User login
Damian McNamara is a journalist for Medscape Medical News and MDedge. He worked full-time for MDedge as the Miami Bureau covering a dozen medical specialties during 2001-2012, then as a freelancer for Medscape and MDedge, before being hired on staff by Medscape in 2018. Now the two companies are one. He uses what he learned in school – Damian has a BS in chemistry and an MS in science, health and environmental reporting/journalism. He works out of a home office in Miami, with a 100-pound chocolate lab known to snore under his desk during work hours.
COVID-19 linked to large vessel stroke in young adults
In a rapid communication to be published online April 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine, investigators led by Thomas Oxley, MD, PhD, of the department of neurosurgery at Mount Sinai Health System, reported five cases of large vessel stroke over a 2-week period in COVID-19 patients under age 50 years. This represents a sevenfold increase in what would normally be expected.
The five cases had either no, or mild, COVID-19 symptoms.
“It’s been surprising to learn that the virus appears to cause disease through a process of blood clotting,” Dr. Oxley said in an interview.
The message for neurologists and other physicians is “we’re learning that this can disproportionally affect large vessels more than small vessels in terms of presentation of stroke,” he said.
Inflammation in the blood vessel walls may be driving thrombosis formation, Dr. Oxley added. This report joins other research pointing to this emerging phenomenon.
Recently, investigators in the Netherlands found a “remarkably high” 31% rate of thrombotic complications among 184 critical care patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
Dr. Oxley and colleagues also suggested that, since the onset of the pandemic, fewer patients may be calling emergency services when they experience signs of a stroke. The physicians noted that two of the five cases in the report delayed calling an ambulance.
“I understand why people do not want to leave the household. I think people are more willing to ignore other [non–COVID-19] symptoms in this environment,” he said.
As previously reported, physicians in hospitals across the United States and elsewhere have reported a significant drop in stroke patients since the COVID-19 pandemic took hold, which suggests that patients may indeed be foregoing emergency care.
The observations from Dr. Oxley and colleagues call for greater awareness of the association between COVID-19 and large vessel strokes in this age group, they add.
One patient in the case series died, one remains hospitalized, two are undergoing rehabilitation, and one was discharged home as of April 24.
Dr. Oxley and colleagues dedicated their report to “our inspiring colleague Gary Sclar, MD, a stroke physician who succumbed to COVID-19 while caring for his patients.”
Dr. Oxley has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In a rapid communication to be published online April 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine, investigators led by Thomas Oxley, MD, PhD, of the department of neurosurgery at Mount Sinai Health System, reported five cases of large vessel stroke over a 2-week period in COVID-19 patients under age 50 years. This represents a sevenfold increase in what would normally be expected.
The five cases had either no, or mild, COVID-19 symptoms.
“It’s been surprising to learn that the virus appears to cause disease through a process of blood clotting,” Dr. Oxley said in an interview.
The message for neurologists and other physicians is “we’re learning that this can disproportionally affect large vessels more than small vessels in terms of presentation of stroke,” he said.
Inflammation in the blood vessel walls may be driving thrombosis formation, Dr. Oxley added. This report joins other research pointing to this emerging phenomenon.
Recently, investigators in the Netherlands found a “remarkably high” 31% rate of thrombotic complications among 184 critical care patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
Dr. Oxley and colleagues also suggested that, since the onset of the pandemic, fewer patients may be calling emergency services when they experience signs of a stroke. The physicians noted that two of the five cases in the report delayed calling an ambulance.
“I understand why people do not want to leave the household. I think people are more willing to ignore other [non–COVID-19] symptoms in this environment,” he said.
As previously reported, physicians in hospitals across the United States and elsewhere have reported a significant drop in stroke patients since the COVID-19 pandemic took hold, which suggests that patients may indeed be foregoing emergency care.
The observations from Dr. Oxley and colleagues call for greater awareness of the association between COVID-19 and large vessel strokes in this age group, they add.
One patient in the case series died, one remains hospitalized, two are undergoing rehabilitation, and one was discharged home as of April 24.
Dr. Oxley and colleagues dedicated their report to “our inspiring colleague Gary Sclar, MD, a stroke physician who succumbed to COVID-19 while caring for his patients.”
Dr. Oxley has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In a rapid communication to be published online April 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine, investigators led by Thomas Oxley, MD, PhD, of the department of neurosurgery at Mount Sinai Health System, reported five cases of large vessel stroke over a 2-week period in COVID-19 patients under age 50 years. This represents a sevenfold increase in what would normally be expected.
The five cases had either no, or mild, COVID-19 symptoms.
“It’s been surprising to learn that the virus appears to cause disease through a process of blood clotting,” Dr. Oxley said in an interview.
The message for neurologists and other physicians is “we’re learning that this can disproportionally affect large vessels more than small vessels in terms of presentation of stroke,” he said.
Inflammation in the blood vessel walls may be driving thrombosis formation, Dr. Oxley added. This report joins other research pointing to this emerging phenomenon.
Recently, investigators in the Netherlands found a “remarkably high” 31% rate of thrombotic complications among 184 critical care patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
Dr. Oxley and colleagues also suggested that, since the onset of the pandemic, fewer patients may be calling emergency services when they experience signs of a stroke. The physicians noted that two of the five cases in the report delayed calling an ambulance.
“I understand why people do not want to leave the household. I think people are more willing to ignore other [non–COVID-19] symptoms in this environment,” he said.
As previously reported, physicians in hospitals across the United States and elsewhere have reported a significant drop in stroke patients since the COVID-19 pandemic took hold, which suggests that patients may indeed be foregoing emergency care.
The observations from Dr. Oxley and colleagues call for greater awareness of the association between COVID-19 and large vessel strokes in this age group, they add.
One patient in the case series died, one remains hospitalized, two are undergoing rehabilitation, and one was discharged home as of April 24.
Dr. Oxley and colleagues dedicated their report to “our inspiring colleague Gary Sclar, MD, a stroke physician who succumbed to COVID-19 while caring for his patients.”
Dr. Oxley has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19: Are acute stroke patients avoiding emergency care?
(EDs).
Stroke specialists in New Orleans, Chicago, Seattle, and elsewhere told Medscape Medical News they are seeing a precipitous drop in the number of acute strokes at their institutions – and not just in the number of milder cases. Doctors on Twitter are sharing similar reports and are using social media to highlight this issue.
Gabriel Vidal, MD, a vascular and interventional neurologist at the Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, Louisiana, said there are “definitely” fewer patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA) seeking care at his facility and others throughout the New Orleans area, which has been hard hit by COVID-19.
“Even in Louisiana, we have a very large 53-hospital telestroke network, and the number of consults has diminished greatly,” Vidal added.
In Chicago, emergency medical service activations for patients with suspected strokes are down about 30%, Shyam Prabhakaran, MD, professor and chair of neurology at the University of Chicago Biological Sciences, Illinois, told Medscape Medical News.
“It appears to be that mild stroke and TIA patients may be more likely to stay at home and seek alternative care rather than come to the ED,” Prabhakaran said. However, “the severe strokes may be less affected and continue to come to emergency departments.”
“Getting the Word Out”
That may not be the whole story in Seattle, Washington, where a stroke specialist at Harborview Medical Center reported a drop in patients across the stroke-severity spectrum.
Some patients with milder strokes no longer come to Harborview for a comprehensive evaluation and workup, but that is only “a partial explanation,” said David Tirschwell, MD, medical director of comprehensive stroke care at the University of Washington (UW) Medicine Stroke Center at Harborview and a professor of neurology at UW.
“The thrombectomies are down also,” he added. “It’s hard to have great numbers in real time, but it’s probably safe to say it’s at least a 50% reduction in the number of admissions.”
As a stroke referral center, his institution is seeing fewer local cases and referrals from outside hospitals. “I think both of those sources for admissions of stroke cases are down,” Tirschwell said.
Recognizing the seriousness of forgoing essential care for acute stroke, neurologists, institutions, and medical groups are taking to social media to potentially save lives.
“Across our @FLStrokeReg we are seeing less patients with #stroke symptoms coming to our hospitals. We need to get the word out that our teams are working hard to safely provide care when needed during #COVID19,” tweeted Ralph Sacco, MD, chief and professor of neurology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine in South Florida.
Although Florida Stroke Registry data are not publicly available, anecdotal reports suggest that stroke admissions are down among many hospitals, Sacco told Medscape Medical News.
Furthermore, this is not a phenomenon only in the United States. “This has also been reported in other nations hit by COVID-19,” he said.
China is a prime example. There, many stroke centers have shown reduced functioning “because of fear of in-hospital cross infection and lack of experienced stroke care experts,” Jing Zhao, MD, PhD, and colleagues write in an editorial published online March 31 in Stroke.
Preliminary data show that “thrombectomies in Shanghai decreased by 50% in the first month after the Spring Festival compared with the same period in 2019,” write the editorialists, who are from Kings College London and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“Although the control of the COVID-19 is very important, at the same time, the management of stroke must not be neglected,” they add.
“Over 9000 new stroke cases occur each day in China alone. It cannot be right that treatment for one potentially curable disease is euthanized at the expense of another.”
Fear Factor?
The reasons individuals who may have experienced a stroke are avoiding emergency care is unclear at the moment. “I’m not really sure anyone really understands why, quite honestly,” Tirschwell said.
Until survey data or other data emerge, many experts are assuming that fear of COVID-19 is trumping other medical concerns, including emergency treatment of stroke.
“We believe this could represent patients being fearful to come to medical facilities with stroke-like symptoms, given the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Sacco, who is also incoming editor-in-chief of Stroke.
The BBC has been getting the word out in the United Kingdom via social media, with a tweet to “Dial 999 for stroke emergencies despite coronavirus.”
The World Stroke Campaign is also using Twitter to emphasize the need for urgent stroke care when appropriate:
“Don’t let concerns about COVID19 prevent you from seeking emergency treatment for stroke. If you spot the signs of stroke act FAST. Get emergency medical assistance,” the group urged in a tweet.
Don’t Hesitate
The American Heart Association (AHA) has addressed this troubling trend as well.
“People with serious symptoms shouldn’t ignore them,” Sarah Perlman, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver, states in an article on the AHA website.
Perlman added that some individuals who have signs of stroke and heart disease may hesitate to seek care because of fear that they are adding to an overburdened healthcare staff and system. However, she dismissed those concerns outright.
“If you’re experiencing warning signs of a heart attack or stroke, call 911,” she said. “Clearly, if there’s an emergency, we are available and capable and eager to take care of you.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(EDs).
Stroke specialists in New Orleans, Chicago, Seattle, and elsewhere told Medscape Medical News they are seeing a precipitous drop in the number of acute strokes at their institutions – and not just in the number of milder cases. Doctors on Twitter are sharing similar reports and are using social media to highlight this issue.
Gabriel Vidal, MD, a vascular and interventional neurologist at the Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, Louisiana, said there are “definitely” fewer patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA) seeking care at his facility and others throughout the New Orleans area, which has been hard hit by COVID-19.
“Even in Louisiana, we have a very large 53-hospital telestroke network, and the number of consults has diminished greatly,” Vidal added.
In Chicago, emergency medical service activations for patients with suspected strokes are down about 30%, Shyam Prabhakaran, MD, professor and chair of neurology at the University of Chicago Biological Sciences, Illinois, told Medscape Medical News.
“It appears to be that mild stroke and TIA patients may be more likely to stay at home and seek alternative care rather than come to the ED,” Prabhakaran said. However, “the severe strokes may be less affected and continue to come to emergency departments.”
“Getting the Word Out”
That may not be the whole story in Seattle, Washington, where a stroke specialist at Harborview Medical Center reported a drop in patients across the stroke-severity spectrum.
Some patients with milder strokes no longer come to Harborview for a comprehensive evaluation and workup, but that is only “a partial explanation,” said David Tirschwell, MD, medical director of comprehensive stroke care at the University of Washington (UW) Medicine Stroke Center at Harborview and a professor of neurology at UW.
“The thrombectomies are down also,” he added. “It’s hard to have great numbers in real time, but it’s probably safe to say it’s at least a 50% reduction in the number of admissions.”
As a stroke referral center, his institution is seeing fewer local cases and referrals from outside hospitals. “I think both of those sources for admissions of stroke cases are down,” Tirschwell said.
Recognizing the seriousness of forgoing essential care for acute stroke, neurologists, institutions, and medical groups are taking to social media to potentially save lives.
“Across our @FLStrokeReg we are seeing less patients with #stroke symptoms coming to our hospitals. We need to get the word out that our teams are working hard to safely provide care when needed during #COVID19,” tweeted Ralph Sacco, MD, chief and professor of neurology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine in South Florida.
Although Florida Stroke Registry data are not publicly available, anecdotal reports suggest that stroke admissions are down among many hospitals, Sacco told Medscape Medical News.
Furthermore, this is not a phenomenon only in the United States. “This has also been reported in other nations hit by COVID-19,” he said.
China is a prime example. There, many stroke centers have shown reduced functioning “because of fear of in-hospital cross infection and lack of experienced stroke care experts,” Jing Zhao, MD, PhD, and colleagues write in an editorial published online March 31 in Stroke.
Preliminary data show that “thrombectomies in Shanghai decreased by 50% in the first month after the Spring Festival compared with the same period in 2019,” write the editorialists, who are from Kings College London and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“Although the control of the COVID-19 is very important, at the same time, the management of stroke must not be neglected,” they add.
“Over 9000 new stroke cases occur each day in China alone. It cannot be right that treatment for one potentially curable disease is euthanized at the expense of another.”
Fear Factor?
The reasons individuals who may have experienced a stroke are avoiding emergency care is unclear at the moment. “I’m not really sure anyone really understands why, quite honestly,” Tirschwell said.
Until survey data or other data emerge, many experts are assuming that fear of COVID-19 is trumping other medical concerns, including emergency treatment of stroke.
“We believe this could represent patients being fearful to come to medical facilities with stroke-like symptoms, given the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Sacco, who is also incoming editor-in-chief of Stroke.
The BBC has been getting the word out in the United Kingdom via social media, with a tweet to “Dial 999 for stroke emergencies despite coronavirus.”
The World Stroke Campaign is also using Twitter to emphasize the need for urgent stroke care when appropriate:
“Don’t let concerns about COVID19 prevent you from seeking emergency treatment for stroke. If you spot the signs of stroke act FAST. Get emergency medical assistance,” the group urged in a tweet.
Don’t Hesitate
The American Heart Association (AHA) has addressed this troubling trend as well.
“People with serious symptoms shouldn’t ignore them,” Sarah Perlman, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver, states in an article on the AHA website.
Perlman added that some individuals who have signs of stroke and heart disease may hesitate to seek care because of fear that they are adding to an overburdened healthcare staff and system. However, she dismissed those concerns outright.
“If you’re experiencing warning signs of a heart attack or stroke, call 911,” she said. “Clearly, if there’s an emergency, we are available and capable and eager to take care of you.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(EDs).
Stroke specialists in New Orleans, Chicago, Seattle, and elsewhere told Medscape Medical News they are seeing a precipitous drop in the number of acute strokes at their institutions – and not just in the number of milder cases. Doctors on Twitter are sharing similar reports and are using social media to highlight this issue.
Gabriel Vidal, MD, a vascular and interventional neurologist at the Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, Louisiana, said there are “definitely” fewer patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA) seeking care at his facility and others throughout the New Orleans area, which has been hard hit by COVID-19.
“Even in Louisiana, we have a very large 53-hospital telestroke network, and the number of consults has diminished greatly,” Vidal added.
In Chicago, emergency medical service activations for patients with suspected strokes are down about 30%, Shyam Prabhakaran, MD, professor and chair of neurology at the University of Chicago Biological Sciences, Illinois, told Medscape Medical News.
“It appears to be that mild stroke and TIA patients may be more likely to stay at home and seek alternative care rather than come to the ED,” Prabhakaran said. However, “the severe strokes may be less affected and continue to come to emergency departments.”
“Getting the Word Out”
That may not be the whole story in Seattle, Washington, where a stroke specialist at Harborview Medical Center reported a drop in patients across the stroke-severity spectrum.
Some patients with milder strokes no longer come to Harborview for a comprehensive evaluation and workup, but that is only “a partial explanation,” said David Tirschwell, MD, medical director of comprehensive stroke care at the University of Washington (UW) Medicine Stroke Center at Harborview and a professor of neurology at UW.
“The thrombectomies are down also,” he added. “It’s hard to have great numbers in real time, but it’s probably safe to say it’s at least a 50% reduction in the number of admissions.”
As a stroke referral center, his institution is seeing fewer local cases and referrals from outside hospitals. “I think both of those sources for admissions of stroke cases are down,” Tirschwell said.
Recognizing the seriousness of forgoing essential care for acute stroke, neurologists, institutions, and medical groups are taking to social media to potentially save lives.
“Across our @FLStrokeReg we are seeing less patients with #stroke symptoms coming to our hospitals. We need to get the word out that our teams are working hard to safely provide care when needed during #COVID19,” tweeted Ralph Sacco, MD, chief and professor of neurology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine in South Florida.
Although Florida Stroke Registry data are not publicly available, anecdotal reports suggest that stroke admissions are down among many hospitals, Sacco told Medscape Medical News.
Furthermore, this is not a phenomenon only in the United States. “This has also been reported in other nations hit by COVID-19,” he said.
China is a prime example. There, many stroke centers have shown reduced functioning “because of fear of in-hospital cross infection and lack of experienced stroke care experts,” Jing Zhao, MD, PhD, and colleagues write in an editorial published online March 31 in Stroke.
Preliminary data show that “thrombectomies in Shanghai decreased by 50% in the first month after the Spring Festival compared with the same period in 2019,” write the editorialists, who are from Kings College London and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“Although the control of the COVID-19 is very important, at the same time, the management of stroke must not be neglected,” they add.
“Over 9000 new stroke cases occur each day in China alone. It cannot be right that treatment for one potentially curable disease is euthanized at the expense of another.”
Fear Factor?
The reasons individuals who may have experienced a stroke are avoiding emergency care is unclear at the moment. “I’m not really sure anyone really understands why, quite honestly,” Tirschwell said.
Until survey data or other data emerge, many experts are assuming that fear of COVID-19 is trumping other medical concerns, including emergency treatment of stroke.
“We believe this could represent patients being fearful to come to medical facilities with stroke-like symptoms, given the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Sacco, who is also incoming editor-in-chief of Stroke.
The BBC has been getting the word out in the United Kingdom via social media, with a tweet to “Dial 999 for stroke emergencies despite coronavirus.”
The World Stroke Campaign is also using Twitter to emphasize the need for urgent stroke care when appropriate:
“Don’t let concerns about COVID19 prevent you from seeking emergency treatment for stroke. If you spot the signs of stroke act FAST. Get emergency medical assistance,” the group urged in a tweet.
Don’t Hesitate
The American Heart Association (AHA) has addressed this troubling trend as well.
“People with serious symptoms shouldn’t ignore them,” Sarah Perlman, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver, states in an article on the AHA website.
Perlman added that some individuals who have signs of stroke and heart disease may hesitate to seek care because of fear that they are adding to an overburdened healthcare staff and system. However, she dismissed those concerns outright.
“If you’re experiencing warning signs of a heart attack or stroke, call 911,” she said. “Clearly, if there’s an emergency, we are available and capable and eager to take care of you.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Neurologic symptoms and COVID-19: What’s known, what isn’t
Since the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmed the first US case of novel coronavirus infection on January 20, much of the clinical focus has naturally centered on the virus’ prodromal symptoms and severe respiratory effects.
However,
“I am hearing about strokes, ataxia, myelitis, etc,” Stephan Mayer, MD, a neurointensivist in Troy, Michigan, posted on Twitter on March 26.
Other possible signs and symptoms include subtle neurologic deficits, severe fatigue, trigeminal neuralgia, complete/severe anosmia, and myalgia as reported by clinicians who responded to the tweet.
On March 31, the first presumptive case of encephalitis linked to COVID-19 was documented in a 58-year-old woman treated at Henry Ford Health System in Detroit.
Physicians who reported the acute necrotizing hemorrhagic encephalopathy case in the journal Radiology counseled neurologists to suspect the virus in patients presenting with altered levels of consciousness.
Researchers in China also reported the first presumptive case of Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) associated with COVID-19. A 61-year-old woman initially presented with signs of the autoimmune neuropathy GBS, including leg weakness, and severe fatigue after returning from Wuhan, China. She did not initially present with the common COVID-19 symptoms of fever, cough, or chest pain.
Her muscle weakness and distal areflexia progressed over time. On day 8, the patient developed more characteristic COVID-19 signs, including ‘ground glass’ lung opacities, dry cough, and fever. She was treated with antivirals, immunoglobulins, and supportive care, recovering slowly until discharge on day 30.
“Our single-case report only suggests a possible association between GBS and SARS-CoV-2 infection. It may or may not have causal relationship. More cases with epidemiological data are necessary,” said senior author Sheng Chen, MD, PhD.
However, “we still suggest physicians who encounter acute GBS patients from pandemic areas protect themselves carefully and test for the virus on admission. If the results are positive, the patient needs to be isolated,” added Dr. Chen, a neurologist at Shanghai Ruijin Hospital and Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in China.
Neurologic presentations of COVID-19 “are not common, but could happen,” Dr. Chen added. Headache, muscle weakness, and myalgias have been documented in other patients in China, he said.
Early days
Despite this growing number of anecdotal reports and observational data documenting neurologic effects, the majority of patients with COVID-19 do not present with such symptoms.
“Most COVID-19 patients we have seen have a normal neurological presentation. Abnormal neurological findings we have seen include loss of smell and taste sensation, and states of altered mental status including confusion, lethargy, and coma,” said Robert Stevens, MD, who focuses on neuroscience critical care at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland.
Other groups are reporting seizures, spinal cord disease, and brain stem disease. It has been suggested that brain stem dysfunction may account for the loss of hypoxic respiratory drive seen in a subset of patients with severe COVID-19 disease, he added.
However, Dr. Stevens, who plans to track neurologic outcomes in COVID-19 patients, also cautioned that it’s still early and these case reports are preliminary.
“An important caveat is that our knowledge of the different neurological presentations reported in association with COVID-19 is purely descriptive. We know almost nothing about the potential interactions between COVID-19 and the nervous system,” he noted.
He added it’s likely that some of the neurologic phenomena in COVID-19 are not causally related to the virus.
“This is why we have decided to establish a multisite neuro–COVID-19 data registry, so that we can gain epidemiological and mechanistic insight on these phenomena,” he said.
Nevertheless, in an online report February 27 in the Journal of Medical Virology, Yan-Chao Li, MD, and colleagues wrote that “increasing evidence shows that coronaviruses are not always confined to the respiratory tract and that they may also invade the central nervous system, inducing neurological diseases.”
Dr. Li is affiliated with the Department of Histology and Embryology, College of Basic Medical Sciences, Norman Bethune College of Medicine, Jilin University, Changchun, China.
A global view
Scientists observed SARS-CoV in the brains of infected people and animals, particularly the brainstem, they noted. Given the similarity of SARS-CoV to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, the researchers suggest a similar invasive mechanism could be occurring in some patients.
Although it hasn’t been proven, Dr. Li and colleagues suggest COVID-19 could act beyond receptors in the lungs, traveling via “a synapse‐connected route to the medullary cardiorespiratory center” in the brain. This action, in turn, could add to the acute respiratory failure observed in many people with COVID-19.
Other neurologists tracking and monitoring case reports of neurologic symptoms potentially related to COVID-19 include Dr. Mayer and Amelia Boehme, PhD, MSPH, an epidemiologist at Columbia University specializing in stroke and cardiovascular disease.
Dr. Boehme suggested on Twitter that the neurology community conduct a multicenter study to examine the relationship between the virus and neurologic symptoms/sequelae.
Medscape Medical News interviewed Michel Dib, MD, a neurologist at the Pitié Salpêtrière hospital in Paris, who said primary neurologic presentations of COVID-19 occur rarely – and primarily in older adults. As other clinicians note, these include confusion and disorientation. He also reports cases of encephalitis and one patient who initially presented with epilepsy.
Initial reports also came from neurologists in countries where COVID-19 struck first. For example, stroke, delirium, epileptic seizures and more are being treated by neurologists at the University of Brescia in Italy in a dedicated unit designed to treat both COVID-19 and neurologic syndromes, Alessandro Pezzini, MD, reported in Neurology Today, a publication of the American Academy of Neurology.
Dr. Pezzini noted that the mechanisms behind the observed increase in vascular complications warrant further investigation. He and colleagues are planning a multicenter study in Italy to dive deeper into the central nervous system effects of COVID-19 infection.
Clinicians in China also report neurologic symptoms in some patients. A study of 221 consecutive COVID-19 patients in Wuhan revealed 11 patients developed acute ischemic stroke, one experienced cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, and another experienced cerebral hemorrhage.
Older age and more severe disease were associated with a greater likelihood for cerebrovascular disease, the authors reported.
Drs. Chen and Li have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmed the first US case of novel coronavirus infection on January 20, much of the clinical focus has naturally centered on the virus’ prodromal symptoms and severe respiratory effects.
However,
“I am hearing about strokes, ataxia, myelitis, etc,” Stephan Mayer, MD, a neurointensivist in Troy, Michigan, posted on Twitter on March 26.
Other possible signs and symptoms include subtle neurologic deficits, severe fatigue, trigeminal neuralgia, complete/severe anosmia, and myalgia as reported by clinicians who responded to the tweet.
On March 31, the first presumptive case of encephalitis linked to COVID-19 was documented in a 58-year-old woman treated at Henry Ford Health System in Detroit.
Physicians who reported the acute necrotizing hemorrhagic encephalopathy case in the journal Radiology counseled neurologists to suspect the virus in patients presenting with altered levels of consciousness.
Researchers in China also reported the first presumptive case of Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) associated with COVID-19. A 61-year-old woman initially presented with signs of the autoimmune neuropathy GBS, including leg weakness, and severe fatigue after returning from Wuhan, China. She did not initially present with the common COVID-19 symptoms of fever, cough, or chest pain.
Her muscle weakness and distal areflexia progressed over time. On day 8, the patient developed more characteristic COVID-19 signs, including ‘ground glass’ lung opacities, dry cough, and fever. She was treated with antivirals, immunoglobulins, and supportive care, recovering slowly until discharge on day 30.
“Our single-case report only suggests a possible association between GBS and SARS-CoV-2 infection. It may or may not have causal relationship. More cases with epidemiological data are necessary,” said senior author Sheng Chen, MD, PhD.
However, “we still suggest physicians who encounter acute GBS patients from pandemic areas protect themselves carefully and test for the virus on admission. If the results are positive, the patient needs to be isolated,” added Dr. Chen, a neurologist at Shanghai Ruijin Hospital and Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in China.
Neurologic presentations of COVID-19 “are not common, but could happen,” Dr. Chen added. Headache, muscle weakness, and myalgias have been documented in other patients in China, he said.
Early days
Despite this growing number of anecdotal reports and observational data documenting neurologic effects, the majority of patients with COVID-19 do not present with such symptoms.
“Most COVID-19 patients we have seen have a normal neurological presentation. Abnormal neurological findings we have seen include loss of smell and taste sensation, and states of altered mental status including confusion, lethargy, and coma,” said Robert Stevens, MD, who focuses on neuroscience critical care at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland.
Other groups are reporting seizures, spinal cord disease, and brain stem disease. It has been suggested that brain stem dysfunction may account for the loss of hypoxic respiratory drive seen in a subset of patients with severe COVID-19 disease, he added.
However, Dr. Stevens, who plans to track neurologic outcomes in COVID-19 patients, also cautioned that it’s still early and these case reports are preliminary.
“An important caveat is that our knowledge of the different neurological presentations reported in association with COVID-19 is purely descriptive. We know almost nothing about the potential interactions between COVID-19 and the nervous system,” he noted.
He added it’s likely that some of the neurologic phenomena in COVID-19 are not causally related to the virus.
“This is why we have decided to establish a multisite neuro–COVID-19 data registry, so that we can gain epidemiological and mechanistic insight on these phenomena,” he said.
Nevertheless, in an online report February 27 in the Journal of Medical Virology, Yan-Chao Li, MD, and colleagues wrote that “increasing evidence shows that coronaviruses are not always confined to the respiratory tract and that they may also invade the central nervous system, inducing neurological diseases.”
Dr. Li is affiliated with the Department of Histology and Embryology, College of Basic Medical Sciences, Norman Bethune College of Medicine, Jilin University, Changchun, China.
A global view
Scientists observed SARS-CoV in the brains of infected people and animals, particularly the brainstem, they noted. Given the similarity of SARS-CoV to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, the researchers suggest a similar invasive mechanism could be occurring in some patients.
Although it hasn’t been proven, Dr. Li and colleagues suggest COVID-19 could act beyond receptors in the lungs, traveling via “a synapse‐connected route to the medullary cardiorespiratory center” in the brain. This action, in turn, could add to the acute respiratory failure observed in many people with COVID-19.
Other neurologists tracking and monitoring case reports of neurologic symptoms potentially related to COVID-19 include Dr. Mayer and Amelia Boehme, PhD, MSPH, an epidemiologist at Columbia University specializing in stroke and cardiovascular disease.
Dr. Boehme suggested on Twitter that the neurology community conduct a multicenter study to examine the relationship between the virus and neurologic symptoms/sequelae.
Medscape Medical News interviewed Michel Dib, MD, a neurologist at the Pitié Salpêtrière hospital in Paris, who said primary neurologic presentations of COVID-19 occur rarely – and primarily in older adults. As other clinicians note, these include confusion and disorientation. He also reports cases of encephalitis and one patient who initially presented with epilepsy.
Initial reports also came from neurologists in countries where COVID-19 struck first. For example, stroke, delirium, epileptic seizures and more are being treated by neurologists at the University of Brescia in Italy in a dedicated unit designed to treat both COVID-19 and neurologic syndromes, Alessandro Pezzini, MD, reported in Neurology Today, a publication of the American Academy of Neurology.
Dr. Pezzini noted that the mechanisms behind the observed increase in vascular complications warrant further investigation. He and colleagues are planning a multicenter study in Italy to dive deeper into the central nervous system effects of COVID-19 infection.
Clinicians in China also report neurologic symptoms in some patients. A study of 221 consecutive COVID-19 patients in Wuhan revealed 11 patients developed acute ischemic stroke, one experienced cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, and another experienced cerebral hemorrhage.
Older age and more severe disease were associated with a greater likelihood for cerebrovascular disease, the authors reported.
Drs. Chen and Li have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmed the first US case of novel coronavirus infection on January 20, much of the clinical focus has naturally centered on the virus’ prodromal symptoms and severe respiratory effects.
However,
“I am hearing about strokes, ataxia, myelitis, etc,” Stephan Mayer, MD, a neurointensivist in Troy, Michigan, posted on Twitter on March 26.
Other possible signs and symptoms include subtle neurologic deficits, severe fatigue, trigeminal neuralgia, complete/severe anosmia, and myalgia as reported by clinicians who responded to the tweet.
On March 31, the first presumptive case of encephalitis linked to COVID-19 was documented in a 58-year-old woman treated at Henry Ford Health System in Detroit.
Physicians who reported the acute necrotizing hemorrhagic encephalopathy case in the journal Radiology counseled neurologists to suspect the virus in patients presenting with altered levels of consciousness.
Researchers in China also reported the first presumptive case of Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) associated with COVID-19. A 61-year-old woman initially presented with signs of the autoimmune neuropathy GBS, including leg weakness, and severe fatigue after returning from Wuhan, China. She did not initially present with the common COVID-19 symptoms of fever, cough, or chest pain.
Her muscle weakness and distal areflexia progressed over time. On day 8, the patient developed more characteristic COVID-19 signs, including ‘ground glass’ lung opacities, dry cough, and fever. She was treated with antivirals, immunoglobulins, and supportive care, recovering slowly until discharge on day 30.
“Our single-case report only suggests a possible association between GBS and SARS-CoV-2 infection. It may or may not have causal relationship. More cases with epidemiological data are necessary,” said senior author Sheng Chen, MD, PhD.
However, “we still suggest physicians who encounter acute GBS patients from pandemic areas protect themselves carefully and test for the virus on admission. If the results are positive, the patient needs to be isolated,” added Dr. Chen, a neurologist at Shanghai Ruijin Hospital and Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in China.
Neurologic presentations of COVID-19 “are not common, but could happen,” Dr. Chen added. Headache, muscle weakness, and myalgias have been documented in other patients in China, he said.
Early days
Despite this growing number of anecdotal reports and observational data documenting neurologic effects, the majority of patients with COVID-19 do not present with such symptoms.
“Most COVID-19 patients we have seen have a normal neurological presentation. Abnormal neurological findings we have seen include loss of smell and taste sensation, and states of altered mental status including confusion, lethargy, and coma,” said Robert Stevens, MD, who focuses on neuroscience critical care at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland.
Other groups are reporting seizures, spinal cord disease, and brain stem disease. It has been suggested that brain stem dysfunction may account for the loss of hypoxic respiratory drive seen in a subset of patients with severe COVID-19 disease, he added.
However, Dr. Stevens, who plans to track neurologic outcomes in COVID-19 patients, also cautioned that it’s still early and these case reports are preliminary.
“An important caveat is that our knowledge of the different neurological presentations reported in association with COVID-19 is purely descriptive. We know almost nothing about the potential interactions between COVID-19 and the nervous system,” he noted.
He added it’s likely that some of the neurologic phenomena in COVID-19 are not causally related to the virus.
“This is why we have decided to establish a multisite neuro–COVID-19 data registry, so that we can gain epidemiological and mechanistic insight on these phenomena,” he said.
Nevertheless, in an online report February 27 in the Journal of Medical Virology, Yan-Chao Li, MD, and colleagues wrote that “increasing evidence shows that coronaviruses are not always confined to the respiratory tract and that they may also invade the central nervous system, inducing neurological diseases.”
Dr. Li is affiliated with the Department of Histology and Embryology, College of Basic Medical Sciences, Norman Bethune College of Medicine, Jilin University, Changchun, China.
A global view
Scientists observed SARS-CoV in the brains of infected people and animals, particularly the brainstem, they noted. Given the similarity of SARS-CoV to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, the researchers suggest a similar invasive mechanism could be occurring in some patients.
Although it hasn’t been proven, Dr. Li and colleagues suggest COVID-19 could act beyond receptors in the lungs, traveling via “a synapse‐connected route to the medullary cardiorespiratory center” in the brain. This action, in turn, could add to the acute respiratory failure observed in many people with COVID-19.
Other neurologists tracking and monitoring case reports of neurologic symptoms potentially related to COVID-19 include Dr. Mayer and Amelia Boehme, PhD, MSPH, an epidemiologist at Columbia University specializing in stroke and cardiovascular disease.
Dr. Boehme suggested on Twitter that the neurology community conduct a multicenter study to examine the relationship between the virus and neurologic symptoms/sequelae.
Medscape Medical News interviewed Michel Dib, MD, a neurologist at the Pitié Salpêtrière hospital in Paris, who said primary neurologic presentations of COVID-19 occur rarely – and primarily in older adults. As other clinicians note, these include confusion and disorientation. He also reports cases of encephalitis and one patient who initially presented with epilepsy.
Initial reports also came from neurologists in countries where COVID-19 struck first. For example, stroke, delirium, epileptic seizures and more are being treated by neurologists at the University of Brescia in Italy in a dedicated unit designed to treat both COVID-19 and neurologic syndromes, Alessandro Pezzini, MD, reported in Neurology Today, a publication of the American Academy of Neurology.
Dr. Pezzini noted that the mechanisms behind the observed increase in vascular complications warrant further investigation. He and colleagues are planning a multicenter study in Italy to dive deeper into the central nervous system effects of COVID-19 infection.
Clinicians in China also report neurologic symptoms in some patients. A study of 221 consecutive COVID-19 patients in Wuhan revealed 11 patients developed acute ischemic stroke, one experienced cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, and another experienced cerebral hemorrhage.
Older age and more severe disease were associated with a greater likelihood for cerebrovascular disease, the authors reported.
Drs. Chen and Li have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More evidence backs LDL below 70 to reduce recurrent stroke
LOS ANGELES – In a subanalysis of the TST (Treat Stroke to Target) trial, restricting analysis to only French participants followed for an average of 5 years demonstrated an even more robust potential to reduce recurrent stroke and other major cardiovascular events by treating patients to an LDL target of below 70 mg/dL. Treating LDL to a mean of 66 mg/dL versus 96 mg/dL was associated with a 26% relative risk reduction for the composite endpoint of ischemic stroke, MI, new symptoms requiring urgent coronary or carotid revascularization, and vascular death in an adjusted analysis.
“The results are similar to the main paper but even more spectacular, with no increase in hemorrhagic stroke whatsoever, and positive results on any stroke,” study investigator Pierre Amarenco, MD, professor and chair of the department of neurology and Stroke Centre, Bichat University Hospital, Paris, said.
Dr. Amarenco presented the findings as a late-breaking abstract at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association. The trial was published simultaneously in the journal Stroke.
In the full TST trial population, risk was reduced by 22% with more-aggressive LDL-lowering treatment, compared with the more lax 90-110 mg/dL target.
The TST cohort included both French and Korean participants. Dr. Amarenco and colleagues focused on the French population in the current study because the group was larger (2,148 vs. 742 Korean participants) and had a longer follow-up, an average of 5.3 years compared to 2.0 years among Korean patients. The initial study had shown “very significant results in the French patients and no apparent effect in Korean patients,” he said. The longer duration of treatment in the French cohort could have contributed to the greater risk reduction, said Dr. Amarenco.
A 2017 European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel statement noted that exposure time to lipid-lowering drugs correlates with outcomes. The European Stroke Organization and the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association guidelines each recommend intensive statin treatment to lower serum lipids following an ischemic stroke of atherosclerotic origin or after a transient ischemic attack (TIA). However, the current researchers noted that the recommendations do not specify specific target numbers.
“Therefore, there is uncertainty about the target levels of LDL cholesterol,” he said.
Aiming at different targets
To learn more, Dr. Amarenco and colleagues randomly assigned 1,073 of the French patients to a target LDL treatment group of 70 mg/dL and another 1,075 to a target range of 90-110 mg/dL. They enrolled participants at 61 sites in France. Mean age was 67 years. All participants had experienced an ischemic stroke within 3 months or a TIA within 15 days of baseline. They presented either with a modified Rankin Scale poststroke score of 0-3 or a TIA that included at least arm and leg motor deficit or speech disturbance that lasted more than 10 minutes.
Investigators could use any type and any dose of statin to reach the respective targets. Statins could be prescribed as monotherapy or in combination with ezetimibe (Zetia) or other agents. The baseline mean LDL cholesterol level was 137 mg/dL in the lower target group and 138 mg/dL in the higher target group, respectively (3.5 mmol/L in both groups). Dr. Amarenco and colleagues measured LDL cholesterol levels at 3 weeks postrandomization and then every 6 months.
A smaller proportion of the lower LDL cholesterol target group experienced the adverse composite outcome, 9.6%, compared with 12.9% of the higher LDL cholesterol target group. This translated to a hazard ratio of 0.73 (95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.94; P = .015). The absolute risk reduction was 3.3% with a number needed to treat of 30.
An analysis adjusted for covariates showed a hazard ratio of 0.74 (95% CI, 0.57-0.95; P = .019).
Cerebral infarction and acute cerebral artery revascularization were reduced by 27% (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.54-0.99; P = .046). Cerebral infarction or intracranial hemorrhage (all strokes) were reduced by 28% (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.54-0.98; P = .023). In this case, there was an absolute risk reduction of 2.9% and a number needed to treat of 34.
In contrast, MI or urgent coronary revascularization following new symptoms were not significantly reduced (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.67-1.20; P = .18). The investigators also reported nonsignificant results regarding vascular death (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.44-1.32; P = .32] and all deaths (HR, 1.0; 95% CI, 0.74-1.35; P = .99).
Dr. Amarenco and colleagues also tracked adverse events. They found intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 13 (1.2%) patients assigned an LDL cholesterol below 70 mg/dL and in 11 (1%) patients assigned an LDL cholesterol of 100 ± 10 mg/dL. In this analysis, the hazard ratio was 1.17 (95% CI, 0.53-2.62; P = .70), and the absolute difference was 0.2%.
The investigators also reported that 10.3% of the lower LDL target group vs 13.6% of the higher LDL target group experienced either the primary outcome or intracranial hemorrhage. This translated to a 25% relative risk reduction (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.58-0.96; P = .021), an absolute risk reduction of 3.3% and a number needed to treat of 30.
Avoiding one in four events
Assessing the French participants in the TST trial showed that targeting LDL below 70 mg/dL for more than 5 years avoided more than one in four subsequent major cardiovascular events among adults who experienced a recent ischemic stroke or TIA.
Furthermore, more intense LDL lowering also avoided more than one in four recurrent cerebral infarctions or urgent carotid revascularizations following a TIA, as well as one in four recurrent cerebral infarctions or hemorrhages (all strokes), compared with the higher LDL target.
“This was obtained without increasing the risk of intracranial hemorrhage with a number needed to treat of 30,” the researchers noted. “In the context of all randomized clinical trials with statin and other lipid-lowering drugs, there is no reason to think that Asian patients do not benefit from statin treatment and from a lower target LDL cholesterol,” the researchers added.
Therefore, they plan to continue assessing the 742 Korean participants until they reach a median of 5 years of follow-up.
Clinically validating results
“My feeling is that these data are highly supportive of a practice that many of us have been using for years without this level of evidence,” Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, said when asked to comment on the study.
Prior secondary analyses of studies, including research into patients with intracranial atherosclerosis, demonstrated benefit from treating to this lower LDL cholesterol target. “These studies were suggestive enough that many of us were treating patients aggressively with statins,” added Dr. Elkind, professor of neurology and epidemiology and chief of the division of neurology clinical outcomes research and population sciences at Columbia University in New York.
“But this really confirms that [fact] with clinical trial evidence,” said Dr. Elkind, “and I think will be very useful to us as clinicians.”
The results could be used to counsel patients about the potential benefits of statin therapy or to motivate primary care providers to treat patients more aggressively, said Dr. Elkind, who will begin his term as president of the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association in July.
This study was supported by a grant from the French Ministry of Health and from SOS-Attaque Cérébrale Association, with unrestricted grants from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Merck for French sites and from Pfizer for South Korean sites.
Dr. Amarenco receives research grant support and consulting fees from Pfizer, Merck, and AstraZeneca. Elkind had has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SOURCE: Amarenko P et al. ISC 2020. Late-breaking abstract 9.
LOS ANGELES – In a subanalysis of the TST (Treat Stroke to Target) trial, restricting analysis to only French participants followed for an average of 5 years demonstrated an even more robust potential to reduce recurrent stroke and other major cardiovascular events by treating patients to an LDL target of below 70 mg/dL. Treating LDL to a mean of 66 mg/dL versus 96 mg/dL was associated with a 26% relative risk reduction for the composite endpoint of ischemic stroke, MI, new symptoms requiring urgent coronary or carotid revascularization, and vascular death in an adjusted analysis.
“The results are similar to the main paper but even more spectacular, with no increase in hemorrhagic stroke whatsoever, and positive results on any stroke,” study investigator Pierre Amarenco, MD, professor and chair of the department of neurology and Stroke Centre, Bichat University Hospital, Paris, said.
Dr. Amarenco presented the findings as a late-breaking abstract at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association. The trial was published simultaneously in the journal Stroke.
In the full TST trial population, risk was reduced by 22% with more-aggressive LDL-lowering treatment, compared with the more lax 90-110 mg/dL target.
The TST cohort included both French and Korean participants. Dr. Amarenco and colleagues focused on the French population in the current study because the group was larger (2,148 vs. 742 Korean participants) and had a longer follow-up, an average of 5.3 years compared to 2.0 years among Korean patients. The initial study had shown “very significant results in the French patients and no apparent effect in Korean patients,” he said. The longer duration of treatment in the French cohort could have contributed to the greater risk reduction, said Dr. Amarenco.
A 2017 European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel statement noted that exposure time to lipid-lowering drugs correlates with outcomes. The European Stroke Organization and the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association guidelines each recommend intensive statin treatment to lower serum lipids following an ischemic stroke of atherosclerotic origin or after a transient ischemic attack (TIA). However, the current researchers noted that the recommendations do not specify specific target numbers.
“Therefore, there is uncertainty about the target levels of LDL cholesterol,” he said.
Aiming at different targets
To learn more, Dr. Amarenco and colleagues randomly assigned 1,073 of the French patients to a target LDL treatment group of 70 mg/dL and another 1,075 to a target range of 90-110 mg/dL. They enrolled participants at 61 sites in France. Mean age was 67 years. All participants had experienced an ischemic stroke within 3 months or a TIA within 15 days of baseline. They presented either with a modified Rankin Scale poststroke score of 0-3 or a TIA that included at least arm and leg motor deficit or speech disturbance that lasted more than 10 minutes.
Investigators could use any type and any dose of statin to reach the respective targets. Statins could be prescribed as monotherapy or in combination with ezetimibe (Zetia) or other agents. The baseline mean LDL cholesterol level was 137 mg/dL in the lower target group and 138 mg/dL in the higher target group, respectively (3.5 mmol/L in both groups). Dr. Amarenco and colleagues measured LDL cholesterol levels at 3 weeks postrandomization and then every 6 months.
A smaller proportion of the lower LDL cholesterol target group experienced the adverse composite outcome, 9.6%, compared with 12.9% of the higher LDL cholesterol target group. This translated to a hazard ratio of 0.73 (95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.94; P = .015). The absolute risk reduction was 3.3% with a number needed to treat of 30.
An analysis adjusted for covariates showed a hazard ratio of 0.74 (95% CI, 0.57-0.95; P = .019).
Cerebral infarction and acute cerebral artery revascularization were reduced by 27% (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.54-0.99; P = .046). Cerebral infarction or intracranial hemorrhage (all strokes) were reduced by 28% (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.54-0.98; P = .023). In this case, there was an absolute risk reduction of 2.9% and a number needed to treat of 34.
In contrast, MI or urgent coronary revascularization following new symptoms were not significantly reduced (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.67-1.20; P = .18). The investigators also reported nonsignificant results regarding vascular death (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.44-1.32; P = .32] and all deaths (HR, 1.0; 95% CI, 0.74-1.35; P = .99).
Dr. Amarenco and colleagues also tracked adverse events. They found intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 13 (1.2%) patients assigned an LDL cholesterol below 70 mg/dL and in 11 (1%) patients assigned an LDL cholesterol of 100 ± 10 mg/dL. In this analysis, the hazard ratio was 1.17 (95% CI, 0.53-2.62; P = .70), and the absolute difference was 0.2%.
The investigators also reported that 10.3% of the lower LDL target group vs 13.6% of the higher LDL target group experienced either the primary outcome or intracranial hemorrhage. This translated to a 25% relative risk reduction (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.58-0.96; P = .021), an absolute risk reduction of 3.3% and a number needed to treat of 30.
Avoiding one in four events
Assessing the French participants in the TST trial showed that targeting LDL below 70 mg/dL for more than 5 years avoided more than one in four subsequent major cardiovascular events among adults who experienced a recent ischemic stroke or TIA.
Furthermore, more intense LDL lowering also avoided more than one in four recurrent cerebral infarctions or urgent carotid revascularizations following a TIA, as well as one in four recurrent cerebral infarctions or hemorrhages (all strokes), compared with the higher LDL target.
“This was obtained without increasing the risk of intracranial hemorrhage with a number needed to treat of 30,” the researchers noted. “In the context of all randomized clinical trials with statin and other lipid-lowering drugs, there is no reason to think that Asian patients do not benefit from statin treatment and from a lower target LDL cholesterol,” the researchers added.
Therefore, they plan to continue assessing the 742 Korean participants until they reach a median of 5 years of follow-up.
Clinically validating results
“My feeling is that these data are highly supportive of a practice that many of us have been using for years without this level of evidence,” Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, said when asked to comment on the study.
Prior secondary analyses of studies, including research into patients with intracranial atherosclerosis, demonstrated benefit from treating to this lower LDL cholesterol target. “These studies were suggestive enough that many of us were treating patients aggressively with statins,” added Dr. Elkind, professor of neurology and epidemiology and chief of the division of neurology clinical outcomes research and population sciences at Columbia University in New York.
“But this really confirms that [fact] with clinical trial evidence,” said Dr. Elkind, “and I think will be very useful to us as clinicians.”
The results could be used to counsel patients about the potential benefits of statin therapy or to motivate primary care providers to treat patients more aggressively, said Dr. Elkind, who will begin his term as president of the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association in July.
This study was supported by a grant from the French Ministry of Health and from SOS-Attaque Cérébrale Association, with unrestricted grants from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Merck for French sites and from Pfizer for South Korean sites.
Dr. Amarenco receives research grant support and consulting fees from Pfizer, Merck, and AstraZeneca. Elkind had has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SOURCE: Amarenko P et al. ISC 2020. Late-breaking abstract 9.
LOS ANGELES – In a subanalysis of the TST (Treat Stroke to Target) trial, restricting analysis to only French participants followed for an average of 5 years demonstrated an even more robust potential to reduce recurrent stroke and other major cardiovascular events by treating patients to an LDL target of below 70 mg/dL. Treating LDL to a mean of 66 mg/dL versus 96 mg/dL was associated with a 26% relative risk reduction for the composite endpoint of ischemic stroke, MI, new symptoms requiring urgent coronary or carotid revascularization, and vascular death in an adjusted analysis.
“The results are similar to the main paper but even more spectacular, with no increase in hemorrhagic stroke whatsoever, and positive results on any stroke,” study investigator Pierre Amarenco, MD, professor and chair of the department of neurology and Stroke Centre, Bichat University Hospital, Paris, said.
Dr. Amarenco presented the findings as a late-breaking abstract at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association. The trial was published simultaneously in the journal Stroke.
In the full TST trial population, risk was reduced by 22% with more-aggressive LDL-lowering treatment, compared with the more lax 90-110 mg/dL target.
The TST cohort included both French and Korean participants. Dr. Amarenco and colleagues focused on the French population in the current study because the group was larger (2,148 vs. 742 Korean participants) and had a longer follow-up, an average of 5.3 years compared to 2.0 years among Korean patients. The initial study had shown “very significant results in the French patients and no apparent effect in Korean patients,” he said. The longer duration of treatment in the French cohort could have contributed to the greater risk reduction, said Dr. Amarenco.
A 2017 European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel statement noted that exposure time to lipid-lowering drugs correlates with outcomes. The European Stroke Organization and the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association guidelines each recommend intensive statin treatment to lower serum lipids following an ischemic stroke of atherosclerotic origin or after a transient ischemic attack (TIA). However, the current researchers noted that the recommendations do not specify specific target numbers.
“Therefore, there is uncertainty about the target levels of LDL cholesterol,” he said.
Aiming at different targets
To learn more, Dr. Amarenco and colleagues randomly assigned 1,073 of the French patients to a target LDL treatment group of 70 mg/dL and another 1,075 to a target range of 90-110 mg/dL. They enrolled participants at 61 sites in France. Mean age was 67 years. All participants had experienced an ischemic stroke within 3 months or a TIA within 15 days of baseline. They presented either with a modified Rankin Scale poststroke score of 0-3 or a TIA that included at least arm and leg motor deficit or speech disturbance that lasted more than 10 minutes.
Investigators could use any type and any dose of statin to reach the respective targets. Statins could be prescribed as monotherapy or in combination with ezetimibe (Zetia) or other agents. The baseline mean LDL cholesterol level was 137 mg/dL in the lower target group and 138 mg/dL in the higher target group, respectively (3.5 mmol/L in both groups). Dr. Amarenco and colleagues measured LDL cholesterol levels at 3 weeks postrandomization and then every 6 months.
A smaller proportion of the lower LDL cholesterol target group experienced the adverse composite outcome, 9.6%, compared with 12.9% of the higher LDL cholesterol target group. This translated to a hazard ratio of 0.73 (95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.94; P = .015). The absolute risk reduction was 3.3% with a number needed to treat of 30.
An analysis adjusted for covariates showed a hazard ratio of 0.74 (95% CI, 0.57-0.95; P = .019).
Cerebral infarction and acute cerebral artery revascularization were reduced by 27% (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.54-0.99; P = .046). Cerebral infarction or intracranial hemorrhage (all strokes) were reduced by 28% (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.54-0.98; P = .023). In this case, there was an absolute risk reduction of 2.9% and a number needed to treat of 34.
In contrast, MI or urgent coronary revascularization following new symptoms were not significantly reduced (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.67-1.20; P = .18). The investigators also reported nonsignificant results regarding vascular death (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.44-1.32; P = .32] and all deaths (HR, 1.0; 95% CI, 0.74-1.35; P = .99).
Dr. Amarenco and colleagues also tracked adverse events. They found intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 13 (1.2%) patients assigned an LDL cholesterol below 70 mg/dL and in 11 (1%) patients assigned an LDL cholesterol of 100 ± 10 mg/dL. In this analysis, the hazard ratio was 1.17 (95% CI, 0.53-2.62; P = .70), and the absolute difference was 0.2%.
The investigators also reported that 10.3% of the lower LDL target group vs 13.6% of the higher LDL target group experienced either the primary outcome or intracranial hemorrhage. This translated to a 25% relative risk reduction (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.58-0.96; P = .021), an absolute risk reduction of 3.3% and a number needed to treat of 30.
Avoiding one in four events
Assessing the French participants in the TST trial showed that targeting LDL below 70 mg/dL for more than 5 years avoided more than one in four subsequent major cardiovascular events among adults who experienced a recent ischemic stroke or TIA.
Furthermore, more intense LDL lowering also avoided more than one in four recurrent cerebral infarctions or urgent carotid revascularizations following a TIA, as well as one in four recurrent cerebral infarctions or hemorrhages (all strokes), compared with the higher LDL target.
“This was obtained without increasing the risk of intracranial hemorrhage with a number needed to treat of 30,” the researchers noted. “In the context of all randomized clinical trials with statin and other lipid-lowering drugs, there is no reason to think that Asian patients do not benefit from statin treatment and from a lower target LDL cholesterol,” the researchers added.
Therefore, they plan to continue assessing the 742 Korean participants until they reach a median of 5 years of follow-up.
Clinically validating results
“My feeling is that these data are highly supportive of a practice that many of us have been using for years without this level of evidence,” Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, said when asked to comment on the study.
Prior secondary analyses of studies, including research into patients with intracranial atherosclerosis, demonstrated benefit from treating to this lower LDL cholesterol target. “These studies were suggestive enough that many of us were treating patients aggressively with statins,” added Dr. Elkind, professor of neurology and epidemiology and chief of the division of neurology clinical outcomes research and population sciences at Columbia University in New York.
“But this really confirms that [fact] with clinical trial evidence,” said Dr. Elkind, “and I think will be very useful to us as clinicians.”
The results could be used to counsel patients about the potential benefits of statin therapy or to motivate primary care providers to treat patients more aggressively, said Dr. Elkind, who will begin his term as president of the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association in July.
This study was supported by a grant from the French Ministry of Health and from SOS-Attaque Cérébrale Association, with unrestricted grants from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Merck for French sites and from Pfizer for South Korean sites.
Dr. Amarenco receives research grant support and consulting fees from Pfizer, Merck, and AstraZeneca. Elkind had has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SOURCE: Amarenko P et al. ISC 2020. Late-breaking abstract 9.
REPORTING FROM ISC 2020
BASILAR: Endovascular treatment improves outcomes in BAO stroke
LOS ANGELES – Endovascular therapy significantly improved functional outcomes and reduced mortality at 90 days, compared with standard thrombolysis alone, new evidence from a large, prospective registry study suggests.
Participants who received both interventions were almost five times more likely to be able to walk independently at 90 days compared with those who received thrombolysis alone.
Despite multiple trials supporting the potential benefits of endovascular therapy for anterior stroke, little prospective research addresses outcomes associated with an ischemic stroke caused by a posterior basilar artery occlusion (BAO).
“Basilar artery occlusion is the ‘orphan’ of the large vessel occlusions,” Raul Gomes Nogueira, MD, PhD, said here at a late-breaking abstract session at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
“They account for about 5% of the large vessel occlusions – but have the most dismal prognosis.” Severe disability and mortality rates associated with BAO, for example, reach an estimated 68% to 78%, he said.
The results, from the EVT for Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion Study (BASILAR), were also simultaneously published in JAMA Neurology.
Prior studies in this patient population are generally single-center, retrospective studies and “the numbers tend to be small,” said Nogueira, who is affiliated with the Marcus Stroke and Neuroscience Center, Grady Memorial Hospital, Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
Nogueira and colleagues studied 829 consecutive adults who presented with an acute, symptomatic BAO. They examined a nationwide prospective registry study of people with radiologically confirmed BAO in 47 comprehensive stroke centers across 15 provinces in China.
The median age was 65 years and 74% were men. A total 182 participants received thrombolysis therapy within 6 hours of estimated BAO onset. The 647 people in the dual intervention group also received endovascular therapy within 24 hours.
Standard medical treatment included intravenous rt-PA or urokinase, antiplatelet drugs and systematic anticoagulation alone or in combination. Endovascular therapy included mechanical thrombectomy with stent retrievers and/or thromboaspiration, balloon angioplasty, stenting, intra-arterial thrombolysis, or a combination of these interventions.
Interestingly, participants were not randomly assigned, in part because of the favorable outcomes associated with endovascular therapy. “The high number of patients who received [the dual intervention] may suggest the existence of a lack of equipoise among participating centers,” the researchers note.
Key Efficacy Endpoints
A significantly higher proportion of people in the dual treatment group achieved the primary outcome, functional improvement at 90 days, at 32%, compared with 9.3% in the thrombolysis-only group. This endpoint was defined as a modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 3 or less, which reflects an ability to walk independently. The difference was statistically significant (P < .001).
The absolute difference between groups was 22.7% (95% confidence interval, 17.1%-28.2%) with an adjusted odds ratio of 4.70 (95% CI, 2.53-8.75; P < .001) in favor of dual intervention.
The number needed to treat for one additional patient to be able to walk unassisted was 4.4.
Other outcomes, including differences in National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale scores from baseline to 5 to 7 days or discharge, as well as propensity score matching and subgroup analyses, likewise supported the superiority of using both interventions.
Safety Outcomes
Nogueira and colleagues also assessed safety. They found that symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) occurred in 45 patients, or 7.1% of the endovascular treatment group. In contrast, only one patient, or 0.5%, of the standard medical treatment alone cohort experienced an ICH. This difference was statistically significant (P < .001).
Mortality at 90 days was significantly lower in the endovascular therapy plus medical therapy group, 46.2%, compared with 71.4% in the standard medical treatment alone group (P < .001).
The absolute difference in mortality was 25.2% (95% CI, 17.6%-2.8%) favoring dual treatment, with an adjusted odds ratio of 2.93 (95% CI, 1.95-4.40; P < .001).
Rates of other serious adverse events during the 90-day follow-up period were similar in the two study groups, Nogueira said.
He acknowledged that the nonrandomized design was a limitation of the registry study, adding that “sometimes in life it’s important to acknowledge the best of what can be done. It’s very hard when you have access to thrombectomy to randomize people.”
However, other researchers have attempted or are enrolling people with BAO into trials that randomly assign them to endovascular therapy and standard medical treatment or medical treatment alone.
The BEST trial in China, for example, randomly assigned 131 patients to these groups but was stopped early in September 2017. “The BEST trial was terminated prematurely because of loss of equipoise that led to a high crossover rate and drop in valid recruitment,” the current researchers note.
“The other two trials…are facing the challenge of whether they will achieve their inclusion target,” they add, “because a growing number of stroke centers are unwilling to randomize patients to standard medical treatment alone after the many positive results of trials for endovascular treatment in patients with anterior-circulation stroke.”
The BAOCHE trial from China, for example, is ongoing with approximately 110 patients enrolled so far.
Investigators for the Basilar Artery International Cooperation Study (BASICS) in the Netherlands just completed enrollment of their 300th and final patient in December 2019.
“We are hopeful BASICS trial will shed additional light,” Nogueira said. The results are expected to be presented at the European Stroke Organization Conference in Vienna in May 2020.
More Guidance From MRI?
“With the advent of the stent retrievers and successful recanalization, we know there can be better outcomes for patients. And we know the morbidity and mortality of the basilar artery occlusions are so poor that we tend to want to be aggressive in these cases,” session comoderator Shlee S. Song, MD, director of the Comprehensive Stroke Center and associate professor of neurology at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, California, told Medscape Medical News when asked to comment on the study.
“I agree that we’ve lost equipoise in this cohort – that we really cannot do a randomized trial anymore. You know if you don’t do anything, 90% of the time there will be a poor outcome,” she added.
This is an important study for showing how BAO patients fare after endovascular treatment, Song said.
One unanswered question from the study is if any of the centers in China used magnetic resonance imaging to help determine the most appropriate candidates for endovascular treatment of these posterior circulation strokes, which is a common practice in the United States, she said.
The study was supported by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, Chongqing Major Disease Prevention and Control Technology Research Project, Army Medical University Clinical Medical Research Talent Training Program, and Major Clinical Innovation Technology Project of the Second Affiliated Hospital of the Army Military Medical University. Sing had no relevant disclosures. Nogueira’s financial disclosures include working as a consultant for Stryker Neurovascular; as a principal investigator on the Imperative trial and the PROST trial; as a steering committee member for Biogen for the CHARM trial; as an advisory board member for Cerenovus/Neuravi, Phenox, Anaconda, Genentech, Biogen, Prolong Pharmaceuticals and Brainomix; and as an advisory board member with stock options for Viz.ai, Corindus Vascular Robotics, Vesalio, Ceretrieve, Astrocyte Pharmaceuticals, and Cerebrotech.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SOURCE: Nogueira RG et al. ISC 2020. Late-breaking abstract 17.
LOS ANGELES – Endovascular therapy significantly improved functional outcomes and reduced mortality at 90 days, compared with standard thrombolysis alone, new evidence from a large, prospective registry study suggests.
Participants who received both interventions were almost five times more likely to be able to walk independently at 90 days compared with those who received thrombolysis alone.
Despite multiple trials supporting the potential benefits of endovascular therapy for anterior stroke, little prospective research addresses outcomes associated with an ischemic stroke caused by a posterior basilar artery occlusion (BAO).
“Basilar artery occlusion is the ‘orphan’ of the large vessel occlusions,” Raul Gomes Nogueira, MD, PhD, said here at a late-breaking abstract session at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
“They account for about 5% of the large vessel occlusions – but have the most dismal prognosis.” Severe disability and mortality rates associated with BAO, for example, reach an estimated 68% to 78%, he said.
The results, from the EVT for Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion Study (BASILAR), were also simultaneously published in JAMA Neurology.
Prior studies in this patient population are generally single-center, retrospective studies and “the numbers tend to be small,” said Nogueira, who is affiliated with the Marcus Stroke and Neuroscience Center, Grady Memorial Hospital, Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
Nogueira and colleagues studied 829 consecutive adults who presented with an acute, symptomatic BAO. They examined a nationwide prospective registry study of people with radiologically confirmed BAO in 47 comprehensive stroke centers across 15 provinces in China.
The median age was 65 years and 74% were men. A total 182 participants received thrombolysis therapy within 6 hours of estimated BAO onset. The 647 people in the dual intervention group also received endovascular therapy within 24 hours.
Standard medical treatment included intravenous rt-PA or urokinase, antiplatelet drugs and systematic anticoagulation alone or in combination. Endovascular therapy included mechanical thrombectomy with stent retrievers and/or thromboaspiration, balloon angioplasty, stenting, intra-arterial thrombolysis, or a combination of these interventions.
Interestingly, participants were not randomly assigned, in part because of the favorable outcomes associated with endovascular therapy. “The high number of patients who received [the dual intervention] may suggest the existence of a lack of equipoise among participating centers,” the researchers note.
Key Efficacy Endpoints
A significantly higher proportion of people in the dual treatment group achieved the primary outcome, functional improvement at 90 days, at 32%, compared with 9.3% in the thrombolysis-only group. This endpoint was defined as a modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 3 or less, which reflects an ability to walk independently. The difference was statistically significant (P < .001).
The absolute difference between groups was 22.7% (95% confidence interval, 17.1%-28.2%) with an adjusted odds ratio of 4.70 (95% CI, 2.53-8.75; P < .001) in favor of dual intervention.
The number needed to treat for one additional patient to be able to walk unassisted was 4.4.
Other outcomes, including differences in National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale scores from baseline to 5 to 7 days or discharge, as well as propensity score matching and subgroup analyses, likewise supported the superiority of using both interventions.
Safety Outcomes
Nogueira and colleagues also assessed safety. They found that symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) occurred in 45 patients, or 7.1% of the endovascular treatment group. In contrast, only one patient, or 0.5%, of the standard medical treatment alone cohort experienced an ICH. This difference was statistically significant (P < .001).
Mortality at 90 days was significantly lower in the endovascular therapy plus medical therapy group, 46.2%, compared with 71.4% in the standard medical treatment alone group (P < .001).
The absolute difference in mortality was 25.2% (95% CI, 17.6%-2.8%) favoring dual treatment, with an adjusted odds ratio of 2.93 (95% CI, 1.95-4.40; P < .001).
Rates of other serious adverse events during the 90-day follow-up period were similar in the two study groups, Nogueira said.
He acknowledged that the nonrandomized design was a limitation of the registry study, adding that “sometimes in life it’s important to acknowledge the best of what can be done. It’s very hard when you have access to thrombectomy to randomize people.”
However, other researchers have attempted or are enrolling people with BAO into trials that randomly assign them to endovascular therapy and standard medical treatment or medical treatment alone.
The BEST trial in China, for example, randomly assigned 131 patients to these groups but was stopped early in September 2017. “The BEST trial was terminated prematurely because of loss of equipoise that led to a high crossover rate and drop in valid recruitment,” the current researchers note.
“The other two trials…are facing the challenge of whether they will achieve their inclusion target,” they add, “because a growing number of stroke centers are unwilling to randomize patients to standard medical treatment alone after the many positive results of trials for endovascular treatment in patients with anterior-circulation stroke.”
The BAOCHE trial from China, for example, is ongoing with approximately 110 patients enrolled so far.
Investigators for the Basilar Artery International Cooperation Study (BASICS) in the Netherlands just completed enrollment of their 300th and final patient in December 2019.
“We are hopeful BASICS trial will shed additional light,” Nogueira said. The results are expected to be presented at the European Stroke Organization Conference in Vienna in May 2020.
More Guidance From MRI?
“With the advent of the stent retrievers and successful recanalization, we know there can be better outcomes for patients. And we know the morbidity and mortality of the basilar artery occlusions are so poor that we tend to want to be aggressive in these cases,” session comoderator Shlee S. Song, MD, director of the Comprehensive Stroke Center and associate professor of neurology at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, California, told Medscape Medical News when asked to comment on the study.
“I agree that we’ve lost equipoise in this cohort – that we really cannot do a randomized trial anymore. You know if you don’t do anything, 90% of the time there will be a poor outcome,” she added.
This is an important study for showing how BAO patients fare after endovascular treatment, Song said.
One unanswered question from the study is if any of the centers in China used magnetic resonance imaging to help determine the most appropriate candidates for endovascular treatment of these posterior circulation strokes, which is a common practice in the United States, she said.
The study was supported by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, Chongqing Major Disease Prevention and Control Technology Research Project, Army Medical University Clinical Medical Research Talent Training Program, and Major Clinical Innovation Technology Project of the Second Affiliated Hospital of the Army Military Medical University. Sing had no relevant disclosures. Nogueira’s financial disclosures include working as a consultant for Stryker Neurovascular; as a principal investigator on the Imperative trial and the PROST trial; as a steering committee member for Biogen for the CHARM trial; as an advisory board member for Cerenovus/Neuravi, Phenox, Anaconda, Genentech, Biogen, Prolong Pharmaceuticals and Brainomix; and as an advisory board member with stock options for Viz.ai, Corindus Vascular Robotics, Vesalio, Ceretrieve, Astrocyte Pharmaceuticals, and Cerebrotech.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SOURCE: Nogueira RG et al. ISC 2020. Late-breaking abstract 17.
LOS ANGELES – Endovascular therapy significantly improved functional outcomes and reduced mortality at 90 days, compared with standard thrombolysis alone, new evidence from a large, prospective registry study suggests.
Participants who received both interventions were almost five times more likely to be able to walk independently at 90 days compared with those who received thrombolysis alone.
Despite multiple trials supporting the potential benefits of endovascular therapy for anterior stroke, little prospective research addresses outcomes associated with an ischemic stroke caused by a posterior basilar artery occlusion (BAO).
“Basilar artery occlusion is the ‘orphan’ of the large vessel occlusions,” Raul Gomes Nogueira, MD, PhD, said here at a late-breaking abstract session at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
“They account for about 5% of the large vessel occlusions – but have the most dismal prognosis.” Severe disability and mortality rates associated with BAO, for example, reach an estimated 68% to 78%, he said.
The results, from the EVT for Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion Study (BASILAR), were also simultaneously published in JAMA Neurology.
Prior studies in this patient population are generally single-center, retrospective studies and “the numbers tend to be small,” said Nogueira, who is affiliated with the Marcus Stroke and Neuroscience Center, Grady Memorial Hospital, Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
Nogueira and colleagues studied 829 consecutive adults who presented with an acute, symptomatic BAO. They examined a nationwide prospective registry study of people with radiologically confirmed BAO in 47 comprehensive stroke centers across 15 provinces in China.
The median age was 65 years and 74% were men. A total 182 participants received thrombolysis therapy within 6 hours of estimated BAO onset. The 647 people in the dual intervention group also received endovascular therapy within 24 hours.
Standard medical treatment included intravenous rt-PA or urokinase, antiplatelet drugs and systematic anticoagulation alone or in combination. Endovascular therapy included mechanical thrombectomy with stent retrievers and/or thromboaspiration, balloon angioplasty, stenting, intra-arterial thrombolysis, or a combination of these interventions.
Interestingly, participants were not randomly assigned, in part because of the favorable outcomes associated with endovascular therapy. “The high number of patients who received [the dual intervention] may suggest the existence of a lack of equipoise among participating centers,” the researchers note.
Key Efficacy Endpoints
A significantly higher proportion of people in the dual treatment group achieved the primary outcome, functional improvement at 90 days, at 32%, compared with 9.3% in the thrombolysis-only group. This endpoint was defined as a modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 3 or less, which reflects an ability to walk independently. The difference was statistically significant (P < .001).
The absolute difference between groups was 22.7% (95% confidence interval, 17.1%-28.2%) with an adjusted odds ratio of 4.70 (95% CI, 2.53-8.75; P < .001) in favor of dual intervention.
The number needed to treat for one additional patient to be able to walk unassisted was 4.4.
Other outcomes, including differences in National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale scores from baseline to 5 to 7 days or discharge, as well as propensity score matching and subgroup analyses, likewise supported the superiority of using both interventions.
Safety Outcomes
Nogueira and colleagues also assessed safety. They found that symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) occurred in 45 patients, or 7.1% of the endovascular treatment group. In contrast, only one patient, or 0.5%, of the standard medical treatment alone cohort experienced an ICH. This difference was statistically significant (P < .001).
Mortality at 90 days was significantly lower in the endovascular therapy plus medical therapy group, 46.2%, compared with 71.4% in the standard medical treatment alone group (P < .001).
The absolute difference in mortality was 25.2% (95% CI, 17.6%-2.8%) favoring dual treatment, with an adjusted odds ratio of 2.93 (95% CI, 1.95-4.40; P < .001).
Rates of other serious adverse events during the 90-day follow-up period were similar in the two study groups, Nogueira said.
He acknowledged that the nonrandomized design was a limitation of the registry study, adding that “sometimes in life it’s important to acknowledge the best of what can be done. It’s very hard when you have access to thrombectomy to randomize people.”
However, other researchers have attempted or are enrolling people with BAO into trials that randomly assign them to endovascular therapy and standard medical treatment or medical treatment alone.
The BEST trial in China, for example, randomly assigned 131 patients to these groups but was stopped early in September 2017. “The BEST trial was terminated prematurely because of loss of equipoise that led to a high crossover rate and drop in valid recruitment,” the current researchers note.
“The other two trials…are facing the challenge of whether they will achieve their inclusion target,” they add, “because a growing number of stroke centers are unwilling to randomize patients to standard medical treatment alone after the many positive results of trials for endovascular treatment in patients with anterior-circulation stroke.”
The BAOCHE trial from China, for example, is ongoing with approximately 110 patients enrolled so far.
Investigators for the Basilar Artery International Cooperation Study (BASICS) in the Netherlands just completed enrollment of their 300th and final patient in December 2019.
“We are hopeful BASICS trial will shed additional light,” Nogueira said. The results are expected to be presented at the European Stroke Organization Conference in Vienna in May 2020.
More Guidance From MRI?
“With the advent of the stent retrievers and successful recanalization, we know there can be better outcomes for patients. And we know the morbidity and mortality of the basilar artery occlusions are so poor that we tend to want to be aggressive in these cases,” session comoderator Shlee S. Song, MD, director of the Comprehensive Stroke Center and associate professor of neurology at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, California, told Medscape Medical News when asked to comment on the study.
“I agree that we’ve lost equipoise in this cohort – that we really cannot do a randomized trial anymore. You know if you don’t do anything, 90% of the time there will be a poor outcome,” she added.
This is an important study for showing how BAO patients fare after endovascular treatment, Song said.
One unanswered question from the study is if any of the centers in China used magnetic resonance imaging to help determine the most appropriate candidates for endovascular treatment of these posterior circulation strokes, which is a common practice in the United States, she said.
The study was supported by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, Chongqing Major Disease Prevention and Control Technology Research Project, Army Medical University Clinical Medical Research Talent Training Program, and Major Clinical Innovation Technology Project of the Second Affiliated Hospital of the Army Military Medical University. Sing had no relevant disclosures. Nogueira’s financial disclosures include working as a consultant for Stryker Neurovascular; as a principal investigator on the Imperative trial and the PROST trial; as a steering committee member for Biogen for the CHARM trial; as an advisory board member for Cerenovus/Neuravi, Phenox, Anaconda, Genentech, Biogen, Prolong Pharmaceuticals and Brainomix; and as an advisory board member with stock options for Viz.ai, Corindus Vascular Robotics, Vesalio, Ceretrieve, Astrocyte Pharmaceuticals, and Cerebrotech.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SOURCE: Nogueira RG et al. ISC 2020. Late-breaking abstract 17.
REPORTING FROM ISC 2020
ARCADIA: Predicting risk of atrial cardiopathy poststroke
LOS ANGELES – Older age, female sex, black race, relative anemia, and a history of cardiovascular disease are associated with greater risk for atrial cardiopathy among people who experienced an embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS), new evidence suggests.
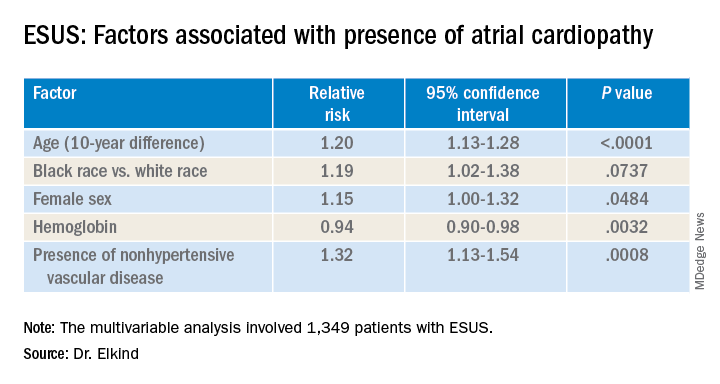
Atrial cardiopathy is a suspected cause of ESUS independent of atrial fibrillation. However, clinical predictors to help physicians identify which ESUS patients are at increased risk remain unknown.
The risk for atrial cardiopathy was 34% higher for women versus men with ESUS in this analysis. In addition, black participants had a 29% increased risk, compared with others, and each 10 years of age increased risk for atrial cardiopathy by 30% in an univariable analysis.
“Modest effects of these associations suggest that all ESUS patients, regardless of underlying demographic and risk factors, may have atrial cardiopathy,” principal investigator Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, of Columbia University, New York, said when presenting results at the 2020 International Stroke Conference, sponsored by the American Heart Association.
For this reason, he added, all people with ESUS should be considered for recruitment into the ongoing ARCADIA (AtRial Cardiopathy and Antithrombotic Drugs In Prevention After Cryptogenic Stroke) trial, of which he is one of the principal investigators.
ESUS is a heterogeneous condition, and some patients may be responsive to anticoagulants and some might not, Elkind said. This observation “led us to consider alternative ways for ischemic disease to lead to stroke. We would hypothesize that the underlying atrium can be a risk for stroke by itself.”
Not yet available is the primary efficacy outcome of the multicenter, randomized ARCADIA trial comparing apixaban with aspirin in reducing risk for recurrent stroke of any type. However, Dr. Elkind and colleagues have recruited 1,505 patients to date, enough to analyze factors that predict risk for recurrent stroke among people with evidence of atrial cardiopathy.
All ARCADIA participants are 45 years of age or older and have no history of atrial fibrillation. Atrial cardiopathy was defined by presence of at least one of three biomarkers: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), P wave terminal force velocity, or evidence of a left atrial diameter of 3 cm/m2 or larger on echocardiography.
Of the 1,349 ARCADIA participants eligible for the current analysis, approximately one-third met one or more of these criteria for atrial cardiopathy.
Those with atrial cardiopathy were “more likely to be black and be women, and tended to have shorter time from stroke to screening,” Dr. Elkind said. In addition, heart failure, hypertension, and peripheral artery disease were more common in those with atrial cardiopathy. This group also was more likely to have an elevation in creatinine and lower hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.
“Heart disease, ischemic heart disease and non-hypertensive vascular disease were significant risk factors” for recurrent stroke in the study, Dr. Elkind added.
Elkind said that, surprisingly, there was no independent association between the time to measurement of NT-proBNP and risk, suggesting that this biomarker “does not rise simply in response to stroke, but reflects a stable condition.”
The multicenter ARCADIA trial is recruiting additional participants at 142 sites now, Dr. Elkind said, “and we are still looking for more sites.”
Which comes first?
“He is looking at what the predictors are for cardiopathy in these patients, which is fascinating for all of us,” session moderator Michelle Christina Johansen, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview when asked to comment.
There is always the conundrum of what came first — the chicken or the egg, Johansen said. Do these patients have stroke that then somehow led to a state that predisposes them to have atrial cardiopathy? Or, rather, was it an atrial cardiopathy state independent of atrial fibrillation that then led to stroke?
“That is why looking at predictors in this population is of such interest,” she said. The study could help identify a subgroup of patients at higher risk for atrial cardiopathy and guide clinical decision-making when patients present with ESUS.
“One of the things I found interesting was that he found that atrial cardiopathy patients were older [a mean 69 years]. This was amazing, because ESUS patients in general tend to be younger,” Dr. Johansen said.
“And there is about a 4-5% risk of recurrence with these patients. So. it was interesting that prior stroke or [transient ischemic attack] was not associated.”*
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the BMS-Pfizer Alliance, and Roche provide funding for ARCADIA. Dr. Elkind and Dr. Johansen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Elkind M et al. ISC 2020, Abstract 26.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*Correction, 4/28/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the risk of recurrence.
LOS ANGELES – Older age, female sex, black race, relative anemia, and a history of cardiovascular disease are associated with greater risk for atrial cardiopathy among people who experienced an embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS), new evidence suggests.

Atrial cardiopathy is a suspected cause of ESUS independent of atrial fibrillation. However, clinical predictors to help physicians identify which ESUS patients are at increased risk remain unknown.
The risk for atrial cardiopathy was 34% higher for women versus men with ESUS in this analysis. In addition, black participants had a 29% increased risk, compared with others, and each 10 years of age increased risk for atrial cardiopathy by 30% in an univariable analysis.
“Modest effects of these associations suggest that all ESUS patients, regardless of underlying demographic and risk factors, may have atrial cardiopathy,” principal investigator Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, of Columbia University, New York, said when presenting results at the 2020 International Stroke Conference, sponsored by the American Heart Association.
For this reason, he added, all people with ESUS should be considered for recruitment into the ongoing ARCADIA (AtRial Cardiopathy and Antithrombotic Drugs In Prevention After Cryptogenic Stroke) trial, of which he is one of the principal investigators.
ESUS is a heterogeneous condition, and some patients may be responsive to anticoagulants and some might not, Elkind said. This observation “led us to consider alternative ways for ischemic disease to lead to stroke. We would hypothesize that the underlying atrium can be a risk for stroke by itself.”
Not yet available is the primary efficacy outcome of the multicenter, randomized ARCADIA trial comparing apixaban with aspirin in reducing risk for recurrent stroke of any type. However, Dr. Elkind and colleagues have recruited 1,505 patients to date, enough to analyze factors that predict risk for recurrent stroke among people with evidence of atrial cardiopathy.
All ARCADIA participants are 45 years of age or older and have no history of atrial fibrillation. Atrial cardiopathy was defined by presence of at least one of three biomarkers: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), P wave terminal force velocity, or evidence of a left atrial diameter of 3 cm/m2 or larger on echocardiography.
Of the 1,349 ARCADIA participants eligible for the current analysis, approximately one-third met one or more of these criteria for atrial cardiopathy.
Those with atrial cardiopathy were “more likely to be black and be women, and tended to have shorter time from stroke to screening,” Dr. Elkind said. In addition, heart failure, hypertension, and peripheral artery disease were more common in those with atrial cardiopathy. This group also was more likely to have an elevation in creatinine and lower hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.
“Heart disease, ischemic heart disease and non-hypertensive vascular disease were significant risk factors” for recurrent stroke in the study, Dr. Elkind added.
Elkind said that, surprisingly, there was no independent association between the time to measurement of NT-proBNP and risk, suggesting that this biomarker “does not rise simply in response to stroke, but reflects a stable condition.”
The multicenter ARCADIA trial is recruiting additional participants at 142 sites now, Dr. Elkind said, “and we are still looking for more sites.”
Which comes first?
“He is looking at what the predictors are for cardiopathy in these patients, which is fascinating for all of us,” session moderator Michelle Christina Johansen, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview when asked to comment.
There is always the conundrum of what came first — the chicken or the egg, Johansen said. Do these patients have stroke that then somehow led to a state that predisposes them to have atrial cardiopathy? Or, rather, was it an atrial cardiopathy state independent of atrial fibrillation that then led to stroke?
“That is why looking at predictors in this population is of such interest,” she said. The study could help identify a subgroup of patients at higher risk for atrial cardiopathy and guide clinical decision-making when patients present with ESUS.
“One of the things I found interesting was that he found that atrial cardiopathy patients were older [a mean 69 years]. This was amazing, because ESUS patients in general tend to be younger,” Dr. Johansen said.
“And there is about a 4-5% risk of recurrence with these patients. So. it was interesting that prior stroke or [transient ischemic attack] was not associated.”*
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the BMS-Pfizer Alliance, and Roche provide funding for ARCADIA. Dr. Elkind and Dr. Johansen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Elkind M et al. ISC 2020, Abstract 26.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*Correction, 4/28/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the risk of recurrence.
LOS ANGELES – Older age, female sex, black race, relative anemia, and a history of cardiovascular disease are associated with greater risk for atrial cardiopathy among people who experienced an embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS), new evidence suggests.

Atrial cardiopathy is a suspected cause of ESUS independent of atrial fibrillation. However, clinical predictors to help physicians identify which ESUS patients are at increased risk remain unknown.
The risk for atrial cardiopathy was 34% higher for women versus men with ESUS in this analysis. In addition, black participants had a 29% increased risk, compared with others, and each 10 years of age increased risk for atrial cardiopathy by 30% in an univariable analysis.
“Modest effects of these associations suggest that all ESUS patients, regardless of underlying demographic and risk factors, may have atrial cardiopathy,” principal investigator Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, of Columbia University, New York, said when presenting results at the 2020 International Stroke Conference, sponsored by the American Heart Association.
For this reason, he added, all people with ESUS should be considered for recruitment into the ongoing ARCADIA (AtRial Cardiopathy and Antithrombotic Drugs In Prevention After Cryptogenic Stroke) trial, of which he is one of the principal investigators.
ESUS is a heterogeneous condition, and some patients may be responsive to anticoagulants and some might not, Elkind said. This observation “led us to consider alternative ways for ischemic disease to lead to stroke. We would hypothesize that the underlying atrium can be a risk for stroke by itself.”
Not yet available is the primary efficacy outcome of the multicenter, randomized ARCADIA trial comparing apixaban with aspirin in reducing risk for recurrent stroke of any type. However, Dr. Elkind and colleagues have recruited 1,505 patients to date, enough to analyze factors that predict risk for recurrent stroke among people with evidence of atrial cardiopathy.
All ARCADIA participants are 45 years of age or older and have no history of atrial fibrillation. Atrial cardiopathy was defined by presence of at least one of three biomarkers: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), P wave terminal force velocity, or evidence of a left atrial diameter of 3 cm/m2 or larger on echocardiography.
Of the 1,349 ARCADIA participants eligible for the current analysis, approximately one-third met one or more of these criteria for atrial cardiopathy.
Those with atrial cardiopathy were “more likely to be black and be women, and tended to have shorter time from stroke to screening,” Dr. Elkind said. In addition, heart failure, hypertension, and peripheral artery disease were more common in those with atrial cardiopathy. This group also was more likely to have an elevation in creatinine and lower hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.
“Heart disease, ischemic heart disease and non-hypertensive vascular disease were significant risk factors” for recurrent stroke in the study, Dr. Elkind added.
Elkind said that, surprisingly, there was no independent association between the time to measurement of NT-proBNP and risk, suggesting that this biomarker “does not rise simply in response to stroke, but reflects a stable condition.”
The multicenter ARCADIA trial is recruiting additional participants at 142 sites now, Dr. Elkind said, “and we are still looking for more sites.”
Which comes first?
“He is looking at what the predictors are for cardiopathy in these patients, which is fascinating for all of us,” session moderator Michelle Christina Johansen, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview when asked to comment.
There is always the conundrum of what came first — the chicken or the egg, Johansen said. Do these patients have stroke that then somehow led to a state that predisposes them to have atrial cardiopathy? Or, rather, was it an atrial cardiopathy state independent of atrial fibrillation that then led to stroke?
“That is why looking at predictors in this population is of such interest,” she said. The study could help identify a subgroup of patients at higher risk for atrial cardiopathy and guide clinical decision-making when patients present with ESUS.
“One of the things I found interesting was that he found that atrial cardiopathy patients were older [a mean 69 years]. This was amazing, because ESUS patients in general tend to be younger,” Dr. Johansen said.
“And there is about a 4-5% risk of recurrence with these patients. So. it was interesting that prior stroke or [transient ischemic attack] was not associated.”*
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the BMS-Pfizer Alliance, and Roche provide funding for ARCADIA. Dr. Elkind and Dr. Johansen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Elkind M et al. ISC 2020, Abstract 26.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*Correction, 4/28/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the risk of recurrence.
REPORTING FROM ISC 2020
Shingles vaccine linked to lower stroke risk
LOS ANGELES – Prevention of shingles with the Zoster Vaccine Live may reduce the risk of subsequent stroke among older adults as well, the first study to examine this association suggests. Shingles vaccination was linked to a 20% decrease in stroke risk in people younger than 80 years of age in the large Medicare cohort study. Older participants showed a 10% reduced risk, according to data released in advance of formal presentation at this week’s International Stroke Conference, sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Reductions were seen for both ischemic and hemorrhagic events.
“Our findings might encourage people age 50 or older to get vaccinated against shingles and to prevent shingles-associated stroke risk,” Quanhe Yang, PhD, lead study author and senior scientist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in an interview.
Dr. Yang and colleagues evaluated the only shingles vaccine available at the time of the study, Zoster Vaccine Live (Zostavax). However, the CDC now calls an adjuvanted, nonlive recombinant vaccine (Shingrix) the preferred shingles vaccine for healthy adults aged 50 years and older. Shingrix was approved in 2017. Zostavax, approved in 2006, can still be used in healthy adults aged 60 years and older, the agency states.
A reduction in inflammation from Zoster Vaccine Live may be the mechanism by which stroke risk is reduced, Dr. Yang said. The newer vaccine, which the CDC notes is more than 90% effective, might provide even greater protection against stroke, although more research is needed, he added.
Interestingly, prior research suggested that, once a person develops shingles, it may be too late. Dr. Yang and colleagues showed vaccination or antiviral treatment after a shingles episode was not effective at reducing stroke risk in research presented at the 2019 International Stroke Conference.
Shingles can present as a painful reactivation of chickenpox, also known as the varicella-zoster virus. Shingles is also common; Dr. Yang estimated one in three people who had chickenpox will develop the condition at some point in their lifetime. In addition, researchers have linked shingles to an elevated risk of stroke.
To assess the vaccine’s protective effect on stroke, Dr. Yang and colleagues reviewed health records for 1.38 million Medicare recipients. All participants were aged 66 years or older, had no history of stroke at baseline, and received the Zoster Vaccine Live during 2008-2016. The investigators compared the stroke rate in this vaccinated group with the rate in a matched control group of the same number of Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries who did not receive the vaccination. They adjusted their analysis for age, sex, race, medications, and comorbidities.
The overall decrease of 16% in stroke risk associated with vaccination included a 12% drop in hemorrhagic stroke and 18% decrease in ischemic stroke over a median follow-up of 3.9 years follow-up (interquartile range, 2.7-5.4).
The adjusted hazard ratios comparing the vaccinated with control groups were 0.84 (95% confidence interval, 0.83-0.85) for all stroke; 0.82 (95% CI, 0.81-0.83) for acute ischemic stroke; and 0.88 (95% CI, 0.84-0.91) for hemorrhagic stroke.
The vaccinated group experienced 42,267 stroke events during that time. This rate included 33,510 acute ischemic strokes and 4,318 hemorrhagic strokes. At the same time, 48,139 strokes occurred in the control group. The breakdown included 39,334 ischemic and 4,713 hemorrhagic events.
“Approximately 1 million people in the United States get shingles each year, yet there is a vaccine to help prevent it,” Dr. Yang stated in a news release. “Our study results may encourage people ages 50 and older to follow the recommendation and get vaccinated against shingles. You are reducing the risk of shingles, and at the same time, you may be reducing your risk of stroke.”
“Further studies are needed to confirm our findings of association between Zostavax vaccine and risk of stroke,” Dr. Yang said.
Because the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommended Shingrix vaccine only for healthy adults 50 years and older in 2017, there were insufficient data in Medicare to study the association between that vaccine and risk of stroke at the time of the current study.
“However, two doses of Shingrix are more than 90% effective at preventing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia, and higher than that of Zostavax,” Dr. Yang said.
‘Very intriguing’ research
“This is a very interesting study,” Ralph L. Sacco, MD, past president of the American Heart Association, said in a video commentary released in advance of the conference. It was a very large sample, he noted, and those older than age 60 years who had the vaccine were protected with a lower risk for both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
“So it is very intriguing,” added Dr. Sacco, chairman of the department of neurology at the University of Miami. “We know things like shingles can increase inflammation and increase the risk of stroke,” Dr. Sacco said, “but this is the first time in a very large Medicare database that it was shown that those who had the vaccine had a lower risk of stroke.”
The CDC funded this study. Dr. Yang and Dr. Sacco have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Yang Q et al. ISC 2020, Abstract TP493.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES – Prevention of shingles with the Zoster Vaccine Live may reduce the risk of subsequent stroke among older adults as well, the first study to examine this association suggests. Shingles vaccination was linked to a 20% decrease in stroke risk in people younger than 80 years of age in the large Medicare cohort study. Older participants showed a 10% reduced risk, according to data released in advance of formal presentation at this week’s International Stroke Conference, sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Reductions were seen for both ischemic and hemorrhagic events.
“Our findings might encourage people age 50 or older to get vaccinated against shingles and to prevent shingles-associated stroke risk,” Quanhe Yang, PhD, lead study author and senior scientist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in an interview.
Dr. Yang and colleagues evaluated the only shingles vaccine available at the time of the study, Zoster Vaccine Live (Zostavax). However, the CDC now calls an adjuvanted, nonlive recombinant vaccine (Shingrix) the preferred shingles vaccine for healthy adults aged 50 years and older. Shingrix was approved in 2017. Zostavax, approved in 2006, can still be used in healthy adults aged 60 years and older, the agency states.
A reduction in inflammation from Zoster Vaccine Live may be the mechanism by which stroke risk is reduced, Dr. Yang said. The newer vaccine, which the CDC notes is more than 90% effective, might provide even greater protection against stroke, although more research is needed, he added.
Interestingly, prior research suggested that, once a person develops shingles, it may be too late. Dr. Yang and colleagues showed vaccination or antiviral treatment after a shingles episode was not effective at reducing stroke risk in research presented at the 2019 International Stroke Conference.
Shingles can present as a painful reactivation of chickenpox, also known as the varicella-zoster virus. Shingles is also common; Dr. Yang estimated one in three people who had chickenpox will develop the condition at some point in their lifetime. In addition, researchers have linked shingles to an elevated risk of stroke.
To assess the vaccine’s protective effect on stroke, Dr. Yang and colleagues reviewed health records for 1.38 million Medicare recipients. All participants were aged 66 years or older, had no history of stroke at baseline, and received the Zoster Vaccine Live during 2008-2016. The investigators compared the stroke rate in this vaccinated group with the rate in a matched control group of the same number of Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries who did not receive the vaccination. They adjusted their analysis for age, sex, race, medications, and comorbidities.
The overall decrease of 16% in stroke risk associated with vaccination included a 12% drop in hemorrhagic stroke and 18% decrease in ischemic stroke over a median follow-up of 3.9 years follow-up (interquartile range, 2.7-5.4).
The adjusted hazard ratios comparing the vaccinated with control groups were 0.84 (95% confidence interval, 0.83-0.85) for all stroke; 0.82 (95% CI, 0.81-0.83) for acute ischemic stroke; and 0.88 (95% CI, 0.84-0.91) for hemorrhagic stroke.
The vaccinated group experienced 42,267 stroke events during that time. This rate included 33,510 acute ischemic strokes and 4,318 hemorrhagic strokes. At the same time, 48,139 strokes occurred in the control group. The breakdown included 39,334 ischemic and 4,713 hemorrhagic events.
“Approximately 1 million people in the United States get shingles each year, yet there is a vaccine to help prevent it,” Dr. Yang stated in a news release. “Our study results may encourage people ages 50 and older to follow the recommendation and get vaccinated against shingles. You are reducing the risk of shingles, and at the same time, you may be reducing your risk of stroke.”
“Further studies are needed to confirm our findings of association between Zostavax vaccine and risk of stroke,” Dr. Yang said.
Because the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommended Shingrix vaccine only for healthy adults 50 years and older in 2017, there were insufficient data in Medicare to study the association between that vaccine and risk of stroke at the time of the current study.
“However, two doses of Shingrix are more than 90% effective at preventing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia, and higher than that of Zostavax,” Dr. Yang said.
‘Very intriguing’ research
“This is a very interesting study,” Ralph L. Sacco, MD, past president of the American Heart Association, said in a video commentary released in advance of the conference. It was a very large sample, he noted, and those older than age 60 years who had the vaccine were protected with a lower risk for both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
“So it is very intriguing,” added Dr. Sacco, chairman of the department of neurology at the University of Miami. “We know things like shingles can increase inflammation and increase the risk of stroke,” Dr. Sacco said, “but this is the first time in a very large Medicare database that it was shown that those who had the vaccine had a lower risk of stroke.”
The CDC funded this study. Dr. Yang and Dr. Sacco have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Yang Q et al. ISC 2020, Abstract TP493.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES – Prevention of shingles with the Zoster Vaccine Live may reduce the risk of subsequent stroke among older adults as well, the first study to examine this association suggests. Shingles vaccination was linked to a 20% decrease in stroke risk in people younger than 80 years of age in the large Medicare cohort study. Older participants showed a 10% reduced risk, according to data released in advance of formal presentation at this week’s International Stroke Conference, sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Reductions were seen for both ischemic and hemorrhagic events.
“Our findings might encourage people age 50 or older to get vaccinated against shingles and to prevent shingles-associated stroke risk,” Quanhe Yang, PhD, lead study author and senior scientist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in an interview.
Dr. Yang and colleagues evaluated the only shingles vaccine available at the time of the study, Zoster Vaccine Live (Zostavax). However, the CDC now calls an adjuvanted, nonlive recombinant vaccine (Shingrix) the preferred shingles vaccine for healthy adults aged 50 years and older. Shingrix was approved in 2017. Zostavax, approved in 2006, can still be used in healthy adults aged 60 years and older, the agency states.
A reduction in inflammation from Zoster Vaccine Live may be the mechanism by which stroke risk is reduced, Dr. Yang said. The newer vaccine, which the CDC notes is more than 90% effective, might provide even greater protection against stroke, although more research is needed, he added.
Interestingly, prior research suggested that, once a person develops shingles, it may be too late. Dr. Yang and colleagues showed vaccination or antiviral treatment after a shingles episode was not effective at reducing stroke risk in research presented at the 2019 International Stroke Conference.
Shingles can present as a painful reactivation of chickenpox, also known as the varicella-zoster virus. Shingles is also common; Dr. Yang estimated one in three people who had chickenpox will develop the condition at some point in their lifetime. In addition, researchers have linked shingles to an elevated risk of stroke.
To assess the vaccine’s protective effect on stroke, Dr. Yang and colleagues reviewed health records for 1.38 million Medicare recipients. All participants were aged 66 years or older, had no history of stroke at baseline, and received the Zoster Vaccine Live during 2008-2016. The investigators compared the stroke rate in this vaccinated group with the rate in a matched control group of the same number of Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries who did not receive the vaccination. They adjusted their analysis for age, sex, race, medications, and comorbidities.
The overall decrease of 16% in stroke risk associated with vaccination included a 12% drop in hemorrhagic stroke and 18% decrease in ischemic stroke over a median follow-up of 3.9 years follow-up (interquartile range, 2.7-5.4).
The adjusted hazard ratios comparing the vaccinated with control groups were 0.84 (95% confidence interval, 0.83-0.85) for all stroke; 0.82 (95% CI, 0.81-0.83) for acute ischemic stroke; and 0.88 (95% CI, 0.84-0.91) for hemorrhagic stroke.
The vaccinated group experienced 42,267 stroke events during that time. This rate included 33,510 acute ischemic strokes and 4,318 hemorrhagic strokes. At the same time, 48,139 strokes occurred in the control group. The breakdown included 39,334 ischemic and 4,713 hemorrhagic events.
“Approximately 1 million people in the United States get shingles each year, yet there is a vaccine to help prevent it,” Dr. Yang stated in a news release. “Our study results may encourage people ages 50 and older to follow the recommendation and get vaccinated against shingles. You are reducing the risk of shingles, and at the same time, you may be reducing your risk of stroke.”
“Further studies are needed to confirm our findings of association between Zostavax vaccine and risk of stroke,” Dr. Yang said.
Because the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommended Shingrix vaccine only for healthy adults 50 years and older in 2017, there were insufficient data in Medicare to study the association between that vaccine and risk of stroke at the time of the current study.
“However, two doses of Shingrix are more than 90% effective at preventing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia, and higher than that of Zostavax,” Dr. Yang said.
‘Very intriguing’ research
“This is a very interesting study,” Ralph L. Sacco, MD, past president of the American Heart Association, said in a video commentary released in advance of the conference. It was a very large sample, he noted, and those older than age 60 years who had the vaccine were protected with a lower risk for both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
“So it is very intriguing,” added Dr. Sacco, chairman of the department of neurology at the University of Miami. “We know things like shingles can increase inflammation and increase the risk of stroke,” Dr. Sacco said, “but this is the first time in a very large Medicare database that it was shown that those who had the vaccine had a lower risk of stroke.”
The CDC funded this study. Dr. Yang and Dr. Sacco have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Yang Q et al. ISC 2020, Abstract TP493.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
REPORTING FROM ISC 2020
Stroke risk tied to diabetic retinopathy may not be modifiable
LOS ANGELES – Evidence continues to mount that diabetic retinopathy predicts elevated risk for stroke.
In a new study with nearly 3,000 people, those with diabetic retinopathy were 60% more likely than others with diabetes to develop an incident stroke over time. Investigators also found that addressing glucose, lipids, and blood pressure levels did not mitigate this risk in this secondary analysis of the ACCORD Eye Study.
“We are not surprised with the finding that diabetic retinopathy increases the risk of stroke — as diabetic retinopathy is common microvascular disease that is an established risk factor for cardiovascular disease,” lead author Ka-Ho Wong, BS, MBA, said in an interview.
However, “we were surprised that none of the trial interventions mitigated this risk, in particular the intensive blood pressure reduction, because hypertension is the most important cause of microvascular disease,” he said. Mr. Wong is clinical research coordinator and lab manager of the de Havenon Lab at the University of Utah Health Hospitals and Clinics in Salt Lake City.
The study findings were released Feb. 12, 2020, in advance of formal presentation at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Common predictor of vascular disease
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common complication of diabetes mellitus, affecting up to 50% of people living with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In addition, previous research suggests that macrovascular diabetes complications, including stroke, could share a common or synergistic pathway.
This small vessel damage in the eye also has been linked to an increased risk of adverse cardiac events, including heart failure, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
To find out more, Mr. Wong and colleagues analyzed 2,828 participants in the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) Eye Study. They compared the stroke risk between 874 people with diabetic retinopathy and another 1,954 diabetics without this complication. The average age was 62 years and 62% were men.
Diabetic neuropathy at baseline was diagnosed using the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Severity Scale using seven-field stereoscopic fundus photographs.
A total of 117 participants experienced a stroke during a mean follow-up of 5.4 years.
The investigators found that diabetic retinopathy was more common among patients who had a stroke (41%) versus 31% of those without a stroke (P = .016). The link between diabetic retinopathy and stroke remained in an analysis adjusted for multiple factors, including baseline age, gender, race, total cholesterol, A1c, smoking, and more. Risk remained elevated, with a hazard ratio of 1.60 (95% confidence interval, 1.10-2.32; P = .015).
Regarding the potential for modifying this risk, the association was unaffected among participants randomly assigned to the ACCORD glucose intervention (P = .305), lipid intervention (P = .546), or blood pressure intervention (P = .422).
The study was a secondary analysis, so information on stroke type and location were unavailable.
The big picture
“Diabetic retinopathy is associated with an increased risk of stroke, which suggests that the microvascular pathology inherent to diabetic retinopathy has larger cardiovascular implications,” the researchers noted.
Despite these findings, the researchers suggest that patients with diabetic retinopathy receive aggressive medical management to try to reduce their stroke risk.
“It’s important for everyone with diabetes to maintain good blood glucose control, and those with established diabetic retinopathy should pay particular attention to meeting all the stroke prevention guidelines that are established by the American Stroke Association,” said Mr. Wong.
“Patients with established diabetic retinopathy should pay particular attention to meeting all stroke prevention guidelines established by the [American Heart Association],” he added.
Mr. Wong and colleagues would like to expand on these findings. Pending grant application and funding support, they propose conducting a prospective, observational trial in stroke patients with baseline diabetic retinopathy. One aim would be to identify the most common mechanisms leading to stroke in this population, “which would have important implications for prevention efforts,” he said.
Consistent Findings
“The results of the study showing that having diabetic retinopathy is also associated with an increase in stroke really isn’t surprising. There have been other studies, population-based studies, done in the past, that have found a similar relationship,” Larry B. Goldstein, MD, said in a video commentary on the findings.
“The results are actually quite consistent with several other studies that have evaluated the same relationship,” added Dr. Goldstein, who is chair of the department of neurology and codirector of the Kentucky Neuroscience Institute, University of Kentucky HealthCare, Lexington.
Mr. Wong and Dr. Goldstein have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The NIH’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke funded the study.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES – Evidence continues to mount that diabetic retinopathy predicts elevated risk for stroke.
In a new study with nearly 3,000 people, those with diabetic retinopathy were 60% more likely than others with diabetes to develop an incident stroke over time. Investigators also found that addressing glucose, lipids, and blood pressure levels did not mitigate this risk in this secondary analysis of the ACCORD Eye Study.
“We are not surprised with the finding that diabetic retinopathy increases the risk of stroke — as diabetic retinopathy is common microvascular disease that is an established risk factor for cardiovascular disease,” lead author Ka-Ho Wong, BS, MBA, said in an interview.
However, “we were surprised that none of the trial interventions mitigated this risk, in particular the intensive blood pressure reduction, because hypertension is the most important cause of microvascular disease,” he said. Mr. Wong is clinical research coordinator and lab manager of the de Havenon Lab at the University of Utah Health Hospitals and Clinics in Salt Lake City.
The study findings were released Feb. 12, 2020, in advance of formal presentation at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Common predictor of vascular disease
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common complication of diabetes mellitus, affecting up to 50% of people living with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In addition, previous research suggests that macrovascular diabetes complications, including stroke, could share a common or synergistic pathway.
This small vessel damage in the eye also has been linked to an increased risk of adverse cardiac events, including heart failure, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
To find out more, Mr. Wong and colleagues analyzed 2,828 participants in the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) Eye Study. They compared the stroke risk between 874 people with diabetic retinopathy and another 1,954 diabetics without this complication. The average age was 62 years and 62% were men.
Diabetic neuropathy at baseline was diagnosed using the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Severity Scale using seven-field stereoscopic fundus photographs.
A total of 117 participants experienced a stroke during a mean follow-up of 5.4 years.
The investigators found that diabetic retinopathy was more common among patients who had a stroke (41%) versus 31% of those without a stroke (P = .016). The link between diabetic retinopathy and stroke remained in an analysis adjusted for multiple factors, including baseline age, gender, race, total cholesterol, A1c, smoking, and more. Risk remained elevated, with a hazard ratio of 1.60 (95% confidence interval, 1.10-2.32; P = .015).
Regarding the potential for modifying this risk, the association was unaffected among participants randomly assigned to the ACCORD glucose intervention (P = .305), lipid intervention (P = .546), or blood pressure intervention (P = .422).
The study was a secondary analysis, so information on stroke type and location were unavailable.
The big picture
“Diabetic retinopathy is associated with an increased risk of stroke, which suggests that the microvascular pathology inherent to diabetic retinopathy has larger cardiovascular implications,” the researchers noted.
Despite these findings, the researchers suggest that patients with diabetic retinopathy receive aggressive medical management to try to reduce their stroke risk.
“It’s important for everyone with diabetes to maintain good blood glucose control, and those with established diabetic retinopathy should pay particular attention to meeting all the stroke prevention guidelines that are established by the American Stroke Association,” said Mr. Wong.
“Patients with established diabetic retinopathy should pay particular attention to meeting all stroke prevention guidelines established by the [American Heart Association],” he added.
Mr. Wong and colleagues would like to expand on these findings. Pending grant application and funding support, they propose conducting a prospective, observational trial in stroke patients with baseline diabetic retinopathy. One aim would be to identify the most common mechanisms leading to stroke in this population, “which would have important implications for prevention efforts,” he said.
Consistent Findings
“The results of the study showing that having diabetic retinopathy is also associated with an increase in stroke really isn’t surprising. There have been other studies, population-based studies, done in the past, that have found a similar relationship,” Larry B. Goldstein, MD, said in a video commentary on the findings.
“The results are actually quite consistent with several other studies that have evaluated the same relationship,” added Dr. Goldstein, who is chair of the department of neurology and codirector of the Kentucky Neuroscience Institute, University of Kentucky HealthCare, Lexington.
Mr. Wong and Dr. Goldstein have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The NIH’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke funded the study.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES – Evidence continues to mount that diabetic retinopathy predicts elevated risk for stroke.
In a new study with nearly 3,000 people, those with diabetic retinopathy were 60% more likely than others with diabetes to develop an incident stroke over time. Investigators also found that addressing glucose, lipids, and blood pressure levels did not mitigate this risk in this secondary analysis of the ACCORD Eye Study.
“We are not surprised with the finding that diabetic retinopathy increases the risk of stroke — as diabetic retinopathy is common microvascular disease that is an established risk factor for cardiovascular disease,” lead author Ka-Ho Wong, BS, MBA, said in an interview.
However, “we were surprised that none of the trial interventions mitigated this risk, in particular the intensive blood pressure reduction, because hypertension is the most important cause of microvascular disease,” he said. Mr. Wong is clinical research coordinator and lab manager of the de Havenon Lab at the University of Utah Health Hospitals and Clinics in Salt Lake City.
The study findings were released Feb. 12, 2020, in advance of formal presentation at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Common predictor of vascular disease
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common complication of diabetes mellitus, affecting up to 50% of people living with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In addition, previous research suggests that macrovascular diabetes complications, including stroke, could share a common or synergistic pathway.
This small vessel damage in the eye also has been linked to an increased risk of adverse cardiac events, including heart failure, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
To find out more, Mr. Wong and colleagues analyzed 2,828 participants in the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) Eye Study. They compared the stroke risk between 874 people with diabetic retinopathy and another 1,954 diabetics without this complication. The average age was 62 years and 62% were men.
Diabetic neuropathy at baseline was diagnosed using the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Severity Scale using seven-field stereoscopic fundus photographs.
A total of 117 participants experienced a stroke during a mean follow-up of 5.4 years.
The investigators found that diabetic retinopathy was more common among patients who had a stroke (41%) versus 31% of those without a stroke (P = .016). The link between diabetic retinopathy and stroke remained in an analysis adjusted for multiple factors, including baseline age, gender, race, total cholesterol, A1c, smoking, and more. Risk remained elevated, with a hazard ratio of 1.60 (95% confidence interval, 1.10-2.32; P = .015).
Regarding the potential for modifying this risk, the association was unaffected among participants randomly assigned to the ACCORD glucose intervention (P = .305), lipid intervention (P = .546), or blood pressure intervention (P = .422).
The study was a secondary analysis, so information on stroke type and location were unavailable.
The big picture
“Diabetic retinopathy is associated with an increased risk of stroke, which suggests that the microvascular pathology inherent to diabetic retinopathy has larger cardiovascular implications,” the researchers noted.
Despite these findings, the researchers suggest that patients with diabetic retinopathy receive aggressive medical management to try to reduce their stroke risk.
“It’s important for everyone with diabetes to maintain good blood glucose control, and those with established diabetic retinopathy should pay particular attention to meeting all the stroke prevention guidelines that are established by the American Stroke Association,” said Mr. Wong.
“Patients with established diabetic retinopathy should pay particular attention to meeting all stroke prevention guidelines established by the [American Heart Association],” he added.
Mr. Wong and colleagues would like to expand on these findings. Pending grant application and funding support, they propose conducting a prospective, observational trial in stroke patients with baseline diabetic retinopathy. One aim would be to identify the most common mechanisms leading to stroke in this population, “which would have important implications for prevention efforts,” he said.
Consistent Findings
“The results of the study showing that having diabetic retinopathy is also associated with an increase in stroke really isn’t surprising. There have been other studies, population-based studies, done in the past, that have found a similar relationship,” Larry B. Goldstein, MD, said in a video commentary on the findings.
“The results are actually quite consistent with several other studies that have evaluated the same relationship,” added Dr. Goldstein, who is chair of the department of neurology and codirector of the Kentucky Neuroscience Institute, University of Kentucky HealthCare, Lexington.
Mr. Wong and Dr. Goldstein have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The NIH’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke funded the study.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
REPORTING FROM ISC 2020
Treating LDL to below 70 reduces recurrent stroke
PHILADELPHIA – Treating patients to a lower LDL target after an ischemic stroke of atherosclerotic origin resulted in fewer recurrent strokes or major cardiovascular events, compared with a higher LDL goal, even though the international trial was stopped early because of lack of funding.
“In the Treat Stroke to Target [TST] trial we showed that the group of patients with an atherosclerotic stroke achieving an LDL cholesterol of less than 70 mg/dL had 22% less recurrent ischemic stroke or other major vascular events than the group achieving a LDL cholesterol between 90 and 110 mg/dL,” lead author Pierre Amarenco, MD, chairman of the department of neurology and the stroke center at Bichat Hospital in Paris, said in an interview.
“We avoided more than one in recurrence in five,” he added.
The findings of the investigator-initiated trial were reported during a late-breaking research session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions and simultaneously published online Nov. 18 in the New England Journal of Medicine (doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910355).
Discussant Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, president-elect of the American Heart Association, called the TST findings “practice confirming” of a strategy many cardiologists already follow for stroke patients.
“The TST study is only the second trial that was done in neurology for stroke prevention using statins and lipid-lowering therapy, and that’s what makes it a hopeful and real advance,” he said in an interview.
To achieve the LDL-lowering goal, two-thirds of patients received a high-dose statin therapy while the remainder received both high-dose statin and ezetimibe (Zetia, Merck). There were no significant increases in intracranial hemorrhage observed between lower- and higher-target groups.
“Now guidelines should move to recommending a target LDL cholesterol of less than 70 mg/dL in all patients with a proven ischemic stroke of atherosclerotic origin,” said Dr. Amarenco, who is also a professor of neurology at Denis Diderot Paris University.
Rare lipid study following stroke
American Heart Association/American Stroke Association guidelines recommend intense statin therapy after an atherothrombotic stroke “but no target level is given to the practitioners,” Dr. Amarenco said. “In reality, most patients receive a reduced dose of statin.”
For example, despite 70% of patients receiving a statin, the average LDL cholesterol level was 92 mg/dL in a real-world registry.
The TST trial is the first major study to evaluate treating to target LDL levels in the ischemic stroke population since the SPARCL trial in 2006. SPARCL was the first randomized, controlled clinical trial to evaluate whether daily statin therapy could reduce the risk of stroke in patients who had suffered a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
SPARCL demonstrated a 16% risk reduction with atorvastatin 80 mg daily versus placebo, and further risk reduction of 33% among those with carotid stenosis, over 5 years. There was some concern about safety for a time; post-hoc analysis showed what appeared to be an increased risk for intracranial hemorrhage with statin treatment. Subsequent analyses seemed to suggest the finding may have been a chance one, however.
For the TST study, Dr. Amarenco and colleagues enrolled participants between March 2010 and December 2018 at one of 61 centers in France. In 2015, the study expanded to include 16 sites in South Korea.
Investigators evaluated participants after an ischemic stroke or a TIA with evidence of atherosclerosis. Blood pressure, smoking cessation, and diabetes were well controlled, he said.
Dr. Amarenco and colleagues randomly assigned 1,430 participants to the low–LDL cholesterol target group, less than 70 mg/dL, and another 1,430 to a high-LDL group with a target of 100 mg/dL.
Assessments were every 6 months and up to 1 year after the last patient joined the study.
Treatment with any available statin on the market was allowed. Ezetimibe could be added on top of statin therapy as necessary. A total of 55% were statin naive at study entry.
Study stopped early
The trial was stopped in May 2019 after allocated funds ran out. At this point, researchers had 277 events to analyze, although their initial goal was to reach 385.
The primary endpoint of this event-driven trial was a composite of nonfatal stroke, nonfatal MI, and unstable angina followed by urgent coronary revascularization; TIA followed by urgent carotid revascularization; or cardiovascular death, including sudden deaths.
The endpoint was experienced by 8.5% of participants in the lower-target group versus 10.9% of those in the higher-target group. This translated to a 22% relative risk reduction (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.68-0.98; P =.04).
A total of 86% of participants had an ischemic stroke confirmed by brain MRI or CT scan. In this group, the relative risk reduction was 33% – “meaning that we could avoid one-third of recurrent major vascular events,” Dr. Amarenco said.
Furthermore, targeting the lower LDL levels was associated with a relative risk reduction of 40% among those with diabetes.
Secondary outcomes not significant
The investigators used hierarchical testing to compare two outcomes at a time in a prespecified order. They planned to continue this strategy until a comparison emerged as nonsignificant.
This occurred right away when their first composite secondary endpoint comparison between nonfatal MI and urgent revascularization was found to be not significantly different between groups (P = .12).
The early ending “weakened the results of the trial, and the results should be taken with caution because of that,” Dr. Amarenco said.
In addition, the number of hemorrhagic strokes did not differ significantly between groups. There were 18 of these events in the lower-target group and 13 in the higher-target cohort.
That numerical increase in intracranial hemorrhage was “driven by the Korean patients. … and that is something we will report soon,” Dr. Amarenco said.
Interestingly, the researchers also evaluated how much time participants spent within the target LDL cholesterol range, averaged by study site. They found that 53% of the lower–LDL target group, for example, was in the therapeutic range on average during the study.
When Dr. Amarenco and colleagues looked at participants who managed to spend 50%-100% in the target range, the relative risk reduction was 36%.
“So we can hypothesize that, if we had used a more potent drug like PCSK9 inhibitors to be closer to 100% in the therapeutic range, we may have had a greater effect size,” Dr. Amarenco said.
“Our results suggest that LDL cholesterol is causally related to atherosclerosis and confirm that the lower the LDL cholesterol the better,” Dr. Amarenco said.
“Future trials should explore the efficacy and safety of lowering LDL cholesterol to very low levels such as less than 55 mg/dL or even 30 mg/dL (as obtained in the FOURIER trial) by using PCSK9 inhibitors or equivalent in patients with an ischemic stroke due to atherosclerotic disease,” Dr. Amarenco said.
‘Practice-confirming’ findings
The findings are also in line with secondary analyses of the WASID (Neurology. 1995 Aug;45[8]:1488-93) and SAMMPRIS trials, which should dispel some concerns that persist about taking LDL to such low levels that it increases risk of intracerebral hemorrhage, Dr. Amarenco noted.
However, TST, he said, didn’t provide clear answers on what specific subgroups of patients with a stroke history would benefit from aggressive lipid lowering.
“What is stroke without atherosclerotic disease?” he said. “Some people say small-vessel disease is also a form of atherosclerosis, and most patients with atrial fibrillation, which is increasingly recognized as a cause of stroke, are also going to have atherosclerosis of the heart as well as the brain and blood vessels.
“Many, many stroke patients will fall into this category,” Dr. Elkind said, “and the question is, should they be treated more aggressively with lipid lowering?”
“The results of this study fit pretty nicely into the rubric of the AHA cholesterol guidelines,” said Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, chairman, department of preventive medicine at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, and chair of the AHA’s 2019 Council on Scientific Sessions Programming. Dr. Lloyd-Jones was also a member of the guideline committee.
Stroke patients are not “garden variety coronary patients,” he said. “The concern about intracerebral hemorrhage continues to be something that we wonder about: Should we be driving our stroke patients as low as our coronary patients? I think these data will certainly help us.”
Consideration for future guidelines
The study would have been more helpful if it provided more detail about the treatment regimens used, Jennifer Robinson, MD, director of the prevention intervention center, department of epidemiology, University of Iowa, said in an interview.
“What was the dose intensity of statins the patients were on?” Dr. Robinson said. “Part of our struggle has been to convince people to use high-intensity statins – get the maximum from statins that are generic now and cost saving in even very low-risk primary prevention patients.”
She said that a third of patients in TST also took ezetimibe with the statin “makes sense” because of its generic status.
Nonetheless, Dr. Robinson said, TST adds to the evidence that LDL of 100 mg/dL is not good enough, that high-intensity statin therapy is superior to a moderate regimen and that adding a nonstatin – ezetimibe in TST – can derive added benefit.
The TST findings may give guideline writers direction going forward, she said. “We really need to start thinking about the potential for net benefit from added therapy, whether it’s from intensifying LDL lowering, adding icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), which seems to have remarkable benefits, or SGLT2 inhibitor,” she said.
“There are a lot of options,” Dr. Robinson said. “We need to have an outlook beyond just treating to target with what really is the best maximized accepted therapy.”
TST was funded primarily by French Government, but also with grants from Pfizer, Astra Zeneca and Merck. Dr. Amarenco disclosed that he is a consultant or advisor to Modest, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Amgen; receives honoraria from Modest, Amgen, Kowa, Shing Poon, Kowa, Bayer, GSK, Fibrogen, and AstraZeneca. He also receives research grants from Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, Sanofi, BMS, Merck, Boston Scientific, and the French Government.
This article also appears on Medscape.com.
SOURCE: Amarenco P. ACC 2019, Late Breaking Science 6 session.
PHILADELPHIA – Treating patients to a lower LDL target after an ischemic stroke of atherosclerotic origin resulted in fewer recurrent strokes or major cardiovascular events, compared with a higher LDL goal, even though the international trial was stopped early because of lack of funding.
“In the Treat Stroke to Target [TST] trial we showed that the group of patients with an atherosclerotic stroke achieving an LDL cholesterol of less than 70 mg/dL had 22% less recurrent ischemic stroke or other major vascular events than the group achieving a LDL cholesterol between 90 and 110 mg/dL,” lead author Pierre Amarenco, MD, chairman of the department of neurology and the stroke center at Bichat Hospital in Paris, said in an interview.
“We avoided more than one in recurrence in five,” he added.
The findings of the investigator-initiated trial were reported during a late-breaking research session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions and simultaneously published online Nov. 18 in the New England Journal of Medicine (doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910355).
Discussant Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, president-elect of the American Heart Association, called the TST findings “practice confirming” of a strategy many cardiologists already follow for stroke patients.
“The TST study is only the second trial that was done in neurology for stroke prevention using statins and lipid-lowering therapy, and that’s what makes it a hopeful and real advance,” he said in an interview.
To achieve the LDL-lowering goal, two-thirds of patients received a high-dose statin therapy while the remainder received both high-dose statin and ezetimibe (Zetia, Merck). There were no significant increases in intracranial hemorrhage observed between lower- and higher-target groups.
“Now guidelines should move to recommending a target LDL cholesterol of less than 70 mg/dL in all patients with a proven ischemic stroke of atherosclerotic origin,” said Dr. Amarenco, who is also a professor of neurology at Denis Diderot Paris University.
Rare lipid study following stroke
American Heart Association/American Stroke Association guidelines recommend intense statin therapy after an atherothrombotic stroke “but no target level is given to the practitioners,” Dr. Amarenco said. “In reality, most patients receive a reduced dose of statin.”
For example, despite 70% of patients receiving a statin, the average LDL cholesterol level was 92 mg/dL in a real-world registry.
The TST trial is the first major study to evaluate treating to target LDL levels in the ischemic stroke population since the SPARCL trial in 2006. SPARCL was the first randomized, controlled clinical trial to evaluate whether daily statin therapy could reduce the risk of stroke in patients who had suffered a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
SPARCL demonstrated a 16% risk reduction with atorvastatin 80 mg daily versus placebo, and further risk reduction of 33% among those with carotid stenosis, over 5 years. There was some concern about safety for a time; post-hoc analysis showed what appeared to be an increased risk for intracranial hemorrhage with statin treatment. Subsequent analyses seemed to suggest the finding may have been a chance one, however.
For the TST study, Dr. Amarenco and colleagues enrolled participants between March 2010 and December 2018 at one of 61 centers in France. In 2015, the study expanded to include 16 sites in South Korea.
Investigators evaluated participants after an ischemic stroke or a TIA with evidence of atherosclerosis. Blood pressure, smoking cessation, and diabetes were well controlled, he said.
Dr. Amarenco and colleagues randomly assigned 1,430 participants to the low–LDL cholesterol target group, less than 70 mg/dL, and another 1,430 to a high-LDL group with a target of 100 mg/dL.
Assessments were every 6 months and up to 1 year after the last patient joined the study.
Treatment with any available statin on the market was allowed. Ezetimibe could be added on top of statin therapy as necessary. A total of 55% were statin naive at study entry.
Study stopped early
The trial was stopped in May 2019 after allocated funds ran out. At this point, researchers had 277 events to analyze, although their initial goal was to reach 385.
The primary endpoint of this event-driven trial was a composite of nonfatal stroke, nonfatal MI, and unstable angina followed by urgent coronary revascularization; TIA followed by urgent carotid revascularization; or cardiovascular death, including sudden deaths.
The endpoint was experienced by 8.5% of participants in the lower-target group versus 10.9% of those in the higher-target group. This translated to a 22% relative risk reduction (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.68-0.98; P =.04).
A total of 86% of participants had an ischemic stroke confirmed by brain MRI or CT scan. In this group, the relative risk reduction was 33% – “meaning that we could avoid one-third of recurrent major vascular events,” Dr. Amarenco said.
Furthermore, targeting the lower LDL levels was associated with a relative risk reduction of 40% among those with diabetes.
Secondary outcomes not significant
The investigators used hierarchical testing to compare two outcomes at a time in a prespecified order. They planned to continue this strategy until a comparison emerged as nonsignificant.
This occurred right away when their first composite secondary endpoint comparison between nonfatal MI and urgent revascularization was found to be not significantly different between groups (P = .12).
The early ending “weakened the results of the trial, and the results should be taken with caution because of that,” Dr. Amarenco said.
In addition, the number of hemorrhagic strokes did not differ significantly between groups. There were 18 of these events in the lower-target group and 13 in the higher-target cohort.
That numerical increase in intracranial hemorrhage was “driven by the Korean patients. … and that is something we will report soon,” Dr. Amarenco said.
Interestingly, the researchers also evaluated how much time participants spent within the target LDL cholesterol range, averaged by study site. They found that 53% of the lower–LDL target group, for example, was in the therapeutic range on average during the study.
When Dr. Amarenco and colleagues looked at participants who managed to spend 50%-100% in the target range, the relative risk reduction was 36%.
“So we can hypothesize that, if we had used a more potent drug like PCSK9 inhibitors to be closer to 100% in the therapeutic range, we may have had a greater effect size,” Dr. Amarenco said.
“Our results suggest that LDL cholesterol is causally related to atherosclerosis and confirm that the lower the LDL cholesterol the better,” Dr. Amarenco said.
“Future trials should explore the efficacy and safety of lowering LDL cholesterol to very low levels such as less than 55 mg/dL or even 30 mg/dL (as obtained in the FOURIER trial) by using PCSK9 inhibitors or equivalent in patients with an ischemic stroke due to atherosclerotic disease,” Dr. Amarenco said.
‘Practice-confirming’ findings
The findings are also in line with secondary analyses of the WASID (Neurology. 1995 Aug;45[8]:1488-93) and SAMMPRIS trials, which should dispel some concerns that persist about taking LDL to such low levels that it increases risk of intracerebral hemorrhage, Dr. Amarenco noted.
However, TST, he said, didn’t provide clear answers on what specific subgroups of patients with a stroke history would benefit from aggressive lipid lowering.
“What is stroke without atherosclerotic disease?” he said. “Some people say small-vessel disease is also a form of atherosclerosis, and most patients with atrial fibrillation, which is increasingly recognized as a cause of stroke, are also going to have atherosclerosis of the heart as well as the brain and blood vessels.
“Many, many stroke patients will fall into this category,” Dr. Elkind said, “and the question is, should they be treated more aggressively with lipid lowering?”
“The results of this study fit pretty nicely into the rubric of the AHA cholesterol guidelines,” said Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, chairman, department of preventive medicine at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, and chair of the AHA’s 2019 Council on Scientific Sessions Programming. Dr. Lloyd-Jones was also a member of the guideline committee.
Stroke patients are not “garden variety coronary patients,” he said. “The concern about intracerebral hemorrhage continues to be something that we wonder about: Should we be driving our stroke patients as low as our coronary patients? I think these data will certainly help us.”
Consideration for future guidelines
The study would have been more helpful if it provided more detail about the treatment regimens used, Jennifer Robinson, MD, director of the prevention intervention center, department of epidemiology, University of Iowa, said in an interview.
“What was the dose intensity of statins the patients were on?” Dr. Robinson said. “Part of our struggle has been to convince people to use high-intensity statins – get the maximum from statins that are generic now and cost saving in even very low-risk primary prevention patients.”
She said that a third of patients in TST also took ezetimibe with the statin “makes sense” because of its generic status.
Nonetheless, Dr. Robinson said, TST adds to the evidence that LDL of 100 mg/dL is not good enough, that high-intensity statin therapy is superior to a moderate regimen and that adding a nonstatin – ezetimibe in TST – can derive added benefit.
The TST findings may give guideline writers direction going forward, she said. “We really need to start thinking about the potential for net benefit from added therapy, whether it’s from intensifying LDL lowering, adding icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), which seems to have remarkable benefits, or SGLT2 inhibitor,” she said.
“There are a lot of options,” Dr. Robinson said. “We need to have an outlook beyond just treating to target with what really is the best maximized accepted therapy.”
TST was funded primarily by French Government, but also with grants from Pfizer, Astra Zeneca and Merck. Dr. Amarenco disclosed that he is a consultant or advisor to Modest, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Amgen; receives honoraria from Modest, Amgen, Kowa, Shing Poon, Kowa, Bayer, GSK, Fibrogen, and AstraZeneca. He also receives research grants from Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, Sanofi, BMS, Merck, Boston Scientific, and the French Government.
This article also appears on Medscape.com.
SOURCE: Amarenco P. ACC 2019, Late Breaking Science 6 session.
PHILADELPHIA – Treating patients to a lower LDL target after an ischemic stroke of atherosclerotic origin resulted in fewer recurrent strokes or major cardiovascular events, compared with a higher LDL goal, even though the international trial was stopped early because of lack of funding.
“In the Treat Stroke to Target [TST] trial we showed that the group of patients with an atherosclerotic stroke achieving an LDL cholesterol of less than 70 mg/dL had 22% less recurrent ischemic stroke or other major vascular events than the group achieving a LDL cholesterol between 90 and 110 mg/dL,” lead author Pierre Amarenco, MD, chairman of the department of neurology and the stroke center at Bichat Hospital in Paris, said in an interview.
“We avoided more than one in recurrence in five,” he added.
The findings of the investigator-initiated trial were reported during a late-breaking research session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions and simultaneously published online Nov. 18 in the New England Journal of Medicine (doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910355).
Discussant Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, president-elect of the American Heart Association, called the TST findings “practice confirming” of a strategy many cardiologists already follow for stroke patients.
“The TST study is only the second trial that was done in neurology for stroke prevention using statins and lipid-lowering therapy, and that’s what makes it a hopeful and real advance,” he said in an interview.
To achieve the LDL-lowering goal, two-thirds of patients received a high-dose statin therapy while the remainder received both high-dose statin and ezetimibe (Zetia, Merck). There were no significant increases in intracranial hemorrhage observed between lower- and higher-target groups.
“Now guidelines should move to recommending a target LDL cholesterol of less than 70 mg/dL in all patients with a proven ischemic stroke of atherosclerotic origin,” said Dr. Amarenco, who is also a professor of neurology at Denis Diderot Paris University.
Rare lipid study following stroke
American Heart Association/American Stroke Association guidelines recommend intense statin therapy after an atherothrombotic stroke “but no target level is given to the practitioners,” Dr. Amarenco said. “In reality, most patients receive a reduced dose of statin.”
For example, despite 70% of patients receiving a statin, the average LDL cholesterol level was 92 mg/dL in a real-world registry.
The TST trial is the first major study to evaluate treating to target LDL levels in the ischemic stroke population since the SPARCL trial in 2006. SPARCL was the first randomized, controlled clinical trial to evaluate whether daily statin therapy could reduce the risk of stroke in patients who had suffered a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
SPARCL demonstrated a 16% risk reduction with atorvastatin 80 mg daily versus placebo, and further risk reduction of 33% among those with carotid stenosis, over 5 years. There was some concern about safety for a time; post-hoc analysis showed what appeared to be an increased risk for intracranial hemorrhage with statin treatment. Subsequent analyses seemed to suggest the finding may have been a chance one, however.
For the TST study, Dr. Amarenco and colleagues enrolled participants between March 2010 and December 2018 at one of 61 centers in France. In 2015, the study expanded to include 16 sites in South Korea.
Investigators evaluated participants after an ischemic stroke or a TIA with evidence of atherosclerosis. Blood pressure, smoking cessation, and diabetes were well controlled, he said.
Dr. Amarenco and colleagues randomly assigned 1,430 participants to the low–LDL cholesterol target group, less than 70 mg/dL, and another 1,430 to a high-LDL group with a target of 100 mg/dL.
Assessments were every 6 months and up to 1 year after the last patient joined the study.
Treatment with any available statin on the market was allowed. Ezetimibe could be added on top of statin therapy as necessary. A total of 55% were statin naive at study entry.
Study stopped early
The trial was stopped in May 2019 after allocated funds ran out. At this point, researchers had 277 events to analyze, although their initial goal was to reach 385.
The primary endpoint of this event-driven trial was a composite of nonfatal stroke, nonfatal MI, and unstable angina followed by urgent coronary revascularization; TIA followed by urgent carotid revascularization; or cardiovascular death, including sudden deaths.
The endpoint was experienced by 8.5% of participants in the lower-target group versus 10.9% of those in the higher-target group. This translated to a 22% relative risk reduction (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.68-0.98; P =.04).
A total of 86% of participants had an ischemic stroke confirmed by brain MRI or CT scan. In this group, the relative risk reduction was 33% – “meaning that we could avoid one-third of recurrent major vascular events,” Dr. Amarenco said.
Furthermore, targeting the lower LDL levels was associated with a relative risk reduction of 40% among those with diabetes.
Secondary outcomes not significant
The investigators used hierarchical testing to compare two outcomes at a time in a prespecified order. They planned to continue this strategy until a comparison emerged as nonsignificant.
This occurred right away when their first composite secondary endpoint comparison between nonfatal MI and urgent revascularization was found to be not significantly different between groups (P = .12).
The early ending “weakened the results of the trial, and the results should be taken with caution because of that,” Dr. Amarenco said.
In addition, the number of hemorrhagic strokes did not differ significantly between groups. There were 18 of these events in the lower-target group and 13 in the higher-target cohort.
That numerical increase in intracranial hemorrhage was “driven by the Korean patients. … and that is something we will report soon,” Dr. Amarenco said.
Interestingly, the researchers also evaluated how much time participants spent within the target LDL cholesterol range, averaged by study site. They found that 53% of the lower–LDL target group, for example, was in the therapeutic range on average during the study.
When Dr. Amarenco and colleagues looked at participants who managed to spend 50%-100% in the target range, the relative risk reduction was 36%.
“So we can hypothesize that, if we had used a more potent drug like PCSK9 inhibitors to be closer to 100% in the therapeutic range, we may have had a greater effect size,” Dr. Amarenco said.
“Our results suggest that LDL cholesterol is causally related to atherosclerosis and confirm that the lower the LDL cholesterol the better,” Dr. Amarenco said.
“Future trials should explore the efficacy and safety of lowering LDL cholesterol to very low levels such as less than 55 mg/dL or even 30 mg/dL (as obtained in the FOURIER trial) by using PCSK9 inhibitors or equivalent in patients with an ischemic stroke due to atherosclerotic disease,” Dr. Amarenco said.
‘Practice-confirming’ findings
The findings are also in line with secondary analyses of the WASID (Neurology. 1995 Aug;45[8]:1488-93) and SAMMPRIS trials, which should dispel some concerns that persist about taking LDL to such low levels that it increases risk of intracerebral hemorrhage, Dr. Amarenco noted.
However, TST, he said, didn’t provide clear answers on what specific subgroups of patients with a stroke history would benefit from aggressive lipid lowering.
“What is stroke without atherosclerotic disease?” he said. “Some people say small-vessel disease is also a form of atherosclerosis, and most patients with atrial fibrillation, which is increasingly recognized as a cause of stroke, are also going to have atherosclerosis of the heart as well as the brain and blood vessels.
“Many, many stroke patients will fall into this category,” Dr. Elkind said, “and the question is, should they be treated more aggressively with lipid lowering?”
“The results of this study fit pretty nicely into the rubric of the AHA cholesterol guidelines,” said Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, chairman, department of preventive medicine at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, and chair of the AHA’s 2019 Council on Scientific Sessions Programming. Dr. Lloyd-Jones was also a member of the guideline committee.
Stroke patients are not “garden variety coronary patients,” he said. “The concern about intracerebral hemorrhage continues to be something that we wonder about: Should we be driving our stroke patients as low as our coronary patients? I think these data will certainly help us.”
Consideration for future guidelines
The study would have been more helpful if it provided more detail about the treatment regimens used, Jennifer Robinson, MD, director of the prevention intervention center, department of epidemiology, University of Iowa, said in an interview.
“What was the dose intensity of statins the patients were on?” Dr. Robinson said. “Part of our struggle has been to convince people to use high-intensity statins – get the maximum from statins that are generic now and cost saving in even very low-risk primary prevention patients.”
She said that a third of patients in TST also took ezetimibe with the statin “makes sense” because of its generic status.
Nonetheless, Dr. Robinson said, TST adds to the evidence that LDL of 100 mg/dL is not good enough, that high-intensity statin therapy is superior to a moderate regimen and that adding a nonstatin – ezetimibe in TST – can derive added benefit.
The TST findings may give guideline writers direction going forward, she said. “We really need to start thinking about the potential for net benefit from added therapy, whether it’s from intensifying LDL lowering, adding icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), which seems to have remarkable benefits, or SGLT2 inhibitor,” she said.
“There are a lot of options,” Dr. Robinson said. “We need to have an outlook beyond just treating to target with what really is the best maximized accepted therapy.”
TST was funded primarily by French Government, but also with grants from Pfizer, Astra Zeneca and Merck. Dr. Amarenco disclosed that he is a consultant or advisor to Modest, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Amgen; receives honoraria from Modest, Amgen, Kowa, Shing Poon, Kowa, Bayer, GSK, Fibrogen, and AstraZeneca. He also receives research grants from Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, Sanofi, BMS, Merck, Boston Scientific, and the French Government.
This article also appears on Medscape.com.
SOURCE: Amarenco P. ACC 2019, Late Breaking Science 6 session.
REPORTING FROM AHA 2019
PASI responses with biologics similar among white, nonwhite individuals, study finds
MIAMI – Skin clearance rates among people with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis treated with brodalumab were superior to clearance rates among those treated with ustekinumab in a study that also provided comparisons between white and nonwhite patients.
In the study, presented in a poster at the 2018 Orlando Dermatology Aesthetic and Clinical Conference, there were no significant difference in overall efficacy, safety, or health-related quality of life outcomes between white and nonwhite patients treated with either biologic.
Additional analyses specific to patients with skin of color can be beneficial, Amy McMichael, MD, one of the investigators, said in an interview. “Patients with skin of color experience differences in psoriasis-related symptoms,” noted Dr. McMichael, chair of dermatology at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center in Winston-Salem, N.C. “Greater degrees of skin involvement have been shown in African-American patients, as have differences in erythema, scaling, dyspigmentation, and plaque thickness.”
She and her colleagues evaluated 1,849 participants in phase 3 brodalumab clinical trials, which included ustekinumab-treated patients as a comparison group. Approximately 10% of the AMAGINE-2 and AMAGINE-3 study populations were skin of color participants. The results reported at the meeting were from their ad hoc study of 12-week induction findings from the 52-week clinical trials.
At week 12, 70% of white and 63% of nonwhite participants treated with ustekinumab achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75. At the same time, 86% of white and 88% of nonwhite patients treated with brodalumab achieved the same outcome. Similarly, PASI 90 and PASI 100 scores did not differ significantly between the 1,667 white and 182 skin of color participants.
The two biologics act on different aspects of the molecular pathway involved in psoriasis. Brodalumab (Siliq) specifically blocks the interleukin-17 receptor, whereas other biologics used to treat psoriasis, including ustekinumab (Stelara), an IL-12 and -23 antagonist, target upstream molecules in the inflammatory pathway. Dr. McMichael said, “The superior skin clearance rates seen in patients treated with brodalumab may be due to its target being a receptor as opposed to a ligand.”
Treatment-emergent adverse event rates were similar between the white and nonwhite patients. Treatment-emergent adverse events were reported in 58% and 57% of the white brodalumab and ustekinumab groups, respectively, and in 53% and 47% of the nonwhite brodalumab and ustekinumab groups, respectively. Serious adverse events occurred in 1.2% and 1.1% of the white brodalumab and ustekinumab cohorts, respectively, and in 1.7% and 0% of the nonwhite participants, respectively.
The investigators also assessed health-related quality of life and again found outcomes were similar between white and nonwhite participants. For example, among those treated with brodalumab, 80% of white and 78% of nonwhite patients achieved a score improvement of 5 or greater on the Dermatology Life Quality Index. Of those randomized to ustekinumab, 76% of white patients and 73% of nonwhite patients achieved the same outcome.
“We plan to perform a further analysis evaluating the Dr. McMichael said. Additionally, a population-based study to investigate treatment patterns in patients with psoriasis across racial and socioeconomic groups could also shed light on how patients with skin of color manage their psoriasis, she added.
Dr. McMichael’s disclosures include having been an investigator for Allergan, Incyte, and Samumed and a consultant to Aclaris, Galderma, IntraDerm, Johnson & Johnson, Merz, Pfizer, and Procter & Gamble.
SOURCE: McMichael A et al. ODAC 2018.
MIAMI – Skin clearance rates among people with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis treated with brodalumab were superior to clearance rates among those treated with ustekinumab in a study that also provided comparisons between white and nonwhite patients.
In the study, presented in a poster at the 2018 Orlando Dermatology Aesthetic and Clinical Conference, there were no significant difference in overall efficacy, safety, or health-related quality of life outcomes between white and nonwhite patients treated with either biologic.
Additional analyses specific to patients with skin of color can be beneficial, Amy McMichael, MD, one of the investigators, said in an interview. “Patients with skin of color experience differences in psoriasis-related symptoms,” noted Dr. McMichael, chair of dermatology at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center in Winston-Salem, N.C. “Greater degrees of skin involvement have been shown in African-American patients, as have differences in erythema, scaling, dyspigmentation, and plaque thickness.”
She and her colleagues evaluated 1,849 participants in phase 3 brodalumab clinical trials, which included ustekinumab-treated patients as a comparison group. Approximately 10% of the AMAGINE-2 and AMAGINE-3 study populations were skin of color participants. The results reported at the meeting were from their ad hoc study of 12-week induction findings from the 52-week clinical trials.
At week 12, 70% of white and 63% of nonwhite participants treated with ustekinumab achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75. At the same time, 86% of white and 88% of nonwhite patients treated with brodalumab achieved the same outcome. Similarly, PASI 90 and PASI 100 scores did not differ significantly between the 1,667 white and 182 skin of color participants.
The two biologics act on different aspects of the molecular pathway involved in psoriasis. Brodalumab (Siliq) specifically blocks the interleukin-17 receptor, whereas other biologics used to treat psoriasis, including ustekinumab (Stelara), an IL-12 and -23 antagonist, target upstream molecules in the inflammatory pathway. Dr. McMichael said, “The superior skin clearance rates seen in patients treated with brodalumab may be due to its target being a receptor as opposed to a ligand.”
Treatment-emergent adverse event rates were similar between the white and nonwhite patients. Treatment-emergent adverse events were reported in 58% and 57% of the white brodalumab and ustekinumab groups, respectively, and in 53% and 47% of the nonwhite brodalumab and ustekinumab groups, respectively. Serious adverse events occurred in 1.2% and 1.1% of the white brodalumab and ustekinumab cohorts, respectively, and in 1.7% and 0% of the nonwhite participants, respectively.
The investigators also assessed health-related quality of life and again found outcomes were similar between white and nonwhite participants. For example, among those treated with brodalumab, 80% of white and 78% of nonwhite patients achieved a score improvement of 5 or greater on the Dermatology Life Quality Index. Of those randomized to ustekinumab, 76% of white patients and 73% of nonwhite patients achieved the same outcome.
“We plan to perform a further analysis evaluating the Dr. McMichael said. Additionally, a population-based study to investigate treatment patterns in patients with psoriasis across racial and socioeconomic groups could also shed light on how patients with skin of color manage their psoriasis, she added.
Dr. McMichael’s disclosures include having been an investigator for Allergan, Incyte, and Samumed and a consultant to Aclaris, Galderma, IntraDerm, Johnson & Johnson, Merz, Pfizer, and Procter & Gamble.
SOURCE: McMichael A et al. ODAC 2018.
MIAMI – Skin clearance rates among people with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis treated with brodalumab were superior to clearance rates among those treated with ustekinumab in a study that also provided comparisons between white and nonwhite patients.
In the study, presented in a poster at the 2018 Orlando Dermatology Aesthetic and Clinical Conference, there were no significant difference in overall efficacy, safety, or health-related quality of life outcomes between white and nonwhite patients treated with either biologic.
Additional analyses specific to patients with skin of color can be beneficial, Amy McMichael, MD, one of the investigators, said in an interview. “Patients with skin of color experience differences in psoriasis-related symptoms,” noted Dr. McMichael, chair of dermatology at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center in Winston-Salem, N.C. “Greater degrees of skin involvement have been shown in African-American patients, as have differences in erythema, scaling, dyspigmentation, and plaque thickness.”
She and her colleagues evaluated 1,849 participants in phase 3 brodalumab clinical trials, which included ustekinumab-treated patients as a comparison group. Approximately 10% of the AMAGINE-2 and AMAGINE-3 study populations were skin of color participants. The results reported at the meeting were from their ad hoc study of 12-week induction findings from the 52-week clinical trials.
At week 12, 70% of white and 63% of nonwhite participants treated with ustekinumab achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75. At the same time, 86% of white and 88% of nonwhite patients treated with brodalumab achieved the same outcome. Similarly, PASI 90 and PASI 100 scores did not differ significantly between the 1,667 white and 182 skin of color participants.
The two biologics act on different aspects of the molecular pathway involved in psoriasis. Brodalumab (Siliq) specifically blocks the interleukin-17 receptor, whereas other biologics used to treat psoriasis, including ustekinumab (Stelara), an IL-12 and -23 antagonist, target upstream molecules in the inflammatory pathway. Dr. McMichael said, “The superior skin clearance rates seen in patients treated with brodalumab may be due to its target being a receptor as opposed to a ligand.”
Treatment-emergent adverse event rates were similar between the white and nonwhite patients. Treatment-emergent adverse events were reported in 58% and 57% of the white brodalumab and ustekinumab groups, respectively, and in 53% and 47% of the nonwhite brodalumab and ustekinumab groups, respectively. Serious adverse events occurred in 1.2% and 1.1% of the white brodalumab and ustekinumab cohorts, respectively, and in 1.7% and 0% of the nonwhite participants, respectively.
The investigators also assessed health-related quality of life and again found outcomes were similar between white and nonwhite participants. For example, among those treated with brodalumab, 80% of white and 78% of nonwhite patients achieved a score improvement of 5 or greater on the Dermatology Life Quality Index. Of those randomized to ustekinumab, 76% of white patients and 73% of nonwhite patients achieved the same outcome.
“We plan to perform a further analysis evaluating the Dr. McMichael said. Additionally, a population-based study to investigate treatment patterns in patients with psoriasis across racial and socioeconomic groups could also shed light on how patients with skin of color manage their psoriasis, she added.
Dr. McMichael’s disclosures include having been an investigator for Allergan, Incyte, and Samumed and a consultant to Aclaris, Galderma, IntraDerm, Johnson & Johnson, Merz, Pfizer, and Procter & Gamble.
SOURCE: McMichael A et al. ODAC 2018.
REPORTING FROM ODAC 2018
Key clinical point: Responses to brodalumab and ustekinumab were comparable in nonwhite and white patients with psoriasis.
Major finding: At week 12, 70% of white and 63% of nonwhite participants treated with ustekinumab achieved PASI 75, a nonsignificant difference.
Study details: An ad hoc comparison of week 12 phase 3 study data in 1,849 patients including 182 patients with skin of color.
Disclosures: Dr. McMichael’s disclosures include having been an investigator for Allergan, Incyte, and Samumed; and a consultant to Aclaris, Galderma, IntraDerm, Johnson & Johnson, Merz, Pfizer, and Procter & Gamble.
Source: McMichael A et al. ODAC 2018.

