User login
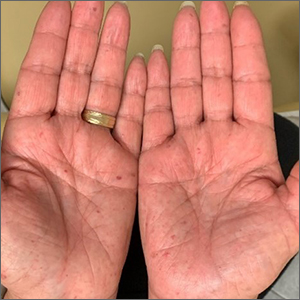
Bilateral palmar rash
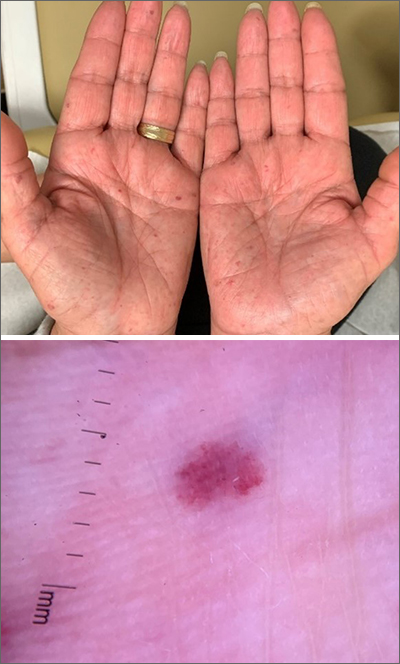
A biopsy was performed and the pathology report showed ectatic, thin-walled vessels consistent with telangiectasias. There were no other inflammatory, infectious, or malignant changes.
Telangiectasias are caused by permanent dilatation of subpapillary plexus end vessels. Unlike petechiae and angiomata, telangiectasias blanch with pressure. They usually manifest as small, bright red, nonpulsatile vascular lesions with a fine, netlike pattern on the surface of the skin. Telangiectasis can affect many organs (eg, intestines, bladder, brain, eyes) and may occur in patients with certain genetic disorders and environmental exposures (eg, radiation).1
Palmar telangiectasias are specifically associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, dermatomyositis, Grave disease, CREST syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, and smoking.2 Sun exposure and smoking are the main risk factors for the development of telangiectasias.1
This patient had no history of autoimmune disease or hyperthyroidism, and no one in her family had telangiectasis. Thus, the likely cause of her lesions was smoking. While the pathophysiology is not fully understood, it is likely related to the vasoconstrictive quality of nicotine, causing ischemia in the dermis. This chronic, low-grade ischemia may trigger the compensatory development of telangiectasias.2
This patient was informed that her telangiectasias were most likely caused by her smoking and that the lesions themselves did not require treatment. She was encouraged to continue her smoking cessation efforts with her primary care provider.
Photos courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD. Text courtesy of Mia MJ Coleman, BA, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Schieving JH, Shoenaker MHD, Weemaes CM, et al. Telangiectasias: Small lesions referring to serious disorders. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2017;21:807-815. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2017.07.016
2. Levi A, Shechter R, Lapidoth M, et al. Palmar telangiectasias: a cutaneous sign for smoking. Dermatology. 2017;233:390-395. doi: 10.1159/000481855

A biopsy was performed and the pathology report showed ectatic, thin-walled vessels consistent with telangiectasias. There were no other inflammatory, infectious, or malignant changes.
Telangiectasias are caused by permanent dilatation of subpapillary plexus end vessels. Unlike petechiae and angiomata, telangiectasias blanch with pressure. They usually manifest as small, bright red, nonpulsatile vascular lesions with a fine, netlike pattern on the surface of the skin. Telangiectasis can affect many organs (eg, intestines, bladder, brain, eyes) and may occur in patients with certain genetic disorders and environmental exposures (eg, radiation).1
Palmar telangiectasias are specifically associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, dermatomyositis, Grave disease, CREST syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, and smoking.2 Sun exposure and smoking are the main risk factors for the development of telangiectasias.1
This patient had no history of autoimmune disease or hyperthyroidism, and no one in her family had telangiectasis. Thus, the likely cause of her lesions was smoking. While the pathophysiology is not fully understood, it is likely related to the vasoconstrictive quality of nicotine, causing ischemia in the dermis. This chronic, low-grade ischemia may trigger the compensatory development of telangiectasias.2
This patient was informed that her telangiectasias were most likely caused by her smoking and that the lesions themselves did not require treatment. She was encouraged to continue her smoking cessation efforts with her primary care provider.
Photos courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD. Text courtesy of Mia MJ Coleman, BA, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

A biopsy was performed and the pathology report showed ectatic, thin-walled vessels consistent with telangiectasias. There were no other inflammatory, infectious, or malignant changes.
Telangiectasias are caused by permanent dilatation of subpapillary plexus end vessels. Unlike petechiae and angiomata, telangiectasias blanch with pressure. They usually manifest as small, bright red, nonpulsatile vascular lesions with a fine, netlike pattern on the surface of the skin. Telangiectasis can affect many organs (eg, intestines, bladder, brain, eyes) and may occur in patients with certain genetic disorders and environmental exposures (eg, radiation).1
Palmar telangiectasias are specifically associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, dermatomyositis, Grave disease, CREST syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, and smoking.2 Sun exposure and smoking are the main risk factors for the development of telangiectasias.1
This patient had no history of autoimmune disease or hyperthyroidism, and no one in her family had telangiectasis. Thus, the likely cause of her lesions was smoking. While the pathophysiology is not fully understood, it is likely related to the vasoconstrictive quality of nicotine, causing ischemia in the dermis. This chronic, low-grade ischemia may trigger the compensatory development of telangiectasias.2
This patient was informed that her telangiectasias were most likely caused by her smoking and that the lesions themselves did not require treatment. She was encouraged to continue her smoking cessation efforts with her primary care provider.
Photos courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD. Text courtesy of Mia MJ Coleman, BA, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Schieving JH, Shoenaker MHD, Weemaes CM, et al. Telangiectasias: Small lesions referring to serious disorders. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2017;21:807-815. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2017.07.016
2. Levi A, Shechter R, Lapidoth M, et al. Palmar telangiectasias: a cutaneous sign for smoking. Dermatology. 2017;233:390-395. doi: 10.1159/000481855
1. Schieving JH, Shoenaker MHD, Weemaes CM, et al. Telangiectasias: Small lesions referring to serious disorders. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2017;21:807-815. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2017.07.016
2. Levi A, Shechter R, Lapidoth M, et al. Palmar telangiectasias: a cutaneous sign for smoking. Dermatology. 2017;233:390-395. doi: 10.1159/000481855
Tech Glitches at One VA Site Raise Concerns About a Nationwide Rollout
Spokane, Washington, was supposed to be the center of the Department of Veterans Affairs’ tech reinvention, the first site in the agency’s decade-long project to change its medical records software. But one morning in early March, the latest system malfunction made some clinicians snap.
At Spokane’s Mann-Grandstaff VA Medical Center, the records system — developed by Cerner Corp., based in North Kansas City, Missouri — went down. Staffers, inside the hospital and its outpatient facilities, were back to relying on pen and paper. Computerized schedules were inaccessible. Physicians couldn’t enter new orders or change patients’ medications.
By the next day, the electronic health records were only partially available. Dozens of records remained “sequestered,” meaning that doctors and nurses struggled to update patient charts.
The snafu, the latest in a series at Mann-Grandstaff, heightened Spokane medical staff members’ frustration with a system that has been problematic since it was installed a year and a half ago. The VA said no patients had been harmed because of the problems.
But physicians on the ground there said it’s only a matter of time before serious safety problems — those causing injury or death — emerge, pointing to the program’s ongoing weaknesses amid VA leadership’s full-bore push toward implementation nationwide. One provider said she was glad she didn’t have a relative in Mann-Grandstaff.
The one-two punch of a dangerous outage and staff grievances is the latest setback in the VA’s more than $16 billion effort to upgrade its record-keeping technology. The issues have at times forced clinicians to see fewer patients and file tens of thousands of requests for help to Cerner with patient-safety problems, congressional and agency watchdog reviews show.
If those issues multiply over the vast VA system — which employs more than a quarter-million workers and serves 6.3 million active patients — it could create rampant patient-safety and productivity problems. Despite the VA’s goals of using the technology upgrade to provide seamless records for patients from enlistment in the military until discharge, the doctors and clinicians who spoke to KHN are convinced that the problems experienced in Spokane will be repeated again and again.
The records system, scheduled for deployment at multiple VA facilities in the Pacific Northwest in the coming weeks and months, most recently rolled out at Jonathan M. Wainwright Memorial VA Medical Center in Walla Walla, Washington.
Both Cerner and Mann-Grandstaff officials declined to comment and referred KHN to officials at VA headquarters in Washington, D.C.
“If it’s a total meltdown” in Walla Walla, said Katie Purswell, the American Legion’s director of veterans affairs and rehabilitation, it’s a problem for the department and its decade-long initiative. Initial impressions from staffers are positive, but the issues in Spokane appeared over the course of weeks after the system was turned on.
The distress was particularly acute in early March. On March 2, Cerner turned on a software update to a database containing patient identification information. Problems emerged the next morning. In the record of a patient who was checking in for surgery, staff members discovered incorrect data, including gender information for a different patient. About an hour later, a staffer from the national VA’s medical records office told some clinicians at Mann-Grandstaff to “log out.”
Robert Fischer, Mann-Grandstaff’s medical center director, sent a dire warning later that morning. “Assume all electronic data is corrupted/inaccurate,” Fischer said in an email. He urged clinicians to limit orders for lab work, imaging studies, and medications. The facility shifted to “downtime procedures,” meaning a reliance on paper.
Some staffers didn’t absorb the late-morning message and continued entering information in the mixed-up records, adding to the stew of erroneous data.
According to information provided to Congress later by the VA, Cerner had informed Mann-Grandstaff of a “complete degradation” the night before — leading to questions from staffers about why it took until late morning the next day to shut down the system. Agency spokesperson Erin Crowe told KHN there wasn’t any delay in notifying staff.
Problems stretched into the following week. Some records — 70 as of March 10, according to a briefing provided to Congress — remained unusable while auditors tried to ascertain what information had been mixed in from other charts. This left clinicians in some instances unable to keep track of patients’ care. Doctors said it became a confusing and chaotic environment. They couldn’t, for example, help patients refill prescriptions.
Members of Congress are concerned — not only about the outage but also VA’s explanations about it. In a letter to agency leadership, the leading Republicans on the House Veterans’ Affairs Committee and the subcommittee overseeing technology, Rep. Mike Bost of Illinois and Rep. Matt Rosendale of Montana, expressed worries the agency was “soft-pedal[ing]” its communications and argued that veterans were misled by assurances that records had been corrected.
The full committee plans to do a deeper examination soon. It has scheduled a closed-door roundtable with VA staffers from Spokane and Walla Walla on April 5.
The outage deepened unhappiness at Mann-Grandstaff. Clinicians there were already frazzled by a deeply buggy system. Downtime was common, a congressional aide told KHN.
A March 17 VA inspector general report documented nearly 39,000 requests for technical help or improvement since the October 2020 deployment of the new records system. Cerner employees often closed requests without resolving the underlying problems, the report said. Mann-Grandstaff staffers became disengaged or devised shortcuts to bypass the malfunctioning software, the inspector general wrote — each a potential root of patient-safety incidents.
The department said the shortcuts — or workarounds — aren’t its policy. “Workarounds are not authorized nor encouraged,” Crowe said.
The Biden administration tried to overhaul the software initiative, putting the program on hiatus before installing new leadership in the medical records office at the end of 2021. But by then, low morale had sunk in. “People in Spokane VA are … demoralized and unhappy,” Rep. Frank Mrvan (D-Ind.), chair of the House subcommittee focused on the VA’s technology modernization programs, told agency leaders during a November congressional hearing. He said staffers told him they felt as though they were beating their heads against a wall to make things function.
Other observers shared Mrvan’s concerns.
Purswell of the American Legion questioned whether appropriate steps are being taken to prepare the Walla Walla facility and its staff for the technology rollout. She asked whether staffers feel as if the Cerner system has been thrust upon them or are excited about the change.
Whether the VA has been persuasive about the benefits of the program is unclear. “I think it’s incumbent on us to demonstrate it’s not a loss,” said Dr. Terry Adirim, the leader of the VA office in charge of implementing the new records technology. “We might have dropped the ball on explaining what a benefit this is.”
Indeed, Adirim conducted a virtual town hall meeting March 21 for veterans in the Walla Walla area — where she was pressed about the problems in Spokane. “If Spokane has been a year figuring this out, why is this moving forward?” one questioner asked, expressing a point made frequently during the call. Adirim said the VA had made “thousands of changes” since the initial rollout.
Medical staffers at the Spokane and Walla Walla VA facilities are part of informal networks sharing their often-negative experiences about the program despite a perception among staff members that dissent will hurt their careers.
Adirim thinks negative feelings can be addressed by stepping up technical support. She also said training programs have been overhauled since the deployment in Spokane. Bottom line: The VA is proceeding.
“People want to revert back to what they did before,” Adirim said, but that’s not going to happen.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Subscribe to KHN's free Morning Briefing.
Spokane, Washington, was supposed to be the center of the Department of Veterans Affairs’ tech reinvention, the first site in the agency’s decade-long project to change its medical records software. But one morning in early March, the latest system malfunction made some clinicians snap.
At Spokane’s Mann-Grandstaff VA Medical Center, the records system — developed by Cerner Corp., based in North Kansas City, Missouri — went down. Staffers, inside the hospital and its outpatient facilities, were back to relying on pen and paper. Computerized schedules were inaccessible. Physicians couldn’t enter new orders or change patients’ medications.
By the next day, the electronic health records were only partially available. Dozens of records remained “sequestered,” meaning that doctors and nurses struggled to update patient charts.
The snafu, the latest in a series at Mann-Grandstaff, heightened Spokane medical staff members’ frustration with a system that has been problematic since it was installed a year and a half ago. The VA said no patients had been harmed because of the problems.
But physicians on the ground there said it’s only a matter of time before serious safety problems — those causing injury or death — emerge, pointing to the program’s ongoing weaknesses amid VA leadership’s full-bore push toward implementation nationwide. One provider said she was glad she didn’t have a relative in Mann-Grandstaff.
The one-two punch of a dangerous outage and staff grievances is the latest setback in the VA’s more than $16 billion effort to upgrade its record-keeping technology. The issues have at times forced clinicians to see fewer patients and file tens of thousands of requests for help to Cerner with patient-safety problems, congressional and agency watchdog reviews show.
If those issues multiply over the vast VA system — which employs more than a quarter-million workers and serves 6.3 million active patients — it could create rampant patient-safety and productivity problems. Despite the VA’s goals of using the technology upgrade to provide seamless records for patients from enlistment in the military until discharge, the doctors and clinicians who spoke to KHN are convinced that the problems experienced in Spokane will be repeated again and again.
The records system, scheduled for deployment at multiple VA facilities in the Pacific Northwest in the coming weeks and months, most recently rolled out at Jonathan M. Wainwright Memorial VA Medical Center in Walla Walla, Washington.
Both Cerner and Mann-Grandstaff officials declined to comment and referred KHN to officials at VA headquarters in Washington, D.C.
“If it’s a total meltdown” in Walla Walla, said Katie Purswell, the American Legion’s director of veterans affairs and rehabilitation, it’s a problem for the department and its decade-long initiative. Initial impressions from staffers are positive, but the issues in Spokane appeared over the course of weeks after the system was turned on.
The distress was particularly acute in early March. On March 2, Cerner turned on a software update to a database containing patient identification information. Problems emerged the next morning. In the record of a patient who was checking in for surgery, staff members discovered incorrect data, including gender information for a different patient. About an hour later, a staffer from the national VA’s medical records office told some clinicians at Mann-Grandstaff to “log out.”
Robert Fischer, Mann-Grandstaff’s medical center director, sent a dire warning later that morning. “Assume all electronic data is corrupted/inaccurate,” Fischer said in an email. He urged clinicians to limit orders for lab work, imaging studies, and medications. The facility shifted to “downtime procedures,” meaning a reliance on paper.
Some staffers didn’t absorb the late-morning message and continued entering information in the mixed-up records, adding to the stew of erroneous data.
According to information provided to Congress later by the VA, Cerner had informed Mann-Grandstaff of a “complete degradation” the night before — leading to questions from staffers about why it took until late morning the next day to shut down the system. Agency spokesperson Erin Crowe told KHN there wasn’t any delay in notifying staff.
Problems stretched into the following week. Some records — 70 as of March 10, according to a briefing provided to Congress — remained unusable while auditors tried to ascertain what information had been mixed in from other charts. This left clinicians in some instances unable to keep track of patients’ care. Doctors said it became a confusing and chaotic environment. They couldn’t, for example, help patients refill prescriptions.
Members of Congress are concerned — not only about the outage but also VA’s explanations about it. In a letter to agency leadership, the leading Republicans on the House Veterans’ Affairs Committee and the subcommittee overseeing technology, Rep. Mike Bost of Illinois and Rep. Matt Rosendale of Montana, expressed worries the agency was “soft-pedal[ing]” its communications and argued that veterans were misled by assurances that records had been corrected.
The full committee plans to do a deeper examination soon. It has scheduled a closed-door roundtable with VA staffers from Spokane and Walla Walla on April 5.
The outage deepened unhappiness at Mann-Grandstaff. Clinicians there were already frazzled by a deeply buggy system. Downtime was common, a congressional aide told KHN.
A March 17 VA inspector general report documented nearly 39,000 requests for technical help or improvement since the October 2020 deployment of the new records system. Cerner employees often closed requests without resolving the underlying problems, the report said. Mann-Grandstaff staffers became disengaged or devised shortcuts to bypass the malfunctioning software, the inspector general wrote — each a potential root of patient-safety incidents.
The department said the shortcuts — or workarounds — aren’t its policy. “Workarounds are not authorized nor encouraged,” Crowe said.
The Biden administration tried to overhaul the software initiative, putting the program on hiatus before installing new leadership in the medical records office at the end of 2021. But by then, low morale had sunk in. “People in Spokane VA are … demoralized and unhappy,” Rep. Frank Mrvan (D-Ind.), chair of the House subcommittee focused on the VA’s technology modernization programs, told agency leaders during a November congressional hearing. He said staffers told him they felt as though they were beating their heads against a wall to make things function.
Other observers shared Mrvan’s concerns.
Purswell of the American Legion questioned whether appropriate steps are being taken to prepare the Walla Walla facility and its staff for the technology rollout. She asked whether staffers feel as if the Cerner system has been thrust upon them or are excited about the change.
Whether the VA has been persuasive about the benefits of the program is unclear. “I think it’s incumbent on us to demonstrate it’s not a loss,” said Dr. Terry Adirim, the leader of the VA office in charge of implementing the new records technology. “We might have dropped the ball on explaining what a benefit this is.”
Indeed, Adirim conducted a virtual town hall meeting March 21 for veterans in the Walla Walla area — where she was pressed about the problems in Spokane. “If Spokane has been a year figuring this out, why is this moving forward?” one questioner asked, expressing a point made frequently during the call. Adirim said the VA had made “thousands of changes” since the initial rollout.
Medical staffers at the Spokane and Walla Walla VA facilities are part of informal networks sharing their often-negative experiences about the program despite a perception among staff members that dissent will hurt their careers.
Adirim thinks negative feelings can be addressed by stepping up technical support. She also said training programs have been overhauled since the deployment in Spokane. Bottom line: The VA is proceeding.
“People want to revert back to what they did before,” Adirim said, but that’s not going to happen.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Subscribe to KHN's free Morning Briefing.
Spokane, Washington, was supposed to be the center of the Department of Veterans Affairs’ tech reinvention, the first site in the agency’s decade-long project to change its medical records software. But one morning in early March, the latest system malfunction made some clinicians snap.
At Spokane’s Mann-Grandstaff VA Medical Center, the records system — developed by Cerner Corp., based in North Kansas City, Missouri — went down. Staffers, inside the hospital and its outpatient facilities, were back to relying on pen and paper. Computerized schedules were inaccessible. Physicians couldn’t enter new orders or change patients’ medications.
By the next day, the electronic health records were only partially available. Dozens of records remained “sequestered,” meaning that doctors and nurses struggled to update patient charts.
The snafu, the latest in a series at Mann-Grandstaff, heightened Spokane medical staff members’ frustration with a system that has been problematic since it was installed a year and a half ago. The VA said no patients had been harmed because of the problems.
But physicians on the ground there said it’s only a matter of time before serious safety problems — those causing injury or death — emerge, pointing to the program’s ongoing weaknesses amid VA leadership’s full-bore push toward implementation nationwide. One provider said she was glad she didn’t have a relative in Mann-Grandstaff.
The one-two punch of a dangerous outage and staff grievances is the latest setback in the VA’s more than $16 billion effort to upgrade its record-keeping technology. The issues have at times forced clinicians to see fewer patients and file tens of thousands of requests for help to Cerner with patient-safety problems, congressional and agency watchdog reviews show.
If those issues multiply over the vast VA system — which employs more than a quarter-million workers and serves 6.3 million active patients — it could create rampant patient-safety and productivity problems. Despite the VA’s goals of using the technology upgrade to provide seamless records for patients from enlistment in the military until discharge, the doctors and clinicians who spoke to KHN are convinced that the problems experienced in Spokane will be repeated again and again.
The records system, scheduled for deployment at multiple VA facilities in the Pacific Northwest in the coming weeks and months, most recently rolled out at Jonathan M. Wainwright Memorial VA Medical Center in Walla Walla, Washington.
Both Cerner and Mann-Grandstaff officials declined to comment and referred KHN to officials at VA headquarters in Washington, D.C.
“If it’s a total meltdown” in Walla Walla, said Katie Purswell, the American Legion’s director of veterans affairs and rehabilitation, it’s a problem for the department and its decade-long initiative. Initial impressions from staffers are positive, but the issues in Spokane appeared over the course of weeks after the system was turned on.
The distress was particularly acute in early March. On March 2, Cerner turned on a software update to a database containing patient identification information. Problems emerged the next morning. In the record of a patient who was checking in for surgery, staff members discovered incorrect data, including gender information for a different patient. About an hour later, a staffer from the national VA’s medical records office told some clinicians at Mann-Grandstaff to “log out.”
Robert Fischer, Mann-Grandstaff’s medical center director, sent a dire warning later that morning. “Assume all electronic data is corrupted/inaccurate,” Fischer said in an email. He urged clinicians to limit orders for lab work, imaging studies, and medications. The facility shifted to “downtime procedures,” meaning a reliance on paper.
Some staffers didn’t absorb the late-morning message and continued entering information in the mixed-up records, adding to the stew of erroneous data.
According to information provided to Congress later by the VA, Cerner had informed Mann-Grandstaff of a “complete degradation” the night before — leading to questions from staffers about why it took until late morning the next day to shut down the system. Agency spokesperson Erin Crowe told KHN there wasn’t any delay in notifying staff.
Problems stretched into the following week. Some records — 70 as of March 10, according to a briefing provided to Congress — remained unusable while auditors tried to ascertain what information had been mixed in from other charts. This left clinicians in some instances unable to keep track of patients’ care. Doctors said it became a confusing and chaotic environment. They couldn’t, for example, help patients refill prescriptions.
Members of Congress are concerned — not only about the outage but also VA’s explanations about it. In a letter to agency leadership, the leading Republicans on the House Veterans’ Affairs Committee and the subcommittee overseeing technology, Rep. Mike Bost of Illinois and Rep. Matt Rosendale of Montana, expressed worries the agency was “soft-pedal[ing]” its communications and argued that veterans were misled by assurances that records had been corrected.
The full committee plans to do a deeper examination soon. It has scheduled a closed-door roundtable with VA staffers from Spokane and Walla Walla on April 5.
The outage deepened unhappiness at Mann-Grandstaff. Clinicians there were already frazzled by a deeply buggy system. Downtime was common, a congressional aide told KHN.
A March 17 VA inspector general report documented nearly 39,000 requests for technical help or improvement since the October 2020 deployment of the new records system. Cerner employees often closed requests without resolving the underlying problems, the report said. Mann-Grandstaff staffers became disengaged or devised shortcuts to bypass the malfunctioning software, the inspector general wrote — each a potential root of patient-safety incidents.
The department said the shortcuts — or workarounds — aren’t its policy. “Workarounds are not authorized nor encouraged,” Crowe said.
The Biden administration tried to overhaul the software initiative, putting the program on hiatus before installing new leadership in the medical records office at the end of 2021. But by then, low morale had sunk in. “People in Spokane VA are … demoralized and unhappy,” Rep. Frank Mrvan (D-Ind.), chair of the House subcommittee focused on the VA’s technology modernization programs, told agency leaders during a November congressional hearing. He said staffers told him they felt as though they were beating their heads against a wall to make things function.
Other observers shared Mrvan’s concerns.
Purswell of the American Legion questioned whether appropriate steps are being taken to prepare the Walla Walla facility and its staff for the technology rollout. She asked whether staffers feel as if the Cerner system has been thrust upon them or are excited about the change.
Whether the VA has been persuasive about the benefits of the program is unclear. “I think it’s incumbent on us to demonstrate it’s not a loss,” said Dr. Terry Adirim, the leader of the VA office in charge of implementing the new records technology. “We might have dropped the ball on explaining what a benefit this is.”
Indeed, Adirim conducted a virtual town hall meeting March 21 for veterans in the Walla Walla area — where she was pressed about the problems in Spokane. “If Spokane has been a year figuring this out, why is this moving forward?” one questioner asked, expressing a point made frequently during the call. Adirim said the VA had made “thousands of changes” since the initial rollout.
Medical staffers at the Spokane and Walla Walla VA facilities are part of informal networks sharing their often-negative experiences about the program despite a perception among staff members that dissent will hurt their careers.
Adirim thinks negative feelings can be addressed by stepping up technical support. She also said training programs have been overhauled since the deployment in Spokane. Bottom line: The VA is proceeding.
“People want to revert back to what they did before,” Adirim said, but that’s not going to happen.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Subscribe to KHN's free Morning Briefing.
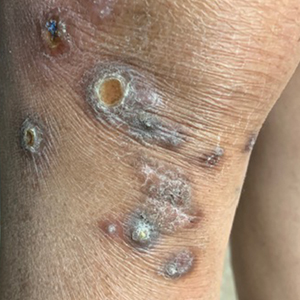
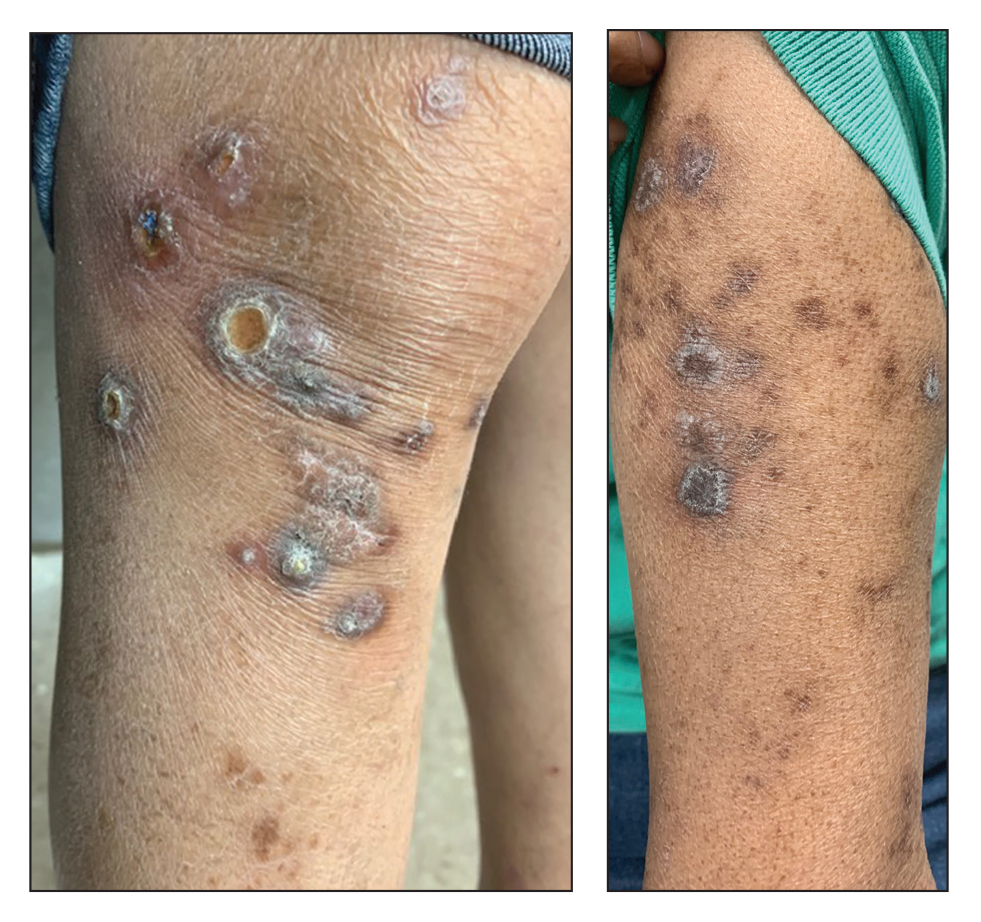
Excoriated Papules and Plaques on the Arms and Legs
The Diagnosis: Reactive Perforating Collagenosis
Reactive perforating collagenosis (RPC) may be either acquired or inherited. It is 1 of 4 classical forms of transepithelial elimination, which also includes elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS) as well as perforating folliculitis and Kyrle disease. These 4 forms of transepithelial elimination share characteristics of the elimination of altered dermal components through the epidermis.1 The acquired subtype of RPC frequently occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease,2 both present in our patient.
Clinical presentation typically shows pruritic hyperkeratotic papules with a central crater filled with crust that frequently are distributed on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, often in a linear pattern.3 The perforating papules and nodules occasionally may involve the trunk and face.4 Histopathologic examination is characterized by the elimination of altered collagen through the epidermis. Established lesions may show a cup-shaped depression of the epidermis filled with a keratin plug. The underlying dermis will show vertically oriented basophilic collagen fibers with focal extrusion through the epidermis, and elastic fibers will be absent.5 The exact pathophysiology of this disease is unknown, but it may represent a cutaneous response to superficial trauma caused by intense scratching.6
Standard treatment protocols are not well established for this condition, but some evidence shows that a combination of treatments can help ameliorate symptoms, even if they are not curative.7 Treatments without strong evidence have included a wide range of topical, systemic, and other therapies. Case series and anecdotal reports have used retinoids, corticosteroids, menthol, antibiotics, allopurinol antihistamines, cryotherapy, and lasers.8 One case was treated with a combination of narrowband UVB phototherapy and doxycycline with resolution in approximately 6 weeks.9 Other cases have been cured using triple therapy with antihistamines, topical or injected steroids, and emollients or oral antibiotics.7 Evidence shows that there may be benefit to combining multiple different treatment types that target pruritus, inflammation, and collagen damage.7,9 This disease usually cannot be cured, but it may be improved by the available treatments.
The differential diagnosis includes delusional parasitosis, EPS, perforating folliculitis, and prurigo nodularis. Delusional parasitosis also can be characterized by excoriated plaques and a sensation of parasites infesting the skin, as our patient described.10 However, it can be differentiated from RPC by the fact that it is a diagnosis of exclusion, which would not have the histopathologic findings of the elimination of collagen from the epidermis, as was demonstrated in our patient.11 Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is in the same family of perforating diseases as RPC; however, EPS typically appears in children or young adults and often is associated with other genetic disorders. Physical examination in a patient with EPS would reveal keratotic papules in a serpiginous pattern, whereas our patient had discrete lesions without any serpiginous pattern. The histopathologic appearance of EPS would reveal plugs of elastic fibers rather than collagen fibers, as was demonstrated in our patient.8 Perforating folliculitis, while also demonstrating transepithelial elimination similar to RPC, would appear as erythematous follicular papules with small central keratotic plugs and histopathologic findings of a widely dilated follicle with a mass of keratotic debris.12 Prurigo nodularis would appear as dome-shaped papulonodules with varying degrees of scale, crust, and erosion, with a histopathologic appearance of hyperplasia and thick hyperkeratosis.11
Overall, the histopathology is paramount in differentiating RPC from the alternative diagnoses, with the extrusion of collagen from the epidermis not being seen in these other conditions. The coupling of the medical history (type 2 diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease) with the clinical presentation and skin biopsy findings confirmed the diagnosis of RPC.
- Fei C, Wang Y, Gong Y, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a report of a typical case. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E4305.
- Matsui A, Nakano H, Aizu T, et al. Treatment of acquired reactive perforating collagenosis with 308‐nm excimer laser. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:820-821.
- Dey AK. Reactive perforating collagenosis: an important differential diagnosis in hemodialysis patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2018;29:422-425.
- Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 9th ed. McGraw-Hill Education LLC; 2012.
- Plaza JA, Prieto VG. Inflammatory Skin Disorders. Demos Medical Publishing LLC; 2012.
- Kreuter A, Gambichler T. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. CMAJ. 2010;182:E184.
- Zhang X, Yang Y, Shao S. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99:E20391.
- Rapini RP. Perforating diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1690-1696.
- Gao L, Gu L, Chen Z, et al. Doxycycline combined with NB-UVB phototherapy for acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020;16:917-921.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Psychocutaneous disorders. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:50-55. 11. Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Pruritus and dysesthesia. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:39-49. 12. Rubio FA, Herranz P, Robayna G, et al. Perforating folliculitis: report of a case in an HIV-infected man. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:300-302.
The Diagnosis: Reactive Perforating Collagenosis
Reactive perforating collagenosis (RPC) may be either acquired or inherited. It is 1 of 4 classical forms of transepithelial elimination, which also includes elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS) as well as perforating folliculitis and Kyrle disease. These 4 forms of transepithelial elimination share characteristics of the elimination of altered dermal components through the epidermis.1 The acquired subtype of RPC frequently occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease,2 both present in our patient.
Clinical presentation typically shows pruritic hyperkeratotic papules with a central crater filled with crust that frequently are distributed on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, often in a linear pattern.3 The perforating papules and nodules occasionally may involve the trunk and face.4 Histopathologic examination is characterized by the elimination of altered collagen through the epidermis. Established lesions may show a cup-shaped depression of the epidermis filled with a keratin plug. The underlying dermis will show vertically oriented basophilic collagen fibers with focal extrusion through the epidermis, and elastic fibers will be absent.5 The exact pathophysiology of this disease is unknown, but it may represent a cutaneous response to superficial trauma caused by intense scratching.6
Standard treatment protocols are not well established for this condition, but some evidence shows that a combination of treatments can help ameliorate symptoms, even if they are not curative.7 Treatments without strong evidence have included a wide range of topical, systemic, and other therapies. Case series and anecdotal reports have used retinoids, corticosteroids, menthol, antibiotics, allopurinol antihistamines, cryotherapy, and lasers.8 One case was treated with a combination of narrowband UVB phototherapy and doxycycline with resolution in approximately 6 weeks.9 Other cases have been cured using triple therapy with antihistamines, topical or injected steroids, and emollients or oral antibiotics.7 Evidence shows that there may be benefit to combining multiple different treatment types that target pruritus, inflammation, and collagen damage.7,9 This disease usually cannot be cured, but it may be improved by the available treatments.
The differential diagnosis includes delusional parasitosis, EPS, perforating folliculitis, and prurigo nodularis. Delusional parasitosis also can be characterized by excoriated plaques and a sensation of parasites infesting the skin, as our patient described.10 However, it can be differentiated from RPC by the fact that it is a diagnosis of exclusion, which would not have the histopathologic findings of the elimination of collagen from the epidermis, as was demonstrated in our patient.11 Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is in the same family of perforating diseases as RPC; however, EPS typically appears in children or young adults and often is associated with other genetic disorders. Physical examination in a patient with EPS would reveal keratotic papules in a serpiginous pattern, whereas our patient had discrete lesions without any serpiginous pattern. The histopathologic appearance of EPS would reveal plugs of elastic fibers rather than collagen fibers, as was demonstrated in our patient.8 Perforating folliculitis, while also demonstrating transepithelial elimination similar to RPC, would appear as erythematous follicular papules with small central keratotic plugs and histopathologic findings of a widely dilated follicle with a mass of keratotic debris.12 Prurigo nodularis would appear as dome-shaped papulonodules with varying degrees of scale, crust, and erosion, with a histopathologic appearance of hyperplasia and thick hyperkeratosis.11
Overall, the histopathology is paramount in differentiating RPC from the alternative diagnoses, with the extrusion of collagen from the epidermis not being seen in these other conditions. The coupling of the medical history (type 2 diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease) with the clinical presentation and skin biopsy findings confirmed the diagnosis of RPC.
The Diagnosis: Reactive Perforating Collagenosis
Reactive perforating collagenosis (RPC) may be either acquired or inherited. It is 1 of 4 classical forms of transepithelial elimination, which also includes elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS) as well as perforating folliculitis and Kyrle disease. These 4 forms of transepithelial elimination share characteristics of the elimination of altered dermal components through the epidermis.1 The acquired subtype of RPC frequently occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease,2 both present in our patient.
Clinical presentation typically shows pruritic hyperkeratotic papules with a central crater filled with crust that frequently are distributed on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, often in a linear pattern.3 The perforating papules and nodules occasionally may involve the trunk and face.4 Histopathologic examination is characterized by the elimination of altered collagen through the epidermis. Established lesions may show a cup-shaped depression of the epidermis filled with a keratin plug. The underlying dermis will show vertically oriented basophilic collagen fibers with focal extrusion through the epidermis, and elastic fibers will be absent.5 The exact pathophysiology of this disease is unknown, but it may represent a cutaneous response to superficial trauma caused by intense scratching.6
Standard treatment protocols are not well established for this condition, but some evidence shows that a combination of treatments can help ameliorate symptoms, even if they are not curative.7 Treatments without strong evidence have included a wide range of topical, systemic, and other therapies. Case series and anecdotal reports have used retinoids, corticosteroids, menthol, antibiotics, allopurinol antihistamines, cryotherapy, and lasers.8 One case was treated with a combination of narrowband UVB phototherapy and doxycycline with resolution in approximately 6 weeks.9 Other cases have been cured using triple therapy with antihistamines, topical or injected steroids, and emollients or oral antibiotics.7 Evidence shows that there may be benefit to combining multiple different treatment types that target pruritus, inflammation, and collagen damage.7,9 This disease usually cannot be cured, but it may be improved by the available treatments.
The differential diagnosis includes delusional parasitosis, EPS, perforating folliculitis, and prurigo nodularis. Delusional parasitosis also can be characterized by excoriated plaques and a sensation of parasites infesting the skin, as our patient described.10 However, it can be differentiated from RPC by the fact that it is a diagnosis of exclusion, which would not have the histopathologic findings of the elimination of collagen from the epidermis, as was demonstrated in our patient.11 Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is in the same family of perforating diseases as RPC; however, EPS typically appears in children or young adults and often is associated with other genetic disorders. Physical examination in a patient with EPS would reveal keratotic papules in a serpiginous pattern, whereas our patient had discrete lesions without any serpiginous pattern. The histopathologic appearance of EPS would reveal plugs of elastic fibers rather than collagen fibers, as was demonstrated in our patient.8 Perforating folliculitis, while also demonstrating transepithelial elimination similar to RPC, would appear as erythematous follicular papules with small central keratotic plugs and histopathologic findings of a widely dilated follicle with a mass of keratotic debris.12 Prurigo nodularis would appear as dome-shaped papulonodules with varying degrees of scale, crust, and erosion, with a histopathologic appearance of hyperplasia and thick hyperkeratosis.11
Overall, the histopathology is paramount in differentiating RPC from the alternative diagnoses, with the extrusion of collagen from the epidermis not being seen in these other conditions. The coupling of the medical history (type 2 diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease) with the clinical presentation and skin biopsy findings confirmed the diagnosis of RPC.
- Fei C, Wang Y, Gong Y, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a report of a typical case. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E4305.
- Matsui A, Nakano H, Aizu T, et al. Treatment of acquired reactive perforating collagenosis with 308‐nm excimer laser. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:820-821.
- Dey AK. Reactive perforating collagenosis: an important differential diagnosis in hemodialysis patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2018;29:422-425.
- Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 9th ed. McGraw-Hill Education LLC; 2012.
- Plaza JA, Prieto VG. Inflammatory Skin Disorders. Demos Medical Publishing LLC; 2012.
- Kreuter A, Gambichler T. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. CMAJ. 2010;182:E184.
- Zhang X, Yang Y, Shao S. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99:E20391.
- Rapini RP. Perforating diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1690-1696.
- Gao L, Gu L, Chen Z, et al. Doxycycline combined with NB-UVB phototherapy for acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020;16:917-921.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Psychocutaneous disorders. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:50-55. 11. Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Pruritus and dysesthesia. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:39-49. 12. Rubio FA, Herranz P, Robayna G, et al. Perforating folliculitis: report of a case in an HIV-infected man. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:300-302.
- Fei C, Wang Y, Gong Y, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a report of a typical case. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E4305.
- Matsui A, Nakano H, Aizu T, et al. Treatment of acquired reactive perforating collagenosis with 308‐nm excimer laser. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:820-821.
- Dey AK. Reactive perforating collagenosis: an important differential diagnosis in hemodialysis patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2018;29:422-425.
- Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 9th ed. McGraw-Hill Education LLC; 2012.
- Plaza JA, Prieto VG. Inflammatory Skin Disorders. Demos Medical Publishing LLC; 2012.
- Kreuter A, Gambichler T. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. CMAJ. 2010;182:E184.
- Zhang X, Yang Y, Shao S. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99:E20391.
- Rapini RP. Perforating diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1690-1696.
- Gao L, Gu L, Chen Z, et al. Doxycycline combined with NB-UVB phototherapy for acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020;16:917-921.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Psychocutaneous disorders. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:50-55. 11. Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Pruritus and dysesthesia. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:39-49. 12. Rubio FA, Herranz P, Robayna G, et al. Perforating folliculitis: report of a case in an HIV-infected man. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:300-302.
A 73-year-old woman presented for evaluation of a rash on the arms and legs of 3 months’ duration. The rash had developed abruptly, and she believed it was caused by bugs in the skin; her husband noted that she constantly picked at her arms and legs. She had a medical history of hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and endstage renal disease on dialysis. Physical examination revealed multiple pigmented papules and plaques, some with keratotic scale, on the lower legs (left) and arms, with greater involvement on the left arm (right). The lesions were of various sizes and shapes, some with a central keratotic core, and several lesions demonstrated erosion, excoriation, or ulceration. Histopathologic examination revealed slight attenuation of the epidermis with loss of normal rete peg architecture, alternating areas of hypergranulosis and hypogranulosis, central ulceration with inflammatory cells, and a basophilic hue to the ulcer base with sweeping up of the collagen fibers.
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Atopic Dermatitis April 2022
Dupilumab is a subcutaneous injection therapy that inhibits the interleukin 4 receptor alpha subunit. It has been approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with moderate-to-severe AD since 2017 and has since been approved for children and adolescents older than 6 years. Many real-world studies of the effectiveness of dupilumab have been published over the past few years. Kojanova and colleagues reported findings from a retrospective, multicenter study of 360 adults with severe AD who received dupilumab. They found that a high proportion of patients achieved a 75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75) at week 16 (66.6%), 1 year (89.5%), and 2 years (95.8%). Drug persistence rates were very high (> 90%) throughout the 2 years of therapy, suggesting that dupilumab was effective and well-tolerated.
Dupilumab was previously found to be associated with increased conjunctivitis in clinical trials and real-world studies. Schneeweiss and colleagues conducted a population-based longitudinal study of 5,004,117 patients with AD who newly initiated dupilumab, methotrexate, mycophenolate, and cyclosporine. They found that the risk of developing conjunctivitis diagnosed in clinical practice within 6 months of treatment initiation was approximately double with dupilumab compared with methotrexate, mycophenolate, or cyclosporine. Interestingly, comorbid asthma was found to be a risk factor for conjunctivitis in dupilumab initiators. This study provides insight into how commonly clinically significant conjunctivitis occurs with dupilumab treatment. Of note, the study results may underestimate the incidence of conjunctivitis because milder cases may go undetected.
Upadacitinib is an oral selective Janus kinase (JAK) 1 inhibitor that was approved in the United States in 2022 for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD. Simpson and colleagues reported on the long-term efficacy and safety of oral upadacitinib from the phase 3 double-blind, randomized controlled trials Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2 in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis ho had an inadequate response to topical therapy. The initial phase of the Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2 studies was 16 weeks in duration, with a placebo control group. At week 16, patients who received 15 or 30 mg upadacitinib in the initial 16 weeks of the study continued to receive that dose. Patients who received placebo in the initial 16 weeks were randomly assigned to receive oral 15 mg or 30 mg upadacitinib daily. So, in the long run, all patients received upadacitinib in the second phase of the study but were blinded to the dose they were receiving. The results from the first 16 weeks of treatment were previously published. Simpson and colleagues reported on the results up to week 52 from the second phase of the study. They showed that at week 52, 82.0% and 79.1% of patients in Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2 achieved a 75% improvement in EASI-75 when continuing on 15 mg upadacitinib and 84.9% and 84.3% in patients continuing 30 mg upadacitinib, respectively. More than 80% of patients who switched from placebo to upadacitinib at week 16 achieved EASI-75 at week 52. No safety signals were observed in this phase of the study that were not previously observed in other studies of upadacitinib for atopic dermatitis and other indications (rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis). These results indicate that upadacitinib has durable efficacy with long-term treatment in moderate-to-severe AD. These studies are ongoing, and I look forward to future results reporting for even longer-term treatment.
It is an exciting time in dermatology with the arrival of multiple novel therapies for atopic dermatitis. The field has already benefited so much by the tremendous interest and research effort into understanding how to best manage this disease. With so many more treatments in the pipeline, perhaps the best is yet to come.
Dupilumab is a subcutaneous injection therapy that inhibits the interleukin 4 receptor alpha subunit. It has been approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with moderate-to-severe AD since 2017 and has since been approved for children and adolescents older than 6 years. Many real-world studies of the effectiveness of dupilumab have been published over the past few years. Kojanova and colleagues reported findings from a retrospective, multicenter study of 360 adults with severe AD who received dupilumab. They found that a high proportion of patients achieved a 75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75) at week 16 (66.6%), 1 year (89.5%), and 2 years (95.8%). Drug persistence rates were very high (> 90%) throughout the 2 years of therapy, suggesting that dupilumab was effective and well-tolerated.
Dupilumab was previously found to be associated with increased conjunctivitis in clinical trials and real-world studies. Schneeweiss and colleagues conducted a population-based longitudinal study of 5,004,117 patients with AD who newly initiated dupilumab, methotrexate, mycophenolate, and cyclosporine. They found that the risk of developing conjunctivitis diagnosed in clinical practice within 6 months of treatment initiation was approximately double with dupilumab compared with methotrexate, mycophenolate, or cyclosporine. Interestingly, comorbid asthma was found to be a risk factor for conjunctivitis in dupilumab initiators. This study provides insight into how commonly clinically significant conjunctivitis occurs with dupilumab treatment. Of note, the study results may underestimate the incidence of conjunctivitis because milder cases may go undetected.
Upadacitinib is an oral selective Janus kinase (JAK) 1 inhibitor that was approved in the United States in 2022 for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD. Simpson and colleagues reported on the long-term efficacy and safety of oral upadacitinib from the phase 3 double-blind, randomized controlled trials Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2 in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis ho had an inadequate response to topical therapy. The initial phase of the Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2 studies was 16 weeks in duration, with a placebo control group. At week 16, patients who received 15 or 30 mg upadacitinib in the initial 16 weeks of the study continued to receive that dose. Patients who received placebo in the initial 16 weeks were randomly assigned to receive oral 15 mg or 30 mg upadacitinib daily. So, in the long run, all patients received upadacitinib in the second phase of the study but were blinded to the dose they were receiving. The results from the first 16 weeks of treatment were previously published. Simpson and colleagues reported on the results up to week 52 from the second phase of the study. They showed that at week 52, 82.0% and 79.1% of patients in Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2 achieved a 75% improvement in EASI-75 when continuing on 15 mg upadacitinib and 84.9% and 84.3% in patients continuing 30 mg upadacitinib, respectively. More than 80% of patients who switched from placebo to upadacitinib at week 16 achieved EASI-75 at week 52. No safety signals were observed in this phase of the study that were not previously observed in other studies of upadacitinib for atopic dermatitis and other indications (rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis). These results indicate that upadacitinib has durable efficacy with long-term treatment in moderate-to-severe AD. These studies are ongoing, and I look forward to future results reporting for even longer-term treatment.
It is an exciting time in dermatology with the arrival of multiple novel therapies for atopic dermatitis. The field has already benefited so much by the tremendous interest and research effort into understanding how to best manage this disease. With so many more treatments in the pipeline, perhaps the best is yet to come.
Dupilumab is a subcutaneous injection therapy that inhibits the interleukin 4 receptor alpha subunit. It has been approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with moderate-to-severe AD since 2017 and has since been approved for children and adolescents older than 6 years. Many real-world studies of the effectiveness of dupilumab have been published over the past few years. Kojanova and colleagues reported findings from a retrospective, multicenter study of 360 adults with severe AD who received dupilumab. They found that a high proportion of patients achieved a 75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75) at week 16 (66.6%), 1 year (89.5%), and 2 years (95.8%). Drug persistence rates were very high (> 90%) throughout the 2 years of therapy, suggesting that dupilumab was effective and well-tolerated.
Dupilumab was previously found to be associated with increased conjunctivitis in clinical trials and real-world studies. Schneeweiss and colleagues conducted a population-based longitudinal study of 5,004,117 patients with AD who newly initiated dupilumab, methotrexate, mycophenolate, and cyclosporine. They found that the risk of developing conjunctivitis diagnosed in clinical practice within 6 months of treatment initiation was approximately double with dupilumab compared with methotrexate, mycophenolate, or cyclosporine. Interestingly, comorbid asthma was found to be a risk factor for conjunctivitis in dupilumab initiators. This study provides insight into how commonly clinically significant conjunctivitis occurs with dupilumab treatment. Of note, the study results may underestimate the incidence of conjunctivitis because milder cases may go undetected.
Upadacitinib is an oral selective Janus kinase (JAK) 1 inhibitor that was approved in the United States in 2022 for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD. Simpson and colleagues reported on the long-term efficacy and safety of oral upadacitinib from the phase 3 double-blind, randomized controlled trials Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2 in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis ho had an inadequate response to topical therapy. The initial phase of the Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2 studies was 16 weeks in duration, with a placebo control group. At week 16, patients who received 15 or 30 mg upadacitinib in the initial 16 weeks of the study continued to receive that dose. Patients who received placebo in the initial 16 weeks were randomly assigned to receive oral 15 mg or 30 mg upadacitinib daily. So, in the long run, all patients received upadacitinib in the second phase of the study but were blinded to the dose they were receiving. The results from the first 16 weeks of treatment were previously published. Simpson and colleagues reported on the results up to week 52 from the second phase of the study. They showed that at week 52, 82.0% and 79.1% of patients in Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2 achieved a 75% improvement in EASI-75 when continuing on 15 mg upadacitinib and 84.9% and 84.3% in patients continuing 30 mg upadacitinib, respectively. More than 80% of patients who switched from placebo to upadacitinib at week 16 achieved EASI-75 at week 52. No safety signals were observed in this phase of the study that were not previously observed in other studies of upadacitinib for atopic dermatitis and other indications (rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis). These results indicate that upadacitinib has durable efficacy with long-term treatment in moderate-to-severe AD. These studies are ongoing, and I look forward to future results reporting for even longer-term treatment.
It is an exciting time in dermatology with the arrival of multiple novel therapies for atopic dermatitis. The field has already benefited so much by the tremendous interest and research effort into understanding how to best manage this disease. With so many more treatments in the pipeline, perhaps the best is yet to come.
Infectious disease pop quiz: Clinical challenge #21 for the ObGyn
What prophylactic antibiotic should be administered intrapartum to a pregnant woman who is colonized with group B streptococci but who has a mild allergy to penicillin?
Continue to the answer...
In this situation, the drug of choice is intravenous cefazolin, 2 g initially then 1 g every 8 hours until delivery. For patients with a severe allergy to penicillin, the drugs of choice are either clindamycin, 900 mg intravenously every 8 hours (if sensitivity of the organism is confirmed), or vancomycin, 20 mg/kg intravenously every 8 hours (maximum of 2 g per single dose).
- Duff P. Maternal and perinatal infections: bacterial. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al. Gabbe’s Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021:1124-1146.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TJ, et al. Creasy & Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019:862-919.
What prophylactic antibiotic should be administered intrapartum to a pregnant woman who is colonized with group B streptococci but who has a mild allergy to penicillin?
Continue to the answer...
In this situation, the drug of choice is intravenous cefazolin, 2 g initially then 1 g every 8 hours until delivery. For patients with a severe allergy to penicillin, the drugs of choice are either clindamycin, 900 mg intravenously every 8 hours (if sensitivity of the organism is confirmed), or vancomycin, 20 mg/kg intravenously every 8 hours (maximum of 2 g per single dose).
What prophylactic antibiotic should be administered intrapartum to a pregnant woman who is colonized with group B streptococci but who has a mild allergy to penicillin?
Continue to the answer...
In this situation, the drug of choice is intravenous cefazolin, 2 g initially then 1 g every 8 hours until delivery. For patients with a severe allergy to penicillin, the drugs of choice are either clindamycin, 900 mg intravenously every 8 hours (if sensitivity of the organism is confirmed), or vancomycin, 20 mg/kg intravenously every 8 hours (maximum of 2 g per single dose).
- Duff P. Maternal and perinatal infections: bacterial. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al. Gabbe’s Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021:1124-1146.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TJ, et al. Creasy & Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019:862-919.
- Duff P. Maternal and perinatal infections: bacterial. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al. Gabbe’s Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021:1124-1146.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TJ, et al. Creasy & Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019:862-919.
Do no harm: Benztropine revisited
Ms. P, a 63-year-old woman with a history of schizophrenia whose symptoms have been stable on haloperidol 10 mg/d and ziprasidone 40 mg twice daily, presents to the outpatient clinic for a medication review. She mentions that she has noticed problems with her “memory.” She says she has had difficulty remembering names of people and places as well as difficulty concentrating while reading and writing, which she did months ago with ease. A Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is conducted, and Ms. P scores 13/30, indicating moderate cognitive impairment. Visuospatial tasks and clock drawing are intact, but she exhibits impairments in working memory, attention, and concentration. One year ago, Ms. P’s MoCA score was 27/30. She agrees to a neurologic assessment and is referred to neurology for work-up.
Ms. P’s physical examination and routine laboratory tests are all within normal limits. The neurologic exam reveals deficits in working memory, concentration, and attention, but is otherwise unremarkable. MRI reveals mild chronic microvascular changes. The neurology service does not rule out cognitive impairment but recommends adjusting the dosage of Ms. P’s psychiatric medications to elucidate if her impairment of memory and attention is due to medications. However, Ms. P had been managed on her current regimen for several years and had not been hospitalized in many years. Previous attempts to taper her antipsychotics had resulted in worsening symptoms. Ms. P is reluctant to attempt a taper of her antipsychotics because she fears decompensation of her chronic illness. The treating team reviews Ms. P’s medication regimen, and notes that she is receiving benztropine 1 mg twice daily for prophylaxis of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). Ms. P denies past or present symptoms of drug-induced parkinsonism, dystonia, or akathisia as well as constipation, sialorrhea, blurry vision, palpitations, or urinary retention.
Benztropine is a tropane alkaloid that was synthetized by combining the tropine portion of atropine with the benzhydryl portion of diphenhydramine hydrochloride. It has anticholinergic and antihistaminic properties1 and seems to inhibit the dopamine transporter. Benztropine is indicated for all forms of parkinsonism, including antipsychotic-induced parkinsonism, but is also prescribed for many off-label uses, including sialorrhea and akathisia (although many authors do not recommend anticholinergics for this purpose2,3), and for prophylaxis of EPS. Benztropine can be administered intravenously, intramuscularly, or orally. Given orally, the typical dosing is twice daily with a maximum dose of 6 mg/d. Benztropine is preferred over diphenhydramine and trihexyphenidyl due to adverse effects of sedation or potential for misuse of the medication.1
Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) have been associated with lower rates of neurologic adverse effects compared with first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs). Because SGAs are increasingly prescribed, the use of benztropine (along with other agents such as trihexyphenidyl) for EPS prophylaxis is not an evidence-based practice. However, despite a movement away from prophylactic management of movement disorders, benztropine continues to be prescribed for EPS and/or cholinergic symptoms, despite the peripheral and cognitive adverse effects of this agent and, in many instances, the lack of clear indication for its use.
According to the most recent edition of the American Psychiatric Association’s (APA) Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Schizophrenia,4 anticholinergics should only be used for preventing acute dystonia in conjunction with a long-acting injectable antipsychotic. Furthermore, the APA Guideline states anticholinergics may be used for drug-induced parkinsonism when the dose of an antipsychotic cannot be reduced and an alternative agent is required. However, the first-line agent for drug-induced parkinsonism is amantadine, and benztropine should only be considered if amantadine is contraindicated.4 The rationale for this guideline and for judicious use of anticholinergics is that like any pharmacologic treatment, anticholinergics (including benztropine) carry the potential for adverse effects. For benztropine, these range from mild effects such as tachycardia and constipation to paralytic ileus, increased falls, worsening of tardive dyskinesia (TD), and potential cognitive impairment. Literature suggests that the first step in managing cognitive concerns in a patient with schizophrenia should be a close review of medications, and avoidance of agents with anticholinergic properties.5
Prescribing benztropine for EPS
EPS, which include dystonia, akathisia, drug-induced parkinsonism, and TD, are very frequent adverse effects noted with antipsychotics. Benztropine has demonstrated benefit in managing acute dystonia and the APA Guideline recommends IM administration of either benztropine 1 mg or diphenhydramine 25 mg for this purpose.4 However, in our experience, the most frequent indication for long-term prescribing of benztropine is prophylaxis of antipsychoticinduced dystonia. This use was suggested by some older studies. In a 1987 study by Boyer et al,6 patients who were administered benztropine with haloperidol did not develop acute dystonia, while patients who received haloperidol alone developed dystonia. However, this was a small retrospective study with methodological issues. Boyer et al6 suggested discontinuing prophylaxis with benztropine within 1 week, as acute dystonia occurred within 2.5 days. Other researchers7,8 have argued that short-term prophylaxis with benztropine for 1 week may work, especially during treatment with high-potency antipsychotics. However, in a review of the use of anticholinergics in conjunction with antipsychotics, Desmarais et al5 concluded that there is no need for prophylaxis and recommended alternative treatments. As we have noticed in Ms. P and other patients treated in our facilities, benztropine is frequently continued indefinitely without a clinical indication for its continuous use. Assessment and indication for continued use of benztropine should be considered regularly, and it should be discontinued when there is no clear indication for its use or when adverse effects emerge.
Prescribing benztropine for TD
TD is a subtype of tardive syndromes associated with the use of antipsychotics. It is characterized by repetitive involuntary movements such as lip smacking, puckering, chewing, or tongue protrusion. Proposed pathophysiological mechanisms include dopamine receptor hypersensitivity, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor excitotoxicity, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-containing neuron activity.
According to the APA Guideline, evidence of benztropine’s efficacy for the prevention of TD is lacking.4 A 2018 Cochrane systematic review9 was unable to provide a definitive conclusion regarding the effectiveness of benztropine and other anticholinergics for the treatment of antipsychotic-induced TD. While many clinicians believe that benztropine can be used to treat all types of EPS, there are no clear instances in reviewed literature where the efficacy of benztropine for treating TD could be reliably demonstrated. Furthermore, some literature suggests that anticholinergics such as benztropine increase the risk of developing TD.5,10 The mechanism underlying benztropine’s ability to precipitate or exacerbate abnormal movements is unclear, though it is theorized that anticholinergic medications may inhibit dopamine reuptake into neurons, thus leading to an excess of dopamine in the synaptic cleft that manifests as dyskinesias.10 Some authors also recommend that the first step in the management of TD should be to gradually discontinue anticholinergics, as this has been associated with improvement in TD.11
Continue to: Prescribing anticholinergics in specific patient populations...
Prescribing anticholinergics in specific patient populations
In addition to the adverse effects described above, benztropine can affect cognition, as we observed in Ms. P. The cholinergic system plays a role in human cognition, and blockade of muscarinic receptors has been associated with impairments in working memory and prefrontal tasks.12 These adverse cognitive effects are more pronounced in certain populations, including patients with schizophrenia and older adults.
Schizophrenia is associated with declining cognitive function, and the cognitive faculties of patients with schizophrenia may be worsened by anticholinergics. In patients with schizophrenia, social interactions and social integration are often impacted by profound negative symptoms such as social withdrawal and poverty of thought and speech.13 In a double-blind study by Baker et al,14 benztropine was found to have an impact on attention and concentration in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Baker et al14 found that patients with schizophrenia who were switched from benztropine to placebo increased their overall Wechsler Memory Scale scores compared to those maintained on benztropine. One crosssectional analysis found that a higher anticholinergic burden was associated with impairments across all cognitive domains, including memory, attention/control, executive and visuospatial functioning, and motor speed domains.15 Importantly, a higher anticholinergic medication burden was associated with worse cognitive performance.15 In addition to impairments in cognitive processing, anticholinergics have been associated with a decreased ability to benefit from psychosocial programs and impaired abilities to manage activities of daily living.4 In another study exploring the effects of discontinuing anticholinergics and the impact on movement disorders, Desmarais et al16 found patients experienced a significant improvement in scores on the Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia after discontinuing anticholinergics. Vinogradov et al17 noted that “serum anticholinergic activity in schizophrenia patients shows a significant association with impaired performance in measures of verbal working memory and verbal learning memory and was significantly associated with a lowered response to an intensive course of computerized cognitive training.” They felt their findings underscored the cognitive cost of medications with high anticholinergic burden.
Geriatric patients. Careful consideration should be given before starting benztropine in patients age ≥65. The 2019 American Geriatric Society’s Beers Criteria18 recommend avoiding benztropine in geriatric patients; the level of recommendation is strong. Furthermore, the American Geriatric Society designates benztropine as a medication that should be avoided, and a nondrug approach or alternative medication be prescribed independent of the patient’s condition or diagnosis. In a recently published case report, Esang et al19 highlighted several salient findings from previous studies on the risks associated with anticholinergic use:
- any medications a patient takes with anticholinergic properties contribute to the overall anticholinergic load of a patient’s medication regimen
- the higher the anticholinergic burden, the greater the cognitive deficits
- switching from an FGA to an SGA may decrease the risk of EPS and may limit the need for anticholinergic medications such as benztropine for a particular patient.
One must also consider that the effects of multiple medications with anticholinergic properties is probably cumulative.
Alternatives for treating drug-induced parkinsonism
Antipsychotics exert their effects through antagonism of the D2 receptor, and this is the same mechanism that leads to parkinsonism. Specifically, the mechanism is believed to be D2 receptor antagonism in the striatum leading to disinhibition of striatal neurons containing GABA.11 This disinhibition of medium spiny neurons is propagated when acetylcholine is released from cholinergic interneurons. Anticholinergics such as benztropine can remedy symptoms by blocking the signal of acetylcholine on the M1 receptors on medium spiny neurons. However, benztropine also has the propensity to decrease cholinergic transmission, thereby impairing storage of new information into long-term memory as well as impair perception of time—similar to effects seen with (for instance) diphenhydramine.20
The first step in managing drug-induced parkinsonism is to monitor symptoms. The APA Guideline recommends monitoring for acute-onset EPS at weekly intervals when beginning treatment and until stable for 2 weeks, and then monitoring at every follow-up visit thereafter.4 The next recommendation for long-term management of drug-induced parkinsonism is reducing the antipsychotic dose, or replacing the patient’s antipsychotic with an antipsychotic that is less likely to precipitate parkinsonism,4 such as quetiapine, iloperidone, or clozapine.11 If dose reduction is not possible, and the patient’s symptoms are severe, pharmacologic management is indicated. The APA Guideline recommends amantadine as a first-line agent because it is associated with fewer peripheral adverse effects and less impairment in cognition compared with benztropine.4 In a small (N = 60) doubleblind crossover trial, Gelenberg et al20 found benztropine 4 mg/d—but not amantadine 200 mg/d—impaired free recall and perception of time, and participants’ perception of their own memory impairment was significantly greater with benztropine. Amantadine has also been compared to biperiden, a relatively selective M1 muscarinic receptor muscarinic agent. In a separate double-blind crossover study of 26 patients with chronic schizophrenia, Silver and Geraisy21 found that compared to amantadine, biperiden was associated with worse memory performance. The recommended starting dose of amantadine for parkinsonism is 100 mg in the morning, increased to 100 mg twice a day and titrated to a maximum daily dose of 300 mg/d in divided doses.4
Continue to: Alternatives for treating drug-induced akathisia...
Alternatives for treating drug-induced akathisia
Akathisia remains a relatively common adverse effect of SGAs, and the profound physical distress and impaired functioning caused by akathisia necessitates pharmacologic treatment. Despite frequent use in practice for presumed benefit in akathisia, benztropine is not effective for the treatment of akathisia and the APA Guideline recommends that long-term management should begin with an antipsychotic dose reduction, followed by a switch to an agent with less propensity to incite akathisia.4 Acute manifestations of akathisia must be treated, and mirtazapine, propranolol, or clonazepam may be considered as alternatives.4 Mirtazapine is dosed 7.5 mg to 10 mg nightly for akathisia, though it should be used in caution in patients at risk for mania.4 Mirtazapine’s potent 5-HT2A blockade at low doses may contribute to its utility in treating akathisia.2 Propranolol, a nonselective lipophilic beta-adrenergic antagonist, also has demonstrated efficacy in managing akathisia, with recommended dosing of 40 mg to 80 mg twice daily.2 Benzodiazepines such as clonazepam require judicious use for akathisia because they may also precipitate or exacerbate cognitive impairment.4
Alternatives for treating TD
As mentioned above, benztropine is not recommended for the treatment of TD.1 The Box4,22,23 outlines potential treatment options for TD.
Box
Monitoring is the first step in the prevention of tardive dyskinesia (TD). The American Psychiatric Association’s (APA) Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Schizophrenia recommends patients receiving first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs) be monitored every 6 months, those prescribed second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) be monitored every 12 months, and twice as frequent monitoring for geriatric patients and those who developed involuntary movements rapidly after starting an antipsychotic.4
The APA Guideline recommends decreasing or gradually tapering antipsychotics as another strategy for preventing TD.4 However, these recommendations should be weighed against the risk of short-term antipsychotic withdrawal. Withdrawal of D2 antagonists is associated with worsening of dyskinesias or withdrawal dyskinesia and psychotic decompensation.22
Current treatment recommendations give preference to the importance of preventing development of TD by tapering to the lowest dose of antipsychotic needed to control symptoms for the shortest duration possible.22 Thereafter, if treatment intervention is needed, consideration should be given to the following pharmacological interventions in order from highest level of recommendation (Grade A) to lowest (Grade C):
A: vesicular monoamine transporter-2 inhibitors deutetrabenazine and valbenazine
B: clonazepam, ginkgo biloba
C: amantadine, tetrabenazine, and globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation.22
There is insufficient evidence to support or refute withdrawing causative agents or switching from FGAs to SGAs to treat TD.22 Furthermore, for many patients with schizophrenia, a gradual discontinuation of their antipsychotic must be weighed against the risk of relapse.23
Valbenazine and deutetrabenazine have been demonstrated to be efficacious and are FDA-approved for managing TD. The initial dose of valbenazine is 40 mg/d. Common adverse effects include somnolence and fatigue/ sedation. Valbenazine should be avoided in patients with QT prolongation or arrhythmias. Deutetrabenazine has less impact on the cytochrome P450 2D6 enzyme and therefore does not require genotyping as would be the case for patients who are receiving >50 mg/d of tetrabenazine. The starting dose of deutetrabenazine is 6 mg/d. Adverse effects include depression, suicidality, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, parkinsonism, and QT prolongation. Deutetrabenazine is contraindicated in patients who are suicidal or have untreated depression, hepatic impairment, or concomitant use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors.22 Deutetrabenazine is an isomer of tetrabenazine; however, evidence supporting the parent compound suggests limited use due to increased risk of adverse effects compared with valbenazine and deutetrabenazine.23 Tetrabenazine may be considered as an adjunctive treatment or used as a single agent if valbenazine or deutetrabenazine are not accessible.22
Discontinuing benztropine
Benztropine is recommended as a firstline agent for the management of acute dystonia, and it may be used temporarily for drug-induced parkinsonism, but it is not recommended to prevent EPS or TD. Given the multitude of adverse effects and cognitive impairment noted with anticholinergics, tapering should be considered for patients receiving an anticholinergic agent such as benztropine. Based on their review of earlier studies, Desmarais et al5 suggest a gradual 3-month discontinuation of benztropine. Multiple studies have demonstrated an ability to taper anticholinergics in days to months.4 However, gradual discontinuation is advisable to avoid cholinergic rebound and the reemergence of EPS, and to decrease the risk of neuroleptic malignant syndrome associated with sudden discontinuation.5 One suggested taper regimen is a decrease of 0.5 mg benztropine every week. Amantadine may be considered if parkinsonism is noted during the taper. Patients on benztropine may develop rebound symptoms, such as vivid dreams/nightmares; if this occurs, the taper rate can be slowed to a decrease of 0.5 mg every 2 weeks.4
Continue to: First do no harm...
First do no harm
Psychiatrists commonly prescribe benztropine to prevent EPS and TD, but available literature does not support the efficacy of benztropine for mitigating drug-induced parkinsonism, and studies report benztropine may significantly worsen cognitive processes and exacerbate TD.16 In addition, benztropine misuse has been correlated with euphoria and psychosis.16 More than 3 decades ago, the World Health Organization Heads of Centres Collaborating in WHO-Coordinated Studies on Biological Aspects of Mental Illness issued a consensus statement24 discouraging the prophylactic use of anticholinergics for patients receiving antipsychotics, yet we still see patients on an indefinite regimen of benztropine.
As clinicians, our goals should be to optimize a patient’s functioning and quality of life, and to use the lowest dose of medication along with the fewest medications necessary to avoid adverse effects such as EPS. Benztropine is recommended as a first-line agent for the management of acute dystonia, but its continued or indefinite use to prevent antipsychotic-induced adverse effects is not recommended. While all pharmacologic interventions carry a risk of adverse effects, weighing the risk of those effects against the clinical benefits is the prerogative of a skilled clinician. Benztropine and other anticholinergics prescribed for prophylactic purposes have numerous adverse effects, limited clinical utility, and a deleterious effect on quality of life. Furthermore, benztropine prophylaxis of drug-induced parkinsonism does not seem to be warranted, and the risks do not seem to outweigh the harm benztropine may cause, with the possible exception of “prophylactic” treatment of dystonia that is discontinued in a few days, as some researchers have suggested.6-8 The preventive value of benztropine has not been demonstrated. It is time we took inventory of medications that might cause more harm than good, rely on current treatment guidelines instead of habit, and use these agents judiciously while considering replacement with novel, safer medications whenever possible.
CASE CONTINUED
The clinical team considers benztropine’s ability to cause cognitive effects, and decides to taper and discontinue it over 1 month. Ms. P is seen in an outpatient clinic within 1 month of discontinuing benztropine. She reports that her difficulty remembering words and details has improved. She also says that she is now able to concentrate on writing and reading. The consulting neurologist also notes improvement. Ms. P continues to report improvement in symptoms over the next 2 months of follow-up, and says that her mood improved and she has less apathy.
Bottom Line
Benztropine is a first-line medication for acute dystonia, but its continued or indefinite use for preventing antipsychotic-induced adverse effects is not recommended. Given the multitude of adverse effects and cognitive impairment noted with anticholinergics, tapering should be considered for patients receiving an anticholinergic medication such as benztropine.
1. Cogentin [package insert]. McPherson, KS: Lundbeck Inc; 2013.
2. Poyurovsky M, Weizman A. Treatment of antipsychoticrelated akathisia revisited. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015; 35(6):711-714.
3. Salem H, Nagpal C, Pigott T, et al. Revisiting antipsychoticinduced akathisia: current issues and prospective challenges. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(5):789-798.
4. The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Schizophrenia. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2021.
5. Desmarais JE, Beauclair L, Margolese HC. Anticholinergics in the era of atypical antipsychotics: short-term or long-term treatment? J Psychopharmacol. 2012;26(9):1167-1174.
6. Boyer WF, Bakalar NH, Lake CR. Anticholinergic prophylaxis of acute haloperidol-induced acute dystonic reactions. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1987;7(3):164-166.
7. Winslow RS, Stillner V, Coons DJ, et al. Prevention of acute dystonic reactions in patients beginning high-potency neuroleptics. Am J Psychiatry. 1986;143(6):706-710.
8. Stern TA, Anderson WH. Benztropine prophylaxis of dystonic reactions. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1979; 61(3):261-262.
9. Bergman H, Soares‐Weiser K. Anticholinergic medication for antipsychotic‐induced tardive dyskinesia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;1(1):CD000204. doi:10.1002/ 14651858.CD000204.pub2
10. Howrie DL, Rowley AH, Krenzelok EP. Benztropineinduced acute dystonic reaction. Ann Emerg Med. 1986;15(5):594-596.
11. Ward KM, Citrome L. Antipsychotic-related movement disorders: drug-induced parkinsonism vs. tardive dyskinesia--key differences in pathophysiology and clinical management. Neurol Ther. 2018;7(2): 233-248.
12. Wijegunaratne H, Qazi H, Koola M. Chronic and bedtime use of benztropine with antipsychotics: is it necessary? Schizophr Res. 2014;153(1-3):248-249.
13. Möller HJ. The relevance of negative symptoms in schizophrenia and how to treat them with psychopharmaceuticals? Psychiatr Danub. 2016;28(4):435-440.
14. Baker LA, Cheng LY, Amara IB. The withdrawal of benztropine mesylate in chronic schizophrenic patients. Br J Psychiatry. 1983;143:584-590.
15. Joshi YB, Thomas ML, Braff DL, et al. Anticholinergic medication burden-associated cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(9):838-847.
16. Desmarais JE, Beauclair E, Annable L, et al. Effects of discontinuing anticholinergic treatment on movement disorders, cognition and psychopathology in patients with schizophrenia. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2014;4(6): 257-267.
17. Vinogradov S, Fisher M, Warm H, et al. The cognitive cost of anticholinergic burden: decreased response to cognitive training in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166(9): 1055-1062.
18. American Geriatrics Society 2019 Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society updated Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(4):674-694.
19. Esang M, Person US, Izekor OO, et al. An unlikely case of benztropine misuse in an elderly schizophrenic. Cureus. 2021;13(2):e13434. doi:10.7759/cureus.13434
20. Gelenberg AJ, Van Putten T, Lavori PW, et al. Anticholinergic effects on memory: benztropine versus amantadine. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1989;9(3):180-185.
21. Silver H, Geraisy N. Effects of biperiden and amantadine on memory in medicated chronic schizophrenic patients. A double-blind cross-over study. Br J Psychiatry. 1995; 166(2):241-243.
22. Bhidayasiri R, Jitkritsadakul O, Friedman J, et al. Updating the recommendations for treatment of tardive syndromes: a systematic review of new evidence and practical treatment algorithm. J Neurol Sci. 2018;389:67-75.
23. Ricciardi L, Pringsheim T, Barnes TRE, et al. Treatment recommendations for tardive dyskinesia. Canadian J Psychiatry. 2019;64(6):388-399.
24. Prophylactic use of anticholinergics in patients on long-term neuroleptic treatment. A consensus statement. World Health Organization heads of centres collaborating in WHO coordinated studies on biological aspects of mental illness. Br J Psychiatry. 1990;156:412.
Ms. P, a 63-year-old woman with a history of schizophrenia whose symptoms have been stable on haloperidol 10 mg/d and ziprasidone 40 mg twice daily, presents to the outpatient clinic for a medication review. She mentions that she has noticed problems with her “memory.” She says she has had difficulty remembering names of people and places as well as difficulty concentrating while reading and writing, which she did months ago with ease. A Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is conducted, and Ms. P scores 13/30, indicating moderate cognitive impairment. Visuospatial tasks and clock drawing are intact, but she exhibits impairments in working memory, attention, and concentration. One year ago, Ms. P’s MoCA score was 27/30. She agrees to a neurologic assessment and is referred to neurology for work-up.
Ms. P’s physical examination and routine laboratory tests are all within normal limits. The neurologic exam reveals deficits in working memory, concentration, and attention, but is otherwise unremarkable. MRI reveals mild chronic microvascular changes. The neurology service does not rule out cognitive impairment but recommends adjusting the dosage of Ms. P’s psychiatric medications to elucidate if her impairment of memory and attention is due to medications. However, Ms. P had been managed on her current regimen for several years and had not been hospitalized in many years. Previous attempts to taper her antipsychotics had resulted in worsening symptoms. Ms. P is reluctant to attempt a taper of her antipsychotics because she fears decompensation of her chronic illness. The treating team reviews Ms. P’s medication regimen, and notes that she is receiving benztropine 1 mg twice daily for prophylaxis of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). Ms. P denies past or present symptoms of drug-induced parkinsonism, dystonia, or akathisia as well as constipation, sialorrhea, blurry vision, palpitations, or urinary retention.
Benztropine is a tropane alkaloid that was synthetized by combining the tropine portion of atropine with the benzhydryl portion of diphenhydramine hydrochloride. It has anticholinergic and antihistaminic properties1 and seems to inhibit the dopamine transporter. Benztropine is indicated for all forms of parkinsonism, including antipsychotic-induced parkinsonism, but is also prescribed for many off-label uses, including sialorrhea and akathisia (although many authors do not recommend anticholinergics for this purpose2,3), and for prophylaxis of EPS. Benztropine can be administered intravenously, intramuscularly, or orally. Given orally, the typical dosing is twice daily with a maximum dose of 6 mg/d. Benztropine is preferred over diphenhydramine and trihexyphenidyl due to adverse effects of sedation or potential for misuse of the medication.1
Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) have been associated with lower rates of neurologic adverse effects compared with first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs). Because SGAs are increasingly prescribed, the use of benztropine (along with other agents such as trihexyphenidyl) for EPS prophylaxis is not an evidence-based practice. However, despite a movement away from prophylactic management of movement disorders, benztropine continues to be prescribed for EPS and/or cholinergic symptoms, despite the peripheral and cognitive adverse effects of this agent and, in many instances, the lack of clear indication for its use.
According to the most recent edition of the American Psychiatric Association’s (APA) Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Schizophrenia,4 anticholinergics should only be used for preventing acute dystonia in conjunction with a long-acting injectable antipsychotic. Furthermore, the APA Guideline states anticholinergics may be used for drug-induced parkinsonism when the dose of an antipsychotic cannot be reduced and an alternative agent is required. However, the first-line agent for drug-induced parkinsonism is amantadine, and benztropine should only be considered if amantadine is contraindicated.4 The rationale for this guideline and for judicious use of anticholinergics is that like any pharmacologic treatment, anticholinergics (including benztropine) carry the potential for adverse effects. For benztropine, these range from mild effects such as tachycardia and constipation to paralytic ileus, increased falls, worsening of tardive dyskinesia (TD), and potential cognitive impairment. Literature suggests that the first step in managing cognitive concerns in a patient with schizophrenia should be a close review of medications, and avoidance of agents with anticholinergic properties.5
Prescribing benztropine for EPS
EPS, which include dystonia, akathisia, drug-induced parkinsonism, and TD, are very frequent adverse effects noted with antipsychotics. Benztropine has demonstrated benefit in managing acute dystonia and the APA Guideline recommends IM administration of either benztropine 1 mg or diphenhydramine 25 mg for this purpose.4 However, in our experience, the most frequent indication for long-term prescribing of benztropine is prophylaxis of antipsychoticinduced dystonia. This use was suggested by some older studies. In a 1987 study by Boyer et al,6 patients who were administered benztropine with haloperidol did not develop acute dystonia, while patients who received haloperidol alone developed dystonia. However, this was a small retrospective study with methodological issues. Boyer et al6 suggested discontinuing prophylaxis with benztropine within 1 week, as acute dystonia occurred within 2.5 days. Other researchers7,8 have argued that short-term prophylaxis with benztropine for 1 week may work, especially during treatment with high-potency antipsychotics. However, in a review of the use of anticholinergics in conjunction with antipsychotics, Desmarais et al5 concluded that there is no need for prophylaxis and recommended alternative treatments. As we have noticed in Ms. P and other patients treated in our facilities, benztropine is frequently continued indefinitely without a clinical indication for its continuous use. Assessment and indication for continued use of benztropine should be considered regularly, and it should be discontinued when there is no clear indication for its use or when adverse effects emerge.
Prescribing benztropine for TD
TD is a subtype of tardive syndromes associated with the use of antipsychotics. It is characterized by repetitive involuntary movements such as lip smacking, puckering, chewing, or tongue protrusion. Proposed pathophysiological mechanisms include dopamine receptor hypersensitivity, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor excitotoxicity, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-containing neuron activity.
According to the APA Guideline, evidence of benztropine’s efficacy for the prevention of TD is lacking.4 A 2018 Cochrane systematic review9 was unable to provide a definitive conclusion regarding the effectiveness of benztropine and other anticholinergics for the treatment of antipsychotic-induced TD. While many clinicians believe that benztropine can be used to treat all types of EPS, there are no clear instances in reviewed literature where the efficacy of benztropine for treating TD could be reliably demonstrated. Furthermore, some literature suggests that anticholinergics such as benztropine increase the risk of developing TD.5,10 The mechanism underlying benztropine’s ability to precipitate or exacerbate abnormal movements is unclear, though it is theorized that anticholinergic medications may inhibit dopamine reuptake into neurons, thus leading to an excess of dopamine in the synaptic cleft that manifests as dyskinesias.10 Some authors also recommend that the first step in the management of TD should be to gradually discontinue anticholinergics, as this has been associated with improvement in TD.11
Continue to: Prescribing anticholinergics in specific patient populations...
Prescribing anticholinergics in specific patient populations
In addition to the adverse effects described above, benztropine can affect cognition, as we observed in Ms. P. The cholinergic system plays a role in human cognition, and blockade of muscarinic receptors has been associated with impairments in working memory and prefrontal tasks.12 These adverse cognitive effects are more pronounced in certain populations, including patients with schizophrenia and older adults.
Schizophrenia is associated with declining cognitive function, and the cognitive faculties of patients with schizophrenia may be worsened by anticholinergics. In patients with schizophrenia, social interactions and social integration are often impacted by profound negative symptoms such as social withdrawal and poverty of thought and speech.13 In a double-blind study by Baker et al,14 benztropine was found to have an impact on attention and concentration in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Baker et al14 found that patients with schizophrenia who were switched from benztropine to placebo increased their overall Wechsler Memory Scale scores compared to those maintained on benztropine. One crosssectional analysis found that a higher anticholinergic burden was associated with impairments across all cognitive domains, including memory, attention/control, executive and visuospatial functioning, and motor speed domains.15 Importantly, a higher anticholinergic medication burden was associated with worse cognitive performance.15 In addition to impairments in cognitive processing, anticholinergics have been associated with a decreased ability to benefit from psychosocial programs and impaired abilities to manage activities of daily living.4 In another study exploring the effects of discontinuing anticholinergics and the impact on movement disorders, Desmarais et al16 found patients experienced a significant improvement in scores on the Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia after discontinuing anticholinergics. Vinogradov et al17 noted that “serum anticholinergic activity in schizophrenia patients shows a significant association with impaired performance in measures of verbal working memory and verbal learning memory and was significantly associated with a lowered response to an intensive course of computerized cognitive training.” They felt their findings underscored the cognitive cost of medications with high anticholinergic burden.
Geriatric patients. Careful consideration should be given before starting benztropine in patients age ≥65. The 2019 American Geriatric Society’s Beers Criteria18 recommend avoiding benztropine in geriatric patients; the level of recommendation is strong. Furthermore, the American Geriatric Society designates benztropine as a medication that should be avoided, and a nondrug approach or alternative medication be prescribed independent of the patient’s condition or diagnosis. In a recently published case report, Esang et al19 highlighted several salient findings from previous studies on the risks associated with anticholinergic use:
- any medications a patient takes with anticholinergic properties contribute to the overall anticholinergic load of a patient’s medication regimen
- the higher the anticholinergic burden, the greater the cognitive deficits
- switching from an FGA to an SGA may decrease the risk of EPS and may limit the need for anticholinergic medications such as benztropine for a particular patient.
One must also consider that the effects of multiple medications with anticholinergic properties is probably cumulative.
Alternatives for treating drug-induced parkinsonism
Antipsychotics exert their effects through antagonism of the D2 receptor, and this is the same mechanism that leads to parkinsonism. Specifically, the mechanism is believed to be D2 receptor antagonism in the striatum leading to disinhibition of striatal neurons containing GABA.11 This disinhibition of medium spiny neurons is propagated when acetylcholine is released from cholinergic interneurons. Anticholinergics such as benztropine can remedy symptoms by blocking the signal of acetylcholine on the M1 receptors on medium spiny neurons. However, benztropine also has the propensity to decrease cholinergic transmission, thereby impairing storage of new information into long-term memory as well as impair perception of time—similar to effects seen with (for instance) diphenhydramine.20
The first step in managing drug-induced parkinsonism is to monitor symptoms. The APA Guideline recommends monitoring for acute-onset EPS at weekly intervals when beginning treatment and until stable for 2 weeks, and then monitoring at every follow-up visit thereafter.4 The next recommendation for long-term management of drug-induced parkinsonism is reducing the antipsychotic dose, or replacing the patient’s antipsychotic with an antipsychotic that is less likely to precipitate parkinsonism,4 such as quetiapine, iloperidone, or clozapine.11 If dose reduction is not possible, and the patient’s symptoms are severe, pharmacologic management is indicated. The APA Guideline recommends amantadine as a first-line agent because it is associated with fewer peripheral adverse effects and less impairment in cognition compared with benztropine.4 In a small (N = 60) doubleblind crossover trial, Gelenberg et al20 found benztropine 4 mg/d—but not amantadine 200 mg/d—impaired free recall and perception of time, and participants’ perception of their own memory impairment was significantly greater with benztropine. Amantadine has also been compared to biperiden, a relatively selective M1 muscarinic receptor muscarinic agent. In a separate double-blind crossover study of 26 patients with chronic schizophrenia, Silver and Geraisy21 found that compared to amantadine, biperiden was associated with worse memory performance. The recommended starting dose of amantadine for parkinsonism is 100 mg in the morning, increased to 100 mg twice a day and titrated to a maximum daily dose of 300 mg/d in divided doses.4
Continue to: Alternatives for treating drug-induced akathisia...
Alternatives for treating drug-induced akathisia
Akathisia remains a relatively common adverse effect of SGAs, and the profound physical distress and impaired functioning caused by akathisia necessitates pharmacologic treatment. Despite frequent use in practice for presumed benefit in akathisia, benztropine is not effective for the treatment of akathisia and the APA Guideline recommends that long-term management should begin with an antipsychotic dose reduction, followed by a switch to an agent with less propensity to incite akathisia.4 Acute manifestations of akathisia must be treated, and mirtazapine, propranolol, or clonazepam may be considered as alternatives.4 Mirtazapine is dosed 7.5 mg to 10 mg nightly for akathisia, though it should be used in caution in patients at risk for mania.4 Mirtazapine’s potent 5-HT2A blockade at low doses may contribute to its utility in treating akathisia.2 Propranolol, a nonselective lipophilic beta-adrenergic antagonist, also has demonstrated efficacy in managing akathisia, with recommended dosing of 40 mg to 80 mg twice daily.2 Benzodiazepines such as clonazepam require judicious use for akathisia because they may also precipitate or exacerbate cognitive impairment.4
Alternatives for treating TD
As mentioned above, benztropine is not recommended for the treatment of TD.1 The Box4,22,23 outlines potential treatment options for TD.
Box
Monitoring is the first step in the prevention of tardive dyskinesia (TD). The American Psychiatric Association’s (APA) Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Schizophrenia recommends patients receiving first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs) be monitored every 6 months, those prescribed second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) be monitored every 12 months, and twice as frequent monitoring for geriatric patients and those who developed involuntary movements rapidly after starting an antipsychotic.4
The APA Guideline recommends decreasing or gradually tapering antipsychotics as another strategy for preventing TD.4 However, these recommendations should be weighed against the risk of short-term antipsychotic withdrawal. Withdrawal of D2 antagonists is associated with worsening of dyskinesias or withdrawal dyskinesia and psychotic decompensation.22
Current treatment recommendations give preference to the importance of preventing development of TD by tapering to the lowest dose of antipsychotic needed to control symptoms for the shortest duration possible.22 Thereafter, if treatment intervention is needed, consideration should be given to the following pharmacological interventions in order from highest level of recommendation (Grade A) to lowest (Grade C):
A: vesicular monoamine transporter-2 inhibitors deutetrabenazine and valbenazine
B: clonazepam, ginkgo biloba
C: amantadine, tetrabenazine, and globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation.22
There is insufficient evidence to support or refute withdrawing causative agents or switching from FGAs to SGAs to treat TD.22 Furthermore, for many patients with schizophrenia, a gradual discontinuation of their antipsychotic must be weighed against the risk of relapse.23
Valbenazine and deutetrabenazine have been demonstrated to be efficacious and are FDA-approved for managing TD. The initial dose of valbenazine is 40 mg/d. Common adverse effects include somnolence and fatigue/ sedation. Valbenazine should be avoided in patients with QT prolongation or arrhythmias. Deutetrabenazine has less impact on the cytochrome P450 2D6 enzyme and therefore does not require genotyping as would be the case for patients who are receiving >50 mg/d of tetrabenazine. The starting dose of deutetrabenazine is 6 mg/d. Adverse effects include depression, suicidality, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, parkinsonism, and QT prolongation. Deutetrabenazine is contraindicated in patients who are suicidal or have untreated depression, hepatic impairment, or concomitant use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors.22 Deutetrabenazine is an isomer of tetrabenazine; however, evidence supporting the parent compound suggests limited use due to increased risk of adverse effects compared with valbenazine and deutetrabenazine.23 Tetrabenazine may be considered as an adjunctive treatment or used as a single agent if valbenazine or deutetrabenazine are not accessible.22
Discontinuing benztropine
Benztropine is recommended as a firstline agent for the management of acute dystonia, and it may be used temporarily for drug-induced parkinsonism, but it is not recommended to prevent EPS or TD. Given the multitude of adverse effects and cognitive impairment noted with anticholinergics, tapering should be considered for patients receiving an anticholinergic agent such as benztropine. Based on their review of earlier studies, Desmarais et al5 suggest a gradual 3-month discontinuation of benztropine. Multiple studies have demonstrated an ability to taper anticholinergics in days to months.4 However, gradual discontinuation is advisable to avoid cholinergic rebound and the reemergence of EPS, and to decrease the risk of neuroleptic malignant syndrome associated with sudden discontinuation.5 One suggested taper regimen is a decrease of 0.5 mg benztropine every week. Amantadine may be considered if parkinsonism is noted during the taper. Patients on benztropine may develop rebound symptoms, such as vivid dreams/nightmares; if this occurs, the taper rate can be slowed to a decrease of 0.5 mg every 2 weeks.4
Continue to: First do no harm...
First do no harm
Psychiatrists commonly prescribe benztropine to prevent EPS and TD, but available literature does not support the efficacy of benztropine for mitigating drug-induced parkinsonism, and studies report benztropine may significantly worsen cognitive processes and exacerbate TD.16 In addition, benztropine misuse has been correlated with euphoria and psychosis.16 More than 3 decades ago, the World Health Organization Heads of Centres Collaborating in WHO-Coordinated Studies on Biological Aspects of Mental Illness issued a consensus statement24 discouraging the prophylactic use of anticholinergics for patients receiving antipsychotics, yet we still see patients on an indefinite regimen of benztropine.
As clinicians, our goals should be to optimize a patient’s functioning and quality of life, and to use the lowest dose of medication along with the fewest medications necessary to avoid adverse effects such as EPS. Benztropine is recommended as a first-line agent for the management of acute dystonia, but its continued or indefinite use to prevent antipsychotic-induced adverse effects is not recommended. While all pharmacologic interventions carry a risk of adverse effects, weighing the risk of those effects against the clinical benefits is the prerogative of a skilled clinician. Benztropine and other anticholinergics prescribed for prophylactic purposes have numerous adverse effects, limited clinical utility, and a deleterious effect on quality of life. Furthermore, benztropine prophylaxis of drug-induced parkinsonism does not seem to be warranted, and the risks do not seem to outweigh the harm benztropine may cause, with the possible exception of “prophylactic” treatment of dystonia that is discontinued in a few days, as some researchers have suggested.6-8 The preventive value of benztropine has not been demonstrated. It is time we took inventory of medications that might cause more harm than good, rely on current treatment guidelines instead of habit, and use these agents judiciously while considering replacement with novel, safer medications whenever possible.
CASE CONTINUED
The clinical team considers benztropine’s ability to cause cognitive effects, and decides to taper and discontinue it over 1 month. Ms. P is seen in an outpatient clinic within 1 month of discontinuing benztropine. She reports that her difficulty remembering words and details has improved. She also says that she is now able to concentrate on writing and reading. The consulting neurologist also notes improvement. Ms. P continues to report improvement in symptoms over the next 2 months of follow-up, and says that her mood improved and she has less apathy.
Bottom Line
Benztropine is a first-line medication for acute dystonia, but its continued or indefinite use for preventing antipsychotic-induced adverse effects is not recommended. Given the multitude of adverse effects and cognitive impairment noted with anticholinergics, tapering should be considered for patients receiving an anticholinergic medication such as benztropine.
Ms. P, a 63-year-old woman with a history of schizophrenia whose symptoms have been stable on haloperidol 10 mg/d and ziprasidone 40 mg twice daily, presents to the outpatient clinic for a medication review. She mentions that she has noticed problems with her “memory.” She says she has had difficulty remembering names of people and places as well as difficulty concentrating while reading and writing, which she did months ago with ease. A Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is conducted, and Ms. P scores 13/30, indicating moderate cognitive impairment. Visuospatial tasks and clock drawing are intact, but she exhibits impairments in working memory, attention, and concentration. One year ago, Ms. P’s MoCA score was 27/30. She agrees to a neurologic assessment and is referred to neurology for work-up.
Ms. P’s physical examination and routine laboratory tests are all within normal limits. The neurologic exam reveals deficits in working memory, concentration, and attention, but is otherwise unremarkable. MRI reveals mild chronic microvascular changes. The neurology service does not rule out cognitive impairment but recommends adjusting the dosage of Ms. P’s psychiatric medications to elucidate if her impairment of memory and attention is due to medications. However, Ms. P had been managed on her current regimen for several years and had not been hospitalized in many years. Previous attempts to taper her antipsychotics had resulted in worsening symptoms. Ms. P is reluctant to attempt a taper of her antipsychotics because she fears decompensation of her chronic illness. The treating team reviews Ms. P’s medication regimen, and notes that she is receiving benztropine 1 mg twice daily for prophylaxis of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). Ms. P denies past or present symptoms of drug-induced parkinsonism, dystonia, or akathisia as well as constipation, sialorrhea, blurry vision, palpitations, or urinary retention.
Benztropine is a tropane alkaloid that was synthetized by combining the tropine portion of atropine with the benzhydryl portion of diphenhydramine hydrochloride. It has anticholinergic and antihistaminic properties1 and seems to inhibit the dopamine transporter. Benztropine is indicated for all forms of parkinsonism, including antipsychotic-induced parkinsonism, but is also prescribed for many off-label uses, including sialorrhea and akathisia (although many authors do not recommend anticholinergics for this purpose2,3), and for prophylaxis of EPS. Benztropine can be administered intravenously, intramuscularly, or orally. Given orally, the typical dosing is twice daily with a maximum dose of 6 mg/d. Benztropine is preferred over diphenhydramine and trihexyphenidyl due to adverse effects of sedation or potential for misuse of the medication.1
Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) have been associated with lower rates of neurologic adverse effects compared with first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs). Because SGAs are increasingly prescribed, the use of benztropine (along with other agents such as trihexyphenidyl) for EPS prophylaxis is not an evidence-based practice. However, despite a movement away from prophylactic management of movement disorders, benztropine continues to be prescribed for EPS and/or cholinergic symptoms, despite the peripheral and cognitive adverse effects of this agent and, in many instances, the lack of clear indication for its use.
According to the most recent edition of the American Psychiatric Association’s (APA) Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Schizophrenia,4 anticholinergics should only be used for preventing acute dystonia in conjunction with a long-acting injectable antipsychotic. Furthermore, the APA Guideline states anticholinergics may be used for drug-induced parkinsonism when the dose of an antipsychotic cannot be reduced and an alternative agent is required. However, the first-line agent for drug-induced parkinsonism is amantadine, and benztropine should only be considered if amantadine is contraindicated.4 The rationale for this guideline and for judicious use of anticholinergics is that like any pharmacologic treatment, anticholinergics (including benztropine) carry the potential for adverse effects. For benztropine, these range from mild effects such as tachycardia and constipation to paralytic ileus, increased falls, worsening of tardive dyskinesia (TD), and potential cognitive impairment. Literature suggests that the first step in managing cognitive concerns in a patient with schizophrenia should be a close review of medications, and avoidance of agents with anticholinergic properties.5
Prescribing benztropine for EPS
EPS, which include dystonia, akathisia, drug-induced parkinsonism, and TD, are very frequent adverse effects noted with antipsychotics. Benztropine has demonstrated benefit in managing acute dystonia and the APA Guideline recommends IM administration of either benztropine 1 mg or diphenhydramine 25 mg for this purpose.4 However, in our experience, the most frequent indication for long-term prescribing of benztropine is prophylaxis of antipsychoticinduced dystonia. This use was suggested by some older studies. In a 1987 study by Boyer et al,6 patients who were administered benztropine with haloperidol did not develop acute dystonia, while patients who received haloperidol alone developed dystonia. However, this was a small retrospective study with methodological issues. Boyer et al6 suggested discontinuing prophylaxis with benztropine within 1 week, as acute dystonia occurred within 2.5 days. Other researchers7,8 have argued that short-term prophylaxis with benztropine for 1 week may work, especially during treatment with high-potency antipsychotics. However, in a review of the use of anticholinergics in conjunction with antipsychotics, Desmarais et al5 concluded that there is no need for prophylaxis and recommended alternative treatments. As we have noticed in Ms. P and other patients treated in our facilities, benztropine is frequently continued indefinitely without a clinical indication for its continuous use. Assessment and indication for continued use of benztropine should be considered regularly, and it should be discontinued when there is no clear indication for its use or when adverse effects emerge.
Prescribing benztropine for TD
TD is a subtype of tardive syndromes associated with the use of antipsychotics. It is characterized by repetitive involuntary movements such as lip smacking, puckering, chewing, or tongue protrusion. Proposed pathophysiological mechanisms include dopamine receptor hypersensitivity, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor excitotoxicity, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-containing neuron activity.
According to the APA Guideline, evidence of benztropine’s efficacy for the prevention of TD is lacking.4 A 2018 Cochrane systematic review9 was unable to provide a definitive conclusion regarding the effectiveness of benztropine and other anticholinergics for the treatment of antipsychotic-induced TD. While many clinicians believe that benztropine can be used to treat all types of EPS, there are no clear instances in reviewed literature where the efficacy of benztropine for treating TD could be reliably demonstrated. Furthermore, some literature suggests that anticholinergics such as benztropine increase the risk of developing TD.5,10 The mechanism underlying benztropine’s ability to precipitate or exacerbate abnormal movements is unclear, though it is theorized that anticholinergic medications may inhibit dopamine reuptake into neurons, thus leading to an excess of dopamine in the synaptic cleft that manifests as dyskinesias.10 Some authors also recommend that the first step in the management of TD should be to gradually discontinue anticholinergics, as this has been associated with improvement in TD.11
Continue to: Prescribing anticholinergics in specific patient populations...
Prescribing anticholinergics in specific patient populations
In addition to the adverse effects described above, benztropine can affect cognition, as we observed in Ms. P. The cholinergic system plays a role in human cognition, and blockade of muscarinic receptors has been associated with impairments in working memory and prefrontal tasks.12 These adverse cognitive effects are more pronounced in certain populations, including patients with schizophrenia and older adults.
Schizophrenia is associated with declining cognitive function, and the cognitive faculties of patients with schizophrenia may be worsened by anticholinergics. In patients with schizophrenia, social interactions and social integration are often impacted by profound negative symptoms such as social withdrawal and poverty of thought and speech.13 In a double-blind study by Baker et al,14 benztropine was found to have an impact on attention and concentration in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Baker et al14 found that patients with schizophrenia who were switched from benztropine to placebo increased their overall Wechsler Memory Scale scores compared to those maintained on benztropine. One crosssectional analysis found that a higher anticholinergic burden was associated with impairments across all cognitive domains, including memory, attention/control, executive and visuospatial functioning, and motor speed domains.15 Importantly, a higher anticholinergic medication burden was associated with worse cognitive performance.15 In addition to impairments in cognitive processing, anticholinergics have been associated with a decreased ability to benefit from psychosocial programs and impaired abilities to manage activities of daily living.4 In another study exploring the effects of discontinuing anticholinergics and the impact on movement disorders, Desmarais et al16 found patients experienced a significant improvement in scores on the Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia after discontinuing anticholinergics. Vinogradov et al17 noted that “serum anticholinergic activity in schizophrenia patients shows a significant association with impaired performance in measures of verbal working memory and verbal learning memory and was significantly associated with a lowered response to an intensive course of computerized cognitive training.” They felt their findings underscored the cognitive cost of medications with high anticholinergic burden.
Geriatric patients. Careful consideration should be given before starting benztropine in patients age ≥65. The 2019 American Geriatric Society’s Beers Criteria18 recommend avoiding benztropine in geriatric patients; the level of recommendation is strong. Furthermore, the American Geriatric Society designates benztropine as a medication that should be avoided, and a nondrug approach or alternative medication be prescribed independent of the patient’s condition or diagnosis. In a recently published case report, Esang et al19 highlighted several salient findings from previous studies on the risks associated with anticholinergic use:
- any medications a patient takes with anticholinergic properties contribute to the overall anticholinergic load of a patient’s medication regimen
- the higher the anticholinergic burden, the greater the cognitive deficits
- switching from an FGA to an SGA may decrease the risk of EPS and may limit the need for anticholinergic medications such as benztropine for a particular patient.
One must also consider that the effects of multiple medications with anticholinergic properties is probably cumulative.
Alternatives for treating drug-induced parkinsonism
Antipsychotics exert their effects through antagonism of the D2 receptor, and this is the same mechanism that leads to parkinsonism. Specifically, the mechanism is believed to be D2 receptor antagonism in the striatum leading to disinhibition of striatal neurons containing GABA.11 This disinhibition of medium spiny neurons is propagated when acetylcholine is released from cholinergic interneurons. Anticholinergics such as benztropine can remedy symptoms by blocking the signal of acetylcholine on the M1 receptors on medium spiny neurons. However, benztropine also has the propensity to decrease cholinergic transmission, thereby impairing storage of new information into long-term memory as well as impair perception of time—similar to effects seen with (for instance) diphenhydramine.20
The first step in managing drug-induced parkinsonism is to monitor symptoms. The APA Guideline recommends monitoring for acute-onset EPS at weekly intervals when beginning treatment and until stable for 2 weeks, and then monitoring at every follow-up visit thereafter.4 The next recommendation for long-term management of drug-induced parkinsonism is reducing the antipsychotic dose, or replacing the patient’s antipsychotic with an antipsychotic that is less likely to precipitate parkinsonism,4 such as quetiapine, iloperidone, or clozapine.11 If dose reduction is not possible, and the patient’s symptoms are severe, pharmacologic management is indicated. The APA Guideline recommends amantadine as a first-line agent because it is associated with fewer peripheral adverse effects and less impairment in cognition compared with benztropine.4 In a small (N = 60) doubleblind crossover trial, Gelenberg et al20 found benztropine 4 mg/d—but not amantadine 200 mg/d—impaired free recall and perception of time, and participants’ perception of their own memory impairment was significantly greater with benztropine. Amantadine has also been compared to biperiden, a relatively selective M1 muscarinic receptor muscarinic agent. In a separate double-blind crossover study of 26 patients with chronic schizophrenia, Silver and Geraisy21 found that compared to amantadine, biperiden was associated with worse memory performance. The recommended starting dose of amantadine for parkinsonism is 100 mg in the morning, increased to 100 mg twice a day and titrated to a maximum daily dose of 300 mg/d in divided doses.4
Continue to: Alternatives for treating drug-induced akathisia...
Alternatives for treating drug-induced akathisia
Akathisia remains a relatively common adverse effect of SGAs, and the profound physical distress and impaired functioning caused by akathisia necessitates pharmacologic treatment. Despite frequent use in practice for presumed benefit in akathisia, benztropine is not effective for the treatment of akathisia and the APA Guideline recommends that long-term management should begin with an antipsychotic dose reduction, followed by a switch to an agent with less propensity to incite akathisia.4 Acute manifestations of akathisia must be treated, and mirtazapine, propranolol, or clonazepam may be considered as alternatives.4 Mirtazapine is dosed 7.5 mg to 10 mg nightly for akathisia, though it should be used in caution in patients at risk for mania.4 Mirtazapine’s potent 5-HT2A blockade at low doses may contribute to its utility in treating akathisia.2 Propranolol, a nonselective lipophilic beta-adrenergic antagonist, also has demonstrated efficacy in managing akathisia, with recommended dosing of 40 mg to 80 mg twice daily.2 Benzodiazepines such as clonazepam require judicious use for akathisia because they may also precipitate or exacerbate cognitive impairment.4
Alternatives for treating TD
As mentioned above, benztropine is not recommended for the treatment of TD.1 The Box4,22,23 outlines potential treatment options for TD.
Box
Monitoring is the first step in the prevention of tardive dyskinesia (TD). The American Psychiatric Association’s (APA) Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Schizophrenia recommends patients receiving first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs) be monitored every 6 months, those prescribed second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) be monitored every 12 months, and twice as frequent monitoring for geriatric patients and those who developed involuntary movements rapidly after starting an antipsychotic.4
The APA Guideline recommends decreasing or gradually tapering antipsychotics as another strategy for preventing TD.4 However, these recommendations should be weighed against the risk of short-term antipsychotic withdrawal. Withdrawal of D2 antagonists is associated with worsening of dyskinesias or withdrawal dyskinesia and psychotic decompensation.22
Current treatment recommendations give preference to the importance of preventing development of TD by tapering to the lowest dose of antipsychotic needed to control symptoms for the shortest duration possible.22 Thereafter, if treatment intervention is needed, consideration should be given to the following pharmacological interventions in order from highest level of recommendation (Grade A) to lowest (Grade C):
A: vesicular monoamine transporter-2 inhibitors deutetrabenazine and valbenazine
B: clonazepam, ginkgo biloba
C: amantadine, tetrabenazine, and globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation.22
There is insufficient evidence to support or refute withdrawing causative agents or switching from FGAs to SGAs to treat TD.22 Furthermore, for many patients with schizophrenia, a gradual discontinuation of their antipsychotic must be weighed against the risk of relapse.23
Valbenazine and deutetrabenazine have been demonstrated to be efficacious and are FDA-approved for managing TD. The initial dose of valbenazine is 40 mg/d. Common adverse effects include somnolence and fatigue/ sedation. Valbenazine should be avoided in patients with QT prolongation or arrhythmias. Deutetrabenazine has less impact on the cytochrome P450 2D6 enzyme and therefore does not require genotyping as would be the case for patients who are receiving >50 mg/d of tetrabenazine. The starting dose of deutetrabenazine is 6 mg/d. Adverse effects include depression, suicidality, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, parkinsonism, and QT prolongation. Deutetrabenazine is contraindicated in patients who are suicidal or have untreated depression, hepatic impairment, or concomitant use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors.22 Deutetrabenazine is an isomer of tetrabenazine; however, evidence supporting the parent compound suggests limited use due to increased risk of adverse effects compared with valbenazine and deutetrabenazine.23 Tetrabenazine may be considered as an adjunctive treatment or used as a single agent if valbenazine or deutetrabenazine are not accessible.22
Discontinuing benztropine
Benztropine is recommended as a firstline agent for the management of acute dystonia, and it may be used temporarily for drug-induced parkinsonism, but it is not recommended to prevent EPS or TD. Given the multitude of adverse effects and cognitive impairment noted with anticholinergics, tapering should be considered for patients receiving an anticholinergic agent such as benztropine. Based on their review of earlier studies, Desmarais et al5 suggest a gradual 3-month discontinuation of benztropine. Multiple studies have demonstrated an ability to taper anticholinergics in days to months.4 However, gradual discontinuation is advisable to avoid cholinergic rebound and the reemergence of EPS, and to decrease the risk of neuroleptic malignant syndrome associated with sudden discontinuation.5 One suggested taper regimen is a decrease of 0.5 mg benztropine every week. Amantadine may be considered if parkinsonism is noted during the taper. Patients on benztropine may develop rebound symptoms, such as vivid dreams/nightmares; if this occurs, the taper rate can be slowed to a decrease of 0.5 mg every 2 weeks.4
Continue to: First do no harm...
First do no harm
Psychiatrists commonly prescribe benztropine to prevent EPS and TD, but available literature does not support the efficacy of benztropine for mitigating drug-induced parkinsonism, and studies report benztropine may significantly worsen cognitive processes and exacerbate TD.16 In addition, benztropine misuse has been correlated with euphoria and psychosis.16 More than 3 decades ago, the World Health Organization Heads of Centres Collaborating in WHO-Coordinated Studies on Biological Aspects of Mental Illness issued a consensus statement24 discouraging the prophylactic use of anticholinergics for patients receiving antipsychotics, yet we still see patients on an indefinite regimen of benztropine.
As clinicians, our goals should be to optimize a patient’s functioning and quality of life, and to use the lowest dose of medication along with the fewest medications necessary to avoid adverse effects such as EPS. Benztropine is recommended as a first-line agent for the management of acute dystonia, but its continued or indefinite use to prevent antipsychotic-induced adverse effects is not recommended. While all pharmacologic interventions carry a risk of adverse effects, weighing the risk of those effects against the clinical benefits is the prerogative of a skilled clinician. Benztropine and other anticholinergics prescribed for prophylactic purposes have numerous adverse effects, limited clinical utility, and a deleterious effect on quality of life. Furthermore, benztropine prophylaxis of drug-induced parkinsonism does not seem to be warranted, and the risks do not seem to outweigh the harm benztropine may cause, with the possible exception of “prophylactic” treatment of dystonia that is discontinued in a few days, as some researchers have suggested.6-8 The preventive value of benztropine has not been demonstrated. It is time we took inventory of medications that might cause more harm than good, rely on current treatment guidelines instead of habit, and use these agents judiciously while considering replacement with novel, safer medications whenever possible.
CASE CONTINUED
The clinical team considers benztropine’s ability to cause cognitive effects, and decides to taper and discontinue it over 1 month. Ms. P is seen in an outpatient clinic within 1 month of discontinuing benztropine. She reports that her difficulty remembering words and details has improved. She also says that she is now able to concentrate on writing and reading. The consulting neurologist also notes improvement. Ms. P continues to report improvement in symptoms over the next 2 months of follow-up, and says that her mood improved and she has less apathy.
Bottom Line
Benztropine is a first-line medication for acute dystonia, but its continued or indefinite use for preventing antipsychotic-induced adverse effects is not recommended. Given the multitude of adverse effects and cognitive impairment noted with anticholinergics, tapering should be considered for patients receiving an anticholinergic medication such as benztropine.
1. Cogentin [package insert]. McPherson, KS: Lundbeck Inc; 2013.
2. Poyurovsky M, Weizman A. Treatment of antipsychoticrelated akathisia revisited. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015; 35(6):711-714.
3. Salem H, Nagpal C, Pigott T, et al. Revisiting antipsychoticinduced akathisia: current issues and prospective challenges. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(5):789-798.
4. The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Schizophrenia. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2021.
5. Desmarais JE, Beauclair L, Margolese HC. Anticholinergics in the era of atypical antipsychotics: short-term or long-term treatment? J Psychopharmacol. 2012;26(9):1167-1174.
6. Boyer WF, Bakalar NH, Lake CR. Anticholinergic prophylaxis of acute haloperidol-induced acute dystonic reactions. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1987;7(3):164-166.
7. Winslow RS, Stillner V, Coons DJ, et al. Prevention of acute dystonic reactions in patients beginning high-potency neuroleptics. Am J Psychiatry. 1986;143(6):706-710.
8. Stern TA, Anderson WH. Benztropine prophylaxis of dystonic reactions. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1979; 61(3):261-262.
9. Bergman H, Soares‐Weiser K. Anticholinergic medication for antipsychotic‐induced tardive dyskinesia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;1(1):CD000204. doi:10.1002/ 14651858.CD000204.pub2
10. Howrie DL, Rowley AH, Krenzelok EP. Benztropineinduced acute dystonic reaction. Ann Emerg Med. 1986;15(5):594-596.
11. Ward KM, Citrome L. Antipsychotic-related movement disorders: drug-induced parkinsonism vs. tardive dyskinesia--key differences in pathophysiology and clinical management. Neurol Ther. 2018;7(2): 233-248.
12. Wijegunaratne H, Qazi H, Koola M. Chronic and bedtime use of benztropine with antipsychotics: is it necessary? Schizophr Res. 2014;153(1-3):248-249.
13. Möller HJ. The relevance of negative symptoms in schizophrenia and how to treat them with psychopharmaceuticals? Psychiatr Danub. 2016;28(4):435-440.
14. Baker LA, Cheng LY, Amara IB. The withdrawal of benztropine mesylate in chronic schizophrenic patients. Br J Psychiatry. 1983;143:584-590.
15. Joshi YB, Thomas ML, Braff DL, et al. Anticholinergic medication burden-associated cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(9):838-847.
16. Desmarais JE, Beauclair E, Annable L, et al. Effects of discontinuing anticholinergic treatment on movement disorders, cognition and psychopathology in patients with schizophrenia. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2014;4(6): 257-267.
17. Vinogradov S, Fisher M, Warm H, et al. The cognitive cost of anticholinergic burden: decreased response to cognitive training in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166(9): 1055-1062.
18. American Geriatrics Society 2019 Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society updated Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(4):674-694.
19. Esang M, Person US, Izekor OO, et al. An unlikely case of benztropine misuse in an elderly schizophrenic. Cureus. 2021;13(2):e13434. doi:10.7759/cureus.13434
20. Gelenberg AJ, Van Putten T, Lavori PW, et al. Anticholinergic effects on memory: benztropine versus amantadine. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1989;9(3):180-185.
21. Silver H, Geraisy N. Effects of biperiden and amantadine on memory in medicated chronic schizophrenic patients. A double-blind cross-over study. Br J Psychiatry. 1995; 166(2):241-243.
22. Bhidayasiri R, Jitkritsadakul O, Friedman J, et al. Updating the recommendations for treatment of tardive syndromes: a systematic review of new evidence and practical treatment algorithm. J Neurol Sci. 2018;389:67-75.
23. Ricciardi L, Pringsheim T, Barnes TRE, et al. Treatment recommendations for tardive dyskinesia. Canadian J Psychiatry. 2019;64(6):388-399.
24. Prophylactic use of anticholinergics in patients on long-term neuroleptic treatment. A consensus statement. World Health Organization heads of centres collaborating in WHO coordinated studies on biological aspects of mental illness. Br J Psychiatry. 1990;156:412.
1. Cogentin [package insert]. McPherson, KS: Lundbeck Inc; 2013.
2. Poyurovsky M, Weizman A. Treatment of antipsychoticrelated akathisia revisited. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015; 35(6):711-714.
3. Salem H, Nagpal C, Pigott T, et al. Revisiting antipsychoticinduced akathisia: current issues and prospective challenges. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(5):789-798.
4. The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Schizophrenia. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2021.
5. Desmarais JE, Beauclair L, Margolese HC. Anticholinergics in the era of atypical antipsychotics: short-term or long-term treatment? J Psychopharmacol. 2012;26(9):1167-1174.
6. Boyer WF, Bakalar NH, Lake CR. Anticholinergic prophylaxis of acute haloperidol-induced acute dystonic reactions. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1987;7(3):164-166.
7. Winslow RS, Stillner V, Coons DJ, et al. Prevention of acute dystonic reactions in patients beginning high-potency neuroleptics. Am J Psychiatry. 1986;143(6):706-710.
8. Stern TA, Anderson WH. Benztropine prophylaxis of dystonic reactions. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1979; 61(3):261-262.
9. Bergman H, Soares‐Weiser K. Anticholinergic medication for antipsychotic‐induced tardive dyskinesia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;1(1):CD000204. doi:10.1002/ 14651858.CD000204.pub2
10. Howrie DL, Rowley AH, Krenzelok EP. Benztropineinduced acute dystonic reaction. Ann Emerg Med. 1986;15(5):594-596.
11. Ward KM, Citrome L. Antipsychotic-related movement disorders: drug-induced parkinsonism vs. tardive dyskinesia--key differences in pathophysiology and clinical management. Neurol Ther. 2018;7(2): 233-248.
12. Wijegunaratne H, Qazi H, Koola M. Chronic and bedtime use of benztropine with antipsychotics: is it necessary? Schizophr Res. 2014;153(1-3):248-249.
13. Möller HJ. The relevance of negative symptoms in schizophrenia and how to treat them with psychopharmaceuticals? Psychiatr Danub. 2016;28(4):435-440.
14. Baker LA, Cheng LY, Amara IB. The withdrawal of benztropine mesylate in chronic schizophrenic patients. Br J Psychiatry. 1983;143:584-590.
15. Joshi YB, Thomas ML, Braff DL, et al. Anticholinergic medication burden-associated cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(9):838-847.
16. Desmarais JE, Beauclair E, Annable L, et al. Effects of discontinuing anticholinergic treatment on movement disorders, cognition and psychopathology in patients with schizophrenia. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2014;4(6): 257-267.
17. Vinogradov S, Fisher M, Warm H, et al. The cognitive cost of anticholinergic burden: decreased response to cognitive training in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166(9): 1055-1062.
18. American Geriatrics Society 2019 Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society updated Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(4):674-694.
19. Esang M, Person US, Izekor OO, et al. An unlikely case of benztropine misuse in an elderly schizophrenic. Cureus. 2021;13(2):e13434. doi:10.7759/cureus.13434
20. Gelenberg AJ, Van Putten T, Lavori PW, et al. Anticholinergic effects on memory: benztropine versus amantadine. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1989;9(3):180-185.
21. Silver H, Geraisy N. Effects of biperiden and amantadine on memory in medicated chronic schizophrenic patients. A double-blind cross-over study. Br J Psychiatry. 1995; 166(2):241-243.
22. Bhidayasiri R, Jitkritsadakul O, Friedman J, et al. Updating the recommendations for treatment of tardive syndromes: a systematic review of new evidence and practical treatment algorithm. J Neurol Sci. 2018;389:67-75.
23. Ricciardi L, Pringsheim T, Barnes TRE, et al. Treatment recommendations for tardive dyskinesia. Canadian J Psychiatry. 2019;64(6):388-399.
24. Prophylactic use of anticholinergics in patients on long-term neuroleptic treatment. A consensus statement. World Health Organization heads of centres collaborating in WHO coordinated studies on biological aspects of mental illness. Br J Psychiatry. 1990;156:412.
Autism spectrum disorder in children and adolescents: Treatment options
SECOND OF 2 PARTS
Evidence supports the crucial role of early intervention and nonpharmacologic approaches
A large percentage of individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience persisting significant social deficits in adulthood,1 which often leads to isolation, depressive symptoms, and poor occupational and relationship functioning.2,3 Childhood is a vital time for making the most significant and lasting changes that can improve functioning of individuals with ASD. Psychiatrists and other physicians who treat children are in a key role to influence outcomes of children at risk for or diagnosed with ASD.
This article provides updates on various aspects of ASD diagnosis and treatment (based on available evidence up to March 2020). Part 1 (
A comprehensive approach is essential
Multiple treatment modalities have been recommended for ASD.5 It is essential to address all aspects of ASD through cognitive, developmental, social-communication, sensory-motor, and behavioral interventions. Nonpharmacologic interventions are crucial in improving long-term outcomes of children with ASD.6
Nonpharmacologic treatments
Nonpharmacologic interventions commonly utilized for children with ASD include behavioral therapies, other psychological therapies, speech-language therapy, occupational therapy, educational interventions, parent coaching/training, developmental social interventions, and other modalities of therapy that are delivered in school, home, and clinic settings.5,7
A recent study examining ASD treatment trends via caregivers’ reports (N = 5,122) from the SPARK (Simons Foundation Powering Autism Research for Knowledge) cohort in the United States reported that 80% of children received speech-language therapy or occupational therapy; 52% got both.5 The study revealed that approximately one-quarter utilized 3 therapies simultaneously; two-thirds had utilized 3 or more therapies in the previous year.5
Interventions for children with ASD need to be individualized.1,8 Evidence-based behavioral interventions for ASD fall into 2 broad categories: Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), and Naturalistic Developmental Behavioral Interventions (NDBI). Traditionally, ABA has been a key model, guiding treatment for enhancing social-communicating skills and lowering maladaptive behaviors in ASD.9 ABA follows a structured and prescribed format,10,11 and has been shown to be efficacious.1,7 More recently, NDBI, in which interventions are “embedded” in the natural environment of the young child and more actively incorporate a developmental perspective, has been shown to be beneficial in improving and generalizing social-communication skills in young children with ASD.7,11
Early Start Denver Model (ESDM) is an intensive, naturalistic behavioral intervention4 that has been shown to be efficacious for enhancing communication and adaptive behavior in children with ASD.7,8,12 A multisite randomized controlled trial (RCT) by Rogers et al12 that examined the efficacy of ESDM in 118 children (age 14 to 24 months) with ASD found the treatment was beneficial and superior compared with a “community intervention” group, in regards to language ability measured in time by group analyses.The ESDM intervention in this study involved weekly parent coaching for 3 months, along with 24 months of 15 hours/week of one-on-one treatment provided by therapy professionals.12
Reciprocal imitation training (RIT) is another naturalistic intervention that has shown benefit in training children with ASD in imitation skills during play.13 Studies have found that both RIT and ESDM can be parent-implemented, after parents receive training.13,14
Parent-mediated, parent-implemented interventions may have a role in improving outcomes in childhood ASD,7,15 particularly “better generalization and maintenance of skills than therapist-implemented intervention” for lowering challenging behaviors and enhancing verbal and nonverbal communication.16
Various social skills interventions have also been found effective for children with ASD.1 Such interventions are often provided in the school setting.7 Coordination with the child’s school to discuss and advocating for adequate and suitable interventions, educational services, and placement is an essential aspect of ASD treatment.7
Two other school-based, comprehensive treatment model interventions—Learning Experiences and Alternative Programs for Preschoolers and their Parents (LEAP), and TEACCH—have some evidence of leading to improvement in children with ASD.7,17
Some studies have found that music therapy may have high efficacy for children with ASD, even with smaller length and intensity of treatment, particularly in improving social interaction, engagement with parents, joint attention, and communication.3,18 Further research is needed to conclusively establish the efficacy of music therapy for ASD in children and adolescents.
A few studies have assessed the long-term outcomes of interventions for ASD; however, more research is needed.19 Pickles et al19 conducted a follow-up to determine the long-term effects of the Preschool Autism Communication Trial (PACT), an RCT of parent-mediated social communication therapy for children age 2 to 4 with ASD. The children’s average age at follow-up was 10 years. The authors found a significant long-term decrease in ASD symptoms and enhancement of social communication with parents (N = 152).
Technology-based interventions, including games and robotics, have been investigated in recent years, for treatment of children with ASD (eg, for improving social skills).20
Research suggests that the intensity (number of hours) and duration of nonpharmacologic treatments for ASD is critical to improving outcomes (Box1,3,5,7,10,16).
Box
A higher intensity of nonpharmacologic intervention (greater number of hours) has been associated with greater benefit for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), in the form of enhancements in IQ and adaptive behavior.1,10,16 In the United States, the intensity of interventions commonly ranges from 30 to 200 or more minutes per week.3 This may mean that a child with ASD who is receiving 30 minutes of speech therapy at school and continues to exhibit significant deficits in speech-language or social-communication may likely benefit from additional hours of speech therapy and/or social-communication skill training, and should be referred accordingly, even for private therapy services if needed and feasible.7 Guidelines created through a systematic review of evidence recommend at least 25 hours per week of comprehensive treatment interventions for children with ASD to address language, social deficits, and behavioral difficulties.1 The duration of intervention has also been shown to play a role in outcomes.1,3,10 Given the complexity and extent of impairment often associated with ASD, it is not surprising that in recent research examining trends in ASD treatment in the United States, most caregivers reported therapy as ongoing.5 The exact intensity and duration of nonpharmacologic interventions may depend on several factors, such as severity of ASD and of the specific deficit being targeted, type of intervention, and therapist skill. The quality of skills of the care provider has also been shown to affect the benefits gained from the intervention.3
Continue to: Pharmacotherapy...
Pharmacotherapy
Medications cannot resolve core features of ASD.21 However, certain medications may help address associated comorbidities, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, or others, when these conditions have not responded to nonpharmacologic interventions.7,22 Common symptoms that are often treated with pharmacotherapy include aggression, irritability, hyperactivity, attentional difficulties, tics, self-injurious behavior, obsessive-compulsive symptoms, and mood dysregulation/lability.23 Generally speaking, medications might be considered if symptoms are severe and markedly impair functioning. For mild to moderate conditions, psychotherapy and other nonpharmacologic interventions are generally considered first-line. Since none of the medications described below are specific to ASD and psychiatrists generally receive training in prescribing them for other indications, a comprehensive review of their risks and benefits is beyond the scope of this article. No psychotropic medications are known to have robust evidence for safety in preschool children with ASD, and thus are best avoided.
Antipsychotics. Risperidone (for age 5 and older) and aripiprazole (age 6 to 17) are the only medications FDA-approved for use in children and adolescents with ASD, specifically for irritability associated with ASD.21,24 These 2 second-generation antipsychotics may also assist in lowering aggression in patients with ASD.24 First-generation antipsychotics such as haloperidol have been shown to be effective for irritability and aggression in ASD, but the risk of significant adverse effects such as dyskinesias and extrapyramidal symptoms limit their use.24 Two studies (a double-blind study and an open-label extension of that study) in children and adolescents with ASD found that risperidone was more effective and better tolerated than haloperidol in behavioral measures, impulsivity, and even in the social domain.25,26 In addition to other adverse effects and risks, increased prolactin secondary to risperidone use requires close monitoring and caution.24-26 As is the case with the use of other psychotropic medications in children and adolescents, those with ASD who receive antipsychotics should also be periodically reassessed to determine the need for continued use of these medications.27 A multicenter relapse prevention RCT found no statistically significant difference in the time to relapse between aripiprazole and placebo.27 Metabolic syndrome, cardiac risks, and other risks need to be considered before prescribing an antipsychotic.28 Given their serious adverse effects profile, use should be considered only when there is severe impairment or risk of injury, after carefully weighing risks/benefits.
Medications for attentional difficulties. A multisite, randomized, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the use of extended-release guanfacine in children with ASD (N = 62) found the rate of positive response on the Clinical Global Impressions–Improvement scale was 50% for guanfacine vs 9.4% for placebo.29 Clinicians need to monitor for adverse effects of guanfacine, such as fatigue, drowsiness, lightheadedness, lowering of blood pressure and heart rate, and other effects.29 A randomized, double-blind trial of 97 children and adolescents with ASD and ADHD found that atomoxetine had moderate benefit for ADHD symptoms.30 The study reported no serious adverse effects.30 However, it is especially important to monitor for hepatic and cardiac adverse effects (in addition to monitoring for risk of increase in suicidal thoughts/behavior, as in the case of antidepressants) when using atomoxetine, in addition to other side effects and risks. Some evidence suggests that methylphenidate may be effective for attentional difficulties in children and adolescents with ASD21 but may pose a higher risk of adverse effects in this population compared with neurotypical patients.31
Antidepressants. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are sometimes used to reduce obsessive-compulsive symptoms, repetitive behavior, or depressive symptoms in children with ASD, but are not FDA-approved for children or adolescents with ASD. In general, there is inadequate evidence to support the use of SSRIs for ASD in children.31-34 In addition, children with ASD may be at a greater risk of adverse effects from SSRIs.32,34 Despite this, SSRIs are the most commonly prescribed psychotropic medications in children with ASD.32
An RCT examining the efficacy of fluoxetine in 158 children and adolescents with ASD found no significant difference in Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (CY-BOCS) score after 14 weeks of treatment; activation was a common adverse effect.35 A 2005 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 45 children/adolescents with ASD found that low-dose liquid fluoxetine was more effective than placebo for reducing repetitive behaviors in this population.36 Larger studies are warranted to further evaluate the efficacy and safety of fluoxetine (and of SSRIs in general, particularly in the long term) for children and adolescents with ASD.36 A 2009 randomized, placebo-controlled trial of 149 children with ASD revealed no significant difference between citalopram and placebo as measured by Clinical Global Impressions scale or CY-BOCS scores, and noted a significantly elevated likelihood of adverse effects.37
Other antidepressants. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of any other antidepressants in children and adolescents with ASD. A few studies38,39 have examined the use of venlafaxine in children with ASD; however, further research and controlled studies with large sample sizes are required to conclusively establish its benefits. There is a dearth of evidence examining the use of the tetracyclic antidepressant mirtazapine, or other classes of medications such as tricyclic antidepressants or mood stabilizers, in children with ASD; only a few small studies have assessed the efficacy and adverse effects of these medications for such patients.31
Polypharmacy. Although there is no evidence to support polypharmacy in children and adolescents with ASD, the practice appears to be rampant in these patients.28,40 A 2013 retrospective, observational study of psychotropic medication use in children with ASD (N = 33,565) found that 64% were prescribed psychotropic medications, and 35% exhibited evidence of polypharmacy.40 In this study, the total duration of polypharmacy averaged 525 days.40 When addressing polypharmacy, systematic deprescribing or simplification of the psychotropic medication regimen may be needed,28 while taking into account the patient’s complete clinical situation, including (but not limited to) tolerability of the medication regimen, presence or absence of current stressors, presence or absence of adequate supports, use of nonpharmacologic treatments where appropriate, and other factors.
More studies assessing the efficacy and safety of psychotropic medications for children and adolescents with ASD are needed,32 especially studies that evaluate the effects of long-term use, because evidence for pharmacologic treatments for children with ASD is mixed and insufficient.33 There is also a need for evidence-based standards for prescribing psychotropic medications in children and adolescents with ASD.
Psychotropic medications, if used in ASD, should be used only in conjunction with other evidence-based treatment modalities, and not as monotherapy.21 Children and adolescents with ASD may be particularly susceptible to side effects or adverse effects of certain psychotropic medications.31 When considering medications, carefully weigh the risks and benefits.7,21,24,28 Starting low and going slow is generally the preferred strategy.31,32 As always, when recommending medications, discuss in detail with parents the potential side effects, benefits, risks, interactions, and alternatives.
Other agents. Several double-blind, placebo-controlled trials have evaluated using melatonin for sleep difficulties in children and adolescents with ASD.41 A randomized, placebo-controlled, 12-week trial that assessed 160 children with ASD and insomnia found that melatonin plus cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) was superior in efficacy to melatonin alone, CBT alone, or placebo.41
The evidence regarding oxytocin use for children with ASD is mixed.31 Some small studies have associated improvement in the social domain with its use. Guastella et al42 conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of oxytocin nasal spray for 16 participants (age 12 to 19) with ASD, and found oxytocin enhanced emotional identification. Gordon et al43 conducted a functional MRI study of brain activity with oxytocin use in children with high-functioning ASD (N = 17). They found that oxytocin may augment “salience and hedonic evaluations of socially meaningful stimuli in children with ASD” and thus help social attunement. Further research is needed to evaluate the impact of oxytocin on social behavior.
Complementary and alternative medicine. Although there is limited and inconclusive evidence about the use of complementary and alternative medicine in children and adolescents with ASD, these therapies continue to be commonly used.44-46 A recent survey of parents (N = 211) of children with ASD from academic ASD outpatient clinics in Germany found that 46% reported their child was using or had used some type of complementary and alternative medicine.44 There is inadequate evidence to support the use of a gluten-free, casein-free diet for children/adolescents with ASD.46 A recent cross-sectional study assessing supplement use in 210 children with ASD in Canada found that 75% used supplements, such as multivitamins (77.8%), vitamin D (44.9%), omega 3 (42.5%), probiotics (36.5%), and magnesium (28.1%), despite insufficient evidence to support their safety or efficacy for children with ASD.47 Importantly, 33.5% of parents in this study reported that they did not inform the physician about all their child’s supplements.47 Some of the reasons the parents in this study provided for not disclosing information about supplements to their physicians were “physician lack of knowledge,” “no benefit,” “too time-consuming,” and “scared of judgment.”47 Semi-structured interviews of parents of 21 children with ASD in Australia revealed that parents found information on complementary and alternative medicine and therapies complex and often conflicting.45 In addition to recommendations from health care professionals, evidence suggests that parents often consider the opinions of media, friends, and family when making a decision on using complementary and alternative medicine modalities for children/adolescents with ASD.46 Such findings can inform physician practices regarding supplement use, and highlight the need to educate parents about the evidence regarding these therapies and potential adverse effects and interactions of such therapies,46 along with the need to develop a centralized, evidence-based resource for parents regarding their use.45
Omega 3 supplementation has in general shown few adverse effects47; still, risks/benefits need to be weighed before use. Some evidence suggests that it may decrease hyperactivity in children with ASD.31,48 However, further research, particularly controlled trials with large sample sizes, are needed for a definitive determination of efficacy.31,48 A meta-analysis that included 27 RCTs assessing the efficacy of dietary interventions for various ASD symptoms found that omega 3 supplementation was more effective than placebo, but compared with placebo, the effect size was small.49 A RCT of 73 children with ASD in New Zealand found that omega 3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids may benefit some core symptoms of ASD; the authors suggested that further research is needed to conclusively establish efficacy.50
Continue to: A need for advocacy and research..
A need for advocacy and research
Physicians who treat children with ASD can not only make appropriate referrals and educate parents, but also educate their patients’ schools and advocate for their patients to get the level of services they need.23,28
A recent study in the United States found that behavior therapy and speech-language therapy were used less often in the treatment of children with ASD in rural areas compared with those in metro areas.5 This suggests that in addition to increasing parents’ awareness and use of ASD services and providing referrals where appropriate, physicians are in a unique position to advocate for public health policies to improve access, coverage, and training for the provision of such services in rural areas.
There is need for ongoing research to further examine the efficacy and nuances of effects of various treatment interventions for ASD, especially long-term studies with larger sample sizes.11,51 Additionally, research is warranted to better understand the underlying genetic and neurobiological mechanisms of ASD, which would help guide the development of biomarkers,52 innovative treatments, and disease-modifying agents for ASD.7,22 Exploring the effects of potential alliances or joint action between biological and psychosocial interventions for ASD is also an area that needs further research.51
Bottom Line
A combination of treatment modalities (such as speech-language therapy, social skills training, behavior therapy/other psychotherapy, and occupational therapy for sensory sensitivities) is generally needed to improve the long-term outcomes of children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). In addition to the importance of early intervention, the intensity and duration of nonpharmacologic treatments are vital to improving outcomes in ASD.
1. Maglione MA, Gans D, Das L, et al. Nonmedical interventions for children with ASD: recommended guidelines and further research needs. Pediatrics. 2012;30(Suppl 2):S169-S178.
2. Simms MD, Jin XM. Autism, language disorder, and social (pragmatic) communication disorder: DSM-V and differential diagnoses. Pediatr Rev. 2015;36(8):355-363. doi:10.1542/pir.36-8-355
3. Su Maw S, Haga C. Effectiveness of cognitive, developmental, and behavioural interventions for autism spectrum disorder in preschool-aged children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon. 2018;4(9):e00763. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00763
4. Charman T. Editorial: trials and tribulations in early autism intervention research. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;58(9):846-848. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2019.03.004
5. Monz BU, Houghton R, Law K, et al. Treatment patterns in children with autism in the United States. Autism Res. 2019;12(3):517-526. doi:10.1002/aur.2070
6. Sperdin HF, Schaer M. Aberrant development of speech processing in young children with autism: new insights from neuroimaging biomarkers. Front Neurosci. 2016;10:393. doi:10.3389/fnins.2016.00393
7. Hyman SL, Levy SE, Myers SM, et al. Identification, evaluation, and management of children with autism spectrum disorder. Pediatrics. 2020;145(1):e20193447. doi:10.1542/peds.2019-3447
8. Contaldo A, Colombi C, Pierotti C, et al. Outcomes and moderators of Early Start Denver Model intervention in young children with autism spectrum disorder delivered in a mixed individual and group setting. Autism. 2020;24(3):718-729. doi:10.1177/1362361319888344
9. Lei J, Ventola P. Pivotal response treatment for autism spectrum disorder: current perspectives. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017;13:1613-1626. doi:10.2147/NDT.S120710
10. Landa RJ. Efficacy of early interventions for infants and young children with, and at risk for, autism spectrum disorders. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2018;30(1):25-39. doi:10.1080/09540261.2018.1432574
11. Schreibman L, Dawson G, Stahmer AC, et al. Naturalistic developmental behavioral interventions: empirically validated treatments for autism spectrum disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. 2015;45(8):2411-2428. doi:10.1007/s10803-015-2407-8
12. Rogers SJ, Estes A, Lord C, et al. A multisite randomized controlled two-phase trial of the Early Start Denver Model compared to treatment as usual. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;58(9):853-865. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2019.01.004
13. Ingersoll B, Gergans S. The effect of a parent-implemented imitation intervention on spontaneous imitation skills in young children with autism. Res Dev Disabil. 2007;28(2):163-175.
14. Waddington H, van der Meer L, Sigafoos J, et al. Examining parent use of specific intervention techniques during a 12-week training program based on the Early Start Denver Model. Autism. 2020;24(2):484-498. doi:10.1177/1362361319876495
15. Trembath D, Gurm M, Scheerer NE, et al. Systematic review of factors that may influence the outcomes and generalizability of parent‐mediated interventions for young children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2019;12(9):1304-1321.
16. Rogers SJ, Estes A, Lord C, et al. Effects of a brief Early Start Denver Model (ESDM)-based parent intervention on toddlers at risk for autism spectrum disorders: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(10):1052-1065. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2012.08.003
17. Boyd BA, Hume K, McBee MT, et al. Comparative efficacy of LEAP, TEACCH and non-model-specific special education programs for preschoolers with autism spectrum disorders. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44(2):366-380. doi:10.1007/s10803-013-1877-9
18. Thompson GA, McFerran KS, Gold C. Family-centred music therapy to promote social engagement in young children with severe autism spectrum disorder: a randomized controlled study. Child Care Health Dev. 2014;40(6):840-852. doi:10.1111/cch.12121
19. Pickles A, Le Couteur A, Leadbitter K, et al. Parent-mediated social communication therapy for young children with autism (PACT): long-term follow-up of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2501-2509.
20. Grossard C, Palestra G, Xavier J, et al. ICT and autism care: state of the art. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2018;31(6):474-483. doi:10.1097/YCO.0000000000000455
21. Cukier S, Barrios N. Pharmacological interventions for intellectual disability and autism. Vertex. 2019;XXX(143)52-63.
22. Sharma SR, Gonda X, Tarazi FI. Autism spectrum disorder: classification, diagnosis and therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;190:91-104.
23. Volkmar F, Siegel M, Woodbury-Smith M, et al. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;53(2):237-257.
24. LeClerc S, Easley D. Pharmacological therapies for autism spectrum disorder: a review. P T. 2015;40(6):389-397.
25. Gencer O, Emiroglu FN, Miral S, et al. Comparison of long-term efficacy and safety of risperidone and haloperidol in children and adolescents with autistic disorder. An open label maintenance study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;17(4):217-225.
26. Miral S, Gencer O, Inal-Emiroglu FN, et al. Risperidone versus haloperidol in children and adolescents with AD: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;17(1):1-8.
27. Findling RL, Mankoski R, Timko K, et al. A randomized controlled trial investigating the safety and efficacy of aripiprazole in the long-term maintenance treatment of pediatric patients with irritability associated with autistic disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2014;75(1):22-30. doi:10.4088/jcp.13m08500
28. McLennan JD. Deprescribing in a youth with an intellectual disability, autism, behavioural problems, and medication-related obesity: a case study. J Can Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;28(3):141-146.
29. Scahill L, McCracken JT, King B, et al. Extended-release guanfacine for hyperactivity in children with autism spectrum disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2015;172(12):1197-1206. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15010055
30. Harfterkamp M, van de Loo-Neus G, Minderaa RB, et al. A randomized double-blind study of atomoxetine versus placebo for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in children with autism spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(7):733-741. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2012.04.011
31. DeFilippis M, Wagner KD. Treatment of autism spectrum disorder in children and adolescents. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2016;46(2):18-41.
32. DeFilippis M. Depression in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Children (Basel). 2018;5(9):112. doi:10.3390/children5090112
33. Goel R, Hong JS, Findling RL, et al. An update on pharmacotherapy of autism spectrum disorder in children and adolescents. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2018;30(1):78-95. doi:10.1080/09540261.2018.1458706
34. Williams K, Brignell A, Randall M, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(8):CD004677. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004677.pub3
35. Herscu P, Handen BL, Arnold LE, et al. The SOFIA study: negative multi-center study of low dose fluoxetine on repetitive behaviors in children and adolescents with autistic disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020;50(9):3233-3244. doi:10.1007/s10803-019-04120-y
36. Hollander E, Phillips A, Chaplin W, et al. A placebo controlled crossover trial of liquid fluoxetine on repetitive behaviors in childhood and adolescent autism. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30(3):582-589.
37. King BH, Hollander E, Sikich L, et al. Lack of efficacy of citalopram in children with autism spectrum disorders and high levels of repetitive behavior: citalopram ineffective in children with autism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(6):583-590. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.30
38. Hollander E, Kaplan A, Cartwright C, et al. Venlafaxine in children, adolescents, and young adults with autism spectrum disorders: an open retrospective clinical report. J Child Neurol. 2000;15(2):132-135.
39. Carminati GG, Deriaz N, Bertschy G. Low-dose venlafaxine in three adolescents and young adults with autistic disorder improves self-injurious behavior and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorders (ADHD)-like symptoms. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2006;30(2):312-315.
40. Spencer D, Marshall J, Post B, et al. Psychotropic medication use and polypharmacy in children with autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics. 2013;132(5):833-840. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-3774
41. Cortesi F, Giannotti F, Sebastiani T, et al. Controlled-release melatonin, singly and combined with cognitive behavioural therapy, for persistent insomnia in children with autism spectrum disorders: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Sleep Res. 2012;21(6):700-709. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2869.2012.01021.x
42. Guastella AJ, Einfeld SL, Gray KM, et al. Intranasal oxytocin improves emotion recognition for youth with autism spectrum disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67(7):692-694. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.09.020
43. Gordon I, Vander Wyk BC, Bennett RH, et al. Oxytocin enhances brain function in children with autism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(52):20953-20958. doi:10.1073/pnas.1312857110
44. Höfer J, Bachmann C, Kamp-Becker I, et al. Willingness to try and lifetime use of complementary and alternative medicine in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder in Germany: a survey of parents. Autism. 2019;23(7):1865-1870. doi:10.1177/1362361318823545
45. Smith CA, Parton C, King M, et al. Parents’ experiences of information-seeking and decision-making regarding complementary medicine for children with autism spectrum disorder: a qualitative study. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020;20(1):4. doi:10.1186/s12906-019-2805-0
46. Marsden REF, Francis J, Garner I. Use of GFCF diets in children with ASD. An investigation into parents’ beliefs using the theory of planned behaviour. J Autism Dev Disord. 2019;49(9):3716-3731. doi:10.1007/s10803-019-04035-8
47. Trudeau MS, Madden RF, Parnell JA, et al. Dietary and supplement-based complementary and alternative medicine use in pediatric autism spectrum disorder. Nutrients. 2019;11(8):1783. doi:10.3390/nu11081783
48. Bent S, Hendren RL, Zandi T, et al. Internet-based, randomized, controlled trial of omega-3 fatty acids for hyperactivity in autism. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;53(6):658-666. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2014.01.018
49. Fraguas D, Díaz-Caneja C, Pina-Camacho L, et al. Dietary interventions for autism spectrum disorder: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 144(5):e20183218.
50. Mazahery H, Conlon CA, Beck KL, et al. A randomised-controlled trial of vitamin D and omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in the treatment of core symptoms of autism spectrum disorder in children. J Autism Dev Disord. 2019;49(5):1778-1794. doi:10.1007/s10803-018-3860-y
51. Green J, Garg S. Annual research review: the state of autism intervention science: progress, target psychological and biological mechanisms and future prospects. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018;59(4):424-443. doi:10.1111/jcpp.1289
52. Frye RE, Vassall S, Kaur G, et al. Emerging biomarkers in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(23):792. doi:10.21037/atm.2019.11.53
SECOND OF 2 PARTS
Evidence supports the crucial role of early intervention and nonpharmacologic approaches
A large percentage of individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience persisting significant social deficits in adulthood,1 which often leads to isolation, depressive symptoms, and poor occupational and relationship functioning.2,3 Childhood is a vital time for making the most significant and lasting changes that can improve functioning of individuals with ASD. Psychiatrists and other physicians who treat children are in a key role to influence outcomes of children at risk for or diagnosed with ASD.
This article provides updates on various aspects of ASD diagnosis and treatment (based on available evidence up to March 2020). Part 1 (
A comprehensive approach is essential
Multiple treatment modalities have been recommended for ASD.5 It is essential to address all aspects of ASD through cognitive, developmental, social-communication, sensory-motor, and behavioral interventions. Nonpharmacologic interventions are crucial in improving long-term outcomes of children with ASD.6
Nonpharmacologic treatments
Nonpharmacologic interventions commonly utilized for children with ASD include behavioral therapies, other psychological therapies, speech-language therapy, occupational therapy, educational interventions, parent coaching/training, developmental social interventions, and other modalities of therapy that are delivered in school, home, and clinic settings.5,7
A recent study examining ASD treatment trends via caregivers’ reports (N = 5,122) from the SPARK (Simons Foundation Powering Autism Research for Knowledge) cohort in the United States reported that 80% of children received speech-language therapy or occupational therapy; 52% got both.5 The study revealed that approximately one-quarter utilized 3 therapies simultaneously; two-thirds had utilized 3 or more therapies in the previous year.5
Interventions for children with ASD need to be individualized.1,8 Evidence-based behavioral interventions for ASD fall into 2 broad categories: Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), and Naturalistic Developmental Behavioral Interventions (NDBI). Traditionally, ABA has been a key model, guiding treatment for enhancing social-communicating skills and lowering maladaptive behaviors in ASD.9 ABA follows a structured and prescribed format,10,11 and has been shown to be efficacious.1,7 More recently, NDBI, in which interventions are “embedded” in the natural environment of the young child and more actively incorporate a developmental perspective, has been shown to be beneficial in improving and generalizing social-communication skills in young children with ASD.7,11
Early Start Denver Model (ESDM) is an intensive, naturalistic behavioral intervention4 that has been shown to be efficacious for enhancing communication and adaptive behavior in children with ASD.7,8,12 A multisite randomized controlled trial (RCT) by Rogers et al12 that examined the efficacy of ESDM in 118 children (age 14 to 24 months) with ASD found the treatment was beneficial and superior compared with a “community intervention” group, in regards to language ability measured in time by group analyses.The ESDM intervention in this study involved weekly parent coaching for 3 months, along with 24 months of 15 hours/week of one-on-one treatment provided by therapy professionals.12
Reciprocal imitation training (RIT) is another naturalistic intervention that has shown benefit in training children with ASD in imitation skills during play.13 Studies have found that both RIT and ESDM can be parent-implemented, after parents receive training.13,14
Parent-mediated, parent-implemented interventions may have a role in improving outcomes in childhood ASD,7,15 particularly “better generalization and maintenance of skills than therapist-implemented intervention” for lowering challenging behaviors and enhancing verbal and nonverbal communication.16
Various social skills interventions have also been found effective for children with ASD.1 Such interventions are often provided in the school setting.7 Coordination with the child’s school to discuss and advocating for adequate and suitable interventions, educational services, and placement is an essential aspect of ASD treatment.7
Two other school-based, comprehensive treatment model interventions—Learning Experiences and Alternative Programs for Preschoolers and their Parents (LEAP), and TEACCH—have some evidence of leading to improvement in children with ASD.7,17
Some studies have found that music therapy may have high efficacy for children with ASD, even with smaller length and intensity of treatment, particularly in improving social interaction, engagement with parents, joint attention, and communication.3,18 Further research is needed to conclusively establish the efficacy of music therapy for ASD in children and adolescents.
A few studies have assessed the long-term outcomes of interventions for ASD; however, more research is needed.19 Pickles et al19 conducted a follow-up to determine the long-term effects of the Preschool Autism Communication Trial (PACT), an RCT of parent-mediated social communication therapy for children age 2 to 4 with ASD. The children’s average age at follow-up was 10 years. The authors found a significant long-term decrease in ASD symptoms and enhancement of social communication with parents (N = 152).
Technology-based interventions, including games and robotics, have been investigated in recent years, for treatment of children with ASD (eg, for improving social skills).20
Research suggests that the intensity (number of hours) and duration of nonpharmacologic treatments for ASD is critical to improving outcomes (Box1,3,5,7,10,16).
Box
A higher intensity of nonpharmacologic intervention (greater number of hours) has been associated with greater benefit for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), in the form of enhancements in IQ and adaptive behavior.1,10,16 In the United States, the intensity of interventions commonly ranges from 30 to 200 or more minutes per week.3 This may mean that a child with ASD who is receiving 30 minutes of speech therapy at school and continues to exhibit significant deficits in speech-language or social-communication may likely benefit from additional hours of speech therapy and/or social-communication skill training, and should be referred accordingly, even for private therapy services if needed and feasible.7 Guidelines created through a systematic review of evidence recommend at least 25 hours per week of comprehensive treatment interventions for children with ASD to address language, social deficits, and behavioral difficulties.1 The duration of intervention has also been shown to play a role in outcomes.1,3,10 Given the complexity and extent of impairment often associated with ASD, it is not surprising that in recent research examining trends in ASD treatment in the United States, most caregivers reported therapy as ongoing.5 The exact intensity and duration of nonpharmacologic interventions may depend on several factors, such as severity of ASD and of the specific deficit being targeted, type of intervention, and therapist skill. The quality of skills of the care provider has also been shown to affect the benefits gained from the intervention.3
Continue to: Pharmacotherapy...
Pharmacotherapy
Medications cannot resolve core features of ASD.21 However, certain medications may help address associated comorbidities, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, or others, when these conditions have not responded to nonpharmacologic interventions.7,22 Common symptoms that are often treated with pharmacotherapy include aggression, irritability, hyperactivity, attentional difficulties, tics, self-injurious behavior, obsessive-compulsive symptoms, and mood dysregulation/lability.23 Generally speaking, medications might be considered if symptoms are severe and markedly impair functioning. For mild to moderate conditions, psychotherapy and other nonpharmacologic interventions are generally considered first-line. Since none of the medications described below are specific to ASD and psychiatrists generally receive training in prescribing them for other indications, a comprehensive review of their risks and benefits is beyond the scope of this article. No psychotropic medications are known to have robust evidence for safety in preschool children with ASD, and thus are best avoided.
Antipsychotics. Risperidone (for age 5 and older) and aripiprazole (age 6 to 17) are the only medications FDA-approved for use in children and adolescents with ASD, specifically for irritability associated with ASD.21,24 These 2 second-generation antipsychotics may also assist in lowering aggression in patients with ASD.24 First-generation antipsychotics such as haloperidol have been shown to be effective for irritability and aggression in ASD, but the risk of significant adverse effects such as dyskinesias and extrapyramidal symptoms limit their use.24 Two studies (a double-blind study and an open-label extension of that study) in children and adolescents with ASD found that risperidone was more effective and better tolerated than haloperidol in behavioral measures, impulsivity, and even in the social domain.25,26 In addition to other adverse effects and risks, increased prolactin secondary to risperidone use requires close monitoring and caution.24-26 As is the case with the use of other psychotropic medications in children and adolescents, those with ASD who receive antipsychotics should also be periodically reassessed to determine the need for continued use of these medications.27 A multicenter relapse prevention RCT found no statistically significant difference in the time to relapse between aripiprazole and placebo.27 Metabolic syndrome, cardiac risks, and other risks need to be considered before prescribing an antipsychotic.28 Given their serious adverse effects profile, use should be considered only when there is severe impairment or risk of injury, after carefully weighing risks/benefits.
Medications for attentional difficulties. A multisite, randomized, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the use of extended-release guanfacine in children with ASD (N = 62) found the rate of positive response on the Clinical Global Impressions–Improvement scale was 50% for guanfacine vs 9.4% for placebo.29 Clinicians need to monitor for adverse effects of guanfacine, such as fatigue, drowsiness, lightheadedness, lowering of blood pressure and heart rate, and other effects.29 A randomized, double-blind trial of 97 children and adolescents with ASD and ADHD found that atomoxetine had moderate benefit for ADHD symptoms.30 The study reported no serious adverse effects.30 However, it is especially important to monitor for hepatic and cardiac adverse effects (in addition to monitoring for risk of increase in suicidal thoughts/behavior, as in the case of antidepressants) when using atomoxetine, in addition to other side effects and risks. Some evidence suggests that methylphenidate may be effective for attentional difficulties in children and adolescents with ASD21 but may pose a higher risk of adverse effects in this population compared with neurotypical patients.31
Antidepressants. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are sometimes used to reduce obsessive-compulsive symptoms, repetitive behavior, or depressive symptoms in children with ASD, but are not FDA-approved for children or adolescents with ASD. In general, there is inadequate evidence to support the use of SSRIs for ASD in children.31-34 In addition, children with ASD may be at a greater risk of adverse effects from SSRIs.32,34 Despite this, SSRIs are the most commonly prescribed psychotropic medications in children with ASD.32
An RCT examining the efficacy of fluoxetine in 158 children and adolescents with ASD found no significant difference in Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (CY-BOCS) score after 14 weeks of treatment; activation was a common adverse effect.35 A 2005 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 45 children/adolescents with ASD found that low-dose liquid fluoxetine was more effective than placebo for reducing repetitive behaviors in this population.36 Larger studies are warranted to further evaluate the efficacy and safety of fluoxetine (and of SSRIs in general, particularly in the long term) for children and adolescents with ASD.36 A 2009 randomized, placebo-controlled trial of 149 children with ASD revealed no significant difference between citalopram and placebo as measured by Clinical Global Impressions scale or CY-BOCS scores, and noted a significantly elevated likelihood of adverse effects.37
Other antidepressants. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of any other antidepressants in children and adolescents with ASD. A few studies38,39 have examined the use of venlafaxine in children with ASD; however, further research and controlled studies with large sample sizes are required to conclusively establish its benefits. There is a dearth of evidence examining the use of the tetracyclic antidepressant mirtazapine, or other classes of medications such as tricyclic antidepressants or mood stabilizers, in children with ASD; only a few small studies have assessed the efficacy and adverse effects of these medications for such patients.31
Polypharmacy. Although there is no evidence to support polypharmacy in children and adolescents with ASD, the practice appears to be rampant in these patients.28,40 A 2013 retrospective, observational study of psychotropic medication use in children with ASD (N = 33,565) found that 64% were prescribed psychotropic medications, and 35% exhibited evidence of polypharmacy.40 In this study, the total duration of polypharmacy averaged 525 days.40 When addressing polypharmacy, systematic deprescribing or simplification of the psychotropic medication regimen may be needed,28 while taking into account the patient’s complete clinical situation, including (but not limited to) tolerability of the medication regimen, presence or absence of current stressors, presence or absence of adequate supports, use of nonpharmacologic treatments where appropriate, and other factors.
More studies assessing the efficacy and safety of psychotropic medications for children and adolescents with ASD are needed,32 especially studies that evaluate the effects of long-term use, because evidence for pharmacologic treatments for children with ASD is mixed and insufficient.33 There is also a need for evidence-based standards for prescribing psychotropic medications in children and adolescents with ASD.
Psychotropic medications, if used in ASD, should be used only in conjunction with other evidence-based treatment modalities, and not as monotherapy.21 Children and adolescents with ASD may be particularly susceptible to side effects or adverse effects of certain psychotropic medications.31 When considering medications, carefully weigh the risks and benefits.7,21,24,28 Starting low and going slow is generally the preferred strategy.31,32 As always, when recommending medications, discuss in detail with parents the potential side effects, benefits, risks, interactions, and alternatives.
Other agents. Several double-blind, placebo-controlled trials have evaluated using melatonin for sleep difficulties in children and adolescents with ASD.41 A randomized, placebo-controlled, 12-week trial that assessed 160 children with ASD and insomnia found that melatonin plus cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) was superior in efficacy to melatonin alone, CBT alone, or placebo.41
The evidence regarding oxytocin use for children with ASD is mixed.31 Some small studies have associated improvement in the social domain with its use. Guastella et al42 conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of oxytocin nasal spray for 16 participants (age 12 to 19) with ASD, and found oxytocin enhanced emotional identification. Gordon et al43 conducted a functional MRI study of brain activity with oxytocin use in children with high-functioning ASD (N = 17). They found that oxytocin may augment “salience and hedonic evaluations of socially meaningful stimuli in children with ASD” and thus help social attunement. Further research is needed to evaluate the impact of oxytocin on social behavior.
Complementary and alternative medicine. Although there is limited and inconclusive evidence about the use of complementary and alternative medicine in children and adolescents with ASD, these therapies continue to be commonly used.44-46 A recent survey of parents (N = 211) of children with ASD from academic ASD outpatient clinics in Germany found that 46% reported their child was using or had used some type of complementary and alternative medicine.44 There is inadequate evidence to support the use of a gluten-free, casein-free diet for children/adolescents with ASD.46 A recent cross-sectional study assessing supplement use in 210 children with ASD in Canada found that 75% used supplements, such as multivitamins (77.8%), vitamin D (44.9%), omega 3 (42.5%), probiotics (36.5%), and magnesium (28.1%), despite insufficient evidence to support their safety or efficacy for children with ASD.47 Importantly, 33.5% of parents in this study reported that they did not inform the physician about all their child’s supplements.47 Some of the reasons the parents in this study provided for not disclosing information about supplements to their physicians were “physician lack of knowledge,” “no benefit,” “too time-consuming,” and “scared of judgment.”47 Semi-structured interviews of parents of 21 children with ASD in Australia revealed that parents found information on complementary and alternative medicine and therapies complex and often conflicting.45 In addition to recommendations from health care professionals, evidence suggests that parents often consider the opinions of media, friends, and family when making a decision on using complementary and alternative medicine modalities for children/adolescents with ASD.46 Such findings can inform physician practices regarding supplement use, and highlight the need to educate parents about the evidence regarding these therapies and potential adverse effects and interactions of such therapies,46 along with the need to develop a centralized, evidence-based resource for parents regarding their use.45
Omega 3 supplementation has in general shown few adverse effects47; still, risks/benefits need to be weighed before use. Some evidence suggests that it may decrease hyperactivity in children with ASD.31,48 However, further research, particularly controlled trials with large sample sizes, are needed for a definitive determination of efficacy.31,48 A meta-analysis that included 27 RCTs assessing the efficacy of dietary interventions for various ASD symptoms found that omega 3 supplementation was more effective than placebo, but compared with placebo, the effect size was small.49 A RCT of 73 children with ASD in New Zealand found that omega 3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids may benefit some core symptoms of ASD; the authors suggested that further research is needed to conclusively establish efficacy.50
Continue to: A need for advocacy and research..
A need for advocacy and research
Physicians who treat children with ASD can not only make appropriate referrals and educate parents, but also educate their patients’ schools and advocate for their patients to get the level of services they need.23,28
A recent study in the United States found that behavior therapy and speech-language therapy were used less often in the treatment of children with ASD in rural areas compared with those in metro areas.5 This suggests that in addition to increasing parents’ awareness and use of ASD services and providing referrals where appropriate, physicians are in a unique position to advocate for public health policies to improve access, coverage, and training for the provision of such services in rural areas.
There is need for ongoing research to further examine the efficacy and nuances of effects of various treatment interventions for ASD, especially long-term studies with larger sample sizes.11,51 Additionally, research is warranted to better understand the underlying genetic and neurobiological mechanisms of ASD, which would help guide the development of biomarkers,52 innovative treatments, and disease-modifying agents for ASD.7,22 Exploring the effects of potential alliances or joint action between biological and psychosocial interventions for ASD is also an area that needs further research.51
Bottom Line
A combination of treatment modalities (such as speech-language therapy, social skills training, behavior therapy/other psychotherapy, and occupational therapy for sensory sensitivities) is generally needed to improve the long-term outcomes of children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). In addition to the importance of early intervention, the intensity and duration of nonpharmacologic treatments are vital to improving outcomes in ASD.
SECOND OF 2 PARTS
Evidence supports the crucial role of early intervention and nonpharmacologic approaches
A large percentage of individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience persisting significant social deficits in adulthood,1 which often leads to isolation, depressive symptoms, and poor occupational and relationship functioning.2,3 Childhood is a vital time for making the most significant and lasting changes that can improve functioning of individuals with ASD. Psychiatrists and other physicians who treat children are in a key role to influence outcomes of children at risk for or diagnosed with ASD.
This article provides updates on various aspects of ASD diagnosis and treatment (based on available evidence up to March 2020). Part 1 (
A comprehensive approach is essential
Multiple treatment modalities have been recommended for ASD.5 It is essential to address all aspects of ASD through cognitive, developmental, social-communication, sensory-motor, and behavioral interventions. Nonpharmacologic interventions are crucial in improving long-term outcomes of children with ASD.6
Nonpharmacologic treatments
Nonpharmacologic interventions commonly utilized for children with ASD include behavioral therapies, other psychological therapies, speech-language therapy, occupational therapy, educational interventions, parent coaching/training, developmental social interventions, and other modalities of therapy that are delivered in school, home, and clinic settings.5,7
A recent study examining ASD treatment trends via caregivers’ reports (N = 5,122) from the SPARK (Simons Foundation Powering Autism Research for Knowledge) cohort in the United States reported that 80% of children received speech-language therapy or occupational therapy; 52% got both.5 The study revealed that approximately one-quarter utilized 3 therapies simultaneously; two-thirds had utilized 3 or more therapies in the previous year.5
Interventions for children with ASD need to be individualized.1,8 Evidence-based behavioral interventions for ASD fall into 2 broad categories: Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), and Naturalistic Developmental Behavioral Interventions (NDBI). Traditionally, ABA has been a key model, guiding treatment for enhancing social-communicating skills and lowering maladaptive behaviors in ASD.9 ABA follows a structured and prescribed format,10,11 and has been shown to be efficacious.1,7 More recently, NDBI, in which interventions are “embedded” in the natural environment of the young child and more actively incorporate a developmental perspective, has been shown to be beneficial in improving and generalizing social-communication skills in young children with ASD.7,11
Early Start Denver Model (ESDM) is an intensive, naturalistic behavioral intervention4 that has been shown to be efficacious for enhancing communication and adaptive behavior in children with ASD.7,8,12 A multisite randomized controlled trial (RCT) by Rogers et al12 that examined the efficacy of ESDM in 118 children (age 14 to 24 months) with ASD found the treatment was beneficial and superior compared with a “community intervention” group, in regards to language ability measured in time by group analyses.The ESDM intervention in this study involved weekly parent coaching for 3 months, along with 24 months of 15 hours/week of one-on-one treatment provided by therapy professionals.12
Reciprocal imitation training (RIT) is another naturalistic intervention that has shown benefit in training children with ASD in imitation skills during play.13 Studies have found that both RIT and ESDM can be parent-implemented, after parents receive training.13,14
Parent-mediated, parent-implemented interventions may have a role in improving outcomes in childhood ASD,7,15 particularly “better generalization and maintenance of skills than therapist-implemented intervention” for lowering challenging behaviors and enhancing verbal and nonverbal communication.16
Various social skills interventions have also been found effective for children with ASD.1 Such interventions are often provided in the school setting.7 Coordination with the child’s school to discuss and advocating for adequate and suitable interventions, educational services, and placement is an essential aspect of ASD treatment.7
Two other school-based, comprehensive treatment model interventions—Learning Experiences and Alternative Programs for Preschoolers and their Parents (LEAP), and TEACCH—have some evidence of leading to improvement in children with ASD.7,17
Some studies have found that music therapy may have high efficacy for children with ASD, even with smaller length and intensity of treatment, particularly in improving social interaction, engagement with parents, joint attention, and communication.3,18 Further research is needed to conclusively establish the efficacy of music therapy for ASD in children and adolescents.
A few studies have assessed the long-term outcomes of interventions for ASD; however, more research is needed.19 Pickles et al19 conducted a follow-up to determine the long-term effects of the Preschool Autism Communication Trial (PACT), an RCT of parent-mediated social communication therapy for children age 2 to 4 with ASD. The children’s average age at follow-up was 10 years. The authors found a significant long-term decrease in ASD symptoms and enhancement of social communication with parents (N = 152).
Technology-based interventions, including games and robotics, have been investigated in recent years, for treatment of children with ASD (eg, for improving social skills).20
Research suggests that the intensity (number of hours) and duration of nonpharmacologic treatments for ASD is critical to improving outcomes (Box1,3,5,7,10,16).
Box
A higher intensity of nonpharmacologic intervention (greater number of hours) has been associated with greater benefit for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), in the form of enhancements in IQ and adaptive behavior.1,10,16 In the United States, the intensity of interventions commonly ranges from 30 to 200 or more minutes per week.3 This may mean that a child with ASD who is receiving 30 minutes of speech therapy at school and continues to exhibit significant deficits in speech-language or social-communication may likely benefit from additional hours of speech therapy and/or social-communication skill training, and should be referred accordingly, even for private therapy services if needed and feasible.7 Guidelines created through a systematic review of evidence recommend at least 25 hours per week of comprehensive treatment interventions for children with ASD to address language, social deficits, and behavioral difficulties.1 The duration of intervention has also been shown to play a role in outcomes.1,3,10 Given the complexity and extent of impairment often associated with ASD, it is not surprising that in recent research examining trends in ASD treatment in the United States, most caregivers reported therapy as ongoing.5 The exact intensity and duration of nonpharmacologic interventions may depend on several factors, such as severity of ASD and of the specific deficit being targeted, type of intervention, and therapist skill. The quality of skills of the care provider has also been shown to affect the benefits gained from the intervention.3
Continue to: Pharmacotherapy...
Pharmacotherapy
Medications cannot resolve core features of ASD.21 However, certain medications may help address associated comorbidities, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, or others, when these conditions have not responded to nonpharmacologic interventions.7,22 Common symptoms that are often treated with pharmacotherapy include aggression, irritability, hyperactivity, attentional difficulties, tics, self-injurious behavior, obsessive-compulsive symptoms, and mood dysregulation/lability.23 Generally speaking, medications might be considered if symptoms are severe and markedly impair functioning. For mild to moderate conditions, psychotherapy and other nonpharmacologic interventions are generally considered first-line. Since none of the medications described below are specific to ASD and psychiatrists generally receive training in prescribing them for other indications, a comprehensive review of their risks and benefits is beyond the scope of this article. No psychotropic medications are known to have robust evidence for safety in preschool children with ASD, and thus are best avoided.
Antipsychotics. Risperidone (for age 5 and older) and aripiprazole (age 6 to 17) are the only medications FDA-approved for use in children and adolescents with ASD, specifically for irritability associated with ASD.21,24 These 2 second-generation antipsychotics may also assist in lowering aggression in patients with ASD.24 First-generation antipsychotics such as haloperidol have been shown to be effective for irritability and aggression in ASD, but the risk of significant adverse effects such as dyskinesias and extrapyramidal symptoms limit their use.24 Two studies (a double-blind study and an open-label extension of that study) in children and adolescents with ASD found that risperidone was more effective and better tolerated than haloperidol in behavioral measures, impulsivity, and even in the social domain.25,26 In addition to other adverse effects and risks, increased prolactin secondary to risperidone use requires close monitoring and caution.24-26 As is the case with the use of other psychotropic medications in children and adolescents, those with ASD who receive antipsychotics should also be periodically reassessed to determine the need for continued use of these medications.27 A multicenter relapse prevention RCT found no statistically significant difference in the time to relapse between aripiprazole and placebo.27 Metabolic syndrome, cardiac risks, and other risks need to be considered before prescribing an antipsychotic.28 Given their serious adverse effects profile, use should be considered only when there is severe impairment or risk of injury, after carefully weighing risks/benefits.
Medications for attentional difficulties. A multisite, randomized, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the use of extended-release guanfacine in children with ASD (N = 62) found the rate of positive response on the Clinical Global Impressions–Improvement scale was 50% for guanfacine vs 9.4% for placebo.29 Clinicians need to monitor for adverse effects of guanfacine, such as fatigue, drowsiness, lightheadedness, lowering of blood pressure and heart rate, and other effects.29 A randomized, double-blind trial of 97 children and adolescents with ASD and ADHD found that atomoxetine had moderate benefit for ADHD symptoms.30 The study reported no serious adverse effects.30 However, it is especially important to monitor for hepatic and cardiac adverse effects (in addition to monitoring for risk of increase in suicidal thoughts/behavior, as in the case of antidepressants) when using atomoxetine, in addition to other side effects and risks. Some evidence suggests that methylphenidate may be effective for attentional difficulties in children and adolescents with ASD21 but may pose a higher risk of adverse effects in this population compared with neurotypical patients.31
Antidepressants. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are sometimes used to reduce obsessive-compulsive symptoms, repetitive behavior, or depressive symptoms in children with ASD, but are not FDA-approved for children or adolescents with ASD. In general, there is inadequate evidence to support the use of SSRIs for ASD in children.31-34 In addition, children with ASD may be at a greater risk of adverse effects from SSRIs.32,34 Despite this, SSRIs are the most commonly prescribed psychotropic medications in children with ASD.32
An RCT examining the efficacy of fluoxetine in 158 children and adolescents with ASD found no significant difference in Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (CY-BOCS) score after 14 weeks of treatment; activation was a common adverse effect.35 A 2005 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 45 children/adolescents with ASD found that low-dose liquid fluoxetine was more effective than placebo for reducing repetitive behaviors in this population.36 Larger studies are warranted to further evaluate the efficacy and safety of fluoxetine (and of SSRIs in general, particularly in the long term) for children and adolescents with ASD.36 A 2009 randomized, placebo-controlled trial of 149 children with ASD revealed no significant difference between citalopram and placebo as measured by Clinical Global Impressions scale or CY-BOCS scores, and noted a significantly elevated likelihood of adverse effects.37
Other antidepressants. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of any other antidepressants in children and adolescents with ASD. A few studies38,39 have examined the use of venlafaxine in children with ASD; however, further research and controlled studies with large sample sizes are required to conclusively establish its benefits. There is a dearth of evidence examining the use of the tetracyclic antidepressant mirtazapine, or other classes of medications such as tricyclic antidepressants or mood stabilizers, in children with ASD; only a few small studies have assessed the efficacy and adverse effects of these medications for such patients.31
Polypharmacy. Although there is no evidence to support polypharmacy in children and adolescents with ASD, the practice appears to be rampant in these patients.28,40 A 2013 retrospective, observational study of psychotropic medication use in children with ASD (N = 33,565) found that 64% were prescribed psychotropic medications, and 35% exhibited evidence of polypharmacy.40 In this study, the total duration of polypharmacy averaged 525 days.40 When addressing polypharmacy, systematic deprescribing or simplification of the psychotropic medication regimen may be needed,28 while taking into account the patient’s complete clinical situation, including (but not limited to) tolerability of the medication regimen, presence or absence of current stressors, presence or absence of adequate supports, use of nonpharmacologic treatments where appropriate, and other factors.
More studies assessing the efficacy and safety of psychotropic medications for children and adolescents with ASD are needed,32 especially studies that evaluate the effects of long-term use, because evidence for pharmacologic treatments for children with ASD is mixed and insufficient.33 There is also a need for evidence-based standards for prescribing psychotropic medications in children and adolescents with ASD.
Psychotropic medications, if used in ASD, should be used only in conjunction with other evidence-based treatment modalities, and not as monotherapy.21 Children and adolescents with ASD may be particularly susceptible to side effects or adverse effects of certain psychotropic medications.31 When considering medications, carefully weigh the risks and benefits.7,21,24,28 Starting low and going slow is generally the preferred strategy.31,32 As always, when recommending medications, discuss in detail with parents the potential side effects, benefits, risks, interactions, and alternatives.
Other agents. Several double-blind, placebo-controlled trials have evaluated using melatonin for sleep difficulties in children and adolescents with ASD.41 A randomized, placebo-controlled, 12-week trial that assessed 160 children with ASD and insomnia found that melatonin plus cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) was superior in efficacy to melatonin alone, CBT alone, or placebo.41
The evidence regarding oxytocin use for children with ASD is mixed.31 Some small studies have associated improvement in the social domain with its use. Guastella et al42 conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of oxytocin nasal spray for 16 participants (age 12 to 19) with ASD, and found oxytocin enhanced emotional identification. Gordon et al43 conducted a functional MRI study of brain activity with oxytocin use in children with high-functioning ASD (N = 17). They found that oxytocin may augment “salience and hedonic evaluations of socially meaningful stimuli in children with ASD” and thus help social attunement. Further research is needed to evaluate the impact of oxytocin on social behavior.
Complementary and alternative medicine. Although there is limited and inconclusive evidence about the use of complementary and alternative medicine in children and adolescents with ASD, these therapies continue to be commonly used.44-46 A recent survey of parents (N = 211) of children with ASD from academic ASD outpatient clinics in Germany found that 46% reported their child was using or had used some type of complementary and alternative medicine.44 There is inadequate evidence to support the use of a gluten-free, casein-free diet for children/adolescents with ASD.46 A recent cross-sectional study assessing supplement use in 210 children with ASD in Canada found that 75% used supplements, such as multivitamins (77.8%), vitamin D (44.9%), omega 3 (42.5%), probiotics (36.5%), and magnesium (28.1%), despite insufficient evidence to support their safety or efficacy for children with ASD.47 Importantly, 33.5% of parents in this study reported that they did not inform the physician about all their child’s supplements.47 Some of the reasons the parents in this study provided for not disclosing information about supplements to their physicians were “physician lack of knowledge,” “no benefit,” “too time-consuming,” and “scared of judgment.”47 Semi-structured interviews of parents of 21 children with ASD in Australia revealed that parents found information on complementary and alternative medicine and therapies complex and often conflicting.45 In addition to recommendations from health care professionals, evidence suggests that parents often consider the opinions of media, friends, and family when making a decision on using complementary and alternative medicine modalities for children/adolescents with ASD.46 Such findings can inform physician practices regarding supplement use, and highlight the need to educate parents about the evidence regarding these therapies and potential adverse effects and interactions of such therapies,46 along with the need to develop a centralized, evidence-based resource for parents regarding their use.45
Omega 3 supplementation has in general shown few adverse effects47; still, risks/benefits need to be weighed before use. Some evidence suggests that it may decrease hyperactivity in children with ASD.31,48 However, further research, particularly controlled trials with large sample sizes, are needed for a definitive determination of efficacy.31,48 A meta-analysis that included 27 RCTs assessing the efficacy of dietary interventions for various ASD symptoms found that omega 3 supplementation was more effective than placebo, but compared with placebo, the effect size was small.49 A RCT of 73 children with ASD in New Zealand found that omega 3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids may benefit some core symptoms of ASD; the authors suggested that further research is needed to conclusively establish efficacy.50
Continue to: A need for advocacy and research..
A need for advocacy and research
Physicians who treat children with ASD can not only make appropriate referrals and educate parents, but also educate their patients’ schools and advocate for their patients to get the level of services they need.23,28
A recent study in the United States found that behavior therapy and speech-language therapy were used less often in the treatment of children with ASD in rural areas compared with those in metro areas.5 This suggests that in addition to increasing parents’ awareness and use of ASD services and providing referrals where appropriate, physicians are in a unique position to advocate for public health policies to improve access, coverage, and training for the provision of such services in rural areas.
There is need for ongoing research to further examine the efficacy and nuances of effects of various treatment interventions for ASD, especially long-term studies with larger sample sizes.11,51 Additionally, research is warranted to better understand the underlying genetic and neurobiological mechanisms of ASD, which would help guide the development of biomarkers,52 innovative treatments, and disease-modifying agents for ASD.7,22 Exploring the effects of potential alliances or joint action between biological and psychosocial interventions for ASD is also an area that needs further research.51
Bottom Line
A combination of treatment modalities (such as speech-language therapy, social skills training, behavior therapy/other psychotherapy, and occupational therapy for sensory sensitivities) is generally needed to improve the long-term outcomes of children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). In addition to the importance of early intervention, the intensity and duration of nonpharmacologic treatments are vital to improving outcomes in ASD.
1. Maglione MA, Gans D, Das L, et al. Nonmedical interventions for children with ASD: recommended guidelines and further research needs. Pediatrics. 2012;30(Suppl 2):S169-S178.
2. Simms MD, Jin XM. Autism, language disorder, and social (pragmatic) communication disorder: DSM-V and differential diagnoses. Pediatr Rev. 2015;36(8):355-363. doi:10.1542/pir.36-8-355
3. Su Maw S, Haga C. Effectiveness of cognitive, developmental, and behavioural interventions for autism spectrum disorder in preschool-aged children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon. 2018;4(9):e00763. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00763
4. Charman T. Editorial: trials and tribulations in early autism intervention research. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;58(9):846-848. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2019.03.004
5. Monz BU, Houghton R, Law K, et al. Treatment patterns in children with autism in the United States. Autism Res. 2019;12(3):517-526. doi:10.1002/aur.2070
6. Sperdin HF, Schaer M. Aberrant development of speech processing in young children with autism: new insights from neuroimaging biomarkers. Front Neurosci. 2016;10:393. doi:10.3389/fnins.2016.00393
7. Hyman SL, Levy SE, Myers SM, et al. Identification, evaluation, and management of children with autism spectrum disorder. Pediatrics. 2020;145(1):e20193447. doi:10.1542/peds.2019-3447
8. Contaldo A, Colombi C, Pierotti C, et al. Outcomes and moderators of Early Start Denver Model intervention in young children with autism spectrum disorder delivered in a mixed individual and group setting. Autism. 2020;24(3):718-729. doi:10.1177/1362361319888344
9. Lei J, Ventola P. Pivotal response treatment for autism spectrum disorder: current perspectives. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017;13:1613-1626. doi:10.2147/NDT.S120710
10. Landa RJ. Efficacy of early interventions for infants and young children with, and at risk for, autism spectrum disorders. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2018;30(1):25-39. doi:10.1080/09540261.2018.1432574
11. Schreibman L, Dawson G, Stahmer AC, et al. Naturalistic developmental behavioral interventions: empirically validated treatments for autism spectrum disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. 2015;45(8):2411-2428. doi:10.1007/s10803-015-2407-8
12. Rogers SJ, Estes A, Lord C, et al. A multisite randomized controlled two-phase trial of the Early Start Denver Model compared to treatment as usual. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;58(9):853-865. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2019.01.004
13. Ingersoll B, Gergans S. The effect of a parent-implemented imitation intervention on spontaneous imitation skills in young children with autism. Res Dev Disabil. 2007;28(2):163-175.
14. Waddington H, van der Meer L, Sigafoos J, et al. Examining parent use of specific intervention techniques during a 12-week training program based on the Early Start Denver Model. Autism. 2020;24(2):484-498. doi:10.1177/1362361319876495
15. Trembath D, Gurm M, Scheerer NE, et al. Systematic review of factors that may influence the outcomes and generalizability of parent‐mediated interventions for young children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2019;12(9):1304-1321.
16. Rogers SJ, Estes A, Lord C, et al. Effects of a brief Early Start Denver Model (ESDM)-based parent intervention on toddlers at risk for autism spectrum disorders: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(10):1052-1065. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2012.08.003
17. Boyd BA, Hume K, McBee MT, et al. Comparative efficacy of LEAP, TEACCH and non-model-specific special education programs for preschoolers with autism spectrum disorders. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44(2):366-380. doi:10.1007/s10803-013-1877-9
18. Thompson GA, McFerran KS, Gold C. Family-centred music therapy to promote social engagement in young children with severe autism spectrum disorder: a randomized controlled study. Child Care Health Dev. 2014;40(6):840-852. doi:10.1111/cch.12121
19. Pickles A, Le Couteur A, Leadbitter K, et al. Parent-mediated social communication therapy for young children with autism (PACT): long-term follow-up of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2501-2509.
20. Grossard C, Palestra G, Xavier J, et al. ICT and autism care: state of the art. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2018;31(6):474-483. doi:10.1097/YCO.0000000000000455
21. Cukier S, Barrios N. Pharmacological interventions for intellectual disability and autism. Vertex. 2019;XXX(143)52-63.
22. Sharma SR, Gonda X, Tarazi FI. Autism spectrum disorder: classification, diagnosis and therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;190:91-104.
23. Volkmar F, Siegel M, Woodbury-Smith M, et al. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;53(2):237-257.
24. LeClerc S, Easley D. Pharmacological therapies for autism spectrum disorder: a review. P T. 2015;40(6):389-397.
25. Gencer O, Emiroglu FN, Miral S, et al. Comparison of long-term efficacy and safety of risperidone and haloperidol in children and adolescents with autistic disorder. An open label maintenance study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;17(4):217-225.
26. Miral S, Gencer O, Inal-Emiroglu FN, et al. Risperidone versus haloperidol in children and adolescents with AD: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;17(1):1-8.
27. Findling RL, Mankoski R, Timko K, et al. A randomized controlled trial investigating the safety and efficacy of aripiprazole in the long-term maintenance treatment of pediatric patients with irritability associated with autistic disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2014;75(1):22-30. doi:10.4088/jcp.13m08500
28. McLennan JD. Deprescribing in a youth with an intellectual disability, autism, behavioural problems, and medication-related obesity: a case study. J Can Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;28(3):141-146.
29. Scahill L, McCracken JT, King B, et al. Extended-release guanfacine for hyperactivity in children with autism spectrum disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2015;172(12):1197-1206. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15010055
30. Harfterkamp M, van de Loo-Neus G, Minderaa RB, et al. A randomized double-blind study of atomoxetine versus placebo for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in children with autism spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(7):733-741. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2012.04.011
31. DeFilippis M, Wagner KD. Treatment of autism spectrum disorder in children and adolescents. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2016;46(2):18-41.
32. DeFilippis M. Depression in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Children (Basel). 2018;5(9):112. doi:10.3390/children5090112
33. Goel R, Hong JS, Findling RL, et al. An update on pharmacotherapy of autism spectrum disorder in children and adolescents. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2018;30(1):78-95. doi:10.1080/09540261.2018.1458706
34. Williams K, Brignell A, Randall M, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(8):CD004677. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004677.pub3
35. Herscu P, Handen BL, Arnold LE, et al. The SOFIA study: negative multi-center study of low dose fluoxetine on repetitive behaviors in children and adolescents with autistic disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020;50(9):3233-3244. doi:10.1007/s10803-019-04120-y
36. Hollander E, Phillips A, Chaplin W, et al. A placebo controlled crossover trial of liquid fluoxetine on repetitive behaviors in childhood and adolescent autism. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30(3):582-589.
37. King BH, Hollander E, Sikich L, et al. Lack of efficacy of citalopram in children with autism spectrum disorders and high levels of repetitive behavior: citalopram ineffective in children with autism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(6):583-590. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.30
38. Hollander E, Kaplan A, Cartwright C, et al. Venlafaxine in children, adolescents, and young adults with autism spectrum disorders: an open retrospective clinical report. J Child Neurol. 2000;15(2):132-135.
39. Carminati GG, Deriaz N, Bertschy G. Low-dose venlafaxine in three adolescents and young adults with autistic disorder improves self-injurious behavior and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorders (ADHD)-like symptoms. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2006;30(2):312-315.
40. Spencer D, Marshall J, Post B, et al. Psychotropic medication use and polypharmacy in children with autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics. 2013;132(5):833-840. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-3774
41. Cortesi F, Giannotti F, Sebastiani T, et al. Controlled-release melatonin, singly and combined with cognitive behavioural therapy, for persistent insomnia in children with autism spectrum disorders: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Sleep Res. 2012;21(6):700-709. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2869.2012.01021.x
42. Guastella AJ, Einfeld SL, Gray KM, et al. Intranasal oxytocin improves emotion recognition for youth with autism spectrum disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67(7):692-694. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.09.020
43. Gordon I, Vander Wyk BC, Bennett RH, et al. Oxytocin enhances brain function in children with autism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(52):20953-20958. doi:10.1073/pnas.1312857110
44. Höfer J, Bachmann C, Kamp-Becker I, et al. Willingness to try and lifetime use of complementary and alternative medicine in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder in Germany: a survey of parents. Autism. 2019;23(7):1865-1870. doi:10.1177/1362361318823545
45. Smith CA, Parton C, King M, et al. Parents’ experiences of information-seeking and decision-making regarding complementary medicine for children with autism spectrum disorder: a qualitative study. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020;20(1):4. doi:10.1186/s12906-019-2805-0
46. Marsden REF, Francis J, Garner I. Use of GFCF diets in children with ASD. An investigation into parents’ beliefs using the theory of planned behaviour. J Autism Dev Disord. 2019;49(9):3716-3731. doi:10.1007/s10803-019-04035-8
47. Trudeau MS, Madden RF, Parnell JA, et al. Dietary and supplement-based complementary and alternative medicine use in pediatric autism spectrum disorder. Nutrients. 2019;11(8):1783. doi:10.3390/nu11081783
48. Bent S, Hendren RL, Zandi T, et al. Internet-based, randomized, controlled trial of omega-3 fatty acids for hyperactivity in autism. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;53(6):658-666. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2014.01.018
49. Fraguas D, Díaz-Caneja C, Pina-Camacho L, et al. Dietary interventions for autism spectrum disorder: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 144(5):e20183218.
50. Mazahery H, Conlon CA, Beck KL, et al. A randomised-controlled trial of vitamin D and omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in the treatment of core symptoms of autism spectrum disorder in children. J Autism Dev Disord. 2019;49(5):1778-1794. doi:10.1007/s10803-018-3860-y
51. Green J, Garg S. Annual research review: the state of autism intervention science: progress, target psychological and biological mechanisms and future prospects. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018;59(4):424-443. doi:10.1111/jcpp.1289
52. Frye RE, Vassall S, Kaur G, et al. Emerging biomarkers in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(23):792. doi:10.21037/atm.2019.11.53
1. Maglione MA, Gans D, Das L, et al. Nonmedical interventions for children with ASD: recommended guidelines and further research needs. Pediatrics. 2012;30(Suppl 2):S169-S178.
2. Simms MD, Jin XM. Autism, language disorder, and social (pragmatic) communication disorder: DSM-V and differential diagnoses. Pediatr Rev. 2015;36(8):355-363. doi:10.1542/pir.36-8-355
3. Su Maw S, Haga C. Effectiveness of cognitive, developmental, and behavioural interventions for autism spectrum disorder in preschool-aged children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon. 2018;4(9):e00763. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00763
4. Charman T. Editorial: trials and tribulations in early autism intervention research. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;58(9):846-848. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2019.03.004
5. Monz BU, Houghton R, Law K, et al. Treatment patterns in children with autism in the United States. Autism Res. 2019;12(3):517-526. doi:10.1002/aur.2070
6. Sperdin HF, Schaer M. Aberrant development of speech processing in young children with autism: new insights from neuroimaging biomarkers. Front Neurosci. 2016;10:393. doi:10.3389/fnins.2016.00393
7. Hyman SL, Levy SE, Myers SM, et al. Identification, evaluation, and management of children with autism spectrum disorder. Pediatrics. 2020;145(1):e20193447. doi:10.1542/peds.2019-3447
8. Contaldo A, Colombi C, Pierotti C, et al. Outcomes and moderators of Early Start Denver Model intervention in young children with autism spectrum disorder delivered in a mixed individual and group setting. Autism. 2020;24(3):718-729. doi:10.1177/1362361319888344
9. Lei J, Ventola P. Pivotal response treatment for autism spectrum disorder: current perspectives. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017;13:1613-1626. doi:10.2147/NDT.S120710
10. Landa RJ. Efficacy of early interventions for infants and young children with, and at risk for, autism spectrum disorders. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2018;30(1):25-39. doi:10.1080/09540261.2018.1432574
11. Schreibman L, Dawson G, Stahmer AC, et al. Naturalistic developmental behavioral interventions: empirically validated treatments for autism spectrum disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. 2015;45(8):2411-2428. doi:10.1007/s10803-015-2407-8
12. Rogers SJ, Estes A, Lord C, et al. A multisite randomized controlled two-phase trial of the Early Start Denver Model compared to treatment as usual. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;58(9):853-865. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2019.01.004
13. Ingersoll B, Gergans S. The effect of a parent-implemented imitation intervention on spontaneous imitation skills in young children with autism. Res Dev Disabil. 2007;28(2):163-175.
14. Waddington H, van der Meer L, Sigafoos J, et al. Examining parent use of specific intervention techniques during a 12-week training program based on the Early Start Denver Model. Autism. 2020;24(2):484-498. doi:10.1177/1362361319876495
15. Trembath D, Gurm M, Scheerer NE, et al. Systematic review of factors that may influence the outcomes and generalizability of parent‐mediated interventions for young children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2019;12(9):1304-1321.
16. Rogers SJ, Estes A, Lord C, et al. Effects of a brief Early Start Denver Model (ESDM)-based parent intervention on toddlers at risk for autism spectrum disorders: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(10):1052-1065. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2012.08.003
17. Boyd BA, Hume K, McBee MT, et al. Comparative efficacy of LEAP, TEACCH and non-model-specific special education programs for preschoolers with autism spectrum disorders. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44(2):366-380. doi:10.1007/s10803-013-1877-9
18. Thompson GA, McFerran KS, Gold C. Family-centred music therapy to promote social engagement in young children with severe autism spectrum disorder: a randomized controlled study. Child Care Health Dev. 2014;40(6):840-852. doi:10.1111/cch.12121
19. Pickles A, Le Couteur A, Leadbitter K, et al. Parent-mediated social communication therapy for young children with autism (PACT): long-term follow-up of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2501-2509.
20. Grossard C, Palestra G, Xavier J, et al. ICT and autism care: state of the art. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2018;31(6):474-483. doi:10.1097/YCO.0000000000000455
21. Cukier S, Barrios N. Pharmacological interventions for intellectual disability and autism. Vertex. 2019;XXX(143)52-63.
22. Sharma SR, Gonda X, Tarazi FI. Autism spectrum disorder: classification, diagnosis and therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;190:91-104.
23. Volkmar F, Siegel M, Woodbury-Smith M, et al. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;53(2):237-257.
24. LeClerc S, Easley D. Pharmacological therapies for autism spectrum disorder: a review. P T. 2015;40(6):389-397.
25. Gencer O, Emiroglu FN, Miral S, et al. Comparison of long-term efficacy and safety of risperidone and haloperidol in children and adolescents with autistic disorder. An open label maintenance study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;17(4):217-225.
26. Miral S, Gencer O, Inal-Emiroglu FN, et al. Risperidone versus haloperidol in children and adolescents with AD: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;17(1):1-8.
27. Findling RL, Mankoski R, Timko K, et al. A randomized controlled trial investigating the safety and efficacy of aripiprazole in the long-term maintenance treatment of pediatric patients with irritability associated with autistic disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2014;75(1):22-30. doi:10.4088/jcp.13m08500
28. McLennan JD. Deprescribing in a youth with an intellectual disability, autism, behavioural problems, and medication-related obesity: a case study. J Can Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;28(3):141-146.
29. Scahill L, McCracken JT, King B, et al. Extended-release guanfacine for hyperactivity in children with autism spectrum disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2015;172(12):1197-1206. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15010055
30. Harfterkamp M, van de Loo-Neus G, Minderaa RB, et al. A randomized double-blind study of atomoxetine versus placebo for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in children with autism spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(7):733-741. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2012.04.011
31. DeFilippis M, Wagner KD. Treatment of autism spectrum disorder in children and adolescents. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2016;46(2):18-41.
32. DeFilippis M. Depression in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Children (Basel). 2018;5(9):112. doi:10.3390/children5090112
33. Goel R, Hong JS, Findling RL, et al. An update on pharmacotherapy of autism spectrum disorder in children and adolescents. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2018;30(1):78-95. doi:10.1080/09540261.2018.1458706
34. Williams K, Brignell A, Randall M, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(8):CD004677. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004677.pub3
35. Herscu P, Handen BL, Arnold LE, et al. The SOFIA study: negative multi-center study of low dose fluoxetine on repetitive behaviors in children and adolescents with autistic disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020;50(9):3233-3244. doi:10.1007/s10803-019-04120-y
36. Hollander E, Phillips A, Chaplin W, et al. A placebo controlled crossover trial of liquid fluoxetine on repetitive behaviors in childhood and adolescent autism. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30(3):582-589.
37. King BH, Hollander E, Sikich L, et al. Lack of efficacy of citalopram in children with autism spectrum disorders and high levels of repetitive behavior: citalopram ineffective in children with autism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(6):583-590. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.30
38. Hollander E, Kaplan A, Cartwright C, et al. Venlafaxine in children, adolescents, and young adults with autism spectrum disorders: an open retrospective clinical report. J Child Neurol. 2000;15(2):132-135.
39. Carminati GG, Deriaz N, Bertschy G. Low-dose venlafaxine in three adolescents and young adults with autistic disorder improves self-injurious behavior and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorders (ADHD)-like symptoms. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2006;30(2):312-315.
40. Spencer D, Marshall J, Post B, et al. Psychotropic medication use and polypharmacy in children with autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics. 2013;132(5):833-840. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-3774
41. Cortesi F, Giannotti F, Sebastiani T, et al. Controlled-release melatonin, singly and combined with cognitive behavioural therapy, for persistent insomnia in children with autism spectrum disorders: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Sleep Res. 2012;21(6):700-709. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2869.2012.01021.x
42. Guastella AJ, Einfeld SL, Gray KM, et al. Intranasal oxytocin improves emotion recognition for youth with autism spectrum disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67(7):692-694. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.09.020
43. Gordon I, Vander Wyk BC, Bennett RH, et al. Oxytocin enhances brain function in children with autism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(52):20953-20958. doi:10.1073/pnas.1312857110
44. Höfer J, Bachmann C, Kamp-Becker I, et al. Willingness to try and lifetime use of complementary and alternative medicine in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder in Germany: a survey of parents. Autism. 2019;23(7):1865-1870. doi:10.1177/1362361318823545
45. Smith CA, Parton C, King M, et al. Parents’ experiences of information-seeking and decision-making regarding complementary medicine for children with autism spectrum disorder: a qualitative study. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020;20(1):4. doi:10.1186/s12906-019-2805-0
46. Marsden REF, Francis J, Garner I. Use of GFCF diets in children with ASD. An investigation into parents’ beliefs using the theory of planned behaviour. J Autism Dev Disord. 2019;49(9):3716-3731. doi:10.1007/s10803-019-04035-8
47. Trudeau MS, Madden RF, Parnell JA, et al. Dietary and supplement-based complementary and alternative medicine use in pediatric autism spectrum disorder. Nutrients. 2019;11(8):1783. doi:10.3390/nu11081783
48. Bent S, Hendren RL, Zandi T, et al. Internet-based, randomized, controlled trial of omega-3 fatty acids for hyperactivity in autism. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;53(6):658-666. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2014.01.018
49. Fraguas D, Díaz-Caneja C, Pina-Camacho L, et al. Dietary interventions for autism spectrum disorder: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 144(5):e20183218.
50. Mazahery H, Conlon CA, Beck KL, et al. A randomised-controlled trial of vitamin D and omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in the treatment of core symptoms of autism spectrum disorder in children. J Autism Dev Disord. 2019;49(5):1778-1794. doi:10.1007/s10803-018-3860-y
51. Green J, Garg S. Annual research review: the state of autism intervention science: progress, target psychological and biological mechanisms and future prospects. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018;59(4):424-443. doi:10.1111/jcpp.1289
52. Frye RE, Vassall S, Kaur G, et al. Emerging biomarkers in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(23):792. doi:10.21037/atm.2019.11.53
COVID-19 and the psychiatrist/psychoanalyst: My experience
COVID-19 affected all aspects of psychiatric care. As a psychiatrist who is also a psychoanalyst, I faced some unique challenges to caring for my patients during the pandemic. In this article, I describe how COVID-19 impacted my practice, and how I adjusted to ensure that my patients received the best possible care.
The loss of ‘normal’
Our recognition of the loss was not immediate since no one knew what to expect. From March 11, 2020 through the end of the warm weather, when we could be outdoors, personal life was still gratifying. There was even a new spirit of togetherness in my neighborhood, with people seamlessly cooperating by crossing the street to avoid getting too close to one another, practicing proper social distancing in the grocery line, and smiling at everyone.
November 2020 through Spring 2021 was an unprecedented period of no socialization and spending time exclusively with my husband. By the end, I was finally aware of the exhaustion I felt trying to work with patients via phone and video sessions. Beyond that, we were (and still are) conducting administrative meetings and national organization meetings by video.
Spring 2021 until the arrival of cold weather felt more relaxed, as socializing outside again became possible. But from Winter 2021 to now has been a weary repeat of isolation, and a realization that my work life might never go back to “normal.” I would have to make peace with various sorts of losses of gratification in my work.
Life before COVID-19
I am a psychiatrist and psychoanalyst in a group private practice near the University of Cincinnati Medical Center. As a former full-time faculty member there, I maintain some teaching and supervision of residents. I typically see patients from 8:30 AM until 6:30 PM, and for years have had an average of 5 patients in psychoanalysis on the couch for 3 to 4 sessions per week. I see some psychotherapy patients weekly or twice a week and have some hours for new diagnostic evaluations and medication management. In addition, as a faculty member of the Cincinnati Psychoanalytic Institute, I take part in several committees, teach in the psychotherapy program and psychoanalytic training program, and supervise students and candidates. Most weeks, I see between 35 and 40 patients, with 4 to 6 weeks of vacation time per year.
Major changes with the onset of the pandemic
Once the threat from COVID-19 became clear in March 2020, I thought through my options. My office comprises 5 professional offices, a waiting room, and an administrative area. Our administrative assistant and 1 or 2 practitioners were in the office with me most days. We maintained appropriate distance from each another and wore masks in common areas. The practice group was exemplary in immediately setting up safe practices. I learned a few colleagues were seeing patients outside using lawn chairs in the back of our lot where there was some privacy, but many stopped coming to the building altogether.
I felt real sadness having to tell patients I could no longer see them in my office. However, I was relieved to find how quickly many patients made an immediate transition to telephone or video sessions. Since I was alone in my office and not distracted by barking dogs, ringing doorbells, or loud lawnmowers, I continued to come to the office, and never switched to working from home.
Since I was not vis-à-vis with patients on the couch, those sessions shifted to the telephone. I offered psychotherapy patients the option of video sessions via the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act–compliant Doximity app (doxy.me) or telephone, and found that approximately 75% preferred video. When I used the telephone, I used a professional-grade headset, which made it less onerous than being tied to a receiver, and I occasionally used the speaker option. I also installed a desk platform that allows me to raise and lower my computer from sitting to standing height.
I worried a great deal about patients I felt would do poorly with video or telephone sessions: older adults who found comfort in human contact that was sometimes curative, less well-integrated individuals who needed real contact in order to feel there was a treatment process, those with serious mental illnesses who needed reassurance at their reality-testing, and new patients who I couldn’t fully assess without in-person meetings.
In the beginning of the pandemic, as we were still learning about the virus, nothing seemed safe. We were washing our hands constantly, afraid to touch doorknobs, mail, or groceries. Thankfully, we learned that COVID-19 transmission occurs primarily through inhalation of droplets and particles containing the virus.1 Masks, good ventilation, and adequate distance from others considerably cut infection rates. By January 2021, the availability of a vaccine made an enormous difference in vulnerability to severe illness.
When I stopped seeing patients in my office, I set up the conference room that had doors on either end so I could sit on one end of a table and have the patient at the other end, keeping about 8 feet between us. I also kept a fan blowing air away from me and parallel to the patient. After each session, I opened both doors to allow for full ventilation of the room. This provided a solution for the patients I knew I needed to meet with in person.
Continue to: Case examples: How it worked...
Case examples: How it worked
The following case examples illustrate how I provided care during this time. To protect patient anonymity, these vignettes are composites.
Psychotherapy patients
Established patients in psychotherapy have seemed to work well with video or telephone sessions. The video option added a new element I never appreciated: seeing patients in their homes or cars allowed me to gain a new set of impressions about them. The use of technology is clearly another element I would not have identified before. Less technically adept older patients are likely to join a video session with only the top of their head visible, or with insufficient lighting. In some cases, I coached patients to rearrange their computer so I could see their faces, but only if it seemed that doing so would not cause them greater distress.
Ms. A, age 74, is a widow who retired from a high-level professional position 5 years ago. She was brought to the hospital due to ongoing anxiety, especially about her health. Ms. A maintained a wide range of relationships with friends, colleagues she mentored, and neighbors who provided a satisfying social network, and she continued to contribute to her field via scholarly writing projects. Before the pandemic, she found occasional sessions helpful in putting her health fears into perspective. When the pandemic led her to isolate at home, Ms. A became anxious and depressed to an unprecedented extent. Video sessions were unsatisfying, and she was terrified of taking tranquilizers or other medications. Once COVID-19 vaccinations became available and both she and I received both doses, we switched to meeting in the conference room every 2 to 3 weeks, with considerably better results.
Mr. B, age 41, is a single male who I diagnosed with schizophrenia at age 19 when he developed paranoid delusions and auditory hallucinations. Mr. B was not interested in taking antipsychotic medications, and his situation did not improve even when he did try taking them. He volunteered at a local emergency department doing odd jobs—moving gurneys, cleaning rooms, hauling boxes of supplies—for many years, and had always been employed in jobs such as grocery stocking or janitorial work that did not involve extensive interactions with people. He repeatedly enrolled in programs that would provide a skill such as phlebotomy or medical billing, only to find that he was never hired for such work. We talked once a month for 30 minutes about his frustrations trying to find women to date and marry, and how he was repeatedly taken advantage of (one “date” from an escort service took him to an ATM and got him to withdraw most of the money in his account).
Coincident with COVID-19, Mr. B’s father died from widespread metastatic cancer. His father had been Mr. B’s guide, friend, payee for Social Security Disability Insurance funds, and source of advice. To provide humane and somewhat effective treatment, I saw Mr. B in the conference room. His capacity to express grief and distress at the loss of his father has been impressive, as has his initiative in finding a grief group to attend, which he has done consistently.
Several patients who had been seeing me for weekly psychotherapy chose not to continue, many without specifically informing me of their decision. I understood the situation was in flux, and it would not be clear to anyone what to expect for the future. To avoid pressuring anyone, I chose not to contact patients to inquire about their plans.
Ms. C, age 50, is a professional with 3 children whose marriage had been highly dissatisfying for years, and she was now ready to investigate it. She was very successful in her career, having taken on a leadership role in her firm and earning a high income, while her husband was erratic, unreliable, and self-absorbed. Though he was well-educated and competent in his field, he could not maintain employment in a corporate environment and worked as a consultant with relatively little success. Along with the hours she spent working, Ms. C took responsibility for the family finances, was the chief wage earner, managed the needs of their children, made sure meals were prepared, and took on many other responsibilities.
Continue to: Case examples: How it worked (cont.)...
We agreed to a weekly session that fit Ms. C’s schedule, and she seemed able to relax and talk about herself. I found Ms. C quite likeable and enjoyed meeting with her, though I worried about whether we would need a greater intensity to get at the reasons such a successful and intelligent woman would fear setting limits with her husband or even considering ending the relationship. The reasons were clear as we put together the story of her early life, but conviction only develops with full emotional awareness (transference provides this in psychoanalysis).
The pandemic started approximately 18 months into our work, and Ms. C disappeared. She called my administrative assistant to cancel further appointments but did not ask to speak with me directly. While I knew this might represent resistance, I also felt unwilling to pressure Ms. C if she chose not to continue. I remain hopeful that I will hear from her once again; if not, I will send a note by mail to say that I enjoyed working with her, am happy to see her again, and hope she found some benefit from our work.
Mr. D contacted me for psychotherapy following the death of his father, who I had seen as a patient many years earlier. I was aware of the likely impact of his father’s outsized personality and emotional dysregulation on Mr. D and agreed to meet with him. He had taken over the family business and had made it an even greater success, but had trouble feeling confident about setting limits with employees who he knew took advantage of his avoidance.
Mr. D and I met weekly for several months and then moved to every other week, a form of resistance I expected as we got closer to his feeling pain. At the same time, I recognize that many patients use this tactic to “dose” themselves with the intensity they can tolerate, and Mr. D was quite observant and able to pick up themes where we’d left off.
When the pandemic shut down office visits, Mr. D immediately agreed to video sessions, which he has continued at roughly the same frequency. While I miss sitting with him, we continue to make progress towards his goal of learning to see himself as able to compete with his father.
Psychoanalysis patients
I found that patients in psychoanalysis had no trouble with the transition to telephone sessions, and the intensity of the work was not diluted. In some ways, audio-only communication is more intimate and might encourage patients to talk about topics they may not have otherwise brought up. I have not seen any evidence of less progress among these patients.
Dr. E, age 45, is a divorced physician who began psychoanalysis 3 times per week on the couch in 2018 for problems with frustration and confusion about his career, his identity as a father, and intense loneliness. He had worked up to 80 hours per week to earn as much money as he could, but also to avoid time at home with his then-wife and young children. The lack of time to recover led him to hate his work, left no time for social connections, and led to binges of heavy drinking. Our work had begun to allow him to develop a narrative about his early life that had never been considered, and to identify patterns of repetition of old defensive strategies that had never served him well.
At the onset of the pandemic, I told Dr. E that we would have to switch to telephone sessions, and he agreed immediately. In fact, he came to prefer telephone work since it spared him the 2 hours per day he had spent coming to my office. While I found it less satisfying than working in person, we have continued the same schedule and with the same intensity and trajectory established before the pandemic.
Continue to: Working with new patients...
Working with new patients
Seeing new patients for diagnostic evaluation is always best done in person, because the information I gain from the patient’s appearance, clothing, demeanor, gait, postures, gesturing, and facial expressions (among other elements) gives me important impressions I miss with video or telephone. In many cases, patients gain a sense of who I am from sitting in my office, and using the conference room eliminates that benefit. I attempted to create a warm environment in the conference room by obtaining lamps that produce warmer indirect light and hanging artwork that reflects my tastes. There are clocks in places that allow me and my patient to keep track of time. In meeting new patients by video, I get some impressions about their surroundings that add to the information I get through our interview. I have done many diagnostic evaluations during the pandemic and gotten treatments (whether medication, psychotherapy, or both) underway without discernible problems in the outcomes. Patients who started with me in person have mostly wanted to continue with in-person meetings, but as many have told me, interspersed video sessions save them travel time.
What about vaccination?
Once COVID-19 vaccinations were widely available, I assumed patients would be as eager to get them as I had been. When I began asking patients about whether they had gotten their vaccines, I was surprised to hear that a few were not going to get vaccinated, clearly based on political views and misinformation about the danger of vaccines. (The topic of political beliefs and their impact on psychological treatment is beyond the scope of this commentary.) I tried to counter obvious misinformation, repeated my recommendation that the patient get vaccinated, and then turned to other topics. I later decided to tell all patients that vaccination was required to enter the office. Only 1 patient who had been coming to the office dropped out, and she eventually returned to meeting by video.
COVID-19’s toll on the therapist
While the first several months of the pandemic were so full of uncertainty about the future, once vaccinations were available, it seemed cause for hope of a return to normalcy. As time went on, however, it became clear that normal was still a long way off. With vaccine refusal and new variants upending my naïve view that we were near the end, I began to feel aware of the impact this had on me, and began to focus on self-care (Box). I had always seen myself as unusually lucky to have a full practice, a supportive partnership with my husband, grown children who didn’t need me to homeschool them, a strong social network of friends who could share the burden and cheer each other up at outdoor gatherings, and a wonderful group of siblings and in-laws (all in different cities) who stayed in touch via video calls and quarantined in advance of getting together in someone’s home.
Box
Self-care has always been a requirement of doing psychotherapeutic work, and I encourage practitioners to be sure they are attending to themselves. We can’t be effective as listeners, empathizers, diagnosticians, and problem-solvers if we ourselves aren’t healthy. We evaluate our patients in terms of mood, outlook, sleep, appetite, energy, motivation, and energy; we also investigate their capacity for relationships that are sustaining. Self-care is the same, taking care of both our physical and relationship beings. Getting enough sleep, exercising daily, cooking healthy meals, and making time to relax are all ways of caring for our physical identities that should have been in place before COVID-19. Making personal time for ourselves in the face of constant demands for time from patients, colleagues, partners, children, parents, siblings, and friends never happens without the resolve to do it. As a psychiatrist who is used to sitting for up to 10 hours per day, I strongly recommend making a daily habit of walking, running, biking, or using an elliptical trainer, treadmill, or stationary bike for 30 minutes or more. Sleep is necessary for adequate concentration and attention to patient after patient. If you have trouble sleeping, talk with your doctor about remedies. If you use a sleep aid, I strongly recommend alternating medications so you don’t develop tolerance to any of them. Plan your food and cooking ahead of time so you aren’t tempted to order out. If you cook simple meals yourself (ideally with your partner helping or in range so you can chat), you will consume fewer calories, less sodium, and more nutrients. Even if you have a spouse and young children at home, work out a plan with your partner that allows each of you time for exercise or to recoup after a long day with patients. Babysitters allow you to take the time to be with each other that is necessary to sustaining a connection. Think about time for sexual intimacy if that has dropped off the calendar. Relationships with others, such as parents, siblings and their families, and friends are invaluable. The time spent with others might seem inconsequential, but is critical to our internal sense of security, even in the face of external disorder.
Staying busy and engaged with my practice, spouse, family, and friends kept sadness away most of the time. But I surprised myself a few months ago when I sat down to reflect and check in with myself. I felt enormous loss, resentment, and exhaustion at the privations of the pandemic: every trip to the grocery story felt dangerous. I hadn’t seen the inside of a concert hall, movie theater, restaurant, or museum in nearly 2 years. Travel for meetings and visits to family and friends and various adventures had been abruptly stopped. I lost both parents (not to COVID-19) during 2020; both were older adults living in senior communities that could not allow visitors. The usual grieving process would include attending services at my synagogue where I could say Kaddish for them, and video services were simply not tolerable.
Most of us have become experts at video meetings and likely have come to despise them. While our Institute has always held classes with some out-of-town students joining by video, with a very sophisticated system that provides excellent sound and visual fidelity, teaching entirely by video is another matter. I now teach students I have never met in person and might not recognize if I passed them in public. The art of creating discussion around a table is much more difficult on a computer screen. The first class I taught to residents during the pandemic was completely disorienting as I faced a wall of black screens with names and silence. Each student had turned off their camera and muted their microphone, so I was lecturing to a computer. That never happened again after I insisted on seeing everyone’s face and hearing their voices.
Thankfully, my usual experience of a long day seeing patients followed by chatting while cooking dinner with my husband and walking the dogs before settling down to read didn’t change. But the pleasure of sitting with patients was replaced by the daily grind of figuring out who will need a video link, who will be on the telephone, and who will come to the office, and it doesn’t feel the same. Again, in the big picture, I realize how fortunate I have been, but it’s been a big change in the world of the psychotherapist.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 frequently asked questions. Accessed March 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/faq.html#Spread
COVID-19 affected all aspects of psychiatric care. As a psychiatrist who is also a psychoanalyst, I faced some unique challenges to caring for my patients during the pandemic. In this article, I describe how COVID-19 impacted my practice, and how I adjusted to ensure that my patients received the best possible care.
The loss of ‘normal’
Our recognition of the loss was not immediate since no one knew what to expect. From March 11, 2020 through the end of the warm weather, when we could be outdoors, personal life was still gratifying. There was even a new spirit of togetherness in my neighborhood, with people seamlessly cooperating by crossing the street to avoid getting too close to one another, practicing proper social distancing in the grocery line, and smiling at everyone.
November 2020 through Spring 2021 was an unprecedented period of no socialization and spending time exclusively with my husband. By the end, I was finally aware of the exhaustion I felt trying to work with patients via phone and video sessions. Beyond that, we were (and still are) conducting administrative meetings and national organization meetings by video.
Spring 2021 until the arrival of cold weather felt more relaxed, as socializing outside again became possible. But from Winter 2021 to now has been a weary repeat of isolation, and a realization that my work life might never go back to “normal.” I would have to make peace with various sorts of losses of gratification in my work.
Life before COVID-19
I am a psychiatrist and psychoanalyst in a group private practice near the University of Cincinnati Medical Center. As a former full-time faculty member there, I maintain some teaching and supervision of residents. I typically see patients from 8:30 AM until 6:30 PM, and for years have had an average of 5 patients in psychoanalysis on the couch for 3 to 4 sessions per week. I see some psychotherapy patients weekly or twice a week and have some hours for new diagnostic evaluations and medication management. In addition, as a faculty member of the Cincinnati Psychoanalytic Institute, I take part in several committees, teach in the psychotherapy program and psychoanalytic training program, and supervise students and candidates. Most weeks, I see between 35 and 40 patients, with 4 to 6 weeks of vacation time per year.
Major changes with the onset of the pandemic
Once the threat from COVID-19 became clear in March 2020, I thought through my options. My office comprises 5 professional offices, a waiting room, and an administrative area. Our administrative assistant and 1 or 2 practitioners were in the office with me most days. We maintained appropriate distance from each another and wore masks in common areas. The practice group was exemplary in immediately setting up safe practices. I learned a few colleagues were seeing patients outside using lawn chairs in the back of our lot where there was some privacy, but many stopped coming to the building altogether.
I felt real sadness having to tell patients I could no longer see them in my office. However, I was relieved to find how quickly many patients made an immediate transition to telephone or video sessions. Since I was alone in my office and not distracted by barking dogs, ringing doorbells, or loud lawnmowers, I continued to come to the office, and never switched to working from home.
Since I was not vis-à-vis with patients on the couch, those sessions shifted to the telephone. I offered psychotherapy patients the option of video sessions via the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act–compliant Doximity app (doxy.me) or telephone, and found that approximately 75% preferred video. When I used the telephone, I used a professional-grade headset, which made it less onerous than being tied to a receiver, and I occasionally used the speaker option. I also installed a desk platform that allows me to raise and lower my computer from sitting to standing height.
I worried a great deal about patients I felt would do poorly with video or telephone sessions: older adults who found comfort in human contact that was sometimes curative, less well-integrated individuals who needed real contact in order to feel there was a treatment process, those with serious mental illnesses who needed reassurance at their reality-testing, and new patients who I couldn’t fully assess without in-person meetings.
In the beginning of the pandemic, as we were still learning about the virus, nothing seemed safe. We were washing our hands constantly, afraid to touch doorknobs, mail, or groceries. Thankfully, we learned that COVID-19 transmission occurs primarily through inhalation of droplets and particles containing the virus.1 Masks, good ventilation, and adequate distance from others considerably cut infection rates. By January 2021, the availability of a vaccine made an enormous difference in vulnerability to severe illness.
When I stopped seeing patients in my office, I set up the conference room that had doors on either end so I could sit on one end of a table and have the patient at the other end, keeping about 8 feet between us. I also kept a fan blowing air away from me and parallel to the patient. After each session, I opened both doors to allow for full ventilation of the room. This provided a solution for the patients I knew I needed to meet with in person.
Continue to: Case examples: How it worked...
Case examples: How it worked
The following case examples illustrate how I provided care during this time. To protect patient anonymity, these vignettes are composites.
Psychotherapy patients
Established patients in psychotherapy have seemed to work well with video or telephone sessions. The video option added a new element I never appreciated: seeing patients in their homes or cars allowed me to gain a new set of impressions about them. The use of technology is clearly another element I would not have identified before. Less technically adept older patients are likely to join a video session with only the top of their head visible, or with insufficient lighting. In some cases, I coached patients to rearrange their computer so I could see their faces, but only if it seemed that doing so would not cause them greater distress.
Ms. A, age 74, is a widow who retired from a high-level professional position 5 years ago. She was brought to the hospital due to ongoing anxiety, especially about her health. Ms. A maintained a wide range of relationships with friends, colleagues she mentored, and neighbors who provided a satisfying social network, and she continued to contribute to her field via scholarly writing projects. Before the pandemic, she found occasional sessions helpful in putting her health fears into perspective. When the pandemic led her to isolate at home, Ms. A became anxious and depressed to an unprecedented extent. Video sessions were unsatisfying, and she was terrified of taking tranquilizers or other medications. Once COVID-19 vaccinations became available and both she and I received both doses, we switched to meeting in the conference room every 2 to 3 weeks, with considerably better results.
Mr. B, age 41, is a single male who I diagnosed with schizophrenia at age 19 when he developed paranoid delusions and auditory hallucinations. Mr. B was not interested in taking antipsychotic medications, and his situation did not improve even when he did try taking them. He volunteered at a local emergency department doing odd jobs—moving gurneys, cleaning rooms, hauling boxes of supplies—for many years, and had always been employed in jobs such as grocery stocking or janitorial work that did not involve extensive interactions with people. He repeatedly enrolled in programs that would provide a skill such as phlebotomy or medical billing, only to find that he was never hired for such work. We talked once a month for 30 minutes about his frustrations trying to find women to date and marry, and how he was repeatedly taken advantage of (one “date” from an escort service took him to an ATM and got him to withdraw most of the money in his account).
Coincident with COVID-19, Mr. B’s father died from widespread metastatic cancer. His father had been Mr. B’s guide, friend, payee for Social Security Disability Insurance funds, and source of advice. To provide humane and somewhat effective treatment, I saw Mr. B in the conference room. His capacity to express grief and distress at the loss of his father has been impressive, as has his initiative in finding a grief group to attend, which he has done consistently.
Several patients who had been seeing me for weekly psychotherapy chose not to continue, many without specifically informing me of their decision. I understood the situation was in flux, and it would not be clear to anyone what to expect for the future. To avoid pressuring anyone, I chose not to contact patients to inquire about their plans.
Ms. C, age 50, is a professional with 3 children whose marriage had been highly dissatisfying for years, and she was now ready to investigate it. She was very successful in her career, having taken on a leadership role in her firm and earning a high income, while her husband was erratic, unreliable, and self-absorbed. Though he was well-educated and competent in his field, he could not maintain employment in a corporate environment and worked as a consultant with relatively little success. Along with the hours she spent working, Ms. C took responsibility for the family finances, was the chief wage earner, managed the needs of their children, made sure meals were prepared, and took on many other responsibilities.
Continue to: Case examples: How it worked (cont.)...
We agreed to a weekly session that fit Ms. C’s schedule, and she seemed able to relax and talk about herself. I found Ms. C quite likeable and enjoyed meeting with her, though I worried about whether we would need a greater intensity to get at the reasons such a successful and intelligent woman would fear setting limits with her husband or even considering ending the relationship. The reasons were clear as we put together the story of her early life, but conviction only develops with full emotional awareness (transference provides this in psychoanalysis).
The pandemic started approximately 18 months into our work, and Ms. C disappeared. She called my administrative assistant to cancel further appointments but did not ask to speak with me directly. While I knew this might represent resistance, I also felt unwilling to pressure Ms. C if she chose not to continue. I remain hopeful that I will hear from her once again; if not, I will send a note by mail to say that I enjoyed working with her, am happy to see her again, and hope she found some benefit from our work.
Mr. D contacted me for psychotherapy following the death of his father, who I had seen as a patient many years earlier. I was aware of the likely impact of his father’s outsized personality and emotional dysregulation on Mr. D and agreed to meet with him. He had taken over the family business and had made it an even greater success, but had trouble feeling confident about setting limits with employees who he knew took advantage of his avoidance.
Mr. D and I met weekly for several months and then moved to every other week, a form of resistance I expected as we got closer to his feeling pain. At the same time, I recognize that many patients use this tactic to “dose” themselves with the intensity they can tolerate, and Mr. D was quite observant and able to pick up themes where we’d left off.
When the pandemic shut down office visits, Mr. D immediately agreed to video sessions, which he has continued at roughly the same frequency. While I miss sitting with him, we continue to make progress towards his goal of learning to see himself as able to compete with his father.
Psychoanalysis patients
I found that patients in psychoanalysis had no trouble with the transition to telephone sessions, and the intensity of the work was not diluted. In some ways, audio-only communication is more intimate and might encourage patients to talk about topics they may not have otherwise brought up. I have not seen any evidence of less progress among these patients.
Dr. E, age 45, is a divorced physician who began psychoanalysis 3 times per week on the couch in 2018 for problems with frustration and confusion about his career, his identity as a father, and intense loneliness. He had worked up to 80 hours per week to earn as much money as he could, but also to avoid time at home with his then-wife and young children. The lack of time to recover led him to hate his work, left no time for social connections, and led to binges of heavy drinking. Our work had begun to allow him to develop a narrative about his early life that had never been considered, and to identify patterns of repetition of old defensive strategies that had never served him well.
At the onset of the pandemic, I told Dr. E that we would have to switch to telephone sessions, and he agreed immediately. In fact, he came to prefer telephone work since it spared him the 2 hours per day he had spent coming to my office. While I found it less satisfying than working in person, we have continued the same schedule and with the same intensity and trajectory established before the pandemic.
Continue to: Working with new patients...
Working with new patients
Seeing new patients for diagnostic evaluation is always best done in person, because the information I gain from the patient’s appearance, clothing, demeanor, gait, postures, gesturing, and facial expressions (among other elements) gives me important impressions I miss with video or telephone. In many cases, patients gain a sense of who I am from sitting in my office, and using the conference room eliminates that benefit. I attempted to create a warm environment in the conference room by obtaining lamps that produce warmer indirect light and hanging artwork that reflects my tastes. There are clocks in places that allow me and my patient to keep track of time. In meeting new patients by video, I get some impressions about their surroundings that add to the information I get through our interview. I have done many diagnostic evaluations during the pandemic and gotten treatments (whether medication, psychotherapy, or both) underway without discernible problems in the outcomes. Patients who started with me in person have mostly wanted to continue with in-person meetings, but as many have told me, interspersed video sessions save them travel time.
What about vaccination?
Once COVID-19 vaccinations were widely available, I assumed patients would be as eager to get them as I had been. When I began asking patients about whether they had gotten their vaccines, I was surprised to hear that a few were not going to get vaccinated, clearly based on political views and misinformation about the danger of vaccines. (The topic of political beliefs and their impact on psychological treatment is beyond the scope of this commentary.) I tried to counter obvious misinformation, repeated my recommendation that the patient get vaccinated, and then turned to other topics. I later decided to tell all patients that vaccination was required to enter the office. Only 1 patient who had been coming to the office dropped out, and she eventually returned to meeting by video.
COVID-19’s toll on the therapist
While the first several months of the pandemic were so full of uncertainty about the future, once vaccinations were available, it seemed cause for hope of a return to normalcy. As time went on, however, it became clear that normal was still a long way off. With vaccine refusal and new variants upending my naïve view that we were near the end, I began to feel aware of the impact this had on me, and began to focus on self-care (Box). I had always seen myself as unusually lucky to have a full practice, a supportive partnership with my husband, grown children who didn’t need me to homeschool them, a strong social network of friends who could share the burden and cheer each other up at outdoor gatherings, and a wonderful group of siblings and in-laws (all in different cities) who stayed in touch via video calls and quarantined in advance of getting together in someone’s home.
Box
Self-care has always been a requirement of doing psychotherapeutic work, and I encourage practitioners to be sure they are attending to themselves. We can’t be effective as listeners, empathizers, diagnosticians, and problem-solvers if we ourselves aren’t healthy. We evaluate our patients in terms of mood, outlook, sleep, appetite, energy, motivation, and energy; we also investigate their capacity for relationships that are sustaining. Self-care is the same, taking care of both our physical and relationship beings. Getting enough sleep, exercising daily, cooking healthy meals, and making time to relax are all ways of caring for our physical identities that should have been in place before COVID-19. Making personal time for ourselves in the face of constant demands for time from patients, colleagues, partners, children, parents, siblings, and friends never happens without the resolve to do it. As a psychiatrist who is used to sitting for up to 10 hours per day, I strongly recommend making a daily habit of walking, running, biking, or using an elliptical trainer, treadmill, or stationary bike for 30 minutes or more. Sleep is necessary for adequate concentration and attention to patient after patient. If you have trouble sleeping, talk with your doctor about remedies. If you use a sleep aid, I strongly recommend alternating medications so you don’t develop tolerance to any of them. Plan your food and cooking ahead of time so you aren’t tempted to order out. If you cook simple meals yourself (ideally with your partner helping or in range so you can chat), you will consume fewer calories, less sodium, and more nutrients. Even if you have a spouse and young children at home, work out a plan with your partner that allows each of you time for exercise or to recoup after a long day with patients. Babysitters allow you to take the time to be with each other that is necessary to sustaining a connection. Think about time for sexual intimacy if that has dropped off the calendar. Relationships with others, such as parents, siblings and their families, and friends are invaluable. The time spent with others might seem inconsequential, but is critical to our internal sense of security, even in the face of external disorder.
Staying busy and engaged with my practice, spouse, family, and friends kept sadness away most of the time. But I surprised myself a few months ago when I sat down to reflect and check in with myself. I felt enormous loss, resentment, and exhaustion at the privations of the pandemic: every trip to the grocery story felt dangerous. I hadn’t seen the inside of a concert hall, movie theater, restaurant, or museum in nearly 2 years. Travel for meetings and visits to family and friends and various adventures had been abruptly stopped. I lost both parents (not to COVID-19) during 2020; both were older adults living in senior communities that could not allow visitors. The usual grieving process would include attending services at my synagogue where I could say Kaddish for them, and video services were simply not tolerable.
Most of us have become experts at video meetings and likely have come to despise them. While our Institute has always held classes with some out-of-town students joining by video, with a very sophisticated system that provides excellent sound and visual fidelity, teaching entirely by video is another matter. I now teach students I have never met in person and might not recognize if I passed them in public. The art of creating discussion around a table is much more difficult on a computer screen. The first class I taught to residents during the pandemic was completely disorienting as I faced a wall of black screens with names and silence. Each student had turned off their camera and muted their microphone, so I was lecturing to a computer. That never happened again after I insisted on seeing everyone’s face and hearing their voices.
Thankfully, my usual experience of a long day seeing patients followed by chatting while cooking dinner with my husband and walking the dogs before settling down to read didn’t change. But the pleasure of sitting with patients was replaced by the daily grind of figuring out who will need a video link, who will be on the telephone, and who will come to the office, and it doesn’t feel the same. Again, in the big picture, I realize how fortunate I have been, but it’s been a big change in the world of the psychotherapist.
COVID-19 affected all aspects of psychiatric care. As a psychiatrist who is also a psychoanalyst, I faced some unique challenges to caring for my patients during the pandemic. In this article, I describe how COVID-19 impacted my practice, and how I adjusted to ensure that my patients received the best possible care.
The loss of ‘normal’
Our recognition of the loss was not immediate since no one knew what to expect. From March 11, 2020 through the end of the warm weather, when we could be outdoors, personal life was still gratifying. There was even a new spirit of togetherness in my neighborhood, with people seamlessly cooperating by crossing the street to avoid getting too close to one another, practicing proper social distancing in the grocery line, and smiling at everyone.
November 2020 through Spring 2021 was an unprecedented period of no socialization and spending time exclusively with my husband. By the end, I was finally aware of the exhaustion I felt trying to work with patients via phone and video sessions. Beyond that, we were (and still are) conducting administrative meetings and national organization meetings by video.
Spring 2021 until the arrival of cold weather felt more relaxed, as socializing outside again became possible. But from Winter 2021 to now has been a weary repeat of isolation, and a realization that my work life might never go back to “normal.” I would have to make peace with various sorts of losses of gratification in my work.
Life before COVID-19
I am a psychiatrist and psychoanalyst in a group private practice near the University of Cincinnati Medical Center. As a former full-time faculty member there, I maintain some teaching and supervision of residents. I typically see patients from 8:30 AM until 6:30 PM, and for years have had an average of 5 patients in psychoanalysis on the couch for 3 to 4 sessions per week. I see some psychotherapy patients weekly or twice a week and have some hours for new diagnostic evaluations and medication management. In addition, as a faculty member of the Cincinnati Psychoanalytic Institute, I take part in several committees, teach in the psychotherapy program and psychoanalytic training program, and supervise students and candidates. Most weeks, I see between 35 and 40 patients, with 4 to 6 weeks of vacation time per year.
Major changes with the onset of the pandemic
Once the threat from COVID-19 became clear in March 2020, I thought through my options. My office comprises 5 professional offices, a waiting room, and an administrative area. Our administrative assistant and 1 or 2 practitioners were in the office with me most days. We maintained appropriate distance from each another and wore masks in common areas. The practice group was exemplary in immediately setting up safe practices. I learned a few colleagues were seeing patients outside using lawn chairs in the back of our lot where there was some privacy, but many stopped coming to the building altogether.
I felt real sadness having to tell patients I could no longer see them in my office. However, I was relieved to find how quickly many patients made an immediate transition to telephone or video sessions. Since I was alone in my office and not distracted by barking dogs, ringing doorbells, or loud lawnmowers, I continued to come to the office, and never switched to working from home.
Since I was not vis-à-vis with patients on the couch, those sessions shifted to the telephone. I offered psychotherapy patients the option of video sessions via the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act–compliant Doximity app (doxy.me) or telephone, and found that approximately 75% preferred video. When I used the telephone, I used a professional-grade headset, which made it less onerous than being tied to a receiver, and I occasionally used the speaker option. I also installed a desk platform that allows me to raise and lower my computer from sitting to standing height.
I worried a great deal about patients I felt would do poorly with video or telephone sessions: older adults who found comfort in human contact that was sometimes curative, less well-integrated individuals who needed real contact in order to feel there was a treatment process, those with serious mental illnesses who needed reassurance at their reality-testing, and new patients who I couldn’t fully assess without in-person meetings.
In the beginning of the pandemic, as we were still learning about the virus, nothing seemed safe. We were washing our hands constantly, afraid to touch doorknobs, mail, or groceries. Thankfully, we learned that COVID-19 transmission occurs primarily through inhalation of droplets and particles containing the virus.1 Masks, good ventilation, and adequate distance from others considerably cut infection rates. By January 2021, the availability of a vaccine made an enormous difference in vulnerability to severe illness.
When I stopped seeing patients in my office, I set up the conference room that had doors on either end so I could sit on one end of a table and have the patient at the other end, keeping about 8 feet between us. I also kept a fan blowing air away from me and parallel to the patient. After each session, I opened both doors to allow for full ventilation of the room. This provided a solution for the patients I knew I needed to meet with in person.
Continue to: Case examples: How it worked...
Case examples: How it worked
The following case examples illustrate how I provided care during this time. To protect patient anonymity, these vignettes are composites.
Psychotherapy patients
Established patients in psychotherapy have seemed to work well with video or telephone sessions. The video option added a new element I never appreciated: seeing patients in their homes or cars allowed me to gain a new set of impressions about them. The use of technology is clearly another element I would not have identified before. Less technically adept older patients are likely to join a video session with only the top of their head visible, or with insufficient lighting. In some cases, I coached patients to rearrange their computer so I could see their faces, but only if it seemed that doing so would not cause them greater distress.
Ms. A, age 74, is a widow who retired from a high-level professional position 5 years ago. She was brought to the hospital due to ongoing anxiety, especially about her health. Ms. A maintained a wide range of relationships with friends, colleagues she mentored, and neighbors who provided a satisfying social network, and she continued to contribute to her field via scholarly writing projects. Before the pandemic, she found occasional sessions helpful in putting her health fears into perspective. When the pandemic led her to isolate at home, Ms. A became anxious and depressed to an unprecedented extent. Video sessions were unsatisfying, and she was terrified of taking tranquilizers or other medications. Once COVID-19 vaccinations became available and both she and I received both doses, we switched to meeting in the conference room every 2 to 3 weeks, with considerably better results.
Mr. B, age 41, is a single male who I diagnosed with schizophrenia at age 19 when he developed paranoid delusions and auditory hallucinations. Mr. B was not interested in taking antipsychotic medications, and his situation did not improve even when he did try taking them. He volunteered at a local emergency department doing odd jobs—moving gurneys, cleaning rooms, hauling boxes of supplies—for many years, and had always been employed in jobs such as grocery stocking or janitorial work that did not involve extensive interactions with people. He repeatedly enrolled in programs that would provide a skill such as phlebotomy or medical billing, only to find that he was never hired for such work. We talked once a month for 30 minutes about his frustrations trying to find women to date and marry, and how he was repeatedly taken advantage of (one “date” from an escort service took him to an ATM and got him to withdraw most of the money in his account).
Coincident with COVID-19, Mr. B’s father died from widespread metastatic cancer. His father had been Mr. B’s guide, friend, payee for Social Security Disability Insurance funds, and source of advice. To provide humane and somewhat effective treatment, I saw Mr. B in the conference room. His capacity to express grief and distress at the loss of his father has been impressive, as has his initiative in finding a grief group to attend, which he has done consistently.
Several patients who had been seeing me for weekly psychotherapy chose not to continue, many without specifically informing me of their decision. I understood the situation was in flux, and it would not be clear to anyone what to expect for the future. To avoid pressuring anyone, I chose not to contact patients to inquire about their plans.
Ms. C, age 50, is a professional with 3 children whose marriage had been highly dissatisfying for years, and she was now ready to investigate it. She was very successful in her career, having taken on a leadership role in her firm and earning a high income, while her husband was erratic, unreliable, and self-absorbed. Though he was well-educated and competent in his field, he could not maintain employment in a corporate environment and worked as a consultant with relatively little success. Along with the hours she spent working, Ms. C took responsibility for the family finances, was the chief wage earner, managed the needs of their children, made sure meals were prepared, and took on many other responsibilities.
Continue to: Case examples: How it worked (cont.)...
We agreed to a weekly session that fit Ms. C’s schedule, and she seemed able to relax and talk about herself. I found Ms. C quite likeable and enjoyed meeting with her, though I worried about whether we would need a greater intensity to get at the reasons such a successful and intelligent woman would fear setting limits with her husband or even considering ending the relationship. The reasons were clear as we put together the story of her early life, but conviction only develops with full emotional awareness (transference provides this in psychoanalysis).
The pandemic started approximately 18 months into our work, and Ms. C disappeared. She called my administrative assistant to cancel further appointments but did not ask to speak with me directly. While I knew this might represent resistance, I also felt unwilling to pressure Ms. C if she chose not to continue. I remain hopeful that I will hear from her once again; if not, I will send a note by mail to say that I enjoyed working with her, am happy to see her again, and hope she found some benefit from our work.
Mr. D contacted me for psychotherapy following the death of his father, who I had seen as a patient many years earlier. I was aware of the likely impact of his father’s outsized personality and emotional dysregulation on Mr. D and agreed to meet with him. He had taken over the family business and had made it an even greater success, but had trouble feeling confident about setting limits with employees who he knew took advantage of his avoidance.
Mr. D and I met weekly for several months and then moved to every other week, a form of resistance I expected as we got closer to his feeling pain. At the same time, I recognize that many patients use this tactic to “dose” themselves with the intensity they can tolerate, and Mr. D was quite observant and able to pick up themes where we’d left off.
When the pandemic shut down office visits, Mr. D immediately agreed to video sessions, which he has continued at roughly the same frequency. While I miss sitting with him, we continue to make progress towards his goal of learning to see himself as able to compete with his father.
Psychoanalysis patients
I found that patients in psychoanalysis had no trouble with the transition to telephone sessions, and the intensity of the work was not diluted. In some ways, audio-only communication is more intimate and might encourage patients to talk about topics they may not have otherwise brought up. I have not seen any evidence of less progress among these patients.
Dr. E, age 45, is a divorced physician who began psychoanalysis 3 times per week on the couch in 2018 for problems with frustration and confusion about his career, his identity as a father, and intense loneliness. He had worked up to 80 hours per week to earn as much money as he could, but also to avoid time at home with his then-wife and young children. The lack of time to recover led him to hate his work, left no time for social connections, and led to binges of heavy drinking. Our work had begun to allow him to develop a narrative about his early life that had never been considered, and to identify patterns of repetition of old defensive strategies that had never served him well.
At the onset of the pandemic, I told Dr. E that we would have to switch to telephone sessions, and he agreed immediately. In fact, he came to prefer telephone work since it spared him the 2 hours per day he had spent coming to my office. While I found it less satisfying than working in person, we have continued the same schedule and with the same intensity and trajectory established before the pandemic.
Continue to: Working with new patients...
Working with new patients
Seeing new patients for diagnostic evaluation is always best done in person, because the information I gain from the patient’s appearance, clothing, demeanor, gait, postures, gesturing, and facial expressions (among other elements) gives me important impressions I miss with video or telephone. In many cases, patients gain a sense of who I am from sitting in my office, and using the conference room eliminates that benefit. I attempted to create a warm environment in the conference room by obtaining lamps that produce warmer indirect light and hanging artwork that reflects my tastes. There are clocks in places that allow me and my patient to keep track of time. In meeting new patients by video, I get some impressions about their surroundings that add to the information I get through our interview. I have done many diagnostic evaluations during the pandemic and gotten treatments (whether medication, psychotherapy, or both) underway without discernible problems in the outcomes. Patients who started with me in person have mostly wanted to continue with in-person meetings, but as many have told me, interspersed video sessions save them travel time.
What about vaccination?
Once COVID-19 vaccinations were widely available, I assumed patients would be as eager to get them as I had been. When I began asking patients about whether they had gotten their vaccines, I was surprised to hear that a few were not going to get vaccinated, clearly based on political views and misinformation about the danger of vaccines. (The topic of political beliefs and their impact on psychological treatment is beyond the scope of this commentary.) I tried to counter obvious misinformation, repeated my recommendation that the patient get vaccinated, and then turned to other topics. I later decided to tell all patients that vaccination was required to enter the office. Only 1 patient who had been coming to the office dropped out, and she eventually returned to meeting by video.
COVID-19’s toll on the therapist
While the first several months of the pandemic were so full of uncertainty about the future, once vaccinations were available, it seemed cause for hope of a return to normalcy. As time went on, however, it became clear that normal was still a long way off. With vaccine refusal and new variants upending my naïve view that we were near the end, I began to feel aware of the impact this had on me, and began to focus on self-care (Box). I had always seen myself as unusually lucky to have a full practice, a supportive partnership with my husband, grown children who didn’t need me to homeschool them, a strong social network of friends who could share the burden and cheer each other up at outdoor gatherings, and a wonderful group of siblings and in-laws (all in different cities) who stayed in touch via video calls and quarantined in advance of getting together in someone’s home.
Box
Self-care has always been a requirement of doing psychotherapeutic work, and I encourage practitioners to be sure they are attending to themselves. We can’t be effective as listeners, empathizers, diagnosticians, and problem-solvers if we ourselves aren’t healthy. We evaluate our patients in terms of mood, outlook, sleep, appetite, energy, motivation, and energy; we also investigate their capacity for relationships that are sustaining. Self-care is the same, taking care of both our physical and relationship beings. Getting enough sleep, exercising daily, cooking healthy meals, and making time to relax are all ways of caring for our physical identities that should have been in place before COVID-19. Making personal time for ourselves in the face of constant demands for time from patients, colleagues, partners, children, parents, siblings, and friends never happens without the resolve to do it. As a psychiatrist who is used to sitting for up to 10 hours per day, I strongly recommend making a daily habit of walking, running, biking, or using an elliptical trainer, treadmill, or stationary bike for 30 minutes or more. Sleep is necessary for adequate concentration and attention to patient after patient. If you have trouble sleeping, talk with your doctor about remedies. If you use a sleep aid, I strongly recommend alternating medications so you don’t develop tolerance to any of them. Plan your food and cooking ahead of time so you aren’t tempted to order out. If you cook simple meals yourself (ideally with your partner helping or in range so you can chat), you will consume fewer calories, less sodium, and more nutrients. Even if you have a spouse and young children at home, work out a plan with your partner that allows each of you time for exercise or to recoup after a long day with patients. Babysitters allow you to take the time to be with each other that is necessary to sustaining a connection. Think about time for sexual intimacy if that has dropped off the calendar. Relationships with others, such as parents, siblings and their families, and friends are invaluable. The time spent with others might seem inconsequential, but is critical to our internal sense of security, even in the face of external disorder.
Staying busy and engaged with my practice, spouse, family, and friends kept sadness away most of the time. But I surprised myself a few months ago when I sat down to reflect and check in with myself. I felt enormous loss, resentment, and exhaustion at the privations of the pandemic: every trip to the grocery story felt dangerous. I hadn’t seen the inside of a concert hall, movie theater, restaurant, or museum in nearly 2 years. Travel for meetings and visits to family and friends and various adventures had been abruptly stopped. I lost both parents (not to COVID-19) during 2020; both were older adults living in senior communities that could not allow visitors. The usual grieving process would include attending services at my synagogue where I could say Kaddish for them, and video services were simply not tolerable.
Most of us have become experts at video meetings and likely have come to despise them. While our Institute has always held classes with some out-of-town students joining by video, with a very sophisticated system that provides excellent sound and visual fidelity, teaching entirely by video is another matter. I now teach students I have never met in person and might not recognize if I passed them in public. The art of creating discussion around a table is much more difficult on a computer screen. The first class I taught to residents during the pandemic was completely disorienting as I faced a wall of black screens with names and silence. Each student had turned off their camera and muted their microphone, so I was lecturing to a computer. That never happened again after I insisted on seeing everyone’s face and hearing their voices.
Thankfully, my usual experience of a long day seeing patients followed by chatting while cooking dinner with my husband and walking the dogs before settling down to read didn’t change. But the pleasure of sitting with patients was replaced by the daily grind of figuring out who will need a video link, who will be on the telephone, and who will come to the office, and it doesn’t feel the same. Again, in the big picture, I realize how fortunate I have been, but it’s been a big change in the world of the psychotherapist.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 frequently asked questions. Accessed March 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/faq.html#Spread
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 frequently asked questions. Accessed March 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/faq.html#Spread
Sexual activity alters the microbiome, with potential psychiatric implications
Evidence is strong that sexual partners transmit microbiota (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and archaea) to each other. While microbial flora are abundant in the gastrointestinal tract, they are also present in the vagina, penis, urethra, mouth, and skin.1 For better or worse, sexual contact of all types means that participants will acquire each other’s microbiota.
The 39 trillion microbiota in the body (which exceed the 30 trillion cells in the body) are commensal and influence both the larger brain in the skull and the smaller enteric brain in the gut. The microbiota and their microbiome genes (1,000 times larger than the human genome) have been linked to depression, anxiety, psychosis, and autism.2-4 They produce 90% of the body’s serotonin, as well as catecholamines (norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine), make hormones (eg, cortisol), and modulate the immune system. Microbiota have several important functions, including food digestion, synthesis of vitamins, autoimmunity, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation, and CNS modulation.
Consequences of dysbiosis
Everyone should be concerned about maintaining a healthy diversity of microbiota in their body, with a predominance of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bacteroides, and avoiding acquiring pathogenic bacteria such as Gardnerella, Prevotella, and Atopobium. Sexual activity involving a partner with unhealthy microbiota may increase the risk of dysbiosis, defined as a reduction in microbiota diversity, including a loss of beneficial bacteria and a rise in harmful bacteria.
Dysbiosis is associated with multiple symptoms, including5:
- brain “fog,” irritability, mood changes, and anxiety
- bloating, loss of intestinal permeability, and insufficient reclamation of nutrients
- congestion of certain organs, such as the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
- production of antigen-antibody complexes in response to chemicals in partially digested food
- aggravation of inflammatory disorders such as migraine, arthritis, and autoimmune disorders.
Apart from intimate sexual contact, simply sharing a household with someone leads to sharing of gut microflora. Persons who live together, whether genetically related or not, have similar microbiota. Compared with people living in separate households, cohabiting human pairs, dog pairs, and human-dog pairs share most of their microbiota (especially in the skin).
A consequence of acquiring pathogenic microbiota in the vagina is bacterial vaginosis (BV), which is not an infection but an ecologic imbalance in the composition of the vaginal microbiota. BV is caused by a significant decline in the beneficial vaginal Lactobacillus and a marked increase in the non-Lactobacillus taxa (especially Gardnerella and Atopobium).6 It can last for a least 1 week after sexual intercourse. BV is rare or absent among virgins. For a male partner, penile microbiota changes significantly after unprotected sex.6
Pathogenic bacteria can be cultivated from the glans, the coronal sulcus, and the prepuce, as well as from the penile skin, semen, urethra, and urine.6 Diverse bacteria exist in human semen, regardless if the male is fertile or infertile.7Anaerococcus is a biomarker for low sperm quality. Many of the semen bacteria are also found in the vagina of women with BV.7 Semen is a medium for the transmission of bacteria and viruses between men and women, and can contribute to sexually transmitted diseases.8
There are approximately 21 million cases of BV in the United States each year, and BV can also increase the risk of HIV and poor obstetric outcomes.9 The microbiota in the penile skin and urethra in males who have monogamous relationships with females are very similar to the vaginal microbiota of their female partner.
Consequences of BV include:
- decrease in hydrogen peroxide–producing bacilli
- prevalence of anaerobic bacteria (Prevotella, Gardnerella, and Atopobium)
- alkalinization, fishy odor, and gray-white vaginal discharge
- increase in the rate of pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, preterm birth, and tubal factor infertility.9
Circumcision decreases the risk of BV. There is an increased rate of BV bacterial taxa in men with extramarital affairs and in women with multiple partners. Both oral and vaginal sex increase the abundance of Lactobacillus in the male oral and penile microbiota. Gingivitis has also been reported after oral sex.10
A link to psychiatric disorders
Given that all forms of sexual contact (vaginal, oral, anal, or skin) can transmit microbiota bidirectionally between partners, it is vital to practice safe sex and consider a monogamous relationship rather than indiscriminate promiscuity. Unfortunately, certain psychiatric disorders, such as bipolar disorder, are associated with hypersexuality and multiple partners, which may disrupt the microbiota. This can further disrupt the diversity of an individual’s microbiome and may put them at risk for mood, anxiety, and other psychiatric disorders. Another problem is sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea or syphilis require antibiotic therapy. It is well established that antibiotics kill both the bad pathogenic and the good nonpathogenic microbiota, further exacerbating dysbiosis and leading to disruptions in the microbiota-gut-brain (MGB) axis, which then results in psychiatric disorders.
The MGB axis modulates neurological processes via the vagus nerve, the major “highway” connecting the gut and brain for bidirectional traffic. The MGB axis produces microbial metabolites and immune factors that can lead to changes in brain neurotransmitters as well as neuroinflammation and psychiatric symptoms such as depression and anxiety.5
Many researchers are focusing on how to exploit the microbiome to develop novel therapeutic strategies, and encouraging advances are emerging.5 But the exact mechanisms by which the gut microbiome can impact mental health is still a work in progress. It is highly likely that dysbiosis is associated with mood and anxiety symptoms.
The bottom line: Sexual activity—whether it is heavy kissing, vaginal intercourse, oral sex, anal sex, or extensive skin contact—can lead to the exchange of microbiota. If an individual has dysbiosis, that could impact the mental health of their sexual partner(s). This raises the question of whether counseling patients about avoiding indiscriminate sex and practicing safe sex is as important for mental health as diet and exercise counseling is for physical health.
1. Reid G, Younes JA, Van der Mei HC, et al. Microbiota restoration: natural and supplemented recovery of human microbial communities. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9(1):27-38.
2. Cryan JF, Dinan TG. Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13(10):701-712.
3. Peirce JM, Alviña K. The role of inflammation and the gut microbiome in depression and anxiety. J Neurosci Res. 2019;97(10):1223-1241.
4. Yolken R, Prandovszky E, Severance EG, et al. The oropharyngeal microbiome is altered in individuals with schizophrenia and mania. Schizophr Res. 2021;234:51-57.
5. Capuco A, Urits I, Hasoon J, et al. Current perspectives on gut microbiome dysbiosis and depression. Adv Ther. 2020;37(4):1328-1346.
6. Zozaya M, Ferris MJ, Siren JD, et al. Bacterial communities in penile skin, male urethra, and vagina of heterosexual couples with and without bacterial vaginosis. Microbiome. 2016;4:16. doi:10.1186/s40168-016-0161-6
7. Hou D, Zhou X, Zhong X, et al. Microbiota of the seminal fluid from healthy and infertile men. Fertil Steril. 2013;100(5):1261-1269.
8. Gallo MF, Warner L, King CC, et al. Association between semen exposure and incident bacterial vaginosis. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 2011;2011:842652.
9. Liu CM, Hungate BA, Tobian AA, et al. Penile microbiota and female partner bacterial vaginosis in Rakai, Uganda. mBio. 2015;6(3):e00589. doi:10.1128/mBio.00589-15
10. Carda-Diéguez M, Cárdenas N, Aparicio M, et al. Variations in vaginal, penile, and oral microbiota after sexual intercourse: a case report. Front Med. 2019;6:178. doi:10.3389/fmed.2019.00178
Evidence is strong that sexual partners transmit microbiota (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and archaea) to each other. While microbial flora are abundant in the gastrointestinal tract, they are also present in the vagina, penis, urethra, mouth, and skin.1 For better or worse, sexual contact of all types means that participants will acquire each other’s microbiota.
The 39 trillion microbiota in the body (which exceed the 30 trillion cells in the body) are commensal and influence both the larger brain in the skull and the smaller enteric brain in the gut. The microbiota and their microbiome genes (1,000 times larger than the human genome) have been linked to depression, anxiety, psychosis, and autism.2-4 They produce 90% of the body’s serotonin, as well as catecholamines (norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine), make hormones (eg, cortisol), and modulate the immune system. Microbiota have several important functions, including food digestion, synthesis of vitamins, autoimmunity, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation, and CNS modulation.
Consequences of dysbiosis
Everyone should be concerned about maintaining a healthy diversity of microbiota in their body, with a predominance of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bacteroides, and avoiding acquiring pathogenic bacteria such as Gardnerella, Prevotella, and Atopobium. Sexual activity involving a partner with unhealthy microbiota may increase the risk of dysbiosis, defined as a reduction in microbiota diversity, including a loss of beneficial bacteria and a rise in harmful bacteria.
Dysbiosis is associated with multiple symptoms, including5:
- brain “fog,” irritability, mood changes, and anxiety
- bloating, loss of intestinal permeability, and insufficient reclamation of nutrients
- congestion of certain organs, such as the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
- production of antigen-antibody complexes in response to chemicals in partially digested food
- aggravation of inflammatory disorders such as migraine, arthritis, and autoimmune disorders.
Apart from intimate sexual contact, simply sharing a household with someone leads to sharing of gut microflora. Persons who live together, whether genetically related or not, have similar microbiota. Compared with people living in separate households, cohabiting human pairs, dog pairs, and human-dog pairs share most of their microbiota (especially in the skin).
A consequence of acquiring pathogenic microbiota in the vagina is bacterial vaginosis (BV), which is not an infection but an ecologic imbalance in the composition of the vaginal microbiota. BV is caused by a significant decline in the beneficial vaginal Lactobacillus and a marked increase in the non-Lactobacillus taxa (especially Gardnerella and Atopobium).6 It can last for a least 1 week after sexual intercourse. BV is rare or absent among virgins. For a male partner, penile microbiota changes significantly after unprotected sex.6
Pathogenic bacteria can be cultivated from the glans, the coronal sulcus, and the prepuce, as well as from the penile skin, semen, urethra, and urine.6 Diverse bacteria exist in human semen, regardless if the male is fertile or infertile.7Anaerococcus is a biomarker for low sperm quality. Many of the semen bacteria are also found in the vagina of women with BV.7 Semen is a medium for the transmission of bacteria and viruses between men and women, and can contribute to sexually transmitted diseases.8
There are approximately 21 million cases of BV in the United States each year, and BV can also increase the risk of HIV and poor obstetric outcomes.9 The microbiota in the penile skin and urethra in males who have monogamous relationships with females are very similar to the vaginal microbiota of their female partner.
Consequences of BV include:
- decrease in hydrogen peroxide–producing bacilli
- prevalence of anaerobic bacteria (Prevotella, Gardnerella, and Atopobium)
- alkalinization, fishy odor, and gray-white vaginal discharge
- increase in the rate of pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, preterm birth, and tubal factor infertility.9
Circumcision decreases the risk of BV. There is an increased rate of BV bacterial taxa in men with extramarital affairs and in women with multiple partners. Both oral and vaginal sex increase the abundance of Lactobacillus in the male oral and penile microbiota. Gingivitis has also been reported after oral sex.10
A link to psychiatric disorders
Given that all forms of sexual contact (vaginal, oral, anal, or skin) can transmit microbiota bidirectionally between partners, it is vital to practice safe sex and consider a monogamous relationship rather than indiscriminate promiscuity. Unfortunately, certain psychiatric disorders, such as bipolar disorder, are associated with hypersexuality and multiple partners, which may disrupt the microbiota. This can further disrupt the diversity of an individual’s microbiome and may put them at risk for mood, anxiety, and other psychiatric disorders. Another problem is sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea or syphilis require antibiotic therapy. It is well established that antibiotics kill both the bad pathogenic and the good nonpathogenic microbiota, further exacerbating dysbiosis and leading to disruptions in the microbiota-gut-brain (MGB) axis, which then results in psychiatric disorders.
The MGB axis modulates neurological processes via the vagus nerve, the major “highway” connecting the gut and brain for bidirectional traffic. The MGB axis produces microbial metabolites and immune factors that can lead to changes in brain neurotransmitters as well as neuroinflammation and psychiatric symptoms such as depression and anxiety.5
Many researchers are focusing on how to exploit the microbiome to develop novel therapeutic strategies, and encouraging advances are emerging.5 But the exact mechanisms by which the gut microbiome can impact mental health is still a work in progress. It is highly likely that dysbiosis is associated with mood and anxiety symptoms.
The bottom line: Sexual activity—whether it is heavy kissing, vaginal intercourse, oral sex, anal sex, or extensive skin contact—can lead to the exchange of microbiota. If an individual has dysbiosis, that could impact the mental health of their sexual partner(s). This raises the question of whether counseling patients about avoiding indiscriminate sex and practicing safe sex is as important for mental health as diet and exercise counseling is for physical health.
Evidence is strong that sexual partners transmit microbiota (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and archaea) to each other. While microbial flora are abundant in the gastrointestinal tract, they are also present in the vagina, penis, urethra, mouth, and skin.1 For better or worse, sexual contact of all types means that participants will acquire each other’s microbiota.
The 39 trillion microbiota in the body (which exceed the 30 trillion cells in the body) are commensal and influence both the larger brain in the skull and the smaller enteric brain in the gut. The microbiota and their microbiome genes (1,000 times larger than the human genome) have been linked to depression, anxiety, psychosis, and autism.2-4 They produce 90% of the body’s serotonin, as well as catecholamines (norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine), make hormones (eg, cortisol), and modulate the immune system. Microbiota have several important functions, including food digestion, synthesis of vitamins, autoimmunity, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation, and CNS modulation.
Consequences of dysbiosis
Everyone should be concerned about maintaining a healthy diversity of microbiota in their body, with a predominance of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bacteroides, and avoiding acquiring pathogenic bacteria such as Gardnerella, Prevotella, and Atopobium. Sexual activity involving a partner with unhealthy microbiota may increase the risk of dysbiosis, defined as a reduction in microbiota diversity, including a loss of beneficial bacteria and a rise in harmful bacteria.
Dysbiosis is associated with multiple symptoms, including5:
- brain “fog,” irritability, mood changes, and anxiety
- bloating, loss of intestinal permeability, and insufficient reclamation of nutrients
- congestion of certain organs, such as the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
- production of antigen-antibody complexes in response to chemicals in partially digested food
- aggravation of inflammatory disorders such as migraine, arthritis, and autoimmune disorders.
Apart from intimate sexual contact, simply sharing a household with someone leads to sharing of gut microflora. Persons who live together, whether genetically related or not, have similar microbiota. Compared with people living in separate households, cohabiting human pairs, dog pairs, and human-dog pairs share most of their microbiota (especially in the skin).
A consequence of acquiring pathogenic microbiota in the vagina is bacterial vaginosis (BV), which is not an infection but an ecologic imbalance in the composition of the vaginal microbiota. BV is caused by a significant decline in the beneficial vaginal Lactobacillus and a marked increase in the non-Lactobacillus taxa (especially Gardnerella and Atopobium).6 It can last for a least 1 week after sexual intercourse. BV is rare or absent among virgins. For a male partner, penile microbiota changes significantly after unprotected sex.6
Pathogenic bacteria can be cultivated from the glans, the coronal sulcus, and the prepuce, as well as from the penile skin, semen, urethra, and urine.6 Diverse bacteria exist in human semen, regardless if the male is fertile or infertile.7Anaerococcus is a biomarker for low sperm quality. Many of the semen bacteria are also found in the vagina of women with BV.7 Semen is a medium for the transmission of bacteria and viruses between men and women, and can contribute to sexually transmitted diseases.8
There are approximately 21 million cases of BV in the United States each year, and BV can also increase the risk of HIV and poor obstetric outcomes.9 The microbiota in the penile skin and urethra in males who have monogamous relationships with females are very similar to the vaginal microbiota of their female partner.
Consequences of BV include:
- decrease in hydrogen peroxide–producing bacilli
- prevalence of anaerobic bacteria (Prevotella, Gardnerella, and Atopobium)
- alkalinization, fishy odor, and gray-white vaginal discharge
- increase in the rate of pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, preterm birth, and tubal factor infertility.9
Circumcision decreases the risk of BV. There is an increased rate of BV bacterial taxa in men with extramarital affairs and in women with multiple partners. Both oral and vaginal sex increase the abundance of Lactobacillus in the male oral and penile microbiota. Gingivitis has also been reported after oral sex.10
A link to psychiatric disorders
Given that all forms of sexual contact (vaginal, oral, anal, or skin) can transmit microbiota bidirectionally between partners, it is vital to practice safe sex and consider a monogamous relationship rather than indiscriminate promiscuity. Unfortunately, certain psychiatric disorders, such as bipolar disorder, are associated with hypersexuality and multiple partners, which may disrupt the microbiota. This can further disrupt the diversity of an individual’s microbiome and may put them at risk for mood, anxiety, and other psychiatric disorders. Another problem is sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea or syphilis require antibiotic therapy. It is well established that antibiotics kill both the bad pathogenic and the good nonpathogenic microbiota, further exacerbating dysbiosis and leading to disruptions in the microbiota-gut-brain (MGB) axis, which then results in psychiatric disorders.
The MGB axis modulates neurological processes via the vagus nerve, the major “highway” connecting the gut and brain for bidirectional traffic. The MGB axis produces microbial metabolites and immune factors that can lead to changes in brain neurotransmitters as well as neuroinflammation and psychiatric symptoms such as depression and anxiety.5
Many researchers are focusing on how to exploit the microbiome to develop novel therapeutic strategies, and encouraging advances are emerging.5 But the exact mechanisms by which the gut microbiome can impact mental health is still a work in progress. It is highly likely that dysbiosis is associated with mood and anxiety symptoms.
The bottom line: Sexual activity—whether it is heavy kissing, vaginal intercourse, oral sex, anal sex, or extensive skin contact—can lead to the exchange of microbiota. If an individual has dysbiosis, that could impact the mental health of their sexual partner(s). This raises the question of whether counseling patients about avoiding indiscriminate sex and practicing safe sex is as important for mental health as diet and exercise counseling is for physical health.
1. Reid G, Younes JA, Van der Mei HC, et al. Microbiota restoration: natural and supplemented recovery of human microbial communities. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9(1):27-38.
2. Cryan JF, Dinan TG. Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13(10):701-712.
3. Peirce JM, Alviña K. The role of inflammation and the gut microbiome in depression and anxiety. J Neurosci Res. 2019;97(10):1223-1241.
4. Yolken R, Prandovszky E, Severance EG, et al. The oropharyngeal microbiome is altered in individuals with schizophrenia and mania. Schizophr Res. 2021;234:51-57.
5. Capuco A, Urits I, Hasoon J, et al. Current perspectives on gut microbiome dysbiosis and depression. Adv Ther. 2020;37(4):1328-1346.
6. Zozaya M, Ferris MJ, Siren JD, et al. Bacterial communities in penile skin, male urethra, and vagina of heterosexual couples with and without bacterial vaginosis. Microbiome. 2016;4:16. doi:10.1186/s40168-016-0161-6
7. Hou D, Zhou X, Zhong X, et al. Microbiota of the seminal fluid from healthy and infertile men. Fertil Steril. 2013;100(5):1261-1269.
8. Gallo MF, Warner L, King CC, et al. Association between semen exposure and incident bacterial vaginosis. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 2011;2011:842652.
9. Liu CM, Hungate BA, Tobian AA, et al. Penile microbiota and female partner bacterial vaginosis in Rakai, Uganda. mBio. 2015;6(3):e00589. doi:10.1128/mBio.00589-15
10. Carda-Diéguez M, Cárdenas N, Aparicio M, et al. Variations in vaginal, penile, and oral microbiota after sexual intercourse: a case report. Front Med. 2019;6:178. doi:10.3389/fmed.2019.00178
1. Reid G, Younes JA, Van der Mei HC, et al. Microbiota restoration: natural and supplemented recovery of human microbial communities. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9(1):27-38.
2. Cryan JF, Dinan TG. Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13(10):701-712.
3. Peirce JM, Alviña K. The role of inflammation and the gut microbiome in depression and anxiety. J Neurosci Res. 2019;97(10):1223-1241.
4. Yolken R, Prandovszky E, Severance EG, et al. The oropharyngeal microbiome is altered in individuals with schizophrenia and mania. Schizophr Res. 2021;234:51-57.
5. Capuco A, Urits I, Hasoon J, et al. Current perspectives on gut microbiome dysbiosis and depression. Adv Ther. 2020;37(4):1328-1346.
6. Zozaya M, Ferris MJ, Siren JD, et al. Bacterial communities in penile skin, male urethra, and vagina of heterosexual couples with and without bacterial vaginosis. Microbiome. 2016;4:16. doi:10.1186/s40168-016-0161-6
7. Hou D, Zhou X, Zhong X, et al. Microbiota of the seminal fluid from healthy and infertile men. Fertil Steril. 2013;100(5):1261-1269.
8. Gallo MF, Warner L, King CC, et al. Association between semen exposure and incident bacterial vaginosis. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 2011;2011:842652.
9. Liu CM, Hungate BA, Tobian AA, et al. Penile microbiota and female partner bacterial vaginosis in Rakai, Uganda. mBio. 2015;6(3):e00589. doi:10.1128/mBio.00589-15
10. Carda-Diéguez M, Cárdenas N, Aparicio M, et al. Variations in vaginal, penile, and oral microbiota after sexual intercourse: a case report. Front Med. 2019;6:178. doi:10.3389/fmed.2019.00178
Psychiatric and nonpsychiatric indications for mood stabilizers and select antiepileptics
Mr. B, age 64, is being treated in the psychiatric clinic for generalized anxiety disorder. He also has a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis. His present medications include metformin 500 mg twice daily, escitalopram 20 mg/d, and a multivitamin.
Three months after a shingles outbreak on his left trunk, Mr. B develops a sharp, burning pain and hypersensitivity to light in the same area as the shingles flare-up. He is diagnosed with postherpetic neuralgia. Despite a 12-week trial of cognitive-behavioral therapy, Mr. B continues to report excessive worry, irritability, poor concentration, psychomotor restlessness, and poor sleep.
Contrasting with the serendipitous discovery of iproniazid and chlorpromazine leading to the development of the current spectrum of antidepressant and antipsychotic agents, discovery of the benefits various antiepileptic agents have in bipolar disorder has not led to a similar proliferation of medication development for bipolar mania or depression.1-3 Divalproex, one of the most commonly used antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) in psychiatry, was thought to be an inactive organic solvent until it was used in 1962 to test the anticonvulsant activity of other compounds. This led to the discovery and subsequent use of divalproex in patients with epilepsy, followed by FDA approval in bipolar disorder.4,5 Off-label use of many AEDs as mood-stabilizing agents in bipolar disorder led to the emergence of carbamazepine, divalproex, and lamotrigine, which joined lithium as classic mood-stabilizing agents.4,6-8 Amid varying definitions of “mood stabilizer,” many AEDs have failed to demonstrate mood-stabilizing effects in bipolar disorder and therefore should not all be considered mood stabilizers.9 Nonetheless, the dual use of a single AED for both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric indications can decrease polypharmacy and increase acceptability of medications in patients who have low insight into their illness.10,11
Because AEDs were originally purposed to treat neurologic disease, psychiatric indications must first be established before considering other indications. AEDs as a class have broad pharmacologic actions, but are generally CNS depressants, decreasing brain signaling through mechanisms such as ion channel antagonism (carbamazepine, gabapentin) or alterations to gamma-aminobutyric acid/glutamate signaling (divalproex, topiramate).4,6,12,13 Compared to antidepressants and antipsychotics, whose primary use for psychiatric conditions is firmly rooted in evidence, rational use of AEDs for psychiatric conditions and symptoms depends on the agent-specific efficacy. Patients with comorbid psychiatric and neurologic disorders are ideal candidates for dually indicated AEDs due to these agents’ class effects rooted in epilepsy. Due to the history of positive psychiatric benefits with AEDs, newer agents may be psychiatrically beneficial but will likely follow the discovery of these benefits in patients for whom epilepsy is the primary diagnosis.
Consider the limitations
Using AEDs to reduce polypharmacy should be done judiciously from a drug-drug interaction perspective, because certain AEDs (eg, carbamazepine, divalproex) can greatly influence the metabolism of other medications, which may defeat the best intentions of the original intervention.4,6
Several other limitations should be considered. This article does not include all AEDs, only those commonly used for psychiatric indications with known nonpsychiatric benefits. Some may worsen psychiatric conditions (such as rage and irritability in the case of levetiracetam), and all AEDs have an FDA warning regarding suicidal behaviors and ideation.14,15 Another important limitation is the potential for differential dosing across indications; tolerability concerns may limit adequate dosing across multiple uses. For example, topiramate’s migraine prophylaxis effect can be achieved at much lower doses than the patient-specific efficacy dosing seen in binge eating disorder, with higher doses increasing the propensity for adverse effects.13,16Dual-use AEDs should be considered wherever possible, but judicious review of evidence is necessary to appropriately adjudicate a specific patient’s risk vs benefit. The Table4,6-9,12,13,16-68 provides information on select AEDs with both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric indications, including both FDA-approved and common off-label uses. These indications are limited to adult use only.
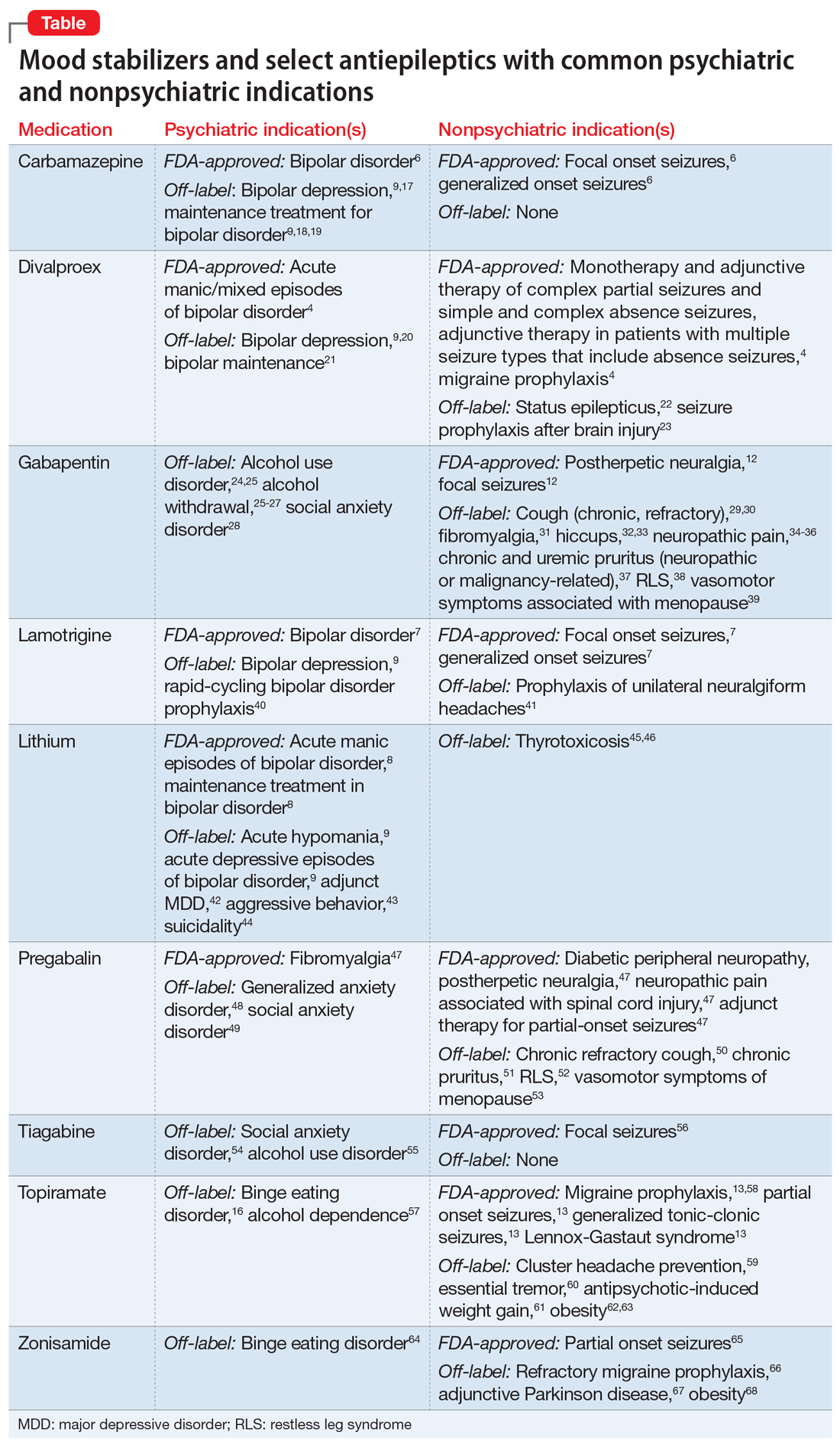
CASE CONTINUED
After reviewing Mr. B’s medical history, the treating medical team decides to cross-taper escitalopram to duloxetine 30 mg twice daily. Though his pain lessens after several weeks, it persists enough to interfere with Mr. B’s daily life. In addition to duloxetine, he is started on pregabalin 50 mg 3 times a day. Mr. B’s pain decreases to a tolerable level, and he reports decreased worrying and restlessness, and improvements in concentration and sleep.
1. Meyer JM. A concise guide to monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(12):14-16,18-23,47,A.
2. Ban TA. Fifty years chlorpromazine: a historical perspective. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2007;3(4):495-500.
3. López-Mun
4. Depakote [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie, Inc; 2021.
5. Henry TR. The history of valproate in clinical neuroscience. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2003;37 Suppl 2:5-16.
6. Tegretol and Tegretol-XR [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ: Pharmaceuticals Co.; 2020.
7. Lamictal [package insert]. Research Triangle Park, NC: GlaxoSmithKline; 2009.
8. Lithobid [package insert]. Baudette, MN: ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2009.
9. Yatham LN, Kennedy SH, Parikh SV, et al. Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) and International Society for Bipolar Disorders (ISBD) 2018 guidelines for the management of patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2018;20(2):97-170.
10. National Alliance on Mental Illness. Anosognosia. Common with mental illness. Accessed March 3, 2022. https://www.nami.org/About-Mental-Illness/Common-with-Mental-Illness/Anosognosia
11. Hales CM, Servais J, Martin CB, et al. Prescription drug use among adults aged 40-79 in the United States and Canada. NCHS Data Brief. 2019(347):1-8.
12. Neurontin [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer; 2017.
13. Topamax [package insert]. Titusville, NJ: Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2009.
14. Molokwu OA, Ezeala-Adikaibe BA, Onwuekwe IO. Levetiracetam-induced rage and suicidality: two case reports and review of literature. Epilepsy Behav Case Rep. 2015;4:79-81.
15. U.S. Food & Drug Administration. FDA Statistical Review and Evaluation. Antiepileptic Drugs and Suicidality. 2008. Accessed March 3, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Statistical-Review-and-Evaluation--Antiepileptic-Drugs-and-Suicidality.pdf
16. McElroy SL, Hudson JI, Capece JA, et al. Topiramate for the treatment of binge eating disorder associated with obesity: a placebo-controlled study. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;61(9):1039-1048.
17. Zhang ZJ, Kang WH, Tan QR, et al. Adjunctive herbal medicine with carbamazepine for bipolar disorders: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Psychiatr Res. 2007;41(3-4):360-369.
18. Kleindienst N, Greil W. Differential efficacy of lithium and carbamazepine in the prophylaxis of bipolar disorder: results of the MAP study. Neuropsychobiology. 2000;42 Suppl 1:2-10.
19. Goodwin GM, Haddad PM, Ferrier IN, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for treating bipolar disorder: revised third edition recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(6):495-553.
20. Davis LL, Bartolucci A, Petty F. Divalproex in the treatment of bipolar depression: a placebo-controlled study. J Affect Disord. 2005;85(3):259-266.
21. Gyulai L, Bowden CL, McElroy SL, et al. Maintenance efficacy of divalproex in the prevention of bipolar depression. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28(7):1374-1382.
22. Limdi NA, Shimpi AV, Faught E, et al. Efficacy of rapid IV administration of valproic acid for status epilepticus. Neurology. 2005;64(2):353-355.
23. Temkin NR, Dikmen SS, Anderson GD, et al. Valproate therapy for prevention of posttraumatic seizures: a randomized trial. J Neurosurg. 1999; 91(4):593-600.
24. Reus VI, Fochtmann LJ, Bukstein O, et al. The American Psychiatric Association practice guideline for the pharmacological treatment of patients with alcohol use disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(1):86-90.
25. US Dept of Veterans Affairs, US Dept of Defense, The Management of Substance Use Disorders Work Group. VA/DoD clinical practice guideline for the management of substance use disorders. US Dept of Veterans Affairs/Dept of Defense; 2015. Accessed March 3, 2022. http://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/MH/sud/VADoDSUDCPGRevised22216.pdf
26. Myrick H, Malcolm R, Randall PK, et al. A double-blind trial of gabapentin versus lorazepam in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009;33(9):1582-1588.
27. Ahmed S, Stanciu CN, Kotapati PV, et al. Effectiveness of gabapentin in reducing cravings and withdrawal in alcohol use disorder: a meta-analytic review. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2019;21(4):19r02465.
28. Pande AC, Davidson JR, Jefferson JW, et al. Treatment of social phobia with gabapentin: a placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1999;19(4):341-348.
29. Ryan NM, Birring SS, Gibson PG. Gabapentin for refractory chronic cough: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380(9853):1583-1589.
30. Gibson P, Wang G, McGarvey L, et al. Treatment of unexplained chronic cough: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016;149(1):27-44.
31. Arnold LM, Goldenberg DL, Stanford SB, et al. Gabapentin in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(4):1336-1344.
32. Alonso-Navarro H, Rubio L, Jiménez-Jiménez FJ. Refractory hiccup: successful treatment with gabapentin. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2007;30(3):186-187.
33. Jatzko A, Stegmeier-Petroianu A, Petroianu GA. Alpha-2-delta ligands for singultus (hiccup) treatment: three case reports. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007;33(6):756-760.
34. Finnerup NB, Attal N, Haroutounian S, et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(2):162-173.
35. Moore RA, Wiffen PJ, Derry S, et al. Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014(4):CD007938.
36. Yuan M, Zhou HY, Xiao ZL, et al. Efficacy and safety of gabapentin vs. carbamazepine in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: a meta-analysis. Pain Pract. 2016;16(8):1083-1091.
37. Weisshaar E, Szepietowski JC, Darsow U, et al. European guideline on chronic pruritus. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92(5):563-581.
38. Garcia-Borreguero D, Silber MH, Winkelman JW, et al. Guidelines for the first-line treatment of restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease, prevention and treatment of dopaminergic augmentation: a combined task force of the IRLSSG, EURLSSG, and the RLS-Foundation. Sleep Med. 2016;21:1-11.
39. Cobin RH, Goodman NF; AACE Reproductive Endocrinology Scientific Committee. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology position statement on menopause—2017 update [published correction appears in Endocr Pract. 2017;23 (12):1488]. Endocr Pract. 2017;23(7):869-880.
40. Calabrese JR, Suppes T, Bowden CL, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, prophylaxis study of lamotrigine in rapid-cycling bipolar disorder: Lamictal 614 Study Group. J Clin Psychiatry. 2000;60(11):841-850.
41. May A, Leone M, Afra J, et al. EFNS guidelines on the treatment of cluster headache and other trigeminal-autonomic cephalalgias. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13(10):1066-1077.
42. Stein G, Bernadt M. Lithium augmentation therapy in tricyclic-resistant depression. A controlled trial using lithium in low and normal doses. Br J Psychiatry. 1993;162:634-640.
43. Craft M, Ismail IA, Krishnamurti D, et al. Lithium in the treatment of aggression in mentally handicapped patients: a double-blind trial. Br J Psychiatry. 1987;150:685-689.
44. Cipriani A, Pretty H, Hawton K, et al. Lithium in the prevention of suicidal behavior and all-cause mortality in patients with mood disorders: a systematic review of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(10):1805-1819.
45. Dickstein G, Shechner C, Adawi F, et al. Lithium treatment in amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis. Am J Med. 1997;102(5):454-458.
46. Bogazzi F, Bartalena L, Brogioni S, et al. Comparison of radioiodine with radioiodine plus lithium in the treatment of Graves’ hyperthyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84(2):499-503.
47. Lyrica [package insert]. New York, NY: Parke-Davis, Division of Pfizer Inc; 2020.
48. Lydiard RB, Rickels K, Herman B, et al. Comparative efficacy of pregabalin and benzodiazepines in treating the psychic and somatic symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13(2):229-241.
49. Pande AC, Feltner DE, Jefferson JW, et al. Efficacy of the novel anxiolytic pregabalin in social anxiety disorder: a placebo-controlled, multicenter study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2004;24(2):141-149.
50. Vertigan AE, Kapela SL, Ryan NM, et al. Pregabalin and speech pathology combination therapy for refractory chronic cough: a randomized controlled trial. Chest. 2016;149(3):639-648.
51. Matsuda KM, Sharma D, Schonfeld AR, et al. Gabapentin and pregabalin for the treatment of chronic pruritus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75(3):619-625.e6.
52. Allen R, Chen C, Soaita A, et al. A randomized, double-blind, 6-week, dose-ranging study of pregabalin in patients with restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2010;11(6):512-519.
53. Loprinzi CL, Qin R, Balcueva EP, et al. Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation of pregabalin for alleviating hot flashes, N07C1 [published correction appears in J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(10):1808]. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(4):641-647.
54. Dunlop BW, Papp L, Garlow SJ, et al. Tiagabine for social anxiety disorder. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2007;22(4):241-244.
55. Paparrigopoulos T, Tzavellas E, Karaiskos D, et al. An open pilot study of tiagabine in alcohol dependence: tolerability and clinical effects. J Psychopharmacol. 2010;24(9):1375-1380.
56. Gabitril [package insert]. North Wales, PA: Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc; 2015.
57. Johnson BA, Ait-Daoud N, Bowden C, et al. Oral topiramate for treatment of alcohol dependence: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361(9370):1677-1685.
58. Linde M, Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP, et al. Topiramate for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013(6):CD010610.
59. Pascual J, Láinez MJ, Dodick D, et al. Antiepileptic drugs for the treatment of chronic and episodic cluster headache: a review. Headache. 2007;47(1):81-89.
60. Ondo WG, Jankovic J, Connor GS, et al. Topiramate in essential tremor: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neurology. 2006;66(5):672-677.
61. Ko YH, Joe SH, Jung IK, et al. Topiramate as an adjuvant treatment with atypical antipsychotics in schizophrenic patients experiencing weight gain. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2005;28(4):169-175.
62. Wilding J, Van Gaal L, Rissanen A, et al. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study of the long-term efficacy and safety of topiramate in the treatment of obese subjects. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28(11):1399-1410.
63. Rosenstock J, Hollander P, Gadde KM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study to assess the efficacy and safety of topiramate controlled release in the treatment of obese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30(6):1480-1486.
64. McElroy SL, Kotwal R, Guerdjikova AI, et al. Zonisamide in the treatment of binge eating disorder with obesity: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(12):1897-1906.
65. Zonegran [package insert]. Teaneck, NJ: Eisai Inc; 2006.
66. Drake ME Jr, Greathouse NI, Renner JB, et al. Open-label zonisamide for refractory migraine. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2004;27(6):278-280.
67. Matsunaga S, Kishi T, Iwata N. Combination therapy with zonisamide and antiparkinson drugs for Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;56(4):1229-1239.
68. Gadde KM, Kopping MF, Wagner HR 2nd, et al. Zonisamide for weight reduction in obese adults: a 1-year randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(20):1557-1564.
Mr. B, age 64, is being treated in the psychiatric clinic for generalized anxiety disorder. He also has a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis. His present medications include metformin 500 mg twice daily, escitalopram 20 mg/d, and a multivitamin.
Three months after a shingles outbreak on his left trunk, Mr. B develops a sharp, burning pain and hypersensitivity to light in the same area as the shingles flare-up. He is diagnosed with postherpetic neuralgia. Despite a 12-week trial of cognitive-behavioral therapy, Mr. B continues to report excessive worry, irritability, poor concentration, psychomotor restlessness, and poor sleep.
Contrasting with the serendipitous discovery of iproniazid and chlorpromazine leading to the development of the current spectrum of antidepressant and antipsychotic agents, discovery of the benefits various antiepileptic agents have in bipolar disorder has not led to a similar proliferation of medication development for bipolar mania or depression.1-3 Divalproex, one of the most commonly used antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) in psychiatry, was thought to be an inactive organic solvent until it was used in 1962 to test the anticonvulsant activity of other compounds. This led to the discovery and subsequent use of divalproex in patients with epilepsy, followed by FDA approval in bipolar disorder.4,5 Off-label use of many AEDs as mood-stabilizing agents in bipolar disorder led to the emergence of carbamazepine, divalproex, and lamotrigine, which joined lithium as classic mood-stabilizing agents.4,6-8 Amid varying definitions of “mood stabilizer,” many AEDs have failed to demonstrate mood-stabilizing effects in bipolar disorder and therefore should not all be considered mood stabilizers.9 Nonetheless, the dual use of a single AED for both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric indications can decrease polypharmacy and increase acceptability of medications in patients who have low insight into their illness.10,11
Because AEDs were originally purposed to treat neurologic disease, psychiatric indications must first be established before considering other indications. AEDs as a class have broad pharmacologic actions, but are generally CNS depressants, decreasing brain signaling through mechanisms such as ion channel antagonism (carbamazepine, gabapentin) or alterations to gamma-aminobutyric acid/glutamate signaling (divalproex, topiramate).4,6,12,13 Compared to antidepressants and antipsychotics, whose primary use for psychiatric conditions is firmly rooted in evidence, rational use of AEDs for psychiatric conditions and symptoms depends on the agent-specific efficacy. Patients with comorbid psychiatric and neurologic disorders are ideal candidates for dually indicated AEDs due to these agents’ class effects rooted in epilepsy. Due to the history of positive psychiatric benefits with AEDs, newer agents may be psychiatrically beneficial but will likely follow the discovery of these benefits in patients for whom epilepsy is the primary diagnosis.
Consider the limitations
Using AEDs to reduce polypharmacy should be done judiciously from a drug-drug interaction perspective, because certain AEDs (eg, carbamazepine, divalproex) can greatly influence the metabolism of other medications, which may defeat the best intentions of the original intervention.4,6
Several other limitations should be considered. This article does not include all AEDs, only those commonly used for psychiatric indications with known nonpsychiatric benefits. Some may worsen psychiatric conditions (such as rage and irritability in the case of levetiracetam), and all AEDs have an FDA warning regarding suicidal behaviors and ideation.14,15 Another important limitation is the potential for differential dosing across indications; tolerability concerns may limit adequate dosing across multiple uses. For example, topiramate’s migraine prophylaxis effect can be achieved at much lower doses than the patient-specific efficacy dosing seen in binge eating disorder, with higher doses increasing the propensity for adverse effects.13,16Dual-use AEDs should be considered wherever possible, but judicious review of evidence is necessary to appropriately adjudicate a specific patient’s risk vs benefit. The Table4,6-9,12,13,16-68 provides information on select AEDs with both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric indications, including both FDA-approved and common off-label uses. These indications are limited to adult use only.

CASE CONTINUED
After reviewing Mr. B’s medical history, the treating medical team decides to cross-taper escitalopram to duloxetine 30 mg twice daily. Though his pain lessens after several weeks, it persists enough to interfere with Mr. B’s daily life. In addition to duloxetine, he is started on pregabalin 50 mg 3 times a day. Mr. B’s pain decreases to a tolerable level, and he reports decreased worrying and restlessness, and improvements in concentration and sleep.
Mr. B, age 64, is being treated in the psychiatric clinic for generalized anxiety disorder. He also has a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis. His present medications include metformin 500 mg twice daily, escitalopram 20 mg/d, and a multivitamin.
Three months after a shingles outbreak on his left trunk, Mr. B develops a sharp, burning pain and hypersensitivity to light in the same area as the shingles flare-up. He is diagnosed with postherpetic neuralgia. Despite a 12-week trial of cognitive-behavioral therapy, Mr. B continues to report excessive worry, irritability, poor concentration, psychomotor restlessness, and poor sleep.
Contrasting with the serendipitous discovery of iproniazid and chlorpromazine leading to the development of the current spectrum of antidepressant and antipsychotic agents, discovery of the benefits various antiepileptic agents have in bipolar disorder has not led to a similar proliferation of medication development for bipolar mania or depression.1-3 Divalproex, one of the most commonly used antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) in psychiatry, was thought to be an inactive organic solvent until it was used in 1962 to test the anticonvulsant activity of other compounds. This led to the discovery and subsequent use of divalproex in patients with epilepsy, followed by FDA approval in bipolar disorder.4,5 Off-label use of many AEDs as mood-stabilizing agents in bipolar disorder led to the emergence of carbamazepine, divalproex, and lamotrigine, which joined lithium as classic mood-stabilizing agents.4,6-8 Amid varying definitions of “mood stabilizer,” many AEDs have failed to demonstrate mood-stabilizing effects in bipolar disorder and therefore should not all be considered mood stabilizers.9 Nonetheless, the dual use of a single AED for both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric indications can decrease polypharmacy and increase acceptability of medications in patients who have low insight into their illness.10,11
Because AEDs were originally purposed to treat neurologic disease, psychiatric indications must first be established before considering other indications. AEDs as a class have broad pharmacologic actions, but are generally CNS depressants, decreasing brain signaling through mechanisms such as ion channel antagonism (carbamazepine, gabapentin) or alterations to gamma-aminobutyric acid/glutamate signaling (divalproex, topiramate).4,6,12,13 Compared to antidepressants and antipsychotics, whose primary use for psychiatric conditions is firmly rooted in evidence, rational use of AEDs for psychiatric conditions and symptoms depends on the agent-specific efficacy. Patients with comorbid psychiatric and neurologic disorders are ideal candidates for dually indicated AEDs due to these agents’ class effects rooted in epilepsy. Due to the history of positive psychiatric benefits with AEDs, newer agents may be psychiatrically beneficial but will likely follow the discovery of these benefits in patients for whom epilepsy is the primary diagnosis.
Consider the limitations
Using AEDs to reduce polypharmacy should be done judiciously from a drug-drug interaction perspective, because certain AEDs (eg, carbamazepine, divalproex) can greatly influence the metabolism of other medications, which may defeat the best intentions of the original intervention.4,6
Several other limitations should be considered. This article does not include all AEDs, only those commonly used for psychiatric indications with known nonpsychiatric benefits. Some may worsen psychiatric conditions (such as rage and irritability in the case of levetiracetam), and all AEDs have an FDA warning regarding suicidal behaviors and ideation.14,15 Another important limitation is the potential for differential dosing across indications; tolerability concerns may limit adequate dosing across multiple uses. For example, topiramate’s migraine prophylaxis effect can be achieved at much lower doses than the patient-specific efficacy dosing seen in binge eating disorder, with higher doses increasing the propensity for adverse effects.13,16Dual-use AEDs should be considered wherever possible, but judicious review of evidence is necessary to appropriately adjudicate a specific patient’s risk vs benefit. The Table4,6-9,12,13,16-68 provides information on select AEDs with both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric indications, including both FDA-approved and common off-label uses. These indications are limited to adult use only.

CASE CONTINUED
After reviewing Mr. B’s medical history, the treating medical team decides to cross-taper escitalopram to duloxetine 30 mg twice daily. Though his pain lessens after several weeks, it persists enough to interfere with Mr. B’s daily life. In addition to duloxetine, he is started on pregabalin 50 mg 3 times a day. Mr. B’s pain decreases to a tolerable level, and he reports decreased worrying and restlessness, and improvements in concentration and sleep.
1. Meyer JM. A concise guide to monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(12):14-16,18-23,47,A.
2. Ban TA. Fifty years chlorpromazine: a historical perspective. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2007;3(4):495-500.
3. López-Mun
4. Depakote [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie, Inc; 2021.
5. Henry TR. The history of valproate in clinical neuroscience. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2003;37 Suppl 2:5-16.
6. Tegretol and Tegretol-XR [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ: Pharmaceuticals Co.; 2020.
7. Lamictal [package insert]. Research Triangle Park, NC: GlaxoSmithKline; 2009.
8. Lithobid [package insert]. Baudette, MN: ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2009.
9. Yatham LN, Kennedy SH, Parikh SV, et al. Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) and International Society for Bipolar Disorders (ISBD) 2018 guidelines for the management of patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2018;20(2):97-170.
10. National Alliance on Mental Illness. Anosognosia. Common with mental illness. Accessed March 3, 2022. https://www.nami.org/About-Mental-Illness/Common-with-Mental-Illness/Anosognosia
11. Hales CM, Servais J, Martin CB, et al. Prescription drug use among adults aged 40-79 in the United States and Canada. NCHS Data Brief. 2019(347):1-8.
12. Neurontin [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer; 2017.
13. Topamax [package insert]. Titusville, NJ: Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2009.
14. Molokwu OA, Ezeala-Adikaibe BA, Onwuekwe IO. Levetiracetam-induced rage and suicidality: two case reports and review of literature. Epilepsy Behav Case Rep. 2015;4:79-81.
15. U.S. Food & Drug Administration. FDA Statistical Review and Evaluation. Antiepileptic Drugs and Suicidality. 2008. Accessed March 3, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Statistical-Review-and-Evaluation--Antiepileptic-Drugs-and-Suicidality.pdf
16. McElroy SL, Hudson JI, Capece JA, et al. Topiramate for the treatment of binge eating disorder associated with obesity: a placebo-controlled study. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;61(9):1039-1048.
17. Zhang ZJ, Kang WH, Tan QR, et al. Adjunctive herbal medicine with carbamazepine for bipolar disorders: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Psychiatr Res. 2007;41(3-4):360-369.
18. Kleindienst N, Greil W. Differential efficacy of lithium and carbamazepine in the prophylaxis of bipolar disorder: results of the MAP study. Neuropsychobiology. 2000;42 Suppl 1:2-10.
19. Goodwin GM, Haddad PM, Ferrier IN, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for treating bipolar disorder: revised third edition recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(6):495-553.
20. Davis LL, Bartolucci A, Petty F. Divalproex in the treatment of bipolar depression: a placebo-controlled study. J Affect Disord. 2005;85(3):259-266.
21. Gyulai L, Bowden CL, McElroy SL, et al. Maintenance efficacy of divalproex in the prevention of bipolar depression. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28(7):1374-1382.
22. Limdi NA, Shimpi AV, Faught E, et al. Efficacy of rapid IV administration of valproic acid for status epilepticus. Neurology. 2005;64(2):353-355.
23. Temkin NR, Dikmen SS, Anderson GD, et al. Valproate therapy for prevention of posttraumatic seizures: a randomized trial. J Neurosurg. 1999; 91(4):593-600.
24. Reus VI, Fochtmann LJ, Bukstein O, et al. The American Psychiatric Association practice guideline for the pharmacological treatment of patients with alcohol use disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(1):86-90.
25. US Dept of Veterans Affairs, US Dept of Defense, The Management of Substance Use Disorders Work Group. VA/DoD clinical practice guideline for the management of substance use disorders. US Dept of Veterans Affairs/Dept of Defense; 2015. Accessed March 3, 2022. http://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/MH/sud/VADoDSUDCPGRevised22216.pdf
26. Myrick H, Malcolm R, Randall PK, et al. A double-blind trial of gabapentin versus lorazepam in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009;33(9):1582-1588.
27. Ahmed S, Stanciu CN, Kotapati PV, et al. Effectiveness of gabapentin in reducing cravings and withdrawal in alcohol use disorder: a meta-analytic review. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2019;21(4):19r02465.
28. Pande AC, Davidson JR, Jefferson JW, et al. Treatment of social phobia with gabapentin: a placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1999;19(4):341-348.
29. Ryan NM, Birring SS, Gibson PG. Gabapentin for refractory chronic cough: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380(9853):1583-1589.
30. Gibson P, Wang G, McGarvey L, et al. Treatment of unexplained chronic cough: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016;149(1):27-44.
31. Arnold LM, Goldenberg DL, Stanford SB, et al. Gabapentin in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(4):1336-1344.
32. Alonso-Navarro H, Rubio L, Jiménez-Jiménez FJ. Refractory hiccup: successful treatment with gabapentin. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2007;30(3):186-187.
33. Jatzko A, Stegmeier-Petroianu A, Petroianu GA. Alpha-2-delta ligands for singultus (hiccup) treatment: three case reports. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007;33(6):756-760.
34. Finnerup NB, Attal N, Haroutounian S, et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(2):162-173.
35. Moore RA, Wiffen PJ, Derry S, et al. Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014(4):CD007938.
36. Yuan M, Zhou HY, Xiao ZL, et al. Efficacy and safety of gabapentin vs. carbamazepine in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: a meta-analysis. Pain Pract. 2016;16(8):1083-1091.
37. Weisshaar E, Szepietowski JC, Darsow U, et al. European guideline on chronic pruritus. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92(5):563-581.
38. Garcia-Borreguero D, Silber MH, Winkelman JW, et al. Guidelines for the first-line treatment of restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease, prevention and treatment of dopaminergic augmentation: a combined task force of the IRLSSG, EURLSSG, and the RLS-Foundation. Sleep Med. 2016;21:1-11.
39. Cobin RH, Goodman NF; AACE Reproductive Endocrinology Scientific Committee. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology position statement on menopause—2017 update [published correction appears in Endocr Pract. 2017;23 (12):1488]. Endocr Pract. 2017;23(7):869-880.
40. Calabrese JR, Suppes T, Bowden CL, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, prophylaxis study of lamotrigine in rapid-cycling bipolar disorder: Lamictal 614 Study Group. J Clin Psychiatry. 2000;60(11):841-850.
41. May A, Leone M, Afra J, et al. EFNS guidelines on the treatment of cluster headache and other trigeminal-autonomic cephalalgias. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13(10):1066-1077.
42. Stein G, Bernadt M. Lithium augmentation therapy in tricyclic-resistant depression. A controlled trial using lithium in low and normal doses. Br J Psychiatry. 1993;162:634-640.
43. Craft M, Ismail IA, Krishnamurti D, et al. Lithium in the treatment of aggression in mentally handicapped patients: a double-blind trial. Br J Psychiatry. 1987;150:685-689.
44. Cipriani A, Pretty H, Hawton K, et al. Lithium in the prevention of suicidal behavior and all-cause mortality in patients with mood disorders: a systematic review of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(10):1805-1819.
45. Dickstein G, Shechner C, Adawi F, et al. Lithium treatment in amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis. Am J Med. 1997;102(5):454-458.
46. Bogazzi F, Bartalena L, Brogioni S, et al. Comparison of radioiodine with radioiodine plus lithium in the treatment of Graves’ hyperthyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84(2):499-503.
47. Lyrica [package insert]. New York, NY: Parke-Davis, Division of Pfizer Inc; 2020.
48. Lydiard RB, Rickels K, Herman B, et al. Comparative efficacy of pregabalin and benzodiazepines in treating the psychic and somatic symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13(2):229-241.
49. Pande AC, Feltner DE, Jefferson JW, et al. Efficacy of the novel anxiolytic pregabalin in social anxiety disorder: a placebo-controlled, multicenter study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2004;24(2):141-149.
50. Vertigan AE, Kapela SL, Ryan NM, et al. Pregabalin and speech pathology combination therapy for refractory chronic cough: a randomized controlled trial. Chest. 2016;149(3):639-648.
51. Matsuda KM, Sharma D, Schonfeld AR, et al. Gabapentin and pregabalin for the treatment of chronic pruritus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75(3):619-625.e6.
52. Allen R, Chen C, Soaita A, et al. A randomized, double-blind, 6-week, dose-ranging study of pregabalin in patients with restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2010;11(6):512-519.
53. Loprinzi CL, Qin R, Balcueva EP, et al. Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation of pregabalin for alleviating hot flashes, N07C1 [published correction appears in J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(10):1808]. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(4):641-647.
54. Dunlop BW, Papp L, Garlow SJ, et al. Tiagabine for social anxiety disorder. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2007;22(4):241-244.
55. Paparrigopoulos T, Tzavellas E, Karaiskos D, et al. An open pilot study of tiagabine in alcohol dependence: tolerability and clinical effects. J Psychopharmacol. 2010;24(9):1375-1380.
56. Gabitril [package insert]. North Wales, PA: Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc; 2015.
57. Johnson BA, Ait-Daoud N, Bowden C, et al. Oral topiramate for treatment of alcohol dependence: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361(9370):1677-1685.
58. Linde M, Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP, et al. Topiramate for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013(6):CD010610.
59. Pascual J, Láinez MJ, Dodick D, et al. Antiepileptic drugs for the treatment of chronic and episodic cluster headache: a review. Headache. 2007;47(1):81-89.
60. Ondo WG, Jankovic J, Connor GS, et al. Topiramate in essential tremor: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neurology. 2006;66(5):672-677.
61. Ko YH, Joe SH, Jung IK, et al. Topiramate as an adjuvant treatment with atypical antipsychotics in schizophrenic patients experiencing weight gain. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2005;28(4):169-175.
62. Wilding J, Van Gaal L, Rissanen A, et al. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study of the long-term efficacy and safety of topiramate in the treatment of obese subjects. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28(11):1399-1410.
63. Rosenstock J, Hollander P, Gadde KM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study to assess the efficacy and safety of topiramate controlled release in the treatment of obese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30(6):1480-1486.
64. McElroy SL, Kotwal R, Guerdjikova AI, et al. Zonisamide in the treatment of binge eating disorder with obesity: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(12):1897-1906.
65. Zonegran [package insert]. Teaneck, NJ: Eisai Inc; 2006.
66. Drake ME Jr, Greathouse NI, Renner JB, et al. Open-label zonisamide for refractory migraine. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2004;27(6):278-280.
67. Matsunaga S, Kishi T, Iwata N. Combination therapy with zonisamide and antiparkinson drugs for Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;56(4):1229-1239.
68. Gadde KM, Kopping MF, Wagner HR 2nd, et al. Zonisamide for weight reduction in obese adults: a 1-year randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(20):1557-1564.
1. Meyer JM. A concise guide to monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(12):14-16,18-23,47,A.
2. Ban TA. Fifty years chlorpromazine: a historical perspective. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2007;3(4):495-500.
3. López-Mun
4. Depakote [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie, Inc; 2021.
5. Henry TR. The history of valproate in clinical neuroscience. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2003;37 Suppl 2:5-16.
6. Tegretol and Tegretol-XR [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ: Pharmaceuticals Co.; 2020.
7. Lamictal [package insert]. Research Triangle Park, NC: GlaxoSmithKline; 2009.
8. Lithobid [package insert]. Baudette, MN: ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2009.
9. Yatham LN, Kennedy SH, Parikh SV, et al. Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) and International Society for Bipolar Disorders (ISBD) 2018 guidelines for the management of patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2018;20(2):97-170.
10. National Alliance on Mental Illness. Anosognosia. Common with mental illness. Accessed March 3, 2022. https://www.nami.org/About-Mental-Illness/Common-with-Mental-Illness/Anosognosia
11. Hales CM, Servais J, Martin CB, et al. Prescription drug use among adults aged 40-79 in the United States and Canada. NCHS Data Brief. 2019(347):1-8.
12. Neurontin [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer; 2017.
13. Topamax [package insert]. Titusville, NJ: Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2009.
14. Molokwu OA, Ezeala-Adikaibe BA, Onwuekwe IO. Levetiracetam-induced rage and suicidality: two case reports and review of literature. Epilepsy Behav Case Rep. 2015;4:79-81.
15. U.S. Food & Drug Administration. FDA Statistical Review and Evaluation. Antiepileptic Drugs and Suicidality. 2008. Accessed March 3, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Statistical-Review-and-Evaluation--Antiepileptic-Drugs-and-Suicidality.pdf
16. McElroy SL, Hudson JI, Capece JA, et al. Topiramate for the treatment of binge eating disorder associated with obesity: a placebo-controlled study. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;61(9):1039-1048.
17. Zhang ZJ, Kang WH, Tan QR, et al. Adjunctive herbal medicine with carbamazepine for bipolar disorders: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Psychiatr Res. 2007;41(3-4):360-369.
18. Kleindienst N, Greil W. Differential efficacy of lithium and carbamazepine in the prophylaxis of bipolar disorder: results of the MAP study. Neuropsychobiology. 2000;42 Suppl 1:2-10.
19. Goodwin GM, Haddad PM, Ferrier IN, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for treating bipolar disorder: revised third edition recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(6):495-553.
20. Davis LL, Bartolucci A, Petty F. Divalproex in the treatment of bipolar depression: a placebo-controlled study. J Affect Disord. 2005;85(3):259-266.
21. Gyulai L, Bowden CL, McElroy SL, et al. Maintenance efficacy of divalproex in the prevention of bipolar depression. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28(7):1374-1382.
22. Limdi NA, Shimpi AV, Faught E, et al. Efficacy of rapid IV administration of valproic acid for status epilepticus. Neurology. 2005;64(2):353-355.
23. Temkin NR, Dikmen SS, Anderson GD, et al. Valproate therapy for prevention of posttraumatic seizures: a randomized trial. J Neurosurg. 1999; 91(4):593-600.
24. Reus VI, Fochtmann LJ, Bukstein O, et al. The American Psychiatric Association practice guideline for the pharmacological treatment of patients with alcohol use disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(1):86-90.
25. US Dept of Veterans Affairs, US Dept of Defense, The Management of Substance Use Disorders Work Group. VA/DoD clinical practice guideline for the management of substance use disorders. US Dept of Veterans Affairs/Dept of Defense; 2015. Accessed March 3, 2022. http://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/MH/sud/VADoDSUDCPGRevised22216.pdf
26. Myrick H, Malcolm R, Randall PK, et al. A double-blind trial of gabapentin versus lorazepam in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009;33(9):1582-1588.
27. Ahmed S, Stanciu CN, Kotapati PV, et al. Effectiveness of gabapentin in reducing cravings and withdrawal in alcohol use disorder: a meta-analytic review. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2019;21(4):19r02465.
28. Pande AC, Davidson JR, Jefferson JW, et al. Treatment of social phobia with gabapentin: a placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1999;19(4):341-348.
29. Ryan NM, Birring SS, Gibson PG. Gabapentin for refractory chronic cough: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380(9853):1583-1589.
30. Gibson P, Wang G, McGarvey L, et al. Treatment of unexplained chronic cough: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016;149(1):27-44.
31. Arnold LM, Goldenberg DL, Stanford SB, et al. Gabapentin in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(4):1336-1344.
32. Alonso-Navarro H, Rubio L, Jiménez-Jiménez FJ. Refractory hiccup: successful treatment with gabapentin. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2007;30(3):186-187.
33. Jatzko A, Stegmeier-Petroianu A, Petroianu GA. Alpha-2-delta ligands for singultus (hiccup) treatment: three case reports. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007;33(6):756-760.
34. Finnerup NB, Attal N, Haroutounian S, et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(2):162-173.
35. Moore RA, Wiffen PJ, Derry S, et al. Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014(4):CD007938.
36. Yuan M, Zhou HY, Xiao ZL, et al. Efficacy and safety of gabapentin vs. carbamazepine in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: a meta-analysis. Pain Pract. 2016;16(8):1083-1091.
37. Weisshaar E, Szepietowski JC, Darsow U, et al. European guideline on chronic pruritus. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92(5):563-581.
38. Garcia-Borreguero D, Silber MH, Winkelman JW, et al. Guidelines for the first-line treatment of restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease, prevention and treatment of dopaminergic augmentation: a combined task force of the IRLSSG, EURLSSG, and the RLS-Foundation. Sleep Med. 2016;21:1-11.
39. Cobin RH, Goodman NF; AACE Reproductive Endocrinology Scientific Committee. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology position statement on menopause—2017 update [published correction appears in Endocr Pract. 2017;23 (12):1488]. Endocr Pract. 2017;23(7):869-880.
40. Calabrese JR, Suppes T, Bowden CL, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, prophylaxis study of lamotrigine in rapid-cycling bipolar disorder: Lamictal 614 Study Group. J Clin Psychiatry. 2000;60(11):841-850.
41. May A, Leone M, Afra J, et al. EFNS guidelines on the treatment of cluster headache and other trigeminal-autonomic cephalalgias. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13(10):1066-1077.
42. Stein G, Bernadt M. Lithium augmentation therapy in tricyclic-resistant depression. A controlled trial using lithium in low and normal doses. Br J Psychiatry. 1993;162:634-640.
43. Craft M, Ismail IA, Krishnamurti D, et al. Lithium in the treatment of aggression in mentally handicapped patients: a double-blind trial. Br J Psychiatry. 1987;150:685-689.
44. Cipriani A, Pretty H, Hawton K, et al. Lithium in the prevention of suicidal behavior and all-cause mortality in patients with mood disorders: a systematic review of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(10):1805-1819.
45. Dickstein G, Shechner C, Adawi F, et al. Lithium treatment in amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis. Am J Med. 1997;102(5):454-458.
46. Bogazzi F, Bartalena L, Brogioni S, et al. Comparison of radioiodine with radioiodine plus lithium in the treatment of Graves’ hyperthyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84(2):499-503.
47. Lyrica [package insert]. New York, NY: Parke-Davis, Division of Pfizer Inc; 2020.
48. Lydiard RB, Rickels K, Herman B, et al. Comparative efficacy of pregabalin and benzodiazepines in treating the psychic and somatic symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13(2):229-241.
49. Pande AC, Feltner DE, Jefferson JW, et al. Efficacy of the novel anxiolytic pregabalin in social anxiety disorder: a placebo-controlled, multicenter study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2004;24(2):141-149.
50. Vertigan AE, Kapela SL, Ryan NM, et al. Pregabalin and speech pathology combination therapy for refractory chronic cough: a randomized controlled trial. Chest. 2016;149(3):639-648.
51. Matsuda KM, Sharma D, Schonfeld AR, et al. Gabapentin and pregabalin for the treatment of chronic pruritus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75(3):619-625.e6.
52. Allen R, Chen C, Soaita A, et al. A randomized, double-blind, 6-week, dose-ranging study of pregabalin in patients with restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2010;11(6):512-519.
53. Loprinzi CL, Qin R, Balcueva EP, et al. Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation of pregabalin for alleviating hot flashes, N07C1 [published correction appears in J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(10):1808]. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(4):641-647.
54. Dunlop BW, Papp L, Garlow SJ, et al. Tiagabine for social anxiety disorder. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2007;22(4):241-244.
55. Paparrigopoulos T, Tzavellas E, Karaiskos D, et al. An open pilot study of tiagabine in alcohol dependence: tolerability and clinical effects. J Psychopharmacol. 2010;24(9):1375-1380.
56. Gabitril [package insert]. North Wales, PA: Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc; 2015.
57. Johnson BA, Ait-Daoud N, Bowden C, et al. Oral topiramate for treatment of alcohol dependence: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361(9370):1677-1685.
58. Linde M, Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP, et al. Topiramate for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013(6):CD010610.
59. Pascual J, Láinez MJ, Dodick D, et al. Antiepileptic drugs for the treatment of chronic and episodic cluster headache: a review. Headache. 2007;47(1):81-89.
60. Ondo WG, Jankovic J, Connor GS, et al. Topiramate in essential tremor: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neurology. 2006;66(5):672-677.
61. Ko YH, Joe SH, Jung IK, et al. Topiramate as an adjuvant treatment with atypical antipsychotics in schizophrenic patients experiencing weight gain. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2005;28(4):169-175.
62. Wilding J, Van Gaal L, Rissanen A, et al. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study of the long-term efficacy and safety of topiramate in the treatment of obese subjects. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28(11):1399-1410.
63. Rosenstock J, Hollander P, Gadde KM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study to assess the efficacy and safety of topiramate controlled release in the treatment of obese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30(6):1480-1486.
64. McElroy SL, Kotwal R, Guerdjikova AI, et al. Zonisamide in the treatment of binge eating disorder with obesity: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(12):1897-1906.
65. Zonegran [package insert]. Teaneck, NJ: Eisai Inc; 2006.
66. Drake ME Jr, Greathouse NI, Renner JB, et al. Open-label zonisamide for refractory migraine. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2004;27(6):278-280.
67. Matsunaga S, Kishi T, Iwata N. Combination therapy with zonisamide and antiparkinson drugs for Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;56(4):1229-1239.
68. Gadde KM, Kopping MF, Wagner HR 2nd, et al. Zonisamide for weight reduction in obese adults: a 1-year randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(20):1557-1564.