User login
The significance of Transgender Awareness Week
As I sit down to write this article, I cannot help but reflect on the significance of today and the upcoming week – Transgender Awareness Week. While it may seem that the transgender community has made great strides in political, social, and health care forums, this week serves as a cold and grave reality check for members of the community and its allies. We still have a long way to go.
This annual tradition began in 1998 in response to the murder of a transgender woman, Rita Hester. Now Transgender Awareness Week, which occurs from Nov. 13th through the 19th is a week dedicated to help raise awareness and improve visibility of transgender people and the issues they face.1 The week culminates on Nov. 20 with The Transgender Day of Remembrance (TDOR). The day is an annual observance to honor the memory of the transgender people who lost their lives to acts of antitransgender violence during that year.1
Unfortunately, 2021 marks the worst year in recent history for transgender violence and anti-LGBT legislation. Over this past year, 375 transgender people were killed – 96% of whom were black and migrant trans women of color and over half (58%) of whom were sex workers.2 What is even more shocking is that one in four of these victims were murdered in their own homes.2 Compared with 2015, which previously held the title of “worst year,” 250 anti-LGBT bills have been introduced in state legislatures in 2021; 17 of which have been already enacted into law.3 The recently passed laws involve antitrans sports bans, religious refusal, anti-LGBTQ education, antitrans medical care, antitrans birth certificates, and an anti–all comers bill.3 In evaluating the 250 anti-LGBT bills introduced into state legislatures, at least 35 of these would prohibit transgender youth from accessing gender-affirming medical care and an additional 43 bills would allow people to deny or not provide services (including all medical care) by asserting religious freedom.3 The current bills exhibit a flagrant disregard for current best practices, which have demonstrated the benefits of gender-affirming medical care. Furthermore, they can increase the already high death toll for transgender patients by allowing providers and institutions to deny care to patients seeking services unrelated to their gender identity or sexual orientation.
Even if providers are not directly prescribing hormone therapy or performing gender-affirming procedures, all providers have encountered and will treat an LGBTQ patient at some point during their career. It is necessary for all obstetrician-gynecologists to be aware of the systemic damages and threats that LGBTQ patients face, as well as pending legislation that can significantly affect and harm patient care. As a result, we need to screen these patients for depression and history of self-harm, and to assess social support, as well as challenge legislation that can negatively affect LGBTQ care. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has not only issued formal statements condemning discrimination on the basis of gender identity and sexual orientation, but also advocates for inclusive, thoughtful, and affirming care for transgender individuals.4 In a time when our patients may not feel as though they can advocate for themselves, we as providers must use our voices and medical knowledge to enact these changes to encourage equitable and safe health care for all.
Dr. Brandt is an an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Transgender awareness month 2021. Fenway Health. 2021 Nov 1.
2. Wareham J. 375 transgender people murdered in 2021 – ‘Deadliest year’ since records began. Forbes. 2021 Nov 11..
3. Ronan R. 2021 officially becomes worst year in recent history for LGBTQ state legislative attacks as unprecedented number of states enact record-shattering number of anti-LGBTQ measures into law. Human Rights Campaign Press Release. 2021 May 7..
4. Practice Guideline. Health care for transgender and gender diverse individuals: ACOG Committee Opinion, No. 823. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
As I sit down to write this article, I cannot help but reflect on the significance of today and the upcoming week – Transgender Awareness Week. While it may seem that the transgender community has made great strides in political, social, and health care forums, this week serves as a cold and grave reality check for members of the community and its allies. We still have a long way to go.
This annual tradition began in 1998 in response to the murder of a transgender woman, Rita Hester. Now Transgender Awareness Week, which occurs from Nov. 13th through the 19th is a week dedicated to help raise awareness and improve visibility of transgender people and the issues they face.1 The week culminates on Nov. 20 with The Transgender Day of Remembrance (TDOR). The day is an annual observance to honor the memory of the transgender people who lost their lives to acts of antitransgender violence during that year.1
Unfortunately, 2021 marks the worst year in recent history for transgender violence and anti-LGBT legislation. Over this past year, 375 transgender people were killed – 96% of whom were black and migrant trans women of color and over half (58%) of whom were sex workers.2 What is even more shocking is that one in four of these victims were murdered in their own homes.2 Compared with 2015, which previously held the title of “worst year,” 250 anti-LGBT bills have been introduced in state legislatures in 2021; 17 of which have been already enacted into law.3 The recently passed laws involve antitrans sports bans, religious refusal, anti-LGBTQ education, antitrans medical care, antitrans birth certificates, and an anti–all comers bill.3 In evaluating the 250 anti-LGBT bills introduced into state legislatures, at least 35 of these would prohibit transgender youth from accessing gender-affirming medical care and an additional 43 bills would allow people to deny or not provide services (including all medical care) by asserting religious freedom.3 The current bills exhibit a flagrant disregard for current best practices, which have demonstrated the benefits of gender-affirming medical care. Furthermore, they can increase the already high death toll for transgender patients by allowing providers and institutions to deny care to patients seeking services unrelated to their gender identity or sexual orientation.
Even if providers are not directly prescribing hormone therapy or performing gender-affirming procedures, all providers have encountered and will treat an LGBTQ patient at some point during their career. It is necessary for all obstetrician-gynecologists to be aware of the systemic damages and threats that LGBTQ patients face, as well as pending legislation that can significantly affect and harm patient care. As a result, we need to screen these patients for depression and history of self-harm, and to assess social support, as well as challenge legislation that can negatively affect LGBTQ care. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has not only issued formal statements condemning discrimination on the basis of gender identity and sexual orientation, but also advocates for inclusive, thoughtful, and affirming care for transgender individuals.4 In a time when our patients may not feel as though they can advocate for themselves, we as providers must use our voices and medical knowledge to enact these changes to encourage equitable and safe health care for all.
Dr. Brandt is an an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Transgender awareness month 2021. Fenway Health. 2021 Nov 1.
2. Wareham J. 375 transgender people murdered in 2021 – ‘Deadliest year’ since records began. Forbes. 2021 Nov 11..
3. Ronan R. 2021 officially becomes worst year in recent history for LGBTQ state legislative attacks as unprecedented number of states enact record-shattering number of anti-LGBTQ measures into law. Human Rights Campaign Press Release. 2021 May 7..
4. Practice Guideline. Health care for transgender and gender diverse individuals: ACOG Committee Opinion, No. 823. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
As I sit down to write this article, I cannot help but reflect on the significance of today and the upcoming week – Transgender Awareness Week. While it may seem that the transgender community has made great strides in political, social, and health care forums, this week serves as a cold and grave reality check for members of the community and its allies. We still have a long way to go.
This annual tradition began in 1998 in response to the murder of a transgender woman, Rita Hester. Now Transgender Awareness Week, which occurs from Nov. 13th through the 19th is a week dedicated to help raise awareness and improve visibility of transgender people and the issues they face.1 The week culminates on Nov. 20 with The Transgender Day of Remembrance (TDOR). The day is an annual observance to honor the memory of the transgender people who lost their lives to acts of antitransgender violence during that year.1
Unfortunately, 2021 marks the worst year in recent history for transgender violence and anti-LGBT legislation. Over this past year, 375 transgender people were killed – 96% of whom were black and migrant trans women of color and over half (58%) of whom were sex workers.2 What is even more shocking is that one in four of these victims were murdered in their own homes.2 Compared with 2015, which previously held the title of “worst year,” 250 anti-LGBT bills have been introduced in state legislatures in 2021; 17 of which have been already enacted into law.3 The recently passed laws involve antitrans sports bans, religious refusal, anti-LGBTQ education, antitrans medical care, antitrans birth certificates, and an anti–all comers bill.3 In evaluating the 250 anti-LGBT bills introduced into state legislatures, at least 35 of these would prohibit transgender youth from accessing gender-affirming medical care and an additional 43 bills would allow people to deny or not provide services (including all medical care) by asserting religious freedom.3 The current bills exhibit a flagrant disregard for current best practices, which have demonstrated the benefits of gender-affirming medical care. Furthermore, they can increase the already high death toll for transgender patients by allowing providers and institutions to deny care to patients seeking services unrelated to their gender identity or sexual orientation.
Even if providers are not directly prescribing hormone therapy or performing gender-affirming procedures, all providers have encountered and will treat an LGBTQ patient at some point during their career. It is necessary for all obstetrician-gynecologists to be aware of the systemic damages and threats that LGBTQ patients face, as well as pending legislation that can significantly affect and harm patient care. As a result, we need to screen these patients for depression and history of self-harm, and to assess social support, as well as challenge legislation that can negatively affect LGBTQ care. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has not only issued formal statements condemning discrimination on the basis of gender identity and sexual orientation, but also advocates for inclusive, thoughtful, and affirming care for transgender individuals.4 In a time when our patients may not feel as though they can advocate for themselves, we as providers must use our voices and medical knowledge to enact these changes to encourage equitable and safe health care for all.
Dr. Brandt is an an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Transgender awareness month 2021. Fenway Health. 2021 Nov 1.
2. Wareham J. 375 transgender people murdered in 2021 – ‘Deadliest year’ since records began. Forbes. 2021 Nov 11..
3. Ronan R. 2021 officially becomes worst year in recent history for LGBTQ state legislative attacks as unprecedented number of states enact record-shattering number of anti-LGBTQ measures into law. Human Rights Campaign Press Release. 2021 May 7..
4. Practice Guideline. Health care for transgender and gender diverse individuals: ACOG Committee Opinion, No. 823. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Medical technology should keep patient in mind
Indeed, science and technology provide opportunities to improve outcomes in ways not even imagined 100 years ago, yet we must acknowledge that technology also threatens to erect barriers between us and our patients. We can be easily tempted to confuse new care delivery tools with the actual care itself.
Threats to the physician-patient relationship
Medical history provides many examples of how our zeal to innovate can have untoward consequences to the physician-patient relationship.
In the late 1800s, for example, to convey a sense of science, purity of intent, and trust, the medical community began wearing white coats. Those white coats have been discussed as creating emotional distance between physicians and their patients.1
Even when we in the medical community are slow and reluctant to change, the external forces propelling us forward often seem unstoppable; kinetic aspirations to innovate electronic information systems and new applications seem suddenly to revolutionize care delivery when we least expect it. The rapidity of change in technology can sometimes be dizzying but can at the same time can occur so swiftly we don’t even notice it.
After René Laennec invented the stethoscope in the early 1800s, clinicians no longer needed to physically lean in and place an ear directly onto patients to hear their hearts beating. This created a distance from patients that was still lamented 50 years later, when a professor of medicine is reported to have said, “he that hath ears to hear, let him use his ears and not a stethoscope.” Still, while the stethoscope has literally distanced us from patients, it is such an important tool that we no longer think about this distancing. We have adapted over time to remain close to our patients, to sincerely listen to their thoughts and reassure them that we hear them without the need to feel our ears on their chests.
Francis Peabody, the eminent Harvard physician, wrote an essay in 1927 titled, “The Care of the Patient.” At the end of the first paragraph, he states: “The most common criticism made at present by older practitioners is that young graduates ... are too “scientific” and do not know how to take care of patients.” He goes on to say that “one of the essential qualities of the clinician is interest in humanity, for the secret of the care of the patient is in caring for the patient.”2
We agree with Dr. Peabody. As we embrace science and technology that can change health outcomes, our patients’ needs to feel understood and cared for will not diminish. Instead, that need will continue to be an important aspect of our struggle and joy in providing holistic, humane, competent care into the future.
Twenty-first century physicians have access to an ever-growing trove of data, yet our ability to truly know our patients seems somehow less accessible. Home health devices have begun to provide a flow of information about parameters, ranging from continuous glucose readings to home blood pressures, weights, and inspiratory flow readings. These data can provide much more accurate insight into patients than what we can glean from one point in time during an office visit. Yet we need to remember that behind the data are people with dreams and desires, not just table entries in an electronic health record.
In 1923, the German philosopher Martin Buber published the book for which he is best known, “I and Thou.” In that book, Mr. Buber says that there are two ways we can approach relationships: “I-Thou” or “I-It.” In I-It relationships, we view the other person as an “it” to be used to accomplish a purpose, or to be experienced without his or her full involvement. In an I-Thou relationship, we appreciate the other people for all their complexity, in their full humanness. We must consciously remind ourselves amid the rush of technology that there are real people behind those data. We must acknowledge and approach each person as a unique individual who has dreams, goals, fears, and wishes that may be different from ours but to which we can still relate.
‘From the Beating End of the Stethoscope’
John Ciardi, an American poet, said the following in a poem titled, “Lines From the Beating End of the Stethoscope”:
I speak, as I say, the patient’s point of view.
But, given time, doctors are patients, too.
And there’s our bond: beyond anatomy,
Or in it, through it, to the mystery
Medicine takes the pulse of and lets go
Forever unexplained. It’s art, we know,
Not science at the heart. Doctor be whole,
I won’t insist the patient is a soul,
But he’s a something, possibly laughable,
Or possibly sublime, but not quite graphable.
Not quite containable on a bed chart.
Where science touches man it turns to art.3
This poem is a reminder of the subtle needs of patients during their encounters with doctors, especially around many of the most important decisions and events in their lives. Patients’ needs are varied, complex, difficult to discern, and not able to be fully explained or understood through math and science.
Einstein warned us that the modern age would be characterized by a perfection of means and a confusion of goals.4 As clinicians, we should strive to clarify and align our goals with those of our patients, providing care that is real, compassionate, and personal, not just an optimized means to achieve standardized metrics. While technology can assist us in this pursuit, we’ll need be careful that our enchantment with innovation does not cloud our actual goal: truly caring for our patients.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Jones VA. The white coat: Why not follow suit? JAMA. 1999;281(5):478. doi: 10.1001/jama.281.5.478-JMS0203-5-1
2. Peabody, Francis (1927). “The care of the patient.” JAMA. 88(12):877-82. doi: 10.1001/jama.1927.02680380001001.
3. Ciardi, John. Lines from the Beating End of the Stethoscope. Saturday Review, Nov. 18, 1968.
4. Albert Einstein, Out of My Later Years, 1950.
Indeed, science and technology provide opportunities to improve outcomes in ways not even imagined 100 years ago, yet we must acknowledge that technology also threatens to erect barriers between us and our patients. We can be easily tempted to confuse new care delivery tools with the actual care itself.
Threats to the physician-patient relationship
Medical history provides many examples of how our zeal to innovate can have untoward consequences to the physician-patient relationship.
In the late 1800s, for example, to convey a sense of science, purity of intent, and trust, the medical community began wearing white coats. Those white coats have been discussed as creating emotional distance between physicians and their patients.1
Even when we in the medical community are slow and reluctant to change, the external forces propelling us forward often seem unstoppable; kinetic aspirations to innovate electronic information systems and new applications seem suddenly to revolutionize care delivery when we least expect it. The rapidity of change in technology can sometimes be dizzying but can at the same time can occur so swiftly we don’t even notice it.
After René Laennec invented the stethoscope in the early 1800s, clinicians no longer needed to physically lean in and place an ear directly onto patients to hear their hearts beating. This created a distance from patients that was still lamented 50 years later, when a professor of medicine is reported to have said, “he that hath ears to hear, let him use his ears and not a stethoscope.” Still, while the stethoscope has literally distanced us from patients, it is such an important tool that we no longer think about this distancing. We have adapted over time to remain close to our patients, to sincerely listen to their thoughts and reassure them that we hear them without the need to feel our ears on their chests.
Francis Peabody, the eminent Harvard physician, wrote an essay in 1927 titled, “The Care of the Patient.” At the end of the first paragraph, he states: “The most common criticism made at present by older practitioners is that young graduates ... are too “scientific” and do not know how to take care of patients.” He goes on to say that “one of the essential qualities of the clinician is interest in humanity, for the secret of the care of the patient is in caring for the patient.”2
We agree with Dr. Peabody. As we embrace science and technology that can change health outcomes, our patients’ needs to feel understood and cared for will not diminish. Instead, that need will continue to be an important aspect of our struggle and joy in providing holistic, humane, competent care into the future.
Twenty-first century physicians have access to an ever-growing trove of data, yet our ability to truly know our patients seems somehow less accessible. Home health devices have begun to provide a flow of information about parameters, ranging from continuous glucose readings to home blood pressures, weights, and inspiratory flow readings. These data can provide much more accurate insight into patients than what we can glean from one point in time during an office visit. Yet we need to remember that behind the data are people with dreams and desires, not just table entries in an electronic health record.
In 1923, the German philosopher Martin Buber published the book for which he is best known, “I and Thou.” In that book, Mr. Buber says that there are two ways we can approach relationships: “I-Thou” or “I-It.” In I-It relationships, we view the other person as an “it” to be used to accomplish a purpose, or to be experienced without his or her full involvement. In an I-Thou relationship, we appreciate the other people for all their complexity, in their full humanness. We must consciously remind ourselves amid the rush of technology that there are real people behind those data. We must acknowledge and approach each person as a unique individual who has dreams, goals, fears, and wishes that may be different from ours but to which we can still relate.
‘From the Beating End of the Stethoscope’
John Ciardi, an American poet, said the following in a poem titled, “Lines From the Beating End of the Stethoscope”:
I speak, as I say, the patient’s point of view.
But, given time, doctors are patients, too.
And there’s our bond: beyond anatomy,
Or in it, through it, to the mystery
Medicine takes the pulse of and lets go
Forever unexplained. It’s art, we know,
Not science at the heart. Doctor be whole,
I won’t insist the patient is a soul,
But he’s a something, possibly laughable,
Or possibly sublime, but not quite graphable.
Not quite containable on a bed chart.
Where science touches man it turns to art.3
This poem is a reminder of the subtle needs of patients during their encounters with doctors, especially around many of the most important decisions and events in their lives. Patients’ needs are varied, complex, difficult to discern, and not able to be fully explained or understood through math and science.
Einstein warned us that the modern age would be characterized by a perfection of means and a confusion of goals.4 As clinicians, we should strive to clarify and align our goals with those of our patients, providing care that is real, compassionate, and personal, not just an optimized means to achieve standardized metrics. While technology can assist us in this pursuit, we’ll need be careful that our enchantment with innovation does not cloud our actual goal: truly caring for our patients.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Jones VA. The white coat: Why not follow suit? JAMA. 1999;281(5):478. doi: 10.1001/jama.281.5.478-JMS0203-5-1
2. Peabody, Francis (1927). “The care of the patient.” JAMA. 88(12):877-82. doi: 10.1001/jama.1927.02680380001001.
3. Ciardi, John. Lines from the Beating End of the Stethoscope. Saturday Review, Nov. 18, 1968.
4. Albert Einstein, Out of My Later Years, 1950.
Indeed, science and technology provide opportunities to improve outcomes in ways not even imagined 100 years ago, yet we must acknowledge that technology also threatens to erect barriers between us and our patients. We can be easily tempted to confuse new care delivery tools with the actual care itself.
Threats to the physician-patient relationship
Medical history provides many examples of how our zeal to innovate can have untoward consequences to the physician-patient relationship.
In the late 1800s, for example, to convey a sense of science, purity of intent, and trust, the medical community began wearing white coats. Those white coats have been discussed as creating emotional distance between physicians and their patients.1
Even when we in the medical community are slow and reluctant to change, the external forces propelling us forward often seem unstoppable; kinetic aspirations to innovate electronic information systems and new applications seem suddenly to revolutionize care delivery when we least expect it. The rapidity of change in technology can sometimes be dizzying but can at the same time can occur so swiftly we don’t even notice it.
After René Laennec invented the stethoscope in the early 1800s, clinicians no longer needed to physically lean in and place an ear directly onto patients to hear their hearts beating. This created a distance from patients that was still lamented 50 years later, when a professor of medicine is reported to have said, “he that hath ears to hear, let him use his ears and not a stethoscope.” Still, while the stethoscope has literally distanced us from patients, it is such an important tool that we no longer think about this distancing. We have adapted over time to remain close to our patients, to sincerely listen to their thoughts and reassure them that we hear them without the need to feel our ears on their chests.
Francis Peabody, the eminent Harvard physician, wrote an essay in 1927 titled, “The Care of the Patient.” At the end of the first paragraph, he states: “The most common criticism made at present by older practitioners is that young graduates ... are too “scientific” and do not know how to take care of patients.” He goes on to say that “one of the essential qualities of the clinician is interest in humanity, for the secret of the care of the patient is in caring for the patient.”2
We agree with Dr. Peabody. As we embrace science and technology that can change health outcomes, our patients’ needs to feel understood and cared for will not diminish. Instead, that need will continue to be an important aspect of our struggle and joy in providing holistic, humane, competent care into the future.
Twenty-first century physicians have access to an ever-growing trove of data, yet our ability to truly know our patients seems somehow less accessible. Home health devices have begun to provide a flow of information about parameters, ranging from continuous glucose readings to home blood pressures, weights, and inspiratory flow readings. These data can provide much more accurate insight into patients than what we can glean from one point in time during an office visit. Yet we need to remember that behind the data are people with dreams and desires, not just table entries in an electronic health record.
In 1923, the German philosopher Martin Buber published the book for which he is best known, “I and Thou.” In that book, Mr. Buber says that there are two ways we can approach relationships: “I-Thou” or “I-It.” In I-It relationships, we view the other person as an “it” to be used to accomplish a purpose, or to be experienced without his or her full involvement. In an I-Thou relationship, we appreciate the other people for all their complexity, in their full humanness. We must consciously remind ourselves amid the rush of technology that there are real people behind those data. We must acknowledge and approach each person as a unique individual who has dreams, goals, fears, and wishes that may be different from ours but to which we can still relate.
‘From the Beating End of the Stethoscope’
John Ciardi, an American poet, said the following in a poem titled, “Lines From the Beating End of the Stethoscope”:
I speak, as I say, the patient’s point of view.
But, given time, doctors are patients, too.
And there’s our bond: beyond anatomy,
Or in it, through it, to the mystery
Medicine takes the pulse of and lets go
Forever unexplained. It’s art, we know,
Not science at the heart. Doctor be whole,
I won’t insist the patient is a soul,
But he’s a something, possibly laughable,
Or possibly sublime, but not quite graphable.
Not quite containable on a bed chart.
Where science touches man it turns to art.3
This poem is a reminder of the subtle needs of patients during their encounters with doctors, especially around many of the most important decisions and events in their lives. Patients’ needs are varied, complex, difficult to discern, and not able to be fully explained or understood through math and science.
Einstein warned us that the modern age would be characterized by a perfection of means and a confusion of goals.4 As clinicians, we should strive to clarify and align our goals with those of our patients, providing care that is real, compassionate, and personal, not just an optimized means to achieve standardized metrics. While technology can assist us in this pursuit, we’ll need be careful that our enchantment with innovation does not cloud our actual goal: truly caring for our patients.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Jones VA. The white coat: Why not follow suit? JAMA. 1999;281(5):478. doi: 10.1001/jama.281.5.478-JMS0203-5-1
2. Peabody, Francis (1927). “The care of the patient.” JAMA. 88(12):877-82. doi: 10.1001/jama.1927.02680380001001.
3. Ciardi, John. Lines from the Beating End of the Stethoscope. Saturday Review, Nov. 18, 1968.
4. Albert Einstein, Out of My Later Years, 1950.
More tools for the COVID toolbox
I was recently asked to see a 16-year-old, unvaccinated (against COVID-19) adolescent with hypothyroidism and obesity (body mass index 37 kg/m2) seen in the pediatric emergency department with tachycardia, O2 saturation 96%, urinary tract infection, poor appetite, and nausea. Her chest x-ray had low lung volumes but no infiltrates. She was noted to be dehydrated. Testing for COVID-19 was PCR positive.1
She was observed overnight, tolerated oral rehydration, and was being readied for discharge. Pediatric Infectious Diseases was called about prescribing remdesivir.
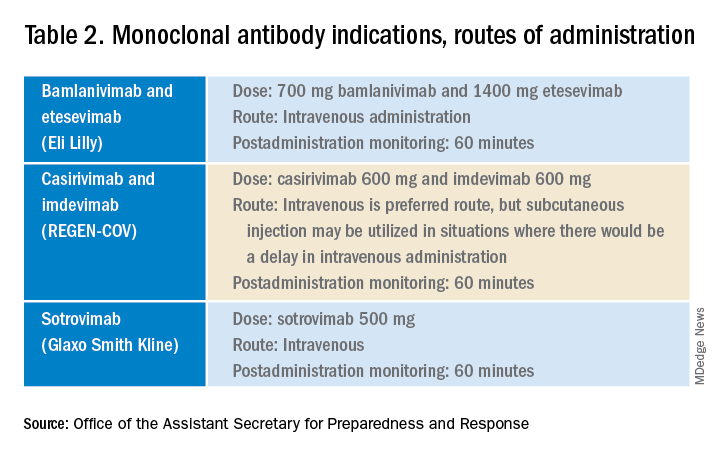
Remdesivir was not indicated as its current use is limited to inpatients with oxygen desaturations less than 94%. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines do recommend the use of monoclonal antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein for prevention of COVID disease progression in high-risk individuals. Specifically, the IDSA guidelines say, “Among ambulatory patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 at high risk for progression to severe disease, bamlanivimab/etesevimab, casirivimab/imdevimab, or sotrovimab rather than no neutralizing antibody treatment.”
The Food and Drug Administration’s Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) allowed use of specific monoclonal antibodies (casirivimab/imdevimab in combination, bamlanivimab/etesevimab in combination, and sotrovimab alone) for individuals 12 years and above with a minimum weight of 40 kg with high-risk conditions, describing the evidence as moderate certainty.2
Several questions have arisen regarding their use. Which children qualify under the EUA? Are the available monoclonal antibodies effective for SARS-CoV-2 variants? What adverse events were observed? Are there implementation hurdles?
Unlike the EUA for prophylactic use, which targeted unvaccinated individuals and those unlikely to have a good antibody response to vaccine, use of monoclonal antibody for prevention of progression does not have such restrictions. Effectiveness may vary by local variant susceptibility and should be considered in the choice of the most appropriate monoclonal antibody therapy. Reductions in hospitalization and progression to critical disease status were reported from phase 3 studies; reductions were also observed in mortality in some, but not all, studies. Enhanced viral clearance on day 7 was observed with few subjects having persistent high viral load.
Which children qualify under the EUA? Adolescents 12 years and older and over 40 kg are eligible if a high risk condition is present. High-risk conditions include body mass index at the 85th percentile or higher, immunosuppressive disease, or receipt of immunosuppressive therapies, or baseline (pre-COVID infection) medical-related technological dependence such as tracheostomy or positive pressure ventilation. Additional high-risk conditions are neurodevelopmental disorders, sickle cell disease, congenital or acquired heart disease, asthma, or reactive airway or other chronic respiratory disease that requires daily medication for control, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or pregnancy.3
Are the available monoclonal antibodies effective for SARS-CoV-2 variants? Of course, this is a critical question and relies on knowledge of the dominant variant in a specific geographic location. The CDC data on which variants are susceptible to which monoclonal therapies were updated as of Oct. 21 online (see Table 1). Local departments of public health often will have current data on the dominant variant in the community. Currently, the dominant variant in the United States is Delta and it is anticipated to be susceptible to the three monoclonal treatments authorized under the EUA based on in vitro neutralizing assays.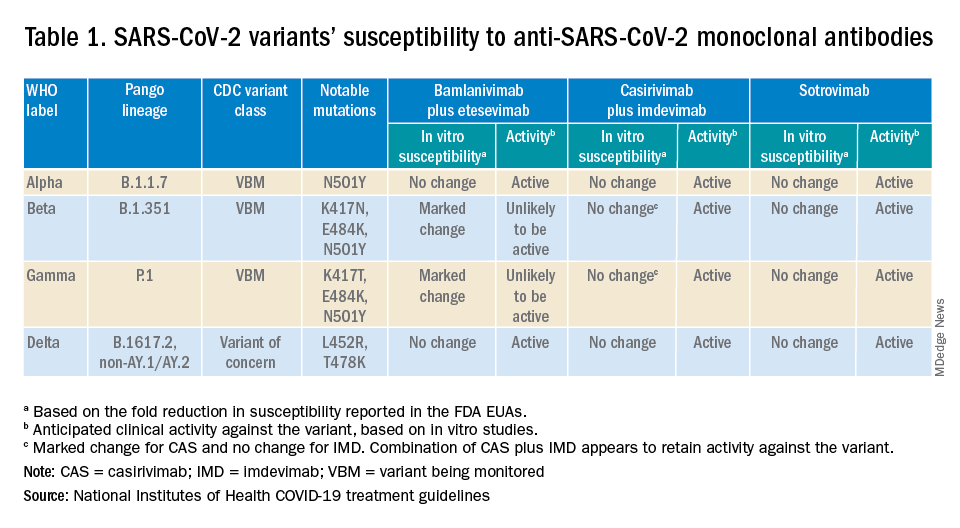
What adverse events were observed? Monoclonal antibody infusions are in general safe but anaphylaxis has been reported. Other infusion-related adverse events include urticaria, pruritis, flushing, pyrexia, shortness of breath, chest tightness, nausea, vomiting, and rash. Nearly all events were grade 1, mild, or grade 2, moderate. For nonsevere infusion-related reactions, consider slowing the infusion; if necessary, the infusion should be stopped.
Implementation challenges
The first challenge is finding a location to infuse the monoclonal antibodies. Although they can be given subcutaneously, the dose is large and little, if any, time is saved as the recommendation is for observation post administration for 1 hour. The challenge we and other centers may face is that the patients are COVID PCR+ and therefore our usual infusion program, which often is occupied by individuals already compromised and at high risk for severe COVID, is an undesirable location. We are planning to use the emergency department to accommodate such patients currently, but even that solution creates challenges for a busy, urban medical center.
Summary
Anti–SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies are an important part of the therapeutic approach to minimizing disease severity. Clinicians should review high-risk conditions in adolescents who are PCR+ for SARS-CoV-2 and have mild to moderate symptoms. Medical care systems should implement programs to make monoclonal infusions available for such high-risk adolescents.4 Obesity and asthma reactive airways or requiring daily medication for control are the two most common conditions that place adolescents with COVID-19 at risk for progression to hospitalization and severe disease in addition to the more traditional immune-compromising conditions and medical fragility.
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University schools of medicine and public health and senior attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases, Boston Medical Center. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Federal Response to COVID-19: Monoclonal Antibody Clinical Implementation Guide. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2021 Sep 2.
2. Bhimraj A et al. IDSA Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19. Last updated 2021 Nov 9.
3. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies. National Institutes of Health’s COVID 19 Treatment Guidelines. Last updated 2021 Oct 19.
4. Spreading the Word on the Benefits of Monoclonal Antibodies for COVID-19, by Hannah R. Buchdahl. CDC Foundation, 2021 Jul 2.
I was recently asked to see a 16-year-old, unvaccinated (against COVID-19) adolescent with hypothyroidism and obesity (body mass index 37 kg/m2) seen in the pediatric emergency department with tachycardia, O2 saturation 96%, urinary tract infection, poor appetite, and nausea. Her chest x-ray had low lung volumes but no infiltrates. She was noted to be dehydrated. Testing for COVID-19 was PCR positive.1
She was observed overnight, tolerated oral rehydration, and was being readied for discharge. Pediatric Infectious Diseases was called about prescribing remdesivir.
Remdesivir was not indicated as its current use is limited to inpatients with oxygen desaturations less than 94%. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines do recommend the use of monoclonal antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein for prevention of COVID disease progression in high-risk individuals. Specifically, the IDSA guidelines say, “Among ambulatory patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 at high risk for progression to severe disease, bamlanivimab/etesevimab, casirivimab/imdevimab, or sotrovimab rather than no neutralizing antibody treatment.”
The Food and Drug Administration’s Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) allowed use of specific monoclonal antibodies (casirivimab/imdevimab in combination, bamlanivimab/etesevimab in combination, and sotrovimab alone) for individuals 12 years and above with a minimum weight of 40 kg with high-risk conditions, describing the evidence as moderate certainty.2
Several questions have arisen regarding their use. Which children qualify under the EUA? Are the available monoclonal antibodies effective for SARS-CoV-2 variants? What adverse events were observed? Are there implementation hurdles?
Unlike the EUA for prophylactic use, which targeted unvaccinated individuals and those unlikely to have a good antibody response to vaccine, use of monoclonal antibody for prevention of progression does not have such restrictions. Effectiveness may vary by local variant susceptibility and should be considered in the choice of the most appropriate monoclonal antibody therapy. Reductions in hospitalization and progression to critical disease status were reported from phase 3 studies; reductions were also observed in mortality in some, but not all, studies. Enhanced viral clearance on day 7 was observed with few subjects having persistent high viral load.
Which children qualify under the EUA? Adolescents 12 years and older and over 40 kg are eligible if a high risk condition is present. High-risk conditions include body mass index at the 85th percentile or higher, immunosuppressive disease, or receipt of immunosuppressive therapies, or baseline (pre-COVID infection) medical-related technological dependence such as tracheostomy or positive pressure ventilation. Additional high-risk conditions are neurodevelopmental disorders, sickle cell disease, congenital or acquired heart disease, asthma, or reactive airway or other chronic respiratory disease that requires daily medication for control, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or pregnancy.3
Are the available monoclonal antibodies effective for SARS-CoV-2 variants? Of course, this is a critical question and relies on knowledge of the dominant variant in a specific geographic location. The CDC data on which variants are susceptible to which monoclonal therapies were updated as of Oct. 21 online (see Table 1). Local departments of public health often will have current data on the dominant variant in the community. Currently, the dominant variant in the United States is Delta and it is anticipated to be susceptible to the three monoclonal treatments authorized under the EUA based on in vitro neutralizing assays.
What adverse events were observed? Monoclonal antibody infusions are in general safe but anaphylaxis has been reported. Other infusion-related adverse events include urticaria, pruritis, flushing, pyrexia, shortness of breath, chest tightness, nausea, vomiting, and rash. Nearly all events were grade 1, mild, or grade 2, moderate. For nonsevere infusion-related reactions, consider slowing the infusion; if necessary, the infusion should be stopped.
Implementation challenges
The first challenge is finding a location to infuse the monoclonal antibodies. Although they can be given subcutaneously, the dose is large and little, if any, time is saved as the recommendation is for observation post administration for 1 hour. The challenge we and other centers may face is that the patients are COVID PCR+ and therefore our usual infusion program, which often is occupied by individuals already compromised and at high risk for severe COVID, is an undesirable location. We are planning to use the emergency department to accommodate such patients currently, but even that solution creates challenges for a busy, urban medical center.

Summary
Anti–SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies are an important part of the therapeutic approach to minimizing disease severity. Clinicians should review high-risk conditions in adolescents who are PCR+ for SARS-CoV-2 and have mild to moderate symptoms. Medical care systems should implement programs to make monoclonal infusions available for such high-risk adolescents.4 Obesity and asthma reactive airways or requiring daily medication for control are the two most common conditions that place adolescents with COVID-19 at risk for progression to hospitalization and severe disease in addition to the more traditional immune-compromising conditions and medical fragility.
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University schools of medicine and public health and senior attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases, Boston Medical Center. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Federal Response to COVID-19: Monoclonal Antibody Clinical Implementation Guide. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2021 Sep 2.
2. Bhimraj A et al. IDSA Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19. Last updated 2021 Nov 9.
3. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies. National Institutes of Health’s COVID 19 Treatment Guidelines. Last updated 2021 Oct 19.
4. Spreading the Word on the Benefits of Monoclonal Antibodies for COVID-19, by Hannah R. Buchdahl. CDC Foundation, 2021 Jul 2.
I was recently asked to see a 16-year-old, unvaccinated (against COVID-19) adolescent with hypothyroidism and obesity (body mass index 37 kg/m2) seen in the pediatric emergency department with tachycardia, O2 saturation 96%, urinary tract infection, poor appetite, and nausea. Her chest x-ray had low lung volumes but no infiltrates. She was noted to be dehydrated. Testing for COVID-19 was PCR positive.1
She was observed overnight, tolerated oral rehydration, and was being readied for discharge. Pediatric Infectious Diseases was called about prescribing remdesivir.
Remdesivir was not indicated as its current use is limited to inpatients with oxygen desaturations less than 94%. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines do recommend the use of monoclonal antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein for prevention of COVID disease progression in high-risk individuals. Specifically, the IDSA guidelines say, “Among ambulatory patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 at high risk for progression to severe disease, bamlanivimab/etesevimab, casirivimab/imdevimab, or sotrovimab rather than no neutralizing antibody treatment.”
The Food and Drug Administration’s Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) allowed use of specific monoclonal antibodies (casirivimab/imdevimab in combination, bamlanivimab/etesevimab in combination, and sotrovimab alone) for individuals 12 years and above with a minimum weight of 40 kg with high-risk conditions, describing the evidence as moderate certainty.2
Several questions have arisen regarding their use. Which children qualify under the EUA? Are the available monoclonal antibodies effective for SARS-CoV-2 variants? What adverse events were observed? Are there implementation hurdles?
Unlike the EUA for prophylactic use, which targeted unvaccinated individuals and those unlikely to have a good antibody response to vaccine, use of monoclonal antibody for prevention of progression does not have such restrictions. Effectiveness may vary by local variant susceptibility and should be considered in the choice of the most appropriate monoclonal antibody therapy. Reductions in hospitalization and progression to critical disease status were reported from phase 3 studies; reductions were also observed in mortality in some, but not all, studies. Enhanced viral clearance on day 7 was observed with few subjects having persistent high viral load.
Which children qualify under the EUA? Adolescents 12 years and older and over 40 kg are eligible if a high risk condition is present. High-risk conditions include body mass index at the 85th percentile or higher, immunosuppressive disease, or receipt of immunosuppressive therapies, or baseline (pre-COVID infection) medical-related technological dependence such as tracheostomy or positive pressure ventilation. Additional high-risk conditions are neurodevelopmental disorders, sickle cell disease, congenital or acquired heart disease, asthma, or reactive airway or other chronic respiratory disease that requires daily medication for control, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or pregnancy.3
Are the available monoclonal antibodies effective for SARS-CoV-2 variants? Of course, this is a critical question and relies on knowledge of the dominant variant in a specific geographic location. The CDC data on which variants are susceptible to which monoclonal therapies were updated as of Oct. 21 online (see Table 1). Local departments of public health often will have current data on the dominant variant in the community. Currently, the dominant variant in the United States is Delta and it is anticipated to be susceptible to the three monoclonal treatments authorized under the EUA based on in vitro neutralizing assays.
What adverse events were observed? Monoclonal antibody infusions are in general safe but anaphylaxis has been reported. Other infusion-related adverse events include urticaria, pruritis, flushing, pyrexia, shortness of breath, chest tightness, nausea, vomiting, and rash. Nearly all events were grade 1, mild, or grade 2, moderate. For nonsevere infusion-related reactions, consider slowing the infusion; if necessary, the infusion should be stopped.
Implementation challenges
The first challenge is finding a location to infuse the monoclonal antibodies. Although they can be given subcutaneously, the dose is large and little, if any, time is saved as the recommendation is for observation post administration for 1 hour. The challenge we and other centers may face is that the patients are COVID PCR+ and therefore our usual infusion program, which often is occupied by individuals already compromised and at high risk for severe COVID, is an undesirable location. We are planning to use the emergency department to accommodate such patients currently, but even that solution creates challenges for a busy, urban medical center.

Summary
Anti–SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies are an important part of the therapeutic approach to minimizing disease severity. Clinicians should review high-risk conditions in adolescents who are PCR+ for SARS-CoV-2 and have mild to moderate symptoms. Medical care systems should implement programs to make monoclonal infusions available for such high-risk adolescents.4 Obesity and asthma reactive airways or requiring daily medication for control are the two most common conditions that place adolescents with COVID-19 at risk for progression to hospitalization and severe disease in addition to the more traditional immune-compromising conditions and medical fragility.
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University schools of medicine and public health and senior attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases, Boston Medical Center. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Federal Response to COVID-19: Monoclonal Antibody Clinical Implementation Guide. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2021 Sep 2.
2. Bhimraj A et al. IDSA Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19. Last updated 2021 Nov 9.
3. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies. National Institutes of Health’s COVID 19 Treatment Guidelines. Last updated 2021 Oct 19.
4. Spreading the Word on the Benefits of Monoclonal Antibodies for COVID-19, by Hannah R. Buchdahl. CDC Foundation, 2021 Jul 2.
Case: Older patient with T2D has recurrent flushing
He has had no other symptoms. His only abnormalities on physical exam are a blood pressure of 160/100 and mild peripheral edema.
His current medications include: Famotidine 20 mg b.i.d., Pseudoephedrine/guaifenesin SR b.i.d., Metformin 1,000 mg twice a day, Nifedipine 60 mg XL once a day, and Atorvastatin 20 mg once a day.
His laboratory work up includes: blood urea nitrogen: 20, creatinine: 1.3, sodium: 140, Chloride: 104, potassium: 3.9, glucose: 205, white blood cell count: 6,000, hematocrit: 41, 24-hour urine 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5HIAA) test: 12 mg/day (normal 2-8 mg/day), free catecholamines: 80 mg/24 hours (normal less than 100 mg/24 hours).
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Drug effect
B. Pheochromocytoma
C. Carcinoid syndrome
D. Mastocytosis
E. Medullary thyroid cancer
The most likely diagnosis is a drug effect. His flushing is likely caused by nifedipine.
Flushing is one of the most common side effects of this drug.1 This patient had lab testing done for carcinoid (urine 5HIAA), presumably because he had flushing. This lab test result was a false positive, likely because of guaifenesin ingestion, which can cause false-positive 5HIAA results.2
Carcinoid syndrome is very rare (estimates from less than 1 patient/100,000), and the vast majority of patients who have it present with metastatic disease at presentation. Drug side effects are common, and usually are much more likely than rare diseases.
Four principles for assisting with making a diagnosis
This case points out the following four principles that I will touch on to help us make diagnoses in challenging cases.
1. Trigger symptoms: These are symptoms that make us think of a rare disease. In this case, the symptom is flushing, which may make you think of carcinoid syndrome.
Another good example of a trigger symptom is night sweats, where you may think of tuberculosis or lymphoma. These symptoms almost always have a much more common and likely cause, which in this case is a common drug side effect.
Trigger symptoms are great to pay attention to, but do not jump to working up the rare diagnosis without more evidence that it is a plausible diagnosis. Working up rare diseases without a reasonable pretest probability will lead to significant false-positive results.
2. Distinguishing features: These are findings, or combinations of findings, that make rarer diseases more likely. For example, flushing, although seen in many patients with carcinoid syndrome, is much more commonly caused by rosacea, medications, or estrogen/testosterone deficiency.
If a patient presents with flushing plus diarrhea, carcinoid syndrome becomes more likely in differentials. An example of a specific distinguishing feature is transient visual obstructions in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH or pseudotumor cerebri).
Sudden transient visual loss is not a symptom we see often, but headaches and obesity are problems we see every day. A patient with headaches and obesity is very likely to have IIH if they have transient visual obstructions along with headaches and obesity.
3. Intentional physical exams: Do the physical exam focusing on what findings will change your diagnostic probabilities. For example, in this case, if you are considering carcinoid, do a careful abdominal exam, with close attention to the liver, as 75% of patients with carcinoid syndrome have liver metastases.
If you are thinking about IIH, a fundoscopic exam is mandatory, as papilledema is a key feature of this diagnosis.
Read about the rare diagnosis you are considering, this will help with targeting your exam.
4. Remember the unusual presentation of a common disease is more common than the common presentation of a rare disease: Good examples of this are sleep apnea and gastroesophageal reflux disease causing night sweats more commonly than finding lymphomas or active tuberculosis (in the United States) as the cause.3
Pearl: Trigger symptoms help us think of rare diseases, but distinguishing features are most helpful in including or excluding the diagnosis.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Gueret P et al. Drugs. 1990;39 Suppl 2:67-72.
2. Corcuff J et al. Endocr Connect. 2017;6:R87.
3. Smith CS and Paauw DS. J Am Board Fam Pract. 2000;13:424-9.
He has had no other symptoms. His only abnormalities on physical exam are a blood pressure of 160/100 and mild peripheral edema.
His current medications include: Famotidine 20 mg b.i.d., Pseudoephedrine/guaifenesin SR b.i.d., Metformin 1,000 mg twice a day, Nifedipine 60 mg XL once a day, and Atorvastatin 20 mg once a day.
His laboratory work up includes: blood urea nitrogen: 20, creatinine: 1.3, sodium: 140, Chloride: 104, potassium: 3.9, glucose: 205, white blood cell count: 6,000, hematocrit: 41, 24-hour urine 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5HIAA) test: 12 mg/day (normal 2-8 mg/day), free catecholamines: 80 mg/24 hours (normal less than 100 mg/24 hours).
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Drug effect
B. Pheochromocytoma
C. Carcinoid syndrome
D. Mastocytosis
E. Medullary thyroid cancer
The most likely diagnosis is a drug effect. His flushing is likely caused by nifedipine.
Flushing is one of the most common side effects of this drug.1 This patient had lab testing done for carcinoid (urine 5HIAA), presumably because he had flushing. This lab test result was a false positive, likely because of guaifenesin ingestion, which can cause false-positive 5HIAA results.2
Carcinoid syndrome is very rare (estimates from less than 1 patient/100,000), and the vast majority of patients who have it present with metastatic disease at presentation. Drug side effects are common, and usually are much more likely than rare diseases.
Four principles for assisting with making a diagnosis
This case points out the following four principles that I will touch on to help us make diagnoses in challenging cases.
1. Trigger symptoms: These are symptoms that make us think of a rare disease. In this case, the symptom is flushing, which may make you think of carcinoid syndrome.
Another good example of a trigger symptom is night sweats, where you may think of tuberculosis or lymphoma. These symptoms almost always have a much more common and likely cause, which in this case is a common drug side effect.
Trigger symptoms are great to pay attention to, but do not jump to working up the rare diagnosis without more evidence that it is a plausible diagnosis. Working up rare diseases without a reasonable pretest probability will lead to significant false-positive results.
2. Distinguishing features: These are findings, or combinations of findings, that make rarer diseases more likely. For example, flushing, although seen in many patients with carcinoid syndrome, is much more commonly caused by rosacea, medications, or estrogen/testosterone deficiency.
If a patient presents with flushing plus diarrhea, carcinoid syndrome becomes more likely in differentials. An example of a specific distinguishing feature is transient visual obstructions in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH or pseudotumor cerebri).
Sudden transient visual loss is not a symptom we see often, but headaches and obesity are problems we see every day. A patient with headaches and obesity is very likely to have IIH if they have transient visual obstructions along with headaches and obesity.
3. Intentional physical exams: Do the physical exam focusing on what findings will change your diagnostic probabilities. For example, in this case, if you are considering carcinoid, do a careful abdominal exam, with close attention to the liver, as 75% of patients with carcinoid syndrome have liver metastases.
If you are thinking about IIH, a fundoscopic exam is mandatory, as papilledema is a key feature of this diagnosis.
Read about the rare diagnosis you are considering, this will help with targeting your exam.
4. Remember the unusual presentation of a common disease is more common than the common presentation of a rare disease: Good examples of this are sleep apnea and gastroesophageal reflux disease causing night sweats more commonly than finding lymphomas or active tuberculosis (in the United States) as the cause.3
Pearl: Trigger symptoms help us think of rare diseases, but distinguishing features are most helpful in including or excluding the diagnosis.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Gueret P et al. Drugs. 1990;39 Suppl 2:67-72.
2. Corcuff J et al. Endocr Connect. 2017;6:R87.
3. Smith CS and Paauw DS. J Am Board Fam Pract. 2000;13:424-9.
He has had no other symptoms. His only abnormalities on physical exam are a blood pressure of 160/100 and mild peripheral edema.
His current medications include: Famotidine 20 mg b.i.d., Pseudoephedrine/guaifenesin SR b.i.d., Metformin 1,000 mg twice a day, Nifedipine 60 mg XL once a day, and Atorvastatin 20 mg once a day.
His laboratory work up includes: blood urea nitrogen: 20, creatinine: 1.3, sodium: 140, Chloride: 104, potassium: 3.9, glucose: 205, white blood cell count: 6,000, hematocrit: 41, 24-hour urine 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5HIAA) test: 12 mg/day (normal 2-8 mg/day), free catecholamines: 80 mg/24 hours (normal less than 100 mg/24 hours).
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Drug effect
B. Pheochromocytoma
C. Carcinoid syndrome
D. Mastocytosis
E. Medullary thyroid cancer
The most likely diagnosis is a drug effect. His flushing is likely caused by nifedipine.
Flushing is one of the most common side effects of this drug.1 This patient had lab testing done for carcinoid (urine 5HIAA), presumably because he had flushing. This lab test result was a false positive, likely because of guaifenesin ingestion, which can cause false-positive 5HIAA results.2
Carcinoid syndrome is very rare (estimates from less than 1 patient/100,000), and the vast majority of patients who have it present with metastatic disease at presentation. Drug side effects are common, and usually are much more likely than rare diseases.
Four principles for assisting with making a diagnosis
This case points out the following four principles that I will touch on to help us make diagnoses in challenging cases.
1. Trigger symptoms: These are symptoms that make us think of a rare disease. In this case, the symptom is flushing, which may make you think of carcinoid syndrome.
Another good example of a trigger symptom is night sweats, where you may think of tuberculosis or lymphoma. These symptoms almost always have a much more common and likely cause, which in this case is a common drug side effect.
Trigger symptoms are great to pay attention to, but do not jump to working up the rare diagnosis without more evidence that it is a plausible diagnosis. Working up rare diseases without a reasonable pretest probability will lead to significant false-positive results.
2. Distinguishing features: These are findings, or combinations of findings, that make rarer diseases more likely. For example, flushing, although seen in many patients with carcinoid syndrome, is much more commonly caused by rosacea, medications, or estrogen/testosterone deficiency.
If a patient presents with flushing plus diarrhea, carcinoid syndrome becomes more likely in differentials. An example of a specific distinguishing feature is transient visual obstructions in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH or pseudotumor cerebri).
Sudden transient visual loss is not a symptom we see often, but headaches and obesity are problems we see every day. A patient with headaches and obesity is very likely to have IIH if they have transient visual obstructions along with headaches and obesity.
3. Intentional physical exams: Do the physical exam focusing on what findings will change your diagnostic probabilities. For example, in this case, if you are considering carcinoid, do a careful abdominal exam, with close attention to the liver, as 75% of patients with carcinoid syndrome have liver metastases.
If you are thinking about IIH, a fundoscopic exam is mandatory, as papilledema is a key feature of this diagnosis.
Read about the rare diagnosis you are considering, this will help with targeting your exam.
4. Remember the unusual presentation of a common disease is more common than the common presentation of a rare disease: Good examples of this are sleep apnea and gastroesophageal reflux disease causing night sweats more commonly than finding lymphomas or active tuberculosis (in the United States) as the cause.3
Pearl: Trigger symptoms help us think of rare diseases, but distinguishing features are most helpful in including or excluding the diagnosis.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Gueret P et al. Drugs. 1990;39 Suppl 2:67-72.
2. Corcuff J et al. Endocr Connect. 2017;6:R87.
3. Smith CS and Paauw DS. J Am Board Fam Pract. 2000;13:424-9.
Perinatal research and the Tooth Fairy
How much did you get per tooth from the Tooth Fairy? How much do your children or grandchildren receive each time they lose a baby tooth? In my family the Tooth Fairy seems to be more than keeping with inflation. Has she ever been caught in the act of swapping cash for enamel in your home? Has she every slipped up one night but managed to resurrect her credibility the following night by doubling the reward? And, by the way, what does the Tooth Fairy do with all those teeth, and who’s funding her nocturnal switcheroos?
A recent study from the Center for Genomic Medicine at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston may provide an answer to at least one of those questions. It turns out some researchers have been collecting baby teeth in hopes of assessing prenatal and perinatal stress in infants.
Not surprisingly, teeth are like trees, preserving a history of the environment in their growth rings. The Boston researchers hypothesized that the thickness of one particular growth line referred to as the neonatal line (NNL) might reflect prenatal and immediate postnatal environmental stress. Using data and naturally shed teeth collected in an English longitudinal study, the authors discovered that the teeth of children whose mothers had a long history of severe depression or other psychiatric problems and children of mothers who at 32 weeks’ gestation experienced anxiety and/or depression were more likely to have thicker NNLs. On the other hand, the teeth of children whose mothers had received “significant social support” in the immediate postnatal period exhibited thinner NNLs.
Based on anecdotal observations, I think most of us already suspected that the children whose mothers had significant psychiatric illness began life with a challenge, but it is nice to know that we may now have a tool to document one small bit of evidence of the structural damage that occurred during this period of stress. Of course, the prior owners of these baby teeth won’t benefit from the findings in this study; however, the evidence that social support during the critical perinatal period can ameliorate the damage might stimulate more robust prenatal programs for mother and infants at risk in the future.
It will be interesting to see if this investigative tool becomes more widely used to determine the degree to which a variety of potential perinatal stressors are manifesting themselves in structural change in newborns. For example, collecting baby teeth from neonatal ICU graduates may answer some questions about how certain environmental conditions such as sound, vibration, bright light, and temperature may result in long-term damage to the infants. Most of us suspect that skin-to-skin contact with mother and kangaroo care are beneficial. A study that includes a survey of NNLs might go a long way toward supporting our suspicions.
I can even imagine that a deep retrospective study of NNLs in baby teeth collected over the last 100 years might demonstrate the effect of phenomena such as wars, natural disasters, forced migration, and pandemics, to name a few.
It may be time to put out a nationwide call to all Tooth Fairies both active and retired to dig deep in their top bureau drawers. Those little bits of long-forgotten enamel may hold the answers to a plethora of unanswered questions about those critical months surrounding the birth of a child.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
How much did you get per tooth from the Tooth Fairy? How much do your children or grandchildren receive each time they lose a baby tooth? In my family the Tooth Fairy seems to be more than keeping with inflation. Has she ever been caught in the act of swapping cash for enamel in your home? Has she every slipped up one night but managed to resurrect her credibility the following night by doubling the reward? And, by the way, what does the Tooth Fairy do with all those teeth, and who’s funding her nocturnal switcheroos?
A recent study from the Center for Genomic Medicine at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston may provide an answer to at least one of those questions. It turns out some researchers have been collecting baby teeth in hopes of assessing prenatal and perinatal stress in infants.
Not surprisingly, teeth are like trees, preserving a history of the environment in their growth rings. The Boston researchers hypothesized that the thickness of one particular growth line referred to as the neonatal line (NNL) might reflect prenatal and immediate postnatal environmental stress. Using data and naturally shed teeth collected in an English longitudinal study, the authors discovered that the teeth of children whose mothers had a long history of severe depression or other psychiatric problems and children of mothers who at 32 weeks’ gestation experienced anxiety and/or depression were more likely to have thicker NNLs. On the other hand, the teeth of children whose mothers had received “significant social support” in the immediate postnatal period exhibited thinner NNLs.
Based on anecdotal observations, I think most of us already suspected that the children whose mothers had significant psychiatric illness began life with a challenge, but it is nice to know that we may now have a tool to document one small bit of evidence of the structural damage that occurred during this period of stress. Of course, the prior owners of these baby teeth won’t benefit from the findings in this study; however, the evidence that social support during the critical perinatal period can ameliorate the damage might stimulate more robust prenatal programs for mother and infants at risk in the future.
It will be interesting to see if this investigative tool becomes more widely used to determine the degree to which a variety of potential perinatal stressors are manifesting themselves in structural change in newborns. For example, collecting baby teeth from neonatal ICU graduates may answer some questions about how certain environmental conditions such as sound, vibration, bright light, and temperature may result in long-term damage to the infants. Most of us suspect that skin-to-skin contact with mother and kangaroo care are beneficial. A study that includes a survey of NNLs might go a long way toward supporting our suspicions.
I can even imagine that a deep retrospective study of NNLs in baby teeth collected over the last 100 years might demonstrate the effect of phenomena such as wars, natural disasters, forced migration, and pandemics, to name a few.
It may be time to put out a nationwide call to all Tooth Fairies both active and retired to dig deep in their top bureau drawers. Those little bits of long-forgotten enamel may hold the answers to a plethora of unanswered questions about those critical months surrounding the birth of a child.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
How much did you get per tooth from the Tooth Fairy? How much do your children or grandchildren receive each time they lose a baby tooth? In my family the Tooth Fairy seems to be more than keeping with inflation. Has she ever been caught in the act of swapping cash for enamel in your home? Has she every slipped up one night but managed to resurrect her credibility the following night by doubling the reward? And, by the way, what does the Tooth Fairy do with all those teeth, and who’s funding her nocturnal switcheroos?
A recent study from the Center for Genomic Medicine at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston may provide an answer to at least one of those questions. It turns out some researchers have been collecting baby teeth in hopes of assessing prenatal and perinatal stress in infants.
Not surprisingly, teeth are like trees, preserving a history of the environment in their growth rings. The Boston researchers hypothesized that the thickness of one particular growth line referred to as the neonatal line (NNL) might reflect prenatal and immediate postnatal environmental stress. Using data and naturally shed teeth collected in an English longitudinal study, the authors discovered that the teeth of children whose mothers had a long history of severe depression or other psychiatric problems and children of mothers who at 32 weeks’ gestation experienced anxiety and/or depression were more likely to have thicker NNLs. On the other hand, the teeth of children whose mothers had received “significant social support” in the immediate postnatal period exhibited thinner NNLs.
Based on anecdotal observations, I think most of us already suspected that the children whose mothers had significant psychiatric illness began life with a challenge, but it is nice to know that we may now have a tool to document one small bit of evidence of the structural damage that occurred during this period of stress. Of course, the prior owners of these baby teeth won’t benefit from the findings in this study; however, the evidence that social support during the critical perinatal period can ameliorate the damage might stimulate more robust prenatal programs for mother and infants at risk in the future.
It will be interesting to see if this investigative tool becomes more widely used to determine the degree to which a variety of potential perinatal stressors are manifesting themselves in structural change in newborns. For example, collecting baby teeth from neonatal ICU graduates may answer some questions about how certain environmental conditions such as sound, vibration, bright light, and temperature may result in long-term damage to the infants. Most of us suspect that skin-to-skin contact with mother and kangaroo care are beneficial. A study that includes a survey of NNLs might go a long way toward supporting our suspicions.
I can even imagine that a deep retrospective study of NNLs in baby teeth collected over the last 100 years might demonstrate the effect of phenomena such as wars, natural disasters, forced migration, and pandemics, to name a few.
It may be time to put out a nationwide call to all Tooth Fairies both active and retired to dig deep in their top bureau drawers. Those little bits of long-forgotten enamel may hold the answers to a plethora of unanswered questions about those critical months surrounding the birth of a child.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Improving statewide reporting of melanoma cases
For years, . I have audited my melanoma cases (biopsies and excisions sent to me) and discovered that of the 240 cases confirmed over the past 5 years, only 41 were reported to the Ohio state health department and are in that database. That amounts to 199 unreported cases – nearly 83% of the total.
This raises the question as to who is responsible for reporting these cases. Dermatology is unique in that our pathology specimens are not routinely passed through a hospital pathology laboratory. The big difference in reporting is that hospital labs have trained data registrars to report all reportable cancers to state health departments. Therefore, in my case, only patients sent to a hospital-based surgeon for sentinel node biopsies or exceptionally large excisions get reported. When I have spoken about this to my dermatology lab and biopsying physicians, the discussion rapidly turns into a finger pointing game of who is responsible. No one, except perhaps the dermatologist who did the biopsy, has all the data.
Unfortunately, these cases are tedious and time consuming to report. Despite state laws requiring reporting, even with penalties for nonreporters, many small dermatology practices do not report these cases and expect their dermatopathology labs to do so, but the labs expect the biopsying dermatologist to report the cases. This is a classic case of an unfunded mandate since small dermatology practices do not have the time or resources for reporting.
I have worked with the Ohio Department of Health to remove any unnecessary data fields and they have managed to reduce the reporting fields (to 59!). This is the minimum amount required to be included in the National Cancer Institute’s SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) database. Many of these fields are not applicable to thin melanomas and after reviewing the 1-hour online training course, each patient can be entered (once the necessary data are collected) in about 15 minutes. This is still a formidable task for small offices, which cannot be blamed for ducking and hoping someone else reports.
While there is controversy regarding the relevance of thin melanomas to overall survival, more accurate reporting can only bolster either argument.
A solution to underreporting
I believe we have developed a unique solution to this conundrum. Our office is partnering with the local melanoma support group (Melanoma Know More) to train volunteers to help with the data collection and reporting of these thin melanomas. We have also discovered that the local community college has students who are majoring in pathology data registry reporting and are happy to gain a little experience before graduating.
We eventually hope to become a clearinghouse for the entire state of Ohio. The state health department has agreed not to apply punitive measures to physicians who are new reporters. It is our plan to obtain melanoma pathology reports, run these past the state database, identify unreported cases, and obtain further data as needed from the biopsying physicians, and then complete the reporting.
I think dermatologic oncologists in every state should view this as an opportunity for a significant quality improvement project, and as a terrific service to the general dermatology community.
The ramifications of more comprehensive reporting of melanomas are great. I would expect more attention to the disease by researchers, and much more clout with state and national legislators. Think about increased funding for melanoma research, allowing sunscreen use for school children, sunshades for playgrounds, and more responsible tanning bed restrictions.
Now, I must inform you that this is my last column, but I plan to continue writing. Over the past 6 years, I have been able to cover a wide range of topics ranging from human trafficking and the American Medical Association, to the many problems faced by small practices. I have enjoyed myself hugely. To quote Douglas Adams, from The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy, “So long and thanks for all the fish!” Keep in touch at [email protected].
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected].
For years, . I have audited my melanoma cases (biopsies and excisions sent to me) and discovered that of the 240 cases confirmed over the past 5 years, only 41 were reported to the Ohio state health department and are in that database. That amounts to 199 unreported cases – nearly 83% of the total.
This raises the question as to who is responsible for reporting these cases. Dermatology is unique in that our pathology specimens are not routinely passed through a hospital pathology laboratory. The big difference in reporting is that hospital labs have trained data registrars to report all reportable cancers to state health departments. Therefore, in my case, only patients sent to a hospital-based surgeon for sentinel node biopsies or exceptionally large excisions get reported. When I have spoken about this to my dermatology lab and biopsying physicians, the discussion rapidly turns into a finger pointing game of who is responsible. No one, except perhaps the dermatologist who did the biopsy, has all the data.
Unfortunately, these cases are tedious and time consuming to report. Despite state laws requiring reporting, even with penalties for nonreporters, many small dermatology practices do not report these cases and expect their dermatopathology labs to do so, but the labs expect the biopsying dermatologist to report the cases. This is a classic case of an unfunded mandate since small dermatology practices do not have the time or resources for reporting.
I have worked with the Ohio Department of Health to remove any unnecessary data fields and they have managed to reduce the reporting fields (to 59!). This is the minimum amount required to be included in the National Cancer Institute’s SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) database. Many of these fields are not applicable to thin melanomas and after reviewing the 1-hour online training course, each patient can be entered (once the necessary data are collected) in about 15 minutes. This is still a formidable task for small offices, which cannot be blamed for ducking and hoping someone else reports.
While there is controversy regarding the relevance of thin melanomas to overall survival, more accurate reporting can only bolster either argument.
A solution to underreporting
I believe we have developed a unique solution to this conundrum. Our office is partnering with the local melanoma support group (Melanoma Know More) to train volunteers to help with the data collection and reporting of these thin melanomas. We have also discovered that the local community college has students who are majoring in pathology data registry reporting and are happy to gain a little experience before graduating.
We eventually hope to become a clearinghouse for the entire state of Ohio. The state health department has agreed not to apply punitive measures to physicians who are new reporters. It is our plan to obtain melanoma pathology reports, run these past the state database, identify unreported cases, and obtain further data as needed from the biopsying physicians, and then complete the reporting.
I think dermatologic oncologists in every state should view this as an opportunity for a significant quality improvement project, and as a terrific service to the general dermatology community.
The ramifications of more comprehensive reporting of melanomas are great. I would expect more attention to the disease by researchers, and much more clout with state and national legislators. Think about increased funding for melanoma research, allowing sunscreen use for school children, sunshades for playgrounds, and more responsible tanning bed restrictions.
Now, I must inform you that this is my last column, but I plan to continue writing. Over the past 6 years, I have been able to cover a wide range of topics ranging from human trafficking and the American Medical Association, to the many problems faced by small practices. I have enjoyed myself hugely. To quote Douglas Adams, from The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy, “So long and thanks for all the fish!” Keep in touch at [email protected].
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected].
For years, . I have audited my melanoma cases (biopsies and excisions sent to me) and discovered that of the 240 cases confirmed over the past 5 years, only 41 were reported to the Ohio state health department and are in that database. That amounts to 199 unreported cases – nearly 83% of the total.
This raises the question as to who is responsible for reporting these cases. Dermatology is unique in that our pathology specimens are not routinely passed through a hospital pathology laboratory. The big difference in reporting is that hospital labs have trained data registrars to report all reportable cancers to state health departments. Therefore, in my case, only patients sent to a hospital-based surgeon for sentinel node biopsies or exceptionally large excisions get reported. When I have spoken about this to my dermatology lab and biopsying physicians, the discussion rapidly turns into a finger pointing game of who is responsible. No one, except perhaps the dermatologist who did the biopsy, has all the data.
Unfortunately, these cases are tedious and time consuming to report. Despite state laws requiring reporting, even with penalties for nonreporters, many small dermatology practices do not report these cases and expect their dermatopathology labs to do so, but the labs expect the biopsying dermatologist to report the cases. This is a classic case of an unfunded mandate since small dermatology practices do not have the time or resources for reporting.
I have worked with the Ohio Department of Health to remove any unnecessary data fields and they have managed to reduce the reporting fields (to 59!). This is the minimum amount required to be included in the National Cancer Institute’s SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) database. Many of these fields are not applicable to thin melanomas and after reviewing the 1-hour online training course, each patient can be entered (once the necessary data are collected) in about 15 minutes. This is still a formidable task for small offices, which cannot be blamed for ducking and hoping someone else reports.
While there is controversy regarding the relevance of thin melanomas to overall survival, more accurate reporting can only bolster either argument.
A solution to underreporting
I believe we have developed a unique solution to this conundrum. Our office is partnering with the local melanoma support group (Melanoma Know More) to train volunteers to help with the data collection and reporting of these thin melanomas. We have also discovered that the local community college has students who are majoring in pathology data registry reporting and are happy to gain a little experience before graduating.
We eventually hope to become a clearinghouse for the entire state of Ohio. The state health department has agreed not to apply punitive measures to physicians who are new reporters. It is our plan to obtain melanoma pathology reports, run these past the state database, identify unreported cases, and obtain further data as needed from the biopsying physicians, and then complete the reporting.
I think dermatologic oncologists in every state should view this as an opportunity for a significant quality improvement project, and as a terrific service to the general dermatology community.
The ramifications of more comprehensive reporting of melanomas are great. I would expect more attention to the disease by researchers, and much more clout with state and national legislators. Think about increased funding for melanoma research, allowing sunscreen use for school children, sunshades for playgrounds, and more responsible tanning bed restrictions.
Now, I must inform you that this is my last column, but I plan to continue writing. Over the past 6 years, I have been able to cover a wide range of topics ranging from human trafficking and the American Medical Association, to the many problems faced by small practices. I have enjoyed myself hugely. To quote Douglas Adams, from The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy, “So long and thanks for all the fish!” Keep in touch at [email protected].
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected].
A fair trade-off
In the mid-90s, as a resident, I gave tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) one night to the first patient my institution registered in the study that got it approved by the Food and Drug Administration. Our director of stroke gave me a bottle of champagne the next day to thank me. That was where my career in acute inpatient neurology began.
Like many docs of my age, my hospital work has been dwindling with time, and was down to just 1-2 weekends a month in a small three-doc rotation. Not much, but it still made for some busy weekends.
The first wave of mass quarantining happened to fall just as our quarterly schedule was ending. In fact, I’d been working on writing it up for the next quarter when things began.
But then, in the course of a few days, one of us decided to retire early, and the other doc and I couldn’t agree on how to handle the rotation with only two people (somewhat naively, I told him the whole COVID thing would be over in 2-3 months; obviously I was WAY wrong).
So I finished up my last scheduled hospital call, figuring I’d be back in a few months.
So far that hasn’t happened. I’m now 17 months out since the last time I rounded on hospital patients.
And I don’t miss it at all.
This surprises me. I mean, we all start out, in medical school and residency, immersed in the hospital. It’s where the action is. Rounding, checking tests results, talking to patients, families, and nurses is ingrained into us. When I started in 1998 I hustled between four hospitals and enjoyed it (the work, not the driving).
Now I realize that my inpatient days are probably behind me, and I’m not bothered by it. That’s not to say I may not go back. Circumstances change, so, as before, I try to keep up on both inpatient and outpatient neurologic care and developments.
But for now, I’m happier without it. My weekends are my own. I don’t dread the Friday afternoon switchover where new consults suddenly start showing up on my cell phone. I don’t have to worry about running in at 2:00 a.m. to decide tPA or not tPA. My wife and I don’t have to take separate cars to go out to dinner, just in case I have to leave.
I’m sure I’ve lost some revenue because of it, but in the overall downturn of the pandemic it’s hard to know how much.
But I do know that I’ve gained time at home. With my wife, my kids, my dogs, and even just myself. My start and stop times on weekdays, and now plans for weekends, are now more predictable.
At some point those things are worth the money lost, and I’m happy to take them.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
In the mid-90s, as a resident, I gave tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) one night to the first patient my institution registered in the study that got it approved by the Food and Drug Administration. Our director of stroke gave me a bottle of champagne the next day to thank me. That was where my career in acute inpatient neurology began.
Like many docs of my age, my hospital work has been dwindling with time, and was down to just 1-2 weekends a month in a small three-doc rotation. Not much, but it still made for some busy weekends.
The first wave of mass quarantining happened to fall just as our quarterly schedule was ending. In fact, I’d been working on writing it up for the next quarter when things began.
But then, in the course of a few days, one of us decided to retire early, and the other doc and I couldn’t agree on how to handle the rotation with only two people (somewhat naively, I told him the whole COVID thing would be over in 2-3 months; obviously I was WAY wrong).
So I finished up my last scheduled hospital call, figuring I’d be back in a few months.
So far that hasn’t happened. I’m now 17 months out since the last time I rounded on hospital patients.
And I don’t miss it at all.
This surprises me. I mean, we all start out, in medical school and residency, immersed in the hospital. It’s where the action is. Rounding, checking tests results, talking to patients, families, and nurses is ingrained into us. When I started in 1998 I hustled between four hospitals and enjoyed it (the work, not the driving).
Now I realize that my inpatient days are probably behind me, and I’m not bothered by it. That’s not to say I may not go back. Circumstances change, so, as before, I try to keep up on both inpatient and outpatient neurologic care and developments.
But for now, I’m happier without it. My weekends are my own. I don’t dread the Friday afternoon switchover where new consults suddenly start showing up on my cell phone. I don’t have to worry about running in at 2:00 a.m. to decide tPA or not tPA. My wife and I don’t have to take separate cars to go out to dinner, just in case I have to leave.
I’m sure I’ve lost some revenue because of it, but in the overall downturn of the pandemic it’s hard to know how much.
But I do know that I’ve gained time at home. With my wife, my kids, my dogs, and even just myself. My start and stop times on weekdays, and now plans for weekends, are now more predictable.
At some point those things are worth the money lost, and I’m happy to take them.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
In the mid-90s, as a resident, I gave tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) one night to the first patient my institution registered in the study that got it approved by the Food and Drug Administration. Our director of stroke gave me a bottle of champagne the next day to thank me. That was where my career in acute inpatient neurology began.
Like many docs of my age, my hospital work has been dwindling with time, and was down to just 1-2 weekends a month in a small three-doc rotation. Not much, but it still made for some busy weekends.
The first wave of mass quarantining happened to fall just as our quarterly schedule was ending. In fact, I’d been working on writing it up for the next quarter when things began.
But then, in the course of a few days, one of us decided to retire early, and the other doc and I couldn’t agree on how to handle the rotation with only two people (somewhat naively, I told him the whole COVID thing would be over in 2-3 months; obviously I was WAY wrong).
So I finished up my last scheduled hospital call, figuring I’d be back in a few months.
So far that hasn’t happened. I’m now 17 months out since the last time I rounded on hospital patients.
And I don’t miss it at all.
This surprises me. I mean, we all start out, in medical school and residency, immersed in the hospital. It’s where the action is. Rounding, checking tests results, talking to patients, families, and nurses is ingrained into us. When I started in 1998 I hustled between four hospitals and enjoyed it (the work, not the driving).
Now I realize that my inpatient days are probably behind me, and I’m not bothered by it. That’s not to say I may not go back. Circumstances change, so, as before, I try to keep up on both inpatient and outpatient neurologic care and developments.
But for now, I’m happier without it. My weekends are my own. I don’t dread the Friday afternoon switchover where new consults suddenly start showing up on my cell phone. I don’t have to worry about running in at 2:00 a.m. to decide tPA or not tPA. My wife and I don’t have to take separate cars to go out to dinner, just in case I have to leave.
I’m sure I’ve lost some revenue because of it, but in the overall downturn of the pandemic it’s hard to know how much.
But I do know that I’ve gained time at home. With my wife, my kids, my dogs, and even just myself. My start and stop times on weekdays, and now plans for weekends, are now more predictable.
At some point those things are worth the money lost, and I’m happy to take them.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
A 73-year-old White male presented with 2 days of a very pruritic rash
Reactions can occur anytime from within the first 2 weeks of treatment up to 10 days after the treatment has been discontinued. If a drug is rechallenged, eruptions may occur sooner. Pruritus is commonly seen. Clinically, erythematous papules and macules present symmetrically on the trunk and upper extremities and then become more generalized. A low-grade fever may be present.
Antibiotics are the most common causes of exanthematous drug eruptions. Penicillins and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are common offenders. Cephalosporins, anticonvulsants, and allopurinol may also induce a reaction. As this condition is diagnosed clinically, skin biopsy is often not necessary. Histology is nonspecific and shows a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and few epidermal necrotic keratinocytes.
In drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), symptoms present 2-6 weeks after the offending medication has been started. The cutaneous rash appears similar to an exanthematous drug eruption; however, lesions will also present on the face, and facial edema may occur. Fever is often present. Laboratory findings include a marked peripheral blood hypereosinophilia. Elevated liver function tests may be seen. Viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus, enteroviruses, adenovirus, early HIV, human herpesvirus 6, and parvovirus B19 have a similar clinical appearance to an exanthematous drug eruption. A mild eosinophilia, as seen in a drug eruption, helps to distinguish between a drug eruption and viral exanthem. In Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, mucosal membranes are involved and skin is often painful or appears dusky.
Treatment of exanthematous drug eruptions is largely supportive. Discontinuing the drug will help speed resolution and topical steroids may alleviate pruritus.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Bolognia J et al. “Dermatology” (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
2. James W et al. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. (Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006).
Reactions can occur anytime from within the first 2 weeks of treatment up to 10 days after the treatment has been discontinued. If a drug is rechallenged, eruptions may occur sooner. Pruritus is commonly seen. Clinically, erythematous papules and macules present symmetrically on the trunk and upper extremities and then become more generalized. A low-grade fever may be present.
Antibiotics are the most common causes of exanthematous drug eruptions. Penicillins and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are common offenders. Cephalosporins, anticonvulsants, and allopurinol may also induce a reaction. As this condition is diagnosed clinically, skin biopsy is often not necessary. Histology is nonspecific and shows a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and few epidermal necrotic keratinocytes.
In drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), symptoms present 2-6 weeks after the offending medication has been started. The cutaneous rash appears similar to an exanthematous drug eruption; however, lesions will also present on the face, and facial edema may occur. Fever is often present. Laboratory findings include a marked peripheral blood hypereosinophilia. Elevated liver function tests may be seen. Viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus, enteroviruses, adenovirus, early HIV, human herpesvirus 6, and parvovirus B19 have a similar clinical appearance to an exanthematous drug eruption. A mild eosinophilia, as seen in a drug eruption, helps to distinguish between a drug eruption and viral exanthem. In Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, mucosal membranes are involved and skin is often painful or appears dusky.
Treatment of exanthematous drug eruptions is largely supportive. Discontinuing the drug will help speed resolution and topical steroids may alleviate pruritus.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Bolognia J et al. “Dermatology” (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
2. James W et al. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. (Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006).
Reactions can occur anytime from within the first 2 weeks of treatment up to 10 days after the treatment has been discontinued. If a drug is rechallenged, eruptions may occur sooner. Pruritus is commonly seen. Clinically, erythematous papules and macules present symmetrically on the trunk and upper extremities and then become more generalized. A low-grade fever may be present.
Antibiotics are the most common causes of exanthematous drug eruptions. Penicillins and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are common offenders. Cephalosporins, anticonvulsants, and allopurinol may also induce a reaction. As this condition is diagnosed clinically, skin biopsy is often not necessary. Histology is nonspecific and shows a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and few epidermal necrotic keratinocytes.
In drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), symptoms present 2-6 weeks after the offending medication has been started. The cutaneous rash appears similar to an exanthematous drug eruption; however, lesions will also present on the face, and facial edema may occur. Fever is often present. Laboratory findings include a marked peripheral blood hypereosinophilia. Elevated liver function tests may be seen. Viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus, enteroviruses, adenovirus, early HIV, human herpesvirus 6, and parvovirus B19 have a similar clinical appearance to an exanthematous drug eruption. A mild eosinophilia, as seen in a drug eruption, helps to distinguish between a drug eruption and viral exanthem. In Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, mucosal membranes are involved and skin is often painful or appears dusky.
Treatment of exanthematous drug eruptions is largely supportive. Discontinuing the drug will help speed resolution and topical steroids may alleviate pruritus.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Bolognia J et al. “Dermatology” (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
2. James W et al. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. (Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006).
Words from the wise
“When 900-years-old you reach, look as good you will not.” –Yoda
I’ve been on a roll lately: 100, 94, 90, 97, 94. These aren’t grades or even what I scratched on my scorecard for 18 holes (that’s more like 112), but rather patients I’ve seen.
Our oldest-old have been in COVID-19 protection for the last couple of years and only now feel safe to come out again. Many have skin cancers. Some of them have many. I’m grateful that for all their health problems, basal cell carcinomas at least I can cure. And
From a 94-year-old woman who was just discharged from the hospital for sepsis: First, sepsis can sneak up from behind and jump you when you’re 94. She was sitting in a waiting room for a routine exam when she passed out and woke up in the ICU. She made it home and is back on her feet, literally. When I asked her how she made it though, she was very matter of fact. Trust that the doctors know what’s right. Trust that someone will tell you what to do next. Trust that you know your own body and what you can and cannot do. Ask for help, then simply trust it will all work out. It usually does.
From a 97-year-old fighter pilot who fought in the Korean War: Let regrets drop away and live to fight another day. He’s had multiple marriages, built and lost companies, been fired and fired at, and made some doozy mistakes, some that caused considerable pain and collateral damage. But each day is new and requires your best. He has lived long enough to love dozens of grandkids and give away more than what most people ever make. His bottom line, if you worry and fret and regret, you’ll make even more mistakes ahead. Look ahead, the ground never comes up from behind you.
From a 94-year-old whose son was killed in a car accident nearly 60 years ago: You can be both happy and sad. When she retold the story of how the police knocked on her door with the news that her son was dead, she started to cry. Even 60 years isn’t long enough to blunt such pain. She still thinks of him often and to this day sometimes finds it difficult to believe he’s gone. Such pain never leaves you. But she is still a happy person with countless joys and is still having such fun. If you live long enough, both will likely be true.
From a 90-year old who still played tennis: “Just one and one.” That is, one beer and one shot, every day. No more. No less. I daren’t say I recommend this one; however, it might also be the social aspect of drinking that matters. He also advised to be free with friendships. You’ll have many people come in and out of your life; be open to new ones all the time. Also sometimes let your friends win.
From a 100-year-old, I asked how he managed to get through the Great Depression, WWII, civil unrest of the 1950s, and the Vietnam War. His reply? “To be honest, I’ve never seen anything quite like this before.”
When there’s time, consider asking for advice from those elders who happen to have an appointment with you. Bring you wisdom, they will.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
“When 900-years-old you reach, look as good you will not.” –Yoda
I’ve been on a roll lately: 100, 94, 90, 97, 94. These aren’t grades or even what I scratched on my scorecard for 18 holes (that’s more like 112), but rather patients I’ve seen.
Our oldest-old have been in COVID-19 protection for the last couple of years and only now feel safe to come out again. Many have skin cancers. Some of them have many. I’m grateful that for all their health problems, basal cell carcinomas at least I can cure. And
From a 94-year-old woman who was just discharged from the hospital for sepsis: First, sepsis can sneak up from behind and jump you when you’re 94. She was sitting in a waiting room for a routine exam when she passed out and woke up in the ICU. She made it home and is back on her feet, literally. When I asked her how she made it though, she was very matter of fact. Trust that the doctors know what’s right. Trust that someone will tell you what to do next. Trust that you know your own body and what you can and cannot do. Ask for help, then simply trust it will all work out. It usually does.
From a 97-year-old fighter pilot who fought in the Korean War: Let regrets drop away and live to fight another day. He’s had multiple marriages, built and lost companies, been fired and fired at, and made some doozy mistakes, some that caused considerable pain and collateral damage. But each day is new and requires your best. He has lived long enough to love dozens of grandkids and give away more than what most people ever make. His bottom line, if you worry and fret and regret, you’ll make even more mistakes ahead. Look ahead, the ground never comes up from behind you.
From a 94-year-old whose son was killed in a car accident nearly 60 years ago: You can be both happy and sad. When she retold the story of how the police knocked on her door with the news that her son was dead, she started to cry. Even 60 years isn’t long enough to blunt such pain. She still thinks of him often and to this day sometimes finds it difficult to believe he’s gone. Such pain never leaves you. But she is still a happy person with countless joys and is still having such fun. If you live long enough, both will likely be true.
From a 90-year old who still played tennis: “Just one and one.” That is, one beer and one shot, every day. No more. No less. I daren’t say I recommend this one; however, it might also be the social aspect of drinking that matters. He also advised to be free with friendships. You’ll have many people come in and out of your life; be open to new ones all the time. Also sometimes let your friends win.
From a 100-year-old, I asked how he managed to get through the Great Depression, WWII, civil unrest of the 1950s, and the Vietnam War. His reply? “To be honest, I’ve never seen anything quite like this before.”
When there’s time, consider asking for advice from those elders who happen to have an appointment with you. Bring you wisdom, they will.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
“When 900-years-old you reach, look as good you will not.” –Yoda
I’ve been on a roll lately: 100, 94, 90, 97, 94. These aren’t grades or even what I scratched on my scorecard for 18 holes (that’s more like 112), but rather patients I’ve seen.
Our oldest-old have been in COVID-19 protection for the last couple of years and only now feel safe to come out again. Many have skin cancers. Some of them have many. I’m grateful that for all their health problems, basal cell carcinomas at least I can cure. And
From a 94-year-old woman who was just discharged from the hospital for sepsis: First, sepsis can sneak up from behind and jump you when you’re 94. She was sitting in a waiting room for a routine exam when she passed out and woke up in the ICU. She made it home and is back on her feet, literally. When I asked her how she made it though, she was very matter of fact. Trust that the doctors know what’s right. Trust that someone will tell you what to do next. Trust that you know your own body and what you can and cannot do. Ask for help, then simply trust it will all work out. It usually does.
From a 97-year-old fighter pilot who fought in the Korean War: Let regrets drop away and live to fight another day. He’s had multiple marriages, built and lost companies, been fired and fired at, and made some doozy mistakes, some that caused considerable pain and collateral damage. But each day is new and requires your best. He has lived long enough to love dozens of grandkids and give away more than what most people ever make. His bottom line, if you worry and fret and regret, you’ll make even more mistakes ahead. Look ahead, the ground never comes up from behind you.
From a 94-year-old whose son was killed in a car accident nearly 60 years ago: You can be both happy and sad. When she retold the story of how the police knocked on her door with the news that her son was dead, she started to cry. Even 60 years isn’t long enough to blunt such pain. She still thinks of him often and to this day sometimes finds it difficult to believe he’s gone. Such pain never leaves you. But she is still a happy person with countless joys and is still having such fun. If you live long enough, both will likely be true.
From a 90-year old who still played tennis: “Just one and one.” That is, one beer and one shot, every day. No more. No less. I daren’t say I recommend this one; however, it might also be the social aspect of drinking that matters. He also advised to be free with friendships. You’ll have many people come in and out of your life; be open to new ones all the time. Also sometimes let your friends win.
From a 100-year-old, I asked how he managed to get through the Great Depression, WWII, civil unrest of the 1950s, and the Vietnam War. His reply? “To be honest, I’ve never seen anything quite like this before.”
When there’s time, consider asking for advice from those elders who happen to have an appointment with you. Bring you wisdom, they will.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Britney Spears – Reflections on conservatorship
If you are a psychiatrist who has done a public lecture in the past year, you likely encountered the question, “What about Britney’s conservatorship?” Many psychiatrists are far removed from conservatorship evaluations, doing the different yet still important work of alleviating mental suffering without paddling in the controversial waters of involuntary treatment. Others judiciously hide behind the veil of the prudent Goldwater Rule in avoiding such discussions altogether. Regardless of whether psychiatry attempts to stay out of such affairs publicly, our field remains intimately involved in the process itself. This can lead to negative views of psychiatry among the public – that of a medical specialty with ulterior motives operating at the behest of the state.
Some psychiatrists simplistically advocate against any form of involuntary treatment.1 In many ways, this may appear noble. However, the reality of mental illness, with its potential harm to self and others, introduces the potential for dire consequences of such a position. If society is unwilling to accept behavior that may lead to harm, but psychiatry is unwilling to intervene, then other avenues of restricting such behavior will emerge. Those avenues traditionally have included conscription of law enforcement and the incarceration of patients with mental illness.
Yet, therein lies the conundrum of Ms. Spears and other celebrities on conservatorship. At face value, they do not appear to require conservatorship. We do not think it violates the Goldwater Rule to render this observation. In fact, it may reassure the public if the American Psychiatric Association, as well as individual psychiatrists, were more open about the goal, intent, and limitations of conservatorships.
The process of establishing conservatorships is not driven solely by mental health professionals. Rather, conservatorship laws permit society to enact, through psychiatrists, its desire to alleviate behaviors considered unacceptable in the context of mental illness.
In California, it has resulted in our famous or infamous “5150,” which asks psychiatrists to comment on the danger to self, danger to others, and grave disability of our patients. It can be helpful to frame these criteria regarding the relationship between society and our patients. The criteria of danger to self represents society’s wish to intervene in cases of patients with imminent intent of self-harm, operating under the presumption that a suicide can be prevented. Danger to others represents the societal angst, at times exaggerated,2 about people with mental illness perpetuating homicides, especially when off their medication. Grave disability represents public shame at the thought of persons so lost to mental illness they are unable to provide for themselves or even accept food, clothing, and shelter.
While an involuntary hold is necessary at times, working against our patients engenders revolting feelings. We often rationalize involuntary holds as illustrative of sincere compassion for our patients’ suffering and an attempt to lift them out of such tragic conditions. Our patients regularly do not feel our compassion when we are making an argument in a hearing for the restriction of their rights. They see our efforts as an attempt to lock them away “for their own good” because of society’s discomfort with homelessness. As such, we wonder whether our role becomes one of doctors for society, prescribing a treatment for the emotional distress of the community, and at times for ourselves, rather than that of the patient.
One may be perplexed as to how a celebrity could be considered gravely disabled. Celebrities generally have enough income to afford food, clothing, and shelter. One could justifiably ask why an individual with no history of violence would be considered a danger to others. Similarly, one may wonder how, in the absence of any reported attempts to engage in self-harm, with no visible marks of self-harm, someone is determined to be a danger to himself or herself. The bafflement on the part of one on the outside of these determinations can be sharply contrasted by the desperation felt by family members whose loved ones with mental illness appear to meet those criteria yet are consistently turned away by mental health programs and hospitals.
Not uncommonly, it is families advocating for involuntary hospitalization – while lamenting our strict criteria – that prevent doctors from intervening until some tragic fate befalls their loved ones. They criticize what they consider to be too-stringent mental health laws and are infuriated by seemingly obtuse insurance policies limiting care to patients. Most of our colleagues working with those who have severe mental illness share the frustration of these families over the scarcity of psychiatry beds. Therefore, it is particularly shocking when the most mediatized story about conservatorship is not about how hard it is to obtain. The story is about a singer who was seemingly safe, caring for herself, and yet still ended up on a conservatorship.
We wonder whether there is a question of magnitude. Are homeless patients more difficult to place on conservatorship because society sees a lesser stake? One could argue that Ms. Spears and other celebrities would have so much to lose in a single episode of mental illness. A week with mania or psychosis could cause irreparable damage to their persona, opportunity for employment, and their fortune. On the contrary, many of our patients on conservatorship have little to their names, and no one keeping up on their reputation. Triers of facts should ask themselves about the nature of their motivations. Envy, a desire to live vicariously through celebrities, or even less ethical motivations – such as a desire to control and exert authority over those individuals – can influence our decisions.
Throughout the past year, when asked about Ms. Spears, we have pointed out the obvious – she seemingly has a life incompatible with meeting criteria for a psychiatric conservatorship. We have outlined the role, history, and limitations of psychiatric conservatorship. We have shared how such cases are often approached, when required for our own patients or when asked by the court to do so. We have discussed the significant oversight of the system, including the public conservator’s office, which frequently refuses petitions outright. There are hearing officers, who, in the early stages of this process, weigh our case against that of the patients, aided by passionately driven patient advocates. There is the public defender’s office, which, at least in San Diego, vigorously defends the rights of those with mental illness. Most importantly, there are judges who adjudicate those cases with diligence and humility.
As the story has continued to be in the news, we have had numerous conversations about Ms. Spears’ conservatorship with colleagues sharing strong opinions on her case. Many of these colleagues do not have forensic practices and we inevitably find ourselves responding along the lines of, “It is easy to say this, but quite a different thing to prove it in court.” It is hard not to imagine testifying in such a high-profile conservatorship case; testifying, in front of jurors, about a celebrity who may have engaged in what some considered to be unusual behavior.
Conservatorship laws are not about the minutia or criteria of a specific mental health disorder. Patients do not meet criteria for conservatorship by having a certain number of delusional thoughts or a specific type of hallucination. Patients meet criteria for conservatorship because of state-enacted laws based on social factors – such as danger and self-care – the population wishes to treat, even if against the will of those treated. Under this light, one must recognize that a conservatorship trial is not just about mental illness but about how society wants to care for human beings. Psychiatric illness itself is not grounds for conservatorship. Oftentimes, severely ill patients win a hearing for grave disability by simply accepting a referral for housing, showing up to court clothed, and eating the meals provided at the hospital.
With understanding that these laws pertain specifically to behaviors resulting from mental illness that society finds unacceptable, the narrative of a celebrity conservatorship can be considered differently. The stories of celebrities being used and abused by deleterious beings and deleterious conditions have become a genre. Paul Prenter’s treatment of Freddie Mercury documented in the 2018 movie “Bohemian Rhapsody” and John Reid’s alleged betrayal of Elton John, who was suffering from a substance use disorder, documented in the 2019 movie “Rocketman,” are recent examples, among many.
Imagine yourself, as a juror, deciding on the fate of a celebrity. Would you require them to have lost all property, including the clothing on their backs, before intervening? Consider the next time you hear of a celebrity swindled from his or her fortune in a time of crisis and whether it would have been righteous to prevent it. We personally have, at times, argued for restraint in psychiatry’s desire to have more power. This concern extends not only to our ability to control people, but also our ability to force them into being subjected to psychotropic medications with well-known side effects.
At the same time, we remain cognizant of the magnified impact of adverse outcomes on public figures. John Hinckley Jr. did not attempt to murder a bystander; he attempted to kill the president of the United States when he shot at President Ronald Reagan in 1981. That incident led to considerable changes in our laws about insanity. More recently, society was particularly affected by Tom Hanks’ COVID-19 diagnosis. Mr. Hanks’ illness led to scientifically measurable changes in the public’s beliefs regarding the pandemic.3
On the other hand, and of equal importance to the desire to protect public figures from adverse events, is the risk that those same laws intended to protect will harm. From unsanitary asylums to disproportionate placements of minorities on psychiatric holds, we are concerned with unbridled control in the hands of those meant to cure and care. Sadly, there is also a cinematic genre of unprincipled and detrimental mental health treatment, from Brian Wilson’s treatment by his psychologist documented in “Love & Mercy,” to the upcoming “The Shrink Next Door,” featuring a psychiatrist swindling his patient.
With this additional understanding and analysis, we now ask our colleagues what it would take for them to intervene. Would a celebrity losing $100,000,000 because of mental illness constitute a form of grave disability despite remaining dressed? Would a celebrity engaging in significant drug use constitute a form of self-harm despite still recording albums? Would a celebrity failing to fulfill a social commitment to others, including children, constitute a form of harm to others? Those are not trivial questions to answer, and we are glad the Goldwater Rule reminds us of the limitations of speculating on people we do not know.
Nonetheless, the question of conservatorship is more complex than simply saying: “They make money; they have clothes on; this is absurd.” While this may be a catchy, compelling, and relevant argument, when confronted with a more complete narrative, triers of facts may feel compelled to intervene because, in the end, conservatorship laws are about what society is willing to accept rather than an enumeration of psychiatric symptoms.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. Dr. Compton is a psychiatry resident at University of California, San Diego. His background includes medical education, mental health advocacy, work with underserved populations, and brain cancer research.
References
1. Badre N et al. “Coercion and the critical psychiatrist.” In Critical Psychiatry. Springer, Cham, 2019. doi: 10.1007/97-3-030-02732-2_7.
2. Barnes SS and Badre N. Psychiatr Serv. 2016 Jul 1;67(7)784-6.
3. Myrick JG and Willoughby JF. Health Commun. 2021 Jan 14;1-9.
If you are a psychiatrist who has done a public lecture in the past year, you likely encountered the question, “What about Britney’s conservatorship?” Many psychiatrists are far removed from conservatorship evaluations, doing the different yet still important work of alleviating mental suffering without paddling in the controversial waters of involuntary treatment. Others judiciously hide behind the veil of the prudent Goldwater Rule in avoiding such discussions altogether. Regardless of whether psychiatry attempts to stay out of such affairs publicly, our field remains intimately involved in the process itself. This can lead to negative views of psychiatry among the public – that of a medical specialty with ulterior motives operating at the behest of the state.
Some psychiatrists simplistically advocate against any form of involuntary treatment.1 In many ways, this may appear noble. However, the reality of mental illness, with its potential harm to self and others, introduces the potential for dire consequences of such a position. If society is unwilling to accept behavior that may lead to harm, but psychiatry is unwilling to intervene, then other avenues of restricting such behavior will emerge. Those avenues traditionally have included conscription of law enforcement and the incarceration of patients with mental illness.
Yet, therein lies the conundrum of Ms. Spears and other celebrities on conservatorship. At face value, they do not appear to require conservatorship. We do not think it violates the Goldwater Rule to render this observation. In fact, it may reassure the public if the American Psychiatric Association, as well as individual psychiatrists, were more open about the goal, intent, and limitations of conservatorships.
The process of establishing conservatorships is not driven solely by mental health professionals. Rather, conservatorship laws permit society to enact, through psychiatrists, its desire to alleviate behaviors considered unacceptable in the context of mental illness.
In California, it has resulted in our famous or infamous “5150,” which asks psychiatrists to comment on the danger to self, danger to others, and grave disability of our patients. It can be helpful to frame these criteria regarding the relationship between society and our patients. The criteria of danger to self represents society’s wish to intervene in cases of patients with imminent intent of self-harm, operating under the presumption that a suicide can be prevented. Danger to others represents the societal angst, at times exaggerated,2 about people with mental illness perpetuating homicides, especially when off their medication. Grave disability represents public shame at the thought of persons so lost to mental illness they are unable to provide for themselves or even accept food, clothing, and shelter.
While an involuntary hold is necessary at times, working against our patients engenders revolting feelings. We often rationalize involuntary holds as illustrative of sincere compassion for our patients’ suffering and an attempt to lift them out of such tragic conditions. Our patients regularly do not feel our compassion when we are making an argument in a hearing for the restriction of their rights. They see our efforts as an attempt to lock them away “for their own good” because of society’s discomfort with homelessness. As such, we wonder whether our role becomes one of doctors for society, prescribing a treatment for the emotional distress of the community, and at times for ourselves, rather than that of the patient.
One may be perplexed as to how a celebrity could be considered gravely disabled. Celebrities generally have enough income to afford food, clothing, and shelter. One could justifiably ask why an individual with no history of violence would be considered a danger to others. Similarly, one may wonder how, in the absence of any reported attempts to engage in self-harm, with no visible marks of self-harm, someone is determined to be a danger to himself or herself. The bafflement on the part of one on the outside of these determinations can be sharply contrasted by the desperation felt by family members whose loved ones with mental illness appear to meet those criteria yet are consistently turned away by mental health programs and hospitals.
Not uncommonly, it is families advocating for involuntary hospitalization – while lamenting our strict criteria – that prevent doctors from intervening until some tragic fate befalls their loved ones. They criticize what they consider to be too-stringent mental health laws and are infuriated by seemingly obtuse insurance policies limiting care to patients. Most of our colleagues working with those who have severe mental illness share the frustration of these families over the scarcity of psychiatry beds. Therefore, it is particularly shocking when the most mediatized story about conservatorship is not about how hard it is to obtain. The story is about a singer who was seemingly safe, caring for herself, and yet still ended up on a conservatorship.
We wonder whether there is a question of magnitude. Are homeless patients more difficult to place on conservatorship because society sees a lesser stake? One could argue that Ms. Spears and other celebrities would have so much to lose in a single episode of mental illness. A week with mania or psychosis could cause irreparable damage to their persona, opportunity for employment, and their fortune. On the contrary, many of our patients on conservatorship have little to their names, and no one keeping up on their reputation. Triers of facts should ask themselves about the nature of their motivations. Envy, a desire to live vicariously through celebrities, or even less ethical motivations – such as a desire to control and exert authority over those individuals – can influence our decisions.
Throughout the past year, when asked about Ms. Spears, we have pointed out the obvious – she seemingly has a life incompatible with meeting criteria for a psychiatric conservatorship. We have outlined the role, history, and limitations of psychiatric conservatorship. We have shared how such cases are often approached, when required for our own patients or when asked by the court to do so. We have discussed the significant oversight of the system, including the public conservator’s office, which frequently refuses petitions outright. There are hearing officers, who, in the early stages of this process, weigh our case against that of the patients, aided by passionately driven patient advocates. There is the public defender’s office, which, at least in San Diego, vigorously defends the rights of those with mental illness. Most importantly, there are judges who adjudicate those cases with diligence and humility.
As the story has continued to be in the news, we have had numerous conversations about Ms. Spears’ conservatorship with colleagues sharing strong opinions on her case. Many of these colleagues do not have forensic practices and we inevitably find ourselves responding along the lines of, “It is easy to say this, but quite a different thing to prove it in court.” It is hard not to imagine testifying in such a high-profile conservatorship case; testifying, in front of jurors, about a celebrity who may have engaged in what some considered to be unusual behavior.
Conservatorship laws are not about the minutia or criteria of a specific mental health disorder. Patients do not meet criteria for conservatorship by having a certain number of delusional thoughts or a specific type of hallucination. Patients meet criteria for conservatorship because of state-enacted laws based on social factors – such as danger and self-care – the population wishes to treat, even if against the will of those treated. Under this light, one must recognize that a conservatorship trial is not just about mental illness but about how society wants to care for human beings. Psychiatric illness itself is not grounds for conservatorship. Oftentimes, severely ill patients win a hearing for grave disability by simply accepting a referral for housing, showing up to court clothed, and eating the meals provided at the hospital.
With understanding that these laws pertain specifically to behaviors resulting from mental illness that society finds unacceptable, the narrative of a celebrity conservatorship can be considered differently. The stories of celebrities being used and abused by deleterious beings and deleterious conditions have become a genre. Paul Prenter’s treatment of Freddie Mercury documented in the 2018 movie “Bohemian Rhapsody” and John Reid’s alleged betrayal of Elton John, who was suffering from a substance use disorder, documented in the 2019 movie “Rocketman,” are recent examples, among many.
Imagine yourself, as a juror, deciding on the fate of a celebrity. Would you require them to have lost all property, including the clothing on their backs, before intervening? Consider the next time you hear of a celebrity swindled from his or her fortune in a time of crisis and whether it would have been righteous to prevent it. We personally have, at times, argued for restraint in psychiatry’s desire to have more power. This concern extends not only to our ability to control people, but also our ability to force them into being subjected to psychotropic medications with well-known side effects.
At the same time, we remain cognizant of the magnified impact of adverse outcomes on public figures. John Hinckley Jr. did not attempt to murder a bystander; he attempted to kill the president of the United States when he shot at President Ronald Reagan in 1981. That incident led to considerable changes in our laws about insanity. More recently, society was particularly affected by Tom Hanks’ COVID-19 diagnosis. Mr. Hanks’ illness led to scientifically measurable changes in the public’s beliefs regarding the pandemic.3
On the other hand, and of equal importance to the desire to protect public figures from adverse events, is the risk that those same laws intended to protect will harm. From unsanitary asylums to disproportionate placements of minorities on psychiatric holds, we are concerned with unbridled control in the hands of those meant to cure and care. Sadly, there is also a cinematic genre of unprincipled and detrimental mental health treatment, from Brian Wilson’s treatment by his psychologist documented in “Love & Mercy,” to the upcoming “The Shrink Next Door,” featuring a psychiatrist swindling his patient.
With this additional understanding and analysis, we now ask our colleagues what it would take for them to intervene. Would a celebrity losing $100,000,000 because of mental illness constitute a form of grave disability despite remaining dressed? Would a celebrity engaging in significant drug use constitute a form of self-harm despite still recording albums? Would a celebrity failing to fulfill a social commitment to others, including children, constitute a form of harm to others? Those are not trivial questions to answer, and we are glad the Goldwater Rule reminds us of the limitations of speculating on people we do not know.
Nonetheless, the question of conservatorship is more complex than simply saying: “They make money; they have clothes on; this is absurd.” While this may be a catchy, compelling, and relevant argument, when confronted with a more complete narrative, triers of facts may feel compelled to intervene because, in the end, conservatorship laws are about what society is willing to accept rather than an enumeration of psychiatric symptoms.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. Dr. Compton is a psychiatry resident at University of California, San Diego. His background includes medical education, mental health advocacy, work with underserved populations, and brain cancer research.
References
1. Badre N et al. “Coercion and the critical psychiatrist.” In Critical Psychiatry. Springer, Cham, 2019. doi: 10.1007/97-3-030-02732-2_7.
2. Barnes SS and Badre N. Psychiatr Serv. 2016 Jul 1;67(7)784-6.
3. Myrick JG and Willoughby JF. Health Commun. 2021 Jan 14;1-9.
If you are a psychiatrist who has done a public lecture in the past year, you likely encountered the question, “What about Britney’s conservatorship?” Many psychiatrists are far removed from conservatorship evaluations, doing the different yet still important work of alleviating mental suffering without paddling in the controversial waters of involuntary treatment. Others judiciously hide behind the veil of the prudent Goldwater Rule in avoiding such discussions altogether. Regardless of whether psychiatry attempts to stay out of such affairs publicly, our field remains intimately involved in the process itself. This can lead to negative views of psychiatry among the public – that of a medical specialty with ulterior motives operating at the behest of the state.
Some psychiatrists simplistically advocate against any form of involuntary treatment.1 In many ways, this may appear noble. However, the reality of mental illness, with its potential harm to self and others, introduces the potential for dire consequences of such a position. If society is unwilling to accept behavior that may lead to harm, but psychiatry is unwilling to intervene, then other avenues of restricting such behavior will emerge. Those avenues traditionally have included conscription of law enforcement and the incarceration of patients with mental illness.
Yet, therein lies the conundrum of Ms. Spears and other celebrities on conservatorship. At face value, they do not appear to require conservatorship. We do not think it violates the Goldwater Rule to render this observation. In fact, it may reassure the public if the American Psychiatric Association, as well as individual psychiatrists, were more open about the goal, intent, and limitations of conservatorships.
The process of establishing conservatorships is not driven solely by mental health professionals. Rather, conservatorship laws permit society to enact, through psychiatrists, its desire to alleviate behaviors considered unacceptable in the context of mental illness.
In California, it has resulted in our famous or infamous “5150,” which asks psychiatrists to comment on the danger to self, danger to others, and grave disability of our patients. It can be helpful to frame these criteria regarding the relationship between society and our patients. The criteria of danger to self represents society’s wish to intervene in cases of patients with imminent intent of self-harm, operating under the presumption that a suicide can be prevented. Danger to others represents the societal angst, at times exaggerated,2 about people with mental illness perpetuating homicides, especially when off their medication. Grave disability represents public shame at the thought of persons so lost to mental illness they are unable to provide for themselves or even accept food, clothing, and shelter.
While an involuntary hold is necessary at times, working against our patients engenders revolting feelings. We often rationalize involuntary holds as illustrative of sincere compassion for our patients’ suffering and an attempt to lift them out of such tragic conditions. Our patients regularly do not feel our compassion when we are making an argument in a hearing for the restriction of their rights. They see our efforts as an attempt to lock them away “for their own good” because of society’s discomfort with homelessness. As such, we wonder whether our role becomes one of doctors for society, prescribing a treatment for the emotional distress of the community, and at times for ourselves, rather than that of the patient.
One may be perplexed as to how a celebrity could be considered gravely disabled. Celebrities generally have enough income to afford food, clothing, and shelter. One could justifiably ask why an individual with no history of violence would be considered a danger to others. Similarly, one may wonder how, in the absence of any reported attempts to engage in self-harm, with no visible marks of self-harm, someone is determined to be a danger to himself or herself. The bafflement on the part of one on the outside of these determinations can be sharply contrasted by the desperation felt by family members whose loved ones with mental illness appear to meet those criteria yet are consistently turned away by mental health programs and hospitals.
Not uncommonly, it is families advocating for involuntary hospitalization – while lamenting our strict criteria – that prevent doctors from intervening until some tragic fate befalls their loved ones. They criticize what they consider to be too-stringent mental health laws and are infuriated by seemingly obtuse insurance policies limiting care to patients. Most of our colleagues working with those who have severe mental illness share the frustration of these families over the scarcity of psychiatry beds. Therefore, it is particularly shocking when the most mediatized story about conservatorship is not about how hard it is to obtain. The story is about a singer who was seemingly safe, caring for herself, and yet still ended up on a conservatorship.
We wonder whether there is a question of magnitude. Are homeless patients more difficult to place on conservatorship because society sees a lesser stake? One could argue that Ms. Spears and other celebrities would have so much to lose in a single episode of mental illness. A week with mania or psychosis could cause irreparable damage to their persona, opportunity for employment, and their fortune. On the contrary, many of our patients on conservatorship have little to their names, and no one keeping up on their reputation. Triers of facts should ask themselves about the nature of their motivations. Envy, a desire to live vicariously through celebrities, or even less ethical motivations – such as a desire to control and exert authority over those individuals – can influence our decisions.
Throughout the past year, when asked about Ms. Spears, we have pointed out the obvious – she seemingly has a life incompatible with meeting criteria for a psychiatric conservatorship. We have outlined the role, history, and limitations of psychiatric conservatorship. We have shared how such cases are often approached, when required for our own patients or when asked by the court to do so. We have discussed the significant oversight of the system, including the public conservator’s office, which frequently refuses petitions outright. There are hearing officers, who, in the early stages of this process, weigh our case against that of the patients, aided by passionately driven patient advocates. There is the public defender’s office, which, at least in San Diego, vigorously defends the rights of those with mental illness. Most importantly, there are judges who adjudicate those cases with diligence and humility.
As the story has continued to be in the news, we have had numerous conversations about Ms. Spears’ conservatorship with colleagues sharing strong opinions on her case. Many of these colleagues do not have forensic practices and we inevitably find ourselves responding along the lines of, “It is easy to say this, but quite a different thing to prove it in court.” It is hard not to imagine testifying in such a high-profile conservatorship case; testifying, in front of jurors, about a celebrity who may have engaged in what some considered to be unusual behavior.
Conservatorship laws are not about the minutia or criteria of a specific mental health disorder. Patients do not meet criteria for conservatorship by having a certain number of delusional thoughts or a specific type of hallucination. Patients meet criteria for conservatorship because of state-enacted laws based on social factors – such as danger and self-care – the population wishes to treat, even if against the will of those treated. Under this light, one must recognize that a conservatorship trial is not just about mental illness but about how society wants to care for human beings. Psychiatric illness itself is not grounds for conservatorship. Oftentimes, severely ill patients win a hearing for grave disability by simply accepting a referral for housing, showing up to court clothed, and eating the meals provided at the hospital.
With understanding that these laws pertain specifically to behaviors resulting from mental illness that society finds unacceptable, the narrative of a celebrity conservatorship can be considered differently. The stories of celebrities being used and abused by deleterious beings and deleterious conditions have become a genre. Paul Prenter’s treatment of Freddie Mercury documented in the 2018 movie “Bohemian Rhapsody” and John Reid’s alleged betrayal of Elton John, who was suffering from a substance use disorder, documented in the 2019 movie “Rocketman,” are recent examples, among many.
Imagine yourself, as a juror, deciding on the fate of a celebrity. Would you require them to have lost all property, including the clothing on their backs, before intervening? Consider the next time you hear of a celebrity swindled from his or her fortune in a time of crisis and whether it would have been righteous to prevent it. We personally have, at times, argued for restraint in psychiatry’s desire to have more power. This concern extends not only to our ability to control people, but also our ability to force them into being subjected to psychotropic medications with well-known side effects.
At the same time, we remain cognizant of the magnified impact of adverse outcomes on public figures. John Hinckley Jr. did not attempt to murder a bystander; he attempted to kill the president of the United States when he shot at President Ronald Reagan in 1981. That incident led to considerable changes in our laws about insanity. More recently, society was particularly affected by Tom Hanks’ COVID-19 diagnosis. Mr. Hanks’ illness led to scientifically measurable changes in the public’s beliefs regarding the pandemic.3
On the other hand, and of equal importance to the desire to protect public figures from adverse events, is the risk that those same laws intended to protect will harm. From unsanitary asylums to disproportionate placements of minorities on psychiatric holds, we are concerned with unbridled control in the hands of those meant to cure and care. Sadly, there is also a cinematic genre of unprincipled and detrimental mental health treatment, from Brian Wilson’s treatment by his psychologist documented in “Love & Mercy,” to the upcoming “The Shrink Next Door,” featuring a psychiatrist swindling his patient.
With this additional understanding and analysis, we now ask our colleagues what it would take for them to intervene. Would a celebrity losing $100,000,000 because of mental illness constitute a form of grave disability despite remaining dressed? Would a celebrity engaging in significant drug use constitute a form of self-harm despite still recording albums? Would a celebrity failing to fulfill a social commitment to others, including children, constitute a form of harm to others? Those are not trivial questions to answer, and we are glad the Goldwater Rule reminds us of the limitations of speculating on people we do not know.
Nonetheless, the question of conservatorship is more complex than simply saying: “They make money; they have clothes on; this is absurd.” While this may be a catchy, compelling, and relevant argument, when confronted with a more complete narrative, triers of facts may feel compelled to intervene because, in the end, conservatorship laws are about what society is willing to accept rather than an enumeration of psychiatric symptoms.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. Dr. Compton is a psychiatry resident at University of California, San Diego. His background includes medical education, mental health advocacy, work with underserved populations, and brain cancer research.
References
1. Badre N et al. “Coercion and the critical psychiatrist.” In Critical Psychiatry. Springer, Cham, 2019. doi: 10.1007/97-3-030-02732-2_7.
2. Barnes SS and Badre N. Psychiatr Serv. 2016 Jul 1;67(7)784-6.
3. Myrick JG and Willoughby JF. Health Commun. 2021 Jan 14;1-9.