User login
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Migraine May 2022
Cefaly is a commonly used nonprescription device that uses external trigeminal nerve stimulation (e-TNS) to either abort or prevent migraine attacks. The pivotal Cefaly study was published about 10 years ago, and Cefaly was the first US Food and Drug Administration–cleared neurostimulation device for headache. The initial acute data were gathered primarily in the hospital setting, and the investigators in the study by Kuruvilla and colleagues intended to replicate a more real-world scenario for the acute use of Cefaly.
This was a prospective, multicenter, sham-controlled study. Patients were enrolled if they developed migraine prior to age 50 years and experienced two to eight attacks per month of moderate to severe intensity. Patients were randomized to either Cefaly or a sham device. The Cefaly device itself has two setting: acute and preventive. For this study, the acute setting was used for 2 hours at a time during an acute attack (within the first 4 hours). The supraorbital and supratrochlear branches of trigeminal nerves bilaterally are stimulated with a continuous stimulation via a self-adhesive electrode. This has previously been shown to be safe and effective with the most common side effect noted to be skin irritation at the electrode site.
Patients collected data about their headaches in an e-diary and continued to treat for 2 months. The co-primary outcomes were headache freedom and resolution of most bothersome syndrome at 2 hours. Secondary outcomes were pain relief at 2 hours, resolution of any migraine-associated symptom at 2 hours after beginning e-TNS treatment, sustained pain freedom (defined as pain freedom at 2 hours and pain freedom at 24 hours without the use of antimigraine medication during those 24 hours), and use of a rescue medication between 2 and 24 hours after beginning an e-TNS session.
A total of 538 patients were enrolled. The percentage of patients with both freedom from pain and resolution of the most bothersome symptoms were statistically different in the intervention and sham groups. The secondary outcomes were also statistically improved in the device group, with the exception of use of rescue medications between 2 and 24 hours. The most common adverse events were forehead discomfort and paresthesia.
This study does show the effectiveness of Cefaly, especially when used for longer periods of time than had been previously recommended. The outcomes were all met with the exception of rescue medication use, and there is no contraindication to using any rescue medication while using the Cefaly device. Cefaly can be an excellent add-on for acute treatment, especially in patients that may need to use more than one intervention acutely for their migraine attacks.
Providers often discuss when to start medications but do not as often discuss when to stop medications. This is especially true for preventive medications for migraine. The best-case scenario is that a preventive medication is so effective that it is no longer necessary; but in other circumstances, preventive medications have to be stopped, for instance, during pregnancy planning. One concern especially when starting and stopping a monoclonal antibody (mAb) medication is the development of neutralizing antibodies to negate the effect of restarting the medication. This study was designed to determine whether restarting calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)–mAb medications was still effective after having been previously stopped.
Raffaelli and colleagues managed a small (39 patients) open-label prospective study. Patients either had a diagnosis of episodic or chronic migraine and were initially given CGRP-mAbs for at least 8 months. They then stopped the therapy for at least 3 months and were restarted on the same mAb that they had initially used. They tracked their headache symptoms for 3 months after restarting therapy. If another treatment had been started in between, those patients were excluded.
The primary outcome was change in mean monthly migraine days between the last 4 weeks of treatment discontinuation and weeks 9-12 after restarting therapy. Secondary endpoints were the changes in mean monthly headache days across the other observation points and Headache Impact Test-6 (HIT-6) sum scores. Of the 39 patients enrolled, 16 were given erenumab, 15 galcanezumab, and 8 fremanezumab.
Mean migraine days and mean headache days were shown to have a statistically significant decrease after resumption of therapy. Restarting CGRP medications was not associated with other adverse events associated with these medications. This gives us evidence in favor of restarting the same CGRP medication when a patient's symptoms start to worsen after they have discontinued because of improvement or after pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The use of implanted devices for migraine treatment is considered somewhat controversial. Surgical interventions and implantations for migraine have not been well studied; however small case series have been published, and non-neurologists report anecdotally that these interventions can be helpful for refractory headache disorders. The study by Evans and colleagues reviewed via meta-analysis much of the prior data for nerve stimulation in migraine.
Studies included in this meta-analysis were English-language, peer-reviewed articles of prospective studies with patients over age 18 years for migraine diagnosed according to International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD) criteria. The devices were transcutaneous nerve stimulator devices in a single region of the head (occipital, supraorbital/supratrochlear areas) and enrolled a minimum of 10 patients in the treatment groups. A total of 14 studies were identified; 13 of the studies did report significant adverse events related to treatment.
Regarding migraine frequency, only four of the studies were considered comparable, investigating episodic migraine with 2-3 months of transcutaneous stimulation, and two were comparable in investigating chronic migraine. The episodic migraine studies had a pooled reduction by 2.8 days of migraine per month; chronic migraine was noted to be 2.97 days fewer per month. Three comparable studies for episodic migraine showed a pooled reduction in severity by 2.23 points after 3 months.
Occipital and other trigeminal branch stimulation implants are invasive and associated with risk, most prominently leading to migration and worsening headache and neck pain. This meta-analysis did reveal important pooled data, but it becomes less impressive when considering the published data for standard oral or injection therapies. The fact that there can be long-term worsening and adverse events with surgical implantation makes this choice a higher risk. Of note, there are now neurostimulation devices, such as Cefaly, that allow similar transcutaneous stimulation without the risk of surgery.
Cefaly is a commonly used nonprescription device that uses external trigeminal nerve stimulation (e-TNS) to either abort or prevent migraine attacks. The pivotal Cefaly study was published about 10 years ago, and Cefaly was the first US Food and Drug Administration–cleared neurostimulation device for headache. The initial acute data were gathered primarily in the hospital setting, and the investigators in the study by Kuruvilla and colleagues intended to replicate a more real-world scenario for the acute use of Cefaly.
This was a prospective, multicenter, sham-controlled study. Patients were enrolled if they developed migraine prior to age 50 years and experienced two to eight attacks per month of moderate to severe intensity. Patients were randomized to either Cefaly or a sham device. The Cefaly device itself has two setting: acute and preventive. For this study, the acute setting was used for 2 hours at a time during an acute attack (within the first 4 hours). The supraorbital and supratrochlear branches of trigeminal nerves bilaterally are stimulated with a continuous stimulation via a self-adhesive electrode. This has previously been shown to be safe and effective with the most common side effect noted to be skin irritation at the electrode site.
Patients collected data about their headaches in an e-diary and continued to treat for 2 months. The co-primary outcomes were headache freedom and resolution of most bothersome syndrome at 2 hours. Secondary outcomes were pain relief at 2 hours, resolution of any migraine-associated symptom at 2 hours after beginning e-TNS treatment, sustained pain freedom (defined as pain freedom at 2 hours and pain freedom at 24 hours without the use of antimigraine medication during those 24 hours), and use of a rescue medication between 2 and 24 hours after beginning an e-TNS session.
A total of 538 patients were enrolled. The percentage of patients with both freedom from pain and resolution of the most bothersome symptoms were statistically different in the intervention and sham groups. The secondary outcomes were also statistically improved in the device group, with the exception of use of rescue medications between 2 and 24 hours. The most common adverse events were forehead discomfort and paresthesia.
This study does show the effectiveness of Cefaly, especially when used for longer periods of time than had been previously recommended. The outcomes were all met with the exception of rescue medication use, and there is no contraindication to using any rescue medication while using the Cefaly device. Cefaly can be an excellent add-on for acute treatment, especially in patients that may need to use more than one intervention acutely for their migraine attacks.
Providers often discuss when to start medications but do not as often discuss when to stop medications. This is especially true for preventive medications for migraine. The best-case scenario is that a preventive medication is so effective that it is no longer necessary; but in other circumstances, preventive medications have to be stopped, for instance, during pregnancy planning. One concern especially when starting and stopping a monoclonal antibody (mAb) medication is the development of neutralizing antibodies to negate the effect of restarting the medication. This study was designed to determine whether restarting calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)–mAb medications was still effective after having been previously stopped.
Raffaelli and colleagues managed a small (39 patients) open-label prospective study. Patients either had a diagnosis of episodic or chronic migraine and were initially given CGRP-mAbs for at least 8 months. They then stopped the therapy for at least 3 months and were restarted on the same mAb that they had initially used. They tracked their headache symptoms for 3 months after restarting therapy. If another treatment had been started in between, those patients were excluded.
The primary outcome was change in mean monthly migraine days between the last 4 weeks of treatment discontinuation and weeks 9-12 after restarting therapy. Secondary endpoints were the changes in mean monthly headache days across the other observation points and Headache Impact Test-6 (HIT-6) sum scores. Of the 39 patients enrolled, 16 were given erenumab, 15 galcanezumab, and 8 fremanezumab.
Mean migraine days and mean headache days were shown to have a statistically significant decrease after resumption of therapy. Restarting CGRP medications was not associated with other adverse events associated with these medications. This gives us evidence in favor of restarting the same CGRP medication when a patient's symptoms start to worsen after they have discontinued because of improvement or after pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The use of implanted devices for migraine treatment is considered somewhat controversial. Surgical interventions and implantations for migraine have not been well studied; however small case series have been published, and non-neurologists report anecdotally that these interventions can be helpful for refractory headache disorders. The study by Evans and colleagues reviewed via meta-analysis much of the prior data for nerve stimulation in migraine.
Studies included in this meta-analysis were English-language, peer-reviewed articles of prospective studies with patients over age 18 years for migraine diagnosed according to International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD) criteria. The devices were transcutaneous nerve stimulator devices in a single region of the head (occipital, supraorbital/supratrochlear areas) and enrolled a minimum of 10 patients in the treatment groups. A total of 14 studies were identified; 13 of the studies did report significant adverse events related to treatment.
Regarding migraine frequency, only four of the studies were considered comparable, investigating episodic migraine with 2-3 months of transcutaneous stimulation, and two were comparable in investigating chronic migraine. The episodic migraine studies had a pooled reduction by 2.8 days of migraine per month; chronic migraine was noted to be 2.97 days fewer per month. Three comparable studies for episodic migraine showed a pooled reduction in severity by 2.23 points after 3 months.
Occipital and other trigeminal branch stimulation implants are invasive and associated with risk, most prominently leading to migration and worsening headache and neck pain. This meta-analysis did reveal important pooled data, but it becomes less impressive when considering the published data for standard oral or injection therapies. The fact that there can be long-term worsening and adverse events with surgical implantation makes this choice a higher risk. Of note, there are now neurostimulation devices, such as Cefaly, that allow similar transcutaneous stimulation without the risk of surgery.
Cefaly is a commonly used nonprescription device that uses external trigeminal nerve stimulation (e-TNS) to either abort or prevent migraine attacks. The pivotal Cefaly study was published about 10 years ago, and Cefaly was the first US Food and Drug Administration–cleared neurostimulation device for headache. The initial acute data were gathered primarily in the hospital setting, and the investigators in the study by Kuruvilla and colleagues intended to replicate a more real-world scenario for the acute use of Cefaly.
This was a prospective, multicenter, sham-controlled study. Patients were enrolled if they developed migraine prior to age 50 years and experienced two to eight attacks per month of moderate to severe intensity. Patients were randomized to either Cefaly or a sham device. The Cefaly device itself has two setting: acute and preventive. For this study, the acute setting was used for 2 hours at a time during an acute attack (within the first 4 hours). The supraorbital and supratrochlear branches of trigeminal nerves bilaterally are stimulated with a continuous stimulation via a self-adhesive electrode. This has previously been shown to be safe and effective with the most common side effect noted to be skin irritation at the electrode site.
Patients collected data about their headaches in an e-diary and continued to treat for 2 months. The co-primary outcomes were headache freedom and resolution of most bothersome syndrome at 2 hours. Secondary outcomes were pain relief at 2 hours, resolution of any migraine-associated symptom at 2 hours after beginning e-TNS treatment, sustained pain freedom (defined as pain freedom at 2 hours and pain freedom at 24 hours without the use of antimigraine medication during those 24 hours), and use of a rescue medication between 2 and 24 hours after beginning an e-TNS session.
A total of 538 patients were enrolled. The percentage of patients with both freedom from pain and resolution of the most bothersome symptoms were statistically different in the intervention and sham groups. The secondary outcomes were also statistically improved in the device group, with the exception of use of rescue medications between 2 and 24 hours. The most common adverse events were forehead discomfort and paresthesia.
This study does show the effectiveness of Cefaly, especially when used for longer periods of time than had been previously recommended. The outcomes were all met with the exception of rescue medication use, and there is no contraindication to using any rescue medication while using the Cefaly device. Cefaly can be an excellent add-on for acute treatment, especially in patients that may need to use more than one intervention acutely for their migraine attacks.
Providers often discuss when to start medications but do not as often discuss when to stop medications. This is especially true for preventive medications for migraine. The best-case scenario is that a preventive medication is so effective that it is no longer necessary; but in other circumstances, preventive medications have to be stopped, for instance, during pregnancy planning. One concern especially when starting and stopping a monoclonal antibody (mAb) medication is the development of neutralizing antibodies to negate the effect of restarting the medication. This study was designed to determine whether restarting calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)–mAb medications was still effective after having been previously stopped.
Raffaelli and colleagues managed a small (39 patients) open-label prospective study. Patients either had a diagnosis of episodic or chronic migraine and were initially given CGRP-mAbs for at least 8 months. They then stopped the therapy for at least 3 months and were restarted on the same mAb that they had initially used. They tracked their headache symptoms for 3 months after restarting therapy. If another treatment had been started in between, those patients were excluded.
The primary outcome was change in mean monthly migraine days between the last 4 weeks of treatment discontinuation and weeks 9-12 after restarting therapy. Secondary endpoints were the changes in mean monthly headache days across the other observation points and Headache Impact Test-6 (HIT-6) sum scores. Of the 39 patients enrolled, 16 were given erenumab, 15 galcanezumab, and 8 fremanezumab.
Mean migraine days and mean headache days were shown to have a statistically significant decrease after resumption of therapy. Restarting CGRP medications was not associated with other adverse events associated with these medications. This gives us evidence in favor of restarting the same CGRP medication when a patient's symptoms start to worsen after they have discontinued because of improvement or after pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The use of implanted devices for migraine treatment is considered somewhat controversial. Surgical interventions and implantations for migraine have not been well studied; however small case series have been published, and non-neurologists report anecdotally that these interventions can be helpful for refractory headache disorders. The study by Evans and colleagues reviewed via meta-analysis much of the prior data for nerve stimulation in migraine.
Studies included in this meta-analysis were English-language, peer-reviewed articles of prospective studies with patients over age 18 years for migraine diagnosed according to International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD) criteria. The devices were transcutaneous nerve stimulator devices in a single region of the head (occipital, supraorbital/supratrochlear areas) and enrolled a minimum of 10 patients in the treatment groups. A total of 14 studies were identified; 13 of the studies did report significant adverse events related to treatment.
Regarding migraine frequency, only four of the studies were considered comparable, investigating episodic migraine with 2-3 months of transcutaneous stimulation, and two were comparable in investigating chronic migraine. The episodic migraine studies had a pooled reduction by 2.8 days of migraine per month; chronic migraine was noted to be 2.97 days fewer per month. Three comparable studies for episodic migraine showed a pooled reduction in severity by 2.23 points after 3 months.
Occipital and other trigeminal branch stimulation implants are invasive and associated with risk, most prominently leading to migration and worsening headache and neck pain. This meta-analysis did reveal important pooled data, but it becomes less impressive when considering the published data for standard oral or injection therapies. The fact that there can be long-term worsening and adverse events with surgical implantation makes this choice a higher risk. Of note, there are now neurostimulation devices, such as Cefaly, that allow similar transcutaneous stimulation without the risk of surgery.
Focal hair loss
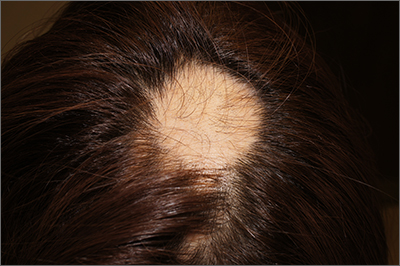
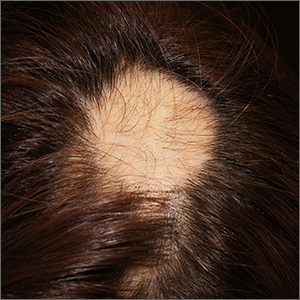
The findings of smooth, round alopecia occurring rapidly without associated scarring, pain, or itching, is consistent with the diagnosis of alopecia areata.
Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disease caused by T lymphocytes targeting hair follicles and resulting in rapid and nonscarring hair loss. It is usually self-resolving and about 2% of all individuals are affected at some point during their lifetime, with an average age of onset of 33 years.1 Some patients may progress to loss of all scalp hair (alopecia totalis) or all hair on the scalp and body (alopecia universalis).1
It is important to inspect a patient’s scalp, face, and body for more subtle areas of loss that could signal other disorders, such as lichen planopilaris, discoid lupus, or telogen effluvium. It is worth noting that alopecia areata is not associated with scalp lesions, crusting, or scars without follicles. Such findings should be further investigated with a 4-mm punch biopsy of affected and adjacent follicular units. Carefully labeling biopsy specimens as scalp specimens for hair loss will aid in a correct histopathologic diagnosis.
Systematic data comparing treatments for alopecia areata are lacking. For localized disease, topical or intradermal triamcinolone injections at a concentration of 5 to 10 mg/mL, with about 0.1 mL to 0.05 mL injected every square centimeter of affected area (up to 40 mg per visit), can provide rapid regrowth.1 Within 4 months of the monthly injections, 63% of patients experience complete regrowth.1 Despite this favorable outcome, there is also a high rate of recurrence.
For more widespread disease, contact immunotherapy with squaric acid dibutyl ester or diphencyprone can provoke a low-grade contact allergy and induce antigenic completion. This therapy is painless but can be itchy; medications must be compounded and titrated to activity.
The patient in this case opted to receive monthly triamcinolone injections in an undiluted concentration of 10 mg/mL for 3 months, at which point she experienced excellent hair regrowth. A small patch of recurrence was noted a year later and treated twice with monthly triamcinolone injections.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Darwin E, Hirt PA, Fertig R, et al. Alopecia areata: review of epidemiology, clinical features, pathogenesis, and new treatment options. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:51-60. doi: 10.4103/ijt.ijt_99_17

The findings of smooth, round alopecia occurring rapidly without associated scarring, pain, or itching, is consistent with the diagnosis of alopecia areata.
Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disease caused by T lymphocytes targeting hair follicles and resulting in rapid and nonscarring hair loss. It is usually self-resolving and about 2% of all individuals are affected at some point during their lifetime, with an average age of onset of 33 years.1 Some patients may progress to loss of all scalp hair (alopecia totalis) or all hair on the scalp and body (alopecia universalis).1
It is important to inspect a patient’s scalp, face, and body for more subtle areas of loss that could signal other disorders, such as lichen planopilaris, discoid lupus, or telogen effluvium. It is worth noting that alopecia areata is not associated with scalp lesions, crusting, or scars without follicles. Such findings should be further investigated with a 4-mm punch biopsy of affected and adjacent follicular units. Carefully labeling biopsy specimens as scalp specimens for hair loss will aid in a correct histopathologic diagnosis.
Systematic data comparing treatments for alopecia areata are lacking. For localized disease, topical or intradermal triamcinolone injections at a concentration of 5 to 10 mg/mL, with about 0.1 mL to 0.05 mL injected every square centimeter of affected area (up to 40 mg per visit), can provide rapid regrowth.1 Within 4 months of the monthly injections, 63% of patients experience complete regrowth.1 Despite this favorable outcome, there is also a high rate of recurrence.
For more widespread disease, contact immunotherapy with squaric acid dibutyl ester or diphencyprone can provoke a low-grade contact allergy and induce antigenic completion. This therapy is painless but can be itchy; medications must be compounded and titrated to activity.
The patient in this case opted to receive monthly triamcinolone injections in an undiluted concentration of 10 mg/mL for 3 months, at which point she experienced excellent hair regrowth. A small patch of recurrence was noted a year later and treated twice with monthly triamcinolone injections.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

The findings of smooth, round alopecia occurring rapidly without associated scarring, pain, or itching, is consistent with the diagnosis of alopecia areata.
Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disease caused by T lymphocytes targeting hair follicles and resulting in rapid and nonscarring hair loss. It is usually self-resolving and about 2% of all individuals are affected at some point during their lifetime, with an average age of onset of 33 years.1 Some patients may progress to loss of all scalp hair (alopecia totalis) or all hair on the scalp and body (alopecia universalis).1
It is important to inspect a patient’s scalp, face, and body for more subtle areas of loss that could signal other disorders, such as lichen planopilaris, discoid lupus, or telogen effluvium. It is worth noting that alopecia areata is not associated with scalp lesions, crusting, or scars without follicles. Such findings should be further investigated with a 4-mm punch biopsy of affected and adjacent follicular units. Carefully labeling biopsy specimens as scalp specimens for hair loss will aid in a correct histopathologic diagnosis.
Systematic data comparing treatments for alopecia areata are lacking. For localized disease, topical or intradermal triamcinolone injections at a concentration of 5 to 10 mg/mL, with about 0.1 mL to 0.05 mL injected every square centimeter of affected area (up to 40 mg per visit), can provide rapid regrowth.1 Within 4 months of the monthly injections, 63% of patients experience complete regrowth.1 Despite this favorable outcome, there is also a high rate of recurrence.
For more widespread disease, contact immunotherapy with squaric acid dibutyl ester or diphencyprone can provoke a low-grade contact allergy and induce antigenic completion. This therapy is painless but can be itchy; medications must be compounded and titrated to activity.
The patient in this case opted to receive monthly triamcinolone injections in an undiluted concentration of 10 mg/mL for 3 months, at which point she experienced excellent hair regrowth. A small patch of recurrence was noted a year later and treated twice with monthly triamcinolone injections.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Darwin E, Hirt PA, Fertig R, et al. Alopecia areata: review of epidemiology, clinical features, pathogenesis, and new treatment options. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:51-60. doi: 10.4103/ijt.ijt_99_17
1. Darwin E, Hirt PA, Fertig R, et al. Alopecia areata: review of epidemiology, clinical features, pathogenesis, and new treatment options. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:51-60. doi: 10.4103/ijt.ijt_99_17
Reading Chekhov on the Cancer Ward
Burnout and other forms of psychosocial distress are common among health care professionals necessitating measures to promote well-being and reduce burnout.1 Studies have shown that nonmedical reading is associated with low burnout and that small group study sections can promote wellness.2,3 Narrative medicine, which proposes a model for humane and effective medical practice, advocates for the necessity of narrative competence.
Short Story Club
Narrative competence is the ability to acknowledge, interpret, and act on the stories of others. The narrative skill of close reading also encourages reflective practice, equipping practitioners to better weather the tides of illness.4 In our case, we formed a short story club intervention to closely read, or read and reflect, on literary fiction. We explored how reading and reflecting would result in profound changes in thinking and feeling and noted different ways by which they can cause such well-being. We describe here the 7 ways in which stories led us to increase bonding, improve empathy, and promote meaning in medicine.
Slowing Down
The short story club helped to bond us together and increase our sense of meaning in medicine by slowing us down. One member of the group likened the experience to increasing the pixels in a painting, thereby improving the resolution and seeing more clearly. Another member mentioned the experience as a form of meditation in slowing down the brain, breathing in the story, and breathing out impressions. One story by Anatole Broyard emphasized the importance of slowing down and “brooding” over a patient.5 The author describes his experience as a prostate cancer patient, in which his body was treated but his story was ignored. He begged his doctors to pay more attention to his story to listen and to brood over him. This story was enlightening to us; we saw how desperate our patients are to tell their stories, and for us to hear their stories.
Mirrors and Windows
Another way reading and reflecting on short stories helped was by reflecting our practices to ourselves, as though looking into a mirror to see ourselves and out of a window to see others. We found that stories mirrored our own world and allowed us to discuss issues close to us without the embarrassment or stigma of owning the story. In one session we read “The Doctor’s Visit” by Anton Chekhov.6 Some of the members resonated with the doctor of this story who awkwardly attended to his lady patient whose son was dying of a brain tumor. The doctor was nervous, insecure, and unable to express any empathy. He was also the father of the child who was dying and refused to admit any responsibility. One member of the group stated that he could relate to the doctor’s insecurities and mentioned that he too felt insecure and even sometimes felt like an imposter. This led to a discussion of insecurities, ways to bolster self-confidence, and ways to accept and respect limitations. This was a conversation that may not have taken place without the story as anchor to discuss insecurities that we individually may not have been willing to admit to the group.
In a different session, we discussed the story “Interpreter of Maladies” by Jhumpa Lahiri in which a settled Indian American family returns to India to tour and learn about their heritage from a guide (the interpreter of maladies) who interpreted the culture for them.7 The family professed to be interested in knowing about the culture but could not concentrate: the wife stayed busy flirting with the guide and revealing outrageous secrets to him, the children were engrossed in their squabbles, and the father was essentially absent taking photographs as souvenirs instead of seeing the sites firsthand. Some of the members of the group were Indian American and could relate to the alienation from their home and nostalgia for their country, while others could relate to the same alienation, albeit from other cultures and countries. This allowed us to talk about deeply personal topics, without having to own the topic or reveal personal issues. The discussion led to a deep understanding and empathy for us and our colleagues knowing the pain of alienation that some of them felt but could not discuss.
The stories also served as windows into the world of others which enabled us to see and become the other. For example, in one session we reflected on “Babylon Revisited” by F. Scott Fitzgerald.8 In this story, an American man returns to Paris after the Great Depression and recalls his life as a young artist in the American artist expatriate community of Paris in the 1920s and 1930s. During that time, he partied, drank in excess, lost his wife to pneumonia (for which he was at least partially responsible), lost custody of his daughter, and lost his fortune. As he returned to Paris to try to reclaim his daughter, we feel his pain as he tries but fails to overcome chronic alcoholism, sexual indiscretions, and losses. This gave rise to discussion of losses in general as we became one with the main character. This increased our empathy for others in a way that could not have been possible without this short story as anchor.
In another session we reflected on “Hills Like White Elephants” by Ernest Hemingway, in which a man is waiting for a train while proposing his girlfriend get an abortion.9 She agonizes over her choices and makes no decision in this story. Yet, we the reader could “become” the woman in the story faced with hard choices of having a baby but losing the man she loves, or having an abortion and maybe losing him anyway. In becoming this woman, we could experience the complex emotions and feel an experience of the other.
Exploring the Taboo
A third aspect of the club was enabling discussion of controversial topics. There were topics that arose in the group which never would have arisen in clinical practice discussions. These had to do with the taboo topics such as romantic attachments to patients. We read “The Caves of Lascaux” and reflected on the story of a young doctor who becomes enamored and obsessed with his beautiful but dying patient.10 He becomes so obsessed with her that he almost abandons his wife, family, and stable livelihood to descend with her into the caves. This story gave rise to discussions about romantic attachment to patients and how to handle and extricate one from the situation. The senior doctors explained some of their relevant experiences and how they either transferred care or sought counseling to extricate themselves from a potentially dangerous situation, especially when they too fell under the spell of forbidden romance.
Moral Grounding
These sessions also served to define the moral basis of our own practice. Much of health care psychosocial distress is related to moral injury in which health care professionals do the wrong thing or fail to do the right thing at the right time, due to external pressures related to financial or other gains. Reading and reflecting put us face-to-face with moral dilemmas and let us find our moral grounding. In reading “The Haircut” by Ring Lardner, we explored the disruptive town scoundrel who harassed and tortured his friends and neighbors but in such outrageous ways that he was considered a comedian rather than an abuser.11 Despite his hurtful acts, the townspeople (including the narrator) considered him a clown and laughed at his racist and sexist statements as well as his tricks.He faced no consequences such as confrontation, until the end when fate caught up. This story gave rise to a discussion of how we handle unkind, racist, sexist, or other comments which are disguised as humor, and to what extent we tolerate such controversial behavior. Do we go along with the scoundrel and laugh, or do we confront such people and insist that they respect and honor other people? The story sensitized the group to the ways in which prejudice and racism or sexism can be masked as humor, and to consider our moral responsibilities in society.
In another session we read and reflected on “Three Questions” by Leo Tolstoy.12 In this story, a king travels to another territory but gets distracted by helping a neighbor in need, and thereby inadvertently and fortunately avoids the trap that had been devised to kill him. The author gives us his moral basis by asking and answering 3 questions: Who is the most important person? What is the most important thing to do? What is the most important thing to do now? His answers provided his moral grounding. We discussed our answers and the basis of our moral grounding, whether it be the injunction do no harm, the more complex religious backgrounds of our childhood, or otherwise.
Symbols and Metaphors
The practice of reading and reflecting also taught us symbols and metaphors. Symbols and metaphors are the essence of storytelling, and they provide keys to understanding people. We sought out and studied the metaphors and symbols in each of the stories we read. In “I Stood There Ironing”, a woman is ironing as she is being questioned by a social worker on the upbringing of her first daughter, and its impact on her psychosocial distress.13 The woman remembers the hardships in raising her daughter and her neglect and abuse of the child due to circumstances beyond her control. She keeps ironing back and forth as she recounts the ways in which she neglected her child. The ironing provides a metaphor for attempting to straighten out her life and for recognizing finally at the end of the story that the daughter should not be the dress, under which her iron is pressing. This gave rise to a discussion of metaphors in our lives and the meanings they carry.
Problem-solving Guide
A sixth way the reflections helped was by serving as a guide to solving our problems. Some of the stories we read resonated deeply with members of the group and provided guides to solving problems. In one meeting we discussed “Those Are as Brothers” by Nancy Hale, a story in which a Nazi concentration camp survivor finds refuge in a country home and develops a friendship with a survivor of an abusive marriage.14 Reading and reflecting on this story enabled us to see the impact of trauma on ourselves, our life choices, professions, ways of being, philosophies, and even on our next generation. The story was personal for several members of the group, some of whom were second-generation Holocaust survivors, and for one who admitted to severe trauma as a child. Discussing our backgrounds together, we empathized with each other and helped each other heal. The story also provided a guide to healing from trauma, as its title indicates: sharing stories together can be a way to heal. The solidarity of standing together, as brothers, heals. The concentration camp survivor was mistreated in his job, but the abuse trauma victim rushes to his defense and vows her friendship and support. This soothed his soul and healed his mind. The guidance is clear: we can do the same, find friends, treat them like brothers, support each other and heal.
Bonding Through Shared Experience
The final and possibly most important way in which the club helped was by serving as an adventure to bond group members together through shared experience. We believe that literature can capture imagination in extraordinary ways and provide an opportunity to undertake remarkable journeys. As such, together we traveled to the ends of the earth from the beginning to the end of time and beyond. We traveled through the hills of Africa, meandered in the streets of Russia and Poland, watched the racetracks in Italy, toured the Taj Mahal in India, and descended into the caves of Lascaux, all while working in Little Rock, Arkansas. We shared a wide array of experiences together, which allowed us to know ourselves and others better, to share stories, and to develop a common vision, common ground, and common culture.
Conclusions
Through reading and reflecting on stories, we bonded as a group, increased our empathy for each other and others, and found meaning in medicine. Other studies have shown that participation in small study groups promote physician well-being, improve job satisfaction, and decrease burnout.3 We synergized this effort by reading nonmedical stories on a consistent basis, hoping to gain resilience to psychosocial distress.3 We chose short stories rather than novels to minimize any stress from excess reading. Combining these interventions, small group studies and nonmedical reading, into a single intervention as is typical in the practice of narrative medicine may provide a way to improve team functioning.
This pilot study showed that it is possible to form short story clubs even in a busy oncology program and that such programs benefit participants in a variety of ways with no apparent adverse effects. Further research is needed to study the impact of reading and reflecting on medical work in small study groups in larger numbers of subjects and to evaluate their impact on burnout. Further study is also needed to develop narrative medicine curricula that best address the needs of particular subspecialties and to determine the optimal conditions for implementation.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Dr. Erick Messias for inspiring and encouraging this project at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences where he was Associate Dean for Faculty Affairs. He is presently Chair of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neuroscience at the St. Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri.
1. Messias E, Gathright MM, Freeman ES, et al. Differences in burnout prevalence between clinical professionals and biomedical scientists in an academic medical centre: a cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open. 2019;9(2):e023506. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023506
2. Marchalik D, Rodriguez A, Namath A, et al. The impact of non-medical reading on clinical burnout: a national survey of palliative care providers. Ann Palliat Med. 2019;8(4):428-435. doi:10.21037/apm.2019.05.02
3. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Rabatin JT, et al. Intervention to promote physician well-being, job satisfaction, and professionalism: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(4):527-533. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.14387
4. Charon R. Narrative medicine: a model for empathy, reflection, profession, and tust. JAMA. 2001;286(15):1897–1902. doi:10.1001/jama.286.15.1897
5. Broyard A. Doctor Talk to Me. August 26, 1990. Accessed September 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/1990/08/26/magazine/doctor-talk-to-me.html
6. Chekhov A. A Doctor’s Visit,. In: Reynolds R, Stone J, eds. On Doctoring. Simon and Shuster;1995:50-59.
7. Lahiri J. Interpreter of Maladies. In: Lahiri J. Interpreter of Maladies. Mariner Books;2019.
8. Fitzgerald FS. Babylon Revisited. In: Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:62-81.
9. Hemingway E. Hills like White Elephants. In: Reynolds R, Stone J, eds. On Doctoring. Simon and Shuster;1995:108-111.
10. Karmel M. Caves of Lascaux. In: Ofri D, Staff of the Bellavue Literary Review, eds. The Best of the Bellevue Literary Review. Bellevue Literary Press;2008:168-174.
11. Lardner R. The Haircut. In Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:48-61.
12. Tolstoy L. The Three Questions. Accessed September 2021. https://www.plough.com/en/topics/culture/short-stories/the-three-questions
13. Olsen T. I Stand Here Ironing. In Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:173-180.
14. Hale N. Those Are as Brothers. In: Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:132-141.
Burnout and other forms of psychosocial distress are common among health care professionals necessitating measures to promote well-being and reduce burnout.1 Studies have shown that nonmedical reading is associated with low burnout and that small group study sections can promote wellness.2,3 Narrative medicine, which proposes a model for humane and effective medical practice, advocates for the necessity of narrative competence.
Short Story Club
Narrative competence is the ability to acknowledge, interpret, and act on the stories of others. The narrative skill of close reading also encourages reflective practice, equipping practitioners to better weather the tides of illness.4 In our case, we formed a short story club intervention to closely read, or read and reflect, on literary fiction. We explored how reading and reflecting would result in profound changes in thinking and feeling and noted different ways by which they can cause such well-being. We describe here the 7 ways in which stories led us to increase bonding, improve empathy, and promote meaning in medicine.
Slowing Down
The short story club helped to bond us together and increase our sense of meaning in medicine by slowing us down. One member of the group likened the experience to increasing the pixels in a painting, thereby improving the resolution and seeing more clearly. Another member mentioned the experience as a form of meditation in slowing down the brain, breathing in the story, and breathing out impressions. One story by Anatole Broyard emphasized the importance of slowing down and “brooding” over a patient.5 The author describes his experience as a prostate cancer patient, in which his body was treated but his story was ignored. He begged his doctors to pay more attention to his story to listen and to brood over him. This story was enlightening to us; we saw how desperate our patients are to tell their stories, and for us to hear their stories.
Mirrors and Windows
Another way reading and reflecting on short stories helped was by reflecting our practices to ourselves, as though looking into a mirror to see ourselves and out of a window to see others. We found that stories mirrored our own world and allowed us to discuss issues close to us without the embarrassment or stigma of owning the story. In one session we read “The Doctor’s Visit” by Anton Chekhov.6 Some of the members resonated with the doctor of this story who awkwardly attended to his lady patient whose son was dying of a brain tumor. The doctor was nervous, insecure, and unable to express any empathy. He was also the father of the child who was dying and refused to admit any responsibility. One member of the group stated that he could relate to the doctor’s insecurities and mentioned that he too felt insecure and even sometimes felt like an imposter. This led to a discussion of insecurities, ways to bolster self-confidence, and ways to accept and respect limitations. This was a conversation that may not have taken place without the story as anchor to discuss insecurities that we individually may not have been willing to admit to the group.
In a different session, we discussed the story “Interpreter of Maladies” by Jhumpa Lahiri in which a settled Indian American family returns to India to tour and learn about their heritage from a guide (the interpreter of maladies) who interpreted the culture for them.7 The family professed to be interested in knowing about the culture but could not concentrate: the wife stayed busy flirting with the guide and revealing outrageous secrets to him, the children were engrossed in their squabbles, and the father was essentially absent taking photographs as souvenirs instead of seeing the sites firsthand. Some of the members of the group were Indian American and could relate to the alienation from their home and nostalgia for their country, while others could relate to the same alienation, albeit from other cultures and countries. This allowed us to talk about deeply personal topics, without having to own the topic or reveal personal issues. The discussion led to a deep understanding and empathy for us and our colleagues knowing the pain of alienation that some of them felt but could not discuss.
The stories also served as windows into the world of others which enabled us to see and become the other. For example, in one session we reflected on “Babylon Revisited” by F. Scott Fitzgerald.8 In this story, an American man returns to Paris after the Great Depression and recalls his life as a young artist in the American artist expatriate community of Paris in the 1920s and 1930s. During that time, he partied, drank in excess, lost his wife to pneumonia (for which he was at least partially responsible), lost custody of his daughter, and lost his fortune. As he returned to Paris to try to reclaim his daughter, we feel his pain as he tries but fails to overcome chronic alcoholism, sexual indiscretions, and losses. This gave rise to discussion of losses in general as we became one with the main character. This increased our empathy for others in a way that could not have been possible without this short story as anchor.
In another session we reflected on “Hills Like White Elephants” by Ernest Hemingway, in which a man is waiting for a train while proposing his girlfriend get an abortion.9 She agonizes over her choices and makes no decision in this story. Yet, we the reader could “become” the woman in the story faced with hard choices of having a baby but losing the man she loves, or having an abortion and maybe losing him anyway. In becoming this woman, we could experience the complex emotions and feel an experience of the other.
Exploring the Taboo
A third aspect of the club was enabling discussion of controversial topics. There were topics that arose in the group which never would have arisen in clinical practice discussions. These had to do with the taboo topics such as romantic attachments to patients. We read “The Caves of Lascaux” and reflected on the story of a young doctor who becomes enamored and obsessed with his beautiful but dying patient.10 He becomes so obsessed with her that he almost abandons his wife, family, and stable livelihood to descend with her into the caves. This story gave rise to discussions about romantic attachment to patients and how to handle and extricate one from the situation. The senior doctors explained some of their relevant experiences and how they either transferred care or sought counseling to extricate themselves from a potentially dangerous situation, especially when they too fell under the spell of forbidden romance.
Moral Grounding
These sessions also served to define the moral basis of our own practice. Much of health care psychosocial distress is related to moral injury in which health care professionals do the wrong thing or fail to do the right thing at the right time, due to external pressures related to financial or other gains. Reading and reflecting put us face-to-face with moral dilemmas and let us find our moral grounding. In reading “The Haircut” by Ring Lardner, we explored the disruptive town scoundrel who harassed and tortured his friends and neighbors but in such outrageous ways that he was considered a comedian rather than an abuser.11 Despite his hurtful acts, the townspeople (including the narrator) considered him a clown and laughed at his racist and sexist statements as well as his tricks.He faced no consequences such as confrontation, until the end when fate caught up. This story gave rise to a discussion of how we handle unkind, racist, sexist, or other comments which are disguised as humor, and to what extent we tolerate such controversial behavior. Do we go along with the scoundrel and laugh, or do we confront such people and insist that they respect and honor other people? The story sensitized the group to the ways in which prejudice and racism or sexism can be masked as humor, and to consider our moral responsibilities in society.
In another session we read and reflected on “Three Questions” by Leo Tolstoy.12 In this story, a king travels to another territory but gets distracted by helping a neighbor in need, and thereby inadvertently and fortunately avoids the trap that had been devised to kill him. The author gives us his moral basis by asking and answering 3 questions: Who is the most important person? What is the most important thing to do? What is the most important thing to do now? His answers provided his moral grounding. We discussed our answers and the basis of our moral grounding, whether it be the injunction do no harm, the more complex religious backgrounds of our childhood, or otherwise.
Symbols and Metaphors
The practice of reading and reflecting also taught us symbols and metaphors. Symbols and metaphors are the essence of storytelling, and they provide keys to understanding people. We sought out and studied the metaphors and symbols in each of the stories we read. In “I Stood There Ironing”, a woman is ironing as she is being questioned by a social worker on the upbringing of her first daughter, and its impact on her psychosocial distress.13 The woman remembers the hardships in raising her daughter and her neglect and abuse of the child due to circumstances beyond her control. She keeps ironing back and forth as she recounts the ways in which she neglected her child. The ironing provides a metaphor for attempting to straighten out her life and for recognizing finally at the end of the story that the daughter should not be the dress, under which her iron is pressing. This gave rise to a discussion of metaphors in our lives and the meanings they carry.
Problem-solving Guide
A sixth way the reflections helped was by serving as a guide to solving our problems. Some of the stories we read resonated deeply with members of the group and provided guides to solving problems. In one meeting we discussed “Those Are as Brothers” by Nancy Hale, a story in which a Nazi concentration camp survivor finds refuge in a country home and develops a friendship with a survivor of an abusive marriage.14 Reading and reflecting on this story enabled us to see the impact of trauma on ourselves, our life choices, professions, ways of being, philosophies, and even on our next generation. The story was personal for several members of the group, some of whom were second-generation Holocaust survivors, and for one who admitted to severe trauma as a child. Discussing our backgrounds together, we empathized with each other and helped each other heal. The story also provided a guide to healing from trauma, as its title indicates: sharing stories together can be a way to heal. The solidarity of standing together, as brothers, heals. The concentration camp survivor was mistreated in his job, but the abuse trauma victim rushes to his defense and vows her friendship and support. This soothed his soul and healed his mind. The guidance is clear: we can do the same, find friends, treat them like brothers, support each other and heal.
Bonding Through Shared Experience
The final and possibly most important way in which the club helped was by serving as an adventure to bond group members together through shared experience. We believe that literature can capture imagination in extraordinary ways and provide an opportunity to undertake remarkable journeys. As such, together we traveled to the ends of the earth from the beginning to the end of time and beyond. We traveled through the hills of Africa, meandered in the streets of Russia and Poland, watched the racetracks in Italy, toured the Taj Mahal in India, and descended into the caves of Lascaux, all while working in Little Rock, Arkansas. We shared a wide array of experiences together, which allowed us to know ourselves and others better, to share stories, and to develop a common vision, common ground, and common culture.
Conclusions
Through reading and reflecting on stories, we bonded as a group, increased our empathy for each other and others, and found meaning in medicine. Other studies have shown that participation in small study groups promote physician well-being, improve job satisfaction, and decrease burnout.3 We synergized this effort by reading nonmedical stories on a consistent basis, hoping to gain resilience to psychosocial distress.3 We chose short stories rather than novels to minimize any stress from excess reading. Combining these interventions, small group studies and nonmedical reading, into a single intervention as is typical in the practice of narrative medicine may provide a way to improve team functioning.
This pilot study showed that it is possible to form short story clubs even in a busy oncology program and that such programs benefit participants in a variety of ways with no apparent adverse effects. Further research is needed to study the impact of reading and reflecting on medical work in small study groups in larger numbers of subjects and to evaluate their impact on burnout. Further study is also needed to develop narrative medicine curricula that best address the needs of particular subspecialties and to determine the optimal conditions for implementation.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Dr. Erick Messias for inspiring and encouraging this project at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences where he was Associate Dean for Faculty Affairs. He is presently Chair of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neuroscience at the St. Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri.
Burnout and other forms of psychosocial distress are common among health care professionals necessitating measures to promote well-being and reduce burnout.1 Studies have shown that nonmedical reading is associated with low burnout and that small group study sections can promote wellness.2,3 Narrative medicine, which proposes a model for humane and effective medical practice, advocates for the necessity of narrative competence.
Short Story Club
Narrative competence is the ability to acknowledge, interpret, and act on the stories of others. The narrative skill of close reading also encourages reflective practice, equipping practitioners to better weather the tides of illness.4 In our case, we formed a short story club intervention to closely read, or read and reflect, on literary fiction. We explored how reading and reflecting would result in profound changes in thinking and feeling and noted different ways by which they can cause such well-being. We describe here the 7 ways in which stories led us to increase bonding, improve empathy, and promote meaning in medicine.
Slowing Down
The short story club helped to bond us together and increase our sense of meaning in medicine by slowing us down. One member of the group likened the experience to increasing the pixels in a painting, thereby improving the resolution and seeing more clearly. Another member mentioned the experience as a form of meditation in slowing down the brain, breathing in the story, and breathing out impressions. One story by Anatole Broyard emphasized the importance of slowing down and “brooding” over a patient.5 The author describes his experience as a prostate cancer patient, in which his body was treated but his story was ignored. He begged his doctors to pay more attention to his story to listen and to brood over him. This story was enlightening to us; we saw how desperate our patients are to tell their stories, and for us to hear their stories.
Mirrors and Windows
Another way reading and reflecting on short stories helped was by reflecting our practices to ourselves, as though looking into a mirror to see ourselves and out of a window to see others. We found that stories mirrored our own world and allowed us to discuss issues close to us without the embarrassment or stigma of owning the story. In one session we read “The Doctor’s Visit” by Anton Chekhov.6 Some of the members resonated with the doctor of this story who awkwardly attended to his lady patient whose son was dying of a brain tumor. The doctor was nervous, insecure, and unable to express any empathy. He was also the father of the child who was dying and refused to admit any responsibility. One member of the group stated that he could relate to the doctor’s insecurities and mentioned that he too felt insecure and even sometimes felt like an imposter. This led to a discussion of insecurities, ways to bolster self-confidence, and ways to accept and respect limitations. This was a conversation that may not have taken place without the story as anchor to discuss insecurities that we individually may not have been willing to admit to the group.
In a different session, we discussed the story “Interpreter of Maladies” by Jhumpa Lahiri in which a settled Indian American family returns to India to tour and learn about their heritage from a guide (the interpreter of maladies) who interpreted the culture for them.7 The family professed to be interested in knowing about the culture but could not concentrate: the wife stayed busy flirting with the guide and revealing outrageous secrets to him, the children were engrossed in their squabbles, and the father was essentially absent taking photographs as souvenirs instead of seeing the sites firsthand. Some of the members of the group were Indian American and could relate to the alienation from their home and nostalgia for their country, while others could relate to the same alienation, albeit from other cultures and countries. This allowed us to talk about deeply personal topics, without having to own the topic or reveal personal issues. The discussion led to a deep understanding and empathy for us and our colleagues knowing the pain of alienation that some of them felt but could not discuss.
The stories also served as windows into the world of others which enabled us to see and become the other. For example, in one session we reflected on “Babylon Revisited” by F. Scott Fitzgerald.8 In this story, an American man returns to Paris after the Great Depression and recalls his life as a young artist in the American artist expatriate community of Paris in the 1920s and 1930s. During that time, he partied, drank in excess, lost his wife to pneumonia (for which he was at least partially responsible), lost custody of his daughter, and lost his fortune. As he returned to Paris to try to reclaim his daughter, we feel his pain as he tries but fails to overcome chronic alcoholism, sexual indiscretions, and losses. This gave rise to discussion of losses in general as we became one with the main character. This increased our empathy for others in a way that could not have been possible without this short story as anchor.
In another session we reflected on “Hills Like White Elephants” by Ernest Hemingway, in which a man is waiting for a train while proposing his girlfriend get an abortion.9 She agonizes over her choices and makes no decision in this story. Yet, we the reader could “become” the woman in the story faced with hard choices of having a baby but losing the man she loves, or having an abortion and maybe losing him anyway. In becoming this woman, we could experience the complex emotions and feel an experience of the other.
Exploring the Taboo
A third aspect of the club was enabling discussion of controversial topics. There were topics that arose in the group which never would have arisen in clinical practice discussions. These had to do with the taboo topics such as romantic attachments to patients. We read “The Caves of Lascaux” and reflected on the story of a young doctor who becomes enamored and obsessed with his beautiful but dying patient.10 He becomes so obsessed with her that he almost abandons his wife, family, and stable livelihood to descend with her into the caves. This story gave rise to discussions about romantic attachment to patients and how to handle and extricate one from the situation. The senior doctors explained some of their relevant experiences and how they either transferred care or sought counseling to extricate themselves from a potentially dangerous situation, especially when they too fell under the spell of forbidden romance.
Moral Grounding
These sessions also served to define the moral basis of our own practice. Much of health care psychosocial distress is related to moral injury in which health care professionals do the wrong thing or fail to do the right thing at the right time, due to external pressures related to financial or other gains. Reading and reflecting put us face-to-face with moral dilemmas and let us find our moral grounding. In reading “The Haircut” by Ring Lardner, we explored the disruptive town scoundrel who harassed and tortured his friends and neighbors but in such outrageous ways that he was considered a comedian rather than an abuser.11 Despite his hurtful acts, the townspeople (including the narrator) considered him a clown and laughed at his racist and sexist statements as well as his tricks.He faced no consequences such as confrontation, until the end when fate caught up. This story gave rise to a discussion of how we handle unkind, racist, sexist, or other comments which are disguised as humor, and to what extent we tolerate such controversial behavior. Do we go along with the scoundrel and laugh, or do we confront such people and insist that they respect and honor other people? The story sensitized the group to the ways in which prejudice and racism or sexism can be masked as humor, and to consider our moral responsibilities in society.
In another session we read and reflected on “Three Questions” by Leo Tolstoy.12 In this story, a king travels to another territory but gets distracted by helping a neighbor in need, and thereby inadvertently and fortunately avoids the trap that had been devised to kill him. The author gives us his moral basis by asking and answering 3 questions: Who is the most important person? What is the most important thing to do? What is the most important thing to do now? His answers provided his moral grounding. We discussed our answers and the basis of our moral grounding, whether it be the injunction do no harm, the more complex religious backgrounds of our childhood, or otherwise.
Symbols and Metaphors
The practice of reading and reflecting also taught us symbols and metaphors. Symbols and metaphors are the essence of storytelling, and they provide keys to understanding people. We sought out and studied the metaphors and symbols in each of the stories we read. In “I Stood There Ironing”, a woman is ironing as she is being questioned by a social worker on the upbringing of her first daughter, and its impact on her psychosocial distress.13 The woman remembers the hardships in raising her daughter and her neglect and abuse of the child due to circumstances beyond her control. She keeps ironing back and forth as she recounts the ways in which she neglected her child. The ironing provides a metaphor for attempting to straighten out her life and for recognizing finally at the end of the story that the daughter should not be the dress, under which her iron is pressing. This gave rise to a discussion of metaphors in our lives and the meanings they carry.
Problem-solving Guide
A sixth way the reflections helped was by serving as a guide to solving our problems. Some of the stories we read resonated deeply with members of the group and provided guides to solving problems. In one meeting we discussed “Those Are as Brothers” by Nancy Hale, a story in which a Nazi concentration camp survivor finds refuge in a country home and develops a friendship with a survivor of an abusive marriage.14 Reading and reflecting on this story enabled us to see the impact of trauma on ourselves, our life choices, professions, ways of being, philosophies, and even on our next generation. The story was personal for several members of the group, some of whom were second-generation Holocaust survivors, and for one who admitted to severe trauma as a child. Discussing our backgrounds together, we empathized with each other and helped each other heal. The story also provided a guide to healing from trauma, as its title indicates: sharing stories together can be a way to heal. The solidarity of standing together, as brothers, heals. The concentration camp survivor was mistreated in his job, but the abuse trauma victim rushes to his defense and vows her friendship and support. This soothed his soul and healed his mind. The guidance is clear: we can do the same, find friends, treat them like brothers, support each other and heal.
Bonding Through Shared Experience
The final and possibly most important way in which the club helped was by serving as an adventure to bond group members together through shared experience. We believe that literature can capture imagination in extraordinary ways and provide an opportunity to undertake remarkable journeys. As such, together we traveled to the ends of the earth from the beginning to the end of time and beyond. We traveled through the hills of Africa, meandered in the streets of Russia and Poland, watched the racetracks in Italy, toured the Taj Mahal in India, and descended into the caves of Lascaux, all while working in Little Rock, Arkansas. We shared a wide array of experiences together, which allowed us to know ourselves and others better, to share stories, and to develop a common vision, common ground, and common culture.
Conclusions
Through reading and reflecting on stories, we bonded as a group, increased our empathy for each other and others, and found meaning in medicine. Other studies have shown that participation in small study groups promote physician well-being, improve job satisfaction, and decrease burnout.3 We synergized this effort by reading nonmedical stories on a consistent basis, hoping to gain resilience to psychosocial distress.3 We chose short stories rather than novels to minimize any stress from excess reading. Combining these interventions, small group studies and nonmedical reading, into a single intervention as is typical in the practice of narrative medicine may provide a way to improve team functioning.
This pilot study showed that it is possible to form short story clubs even in a busy oncology program and that such programs benefit participants in a variety of ways with no apparent adverse effects. Further research is needed to study the impact of reading and reflecting on medical work in small study groups in larger numbers of subjects and to evaluate their impact on burnout. Further study is also needed to develop narrative medicine curricula that best address the needs of particular subspecialties and to determine the optimal conditions for implementation.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Dr. Erick Messias for inspiring and encouraging this project at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences where he was Associate Dean for Faculty Affairs. He is presently Chair of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neuroscience at the St. Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri.
1. Messias E, Gathright MM, Freeman ES, et al. Differences in burnout prevalence between clinical professionals and biomedical scientists in an academic medical centre: a cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open. 2019;9(2):e023506. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023506
2. Marchalik D, Rodriguez A, Namath A, et al. The impact of non-medical reading on clinical burnout: a national survey of palliative care providers. Ann Palliat Med. 2019;8(4):428-435. doi:10.21037/apm.2019.05.02
3. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Rabatin JT, et al. Intervention to promote physician well-being, job satisfaction, and professionalism: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(4):527-533. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.14387
4. Charon R. Narrative medicine: a model for empathy, reflection, profession, and tust. JAMA. 2001;286(15):1897–1902. doi:10.1001/jama.286.15.1897
5. Broyard A. Doctor Talk to Me. August 26, 1990. Accessed September 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/1990/08/26/magazine/doctor-talk-to-me.html
6. Chekhov A. A Doctor’s Visit,. In: Reynolds R, Stone J, eds. On Doctoring. Simon and Shuster;1995:50-59.
7. Lahiri J. Interpreter of Maladies. In: Lahiri J. Interpreter of Maladies. Mariner Books;2019.
8. Fitzgerald FS. Babylon Revisited. In: Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:62-81.
9. Hemingway E. Hills like White Elephants. In: Reynolds R, Stone J, eds. On Doctoring. Simon and Shuster;1995:108-111.
10. Karmel M. Caves of Lascaux. In: Ofri D, Staff of the Bellavue Literary Review, eds. The Best of the Bellevue Literary Review. Bellevue Literary Press;2008:168-174.
11. Lardner R. The Haircut. In Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:48-61.
12. Tolstoy L. The Three Questions. Accessed September 2021. https://www.plough.com/en/topics/culture/short-stories/the-three-questions
13. Olsen T. I Stand Here Ironing. In Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:173-180.
14. Hale N. Those Are as Brothers. In: Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:132-141.
1. Messias E, Gathright MM, Freeman ES, et al. Differences in burnout prevalence between clinical professionals and biomedical scientists in an academic medical centre: a cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open. 2019;9(2):e023506. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023506
2. Marchalik D, Rodriguez A, Namath A, et al. The impact of non-medical reading on clinical burnout: a national survey of palliative care providers. Ann Palliat Med. 2019;8(4):428-435. doi:10.21037/apm.2019.05.02
3. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Rabatin JT, et al. Intervention to promote physician well-being, job satisfaction, and professionalism: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(4):527-533. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.14387
4. Charon R. Narrative medicine: a model for empathy, reflection, profession, and tust. JAMA. 2001;286(15):1897–1902. doi:10.1001/jama.286.15.1897
5. Broyard A. Doctor Talk to Me. August 26, 1990. Accessed September 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/1990/08/26/magazine/doctor-talk-to-me.html
6. Chekhov A. A Doctor’s Visit,. In: Reynolds R, Stone J, eds. On Doctoring. Simon and Shuster;1995:50-59.
7. Lahiri J. Interpreter of Maladies. In: Lahiri J. Interpreter of Maladies. Mariner Books;2019.
8. Fitzgerald FS. Babylon Revisited. In: Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:62-81.
9. Hemingway E. Hills like White Elephants. In: Reynolds R, Stone J, eds. On Doctoring. Simon and Shuster;1995:108-111.
10. Karmel M. Caves of Lascaux. In: Ofri D, Staff of the Bellavue Literary Review, eds. The Best of the Bellevue Literary Review. Bellevue Literary Press;2008:168-174.
11. Lardner R. The Haircut. In Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:48-61.
12. Tolstoy L. The Three Questions. Accessed September 2021. https://www.plough.com/en/topics/culture/short-stories/the-three-questions
13. Olsen T. I Stand Here Ironing. In Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:173-180.
14. Hale N. Those Are as Brothers. In: Moore L, Pitlor H, eds. 100 Years of the Best American Short Stories. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt;2015:132-141.
Should you be screening for eating disorders?
The US Preventive Services Task Force recently released its findings on screening for eating disorders—including binge eating, bulimia nervosa, and anorexia nervosa—in adolescents and adults.1 This is the first time the Task Force has addressed this topic.
For those who have no signs or symptoms of an eating disorder, the Task Force found insufficient evidence to assess the benefits and harms of screening. Signs and symptoms of an eating disorder include rapid changes in weight (gain or loss), delayed puberty, bradycardia, oligomenorrhea, or amenorrhea.1
Screening vs diagnostic work-up. The term screening means looking for the presence of a condition in an asymptomatic person. Those who have signs or symptoms that could be due to an eating disorder should be assessed for these conditions, but this would be classified as diagnostic testing rather than preventive screening.
Relatively uncommon but serious. The estimated lifetime prevalence of anorexia is 1.42% in women and 0.12% in men; for bulimia, 0.46% in women and 0.08% in men; and for binge eating, 1.25% in women and 0.42% in men.1 Those suspected of having an eating disorder need psychological, behavioral, medical, and nutritional care provided by those with expertise in diagnosing and treating these disorders. (A systematic review of treatment options was recently published in American Family Physician.2)
If you suspect an eating disorder … Several tools for the assessment of eating disorders have been described in the literature, including the Eating Disorder Screen for Primary Care (EDS-PC) tool, but the Task Force identified enough evidence to comment on the accuracy of only one: the SCOFF questionnaire. There is adequate evidence on its accuracy for use in adult women but not in adolescents or males.1
The SCOFF tool, which originated in the United Kingdom, consists of 5 questions3:
- Do you make yourself Sick because you feel uncomfortably full?
- Do you worry that you have lost Control over how much you eat?
- Have you recently lost more than One stone (14 lb) in a 3-month period?
- Do you believe yourself to be Fat when others say you are too thin?
- Would you say that Food dominates your life?
A threshold of 2 or more “Yes” answers on the SCOFF questionnaire has a pooled sensitivity of 84% for all 3 disorders combined and a pooled specificity of 80%.4
What should you do routinely? For adolescents and adults who have no indication of an eating disorder, there is no proven value to screening. Measuring height and weight, calculating body mass index, and continuing to track these measurements for all patients over time is considered standard practice. For those patients who have signs or symptoms that could be due to an eating disorder, administer the SCOFF tool; further assess those with 2 or more positive responses, and refer for diagnosis and treatment those suspected of having an eating disorder.
1. USPSTF. Screening for eating disorders in adolescents and adults. JAMA. 2022;327:1061-1066. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.1806
2. Klein DA, Sylvester JE, Schvey NA. Eating disorders in primary care: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2021;103:22-32.
3. Morgan JF, Reid F, Lacy JH. The SCOFF questionnaire: a new screening tool for eating disorders. West J Med. 2000;172:164-165. doi: 10.1136/ewjm.172.3.164
4. Feltner C, Peat C, Reddy S, et al. Evidence Synthesis No 212: Screening for eating disorders in adolescents and adults: an evidence review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Published March 2022. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/document/final-evidence-review/screening-eating-disorders-adolescents-adults
The US Preventive Services Task Force recently released its findings on screening for eating disorders—including binge eating, bulimia nervosa, and anorexia nervosa—in adolescents and adults.1 This is the first time the Task Force has addressed this topic.
For those who have no signs or symptoms of an eating disorder, the Task Force found insufficient evidence to assess the benefits and harms of screening. Signs and symptoms of an eating disorder include rapid changes in weight (gain or loss), delayed puberty, bradycardia, oligomenorrhea, or amenorrhea.1
Screening vs diagnostic work-up. The term screening means looking for the presence of a condition in an asymptomatic person. Those who have signs or symptoms that could be due to an eating disorder should be assessed for these conditions, but this would be classified as diagnostic testing rather than preventive screening.
Relatively uncommon but serious. The estimated lifetime prevalence of anorexia is 1.42% in women and 0.12% in men; for bulimia, 0.46% in women and 0.08% in men; and for binge eating, 1.25% in women and 0.42% in men.1 Those suspected of having an eating disorder need psychological, behavioral, medical, and nutritional care provided by those with expertise in diagnosing and treating these disorders. (A systematic review of treatment options was recently published in American Family Physician.2)
If you suspect an eating disorder … Several tools for the assessment of eating disorders have been described in the literature, including the Eating Disorder Screen for Primary Care (EDS-PC) tool, but the Task Force identified enough evidence to comment on the accuracy of only one: the SCOFF questionnaire. There is adequate evidence on its accuracy for use in adult women but not in adolescents or males.1
The SCOFF tool, which originated in the United Kingdom, consists of 5 questions3:
- Do you make yourself Sick because you feel uncomfortably full?
- Do you worry that you have lost Control over how much you eat?
- Have you recently lost more than One stone (14 lb) in a 3-month period?
- Do you believe yourself to be Fat when others say you are too thin?
- Would you say that Food dominates your life?
A threshold of 2 or more “Yes” answers on the SCOFF questionnaire has a pooled sensitivity of 84% for all 3 disorders combined and a pooled specificity of 80%.4
What should you do routinely? For adolescents and adults who have no indication of an eating disorder, there is no proven value to screening. Measuring height and weight, calculating body mass index, and continuing to track these measurements for all patients over time is considered standard practice. For those patients who have signs or symptoms that could be due to an eating disorder, administer the SCOFF tool; further assess those with 2 or more positive responses, and refer for diagnosis and treatment those suspected of having an eating disorder.
The US Preventive Services Task Force recently released its findings on screening for eating disorders—including binge eating, bulimia nervosa, and anorexia nervosa—in adolescents and adults.1 This is the first time the Task Force has addressed this topic.
For those who have no signs or symptoms of an eating disorder, the Task Force found insufficient evidence to assess the benefits and harms of screening. Signs and symptoms of an eating disorder include rapid changes in weight (gain or loss), delayed puberty, bradycardia, oligomenorrhea, or amenorrhea.1
Screening vs diagnostic work-up. The term screening means looking for the presence of a condition in an asymptomatic person. Those who have signs or symptoms that could be due to an eating disorder should be assessed for these conditions, but this would be classified as diagnostic testing rather than preventive screening.
Relatively uncommon but serious. The estimated lifetime prevalence of anorexia is 1.42% in women and 0.12% in men; for bulimia, 0.46% in women and 0.08% in men; and for binge eating, 1.25% in women and 0.42% in men.1 Those suspected of having an eating disorder need psychological, behavioral, medical, and nutritional care provided by those with expertise in diagnosing and treating these disorders. (A systematic review of treatment options was recently published in American Family Physician.2)
If you suspect an eating disorder … Several tools for the assessment of eating disorders have been described in the literature, including the Eating Disorder Screen for Primary Care (EDS-PC) tool, but the Task Force identified enough evidence to comment on the accuracy of only one: the SCOFF questionnaire. There is adequate evidence on its accuracy for use in adult women but not in adolescents or males.1
The SCOFF tool, which originated in the United Kingdom, consists of 5 questions3:
- Do you make yourself Sick because you feel uncomfortably full?
- Do you worry that you have lost Control over how much you eat?
- Have you recently lost more than One stone (14 lb) in a 3-month period?
- Do you believe yourself to be Fat when others say you are too thin?
- Would you say that Food dominates your life?
A threshold of 2 or more “Yes” answers on the SCOFF questionnaire has a pooled sensitivity of 84% for all 3 disorders combined and a pooled specificity of 80%.4
What should you do routinely? For adolescents and adults who have no indication of an eating disorder, there is no proven value to screening. Measuring height and weight, calculating body mass index, and continuing to track these measurements for all patients over time is considered standard practice. For those patients who have signs or symptoms that could be due to an eating disorder, administer the SCOFF tool; further assess those with 2 or more positive responses, and refer for diagnosis and treatment those suspected of having an eating disorder.
1. USPSTF. Screening for eating disorders in adolescents and adults. JAMA. 2022;327:1061-1066. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.1806
2. Klein DA, Sylvester JE, Schvey NA. Eating disorders in primary care: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2021;103:22-32.
3. Morgan JF, Reid F, Lacy JH. The SCOFF questionnaire: a new screening tool for eating disorders. West J Med. 2000;172:164-165. doi: 10.1136/ewjm.172.3.164
4. Feltner C, Peat C, Reddy S, et al. Evidence Synthesis No 212: Screening for eating disorders in adolescents and adults: an evidence review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Published March 2022. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/document/final-evidence-review/screening-eating-disorders-adolescents-adults
1. USPSTF. Screening for eating disorders in adolescents and adults. JAMA. 2022;327:1061-1066. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.1806
2. Klein DA, Sylvester JE, Schvey NA. Eating disorders in primary care: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2021;103:22-32.
3. Morgan JF, Reid F, Lacy JH. The SCOFF questionnaire: a new screening tool for eating disorders. West J Med. 2000;172:164-165. doi: 10.1136/ewjm.172.3.164
4. Feltner C, Peat C, Reddy S, et al. Evidence Synthesis No 212: Screening for eating disorders in adolescents and adults: an evidence review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Published March 2022. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/document/final-evidence-review/screening-eating-disorders-adolescents-adults
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Recent Lung Cancer Trial Results, May 2022
In a European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Plenary session, Dr Paz-Ares and colleagues presented interim analysis of the PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091 study of adjuvant pembrolizumab. In this triple-blind phase 3 trial, 1177 patients with stage IB (tumor ≥ 4 cm) to IIIA non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (per American Joint Committee on Cancer [AJCC], version 7) were randomly assigned to receive pembrolizumab vs placebo. The dual primary endpoints were disease-free survival (DFS) in the overall population and in the population with high programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) (tumor proportion score [TPS] ≥ 50%). The study met its primary endpoint where improved DFS was observed in the overall population that included lung cancers, whether they were PD-L1–negative (TPS = 0%) or –positive (TPS ≥ 1%) (53.6 months in the pembrolizumab group vs 42.0 months in the placebo group [hazard ratio (HR) 0.76; P = .0014]). Overall survival data are not yet clear. Of note, in the interim analysis presented, the subset of patients with high PD-L1 NSCLC (TPS ≥ 50%) did not show a DFS benefit whereas in other adjuvant and neoadjuvant studies, such as IMpower010 and CheckMate 816, the subset of high PD-L1 patients appeared to derive the most benefit. The results from the high PD-L1 subset and other subsets may change with future updated analyses as more events occur. The major co-primary endpoint was clearly met with the overall population clearly showing a positive DFS benefit. The results of the PEARLS trial adds to the current landscape of systemic treatment of early-stage NSCLC where neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus nivolumab is US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved for stage IB (≥ 4 cm) to IIIA resected NSCLC regardless of level of PD-L1 expression, as is adjuvant atezolizumab after consideration of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients that are PD-L1–positive (≥ 1%) on the basis of a DFS benefit observed in this population.1,2 For the future, it is important to see if the DFS benefit observed in these studies translates into a meaningful overall survival benefit.
Plasma cfDNA Levels as a Prognostic Marker in ALK+ NSCLC in the ALEX Trial
The ALEX trial is a pivotal global phase 3 randomized control trial that demonstrated superior progression-free survival (PFS) with the next-generation ALK inhibitor alectinib compared with the first-generation ALK inhibitor crizotinib as first-line treatment of ALK-positive NSCLC (HR 0.43; 95% CI 0.32-0.58; median PFS 34.8 vs 10.9 months crizotinib).3 In a study recently published in Clinical Cancer Research, Dr Dziadziuszko and colleagues retrospectively assessed the prognostic value of baseline cell-free DNA (cfDNA) levels in patients treated in the ALEX trial. Baseline plasma for cfDNA was quantified by the Foundation ACT next-generation sequencing assay. Clinical outcomes were assessed by quantitative cfDNA level stratified by the median value. In both the alectinib and crizotinib treatment arms, patients with cfDNA levels above the median were more likely to experience disease progression (alectinib adjusted HR 2.04; 95% CI 1.07-3.89; P = .03 and crizotinib adjusted HR 1.83; 95% CI 1.11-3.00, P = .016). Though survival data are incomplete, the study also suggested survival probability was lower when baseline cfDNA was above the median in both the alectinib and crizotinib treatment arms. Regardless of cfDNA levels, PFS was improved with alectinib compared with crizotinib. Previous studies have shown the value of cfDNA analysis at the time of progression to guide further treatment and target resistance mechanisms to ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI), such as G1202R, or bypass tract pathways, such as MET amplification.4,5 Assessment of the EML4-ALK variant type (V1 vs V3) has been shown to associate with certain types of resistance mechanisms (ie, on target ALK mutations, such as G1202R in V3) and clinical activity of specific ALK TKI (V3 > V1 for PFS with lorlatinib).6 This study examining baseline cfDNA levels and clinical outcomes on the ALEX trial shows the potential utility of baseline cfDNA levels as a prognostic factor for ALK TKI.
Lorlatinib in ROS1-Rearranged NSCLC After Progression on Prior ROS1 TKI
ROS1 rearrangements represent about 1.5% of lung adenocarcinoma. In advanced disease, both crizotinib and entrectinib are FDA-approved as agents targeting ROS1 with robust PFS. The third-generation TKI lorlatinib is approved and has substantial activity in ALK-rearranged NSCLC. In a recently published retrospective real-world cohort study by Girard and colleagues (LORLATU), 80 patients with ROS1-rearranged NSCLC were treated with lorlatinib as second-line treatment or beyond and after failure on at least one prior ROS1 TKI. Median PFS was 7.1 months (95% CI 5.0-9.9) and median overall survival was 19.6 months (95% CI 12.3-27.5). The overall response rate was 45% and the disease control rate was 82%. The central nervous system response rate was 72%. There were no new safety signals. This retrospective cohort study demonstrates that lorlatinib is a major targeted therapy treatment option in ROS1-rearranged NSCLC.
Checkmate 816: Neoadjuvant Nivolumab Plus Chemotherapy in Resectable NSCLC
In this open-label, phase 3 trial, 358 patients with stage IB (T ³ 4cm) to IIIA (per AJCC v7) resectable NSCLC were randomized 1:1 to receive nivolumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy or platinum-based chemotherapy alone for three cycles, followed by surgical resection. The primary endpoints were event-free survival (EFS) and pathological complete response (pCR) (0% viable tumor in resected lung and lymph nodes), both evaluated by blinded independent review. The median EFS was significantly increased in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm compared to chemotherapy alone: 31.6 months (95% CI 30.2 to not reached) vs 20.8 months (95% CI 14.0 to 26.7) (HR 0.63; 97.38% CI 0.43 to 0.91; P = .005). pCR rate was also increased in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm (24.0% vs 2.2%, respectively; odds ratio 13.94; 99% CI 3.49 to 55.75; P < .001). At the first prespecified interim analysis, the hazard ratio for death was 0.57 (99.67% CI 0.30 to 1.07), which currently does not meet the criterion for statistical significance. Of the randomized patients, 83.2% of those in the nivolumab-plus chemotherapy group and 75.4% of those in the chemotherapy-alone group were able to undergo surgery. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 33.5% of the patients in the nivolumab-plus-chemotherapy group and in 36.9% of those in the chemotherapy-alone group. In an exploratory analysis, EFS was longer in patients with pCR than patients without a pCR. In a subset analysis, patients with high PD-L1 expression (³50%) stood out in terms of particular benefit (HR 0.24, 95% CI 0.10–0.61). The Checkmate 816 trial is a landmark study. Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy represents a new standard of care in the systemic treatment of resectable NSCLC that is at a stage that warrants systemic treatment. It is FDA approved regardless of PD-L1 expression level including PD-L1 negative (0%) patients.2 Adjuvant atezolizumab after adjuvant chemotherapy is also an FDA-approved treatment option for patients that are PD-L1 positive (³1%) based upon the IMpower 010 study.1 It will be important to assess the overall survival benefit as the trial data matures, which seems to be trending in the right direction. Additional neoadjuvant clinical trials with chemoimmunotherapy have completed accrual and some of these trials also continued PD-(L)1 immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in the adjuvant setting after surgery. An important question for the future is if combination of PD-(L)1 immune checkpoint blockade with chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant setting along with continuation of immunotherapy in the adjuvant setting post-surgery will further improve clinical outcomes.
References
- Felip E, Altorki N, Zhou C, et al. Adjuvant atezolizumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower010): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398(10308):1344-57. Doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02098-5 Source
- Forde PM, Spicer J, Lu S, et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. April 11, 2022. Doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2202170 Source
- Mok T, Camige DR, Gadgeel SM, et al. Updated overall survival and final progression-free survival data for patients with treatment-naive advanced ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the ALEX study. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1056-1064. Doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.478 Source
- Shaw AT, Solomon BJ, Chiari R, et al. Lorlatinib in advanced ROS1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:1691-1701. Doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30655-2 Source
- Lawrence MN, Tamen RM, Martinez P, et al. SPACEWALK: A remote participation study of ALK resistance leveraging plasma cell-free DNA genotyping. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2021;2:100151. Doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2021.100151 Source
- Lin JJ, Zhu VW, Yoda S, et al. Impact of EML4-ALK variant on resistance mechanisms and clinical outcomes in ALK-positive lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:1199-1206. Doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.2294 Source
In a European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Plenary session, Dr Paz-Ares and colleagues presented interim analysis of the PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091 study of adjuvant pembrolizumab. In this triple-blind phase 3 trial, 1177 patients with stage IB (tumor ≥ 4 cm) to IIIA non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (per American Joint Committee on Cancer [AJCC], version 7) were randomly assigned to receive pembrolizumab vs placebo. The dual primary endpoints were disease-free survival (DFS) in the overall population and in the population with high programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) (tumor proportion score [TPS] ≥ 50%). The study met its primary endpoint where improved DFS was observed in the overall population that included lung cancers, whether they were PD-L1–negative (TPS = 0%) or –positive (TPS ≥ 1%) (53.6 months in the pembrolizumab group vs 42.0 months in the placebo group [hazard ratio (HR) 0.76; P = .0014]). Overall survival data are not yet clear. Of note, in the interim analysis presented, the subset of patients with high PD-L1 NSCLC (TPS ≥ 50%) did not show a DFS benefit whereas in other adjuvant and neoadjuvant studies, such as IMpower010 and CheckMate 816, the subset of high PD-L1 patients appeared to derive the most benefit. The results from the high PD-L1 subset and other subsets may change with future updated analyses as more events occur. The major co-primary endpoint was clearly met with the overall population clearly showing a positive DFS benefit. The results of the PEARLS trial adds to the current landscape of systemic treatment of early-stage NSCLC where neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus nivolumab is US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved for stage IB (≥ 4 cm) to IIIA resected NSCLC regardless of level of PD-L1 expression, as is adjuvant atezolizumab after consideration of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients that are PD-L1–positive (≥ 1%) on the basis of a DFS benefit observed in this population.1,2 For the future, it is important to see if the DFS benefit observed in these studies translates into a meaningful overall survival benefit.
Plasma cfDNA Levels as a Prognostic Marker in ALK+ NSCLC in the ALEX Trial
The ALEX trial is a pivotal global phase 3 randomized control trial that demonstrated superior progression-free survival (PFS) with the next-generation ALK inhibitor alectinib compared with the first-generation ALK inhibitor crizotinib as first-line treatment of ALK-positive NSCLC (HR 0.43; 95% CI 0.32-0.58; median PFS 34.8 vs 10.9 months crizotinib).3 In a study recently published in Clinical Cancer Research, Dr Dziadziuszko and colleagues retrospectively assessed the prognostic value of baseline cell-free DNA (cfDNA) levels in patients treated in the ALEX trial. Baseline plasma for cfDNA was quantified by the Foundation ACT next-generation sequencing assay. Clinical outcomes were assessed by quantitative cfDNA level stratified by the median value. In both the alectinib and crizotinib treatment arms, patients with cfDNA levels above the median were more likely to experience disease progression (alectinib adjusted HR 2.04; 95% CI 1.07-3.89; P = .03 and crizotinib adjusted HR 1.83; 95% CI 1.11-3.00, P = .016). Though survival data are incomplete, the study also suggested survival probability was lower when baseline cfDNA was above the median in both the alectinib and crizotinib treatment arms. Regardless of cfDNA levels, PFS was improved with alectinib compared with crizotinib. Previous studies have shown the value of cfDNA analysis at the time of progression to guide further treatment and target resistance mechanisms to ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI), such as G1202R, or bypass tract pathways, such as MET amplification.4,5 Assessment of the EML4-ALK variant type (V1 vs V3) has been shown to associate with certain types of resistance mechanisms (ie, on target ALK mutations, such as G1202R in V3) and clinical activity of specific ALK TKI (V3 > V1 for PFS with lorlatinib).6 This study examining baseline cfDNA levels and clinical outcomes on the ALEX trial shows the potential utility of baseline cfDNA levels as a prognostic factor for ALK TKI.
Lorlatinib in ROS1-Rearranged NSCLC After Progression on Prior ROS1 TKI
ROS1 rearrangements represent about 1.5% of lung adenocarcinoma. In advanced disease, both crizotinib and entrectinib are FDA-approved as agents targeting ROS1 with robust PFS. The third-generation TKI lorlatinib is approved and has substantial activity in ALK-rearranged NSCLC. In a recently published retrospective real-world cohort study by Girard and colleagues (LORLATU), 80 patients with ROS1-rearranged NSCLC were treated with lorlatinib as second-line treatment or beyond and after failure on at least one prior ROS1 TKI. Median PFS was 7.1 months (95% CI 5.0-9.9) and median overall survival was 19.6 months (95% CI 12.3-27.5). The overall response rate was 45% and the disease control rate was 82%. The central nervous system response rate was 72%. There were no new safety signals. This retrospective cohort study demonstrates that lorlatinib is a major targeted therapy treatment option in ROS1-rearranged NSCLC.
Checkmate 816: Neoadjuvant Nivolumab Plus Chemotherapy in Resectable NSCLC
In this open-label, phase 3 trial, 358 patients with stage IB (T ³ 4cm) to IIIA (per AJCC v7) resectable NSCLC were randomized 1:1 to receive nivolumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy or platinum-based chemotherapy alone for three cycles, followed by surgical resection. The primary endpoints were event-free survival (EFS) and pathological complete response (pCR) (0% viable tumor in resected lung and lymph nodes), both evaluated by blinded independent review. The median EFS was significantly increased in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm compared to chemotherapy alone: 31.6 months (95% CI 30.2 to not reached) vs 20.8 months (95% CI 14.0 to 26.7) (HR 0.63; 97.38% CI 0.43 to 0.91; P = .005). pCR rate was also increased in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm (24.0% vs 2.2%, respectively; odds ratio 13.94; 99% CI 3.49 to 55.75; P < .001). At the first prespecified interim analysis, the hazard ratio for death was 0.57 (99.67% CI 0.30 to 1.07), which currently does not meet the criterion for statistical significance. Of the randomized patients, 83.2% of those in the nivolumab-plus chemotherapy group and 75.4% of those in the chemotherapy-alone group were able to undergo surgery. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 33.5% of the patients in the nivolumab-plus-chemotherapy group and in 36.9% of those in the chemotherapy-alone group. In an exploratory analysis, EFS was longer in patients with pCR than patients without a pCR. In a subset analysis, patients with high PD-L1 expression (³50%) stood out in terms of particular benefit (HR 0.24, 95% CI 0.10–0.61). The Checkmate 816 trial is a landmark study. Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy represents a new standard of care in the systemic treatment of resectable NSCLC that is at a stage that warrants systemic treatment. It is FDA approved regardless of PD-L1 expression level including PD-L1 negative (0%) patients.2 Adjuvant atezolizumab after adjuvant chemotherapy is also an FDA-approved treatment option for patients that are PD-L1 positive (³1%) based upon the IMpower 010 study.1 It will be important to assess the overall survival benefit as the trial data matures, which seems to be trending in the right direction. Additional neoadjuvant clinical trials with chemoimmunotherapy have completed accrual and some of these trials also continued PD-(L)1 immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in the adjuvant setting after surgery. An important question for the future is if combination of PD-(L)1 immune checkpoint blockade with chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant setting along with continuation of immunotherapy in the adjuvant setting post-surgery will further improve clinical outcomes.
References
- Felip E, Altorki N, Zhou C, et al. Adjuvant atezolizumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower010): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398(10308):1344-57. Doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02098-5 Source
- Forde PM, Spicer J, Lu S, et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. April 11, 2022. Doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2202170 Source
- Mok T, Camige DR, Gadgeel SM, et al. Updated overall survival and final progression-free survival data for patients with treatment-naive advanced ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the ALEX study. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1056-1064. Doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.478 Source
- Shaw AT, Solomon BJ, Chiari R, et al. Lorlatinib in advanced ROS1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:1691-1701. Doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30655-2 Source
- Lawrence MN, Tamen RM, Martinez P, et al. SPACEWALK: A remote participation study of ALK resistance leveraging plasma cell-free DNA genotyping. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2021;2:100151. Doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2021.100151 Source
- Lin JJ, Zhu VW, Yoda S, et al. Impact of EML4-ALK variant on resistance mechanisms and clinical outcomes in ALK-positive lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:1199-1206. Doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.2294 Source
In a European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Plenary session, Dr Paz-Ares and colleagues presented interim analysis of the PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091 study of adjuvant pembrolizumab. In this triple-blind phase 3 trial, 1177 patients with stage IB (tumor ≥ 4 cm) to IIIA non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (per American Joint Committee on Cancer [AJCC], version 7) were randomly assigned to receive pembrolizumab vs placebo. The dual primary endpoints were disease-free survival (DFS) in the overall population and in the population with high programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) (tumor proportion score [TPS] ≥ 50%). The study met its primary endpoint where improved DFS was observed in the overall population that included lung cancers, whether they were PD-L1–negative (TPS = 0%) or –positive (TPS ≥ 1%) (53.6 months in the pembrolizumab group vs 42.0 months in the placebo group [hazard ratio (HR) 0.76; P = .0014]). Overall survival data are not yet clear. Of note, in the interim analysis presented, the subset of patients with high PD-L1 NSCLC (TPS ≥ 50%) did not show a DFS benefit whereas in other adjuvant and neoadjuvant studies, such as IMpower010 and CheckMate 816, the subset of high PD-L1 patients appeared to derive the most benefit. The results from the high PD-L1 subset and other subsets may change with future updated analyses as more events occur. The major co-primary endpoint was clearly met with the overall population clearly showing a positive DFS benefit. The results of the PEARLS trial adds to the current landscape of systemic treatment of early-stage NSCLC where neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus nivolumab is US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved for stage IB (≥ 4 cm) to IIIA resected NSCLC regardless of level of PD-L1 expression, as is adjuvant atezolizumab after consideration of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients that are PD-L1–positive (≥ 1%) on the basis of a DFS benefit observed in this population.1,2 For the future, it is important to see if the DFS benefit observed in these studies translates into a meaningful overall survival benefit.
Plasma cfDNA Levels as a Prognostic Marker in ALK+ NSCLC in the ALEX Trial
The ALEX trial is a pivotal global phase 3 randomized control trial that demonstrated superior progression-free survival (PFS) with the next-generation ALK inhibitor alectinib compared with the first-generation ALK inhibitor crizotinib as first-line treatment of ALK-positive NSCLC (HR 0.43; 95% CI 0.32-0.58; median PFS 34.8 vs 10.9 months crizotinib).3 In a study recently published in Clinical Cancer Research, Dr Dziadziuszko and colleagues retrospectively assessed the prognostic value of baseline cell-free DNA (cfDNA) levels in patients treated in the ALEX trial. Baseline plasma for cfDNA was quantified by the Foundation ACT next-generation sequencing assay. Clinical outcomes were assessed by quantitative cfDNA level stratified by the median value. In both the alectinib and crizotinib treatment arms, patients with cfDNA levels above the median were more likely to experience disease progression (alectinib adjusted HR 2.04; 95% CI 1.07-3.89; P = .03 and crizotinib adjusted HR 1.83; 95% CI 1.11-3.00, P = .016). Though survival data are incomplete, the study also suggested survival probability was lower when baseline cfDNA was above the median in both the alectinib and crizotinib treatment arms. Regardless of cfDNA levels, PFS was improved with alectinib compared with crizotinib. Previous studies have shown the value of cfDNA analysis at the time of progression to guide further treatment and target resistance mechanisms to ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI), such as G1202R, or bypass tract pathways, such as MET amplification.4,5 Assessment of the EML4-ALK variant type (V1 vs V3) has been shown to associate with certain types of resistance mechanisms (ie, on target ALK mutations, such as G1202R in V3) and clinical activity of specific ALK TKI (V3 > V1 for PFS with lorlatinib).6 This study examining baseline cfDNA levels and clinical outcomes on the ALEX trial shows the potential utility of baseline cfDNA levels as a prognostic factor for ALK TKI.
Lorlatinib in ROS1-Rearranged NSCLC After Progression on Prior ROS1 TKI
ROS1 rearrangements represent about 1.5% of lung adenocarcinoma. In advanced disease, both crizotinib and entrectinib are FDA-approved as agents targeting ROS1 with robust PFS. The third-generation TKI lorlatinib is approved and has substantial activity in ALK-rearranged NSCLC. In a recently published retrospective real-world cohort study by Girard and colleagues (LORLATU), 80 patients with ROS1-rearranged NSCLC were treated with lorlatinib as second-line treatment or beyond and after failure on at least one prior ROS1 TKI. Median PFS was 7.1 months (95% CI 5.0-9.9) and median overall survival was 19.6 months (95% CI 12.3-27.5). The overall response rate was 45% and the disease control rate was 82%. The central nervous system response rate was 72%. There were no new safety signals. This retrospective cohort study demonstrates that lorlatinib is a major targeted therapy treatment option in ROS1-rearranged NSCLC.
Checkmate 816: Neoadjuvant Nivolumab Plus Chemotherapy in Resectable NSCLC
In this open-label, phase 3 trial, 358 patients with stage IB (T ³ 4cm) to IIIA (per AJCC v7) resectable NSCLC were randomized 1:1 to receive nivolumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy or platinum-based chemotherapy alone for three cycles, followed by surgical resection. The primary endpoints were event-free survival (EFS) and pathological complete response (pCR) (0% viable tumor in resected lung and lymph nodes), both evaluated by blinded independent review. The median EFS was significantly increased in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm compared to chemotherapy alone: 31.6 months (95% CI 30.2 to not reached) vs 20.8 months (95% CI 14.0 to 26.7) (HR 0.63; 97.38% CI 0.43 to 0.91; P = .005). pCR rate was also increased in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm (24.0% vs 2.2%, respectively; odds ratio 13.94; 99% CI 3.49 to 55.75; P < .001). At the first prespecified interim analysis, the hazard ratio for death was 0.57 (99.67% CI 0.30 to 1.07), which currently does not meet the criterion for statistical significance. Of the randomized patients, 83.2% of those in the nivolumab-plus chemotherapy group and 75.4% of those in the chemotherapy-alone group were able to undergo surgery. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 33.5% of the patients in the nivolumab-plus-chemotherapy group and in 36.9% of those in the chemotherapy-alone group. In an exploratory analysis, EFS was longer in patients with pCR than patients without a pCR. In a subset analysis, patients with high PD-L1 expression (³50%) stood out in terms of particular benefit (HR 0.24, 95% CI 0.10–0.61). The Checkmate 816 trial is a landmark study. Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy represents a new standard of care in the systemic treatment of resectable NSCLC that is at a stage that warrants systemic treatment. It is FDA approved regardless of PD-L1 expression level including PD-L1 negative (0%) patients.2 Adjuvant atezolizumab after adjuvant chemotherapy is also an FDA-approved treatment option for patients that are PD-L1 positive (³1%) based upon the IMpower 010 study.1 It will be important to assess the overall survival benefit as the trial data matures, which seems to be trending in the right direction. Additional neoadjuvant clinical trials with chemoimmunotherapy have completed accrual and some of these trials also continued PD-(L)1 immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in the adjuvant setting after surgery. An important question for the future is if combination of PD-(L)1 immune checkpoint blockade with chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant setting along with continuation of immunotherapy in the adjuvant setting post-surgery will further improve clinical outcomes.
References
- Felip E, Altorki N, Zhou C, et al. Adjuvant atezolizumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower010): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398(10308):1344-57. Doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02098-5 Source
- Forde PM, Spicer J, Lu S, et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. April 11, 2022. Doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2202170 Source
- Mok T, Camige DR, Gadgeel SM, et al. Updated overall survival and final progression-free survival data for patients with treatment-naive advanced ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the ALEX study. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1056-1064. Doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.478 Source
- Shaw AT, Solomon BJ, Chiari R, et al. Lorlatinib in advanced ROS1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:1691-1701. Doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30655-2 Source
- Lawrence MN, Tamen RM, Martinez P, et al. SPACEWALK: A remote participation study of ALK resistance leveraging plasma cell-free DNA genotyping. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2021;2:100151. Doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2021.100151 Source
- Lin JJ, Zhu VW, Yoda S, et al. Impact of EML4-ALK variant on resistance mechanisms and clinical outcomes in ALK-positive lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:1199-1206. Doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.2294 Source
OIG Finds More Problems in the VA’s Problem-Prone EHR Rollout
Scheduling delays. Disappearing lab orders. Bad links for telehealth appointments. Erroneous medication dispensing. Time-consuming workarounds.
The rollout of the $16 billion electronic health record (EHR) system at the US Department of Veterans Affair (VA) has met some fairly large bumps in the past few years. And now, the VA Office of the Inspector General (OIG) has pronounced on a “range of allegations” at the Mann-Grandstaff VA Medical Center in Spokane, Washington, the first of several hospitals and clinics in the Pacific Northwest set to implement the new system.
VA Inspector General Michael Missal issued 3 reports in mid-March on how the “go-live” process was faring: one on medication management deficiencies, one on care coordination deficiencies, and one on technical issues.
The reports document the OIG’s “concerns” with the new process. According to the technical report, for instance, between October 2020 and March 2021, new EHR users placed more than 38,700 requests for assistance. Of those, 33% were closed without a documented resolution. The OIG also reviewed 210 tickets related to care coordination and found that 1% were closed without a documented resolution.
The OIG said EHR implementation had “created difficulties” for end users in 8 areas:
- Patient record flags, including failures to transfer flags and information related to patients at high risk for suicide;
- Data migration errors leading to inaccurate name, sex, and contact information;
- Scheduling process issues, such as delays in primary care scheduling;
- VA Video Connect problems, including inoperable and misdirected links;
- Referral management deficiencies, including lost or unaddressed referrals;
- Laboratory orders “disappearing” that affected workflow and tracking, and delayed results;
- Patient portal and secure messaging being inaccessible; and
- Documentation processes, including creating additional work and limiting the ability to correctly code patient diagnoses.
The OIG’s technical report identified 5 factors that contributed to the headaches: EHR usability problems, training deficits, interoperability challenges, post–go-live fixes and refinement needs, and problem-resolution process challenges.
The OIG did not identify any associated patient deaths during the inspection but says “future deployment of the new EHR without resolving deficiencies can increase risks to patient safety.”
The technological overhaul has been handled by Cerner. The VA initially awarded Cerner $113 million for EHR modernization, and in 2018 the company secured a 10-year, $10 billion contract to help the VA rebuild its system, similar to the way it did for the US Department of Defense (DoD) with MHS GENESIS. The Cerner DoD project, which has been called “the most lucrative electronic health record contract in history” was launched at the Fairchild Air Force Base in Spokane, Washington, in 2017, and is expected to be operational in more than half of military hospitals and clinics by the end of this year. In 2021, Cerner received an 18-month, $134.1 million task order to deploy the company’s EHR platform at VA medical centers.
This isn’t the first time the VA/Cerner EHR project has hit snags. In 2021, the VA scrapped the schedule, trading it for a 6-month pause after a strategic review ordered by VA Secretary Denis McDonough found problems with governance and management. McDonough told the Senate Veterans’ Affairs Committee that a 3-month internal review had found too many structural problems to warrant continuing the rollout. The sole-source contract with Cerner also raised concerns, as did the influence of 3 confidants of Present Trump on the process. Moreover, cost estimates kept growing—from $10 billion to $16 billion—in part because VA leaders during the Trump administration did not budget for technology and hospital upgrades to allow the new platform to work, according to an article in The Washington Post.
During the senate hearing, committee chair Sen. Jon Tester (D-MT) said, “There’s been damn little accountability. I hope Cerner’s watching this. If they’re not open to making a user-friendly health medical record, they ought to admit it so we can get the money back and start all over.” He told McDonough that the failures were “not all your fault—I don’t know if any of it is your fault.”
“It’s a lot of money you’ve entrusted to us,” McDonough told the committee. The serious problems, he said, were “on us.” He added, “We are taking swift and decisive action to incorporate the management rigor and enterprise jointness required for this program to deliver on its intended purpose: seamless excellence in VA care for veterans. VA’s first implementation of the [project] did not live up to that promise, either for our veterans or for our providers.”
He said he had ordered an overhaul that will include better training for clinical staff, more reliable testing and oversight of Cerner, and a leadership shake-up. He also said he had installed a patient safety team at the Spokane hospital.
Terry Adirim, MD, formerly with the DoD, took over the EHR program in January. In an interview, she said, “[W]e’ve made a substantial number of changes,” such as a new round of training for the hospital’s medical staff. “These deployments are really complex and they’re really hard,” Adirim said, noting that about half of digital medical records programs at private hospitals fail at first. She pointed to the revamped DoD program, which also had its flaws but is running much more smoothly. One of the issues, she said, is that many physicians did not realize that the Cerner system would differ so dramatically from VistA, the system it’s replacing.
The first installment of the rocky rollout left hospital staff confused and worn out. Sen. Patty Murphy (D-WA) said in 2021 that the Spokane staff had filed hundreds of reports of patient safety issues caused by the new system. “Patients are not getting accurate meds. Meds are sent to the wrong address. What used to take a few clicks is now a lot more complicated. Providers are burning out.”
A year later, in a statement, echoing her earlier comments, she said, “We need to put a pause on this rollout right now.”
But Adirim has said the VA is moving ahead with the rollout. The VA has added extra support staff and plans to have physicians from outside the hospital on hand in case things go wrong. According to the Washington Post, Deputy VA Secretary Donald Remy told the OIG that the VA is working to address the outstanding issues and hopes to resolve them by mid-May.
Meanwhile, the beleaguered project ran into another obstacle in early March, when computers went down at Mann-Grandstaff, leading to 20 hours of yet more confusion about medications and surgeries. The VA said the IT system outage also happened at Columbus, Ohio (another of the planned pilot spots). The system was back online the next day, with no known patient safety issues.
Eastern Washington Congresswoman Cathy McMorris Rodgers released a statement saying, “The shutdown of Mann-Grandstaff VA yesterday is another event in a series of challenges that the new electronic health record has created for staff and veterans at the facility. My understanding is that an update made to help the VA’s database for demographic data better communicate with the Cerner system was not performed correctly. Mann-Grandstaff leadership rightly took the system offline until the scope of the problem was understood, so no patients were harmed.”
However, Sen. Murphy called the technical failure “absolutely unacceptable.” In a more recent statement about the rollout, she said, “This is about patient safety and it needs to get fixed—period. VA needs to be upfront about issues like this in real time—Congress absolutely requires transparency when it comes to failures as serious as this. I should be hearing about this from local reporting first.”
If the high-quality care veterans deserve is uncertain at any point, she added, “the rollout should be delayed.” Again.
Scheduling delays. Disappearing lab orders. Bad links for telehealth appointments. Erroneous medication dispensing. Time-consuming workarounds.
The rollout of the $16 billion electronic health record (EHR) system at the US Department of Veterans Affair (VA) has met some fairly large bumps in the past few years. And now, the VA Office of the Inspector General (OIG) has pronounced on a “range of allegations” at the Mann-Grandstaff VA Medical Center in Spokane, Washington, the first of several hospitals and clinics in the Pacific Northwest set to implement the new system.
VA Inspector General Michael Missal issued 3 reports in mid-March on how the “go-live” process was faring: one on medication management deficiencies, one on care coordination deficiencies, and one on technical issues.
The reports document the OIG’s “concerns” with the new process. According to the technical report, for instance, between October 2020 and March 2021, new EHR users placed more than 38,700 requests for assistance. Of those, 33% were closed without a documented resolution. The OIG also reviewed 210 tickets related to care coordination and found that 1% were closed without a documented resolution.
The OIG said EHR implementation had “created difficulties” for end users in 8 areas:
- Patient record flags, including failures to transfer flags and information related to patients at high risk for suicide;
- Data migration errors leading to inaccurate name, sex, and contact information;
- Scheduling process issues, such as delays in primary care scheduling;
- VA Video Connect problems, including inoperable and misdirected links;
- Referral management deficiencies, including lost or unaddressed referrals;
- Laboratory orders “disappearing” that affected workflow and tracking, and delayed results;
- Patient portal and secure messaging being inaccessible; and
- Documentation processes, including creating additional work and limiting the ability to correctly code patient diagnoses.
The OIG’s technical report identified 5 factors that contributed to the headaches: EHR usability problems, training deficits, interoperability challenges, post–go-live fixes and refinement needs, and problem-resolution process challenges.
The OIG did not identify any associated patient deaths during the inspection but says “future deployment of the new EHR without resolving deficiencies can increase risks to patient safety.”
The technological overhaul has been handled by Cerner. The VA initially awarded Cerner $113 million for EHR modernization, and in 2018 the company secured a 10-year, $10 billion contract to help the VA rebuild its system, similar to the way it did for the US Department of Defense (DoD) with MHS GENESIS. The Cerner DoD project, which has been called “the most lucrative electronic health record contract in history” was launched at the Fairchild Air Force Base in Spokane, Washington, in 2017, and is expected to be operational in more than half of military hospitals and clinics by the end of this year. In 2021, Cerner received an 18-month, $134.1 million task order to deploy the company’s EHR platform at VA medical centers.
This isn’t the first time the VA/Cerner EHR project has hit snags. In 2021, the VA scrapped the schedule, trading it for a 6-month pause after a strategic review ordered by VA Secretary Denis McDonough found problems with governance and management. McDonough told the Senate Veterans’ Affairs Committee that a 3-month internal review had found too many structural problems to warrant continuing the rollout. The sole-source contract with Cerner also raised concerns, as did the influence of 3 confidants of Present Trump on the process. Moreover, cost estimates kept growing—from $10 billion to $16 billion—in part because VA leaders during the Trump administration did not budget for technology and hospital upgrades to allow the new platform to work, according to an article in The Washington Post.
During the senate hearing, committee chair Sen. Jon Tester (D-MT) said, “There’s been damn little accountability. I hope Cerner’s watching this. If they’re not open to making a user-friendly health medical record, they ought to admit it so we can get the money back and start all over.” He told McDonough that the failures were “not all your fault—I don’t know if any of it is your fault.”
“It’s a lot of money you’ve entrusted to us,” McDonough told the committee. The serious problems, he said, were “on us.” He added, “We are taking swift and decisive action to incorporate the management rigor and enterprise jointness required for this program to deliver on its intended purpose: seamless excellence in VA care for veterans. VA’s first implementation of the [project] did not live up to that promise, either for our veterans or for our providers.”
He said he had ordered an overhaul that will include better training for clinical staff, more reliable testing and oversight of Cerner, and a leadership shake-up. He also said he had installed a patient safety team at the Spokane hospital.
Terry Adirim, MD, formerly with the DoD, took over the EHR program in January. In an interview, she said, “[W]e’ve made a substantial number of changes,” such as a new round of training for the hospital’s medical staff. “These deployments are really complex and they’re really hard,” Adirim said, noting that about half of digital medical records programs at private hospitals fail at first. She pointed to the revamped DoD program, which also had its flaws but is running much more smoothly. One of the issues, she said, is that many physicians did not realize that the Cerner system would differ so dramatically from VistA, the system it’s replacing.
The first installment of the rocky rollout left hospital staff confused and worn out. Sen. Patty Murphy (D-WA) said in 2021 that the Spokane staff had filed hundreds of reports of patient safety issues caused by the new system. “Patients are not getting accurate meds. Meds are sent to the wrong address. What used to take a few clicks is now a lot more complicated. Providers are burning out.”
A year later, in a statement, echoing her earlier comments, she said, “We need to put a pause on this rollout right now.”
But Adirim has said the VA is moving ahead with the rollout. The VA has added extra support staff and plans to have physicians from outside the hospital on hand in case things go wrong. According to the Washington Post, Deputy VA Secretary Donald Remy told the OIG that the VA is working to address the outstanding issues and hopes to resolve them by mid-May.
Meanwhile, the beleaguered project ran into another obstacle in early March, when computers went down at Mann-Grandstaff, leading to 20 hours of yet more confusion about medications and surgeries. The VA said the IT system outage also happened at Columbus, Ohio (another of the planned pilot spots). The system was back online the next day, with no known patient safety issues.
Eastern Washington Congresswoman Cathy McMorris Rodgers released a statement saying, “The shutdown of Mann-Grandstaff VA yesterday is another event in a series of challenges that the new electronic health record has created for staff and veterans at the facility. My understanding is that an update made to help the VA’s database for demographic data better communicate with the Cerner system was not performed correctly. Mann-Grandstaff leadership rightly took the system offline until the scope of the problem was understood, so no patients were harmed.”
However, Sen. Murphy called the technical failure “absolutely unacceptable.” In a more recent statement about the rollout, she said, “This is about patient safety and it needs to get fixed—period. VA needs to be upfront about issues like this in real time—Congress absolutely requires transparency when it comes to failures as serious as this. I should be hearing about this from local reporting first.”
If the high-quality care veterans deserve is uncertain at any point, she added, “the rollout should be delayed.” Again.
Scheduling delays. Disappearing lab orders. Bad links for telehealth appointments. Erroneous medication dispensing. Time-consuming workarounds.
The rollout of the $16 billion electronic health record (EHR) system at the US Department of Veterans Affair (VA) has met some fairly large bumps in the past few years. And now, the VA Office of the Inspector General (OIG) has pronounced on a “range of allegations” at the Mann-Grandstaff VA Medical Center in Spokane, Washington, the first of several hospitals and clinics in the Pacific Northwest set to implement the new system.
VA Inspector General Michael Missal issued 3 reports in mid-March on how the “go-live” process was faring: one on medication management deficiencies, one on care coordination deficiencies, and one on technical issues.
The reports document the OIG’s “concerns” with the new process. According to the technical report, for instance, between October 2020 and March 2021, new EHR users placed more than 38,700 requests for assistance. Of those, 33% were closed without a documented resolution. The OIG also reviewed 210 tickets related to care coordination and found that 1% were closed without a documented resolution.
The OIG said EHR implementation had “created difficulties” for end users in 8 areas:
- Patient record flags, including failures to transfer flags and information related to patients at high risk for suicide;
- Data migration errors leading to inaccurate name, sex, and contact information;
- Scheduling process issues, such as delays in primary care scheduling;
- VA Video Connect problems, including inoperable and misdirected links;
- Referral management deficiencies, including lost or unaddressed referrals;
- Laboratory orders “disappearing” that affected workflow and tracking, and delayed results;
- Patient portal and secure messaging being inaccessible; and
- Documentation processes, including creating additional work and limiting the ability to correctly code patient diagnoses.
The OIG’s technical report identified 5 factors that contributed to the headaches: EHR usability problems, training deficits, interoperability challenges, post–go-live fixes and refinement needs, and problem-resolution process challenges.
The OIG did not identify any associated patient deaths during the inspection but says “future deployment of the new EHR without resolving deficiencies can increase risks to patient safety.”
The technological overhaul has been handled by Cerner. The VA initially awarded Cerner $113 million for EHR modernization, and in 2018 the company secured a 10-year, $10 billion contract to help the VA rebuild its system, similar to the way it did for the US Department of Defense (DoD) with MHS GENESIS. The Cerner DoD project, which has been called “the most lucrative electronic health record contract in history” was launched at the Fairchild Air Force Base in Spokane, Washington, in 2017, and is expected to be operational in more than half of military hospitals and clinics by the end of this year. In 2021, Cerner received an 18-month, $134.1 million task order to deploy the company’s EHR platform at VA medical centers.
This isn’t the first time the VA/Cerner EHR project has hit snags. In 2021, the VA scrapped the schedule, trading it for a 6-month pause after a strategic review ordered by VA Secretary Denis McDonough found problems with governance and management. McDonough told the Senate Veterans’ Affairs Committee that a 3-month internal review had found too many structural problems to warrant continuing the rollout. The sole-source contract with Cerner also raised concerns, as did the influence of 3 confidants of Present Trump on the process. Moreover, cost estimates kept growing—from $10 billion to $16 billion—in part because VA leaders during the Trump administration did not budget for technology and hospital upgrades to allow the new platform to work, according to an article in The Washington Post.
During the senate hearing, committee chair Sen. Jon Tester (D-MT) said, “There’s been damn little accountability. I hope Cerner’s watching this. If they’re not open to making a user-friendly health medical record, they ought to admit it so we can get the money back and start all over.” He told McDonough that the failures were “not all your fault—I don’t know if any of it is your fault.”
“It’s a lot of money you’ve entrusted to us,” McDonough told the committee. The serious problems, he said, were “on us.” He added, “We are taking swift and decisive action to incorporate the management rigor and enterprise jointness required for this program to deliver on its intended purpose: seamless excellence in VA care for veterans. VA’s first implementation of the [project] did not live up to that promise, either for our veterans or for our providers.”
He said he had ordered an overhaul that will include better training for clinical staff, more reliable testing and oversight of Cerner, and a leadership shake-up. He also said he had installed a patient safety team at the Spokane hospital.
Terry Adirim, MD, formerly with the DoD, took over the EHR program in January. In an interview, she said, “[W]e’ve made a substantial number of changes,” such as a new round of training for the hospital’s medical staff. “These deployments are really complex and they’re really hard,” Adirim said, noting that about half of digital medical records programs at private hospitals fail at first. She pointed to the revamped DoD program, which also had its flaws but is running much more smoothly. One of the issues, she said, is that many physicians did not realize that the Cerner system would differ so dramatically from VistA, the system it’s replacing.
The first installment of the rocky rollout left hospital staff confused and worn out. Sen. Patty Murphy (D-WA) said in 2021 that the Spokane staff had filed hundreds of reports of patient safety issues caused by the new system. “Patients are not getting accurate meds. Meds are sent to the wrong address. What used to take a few clicks is now a lot more complicated. Providers are burning out.”
A year later, in a statement, echoing her earlier comments, she said, “We need to put a pause on this rollout right now.”
But Adirim has said the VA is moving ahead with the rollout. The VA has added extra support staff and plans to have physicians from outside the hospital on hand in case things go wrong. According to the Washington Post, Deputy VA Secretary Donald Remy told the OIG that the VA is working to address the outstanding issues and hopes to resolve them by mid-May.
Meanwhile, the beleaguered project ran into another obstacle in early March, when computers went down at Mann-Grandstaff, leading to 20 hours of yet more confusion about medications and surgeries. The VA said the IT system outage also happened at Columbus, Ohio (another of the planned pilot spots). The system was back online the next day, with no known patient safety issues.
Eastern Washington Congresswoman Cathy McMorris Rodgers released a statement saying, “The shutdown of Mann-Grandstaff VA yesterday is another event in a series of challenges that the new electronic health record has created for staff and veterans at the facility. My understanding is that an update made to help the VA’s database for demographic data better communicate with the Cerner system was not performed correctly. Mann-Grandstaff leadership rightly took the system offline until the scope of the problem was understood, so no patients were harmed.”
However, Sen. Murphy called the technical failure “absolutely unacceptable.” In a more recent statement about the rollout, she said, “This is about patient safety and it needs to get fixed—period. VA needs to be upfront about issues like this in real time—Congress absolutely requires transparency when it comes to failures as serious as this. I should be hearing about this from local reporting first.”
If the high-quality care veterans deserve is uncertain at any point, she added, “the rollout should be delayed.” Again.
Melanoma
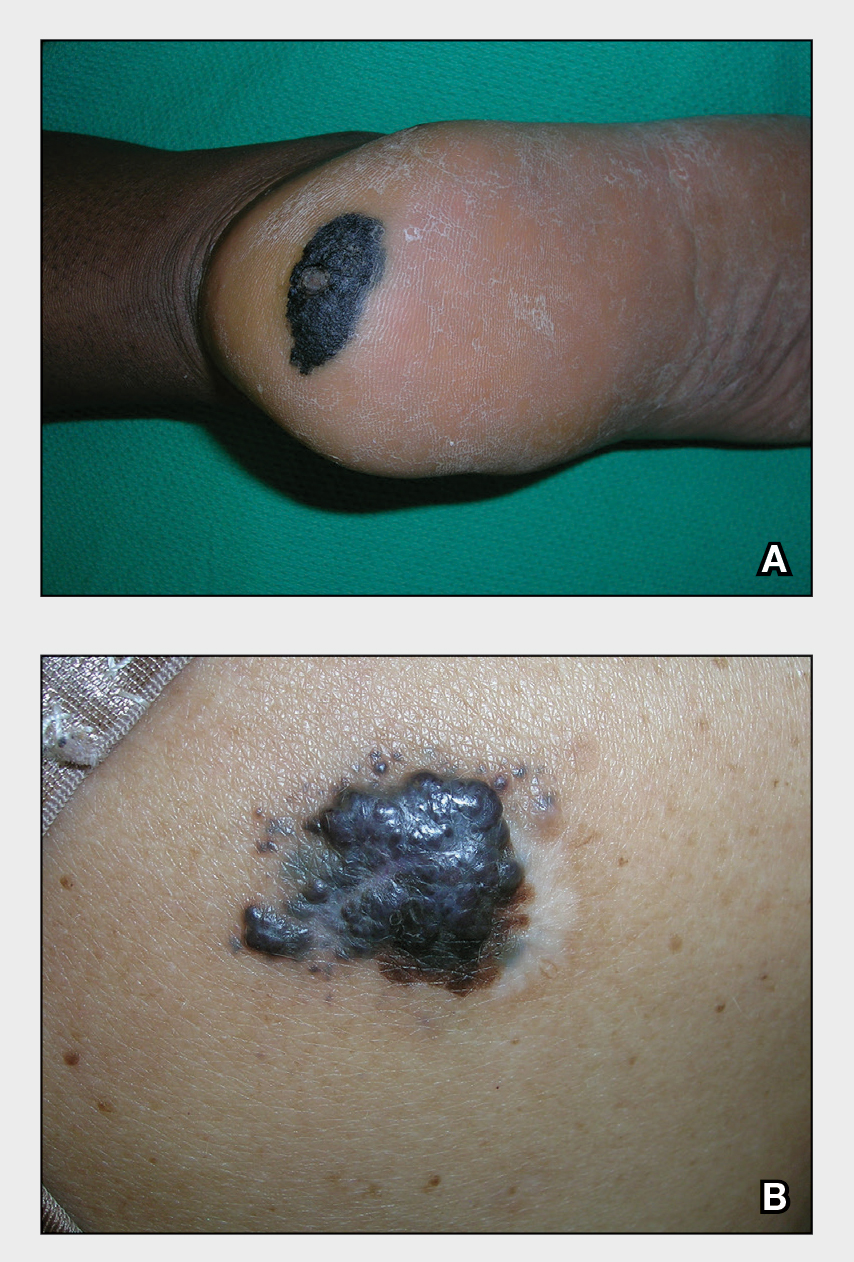
THE COMPARISON
A Acral lentiginous melanoma on the sole of the foot in a 30-year-old Black woman. The depth of the lesion was 2 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
B Nodular melanoma on the shoulder of a 63-year-old Hispanic woman. The depth of the lesion was 5.5 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Melanoma occurs less frequently in individuals with darker skin types than in lighter skin types but is associated with higher rates of morbidity and mortality in this patient population.1-7 In the cases shown here (A and B), both patients had advanced melanomas with large primary lesions and lymph node metastases.
Epidemiology
A systematic review by Higgins et al6 reported the following on the epidemiology of melanomas in patients with skin of color:
- African Americans have deeper tumors at the time of diagnosis, in addition to increased rates of regionally advanced and distant disease. Lesions generally are located on the lower extremities and have an increased propensity for ulceration. Acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype found in African American patients.6
- In Hispanic individuals, superficial spreading melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype. Lower extremity lesions are more common relative to White individuals. Hispanic individuals have the highest rate of oral cavity melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
- In Asian individuals, acral and subungual sites are most common. Specifically, Pacific Islanders have the highest proportion of mucosal melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Melanomas are found more often on the palms, soles, nail units, oral cavity, and mucosae.6 The melanomas have the same clinical and dermoscopic features found in individuals with lighter skin tones.
Worth noting
Factors that may contribute to the diagnosis of more advanced melanomas in racial/ethnic minorities in the United States include:
- decreased access to health care based on lack of health insurance and low socioeconomic status,
- less awareness of the risk of melanoma among patients and health care providers because melanoma is less common in persons of color, and
- lesions found in areas less likely to be seen in screening examinations, such as the soles of the feet and the oral and genital mucosae.
Health disparity highlight
- In a large US study of 96,953 patients with a diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma from 1992 to 2009, the proportion of later-stage melanoma—stages II to IV—was greater in Black patients compared to White patients.7
- Based on this same data set, White patients had the longest survival time (P<.05), followed by Hispanic (P<.05), Asian American/Native American/Pacific Islander (P<.05), and Black (P<.05) patients, respectively.7
- In Miami-Dade County, one study of 1690 melanoma cases found that 48% of Black patients had regional or distant disease at presentation compared to 22% of White patients (P=.015).5 Analysis of multiple factors found that only race was a significant predictor for late-stage melanoma (P<.001). Black patients in this study were 3 times more likely than others to be diagnosed with melanoma at a late stage (P=.07).5
- Black patients in the United States are more likely to have a delayed time from diagnosis to definitive surgery even when controlled for type of health insurance and stage of diagnosis.8
Final thoughts
Efforts are needed to overcome these disparities by:
- educating patients with skin of color and their health care providers about the risks of advanced melanoma with the goal of prevention and earlier diagnosis;
- breaking down barriers to care caused by poverty, lack of health insurance, and systemic racism; and
- eliminating factors that lead to delays from diagnosis to definitive surgery.
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2001.05.034
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.17.1907
- Cress RD, Holly EA. Incidence of cutaneous melanoma among non-Hispanic whites, Hispanics, Asians, and blacks: an analysis of California cancer registry data, 1988-93. Cancer Causes Control. 1997;8:246-252. doi:10.1023/a:1018432632528
- Hu S, Parker DF, Thomas AG, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans: the Miami-Dade County experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:1031-1032. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2004.05.005
- Hu S, Soza-Vento RM, Parker DF, et al. Comparison of stage at diagnosis of melanoma among Hispanic, black, and white patients in Miami-Dade County, Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:704-708. doi:10.1001/archderm.142.6.704
- Higgins S, Nazemi A, Feinstein S, et al. Clinical presentations of melanoma in African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:791-801. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001759
- Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival [published online July 28, 2016]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.06.006
- Qian Y, Johannet P, Sawyers A, et al. The ongoing racial disparities in melanoma: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (1975-2016)[published online August 27, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1585-1593. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2020.08.097

THE COMPARISON
A Acral lentiginous melanoma on the sole of the foot in a 30-year-old Black woman. The depth of the lesion was 2 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
B Nodular melanoma on the shoulder of a 63-year-old Hispanic woman. The depth of the lesion was 5.5 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Melanoma occurs less frequently in individuals with darker skin types than in lighter skin types but is associated with higher rates of morbidity and mortality in this patient population.1-7 In the cases shown here (A and B), both patients had advanced melanomas with large primary lesions and lymph node metastases.
Epidemiology
A systematic review by Higgins et al6 reported the following on the epidemiology of melanomas in patients with skin of color:
- African Americans have deeper tumors at the time of diagnosis, in addition to increased rates of regionally advanced and distant disease. Lesions generally are located on the lower extremities and have an increased propensity for ulceration. Acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype found in African American patients.6
- In Hispanic individuals, superficial spreading melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype. Lower extremity lesions are more common relative to White individuals. Hispanic individuals have the highest rate of oral cavity melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
- In Asian individuals, acral and subungual sites are most common. Specifically, Pacific Islanders have the highest proportion of mucosal melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Melanomas are found more often on the palms, soles, nail units, oral cavity, and mucosae.6 The melanomas have the same clinical and dermoscopic features found in individuals with lighter skin tones.
Worth noting
Factors that may contribute to the diagnosis of more advanced melanomas in racial/ethnic minorities in the United States include:
- decreased access to health care based on lack of health insurance and low socioeconomic status,
- less awareness of the risk of melanoma among patients and health care providers because melanoma is less common in persons of color, and
- lesions found in areas less likely to be seen in screening examinations, such as the soles of the feet and the oral and genital mucosae.
Health disparity highlight
- In a large US study of 96,953 patients with a diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma from 1992 to 2009, the proportion of later-stage melanoma—stages II to IV—was greater in Black patients compared to White patients.7
- Based on this same data set, White patients had the longest survival time (P<.05), followed by Hispanic (P<.05), Asian American/Native American/Pacific Islander (P<.05), and Black (P<.05) patients, respectively.7
- In Miami-Dade County, one study of 1690 melanoma cases found that 48% of Black patients had regional or distant disease at presentation compared to 22% of White patients (P=.015).5 Analysis of multiple factors found that only race was a significant predictor for late-stage melanoma (P<.001). Black patients in this study were 3 times more likely than others to be diagnosed with melanoma at a late stage (P=.07).5
- Black patients in the United States are more likely to have a delayed time from diagnosis to definitive surgery even when controlled for type of health insurance and stage of diagnosis.8
Final thoughts
Efforts are needed to overcome these disparities by:
- educating patients with skin of color and their health care providers about the risks of advanced melanoma with the goal of prevention and earlier diagnosis;
- breaking down barriers to care caused by poverty, lack of health insurance, and systemic racism; and
- eliminating factors that lead to delays from diagnosis to definitive surgery.

THE COMPARISON
A Acral lentiginous melanoma on the sole of the foot in a 30-year-old Black woman. The depth of the lesion was 2 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
B Nodular melanoma on the shoulder of a 63-year-old Hispanic woman. The depth of the lesion was 5.5 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Melanoma occurs less frequently in individuals with darker skin types than in lighter skin types but is associated with higher rates of morbidity and mortality in this patient population.1-7 In the cases shown here (A and B), both patients had advanced melanomas with large primary lesions and lymph node metastases.
Epidemiology
A systematic review by Higgins et al6 reported the following on the epidemiology of melanomas in patients with skin of color:
- African Americans have deeper tumors at the time of diagnosis, in addition to increased rates of regionally advanced and distant disease. Lesions generally are located on the lower extremities and have an increased propensity for ulceration. Acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype found in African American patients.6
- In Hispanic individuals, superficial spreading melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype. Lower extremity lesions are more common relative to White individuals. Hispanic individuals have the highest rate of oral cavity melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
- In Asian individuals, acral and subungual sites are most common. Specifically, Pacific Islanders have the highest proportion of mucosal melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Melanomas are found more often on the palms, soles, nail units, oral cavity, and mucosae.6 The melanomas have the same clinical and dermoscopic features found in individuals with lighter skin tones.
Worth noting
Factors that may contribute to the diagnosis of more advanced melanomas in racial/ethnic minorities in the United States include:
- decreased access to health care based on lack of health insurance and low socioeconomic status,
- less awareness of the risk of melanoma among patients and health care providers because melanoma is less common in persons of color, and
- lesions found in areas less likely to be seen in screening examinations, such as the soles of the feet and the oral and genital mucosae.
Health disparity highlight
- In a large US study of 96,953 patients with a diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma from 1992 to 2009, the proportion of later-stage melanoma—stages II to IV—was greater in Black patients compared to White patients.7
- Based on this same data set, White patients had the longest survival time (P<.05), followed by Hispanic (P<.05), Asian American/Native American/Pacific Islander (P<.05), and Black (P<.05) patients, respectively.7
- In Miami-Dade County, one study of 1690 melanoma cases found that 48% of Black patients had regional or distant disease at presentation compared to 22% of White patients (P=.015).5 Analysis of multiple factors found that only race was a significant predictor for late-stage melanoma (P<.001). Black patients in this study were 3 times more likely than others to be diagnosed with melanoma at a late stage (P=.07).5
- Black patients in the United States are more likely to have a delayed time from diagnosis to definitive surgery even when controlled for type of health insurance and stage of diagnosis.8
Final thoughts
Efforts are needed to overcome these disparities by:
- educating patients with skin of color and their health care providers about the risks of advanced melanoma with the goal of prevention and earlier diagnosis;
- breaking down barriers to care caused by poverty, lack of health insurance, and systemic racism; and
- eliminating factors that lead to delays from diagnosis to definitive surgery.
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2001.05.034
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.17.1907
- Cress RD, Holly EA. Incidence of cutaneous melanoma among non-Hispanic whites, Hispanics, Asians, and blacks: an analysis of California cancer registry data, 1988-93. Cancer Causes Control. 1997;8:246-252. doi:10.1023/a:1018432632528
- Hu S, Parker DF, Thomas AG, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans: the Miami-Dade County experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:1031-1032. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2004.05.005
- Hu S, Soza-Vento RM, Parker DF, et al. Comparison of stage at diagnosis of melanoma among Hispanic, black, and white patients in Miami-Dade County, Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:704-708. doi:10.1001/archderm.142.6.704
- Higgins S, Nazemi A, Feinstein S, et al. Clinical presentations of melanoma in African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:791-801. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001759
- Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival [published online July 28, 2016]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.06.006
- Qian Y, Johannet P, Sawyers A, et al. The ongoing racial disparities in melanoma: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (1975-2016)[published online August 27, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1585-1593. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2020.08.097
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2001.05.034
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.17.1907
- Cress RD, Holly EA. Incidence of cutaneous melanoma among non-Hispanic whites, Hispanics, Asians, and blacks: an analysis of California cancer registry data, 1988-93. Cancer Causes Control. 1997;8:246-252. doi:10.1023/a:1018432632528
- Hu S, Parker DF, Thomas AG, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans: the Miami-Dade County experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:1031-1032. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2004.05.005
- Hu S, Soza-Vento RM, Parker DF, et al. Comparison of stage at diagnosis of melanoma among Hispanic, black, and white patients in Miami-Dade County, Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:704-708. doi:10.1001/archderm.142.6.704
- Higgins S, Nazemi A, Feinstein S, et al. Clinical presentations of melanoma in African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:791-801. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001759
- Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival [published online July 28, 2016]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.06.006
- Qian Y, Johannet P, Sawyers A, et al. The ongoing racial disparities in melanoma: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (1975-2016)[published online August 27, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1585-1593. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2020.08.097
Painful Fungating Perianal Mass
The Diagnosis: Condyloma Latum
A punch biopsy of the perianal mass revealed epidermal acanthosis with elongated slender rete ridges, scattered intraepidermal neutrophils, and a dense dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Figure, A) with a prominent plasma cell component (Figure, B). A treponemal immunohistochemical stain revealed numerous coiled spirochetes concentrated in the lower epidermis (Figure, C). Serologic test results including rapid plasma reagin (titer 1:1024) and Treponema pallidum antibody were reactive, confirming the diagnosis of secondary syphilis with condyloma latum. The patient was treated with intramuscular penicillin G with resolution of the lesion 2 weeks later.
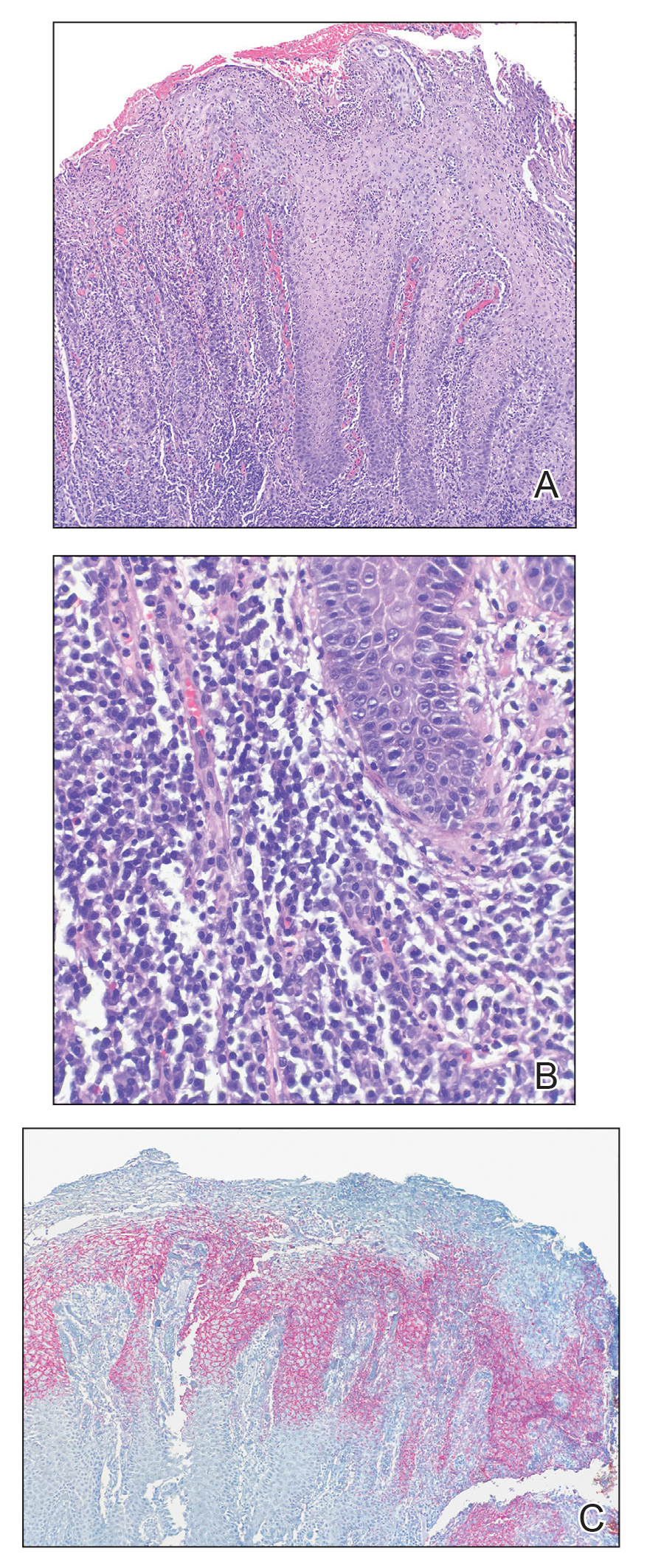
Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the spirochete T pallidum, reached historically low rates in the United States in the early 2000s due to the widespread use of penicillin and effective public health efforts.1 However, the rates of primary and secondary syphilis infections recently have markedly increased, resulting in the current epidemic of syphilis in the United States and Europe.1,2 Its wide variety of clinical and histopathologic manifestations make recognition challenging and lend it the moniker “the great imitator.”
Secondary syphilis results from the systemic spread of T pallidum and classically is characterized by the triad of a skin rash that frequently involves the palms and soles, mucosal ulceration such as condyloma latum, and lymphadenopathy.2,3 However, condyloma latum may represent the only manifestation of secondary syphilis in a subset of patients,4 as observed in our patient.
In the 2 months prior to diagnosis, our patient was evaluated at multiple emergency departments and primary care clinics, receiving diagnoses of condyloma acuminatum, genital herpes simplex virus, hemorrhoids, and suspicion for malignancy—entities that comprise the differential diagnosis for condyloma latum.2,5 Despite some degree of overlap in patient populations, risk factors, and presentations between these diagnostic considerations, recognition of certain clinical features, in addition to histopathologic evaluation, may facilitate navigation of this differential diagnosis.
Primary and secondary syphilis infections have been predominantly observed in men, mostly men who have sex with men and/or those who are infected with HIV.1 Condyloma acuminata, genital herpes simplex virus, and chancroid also are seen in younger individuals, more commonly in those with multiple sexual partners, but show a more even gender distribution and are not restricted to those partaking in anal intercourse. The clinical presentation of condyloma latum can be differentiated by its painless, flat, smooth, and commonly hypopigmented appearance, often with associated surface erosion and a gray exudate, in contrast to condyloma acuminatum, which typically presents as nontender, flesh-colored or hyperpigmented, exophytic papules that may coalesce into plaques.2,3,6 Genital herpes simplex virus infection presents with multiple small papulovesicular lesions with ulceration, most commonly on the tip or shaft of the penis, though perianal lesions may be seen in men who have sex with men.7 Similarly, chancroid presents with painful necrotizing genital ulcers most commonly on the penis, though perianal lesions also may be seen.8 Hemorrhoids classically are seen in middle-aged adults with a history of constipation, present with rectal bleeding, and may be associated with pain in the setting of thrombosis or ulceration.9 Finally, perianal squamous cell carcinoma primarily occurs in older adults, typically in the sixth decade of life. Verrucous carcinoma most commonly arises in the oropharynx or anogenital region in sites of chronic irritation and presents as a slow-growing exophytic mass. Classic squamous cell carcinoma most commonly occurs in association with human papillomavirus infection and presents with scaly erythematous papules or plaques.10
Our case highlighted the clinical difficulty in recognizing condyloma latum, as this lesion remained undiagnosed for 2 months, and our patient presumptively was treated for multiple perianal pathologies prior to a biopsy being performed. Due to the clinical similarity of various perianal lesions, the diagnosis of condyloma latum should be considered, and serologic studies should be performed in fitting clinical contexts, especially in light of recently rising rates of syphilis infection.1,2
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Tayal S, Shaban F, Dasgupta K, et al. A case of syphilitic anal condylomata lata mimicking malignancy. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015; 17:69-71.
- Aung PP, Wimmer DB, Lester TR, et al. Perianal condylomata lata mimicking carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2022;49:209-214.
- Pourang A, Fung MA, Tartar D, et al. Condyloma lata in secondary syphilis. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;10:18-21.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJ, de Vries HJ. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259.
- Leslie SW, Sajjad H, Kumar S. Genital warts. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Groves MJ. Genital herpes: a review. Am Fam Physician. 2016; 93:928-934.
- Irizarry L, Velasquez J, Wray AA. Chancroid. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Mounsey AL, Halladay J, Sadiq TS. Hemorrhoids. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:204-210.
- Abbass MA, Valente MA. Premalignant and malignant perianal lesions. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2019;32:386-393.
The Diagnosis: Condyloma Latum
A punch biopsy of the perianal mass revealed epidermal acanthosis with elongated slender rete ridges, scattered intraepidermal neutrophils, and a dense dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Figure, A) with a prominent plasma cell component (Figure, B). A treponemal immunohistochemical stain revealed numerous coiled spirochetes concentrated in the lower epidermis (Figure, C). Serologic test results including rapid plasma reagin (titer 1:1024) and Treponema pallidum antibody were reactive, confirming the diagnosis of secondary syphilis with condyloma latum. The patient was treated with intramuscular penicillin G with resolution of the lesion 2 weeks later.

Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the spirochete T pallidum, reached historically low rates in the United States in the early 2000s due to the widespread use of penicillin and effective public health efforts.1 However, the rates of primary and secondary syphilis infections recently have markedly increased, resulting in the current epidemic of syphilis in the United States and Europe.1,2 Its wide variety of clinical and histopathologic manifestations make recognition challenging and lend it the moniker “the great imitator.”
Secondary syphilis results from the systemic spread of T pallidum and classically is characterized by the triad of a skin rash that frequently involves the palms and soles, mucosal ulceration such as condyloma latum, and lymphadenopathy.2,3 However, condyloma latum may represent the only manifestation of secondary syphilis in a subset of patients,4 as observed in our patient.
In the 2 months prior to diagnosis, our patient was evaluated at multiple emergency departments and primary care clinics, receiving diagnoses of condyloma acuminatum, genital herpes simplex virus, hemorrhoids, and suspicion for malignancy—entities that comprise the differential diagnosis for condyloma latum.2,5 Despite some degree of overlap in patient populations, risk factors, and presentations between these diagnostic considerations, recognition of certain clinical features, in addition to histopathologic evaluation, may facilitate navigation of this differential diagnosis.
Primary and secondary syphilis infections have been predominantly observed in men, mostly men who have sex with men and/or those who are infected with HIV.1 Condyloma acuminata, genital herpes simplex virus, and chancroid also are seen in younger individuals, more commonly in those with multiple sexual partners, but show a more even gender distribution and are not restricted to those partaking in anal intercourse. The clinical presentation of condyloma latum can be differentiated by its painless, flat, smooth, and commonly hypopigmented appearance, often with associated surface erosion and a gray exudate, in contrast to condyloma acuminatum, which typically presents as nontender, flesh-colored or hyperpigmented, exophytic papules that may coalesce into plaques.2,3,6 Genital herpes simplex virus infection presents with multiple small papulovesicular lesions with ulceration, most commonly on the tip or shaft of the penis, though perianal lesions may be seen in men who have sex with men.7 Similarly, chancroid presents with painful necrotizing genital ulcers most commonly on the penis, though perianal lesions also may be seen.8 Hemorrhoids classically are seen in middle-aged adults with a history of constipation, present with rectal bleeding, and may be associated with pain in the setting of thrombosis or ulceration.9 Finally, perianal squamous cell carcinoma primarily occurs in older adults, typically in the sixth decade of life. Verrucous carcinoma most commonly arises in the oropharynx or anogenital region in sites of chronic irritation and presents as a slow-growing exophytic mass. Classic squamous cell carcinoma most commonly occurs in association with human papillomavirus infection and presents with scaly erythematous papules or plaques.10
Our case highlighted the clinical difficulty in recognizing condyloma latum, as this lesion remained undiagnosed for 2 months, and our patient presumptively was treated for multiple perianal pathologies prior to a biopsy being performed. Due to the clinical similarity of various perianal lesions, the diagnosis of condyloma latum should be considered, and serologic studies should be performed in fitting clinical contexts, especially in light of recently rising rates of syphilis infection.1,2
The Diagnosis: Condyloma Latum
A punch biopsy of the perianal mass revealed epidermal acanthosis with elongated slender rete ridges, scattered intraepidermal neutrophils, and a dense dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Figure, A) with a prominent plasma cell component (Figure, B). A treponemal immunohistochemical stain revealed numerous coiled spirochetes concentrated in the lower epidermis (Figure, C). Serologic test results including rapid plasma reagin (titer 1:1024) and Treponema pallidum antibody were reactive, confirming the diagnosis of secondary syphilis with condyloma latum. The patient was treated with intramuscular penicillin G with resolution of the lesion 2 weeks later.

Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the spirochete T pallidum, reached historically low rates in the United States in the early 2000s due to the widespread use of penicillin and effective public health efforts.1 However, the rates of primary and secondary syphilis infections recently have markedly increased, resulting in the current epidemic of syphilis in the United States and Europe.1,2 Its wide variety of clinical and histopathologic manifestations make recognition challenging and lend it the moniker “the great imitator.”
Secondary syphilis results from the systemic spread of T pallidum and classically is characterized by the triad of a skin rash that frequently involves the palms and soles, mucosal ulceration such as condyloma latum, and lymphadenopathy.2,3 However, condyloma latum may represent the only manifestation of secondary syphilis in a subset of patients,4 as observed in our patient.
In the 2 months prior to diagnosis, our patient was evaluated at multiple emergency departments and primary care clinics, receiving diagnoses of condyloma acuminatum, genital herpes simplex virus, hemorrhoids, and suspicion for malignancy—entities that comprise the differential diagnosis for condyloma latum.2,5 Despite some degree of overlap in patient populations, risk factors, and presentations between these diagnostic considerations, recognition of certain clinical features, in addition to histopathologic evaluation, may facilitate navigation of this differential diagnosis.
Primary and secondary syphilis infections have been predominantly observed in men, mostly men who have sex with men and/or those who are infected with HIV.1 Condyloma acuminata, genital herpes simplex virus, and chancroid also are seen in younger individuals, more commonly in those with multiple sexual partners, but show a more even gender distribution and are not restricted to those partaking in anal intercourse. The clinical presentation of condyloma latum can be differentiated by its painless, flat, smooth, and commonly hypopigmented appearance, often with associated surface erosion and a gray exudate, in contrast to condyloma acuminatum, which typically presents as nontender, flesh-colored or hyperpigmented, exophytic papules that may coalesce into plaques.2,3,6 Genital herpes simplex virus infection presents with multiple small papulovesicular lesions with ulceration, most commonly on the tip or shaft of the penis, though perianal lesions may be seen in men who have sex with men.7 Similarly, chancroid presents with painful necrotizing genital ulcers most commonly on the penis, though perianal lesions also may be seen.8 Hemorrhoids classically are seen in middle-aged adults with a history of constipation, present with rectal bleeding, and may be associated with pain in the setting of thrombosis or ulceration.9 Finally, perianal squamous cell carcinoma primarily occurs in older adults, typically in the sixth decade of life. Verrucous carcinoma most commonly arises in the oropharynx or anogenital region in sites of chronic irritation and presents as a slow-growing exophytic mass. Classic squamous cell carcinoma most commonly occurs in association with human papillomavirus infection and presents with scaly erythematous papules or plaques.10
Our case highlighted the clinical difficulty in recognizing condyloma latum, as this lesion remained undiagnosed for 2 months, and our patient presumptively was treated for multiple perianal pathologies prior to a biopsy being performed. Due to the clinical similarity of various perianal lesions, the diagnosis of condyloma latum should be considered, and serologic studies should be performed in fitting clinical contexts, especially in light of recently rising rates of syphilis infection.1,2
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Tayal S, Shaban F, Dasgupta K, et al. A case of syphilitic anal condylomata lata mimicking malignancy. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015; 17:69-71.
- Aung PP, Wimmer DB, Lester TR, et al. Perianal condylomata lata mimicking carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2022;49:209-214.
- Pourang A, Fung MA, Tartar D, et al. Condyloma lata in secondary syphilis. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;10:18-21.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJ, de Vries HJ. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259.
- Leslie SW, Sajjad H, Kumar S. Genital warts. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Groves MJ. Genital herpes: a review. Am Fam Physician. 2016; 93:928-934.
- Irizarry L, Velasquez J, Wray AA. Chancroid. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Mounsey AL, Halladay J, Sadiq TS. Hemorrhoids. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:204-210.
- Abbass MA, Valente MA. Premalignant and malignant perianal lesions. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2019;32:386-393.
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Tayal S, Shaban F, Dasgupta K, et al. A case of syphilitic anal condylomata lata mimicking malignancy. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015; 17:69-71.
- Aung PP, Wimmer DB, Lester TR, et al. Perianal condylomata lata mimicking carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2022;49:209-214.
- Pourang A, Fung MA, Tartar D, et al. Condyloma lata in secondary syphilis. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;10:18-21.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJ, de Vries HJ. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259.
- Leslie SW, Sajjad H, Kumar S. Genital warts. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Groves MJ. Genital herpes: a review. Am Fam Physician. 2016; 93:928-934.
- Irizarry L, Velasquez J, Wray AA. Chancroid. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Mounsey AL, Halladay J, Sadiq TS. Hemorrhoids. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:204-210.
- Abbass MA, Valente MA. Premalignant and malignant perianal lesions. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2019;32:386-393.
A 21-year-old man presented to our clinic with rectal pain of 2 months’ duration that occurred in association with bowel movements and rectal bleeding in the setting of constipation. The patient’s symptoms had persisted despite multiple clinical encounters and treatment with sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, clotrimazole, valacyclovir, topical hydrocortisone and pramoxine, topical lidocaine, imiquimod, and psyllium seed. The patient denied engaging in receptive anal intercourse and had no notable medical or surgical history. Physical examination revealed a 6-cm hypopigmented fungating mass on the left gluteal cleft just external to the anal verge; there were no other abnormal findings. The patient denied any other systemic symptoms.
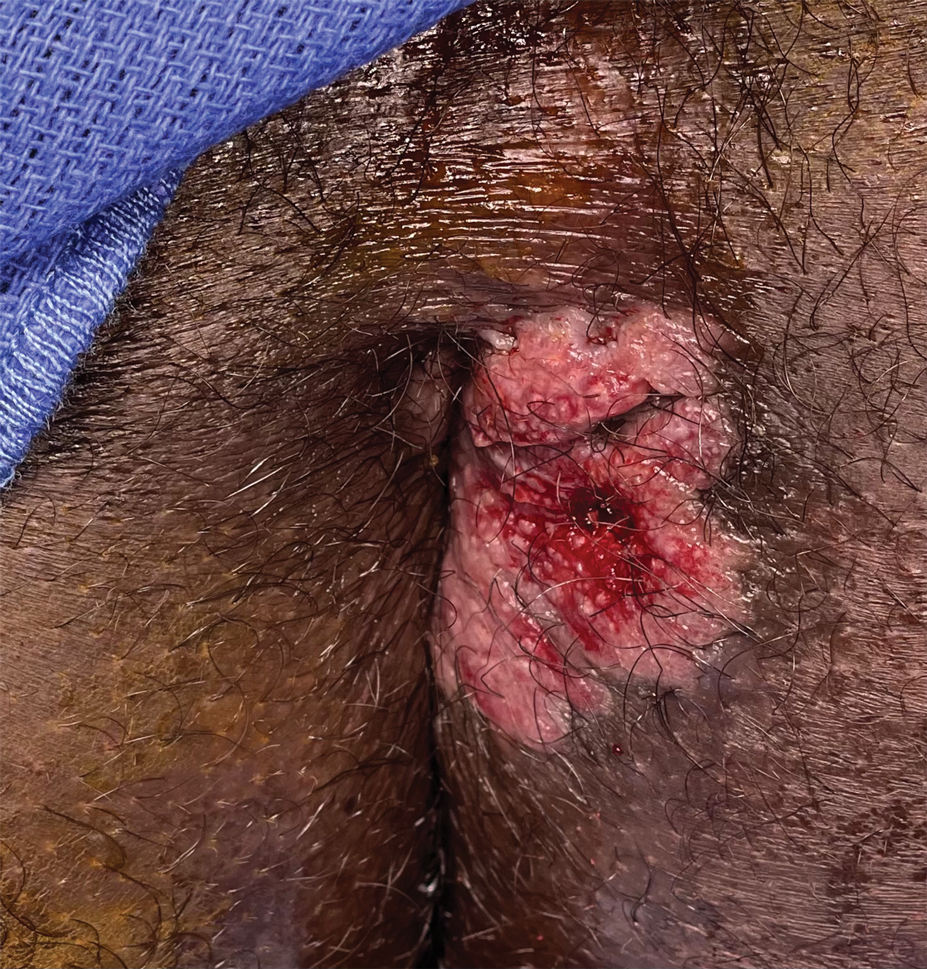
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Atopic Dermatitis May 2022
- Dupilumab is a subcutaneous injection therapy that inhibits the interleukin 4-receptor alpha subunit. It was approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe AD in 2017 and has since been approved for children and adolescents down to 6 years of age. Ungar and colleagues studied the effects of dupilumab on SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses in patients with moderate to severe AD. They previously found that dupilumab was associated with milder COVID-19 illness. In this study, they similarly found that dupilumab was associated with lower immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody levels to SARS-CoV-2, consistent with less severe COVID-19 illness. Future studies are needed to confirm these results. However, these results reassure that taking dupilumab does not pose any major harms in regard to COVID-19 outcomes.
- My patients with AD ask me on an almost daily basis about whether they should get vaccinated for SARS-CoV-2. I recommended that my patients get vaccinated, based on data from vaccine studies. However, there has been a dearth of data on the efficacy and safety of SARS-CoV-2 specifically in AD patients. Kridin and colleagues performed a population-based cohort study including 77,682 adults with AD, of which 58,582 patients had completed two doses of the BioNTech-Pfizer SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. They found that patients with AD who received both vs no vaccine doses had significantly lower risk for COVID-19, hospitalization, and mortality. These are the best data to date in support of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with AD. Of note, there was no significant impact of immunosuppressive drugs on vaccine efficacy against COVID-19. However, previous studies in other immune-mediated disorders suggest that immunosuppressants may lower vaccine immune responses.1,2 Some authors have advocated for temporarily discontinuing immunosuppressive agents for 1-2 weeks before and after administering SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Currently, there is insufficient evidence to make strong recommendations.
Numerous in utero and early-life risk factors for AD have been examined over the years. Maternal stress and depression have been considered as potential risk factors for AD in children.
- My research group showed a while back that depression during pregnancy and in the postpartum period was associated with higher likelihood of AD in children.3
- Kawaguchi and colleagues recently analyzed data from the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project Birth and Three-Generation Cohort Study in Japan, including 8377 mother-child dyads where the child had not developed AD by the age of 1 year. They found that mothers with vs without psychological distress in both prenatal and postnatal periods or even only in the postnatal period had significantly increased risk of their children developing AD at 1-2 years of age. It seems prudent that mothers try to minimize stress during pregnancy and postpartum, though, understandably, this is not always feasible. Additionally, children of mothers who experience a lot of stress during pregnancy or postpartum may benefit from closer surveillance for the development of AD and other atopic diseases.
Additional References
1. Dayam RM, Law JC, Goetbebuer RL, et al. Accelerated waning of immunity to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with immune mediated inflammatory diseases. JCI Insight. 2022 (Apr 26). Doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.159721 Source
2. Medeiros-Ribeiro AC, Bonfiglioli KR, Domiciano DS, et al. Distinct impact of DMARD combination and monotherapy in immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81:710-719. Doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221735 Source
3. McKenzie C, Silverberg JI. Maternal depression and atopic dermatitis in American children and adolescents. Dermatitis. 2020;31:75-80. Doi: 10.1097/DER.0000000000000548 Source
- Dupilumab is a subcutaneous injection therapy that inhibits the interleukin 4-receptor alpha subunit. It was approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe AD in 2017 and has since been approved for children and adolescents down to 6 years of age. Ungar and colleagues studied the effects of dupilumab on SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses in patients with moderate to severe AD. They previously found that dupilumab was associated with milder COVID-19 illness. In this study, they similarly found that dupilumab was associated with lower immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody levels to SARS-CoV-2, consistent with less severe COVID-19 illness. Future studies are needed to confirm these results. However, these results reassure that taking dupilumab does not pose any major harms in regard to COVID-19 outcomes.
- My patients with AD ask me on an almost daily basis about whether they should get vaccinated for SARS-CoV-2. I recommended that my patients get vaccinated, based on data from vaccine studies. However, there has been a dearth of data on the efficacy and safety of SARS-CoV-2 specifically in AD patients. Kridin and colleagues performed a population-based cohort study including 77,682 adults with AD, of which 58,582 patients had completed two doses of the BioNTech-Pfizer SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. They found that patients with AD who received both vs no vaccine doses had significantly lower risk for COVID-19, hospitalization, and mortality. These are the best data to date in support of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with AD. Of note, there was no significant impact of immunosuppressive drugs on vaccine efficacy against COVID-19. However, previous studies in other immune-mediated disorders suggest that immunosuppressants may lower vaccine immune responses.1,2 Some authors have advocated for temporarily discontinuing immunosuppressive agents for 1-2 weeks before and after administering SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Currently, there is insufficient evidence to make strong recommendations.
Numerous in utero and early-life risk factors for AD have been examined over the years. Maternal stress and depression have been considered as potential risk factors for AD in children.
- My research group showed a while back that depression during pregnancy and in the postpartum period was associated with higher likelihood of AD in children.3
- Kawaguchi and colleagues recently analyzed data from the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project Birth and Three-Generation Cohort Study in Japan, including 8377 mother-child dyads where the child had not developed AD by the age of 1 year. They found that mothers with vs without psychological distress in both prenatal and postnatal periods or even only in the postnatal period had significantly increased risk of their children developing AD at 1-2 years of age. It seems prudent that mothers try to minimize stress during pregnancy and postpartum, though, understandably, this is not always feasible. Additionally, children of mothers who experience a lot of stress during pregnancy or postpartum may benefit from closer surveillance for the development of AD and other atopic diseases.
Additional References
1. Dayam RM, Law JC, Goetbebuer RL, et al. Accelerated waning of immunity to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with immune mediated inflammatory diseases. JCI Insight. 2022 (Apr 26). Doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.159721 Source
2. Medeiros-Ribeiro AC, Bonfiglioli KR, Domiciano DS, et al. Distinct impact of DMARD combination and monotherapy in immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81:710-719. Doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221735 Source
3. McKenzie C, Silverberg JI. Maternal depression and atopic dermatitis in American children and adolescents. Dermatitis. 2020;31:75-80. Doi: 10.1097/DER.0000000000000548 Source
- Dupilumab is a subcutaneous injection therapy that inhibits the interleukin 4-receptor alpha subunit. It was approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe AD in 2017 and has since been approved for children and adolescents down to 6 years of age. Ungar and colleagues studied the effects of dupilumab on SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses in patients with moderate to severe AD. They previously found that dupilumab was associated with milder COVID-19 illness. In this study, they similarly found that dupilumab was associated with lower immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody levels to SARS-CoV-2, consistent with less severe COVID-19 illness. Future studies are needed to confirm these results. However, these results reassure that taking dupilumab does not pose any major harms in regard to COVID-19 outcomes.
- My patients with AD ask me on an almost daily basis about whether they should get vaccinated for SARS-CoV-2. I recommended that my patients get vaccinated, based on data from vaccine studies. However, there has been a dearth of data on the efficacy and safety of SARS-CoV-2 specifically in AD patients. Kridin and colleagues performed a population-based cohort study including 77,682 adults with AD, of which 58,582 patients had completed two doses of the BioNTech-Pfizer SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. They found that patients with AD who received both vs no vaccine doses had significantly lower risk for COVID-19, hospitalization, and mortality. These are the best data to date in support of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with AD. Of note, there was no significant impact of immunosuppressive drugs on vaccine efficacy against COVID-19. However, previous studies in other immune-mediated disorders suggest that immunosuppressants may lower vaccine immune responses.1,2 Some authors have advocated for temporarily discontinuing immunosuppressive agents for 1-2 weeks before and after administering SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Currently, there is insufficient evidence to make strong recommendations.
Numerous in utero and early-life risk factors for AD have been examined over the years. Maternal stress and depression have been considered as potential risk factors for AD in children.
- My research group showed a while back that depression during pregnancy and in the postpartum period was associated with higher likelihood of AD in children.3
- Kawaguchi and colleagues recently analyzed data from the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project Birth and Three-Generation Cohort Study in Japan, including 8377 mother-child dyads where the child had not developed AD by the age of 1 year. They found that mothers with vs without psychological distress in both prenatal and postnatal periods or even only in the postnatal period had significantly increased risk of their children developing AD at 1-2 years of age. It seems prudent that mothers try to minimize stress during pregnancy and postpartum, though, understandably, this is not always feasible. Additionally, children of mothers who experience a lot of stress during pregnancy or postpartum may benefit from closer surveillance for the development of AD and other atopic diseases.
Additional References
1. Dayam RM, Law JC, Goetbebuer RL, et al. Accelerated waning of immunity to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with immune mediated inflammatory diseases. JCI Insight. 2022 (Apr 26). Doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.159721 Source
2. Medeiros-Ribeiro AC, Bonfiglioli KR, Domiciano DS, et al. Distinct impact of DMARD combination and monotherapy in immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81:710-719. Doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221735 Source
3. McKenzie C, Silverberg JI. Maternal depression and atopic dermatitis in American children and adolescents. Dermatitis. 2020;31:75-80. Doi: 10.1097/DER.0000000000000548 Source
A New Approach to an Old Problem: Not Just the Azoles for Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
At the conclusion of this activity, the participant will be able to:
• Appreciate the scope of the problem of Candida infection in terms of cost, lost productivity, and medical visits
• Learn current diagnostic and treatment patterns for vulvovaginal candidiasis
• Appreciate the attributes of the new antifungal class (triterpenoids) for vulvovaginal candidiasis
• Analyze clinical trial data with the non-azole approach to vulvovaginal candidiasis
Click here to read this supplement
To access post-test and evaluation, visit www.worldclasscme.com/online-courses/new-approach-old-problem-no-longer-just-azoles-candida
World Class CME designates this journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.0 AMA PRA Category1 Credit™.
At the conclusion of this activity, the participant will be able to:
• Appreciate the scope of the problem of Candida infection in terms of cost, lost productivity, and medical visits
• Learn current diagnostic and treatment patterns for vulvovaginal candidiasis
• Appreciate the attributes of the new antifungal class (triterpenoids) for vulvovaginal candidiasis
• Analyze clinical trial data with the non-azole approach to vulvovaginal candidiasis
Click here to read this supplement
To access post-test and evaluation, visit www.worldclasscme.com/online-courses/new-approach-old-problem-no-longer-just-azoles-candida
World Class CME designates this journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.0 AMA PRA Category1 Credit™.
At the conclusion of this activity, the participant will be able to:
• Appreciate the scope of the problem of Candida infection in terms of cost, lost productivity, and medical visits
• Learn current diagnostic and treatment patterns for vulvovaginal candidiasis
• Appreciate the attributes of the new antifungal class (triterpenoids) for vulvovaginal candidiasis
• Analyze clinical trial data with the non-azole approach to vulvovaginal candidiasis
Click here to read this supplement
To access post-test and evaluation, visit www.worldclasscme.com/online-courses/new-approach-old-problem-no-longer-just-azoles-candida
World Class CME designates this journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.0 AMA PRA Category1 Credit™.