User login
Acquired Perforating Dermatosis in a Skin Graft
Case Report
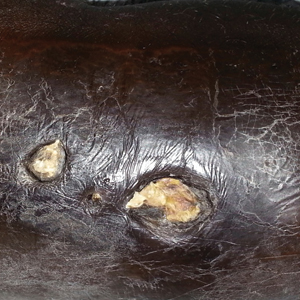
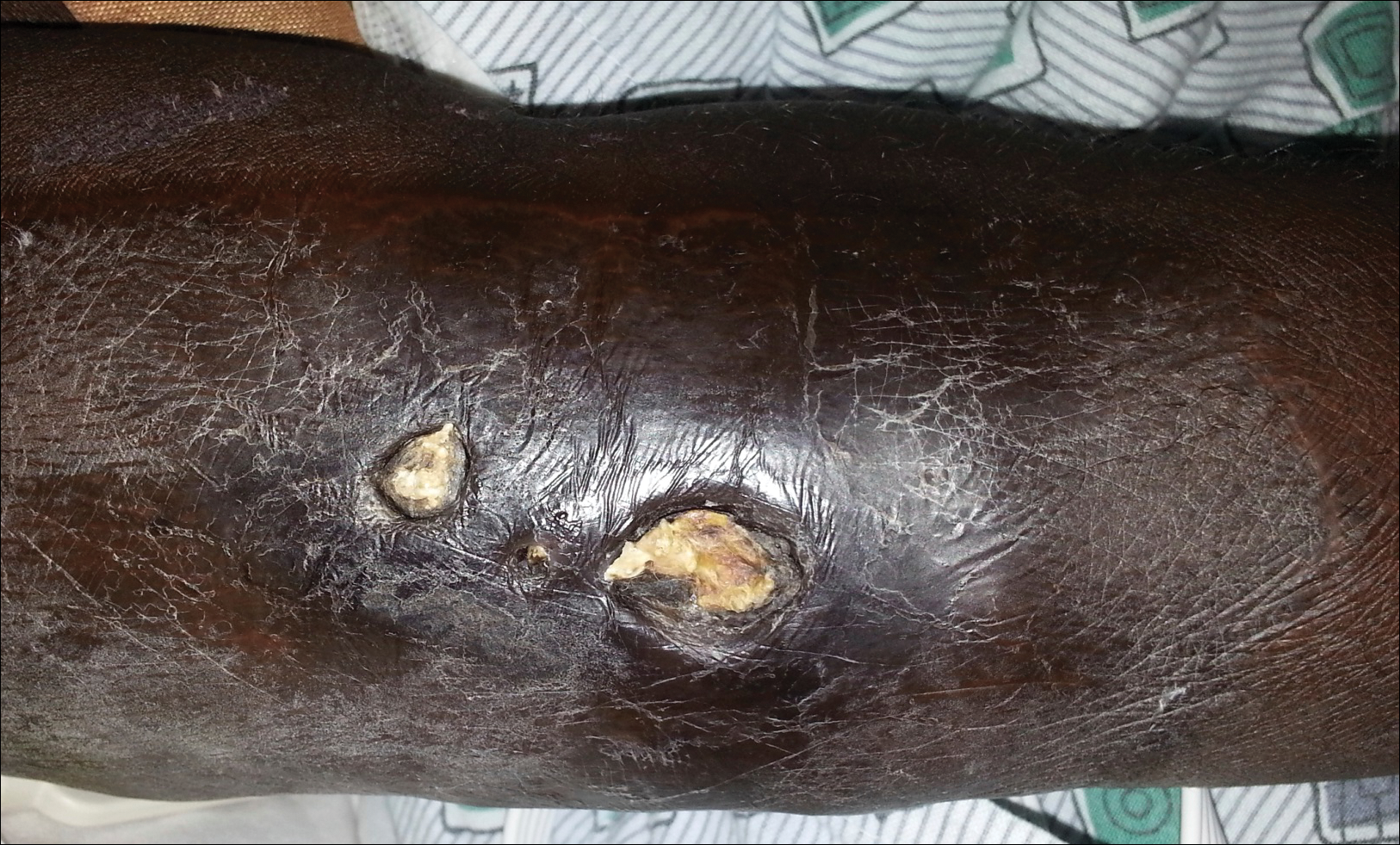
A 57-year-old black woman with a history of dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease, diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension, diastolic congestive heart failure, and chronic bronchitis was admitted to Howard University Hospital (Washington, DC) for acute chest pain and shortness of breath. During her hospital stay the dermatology team was consulted for evaluation of two 1.6-cm teardrop-shaped, yellow-white-chalky plaques noted in the center of an atrophic, hyperpigmented, shiny, contracted split-thickness skin graft (STSG) on the right posterior forearm (Figure 1). Twenty years prior, the patient received STSGs on the right and left forearm secondary to caustic burns. Two months before the current admission she noticed 2 adjacent teardrop-shaped white plaques within the center of the STSG on the right forearm. At a 3-month follow-up, she had developed more lesions within both graft sites of the bilateral forearm. There was no notable pruritus associated with the lesions.
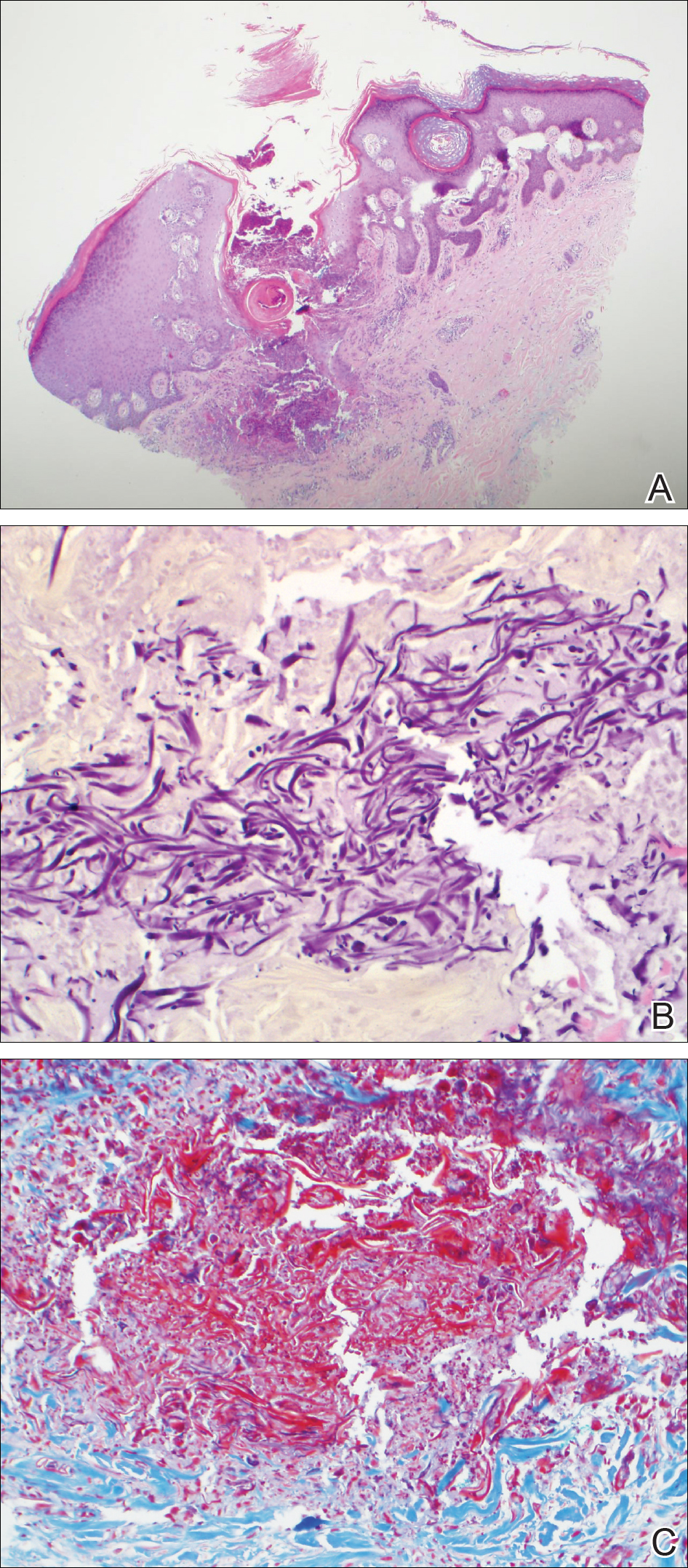
A 4-mm punch biopsy showed an orthokeratotic plug with basophilic inflammatory debris adjacent to acanthotic epidermis, necrotic basophilic debris at the superficial dermis with epidermal canals extending from the base of the lesion superiorly, and transepidermal elimination of elastic fibers (Figure 2A). A Verhoeff-van Gieson stain revealed the necrotic basophilic debris located in the superficial dermis admixed with a cluster of black wavy elastic fibers establishing the identity of the perforating substance (Figure 2B). Masson trichrome stain revealed loss of collagen structure within the aggregate of elastic fibers adjacent to the epidermis and no collagen within epidermal canals (Figure 2C). These histopathologic findings together with the clinical presentation were consistent with a diagnosis of acquired perforating dermatosis (APD).
Comment
Presentation
Acquired perforating dermatosis is a dermatologic condition characterized by multiple pruritic, dome-shaped papules and plaques with central keratotic plugs giving a craterlike appearance.1-4 A green-brown or black crust with an erythematous border typically surrounds the primary lesions.4 Acquired perforating dermatosis favors a distribution over the trunk, gluteal region, and the extensor surfaces of the upper and lower extremities. Palmoplantar, intertriginous, and mucous membrane regions typically are spared.4 Occasionally, APD may present as generalized nodules and papules. Our case consisting of lesions that were localized to STSGs on the forearms supports the typical distribution; however, the presentation of APD occurring within a skin graft is unique.
From an epidemiologic standpoint, APD is more likely to affect men than women (1.5:1 ratio). Additionally, APD’s affected age range is 29 to 96 years (mean, 56.8 years),5 which is consistent with our patient’s age. Acquired perforating dermatosis has no racial predilection, though there is a predominance among black patients with concomitant chronic renal failure, as seen in our patient.3
Pathogenesis
The etiology of APD remains unknown.6 Some believe that the uremic or calcium deposits on the skin of patients with chronic kidney disease may trigger chronic pruritus, leading to epithelial hyperplasia and the development of perforating lesions.1,3 A prominent theory in the literature is that superficial trauma, such as scratching, induces necrosis of tissue, facilitating transepidermal elimination of connective tissue components.7 The Köbner phenomenon, which can easily be induced by scratching the skin, supports this idea.8 Fujimoto et al9 suggested that scratching exposes keratinocytes to advanced glycation end product–modified extracellular matrix proteins, particularly types I and III collagen. This exposure leads to the terminal differentiation of keratinocytes with the advanced glycation end receptor (CD36) followed by the upward movement of keratinocytes with glycated collagen. Others postulate fibronectin, involved in epidermal cell signaling, locomotion, and differentiation, is an antigenic trigger because patients with DM and uremia have increased levels of fibronectin in the serum and at sites of perforating skin lesions.10
Diseases Associated With APD
Acquired perforating dermatosis is an umbrella term for perforating disease found in adults. It is associated with systemic diseases, such as DM and pruritus of renal failure.11 Our patient had both dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease and DM. Acquired perforating dermatosis is observed in 4.5% to 11% of patients on hemodialysis12,13; however, APD may occur prior to or in the absence of dialysis.3 Other examples of systemic conditions associated with APD include obstructive uropathy, chronic nephritis, anuria, and hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Koebnerization also may trigger lesions to manifest in a linear pattern after localized trauma to the skin.7 Acquired perforating dermatosis is associated with other types of trauma, such as healing herpes zoster, or following exposure to drugs, such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors, bevacizumab, telaprevir, sorafenib, sirolimus, and indinavir.14-16 Rarely, there have been associations with a history of insect bites, scabies, lymphoma, and hepatobiliary disease.1-3
Histopathology
Acquired perforating dermatosis is classified as a perforating disease, along with reactive perforating collagenosis, elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS), perforating folliculitis, and perforating calcific elastosis. Perforating diseases are histologically characterized by the transepidermal penetration and elimination of altered connective tissue and inflammatory cells.5 Each disease differs based on their clinical and histological characteristics.
Histologic sections of APD show a plug of crusting or hyperkeratosis with variable parakeratosis, acanthosis, and occasional dyskeratotic keratinocytes. In the dermis, aggregates of neutrophils, lymphocytes, macrophages, or multinucleated giant cells may be found.17 The histologic findings vary depending on the stage of evolution of the individual lesion. Early lesions show a concave depression with acanthosis, vacuolation of basal keratinocytes, and dermal inflammation.4 Additionally, transepidermal channels filled with keratin, pyknotic nuclear debris, inflammatory cells, elastin, or collagen can be noted.3 Over time, the elastic fibers, as detected by the Verhoeff-van Gieson stain, dissipate and the collagen acquires a basophilic staining. Adjacent to the channels, the basement membrane remains intact in early lesions but later shows discontinuities and electron-dense fibrinlike material.3 Occasionally, amorphous degenerated material within the perforations is the major histologic finding.11 Usually, the material cannot be clearly identified as collagen or elastin, but sometimes both are present.
In our case, we identified elastin as the perforating substance, which is less common than collagen, the typical perforating substance in APD. Elastin has occasionally been seen to serve as the only perforating substance from APD lesions among patients. Abe et al18 reported that the biopsy of a Japanese patient with keratotic follicular papules and serpiginous-arranged papules demonstrated elimination of atypical elastin fibers from the transepidermal channels. This patient was diagnosed with APD as well as EPS and perforating folliculitis based on the clinical presentation.18 Kim et al19 studied 30 Korean patients with APD. One had serpiginous hyperkeratotic plaques along the upper extremity and trunk that revealed transepidermal channels containing coarse elastic fibers and basophilic debris; however, due to the serpiginous morphology of lesions, both Abe et al18 and Kim et al19 favored a diagnosis of acquired EPS. Saray et al20 conducted a retrospective study of 22 Turkish patients with APD; 1 patient had a painful hyperkeratotic papule on the auricle that on histopathology showed degenerated elastin perforating through the keratotic plug, features similar to our case.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnoses include perforating diseases14,19 as well as other disorders that exhibit the Köbner phenomenon, such as psoriasis, lichen planus, and verruca vulgaris.21,22 Also, it is not uncommon for patients with APD to have coexisting folliculitis or prurigo nodularis.22
Treatment
Management is focused on treating the symptoms. For pruritus, sedating antihistamines and other antipruritic agents are efficacious.23 Topical, intra-lesional, or systemic corticosteroids and topical retinoids have shown variable resolution in APD lesions.24 Some case reports describe topical menthol, salicylic acid, sulfur, benzoyl peroxide, systemic antibiotics (eg, clindamycin, doxycycline), and allopurinol for elevated uric acid levels as effective treatment methods.6 Narrowband UVB phototherapy is beneficial for APD and renal disease.25,26 Renal transplantation has been curative for some patients with APD.27 Given that our patient’s lesions were asymptomatic, no treatment was offered at the time.
Conclusion
Our patient presented with APD localized exclusively to the site of a skin graft, and histologic examination identified elastin as the primary perforating substance. A medical history of DM and chronic kidney disease predisposes patients to APD. This case suggests that skin graft sites may be predisposed to the development of APD.
- Rodney IJ, Taylor CS, Cohen G. Derm Dx: what are these pruritic nodules? The Dermatologist. October 15, 2009. http://www.the-dermatologist.com/content/derm-dx-what-are-these-pruritic-nodules. Accessed September 18, 2018.
- Gagnon, AL, Desai T. Dermatological diseases in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Nephropathol. 2013;2:104-109.
- Kurban MS, Boueiz A, Kibbi AG. Cutaneous manifestations of chronic kidney disease. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:255-264.
- Wagner G, Sachse MM. Acquired reactive perforating dermatosis [published online May 29, 2013]. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:723-729; 723-730.
- Karpouzis A, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: current status. J Dermatol. 2010;37:585-592.
- Healy R, Cerio R, Hollingsworth A, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with pregnancy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:621-623.
- Cordova KB, Oberg TJ, Malik M, et al. Dermatologic conditions seen in end-stage renal disease. Semin Dial. 2009;22:45-55.
- Satchell AC, Crotty K, Lee S. Reactive perforating collagenosis: a condition that may be underdiagnosed. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:284-287.
- Fujimoto E, Kobayashi T, Fujimoto N, et al. AGE-modified collagens I and III induce keratinocyte terminal differentiation through AGE receptor CD36: epidermal-dermal interaction in acquired perforating dermatosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130:405-414.
- Bilezikci B, Sechkin D, Demirhan B. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure: a possible role for fibronectin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:230-232.
- Rapini RP, Herbert AA, Drucker CR. Acquired perforating dermatosis. evidence for combined transepidermal elimination of both collagen and elastic fibers. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:1074-1078.
- Hurwitz RM, Melton ME, Creech FT, et al. Perforating folliculitis in association with hemodialysis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1982;4:101-108.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Lübbe J, Sorg O, Malé PJ, et al. Sirolimus-induced inflammatory papules with acquired reactive perforating collagenosis [published online January 9, 2008]. Dermatology. 2008;216:239-242.
- Pernet C, Pageaux GP, Guillot B, et al. Telaprevir-induced acquired perforating dermatosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1371-1372.
- Severino-Freire M, Sibaud V, Tournier E, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with sorafenib therapy [published online September 11, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:328-330.
- Zelger B, Hintner H, Auböck J, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis. transepidermal elimination of DNA material and possible role of leukocytes in pathogenesis. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:695-700.
- Abe R, Murase S, Nomura Y, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis appearing as elastosis perforans serpiginosa and perforating folliculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008;33:653-654.
- Kim SW, Kim MS, Lee JH, et al. A clinicopathologic study of thirty cases of acquired perforating dermatosis in Korea. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:162-171.
- Saray Y, Seçkin D, Bilezikçi B. Acquired perforating dermatosis: clinicopathological features in twenty-two cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:679-688.
- Carter VH, Constantine VS. Kyrle’s disease. I. clinical findings in five cases and review of literature. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:624-632.
- Robinson-Bostom L, Digiovanna JJ. Cutaneous manifestations of end-stage renal disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:975-986.
- Hong SB, Park JH, Ihm CG, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure and diabetes mellitus. J Korean Med Sci. 2004;19:283-288.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Ohe S, Danno K, Sasaki H, et al. Treatment of acquired perforating dermatosis with narrowband ultraviolet B. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:892-894.
- Sezer E, Erkek E. Acquired perforating dermatosis successfully treated with photodynamic therapy. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2012;28:50-52.
- Saldanha LF, Gonick HC, Rodriguez HJ, et al. Silicon-related syndrome in dialysis patients. Nephron. 1997;77:48-56.
Case Report
A 57-year-old black woman with a history of dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease, diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension, diastolic congestive heart failure, and chronic bronchitis was admitted to Howard University Hospital (Washington, DC) for acute chest pain and shortness of breath. During her hospital stay the dermatology team was consulted for evaluation of two 1.6-cm teardrop-shaped, yellow-white-chalky plaques noted in the center of an atrophic, hyperpigmented, shiny, contracted split-thickness skin graft (STSG) on the right posterior forearm (Figure 1). Twenty years prior, the patient received STSGs on the right and left forearm secondary to caustic burns. Two months before the current admission she noticed 2 adjacent teardrop-shaped white plaques within the center of the STSG on the right forearm. At a 3-month follow-up, she had developed more lesions within both graft sites of the bilateral forearm. There was no notable pruritus associated with the lesions.

A 4-mm punch biopsy showed an orthokeratotic plug with basophilic inflammatory debris adjacent to acanthotic epidermis, necrotic basophilic debris at the superficial dermis with epidermal canals extending from the base of the lesion superiorly, and transepidermal elimination of elastic fibers (Figure 2A). A Verhoeff-van Gieson stain revealed the necrotic basophilic debris located in the superficial dermis admixed with a cluster of black wavy elastic fibers establishing the identity of the perforating substance (Figure 2B). Masson trichrome stain revealed loss of collagen structure within the aggregate of elastic fibers adjacent to the epidermis and no collagen within epidermal canals (Figure 2C). These histopathologic findings together with the clinical presentation were consistent with a diagnosis of acquired perforating dermatosis (APD).

Comment
Presentation
Acquired perforating dermatosis is a dermatologic condition characterized by multiple pruritic, dome-shaped papules and plaques with central keratotic plugs giving a craterlike appearance.1-4 A green-brown or black crust with an erythematous border typically surrounds the primary lesions.4 Acquired perforating dermatosis favors a distribution over the trunk, gluteal region, and the extensor surfaces of the upper and lower extremities. Palmoplantar, intertriginous, and mucous membrane regions typically are spared.4 Occasionally, APD may present as generalized nodules and papules. Our case consisting of lesions that were localized to STSGs on the forearms supports the typical distribution; however, the presentation of APD occurring within a skin graft is unique.
From an epidemiologic standpoint, APD is more likely to affect men than women (1.5:1 ratio). Additionally, APD’s affected age range is 29 to 96 years (mean, 56.8 years),5 which is consistent with our patient’s age. Acquired perforating dermatosis has no racial predilection, though there is a predominance among black patients with concomitant chronic renal failure, as seen in our patient.3
Pathogenesis
The etiology of APD remains unknown.6 Some believe that the uremic or calcium deposits on the skin of patients with chronic kidney disease may trigger chronic pruritus, leading to epithelial hyperplasia and the development of perforating lesions.1,3 A prominent theory in the literature is that superficial trauma, such as scratching, induces necrosis of tissue, facilitating transepidermal elimination of connective tissue components.7 The Köbner phenomenon, which can easily be induced by scratching the skin, supports this idea.8 Fujimoto et al9 suggested that scratching exposes keratinocytes to advanced glycation end product–modified extracellular matrix proteins, particularly types I and III collagen. This exposure leads to the terminal differentiation of keratinocytes with the advanced glycation end receptor (CD36) followed by the upward movement of keratinocytes with glycated collagen. Others postulate fibronectin, involved in epidermal cell signaling, locomotion, and differentiation, is an antigenic trigger because patients with DM and uremia have increased levels of fibronectin in the serum and at sites of perforating skin lesions.10
Diseases Associated With APD
Acquired perforating dermatosis is an umbrella term for perforating disease found in adults. It is associated with systemic diseases, such as DM and pruritus of renal failure.11 Our patient had both dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease and DM. Acquired perforating dermatosis is observed in 4.5% to 11% of patients on hemodialysis12,13; however, APD may occur prior to or in the absence of dialysis.3 Other examples of systemic conditions associated with APD include obstructive uropathy, chronic nephritis, anuria, and hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Koebnerization also may trigger lesions to manifest in a linear pattern after localized trauma to the skin.7 Acquired perforating dermatosis is associated with other types of trauma, such as healing herpes zoster, or following exposure to drugs, such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors, bevacizumab, telaprevir, sorafenib, sirolimus, and indinavir.14-16 Rarely, there have been associations with a history of insect bites, scabies, lymphoma, and hepatobiliary disease.1-3
Histopathology
Acquired perforating dermatosis is classified as a perforating disease, along with reactive perforating collagenosis, elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS), perforating folliculitis, and perforating calcific elastosis. Perforating diseases are histologically characterized by the transepidermal penetration and elimination of altered connective tissue and inflammatory cells.5 Each disease differs based on their clinical and histological characteristics.
Histologic sections of APD show a plug of crusting or hyperkeratosis with variable parakeratosis, acanthosis, and occasional dyskeratotic keratinocytes. In the dermis, aggregates of neutrophils, lymphocytes, macrophages, or multinucleated giant cells may be found.17 The histologic findings vary depending on the stage of evolution of the individual lesion. Early lesions show a concave depression with acanthosis, vacuolation of basal keratinocytes, and dermal inflammation.4 Additionally, transepidermal channels filled with keratin, pyknotic nuclear debris, inflammatory cells, elastin, or collagen can be noted.3 Over time, the elastic fibers, as detected by the Verhoeff-van Gieson stain, dissipate and the collagen acquires a basophilic staining. Adjacent to the channels, the basement membrane remains intact in early lesions but later shows discontinuities and electron-dense fibrinlike material.3 Occasionally, amorphous degenerated material within the perforations is the major histologic finding.11 Usually, the material cannot be clearly identified as collagen or elastin, but sometimes both are present.
In our case, we identified elastin as the perforating substance, which is less common than collagen, the typical perforating substance in APD. Elastin has occasionally been seen to serve as the only perforating substance from APD lesions among patients. Abe et al18 reported that the biopsy of a Japanese patient with keratotic follicular papules and serpiginous-arranged papules demonstrated elimination of atypical elastin fibers from the transepidermal channels. This patient was diagnosed with APD as well as EPS and perforating folliculitis based on the clinical presentation.18 Kim et al19 studied 30 Korean patients with APD. One had serpiginous hyperkeratotic plaques along the upper extremity and trunk that revealed transepidermal channels containing coarse elastic fibers and basophilic debris; however, due to the serpiginous morphology of lesions, both Abe et al18 and Kim et al19 favored a diagnosis of acquired EPS. Saray et al20 conducted a retrospective study of 22 Turkish patients with APD; 1 patient had a painful hyperkeratotic papule on the auricle that on histopathology showed degenerated elastin perforating through the keratotic plug, features similar to our case.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnoses include perforating diseases14,19 as well as other disorders that exhibit the Köbner phenomenon, such as psoriasis, lichen planus, and verruca vulgaris.21,22 Also, it is not uncommon for patients with APD to have coexisting folliculitis or prurigo nodularis.22
Treatment
Management is focused on treating the symptoms. For pruritus, sedating antihistamines and other antipruritic agents are efficacious.23 Topical, intra-lesional, or systemic corticosteroids and topical retinoids have shown variable resolution in APD lesions.24 Some case reports describe topical menthol, salicylic acid, sulfur, benzoyl peroxide, systemic antibiotics (eg, clindamycin, doxycycline), and allopurinol for elevated uric acid levels as effective treatment methods.6 Narrowband UVB phototherapy is beneficial for APD and renal disease.25,26 Renal transplantation has been curative for some patients with APD.27 Given that our patient’s lesions were asymptomatic, no treatment was offered at the time.
Conclusion
Our patient presented with APD localized exclusively to the site of a skin graft, and histologic examination identified elastin as the primary perforating substance. A medical history of DM and chronic kidney disease predisposes patients to APD. This case suggests that skin graft sites may be predisposed to the development of APD.
Case Report
A 57-year-old black woman with a history of dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease, diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension, diastolic congestive heart failure, and chronic bronchitis was admitted to Howard University Hospital (Washington, DC) for acute chest pain and shortness of breath. During her hospital stay the dermatology team was consulted for evaluation of two 1.6-cm teardrop-shaped, yellow-white-chalky plaques noted in the center of an atrophic, hyperpigmented, shiny, contracted split-thickness skin graft (STSG) on the right posterior forearm (Figure 1). Twenty years prior, the patient received STSGs on the right and left forearm secondary to caustic burns. Two months before the current admission she noticed 2 adjacent teardrop-shaped white plaques within the center of the STSG on the right forearm. At a 3-month follow-up, she had developed more lesions within both graft sites of the bilateral forearm. There was no notable pruritus associated with the lesions.

A 4-mm punch biopsy showed an orthokeratotic plug with basophilic inflammatory debris adjacent to acanthotic epidermis, necrotic basophilic debris at the superficial dermis with epidermal canals extending from the base of the lesion superiorly, and transepidermal elimination of elastic fibers (Figure 2A). A Verhoeff-van Gieson stain revealed the necrotic basophilic debris located in the superficial dermis admixed with a cluster of black wavy elastic fibers establishing the identity of the perforating substance (Figure 2B). Masson trichrome stain revealed loss of collagen structure within the aggregate of elastic fibers adjacent to the epidermis and no collagen within epidermal canals (Figure 2C). These histopathologic findings together with the clinical presentation were consistent with a diagnosis of acquired perforating dermatosis (APD).

Comment
Presentation
Acquired perforating dermatosis is a dermatologic condition characterized by multiple pruritic, dome-shaped papules and plaques with central keratotic plugs giving a craterlike appearance.1-4 A green-brown or black crust with an erythematous border typically surrounds the primary lesions.4 Acquired perforating dermatosis favors a distribution over the trunk, gluteal region, and the extensor surfaces of the upper and lower extremities. Palmoplantar, intertriginous, and mucous membrane regions typically are spared.4 Occasionally, APD may present as generalized nodules and papules. Our case consisting of lesions that were localized to STSGs on the forearms supports the typical distribution; however, the presentation of APD occurring within a skin graft is unique.
From an epidemiologic standpoint, APD is more likely to affect men than women (1.5:1 ratio). Additionally, APD’s affected age range is 29 to 96 years (mean, 56.8 years),5 which is consistent with our patient’s age. Acquired perforating dermatosis has no racial predilection, though there is a predominance among black patients with concomitant chronic renal failure, as seen in our patient.3
Pathogenesis
The etiology of APD remains unknown.6 Some believe that the uremic or calcium deposits on the skin of patients with chronic kidney disease may trigger chronic pruritus, leading to epithelial hyperplasia and the development of perforating lesions.1,3 A prominent theory in the literature is that superficial trauma, such as scratching, induces necrosis of tissue, facilitating transepidermal elimination of connective tissue components.7 The Köbner phenomenon, which can easily be induced by scratching the skin, supports this idea.8 Fujimoto et al9 suggested that scratching exposes keratinocytes to advanced glycation end product–modified extracellular matrix proteins, particularly types I and III collagen. This exposure leads to the terminal differentiation of keratinocytes with the advanced glycation end receptor (CD36) followed by the upward movement of keratinocytes with glycated collagen. Others postulate fibronectin, involved in epidermal cell signaling, locomotion, and differentiation, is an antigenic trigger because patients with DM and uremia have increased levels of fibronectin in the serum and at sites of perforating skin lesions.10
Diseases Associated With APD
Acquired perforating dermatosis is an umbrella term for perforating disease found in adults. It is associated with systemic diseases, such as DM and pruritus of renal failure.11 Our patient had both dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease and DM. Acquired perforating dermatosis is observed in 4.5% to 11% of patients on hemodialysis12,13; however, APD may occur prior to or in the absence of dialysis.3 Other examples of systemic conditions associated with APD include obstructive uropathy, chronic nephritis, anuria, and hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Koebnerization also may trigger lesions to manifest in a linear pattern after localized trauma to the skin.7 Acquired perforating dermatosis is associated with other types of trauma, such as healing herpes zoster, or following exposure to drugs, such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors, bevacizumab, telaprevir, sorafenib, sirolimus, and indinavir.14-16 Rarely, there have been associations with a history of insect bites, scabies, lymphoma, and hepatobiliary disease.1-3
Histopathology
Acquired perforating dermatosis is classified as a perforating disease, along with reactive perforating collagenosis, elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS), perforating folliculitis, and perforating calcific elastosis. Perforating diseases are histologically characterized by the transepidermal penetration and elimination of altered connective tissue and inflammatory cells.5 Each disease differs based on their clinical and histological characteristics.
Histologic sections of APD show a plug of crusting or hyperkeratosis with variable parakeratosis, acanthosis, and occasional dyskeratotic keratinocytes. In the dermis, aggregates of neutrophils, lymphocytes, macrophages, or multinucleated giant cells may be found.17 The histologic findings vary depending on the stage of evolution of the individual lesion. Early lesions show a concave depression with acanthosis, vacuolation of basal keratinocytes, and dermal inflammation.4 Additionally, transepidermal channels filled with keratin, pyknotic nuclear debris, inflammatory cells, elastin, or collagen can be noted.3 Over time, the elastic fibers, as detected by the Verhoeff-van Gieson stain, dissipate and the collagen acquires a basophilic staining. Adjacent to the channels, the basement membrane remains intact in early lesions but later shows discontinuities and electron-dense fibrinlike material.3 Occasionally, amorphous degenerated material within the perforations is the major histologic finding.11 Usually, the material cannot be clearly identified as collagen or elastin, but sometimes both are present.
In our case, we identified elastin as the perforating substance, which is less common than collagen, the typical perforating substance in APD. Elastin has occasionally been seen to serve as the only perforating substance from APD lesions among patients. Abe et al18 reported that the biopsy of a Japanese patient with keratotic follicular papules and serpiginous-arranged papules demonstrated elimination of atypical elastin fibers from the transepidermal channels. This patient was diagnosed with APD as well as EPS and perforating folliculitis based on the clinical presentation.18 Kim et al19 studied 30 Korean patients with APD. One had serpiginous hyperkeratotic plaques along the upper extremity and trunk that revealed transepidermal channels containing coarse elastic fibers and basophilic debris; however, due to the serpiginous morphology of lesions, both Abe et al18 and Kim et al19 favored a diagnosis of acquired EPS. Saray et al20 conducted a retrospective study of 22 Turkish patients with APD; 1 patient had a painful hyperkeratotic papule on the auricle that on histopathology showed degenerated elastin perforating through the keratotic plug, features similar to our case.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnoses include perforating diseases14,19 as well as other disorders that exhibit the Köbner phenomenon, such as psoriasis, lichen planus, and verruca vulgaris.21,22 Also, it is not uncommon for patients with APD to have coexisting folliculitis or prurigo nodularis.22
Treatment
Management is focused on treating the symptoms. For pruritus, sedating antihistamines and other antipruritic agents are efficacious.23 Topical, intra-lesional, or systemic corticosteroids and topical retinoids have shown variable resolution in APD lesions.24 Some case reports describe topical menthol, salicylic acid, sulfur, benzoyl peroxide, systemic antibiotics (eg, clindamycin, doxycycline), and allopurinol for elevated uric acid levels as effective treatment methods.6 Narrowband UVB phototherapy is beneficial for APD and renal disease.25,26 Renal transplantation has been curative for some patients with APD.27 Given that our patient’s lesions were asymptomatic, no treatment was offered at the time.
Conclusion
Our patient presented with APD localized exclusively to the site of a skin graft, and histologic examination identified elastin as the primary perforating substance. A medical history of DM and chronic kidney disease predisposes patients to APD. This case suggests that skin graft sites may be predisposed to the development of APD.
- Rodney IJ, Taylor CS, Cohen G. Derm Dx: what are these pruritic nodules? The Dermatologist. October 15, 2009. http://www.the-dermatologist.com/content/derm-dx-what-are-these-pruritic-nodules. Accessed September 18, 2018.
- Gagnon, AL, Desai T. Dermatological diseases in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Nephropathol. 2013;2:104-109.
- Kurban MS, Boueiz A, Kibbi AG. Cutaneous manifestations of chronic kidney disease. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:255-264.
- Wagner G, Sachse MM. Acquired reactive perforating dermatosis [published online May 29, 2013]. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:723-729; 723-730.
- Karpouzis A, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: current status. J Dermatol. 2010;37:585-592.
- Healy R, Cerio R, Hollingsworth A, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with pregnancy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:621-623.
- Cordova KB, Oberg TJ, Malik M, et al. Dermatologic conditions seen in end-stage renal disease. Semin Dial. 2009;22:45-55.
- Satchell AC, Crotty K, Lee S. Reactive perforating collagenosis: a condition that may be underdiagnosed. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:284-287.
- Fujimoto E, Kobayashi T, Fujimoto N, et al. AGE-modified collagens I and III induce keratinocyte terminal differentiation through AGE receptor CD36: epidermal-dermal interaction in acquired perforating dermatosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130:405-414.
- Bilezikci B, Sechkin D, Demirhan B. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure: a possible role for fibronectin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:230-232.
- Rapini RP, Herbert AA, Drucker CR. Acquired perforating dermatosis. evidence for combined transepidermal elimination of both collagen and elastic fibers. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:1074-1078.
- Hurwitz RM, Melton ME, Creech FT, et al. Perforating folliculitis in association with hemodialysis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1982;4:101-108.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Lübbe J, Sorg O, Malé PJ, et al. Sirolimus-induced inflammatory papules with acquired reactive perforating collagenosis [published online January 9, 2008]. Dermatology. 2008;216:239-242.
- Pernet C, Pageaux GP, Guillot B, et al. Telaprevir-induced acquired perforating dermatosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1371-1372.
- Severino-Freire M, Sibaud V, Tournier E, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with sorafenib therapy [published online September 11, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:328-330.
- Zelger B, Hintner H, Auböck J, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis. transepidermal elimination of DNA material and possible role of leukocytes in pathogenesis. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:695-700.
- Abe R, Murase S, Nomura Y, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis appearing as elastosis perforans serpiginosa and perforating folliculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008;33:653-654.
- Kim SW, Kim MS, Lee JH, et al. A clinicopathologic study of thirty cases of acquired perforating dermatosis in Korea. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:162-171.
- Saray Y, Seçkin D, Bilezikçi B. Acquired perforating dermatosis: clinicopathological features in twenty-two cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:679-688.
- Carter VH, Constantine VS. Kyrle’s disease. I. clinical findings in five cases and review of literature. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:624-632.
- Robinson-Bostom L, Digiovanna JJ. Cutaneous manifestations of end-stage renal disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:975-986.
- Hong SB, Park JH, Ihm CG, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure and diabetes mellitus. J Korean Med Sci. 2004;19:283-288.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Ohe S, Danno K, Sasaki H, et al. Treatment of acquired perforating dermatosis with narrowband ultraviolet B. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:892-894.
- Sezer E, Erkek E. Acquired perforating dermatosis successfully treated with photodynamic therapy. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2012;28:50-52.
- Saldanha LF, Gonick HC, Rodriguez HJ, et al. Silicon-related syndrome in dialysis patients. Nephron. 1997;77:48-56.
- Rodney IJ, Taylor CS, Cohen G. Derm Dx: what are these pruritic nodules? The Dermatologist. October 15, 2009. http://www.the-dermatologist.com/content/derm-dx-what-are-these-pruritic-nodules. Accessed September 18, 2018.
- Gagnon, AL, Desai T. Dermatological diseases in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Nephropathol. 2013;2:104-109.
- Kurban MS, Boueiz A, Kibbi AG. Cutaneous manifestations of chronic kidney disease. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:255-264.
- Wagner G, Sachse MM. Acquired reactive perforating dermatosis [published online May 29, 2013]. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:723-729; 723-730.
- Karpouzis A, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: current status. J Dermatol. 2010;37:585-592.
- Healy R, Cerio R, Hollingsworth A, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with pregnancy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:621-623.
- Cordova KB, Oberg TJ, Malik M, et al. Dermatologic conditions seen in end-stage renal disease. Semin Dial. 2009;22:45-55.
- Satchell AC, Crotty K, Lee S. Reactive perforating collagenosis: a condition that may be underdiagnosed. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:284-287.
- Fujimoto E, Kobayashi T, Fujimoto N, et al. AGE-modified collagens I and III induce keratinocyte terminal differentiation through AGE receptor CD36: epidermal-dermal interaction in acquired perforating dermatosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130:405-414.
- Bilezikci B, Sechkin D, Demirhan B. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure: a possible role for fibronectin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:230-232.
- Rapini RP, Herbert AA, Drucker CR. Acquired perforating dermatosis. evidence for combined transepidermal elimination of both collagen and elastic fibers. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:1074-1078.
- Hurwitz RM, Melton ME, Creech FT, et al. Perforating folliculitis in association with hemodialysis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1982;4:101-108.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Lübbe J, Sorg O, Malé PJ, et al. Sirolimus-induced inflammatory papules with acquired reactive perforating collagenosis [published online January 9, 2008]. Dermatology. 2008;216:239-242.
- Pernet C, Pageaux GP, Guillot B, et al. Telaprevir-induced acquired perforating dermatosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1371-1372.
- Severino-Freire M, Sibaud V, Tournier E, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with sorafenib therapy [published online September 11, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:328-330.
- Zelger B, Hintner H, Auböck J, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis. transepidermal elimination of DNA material and possible role of leukocytes in pathogenesis. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:695-700.
- Abe R, Murase S, Nomura Y, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis appearing as elastosis perforans serpiginosa and perforating folliculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008;33:653-654.
- Kim SW, Kim MS, Lee JH, et al. A clinicopathologic study of thirty cases of acquired perforating dermatosis in Korea. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:162-171.
- Saray Y, Seçkin D, Bilezikçi B. Acquired perforating dermatosis: clinicopathological features in twenty-two cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:679-688.
- Carter VH, Constantine VS. Kyrle’s disease. I. clinical findings in five cases and review of literature. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:624-632.
- Robinson-Bostom L, Digiovanna JJ. Cutaneous manifestations of end-stage renal disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:975-986.
- Hong SB, Park JH, Ihm CG, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure and diabetes mellitus. J Korean Med Sci. 2004;19:283-288.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Ohe S, Danno K, Sasaki H, et al. Treatment of acquired perforating dermatosis with narrowband ultraviolet B. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:892-894.
- Sezer E, Erkek E. Acquired perforating dermatosis successfully treated with photodynamic therapy. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2012;28:50-52.
- Saldanha LF, Gonick HC, Rodriguez HJ, et al. Silicon-related syndrome in dialysis patients. Nephron. 1997;77:48-56.
Practice Points
- Acquired perforating dermatosis (APD) presents as pruritic crateriform papules and plaques with central keratotic plugs.
- A medical history of diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease predisposes patients to APD. This case suggests that skin graft sites may be predisposed to the development of APD.