User login
Multidisciplinary lifestyle program improves outcomes in RA
Key clinical point: “Plants for Joints” (PFJ), a 16-week multidisciplinary lifestyle program based on whole food plant-based diet, physical activity, and stress management in addition to usual care, significantly improved disease activity compared with usual care alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and low-to-moderate disease activity.
Major finding: After 16 weeks, patients receiving PFJ vs usual care alone had a greater reduction in disease activity score of 28 joints (DAS28; mean difference −0.90; P < .0001) and were more likely to achieve DAS28 <2.60 (odds ratio [OR] 4.6) and European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology Good Response (OR 4.3; both P < .001). No serious adverse events were reported.
Study details: This randomized controlled trial, “Plants for Joints,” included 77 patients with RA and low-to-moderate disease activity who were randomly assigned to receive PFJ intervention plus usual care or usual care alone.
Disclosures: The trial was funded by Reade (The Netherlands) and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Walrabenstein W et al. A multidisciplinary lifestyle program for rheumatoid arthritis: The “Plants for Joints” randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 (Jan 6). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac693
Key clinical point: “Plants for Joints” (PFJ), a 16-week multidisciplinary lifestyle program based on whole food plant-based diet, physical activity, and stress management in addition to usual care, significantly improved disease activity compared with usual care alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and low-to-moderate disease activity.
Major finding: After 16 weeks, patients receiving PFJ vs usual care alone had a greater reduction in disease activity score of 28 joints (DAS28; mean difference −0.90; P < .0001) and were more likely to achieve DAS28 <2.60 (odds ratio [OR] 4.6) and European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology Good Response (OR 4.3; both P < .001). No serious adverse events were reported.
Study details: This randomized controlled trial, “Plants for Joints,” included 77 patients with RA and low-to-moderate disease activity who were randomly assigned to receive PFJ intervention plus usual care or usual care alone.
Disclosures: The trial was funded by Reade (The Netherlands) and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Walrabenstein W et al. A multidisciplinary lifestyle program for rheumatoid arthritis: The “Plants for Joints” randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 (Jan 6). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac693
Key clinical point: “Plants for Joints” (PFJ), a 16-week multidisciplinary lifestyle program based on whole food plant-based diet, physical activity, and stress management in addition to usual care, significantly improved disease activity compared with usual care alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and low-to-moderate disease activity.
Major finding: After 16 weeks, patients receiving PFJ vs usual care alone had a greater reduction in disease activity score of 28 joints (DAS28; mean difference −0.90; P < .0001) and were more likely to achieve DAS28 <2.60 (odds ratio [OR] 4.6) and European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology Good Response (OR 4.3; both P < .001). No serious adverse events were reported.
Study details: This randomized controlled trial, “Plants for Joints,” included 77 patients with RA and low-to-moderate disease activity who were randomly assigned to receive PFJ intervention plus usual care or usual care alone.
Disclosures: The trial was funded by Reade (The Netherlands) and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Walrabenstein W et al. A multidisciplinary lifestyle program for rheumatoid arthritis: The “Plants for Joints” randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 (Jan 6). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac693
Tapering glucocorticoids to ≤2.5 mg/day increases the risk for flare in patients receiving bDMARD in RA
Key clinical point: Tapering glucocorticoids to doses >2.5 mg/day was effective with no increase in the risk for flare, whereas tapering to doses ≤2.5 mg/day significantly increased the risk for flare in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receiving biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD).
Major finding: Discontinuation of glucocorticoids (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.45; 95% CI 1.13-2.24) and tapering of glucocorticoid dose to 0-2.5 mg/day (aOR 1.37; 95% CI 1.06-2.01) were significantly associated with an increased risk for flare, whereas tapering of glucocorticoid dose to >2.5 mg/day did not significantly increase the risk for flare compared with no tapering.
Study details: The data come from a case-crossover study including 508 patients with RA receiving bDMARD with or without glucocorticoids, of which 52.5% of patients reported at least one flare.
Disclosures: This study did not declare any specific funding. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Source: Adami G et al. Tapering glucocorticoids and risk of flare in rheumatoid arthritis on biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs). RMD Open. 2023;9(1):e002792 (Jan 4). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002792
Key clinical point: Tapering glucocorticoids to doses >2.5 mg/day was effective with no increase in the risk for flare, whereas tapering to doses ≤2.5 mg/day significantly increased the risk for flare in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receiving biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD).
Major finding: Discontinuation of glucocorticoids (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.45; 95% CI 1.13-2.24) and tapering of glucocorticoid dose to 0-2.5 mg/day (aOR 1.37; 95% CI 1.06-2.01) were significantly associated with an increased risk for flare, whereas tapering of glucocorticoid dose to >2.5 mg/day did not significantly increase the risk for flare compared with no tapering.
Study details: The data come from a case-crossover study including 508 patients with RA receiving bDMARD with or without glucocorticoids, of which 52.5% of patients reported at least one flare.
Disclosures: This study did not declare any specific funding. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Source: Adami G et al. Tapering glucocorticoids and risk of flare in rheumatoid arthritis on biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs). RMD Open. 2023;9(1):e002792 (Jan 4). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002792
Key clinical point: Tapering glucocorticoids to doses >2.5 mg/day was effective with no increase in the risk for flare, whereas tapering to doses ≤2.5 mg/day significantly increased the risk for flare in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receiving biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD).
Major finding: Discontinuation of glucocorticoids (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.45; 95% CI 1.13-2.24) and tapering of glucocorticoid dose to 0-2.5 mg/day (aOR 1.37; 95% CI 1.06-2.01) were significantly associated with an increased risk for flare, whereas tapering of glucocorticoid dose to >2.5 mg/day did not significantly increase the risk for flare compared with no tapering.
Study details: The data come from a case-crossover study including 508 patients with RA receiving bDMARD with or without glucocorticoids, of which 52.5% of patients reported at least one flare.
Disclosures: This study did not declare any specific funding. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Source: Adami G et al. Tapering glucocorticoids and risk of flare in rheumatoid arthritis on biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs). RMD Open. 2023;9(1):e002792 (Jan 4). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002792
Comorbidity burden tied to lower likelihood of achieving quality care in RA
Key clinical point: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who were males or had multiple comorbidities were less likely to achieve quality care markers, thereby highlighting the need to prioritize early treatment in the vulnerable patient population.
Major finding: Among patients with RA, males (odds ratio [OR] 0.72; 95% CI 0.72-0.73) and those with a Rheumatic Disease Comorbidity Index >2 (OR 0.88; 95% CI 0.86-0.90) were less likely to receive a rheumatologist referral, with findings being similar for annual physical examination. Additionally, the presence of diabetes was associated with reduced odds of receiving a rheumatologist referral (OR 0.77; 95% CI 0.76-0.78) or annual physical examination (OR 0.59; 95% CI 0.56-0.62).
Study details: This retrospective observational cohort study included 581,770 patients with incident RA.
Disclosures: This study was funded by joint grants from Chang Gung Memorial Hospital-University of Michigan Medical Center to two authors. KC Chung reported receiving funding, research grant, and book royalties from various sources.
Source: Seyferth AV et al. Factors associated with quality care among adults with rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(12):e2246299 (Dec 12). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.46299.
Key clinical point: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who were males or had multiple comorbidities were less likely to achieve quality care markers, thereby highlighting the need to prioritize early treatment in the vulnerable patient population.
Major finding: Among patients with RA, males (odds ratio [OR] 0.72; 95% CI 0.72-0.73) and those with a Rheumatic Disease Comorbidity Index >2 (OR 0.88; 95% CI 0.86-0.90) were less likely to receive a rheumatologist referral, with findings being similar for annual physical examination. Additionally, the presence of diabetes was associated with reduced odds of receiving a rheumatologist referral (OR 0.77; 95% CI 0.76-0.78) or annual physical examination (OR 0.59; 95% CI 0.56-0.62).
Study details: This retrospective observational cohort study included 581,770 patients with incident RA.
Disclosures: This study was funded by joint grants from Chang Gung Memorial Hospital-University of Michigan Medical Center to two authors. KC Chung reported receiving funding, research grant, and book royalties from various sources.
Source: Seyferth AV et al. Factors associated with quality care among adults with rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(12):e2246299 (Dec 12). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.46299.
Key clinical point: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who were males or had multiple comorbidities were less likely to achieve quality care markers, thereby highlighting the need to prioritize early treatment in the vulnerable patient population.
Major finding: Among patients with RA, males (odds ratio [OR] 0.72; 95% CI 0.72-0.73) and those with a Rheumatic Disease Comorbidity Index >2 (OR 0.88; 95% CI 0.86-0.90) were less likely to receive a rheumatologist referral, with findings being similar for annual physical examination. Additionally, the presence of diabetes was associated with reduced odds of receiving a rheumatologist referral (OR 0.77; 95% CI 0.76-0.78) or annual physical examination (OR 0.59; 95% CI 0.56-0.62).
Study details: This retrospective observational cohort study included 581,770 patients with incident RA.
Disclosures: This study was funded by joint grants from Chang Gung Memorial Hospital-University of Michigan Medical Center to two authors. KC Chung reported receiving funding, research grant, and book royalties from various sources.
Source: Seyferth AV et al. Factors associated with quality care among adults with rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(12):e2246299 (Dec 12). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.46299.
Oral glucocorticoid use raises risk for Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in RA
Key clinical point: Current use of oral glucocorticoids significantly increased the risk for Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (SAB) in a dose-dependent manner in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but the absolute risk was low with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) use.
Major finding: Relative risk for SAB was 2.2-fold (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 2.2; 95% CI 1.3-4.0) and 9.5-fold (aOR 9.5; 95% CI 3.9-22.7) higher with current use of ≤7.5 and >7.5 mg/day prednisolone-equivalent oral glucocorticoids, respectively. The number needed to harm was approximately 10 times higher with the current use of bDMARD vs >7.5 mg/day oral glucocorticoids (1172 vs 110).
Study details: This nested case-control study included 180 patients with first-time SAB who received glucocorticoids or bDMARD and 720 age- and sex-matched control individuals from a cohort of 30,479 patients with RA.
Disclosures: This study was supported by The Danish Rheumatism Association (TDRA) and Beckett-Fonden. Several authors reported ties with various sources, including TDRA and Beckett-Fonden.
Source: Dieperink SS et al. Antirheumatic treatment, disease activity and risk of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in rheumatoid arthritis: A nationwide nested case-control study. RMD Open. 2022;8(2):e002636 (Dec 14). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002636
Key clinical point: Current use of oral glucocorticoids significantly increased the risk for Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (SAB) in a dose-dependent manner in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but the absolute risk was low with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) use.
Major finding: Relative risk for SAB was 2.2-fold (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 2.2; 95% CI 1.3-4.0) and 9.5-fold (aOR 9.5; 95% CI 3.9-22.7) higher with current use of ≤7.5 and >7.5 mg/day prednisolone-equivalent oral glucocorticoids, respectively. The number needed to harm was approximately 10 times higher with the current use of bDMARD vs >7.5 mg/day oral glucocorticoids (1172 vs 110).
Study details: This nested case-control study included 180 patients with first-time SAB who received glucocorticoids or bDMARD and 720 age- and sex-matched control individuals from a cohort of 30,479 patients with RA.
Disclosures: This study was supported by The Danish Rheumatism Association (TDRA) and Beckett-Fonden. Several authors reported ties with various sources, including TDRA and Beckett-Fonden.
Source: Dieperink SS et al. Antirheumatic treatment, disease activity and risk of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in rheumatoid arthritis: A nationwide nested case-control study. RMD Open. 2022;8(2):e002636 (Dec 14). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002636
Key clinical point: Current use of oral glucocorticoids significantly increased the risk for Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (SAB) in a dose-dependent manner in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but the absolute risk was low with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) use.
Major finding: Relative risk for SAB was 2.2-fold (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 2.2; 95% CI 1.3-4.0) and 9.5-fold (aOR 9.5; 95% CI 3.9-22.7) higher with current use of ≤7.5 and >7.5 mg/day prednisolone-equivalent oral glucocorticoids, respectively. The number needed to harm was approximately 10 times higher with the current use of bDMARD vs >7.5 mg/day oral glucocorticoids (1172 vs 110).
Study details: This nested case-control study included 180 patients with first-time SAB who received glucocorticoids or bDMARD and 720 age- and sex-matched control individuals from a cohort of 30,479 patients with RA.
Disclosures: This study was supported by The Danish Rheumatism Association (TDRA) and Beckett-Fonden. Several authors reported ties with various sources, including TDRA and Beckett-Fonden.
Source: Dieperink SS et al. Antirheumatic treatment, disease activity and risk of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in rheumatoid arthritis: A nationwide nested case-control study. RMD Open. 2022;8(2):e002636 (Dec 14). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002636
Most patients successfully discontinue glucocorticoids after initiation as bridging therapy in RA
Key clinical point: The probability of continued use of glucocorticoids after bridging was low among patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), with a shorter oral bridging schedule and lower initial dose being associated with fewer patients taking glucocorticoids at 18 months after bridging.
Major finding: The probability of using or restarting glucocorticoids decreased from 0.18 at 1 month to 0.07 at 6, 12, and 18 months of ending glucocorticoid bridging therapy. A longer duration of bridging schedule (odds ratio [OR] 1.14; 95% CI 1.05-1.24) and higher initial glucocorticoid dose (OR 1.04; 95% CI 1.01-1.06) were associated with more patients taking glucocorticoids at 18 months after bridging.
Study details: This individual patient data meta-analysis of seven clinical trials included 1653 patients with newly diagnosed RA, undifferentiated arthritis, or a high-risk profile for persistent arthritis who received glucocorticoids bridging therapy as initial treatment.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. Several authors reported ties with various sources.
Source: van Ouwerkerk L et al. Individual patient data meta-analysis on continued use of glucocorticoids after their initiation as bridging therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022 (Dec 16). Doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223443
Key clinical point: The probability of continued use of glucocorticoids after bridging was low among patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), with a shorter oral bridging schedule and lower initial dose being associated with fewer patients taking glucocorticoids at 18 months after bridging.
Major finding: The probability of using or restarting glucocorticoids decreased from 0.18 at 1 month to 0.07 at 6, 12, and 18 months of ending glucocorticoid bridging therapy. A longer duration of bridging schedule (odds ratio [OR] 1.14; 95% CI 1.05-1.24) and higher initial glucocorticoid dose (OR 1.04; 95% CI 1.01-1.06) were associated with more patients taking glucocorticoids at 18 months after bridging.
Study details: This individual patient data meta-analysis of seven clinical trials included 1653 patients with newly diagnosed RA, undifferentiated arthritis, or a high-risk profile for persistent arthritis who received glucocorticoids bridging therapy as initial treatment.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. Several authors reported ties with various sources.
Source: van Ouwerkerk L et al. Individual patient data meta-analysis on continued use of glucocorticoids after their initiation as bridging therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022 (Dec 16). Doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223443
Key clinical point: The probability of continued use of glucocorticoids after bridging was low among patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), with a shorter oral bridging schedule and lower initial dose being associated with fewer patients taking glucocorticoids at 18 months after bridging.
Major finding: The probability of using or restarting glucocorticoids decreased from 0.18 at 1 month to 0.07 at 6, 12, and 18 months of ending glucocorticoid bridging therapy. A longer duration of bridging schedule (odds ratio [OR] 1.14; 95% CI 1.05-1.24) and higher initial glucocorticoid dose (OR 1.04; 95% CI 1.01-1.06) were associated with more patients taking glucocorticoids at 18 months after bridging.
Study details: This individual patient data meta-analysis of seven clinical trials included 1653 patients with newly diagnosed RA, undifferentiated arthritis, or a high-risk profile for persistent arthritis who received glucocorticoids bridging therapy as initial treatment.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. Several authors reported ties with various sources.
Source: van Ouwerkerk L et al. Individual patient data meta-analysis on continued use of glucocorticoids after their initiation as bridging therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022 (Dec 16). Doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223443
Methotrexate use needs close monitoring in patients with RA of childbearing age
Key clinical point: Methotrexate use before conception increased the risk for pregnancy losses and abortion in childbearing-age women with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), with the risk for elective termination of pregnancy (ETOP) being significantly higher with methotrexate use in the period close to conception.
Major finding: Methotrexate use any time before conception was significantly associated with a higher risk for pregnancy losses (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 2.22; P < .001) and abortion (aOR 1.76; P < .01) in women with vs without RA, with the risk for ETOP being almost 4-fold higher with methotrexate use in the 3-month window before conception (aOR 4.77; P < .05).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including childbearing-age women with RA who did (n = 223) and did not (n = 323) receive methotrexate and those without RA who did not receive methotrexate (n = 1690).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Italian Society for Rheumatology. This authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
Source: Zanetti A et al. Impact of rheumatoid arthritis and methotrexate on pregnancy outcomes: Retrospective cohort study of the Italian Society for Rheumatology. RMD Open. 2022;8(2):e002412 (Dec 12). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002412
Key clinical point: Methotrexate use before conception increased the risk for pregnancy losses and abortion in childbearing-age women with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), with the risk for elective termination of pregnancy (ETOP) being significantly higher with methotrexate use in the period close to conception.
Major finding: Methotrexate use any time before conception was significantly associated with a higher risk for pregnancy losses (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 2.22; P < .001) and abortion (aOR 1.76; P < .01) in women with vs without RA, with the risk for ETOP being almost 4-fold higher with methotrexate use in the 3-month window before conception (aOR 4.77; P < .05).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including childbearing-age women with RA who did (n = 223) and did not (n = 323) receive methotrexate and those without RA who did not receive methotrexate (n = 1690).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Italian Society for Rheumatology. This authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
Source: Zanetti A et al. Impact of rheumatoid arthritis and methotrexate on pregnancy outcomes: Retrospective cohort study of the Italian Society for Rheumatology. RMD Open. 2022;8(2):e002412 (Dec 12). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002412
Key clinical point: Methotrexate use before conception increased the risk for pregnancy losses and abortion in childbearing-age women with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), with the risk for elective termination of pregnancy (ETOP) being significantly higher with methotrexate use in the period close to conception.
Major finding: Methotrexate use any time before conception was significantly associated with a higher risk for pregnancy losses (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 2.22; P < .001) and abortion (aOR 1.76; P < .01) in women with vs without RA, with the risk for ETOP being almost 4-fold higher with methotrexate use in the 3-month window before conception (aOR 4.77; P < .05).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including childbearing-age women with RA who did (n = 223) and did not (n = 323) receive methotrexate and those without RA who did not receive methotrexate (n = 1690).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Italian Society for Rheumatology. This authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
Source: Zanetti A et al. Impact of rheumatoid arthritis and methotrexate on pregnancy outcomes: Retrospective cohort study of the Italian Society for Rheumatology. RMD Open. 2022;8(2):e002412 (Dec 12). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002412
Managing patients with comorbid opioid and alcohol use disorders
When left untreated, opioid use disorder (OUD) is a debilitating and potentially lethal illness. Despite the availability of safe and effective medications for OUD, the prevalence of opioid use and overdose deaths has been increasing every year.1 An additional challenge in OUD treatment is the high prevalence of comorbid alcohol use disorder (AUD).2-6 A Clinical Trials Network survey from the National Institute on Drug Abuse found 38% of persons seeking treatment for OUD also had AUD.7 Other analyses have found alcohol was involved in approximately one-fifth of opioid-related deaths.8 Research also reveals that comorbid OUD and AUD contributes to poor treatment outcomes, more medical comorbidities, and a high risk of death (including overdose death).4,9 There is no standard of care for this particular patient population.3 This article reviews the evidence and summarizes practical considerations regarding the clinical management of patients with comorbid OUD and AUD.
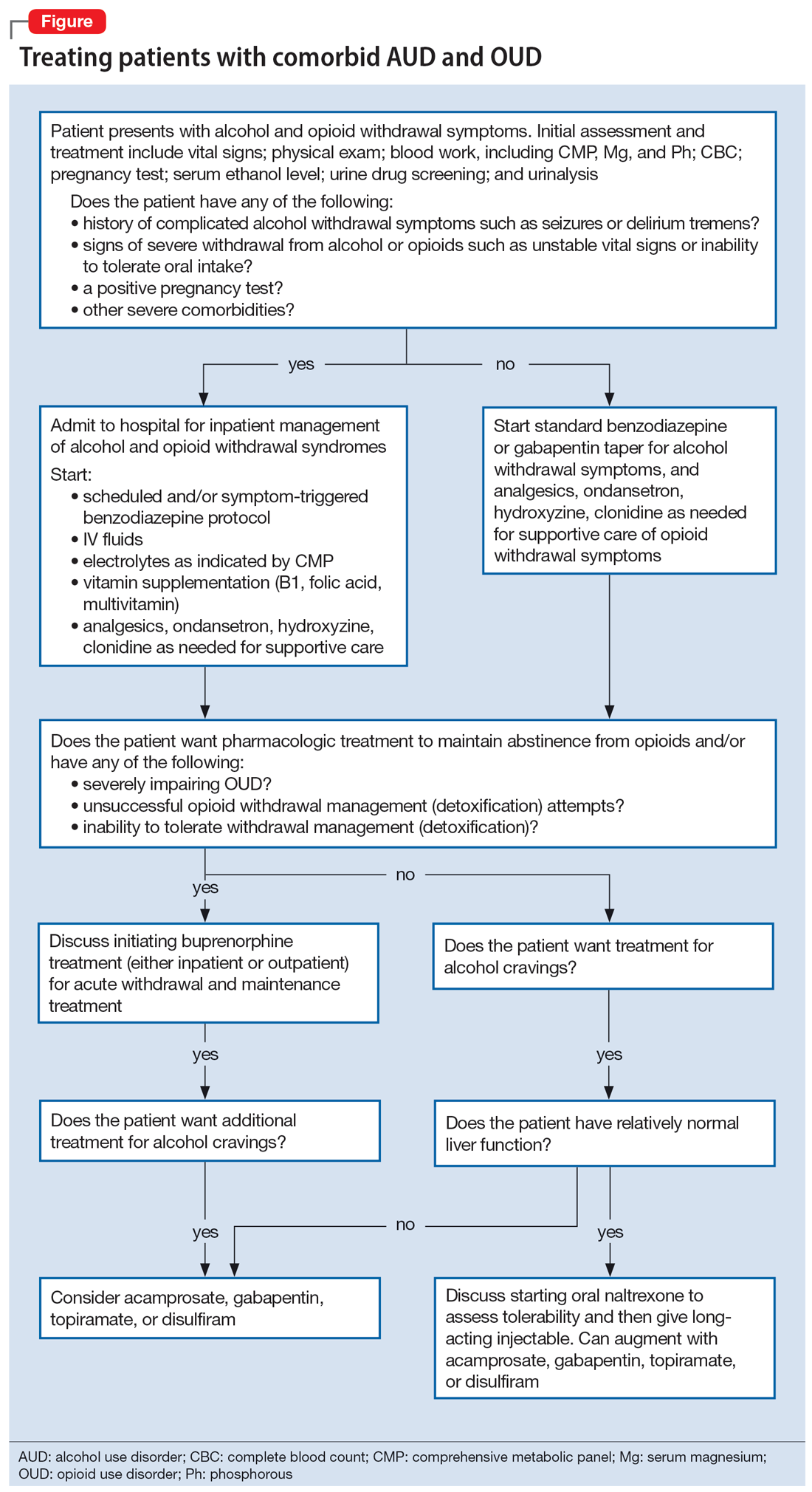
To illustrate the various decision points, we will follow 2 hypothetical patients through various stages of treatment (Figure), from their presentation in the emergency department (ED) or outpatient clinic, through their hospital admission (if needed), and into their outpatient follow-up treatment.
CASE REPORTS
Ms. A and Ms. B present to the ED for evaluation of nausea, vomiting, sweating, anxiety, and tremor. Both patients describe their most recent use of both alcohol and opioids approximately 12 hours ago, and each has been attempting to stop using both substances at home.
Decision-making in the emergency setting
In the ED, a few important decisions need to be made regarding treatment:
- Are the presenting symptoms primarily due to alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS), opioid withdrawal syndrome (OWS), or both?
- Does the patient require inpatient medical withdrawal management (detoxification) based on the history and severity of the withdrawal symptoms?
- What are the patient’s treatment goals for their AUD and OUD?
- Is maintenance medication for OUD indicated? If so, which medication is most appropriate?
In the ED, the presentation of individuals affected by both OUD and AUD can be challenging because OWS shares overlapping features with AWS, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, sweating, anxiety, and tremor. However, although acute OWS is typically very uncomfortable, it is rarely lethal. On the other hand, severe AWS may result in delirium, seizures, and death,10 which makes it essential to recognize and treat appropriately.
Both Ms. A and Ms. B should be medically evaluated and treated by an emergency medicine physician in conjunction with psychiatric (or addiction medicine) consultation. The ED assessment of a patient presenting with both AUD and OUD should include vital signs monitoring; physical examination; blood work including comprehensive metabolic panel, serum magnesium, and phosphorus; complete blood count; pregnancy test for women of reproductive age; urine drug screen (UDS); urinalysis; and serum ethanol level. Of note, sympathetic hyperactivity is found in both alcohol and opioid withdrawal, and patients with alcohol withdrawal may also have hypokalemia, a condition associated with an increased risk of arrhythmia. Furthermore, a prolonged QTc would affect clinical decision-making about medications for OUD (ie, methadone) and withdrawal management (ie, ondansetron, trazodone, and hydroxyzine). Therefore, an electrocardiogram should be conducted, where appropriate.
Initial treatment of AWS includes vitamin supplementation (thiamine, folic acid, and multivitamins) and benzodiazepine administration (symptom-triggered and/or scheduled taper). It may also include IV fluid resuscitation, analgesics for pain, ondansetron for nausea and vomiting, and other electrolyte repletion as indicated by the laboratory results.11 Additional measures for patients in opioid withdrawal should include alpha-2 agonists such as clonidine or lofexidine for adrenergic symptoms, antiemetics, antidiarrheals, muscle relaxants, anxiolytics such as hydroxyzine, and sleep medications such as trazodone.12
Continue to: The next decision...
The next decision is whether the patient needs to be admitted for inpatient treatment. This decision is based primarily on the risk assessment and severity of AWS, including a compelling history of complicated AWS such as seizures or delirium tremens as well as consideration of the complexity and severity of any comorbid medical or psychiatric conditions. Other indications for medical withdrawal management include a history of unsuccessful ambulatory withdrawal management and pregnancy. For severe AWS, a scheduled benzodiazepine taper in addition to the symptom-triggered protocol should be considered.13-15 A psychiatric evaluation may be obtained in the ED, as long as the patient is sober enough to meaningfully participate in the psychiatric interview. Wherever possible, psychiatric interviews should be supplemented by collateral information.
CASE REPORTS CONTINUED
Ms. A admits to a 5-year history of alcohol and opioid use that meets the criteria for severe AUD and severe OUD. She has previously required inpatient treatment for seizures related to AWS. Laboratory results are notable for a serum ethanol level of 380 mg/dL, UDS positive for opioids, and a negative pregnancy test.
Disposition of patients in alcohol and opioid withdrawal
Given Ms. A’s history of seizures while withdrawing from alcohol, she is appropriate for hospital admission for medically managed withdrawal observation. As previously mentioned, there is clinical overlap between AWS and OWS, and differentiating between the 2 syndromes is essential and may be lifesaving. Whereas anxiety, agitation, diaphoresis, tachycardia, hypertension, and insomnia can be seen in both opioid and alcohol withdrawal, OWS-specific symptoms include mydriasis, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, bone or joint aches, yawning, and piloerection. AWS may present with visual or tactile hallucinations, delirium, and grand mal seizures.15
The details of inpatient management are beyond the scope of this article; however, both patients should be started on thiamine, folic acid, and a multivitamin. For patients in alcohol withdrawal with a history of poor diet who appear malnourished or have a history of malabsorption (such as gastric bypass surgery), thiamine 100 mg/d IV should be given for 3 to 5 days to prevent Wernicke encephalopathy.16 Where there is any concern the patient may be exhibiting signs of Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome (impaired cognition, evident malnourishment, ataxia, or eye movement abnormalities), high-dose thiamine IV should be given presumptively as follows: 500 mg IV 3 times a day for 3 days, 250 mg/d IV for 5 days, and then oral supplementation 100 mg/d for at least 30 days.17
In summary, on presentation to the ED, both patients should be medically stabilized and started on benzodiazepines for alcohol withdrawal. The risk assessment and the severity of the AWS often determines the level of care.
CASE REPORTS CONTINUED
On hospital Day 2, Ms. A tells the consulting psychiatrist she would like to start medications to treat her substance use disorders. She has a long history of failed attempts to achieve abstinence from opioids, so she and the psychiatrist agree to initiate a trial of buprenorphine/naloxone for her OUD, 4 mg/1 mg to 8 mg/2 mg for Day 1. Although buprenorphine/naloxone seems to help her alcohol cravings somewhat, she requests additional help. She experiences migraine headaches, which is in part why she began using opioid medications. Via joint decision making with her psychiatrist, she agrees to a trial of topiramate, with a slow titration schedule starting at 25 mg/d.
Continue to: Management decisions
Management decisions: Buprenorphine for OUD
The next issue is to determine the appropriate treatment for the patient’s OUD. Although treating OWS is important in improving the patient’s health, decreasing their discomfort, and facilitating their participation in a psychosocial treatment program,18 current evidence suggests that opioid withdrawal management alone without medication for OUD rarely leads to long-term recovery.19,20 Some research suggests that the risk of accidental opioid overdose immediately following acute withdrawal management may actually be increased due to decreased tolerance in these patients.12,21,22
Three medications have the most evidence for OUD treatment: buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone.15 The decision to use buprenorphine, methadone, or naltrexone depends on a variety of factors, including the severity of the OUD, patient history of prior treatment successes and failures, comorbid medical and psychiatric conditions, and patient preference.4 Treatment with buprenorphine or methadone is preferred over naltrexone for patients who do not want to or cannot tolerate the physical and emotional discomfort of the opioid withdrawal process, who experience moderate to severe OUD, who have a history of failed abstinence-based treatment, or who have more severe physiological tolerance/dependence.12 Buprenorphine is a mu opioid receptor partial agonist that has been shown to reduce opioid cravings,23 provide moderate pain relief,24 and ameliorate OWS.12 It does not typically result in significant respiratory depression, which is the biggest safety concern for opioid use.12 Buprenorphine may also treat comorbid AUD at higher doses; however, the data are inconclusive.25,26 Buprenorphine should be prescribed with caution to patients with comorbid, uncontrolled AUD, due to the risk of respiratory depression when combined with alcohol. Patients who continue to drink alcohol but are able to abstain from opioids may consider starting an AUD-specific medication. Pharmacologic options are discussed in more detail in the next section.
For patients who have higher physiological dependence or more severe OUD, methadone may be a reasonable alternative to buprenorphine. Methadone, a mu-opioid receptor agonist, ameliorates OWS, reduces opioid cravings, and reduces the euphoric effects of opioid ingestion if the patient relapses. However, methadone can only be dispensed for the treatment of OUD by a federally-certified treatment program governed by restrictive and federally mandated guidelines. Compared to buprenorphine, methadone is more dangerous in overdose, has more drug interactions, and is more commonly diverted for recreational use.27 Furthermore, methadone should be prescribed with caution to patients with comorbid, uncontrolled AUD, because both alcohol and methadone can result in respiratory depression.
By contrast, the first-line treatment for individuals experiencing moderateto severe AUD is typically naltrexone.28 Naltrexone is contraindicated in Ms. A because she has a severe OUD and is unlikely to tolerate the opioid withdrawal process. Research suggests that the use of naltrexone for OUD should be limited to patients who have a mild disorder or who show low physiological dependence.29 Alternatively, acamprosate, disulfiram, topiramate, or gabapentin should be considered for Ms. A.4,28,30 Because each of these medications have specific strengths and weaknesses, medication selection should be based on individual patient factors such as comorbid psychiatric and medical conditions and/or patient preference.28
Management decisions: AUD augmentation strategies
Naltrexone is contraindicated for patients who are receiving opioids, including opioid agonist therapy for OUD. Therefore, clinicians need to consider other options for these individuals. There are several medications with good evidence, including acamprosate, disulfiram, topiramate, and gabapentin. Acamprosate and disulfiram are FDA-approved for AUD; the latter 2 have been used off-label.
Continue to: Acamprosate is a glutamate receptor modulator...
Acamprosate is a glutamate receptor modulator that reduces alcohol cravings and is recommended for patients who have achieved and wish to maintain abstinence. It can be used in patients with liver disease, because it is not hepatically metabolized.30 Topiramate is also used to reduce alcohol cravings. It antagonizes glutamate at alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate (AMPA) and kainite receptors, facilitates gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) function, and reduces the extracellular release of dopamine in the mesocorticolimbic regions of the brain.30 Topiramate is a reasonable option for patients with a seizure disorder, a history of migraine headaches,30 or who are overweight or obese and wish to lose weight.31 In a nonrandomized study, topiramate reduced alcohol intake and cravings more than naltrexone.32
Disulfiram is another second-line therapy for AUD. It is best used under close supervision because it does not reduce alcohol cravings but makes ingesting alcohol extremely aversive by preventing the breakdown of the alcohol metabolite acetaldehyde, and in doing so causes a cluster of unpleasant symptoms, including sweating, palpitations, flushing, nausea/vomiting, and increased sympathetic tone.28 Disulfiram only works if it is taken daily, and it requires a high degree of motivation and/or daily supervision at home or in the clinic.33 It is not recommended to be used as a first-line treatment based on its potential toxicity, adverse effects, and mixed findings on its efficacy. In addition, it should not be given to medically vulnerable/fragile individuals.
Lastly, gabapentin, a voltage-gated calcium channel modulator, may also be used as a second-line agent for AUD. Patients who have started alcohol withdrawal management with gabapentin may wish to continue treatment to assist with craving suppression.30 It is also a good choice for patients who have comorbid diabetic neuropathy or other neuropathic pain conditions, anxiety, or insomnia.30,34 Of note, there have been reports of gabapentin misuse.
CASE REPORTS CONTINUED
Ms. B presents to the ED with a 5-year history of moderate AUD and a 2-year history of mild OUD. She denies a history of severe or complicated AWS. Her laboratory results are significant for a serum ethanol level of 250 mg/dL, UDS positive for opioids, and a negative pregnancy test.
Management decisions: Naltrexone for OUD
In contrast to Ms. A, Ms. B is likely able to complete the opioid withdrawal management process. It is reasonable to treat her uncomplicated, moderate alcohol withdrawal as an outpatient with gabapentin or a benzodiazepine taper. Had her AUD been as severe as Ms. A’s, or if she were unsuccessful with ambulatory withdrawal treatment attempts, Ms. B would also be a candidate for inpatient medical treatment for alcohol withdrawal regardless of the severity of her OUD. Ongoing pharmacotherapy for her AUD after withdrawal management is the same as previously outlined. After Ms. B completes the taper (typically 1 week after the ED visit), she should follow up for initiation of pharmacotherapy for AUD. Ms. B is an ideal candidate for naltrexone, which targets both AUD and OUD.
Continue to: Naltrexone is a semi-synthetic...
Naltrexone is a semi-synthetic competitive antagonist at mu-opioid receptors and a partial agonist at kappa receptors; it has little to no activity at delta receptors. Naltrexone has been shown to reduce alcohol cravings and diminish the euphoric effects of alcohol by reducing endogenous opioid release and receptor activation.35 Thus, even when patients do use alcohol while taking naltrexone, the amount of alcohol they use is typically substantially reduced.36 In fact, at a standard dose of 50 mg/d, 95% of mu-opioid receptors are occupied and are shown to yield approximately 40% alcohol abstinence rates at 1 year.36
Once Ms. B has completed withdrawal management from both alcohol and opioids, she should have a trial period of oral naltrexone to prove tolerability, and then transition to the long-acting injectable (LAI) formulation. Patients able to complete withdrawal management from opioids and transition to LAI naltrexone have been shown to have equivalent rates of successful abstinence from opioids compared to buprenorphine.37 Though Ms. B could opt to try buprenorphine to treat her mild OUD, naltrexone would be the preferred option because it has 3 advantages:
- it blocks the mu-opioid receptor, which prevents euphoria if an illicit substance is used
- it does not cause physiologic dependence or withdrawal syndrome if/when stopped
- if it is not effective, it is easy to switch to buprenorphine.
Lastly, all patients with OUD should be prescribed a rescue naloxone kit, in accordance with harm-reduction guidelines. Naloxone, a potent opioid receptor antagonist, is used to prevent or reverse respiratory depression in opioid overdose. Naloxone rescue kits include intranasal naloxone, which makes it easy for nonclinician bystanders to administer while waiting for emergency transport.38 Most states allow naloxone kits to be prescribed to individuals who have a concern for overdose among friends, family, or others in the community. The wide distribution and easy availability of naloxone rescue kits have been essential in decreasing overdose deaths among patients who misuse opioids.39
Take-home points
Patients with both OUD and AUD are relatively common and often pose significant management challenges when they present to the clinic or the ED in withdrawal. Because severe AWS can be life-threatening, hospitalization should be considered. OWS is often accompanied by intense cravings that can lead to relapse and the risk of accidental opioid overdose/death. As soon as patients are able to engage in a discussion about their treatment options, clinicians need to clarify the patient’s goals and priorities. In medications for OUD, the decision of whether to use buprenorphine, naltrexone, or methadone is guided by the severity of the OUD, the patient’s past treatment experience (illicit as well as prescribed), and patient preference. If the OUD is mild or if the patient prefers to avoid opioid agonist medications and can tolerate the opioid withdrawal process, both the AUD and OUD can be treated with naltrexone, preferably with the LAI formulation. Other AUD medications and outpatient psychotherapy may be used to augment treatment outcomes. For patients with a moderate to severe OUD, buprenorphine (preferably with immediate initiation) or methadone therapy should be offered. Patients with comorbid OUD and AUD who are treated with opioid agonists should be offered medication for AUD other than naltrexone, as outlined above. All patients with substance use disorders would benefit from psychosocial interventions, including group and individual therapy as well as community sober support groups.
Bottom Line
Patients with comorbid opioid use disorder (OUD) and alcohol use disorder (AUD) often pose significant management challenges when they present in withdrawal. This article reviews the evidence and summarizes practical considerations regarding the clinical management of patients with comorbid OUD and AUD.
Related Resources
- Chaney L, Mathia C, Cole T. Transitioning patients with opioid use disorder from methadone to buprenorphine. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(12):23-24,28. doi:10.12788/ cp.0305
- Eatmon CV, Trent K. Pharmacotherapy for alcohol use disorder in patients with hepatic impairment. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(12):25-28. doi:10.12788/cp.0068
Drug Brand Names
Acamprosate • Campral
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone, Zubsolv
Clonidine • Catapres
Disulfiram • Antabuse
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Hydroxyzine • Vistaril
Lofexidine • Lucemyra
Methadone • Methadose, Dolophine
Naloxone • Narcan
Naltrexone • ReVia, Vivitrol
Ondansetron • Zofran
Topiramate • Topamax
Trazodone • Desyrel, Oleptro
1. Mattson CL, Tanz LJ, Quinn K, et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths - United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(6):202-207.
2. Hartzler B, Donovan DM, Huang Z. Comparison of opiate-primary treatment seekers with and without alcohol use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010;39(2):114-123.
3. Nolan S, Klimas J, Wood E. Alcohol use in opioid agonist treatment. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2016;11(1):17.
4. Hood LE, Leyrer-Hackson JM, Olive MF. Pharmacotherapeutic management of co-morbid alcohol and opioid use. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020;21(7):823-839.
5. Pikovsky M, Peacock A, Larney S, et al. Alcohol use disorder and associated physical health complications and treatment amongst individuals with and without opioid dependence: a case-control study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018;188:304-310.
6. Jones CM, McCance-Katz EF. Co-occurring substance use and mental disorders among adults with opioid use disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;197:78-82.
7. Hartzler B, Donovan DM, Huang Z. Comparison of opiate-primary treatment seekers with and without alcohol use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010;39(2):114-123.
8. Jones CM, Paulozzi LJ, Mack KA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Alcohol involvement in opioid pain reliever and benzodiazepine drug abuse-related emergency department visits and drug-related deaths - United States, 2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63(40):881-885.
9. Stapleton RD, Comiskey CM. Alcohol usage and associated treatment outcomes for opiate users entering treatment in Ireland. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010;107(1):56-61.
10. Turner RC, Lichstein PR, Peden JG Jr, et al. Alcohol withdrawal syndromes: a review of pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment. J Gen Intern Med. 1989;4(5):432-444.
11. Boba A. Management of acute alcohol intoxication. Am J Emerg Med. 1999;17(4):431.
12. The ASAM national practice guideline for the treatment of opioid use disorder: 2020 focused update. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2S Suppl1):1-91.
13. Shaw JM, Kolesar GS, Sellers EM, et al. Development of optimal treatment tactics for alcohol withdrawal. I. Assessment and effectiveness of supportive care. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1981;1(6):382-389.
14. Naranjo CA, Sellers EM. Clinical assessment and pharmacotherapy of the alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Recent Dev Alcohol. 1986;4:265-281.
15. Kampman K, Jarvis M. American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) national practice guideline for the use of medications in the treatment of addiction involving opioid use. J Addict Med. 2015;9(5):358-367.
16. The ASAM clinical practice guideline on alcohol withdrawal management. J Addict Med. 2020;14(3S Suppl 1):1-72.
17. Isenberg-Grzeda E, Kutner HE, Nicolson SE. Wernicke-Korsakoff-syndrome: under-recognized and under-treated. Psychosomatics. 2012;53(6):507-516.
18. Schuckit MA. Treatment of opioid-use disorders. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(4):357-368.
19. Tang Y-L, Hao W. Improving drug addiction treatment in China. Addiction. 2007;102(7):1057-1063.
20. Wakeman SE, Larochelle MR, Ameli O, et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(2):e1920622.
21. Wines JD Jr, Saitz R, Horton NJ, et al. Overdose after detoxification: a prospective study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007;89(2-3):161-169.
22. Maughan BC, Becker EA. Drug-related mortality after discharge from treatment: a record-linkage study of substance abuse clients in Texas, 2006-2012. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;204:107473.
23. Gowing L, Ali R, White J. Buprenorphine for the management of opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD002025.
24. Malinoff HL, Barkin RL, Wilson G. Sublingual buprenorphine is effective in the treatment of chronic pain syndrome. Am J Ther. 2005;12(5):379-384.
25. Nava F, Manzato E, Leonardi C, et al. Opioid maintenance therapy suppresses alcohol intake in heroin addicts with alcohol dependence: preliminary results of an open randomized study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008;32(8):1867-1872.
26. Srivastava A, Kahan M, Ross S. The effect of methadone maintenance treatment on alcohol consumption: a systematic review. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2008;34(2):215-223.
27. Davids E, Gastpar M. Buprenorphine in the treatment of opioid dependence. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004;14(3):209-216.
28. American Psychiatric Association. Practice Guideline for the Pharmacological Treatment of Patients With Alcohol Use Disorder. American Psychiatric Association; 2018.
29. Hassanian-Moghaddam H, Afzali S, Pooya A. Withdrawal syndrome caused by naltrexone in opioid abusers. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2014;33(6):561-567.
30. Fairbanks J, Umbreit A, Kolla BP, et al. Evidence-based pharmacotherapies for alcohol use disorder: clinical pearls. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(9):1964-1977.
31. Verrotti A, Scaparrotta A, Agostinelli S, et al. Topiramate-induced weight loss: a review. Epilepsy Res. 2011;95(3):189-199.
32. Flórez G, García-Portilla P, Alvarez S, et al. Using topiramate or naltrexone for the treatment of alcohol-dependent patients. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008;32(7):1251-1259.
33. Jørgensen CH, Pedersen B, Tønnesen H. The efficacy of disulfiram for the treatment of alcohol use disorder. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011;35(10):1749-1758.
34. Mason BJ, Quello S, Shadan F. Gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018;27(1):113-124.
35. Sudakin D. Naltrexone: not just for opioids anymore. J Med Toxicol. 2016;12(1):71-75.
36. Rubio G, Jiménez-Arrieri MA, Ponce G, et al. Naltrexone versus acamprosate: one year follow-up of alcohol dependence treatment. Alcohol Alcohol. 2001;36(5):419-425.
37. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318.
38. Clark AK, Wilder CM, Winstanley EL. A systematic review of community opioid overdose prevention and naloxone distribution programs. J Addict Med. 2014;8(3):153-163.
39. Dunne RB. Prescribing naloxone for opioid overdose intervention. Pain Manag. 2018;8(3):197-208.
When left untreated, opioid use disorder (OUD) is a debilitating and potentially lethal illness. Despite the availability of safe and effective medications for OUD, the prevalence of opioid use and overdose deaths has been increasing every year.1 An additional challenge in OUD treatment is the high prevalence of comorbid alcohol use disorder (AUD).2-6 A Clinical Trials Network survey from the National Institute on Drug Abuse found 38% of persons seeking treatment for OUD also had AUD.7 Other analyses have found alcohol was involved in approximately one-fifth of opioid-related deaths.8 Research also reveals that comorbid OUD and AUD contributes to poor treatment outcomes, more medical comorbidities, and a high risk of death (including overdose death).4,9 There is no standard of care for this particular patient population.3 This article reviews the evidence and summarizes practical considerations regarding the clinical management of patients with comorbid OUD and AUD.
To illustrate the various decision points, we will follow 2 hypothetical patients through various stages of treatment (Figure), from their presentation in the emergency department (ED) or outpatient clinic, through their hospital admission (if needed), and into their outpatient follow-up treatment.

CASE REPORTS
Ms. A and Ms. B present to the ED for evaluation of nausea, vomiting, sweating, anxiety, and tremor. Both patients describe their most recent use of both alcohol and opioids approximately 12 hours ago, and each has been attempting to stop using both substances at home.
Decision-making in the emergency setting
In the ED, a few important decisions need to be made regarding treatment:
- Are the presenting symptoms primarily due to alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS), opioid withdrawal syndrome (OWS), or both?
- Does the patient require inpatient medical withdrawal management (detoxification) based on the history and severity of the withdrawal symptoms?
- What are the patient’s treatment goals for their AUD and OUD?
- Is maintenance medication for OUD indicated? If so, which medication is most appropriate?
In the ED, the presentation of individuals affected by both OUD and AUD can be challenging because OWS shares overlapping features with AWS, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, sweating, anxiety, and tremor. However, although acute OWS is typically very uncomfortable, it is rarely lethal. On the other hand, severe AWS may result in delirium, seizures, and death,10 which makes it essential to recognize and treat appropriately.
Both Ms. A and Ms. B should be medically evaluated and treated by an emergency medicine physician in conjunction with psychiatric (or addiction medicine) consultation. The ED assessment of a patient presenting with both AUD and OUD should include vital signs monitoring; physical examination; blood work including comprehensive metabolic panel, serum magnesium, and phosphorus; complete blood count; pregnancy test for women of reproductive age; urine drug screen (UDS); urinalysis; and serum ethanol level. Of note, sympathetic hyperactivity is found in both alcohol and opioid withdrawal, and patients with alcohol withdrawal may also have hypokalemia, a condition associated with an increased risk of arrhythmia. Furthermore, a prolonged QTc would affect clinical decision-making about medications for OUD (ie, methadone) and withdrawal management (ie, ondansetron, trazodone, and hydroxyzine). Therefore, an electrocardiogram should be conducted, where appropriate.
Initial treatment of AWS includes vitamin supplementation (thiamine, folic acid, and multivitamins) and benzodiazepine administration (symptom-triggered and/or scheduled taper). It may also include IV fluid resuscitation, analgesics for pain, ondansetron for nausea and vomiting, and other electrolyte repletion as indicated by the laboratory results.11 Additional measures for patients in opioid withdrawal should include alpha-2 agonists such as clonidine or lofexidine for adrenergic symptoms, antiemetics, antidiarrheals, muscle relaxants, anxiolytics such as hydroxyzine, and sleep medications such as trazodone.12
Continue to: The next decision...
The next decision is whether the patient needs to be admitted for inpatient treatment. This decision is based primarily on the risk assessment and severity of AWS, including a compelling history of complicated AWS such as seizures or delirium tremens as well as consideration of the complexity and severity of any comorbid medical or psychiatric conditions. Other indications for medical withdrawal management include a history of unsuccessful ambulatory withdrawal management and pregnancy. For severe AWS, a scheduled benzodiazepine taper in addition to the symptom-triggered protocol should be considered.13-15 A psychiatric evaluation may be obtained in the ED, as long as the patient is sober enough to meaningfully participate in the psychiatric interview. Wherever possible, psychiatric interviews should be supplemented by collateral information.
CASE REPORTS CONTINUED
Ms. A admits to a 5-year history of alcohol and opioid use that meets the criteria for severe AUD and severe OUD. She has previously required inpatient treatment for seizures related to AWS. Laboratory results are notable for a serum ethanol level of 380 mg/dL, UDS positive for opioids, and a negative pregnancy test.
Disposition of patients in alcohol and opioid withdrawal
Given Ms. A’s history of seizures while withdrawing from alcohol, she is appropriate for hospital admission for medically managed withdrawal observation. As previously mentioned, there is clinical overlap between AWS and OWS, and differentiating between the 2 syndromes is essential and may be lifesaving. Whereas anxiety, agitation, diaphoresis, tachycardia, hypertension, and insomnia can be seen in both opioid and alcohol withdrawal, OWS-specific symptoms include mydriasis, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, bone or joint aches, yawning, and piloerection. AWS may present with visual or tactile hallucinations, delirium, and grand mal seizures.15
The details of inpatient management are beyond the scope of this article; however, both patients should be started on thiamine, folic acid, and a multivitamin. For patients in alcohol withdrawal with a history of poor diet who appear malnourished or have a history of malabsorption (such as gastric bypass surgery), thiamine 100 mg/d IV should be given for 3 to 5 days to prevent Wernicke encephalopathy.16 Where there is any concern the patient may be exhibiting signs of Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome (impaired cognition, evident malnourishment, ataxia, or eye movement abnormalities), high-dose thiamine IV should be given presumptively as follows: 500 mg IV 3 times a day for 3 days, 250 mg/d IV for 5 days, and then oral supplementation 100 mg/d for at least 30 days.17
In summary, on presentation to the ED, both patients should be medically stabilized and started on benzodiazepines for alcohol withdrawal. The risk assessment and the severity of the AWS often determines the level of care.
CASE REPORTS CONTINUED
On hospital Day 2, Ms. A tells the consulting psychiatrist she would like to start medications to treat her substance use disorders. She has a long history of failed attempts to achieve abstinence from opioids, so she and the psychiatrist agree to initiate a trial of buprenorphine/naloxone for her OUD, 4 mg/1 mg to 8 mg/2 mg for Day 1. Although buprenorphine/naloxone seems to help her alcohol cravings somewhat, she requests additional help. She experiences migraine headaches, which is in part why she began using opioid medications. Via joint decision making with her psychiatrist, she agrees to a trial of topiramate, with a slow titration schedule starting at 25 mg/d.
Continue to: Management decisions
Management decisions: Buprenorphine for OUD
The next issue is to determine the appropriate treatment for the patient’s OUD. Although treating OWS is important in improving the patient’s health, decreasing their discomfort, and facilitating their participation in a psychosocial treatment program,18 current evidence suggests that opioid withdrawal management alone without medication for OUD rarely leads to long-term recovery.19,20 Some research suggests that the risk of accidental opioid overdose immediately following acute withdrawal management may actually be increased due to decreased tolerance in these patients.12,21,22
Three medications have the most evidence for OUD treatment: buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone.15 The decision to use buprenorphine, methadone, or naltrexone depends on a variety of factors, including the severity of the OUD, patient history of prior treatment successes and failures, comorbid medical and psychiatric conditions, and patient preference.4 Treatment with buprenorphine or methadone is preferred over naltrexone for patients who do not want to or cannot tolerate the physical and emotional discomfort of the opioid withdrawal process, who experience moderate to severe OUD, who have a history of failed abstinence-based treatment, or who have more severe physiological tolerance/dependence.12 Buprenorphine is a mu opioid receptor partial agonist that has been shown to reduce opioid cravings,23 provide moderate pain relief,24 and ameliorate OWS.12 It does not typically result in significant respiratory depression, which is the biggest safety concern for opioid use.12 Buprenorphine may also treat comorbid AUD at higher doses; however, the data are inconclusive.25,26 Buprenorphine should be prescribed with caution to patients with comorbid, uncontrolled AUD, due to the risk of respiratory depression when combined with alcohol. Patients who continue to drink alcohol but are able to abstain from opioids may consider starting an AUD-specific medication. Pharmacologic options are discussed in more detail in the next section.
For patients who have higher physiological dependence or more severe OUD, methadone may be a reasonable alternative to buprenorphine. Methadone, a mu-opioid receptor agonist, ameliorates OWS, reduces opioid cravings, and reduces the euphoric effects of opioid ingestion if the patient relapses. However, methadone can only be dispensed for the treatment of OUD by a federally-certified treatment program governed by restrictive and federally mandated guidelines. Compared to buprenorphine, methadone is more dangerous in overdose, has more drug interactions, and is more commonly diverted for recreational use.27 Furthermore, methadone should be prescribed with caution to patients with comorbid, uncontrolled AUD, because both alcohol and methadone can result in respiratory depression.
By contrast, the first-line treatment for individuals experiencing moderateto severe AUD is typically naltrexone.28 Naltrexone is contraindicated in Ms. A because she has a severe OUD and is unlikely to tolerate the opioid withdrawal process. Research suggests that the use of naltrexone for OUD should be limited to patients who have a mild disorder or who show low physiological dependence.29 Alternatively, acamprosate, disulfiram, topiramate, or gabapentin should be considered for Ms. A.4,28,30 Because each of these medications have specific strengths and weaknesses, medication selection should be based on individual patient factors such as comorbid psychiatric and medical conditions and/or patient preference.28
Management decisions: AUD augmentation strategies
Naltrexone is contraindicated for patients who are receiving opioids, including opioid agonist therapy for OUD. Therefore, clinicians need to consider other options for these individuals. There are several medications with good evidence, including acamprosate, disulfiram, topiramate, and gabapentin. Acamprosate and disulfiram are FDA-approved for AUD; the latter 2 have been used off-label.
Continue to: Acamprosate is a glutamate receptor modulator...
Acamprosate is a glutamate receptor modulator that reduces alcohol cravings and is recommended for patients who have achieved and wish to maintain abstinence. It can be used in patients with liver disease, because it is not hepatically metabolized.30 Topiramate is also used to reduce alcohol cravings. It antagonizes glutamate at alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate (AMPA) and kainite receptors, facilitates gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) function, and reduces the extracellular release of dopamine in the mesocorticolimbic regions of the brain.30 Topiramate is a reasonable option for patients with a seizure disorder, a history of migraine headaches,30 or who are overweight or obese and wish to lose weight.31 In a nonrandomized study, topiramate reduced alcohol intake and cravings more than naltrexone.32
Disulfiram is another second-line therapy for AUD. It is best used under close supervision because it does not reduce alcohol cravings but makes ingesting alcohol extremely aversive by preventing the breakdown of the alcohol metabolite acetaldehyde, and in doing so causes a cluster of unpleasant symptoms, including sweating, palpitations, flushing, nausea/vomiting, and increased sympathetic tone.28 Disulfiram only works if it is taken daily, and it requires a high degree of motivation and/or daily supervision at home or in the clinic.33 It is not recommended to be used as a first-line treatment based on its potential toxicity, adverse effects, and mixed findings on its efficacy. In addition, it should not be given to medically vulnerable/fragile individuals.
Lastly, gabapentin, a voltage-gated calcium channel modulator, may also be used as a second-line agent for AUD. Patients who have started alcohol withdrawal management with gabapentin may wish to continue treatment to assist with craving suppression.30 It is also a good choice for patients who have comorbid diabetic neuropathy or other neuropathic pain conditions, anxiety, or insomnia.30,34 Of note, there have been reports of gabapentin misuse.
CASE REPORTS CONTINUED
Ms. B presents to the ED with a 5-year history of moderate AUD and a 2-year history of mild OUD. She denies a history of severe or complicated AWS. Her laboratory results are significant for a serum ethanol level of 250 mg/dL, UDS positive for opioids, and a negative pregnancy test.
Management decisions: Naltrexone for OUD
In contrast to Ms. A, Ms. B is likely able to complete the opioid withdrawal management process. It is reasonable to treat her uncomplicated, moderate alcohol withdrawal as an outpatient with gabapentin or a benzodiazepine taper. Had her AUD been as severe as Ms. A’s, or if she were unsuccessful with ambulatory withdrawal treatment attempts, Ms. B would also be a candidate for inpatient medical treatment for alcohol withdrawal regardless of the severity of her OUD. Ongoing pharmacotherapy for her AUD after withdrawal management is the same as previously outlined. After Ms. B completes the taper (typically 1 week after the ED visit), she should follow up for initiation of pharmacotherapy for AUD. Ms. B is an ideal candidate for naltrexone, which targets both AUD and OUD.
Continue to: Naltrexone is a semi-synthetic...
Naltrexone is a semi-synthetic competitive antagonist at mu-opioid receptors and a partial agonist at kappa receptors; it has little to no activity at delta receptors. Naltrexone has been shown to reduce alcohol cravings and diminish the euphoric effects of alcohol by reducing endogenous opioid release and receptor activation.35 Thus, even when patients do use alcohol while taking naltrexone, the amount of alcohol they use is typically substantially reduced.36 In fact, at a standard dose of 50 mg/d, 95% of mu-opioid receptors are occupied and are shown to yield approximately 40% alcohol abstinence rates at 1 year.36
Once Ms. B has completed withdrawal management from both alcohol and opioids, she should have a trial period of oral naltrexone to prove tolerability, and then transition to the long-acting injectable (LAI) formulation. Patients able to complete withdrawal management from opioids and transition to LAI naltrexone have been shown to have equivalent rates of successful abstinence from opioids compared to buprenorphine.37 Though Ms. B could opt to try buprenorphine to treat her mild OUD, naltrexone would be the preferred option because it has 3 advantages:
- it blocks the mu-opioid receptor, which prevents euphoria if an illicit substance is used
- it does not cause physiologic dependence or withdrawal syndrome if/when stopped
- if it is not effective, it is easy to switch to buprenorphine.
Lastly, all patients with OUD should be prescribed a rescue naloxone kit, in accordance with harm-reduction guidelines. Naloxone, a potent opioid receptor antagonist, is used to prevent or reverse respiratory depression in opioid overdose. Naloxone rescue kits include intranasal naloxone, which makes it easy for nonclinician bystanders to administer while waiting for emergency transport.38 Most states allow naloxone kits to be prescribed to individuals who have a concern for overdose among friends, family, or others in the community. The wide distribution and easy availability of naloxone rescue kits have been essential in decreasing overdose deaths among patients who misuse opioids.39
Take-home points
Patients with both OUD and AUD are relatively common and often pose significant management challenges when they present to the clinic or the ED in withdrawal. Because severe AWS can be life-threatening, hospitalization should be considered. OWS is often accompanied by intense cravings that can lead to relapse and the risk of accidental opioid overdose/death. As soon as patients are able to engage in a discussion about their treatment options, clinicians need to clarify the patient’s goals and priorities. In medications for OUD, the decision of whether to use buprenorphine, naltrexone, or methadone is guided by the severity of the OUD, the patient’s past treatment experience (illicit as well as prescribed), and patient preference. If the OUD is mild or if the patient prefers to avoid opioid agonist medications and can tolerate the opioid withdrawal process, both the AUD and OUD can be treated with naltrexone, preferably with the LAI formulation. Other AUD medications and outpatient psychotherapy may be used to augment treatment outcomes. For patients with a moderate to severe OUD, buprenorphine (preferably with immediate initiation) or methadone therapy should be offered. Patients with comorbid OUD and AUD who are treated with opioid agonists should be offered medication for AUD other than naltrexone, as outlined above. All patients with substance use disorders would benefit from psychosocial interventions, including group and individual therapy as well as community sober support groups.
Bottom Line
Patients with comorbid opioid use disorder (OUD) and alcohol use disorder (AUD) often pose significant management challenges when they present in withdrawal. This article reviews the evidence and summarizes practical considerations regarding the clinical management of patients with comorbid OUD and AUD.
Related Resources
- Chaney L, Mathia C, Cole T. Transitioning patients with opioid use disorder from methadone to buprenorphine. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(12):23-24,28. doi:10.12788/ cp.0305
- Eatmon CV, Trent K. Pharmacotherapy for alcohol use disorder in patients with hepatic impairment. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(12):25-28. doi:10.12788/cp.0068
Drug Brand Names
Acamprosate • Campral
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone, Zubsolv
Clonidine • Catapres
Disulfiram • Antabuse
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Hydroxyzine • Vistaril
Lofexidine • Lucemyra
Methadone • Methadose, Dolophine
Naloxone • Narcan
Naltrexone • ReVia, Vivitrol
Ondansetron • Zofran
Topiramate • Topamax
Trazodone • Desyrel, Oleptro
When left untreated, opioid use disorder (OUD) is a debilitating and potentially lethal illness. Despite the availability of safe and effective medications for OUD, the prevalence of opioid use and overdose deaths has been increasing every year.1 An additional challenge in OUD treatment is the high prevalence of comorbid alcohol use disorder (AUD).2-6 A Clinical Trials Network survey from the National Institute on Drug Abuse found 38% of persons seeking treatment for OUD also had AUD.7 Other analyses have found alcohol was involved in approximately one-fifth of opioid-related deaths.8 Research also reveals that comorbid OUD and AUD contributes to poor treatment outcomes, more medical comorbidities, and a high risk of death (including overdose death).4,9 There is no standard of care for this particular patient population.3 This article reviews the evidence and summarizes practical considerations regarding the clinical management of patients with comorbid OUD and AUD.
To illustrate the various decision points, we will follow 2 hypothetical patients through various stages of treatment (Figure), from their presentation in the emergency department (ED) or outpatient clinic, through their hospital admission (if needed), and into their outpatient follow-up treatment.

CASE REPORTS
Ms. A and Ms. B present to the ED for evaluation of nausea, vomiting, sweating, anxiety, and tremor. Both patients describe their most recent use of both alcohol and opioids approximately 12 hours ago, and each has been attempting to stop using both substances at home.
Decision-making in the emergency setting
In the ED, a few important decisions need to be made regarding treatment:
- Are the presenting symptoms primarily due to alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS), opioid withdrawal syndrome (OWS), or both?
- Does the patient require inpatient medical withdrawal management (detoxification) based on the history and severity of the withdrawal symptoms?
- What are the patient’s treatment goals for their AUD and OUD?
- Is maintenance medication for OUD indicated? If so, which medication is most appropriate?
In the ED, the presentation of individuals affected by both OUD and AUD can be challenging because OWS shares overlapping features with AWS, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, sweating, anxiety, and tremor. However, although acute OWS is typically very uncomfortable, it is rarely lethal. On the other hand, severe AWS may result in delirium, seizures, and death,10 which makes it essential to recognize and treat appropriately.
Both Ms. A and Ms. B should be medically evaluated and treated by an emergency medicine physician in conjunction with psychiatric (or addiction medicine) consultation. The ED assessment of a patient presenting with both AUD and OUD should include vital signs monitoring; physical examination; blood work including comprehensive metabolic panel, serum magnesium, and phosphorus; complete blood count; pregnancy test for women of reproductive age; urine drug screen (UDS); urinalysis; and serum ethanol level. Of note, sympathetic hyperactivity is found in both alcohol and opioid withdrawal, and patients with alcohol withdrawal may also have hypokalemia, a condition associated with an increased risk of arrhythmia. Furthermore, a prolonged QTc would affect clinical decision-making about medications for OUD (ie, methadone) and withdrawal management (ie, ondansetron, trazodone, and hydroxyzine). Therefore, an electrocardiogram should be conducted, where appropriate.
Initial treatment of AWS includes vitamin supplementation (thiamine, folic acid, and multivitamins) and benzodiazepine administration (symptom-triggered and/or scheduled taper). It may also include IV fluid resuscitation, analgesics for pain, ondansetron for nausea and vomiting, and other electrolyte repletion as indicated by the laboratory results.11 Additional measures for patients in opioid withdrawal should include alpha-2 agonists such as clonidine or lofexidine for adrenergic symptoms, antiemetics, antidiarrheals, muscle relaxants, anxiolytics such as hydroxyzine, and sleep medications such as trazodone.12
Continue to: The next decision...
The next decision is whether the patient needs to be admitted for inpatient treatment. This decision is based primarily on the risk assessment and severity of AWS, including a compelling history of complicated AWS such as seizures or delirium tremens as well as consideration of the complexity and severity of any comorbid medical or psychiatric conditions. Other indications for medical withdrawal management include a history of unsuccessful ambulatory withdrawal management and pregnancy. For severe AWS, a scheduled benzodiazepine taper in addition to the symptom-triggered protocol should be considered.13-15 A psychiatric evaluation may be obtained in the ED, as long as the patient is sober enough to meaningfully participate in the psychiatric interview. Wherever possible, psychiatric interviews should be supplemented by collateral information.
CASE REPORTS CONTINUED
Ms. A admits to a 5-year history of alcohol and opioid use that meets the criteria for severe AUD and severe OUD. She has previously required inpatient treatment for seizures related to AWS. Laboratory results are notable for a serum ethanol level of 380 mg/dL, UDS positive for opioids, and a negative pregnancy test.
Disposition of patients in alcohol and opioid withdrawal
Given Ms. A’s history of seizures while withdrawing from alcohol, she is appropriate for hospital admission for medically managed withdrawal observation. As previously mentioned, there is clinical overlap between AWS and OWS, and differentiating between the 2 syndromes is essential and may be lifesaving. Whereas anxiety, agitation, diaphoresis, tachycardia, hypertension, and insomnia can be seen in both opioid and alcohol withdrawal, OWS-specific symptoms include mydriasis, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, bone or joint aches, yawning, and piloerection. AWS may present with visual or tactile hallucinations, delirium, and grand mal seizures.15
The details of inpatient management are beyond the scope of this article; however, both patients should be started on thiamine, folic acid, and a multivitamin. For patients in alcohol withdrawal with a history of poor diet who appear malnourished or have a history of malabsorption (such as gastric bypass surgery), thiamine 100 mg/d IV should be given for 3 to 5 days to prevent Wernicke encephalopathy.16 Where there is any concern the patient may be exhibiting signs of Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome (impaired cognition, evident malnourishment, ataxia, or eye movement abnormalities), high-dose thiamine IV should be given presumptively as follows: 500 mg IV 3 times a day for 3 days, 250 mg/d IV for 5 days, and then oral supplementation 100 mg/d for at least 30 days.17
In summary, on presentation to the ED, both patients should be medically stabilized and started on benzodiazepines for alcohol withdrawal. The risk assessment and the severity of the AWS often determines the level of care.
CASE REPORTS CONTINUED
On hospital Day 2, Ms. A tells the consulting psychiatrist she would like to start medications to treat her substance use disorders. She has a long history of failed attempts to achieve abstinence from opioids, so she and the psychiatrist agree to initiate a trial of buprenorphine/naloxone for her OUD, 4 mg/1 mg to 8 mg/2 mg for Day 1. Although buprenorphine/naloxone seems to help her alcohol cravings somewhat, she requests additional help. She experiences migraine headaches, which is in part why she began using opioid medications. Via joint decision making with her psychiatrist, she agrees to a trial of topiramate, with a slow titration schedule starting at 25 mg/d.
Continue to: Management decisions
Management decisions: Buprenorphine for OUD
The next issue is to determine the appropriate treatment for the patient’s OUD. Although treating OWS is important in improving the patient’s health, decreasing their discomfort, and facilitating their participation in a psychosocial treatment program,18 current evidence suggests that opioid withdrawal management alone without medication for OUD rarely leads to long-term recovery.19,20 Some research suggests that the risk of accidental opioid overdose immediately following acute withdrawal management may actually be increased due to decreased tolerance in these patients.12,21,22
Three medications have the most evidence for OUD treatment: buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone.15 The decision to use buprenorphine, methadone, or naltrexone depends on a variety of factors, including the severity of the OUD, patient history of prior treatment successes and failures, comorbid medical and psychiatric conditions, and patient preference.4 Treatment with buprenorphine or methadone is preferred over naltrexone for patients who do not want to or cannot tolerate the physical and emotional discomfort of the opioid withdrawal process, who experience moderate to severe OUD, who have a history of failed abstinence-based treatment, or who have more severe physiological tolerance/dependence.12 Buprenorphine is a mu opioid receptor partial agonist that has been shown to reduce opioid cravings,23 provide moderate pain relief,24 and ameliorate OWS.12 It does not typically result in significant respiratory depression, which is the biggest safety concern for opioid use.12 Buprenorphine may also treat comorbid AUD at higher doses; however, the data are inconclusive.25,26 Buprenorphine should be prescribed with caution to patients with comorbid, uncontrolled AUD, due to the risk of respiratory depression when combined with alcohol. Patients who continue to drink alcohol but are able to abstain from opioids may consider starting an AUD-specific medication. Pharmacologic options are discussed in more detail in the next section.
For patients who have higher physiological dependence or more severe OUD, methadone may be a reasonable alternative to buprenorphine. Methadone, a mu-opioid receptor agonist, ameliorates OWS, reduces opioid cravings, and reduces the euphoric effects of opioid ingestion if the patient relapses. However, methadone can only be dispensed for the treatment of OUD by a federally-certified treatment program governed by restrictive and federally mandated guidelines. Compared to buprenorphine, methadone is more dangerous in overdose, has more drug interactions, and is more commonly diverted for recreational use.27 Furthermore, methadone should be prescribed with caution to patients with comorbid, uncontrolled AUD, because both alcohol and methadone can result in respiratory depression.
By contrast, the first-line treatment for individuals experiencing moderateto severe AUD is typically naltrexone.28 Naltrexone is contraindicated in Ms. A because she has a severe OUD and is unlikely to tolerate the opioid withdrawal process. Research suggests that the use of naltrexone for OUD should be limited to patients who have a mild disorder or who show low physiological dependence.29 Alternatively, acamprosate, disulfiram, topiramate, or gabapentin should be considered for Ms. A.4,28,30 Because each of these medications have specific strengths and weaknesses, medication selection should be based on individual patient factors such as comorbid psychiatric and medical conditions and/or patient preference.28
Management decisions: AUD augmentation strategies
Naltrexone is contraindicated for patients who are receiving opioids, including opioid agonist therapy for OUD. Therefore, clinicians need to consider other options for these individuals. There are several medications with good evidence, including acamprosate, disulfiram, topiramate, and gabapentin. Acamprosate and disulfiram are FDA-approved for AUD; the latter 2 have been used off-label.
Continue to: Acamprosate is a glutamate receptor modulator...
Acamprosate is a glutamate receptor modulator that reduces alcohol cravings and is recommended for patients who have achieved and wish to maintain abstinence. It can be used in patients with liver disease, because it is not hepatically metabolized.30 Topiramate is also used to reduce alcohol cravings. It antagonizes glutamate at alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate (AMPA) and kainite receptors, facilitates gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) function, and reduces the extracellular release of dopamine in the mesocorticolimbic regions of the brain.30 Topiramate is a reasonable option for patients with a seizure disorder, a history of migraine headaches,30 or who are overweight or obese and wish to lose weight.31 In a nonrandomized study, topiramate reduced alcohol intake and cravings more than naltrexone.32
Disulfiram is another second-line therapy for AUD. It is best used under close supervision because it does not reduce alcohol cravings but makes ingesting alcohol extremely aversive by preventing the breakdown of the alcohol metabolite acetaldehyde, and in doing so causes a cluster of unpleasant symptoms, including sweating, palpitations, flushing, nausea/vomiting, and increased sympathetic tone.28 Disulfiram only works if it is taken daily, and it requires a high degree of motivation and/or daily supervision at home or in the clinic.33 It is not recommended to be used as a first-line treatment based on its potential toxicity, adverse effects, and mixed findings on its efficacy. In addition, it should not be given to medically vulnerable/fragile individuals.
Lastly, gabapentin, a voltage-gated calcium channel modulator, may also be used as a second-line agent for AUD. Patients who have started alcohol withdrawal management with gabapentin may wish to continue treatment to assist with craving suppression.30 It is also a good choice for patients who have comorbid diabetic neuropathy or other neuropathic pain conditions, anxiety, or insomnia.30,34 Of note, there have been reports of gabapentin misuse.
CASE REPORTS CONTINUED
Ms. B presents to the ED with a 5-year history of moderate AUD and a 2-year history of mild OUD. She denies a history of severe or complicated AWS. Her laboratory results are significant for a serum ethanol level of 250 mg/dL, UDS positive for opioids, and a negative pregnancy test.
Management decisions: Naltrexone for OUD
In contrast to Ms. A, Ms. B is likely able to complete the opioid withdrawal management process. It is reasonable to treat her uncomplicated, moderate alcohol withdrawal as an outpatient with gabapentin or a benzodiazepine taper. Had her AUD been as severe as Ms. A’s, or if she were unsuccessful with ambulatory withdrawal treatment attempts, Ms. B would also be a candidate for inpatient medical treatment for alcohol withdrawal regardless of the severity of her OUD. Ongoing pharmacotherapy for her AUD after withdrawal management is the same as previously outlined. After Ms. B completes the taper (typically 1 week after the ED visit), she should follow up for initiation of pharmacotherapy for AUD. Ms. B is an ideal candidate for naltrexone, which targets both AUD and OUD.
Continue to: Naltrexone is a semi-synthetic...
Naltrexone is a semi-synthetic competitive antagonist at mu-opioid receptors and a partial agonist at kappa receptors; it has little to no activity at delta receptors. Naltrexone has been shown to reduce alcohol cravings and diminish the euphoric effects of alcohol by reducing endogenous opioid release and receptor activation.35 Thus, even when patients do use alcohol while taking naltrexone, the amount of alcohol they use is typically substantially reduced.36 In fact, at a standard dose of 50 mg/d, 95% of mu-opioid receptors are occupied and are shown to yield approximately 40% alcohol abstinence rates at 1 year.36
Once Ms. B has completed withdrawal management from both alcohol and opioids, she should have a trial period of oral naltrexone to prove tolerability, and then transition to the long-acting injectable (LAI) formulation. Patients able to complete withdrawal management from opioids and transition to LAI naltrexone have been shown to have equivalent rates of successful abstinence from opioids compared to buprenorphine.37 Though Ms. B could opt to try buprenorphine to treat her mild OUD, naltrexone would be the preferred option because it has 3 advantages:
- it blocks the mu-opioid receptor, which prevents euphoria if an illicit substance is used
- it does not cause physiologic dependence or withdrawal syndrome if/when stopped
- if it is not effective, it is easy to switch to buprenorphine.
Lastly, all patients with OUD should be prescribed a rescue naloxone kit, in accordance with harm-reduction guidelines. Naloxone, a potent opioid receptor antagonist, is used to prevent or reverse respiratory depression in opioid overdose. Naloxone rescue kits include intranasal naloxone, which makes it easy for nonclinician bystanders to administer while waiting for emergency transport.38 Most states allow naloxone kits to be prescribed to individuals who have a concern for overdose among friends, family, or others in the community. The wide distribution and easy availability of naloxone rescue kits have been essential in decreasing overdose deaths among patients who misuse opioids.39
Take-home points
Patients with both OUD and AUD are relatively common and often pose significant management challenges when they present to the clinic or the ED in withdrawal. Because severe AWS can be life-threatening, hospitalization should be considered. OWS is often accompanied by intense cravings that can lead to relapse and the risk of accidental opioid overdose/death. As soon as patients are able to engage in a discussion about their treatment options, clinicians need to clarify the patient’s goals and priorities. In medications for OUD, the decision of whether to use buprenorphine, naltrexone, or methadone is guided by the severity of the OUD, the patient’s past treatment experience (illicit as well as prescribed), and patient preference. If the OUD is mild or if the patient prefers to avoid opioid agonist medications and can tolerate the opioid withdrawal process, both the AUD and OUD can be treated with naltrexone, preferably with the LAI formulation. Other AUD medications and outpatient psychotherapy may be used to augment treatment outcomes. For patients with a moderate to severe OUD, buprenorphine (preferably with immediate initiation) or methadone therapy should be offered. Patients with comorbid OUD and AUD who are treated with opioid agonists should be offered medication for AUD other than naltrexone, as outlined above. All patients with substance use disorders would benefit from psychosocial interventions, including group and individual therapy as well as community sober support groups.
Bottom Line
Patients with comorbid opioid use disorder (OUD) and alcohol use disorder (AUD) often pose significant management challenges when they present in withdrawal. This article reviews the evidence and summarizes practical considerations regarding the clinical management of patients with comorbid OUD and AUD.
Related Resources
- Chaney L, Mathia C, Cole T. Transitioning patients with opioid use disorder from methadone to buprenorphine. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(12):23-24,28. doi:10.12788/ cp.0305
- Eatmon CV, Trent K. Pharmacotherapy for alcohol use disorder in patients with hepatic impairment. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(12):25-28. doi:10.12788/cp.0068
Drug Brand Names
Acamprosate • Campral
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone, Zubsolv
Clonidine • Catapres
Disulfiram • Antabuse
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Hydroxyzine • Vistaril
Lofexidine • Lucemyra
Methadone • Methadose, Dolophine
Naloxone • Narcan
Naltrexone • ReVia, Vivitrol
Ondansetron • Zofran
Topiramate • Topamax
Trazodone • Desyrel, Oleptro
1. Mattson CL, Tanz LJ, Quinn K, et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths - United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(6):202-207.
2. Hartzler B, Donovan DM, Huang Z. Comparison of opiate-primary treatment seekers with and without alcohol use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010;39(2):114-123.
3. Nolan S, Klimas J, Wood E. Alcohol use in opioid agonist treatment. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2016;11(1):17.
4. Hood LE, Leyrer-Hackson JM, Olive MF. Pharmacotherapeutic management of co-morbid alcohol and opioid use. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020;21(7):823-839.
5. Pikovsky M, Peacock A, Larney S, et al. Alcohol use disorder and associated physical health complications and treatment amongst individuals with and without opioid dependence: a case-control study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018;188:304-310.
6. Jones CM, McCance-Katz EF. Co-occurring substance use and mental disorders among adults with opioid use disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;197:78-82.
7. Hartzler B, Donovan DM, Huang Z. Comparison of opiate-primary treatment seekers with and without alcohol use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010;39(2):114-123.
8. Jones CM, Paulozzi LJ, Mack KA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Alcohol involvement in opioid pain reliever and benzodiazepine drug abuse-related emergency department visits and drug-related deaths - United States, 2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63(40):881-885.
9. Stapleton RD, Comiskey CM. Alcohol usage and associated treatment outcomes for opiate users entering treatment in Ireland. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010;107(1):56-61.
10. Turner RC, Lichstein PR, Peden JG Jr, et al. Alcohol withdrawal syndromes: a review of pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment. J Gen Intern Med. 1989;4(5):432-444.
11. Boba A. Management of acute alcohol intoxication. Am J Emerg Med. 1999;17(4):431.
12. The ASAM national practice guideline for the treatment of opioid use disorder: 2020 focused update. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2S Suppl1):1-91.
13. Shaw JM, Kolesar GS, Sellers EM, et al. Development of optimal treatment tactics for alcohol withdrawal. I. Assessment and effectiveness of supportive care. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1981;1(6):382-389.
14. Naranjo CA, Sellers EM. Clinical assessment and pharmacotherapy of the alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Recent Dev Alcohol. 1986;4:265-281.
15. Kampman K, Jarvis M. American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) national practice guideline for the use of medications in the treatment of addiction involving opioid use. J Addict Med. 2015;9(5):358-367.
16. The ASAM clinical practice guideline on alcohol withdrawal management. J Addict Med. 2020;14(3S Suppl 1):1-72.
17. Isenberg-Grzeda E, Kutner HE, Nicolson SE. Wernicke-Korsakoff-syndrome: under-recognized and under-treated. Psychosomatics. 2012;53(6):507-516.
18. Schuckit MA. Treatment of opioid-use disorders. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(4):357-368.
19. Tang Y-L, Hao W. Improving drug addiction treatment in China. Addiction. 2007;102(7):1057-1063.
20. Wakeman SE, Larochelle MR, Ameli O, et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(2):e1920622.
21. Wines JD Jr, Saitz R, Horton NJ, et al. Overdose after detoxification: a prospective study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007;89(2-3):161-169.
22. Maughan BC, Becker EA. Drug-related mortality after discharge from treatment: a record-linkage study of substance abuse clients in Texas, 2006-2012. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;204:107473.
23. Gowing L, Ali R, White J. Buprenorphine for the management of opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD002025.
24. Malinoff HL, Barkin RL, Wilson G. Sublingual buprenorphine is effective in the treatment of chronic pain syndrome. Am J Ther. 2005;12(5):379-384.
25. Nava F, Manzato E, Leonardi C, et al. Opioid maintenance therapy suppresses alcohol intake in heroin addicts with alcohol dependence: preliminary results of an open randomized study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008;32(8):1867-1872.
26. Srivastava A, Kahan M, Ross S. The effect of methadone maintenance treatment on alcohol consumption: a systematic review. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2008;34(2):215-223.
27. Davids E, Gastpar M. Buprenorphine in the treatment of opioid dependence. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004;14(3):209-216.
28. American Psychiatric Association. Practice Guideline for the Pharmacological Treatment of Patients With Alcohol Use Disorder. American Psychiatric Association; 2018.
29. Hassanian-Moghaddam H, Afzali S, Pooya A. Withdrawal syndrome caused by naltrexone in opioid abusers. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2014;33(6):561-567.
30. Fairbanks J, Umbreit A, Kolla BP, et al. Evidence-based pharmacotherapies for alcohol use disorder: clinical pearls. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(9):1964-1977.
31. Verrotti A, Scaparrotta A, Agostinelli S, et al. Topiramate-induced weight loss: a review. Epilepsy Res. 2011;95(3):189-199.
32. Flórez G, García-Portilla P, Alvarez S, et al. Using topiramate or naltrexone for the treatment of alcohol-dependent patients. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008;32(7):1251-1259.
33. Jørgensen CH, Pedersen B, Tønnesen H. The efficacy of disulfiram for the treatment of alcohol use disorder. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011;35(10):1749-1758.
34. Mason BJ, Quello S, Shadan F. Gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018;27(1):113-124.
35. Sudakin D. Naltrexone: not just for opioids anymore. J Med Toxicol. 2016;12(1):71-75.
36. Rubio G, Jiménez-Arrieri MA, Ponce G, et al. Naltrexone versus acamprosate: one year follow-up of alcohol dependence treatment. Alcohol Alcohol. 2001;36(5):419-425.
37. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318.
38. Clark AK, Wilder CM, Winstanley EL. A systematic review of community opioid overdose prevention and naloxone distribution programs. J Addict Med. 2014;8(3):153-163.
39. Dunne RB. Prescribing naloxone for opioid overdose intervention. Pain Manag. 2018;8(3):197-208.
1. Mattson CL, Tanz LJ, Quinn K, et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths - United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(6):202-207.
2. Hartzler B, Donovan DM, Huang Z. Comparison of opiate-primary treatment seekers with and without alcohol use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010;39(2):114-123.
3. Nolan S, Klimas J, Wood E. Alcohol use in opioid agonist treatment. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2016;11(1):17.
4. Hood LE, Leyrer-Hackson JM, Olive MF. Pharmacotherapeutic management of co-morbid alcohol and opioid use. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020;21(7):823-839.
5. Pikovsky M, Peacock A, Larney S, et al. Alcohol use disorder and associated physical health complications and treatment amongst individuals with and without opioid dependence: a case-control study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018;188:304-310.
6. Jones CM, McCance-Katz EF. Co-occurring substance use and mental disorders among adults with opioid use disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;197:78-82.
7. Hartzler B, Donovan DM, Huang Z. Comparison of opiate-primary treatment seekers with and without alcohol use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010;39(2):114-123.
8. Jones CM, Paulozzi LJ, Mack KA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Alcohol involvement in opioid pain reliever and benzodiazepine drug abuse-related emergency department visits and drug-related deaths - United States, 2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63(40):881-885.
9. Stapleton RD, Comiskey CM. Alcohol usage and associated treatment outcomes for opiate users entering treatment in Ireland. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010;107(1):56-61.
10. Turner RC, Lichstein PR, Peden JG Jr, et al. Alcohol withdrawal syndromes: a review of pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment. J Gen Intern Med. 1989;4(5):432-444.
11. Boba A. Management of acute alcohol intoxication. Am J Emerg Med. 1999;17(4):431.
12. The ASAM national practice guideline for the treatment of opioid use disorder: 2020 focused update. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2S Suppl1):1-91.
13. Shaw JM, Kolesar GS, Sellers EM, et al. Development of optimal treatment tactics for alcohol withdrawal. I. Assessment and effectiveness of supportive care. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1981;1(6):382-389.
14. Naranjo CA, Sellers EM. Clinical assessment and pharmacotherapy of the alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Recent Dev Alcohol. 1986;4:265-281.
15. Kampman K, Jarvis M. American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) national practice guideline for the use of medications in the treatment of addiction involving opioid use. J Addict Med. 2015;9(5):358-367.
16. The ASAM clinical practice guideline on alcohol withdrawal management. J Addict Med. 2020;14(3S Suppl 1):1-72.
17. Isenberg-Grzeda E, Kutner HE, Nicolson SE. Wernicke-Korsakoff-syndrome: under-recognized and under-treated. Psychosomatics. 2012;53(6):507-516.
18. Schuckit MA. Treatment of opioid-use disorders. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(4):357-368.
19. Tang Y-L, Hao W. Improving drug addiction treatment in China. Addiction. 2007;102(7):1057-1063.
20. Wakeman SE, Larochelle MR, Ameli O, et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(2):e1920622.
21. Wines JD Jr, Saitz R, Horton NJ, et al. Overdose after detoxification: a prospective study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007;89(2-3):161-169.
22. Maughan BC, Becker EA. Drug-related mortality after discharge from treatment: a record-linkage study of substance abuse clients in Texas, 2006-2012. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;204:107473.
23. Gowing L, Ali R, White J. Buprenorphine for the management of opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD002025.
24. Malinoff HL, Barkin RL, Wilson G. Sublingual buprenorphine is effective in the treatment of chronic pain syndrome. Am J Ther. 2005;12(5):379-384.
25. Nava F, Manzato E, Leonardi C, et al. Opioid maintenance therapy suppresses alcohol intake in heroin addicts with alcohol dependence: preliminary results of an open randomized study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008;32(8):1867-1872.
26. Srivastava A, Kahan M, Ross S. The effect of methadone maintenance treatment on alcohol consumption: a systematic review. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2008;34(2):215-223.
27. Davids E, Gastpar M. Buprenorphine in the treatment of opioid dependence. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004;14(3):209-216.
28. American Psychiatric Association. Practice Guideline for the Pharmacological Treatment of Patients With Alcohol Use Disorder. American Psychiatric Association; 2018.
29. Hassanian-Moghaddam H, Afzali S, Pooya A. Withdrawal syndrome caused by naltrexone in opioid abusers. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2014;33(6):561-567.
30. Fairbanks J, Umbreit A, Kolla BP, et al. Evidence-based pharmacotherapies for alcohol use disorder: clinical pearls. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(9):1964-1977.
31. Verrotti A, Scaparrotta A, Agostinelli S, et al. Topiramate-induced weight loss: a review. Epilepsy Res. 2011;95(3):189-199.
32. Flórez G, García-Portilla P, Alvarez S, et al. Using topiramate or naltrexone for the treatment of alcohol-dependent patients. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008;32(7):1251-1259.
33. Jørgensen CH, Pedersen B, Tønnesen H. The efficacy of disulfiram for the treatment of alcohol use disorder. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011;35(10):1749-1758.
34. Mason BJ, Quello S, Shadan F. Gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018;27(1):113-124.
35. Sudakin D. Naltrexone: not just for opioids anymore. J Med Toxicol. 2016;12(1):71-75.
36. Rubio G, Jiménez-Arrieri MA, Ponce G, et al. Naltrexone versus acamprosate: one year follow-up of alcohol dependence treatment. Alcohol Alcohol. 2001;36(5):419-425.
37. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318.
38. Clark AK, Wilder CM, Winstanley EL. A systematic review of community opioid overdose prevention and naloxone distribution programs. J Addict Med. 2014;8(3):153-163.
39. Dunne RB. Prescribing naloxone for opioid overdose intervention. Pain Manag. 2018;8(3):197-208.
Evaluation after a suicide attempt: What to ask
In 2021, suicide was the 11th leading cause of death in the United States.1 Suicide resulted in 49,000 US deaths during 2021; it was the second most common cause of death in individuals age 10 to 34, and the fifth leading cause among children.1,2 Women are 3 to 4 times more likely than men to attempt suicide, but men are 4 times more likely to die by suicide.2
The evaluation of patients with suicidal ideation who have not made an attempt generally involves assessing 4 factors: the specific plan, access to lethal means, any recent social stressors, and the presence of a psychiatric disorder.3 The clinician should also assess which potential deterrents, such as religious beliefs or dependent children, might be present.
Mental health clinicians are often called upon to evaluate a patient after a suicide attempt to assess intent for continued self-harm and to determine appropriate disposition. Such an evaluation must consider multiple factors, including the method used, premeditation, consequences of the attempt, the presence of severe depression and/or psychosis, and the role of substance use. Assessment after a suicide attempt differs from the examination of individuals who harbor suicidal thoughts but have not made an attempt; the latter group may be more likely to respond to interventions such as intensive outpatient care, mobilization of family support, and religious proscriptions against suicide. However, for patients who make an attempt to end their life, whatever potential safeguards or deterrents to suicide that were in place obviously did not prevent the self-harm act. The consequences of the attempt, such as disabling injuries or medical complications, and possible involuntary commitment, need to be considered. Assessment of the patient’s feelings about having survived the attempt is important because the psychological impact of the attempt on family members may serve to intensify the patient’s depression and make a subsequent attempt more likely.
Many individuals who think of suicide have communicated self-harm thoughts or intentions, but such comments are often minimized or ignored. There is a common but erroneous belief that if patients are encouraged to discuss thoughts of self-harm, they will be more likely to act upon them. Because the opposite is true,4 clinicians should ask vulnerable patients about suicidal ideation or intent. Importantly, noncompliance with life-saving medical care, risk-taking behaviors, and substance use may also signal a desire for self-harm. Passive thoughts of death, typified by comments such as “I don’t care whether I wake up or not,” should also be elicited. Many patients who think of suicide speak of being in a “bad place” where reason and logic give way to an intense desire to end their misery.

The evaluation of a patient who has attempted suicide is an important component of providing psychiatric care. This article reflects our 45 years of evaluating such patients. As such, it reflects our clinical experience and is not evidence-based. We offer a checklist of 14 questions that we have found helpful when determining if it would be best for a patient to receive inpatient psychiatric hospitalization or a discharge referral for outpatient care (Table). Questions 1 through 6 are specific for patients who have made a suicide attempt, while questions 7 through 14 are helpful for assessing global risk factors for suicide.
1. Was the attempt premeditated?
Determining premeditation vs impulsivity is an essential element of the assessment following a suicide attempt. Many such acts may occur without forethought in response to an unexpected stressor, such as an altercation between partners or family conflicts. Impulsive attempts can occur when an individual is involved in a distressing event and/or while intoxicated. Conversely, premeditation involves forethought and planning, which may increase the risk of suicide in the near future.
Examples of premeditated behavior include:
- Contemplating the attempt days or weeks beforehand
- Researching the effects of a medication or combination of medications in terms of potential lethality
- Engaging in behavior that would decrease the likelihood of their body being discovered after the attempt
- Obtaining weapons and/or stockpiling pills
- Canvassing potential sites such as bridges or tall buildings
- Engaging in a suicide attempt “practice run”
- Leaving a suicide note or message on social media
- Making funeral arrangements, such as choosing burial clothing
- Writing a will and arranging for the custody of dependent children
- Purchasing life insurance that does not deny payment of benefits in cases of death by suicide.
Continue to: Patients with a premeditated...
Patients with a premeditated suicide attempt generally do not expect to survive and are often surprised or upset that the act was not fatal. The presence of indicators that the attempt was premeditated should direct the disposition more toward hospitalization than discharge. In assessing the impact of premeditation, it is important to gauge not just the examples listed above, but also the patient’s perception of these issues (such as potential loss of child custody). Consider how much the patient is emotionally affected by such thinking.
2. What were the consequences of the attempt?
Assessing the reason for the attempt (if any) and determining whether the inciting circumstance has changed due to the suicide attempt are an important part of the evaluation. A suicide attempt may result in reconciliation with and/or renewed support from family members or partners, who might not have been aware of the patient’s emotional distress. Such unexpected support often results in the patient exhibiting improved mood and affect, and possibly temporary resolution of suicidal thoughts. This “flight into health” may be short-lived, but it also may be enough to engage the patient in a therapeutic alliance. That may permit a discharge with safe disposition to the outpatient clinic while in the custody of a family member, partner, or close friend.
Alternatively, some people experience a troubling worsening of precipitants following a suicide attempt. Preexisting medical conditions and financial, occupational, and/or social woes may be exacerbated. Child custody determinations may be affected, assuming the patient understands the possibility of this adverse consequence. Violent methods may result in disfigurement and body image issues. Individuals from small, close-knit communities may experience stigmatization and unwanted notoriety because of their suicide attempt. Such negative consequences may render some patients more likely to make another attempt to die by suicide. It is crucial to consider how a suicide attempt may have changed the original stress that led to the attempt.
3. Which method was used?
Most fatal suicides in the US are by firearms, and many individuals who survive such attempts do so because of unfamiliarity with the weapon, gun malfunction, faulty aim, or alcohol use.5-7 Some survivors report intending to shoot themselves in the heart, but instead suffered shoulder injuries. Unfortunately, for a patient who survives self-inflicted gunshot wounds, the sequelae of chronic pain, multiple surgical procedures, disability, and disfigurement may serve as constant negative reminders of the event. Some individuals with suicidal intent eschew the idea of using firearms because they hope to avoid having a family member be the first to discover them. Witnessing the aftermath of a fatal suicide by gunshot can induce symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder in family members and/or partners.8
For a patient with self-inflicted gunshot wounds, always determine whether the weapon has been secured or if the patient still has access to it. Asking about weapon availability is essential during the evaluation of any patient with depression, major life crises, or other factors that may yield a desire to die; this is especially true for individuals with substance use disorders (SUDs). Whenever readily available to such individuals, weapons need to be safely removed.
Continue to: Other self-harm methods...
Other self-harm methods with a high degree of lethality include jumping from bridges or buildings, poisonings, self-immolation, cutting, and hangings. Individuals who choose these approaches generally do not intend to survive. Many of these methods also entail premeditation, as in the case of individuals who canvass bridges and note time when traffic is light so they are less likely to be interrupted. Between 1937 and 2012, there were >1,600 deaths by suicide from San Francisco’s Golden Gate Bridge.9 Patients who choose highly lethal methods are often irritated during the postattempt evaluation because their plans were not fatal. Usually, patients who choose such potentially lethal methods are hospitalized initially on medical and surgical floors, and receive most of their psychiatric care from consultation psychiatrists. Following discharge, these patients may be at high risk for subsequent suicide attempts.
In the US, the most common method of attempting suicide is by overdose.4 Lethality is determined by the agent or combination of substances ingested, the amount taken, the person’s health status, and the length of time before they are discovered. Many patients mistakenly assume that readily available agents such as acetaminophen and aspirin are less likely to be fatal than prescription medications. Evaluators may want to assess for suicidality in individuals with erratic, risk-taking behaviors, who are at especially high risk for death. Learning about the method the patient used can help the clinician determine the imminent risk of another suicide attempt. The more potentially fatal the patient’s method, the more serious their suicide intent, and the higher the risk they will make another suicide attempt, possibly using an even more lethal method.
4. What was the intent?
“What did you want to happen when you made this attempt?” Many patients will respond that they wanted to die, sleep, not wake up, or did not care what happened. Others say it was a gesture to evoke a certain response from another person. If this is the case, it is important to know whether the desired outcome was achieved. These so-called gestures often involve making sure the intended person is aware of the attempt, often by writing a letter, sending a text, or posting on social media. Such behaviors may be exhibited by patients with personality disorders. While such attempts often are impulsive, if the attempt fails to generate the anticipated effect, the patient may try to gain more attention by escalating their suicide actions.
Conversely, if a spouse or partner reconciles with the patient solely because of a suicide attempt, this may set a pattern for future self-harm events in which the patient hopes to achieve the same outcome. Nevertheless, it is better to err for safety because some of these patients will make another attempt, just to prove that they should have been taken more seriously. An exploration of such intent can help the evaluation because even supposed “gestures” can have dangerous consequences. Acts that do not result in the desired outcome should precipitate hospitalization rather than discharge.
5. What facilitated the patient’s rescue?
“Why is this patient still alive?” Determine if the patient did anything to save themself, such as calling an ambulance, inducing emesis, telling someone what they did, or coming to the hospital on their own. If yes, asking them what changed their mind may provide information about what exists in their lives to potentially prevent future attempts, or about wishes to stay alive. These issues can be used to guide outpatient therapy.
Continue to: How does the patient feel about having survived?
6. How does the patient feel about having survived?
When a patient is asked how they feel about having survived a suicide attempt, some will label their act “stupid” and profess embarrassment. Others exhibit future-oriented thought, which is a very good prognostic sign. More ominous is subsequent dysphoria or lamenting that “I could not even do this right.” Patients often express anger toward anyone who rescued them, especially those whose attempts were carefully planned or were discovered by accident. Some patients might also express ambivalence about having survived.
The patient’s response to this question may be shaped by their desire to avoid hospitalization, so beyond their verbal answers, be attentive to clinical cues that may suggest the patient is not being fully transparent. Anger or ambivalence about having survived, a lack of future-oriented thought, and a restricted affect despite verbalizing joy about still being alive are features that suggest psychiatric hospitalization may be warranted.
7. Has the patient made previous suicide attempts?
Compared to individuals with no previous suicide attempts, patients with a history of suicide attempts are 30 to 40 times more likely to die by suicide.2 Many patients who present after a suicide attempt have tried to kill themselves multiple times. Exploring the number of past attempts, how recent the attempts were, and what dispositions were made can be of benefit. Reviewing the potential lethality of past attempts (eg, was hospitalization required, was the patient placed in an intensive care unit, and/or was intubation needed) is recommended. If outpatient care was suggested or medication prescribed, was the patient adherent? Consider asking about passive suicidal behavior, such as not seeking care for medical issues, discontinuing life-saving medication, or engaging in reckless behavior. While such behaviors may not have been classified as a suicide attempt, it might indicate a feeling of indifference toward staying alive. A patient with a past attempt, especially if recent, merits consideration for inpatient care. Once again, referring previously nonadherent patients to outpatient treatment is less likely to be effective.
8. Does the patient have a support network?
Before discharging a patient who has made a suicide attempt, consider the quality of their support network. Gauging the response of the family and friends to the patient’s attempt can be beneficial. Indifference or resentment on the part of loved ones is a bad sign. Some patients have access to support networks they either did not know were available or chose not to utilize. In other instances, after realizing how depressed the patient has been, the family might provide a new safety net. Strong religious affiliations can also be valuable because devout spirituality can be a deterrent to suicide behaviors.10 For an individual whose attempt was motivated by loneliness or feeling unloved or underappreciated, a newly realized support network can be an additional protective deterrent.
9. Does the patient have a family history of suicide?
There may be a familial component to suicide. Knowing about any suicide history in the family contributes to future therapeutic planning. The clinician may want to explore the patient’s family suicide history in detail because such information can have substantial impact on the patient’s motivation for attempting suicide. The evaluator may want to determine if the anniversary of a family suicide is coming. Triggers for a suicide attempt could include the anniversary of a death, birthdays, family-oriented holidays, and similar events. It is productive to understand how the patient feels about family members who have died by suicide. Some will empathize with the deceased, commenting that they did the “right thing.” Others, upon realizing how their own attempt affected others, will be remorseful and determined not to inflict more pain on their family. Such patients may need to be reminded of the misery associated with their family being left without them. These understandings are helpful at setting a safe disposition. However, a history of death by suicide in the family should always be thoroughly evaluated, regardless of the patient’s attitude about that death.
Continue to: Was the attempt the result of depression?
10. Was the attempt the result of depression?
For a patient experiencing depressive symptoms, the prognosis is less positive; they are more likely to harbor serious intent, premeditation, hopelessness, and social isolation, and less likely to express future-oriented thought. They often exhibit a temporary “flight into health.” Such progress is often transitory and may not represent recovery. Because mood disorders may still be present despite a temporary improvement, inpatient and pharmacologic treatment may be needed. If a patient’s suicide attempt occurred as a result of severe depression, it is possible they will make another suicide attempt unless their depression is addressed in a safe and secure setting, such as inpatient hospitalization, or through close family observation while the patient is receiving intensive outpatient treatment.
11. Does the patient have a psychotic disorder?
Many patients with a psychotic illness die following their first attempt without ever having contact with a mental health professional.11 Features of psychosis might include malevolent auditory hallucinations that suggest self-destruction.11 Such “voices” can be intense and self-deprecating; many patients with this type of hallucination report having made a suicide attempt “just to make the voices stop.”
Symptoms of paranoia can make it less likely for individuals with psychosis to confide in family members, friends, or medical personnel. Religious elements are often of a delusional nature and can be dangerous. Psychosis is more difficult to hide than depression and the presence of psychoses concurrent with major depressive disorder (MDD) increases the probability of suicidality.11 Psychosis secondary to substance use may diminish inhibitions and heighten impulsivity, thereby exacerbating the likelihood of self-harm. Usually, the presence of psychotic features precipitating or following a suicide attempt leads to psychiatric hospitalization.
12. Is the patient in a high-risk demographic group?
When evaluating a patient who has attempted suicide, it helps to consider not just what they did, but who they are. Specifically, does the individual belong to a demographic group that traditionally has a high rate of suicide? For example, patients who are Native American or Alaska Natives warrant extra caution.2 Older White males, especially those who are divorced, widowed, retired, and/or have chronic health problems, are also at greater risk. Compared to the general population, individuals age >80 have a massively elevated chance for self-induced death.12 Some of the reasons include:
- medical comorbidities make surviving an attempt less likely
- access to large amounts of medications
- more irreversible issues, such as chronic pain, disability, or widowhood
- living alone, which may delay discovery.
Patients who are members of any of these demographic groups may deserve serious consideration for inpatient psychiatric admission, regardless of other factors.
Continue to: Were drugs or alcohol involved?
13. Were drugs or alcohol involved?
This factor is unique in that it is both a chronic risk factor (SUDs) and a warning sign for imminent suicide, as in the case of an individual who gets intoxicated to disinhibit their fear of death so they can attempt suicide. Alcohol use disorders are associated with depression and suicide. Overdoses by fentanyl and other opiates have become more frequent.13 In many cases, fatalities are unintentional because users overestimate their tolerance or ingest contaminated substances.14 Disinhibition by alcohol and/or other drugs is a risk factor for attempting suicide and can intensify the depth of MDD. Some patients will ingest substances before an attempt just to give them the courage to act; many think of suicide only when intoxicated. Toxicology screens are indicated as part of the evaluation after a suicide attempt.
Depressive and suicidal thoughts often occur in people “coming down” from cocaine or other stimulants. These circumstances require determining whether to refer the patient for treatment for an SUD or psychiatric hospitalization.
In summary, getting intoxicated solely to diminish anxiety about suicide is a dangerous feature, whereas attempting suicide due to intoxication is less concerning. The latter patient may not consider suicide unless they become intoxicated again. When available, dual diagnosis treatment facilities can be an appropriate referral for such patients. Emergency department holding beds can allow these individuals to detoxify prior to the evaluation.
14. Does the patient have future-oriented thoughts?
When evaluating a patient who has attempted suicide, the presence of future planning and anticipation can be reassuring, but these features should be carefully assessed.14-16
After-the-fact comments may be more reliable when a patient offers them spontaneously, as opposed to in response to direct questioning.
- the specificity of the future plans
- corroboration from the family and others about the patient’s previous investment in the upcoming event
- whether the patient mentions such plans spontaneously or only in response to direct questioning
- the patient’s emotional expression or affect when discussing their future
- whether such plans are reasonable, grandiose, and/or unrealistic.
Bottom Line
When assessing a patient after a suicide attempt, both the patient’s presentation and history and the clinician’s instincts are important. Careful consideration of the method, stated intent, premeditation vs impulsivity, feelings about having survived, presence of psychiatric illness, high-risk demographic, postattempt demeanor and affect, quality of support, presence of self-rescue behaviors, future-oriented thoughts, and other factors can help in making the appropriate disposition.
Related Resources
- Kim H, Kim Y, Shin MH, et al. Early psychiatric referral after attempted suicide helps prevent suicide reattempts: a longitudinal national cohort study in South Korea. Front Psychiatry. 2022;13:607892. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2022.607892
- Michaud L, Berva S, Ostertag L, et al. When to discharge and when to voluntary or compulsory hospitalize? Factors associated with treatment decision after self-harm. Psychiatry Res. 2022;317:114810. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114810
1. Ten Leading Causes of Death, United States 2020. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention WISQARS. Accessed March 4, 2022. https://wisqars.cdc.gov/data/lcd/home
2. Norris D, Clark MS. Evaluation and treatment of suicidal patients. Am Fam Physician. 2012;15;85(6):602-605.
3. Gliatto MF, Rai AK. Evaluation and treatment patients with suicidal ideation. Am Fam Phys. 1999;59(6):1500-1506.
4. Dazzi T, Gribble R, Wessely S, et al. Does asking about suicide and related behaviors induce suicidal ideation? What is the evidence? Psychol Med. 2014;44(16):3361-3363.
5. Lewiecki EM, Miller SA. Suicide, guns and public policy. Am J Public Health. 2013;103(1):27-31.
6. Frierson RL. Women who shoot themselves. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1989;40(8):841-843.
7. Frierson RL, Lippmann SB. Psychiatric consultation for patients with self-inflicted gunshot wounds. Psychosomatics. 1990;31(1):67-74.
8. Mitchell AM, Terhorst L. PTSD symptoms in survivors bereaved by the suicide of a significant other. J Am Psychiatr Nurses Assoc. 2017;23(1):61-65.
9. Bateson J. The Golden Gate Bridge’s fatal flaw. Los Angeles Times. May 25, 2012. Accessed March 2, 2022. https://www.latimes.com/opinion/la-xpm-2012-may-25-la-oe-adv-bateson-golden-gate-20120525-story.html
10. Dervic K, Oquendoma MA, Grunebaum MF, et al. Religious affiliation and suicide attempt. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161(12):2303-2308.
11. Nordentoft H, Madsen T, Fedyszyn IF. Suicidal behavior and mortality in first episode psychosis. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2015;203(5):387-392.
12. Frierson R, Lippmann S. Suicide attempts by the old and the very old. Arch Intern Med. 1991;151(1):141-144.
13. Braden JB, Edlund MJ, Sullivan MD. Suicide deaths with opiate poisonings in the United States: 1999-2014. Am J Public Health. 2017;107(3):421-426.
14. Morin KA, Acharya S, Eibl JK, et al: Evidence of increased fentanyl use during the COVID-19 pandemic among opioid agonist treated patients in Ontario, Canada. Int J Drug Policy. 2021;90:103088.
15. Shobassy A, Abu-Mohammad AS. Assessing imminent suicide risk: what about future planning? Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(2):12-17.
16. MacLeod AK, Pankhania B, Lee M, et al. Parasuicide, depression and the anticipation of positive and negative future experiences. Psychol Med. 1997;27(4):973-977.
17. Macleod AK, Tata P, Tyrer P, et al. Hopelessness and positive and negative future thinking in parasuicide. Br J Clin Psychol. 2010;44(Pt 4):495-504.
In 2021, suicide was the 11th leading cause of death in the United States.1 Suicide resulted in 49,000 US deaths during 2021; it was the second most common cause of death in individuals age 10 to 34, and the fifth leading cause among children.1,2 Women are 3 to 4 times more likely than men to attempt suicide, but men are 4 times more likely to die by suicide.2
The evaluation of patients with suicidal ideation who have not made an attempt generally involves assessing 4 factors: the specific plan, access to lethal means, any recent social stressors, and the presence of a psychiatric disorder.3 The clinician should also assess which potential deterrents, such as religious beliefs or dependent children, might be present.
Mental health clinicians are often called upon to evaluate a patient after a suicide attempt to assess intent for continued self-harm and to determine appropriate disposition. Such an evaluation must consider multiple factors, including the method used, premeditation, consequences of the attempt, the presence of severe depression and/or psychosis, and the role of substance use. Assessment after a suicide attempt differs from the examination of individuals who harbor suicidal thoughts but have not made an attempt; the latter group may be more likely to respond to interventions such as intensive outpatient care, mobilization of family support, and religious proscriptions against suicide. However, for patients who make an attempt to end their life, whatever potential safeguards or deterrents to suicide that were in place obviously did not prevent the self-harm act. The consequences of the attempt, such as disabling injuries or medical complications, and possible involuntary commitment, need to be considered. Assessment of the patient’s feelings about having survived the attempt is important because the psychological impact of the attempt on family members may serve to intensify the patient’s depression and make a subsequent attempt more likely.
Many individuals who think of suicide have communicated self-harm thoughts or intentions, but such comments are often minimized or ignored. There is a common but erroneous belief that if patients are encouraged to discuss thoughts of self-harm, they will be more likely to act upon them. Because the opposite is true,4 clinicians should ask vulnerable patients about suicidal ideation or intent. Importantly, noncompliance with life-saving medical care, risk-taking behaviors, and substance use may also signal a desire for self-harm. Passive thoughts of death, typified by comments such as “I don’t care whether I wake up or not,” should also be elicited. Many patients who think of suicide speak of being in a “bad place” where reason and logic give way to an intense desire to end their misery.

The evaluation of a patient who has attempted suicide is an important component of providing psychiatric care. This article reflects our 45 years of evaluating such patients. As such, it reflects our clinical experience and is not evidence-based. We offer a checklist of 14 questions that we have found helpful when determining if it would be best for a patient to receive inpatient psychiatric hospitalization or a discharge referral for outpatient care (Table). Questions 1 through 6 are specific for patients who have made a suicide attempt, while questions 7 through 14 are helpful for assessing global risk factors for suicide.
1. Was the attempt premeditated?
Determining premeditation vs impulsivity is an essential element of the assessment following a suicide attempt. Many such acts may occur without forethought in response to an unexpected stressor, such as an altercation between partners or family conflicts. Impulsive attempts can occur when an individual is involved in a distressing event and/or while intoxicated. Conversely, premeditation involves forethought and planning, which may increase the risk of suicide in the near future.
Examples of premeditated behavior include:
- Contemplating the attempt days or weeks beforehand
- Researching the effects of a medication or combination of medications in terms of potential lethality
- Engaging in behavior that would decrease the likelihood of their body being discovered after the attempt
- Obtaining weapons and/or stockpiling pills
- Canvassing potential sites such as bridges or tall buildings
- Engaging in a suicide attempt “practice run”
- Leaving a suicide note or message on social media
- Making funeral arrangements, such as choosing burial clothing
- Writing a will and arranging for the custody of dependent children
- Purchasing life insurance that does not deny payment of benefits in cases of death by suicide.
Continue to: Patients with a premeditated...
Patients with a premeditated suicide attempt generally do not expect to survive and are often surprised or upset that the act was not fatal. The presence of indicators that the attempt was premeditated should direct the disposition more toward hospitalization than discharge. In assessing the impact of premeditation, it is important to gauge not just the examples listed above, but also the patient’s perception of these issues (such as potential loss of child custody). Consider how much the patient is emotionally affected by such thinking.
2. What were the consequences of the attempt?
Assessing the reason for the attempt (if any) and determining whether the inciting circumstance has changed due to the suicide attempt are an important part of the evaluation. A suicide attempt may result in reconciliation with and/or renewed support from family members or partners, who might not have been aware of the patient’s emotional distress. Such unexpected support often results in the patient exhibiting improved mood and affect, and possibly temporary resolution of suicidal thoughts. This “flight into health” may be short-lived, but it also may be enough to engage the patient in a therapeutic alliance. That may permit a discharge with safe disposition to the outpatient clinic while in the custody of a family member, partner, or close friend.
Alternatively, some people experience a troubling worsening of precipitants following a suicide attempt. Preexisting medical conditions and financial, occupational, and/or social woes may be exacerbated. Child custody determinations may be affected, assuming the patient understands the possibility of this adverse consequence. Violent methods may result in disfigurement and body image issues. Individuals from small, close-knit communities may experience stigmatization and unwanted notoriety because of their suicide attempt. Such negative consequences may render some patients more likely to make another attempt to die by suicide. It is crucial to consider how a suicide attempt may have changed the original stress that led to the attempt.
3. Which method was used?
Most fatal suicides in the US are by firearms, and many individuals who survive such attempts do so because of unfamiliarity with the weapon, gun malfunction, faulty aim, or alcohol use.5-7 Some survivors report intending to shoot themselves in the heart, but instead suffered shoulder injuries. Unfortunately, for a patient who survives self-inflicted gunshot wounds, the sequelae of chronic pain, multiple surgical procedures, disability, and disfigurement may serve as constant negative reminders of the event. Some individuals with suicidal intent eschew the idea of using firearms because they hope to avoid having a family member be the first to discover them. Witnessing the aftermath of a fatal suicide by gunshot can induce symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder in family members and/or partners.8
For a patient with self-inflicted gunshot wounds, always determine whether the weapon has been secured or if the patient still has access to it. Asking about weapon availability is essential during the evaluation of any patient with depression, major life crises, or other factors that may yield a desire to die; this is especially true for individuals with substance use disorders (SUDs). Whenever readily available to such individuals, weapons need to be safely removed.
Continue to: Other self-harm methods...
Other self-harm methods with a high degree of lethality include jumping from bridges or buildings, poisonings, self-immolation, cutting, and hangings. Individuals who choose these approaches generally do not intend to survive. Many of these methods also entail premeditation, as in the case of individuals who canvass bridges and note time when traffic is light so they are less likely to be interrupted. Between 1937 and 2012, there were >1,600 deaths by suicide from San Francisco’s Golden Gate Bridge.9 Patients who choose highly lethal methods are often irritated during the postattempt evaluation because their plans were not fatal. Usually, patients who choose such potentially lethal methods are hospitalized initially on medical and surgical floors, and receive most of their psychiatric care from consultation psychiatrists. Following discharge, these patients may be at high risk for subsequent suicide attempts.
In the US, the most common method of attempting suicide is by overdose.4 Lethality is determined by the agent or combination of substances ingested, the amount taken, the person’s health status, and the length of time before they are discovered. Many patients mistakenly assume that readily available agents such as acetaminophen and aspirin are less likely to be fatal than prescription medications. Evaluators may want to assess for suicidality in individuals with erratic, risk-taking behaviors, who are at especially high risk for death. Learning about the method the patient used can help the clinician determine the imminent risk of another suicide attempt. The more potentially fatal the patient’s method, the more serious their suicide intent, and the higher the risk they will make another suicide attempt, possibly using an even more lethal method.
4. What was the intent?
“What did you want to happen when you made this attempt?” Many patients will respond that they wanted to die, sleep, not wake up, or did not care what happened. Others say it was a gesture to evoke a certain response from another person. If this is the case, it is important to know whether the desired outcome was achieved. These so-called gestures often involve making sure the intended person is aware of the attempt, often by writing a letter, sending a text, or posting on social media. Such behaviors may be exhibited by patients with personality disorders. While such attempts often are impulsive, if the attempt fails to generate the anticipated effect, the patient may try to gain more attention by escalating their suicide actions.
Conversely, if a spouse or partner reconciles with the patient solely because of a suicide attempt, this may set a pattern for future self-harm events in which the patient hopes to achieve the same outcome. Nevertheless, it is better to err for safety because some of these patients will make another attempt, just to prove that they should have been taken more seriously. An exploration of such intent can help the evaluation because even supposed “gestures” can have dangerous consequences. Acts that do not result in the desired outcome should precipitate hospitalization rather than discharge.
5. What facilitated the patient’s rescue?
“Why is this patient still alive?” Determine if the patient did anything to save themself, such as calling an ambulance, inducing emesis, telling someone what they did, or coming to the hospital on their own. If yes, asking them what changed their mind may provide information about what exists in their lives to potentially prevent future attempts, or about wishes to stay alive. These issues can be used to guide outpatient therapy.
Continue to: How does the patient feel about having survived?
6. How does the patient feel about having survived?
When a patient is asked how they feel about having survived a suicide attempt, some will label their act “stupid” and profess embarrassment. Others exhibit future-oriented thought, which is a very good prognostic sign. More ominous is subsequent dysphoria or lamenting that “I could not even do this right.” Patients often express anger toward anyone who rescued them, especially those whose attempts were carefully planned or were discovered by accident. Some patients might also express ambivalence about having survived.
The patient’s response to this question may be shaped by their desire to avoid hospitalization, so beyond their verbal answers, be attentive to clinical cues that may suggest the patient is not being fully transparent. Anger or ambivalence about having survived, a lack of future-oriented thought, and a restricted affect despite verbalizing joy about still being alive are features that suggest psychiatric hospitalization may be warranted.
7. Has the patient made previous suicide attempts?
Compared to individuals with no previous suicide attempts, patients with a history of suicide attempts are 30 to 40 times more likely to die by suicide.2 Many patients who present after a suicide attempt have tried to kill themselves multiple times. Exploring the number of past attempts, how recent the attempts were, and what dispositions were made can be of benefit. Reviewing the potential lethality of past attempts (eg, was hospitalization required, was the patient placed in an intensive care unit, and/or was intubation needed) is recommended. If outpatient care was suggested or medication prescribed, was the patient adherent? Consider asking about passive suicidal behavior, such as not seeking care for medical issues, discontinuing life-saving medication, or engaging in reckless behavior. While such behaviors may not have been classified as a suicide attempt, it might indicate a feeling of indifference toward staying alive. A patient with a past attempt, especially if recent, merits consideration for inpatient care. Once again, referring previously nonadherent patients to outpatient treatment is less likely to be effective.
8. Does the patient have a support network?
Before discharging a patient who has made a suicide attempt, consider the quality of their support network. Gauging the response of the family and friends to the patient’s attempt can be beneficial. Indifference or resentment on the part of loved ones is a bad sign. Some patients have access to support networks they either did not know were available or chose not to utilize. In other instances, after realizing how depressed the patient has been, the family might provide a new safety net. Strong religious affiliations can also be valuable because devout spirituality can be a deterrent to suicide behaviors.10 For an individual whose attempt was motivated by loneliness or feeling unloved or underappreciated, a newly realized support network can be an additional protective deterrent.
9. Does the patient have a family history of suicide?
There may be a familial component to suicide. Knowing about any suicide history in the family contributes to future therapeutic planning. The clinician may want to explore the patient’s family suicide history in detail because such information can have substantial impact on the patient’s motivation for attempting suicide. The evaluator may want to determine if the anniversary of a family suicide is coming. Triggers for a suicide attempt could include the anniversary of a death, birthdays, family-oriented holidays, and similar events. It is productive to understand how the patient feels about family members who have died by suicide. Some will empathize with the deceased, commenting that they did the “right thing.” Others, upon realizing how their own attempt affected others, will be remorseful and determined not to inflict more pain on their family. Such patients may need to be reminded of the misery associated with their family being left without them. These understandings are helpful at setting a safe disposition. However, a history of death by suicide in the family should always be thoroughly evaluated, regardless of the patient’s attitude about that death.
Continue to: Was the attempt the result of depression?
10. Was the attempt the result of depression?
For a patient experiencing depressive symptoms, the prognosis is less positive; they are more likely to harbor serious intent, premeditation, hopelessness, and social isolation, and less likely to express future-oriented thought. They often exhibit a temporary “flight into health.” Such progress is often transitory and may not represent recovery. Because mood disorders may still be present despite a temporary improvement, inpatient and pharmacologic treatment may be needed. If a patient’s suicide attempt occurred as a result of severe depression, it is possible they will make another suicide attempt unless their depression is addressed in a safe and secure setting, such as inpatient hospitalization, or through close family observation while the patient is receiving intensive outpatient treatment.
11. Does the patient have a psychotic disorder?
Many patients with a psychotic illness die following their first attempt without ever having contact with a mental health professional.11 Features of psychosis might include malevolent auditory hallucinations that suggest self-destruction.11 Such “voices” can be intense and self-deprecating; many patients with this type of hallucination report having made a suicide attempt “just to make the voices stop.”
Symptoms of paranoia can make it less likely for individuals with psychosis to confide in family members, friends, or medical personnel. Religious elements are often of a delusional nature and can be dangerous. Psychosis is more difficult to hide than depression and the presence of psychoses concurrent with major depressive disorder (MDD) increases the probability of suicidality.11 Psychosis secondary to substance use may diminish inhibitions and heighten impulsivity, thereby exacerbating the likelihood of self-harm. Usually, the presence of psychotic features precipitating or following a suicide attempt leads to psychiatric hospitalization.
12. Is the patient in a high-risk demographic group?
When evaluating a patient who has attempted suicide, it helps to consider not just what they did, but who they are. Specifically, does the individual belong to a demographic group that traditionally has a high rate of suicide? For example, patients who are Native American or Alaska Natives warrant extra caution.2 Older White males, especially those who are divorced, widowed, retired, and/or have chronic health problems, are also at greater risk. Compared to the general population, individuals age >80 have a massively elevated chance for self-induced death.12 Some of the reasons include:
- medical comorbidities make surviving an attempt less likely
- access to large amounts of medications
- more irreversible issues, such as chronic pain, disability, or widowhood
- living alone, which may delay discovery.
Patients who are members of any of these demographic groups may deserve serious consideration for inpatient psychiatric admission, regardless of other factors.
Continue to: Were drugs or alcohol involved?
13. Were drugs or alcohol involved?
This factor is unique in that it is both a chronic risk factor (SUDs) and a warning sign for imminent suicide, as in the case of an individual who gets intoxicated to disinhibit their fear of death so they can attempt suicide. Alcohol use disorders are associated with depression and suicide. Overdoses by fentanyl and other opiates have become more frequent.13 In many cases, fatalities are unintentional because users overestimate their tolerance or ingest contaminated substances.14 Disinhibition by alcohol and/or other drugs is a risk factor for attempting suicide and can intensify the depth of MDD. Some patients will ingest substances before an attempt just to give them the courage to act; many think of suicide only when intoxicated. Toxicology screens are indicated as part of the evaluation after a suicide attempt.
Depressive and suicidal thoughts often occur in people “coming down” from cocaine or other stimulants. These circumstances require determining whether to refer the patient for treatment for an SUD or psychiatric hospitalization.
In summary, getting intoxicated solely to diminish anxiety about suicide is a dangerous feature, whereas attempting suicide due to intoxication is less concerning. The latter patient may not consider suicide unless they become intoxicated again. When available, dual diagnosis treatment facilities can be an appropriate referral for such patients. Emergency department holding beds can allow these individuals to detoxify prior to the evaluation.
14. Does the patient have future-oriented thoughts?
When evaluating a patient who has attempted suicide, the presence of future planning and anticipation can be reassuring, but these features should be carefully assessed.14-16
After-the-fact comments may be more reliable when a patient offers them spontaneously, as opposed to in response to direct questioning.
- the specificity of the future plans
- corroboration from the family and others about the patient’s previous investment in the upcoming event
- whether the patient mentions such plans spontaneously or only in response to direct questioning
- the patient’s emotional expression or affect when discussing their future
- whether such plans are reasonable, grandiose, and/or unrealistic.
Bottom Line
When assessing a patient after a suicide attempt, both the patient’s presentation and history and the clinician’s instincts are important. Careful consideration of the method, stated intent, premeditation vs impulsivity, feelings about having survived, presence of psychiatric illness, high-risk demographic, postattempt demeanor and affect, quality of support, presence of self-rescue behaviors, future-oriented thoughts, and other factors can help in making the appropriate disposition.
Related Resources
- Kim H, Kim Y, Shin MH, et al. Early psychiatric referral after attempted suicide helps prevent suicide reattempts: a longitudinal national cohort study in South Korea. Front Psychiatry. 2022;13:607892. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2022.607892
- Michaud L, Berva S, Ostertag L, et al. When to discharge and when to voluntary or compulsory hospitalize? Factors associated with treatment decision after self-harm. Psychiatry Res. 2022;317:114810. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114810
In 2021, suicide was the 11th leading cause of death in the United States.1 Suicide resulted in 49,000 US deaths during 2021; it was the second most common cause of death in individuals age 10 to 34, and the fifth leading cause among children.1,2 Women are 3 to 4 times more likely than men to attempt suicide, but men are 4 times more likely to die by suicide.2
The evaluation of patients with suicidal ideation who have not made an attempt generally involves assessing 4 factors: the specific plan, access to lethal means, any recent social stressors, and the presence of a psychiatric disorder.3 The clinician should also assess which potential deterrents, such as religious beliefs or dependent children, might be present.
Mental health clinicians are often called upon to evaluate a patient after a suicide attempt to assess intent for continued self-harm and to determine appropriate disposition. Such an evaluation must consider multiple factors, including the method used, premeditation, consequences of the attempt, the presence of severe depression and/or psychosis, and the role of substance use. Assessment after a suicide attempt differs from the examination of individuals who harbor suicidal thoughts but have not made an attempt; the latter group may be more likely to respond to interventions such as intensive outpatient care, mobilization of family support, and religious proscriptions against suicide. However, for patients who make an attempt to end their life, whatever potential safeguards or deterrents to suicide that were in place obviously did not prevent the self-harm act. The consequences of the attempt, such as disabling injuries or medical complications, and possible involuntary commitment, need to be considered. Assessment of the patient’s feelings about having survived the attempt is important because the psychological impact of the attempt on family members may serve to intensify the patient’s depression and make a subsequent attempt more likely.
Many individuals who think of suicide have communicated self-harm thoughts or intentions, but such comments are often minimized or ignored. There is a common but erroneous belief that if patients are encouraged to discuss thoughts of self-harm, they will be more likely to act upon them. Because the opposite is true,4 clinicians should ask vulnerable patients about suicidal ideation or intent. Importantly, noncompliance with life-saving medical care, risk-taking behaviors, and substance use may also signal a desire for self-harm. Passive thoughts of death, typified by comments such as “I don’t care whether I wake up or not,” should also be elicited. Many patients who think of suicide speak of being in a “bad place” where reason and logic give way to an intense desire to end their misery.

The evaluation of a patient who has attempted suicide is an important component of providing psychiatric care. This article reflects our 45 years of evaluating such patients. As such, it reflects our clinical experience and is not evidence-based. We offer a checklist of 14 questions that we have found helpful when determining if it would be best for a patient to receive inpatient psychiatric hospitalization or a discharge referral for outpatient care (Table). Questions 1 through 6 are specific for patients who have made a suicide attempt, while questions 7 through 14 are helpful for assessing global risk factors for suicide.
1. Was the attempt premeditated?
Determining premeditation vs impulsivity is an essential element of the assessment following a suicide attempt. Many such acts may occur without forethought in response to an unexpected stressor, such as an altercation between partners or family conflicts. Impulsive attempts can occur when an individual is involved in a distressing event and/or while intoxicated. Conversely, premeditation involves forethought and planning, which may increase the risk of suicide in the near future.
Examples of premeditated behavior include:
- Contemplating the attempt days or weeks beforehand
- Researching the effects of a medication or combination of medications in terms of potential lethality
- Engaging in behavior that would decrease the likelihood of their body being discovered after the attempt
- Obtaining weapons and/or stockpiling pills
- Canvassing potential sites such as bridges or tall buildings
- Engaging in a suicide attempt “practice run”
- Leaving a suicide note or message on social media
- Making funeral arrangements, such as choosing burial clothing
- Writing a will and arranging for the custody of dependent children
- Purchasing life insurance that does not deny payment of benefits in cases of death by suicide.
Continue to: Patients with a premeditated...
Patients with a premeditated suicide attempt generally do not expect to survive and are often surprised or upset that the act was not fatal. The presence of indicators that the attempt was premeditated should direct the disposition more toward hospitalization than discharge. In assessing the impact of premeditation, it is important to gauge not just the examples listed above, but also the patient’s perception of these issues (such as potential loss of child custody). Consider how much the patient is emotionally affected by such thinking.
2. What were the consequences of the attempt?
Assessing the reason for the attempt (if any) and determining whether the inciting circumstance has changed due to the suicide attempt are an important part of the evaluation. A suicide attempt may result in reconciliation with and/or renewed support from family members or partners, who might not have been aware of the patient’s emotional distress. Such unexpected support often results in the patient exhibiting improved mood and affect, and possibly temporary resolution of suicidal thoughts. This “flight into health” may be short-lived, but it also may be enough to engage the patient in a therapeutic alliance. That may permit a discharge with safe disposition to the outpatient clinic while in the custody of a family member, partner, or close friend.
Alternatively, some people experience a troubling worsening of precipitants following a suicide attempt. Preexisting medical conditions and financial, occupational, and/or social woes may be exacerbated. Child custody determinations may be affected, assuming the patient understands the possibility of this adverse consequence. Violent methods may result in disfigurement and body image issues. Individuals from small, close-knit communities may experience stigmatization and unwanted notoriety because of their suicide attempt. Such negative consequences may render some patients more likely to make another attempt to die by suicide. It is crucial to consider how a suicide attempt may have changed the original stress that led to the attempt.
3. Which method was used?
Most fatal suicides in the US are by firearms, and many individuals who survive such attempts do so because of unfamiliarity with the weapon, gun malfunction, faulty aim, or alcohol use.5-7 Some survivors report intending to shoot themselves in the heart, but instead suffered shoulder injuries. Unfortunately, for a patient who survives self-inflicted gunshot wounds, the sequelae of chronic pain, multiple surgical procedures, disability, and disfigurement may serve as constant negative reminders of the event. Some individuals with suicidal intent eschew the idea of using firearms because they hope to avoid having a family member be the first to discover them. Witnessing the aftermath of a fatal suicide by gunshot can induce symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder in family members and/or partners.8
For a patient with self-inflicted gunshot wounds, always determine whether the weapon has been secured or if the patient still has access to it. Asking about weapon availability is essential during the evaluation of any patient with depression, major life crises, or other factors that may yield a desire to die; this is especially true for individuals with substance use disorders (SUDs). Whenever readily available to such individuals, weapons need to be safely removed.
Continue to: Other self-harm methods...
Other self-harm methods with a high degree of lethality include jumping from bridges or buildings, poisonings, self-immolation, cutting, and hangings. Individuals who choose these approaches generally do not intend to survive. Many of these methods also entail premeditation, as in the case of individuals who canvass bridges and note time when traffic is light so they are less likely to be interrupted. Between 1937 and 2012, there were >1,600 deaths by suicide from San Francisco’s Golden Gate Bridge.9 Patients who choose highly lethal methods are often irritated during the postattempt evaluation because their plans were not fatal. Usually, patients who choose such potentially lethal methods are hospitalized initially on medical and surgical floors, and receive most of their psychiatric care from consultation psychiatrists. Following discharge, these patients may be at high risk for subsequent suicide attempts.
In the US, the most common method of attempting suicide is by overdose.4 Lethality is determined by the agent or combination of substances ingested, the amount taken, the person’s health status, and the length of time before they are discovered. Many patients mistakenly assume that readily available agents such as acetaminophen and aspirin are less likely to be fatal than prescription medications. Evaluators may want to assess for suicidality in individuals with erratic, risk-taking behaviors, who are at especially high risk for death. Learning about the method the patient used can help the clinician determine the imminent risk of another suicide attempt. The more potentially fatal the patient’s method, the more serious their suicide intent, and the higher the risk they will make another suicide attempt, possibly using an even more lethal method.
4. What was the intent?
“What did you want to happen when you made this attempt?” Many patients will respond that they wanted to die, sleep, not wake up, or did not care what happened. Others say it was a gesture to evoke a certain response from another person. If this is the case, it is important to know whether the desired outcome was achieved. These so-called gestures often involve making sure the intended person is aware of the attempt, often by writing a letter, sending a text, or posting on social media. Such behaviors may be exhibited by patients with personality disorders. While such attempts often are impulsive, if the attempt fails to generate the anticipated effect, the patient may try to gain more attention by escalating their suicide actions.
Conversely, if a spouse or partner reconciles with the patient solely because of a suicide attempt, this may set a pattern for future self-harm events in which the patient hopes to achieve the same outcome. Nevertheless, it is better to err for safety because some of these patients will make another attempt, just to prove that they should have been taken more seriously. An exploration of such intent can help the evaluation because even supposed “gestures” can have dangerous consequences. Acts that do not result in the desired outcome should precipitate hospitalization rather than discharge.
5. What facilitated the patient’s rescue?
“Why is this patient still alive?” Determine if the patient did anything to save themself, such as calling an ambulance, inducing emesis, telling someone what they did, or coming to the hospital on their own. If yes, asking them what changed their mind may provide information about what exists in their lives to potentially prevent future attempts, or about wishes to stay alive. These issues can be used to guide outpatient therapy.
Continue to: How does the patient feel about having survived?
6. How does the patient feel about having survived?
When a patient is asked how they feel about having survived a suicide attempt, some will label their act “stupid” and profess embarrassment. Others exhibit future-oriented thought, which is a very good prognostic sign. More ominous is subsequent dysphoria or lamenting that “I could not even do this right.” Patients often express anger toward anyone who rescued them, especially those whose attempts were carefully planned or were discovered by accident. Some patients might also express ambivalence about having survived.
The patient’s response to this question may be shaped by their desire to avoid hospitalization, so beyond their verbal answers, be attentive to clinical cues that may suggest the patient is not being fully transparent. Anger or ambivalence about having survived, a lack of future-oriented thought, and a restricted affect despite verbalizing joy about still being alive are features that suggest psychiatric hospitalization may be warranted.
7. Has the patient made previous suicide attempts?
Compared to individuals with no previous suicide attempts, patients with a history of suicide attempts are 30 to 40 times more likely to die by suicide.2 Many patients who present after a suicide attempt have tried to kill themselves multiple times. Exploring the number of past attempts, how recent the attempts were, and what dispositions were made can be of benefit. Reviewing the potential lethality of past attempts (eg, was hospitalization required, was the patient placed in an intensive care unit, and/or was intubation needed) is recommended. If outpatient care was suggested or medication prescribed, was the patient adherent? Consider asking about passive suicidal behavior, such as not seeking care for medical issues, discontinuing life-saving medication, or engaging in reckless behavior. While such behaviors may not have been classified as a suicide attempt, it might indicate a feeling of indifference toward staying alive. A patient with a past attempt, especially if recent, merits consideration for inpatient care. Once again, referring previously nonadherent patients to outpatient treatment is less likely to be effective.
8. Does the patient have a support network?
Before discharging a patient who has made a suicide attempt, consider the quality of their support network. Gauging the response of the family and friends to the patient’s attempt can be beneficial. Indifference or resentment on the part of loved ones is a bad sign. Some patients have access to support networks they either did not know were available or chose not to utilize. In other instances, after realizing how depressed the patient has been, the family might provide a new safety net. Strong religious affiliations can also be valuable because devout spirituality can be a deterrent to suicide behaviors.10 For an individual whose attempt was motivated by loneliness or feeling unloved or underappreciated, a newly realized support network can be an additional protective deterrent.
9. Does the patient have a family history of suicide?
There may be a familial component to suicide. Knowing about any suicide history in the family contributes to future therapeutic planning. The clinician may want to explore the patient’s family suicide history in detail because such information can have substantial impact on the patient’s motivation for attempting suicide. The evaluator may want to determine if the anniversary of a family suicide is coming. Triggers for a suicide attempt could include the anniversary of a death, birthdays, family-oriented holidays, and similar events. It is productive to understand how the patient feels about family members who have died by suicide. Some will empathize with the deceased, commenting that they did the “right thing.” Others, upon realizing how their own attempt affected others, will be remorseful and determined not to inflict more pain on their family. Such patients may need to be reminded of the misery associated with their family being left without them. These understandings are helpful at setting a safe disposition. However, a history of death by suicide in the family should always be thoroughly evaluated, regardless of the patient’s attitude about that death.
Continue to: Was the attempt the result of depression?
10. Was the attempt the result of depression?
For a patient experiencing depressive symptoms, the prognosis is less positive; they are more likely to harbor serious intent, premeditation, hopelessness, and social isolation, and less likely to express future-oriented thought. They often exhibit a temporary “flight into health.” Such progress is often transitory and may not represent recovery. Because mood disorders may still be present despite a temporary improvement, inpatient and pharmacologic treatment may be needed. If a patient’s suicide attempt occurred as a result of severe depression, it is possible they will make another suicide attempt unless their depression is addressed in a safe and secure setting, such as inpatient hospitalization, or through close family observation while the patient is receiving intensive outpatient treatment.
11. Does the patient have a psychotic disorder?
Many patients with a psychotic illness die following their first attempt without ever having contact with a mental health professional.11 Features of psychosis might include malevolent auditory hallucinations that suggest self-destruction.11 Such “voices” can be intense and self-deprecating; many patients with this type of hallucination report having made a suicide attempt “just to make the voices stop.”
Symptoms of paranoia can make it less likely for individuals with psychosis to confide in family members, friends, or medical personnel. Religious elements are often of a delusional nature and can be dangerous. Psychosis is more difficult to hide than depression and the presence of psychoses concurrent with major depressive disorder (MDD) increases the probability of suicidality.11 Psychosis secondary to substance use may diminish inhibitions and heighten impulsivity, thereby exacerbating the likelihood of self-harm. Usually, the presence of psychotic features precipitating or following a suicide attempt leads to psychiatric hospitalization.
12. Is the patient in a high-risk demographic group?
When evaluating a patient who has attempted suicide, it helps to consider not just what they did, but who they are. Specifically, does the individual belong to a demographic group that traditionally has a high rate of suicide? For example, patients who are Native American or Alaska Natives warrant extra caution.2 Older White males, especially those who are divorced, widowed, retired, and/or have chronic health problems, are also at greater risk. Compared to the general population, individuals age >80 have a massively elevated chance for self-induced death.12 Some of the reasons include:
- medical comorbidities make surviving an attempt less likely
- access to large amounts of medications
- more irreversible issues, such as chronic pain, disability, or widowhood
- living alone, which may delay discovery.
Patients who are members of any of these demographic groups may deserve serious consideration for inpatient psychiatric admission, regardless of other factors.
Continue to: Were drugs or alcohol involved?
13. Were drugs or alcohol involved?
This factor is unique in that it is both a chronic risk factor (SUDs) and a warning sign for imminent suicide, as in the case of an individual who gets intoxicated to disinhibit their fear of death so they can attempt suicide. Alcohol use disorders are associated with depression and suicide. Overdoses by fentanyl and other opiates have become more frequent.13 In many cases, fatalities are unintentional because users overestimate their tolerance or ingest contaminated substances.14 Disinhibition by alcohol and/or other drugs is a risk factor for attempting suicide and can intensify the depth of MDD. Some patients will ingest substances before an attempt just to give them the courage to act; many think of suicide only when intoxicated. Toxicology screens are indicated as part of the evaluation after a suicide attempt.
Depressive and suicidal thoughts often occur in people “coming down” from cocaine or other stimulants. These circumstances require determining whether to refer the patient for treatment for an SUD or psychiatric hospitalization.
In summary, getting intoxicated solely to diminish anxiety about suicide is a dangerous feature, whereas attempting suicide due to intoxication is less concerning. The latter patient may not consider suicide unless they become intoxicated again. When available, dual diagnosis treatment facilities can be an appropriate referral for such patients. Emergency department holding beds can allow these individuals to detoxify prior to the evaluation.
14. Does the patient have future-oriented thoughts?
When evaluating a patient who has attempted suicide, the presence of future planning and anticipation can be reassuring, but these features should be carefully assessed.14-16
After-the-fact comments may be more reliable when a patient offers them spontaneously, as opposed to in response to direct questioning.
- the specificity of the future plans
- corroboration from the family and others about the patient’s previous investment in the upcoming event
- whether the patient mentions such plans spontaneously or only in response to direct questioning
- the patient’s emotional expression or affect when discussing their future
- whether such plans are reasonable, grandiose, and/or unrealistic.
Bottom Line
When assessing a patient after a suicide attempt, both the patient’s presentation and history and the clinician’s instincts are important. Careful consideration of the method, stated intent, premeditation vs impulsivity, feelings about having survived, presence of psychiatric illness, high-risk demographic, postattempt demeanor and affect, quality of support, presence of self-rescue behaviors, future-oriented thoughts, and other factors can help in making the appropriate disposition.
Related Resources
- Kim H, Kim Y, Shin MH, et al. Early psychiatric referral after attempted suicide helps prevent suicide reattempts: a longitudinal national cohort study in South Korea. Front Psychiatry. 2022;13:607892. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2022.607892
- Michaud L, Berva S, Ostertag L, et al. When to discharge and when to voluntary or compulsory hospitalize? Factors associated with treatment decision after self-harm. Psychiatry Res. 2022;317:114810. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114810
1. Ten Leading Causes of Death, United States 2020. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention WISQARS. Accessed March 4, 2022. https://wisqars.cdc.gov/data/lcd/home
2. Norris D, Clark MS. Evaluation and treatment of suicidal patients. Am Fam Physician. 2012;15;85(6):602-605.
3. Gliatto MF, Rai AK. Evaluation and treatment patients with suicidal ideation. Am Fam Phys. 1999;59(6):1500-1506.
4. Dazzi T, Gribble R, Wessely S, et al. Does asking about suicide and related behaviors induce suicidal ideation? What is the evidence? Psychol Med. 2014;44(16):3361-3363.
5. Lewiecki EM, Miller SA. Suicide, guns and public policy. Am J Public Health. 2013;103(1):27-31.
6. Frierson RL. Women who shoot themselves. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1989;40(8):841-843.
7. Frierson RL, Lippmann SB. Psychiatric consultation for patients with self-inflicted gunshot wounds. Psychosomatics. 1990;31(1):67-74.
8. Mitchell AM, Terhorst L. PTSD symptoms in survivors bereaved by the suicide of a significant other. J Am Psychiatr Nurses Assoc. 2017;23(1):61-65.
9. Bateson J. The Golden Gate Bridge’s fatal flaw. Los Angeles Times. May 25, 2012. Accessed March 2, 2022. https://www.latimes.com/opinion/la-xpm-2012-may-25-la-oe-adv-bateson-golden-gate-20120525-story.html
10. Dervic K, Oquendoma MA, Grunebaum MF, et al. Religious affiliation and suicide attempt. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161(12):2303-2308.
11. Nordentoft H, Madsen T, Fedyszyn IF. Suicidal behavior and mortality in first episode psychosis. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2015;203(5):387-392.
12. Frierson R, Lippmann S. Suicide attempts by the old and the very old. Arch Intern Med. 1991;151(1):141-144.
13. Braden JB, Edlund MJ, Sullivan MD. Suicide deaths with opiate poisonings in the United States: 1999-2014. Am J Public Health. 2017;107(3):421-426.
14. Morin KA, Acharya S, Eibl JK, et al: Evidence of increased fentanyl use during the COVID-19 pandemic among opioid agonist treated patients in Ontario, Canada. Int J Drug Policy. 2021;90:103088.
15. Shobassy A, Abu-Mohammad AS. Assessing imminent suicide risk: what about future planning? Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(2):12-17.
16. MacLeod AK, Pankhania B, Lee M, et al. Parasuicide, depression and the anticipation of positive and negative future experiences. Psychol Med. 1997;27(4):973-977.
17. Macleod AK, Tata P, Tyrer P, et al. Hopelessness and positive and negative future thinking in parasuicide. Br J Clin Psychol. 2010;44(Pt 4):495-504.
1. Ten Leading Causes of Death, United States 2020. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention WISQARS. Accessed March 4, 2022. https://wisqars.cdc.gov/data/lcd/home
2. Norris D, Clark MS. Evaluation and treatment of suicidal patients. Am Fam Physician. 2012;15;85(6):602-605.
3. Gliatto MF, Rai AK. Evaluation and treatment patients with suicidal ideation. Am Fam Phys. 1999;59(6):1500-1506.
4. Dazzi T, Gribble R, Wessely S, et al. Does asking about suicide and related behaviors induce suicidal ideation? What is the evidence? Psychol Med. 2014;44(16):3361-3363.
5. Lewiecki EM, Miller SA. Suicide, guns and public policy. Am J Public Health. 2013;103(1):27-31.
6. Frierson RL. Women who shoot themselves. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1989;40(8):841-843.
7. Frierson RL, Lippmann SB. Psychiatric consultation for patients with self-inflicted gunshot wounds. Psychosomatics. 1990;31(1):67-74.
8. Mitchell AM, Terhorst L. PTSD symptoms in survivors bereaved by the suicide of a significant other. J Am Psychiatr Nurses Assoc. 2017;23(1):61-65.
9. Bateson J. The Golden Gate Bridge’s fatal flaw. Los Angeles Times. May 25, 2012. Accessed March 2, 2022. https://www.latimes.com/opinion/la-xpm-2012-may-25-la-oe-adv-bateson-golden-gate-20120525-story.html
10. Dervic K, Oquendoma MA, Grunebaum MF, et al. Religious affiliation and suicide attempt. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161(12):2303-2308.
11. Nordentoft H, Madsen T, Fedyszyn IF. Suicidal behavior and mortality in first episode psychosis. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2015;203(5):387-392.
12. Frierson R, Lippmann S. Suicide attempts by the old and the very old. Arch Intern Med. 1991;151(1):141-144.
13. Braden JB, Edlund MJ, Sullivan MD. Suicide deaths with opiate poisonings in the United States: 1999-2014. Am J Public Health. 2017;107(3):421-426.
14. Morin KA, Acharya S, Eibl JK, et al: Evidence of increased fentanyl use during the COVID-19 pandemic among opioid agonist treated patients in Ontario, Canada. Int J Drug Policy. 2021;90:103088.
15. Shobassy A, Abu-Mohammad AS. Assessing imminent suicide risk: what about future planning? Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(2):12-17.
16. MacLeod AK, Pankhania B, Lee M, et al. Parasuicide, depression and the anticipation of positive and negative future experiences. Psychol Med. 1997;27(4):973-977.
17. Macleod AK, Tata P, Tyrer P, et al. Hopelessness and positive and negative future thinking in parasuicide. Br J Clin Psychol. 2010;44(Pt 4):495-504.
Gut microbiota and symptoms of psychosis: Is there a link?
The human microbiota refers to the collection of bacteria, archaea, eukarya, and viruses that reside within the human body. The term gut microbiome indicates the composition of these microbes and genetic codes in the intestine.1 Harkening back to the ancient Greek physician Galen, who treated gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms to relieve mental disturbances such as psychosis, the gut has been a therapeutic target in schizophrenia long before antipsychotics and the DSM.2 In recent years, research into the gut microbiome has drastically increased, with genetic sequencing affording a more precise look into the specific bacteria that call the human intestines their home. This has led to the recognition that the gut microbiome may be severely disrupted in schizophrenia, a condition known as dysbiosis. Preliminary research suggests that gut bacteria are more helpful than many human genes in distinguishing individuals with schizophrenia from their healthy counterparts.3,4 In this article, we discuss the potential role of the gut microbiome in schizophrenia, including new research correlating clinical symptoms of psychosis with dysbiosis. We also provide recommendations for promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
The enteric brain across life
The composition of our bodies is far more microbiota than human. Strikingly, microbiota cells in the gut outnumber human cells, and the distal gut alone hosts bacteria with 100 times the genetic content of the entire genome.5 The intricate meshwork of nerves in the gut is often called the enteric brain because the gut consists of 100 million neurons and synthesizes many neuroactive chemicals implicated in mood disorders and psychosis, including serotonin, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and acetylcholine.6 The variety of neuroimmunologic, hormonal, and metabolic paths by which the gut microbiome and the brain interact are collectively known as the gut-microbiota-brain axis.7
How do we acquire our gut microbiome, and how does it come to influence our brain and behavior? On the first day of life, as babies pass through the birth canal, they are bathed in their mother’s vaginal microbiota. In the following weeks, the microbiome expands and colonizes the gut as bacteria are introduced from environmental sources such as skin-to-skin contact and breastmilk.8 The microbiome continues to evolve throughout early life. As children expand their diets and navigate new aspects of the physical world, additional bacteria join the unseen ecosystem growing inside.9 The development of the microbiome coincides with the development of the brain. From preclinical studies, we know the gut microbiome mediates important aspects of neurodevelopment such as the formation of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), synaptic pruning, glial activation, and myelination.10 Interestingly, many of the risk factors for schizophrenia are associated with gut dysbiosis, including obstetric complications, infections treated with antibiotics, and urbanization.11-15
Throughout human life, the gut and brain remain in close communication. The gut microbiota continue to produce monoamines, along with other metabolites that are able to cross the BBB.6 The HPA axis, stimulation of the immune system, and the vagus nerve all provide highways of communication between the gut and the brain.7 The relationship between the enteric brain and cephalic brain continues through life, even up to a person’s final hour. One autopsy study that is often cited (but soberingly, cannot be found online) allegedly revealed that 92% of schizophrenia patients had developed colitis by the time of death.16,17
First-episode psychosis and antipsychotic treatment
For patients with schizophrenia, first-episode psychosis (FEP) represents a cocktail of mounting genetic and environmental factors. Typically, by the time a patient receives psychiatric care, they present with characteristic psychotic symptoms—hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behavior, and unusual thought process—along with a unique gut microbiome profile.
This disrupted microbiome coincides with a marked state of inflammation in the intestines. Inflammation triggers increased endothelial barrier permeability, similar to the way immune signals increase capillary permeability to allow immune cells into the periphery of the blood. Specific gut bacteria play specific roles in maintaining the gut barrier.18,19 Disruptions in the bacteria that maintain the gut barrier, combined with inflammation, contribute to a leaky gut. A leaky gut barrier allows bacterial and immune products to more easily enter the bloodstream and then the brain, which is a potential source of neuroinflammation in schizophrenia.20 This increase in gut permeability (leaky gut syndrome) is likely one of several reasons low-grade inflammation is common in schizophrenia—numerous studies show higher serum levels of proinflammatory cytokines along with antibacterial immunoglobulins in patients with FEP.21,22
Fortunately, antipsychotics, especially the second-generation agents, help restore a healthy gut microbiome and have substantial anti-inflammatory properties.23,24 These medications interact heavily with the gut microbiome: they have been found to have antibiotic properties, even in doses lower than would normally reach the gut microbiome.25 In humans, a randomized controlled trial of probiotic supplementation for schizophrenia patients taking antipsychotics showed a reduction in GI symptoms but no significant improvement in psychotic symptoms.26
Dysbiosis in schizophrenia: cause or effect?
There is no consensus on what constitutes a healthy gut microbiome because the gut microbiome is highly variable, even among healthy individuals, and can change quickly. Those who adopt new diets, for example, see drastic shifts in the gut microbiome within a few days.27 Despite this variation, the main separation between a healthy and dysbiotic gut comes from the diversity of bacteria present in the gut—a healthy gut microbiome is associated with increased diversity. Numerous disease states have been associated with decreased bacterial diversity, including Clostridium difficile infection, Parkinson disease, depression, Crohn disease, and schizophrenia spectrum disorders.28,29
Although there are ethical limitations to studying causality in humans directly, animal models have provided a great deal of insight into the gut microbiome’s role in the development of schizophrenia. A recent study used fecal transplant to provide the gut microbiome from patients with schizophrenia to a group of germ-free mice and compared these animals to a group of mice that received a fecal transplant from individuals with a healthy gut microbiome. The mice receiving the schizophrenia microbiome showed an increased startle response and hyperactivity.3 This was consistent with mouse models of schizophrenia, although with obvious limitations.30 In addition, the brains of these animals showed changes in glutamate, glutamine, and GABA in the hippocampus; these chemicals play a role in the neurophysiology of schizophrenia.3,31 This study has not yet been replicated, and considerable variation remains within the schizophrenia biosignature.
Continue to: Clinical symptoms of psychosis and the gut microbiome
Clinical symptoms of psychosis and the gut microbiome
Previous literature has grouped patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders as 1 unified study group. But as is the case with many psychiatric conditions, there is a great deal of heterogeneity in neurobiology, genetics, and microbiome composition among individuals with schizophrenia.32
Researchers have begun to investigate ways in which the gut microbiome varies regarding the clinical symptoms of psychosis.33 The Table3,34-39 provides an overview of 7 human studies of gut microbiome changes relating to clinical features of schizophrenia. In these studies, researchers have found correlations between the gut microbiome and a tendency toward violence,37 cognitive deficits,34-36,39 depressive symptoms,35,39 and numerous other clinical features of psychosis. Most of these correlations have not yet been replicated by further studies. But among studies with similar clinical questions, 3 reported changes in gut microbiome correlated with overall symptom severity, and 4 studies correlated changes with negative symptom severity. In 2 studies,3,34 Lachnospiraceae was correlated with worsened symptom severity. However, this may have been the result of poor control for antipsychotic use, as 1 study in bipolar patients found that Lachnospiraceae was increased in those taking antipsychotics compared to those who were not treated with antipsychotics.40 The specific shifts in bacteria seen for overall symptom and negative symptom severity were not consistent across studies. This is not surprising because the gut microbiome varies with diet and geographic region,41 and patients in these studies were from a variety of regions. Multiple studies demonstrated gut microbiome alterations for patients with more severe negative symptoms. This is particularly interesting because negative symptoms are often difficult to treat and do not respond to antipsychotics.42 This research suggests the gut microbiome may be helpful in developing future treatments for patients with negative symptoms that do not respond to existing treatments.
Research of probiotic supplementation for ameliorating symptoms of schizophrenia has yielded mixed results.43 It is possible that studies of probiotic supplementation have failed to consider the variations in the gut microbiome among individuals with schizophrenia. A better understanding of the variations in gut microbiome may allow for the development of more personalized interventions.
Recommendations for a healthy gut microbiome
In addition to antipsychotics, many other evidence-based interventions can be used to help restore a healthy gut microbiome in patients with schizophrenia. To improve the gut microbiome, we suggest discussing the following changes with patients:
- Quitting smoking. Smoking is common among patients with schizophrenia but decreases gut microbiome diversity.44
- Avoiding excessive alcohol use. Excessive alcohol use contributes to dysbiosis and increased intestinal permeability.45 Moderate alcohol consumption does not appear to have the same harmful effects on the microbiome.46
- Avoiding the use of recreational drugs, including marijuana, which impact the gut microbiome.47
- Consuming a diet rich in fiber.48 Presently, there is not enough evidence to recommend probiotic supplementation to reduce symptoms of schizophrenia.41 Similar to probiotics, fermented foods contain Lactobacillus, a bacterial species that produces lactic acid.49 Lactobacillus is enriched in the gut microbiome in some neurodegenerative diseases, and lactic acid can be neurotoxic at high levels.50-52 Therefore, clinicians should not explicitly recommend fermented foods under the assumption of improved brain health. A diet rich in soluble fiber has been consistently shown to promote anti-inflammatory bacteria and is much more likely to be beneficial.53,54 Soluble fiber is found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, beans, and oats.
- Exercising can increase microbiome diversity and provide anti-inflammatory effects in the gut.55,56 A recent review found that steady-state aerobic and high-intensity exercise interventions have positive effects on mood, cognition, and other negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia.55
- Minimizing stress. Psychological stress and physiological stress from untreated medical conditions are toxic to healthy gut bacteria and weaken the gut barrier.57
- Mitigating exposure to pollution. Environmental pollution, including exposures to air pollution, heavy metals, and pesticides, disrupts the gut microbiome.58
The American Heart Association publishes lifestyle recommendations for individuals with heart disease and the National Institutes of Health publishes lifestyle recommendations for patients with chronic kidney disease. This leads us to question why the American Psychiatric Association has not published lifestyle recommendations for those with severe mental illness. The effects of lifestyle on both the gut microbiome and symptom mitigation is critical. With increasingly shortened appointments, standardized guidelines would benefit psychiatrists and patients alike.
Bottom Line
The gut microbiome is connected to the clinical symptoms of psychosis via a variety of hormonal, neuroimmune, and metabolic mechanisms active across the lifespan. Despite advances in research, there is still much to be understood regarding this relationship. Clinicians should discuss with patients ways to promote a healthy gut microbiome, including consuming a diet rich in fiber, avoiding use of recreational drugs, and exercising regularly.
Related Resources
- Nocera A, Nasrallah HA. The association of the gut microbiota with clinical features in schizophrenia. Behav Sci. 2022;12(4):89.
- Nasrallah HA. It takes guts to be mentally ill: microbiota and psychopathology. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(9):4-6.
1. Bäckhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, et al. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science. 2005;307(5717):1915-1920. doi:10.1126/science.1104816
2. Jackson SW. Galen—on mental disorders. J Hist Behav Sci. 1969;5(4):365-384. doi:10.1002/1520-6696(196910)5:4<365::AID-JHBS2300050408>3.0.CO;2-9
3. Zheng P, Zeng B, Liu M, et al. The gut microbiome from patients with schizophrenia modulates the glutamate-glutamine-GABA cycle and schizophrenia-relevant behaviors in mice. Sci Adv. 2019;5(2):eaau8317. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aau8317
4. Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature. 2014;511(7510):421-427. doi:10.1038/nature13595
5. Gill SR, Pop M, DeBoy RT, et al. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science. 2006;312(5778):1355-1359. doi:10.1126/science.1124234
6. Alam R, Abdolmaleky HM, Zhou JR. Microbiome, inflammation, epigenetic alterations, and mental diseases. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017;174(6):651-660. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.32567
7. Cryan JF, O’Riordan KJ, Cowan CSM, et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(4):1877-2013. doi:10.1152/physrev.00018.2018
8. Mueller NT, Bakacs E, Combellick J, et al. The infant microbiome development: mom matters. Trends Mol Med. 2015;21(2):109-117. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2014.12.002
9. Fouhy F, Watkins C, Hill CJ, et al. Perinatal factors affect the gut microbiota up to four years after birth. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1517. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09252-4
10. Sharon G, Sampson TR, Geschwind DH, et al. The central nervous system and the gut microbiome. Cell. 2016;167(4):915-932. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.027
11. Hill CJ, Lynch DB, Murphy K, et al. Evolution of gut microbiota composition from birth to 24 weeks in the INFANTMET Cohort. Microbiome. 2017;5:4. doi:10.1186/s40168-016-0213-y
12. Gareau MG, Wine E, Rodrigues DM, et al. Bacterial infection causes stress-induced memory dysfunction in mice. Gut. 2011;60(3):307-317. doi:10.1136/gut.2009.202515
13. Bokulich NA, Chung J, Battaglia T, et al. Antibiotics, birth mode, and diet shape microbiome maturation during early life. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(343):343ra82. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aad7121
14. Mancabelli L, Milani C, Lugli GA, et al. Meta-analysis of the human gut microbiome from urbanized and pre-agricultural populations. Environ Microbiol. 2017;19(4):1379-1390. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13692
15. Stilo SA, Murray RM. Non-genetic factors in schizophrenia. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21(10):100. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-1091-3
16. Buscaino VM. Patologia extraneurale della schizofrenia: fegato, tubo digerente, sistema reticolo-endoteliale. Acta Neurologica. 1953;VIII:1-60.
17. Hemmings G. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2004;364(9442):1312-1313. doi:10.1016/S0140- 6736(04)17181-X
18. Hooper LV, Gordon JI. Commensal host-bacterial relationships in the gut. Science. 2001;292(5519):1115-1118. doi:10.1126/science.1058709
19. Ewaschuk JB, Diaz H, Meddings L, et al. Secreted bioactive factors from Bifidobacterium infantis enhance epithelial cell barrier function. Am J Physiol-Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;295(5):G1025-G1034. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.90227.2008
20. Alhasson F, Das S, Seth R, et al. Altered gut microbiome in a mouse model of Gulf War Illness causes neuroinflammation and intestinal injury via leaky gut and TLR4 activation. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0172914. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0172914
21. Fillman SG, Cloonan N, Catts VS, et al. Increased inflammatory markers identified in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18(2):206-214. doi:10.1038/mp.2012.110
22. Miller BJ, Buckley P, Seabolt W, et al. Meta-analysis of cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: clinical status and antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;70(7):663-671. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.04.013
23. Al-Amin M, Uddin MMN, Reza HM. Effects of antipsychotics on the inflammatory response system of patients with schizophrenia in peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2013;11(3):144-151. doi:10.9758/cpn.2013.11.3.144
24. Yuan X, Zhang P, Wang Y, et al. Changes in metabolism and microbiota after 24-week risperidone treatment in drug naïve, normal weight patients with first episode schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2018;201:299-306. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2018.05.017
25. Maier L, Pruteanu M, Kuhn M, et al. Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018;555(7698):623-628. doi:10.1038/nature25979
26. Dickerson FB, Stallings C, Origoni A, et al. Effect of probiotic supplementation on schizophrenia symptoms and association with gastrointestinal functioning: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2014;15(1):PCC.13m01579. doi:10.4088/PCC.13m01579
27. David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature. 2014;505(7484):559-563. doi:10.1038/nature12820
28. Bien J, Palagani V, Bozko P. The intestinal microbiota dysbiosis and Clostridium difficile infection: is there a relationship with inflammatory bowel disease? Ther Adv Gastroenterol. 2013;6(1):53-68. doi:10.1177/1756283X12454590
29. Cryan JF, O’Riordan KJ, Sandhu K, et al. The gut microbiome in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(2):179-194. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30356-4
30. Jones CA, Watson DJG, Fone KCF. Animal models of schizophrenia. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;164(4):1162-1194. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01386.x
31. Schmidt MJ, Mirnics K. Neurodevelopment, GABA system dysfunction, and schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40(1):190-206. doi:10.1038/npp.2014.95
32. Nasrallah, HA. The daunting challenge of schizophrenia: hundreds of biotypes and dozens of theories. Curr. Psychiatry 2018;17(12):4-6,50.
33. Nocera A, Nasrallah HA. The association of the gut microbiota with clinical features in schizophrenia. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022;12(4):89. doi:10.3390/bs12040089
34. Schwarz E, Maukonen J, Hyytiäinen T, et al. Analysis of microbiota in first episode psychosis identifies preliminary associations with symptom severity and treatment response. Schizophr Res. 2018;192:398-403. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2017.04.017
35. Nguyen TT, Kosciolek T, Maldonado Y, et al. Differences in gut microbiome composition between persons with chronic schizophrenia and healthy comparison subjects. Schizophr Res. 2019;204:23-29. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2018.09.014
36. Li S, Zhuo M, Huang X, et al. Altered gut microbiota associated with symptom severity in schizophrenia. PeerJ. 2020;8:e9574. doi:10.7717/peerj.9574
37. Chen X, Xu J, Wang H, et al. Profiling the differences of gut microbial structure between schizophrenia patients with and without violent behaviors based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Int J Legal Med. 2021;135(1):131-141. doi:10.1007/s00414-020-02439-1
38. Manchia M, Fontana A, Panebianco C, et al. Involvement of gut microbiota in schizophrenia and treatment resistance to antipsychotics. Biomedicines. 2021;9(8):875. doi:10.3390/biomedicines9080875
39. Zhu C, Zheng M, Ali U, et al. Association between abundance of haemophilus in the gut microbiota and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:685910. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.685910
40. Flowers SA, Evans SJ, Ward KM, et al. Interaction between atypical antipsychotics and the gut microbiome in a bipolar disease cohort. Pharmacotherapy. 2017;37(3):261-267. doi:10.1002/phar.1890
41. Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature. 2012;486(7402):222-227. doi:10.1038/nature11053
42. Buchanan RW. Persistent negative symptoms in schizophrenia: an overview. Schizophr Bull. 2007;33(4):1013-1022. doi:10.1093/schbul/sb1057
43. Liu JCW, Gorbovskaya I, Hahn MK, et al. The gut microbiome in schizophrenia and the potential benefits of prebiotic and probiotic treatment. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1152. doi:10.3390/nu13041152
44. Biedermann L, Zeitz J, Mwinyi J, et al. Smoking cessation induces profound changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota in humans. PloS One. 2013;8(3):e59260. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059260
45. Leclercq S, Matamoros S, Cani PD, et al. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111(42):e4485-e4493. doi:10.1073/pnas.1415174111
46. Hernández-Quiroz F, Nirmalkar K, Villalobos-Flores LE, et al. Influence of moderate beer consumption on human gut microbiota and its impact on fasting glucose and ß-cell function. Alcohol. 2020;85:77-94. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2019.05.006
47. Panee J, Gerschenson M, Chang L. Associations between microbiota, mitochondrial function, and cognition in chronic marijuana users. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018;13(1):113-122. doi:10.1007/s11481-017-9767-0
48. Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science. 2011;334(6052):105-108. doi:10.1126/science.1208344
49. Rezac S, Kok CR, Heermann M, et al. Fermented foods as a dietary source of live organisms. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:1785. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.01785
50. Chen X, Zhang Y, Wang H, et al. The regulatory effects of lactic acid on neuropsychiatric disorders. Discover Ment Health. 2022;2(1). doi:10.1007/s44192-022-00011-4
51. Karbownik MS, Mokros Ł, Dobielska M, et al. Association between consumption of fermented food and food-derived prebiotics with cognitive performance, depressive, and anxiety symptoms in psychiatrically healthy medical students under psychological stress: a prospective cohort study. Front Nutr. 2022;9:850249. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.850249
52. Romano S, Savva GM, Bedarf JR, et al. Meta-analysis of the Parkinson’s disease gut microbiome suggests alterations linked to intestinal inflammation. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2021;7(1):27. doi:10.1038/s41531-021-00156-z
53. Bourassa MW, Alim I, Bultman SJ, et al. Butyrate, neuroepigenetics and the gut microbiome: can a high fiber diet improve brain health? Neurosci Lett. 2016;625:56-63. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2016.02.009
54. Matt SM, Allen JM, Lawson MA, et al. Butyrate and dietary soluble fiber improve neuroinflammation associated with aging in mice. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1832. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.01832
55. Mittal VA, Vargas T, Osborne KJ, et al. Exercise treatments for psychosis: a review. Curr Treat Options Psychiatry. 2017;4(2):152-166. doi:10.1007/s40501-017-0112-2
56. Estaki M, Pither J, Baumeister P, et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness as a predictor of intestinal microbial diversity and distinct metagenomic functions. Microbiome. 2016;4(1):42. doi:10.1186/s40168-016-0189-7
57. Karl JP, Margolis LM, Madslien EH, et al. Changes in intestinal microbiota composition and metabolism coincide with increased intestinal permeability in young adults under prolonged physiological stress. Am J Physiol-Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017;312(6):G559-G571. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00066.2017
58. Claus SP, Guillou H, Ellero-Simatos S. The gut microbiota: a major player in the toxicity of environmental pollutants? NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2016;2:16003. doi:10.1038/npjbiofilms.2016.3
The human microbiota refers to the collection of bacteria, archaea, eukarya, and viruses that reside within the human body. The term gut microbiome indicates the composition of these microbes and genetic codes in the intestine.1 Harkening back to the ancient Greek physician Galen, who treated gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms to relieve mental disturbances such as psychosis, the gut has been a therapeutic target in schizophrenia long before antipsychotics and the DSM.2 In recent years, research into the gut microbiome has drastically increased, with genetic sequencing affording a more precise look into the specific bacteria that call the human intestines their home. This has led to the recognition that the gut microbiome may be severely disrupted in schizophrenia, a condition known as dysbiosis. Preliminary research suggests that gut bacteria are more helpful than many human genes in distinguishing individuals with schizophrenia from their healthy counterparts.3,4 In this article, we discuss the potential role of the gut microbiome in schizophrenia, including new research correlating clinical symptoms of psychosis with dysbiosis. We also provide recommendations for promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
The enteric brain across life
The composition of our bodies is far more microbiota than human. Strikingly, microbiota cells in the gut outnumber human cells, and the distal gut alone hosts bacteria with 100 times the genetic content of the entire genome.5 The intricate meshwork of nerves in the gut is often called the enteric brain because the gut consists of 100 million neurons and synthesizes many neuroactive chemicals implicated in mood disorders and psychosis, including serotonin, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and acetylcholine.6 The variety of neuroimmunologic, hormonal, and metabolic paths by which the gut microbiome and the brain interact are collectively known as the gut-microbiota-brain axis.7
How do we acquire our gut microbiome, and how does it come to influence our brain and behavior? On the first day of life, as babies pass through the birth canal, they are bathed in their mother’s vaginal microbiota. In the following weeks, the microbiome expands and colonizes the gut as bacteria are introduced from environmental sources such as skin-to-skin contact and breastmilk.8 The microbiome continues to evolve throughout early life. As children expand their diets and navigate new aspects of the physical world, additional bacteria join the unseen ecosystem growing inside.9 The development of the microbiome coincides with the development of the brain. From preclinical studies, we know the gut microbiome mediates important aspects of neurodevelopment such as the formation of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), synaptic pruning, glial activation, and myelination.10 Interestingly, many of the risk factors for schizophrenia are associated with gut dysbiosis, including obstetric complications, infections treated with antibiotics, and urbanization.11-15
Throughout human life, the gut and brain remain in close communication. The gut microbiota continue to produce monoamines, along with other metabolites that are able to cross the BBB.6 The HPA axis, stimulation of the immune system, and the vagus nerve all provide highways of communication between the gut and the brain.7 The relationship between the enteric brain and cephalic brain continues through life, even up to a person’s final hour. One autopsy study that is often cited (but soberingly, cannot be found online) allegedly revealed that 92% of schizophrenia patients had developed colitis by the time of death.16,17
First-episode psychosis and antipsychotic treatment
For patients with schizophrenia, first-episode psychosis (FEP) represents a cocktail of mounting genetic and environmental factors. Typically, by the time a patient receives psychiatric care, they present with characteristic psychotic symptoms—hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behavior, and unusual thought process—along with a unique gut microbiome profile.
This disrupted microbiome coincides with a marked state of inflammation in the intestines. Inflammation triggers increased endothelial barrier permeability, similar to the way immune signals increase capillary permeability to allow immune cells into the periphery of the blood. Specific gut bacteria play specific roles in maintaining the gut barrier.18,19 Disruptions in the bacteria that maintain the gut barrier, combined with inflammation, contribute to a leaky gut. A leaky gut barrier allows bacterial and immune products to more easily enter the bloodstream and then the brain, which is a potential source of neuroinflammation in schizophrenia.20 This increase in gut permeability (leaky gut syndrome) is likely one of several reasons low-grade inflammation is common in schizophrenia—numerous studies show higher serum levels of proinflammatory cytokines along with antibacterial immunoglobulins in patients with FEP.21,22
Fortunately, antipsychotics, especially the second-generation agents, help restore a healthy gut microbiome and have substantial anti-inflammatory properties.23,24 These medications interact heavily with the gut microbiome: they have been found to have antibiotic properties, even in doses lower than would normally reach the gut microbiome.25 In humans, a randomized controlled trial of probiotic supplementation for schizophrenia patients taking antipsychotics showed a reduction in GI symptoms but no significant improvement in psychotic symptoms.26
Dysbiosis in schizophrenia: cause or effect?
There is no consensus on what constitutes a healthy gut microbiome because the gut microbiome is highly variable, even among healthy individuals, and can change quickly. Those who adopt new diets, for example, see drastic shifts in the gut microbiome within a few days.27 Despite this variation, the main separation between a healthy and dysbiotic gut comes from the diversity of bacteria present in the gut—a healthy gut microbiome is associated with increased diversity. Numerous disease states have been associated with decreased bacterial diversity, including Clostridium difficile infection, Parkinson disease, depression, Crohn disease, and schizophrenia spectrum disorders.28,29
Although there are ethical limitations to studying causality in humans directly, animal models have provided a great deal of insight into the gut microbiome’s role in the development of schizophrenia. A recent study used fecal transplant to provide the gut microbiome from patients with schizophrenia to a group of germ-free mice and compared these animals to a group of mice that received a fecal transplant from individuals with a healthy gut microbiome. The mice receiving the schizophrenia microbiome showed an increased startle response and hyperactivity.3 This was consistent with mouse models of schizophrenia, although with obvious limitations.30 In addition, the brains of these animals showed changes in glutamate, glutamine, and GABA in the hippocampus; these chemicals play a role in the neurophysiology of schizophrenia.3,31 This study has not yet been replicated, and considerable variation remains within the schizophrenia biosignature.
Continue to: Clinical symptoms of psychosis and the gut microbiome
Clinical symptoms of psychosis and the gut microbiome
Previous literature has grouped patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders as 1 unified study group. But as is the case with many psychiatric conditions, there is a great deal of heterogeneity in neurobiology, genetics, and microbiome composition among individuals with schizophrenia.32
Researchers have begun to investigate ways in which the gut microbiome varies regarding the clinical symptoms of psychosis.33 The Table3,34-39 provides an overview of 7 human studies of gut microbiome changes relating to clinical features of schizophrenia. In these studies, researchers have found correlations between the gut microbiome and a tendency toward violence,37 cognitive deficits,34-36,39 depressive symptoms,35,39 and numerous other clinical features of psychosis. Most of these correlations have not yet been replicated by further studies. But among studies with similar clinical questions, 3 reported changes in gut microbiome correlated with overall symptom severity, and 4 studies correlated changes with negative symptom severity. In 2 studies,3,34 Lachnospiraceae was correlated with worsened symptom severity. However, this may have been the result of poor control for antipsychotic use, as 1 study in bipolar patients found that Lachnospiraceae was increased in those taking antipsychotics compared to those who were not treated with antipsychotics.40 The specific shifts in bacteria seen for overall symptom and negative symptom severity were not consistent across studies. This is not surprising because the gut microbiome varies with diet and geographic region,41 and patients in these studies were from a variety of regions. Multiple studies demonstrated gut microbiome alterations for patients with more severe negative symptoms. This is particularly interesting because negative symptoms are often difficult to treat and do not respond to antipsychotics.42 This research suggests the gut microbiome may be helpful in developing future treatments for patients with negative symptoms that do not respond to existing treatments.
Research of probiotic supplementation for ameliorating symptoms of schizophrenia has yielded mixed results.43 It is possible that studies of probiotic supplementation have failed to consider the variations in the gut microbiome among individuals with schizophrenia. A better understanding of the variations in gut microbiome may allow for the development of more personalized interventions.

Recommendations for a healthy gut microbiome
In addition to antipsychotics, many other evidence-based interventions can be used to help restore a healthy gut microbiome in patients with schizophrenia. To improve the gut microbiome, we suggest discussing the following changes with patients:
- Quitting smoking. Smoking is common among patients with schizophrenia but decreases gut microbiome diversity.44
- Avoiding excessive alcohol use. Excessive alcohol use contributes to dysbiosis and increased intestinal permeability.45 Moderate alcohol consumption does not appear to have the same harmful effects on the microbiome.46
- Avoiding the use of recreational drugs, including marijuana, which impact the gut microbiome.47
- Consuming a diet rich in fiber.48 Presently, there is not enough evidence to recommend probiotic supplementation to reduce symptoms of schizophrenia.41 Similar to probiotics, fermented foods contain Lactobacillus, a bacterial species that produces lactic acid.49 Lactobacillus is enriched in the gut microbiome in some neurodegenerative diseases, and lactic acid can be neurotoxic at high levels.50-52 Therefore, clinicians should not explicitly recommend fermented foods under the assumption of improved brain health. A diet rich in soluble fiber has been consistently shown to promote anti-inflammatory bacteria and is much more likely to be beneficial.53,54 Soluble fiber is found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, beans, and oats.
- Exercising can increase microbiome diversity and provide anti-inflammatory effects in the gut.55,56 A recent review found that steady-state aerobic and high-intensity exercise interventions have positive effects on mood, cognition, and other negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia.55
- Minimizing stress. Psychological stress and physiological stress from untreated medical conditions are toxic to healthy gut bacteria and weaken the gut barrier.57
- Mitigating exposure to pollution. Environmental pollution, including exposures to air pollution, heavy metals, and pesticides, disrupts the gut microbiome.58
The American Heart Association publishes lifestyle recommendations for individuals with heart disease and the National Institutes of Health publishes lifestyle recommendations for patients with chronic kidney disease. This leads us to question why the American Psychiatric Association has not published lifestyle recommendations for those with severe mental illness. The effects of lifestyle on both the gut microbiome and symptom mitigation is critical. With increasingly shortened appointments, standardized guidelines would benefit psychiatrists and patients alike.
Bottom Line
The gut microbiome is connected to the clinical symptoms of psychosis via a variety of hormonal, neuroimmune, and metabolic mechanisms active across the lifespan. Despite advances in research, there is still much to be understood regarding this relationship. Clinicians should discuss with patients ways to promote a healthy gut microbiome, including consuming a diet rich in fiber, avoiding use of recreational drugs, and exercising regularly.
Related Resources
- Nocera A, Nasrallah HA. The association of the gut microbiota with clinical features in schizophrenia. Behav Sci. 2022;12(4):89.
- Nasrallah HA. It takes guts to be mentally ill: microbiota and psychopathology. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(9):4-6.
The human microbiota refers to the collection of bacteria, archaea, eukarya, and viruses that reside within the human body. The term gut microbiome indicates the composition of these microbes and genetic codes in the intestine.1 Harkening back to the ancient Greek physician Galen, who treated gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms to relieve mental disturbances such as psychosis, the gut has been a therapeutic target in schizophrenia long before antipsychotics and the DSM.2 In recent years, research into the gut microbiome has drastically increased, with genetic sequencing affording a more precise look into the specific bacteria that call the human intestines their home. This has led to the recognition that the gut microbiome may be severely disrupted in schizophrenia, a condition known as dysbiosis. Preliminary research suggests that gut bacteria are more helpful than many human genes in distinguishing individuals with schizophrenia from their healthy counterparts.3,4 In this article, we discuss the potential role of the gut microbiome in schizophrenia, including new research correlating clinical symptoms of psychosis with dysbiosis. We also provide recommendations for promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
The enteric brain across life
The composition of our bodies is far more microbiota than human. Strikingly, microbiota cells in the gut outnumber human cells, and the distal gut alone hosts bacteria with 100 times the genetic content of the entire genome.5 The intricate meshwork of nerves in the gut is often called the enteric brain because the gut consists of 100 million neurons and synthesizes many neuroactive chemicals implicated in mood disorders and psychosis, including serotonin, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and acetylcholine.6 The variety of neuroimmunologic, hormonal, and metabolic paths by which the gut microbiome and the brain interact are collectively known as the gut-microbiota-brain axis.7
How do we acquire our gut microbiome, and how does it come to influence our brain and behavior? On the first day of life, as babies pass through the birth canal, they are bathed in their mother’s vaginal microbiota. In the following weeks, the microbiome expands and colonizes the gut as bacteria are introduced from environmental sources such as skin-to-skin contact and breastmilk.8 The microbiome continues to evolve throughout early life. As children expand their diets and navigate new aspects of the physical world, additional bacteria join the unseen ecosystem growing inside.9 The development of the microbiome coincides with the development of the brain. From preclinical studies, we know the gut microbiome mediates important aspects of neurodevelopment such as the formation of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), synaptic pruning, glial activation, and myelination.10 Interestingly, many of the risk factors for schizophrenia are associated with gut dysbiosis, including obstetric complications, infections treated with antibiotics, and urbanization.11-15
Throughout human life, the gut and brain remain in close communication. The gut microbiota continue to produce monoamines, along with other metabolites that are able to cross the BBB.6 The HPA axis, stimulation of the immune system, and the vagus nerve all provide highways of communication between the gut and the brain.7 The relationship between the enteric brain and cephalic brain continues through life, even up to a person’s final hour. One autopsy study that is often cited (but soberingly, cannot be found online) allegedly revealed that 92% of schizophrenia patients had developed colitis by the time of death.16,17
First-episode psychosis and antipsychotic treatment
For patients with schizophrenia, first-episode psychosis (FEP) represents a cocktail of mounting genetic and environmental factors. Typically, by the time a patient receives psychiatric care, they present with characteristic psychotic symptoms—hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behavior, and unusual thought process—along with a unique gut microbiome profile.
This disrupted microbiome coincides with a marked state of inflammation in the intestines. Inflammation triggers increased endothelial barrier permeability, similar to the way immune signals increase capillary permeability to allow immune cells into the periphery of the blood. Specific gut bacteria play specific roles in maintaining the gut barrier.18,19 Disruptions in the bacteria that maintain the gut barrier, combined with inflammation, contribute to a leaky gut. A leaky gut barrier allows bacterial and immune products to more easily enter the bloodstream and then the brain, which is a potential source of neuroinflammation in schizophrenia.20 This increase in gut permeability (leaky gut syndrome) is likely one of several reasons low-grade inflammation is common in schizophrenia—numerous studies show higher serum levels of proinflammatory cytokines along with antibacterial immunoglobulins in patients with FEP.21,22
Fortunately, antipsychotics, especially the second-generation agents, help restore a healthy gut microbiome and have substantial anti-inflammatory properties.23,24 These medications interact heavily with the gut microbiome: they have been found to have antibiotic properties, even in doses lower than would normally reach the gut microbiome.25 In humans, a randomized controlled trial of probiotic supplementation for schizophrenia patients taking antipsychotics showed a reduction in GI symptoms but no significant improvement in psychotic symptoms.26
Dysbiosis in schizophrenia: cause or effect?
There is no consensus on what constitutes a healthy gut microbiome because the gut microbiome is highly variable, even among healthy individuals, and can change quickly. Those who adopt new diets, for example, see drastic shifts in the gut microbiome within a few days.27 Despite this variation, the main separation between a healthy and dysbiotic gut comes from the diversity of bacteria present in the gut—a healthy gut microbiome is associated with increased diversity. Numerous disease states have been associated with decreased bacterial diversity, including Clostridium difficile infection, Parkinson disease, depression, Crohn disease, and schizophrenia spectrum disorders.28,29
Although there are ethical limitations to studying causality in humans directly, animal models have provided a great deal of insight into the gut microbiome’s role in the development of schizophrenia. A recent study used fecal transplant to provide the gut microbiome from patients with schizophrenia to a group of germ-free mice and compared these animals to a group of mice that received a fecal transplant from individuals with a healthy gut microbiome. The mice receiving the schizophrenia microbiome showed an increased startle response and hyperactivity.3 This was consistent with mouse models of schizophrenia, although with obvious limitations.30 In addition, the brains of these animals showed changes in glutamate, glutamine, and GABA in the hippocampus; these chemicals play a role in the neurophysiology of schizophrenia.3,31 This study has not yet been replicated, and considerable variation remains within the schizophrenia biosignature.
Continue to: Clinical symptoms of psychosis and the gut microbiome
Clinical symptoms of psychosis and the gut microbiome
Previous literature has grouped patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders as 1 unified study group. But as is the case with many psychiatric conditions, there is a great deal of heterogeneity in neurobiology, genetics, and microbiome composition among individuals with schizophrenia.32
Researchers have begun to investigate ways in which the gut microbiome varies regarding the clinical symptoms of psychosis.33 The Table3,34-39 provides an overview of 7 human studies of gut microbiome changes relating to clinical features of schizophrenia. In these studies, researchers have found correlations between the gut microbiome and a tendency toward violence,37 cognitive deficits,34-36,39 depressive symptoms,35,39 and numerous other clinical features of psychosis. Most of these correlations have not yet been replicated by further studies. But among studies with similar clinical questions, 3 reported changes in gut microbiome correlated with overall symptom severity, and 4 studies correlated changes with negative symptom severity. In 2 studies,3,34 Lachnospiraceae was correlated with worsened symptom severity. However, this may have been the result of poor control for antipsychotic use, as 1 study in bipolar patients found that Lachnospiraceae was increased in those taking antipsychotics compared to those who were not treated with antipsychotics.40 The specific shifts in bacteria seen for overall symptom and negative symptom severity were not consistent across studies. This is not surprising because the gut microbiome varies with diet and geographic region,41 and patients in these studies were from a variety of regions. Multiple studies demonstrated gut microbiome alterations for patients with more severe negative symptoms. This is particularly interesting because negative symptoms are often difficult to treat and do not respond to antipsychotics.42 This research suggests the gut microbiome may be helpful in developing future treatments for patients with negative symptoms that do not respond to existing treatments.
Research of probiotic supplementation for ameliorating symptoms of schizophrenia has yielded mixed results.43 It is possible that studies of probiotic supplementation have failed to consider the variations in the gut microbiome among individuals with schizophrenia. A better understanding of the variations in gut microbiome may allow for the development of more personalized interventions.

Recommendations for a healthy gut microbiome
In addition to antipsychotics, many other evidence-based interventions can be used to help restore a healthy gut microbiome in patients with schizophrenia. To improve the gut microbiome, we suggest discussing the following changes with patients:
- Quitting smoking. Smoking is common among patients with schizophrenia but decreases gut microbiome diversity.44
- Avoiding excessive alcohol use. Excessive alcohol use contributes to dysbiosis and increased intestinal permeability.45 Moderate alcohol consumption does not appear to have the same harmful effects on the microbiome.46
- Avoiding the use of recreational drugs, including marijuana, which impact the gut microbiome.47
- Consuming a diet rich in fiber.48 Presently, there is not enough evidence to recommend probiotic supplementation to reduce symptoms of schizophrenia.41 Similar to probiotics, fermented foods contain Lactobacillus, a bacterial species that produces lactic acid.49 Lactobacillus is enriched in the gut microbiome in some neurodegenerative diseases, and lactic acid can be neurotoxic at high levels.50-52 Therefore, clinicians should not explicitly recommend fermented foods under the assumption of improved brain health. A diet rich in soluble fiber has been consistently shown to promote anti-inflammatory bacteria and is much more likely to be beneficial.53,54 Soluble fiber is found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, beans, and oats.
- Exercising can increase microbiome diversity and provide anti-inflammatory effects in the gut.55,56 A recent review found that steady-state aerobic and high-intensity exercise interventions have positive effects on mood, cognition, and other negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia.55
- Minimizing stress. Psychological stress and physiological stress from untreated medical conditions are toxic to healthy gut bacteria and weaken the gut barrier.57
- Mitigating exposure to pollution. Environmental pollution, including exposures to air pollution, heavy metals, and pesticides, disrupts the gut microbiome.58
The American Heart Association publishes lifestyle recommendations for individuals with heart disease and the National Institutes of Health publishes lifestyle recommendations for patients with chronic kidney disease. This leads us to question why the American Psychiatric Association has not published lifestyle recommendations for those with severe mental illness. The effects of lifestyle on both the gut microbiome and symptom mitigation is critical. With increasingly shortened appointments, standardized guidelines would benefit psychiatrists and patients alike.
Bottom Line
The gut microbiome is connected to the clinical symptoms of psychosis via a variety of hormonal, neuroimmune, and metabolic mechanisms active across the lifespan. Despite advances in research, there is still much to be understood regarding this relationship. Clinicians should discuss with patients ways to promote a healthy gut microbiome, including consuming a diet rich in fiber, avoiding use of recreational drugs, and exercising regularly.
Related Resources
- Nocera A, Nasrallah HA. The association of the gut microbiota with clinical features in schizophrenia. Behav Sci. 2022;12(4):89.
- Nasrallah HA. It takes guts to be mentally ill: microbiota and psychopathology. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(9):4-6.
1. Bäckhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, et al. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science. 2005;307(5717):1915-1920. doi:10.1126/science.1104816
2. Jackson SW. Galen—on mental disorders. J Hist Behav Sci. 1969;5(4):365-384. doi:10.1002/1520-6696(196910)5:4<365::AID-JHBS2300050408>3.0.CO;2-9
3. Zheng P, Zeng B, Liu M, et al. The gut microbiome from patients with schizophrenia modulates the glutamate-glutamine-GABA cycle and schizophrenia-relevant behaviors in mice. Sci Adv. 2019;5(2):eaau8317. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aau8317
4. Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature. 2014;511(7510):421-427. doi:10.1038/nature13595
5. Gill SR, Pop M, DeBoy RT, et al. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science. 2006;312(5778):1355-1359. doi:10.1126/science.1124234
6. Alam R, Abdolmaleky HM, Zhou JR. Microbiome, inflammation, epigenetic alterations, and mental diseases. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017;174(6):651-660. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.32567
7. Cryan JF, O’Riordan KJ, Cowan CSM, et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(4):1877-2013. doi:10.1152/physrev.00018.2018
8. Mueller NT, Bakacs E, Combellick J, et al. The infant microbiome development: mom matters. Trends Mol Med. 2015;21(2):109-117. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2014.12.002
9. Fouhy F, Watkins C, Hill CJ, et al. Perinatal factors affect the gut microbiota up to four years after birth. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1517. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09252-4
10. Sharon G, Sampson TR, Geschwind DH, et al. The central nervous system and the gut microbiome. Cell. 2016;167(4):915-932. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.027
11. Hill CJ, Lynch DB, Murphy K, et al. Evolution of gut microbiota composition from birth to 24 weeks in the INFANTMET Cohort. Microbiome. 2017;5:4. doi:10.1186/s40168-016-0213-y
12. Gareau MG, Wine E, Rodrigues DM, et al. Bacterial infection causes stress-induced memory dysfunction in mice. Gut. 2011;60(3):307-317. doi:10.1136/gut.2009.202515
13. Bokulich NA, Chung J, Battaglia T, et al. Antibiotics, birth mode, and diet shape microbiome maturation during early life. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(343):343ra82. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aad7121
14. Mancabelli L, Milani C, Lugli GA, et al. Meta-analysis of the human gut microbiome from urbanized and pre-agricultural populations. Environ Microbiol. 2017;19(4):1379-1390. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13692
15. Stilo SA, Murray RM. Non-genetic factors in schizophrenia. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21(10):100. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-1091-3
16. Buscaino VM. Patologia extraneurale della schizofrenia: fegato, tubo digerente, sistema reticolo-endoteliale. Acta Neurologica. 1953;VIII:1-60.
17. Hemmings G. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2004;364(9442):1312-1313. doi:10.1016/S0140- 6736(04)17181-X
18. Hooper LV, Gordon JI. Commensal host-bacterial relationships in the gut. Science. 2001;292(5519):1115-1118. doi:10.1126/science.1058709
19. Ewaschuk JB, Diaz H, Meddings L, et al. Secreted bioactive factors from Bifidobacterium infantis enhance epithelial cell barrier function. Am J Physiol-Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;295(5):G1025-G1034. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.90227.2008
20. Alhasson F, Das S, Seth R, et al. Altered gut microbiome in a mouse model of Gulf War Illness causes neuroinflammation and intestinal injury via leaky gut and TLR4 activation. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0172914. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0172914
21. Fillman SG, Cloonan N, Catts VS, et al. Increased inflammatory markers identified in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18(2):206-214. doi:10.1038/mp.2012.110
22. Miller BJ, Buckley P, Seabolt W, et al. Meta-analysis of cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: clinical status and antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;70(7):663-671. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.04.013
23. Al-Amin M, Uddin MMN, Reza HM. Effects of antipsychotics on the inflammatory response system of patients with schizophrenia in peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2013;11(3):144-151. doi:10.9758/cpn.2013.11.3.144
24. Yuan X, Zhang P, Wang Y, et al. Changes in metabolism and microbiota after 24-week risperidone treatment in drug naïve, normal weight patients with first episode schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2018;201:299-306. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2018.05.017
25. Maier L, Pruteanu M, Kuhn M, et al. Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018;555(7698):623-628. doi:10.1038/nature25979
26. Dickerson FB, Stallings C, Origoni A, et al. Effect of probiotic supplementation on schizophrenia symptoms and association with gastrointestinal functioning: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2014;15(1):PCC.13m01579. doi:10.4088/PCC.13m01579
27. David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature. 2014;505(7484):559-563. doi:10.1038/nature12820
28. Bien J, Palagani V, Bozko P. The intestinal microbiota dysbiosis and Clostridium difficile infection: is there a relationship with inflammatory bowel disease? Ther Adv Gastroenterol. 2013;6(1):53-68. doi:10.1177/1756283X12454590
29. Cryan JF, O’Riordan KJ, Sandhu K, et al. The gut microbiome in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(2):179-194. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30356-4
30. Jones CA, Watson DJG, Fone KCF. Animal models of schizophrenia. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;164(4):1162-1194. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01386.x
31. Schmidt MJ, Mirnics K. Neurodevelopment, GABA system dysfunction, and schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40(1):190-206. doi:10.1038/npp.2014.95
32. Nasrallah, HA. The daunting challenge of schizophrenia: hundreds of biotypes and dozens of theories. Curr. Psychiatry 2018;17(12):4-6,50.
33. Nocera A, Nasrallah HA. The association of the gut microbiota with clinical features in schizophrenia. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022;12(4):89. doi:10.3390/bs12040089
34. Schwarz E, Maukonen J, Hyytiäinen T, et al. Analysis of microbiota in first episode psychosis identifies preliminary associations with symptom severity and treatment response. Schizophr Res. 2018;192:398-403. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2017.04.017
35. Nguyen TT, Kosciolek T, Maldonado Y, et al. Differences in gut microbiome composition between persons with chronic schizophrenia and healthy comparison subjects. Schizophr Res. 2019;204:23-29. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2018.09.014
36. Li S, Zhuo M, Huang X, et al. Altered gut microbiota associated with symptom severity in schizophrenia. PeerJ. 2020;8:e9574. doi:10.7717/peerj.9574
37. Chen X, Xu J, Wang H, et al. Profiling the differences of gut microbial structure between schizophrenia patients with and without violent behaviors based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Int J Legal Med. 2021;135(1):131-141. doi:10.1007/s00414-020-02439-1
38. Manchia M, Fontana A, Panebianco C, et al. Involvement of gut microbiota in schizophrenia and treatment resistance to antipsychotics. Biomedicines. 2021;9(8):875. doi:10.3390/biomedicines9080875
39. Zhu C, Zheng M, Ali U, et al. Association between abundance of haemophilus in the gut microbiota and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:685910. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.685910
40. Flowers SA, Evans SJ, Ward KM, et al. Interaction between atypical antipsychotics and the gut microbiome in a bipolar disease cohort. Pharmacotherapy. 2017;37(3):261-267. doi:10.1002/phar.1890
41. Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature. 2012;486(7402):222-227. doi:10.1038/nature11053
42. Buchanan RW. Persistent negative symptoms in schizophrenia: an overview. Schizophr Bull. 2007;33(4):1013-1022. doi:10.1093/schbul/sb1057
43. Liu JCW, Gorbovskaya I, Hahn MK, et al. The gut microbiome in schizophrenia and the potential benefits of prebiotic and probiotic treatment. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1152. doi:10.3390/nu13041152
44. Biedermann L, Zeitz J, Mwinyi J, et al. Smoking cessation induces profound changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota in humans. PloS One. 2013;8(3):e59260. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059260
45. Leclercq S, Matamoros S, Cani PD, et al. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111(42):e4485-e4493. doi:10.1073/pnas.1415174111
46. Hernández-Quiroz F, Nirmalkar K, Villalobos-Flores LE, et al. Influence of moderate beer consumption on human gut microbiota and its impact on fasting glucose and ß-cell function. Alcohol. 2020;85:77-94. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2019.05.006
47. Panee J, Gerschenson M, Chang L. Associations between microbiota, mitochondrial function, and cognition in chronic marijuana users. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018;13(1):113-122. doi:10.1007/s11481-017-9767-0
48. Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science. 2011;334(6052):105-108. doi:10.1126/science.1208344
49. Rezac S, Kok CR, Heermann M, et al. Fermented foods as a dietary source of live organisms. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:1785. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.01785
50. Chen X, Zhang Y, Wang H, et al. The regulatory effects of lactic acid on neuropsychiatric disorders. Discover Ment Health. 2022;2(1). doi:10.1007/s44192-022-00011-4
51. Karbownik MS, Mokros Ł, Dobielska M, et al. Association between consumption of fermented food and food-derived prebiotics with cognitive performance, depressive, and anxiety symptoms in psychiatrically healthy medical students under psychological stress: a prospective cohort study. Front Nutr. 2022;9:850249. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.850249
52. Romano S, Savva GM, Bedarf JR, et al. Meta-analysis of the Parkinson’s disease gut microbiome suggests alterations linked to intestinal inflammation. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2021;7(1):27. doi:10.1038/s41531-021-00156-z
53. Bourassa MW, Alim I, Bultman SJ, et al. Butyrate, neuroepigenetics and the gut microbiome: can a high fiber diet improve brain health? Neurosci Lett. 2016;625:56-63. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2016.02.009
54. Matt SM, Allen JM, Lawson MA, et al. Butyrate and dietary soluble fiber improve neuroinflammation associated with aging in mice. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1832. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.01832
55. Mittal VA, Vargas T, Osborne KJ, et al. Exercise treatments for psychosis: a review. Curr Treat Options Psychiatry. 2017;4(2):152-166. doi:10.1007/s40501-017-0112-2
56. Estaki M, Pither J, Baumeister P, et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness as a predictor of intestinal microbial diversity and distinct metagenomic functions. Microbiome. 2016;4(1):42. doi:10.1186/s40168-016-0189-7
57. Karl JP, Margolis LM, Madslien EH, et al. Changes in intestinal microbiota composition and metabolism coincide with increased intestinal permeability in young adults under prolonged physiological stress. Am J Physiol-Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017;312(6):G559-G571. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00066.2017
58. Claus SP, Guillou H, Ellero-Simatos S. The gut microbiota: a major player in the toxicity of environmental pollutants? NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2016;2:16003. doi:10.1038/npjbiofilms.2016.3
1. Bäckhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, et al. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science. 2005;307(5717):1915-1920. doi:10.1126/science.1104816
2. Jackson SW. Galen—on mental disorders. J Hist Behav Sci. 1969;5(4):365-384. doi:10.1002/1520-6696(196910)5:4<365::AID-JHBS2300050408>3.0.CO;2-9
3. Zheng P, Zeng B, Liu M, et al. The gut microbiome from patients with schizophrenia modulates the glutamate-glutamine-GABA cycle and schizophrenia-relevant behaviors in mice. Sci Adv. 2019;5(2):eaau8317. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aau8317
4. Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature. 2014;511(7510):421-427. doi:10.1038/nature13595
5. Gill SR, Pop M, DeBoy RT, et al. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science. 2006;312(5778):1355-1359. doi:10.1126/science.1124234
6. Alam R, Abdolmaleky HM, Zhou JR. Microbiome, inflammation, epigenetic alterations, and mental diseases. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017;174(6):651-660. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.32567
7. Cryan JF, O’Riordan KJ, Cowan CSM, et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(4):1877-2013. doi:10.1152/physrev.00018.2018
8. Mueller NT, Bakacs E, Combellick J, et al. The infant microbiome development: mom matters. Trends Mol Med. 2015;21(2):109-117. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2014.12.002
9. Fouhy F, Watkins C, Hill CJ, et al. Perinatal factors affect the gut microbiota up to four years after birth. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1517. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09252-4
10. Sharon G, Sampson TR, Geschwind DH, et al. The central nervous system and the gut microbiome. Cell. 2016;167(4):915-932. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.027
11. Hill CJ, Lynch DB, Murphy K, et al. Evolution of gut microbiota composition from birth to 24 weeks in the INFANTMET Cohort. Microbiome. 2017;5:4. doi:10.1186/s40168-016-0213-y
12. Gareau MG, Wine E, Rodrigues DM, et al. Bacterial infection causes stress-induced memory dysfunction in mice. Gut. 2011;60(3):307-317. doi:10.1136/gut.2009.202515
13. Bokulich NA, Chung J, Battaglia T, et al. Antibiotics, birth mode, and diet shape microbiome maturation during early life. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(343):343ra82. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aad7121
14. Mancabelli L, Milani C, Lugli GA, et al. Meta-analysis of the human gut microbiome from urbanized and pre-agricultural populations. Environ Microbiol. 2017;19(4):1379-1390. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13692
15. Stilo SA, Murray RM. Non-genetic factors in schizophrenia. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21(10):100. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-1091-3
16. Buscaino VM. Patologia extraneurale della schizofrenia: fegato, tubo digerente, sistema reticolo-endoteliale. Acta Neurologica. 1953;VIII:1-60.
17. Hemmings G. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2004;364(9442):1312-1313. doi:10.1016/S0140- 6736(04)17181-X
18. Hooper LV, Gordon JI. Commensal host-bacterial relationships in the gut. Science. 2001;292(5519):1115-1118. doi:10.1126/science.1058709
19. Ewaschuk JB, Diaz H, Meddings L, et al. Secreted bioactive factors from Bifidobacterium infantis enhance epithelial cell barrier function. Am J Physiol-Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;295(5):G1025-G1034. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.90227.2008
20. Alhasson F, Das S, Seth R, et al. Altered gut microbiome in a mouse model of Gulf War Illness causes neuroinflammation and intestinal injury via leaky gut and TLR4 activation. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0172914. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0172914
21. Fillman SG, Cloonan N, Catts VS, et al. Increased inflammatory markers identified in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18(2):206-214. doi:10.1038/mp.2012.110
22. Miller BJ, Buckley P, Seabolt W, et al. Meta-analysis of cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: clinical status and antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;70(7):663-671. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.04.013
23. Al-Amin M, Uddin MMN, Reza HM. Effects of antipsychotics on the inflammatory response system of patients with schizophrenia in peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2013;11(3):144-151. doi:10.9758/cpn.2013.11.3.144
24. Yuan X, Zhang P, Wang Y, et al. Changes in metabolism and microbiota after 24-week risperidone treatment in drug naïve, normal weight patients with first episode schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2018;201:299-306. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2018.05.017
25. Maier L, Pruteanu M, Kuhn M, et al. Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018;555(7698):623-628. doi:10.1038/nature25979
26. Dickerson FB, Stallings C, Origoni A, et al. Effect of probiotic supplementation on schizophrenia symptoms and association with gastrointestinal functioning: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2014;15(1):PCC.13m01579. doi:10.4088/PCC.13m01579
27. David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature. 2014;505(7484):559-563. doi:10.1038/nature12820
28. Bien J, Palagani V, Bozko P. The intestinal microbiota dysbiosis and Clostridium difficile infection: is there a relationship with inflammatory bowel disease? Ther Adv Gastroenterol. 2013;6(1):53-68. doi:10.1177/1756283X12454590
29. Cryan JF, O’Riordan KJ, Sandhu K, et al. The gut microbiome in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(2):179-194. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30356-4
30. Jones CA, Watson DJG, Fone KCF. Animal models of schizophrenia. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;164(4):1162-1194. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01386.x
31. Schmidt MJ, Mirnics K. Neurodevelopment, GABA system dysfunction, and schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40(1):190-206. doi:10.1038/npp.2014.95
32. Nasrallah, HA. The daunting challenge of schizophrenia: hundreds of biotypes and dozens of theories. Curr. Psychiatry 2018;17(12):4-6,50.
33. Nocera A, Nasrallah HA. The association of the gut microbiota with clinical features in schizophrenia. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022;12(4):89. doi:10.3390/bs12040089
34. Schwarz E, Maukonen J, Hyytiäinen T, et al. Analysis of microbiota in first episode psychosis identifies preliminary associations with symptom severity and treatment response. Schizophr Res. 2018;192:398-403. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2017.04.017
35. Nguyen TT, Kosciolek T, Maldonado Y, et al. Differences in gut microbiome composition between persons with chronic schizophrenia and healthy comparison subjects. Schizophr Res. 2019;204:23-29. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2018.09.014
36. Li S, Zhuo M, Huang X, et al. Altered gut microbiota associated with symptom severity in schizophrenia. PeerJ. 2020;8:e9574. doi:10.7717/peerj.9574
37. Chen X, Xu J, Wang H, et al. Profiling the differences of gut microbial structure between schizophrenia patients with and without violent behaviors based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Int J Legal Med. 2021;135(1):131-141. doi:10.1007/s00414-020-02439-1
38. Manchia M, Fontana A, Panebianco C, et al. Involvement of gut microbiota in schizophrenia and treatment resistance to antipsychotics. Biomedicines. 2021;9(8):875. doi:10.3390/biomedicines9080875
39. Zhu C, Zheng M, Ali U, et al. Association between abundance of haemophilus in the gut microbiota and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:685910. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.685910
40. Flowers SA, Evans SJ, Ward KM, et al. Interaction between atypical antipsychotics and the gut microbiome in a bipolar disease cohort. Pharmacotherapy. 2017;37(3):261-267. doi:10.1002/phar.1890
41. Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature. 2012;486(7402):222-227. doi:10.1038/nature11053
42. Buchanan RW. Persistent negative symptoms in schizophrenia: an overview. Schizophr Bull. 2007;33(4):1013-1022. doi:10.1093/schbul/sb1057
43. Liu JCW, Gorbovskaya I, Hahn MK, et al. The gut microbiome in schizophrenia and the potential benefits of prebiotic and probiotic treatment. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1152. doi:10.3390/nu13041152
44. Biedermann L, Zeitz J, Mwinyi J, et al. Smoking cessation induces profound changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota in humans. PloS One. 2013;8(3):e59260. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059260
45. Leclercq S, Matamoros S, Cani PD, et al. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111(42):e4485-e4493. doi:10.1073/pnas.1415174111
46. Hernández-Quiroz F, Nirmalkar K, Villalobos-Flores LE, et al. Influence of moderate beer consumption on human gut microbiota and its impact on fasting glucose and ß-cell function. Alcohol. 2020;85:77-94. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2019.05.006
47. Panee J, Gerschenson M, Chang L. Associations between microbiota, mitochondrial function, and cognition in chronic marijuana users. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018;13(1):113-122. doi:10.1007/s11481-017-9767-0
48. Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science. 2011;334(6052):105-108. doi:10.1126/science.1208344
49. Rezac S, Kok CR, Heermann M, et al. Fermented foods as a dietary source of live organisms. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:1785. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.01785
50. Chen X, Zhang Y, Wang H, et al. The regulatory effects of lactic acid on neuropsychiatric disorders. Discover Ment Health. 2022;2(1). doi:10.1007/s44192-022-00011-4
51. Karbownik MS, Mokros Ł, Dobielska M, et al. Association between consumption of fermented food and food-derived prebiotics with cognitive performance, depressive, and anxiety symptoms in psychiatrically healthy medical students under psychological stress: a prospective cohort study. Front Nutr. 2022;9:850249. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.850249
52. Romano S, Savva GM, Bedarf JR, et al. Meta-analysis of the Parkinson’s disease gut microbiome suggests alterations linked to intestinal inflammation. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2021;7(1):27. doi:10.1038/s41531-021-00156-z
53. Bourassa MW, Alim I, Bultman SJ, et al. Butyrate, neuroepigenetics and the gut microbiome: can a high fiber diet improve brain health? Neurosci Lett. 2016;625:56-63. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2016.02.009
54. Matt SM, Allen JM, Lawson MA, et al. Butyrate and dietary soluble fiber improve neuroinflammation associated with aging in mice. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1832. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.01832
55. Mittal VA, Vargas T, Osborne KJ, et al. Exercise treatments for psychosis: a review. Curr Treat Options Psychiatry. 2017;4(2):152-166. doi:10.1007/s40501-017-0112-2
56. Estaki M, Pither J, Baumeister P, et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness as a predictor of intestinal microbial diversity and distinct metagenomic functions. Microbiome. 2016;4(1):42. doi:10.1186/s40168-016-0189-7
57. Karl JP, Margolis LM, Madslien EH, et al. Changes in intestinal microbiota composition and metabolism coincide with increased intestinal permeability in young adults under prolonged physiological stress. Am J Physiol-Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017;312(6):G559-G571. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00066.2017
58. Claus SP, Guillou H, Ellero-Simatos S. The gut microbiota: a major player in the toxicity of environmental pollutants? NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2016;2:16003. doi:10.1038/npjbiofilms.2016.3
Depression and schizophrenia: Many biological and clinical similarities
Clinicians generally regard major depressive disorder (MDD) and schizophrenia as 2 separate and distinct psychiatric brain disorders. However, despite some differences, those 2 psychiatric syndromes have numerous similarities across clinical features and neurobiologic parameters.
Biological similarities
Both disorders share the following variables:
- Highly genetic in etiology but with environmental influences and epigenetics
- Associated with childhood maltreatment, abuse, or neglect
- Disrupted neuroplasticity, especially shrinkage in hippocampal volume
- Significant drop in brain-derived neurotrophic factor resulting in decreased neurogenesis
- Extensive white matter pathology across interhemispheric and intrahemispheric bundles
- Increased levels of serum cortisol, a stress hormone and inflammatory biomarker
- Hypofrontal cerebral blood flow during acute episodes of both MDD and schizophrenia
- Reduced dendritic spines (in number and size) and impaired experiential neuroplasticity
- Neuroinflammation (eg, cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, C-reactive protein) during acute episodes
- Elevated oxidative stress biomarkers, indicating an increase in free radicals
- Overactive default mode network associated with ruminations in MDD and “daydreaming” in schizophrenia
- Decrease in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and its inhibitory activity, translating into dysregulation of glutamatergic pathways and other neurotransmitters
- Immune dysregulation and comorbid autoimmune disorders
Clinical similarities
- Psychotic symptoms, especially delusional thinking such as paranoia in schizophrenia and severe self-deprecation in MDD
- Significantly elevated lifetime suicide risk
- Cognitive impairment (more severe in schizophrenia across several cognitive functions)
- Similarity of depressive and negative symptoms (especially anhedonia, apathy, restricted facial expression, social withdrawal)
- Antidepressant medications im-prove depressive and negative symptoms (though not completely in the case of negative symptoms of schizophrenia)
- Both have treatment-resistant subtypes that fail to respond to standard therapies
- Both are associated with comorbid generalized anxiety disorder
- Both are associated with comorbid obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Both are associated with serious alcohol and drug use
- Early mortality from general medical conditions, especially cardiovascular risks due to obesity, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia
- Elevated risk of dementia with aging compared to the unaffected general population
- Opioids improve MDD and psychosis (buprenorphine in MDD and morphine in schizophrenia)
- Several second-generation antipsychotic medications are approved for both MDD and schizophrenia
- Electroconvulsive therapy is effective when pharmacotherapy fails in both MDD and schizophrenia
Biological differences
- Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists (eg, ketamine) improve MDD but worsen schizophrenia
- Muscarinic agonists improve psychosis but worsen depression
- High pain threshold in schizophrenia (pain insensitivity) and low threshold in MDD (in which pain is a common comorbidity)
- Cortical thinning more severe in schizophrenia
- Hippocampal atrophy is reversible with successful treatment in MDD but not in schizophrenia
- Hypofrontality is reversible with remission in MDD but not in schizophrenia
Clinical differences
- Auditory and visual hallucinations are more common in schizophrenia than in MDD
- Anosognosia is common in schizophrenia but not in MDD
- Implausible delusions are more common in schizophrenia than in MDD
- Mood-congruent delusions are more common in MDD than in schizophrenia
- Sadness, crying, pessimism, and self-deprecation are common in MDD but not in schizophrenia
- Achieving full remission is more common in MDD than in schizophrenia
- Long-acting injectable medications are available for schizophrenia but not for MDD
- Evidence-based psychotherapy, without pharmacotherapy, is more likely to be effective in MDD than in schizophrenia
A transdiagnostic model of psychopathology
The significant overlap between MDD and schizophrenia should not be surprising. They are both generated by the same organ, the human brain, with disrupted neurochemical and physiological circuits in the brain.
The overlap is also consistent with the emerging transdiagnostic model of psychopathology.1-9 This model proposes that there is a “core” genetic risk for psychopathology with different iterations. The transdiagnostic model is in stark contrast to the prevailing DSM-5, which categorizes psychiatric disorders in “silos,” as if they are completely independent from each other despite many shared features. This is highly debatable according to the substantial evidence that multiple psychiatric disorders share many genes that influence brain development in utero and predispose individuals to a variety of clinical symptoms in adolescence and young adulthood.
The origin of mental illness is being disentangled by emerging research, which is identifying the common links among the various disorders currently listed in DSM-5.10 However, the evolution of psychiatric diagnosis has come full circle from a single entity before DSM, to multiple entities with DSM, and now back to a unified transdiagnostic model that is rapidly emerging.11 This has implications for the FDA’s persistent dogma that clinical trials for new drugs must be targeted for 1 of the DSM-5 categories, a flawed and narrow assumption. Given the accelerating body of evidence for a unified, transdiagnostic model, it makes much more sense for the FDA to approve medications that target a psychiatric symptom that is shared by multiple psychiatric conditions within a transdiagnostic clinical system. When medications are approved for a symptom regardless of a DSM diagnosis, the term “off-label” and its “stigma” will then fade into history, along with the malignant preauthorization racket that was invented by greedy insurance companies that exploit the off-label use of medications (even when an FDA-approved medication for the patient’s condition does not yet exist) simply to deny coverage, lower their expenses, and fatten their profits.
1. Goodkind M, Eickhoff SB, Oathes DJ, et al. Identification of a common neurobiological substrate for mental illness. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72(4):305-315.
2. Caspi A, Moffitt TE. All for one and one for all: mental disorders in one dimension. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(9):831-844.
3. Krueger RF, Easton NR. Transdiagnostic factors in mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2015;14(1):27-29.
4. Hyman SE. New evidence for shared risk architecture for mental disorders. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(3):235-236.
5. Selzam S, Coleman JRI, Caspi A, et al. A polygenic p factor for major psychiatric disorders. Translational Psychiatry. 2018;8(1):205.
6. Barch DM. What it means to be transdiagnostic and how do we know? Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(5):370-372.
7. Nasrallah HA. Is there only 1 neurobiologic psychiatric disorder with different clinical expressions? Current Psychiatry. 2015;14(7):10-12.
8. Nasrallah HA. Pleiotropy of psychiatric disorders will reinvent DSM. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(4):6-7.
9. Nasrallah HA. Beyond DSM-5: clinical and biological features shared by major psychiatric syndromes. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(10):4-7.
10. Marshall M. Roots of mental illness: researchers are beginning to untangle the common biology that links supposedly distinct psychiatric conditions. Nature. 2020;581:19-21.
11. Kendler KS. From many to one to many--the search for causes of psychiatric illness. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(10):1085-1091.
Clinicians generally regard major depressive disorder (MDD) and schizophrenia as 2 separate and distinct psychiatric brain disorders. However, despite some differences, those 2 psychiatric syndromes have numerous similarities across clinical features and neurobiologic parameters.
Biological similarities
Both disorders share the following variables:
- Highly genetic in etiology but with environmental influences and epigenetics
- Associated with childhood maltreatment, abuse, or neglect
- Disrupted neuroplasticity, especially shrinkage in hippocampal volume
- Significant drop in brain-derived neurotrophic factor resulting in decreased neurogenesis
- Extensive white matter pathology across interhemispheric and intrahemispheric bundles
- Increased levels of serum cortisol, a stress hormone and inflammatory biomarker
- Hypofrontal cerebral blood flow during acute episodes of both MDD and schizophrenia
- Reduced dendritic spines (in number and size) and impaired experiential neuroplasticity
- Neuroinflammation (eg, cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, C-reactive protein) during acute episodes
- Elevated oxidative stress biomarkers, indicating an increase in free radicals
- Overactive default mode network associated with ruminations in MDD and “daydreaming” in schizophrenia
- Decrease in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and its inhibitory activity, translating into dysregulation of glutamatergic pathways and other neurotransmitters
- Immune dysregulation and comorbid autoimmune disorders
Clinical similarities
- Psychotic symptoms, especially delusional thinking such as paranoia in schizophrenia and severe self-deprecation in MDD
- Significantly elevated lifetime suicide risk
- Cognitive impairment (more severe in schizophrenia across several cognitive functions)
- Similarity of depressive and negative symptoms (especially anhedonia, apathy, restricted facial expression, social withdrawal)
- Antidepressant medications im-prove depressive and negative symptoms (though not completely in the case of negative symptoms of schizophrenia)
- Both have treatment-resistant subtypes that fail to respond to standard therapies
- Both are associated with comorbid generalized anxiety disorder
- Both are associated with comorbid obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Both are associated with serious alcohol and drug use
- Early mortality from general medical conditions, especially cardiovascular risks due to obesity, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia
- Elevated risk of dementia with aging compared to the unaffected general population
- Opioids improve MDD and psychosis (buprenorphine in MDD and morphine in schizophrenia)
- Several second-generation antipsychotic medications are approved for both MDD and schizophrenia
- Electroconvulsive therapy is effective when pharmacotherapy fails in both MDD and schizophrenia
Biological differences
- Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists (eg, ketamine) improve MDD but worsen schizophrenia
- Muscarinic agonists improve psychosis but worsen depression
- High pain threshold in schizophrenia (pain insensitivity) and low threshold in MDD (in which pain is a common comorbidity)
- Cortical thinning more severe in schizophrenia
- Hippocampal atrophy is reversible with successful treatment in MDD but not in schizophrenia
- Hypofrontality is reversible with remission in MDD but not in schizophrenia
Clinical differences
- Auditory and visual hallucinations are more common in schizophrenia than in MDD
- Anosognosia is common in schizophrenia but not in MDD
- Implausible delusions are more common in schizophrenia than in MDD
- Mood-congruent delusions are more common in MDD than in schizophrenia
- Sadness, crying, pessimism, and self-deprecation are common in MDD but not in schizophrenia
- Achieving full remission is more common in MDD than in schizophrenia
- Long-acting injectable medications are available for schizophrenia but not for MDD
- Evidence-based psychotherapy, without pharmacotherapy, is more likely to be effective in MDD than in schizophrenia
A transdiagnostic model of psychopathology
The significant overlap between MDD and schizophrenia should not be surprising. They are both generated by the same organ, the human brain, with disrupted neurochemical and physiological circuits in the brain.
The overlap is also consistent with the emerging transdiagnostic model of psychopathology.1-9 This model proposes that there is a “core” genetic risk for psychopathology with different iterations. The transdiagnostic model is in stark contrast to the prevailing DSM-5, which categorizes psychiatric disorders in “silos,” as if they are completely independent from each other despite many shared features. This is highly debatable according to the substantial evidence that multiple psychiatric disorders share many genes that influence brain development in utero and predispose individuals to a variety of clinical symptoms in adolescence and young adulthood.
The origin of mental illness is being disentangled by emerging research, which is identifying the common links among the various disorders currently listed in DSM-5.10 However, the evolution of psychiatric diagnosis has come full circle from a single entity before DSM, to multiple entities with DSM, and now back to a unified transdiagnostic model that is rapidly emerging.11 This has implications for the FDA’s persistent dogma that clinical trials for new drugs must be targeted for 1 of the DSM-5 categories, a flawed and narrow assumption. Given the accelerating body of evidence for a unified, transdiagnostic model, it makes much more sense for the FDA to approve medications that target a psychiatric symptom that is shared by multiple psychiatric conditions within a transdiagnostic clinical system. When medications are approved for a symptom regardless of a DSM diagnosis, the term “off-label” and its “stigma” will then fade into history, along with the malignant preauthorization racket that was invented by greedy insurance companies that exploit the off-label use of medications (even when an FDA-approved medication for the patient’s condition does not yet exist) simply to deny coverage, lower their expenses, and fatten their profits.
Clinicians generally regard major depressive disorder (MDD) and schizophrenia as 2 separate and distinct psychiatric brain disorders. However, despite some differences, those 2 psychiatric syndromes have numerous similarities across clinical features and neurobiologic parameters.
Biological similarities
Both disorders share the following variables:
- Highly genetic in etiology but with environmental influences and epigenetics
- Associated with childhood maltreatment, abuse, or neglect
- Disrupted neuroplasticity, especially shrinkage in hippocampal volume
- Significant drop in brain-derived neurotrophic factor resulting in decreased neurogenesis
- Extensive white matter pathology across interhemispheric and intrahemispheric bundles
- Increased levels of serum cortisol, a stress hormone and inflammatory biomarker
- Hypofrontal cerebral blood flow during acute episodes of both MDD and schizophrenia
- Reduced dendritic spines (in number and size) and impaired experiential neuroplasticity
- Neuroinflammation (eg, cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, C-reactive protein) during acute episodes
- Elevated oxidative stress biomarkers, indicating an increase in free radicals
- Overactive default mode network associated with ruminations in MDD and “daydreaming” in schizophrenia
- Decrease in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and its inhibitory activity, translating into dysregulation of glutamatergic pathways and other neurotransmitters
- Immune dysregulation and comorbid autoimmune disorders
Clinical similarities
- Psychotic symptoms, especially delusional thinking such as paranoia in schizophrenia and severe self-deprecation in MDD
- Significantly elevated lifetime suicide risk
- Cognitive impairment (more severe in schizophrenia across several cognitive functions)
- Similarity of depressive and negative symptoms (especially anhedonia, apathy, restricted facial expression, social withdrawal)
- Antidepressant medications im-prove depressive and negative symptoms (though not completely in the case of negative symptoms of schizophrenia)
- Both have treatment-resistant subtypes that fail to respond to standard therapies
- Both are associated with comorbid generalized anxiety disorder
- Both are associated with comorbid obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Both are associated with serious alcohol and drug use
- Early mortality from general medical conditions, especially cardiovascular risks due to obesity, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia
- Elevated risk of dementia with aging compared to the unaffected general population
- Opioids improve MDD and psychosis (buprenorphine in MDD and morphine in schizophrenia)
- Several second-generation antipsychotic medications are approved for both MDD and schizophrenia
- Electroconvulsive therapy is effective when pharmacotherapy fails in both MDD and schizophrenia
Biological differences
- Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists (eg, ketamine) improve MDD but worsen schizophrenia
- Muscarinic agonists improve psychosis but worsen depression
- High pain threshold in schizophrenia (pain insensitivity) and low threshold in MDD (in which pain is a common comorbidity)
- Cortical thinning more severe in schizophrenia
- Hippocampal atrophy is reversible with successful treatment in MDD but not in schizophrenia
- Hypofrontality is reversible with remission in MDD but not in schizophrenia
Clinical differences
- Auditory and visual hallucinations are more common in schizophrenia than in MDD
- Anosognosia is common in schizophrenia but not in MDD
- Implausible delusions are more common in schizophrenia than in MDD
- Mood-congruent delusions are more common in MDD than in schizophrenia
- Sadness, crying, pessimism, and self-deprecation are common in MDD but not in schizophrenia
- Achieving full remission is more common in MDD than in schizophrenia
- Long-acting injectable medications are available for schizophrenia but not for MDD
- Evidence-based psychotherapy, without pharmacotherapy, is more likely to be effective in MDD than in schizophrenia
A transdiagnostic model of psychopathology
The significant overlap between MDD and schizophrenia should not be surprising. They are both generated by the same organ, the human brain, with disrupted neurochemical and physiological circuits in the brain.
The overlap is also consistent with the emerging transdiagnostic model of psychopathology.1-9 This model proposes that there is a “core” genetic risk for psychopathology with different iterations. The transdiagnostic model is in stark contrast to the prevailing DSM-5, which categorizes psychiatric disorders in “silos,” as if they are completely independent from each other despite many shared features. This is highly debatable according to the substantial evidence that multiple psychiatric disorders share many genes that influence brain development in utero and predispose individuals to a variety of clinical symptoms in adolescence and young adulthood.
The origin of mental illness is being disentangled by emerging research, which is identifying the common links among the various disorders currently listed in DSM-5.10 However, the evolution of psychiatric diagnosis has come full circle from a single entity before DSM, to multiple entities with DSM, and now back to a unified transdiagnostic model that is rapidly emerging.11 This has implications for the FDA’s persistent dogma that clinical trials for new drugs must be targeted for 1 of the DSM-5 categories, a flawed and narrow assumption. Given the accelerating body of evidence for a unified, transdiagnostic model, it makes much more sense for the FDA to approve medications that target a psychiatric symptom that is shared by multiple psychiatric conditions within a transdiagnostic clinical system. When medications are approved for a symptom regardless of a DSM diagnosis, the term “off-label” and its “stigma” will then fade into history, along with the malignant preauthorization racket that was invented by greedy insurance companies that exploit the off-label use of medications (even when an FDA-approved medication for the patient’s condition does not yet exist) simply to deny coverage, lower their expenses, and fatten their profits.
1. Goodkind M, Eickhoff SB, Oathes DJ, et al. Identification of a common neurobiological substrate for mental illness. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72(4):305-315.
2. Caspi A, Moffitt TE. All for one and one for all: mental disorders in one dimension. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(9):831-844.
3. Krueger RF, Easton NR. Transdiagnostic factors in mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2015;14(1):27-29.
4. Hyman SE. New evidence for shared risk architecture for mental disorders. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(3):235-236.
5. Selzam S, Coleman JRI, Caspi A, et al. A polygenic p factor for major psychiatric disorders. Translational Psychiatry. 2018;8(1):205.
6. Barch DM. What it means to be transdiagnostic and how do we know? Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(5):370-372.
7. Nasrallah HA. Is there only 1 neurobiologic psychiatric disorder with different clinical expressions? Current Psychiatry. 2015;14(7):10-12.
8. Nasrallah HA. Pleiotropy of psychiatric disorders will reinvent DSM. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(4):6-7.
9. Nasrallah HA. Beyond DSM-5: clinical and biological features shared by major psychiatric syndromes. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(10):4-7.
10. Marshall M. Roots of mental illness: researchers are beginning to untangle the common biology that links supposedly distinct psychiatric conditions. Nature. 2020;581:19-21.
11. Kendler KS. From many to one to many--the search for causes of psychiatric illness. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(10):1085-1091.
1. Goodkind M, Eickhoff SB, Oathes DJ, et al. Identification of a common neurobiological substrate for mental illness. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72(4):305-315.
2. Caspi A, Moffitt TE. All for one and one for all: mental disorders in one dimension. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(9):831-844.
3. Krueger RF, Easton NR. Transdiagnostic factors in mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2015;14(1):27-29.
4. Hyman SE. New evidence for shared risk architecture for mental disorders. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(3):235-236.
5. Selzam S, Coleman JRI, Caspi A, et al. A polygenic p factor for major psychiatric disorders. Translational Psychiatry. 2018;8(1):205.
6. Barch DM. What it means to be transdiagnostic and how do we know? Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(5):370-372.
7. Nasrallah HA. Is there only 1 neurobiologic psychiatric disorder with different clinical expressions? Current Psychiatry. 2015;14(7):10-12.
8. Nasrallah HA. Pleiotropy of psychiatric disorders will reinvent DSM. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(4):6-7.
9. Nasrallah HA. Beyond DSM-5: clinical and biological features shared by major psychiatric syndromes. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(10):4-7.
10. Marshall M. Roots of mental illness: researchers are beginning to untangle the common biology that links supposedly distinct psychiatric conditions. Nature. 2020;581:19-21.
11. Kendler KS. From many to one to many--the search for causes of psychiatric illness. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(10):1085-1091.