User login
Treatment augmentation strategies for OCD: A review of 8 studies
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a chronic, debilitating neuropsychiatric disorder that affects 1% to 3% of the population worldwide.1,2 Together, serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs) and cognitive-behavior therapy (CBT) are considered the first-line treatment for OCD.3 In children and adults, CBT is considered at least as effective as pharmacotherapy.4 Despite being an effective treatment, CBT continues to have barriers to its widespread use, including limited availability of trained CBT therapists, delayed clinical response, and high costs.5
Only approximately one-half of patients with OCD respond to SRI therapy, and a considerable percentage (30% to 40%) show significant residual symptoms even after multiple trials of SRIs.6-8 In addition, SRIs may have adverse effects (eg, sexual dysfunction, gastrointestinal symptoms) that impair patient adherence to these medications.9 Therefore, finding better treatment options is important for managing patients with OCD.
Augmentation strategies are recommended for patients who show partial response to SRI treatment or poor response to multiple SRIs. Augmentation typically includes incorporating additional medications with the primary drug with the goal of boosting the therapeutic efficacy of the primary drug. Typically, these additional medications have different mechanisms of action. However, there are no large-scale randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to inform treatment augmentation after first-line treatments for OCD produce suboptimal outcomes. The available evidence is predominantly based on small-scale RCTs, open-label trials, and case series.
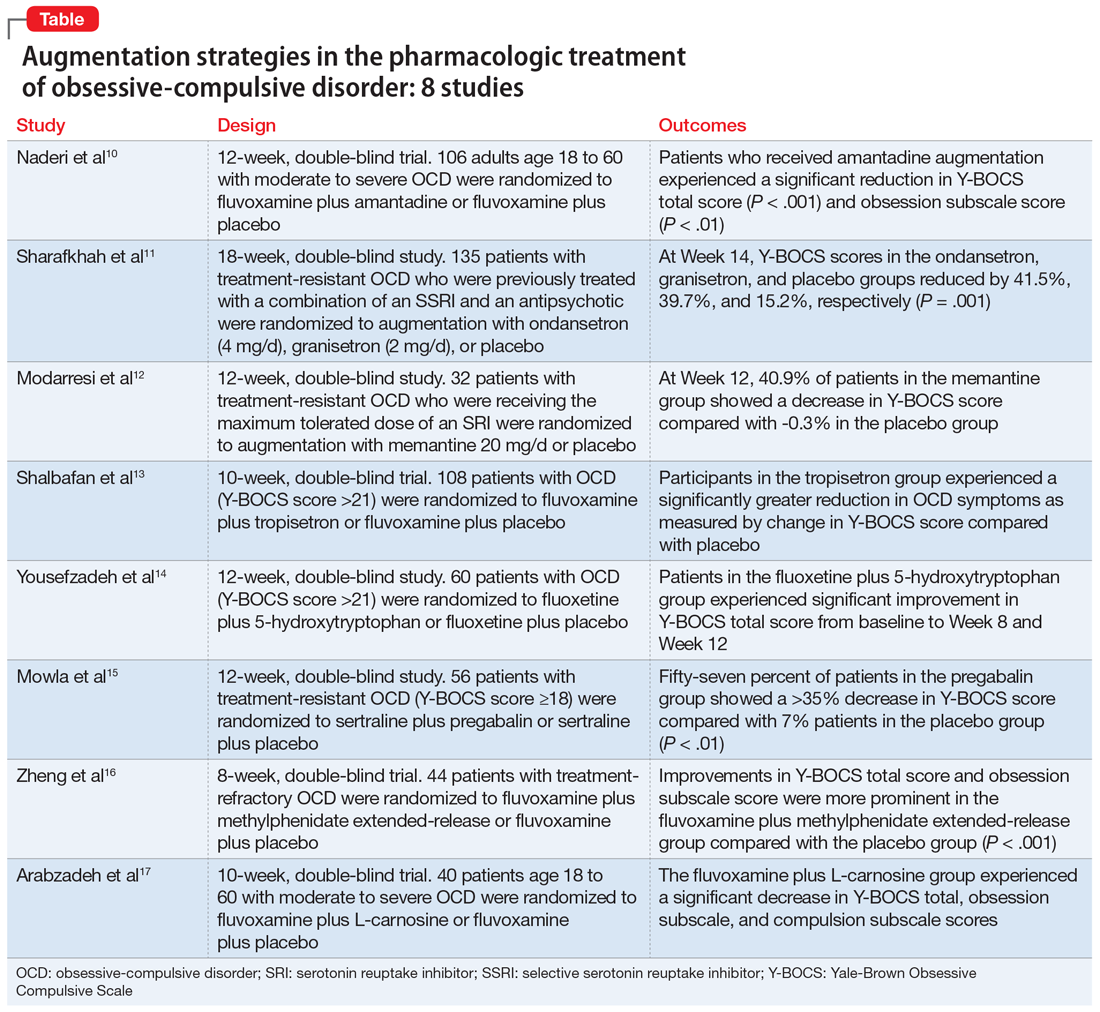
In this article, we review the evidence for treatment augmentation strategies for OCD and summarize 8 studies that show promising results (Table10-17). We focus only on pharmacologic agents and do not include other biological interventions, such as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over supplementary motor area, ablative neurosurgery, or deep brain stimulation.
Continue to: Reference 1...
1. Naderi S, Faghih H , Aqamolaei A, et al. Amantadine as adjuvant therapy in the treatment of moderate to severe obsessivecompulsive disorder: a double-blind randomized trial with placebo control. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019;73(4):169-174. doi:10.1111/ pcn.12803
Numerous studies support the role of glutamate dysregulation in the pathophysiology of OCD. Cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical (CSTC) abnormalities play a major role in the pathophysiology of OCD as suggested by neuroimaging research studies that indicate glutamate is the fundamental neurotransmitter of the CSTC circuit. Dysregulation of glutamatergic signaling within this circuit has been linked to OCD. Patients with OCD have been found to have an increase of glutamate in the CSF. As a result, medications that affect glutamate levels can be used to treat patients with OCD who do not respond to first-line agents. In patients already taking SRIs, augmentation of glutamate-modulating medications can reduce OCD symptoms. As an uncompetitive antagonist of the N-methyl-
Naderi et al10 evaluated amantadine as augmentative therapy to fluvoxamine for treating patients with moderate to severe OCD.
Study design
- This 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of amantadine as an augmentative agent to fluvoxamine in 106 patients age 18 to 60 with moderate to severe OCD.
- Participants met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had a Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS) score >21. Participants were excluded if they had any substance dependence; an IQ <70; any other Axis I mental disorder; any serious cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease; had received psychotropic medications during the last 6 weeks, were pregnant or breastfeeding, or had rising liver transaminases to 3 times the upper limit of normal or higher.
- Participants received fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily plus amantadine 100 mg/d, or fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily plus placebo. All patients received fluvoxamine 100 mg/d for 28 days followed by 200 mg/d for the remainder of the trial.
- The primary outcome measure was difference in Y-BOCS total scores between the amantadine and placebo groups. The secondary outcome was the difference in Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores.
Outcomes
- Patients who received amantadine augmentation experienced a significant reduction in Y-BOCS total score (P < .001) and obsession subscale score (P < .01).
- The amantadine group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
- Amantadine is an effective adjuvant to fluvoxamine for reducing OCD symptoms.
Conclusion
- Ondansetron and granisetron can be beneficial as an augmentation strategy for patients with treatment-resistant OCD.
2. Sharafkhah M, Aghakarim Alamdar M, Massoudifar A, et al. Comparing the efficacy of ondansetron and granisetron augmentation in treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;34(5):222- 233. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000267
Although selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are considered a first-line treatment when teamed with CBT and antipsychotic augmentation, symptom resolution is not always achieved, and treatment resistance is a common problem. Sharafkhah et al11 compared the efficacy of ondansetron and granisetron augmentation specifically for patients with treatment-resistant OCD.
Study Design
- In this 18-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 135 patients with treatment-resistant OCD who were previously treated with a combination of an SSRI and an antipsychotic received augmentation with ondansetron (n = 45, 4 mg/d), granisetron (n = 45, 2 mg/d), or placebo.
- Patients were rated using Y-BOCS every 2 weeks during phase I (intervention period), which lasted 14 weeks. After completing the intervention, patients were followed for 4 more weeks during phase II (discontinuation period).
- The aim of this study was to determine the safety, efficacy, and tolerability of ondansetron vs granisetron as augmentation for patients with treatment-resistant OCD. A secondary aim was to determine the rate of relapse of OCD symptoms after discontinuing ondansetron as compared with granisetron at 4 weeks after intervention.
Outcomes
- At Week 14, the reductions in Y-BOCS scores in the ondansetron, granisetron, and placebo groups were 41.5%, 39.7%, and 15.2%, respectively (P = .001). The reduction in Y-BOCS score in the ondansetron and granisetron groups was significantly greater than placebo at all phase I visits.
- Complete response was higher in the ondansetron group compared with the granisetron group (P = .041).
- Y-BOCS scores increased in both the ondansetron and granisetron groups during the discontinuation phase, but OCD symptoms were not significantly exacerbated.
Conclusion
- Ondansetron and granisetron can be beneficial as an augmentation strategy for patients with treatment-resistant OCD.
3. Modarresi A, Sayyah M, Razooghi S, et al. Memantine augmentation improves symptoms in serotonin reuptake inhibitorrefractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2018;51(6):263-269. doi:10.1055/s-0043-120268
Increased glutamate levels in CSF, glutamatergic overactivity, and polymorphisms of genes coding the NMDA receptor have been shown to contribute to the occurrence of OCD. Memantine is a noncompetitive antagonist of the NMDA receptor. Various control trials have shown augmentation with memantine 5 mg/d to 20 mg/d significantly reduced symptom severity in patients with moderate to severe OCD. Modarresi et al12 evaluated memantine as a treatment option for patients with severe OCD who did not respond to SRI monotherapy.
Study design
- This 12-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy of memantine augmentation in 32 patients age 18 to 40 who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD, had a Y-BOCS score ≥24, and no psychiatric comorbidity. Participants had not responded to ≥3 adequate trials (minimum 3 months) of SRI therapy, 1 of which was clomipramine.
- Individuals were excluded if they were undergoing CBT; had an additional anxiety disorder, mood disorder, or current drug or alcohol use disorder, or any systemic disorder; had a history of seizures; were pregnant or breastfeeding; or had a history of memantine use.
- Participants already receiving the maximum tolerated dose of an SRI received augmentation with memantine 20 mg/d or placebo.
- The primary outcome measure was change in Y-BOCS score from baseline. The secondary outcome was the number of individuals who achieved treatment response (defined as ≥35% reduction in Y-BOCS score).
Continue to: Outcomes...
Outcomes
- There was a statistically significant difference in Y-BOCS score in patients treated with memantine at Week 8 and Week 12 vs those who received placebo. By Week 8, 17.2% of patients in the memantine group showed a decrease in Y-BOCS score, compared with -0.8% patients in the placebo group. The difference became more significant by Week 12, with 40.9% in the memantine group showing a decrease in Y-BOCS score vs -0.3% in the placebo group. This resulted in 73.3% of patients achieving treatment response.
- Eight weeks of memantine augmentation was necessary to observe a significant improvement in OCD symptoms, and 12 weeks was needed for treatment response.
- The mean Y-BOCS total score decreased significantly in the memantine group from Week 4 to Week 8 (16.8%) and again from Week 8 to Week 12 (28.5%).
- The memantine group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Conclusion
- Memantine augmentation in patients with severe OCD who do not respond to an SRI is effective and well-tolerated.
4. Shalbafan M, Malekpour F, Tadayon Najafabadi B, et al. Fluvoxamine combination therapy with tropisetron for obsessive-compulsive disorder patients: a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33(11):1407- 1414. doi:10.1177/0269881119878177
Studies have demonstrated the involvement of the amygdala, medial and lateral orbitofrontal cortex, and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex in OCD. Additionally, studies have also investigated the role of serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate system dysregulation in the pathology of OCD.
The 5-HT3 receptors are ligand-gated ion channels found in the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus. Studies of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists such as ondansetron and granisetron have shown beneficial results in augmentation with SSRIs for patients with OCD.11 Tropisetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, is highly lipophilic and able to cross the blood brain barrier. It also has dopamine-inhibiting properties that could have benefits in OCD management. Shalbafan et al13 evaluated the efficacy of tropisetron augmentation to fluvoxamine for patients with OCD.
Study design
- In a 10-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial, 108 individuals age 18 to 60 who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had a Y-BOCS score >21 received fluvoxamine plus tropisetron or fluvoxamine plus placebo. A total of 48 (44.4%) participants in each group completed the trial. Participants were evaluated using the Y-BOCS scale at baseline and at Week 4 and Week 10.
- The primary outcome was decrease in total Y-BOCS score from baseline to Week 10. The secondary outcome was the difference in change in Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores between the groups.
Outcomes
- The Y-BOCS total score was not significantly different between the 2 groups (P = .975). Repeated measures analysis of variance determined a significant effect for time in both tropisetron and placebo groups (Greenhouse-Geisser F [2.72–2303.84] = 152.25, P < .001; and Greenhouse-Geisser F [1.37–1736.81] = 75.57, P < .001, respectively). At Week 10, 35 participants in the tropisetron group and 19 participants in the placebo group were complete responders.
- The baseline Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscales did not significantly differ between treatment groups.
Conclusion
- Compared with participants in the placebo group, those in the tropisetron group experienced a significantly greater reduction in OCD symptoms as measured by Y-BOCS score. More participants in the tropisetron group experienced complete response and remission.
- This study demonstrated that compared with placebo, when administered as augmentation with fluvoxamine, tropisetron can have beneficial effects for patients with OCD.
Continue to: Reference 5...
5. Yousefzadeh F, Sahebolzamani E, Sadri A, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptophan as adjuvant therapy in treatment of moderate to severe obsessive-compulsive disorder: a doubleblind randomized trial with placebo control. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2020;35(5):254- 262. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000321
Nutraceuticals such as glycine, milk thistle, myoinositol, and serotonin (5-hydroxytryptophan) have been proposed as augmentation options for OCD. Yousefzadeh et al14 investigated the effectiveness of using 5-hydroxytryptophan in treating OCD.
Study design
- In a 12-week, randomized, double-blind study, 60 patients who met DSM-5 criteria for moderate to severe OCD (Y-BOCS score >21) were randomly assigned to receive fluoxetine plus 5-hydroxytryptophan 100 mg twice daily or fluoxetine plus placebo.
- All patients were administered fluoxetine 20 mg/d for the first 4 weeks of the study followed by fluoxetine 60 mg/d for the remainder of the trial.
- Symptoms were assessed using the Y-BOCS at baseline, Week 4, Week 8, and Week 12.
- The primary outcome measure was the difference between the 2 groups in change in Y-BOCS total score from baseline to the end of the trial. Secondary outcome measures were the differences in the Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores from baseline to Week 12.
Outcomes
- Compared to the placebo group, the 5-hydroxytryptophan group experienced a statistically significant greater improvement in Y-BOCS total score from baseline to Week 8 (P = .002) and Week 12 (P < .001).
- General linear model repeated measure showed significant effects for time × treatment interaction on Y-BOCS total (F = 12.07, df = 2.29, P < .001), obsession subscale (F = 8.25, df = 1.91, P = .001), and compulsion subscale scores (F = 6.64, df = 2.01, P = .002).
- The 5-hydroxytryptophan group demonstrated higher partial and complete treatment response rates (P = .032 and P = .001, respectively) as determined by change in Y-BOCS total score.
- The 5-hydroxytryptophan group showed a significant improvement from baseline to Week 12 in Y-BOCS obsession subscale score (5.23 ± 2.33 vs 3.53 ± 2.13, P = .009).
- There was a significant change from baseline to the end of the trial in the Y-BOCS compulsion subscale score (3.88 ± 2.04 vs 2.30 ± 1.37, P = .002).
Conclusion
- This trial demonstrated the potential benefits of 5-hydroxytryptophan in combination with fluoxetine for patients with OCD.
6. Mowla A, Ghaedsharaf M. Pregabalin augmentation for resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. CNS Spectr. 2020;25(4):552-556. doi:10.1017/S1092852919001500
Glutamatergic dysfunction has been identified as a potential cause of OCD. Studies have found elevated levels of glutamatergic transmission in the cortical-striatal-thalamic circuit of the brain and elevated glutamate concentration in the CSF in patients with OCD. Pregabalin has multiple mechanisms of action that inhibit the release of glutamate. Mowla et al15 evaluated pregabalin as an augmentation treatment for resistant OCD.
Study design
- This 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluated the efficacy of adjunctive pregabalin in 56 patients who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had not responded to ≥12 weeks of treatment with an adequate and stable dose of sertraline (baseline Y-BOCS score ≥18).
- Individuals who had other major psychiatric disorders, major medical problems, were pregnant, or had past substance or alcohol abuse were excluded.
- Participants were randomly assigned to receive sertraline plus pregabalin (n = 28) or sertraline plus placebo (n = 28). Mean sertraline dosage was 256.5 mg/d; range was 100 mg/d to 300 mg/d. Pregabalin was started at 75 mg/d and increased by 75 mg increments weekly. The mean dosage was 185.9 mg/d; range was 75 mg/d to 225 mg/d.
- The primary outcome measure was change in Y-BOCS score. A decrease >35% in Y-BOCS score was considered a significant response rate.
Outcomes
- There was a statistically significant decrease in Y-BOCS score in patients who received pregabalin. In the pregabalin group, 57.14% of patients (n = 16) showed a >35% decrease in Y-BOCS score compared with 7.14% of patients (n = 2) in the placebo group (P < .01).
- The pregabalin group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Conclusion
- In patients with treatment-resistant OCD who did not respond to sertraline monotherapy, augmentation with pregabalin significantly decreases Y-BOCS scores compared with placebo.
Continue to: Reference 7...
7. Zheng H, Jia F, Han H, et al. Combined fluvoxamine and extended-release methylphenidate improved treatment response compared to fluvoxamine alone in patients with treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind, placebocontrolled study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019;29(3):397-404. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro. 2018.12.010
Recent evidence suggests dysregulation of serotonin and dopamine in patients with OCD. Methylphenidate is a dopamine and norepinephrine inhibitor and releaser. A limited number of studies have suggested stimulants might be useful for OCD patients. Zheng et al16 conducted a pilot trial to determine whether methylphenidate augmentation may be of benefit in the management of outpatients with OCD.
Study design
- In an 8-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, 44 patients (29 [66%] men, with a mean [SD] age of 24.7 [6]) with treatment-refractory OCD were randomized to receive fluvoxamine 250 mg/d plus methylphenidate extended-release (MPH-ER) 36 mg/d or fluvoxamine 250 mg/d plus placebo. The MPH-ER dose was 18 mg/d for the first 4 weeks and 36 mg/d for the rest of the trial.
- Biweekly assessments consisted of scores on the Y-BOCS, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS), and Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A).
- The primary outcomes were improvement in Y-BOCS score and the clinical response rate. Secondary outcomes included a change in score on the Y-BOCS subscales, HARS, and HAM-A. Data were analyzed with the intention-to-treat sample.
Outcomes
- Forty-one patients finished the trial. The baseline Y-BOCS total scores and subscale scores did not differ significantly between the 2 groups.
- Improvements in Y-BOCS total score and obsession subscale score were more prominent in the fluvoxamine plus MPH-ER group compared with the placebo group (P < .001).
- HDRS score decreased in both the placebo and MPH-ER groups. HAM-A scores decreased significantly in the MPH-ER plus fluvoxamine group compared with the placebo group.
Conclusion
- This study demonstrated that the combination of fluvoxamine and MPH-ER produces a higher and faster response rate than fluvoxamine plus placebo in patients with OCD.
8. Arabzadeh S, Shahhossenie M, Mesgarpour B, et al. L-carnosine as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine in treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind study. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2017;32(4). doi:10.1002/hup.2584
Glutamate dysregulation is implicated in the pathogenesis of OCD. Glutamate-modulating agents have been used to treat OCD. Studies have shown L-carnosine has a neuroprotective role via its modulatory effect on glutamate. Arabzadeh et al17 evaluated the efficacy of L-carnosine as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine for treating OCD.
Study design
- This 10-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy of adjunctive L-carnosine in 40 patients age 18 to 60 who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had moderate to severe OCD (Y-BOCS score ≥21).
- Individuals with any other DSM-5 major psychiatric disorders, serious medical or neurologic illness, substance dependence (other than caffeine or nicotine), mental retardation (based on clinical judgment), were pregnant or breastfeeding, had any contraindication for the use of L‐carnosine or fluvoxamine, or received any psychotropic drugs in the previous 6 weeks were excluded.
- Participants received fluvoxamine 100 mg/d for the first 4 weeks and 200 mg/d for the next 6 weeks plus either L-carnosine 500 mg twice daily or placebo. This dosage of L-carnosine was chosen because previously it had been tolerated and effective.
- The primary outcome measure was difference in Y-BOCS total scores. Secondary outcomes were differences in Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores and differences in change in score on Y-BOCS total and subscale scores from baseline.
Outcomes
- The L-carnosine group experienced a significant decrease in Y-BOCS total score (P < .001), obsession subscale score (P < .01), and compulsion subscale score (P < .01).
- The group that received fluvoxamine plus L-carnosine also experienced a more complete response (P = .03).
- The L-carnosine group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Conclusion
- L-carnosine significantly reduces OCD symptoms when used as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Ruscio AM, Stein DJ, Chiu WT, et al. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15(1):53-63.
3. Eddy KT, Dutra L, Bradley, R, et al. A multidimensional meta-analysis of psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Clin Psychol Rev. 2004;24(8):1011-1030.
4. Franklin ME, Foa EB. Treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2011;7:229-243.
5. Koran LM, Hanna GL, Hollander E, et al. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(7 Suppl):5-53.
6. Pittenger C, Bloch MH. Pharmacological treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2014;37(3):375-391.
7. Pallanti S, Hollander E, Bienstock C, et al. Treatment non-response in OCD: methodological issues and operational definitions. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2002;5(2):181-191.
8. Atmaca M. Treatment-refractory obsessive compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016;70:127-133.
9. Barth M, Kriston L, Klostermann S, et al. Efficacy of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and adverse events: meta-regression and mediation analysis of placebo-controlled trials. Br J Psychiatry. 2016;208(2):114-119.
10. NaderiS, Faghih H, Aqamolaei A, et al. Amantadine as adjuvant therapy in the treatment of moderate to severe obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind randomized trial with placebo control. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019;73(4):169-174. doi:10.1111/pcn.12803
11. SharafkhahM, Aghakarim Alamdar M, MassoudifarA, et al. Comparing the efficacy of ondansetron and granisetron augmentation in treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;34(5):222-233. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000267
12. ModarresiA, Sayyah M, Razooghi S, et al. Memantine augmentation improves symptoms in serotonin reuptake inhibitor-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2018;51(6):263-269. doi:10.1055/s-0043-12026
13. Shalbafan M, Malekpour F, Tadayon Najafabadi B, et al. Fluvoxamine combination therapy with tropisetron for obsessive-compulsive disorder patients: a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33(11):1407-1414. doi:10.1177/0269881119878177
14. Yousefzadeh F, Sahebolzamani E, Sadri A, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptophan as adjuvant therapy in treatment of moderate to severe obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind randomized trial with placebo control. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2020;35(5):254-262. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000321
15. Mowla A, Ghaedsharaf M. Pregabalin augmentation for resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. CNS Spectr. 2020;25(4):552-556. doi:10.1017/S1092852919001500
16. Zheng H, Jia F, Han H, et al.Combined fluvoxamine and extended-release methylphenidate improved treatment response compared to fluvoxamine alone in patients with treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019;29(3):397-404. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.12.010
17. Arabzadeh S, Shahhossenie M, Mesgarpour B, et al. L-carnosine as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine in treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind study. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2017;32(4). doi:10.1002/hup.2584
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a chronic, debilitating neuropsychiatric disorder that affects 1% to 3% of the population worldwide.1,2 Together, serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs) and cognitive-behavior therapy (CBT) are considered the first-line treatment for OCD.3 In children and adults, CBT is considered at least as effective as pharmacotherapy.4 Despite being an effective treatment, CBT continues to have barriers to its widespread use, including limited availability of trained CBT therapists, delayed clinical response, and high costs.5
Only approximately one-half of patients with OCD respond to SRI therapy, and a considerable percentage (30% to 40%) show significant residual symptoms even after multiple trials of SRIs.6-8 In addition, SRIs may have adverse effects (eg, sexual dysfunction, gastrointestinal symptoms) that impair patient adherence to these medications.9 Therefore, finding better treatment options is important for managing patients with OCD.
Augmentation strategies are recommended for patients who show partial response to SRI treatment or poor response to multiple SRIs. Augmentation typically includes incorporating additional medications with the primary drug with the goal of boosting the therapeutic efficacy of the primary drug. Typically, these additional medications have different mechanisms of action. However, there are no large-scale randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to inform treatment augmentation after first-line treatments for OCD produce suboptimal outcomes. The available evidence is predominantly based on small-scale RCTs, open-label trials, and case series.
In this article, we review the evidence for treatment augmentation strategies for OCD and summarize 8 studies that show promising results (Table10-17). We focus only on pharmacologic agents and do not include other biological interventions, such as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over supplementary motor area, ablative neurosurgery, or deep brain stimulation.

Continue to: Reference 1...
1. Naderi S, Faghih H , Aqamolaei A, et al. Amantadine as adjuvant therapy in the treatment of moderate to severe obsessivecompulsive disorder: a double-blind randomized trial with placebo control. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019;73(4):169-174. doi:10.1111/ pcn.12803
Numerous studies support the role of glutamate dysregulation in the pathophysiology of OCD. Cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical (CSTC) abnormalities play a major role in the pathophysiology of OCD as suggested by neuroimaging research studies that indicate glutamate is the fundamental neurotransmitter of the CSTC circuit. Dysregulation of glutamatergic signaling within this circuit has been linked to OCD. Patients with OCD have been found to have an increase of glutamate in the CSF. As a result, medications that affect glutamate levels can be used to treat patients with OCD who do not respond to first-line agents. In patients already taking SRIs, augmentation of glutamate-modulating medications can reduce OCD symptoms. As an uncompetitive antagonist of the N-methyl-
Naderi et al10 evaluated amantadine as augmentative therapy to fluvoxamine for treating patients with moderate to severe OCD.
Study design
- This 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of amantadine as an augmentative agent to fluvoxamine in 106 patients age 18 to 60 with moderate to severe OCD.
- Participants met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had a Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS) score >21. Participants were excluded if they had any substance dependence; an IQ <70; any other Axis I mental disorder; any serious cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease; had received psychotropic medications during the last 6 weeks, were pregnant or breastfeeding, or had rising liver transaminases to 3 times the upper limit of normal or higher.
- Participants received fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily plus amantadine 100 mg/d, or fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily plus placebo. All patients received fluvoxamine 100 mg/d for 28 days followed by 200 mg/d for the remainder of the trial.
- The primary outcome measure was difference in Y-BOCS total scores between the amantadine and placebo groups. The secondary outcome was the difference in Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores.
Outcomes
- Patients who received amantadine augmentation experienced a significant reduction in Y-BOCS total score (P < .001) and obsession subscale score (P < .01).
- The amantadine group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
- Amantadine is an effective adjuvant to fluvoxamine for reducing OCD symptoms.
Conclusion
- Ondansetron and granisetron can be beneficial as an augmentation strategy for patients with treatment-resistant OCD.
2. Sharafkhah M, Aghakarim Alamdar M, Massoudifar A, et al. Comparing the efficacy of ondansetron and granisetron augmentation in treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;34(5):222- 233. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000267
Although selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are considered a first-line treatment when teamed with CBT and antipsychotic augmentation, symptom resolution is not always achieved, and treatment resistance is a common problem. Sharafkhah et al11 compared the efficacy of ondansetron and granisetron augmentation specifically for patients with treatment-resistant OCD.
Study Design
- In this 18-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 135 patients with treatment-resistant OCD who were previously treated with a combination of an SSRI and an antipsychotic received augmentation with ondansetron (n = 45, 4 mg/d), granisetron (n = 45, 2 mg/d), or placebo.
- Patients were rated using Y-BOCS every 2 weeks during phase I (intervention period), which lasted 14 weeks. After completing the intervention, patients were followed for 4 more weeks during phase II (discontinuation period).
- The aim of this study was to determine the safety, efficacy, and tolerability of ondansetron vs granisetron as augmentation for patients with treatment-resistant OCD. A secondary aim was to determine the rate of relapse of OCD symptoms after discontinuing ondansetron as compared with granisetron at 4 weeks after intervention.
Outcomes
- At Week 14, the reductions in Y-BOCS scores in the ondansetron, granisetron, and placebo groups were 41.5%, 39.7%, and 15.2%, respectively (P = .001). The reduction in Y-BOCS score in the ondansetron and granisetron groups was significantly greater than placebo at all phase I visits.
- Complete response was higher in the ondansetron group compared with the granisetron group (P = .041).
- Y-BOCS scores increased in both the ondansetron and granisetron groups during the discontinuation phase, but OCD symptoms were not significantly exacerbated.
Conclusion
- Ondansetron and granisetron can be beneficial as an augmentation strategy for patients with treatment-resistant OCD.
3. Modarresi A, Sayyah M, Razooghi S, et al. Memantine augmentation improves symptoms in serotonin reuptake inhibitorrefractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2018;51(6):263-269. doi:10.1055/s-0043-120268
Increased glutamate levels in CSF, glutamatergic overactivity, and polymorphisms of genes coding the NMDA receptor have been shown to contribute to the occurrence of OCD. Memantine is a noncompetitive antagonist of the NMDA receptor. Various control trials have shown augmentation with memantine 5 mg/d to 20 mg/d significantly reduced symptom severity in patients with moderate to severe OCD. Modarresi et al12 evaluated memantine as a treatment option for patients with severe OCD who did not respond to SRI monotherapy.
Study design
- This 12-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy of memantine augmentation in 32 patients age 18 to 40 who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD, had a Y-BOCS score ≥24, and no psychiatric comorbidity. Participants had not responded to ≥3 adequate trials (minimum 3 months) of SRI therapy, 1 of which was clomipramine.
- Individuals were excluded if they were undergoing CBT; had an additional anxiety disorder, mood disorder, or current drug or alcohol use disorder, or any systemic disorder; had a history of seizures; were pregnant or breastfeeding; or had a history of memantine use.
- Participants already receiving the maximum tolerated dose of an SRI received augmentation with memantine 20 mg/d or placebo.
- The primary outcome measure was change in Y-BOCS score from baseline. The secondary outcome was the number of individuals who achieved treatment response (defined as ≥35% reduction in Y-BOCS score).
Continue to: Outcomes...
Outcomes
- There was a statistically significant difference in Y-BOCS score in patients treated with memantine at Week 8 and Week 12 vs those who received placebo. By Week 8, 17.2% of patients in the memantine group showed a decrease in Y-BOCS score, compared with -0.8% patients in the placebo group. The difference became more significant by Week 12, with 40.9% in the memantine group showing a decrease in Y-BOCS score vs -0.3% in the placebo group. This resulted in 73.3% of patients achieving treatment response.
- Eight weeks of memantine augmentation was necessary to observe a significant improvement in OCD symptoms, and 12 weeks was needed for treatment response.
- The mean Y-BOCS total score decreased significantly in the memantine group from Week 4 to Week 8 (16.8%) and again from Week 8 to Week 12 (28.5%).
- The memantine group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Conclusion
- Memantine augmentation in patients with severe OCD who do not respond to an SRI is effective and well-tolerated.
4. Shalbafan M, Malekpour F, Tadayon Najafabadi B, et al. Fluvoxamine combination therapy with tropisetron for obsessive-compulsive disorder patients: a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33(11):1407- 1414. doi:10.1177/0269881119878177
Studies have demonstrated the involvement of the amygdala, medial and lateral orbitofrontal cortex, and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex in OCD. Additionally, studies have also investigated the role of serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate system dysregulation in the pathology of OCD.
The 5-HT3 receptors are ligand-gated ion channels found in the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus. Studies of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists such as ondansetron and granisetron have shown beneficial results in augmentation with SSRIs for patients with OCD.11 Tropisetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, is highly lipophilic and able to cross the blood brain barrier. It also has dopamine-inhibiting properties that could have benefits in OCD management. Shalbafan et al13 evaluated the efficacy of tropisetron augmentation to fluvoxamine for patients with OCD.
Study design
- In a 10-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial, 108 individuals age 18 to 60 who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had a Y-BOCS score >21 received fluvoxamine plus tropisetron or fluvoxamine plus placebo. A total of 48 (44.4%) participants in each group completed the trial. Participants were evaluated using the Y-BOCS scale at baseline and at Week 4 and Week 10.
- The primary outcome was decrease in total Y-BOCS score from baseline to Week 10. The secondary outcome was the difference in change in Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores between the groups.
Outcomes
- The Y-BOCS total score was not significantly different between the 2 groups (P = .975). Repeated measures analysis of variance determined a significant effect for time in both tropisetron and placebo groups (Greenhouse-Geisser F [2.72–2303.84] = 152.25, P < .001; and Greenhouse-Geisser F [1.37–1736.81] = 75.57, P < .001, respectively). At Week 10, 35 participants in the tropisetron group and 19 participants in the placebo group were complete responders.
- The baseline Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscales did not significantly differ between treatment groups.
Conclusion
- Compared with participants in the placebo group, those in the tropisetron group experienced a significantly greater reduction in OCD symptoms as measured by Y-BOCS score. More participants in the tropisetron group experienced complete response and remission.
- This study demonstrated that compared with placebo, when administered as augmentation with fluvoxamine, tropisetron can have beneficial effects for patients with OCD.
Continue to: Reference 5...
5. Yousefzadeh F, Sahebolzamani E, Sadri A, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptophan as adjuvant therapy in treatment of moderate to severe obsessive-compulsive disorder: a doubleblind randomized trial with placebo control. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2020;35(5):254- 262. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000321
Nutraceuticals such as glycine, milk thistle, myoinositol, and serotonin (5-hydroxytryptophan) have been proposed as augmentation options for OCD. Yousefzadeh et al14 investigated the effectiveness of using 5-hydroxytryptophan in treating OCD.
Study design
- In a 12-week, randomized, double-blind study, 60 patients who met DSM-5 criteria for moderate to severe OCD (Y-BOCS score >21) were randomly assigned to receive fluoxetine plus 5-hydroxytryptophan 100 mg twice daily or fluoxetine plus placebo.
- All patients were administered fluoxetine 20 mg/d for the first 4 weeks of the study followed by fluoxetine 60 mg/d for the remainder of the trial.
- Symptoms were assessed using the Y-BOCS at baseline, Week 4, Week 8, and Week 12.
- The primary outcome measure was the difference between the 2 groups in change in Y-BOCS total score from baseline to the end of the trial. Secondary outcome measures were the differences in the Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores from baseline to Week 12.
Outcomes
- Compared to the placebo group, the 5-hydroxytryptophan group experienced a statistically significant greater improvement in Y-BOCS total score from baseline to Week 8 (P = .002) and Week 12 (P < .001).
- General linear model repeated measure showed significant effects for time × treatment interaction on Y-BOCS total (F = 12.07, df = 2.29, P < .001), obsession subscale (F = 8.25, df = 1.91, P = .001), and compulsion subscale scores (F = 6.64, df = 2.01, P = .002).
- The 5-hydroxytryptophan group demonstrated higher partial and complete treatment response rates (P = .032 and P = .001, respectively) as determined by change in Y-BOCS total score.
- The 5-hydroxytryptophan group showed a significant improvement from baseline to Week 12 in Y-BOCS obsession subscale score (5.23 ± 2.33 vs 3.53 ± 2.13, P = .009).
- There was a significant change from baseline to the end of the trial in the Y-BOCS compulsion subscale score (3.88 ± 2.04 vs 2.30 ± 1.37, P = .002).
Conclusion
- This trial demonstrated the potential benefits of 5-hydroxytryptophan in combination with fluoxetine for patients with OCD.
6. Mowla A, Ghaedsharaf M. Pregabalin augmentation for resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. CNS Spectr. 2020;25(4):552-556. doi:10.1017/S1092852919001500
Glutamatergic dysfunction has been identified as a potential cause of OCD. Studies have found elevated levels of glutamatergic transmission in the cortical-striatal-thalamic circuit of the brain and elevated glutamate concentration in the CSF in patients with OCD. Pregabalin has multiple mechanisms of action that inhibit the release of glutamate. Mowla et al15 evaluated pregabalin as an augmentation treatment for resistant OCD.
Study design
- This 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluated the efficacy of adjunctive pregabalin in 56 patients who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had not responded to ≥12 weeks of treatment with an adequate and stable dose of sertraline (baseline Y-BOCS score ≥18).
- Individuals who had other major psychiatric disorders, major medical problems, were pregnant, or had past substance or alcohol abuse were excluded.
- Participants were randomly assigned to receive sertraline plus pregabalin (n = 28) or sertraline plus placebo (n = 28). Mean sertraline dosage was 256.5 mg/d; range was 100 mg/d to 300 mg/d. Pregabalin was started at 75 mg/d and increased by 75 mg increments weekly. The mean dosage was 185.9 mg/d; range was 75 mg/d to 225 mg/d.
- The primary outcome measure was change in Y-BOCS score. A decrease >35% in Y-BOCS score was considered a significant response rate.
Outcomes
- There was a statistically significant decrease in Y-BOCS score in patients who received pregabalin. In the pregabalin group, 57.14% of patients (n = 16) showed a >35% decrease in Y-BOCS score compared with 7.14% of patients (n = 2) in the placebo group (P < .01).
- The pregabalin group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Conclusion
- In patients with treatment-resistant OCD who did not respond to sertraline monotherapy, augmentation with pregabalin significantly decreases Y-BOCS scores compared with placebo.
Continue to: Reference 7...
7. Zheng H, Jia F, Han H, et al. Combined fluvoxamine and extended-release methylphenidate improved treatment response compared to fluvoxamine alone in patients with treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind, placebocontrolled study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019;29(3):397-404. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro. 2018.12.010
Recent evidence suggests dysregulation of serotonin and dopamine in patients with OCD. Methylphenidate is a dopamine and norepinephrine inhibitor and releaser. A limited number of studies have suggested stimulants might be useful for OCD patients. Zheng et al16 conducted a pilot trial to determine whether methylphenidate augmentation may be of benefit in the management of outpatients with OCD.
Study design
- In an 8-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, 44 patients (29 [66%] men, with a mean [SD] age of 24.7 [6]) with treatment-refractory OCD were randomized to receive fluvoxamine 250 mg/d plus methylphenidate extended-release (MPH-ER) 36 mg/d or fluvoxamine 250 mg/d plus placebo. The MPH-ER dose was 18 mg/d for the first 4 weeks and 36 mg/d for the rest of the trial.
- Biweekly assessments consisted of scores on the Y-BOCS, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS), and Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A).
- The primary outcomes were improvement in Y-BOCS score and the clinical response rate. Secondary outcomes included a change in score on the Y-BOCS subscales, HARS, and HAM-A. Data were analyzed with the intention-to-treat sample.
Outcomes
- Forty-one patients finished the trial. The baseline Y-BOCS total scores and subscale scores did not differ significantly between the 2 groups.
- Improvements in Y-BOCS total score and obsession subscale score were more prominent in the fluvoxamine plus MPH-ER group compared with the placebo group (P < .001).
- HDRS score decreased in both the placebo and MPH-ER groups. HAM-A scores decreased significantly in the MPH-ER plus fluvoxamine group compared with the placebo group.
Conclusion
- This study demonstrated that the combination of fluvoxamine and MPH-ER produces a higher and faster response rate than fluvoxamine plus placebo in patients with OCD.
8. Arabzadeh S, Shahhossenie M, Mesgarpour B, et al. L-carnosine as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine in treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind study. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2017;32(4). doi:10.1002/hup.2584
Glutamate dysregulation is implicated in the pathogenesis of OCD. Glutamate-modulating agents have been used to treat OCD. Studies have shown L-carnosine has a neuroprotective role via its modulatory effect on glutamate. Arabzadeh et al17 evaluated the efficacy of L-carnosine as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine for treating OCD.
Study design
- This 10-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy of adjunctive L-carnosine in 40 patients age 18 to 60 who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had moderate to severe OCD (Y-BOCS score ≥21).
- Individuals with any other DSM-5 major psychiatric disorders, serious medical or neurologic illness, substance dependence (other than caffeine or nicotine), mental retardation (based on clinical judgment), were pregnant or breastfeeding, had any contraindication for the use of L‐carnosine or fluvoxamine, or received any psychotropic drugs in the previous 6 weeks were excluded.
- Participants received fluvoxamine 100 mg/d for the first 4 weeks and 200 mg/d for the next 6 weeks plus either L-carnosine 500 mg twice daily or placebo. This dosage of L-carnosine was chosen because previously it had been tolerated and effective.
- The primary outcome measure was difference in Y-BOCS total scores. Secondary outcomes were differences in Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores and differences in change in score on Y-BOCS total and subscale scores from baseline.
Outcomes
- The L-carnosine group experienced a significant decrease in Y-BOCS total score (P < .001), obsession subscale score (P < .01), and compulsion subscale score (P < .01).
- The group that received fluvoxamine plus L-carnosine also experienced a more complete response (P = .03).
- The L-carnosine group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Conclusion
- L-carnosine significantly reduces OCD symptoms when used as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a chronic, debilitating neuropsychiatric disorder that affects 1% to 3% of the population worldwide.1,2 Together, serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs) and cognitive-behavior therapy (CBT) are considered the first-line treatment for OCD.3 In children and adults, CBT is considered at least as effective as pharmacotherapy.4 Despite being an effective treatment, CBT continues to have barriers to its widespread use, including limited availability of trained CBT therapists, delayed clinical response, and high costs.5
Only approximately one-half of patients with OCD respond to SRI therapy, and a considerable percentage (30% to 40%) show significant residual symptoms even after multiple trials of SRIs.6-8 In addition, SRIs may have adverse effects (eg, sexual dysfunction, gastrointestinal symptoms) that impair patient adherence to these medications.9 Therefore, finding better treatment options is important for managing patients with OCD.
Augmentation strategies are recommended for patients who show partial response to SRI treatment or poor response to multiple SRIs. Augmentation typically includes incorporating additional medications with the primary drug with the goal of boosting the therapeutic efficacy of the primary drug. Typically, these additional medications have different mechanisms of action. However, there are no large-scale randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to inform treatment augmentation after first-line treatments for OCD produce suboptimal outcomes. The available evidence is predominantly based on small-scale RCTs, open-label trials, and case series.
In this article, we review the evidence for treatment augmentation strategies for OCD and summarize 8 studies that show promising results (Table10-17). We focus only on pharmacologic agents and do not include other biological interventions, such as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over supplementary motor area, ablative neurosurgery, or deep brain stimulation.

Continue to: Reference 1...
1. Naderi S, Faghih H , Aqamolaei A, et al. Amantadine as adjuvant therapy in the treatment of moderate to severe obsessivecompulsive disorder: a double-blind randomized trial with placebo control. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019;73(4):169-174. doi:10.1111/ pcn.12803
Numerous studies support the role of glutamate dysregulation in the pathophysiology of OCD. Cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical (CSTC) abnormalities play a major role in the pathophysiology of OCD as suggested by neuroimaging research studies that indicate glutamate is the fundamental neurotransmitter of the CSTC circuit. Dysregulation of glutamatergic signaling within this circuit has been linked to OCD. Patients with OCD have been found to have an increase of glutamate in the CSF. As a result, medications that affect glutamate levels can be used to treat patients with OCD who do not respond to first-line agents. In patients already taking SRIs, augmentation of glutamate-modulating medications can reduce OCD symptoms. As an uncompetitive antagonist of the N-methyl-
Naderi et al10 evaluated amantadine as augmentative therapy to fluvoxamine for treating patients with moderate to severe OCD.
Study design
- This 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of amantadine as an augmentative agent to fluvoxamine in 106 patients age 18 to 60 with moderate to severe OCD.
- Participants met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had a Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS) score >21. Participants were excluded if they had any substance dependence; an IQ <70; any other Axis I mental disorder; any serious cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease; had received psychotropic medications during the last 6 weeks, were pregnant or breastfeeding, or had rising liver transaminases to 3 times the upper limit of normal or higher.
- Participants received fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily plus amantadine 100 mg/d, or fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily plus placebo. All patients received fluvoxamine 100 mg/d for 28 days followed by 200 mg/d for the remainder of the trial.
- The primary outcome measure was difference in Y-BOCS total scores between the amantadine and placebo groups. The secondary outcome was the difference in Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores.
Outcomes
- Patients who received amantadine augmentation experienced a significant reduction in Y-BOCS total score (P < .001) and obsession subscale score (P < .01).
- The amantadine group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
- Amantadine is an effective adjuvant to fluvoxamine for reducing OCD symptoms.
Conclusion
- Ondansetron and granisetron can be beneficial as an augmentation strategy for patients with treatment-resistant OCD.
2. Sharafkhah M, Aghakarim Alamdar M, Massoudifar A, et al. Comparing the efficacy of ondansetron and granisetron augmentation in treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;34(5):222- 233. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000267
Although selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are considered a first-line treatment when teamed with CBT and antipsychotic augmentation, symptom resolution is not always achieved, and treatment resistance is a common problem. Sharafkhah et al11 compared the efficacy of ondansetron and granisetron augmentation specifically for patients with treatment-resistant OCD.
Study Design
- In this 18-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 135 patients with treatment-resistant OCD who were previously treated with a combination of an SSRI and an antipsychotic received augmentation with ondansetron (n = 45, 4 mg/d), granisetron (n = 45, 2 mg/d), or placebo.
- Patients were rated using Y-BOCS every 2 weeks during phase I (intervention period), which lasted 14 weeks. After completing the intervention, patients were followed for 4 more weeks during phase II (discontinuation period).
- The aim of this study was to determine the safety, efficacy, and tolerability of ondansetron vs granisetron as augmentation for patients with treatment-resistant OCD. A secondary aim was to determine the rate of relapse of OCD symptoms after discontinuing ondansetron as compared with granisetron at 4 weeks after intervention.
Outcomes
- At Week 14, the reductions in Y-BOCS scores in the ondansetron, granisetron, and placebo groups were 41.5%, 39.7%, and 15.2%, respectively (P = .001). The reduction in Y-BOCS score in the ondansetron and granisetron groups was significantly greater than placebo at all phase I visits.
- Complete response was higher in the ondansetron group compared with the granisetron group (P = .041).
- Y-BOCS scores increased in both the ondansetron and granisetron groups during the discontinuation phase, but OCD symptoms were not significantly exacerbated.
Conclusion
- Ondansetron and granisetron can be beneficial as an augmentation strategy for patients with treatment-resistant OCD.
3. Modarresi A, Sayyah M, Razooghi S, et al. Memantine augmentation improves symptoms in serotonin reuptake inhibitorrefractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2018;51(6):263-269. doi:10.1055/s-0043-120268
Increased glutamate levels in CSF, glutamatergic overactivity, and polymorphisms of genes coding the NMDA receptor have been shown to contribute to the occurrence of OCD. Memantine is a noncompetitive antagonist of the NMDA receptor. Various control trials have shown augmentation with memantine 5 mg/d to 20 mg/d significantly reduced symptom severity in patients with moderate to severe OCD. Modarresi et al12 evaluated memantine as a treatment option for patients with severe OCD who did not respond to SRI monotherapy.
Study design
- This 12-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy of memantine augmentation in 32 patients age 18 to 40 who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD, had a Y-BOCS score ≥24, and no psychiatric comorbidity. Participants had not responded to ≥3 adequate trials (minimum 3 months) of SRI therapy, 1 of which was clomipramine.
- Individuals were excluded if they were undergoing CBT; had an additional anxiety disorder, mood disorder, or current drug or alcohol use disorder, or any systemic disorder; had a history of seizures; were pregnant or breastfeeding; or had a history of memantine use.
- Participants already receiving the maximum tolerated dose of an SRI received augmentation with memantine 20 mg/d or placebo.
- The primary outcome measure was change in Y-BOCS score from baseline. The secondary outcome was the number of individuals who achieved treatment response (defined as ≥35% reduction in Y-BOCS score).
Continue to: Outcomes...
Outcomes
- There was a statistically significant difference in Y-BOCS score in patients treated with memantine at Week 8 and Week 12 vs those who received placebo. By Week 8, 17.2% of patients in the memantine group showed a decrease in Y-BOCS score, compared with -0.8% patients in the placebo group. The difference became more significant by Week 12, with 40.9% in the memantine group showing a decrease in Y-BOCS score vs -0.3% in the placebo group. This resulted in 73.3% of patients achieving treatment response.
- Eight weeks of memantine augmentation was necessary to observe a significant improvement in OCD symptoms, and 12 weeks was needed for treatment response.
- The mean Y-BOCS total score decreased significantly in the memantine group from Week 4 to Week 8 (16.8%) and again from Week 8 to Week 12 (28.5%).
- The memantine group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Conclusion
- Memantine augmentation in patients with severe OCD who do not respond to an SRI is effective and well-tolerated.
4. Shalbafan M, Malekpour F, Tadayon Najafabadi B, et al. Fluvoxamine combination therapy with tropisetron for obsessive-compulsive disorder patients: a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33(11):1407- 1414. doi:10.1177/0269881119878177
Studies have demonstrated the involvement of the amygdala, medial and lateral orbitofrontal cortex, and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex in OCD. Additionally, studies have also investigated the role of serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate system dysregulation in the pathology of OCD.
The 5-HT3 receptors are ligand-gated ion channels found in the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus. Studies of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists such as ondansetron and granisetron have shown beneficial results in augmentation with SSRIs for patients with OCD.11 Tropisetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, is highly lipophilic and able to cross the blood brain barrier. It also has dopamine-inhibiting properties that could have benefits in OCD management. Shalbafan et al13 evaluated the efficacy of tropisetron augmentation to fluvoxamine for patients with OCD.
Study design
- In a 10-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial, 108 individuals age 18 to 60 who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had a Y-BOCS score >21 received fluvoxamine plus tropisetron or fluvoxamine plus placebo. A total of 48 (44.4%) participants in each group completed the trial. Participants were evaluated using the Y-BOCS scale at baseline and at Week 4 and Week 10.
- The primary outcome was decrease in total Y-BOCS score from baseline to Week 10. The secondary outcome was the difference in change in Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores between the groups.
Outcomes
- The Y-BOCS total score was not significantly different between the 2 groups (P = .975). Repeated measures analysis of variance determined a significant effect for time in both tropisetron and placebo groups (Greenhouse-Geisser F [2.72–2303.84] = 152.25, P < .001; and Greenhouse-Geisser F [1.37–1736.81] = 75.57, P < .001, respectively). At Week 10, 35 participants in the tropisetron group and 19 participants in the placebo group were complete responders.
- The baseline Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscales did not significantly differ between treatment groups.
Conclusion
- Compared with participants in the placebo group, those in the tropisetron group experienced a significantly greater reduction in OCD symptoms as measured by Y-BOCS score. More participants in the tropisetron group experienced complete response and remission.
- This study demonstrated that compared with placebo, when administered as augmentation with fluvoxamine, tropisetron can have beneficial effects for patients with OCD.
Continue to: Reference 5...
5. Yousefzadeh F, Sahebolzamani E, Sadri A, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptophan as adjuvant therapy in treatment of moderate to severe obsessive-compulsive disorder: a doubleblind randomized trial with placebo control. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2020;35(5):254- 262. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000321
Nutraceuticals such as glycine, milk thistle, myoinositol, and serotonin (5-hydroxytryptophan) have been proposed as augmentation options for OCD. Yousefzadeh et al14 investigated the effectiveness of using 5-hydroxytryptophan in treating OCD.
Study design
- In a 12-week, randomized, double-blind study, 60 patients who met DSM-5 criteria for moderate to severe OCD (Y-BOCS score >21) were randomly assigned to receive fluoxetine plus 5-hydroxytryptophan 100 mg twice daily or fluoxetine plus placebo.
- All patients were administered fluoxetine 20 mg/d for the first 4 weeks of the study followed by fluoxetine 60 mg/d for the remainder of the trial.
- Symptoms were assessed using the Y-BOCS at baseline, Week 4, Week 8, and Week 12.
- The primary outcome measure was the difference between the 2 groups in change in Y-BOCS total score from baseline to the end of the trial. Secondary outcome measures were the differences in the Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores from baseline to Week 12.
Outcomes
- Compared to the placebo group, the 5-hydroxytryptophan group experienced a statistically significant greater improvement in Y-BOCS total score from baseline to Week 8 (P = .002) and Week 12 (P < .001).
- General linear model repeated measure showed significant effects for time × treatment interaction on Y-BOCS total (F = 12.07, df = 2.29, P < .001), obsession subscale (F = 8.25, df = 1.91, P = .001), and compulsion subscale scores (F = 6.64, df = 2.01, P = .002).
- The 5-hydroxytryptophan group demonstrated higher partial and complete treatment response rates (P = .032 and P = .001, respectively) as determined by change in Y-BOCS total score.
- The 5-hydroxytryptophan group showed a significant improvement from baseline to Week 12 in Y-BOCS obsession subscale score (5.23 ± 2.33 vs 3.53 ± 2.13, P = .009).
- There was a significant change from baseline to the end of the trial in the Y-BOCS compulsion subscale score (3.88 ± 2.04 vs 2.30 ± 1.37, P = .002).
Conclusion
- This trial demonstrated the potential benefits of 5-hydroxytryptophan in combination with fluoxetine for patients with OCD.
6. Mowla A, Ghaedsharaf M. Pregabalin augmentation for resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. CNS Spectr. 2020;25(4):552-556. doi:10.1017/S1092852919001500
Glutamatergic dysfunction has been identified as a potential cause of OCD. Studies have found elevated levels of glutamatergic transmission in the cortical-striatal-thalamic circuit of the brain and elevated glutamate concentration in the CSF in patients with OCD. Pregabalin has multiple mechanisms of action that inhibit the release of glutamate. Mowla et al15 evaluated pregabalin as an augmentation treatment for resistant OCD.
Study design
- This 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluated the efficacy of adjunctive pregabalin in 56 patients who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had not responded to ≥12 weeks of treatment with an adequate and stable dose of sertraline (baseline Y-BOCS score ≥18).
- Individuals who had other major psychiatric disorders, major medical problems, were pregnant, or had past substance or alcohol abuse were excluded.
- Participants were randomly assigned to receive sertraline plus pregabalin (n = 28) or sertraline plus placebo (n = 28). Mean sertraline dosage was 256.5 mg/d; range was 100 mg/d to 300 mg/d. Pregabalin was started at 75 mg/d and increased by 75 mg increments weekly. The mean dosage was 185.9 mg/d; range was 75 mg/d to 225 mg/d.
- The primary outcome measure was change in Y-BOCS score. A decrease >35% in Y-BOCS score was considered a significant response rate.
Outcomes
- There was a statistically significant decrease in Y-BOCS score in patients who received pregabalin. In the pregabalin group, 57.14% of patients (n = 16) showed a >35% decrease in Y-BOCS score compared with 7.14% of patients (n = 2) in the placebo group (P < .01).
- The pregabalin group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Conclusion
- In patients with treatment-resistant OCD who did not respond to sertraline monotherapy, augmentation with pregabalin significantly decreases Y-BOCS scores compared with placebo.
Continue to: Reference 7...
7. Zheng H, Jia F, Han H, et al. Combined fluvoxamine and extended-release methylphenidate improved treatment response compared to fluvoxamine alone in patients with treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind, placebocontrolled study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019;29(3):397-404. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro. 2018.12.010
Recent evidence suggests dysregulation of serotonin and dopamine in patients with OCD. Methylphenidate is a dopamine and norepinephrine inhibitor and releaser. A limited number of studies have suggested stimulants might be useful for OCD patients. Zheng et al16 conducted a pilot trial to determine whether methylphenidate augmentation may be of benefit in the management of outpatients with OCD.
Study design
- In an 8-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, 44 patients (29 [66%] men, with a mean [SD] age of 24.7 [6]) with treatment-refractory OCD were randomized to receive fluvoxamine 250 mg/d plus methylphenidate extended-release (MPH-ER) 36 mg/d or fluvoxamine 250 mg/d plus placebo. The MPH-ER dose was 18 mg/d for the first 4 weeks and 36 mg/d for the rest of the trial.
- Biweekly assessments consisted of scores on the Y-BOCS, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS), and Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A).
- The primary outcomes were improvement in Y-BOCS score and the clinical response rate. Secondary outcomes included a change in score on the Y-BOCS subscales, HARS, and HAM-A. Data were analyzed with the intention-to-treat sample.
Outcomes
- Forty-one patients finished the trial. The baseline Y-BOCS total scores and subscale scores did not differ significantly between the 2 groups.
- Improvements in Y-BOCS total score and obsession subscale score were more prominent in the fluvoxamine plus MPH-ER group compared with the placebo group (P < .001).
- HDRS score decreased in both the placebo and MPH-ER groups. HAM-A scores decreased significantly in the MPH-ER plus fluvoxamine group compared with the placebo group.
Conclusion
- This study demonstrated that the combination of fluvoxamine and MPH-ER produces a higher and faster response rate than fluvoxamine plus placebo in patients with OCD.
8. Arabzadeh S, Shahhossenie M, Mesgarpour B, et al. L-carnosine as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine in treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind study. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2017;32(4). doi:10.1002/hup.2584
Glutamate dysregulation is implicated in the pathogenesis of OCD. Glutamate-modulating agents have been used to treat OCD. Studies have shown L-carnosine has a neuroprotective role via its modulatory effect on glutamate. Arabzadeh et al17 evaluated the efficacy of L-carnosine as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine for treating OCD.
Study design
- This 10-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy of adjunctive L-carnosine in 40 patients age 18 to 60 who met DSM-5 criteria for OCD and had moderate to severe OCD (Y-BOCS score ≥21).
- Individuals with any other DSM-5 major psychiatric disorders, serious medical or neurologic illness, substance dependence (other than caffeine or nicotine), mental retardation (based on clinical judgment), were pregnant or breastfeeding, had any contraindication for the use of L‐carnosine or fluvoxamine, or received any psychotropic drugs in the previous 6 weeks were excluded.
- Participants received fluvoxamine 100 mg/d for the first 4 weeks and 200 mg/d for the next 6 weeks plus either L-carnosine 500 mg twice daily or placebo. This dosage of L-carnosine was chosen because previously it had been tolerated and effective.
- The primary outcome measure was difference in Y-BOCS total scores. Secondary outcomes were differences in Y-BOCS obsession and compulsion subscale scores and differences in change in score on Y-BOCS total and subscale scores from baseline.
Outcomes
- The L-carnosine group experienced a significant decrease in Y-BOCS total score (P < .001), obsession subscale score (P < .01), and compulsion subscale score (P < .01).
- The group that received fluvoxamine plus L-carnosine also experienced a more complete response (P = .03).
- The L-carnosine group showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Conclusion
- L-carnosine significantly reduces OCD symptoms when used as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Ruscio AM, Stein DJ, Chiu WT, et al. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15(1):53-63.
3. Eddy KT, Dutra L, Bradley, R, et al. A multidimensional meta-analysis of psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Clin Psychol Rev. 2004;24(8):1011-1030.
4. Franklin ME, Foa EB. Treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2011;7:229-243.
5. Koran LM, Hanna GL, Hollander E, et al. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(7 Suppl):5-53.
6. Pittenger C, Bloch MH. Pharmacological treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2014;37(3):375-391.
7. Pallanti S, Hollander E, Bienstock C, et al. Treatment non-response in OCD: methodological issues and operational definitions. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2002;5(2):181-191.
8. Atmaca M. Treatment-refractory obsessive compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016;70:127-133.
9. Barth M, Kriston L, Klostermann S, et al. Efficacy of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and adverse events: meta-regression and mediation analysis of placebo-controlled trials. Br J Psychiatry. 2016;208(2):114-119.
10. NaderiS, Faghih H, Aqamolaei A, et al. Amantadine as adjuvant therapy in the treatment of moderate to severe obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind randomized trial with placebo control. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019;73(4):169-174. doi:10.1111/pcn.12803
11. SharafkhahM, Aghakarim Alamdar M, MassoudifarA, et al. Comparing the efficacy of ondansetron and granisetron augmentation in treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;34(5):222-233. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000267
12. ModarresiA, Sayyah M, Razooghi S, et al. Memantine augmentation improves symptoms in serotonin reuptake inhibitor-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2018;51(6):263-269. doi:10.1055/s-0043-12026
13. Shalbafan M, Malekpour F, Tadayon Najafabadi B, et al. Fluvoxamine combination therapy with tropisetron for obsessive-compulsive disorder patients: a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33(11):1407-1414. doi:10.1177/0269881119878177
14. Yousefzadeh F, Sahebolzamani E, Sadri A, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptophan as adjuvant therapy in treatment of moderate to severe obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind randomized trial with placebo control. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2020;35(5):254-262. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000321
15. Mowla A, Ghaedsharaf M. Pregabalin augmentation for resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. CNS Spectr. 2020;25(4):552-556. doi:10.1017/S1092852919001500
16. Zheng H, Jia F, Han H, et al.Combined fluvoxamine and extended-release methylphenidate improved treatment response compared to fluvoxamine alone in patients with treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019;29(3):397-404. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.12.010
17. Arabzadeh S, Shahhossenie M, Mesgarpour B, et al. L-carnosine as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine in treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind study. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2017;32(4). doi:10.1002/hup.2584
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Ruscio AM, Stein DJ, Chiu WT, et al. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15(1):53-63.
3. Eddy KT, Dutra L, Bradley, R, et al. A multidimensional meta-analysis of psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Clin Psychol Rev. 2004;24(8):1011-1030.
4. Franklin ME, Foa EB. Treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2011;7:229-243.
5. Koran LM, Hanna GL, Hollander E, et al. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(7 Suppl):5-53.
6. Pittenger C, Bloch MH. Pharmacological treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2014;37(3):375-391.
7. Pallanti S, Hollander E, Bienstock C, et al. Treatment non-response in OCD: methodological issues and operational definitions. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2002;5(2):181-191.
8. Atmaca M. Treatment-refractory obsessive compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016;70:127-133.
9. Barth M, Kriston L, Klostermann S, et al. Efficacy of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and adverse events: meta-regression and mediation analysis of placebo-controlled trials. Br J Psychiatry. 2016;208(2):114-119.
10. NaderiS, Faghih H, Aqamolaei A, et al. Amantadine as adjuvant therapy in the treatment of moderate to severe obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind randomized trial with placebo control. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019;73(4):169-174. doi:10.1111/pcn.12803
11. SharafkhahM, Aghakarim Alamdar M, MassoudifarA, et al. Comparing the efficacy of ondansetron and granisetron augmentation in treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;34(5):222-233. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000267
12. ModarresiA, Sayyah M, Razooghi S, et al. Memantine augmentation improves symptoms in serotonin reuptake inhibitor-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2018;51(6):263-269. doi:10.1055/s-0043-12026
13. Shalbafan M, Malekpour F, Tadayon Najafabadi B, et al. Fluvoxamine combination therapy with tropisetron for obsessive-compulsive disorder patients: a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33(11):1407-1414. doi:10.1177/0269881119878177
14. Yousefzadeh F, Sahebolzamani E, Sadri A, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptophan as adjuvant therapy in treatment of moderate to severe obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind randomized trial with placebo control. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2020;35(5):254-262. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000321
15. Mowla A, Ghaedsharaf M. Pregabalin augmentation for resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. CNS Spectr. 2020;25(4):552-556. doi:10.1017/S1092852919001500
16. Zheng H, Jia F, Han H, et al.Combined fluvoxamine and extended-release methylphenidate improved treatment response compared to fluvoxamine alone in patients with treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019;29(3):397-404. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.12.010
17. Arabzadeh S, Shahhossenie M, Mesgarpour B, et al. L-carnosine as an adjuvant to fluvoxamine in treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder: a randomized double-blind study. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2017;32(4). doi:10.1002/hup.2584
Food for thought: Dangerous weight loss in an older adult
CASE Fixated on health and nutrition
At the insistence of her daughter, Ms. L, age 75, presents to the emergency department (ED) for self-neglect and severe weight loss, with a body mass index (BMI) of 13.5 kg/m2 (normal: 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2). When asked why she is in the ED, Ms. L says she doesn’t know. She attributes her significant weight loss (approximately 20 pounds in the last few months) to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). She constantly worries about her esophagus. She had been diagnosed with esophageal dysphagia 7 years ago after undergoing radiofrequency ablation for esophageal cancer. Ms. L fixates on the negative effects certain foods and ingredients might have on her stomach and esophagus.
Following transfer from the ED, Ms. L is involuntarily admitted to our inpatient unit. Although she acknowledges weight loss, she minimizes the severity of her illness and indicates she would like to gain weight, but only by eating healthy foods she is comfortable with, including kale, quinoa, and vegetables. Ms. L says that she has always been interested in “healthful foods” and that she “loves sugar,” but “it’s bad for you,” mentioning that “sugar fuels cancer.” She has daily thoughts about sugar causing cancer. Ms. L also mentions that she stopped eating flour, sugar, fried food, and oils because those foods affect her “stomach acid” and cause “pimples on my face and weight loss.” While in the inpatient unit, Ms. L requests a special diet and demands to know the origin and ingredients of the foods she is offered. She emphasizes that her esophageal cancer diagnosis and dysphagia exacerbate worries that certain foods cause cancer, and wants to continue her diet restrictions. Nonetheless, she says she wants to get healthy, and denies an intense fear of gaining weight or feeling fat.
HISTORY Multiple psychiatric diagnoses
Ms. L lives alone and enjoys spending time with her grandchildren, visiting museums, and listening to classical music. However, her family, social workers, and records from a previous psychiatric hospitalization reveal that Ms. L has a history of psychiatric illness and fears regarding certain types of foods for much of her adult life. Ms. L’s family also described a range of compulsive behaviors, including shoplifting, hoarding art, multiple plastic surgeries, and phases where Ms. L ate only frozen yogurt without sugar.
Ms. L’s daughter reported that Ms. L had seen a psychologist in the late 1990s for depression and had been diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in the early 2000s. In 2006, during a depressive episode after her divorce, Ms. L had a suicide attempt with pills and alcohol, and was hospitalized. Records from that stay described a history of mood dysregulation with fears regarding food and nutrition. Ms. L was treated with aripiprazole 5 mg/d. A trial of trazodone 25 mg/d did not have any effect. When discharged, she was receiving lamotrigine 100 mg/d. However, her daughter believes she stopped taking all psychiatric medications shortly after discharge.
Her daughter says that in the past 2 years, Ms. L has seen multiple doctors for treatment of somatic gastrointestinal (GI) complaints. A 2018 note from a social worker indicated that Ms. L endorsed taking >80 supplements per day and constantly researched nutrition online. In the months leading to her current hospitalization, Ms. L suffered from severe self-neglect and fear regarding foods she felt were not healthy for her. She had stopped leaving her apartment.
Continue to: EVALUATION Poor insight, normal lab results...
EVALUATION Poor insight, normal lab results
During her evaluation, Ms. L appears cachectic and frail. She has a heavily constricted affect and is guarded, dismissive, and vague. Although her thought processes are linear and goal-directed, her insight into her condition is extremely poor and she appears surprised when clinicians inform her that her self-neglect would lead to death. Instead, Ms. L insists she is eating healthily and demonstrates severe anxiety in relation to her GI symptoms.
Ms. L is oriented to person, place, and time. She scores 27/30 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, indicating normal cognition. She denies any depressive symptoms or suicidal intent. She does not appear to be internally preoccupied and denies having auditory or visual hallucinations or manic symptoms.
A neurologic examination reveals that her cranial nerves are normal, and cerebellar function, strength, and sensory testing are intact. Her gait is steady and she walks without a walker. Despite her severely low BMI and recent history of self-neglect, Ms. L’s laboratory results are remarkably normal and show no liver, metabolic, or electrolyte abnormalities, no signs of infection, and normal vitamin B12 levels. She has slightly elevated creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels, but a normal glomerular filtration rate.
Her medical history is significant for squamous cell esophageal cancer, treated with radiofrequency ablation. Although Ms. L is constantly worried about the recurrence of cancer, pathology reports demonstrate no esophageal dysplasia. However, she does show evidence of an approximately 1 cm × 1 cm mild, noncircumferential esophageal stenosis, likely resulting from radiofrequency ablation.
[polldaddy:11079394]
The authors’ observations
Several health- and physical symptom-related psychiatric disorders have overlapping features, which can complicate the differential diagnosis (Table 11). Ms. L presented to the ED with a severely low BMI of 13.5 kg/m2, obsessions regarding specific types of food, and preoccupations regarding her esophagus. Despite her extensive psychiatric history (including intense fears regarding food), we ruled out a primary psychotic disorder because she did not describe auditory or visual hallucinations and never appeared internally preoccupied. While her BMI and persistent minimization of the extent of her disease meet criteria for anorexia nervosa, she denied body dysmorphia and did not have any fear of gaining weight.
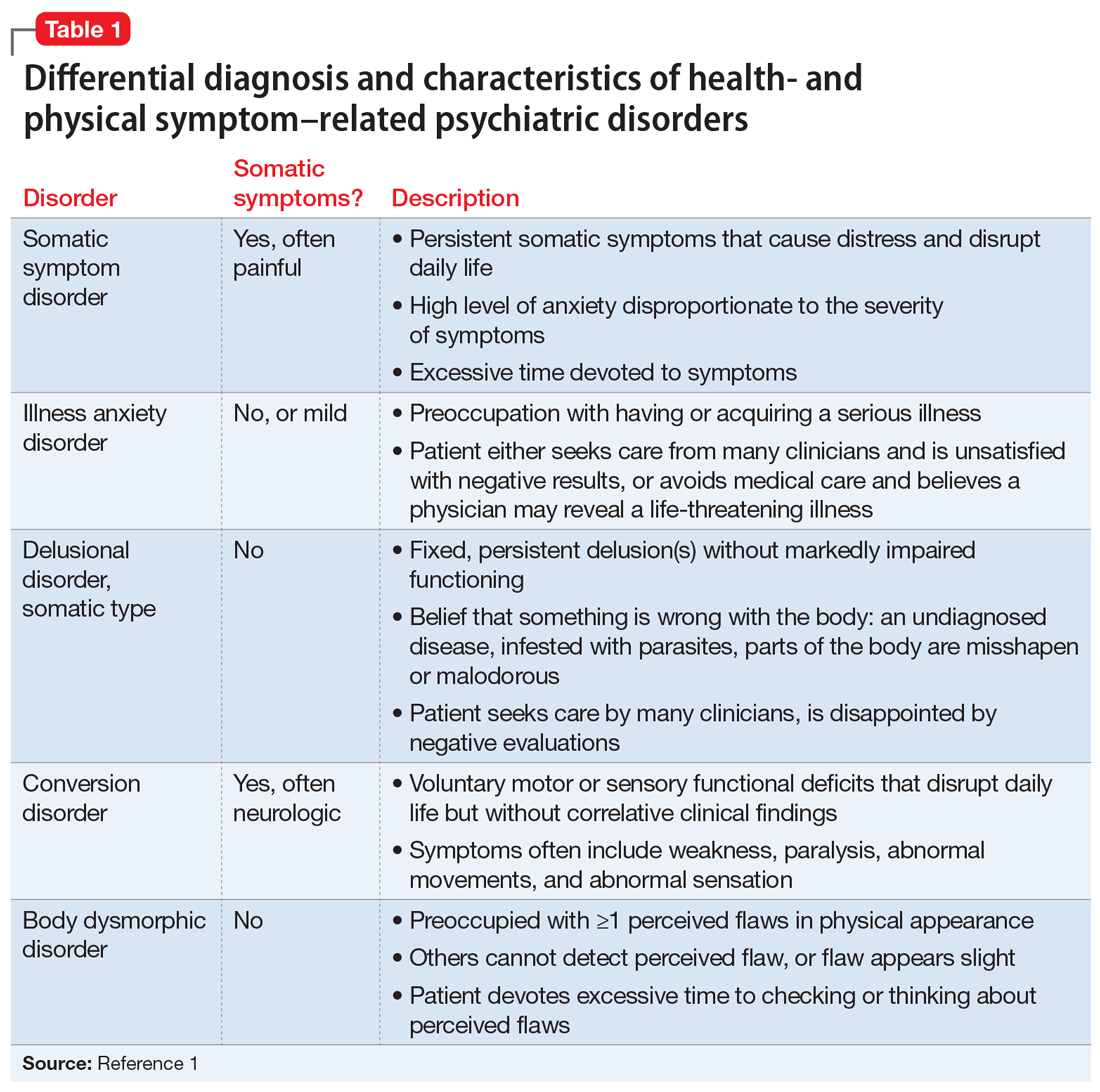
A central element of Ms. L’s presentation was her anxiety regarding how certain types of foods impact her health as well as her anxieties regarding her esophagus. While Ms. L was in remission from esophageal cancer and had a diagnosis of esophageal dysphagia, these preoccupations and obsessions regarding how certain types of foods affect her esophagus drove her to self-neglect and thus represent pathologic thought processes out of proportion to her symptoms. Illness anxiety disorder was considered because Ms. L met many of its criteria: preoccupation with having a serious illness, disproportionate preoccupation with somatic symptoms if they are present, extreme anxiety over health, and performance of health-related behaviors.1 However, illness anxiety disorder is a diagnosis of exclusion, and 1 criterion is that these symptoms cannot be explained by another mental disorder. We felt other diagnoses better fit Ms. L’s condition and ruled out illness anxiety disorder.
Ms. L’s long history of food and non-food–related obsessions and compulsions that interrupted her ability to perform daily activities were strongly suggestive for OCD. Additionally, her intense preoccupation, high level of anxiety, amount of time and energy spent seeking care for her esophagus and GERD symptoms, and the resulting significant disruption of daily life, met criteria for somatic symptom disorder (SSD). However, we did not believe that a diagnosis of OCD and SSD alone explained the entirety of Ms. L’s clinical picture. Despite ruling out anorexia nervosa, Ms. L nonetheless demonstrated disordered eating.
Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID) is an eating disorder in which patients restrict their diet and do not meet nutritional needs for any number of reasons, do not experience body dysmorphia, and do not fear weight gain.1 A common feature of ARFID is a fear of negative consequences from eating specific types of food.2 Table 21,2 summarizes additional clinical features of ARFID. Although ARFID is typically diagnosed in children and adolescents, particularly in individuals with autism with heightened sensory sensitivities, ARFID is also common among adult patients with GI disorders.3 In a retrospective chart review of 410 adults ages 18 to 90 (73% women) referred to a neurogastroenterology care center, 6.3% met the full criteria for ARFID and 17.3% had clinically significant avoidant or restrictive eating behaviors. Among patients with ARFID symptoms, 93% stated that a fear of GI symptoms was the driver of their avoidant or restrictive eating behaviors.2 Patients with GI diseases often develop dietary control and avoidance coping mechanisms to alleviate their symptoms.4 These strategies can exacerbate health anxieties and have a detrimental effect on mental health.5 Patients with GI disorders have a high degree of comorbidity with affective disorders, including anxiety disorders.6 These trends may arise from hypervigilance and the need to gain control over physical symptoms.7 Feeling a need for control, actions driven by anxiety and fear, and the need for compensatory behaviors are cardinal features of OCD and eating disorders.8 Multiple studies have demonstrated comorbidities between irritable bowel syndrome and eating disorders,9 SSD,10 and OCD.11 Taken together with observations that ARFID is also found in patients with GI disorders,2 these findings demonstrate that patients with a history of GI disease are at high risk of developing extreme health anxieties and behavioral coping strategies that can lead to disordered eating.
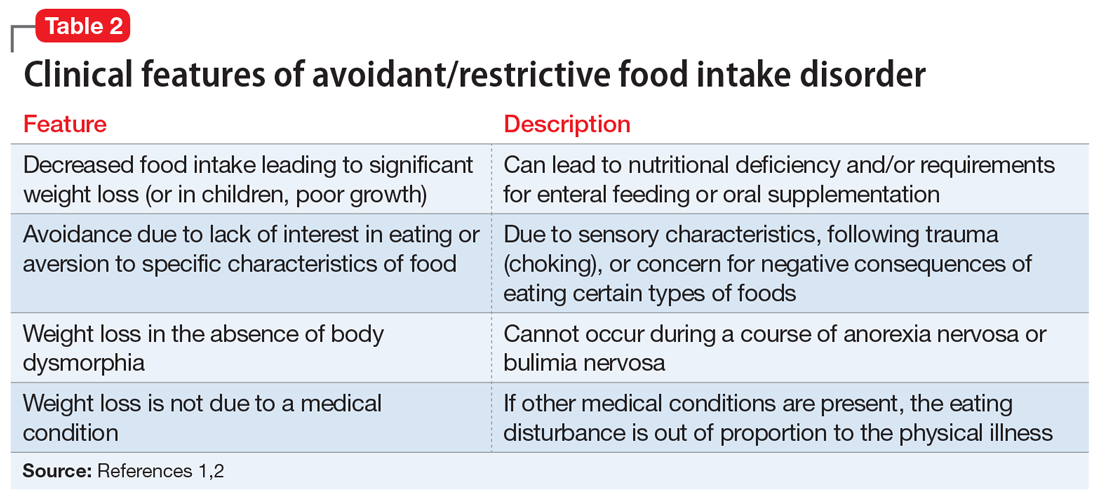
The rise in “healthy” eating materials online—particularly on social media—has created an atmosphere in which misinformation regarding diet and health is common and widespread. For patients with OCD and a predisposition to health anxiety, such as Ms. L, searching online for nutrition information and healthy living habits can exacerbate food-related anxieties and can lead to a pathological drive for purity and health.12Although not included in DSM-5, orthorexia nervosa was identified in 1997 as a proposed eating disorder best characterized as an obsession with healthy eating with associated restrictive behaviors.13 Patients with this disorder are rarely focused on losing weight, and orthorexic eating behaviors have been associated with both SSD and OCD.12,14 As in Ms. L’s case, patients with orthorexia nervosa demonstrate intrusive obsessions with nutrition, spend excessive amount of time researching nutrition, and fixate on food quality.12 Throughout Ms. L’s hospitalization, even as her food-related magical thinking symptoms improved, she constantly informed her care team that she had been “eating healthily” even though she was severely cachectic. Patients with SSD and OCD prone to health anxieties are at risk of developing pathologic food beliefs and dangerous eating behaviors. These patients may benefit from psychoeducation regarding nutrition and media literacy, which are components of effective eating disorder programs.15
[polldaddy:11079399]
Continue to: The authors' observations...
The authors’ observations
How do we approach the pharmacologic treatment of patients with co-occurring eating, somatic symptom, and anxiety disorders? Olanzapine facilitates recovery in children and adolescents with ARFID by promoting eating and weight gain, and decreasing symptoms of depression and anxiety.16 Patients with orthorexia nervosa also may benefit from treatment with olanzapine, which has decreased food-related fixations, magical thinking, and delusions regarding food.17 Further, orthorexic patients with ARFID have also been shown to respond to SSRIs due to those agents’ efficacy for treating intrusive thoughts, obsessions, and preoccupations from OCD and SSD.18,19 Thus, treating Ms. L’s symptoms with olanzapine and fluoxetine targeted the intersection of several diagnoses on our differential. Olanzapine’s propensity to cause weight gain is favorable in this population, particularly patients such as Ms. L, who do not exhibit body dysmorphia or fear of gaining weight.
OUTCOME Weight gain and fewer fears
Ms. L is prescribed olanzapine 5 mg/d and fluoxetine 20 mg/d. She gains 20.6 pounds in 4 weeks. Importantly, she endorses fewer fears related to foods and expands her palate to include foods she previously considered to be unhealthy, including white bread and farm-raised salmon. Further, she spends less time thinking about food and says she has less anxiety regarding the recurrence of GI symptoms.
1. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Murray HB, Bailey AP, Keshishian AC. Prevalence and characteristics of avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder in adult neurogastroenterology patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(9):1995-2002.e1.
3. Görmez A, Kılıç A, Kırpınar İ. Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder: an adult case responding to cognitive behavioral therapy. Clinical Case Studies. 2018;17(6):443-452.
4. Reed-Knight B, Squires M, Chitkara DK, et al. Adolescents with irritable bowel syndrome report increased eating-associated symptoms, changes in dietary composition, and altered eating behaviors: a pilot comparison study to healthy adolescents. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016;28(12):1915-1920.
5. Melchior C, Desprez C, Riachi G, et al. Anxiety and depression profile is associated with eating disorders in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Front Psychiatry. 2020;10:928.
6. Mayer EA, Craske M, Naliboff BD. Depression, anxiety, and the gastrointestinal system. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62 Suppl 8:28-37.
7. Abraham S, Kellow J. Exploring eating disorder quality of life and functional gastrointestinal disorders among eating disorder patients. J Psychosom Res. 2011;70(4):372-377.
8. Swinbourne JM, Touyz SW. The co-morbidity of eating disorders and anxiety disorders: a review. Eur Eat Disord Rev. 2007;15(4):253-274.
9. Perkins SJ, Keville S, Schmidt U, et al. Eating disorders and irritable bowel syndrome: is there a link? J Psychosom Res. 2005;59(2):57-64.
10. Hausteiner-Wiehle C, Henningsen P. Irritable bowel syndrome: relations with functional, mental, and somatoform disorders. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(2):6024-6030.
11. Masand PS, Keuthen NJ, Gupta S, et al. Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in obsessive-compulsive disorder. CNS Spectr. 2006;11(1):21-25.
12. Koven NS, Abry AW. The clinical basis of orthorexia nervosa: emerging perspectives. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:385-394.
13. Bratman S. Health food junkie. Yoga Journal. 1997;136:42-50.
14. Barthels F, Müller R, Schüth T, et al. Orthorexic eating behavior in patients with somatoform disorders. Eat Weight Disord. 2021;26(1):135-143.
15. Ciao AC, Loth K, Neumark-Sztainer D. Preventing eating disorder pathology: common and unique features of successful eating disorders prevention programs. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2014;16(7):453.
16. Brewerton TD, D’Agostino M. Adjunctive use of olanzapine in the treatment of avoidant restrictive food intake disorder in children and adolescents in an eating disorders program. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(10):920-922.
17. Moroze RM, Dunn TM, Craig Holland J, et al. Microthinking about micronutrients: a case of transition from obsessions about healthy eating to near-fatal “orthorexia nervosa” and proposed diagnostic criteria. Psychosomatics. 2015;56(4):397-403.
18. Spettigue W, Norris ML, Santos A, et al. Treatment of children and adolescents with avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder: a case series examining the feasibility of family therapy and adjunctive treatments. J Eat Disord. 2018;6:20.
19. Niedzielski A, Kaźmierczak-Wojtaś N. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa and Its Diagnostic Tools-A Literature Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(10):5488. Published 2021 May 20. doi:10.3390/ijerph18105488 Prevalence of orthorexia nervosa and its diagnostic tools-a literature review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(10):5488.
CASE Fixated on health and nutrition
At the insistence of her daughter, Ms. L, age 75, presents to the emergency department (ED) for self-neglect and severe weight loss, with a body mass index (BMI) of 13.5 kg/m2 (normal: 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2). When asked why she is in the ED, Ms. L says she doesn’t know. She attributes her significant weight loss (approximately 20 pounds in the last few months) to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). She constantly worries about her esophagus. She had been diagnosed with esophageal dysphagia 7 years ago after undergoing radiofrequency ablation for esophageal cancer. Ms. L fixates on the negative effects certain foods and ingredients might have on her stomach and esophagus.
Following transfer from the ED, Ms. L is involuntarily admitted to our inpatient unit. Although she acknowledges weight loss, she minimizes the severity of her illness and indicates she would like to gain weight, but only by eating healthy foods she is comfortable with, including kale, quinoa, and vegetables. Ms. L says that she has always been interested in “healthful foods” and that she “loves sugar,” but “it’s bad for you,” mentioning that “sugar fuels cancer.” She has daily thoughts about sugar causing cancer. Ms. L also mentions that she stopped eating flour, sugar, fried food, and oils because those foods affect her “stomach acid” and cause “pimples on my face and weight loss.” While in the inpatient unit, Ms. L requests a special diet and demands to know the origin and ingredients of the foods she is offered. She emphasizes that her esophageal cancer diagnosis and dysphagia exacerbate worries that certain foods cause cancer, and wants to continue her diet restrictions. Nonetheless, she says she wants to get healthy, and denies an intense fear of gaining weight or feeling fat.
HISTORY Multiple psychiatric diagnoses
Ms. L lives alone and enjoys spending time with her grandchildren, visiting museums, and listening to classical music. However, her family, social workers, and records from a previous psychiatric hospitalization reveal that Ms. L has a history of psychiatric illness and fears regarding certain types of foods for much of her adult life. Ms. L’s family also described a range of compulsive behaviors, including shoplifting, hoarding art, multiple plastic surgeries, and phases where Ms. L ate only frozen yogurt without sugar.
Ms. L’s daughter reported that Ms. L had seen a psychologist in the late 1990s for depression and had been diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in the early 2000s. In 2006, during a depressive episode after her divorce, Ms. L had a suicide attempt with pills and alcohol, and was hospitalized. Records from that stay described a history of mood dysregulation with fears regarding food and nutrition. Ms. L was treated with aripiprazole 5 mg/d. A trial of trazodone 25 mg/d did not have any effect. When discharged, she was receiving lamotrigine 100 mg/d. However, her daughter believes she stopped taking all psychiatric medications shortly after discharge.
Her daughter says that in the past 2 years, Ms. L has seen multiple doctors for treatment of somatic gastrointestinal (GI) complaints. A 2018 note from a social worker indicated that Ms. L endorsed taking >80 supplements per day and constantly researched nutrition online. In the months leading to her current hospitalization, Ms. L suffered from severe self-neglect and fear regarding foods she felt were not healthy for her. She had stopped leaving her apartment.
Continue to: EVALUATION Poor insight, normal lab results...
EVALUATION Poor insight, normal lab results
During her evaluation, Ms. L appears cachectic and frail. She has a heavily constricted affect and is guarded, dismissive, and vague. Although her thought processes are linear and goal-directed, her insight into her condition is extremely poor and she appears surprised when clinicians inform her that her self-neglect would lead to death. Instead, Ms. L insists she is eating healthily and demonstrates severe anxiety in relation to her GI symptoms.
Ms. L is oriented to person, place, and time. She scores 27/30 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, indicating normal cognition. She denies any depressive symptoms or suicidal intent. She does not appear to be internally preoccupied and denies having auditory or visual hallucinations or manic symptoms.
A neurologic examination reveals that her cranial nerves are normal, and cerebellar function, strength, and sensory testing are intact. Her gait is steady and she walks without a walker. Despite her severely low BMI and recent history of self-neglect, Ms. L’s laboratory results are remarkably normal and show no liver, metabolic, or electrolyte abnormalities, no signs of infection, and normal vitamin B12 levels. She has slightly elevated creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels, but a normal glomerular filtration rate.
Her medical history is significant for squamous cell esophageal cancer, treated with radiofrequency ablation. Although Ms. L is constantly worried about the recurrence of cancer, pathology reports demonstrate no esophageal dysplasia. However, she does show evidence of an approximately 1 cm × 1 cm mild, noncircumferential esophageal stenosis, likely resulting from radiofrequency ablation.
[polldaddy:11079394]
The authors’ observations
Several health- and physical symptom-related psychiatric disorders have overlapping features, which can complicate the differential diagnosis (Table 11). Ms. L presented to the ED with a severely low BMI of 13.5 kg/m2, obsessions regarding specific types of food, and preoccupations regarding her esophagus. Despite her extensive psychiatric history (including intense fears regarding food), we ruled out a primary psychotic disorder because she did not describe auditory or visual hallucinations and never appeared internally preoccupied. While her BMI and persistent minimization of the extent of her disease meet criteria for anorexia nervosa, she denied body dysmorphia and did not have any fear of gaining weight.

A central element of Ms. L’s presentation was her anxiety regarding how certain types of foods impact her health as well as her anxieties regarding her esophagus. While Ms. L was in remission from esophageal cancer and had a diagnosis of esophageal dysphagia, these preoccupations and obsessions regarding how certain types of foods affect her esophagus drove her to self-neglect and thus represent pathologic thought processes out of proportion to her symptoms. Illness anxiety disorder was considered because Ms. L met many of its criteria: preoccupation with having a serious illness, disproportionate preoccupation with somatic symptoms if they are present, extreme anxiety over health, and performance of health-related behaviors.1 However, illness anxiety disorder is a diagnosis of exclusion, and 1 criterion is that these symptoms cannot be explained by another mental disorder. We felt other diagnoses better fit Ms. L’s condition and ruled out illness anxiety disorder.
Ms. L’s long history of food and non-food–related obsessions and compulsions that interrupted her ability to perform daily activities were strongly suggestive for OCD. Additionally, her intense preoccupation, high level of anxiety, amount of time and energy spent seeking care for her esophagus and GERD symptoms, and the resulting significant disruption of daily life, met criteria for somatic symptom disorder (SSD). However, we did not believe that a diagnosis of OCD and SSD alone explained the entirety of Ms. L’s clinical picture. Despite ruling out anorexia nervosa, Ms. L nonetheless demonstrated disordered eating.
Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID) is an eating disorder in which patients restrict their diet and do not meet nutritional needs for any number of reasons, do not experience body dysmorphia, and do not fear weight gain.1 A common feature of ARFID is a fear of negative consequences from eating specific types of food.2 Table 21,2 summarizes additional clinical features of ARFID. Although ARFID is typically diagnosed in children and adolescents, particularly in individuals with autism with heightened sensory sensitivities, ARFID is also common among adult patients with GI disorders.3 In a retrospective chart review of 410 adults ages 18 to 90 (73% women) referred to a neurogastroenterology care center, 6.3% met the full criteria for ARFID and 17.3% had clinically significant avoidant or restrictive eating behaviors. Among patients with ARFID symptoms, 93% stated that a fear of GI symptoms was the driver of their avoidant or restrictive eating behaviors.2 Patients with GI diseases often develop dietary control and avoidance coping mechanisms to alleviate their symptoms.4 These strategies can exacerbate health anxieties and have a detrimental effect on mental health.5 Patients with GI disorders have a high degree of comorbidity with affective disorders, including anxiety disorders.6 These trends may arise from hypervigilance and the need to gain control over physical symptoms.7 Feeling a need for control, actions driven by anxiety and fear, and the need for compensatory behaviors are cardinal features of OCD and eating disorders.8 Multiple studies have demonstrated comorbidities between irritable bowel syndrome and eating disorders,9 SSD,10 and OCD.11 Taken together with observations that ARFID is also found in patients with GI disorders,2 these findings demonstrate that patients with a history of GI disease are at high risk of developing extreme health anxieties and behavioral coping strategies that can lead to disordered eating.

The rise in “healthy” eating materials online—particularly on social media—has created an atmosphere in which misinformation regarding diet and health is common and widespread. For patients with OCD and a predisposition to health anxiety, such as Ms. L, searching online for nutrition information and healthy living habits can exacerbate food-related anxieties and can lead to a pathological drive for purity and health.12Although not included in DSM-5, orthorexia nervosa was identified in 1997 as a proposed eating disorder best characterized as an obsession with healthy eating with associated restrictive behaviors.13 Patients with this disorder are rarely focused on losing weight, and orthorexic eating behaviors have been associated with both SSD and OCD.12,14 As in Ms. L’s case, patients with orthorexia nervosa demonstrate intrusive obsessions with nutrition, spend excessive amount of time researching nutrition, and fixate on food quality.12 Throughout Ms. L’s hospitalization, even as her food-related magical thinking symptoms improved, she constantly informed her care team that she had been “eating healthily” even though she was severely cachectic. Patients with SSD and OCD prone to health anxieties are at risk of developing pathologic food beliefs and dangerous eating behaviors. These patients may benefit from psychoeducation regarding nutrition and media literacy, which are components of effective eating disorder programs.15
[polldaddy:11079399]
Continue to: The authors' observations...
The authors’ observations
How do we approach the pharmacologic treatment of patients with co-occurring eating, somatic symptom, and anxiety disorders? Olanzapine facilitates recovery in children and adolescents with ARFID by promoting eating and weight gain, and decreasing symptoms of depression and anxiety.16 Patients with orthorexia nervosa also may benefit from treatment with olanzapine, which has decreased food-related fixations, magical thinking, and delusions regarding food.17 Further, orthorexic patients with ARFID have also been shown to respond to SSRIs due to those agents’ efficacy for treating intrusive thoughts, obsessions, and preoccupations from OCD and SSD.18,19 Thus, treating Ms. L’s symptoms with olanzapine and fluoxetine targeted the intersection of several diagnoses on our differential. Olanzapine’s propensity to cause weight gain is favorable in this population, particularly patients such as Ms. L, who do not exhibit body dysmorphia or fear of gaining weight.
OUTCOME Weight gain and fewer fears
Ms. L is prescribed olanzapine 5 mg/d and fluoxetine 20 mg/d. She gains 20.6 pounds in 4 weeks. Importantly, she endorses fewer fears related to foods and expands her palate to include foods she previously considered to be unhealthy, including white bread and farm-raised salmon. Further, she spends less time thinking about food and says she has less anxiety regarding the recurrence of GI symptoms.
CASE Fixated on health and nutrition
At the insistence of her daughter, Ms. L, age 75, presents to the emergency department (ED) for self-neglect and severe weight loss, with a body mass index (BMI) of 13.5 kg/m2 (normal: 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2). When asked why she is in the ED, Ms. L says she doesn’t know. She attributes her significant weight loss (approximately 20 pounds in the last few months) to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). She constantly worries about her esophagus. She had been diagnosed with esophageal dysphagia 7 years ago after undergoing radiofrequency ablation for esophageal cancer. Ms. L fixates on the negative effects certain foods and ingredients might have on her stomach and esophagus.
Following transfer from the ED, Ms. L is involuntarily admitted to our inpatient unit. Although she acknowledges weight loss, she minimizes the severity of her illness and indicates she would like to gain weight, but only by eating healthy foods she is comfortable with, including kale, quinoa, and vegetables. Ms. L says that she has always been interested in “healthful foods” and that she “loves sugar,” but “it’s bad for you,” mentioning that “sugar fuels cancer.” She has daily thoughts about sugar causing cancer. Ms. L also mentions that she stopped eating flour, sugar, fried food, and oils because those foods affect her “stomach acid” and cause “pimples on my face and weight loss.” While in the inpatient unit, Ms. L requests a special diet and demands to know the origin and ingredients of the foods she is offered. She emphasizes that her esophageal cancer diagnosis and dysphagia exacerbate worries that certain foods cause cancer, and wants to continue her diet restrictions. Nonetheless, she says she wants to get healthy, and denies an intense fear of gaining weight or feeling fat.
HISTORY Multiple psychiatric diagnoses
Ms. L lives alone and enjoys spending time with her grandchildren, visiting museums, and listening to classical music. However, her family, social workers, and records from a previous psychiatric hospitalization reveal that Ms. L has a history of psychiatric illness and fears regarding certain types of foods for much of her adult life. Ms. L’s family also described a range of compulsive behaviors, including shoplifting, hoarding art, multiple plastic surgeries, and phases where Ms. L ate only frozen yogurt without sugar.
Ms. L’s daughter reported that Ms. L had seen a psychologist in the late 1990s for depression and had been diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in the early 2000s. In 2006, during a depressive episode after her divorce, Ms. L had a suicide attempt with pills and alcohol, and was hospitalized. Records from that stay described a history of mood dysregulation with fears regarding food and nutrition. Ms. L was treated with aripiprazole 5 mg/d. A trial of trazodone 25 mg/d did not have any effect. When discharged, she was receiving lamotrigine 100 mg/d. However, her daughter believes she stopped taking all psychiatric medications shortly after discharge.
Her daughter says that in the past 2 years, Ms. L has seen multiple doctors for treatment of somatic gastrointestinal (GI) complaints. A 2018 note from a social worker indicated that Ms. L endorsed taking >80 supplements per day and constantly researched nutrition online. In the months leading to her current hospitalization, Ms. L suffered from severe self-neglect and fear regarding foods she felt were not healthy for her. She had stopped leaving her apartment.
Continue to: EVALUATION Poor insight, normal lab results...
EVALUATION Poor insight, normal lab results
During her evaluation, Ms. L appears cachectic and frail. She has a heavily constricted affect and is guarded, dismissive, and vague. Although her thought processes are linear and goal-directed, her insight into her condition is extremely poor and she appears surprised when clinicians inform her that her self-neglect would lead to death. Instead, Ms. L insists she is eating healthily and demonstrates severe anxiety in relation to her GI symptoms.
Ms. L is oriented to person, place, and time. She scores 27/30 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, indicating normal cognition. She denies any depressive symptoms or suicidal intent. She does not appear to be internally preoccupied and denies having auditory or visual hallucinations or manic symptoms.
A neurologic examination reveals that her cranial nerves are normal, and cerebellar function, strength, and sensory testing are intact. Her gait is steady and she walks without a walker. Despite her severely low BMI and recent history of self-neglect, Ms. L’s laboratory results are remarkably normal and show no liver, metabolic, or electrolyte abnormalities, no signs of infection, and normal vitamin B12 levels. She has slightly elevated creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels, but a normal glomerular filtration rate.
Her medical history is significant for squamous cell esophageal cancer, treated with radiofrequency ablation. Although Ms. L is constantly worried about the recurrence of cancer, pathology reports demonstrate no esophageal dysplasia. However, she does show evidence of an approximately 1 cm × 1 cm mild, noncircumferential esophageal stenosis, likely resulting from radiofrequency ablation.
[polldaddy:11079394]
The authors’ observations
Several health- and physical symptom-related psychiatric disorders have overlapping features, which can complicate the differential diagnosis (Table 11). Ms. L presented to the ED with a severely low BMI of 13.5 kg/m2, obsessions regarding specific types of food, and preoccupations regarding her esophagus. Despite her extensive psychiatric history (including intense fears regarding food), we ruled out a primary psychotic disorder because she did not describe auditory or visual hallucinations and never appeared internally preoccupied. While her BMI and persistent minimization of the extent of her disease meet criteria for anorexia nervosa, she denied body dysmorphia and did not have any fear of gaining weight.

A central element of Ms. L’s presentation was her anxiety regarding how certain types of foods impact her health as well as her anxieties regarding her esophagus. While Ms. L was in remission from esophageal cancer and had a diagnosis of esophageal dysphagia, these preoccupations and obsessions regarding how certain types of foods affect her esophagus drove her to self-neglect and thus represent pathologic thought processes out of proportion to her symptoms. Illness anxiety disorder was considered because Ms. L met many of its criteria: preoccupation with having a serious illness, disproportionate preoccupation with somatic symptoms if they are present, extreme anxiety over health, and performance of health-related behaviors.1 However, illness anxiety disorder is a diagnosis of exclusion, and 1 criterion is that these symptoms cannot be explained by another mental disorder. We felt other diagnoses better fit Ms. L’s condition and ruled out illness anxiety disorder.
Ms. L’s long history of food and non-food–related obsessions and compulsions that interrupted her ability to perform daily activities were strongly suggestive for OCD. Additionally, her intense preoccupation, high level of anxiety, amount of time and energy spent seeking care for her esophagus and GERD symptoms, and the resulting significant disruption of daily life, met criteria for somatic symptom disorder (SSD). However, we did not believe that a diagnosis of OCD and SSD alone explained the entirety of Ms. L’s clinical picture. Despite ruling out anorexia nervosa, Ms. L nonetheless demonstrated disordered eating.
Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID) is an eating disorder in which patients restrict their diet and do not meet nutritional needs for any number of reasons, do not experience body dysmorphia, and do not fear weight gain.1 A common feature of ARFID is a fear of negative consequences from eating specific types of food.2 Table 21,2 summarizes additional clinical features of ARFID. Although ARFID is typically diagnosed in children and adolescents, particularly in individuals with autism with heightened sensory sensitivities, ARFID is also common among adult patients with GI disorders.3 In a retrospective chart review of 410 adults ages 18 to 90 (73% women) referred to a neurogastroenterology care center, 6.3% met the full criteria for ARFID and 17.3% had clinically significant avoidant or restrictive eating behaviors. Among patients with ARFID symptoms, 93% stated that a fear of GI symptoms was the driver of their avoidant or restrictive eating behaviors.2 Patients with GI diseases often develop dietary control and avoidance coping mechanisms to alleviate their symptoms.4 These strategies can exacerbate health anxieties and have a detrimental effect on mental health.5 Patients with GI disorders have a high degree of comorbidity with affective disorders, including anxiety disorders.6 These trends may arise from hypervigilance and the need to gain control over physical symptoms.7 Feeling a need for control, actions driven by anxiety and fear, and the need for compensatory behaviors are cardinal features of OCD and eating disorders.8 Multiple studies have demonstrated comorbidities between irritable bowel syndrome and eating disorders,9 SSD,10 and OCD.11 Taken together with observations that ARFID is also found in patients with GI disorders,2 these findings demonstrate that patients with a history of GI disease are at high risk of developing extreme health anxieties and behavioral coping strategies that can lead to disordered eating.

The rise in “healthy” eating materials online—particularly on social media—has created an atmosphere in which misinformation regarding diet and health is common and widespread. For patients with OCD and a predisposition to health anxiety, such as Ms. L, searching online for nutrition information and healthy living habits can exacerbate food-related anxieties and can lead to a pathological drive for purity and health.12Although not included in DSM-5, orthorexia nervosa was identified in 1997 as a proposed eating disorder best characterized as an obsession with healthy eating with associated restrictive behaviors.13 Patients with this disorder are rarely focused on losing weight, and orthorexic eating behaviors have been associated with both SSD and OCD.12,14 As in Ms. L’s case, patients with orthorexia nervosa demonstrate intrusive obsessions with nutrition, spend excessive amount of time researching nutrition, and fixate on food quality.12 Throughout Ms. L’s hospitalization, even as her food-related magical thinking symptoms improved, she constantly informed her care team that she had been “eating healthily” even though she was severely cachectic. Patients with SSD and OCD prone to health anxieties are at risk of developing pathologic food beliefs and dangerous eating behaviors. These patients may benefit from psychoeducation regarding nutrition and media literacy, which are components of effective eating disorder programs.15
[polldaddy:11079399]
Continue to: The authors' observations...
The authors’ observations
How do we approach the pharmacologic treatment of patients with co-occurring eating, somatic symptom, and anxiety disorders? Olanzapine facilitates recovery in children and adolescents with ARFID by promoting eating and weight gain, and decreasing symptoms of depression and anxiety.16 Patients with orthorexia nervosa also may benefit from treatment with olanzapine, which has decreased food-related fixations, magical thinking, and delusions regarding food.17 Further, orthorexic patients with ARFID have also been shown to respond to SSRIs due to those agents’ efficacy for treating intrusive thoughts, obsessions, and preoccupations from OCD and SSD.18,19 Thus, treating Ms. L’s symptoms with olanzapine and fluoxetine targeted the intersection of several diagnoses on our differential. Olanzapine’s propensity to cause weight gain is favorable in this population, particularly patients such as Ms. L, who do not exhibit body dysmorphia or fear of gaining weight.
OUTCOME Weight gain and fewer fears
Ms. L is prescribed olanzapine 5 mg/d and fluoxetine 20 mg/d. She gains 20.6 pounds in 4 weeks. Importantly, she endorses fewer fears related to foods and expands her palate to include foods she previously considered to be unhealthy, including white bread and farm-raised salmon. Further, she spends less time thinking about food and says she has less anxiety regarding the recurrence of GI symptoms.
1. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Murray HB, Bailey AP, Keshishian AC. Prevalence and characteristics of avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder in adult neurogastroenterology patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(9):1995-2002.e1.
3. Görmez A, Kılıç A, Kırpınar İ. Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder: an adult case responding to cognitive behavioral therapy. Clinical Case Studies. 2018;17(6):443-452.
4. Reed-Knight B, Squires M, Chitkara DK, et al. Adolescents with irritable bowel syndrome report increased eating-associated symptoms, changes in dietary composition, and altered eating behaviors: a pilot comparison study to healthy adolescents. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016;28(12):1915-1920.
5. Melchior C, Desprez C, Riachi G, et al. Anxiety and depression profile is associated with eating disorders in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Front Psychiatry. 2020;10:928.
6. Mayer EA, Craske M, Naliboff BD. Depression, anxiety, and the gastrointestinal system. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62 Suppl 8:28-37.
7. Abraham S, Kellow J. Exploring eating disorder quality of life and functional gastrointestinal disorders among eating disorder patients. J Psychosom Res. 2011;70(4):372-377.
8. Swinbourne JM, Touyz SW. The co-morbidity of eating disorders and anxiety disorders: a review. Eur Eat Disord Rev. 2007;15(4):253-274.
9. Perkins SJ, Keville S, Schmidt U, et al. Eating disorders and irritable bowel syndrome: is there a link? J Psychosom Res. 2005;59(2):57-64.
10. Hausteiner-Wiehle C, Henningsen P. Irritable bowel syndrome: relations with functional, mental, and somatoform disorders. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(2):6024-6030.
11. Masand PS, Keuthen NJ, Gupta S, et al. Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in obsessive-compulsive disorder. CNS Spectr. 2006;11(1):21-25.
12. Koven NS, Abry AW. The clinical basis of orthorexia nervosa: emerging perspectives. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:385-394.
13. Bratman S. Health food junkie. Yoga Journal. 1997;136:42-50.
14. Barthels F, Müller R, Schüth T, et al. Orthorexic eating behavior in patients with somatoform disorders. Eat Weight Disord. 2021;26(1):135-143.
15. Ciao AC, Loth K, Neumark-Sztainer D. Preventing eating disorder pathology: common and unique features of successful eating disorders prevention programs. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2014;16(7):453.
16. Brewerton TD, D’Agostino M. Adjunctive use of olanzapine in the treatment of avoidant restrictive food intake disorder in children and adolescents in an eating disorders program. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(10):920-922.
17. Moroze RM, Dunn TM, Craig Holland J, et al. Microthinking about micronutrients: a case of transition from obsessions about healthy eating to near-fatal “orthorexia nervosa” and proposed diagnostic criteria. Psychosomatics. 2015;56(4):397-403.
18. Spettigue W, Norris ML, Santos A, et al. Treatment of children and adolescents with avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder: a case series examining the feasibility of family therapy and adjunctive treatments. J Eat Disord. 2018;6:20.
19. Niedzielski A, Kaźmierczak-Wojtaś N. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa and Its Diagnostic Tools-A Literature Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(10):5488. Published 2021 May 20. doi:10.3390/ijerph18105488 Prevalence of orthorexia nervosa and its diagnostic tools-a literature review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(10):5488.
1. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Murray HB, Bailey AP, Keshishian AC. Prevalence and characteristics of avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder in adult neurogastroenterology patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(9):1995-2002.e1.
3. Görmez A, Kılıç A, Kırpınar İ. Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder: an adult case responding to cognitive behavioral therapy. Clinical Case Studies. 2018;17(6):443-452.
4. Reed-Knight B, Squires M, Chitkara DK, et al. Adolescents with irritable bowel syndrome report increased eating-associated symptoms, changes in dietary composition, and altered eating behaviors: a pilot comparison study to healthy adolescents. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016;28(12):1915-1920.
5. Melchior C, Desprez C, Riachi G, et al. Anxiety and depression profile is associated with eating disorders in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Front Psychiatry. 2020;10:928.
6. Mayer EA, Craske M, Naliboff BD. Depression, anxiety, and the gastrointestinal system. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62 Suppl 8:28-37.
7. Abraham S, Kellow J. Exploring eating disorder quality of life and functional gastrointestinal disorders among eating disorder patients. J Psychosom Res. 2011;70(4):372-377.
8. Swinbourne JM, Touyz SW. The co-morbidity of eating disorders and anxiety disorders: a review. Eur Eat Disord Rev. 2007;15(4):253-274.
9. Perkins SJ, Keville S, Schmidt U, et al. Eating disorders and irritable bowel syndrome: is there a link? J Psychosom Res. 2005;59(2):57-64.
10. Hausteiner-Wiehle C, Henningsen P. Irritable bowel syndrome: relations with functional, mental, and somatoform disorders. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(2):6024-6030.
11. Masand PS, Keuthen NJ, Gupta S, et al. Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in obsessive-compulsive disorder. CNS Spectr. 2006;11(1):21-25.
12. Koven NS, Abry AW. The clinical basis of orthorexia nervosa: emerging perspectives. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:385-394.
13. Bratman S. Health food junkie. Yoga Journal. 1997;136:42-50.
14. Barthels F, Müller R, Schüth T, et al. Orthorexic eating behavior in patients with somatoform disorders. Eat Weight Disord. 2021;26(1):135-143.
15. Ciao AC, Loth K, Neumark-Sztainer D. Preventing eating disorder pathology: common and unique features of successful eating disorders prevention programs. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2014;16(7):453.
16. Brewerton TD, D’Agostino M. Adjunctive use of olanzapine in the treatment of avoidant restrictive food intake disorder in children and adolescents in an eating disorders program. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(10):920-922.
17. Moroze RM, Dunn TM, Craig Holland J, et al. Microthinking about micronutrients: a case of transition from obsessions about healthy eating to near-fatal “orthorexia nervosa” and proposed diagnostic criteria. Psychosomatics. 2015;56(4):397-403.
18. Spettigue W, Norris ML, Santos A, et al. Treatment of children and adolescents with avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder: a case series examining the feasibility of family therapy and adjunctive treatments. J Eat Disord. 2018;6:20.
19. Niedzielski A, Kaźmierczak-Wojtaś N. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa and Its Diagnostic Tools-A Literature Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(10):5488. Published 2021 May 20. doi:10.3390/ijerph18105488 Prevalence of orthorexia nervosa and its diagnostic tools-a literature review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(10):5488.
I STEP: Recognizing cognitive distortions in posttraumatic stress disorder
Evidence-based cognitive-behavioral therapies for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may employ cognitive restructuring. This psychotherapeutic technique entails recognizing and correcting maladaptive, inaccurate thoughts that perpetuate illness.1 For example, a clinician helps a patient recognize that the negative thought “Nobody loves me” following a romantic breakup is an overgeneralization. The patient is taught to self-correct this to “While my ex-girlfriend doesn’t love me, others do. It only feels like nobody loves me.”2
We introduce the acronym I STEP to help clinicians recognize several common distorted thoughts in PTSD. These tend to occur within stereotyped themes in PTSD,3 as outlined and illustrated below. Recognizing distorted thoughts in these patients will help clinicians understand and address psychological distress following trauma.
Intimacy/In-touch. Intimacy involves comfort in relationships, including but not limited to sexual intimacy. This requires being in touch emotionally with self and others. In trauma involving loss, fear of further loss may impair intimacy with others. Difficulty with self-intimacy impairs commitment to life’s goals and prompts unhelpful avoidance behaviors, such as difficulty being alone or self-injurious use of drugs or alcohol. Comfort in spending some portion of time alone with one’s thoughts and emotions is a life skill necessary to attain optimum function. Patients who are unable to tolerate their own emotions without constant company might have excessive anxiety when social supports are otherwise occupied. Such patients might seek excessive and repeated reassurance rather than learning to tolerate their own emotions and thoughts. They would then find it difficult to engage successfully in solo activities.
Safety. After trauma, patients may view themselves and others as unsafe, and may overestimate risk. For example, a pedestrian who is struck by a vehicle may believe that crossing a street will again result in getting hit by a car without appreciating that people frequently cross streets without injury or that crossing cautiously is an essential life skill. Parents who have suffered from trauma may unduly believe that their children are in danger when engaging in an activity generally considered to be safe. This may create challenges in parenting and impede their children’s ability to develop a sense of independence.
Trust. Trauma victims may unfairly blame themselves, leading them to mistrust their own judgment. Such patients may have difficulty making decisions confidently and independently, such as choosing a job or a romantic partner. When traumatized by another person or people, it can be difficult to maintain positive views of others or to accept others’ positive behaviors as genuine. For example, a common reaction following rape may be a generalized mistrust of all men.
Esteem. Patients’ self-esteem may suffer following trauma due to irrational self-blame or believing the “just world hypothesis”—the idea that bad things only happen to bad people. For example, a patient who suffers an assault by an acquaintance might think “I must be stupid if I couldn’t figure out that my friend was dangerous.”
Power. Traumatic events usually occur outside of one’s control. Survivors of trauma may lose confidence in their ability to control any aspect of their lives. Conversely, they may attempt to gain control of all of life’s circumstances, including those that are beyond anyone’s control. Control can be applied to emotions, behaviors, or events. A driver struck by a vehicle may think “I can’t control other drivers, so I have no power to control my safety while driving,” and hence give up driving. While there are things that are beyond our control, this extreme thought ignores things that we can control, such as wearing seatbelts or having the vehicle’s brakes regularly serviced.
1. Wenzel A. Basic strategies of cognitive behavioral therapy. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2017;40(4):597-609.
2. Beck J. Cognitive behavioral therapy: basics and beyond. 2nd ed. The Guilford Press; 2011.
3. Resick PA, Monson CM, Chard KM. Cognitive processing therapy for PTSD. A comprehensive manual. The Guilford Press; 2017.
Evidence-based cognitive-behavioral therapies for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may employ cognitive restructuring. This psychotherapeutic technique entails recognizing and correcting maladaptive, inaccurate thoughts that perpetuate illness.1 For example, a clinician helps a patient recognize that the negative thought “Nobody loves me” following a romantic breakup is an overgeneralization. The patient is taught to self-correct this to “While my ex-girlfriend doesn’t love me, others do. It only feels like nobody loves me.”2
We introduce the acronym I STEP to help clinicians recognize several common distorted thoughts in PTSD. These tend to occur within stereotyped themes in PTSD,3 as outlined and illustrated below. Recognizing distorted thoughts in these patients will help clinicians understand and address psychological distress following trauma.
Intimacy/In-touch. Intimacy involves comfort in relationships, including but not limited to sexual intimacy. This requires being in touch emotionally with self and others. In trauma involving loss, fear of further loss may impair intimacy with others. Difficulty with self-intimacy impairs commitment to life’s goals and prompts unhelpful avoidance behaviors, such as difficulty being alone or self-injurious use of drugs or alcohol. Comfort in spending some portion of time alone with one’s thoughts and emotions is a life skill necessary to attain optimum function. Patients who are unable to tolerate their own emotions without constant company might have excessive anxiety when social supports are otherwise occupied. Such patients might seek excessive and repeated reassurance rather than learning to tolerate their own emotions and thoughts. They would then find it difficult to engage successfully in solo activities.
Safety. After trauma, patients may view themselves and others as unsafe, and may overestimate risk. For example, a pedestrian who is struck by a vehicle may believe that crossing a street will again result in getting hit by a car without appreciating that people frequently cross streets without injury or that crossing cautiously is an essential life skill. Parents who have suffered from trauma may unduly believe that their children are in danger when engaging in an activity generally considered to be safe. This may create challenges in parenting and impede their children’s ability to develop a sense of independence.
Trust. Trauma victims may unfairly blame themselves, leading them to mistrust their own judgment. Such patients may have difficulty making decisions confidently and independently, such as choosing a job or a romantic partner. When traumatized by another person or people, it can be difficult to maintain positive views of others or to accept others’ positive behaviors as genuine. For example, a common reaction following rape may be a generalized mistrust of all men.
Esteem. Patients’ self-esteem may suffer following trauma due to irrational self-blame or believing the “just world hypothesis”—the idea that bad things only happen to bad people. For example, a patient who suffers an assault by an acquaintance might think “I must be stupid if I couldn’t figure out that my friend was dangerous.”
Power. Traumatic events usually occur outside of one’s control. Survivors of trauma may lose confidence in their ability to control any aspect of their lives. Conversely, they may attempt to gain control of all of life’s circumstances, including those that are beyond anyone’s control. Control can be applied to emotions, behaviors, or events. A driver struck by a vehicle may think “I can’t control other drivers, so I have no power to control my safety while driving,” and hence give up driving. While there are things that are beyond our control, this extreme thought ignores things that we can control, such as wearing seatbelts or having the vehicle’s brakes regularly serviced.
Evidence-based cognitive-behavioral therapies for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may employ cognitive restructuring. This psychotherapeutic technique entails recognizing and correcting maladaptive, inaccurate thoughts that perpetuate illness.1 For example, a clinician helps a patient recognize that the negative thought “Nobody loves me” following a romantic breakup is an overgeneralization. The patient is taught to self-correct this to “While my ex-girlfriend doesn’t love me, others do. It only feels like nobody loves me.”2
We introduce the acronym I STEP to help clinicians recognize several common distorted thoughts in PTSD. These tend to occur within stereotyped themes in PTSD,3 as outlined and illustrated below. Recognizing distorted thoughts in these patients will help clinicians understand and address psychological distress following trauma.
Intimacy/In-touch. Intimacy involves comfort in relationships, including but not limited to sexual intimacy. This requires being in touch emotionally with self and others. In trauma involving loss, fear of further loss may impair intimacy with others. Difficulty with self-intimacy impairs commitment to life’s goals and prompts unhelpful avoidance behaviors, such as difficulty being alone or self-injurious use of drugs or alcohol. Comfort in spending some portion of time alone with one’s thoughts and emotions is a life skill necessary to attain optimum function. Patients who are unable to tolerate their own emotions without constant company might have excessive anxiety when social supports are otherwise occupied. Such patients might seek excessive and repeated reassurance rather than learning to tolerate their own emotions and thoughts. They would then find it difficult to engage successfully in solo activities.
Safety. After trauma, patients may view themselves and others as unsafe, and may overestimate risk. For example, a pedestrian who is struck by a vehicle may believe that crossing a street will again result in getting hit by a car without appreciating that people frequently cross streets without injury or that crossing cautiously is an essential life skill. Parents who have suffered from trauma may unduly believe that their children are in danger when engaging in an activity generally considered to be safe. This may create challenges in parenting and impede their children’s ability to develop a sense of independence.
Trust. Trauma victims may unfairly blame themselves, leading them to mistrust their own judgment. Such patients may have difficulty making decisions confidently and independently, such as choosing a job or a romantic partner. When traumatized by another person or people, it can be difficult to maintain positive views of others or to accept others’ positive behaviors as genuine. For example, a common reaction following rape may be a generalized mistrust of all men.
Esteem. Patients’ self-esteem may suffer following trauma due to irrational self-blame or believing the “just world hypothesis”—the idea that bad things only happen to bad people. For example, a patient who suffers an assault by an acquaintance might think “I must be stupid if I couldn’t figure out that my friend was dangerous.”
Power. Traumatic events usually occur outside of one’s control. Survivors of trauma may lose confidence in their ability to control any aspect of their lives. Conversely, they may attempt to gain control of all of life’s circumstances, including those that are beyond anyone’s control. Control can be applied to emotions, behaviors, or events. A driver struck by a vehicle may think “I can’t control other drivers, so I have no power to control my safety while driving,” and hence give up driving. While there are things that are beyond our control, this extreme thought ignores things that we can control, such as wearing seatbelts or having the vehicle’s brakes regularly serviced.
1. Wenzel A. Basic strategies of cognitive behavioral therapy. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2017;40(4):597-609.
2. Beck J. Cognitive behavioral therapy: basics and beyond. 2nd ed. The Guilford Press; 2011.
3. Resick PA, Monson CM, Chard KM. Cognitive processing therapy for PTSD. A comprehensive manual. The Guilford Press; 2017.
1. Wenzel A. Basic strategies of cognitive behavioral therapy. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2017;40(4):597-609.
2. Beck J. Cognitive behavioral therapy: basics and beyond. 2nd ed. The Guilford Press; 2011.
3. Resick PA, Monson CM, Chard KM. Cognitive processing therapy for PTSD. A comprehensive manual. The Guilford Press; 2017.
Managing a COVID-19–positive psychiatric patient on a medical unit
With the COVID-19 pandemic turning the world on its head, we have seen more first-episode psychotic breaks and quick deterioration in previously stable patients. Early in the pandemic, care was particularly complicated for psychiatric patients who had been infected with the virus. Many of these patients required immediate psychiatric hospitalization. At that time, many community hospital psychiatric inpatient units did not have the capacity, staffing, or infrastructure to safely admit such patients, so they needed to be managed on a medical unit. Here, I discuss the case of a COVID-19–positive woman with psychiatric illness who we managed while she was in quarantine on a medical unit.
Case report
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, Ms. B, a 35-year-old teacher with a history of depression, was evaluated in the emergency department for bizarre behavior and paranoid delusions regarding her family. Initial laboratory and imaging testing was negative for any potential medical causes of her psychiatric symptoms. Psychiatric hospitalization was recommended, but before Ms. B could be transferred to the psychiatric unit, she tested positive for COVID-19. At that time, our community hospital did not have a designated wing on our psychiatric unit for patients infected with COVID-19. Thus, Ms. B was admitted to the medical floor, where she was quarantined in her room. She would need to remain asymptomatic and test negative for COVID-19 before she could be transferred to the psychiatric unit.
Upon arriving at the medical unit, Ms. B was hostile and uncooperative. She frequently attempted to leave her room and required restraints throughout the day. Our consultation-liaison (CL) team was consulted to assist in managing her. During the initial interview, we noticed that she had covered all 4 walls of her room with papers filled with handwritten notes. Ms. B had cut her gown to expose her stomach and legs. She had pressured speech, tangential thinking, and was religiously preoccupied. She denied any visual and auditory hallucinations, but her persecutory delusions involving her family persisted. We believed that her signs and symptoms were consistent with a manic episode from underlying, and likely undiagnosed, bipolar I disorder that was precipitated by her COVID-19 infection.
We first addressed Ms. B’s and the staff’s safety by transferring her to a larger room with a vestibule at the end of the hallway so she had more room to walk and minimal exposure to the stimuli of the medical unit. We initiated one-on-one observation to redirect her and prevent elopement. We incentivized her cooperation with staff by providing her with paper, pencils, reading material, and phone privileges. We started oral risperidone 2 mg twice daily and lorazepam 2 mg 3 times daily for short-term behavioral control and acute treatment of her symptoms, with the goal of deferring additional treatment decisions to the inpatient psychiatry team after she was transferred to the psychiatric unit. Ms. B’s agitation and impulsivity improved. She began participating with the medical team and was eventually transferred out of our medical unit to a psychiatric unit at a different facility.
COVID-19 and psychiatric illness: Clinical concerns
While infection from COVID-19 and widespread social distancing of the general population have been linked to depression and anxiety, manic and psychotic symptoms secondary to the COVID-19 pandemic have not been well described. The association between influenza infection and psychosis has been reported since the Spanish Flu pandemic,1 but there is limited data on the association between COVID-19 and psychosis. A review of 14 studies found that 0.9% to 4% of people exposed to a virus during an epidemic or pandemic develop psychosis or psychotic symptoms.1 Psychosis was associated with viral exposure, treatments used to manage the infection (steroid therapy), and psychosocial stress. This study also found that treatment with low doses of antipsychotic medication—notably aripiprazole—seemed to have been effective.1
Nonetheless, it is important to keep in mind a thorough differential diagnosis and rule out any potential organic etiologies in a COVID-19–positive patient who presents with psychiatric symptoms.2 For Ms. B, we began by ruling out drug-induced psychosis and electrolyte imbalance, and obtained brain imaging to rule out malignancy. We considered an interictal behavior syndrome of temporal lobe epilepsy, a neuropsychiatric disorder characterized by alterations in sexual behavior, religiosity, and extensive and compulsive writing and drawing.3 Neurology was consulted to evaluate the patient and possibly use EEG to detect interictal spikes, a tall task given the patient’s restlessness and paranoia. Ultimately, we determined the patient was most likely exhibiting symptoms of previously undetected bipolar disorder.
Managing patients with psychiatric illness on a medical floor during a pandemic such as COVID-19 requires the psychiatrist to truly serve as a consultant and liaison between the patient and the treatment team.4 Clinical management should address both infection control and psychiatric symptoms.5 We visited with Ms. B frequently, provided psychoeducation, engaged her in treatment, and updated her on the treatment plan.
As the medical world continues to adjust to treating patients during the pandemic, CL psychiatrists may be tasked with managing patients with acute psychiatric illness on the medical unit while they await transfer to a psychiatric unit. A creative, multifaceted, and team-based approach is key to ensure effective care and safety for all involved.
1. Brown E, Gray R, Lo Monaco S, et al. The potential impact of COVID-19 on psychosis: a rapid review of contemporary epidemic and pandemic research. Schizophr Res. 2020;222:79-87. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2020.05.005
2. Byrne P. Managing the acute psychotic episode. BMJ. 2007;334(7595):686-692. doi:10.1136/bmj.39148.668160.80
3. Waxman SG, Geschwind N. The interictal behavior syndrome of temporal lobe epilepsy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1975;32(12):1580-1586. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1975.01760300118011
4. Stern TA, Freudenreich O, Smith FA, et al. Psychotic patients. In: Massachusetts General Hospital: Handbook of General Hospital Psychiatry. Mosby; 1997:109-121.
5. Deshpande S, Livingstone A. First-onset psychosis in older adults: social isolation influence during COVID pandemic—a UK case series. Progress in Neurology and Psychiatry. 2021;25(1):14-18. doi:10.1002/pnp.692
With the COVID-19 pandemic turning the world on its head, we have seen more first-episode psychotic breaks and quick deterioration in previously stable patients. Early in the pandemic, care was particularly complicated for psychiatric patients who had been infected with the virus. Many of these patients required immediate psychiatric hospitalization. At that time, many community hospital psychiatric inpatient units did not have the capacity, staffing, or infrastructure to safely admit such patients, so they needed to be managed on a medical unit. Here, I discuss the case of a COVID-19–positive woman with psychiatric illness who we managed while she was in quarantine on a medical unit.
Case report
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, Ms. B, a 35-year-old teacher with a history of depression, was evaluated in the emergency department for bizarre behavior and paranoid delusions regarding her family. Initial laboratory and imaging testing was negative for any potential medical causes of her psychiatric symptoms. Psychiatric hospitalization was recommended, but before Ms. B could be transferred to the psychiatric unit, she tested positive for COVID-19. At that time, our community hospital did not have a designated wing on our psychiatric unit for patients infected with COVID-19. Thus, Ms. B was admitted to the medical floor, where she was quarantined in her room. She would need to remain asymptomatic and test negative for COVID-19 before she could be transferred to the psychiatric unit.
Upon arriving at the medical unit, Ms. B was hostile and uncooperative. She frequently attempted to leave her room and required restraints throughout the day. Our consultation-liaison (CL) team was consulted to assist in managing her. During the initial interview, we noticed that she had covered all 4 walls of her room with papers filled with handwritten notes. Ms. B had cut her gown to expose her stomach and legs. She had pressured speech, tangential thinking, and was religiously preoccupied. She denied any visual and auditory hallucinations, but her persecutory delusions involving her family persisted. We believed that her signs and symptoms were consistent with a manic episode from underlying, and likely undiagnosed, bipolar I disorder that was precipitated by her COVID-19 infection.
We first addressed Ms. B’s and the staff’s safety by transferring her to a larger room with a vestibule at the end of the hallway so she had more room to walk and minimal exposure to the stimuli of the medical unit. We initiated one-on-one observation to redirect her and prevent elopement. We incentivized her cooperation with staff by providing her with paper, pencils, reading material, and phone privileges. We started oral risperidone 2 mg twice daily and lorazepam 2 mg 3 times daily for short-term behavioral control and acute treatment of her symptoms, with the goal of deferring additional treatment decisions to the inpatient psychiatry team after she was transferred to the psychiatric unit. Ms. B’s agitation and impulsivity improved. She began participating with the medical team and was eventually transferred out of our medical unit to a psychiatric unit at a different facility.
COVID-19 and psychiatric illness: Clinical concerns
While infection from COVID-19 and widespread social distancing of the general population have been linked to depression and anxiety, manic and psychotic symptoms secondary to the COVID-19 pandemic have not been well described. The association between influenza infection and psychosis has been reported since the Spanish Flu pandemic,1 but there is limited data on the association between COVID-19 and psychosis. A review of 14 studies found that 0.9% to 4% of people exposed to a virus during an epidemic or pandemic develop psychosis or psychotic symptoms.1 Psychosis was associated with viral exposure, treatments used to manage the infection (steroid therapy), and psychosocial stress. This study also found that treatment with low doses of antipsychotic medication—notably aripiprazole—seemed to have been effective.1
Nonetheless, it is important to keep in mind a thorough differential diagnosis and rule out any potential organic etiologies in a COVID-19–positive patient who presents with psychiatric symptoms.2 For Ms. B, we began by ruling out drug-induced psychosis and electrolyte imbalance, and obtained brain imaging to rule out malignancy. We considered an interictal behavior syndrome of temporal lobe epilepsy, a neuropsychiatric disorder characterized by alterations in sexual behavior, religiosity, and extensive and compulsive writing and drawing.3 Neurology was consulted to evaluate the patient and possibly use EEG to detect interictal spikes, a tall task given the patient’s restlessness and paranoia. Ultimately, we determined the patient was most likely exhibiting symptoms of previously undetected bipolar disorder.
Managing patients with psychiatric illness on a medical floor during a pandemic such as COVID-19 requires the psychiatrist to truly serve as a consultant and liaison between the patient and the treatment team.4 Clinical management should address both infection control and psychiatric symptoms.5 We visited with Ms. B frequently, provided psychoeducation, engaged her in treatment, and updated her on the treatment plan.
As the medical world continues to adjust to treating patients during the pandemic, CL psychiatrists may be tasked with managing patients with acute psychiatric illness on the medical unit while they await transfer to a psychiatric unit. A creative, multifaceted, and team-based approach is key to ensure effective care and safety for all involved.
With the COVID-19 pandemic turning the world on its head, we have seen more first-episode psychotic breaks and quick deterioration in previously stable patients. Early in the pandemic, care was particularly complicated for psychiatric patients who had been infected with the virus. Many of these patients required immediate psychiatric hospitalization. At that time, many community hospital psychiatric inpatient units did not have the capacity, staffing, or infrastructure to safely admit such patients, so they needed to be managed on a medical unit. Here, I discuss the case of a COVID-19–positive woman with psychiatric illness who we managed while she was in quarantine on a medical unit.
Case report
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, Ms. B, a 35-year-old teacher with a history of depression, was evaluated in the emergency department for bizarre behavior and paranoid delusions regarding her family. Initial laboratory and imaging testing was negative for any potential medical causes of her psychiatric symptoms. Psychiatric hospitalization was recommended, but before Ms. B could be transferred to the psychiatric unit, she tested positive for COVID-19. At that time, our community hospital did not have a designated wing on our psychiatric unit for patients infected with COVID-19. Thus, Ms. B was admitted to the medical floor, where she was quarantined in her room. She would need to remain asymptomatic and test negative for COVID-19 before she could be transferred to the psychiatric unit.
Upon arriving at the medical unit, Ms. B was hostile and uncooperative. She frequently attempted to leave her room and required restraints throughout the day. Our consultation-liaison (CL) team was consulted to assist in managing her. During the initial interview, we noticed that she had covered all 4 walls of her room with papers filled with handwritten notes. Ms. B had cut her gown to expose her stomach and legs. She had pressured speech, tangential thinking, and was religiously preoccupied. She denied any visual and auditory hallucinations, but her persecutory delusions involving her family persisted. We believed that her signs and symptoms were consistent with a manic episode from underlying, and likely undiagnosed, bipolar I disorder that was precipitated by her COVID-19 infection.
We first addressed Ms. B’s and the staff’s safety by transferring her to a larger room with a vestibule at the end of the hallway so she had more room to walk and minimal exposure to the stimuli of the medical unit. We initiated one-on-one observation to redirect her and prevent elopement. We incentivized her cooperation with staff by providing her with paper, pencils, reading material, and phone privileges. We started oral risperidone 2 mg twice daily and lorazepam 2 mg 3 times daily for short-term behavioral control and acute treatment of her symptoms, with the goal of deferring additional treatment decisions to the inpatient psychiatry team after she was transferred to the psychiatric unit. Ms. B’s agitation and impulsivity improved. She began participating with the medical team and was eventually transferred out of our medical unit to a psychiatric unit at a different facility.
COVID-19 and psychiatric illness: Clinical concerns
While infection from COVID-19 and widespread social distancing of the general population have been linked to depression and anxiety, manic and psychotic symptoms secondary to the COVID-19 pandemic have not been well described. The association between influenza infection and psychosis has been reported since the Spanish Flu pandemic,1 but there is limited data on the association between COVID-19 and psychosis. A review of 14 studies found that 0.9% to 4% of people exposed to a virus during an epidemic or pandemic develop psychosis or psychotic symptoms.1 Psychosis was associated with viral exposure, treatments used to manage the infection (steroid therapy), and psychosocial stress. This study also found that treatment with low doses of antipsychotic medication—notably aripiprazole—seemed to have been effective.1
Nonetheless, it is important to keep in mind a thorough differential diagnosis and rule out any potential organic etiologies in a COVID-19–positive patient who presents with psychiatric symptoms.2 For Ms. B, we began by ruling out drug-induced psychosis and electrolyte imbalance, and obtained brain imaging to rule out malignancy. We considered an interictal behavior syndrome of temporal lobe epilepsy, a neuropsychiatric disorder characterized by alterations in sexual behavior, religiosity, and extensive and compulsive writing and drawing.3 Neurology was consulted to evaluate the patient and possibly use EEG to detect interictal spikes, a tall task given the patient’s restlessness and paranoia. Ultimately, we determined the patient was most likely exhibiting symptoms of previously undetected bipolar disorder.
Managing patients with psychiatric illness on a medical floor during a pandemic such as COVID-19 requires the psychiatrist to truly serve as a consultant and liaison between the patient and the treatment team.4 Clinical management should address both infection control and psychiatric symptoms.5 We visited with Ms. B frequently, provided psychoeducation, engaged her in treatment, and updated her on the treatment plan.
As the medical world continues to adjust to treating patients during the pandemic, CL psychiatrists may be tasked with managing patients with acute psychiatric illness on the medical unit while they await transfer to a psychiatric unit. A creative, multifaceted, and team-based approach is key to ensure effective care and safety for all involved.
1. Brown E, Gray R, Lo Monaco S, et al. The potential impact of COVID-19 on psychosis: a rapid review of contemporary epidemic and pandemic research. Schizophr Res. 2020;222:79-87. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2020.05.005
2. Byrne P. Managing the acute psychotic episode. BMJ. 2007;334(7595):686-692. doi:10.1136/bmj.39148.668160.80
3. Waxman SG, Geschwind N. The interictal behavior syndrome of temporal lobe epilepsy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1975;32(12):1580-1586. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1975.01760300118011
4. Stern TA, Freudenreich O, Smith FA, et al. Psychotic patients. In: Massachusetts General Hospital: Handbook of General Hospital Psychiatry. Mosby; 1997:109-121.
5. Deshpande S, Livingstone A. First-onset psychosis in older adults: social isolation influence during COVID pandemic—a UK case series. Progress in Neurology and Psychiatry. 2021;25(1):14-18. doi:10.1002/pnp.692
1. Brown E, Gray R, Lo Monaco S, et al. The potential impact of COVID-19 on psychosis: a rapid review of contemporary epidemic and pandemic research. Schizophr Res. 2020;222:79-87. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2020.05.005
2. Byrne P. Managing the acute psychotic episode. BMJ. 2007;334(7595):686-692. doi:10.1136/bmj.39148.668160.80
3. Waxman SG, Geschwind N. The interictal behavior syndrome of temporal lobe epilepsy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1975;32(12):1580-1586. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1975.01760300118011
4. Stern TA, Freudenreich O, Smith FA, et al. Psychotic patients. In: Massachusetts General Hospital: Handbook of General Hospital Psychiatry. Mosby; 1997:109-121.
5. Deshpande S, Livingstone A. First-onset psychosis in older adults: social isolation influence during COVID pandemic—a UK case series. Progress in Neurology and Psychiatry. 2021;25(1):14-18. doi:10.1002/pnp.692
USPSTF issues draft guidance on statins for primary CVD prevention
On February 22, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) posted draft recommendations on the use of statins as a method of primary prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD).1 This is an update to their 2016 recommendations and reaffirms the guidance published at that time.
What’s recommended. The recommendations have 3 parts and are intended for adults with no evidence or previous diagnosis of CVD.
- Statins should be prescribed for those who meet 3 criteria: (1) are ages 40 through 75 years; (2) have 1 or more CVD risk factors (high blood pressure, dyslipidemia, diabetes, tobacco use); and (3) have a calculated 10-year risk of a CVD event of 10% or greater. (The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association ASCVD Risk Calculator, recommended by the USPSTF, can be found at www.cvriskcalculator.com/.) This is a “B” recommendation.1
- Selectively offer a statin, based on a discussion of benefits and risks and patient preferences, to those who meet criteria 1 and 2 above but who have a calculated CVD risk of 7.5% to 10%. This is a “C” recommendation.1
- For those ages 76 years and older, there is insufficient evidence to assess benefits and harms of statin use. The USPSTF therefore issued an “I” statement for this group.1
What to prescribe. The USPSTF feels that moderate-intensity statin therapy is a reasonable approach for most people who use statins for primary CVD prevention. This would equate to atorvastatin 10 mg, pravastatin 40 mg, or simvastatin 20 to 40 mg daily.1
A few notes on the evidence. Data from 22 studies were included in the evidence review upon which the recommendations are based. The mean duration of follow-up was 3 years. The number needed to treat to prevent 1 stroke was about 256; to prevent 1 myocardial infarction, 112; and to prevent all CVD events, 78.2
What others recommend. These recommendations are mostly consistent with those of the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association, except that those organizations recommend initiating statins in all those with a 10-year CVD risk ≥ 7.5%.1
1. USPSTF. Statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: preventive medication. Published February 22, 2022. Accessed March 18, 2022. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/draft-recommendation/statin-use-primary-prevention-cardiovascular-disease-adults
2. Chou R, Cantor A, Dana T, et al. Statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: a systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Evidence Synthesis No. 219. AHRQ Publication No. 22-05291-EF-1. Published February 2022. Accessed March 18, 2022. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/document/draft-evidence-review/statin-use-primary-prevention-cardiovascular-disease-adults
On February 22, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) posted draft recommendations on the use of statins as a method of primary prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD).1 This is an update to their 2016 recommendations and reaffirms the guidance published at that time.
What’s recommended. The recommendations have 3 parts and are intended for adults with no evidence or previous diagnosis of CVD.
- Statins should be prescribed for those who meet 3 criteria: (1) are ages 40 through 75 years; (2) have 1 or more CVD risk factors (high blood pressure, dyslipidemia, diabetes, tobacco use); and (3) have a calculated 10-year risk of a CVD event of 10% or greater. (The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association ASCVD Risk Calculator, recommended by the USPSTF, can be found at www.cvriskcalculator.com/.) This is a “B” recommendation.1
- Selectively offer a statin, based on a discussion of benefits and risks and patient preferences, to those who meet criteria 1 and 2 above but who have a calculated CVD risk of 7.5% to 10%. This is a “C” recommendation.1
- For those ages 76 years and older, there is insufficient evidence to assess benefits and harms of statin use. The USPSTF therefore issued an “I” statement for this group.1
What to prescribe. The USPSTF feels that moderate-intensity statin therapy is a reasonable approach for most people who use statins for primary CVD prevention. This would equate to atorvastatin 10 mg, pravastatin 40 mg, or simvastatin 20 to 40 mg daily.1
A few notes on the evidence. Data from 22 studies were included in the evidence review upon which the recommendations are based. The mean duration of follow-up was 3 years. The number needed to treat to prevent 1 stroke was about 256; to prevent 1 myocardial infarction, 112; and to prevent all CVD events, 78.2
What others recommend. These recommendations are mostly consistent with those of the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association, except that those organizations recommend initiating statins in all those with a 10-year CVD risk ≥ 7.5%.1
On February 22, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) posted draft recommendations on the use of statins as a method of primary prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD).1 This is an update to their 2016 recommendations and reaffirms the guidance published at that time.
What’s recommended. The recommendations have 3 parts and are intended for adults with no evidence or previous diagnosis of CVD.
- Statins should be prescribed for those who meet 3 criteria: (1) are ages 40 through 75 years; (2) have 1 or more CVD risk factors (high blood pressure, dyslipidemia, diabetes, tobacco use); and (3) have a calculated 10-year risk of a CVD event of 10% or greater. (The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association ASCVD Risk Calculator, recommended by the USPSTF, can be found at www.cvriskcalculator.com/.) This is a “B” recommendation.1
- Selectively offer a statin, based on a discussion of benefits and risks and patient preferences, to those who meet criteria 1 and 2 above but who have a calculated CVD risk of 7.5% to 10%. This is a “C” recommendation.1
- For those ages 76 years and older, there is insufficient evidence to assess benefits and harms of statin use. The USPSTF therefore issued an “I” statement for this group.1
What to prescribe. The USPSTF feels that moderate-intensity statin therapy is a reasonable approach for most people who use statins for primary CVD prevention. This would equate to atorvastatin 10 mg, pravastatin 40 mg, or simvastatin 20 to 40 mg daily.1
A few notes on the evidence. Data from 22 studies were included in the evidence review upon which the recommendations are based. The mean duration of follow-up was 3 years. The number needed to treat to prevent 1 stroke was about 256; to prevent 1 myocardial infarction, 112; and to prevent all CVD events, 78.2
What others recommend. These recommendations are mostly consistent with those of the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association, except that those organizations recommend initiating statins in all those with a 10-year CVD risk ≥ 7.5%.1
1. USPSTF. Statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: preventive medication. Published February 22, 2022. Accessed March 18, 2022. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/draft-recommendation/statin-use-primary-prevention-cardiovascular-disease-adults
2. Chou R, Cantor A, Dana T, et al. Statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: a systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Evidence Synthesis No. 219. AHRQ Publication No. 22-05291-EF-1. Published February 2022. Accessed March 18, 2022. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/document/draft-evidence-review/statin-use-primary-prevention-cardiovascular-disease-adults
1. USPSTF. Statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: preventive medication. Published February 22, 2022. Accessed March 18, 2022. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/draft-recommendation/statin-use-primary-prevention-cardiovascular-disease-adults
2. Chou R, Cantor A, Dana T, et al. Statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: a systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Evidence Synthesis No. 219. AHRQ Publication No. 22-05291-EF-1. Published February 2022. Accessed March 18, 2022. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/document/draft-evidence-review/statin-use-primary-prevention-cardiovascular-disease-adults
Selecting Between CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Advanced HR+/HER2- Breast Cancer
Patients diagnosed with advanced hormone receptor–positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative (HER2-) breast cancer have significantly improved outcomes with the combination of a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor and endocrine therapy compared with endocrine therapy alone.
Dr Sara Hurvitz, director of the Breast Cancer Clinical Trials Program at UCLA, discusses the efficacy, tolerability, and patient quality-of-life factors to consider when deciding which of the three available CDK4/6 inhibitors — palbociclib, ribociclib, or abemaciclib — is appropriate for your patient in the frontline setting.
Reporting on data from the ongoing MONALEESA, MONARCH, and PALOMA trials, Dr Hurvitz spotlights the differences and similarities between agents that may help steer treatment decisions for pre- or perimenopausal patients
--
Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA; Medical Director, Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center Clinical Research Unit; Co-director, Santa Monica-UCLA Outpatient Oncology Practices; Director, Breast Cancer Clinical Trials Program, UCLA, Los Angeles, California
Sara A. Hurvitz, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Ambrx; Amgen; Arvinas; Bayer; BioMarin; Cascadian Therapeutics; Daiichi Sankyo; Dignitana; Genentech/Roche; Gilead Sciences; GlaxoSmithKline; Immunomedics; Lilly; MacroGenics; Merrimack; Novartis; OBI Pharma; Pfizer; Phoenix Molecular Designs; Pieris; Puma Biotechnology; Radius; Samumed; Sanofi; Seattle Genetics; Zymeworks
Has been reimbursed for travel, accommodations, or other expenses by Lilly
Patients diagnosed with advanced hormone receptor–positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative (HER2-) breast cancer have significantly improved outcomes with the combination of a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor and endocrine therapy compared with endocrine therapy alone.
Dr Sara Hurvitz, director of the Breast Cancer Clinical Trials Program at UCLA, discusses the efficacy, tolerability, and patient quality-of-life factors to consider when deciding which of the three available CDK4/6 inhibitors — palbociclib, ribociclib, or abemaciclib — is appropriate for your patient in the frontline setting.
Reporting on data from the ongoing MONALEESA, MONARCH, and PALOMA trials, Dr Hurvitz spotlights the differences and similarities between agents that may help steer treatment decisions for pre- or perimenopausal patients
--
Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA; Medical Director, Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center Clinical Research Unit; Co-director, Santa Monica-UCLA Outpatient Oncology Practices; Director, Breast Cancer Clinical Trials Program, UCLA, Los Angeles, California
Sara A. Hurvitz, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Ambrx; Amgen; Arvinas; Bayer; BioMarin; Cascadian Therapeutics; Daiichi Sankyo; Dignitana; Genentech/Roche; Gilead Sciences; GlaxoSmithKline; Immunomedics; Lilly; MacroGenics; Merrimack; Novartis; OBI Pharma; Pfizer; Phoenix Molecular Designs; Pieris; Puma Biotechnology; Radius; Samumed; Sanofi; Seattle Genetics; Zymeworks
Has been reimbursed for travel, accommodations, or other expenses by Lilly
Patients diagnosed with advanced hormone receptor–positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative (HER2-) breast cancer have significantly improved outcomes with the combination of a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor and endocrine therapy compared with endocrine therapy alone.
Dr Sara Hurvitz, director of the Breast Cancer Clinical Trials Program at UCLA, discusses the efficacy, tolerability, and patient quality-of-life factors to consider when deciding which of the three available CDK4/6 inhibitors — palbociclib, ribociclib, or abemaciclib — is appropriate for your patient in the frontline setting.
Reporting on data from the ongoing MONALEESA, MONARCH, and PALOMA trials, Dr Hurvitz spotlights the differences and similarities between agents that may help steer treatment decisions for pre- or perimenopausal patients
--
Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA; Medical Director, Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center Clinical Research Unit; Co-director, Santa Monica-UCLA Outpatient Oncology Practices; Director, Breast Cancer Clinical Trials Program, UCLA, Los Angeles, California
Sara A. Hurvitz, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Ambrx; Amgen; Arvinas; Bayer; BioMarin; Cascadian Therapeutics; Daiichi Sankyo; Dignitana; Genentech/Roche; Gilead Sciences; GlaxoSmithKline; Immunomedics; Lilly; MacroGenics; Merrimack; Novartis; OBI Pharma; Pfizer; Phoenix Molecular Designs; Pieris; Puma Biotechnology; Radius; Samumed; Sanofi; Seattle Genetics; Zymeworks
Has been reimbursed for travel, accommodations, or other expenses by Lilly

Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency: Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
What is your approach to differentiating EPI from other pancreatic conditions when making a diagnosis?
Dr. Kothari: Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, or EPI, is a condition largely defined by malabsorption as the result of inadequate digestive enzymes. The resulting symptoms from maldigestion include bloating, malodorous gas, abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, and weight change. EPI can be caused by intrinsic pancreatic disorders (such as chronic pancreatitis, acute pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis or pancreatic cancer) or from extra-pancreatic diseases (including the result of gastrointestinal surgery). Thus, EPI should be considered a consequence of an already existing gastrointestinal disorder.
Can you a speak a little bit more about the signs and symptoms or characteristics that are most common in patients with EPI?
Dr. Kothari: The symptoms of EPI can range from bloating and abdominal pain with mild to overt steatorrhea with greasy and oily stools that are difficult to flush with malodorous flatulence, weight loss, and symptoms of vitamin and micronutrient deficiency. The pathophysiology of these symptoms results from inadequate enzymes which are needed for digestion. Particularly, lipase is the major enzyme needed for fat digestion and thus when not present leads to fat maldigestion resulting in symptoms. Furthermore, undigested fats result in alterations in gut motility which can further exacerbate symptoms to include nausea, vomiting, early satiety and inadequate stool evacuation.
Patients who have fat malabsorption, particularly for pancreatic insufficiency, can also have malnutrition as a result of inadequate absorption of nutrients and micronutrients. Particularly, we think about fat-soluble vitamins-- vitamin A, vitamin E, vitamin D, and vitamin K and in the initial evaluation of patients with established EPI, one could consider evaluation of comorbid bone disease.
How crucial is having the correct interpretation of the clinical presentation to pinpointing the diagnosis?
Dr. Kothari: This is a great question because, with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency as there is growing publicity for the disorder and because symptoms can be rather non-specific when mild, it is important to be informed on how best to make this diagnosis. Thus, it is important to review the predisposing conditions that may lead to the diagnosis of EPI. These conditions include cystic fibrosis, chronic pancreatitis, acute pancreatitis, previous pancreatic surgery, history of pancreatic cancer (or suspicion for new pancreatic cancer), history of diabetes, celiac disease, history of luminal surgeries (including bariatric surgery), and inflammatory bowel disease. Further, since EPI can be a result of intrinsic pancreatic pathologies, it is critical to consider the risk factors for chronic pancreatitis which include alcohol and tobacco ingestion, prior episodes of recurrent acute pancreatitis, genetic conditions that may predispose patients to chronic pancreatitis, including cystic fibrosis, and hereditary conditions that also result in pancreatitis. As clinicians, it is our role to obtain an accurate history to best gauge the risk factors for EPI.
After reviewing risk factors, we then must review the clinical presentation to know if the symptoms could be from EPI which include bloating, gas, abdominal pain, weight changes, changes in bowel habits and consequences of vitamin deficiencies. Since the symptoms of mild EPI can be similar to other GI conditions such as SIBO, celiac disease, and functional bowel disorders, gauging whether a patient has risk factors for EPI will help the clinician understand how likely a diagnosis of EPI may be and if and what testing would be appropriate.
In my practice, I consider diagnostic testing in patients who may be at risk for EPI and have mild symptoms such malodorous gas, bloating and mild steatorrhea. For patient with clear evidence of steatorrhea (weight loss and vitamin deficiencies) and have strong risk factors for EPI (i.e. heavy alcohol and tobacco and/or a history of recurrent or severe acute pancreatitis), I might consider imaging and/or empiric therapies as to expedite care.
How difficult is it to diagnose EPI and what steps do you take to ensure that you prescribe patients with the proper therapy?
Dr. Kothari: The diagnosis of pancreatic insufficiency, in my mind, needs to start with assessing the pre-test probability of the patient having EPI, since testing could lead to a false positive.
The test of choice in most scenarios for diagnosing pancreatic insufficiency is a stool test known as the fecal elastase. It is a measurement of pancreatic elastase in the stool. The test itself is a concentration. For any condition that results in a dilute stool sample, that'll result in a falsely low value that can give a patient a false positive test. Now, this can be corrected by the lab concentrating the stool sample before running the test, but that testing center needs to know how to do that.
The other assumption that we make with this stool test is that we assume that the elastase is a stable molecule that can traverse all the gut and be collected adequately. And for any reason, if that enzyme is degraded for any reason, it's also going to provide a low test, a low result, resulting in a false positive.
If they have risk factors for chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic disease and they're presenting with symptoms of EPI, then the usual test that I'll choose is dedicated pancreatic imaging such as an MRI or dedicated CT pancreatic imaging, or endoscopic ultrasound. If we clinch a diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis and they have symptoms of pancreatic insufficiency, I think that’s enough to presume a diagnosis of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and start treatment.
On the other hand, in patients who do not have risk factors for pancreatic disease but there remains some clinical suspicion for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, then it may be reasonable to check a fecal elastase to rule out pancreatic insufficiency. If the test results are low, then follow-up dedicated pancreas imaging would be the next step in delineating intrinsic pancreatic conditions form extra-pancreatic causes. If pancreas imaging effectively rules out pancreatic disease then I consider checking for celiac disease, ruling out small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and considering assessment of luminal motility (either with a capsule or small bowel follow through). Although functional neuroendocrine tumors have been previously considered a cause of EPI, these tumors tend to present with secretory diarrhea which typically present differently (and often more dramatically) than other causes of EPI. Thus, I do not routinely check vasoactive hormone levels.
I think the American Gastroenterological Association has great patient education documents for our patients. Thus, I would encourage our colleagues to use the AGA for their resources for our patients on EPI.
What is your approach to differentiating EPI from other pancreatic conditions when making a diagnosis?
Dr. Kothari: Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, or EPI, is a condition largely defined by malabsorption as the result of inadequate digestive enzymes. The resulting symptoms from maldigestion include bloating, malodorous gas, abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, and weight change. EPI can be caused by intrinsic pancreatic disorders (such as chronic pancreatitis, acute pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis or pancreatic cancer) or from extra-pancreatic diseases (including the result of gastrointestinal surgery). Thus, EPI should be considered a consequence of an already existing gastrointestinal disorder.
Can you a speak a little bit more about the signs and symptoms or characteristics that are most common in patients with EPI?
Dr. Kothari: The symptoms of EPI can range from bloating and abdominal pain with mild to overt steatorrhea with greasy and oily stools that are difficult to flush with malodorous flatulence, weight loss, and symptoms of vitamin and micronutrient deficiency. The pathophysiology of these symptoms results from inadequate enzymes which are needed for digestion. Particularly, lipase is the major enzyme needed for fat digestion and thus when not present leads to fat maldigestion resulting in symptoms. Furthermore, undigested fats result in alterations in gut motility which can further exacerbate symptoms to include nausea, vomiting, early satiety and inadequate stool evacuation.
Patients who have fat malabsorption, particularly for pancreatic insufficiency, can also have malnutrition as a result of inadequate absorption of nutrients and micronutrients. Particularly, we think about fat-soluble vitamins-- vitamin A, vitamin E, vitamin D, and vitamin K and in the initial evaluation of patients with established EPI, one could consider evaluation of comorbid bone disease.
How crucial is having the correct interpretation of the clinical presentation to pinpointing the diagnosis?
Dr. Kothari: This is a great question because, with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency as there is growing publicity for the disorder and because symptoms can be rather non-specific when mild, it is important to be informed on how best to make this diagnosis. Thus, it is important to review the predisposing conditions that may lead to the diagnosis of EPI. These conditions include cystic fibrosis, chronic pancreatitis, acute pancreatitis, previous pancreatic surgery, history of pancreatic cancer (or suspicion for new pancreatic cancer), history of diabetes, celiac disease, history of luminal surgeries (including bariatric surgery), and inflammatory bowel disease. Further, since EPI can be a result of intrinsic pancreatic pathologies, it is critical to consider the risk factors for chronic pancreatitis which include alcohol and tobacco ingestion, prior episodes of recurrent acute pancreatitis, genetic conditions that may predispose patients to chronic pancreatitis, including cystic fibrosis, and hereditary conditions that also result in pancreatitis. As clinicians, it is our role to obtain an accurate history to best gauge the risk factors for EPI.
After reviewing risk factors, we then must review the clinical presentation to know if the symptoms could be from EPI which include bloating, gas, abdominal pain, weight changes, changes in bowel habits and consequences of vitamin deficiencies. Since the symptoms of mild EPI can be similar to other GI conditions such as SIBO, celiac disease, and functional bowel disorders, gauging whether a patient has risk factors for EPI will help the clinician understand how likely a diagnosis of EPI may be and if and what testing would be appropriate.
In my practice, I consider diagnostic testing in patients who may be at risk for EPI and have mild symptoms such malodorous gas, bloating and mild steatorrhea. For patient with clear evidence of steatorrhea (weight loss and vitamin deficiencies) and have strong risk factors for EPI (i.e. heavy alcohol and tobacco and/or a history of recurrent or severe acute pancreatitis), I might consider imaging and/or empiric therapies as to expedite care.
How difficult is it to diagnose EPI and what steps do you take to ensure that you prescribe patients with the proper therapy?
Dr. Kothari: The diagnosis of pancreatic insufficiency, in my mind, needs to start with assessing the pre-test probability of the patient having EPI, since testing could lead to a false positive.
The test of choice in most scenarios for diagnosing pancreatic insufficiency is a stool test known as the fecal elastase. It is a measurement of pancreatic elastase in the stool. The test itself is a concentration. For any condition that results in a dilute stool sample, that'll result in a falsely low value that can give a patient a false positive test. Now, this can be corrected by the lab concentrating the stool sample before running the test, but that testing center needs to know how to do that.
The other assumption that we make with this stool test is that we assume that the elastase is a stable molecule that can traverse all the gut and be collected adequately. And for any reason, if that enzyme is degraded for any reason, it's also going to provide a low test, a low result, resulting in a false positive.
If they have risk factors for chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic disease and they're presenting with symptoms of EPI, then the usual test that I'll choose is dedicated pancreatic imaging such as an MRI or dedicated CT pancreatic imaging, or endoscopic ultrasound. If we clinch a diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis and they have symptoms of pancreatic insufficiency, I think that’s enough to presume a diagnosis of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and start treatment.
On the other hand, in patients who do not have risk factors for pancreatic disease but there remains some clinical suspicion for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, then it may be reasonable to check a fecal elastase to rule out pancreatic insufficiency. If the test results are low, then follow-up dedicated pancreas imaging would be the next step in delineating intrinsic pancreatic conditions form extra-pancreatic causes. If pancreas imaging effectively rules out pancreatic disease then I consider checking for celiac disease, ruling out small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and considering assessment of luminal motility (either with a capsule or small bowel follow through). Although functional neuroendocrine tumors have been previously considered a cause of EPI, these tumors tend to present with secretory diarrhea which typically present differently (and often more dramatically) than other causes of EPI. Thus, I do not routinely check vasoactive hormone levels.
I think the American Gastroenterological Association has great patient education documents for our patients. Thus, I would encourage our colleagues to use the AGA for their resources for our patients on EPI.
What is your approach to differentiating EPI from other pancreatic conditions when making a diagnosis?
Dr. Kothari: Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, or EPI, is a condition largely defined by malabsorption as the result of inadequate digestive enzymes. The resulting symptoms from maldigestion include bloating, malodorous gas, abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, and weight change. EPI can be caused by intrinsic pancreatic disorders (such as chronic pancreatitis, acute pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis or pancreatic cancer) or from extra-pancreatic diseases (including the result of gastrointestinal surgery). Thus, EPI should be considered a consequence of an already existing gastrointestinal disorder.
Can you a speak a little bit more about the signs and symptoms or characteristics that are most common in patients with EPI?
Dr. Kothari: The symptoms of EPI can range from bloating and abdominal pain with mild to overt steatorrhea with greasy and oily stools that are difficult to flush with malodorous flatulence, weight loss, and symptoms of vitamin and micronutrient deficiency. The pathophysiology of these symptoms results from inadequate enzymes which are needed for digestion. Particularly, lipase is the major enzyme needed for fat digestion and thus when not present leads to fat maldigestion resulting in symptoms. Furthermore, undigested fats result in alterations in gut motility which can further exacerbate symptoms to include nausea, vomiting, early satiety and inadequate stool evacuation.
Patients who have fat malabsorption, particularly for pancreatic insufficiency, can also have malnutrition as a result of inadequate absorption of nutrients and micronutrients. Particularly, we think about fat-soluble vitamins-- vitamin A, vitamin E, vitamin D, and vitamin K and in the initial evaluation of patients with established EPI, one could consider evaluation of comorbid bone disease.
How crucial is having the correct interpretation of the clinical presentation to pinpointing the diagnosis?
Dr. Kothari: This is a great question because, with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency as there is growing publicity for the disorder and because symptoms can be rather non-specific when mild, it is important to be informed on how best to make this diagnosis. Thus, it is important to review the predisposing conditions that may lead to the diagnosis of EPI. These conditions include cystic fibrosis, chronic pancreatitis, acute pancreatitis, previous pancreatic surgery, history of pancreatic cancer (or suspicion for new pancreatic cancer), history of diabetes, celiac disease, history of luminal surgeries (including bariatric surgery), and inflammatory bowel disease. Further, since EPI can be a result of intrinsic pancreatic pathologies, it is critical to consider the risk factors for chronic pancreatitis which include alcohol and tobacco ingestion, prior episodes of recurrent acute pancreatitis, genetic conditions that may predispose patients to chronic pancreatitis, including cystic fibrosis, and hereditary conditions that also result in pancreatitis. As clinicians, it is our role to obtain an accurate history to best gauge the risk factors for EPI.
After reviewing risk factors, we then must review the clinical presentation to know if the symptoms could be from EPI which include bloating, gas, abdominal pain, weight changes, changes in bowel habits and consequences of vitamin deficiencies. Since the symptoms of mild EPI can be similar to other GI conditions such as SIBO, celiac disease, and functional bowel disorders, gauging whether a patient has risk factors for EPI will help the clinician understand how likely a diagnosis of EPI may be and if and what testing would be appropriate.
In my practice, I consider diagnostic testing in patients who may be at risk for EPI and have mild symptoms such malodorous gas, bloating and mild steatorrhea. For patient with clear evidence of steatorrhea (weight loss and vitamin deficiencies) and have strong risk factors for EPI (i.e. heavy alcohol and tobacco and/or a history of recurrent or severe acute pancreatitis), I might consider imaging and/or empiric therapies as to expedite care.
How difficult is it to diagnose EPI and what steps do you take to ensure that you prescribe patients with the proper therapy?
Dr. Kothari: The diagnosis of pancreatic insufficiency, in my mind, needs to start with assessing the pre-test probability of the patient having EPI, since testing could lead to a false positive.
The test of choice in most scenarios for diagnosing pancreatic insufficiency is a stool test known as the fecal elastase. It is a measurement of pancreatic elastase in the stool. The test itself is a concentration. For any condition that results in a dilute stool sample, that'll result in a falsely low value that can give a patient a false positive test. Now, this can be corrected by the lab concentrating the stool sample before running the test, but that testing center needs to know how to do that.
The other assumption that we make with this stool test is that we assume that the elastase is a stable molecule that can traverse all the gut and be collected adequately. And for any reason, if that enzyme is degraded for any reason, it's also going to provide a low test, a low result, resulting in a false positive.
If they have risk factors for chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic disease and they're presenting with symptoms of EPI, then the usual test that I'll choose is dedicated pancreatic imaging such as an MRI or dedicated CT pancreatic imaging, or endoscopic ultrasound. If we clinch a diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis and they have symptoms of pancreatic insufficiency, I think that’s enough to presume a diagnosis of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and start treatment.
On the other hand, in patients who do not have risk factors for pancreatic disease but there remains some clinical suspicion for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, then it may be reasonable to check a fecal elastase to rule out pancreatic insufficiency. If the test results are low, then follow-up dedicated pancreas imaging would be the next step in delineating intrinsic pancreatic conditions form extra-pancreatic causes. If pancreas imaging effectively rules out pancreatic disease then I consider checking for celiac disease, ruling out small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and considering assessment of luminal motility (either with a capsule or small bowel follow through). Although functional neuroendocrine tumors have been previously considered a cause of EPI, these tumors tend to present with secretory diarrhea which typically present differently (and often more dramatically) than other causes of EPI. Thus, I do not routinely check vasoactive hormone levels.
I think the American Gastroenterological Association has great patient education documents for our patients. Thus, I would encourage our colleagues to use the AGA for their resources for our patients on EPI.
Question 2
Correct answer: B. Absence of ganglion cells on rectal biopsy.
Rationale
Hirschsprung's disease occurs in approximately 1 out of 5,000 live births and is caused by absence of ganglion cells in the myenteric plexus of the intestine. The condition arises from failure of the neural crest cells to fully migrate caudally along the intestine during early gestation, resulting in a distal portion of the intestine being aganglionic. Rectal and distal sigmoid involvement is seen in around 85% of cases, with the other 15 percent involving more proximal intestine. It can rarely involve the entire colon and small intestine. Ganglion cells inhibit local smooth muscles, resulting in the characteristic inability for aganglionic bowel to relax. This lack of inhibition gives rise to the absence of rectoanal inhibitory reflex (RAIRs) during anorectal manometry. The lack of inhibition also produces a transition zone on contrast enema, with the distal aganglionic bowel being narrow and the more proximal bowel containing ganglia being dilated. Lack of meconium passage in the first 48 hours of life raises concern for Hirschsprung's disease. Other causes for possible failure to pass meconium include cystic fibrosis, anorectal malformation, small left colon syndrome, meconium plug syndrome and megacystis-microcolon-intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome.
References
Kenny, S et al. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2010 Aug;19(3):194-200.
Wyllie R et al. Pediatric Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 4th edition. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, 2011.
Correct answer: B. Absence of ganglion cells on rectal biopsy.
Rationale
Hirschsprung's disease occurs in approximately 1 out of 5,000 live births and is caused by absence of ganglion cells in the myenteric plexus of the intestine. The condition arises from failure of the neural crest cells to fully migrate caudally along the intestine during early gestation, resulting in a distal portion of the intestine being aganglionic. Rectal and distal sigmoid involvement is seen in around 85% of cases, with the other 15 percent involving more proximal intestine. It can rarely involve the entire colon and small intestine. Ganglion cells inhibit local smooth muscles, resulting in the characteristic inability for aganglionic bowel to relax. This lack of inhibition gives rise to the absence of rectoanal inhibitory reflex (RAIRs) during anorectal manometry. The lack of inhibition also produces a transition zone on contrast enema, with the distal aganglionic bowel being narrow and the more proximal bowel containing ganglia being dilated. Lack of meconium passage in the first 48 hours of life raises concern for Hirschsprung's disease. Other causes for possible failure to pass meconium include cystic fibrosis, anorectal malformation, small left colon syndrome, meconium plug syndrome and megacystis-microcolon-intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome.
References
Kenny, S et al. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2010 Aug;19(3):194-200.
Wyllie R et al. Pediatric Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 4th edition. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, 2011.
Correct answer: B. Absence of ganglion cells on rectal biopsy.
Rationale
Hirschsprung's disease occurs in approximately 1 out of 5,000 live births and is caused by absence of ganglion cells in the myenteric plexus of the intestine. The condition arises from failure of the neural crest cells to fully migrate caudally along the intestine during early gestation, resulting in a distal portion of the intestine being aganglionic. Rectal and distal sigmoid involvement is seen in around 85% of cases, with the other 15 percent involving more proximal intestine. It can rarely involve the entire colon and small intestine. Ganglion cells inhibit local smooth muscles, resulting in the characteristic inability for aganglionic bowel to relax. This lack of inhibition gives rise to the absence of rectoanal inhibitory reflex (RAIRs) during anorectal manometry. The lack of inhibition also produces a transition zone on contrast enema, with the distal aganglionic bowel being narrow and the more proximal bowel containing ganglia being dilated. Lack of meconium passage in the first 48 hours of life raises concern for Hirschsprung's disease. Other causes for possible failure to pass meconium include cystic fibrosis, anorectal malformation, small left colon syndrome, meconium plug syndrome and megacystis-microcolon-intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome.
References
Kenny, S et al. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2010 Aug;19(3):194-200.
Wyllie R et al. Pediatric Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 4th edition. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, 2011.
A 2-month-old male presents with abdominal distention and poor appetite. His family notes that the patient has chronic difficulties with constipation, reporting that they have to use a glycerin suppository to help him have a bowel movement every 2-3 days. The family reports that he even needed a suppository in the newborn nursey at day of life 3 due to lack of passage of meconium.
Question 1
Correct answer: A. Amyloidosis involving the small intestine
Rationale
This patient has a protein-losing enteropathy as indicated by his diarrhea, peripheral edema, and positive stool alpha-1 antitrypsin test. Multiple diseases, particularly in their later stages, can be associated with a protein-losing enteropathy including primary intestinal lymphangectasia, Crohn's disease of the small intestine, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), and amyloidosis of the small intestine (A). Celiac disease (B) is not associated with protein-losing enteropathy. While Crohn's disease can be associated with protein-losing enteropathy, ulcerative colitis (C) is not usually associated with it. Small bowel dysmotility (D) does not impact absorption or secretion unless associated with SIBO, making this a wrong answer.
Correct answer: A. Amyloidosis involving the small intestine
Rationale
This patient has a protein-losing enteropathy as indicated by his diarrhea, peripheral edema, and positive stool alpha-1 antitrypsin test. Multiple diseases, particularly in their later stages, can be associated with a protein-losing enteropathy including primary intestinal lymphangectasia, Crohn's disease of the small intestine, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), and amyloidosis of the small intestine (A). Celiac disease (B) is not associated with protein-losing enteropathy. While Crohn's disease can be associated with protein-losing enteropathy, ulcerative colitis (C) is not usually associated with it. Small bowel dysmotility (D) does not impact absorption or secretion unless associated with SIBO, making this a wrong answer.
Correct answer: A. Amyloidosis involving the small intestine
Rationale
This patient has a protein-losing enteropathy as indicated by his diarrhea, peripheral edema, and positive stool alpha-1 antitrypsin test. Multiple diseases, particularly in their later stages, can be associated with a protein-losing enteropathy including primary intestinal lymphangectasia, Crohn's disease of the small intestine, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), and amyloidosis of the small intestine (A). Celiac disease (B) is not associated with protein-losing enteropathy. While Crohn's disease can be associated with protein-losing enteropathy, ulcerative colitis (C) is not usually associated with it. Small bowel dysmotility (D) does not impact absorption or secretion unless associated with SIBO, making this a wrong answer.
A 65-year-old male with no significant past medical history presents with significant diarrhea. He reports that for the past 3 months, he has had four to five bowel movements a day. He characterizes them as greasy and foul smelling, but not entirely watery. He notices no blood or mucous in the stool. Over the same time period, he has also noticed increased swelling in both of his ankles. The physician sends a broad work-up.
Stool testing results include the following:
Clostridioides difficile - Negative.
Stool Ova and Parasite - Negative.
Stool Culture - Negative.
Stool Elastase - within normal limits.
Fecal Fat (spot test) - within normal limits.
Stool Alpha-1 Antitrypsin - Elevated.
Verrucous Carcinoma of the Foot: A Retrospective Study of 19 Cases and Analysis of Prognostic Factors Influencing Recurrence
Verrucous carcinoma is a rare cancer with the greatest predilection for the foot. Multiple case reports with only a few large case series have been published. 1-3 Plantar verrucous carcinoma is characterized as a slowly but relentlessly enlarging warty tumor with low metastatic potential and high risk for local invasion. The tumor occurs most frequently in patients aged 60 to 70 years, predominantly in White males. 1 It often is misdiagnosed for years as an ulcer or wart that is highly resistant to therapy. Size typically ranges from 1 to 12 cm in greatest dimension. 1
The pathogenesis of plantar verrucous carcinoma remains unclear, but some contributing factors have been proposed, including trauma, chronic irritation, infection, and poor local hygiene.2 This tumor has been reported to occur in chronic foot ulcerations, particularly in the diabetic population.4 It has been proposed that abnormal expression of the p53 tumor suppressor protein and several types of human papillomavirus (HPV) may have a role in the pathogenesis of verrucous carcinoma.5
The pathologic hallmarks of this tumor include a verrucous/hyperkeratotic surface with a deeply endophytic, broad, pushing base. Tumor cells are well differentiated, and atypia is either absent or confined to 1 or 2 layers at the base of the tumor. Overt invasion at the base is lacking, except in cases with a component of conventional invasive squamous cell carcinoma. Human papillomavirus viropathic changes are classically absent.1,3 Studies of the histopathology of verrucous carcinoma have been complicated by similar entities, nomenclatural uncertainty, and variable diagnostic criteria. For example, epithelioma cuniculatum variously has been defined as being synonymous with verrucous carcinoma, a distinct clinical verrucous carcinoma subtype occurring on the soles, a histologic subtype (characterized by prominent burrowing sinuses), or a separate entity entirely.1,2,6,7 Furthermore, in the genital area, several different types of carcinomas have verruciform features but display distinct microscopic findings and outcomes from verrucous carcinoma.8
Verrucous carcinoma represents an unusual variant of squamous cell carcinoma and is treated as such. Treatments have included laser surgery; immunotherapy; retinoid therapy; and chemotherapy by oral, intralesional, or iontophoretic routes in select patients.9 Radiotherapy presents another option, though reports have described progression to aggressive squamous cell carcinoma in some cases.9 Surgery is the best course of treatment, and as more case reports have been published, a transition from radical resection to wide excision with tumor-free margins is the treatment of choice.2,3,10,11 To minimize soft-tissue deficits, Mohs micrographic surgery has been discussed as a treatment option for verrucous carcinoma.11-13
Few studies have described verrucous carcinoma recurrence, and none have systematically examined recurrence rate, risk factors, or prognosis
Methods
Patient cases were
Of the 19 cases, 16 were treated at the University of Michigan and are included in the treatment analyses. Specific attention was then paid to the cases with a clinical recurrence despite negative surgical margins. We compared the clinical and surgical differences between recurrent cases and nonrecurrent cases.
Pathology was rereviewed for selected cases, including 2 cases with recurrence and matched primary, 2 cases with recurrence (for which the matched primary was unavailable for review), and 5 representative primary cases that were not complicated by recurrence. Pathology review was conducted in a blinded manner by one of the authors (P.W.H) who is a board-certified dermatopathologist for approximate depth of invasion from the granular layer, perineural invasion, bone invasion, infiltrative growth, presence of conventional squamous cell carcinoma, and margin status.
Statistical analysis was performed when appropriate using an N1 χ2 test or Student t test.
Results
Demographics and Comorbidities—The median age of the patients at the time of diagnosis was 55 years (range, 34–77 years). There were 12 males and 7 females (Table 1). Two patients were Black and 17 were White. Almost all patients had additional comorbidities including tobacco use (68%), alcohol use (47%), and diabetes (47%). Only 1 patient had an autoimmune disease and was on chronic steroids. No significant difference was found between the demographics of patients with recurrent lesions and those without recurrence.
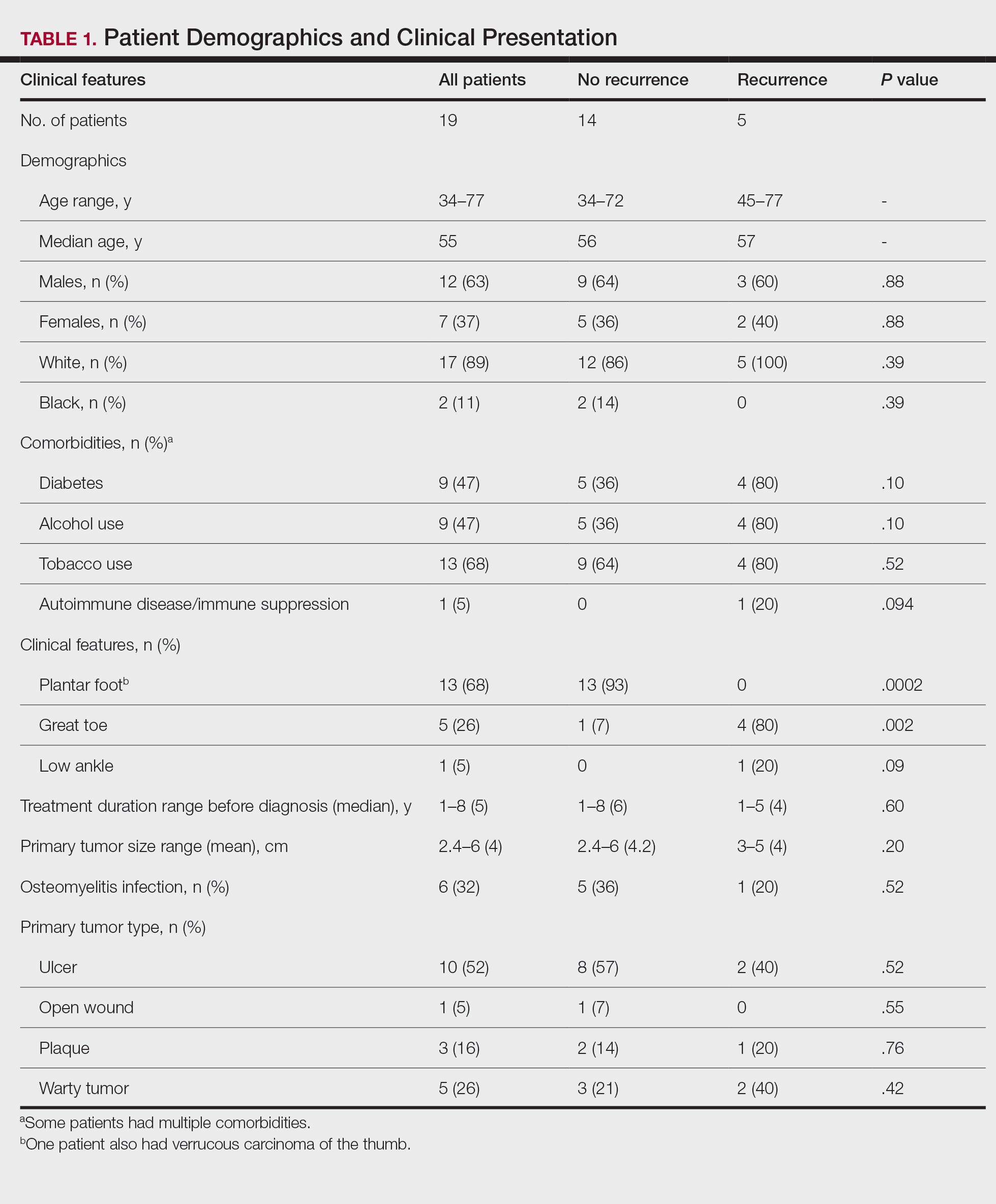
Tumor Location and Clinical Presentation—The most common clinical presentation included a nonhealing ulceration with warty edges, pain, bleeding, and lowered mobility. In most cases, there was history of prior treatment over a duration ranging from 1 to 8 years, with a median of 5 years prior to biopsy-based diagnosis (Table 1). Six patients had a history of osteomyelitis, diagnosed by imaging or biopsy, within a year before tumor diagnosis. The size of the primary tumor ranged from 2.4 to 6 cm, with a mean of 4 cm (P=.20). The clinical presentation, time before diagnosis, and size of the tumors did not differ significantly between recurrent and nonrecurrent cases.
The tumor location for the recurrent cases differed significantly compared to nonrecurrent cases. All 5 of the patients with a recurrence presented with a tumor on the nonglabrous part of the foot. Four patients (80%) had lesions on the dorsal or lateral aspect of the great toe (P=.002), and 1 patient (20%) had a lesion on the low ankle (P=.09)(Table 1). Of the nonrecurrent cases, 1 patient (7%) presented with a tumor on the plantar surface of the great toe (P=.002), 13 patients (93%) presented with tumors on the distal plantar surface of the foot (P=.0002), and 1 patient with a plantar foot tumor (Figure 1) also had verrucous carcinoma on the thumb (Table 1 and Figure 2).
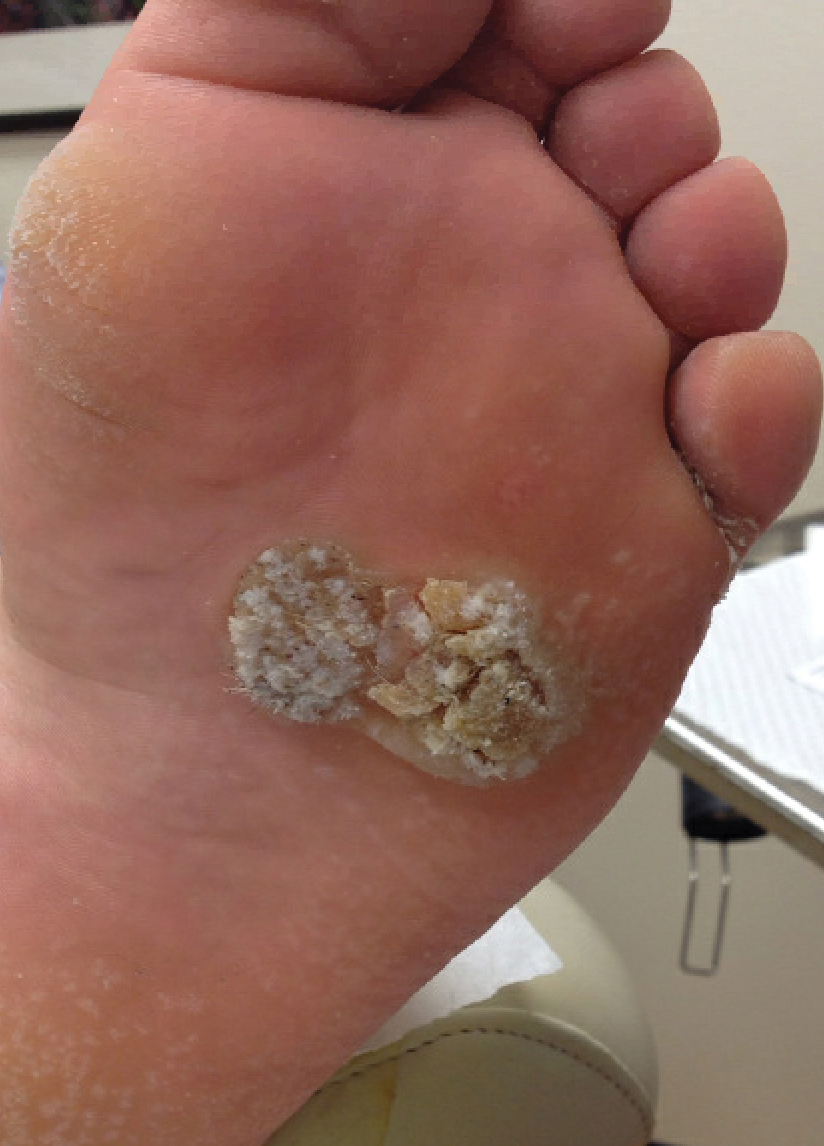
Histopathology—Available pathology slides for recurrent cases of verrucous carcinoma were reviewed alongside representative cases of verrucous carcinomas that did not progress to recurrence. The diagnosis of verrucous carcinoma was confirmed in all cases, with no evidence of conventional squamous cell carcinoma, perineural invasion, extension beyond the dermis, or bone invasion in any case. The median size of the tumors was 4.2 cm and 4 cm for nonrecurrent and recurrent specimens, respectively. Recurrences displayed a trend toward increased depth compared to primary tumors without recurrence (average depth, 5.5 mm vs 3.7 mm); however, this did not reach statistical significance (P=.24). Primary tumors that progressed to recurrence (n=2) displayed similar findings to the other cases, with invasive depths of 3.5 and 5.5 mm, and there was no evidence of conventional squamous cell carcinoma, perineural invasion, or extension beyond the dermis.
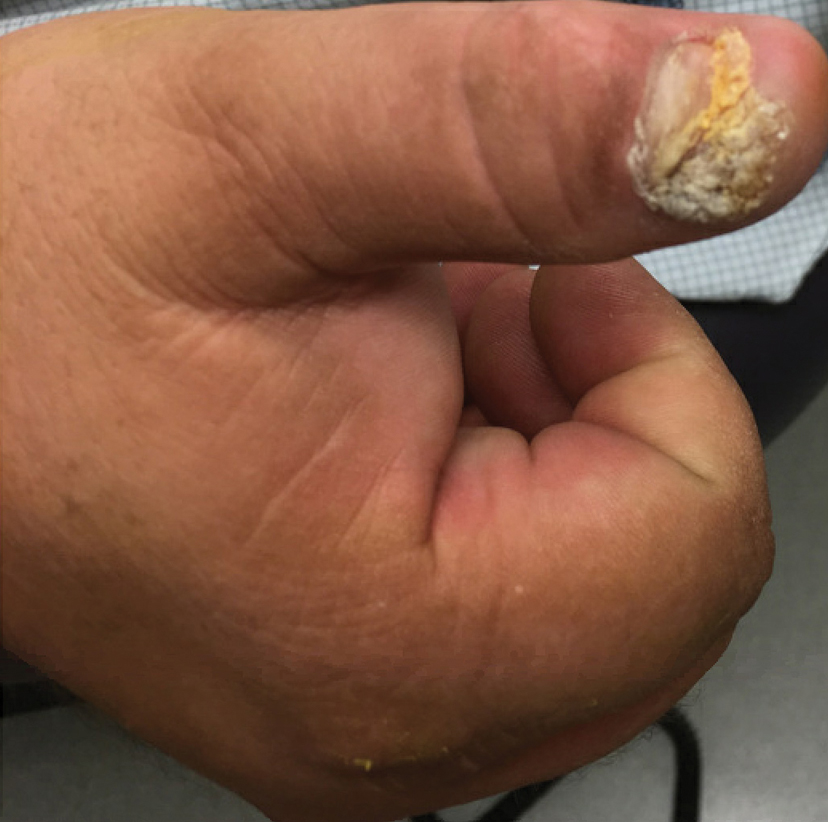
Treatment of Nonrecurrent Cases—Of the 16 total cases treated at the University of Michigan, surgery was the primary mode of therapy in every case (Tables 2 and 3). Of the 11 nonrecurrent cases, 7 patients had wide local excision with a dermal regeneration template, and delayed split-thickness graft reconstruction. Three cases had wide local excision with metatarsal resection, dermal regeneration template, and delayed skin grafting. One case had a great toe amputation
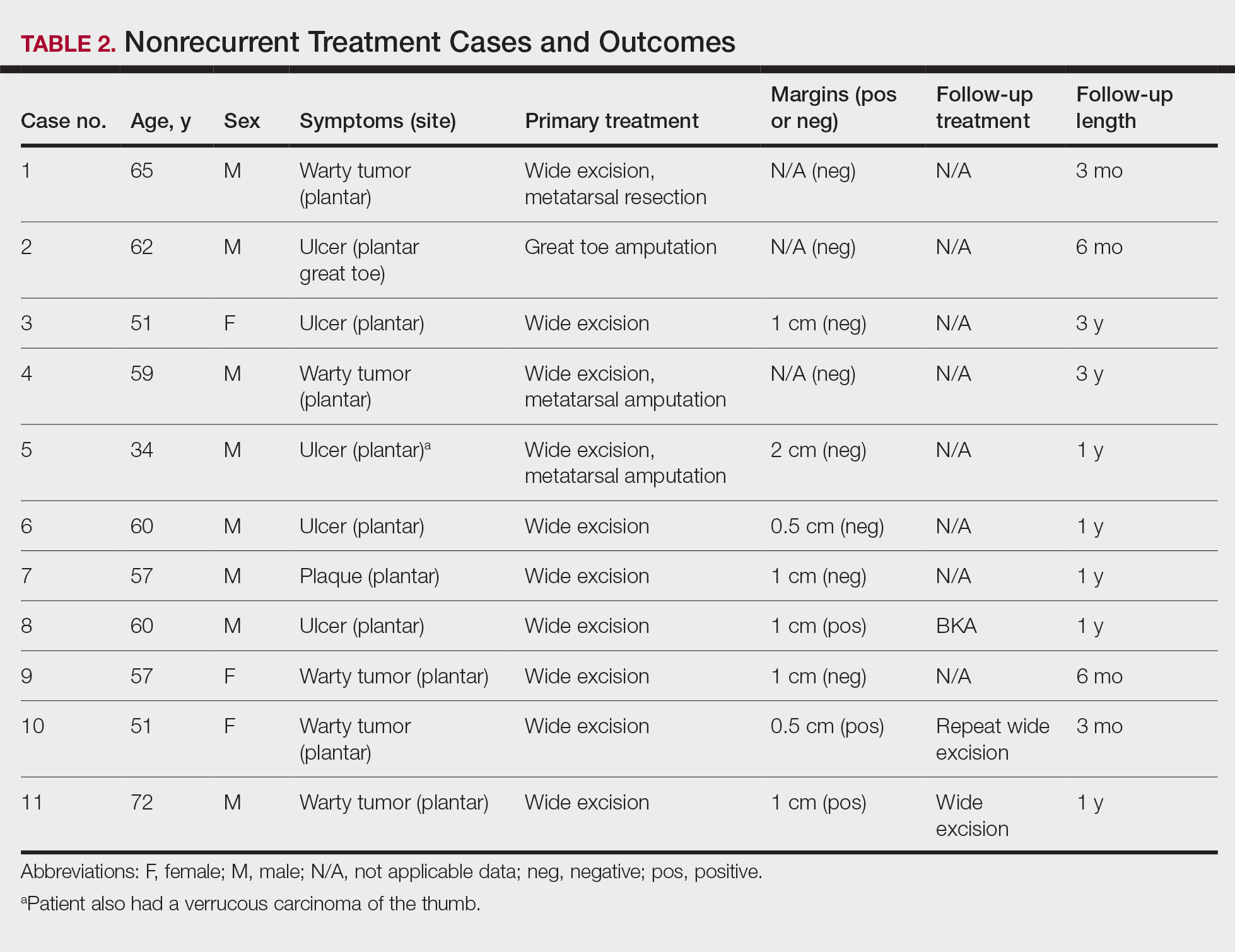
Treatment of Recurrent Cases—For the 5 patients with recurrence, surgical margins were not reported in all the cases but ranged from 0.5 to 2 cm (4/5 [80%] reported). On average, follow-up for this group of patients was 29 months, with a range of 12 to 60 months (Table 3).
The first case with a recurrence (patient 12) initially presented with a chronic calluslike growth of the medial ankle. The lesion initially was treated with wide local excision with negative margins. Reconstruction was performed in a staged fashion with use of a dermal regenerative template followed later by split-thickness skin grafting. Tumor recurrence with negative margins occurred 3 times over the next 2 years despite re-resections with negative pathologic margins. Each recurrence presented as graft breakdown and surrounding hyperkeratosis (Figure 3). After the third graft placement failed, the patient elected for a BKA. There has not been recurrence since the BKA after 5 years total follow-up from the time of primary tumor resection. Of note, this was the only patient in our cohort who was immunosuppressed and evaluated for regional nodal involvement by positron emission tomography.
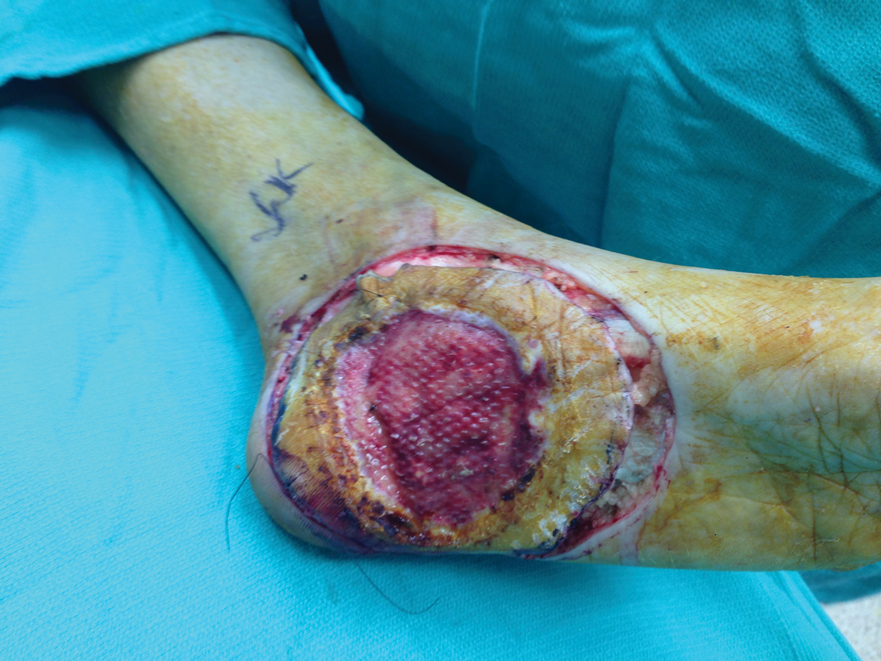
Another patient with recurrence (patient 13) presented with a chronic great toe ulcer of 5 years’ duration that formed on the dorsal aspect of the great toe after a previously excised wart (Figure 4A). This patient underwent mid-proximal metatarsal amputation with 2-cm margins and subsequent skin graft. Pathologic margins were negative. Within 6 months, there was hyperkeratosis and a draining wound (Figure 4B). Biopsy results confirmed recurrent disease that was treated with re-resection, including complete metatarsal amputation with negative margins and skin graft placement. Verrucous carcinoma recurred at the edges of the graft within 8 months, and the patient elected for a BKA. In addition, this patient also presented with a verrucous carcinoma of the contralateral great toe. The tumor presented as a warty ulcer of 4 months’ duration in the setting of osteomyelitis and was resected by great toe amputation that was performed concurrently with the opposite leg BKA; there has been no recurrence. Of note, this was the only patient to have right inguinal sentinel lymph node tissue sampled and HPV testing conducted, which were negative for verrucous carcinoma and high or low strains of HPV.
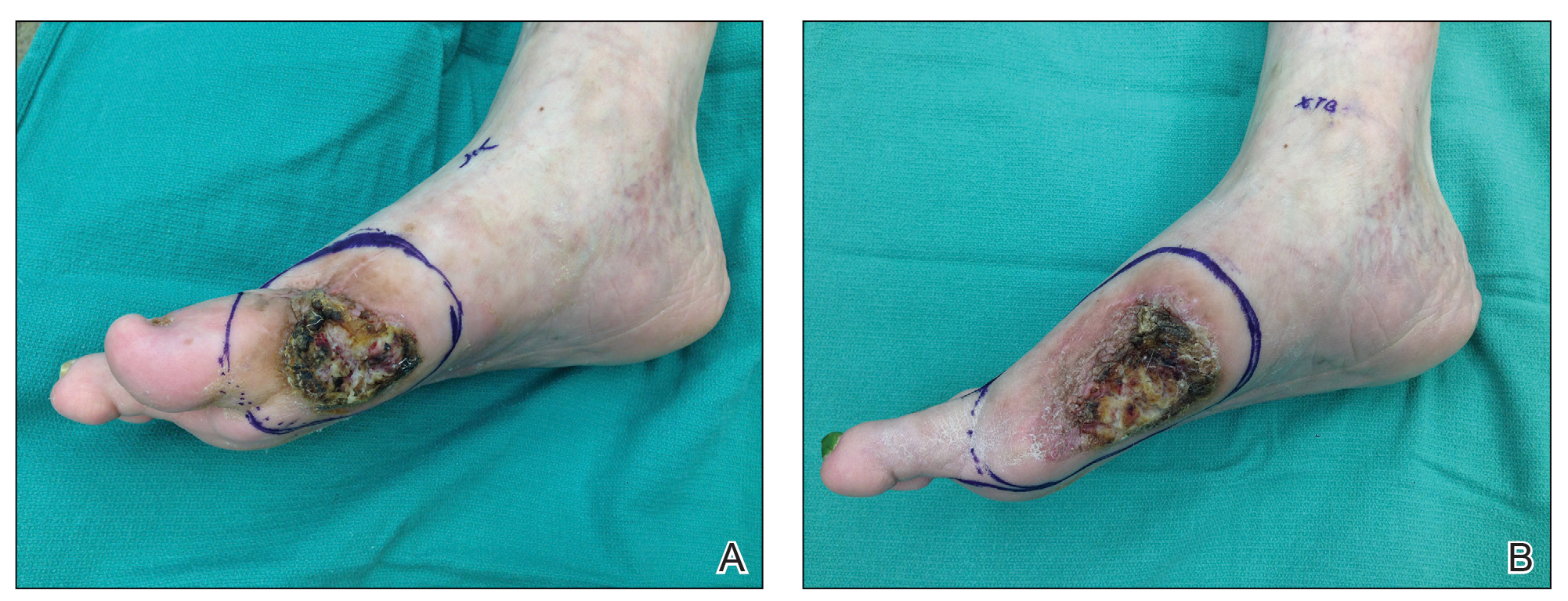
Another recurrent case (patient 14) presented with a large warty lesion on the dorsal great toe positive for verrucous carcinoma. He underwent a complete great toe amputation with skin graft placement. Verrucous carcinoma recurred on the edges of the graft within 6 months, and the patient was lost to follow-up when a BKA was suggested.
The fourth recurrent case (patient 15) initially had been treated for 1 year as a viral verruca of the dorsal aspect of the great toe. He had an exophytic mass positive for verrucous carcinoma growing on the dorsal aspect of the great toe around the prior excision site. After primary wide excision with negative 1-cm margins and graft placement, the tumor was re-excised twice within the next 2 years with pathologic negative margins. The patient underwent a foot amputation due to a severe osteomyelitis infection at the reconstruction site.
The final recurrent case (patient 16) presented with a mass on the lateral great toe that initially was treated as a viral verruca (for unknown duration) that had begun to ulcerate. The patient underwent wide excision with 1-cm margins and graft placement. Final pathology was consistent with verrucous carcinoma with negative margins. Recurrence occurred within 11 months on the edge of the graft, and a great toe amputation through the metatarsal phalangeal joint was performed.
Comment
Our series of 19 cases of verrucous carcinoma adds to the limited number of reported cases in the literature. We sought to evaluate the potential risk factors for early recurrence. Consistent with prior studies, our series found verrucous carcinoma of the foot to occur most frequently in patients aged 50 to 70 years, predominantly in White men.1 These tumors grew in the setting of chronic inflammation, tissue regeneration, multiple comorbidities, and poor wound hygiene. Misdiagnosis of verrucous carcinoma often leads to ineffective treatments and local invasion of nerves, muscle, and bone tissue.9,15,16 Our case series also clearly demonstrated the diagnostic challenge verrucous carcinoma presents, with an average delay in diagnosis of 5 years; correct diagnosis often did not occur until the tumor was 4 cm in size (average) and more than 50% had chronic ulceration.
The histologic features of the tumors showed striking uniformity. Within the literature, there is confusion regarding the use of the terms verrucous carcinoma and carcinoma (epithelioma) cuniculatum and the possible pathologic differences between the two. The World Health Organization’s classification of skin tumors describes epithelioma cuniculatum as verrucous carcinoma located on the sole of the foot.7 Kubik and Rhatigan6 pointed out that carcinoma cuniculatum does not have a warty or verrucous surface, which is a defining feature of verrucous carcinoma. Multiple authors have further surmised that the deep burrowing sinus tracts of epithelioma cuniculatum are different than those seen in verrucous carcinoma formed by the undulations extending from the papillomatous and verrucous surface.1,6 We did not observe these notable pathologic differences in recurrent or nonrecurrent primary tumors or differences between primary and recurrent cases. Although our cohort was small, the findings suggest that standard histologic features do not predict aggressive behavior in verrucous carcinomas. Furthermore, our observations support a model wherein recurrence is an inherent property of certain verrucous carcinomas rather than a consequence of histologic progression to conventional squamous cell carcinoma. The lack of overt malignant features in such cases underscores the need for distinction of verrucous carcinoma from benign mimics such as viral verruca or reactive epidermal hyperplasia.
Our recurrent cases showed a greater predilection for nonplantar surfaces and the great toe (P=.002). Five of 6 cases on the nonplantar surface—1 on the ankle and 5 on the great toe—recurred despite negative pathologic margins. There was no significant difference in demographics, pathogenesis, tumor size, chronicity, phenotype, or metastatic spread in recurrent and nonrecurrent cases in our cohort.
The tumor has only been described in rare instances at extrapedal cutaneous sites including the hand, scalp, and abdomen.14,17,18 Our series did include a case of synchronous presentation with a verrucous carcinoma on the thumb. Given the rarity of this presentation, thus far there are no data supporting any atypical locations of verrucous carcinoma having greater instances of recurrence. Our recurrent cases displaying atypical location on nonglabrous skin could suggest an underlying pathologic mechanism distinct from tumors on glabrous skin and relevant to increased recurrence risk. Such a mechanism might relate to distinct genetic insults, tumor-microenvironment interactions, or field effects. There are few studies regarding physiologic differences between the plantar surface and the nonglabrous surface and how that influences cancer genesis. Within acral melanoma studies, nonglabrous skin of more sun-exposed surfaces has a higher burden of genetic insults including BRAF mutations.19 Genetic testing of verrucous carcinoma is highly limited, with abnormal expression of the p53 tumor suppressor protein and possible association with several types of HPV. Verrucous carcinoma in general has been found to contain HPV types 6 and 11, nononcogenic forms, and higher risk from HPV types 16 and 18.9,20 However, only a few cases of HPV type 16 as well as 1 case each of HPV type 2 and type 11 have been found within verrucous carcinoma of the foot.21,22 In squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, HPV-positive tumors have shown better response to treatment. Further investigation of HPV and genetic contributors in verrucous carcinoma is warranted.
There is notable evidence that surgical resection is the best mode of treatment of verrucous carcinoma.2,3,10,11 Our case series was treated with wide local excision, with partial metatarsal amputation or great toe amputation, in cases with bone invasion or osteomyelitis. Surgical margins were not reported in all the cases but ranged from 0.5 to 2 cm with no significant differences between the recurrent and nonrecurrent groups. After excision, closure was conducted by incorporating primary, secondary, and delayed closure techniques, along with skin grafts for larger defects. Lymph node biopsy traditionally has not been recommended due to reported low metastatic potential. In all 5 recurrent cases, the tumors recurred after multiple attempts at wide excision and greater resection of bone and tissue, with negative margins. The tumors regrew quickly, within months, on the edges of the new graft or in the middle of the graft. The sites of recurrent tumor growth would suggest regrowth in the areas of greatest tissue stress and proliferation. We recommend a low threshold for biopsy and aggressive retreatment in the setting of exophytic growth at reconstruction sites.
Recurrence is uncommon in the setting of verrucous carcinoma, with our series being the first to analyze prognostic factors.3,9,14 Our findings indicate that
- Kao GF, Graham JH, Helwig EB. Carcinoma cuniculatum (verrucous carcinoma of the skin): a clinicopathologic study of 46 cases with ultrastructural observations. Cancer. 1982;49:2395-2403.
- McKee PH, Wilkinson JD, Black M, et al. Carcinoma (epithelioma) cuniculatum: a clinic-pathologic study of nineteen cases and review of the literature. Histopathology. 1981;5:425-436.
- Penera KE, Manji KA, Craig AB, et al. Atypical presentation of verrucous carcinoma: a case study and review of the literature. Foot Ankle Spec. 2013;6:318-322.
- Rosales MA, Martin BR, Armstrong DG, et al. Verrucous hyperplasia: a common and problematic finding in the high-risk diabetic foot. J Am Podiatr Assoc. 2006:4:348-350.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, De Dobbeleer G, et al. p53 Protein overexpression in verrucous carcinoma of the skin. Dermatology. 1996;192:12-15.
- Kubik MJ, Rhatigan RM. Carcinoma cuniculatum: not a verrucous carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:1083-1087
- Elder D, Massi D, Scolver R, et al. Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma. WHO Classification of Tumours (Medicine). Vol 11. 4th ed. International Agency for Research on Cancer: 2018;35-57.
- Chan MP. Verruciform and condyloma-like squamous proliferations in the anogenital region. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2019;143:821-831
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-21.
- Flynn K, Wiemer D. Treatment of an epithelioma cuniculatum plantare by local excision and a plantar skin flap. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1978;4:773-775.
- Spyriounis P, Tentis D, Sparveri I, et al. Plantar epithelioma cuniculatum: a case report with review of the literature. Eur J Plast Surg. 2004;27:253-256.
- Swanson NA, Taylor WB. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: literature review and treatment by the Moh’s chemosurgery technique. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:794-797.
- Alkalay R, Alcalay J, Shiri J. Plantar verrucous carcinoma treated with Mohs micrographic surgery: a case report and literature review. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006:5:68-73.
- Kotwal M, Poflee S, Bobhate, S. Carcinoma cuniculatum at various anatomical sites. Indian J Dermatol. 2005;50:216-220.
- Nagarajan D, Chandrasekhar M, Jebakumar J, et al. Verrucous carcinoma of foot at an unusual site: lessons to be learnt. South Asian J Cancer. 2017;6:63.
- Pempinello C, Bova A, Pempinello R, et al Verrucous carcinoma of the foot with bone invasion: a case report. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2013;2013:135307.
- Vandeweyer E, Sales F, Deramaecker R. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma. Br J Plastic Surg. 2001;54:168-170.
- Joybari A, Azadeh P, Honar B. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma superimposed on chronically inflamed ileostomy site skin. Iran J Pathol. 2018;13:285-288.
- Davis EJ, Johnson DB, Sosman JA, et al. Melanoma: what do all the mutations mean? Cancer. 2018;124:3490-3499.
- Gissmann L, Wolnik L, Ikenberg H, et al. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 DNA sequences in genital and laryngeal papillomas and in some cervical cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983;80:560-563.
- Knobler RM, Schneider S, Neumann RA, et al. DNA dot-blot hybridization implicates human papillomavirus type 11-DNA in epithelioma cuniculatum. J Med Virol. 1989;29:33-37.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, Detremmerie O, et al. Demonstration of human papillomavirus type 2 in a verrucous carcinoma of the foot. Dermatology. 1993;187:58-61.
Verrucous carcinoma is a rare cancer with the greatest predilection for the foot. Multiple case reports with only a few large case series have been published. 1-3 Plantar verrucous carcinoma is characterized as a slowly but relentlessly enlarging warty tumor with low metastatic potential and high risk for local invasion. The tumor occurs most frequently in patients aged 60 to 70 years, predominantly in White males. 1 It often is misdiagnosed for years as an ulcer or wart that is highly resistant to therapy. Size typically ranges from 1 to 12 cm in greatest dimension. 1
The pathogenesis of plantar verrucous carcinoma remains unclear, but some contributing factors have been proposed, including trauma, chronic irritation, infection, and poor local hygiene.2 This tumor has been reported to occur in chronic foot ulcerations, particularly in the diabetic population.4 It has been proposed that abnormal expression of the p53 tumor suppressor protein and several types of human papillomavirus (HPV) may have a role in the pathogenesis of verrucous carcinoma.5
The pathologic hallmarks of this tumor include a verrucous/hyperkeratotic surface with a deeply endophytic, broad, pushing base. Tumor cells are well differentiated, and atypia is either absent or confined to 1 or 2 layers at the base of the tumor. Overt invasion at the base is lacking, except in cases with a component of conventional invasive squamous cell carcinoma. Human papillomavirus viropathic changes are classically absent.1,3 Studies of the histopathology of verrucous carcinoma have been complicated by similar entities, nomenclatural uncertainty, and variable diagnostic criteria. For example, epithelioma cuniculatum variously has been defined as being synonymous with verrucous carcinoma, a distinct clinical verrucous carcinoma subtype occurring on the soles, a histologic subtype (characterized by prominent burrowing sinuses), or a separate entity entirely.1,2,6,7 Furthermore, in the genital area, several different types of carcinomas have verruciform features but display distinct microscopic findings and outcomes from verrucous carcinoma.8
Verrucous carcinoma represents an unusual variant of squamous cell carcinoma and is treated as such. Treatments have included laser surgery; immunotherapy; retinoid therapy; and chemotherapy by oral, intralesional, or iontophoretic routes in select patients.9 Radiotherapy presents another option, though reports have described progression to aggressive squamous cell carcinoma in some cases.9 Surgery is the best course of treatment, and as more case reports have been published, a transition from radical resection to wide excision with tumor-free margins is the treatment of choice.2,3,10,11 To minimize soft-tissue deficits, Mohs micrographic surgery has been discussed as a treatment option for verrucous carcinoma.11-13
Few studies have described verrucous carcinoma recurrence, and none have systematically examined recurrence rate, risk factors, or prognosis
Methods
Patient cases were
Of the 19 cases, 16 were treated at the University of Michigan and are included in the treatment analyses. Specific attention was then paid to the cases with a clinical recurrence despite negative surgical margins. We compared the clinical and surgical differences between recurrent cases and nonrecurrent cases.
Pathology was rereviewed for selected cases, including 2 cases with recurrence and matched primary, 2 cases with recurrence (for which the matched primary was unavailable for review), and 5 representative primary cases that were not complicated by recurrence. Pathology review was conducted in a blinded manner by one of the authors (P.W.H) who is a board-certified dermatopathologist for approximate depth of invasion from the granular layer, perineural invasion, bone invasion, infiltrative growth, presence of conventional squamous cell carcinoma, and margin status.
Statistical analysis was performed when appropriate using an N1 χ2 test or Student t test.
Results
Demographics and Comorbidities—The median age of the patients at the time of diagnosis was 55 years (range, 34–77 years). There were 12 males and 7 females (Table 1). Two patients were Black and 17 were White. Almost all patients had additional comorbidities including tobacco use (68%), alcohol use (47%), and diabetes (47%). Only 1 patient had an autoimmune disease and was on chronic steroids. No significant difference was found between the demographics of patients with recurrent lesions and those without recurrence.

Tumor Location and Clinical Presentation—The most common clinical presentation included a nonhealing ulceration with warty edges, pain, bleeding, and lowered mobility. In most cases, there was history of prior treatment over a duration ranging from 1 to 8 years, with a median of 5 years prior to biopsy-based diagnosis (Table 1). Six patients had a history of osteomyelitis, diagnosed by imaging or biopsy, within a year before tumor diagnosis. The size of the primary tumor ranged from 2.4 to 6 cm, with a mean of 4 cm (P=.20). The clinical presentation, time before diagnosis, and size of the tumors did not differ significantly between recurrent and nonrecurrent cases.
The tumor location for the recurrent cases differed significantly compared to nonrecurrent cases. All 5 of the patients with a recurrence presented with a tumor on the nonglabrous part of the foot. Four patients (80%) had lesions on the dorsal or lateral aspect of the great toe (P=.002), and 1 patient (20%) had a lesion on the low ankle (P=.09)(Table 1). Of the nonrecurrent cases, 1 patient (7%) presented with a tumor on the plantar surface of the great toe (P=.002), 13 patients (93%) presented with tumors on the distal plantar surface of the foot (P=.0002), and 1 patient with a plantar foot tumor (Figure 1) also had verrucous carcinoma on the thumb (Table 1 and Figure 2).

Histopathology—Available pathology slides for recurrent cases of verrucous carcinoma were reviewed alongside representative cases of verrucous carcinomas that did not progress to recurrence. The diagnosis of verrucous carcinoma was confirmed in all cases, with no evidence of conventional squamous cell carcinoma, perineural invasion, extension beyond the dermis, or bone invasion in any case. The median size of the tumors was 4.2 cm and 4 cm for nonrecurrent and recurrent specimens, respectively. Recurrences displayed a trend toward increased depth compared to primary tumors without recurrence (average depth, 5.5 mm vs 3.7 mm); however, this did not reach statistical significance (P=.24). Primary tumors that progressed to recurrence (n=2) displayed similar findings to the other cases, with invasive depths of 3.5 and 5.5 mm, and there was no evidence of conventional squamous cell carcinoma, perineural invasion, or extension beyond the dermis.

Treatment of Nonrecurrent Cases—Of the 16 total cases treated at the University of Michigan, surgery was the primary mode of therapy in every case (Tables 2 and 3). Of the 11 nonrecurrent cases, 7 patients had wide local excision with a dermal regeneration template, and delayed split-thickness graft reconstruction. Three cases had wide local excision with metatarsal resection, dermal regeneration template, and delayed skin grafting. One case had a great toe amputation

Treatment of Recurrent Cases—For the 5 patients with recurrence, surgical margins were not reported in all the cases but ranged from 0.5 to 2 cm (4/5 [80%] reported). On average, follow-up for this group of patients was 29 months, with a range of 12 to 60 months (Table 3).

The first case with a recurrence (patient 12) initially presented with a chronic calluslike growth of the medial ankle. The lesion initially was treated with wide local excision with negative margins. Reconstruction was performed in a staged fashion with use of a dermal regenerative template followed later by split-thickness skin grafting. Tumor recurrence with negative margins occurred 3 times over the next 2 years despite re-resections with negative pathologic margins. Each recurrence presented as graft breakdown and surrounding hyperkeratosis (Figure 3). After the third graft placement failed, the patient elected for a BKA. There has not been recurrence since the BKA after 5 years total follow-up from the time of primary tumor resection. Of note, this was the only patient in our cohort who was immunosuppressed and evaluated for regional nodal involvement by positron emission tomography.

Another patient with recurrence (patient 13) presented with a chronic great toe ulcer of 5 years’ duration that formed on the dorsal aspect of the great toe after a previously excised wart (Figure 4A). This patient underwent mid-proximal metatarsal amputation with 2-cm margins and subsequent skin graft. Pathologic margins were negative. Within 6 months, there was hyperkeratosis and a draining wound (Figure 4B). Biopsy results confirmed recurrent disease that was treated with re-resection, including complete metatarsal amputation with negative margins and skin graft placement. Verrucous carcinoma recurred at the edges of the graft within 8 months, and the patient elected for a BKA. In addition, this patient also presented with a verrucous carcinoma of the contralateral great toe. The tumor presented as a warty ulcer of 4 months’ duration in the setting of osteomyelitis and was resected by great toe amputation that was performed concurrently with the opposite leg BKA; there has been no recurrence. Of note, this was the only patient to have right inguinal sentinel lymph node tissue sampled and HPV testing conducted, which were negative for verrucous carcinoma and high or low strains of HPV.

Another recurrent case (patient 14) presented with a large warty lesion on the dorsal great toe positive for verrucous carcinoma. He underwent a complete great toe amputation with skin graft placement. Verrucous carcinoma recurred on the edges of the graft within 6 months, and the patient was lost to follow-up when a BKA was suggested.
The fourth recurrent case (patient 15) initially had been treated for 1 year as a viral verruca of the dorsal aspect of the great toe. He had an exophytic mass positive for verrucous carcinoma growing on the dorsal aspect of the great toe around the prior excision site. After primary wide excision with negative 1-cm margins and graft placement, the tumor was re-excised twice within the next 2 years with pathologic negative margins. The patient underwent a foot amputation due to a severe osteomyelitis infection at the reconstruction site.
The final recurrent case (patient 16) presented with a mass on the lateral great toe that initially was treated as a viral verruca (for unknown duration) that had begun to ulcerate. The patient underwent wide excision with 1-cm margins and graft placement. Final pathology was consistent with verrucous carcinoma with negative margins. Recurrence occurred within 11 months on the edge of the graft, and a great toe amputation through the metatarsal phalangeal joint was performed.
Comment
Our series of 19 cases of verrucous carcinoma adds to the limited number of reported cases in the literature. We sought to evaluate the potential risk factors for early recurrence. Consistent with prior studies, our series found verrucous carcinoma of the foot to occur most frequently in patients aged 50 to 70 years, predominantly in White men.1 These tumors grew in the setting of chronic inflammation, tissue regeneration, multiple comorbidities, and poor wound hygiene. Misdiagnosis of verrucous carcinoma often leads to ineffective treatments and local invasion of nerves, muscle, and bone tissue.9,15,16 Our case series also clearly demonstrated the diagnostic challenge verrucous carcinoma presents, with an average delay in diagnosis of 5 years; correct diagnosis often did not occur until the tumor was 4 cm in size (average) and more than 50% had chronic ulceration.
The histologic features of the tumors showed striking uniformity. Within the literature, there is confusion regarding the use of the terms verrucous carcinoma and carcinoma (epithelioma) cuniculatum and the possible pathologic differences between the two. The World Health Organization’s classification of skin tumors describes epithelioma cuniculatum as verrucous carcinoma located on the sole of the foot.7 Kubik and Rhatigan6 pointed out that carcinoma cuniculatum does not have a warty or verrucous surface, which is a defining feature of verrucous carcinoma. Multiple authors have further surmised that the deep burrowing sinus tracts of epithelioma cuniculatum are different than those seen in verrucous carcinoma formed by the undulations extending from the papillomatous and verrucous surface.1,6 We did not observe these notable pathologic differences in recurrent or nonrecurrent primary tumors or differences between primary and recurrent cases. Although our cohort was small, the findings suggest that standard histologic features do not predict aggressive behavior in verrucous carcinomas. Furthermore, our observations support a model wherein recurrence is an inherent property of certain verrucous carcinomas rather than a consequence of histologic progression to conventional squamous cell carcinoma. The lack of overt malignant features in such cases underscores the need for distinction of verrucous carcinoma from benign mimics such as viral verruca or reactive epidermal hyperplasia.
Our recurrent cases showed a greater predilection for nonplantar surfaces and the great toe (P=.002). Five of 6 cases on the nonplantar surface—1 on the ankle and 5 on the great toe—recurred despite negative pathologic margins. There was no significant difference in demographics, pathogenesis, tumor size, chronicity, phenotype, or metastatic spread in recurrent and nonrecurrent cases in our cohort.
The tumor has only been described in rare instances at extrapedal cutaneous sites including the hand, scalp, and abdomen.14,17,18 Our series did include a case of synchronous presentation with a verrucous carcinoma on the thumb. Given the rarity of this presentation, thus far there are no data supporting any atypical locations of verrucous carcinoma having greater instances of recurrence. Our recurrent cases displaying atypical location on nonglabrous skin could suggest an underlying pathologic mechanism distinct from tumors on glabrous skin and relevant to increased recurrence risk. Such a mechanism might relate to distinct genetic insults, tumor-microenvironment interactions, or field effects. There are few studies regarding physiologic differences between the plantar surface and the nonglabrous surface and how that influences cancer genesis. Within acral melanoma studies, nonglabrous skin of more sun-exposed surfaces has a higher burden of genetic insults including BRAF mutations.19 Genetic testing of verrucous carcinoma is highly limited, with abnormal expression of the p53 tumor suppressor protein and possible association with several types of HPV. Verrucous carcinoma in general has been found to contain HPV types 6 and 11, nononcogenic forms, and higher risk from HPV types 16 and 18.9,20 However, only a few cases of HPV type 16 as well as 1 case each of HPV type 2 and type 11 have been found within verrucous carcinoma of the foot.21,22 In squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, HPV-positive tumors have shown better response to treatment. Further investigation of HPV and genetic contributors in verrucous carcinoma is warranted.
There is notable evidence that surgical resection is the best mode of treatment of verrucous carcinoma.2,3,10,11 Our case series was treated with wide local excision, with partial metatarsal amputation or great toe amputation, in cases with bone invasion or osteomyelitis. Surgical margins were not reported in all the cases but ranged from 0.5 to 2 cm with no significant differences between the recurrent and nonrecurrent groups. After excision, closure was conducted by incorporating primary, secondary, and delayed closure techniques, along with skin grafts for larger defects. Lymph node biopsy traditionally has not been recommended due to reported low metastatic potential. In all 5 recurrent cases, the tumors recurred after multiple attempts at wide excision and greater resection of bone and tissue, with negative margins. The tumors regrew quickly, within months, on the edges of the new graft or in the middle of the graft. The sites of recurrent tumor growth would suggest regrowth in the areas of greatest tissue stress and proliferation. We recommend a low threshold for biopsy and aggressive retreatment in the setting of exophytic growth at reconstruction sites.
Recurrence is uncommon in the setting of verrucous carcinoma, with our series being the first to analyze prognostic factors.3,9,14 Our findings indicate that
Verrucous carcinoma is a rare cancer with the greatest predilection for the foot. Multiple case reports with only a few large case series have been published. 1-3 Plantar verrucous carcinoma is characterized as a slowly but relentlessly enlarging warty tumor with low metastatic potential and high risk for local invasion. The tumor occurs most frequently in patients aged 60 to 70 years, predominantly in White males. 1 It often is misdiagnosed for years as an ulcer or wart that is highly resistant to therapy. Size typically ranges from 1 to 12 cm in greatest dimension. 1
The pathogenesis of plantar verrucous carcinoma remains unclear, but some contributing factors have been proposed, including trauma, chronic irritation, infection, and poor local hygiene.2 This tumor has been reported to occur in chronic foot ulcerations, particularly in the diabetic population.4 It has been proposed that abnormal expression of the p53 tumor suppressor protein and several types of human papillomavirus (HPV) may have a role in the pathogenesis of verrucous carcinoma.5
The pathologic hallmarks of this tumor include a verrucous/hyperkeratotic surface with a deeply endophytic, broad, pushing base. Tumor cells are well differentiated, and atypia is either absent or confined to 1 or 2 layers at the base of the tumor. Overt invasion at the base is lacking, except in cases with a component of conventional invasive squamous cell carcinoma. Human papillomavirus viropathic changes are classically absent.1,3 Studies of the histopathology of verrucous carcinoma have been complicated by similar entities, nomenclatural uncertainty, and variable diagnostic criteria. For example, epithelioma cuniculatum variously has been defined as being synonymous with verrucous carcinoma, a distinct clinical verrucous carcinoma subtype occurring on the soles, a histologic subtype (characterized by prominent burrowing sinuses), or a separate entity entirely.1,2,6,7 Furthermore, in the genital area, several different types of carcinomas have verruciform features but display distinct microscopic findings and outcomes from verrucous carcinoma.8
Verrucous carcinoma represents an unusual variant of squamous cell carcinoma and is treated as such. Treatments have included laser surgery; immunotherapy; retinoid therapy; and chemotherapy by oral, intralesional, or iontophoretic routes in select patients.9 Radiotherapy presents another option, though reports have described progression to aggressive squamous cell carcinoma in some cases.9 Surgery is the best course of treatment, and as more case reports have been published, a transition from radical resection to wide excision with tumor-free margins is the treatment of choice.2,3,10,11 To minimize soft-tissue deficits, Mohs micrographic surgery has been discussed as a treatment option for verrucous carcinoma.11-13
Few studies have described verrucous carcinoma recurrence, and none have systematically examined recurrence rate, risk factors, or prognosis
Methods
Patient cases were
Of the 19 cases, 16 were treated at the University of Michigan and are included in the treatment analyses. Specific attention was then paid to the cases with a clinical recurrence despite negative surgical margins. We compared the clinical and surgical differences between recurrent cases and nonrecurrent cases.
Pathology was rereviewed for selected cases, including 2 cases with recurrence and matched primary, 2 cases with recurrence (for which the matched primary was unavailable for review), and 5 representative primary cases that were not complicated by recurrence. Pathology review was conducted in a blinded manner by one of the authors (P.W.H) who is a board-certified dermatopathologist for approximate depth of invasion from the granular layer, perineural invasion, bone invasion, infiltrative growth, presence of conventional squamous cell carcinoma, and margin status.
Statistical analysis was performed when appropriate using an N1 χ2 test or Student t test.
Results
Demographics and Comorbidities—The median age of the patients at the time of diagnosis was 55 years (range, 34–77 years). There were 12 males and 7 females (Table 1). Two patients were Black and 17 were White. Almost all patients had additional comorbidities including tobacco use (68%), alcohol use (47%), and diabetes (47%). Only 1 patient had an autoimmune disease and was on chronic steroids. No significant difference was found between the demographics of patients with recurrent lesions and those without recurrence.

Tumor Location and Clinical Presentation—The most common clinical presentation included a nonhealing ulceration with warty edges, pain, bleeding, and lowered mobility. In most cases, there was history of prior treatment over a duration ranging from 1 to 8 years, with a median of 5 years prior to biopsy-based diagnosis (Table 1). Six patients had a history of osteomyelitis, diagnosed by imaging or biopsy, within a year before tumor diagnosis. The size of the primary tumor ranged from 2.4 to 6 cm, with a mean of 4 cm (P=.20). The clinical presentation, time before diagnosis, and size of the tumors did not differ significantly between recurrent and nonrecurrent cases.
The tumor location for the recurrent cases differed significantly compared to nonrecurrent cases. All 5 of the patients with a recurrence presented with a tumor on the nonglabrous part of the foot. Four patients (80%) had lesions on the dorsal or lateral aspect of the great toe (P=.002), and 1 patient (20%) had a lesion on the low ankle (P=.09)(Table 1). Of the nonrecurrent cases, 1 patient (7%) presented with a tumor on the plantar surface of the great toe (P=.002), 13 patients (93%) presented with tumors on the distal plantar surface of the foot (P=.0002), and 1 patient with a plantar foot tumor (Figure 1) also had verrucous carcinoma on the thumb (Table 1 and Figure 2).

Histopathology—Available pathology slides for recurrent cases of verrucous carcinoma were reviewed alongside representative cases of verrucous carcinomas that did not progress to recurrence. The diagnosis of verrucous carcinoma was confirmed in all cases, with no evidence of conventional squamous cell carcinoma, perineural invasion, extension beyond the dermis, or bone invasion in any case. The median size of the tumors was 4.2 cm and 4 cm for nonrecurrent and recurrent specimens, respectively. Recurrences displayed a trend toward increased depth compared to primary tumors without recurrence (average depth, 5.5 mm vs 3.7 mm); however, this did not reach statistical significance (P=.24). Primary tumors that progressed to recurrence (n=2) displayed similar findings to the other cases, with invasive depths of 3.5 and 5.5 mm, and there was no evidence of conventional squamous cell carcinoma, perineural invasion, or extension beyond the dermis.

Treatment of Nonrecurrent Cases—Of the 16 total cases treated at the University of Michigan, surgery was the primary mode of therapy in every case (Tables 2 and 3). Of the 11 nonrecurrent cases, 7 patients had wide local excision with a dermal regeneration template, and delayed split-thickness graft reconstruction. Three cases had wide local excision with metatarsal resection, dermal regeneration template, and delayed skin grafting. One case had a great toe amputation

Treatment of Recurrent Cases—For the 5 patients with recurrence, surgical margins were not reported in all the cases but ranged from 0.5 to 2 cm (4/5 [80%] reported). On average, follow-up for this group of patients was 29 months, with a range of 12 to 60 months (Table 3).

The first case with a recurrence (patient 12) initially presented with a chronic calluslike growth of the medial ankle. The lesion initially was treated with wide local excision with negative margins. Reconstruction was performed in a staged fashion with use of a dermal regenerative template followed later by split-thickness skin grafting. Tumor recurrence with negative margins occurred 3 times over the next 2 years despite re-resections with negative pathologic margins. Each recurrence presented as graft breakdown and surrounding hyperkeratosis (Figure 3). After the third graft placement failed, the patient elected for a BKA. There has not been recurrence since the BKA after 5 years total follow-up from the time of primary tumor resection. Of note, this was the only patient in our cohort who was immunosuppressed and evaluated for regional nodal involvement by positron emission tomography.

Another patient with recurrence (patient 13) presented with a chronic great toe ulcer of 5 years’ duration that formed on the dorsal aspect of the great toe after a previously excised wart (Figure 4A). This patient underwent mid-proximal metatarsal amputation with 2-cm margins and subsequent skin graft. Pathologic margins were negative. Within 6 months, there was hyperkeratosis and a draining wound (Figure 4B). Biopsy results confirmed recurrent disease that was treated with re-resection, including complete metatarsal amputation with negative margins and skin graft placement. Verrucous carcinoma recurred at the edges of the graft within 8 months, and the patient elected for a BKA. In addition, this patient also presented with a verrucous carcinoma of the contralateral great toe. The tumor presented as a warty ulcer of 4 months’ duration in the setting of osteomyelitis and was resected by great toe amputation that was performed concurrently with the opposite leg BKA; there has been no recurrence. Of note, this was the only patient to have right inguinal sentinel lymph node tissue sampled and HPV testing conducted, which were negative for verrucous carcinoma and high or low strains of HPV.

Another recurrent case (patient 14) presented with a large warty lesion on the dorsal great toe positive for verrucous carcinoma. He underwent a complete great toe amputation with skin graft placement. Verrucous carcinoma recurred on the edges of the graft within 6 months, and the patient was lost to follow-up when a BKA was suggested.
The fourth recurrent case (patient 15) initially had been treated for 1 year as a viral verruca of the dorsal aspect of the great toe. He had an exophytic mass positive for verrucous carcinoma growing on the dorsal aspect of the great toe around the prior excision site. After primary wide excision with negative 1-cm margins and graft placement, the tumor was re-excised twice within the next 2 years with pathologic negative margins. The patient underwent a foot amputation due to a severe osteomyelitis infection at the reconstruction site.
The final recurrent case (patient 16) presented with a mass on the lateral great toe that initially was treated as a viral verruca (for unknown duration) that had begun to ulcerate. The patient underwent wide excision with 1-cm margins and graft placement. Final pathology was consistent with verrucous carcinoma with negative margins. Recurrence occurred within 11 months on the edge of the graft, and a great toe amputation through the metatarsal phalangeal joint was performed.
Comment
Our series of 19 cases of verrucous carcinoma adds to the limited number of reported cases in the literature. We sought to evaluate the potential risk factors for early recurrence. Consistent with prior studies, our series found verrucous carcinoma of the foot to occur most frequently in patients aged 50 to 70 years, predominantly in White men.1 These tumors grew in the setting of chronic inflammation, tissue regeneration, multiple comorbidities, and poor wound hygiene. Misdiagnosis of verrucous carcinoma often leads to ineffective treatments and local invasion of nerves, muscle, and bone tissue.9,15,16 Our case series also clearly demonstrated the diagnostic challenge verrucous carcinoma presents, with an average delay in diagnosis of 5 years; correct diagnosis often did not occur until the tumor was 4 cm in size (average) and more than 50% had chronic ulceration.
The histologic features of the tumors showed striking uniformity. Within the literature, there is confusion regarding the use of the terms verrucous carcinoma and carcinoma (epithelioma) cuniculatum and the possible pathologic differences between the two. The World Health Organization’s classification of skin tumors describes epithelioma cuniculatum as verrucous carcinoma located on the sole of the foot.7 Kubik and Rhatigan6 pointed out that carcinoma cuniculatum does not have a warty or verrucous surface, which is a defining feature of verrucous carcinoma. Multiple authors have further surmised that the deep burrowing sinus tracts of epithelioma cuniculatum are different than those seen in verrucous carcinoma formed by the undulations extending from the papillomatous and verrucous surface.1,6 We did not observe these notable pathologic differences in recurrent or nonrecurrent primary tumors or differences between primary and recurrent cases. Although our cohort was small, the findings suggest that standard histologic features do not predict aggressive behavior in verrucous carcinomas. Furthermore, our observations support a model wherein recurrence is an inherent property of certain verrucous carcinomas rather than a consequence of histologic progression to conventional squamous cell carcinoma. The lack of overt malignant features in such cases underscores the need for distinction of verrucous carcinoma from benign mimics such as viral verruca or reactive epidermal hyperplasia.
Our recurrent cases showed a greater predilection for nonplantar surfaces and the great toe (P=.002). Five of 6 cases on the nonplantar surface—1 on the ankle and 5 on the great toe—recurred despite negative pathologic margins. There was no significant difference in demographics, pathogenesis, tumor size, chronicity, phenotype, or metastatic spread in recurrent and nonrecurrent cases in our cohort.
The tumor has only been described in rare instances at extrapedal cutaneous sites including the hand, scalp, and abdomen.14,17,18 Our series did include a case of synchronous presentation with a verrucous carcinoma on the thumb. Given the rarity of this presentation, thus far there are no data supporting any atypical locations of verrucous carcinoma having greater instances of recurrence. Our recurrent cases displaying atypical location on nonglabrous skin could suggest an underlying pathologic mechanism distinct from tumors on glabrous skin and relevant to increased recurrence risk. Such a mechanism might relate to distinct genetic insults, tumor-microenvironment interactions, or field effects. There are few studies regarding physiologic differences between the plantar surface and the nonglabrous surface and how that influences cancer genesis. Within acral melanoma studies, nonglabrous skin of more sun-exposed surfaces has a higher burden of genetic insults including BRAF mutations.19 Genetic testing of verrucous carcinoma is highly limited, with abnormal expression of the p53 tumor suppressor protein and possible association with several types of HPV. Verrucous carcinoma in general has been found to contain HPV types 6 and 11, nononcogenic forms, and higher risk from HPV types 16 and 18.9,20 However, only a few cases of HPV type 16 as well as 1 case each of HPV type 2 and type 11 have been found within verrucous carcinoma of the foot.21,22 In squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, HPV-positive tumors have shown better response to treatment. Further investigation of HPV and genetic contributors in verrucous carcinoma is warranted.
There is notable evidence that surgical resection is the best mode of treatment of verrucous carcinoma.2,3,10,11 Our case series was treated with wide local excision, with partial metatarsal amputation or great toe amputation, in cases with bone invasion or osteomyelitis. Surgical margins were not reported in all the cases but ranged from 0.5 to 2 cm with no significant differences between the recurrent and nonrecurrent groups. After excision, closure was conducted by incorporating primary, secondary, and delayed closure techniques, along with skin grafts for larger defects. Lymph node biopsy traditionally has not been recommended due to reported low metastatic potential. In all 5 recurrent cases, the tumors recurred after multiple attempts at wide excision and greater resection of bone and tissue, with negative margins. The tumors regrew quickly, within months, on the edges of the new graft or in the middle of the graft. The sites of recurrent tumor growth would suggest regrowth in the areas of greatest tissue stress and proliferation. We recommend a low threshold for biopsy and aggressive retreatment in the setting of exophytic growth at reconstruction sites.
Recurrence is uncommon in the setting of verrucous carcinoma, with our series being the first to analyze prognostic factors.3,9,14 Our findings indicate that
- Kao GF, Graham JH, Helwig EB. Carcinoma cuniculatum (verrucous carcinoma of the skin): a clinicopathologic study of 46 cases with ultrastructural observations. Cancer. 1982;49:2395-2403.
- McKee PH, Wilkinson JD, Black M, et al. Carcinoma (epithelioma) cuniculatum: a clinic-pathologic study of nineteen cases and review of the literature. Histopathology. 1981;5:425-436.
- Penera KE, Manji KA, Craig AB, et al. Atypical presentation of verrucous carcinoma: a case study and review of the literature. Foot Ankle Spec. 2013;6:318-322.
- Rosales MA, Martin BR, Armstrong DG, et al. Verrucous hyperplasia: a common and problematic finding in the high-risk diabetic foot. J Am Podiatr Assoc. 2006:4:348-350.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, De Dobbeleer G, et al. p53 Protein overexpression in verrucous carcinoma of the skin. Dermatology. 1996;192:12-15.
- Kubik MJ, Rhatigan RM. Carcinoma cuniculatum: not a verrucous carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:1083-1087
- Elder D, Massi D, Scolver R, et al. Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma. WHO Classification of Tumours (Medicine). Vol 11. 4th ed. International Agency for Research on Cancer: 2018;35-57.
- Chan MP. Verruciform and condyloma-like squamous proliferations in the anogenital region. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2019;143:821-831
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-21.
- Flynn K, Wiemer D. Treatment of an epithelioma cuniculatum plantare by local excision and a plantar skin flap. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1978;4:773-775.
- Spyriounis P, Tentis D, Sparveri I, et al. Plantar epithelioma cuniculatum: a case report with review of the literature. Eur J Plast Surg. 2004;27:253-256.
- Swanson NA, Taylor WB. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: literature review and treatment by the Moh’s chemosurgery technique. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:794-797.
- Alkalay R, Alcalay J, Shiri J. Plantar verrucous carcinoma treated with Mohs micrographic surgery: a case report and literature review. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006:5:68-73.
- Kotwal M, Poflee S, Bobhate, S. Carcinoma cuniculatum at various anatomical sites. Indian J Dermatol. 2005;50:216-220.
- Nagarajan D, Chandrasekhar M, Jebakumar J, et al. Verrucous carcinoma of foot at an unusual site: lessons to be learnt. South Asian J Cancer. 2017;6:63.
- Pempinello C, Bova A, Pempinello R, et al Verrucous carcinoma of the foot with bone invasion: a case report. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2013;2013:135307.
- Vandeweyer E, Sales F, Deramaecker R. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma. Br J Plastic Surg. 2001;54:168-170.
- Joybari A, Azadeh P, Honar B. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma superimposed on chronically inflamed ileostomy site skin. Iran J Pathol. 2018;13:285-288.
- Davis EJ, Johnson DB, Sosman JA, et al. Melanoma: what do all the mutations mean? Cancer. 2018;124:3490-3499.
- Gissmann L, Wolnik L, Ikenberg H, et al. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 DNA sequences in genital and laryngeal papillomas and in some cervical cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983;80:560-563.
- Knobler RM, Schneider S, Neumann RA, et al. DNA dot-blot hybridization implicates human papillomavirus type 11-DNA in epithelioma cuniculatum. J Med Virol. 1989;29:33-37.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, Detremmerie O, et al. Demonstration of human papillomavirus type 2 in a verrucous carcinoma of the foot. Dermatology. 1993;187:58-61.
- Kao GF, Graham JH, Helwig EB. Carcinoma cuniculatum (verrucous carcinoma of the skin): a clinicopathologic study of 46 cases with ultrastructural observations. Cancer. 1982;49:2395-2403.
- McKee PH, Wilkinson JD, Black M, et al. Carcinoma (epithelioma) cuniculatum: a clinic-pathologic study of nineteen cases and review of the literature. Histopathology. 1981;5:425-436.
- Penera KE, Manji KA, Craig AB, et al. Atypical presentation of verrucous carcinoma: a case study and review of the literature. Foot Ankle Spec. 2013;6:318-322.
- Rosales MA, Martin BR, Armstrong DG, et al. Verrucous hyperplasia: a common and problematic finding in the high-risk diabetic foot. J Am Podiatr Assoc. 2006:4:348-350.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, De Dobbeleer G, et al. p53 Protein overexpression in verrucous carcinoma of the skin. Dermatology. 1996;192:12-15.
- Kubik MJ, Rhatigan RM. Carcinoma cuniculatum: not a verrucous carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:1083-1087
- Elder D, Massi D, Scolver R, et al. Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma. WHO Classification of Tumours (Medicine). Vol 11. 4th ed. International Agency for Research on Cancer: 2018;35-57.
- Chan MP. Verruciform and condyloma-like squamous proliferations in the anogenital region. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2019;143:821-831
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-21.
- Flynn K, Wiemer D. Treatment of an epithelioma cuniculatum plantare by local excision and a plantar skin flap. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1978;4:773-775.
- Spyriounis P, Tentis D, Sparveri I, et al. Plantar epithelioma cuniculatum: a case report with review of the literature. Eur J Plast Surg. 2004;27:253-256.
- Swanson NA, Taylor WB. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: literature review and treatment by the Moh’s chemosurgery technique. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:794-797.
- Alkalay R, Alcalay J, Shiri J. Plantar verrucous carcinoma treated with Mohs micrographic surgery: a case report and literature review. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006:5:68-73.
- Kotwal M, Poflee S, Bobhate, S. Carcinoma cuniculatum at various anatomical sites. Indian J Dermatol. 2005;50:216-220.
- Nagarajan D, Chandrasekhar M, Jebakumar J, et al. Verrucous carcinoma of foot at an unusual site: lessons to be learnt. South Asian J Cancer. 2017;6:63.
- Pempinello C, Bova A, Pempinello R, et al Verrucous carcinoma of the foot with bone invasion: a case report. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2013;2013:135307.
- Vandeweyer E, Sales F, Deramaecker R. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma. Br J Plastic Surg. 2001;54:168-170.
- Joybari A, Azadeh P, Honar B. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma superimposed on chronically inflamed ileostomy site skin. Iran J Pathol. 2018;13:285-288.
- Davis EJ, Johnson DB, Sosman JA, et al. Melanoma: what do all the mutations mean? Cancer. 2018;124:3490-3499.
- Gissmann L, Wolnik L, Ikenberg H, et al. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 DNA sequences in genital and laryngeal papillomas and in some cervical cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983;80:560-563.
- Knobler RM, Schneider S, Neumann RA, et al. DNA dot-blot hybridization implicates human papillomavirus type 11-DNA in epithelioma cuniculatum. J Med Virol. 1989;29:33-37.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, Detremmerie O, et al. Demonstration of human papillomavirus type 2 in a verrucous carcinoma of the foot. Dermatology. 1993;187:58-61.
Practice Points
- Clinicians should have a high suspicion for verrucous carcinoma in the setting of a chronic ulceration or warty lesion that is resistant to traditional treatment. Early biopsy with tissue collection of the raised ulcer borders and the deep dermis layer of warty lesions is imperative for diagnosis.
- Verrucous carcinoma originating on the nonglabrous surface of the foot may have a higher rate of recurrence often occurring within months of previous treatment. Patients presenting with nonhealing surgical sites in this area should be treated with a high level of suspicion for recurrence.