User login
In the Future, a Robot Intensivist May Save Your Life
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
They call it the “golden hour”: 60 minutes, give or take, when the chance to save the life of a trauma victim is at its greatest. If the patient can be resuscitated and stabilized in that time window, they stand a good chance of surviving. If not, well, they don’t.
But resuscitation is complicated. It requires blood products, fluids, vasopressors — all given in precise doses in response to rapidly changing hemodynamics. To do it right takes specialized training, advanced life support (ALS). If the patient is in a remote area or an area without ALS-certified emergency medical services, or is far from the nearest trauma center, that golden hour is lost. And the patient may be as well.
But we live in the future. We have robots in factories, self-driving cars, autonomous drones. Why not an autonomous trauma doctor? If you are in a life-threatening accident, would you want to be treated ... by a robot?
Enter “resuscitation based on functional hemodynamic monitoring,” or “ReFit,” introduced in this article appearing in the journal Intensive Care Medicine Experimental.
The idea behind ReFit is straightforward. Resuscitation after trauma should be based on hitting key hemodynamic targets using the tools we have available in the field: blood, fluids, pressors. The researchers wanted to develop a closed-loop system, something that could be used by minimally trained personnel. The input to the system? Hemodynamic data, provided through a single measurement device, an arterial catheter. The output: blood, fluids, and pressors, delivered intravenously.
The body (a prototype) of the system looks like this. You can see various pumps labeled with various fluids, electronic controllers, and so forth.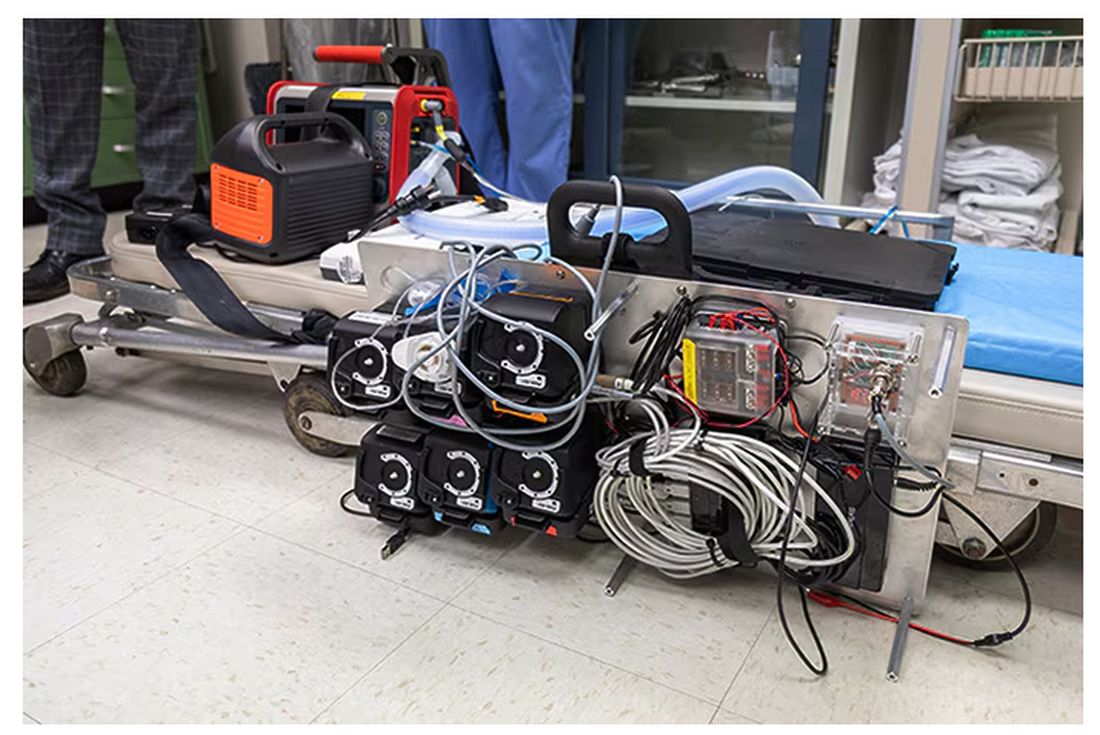
If that’s the body, then this is the brain – a ruggedized laptop interpreting a readout of that arterial catheter.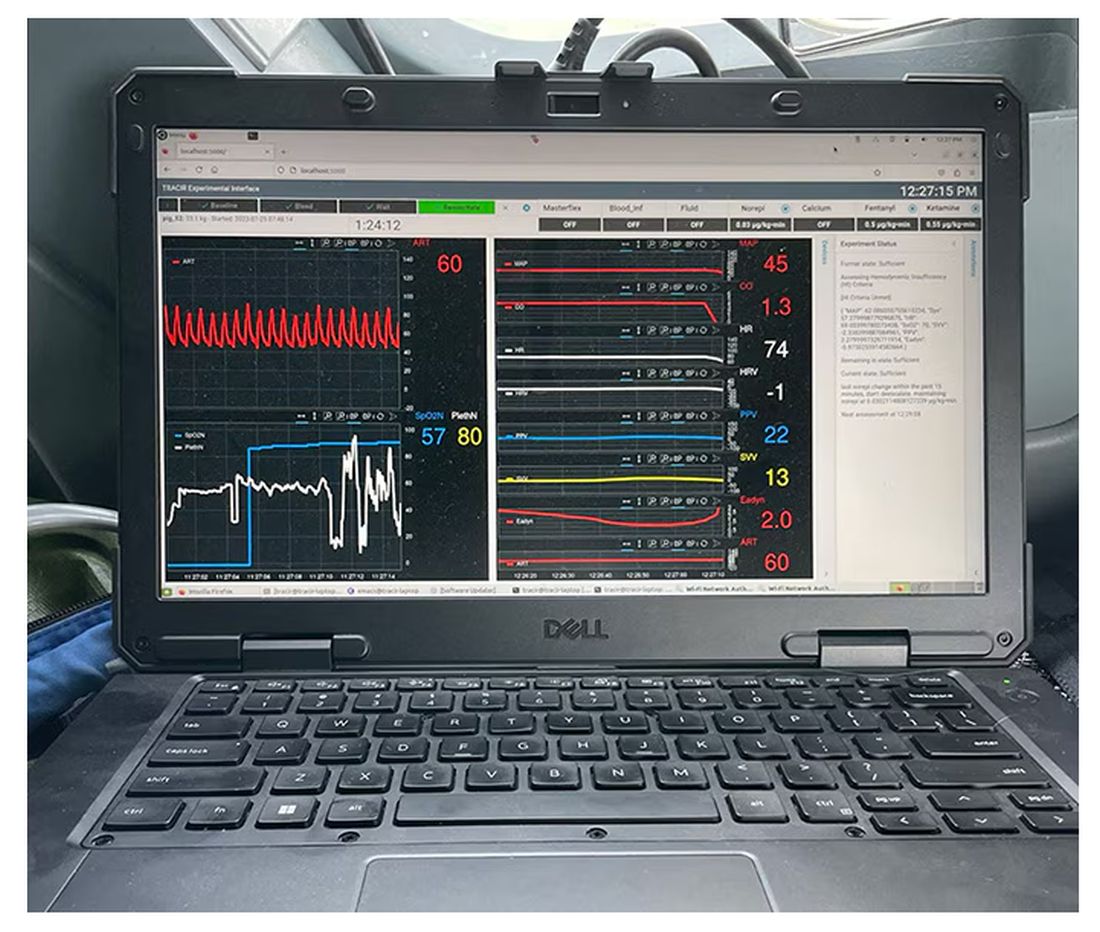
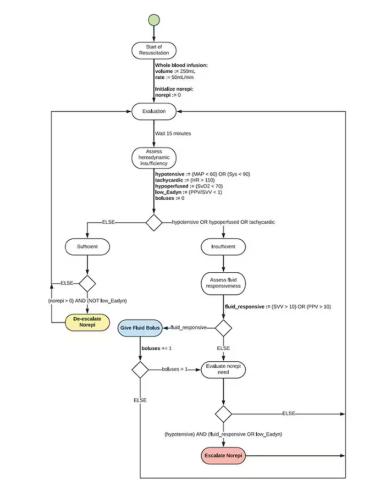
If that’s the brain, then the ReFit algorithm is the mind. The algorithm does its best to leverage all the data it can, so I want to walk through it in a bit of detail.
First, check to see whether the patient is stable, defined as a heart rate < 110 beats/min and a mean arterial pressure > 60 mm Hg. If not, you’re off to the races, starting with a bolus of whole blood.
Next, the algorithm gets really interesting. If the patient is still unstable, the computer assesses fluid responsiveness by giving a test dose of fluid and measuring the pulse pressure variation. Greater pulse pressure variation means more fluid responsiveness and the algorithm gives more fluid. Less pulse pressure variation leads the algorithm to uptitrate pressors — in this case, norepinephrine.
This cycle of evaluation and response keeps repeating. The computer titrates fluids and pressors up and down entirely on its own, in theory freeing the human team members to do other things, like getting the patient to a trauma center for definitive care.
So, how do you test whether something like this works? Clearly, you don’t want the trial run of a system like this to be used on a real human suffering from a real traumatic injury.
Once again, we have animals to thank for research advances — in this case, pigs. Fifteen pigs are described in the study. To simulate a severe, hemorrhagic trauma, they were anesthetized and the liver was lacerated. They were then observed passively until the mean arterial pressure had dropped to below 40 mm Hg.
This is a pretty severe injury. Three unfortunate animals served as controls, two of which died within the 3-hour time window of the study. Eight animals were plugged into the ReFit system.
For a window into what happens during this process, let’s take a look at the mean arterial pressure and heart rate readouts for one of the animals. You see that the blood pressure starts to fall precipitously after the liver laceration. The heart rate quickly picks up to compensate, raising the mean arterial pressure a bit, but this would be unsustainable with ongoing bleeding.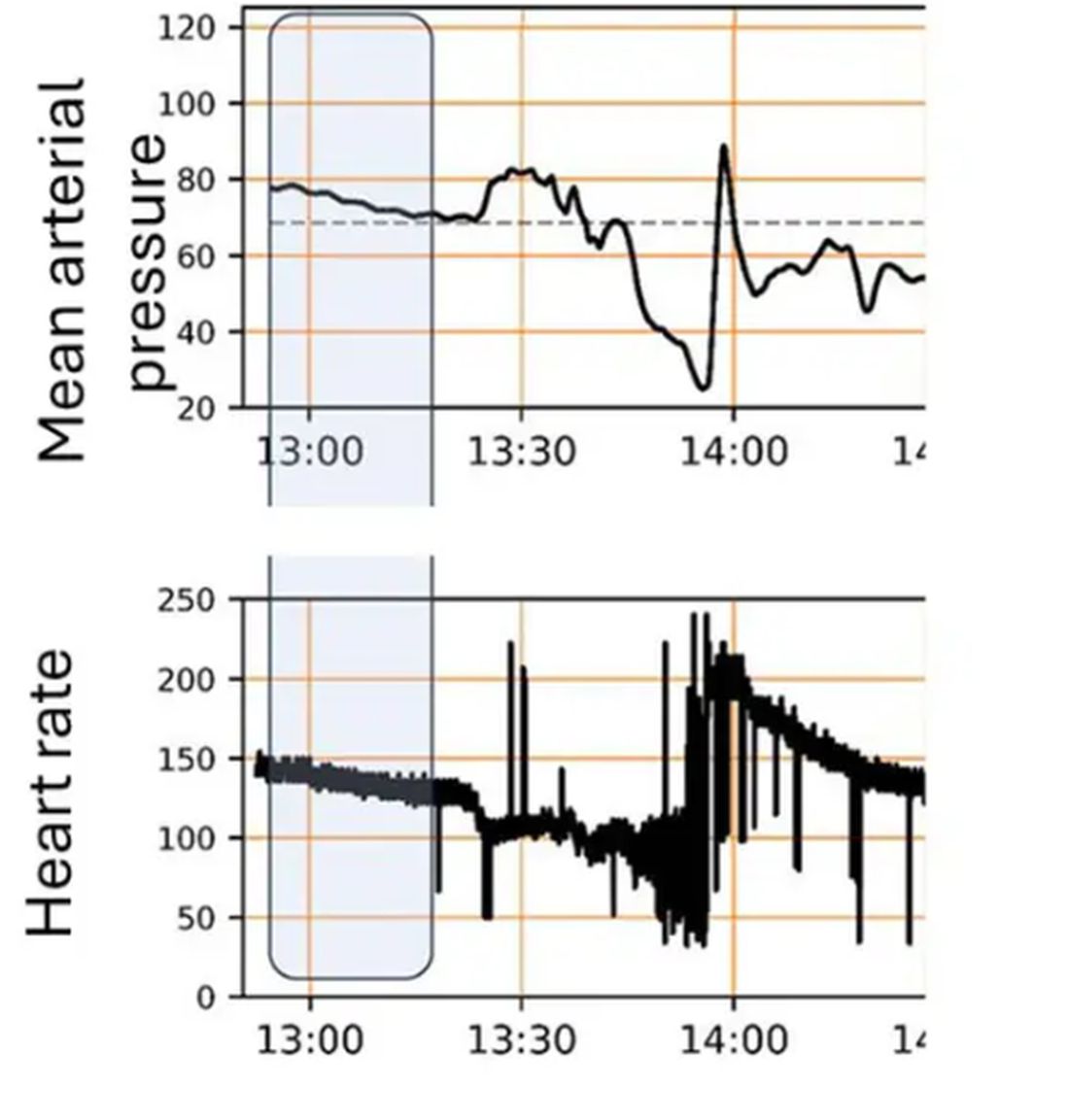
Here, the ReFit system takes over. Autonomously, the system administers two units of blood, followed by fluids, and then norepinephrine or further fluids per the protocol I described earlier. 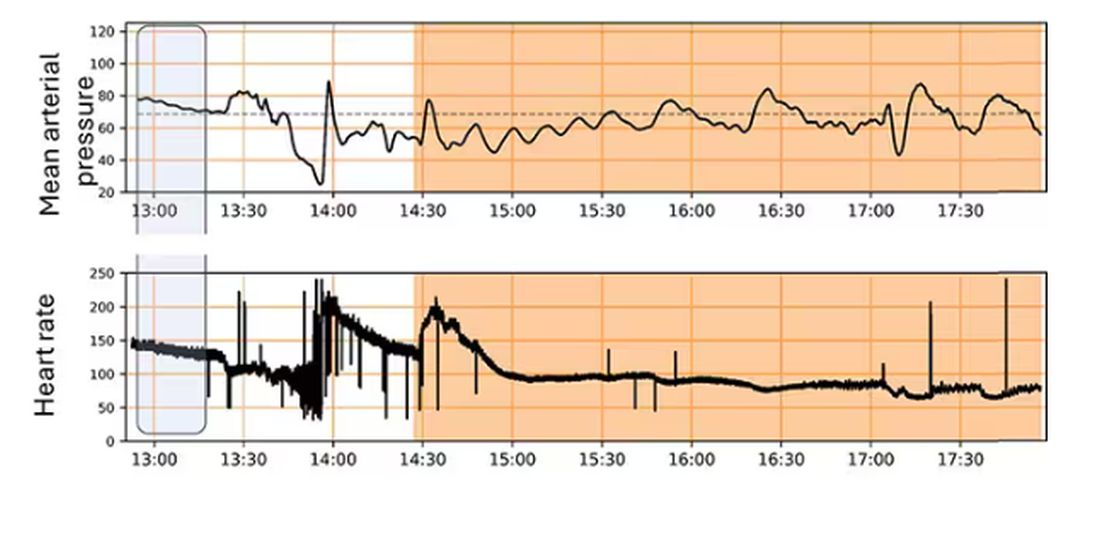
The practical upshot of all of this is stabilization, despite an as-yet untreated liver laceration.
Could an experienced ALS provider do this? Of course. But, as I mentioned before, you aren’t always near an experienced ALS provider.
This is all well and good in the lab, but in the real world, you actually need to transport a trauma patient. The researchers tried this also. To prove feasibility, four pigs were taken from the lab to the top of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, flown to Allegheny County Airport and back. Total time before liver laceration repair? Three hours. And all four survived.
It won’t surprise you to hear that this work was funded by the Department of Defense. You can see how a system like this, made a bit more rugged, a bit smaller, and a bit more self-contained could have real uses in the battlefield. But trauma is not unique to war, and something that can extend the time you have to safely transport a patient to definitive care — well, that’s worth its weight in golden hours.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
They call it the “golden hour”: 60 minutes, give or take, when the chance to save the life of a trauma victim is at its greatest. If the patient can be resuscitated and stabilized in that time window, they stand a good chance of surviving. If not, well, they don’t.
But resuscitation is complicated. It requires blood products, fluids, vasopressors — all given in precise doses in response to rapidly changing hemodynamics. To do it right takes specialized training, advanced life support (ALS). If the patient is in a remote area or an area without ALS-certified emergency medical services, or is far from the nearest trauma center, that golden hour is lost. And the patient may be as well.
But we live in the future. We have robots in factories, self-driving cars, autonomous drones. Why not an autonomous trauma doctor? If you are in a life-threatening accident, would you want to be treated ... by a robot?
Enter “resuscitation based on functional hemodynamic monitoring,” or “ReFit,” introduced in this article appearing in the journal Intensive Care Medicine Experimental.
The idea behind ReFit is straightforward. Resuscitation after trauma should be based on hitting key hemodynamic targets using the tools we have available in the field: blood, fluids, pressors. The researchers wanted to develop a closed-loop system, something that could be used by minimally trained personnel. The input to the system? Hemodynamic data, provided through a single measurement device, an arterial catheter. The output: blood, fluids, and pressors, delivered intravenously.
The body (a prototype) of the system looks like this. You can see various pumps labeled with various fluids, electronic controllers, and so forth.
If that’s the body, then this is the brain – a ruggedized laptop interpreting a readout of that arterial catheter.
If that’s the brain, then the ReFit algorithm is the mind. The algorithm does its best to leverage all the data it can, so I want to walk through it in a bit of detail.
First, check to see whether the patient is stable, defined as a heart rate < 110 beats/min and a mean arterial pressure > 60 mm Hg. If not, you’re off to the races, starting with a bolus of whole blood.
Next, the algorithm gets really interesting. If the patient is still unstable, the computer assesses fluid responsiveness by giving a test dose of fluid and measuring the pulse pressure variation. Greater pulse pressure variation means more fluid responsiveness and the algorithm gives more fluid. Less pulse pressure variation leads the algorithm to uptitrate pressors — in this case, norepinephrine.
This cycle of evaluation and response keeps repeating. The computer titrates fluids and pressors up and down entirely on its own, in theory freeing the human team members to do other things, like getting the patient to a trauma center for definitive care.
So, how do you test whether something like this works? Clearly, you don’t want the trial run of a system like this to be used on a real human suffering from a real traumatic injury.
Once again, we have animals to thank for research advances — in this case, pigs. Fifteen pigs are described in the study. To simulate a severe, hemorrhagic trauma, they were anesthetized and the liver was lacerated. They were then observed passively until the mean arterial pressure had dropped to below 40 mm Hg.
This is a pretty severe injury. Three unfortunate animals served as controls, two of which died within the 3-hour time window of the study. Eight animals were plugged into the ReFit system.
For a window into what happens during this process, let’s take a look at the mean arterial pressure and heart rate readouts for one of the animals. You see that the blood pressure starts to fall precipitously after the liver laceration. The heart rate quickly picks up to compensate, raising the mean arterial pressure a bit, but this would be unsustainable with ongoing bleeding.
Here, the ReFit system takes over. Autonomously, the system administers two units of blood, followed by fluids, and then norepinephrine or further fluids per the protocol I described earlier. 
The practical upshot of all of this is stabilization, despite an as-yet untreated liver laceration.
Could an experienced ALS provider do this? Of course. But, as I mentioned before, you aren’t always near an experienced ALS provider.
This is all well and good in the lab, but in the real world, you actually need to transport a trauma patient. The researchers tried this also. To prove feasibility, four pigs were taken from the lab to the top of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, flown to Allegheny County Airport and back. Total time before liver laceration repair? Three hours. And all four survived.
It won’t surprise you to hear that this work was funded by the Department of Defense. You can see how a system like this, made a bit more rugged, a bit smaller, and a bit more self-contained could have real uses in the battlefield. But trauma is not unique to war, and something that can extend the time you have to safely transport a patient to definitive care — well, that’s worth its weight in golden hours.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
They call it the “golden hour”: 60 minutes, give or take, when the chance to save the life of a trauma victim is at its greatest. If the patient can be resuscitated and stabilized in that time window, they stand a good chance of surviving. If not, well, they don’t.
But resuscitation is complicated. It requires blood products, fluids, vasopressors — all given in precise doses in response to rapidly changing hemodynamics. To do it right takes specialized training, advanced life support (ALS). If the patient is in a remote area or an area without ALS-certified emergency medical services, or is far from the nearest trauma center, that golden hour is lost. And the patient may be as well.
But we live in the future. We have robots in factories, self-driving cars, autonomous drones. Why not an autonomous trauma doctor? If you are in a life-threatening accident, would you want to be treated ... by a robot?
Enter “resuscitation based on functional hemodynamic monitoring,” or “ReFit,” introduced in this article appearing in the journal Intensive Care Medicine Experimental.
The idea behind ReFit is straightforward. Resuscitation after trauma should be based on hitting key hemodynamic targets using the tools we have available in the field: blood, fluids, pressors. The researchers wanted to develop a closed-loop system, something that could be used by minimally trained personnel. The input to the system? Hemodynamic data, provided through a single measurement device, an arterial catheter. The output: blood, fluids, and pressors, delivered intravenously.
The body (a prototype) of the system looks like this. You can see various pumps labeled with various fluids, electronic controllers, and so forth.
If that’s the body, then this is the brain – a ruggedized laptop interpreting a readout of that arterial catheter.
If that’s the brain, then the ReFit algorithm is the mind. The algorithm does its best to leverage all the data it can, so I want to walk through it in a bit of detail.
First, check to see whether the patient is stable, defined as a heart rate < 110 beats/min and a mean arterial pressure > 60 mm Hg. If not, you’re off to the races, starting with a bolus of whole blood.
Next, the algorithm gets really interesting. If the patient is still unstable, the computer assesses fluid responsiveness by giving a test dose of fluid and measuring the pulse pressure variation. Greater pulse pressure variation means more fluid responsiveness and the algorithm gives more fluid. Less pulse pressure variation leads the algorithm to uptitrate pressors — in this case, norepinephrine.
This cycle of evaluation and response keeps repeating. The computer titrates fluids and pressors up and down entirely on its own, in theory freeing the human team members to do other things, like getting the patient to a trauma center for definitive care.
So, how do you test whether something like this works? Clearly, you don’t want the trial run of a system like this to be used on a real human suffering from a real traumatic injury.
Once again, we have animals to thank for research advances — in this case, pigs. Fifteen pigs are described in the study. To simulate a severe, hemorrhagic trauma, they were anesthetized and the liver was lacerated. They were then observed passively until the mean arterial pressure had dropped to below 40 mm Hg.
This is a pretty severe injury. Three unfortunate animals served as controls, two of which died within the 3-hour time window of the study. Eight animals were plugged into the ReFit system.
For a window into what happens during this process, let’s take a look at the mean arterial pressure and heart rate readouts for one of the animals. You see that the blood pressure starts to fall precipitously after the liver laceration. The heart rate quickly picks up to compensate, raising the mean arterial pressure a bit, but this would be unsustainable with ongoing bleeding.
Here, the ReFit system takes over. Autonomously, the system administers two units of blood, followed by fluids, and then norepinephrine or further fluids per the protocol I described earlier. 
The practical upshot of all of this is stabilization, despite an as-yet untreated liver laceration.
Could an experienced ALS provider do this? Of course. But, as I mentioned before, you aren’t always near an experienced ALS provider.
This is all well and good in the lab, but in the real world, you actually need to transport a trauma patient. The researchers tried this also. To prove feasibility, four pigs were taken from the lab to the top of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, flown to Allegheny County Airport and back. Total time before liver laceration repair? Three hours. And all four survived.
It won’t surprise you to hear that this work was funded by the Department of Defense. You can see how a system like this, made a bit more rugged, a bit smaller, and a bit more self-contained could have real uses in the battlefield. But trauma is not unique to war, and something that can extend the time you have to safely transport a patient to definitive care — well, that’s worth its weight in golden hours.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When It Comes to Medicine, ‘Women Are Not Small Men’
Welcome everyone. I’m Dr. John White. I’m the chief medical officer at WebMD. Does your biologic sex impact your health? Does it have any play in how you’re diagnosed, how you’re treated in terms of what symptoms you have? Of course it does. We all know that. But that’s not something that many people believed 5, 10 years ago, certainly not 20 years ago. And it was only because of leaders like my guest today, Phyllis Greenberger, who really championed the need for research on women’s health. She has a new book out, which I love. It’s called Sex Cells: the Fight to Overcome Bias and Discrimination in Women’s Healthcare. Please welcome my very good friend, Phyllis Greenberger.
Thank you.
Phyllis, It’s great to see you today.
It’s great to see you as well.
Now, you and I have been talking about this for easily 2 decades.
At least.
And some people think, oh, of course it makes sense. Although I saw you disagreeing that not everyone still believes that. But what has been that journey? Why has it been so hard to make people understand, as you point out early on in your book, women are not smaller men?
I think the basic reason was that it was just believed that men and women were the same except for their reproductive organs. So minus the reproductive organs, whether it was a device, a diagnostic, or therapeutic, if it was used and successful on a male, that it would be successful on a female. We’re really very far from understanding the differences, and there’s still a lot of distrust and disbelief and ignorance about it. And so there’s still a long way to go.
But you talk about that in the book, that there’s still a long way to go. Why is that? What’s the biggest obstacle? Is it just misinformation, lack of information? People don’t understand the science? There’s still resistance in some areas. Why is that?
I think it’s misinformation, and I gave a presentation, I don’t know how many years ago, at least 20 years ago, about the curriculum. And at the time, there was no women’s health in the curriculum. It was health. So if it was on cardiovascular issues or on osteoporosis, it was sort of the basic. And at the time, there would maybe be one woman whose job was women’s health, and she’d have an office, and otherwise there was nothing. And maybe they talked about breast cancer, who knows. But I spoke to someone just the other day, in view of all the attention that the book is getting now, whether that’s changed, whether it’s necessary and required. And she said it’s not. So, it’s not necessarily on the curriculum of all research and medical institutions, and even if women’s health, quote unquote, is on the curriculum, it doesn’t mean that they’re really looking at sex differences. And the difference is obvious. I mean, gender is really, it’s a social construct, but biological sex is how disease occurs and develops. And so if you’re not looking, and because there’s so little research now on sex differences that I don’t even know, I mean, how much you could actually teach.
So what needs to change? This book is a manifesto in many ways in how we need to include women; we need to make research more inclusive of everyone. But we’re not there yet. So what needs to change, Phyllis?
During this whole saga of trying to get people to listen to me and to the society, we really started out just looking at clinical trials and that, as you mentioned, I mean, there are issues in rural communities. There’s travel issues for women and child care. There’s a lot of disbelief or fear of clinical trials in some ethnicities. I do think, going to the future, that technology can help that. I mean, if people have broadband, which of course is also an issue in rural areas.
What could women do today? What should women listeners hear and then be doing? Should they be saying something to their doctor? Should they be asking specific questions? When they interact with the health care system, how can they make sure they’re getting the best care that’s appropriate for them when we know that sex cells matter?
Well, that’s a good question. It depends on, frankly, if your doctor is aware of this, if he or she has learned anything about this in school, which, I had already said, we’re not sure about that because research is still ongoing and there’s so much we don’t know. So I mean, you used to think, or I used to think, that you go to, you want a physician who’s older and more experienced. But now I think you should be going to a physician who’s younger and hopefully has learned about this, because the physicians that were educated years ago and have been practicing for 20, 30 years, I don’t know how much they know about this, whether they’re even aware of it.
Phyllis, you are a woman of action. You’ve lived in the DC area. You have championed legislative reforms, executive agendas. What do you want done now? What needs to be changed today? The curriculum is going to take time, but what else needs to change?
That’s a good question. I mean, if curriculum is going to take a while and you can ask your doctor if he prescribes the medication, whether it’s been tested on women, but then if it hasn’t been tested on women, but it’s the only thing that there is for your condition, I mean, so it’s very difficult. The Biden administration, as you know, just allocated a hundred million dollars for women’s health research.
What do you hope to accomplish with this book?
Well, what I’m hoping is that I spoke to someone at AMWA and I’m hoping — and AMWA is an association for women medical students. And I’m hoping that’s the audience. The audience needs to be. I mean, obviously everybody that I know that’s not a doctor that’s read it, found it fascinating and didn’t know a lot of the stuff that was in it. So I think it’s an interesting book anyway, and I think women should be aware of it. But really I think it needs to be for medical students.
And to your credit, you built the Society for Women’s Health Research into a powerful force in Washington under your tenure in really promoting the need for Office of Women’s Health and Research in general. The book is entitled Sex Cells, the Fight to Overcome Bias and Discrimination in Women’s Healthcare. Phyllis Greenberger, thank you so much for all that you’ve done for women’s health, for women’s research. We wouldn’t be where we are today if it wasn’t for you. So thanks.
Thank you very much, John. Thank you. I appreciate the opportunity.
Dr. Whyte, is chief medical officer, WebMD, New York, NY. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Greenberger is a women’s health advocate and author of “Sex Cells: The Fight to Overcome Bias and Discrimination in Women’s Healthcare”
This interview originally appeared on WebMD on May 23, 2024. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Welcome everyone. I’m Dr. John White. I’m the chief medical officer at WebMD. Does your biologic sex impact your health? Does it have any play in how you’re diagnosed, how you’re treated in terms of what symptoms you have? Of course it does. We all know that. But that’s not something that many people believed 5, 10 years ago, certainly not 20 years ago. And it was only because of leaders like my guest today, Phyllis Greenberger, who really championed the need for research on women’s health. She has a new book out, which I love. It’s called Sex Cells: the Fight to Overcome Bias and Discrimination in Women’s Healthcare. Please welcome my very good friend, Phyllis Greenberger.
Thank you.
Phyllis, It’s great to see you today.
It’s great to see you as well.
Now, you and I have been talking about this for easily 2 decades.
At least.
And some people think, oh, of course it makes sense. Although I saw you disagreeing that not everyone still believes that. But what has been that journey? Why has it been so hard to make people understand, as you point out early on in your book, women are not smaller men?
I think the basic reason was that it was just believed that men and women were the same except for their reproductive organs. So minus the reproductive organs, whether it was a device, a diagnostic, or therapeutic, if it was used and successful on a male, that it would be successful on a female. We’re really very far from understanding the differences, and there’s still a lot of distrust and disbelief and ignorance about it. And so there’s still a long way to go.
But you talk about that in the book, that there’s still a long way to go. Why is that? What’s the biggest obstacle? Is it just misinformation, lack of information? People don’t understand the science? There’s still resistance in some areas. Why is that?
I think it’s misinformation, and I gave a presentation, I don’t know how many years ago, at least 20 years ago, about the curriculum. And at the time, there was no women’s health in the curriculum. It was health. So if it was on cardiovascular issues or on osteoporosis, it was sort of the basic. And at the time, there would maybe be one woman whose job was women’s health, and she’d have an office, and otherwise there was nothing. And maybe they talked about breast cancer, who knows. But I spoke to someone just the other day, in view of all the attention that the book is getting now, whether that’s changed, whether it’s necessary and required. And she said it’s not. So, it’s not necessarily on the curriculum of all research and medical institutions, and even if women’s health, quote unquote, is on the curriculum, it doesn’t mean that they’re really looking at sex differences. And the difference is obvious. I mean, gender is really, it’s a social construct, but biological sex is how disease occurs and develops. And so if you’re not looking, and because there’s so little research now on sex differences that I don’t even know, I mean, how much you could actually teach.
So what needs to change? This book is a manifesto in many ways in how we need to include women; we need to make research more inclusive of everyone. But we’re not there yet. So what needs to change, Phyllis?
During this whole saga of trying to get people to listen to me and to the society, we really started out just looking at clinical trials and that, as you mentioned, I mean, there are issues in rural communities. There’s travel issues for women and child care. There’s a lot of disbelief or fear of clinical trials in some ethnicities. I do think, going to the future, that technology can help that. I mean, if people have broadband, which of course is also an issue in rural areas.
What could women do today? What should women listeners hear and then be doing? Should they be saying something to their doctor? Should they be asking specific questions? When they interact with the health care system, how can they make sure they’re getting the best care that’s appropriate for them when we know that sex cells matter?
Well, that’s a good question. It depends on, frankly, if your doctor is aware of this, if he or she has learned anything about this in school, which, I had already said, we’re not sure about that because research is still ongoing and there’s so much we don’t know. So I mean, you used to think, or I used to think, that you go to, you want a physician who’s older and more experienced. But now I think you should be going to a physician who’s younger and hopefully has learned about this, because the physicians that were educated years ago and have been practicing for 20, 30 years, I don’t know how much they know about this, whether they’re even aware of it.
Phyllis, you are a woman of action. You’ve lived in the DC area. You have championed legislative reforms, executive agendas. What do you want done now? What needs to be changed today? The curriculum is going to take time, but what else needs to change?
That’s a good question. I mean, if curriculum is going to take a while and you can ask your doctor if he prescribes the medication, whether it’s been tested on women, but then if it hasn’t been tested on women, but it’s the only thing that there is for your condition, I mean, so it’s very difficult. The Biden administration, as you know, just allocated a hundred million dollars for women’s health research.
What do you hope to accomplish with this book?
Well, what I’m hoping is that I spoke to someone at AMWA and I’m hoping — and AMWA is an association for women medical students. And I’m hoping that’s the audience. The audience needs to be. I mean, obviously everybody that I know that’s not a doctor that’s read it, found it fascinating and didn’t know a lot of the stuff that was in it. So I think it’s an interesting book anyway, and I think women should be aware of it. But really I think it needs to be for medical students.
And to your credit, you built the Society for Women’s Health Research into a powerful force in Washington under your tenure in really promoting the need for Office of Women’s Health and Research in general. The book is entitled Sex Cells, the Fight to Overcome Bias and Discrimination in Women’s Healthcare. Phyllis Greenberger, thank you so much for all that you’ve done for women’s health, for women’s research. We wouldn’t be where we are today if it wasn’t for you. So thanks.
Thank you very much, John. Thank you. I appreciate the opportunity.
Dr. Whyte, is chief medical officer, WebMD, New York, NY. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Greenberger is a women’s health advocate and author of “Sex Cells: The Fight to Overcome Bias and Discrimination in Women’s Healthcare”
This interview originally appeared on WebMD on May 23, 2024. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Welcome everyone. I’m Dr. John White. I’m the chief medical officer at WebMD. Does your biologic sex impact your health? Does it have any play in how you’re diagnosed, how you’re treated in terms of what symptoms you have? Of course it does. We all know that. But that’s not something that many people believed 5, 10 years ago, certainly not 20 years ago. And it was only because of leaders like my guest today, Phyllis Greenberger, who really championed the need for research on women’s health. She has a new book out, which I love. It’s called Sex Cells: the Fight to Overcome Bias and Discrimination in Women’s Healthcare. Please welcome my very good friend, Phyllis Greenberger.
Thank you.
Phyllis, It’s great to see you today.
It’s great to see you as well.
Now, you and I have been talking about this for easily 2 decades.
At least.
And some people think, oh, of course it makes sense. Although I saw you disagreeing that not everyone still believes that. But what has been that journey? Why has it been so hard to make people understand, as you point out early on in your book, women are not smaller men?
I think the basic reason was that it was just believed that men and women were the same except for their reproductive organs. So minus the reproductive organs, whether it was a device, a diagnostic, or therapeutic, if it was used and successful on a male, that it would be successful on a female. We’re really very far from understanding the differences, and there’s still a lot of distrust and disbelief and ignorance about it. And so there’s still a long way to go.
But you talk about that in the book, that there’s still a long way to go. Why is that? What’s the biggest obstacle? Is it just misinformation, lack of information? People don’t understand the science? There’s still resistance in some areas. Why is that?
I think it’s misinformation, and I gave a presentation, I don’t know how many years ago, at least 20 years ago, about the curriculum. And at the time, there was no women’s health in the curriculum. It was health. So if it was on cardiovascular issues or on osteoporosis, it was sort of the basic. And at the time, there would maybe be one woman whose job was women’s health, and she’d have an office, and otherwise there was nothing. And maybe they talked about breast cancer, who knows. But I spoke to someone just the other day, in view of all the attention that the book is getting now, whether that’s changed, whether it’s necessary and required. And she said it’s not. So, it’s not necessarily on the curriculum of all research and medical institutions, and even if women’s health, quote unquote, is on the curriculum, it doesn’t mean that they’re really looking at sex differences. And the difference is obvious. I mean, gender is really, it’s a social construct, but biological sex is how disease occurs and develops. And so if you’re not looking, and because there’s so little research now on sex differences that I don’t even know, I mean, how much you could actually teach.
So what needs to change? This book is a manifesto in many ways in how we need to include women; we need to make research more inclusive of everyone. But we’re not there yet. So what needs to change, Phyllis?
During this whole saga of trying to get people to listen to me and to the society, we really started out just looking at clinical trials and that, as you mentioned, I mean, there are issues in rural communities. There’s travel issues for women and child care. There’s a lot of disbelief or fear of clinical trials in some ethnicities. I do think, going to the future, that technology can help that. I mean, if people have broadband, which of course is also an issue in rural areas.
What could women do today? What should women listeners hear and then be doing? Should they be saying something to their doctor? Should they be asking specific questions? When they interact with the health care system, how can they make sure they’re getting the best care that’s appropriate for them when we know that sex cells matter?
Well, that’s a good question. It depends on, frankly, if your doctor is aware of this, if he or she has learned anything about this in school, which, I had already said, we’re not sure about that because research is still ongoing and there’s so much we don’t know. So I mean, you used to think, or I used to think, that you go to, you want a physician who’s older and more experienced. But now I think you should be going to a physician who’s younger and hopefully has learned about this, because the physicians that were educated years ago and have been practicing for 20, 30 years, I don’t know how much they know about this, whether they’re even aware of it.
Phyllis, you are a woman of action. You’ve lived in the DC area. You have championed legislative reforms, executive agendas. What do you want done now? What needs to be changed today? The curriculum is going to take time, but what else needs to change?
That’s a good question. I mean, if curriculum is going to take a while and you can ask your doctor if he prescribes the medication, whether it’s been tested on women, but then if it hasn’t been tested on women, but it’s the only thing that there is for your condition, I mean, so it’s very difficult. The Biden administration, as you know, just allocated a hundred million dollars for women’s health research.
What do you hope to accomplish with this book?
Well, what I’m hoping is that I spoke to someone at AMWA and I’m hoping — and AMWA is an association for women medical students. And I’m hoping that’s the audience. The audience needs to be. I mean, obviously everybody that I know that’s not a doctor that’s read it, found it fascinating and didn’t know a lot of the stuff that was in it. So I think it’s an interesting book anyway, and I think women should be aware of it. But really I think it needs to be for medical students.
And to your credit, you built the Society for Women’s Health Research into a powerful force in Washington under your tenure in really promoting the need for Office of Women’s Health and Research in general. The book is entitled Sex Cells, the Fight to Overcome Bias and Discrimination in Women’s Healthcare. Phyllis Greenberger, thank you so much for all that you’ve done for women’s health, for women’s research. We wouldn’t be where we are today if it wasn’t for you. So thanks.
Thank you very much, John. Thank you. I appreciate the opportunity.
Dr. Whyte, is chief medical officer, WebMD, New York, NY. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Greenberger is a women’s health advocate and author of “Sex Cells: The Fight to Overcome Bias and Discrimination in Women’s Healthcare”
This interview originally appeared on WebMD on May 23, 2024. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Staving Off Obsolescence
I don’t write many checks anymore.
When I started my practice in 2000 I wrote a lot. Paychecks for my staff, my rent, insurance, IRA contributions, federal & state withholding, payments on my EMG machine, pretty much everything.
Checks are old. We’ve been using them in some form for roughly 2000 years.
But the online world has changed a lot of that. Now I write maybe 2-3 a month. I could probably do fewer, but haven’t bothered to set those accounts up that way.
I recently was down to my last few checks, so ordered replacements. The minimum order was 600. As I unpacked the box I realized they’re probably the last ones I’ll need, both because checks are gradually passing by and because there are more days behind in my neurology career than ahead.
The checks are a minor thing, but they do make you think. Certainly we’re in the last generation of people who will ever need to use paper checks. Some phrases like “blank check” will likely be with us long after they’re gone (like “dialing a phone”), but the real deal is heading the same way as 8-Track and VHS tapes.
As my 600 checks dwindle down, realistically, so will my career. There is no rewind button on life. I have no desire to leave medicine right now, but the passage of time changes things.
Does that mean I, like my checks, am also getting obsolete?
I hope not. I’d like to think I still have something to offer. I have 30 years of neurology experience behind me, and try to keep up to date on my field. My patients and staff depend on me to bring my best to the office every day.
I hope to stay that way to the end. I’d rather leave voluntarily, still at the top of my game. Even if I end up leaving a few unused checks behind.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
I don’t write many checks anymore.
When I started my practice in 2000 I wrote a lot. Paychecks for my staff, my rent, insurance, IRA contributions, federal & state withholding, payments on my EMG machine, pretty much everything.
Checks are old. We’ve been using them in some form for roughly 2000 years.
But the online world has changed a lot of that. Now I write maybe 2-3 a month. I could probably do fewer, but haven’t bothered to set those accounts up that way.
I recently was down to my last few checks, so ordered replacements. The minimum order was 600. As I unpacked the box I realized they’re probably the last ones I’ll need, both because checks are gradually passing by and because there are more days behind in my neurology career than ahead.
The checks are a minor thing, but they do make you think. Certainly we’re in the last generation of people who will ever need to use paper checks. Some phrases like “blank check” will likely be with us long after they’re gone (like “dialing a phone”), but the real deal is heading the same way as 8-Track and VHS tapes.
As my 600 checks dwindle down, realistically, so will my career. There is no rewind button on life. I have no desire to leave medicine right now, but the passage of time changes things.
Does that mean I, like my checks, am also getting obsolete?
I hope not. I’d like to think I still have something to offer. I have 30 years of neurology experience behind me, and try to keep up to date on my field. My patients and staff depend on me to bring my best to the office every day.
I hope to stay that way to the end. I’d rather leave voluntarily, still at the top of my game. Even if I end up leaving a few unused checks behind.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
I don’t write many checks anymore.
When I started my practice in 2000 I wrote a lot. Paychecks for my staff, my rent, insurance, IRA contributions, federal & state withholding, payments on my EMG machine, pretty much everything.
Checks are old. We’ve been using them in some form for roughly 2000 years.
But the online world has changed a lot of that. Now I write maybe 2-3 a month. I could probably do fewer, but haven’t bothered to set those accounts up that way.
I recently was down to my last few checks, so ordered replacements. The minimum order was 600. As I unpacked the box I realized they’re probably the last ones I’ll need, both because checks are gradually passing by and because there are more days behind in my neurology career than ahead.
The checks are a minor thing, but they do make you think. Certainly we’re in the last generation of people who will ever need to use paper checks. Some phrases like “blank check” will likely be with us long after they’re gone (like “dialing a phone”), but the real deal is heading the same way as 8-Track and VHS tapes.
As my 600 checks dwindle down, realistically, so will my career. There is no rewind button on life. I have no desire to leave medicine right now, but the passage of time changes things.
Does that mean I, like my checks, am also getting obsolete?
I hope not. I’d like to think I still have something to offer. I have 30 years of neurology experience behind me, and try to keep up to date on my field. My patients and staff depend on me to bring my best to the office every day.
I hope to stay that way to the end. I’d rather leave voluntarily, still at the top of my game. Even if I end up leaving a few unused checks behind.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Rethinking the Rebels
Each month I set out on an expedition to find a topic for this column. I came across a new book Rebel Health by Susannah Fox that I thought might be a good one. It’s both a treatise on the shortcomings of healthcare and a Baedeker for patients on how to find their way to being better served. Her argument is that many patients’ needs are unmet and their conditions are often invisible to us in mainstream healthcare. We fail to find solutions to help them. Patients would benefit from more open access to their records and more resources to take control of their own health, she argues. A few chapters in, I thought, “Oh, here we go, another diatribe on doctors and how we care most about how to keep patients in their rightful, subordinate place.” The “Rebel” title is provocative and implies patients need to overthrow the status quo. Well, I am part of the establishment. I stopped reading. This book doesn’t apply to me, I thought.
After all, I’m a healthcare progressive, right? My notes and results have been open for years. I encourage shared decision-making and try to empower patients as much as treat them. The idea that I or my colleagues are unwilling to do whatever is necessary to meet our patients’ needs was maddening. We dedicate our lives to it. My young daughter often greets me in the morning by asking if I’ll be working tonight. Most nights, I am — answering patient messages, collaborating with colleagues to help patients, keeping up with medical knowledge. I was angry at what felt like unjust criticism, especially that we’d neglect patients because their problems are not obvious or worse, there is not enough money to be made helping them. Harrumph.
That’s when I realized the best thing for me was to read the entire book and digest the arguments. I pride myself on being well-read, but I fall into a common trap: the podcasts I listen to, news I consume, and books I read mostly affirm my beliefs. It is a healthy choice to seek dispositive data and contrasting stories rather than always feeding our personal opinions.
Rebel Health was not written by Robespierre. It was penned by a thoughtful, articulate patient advocate with over 20 years experience. She has far more bona fides than I could achieve in two lifetimes. In the book, she reminds us that She describes four patient archetypes: seekers, networkers, solvers, and champions, and offers a four-quadrant model to visualize how some patients are unhelped by our current healthcare system. She advocates for frictionless, open access to health data and tries to inspire patients to connect, innovate, and create to fill the voids that exist in healthcare. We have come a long way from the immured system of a decade ago; much of that is the result of patient advocates. But healthcare is still too costly, too fragmented and too many patients unhelped. “Community is a superpower,” she writes. I agree, we should assemble all the heroes in the universe for this challenge.
Fox also tells stories of patients who solved diagnostic dilemmas through their own research and advocacy. I thought of my own contrasting experiences of patients whose DIY care was based on misinformation and how their false confidence led to poorer outcomes for them. I want to share with her readers how physicians feel hurt when patients question our competence or place the opinion of an adversarial Redditor over ours. Physicians are sometimes wrong and often in doubt. Most of us care deeply about our patients regardless of how visible their diagnosis or how easy they are to appease.
We don’t have time to engage back-and-forth on an insignificantly abnormal test they find in their open chart or why B12 and hormone testing would not be helpful for their disease. It’s also not the patients’ fault. Having unfettered access to their data might add work, but it also adds value. They are trying to learn and be active in their care. Physicians are frustrated mostly because we don’t have time to meet these unmet needs. Everyone is trying their best and we all want the same thing: patients to be satisfied and well.
As for learning the skill of being open-minded, an excellent reference is Adam Grant’s Think Again. It’s inspiring and instructive of how we can all be more open, including how to have productive arguments rather than fruitless fights. We live in divisive times. Perhaps if we all put in effort to be open-minded, push down righteous indignation, and advance more honest humility we’d all be a bit better off.
Patients are the primary audience for the Rebel Health book. Yet, as we care about them and we all want to make healthcare better, it is worth reading in its entirety. I told my daughter I don’t have to work tonight because I’ve written my article this month. When she’s a little older, I’ll tell her all about it. To be successful, she’ll have to be as open-minded as she is smart. She can learn both.
I have no conflict of interest in the book.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Each month I set out on an expedition to find a topic for this column. I came across a new book Rebel Health by Susannah Fox that I thought might be a good one. It’s both a treatise on the shortcomings of healthcare and a Baedeker for patients on how to find their way to being better served. Her argument is that many patients’ needs are unmet and their conditions are often invisible to us in mainstream healthcare. We fail to find solutions to help them. Patients would benefit from more open access to their records and more resources to take control of their own health, she argues. A few chapters in, I thought, “Oh, here we go, another diatribe on doctors and how we care most about how to keep patients in their rightful, subordinate place.” The “Rebel” title is provocative and implies patients need to overthrow the status quo. Well, I am part of the establishment. I stopped reading. This book doesn’t apply to me, I thought.
After all, I’m a healthcare progressive, right? My notes and results have been open for years. I encourage shared decision-making and try to empower patients as much as treat them. The idea that I or my colleagues are unwilling to do whatever is necessary to meet our patients’ needs was maddening. We dedicate our lives to it. My young daughter often greets me in the morning by asking if I’ll be working tonight. Most nights, I am — answering patient messages, collaborating with colleagues to help patients, keeping up with medical knowledge. I was angry at what felt like unjust criticism, especially that we’d neglect patients because their problems are not obvious or worse, there is not enough money to be made helping them. Harrumph.
That’s when I realized the best thing for me was to read the entire book and digest the arguments. I pride myself on being well-read, but I fall into a common trap: the podcasts I listen to, news I consume, and books I read mostly affirm my beliefs. It is a healthy choice to seek dispositive data and contrasting stories rather than always feeding our personal opinions.
Rebel Health was not written by Robespierre. It was penned by a thoughtful, articulate patient advocate with over 20 years experience. She has far more bona fides than I could achieve in two lifetimes. In the book, she reminds us that She describes four patient archetypes: seekers, networkers, solvers, and champions, and offers a four-quadrant model to visualize how some patients are unhelped by our current healthcare system. She advocates for frictionless, open access to health data and tries to inspire patients to connect, innovate, and create to fill the voids that exist in healthcare. We have come a long way from the immured system of a decade ago; much of that is the result of patient advocates. But healthcare is still too costly, too fragmented and too many patients unhelped. “Community is a superpower,” she writes. I agree, we should assemble all the heroes in the universe for this challenge.
Fox also tells stories of patients who solved diagnostic dilemmas through their own research and advocacy. I thought of my own contrasting experiences of patients whose DIY care was based on misinformation and how their false confidence led to poorer outcomes for them. I want to share with her readers how physicians feel hurt when patients question our competence or place the opinion of an adversarial Redditor over ours. Physicians are sometimes wrong and often in doubt. Most of us care deeply about our patients regardless of how visible their diagnosis or how easy they are to appease.
We don’t have time to engage back-and-forth on an insignificantly abnormal test they find in their open chart or why B12 and hormone testing would not be helpful for their disease. It’s also not the patients’ fault. Having unfettered access to their data might add work, but it also adds value. They are trying to learn and be active in their care. Physicians are frustrated mostly because we don’t have time to meet these unmet needs. Everyone is trying their best and we all want the same thing: patients to be satisfied and well.
As for learning the skill of being open-minded, an excellent reference is Adam Grant’s Think Again. It’s inspiring and instructive of how we can all be more open, including how to have productive arguments rather than fruitless fights. We live in divisive times. Perhaps if we all put in effort to be open-minded, push down righteous indignation, and advance more honest humility we’d all be a bit better off.
Patients are the primary audience for the Rebel Health book. Yet, as we care about them and we all want to make healthcare better, it is worth reading in its entirety. I told my daughter I don’t have to work tonight because I’ve written my article this month. When she’s a little older, I’ll tell her all about it. To be successful, she’ll have to be as open-minded as she is smart. She can learn both.
I have no conflict of interest in the book.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Each month I set out on an expedition to find a topic for this column. I came across a new book Rebel Health by Susannah Fox that I thought might be a good one. It’s both a treatise on the shortcomings of healthcare and a Baedeker for patients on how to find their way to being better served. Her argument is that many patients’ needs are unmet and their conditions are often invisible to us in mainstream healthcare. We fail to find solutions to help them. Patients would benefit from more open access to their records and more resources to take control of their own health, she argues. A few chapters in, I thought, “Oh, here we go, another diatribe on doctors and how we care most about how to keep patients in their rightful, subordinate place.” The “Rebel” title is provocative and implies patients need to overthrow the status quo. Well, I am part of the establishment. I stopped reading. This book doesn’t apply to me, I thought.
After all, I’m a healthcare progressive, right? My notes and results have been open for years. I encourage shared decision-making and try to empower patients as much as treat them. The idea that I or my colleagues are unwilling to do whatever is necessary to meet our patients’ needs was maddening. We dedicate our lives to it. My young daughter often greets me in the morning by asking if I’ll be working tonight. Most nights, I am — answering patient messages, collaborating with colleagues to help patients, keeping up with medical knowledge. I was angry at what felt like unjust criticism, especially that we’d neglect patients because their problems are not obvious or worse, there is not enough money to be made helping them. Harrumph.
That’s when I realized the best thing for me was to read the entire book and digest the arguments. I pride myself on being well-read, but I fall into a common trap: the podcasts I listen to, news I consume, and books I read mostly affirm my beliefs. It is a healthy choice to seek dispositive data and contrasting stories rather than always feeding our personal opinions.
Rebel Health was not written by Robespierre. It was penned by a thoughtful, articulate patient advocate with over 20 years experience. She has far more bona fides than I could achieve in two lifetimes. In the book, she reminds us that She describes four patient archetypes: seekers, networkers, solvers, and champions, and offers a four-quadrant model to visualize how some patients are unhelped by our current healthcare system. She advocates for frictionless, open access to health data and tries to inspire patients to connect, innovate, and create to fill the voids that exist in healthcare. We have come a long way from the immured system of a decade ago; much of that is the result of patient advocates. But healthcare is still too costly, too fragmented and too many patients unhelped. “Community is a superpower,” she writes. I agree, we should assemble all the heroes in the universe for this challenge.
Fox also tells stories of patients who solved diagnostic dilemmas through their own research and advocacy. I thought of my own contrasting experiences of patients whose DIY care was based on misinformation and how their false confidence led to poorer outcomes for them. I want to share with her readers how physicians feel hurt when patients question our competence or place the opinion of an adversarial Redditor over ours. Physicians are sometimes wrong and often in doubt. Most of us care deeply about our patients regardless of how visible their diagnosis or how easy they are to appease.
We don’t have time to engage back-and-forth on an insignificantly abnormal test they find in their open chart or why B12 and hormone testing would not be helpful for their disease. It’s also not the patients’ fault. Having unfettered access to their data might add work, but it also adds value. They are trying to learn and be active in their care. Physicians are frustrated mostly because we don’t have time to meet these unmet needs. Everyone is trying their best and we all want the same thing: patients to be satisfied and well.
As for learning the skill of being open-minded, an excellent reference is Adam Grant’s Think Again. It’s inspiring and instructive of how we can all be more open, including how to have productive arguments rather than fruitless fights. We live in divisive times. Perhaps if we all put in effort to be open-minded, push down righteous indignation, and advance more honest humility we’d all be a bit better off.
Patients are the primary audience for the Rebel Health book. Yet, as we care about them and we all want to make healthcare better, it is worth reading in its entirety. I told my daughter I don’t have to work tonight because I’ve written my article this month. When she’s a little older, I’ll tell her all about it. To be successful, she’ll have to be as open-minded as she is smart. She can learn both.
I have no conflict of interest in the book.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Access to Perinatal Mental Healthcare: What Exactly Are The Obstacles?
The first of May is marked as the World Maternal Mental Health Day, a time for patient groups, medical societies, clinicians, and other colleagues who care for women to highlight maternal mental health and to advocate for increased awareness, enhanced access to care, decrease in stigma, and development of the most effective treatments.
In this spirit, and within the context of greater mental health awareness, I wanted to highlight the ironic dichotomy we see in reproductive psychiatry today. Namely, although we have many useful treatments available in the field to treat maternal psychiatric illness, there are barriers to accessing mental healthcare that prevent women from receiving treatment and getting well.
Thinking back on the last few years from the other side of the pandemic, when COVID concerns turned the experience of motherhood on its side in so many ways, we can only acknowledge that it is an important time in the field of reproductive psychiatry. We have seen not only the development of new pharmacologic (neurosteroids) and nonpharmacologic therapies (transcranial magnetic stimulation, cognitive-behaviorial therapy for perinatal depression), but also the focus on new digital apps for perinatal depression that may be scalable and that may help bridge the voids in access to effective treatment from the most rural to the most urban settings.
In a previous column, I wrote about the potential difficulties of identifying at-risk women with postpartum psychiatric illness, particularly within the context of disparate data collection methods and management of data. Hospital systems that favor paper screening methods rather than digital platforms pose special problems. I also noted an even larger concern: namely, once screened, it can be very challenging to engage women with postpartum depression in treatment, and women may ultimately not navigate to care for a variety of reasons. These components are but one part of the so-called “perinatal treatment cascade.” When we look at access to care, patients would ideally move from depression screening as an example and, following endorsement of significant symptoms, would receive a referral, which would result in the patient being seen, followed up, and getting well. But that is not what is happening.
A recent preliminary study published as a short communication in the Archives of Women’s Mental Health highlighted this issue. The authors used the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) to follow symptoms of depression in 145 pregnant women in ob.gyn. services, and found that there were low levels of adherence to psychiatric screenings and referrals in the perinatal period. Another study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found 30.8% of women with postpartum depression were identified clinically, 15.8% received treatment, and 3.2% achieved remission. That is the gulf, in 2024, that we have not managed to bridge.
The findings show the difficulty women experience accessing perinatal mental health resources. While we’ve known for a long time that the “perinatal treatment cascade” is real, what we don’t understand are the variables in the mix, particularly for patients in marginalized groups. We also do not know where women fall off the curve with regard to accessing care. In my mind, if we’re going to make a difference, we need to know the answer to that question.
Part of the issue is that the research into understanding why women fall off the curve is incomplete. You cannot simply hand a sheet to a woman with an EPDS score of 12 who’s depressed and has a newborn and expect her to navigate to care. What we should really be doing is investing in care navigation for women.
The situation is analogous to diagnosing and treating cardiac abnormalities in a catheterization laboratory. If a patient has a blocked coronary artery and needs a stent, then they need to go to the cath lab. We haven’t yet figured out the process in reproductive psychiatry to optimize the likelihood that patients will be screened and then referred to receive the best available treatment.
Some of our ob.gyn. colleagues have been working to improve access to perinatal mental health services, such as offering on-site services, and offering training and services to patients and providers on screening, assessment, and treatment. At the Center for Women’s Mental Health, we are conducting the Screening and Treatment Enhancement for Postpartum Depression study, which is a universal screening and referral program for women at our center. While some progress is being made, there are still far too many women who are falling through the cracks and not receiving the care they need.
It is both ironic and sad that the growing number of available treatments in reproductive psychiatry are scalable, yet we haven’t figured out how to facilitate access to care. While we should be excited about new treatments, we also need to take the time to understand what the barriers are for at-risk women accessing mental healthcare in the postpartum period.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. STEPS for PPD is funded by the Marriott Foundation. Full disclosure information for Dr. Cohen is available at womensmentalhealth.org. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
The first of May is marked as the World Maternal Mental Health Day, a time for patient groups, medical societies, clinicians, and other colleagues who care for women to highlight maternal mental health and to advocate for increased awareness, enhanced access to care, decrease in stigma, and development of the most effective treatments.
In this spirit, and within the context of greater mental health awareness, I wanted to highlight the ironic dichotomy we see in reproductive psychiatry today. Namely, although we have many useful treatments available in the field to treat maternal psychiatric illness, there are barriers to accessing mental healthcare that prevent women from receiving treatment and getting well.
Thinking back on the last few years from the other side of the pandemic, when COVID concerns turned the experience of motherhood on its side in so many ways, we can only acknowledge that it is an important time in the field of reproductive psychiatry. We have seen not only the development of new pharmacologic (neurosteroids) and nonpharmacologic therapies (transcranial magnetic stimulation, cognitive-behaviorial therapy for perinatal depression), but also the focus on new digital apps for perinatal depression that may be scalable and that may help bridge the voids in access to effective treatment from the most rural to the most urban settings.
In a previous column, I wrote about the potential difficulties of identifying at-risk women with postpartum psychiatric illness, particularly within the context of disparate data collection methods and management of data. Hospital systems that favor paper screening methods rather than digital platforms pose special problems. I also noted an even larger concern: namely, once screened, it can be very challenging to engage women with postpartum depression in treatment, and women may ultimately not navigate to care for a variety of reasons. These components are but one part of the so-called “perinatal treatment cascade.” When we look at access to care, patients would ideally move from depression screening as an example and, following endorsement of significant symptoms, would receive a referral, which would result in the patient being seen, followed up, and getting well. But that is not what is happening.
A recent preliminary study published as a short communication in the Archives of Women’s Mental Health highlighted this issue. The authors used the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) to follow symptoms of depression in 145 pregnant women in ob.gyn. services, and found that there were low levels of adherence to psychiatric screenings and referrals in the perinatal period. Another study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found 30.8% of women with postpartum depression were identified clinically, 15.8% received treatment, and 3.2% achieved remission. That is the gulf, in 2024, that we have not managed to bridge.
The findings show the difficulty women experience accessing perinatal mental health resources. While we’ve known for a long time that the “perinatal treatment cascade” is real, what we don’t understand are the variables in the mix, particularly for patients in marginalized groups. We also do not know where women fall off the curve with regard to accessing care. In my mind, if we’re going to make a difference, we need to know the answer to that question.
Part of the issue is that the research into understanding why women fall off the curve is incomplete. You cannot simply hand a sheet to a woman with an EPDS score of 12 who’s depressed and has a newborn and expect her to navigate to care. What we should really be doing is investing in care navigation for women.
The situation is analogous to diagnosing and treating cardiac abnormalities in a catheterization laboratory. If a patient has a blocked coronary artery and needs a stent, then they need to go to the cath lab. We haven’t yet figured out the process in reproductive psychiatry to optimize the likelihood that patients will be screened and then referred to receive the best available treatment.
Some of our ob.gyn. colleagues have been working to improve access to perinatal mental health services, such as offering on-site services, and offering training and services to patients and providers on screening, assessment, and treatment. At the Center for Women’s Mental Health, we are conducting the Screening and Treatment Enhancement for Postpartum Depression study, which is a universal screening and referral program for women at our center. While some progress is being made, there are still far too many women who are falling through the cracks and not receiving the care they need.
It is both ironic and sad that the growing number of available treatments in reproductive psychiatry are scalable, yet we haven’t figured out how to facilitate access to care. While we should be excited about new treatments, we also need to take the time to understand what the barriers are for at-risk women accessing mental healthcare in the postpartum period.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. STEPS for PPD is funded by the Marriott Foundation. Full disclosure information for Dr. Cohen is available at womensmentalhealth.org. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
The first of May is marked as the World Maternal Mental Health Day, a time for patient groups, medical societies, clinicians, and other colleagues who care for women to highlight maternal mental health and to advocate for increased awareness, enhanced access to care, decrease in stigma, and development of the most effective treatments.
In this spirit, and within the context of greater mental health awareness, I wanted to highlight the ironic dichotomy we see in reproductive psychiatry today. Namely, although we have many useful treatments available in the field to treat maternal psychiatric illness, there are barriers to accessing mental healthcare that prevent women from receiving treatment and getting well.
Thinking back on the last few years from the other side of the pandemic, when COVID concerns turned the experience of motherhood on its side in so many ways, we can only acknowledge that it is an important time in the field of reproductive psychiatry. We have seen not only the development of new pharmacologic (neurosteroids) and nonpharmacologic therapies (transcranial magnetic stimulation, cognitive-behaviorial therapy for perinatal depression), but also the focus on new digital apps for perinatal depression that may be scalable and that may help bridge the voids in access to effective treatment from the most rural to the most urban settings.
In a previous column, I wrote about the potential difficulties of identifying at-risk women with postpartum psychiatric illness, particularly within the context of disparate data collection methods and management of data. Hospital systems that favor paper screening methods rather than digital platforms pose special problems. I also noted an even larger concern: namely, once screened, it can be very challenging to engage women with postpartum depression in treatment, and women may ultimately not navigate to care for a variety of reasons. These components are but one part of the so-called “perinatal treatment cascade.” When we look at access to care, patients would ideally move from depression screening as an example and, following endorsement of significant symptoms, would receive a referral, which would result in the patient being seen, followed up, and getting well. But that is not what is happening.
A recent preliminary study published as a short communication in the Archives of Women’s Mental Health highlighted this issue. The authors used the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) to follow symptoms of depression in 145 pregnant women in ob.gyn. services, and found that there were low levels of adherence to psychiatric screenings and referrals in the perinatal period. Another study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found 30.8% of women with postpartum depression were identified clinically, 15.8% received treatment, and 3.2% achieved remission. That is the gulf, in 2024, that we have not managed to bridge.
The findings show the difficulty women experience accessing perinatal mental health resources. While we’ve known for a long time that the “perinatal treatment cascade” is real, what we don’t understand are the variables in the mix, particularly for patients in marginalized groups. We also do not know where women fall off the curve with regard to accessing care. In my mind, if we’re going to make a difference, we need to know the answer to that question.
Part of the issue is that the research into understanding why women fall off the curve is incomplete. You cannot simply hand a sheet to a woman with an EPDS score of 12 who’s depressed and has a newborn and expect her to navigate to care. What we should really be doing is investing in care navigation for women.
The situation is analogous to diagnosing and treating cardiac abnormalities in a catheterization laboratory. If a patient has a blocked coronary artery and needs a stent, then they need to go to the cath lab. We haven’t yet figured out the process in reproductive psychiatry to optimize the likelihood that patients will be screened and then referred to receive the best available treatment.
Some of our ob.gyn. colleagues have been working to improve access to perinatal mental health services, such as offering on-site services, and offering training and services to patients and providers on screening, assessment, and treatment. At the Center for Women’s Mental Health, we are conducting the Screening and Treatment Enhancement for Postpartum Depression study, which is a universal screening and referral program for women at our center. While some progress is being made, there are still far too many women who are falling through the cracks and not receiving the care they need.
It is both ironic and sad that the growing number of available treatments in reproductive psychiatry are scalable, yet we haven’t figured out how to facilitate access to care. While we should be excited about new treatments, we also need to take the time to understand what the barriers are for at-risk women accessing mental healthcare in the postpartum period.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. STEPS for PPD is funded by the Marriott Foundation. Full disclosure information for Dr. Cohen is available at womensmentalhealth.org. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
Will the Federal Non-Compete Ban Take Effect?
(with very limited exceptions). The final rule will not go into effect until 120 days after its publication in the Federal Register, which took place on May 7, and numerous legal challenges appear to be on the horizon.
The principal components of the rule are as follows:
- After the effective date, most non-compete agreements (which prevent departing employees from signing with a new employer for a defined period within a specific geographic area) are banned nationwide.
- The rule exempts certain “senior executives,” ie individuals who earn more than $151,164 annually and serve in policy-making positions.
- There is another major exception for non-competes connected with a sale of a business.
- While not explicitly stated, the rule arguably exempts non-profits, tax-exempt hospitals, and other tax-exempt entities.
- Employers must provide verbal and written notice to employees regarding existing agreements, which would be voided under the rule.
The final rule is the latest skirmish in an ongoing, years-long debate. Twelve states have already put non-compete bans in place, according to a recent paper, and they may serve as a harbinger of things to come should the federal ban go into effect. Each state rule varies in its specifics as states respond to local market conditions. While some states ban all non-compete agreements outright, others limit them based on variables, such as income and employment circumstances. Of course, should the federal ban take effect, it will supersede whatever rules the individual states have in place.
In drafting the rule, the FTC reasoned that non-compete clauses constitute restraint of trade, and eliminating them could potentially increase worker earnings as well as lower health care costs by billions of dollars. In its statements on the proposed ban, the FTC claimed that it could lower health spending across the board by almost $150 billion per year and return $300 million to workers each year in earnings. The agency cited a large body of research that non-competes make it harder for workers to move between jobs and can raise prices for goods and services, while suppressing wages for workers and inhibiting the creation of new businesses.
Most physicians affected by non-compete agreements heavily favor the new rule, because it would give them more control over their careers and expand their practice and income opportunities. It would allow them to get a new job with a competing organization, bucking a long-standing trend that hospitals and health care systems have heavily relied on to keep staff in place.
The rule would, however, keep in place “non-solicitation” rules that many health care organizations have put in place. That means that if a physician leaves an employer, he or she cannot reach out to former patients and colleagues to bring them along or invite them to join him or her at the new employment venue.
Within that clause, however, the FTC has specified that if such non-solicitation agreement has the “equivalent effect” of a non-compete, the agency would deem it such. That means, even if that rule stands, it could be contested and may be interpreted as violating the non-compete provision. So, there is value in reading all the fine print should the rule move forward.
Physicians in independent practices who employ physician assistants and nurse practitioners have expressed concerns that their expensively trained employees might be tempted to accept a nearby, higher-paying position. The “non-solicitation” clause would theoretically prevent them from taking patients and co-workers with them — unless it were successfully contested. Many questions remain.
Further complicating the non-compete ban issue is how it might impact nonprofit institutions. Most hospitals structured as nonprofits would theoretically be exempt from the rule, although it is not specifically stated in the rule itself, because the FTC Act gives the Commission jurisdiction over for-profit companies only. This would obviously create an unfair advantage for nonprofits, who could continue writing non-compete clauses with impunity.
All of these questions may be moot, of course, because a number of powerful entities with deep pockets have lined up in opposition to the rule. Some of them have even questioned the FTC’s authority to pass the rule at all, on the grounds that Section 5 of the FTC Act does not give it the authority to police labor markets. A lawsuit has already been filed by the US Chamber of Commerce. Other large groups in opposition are the American Medical Group Association, the American Hospital Association, and numerous large hospital and healthcare networks.
Only time will tell whether this issue will be regulated on a national level or remain the purview of each individual state.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
(with very limited exceptions). The final rule will not go into effect until 120 days after its publication in the Federal Register, which took place on May 7, and numerous legal challenges appear to be on the horizon.
The principal components of the rule are as follows:
- After the effective date, most non-compete agreements (which prevent departing employees from signing with a new employer for a defined period within a specific geographic area) are banned nationwide.
- The rule exempts certain “senior executives,” ie individuals who earn more than $151,164 annually and serve in policy-making positions.
- There is another major exception for non-competes connected with a sale of a business.
- While not explicitly stated, the rule arguably exempts non-profits, tax-exempt hospitals, and other tax-exempt entities.
- Employers must provide verbal and written notice to employees regarding existing agreements, which would be voided under the rule.
The final rule is the latest skirmish in an ongoing, years-long debate. Twelve states have already put non-compete bans in place, according to a recent paper, and they may serve as a harbinger of things to come should the federal ban go into effect. Each state rule varies in its specifics as states respond to local market conditions. While some states ban all non-compete agreements outright, others limit them based on variables, such as income and employment circumstances. Of course, should the federal ban take effect, it will supersede whatever rules the individual states have in place.
In drafting the rule, the FTC reasoned that non-compete clauses constitute restraint of trade, and eliminating them could potentially increase worker earnings as well as lower health care costs by billions of dollars. In its statements on the proposed ban, the FTC claimed that it could lower health spending across the board by almost $150 billion per year and return $300 million to workers each year in earnings. The agency cited a large body of research that non-competes make it harder for workers to move between jobs and can raise prices for goods and services, while suppressing wages for workers and inhibiting the creation of new businesses.
Most physicians affected by non-compete agreements heavily favor the new rule, because it would give them more control over their careers and expand their practice and income opportunities. It would allow them to get a new job with a competing organization, bucking a long-standing trend that hospitals and health care systems have heavily relied on to keep staff in place.
The rule would, however, keep in place “non-solicitation” rules that many health care organizations have put in place. That means that if a physician leaves an employer, he or she cannot reach out to former patients and colleagues to bring them along or invite them to join him or her at the new employment venue.
Within that clause, however, the FTC has specified that if such non-solicitation agreement has the “equivalent effect” of a non-compete, the agency would deem it such. That means, even if that rule stands, it could be contested and may be interpreted as violating the non-compete provision. So, there is value in reading all the fine print should the rule move forward.
Physicians in independent practices who employ physician assistants and nurse practitioners have expressed concerns that their expensively trained employees might be tempted to accept a nearby, higher-paying position. The “non-solicitation” clause would theoretically prevent them from taking patients and co-workers with them — unless it were successfully contested. Many questions remain.
Further complicating the non-compete ban issue is how it might impact nonprofit institutions. Most hospitals structured as nonprofits would theoretically be exempt from the rule, although it is not specifically stated in the rule itself, because the FTC Act gives the Commission jurisdiction over for-profit companies only. This would obviously create an unfair advantage for nonprofits, who could continue writing non-compete clauses with impunity.
All of these questions may be moot, of course, because a number of powerful entities with deep pockets have lined up in opposition to the rule. Some of them have even questioned the FTC’s authority to pass the rule at all, on the grounds that Section 5 of the FTC Act does not give it the authority to police labor markets. A lawsuit has already been filed by the US Chamber of Commerce. Other large groups in opposition are the American Medical Group Association, the American Hospital Association, and numerous large hospital and healthcare networks.
Only time will tell whether this issue will be regulated on a national level or remain the purview of each individual state.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
(with very limited exceptions). The final rule will not go into effect until 120 days after its publication in the Federal Register, which took place on May 7, and numerous legal challenges appear to be on the horizon.
The principal components of the rule are as follows:
- After the effective date, most non-compete agreements (which prevent departing employees from signing with a new employer for a defined period within a specific geographic area) are banned nationwide.
- The rule exempts certain “senior executives,” ie individuals who earn more than $151,164 annually and serve in policy-making positions.
- There is another major exception for non-competes connected with a sale of a business.
- While not explicitly stated, the rule arguably exempts non-profits, tax-exempt hospitals, and other tax-exempt entities.
- Employers must provide verbal and written notice to employees regarding existing agreements, which would be voided under the rule.
The final rule is the latest skirmish in an ongoing, years-long debate. Twelve states have already put non-compete bans in place, according to a recent paper, and they may serve as a harbinger of things to come should the federal ban go into effect. Each state rule varies in its specifics as states respond to local market conditions. While some states ban all non-compete agreements outright, others limit them based on variables, such as income and employment circumstances. Of course, should the federal ban take effect, it will supersede whatever rules the individual states have in place.
In drafting the rule, the FTC reasoned that non-compete clauses constitute restraint of trade, and eliminating them could potentially increase worker earnings as well as lower health care costs by billions of dollars. In its statements on the proposed ban, the FTC claimed that it could lower health spending across the board by almost $150 billion per year and return $300 million to workers each year in earnings. The agency cited a large body of research that non-competes make it harder for workers to move between jobs and can raise prices for goods and services, while suppressing wages for workers and inhibiting the creation of new businesses.
Most physicians affected by non-compete agreements heavily favor the new rule, because it would give them more control over their careers and expand their practice and income opportunities. It would allow them to get a new job with a competing organization, bucking a long-standing trend that hospitals and health care systems have heavily relied on to keep staff in place.
The rule would, however, keep in place “non-solicitation” rules that many health care organizations have put in place. That means that if a physician leaves an employer, he or she cannot reach out to former patients and colleagues to bring them along or invite them to join him or her at the new employment venue.
Within that clause, however, the FTC has specified that if such non-solicitation agreement has the “equivalent effect” of a non-compete, the agency would deem it such. That means, even if that rule stands, it could be contested and may be interpreted as violating the non-compete provision. So, there is value in reading all the fine print should the rule move forward.
Physicians in independent practices who employ physician assistants and nurse practitioners have expressed concerns that their expensively trained employees might be tempted to accept a nearby, higher-paying position. The “non-solicitation” clause would theoretically prevent them from taking patients and co-workers with them — unless it were successfully contested. Many questions remain.
Further complicating the non-compete ban issue is how it might impact nonprofit institutions. Most hospitals structured as nonprofits would theoretically be exempt from the rule, although it is not specifically stated in the rule itself, because the FTC Act gives the Commission jurisdiction over for-profit companies only. This would obviously create an unfair advantage for nonprofits, who could continue writing non-compete clauses with impunity.
All of these questions may be moot, of course, because a number of powerful entities with deep pockets have lined up in opposition to the rule. Some of them have even questioned the FTC’s authority to pass the rule at all, on the grounds that Section 5 of the FTC Act does not give it the authority to police labor markets. A lawsuit has already been filed by the US Chamber of Commerce. Other large groups in opposition are the American Medical Group Association, the American Hospital Association, and numerous large hospital and healthcare networks.
Only time will tell whether this issue will be regulated on a national level or remain the purview of each individual state.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
Don’t Miss the Dx: A 24-Year-Old Man With Sudden-Onset Hematuria, Proteinuria, Edema, and Hypertension
Presentation
A 24-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents to urgent care with a 1-week history of sudden-onset dark urine, leg swelling, and unusually high blood pressure readings, with recent values around 160/100 mm Hg. Physical examination reveals pitting edema up to the mid-shins and mild periorbital edema, with an elevated blood pressure of 158/98 mm Hg. Past medical history was significant for frequent upper respiratory tract infections over the past year. Laboratory findings include hematuria, proteinuria, and a raised serum creatinine level at 1.8 mg/dL, indicating a reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 45 mL/min/1.73 m2. Other tests such as a complete blood count and comprehensive metabolic panel (except for creatinine and albumin) are within normal limits. Given these findings, the patient is referred to nephrology for further evaluation to determine the underlying cause of his renal symptoms.
Differential Diagnosis
A glomerular disease can be assumed to be present if the patient manifests glomerular hematuria, glomerular proteinuria, or both, such as in this patient.
Glomerulonephritis occurs due to inflammation in the glomeruli, which leads to blood in urine, variable degrees of protein in urine (sometimes in the nephrotic range), and white blood cells in urine without any urinary tract infection. Patients may also experience hypertension and kidney function impairment. Diagnoses to consider include:
- Postinfectious glomerulonephritis
- Crescentic glomerulonephritis
- Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis
- Glomerulonephritis associated with nonstreptococcal infection
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
- Membranous glomerulonephritis
- Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
- Rapidly Progressive glomerulonephritis
All patients presenting with proteinuria and hematuria should undergo a thorough evaluation for glomerular disease, which generally involves laboratory testing and, in most patients, a kidney biopsy to obtain a definitive diagnosis.
Diagnosis
This patient underwent a renal biopsy, which showed C3-dominant deposition by immunofluorescence; electron microscopy (EM) showed discontinuous, ill-defined intramembranous deposits; and mass spectrometry showed terminal complement components in C3 deposits. The patient was diagnosed with C3 glomerulonephritis (C3G).
The diagnosis of C3G is established by kidney biopsy demonstrating the characteristic findings on immunofluorescence microscopy or EM in a patient with suspected glomerulonephritis. In patients with biopsy-confirmed C3G, additional testing should be performed to help identify the underlying etiology of the glomerulopathy to help determine therapy.
For all patients diagnosed with C3G, especially those who are older than 50 years, it is important to rule out monoclonal gammopathy which can be done through various tests such as serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation, serum free light chains, and urine protein electrophoresis and immunofixation. The presence of a paraprotein, including a monoclonal light chain, can activate the alternative complement cascade and may be responsible for the condition.
Expert opinion recommends a comprehensive complement evaluation for all C3 glomerulopathy patients, including overall complement activity assessment, serum levels measurement of complement proteins and their split products, and autoantibodies screening.
Complement evaluation may include:
- Serum C3 and C4
- Soluble C5b-9 (soluble membrane attack complex)
- Serum factor H
- Serum factor B, factor I, and membrane cofactor protein (MCP; CD46)
All patients with C3G should also undergo screening for autoantibodies:
- C3 nephritic factor (C3NeF)
- C5 nephritic factor (C5NeF)
- C4 nephritic factor (C4NeF)
- Other autoantibodies against factor H, factor B, and/or C3b
It is recommended that genetic testing be considered for patients with C3 glomerulopathy to screen for complement genes including C3, CFB, CFH, CFHR5, and CFI and copy number variations and rearrangements of the CFH-CFHR gene cluster. The value of genetic testing in the clinical setting is still being defined; however, it has been observed that patients with mutations in complement genes generally respond less favorably to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) compared with those who are positive for nephritic factors.
Management
The patient was managed with an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor to treat proteinuria and hypertension and MMF for immunosuppression. Enrollment in a clinical trial of an investigational complement inhibitor was discussed with the patient.
Currently, there are no therapeutic agents specifically designed to target the underlying complement dysregulation that occurs in individuals with C3G, and an optimal treatment for C3 glomerulopathy has not been established.
Various nonspecific therapies have been used to treat C3G, including plasmapheresis, steroids, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, and MMF and have shown positive results. For patients with C3G who have a known genetic variant (eg, CFH mutation) or who have acute kidney injury, plasmapheresis and plasma exchange may be helpful. Using these agents judiciously and in conjunction with optimal blood pressure control is important for maximum benefit in treating C3G. When someone with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) caused by C3G chooses to have a kidney transplant, it is important to know that C3G is likely to return in almost all cases and is the leading cause of transplant failure in 50%-90% of recipients.
Prognosis
The prognosis of C3G varies and is affected by various clinical and histological factors. While some patients may have consistently low levels of protein in their urine and maintain stable kidney function over time, others may experience severe nephrotic syndrome or rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, which often leads to a poor prognosis.
Progression to ESRD is a major complication of C3G, with approximately 70% of affected children and 30%-50% of adults reaching this stage. In addition, disease recurrence is common after kidney transplantation, with about 50% of patients experiencing allograft loss within 10 years. Predictive factors for disease progression, although not robustly established, include initial eGFR at diagnosis, percentage of tubular atrophy, and extent of interstitial fibrosis in the cortical area as observed on kidney biopsies.
Clinical Takeaways
For patients exhibiting symptoms like proteinuria and hematuria indicative of glomerulonephritis, a comprehensive evaluation including laboratory tests and a kidney biopsy is essential to confirm a C3G diagnosis through characteristic findings on immunofluorescence microscopy or electron microscopy.
Additional tests to rule out associated conditions like monoclonal gammopathy and comprehensive complement evaluation are also recommended to understand the underlying etiology and guide therapy.
Though there are no treatments specifically targeting the underlying complement dysregulation unique to C3G, nonspecific therapies like ACE inhibitors, immunosuppressants (eg, MMF), and plasmapheresis are commonly used.
Some anticomplement therapies are available or under investigation, which might offer more targeted intervention options.
The prognosis for patients with C3G can vary widely and factors such as initial eGFR, the extent of tubular atrophy, and interstitial fibrosis are important predictors of disease progression.
Dr. Alper is an associate professor, Nephrology, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, Louisiana. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Presentation
A 24-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents to urgent care with a 1-week history of sudden-onset dark urine, leg swelling, and unusually high blood pressure readings, with recent values around 160/100 mm Hg. Physical examination reveals pitting edema up to the mid-shins and mild periorbital edema, with an elevated blood pressure of 158/98 mm Hg. Past medical history was significant for frequent upper respiratory tract infections over the past year. Laboratory findings include hematuria, proteinuria, and a raised serum creatinine level at 1.8 mg/dL, indicating a reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 45 mL/min/1.73 m2. Other tests such as a complete blood count and comprehensive metabolic panel (except for creatinine and albumin) are within normal limits. Given these findings, the patient is referred to nephrology for further evaluation to determine the underlying cause of his renal symptoms.
Differential Diagnosis
A glomerular disease can be assumed to be present if the patient manifests glomerular hematuria, glomerular proteinuria, or both, such as in this patient.
Glomerulonephritis occurs due to inflammation in the glomeruli, which leads to blood in urine, variable degrees of protein in urine (sometimes in the nephrotic range), and white blood cells in urine without any urinary tract infection. Patients may also experience hypertension and kidney function impairment. Diagnoses to consider include:
- Postinfectious glomerulonephritis
- Crescentic glomerulonephritis
- Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis
- Glomerulonephritis associated with nonstreptococcal infection
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
- Membranous glomerulonephritis
- Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
- Rapidly Progressive glomerulonephritis
All patients presenting with proteinuria and hematuria should undergo a thorough evaluation for glomerular disease, which generally involves laboratory testing and, in most patients, a kidney biopsy to obtain a definitive diagnosis.
Diagnosis
This patient underwent a renal biopsy, which showed C3-dominant deposition by immunofluorescence; electron microscopy (EM) showed discontinuous, ill-defined intramembranous deposits; and mass spectrometry showed terminal complement components in C3 deposits. The patient was diagnosed with C3 glomerulonephritis (C3G).
The diagnosis of C3G is established by kidney biopsy demonstrating the characteristic findings on immunofluorescence microscopy or EM in a patient with suspected glomerulonephritis. In patients with biopsy-confirmed C3G, additional testing should be performed to help identify the underlying etiology of the glomerulopathy to help determine therapy.
For all patients diagnosed with C3G, especially those who are older than 50 years, it is important to rule out monoclonal gammopathy which can be done through various tests such as serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation, serum free light chains, and urine protein electrophoresis and immunofixation. The presence of a paraprotein, including a monoclonal light chain, can activate the alternative complement cascade and may be responsible for the condition.
Expert opinion recommends a comprehensive complement evaluation for all C3 glomerulopathy patients, including overall complement activity assessment, serum levels measurement of complement proteins and their split products, and autoantibodies screening.
Complement evaluation may include:
- Serum C3 and C4
- Soluble C5b-9 (soluble membrane attack complex)
- Serum factor H
- Serum factor B, factor I, and membrane cofactor protein (MCP; CD46)
All patients with C3G should also undergo screening for autoantibodies:
- C3 nephritic factor (C3NeF)
- C5 nephritic factor (C5NeF)
- C4 nephritic factor (C4NeF)
- Other autoantibodies against factor H, factor B, and/or C3b
It is recommended that genetic testing be considered for patients with C3 glomerulopathy to screen for complement genes including C3, CFB, CFH, CFHR5, and CFI and copy number variations and rearrangements of the CFH-CFHR gene cluster. The value of genetic testing in the clinical setting is still being defined; however, it has been observed that patients with mutations in complement genes generally respond less favorably to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) compared with those who are positive for nephritic factors.
Management
The patient was managed with an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor to treat proteinuria and hypertension and MMF for immunosuppression. Enrollment in a clinical trial of an investigational complement inhibitor was discussed with the patient.
Currently, there are no therapeutic agents specifically designed to target the underlying complement dysregulation that occurs in individuals with C3G, and an optimal treatment for C3 glomerulopathy has not been established.
Various nonspecific therapies have been used to treat C3G, including plasmapheresis, steroids, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, and MMF and have shown positive results. For patients with C3G who have a known genetic variant (eg, CFH mutation) or who have acute kidney injury, plasmapheresis and plasma exchange may be helpful. Using these agents judiciously and in conjunction with optimal blood pressure control is important for maximum benefit in treating C3G. When someone with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) caused by C3G chooses to have a kidney transplant, it is important to know that C3G is likely to return in almost all cases and is the leading cause of transplant failure in 50%-90% of recipients.
Prognosis
The prognosis of C3G varies and is affected by various clinical and histological factors. While some patients may have consistently low levels of protein in their urine and maintain stable kidney function over time, others may experience severe nephrotic syndrome or rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, which often leads to a poor prognosis.
Progression to ESRD is a major complication of C3G, with approximately 70% of affected children and 30%-50% of adults reaching this stage. In addition, disease recurrence is common after kidney transplantation, with about 50% of patients experiencing allograft loss within 10 years. Predictive factors for disease progression, although not robustly established, include initial eGFR at diagnosis, percentage of tubular atrophy, and extent of interstitial fibrosis in the cortical area as observed on kidney biopsies.
Clinical Takeaways
For patients exhibiting symptoms like proteinuria and hematuria indicative of glomerulonephritis, a comprehensive evaluation including laboratory tests and a kidney biopsy is essential to confirm a C3G diagnosis through characteristic findings on immunofluorescence microscopy or electron microscopy.
Additional tests to rule out associated conditions like monoclonal gammopathy and comprehensive complement evaluation are also recommended to understand the underlying etiology and guide therapy.
Though there are no treatments specifically targeting the underlying complement dysregulation unique to C3G, nonspecific therapies like ACE inhibitors, immunosuppressants (eg, MMF), and plasmapheresis are commonly used.
Some anticomplement therapies are available or under investigation, which might offer more targeted intervention options.
The prognosis for patients with C3G can vary widely and factors such as initial eGFR, the extent of tubular atrophy, and interstitial fibrosis are important predictors of disease progression.
Dr. Alper is an associate professor, Nephrology, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, Louisiana. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Presentation
A 24-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents to urgent care with a 1-week history of sudden-onset dark urine, leg swelling, and unusually high blood pressure readings, with recent values around 160/100 mm Hg. Physical examination reveals pitting edema up to the mid-shins and mild periorbital edema, with an elevated blood pressure of 158/98 mm Hg. Past medical history was significant for frequent upper respiratory tract infections over the past year. Laboratory findings include hematuria, proteinuria, and a raised serum creatinine level at 1.8 mg/dL, indicating a reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 45 mL/min/1.73 m2. Other tests such as a complete blood count and comprehensive metabolic panel (except for creatinine and albumin) are within normal limits. Given these findings, the patient is referred to nephrology for further evaluation to determine the underlying cause of his renal symptoms.
Differential Diagnosis
A glomerular disease can be assumed to be present if the patient manifests glomerular hematuria, glomerular proteinuria, or both, such as in this patient.
Glomerulonephritis occurs due to inflammation in the glomeruli, which leads to blood in urine, variable degrees of protein in urine (sometimes in the nephrotic range), and white blood cells in urine without any urinary tract infection. Patients may also experience hypertension and kidney function impairment. Diagnoses to consider include:
- Postinfectious glomerulonephritis
- Crescentic glomerulonephritis
- Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis
- Glomerulonephritis associated with nonstreptococcal infection
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
- Membranous glomerulonephritis
- Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
- Rapidly Progressive glomerulonephritis
All patients presenting with proteinuria and hematuria should undergo a thorough evaluation for glomerular disease, which generally involves laboratory testing and, in most patients, a kidney biopsy to obtain a definitive diagnosis.
Diagnosis
This patient underwent a renal biopsy, which showed C3-dominant deposition by immunofluorescence; electron microscopy (EM) showed discontinuous, ill-defined intramembranous deposits; and mass spectrometry showed terminal complement components in C3 deposits. The patient was diagnosed with C3 glomerulonephritis (C3G).
The diagnosis of C3G is established by kidney biopsy demonstrating the characteristic findings on immunofluorescence microscopy or EM in a patient with suspected glomerulonephritis. In patients with biopsy-confirmed C3G, additional testing should be performed to help identify the underlying etiology of the glomerulopathy to help determine therapy.
For all patients diagnosed with C3G, especially those who are older than 50 years, it is important to rule out monoclonal gammopathy which can be done through various tests such as serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation, serum free light chains, and urine protein electrophoresis and immunofixation. The presence of a paraprotein, including a monoclonal light chain, can activate the alternative complement cascade and may be responsible for the condition.
Expert opinion recommends a comprehensive complement evaluation for all C3 glomerulopathy patients, including overall complement activity assessment, serum levels measurement of complement proteins and their split products, and autoantibodies screening.
Complement evaluation may include:
- Serum C3 and C4
- Soluble C5b-9 (soluble membrane attack complex)
- Serum factor H
- Serum factor B, factor I, and membrane cofactor protein (MCP; CD46)
All patients with C3G should also undergo screening for autoantibodies:
- C3 nephritic factor (C3NeF)
- C5 nephritic factor (C5NeF)
- C4 nephritic factor (C4NeF)
- Other autoantibodies against factor H, factor B, and/or C3b
It is recommended that genetic testing be considered for patients with C3 glomerulopathy to screen for complement genes including C3, CFB, CFH, CFHR5, and CFI and copy number variations and rearrangements of the CFH-CFHR gene cluster. The value of genetic testing in the clinical setting is still being defined; however, it has been observed that patients with mutations in complement genes generally respond less favorably to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) compared with those who are positive for nephritic factors.
Management
The patient was managed with an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor to treat proteinuria and hypertension and MMF for immunosuppression. Enrollment in a clinical trial of an investigational complement inhibitor was discussed with the patient.
Currently, there are no therapeutic agents specifically designed to target the underlying complement dysregulation that occurs in individuals with C3G, and an optimal treatment for C3 glomerulopathy has not been established.
Various nonspecific therapies have been used to treat C3G, including plasmapheresis, steroids, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, and MMF and have shown positive results. For patients with C3G who have a known genetic variant (eg, CFH mutation) or who have acute kidney injury, plasmapheresis and plasma exchange may be helpful. Using these agents judiciously and in conjunction with optimal blood pressure control is important for maximum benefit in treating C3G. When someone with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) caused by C3G chooses to have a kidney transplant, it is important to know that C3G is likely to return in almost all cases and is the leading cause of transplant failure in 50%-90% of recipients.
Prognosis
The prognosis of C3G varies and is affected by various clinical and histological factors. While some patients may have consistently low levels of protein in their urine and maintain stable kidney function over time, others may experience severe nephrotic syndrome or rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, which often leads to a poor prognosis.
Progression to ESRD is a major complication of C3G, with approximately 70% of affected children and 30%-50% of adults reaching this stage. In addition, disease recurrence is common after kidney transplantation, with about 50% of patients experiencing allograft loss within 10 years. Predictive factors for disease progression, although not robustly established, include initial eGFR at diagnosis, percentage of tubular atrophy, and extent of interstitial fibrosis in the cortical area as observed on kidney biopsies.
Clinical Takeaways
For patients exhibiting symptoms like proteinuria and hematuria indicative of glomerulonephritis, a comprehensive evaluation including laboratory tests and a kidney biopsy is essential to confirm a C3G diagnosis through characteristic findings on immunofluorescence microscopy or electron microscopy.
Additional tests to rule out associated conditions like monoclonal gammopathy and comprehensive complement evaluation are also recommended to understand the underlying etiology and guide therapy.
Though there are no treatments specifically targeting the underlying complement dysregulation unique to C3G, nonspecific therapies like ACE inhibitors, immunosuppressants (eg, MMF), and plasmapheresis are commonly used.
Some anticomplement therapies are available or under investigation, which might offer more targeted intervention options.
The prognosis for patients with C3G can vary widely and factors such as initial eGFR, the extent of tubular atrophy, and interstitial fibrosis are important predictors of disease progression.
Dr. Alper is an associate professor, Nephrology, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, Louisiana. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An 8-year-old girl presented with papules on her bilateral eyelid margins
, with an equal distribution across genders and ethnicities.1 It is caused by mutations in the ECM1 gene2 on chromosome 1q21. This leads to the abnormal deposition of hyaline material in various tissues across different organ systems, with the classic manifestations known as the “string of pearls” sign and a hoarse cry or voice.
The rarity of lipoid proteinosis often leads to challenges in diagnosis. Particularly when deviating from the common association with consanguinity, the potential for de novo mutations or a broader genetic variability in disease expression is highlighted. Our patient presents with symptoms that are pathognomonic to LP with moniliform blepharosis and hoarseness of the voice, in addition to scarring of the extremities.
Other common clinical manifestations in patients with LP include cobblestoning of the mucosa; hyperkeratosis of the elbows, knees, and hands; and calcification of the amygdala with neuroimaging.3
Genetic testing that identifies a loss-of-function mutation in ECM1 offers diagnostic confirmation. Patients often need multidisciplinary care involving dermatology; ear, nose, throat; neurology; and genetics. Treatment of LP is mostly symptomatic with unsatisfactory resolution of cutaneous changes, with retinoids such as acitretin used as the first-line option and surgery as a consideration for laryngeal hyaline deposits.2 Although LP can affect different organ systems, patients tend to have a normal lifespan.
LP is a rare disorder that dermatologists often learn about during textbook sessions or didactics in residency but do not see in practice for decades, or if ever. This case highlights the need to review the classic presentations of rare conditions.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Chang, BS, Western University of Health Sciences, College of Osteopathic Medicine, Pomona, California; Dr. Connie Chang, Verdugo Dermatology, Glendale, California; and Dr. Yuchieh Kathryn Chang, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Mcgrath JA. Handb Clin Neurol. 2015:132:317-22. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-62702-5.00023-8.
2. Hamada Tet al. Hum Mol Genet. 2002 Apr 1;11(7):833-40. doi: 10.1093/hmg/11.7.833.
3. Frenkel B et al. Clin Oral Investig. 2017 Sep;21(7):2245-51 doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-2017-7.
, with an equal distribution across genders and ethnicities.1 It is caused by mutations in the ECM1 gene2 on chromosome 1q21. This leads to the abnormal deposition of hyaline material in various tissues across different organ systems, with the classic manifestations known as the “string of pearls” sign and a hoarse cry or voice.
The rarity of lipoid proteinosis often leads to challenges in diagnosis. Particularly when deviating from the common association with consanguinity, the potential for de novo mutations or a broader genetic variability in disease expression is highlighted. Our patient presents with symptoms that are pathognomonic to LP with moniliform blepharosis and hoarseness of the voice, in addition to scarring of the extremities.
Other common clinical manifestations in patients with LP include cobblestoning of the mucosa; hyperkeratosis of the elbows, knees, and hands; and calcification of the amygdala with neuroimaging.3
Genetic testing that identifies a loss-of-function mutation in ECM1 offers diagnostic confirmation. Patients often need multidisciplinary care involving dermatology; ear, nose, throat; neurology; and genetics. Treatment of LP is mostly symptomatic with unsatisfactory resolution of cutaneous changes, with retinoids such as acitretin used as the first-line option and surgery as a consideration for laryngeal hyaline deposits.2 Although LP can affect different organ systems, patients tend to have a normal lifespan.
LP is a rare disorder that dermatologists often learn about during textbook sessions or didactics in residency but do not see in practice for decades, or if ever. This case highlights the need to review the classic presentations of rare conditions.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Chang, BS, Western University of Health Sciences, College of Osteopathic Medicine, Pomona, California; Dr. Connie Chang, Verdugo Dermatology, Glendale, California; and Dr. Yuchieh Kathryn Chang, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Mcgrath JA. Handb Clin Neurol. 2015:132:317-22. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-62702-5.00023-8.
2. Hamada Tet al. Hum Mol Genet. 2002 Apr 1;11(7):833-40. doi: 10.1093/hmg/11.7.833.
3. Frenkel B et al. Clin Oral Investig. 2017 Sep;21(7):2245-51 doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-2017-7.
, with an equal distribution across genders and ethnicities.1 It is caused by mutations in the ECM1 gene2 on chromosome 1q21. This leads to the abnormal deposition of hyaline material in various tissues across different organ systems, with the classic manifestations known as the “string of pearls” sign and a hoarse cry or voice.
The rarity of lipoid proteinosis often leads to challenges in diagnosis. Particularly when deviating from the common association with consanguinity, the potential for de novo mutations or a broader genetic variability in disease expression is highlighted. Our patient presents with symptoms that are pathognomonic to LP with moniliform blepharosis and hoarseness of the voice, in addition to scarring of the extremities.
Other common clinical manifestations in patients with LP include cobblestoning of the mucosa; hyperkeratosis of the elbows, knees, and hands; and calcification of the amygdala with neuroimaging.3
Genetic testing that identifies a loss-of-function mutation in ECM1 offers diagnostic confirmation. Patients often need multidisciplinary care involving dermatology; ear, nose, throat; neurology; and genetics. Treatment of LP is mostly symptomatic with unsatisfactory resolution of cutaneous changes, with retinoids such as acitretin used as the first-line option and surgery as a consideration for laryngeal hyaline deposits.2 Although LP can affect different organ systems, patients tend to have a normal lifespan.
LP is a rare disorder that dermatologists often learn about during textbook sessions or didactics in residency but do not see in practice for decades, or if ever. This case highlights the need to review the classic presentations of rare conditions.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Chang, BS, Western University of Health Sciences, College of Osteopathic Medicine, Pomona, California; Dr. Connie Chang, Verdugo Dermatology, Glendale, California; and Dr. Yuchieh Kathryn Chang, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Mcgrath JA. Handb Clin Neurol. 2015:132:317-22. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-62702-5.00023-8.
2. Hamada Tet al. Hum Mol Genet. 2002 Apr 1;11(7):833-40. doi: 10.1093/hmg/11.7.833.
3. Frenkel B et al. Clin Oral Investig. 2017 Sep;21(7):2245-51 doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-2017-7.
Guidance for Practicing Primary Care: Updated Clinical Guidelines Regarding Dry Eye Syndrome
On February 11, 2024, the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) issued new guidelines regarding dry eye syndrome or keratoconjunctivitis sicca. According to the National Eye Institute, dry eye affects approximately 16 million Americans. Dry eye is a multifactorial disease with causes including excessive screen time and refractive surgery. While it may seem that dry eye is a nuisance disease, it can actually damage the cornea if not treated appropriately.
The guidelines state that dry eye can affect the quality of life as well as the outcomes of ocular surgeries such as cataract surgery. It is imperative that we discuss this potential complication before our patients undergo these procedures. As primary care physicians, we have seen that patients may not be well educated on their health conditions by other doctors. We may not be the one performing the surgery but it is likely the patient will seek our advice if any complication arises.
The guidelines say that clinical examination is the gold standard for diagnosing this disease. We need to be proficient at doing eye exams and refer to a specialist when appropriate. The treatment can likely be undertaken in the primary care office unless there are other symptoms such as loss of visual acuity. The guidelines suggest several diagnostic tests, such as the Schirmer test and tear osmolarity test, which may be outside the scope of the primary care setting. Often, clinical history will guide the diagnosis.
Treatments include several Food and Drug Administration–approved eye drops. We need to know what they are and when to prescribe them. We know they will not cure the disease but can keep it under control and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Dry eye may seem a trivial complaint in the sea of diseases we treat on a daily basis. However, it is not trivial to the patient. It can affect their vision and make their life miserable. We need to pay attention when our patients bring this to our attention. We are not just making them comfortable but protecting their corneas. This can be done in conjunction with routine ophthalmologic visits.
According to the authors of these guidelines, approximately 10% of patients with significantly dry eyes and mouth will have Sj
These guidelines also suggest a classification for dry eye including mild, moderate, and severe. Since the treatment varies depending on classification, we need to learn this classification system. They also stress follow-up visits. It is not enough just to diagnose the disease and start treatment, we need to see the patients back for follow-up.
Currently, most people work and play on electronic devices. Dry eye syndrome can make this more difficult and vice versa. While it is typically not a vision-threatening disease, it can be a life-altering one. Ocular symptoms are something we see frequently in our practices, from allergic conjunctivitis to glaucoma. Often, the patient starts seeking help in our office.
Yes, our patients may have more life-threatening diseases. Our job is not just to save lives but to help our patients live healthy lives. If their lives are being affected by any disease, we must step in and do something. Dry eye is not just an inconvenience but something that causes great suffering. Eventually we may end up referring the patient to the ophthalmologist, but if we can do something to ease their discomfort while they are waiting, we would be changing their lives. We must educate ourselves on this disease and appropriate treatments to be prescribed depending on the classification of disease.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ. She has no conflicts of interest.
On February 11, 2024, the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) issued new guidelines regarding dry eye syndrome or keratoconjunctivitis sicca. According to the National Eye Institute, dry eye affects approximately 16 million Americans. Dry eye is a multifactorial disease with causes including excessive screen time and refractive surgery. While it may seem that dry eye is a nuisance disease, it can actually damage the cornea if not treated appropriately.
The guidelines state that dry eye can affect the quality of life as well as the outcomes of ocular surgeries such as cataract surgery. It is imperative that we discuss this potential complication before our patients undergo these procedures. As primary care physicians, we have seen that patients may not be well educated on their health conditions by other doctors. We may not be the one performing the surgery but it is likely the patient will seek our advice if any complication arises.
The guidelines say that clinical examination is the gold standard for diagnosing this disease. We need to be proficient at doing eye exams and refer to a specialist when appropriate. The treatment can likely be undertaken in the primary care office unless there are other symptoms such as loss of visual acuity. The guidelines suggest several diagnostic tests, such as the Schirmer test and tear osmolarity test, which may be outside the scope of the primary care setting. Often, clinical history will guide the diagnosis.
Treatments include several Food and Drug Administration–approved eye drops. We need to know what they are and when to prescribe them. We know they will not cure the disease but can keep it under control and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Dry eye may seem a trivial complaint in the sea of diseases we treat on a daily basis. However, it is not trivial to the patient. It can affect their vision and make their life miserable. We need to pay attention when our patients bring this to our attention. We are not just making them comfortable but protecting their corneas. This can be done in conjunction with routine ophthalmologic visits.
According to the authors of these guidelines, approximately 10% of patients with significantly dry eyes and mouth will have Sj
These guidelines also suggest a classification for dry eye including mild, moderate, and severe. Since the treatment varies depending on classification, we need to learn this classification system. They also stress follow-up visits. It is not enough just to diagnose the disease and start treatment, we need to see the patients back for follow-up.
Currently, most people work and play on electronic devices. Dry eye syndrome can make this more difficult and vice versa. While it is typically not a vision-threatening disease, it can be a life-altering one. Ocular symptoms are something we see frequently in our practices, from allergic conjunctivitis to glaucoma. Often, the patient starts seeking help in our office.
Yes, our patients may have more life-threatening diseases. Our job is not just to save lives but to help our patients live healthy lives. If their lives are being affected by any disease, we must step in and do something. Dry eye is not just an inconvenience but something that causes great suffering. Eventually we may end up referring the patient to the ophthalmologist, but if we can do something to ease their discomfort while they are waiting, we would be changing their lives. We must educate ourselves on this disease and appropriate treatments to be prescribed depending on the classification of disease.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ. She has no conflicts of interest.
On February 11, 2024, the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) issued new guidelines regarding dry eye syndrome or keratoconjunctivitis sicca. According to the National Eye Institute, dry eye affects approximately 16 million Americans. Dry eye is a multifactorial disease with causes including excessive screen time and refractive surgery. While it may seem that dry eye is a nuisance disease, it can actually damage the cornea if not treated appropriately.
The guidelines state that dry eye can affect the quality of life as well as the outcomes of ocular surgeries such as cataract surgery. It is imperative that we discuss this potential complication before our patients undergo these procedures. As primary care physicians, we have seen that patients may not be well educated on their health conditions by other doctors. We may not be the one performing the surgery but it is likely the patient will seek our advice if any complication arises.
The guidelines say that clinical examination is the gold standard for diagnosing this disease. We need to be proficient at doing eye exams and refer to a specialist when appropriate. The treatment can likely be undertaken in the primary care office unless there are other symptoms such as loss of visual acuity. The guidelines suggest several diagnostic tests, such as the Schirmer test and tear osmolarity test, which may be outside the scope of the primary care setting. Often, clinical history will guide the diagnosis.
Treatments include several Food and Drug Administration–approved eye drops. We need to know what they are and when to prescribe them. We know they will not cure the disease but can keep it under control and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Dry eye may seem a trivial complaint in the sea of diseases we treat on a daily basis. However, it is not trivial to the patient. It can affect their vision and make their life miserable. We need to pay attention when our patients bring this to our attention. We are not just making them comfortable but protecting their corneas. This can be done in conjunction with routine ophthalmologic visits.
According to the authors of these guidelines, approximately 10% of patients with significantly dry eyes and mouth will have Sj
These guidelines also suggest a classification for dry eye including mild, moderate, and severe. Since the treatment varies depending on classification, we need to learn this classification system. They also stress follow-up visits. It is not enough just to diagnose the disease and start treatment, we need to see the patients back for follow-up.
Currently, most people work and play on electronic devices. Dry eye syndrome can make this more difficult and vice versa. While it is typically not a vision-threatening disease, it can be a life-altering one. Ocular symptoms are something we see frequently in our practices, from allergic conjunctivitis to glaucoma. Often, the patient starts seeking help in our office.
Yes, our patients may have more life-threatening diseases. Our job is not just to save lives but to help our patients live healthy lives. If their lives are being affected by any disease, we must step in and do something. Dry eye is not just an inconvenience but something that causes great suffering. Eventually we may end up referring the patient to the ophthalmologist, but if we can do something to ease their discomfort while they are waiting, we would be changing their lives. We must educate ourselves on this disease and appropriate treatments to be prescribed depending on the classification of disease.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ. She has no conflicts of interest.
Macadamia and Sapucaia Extracts and the Skin
Macadamia (Macadamia tetraphylla) is endemic to Australia and is now commercially cultivated worldwide.1 It is closely related genetically to the other macadamia plants, including the other main one, M. integrifolia, cultivated for macadamia nuts. Known in Brazil as sapucaia or castanha-de-sapucaia, Lecythis pisonis (also referred to as “cream nut” or “monkey pot”) is a large, deciduous tropical tree and member of the Brazil nut family, Lecythidaceae.2 Various parts of both of these plants have been associated with medicinal properties, including the potential for dermatologic activity. Notably, the leaves of L. pisonis have been used in traditional medicine to treat pruritus.2 .
Macadamia
Extraction to Harness Antioxidant Activity
In 2015, Dailey and Vuong developed an aqueous extraction process to recover the phenolic content and antioxidant functionality from the skin waste of M. tetraphylla using response surface methodology. As an environmentally suitable solvent that is also cheap and safe, water was chosen to maximize the extraction scenario. They identified the proper conditions (90° C, a time of 20 min, and a sample-to-solvent ratio of 5 g/100 mL) to obtain sufficient phenolic compounds, proanthocyanidins, and flavonoids to render robust antioxidant function.1
Early in 2023, Somwongin et al. investigated various green extraction methods for viability in harnessing the cosmetic/cosmeceutical ingredients of M. integrifolia pericarps. Extracts were assessed for total phenolic content as well as antioxidant and anti–skin aging functions. They found that among the green extraction methods (ultrasound, micellar, microwave, and pulsed electric field extraction with water used as a clean solvent), the ultrasound-assisted extraction method netted the greatest yield and total phenolic content. It was also associated with the most robust antioxidant and anti–skin aging activities. Indeed, the researchers reported that its antioxidant activities were comparable to ascorbic acid and Trolox and its anti–skin aging potency on a par with epigallocatechin-3-gallate and oleanolic acid. The ultrasound-assisted extract was also deemed safe as it did not provoke irritation. The authors concluded that this environmentally suitable extraction method for M. integrifolia is appropriate for obtaining effective macadamia extracts for use in cosmetics and cosmeceuticals.3
Anti-Aging Activity
In 2017, Addy et al. set out to characterize skin surface lipid composition and differences in an age- and sex-controlled population as a foundation for developing a botanically derived skin surface lipid mimetic agent. They noted that fatty acids, triglycerides, cholesterol, steryl esters, wax esters, and squalene are the main constituents of skin surface lipids. The investigators obtained skin surface lipid samples from the foreheads of 59 healthy 22-year-old women, analyzed them, and used the raw components of M. integrifolia, Simmondsia chinensis, and Olea europaea to engineer a mimetic product. They reported that the esterification reactions of jojoba, macadamia, and tall oils, combined with squalene derived from O. europaea, yielded an appropriate skin surface lipid mimetic, which, when applied to delipidized skin, assisted in recovering barrier function, enhancing skin hydration, and improving elasticity as well as firmness in aged skin. The researchers concluded that this skin surface lipid mimetic could serve as an effective supplement to human skin surface lipids in aged skin and for conditions in which the stratum corneum is impaired.4
Two years later, Hanum et al. compared the effects of macadamia nut oil nanocream and conventional cream for treating cutaneous aging over a 4-week period. The macadamia nut oil nanocream, which contained macadamia nut oil 10%, tween 80, propylene glycol, cetyl alcohol, methylparaben, propylparaben, and distilled water, was compared with the conventional cream based on effects on moisture, evenness, pore size, melanin, and wrinkling. The macadamia nut oil was found to yield superior anti-aging activity along each parameter as compared with the conventional cream. The researchers concluded that the macadamia nut oil in nanocream can be an effective formulation for providing benefits in addressing cutaneous aging.5
Macadamia nut oil has also been used in an anti-aging emulsion that was evaluated in a small study with 11 volunteers in 2008. Akhtar et al. prepared multiple emulsions of vitamin C and wheat protein using macadamia oil for its abundant supply of palmitoleic acid. Over 4 weeks, the emulsion was found to increase skin moisture without affecting other skin parameters, such as elasticity, erythema, melanin, pH, or sebum levels.6
Sapucaia (L. pisonis), an ornamental tree that is used for timber, produces edible, nutritious nuts that are rich in tocopherols, polyphenols, and fatty acids.7,8 In 2018, Demoliner et al. identified and characterized the phenolic substances present in sapucaia nut extract and its shell. Antioxidant activity conferred by the extract was attributed to the copious supply of catechin, epicatechin, and myricetin, as well as ellagic and ferulic acids, among the 14 phenolic constituents. The shell included 22 phenolic substances along with a significant level of condensed tannins and marked antioxidant function. The authors correlated the substantial activity imparted by the shell with its higher phenolic content, and suggested this robust source of natural antioxidants could be well suited to use in cosmetic products.9
Antifungal Activity
In 2015, Vieira et al. characterized 12 fractions enriched in peptides derived from L. pisonis seeds to determine inhibitory activity against Candida albicans. The fraction that exerted the strongest activity at 10 μg/mL, suppressing C. albicans growth by 38.5% and inducing a 69.3% loss of viability, was identified as similar to plant defensins and thus dubbed “L. pisonis defensin 1 (Lp-Def1).” The investigators concluded that Lp-Def1 acts on C. albicans by slightly elevating the induction of reactive oxygen species and causing a significant reduction in mitochondrial activity. They suggested that their findings support the use of plant defensins, particularly Lp-Def1, in the formulation of antifungal products, especially to address C. albicans.10
Pruritus
In 2012, Silva et al. studied the antipruritic impact of L. pisonis leaf extracts in mice and rats. Pretreatment with the various fractions of L. pisonis as well as constituent mixed triterpenes (ursolic and oleanolic acids) significantly blocked scratching behavior provoked by compound 48/80. The degranulation of rat peritoneal mast cells caused by compound 48/80 was also substantially decreased from pretreatment with the ethanol extract of L. pisonis, ether-L. pisonis fraction, and mixed triterpenes. The L. pisonis ether fraction suppressed edema induced by carrageenan administration and the ethanol extract displayed no toxicity up to an oral dose of 2g/kg. The investigators concluded that their results strongly support the antipruritic effects of L. pisonis leaves as well as the traditional use of the plant to treat pruritus.2
Stability for Cosmetic Creams
In 2020, Rampazzo et al. assessed the stability and cytotoxicity of a cosmetic cream containing sapucaia nut oil. All three tested concentrations (1%, 5%, and 10%) of the cream were found to be stable, with an effective preservative system, and deemed safe for use on human skin. To maintain a pH appropriate for a body cream, the formulation requires a stabilizing agent. The cream with 5% nut oil was identified as the most stable and satisfying for use on the skin.7
More recently, Hertel Pereira et al. investigated the benefits of using L. pisonis pericarp extract, known to exhibit abundant antioxidants, in an all-natural skin cream. They found that formulation instability increased proportionally with the concentration of the extract, but the use of the outer pericarp of L. pisonis was well suited for the cream formulation, with physical-chemical and organoleptic qualities unchanged after the stability test.11
Conclusion
The available literature on the medical applications of macadamia and sapucaia plants is sparse. Some recent findings are promising regarding possible uses in skin health. However, much more research is necessary before considering macadamia and sapucaia as viable sources of botanical agents capable of delivering significant cutaneous benefits.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., an SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Dailey A and Vuong QV. Antioxidants (Basel). 2015 Nov 12;4(4):699-718.
2. Silva LL et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Jan 6;139(1):90-97.
3. Somwongin S et al. Ultrason Sonochem. 2023 Jan;92:106266.
4. Addy J et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2017 Jan/Feb;68(1):59-67.
5. Hanum TI et al. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 Nov 14;7(22):3917-3920.
6. Akhtar N and Yazan Y. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2008 Jan;21(1):45-50.
7. Rampazzo APS et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2020 Sep/Oct;71(5):239-250.
8. Rosa TLM et al. Food Res Int. 2020 Nov;137:109383.
9. Demoliner F et al. Food Res Int. 2018 Oct;112:434-442.
10. Vieira ME et al. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015 Sep;47(9):716-729.
11. Hertel Pereira AC et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2021 Mar-Apr;72(2):155-162.
Macadamia (Macadamia tetraphylla) is endemic to Australia and is now commercially cultivated worldwide.1 It is closely related genetically to the other macadamia plants, including the other main one, M. integrifolia, cultivated for macadamia nuts. Known in Brazil as sapucaia or castanha-de-sapucaia, Lecythis pisonis (also referred to as “cream nut” or “monkey pot”) is a large, deciduous tropical tree and member of the Brazil nut family, Lecythidaceae.2 Various parts of both of these plants have been associated with medicinal properties, including the potential for dermatologic activity. Notably, the leaves of L. pisonis have been used in traditional medicine to treat pruritus.2 .
Macadamia
Extraction to Harness Antioxidant Activity
In 2015, Dailey and Vuong developed an aqueous extraction process to recover the phenolic content and antioxidant functionality from the skin waste of M. tetraphylla using response surface methodology. As an environmentally suitable solvent that is also cheap and safe, water was chosen to maximize the extraction scenario. They identified the proper conditions (90° C, a time of 20 min, and a sample-to-solvent ratio of 5 g/100 mL) to obtain sufficient phenolic compounds, proanthocyanidins, and flavonoids to render robust antioxidant function.1
Early in 2023, Somwongin et al. investigated various green extraction methods for viability in harnessing the cosmetic/cosmeceutical ingredients of M. integrifolia pericarps. Extracts were assessed for total phenolic content as well as antioxidant and anti–skin aging functions. They found that among the green extraction methods (ultrasound, micellar, microwave, and pulsed electric field extraction with water used as a clean solvent), the ultrasound-assisted extraction method netted the greatest yield and total phenolic content. It was also associated with the most robust antioxidant and anti–skin aging activities. Indeed, the researchers reported that its antioxidant activities were comparable to ascorbic acid and Trolox and its anti–skin aging potency on a par with epigallocatechin-3-gallate and oleanolic acid. The ultrasound-assisted extract was also deemed safe as it did not provoke irritation. The authors concluded that this environmentally suitable extraction method for M. integrifolia is appropriate for obtaining effective macadamia extracts for use in cosmetics and cosmeceuticals.3
Anti-Aging Activity
In 2017, Addy et al. set out to characterize skin surface lipid composition and differences in an age- and sex-controlled population as a foundation for developing a botanically derived skin surface lipid mimetic agent. They noted that fatty acids, triglycerides, cholesterol, steryl esters, wax esters, and squalene are the main constituents of skin surface lipids. The investigators obtained skin surface lipid samples from the foreheads of 59 healthy 22-year-old women, analyzed them, and used the raw components of M. integrifolia, Simmondsia chinensis, and Olea europaea to engineer a mimetic product. They reported that the esterification reactions of jojoba, macadamia, and tall oils, combined with squalene derived from O. europaea, yielded an appropriate skin surface lipid mimetic, which, when applied to delipidized skin, assisted in recovering barrier function, enhancing skin hydration, and improving elasticity as well as firmness in aged skin. The researchers concluded that this skin surface lipid mimetic could serve as an effective supplement to human skin surface lipids in aged skin and for conditions in which the stratum corneum is impaired.4
Two years later, Hanum et al. compared the effects of macadamia nut oil nanocream and conventional cream for treating cutaneous aging over a 4-week period. The macadamia nut oil nanocream, which contained macadamia nut oil 10%, tween 80, propylene glycol, cetyl alcohol, methylparaben, propylparaben, and distilled water, was compared with the conventional cream based on effects on moisture, evenness, pore size, melanin, and wrinkling. The macadamia nut oil was found to yield superior anti-aging activity along each parameter as compared with the conventional cream. The researchers concluded that the macadamia nut oil in nanocream can be an effective formulation for providing benefits in addressing cutaneous aging.5
Macadamia nut oil has also been used in an anti-aging emulsion that was evaluated in a small study with 11 volunteers in 2008. Akhtar et al. prepared multiple emulsions of vitamin C and wheat protein using macadamia oil for its abundant supply of palmitoleic acid. Over 4 weeks, the emulsion was found to increase skin moisture without affecting other skin parameters, such as elasticity, erythema, melanin, pH, or sebum levels.6
Sapucaia (L. pisonis), an ornamental tree that is used for timber, produces edible, nutritious nuts that are rich in tocopherols, polyphenols, and fatty acids.7,8 In 2018, Demoliner et al. identified and characterized the phenolic substances present in sapucaia nut extract and its shell. Antioxidant activity conferred by the extract was attributed to the copious supply of catechin, epicatechin, and myricetin, as well as ellagic and ferulic acids, among the 14 phenolic constituents. The shell included 22 phenolic substances along with a significant level of condensed tannins and marked antioxidant function. The authors correlated the substantial activity imparted by the shell with its higher phenolic content, and suggested this robust source of natural antioxidants could be well suited to use in cosmetic products.9
Antifungal Activity
In 2015, Vieira et al. characterized 12 fractions enriched in peptides derived from L. pisonis seeds to determine inhibitory activity against Candida albicans. The fraction that exerted the strongest activity at 10 μg/mL, suppressing C. albicans growth by 38.5% and inducing a 69.3% loss of viability, was identified as similar to plant defensins and thus dubbed “L. pisonis defensin 1 (Lp-Def1).” The investigators concluded that Lp-Def1 acts on C. albicans by slightly elevating the induction of reactive oxygen species and causing a significant reduction in mitochondrial activity. They suggested that their findings support the use of plant defensins, particularly Lp-Def1, in the formulation of antifungal products, especially to address C. albicans.10
Pruritus
In 2012, Silva et al. studied the antipruritic impact of L. pisonis leaf extracts in mice and rats. Pretreatment with the various fractions of L. pisonis as well as constituent mixed triterpenes (ursolic and oleanolic acids) significantly blocked scratching behavior provoked by compound 48/80. The degranulation of rat peritoneal mast cells caused by compound 48/80 was also substantially decreased from pretreatment with the ethanol extract of L. pisonis, ether-L. pisonis fraction, and mixed triterpenes. The L. pisonis ether fraction suppressed edema induced by carrageenan administration and the ethanol extract displayed no toxicity up to an oral dose of 2g/kg. The investigators concluded that their results strongly support the antipruritic effects of L. pisonis leaves as well as the traditional use of the plant to treat pruritus.2
Stability for Cosmetic Creams
In 2020, Rampazzo et al. assessed the stability and cytotoxicity of a cosmetic cream containing sapucaia nut oil. All three tested concentrations (1%, 5%, and 10%) of the cream were found to be stable, with an effective preservative system, and deemed safe for use on human skin. To maintain a pH appropriate for a body cream, the formulation requires a stabilizing agent. The cream with 5% nut oil was identified as the most stable and satisfying for use on the skin.7
More recently, Hertel Pereira et al. investigated the benefits of using L. pisonis pericarp extract, known to exhibit abundant antioxidants, in an all-natural skin cream. They found that formulation instability increased proportionally with the concentration of the extract, but the use of the outer pericarp of L. pisonis was well suited for the cream formulation, with physical-chemical and organoleptic qualities unchanged after the stability test.11
Conclusion
The available literature on the medical applications of macadamia and sapucaia plants is sparse. Some recent findings are promising regarding possible uses in skin health. However, much more research is necessary before considering macadamia and sapucaia as viable sources of botanical agents capable of delivering significant cutaneous benefits.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., an SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Dailey A and Vuong QV. Antioxidants (Basel). 2015 Nov 12;4(4):699-718.
2. Silva LL et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Jan 6;139(1):90-97.
3. Somwongin S et al. Ultrason Sonochem. 2023 Jan;92:106266.
4. Addy J et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2017 Jan/Feb;68(1):59-67.
5. Hanum TI et al. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 Nov 14;7(22):3917-3920.
6. Akhtar N and Yazan Y. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2008 Jan;21(1):45-50.
7. Rampazzo APS et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2020 Sep/Oct;71(5):239-250.
8. Rosa TLM et al. Food Res Int. 2020 Nov;137:109383.
9. Demoliner F et al. Food Res Int. 2018 Oct;112:434-442.
10. Vieira ME et al. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015 Sep;47(9):716-729.
11. Hertel Pereira AC et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2021 Mar-Apr;72(2):155-162.
Macadamia (Macadamia tetraphylla) is endemic to Australia and is now commercially cultivated worldwide.1 It is closely related genetically to the other macadamia plants, including the other main one, M. integrifolia, cultivated for macadamia nuts. Known in Brazil as sapucaia or castanha-de-sapucaia, Lecythis pisonis (also referred to as “cream nut” or “monkey pot”) is a large, deciduous tropical tree and member of the Brazil nut family, Lecythidaceae.2 Various parts of both of these plants have been associated with medicinal properties, including the potential for dermatologic activity. Notably, the leaves of L. pisonis have been used in traditional medicine to treat pruritus.2 .
Macadamia
Extraction to Harness Antioxidant Activity
In 2015, Dailey and Vuong developed an aqueous extraction process to recover the phenolic content and antioxidant functionality from the skin waste of M. tetraphylla using response surface methodology. As an environmentally suitable solvent that is also cheap and safe, water was chosen to maximize the extraction scenario. They identified the proper conditions (90° C, a time of 20 min, and a sample-to-solvent ratio of 5 g/100 mL) to obtain sufficient phenolic compounds, proanthocyanidins, and flavonoids to render robust antioxidant function.1
Early in 2023, Somwongin et al. investigated various green extraction methods for viability in harnessing the cosmetic/cosmeceutical ingredients of M. integrifolia pericarps. Extracts were assessed for total phenolic content as well as antioxidant and anti–skin aging functions. They found that among the green extraction methods (ultrasound, micellar, microwave, and pulsed electric field extraction with water used as a clean solvent), the ultrasound-assisted extraction method netted the greatest yield and total phenolic content. It was also associated with the most robust antioxidant and anti–skin aging activities. Indeed, the researchers reported that its antioxidant activities were comparable to ascorbic acid and Trolox and its anti–skin aging potency on a par with epigallocatechin-3-gallate and oleanolic acid. The ultrasound-assisted extract was also deemed safe as it did not provoke irritation. The authors concluded that this environmentally suitable extraction method for M. integrifolia is appropriate for obtaining effective macadamia extracts for use in cosmetics and cosmeceuticals.3
Anti-Aging Activity
In 2017, Addy et al. set out to characterize skin surface lipid composition and differences in an age- and sex-controlled population as a foundation for developing a botanically derived skin surface lipid mimetic agent. They noted that fatty acids, triglycerides, cholesterol, steryl esters, wax esters, and squalene are the main constituents of skin surface lipids. The investigators obtained skin surface lipid samples from the foreheads of 59 healthy 22-year-old women, analyzed them, and used the raw components of M. integrifolia, Simmondsia chinensis, and Olea europaea to engineer a mimetic product. They reported that the esterification reactions of jojoba, macadamia, and tall oils, combined with squalene derived from O. europaea, yielded an appropriate skin surface lipid mimetic, which, when applied to delipidized skin, assisted in recovering barrier function, enhancing skin hydration, and improving elasticity as well as firmness in aged skin. The researchers concluded that this skin surface lipid mimetic could serve as an effective supplement to human skin surface lipids in aged skin and for conditions in which the stratum corneum is impaired.4
Two years later, Hanum et al. compared the effects of macadamia nut oil nanocream and conventional cream for treating cutaneous aging over a 4-week period. The macadamia nut oil nanocream, which contained macadamia nut oil 10%, tween 80, propylene glycol, cetyl alcohol, methylparaben, propylparaben, and distilled water, was compared with the conventional cream based on effects on moisture, evenness, pore size, melanin, and wrinkling. The macadamia nut oil was found to yield superior anti-aging activity along each parameter as compared with the conventional cream. The researchers concluded that the macadamia nut oil in nanocream can be an effective formulation for providing benefits in addressing cutaneous aging.5
Macadamia nut oil has also been used in an anti-aging emulsion that was evaluated in a small study with 11 volunteers in 2008. Akhtar et al. prepared multiple emulsions of vitamin C and wheat protein using macadamia oil for its abundant supply of palmitoleic acid. Over 4 weeks, the emulsion was found to increase skin moisture without affecting other skin parameters, such as elasticity, erythema, melanin, pH, or sebum levels.6
Sapucaia (L. pisonis), an ornamental tree that is used for timber, produces edible, nutritious nuts that are rich in tocopherols, polyphenols, and fatty acids.7,8 In 2018, Demoliner et al. identified and characterized the phenolic substances present in sapucaia nut extract and its shell. Antioxidant activity conferred by the extract was attributed to the copious supply of catechin, epicatechin, and myricetin, as well as ellagic and ferulic acids, among the 14 phenolic constituents. The shell included 22 phenolic substances along with a significant level of condensed tannins and marked antioxidant function. The authors correlated the substantial activity imparted by the shell with its higher phenolic content, and suggested this robust source of natural antioxidants could be well suited to use in cosmetic products.9
Antifungal Activity
In 2015, Vieira et al. characterized 12 fractions enriched in peptides derived from L. pisonis seeds to determine inhibitory activity against Candida albicans. The fraction that exerted the strongest activity at 10 μg/mL, suppressing C. albicans growth by 38.5% and inducing a 69.3% loss of viability, was identified as similar to plant defensins and thus dubbed “L. pisonis defensin 1 (Lp-Def1).” The investigators concluded that Lp-Def1 acts on C. albicans by slightly elevating the induction of reactive oxygen species and causing a significant reduction in mitochondrial activity. They suggested that their findings support the use of plant defensins, particularly Lp-Def1, in the formulation of antifungal products, especially to address C. albicans.10
Pruritus
In 2012, Silva et al. studied the antipruritic impact of L. pisonis leaf extracts in mice and rats. Pretreatment with the various fractions of L. pisonis as well as constituent mixed triterpenes (ursolic and oleanolic acids) significantly blocked scratching behavior provoked by compound 48/80. The degranulation of rat peritoneal mast cells caused by compound 48/80 was also substantially decreased from pretreatment with the ethanol extract of L. pisonis, ether-L. pisonis fraction, and mixed triterpenes. The L. pisonis ether fraction suppressed edema induced by carrageenan administration and the ethanol extract displayed no toxicity up to an oral dose of 2g/kg. The investigators concluded that their results strongly support the antipruritic effects of L. pisonis leaves as well as the traditional use of the plant to treat pruritus.2
Stability for Cosmetic Creams
In 2020, Rampazzo et al. assessed the stability and cytotoxicity of a cosmetic cream containing sapucaia nut oil. All three tested concentrations (1%, 5%, and 10%) of the cream were found to be stable, with an effective preservative system, and deemed safe for use on human skin. To maintain a pH appropriate for a body cream, the formulation requires a stabilizing agent. The cream with 5% nut oil was identified as the most stable and satisfying for use on the skin.7
More recently, Hertel Pereira et al. investigated the benefits of using L. pisonis pericarp extract, known to exhibit abundant antioxidants, in an all-natural skin cream. They found that formulation instability increased proportionally with the concentration of the extract, but the use of the outer pericarp of L. pisonis was well suited for the cream formulation, with physical-chemical and organoleptic qualities unchanged after the stability test.11
Conclusion
The available literature on the medical applications of macadamia and sapucaia plants is sparse. Some recent findings are promising regarding possible uses in skin health. However, much more research is necessary before considering macadamia and sapucaia as viable sources of botanical agents capable of delivering significant cutaneous benefits.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., an SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Dailey A and Vuong QV. Antioxidants (Basel). 2015 Nov 12;4(4):699-718.
2. Silva LL et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Jan 6;139(1):90-97.
3. Somwongin S et al. Ultrason Sonochem. 2023 Jan;92:106266.
4. Addy J et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2017 Jan/Feb;68(1):59-67.
5. Hanum TI et al. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 Nov 14;7(22):3917-3920.
6. Akhtar N and Yazan Y. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2008 Jan;21(1):45-50.
7. Rampazzo APS et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2020 Sep/Oct;71(5):239-250.
8. Rosa TLM et al. Food Res Int. 2020 Nov;137:109383.
9. Demoliner F et al. Food Res Int. 2018 Oct;112:434-442.
10. Vieira ME et al. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015 Sep;47(9):716-729.
11. Hertel Pereira AC et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2021 Mar-Apr;72(2):155-162.