User login
Richard Franki is the associate editor who writes and creates graphs. He started with the company in 1987, when it was known as the International Medical News Group. In his years as a journalist, Richard has worked for Cap Cities/ABC, Disney, Harcourt, Elsevier, Quadrant, Frontline, and Internet Brands. In the 1990s, he was a contributor to the ill-fated Indications column, predecessor of Livin' on the MDedge.
COVID-19: U.S. sets new weekly high in children
the American Academy of Pediatrics announced Nov. 2.
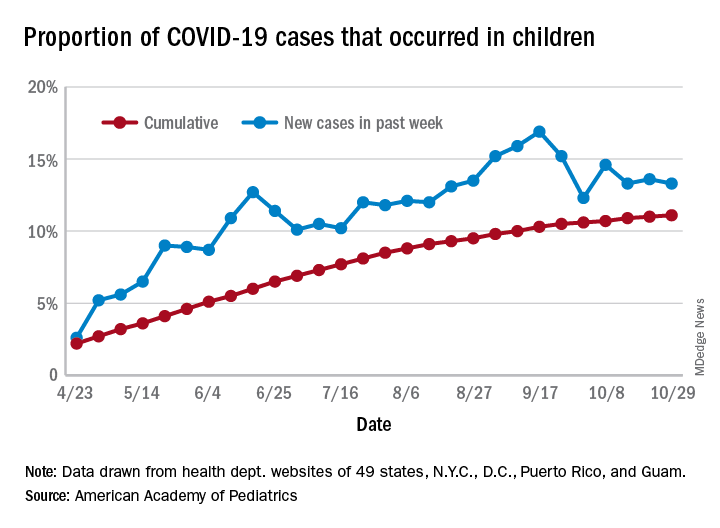
For the week, over 61,000 cases were reported in children, bringing the number of COVID-19 cases for the month of October to nearly 200,000 and the total since the start of the pandemic to over 853,000, the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly report.
“These numbers reflect a disturbing increase in cases throughout most of the United States in all populations, especially among young adults,” Yvonne Maldonado, MD, chair of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases, said in a separate statement. “We are entering a heightened wave of infections around the country. We would encourage family holiday gatherings to be avoided if possible, especially if there are high-risk individuals in the household.”
For the week ending Oct. 29, children represented 13.3% of all cases, possibly constituting a minitrend of stability over the past 3 weeks. For the full length of the pandemic, 11.1% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, although severe illness is much less common: 1.7% of all hospitalizations (data from 24 states and New York City) and 0.06% of all deaths (data from 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA report said.
Other data show that 1,134 per 100,000 children in the United States have been infected by the coronavirus, up from 1,053 the previous week, with state rates ranging from 221 per 100,000 in Vermont to 3,321 in North Dakota. In Wyoming, 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, the highest of any state, while New Jersey has the lowest rate at 4.9%, the AAP/CHA report showed.
In the 10 states making testing data available, children represent the lowest percentage of tests in Iowa (5.0%) and the highest in Indiana (16.9%). Iowa, however, has the highest positivity rate for children at 14.6%, along with Nevada, while West Virginia has the lowest at 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said in the report.
These numbers, however, may not be telling the whole story. “The number of reported COVID-19 cases in children is likely an undercount because children’s symptoms are often mild and they may not be tested for every illness,” the AAP said in its statement.
“We urge policy makers to listen to doctors and public health experts rather than level baseless accusations against them. Physicians, nurses and other health care professionals have put their lives on the line to protect our communities. We can all do our part to protect them, and our communities, by wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and getting our flu immunizations,” AAP President Sally Goza, MD, said in the AAP statement.
the American Academy of Pediatrics announced Nov. 2.

For the week, over 61,000 cases were reported in children, bringing the number of COVID-19 cases for the month of October to nearly 200,000 and the total since the start of the pandemic to over 853,000, the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly report.
“These numbers reflect a disturbing increase in cases throughout most of the United States in all populations, especially among young adults,” Yvonne Maldonado, MD, chair of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases, said in a separate statement. “We are entering a heightened wave of infections around the country. We would encourage family holiday gatherings to be avoided if possible, especially if there are high-risk individuals in the household.”
For the week ending Oct. 29, children represented 13.3% of all cases, possibly constituting a minitrend of stability over the past 3 weeks. For the full length of the pandemic, 11.1% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, although severe illness is much less common: 1.7% of all hospitalizations (data from 24 states and New York City) and 0.06% of all deaths (data from 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA report said.
Other data show that 1,134 per 100,000 children in the United States have been infected by the coronavirus, up from 1,053 the previous week, with state rates ranging from 221 per 100,000 in Vermont to 3,321 in North Dakota. In Wyoming, 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, the highest of any state, while New Jersey has the lowest rate at 4.9%, the AAP/CHA report showed.
In the 10 states making testing data available, children represent the lowest percentage of tests in Iowa (5.0%) and the highest in Indiana (16.9%). Iowa, however, has the highest positivity rate for children at 14.6%, along with Nevada, while West Virginia has the lowest at 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said in the report.
These numbers, however, may not be telling the whole story. “The number of reported COVID-19 cases in children is likely an undercount because children’s symptoms are often mild and they may not be tested for every illness,” the AAP said in its statement.
“We urge policy makers to listen to doctors and public health experts rather than level baseless accusations against them. Physicians, nurses and other health care professionals have put their lives on the line to protect our communities. We can all do our part to protect them, and our communities, by wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and getting our flu immunizations,” AAP President Sally Goza, MD, said in the AAP statement.
the American Academy of Pediatrics announced Nov. 2.

For the week, over 61,000 cases were reported in children, bringing the number of COVID-19 cases for the month of October to nearly 200,000 and the total since the start of the pandemic to over 853,000, the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly report.
“These numbers reflect a disturbing increase in cases throughout most of the United States in all populations, especially among young adults,” Yvonne Maldonado, MD, chair of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases, said in a separate statement. “We are entering a heightened wave of infections around the country. We would encourage family holiday gatherings to be avoided if possible, especially if there are high-risk individuals in the household.”
For the week ending Oct. 29, children represented 13.3% of all cases, possibly constituting a minitrend of stability over the past 3 weeks. For the full length of the pandemic, 11.1% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, although severe illness is much less common: 1.7% of all hospitalizations (data from 24 states and New York City) and 0.06% of all deaths (data from 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA report said.
Other data show that 1,134 per 100,000 children in the United States have been infected by the coronavirus, up from 1,053 the previous week, with state rates ranging from 221 per 100,000 in Vermont to 3,321 in North Dakota. In Wyoming, 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, the highest of any state, while New Jersey has the lowest rate at 4.9%, the AAP/CHA report showed.
In the 10 states making testing data available, children represent the lowest percentage of tests in Iowa (5.0%) and the highest in Indiana (16.9%). Iowa, however, has the highest positivity rate for children at 14.6%, along with Nevada, while West Virginia has the lowest at 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said in the report.
These numbers, however, may not be telling the whole story. “The number of reported COVID-19 cases in children is likely an undercount because children’s symptoms are often mild and they may not be tested for every illness,” the AAP said in its statement.
“We urge policy makers to listen to doctors and public health experts rather than level baseless accusations against them. Physicians, nurses and other health care professionals have put their lives on the line to protect our communities. We can all do our part to protect them, and our communities, by wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and getting our flu immunizations,” AAP President Sally Goza, MD, said in the AAP statement.
Health sector has spent $464 million on lobbying in 2020
, according to the Center for Responsive Politics.
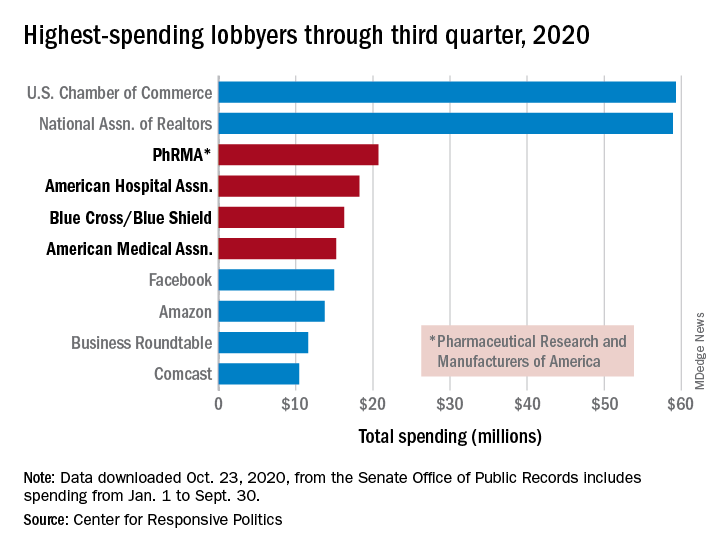
PhRMA spent $20.7 million on lobbying through the end of September, good enough for third on the overall list of U.S. companies and organizations. Three other members of the health sector made the top 10: the American Hospital Association ($18.3 million), BlueCross/BlueShield ($16.3 million), and the American Medical Association ($15.2 million), the center reported.
Total spending by the health sector was $464 million from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30, topping the finance/insurance/real estate sector at $403 million, and miscellaneous business at $371 million. Miscellaneous business is the home of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, the annual leader in such spending for the last 20 years, based on data from the Senate Office of Public Records.
The largest share of health sector spending came from pharmaceuticals/health products, with a total of almost $233 million, just slightly more than the sector’s four other constituents combined: hospitals/nursing homes ($80 million), health services/HMOs ($75 million), health professionals ($67 million), and miscellaneous health ($9.5 million), the center said on OpenSecrets.org.
Taking one step down from the sector level, that $233 million made pharmaceuticals/health products the highest spending of about 100 industries in 2020, nearly doubling the efforts of electronics manufacturing and equipment ($118 million), which came a distant second. Hospitals/nursing homes was eighth on the industry list, the center noted.
, according to the Center for Responsive Politics.

PhRMA spent $20.7 million on lobbying through the end of September, good enough for third on the overall list of U.S. companies and organizations. Three other members of the health sector made the top 10: the American Hospital Association ($18.3 million), BlueCross/BlueShield ($16.3 million), and the American Medical Association ($15.2 million), the center reported.
Total spending by the health sector was $464 million from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30, topping the finance/insurance/real estate sector at $403 million, and miscellaneous business at $371 million. Miscellaneous business is the home of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, the annual leader in such spending for the last 20 years, based on data from the Senate Office of Public Records.
The largest share of health sector spending came from pharmaceuticals/health products, with a total of almost $233 million, just slightly more than the sector’s four other constituents combined: hospitals/nursing homes ($80 million), health services/HMOs ($75 million), health professionals ($67 million), and miscellaneous health ($9.5 million), the center said on OpenSecrets.org.
Taking one step down from the sector level, that $233 million made pharmaceuticals/health products the highest spending of about 100 industries in 2020, nearly doubling the efforts of electronics manufacturing and equipment ($118 million), which came a distant second. Hospitals/nursing homes was eighth on the industry list, the center noted.
, according to the Center for Responsive Politics.

PhRMA spent $20.7 million on lobbying through the end of September, good enough for third on the overall list of U.S. companies and organizations. Three other members of the health sector made the top 10: the American Hospital Association ($18.3 million), BlueCross/BlueShield ($16.3 million), and the American Medical Association ($15.2 million), the center reported.
Total spending by the health sector was $464 million from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30, topping the finance/insurance/real estate sector at $403 million, and miscellaneous business at $371 million. Miscellaneous business is the home of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, the annual leader in such spending for the last 20 years, based on data from the Senate Office of Public Records.
The largest share of health sector spending came from pharmaceuticals/health products, with a total of almost $233 million, just slightly more than the sector’s four other constituents combined: hospitals/nursing homes ($80 million), health services/HMOs ($75 million), health professionals ($67 million), and miscellaneous health ($9.5 million), the center said on OpenSecrets.org.
Taking one step down from the sector level, that $233 million made pharmaceuticals/health products the highest spending of about 100 industries in 2020, nearly doubling the efforts of electronics manufacturing and equipment ($118 million), which came a distant second. Hospitals/nursing homes was eighth on the industry list, the center noted.
The new one-percenters: Children with COVID-19
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
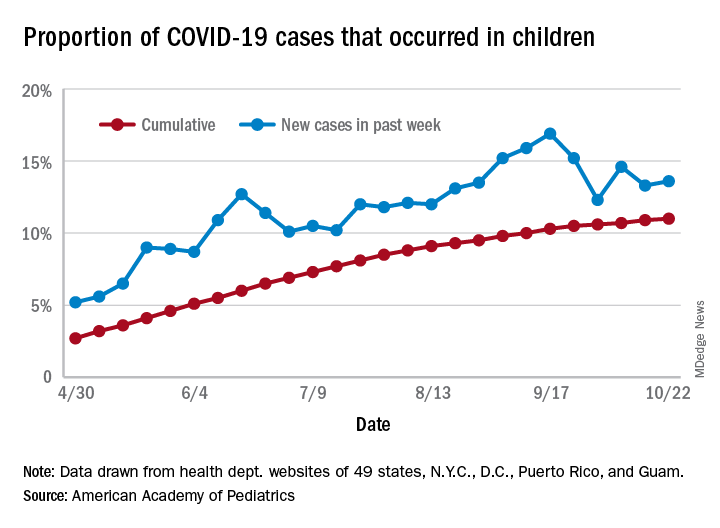
There have been 1,052 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 22, and that works out to 1.05% of all children in the country. The cumulative number of pediatric cases is 792,188, and children now represent 11% of all COVID-19 cases, the AAP and the CHA reported Oct. 26.
There were just over 50,000 new child cases reported in the week ending Oct. 22, which was 13.6% of the national total of almost 370,000. That’s up slightly from the 13.3% the previous week but still down from the spike seen in mid-September, based on the data collected from the websites of 49 state health departments (New York does not report ages), along with the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The state-level data show that California has had more COVID-19 cases in children (92,864) than any other state, although Texas has reported ages for only 7% of its confirmed cases. Illinois is next with 46,006 cases, followed by Florida at 45,575, although Florida is using an age range of 0-14 years to define a child case, the AAP and CHA noted.
Other measures largely put small states at the extremes:
- North Dakota has the highest cumulative rate: 2,954 cases per 100,000 children.
- Vermont has the lowest cumulative rate: 190.5 per 100,000.
- Wyoming has the highest proportion of cases in children: 27.7%.
- New Jersey has the lowest proportion of child cases: 4.6%.
There were no COVID-19–related deaths in children reported the week ending Oct. 22, so the total number remains at 120, which is just 0.06% of the total for all ages, based on data from 42 states and New York City. Hospitalization figures put admissions at almost 5,600 in children, or 1.7% of all hospitalizations, although those data come from just 24 states and New York City, the AAP and CHA said.
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

There have been 1,052 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 22, and that works out to 1.05% of all children in the country. The cumulative number of pediatric cases is 792,188, and children now represent 11% of all COVID-19 cases, the AAP and the CHA reported Oct. 26.
There were just over 50,000 new child cases reported in the week ending Oct. 22, which was 13.6% of the national total of almost 370,000. That’s up slightly from the 13.3% the previous week but still down from the spike seen in mid-September, based on the data collected from the websites of 49 state health departments (New York does not report ages), along with the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The state-level data show that California has had more COVID-19 cases in children (92,864) than any other state, although Texas has reported ages for only 7% of its confirmed cases. Illinois is next with 46,006 cases, followed by Florida at 45,575, although Florida is using an age range of 0-14 years to define a child case, the AAP and CHA noted.
Other measures largely put small states at the extremes:
- North Dakota has the highest cumulative rate: 2,954 cases per 100,000 children.
- Vermont has the lowest cumulative rate: 190.5 per 100,000.
- Wyoming has the highest proportion of cases in children: 27.7%.
- New Jersey has the lowest proportion of child cases: 4.6%.
There were no COVID-19–related deaths in children reported the week ending Oct. 22, so the total number remains at 120, which is just 0.06% of the total for all ages, based on data from 42 states and New York City. Hospitalization figures put admissions at almost 5,600 in children, or 1.7% of all hospitalizations, although those data come from just 24 states and New York City, the AAP and CHA said.
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

There have been 1,052 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 22, and that works out to 1.05% of all children in the country. The cumulative number of pediatric cases is 792,188, and children now represent 11% of all COVID-19 cases, the AAP and the CHA reported Oct. 26.
There were just over 50,000 new child cases reported in the week ending Oct. 22, which was 13.6% of the national total of almost 370,000. That’s up slightly from the 13.3% the previous week but still down from the spike seen in mid-September, based on the data collected from the websites of 49 state health departments (New York does not report ages), along with the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The state-level data show that California has had more COVID-19 cases in children (92,864) than any other state, although Texas has reported ages for only 7% of its confirmed cases. Illinois is next with 46,006 cases, followed by Florida at 45,575, although Florida is using an age range of 0-14 years to define a child case, the AAP and CHA noted.
Other measures largely put small states at the extremes:
- North Dakota has the highest cumulative rate: 2,954 cases per 100,000 children.
- Vermont has the lowest cumulative rate: 190.5 per 100,000.
- Wyoming has the highest proportion of cases in children: 27.7%.
- New Jersey has the lowest proportion of child cases: 4.6%.
There were no COVID-19–related deaths in children reported the week ending Oct. 22, so the total number remains at 120, which is just 0.06% of the total for all ages, based on data from 42 states and New York City. Hospitalization figures put admissions at almost 5,600 in children, or 1.7% of all hospitalizations, although those data come from just 24 states and New York City, the AAP and CHA said.
Survey: Acceptance of COVID-19 vaccine dips below 50%
Less than half of Americans now say that they would get a coronavirus vaccine if one became available, according to a survey conducted Oct. 8-10.
the lowest number since the weekly survey began at the end of February, digital media company Morning Consult reported.
Americans’ willingness to receive such a vaccine reached its high point, 72%, in early April but has been steadily dropping. “Overall willingness has hovered around 50% throughout September, fueled primarily by a sharp drop among Democrats since mid-August, around the time reports of White House interference at the Food and Drug Administration and other federal health agencies began to command more public attention,” Morning Consult noted.
Despite that drop, a majority of Democrats (55%) are still willing to get a COVID-19 vaccine, compared with 48% of Republicans and just 41% of independents. The willingness gap between the two parties was quite a bit wider in the previous poll, conducted Oct. 1-4: 60% of Democrats versus 48% for Republicans, the company said.
“Keeping with longstanding trends, the survey also shows women were less likely to say they’d seek a vaccine than men (42% to 55%), as were people with lower education levels and those who live in rural areas,” the news outlet added.
The latest poll results also show that 33% of respondents (43% of Republicans/25% of Democrats) are socializing in public places. The overall number was just 8% in mid-April but was up to 27% by mid-June. The proportion of all adults who believe in the effectiveness of face masks has been around 80% since April, but there is a significant gap between those who strongly approve of President Trump (66%) and those who strongly disapprove (95%), Morning Consult said.
Less than half of Americans now say that they would get a coronavirus vaccine if one became available, according to a survey conducted Oct. 8-10.
the lowest number since the weekly survey began at the end of February, digital media company Morning Consult reported.
Americans’ willingness to receive such a vaccine reached its high point, 72%, in early April but has been steadily dropping. “Overall willingness has hovered around 50% throughout September, fueled primarily by a sharp drop among Democrats since mid-August, around the time reports of White House interference at the Food and Drug Administration and other federal health agencies began to command more public attention,” Morning Consult noted.
Despite that drop, a majority of Democrats (55%) are still willing to get a COVID-19 vaccine, compared with 48% of Republicans and just 41% of independents. The willingness gap between the two parties was quite a bit wider in the previous poll, conducted Oct. 1-4: 60% of Democrats versus 48% for Republicans, the company said.
“Keeping with longstanding trends, the survey also shows women were less likely to say they’d seek a vaccine than men (42% to 55%), as were people with lower education levels and those who live in rural areas,” the news outlet added.
The latest poll results also show that 33% of respondents (43% of Republicans/25% of Democrats) are socializing in public places. The overall number was just 8% in mid-April but was up to 27% by mid-June. The proportion of all adults who believe in the effectiveness of face masks has been around 80% since April, but there is a significant gap between those who strongly approve of President Trump (66%) and those who strongly disapprove (95%), Morning Consult said.
Less than half of Americans now say that they would get a coronavirus vaccine if one became available, according to a survey conducted Oct. 8-10.
the lowest number since the weekly survey began at the end of February, digital media company Morning Consult reported.
Americans’ willingness to receive such a vaccine reached its high point, 72%, in early April but has been steadily dropping. “Overall willingness has hovered around 50% throughout September, fueled primarily by a sharp drop among Democrats since mid-August, around the time reports of White House interference at the Food and Drug Administration and other federal health agencies began to command more public attention,” Morning Consult noted.
Despite that drop, a majority of Democrats (55%) are still willing to get a COVID-19 vaccine, compared with 48% of Republicans and just 41% of independents. The willingness gap between the two parties was quite a bit wider in the previous poll, conducted Oct. 1-4: 60% of Democrats versus 48% for Republicans, the company said.
“Keeping with longstanding trends, the survey also shows women were less likely to say they’d seek a vaccine than men (42% to 55%), as were people with lower education levels and those who live in rural areas,” the news outlet added.
The latest poll results also show that 33% of respondents (43% of Republicans/25% of Democrats) are socializing in public places. The overall number was just 8% in mid-April but was up to 27% by mid-June. The proportion of all adults who believe in the effectiveness of face masks has been around 80% since April, but there is a significant gap between those who strongly approve of President Trump (66%) and those who strongly disapprove (95%), Morning Consult said.
Latest week brings 44,000 more children with COVID-19
in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
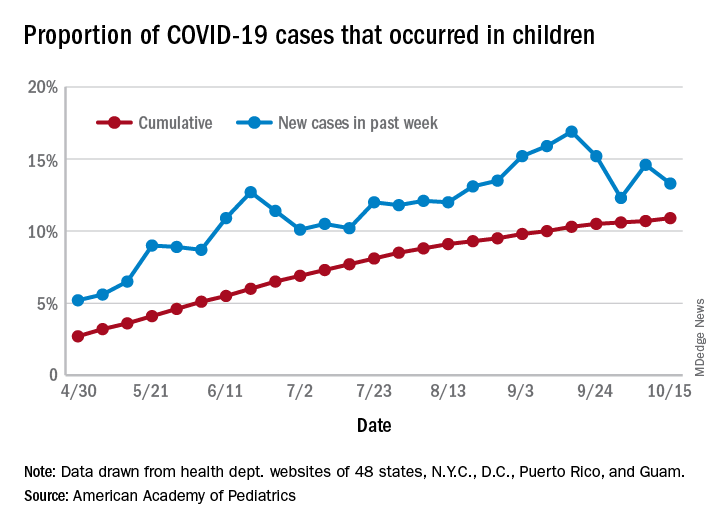
The total number of COVID-19 cases among children was 741,891 as of Oct. 15, which puts the cumulative proportion at 10.9% of the 6.8 million cases reported in all ages by 49 states (New York does not report ages), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The 44,258 new cases in children represented 13.3% of all cases reported during the week ending Oct. 15, down from 14.6% the previous week (children make up almost 23% of the total U.S. population), the AAP/CHA data show.
Those data also indicate that there have been almost 986 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children in the United States. Corresponding rates among the states range from 181 per 100,000 in Vermont to 2,581 per 100,000 in North Dakota. Tennessee (2,277) and South Carolina (2,212) are the only other states above 2,000, according to the report.
California has reported the most child cases, 89,843 (1,010 per 100,000 children), so far, followed by Florida (44,199), Illinois (42,132), and Tennessee (40,137). Seven other states have had over 20,000 cases each, the AAP and CHA noted.
Measures of severe illness continue to be low, although the data are less comprehensive. Children represent only 1.7% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations (24 states and N.Y.C. reporting) and 0.07% of all deaths (42 states and N.Y.C. reporting). Thirteen states and D.C. have had no deaths yet, while Texas has reported three times as many (27) as any other state (Arizona is next with 9, although N.Y.C. has had 15), the AAP/CHA report said.
in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of COVID-19 cases among children was 741,891 as of Oct. 15, which puts the cumulative proportion at 10.9% of the 6.8 million cases reported in all ages by 49 states (New York does not report ages), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The 44,258 new cases in children represented 13.3% of all cases reported during the week ending Oct. 15, down from 14.6% the previous week (children make up almost 23% of the total U.S. population), the AAP/CHA data show.
Those data also indicate that there have been almost 986 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children in the United States. Corresponding rates among the states range from 181 per 100,000 in Vermont to 2,581 per 100,000 in North Dakota. Tennessee (2,277) and South Carolina (2,212) are the only other states above 2,000, according to the report.
California has reported the most child cases, 89,843 (1,010 per 100,000 children), so far, followed by Florida (44,199), Illinois (42,132), and Tennessee (40,137). Seven other states have had over 20,000 cases each, the AAP and CHA noted.
Measures of severe illness continue to be low, although the data are less comprehensive. Children represent only 1.7% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations (24 states and N.Y.C. reporting) and 0.07% of all deaths (42 states and N.Y.C. reporting). Thirteen states and D.C. have had no deaths yet, while Texas has reported three times as many (27) as any other state (Arizona is next with 9, although N.Y.C. has had 15), the AAP/CHA report said.
in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of COVID-19 cases among children was 741,891 as of Oct. 15, which puts the cumulative proportion at 10.9% of the 6.8 million cases reported in all ages by 49 states (New York does not report ages), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The 44,258 new cases in children represented 13.3% of all cases reported during the week ending Oct. 15, down from 14.6% the previous week (children make up almost 23% of the total U.S. population), the AAP/CHA data show.
Those data also indicate that there have been almost 986 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children in the United States. Corresponding rates among the states range from 181 per 100,000 in Vermont to 2,581 per 100,000 in North Dakota. Tennessee (2,277) and South Carolina (2,212) are the only other states above 2,000, according to the report.
California has reported the most child cases, 89,843 (1,010 per 100,000 children), so far, followed by Florida (44,199), Illinois (42,132), and Tennessee (40,137). Seven other states have had over 20,000 cases each, the AAP and CHA noted.
Measures of severe illness continue to be low, although the data are less comprehensive. Children represent only 1.7% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations (24 states and N.Y.C. reporting) and 0.07% of all deaths (42 states and N.Y.C. reporting). Thirteen states and D.C. have had no deaths yet, while Texas has reported three times as many (27) as any other state (Arizona is next with 9, although N.Y.C. has had 15), the AAP/CHA report said.
What’s in a number? 697,633 children with COVID-19
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
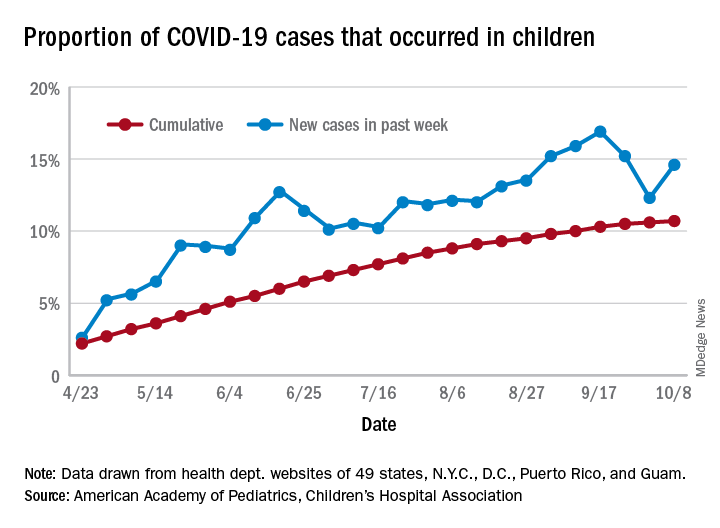
For the week, 14.6% of all COVID-19 cases reported in the United States occurred in children, after 2 consecutive weeks of declines that saw the proportion drop from 16.9% to 12.3%. The cumulative rate of child cases for the entire pandemic is 10.7%, with total child cases in the United States now up to 697,633 and cases among all ages at just over 6.5 million, the AAP and the CHA said Oct. 12 in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Nationally, there were 927 cases reported per 100,000 children as of Oct. 8, with rates at the state level varying from 176 per 100,000 in Vermont to 2,221 per 100,000 in North Dakota. Two other states were over 2,000 cases per 100,000 children: Tennessee (2,155) and South Carolina (2,116), based on data from the health departments of 49 states (New York does not report age distribution), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Severe illness continues to be rare in children, and national (25 states and New York City) hospitalization rates dropped in the last week. The proportion of hospitalizations occurring in children slipped from a pandemic high of 1.8% the previous week to 1.7% during the week of Oct. 8, and the rate of hospitalizations for children with COVID-19 was down to 1.4% from 1.6% the week before and 1.9% on Sept. 3, the AAP and the CHA said.
Mortality data from 42 states and New York City also show a decline. For the third consecutive week, children represented just 0.06% of all COVID-19 deaths in the United States, down from a high of 0.07% on Sept. 17. Only 0.02% of all cases in children have resulted in death, and that figure has been dropping since early June, when it reached 0.06%, according to the AAP/CHA report. As of Oct. 8, there have been 115 total deaths reported in children.
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

For the week, 14.6% of all COVID-19 cases reported in the United States occurred in children, after 2 consecutive weeks of declines that saw the proportion drop from 16.9% to 12.3%. The cumulative rate of child cases for the entire pandemic is 10.7%, with total child cases in the United States now up to 697,633 and cases among all ages at just over 6.5 million, the AAP and the CHA said Oct. 12 in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Nationally, there were 927 cases reported per 100,000 children as of Oct. 8, with rates at the state level varying from 176 per 100,000 in Vermont to 2,221 per 100,000 in North Dakota. Two other states were over 2,000 cases per 100,000 children: Tennessee (2,155) and South Carolina (2,116), based on data from the health departments of 49 states (New York does not report age distribution), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Severe illness continues to be rare in children, and national (25 states and New York City) hospitalization rates dropped in the last week. The proportion of hospitalizations occurring in children slipped from a pandemic high of 1.8% the previous week to 1.7% during the week of Oct. 8, and the rate of hospitalizations for children with COVID-19 was down to 1.4% from 1.6% the week before and 1.9% on Sept. 3, the AAP and the CHA said.
Mortality data from 42 states and New York City also show a decline. For the third consecutive week, children represented just 0.06% of all COVID-19 deaths in the United States, down from a high of 0.07% on Sept. 17. Only 0.02% of all cases in children have resulted in death, and that figure has been dropping since early June, when it reached 0.06%, according to the AAP/CHA report. As of Oct. 8, there have been 115 total deaths reported in children.
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

For the week, 14.6% of all COVID-19 cases reported in the United States occurred in children, after 2 consecutive weeks of declines that saw the proportion drop from 16.9% to 12.3%. The cumulative rate of child cases for the entire pandemic is 10.7%, with total child cases in the United States now up to 697,633 and cases among all ages at just over 6.5 million, the AAP and the CHA said Oct. 12 in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Nationally, there were 927 cases reported per 100,000 children as of Oct. 8, with rates at the state level varying from 176 per 100,000 in Vermont to 2,221 per 100,000 in North Dakota. Two other states were over 2,000 cases per 100,000 children: Tennessee (2,155) and South Carolina (2,116), based on data from the health departments of 49 states (New York does not report age distribution), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Severe illness continues to be rare in children, and national (25 states and New York City) hospitalization rates dropped in the last week. The proportion of hospitalizations occurring in children slipped from a pandemic high of 1.8% the previous week to 1.7% during the week of Oct. 8, and the rate of hospitalizations for children with COVID-19 was down to 1.4% from 1.6% the week before and 1.9% on Sept. 3, the AAP and the CHA said.
Mortality data from 42 states and New York City also show a decline. For the third consecutive week, children represented just 0.06% of all COVID-19 deaths in the United States, down from a high of 0.07% on Sept. 17. Only 0.02% of all cases in children have resulted in death, and that figure has been dropping since early June, when it reached 0.06%, according to the AAP/CHA report. As of Oct. 8, there have been 115 total deaths reported in children.
One measure of child COVID-19 may be trending downward
After increasing for several weeks, the proportion of new COVID-19 cases occurring in children has dropped for the second week in a row, according to data in a new report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
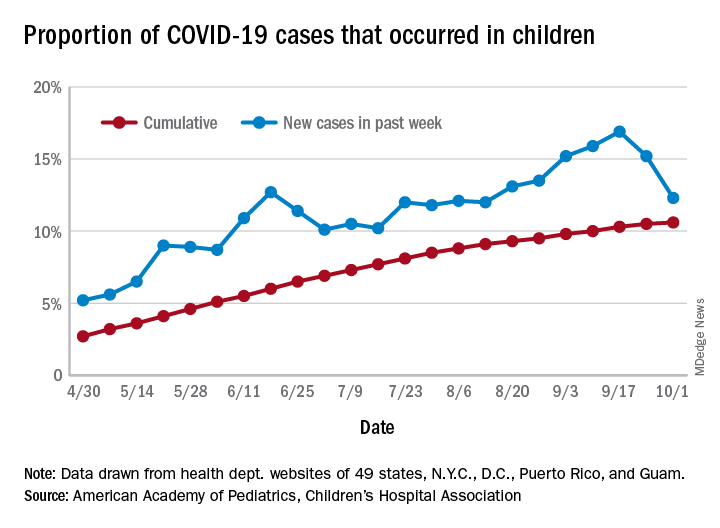
COVID-19 cases in children accounted for 12.3% of all new cases in the United States for the week ending Oct. 1, down from 15.2% the previous week. That measure had reached its highest point, 16.9%, just one week earlier (Sept. 17), the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
based on data from the health departments of 49 states (New York does not provide ages on its website), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The child COVID-19 rate for the United States was 874 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 1, and that figure has doubled since the end of July. At the state level, the highest rates can be found in Tennessee (2,031.4 per 100,000), North Dakota (2,029.6), and South Carolina (2,002.6), with the lowest rates in Vermont (168.9), Maine (229.1), and New Hampshire (268.3), the AAP/CHA report shows.
The children of Wyoming make up the largest share, 22.4%, of any state’s COVID-19 cases, followed by North Dakota and Tennessee, both at 18.3%. New Jersey is lower than any other state at 3.9%, although New York City is a slightly lower 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said.
“The data are limited because the states differ in how they report the data, and it is unknown how many children have been infected but not tested. It is unclear how much of the increase in child cases is due to increased testing capacity,” the AAP said in an earlier statement.
After increasing for several weeks, the proportion of new COVID-19 cases occurring in children has dropped for the second week in a row, according to data in a new report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

COVID-19 cases in children accounted for 12.3% of all new cases in the United States for the week ending Oct. 1, down from 15.2% the previous week. That measure had reached its highest point, 16.9%, just one week earlier (Sept. 17), the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
based on data from the health departments of 49 states (New York does not provide ages on its website), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The child COVID-19 rate for the United States was 874 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 1, and that figure has doubled since the end of July. At the state level, the highest rates can be found in Tennessee (2,031.4 per 100,000), North Dakota (2,029.6), and South Carolina (2,002.6), with the lowest rates in Vermont (168.9), Maine (229.1), and New Hampshire (268.3), the AAP/CHA report shows.
The children of Wyoming make up the largest share, 22.4%, of any state’s COVID-19 cases, followed by North Dakota and Tennessee, both at 18.3%. New Jersey is lower than any other state at 3.9%, although New York City is a slightly lower 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said.
“The data are limited because the states differ in how they report the data, and it is unknown how many children have been infected but not tested. It is unclear how much of the increase in child cases is due to increased testing capacity,” the AAP said in an earlier statement.
After increasing for several weeks, the proportion of new COVID-19 cases occurring in children has dropped for the second week in a row, according to data in a new report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

COVID-19 cases in children accounted for 12.3% of all new cases in the United States for the week ending Oct. 1, down from 15.2% the previous week. That measure had reached its highest point, 16.9%, just one week earlier (Sept. 17), the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
based on data from the health departments of 49 states (New York does not provide ages on its website), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The child COVID-19 rate for the United States was 874 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 1, and that figure has doubled since the end of July. At the state level, the highest rates can be found in Tennessee (2,031.4 per 100,000), North Dakota (2,029.6), and South Carolina (2,002.6), with the lowest rates in Vermont (168.9), Maine (229.1), and New Hampshire (268.3), the AAP/CHA report shows.
The children of Wyoming make up the largest share, 22.4%, of any state’s COVID-19 cases, followed by North Dakota and Tennessee, both at 18.3%. New Jersey is lower than any other state at 3.9%, although New York City is a slightly lower 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said.
“The data are limited because the states differ in how they report the data, and it is unknown how many children have been infected but not tested. It is unclear how much of the increase in child cases is due to increased testing capacity,” the AAP said in an earlier statement.
Counterfeits: An ugly truth in aesthetic medicine
according to the results of two recent surveys of such providers.

“Counterfeit medical devices and injectables may be more prevalent in aesthetic medicine than most practitioners might estimate,” Jordan V. Wang, MD, of Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associates wrote in Dermatologic Surgery, even though “the vast majority [believe] that they are inferior and even potentially harmful.”
In one of the online surveys, conducted among members of the American Society of Dermatologic Surgery, 41.1% of the 616 respondents said they had encountered counterfeit injectables, more than half (56.5%) of whom were solicited to buy such products. Just over 10% had purchased counterfeit injectables, although nearly 80% did so unknowingly, the investigators said.
In the second survey, 37.4% of the 765 respondents (members of the ASDS as well as the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery) said that they had encountered counterfeit medical devices, and nearly half had been approached to purchase such devices. Of those who were approached, 4.6% had actually purchased a counterfeit, but only 6.1% did so unknowingly, Dr. Wang and associates reported.
In the medical device survey, almost a quarter (24.2%) acknowledged that they know of other providers using them, while 29.3% of those surveyed about injectables know of others who use counterfeits, they said.
Over 90% of practitioners in each survey agreed that counterfeits are worse in terms of safety, reliability, and effectiveness, but the proportions were smaller when they were asked if counterfeits were either very or extremely endangering to patient safety: 70.5% for injectables and 59.2% for devices, the investigators said.
Experience with adverse events from counterfeits in patients was reported by 39.7% of respondents to the injectables survey and by 20.1% of those in the device survey, they added.
Majorities in both surveys – 73.7% for injectables and 68.9% for devices – also said that they were either not familiar or only somewhat familiar with the Food and Drug Administration’s regulations on counterfeits. “This is especially problematic considering the potentially severe adverse events and steep punishments,” Dr. Wang and associates wrote.
The authors disclosed that they had no significant interest with commercial supporters. Dr. Wang is now a fellow at the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York.
SOURCE: Wang JV et al. Dermatol. Surg. 2020 Oct;46(10):1323-6.
according to the results of two recent surveys of such providers.

“Counterfeit medical devices and injectables may be more prevalent in aesthetic medicine than most practitioners might estimate,” Jordan V. Wang, MD, of Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associates wrote in Dermatologic Surgery, even though “the vast majority [believe] that they are inferior and even potentially harmful.”
In one of the online surveys, conducted among members of the American Society of Dermatologic Surgery, 41.1% of the 616 respondents said they had encountered counterfeit injectables, more than half (56.5%) of whom were solicited to buy such products. Just over 10% had purchased counterfeit injectables, although nearly 80% did so unknowingly, the investigators said.
In the second survey, 37.4% of the 765 respondents (members of the ASDS as well as the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery) said that they had encountered counterfeit medical devices, and nearly half had been approached to purchase such devices. Of those who were approached, 4.6% had actually purchased a counterfeit, but only 6.1% did so unknowingly, Dr. Wang and associates reported.
In the medical device survey, almost a quarter (24.2%) acknowledged that they know of other providers using them, while 29.3% of those surveyed about injectables know of others who use counterfeits, they said.
Over 90% of practitioners in each survey agreed that counterfeits are worse in terms of safety, reliability, and effectiveness, but the proportions were smaller when they were asked if counterfeits were either very or extremely endangering to patient safety: 70.5% for injectables and 59.2% for devices, the investigators said.
Experience with adverse events from counterfeits in patients was reported by 39.7% of respondents to the injectables survey and by 20.1% of those in the device survey, they added.
Majorities in both surveys – 73.7% for injectables and 68.9% for devices – also said that they were either not familiar or only somewhat familiar with the Food and Drug Administration’s regulations on counterfeits. “This is especially problematic considering the potentially severe adverse events and steep punishments,” Dr. Wang and associates wrote.
The authors disclosed that they had no significant interest with commercial supporters. Dr. Wang is now a fellow at the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York.
SOURCE: Wang JV et al. Dermatol. Surg. 2020 Oct;46(10):1323-6.
according to the results of two recent surveys of such providers.

“Counterfeit medical devices and injectables may be more prevalent in aesthetic medicine than most practitioners might estimate,” Jordan V. Wang, MD, of Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associates wrote in Dermatologic Surgery, even though “the vast majority [believe] that they are inferior and even potentially harmful.”
In one of the online surveys, conducted among members of the American Society of Dermatologic Surgery, 41.1% of the 616 respondents said they had encountered counterfeit injectables, more than half (56.5%) of whom were solicited to buy such products. Just over 10% had purchased counterfeit injectables, although nearly 80% did so unknowingly, the investigators said.
In the second survey, 37.4% of the 765 respondents (members of the ASDS as well as the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery) said that they had encountered counterfeit medical devices, and nearly half had been approached to purchase such devices. Of those who were approached, 4.6% had actually purchased a counterfeit, but only 6.1% did so unknowingly, Dr. Wang and associates reported.
In the medical device survey, almost a quarter (24.2%) acknowledged that they know of other providers using them, while 29.3% of those surveyed about injectables know of others who use counterfeits, they said.
Over 90% of practitioners in each survey agreed that counterfeits are worse in terms of safety, reliability, and effectiveness, but the proportions were smaller when they were asked if counterfeits were either very or extremely endangering to patient safety: 70.5% for injectables and 59.2% for devices, the investigators said.
Experience with adverse events from counterfeits in patients was reported by 39.7% of respondents to the injectables survey and by 20.1% of those in the device survey, they added.
Majorities in both surveys – 73.7% for injectables and 68.9% for devices – also said that they were either not familiar or only somewhat familiar with the Food and Drug Administration’s regulations on counterfeits. “This is especially problematic considering the potentially severe adverse events and steep punishments,” Dr. Wang and associates wrote.
The authors disclosed that they had no significant interest with commercial supporters. Dr. Wang is now a fellow at the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York.
SOURCE: Wang JV et al. Dermatol. Surg. 2020 Oct;46(10):1323-6.
FROM DERMATOLOGIC SURGERY
Children’s opioid harms vary by race, location
or dependence, compared with their White or rural/suburban counterparts, according to a study of 3.2 million Medicaid-enrolled children in North Carolina.
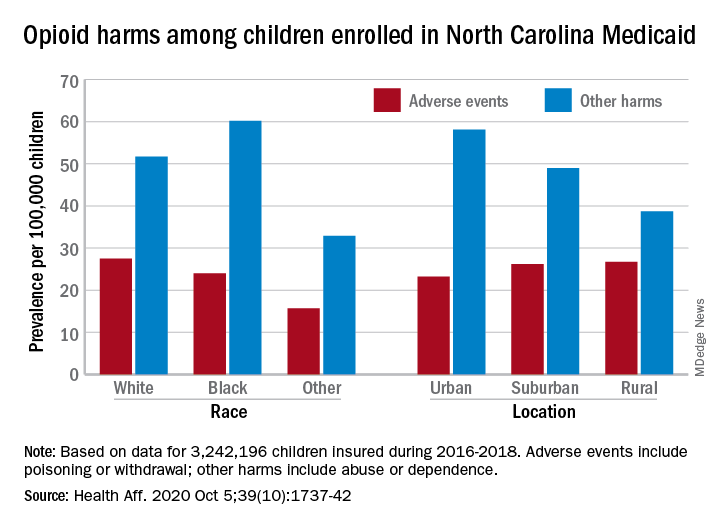
Analysis of the almost 138,000 prescription fills also showed that Black and urban children in North Carolina were less likely to fill a opioid prescription, suggesting a need “for future studies to explore racial and geographic opioid-related inequities in children,” Kelby W. Brown, MA, and associates at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said Oct. 5 in Health Affairs.
In 2016-2018, the prevalence of opioid-related adverse events, such as poisoning or withdrawal, was 24.0 per 100,000 children among Blacks aged 1-17 years, compared with 27.5 per 100,000 for whites. For other opioid-related harms such as abuse or dependence, the order was reversed: 60.2 for Blacks and 51.7 for Whites, the investigators reported. Children of all other races were lowest in both measures.
Geography also appears to play a part. The children in urban areas had the lowest rate of adverse events – 23.2 per 100,000 vs. 26.2 (suburban) and 26.7 (rural) – and the highest rate of other opioid-related harms – 58.1 vs. 49.0 (suburban) and 38.7 (rural), the Medicaid claims data showed.
Analysis of prescription fills revealed that black children aged 1-17 years had a significantly lower rate (2.7%) than Whites (3.1%) or those of other races (3.0%) and that urban children were significantly less likely to fill a prescription (2.7%) for opioids than the other two groups (suburban, 3.1%; rural, 3.4%), Mr. Brown and associates said.
The prescription data also showed that 48.4% of children aged 6-17 years who had an adverse event had filled a prescription for an opioid in the previous 6 months, compared with just 9.4% of those with other opioid-related harms. The median length of time since the last fill? Three days for children with an adverse event and 67 days for those with other harms, they said.
And those prescriptions, it turns out, were not coming just from the physicians of North Carolina. Physicians, with 35.5% of the prescription load, were the main source, but 33.3% of opioid fills in 2016-2018 came from dentists, and another 17.7% were written by advanced practice providers. Among physicians, the leading opioid-prescribing specialists were surgeons, with 17.3% of the total, the investigators reported.
“The distinct and separate groups of clinicians who prescribe opioids to children suggest the need for pediatric opioid prescribing guidelines, particularly for postprocedural pain,” Mr. Brown and associates wrote.
SOURCE: Brown KW et al. Health Aff. 2020;39(10):1737-42.
or dependence, compared with their White or rural/suburban counterparts, according to a study of 3.2 million Medicaid-enrolled children in North Carolina.

Analysis of the almost 138,000 prescription fills also showed that Black and urban children in North Carolina were less likely to fill a opioid prescription, suggesting a need “for future studies to explore racial and geographic opioid-related inequities in children,” Kelby W. Brown, MA, and associates at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said Oct. 5 in Health Affairs.
In 2016-2018, the prevalence of opioid-related adverse events, such as poisoning or withdrawal, was 24.0 per 100,000 children among Blacks aged 1-17 years, compared with 27.5 per 100,000 for whites. For other opioid-related harms such as abuse or dependence, the order was reversed: 60.2 for Blacks and 51.7 for Whites, the investigators reported. Children of all other races were lowest in both measures.
Geography also appears to play a part. The children in urban areas had the lowest rate of adverse events – 23.2 per 100,000 vs. 26.2 (suburban) and 26.7 (rural) – and the highest rate of other opioid-related harms – 58.1 vs. 49.0 (suburban) and 38.7 (rural), the Medicaid claims data showed.
Analysis of prescription fills revealed that black children aged 1-17 years had a significantly lower rate (2.7%) than Whites (3.1%) or those of other races (3.0%) and that urban children were significantly less likely to fill a prescription (2.7%) for opioids than the other two groups (suburban, 3.1%; rural, 3.4%), Mr. Brown and associates said.
The prescription data also showed that 48.4% of children aged 6-17 years who had an adverse event had filled a prescription for an opioid in the previous 6 months, compared with just 9.4% of those with other opioid-related harms. The median length of time since the last fill? Three days for children with an adverse event and 67 days for those with other harms, they said.
And those prescriptions, it turns out, were not coming just from the physicians of North Carolina. Physicians, with 35.5% of the prescription load, were the main source, but 33.3% of opioid fills in 2016-2018 came from dentists, and another 17.7% were written by advanced practice providers. Among physicians, the leading opioid-prescribing specialists were surgeons, with 17.3% of the total, the investigators reported.
“The distinct and separate groups of clinicians who prescribe opioids to children suggest the need for pediatric opioid prescribing guidelines, particularly for postprocedural pain,” Mr. Brown and associates wrote.
SOURCE: Brown KW et al. Health Aff. 2020;39(10):1737-42.
or dependence, compared with their White or rural/suburban counterparts, according to a study of 3.2 million Medicaid-enrolled children in North Carolina.

Analysis of the almost 138,000 prescription fills also showed that Black and urban children in North Carolina were less likely to fill a opioid prescription, suggesting a need “for future studies to explore racial and geographic opioid-related inequities in children,” Kelby W. Brown, MA, and associates at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said Oct. 5 in Health Affairs.
In 2016-2018, the prevalence of opioid-related adverse events, such as poisoning or withdrawal, was 24.0 per 100,000 children among Blacks aged 1-17 years, compared with 27.5 per 100,000 for whites. For other opioid-related harms such as abuse or dependence, the order was reversed: 60.2 for Blacks and 51.7 for Whites, the investigators reported. Children of all other races were lowest in both measures.
Geography also appears to play a part. The children in urban areas had the lowest rate of adverse events – 23.2 per 100,000 vs. 26.2 (suburban) and 26.7 (rural) – and the highest rate of other opioid-related harms – 58.1 vs. 49.0 (suburban) and 38.7 (rural), the Medicaid claims data showed.
Analysis of prescription fills revealed that black children aged 1-17 years had a significantly lower rate (2.7%) than Whites (3.1%) or those of other races (3.0%) and that urban children were significantly less likely to fill a prescription (2.7%) for opioids than the other two groups (suburban, 3.1%; rural, 3.4%), Mr. Brown and associates said.
The prescription data also showed that 48.4% of children aged 6-17 years who had an adverse event had filled a prescription for an opioid in the previous 6 months, compared with just 9.4% of those with other opioid-related harms. The median length of time since the last fill? Three days for children with an adverse event and 67 days for those with other harms, they said.
And those prescriptions, it turns out, were not coming just from the physicians of North Carolina. Physicians, with 35.5% of the prescription load, were the main source, but 33.3% of opioid fills in 2016-2018 came from dentists, and another 17.7% were written by advanced practice providers. Among physicians, the leading opioid-prescribing specialists were surgeons, with 17.3% of the total, the investigators reported.
“The distinct and separate groups of clinicians who prescribe opioids to children suggest the need for pediatric opioid prescribing guidelines, particularly for postprocedural pain,” Mr. Brown and associates wrote.
SOURCE: Brown KW et al. Health Aff. 2020;39(10):1737-42.
FROM HEALTH AFFAIRS
Use of e-cigarettes may be linked to sleep deprivation
compared with those who have never used e-cigarettes, according to the first study to evaluate the association in a large, nationally representative population of young adults.
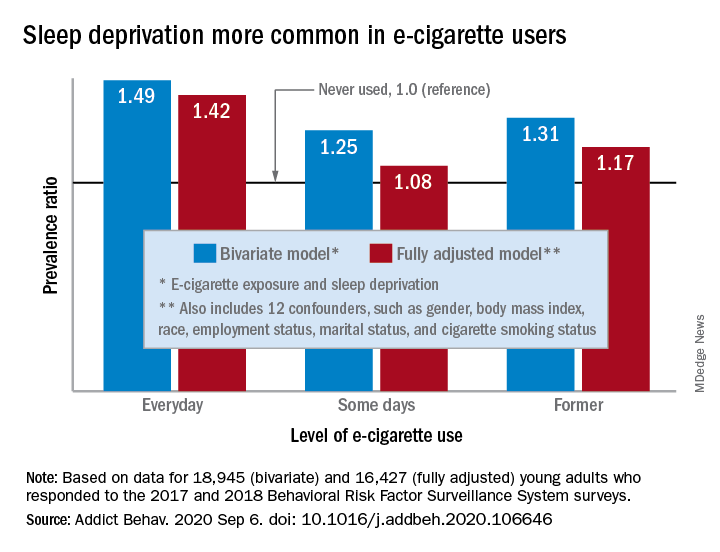
“The e-cigarette use and sleep deprivation association seems to have a dose-response nature as the point estimate of the association increased with increased exposure to e-cigarette,” Sina Kianersi, DVM, and associates at Indiana University, Bloomington, said in Addictive Behaviors.
Sleep deprivation was 49% more prevalent among everyday users of e-cigarettes, compared with nonusers. Prevalence ratios for former users (1.31) and occasional users (1.25) also showed significantly higher sleep deprivation, compared with nonusers, they reported based on a bivariate analysis of data from young adults aged 18-24 years who participated in the 2017 and 2018 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System surveys.
After adjustment for multiple confounders, young adults who currently used e-cigarettes every day were 42% more likely to report sleep deprivation than those who never used e-cigarettes, a difference that was statistically significant. The prevalence of sleep deprivation among those who used e-cigarettes on some days was not significantly higher (prevalence ratio, 1.08), but the ratio between former users and never users was a significant 1.17, the investigators said.
“The nicotine in the inhaled e-cigarette aerosols may have negative effects on sleep architecture and disturb the neurotransmitters that regulate sleep cycle,” they suggested, and since higher doses of nicotine produce greater reductions in sleep duration, “those who use e-cigarette on a daily basis might consume higher doses of nicotine, compared to some days, former, and never users, and therefore get fewer hours of sleep.”
Nicotine withdrawal, on the other hand, has been found to increase sleep duration in a dose-dependent manner, which “could explain the smaller [prevalence ratios] observed for the association between e-cigarette use and sleep deprivation among former and some days e-cigarette users,” Dr. Kianersi and associates added.
The bivariate analysis involved 18,945 survey respondents, of whom 16,427 were included in the fully adjusted model using 12 confounding factors.
SOURCE: Kianersi S et al. Addict Behav. 2020 Sep 6. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106646.
compared with those who have never used e-cigarettes, according to the first study to evaluate the association in a large, nationally representative population of young adults.

“The e-cigarette use and sleep deprivation association seems to have a dose-response nature as the point estimate of the association increased with increased exposure to e-cigarette,” Sina Kianersi, DVM, and associates at Indiana University, Bloomington, said in Addictive Behaviors.
Sleep deprivation was 49% more prevalent among everyday users of e-cigarettes, compared with nonusers. Prevalence ratios for former users (1.31) and occasional users (1.25) also showed significantly higher sleep deprivation, compared with nonusers, they reported based on a bivariate analysis of data from young adults aged 18-24 years who participated in the 2017 and 2018 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System surveys.
After adjustment for multiple confounders, young adults who currently used e-cigarettes every day were 42% more likely to report sleep deprivation than those who never used e-cigarettes, a difference that was statistically significant. The prevalence of sleep deprivation among those who used e-cigarettes on some days was not significantly higher (prevalence ratio, 1.08), but the ratio between former users and never users was a significant 1.17, the investigators said.
“The nicotine in the inhaled e-cigarette aerosols may have negative effects on sleep architecture and disturb the neurotransmitters that regulate sleep cycle,” they suggested, and since higher doses of nicotine produce greater reductions in sleep duration, “those who use e-cigarette on a daily basis might consume higher doses of nicotine, compared to some days, former, and never users, and therefore get fewer hours of sleep.”
Nicotine withdrawal, on the other hand, has been found to increase sleep duration in a dose-dependent manner, which “could explain the smaller [prevalence ratios] observed for the association between e-cigarette use and sleep deprivation among former and some days e-cigarette users,” Dr. Kianersi and associates added.
The bivariate analysis involved 18,945 survey respondents, of whom 16,427 were included in the fully adjusted model using 12 confounding factors.
SOURCE: Kianersi S et al. Addict Behav. 2020 Sep 6. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106646.
compared with those who have never used e-cigarettes, according to the first study to evaluate the association in a large, nationally representative population of young adults.

“The e-cigarette use and sleep deprivation association seems to have a dose-response nature as the point estimate of the association increased with increased exposure to e-cigarette,” Sina Kianersi, DVM, and associates at Indiana University, Bloomington, said in Addictive Behaviors.
Sleep deprivation was 49% more prevalent among everyday users of e-cigarettes, compared with nonusers. Prevalence ratios for former users (1.31) and occasional users (1.25) also showed significantly higher sleep deprivation, compared with nonusers, they reported based on a bivariate analysis of data from young adults aged 18-24 years who participated in the 2017 and 2018 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System surveys.
After adjustment for multiple confounders, young adults who currently used e-cigarettes every day were 42% more likely to report sleep deprivation than those who never used e-cigarettes, a difference that was statistically significant. The prevalence of sleep deprivation among those who used e-cigarettes on some days was not significantly higher (prevalence ratio, 1.08), but the ratio between former users and never users was a significant 1.17, the investigators said.
“The nicotine in the inhaled e-cigarette aerosols may have negative effects on sleep architecture and disturb the neurotransmitters that regulate sleep cycle,” they suggested, and since higher doses of nicotine produce greater reductions in sleep duration, “those who use e-cigarette on a daily basis might consume higher doses of nicotine, compared to some days, former, and never users, and therefore get fewer hours of sleep.”
Nicotine withdrawal, on the other hand, has been found to increase sleep duration in a dose-dependent manner, which “could explain the smaller [prevalence ratios] observed for the association between e-cigarette use and sleep deprivation among former and some days e-cigarette users,” Dr. Kianersi and associates added.
The bivariate analysis involved 18,945 survey respondents, of whom 16,427 were included in the fully adjusted model using 12 confounding factors.
SOURCE: Kianersi S et al. Addict Behav. 2020 Sep 6. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106646.
FROM ADDICTIVE BEHAVIORS