User login
Doug Brunk is a San Diego-based award-winning reporter who began covering health care in 1991. Before joining the company, he wrote for the health sciences division of Columbia University and was an associate editor at Contemporary Long Term Care magazine when it won a Jesse H. Neal Award. His work has been syndicated by the Los Angeles Times and he is the author of two books related to the University of Kentucky Wildcats men's basketball program. Doug has a master’s degree in magazine journalism from the S.I. Newhouse School of Public Communications at Syracuse University. Follow him on Twitter @dougbrunk.
Management of Tinea Capitis in Children Varies, Survey Finds
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The fungal scalp infection tinea capitis affects an estimated 3%-13% of children.
- While international guidelines exist for the treatment of tinea capitis in infants and children, no such document has been developed in the United States.
- Researchers distributed a survey by email to dermatologists through the and the Society for Pediatric Dermatology in the United States, asking about how they treated and managed pediatric patients with tinea capitis; 56 dermatologists participated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Most respondents (88.2%) said they felt comfortable prescribing oral medications prior to confirmation for those aged 2-18 years ( was the most common choice in 60.4% of cases), compared with 81.6% for those aged 2 months to 2 years ( was the most common treatment choice in 41.5% of cases), and 48.7% for those aged 0-2 months ( was the most common choice in 28.6% of cases).
- When asked what topical medication they would start prior to confirmation, most respondents said shampoo (62.3% for those aged 0-2 months and 75.5% each for those aged 2 months to 2 years and those aged 2-18 years), yet between 11.3% and 13% said they would use none.
- The most common form of confirmatory testing was , followed by potassium hydroxide preparation, trichoscopy, and Wood’s lamp.
- More than half of survey respondents would alter their choice of oral medication based on culture results, but most would not change their topical medication preference.
IN PRACTICE:
“The management of tinea capitis in the United States is currently variable, particularly with the introduction of newer antifungals,” the authors wrote. “Future steps involve establishing evidence-based clinical practice guidelines that consider drug efficacy, safety profiles, and costs.”
SOURCE:
Bernard Cohen, MD, of the Departments of Pediatrics and Dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Lower response rates associated with online surveys and predefined age groups restrict the granularity of responses.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The fungal scalp infection tinea capitis affects an estimated 3%-13% of children.
- While international guidelines exist for the treatment of tinea capitis in infants and children, no such document has been developed in the United States.
- Researchers distributed a survey by email to dermatologists through the and the Society for Pediatric Dermatology in the United States, asking about how they treated and managed pediatric patients with tinea capitis; 56 dermatologists participated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Most respondents (88.2%) said they felt comfortable prescribing oral medications prior to confirmation for those aged 2-18 years ( was the most common choice in 60.4% of cases), compared with 81.6% for those aged 2 months to 2 years ( was the most common treatment choice in 41.5% of cases), and 48.7% for those aged 0-2 months ( was the most common choice in 28.6% of cases).
- When asked what topical medication they would start prior to confirmation, most respondents said shampoo (62.3% for those aged 0-2 months and 75.5% each for those aged 2 months to 2 years and those aged 2-18 years), yet between 11.3% and 13% said they would use none.
- The most common form of confirmatory testing was , followed by potassium hydroxide preparation, trichoscopy, and Wood’s lamp.
- More than half of survey respondents would alter their choice of oral medication based on culture results, but most would not change their topical medication preference.
IN PRACTICE:
“The management of tinea capitis in the United States is currently variable, particularly with the introduction of newer antifungals,” the authors wrote. “Future steps involve establishing evidence-based clinical practice guidelines that consider drug efficacy, safety profiles, and costs.”
SOURCE:
Bernard Cohen, MD, of the Departments of Pediatrics and Dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Lower response rates associated with online surveys and predefined age groups restrict the granularity of responses.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The fungal scalp infection tinea capitis affects an estimated 3%-13% of children.
- While international guidelines exist for the treatment of tinea capitis in infants and children, no such document has been developed in the United States.
- Researchers distributed a survey by email to dermatologists through the and the Society for Pediatric Dermatology in the United States, asking about how they treated and managed pediatric patients with tinea capitis; 56 dermatologists participated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Most respondents (88.2%) said they felt comfortable prescribing oral medications prior to confirmation for those aged 2-18 years ( was the most common choice in 60.4% of cases), compared with 81.6% for those aged 2 months to 2 years ( was the most common treatment choice in 41.5% of cases), and 48.7% for those aged 0-2 months ( was the most common choice in 28.6% of cases).
- When asked what topical medication they would start prior to confirmation, most respondents said shampoo (62.3% for those aged 0-2 months and 75.5% each for those aged 2 months to 2 years and those aged 2-18 years), yet between 11.3% and 13% said they would use none.
- The most common form of confirmatory testing was , followed by potassium hydroxide preparation, trichoscopy, and Wood’s lamp.
- More than half of survey respondents would alter their choice of oral medication based on culture results, but most would not change their topical medication preference.
IN PRACTICE:
“The management of tinea capitis in the United States is currently variable, particularly with the introduction of newer antifungals,” the authors wrote. “Future steps involve establishing evidence-based clinical practice guidelines that consider drug efficacy, safety profiles, and costs.”
SOURCE:
Bernard Cohen, MD, of the Departments of Pediatrics and Dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Lower response rates associated with online surveys and predefined age groups restrict the granularity of responses.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Expert Hopes to Expand Ohio Model of Melanoma Case Reporting
SAN DIEGO – Soon after Brett M. Coldiron, MD, launched his Cincinnati-based dermatology and Mohs surgery practice more than 20 years ago, he reported his first three cases of thin melanomas to the Ohio Department of Health, as mandated by state law.
“I got sent reams of paperwork to fill out that I did not understand,” Dr. Coldiron, a past president of the American College of Mohs Surgery and the American Academy of Dermatology, recalled at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “Then, I got chewed out for not reporting sooner and threatened with thousands of dollars in fines if I did not promptly report the forms in the future. It was an obnoxious experience.”
About 15 years later, while testifying at the Ohio Legislature on medical reasons to restrict the use of tanning beds, a lobbyist for the tanning bed industry told him that the melanoma rates had been stable in Ohio for the previous 5 years. “It turns out they were cherry picking certain segments of data to fit their narrative,” Dr. Coldiron said. “I was stunned and it kind of deflated me. I thought about this for a long time, and thought, ‘how do we solve this issue of reporting melanoma cases without adding work to existing staff if you’re a small practice and without spending significant amounts of money? Let’s make this easier.’ ”
In addition to reducing the use of tanning beds, proper reporting of melanoma cases is important for reasons that include efforts to increase sunscreen use and to be counted in ongoing research efforts to obtain a realistic snapshot of melanoma prevalence and incidence, he said.
Quality of melanoma case reporting relies on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Program of Cancer Registries (NPCR), and the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Program, which collects data on the incidence, treatment, staging, and survival for 28% of the US population. All 50 states and US territories require melanoma to be reported to the NPCR, but while most hospital systems have reporting protocols and dedicated data registrars, private practices may not.
Also, many dermatopathology practices operate independently and do not have dedicated registrars and may not report cases. “Melanoma is unique in that it is often completely managed in outpatient settings and these melanomas may never be reported,” said Dr. Coldiron, current president of the Ohio Dermatological Foundation. “That’s the practice gap.” One study published in 2018 found that only 49% of dermatologists knew that melanoma was a reportable disease and only 34% routinely reported newly diagnosed cases to their state’s cancer registry. He characterized melanoma reporting as an unfunded mandate.
“Hospitals are doing the most of them, because they have a registrar,” he said. “Small practices have to assign someone to do this, and it can be difficult to train that person. It’s time consuming. The first time we did it, it took an hour,” but, he said, taking a 2-hour tutorial from the Ohio Department of Health helped.
He noted that there is a lack of awareness and clinicians think it’s the dermatopathologist’s job to report cases, “while the dermatopathologist thinks it’s the clinician’s job,” and many of the entry fields are not applicable to thinner melanomas.
There is also a “patchwork” of ways that state departments of health accept the information, not all electronically, he continued. For example, those in Arizona, Montana, West Virginia, Delaware, Vermont, and Maine accept paper copies only, “meaning you have to download a PDF, fill it out, and fax it back to them,” Dr. Coldiron said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps Cancer Center.
“We have them sign a HIPAA form and take the two-hour online tutorial,” he said. They download data that Ohio dermatologists have faxed to a dedicated secure HIPAA-compliant cloud-based fax line that Dr. Coldiron has set up, and the cases are then sent to the Ohio Department of Health.
Dr. Coldiron and colleagues have also partnered with the University of Cincinnati Clermont, which offers a National Cancer Registries Association–accredited certificate program — one of several nationwide. Students in this program are trained to become cancer registrars. “The university staff are gung-ho about it because they are looking for easy cases to train the students on. Also, the Ohio Department of Health staff are keen to help train the students and even help them find jobs or hire them after they complete the degree. Staff from the department of health and college faculty are fully engaged and supervising. It’s a win-win for all.”
According to Dr. Coldiron, in 2023, 8 Ohio dermatology practices were sending their reports to the fax line he set up and 7 more have signed up in recent months, making 15 practices to date. “It’s self-perpetuating at this point,” he said. “The Ohio Department of Health and the University of Cincinnati are invested in this program long-term.” The fax service costs Dr. Coldiron $42 per month — a small price to pay, he said, for being a clearinghouse for private Ohio dermatology practices looking for a practical way to report their melanoma cases. The model has increased melanoma reporting in Ohio by 2.8% in the last 2 years, “which doesn’t seem like that many, but if there are 6500 cases of melanoma, and you can increase reporting by a couple hundred cases, that’s a lot,” he said.
His goal is to expand this model to more states. “Dermatologists, surgical oncologists, and cancer center administrators should embrace this opportunity to make their practices a clearinghouse for their state,” he said. “This is an opportunity to improve state health, quality improvement projects, help providers, and gain recognition as a center of excellence. The increase in incidence of melanoma will lend great clout to public and legislative requests for prevention, treatment, and research dollars.”
In an interview, Hugh Greenway, MD, the head of Mohs and dermatologic surgery at Scripps Clinic in San Diego, also noted that cutaneous melanoma is significantly underreported in spite of individual state requirements. “As Dr. Coldiron reminds us, the main reason is that in many cases the pathology diagnosis and report come from the dermatologist’s/dermatopathologist’s office,” Dr. Greenway said. “With no hospital or large multispecialty laboratory involved, the reporting may be incomplete or not done. This is not the case with almost all other cancers where a hospital laboratory is involved.”
If widespread adoption of Dr. Coldiron’s model can occur, he added, “then we will have much better melanoma reporting data on which to both help our patients and specialty. He is to be applauded for producing a workable solution to the problem of underreporting.”
Dr. Coldiron reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Greenway reported that he conducts research for Castle Biosciences. He is also course director of the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update.
SAN DIEGO – Soon after Brett M. Coldiron, MD, launched his Cincinnati-based dermatology and Mohs surgery practice more than 20 years ago, he reported his first three cases of thin melanomas to the Ohio Department of Health, as mandated by state law.
“I got sent reams of paperwork to fill out that I did not understand,” Dr. Coldiron, a past president of the American College of Mohs Surgery and the American Academy of Dermatology, recalled at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “Then, I got chewed out for not reporting sooner and threatened with thousands of dollars in fines if I did not promptly report the forms in the future. It was an obnoxious experience.”
About 15 years later, while testifying at the Ohio Legislature on medical reasons to restrict the use of tanning beds, a lobbyist for the tanning bed industry told him that the melanoma rates had been stable in Ohio for the previous 5 years. “It turns out they were cherry picking certain segments of data to fit their narrative,” Dr. Coldiron said. “I was stunned and it kind of deflated me. I thought about this for a long time, and thought, ‘how do we solve this issue of reporting melanoma cases without adding work to existing staff if you’re a small practice and without spending significant amounts of money? Let’s make this easier.’ ”
In addition to reducing the use of tanning beds, proper reporting of melanoma cases is important for reasons that include efforts to increase sunscreen use and to be counted in ongoing research efforts to obtain a realistic snapshot of melanoma prevalence and incidence, he said.
Quality of melanoma case reporting relies on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Program of Cancer Registries (NPCR), and the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Program, which collects data on the incidence, treatment, staging, and survival for 28% of the US population. All 50 states and US territories require melanoma to be reported to the NPCR, but while most hospital systems have reporting protocols and dedicated data registrars, private practices may not.
Also, many dermatopathology practices operate independently and do not have dedicated registrars and may not report cases. “Melanoma is unique in that it is often completely managed in outpatient settings and these melanomas may never be reported,” said Dr. Coldiron, current president of the Ohio Dermatological Foundation. “That’s the practice gap.” One study published in 2018 found that only 49% of dermatologists knew that melanoma was a reportable disease and only 34% routinely reported newly diagnosed cases to their state’s cancer registry. He characterized melanoma reporting as an unfunded mandate.
“Hospitals are doing the most of them, because they have a registrar,” he said. “Small practices have to assign someone to do this, and it can be difficult to train that person. It’s time consuming. The first time we did it, it took an hour,” but, he said, taking a 2-hour tutorial from the Ohio Department of Health helped.
He noted that there is a lack of awareness and clinicians think it’s the dermatopathologist’s job to report cases, “while the dermatopathologist thinks it’s the clinician’s job,” and many of the entry fields are not applicable to thinner melanomas.
There is also a “patchwork” of ways that state departments of health accept the information, not all electronically, he continued. For example, those in Arizona, Montana, West Virginia, Delaware, Vermont, and Maine accept paper copies only, “meaning you have to download a PDF, fill it out, and fax it back to them,” Dr. Coldiron said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps Cancer Center.
“We have them sign a HIPAA form and take the two-hour online tutorial,” he said. They download data that Ohio dermatologists have faxed to a dedicated secure HIPAA-compliant cloud-based fax line that Dr. Coldiron has set up, and the cases are then sent to the Ohio Department of Health.
Dr. Coldiron and colleagues have also partnered with the University of Cincinnati Clermont, which offers a National Cancer Registries Association–accredited certificate program — one of several nationwide. Students in this program are trained to become cancer registrars. “The university staff are gung-ho about it because they are looking for easy cases to train the students on. Also, the Ohio Department of Health staff are keen to help train the students and even help them find jobs or hire them after they complete the degree. Staff from the department of health and college faculty are fully engaged and supervising. It’s a win-win for all.”
According to Dr. Coldiron, in 2023, 8 Ohio dermatology practices were sending their reports to the fax line he set up and 7 more have signed up in recent months, making 15 practices to date. “It’s self-perpetuating at this point,” he said. “The Ohio Department of Health and the University of Cincinnati are invested in this program long-term.” The fax service costs Dr. Coldiron $42 per month — a small price to pay, he said, for being a clearinghouse for private Ohio dermatology practices looking for a practical way to report their melanoma cases. The model has increased melanoma reporting in Ohio by 2.8% in the last 2 years, “which doesn’t seem like that many, but if there are 6500 cases of melanoma, and you can increase reporting by a couple hundred cases, that’s a lot,” he said.
His goal is to expand this model to more states. “Dermatologists, surgical oncologists, and cancer center administrators should embrace this opportunity to make their practices a clearinghouse for their state,” he said. “This is an opportunity to improve state health, quality improvement projects, help providers, and gain recognition as a center of excellence. The increase in incidence of melanoma will lend great clout to public and legislative requests for prevention, treatment, and research dollars.”
In an interview, Hugh Greenway, MD, the head of Mohs and dermatologic surgery at Scripps Clinic in San Diego, also noted that cutaneous melanoma is significantly underreported in spite of individual state requirements. “As Dr. Coldiron reminds us, the main reason is that in many cases the pathology diagnosis and report come from the dermatologist’s/dermatopathologist’s office,” Dr. Greenway said. “With no hospital or large multispecialty laboratory involved, the reporting may be incomplete or not done. This is not the case with almost all other cancers where a hospital laboratory is involved.”
If widespread adoption of Dr. Coldiron’s model can occur, he added, “then we will have much better melanoma reporting data on which to both help our patients and specialty. He is to be applauded for producing a workable solution to the problem of underreporting.”
Dr. Coldiron reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Greenway reported that he conducts research for Castle Biosciences. He is also course director of the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update.
SAN DIEGO – Soon after Brett M. Coldiron, MD, launched his Cincinnati-based dermatology and Mohs surgery practice more than 20 years ago, he reported his first three cases of thin melanomas to the Ohio Department of Health, as mandated by state law.
“I got sent reams of paperwork to fill out that I did not understand,” Dr. Coldiron, a past president of the American College of Mohs Surgery and the American Academy of Dermatology, recalled at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “Then, I got chewed out for not reporting sooner and threatened with thousands of dollars in fines if I did not promptly report the forms in the future. It was an obnoxious experience.”
About 15 years later, while testifying at the Ohio Legislature on medical reasons to restrict the use of tanning beds, a lobbyist for the tanning bed industry told him that the melanoma rates had been stable in Ohio for the previous 5 years. “It turns out they were cherry picking certain segments of data to fit their narrative,” Dr. Coldiron said. “I was stunned and it kind of deflated me. I thought about this for a long time, and thought, ‘how do we solve this issue of reporting melanoma cases without adding work to existing staff if you’re a small practice and without spending significant amounts of money? Let’s make this easier.’ ”
In addition to reducing the use of tanning beds, proper reporting of melanoma cases is important for reasons that include efforts to increase sunscreen use and to be counted in ongoing research efforts to obtain a realistic snapshot of melanoma prevalence and incidence, he said.
Quality of melanoma case reporting relies on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Program of Cancer Registries (NPCR), and the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Program, which collects data on the incidence, treatment, staging, and survival for 28% of the US population. All 50 states and US territories require melanoma to be reported to the NPCR, but while most hospital systems have reporting protocols and dedicated data registrars, private practices may not.
Also, many dermatopathology practices operate independently and do not have dedicated registrars and may not report cases. “Melanoma is unique in that it is often completely managed in outpatient settings and these melanomas may never be reported,” said Dr. Coldiron, current president of the Ohio Dermatological Foundation. “That’s the practice gap.” One study published in 2018 found that only 49% of dermatologists knew that melanoma was a reportable disease and only 34% routinely reported newly diagnosed cases to their state’s cancer registry. He characterized melanoma reporting as an unfunded mandate.
“Hospitals are doing the most of them, because they have a registrar,” he said. “Small practices have to assign someone to do this, and it can be difficult to train that person. It’s time consuming. The first time we did it, it took an hour,” but, he said, taking a 2-hour tutorial from the Ohio Department of Health helped.
He noted that there is a lack of awareness and clinicians think it’s the dermatopathologist’s job to report cases, “while the dermatopathologist thinks it’s the clinician’s job,” and many of the entry fields are not applicable to thinner melanomas.
There is also a “patchwork” of ways that state departments of health accept the information, not all electronically, he continued. For example, those in Arizona, Montana, West Virginia, Delaware, Vermont, and Maine accept paper copies only, “meaning you have to download a PDF, fill it out, and fax it back to them,” Dr. Coldiron said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps Cancer Center.
“We have them sign a HIPAA form and take the two-hour online tutorial,” he said. They download data that Ohio dermatologists have faxed to a dedicated secure HIPAA-compliant cloud-based fax line that Dr. Coldiron has set up, and the cases are then sent to the Ohio Department of Health.
Dr. Coldiron and colleagues have also partnered with the University of Cincinnati Clermont, which offers a National Cancer Registries Association–accredited certificate program — one of several nationwide. Students in this program are trained to become cancer registrars. “The university staff are gung-ho about it because they are looking for easy cases to train the students on. Also, the Ohio Department of Health staff are keen to help train the students and even help them find jobs or hire them after they complete the degree. Staff from the department of health and college faculty are fully engaged and supervising. It’s a win-win for all.”
According to Dr. Coldiron, in 2023, 8 Ohio dermatology practices were sending their reports to the fax line he set up and 7 more have signed up in recent months, making 15 practices to date. “It’s self-perpetuating at this point,” he said. “The Ohio Department of Health and the University of Cincinnati are invested in this program long-term.” The fax service costs Dr. Coldiron $42 per month — a small price to pay, he said, for being a clearinghouse for private Ohio dermatology practices looking for a practical way to report their melanoma cases. The model has increased melanoma reporting in Ohio by 2.8% in the last 2 years, “which doesn’t seem like that many, but if there are 6500 cases of melanoma, and you can increase reporting by a couple hundred cases, that’s a lot,” he said.
His goal is to expand this model to more states. “Dermatologists, surgical oncologists, and cancer center administrators should embrace this opportunity to make their practices a clearinghouse for their state,” he said. “This is an opportunity to improve state health, quality improvement projects, help providers, and gain recognition as a center of excellence. The increase in incidence of melanoma will lend great clout to public and legislative requests for prevention, treatment, and research dollars.”
In an interview, Hugh Greenway, MD, the head of Mohs and dermatologic surgery at Scripps Clinic in San Diego, also noted that cutaneous melanoma is significantly underreported in spite of individual state requirements. “As Dr. Coldiron reminds us, the main reason is that in many cases the pathology diagnosis and report come from the dermatologist’s/dermatopathologist’s office,” Dr. Greenway said. “With no hospital or large multispecialty laboratory involved, the reporting may be incomplete or not done. This is not the case with almost all other cancers where a hospital laboratory is involved.”
If widespread adoption of Dr. Coldiron’s model can occur, he added, “then we will have much better melanoma reporting data on which to both help our patients and specialty. He is to be applauded for producing a workable solution to the problem of underreporting.”
Dr. Coldiron reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Greenway reported that he conducts research for Castle Biosciences. He is also course director of the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update.
FROM MELANOMA 2024
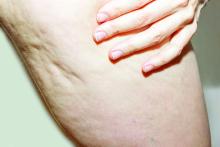
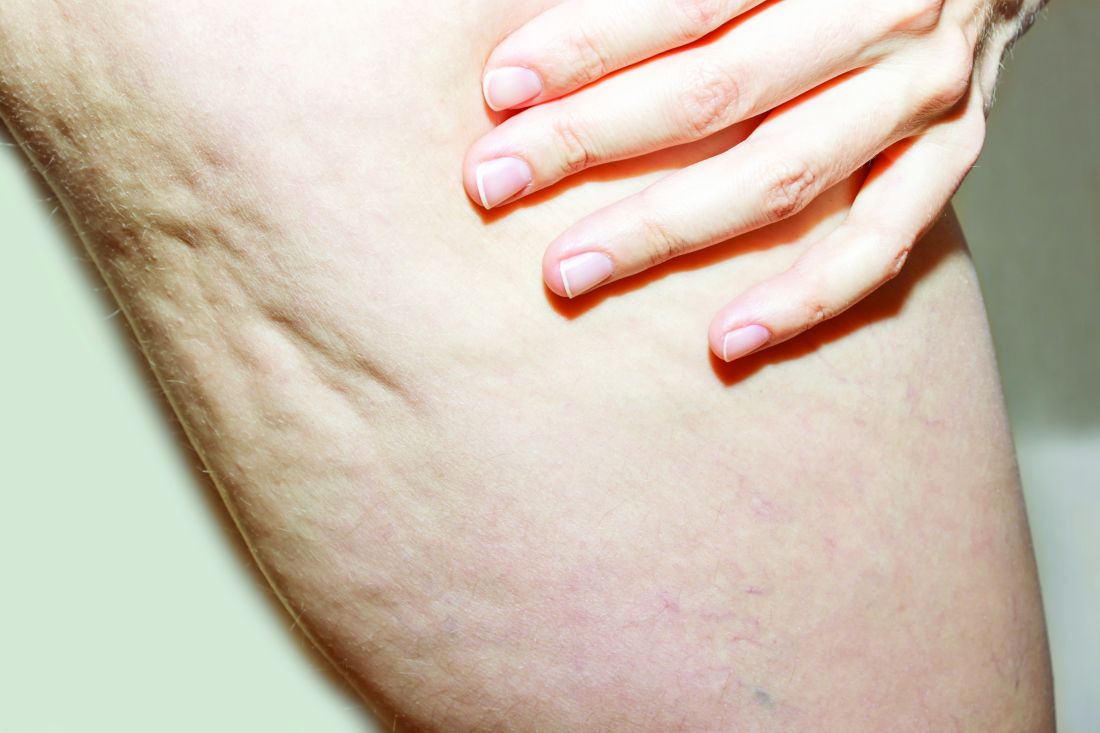
What Do Results from Acoustic Subcision for Cellulite Look Like at One Year?
.
The findings build on results from a 12-week study of the device, marketed as Resonic. In that trial of 56 women with moderate to severe cellulite, a single treatment provided a roughly 1.01-point reduction in the five-point Cellulite Severity Scale (CSS) at 12 weeks, which corresponds to a roughly 29.5% reduction in cellulite from baseline.
The device, which is indicated for long-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite, emits rapid acoustic pulses and shock waves at 50 Hz that are transmitted through the skin. The device “induces physical shearing of fibrous septa through rapid acoustic pulses,” investigators led by Elizabeth Tanzi, MD, who practices cosmetic dermatology in Chevy Chase, Md., wrote in the follow-up study, which was published in Dermatologic Surgery in February “In contrast to current treatment options, the device requires no anesthesia or downtime and was well-tolerated based on an average pain score of 2.4 (on a scale 0–10) during treatment” in the 12-week study, they noted.
To evaluate the long-term efficacy of the acoustic subcision device, Dr. Tanzi and her coauthors at four centers prospectively followed 42 patients who participated in the 12-week trial. The study involved four visits: screening, a single treatment visit, and a follow-up visit 12 weeks after treatment and another after 52 weeks. Because of lockdowns and other reasons related to the COVID-19 pandemic, several participants were unable to make it to follow-up visits and had follow-up visits beyond the 52-week time-point, the authors explained.
Blinded board-certified dermatologists assessed efficacy by correctly identifying post-treatment photographs, from the visit after 52 weeks, and using a 6-point simplified CSS. They also assessed safety and collected data on participant satisfaction. The mean age of the women was 45.5 years, and their mean BMI was 23.9 kg/m2. The blinded reviewers correctly identified post-treatment photographs at the visit after 52 weeks at a rate of 95.2%.
In addition, 70.4% of the study participants had at least a 1-point change in their CSS score from baseline. Overall, their mean reduction in CSS score from baseline was 1.09 at the visit after 52 weeks, and a mean 34.1% reduction in cellulite at that visit, the authors reported.
In other findings, 41 of the 42 study participants (97.6%) rated their cellulite improvement as good and 33 (78.6%) agreed that the treatment was relatively pain free. Immediately following treatment, 85.7% reported an expected adverse event attributable to the device or treatment, which included mild to moderate erythema (76.7%), mild contusion/bruise (5.3%), mild pain (1.7%) and mild heat (1.7%). All adverse events resolved without intervention.
The study authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the lack of a control group and the inability to differentiate effectiveness of the treatment on the buttocks versus the thighs.
“Cellulite is a common complaint among those presenting to cosmetic dermatology clinics, and prior treatment options have been somewhat disappointing in terms of invasiveness, side effects, or lack of improvement,” said Patricia M. Richey, MD, director of Mohs surgery at Boston Medical Center, who also conducts research for the Wellman Center for Photomedicine and the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Acoustic subcision “would potentially be a very attractive and unparalleled option given tolerability and sustained clinical improvement after only one treatment,” she told this news organization. “I agree with the authors that a possible limitation is the lack of comparison between response in different body areas,” namely, the buttocks versus the thighs, she said. “This information would be helpful to set patient expectations, and I suspect future studies will address this.”
Also asked to comment on the study, Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview that while the results were modest after a single treatment, “there is room for further experimentation to see how modifications of settings, treatment numbers, treatment intervals, and location-specific treatment regimens based on tissue depth and tissue band size/dimple size may enhance results.”
She added that cost of treatment and correlation with clinical improvement “will become a more real-world matter when it comes to bringing this more broadly to the clinic settings.”
Soliton sponsored the trial prior to its acquisition by AbbVie. Dr. Tanzi reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Four coauthors reported being employees, consultants, or advisory board members, or having stock options in AbbVie. Dr. Richey and Dr. Sodha were not involved with the study and reported having no disclosures.
.
The findings build on results from a 12-week study of the device, marketed as Resonic. In that trial of 56 women with moderate to severe cellulite, a single treatment provided a roughly 1.01-point reduction in the five-point Cellulite Severity Scale (CSS) at 12 weeks, which corresponds to a roughly 29.5% reduction in cellulite from baseline.
The device, which is indicated for long-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite, emits rapid acoustic pulses and shock waves at 50 Hz that are transmitted through the skin. The device “induces physical shearing of fibrous septa through rapid acoustic pulses,” investigators led by Elizabeth Tanzi, MD, who practices cosmetic dermatology in Chevy Chase, Md., wrote in the follow-up study, which was published in Dermatologic Surgery in February “In contrast to current treatment options, the device requires no anesthesia or downtime and was well-tolerated based on an average pain score of 2.4 (on a scale 0–10) during treatment” in the 12-week study, they noted.
To evaluate the long-term efficacy of the acoustic subcision device, Dr. Tanzi and her coauthors at four centers prospectively followed 42 patients who participated in the 12-week trial. The study involved four visits: screening, a single treatment visit, and a follow-up visit 12 weeks after treatment and another after 52 weeks. Because of lockdowns and other reasons related to the COVID-19 pandemic, several participants were unable to make it to follow-up visits and had follow-up visits beyond the 52-week time-point, the authors explained.
Blinded board-certified dermatologists assessed efficacy by correctly identifying post-treatment photographs, from the visit after 52 weeks, and using a 6-point simplified CSS. They also assessed safety and collected data on participant satisfaction. The mean age of the women was 45.5 years, and their mean BMI was 23.9 kg/m2. The blinded reviewers correctly identified post-treatment photographs at the visit after 52 weeks at a rate of 95.2%.
In addition, 70.4% of the study participants had at least a 1-point change in their CSS score from baseline. Overall, their mean reduction in CSS score from baseline was 1.09 at the visit after 52 weeks, and a mean 34.1% reduction in cellulite at that visit, the authors reported.
In other findings, 41 of the 42 study participants (97.6%) rated their cellulite improvement as good and 33 (78.6%) agreed that the treatment was relatively pain free. Immediately following treatment, 85.7% reported an expected adverse event attributable to the device or treatment, which included mild to moderate erythema (76.7%), mild contusion/bruise (5.3%), mild pain (1.7%) and mild heat (1.7%). All adverse events resolved without intervention.
The study authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the lack of a control group and the inability to differentiate effectiveness of the treatment on the buttocks versus the thighs.
“Cellulite is a common complaint among those presenting to cosmetic dermatology clinics, and prior treatment options have been somewhat disappointing in terms of invasiveness, side effects, or lack of improvement,” said Patricia M. Richey, MD, director of Mohs surgery at Boston Medical Center, who also conducts research for the Wellman Center for Photomedicine and the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Acoustic subcision “would potentially be a very attractive and unparalleled option given tolerability and sustained clinical improvement after only one treatment,” she told this news organization. “I agree with the authors that a possible limitation is the lack of comparison between response in different body areas,” namely, the buttocks versus the thighs, she said. “This information would be helpful to set patient expectations, and I suspect future studies will address this.”
Also asked to comment on the study, Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview that while the results were modest after a single treatment, “there is room for further experimentation to see how modifications of settings, treatment numbers, treatment intervals, and location-specific treatment regimens based on tissue depth and tissue band size/dimple size may enhance results.”
She added that cost of treatment and correlation with clinical improvement “will become a more real-world matter when it comes to bringing this more broadly to the clinic settings.”
Soliton sponsored the trial prior to its acquisition by AbbVie. Dr. Tanzi reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Four coauthors reported being employees, consultants, or advisory board members, or having stock options in AbbVie. Dr. Richey and Dr. Sodha were not involved with the study and reported having no disclosures.
.
The findings build on results from a 12-week study of the device, marketed as Resonic. In that trial of 56 women with moderate to severe cellulite, a single treatment provided a roughly 1.01-point reduction in the five-point Cellulite Severity Scale (CSS) at 12 weeks, which corresponds to a roughly 29.5% reduction in cellulite from baseline.
The device, which is indicated for long-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite, emits rapid acoustic pulses and shock waves at 50 Hz that are transmitted through the skin. The device “induces physical shearing of fibrous septa through rapid acoustic pulses,” investigators led by Elizabeth Tanzi, MD, who practices cosmetic dermatology in Chevy Chase, Md., wrote in the follow-up study, which was published in Dermatologic Surgery in February “In contrast to current treatment options, the device requires no anesthesia or downtime and was well-tolerated based on an average pain score of 2.4 (on a scale 0–10) during treatment” in the 12-week study, they noted.
To evaluate the long-term efficacy of the acoustic subcision device, Dr. Tanzi and her coauthors at four centers prospectively followed 42 patients who participated in the 12-week trial. The study involved four visits: screening, a single treatment visit, and a follow-up visit 12 weeks after treatment and another after 52 weeks. Because of lockdowns and other reasons related to the COVID-19 pandemic, several participants were unable to make it to follow-up visits and had follow-up visits beyond the 52-week time-point, the authors explained.
Blinded board-certified dermatologists assessed efficacy by correctly identifying post-treatment photographs, from the visit after 52 weeks, and using a 6-point simplified CSS. They also assessed safety and collected data on participant satisfaction. The mean age of the women was 45.5 years, and their mean BMI was 23.9 kg/m2. The blinded reviewers correctly identified post-treatment photographs at the visit after 52 weeks at a rate of 95.2%.
In addition, 70.4% of the study participants had at least a 1-point change in their CSS score from baseline. Overall, their mean reduction in CSS score from baseline was 1.09 at the visit after 52 weeks, and a mean 34.1% reduction in cellulite at that visit, the authors reported.
In other findings, 41 of the 42 study participants (97.6%) rated their cellulite improvement as good and 33 (78.6%) agreed that the treatment was relatively pain free. Immediately following treatment, 85.7% reported an expected adverse event attributable to the device or treatment, which included mild to moderate erythema (76.7%), mild contusion/bruise (5.3%), mild pain (1.7%) and mild heat (1.7%). All adverse events resolved without intervention.
The study authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the lack of a control group and the inability to differentiate effectiveness of the treatment on the buttocks versus the thighs.
“Cellulite is a common complaint among those presenting to cosmetic dermatology clinics, and prior treatment options have been somewhat disappointing in terms of invasiveness, side effects, or lack of improvement,” said Patricia M. Richey, MD, director of Mohs surgery at Boston Medical Center, who also conducts research for the Wellman Center for Photomedicine and the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Acoustic subcision “would potentially be a very attractive and unparalleled option given tolerability and sustained clinical improvement after only one treatment,” she told this news organization. “I agree with the authors that a possible limitation is the lack of comparison between response in different body areas,” namely, the buttocks versus the thighs, she said. “This information would be helpful to set patient expectations, and I suspect future studies will address this.”
Also asked to comment on the study, Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview that while the results were modest after a single treatment, “there is room for further experimentation to see how modifications of settings, treatment numbers, treatment intervals, and location-specific treatment regimens based on tissue depth and tissue band size/dimple size may enhance results.”
She added that cost of treatment and correlation with clinical improvement “will become a more real-world matter when it comes to bringing this more broadly to the clinic settings.”
Soliton sponsored the trial prior to its acquisition by AbbVie. Dr. Tanzi reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Four coauthors reported being employees, consultants, or advisory board members, or having stock options in AbbVie. Dr. Richey and Dr. Sodha were not involved with the study and reported having no disclosures.
FROM DERMATOLOGIC SURGERY
OTC Topical Scar Products May Contain Allergens, Study Finds
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- OTC topical scar treatments have the potential to cause an allergic reaction, but the prevalence of North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) core allergens in these products is unclear.
- Researchers used the word scar in a query of Amazon.com and four other retail websites to identify topical scar products for consumers and noted the list of ingredients.
- The investigators also surveyed the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program (CAMP), a resource that helps patients with allergies find personal care products that are safe to use, for pertinent products.
TAKEAWAY:
- The search query identified 156 products. Of these, 119 (76.2%) were gels, creams, or oils and 37 (23.7%) were sheets, strips, or tape.
- Of the 125 products that had a list of ingredients, 69 (55.2%) contained at least one NACDG allergen and 45 (36%) contained more than one.
- The top six most common allergens listed in the ingredients were fragrance (16.8%), phenoxyethanol (16.8%), parabens (14.4%), panthenol (12.8%), sodium benzoate (9.60%), and ethylhexylglycerin (8%).
- Analysis of CAMP revealed that the program only had five unique scar products in its list, suggesting that CAMP might not be a reliable source of scar product information for patients with known allergies to pertinent NACDG allergens.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients can consider trying a ‘use test’ on the inner forearm before applying to the surgical site,” the authors wrote. “It may reveal they are sensitive or sensitized by a product.
SOURCE:
First author Meera Kattapuram, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, led the study, published in the February issue of Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include the selection of five retailers and the top 100 products from each website and the potential for ingredient list inaccuracies.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial conflicts of interest. The research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- OTC topical scar treatments have the potential to cause an allergic reaction, but the prevalence of North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) core allergens in these products is unclear.
- Researchers used the word scar in a query of Amazon.com and four other retail websites to identify topical scar products for consumers and noted the list of ingredients.
- The investigators also surveyed the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program (CAMP), a resource that helps patients with allergies find personal care products that are safe to use, for pertinent products.
TAKEAWAY:
- The search query identified 156 products. Of these, 119 (76.2%) were gels, creams, or oils and 37 (23.7%) were sheets, strips, or tape.
- Of the 125 products that had a list of ingredients, 69 (55.2%) contained at least one NACDG allergen and 45 (36%) contained more than one.
- The top six most common allergens listed in the ingredients were fragrance (16.8%), phenoxyethanol (16.8%), parabens (14.4%), panthenol (12.8%), sodium benzoate (9.60%), and ethylhexylglycerin (8%).
- Analysis of CAMP revealed that the program only had five unique scar products in its list, suggesting that CAMP might not be a reliable source of scar product information for patients with known allergies to pertinent NACDG allergens.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients can consider trying a ‘use test’ on the inner forearm before applying to the surgical site,” the authors wrote. “It may reveal they are sensitive or sensitized by a product.
SOURCE:
First author Meera Kattapuram, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, led the study, published in the February issue of Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include the selection of five retailers and the top 100 products from each website and the potential for ingredient list inaccuracies.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial conflicts of interest. The research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- OTC topical scar treatments have the potential to cause an allergic reaction, but the prevalence of North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) core allergens in these products is unclear.
- Researchers used the word scar in a query of Amazon.com and four other retail websites to identify topical scar products for consumers and noted the list of ingredients.
- The investigators also surveyed the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program (CAMP), a resource that helps patients with allergies find personal care products that are safe to use, for pertinent products.
TAKEAWAY:
- The search query identified 156 products. Of these, 119 (76.2%) were gels, creams, or oils and 37 (23.7%) were sheets, strips, or tape.
- Of the 125 products that had a list of ingredients, 69 (55.2%) contained at least one NACDG allergen and 45 (36%) contained more than one.
- The top six most common allergens listed in the ingredients were fragrance (16.8%), phenoxyethanol (16.8%), parabens (14.4%), panthenol (12.8%), sodium benzoate (9.60%), and ethylhexylglycerin (8%).
- Analysis of CAMP revealed that the program only had five unique scar products in its list, suggesting that CAMP might not be a reliable source of scar product information for patients with known allergies to pertinent NACDG allergens.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients can consider trying a ‘use test’ on the inner forearm before applying to the surgical site,” the authors wrote. “It may reveal they are sensitive or sensitized by a product.
SOURCE:
First author Meera Kattapuram, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, led the study, published in the February issue of Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include the selection of five retailers and the top 100 products from each website and the potential for ingredient list inaccuracies.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial conflicts of interest. The research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite An AI Assist, Imaging Study Shows Disparities in Diagnosing Different Skin Tones
When clinicians in a large-scale study viewed a series of digital images that showed skin diseases across skin tones and were asked to make a diagnosis, the accuracy was 38% among dermatologists and 19% among primary care physicians (PCPs). But when decision support from a deep learning system (DLS) was introduced, diagnostic accuracy increased by 33% among dermatologists and 69% among PCPs, results from a multicenter study showed.
However, the researchers found that across all images, diseases in dark skin (Fitzpatrick skin types 5 and 6) were diagnosed less accurately than diseases in light skin (Fitzpatrick skin types 1-4).
“,” researchers led by Matthew Groh, PhD, of Northwestern University’s Kellogg School of Management, wrote in their study, published online in Nature Medicine.
For the study, 389 board-certified dermatologists and 450 PCPs in 39 countries were presented with 364 images to view spanning 46 skin diseases and asked to submit up to four differential diagnoses. Nearly 80% of the images were of 8 diseases: atopic dermatitis, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), dermatomyositis, lichen planus, Lyme disease, pityriasis rosea, pityriasis rubra pilaris, and secondary syphilis.
Dermatologists and PCPs achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 38% and 19%, respectively, but both groups of clinicians were 4 percentage points less accurate for diagnosis of images of dark skin as compared with light skin. With assistance from DLS decision support, diagnostic accuracy increased by 33% among dermatologists and 69% among primary care physicians. Among dermatologists, DLS support generally increased diagnostic accuracy evenly across skin tones. However, among PCPs, DLS support increased their diagnostic accuracy more in light skin tones than in dark ones.
In the survey component of the study, when the participants were asked, “Do you feel you received sufficient training for diagnosing skin diseases in patients with skin of color (non-white patients)?” 67% of all PCPs and 33% of all dermatologists responded no. “Furthermore, we have found differences in how often BCDs [board-certified dermatologists] and PCPs refer patients with light and dark skin for biopsy,” the authors wrote. “Specifically, for CTCL (a life-threatening disease), we found that both BCDs and PCPs report that they would refer patients for biopsy significantly more often in light skin than dark skin. Moreover, for the common skin diseases atopic dermatitis and pityriasis rosea, we found that BCDs report they would refer patients for biopsy more often in dark skin than light skin, which creates an unnecessary overburden on patients with dark skin.”
In a press release about the study, Dr. Groh emphasized that he and other scientists who investigate human-computer interaction “have to find a way to incorporate underrepresented demographics in our research. That way we will be ready to accurately implement these models in the real world and build AI systems that serve as tools that are designed to avoid the kind of systematic errors we know humans and machines are prone to. Then you can update curricula, you can change norms in different fields and hopefully everyone gets better.”
Ronald Moy, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Beverly Hills, Calif., who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study contributes insights into physician-AI interaction and highlights the need for further training on diagnosing skin diseases in people with darker skin tones. “The strengths of this study include its large sample size of dermatologists and primary care physicians, use of quality-controlled images across skin tones, and thorough evaluation of diagnostic accuracy with and without AI assistance,” said Dr. Moy, who is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, and the American Board of Facial Cosmetic Surgery.
“The study is limited to diagnosis and skin tone estimation based purely on a single image, which does not fully represent a clinical evaluation,” he added. However, “it does provide important benchmark data on diagnostic accuracy disparities across skin tones, but also demonstrates that while AI assistance can improve overall diagnostic accuracy, it may exacerbate disparities for non-specialists.”
Funding for the study was provided by MIT Media Lab consortium members and the Harold Horowitz Student Research Fund. One of the study authors, P. Murali Doraiswamy, MBBS, disclosed that he has received grants, advisory fees, and/or stock from several biotechnology companies outside the scope of this work and that he is a co-inventor on several patents through Duke University. The remaining authors reported having no disclosures. Dr. Moy reported having no disclosures.
When clinicians in a large-scale study viewed a series of digital images that showed skin diseases across skin tones and were asked to make a diagnosis, the accuracy was 38% among dermatologists and 19% among primary care physicians (PCPs). But when decision support from a deep learning system (DLS) was introduced, diagnostic accuracy increased by 33% among dermatologists and 69% among PCPs, results from a multicenter study showed.
However, the researchers found that across all images, diseases in dark skin (Fitzpatrick skin types 5 and 6) were diagnosed less accurately than diseases in light skin (Fitzpatrick skin types 1-4).
“,” researchers led by Matthew Groh, PhD, of Northwestern University’s Kellogg School of Management, wrote in their study, published online in Nature Medicine.
For the study, 389 board-certified dermatologists and 450 PCPs in 39 countries were presented with 364 images to view spanning 46 skin diseases and asked to submit up to four differential diagnoses. Nearly 80% of the images were of 8 diseases: atopic dermatitis, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), dermatomyositis, lichen planus, Lyme disease, pityriasis rosea, pityriasis rubra pilaris, and secondary syphilis.
Dermatologists and PCPs achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 38% and 19%, respectively, but both groups of clinicians were 4 percentage points less accurate for diagnosis of images of dark skin as compared with light skin. With assistance from DLS decision support, diagnostic accuracy increased by 33% among dermatologists and 69% among primary care physicians. Among dermatologists, DLS support generally increased diagnostic accuracy evenly across skin tones. However, among PCPs, DLS support increased their diagnostic accuracy more in light skin tones than in dark ones.
In the survey component of the study, when the participants were asked, “Do you feel you received sufficient training for diagnosing skin diseases in patients with skin of color (non-white patients)?” 67% of all PCPs and 33% of all dermatologists responded no. “Furthermore, we have found differences in how often BCDs [board-certified dermatologists] and PCPs refer patients with light and dark skin for biopsy,” the authors wrote. “Specifically, for CTCL (a life-threatening disease), we found that both BCDs and PCPs report that they would refer patients for biopsy significantly more often in light skin than dark skin. Moreover, for the common skin diseases atopic dermatitis and pityriasis rosea, we found that BCDs report they would refer patients for biopsy more often in dark skin than light skin, which creates an unnecessary overburden on patients with dark skin.”
In a press release about the study, Dr. Groh emphasized that he and other scientists who investigate human-computer interaction “have to find a way to incorporate underrepresented demographics in our research. That way we will be ready to accurately implement these models in the real world and build AI systems that serve as tools that are designed to avoid the kind of systematic errors we know humans and machines are prone to. Then you can update curricula, you can change norms in different fields and hopefully everyone gets better.”
Ronald Moy, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Beverly Hills, Calif., who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study contributes insights into physician-AI interaction and highlights the need for further training on diagnosing skin diseases in people with darker skin tones. “The strengths of this study include its large sample size of dermatologists and primary care physicians, use of quality-controlled images across skin tones, and thorough evaluation of diagnostic accuracy with and without AI assistance,” said Dr. Moy, who is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, and the American Board of Facial Cosmetic Surgery.
“The study is limited to diagnosis and skin tone estimation based purely on a single image, which does not fully represent a clinical evaluation,” he added. However, “it does provide important benchmark data on diagnostic accuracy disparities across skin tones, but also demonstrates that while AI assistance can improve overall diagnostic accuracy, it may exacerbate disparities for non-specialists.”
Funding for the study was provided by MIT Media Lab consortium members and the Harold Horowitz Student Research Fund. One of the study authors, P. Murali Doraiswamy, MBBS, disclosed that he has received grants, advisory fees, and/or stock from several biotechnology companies outside the scope of this work and that he is a co-inventor on several patents through Duke University. The remaining authors reported having no disclosures. Dr. Moy reported having no disclosures.
When clinicians in a large-scale study viewed a series of digital images that showed skin diseases across skin tones and were asked to make a diagnosis, the accuracy was 38% among dermatologists and 19% among primary care physicians (PCPs). But when decision support from a deep learning system (DLS) was introduced, diagnostic accuracy increased by 33% among dermatologists and 69% among PCPs, results from a multicenter study showed.
However, the researchers found that across all images, diseases in dark skin (Fitzpatrick skin types 5 and 6) were diagnosed less accurately than diseases in light skin (Fitzpatrick skin types 1-4).
“,” researchers led by Matthew Groh, PhD, of Northwestern University’s Kellogg School of Management, wrote in their study, published online in Nature Medicine.
For the study, 389 board-certified dermatologists and 450 PCPs in 39 countries were presented with 364 images to view spanning 46 skin diseases and asked to submit up to four differential diagnoses. Nearly 80% of the images were of 8 diseases: atopic dermatitis, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), dermatomyositis, lichen planus, Lyme disease, pityriasis rosea, pityriasis rubra pilaris, and secondary syphilis.
Dermatologists and PCPs achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 38% and 19%, respectively, but both groups of clinicians were 4 percentage points less accurate for diagnosis of images of dark skin as compared with light skin. With assistance from DLS decision support, diagnostic accuracy increased by 33% among dermatologists and 69% among primary care physicians. Among dermatologists, DLS support generally increased diagnostic accuracy evenly across skin tones. However, among PCPs, DLS support increased their diagnostic accuracy more in light skin tones than in dark ones.
In the survey component of the study, when the participants were asked, “Do you feel you received sufficient training for diagnosing skin diseases in patients with skin of color (non-white patients)?” 67% of all PCPs and 33% of all dermatologists responded no. “Furthermore, we have found differences in how often BCDs [board-certified dermatologists] and PCPs refer patients with light and dark skin for biopsy,” the authors wrote. “Specifically, for CTCL (a life-threatening disease), we found that both BCDs and PCPs report that they would refer patients for biopsy significantly more often in light skin than dark skin. Moreover, for the common skin diseases atopic dermatitis and pityriasis rosea, we found that BCDs report they would refer patients for biopsy more often in dark skin than light skin, which creates an unnecessary overburden on patients with dark skin.”
In a press release about the study, Dr. Groh emphasized that he and other scientists who investigate human-computer interaction “have to find a way to incorporate underrepresented demographics in our research. That way we will be ready to accurately implement these models in the real world and build AI systems that serve as tools that are designed to avoid the kind of systematic errors we know humans and machines are prone to. Then you can update curricula, you can change norms in different fields and hopefully everyone gets better.”
Ronald Moy, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Beverly Hills, Calif., who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study contributes insights into physician-AI interaction and highlights the need for further training on diagnosing skin diseases in people with darker skin tones. “The strengths of this study include its large sample size of dermatologists and primary care physicians, use of quality-controlled images across skin tones, and thorough evaluation of diagnostic accuracy with and without AI assistance,” said Dr. Moy, who is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, and the American Board of Facial Cosmetic Surgery.
“The study is limited to diagnosis and skin tone estimation based purely on a single image, which does not fully represent a clinical evaluation,” he added. However, “it does provide important benchmark data on diagnostic accuracy disparities across skin tones, but also demonstrates that while AI assistance can improve overall diagnostic accuracy, it may exacerbate disparities for non-specialists.”
Funding for the study was provided by MIT Media Lab consortium members and the Harold Horowitz Student Research Fund. One of the study authors, P. Murali Doraiswamy, MBBS, disclosed that he has received grants, advisory fees, and/or stock from several biotechnology companies outside the scope of this work and that he is a co-inventor on several patents through Duke University. The remaining authors reported having no disclosures. Dr. Moy reported having no disclosures.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
While Rare, Periocular Melanoma May Be Slightly Increasing
SAN DIEGO — Every year, about 4000 patients in the United States are diagnosed with periocular melanoma, according to Geva Mannor, MD, MPH.
“Though rare, the incidence is thought to be slightly increasing, while the onset tends to occur in patients over age 40 years,” Dr. Mannor, an oculofacial plastic surgeon in the division of ophthalmology at Scripps Clinic, San Diego, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “It may be more common in males and welding is a risk factor. Pain and vision loss are late symptoms, and there are amelanotic variants. Gene expression profiling and other genetic testing can predict metastasis, especially expression of BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1).”
. Extrapolating from the best available data, Dr. Mannor said that the annual incidence of choroidal melanoma in the United States is less than 2500, the annual incidence of eyelid melanoma is less than 750, and the annual incidence of conjunctival melanoma is less than 250 — much lower than for cutaneous melanomas. Put another way, the ratio between cutaneous and choroid melanoma is 80:1, the ratio between cutaneous and eyelid melanoma is 266:1, and the ratio between cutaneous and conjunctival melanoma is 800:1.
According to an article published in 2021 on the topic, risk factors for periocular melanoma include light eye color (blue/gray; relative risk, 1.75), fair skin (RR, 1.80), and inability to tan (RR, 1.64), but not blonde hair. A review of 210 patients with melanoma of the eyelid from 11 studies showed that 57% were located on the lower lid, 13% were on the upper lid (“I think because the brow protects sun exposure to the upper lid,” Dr. Mannor said), 12% were on the brow, 10% were on the lateral canthus, and 2% were on the medial canthus. In addition, 35% of the eyelid melanomas were superficial spreading cases, 31% were lentigo maligna, and 19% were nodular. The mean Breslow depth was 1.36 mm and the mortality rate was 4.9%.
Dr. Mannor said that cheek and brow melanomas can extend to the inside of the eyelid and conjunctiva. “Therefore, you want to examine the inside of upper and lower eyelids,” he said at the meeting, which was hosted by the Scripps Cancer Center. “Margin-control excision of lid melanoma is the standard treatment.”
On a related note, he said that glaucoma eye drops that contain prostaglandin F2alpha induce cutaneous and iris pigmentation with varying rates depending on the specific type of prostaglandin. “There have been case reports of these eye drops causing periocular pigmentation that masquerades as suspicious, melanoma-like skin cancer, often necessitating a skin biopsy,” he said.
Dr. Mannor reported having no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — Every year, about 4000 patients in the United States are diagnosed with periocular melanoma, according to Geva Mannor, MD, MPH.
“Though rare, the incidence is thought to be slightly increasing, while the onset tends to occur in patients over age 40 years,” Dr. Mannor, an oculofacial plastic surgeon in the division of ophthalmology at Scripps Clinic, San Diego, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “It may be more common in males and welding is a risk factor. Pain and vision loss are late symptoms, and there are amelanotic variants. Gene expression profiling and other genetic testing can predict metastasis, especially expression of BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1).”
. Extrapolating from the best available data, Dr. Mannor said that the annual incidence of choroidal melanoma in the United States is less than 2500, the annual incidence of eyelid melanoma is less than 750, and the annual incidence of conjunctival melanoma is less than 250 — much lower than for cutaneous melanomas. Put another way, the ratio between cutaneous and choroid melanoma is 80:1, the ratio between cutaneous and eyelid melanoma is 266:1, and the ratio between cutaneous and conjunctival melanoma is 800:1.
According to an article published in 2021 on the topic, risk factors for periocular melanoma include light eye color (blue/gray; relative risk, 1.75), fair skin (RR, 1.80), and inability to tan (RR, 1.64), but not blonde hair. A review of 210 patients with melanoma of the eyelid from 11 studies showed that 57% were located on the lower lid, 13% were on the upper lid (“I think because the brow protects sun exposure to the upper lid,” Dr. Mannor said), 12% were on the brow, 10% were on the lateral canthus, and 2% were on the medial canthus. In addition, 35% of the eyelid melanomas were superficial spreading cases, 31% were lentigo maligna, and 19% were nodular. The mean Breslow depth was 1.36 mm and the mortality rate was 4.9%.
Dr. Mannor said that cheek and brow melanomas can extend to the inside of the eyelid and conjunctiva. “Therefore, you want to examine the inside of upper and lower eyelids,” he said at the meeting, which was hosted by the Scripps Cancer Center. “Margin-control excision of lid melanoma is the standard treatment.”
On a related note, he said that glaucoma eye drops that contain prostaglandin F2alpha induce cutaneous and iris pigmentation with varying rates depending on the specific type of prostaglandin. “There have been case reports of these eye drops causing periocular pigmentation that masquerades as suspicious, melanoma-like skin cancer, often necessitating a skin biopsy,” he said.
Dr. Mannor reported having no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — Every year, about 4000 patients in the United States are diagnosed with periocular melanoma, according to Geva Mannor, MD, MPH.
“Though rare, the incidence is thought to be slightly increasing, while the onset tends to occur in patients over age 40 years,” Dr. Mannor, an oculofacial plastic surgeon in the division of ophthalmology at Scripps Clinic, San Diego, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “It may be more common in males and welding is a risk factor. Pain and vision loss are late symptoms, and there are amelanotic variants. Gene expression profiling and other genetic testing can predict metastasis, especially expression of BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1).”
. Extrapolating from the best available data, Dr. Mannor said that the annual incidence of choroidal melanoma in the United States is less than 2500, the annual incidence of eyelid melanoma is less than 750, and the annual incidence of conjunctival melanoma is less than 250 — much lower than for cutaneous melanomas. Put another way, the ratio between cutaneous and choroid melanoma is 80:1, the ratio between cutaneous and eyelid melanoma is 266:1, and the ratio between cutaneous and conjunctival melanoma is 800:1.
According to an article published in 2021 on the topic, risk factors for periocular melanoma include light eye color (blue/gray; relative risk, 1.75), fair skin (RR, 1.80), and inability to tan (RR, 1.64), but not blonde hair. A review of 210 patients with melanoma of the eyelid from 11 studies showed that 57% were located on the lower lid, 13% were on the upper lid (“I think because the brow protects sun exposure to the upper lid,” Dr. Mannor said), 12% were on the brow, 10% were on the lateral canthus, and 2% were on the medial canthus. In addition, 35% of the eyelid melanomas were superficial spreading cases, 31% were lentigo maligna, and 19% were nodular. The mean Breslow depth was 1.36 mm and the mortality rate was 4.9%.
Dr. Mannor said that cheek and brow melanomas can extend to the inside of the eyelid and conjunctiva. “Therefore, you want to examine the inside of upper and lower eyelids,” he said at the meeting, which was hosted by the Scripps Cancer Center. “Margin-control excision of lid melanoma is the standard treatment.”
On a related note, he said that glaucoma eye drops that contain prostaglandin F2alpha induce cutaneous and iris pigmentation with varying rates depending on the specific type of prostaglandin. “There have been case reports of these eye drops causing periocular pigmentation that masquerades as suspicious, melanoma-like skin cancer, often necessitating a skin biopsy,” he said.
Dr. Mannor reported having no disclosures.
FROM MELANOMA 2024
Expert Shares Tips for Diagnosing, Managing Spitz Nevi
SAN DIEGO —
“For a pigmented Spitz nevus, we were taught to look for a starburst pattern, a central area of homogeneous pigment, and peripheral symmetrical streaks or pseudopods,” Dr. Piggott, an adult and pediatric dermatologist at Scripps Clinic, San Diego, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “For Spitz nevi without pigment, we were taught to look for symmetric dotted vessels.”
However, results from a retrospective study published in 2015 gave her pause in relying on dermoscopy alone for assessing Spitz nevi. Researchers from Italy, Japan, and Brazil studied excision specimens of 384 Spitzoid-looking lesions in patients 12 years and older. On histology, 86.7% were diagnosed as benign Spitz nevi and 13.3% were diagnosed as melanoma.
When the researchers looked at the dermoscopic images, many cases of atypical Spitz nevi were indistinguishable from the benign Spitz nevi. Now, Dr. Piggott said, “I respect the dermoscopy criteria, but I don’t rely solely on it.”
If a child presents with Spitzoid-looking lesion, biopsy is generally preferred to observation. “The traditional belief was that punch biopsy was preferable, followed by shave biopsy,” she said. “This is always on a case-by-case basis.”
However, results from a retrospective study of the records of 123 cases of biopsy-proven Spitz nevi with incomplete removal on biopsy suggests that the method of biopsy matters. The researchers found that the presence of residual lesion in the re-excision specimen was significantly higher when the initial biopsy was done by punch biopsy (90.9%) when compared with shave biopsy (48.9%) and formal excision (62.5%; P < .05).
“This suggests that shave may better than punch for the initial biopsy, but the study was limited by its retrospective design,” Dr. Piggott said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps Cancer Center. “Even today it remains controversial whether you should do a shave or punch biopsy.”
Parameters for diagnosing Spitzoid tumors that pathologists look for under the microscope are asymmetry, Clark’s level IV/V, lack of maturation, solid growth, nuclear pleomorphism, high nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio, and mitoses that are atypical, deep, or that exceed 6 mm2 in size.
In terms of treatment recommendations for children with biopsy-proven Spitz nevi, Dr. Piggott said that there is no consensus among pediatric dermatologists. If the biopsy comes back as a benign Spitz nevus, the most reasonable approach is observation, “especially if there is no clinical residue — no pigment on exam, no papule left over in the scar,” she said. “You also want to educate the family about the rare potential for transformation down the line. Monitor for recurrence and consider re-excision if recurrence occurs.”
If the initial Spitz nevus biopsy reveals any degree of atypia, excision is preferred. “In young children, you have to weigh the risks of anesthesia for removal,” she said. “If you’re unable to excise the lesion, close observation is recommended at 6 months or 1 year.”
Treatment for borderline atypical Spitz tumor is excision, she continued, but no outcomes data exist that document a survival benefit with sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy. “The decision on whether to do a SLN biopsy is usually made on a case-by-case basis,” Dr. Piggott said. “Nodal metastases from atypical Spitzoid tumors are not uncommon, but death from widespread disease is rare. If the SLN biopsy is positive, complete lymphadenectomy is associated with increased risk of morbidity and no evidence of increased survival. If lymph node disease is found, we in pediatric dermatology would consider referral to a pediatric oncologist for consideration of systemic therapy such as interferon or a newer immunotherapy.”
Dr. Piggott reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO —
“For a pigmented Spitz nevus, we were taught to look for a starburst pattern, a central area of homogeneous pigment, and peripheral symmetrical streaks or pseudopods,” Dr. Piggott, an adult and pediatric dermatologist at Scripps Clinic, San Diego, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “For Spitz nevi without pigment, we were taught to look for symmetric dotted vessels.”
However, results from a retrospective study published in 2015 gave her pause in relying on dermoscopy alone for assessing Spitz nevi. Researchers from Italy, Japan, and Brazil studied excision specimens of 384 Spitzoid-looking lesions in patients 12 years and older. On histology, 86.7% were diagnosed as benign Spitz nevi and 13.3% were diagnosed as melanoma.
When the researchers looked at the dermoscopic images, many cases of atypical Spitz nevi were indistinguishable from the benign Spitz nevi. Now, Dr. Piggott said, “I respect the dermoscopy criteria, but I don’t rely solely on it.”
If a child presents with Spitzoid-looking lesion, biopsy is generally preferred to observation. “The traditional belief was that punch biopsy was preferable, followed by shave biopsy,” she said. “This is always on a case-by-case basis.”
However, results from a retrospective study of the records of 123 cases of biopsy-proven Spitz nevi with incomplete removal on biopsy suggests that the method of biopsy matters. The researchers found that the presence of residual lesion in the re-excision specimen was significantly higher when the initial biopsy was done by punch biopsy (90.9%) when compared with shave biopsy (48.9%) and formal excision (62.5%; P < .05).
“This suggests that shave may better than punch for the initial biopsy, but the study was limited by its retrospective design,” Dr. Piggott said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps Cancer Center. “Even today it remains controversial whether you should do a shave or punch biopsy.”
Parameters for diagnosing Spitzoid tumors that pathologists look for under the microscope are asymmetry, Clark’s level IV/V, lack of maturation, solid growth, nuclear pleomorphism, high nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio, and mitoses that are atypical, deep, or that exceed 6 mm2 in size.
In terms of treatment recommendations for children with biopsy-proven Spitz nevi, Dr. Piggott said that there is no consensus among pediatric dermatologists. If the biopsy comes back as a benign Spitz nevus, the most reasonable approach is observation, “especially if there is no clinical residue — no pigment on exam, no papule left over in the scar,” she said. “You also want to educate the family about the rare potential for transformation down the line. Monitor for recurrence and consider re-excision if recurrence occurs.”
If the initial Spitz nevus biopsy reveals any degree of atypia, excision is preferred. “In young children, you have to weigh the risks of anesthesia for removal,” she said. “If you’re unable to excise the lesion, close observation is recommended at 6 months or 1 year.”
Treatment for borderline atypical Spitz tumor is excision, she continued, but no outcomes data exist that document a survival benefit with sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy. “The decision on whether to do a SLN biopsy is usually made on a case-by-case basis,” Dr. Piggott said. “Nodal metastases from atypical Spitzoid tumors are not uncommon, but death from widespread disease is rare. If the SLN biopsy is positive, complete lymphadenectomy is associated with increased risk of morbidity and no evidence of increased survival. If lymph node disease is found, we in pediatric dermatology would consider referral to a pediatric oncologist for consideration of systemic therapy such as interferon or a newer immunotherapy.”
Dr. Piggott reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO —
“For a pigmented Spitz nevus, we were taught to look for a starburst pattern, a central area of homogeneous pigment, and peripheral symmetrical streaks or pseudopods,” Dr. Piggott, an adult and pediatric dermatologist at Scripps Clinic, San Diego, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “For Spitz nevi without pigment, we were taught to look for symmetric dotted vessels.”
However, results from a retrospective study published in 2015 gave her pause in relying on dermoscopy alone for assessing Spitz nevi. Researchers from Italy, Japan, and Brazil studied excision specimens of 384 Spitzoid-looking lesions in patients 12 years and older. On histology, 86.7% were diagnosed as benign Spitz nevi and 13.3% were diagnosed as melanoma.
When the researchers looked at the dermoscopic images, many cases of atypical Spitz nevi were indistinguishable from the benign Spitz nevi. Now, Dr. Piggott said, “I respect the dermoscopy criteria, but I don’t rely solely on it.”
If a child presents with Spitzoid-looking lesion, biopsy is generally preferred to observation. “The traditional belief was that punch biopsy was preferable, followed by shave biopsy,” she said. “This is always on a case-by-case basis.”
However, results from a retrospective study of the records of 123 cases of biopsy-proven Spitz nevi with incomplete removal on biopsy suggests that the method of biopsy matters. The researchers found that the presence of residual lesion in the re-excision specimen was significantly higher when the initial biopsy was done by punch biopsy (90.9%) when compared with shave biopsy (48.9%) and formal excision (62.5%; P < .05).
“This suggests that shave may better than punch for the initial biopsy, but the study was limited by its retrospective design,” Dr. Piggott said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps Cancer Center. “Even today it remains controversial whether you should do a shave or punch biopsy.”
Parameters for diagnosing Spitzoid tumors that pathologists look for under the microscope are asymmetry, Clark’s level IV/V, lack of maturation, solid growth, nuclear pleomorphism, high nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio, and mitoses that are atypical, deep, or that exceed 6 mm2 in size.
In terms of treatment recommendations for children with biopsy-proven Spitz nevi, Dr. Piggott said that there is no consensus among pediatric dermatologists. If the biopsy comes back as a benign Spitz nevus, the most reasonable approach is observation, “especially if there is no clinical residue — no pigment on exam, no papule left over in the scar,” she said. “You also want to educate the family about the rare potential for transformation down the line. Monitor for recurrence and consider re-excision if recurrence occurs.”
If the initial Spitz nevus biopsy reveals any degree of atypia, excision is preferred. “In young children, you have to weigh the risks of anesthesia for removal,” she said. “If you’re unable to excise the lesion, close observation is recommended at 6 months or 1 year.”
Treatment for borderline atypical Spitz tumor is excision, she continued, but no outcomes data exist that document a survival benefit with sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy. “The decision on whether to do a SLN biopsy is usually made on a case-by-case basis,” Dr. Piggott said. “Nodal metastases from atypical Spitzoid tumors are not uncommon, but death from widespread disease is rare. If the SLN biopsy is positive, complete lymphadenectomy is associated with increased risk of morbidity and no evidence of increased survival. If lymph node disease is found, we in pediatric dermatology would consider referral to a pediatric oncologist for consideration of systemic therapy such as interferon or a newer immunotherapy.”
Dr. Piggott reported having no relevant disclosures.
FROM MELANOMA 2024
AAD Updates Guidelines for Managing Acne
. The guidelines also conditionally recommend the use of topical clascoterone, salicylic acid, azelaic acid, oral minocycline, sarecycline, combined oral contraceptives, and spironolactone.
The development updates the AAD’s 2016 guidelines for managing acne. “Since there have been several important new treatments introduced since the prior guidelines, it was determined that there was a need to update these guidelines,” John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, who cochaired a 16-member multidisciplinary work group that assembled the guidelines, told this news organization.
For the new guidelines, which were published online January 30, 2023, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Barbieri, a dermatologist who directs the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, guidelines cochair Rachel V. Reynolds, MD, a dermatologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and colleagues conducted a systematic review of evidence regarding the management of acne. Next, the work group applied the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach for assessing the certainty of the evidence and formulating and grading clinical recommendations based on relevant randomized trials in the medical literature.
In all, the work group made 18 recommendations and 5 good practice statements. They ranked 7 of the recommendations as “strong” based on the evidence reviewed, and the rest as “conditional.” The “strong” recommendations include the use of benzoyl peroxide, the use of topical retinoids, the use of topical antibiotics, a fixed dose of a combination topical antibiotic with benzoyl peroxide, a fixed dose of a combination topical retinoid with topical antibiotic, a fixed dose combination of a topical retinoid with benzoyl peroxide, and the use of doxycycline.
“Conditional” recommendations include those for the use of clascoterone, salicylic acid, azelaic acid, minocycline, sarecycline, doxycycline over azithromycin; combined oral contraceptive pills, spironolactone, and, for patients with severe acne, traditional daily dosing of isotretinoin over intermittent dosing of isotretinoin.
Meanwhile, good clinical practice statements contained in the document include using topical therapies combining multiple mechanisms of action, limiting systemic antibiotic use, combining topical and systemic antibiotics with benzoyl peroxide and other topical therapies, and adjuvant intralesional corticosteroid injections.
In Dr. Barbieri’s opinion, the recommendations regarding clascoterone and sarecycline represent important developments. “Clascoterone is the first FDA-approved treatment that can address hormonal causes of acne in both men and women,” he told this news organization. “Sarecycline is a narrow-spectrum tetracycline that might have some advantages over other tetracyclines such as doxycycline and minocycline. It will be important to payers to provide coverage to ensure that patients have access to these valuable new treatments.”
Dr. Barbieri added that while no evidence exists to suggest that minocycline is more effective than doxycycline, minocycline can be associated with rare but serious side effects, such as vestibular dysfunction, autoimmune hepatitis, drug-induced lupus, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). “We should consider whether reducing use of minocycline might be beneficial to our overall care of patients with acne,” he said. “In addition, we discuss that use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole should be limited due to risk of severe adverse reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis, and acute respiratory failure.”
Another highlight of the guidelines, he continued, are specific recommendations for young, healthy patients on isotretinoin or spironolactone, which “can help clinicians and patients who are interested in less frequent monitoring feel more comfortable with these approaches,” he said.
Many discussions among work group members dealt with how to best implement the GRADE approach to the project “while ensuring the guidelines were as clinically relevant and actionable as possible,” according to Dr. Barbieri. “I think an important issue going forward will be to consider how to update and modify the GRADE approach to fit the unique needs of creating evidence-based guidelines for the management of skin disease.”
The work group acknowledged limitations of the guidelines, including identification of “important evidence gaps on the use of microbiology and endocrinology testing in acne, the use of systemic antibiotics beyond tetracycline-class antibiotics, physical modalities, complementary and alternative therapies, dietary interventions for the treatment of acne, and cost-effectiveness of acne treatments,” they wrote. “RCTs with long-term follow-up and comparative effectiveness research are necessary to examine and compare patient-centered acne treatment outcomes.”
The AAD funded the project. Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he serves as investigator for the National Institutes of Health and the National Psoriasis Foundation. Many coauthors reported being a speaker for and/or a consultant and advisory board member to many pharmaceutical companies.
. The guidelines also conditionally recommend the use of topical clascoterone, salicylic acid, azelaic acid, oral minocycline, sarecycline, combined oral contraceptives, and spironolactone.
The development updates the AAD’s 2016 guidelines for managing acne. “Since there have been several important new treatments introduced since the prior guidelines, it was determined that there was a need to update these guidelines,” John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, who cochaired a 16-member multidisciplinary work group that assembled the guidelines, told this news organization.
For the new guidelines, which were published online January 30, 2023, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Barbieri, a dermatologist who directs the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, guidelines cochair Rachel V. Reynolds, MD, a dermatologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and colleagues conducted a systematic review of evidence regarding the management of acne. Next, the work group applied the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach for assessing the certainty of the evidence and formulating and grading clinical recommendations based on relevant randomized trials in the medical literature.
In all, the work group made 18 recommendations and 5 good practice statements. They ranked 7 of the recommendations as “strong” based on the evidence reviewed, and the rest as “conditional.” The “strong” recommendations include the use of benzoyl peroxide, the use of topical retinoids, the use of topical antibiotics, a fixed dose of a combination topical antibiotic with benzoyl peroxide, a fixed dose of a combination topical retinoid with topical antibiotic, a fixed dose combination of a topical retinoid with benzoyl peroxide, and the use of doxycycline.
“Conditional” recommendations include those for the use of clascoterone, salicylic acid, azelaic acid, minocycline, sarecycline, doxycycline over azithromycin; combined oral contraceptive pills, spironolactone, and, for patients with severe acne, traditional daily dosing of isotretinoin over intermittent dosing of isotretinoin.
Meanwhile, good clinical practice statements contained in the document include using topical therapies combining multiple mechanisms of action, limiting systemic antibiotic use, combining topical and systemic antibiotics with benzoyl peroxide and other topical therapies, and adjuvant intralesional corticosteroid injections.
In Dr. Barbieri’s opinion, the recommendations regarding clascoterone and sarecycline represent important developments. “Clascoterone is the first FDA-approved treatment that can address hormonal causes of acne in both men and women,” he told this news organization. “Sarecycline is a narrow-spectrum tetracycline that might have some advantages over other tetracyclines such as doxycycline and minocycline. It will be important to payers to provide coverage to ensure that patients have access to these valuable new treatments.”
Dr. Barbieri added that while no evidence exists to suggest that minocycline is more effective than doxycycline, minocycline can be associated with rare but serious side effects, such as vestibular dysfunction, autoimmune hepatitis, drug-induced lupus, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). “We should consider whether reducing use of minocycline might be beneficial to our overall care of patients with acne,” he said. “In addition, we discuss that use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole should be limited due to risk of severe adverse reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis, and acute respiratory failure.”
Another highlight of the guidelines, he continued, are specific recommendations for young, healthy patients on isotretinoin or spironolactone, which “can help clinicians and patients who are interested in less frequent monitoring feel more comfortable with these approaches,” he said.
Many discussions among work group members dealt with how to best implement the GRADE approach to the project “while ensuring the guidelines were as clinically relevant and actionable as possible,” according to Dr. Barbieri. “I think an important issue going forward will be to consider how to update and modify the GRADE approach to fit the unique needs of creating evidence-based guidelines for the management of skin disease.”
The work group acknowledged limitations of the guidelines, including identification of “important evidence gaps on the use of microbiology and endocrinology testing in acne, the use of systemic antibiotics beyond tetracycline-class antibiotics, physical modalities, complementary and alternative therapies, dietary interventions for the treatment of acne, and cost-effectiveness of acne treatments,” they wrote. “RCTs with long-term follow-up and comparative effectiveness research are necessary to examine and compare patient-centered acne treatment outcomes.”
The AAD funded the project. Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he serves as investigator for the National Institutes of Health and the National Psoriasis Foundation. Many coauthors reported being a speaker for and/or a consultant and advisory board member to many pharmaceutical companies.
. The guidelines also conditionally recommend the use of topical clascoterone, salicylic acid, azelaic acid, oral minocycline, sarecycline, combined oral contraceptives, and spironolactone.
The development updates the AAD’s 2016 guidelines for managing acne. “Since there have been several important new treatments introduced since the prior guidelines, it was determined that there was a need to update these guidelines,” John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, who cochaired a 16-member multidisciplinary work group that assembled the guidelines, told this news organization.
For the new guidelines, which were published online January 30, 2023, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Barbieri, a dermatologist who directs the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, guidelines cochair Rachel V. Reynolds, MD, a dermatologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and colleagues conducted a systematic review of evidence regarding the management of acne. Next, the work group applied the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach for assessing the certainty of the evidence and formulating and grading clinical recommendations based on relevant randomized trials in the medical literature.
In all, the work group made 18 recommendations and 5 good practice statements. They ranked 7 of the recommendations as “strong” based on the evidence reviewed, and the rest as “conditional.” The “strong” recommendations include the use of benzoyl peroxide, the use of topical retinoids, the use of topical antibiotics, a fixed dose of a combination topical antibiotic with benzoyl peroxide, a fixed dose of a combination topical retinoid with topical antibiotic, a fixed dose combination of a topical retinoid with benzoyl peroxide, and the use of doxycycline.
“Conditional” recommendations include those for the use of clascoterone, salicylic acid, azelaic acid, minocycline, sarecycline, doxycycline over azithromycin; combined oral contraceptive pills, spironolactone, and, for patients with severe acne, traditional daily dosing of isotretinoin over intermittent dosing of isotretinoin.
Meanwhile, good clinical practice statements contained in the document include using topical therapies combining multiple mechanisms of action, limiting systemic antibiotic use, combining topical and systemic antibiotics with benzoyl peroxide and other topical therapies, and adjuvant intralesional corticosteroid injections.
In Dr. Barbieri’s opinion, the recommendations regarding clascoterone and sarecycline represent important developments. “Clascoterone is the first FDA-approved treatment that can address hormonal causes of acne in both men and women,” he told this news organization. “Sarecycline is a narrow-spectrum tetracycline that might have some advantages over other tetracyclines such as doxycycline and minocycline. It will be important to payers to provide coverage to ensure that patients have access to these valuable new treatments.”
Dr. Barbieri added that while no evidence exists to suggest that minocycline is more effective than doxycycline, minocycline can be associated with rare but serious side effects, such as vestibular dysfunction, autoimmune hepatitis, drug-induced lupus, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). “We should consider whether reducing use of minocycline might be beneficial to our overall care of patients with acne,” he said. “In addition, we discuss that use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole should be limited due to risk of severe adverse reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis, and acute respiratory failure.”
Another highlight of the guidelines, he continued, are specific recommendations for young, healthy patients on isotretinoin or spironolactone, which “can help clinicians and patients who are interested in less frequent monitoring feel more comfortable with these approaches,” he said.
Many discussions among work group members dealt with how to best implement the GRADE approach to the project “while ensuring the guidelines were as clinically relevant and actionable as possible,” according to Dr. Barbieri. “I think an important issue going forward will be to consider how to update and modify the GRADE approach to fit the unique needs of creating evidence-based guidelines for the management of skin disease.”
The work group acknowledged limitations of the guidelines, including identification of “important evidence gaps on the use of microbiology and endocrinology testing in acne, the use of systemic antibiotics beyond tetracycline-class antibiotics, physical modalities, complementary and alternative therapies, dietary interventions for the treatment of acne, and cost-effectiveness of acne treatments,” they wrote. “RCTs with long-term follow-up and comparative effectiveness research are necessary to examine and compare patient-centered acne treatment outcomes.”
The AAD funded the project. Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he serves as investigator for the National Institutes of Health and the National Psoriasis Foundation. Many coauthors reported being a speaker for and/or a consultant and advisory board member to many pharmaceutical companies.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
More Than 100K New Cutaneous Melanoma Diagnoses Expected in 2024
SAN DIEGO — According to data from the
“The incidence of melanoma seems to have continued to go up since the early 1990s,” David E. Kent, MD, a dermatologist at Skin Care Physicians of Georgia, Macon, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “The death rates have been flat and may have slightly decreased.”
In 2024, the ACS estimates that about 100,640 new melanomas will be diagnosed in the United States (59,170 in men and 41,470 in women), and about 8,290 people are expected to die of melanoma (5,430 men and 2,860 women). Meanwhile, the lifetime risk of melanoma is about 3% (1 in 33) for Whites, 0.1% (1 in 1,000) for Blacks, and 0.5% (1 in 200) for Hispanics. In 2019, there were an estimated 1.4 million people in the United States living with cutaneous melanoma, and the overall 5-year survival is 93.7%.
Epidemiologic studies show an increase in melanoma incidence, primarily among White populations. “This is believed to be due to sun exposure, changes in recreational behaviors, and tanning bed exposures,” said Dr. Kent, who holds a faculty position in the department of dermatology at the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta. Increased surveillance and diagnosis also play a role. In the medical literature, annual increases in melanoma incidence vary from 3%-7% per year, “which means that the rate is doubling every 10-20 years,” he said, noting that annual melanoma costs are approximately $3.3 billion.
While incidence rates are lower in non-White, non-Hispanic populations, poor outcomes are disproportionately higher in persons of color, according to a 2023 paper. Black individuals present at diagnosis with more advanced stage disease and are 1.5 times more likely to die from melanoma, he said, while Hispanics are 2.4 times more likely to present with stage III disease and 3.6 times more likely to have distant metastases. Persons of color also have higher rates of mucosal, acral lentiginous, and subungual melanoma.
Risk Factors
Known genetic risk factors for melanoma include having skin types I and II, particularly those with light hair, light eyes, and freckling, and those with a family history have a twofold increased risk. Also, up to 40% of genetic cases are from inherited mutations in CDKN2A, CDK4, BAP1 and MCR1. Other genetic-related risk factors include the number and size of nevi, having atypical nevus syndrome, DNA repair defects, large congenital nevi, and a personal history of melanoma.
Dr. Kent said that genetic testing for melanoma is warranted for individuals who meet criteria for the “rule of 3s.” He defined this as three primary melanomas in an individual, or three cases of melanoma in first- or second-degree relatives, or two cases of melanoma and one pancreatic cancer or astrocytoma in first or second-degree relatives, or one case of melanoma and two of pancreatic cancer/astrocytoma in first- or second-degree relatives.
The main environmental risk factor for melanoma is exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Individuals can track their UV exposure with a variety of wearable devices and apps, including SunSense One Digital UV Tracker, the SunSense App, the UV Index Widget, the SunSmart Global UV App, the SunKnown UV light photometer, and the EPA’s UV Index Mobile App. Other environment-related risk factors include having a high socioeconomic status (SES), being immunosuppressed, as well as exposure to heavy metals, insecticides, or hormones; and ones distance from the equator.
In a study published in 2023, researchers investigated the risk factors associated with first and second primary melanomas in 38,845 patients who were followed in Australia between 2011 and 2018. During a median follow-up of 7.4 years, 1212 patients (3.1%) had a single primary melanoma diagnosis and 245 (0.6%) had a secondary primary melanoma diagnosis. The researchers found that second melanomas were more likely than first melanomas to be in situ; for invasive tumors, second melanomas were more likely to be thin (defined as 1 mm or less) than first melanomas. In addition, having many self-reported moles at age 21 years was more strongly associated with second melanomas compared with first melanomas (hazard ratio, 6.36 vs 3.46, respectively; P = .01), as was having a high genetic predisposition (HR, 3.28 vs. 2.06; P = .03). Second melanomas were also more strongly associated with a history of multiple skin cancer excisions (HR, 2.63 vs 1.86; P = .05).
Dr. Kent noted that while sunscreen use protects against melanoma, a National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey in 2014 found that internists and pediatricians mentioned sunscreen at fewer than 0.1% of visits — even those with patients who have a diagnosis of skin disease. “Physicians need to do better,” he said at the meeting, which was hosted by the Scripps Cancer Center. “We as dermatologists have work to do to help educate them.”
Dr. Kent reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — According to data from the
“The incidence of melanoma seems to have continued to go up since the early 1990s,” David E. Kent, MD, a dermatologist at Skin Care Physicians of Georgia, Macon, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “The death rates have been flat and may have slightly decreased.”
In 2024, the ACS estimates that about 100,640 new melanomas will be diagnosed in the United States (59,170 in men and 41,470 in women), and about 8,290 people are expected to die of melanoma (5,430 men and 2,860 women). Meanwhile, the lifetime risk of melanoma is about 3% (1 in 33) for Whites, 0.1% (1 in 1,000) for Blacks, and 0.5% (1 in 200) for Hispanics. In 2019, there were an estimated 1.4 million people in the United States living with cutaneous melanoma, and the overall 5-year survival is 93.7%.
Epidemiologic studies show an increase in melanoma incidence, primarily among White populations. “This is believed to be due to sun exposure, changes in recreational behaviors, and tanning bed exposures,” said Dr. Kent, who holds a faculty position in the department of dermatology at the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta. Increased surveillance and diagnosis also play a role. In the medical literature, annual increases in melanoma incidence vary from 3%-7% per year, “which means that the rate is doubling every 10-20 years,” he said, noting that annual melanoma costs are approximately $3.3 billion.
While incidence rates are lower in non-White, non-Hispanic populations, poor outcomes are disproportionately higher in persons of color, according to a 2023 paper. Black individuals present at diagnosis with more advanced stage disease and are 1.5 times more likely to die from melanoma, he said, while Hispanics are 2.4 times more likely to present with stage III disease and 3.6 times more likely to have distant metastases. Persons of color also have higher rates of mucosal, acral lentiginous, and subungual melanoma.
Risk Factors
Known genetic risk factors for melanoma include having skin types I and II, particularly those with light hair, light eyes, and freckling, and those with a family history have a twofold increased risk. Also, up to 40% of genetic cases are from inherited mutations in CDKN2A, CDK4, BAP1 and MCR1. Other genetic-related risk factors include the number and size of nevi, having atypical nevus syndrome, DNA repair defects, large congenital nevi, and a personal history of melanoma.
Dr. Kent said that genetic testing for melanoma is warranted for individuals who meet criteria for the “rule of 3s.” He defined this as three primary melanomas in an individual, or three cases of melanoma in first- or second-degree relatives, or two cases of melanoma and one pancreatic cancer or astrocytoma in first or second-degree relatives, or one case of melanoma and two of pancreatic cancer/astrocytoma in first- or second-degree relatives.
The main environmental risk factor for melanoma is exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Individuals can track their UV exposure with a variety of wearable devices and apps, including SunSense One Digital UV Tracker, the SunSense App, the UV Index Widget, the SunSmart Global UV App, the SunKnown UV light photometer, and the EPA’s UV Index Mobile App. Other environment-related risk factors include having a high socioeconomic status (SES), being immunosuppressed, as well as exposure to heavy metals, insecticides, or hormones; and ones distance from the equator.
In a study published in 2023, researchers investigated the risk factors associated with first and second primary melanomas in 38,845 patients who were followed in Australia between 2011 and 2018. During a median follow-up of 7.4 years, 1212 patients (3.1%) had a single primary melanoma diagnosis and 245 (0.6%) had a secondary primary melanoma diagnosis. The researchers found that second melanomas were more likely than first melanomas to be in situ; for invasive tumors, second melanomas were more likely to be thin (defined as 1 mm or less) than first melanomas. In addition, having many self-reported moles at age 21 years was more strongly associated with second melanomas compared with first melanomas (hazard ratio, 6.36 vs 3.46, respectively; P = .01), as was having a high genetic predisposition (HR, 3.28 vs. 2.06; P = .03). Second melanomas were also more strongly associated with a history of multiple skin cancer excisions (HR, 2.63 vs 1.86; P = .05).
Dr. Kent noted that while sunscreen use protects against melanoma, a National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey in 2014 found that internists and pediatricians mentioned sunscreen at fewer than 0.1% of visits — even those with patients who have a diagnosis of skin disease. “Physicians need to do better,” he said at the meeting, which was hosted by the Scripps Cancer Center. “We as dermatologists have work to do to help educate them.”
Dr. Kent reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — According to data from the
“The incidence of melanoma seems to have continued to go up since the early 1990s,” David E. Kent, MD, a dermatologist at Skin Care Physicians of Georgia, Macon, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “The death rates have been flat and may have slightly decreased.”
In 2024, the ACS estimates that about 100,640 new melanomas will be diagnosed in the United States (59,170 in men and 41,470 in women), and about 8,290 people are expected to die of melanoma (5,430 men and 2,860 women). Meanwhile, the lifetime risk of melanoma is about 3% (1 in 33) for Whites, 0.1% (1 in 1,000) for Blacks, and 0.5% (1 in 200) for Hispanics. In 2019, there were an estimated 1.4 million people in the United States living with cutaneous melanoma, and the overall 5-year survival is 93.7%.
Epidemiologic studies show an increase in melanoma incidence, primarily among White populations. “This is believed to be due to sun exposure, changes in recreational behaviors, and tanning bed exposures,” said Dr. Kent, who holds a faculty position in the department of dermatology at the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta. Increased surveillance and diagnosis also play a role. In the medical literature, annual increases in melanoma incidence vary from 3%-7% per year, “which means that the rate is doubling every 10-20 years,” he said, noting that annual melanoma costs are approximately $3.3 billion.
While incidence rates are lower in non-White, non-Hispanic populations, poor outcomes are disproportionately higher in persons of color, according to a 2023 paper. Black individuals present at diagnosis with more advanced stage disease and are 1.5 times more likely to die from melanoma, he said, while Hispanics are 2.4 times more likely to present with stage III disease and 3.6 times more likely to have distant metastases. Persons of color also have higher rates of mucosal, acral lentiginous, and subungual melanoma.
Risk Factors
Known genetic risk factors for melanoma include having skin types I and II, particularly those with light hair, light eyes, and freckling, and those with a family history have a twofold increased risk. Also, up to 40% of genetic cases are from inherited mutations in CDKN2A, CDK4, BAP1 and MCR1. Other genetic-related risk factors include the number and size of nevi, having atypical nevus syndrome, DNA repair defects, large congenital nevi, and a personal history of melanoma.
Dr. Kent said that genetic testing for melanoma is warranted for individuals who meet criteria for the “rule of 3s.” He defined this as three primary melanomas in an individual, or three cases of melanoma in first- or second-degree relatives, or two cases of melanoma and one pancreatic cancer or astrocytoma in first or second-degree relatives, or one case of melanoma and two of pancreatic cancer/astrocytoma in first- or second-degree relatives.
The main environmental risk factor for melanoma is exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Individuals can track their UV exposure with a variety of wearable devices and apps, including SunSense One Digital UV Tracker, the SunSense App, the UV Index Widget, the SunSmart Global UV App, the SunKnown UV light photometer, and the EPA’s UV Index Mobile App. Other environment-related risk factors include having a high socioeconomic status (SES), being immunosuppressed, as well as exposure to heavy metals, insecticides, or hormones; and ones distance from the equator.
In a study published in 2023, researchers investigated the risk factors associated with first and second primary melanomas in 38,845 patients who were followed in Australia between 2011 and 2018. During a median follow-up of 7.4 years, 1212 patients (3.1%) had a single primary melanoma diagnosis and 245 (0.6%) had a secondary primary melanoma diagnosis. The researchers found that second melanomas were more likely than first melanomas to be in situ; for invasive tumors, second melanomas were more likely to be thin (defined as 1 mm or less) than first melanomas. In addition, having many self-reported moles at age 21 years was more strongly associated with second melanomas compared with first melanomas (hazard ratio, 6.36 vs 3.46, respectively; P = .01), as was having a high genetic predisposition (HR, 3.28 vs. 2.06; P = .03). Second melanomas were also more strongly associated with a history of multiple skin cancer excisions (HR, 2.63 vs 1.86; P = .05).
Dr. Kent noted that while sunscreen use protects against melanoma, a National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey in 2014 found that internists and pediatricians mentioned sunscreen at fewer than 0.1% of visits — even those with patients who have a diagnosis of skin disease. “Physicians need to do better,” he said at the meeting, which was hosted by the Scripps Cancer Center. “We as dermatologists have work to do to help educate them.”
Dr. Kent reported having no relevant disclosures.
FROM MELANOMA 2024
Study Concludes Most Melanoma Overdiagnoses Are In Situ
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The increase in melanoma diagnoses in the United States, while mortality has remained flat, has raised concerns about overdiagnosis of melanoma, cases that may not result in harm if left untreated. How much of the overdiagnoses can be attributed to melanoma in situ vs invasive melanoma is unknown.
- To address this question, researchers collected data from the SEER 9 registries database.
- They used DevCan software to calculate the cumulative lifetime risk of White American men and women being diagnosed with melanoma between 1975 and 2018, adjusting for changes in longevity and risk factors over the study period.
- The primary outcome was excess lifetime risk for melanoma diagnosis between 1976 and 2018, adjusted for year 2018 competing mortality and changes in risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers found that between 1975 and 2018, the adjusted lifetime risk of being diagnosed with melanoma in situ increased from 0.17% to 2.7% in White men and 0.08% to 2% in White women.
- An estimated 49.7% and 64.6% of melanomas diagnosed in White men and White women, respectively, were overdiagnosed in 2018.
- Among individuals diagnosed with melanoma in situ, 89.4% of White men and 85.4% of White women were likely overdiagnosed in 2018.
IN PRACTICE:
“A large proportion of overdiagnosed melanomas are in situ cancers, pointing to a potential area to focus for an intervention de-escalation of the intensity of treatment and survivorship care,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Adewole S. Adamson, MD, of the Division of Dermatology at The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, led the research. The study was published in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine on January 19, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis only involved White individuals. Other limitations include a high risk for selection bias and that the researchers assumed no melanoma diagnosis in 1975, which may not be the case.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Adamson disclosed that he is supported by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation through The Harold Amos Medical Faculty Development Program. Coauthor Katy J.L. Bell, MBchB, PhD, of the University of Sydney, is supported by an Australian Government National Health and Medical Research Council Investigator Grant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The increase in melanoma diagnoses in the United States, while mortality has remained flat, has raised concerns about overdiagnosis of melanoma, cases that may not result in harm if left untreated. How much of the overdiagnoses can be attributed to melanoma in situ vs invasive melanoma is unknown.
- To address this question, researchers collected data from the SEER 9 registries database.
- They used DevCan software to calculate the cumulative lifetime risk of White American men and women being diagnosed with melanoma between 1975 and 2018, adjusting for changes in longevity and risk factors over the study period.
- The primary outcome was excess lifetime risk for melanoma diagnosis between 1976 and 2018, adjusted for year 2018 competing mortality and changes in risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers found that between 1975 and 2018, the adjusted lifetime risk of being diagnosed with melanoma in situ increased from 0.17% to 2.7% in White men and 0.08% to 2% in White women.
- An estimated 49.7% and 64.6% of melanomas diagnosed in White men and White women, respectively, were overdiagnosed in 2018.
- Among individuals diagnosed with melanoma in situ, 89.4% of White men and 85.4% of White women were likely overdiagnosed in 2018.
IN PRACTICE:
“A large proportion of overdiagnosed melanomas are in situ cancers, pointing to a potential area to focus for an intervention de-escalation of the intensity of treatment and survivorship care,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Adewole S. Adamson, MD, of the Division of Dermatology at The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, led the research. The study was published in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine on January 19, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis only involved White individuals. Other limitations include a high risk for selection bias and that the researchers assumed no melanoma diagnosis in 1975, which may not be the case.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Adamson disclosed that he is supported by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation through The Harold Amos Medical Faculty Development Program. Coauthor Katy J.L. Bell, MBchB, PhD, of the University of Sydney, is supported by an Australian Government National Health and Medical Research Council Investigator Grant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The increase in melanoma diagnoses in the United States, while mortality has remained flat, has raised concerns about overdiagnosis of melanoma, cases that may not result in harm if left untreated. How much of the overdiagnoses can be attributed to melanoma in situ vs invasive melanoma is unknown.
- To address this question, researchers collected data from the SEER 9 registries database.
- They used DevCan software to calculate the cumulative lifetime risk of White American men and women being diagnosed with melanoma between 1975 and 2018, adjusting for changes in longevity and risk factors over the study period.
- The primary outcome was excess lifetime risk for melanoma diagnosis between 1976 and 2018, adjusted for year 2018 competing mortality and changes in risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers found that between 1975 and 2018, the adjusted lifetime risk of being diagnosed with melanoma in situ increased from 0.17% to 2.7% in White men and 0.08% to 2% in White women.
- An estimated 49.7% and 64.6% of melanomas diagnosed in White men and White women, respectively, were overdiagnosed in 2018.
- Among individuals diagnosed with melanoma in situ, 89.4% of White men and 85.4% of White women were likely overdiagnosed in 2018.
IN PRACTICE:
“A large proportion of overdiagnosed melanomas are in situ cancers, pointing to a potential area to focus for an intervention de-escalation of the intensity of treatment and survivorship care,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Adewole S. Adamson, MD, of the Division of Dermatology at The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, led the research. The study was published in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine on January 19, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis only involved White individuals. Other limitations include a high risk for selection bias and that the researchers assumed no melanoma diagnosis in 1975, which may not be the case.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Adamson disclosed that he is supported by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation through The Harold Amos Medical Faculty Development Program. Coauthor Katy J.L. Bell, MBchB, PhD, of the University of Sydney, is supported by an Australian Government National Health and Medical Research Council Investigator Grant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.