparities between Black and White women cannot be attributed solely to differences in access to care and socioeconomics.
Even in the U.S. military health care system, where all service members have universal access to the same facilities and providers, researchers found substantial racial disparities in cesarean deliveries, maternal ICU admission, and overall severe maternal morbidity and mortality between Black patients and White patients, according to findings from a new study presented Jan. 28, 2021, at a meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
“This was surprising given some of the driving theories behind maternal race disparities encountered in this country, such as access to care and socioeconomic status, are controlled for in this health care system,” Capt. Jameaka Hamilton, MD, who presented the research, said in an interview. “Our findings indicate that there are likely additional factors at play which impact the obstetrical outcomes of women based upon their race, including systems-based barriers to accessing the military health care system which contribute to health care disparities, or in systemic or implicit biases which occur within our health care delivery.”
Plenty of recent research has documented the rise in maternal morbidity and mortality in the United States and the considerable racial disparities within those statistics. Black women are twice as likely to suffer morbidity and three to four times more likely to die in childbirth, compared with White women, Dr. Hamilton, an ob.gyn. from the San Antonio Uniformed Services Health Education Consortium at Ft. Sam Houston in San Antonio, Texas, reminded attendees. So far, much of this disparity has been attributed to social determinants of health.
Military retirees, active-duty personnel, and dependents, however, have equal access to federal health insurance and care at military health care facilities, or at covered civilian facilities where needed. Hence the researchers’ hypothesis that the military medical system would not show the same disparities by race that are seen in civilian populations.
The researchers analyzed maternal morbidity data from the Neonatal Perinatal Information Center from April 2018 to March 2019. The retrospective study included data from 13 military treatment facilities that had more than 1,000 deliveries per year. In addition to statistics on cesarean delivery and adult ICU admission, the researchers compared numbers on overall severe maternal morbidity based on the indicators defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The 15,305 deliveries included 23% Black patients and 77% White patients from the Air Force, Army, and Navy branches.
The cesarean delivery rate ranged from 19.4% to 35.5%. ICU admissions totaled 38 women, 190 women had postpartum hemorrhage, and 282 women experienced severe maternal morbidity. All three measures revealed racial disparities:
- Overall severe maternal morbidity occurred in 2.66% of Black women and 1.66% of White women (P =.0001).
- ICU admission occurred in 0.49% of Black women and 0.18% of White women (P =.0026).
- 31.68% of Black women had a cesarean delivery, compared with 23.58% of White women (P <.0001).
After excluding cases with blood transfusions, Black women were twice as likely to have severe maternal morbidity (0.64% vs. 0.32%). There were no significant differences in postpartum hemorrhage rates between Black and White women, but this analysis was limited by the small overall numbers of postpartum hemorrhage.
Among the study’s limitations were the inability to stratify patients by retiree, active duty, or dependent status, and the lack of data on preeclampsia rates, maternal age, obesity, or other preexisting conditions. In addition, the initial dataset included 61% of patients who reported their race as “other” than Black or White, limiting the number of patients whose data could be analyzed. Since low-volume hospitals were excluded, the outcomes could be skewed if lower-volume facilities are more likely to care for more complex cases, Dr. Hamilton added.
Allison Bryant Mantha, MD, MPH, vice chair for quality, equity, and safety in the ob.gyn. department at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, praised Dr. Hamilton’s work for revealing that differential access – though still problematic – cannot fully explain inequities between Black women and other women.
“The findings are not shocking given that what underlies some of these inequities – namely structural and institutional racism, and differential treatment within the system – are not exclusive to civilian health care settings,” Dr. Bryant Mantha, who moderated the session, said in an interview. “That said, doing the work to demonstrate this is extremely valuable.”
Although the causes of these disparities are systemic, Dr. Hamilton said individual providers can play a role in addressing them.
“There can certainly be more done to address this dangerous trend at the provider, hospital/institution, and national level,” she said. I think we as providers should continue to self-reflect and address our own biases. Hospitals and institutions should continue to develop policies that draw attention health care disparities.”
Completely removing these inequalities, however, will require confronting the racism embedded in U.S. health care at all levels, Dr. Bryant Mantha suggested.
“Ultimately, moving to an antiracist health care system – and criminal justice system, educational system, political system, etc. – and dismantling the existing structural racism in policies and practices will be needed to drive this change,” Dr. Bryant Mantha said. “Individual clinicians can use their voices to advocate for these changes in their health systems, communities, and states. Awareness of these inequities is critical, as is a sense of collective efficacy that we can, indeed, change the status quo.”
Dr. Hamilton and Dr. Bryant Mantha reported no disclosures.
FROM THE PREGNANCY MEETING
Low-dose aspirin did not reduce preterm birth rates but don’t rule it out yet
Women at risk of preterm birth who took daily low-dose aspirin did not have significantly lower rates of preterm birth than those who did not take aspirin, according to preliminary findings from a small randomized controlled trial. There was a trend toward lower rates, especially among those with the highest compliance, but the study was underpowered to detect a difference with statistical significance, said Anadeijda Landman, MD, of the Amsterdam University Medical Center. Dr. Landman presented the findings Jan. 28 at a meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
Preterm birth accounts for a third of all neonatal mortality, she told attendees. Among 15 million preterm births worldwide each year, 65% are spontaneous, indicating the need for effective preventive interventions. Dr. Landman reviewed several mechanisms by which aspirin may help reduce preterm birth via different pathways.
The researchers’ multicenter, placebo-controlled trial involved 8 tertiary care and 26 secondary care hospitals in the Netherlands between May 2016 and June 2019. Starting between 8 and 15 weeks’ gestation, women took either 80 mg of aspirin or a placebo daily until 36 weeks’ gestation or delivery. Women also received progesterone, cerclage, or pessary as indicated according to local protocols.
The study enrolled 406 women with singleton pregnancy and a history of preterm birth delivered between 22 and 37 weeks’ gestation. The final analysis, after exclusions for pregnancy termination, congenital anomalies, multiples pregnancy, or similar reasons, included 193 women in the intervention group and 194 in the placebo group. The women had similar baseline characteristics across both groups except a higher number of past mid-trimester fetal deaths in the aspirin group.
“It’s important to realize these women had multiple preterm births, as one of our inclusion criteria was previous spontaneous preterm birth later than 22 weeks’ gestation, so this particular group is very high risk for cervical insufficiency as a probable cause,” Dr. Landman told attendees.
Among women in the aspirin group, 21.2% delivered before 37 weeks, compared with 25.4% in the placebo group (P = .323). The rate of spontaneous birth was 20.1% in the aspirin group and 23.8% in the placebo group (P = .376). Though still not statistically significant, the difference between the groups was larger when the researchers limited their analysis to the 245 women with at least 80% compliance: 18.5% of women in the aspirin group had a preterm birth, compared with 24.8% of women in the placebo group (P = .238).
There were no significant differences between the groups in composite poor neonatal outcomes or in a range of prespecified newborn complications. The aspirin group did have two stillbirths, two mid-trimester fetal losses, and two extremely preterm newborns (at 24+2 weeks and 25+2 weeks). The placebo group had two mid-trimester fetal losses.
“These deaths are inherent to the study population, and it seems unlikely they are related to the use of aspirin,” Dr. Landman said. “Moreover other aspirin studies have not found an increased perinatal mortality rate, and some large studies indicated the neonatal mortality rate is even reduced.”
Although preterm birth only trended lower in the aspirin group, Dr. Landman said the researchers believe they cannot rule out an effect from aspirin.
“It’s also important to note that our study was underpowered as the recurrence risk of preterm birth in our study was lower than expected, so it’s possible a small treatment effect of aspirin could not be demonstrated in our study,” she said. “And, despite the proper randomization procedure, many more women in the aspirin group had a previous mid-trimester fetal loss. This indicates that the aspirin group might be more at risk for preterm birth than the placebo group, and this imbalance could also have diminished a small protective effect of aspirin.”
In response to an audience question, Dr. Landman acknowledged that more recent studies on aspirin have used 100- to 150-mg dosages, but that evidence was not as clear when their study began in 2015. She added that her research team does not advise changing clinical care currently and believes it is too soon to recommend aspirin to this population.
Tracy Manuck, MD, MS, an associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill, agreed that it is premature to begin prescribing aspirin for preterm birth prevention, but she noted that most of the patients she cares for clinically already meet criteria for aspirin based on their risk factors for preeclampsia.
“Additional research is needed in the form of a well-designed and large [randomized, controlled trial],” Dr Manuck, who moderated the session, said in an interview. “However, such a trial is becoming increasingly difficult to conduct because so many pregnant women qualify to receive aspirin for the prevention of preeclampsia due to their weight, medical comorbidities, or prior pregnancy history.”
She said she anticipates seeing patient-level data meta-analyses in the coming months as more data on aspirin for preterm birth prevention are published.
“Given that these data are supportive of the overall trends seen in prior publications, I do think that low-dose aspirin will eventually bear out as a helpful preventative measure to prevent recurrent preterm birth. Aspirin is low risk, readily available, and is inexpensive,” Dr. Manuck said. “I hope that meta-analysis data will provide additional information regarding the benefit of low-dose aspirin for prematurity prevention.”
The research was funded by the Dutch Organization for Health Care Research and the Dutch Consortium for Research in Women’s Health. Dr. Landman and Dr. Manuck had no disclosures.
Women at risk of preterm birth who took daily low-dose aspirin did not have significantly lower rates of preterm birth than those who did not take aspirin, according to preliminary findings from a small randomized controlled trial. There was a trend toward lower rates, especially among those with the highest compliance, but the study was underpowered to detect a difference with statistical significance, said Anadeijda Landman, MD, of the Amsterdam University Medical Center. Dr. Landman presented the findings Jan. 28 at a meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
Preterm birth accounts for a third of all neonatal mortality, she told attendees. Among 15 million preterm births worldwide each year, 65% are spontaneous, indicating the need for effective preventive interventions. Dr. Landman reviewed several mechanisms by which aspirin may help reduce preterm birth via different pathways.
The researchers’ multicenter, placebo-controlled trial involved 8 tertiary care and 26 secondary care hospitals in the Netherlands between May 2016 and June 2019. Starting between 8 and 15 weeks’ gestation, women took either 80 mg of aspirin or a placebo daily until 36 weeks’ gestation or delivery. Women also received progesterone, cerclage, or pessary as indicated according to local protocols.
The study enrolled 406 women with singleton pregnancy and a history of preterm birth delivered between 22 and 37 weeks’ gestation. The final analysis, after exclusions for pregnancy termination, congenital anomalies, multiples pregnancy, or similar reasons, included 193 women in the intervention group and 194 in the placebo group. The women had similar baseline characteristics across both groups except a higher number of past mid-trimester fetal deaths in the aspirin group.
“It’s important to realize these women had multiple preterm births, as one of our inclusion criteria was previous spontaneous preterm birth later than 22 weeks’ gestation, so this particular group is very high risk for cervical insufficiency as a probable cause,” Dr. Landman told attendees.
Among women in the aspirin group, 21.2% delivered before 37 weeks, compared with 25.4% in the placebo group (P = .323). The rate of spontaneous birth was 20.1% in the aspirin group and 23.8% in the placebo group (P = .376). Though still not statistically significant, the difference between the groups was larger when the researchers limited their analysis to the 245 women with at least 80% compliance: 18.5% of women in the aspirin group had a preterm birth, compared with 24.8% of women in the placebo group (P = .238).
There were no significant differences between the groups in composite poor neonatal outcomes or in a range of prespecified newborn complications. The aspirin group did have two stillbirths, two mid-trimester fetal losses, and two extremely preterm newborns (at 24+2 weeks and 25+2 weeks). The placebo group had two mid-trimester fetal losses.
“These deaths are inherent to the study population, and it seems unlikely they are related to the use of aspirin,” Dr. Landman said. “Moreover other aspirin studies have not found an increased perinatal mortality rate, and some large studies indicated the neonatal mortality rate is even reduced.”
Although preterm birth only trended lower in the aspirin group, Dr. Landman said the researchers believe they cannot rule out an effect from aspirin.
“It’s also important to note that our study was underpowered as the recurrence risk of preterm birth in our study was lower than expected, so it’s possible a small treatment effect of aspirin could not be demonstrated in our study,” she said. “And, despite the proper randomization procedure, many more women in the aspirin group had a previous mid-trimester fetal loss. This indicates that the aspirin group might be more at risk for preterm birth than the placebo group, and this imbalance could also have diminished a small protective effect of aspirin.”
In response to an audience question, Dr. Landman acknowledged that more recent studies on aspirin have used 100- to 150-mg dosages, but that evidence was not as clear when their study began in 2015. She added that her research team does not advise changing clinical care currently and believes it is too soon to recommend aspirin to this population.
Tracy Manuck, MD, MS, an associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill, agreed that it is premature to begin prescribing aspirin for preterm birth prevention, but she noted that most of the patients she cares for clinically already meet criteria for aspirin based on their risk factors for preeclampsia.
“Additional research is needed in the form of a well-designed and large [randomized, controlled trial],” Dr Manuck, who moderated the session, said in an interview. “However, such a trial is becoming increasingly difficult to conduct because so many pregnant women qualify to receive aspirin for the prevention of preeclampsia due to their weight, medical comorbidities, or prior pregnancy history.”
She said she anticipates seeing patient-level data meta-analyses in the coming months as more data on aspirin for preterm birth prevention are published.
“Given that these data are supportive of the overall trends seen in prior publications, I do think that low-dose aspirin will eventually bear out as a helpful preventative measure to prevent recurrent preterm birth. Aspirin is low risk, readily available, and is inexpensive,” Dr. Manuck said. “I hope that meta-analysis data will provide additional information regarding the benefit of low-dose aspirin for prematurity prevention.”
The research was funded by the Dutch Organization for Health Care Research and the Dutch Consortium for Research in Women’s Health. Dr. Landman and Dr. Manuck had no disclosures.
Women at risk of preterm birth who took daily low-dose aspirin did not have significantly lower rates of preterm birth than those who did not take aspirin, according to preliminary findings from a small randomized controlled trial. There was a trend toward lower rates, especially among those with the highest compliance, but the study was underpowered to detect a difference with statistical significance, said Anadeijda Landman, MD, of the Amsterdam University Medical Center. Dr. Landman presented the findings Jan. 28 at a meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
Preterm birth accounts for a third of all neonatal mortality, she told attendees. Among 15 million preterm births worldwide each year, 65% are spontaneous, indicating the need for effective preventive interventions. Dr. Landman reviewed several mechanisms by which aspirin may help reduce preterm birth via different pathways.
The researchers’ multicenter, placebo-controlled trial involved 8 tertiary care and 26 secondary care hospitals in the Netherlands between May 2016 and June 2019. Starting between 8 and 15 weeks’ gestation, women took either 80 mg of aspirin or a placebo daily until 36 weeks’ gestation or delivery. Women also received progesterone, cerclage, or pessary as indicated according to local protocols.
The study enrolled 406 women with singleton pregnancy and a history of preterm birth delivered between 22 and 37 weeks’ gestation. The final analysis, after exclusions for pregnancy termination, congenital anomalies, multiples pregnancy, or similar reasons, included 193 women in the intervention group and 194 in the placebo group. The women had similar baseline characteristics across both groups except a higher number of past mid-trimester fetal deaths in the aspirin group.
“It’s important to realize these women had multiple preterm births, as one of our inclusion criteria was previous spontaneous preterm birth later than 22 weeks’ gestation, so this particular group is very high risk for cervical insufficiency as a probable cause,” Dr. Landman told attendees.
Among women in the aspirin group, 21.2% delivered before 37 weeks, compared with 25.4% in the placebo group (P = .323). The rate of spontaneous birth was 20.1% in the aspirin group and 23.8% in the placebo group (P = .376). Though still not statistically significant, the difference between the groups was larger when the researchers limited their analysis to the 245 women with at least 80% compliance: 18.5% of women in the aspirin group had a preterm birth, compared with 24.8% of women in the placebo group (P = .238).
There were no significant differences between the groups in composite poor neonatal outcomes or in a range of prespecified newborn complications. The aspirin group did have two stillbirths, two mid-trimester fetal losses, and two extremely preterm newborns (at 24+2 weeks and 25+2 weeks). The placebo group had two mid-trimester fetal losses.
“These deaths are inherent to the study population, and it seems unlikely they are related to the use of aspirin,” Dr. Landman said. “Moreover other aspirin studies have not found an increased perinatal mortality rate, and some large studies indicated the neonatal mortality rate is even reduced.”
Although preterm birth only trended lower in the aspirin group, Dr. Landman said the researchers believe they cannot rule out an effect from aspirin.
“It’s also important to note that our study was underpowered as the recurrence risk of preterm birth in our study was lower than expected, so it’s possible a small treatment effect of aspirin could not be demonstrated in our study,” she said. “And, despite the proper randomization procedure, many more women in the aspirin group had a previous mid-trimester fetal loss. This indicates that the aspirin group might be more at risk for preterm birth than the placebo group, and this imbalance could also have diminished a small protective effect of aspirin.”
In response to an audience question, Dr. Landman acknowledged that more recent studies on aspirin have used 100- to 150-mg dosages, but that evidence was not as clear when their study began in 2015. She added that her research team does not advise changing clinical care currently and believes it is too soon to recommend aspirin to this population.
Tracy Manuck, MD, MS, an associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill, agreed that it is premature to begin prescribing aspirin for preterm birth prevention, but she noted that most of the patients she cares for clinically already meet criteria for aspirin based on their risk factors for preeclampsia.
“Additional research is needed in the form of a well-designed and large [randomized, controlled trial],” Dr Manuck, who moderated the session, said in an interview. “However, such a trial is becoming increasingly difficult to conduct because so many pregnant women qualify to receive aspirin for the prevention of preeclampsia due to their weight, medical comorbidities, or prior pregnancy history.”
She said she anticipates seeing patient-level data meta-analyses in the coming months as more data on aspirin for preterm birth prevention are published.
“Given that these data are supportive of the overall trends seen in prior publications, I do think that low-dose aspirin will eventually bear out as a helpful preventative measure to prevent recurrent preterm birth. Aspirin is low risk, readily available, and is inexpensive,” Dr. Manuck said. “I hope that meta-analysis data will provide additional information regarding the benefit of low-dose aspirin for prematurity prevention.”
The research was funded by the Dutch Organization for Health Care Research and the Dutch Consortium for Research in Women’s Health. Dr. Landman and Dr. Manuck had no disclosures.
FROM THE PREGNANCY MEETING
COVID-19 in pregnancy tied to hypertension, preeclampsia
Having COVID-19 during pregnancy is linked to a significantly increased risk for gestational hypertension and preeclampsia compared with not having COVID-19 while pregnant, according to findings from a retrospective study presented Jan. 28 at the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine 2021 Annual Pregnancy Meeting.
“This was not entirely surprising given that inflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of both hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and COVID-19 infection and thus may serve to exacerbate each other,” Nigel Madden, MD, a resident physician in the ob.gyn. department at Columbia University, New York. , told this news organization after she presented the results.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy occur in 10%-15% of all pregnancies and are the leading cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide, Dr. Madden told attendees of the meeting. Although it’s not clear what causes hypertensive diseases in pregnancy generally, “it is possible that the acute inflammatory state of the COVID infection may incite or exacerbate hypertensive disease of pregnancy,” Dr. Madden said.
The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of 1,715 patients who had a singleton pregnancy and who underwent routine nasal polymerase chain reaction testing at admission to one institution’s labor and delivery department between March and June 2020. The researchers excluded patients who had a history of chronic hypertension.
Overall, 10% of the patients tested positive for COVID-19 (n = 167), and 90% tested negative (n = 1,548). There were several differences at baseline between the groups. Those who tested positive tended to be younger, with an average age of 28, compared with an average age of 31 years for the group that tested negative. The group that tested negative also had a higher proportion of mothers aged 35 and older (P < .01). There were also significant differences in the racial makeup of the groups. Half of those in the COVID-positive group reported “other” for their race. The biggest baseline disparity between the groups was with regard to insurance type: 73% of those who tested positive for COVID-19 used Medicaid; only 36% of patients in the COVID-negative group used Medicaid. Those with private insurance were more likely to test negative (43%) than positive (25%) (P < .01).
The researchers defined gestational hypertension as having a systolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 140 mm Hg or a diastolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 90 mm Hg on two occasions at least 4 hours apart. A preeclampsia diagnosis required elevated blood pressure (using the same definition as for hypertension) as well as proteinuria, characterized by a protein/creatine ratio greater than or equal to 0.3 mg/dL or greater than or equal to 300 mg of protein on a 24-hour urine collection. Preeclampsia with severe features required prespecified laboratory abnormalities, pulmonary edema, or symptoms of headache, vision changes, chest pain, shortness of breath, or right upper quadrant pain.
More than twice as many patients with COVID had a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (18%) as those who tested negative (8%). The patients who were COVID positive were significantly more likely than those who tested negative to have gestational hypertension and preeclampsia without severe features. Rates of preeclampsia with severe features were not significantly different between the groups.
The severity of hypertensive disease did not differ between the groups. Limitations of the study included its retrospective design, the small number of COVID-positive patients, and the fact that it was conducted at a single institution in New York. However, the study population was diverse, and it was conducted during the height of infections at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This was a study of great clinical significance,” said Kim Boggess, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, while moderating the session. “I would argue that you guys in New York are the best poised to answer some of the questions that need to be answered as it relates to the effect of coronavirus infection in pregnancy.”
Dr. Boggess asked whether the study examined associations related to the severity of COVID-19. Only 10 of the patients were symptomatic, Dr. Madden said, and only one of those patients developed preeclampsia with severe features.
Michelle Y. Owens, MD, professor and chief of maternal fetal medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, who also moderated the session, said in an interview that the findings call for physicians to remain vigilant about evaluating patients who test positive for COVID-19 for hypertensive disease and disorders.
“Additionally, these women should be educated about hypertensive disorders and the common symptoms to facilitate early diagnosis and treatment when indicated,” Dr. Owens said. “I believe this is of particular interest in those women who are not severely affected by COVID, as these changes may occur while they are undergoing quarantine or being monitored remotely. This amplifies the need for remote assessment or home monitoring of maternal blood pressures.”
Dr. Madden, Dr. Boggess, and Dr. Owens have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having COVID-19 during pregnancy is linked to a significantly increased risk for gestational hypertension and preeclampsia compared with not having COVID-19 while pregnant, according to findings from a retrospective study presented Jan. 28 at the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine 2021 Annual Pregnancy Meeting.
“This was not entirely surprising given that inflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of both hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and COVID-19 infection and thus may serve to exacerbate each other,” Nigel Madden, MD, a resident physician in the ob.gyn. department at Columbia University, New York. , told this news organization after she presented the results.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy occur in 10%-15% of all pregnancies and are the leading cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide, Dr. Madden told attendees of the meeting. Although it’s not clear what causes hypertensive diseases in pregnancy generally, “it is possible that the acute inflammatory state of the COVID infection may incite or exacerbate hypertensive disease of pregnancy,” Dr. Madden said.
The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of 1,715 patients who had a singleton pregnancy and who underwent routine nasal polymerase chain reaction testing at admission to one institution’s labor and delivery department between March and June 2020. The researchers excluded patients who had a history of chronic hypertension.
Overall, 10% of the patients tested positive for COVID-19 (n = 167), and 90% tested negative (n = 1,548). There were several differences at baseline between the groups. Those who tested positive tended to be younger, with an average age of 28, compared with an average age of 31 years for the group that tested negative. The group that tested negative also had a higher proportion of mothers aged 35 and older (P < .01). There were also significant differences in the racial makeup of the groups. Half of those in the COVID-positive group reported “other” for their race. The biggest baseline disparity between the groups was with regard to insurance type: 73% of those who tested positive for COVID-19 used Medicaid; only 36% of patients in the COVID-negative group used Medicaid. Those with private insurance were more likely to test negative (43%) than positive (25%) (P < .01).
The researchers defined gestational hypertension as having a systolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 140 mm Hg or a diastolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 90 mm Hg on two occasions at least 4 hours apart. A preeclampsia diagnosis required elevated blood pressure (using the same definition as for hypertension) as well as proteinuria, characterized by a protein/creatine ratio greater than or equal to 0.3 mg/dL or greater than or equal to 300 mg of protein on a 24-hour urine collection. Preeclampsia with severe features required prespecified laboratory abnormalities, pulmonary edema, or symptoms of headache, vision changes, chest pain, shortness of breath, or right upper quadrant pain.
More than twice as many patients with COVID had a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (18%) as those who tested negative (8%). The patients who were COVID positive were significantly more likely than those who tested negative to have gestational hypertension and preeclampsia without severe features. Rates of preeclampsia with severe features were not significantly different between the groups.
The severity of hypertensive disease did not differ between the groups. Limitations of the study included its retrospective design, the small number of COVID-positive patients, and the fact that it was conducted at a single institution in New York. However, the study population was diverse, and it was conducted during the height of infections at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This was a study of great clinical significance,” said Kim Boggess, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, while moderating the session. “I would argue that you guys in New York are the best poised to answer some of the questions that need to be answered as it relates to the effect of coronavirus infection in pregnancy.”
Dr. Boggess asked whether the study examined associations related to the severity of COVID-19. Only 10 of the patients were symptomatic, Dr. Madden said, and only one of those patients developed preeclampsia with severe features.
Michelle Y. Owens, MD, professor and chief of maternal fetal medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, who also moderated the session, said in an interview that the findings call for physicians to remain vigilant about evaluating patients who test positive for COVID-19 for hypertensive disease and disorders.
“Additionally, these women should be educated about hypertensive disorders and the common symptoms to facilitate early diagnosis and treatment when indicated,” Dr. Owens said. “I believe this is of particular interest in those women who are not severely affected by COVID, as these changes may occur while they are undergoing quarantine or being monitored remotely. This amplifies the need for remote assessment or home monitoring of maternal blood pressures.”
Dr. Madden, Dr. Boggess, and Dr. Owens have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having COVID-19 during pregnancy is linked to a significantly increased risk for gestational hypertension and preeclampsia compared with not having COVID-19 while pregnant, according to findings from a retrospective study presented Jan. 28 at the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine 2021 Annual Pregnancy Meeting.
“This was not entirely surprising given that inflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of both hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and COVID-19 infection and thus may serve to exacerbate each other,” Nigel Madden, MD, a resident physician in the ob.gyn. department at Columbia University, New York. , told this news organization after she presented the results.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy occur in 10%-15% of all pregnancies and are the leading cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide, Dr. Madden told attendees of the meeting. Although it’s not clear what causes hypertensive diseases in pregnancy generally, “it is possible that the acute inflammatory state of the COVID infection may incite or exacerbate hypertensive disease of pregnancy,” Dr. Madden said.
The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of 1,715 patients who had a singleton pregnancy and who underwent routine nasal polymerase chain reaction testing at admission to one institution’s labor and delivery department between March and June 2020. The researchers excluded patients who had a history of chronic hypertension.
Overall, 10% of the patients tested positive for COVID-19 (n = 167), and 90% tested negative (n = 1,548). There were several differences at baseline between the groups. Those who tested positive tended to be younger, with an average age of 28, compared with an average age of 31 years for the group that tested negative. The group that tested negative also had a higher proportion of mothers aged 35 and older (P < .01). There were also significant differences in the racial makeup of the groups. Half of those in the COVID-positive group reported “other” for their race. The biggest baseline disparity between the groups was with regard to insurance type: 73% of those who tested positive for COVID-19 used Medicaid; only 36% of patients in the COVID-negative group used Medicaid. Those with private insurance were more likely to test negative (43%) than positive (25%) (P < .01).
The researchers defined gestational hypertension as having a systolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 140 mm Hg or a diastolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 90 mm Hg on two occasions at least 4 hours apart. A preeclampsia diagnosis required elevated blood pressure (using the same definition as for hypertension) as well as proteinuria, characterized by a protein/creatine ratio greater than or equal to 0.3 mg/dL or greater than or equal to 300 mg of protein on a 24-hour urine collection. Preeclampsia with severe features required prespecified laboratory abnormalities, pulmonary edema, or symptoms of headache, vision changes, chest pain, shortness of breath, or right upper quadrant pain.
More than twice as many patients with COVID had a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (18%) as those who tested negative (8%). The patients who were COVID positive were significantly more likely than those who tested negative to have gestational hypertension and preeclampsia without severe features. Rates of preeclampsia with severe features were not significantly different between the groups.
The severity of hypertensive disease did not differ between the groups. Limitations of the study included its retrospective design, the small number of COVID-positive patients, and the fact that it was conducted at a single institution in New York. However, the study population was diverse, and it was conducted during the height of infections at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This was a study of great clinical significance,” said Kim Boggess, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, while moderating the session. “I would argue that you guys in New York are the best poised to answer some of the questions that need to be answered as it relates to the effect of coronavirus infection in pregnancy.”
Dr. Boggess asked whether the study examined associations related to the severity of COVID-19. Only 10 of the patients were symptomatic, Dr. Madden said, and only one of those patients developed preeclampsia with severe features.
Michelle Y. Owens, MD, professor and chief of maternal fetal medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, who also moderated the session, said in an interview that the findings call for physicians to remain vigilant about evaluating patients who test positive for COVID-19 for hypertensive disease and disorders.
“Additionally, these women should be educated about hypertensive disorders and the common symptoms to facilitate early diagnosis and treatment when indicated,” Dr. Owens said. “I believe this is of particular interest in those women who are not severely affected by COVID, as these changes may occur while they are undergoing quarantine or being monitored remotely. This amplifies the need for remote assessment or home monitoring of maternal blood pressures.”
Dr. Madden, Dr. Boggess, and Dr. Owens have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Maternal COVID antibodies cross placenta, detected in newborns
Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 cross the placenta during pregnancy and are detectable in most newborns born to mothers who had COVID-19 during pregnancy, according to findings from a study presented Jan. 28 at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
“I think the most striking finding is that we noticed a high degree of neutralizing response to natural infection even among asymptomatic infection, but of course a higher degree was seen in those with symptomatic infection,” Naima Joseph, MD, MPH, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“Our data demonstrate maternal capacity to mount an appropriate and robust immune response,” and maternal protective immunity lasted at least 28 days after infection, Dr. Joseph said. “Also, we noted higher neonatal cord blood titers in moms with higher titers, which suggests a relationship, but we need to better understand how transplacental transfer occurs as well as establish neonatal correlates of protection in order to see if and how maternal immunity may also benefit neonates.”
The researchers analyzed the amount of IgG and IgM antibodies in maternal and cord blood samples prospectively collected at delivery from women who tested positive for COVID-19 at any time while pregnant. They used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to assess for antibodies for the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
The 32 pairs of mothers and infants in the study were predominantly non-Hispanic Black (72%) and Hispanic (25%), and 84% used Medicaid as their payer. Most of the mothers (72%) had at least one comorbidity, most commonly obesity, hypertension, and asthma or pulmonary disease. Just over half the women (53%) were symptomatic while they were infected, and 88% were ill with COVID-19 during the third trimester. The average time from infection to delivery was 28 days.
All the mothers had IgG antibodies, 94% had IgM antibodies, and 94% had neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Among the cord blood samples, 91% had IgG antibodies, 9% had IgM antibodies, and 25% had neutralizing antibodies.
“It’s reassuring that, so far, the physiological response is exactly what we expected it to be,” Judette Louis, MD, MPH, an associate professor of ob.gyn. and the ob.gyn. department chair at the University of South Florida, Tampa, said in an interview. “It’s what we would expect, but it’s always helpful to have more data to support that. Otherwise, you’re extrapolating from what you know from other conditions,” said Dr. Louis, who moderated the oral abstracts session.
Symptomatic infection was associated with significantly higher IgG titers than asymptomatic infection (P = .03), but no correlation was seen for IgM or neutralizing antibodies. In addition, although mothers who delivered more than 28 days after their infection had higher IgG titers (P = .05), no differences existed in IgM or neutralizing response.
Infants’ cord blood titers were significantly lower than their corresponding maternal samples, independently of symptoms or latency from infection to delivery (P < .001), Dr. Joseph reported.
“Transplacental efficiency in other pathogens has been shown to be correlated with neonatal immunity when the ratio of cord to maternal blood is greater than 1,” Dr. Joseph said in her presentation. Their data showed “suboptimal efficiency” at a ratio of 0.81.
The study’s small sample size and lack of a control group were weaknesses, but a major strength was having a population at disproportionately higher risk for infection and severe morbidity than the general population.
Implications for maternal COVID-19 vaccination
Although the data are not yet available, Dr. Joseph said they have expanded their protocol to include vaccinated pregnant women.
“The key to developing an effective vaccine [for pregnant people] is in really characterizing adaptive immunity in pregnancy,” Dr. Joseph told SMFM attendees. “I think that these findings inform further vaccine development in demonstrating that maternal immunity is robust.”
The World Health Organization recently recommended withholding COVID-19 vaccines from pregnant people, but the SMFM and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists subsequently issued a joint statement reaffirming that the COVID-19 vaccines authorized by the FDA “should not be withheld from pregnant individuals who choose to receive the vaccine.”
“One of the questions people ask is whether in pregnancy you’re going to mount a good response to the vaccine the way you would outside of pregnancy,” Dr. Louis said. “If we can demonstrate that you do, that may provide the information that some mothers need to make their decisions.” Data such as those from Dr. Joseph’s study can also inform recommendations on timing of maternal vaccination.
“For instance, Dr. Joseph demonstrated that, 28 days out from the infection, you had more antibodies, so there may be a scenario where we say this vaccine may be more beneficial in the middle of the pregnancy for the purpose of forming those antibodies,” Dr. Louis said.
Consensus emerging from maternal antibodies data
The findings from Dr. Joseph’s study mirror those reported in a study published online Jan. 29 in JAMA Pediatrics. That study, led by Dustin D. Flannery, DO, MSCE, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, also examined maternal and neonatal levels of IgG and IgM antibodies against the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. They also found a positive correlation between cord blood and maternal IgG concentrations (P < .001), but notably, the ratio of cord to maternal blood titers was greater than 1, unlike in Dr. Joseph’s study.
For their study, Dr. Flannery and colleagues obtained maternal and cord blood sera at the time of delivery from 1471 pairs of mothers and infants, independently of COVID status during pregnancy. The average maternal age was 32 years, and just over a quarter of the population (26%) were Black, non-Hispanic women. About half (51%) were White, 12% were Hispanic, and 7% were Asian.
About 6% of the women had either IgG or IgM antibodies at delivery, and 87% of infants born to those mothers had measurable IgG in their cord blood. No infants had IgM antibodies. As with the study presented at SMFM, the mothers’ infections included asymptomatic, mild, moderate, and severe cases, and the degree of severity of cases had no apparent effect on infant antibody concentrations. Most of the women who tested positive for COVID-19 (60%) were asymptomatic.
Among the 11 mothers who had antibodies but whose infants’ cord blood did not, 5 had only IgM antibodies, and 6 had significantly lower IgG concentrations than those seen in the other mothers.
In a commentary about the JAMA Pediatrics study, Flor Munoz, MD, of the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, suggested that the findings are grounds for optimism about a maternal vaccination strategy to protect infants from COVID-19.
“However, the timing of maternal vaccination to protect the infant, as opposed to the mother alone, would necessitate an adequate interval from vaccination to delivery (of at least 4 weeks), while vaccination early in gestation and even late in the third trimester could still be protective for the mother,” Dr. Munoz wrote.
Given the interval between two-dose vaccination regimens and the fact that transplacental transfer begins at about the 17th week of gestation, “maternal vaccination starting in the early second trimester of gestation might be optimal to achieve the highest levels of antibodies in the newborn,” Dr. Munoz wrote. But questions remain, such as how effective the neonatal antibodies would be in protecting against COVID-19 and how long they last after birth.
No external funding was used in Dr. Joseph’s study. Dr. Joseph and Dr. Louis have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The JAMA Pediatrics study was funded by the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. One coauthor received consultancy fees from Sanofi Pasteur, Lumen, Novavax, and Merck unrelated to the study. Dr. Munoz served on the data and safety monitoring boards of Moderna, Pfizer, Virometix, and Meissa Vaccines and has received grants from Novavax Research and Gilead Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 cross the placenta during pregnancy and are detectable in most newborns born to mothers who had COVID-19 during pregnancy, according to findings from a study presented Jan. 28 at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
“I think the most striking finding is that we noticed a high degree of neutralizing response to natural infection even among asymptomatic infection, but of course a higher degree was seen in those with symptomatic infection,” Naima Joseph, MD, MPH, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“Our data demonstrate maternal capacity to mount an appropriate and robust immune response,” and maternal protective immunity lasted at least 28 days after infection, Dr. Joseph said. “Also, we noted higher neonatal cord blood titers in moms with higher titers, which suggests a relationship, but we need to better understand how transplacental transfer occurs as well as establish neonatal correlates of protection in order to see if and how maternal immunity may also benefit neonates.”
The researchers analyzed the amount of IgG and IgM antibodies in maternal and cord blood samples prospectively collected at delivery from women who tested positive for COVID-19 at any time while pregnant. They used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to assess for antibodies for the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
The 32 pairs of mothers and infants in the study were predominantly non-Hispanic Black (72%) and Hispanic (25%), and 84% used Medicaid as their payer. Most of the mothers (72%) had at least one comorbidity, most commonly obesity, hypertension, and asthma or pulmonary disease. Just over half the women (53%) were symptomatic while they were infected, and 88% were ill with COVID-19 during the third trimester. The average time from infection to delivery was 28 days.
All the mothers had IgG antibodies, 94% had IgM antibodies, and 94% had neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Among the cord blood samples, 91% had IgG antibodies, 9% had IgM antibodies, and 25% had neutralizing antibodies.
“It’s reassuring that, so far, the physiological response is exactly what we expected it to be,” Judette Louis, MD, MPH, an associate professor of ob.gyn. and the ob.gyn. department chair at the University of South Florida, Tampa, said in an interview. “It’s what we would expect, but it’s always helpful to have more data to support that. Otherwise, you’re extrapolating from what you know from other conditions,” said Dr. Louis, who moderated the oral abstracts session.
Symptomatic infection was associated with significantly higher IgG titers than asymptomatic infection (P = .03), but no correlation was seen for IgM or neutralizing antibodies. In addition, although mothers who delivered more than 28 days after their infection had higher IgG titers (P = .05), no differences existed in IgM or neutralizing response.
Infants’ cord blood titers were significantly lower than their corresponding maternal samples, independently of symptoms or latency from infection to delivery (P < .001), Dr. Joseph reported.
“Transplacental efficiency in other pathogens has been shown to be correlated with neonatal immunity when the ratio of cord to maternal blood is greater than 1,” Dr. Joseph said in her presentation. Their data showed “suboptimal efficiency” at a ratio of 0.81.
The study’s small sample size and lack of a control group were weaknesses, but a major strength was having a population at disproportionately higher risk for infection and severe morbidity than the general population.
Implications for maternal COVID-19 vaccination
Although the data are not yet available, Dr. Joseph said they have expanded their protocol to include vaccinated pregnant women.
“The key to developing an effective vaccine [for pregnant people] is in really characterizing adaptive immunity in pregnancy,” Dr. Joseph told SMFM attendees. “I think that these findings inform further vaccine development in demonstrating that maternal immunity is robust.”
The World Health Organization recently recommended withholding COVID-19 vaccines from pregnant people, but the SMFM and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists subsequently issued a joint statement reaffirming that the COVID-19 vaccines authorized by the FDA “should not be withheld from pregnant individuals who choose to receive the vaccine.”
“One of the questions people ask is whether in pregnancy you’re going to mount a good response to the vaccine the way you would outside of pregnancy,” Dr. Louis said. “If we can demonstrate that you do, that may provide the information that some mothers need to make their decisions.” Data such as those from Dr. Joseph’s study can also inform recommendations on timing of maternal vaccination.
“For instance, Dr. Joseph demonstrated that, 28 days out from the infection, you had more antibodies, so there may be a scenario where we say this vaccine may be more beneficial in the middle of the pregnancy for the purpose of forming those antibodies,” Dr. Louis said.
Consensus emerging from maternal antibodies data
The findings from Dr. Joseph’s study mirror those reported in a study published online Jan. 29 in JAMA Pediatrics. That study, led by Dustin D. Flannery, DO, MSCE, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, also examined maternal and neonatal levels of IgG and IgM antibodies against the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. They also found a positive correlation between cord blood and maternal IgG concentrations (P < .001), but notably, the ratio of cord to maternal blood titers was greater than 1, unlike in Dr. Joseph’s study.
For their study, Dr. Flannery and colleagues obtained maternal and cord blood sera at the time of delivery from 1471 pairs of mothers and infants, independently of COVID status during pregnancy. The average maternal age was 32 years, and just over a quarter of the population (26%) were Black, non-Hispanic women. About half (51%) were White, 12% were Hispanic, and 7% were Asian.
About 6% of the women had either IgG or IgM antibodies at delivery, and 87% of infants born to those mothers had measurable IgG in their cord blood. No infants had IgM antibodies. As with the study presented at SMFM, the mothers’ infections included asymptomatic, mild, moderate, and severe cases, and the degree of severity of cases had no apparent effect on infant antibody concentrations. Most of the women who tested positive for COVID-19 (60%) were asymptomatic.
Among the 11 mothers who had antibodies but whose infants’ cord blood did not, 5 had only IgM antibodies, and 6 had significantly lower IgG concentrations than those seen in the other mothers.
In a commentary about the JAMA Pediatrics study, Flor Munoz, MD, of the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, suggested that the findings are grounds for optimism about a maternal vaccination strategy to protect infants from COVID-19.
“However, the timing of maternal vaccination to protect the infant, as opposed to the mother alone, would necessitate an adequate interval from vaccination to delivery (of at least 4 weeks), while vaccination early in gestation and even late in the third trimester could still be protective for the mother,” Dr. Munoz wrote.
Given the interval between two-dose vaccination regimens and the fact that transplacental transfer begins at about the 17th week of gestation, “maternal vaccination starting in the early second trimester of gestation might be optimal to achieve the highest levels of antibodies in the newborn,” Dr. Munoz wrote. But questions remain, such as how effective the neonatal antibodies would be in protecting against COVID-19 and how long they last after birth.
No external funding was used in Dr. Joseph’s study. Dr. Joseph and Dr. Louis have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The JAMA Pediatrics study was funded by the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. One coauthor received consultancy fees from Sanofi Pasteur, Lumen, Novavax, and Merck unrelated to the study. Dr. Munoz served on the data and safety monitoring boards of Moderna, Pfizer, Virometix, and Meissa Vaccines and has received grants from Novavax Research and Gilead Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 cross the placenta during pregnancy and are detectable in most newborns born to mothers who had COVID-19 during pregnancy, according to findings from a study presented Jan. 28 at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
“I think the most striking finding is that we noticed a high degree of neutralizing response to natural infection even among asymptomatic infection, but of course a higher degree was seen in those with symptomatic infection,” Naima Joseph, MD, MPH, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“Our data demonstrate maternal capacity to mount an appropriate and robust immune response,” and maternal protective immunity lasted at least 28 days after infection, Dr. Joseph said. “Also, we noted higher neonatal cord blood titers in moms with higher titers, which suggests a relationship, but we need to better understand how transplacental transfer occurs as well as establish neonatal correlates of protection in order to see if and how maternal immunity may also benefit neonates.”
The researchers analyzed the amount of IgG and IgM antibodies in maternal and cord blood samples prospectively collected at delivery from women who tested positive for COVID-19 at any time while pregnant. They used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to assess for antibodies for the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
The 32 pairs of mothers and infants in the study were predominantly non-Hispanic Black (72%) and Hispanic (25%), and 84% used Medicaid as their payer. Most of the mothers (72%) had at least one comorbidity, most commonly obesity, hypertension, and asthma or pulmonary disease. Just over half the women (53%) were symptomatic while they were infected, and 88% were ill with COVID-19 during the third trimester. The average time from infection to delivery was 28 days.
All the mothers had IgG antibodies, 94% had IgM antibodies, and 94% had neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Among the cord blood samples, 91% had IgG antibodies, 9% had IgM antibodies, and 25% had neutralizing antibodies.
“It’s reassuring that, so far, the physiological response is exactly what we expected it to be,” Judette Louis, MD, MPH, an associate professor of ob.gyn. and the ob.gyn. department chair at the University of South Florida, Tampa, said in an interview. “It’s what we would expect, but it’s always helpful to have more data to support that. Otherwise, you’re extrapolating from what you know from other conditions,” said Dr. Louis, who moderated the oral abstracts session.
Symptomatic infection was associated with significantly higher IgG titers than asymptomatic infection (P = .03), but no correlation was seen for IgM or neutralizing antibodies. In addition, although mothers who delivered more than 28 days after their infection had higher IgG titers (P = .05), no differences existed in IgM or neutralizing response.
Infants’ cord blood titers were significantly lower than their corresponding maternal samples, independently of symptoms or latency from infection to delivery (P < .001), Dr. Joseph reported.
“Transplacental efficiency in other pathogens has been shown to be correlated with neonatal immunity when the ratio of cord to maternal blood is greater than 1,” Dr. Joseph said in her presentation. Their data showed “suboptimal efficiency” at a ratio of 0.81.
The study’s small sample size and lack of a control group were weaknesses, but a major strength was having a population at disproportionately higher risk for infection and severe morbidity than the general population.
Implications for maternal COVID-19 vaccination
Although the data are not yet available, Dr. Joseph said they have expanded their protocol to include vaccinated pregnant women.
“The key to developing an effective vaccine [for pregnant people] is in really characterizing adaptive immunity in pregnancy,” Dr. Joseph told SMFM attendees. “I think that these findings inform further vaccine development in demonstrating that maternal immunity is robust.”
The World Health Organization recently recommended withholding COVID-19 vaccines from pregnant people, but the SMFM and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists subsequently issued a joint statement reaffirming that the COVID-19 vaccines authorized by the FDA “should not be withheld from pregnant individuals who choose to receive the vaccine.”
“One of the questions people ask is whether in pregnancy you’re going to mount a good response to the vaccine the way you would outside of pregnancy,” Dr. Louis said. “If we can demonstrate that you do, that may provide the information that some mothers need to make their decisions.” Data such as those from Dr. Joseph’s study can also inform recommendations on timing of maternal vaccination.
“For instance, Dr. Joseph demonstrated that, 28 days out from the infection, you had more antibodies, so there may be a scenario where we say this vaccine may be more beneficial in the middle of the pregnancy for the purpose of forming those antibodies,” Dr. Louis said.
Consensus emerging from maternal antibodies data
The findings from Dr. Joseph’s study mirror those reported in a study published online Jan. 29 in JAMA Pediatrics. That study, led by Dustin D. Flannery, DO, MSCE, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, also examined maternal and neonatal levels of IgG and IgM antibodies against the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. They also found a positive correlation between cord blood and maternal IgG concentrations (P < .001), but notably, the ratio of cord to maternal blood titers was greater than 1, unlike in Dr. Joseph’s study.
For their study, Dr. Flannery and colleagues obtained maternal and cord blood sera at the time of delivery from 1471 pairs of mothers and infants, independently of COVID status during pregnancy. The average maternal age was 32 years, and just over a quarter of the population (26%) were Black, non-Hispanic women. About half (51%) were White, 12% were Hispanic, and 7% were Asian.
About 6% of the women had either IgG or IgM antibodies at delivery, and 87% of infants born to those mothers had measurable IgG in their cord blood. No infants had IgM antibodies. As with the study presented at SMFM, the mothers’ infections included asymptomatic, mild, moderate, and severe cases, and the degree of severity of cases had no apparent effect on infant antibody concentrations. Most of the women who tested positive for COVID-19 (60%) were asymptomatic.
Among the 11 mothers who had antibodies but whose infants’ cord blood did not, 5 had only IgM antibodies, and 6 had significantly lower IgG concentrations than those seen in the other mothers.
In a commentary about the JAMA Pediatrics study, Flor Munoz, MD, of the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, suggested that the findings are grounds for optimism about a maternal vaccination strategy to protect infants from COVID-19.
“However, the timing of maternal vaccination to protect the infant, as opposed to the mother alone, would necessitate an adequate interval from vaccination to delivery (of at least 4 weeks), while vaccination early in gestation and even late in the third trimester could still be protective for the mother,” Dr. Munoz wrote.
Given the interval between two-dose vaccination regimens and the fact that transplacental transfer begins at about the 17th week of gestation, “maternal vaccination starting in the early second trimester of gestation might be optimal to achieve the highest levels of antibodies in the newborn,” Dr. Munoz wrote. But questions remain, such as how effective the neonatal antibodies would be in protecting against COVID-19 and how long they last after birth.
No external funding was used in Dr. Joseph’s study. Dr. Joseph and Dr. Louis have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The JAMA Pediatrics study was funded by the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. One coauthor received consultancy fees from Sanofi Pasteur, Lumen, Novavax, and Merck unrelated to the study. Dr. Munoz served on the data and safety monitoring boards of Moderna, Pfizer, Virometix, and Meissa Vaccines and has received grants from Novavax Research and Gilead Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Disparities in child abuse evaluation arise from implicit bias
according to research discussed by Tiffani J. Johnson, MD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine at the University of California, Davis.
“These disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting are bidirectional,” she said. “We also recognize that abuse is more likely to be unrecognized in White children.”
Dr. Johnson presented data on the health disparities in child abuse reporting in a session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. Health care disparities, as defined by the National Academy of Sciences, refers to differences in the quality of care between minority and nonminority populations that are not caused by clinical appropriateness, access, need, or patient preference, she explained. Instead, they result from discrimination, bias, stereotyping, and uncertainty.
Disparities lead to harm in all children
For example, a 2018 systematic review found that Black and other non-White children were significantly more likely than White children to be evaluated with a skeletal survey. In one of the studies included, at a large urban academic center, Black and Latinx children with accidental fractures were 8.75 times more likely to undergo a skeletal survey than White children and 4.3 times more likely to be reported to child protective services.
“And let me emphasize that these are children who were ultimately found to have accidental fractures,” Dr. Johnson said.
Meanwhile, in an analysis of known cases of head trauma, researchers found that abuse was missed in 37% of White children, compared with 19% of non-White children.
“These only represent the tip of the iceberg as a true number of cases of abuse may never really be detected because some cases are still unknown,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. And the harm of these disparities runs in both directions.
“Failing to diagnose abuse in White children clearly puts them at increased risk for return visits and return evaluations for repeated abuse by the perpetrators,” she said. But harm also can result from overreporting and investigation, including psychological trauma and a waste of limited resources. Overinvestigation also can erode family-physician relationships and perpetuate distrust of medical care in communities of color.
Yet at the same time, it’s clear that Black children, adolescents, and young adults are not protected from harm in society more generally, when at home, where they learn, or where they play, Dr. Johnson said, referencing the deaths of Breonna Taylor and Tamir Rice as examples.
“And now we’re seeing increased evidence that children are not protected in the health care center when we think about the many disparities that have been identified in the care and outcomes of children, including the disproportionality in terms of child abuse evaluation and referrals,” Dr. Johnson said.
Racism is a root cause of that harm to Black children, she said, as the systemic structure of opportunities unfairly disadvantages some individuals and communities while unfairly advantaging others, thereby “sapping the strength of the whole society through the waste of human resources.”
Tonya Chaffee, MD, MPH, a clinical professor of health sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, who attended the session, said she particularly appreciated “seeing data on which racial/ethnic populations have child abuse reports made and the disparities that exist that are similar to what we are noticing in our own institution.”
Role of individual-level implicit bias and racism
While institutional and structural racism play a substantial role in health care disparities, Dr. Johnson focused primarily on the impact of personal racism when it comes to child abuse evaluations, through overt discrimination, explicit bias, implicit bias, and stigmatization. The most challenging of these to identify and acknowledge is often implicit bias, a tendency to believe, even unconsciously, that some people or ideas are better than others, which results in unfair treatment.
For example, a 2016 study found that half of medical students and residents held at least one biological belief about differences between Black and White individuals that was actually false, such as Black people having more pain tolerance or stronger bones than White people, which then affected treatment recommendations.
“Implicit bias refers to our attitudes that lie below the surface, but they can still influence our behaviors,” Dr. Johnson explained. She encouraged providers to take the implicit bias test online to learn about their own unrecognized implicit biases. These biases have a hand in influencing decisions particularly in fast-paced environments where cognitive load is high – such as EDs, where many child abuse evaluations occur.
For example, in one study Dr. Johnson led, the researchers measured implicit bias in participants before and after an ED shift to assess how cognitive load affected bias. They found that participants who care for more than 10 patients, the average score for implicit bias increased.
Similarly, “when the ED was more overcrowded, there was also increased bias at the end of the shift, compared to the beginning of the shift,” Dr. Johnson said. She asked clinicians to take into consideration that at the start of the shift, they may feel well rested and freshly caffeinated, able to suppress or overcome the biases that they know they have.
“But our biases [are] more likely to come into play with every subsequent decision that we make throughout the day when we’re engaged in clinical encounters,” such as who does and does not receive a skeletal survey or get referred to child protective services, she said.
In another study where she hypothesized that resident physicians would have less bias on the child race implicit bias test than on the adult race one, Dr. Johnson reported that 85% of 91 residents working in an ED had an implicit pro-White/anti-Black bias in the test on adult race, but an even higher bias score – 91% – with child race.
Research has found that even children’s names can conjure implicit bias when it comes to stereotypically “White-sounding” names versus stereotypically “Black-sounding names.”
The implicit bias among clinicians extends beyond care of different children. Research has also identified association between higher implicit bias scores and less interpersonal treatment, less supportive communication, less patient-centered communication, poorer patient ratings of satisfaction, and greater patient-reported difficulty with following recommendations, Dr. Johnson said.
“I want you to think about that because I know that when we’re engaging with parents and making decisions about whether or not we’re going to do a skeletal survey or report someone for it, there is a lot of subjectivity that comes into play with how you’re interacting with families,” Dr. Johnson said. Those verbal and nonverbal cues may be triggering to parents, which then affects your interaction with them. Further, research shows that these biases may impact treatment decisions as well.
Personal-mediated racism also shows up in the use of stigmatizing language, Dr. Johnson said.
“When providers read stigmatizing language in the patient’s medical records, it was associated with them having more negative attitudes about that patient,” which then influenced their clinical decision-making, she said. “So when providers got primed with stigmatizing language, they subsequently had less aggressive pain management for those patients.”
Clinical implications for patient care
Dr. Johnson encouraged attendees to be careful about the language and tone they use in communicating with other health care providers and during documentation in medical records. Disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting tend to be greater in EDs with more subjective conditions, whereas disparities are lower in departments with more established protocols.
She recommended several changes to practice that can reduce the impact of implicit bias. Universal screening for child abuse can increase how many injuries are found, but usually at the cost of increased resources and radiation. Another option is use of validated clinical decision support rules to identify who is at high or low risk for maltreatment, something Dr. Johnson is working on in her research.
But it’s also important for individual providers to confront their personal biases. Evidence-based strategies for reducing bias include perspective taking, focusing on common identities with patients, using counter-stereotypical imaging, seeking increased opportunity for cross-cultural contact, and mindfulness meditation.
“When you interact with people of different backgrounds, it helps to reduce the impact of stereotypes in society about those individuals,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. It’s also important to recognize how diversity in your clinical team can reduce bias.
“We need to work with our institutions to confront racial biases in child abuse reporting and develop quality improvement projects to ensure reporting is done objectively,” Dr. Chaffee said in an interview after attending the session. “This will require training and likely policy changes, including how reports are made to child welfare and/or the police moving forward.”
according to research discussed by Tiffani J. Johnson, MD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine at the University of California, Davis.
“These disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting are bidirectional,” she said. “We also recognize that abuse is more likely to be unrecognized in White children.”
Dr. Johnson presented data on the health disparities in child abuse reporting in a session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. Health care disparities, as defined by the National Academy of Sciences, refers to differences in the quality of care between minority and nonminority populations that are not caused by clinical appropriateness, access, need, or patient preference, she explained. Instead, they result from discrimination, bias, stereotyping, and uncertainty.
Disparities lead to harm in all children
For example, a 2018 systematic review found that Black and other non-White children were significantly more likely than White children to be evaluated with a skeletal survey. In one of the studies included, at a large urban academic center, Black and Latinx children with accidental fractures were 8.75 times more likely to undergo a skeletal survey than White children and 4.3 times more likely to be reported to child protective services.
“And let me emphasize that these are children who were ultimately found to have accidental fractures,” Dr. Johnson said.
Meanwhile, in an analysis of known cases of head trauma, researchers found that abuse was missed in 37% of White children, compared with 19% of non-White children.
“These only represent the tip of the iceberg as a true number of cases of abuse may never really be detected because some cases are still unknown,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. And the harm of these disparities runs in both directions.
“Failing to diagnose abuse in White children clearly puts them at increased risk for return visits and return evaluations for repeated abuse by the perpetrators,” she said. But harm also can result from overreporting and investigation, including psychological trauma and a waste of limited resources. Overinvestigation also can erode family-physician relationships and perpetuate distrust of medical care in communities of color.
Yet at the same time, it’s clear that Black children, adolescents, and young adults are not protected from harm in society more generally, when at home, where they learn, or where they play, Dr. Johnson said, referencing the deaths of Breonna Taylor and Tamir Rice as examples.
“And now we’re seeing increased evidence that children are not protected in the health care center when we think about the many disparities that have been identified in the care and outcomes of children, including the disproportionality in terms of child abuse evaluation and referrals,” Dr. Johnson said.
Racism is a root cause of that harm to Black children, she said, as the systemic structure of opportunities unfairly disadvantages some individuals and communities while unfairly advantaging others, thereby “sapping the strength of the whole society through the waste of human resources.”
Tonya Chaffee, MD, MPH, a clinical professor of health sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, who attended the session, said she particularly appreciated “seeing data on which racial/ethnic populations have child abuse reports made and the disparities that exist that are similar to what we are noticing in our own institution.”
Role of individual-level implicit bias and racism
While institutional and structural racism play a substantial role in health care disparities, Dr. Johnson focused primarily on the impact of personal racism when it comes to child abuse evaluations, through overt discrimination, explicit bias, implicit bias, and stigmatization. The most challenging of these to identify and acknowledge is often implicit bias, a tendency to believe, even unconsciously, that some people or ideas are better than others, which results in unfair treatment.
For example, a 2016 study found that half of medical students and residents held at least one biological belief about differences between Black and White individuals that was actually false, such as Black people having more pain tolerance or stronger bones than White people, which then affected treatment recommendations.
“Implicit bias refers to our attitudes that lie below the surface, but they can still influence our behaviors,” Dr. Johnson explained. She encouraged providers to take the implicit bias test online to learn about their own unrecognized implicit biases. These biases have a hand in influencing decisions particularly in fast-paced environments where cognitive load is high – such as EDs, where many child abuse evaluations occur.
For example, in one study Dr. Johnson led, the researchers measured implicit bias in participants before and after an ED shift to assess how cognitive load affected bias. They found that participants who care for more than 10 patients, the average score for implicit bias increased.
Similarly, “when the ED was more overcrowded, there was also increased bias at the end of the shift, compared to the beginning of the shift,” Dr. Johnson said. She asked clinicians to take into consideration that at the start of the shift, they may feel well rested and freshly caffeinated, able to suppress or overcome the biases that they know they have.
“But our biases [are] more likely to come into play with every subsequent decision that we make throughout the day when we’re engaged in clinical encounters,” such as who does and does not receive a skeletal survey or get referred to child protective services, she said.
In another study where she hypothesized that resident physicians would have less bias on the child race implicit bias test than on the adult race one, Dr. Johnson reported that 85% of 91 residents working in an ED had an implicit pro-White/anti-Black bias in the test on adult race, but an even higher bias score – 91% – with child race.
Research has found that even children’s names can conjure implicit bias when it comes to stereotypically “White-sounding” names versus stereotypically “Black-sounding names.”
The implicit bias among clinicians extends beyond care of different children. Research has also identified association between higher implicit bias scores and less interpersonal treatment, less supportive communication, less patient-centered communication, poorer patient ratings of satisfaction, and greater patient-reported difficulty with following recommendations, Dr. Johnson said.
“I want you to think about that because I know that when we’re engaging with parents and making decisions about whether or not we’re going to do a skeletal survey or report someone for it, there is a lot of subjectivity that comes into play with how you’re interacting with families,” Dr. Johnson said. Those verbal and nonverbal cues may be triggering to parents, which then affects your interaction with them. Further, research shows that these biases may impact treatment decisions as well.
Personal-mediated racism also shows up in the use of stigmatizing language, Dr. Johnson said.
“When providers read stigmatizing language in the patient’s medical records, it was associated with them having more negative attitudes about that patient,” which then influenced their clinical decision-making, she said. “So when providers got primed with stigmatizing language, they subsequently had less aggressive pain management for those patients.”
Clinical implications for patient care
Dr. Johnson encouraged attendees to be careful about the language and tone they use in communicating with other health care providers and during documentation in medical records. Disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting tend to be greater in EDs with more subjective conditions, whereas disparities are lower in departments with more established protocols.
She recommended several changes to practice that can reduce the impact of implicit bias. Universal screening for child abuse can increase how many injuries are found, but usually at the cost of increased resources and radiation. Another option is use of validated clinical decision support rules to identify who is at high or low risk for maltreatment, something Dr. Johnson is working on in her research.
But it’s also important for individual providers to confront their personal biases. Evidence-based strategies for reducing bias include perspective taking, focusing on common identities with patients, using counter-stereotypical imaging, seeking increased opportunity for cross-cultural contact, and mindfulness meditation.
“When you interact with people of different backgrounds, it helps to reduce the impact of stereotypes in society about those individuals,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. It’s also important to recognize how diversity in your clinical team can reduce bias.
“We need to work with our institutions to confront racial biases in child abuse reporting and develop quality improvement projects to ensure reporting is done objectively,” Dr. Chaffee said in an interview after attending the session. “This will require training and likely policy changes, including how reports are made to child welfare and/or the police moving forward.”
according to research discussed by Tiffani J. Johnson, MD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine at the University of California, Davis.
“These disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting are bidirectional,” she said. “We also recognize that abuse is more likely to be unrecognized in White children.”
Dr. Johnson presented data on the health disparities in child abuse reporting in a session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. Health care disparities, as defined by the National Academy of Sciences, refers to differences in the quality of care between minority and nonminority populations that are not caused by clinical appropriateness, access, need, or patient preference, she explained. Instead, they result from discrimination, bias, stereotyping, and uncertainty.
Disparities lead to harm in all children
For example, a 2018 systematic review found that Black and other non-White children were significantly more likely than White children to be evaluated with a skeletal survey. In one of the studies included, at a large urban academic center, Black and Latinx children with accidental fractures were 8.75 times more likely to undergo a skeletal survey than White children and 4.3 times more likely to be reported to child protective services.
“And let me emphasize that these are children who were ultimately found to have accidental fractures,” Dr. Johnson said.
Meanwhile, in an analysis of known cases of head trauma, researchers found that abuse was missed in 37% of White children, compared with 19% of non-White children.
“These only represent the tip of the iceberg as a true number of cases of abuse may never really be detected because some cases are still unknown,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. And the harm of these disparities runs in both directions.
“Failing to diagnose abuse in White children clearly puts them at increased risk for return visits and return evaluations for repeated abuse by the perpetrators,” she said. But harm also can result from overreporting and investigation, including psychological trauma and a waste of limited resources. Overinvestigation also can erode family-physician relationships and perpetuate distrust of medical care in communities of color.
Yet at the same time, it’s clear that Black children, adolescents, and young adults are not protected from harm in society more generally, when at home, where they learn, or where they play, Dr. Johnson said, referencing the deaths of Breonna Taylor and Tamir Rice as examples.
“And now we’re seeing increased evidence that children are not protected in the health care center when we think about the many disparities that have been identified in the care and outcomes of children, including the disproportionality in terms of child abuse evaluation and referrals,” Dr. Johnson said.
Racism is a root cause of that harm to Black children, she said, as the systemic structure of opportunities unfairly disadvantages some individuals and communities while unfairly advantaging others, thereby “sapping the strength of the whole society through the waste of human resources.”
Tonya Chaffee, MD, MPH, a clinical professor of health sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, who attended the session, said she particularly appreciated “seeing data on which racial/ethnic populations have child abuse reports made and the disparities that exist that are similar to what we are noticing in our own institution.”
Role of individual-level implicit bias and racism
While institutional and structural racism play a substantial role in health care disparities, Dr. Johnson focused primarily on the impact of personal racism when it comes to child abuse evaluations, through overt discrimination, explicit bias, implicit bias, and stigmatization. The most challenging of these to identify and acknowledge is often implicit bias, a tendency to believe, even unconsciously, that some people or ideas are better than others, which results in unfair treatment.
For example, a 2016 study found that half of medical students and residents held at least one biological belief about differences between Black and White individuals that was actually false, such as Black people having more pain tolerance or stronger bones than White people, which then affected treatment recommendations.
“Implicit bias refers to our attitudes that lie below the surface, but they can still influence our behaviors,” Dr. Johnson explained. She encouraged providers to take the implicit bias test online to learn about their own unrecognized implicit biases. These biases have a hand in influencing decisions particularly in fast-paced environments where cognitive load is high – such as EDs, where many child abuse evaluations occur.
For example, in one study Dr. Johnson led, the researchers measured implicit bias in participants before and after an ED shift to assess how cognitive load affected bias. They found that participants who care for more than 10 patients, the average score for implicit bias increased.
Similarly, “when the ED was more overcrowded, there was also increased bias at the end of the shift, compared to the beginning of the shift,” Dr. Johnson said. She asked clinicians to take into consideration that at the start of the shift, they may feel well rested and freshly caffeinated, able to suppress or overcome the biases that they know they have.
“But our biases [are] more likely to come into play with every subsequent decision that we make throughout the day when we’re engaged in clinical encounters,” such as who does and does not receive a skeletal survey or get referred to child protective services, she said.
In another study where she hypothesized that resident physicians would have less bias on the child race implicit bias test than on the adult race one, Dr. Johnson reported that 85% of 91 residents working in an ED had an implicit pro-White/anti-Black bias in the test on adult race, but an even higher bias score – 91% – with child race.
Research has found that even children’s names can conjure implicit bias when it comes to stereotypically “White-sounding” names versus stereotypically “Black-sounding names.”
The implicit bias among clinicians extends beyond care of different children. Research has also identified association between higher implicit bias scores and less interpersonal treatment, less supportive communication, less patient-centered communication, poorer patient ratings of satisfaction, and greater patient-reported difficulty with following recommendations, Dr. Johnson said.
“I want you to think about that because I know that when we’re engaging with parents and making decisions about whether or not we’re going to do a skeletal survey or report someone for it, there is a lot of subjectivity that comes into play with how you’re interacting with families,” Dr. Johnson said. Those verbal and nonverbal cues may be triggering to parents, which then affects your interaction with them. Further, research shows that these biases may impact treatment decisions as well.
Personal-mediated racism also shows up in the use of stigmatizing language, Dr. Johnson said.
“When providers read stigmatizing language in the patient’s medical records, it was associated with them having more negative attitudes about that patient,” which then influenced their clinical decision-making, she said. “So when providers got primed with stigmatizing language, they subsequently had less aggressive pain management for those patients.”
Clinical implications for patient care
Dr. Johnson encouraged attendees to be careful about the language and tone they use in communicating with other health care providers and during documentation in medical records. Disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting tend to be greater in EDs with more subjective conditions, whereas disparities are lower in departments with more established protocols.
She recommended several changes to practice that can reduce the impact of implicit bias. Universal screening for child abuse can increase how many injuries are found, but usually at the cost of increased resources and radiation. Another option is use of validated clinical decision support rules to identify who is at high or low risk for maltreatment, something Dr. Johnson is working on in her research.
But it’s also important for individual providers to confront their personal biases. Evidence-based strategies for reducing bias include perspective taking, focusing on common identities with patients, using counter-stereotypical imaging, seeking increased opportunity for cross-cultural contact, and mindfulness meditation.
“When you interact with people of different backgrounds, it helps to reduce the impact of stereotypes in society about those individuals,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. It’s also important to recognize how diversity in your clinical team can reduce bias.
“We need to work with our institutions to confront racial biases in child abuse reporting and develop quality improvement projects to ensure reporting is done objectively,” Dr. Chaffee said in an interview after attending the session. “This will require training and likely policy changes, including how reports are made to child welfare and/or the police moving forward.”
FROM AAP 2020
LGBTQ+ youth issues include fertility counseling and foster care
Caring for LGBTQ+ pediatric patients often requires physicians to consider issues – such as preservation of fertility for transgender youth and resource allocation to sexual-minority youth in the foster-care system – that they may not think about as frequently with their other patients.
“It’s important to engage transgender and gender-diverse youth and families in fertility counseling early in their gender affirmation process,” but it does not happen as often as it should, said Jason Rafferty, MD (he/him/his), a clinical assistant professor of psychiatry and human behavior at the Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Rafferty discussed two studies at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year: one on fertility outcomes among a small transgender sample and another finding that sexual-minority youth are 2.5 times more likely to be involved in the foster-care system.
“We need to recognize and address disparities in health that place sexual-minority youth at increased risk for child welfare involvement,” he told attendees.
Fertility preservation and counseling for transgender patients
Evidence suggests gender-affirming hormone treatment affects gonadal structures and functions in ways that may decrease fertility potential, Dr. Rafferty said. “Yet, there’s very little [research] into the reversibility or thresholds above which fertility potential is affected.”
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) recommends that doctors discuss the possible adverse health effects of feminizing or masculinizing treatments and the patient’s reproductive options before starting hormone therapy, although the extent to which this therapy may impair fertility isn’t known.
The first study Dr. Rafferty discussed was an assessment of semen cryopreservation outcomes among youth asserting a female identity. The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review on a convenience sample of 11 transgender and gender-diverse adolescents and young adults who had been referred for fertility preservation between January 2015 and September 2018 at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Children’s Hospital and the UPMC Magee-Womens Hospital in Pittsburgh.
Of the 11, 1 did not provide a sample, and another discarded their sample after 4 months. The seven patients without prior gender-affirming hormone treatment (average age 19 at time of fertility consultation) were all able to produce a semen sample, which showed normal parameters, except for some abnormal morphology. The significance of that one abnormal finding was unclear without a control group, Dr. Rafferty said. All seven began gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist therapy, and four also began estradiol therapy, although Dr. Rafferty questioned why GnRH agonist therapy was started at such late ages.
Regardless, he said, the takeaway from this first group was the efficiency and effectiveness of getting a semen sample before beginning gender-affirming hormone therapy. The second group offered a different takeaway.
“What I think is probably the most unique aspect of this study is this second group of two individuals who had previously received hormones or blockers,” Dr. Rafferty told attendees. The first patient was 13 years of age at gender dysphoria onset and 18 years at the time of their fertility consultation. They had been on GnRH agonists for 6 months before semen collection. Their first sample, at 3 months after discontinuing hormones, was low-quality, but they did produce a viable sample 2 months later.
The other patient, who underwent fertility consultation at age 19, had taken estrogen and spironolactone for 26 months before semen collection and were not able to produce sperm 4 months after stopping the treatment. They did not try again because they underwent an orchiectomy.
Despite the small sample size and lack of confounding data, such as smoking and stress, the study remains the first to show successful sampling after gender-affirming hormone therapy in a teen, Dr. Rafferty said. It also shows that sampling after beginning hormone therapy may require discontinuation for several months before a successful sample is possible, thereby supporting WPATH’s recommendation for early fertility counseling.
“However, the standard of providing fertility counseling before intervention does not always occur,” Dr. Rafferty said, citing research that found low percentages of teens had received fertility counseling or discussed negative effects of therapy on fertility prior to starting it. These low numbers may result from changes in youths’ interest in fertility throughout development, but they could also relate to youths’ reluctance to discuss family planning while they feel uncomfortable in their bodies.
“My experience, and there is some empirical evidence for this, is that many transgender and gender-diverse youth feel more comfortable conceptualizing and pursuing intimate partner relationships and family planning after they start gender affirmation interventions,” Dr. Rafferty said. The stress associated with gender dysphoria can further complicate fertility discussions, and providers have to consider whether it’s more stressful to hold off on gender-affirming hormone therapy until the patient gets a successful semen sample or to start therapy and then discontinue for several months to get a sample later.
While decisions about fertility services should be fully up to the patient, in reality, multiple barriers – such as high cost, low insurance coverage, a dearth of specialists who can do the procedures, and inaccurate assumptions about transgender people’s interest in family planning – complicate the decision,.
“Systemically denying a marginalized population the ability to reproduce, or at least the ability to make a free choice about reproduction and family planning, is a reproductive justice issue that’s not getting the attention it deserves,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Clair Kronk, BSc, a session attendee from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center, said in an interview that she appreciated the session even while she lamented the lack of adequate evidence on transgender and gender-diverse care.
“I do feel like there are a lot of provider-based questions with no sufficient guidelines right now when it comes to transgender care,” Ms. Kronk said. “Despite being nearly a century old, treatment of trans patients is somehow still a ‘Wild West’ of medical care, which is sad to see.” She is grateful to see attention finally reaching this population.
“It is imperative that medical institutions focus on real, advanceable diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives which center marginalized groups,” she said. “Centering minoritized and marginalized peoples in improving care is the only way lasting change will happen.”
Sexual-minority youth in foster care
The second study Dr. Rafferty discussed was the first nationally representative systemic assessment of the prevalence of sexual-minority youth in foster care, child welfare, and out-of-home placement. Anecdotal evidence and community samples already suggest that a disproportionately higher number of sexual-minority youth enter foster care, he said, possibly resulting in part from family conflict about sexual orientation. In addition, LGBTQ+ youth already experience higher rates of psychological and physical abuse at home – a top reason for entry into child welfare – and this population has high rates of running away, particularly around the time of coming out.
Past research has found that sexual-minority youth experience higher rates of maltreatment and discrimination than do their peers from foster parents, siblings, and agency staff, which translates to fewer support services and lower levels of reunification or adoption.
In the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health involving 14,154 respondents, 6.3% reported any same-sex attraction, and 2.1% were involved in the foster-care system. The researchers determined that 4.3% of sexual-minority youth were involved in foster care, compared with just 1.9% of heterosexual youth (P = .002) – a 2.5 times greater rate – with a stronger effect among those with exclusively same-sex attraction.
In the second part of the study, the researchers looked at 1,014 youths in the foster-care system, of whom 80% had experienced an out-of-home placement. The 16% of youth in foster care reporting same sex attraction did not have a higher rate of out-of-home placement than did heterosexual youth within the system. However, there were twice as many sexual-minority youth in child welfare and four times as many in out-of-home placement, compared with their heterosexual peers, possibly suggesting that sexual-minority youth are less likely to exit the system, Dr. Rafferty said.
“Many studies have shown that family acceptance is a critical factor in building resiliency, while rejection is tied to poor physical and emotional outcomes,” he said. “It would follow that we’re identifying a critical at-risk group of sexual-minority youth lacking in fundamental and essential family support.”
This population “experiences the intersection of multiple forces of marginalization, including out-of-home placement, socioeconomic stress, sexual minority status, and likely, race,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Ms. Kronk commented during the session that fertility services and collection are extremely expensive, often forcing trans people into the absurd situation of having to choose between paying for hormone therapy or paying for fertility treatment.
“This makes a really strong argument for resource allocation based on risk” and has ramifications for the higher proportions of sexual-minority youth facing transition without adequate support services, Dr. Rafferty said.
It also suggests the need for providers to help patients feel comfortable and safe talking about their needs, Ms. Kronk said.
“Unfortunately, LGBTQIA+ health care is not taught very comprehensively in the United States [and most other countries],” she said. “Oftentimes, this leads to awkward situations where patients are more knowledgeable than their providers. Listening, learning, supporting, and being open to change are what every provider should take to heart.”
Dr. Rafferty and Ms. Kronk had no relevant financial disclosures.
Caring for LGBTQ+ pediatric patients often requires physicians to consider issues – such as preservation of fertility for transgender youth and resource allocation to sexual-minority youth in the foster-care system – that they may not think about as frequently with their other patients.
“It’s important to engage transgender and gender-diverse youth and families in fertility counseling early in their gender affirmation process,” but it does not happen as often as it should, said Jason Rafferty, MD (he/him/his), a clinical assistant professor of psychiatry and human behavior at the Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Rafferty discussed two studies at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year: one on fertility outcomes among a small transgender sample and another finding that sexual-minority youth are 2.5 times more likely to be involved in the foster-care system.
“We need to recognize and address disparities in health that place sexual-minority youth at increased risk for child welfare involvement,” he told attendees.
Fertility preservation and counseling for transgender patients
Evidence suggests gender-affirming hormone treatment affects gonadal structures and functions in ways that may decrease fertility potential, Dr. Rafferty said. “Yet, there’s very little [research] into the reversibility or thresholds above which fertility potential is affected.”
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) recommends that doctors discuss the possible adverse health effects of feminizing or masculinizing treatments and the patient’s reproductive options before starting hormone therapy, although the extent to which this therapy may impair fertility isn’t known.
The first study Dr. Rafferty discussed was an assessment of semen cryopreservation outcomes among youth asserting a female identity. The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review on a convenience sample of 11 transgender and gender-diverse adolescents and young adults who had been referred for fertility preservation between January 2015 and September 2018 at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Children’s Hospital and the UPMC Magee-Womens Hospital in Pittsburgh.
Of the 11, 1 did not provide a sample, and another discarded their sample after 4 months. The seven patients without prior gender-affirming hormone treatment (average age 19 at time of fertility consultation) were all able to produce a semen sample, which showed normal parameters, except for some abnormal morphology. The significance of that one abnormal finding was unclear without a control group, Dr. Rafferty said. All seven began gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist therapy, and four also began estradiol therapy, although Dr. Rafferty questioned why GnRH agonist therapy was started at such late ages.
Regardless, he said, the takeaway from this first group was the efficiency and effectiveness of getting a semen sample before beginning gender-affirming hormone therapy. The second group offered a different takeaway.
“What I think is probably the most unique aspect of this study is this second group of two individuals who had previously received hormones or blockers,” Dr. Rafferty told attendees. The first patient was 13 years of age at gender dysphoria onset and 18 years at the time of their fertility consultation. They had been on GnRH agonists for 6 months before semen collection. Their first sample, at 3 months after discontinuing hormones, was low-quality, but they did produce a viable sample 2 months later.
The other patient, who underwent fertility consultation at age 19, had taken estrogen and spironolactone for 26 months before semen collection and were not able to produce sperm 4 months after stopping the treatment. They did not try again because they underwent an orchiectomy.
Despite the small sample size and lack of confounding data, such as smoking and stress, the study remains the first to show successful sampling after gender-affirming hormone therapy in a teen, Dr. Rafferty said. It also shows that sampling after beginning hormone therapy may require discontinuation for several months before a successful sample is possible, thereby supporting WPATH’s recommendation for early fertility counseling.
“However, the standard of providing fertility counseling before intervention does not always occur,” Dr. Rafferty said, citing research that found low percentages of teens had received fertility counseling or discussed negative effects of therapy on fertility prior to starting it. These low numbers may result from changes in youths’ interest in fertility throughout development, but they could also relate to youths’ reluctance to discuss family planning while they feel uncomfortable in their bodies.
“My experience, and there is some empirical evidence for this, is that many transgender and gender-diverse youth feel more comfortable conceptualizing and pursuing intimate partner relationships and family planning after they start gender affirmation interventions,” Dr. Rafferty said. The stress associated with gender dysphoria can further complicate fertility discussions, and providers have to consider whether it’s more stressful to hold off on gender-affirming hormone therapy until the patient gets a successful semen sample or to start therapy and then discontinue for several months to get a sample later.
While decisions about fertility services should be fully up to the patient, in reality, multiple barriers – such as high cost, low insurance coverage, a dearth of specialists who can do the procedures, and inaccurate assumptions about transgender people’s interest in family planning – complicate the decision,.
“Systemically denying a marginalized population the ability to reproduce, or at least the ability to make a free choice about reproduction and family planning, is a reproductive justice issue that’s not getting the attention it deserves,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Clair Kronk, BSc, a session attendee from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center, said in an interview that she appreciated the session even while she lamented the lack of adequate evidence on transgender and gender-diverse care.
“I do feel like there are a lot of provider-based questions with no sufficient guidelines right now when it comes to transgender care,” Ms. Kronk said. “Despite being nearly a century old, treatment of trans patients is somehow still a ‘Wild West’ of medical care, which is sad to see.” She is grateful to see attention finally reaching this population.
“It is imperative that medical institutions focus on real, advanceable diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives which center marginalized groups,” she said. “Centering minoritized and marginalized peoples in improving care is the only way lasting change will happen.”
Sexual-minority youth in foster care
The second study Dr. Rafferty discussed was the first nationally representative systemic assessment of the prevalence of sexual-minority youth in foster care, child welfare, and out-of-home placement. Anecdotal evidence and community samples already suggest that a disproportionately higher number of sexual-minority youth enter foster care, he said, possibly resulting in part from family conflict about sexual orientation. In addition, LGBTQ+ youth already experience higher rates of psychological and physical abuse at home – a top reason for entry into child welfare – and this population has high rates of running away, particularly around the time of coming out.
Past research has found that sexual-minority youth experience higher rates of maltreatment and discrimination than do their peers from foster parents, siblings, and agency staff, which translates to fewer support services and lower levels of reunification or adoption.
In the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health involving 14,154 respondents, 6.3% reported any same-sex attraction, and 2.1% were involved in the foster-care system. The researchers determined that 4.3% of sexual-minority youth were involved in foster care, compared with just 1.9% of heterosexual youth (P = .002) – a 2.5 times greater rate – with a stronger effect among those with exclusively same-sex attraction.
In the second part of the study, the researchers looked at 1,014 youths in the foster-care system, of whom 80% had experienced an out-of-home placement. The 16% of youth in foster care reporting same sex attraction did not have a higher rate of out-of-home placement than did heterosexual youth within the system. However, there were twice as many sexual-minority youth in child welfare and four times as many in out-of-home placement, compared with their heterosexual peers, possibly suggesting that sexual-minority youth are less likely to exit the system, Dr. Rafferty said.
“Many studies have shown that family acceptance is a critical factor in building resiliency, while rejection is tied to poor physical and emotional outcomes,” he said. “It would follow that we’re identifying a critical at-risk group of sexual-minority youth lacking in fundamental and essential family support.”
This population “experiences the intersection of multiple forces of marginalization, including out-of-home placement, socioeconomic stress, sexual minority status, and likely, race,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Ms. Kronk commented during the session that fertility services and collection are extremely expensive, often forcing trans people into the absurd situation of having to choose between paying for hormone therapy or paying for fertility treatment.
“This makes a really strong argument for resource allocation based on risk” and has ramifications for the higher proportions of sexual-minority youth facing transition without adequate support services, Dr. Rafferty said.
It also suggests the need for providers to help patients feel comfortable and safe talking about their needs, Ms. Kronk said.
“Unfortunately, LGBTQIA+ health care is not taught very comprehensively in the United States [and most other countries],” she said. “Oftentimes, this leads to awkward situations where patients are more knowledgeable than their providers. Listening, learning, supporting, and being open to change are what every provider should take to heart.”
Dr. Rafferty and Ms. Kronk had no relevant financial disclosures.
Caring for LGBTQ+ pediatric patients often requires physicians to consider issues – such as preservation of fertility for transgender youth and resource allocation to sexual-minority youth in the foster-care system – that they may not think about as frequently with their other patients.
“It’s important to engage transgender and gender-diverse youth and families in fertility counseling early in their gender affirmation process,” but it does not happen as often as it should, said Jason Rafferty, MD (he/him/his), a clinical assistant professor of psychiatry and human behavior at the Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Rafferty discussed two studies at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year: one on fertility outcomes among a small transgender sample and another finding that sexual-minority youth are 2.5 times more likely to be involved in the foster-care system.
“We need to recognize and address disparities in health that place sexual-minority youth at increased risk for child welfare involvement,” he told attendees.
Fertility preservation and counseling for transgender patients
Evidence suggests gender-affirming hormone treatment affects gonadal structures and functions in ways that may decrease fertility potential, Dr. Rafferty said. “Yet, there’s very little [research] into the reversibility or thresholds above which fertility potential is affected.”
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) recommends that doctors discuss the possible adverse health effects of feminizing or masculinizing treatments and the patient’s reproductive options before starting hormone therapy, although the extent to which this therapy may impair fertility isn’t known.
The first study Dr. Rafferty discussed was an assessment of semen cryopreservation outcomes among youth asserting a female identity. The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review on a convenience sample of 11 transgender and gender-diverse adolescents and young adults who had been referred for fertility preservation between January 2015 and September 2018 at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Children’s Hospital and the UPMC Magee-Womens Hospital in Pittsburgh.
Of the 11, 1 did not provide a sample, and another discarded their sample after 4 months. The seven patients without prior gender-affirming hormone treatment (average age 19 at time of fertility consultation) were all able to produce a semen sample, which showed normal parameters, except for some abnormal morphology. The significance of that one abnormal finding was unclear without a control group, Dr. Rafferty said. All seven began gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist therapy, and four also began estradiol therapy, although Dr. Rafferty questioned why GnRH agonist therapy was started at such late ages.
Regardless, he said, the takeaway from this first group was the efficiency and effectiveness of getting a semen sample before beginning gender-affirming hormone therapy. The second group offered a different takeaway.
“What I think is probably the most unique aspect of this study is this second group of two individuals who had previously received hormones or blockers,” Dr. Rafferty told attendees. The first patient was 13 years of age at gender dysphoria onset and 18 years at the time of their fertility consultation. They had been on GnRH agonists for 6 months before semen collection. Their first sample, at 3 months after discontinuing hormones, was low-quality, but they did produce a viable sample 2 months later.
The other patient, who underwent fertility consultation at age 19, had taken estrogen and spironolactone for 26 months before semen collection and were not able to produce sperm 4 months after stopping the treatment. They did not try again because they underwent an orchiectomy.
Despite the small sample size and lack of confounding data, such as smoking and stress, the study remains the first to show successful sampling after gender-affirming hormone therapy in a teen, Dr. Rafferty said. It also shows that sampling after beginning hormone therapy may require discontinuation for several months before a successful sample is possible, thereby supporting WPATH’s recommendation for early fertility counseling.
“However, the standard of providing fertility counseling before intervention does not always occur,” Dr. Rafferty said, citing research that found low percentages of teens had received fertility counseling or discussed negative effects of therapy on fertility prior to starting it. These low numbers may result from changes in youths’ interest in fertility throughout development, but they could also relate to youths’ reluctance to discuss family planning while they feel uncomfortable in their bodies.
“My experience, and there is some empirical evidence for this, is that many transgender and gender-diverse youth feel more comfortable conceptualizing and pursuing intimate partner relationships and family planning after they start gender affirmation interventions,” Dr. Rafferty said. The stress associated with gender dysphoria can further complicate fertility discussions, and providers have to consider whether it’s more stressful to hold off on gender-affirming hormone therapy until the patient gets a successful semen sample or to start therapy and then discontinue for several months to get a sample later.
While decisions about fertility services should be fully up to the patient, in reality, multiple barriers – such as high cost, low insurance coverage, a dearth of specialists who can do the procedures, and inaccurate assumptions about transgender people’s interest in family planning – complicate the decision,.
“Systemically denying a marginalized population the ability to reproduce, or at least the ability to make a free choice about reproduction and family planning, is a reproductive justice issue that’s not getting the attention it deserves,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Clair Kronk, BSc, a session attendee from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center, said in an interview that she appreciated the session even while she lamented the lack of adequate evidence on transgender and gender-diverse care.
“I do feel like there are a lot of provider-based questions with no sufficient guidelines right now when it comes to transgender care,” Ms. Kronk said. “Despite being nearly a century old, treatment of trans patients is somehow still a ‘Wild West’ of medical care, which is sad to see.” She is grateful to see attention finally reaching this population.
“It is imperative that medical institutions focus on real, advanceable diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives which center marginalized groups,” she said. “Centering minoritized and marginalized peoples in improving care is the only way lasting change will happen.”
Sexual-minority youth in foster care
The second study Dr. Rafferty discussed was the first nationally representative systemic assessment of the prevalence of sexual-minority youth in foster care, child welfare, and out-of-home placement. Anecdotal evidence and community samples already suggest that a disproportionately higher number of sexual-minority youth enter foster care, he said, possibly resulting in part from family conflict about sexual orientation. In addition, LGBTQ+ youth already experience higher rates of psychological and physical abuse at home – a top reason for entry into child welfare – and this population has high rates of running away, particularly around the time of coming out.
Past research has found that sexual-minority youth experience higher rates of maltreatment and discrimination than do their peers from foster parents, siblings, and agency staff, which translates to fewer support services and lower levels of reunification or adoption.
In the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health involving 14,154 respondents, 6.3% reported any same-sex attraction, and 2.1% were involved in the foster-care system. The researchers determined that 4.3% of sexual-minority youth were involved in foster care, compared with just 1.9% of heterosexual youth (P = .002) – a 2.5 times greater rate – with a stronger effect among those with exclusively same-sex attraction.
In the second part of the study, the researchers looked at 1,014 youths in the foster-care system, of whom 80% had experienced an out-of-home placement. The 16% of youth in foster care reporting same sex attraction did not have a higher rate of out-of-home placement than did heterosexual youth within the system. However, there were twice as many sexual-minority youth in child welfare and four times as many in out-of-home placement, compared with their heterosexual peers, possibly suggesting that sexual-minority youth are less likely to exit the system, Dr. Rafferty said.
“Many studies have shown that family acceptance is a critical factor in building resiliency, while rejection is tied to poor physical and emotional outcomes,” he said. “It would follow that we’re identifying a critical at-risk group of sexual-minority youth lacking in fundamental and essential family support.”
This population “experiences the intersection of multiple forces of marginalization, including out-of-home placement, socioeconomic stress, sexual minority status, and likely, race,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Ms. Kronk commented during the session that fertility services and collection are extremely expensive, often forcing trans people into the absurd situation of having to choose between paying for hormone therapy or paying for fertility treatment.
“This makes a really strong argument for resource allocation based on risk” and has ramifications for the higher proportions of sexual-minority youth facing transition without adequate support services, Dr. Rafferty said.
It also suggests the need for providers to help patients feel comfortable and safe talking about their needs, Ms. Kronk said.
“Unfortunately, LGBTQIA+ health care is not taught very comprehensively in the United States [and most other countries],” she said. “Oftentimes, this leads to awkward situations where patients are more knowledgeable than their providers. Listening, learning, supporting, and being open to change are what every provider should take to heart.”
Dr. Rafferty and Ms. Kronk had no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AAP 2020
Understanding and addressing suicide risk in LGBTQ+ youth
Even as dozens of state legislature bills attempt to limit the rights of sexual-diverse and gender-diverse youth, researchers are learning more and more that can help pediatricians better support this population in their practices, according to David Inwards-Breland, MD, MPH, a professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
Dr. Inwards-Breland highlighted two key studies in recent years during the LGBTQ+ section at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually in 2020.
High suicide rates among sexual minority youth
Past research has found that adolescents who identify as sexual minorities have nearly five times the rate of suicide attempts, compared with their heterosexual peers, Dr. Inwards-Breland said as he introduced a recent study on disparities in adolescent suicide.
“This may be from a disproportionate burden of poor mental health that has been linked to stigma,” he said, adding that an estimated 125 state bills have been introduced in the United States that would restrict the rights of sexual minorities.
The study, published in Pediatrics in March 2020, compiled data from 110,243 adolescents in six states on sexual orientation identity; 25,994 adolescents in four states on same-sex sexual contact and sexual assault; and 20,655 adolescents in three states on sexual orientation identity, the sex of sexual contacts, and sexual assault.
The authors found that heterosexual identity dropped from 93% to 86% between 2009 and 2017, but sexual minority youth accounted for an increasing share of suicide attempts over the same period. A quarter of adolescents who attempted suicide in 2009 were sexual minorities, which increased to 36% in 2017. Similarly, among sexually active teens who attempted suicide, the proportion of those who had same-sex contact nearly doubled, from 16% to 30%.
The good news, Dr. Inwards-Breland said, was that overall suicide attempts declined among sexual minorities, but they remain three times as likely to attempt suicide, compared with their heterosexual counterparts.
“As the number of adolescents increase in our country, there will be increasing numbers of adolescents identifying as sexual minorities or who have had same-sex sexual contact,” Dr. Inwards-Breland said. “Therefore, providing confidential services is even more important to allow youth to feel comfortable with their health care provider.” He also emphasized the importance of consistent universal depression screening and advocacy to eliminate and prevent policies that harm these youth.
Using youths’ chosen names
Transgender and nonbinary youth – those who do not identify as male or female – have a higher risk of poor mental health and higher levels of suicidal ideation and behaviors, compared with their “cis” peers, those who identify with the gender they were assigned at birth, Dr. Inwards-Breland said. However, using the chosen, or assertive, name of transgender and nonbinary youth predicted fewer depressive symptoms and less suicidal ideation and behavior in a study published in the Journal of Adolescent Health in October 2018.
“Choosing a name is an important part of social transition of transgender individuals, yet they’re unable to use their name because of interpersonal or institutional barriers,” he said. In addition, using a name other than their legally given name can subject them to discrimination and victimization.
The study, drawing from a larger cohort of LGBTQ youth, involved 129 transgender and nonbinary adolescents, aged 15-21, of whom 74 had a chosen name. No other differences in personal characteristics were associated with depressive symptoms or suicidal ideation besides increased use of their assertive name in different life contexts.
An increase in one context where chosen name could be used predicted a 5.37-unit decrease in depressive symptoms, a 29% decrease in suicidal ideation, and a 56% decrease in suicidal behavior, the study found. All three outcomes were at their lowest levels when chosen names were used in all four contexts explored in the study.
“The chosen name affirms their gender identity,” Dr. Inwards-Breland said, but “the legal name change process is very onerous.” He highlighted the need for institutions to adjust regulations and information systems, for policies that promote the transition process, and for youths’ names to be affirmed in multiple contexts.
“We as pediatricians, specialists, and primary care doctors can support families as they adjust the transition process by helping them with assertive names and pronouns and giving them resources,” Dr. Inwards-Breland said. He also called for school policies and teacher/staff training that promote the use of assertive names and pronouns, and ensuring that the assertive name and pronouns are in the medical record and used by office staff and other medical professionals.
‘A light in the dark’ for LGBTQ+ youth
Clair Kronk of the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center attended the LGBTQ+ section at the AAP meeting because of concerns about she and her transgender siblings have been treated by the medical community.
“It has always been important to be ‘on the pulse’ of what is happening in the medical community, especially with new, more discriminatory policies being passed seemingly willy-nilly these days, both in the medical realm and outside of it,” Ms. Kronk said in an interview. “I was overjoyed to see how many people seemed to care so much about the transgender community and LGBTQIA+ people generally.”
As an ontologist and bioinformatician, she did not recall many big clinical takeaways for her particular work, but she appreciated how many areas the session covered, especially given the dearth of instruction about LGBTQ+ care in medical training.
“This session was a bit of a light in the dark given the state of LGBTQIA+ health care rights,” she said. “There is a lot at stake in the next year or so, and providers’ and LGBTQIA+ persons’ voices need to be heard right now more than ever.”
Sonia Khan, MD, a pediatrician and the medical director of the substance use disorder counseling program in the department of health and human services in Fremont, Calif., also attended the session and came away feeling invigorated.
“These data make me feel more optimistic than I have been in ages in terms of increasing the safety of young people being able to come out,” Dr. Khan said in the comments during the session. “These last 4 years felt so regressive. [It’s] good to get the big picture.”
The presenters and commentators had no disclosures.
Even as dozens of state legislature bills attempt to limit the rights of sexual-diverse and gender-diverse youth, researchers are learning more and more that can help pediatricians better support this population in their practices, according to David Inwards-Breland, MD, MPH, a professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
Dr. Inwards-Breland highlighted two key studies in recent years during the LGBTQ+ section at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually in 2020.
High suicide rates among sexual minority youth
Past research has found that adolescents who identify as sexual minorities have nearly five times the rate of suicide attempts, compared with their heterosexual peers, Dr. Inwards-Breland said as he introduced a recent study on disparities in adolescent suicide.
“This may be from a disproportionate burden of poor mental health that has been linked to stigma,” he said, adding that an estimated 125 state bills have been introduced in the United States that would restrict the rights of sexual minorities.
The study, published in Pediatrics in March 2020, compiled data from 110,243 adolescents in six states on sexual orientation identity; 25,994 adolescents in four states on same-sex sexual contact and sexual assault; and 20,655 adolescents in three states on sexual orientation identity, the sex of sexual contacts, and sexual assault.
The authors found that heterosexual identity dropped from 93% to 86% between 2009 and 2017, but sexual minority youth accounted for an increasing share of suicide attempts over the same period. A quarter of adolescents who attempted suicide in 2009 were sexual minorities, which increased to 36% in 2017. Similarly, among sexually active teens who attempted suicide, the proportion of those who had same-sex contact nearly doubled, from 16% to 30%.
The good news, Dr. Inwards-Breland said, was that overall suicide attempts declined among sexual minorities, but they remain three times as likely to attempt suicide, compared with their heterosexual counterparts.
“As the number of adolescents increase in our country, there will be increasing numbers of adolescents identifying as sexual minorities or who have had same-sex sexual contact,” Dr. Inwards-Breland said. “Therefore, providing confidential services is even more important to allow youth to feel comfortable with their health care provider.” He also emphasized the importance of consistent universal depression screening and advocacy to eliminate and prevent policies that harm these youth.
Using youths’ chosen names
Transgender and nonbinary youth – those who do not identify as male or female – have a higher risk of poor mental health and higher levels of suicidal ideation and behaviors, compared with their “cis” peers, those who identify with the gender they were assigned at birth, Dr. Inwards-Breland said. However, using the chosen, or assertive, name of transgender and nonbinary youth predicted fewer depressive symptoms and less suicidal ideation and behavior in a study published in the Journal of Adolescent Health in October 2018.
“Choosing a name is an important part of social transition of transgender individuals, yet they’re unable to use their name because of interpersonal or institutional barriers,” he said. In addition, using a name other than their legally given name can subject them to discrimination and victimization.
The study, drawing from a larger cohort of LGBTQ youth, involved 129 transgender and nonbinary adolescents, aged 15-21, of whom 74 had a chosen name. No other differences in personal characteristics were associated with depressive symptoms or suicidal ideation besides increased use of their assertive name in different life contexts.
An increase in one context where chosen name could be used predicted a 5.37-unit decrease in depressive symptoms, a 29% decrease in suicidal ideation, and a 56% decrease in suicidal behavior, the study found. All three outcomes were at their lowest levels when chosen names were used in all four contexts explored in the study.
“The chosen name affirms their gender identity,” Dr. Inwards-Breland said, but “the legal name change process is very onerous.” He highlighted the need for institutions to adjust regulations and information systems, for policies that promote the transition process, and for youths’ names to be affirmed in multiple contexts.
“We as pediatricians, specialists, and primary care doctors can support families as they adjust the transition process by helping them with assertive names and pronouns and giving them resources,” Dr. Inwards-Breland said. He also called for school policies and teacher/staff training that promote the use of assertive names and pronouns, and ensuring that the assertive name and pronouns are in the medical record and used by office staff and other medical professionals.
‘A light in the dark’ for LGBTQ+ youth
Clair Kronk of the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center attended the LGBTQ+ section at the AAP meeting because of concerns about she and her transgender siblings have been treated by the medical community.
“It has always been important to be ‘on the pulse’ of what is happening in the medical community, especially with new, more discriminatory policies being passed seemingly willy-nilly these days, both in the medical realm and outside of it,” Ms. Kronk said in an interview. “I was overjoyed to see how many people seemed to care so much about the transgender community and LGBTQIA+ people generally.”
As an ontologist and bioinformatician, she did not recall many big clinical takeaways for her particular work, but she appreciated how many areas the session covered, especially given the dearth of instruction about LGBTQ+ care in medical training.
“This session was a bit of a light in the dark given the state of LGBTQIA+ health care rights,” she said. “There is a lot at stake in the next year or so, and providers’ and LGBTQIA+ persons’ voices need to be heard right now more than ever.”
Sonia Khan, MD, a pediatrician and the medical director of the substance use disorder counseling program in the department of health and human services in Fremont, Calif., also attended the session and came away feeling invigorated.
“These data make me feel more optimistic than I have been in ages in terms of increasing the safety of young people being able to come out,” Dr. Khan said in the comments during the session. “These last 4 years felt so regressive. [It’s] good to get the big picture.”
The presenters and commentators had no disclosures.
Even as dozens of state legislature bills attempt to limit the rights of sexual-diverse and gender-diverse youth, researchers are learning more and more that can help pediatricians better support this population in their practices, according to David Inwards-Breland, MD, MPH, a professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
Dr. Inwards-Breland highlighted two key studies in recent years during the LGBTQ+ section at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually in 2020.
High suicide rates among sexual minority youth
Past research has found that adolescents who identify as sexual minorities have nearly five times the rate of suicide attempts, compared with their heterosexual peers, Dr. Inwards-Breland said as he introduced a recent study on disparities in adolescent suicide.
“This may be from a disproportionate burden of poor mental health that has been linked to stigma,” he said, adding that an estimated 125 state bills have been introduced in the United States that would restrict the rights of sexual minorities.
The study, published in Pediatrics in March 2020, compiled data from 110,243 adolescents in six states on sexual orientation identity; 25,994 adolescents in four states on same-sex sexual contact and sexual assault; and 20,655 adolescents in three states on sexual orientation identity, the sex of sexual contacts, and sexual assault.
The authors found that heterosexual identity dropped from 93% to 86% between 2009 and 2017, but sexual minority youth accounted for an increasing share of suicide attempts over the same period. A quarter of adolescents who attempted suicide in 2009 were sexual minorities, which increased to 36% in 2017. Similarly, among sexually active teens who attempted suicide, the proportion of those who had same-sex contact nearly doubled, from 16% to 30%.
The good news, Dr. Inwards-Breland said, was that overall suicide attempts declined among sexual minorities, but they remain three times as likely to attempt suicide, compared with their heterosexual counterparts.
“As the number of adolescents increase in our country, there will be increasing numbers of adolescents identifying as sexual minorities or who have had same-sex sexual contact,” Dr. Inwards-Breland said. “Therefore, providing confidential services is even more important to allow youth to feel comfortable with their health care provider.” He also emphasized the importance of consistent universal depression screening and advocacy to eliminate and prevent policies that harm these youth.
Using youths’ chosen names
Transgender and nonbinary youth – those who do not identify as male or female – have a higher risk of poor mental health and higher levels of suicidal ideation and behaviors, compared with their “cis” peers, those who identify with the gender they were assigned at birth, Dr. Inwards-Breland said. However, using the chosen, or assertive, name of transgender and nonbinary youth predicted fewer depressive symptoms and less suicidal ideation and behavior in a study published in the Journal of Adolescent Health in October 2018.
“Choosing a name is an important part of social transition of transgender individuals, yet they’re unable to use their name because of interpersonal or institutional barriers,” he said. In addition, using a name other than their legally given name can subject them to discrimination and victimization.
The study, drawing from a larger cohort of LGBTQ youth, involved 129 transgender and nonbinary adolescents, aged 15-21, of whom 74 had a chosen name. No other differences in personal characteristics were associated with depressive symptoms or suicidal ideation besides increased use of their assertive name in different life contexts.
An increase in one context where chosen name could be used predicted a 5.37-unit decrease in depressive symptoms, a 29% decrease in suicidal ideation, and a 56% decrease in suicidal behavior, the study found. All three outcomes were at their lowest levels when chosen names were used in all four contexts explored in the study.
“The chosen name affirms their gender identity,” Dr. Inwards-Breland said, but “the legal name change process is very onerous.” He highlighted the need for institutions to adjust regulations and information systems, for policies that promote the transition process, and for youths’ names to be affirmed in multiple contexts.
“We as pediatricians, specialists, and primary care doctors can support families as they adjust the transition process by helping them with assertive names and pronouns and giving them resources,” Dr. Inwards-Breland said. He also called for school policies and teacher/staff training that promote the use of assertive names and pronouns, and ensuring that the assertive name and pronouns are in the medical record and used by office staff and other medical professionals.
‘A light in the dark’ for LGBTQ+ youth
Clair Kronk of the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center attended the LGBTQ+ section at the AAP meeting because of concerns about she and her transgender siblings have been treated by the medical community.
“It has always been important to be ‘on the pulse’ of what is happening in the medical community, especially with new, more discriminatory policies being passed seemingly willy-nilly these days, both in the medical realm and outside of it,” Ms. Kronk said in an interview. “I was overjoyed to see how many people seemed to care so much about the transgender community and LGBTQIA+ people generally.”
As an ontologist and bioinformatician, she did not recall many big clinical takeaways for her particular work, but she appreciated how many areas the session covered, especially given the dearth of instruction about LGBTQ+ care in medical training.
“This session was a bit of a light in the dark given the state of LGBTQIA+ health care rights,” she said. “There is a lot at stake in the next year or so, and providers’ and LGBTQIA+ persons’ voices need to be heard right now more than ever.”
Sonia Khan, MD, a pediatrician and the medical director of the substance use disorder counseling program in the department of health and human services in Fremont, Calif., also attended the session and came away feeling invigorated.
“These data make me feel more optimistic than I have been in ages in terms of increasing the safety of young people being able to come out,” Dr. Khan said in the comments during the session. “These last 4 years felt so regressive. [It’s] good to get the big picture.”
The presenters and commentators had no disclosures.
FROM AAP 2020
Watch for cognitive traps that lead diagnostics astray
While it’s important not to think immediately of zebras when hearing hoofbeats, it’s just as important not to assume it’s always a horse. The delicate balance between not jumping to the seemingly obvious diagnosis without overanalyzing and overtesting is familiar to all physicians, and
“When these errors are made, it’s not because physicians lack knowledge, but they go down a wrong path in their thinking process,” Richard Scarfone, MD, a pediatric emergency medicine physician at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, told attendees at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. “An important point to be made here is that how physicians think seems to be much more important than what physicians know.”
Dr. Scarfone and Joshua Nagler, MD, MHPEd, director, pediatric emergency medicine fellowship program at Children’s Hospital Boston, presented a session on the cognitive biases that can trip up clinicians when making diagnoses and how to avoid them. Research shows that the rate of diagnostic error is approximately 15%. Although those findings come from studies in adults, the rates are likely similar in pediatrics, Dr. Scarfone said.
A wide range of clinical factors contribute to diagnostic errors: limited information, vague or undifferentiated symptoms, incomplete history, multiple transitions of care, diagnostic uncertainty, daily decision density, and reliance on pattern recognition, among others. Personal contributing factors can play a role as well, such as atypical work hours, fatigue, one’s emotional or affective state, a high cognitive load, and others. On top of all that, medical decision-making can be really complex on its own, Dr. Scarfone said. He compared differential diagnosis with a tree where a single leaf is the correct diagnosis.
System 1 thinking: Pros and cons
Dr. Scarfone and Dr. Nagler explained system 1 and system 2 thinking, two different ways of thinking that can influence decision-making that Daniel Kahneman explained in his book “Thinking, Fast and Slow.” System 1 refers to the snap judgments that rely on heuristics while system 2 refers to a more analytic, slower process.
Neither system 1 nor 2 is inherently “right or wrong,” Dr. Scarfone said. “The diagnostic sweet spot is to try to apply the correct system to the correct patient.”
Heuristics are the mental shortcuts people use to make decisions based on past experience. They exist because they’re useful, enabling people to focus only on what they need to accomplish everyday tasks, such as driving or brushing teeth. But heuristics can also lead to predictable cognitive errors.
“The good news about heuristics and system 1 thinking is that it’s efficient and simple, and we desire that in a busy practice or ED setting, but we should recognize that the trade-off is that it may be at the expense of accuracy,” Dr. Scarfone said.
The advantage to system 1 thinking is easy, simple, rapid, and efficient decision-making that rejects ambiguity. It’s also usually accurate, which rewards the approach, and accuracy increases with time based on memory, experience, and pattern recognition. Doctors develop “illness scripts” that help in identifying diagnoses.
“Illness scripts are common patterns of clinical presentations that usually lead us to a diagnostic possibility,” Dr. Scarfone said. “A classic illness script might be a 4-week-old firstborn male with forceful vomiting, and immediately your mind may go to pyloric stenosis as a likely diagnosis.” But the patient may have a different diagnosis than the initial impression your system 1 thinking leads you to believe.
“Generally, the more experience a clinician has, the more accurate they’ll be in using system 1,” he said. “Seasoned physicians are much more likely to employ system 1 than a newer physician or trainee,” which is why heuristics shouldn’t be thought of as hindrances. Dr. Scarfone quoted Kevin Eva in a 2005 review on clinical reasoning: “Successful heuristics should be embraced rather than overcome.”
A drawback to system 1 thinking, however, is thinking that “what you see is all there is,” which can lead to cognitive errors. Feeling wrong feels the same as feeling right, so you may not realize when you’re off target and therefore neglect to consider alternatives.
“When we learn a little about our patient’s complaint, it’s easier to fit everything into a coherent explanation,” Dr. Scarfone said, but “don’t ask, don’t tell doesn’t work in medicine.”
Another challenge with system 1 thinking is that pattern recognition can be unreliable because it’s dependent on context. For example, consider the difference in assessing a patient’s sore throat in a primary care office versus a resuscitation bay. “Clearly our consideration of what may be going on with the patient and what the diagnosis may be is likely to vary in those two settings,” he said.
System 2 thinking: Of zebras and horses
System 2 is the analytic thinking that involves pondering and seek out the optimal answer rather than the “good-enough” answer.
“The good news about system 2 is that it really can monitor system 1,” said Dr. Nagler, who has a master’s degree in health professions education. “If you spend the time to do analytic reasoning, you can actually mitigate some of those errors that may occur from intuitive judgments from system 1 thinking. System 2 spends the time to say ‘let’s make sure we’re doing this right.’ ” In multiple-choice tests, for example, people are twice as likely to change a wrong answer to a right one than a right one to a wrong one.
System 2 thinking allows for the reasoning to assess questions in the gray zone. It’s vigilant, it’s reliable, it’s effective, it acknowledges uncertainty and doubt, it can be safe in terms of providing care, and it has high scientific rigor. But it also has disadvantages, starting with the fact that it’s slower and more time-consuming. System 2 thinking is resource intensive, requiring a higher cognitive demand and more time and effort.
“Sometimes the quick judgment is the best judgment,” Dr. Nagler said. System 2 thinking also is sometimes unnecessary and counter to value-based care. “If you start to think about all the possibilities of what a presentation may be, all of a sudden you might find yourself wanting to do all kinds of tests and all kinds of referrals and other things, which is not necessarily value-based care.” When system 2 thinking goes astray, it makes us think everything we see is a zebra rather than a horse.
Sonia Khan, MD, a pediatrician in Fremont, Calif., found this session particularly worthwhile.
“It really tries to explain the difference between leaping to conclusions and learning how to hold your horses and do a bit more, to double check that you’re not locking everything into a horse stall and missing a zebra, and avoiding go too far with system 2 and thinking that everything’s a zebra,” Dr. Khan said. “It’s a difficult talk to have because you’re asking pediatricians to look in the mirror and own up, to learn to step back and reconsider the picture, and consider the biases that may come into your decision-making; then learn to extrude them, and rethink the case to be sure your knee-jerk diagnostic response is correct.”
Types of cognitive errors
The presenters listed some of the most common cognitive errors, although their list is far from exhaustive.
- Affective error. Avoiding unpleasant but necessary tests or examinations because of sympathy for the patient, such as avoiding blood work to spare a needle stick in a cancer patient with abdominal pain because the mother is convinced it’s constipation from opioids. This is similar to omission bias, which places excessive concern on avoiding a therapy’s adverse effects when the therapy could be highly effective.
- Anchoring. Clinging to an initial impression or salient features of initial presentation, even as conflicting and contradictory data accumulate, such as diagnosing a patient with fever and vomiting with gastroenteritis even when the patient has an oxygen saturation of 94% and tachypnea.
- Attribution errors. Negative stereotypes lead clinicians to ignore or minimize the possibility of serious disease, such as evaluating a confused teen covered in piercings and tattoos for drug ingestion when the actual diagnosis is new-onset diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Availability bias. Overestimating or underestimating the probability of disease because of recent experience, what was most recently “available” to your brain cognitively, such as getting head imaging on several vomiting patients in a row because you recently had one with a new brain tumor diagnosis.
- Bandwagon effect. Accepting the group’s opinion without assessing a clinical situation yourself, such as sending home a crying, vomiting infant with a presumed viral infection only to see the infant return later with intussusception.
- Base rate neglect. Ignoring the true prevalence of disease by either inflating it or reducing it, such as searching for cardiac disease in all pediatric patients with chest pain.
- Commission. A tendency toward action with the belief that harm may only be prevented by action, such as ordering every possible test for a patient with fever to “rule everything out.”
- Confirmation bias. Subconscious cherry-picking: A tendency to look for, notice, and remember information that fits with preexisting expectations while disregarding information that contradicts those expectations.
- Diagnostic momentum. Clinging to that initial diagnostic impression that may have been generated by others, which is particularly common during transitions of care.
- Premature closure. Narrowing down to a diagnosis without thinking about other diagnoses or asking enough questions about other symptoms that may have opened up other diagnostic possibilities.
- Representation bias. Making a decision in the absence of appropriate context by incorrectly comparing two situations because of a perceived similarity between them, or on the flip side, evaluating a situation without comparing it with other situations.
- Overconfidence. Making a decision without enough supportive evidence yet feeling confident about the diagnosis.
- Search satisfying. Stopping the search for additional diagnoses after the anticipated diagnosis has been made.
Cognitive pills for cognitive ills
Being aware of the pitfalls of cognitive errors is the first step to avoiding and mitigating them. “It really does start with preparation and awareness,” Dr. Scarfone said before presenting strategies to build a cognitive “firewall” that can help physicians practice reflectively instead of reflexively.
First, be aware of your cognitive style. People usually have the same thinking pattern in everyday life as in the clinical setting, so determine whether you’re more of a system 1 or system 2 thinker. System 1 thinkers need to watch out for framing (relying too heavily on context), premature closure, diagnostic momentum, anchoring, and confirmation bias. System 2 thinkers need to watch out for commission, availability bias, and base rate neglect.
“Neither system is inherently right or wrong,” Dr. Scarfone reiterated. “In the perfect world, you may use system 1 to form an initial impression, but then system 2 should really act as a check and balance system to cause you to reflect on your initial diagnostic impressions.”
Additional strategies include being a good history taker and performing a meticulous physical exam: be a good listener, clarify unclear aspects of the history, and identify and address the main concern.
“Remember children and families have a story to tell, and if we listen carefully enough, the diagnostic clues are there,” Dr. Scarfone said. “Sometimes they may be quite subtle.” He recommended doctors perform each part of the physical exam as if expecting an abnormality.
Another strategy is using meta-cognition, a forced analysis of the thinking that led to a diagnosis. It involves asking: “If I had to explain my medical decision-making to others, would this make inherent sense?” Dr. Scarfone said. “If you’re testing, try to avoid anchoring and confirmation biases.”
Finally, take a diagnostic time-out with a checklist that asks these questions:
- Does my presumptive diagnosis make sense?
- What evidence supports or refutes it?
- Did I arrive at it via cognitive biases?
- Are there other diagnostic possibilities that should be considered?
One way to do this is creating a table listing the complaint/finding, diagnostic possibilities with system 1 thinking, diagnostic possibilities with system 2 thinking, and then going beyond system 2 – the potential zebras – when even system 2 diagnostic possibilities don’t account for what the patient is saying or what the exam shows.
Enough overlap exists between these cognitive biases and the intrinsic bias related to individual characteristics that Dr. Khan appreciated the talk on another level as well.
“For me, as a brown Muslim immigrant woman of color, I can sometimes see cognitive biases in action with my colleagues and realize that they are oblivious to it,” Dr. Khan said. “It’s really refreshing to see this issue come up and being discussed at the [AAP] National Conference and Exhibition.”
Dr. Scarfone, Dr. Nagler and Dr. Khan have no relevant financial disclosures.
This article was updated 12/8/2020.
While it’s important not to think immediately of zebras when hearing hoofbeats, it’s just as important not to assume it’s always a horse. The delicate balance between not jumping to the seemingly obvious diagnosis without overanalyzing and overtesting is familiar to all physicians, and
“When these errors are made, it’s not because physicians lack knowledge, but they go down a wrong path in their thinking process,” Richard Scarfone, MD, a pediatric emergency medicine physician at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, told attendees at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. “An important point to be made here is that how physicians think seems to be much more important than what physicians know.”
Dr. Scarfone and Joshua Nagler, MD, MHPEd, director, pediatric emergency medicine fellowship program at Children’s Hospital Boston, presented a session on the cognitive biases that can trip up clinicians when making diagnoses and how to avoid them. Research shows that the rate of diagnostic error is approximately 15%. Although those findings come from studies in adults, the rates are likely similar in pediatrics, Dr. Scarfone said.
A wide range of clinical factors contribute to diagnostic errors: limited information, vague or undifferentiated symptoms, incomplete history, multiple transitions of care, diagnostic uncertainty, daily decision density, and reliance on pattern recognition, among others. Personal contributing factors can play a role as well, such as atypical work hours, fatigue, one’s emotional or affective state, a high cognitive load, and others. On top of all that, medical decision-making can be really complex on its own, Dr. Scarfone said. He compared differential diagnosis with a tree where a single leaf is the correct diagnosis.
System 1 thinking: Pros and cons
Dr. Scarfone and Dr. Nagler explained system 1 and system 2 thinking, two different ways of thinking that can influence decision-making that Daniel Kahneman explained in his book “Thinking, Fast and Slow.” System 1 refers to the snap judgments that rely on heuristics while system 2 refers to a more analytic, slower process.
Neither system 1 nor 2 is inherently “right or wrong,” Dr. Scarfone said. “The diagnostic sweet spot is to try to apply the correct system to the correct patient.”
Heuristics are the mental shortcuts people use to make decisions based on past experience. They exist because they’re useful, enabling people to focus only on what they need to accomplish everyday tasks, such as driving or brushing teeth. But heuristics can also lead to predictable cognitive errors.
“The good news about heuristics and system 1 thinking is that it’s efficient and simple, and we desire that in a busy practice or ED setting, but we should recognize that the trade-off is that it may be at the expense of accuracy,” Dr. Scarfone said.
The advantage to system 1 thinking is easy, simple, rapid, and efficient decision-making that rejects ambiguity. It’s also usually accurate, which rewards the approach, and accuracy increases with time based on memory, experience, and pattern recognition. Doctors develop “illness scripts” that help in identifying diagnoses.
“Illness scripts are common patterns of clinical presentations that usually lead us to a diagnostic possibility,” Dr. Scarfone said. “A classic illness script might be a 4-week-old firstborn male with forceful vomiting, and immediately your mind may go to pyloric stenosis as a likely diagnosis.” But the patient may have a different diagnosis than the initial impression your system 1 thinking leads you to believe.
“Generally, the more experience a clinician has, the more accurate they’ll be in using system 1,” he said. “Seasoned physicians are much more likely to employ system 1 than a newer physician or trainee,” which is why heuristics shouldn’t be thought of as hindrances. Dr. Scarfone quoted Kevin Eva in a 2005 review on clinical reasoning: “Successful heuristics should be embraced rather than overcome.”
A drawback to system 1 thinking, however, is thinking that “what you see is all there is,” which can lead to cognitive errors. Feeling wrong feels the same as feeling right, so you may not realize when you’re off target and therefore neglect to consider alternatives.
“When we learn a little about our patient’s complaint, it’s easier to fit everything into a coherent explanation,” Dr. Scarfone said, but “don’t ask, don’t tell doesn’t work in medicine.”
Another challenge with system 1 thinking is that pattern recognition can be unreliable because it’s dependent on context. For example, consider the difference in assessing a patient’s sore throat in a primary care office versus a resuscitation bay. “Clearly our consideration of what may be going on with the patient and what the diagnosis may be is likely to vary in those two settings,” he said.
System 2 thinking: Of zebras and horses
System 2 is the analytic thinking that involves pondering and seek out the optimal answer rather than the “good-enough” answer.
“The good news about system 2 is that it really can monitor system 1,” said Dr. Nagler, who has a master’s degree in health professions education. “If you spend the time to do analytic reasoning, you can actually mitigate some of those errors that may occur from intuitive judgments from system 1 thinking. System 2 spends the time to say ‘let’s make sure we’re doing this right.’ ” In multiple-choice tests, for example, people are twice as likely to change a wrong answer to a right one than a right one to a wrong one.
System 2 thinking allows for the reasoning to assess questions in the gray zone. It’s vigilant, it’s reliable, it’s effective, it acknowledges uncertainty and doubt, it can be safe in terms of providing care, and it has high scientific rigor. But it also has disadvantages, starting with the fact that it’s slower and more time-consuming. System 2 thinking is resource intensive, requiring a higher cognitive demand and more time and effort.
“Sometimes the quick judgment is the best judgment,” Dr. Nagler said. System 2 thinking also is sometimes unnecessary and counter to value-based care. “If you start to think about all the possibilities of what a presentation may be, all of a sudden you might find yourself wanting to do all kinds of tests and all kinds of referrals and other things, which is not necessarily value-based care.” When system 2 thinking goes astray, it makes us think everything we see is a zebra rather than a horse.
Sonia Khan, MD, a pediatrician in Fremont, Calif., found this session particularly worthwhile.
“It really tries to explain the difference between leaping to conclusions and learning how to hold your horses and do a bit more, to double check that you’re not locking everything into a horse stall and missing a zebra, and avoiding go too far with system 2 and thinking that everything’s a zebra,” Dr. Khan said. “It’s a difficult talk to have because you’re asking pediatricians to look in the mirror and own up, to learn to step back and reconsider the picture, and consider the biases that may come into your decision-making; then learn to extrude them, and rethink the case to be sure your knee-jerk diagnostic response is correct.”
Types of cognitive errors
The presenters listed some of the most common cognitive errors, although their list is far from exhaustive.
- Affective error. Avoiding unpleasant but necessary tests or examinations because of sympathy for the patient, such as avoiding blood work to spare a needle stick in a cancer patient with abdominal pain because the mother is convinced it’s constipation from opioids. This is similar to omission bias, which places excessive concern on avoiding a therapy’s adverse effects when the therapy could be highly effective.
- Anchoring. Clinging to an initial impression or salient features of initial presentation, even as conflicting and contradictory data accumulate, such as diagnosing a patient with fever and vomiting with gastroenteritis even when the patient has an oxygen saturation of 94% and tachypnea.
- Attribution errors. Negative stereotypes lead clinicians to ignore or minimize the possibility of serious disease, such as evaluating a confused teen covered in piercings and tattoos for drug ingestion when the actual diagnosis is new-onset diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Availability bias. Overestimating or underestimating the probability of disease because of recent experience, what was most recently “available” to your brain cognitively, such as getting head imaging on several vomiting patients in a row because you recently had one with a new brain tumor diagnosis.
- Bandwagon effect. Accepting the group’s opinion without assessing a clinical situation yourself, such as sending home a crying, vomiting infant with a presumed viral infection only to see the infant return later with intussusception.
- Base rate neglect. Ignoring the true prevalence of disease by either inflating it or reducing it, such as searching for cardiac disease in all pediatric patients with chest pain.
- Commission. A tendency toward action with the belief that harm may only be prevented by action, such as ordering every possible test for a patient with fever to “rule everything out.”
- Confirmation bias. Subconscious cherry-picking: A tendency to look for, notice, and remember information that fits with preexisting expectations while disregarding information that contradicts those expectations.
- Diagnostic momentum. Clinging to that initial diagnostic impression that may have been generated by others, which is particularly common during transitions of care.
- Premature closure. Narrowing down to a diagnosis without thinking about other diagnoses or asking enough questions about other symptoms that may have opened up other diagnostic possibilities.
- Representation bias. Making a decision in the absence of appropriate context by incorrectly comparing two situations because of a perceived similarity between them, or on the flip side, evaluating a situation without comparing it with other situations.
- Overconfidence. Making a decision without enough supportive evidence yet feeling confident about the diagnosis.
- Search satisfying. Stopping the search for additional diagnoses after the anticipated diagnosis has been made.
Cognitive pills for cognitive ills
Being aware of the pitfalls of cognitive errors is the first step to avoiding and mitigating them. “It really does start with preparation and awareness,” Dr. Scarfone said before presenting strategies to build a cognitive “firewall” that can help physicians practice reflectively instead of reflexively.
First, be aware of your cognitive style. People usually have the same thinking pattern in everyday life as in the clinical setting, so determine whether you’re more of a system 1 or system 2 thinker. System 1 thinkers need to watch out for framing (relying too heavily on context), premature closure, diagnostic momentum, anchoring, and confirmation bias. System 2 thinkers need to watch out for commission, availability bias, and base rate neglect.
“Neither system is inherently right or wrong,” Dr. Scarfone reiterated. “In the perfect world, you may use system 1 to form an initial impression, but then system 2 should really act as a check and balance system to cause you to reflect on your initial diagnostic impressions.”
Additional strategies include being a good history taker and performing a meticulous physical exam: be a good listener, clarify unclear aspects of the history, and identify and address the main concern.
“Remember children and families have a story to tell, and if we listen carefully enough, the diagnostic clues are there,” Dr. Scarfone said. “Sometimes they may be quite subtle.” He recommended doctors perform each part of the physical exam as if expecting an abnormality.
Another strategy is using meta-cognition, a forced analysis of the thinking that led to a diagnosis. It involves asking: “If I had to explain my medical decision-making to others, would this make inherent sense?” Dr. Scarfone said. “If you’re testing, try to avoid anchoring and confirmation biases.”
Finally, take a diagnostic time-out with a checklist that asks these questions:
- Does my presumptive diagnosis make sense?
- What evidence supports or refutes it?
- Did I arrive at it via cognitive biases?
- Are there other diagnostic possibilities that should be considered?
One way to do this is creating a table listing the complaint/finding, diagnostic possibilities with system 1 thinking, diagnostic possibilities with system 2 thinking, and then going beyond system 2 – the potential zebras – when even system 2 diagnostic possibilities don’t account for what the patient is saying or what the exam shows.
Enough overlap exists between these cognitive biases and the intrinsic bias related to individual characteristics that Dr. Khan appreciated the talk on another level as well.
“For me, as a brown Muslim immigrant woman of color, I can sometimes see cognitive biases in action with my colleagues and realize that they are oblivious to it,” Dr. Khan said. “It’s really refreshing to see this issue come up and being discussed at the [AAP] National Conference and Exhibition.”
Dr. Scarfone, Dr. Nagler and Dr. Khan have no relevant financial disclosures.
This article was updated 12/8/2020.
While it’s important not to think immediately of zebras when hearing hoofbeats, it’s just as important not to assume it’s always a horse. The delicate balance between not jumping to the seemingly obvious diagnosis without overanalyzing and overtesting is familiar to all physicians, and
“When these errors are made, it’s not because physicians lack knowledge, but they go down a wrong path in their thinking process,” Richard Scarfone, MD, a pediatric emergency medicine physician at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, told attendees at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. “An important point to be made here is that how physicians think seems to be much more important than what physicians know.”
Dr. Scarfone and Joshua Nagler, MD, MHPEd, director, pediatric emergency medicine fellowship program at Children’s Hospital Boston, presented a session on the cognitive biases that can trip up clinicians when making diagnoses and how to avoid them. Research shows that the rate of diagnostic error is approximately 15%. Although those findings come from studies in adults, the rates are likely similar in pediatrics, Dr. Scarfone said.
A wide range of clinical factors contribute to diagnostic errors: limited information, vague or undifferentiated symptoms, incomplete history, multiple transitions of care, diagnostic uncertainty, daily decision density, and reliance on pattern recognition, among others. Personal contributing factors can play a role as well, such as atypical work hours, fatigue, one’s emotional or affective state, a high cognitive load, and others. On top of all that, medical decision-making can be really complex on its own, Dr. Scarfone said. He compared differential diagnosis with a tree where a single leaf is the correct diagnosis.
System 1 thinking: Pros and cons
Dr. Scarfone and Dr. Nagler explained system 1 and system 2 thinking, two different ways of thinking that can influence decision-making that Daniel Kahneman explained in his book “Thinking, Fast and Slow.” System 1 refers to the snap judgments that rely on heuristics while system 2 refers to a more analytic, slower process.
Neither system 1 nor 2 is inherently “right or wrong,” Dr. Scarfone said. “The diagnostic sweet spot is to try to apply the correct system to the correct patient.”
Heuristics are the mental shortcuts people use to make decisions based on past experience. They exist because they’re useful, enabling people to focus only on what they need to accomplish everyday tasks, such as driving or brushing teeth. But heuristics can also lead to predictable cognitive errors.
“The good news about heuristics and system 1 thinking is that it’s efficient and simple, and we desire that in a busy practice or ED setting, but we should recognize that the trade-off is that it may be at the expense of accuracy,” Dr. Scarfone said.
The advantage to system 1 thinking is easy, simple, rapid, and efficient decision-making that rejects ambiguity. It’s also usually accurate, which rewards the approach, and accuracy increases with time based on memory, experience, and pattern recognition. Doctors develop “illness scripts” that help in identifying diagnoses.
“Illness scripts are common patterns of clinical presentations that usually lead us to a diagnostic possibility,” Dr. Scarfone said. “A classic illness script might be a 4-week-old firstborn male with forceful vomiting, and immediately your mind may go to pyloric stenosis as a likely diagnosis.” But the patient may have a different diagnosis than the initial impression your system 1 thinking leads you to believe.
“Generally, the more experience a clinician has, the more accurate they’ll be in using system 1,” he said. “Seasoned physicians are much more likely to employ system 1 than a newer physician or trainee,” which is why heuristics shouldn’t be thought of as hindrances. Dr. Scarfone quoted Kevin Eva in a 2005 review on clinical reasoning: “Successful heuristics should be embraced rather than overcome.”
A drawback to system 1 thinking, however, is thinking that “what you see is all there is,” which can lead to cognitive errors. Feeling wrong feels the same as feeling right, so you may not realize when you’re off target and therefore neglect to consider alternatives.
“When we learn a little about our patient’s complaint, it’s easier to fit everything into a coherent explanation,” Dr. Scarfone said, but “don’t ask, don’t tell doesn’t work in medicine.”
Another challenge with system 1 thinking is that pattern recognition can be unreliable because it’s dependent on context. For example, consider the difference in assessing a patient’s sore throat in a primary care office versus a resuscitation bay. “Clearly our consideration of what may be going on with the patient and what the diagnosis may be is likely to vary in those two settings,” he said.
System 2 thinking: Of zebras and horses
System 2 is the analytic thinking that involves pondering and seek out the optimal answer rather than the “good-enough” answer.
“The good news about system 2 is that it really can monitor system 1,” said Dr. Nagler, who has a master’s degree in health professions education. “If you spend the time to do analytic reasoning, you can actually mitigate some of those errors that may occur from intuitive judgments from system 1 thinking. System 2 spends the time to say ‘let’s make sure we’re doing this right.’ ” In multiple-choice tests, for example, people are twice as likely to change a wrong answer to a right one than a right one to a wrong one.
System 2 thinking allows for the reasoning to assess questions in the gray zone. It’s vigilant, it’s reliable, it’s effective, it acknowledges uncertainty and doubt, it can be safe in terms of providing care, and it has high scientific rigor. But it also has disadvantages, starting with the fact that it’s slower and more time-consuming. System 2 thinking is resource intensive, requiring a higher cognitive demand and more time and effort.
“Sometimes the quick judgment is the best judgment,” Dr. Nagler said. System 2 thinking also is sometimes unnecessary and counter to value-based care. “If you start to think about all the possibilities of what a presentation may be, all of a sudden you might find yourself wanting to do all kinds of tests and all kinds of referrals and other things, which is not necessarily value-based care.” When system 2 thinking goes astray, it makes us think everything we see is a zebra rather than a horse.
Sonia Khan, MD, a pediatrician in Fremont, Calif., found this session particularly worthwhile.
“It really tries to explain the difference between leaping to conclusions and learning how to hold your horses and do a bit more, to double check that you’re not locking everything into a horse stall and missing a zebra, and avoiding go too far with system 2 and thinking that everything’s a zebra,” Dr. Khan said. “It’s a difficult talk to have because you’re asking pediatricians to look in the mirror and own up, to learn to step back and reconsider the picture, and consider the biases that may come into your decision-making; then learn to extrude them, and rethink the case to be sure your knee-jerk diagnostic response is correct.”
Types of cognitive errors
The presenters listed some of the most common cognitive errors, although their list is far from exhaustive.
- Affective error. Avoiding unpleasant but necessary tests or examinations because of sympathy for the patient, such as avoiding blood work to spare a needle stick in a cancer patient with abdominal pain because the mother is convinced it’s constipation from opioids. This is similar to omission bias, which places excessive concern on avoiding a therapy’s adverse effects when the therapy could be highly effective.
- Anchoring. Clinging to an initial impression or salient features of initial presentation, even as conflicting and contradictory data accumulate, such as diagnosing a patient with fever and vomiting with gastroenteritis even when the patient has an oxygen saturation of 94% and tachypnea.
- Attribution errors. Negative stereotypes lead clinicians to ignore or minimize the possibility of serious disease, such as evaluating a confused teen covered in piercings and tattoos for drug ingestion when the actual diagnosis is new-onset diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Availability bias. Overestimating or underestimating the probability of disease because of recent experience, what was most recently “available” to your brain cognitively, such as getting head imaging on several vomiting patients in a row because you recently had one with a new brain tumor diagnosis.
- Bandwagon effect. Accepting the group’s opinion without assessing a clinical situation yourself, such as sending home a crying, vomiting infant with a presumed viral infection only to see the infant return later with intussusception.
- Base rate neglect. Ignoring the true prevalence of disease by either inflating it or reducing it, such as searching for cardiac disease in all pediatric patients with chest pain.
- Commission. A tendency toward action with the belief that harm may only be prevented by action, such as ordering every possible test for a patient with fever to “rule everything out.”
- Confirmation bias. Subconscious cherry-picking: A tendency to look for, notice, and remember information that fits with preexisting expectations while disregarding information that contradicts those expectations.
- Diagnostic momentum. Clinging to that initial diagnostic impression that may have been generated by others, which is particularly common during transitions of care.
- Premature closure. Narrowing down to a diagnosis without thinking about other diagnoses or asking enough questions about other symptoms that may have opened up other diagnostic possibilities.
- Representation bias. Making a decision in the absence of appropriate context by incorrectly comparing two situations because of a perceived similarity between them, or on the flip side, evaluating a situation without comparing it with other situations.
- Overconfidence. Making a decision without enough supportive evidence yet feeling confident about the diagnosis.
- Search satisfying. Stopping the search for additional diagnoses after the anticipated diagnosis has been made.
Cognitive pills for cognitive ills
Being aware of the pitfalls of cognitive errors is the first step to avoiding and mitigating them. “It really does start with preparation and awareness,” Dr. Scarfone said before presenting strategies to build a cognitive “firewall” that can help physicians practice reflectively instead of reflexively.
First, be aware of your cognitive style. People usually have the same thinking pattern in everyday life as in the clinical setting, so determine whether you’re more of a system 1 or system 2 thinker. System 1 thinkers need to watch out for framing (relying too heavily on context), premature closure, diagnostic momentum, anchoring, and confirmation bias. System 2 thinkers need to watch out for commission, availability bias, and base rate neglect.
“Neither system is inherently right or wrong,” Dr. Scarfone reiterated. “In the perfect world, you may use system 1 to form an initial impression, but then system 2 should really act as a check and balance system to cause you to reflect on your initial diagnostic impressions.”
Additional strategies include being a good history taker and performing a meticulous physical exam: be a good listener, clarify unclear aspects of the history, and identify and address the main concern.
“Remember children and families have a story to tell, and if we listen carefully enough, the diagnostic clues are there,” Dr. Scarfone said. “Sometimes they may be quite subtle.” He recommended doctors perform each part of the physical exam as if expecting an abnormality.
Another strategy is using meta-cognition, a forced analysis of the thinking that led to a diagnosis. It involves asking: “If I had to explain my medical decision-making to others, would this make inherent sense?” Dr. Scarfone said. “If you’re testing, try to avoid anchoring and confirmation biases.”
Finally, take a diagnostic time-out with a checklist that asks these questions:
- Does my presumptive diagnosis make sense?
- What evidence supports or refutes it?
- Did I arrive at it via cognitive biases?
- Are there other diagnostic possibilities that should be considered?
One way to do this is creating a table listing the complaint/finding, diagnostic possibilities with system 1 thinking, diagnostic possibilities with system 2 thinking, and then going beyond system 2 – the potential zebras – when even system 2 diagnostic possibilities don’t account for what the patient is saying or what the exam shows.
Enough overlap exists between these cognitive biases and the intrinsic bias related to individual characteristics that Dr. Khan appreciated the talk on another level as well.
“For me, as a brown Muslim immigrant woman of color, I can sometimes see cognitive biases in action with my colleagues and realize that they are oblivious to it,” Dr. Khan said. “It’s really refreshing to see this issue come up and being discussed at the [AAP] National Conference and Exhibition.”
Dr. Scarfone, Dr. Nagler and Dr. Khan have no relevant financial disclosures.
This article was updated 12/8/2020.
FROM AAP 2020
Food insecurity called urgent issue you must address
and advocate on behalf of those experiencing or at risk of food insecurity, according to Kofi Essel, MD, MPH, a pediatrician at Children’s National Hospital in Washington.
More than one in four adults are dealing with food access hardships during the pandemic, Dr. Essel said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Food insecurity is often interchangeable with hunger and refers to limited or uncertain availability of foods that are nutritious and safe.
“Food insecurity is as much about the threat of deprivation as it is about deprivation itself: A food-insecure life means a life lived in fear of hunger, and the psychological toll that takes,” according to a 2020 New York Times photo feature on food insecurity by Brenda Ann Kenneally that Dr. Essel quoted.
The lived experience of food insecure households includes food anxiety, a preoccupation with being able to get enough food that takes up cognitive bandwidth and prevents people from being able to focus on other important things. Another feature of food-insecure homes is a monotony of diet, which often involves an increase in caloric density and decrease in nutritional quality. As food insecurity grows more dire, adults’ food intake decreases, and then children’s intake decreases as adults seek out any way to get food, including “socially unacceptable” ways, which can include food pantries and bartering for food.
Food insecurity is associated with a wide range of negative outcomes even after accounting for other confounders, including decreased overall health, mental health, and educational outcomes. It’s also associated with an increase in developmental delays, hospitalizations, iron deficiency, asthma, and birth defects, among other problems. Somewhat paradoxically, it’s associated with both an increase and a decrease in obesity in the research.
Megan J. Gray, MD, MPH, assistant professor of pediatrics and population health at Dell Medical School at the The University of Texas at Austin, attended Dr. Essel’s session because food insecurity during COVID-19 now affects about half her patients, according to screening research she’s conducted.
“I wanted to learn more about the nuances of screening and using language and talking points that are helpful with families and with staff in building a culture of discussing food insecurity in our clinics,” Dr. Gray said in an interview. “What I’ve learned in my clinic is that if we don’t ask about it, families aren’t telling us – food insecurity is hiding in plain sight.”
She particularly appreciated Dr. Essel’s slides on the progression of food insecurity and how they acknowledged the mental health burden of food insecurity among parents.
“Right now during COVID-19, I see more patients I would call ‘socially complex’ rather than ‘medically complex,’ ” she said. “We all need to get a crash course in social work and Dr. Essel’s presentation is a great starting place.”
Screening for food insecurity
Beginning in 2015, an AAP policy statement charged pediatricians to “screen and intervene” with regard to food insecurity and their patients, Dr. Essel said. The statement also called for pediatricians to advocate for programs and policies that end childhood food insecurity.
The policy statement recommended a validated two-question screening tool called the Hunger Vital Sign:
1. “Within the past 12 months, we worried whether our food would run out before we got money to buy more.”
2. “Within the past 12 months, the food that we bought just didn’t last and we didn’t have money to get more.”
But in screening, you need to be conscious of how dignity intersects with food insecurity concerns, Dr. Essel said.
“We need to create dignity for our families,” he said. “We need to create a safe environment for our families and use appropriate tools when necessary to be able to identify families that are struggling with food insecurity.”
That need is seen in research on food screening. The Hunger Vital Signs questions can be asked with a dichotomous variable, as a yes/no question, or on a Likert scale, though the latter is a more complex way to ask.
A 2017 study found, however, that asking with “yes/no” answers missed more than a quarter of at-risk families. In the AAP survey using “yes/no” answers, 31% of families screened positive for being at risk of food insecurity, compared with 46% when the same question was asked on a Likert scale. It seems the ability to answer with “sometimes” feels “safer” than answering “yes,” Dr. Essel said.
Another factor that potentially affects answers is how doctors ask. In a March 2020 study at a single primary care practice, 16% of families screened positive with yes/no responses to a food insecurity screen when the questions were written, compared with 10% of positive screens with verbal responses (P < .001).
Epidemiology of food insecurity
The most updated United States Department of Agriculture report on food insecurity released in September shows the United States finally reached prerecession levels in 2019, with 11% of families designated as “food insecure.” But 2019 data cannot show what has occurred since the pandemic.
Further, the numbers are higher in households with children: Fourteen percent, or one in seven households with children, are experiencing food insecurity. Racial and ethnic disparities in food insecurity have remained consistent over the past 2 decades, with about twice as many Black and Hispanic homes experiencing food insecurity as White homes.
More recent research using Census Household Pulse Surveys has found a tremendous increase in food insecurity for children in 2020. One in three Black children and one in four Hispanic children are food insecure, according to these surveys. The rates are one in six for Asian households and one in ten for White households.
“The disparity is consistent,” Dr. Essel said. “We see what COVID has done. We once may have described it as a great equalizer – everyone is touched in the same way – but the reality is, this is actually a great magnifier. It’s revealing to us and magnifying disparities that have existed for far too long and has really allowed us to see it in a new way.”
A big part of disparities in food insecurity is disparities in wealth, “the safety net or cushion for families when things go wrong,” Dr. Essel said. The median wealth of White Americans in 2016 was $171,000, compared to $20,700 among Latinx Americans and $17,600 among Black Americans, according to the Federal Reserve Board Survey of Consumer Finances.
Food insecurity interventions
Federal nutrition programs – such as Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC), and school meal programs – are key to addressing food insecurity, Dr. Essel said.
“They have a long track record of rescuing families out of poverty, of rescuing families from food security and improving overall health of families,” he said.
But emergency food relief programs are important as well. Four in 10 families currently coming into food pantries are new recipients, and these resources have seen a 60% increase in clients, he said.
“This is utterly unreasonable for them to be able to manage,” he said. “Food pantries are essential but inadequate to compensate for large numbers of families,” even while they also may be the only option for families unable or unwilling to access federal programs. For example, for every one meal that food banks can provide, SNAP can provide nine meals, Dr. Essel said. Further, during times of economic downtown, every SNAP $1 spent generates $1.50 to $2 in economic activity.
Currently, the Pandemic Electronic Benefit Transfer (P-EBT) program provides benefits to families for school breakfast and lunch and has been extended through December 2021. Another federal pandemic response was to increase SNAP to the maximum household benefit for families, about $646 for a family of four, although 40% of households were already receiving the maximum benefit.
Food insecurity advocacy
You can advocate for any one of multiple pillars when it comes to food insecurity, Dr. Essel said. “Food cannot solve food insecurity by itself,” he said. “We have to think about root causes – systemic causes – and think about unemployment, livable wage, systemic racism, oppression, an inequitable food system. All of these things are pillars that any of you can advocate for when recognizing a family that is struggling with food insecurity.”
He offered several suggestions for advocacy:
- Join your local AAP chapter and prioritize food insecurity.
- Join a local antihunger task force.
- Make your clinical environment as safe as possible for families to respond to questions about food insecurity.
- Know what’s happening in your community immigrant populations.
- Provide up-to-date information to families about eligibility for federal programs.
- Share stories through op-eds and letters to the editor, and by contacting congressional representatives and providing expert testimony to school boards and city councils.
- Educate others about food insecurity through the above channels and on social media.
Jessica Lazerov, MD, a general pediatrician at Children’s National Anacostia and assistant professor of pediatrics at George Washington University, Washington, said the session was fantastic.
“Dr. Essel went beyond the basics of food insecurity, delving into the root causes, potential solutions, and important considerations when screening for food insecurity in practice,” Dr. Lazerov said in an interview. “I enjoyed his focus on advocacy, as well as the fact that he spent a bit of time reviewing how the COVID pandemic has affected food insecurity. I truly felt empowered to take my advocacy efforts a step further as Dr. Essel laid out concrete, actionable next steps, as well as a review of the most relevant and current information about food insecurity.”
Dr. Essel, Dr. Lazerov, and Dr. Gray have no relevant financial disclosures.
and advocate on behalf of those experiencing or at risk of food insecurity, according to Kofi Essel, MD, MPH, a pediatrician at Children’s National Hospital in Washington.
More than one in four adults are dealing with food access hardships during the pandemic, Dr. Essel said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Food insecurity is often interchangeable with hunger and refers to limited or uncertain availability of foods that are nutritious and safe.
“Food insecurity is as much about the threat of deprivation as it is about deprivation itself: A food-insecure life means a life lived in fear of hunger, and the psychological toll that takes,” according to a 2020 New York Times photo feature on food insecurity by Brenda Ann Kenneally that Dr. Essel quoted.
The lived experience of food insecure households includes food anxiety, a preoccupation with being able to get enough food that takes up cognitive bandwidth and prevents people from being able to focus on other important things. Another feature of food-insecure homes is a monotony of diet, which often involves an increase in caloric density and decrease in nutritional quality. As food insecurity grows more dire, adults’ food intake decreases, and then children’s intake decreases as adults seek out any way to get food, including “socially unacceptable” ways, which can include food pantries and bartering for food.
Food insecurity is associated with a wide range of negative outcomes even after accounting for other confounders, including decreased overall health, mental health, and educational outcomes. It’s also associated with an increase in developmental delays, hospitalizations, iron deficiency, asthma, and birth defects, among other problems. Somewhat paradoxically, it’s associated with both an increase and a decrease in obesity in the research.
Megan J. Gray, MD, MPH, assistant professor of pediatrics and population health at Dell Medical School at the The University of Texas at Austin, attended Dr. Essel’s session because food insecurity during COVID-19 now affects about half her patients, according to screening research she’s conducted.
“I wanted to learn more about the nuances of screening and using language and talking points that are helpful with families and with staff in building a culture of discussing food insecurity in our clinics,” Dr. Gray said in an interview. “What I’ve learned in my clinic is that if we don’t ask about it, families aren’t telling us – food insecurity is hiding in plain sight.”
She particularly appreciated Dr. Essel’s slides on the progression of food insecurity and how they acknowledged the mental health burden of food insecurity among parents.
“Right now during COVID-19, I see more patients I would call ‘socially complex’ rather than ‘medically complex,’ ” she said. “We all need to get a crash course in social work and Dr. Essel’s presentation is a great starting place.”
Screening for food insecurity
Beginning in 2015, an AAP policy statement charged pediatricians to “screen and intervene” with regard to food insecurity and their patients, Dr. Essel said. The statement also called for pediatricians to advocate for programs and policies that end childhood food insecurity.
The policy statement recommended a validated two-question screening tool called the Hunger Vital Sign:
1. “Within the past 12 months, we worried whether our food would run out before we got money to buy more.”
2. “Within the past 12 months, the food that we bought just didn’t last and we didn’t have money to get more.”
But in screening, you need to be conscious of how dignity intersects with food insecurity concerns, Dr. Essel said.
“We need to create dignity for our families,” he said. “We need to create a safe environment for our families and use appropriate tools when necessary to be able to identify families that are struggling with food insecurity.”
That need is seen in research on food screening. The Hunger Vital Signs questions can be asked with a dichotomous variable, as a yes/no question, or on a Likert scale, though the latter is a more complex way to ask.
A 2017 study found, however, that asking with “yes/no” answers missed more than a quarter of at-risk families. In the AAP survey using “yes/no” answers, 31% of families screened positive for being at risk of food insecurity, compared with 46% when the same question was asked on a Likert scale. It seems the ability to answer with “sometimes” feels “safer” than answering “yes,” Dr. Essel said.
Another factor that potentially affects answers is how doctors ask. In a March 2020 study at a single primary care practice, 16% of families screened positive with yes/no responses to a food insecurity screen when the questions were written, compared with 10% of positive screens with verbal responses (P < .001).
Epidemiology of food insecurity
The most updated United States Department of Agriculture report on food insecurity released in September shows the United States finally reached prerecession levels in 2019, with 11% of families designated as “food insecure.” But 2019 data cannot show what has occurred since the pandemic.
Further, the numbers are higher in households with children: Fourteen percent, or one in seven households with children, are experiencing food insecurity. Racial and ethnic disparities in food insecurity have remained consistent over the past 2 decades, with about twice as many Black and Hispanic homes experiencing food insecurity as White homes.
More recent research using Census Household Pulse Surveys has found a tremendous increase in food insecurity for children in 2020. One in three Black children and one in four Hispanic children are food insecure, according to these surveys. The rates are one in six for Asian households and one in ten for White households.
“The disparity is consistent,” Dr. Essel said. “We see what COVID has done. We once may have described it as a great equalizer – everyone is touched in the same way – but the reality is, this is actually a great magnifier. It’s revealing to us and magnifying disparities that have existed for far too long and has really allowed us to see it in a new way.”
A big part of disparities in food insecurity is disparities in wealth, “the safety net or cushion for families when things go wrong,” Dr. Essel said. The median wealth of White Americans in 2016 was $171,000, compared to $20,700 among Latinx Americans and $17,600 among Black Americans, according to the Federal Reserve Board Survey of Consumer Finances.
Food insecurity interventions
Federal nutrition programs – such as Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC), and school meal programs – are key to addressing food insecurity, Dr. Essel said.
“They have a long track record of rescuing families out of poverty, of rescuing families from food security and improving overall health of families,” he said.
But emergency food relief programs are important as well. Four in 10 families currently coming into food pantries are new recipients, and these resources have seen a 60% increase in clients, he said.
“This is utterly unreasonable for them to be able to manage,” he said. “Food pantries are essential but inadequate to compensate for large numbers of families,” even while they also may be the only option for families unable or unwilling to access federal programs. For example, for every one meal that food banks can provide, SNAP can provide nine meals, Dr. Essel said. Further, during times of economic downtown, every SNAP $1 spent generates $1.50 to $2 in economic activity.
Currently, the Pandemic Electronic Benefit Transfer (P-EBT) program provides benefits to families for school breakfast and lunch and has been extended through December 2021. Another federal pandemic response was to increase SNAP to the maximum household benefit for families, about $646 for a family of four, although 40% of households were already receiving the maximum benefit.
Food insecurity advocacy
You can advocate for any one of multiple pillars when it comes to food insecurity, Dr. Essel said. “Food cannot solve food insecurity by itself,” he said. “We have to think about root causes – systemic causes – and think about unemployment, livable wage, systemic racism, oppression, an inequitable food system. All of these things are pillars that any of you can advocate for when recognizing a family that is struggling with food insecurity.”
He offered several suggestions for advocacy:
- Join your local AAP chapter and prioritize food insecurity.
- Join a local antihunger task force.
- Make your clinical environment as safe as possible for families to respond to questions about food insecurity.
- Know what’s happening in your community immigrant populations.
- Provide up-to-date information to families about eligibility for federal programs.
- Share stories through op-eds and letters to the editor, and by contacting congressional representatives and providing expert testimony to school boards and city councils.
- Educate others about food insecurity through the above channels and on social media.
Jessica Lazerov, MD, a general pediatrician at Children’s National Anacostia and assistant professor of pediatrics at George Washington University, Washington, said the session was fantastic.
“Dr. Essel went beyond the basics of food insecurity, delving into the root causes, potential solutions, and important considerations when screening for food insecurity in practice,” Dr. Lazerov said in an interview. “I enjoyed his focus on advocacy, as well as the fact that he spent a bit of time reviewing how the COVID pandemic has affected food insecurity. I truly felt empowered to take my advocacy efforts a step further as Dr. Essel laid out concrete, actionable next steps, as well as a review of the most relevant and current information about food insecurity.”
Dr. Essel, Dr. Lazerov, and Dr. Gray have no relevant financial disclosures.
and advocate on behalf of those experiencing or at risk of food insecurity, according to Kofi Essel, MD, MPH, a pediatrician at Children’s National Hospital in Washington.
More than one in four adults are dealing with food access hardships during the pandemic, Dr. Essel said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Food insecurity is often interchangeable with hunger and refers to limited or uncertain availability of foods that are nutritious and safe.
“Food insecurity is as much about the threat of deprivation as it is about deprivation itself: A food-insecure life means a life lived in fear of hunger, and the psychological toll that takes,” according to a 2020 New York Times photo feature on food insecurity by Brenda Ann Kenneally that Dr. Essel quoted.
The lived experience of food insecure households includes food anxiety, a preoccupation with being able to get enough food that takes up cognitive bandwidth and prevents people from being able to focus on other important things. Another feature of food-insecure homes is a monotony of diet, which often involves an increase in caloric density and decrease in nutritional quality. As food insecurity grows more dire, adults’ food intake decreases, and then children’s intake decreases as adults seek out any way to get food, including “socially unacceptable” ways, which can include food pantries and bartering for food.
Food insecurity is associated with a wide range of negative outcomes even after accounting for other confounders, including decreased overall health, mental health, and educational outcomes. It’s also associated with an increase in developmental delays, hospitalizations, iron deficiency, asthma, and birth defects, among other problems. Somewhat paradoxically, it’s associated with both an increase and a decrease in obesity in the research.
Megan J. Gray, MD, MPH, assistant professor of pediatrics and population health at Dell Medical School at the The University of Texas at Austin, attended Dr. Essel’s session because food insecurity during COVID-19 now affects about half her patients, according to screening research she’s conducted.
“I wanted to learn more about the nuances of screening and using language and talking points that are helpful with families and with staff in building a culture of discussing food insecurity in our clinics,” Dr. Gray said in an interview. “What I’ve learned in my clinic is that if we don’t ask about it, families aren’t telling us – food insecurity is hiding in plain sight.”
She particularly appreciated Dr. Essel’s slides on the progression of food insecurity and how they acknowledged the mental health burden of food insecurity among parents.
“Right now during COVID-19, I see more patients I would call ‘socially complex’ rather than ‘medically complex,’ ” she said. “We all need to get a crash course in social work and Dr. Essel’s presentation is a great starting place.”
Screening for food insecurity
Beginning in 2015, an AAP policy statement charged pediatricians to “screen and intervene” with regard to food insecurity and their patients, Dr. Essel said. The statement also called for pediatricians to advocate for programs and policies that end childhood food insecurity.
The policy statement recommended a validated two-question screening tool called the Hunger Vital Sign:
1. “Within the past 12 months, we worried whether our food would run out before we got money to buy more.”
2. “Within the past 12 months, the food that we bought just didn’t last and we didn’t have money to get more.”
But in screening, you need to be conscious of how dignity intersects with food insecurity concerns, Dr. Essel said.
“We need to create dignity for our families,” he said. “We need to create a safe environment for our families and use appropriate tools when necessary to be able to identify families that are struggling with food insecurity.”
That need is seen in research on food screening. The Hunger Vital Signs questions can be asked with a dichotomous variable, as a yes/no question, or on a Likert scale, though the latter is a more complex way to ask.
A 2017 study found, however, that asking with “yes/no” answers missed more than a quarter of at-risk families. In the AAP survey using “yes/no” answers, 31% of families screened positive for being at risk of food insecurity, compared with 46% when the same question was asked on a Likert scale. It seems the ability to answer with “sometimes” feels “safer” than answering “yes,” Dr. Essel said.
Another factor that potentially affects answers is how doctors ask. In a March 2020 study at a single primary care practice, 16% of families screened positive with yes/no responses to a food insecurity screen when the questions were written, compared with 10% of positive screens with verbal responses (P < .001).
Epidemiology of food insecurity
The most updated United States Department of Agriculture report on food insecurity released in September shows the United States finally reached prerecession levels in 2019, with 11% of families designated as “food insecure.” But 2019 data cannot show what has occurred since the pandemic.
Further, the numbers are higher in households with children: Fourteen percent, or one in seven households with children, are experiencing food insecurity. Racial and ethnic disparities in food insecurity have remained consistent over the past 2 decades, with about twice as many Black and Hispanic homes experiencing food insecurity as White homes.
More recent research using Census Household Pulse Surveys has found a tremendous increase in food insecurity for children in 2020. One in three Black children and one in four Hispanic children are food insecure, according to these surveys. The rates are one in six for Asian households and one in ten for White households.
“The disparity is consistent,” Dr. Essel said. “We see what COVID has done. We once may have described it as a great equalizer – everyone is touched in the same way – but the reality is, this is actually a great magnifier. It’s revealing to us and magnifying disparities that have existed for far too long and has really allowed us to see it in a new way.”
A big part of disparities in food insecurity is disparities in wealth, “the safety net or cushion for families when things go wrong,” Dr. Essel said. The median wealth of White Americans in 2016 was $171,000, compared to $20,700 among Latinx Americans and $17,600 among Black Americans, according to the Federal Reserve Board Survey of Consumer Finances.
Food insecurity interventions
Federal nutrition programs – such as Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC), and school meal programs – are key to addressing food insecurity, Dr. Essel said.
“They have a long track record of rescuing families out of poverty, of rescuing families from food security and improving overall health of families,” he said.
But emergency food relief programs are important as well. Four in 10 families currently coming into food pantries are new recipients, and these resources have seen a 60% increase in clients, he said.
“This is utterly unreasonable for them to be able to manage,” he said. “Food pantries are essential but inadequate to compensate for large numbers of families,” even while they also may be the only option for families unable or unwilling to access federal programs. For example, for every one meal that food banks can provide, SNAP can provide nine meals, Dr. Essel said. Further, during times of economic downtown, every SNAP $1 spent generates $1.50 to $2 in economic activity.
Currently, the Pandemic Electronic Benefit Transfer (P-EBT) program provides benefits to families for school breakfast and lunch and has been extended through December 2021. Another federal pandemic response was to increase SNAP to the maximum household benefit for families, about $646 for a family of four, although 40% of households were already receiving the maximum benefit.
Food insecurity advocacy
You can advocate for any one of multiple pillars when it comes to food insecurity, Dr. Essel said. “Food cannot solve food insecurity by itself,” he said. “We have to think about root causes – systemic causes – and think about unemployment, livable wage, systemic racism, oppression, an inequitable food system. All of these things are pillars that any of you can advocate for when recognizing a family that is struggling with food insecurity.”
He offered several suggestions for advocacy:
- Join your local AAP chapter and prioritize food insecurity.
- Join a local antihunger task force.
- Make your clinical environment as safe as possible for families to respond to questions about food insecurity.
- Know what’s happening in your community immigrant populations.
- Provide up-to-date information to families about eligibility for federal programs.
- Share stories through op-eds and letters to the editor, and by contacting congressional representatives and providing expert testimony to school boards and city councils.
- Educate others about food insecurity through the above channels and on social media.
Jessica Lazerov, MD, a general pediatrician at Children’s National Anacostia and assistant professor of pediatrics at George Washington University, Washington, said the session was fantastic.
“Dr. Essel went beyond the basics of food insecurity, delving into the root causes, potential solutions, and important considerations when screening for food insecurity in practice,” Dr. Lazerov said in an interview. “I enjoyed his focus on advocacy, as well as the fact that he spent a bit of time reviewing how the COVID pandemic has affected food insecurity. I truly felt empowered to take my advocacy efforts a step further as Dr. Essel laid out concrete, actionable next steps, as well as a review of the most relevant and current information about food insecurity.”
Dr. Essel, Dr. Lazerov, and Dr. Gray have no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AAP 2020
Infectious disease is an increasing threat from climate change
“I would argue that the most important reason to care about climate change is because of our children,” Saul Hymes, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year.
“Being able to point out to people how climate change harms the health of their children and affects their children’s risk of infections is a particularly effective argument to make,” said Dr. Hymes, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
Rachel Boykan, MD, a pediatrician at the university, found Dr. Hymes’ presentation excellent and highly relevant to issues all health care workers treating children face, even beyond infectious disease.
“It was data focused but also understandable for a broad audience,” Dr. Boykan, who was not involved in the presentation, said in an interview. “He explained the science of climate change in a way that all physicians, but especially pediatricians, would find relevant. I suspect if people who were listening didn’t already prioritize the issues of climate change, they certainly did after hearing the talk.”
She also appreciated that Dr. Hymes addressed how climate change affects everyone in both their professional and personal lives.
“We need to be prepared to address the clinical issues that ensue after a natural disaster, and we need to be advocates for change so that we can slow down the climate changes we are all dealing with,” said Dr. Boykan, adding that the presentation was also inspiring. “He presented many different viewpoints and many ways to be involved and to be an advocate. I would think that a good number of people who were there would be energized to do something differently to combat climate change.”
The multitudinous impacts of climate change
The impact of climate change on human health is broad and far-reaching, Dr. Hymes said. It doesn’t require much imagination to recognize that rising global temperatures can lead to prolonged extreme heat waves that can cause heat-related deaths and illnesses. But other effects can be more gradual or subtle. Changes in outdoor air quality can affect weather patterns, pollen counts, and air pollution that can increase risk of asthma, allergies, as well as acute and chronic respiratory and cardiovascular disease.
Sea level rise, more frequent and severe hurricanes, storm surges, and extreme precipitation all can lead to contaminated water and destruction of essential infrastructure. In addition to drowning and injuries from the storms themselves, these changes have mental health consequences, and can lead to gastrointestinal and other illnesses, including water-borne infectious disease. The distribution and prevalence of vector-borne diseases also will shift with changes in temperature, precipitation, and other weather patterns.
Distribution, prevalence of vector-borne diseases shift with climate change
One of the most common bacteria transmitted by vectors in the United States is Borrelia burgdorferi, the cause of Lyme disease. Transmitted by deer ticks, Lyme disease is listed by the Environmental Protection Agency as an indicator of climate change’s impact on human health and is becoming more common every year. Cases doubled from 1990 to 2014, from 4 to 8 cases per 100,000 people.
Increases were most dramatic in the Northeast, where Lyme disease is endemic. States such as Maine, Vermont, and New Hampshire all saw increases of 80-100 more cases per 100,000 people. Evidence now shows that Lyme disease is moving north as the climate warms. Toronto, for example, has seen more than a 400% increase in cases in less than a decade, from 128 cases per 100,000 people in 2009 to 700 cases per 100,000 in 2015.
“It’s a known phenomenon that climate change affects more northerly latitudes disproportionately to more than southerly latitudes,” Dr. Hymes said. He shared a 2013 study providing evidence that climate change is expanding the range of Lyme disease. Even when controlling for other confounding factors, the research found that areas being warmed proportionately more by climate change also are experiencing greater Lyme incidence. While Lyme cases declined in several Western and Deep South states, it significantly increased in nearly every Northeast state as well as Idaho, Arizona, and states in the northern Midwest near the Great Lakes.
“We find that this impact of climate change on the movement of vectors like ticks affects more than just Lyme disease,” Dr. Hymes said. Amblyomma americanum, the Lone Star tick, has historically been restricted to the southern United States but is now found further north, even up to New England. It carries bacteria that can cause multiple illnesses, including ehrlichiosis, heartland virus, and tularemia.
An alpha-gal meat allergy associated with this tick can lead to anaphylaxis about 6 hours after a person eats red meat or pork. Prevalence of this allergy, first reported in Georgia in 1989-1991, has been increasing and moving further north, and the Lone Star tick is a particularly heat-tolerant and heat-loving tick.
Climate change also affects how long during the year people are at risk. Lyme disease, for example, typically lasted from April/May to October, when ticks then hibernated during the cold weather. But the warming climate has expanded Lyme season: Local Lyme cases have begun occurring into November through January on Long Island over the past 5 years.
The impact of seasonal changes on infectious diseases overall is difficult to predict. The seasons for cold weather diseases such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, for example, may become shorter or milder while viruses more common in the summer, such as enteroviruses, may become a risk year-round.
Natural disasters pose multiple risks
Natural disasters can pose immediate dangers to families and have a significant impact on mental health, but that’s not their only potential impact.
“Severe weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes are well established in the climate change literature as an effect of increased temperatures and more volatile weather systems, but they also have a significant effect on infectious diseases and on children in particular,” Dr. Hymes said. “Hurricanes and flash floods can cause increases in infectious disease outbreaks through a variety of different ways.”
They can bring saltwater, freshwater, and sometimes soil organisms into the food and water supplies, and lead to sewage contamination from overloaded sewers, overflowing storm drains, and loss of power or pumps. Displaced animal vectors, such as rats, can lead to spread of other diseases, such as plague, hantavirus, typhus, and rabies.
Examples of saltwater organisms include Vibrio, Aeromonas, and Mycobacterium marinum, all of which can cause infections in wounds and/or diarrheal illness or bacteremia. Similarly, organisms from freshwater and soil that can cause serious illness or death include Aeromonas, Pseudomonas, Amebiasis, Giardia, and Legionella. Without access to clean water, or with contamination from overflowing sewage, cryptosporidium, Escherichia coli, salmonella, typhoid, norovirus, hepatitis A and E, and even cholera can also become problems as well.
In Houston following Hurricane Harvey, for example, cellulitis cases doubled and included infections from organisms different from the usual suspects. Scrapes and cuts that occurred during the storm also festered sooner.
Cases of disease linked to Hurricane Katrina in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report included 6 cases of cholera, 17 cases of other vibrio – including five that resulted in death – and reported cases of norovirus, Escherichia coli, salmonella, and influenza and pneumonia from overcrowding of evacuees.
You can help in a variety of ways
You can play several key roles as the world’s climate changes, starting with preparing for the changes. You should familiarize themselves with new and emerging infections, or those that have been around a while but not seen in your areas, such as Lyme, Zika, and Dengue.
“If you haven’t seen them already, you likely will due to movements of vector-borne infections that can occur due to climate change,” Dr. Hymes said. “You also want to expect the usual common diseases, but maybe at unsuspected times,” he added. “If you have a pediatric patient who looks like they have Coxsackie virus but it’s February, if it’s been a warm February, it may very well be Coxsackie virus.”
Following natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes and tornadoes, consider who your patients are. If they’re evacuees, are they living in overcrowded conditions? Do they have access to clean water? If not, explain the need to boil water if they can, or to use iodine tablets or a portable pump filter. Consider that some infections may involve unexpected or odd organisms, such as legionella pneumonia or vibrio cellulitis, and contact your local infectious disease doctor as needed.
You also can make personal lifestyle changes that, while small, can add up in the aggregate in reducing carbon footprints, such as purchasing an electric or hybrid car and converting their homes to solar power.
“For very little money, you can purchase carbon offsets,” Dr. Hymes said, such as $10-$15 a month for wind power offsets with home electricity or $5-$10 a month for car or plane travel.
“But really, the most important thing we can do as pediatricians is educate,” Dr. Hymes said. “Taking opportunities every day in your office to educate your patients and educate your colleagues about the importance of climate change in our patients’ health and our own children’s health is super, super important.”
Dr. Hymes and Dr. Boykan had no relevant financial disclosures.
“I would argue that the most important reason to care about climate change is because of our children,” Saul Hymes, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year.
“Being able to point out to people how climate change harms the health of their children and affects their children’s risk of infections is a particularly effective argument to make,” said Dr. Hymes, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
Rachel Boykan, MD, a pediatrician at the university, found Dr. Hymes’ presentation excellent and highly relevant to issues all health care workers treating children face, even beyond infectious disease.
“It was data focused but also understandable for a broad audience,” Dr. Boykan, who was not involved in the presentation, said in an interview. “He explained the science of climate change in a way that all physicians, but especially pediatricians, would find relevant. I suspect if people who were listening didn’t already prioritize the issues of climate change, they certainly did after hearing the talk.”
She also appreciated that Dr. Hymes addressed how climate change affects everyone in both their professional and personal lives.
“We need to be prepared to address the clinical issues that ensue after a natural disaster, and we need to be advocates for change so that we can slow down the climate changes we are all dealing with,” said Dr. Boykan, adding that the presentation was also inspiring. “He presented many different viewpoints and many ways to be involved and to be an advocate. I would think that a good number of people who were there would be energized to do something differently to combat climate change.”
The multitudinous impacts of climate change
The impact of climate change on human health is broad and far-reaching, Dr. Hymes said. It doesn’t require much imagination to recognize that rising global temperatures can lead to prolonged extreme heat waves that can cause heat-related deaths and illnesses. But other effects can be more gradual or subtle. Changes in outdoor air quality can affect weather patterns, pollen counts, and air pollution that can increase risk of asthma, allergies, as well as acute and chronic respiratory and cardiovascular disease.
Sea level rise, more frequent and severe hurricanes, storm surges, and extreme precipitation all can lead to contaminated water and destruction of essential infrastructure. In addition to drowning and injuries from the storms themselves, these changes have mental health consequences, and can lead to gastrointestinal and other illnesses, including water-borne infectious disease. The distribution and prevalence of vector-borne diseases also will shift with changes in temperature, precipitation, and other weather patterns.
Distribution, prevalence of vector-borne diseases shift with climate change
One of the most common bacteria transmitted by vectors in the United States is Borrelia burgdorferi, the cause of Lyme disease. Transmitted by deer ticks, Lyme disease is listed by the Environmental Protection Agency as an indicator of climate change’s impact on human health and is becoming more common every year. Cases doubled from 1990 to 2014, from 4 to 8 cases per 100,000 people.
Increases were most dramatic in the Northeast, where Lyme disease is endemic. States such as Maine, Vermont, and New Hampshire all saw increases of 80-100 more cases per 100,000 people. Evidence now shows that Lyme disease is moving north as the climate warms. Toronto, for example, has seen more than a 400% increase in cases in less than a decade, from 128 cases per 100,000 people in 2009 to 700 cases per 100,000 in 2015.
“It’s a known phenomenon that climate change affects more northerly latitudes disproportionately to more than southerly latitudes,” Dr. Hymes said. He shared a 2013 study providing evidence that climate change is expanding the range of Lyme disease. Even when controlling for other confounding factors, the research found that areas being warmed proportionately more by climate change also are experiencing greater Lyme incidence. While Lyme cases declined in several Western and Deep South states, it significantly increased in nearly every Northeast state as well as Idaho, Arizona, and states in the northern Midwest near the Great Lakes.
“We find that this impact of climate change on the movement of vectors like ticks affects more than just Lyme disease,” Dr. Hymes said. Amblyomma americanum, the Lone Star tick, has historically been restricted to the southern United States but is now found further north, even up to New England. It carries bacteria that can cause multiple illnesses, including ehrlichiosis, heartland virus, and tularemia.
An alpha-gal meat allergy associated with this tick can lead to anaphylaxis about 6 hours after a person eats red meat or pork. Prevalence of this allergy, first reported in Georgia in 1989-1991, has been increasing and moving further north, and the Lone Star tick is a particularly heat-tolerant and heat-loving tick.
Climate change also affects how long during the year people are at risk. Lyme disease, for example, typically lasted from April/May to October, when ticks then hibernated during the cold weather. But the warming climate has expanded Lyme season: Local Lyme cases have begun occurring into November through January on Long Island over the past 5 years.
The impact of seasonal changes on infectious diseases overall is difficult to predict. The seasons for cold weather diseases such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, for example, may become shorter or milder while viruses more common in the summer, such as enteroviruses, may become a risk year-round.
Natural disasters pose multiple risks
Natural disasters can pose immediate dangers to families and have a significant impact on mental health, but that’s not their only potential impact.
“Severe weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes are well established in the climate change literature as an effect of increased temperatures and more volatile weather systems, but they also have a significant effect on infectious diseases and on children in particular,” Dr. Hymes said. “Hurricanes and flash floods can cause increases in infectious disease outbreaks through a variety of different ways.”
They can bring saltwater, freshwater, and sometimes soil organisms into the food and water supplies, and lead to sewage contamination from overloaded sewers, overflowing storm drains, and loss of power or pumps. Displaced animal vectors, such as rats, can lead to spread of other diseases, such as plague, hantavirus, typhus, and rabies.
Examples of saltwater organisms include Vibrio, Aeromonas, and Mycobacterium marinum, all of which can cause infections in wounds and/or diarrheal illness or bacteremia. Similarly, organisms from freshwater and soil that can cause serious illness or death include Aeromonas, Pseudomonas, Amebiasis, Giardia, and Legionella. Without access to clean water, or with contamination from overflowing sewage, cryptosporidium, Escherichia coli, salmonella, typhoid, norovirus, hepatitis A and E, and even cholera can also become problems as well.
In Houston following Hurricane Harvey, for example, cellulitis cases doubled and included infections from organisms different from the usual suspects. Scrapes and cuts that occurred during the storm also festered sooner.
Cases of disease linked to Hurricane Katrina in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report included 6 cases of cholera, 17 cases of other vibrio – including five that resulted in death – and reported cases of norovirus, Escherichia coli, salmonella, and influenza and pneumonia from overcrowding of evacuees.
You can help in a variety of ways
You can play several key roles as the world’s climate changes, starting with preparing for the changes. You should familiarize themselves with new and emerging infections, or those that have been around a while but not seen in your areas, such as Lyme, Zika, and Dengue.
“If you haven’t seen them already, you likely will due to movements of vector-borne infections that can occur due to climate change,” Dr. Hymes said. “You also want to expect the usual common diseases, but maybe at unsuspected times,” he added. “If you have a pediatric patient who looks like they have Coxsackie virus but it’s February, if it’s been a warm February, it may very well be Coxsackie virus.”
Following natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes and tornadoes, consider who your patients are. If they’re evacuees, are they living in overcrowded conditions? Do they have access to clean water? If not, explain the need to boil water if they can, or to use iodine tablets or a portable pump filter. Consider that some infections may involve unexpected or odd organisms, such as legionella pneumonia or vibrio cellulitis, and contact your local infectious disease doctor as needed.
You also can make personal lifestyle changes that, while small, can add up in the aggregate in reducing carbon footprints, such as purchasing an electric or hybrid car and converting their homes to solar power.
“For very little money, you can purchase carbon offsets,” Dr. Hymes said, such as $10-$15 a month for wind power offsets with home electricity or $5-$10 a month for car or plane travel.
“But really, the most important thing we can do as pediatricians is educate,” Dr. Hymes said. “Taking opportunities every day in your office to educate your patients and educate your colleagues about the importance of climate change in our patients’ health and our own children’s health is super, super important.”
Dr. Hymes and Dr. Boykan had no relevant financial disclosures.
“I would argue that the most important reason to care about climate change is because of our children,” Saul Hymes, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year.
“Being able to point out to people how climate change harms the health of their children and affects their children’s risk of infections is a particularly effective argument to make,” said Dr. Hymes, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
Rachel Boykan, MD, a pediatrician at the university, found Dr. Hymes’ presentation excellent and highly relevant to issues all health care workers treating children face, even beyond infectious disease.
“It was data focused but also understandable for a broad audience,” Dr. Boykan, who was not involved in the presentation, said in an interview. “He explained the science of climate change in a way that all physicians, but especially pediatricians, would find relevant. I suspect if people who were listening didn’t already prioritize the issues of climate change, they certainly did after hearing the talk.”
She also appreciated that Dr. Hymes addressed how climate change affects everyone in both their professional and personal lives.
“We need to be prepared to address the clinical issues that ensue after a natural disaster, and we need to be advocates for change so that we can slow down the climate changes we are all dealing with,” said Dr. Boykan, adding that the presentation was also inspiring. “He presented many different viewpoints and many ways to be involved and to be an advocate. I would think that a good number of people who were there would be energized to do something differently to combat climate change.”
The multitudinous impacts of climate change
The impact of climate change on human health is broad and far-reaching, Dr. Hymes said. It doesn’t require much imagination to recognize that rising global temperatures can lead to prolonged extreme heat waves that can cause heat-related deaths and illnesses. But other effects can be more gradual or subtle. Changes in outdoor air quality can affect weather patterns, pollen counts, and air pollution that can increase risk of asthma, allergies, as well as acute and chronic respiratory and cardiovascular disease.
Sea level rise, more frequent and severe hurricanes, storm surges, and extreme precipitation all can lead to contaminated water and destruction of essential infrastructure. In addition to drowning and injuries from the storms themselves, these changes have mental health consequences, and can lead to gastrointestinal and other illnesses, including water-borne infectious disease. The distribution and prevalence of vector-borne diseases also will shift with changes in temperature, precipitation, and other weather patterns.
Distribution, prevalence of vector-borne diseases shift with climate change
One of the most common bacteria transmitted by vectors in the United States is Borrelia burgdorferi, the cause of Lyme disease. Transmitted by deer ticks, Lyme disease is listed by the Environmental Protection Agency as an indicator of climate change’s impact on human health and is becoming more common every year. Cases doubled from 1990 to 2014, from 4 to 8 cases per 100,000 people.
Increases were most dramatic in the Northeast, where Lyme disease is endemic. States such as Maine, Vermont, and New Hampshire all saw increases of 80-100 more cases per 100,000 people. Evidence now shows that Lyme disease is moving north as the climate warms. Toronto, for example, has seen more than a 400% increase in cases in less than a decade, from 128 cases per 100,000 people in 2009 to 700 cases per 100,000 in 2015.
“It’s a known phenomenon that climate change affects more northerly latitudes disproportionately to more than southerly latitudes,” Dr. Hymes said. He shared a 2013 study providing evidence that climate change is expanding the range of Lyme disease. Even when controlling for other confounding factors, the research found that areas being warmed proportionately more by climate change also are experiencing greater Lyme incidence. While Lyme cases declined in several Western and Deep South states, it significantly increased in nearly every Northeast state as well as Idaho, Arizona, and states in the northern Midwest near the Great Lakes.
“We find that this impact of climate change on the movement of vectors like ticks affects more than just Lyme disease,” Dr. Hymes said. Amblyomma americanum, the Lone Star tick, has historically been restricted to the southern United States but is now found further north, even up to New England. It carries bacteria that can cause multiple illnesses, including ehrlichiosis, heartland virus, and tularemia.
An alpha-gal meat allergy associated with this tick can lead to anaphylaxis about 6 hours after a person eats red meat or pork. Prevalence of this allergy, first reported in Georgia in 1989-1991, has been increasing and moving further north, and the Lone Star tick is a particularly heat-tolerant and heat-loving tick.
Climate change also affects how long during the year people are at risk. Lyme disease, for example, typically lasted from April/May to October, when ticks then hibernated during the cold weather. But the warming climate has expanded Lyme season: Local Lyme cases have begun occurring into November through January on Long Island over the past 5 years.
The impact of seasonal changes on infectious diseases overall is difficult to predict. The seasons for cold weather diseases such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, for example, may become shorter or milder while viruses more common in the summer, such as enteroviruses, may become a risk year-round.
Natural disasters pose multiple risks
Natural disasters can pose immediate dangers to families and have a significant impact on mental health, but that’s not their only potential impact.
“Severe weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes are well established in the climate change literature as an effect of increased temperatures and more volatile weather systems, but they also have a significant effect on infectious diseases and on children in particular,” Dr. Hymes said. “Hurricanes and flash floods can cause increases in infectious disease outbreaks through a variety of different ways.”
They can bring saltwater, freshwater, and sometimes soil organisms into the food and water supplies, and lead to sewage contamination from overloaded sewers, overflowing storm drains, and loss of power or pumps. Displaced animal vectors, such as rats, can lead to spread of other diseases, such as plague, hantavirus, typhus, and rabies.
Examples of saltwater organisms include Vibrio, Aeromonas, and Mycobacterium marinum, all of which can cause infections in wounds and/or diarrheal illness or bacteremia. Similarly, organisms from freshwater and soil that can cause serious illness or death include Aeromonas, Pseudomonas, Amebiasis, Giardia, and Legionella. Without access to clean water, or with contamination from overflowing sewage, cryptosporidium, Escherichia coli, salmonella, typhoid, norovirus, hepatitis A and E, and even cholera can also become problems as well.
In Houston following Hurricane Harvey, for example, cellulitis cases doubled and included infections from organisms different from the usual suspects. Scrapes and cuts that occurred during the storm also festered sooner.
Cases of disease linked to Hurricane Katrina in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report included 6 cases of cholera, 17 cases of other vibrio – including five that resulted in death – and reported cases of norovirus, Escherichia coli, salmonella, and influenza and pneumonia from overcrowding of evacuees.
You can help in a variety of ways
You can play several key roles as the world’s climate changes, starting with preparing for the changes. You should familiarize themselves with new and emerging infections, or those that have been around a while but not seen in your areas, such as Lyme, Zika, and Dengue.
“If you haven’t seen them already, you likely will due to movements of vector-borne infections that can occur due to climate change,” Dr. Hymes said. “You also want to expect the usual common diseases, but maybe at unsuspected times,” he added. “If you have a pediatric patient who looks like they have Coxsackie virus but it’s February, if it’s been a warm February, it may very well be Coxsackie virus.”
Following natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes and tornadoes, consider who your patients are. If they’re evacuees, are they living in overcrowded conditions? Do they have access to clean water? If not, explain the need to boil water if they can, or to use iodine tablets or a portable pump filter. Consider that some infections may involve unexpected or odd organisms, such as legionella pneumonia or vibrio cellulitis, and contact your local infectious disease doctor as needed.
You also can make personal lifestyle changes that, while small, can add up in the aggregate in reducing carbon footprints, such as purchasing an electric or hybrid car and converting their homes to solar power.
“For very little money, you can purchase carbon offsets,” Dr. Hymes said, such as $10-$15 a month for wind power offsets with home electricity or $5-$10 a month for car or plane travel.
“But really, the most important thing we can do as pediatricians is educate,” Dr. Hymes said. “Taking opportunities every day in your office to educate your patients and educate your colleagues about the importance of climate change in our patients’ health and our own children’s health is super, super important.”
Dr. Hymes and Dr. Boykan had no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM AAP 2020